Patents
Literature
72 results about "Adaptive beamformer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An adaptive beamformer is a system that performs adaptive spatial signal processing with an array of transmitters or receivers. The signals are combined in a manner which increases the signal strength to/from a chosen direction. Signals to/from other directions are combined in a benign or destructive manner, resulting in degradation of the signal to/from the undesired direction. This technique is used in both radio frequency and acoustic arrays, and provides for directional sensitivity without physically moving an array of receivers or transmitters.
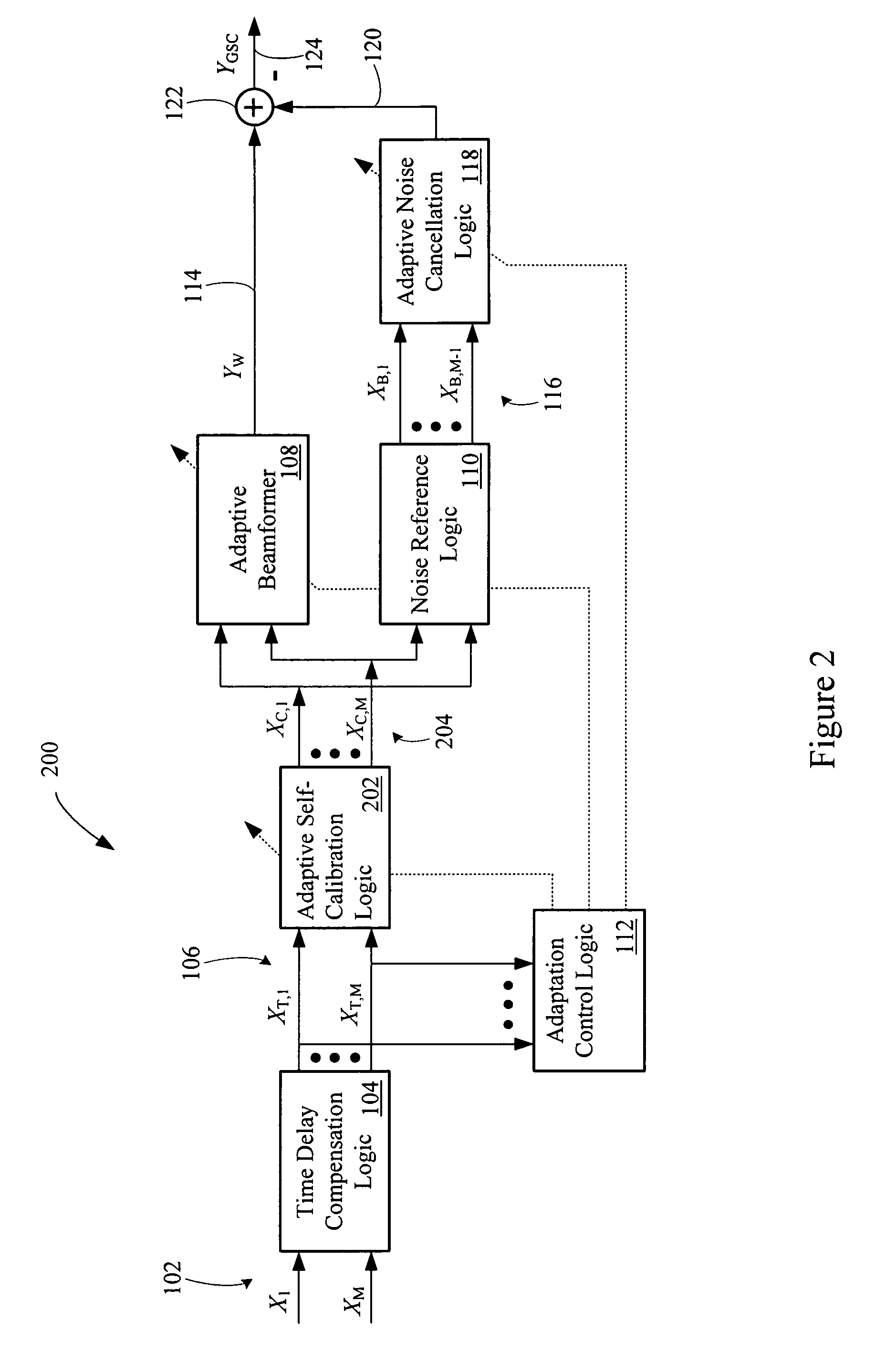
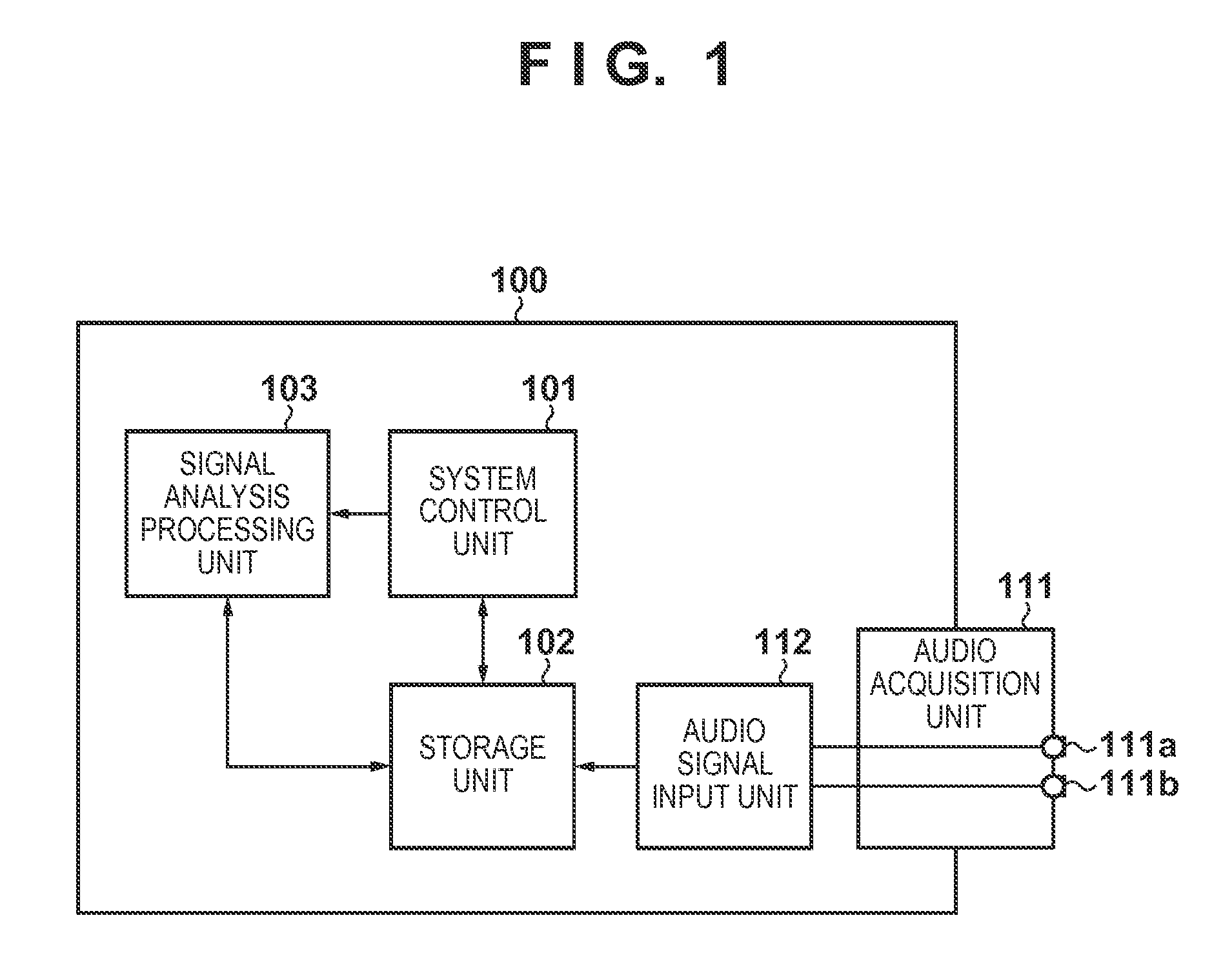
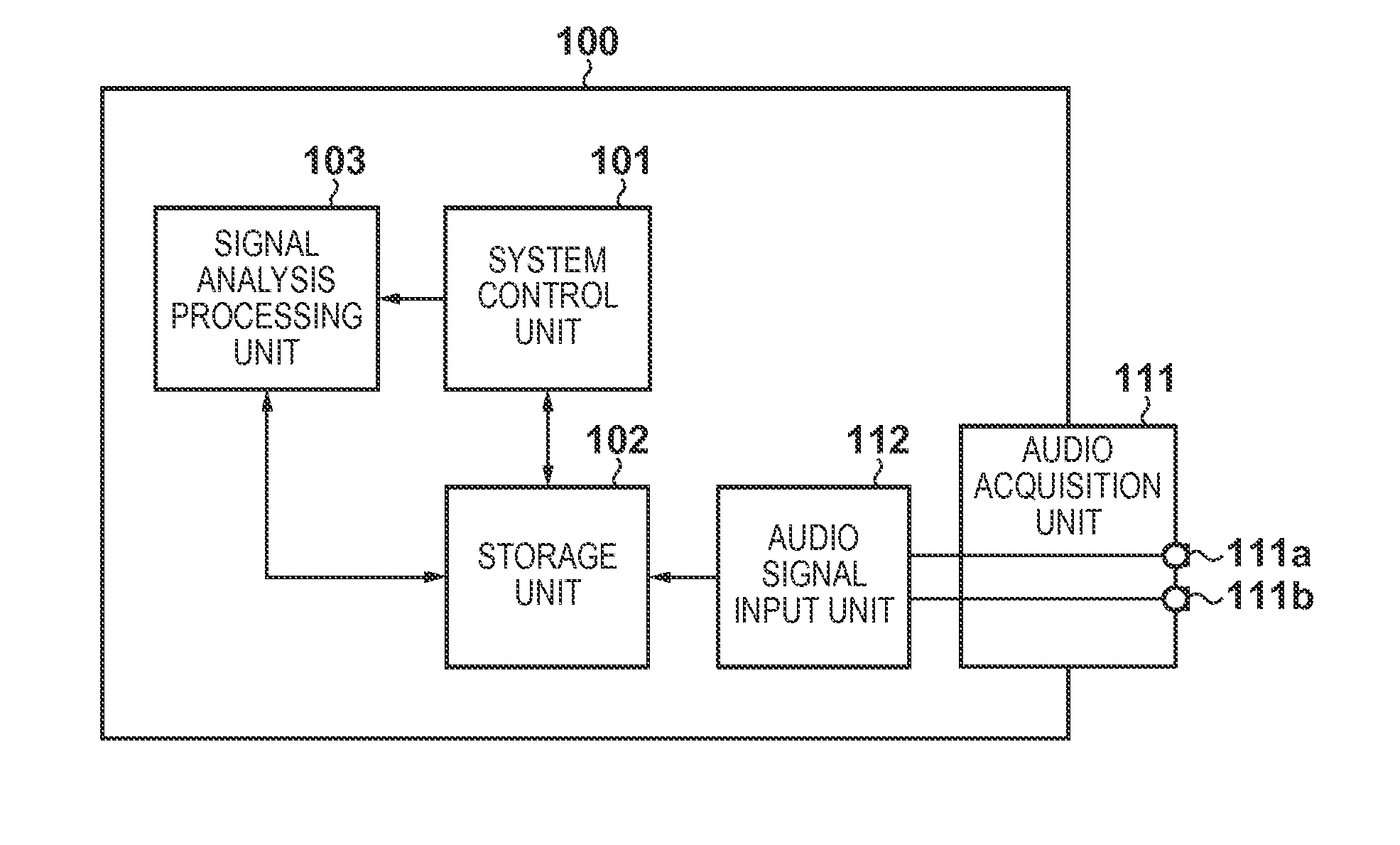
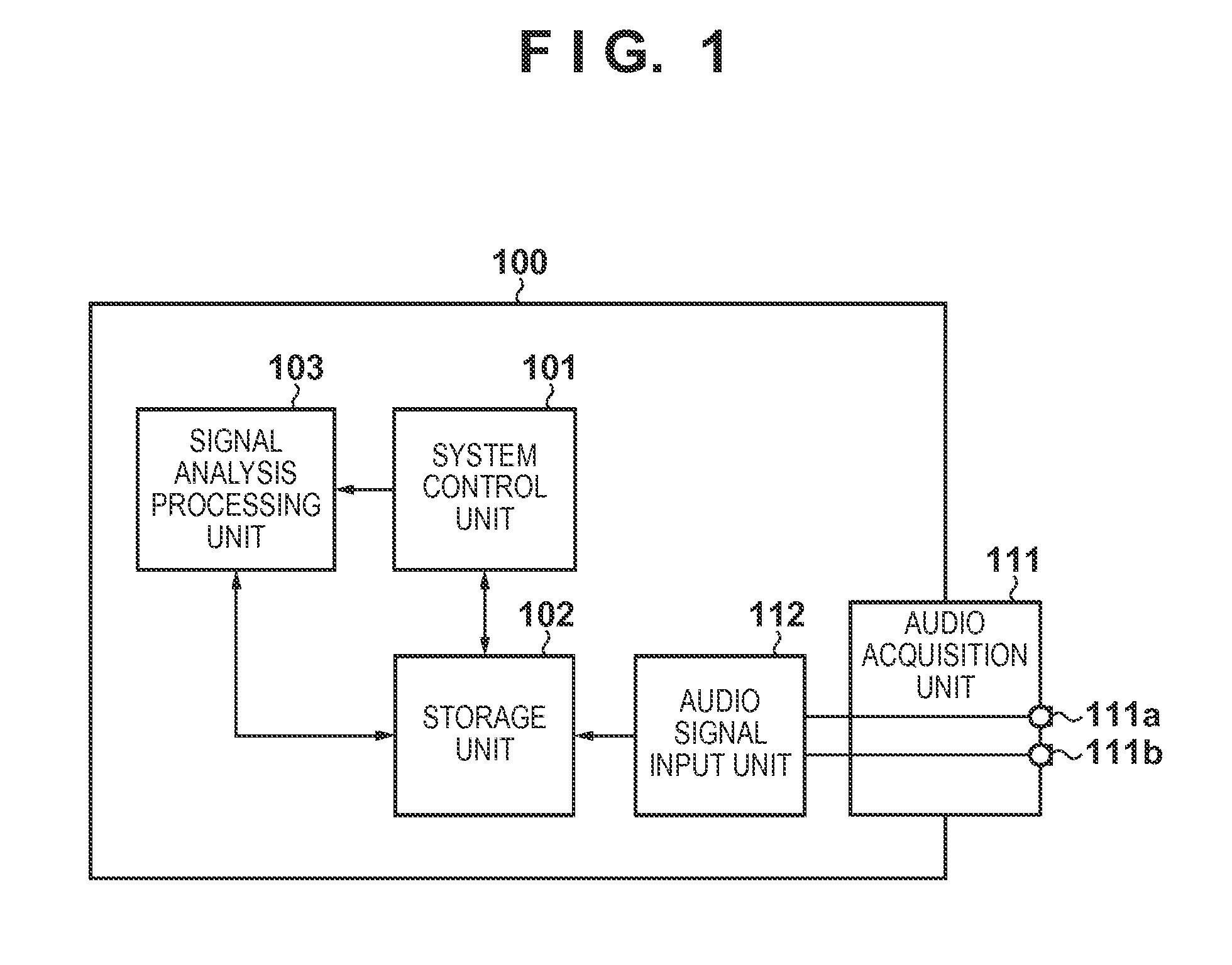
Multi-channel adaptive speech signal processing system with noise reduction
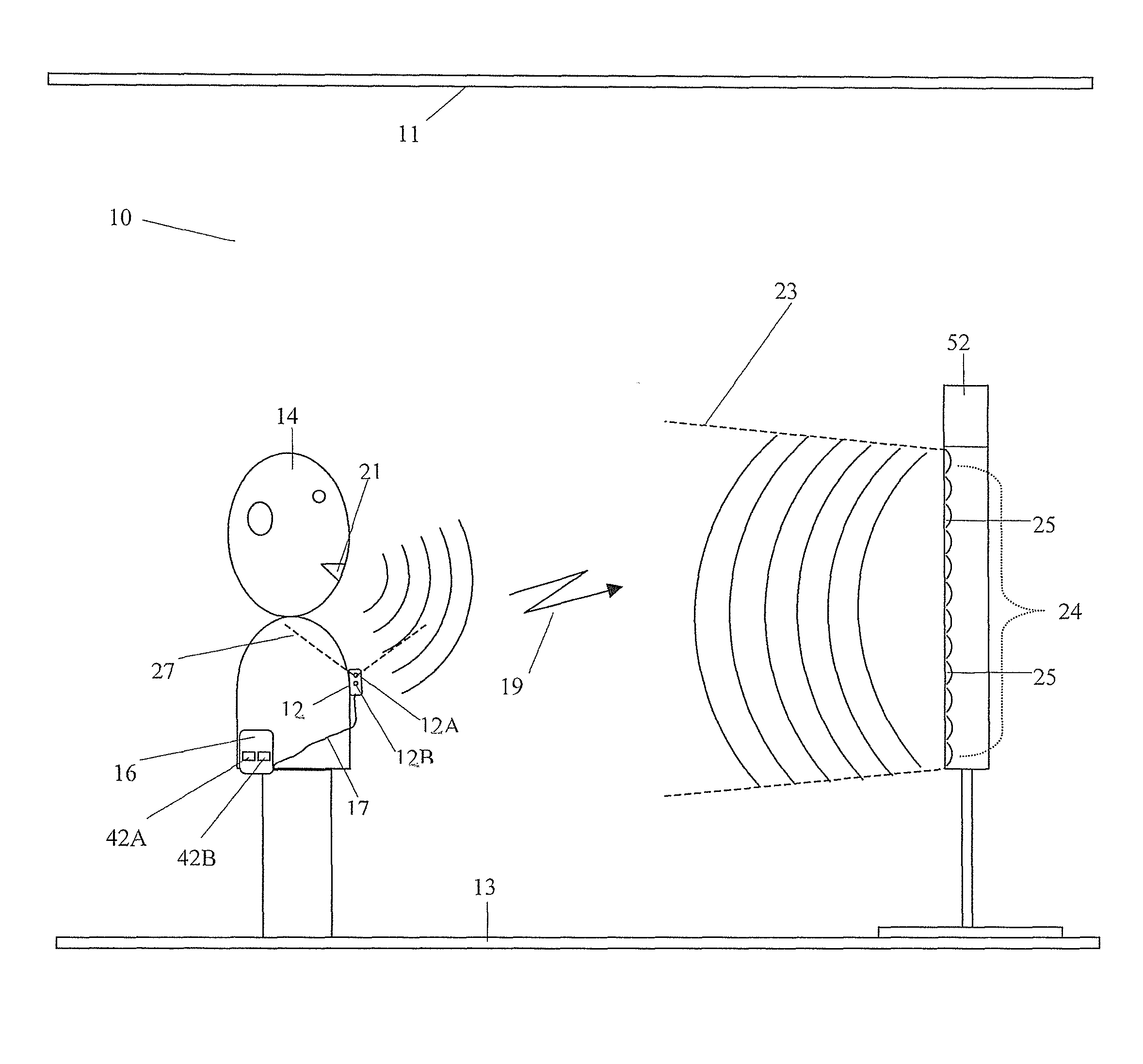
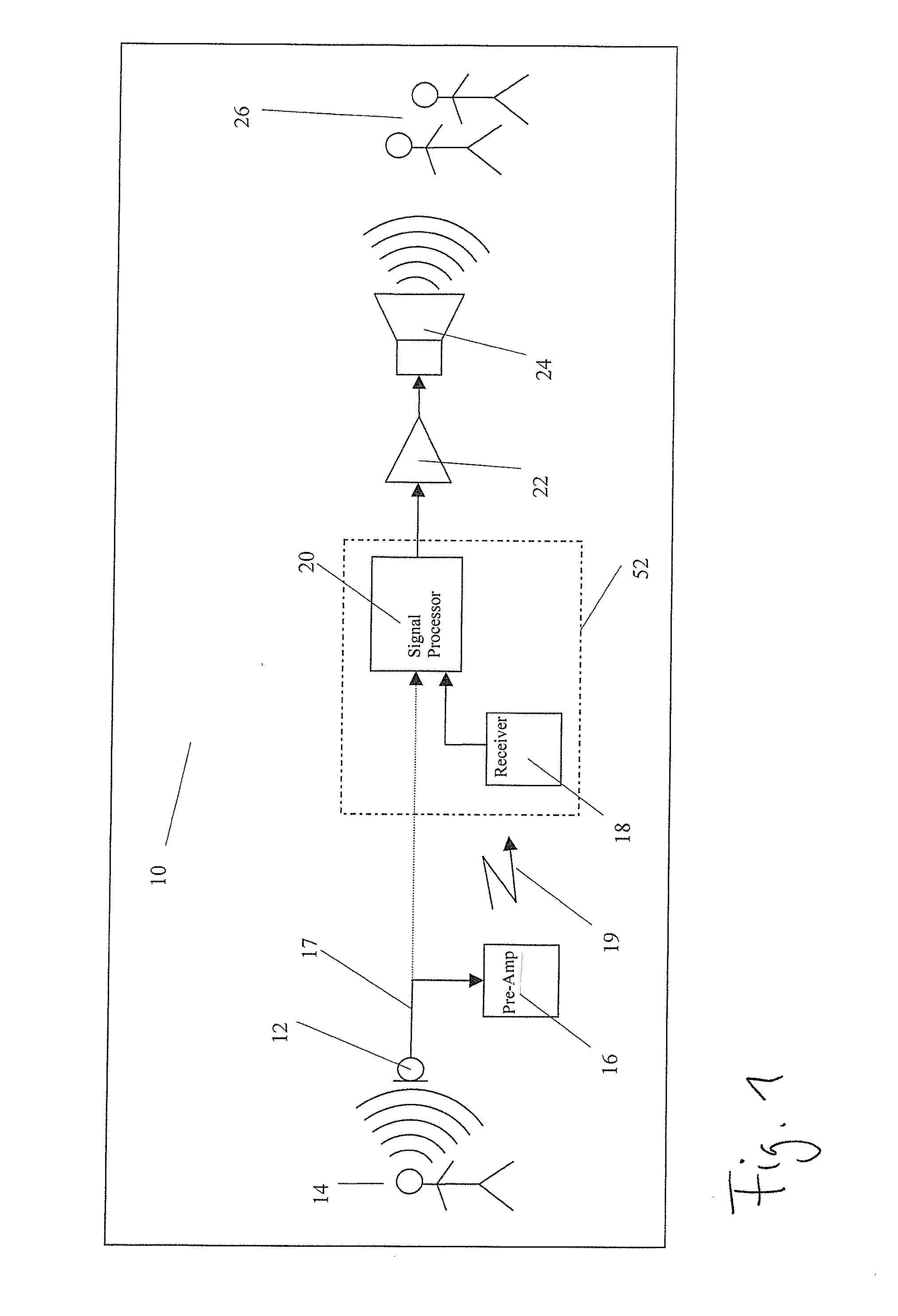
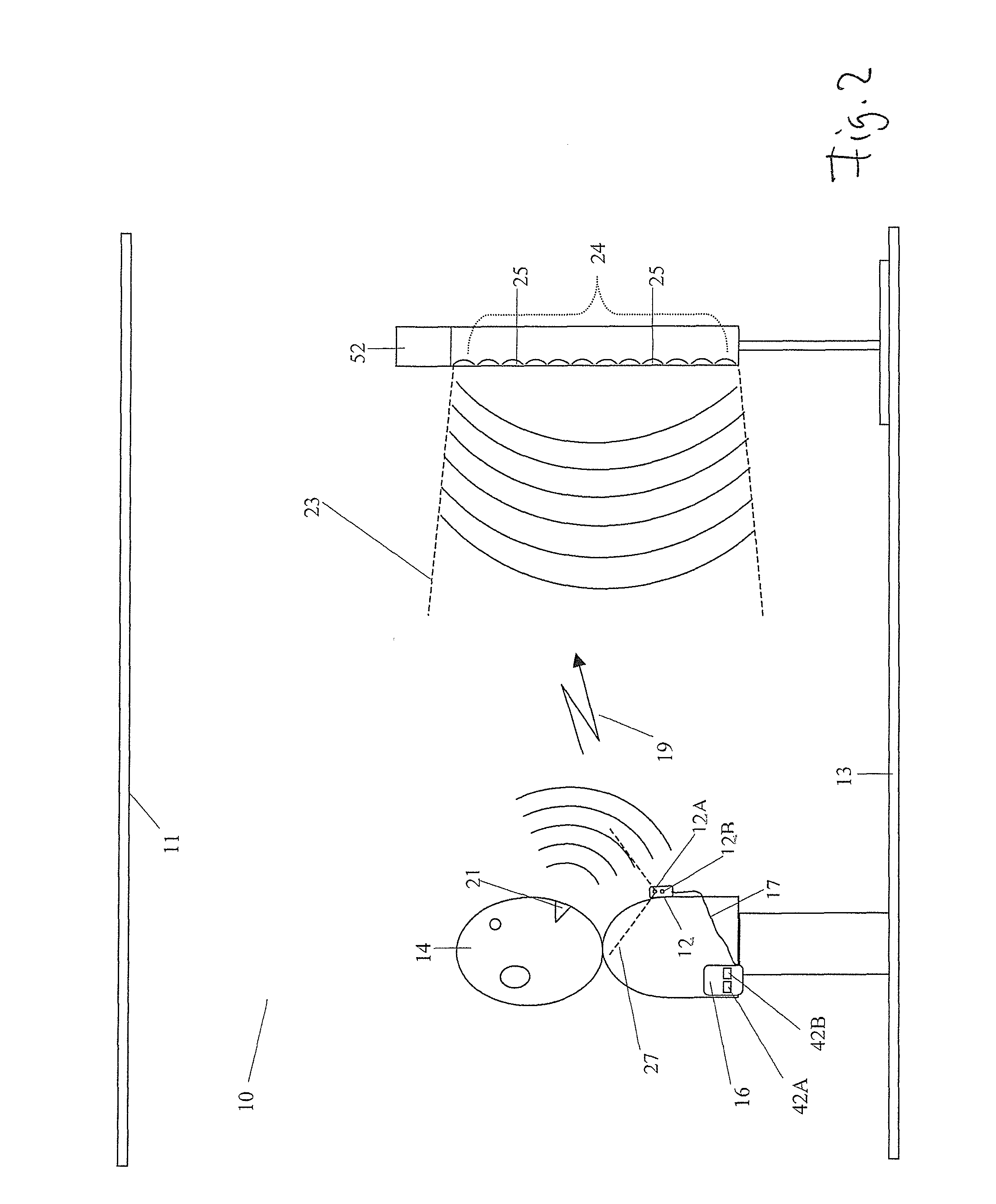
ActiveUS20060222184A1Improved speech signal clarityImprove intelligibilitySignal processingEar treatmentLow noiseHigh energy
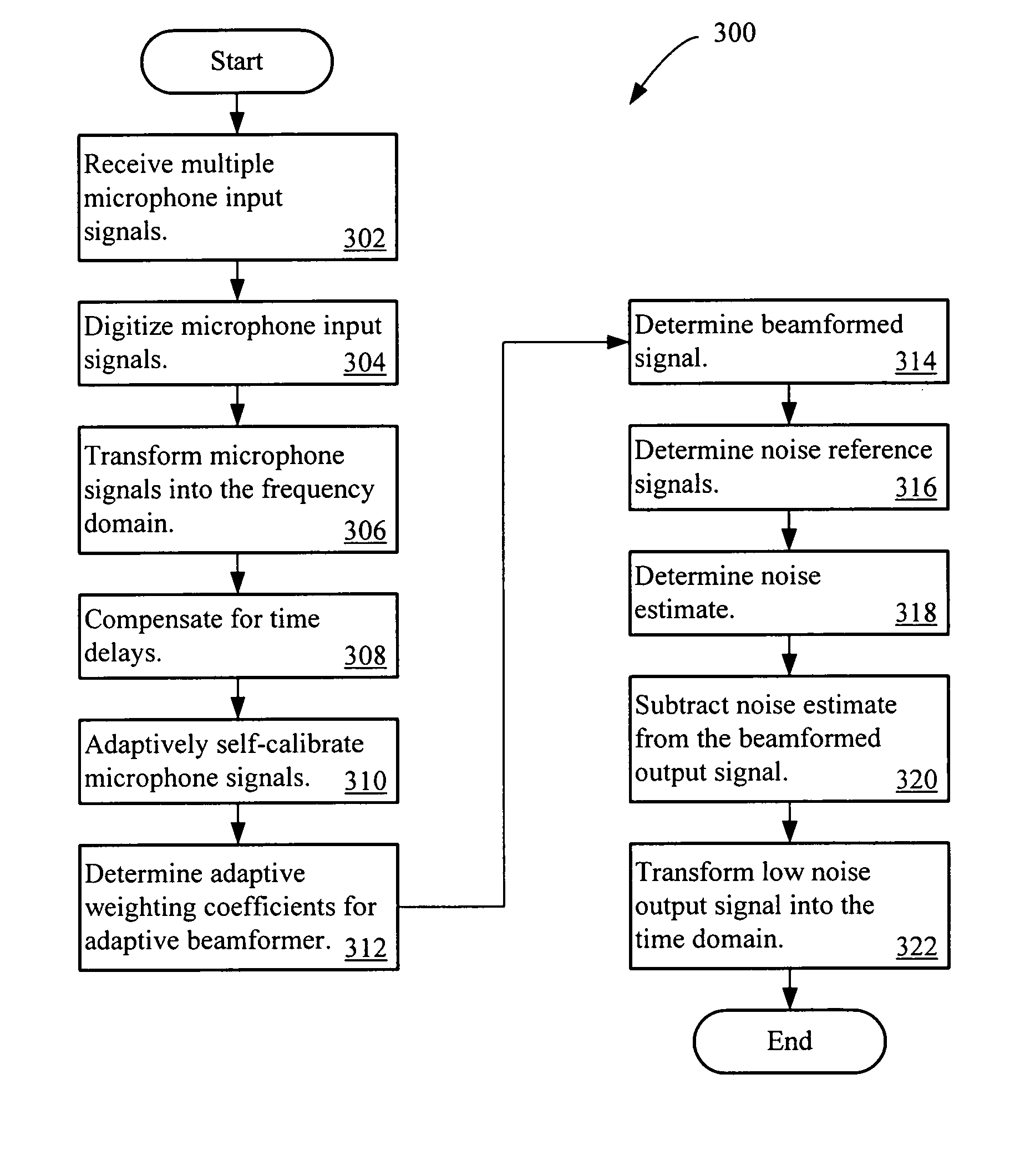
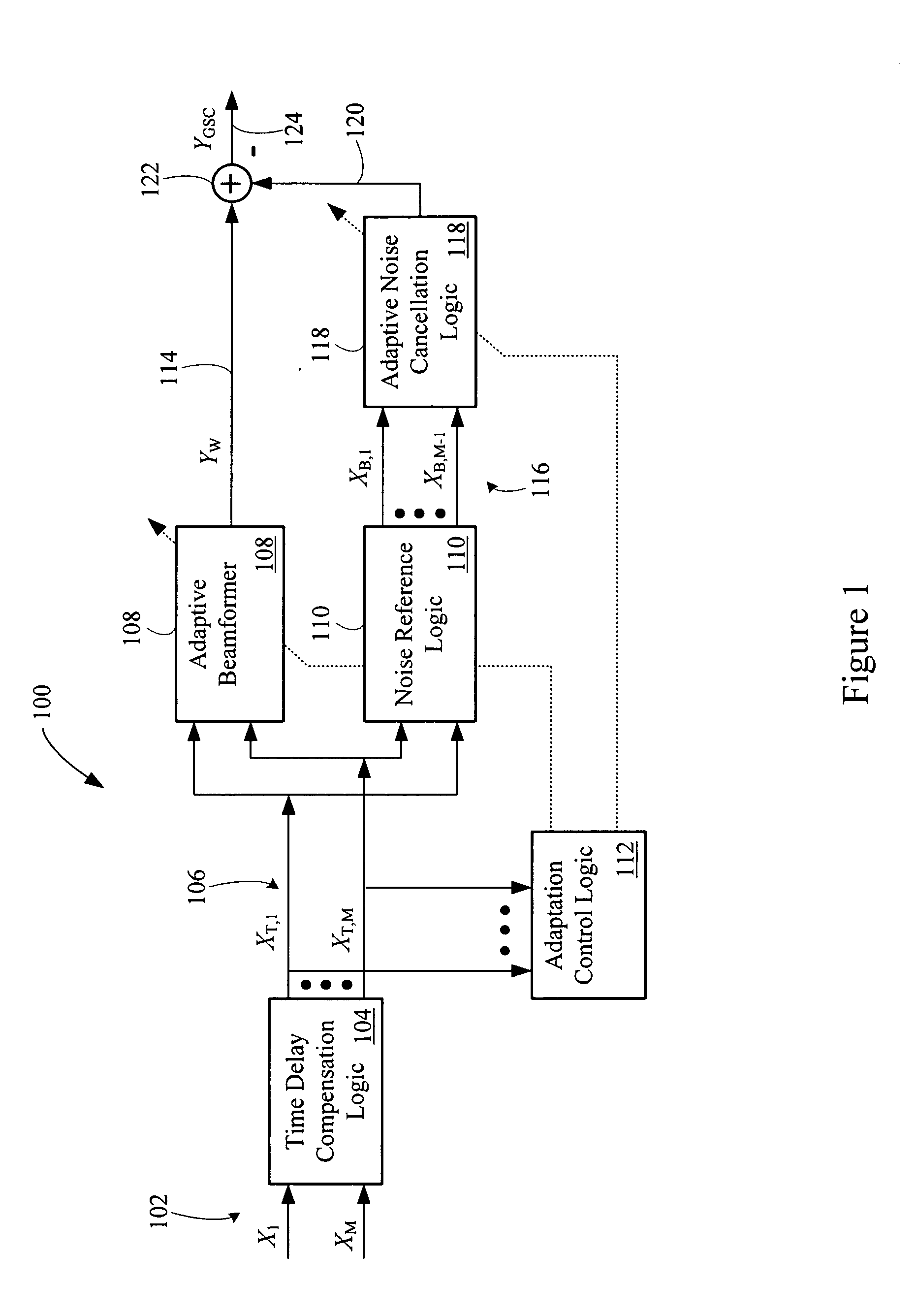
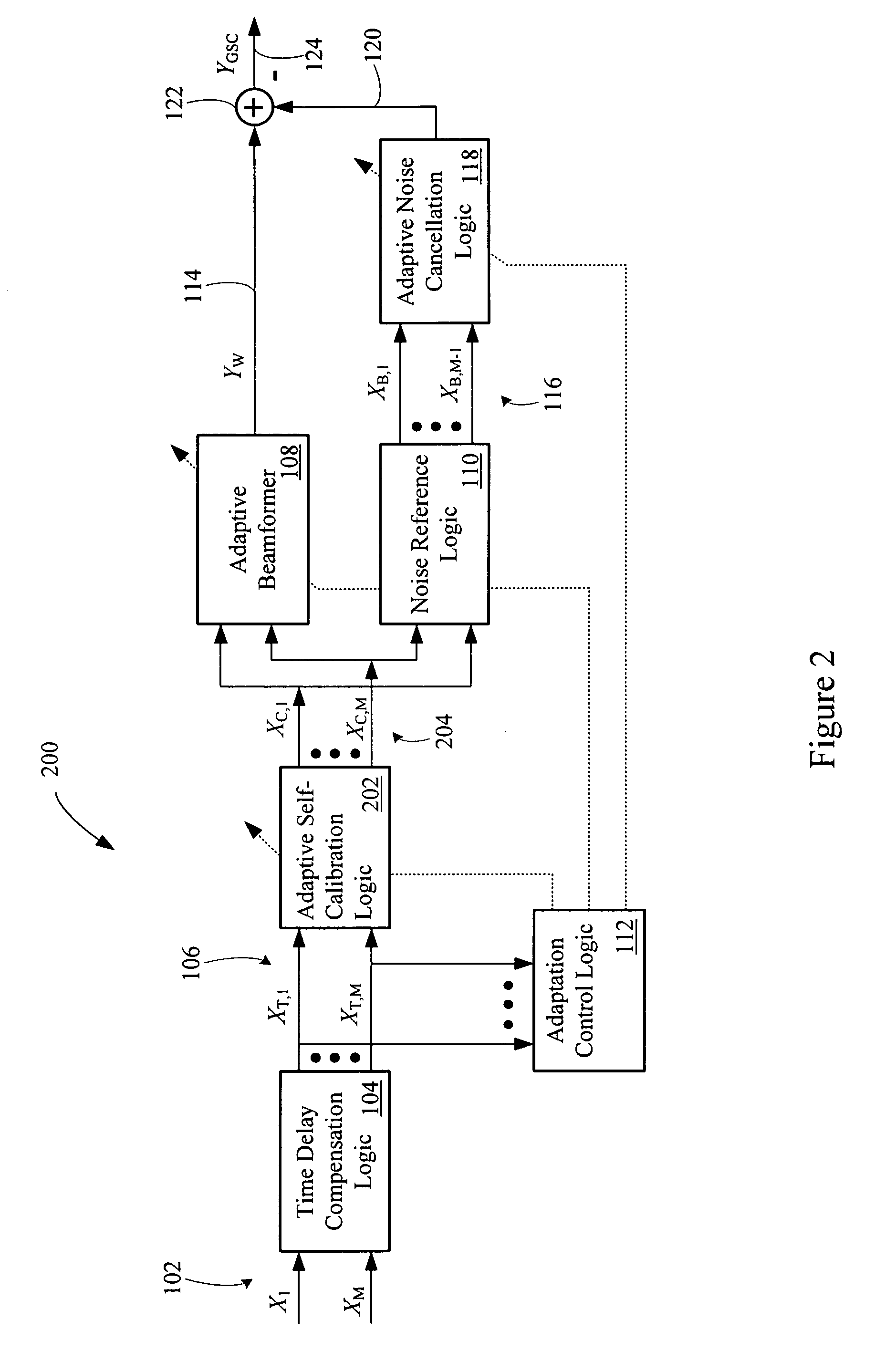
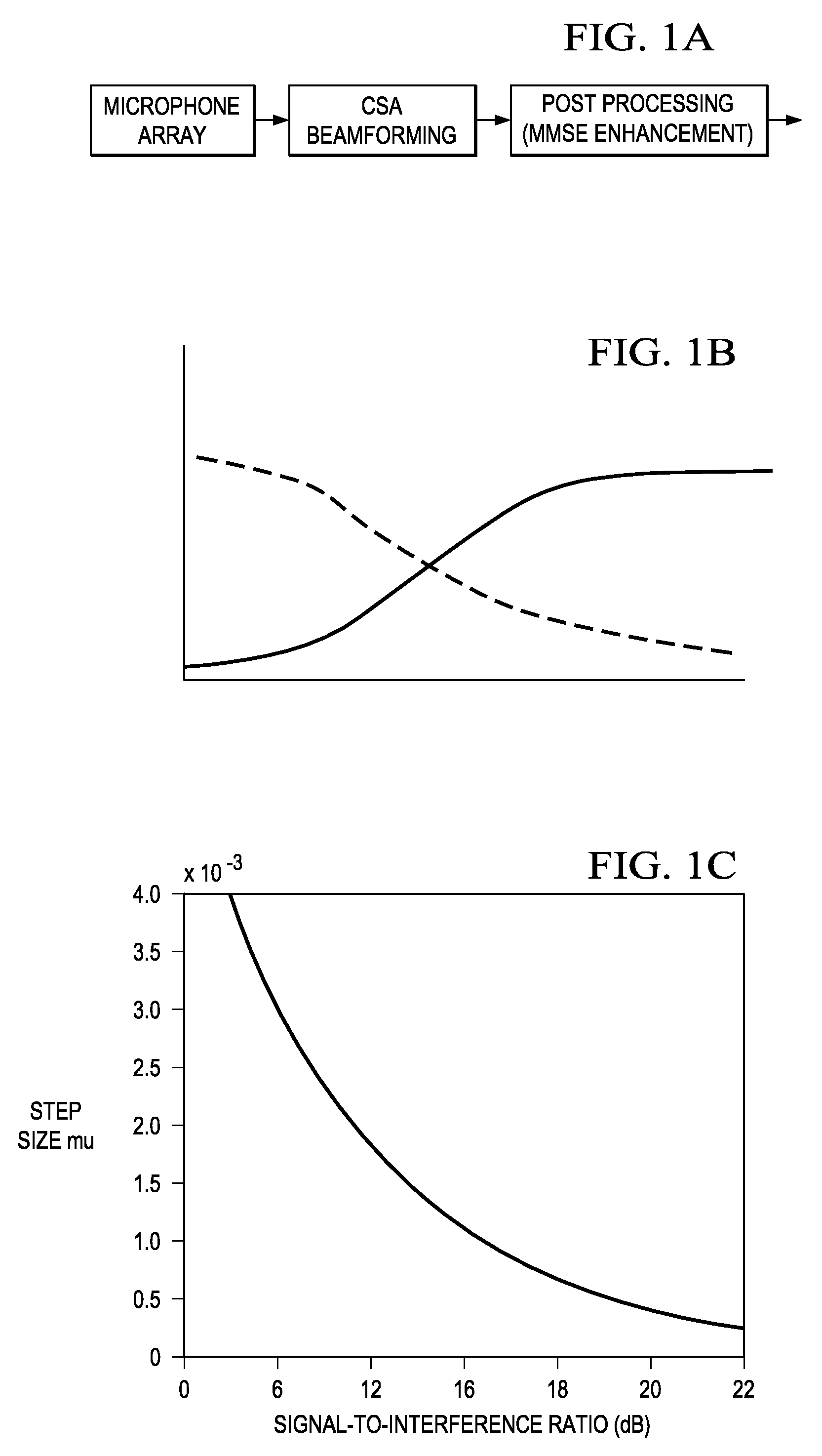
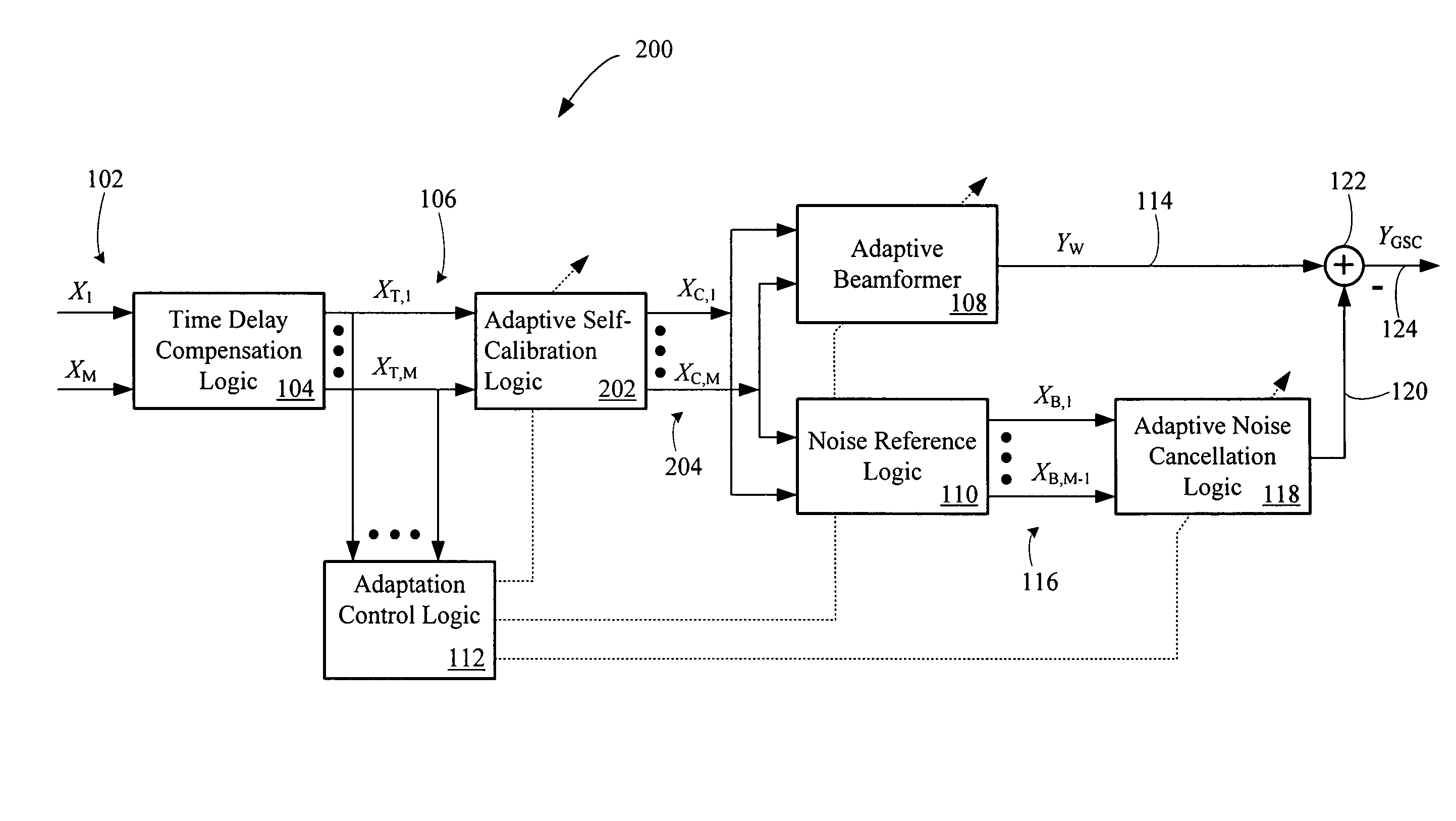
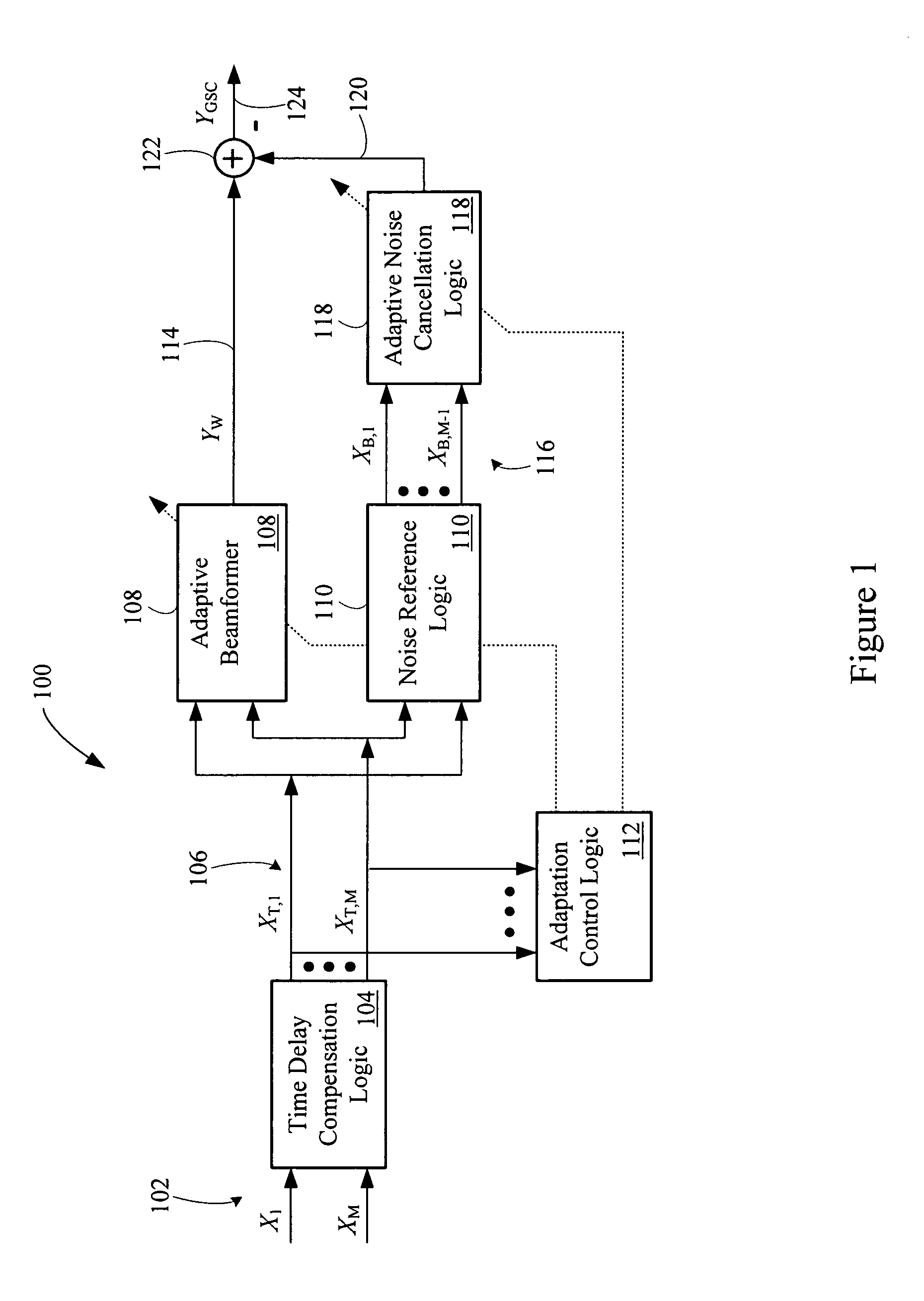
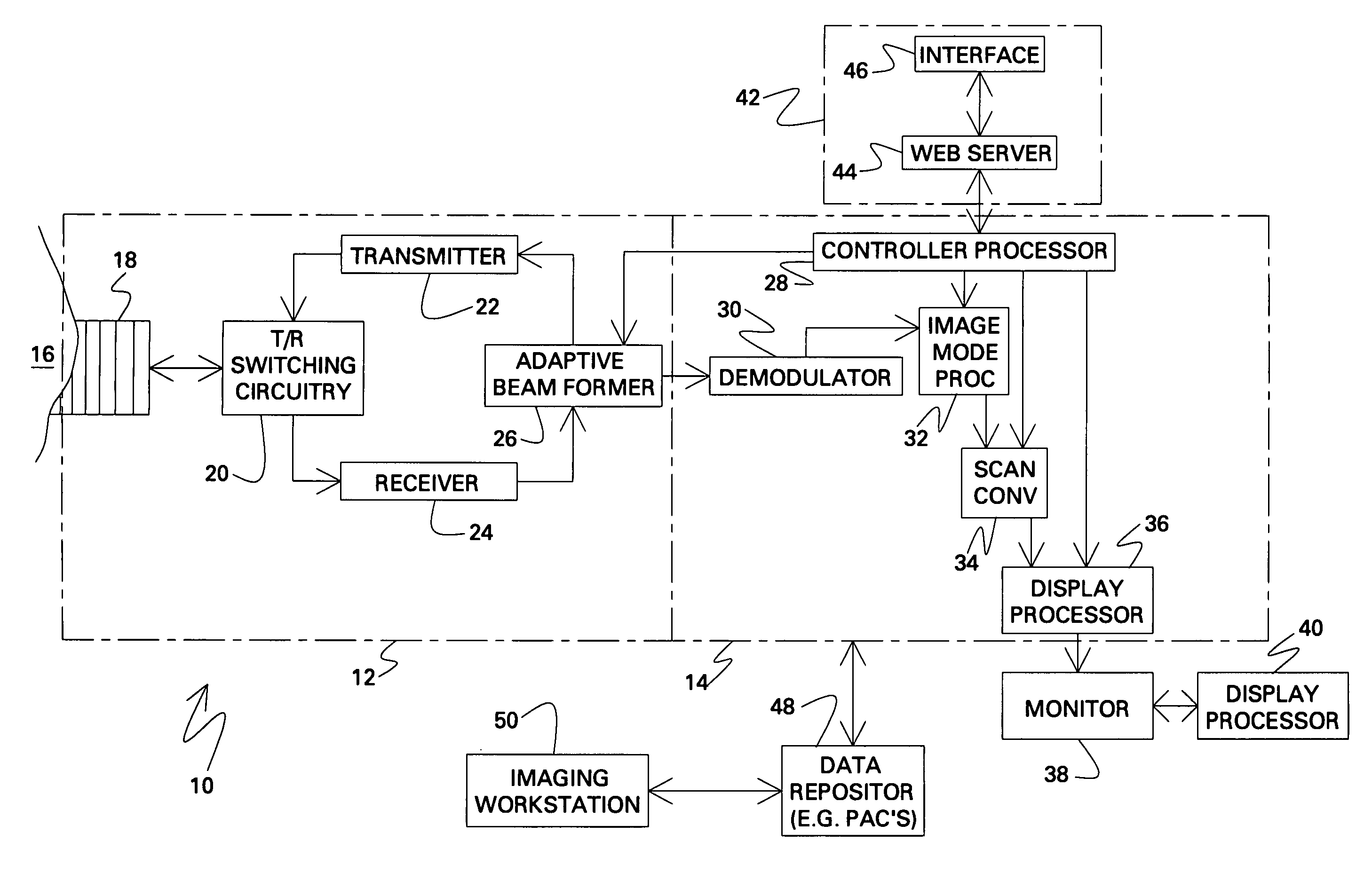
An adaptive signal processing system eliminates noise from input signals while retaining desired signal content, such as speech. The resulting low noise output signal delivers improved clarity and intelligibility. The low noise output signal also improves the performance of subsequent signal processing systems, including speech recognition systems. An adaptive beamformer in the signal processing system consistently updates beamforming signal weights in response to changing microphone signal conditions. The adaptive weights emphasize the contribution of high energy microphone signals to the beamformed output signal. In addition, adaptive noise cancellation logic removes residual noise from the beamformed output signal based on a noise estimate derived from the microphone input signals.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST WAVEMAKERS
Telephony Device with Improved Noise Suppression
InactiveUS20070230712A1Unwanted noise signalMaximize qualityEar treatmentMicrophone structural associationFrequency spectrumPost processor
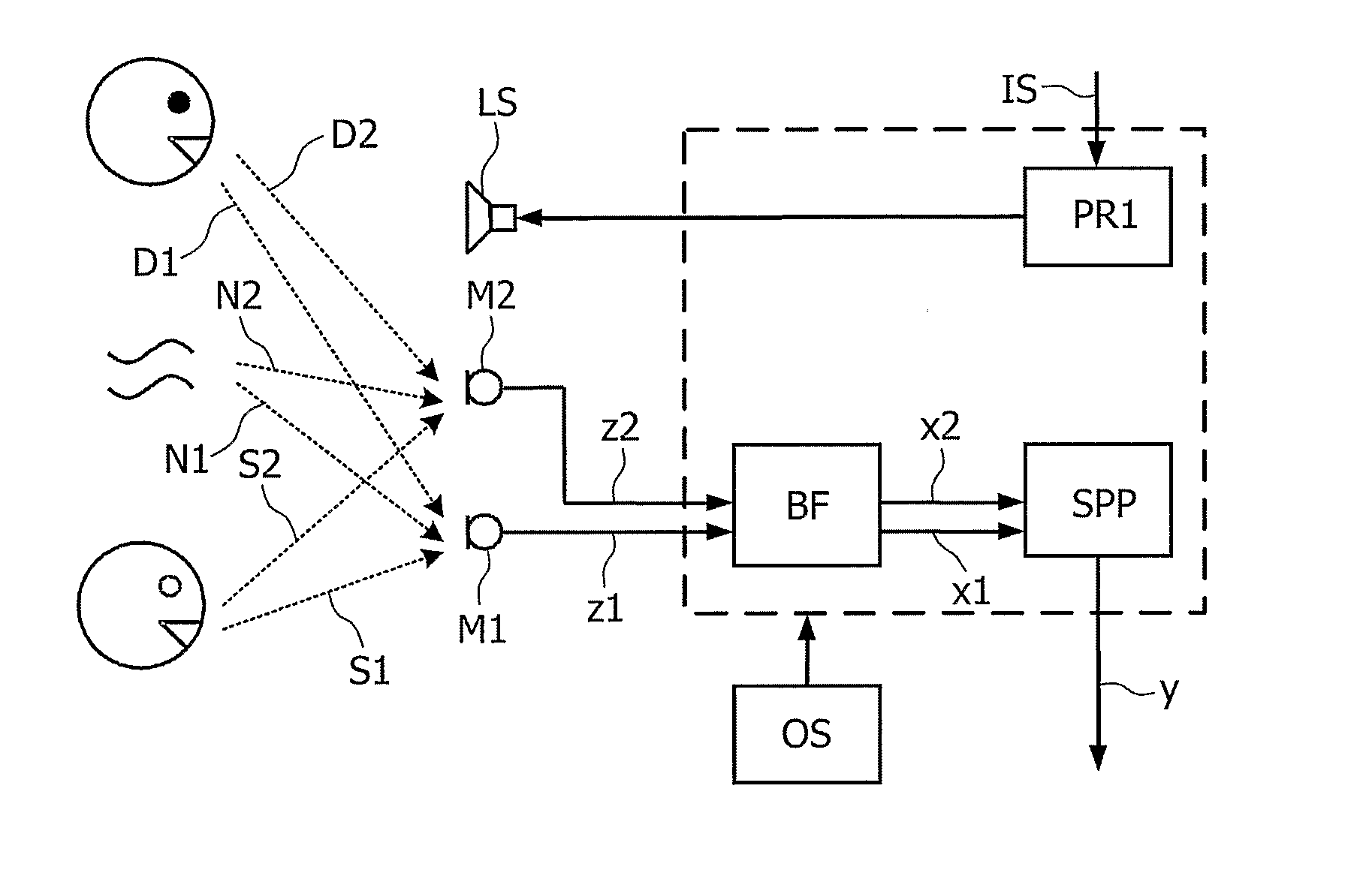
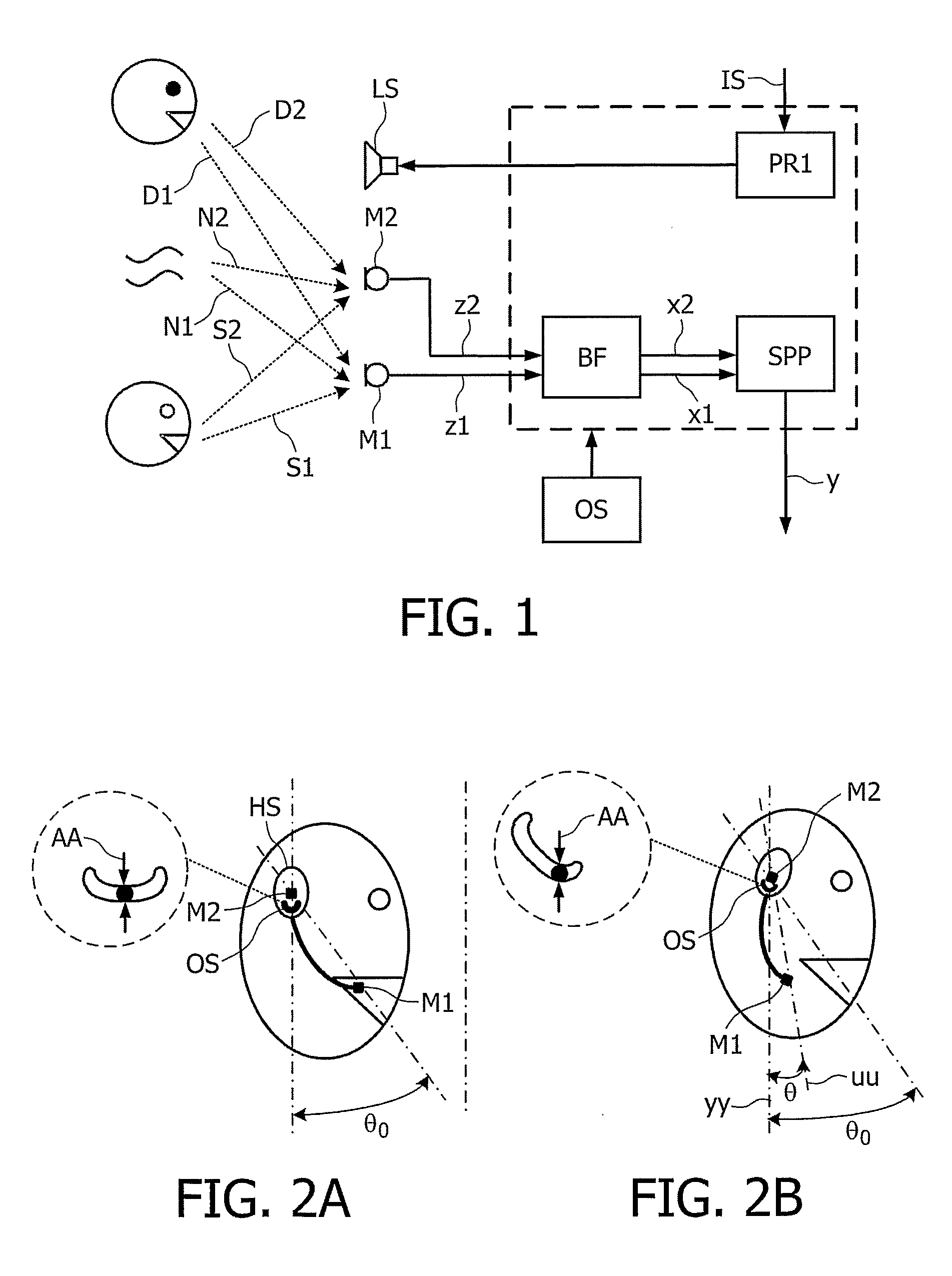
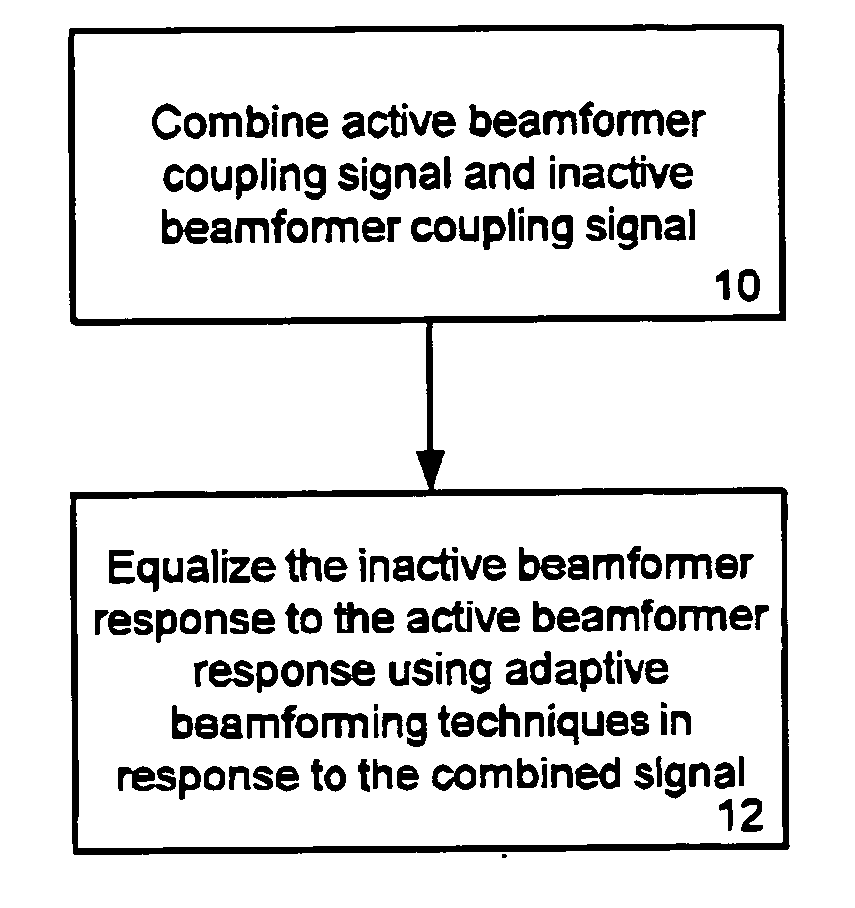
The present invention relates to a telephony device comprising a near-mouth microphone (M1) for picking up an input acoustic signal including the speaker's voice signal (S1) and an unwanted noise signal (N1,D1), a far-mouth microphone (M2) for picking up an unwanted noise signal (N2,D2) in addition to the near-end speaker's voice signal (S2), said speaker's voice signal being at a lower level than the near-mouth microphone, and an orientation sensor for measuring an orientation indication of said mobile device. The telephony device further comprises an audio processing unit comprising an adaptive beamformer (BF) coupled to the near-mouth and far-mouth microphones, including spatial filters for spatially filtering the input signals (z1,z2) delivered by the two microphones, and a spectral post-processor (SPP) for post-processing the signal delivered by the beam-former so as to separate the desired voice signal from the unwanted noise signal so as to deliver the output signal (y).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
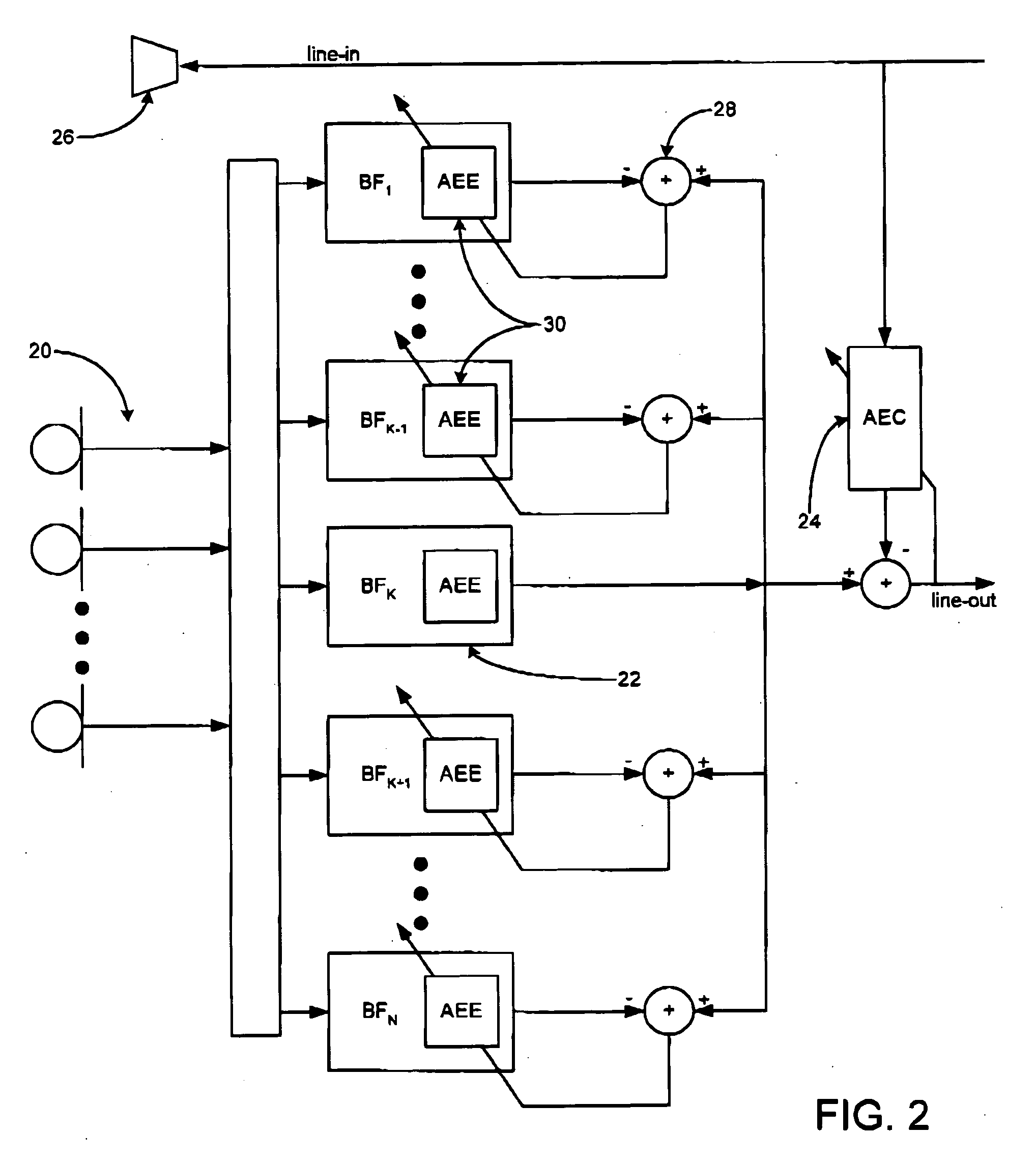
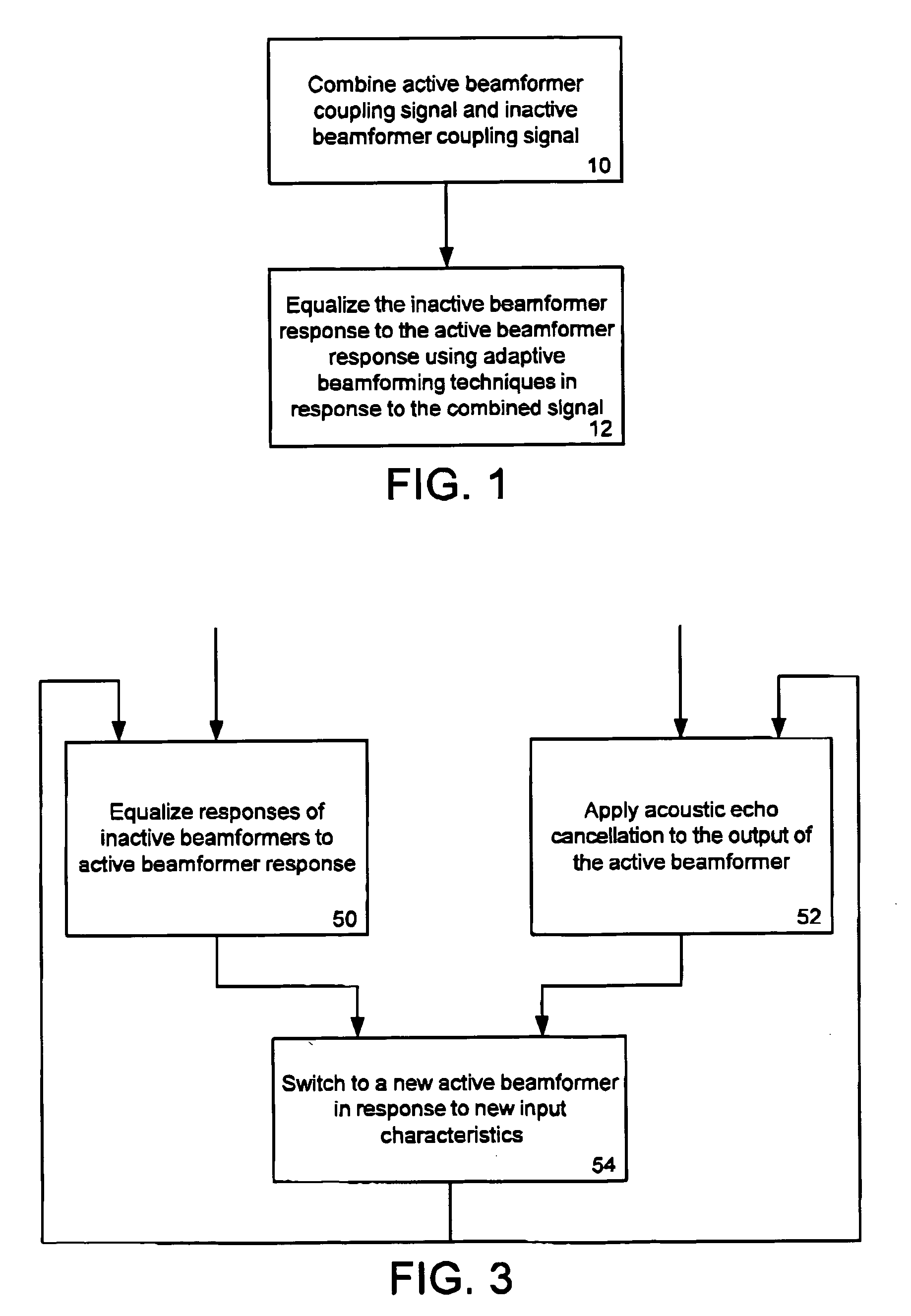
Adaptive coupling equalization in beamforming-based communication systems
ActiveUS20070093714A1Fast convergenceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMicrophonesCommunications systemTemporal change
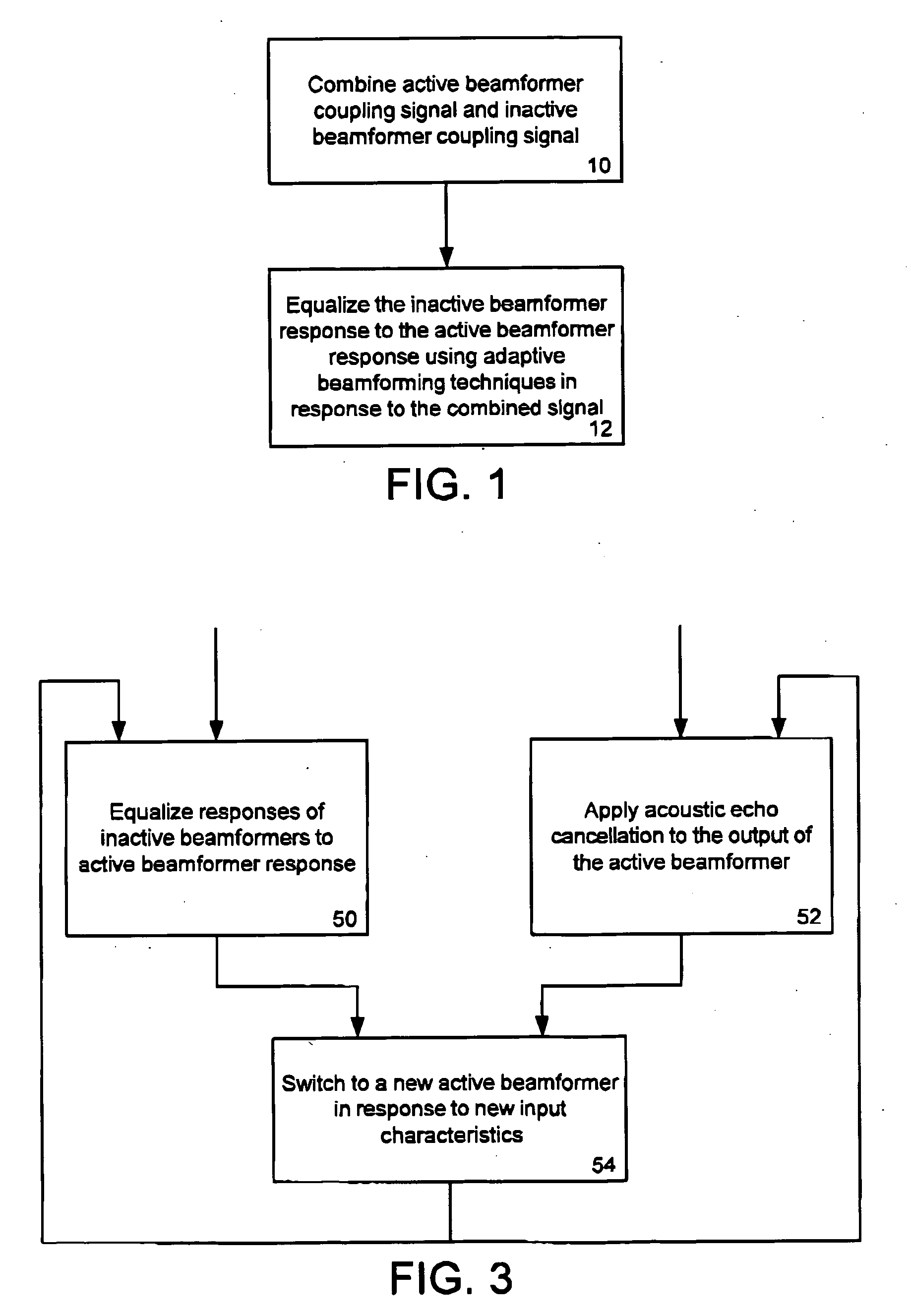
A method and system for rapid adaptive coupling equalization in beamforming-based communication systems, particularly sector-based beamforming systems, provides smooth transitions for AEC when the look direction of the communication system changes and when the acoustic environment varies with time. The coefficients of inactive beamformers are modified in real-time, using adaptive beamforming techniques based on the real-time loudspeaker-coupling signal, in order to force the outputs of inactive beamformers to have the same response to the loudspeaker coupling signal as the active beamformer does.
Owner:MITEL
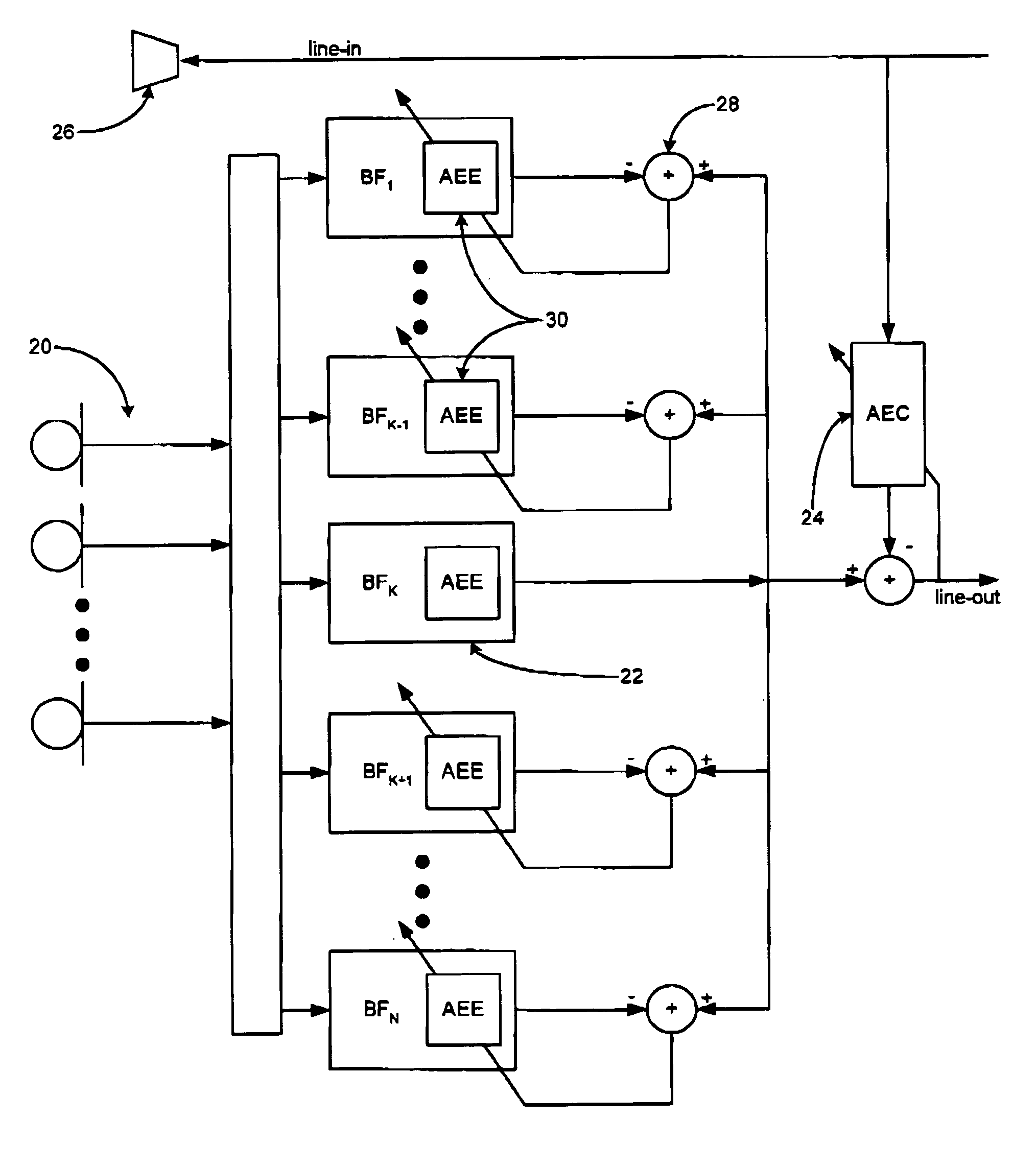
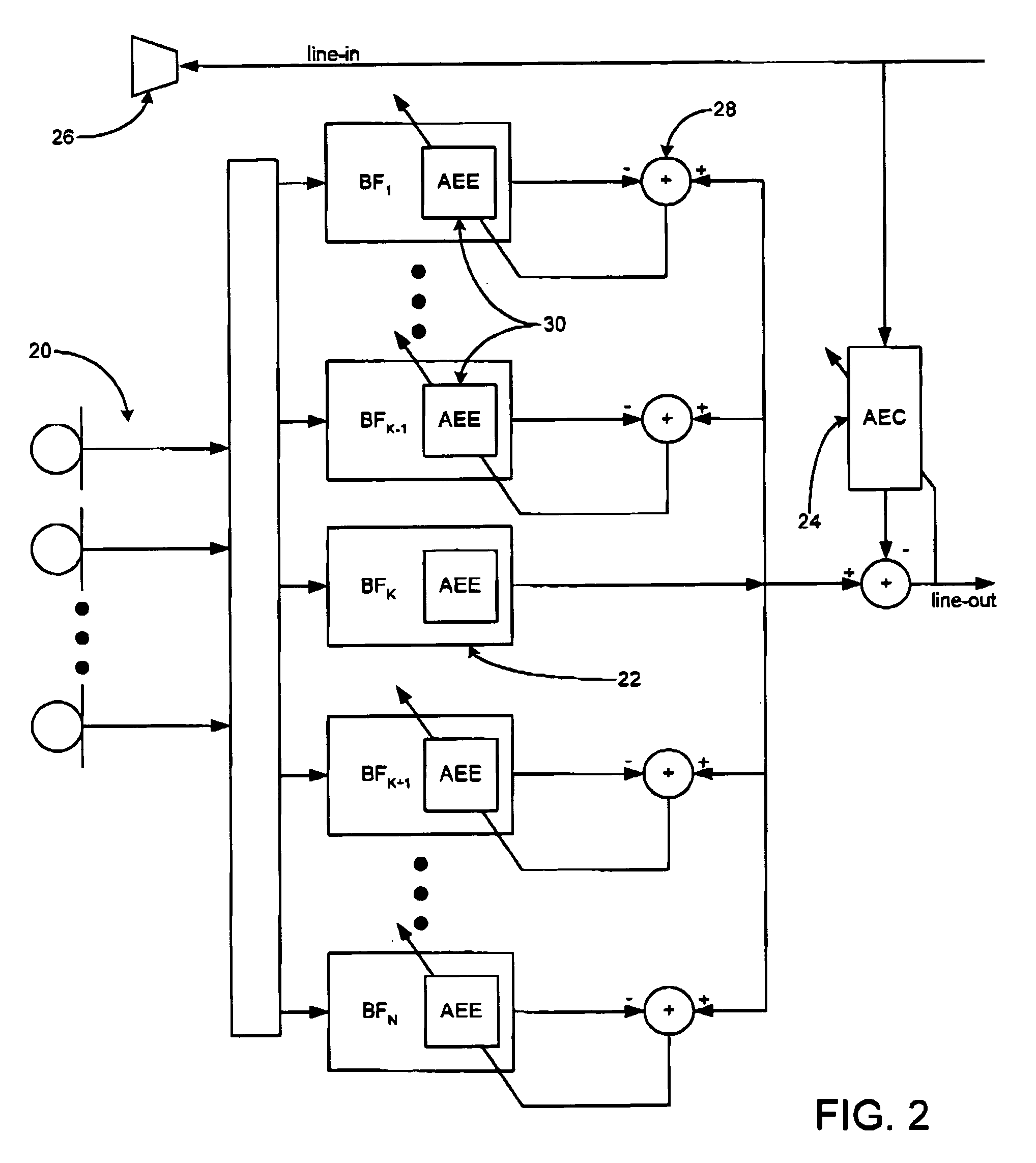
Adaptive coupling equalization in beamforming-based communication systems
ActiveUS7970123B2Fast convergenceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsTemporal changeCommunications system
A method and system for rapid adaptive coupling equalization in beamforming-based communication systems, particularly sector-based beamforming systems, provides smooth transitions for AEC when the look direction of the communication system changes and when the acoustic environment varies with time. The coefficients of inactive beamformers are modified in real-time, using adaptive beamforming techniques based on the real-time loudspeaker-coupling signal, in order to force the outputs of inactive beamformers to have the same response to the loudspeaker coupling signal as the active beamformer does.
Owner:MITEL
Noise suppression system and method for phased-array based systems
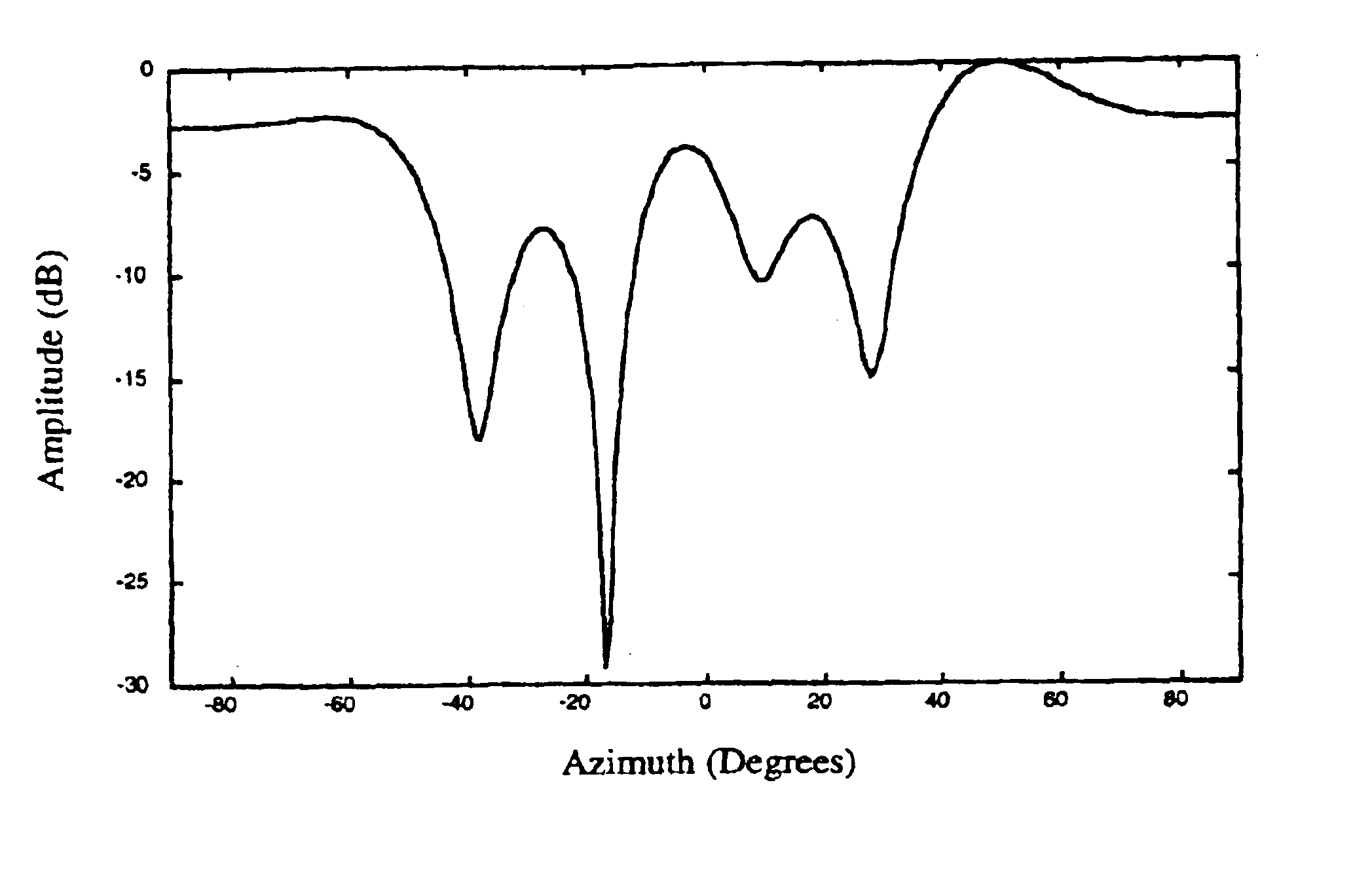
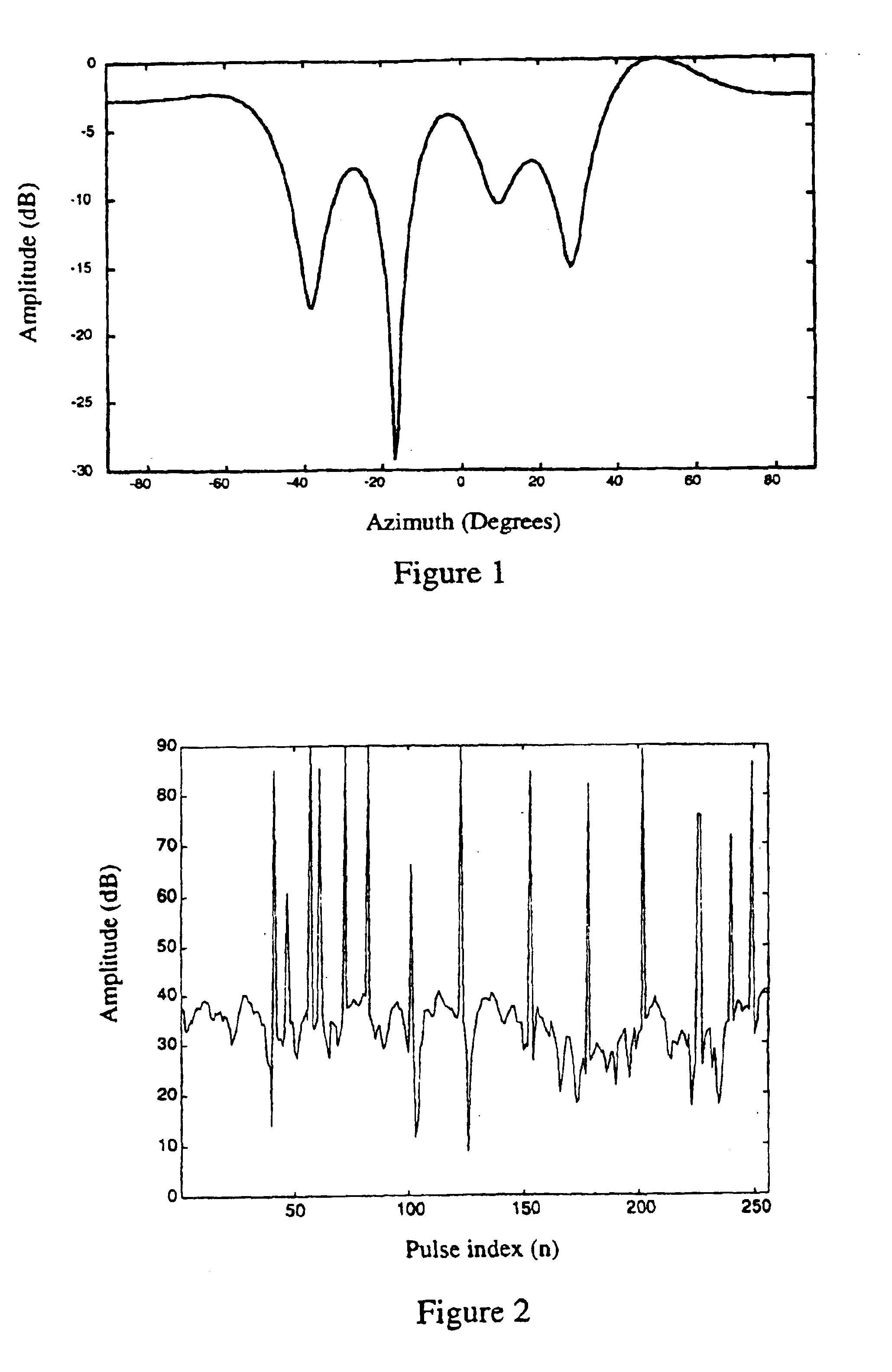
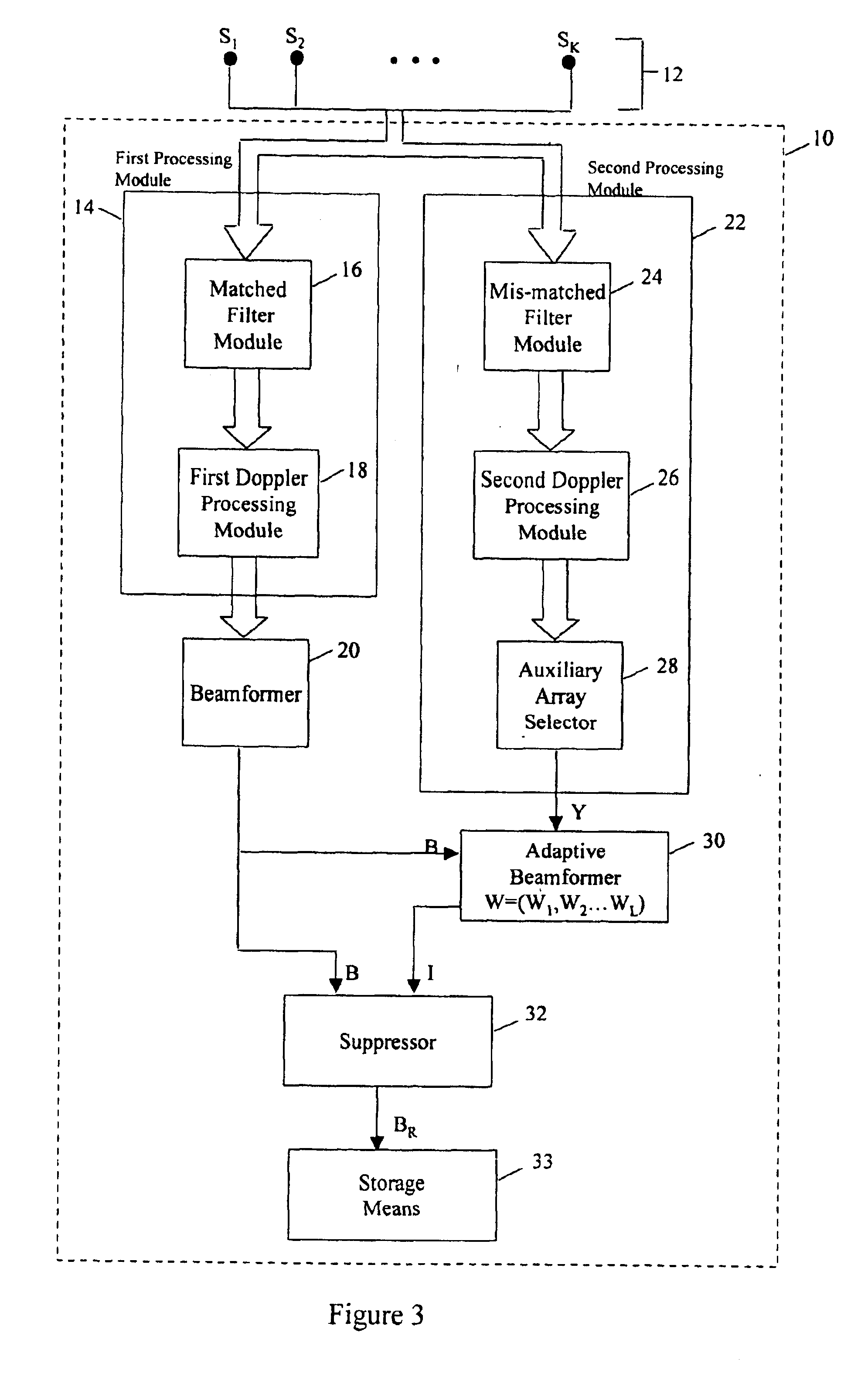
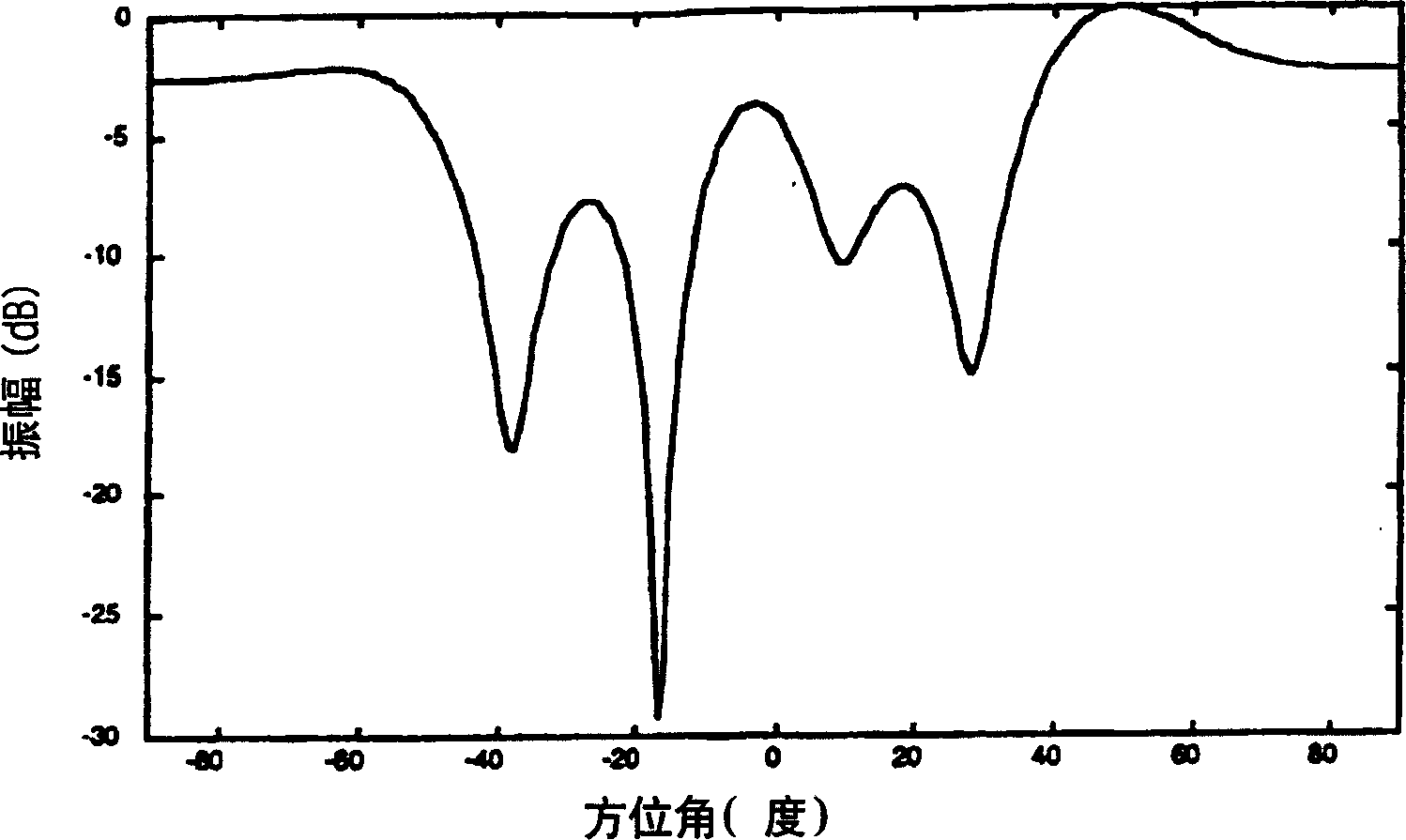
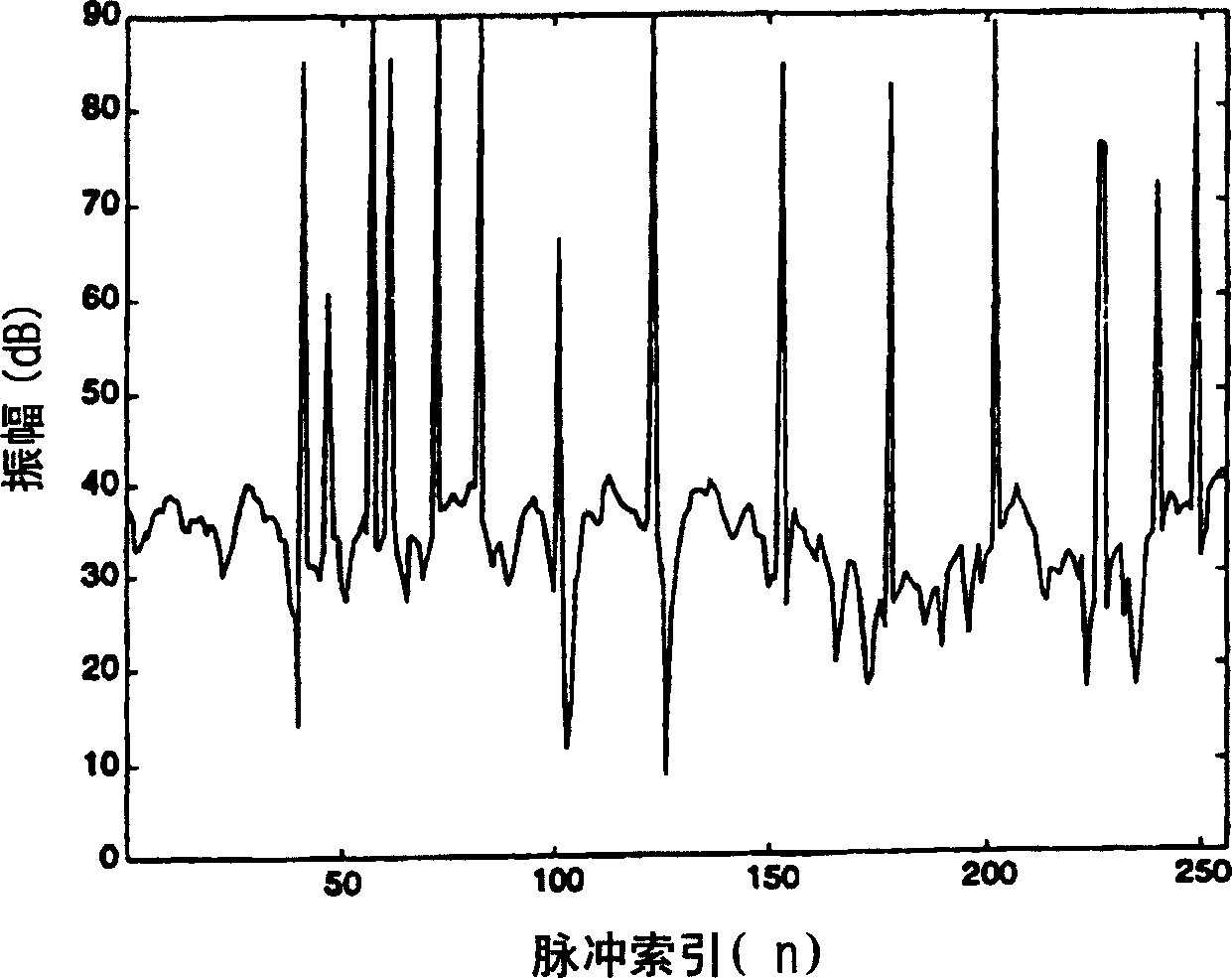
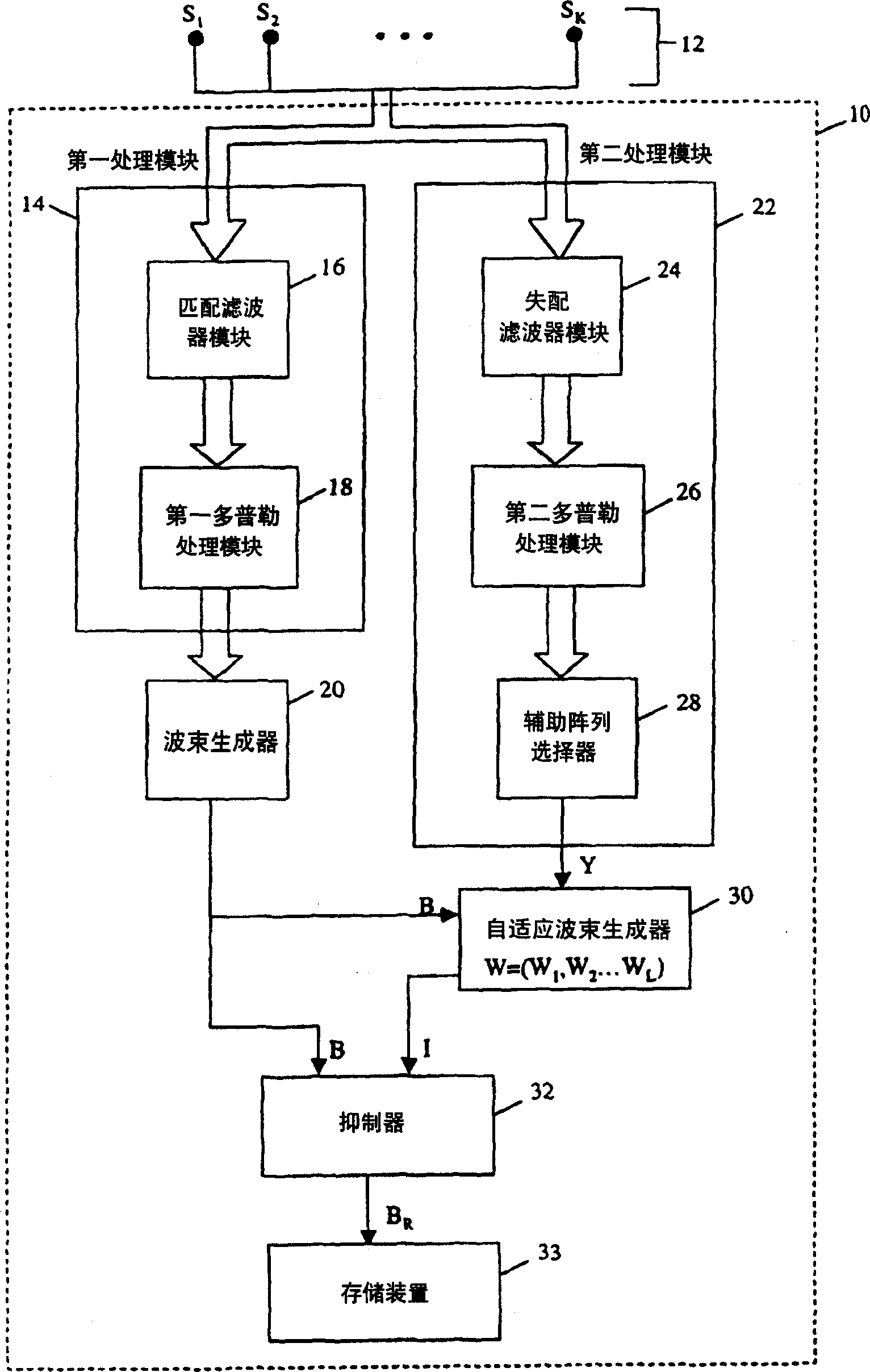
ActiveUS6867731B2Avoiding azimuthal degradationPrevent degradationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSensor arrayRadar
This invention relates to a system and method for suppressing external interference in radar data provided by a plurality of sensors from a main sensor array, the data being pre-processed. The noise suppression system includes a first processing module and a second processing module. The first processing module receives the radar data and produces matched radar data while the second processing module receives the radar data and produces mis-matched radar data. The system further includes a beamformer that is in communication with the first processing module and an adaptive beamformer that is in communication with the second processing module and the beamformer. The beamformer receives the matched radar data and produces beamformed matched radar data.
Owner:RAYTHEON CANADA LTD
Constrainted switched adaptive beamforming
InactiveUS20090034752A1Microphones signal combinationTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsAdaptive filterEngineering
An audio device, comprising a microphone array, a constrained switched adaptive beamformer with input coupled to said microphone array, said beamformer including (i) a first stage speech adaptive beamformer with first adaptive filters having a first adaptive step size, and (ii) a second stage noise adaptive beamformer with second adaptive filters having a second adaptive step size, and a single channel speech enhancer with input coupled to an output of said constrained switched adaptive beamformer.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multi-channel adaptive speech signal processing system with noise reduction
ActiveUS8194872B2Improve clarityImprove intelligibilitySignal processingEar treatmentLow noiseHigh energy
An adaptive signal processing system eliminates noise from input signals while retaining desired signal content, such as speech. The resulting low noise output signal delivers improved clarity and intelligibility. The low noise output signal also improves the performance of subsequent signal processing systems, including speech recognition systems. An adaptive beamformer in the signal processing system consistently updates beamforming signal weights in response to changing microphone signal conditions. The adaptive weights emphasize the contribution of high energy microphone signals to the beamformed output signal. In addition, adaptive noise cancellation logic removes residual noise from the beamformed output signal based on a noise estimate derived from the microphone input signals.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST WAVEMAKERS
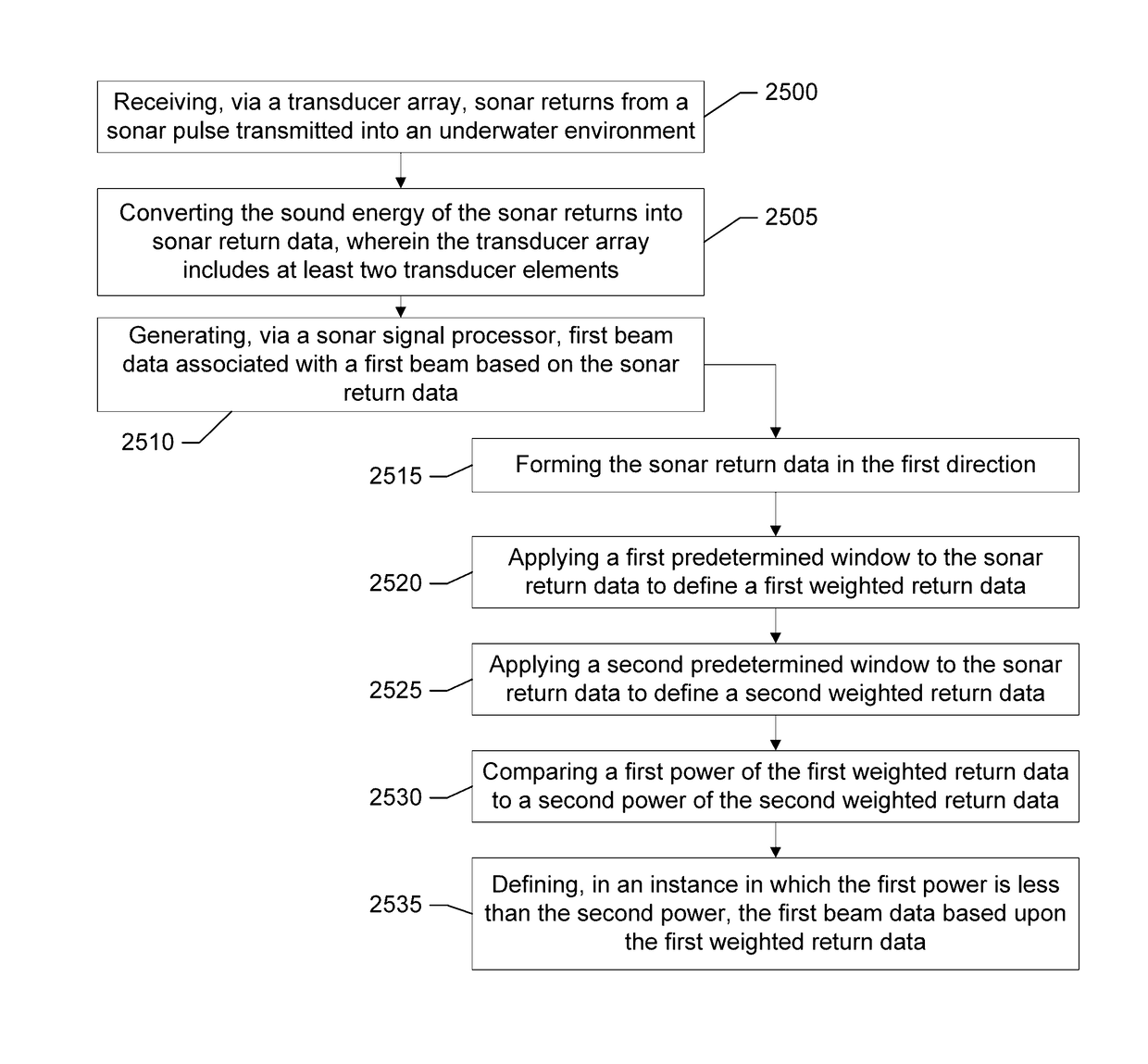
Adaptive beamformer for sonar imaging
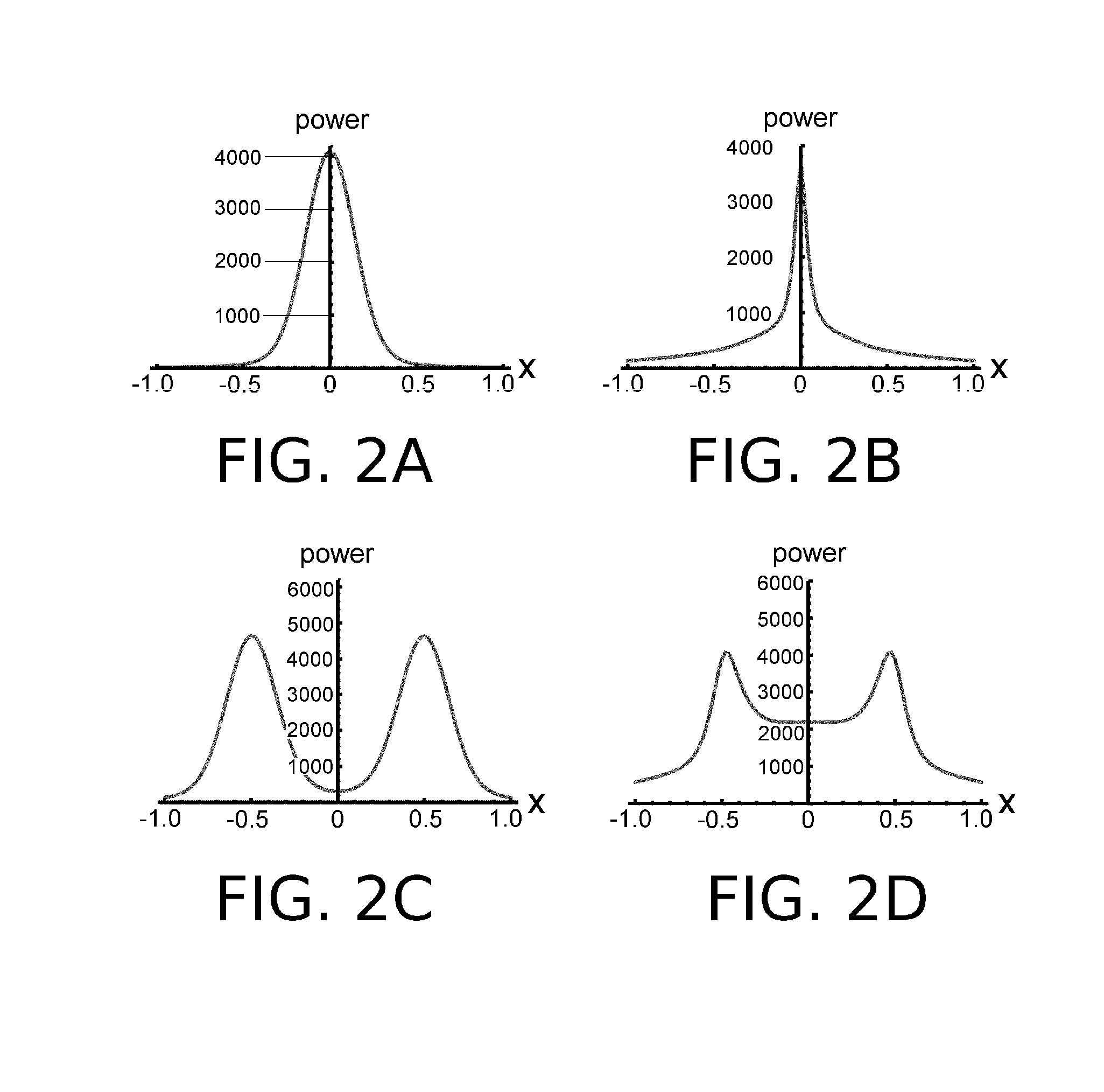
Provided are method, system, and computer program product for imaging an underwater environment. The method may include receiving sonar returns and converting the sound energy of the sonar returns into sonar return data, and generating first beam data associated with a first beam having at least one first main lobe oriented in a first direction. Generating the first beam data may include: forming the sonar return data in the first direction; applying a first predetermined window to the sonar return data to define a first weighted return data; applying a second predetermined window to the sonar return data to define a second weighted return data; comparing a first power of the first weighted return data to a second power of the second weighted return data; and defining, when the first power is less than the second power, the first beam data based upon the first weighted return data.
Owner:NAVICO HLDG
Receiving apparatus including adaptive beamformers
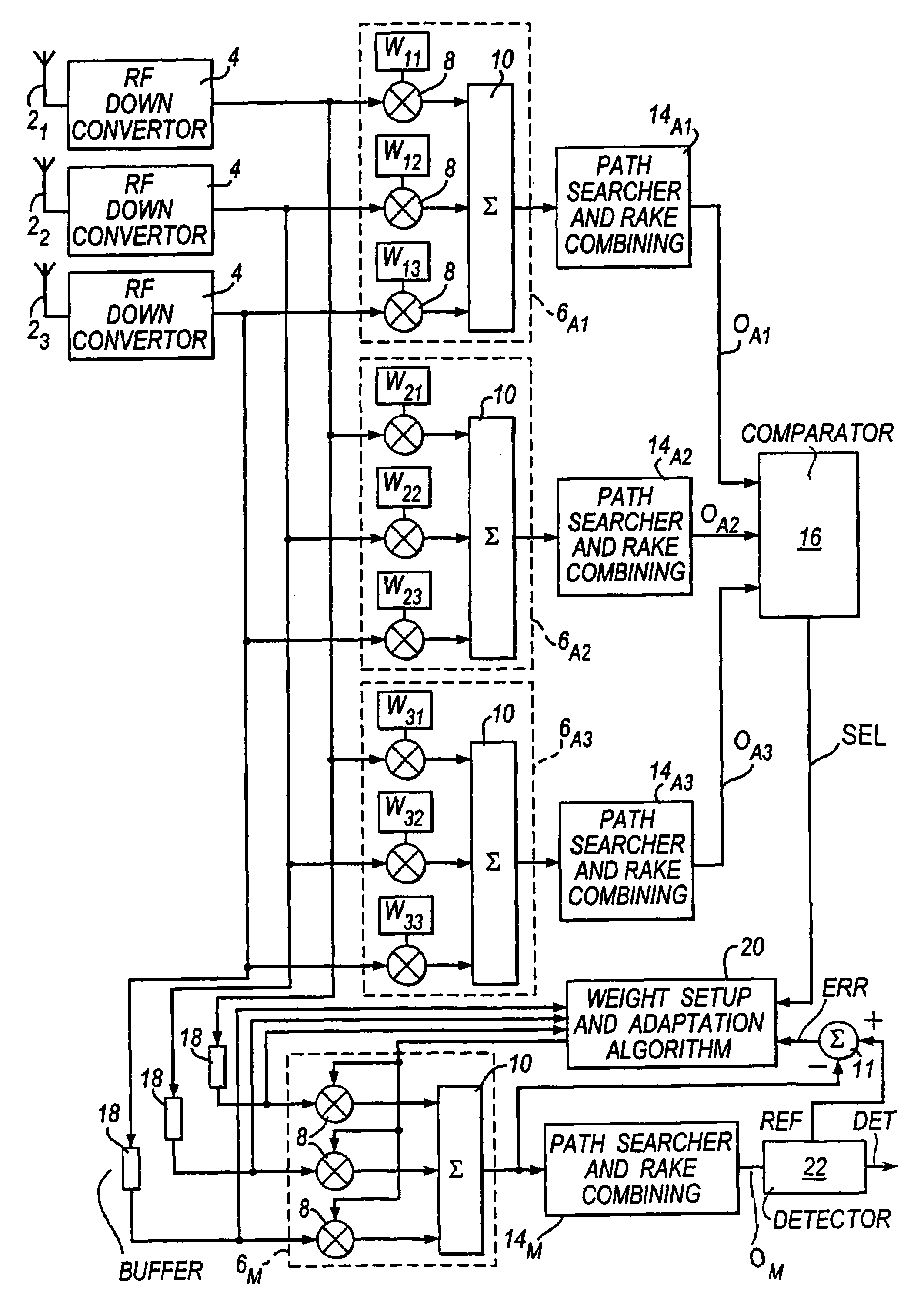
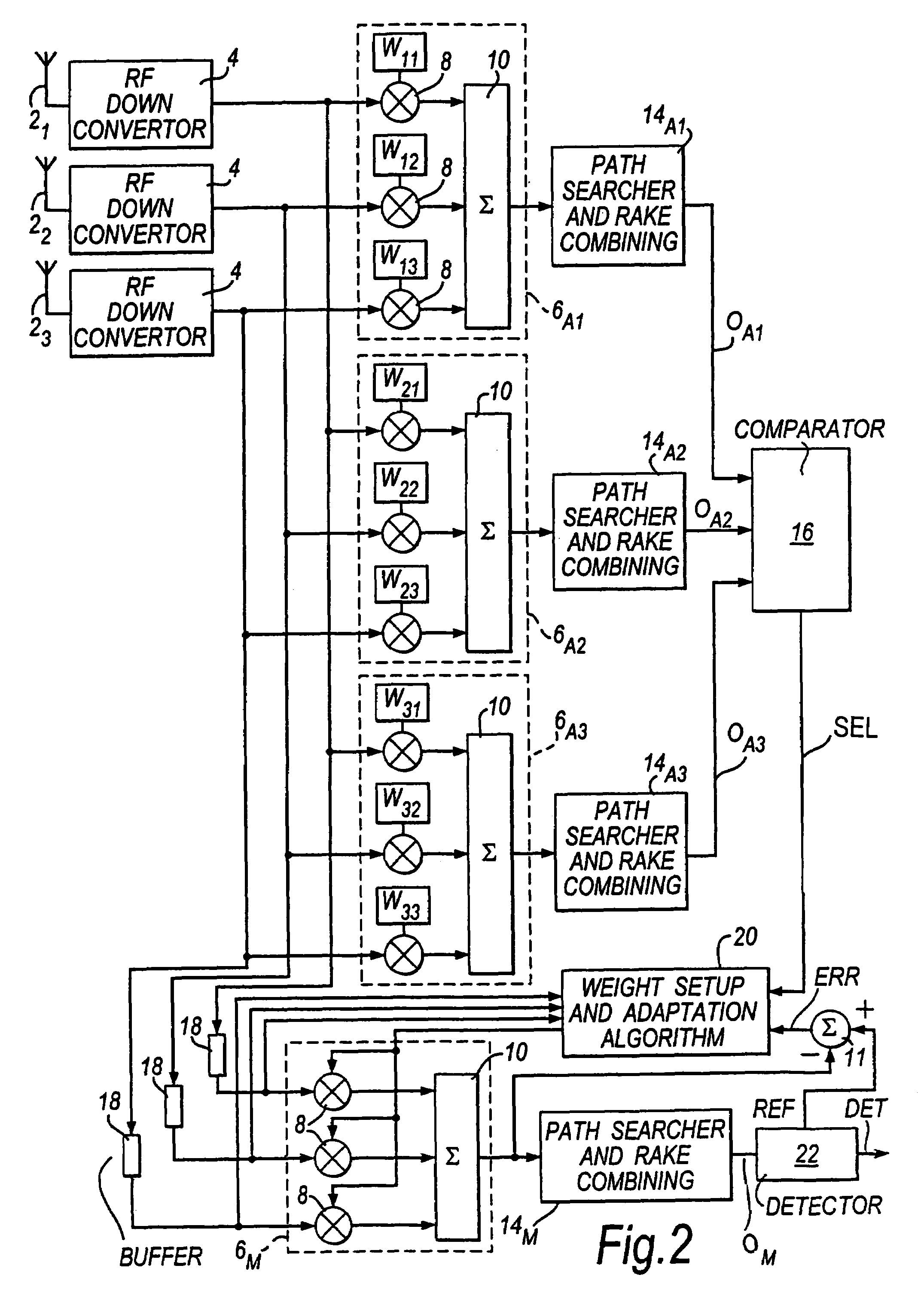
InactiveUS7016399B1Low costFast convergenceSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityCommunications systemBeam pattern
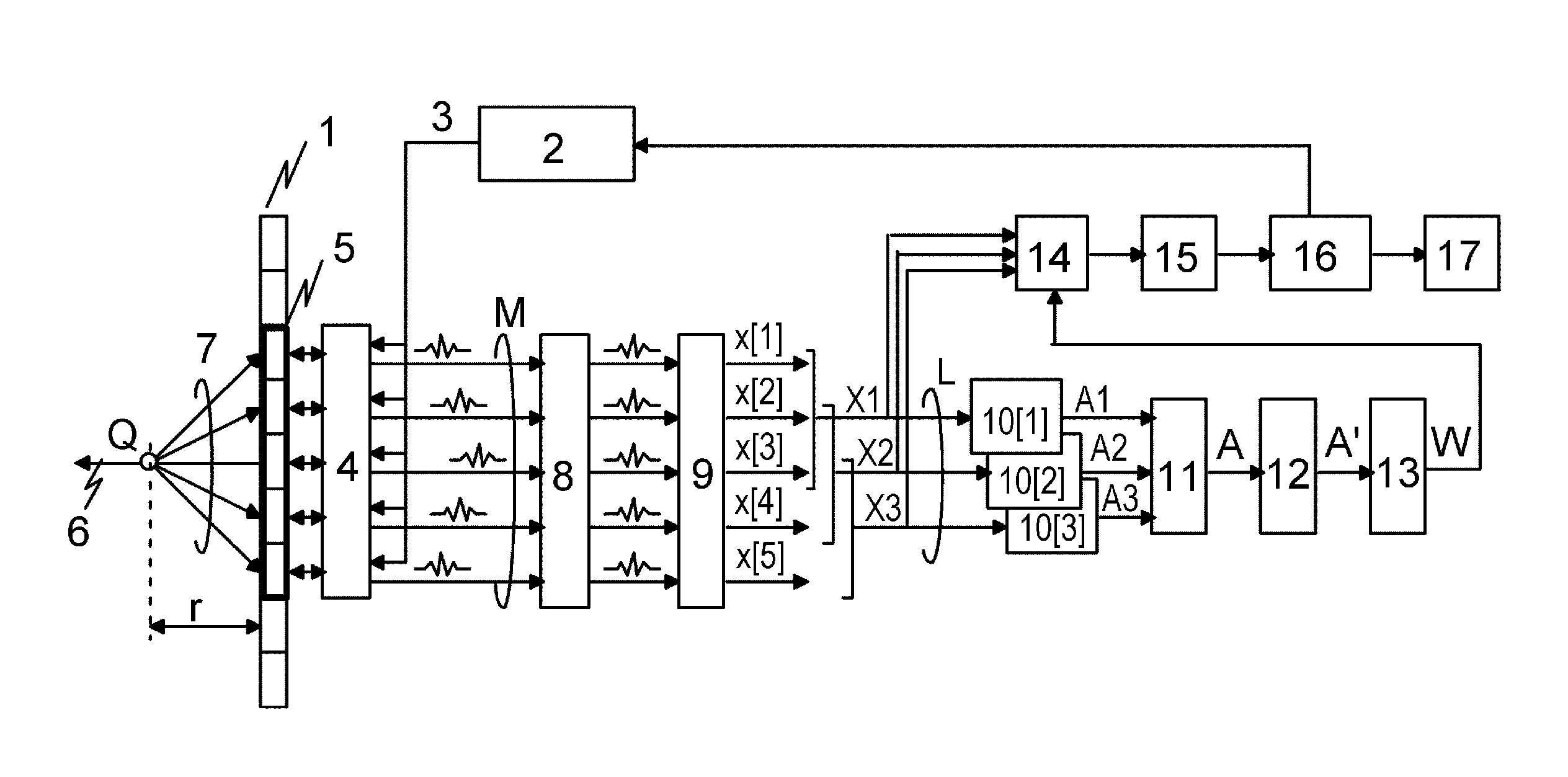
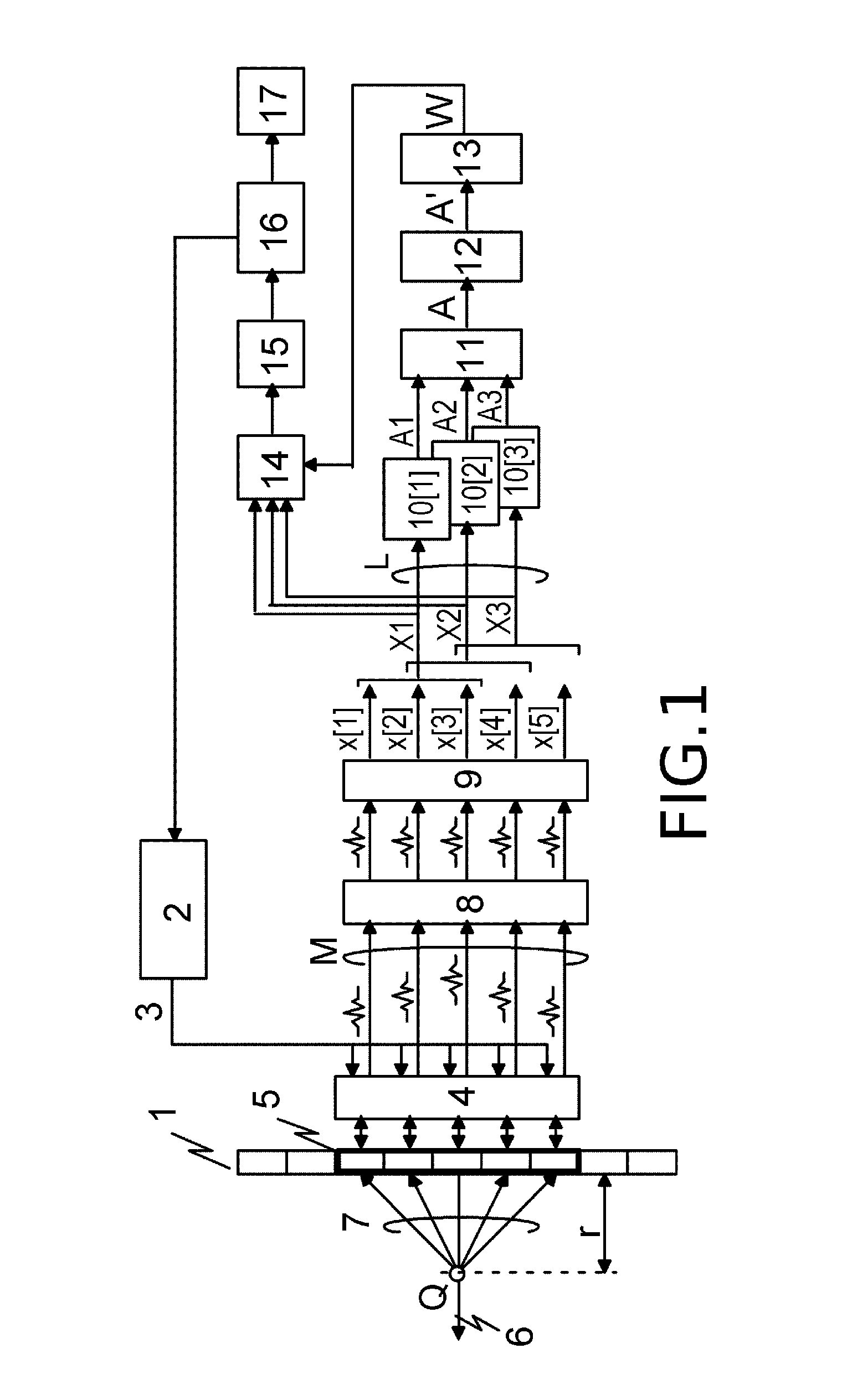
Receiving apparatus, for receiving a transmission signal in a cellular mobile communications system, comprises a main beamformer (6M, 14M) which processes received signals, representing the said transmission signal, in accordance with a main beam pattern. This main beam pattern is determined by beam control information applied to the main beamformer. The main beam pattern is adjusted as necessary during use of the receiving apparatus to facilitate reception of the said transmission signal.The apparatus also has three assistant beamformers (6A1, 14A2; 6A2, 14A2; 6A3, 14A3) that, in an initial operating phase of the apparatus, process such received signals in accordance with three different assistant beam patterns. Each such pattern is determined by beam control information (W1–W33) corresponding individually thereto. The three assistant beamformers produce output signals (OA1, OA2, OA3) corresponding respectively to the different assistant beam patterns.A beam control information setting unit (16, 20) employs the output signals and the beam control information (W11 to W33) corresponding respectively to the said assistant beam patterns to make an initial estimate of the beam control information for the main beamformer.Such receiving apparatus can permit fast setup of the initial beam control information for the main beamformer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
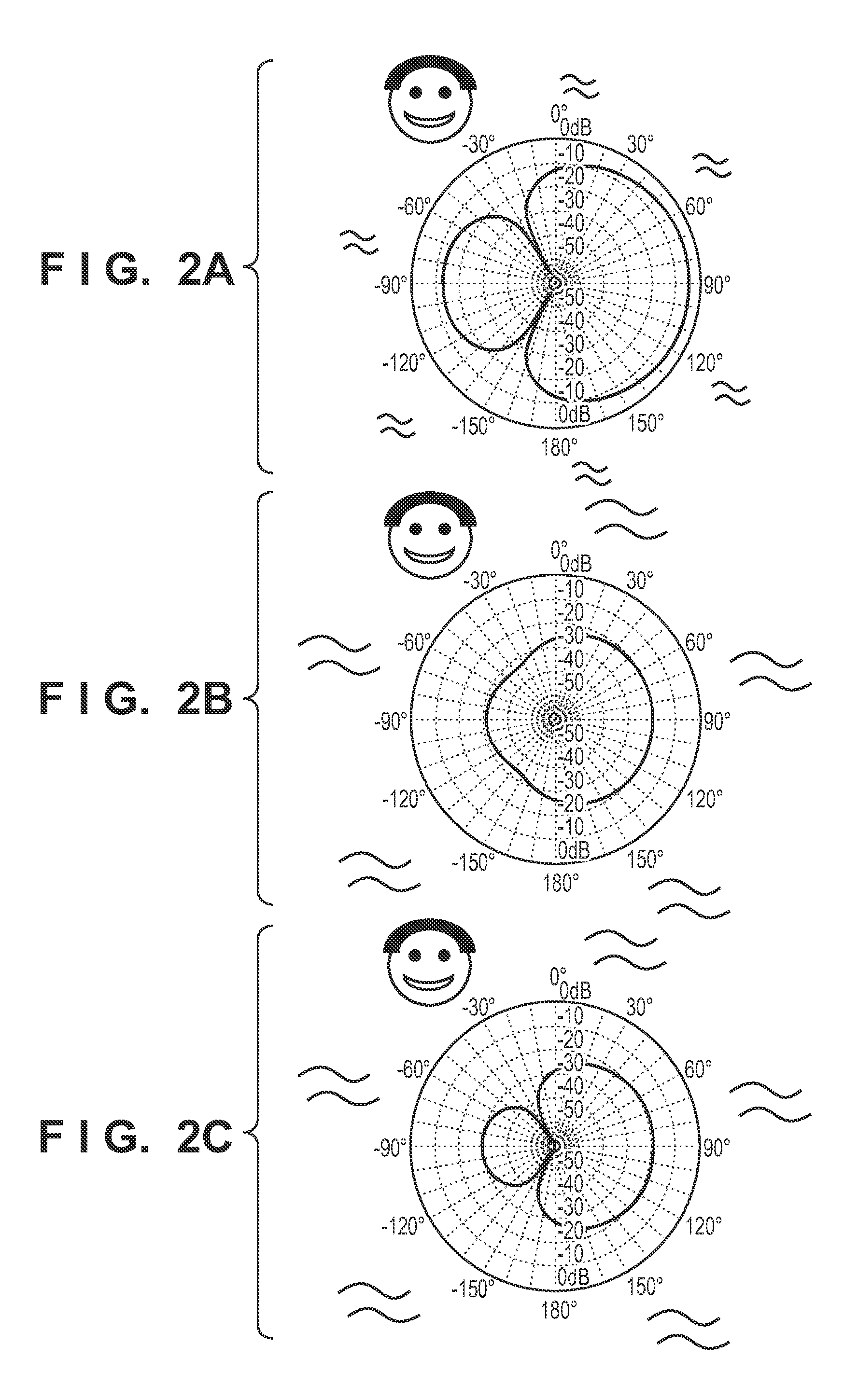
Noise suppression apparatus and control method thereof
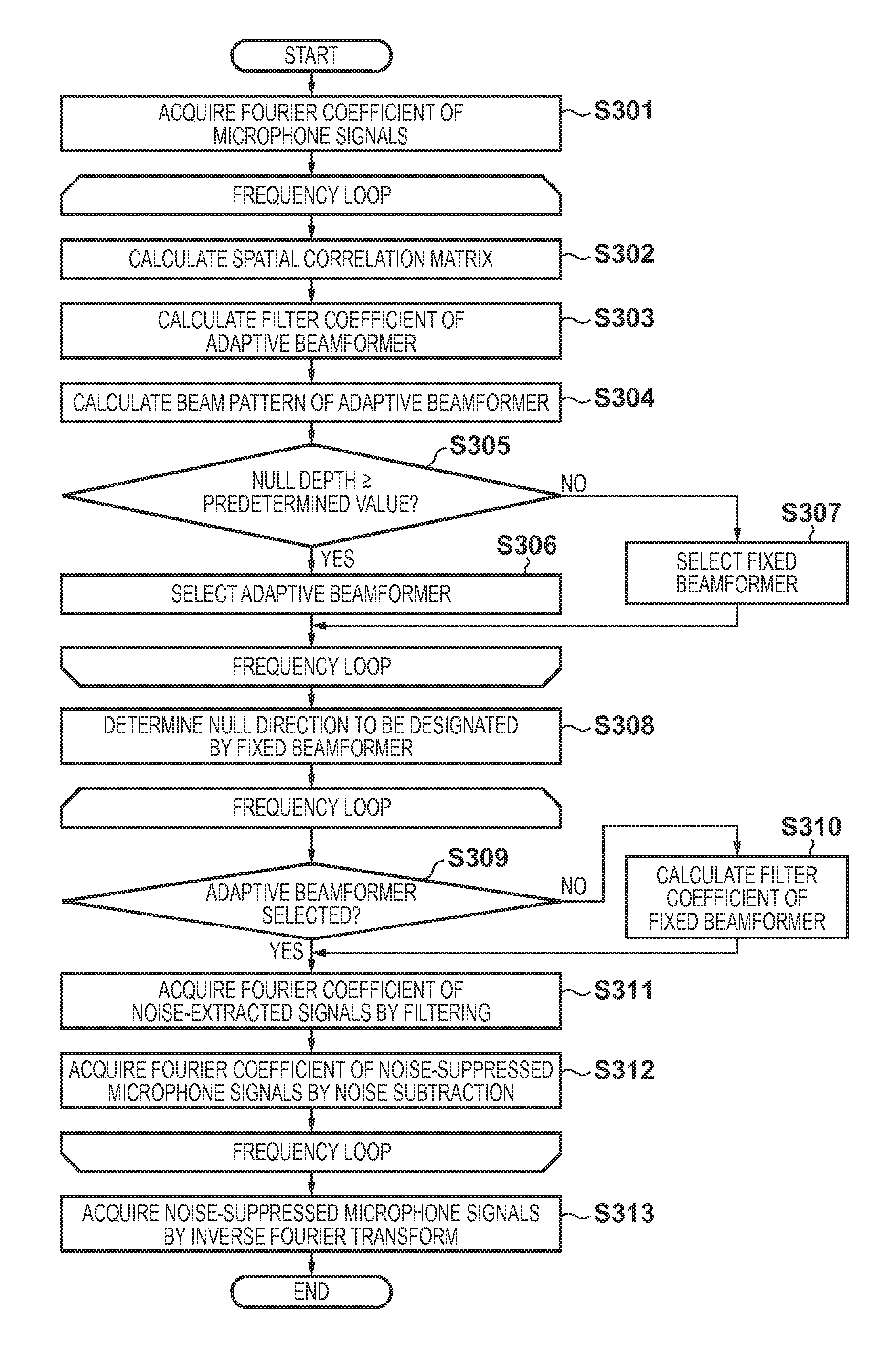
ActiveUS9280985B2Accurately suppress only noise from the audio signalSpeech analysisMinimum normEngineering
A noise suppression apparatus selectively uses an adaptive beamformer and fixed beamformer for each frequency. A direction of a null of the fixed beamformer is determined from a direction of a null automatically formed by the adaptive beamformer. Filter coefficients of the adaptive beamformer based on an output power minimization rule are calculated by a minimum norm method using a norm of the filter coefficients as a constraint. The above selection is made based on, for example, a depth of a null automatically formed by the adaptive beamformer in the selection.
Owner:CANON KK
Noise suppression apparatus and control method thereof
ActiveUS20140185826A1Accurately suppress only noise from the audio signalSpeech analysisTransmission noise suppressionMinimum normEngineering
A noise suppression apparatus selectively uses an adaptive beamformer and fixed beamformer for each frequency. A direction of a null of the fixed beamformer is determined from a direction of a null automatically formed by the adaptive beamformer. Filter coefficients of the adaptive beamformer based on an output power minimization rule are calculated by a minimum norm method using a norm of the filter coefficients as a constraint. The above selection is made based on, for example, a depth of a null automatically formed by the adaptive beamformer in the selection.
Owner:CANON KK
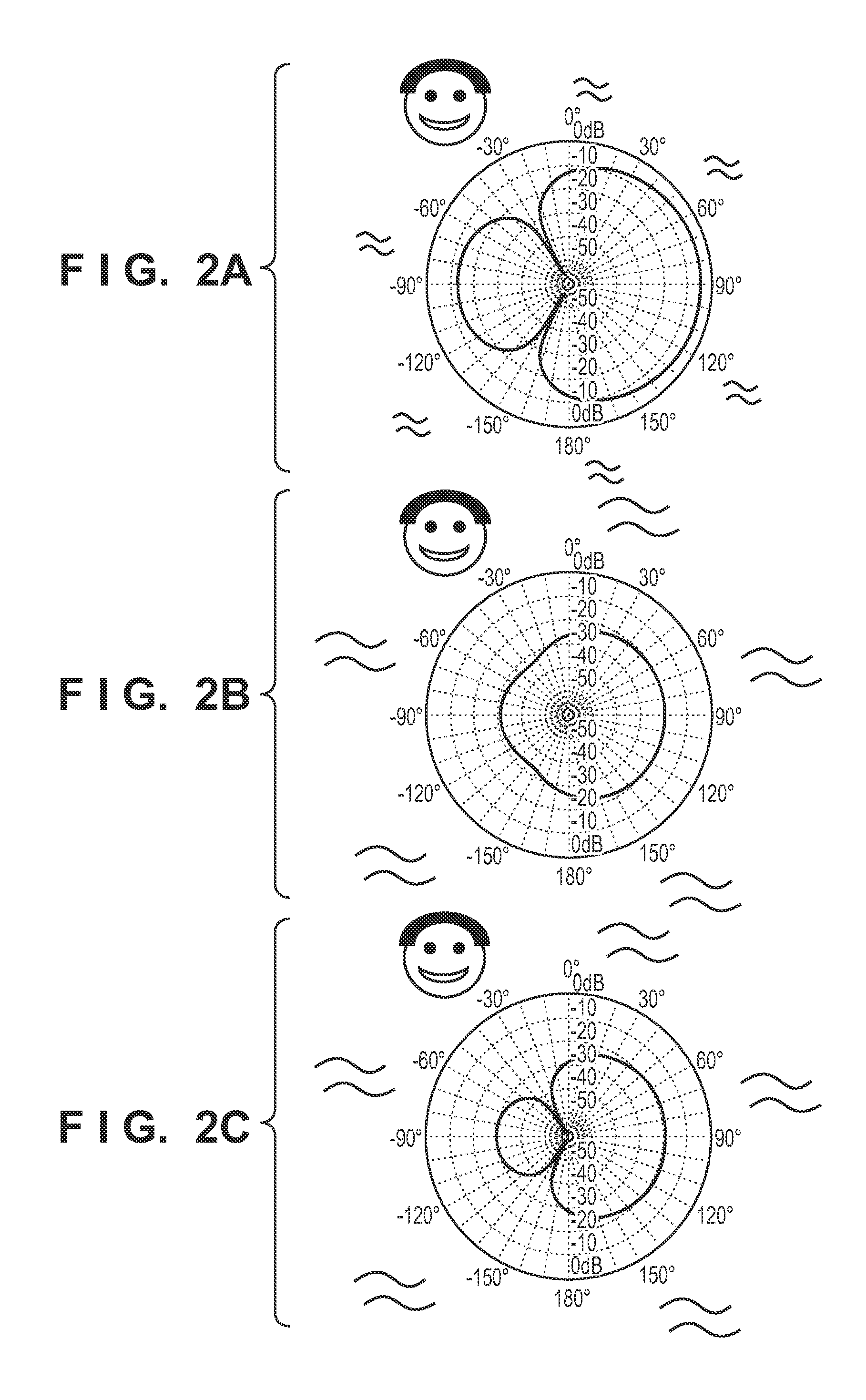
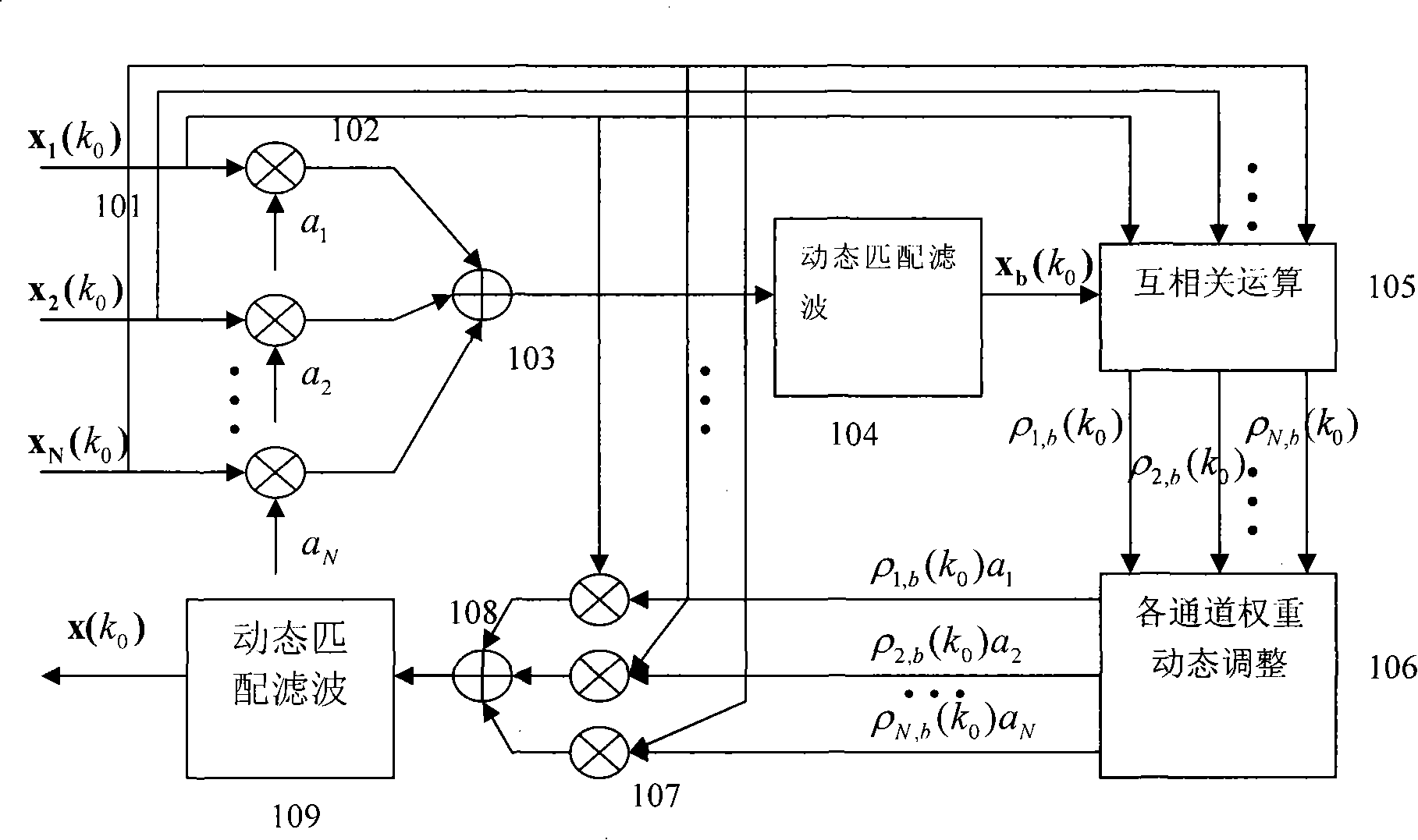
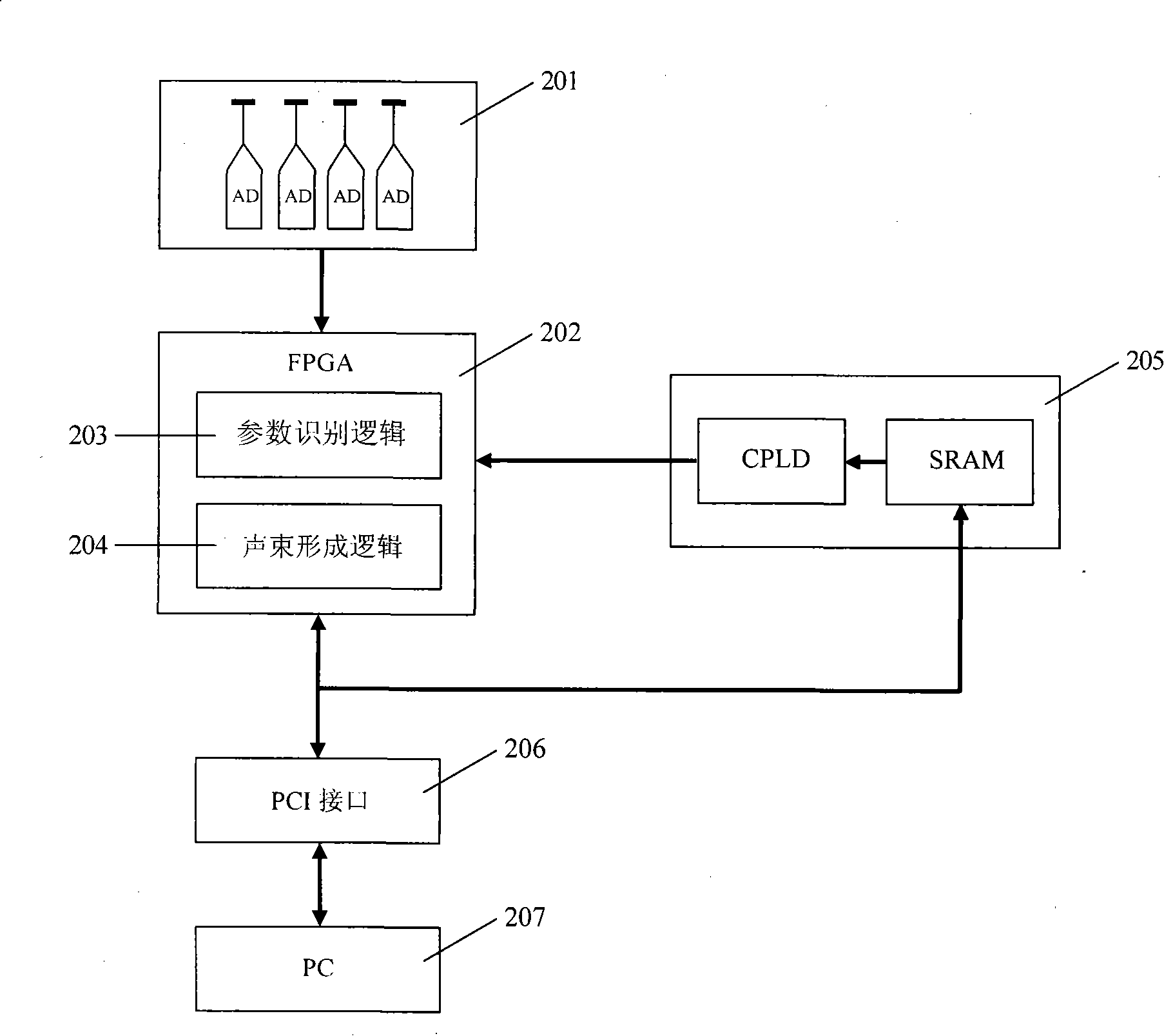
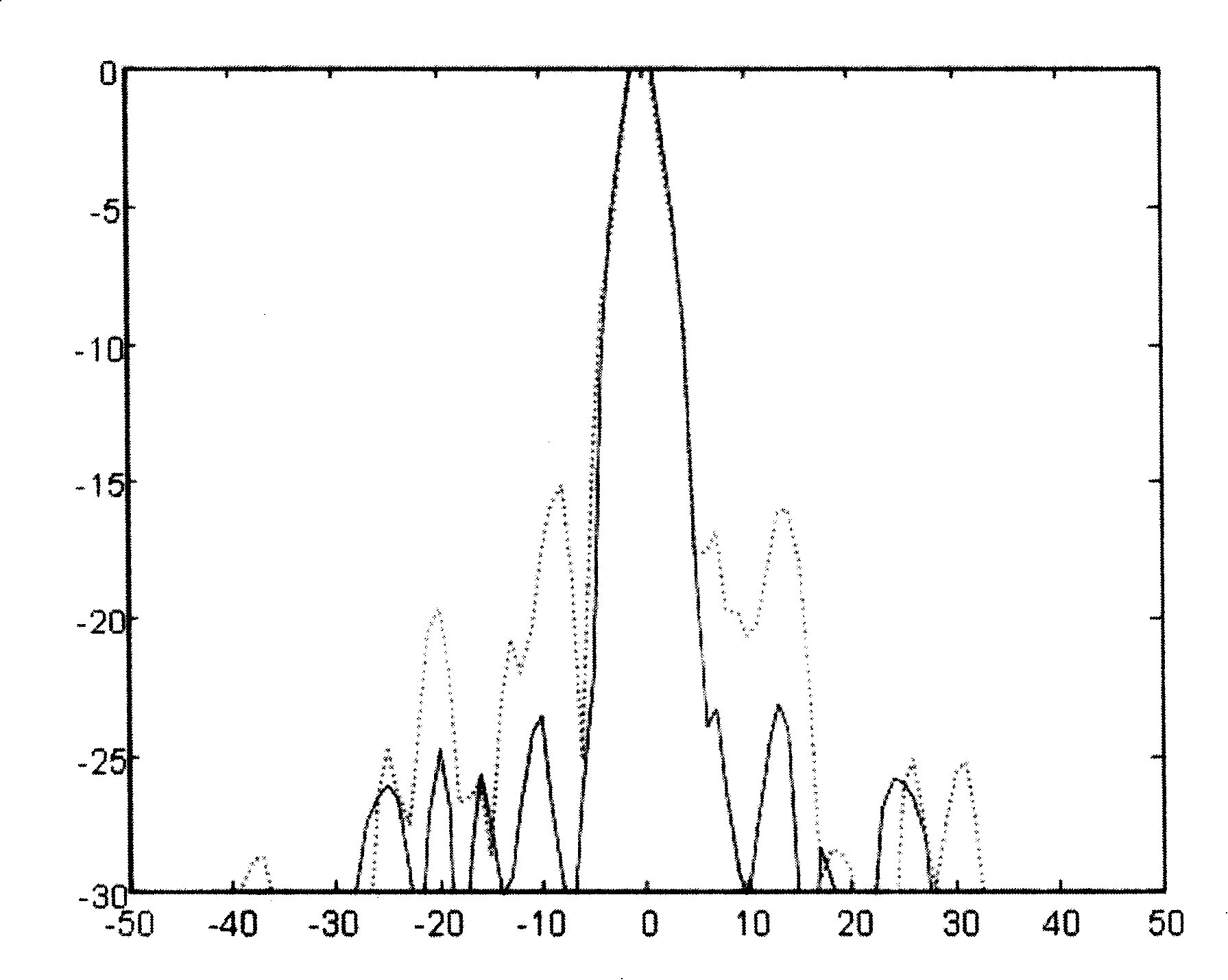
Ultrasonic imaging system self-adaption beam former based on correlation analysis
InactiveCN101238992AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationCorrelation analysis
An adaptive beamforming device belongs to medicine ultrasound imaging field. The invention provides an adaptive beamforming technique based on correlativity analysis, directing towards the difficulty that the traditional beamforming device can not completely restrain sidelobe effect resulted from interchannel random phase error and not affect the focusing effect along with the dynamic alignment of detection position. The technique divides the echo signal obtained from each channel into several segments, direct towards each segment, firstly the reference signal is obtained by a classical beam forming method, and then the signal of each channel is mutually correlated with the reference signal, furthermore weight of channel in each segment is dynamically adjusted using correlation coefficient, finally signals of each channel are synthesized to obtain final beam output using adjusted weight. The adaptive beamforming device adaptively detects the variance of enviroment using dynamic apodization and restrains the sidelobe effect resulted from interchannel random phase error. The adaptive beamforming device has wide application prospect in ultrasound imaging field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
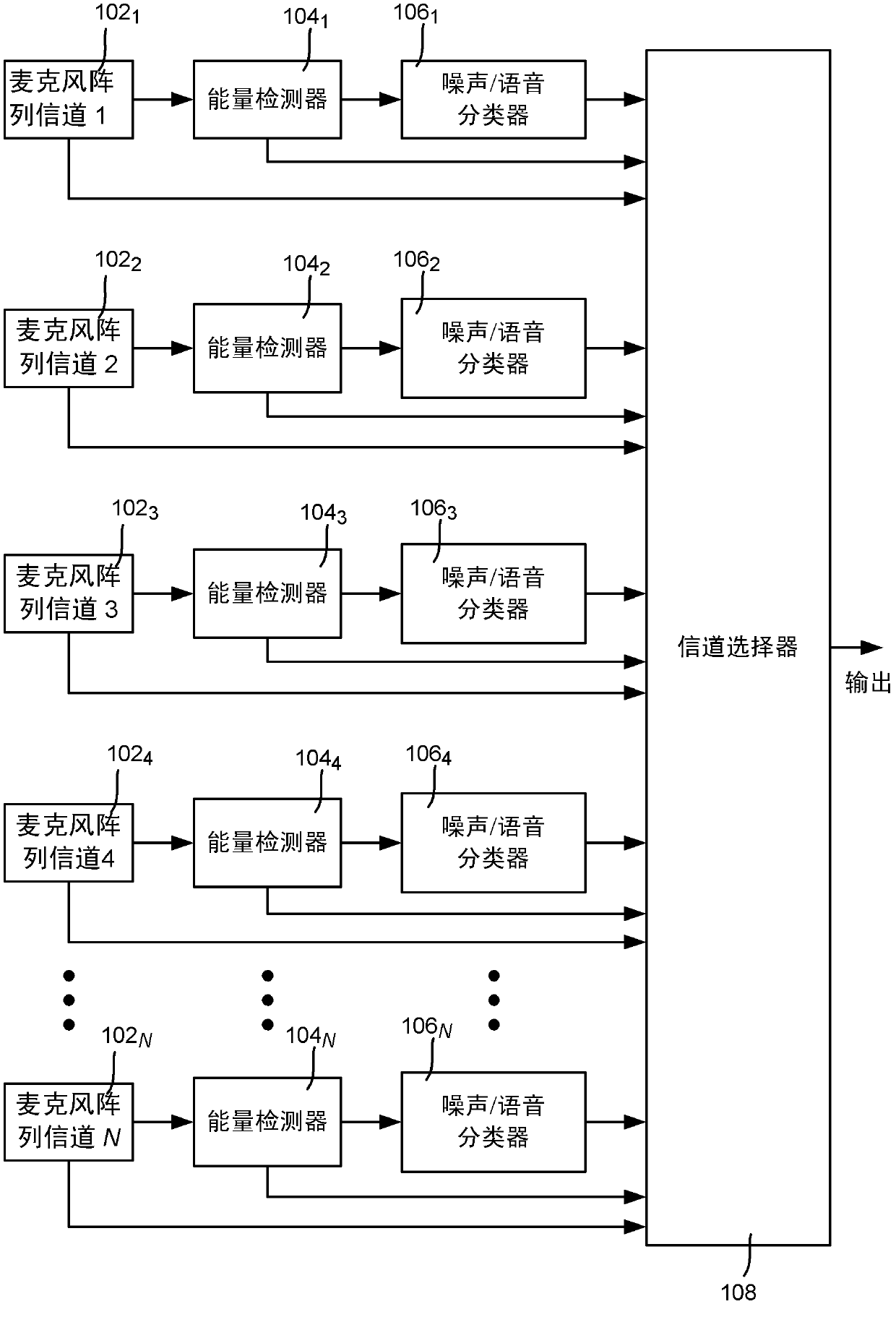
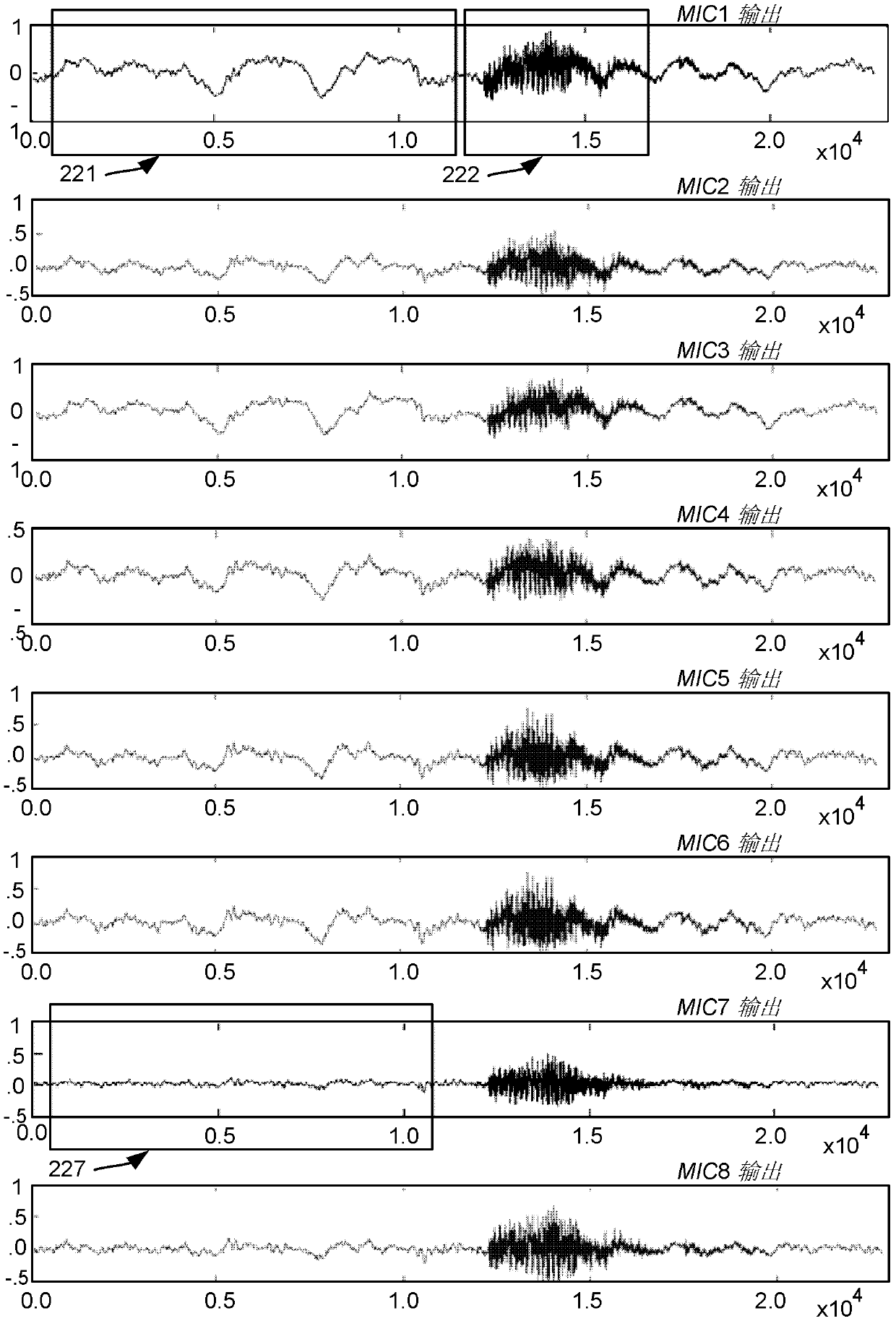
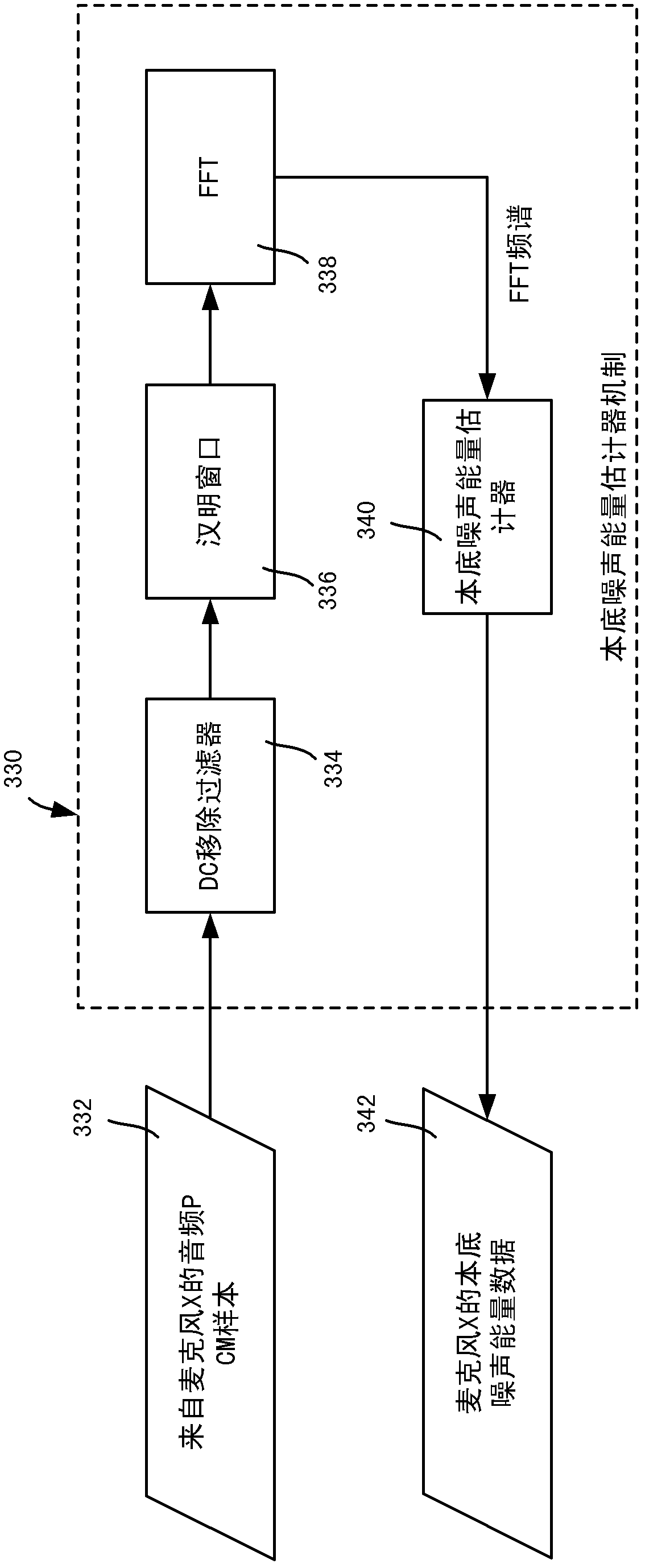
Noise adaptive beamforming for microphone arrays
The subject disclosure is directed towards a noise adaptive beamformer that dynamically selects between microphone array channels, based upon noise energy floor levels that are measured when no actual signal (e.g., no speech) is present. When speech (or a similar desired signal) is detected, the beamformer selects which microphone signal to use in signal processing, e.g., corresponding to the lowest noise channel. Multiple channels may be selected, with their signals combined. The beamformer transitions back to the noise measurement phase when the actual signal is no longer detected, so that the beamformer dynamically adapts as noise levels change, including on a per-microphone basis, to account for microphone hardware differences, changing noise sources, and individual microphone deterioration.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
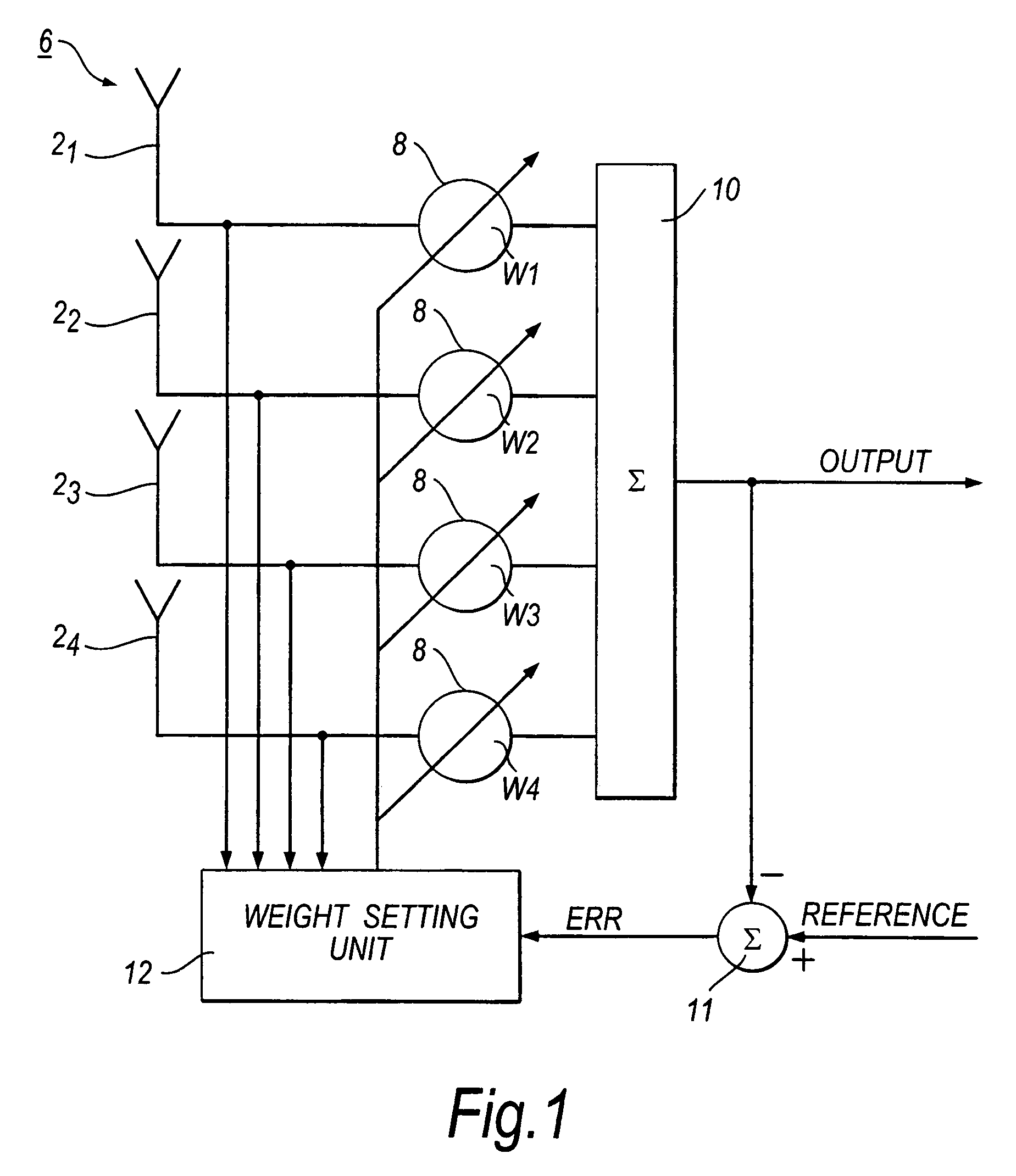
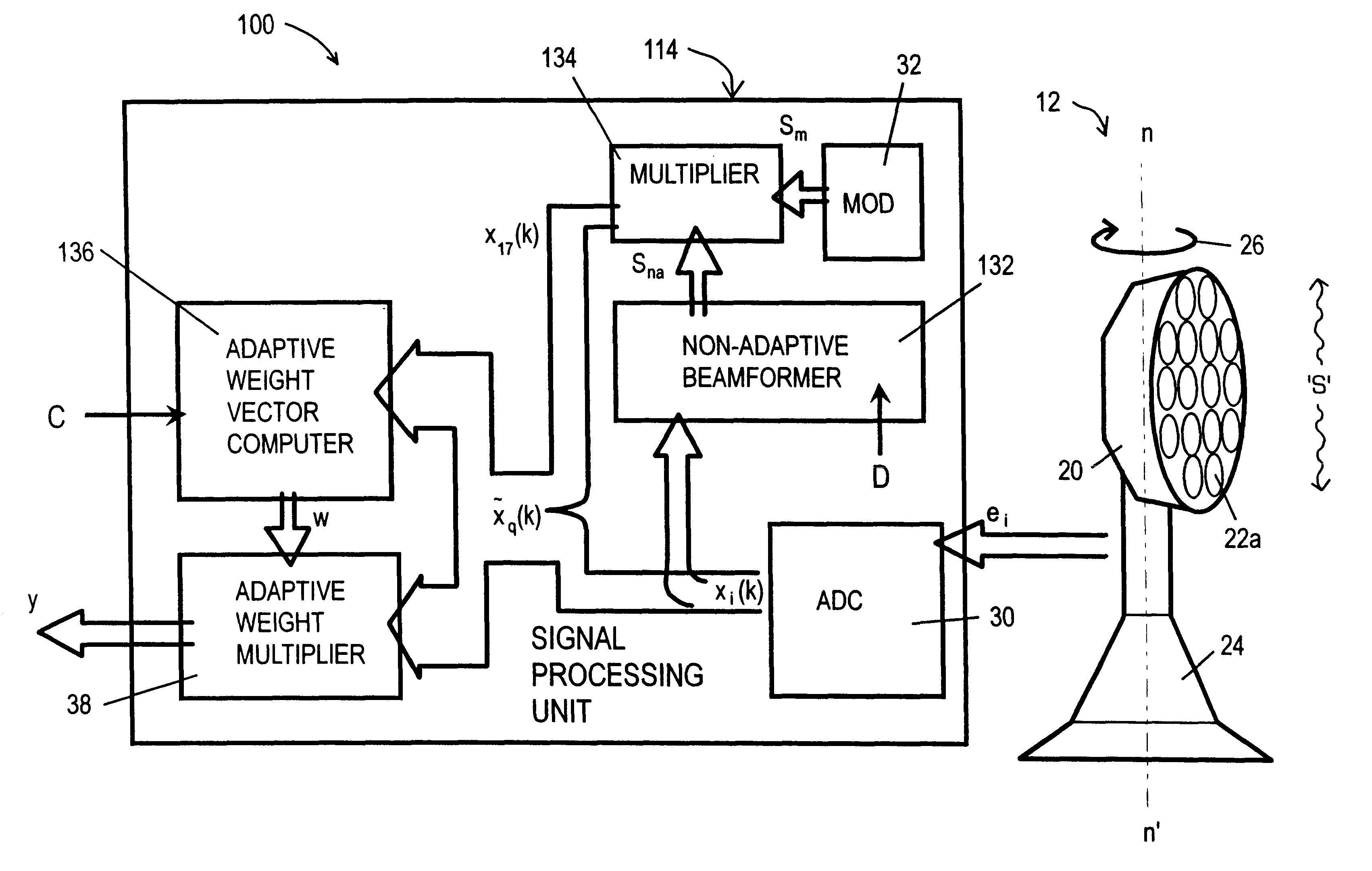
Adaptive sensor array apparatus
InactiveUS6452988B1Increased rejectImprove featuresError preventionAdaptive networkSensor arrayEngineering
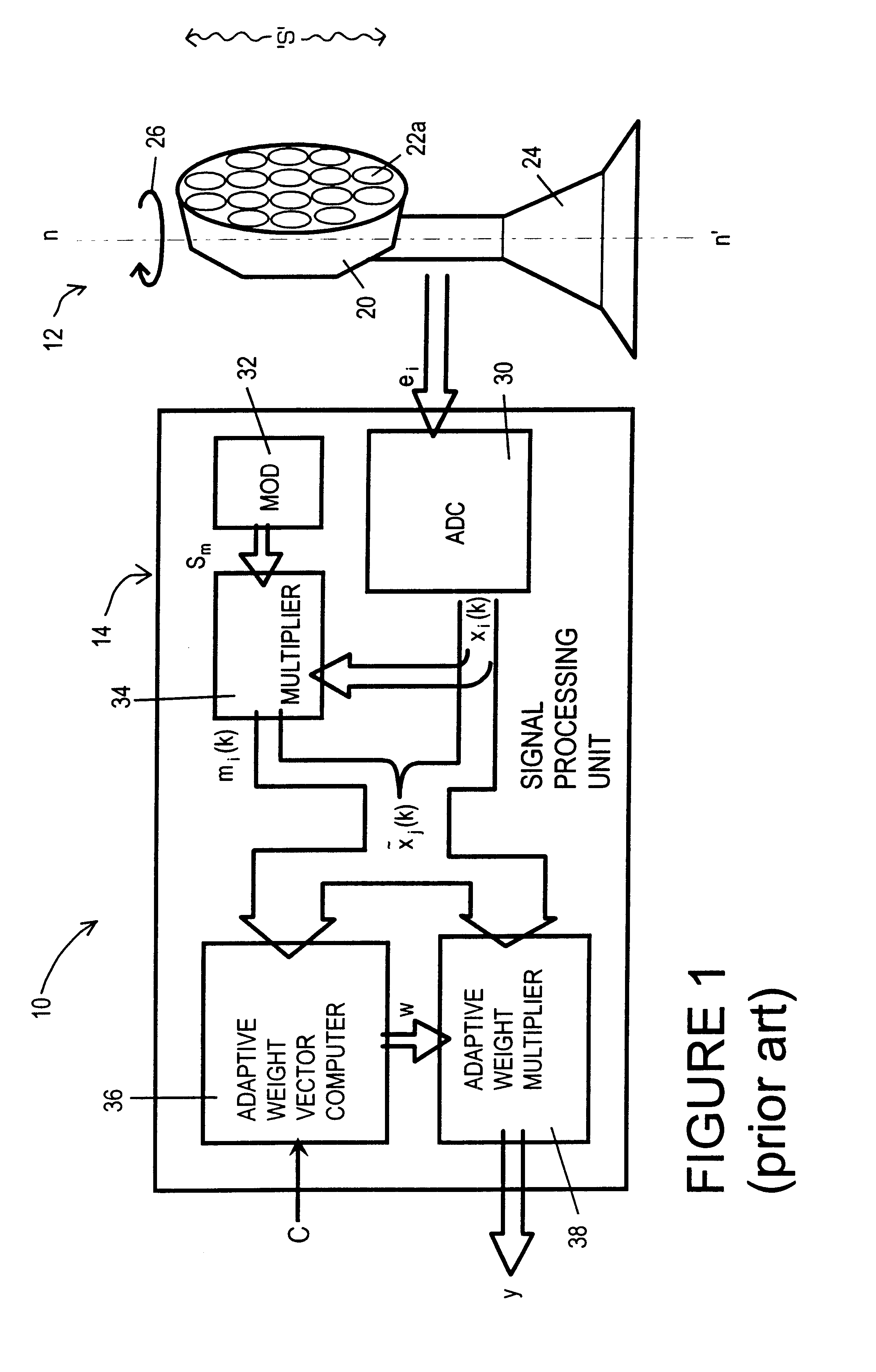
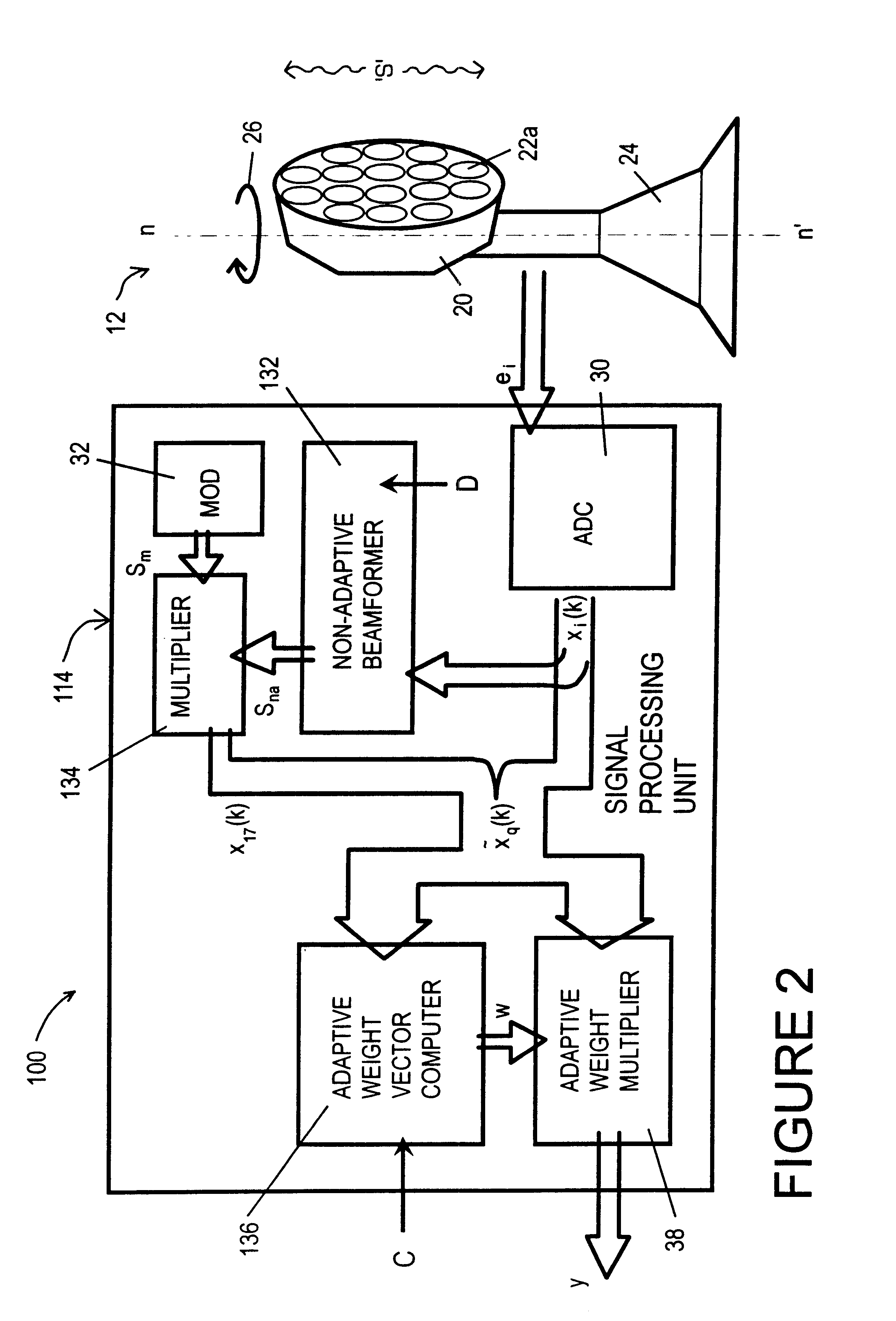
The invention provides an adaptive sensor array apparatus (100) incorporating a multielement antenna (12) for receiving radiation from a scene ("S') and generating signals (e) in response thereto and a processing unit (114) for processing the signals (e) to provide an output signal (y). The unit (114) comprises an adaptive weight computer (136) arranged to generate weighting vectors (w) which are used in the unit (114) to attenuate contributions to the output signal (y) arising from sources of jamming radiation in the scene and transmit contributions to the output signal (y) arising from wanted targets therein. The apparatus (100) incorporates a non-adaptive beamformer unit (132) for preconditioning the signals (e) before they are passed to the computer (136). Preconditioning the signals (e) enhances performance of the apparatus (100) relative to conventional adaptive sensor array apparatus (10).
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Hybrid adaptive beamformer
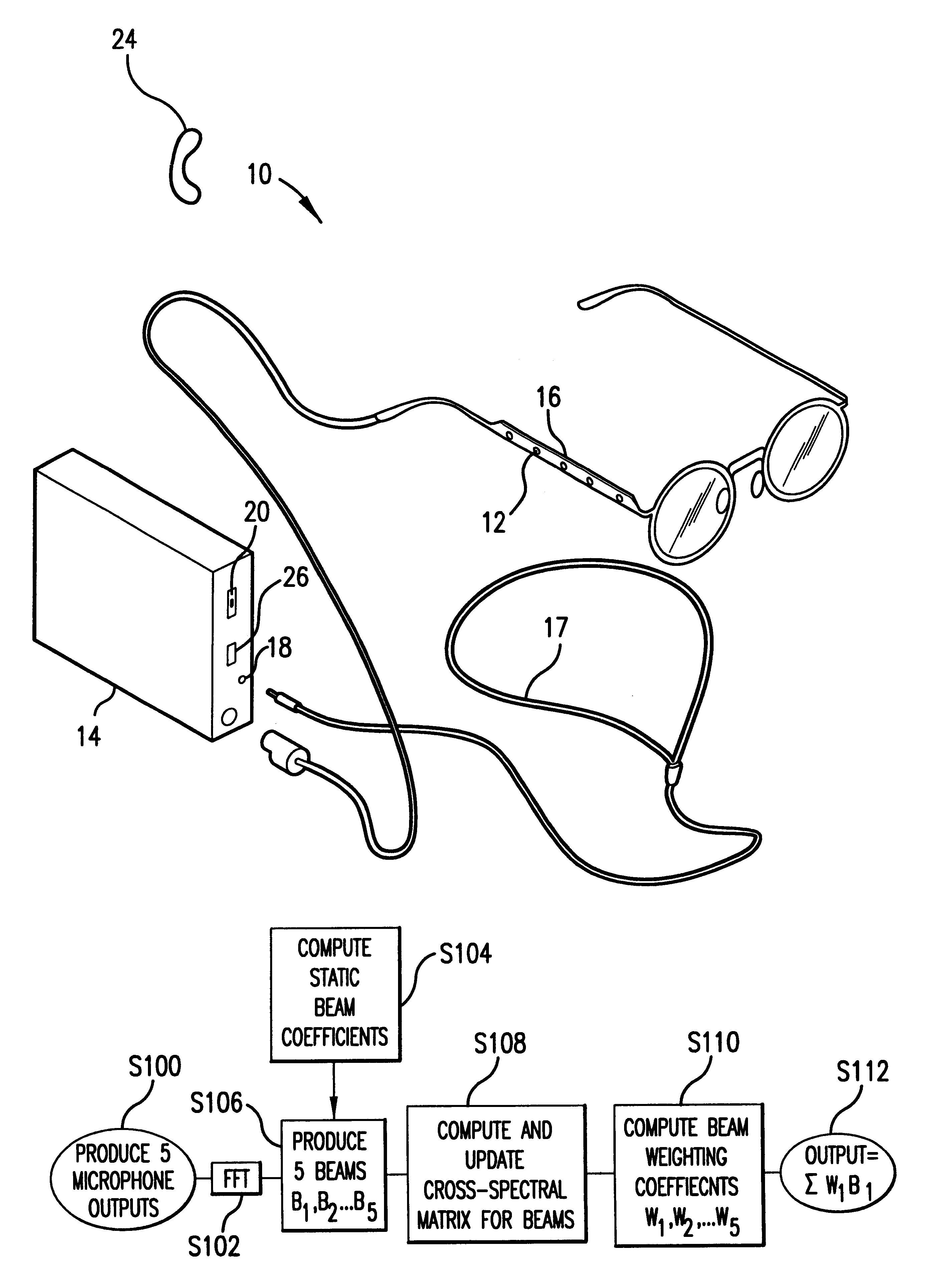
The hybrid adaptive beamformer of the present invention includes a plurality of microphones for receiving sound energy from an external environment and for producing a plurality of microphone outputs from the sound energy. A processor produces a plurality of first order beams based on the microphone outputs. The processor determines an amount of reverberation in the external environment and adaptively produces a second order output beam taking into consideration the determined amount of reverberation. The processor may determine the amount of reverberation based on a comparison of the first order beams. The processor may produce the second order output beam by adaptively combining the plurality of first order beams, as further described below, or by adaptively combining the microphone outputs. The adaptation varies taking into consideration the determined amount of reverberation. Alternatively, the adaptation may vary by measuring the signal-to-noise ratio of the first order beams and adaptively combining the first order beams based on the determined signal-to-noise ratios.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
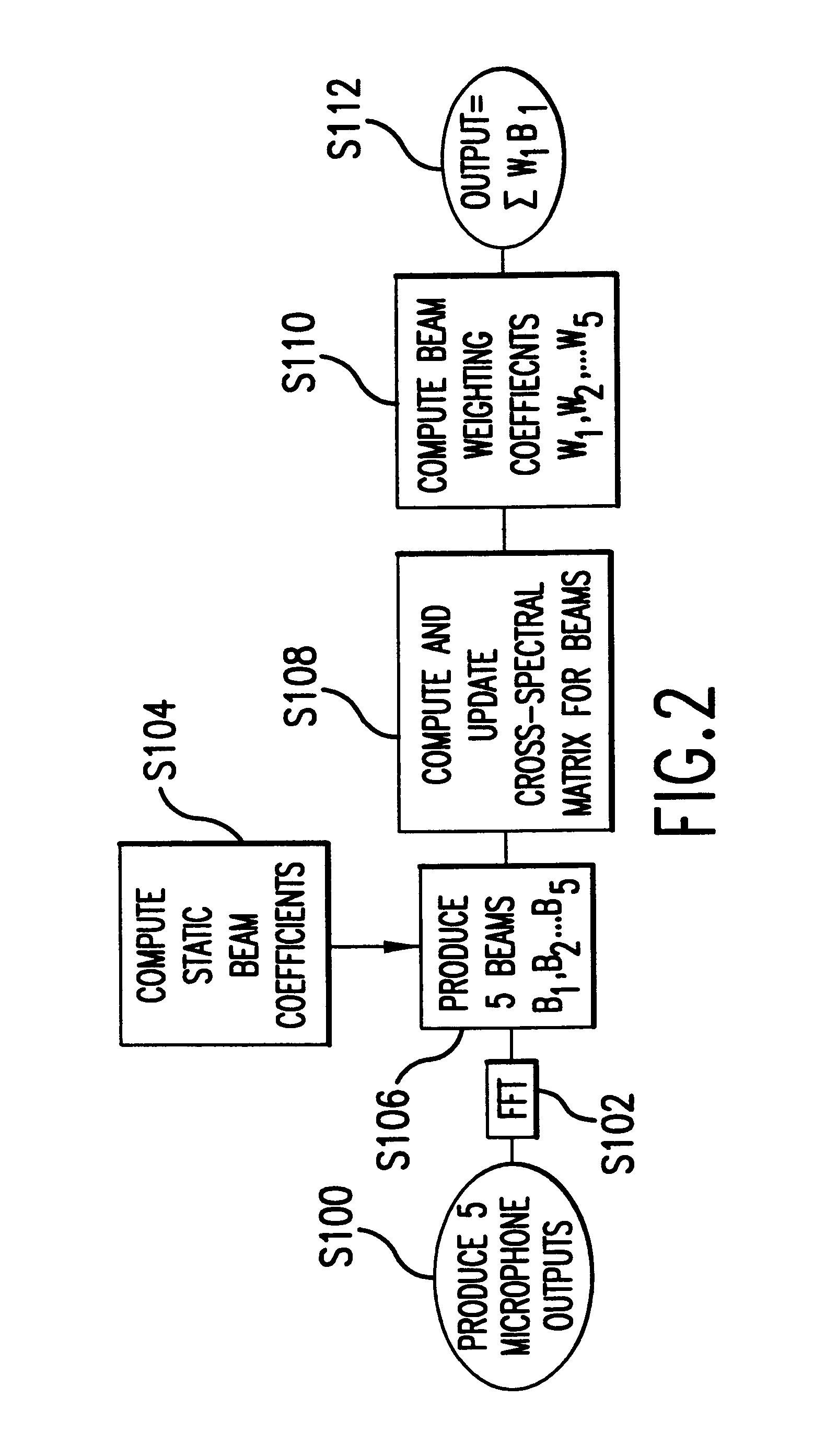
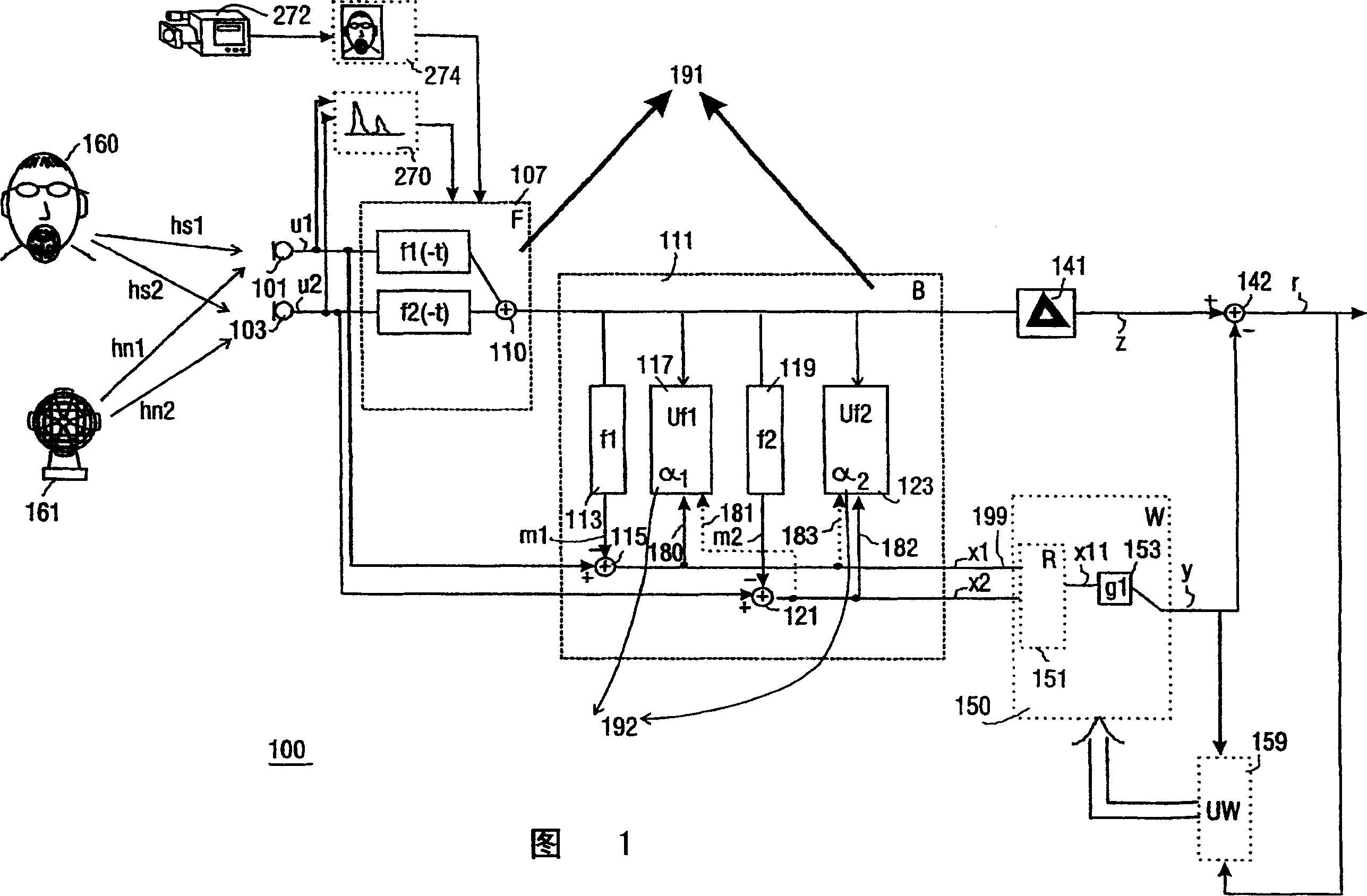
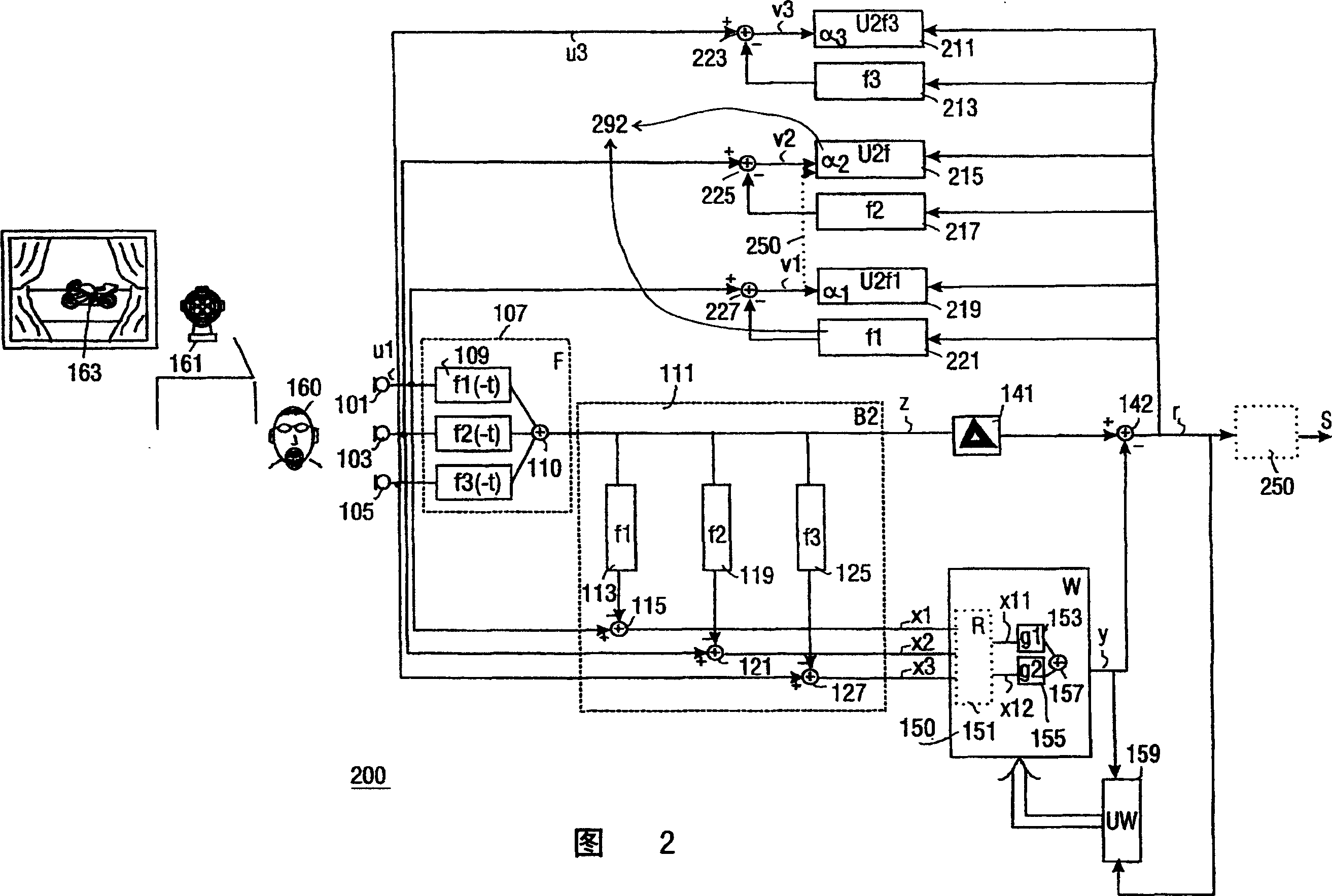
Adaptive beamformer, sidelobe canceller, handsfree speech communication device
The adaptive beamformer unit (191) comprises: a filtered sum beamformer (107) arranged to process input audio signals (u l, u2) from an array of respective microphones (101, 103), and arranged to yield as an output a first audio signal (z) predominantly corresponding to sound from a desired audio source (160) by filtering with a first adaptive filter (fl (-t)) a first one of the input audio signals (u l) and with a second adaptive filter (f2(-t)) a second one of the input audio signals (u2), the coefficients of the first filter (fl(-t)) and the second filter (f2(-t)) being adaptable with a first step size (al) and a second step size ((x2) respectively; noise measure derivation means (111) arranged to derive from the input audio signals (ul, u2) a first noise measure (xl) and a second noise measure (x2); and an updating unit (192) arranged to determine the first and second step size (al, (x2) with an equation comprising in a denominator the first noise measure (xl) for the first step size (al), respectively the second noise measure (x2) for the second step size (a2). This makes the beamformer relatively robust against the influence of correlated audio interference. The beamformer may also be incorporated in a sidelobe canceller topology yielding a more noise cleaned desired sound estimate, which can be used in a related, more advanced adaptive filter (fl (-t), f2(-t)) updating. Such a beamformer is typically useful for application in handsfree speech communication systems.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
A noise suppression system and method for phased-array based systems
Owner:RAYTHEON CANADA LTD
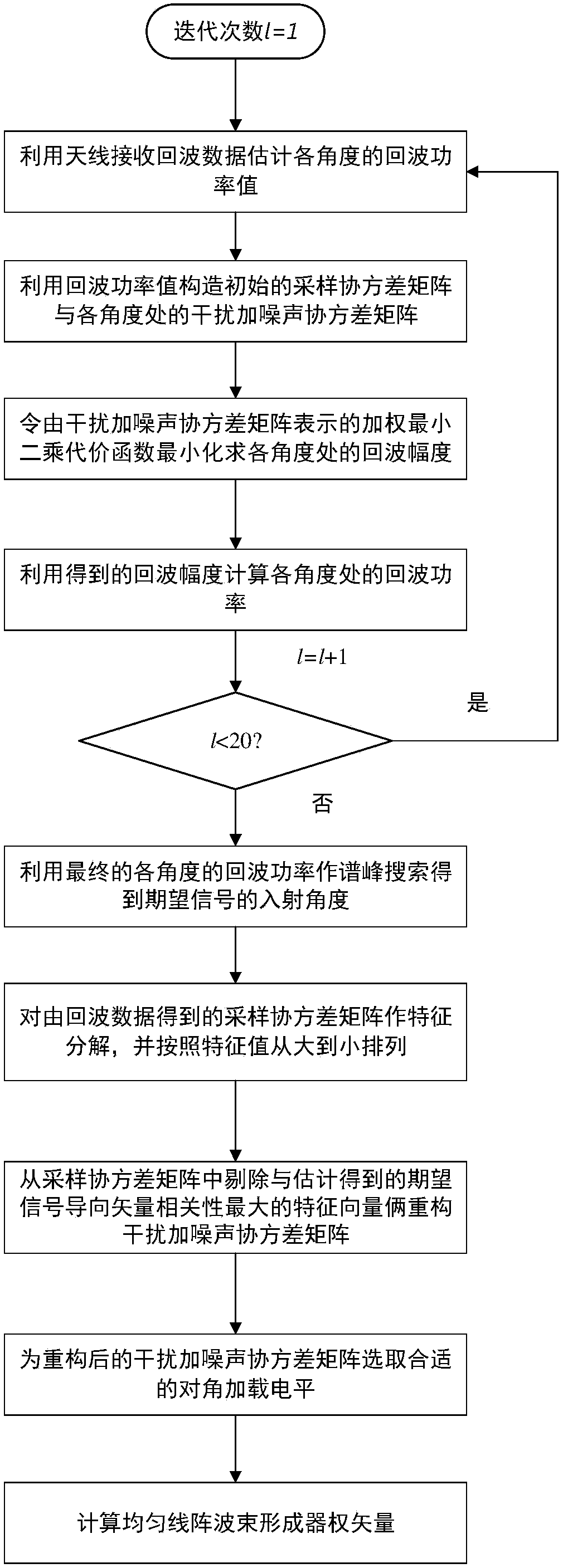
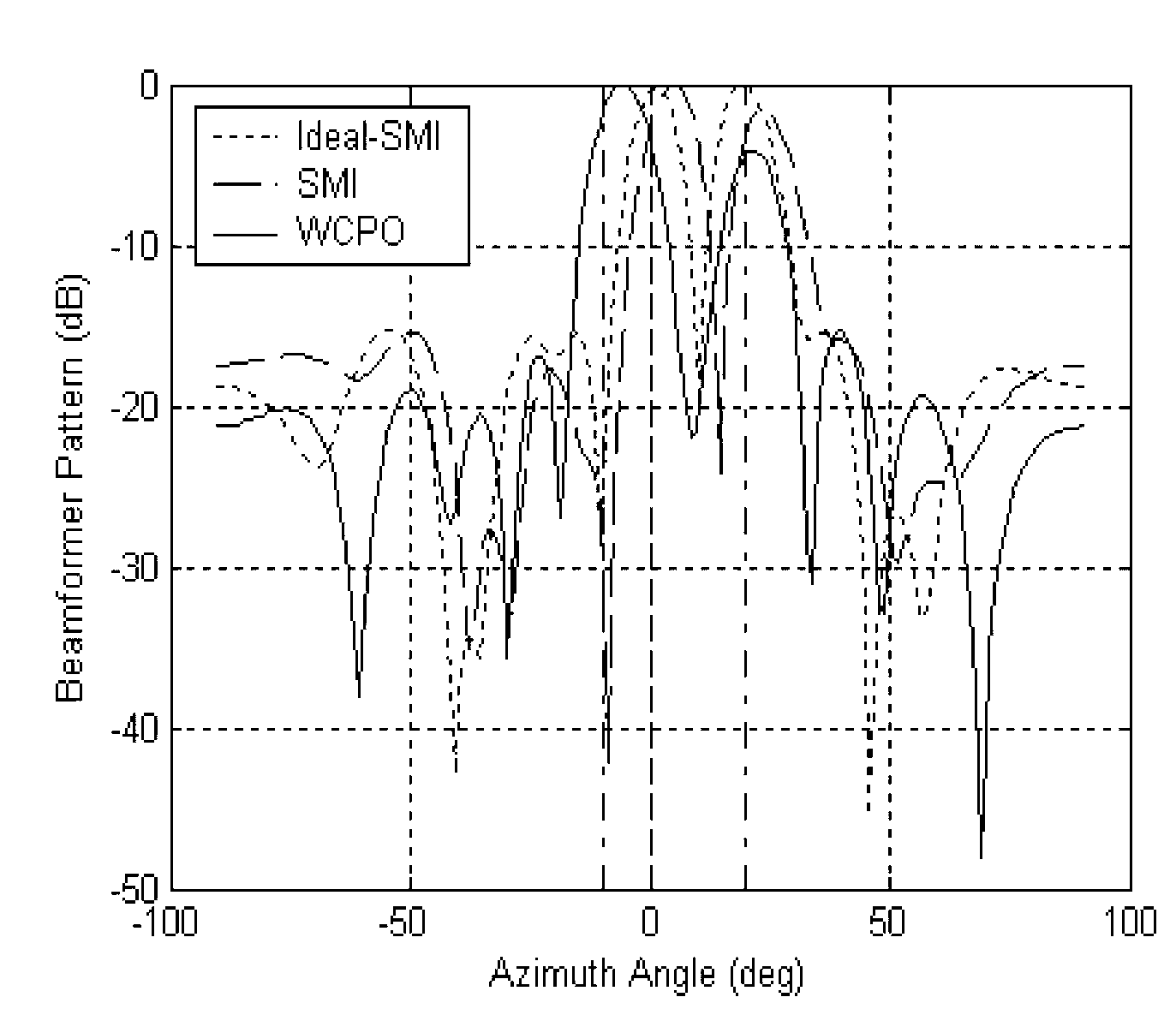
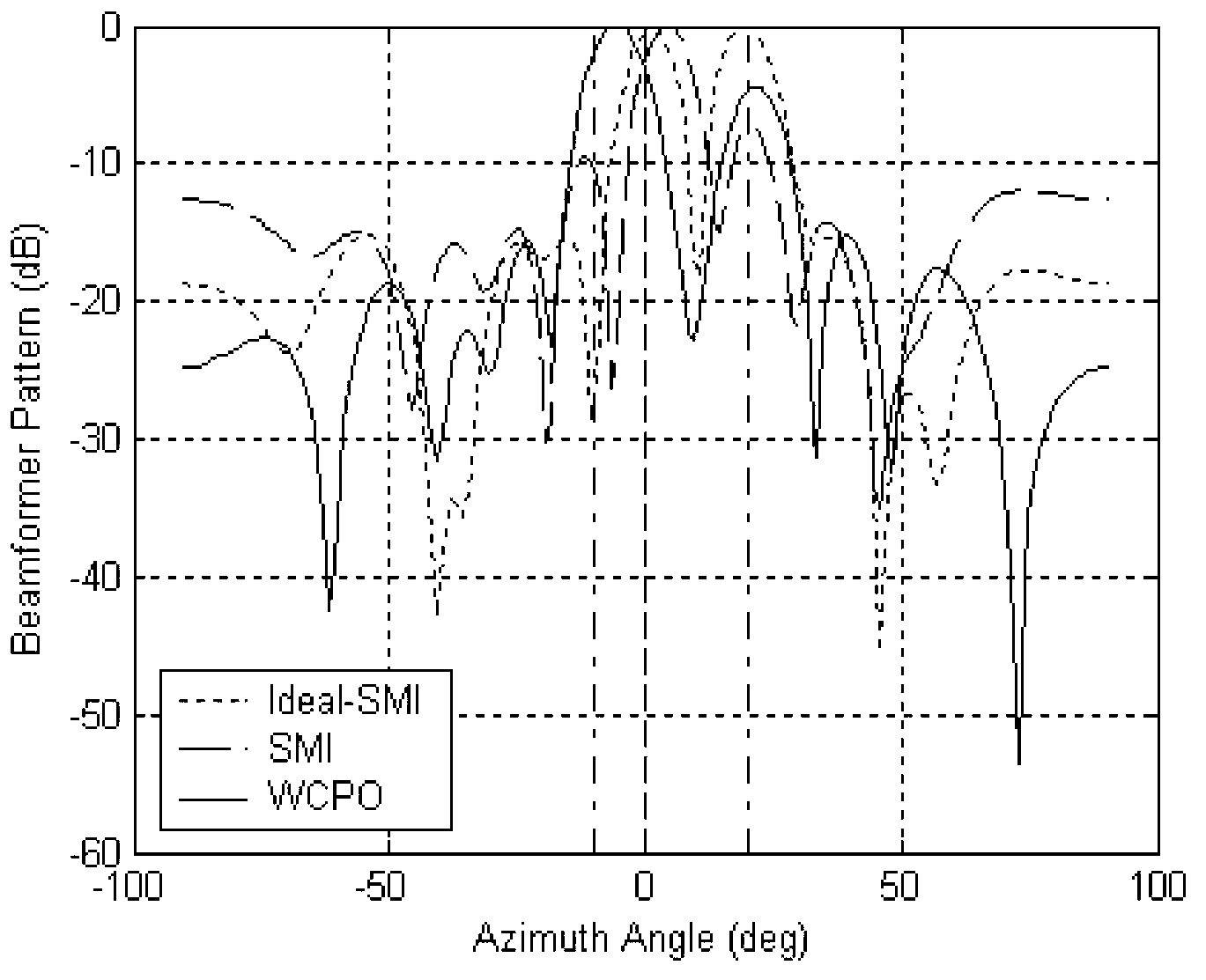
Robust beam forming method based on steering vector and space power estimation
ActiveCN109450499AAccurate estimateImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringCorrelation coefficientSpace power
The invention provides a robust beam forming method based on a steering vector and space power estimation, so as to improve the robustness of random errors on an incoming wave direction and to realizeaccurate signal steering vector estimation under the condition of interference in a main lobe of a beam. The invention provides a signal plus interference covariance matrix reconstruction algorithm,which introduces a correlation coefficient to serve as a signal subspace selection criterion, reconstructs a sampling covariance matrix signal plus interference subspace, and performs alternate projection in combination with a covariance matrix containing a signal subspace and obtained by signal angle interval discrete sampling, so as to perform the accurate signal steering vector estimation and to design a robust adaptive beam former under the condition of interference in the main lobe of the beam.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
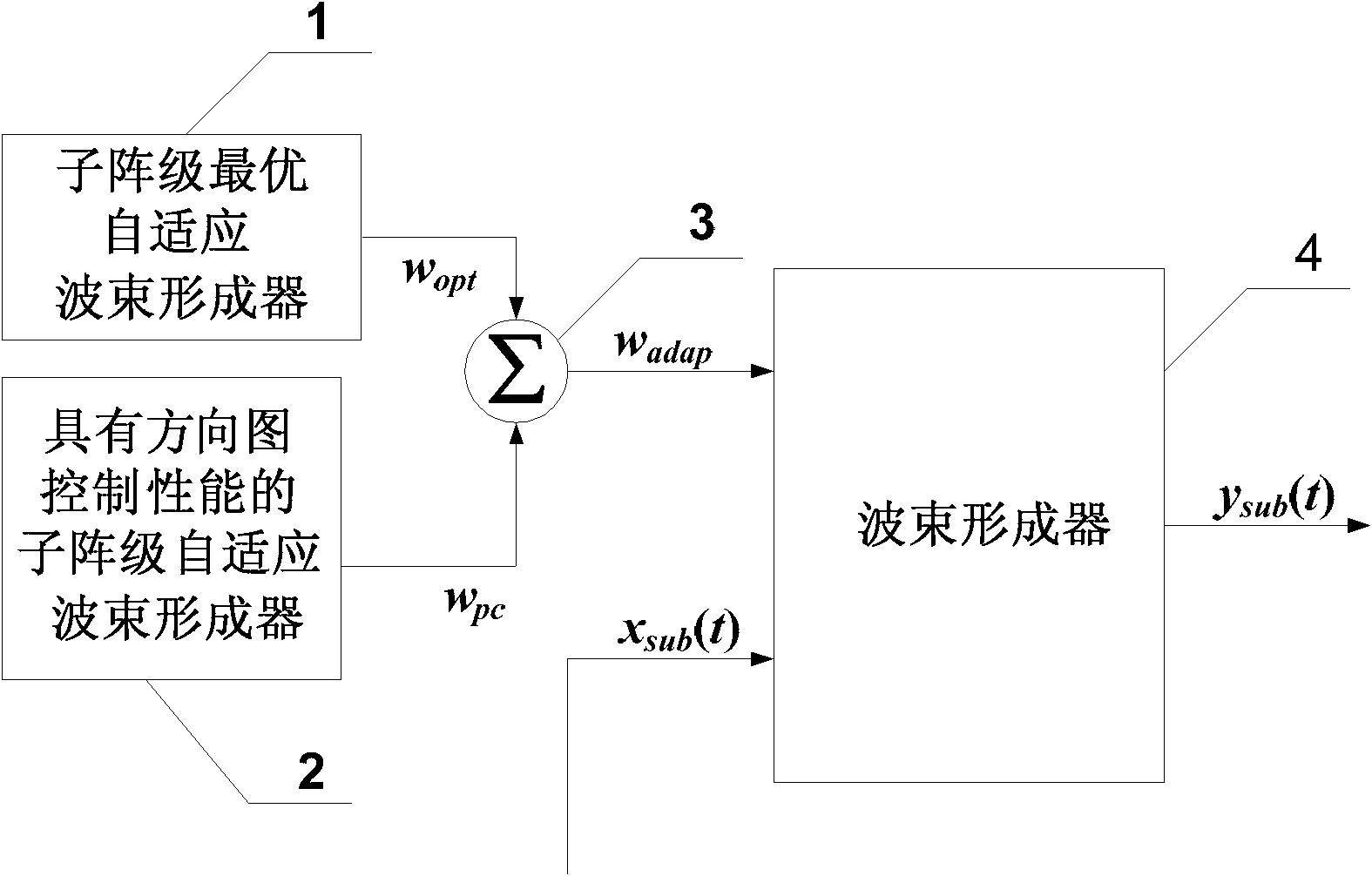
Sub-array-class adaptive digital beam forming device with low side-lobe characteristics
InactiveCN102142609AIncrease flexibilityImproved sidelobe performanceAntenna arraysSide lobeEngineering
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
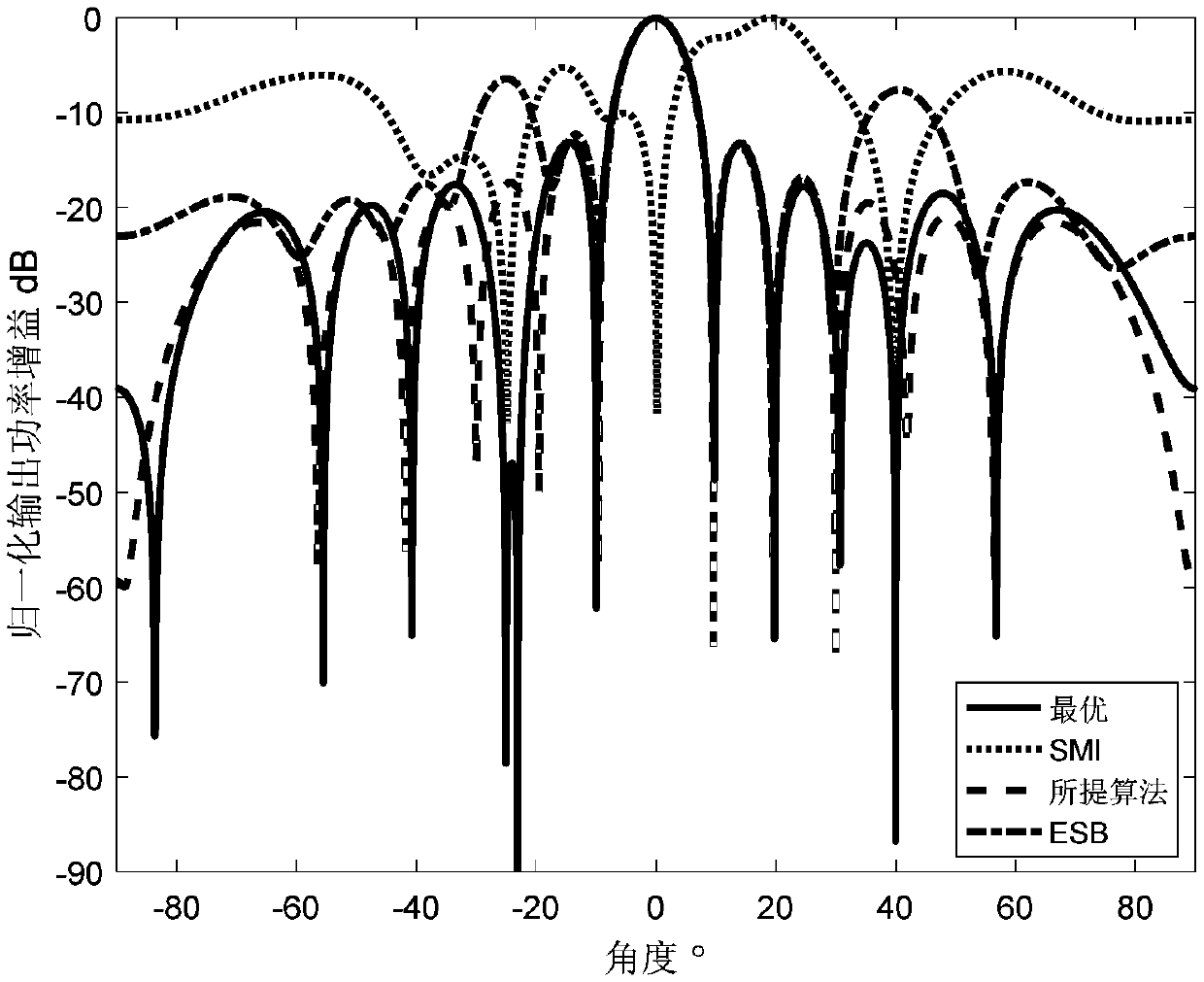
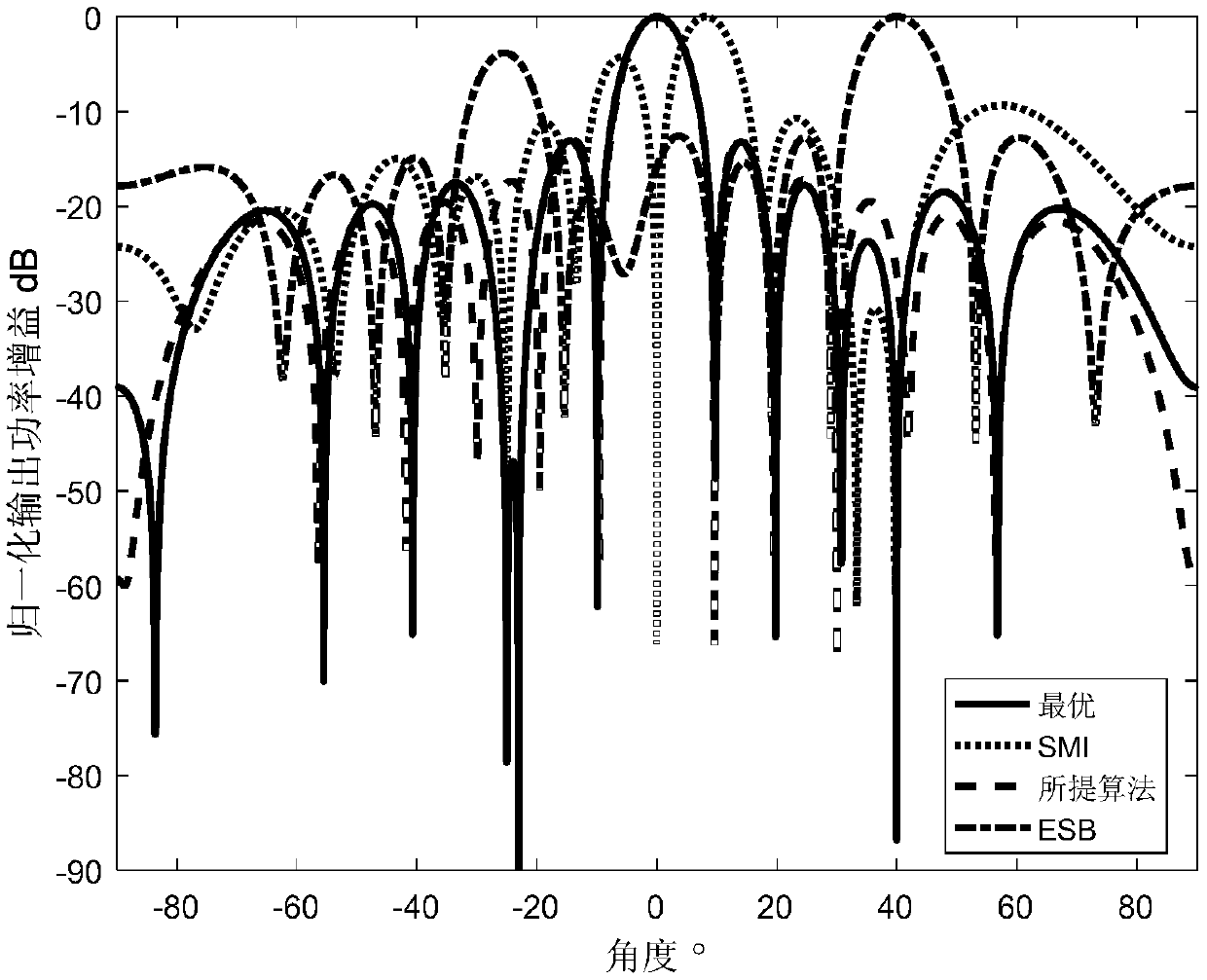
Reconstruction robust beam forming method based IAA interference plus noise covariance matrix
ActiveCN108663668AHigh output SINRImprove robustnessWave based measurement systemsLoading factorFeature vector
The invention belongs to the technical field of antenna beam forming, and discloses a reconstruction robust beam forming method based on IAA interference plus noise covariance matrix. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, estimating the direction of a signal more accurately in an iterative mode by using IAA method, then selecting the characteristic vector with the maximum correlation with the steering vector calculated by using the estimated direction of the desired signal from sampling covariance matrix characteristic vectors and rejecting the characteristic vector from the sampling covariance matrix, finally, selecting a proper diagonal loading factor to carry out diagonal loading on the matrix in order to prevent the covariance matrix after rejecting the signal from generating singular, in the case that the sample contains the desired signal, the signal to noise ratio of a self-adaptive beam former is improved and the robust performance of the self-adaptive beam former is improved in the case of a mismatch steering vector.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Mutual coupling correction-based radar array adaptive beamforming method
ActiveCN106707250AReduce performanceImprove object detection performanceWave based measurement systemsCouplingRadar
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
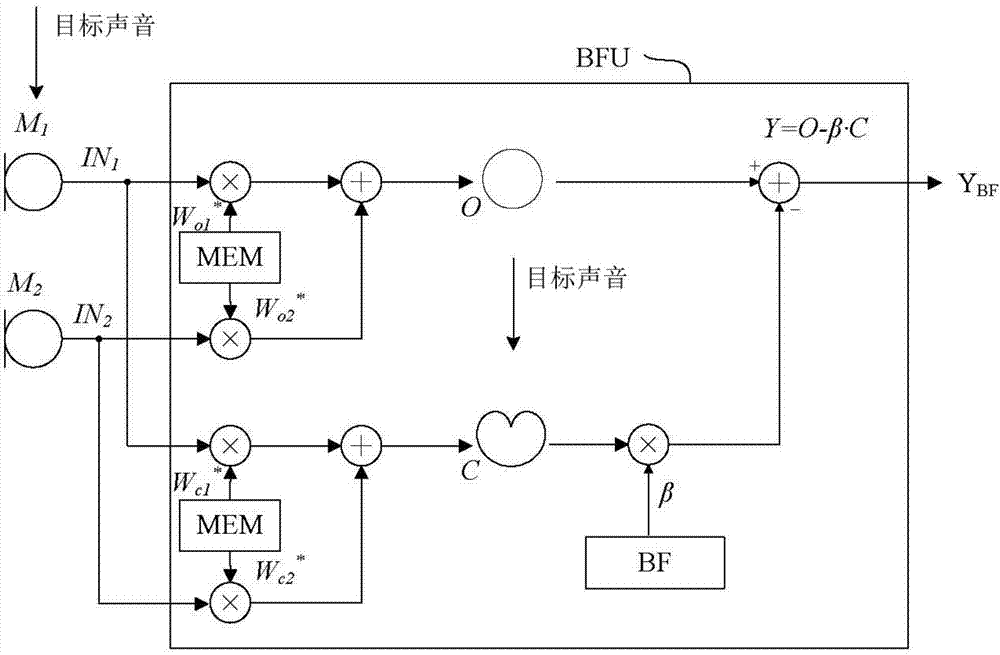
Hearing device comprising a beamformer filtering unit
A hearing aid comprises a) first and second microphones b) an adaptive beamformer filtering unit comprising, b1) a first and second memories comprising a first and second sets of complex frequency dependent weighting parameters representing a first and second beam patterns, where said first and second sets of weighting parameters are predetermined initial values or values updated during operation of the hearing aid, b3) an adaptive beamformer processing unit providing an adaptation parameter representing an adaptive beam pattern configured to attenuate unwanted noise under the constraint that sound from a target direction is essentially unaltered, b4) a third memory comprising a fixed adaptation parameter representing a third, fixed beam pattern, a mixing unit providing a resulting complex, frequency dependent adaptation parameter as a combination of said fixed and adaptively determined frequency dependent adaptation parameters, respectively, and a resulting beamformer for providing a resulting beamformed signal YBF based on first and second microphone signals, said first and second sets of complex frequency dependent weighting parameters, and said resulting complex, frequency dependent adaptation parameter .
Owner:OTICON
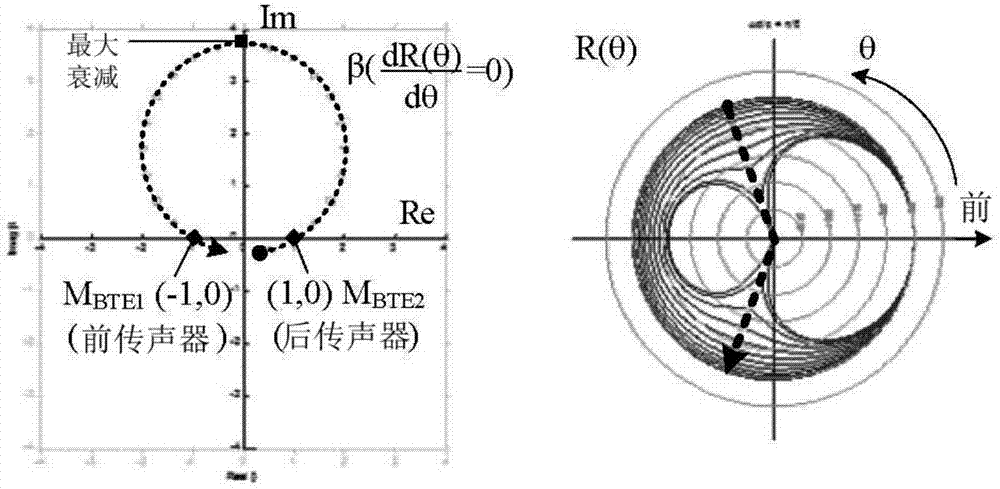
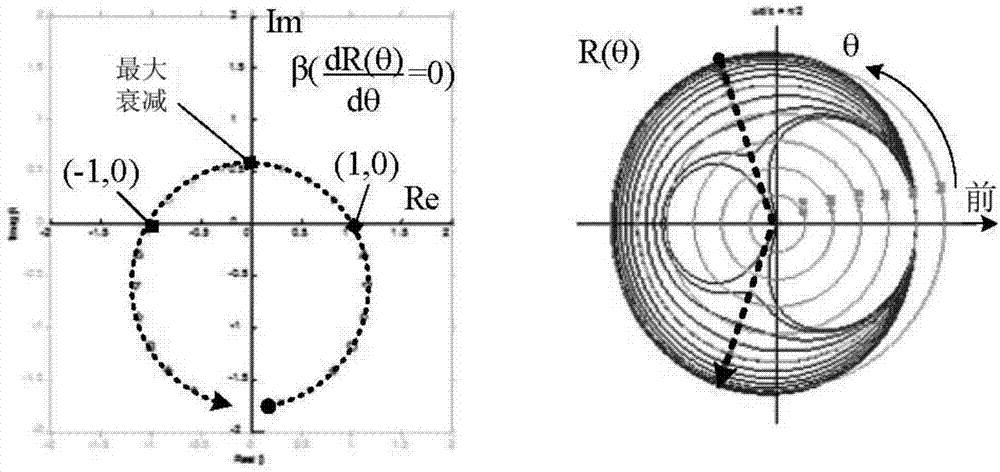
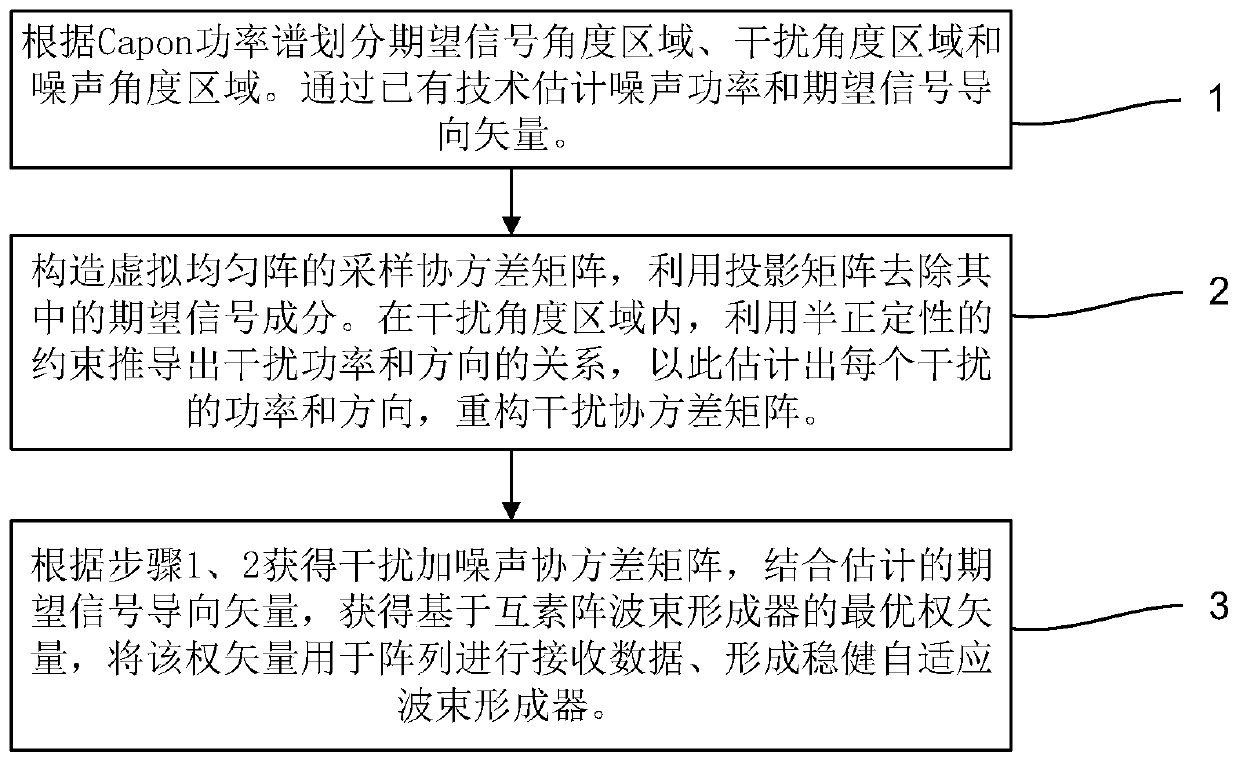
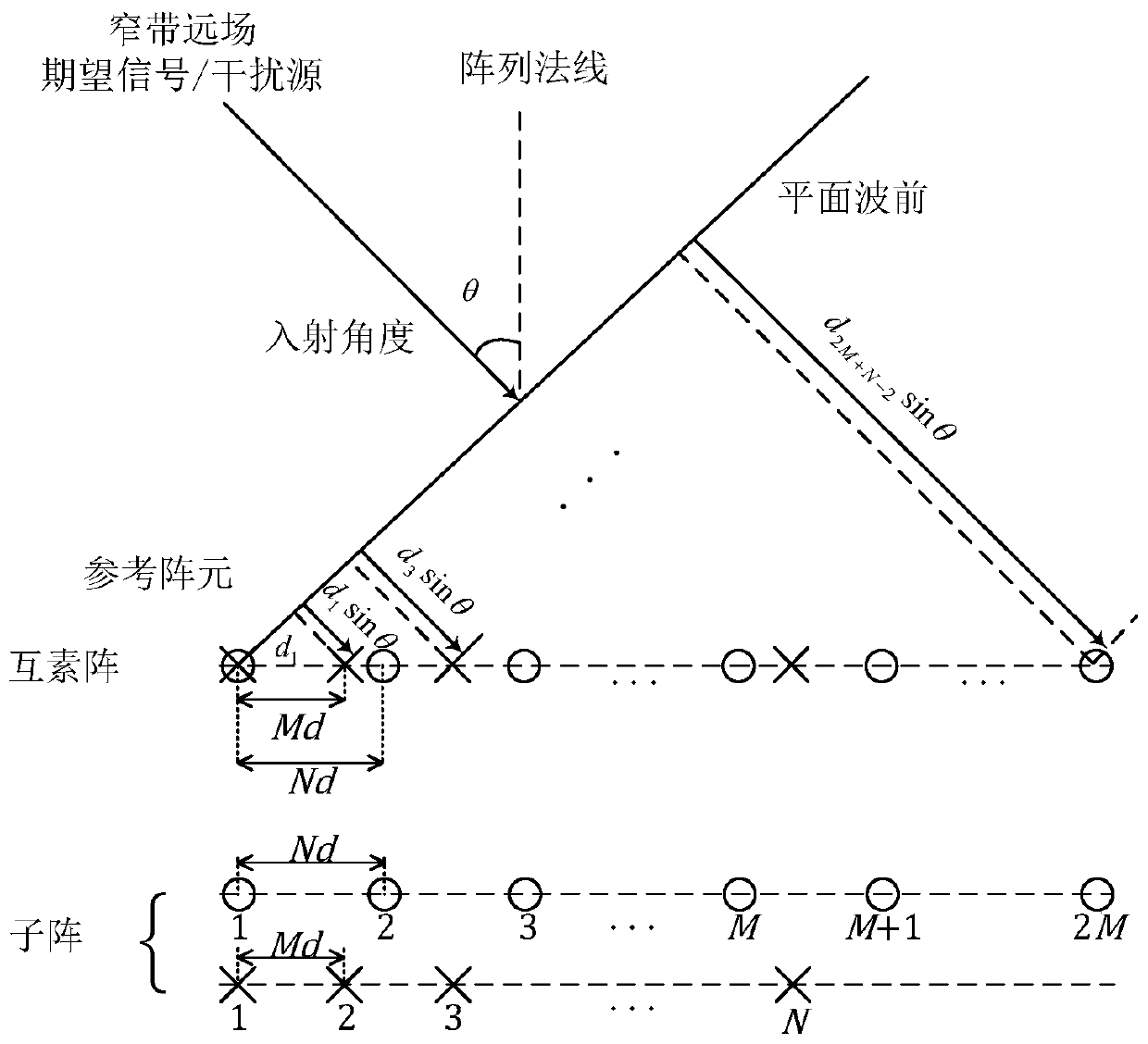
Co-prime array robust adaptive beamforming method based on interference covariance matrix reconstruction
The invention discloses a co-prime array robust adaptive beamforming method based on interference covariance matrix reconstruction. The method comprises the following steps of reconstructing a sampling covariance matrix on the virtual uniform matrix, removing expected signal components in the sampling covariance matrix by using projection, estimating accurate power and direction of each interference according to semi-positive qualitative constraints, reconstructing an interference covariance matrix, estimating noise power in a noise angle area, and obtaining an interference and noise covariance matrix; and taking the main characteristic value of the reconstructed expected signal covariance matrix as an expected signal steering vector, thereby obtaining a weight vector of the robust adaptive beamformer based on the co-prime matrix, and forming the output of the robust adaptive beamformer.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Control interval expansion of variable time delay control structure for channel matching
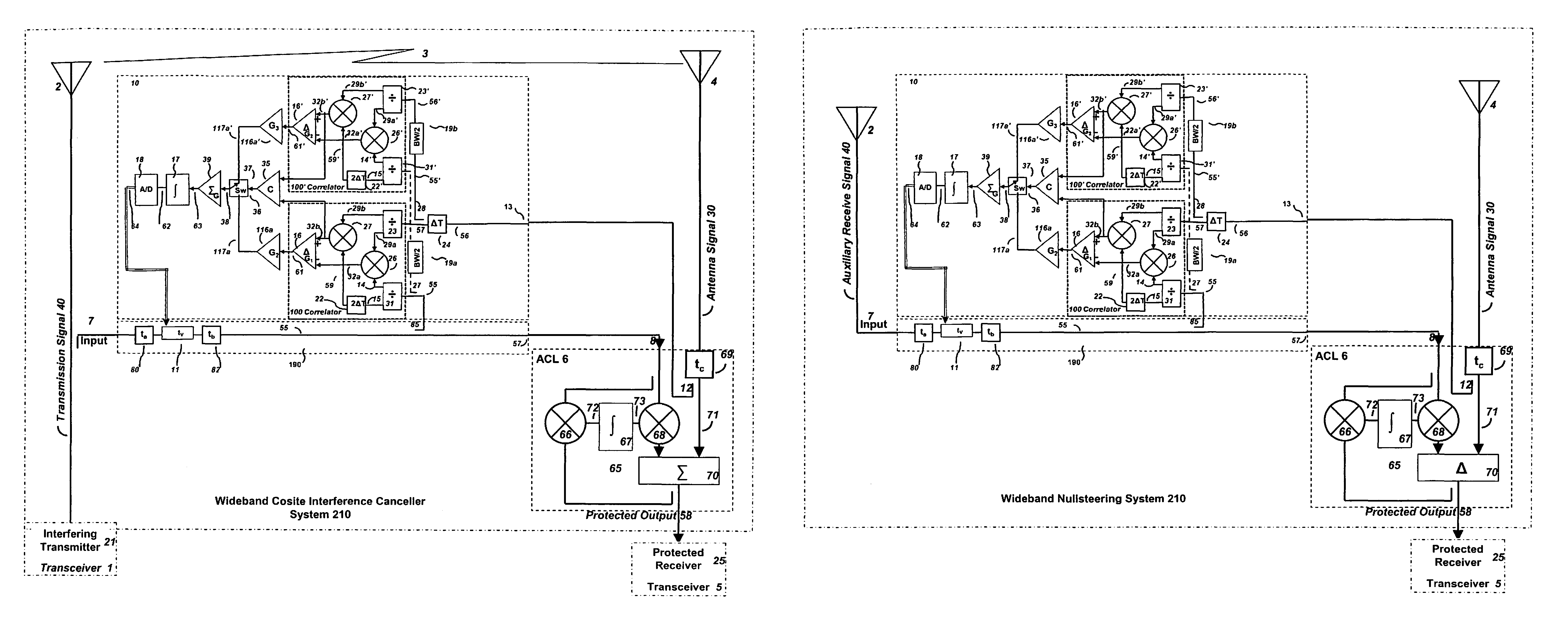
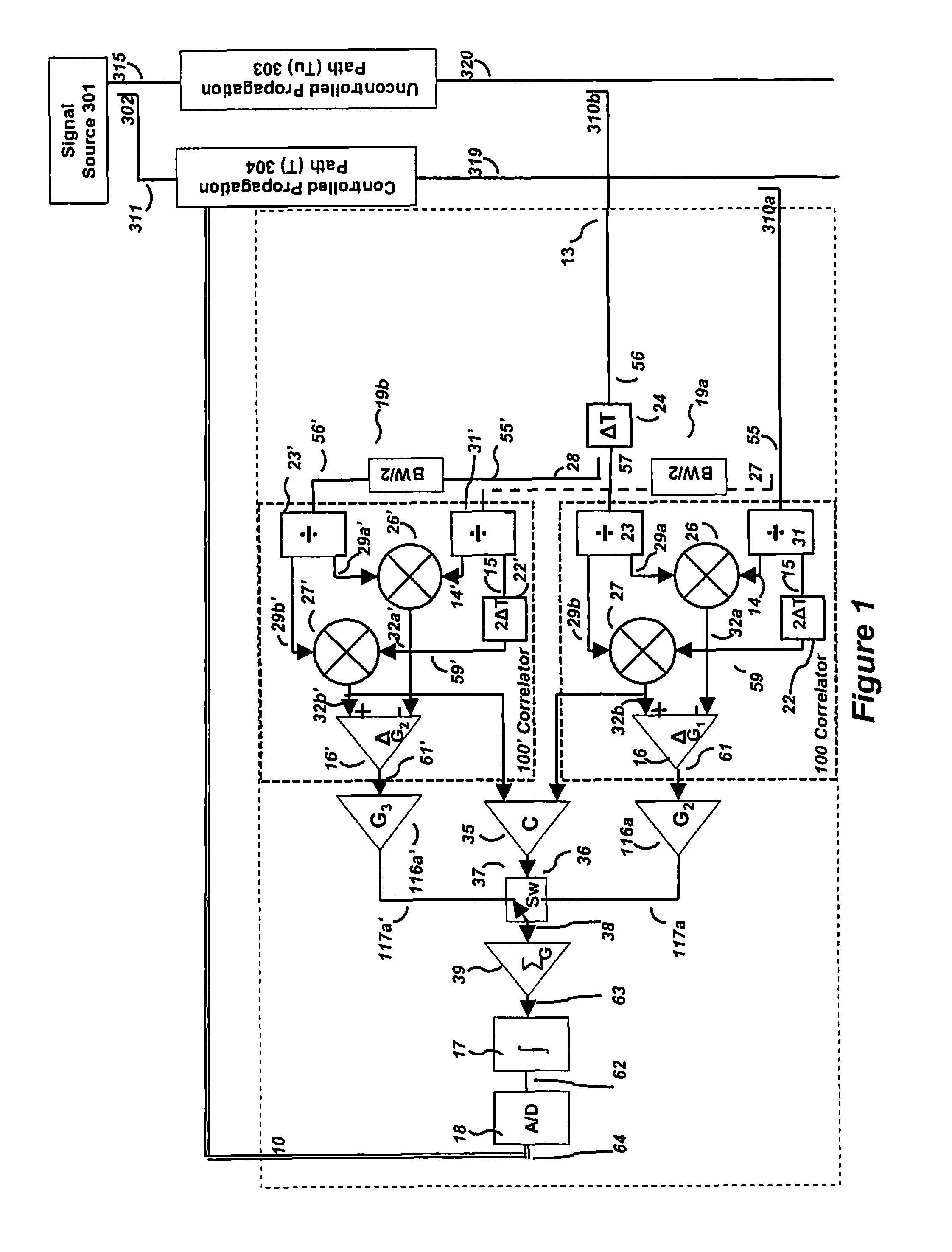
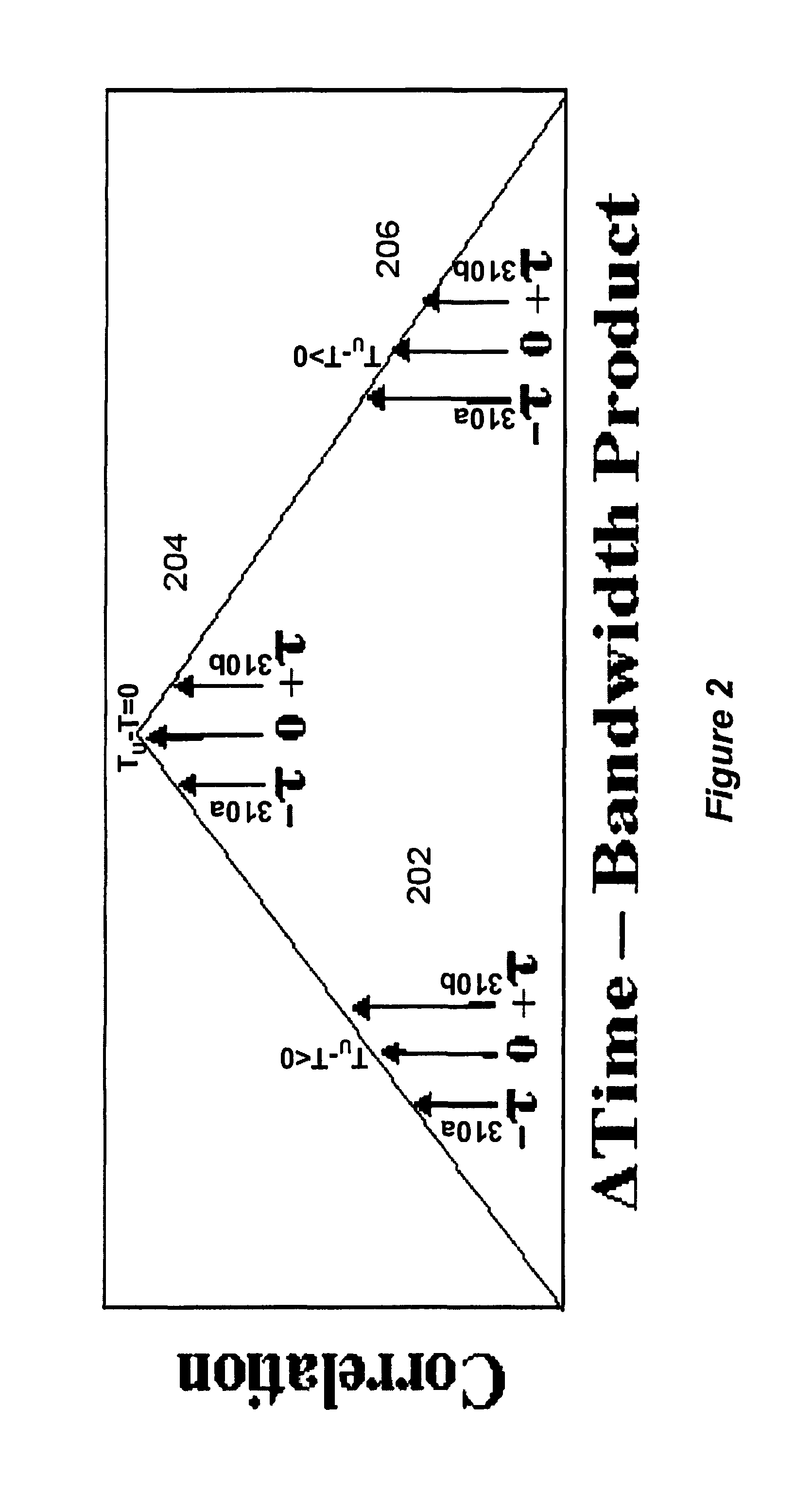
ActiveUS8571154B1Improve performanceImproved signal rejectionPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsInterference cancellerTime delays
An adaptive time delay control system is provided for matching the propagation time delay between two samples of a signal traveling through two independent paths so that they can be coherently combined for additional signal processing functions such as cosite interference cancellers, adaptive interference cancellers and adaptive beam formers. The adaptive time delay control system and associated method advantageously provide improved continuous matching of the two channels over a wider adjustment range while preserving both convergence speed over the full range and minimum jitter upon convergence by using composite autocorrelation functions to control (adjusting) a matching time delay in one channel.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Speech enhancement system and method
ActiveUS20140161272A1Minimize presenceEasy to FeedbackEar treatmentSpeech analysisAdaptive filterLoudspeaker
A system for speech enhancement in a room having a directional lapel microphone arrangement for capturing an audio signal from a speaker's voice; audio signal processor for generating a processed audio signal from the captured audio signal, and an adaptive beamformer unit for imparting directivity to the microphone arrangement provides maximum sensitivity towards the speaker's mouth and minimum sensitivity towards noise sources identified by the beamformer unit. A unit shifts the frequency of components of the audio signal above a frequency threshold value only. A feedback cancelling unit has an adaptive filter and a selection unit which automatically switches between a first mode causing the audio signal to by-pass the adaptive filter and a second mode in which the audio signal is filtered by the adaptive filter. A loudspeaker arrangement generates sound according to the processed audio signal and has plural loudspeakers arranged to form a directional loudspeaker array.
Owner:SONOVA AG
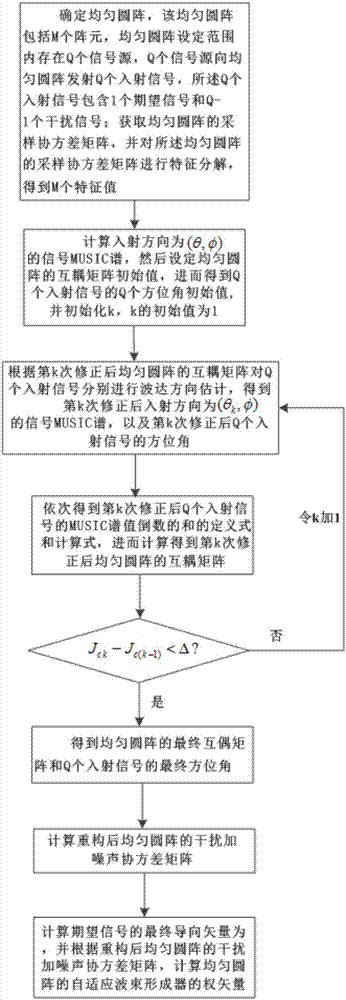
Radar covariance matrix reconstruction beam forming method based on iteration mutual coupling calibration
ActiveCN107102298AImprove robustnessImprove real-time performanceWave based measurement systemsRadarDecomposition
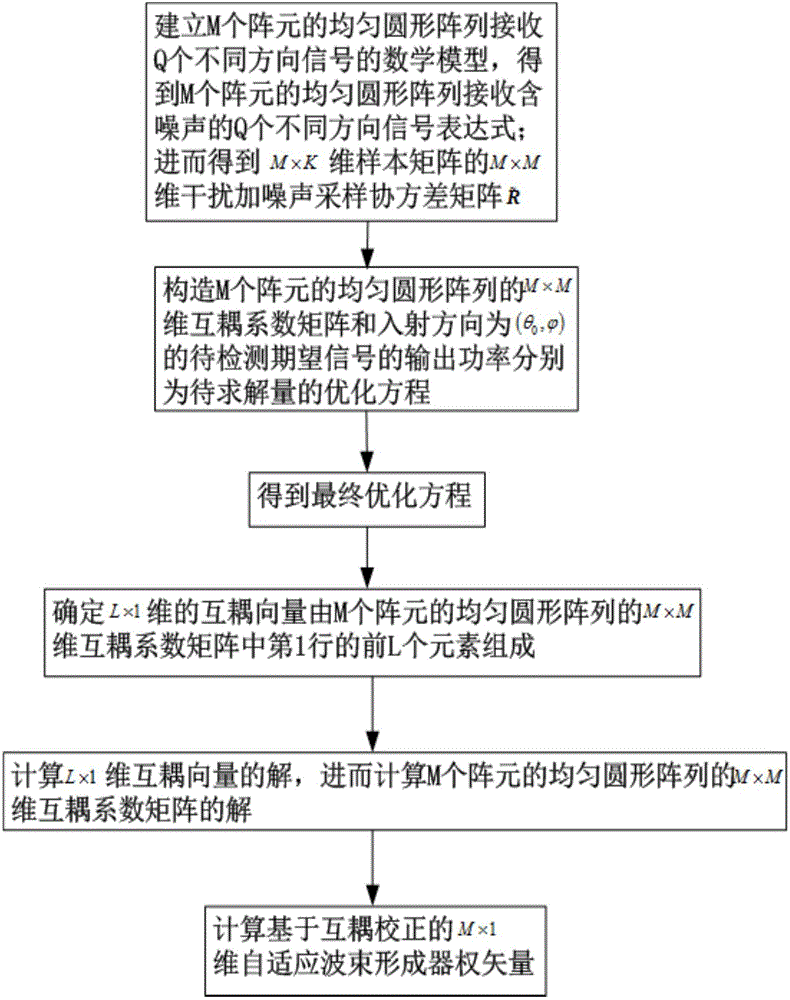
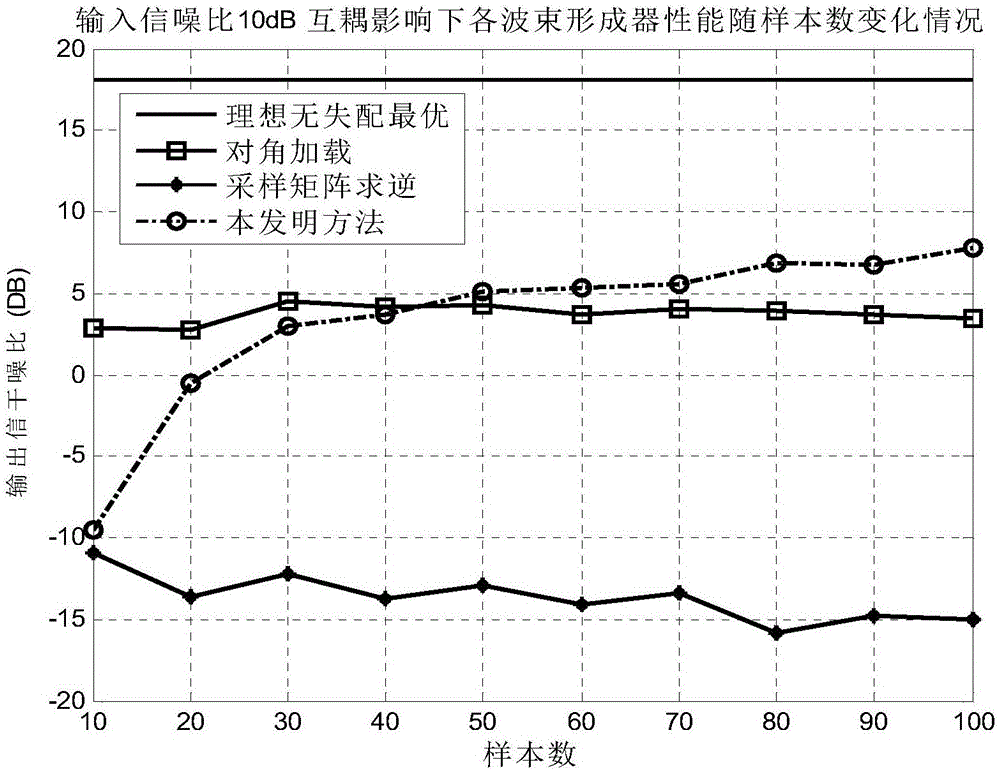
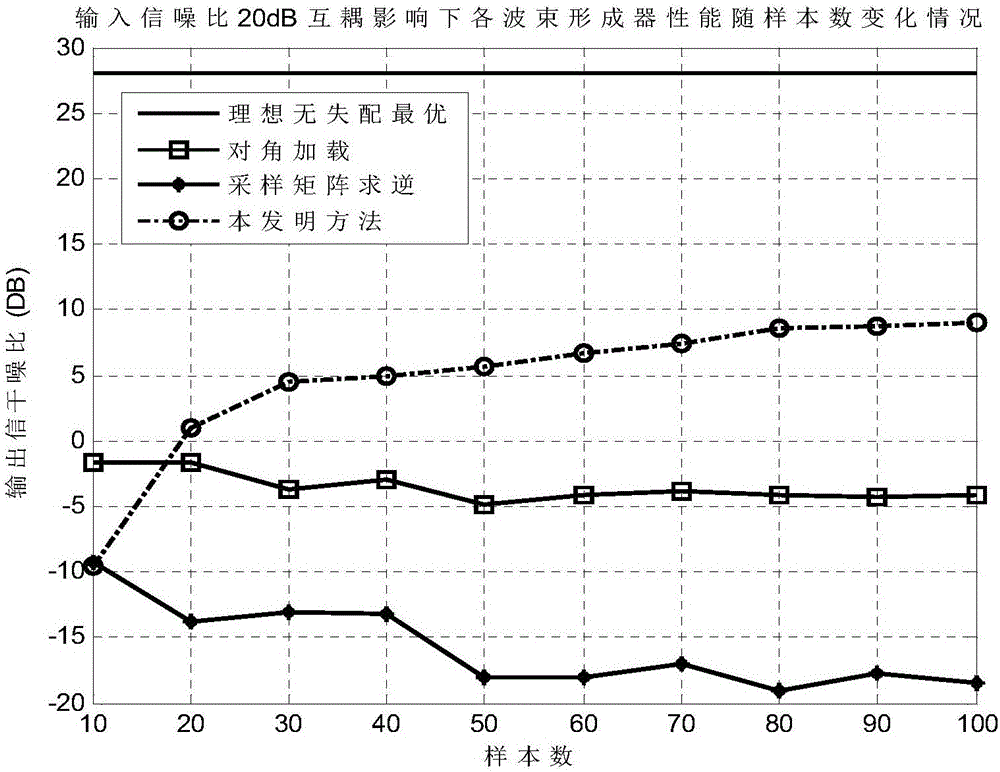
The present invention discloses a radar covariance matrix reconstruction beam forming method based on iteration mutual coupling calibration. The method thinking comprises: an uniform circular array is determined, the uniform circular array comprises M array elements, there are Q signal sources in the setting range of the uniform circular array, the Q signal sources emit Q incident signals to the uniform circular array, and the Q incident signals comprise one desired signal and Q-1 interference signals; the sampling covariance matrix R of the uniform circular array is obtained, the characteristic decomposition is performed, and M characteristic values are obtained; a signal MUSIC spectrum having an incident direction of ([Theta], [Phi]) is calculated, the mutual coupling matrix initial value of the uniform circular array is set to obtain Q azimuth initial values of the Q incident signals, and a final mutual coupling matrix of the uniform circular array (img file='DDA0001335531130000011.TIF' wi='43' he='57' / ) and the final azimuths of the Q incident signals (img file='DDA0001335531130000012.TIF' wi='67' he='58' / ) are obtained; and the interference-plus-noise covariance matrix of the uniform circular array after the reconstruction (img file='DDA0001335531130000013.TIF' wi='116' he='73' / ) is calculated to obtain the weight vector of the adaptive beam former of the uniform circular array so as to complete the reconstruction of the interference-plus-noise covariance matrix of the uniform circular array based on the iteration mutual coupling calibration.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Self-adaptive beamforming method based on interference and noise covariance matrix reconstruction
ActiveCN106842135ASteps to avoid estimatingImprove the output signal-to-noise ratioWave based measurement systemsSelf adaptiveSignal processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of array signal processing and discloses a self-adaptive beamforming method based on interference and noise covariance matrix reconstruction. The self-adaptive beamforming method comprises the steps that a uniform linear array is established and is used for detecting far-field narrow-band signals including one desired signal to be detected and Q-1 interference signals to obtain receiving signals; the receiving signals are sampled to obtain K receiving signal samples, a sample matrix is formed, and an interference and noise sampling covariance matrix of the sample matrix is calculated; a weighting matrix is constructed, and the interference and noise sampling covariance matrix is weighted to obtain a weighted covariance matrix; a sampling matrix is constructed, and further a first interference and noise covariance matrix is constructed; the first interference and noise covariance matrix is weighted again according to the weighting matrix to obtain a second interference and noise covariance matrix; the self-adaptive weight vector of a self-adaptive beamformer is calculated according to the second interference and noise covariance matrix; the calculating amount can be decreased on the basis that a detection effect of desired signals is ensured.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Object information acquiring apparatus, information processing apparatus and object information acquiring method
ActiveUS20140058262A1High resolutionImprove robustnessDiagnostic recording/measuringInfrasonic diagnosticsInformation processingDelay and sum
An object information acquiring apparatus is provided that includes: a plurality of receiving elements which receive an acoustic wave that propagates from an object, and which convert the acoustic wave to a reception signal; an adaptive beamformer that performs adaptive beamforming of adjusting reception directionality in accordance with the reception signal in use of the reception signal; a delay-and-sum beamformer that performs delay-and-sum beamforming having preset directionality in use of the reception signal; an amplitude modulator that uses one output signal of one of the adaptive beamformer and the delay-and-sum beamformer, to perform amplitude modulation on an output signal of the other one of the beamformers; and a generator that, on the basis of a signal outputted by the amplitude modulator, generates image data on the interior of the object.
Owner:CANON KK
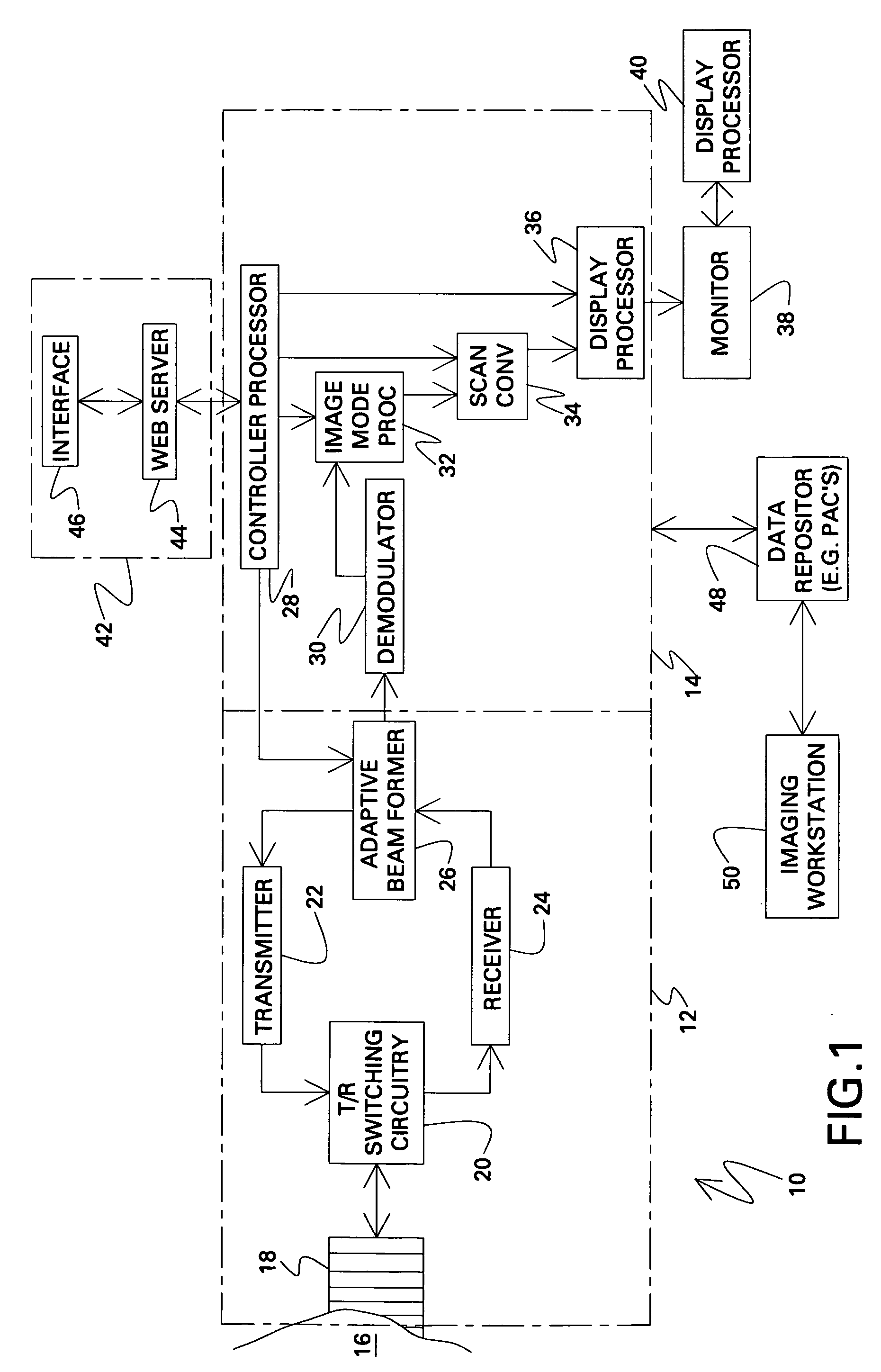
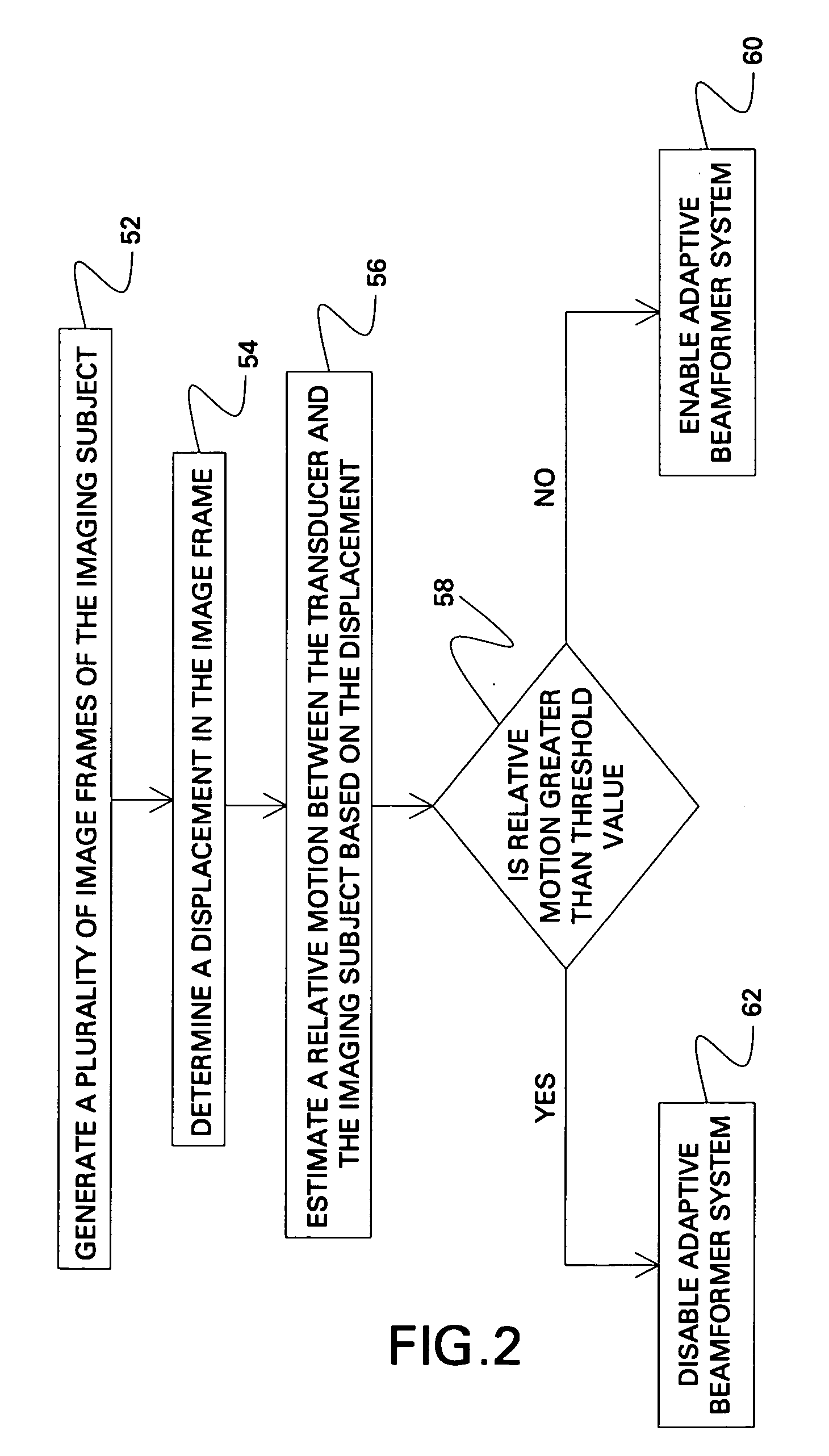
Adaptive ultrasound imaging system
A method and system for operating an ultrasound system is provided. The method comprising estimating a relative motion between a transducer and an imaging subject and controlling an adaptive beamformer system in response to to an estimation of the relative motion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method of forming stable adaptive wave beams of space distribution scattering source
InactiveCN103259584ASolve the blockageEasy to implementSpatial transmit diversityRadarMedical imaging
The invention discloses a method of forming stable adaptive wave beams of a space distribution scattering source. Firstly, received data are utilized to form a covariance matrix, secondly, mismatch constrained parameters are selected and an optimum weighting vector of an adaptive beam former is calculated according to the method of forming the stable adaptive wave beams of the space distribution scattering source, and finally the method of forming the stable adaptive wave beams is obtained. The method of forming the stable adaptive wave beams of the space distribution scattering source can solve the problem how to improve sharp performance reduction of the adaptive beam former when an assumed signal array response is not matched with an actual value, and the technical problem that the performance of the adaptive beam former is reduced due to signal mismatch and other mismatches under the condition that all mismatches exist, and can be widely applied to adaptive array processing in the field of radars, communication, medical imaging, microphone micro-arrays, seismic exploration and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGXIN TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com