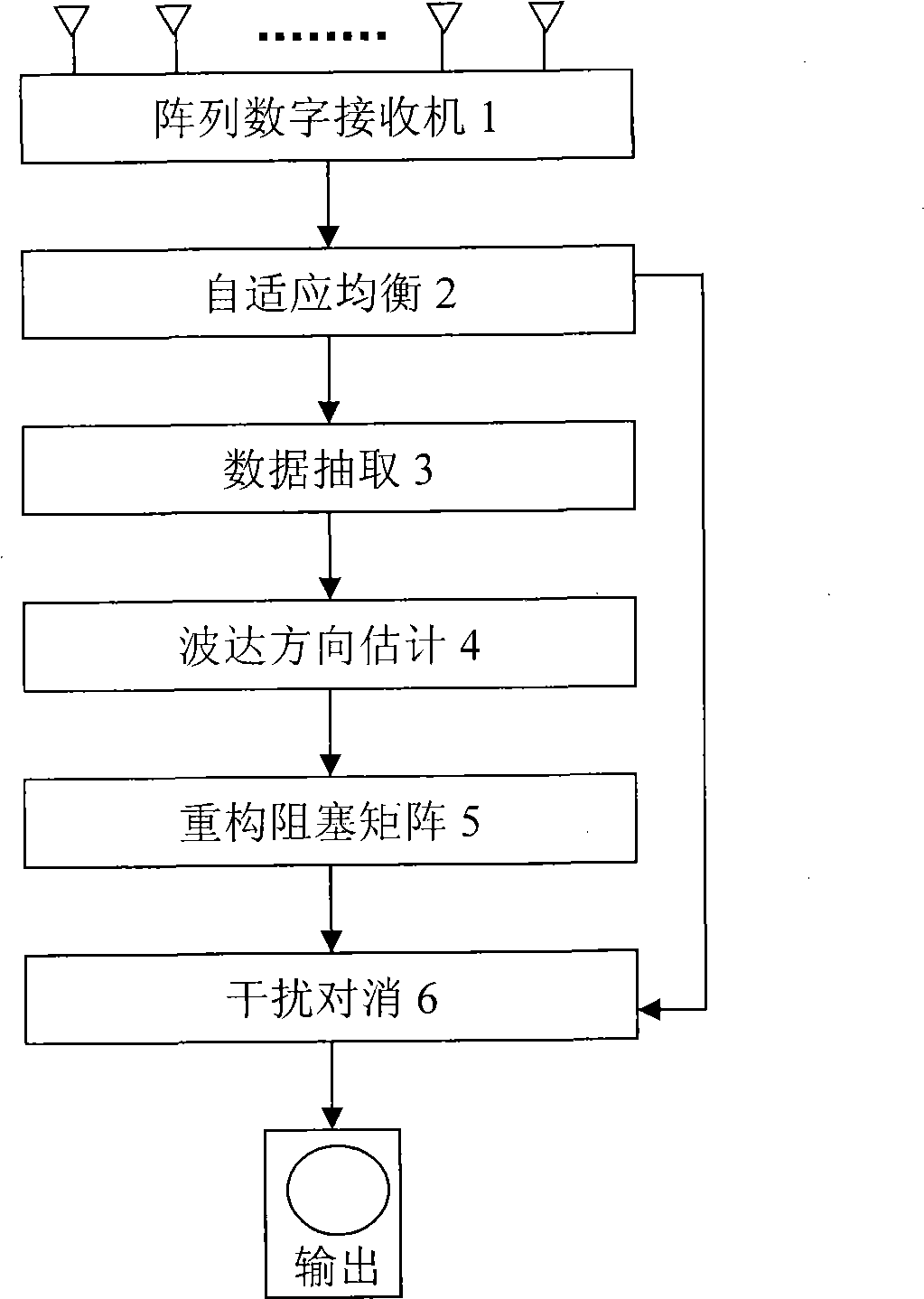
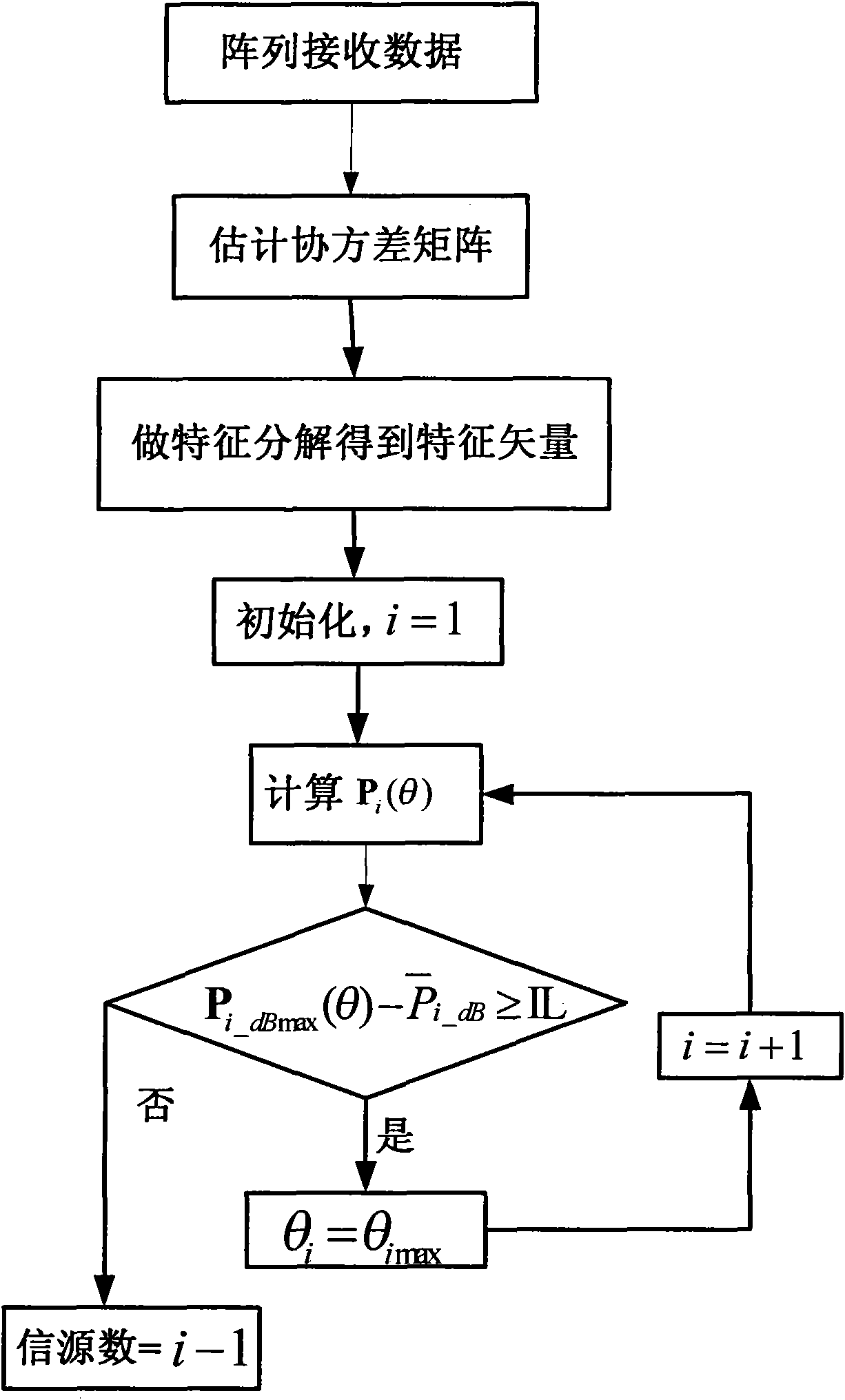
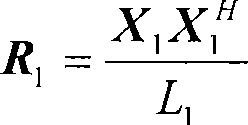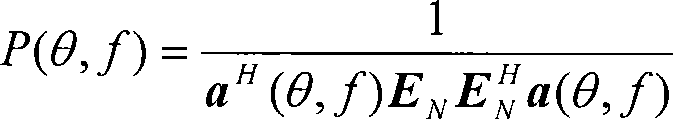Patents
Literature
1037 results about "Main lobe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
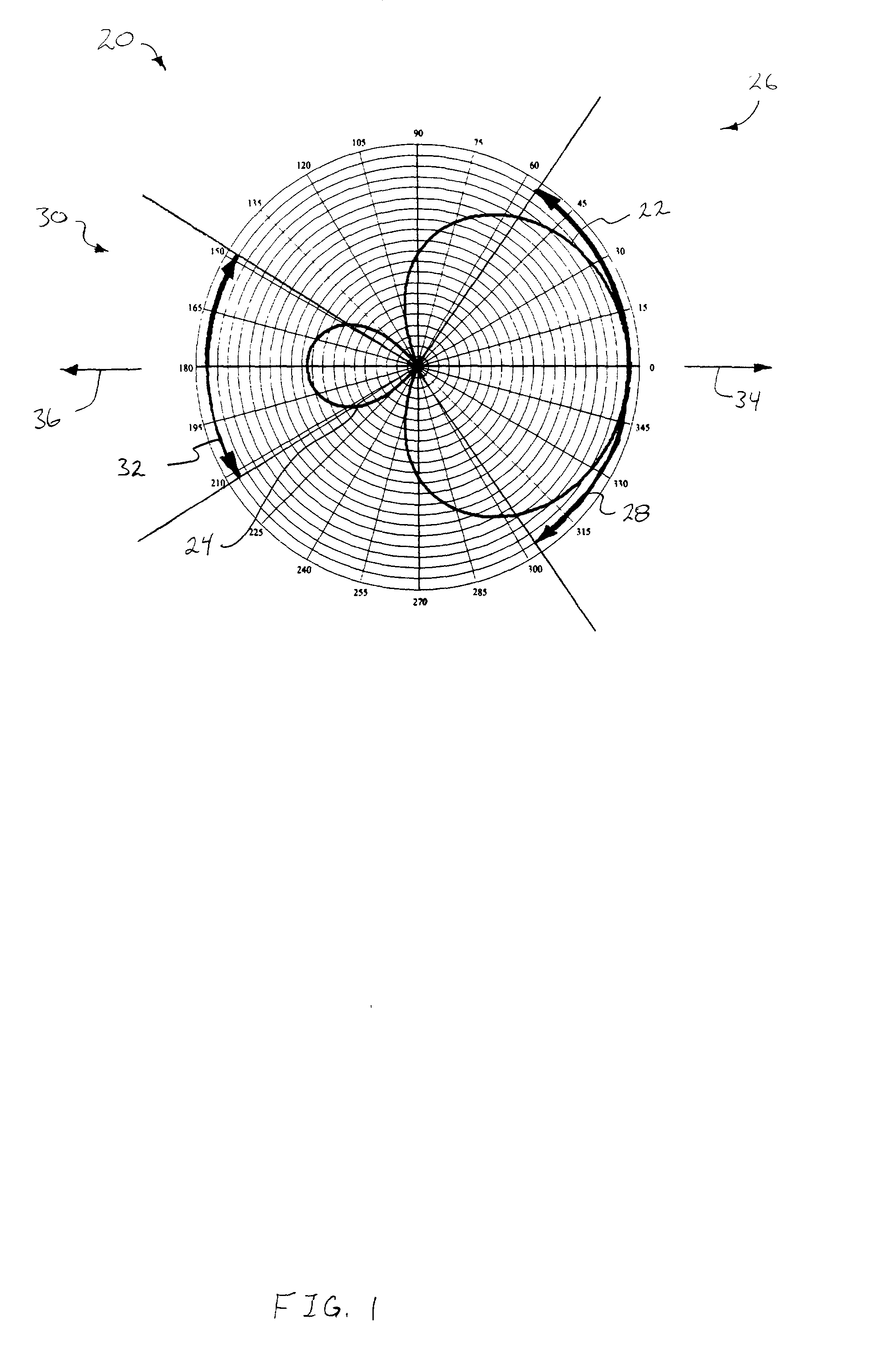
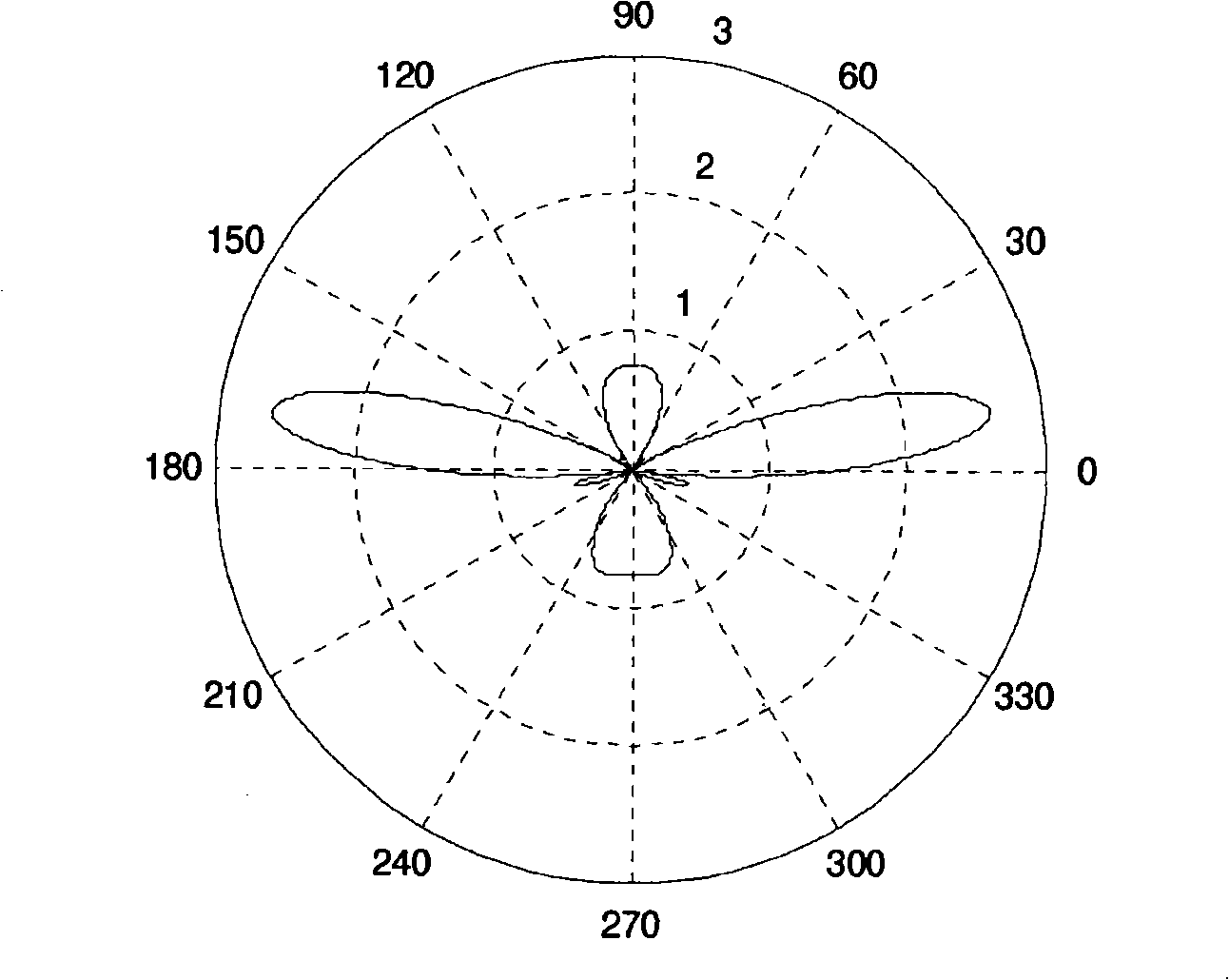
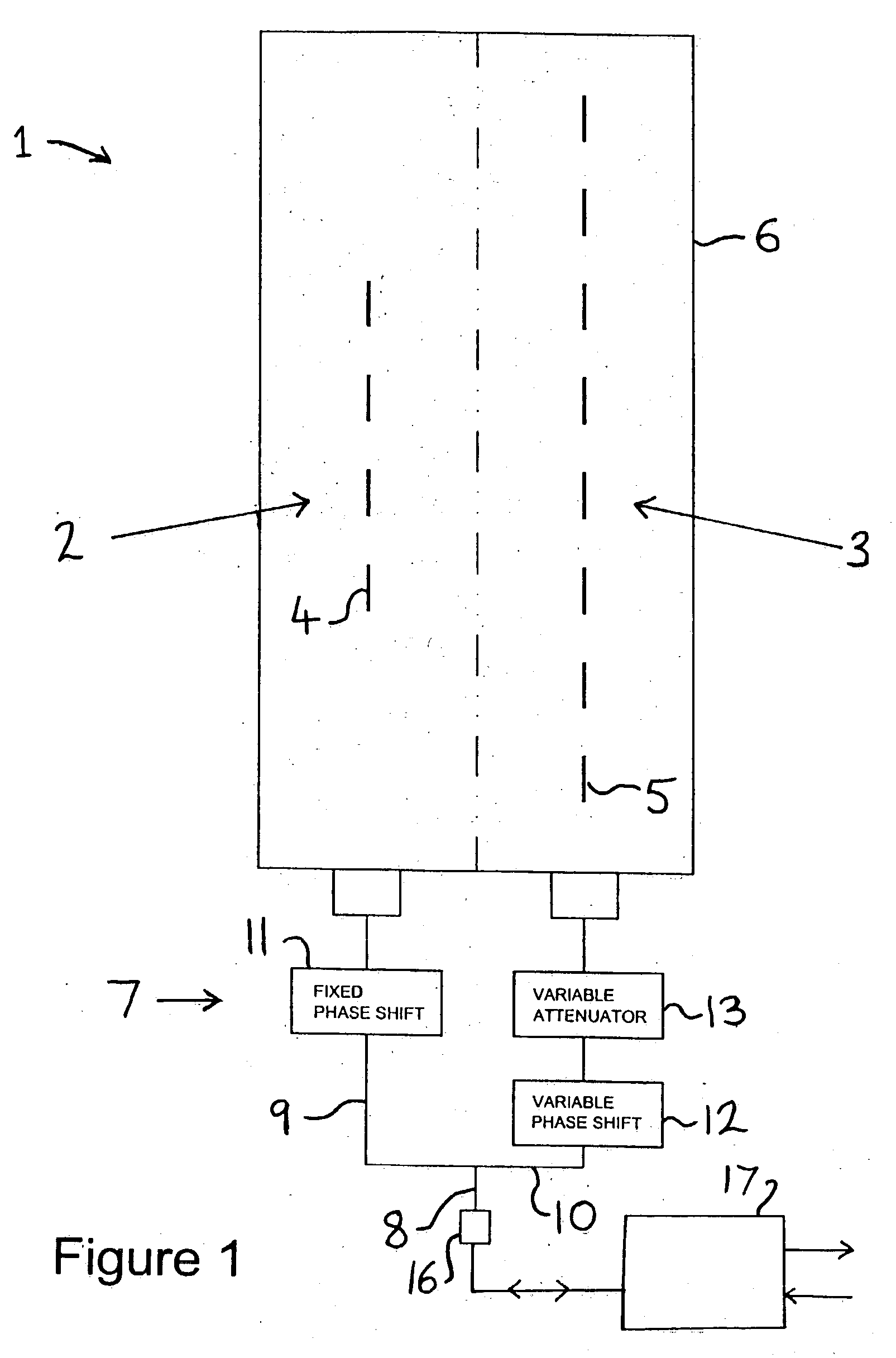
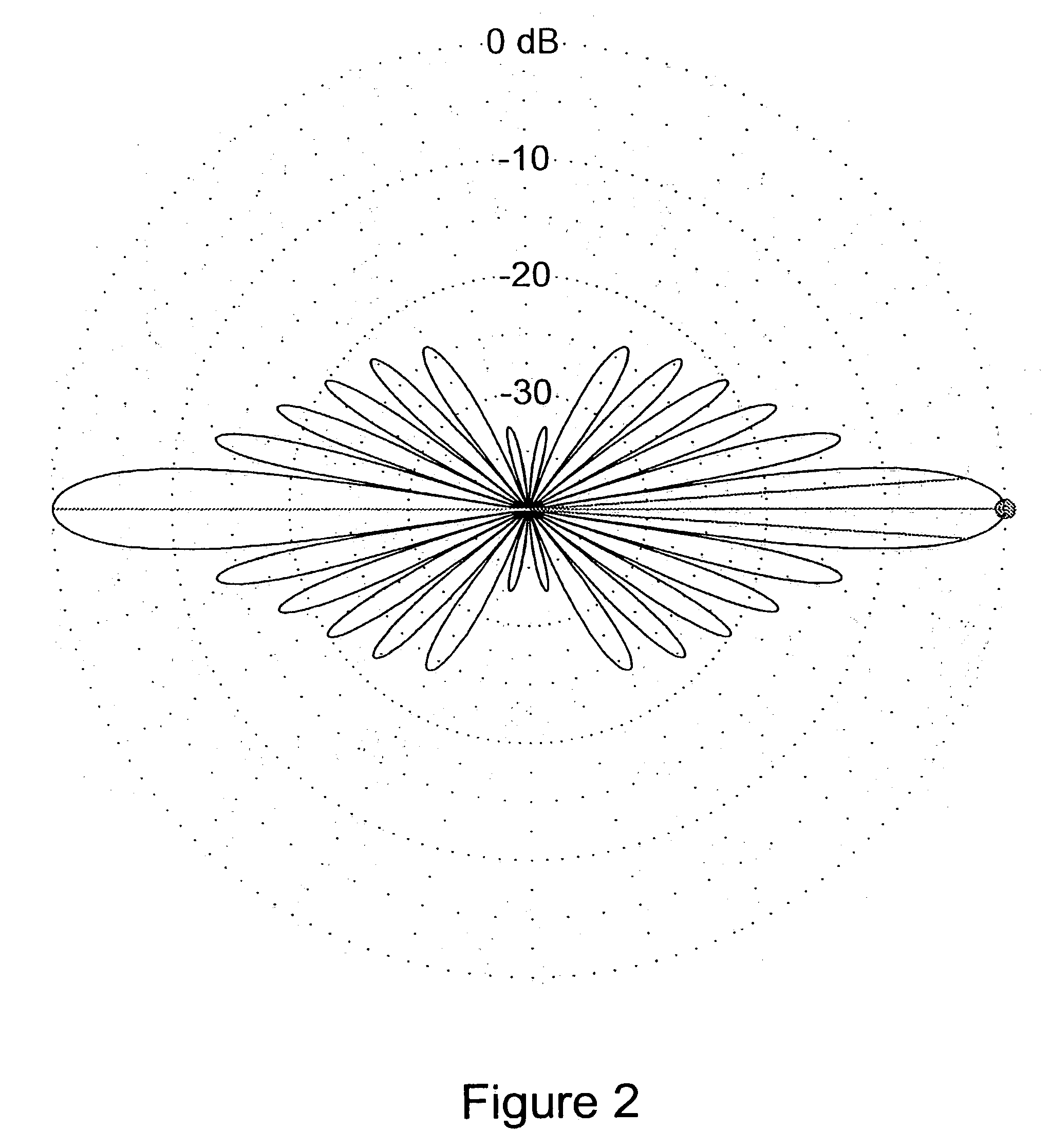
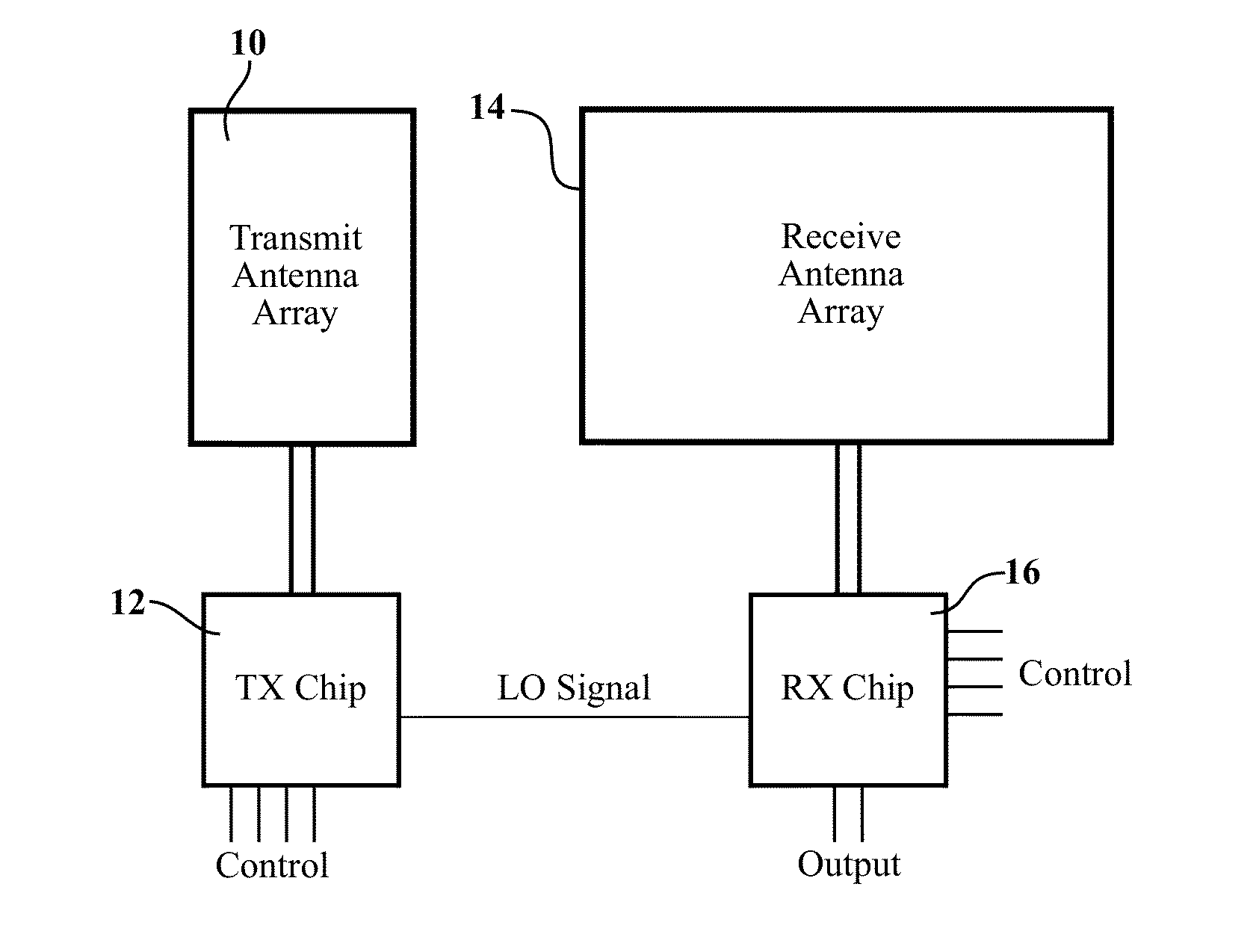
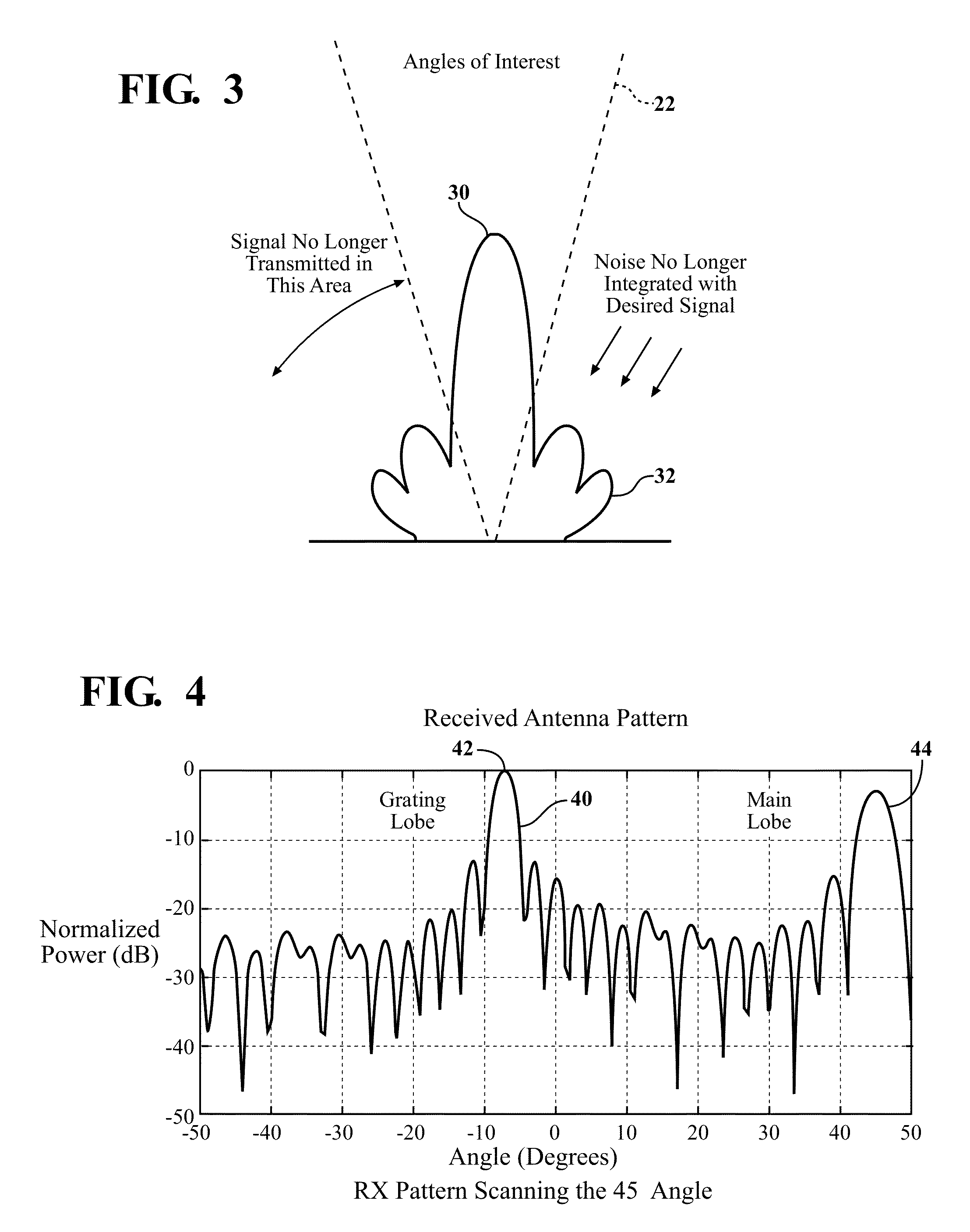
In a radio antenna's radiation pattern, the main lobe, or main beam, is the lobe containing the higher power. This is the lobe that exhibits the greater field strength. The radiation pattern of most antennas shows a pattern of "lobes" at various angles, directions where the radiated signal strength reaches a maximum, separated by "nulls", angles at which the radiation falls to zero. In a directional antenna in which the objective is to emit the radio waves in one direction, the lobe in that direction is designed to have higher field strength than the others, so on a graph of the radiation pattern it appears biggest; this is the main lobe. The other lobes are called "sidelobes", and usually represent unwanted radiation in undesired directions. The sidelobe in the opposite direction from the main lobe is called the "backlobe".
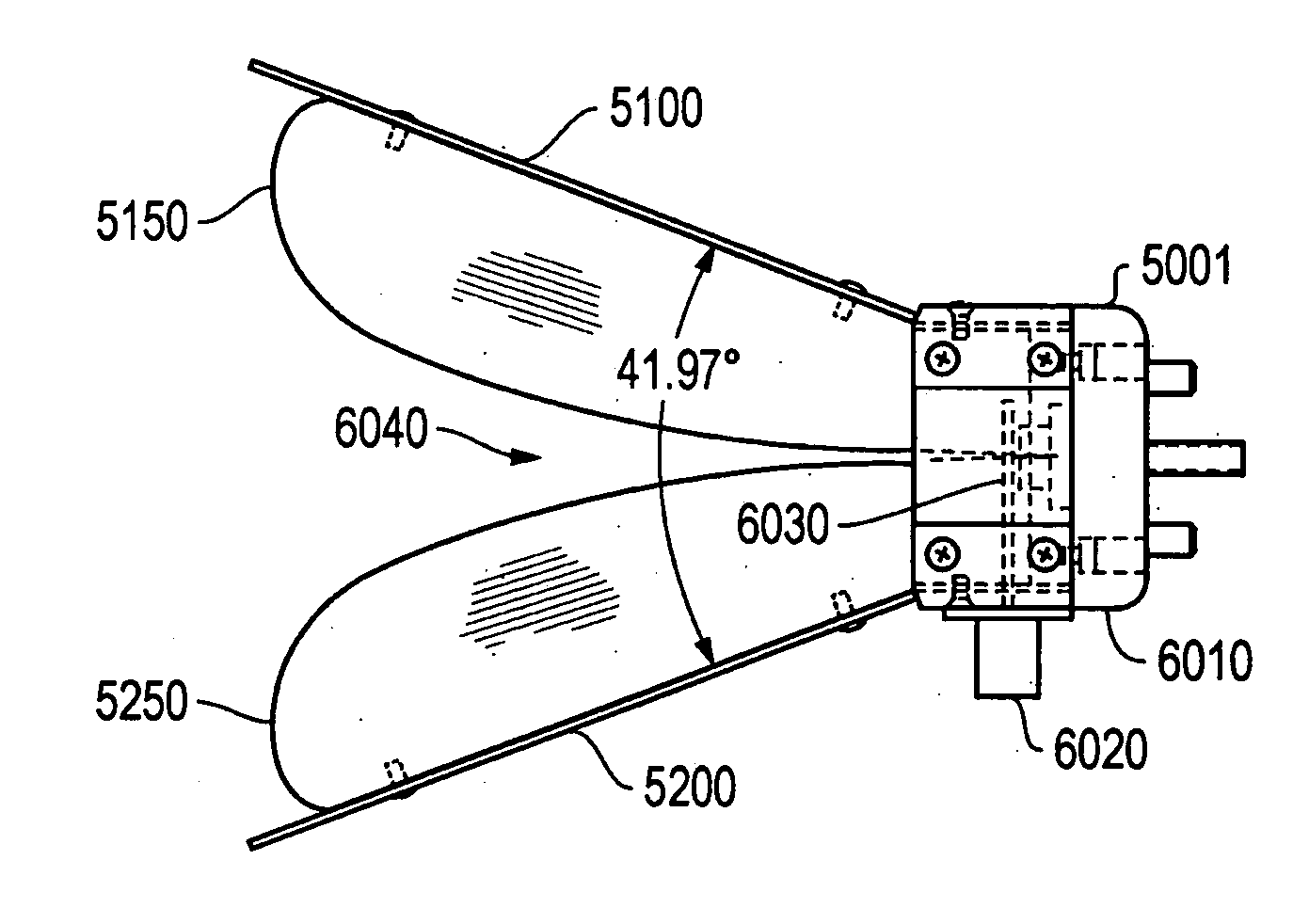
Fluid mixer with an integral fluid capture ducts forming auxiliary secondary chutes at the discharge end of said ducts
ActiveUS7434384B2Improve performanceEfficient capturePower plant exhaust arrangementsPower plant constructionEngineeringMain lobe
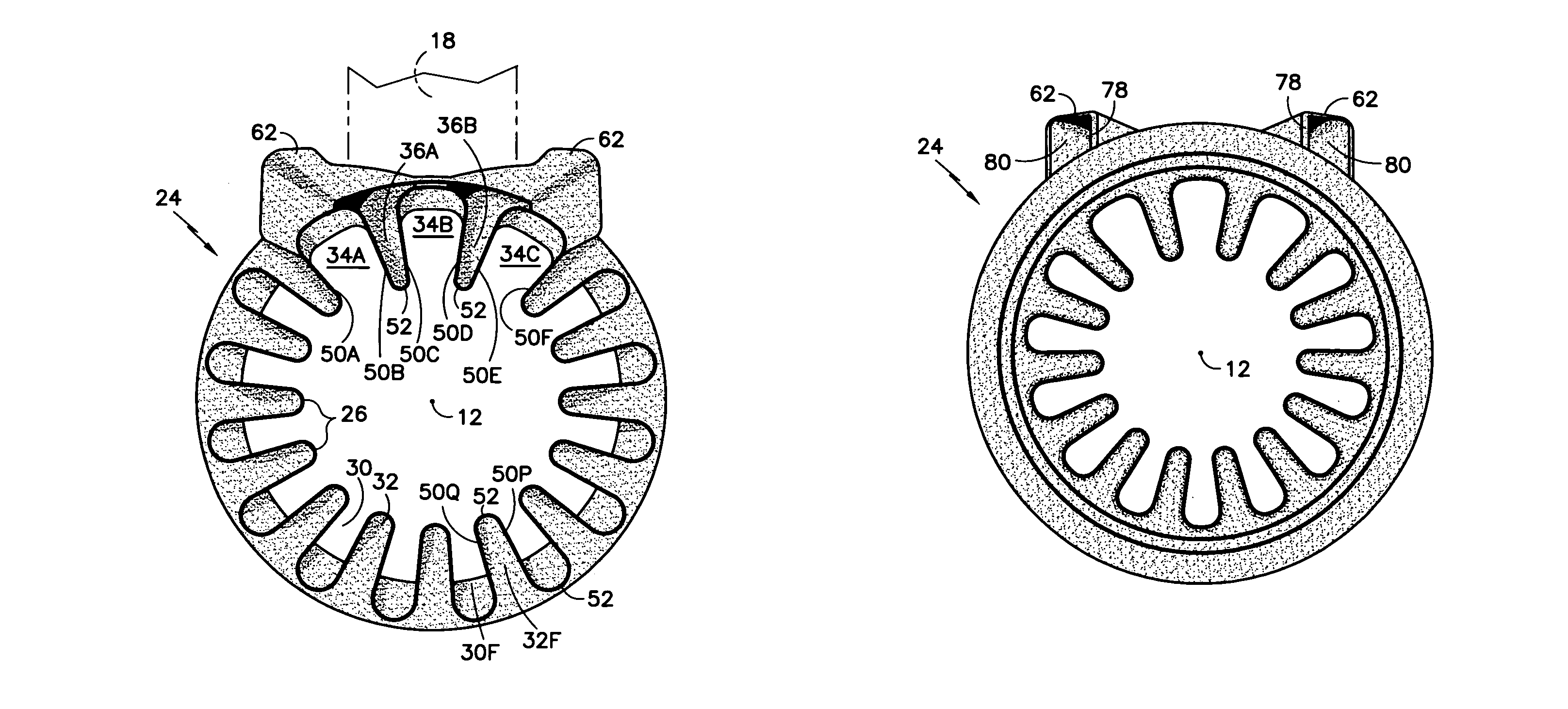
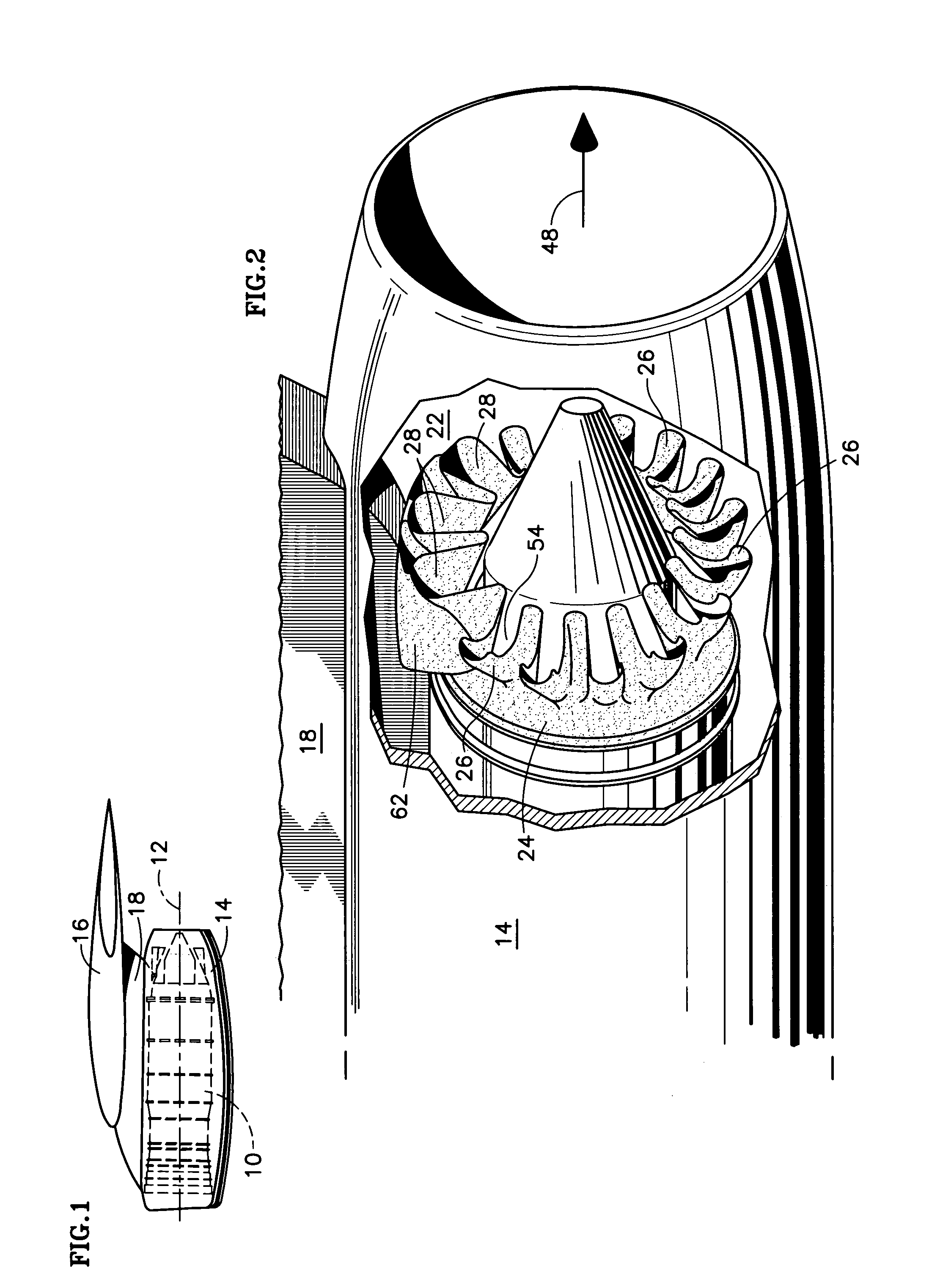
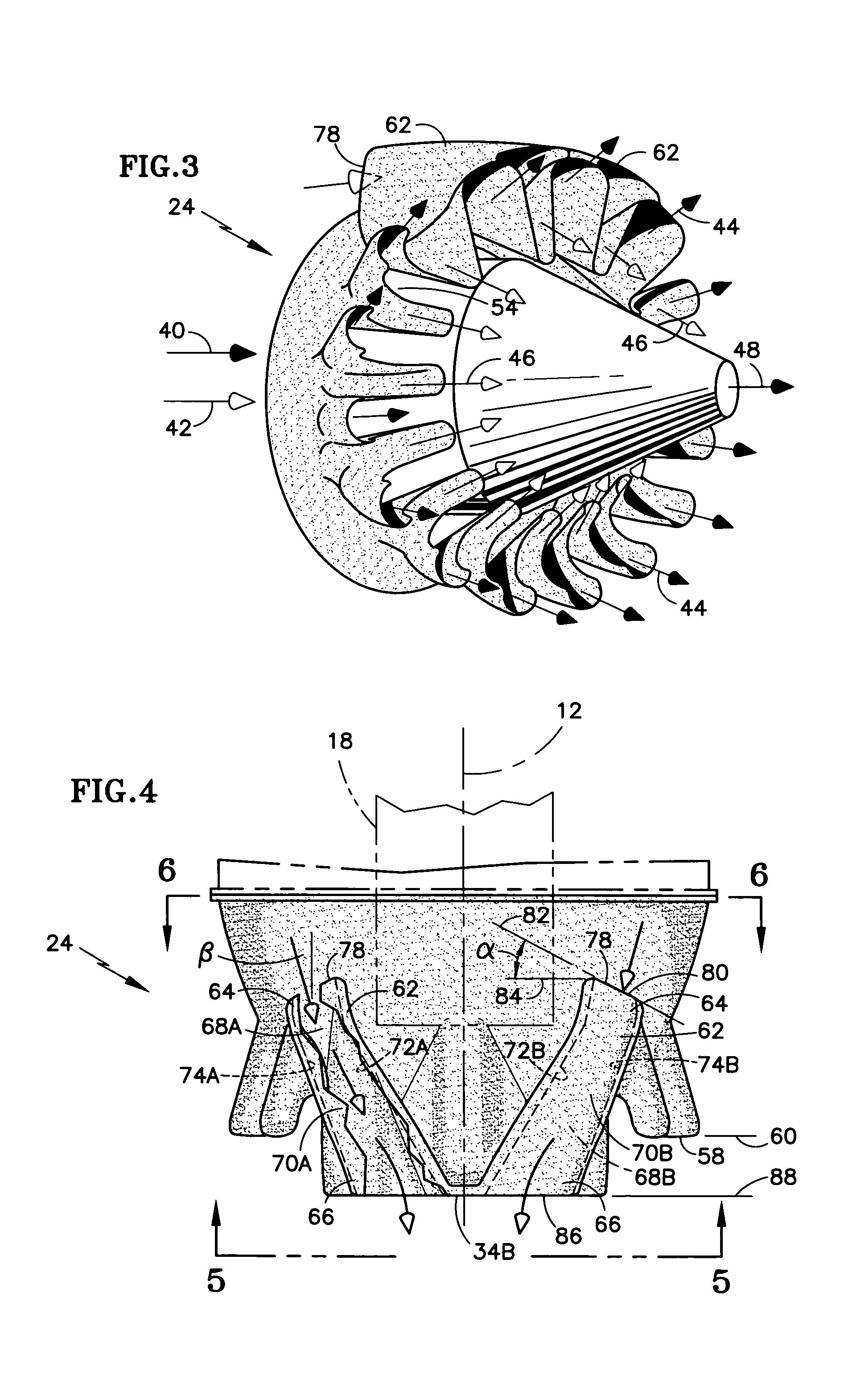
A fluid mixer for mixing two fluid streams 40, 42 includes a set of main lobes 26 defining alternating primary and secondary main chutes 30, 32, one or more auxiliary lobes 28 intermediate two of the main lobes, and an auxiliary fluid capture duct 62. The auxiliary lobes are defined, at least in part, by the discharge end of the duct. In operation, the duct conveys secondary fluid to secondary chutes 36 defined by the lobes thereby improving the performance of the mixer despite the presence of an obstruction 18 that would otherwise impede thorough mixing of two fluid streams.
Owner:RTX CORP
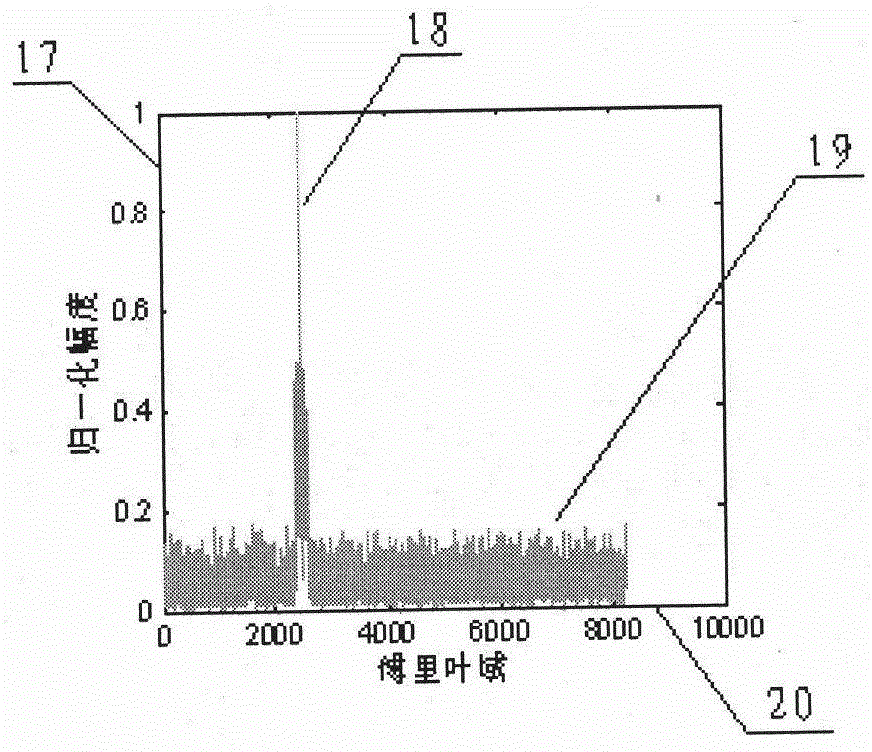
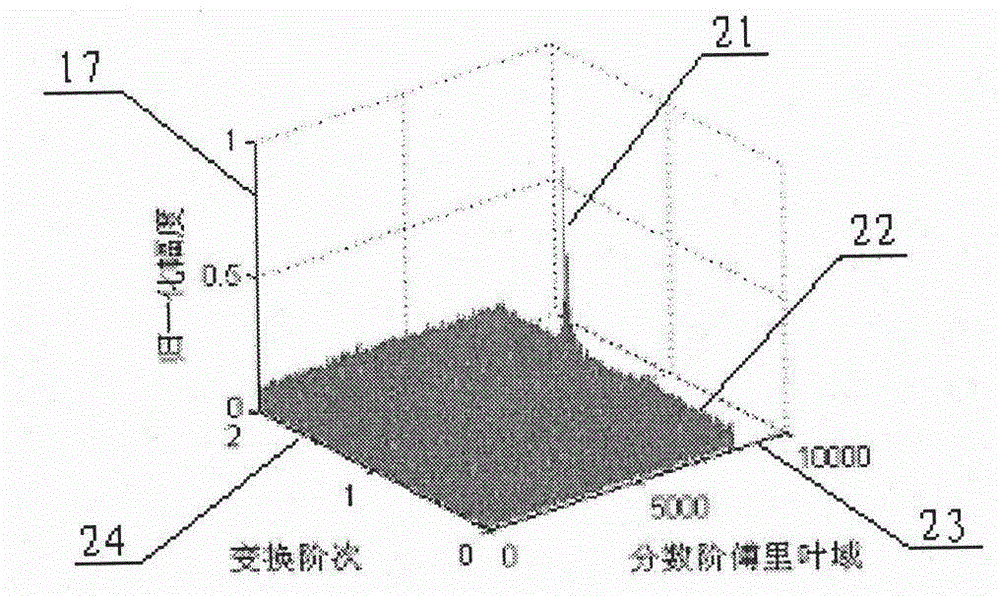
Multi-target detection method based on short-time Fourier transform and fractional Fourier transform
InactiveCN102866391AHigh-resolutionSolve the separation problemWave based measurement systemsMulti methodFrequency modulation
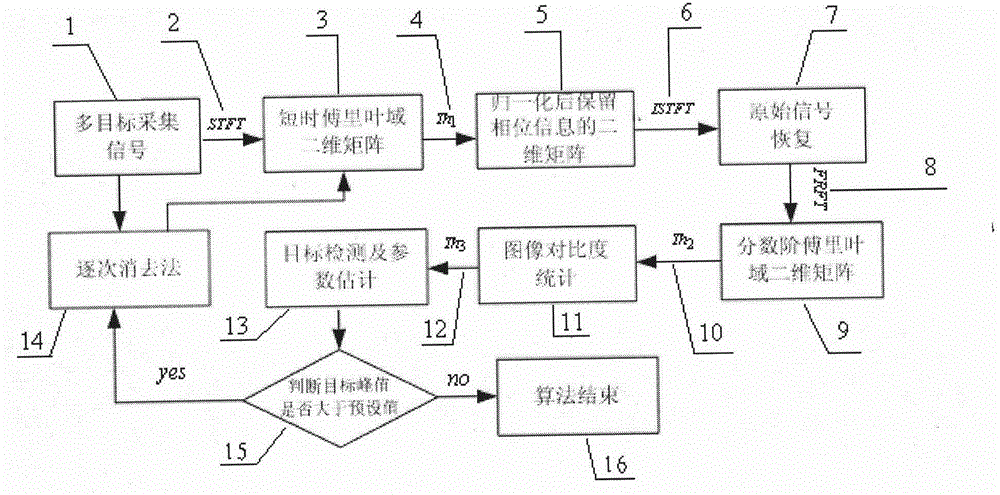
The invention discloses a multi-target detection method based on short-time Fourier transform and fractional Fourier transform, which belongs to the technical field of the radar target detection. The method comprises the following steps that the short-time Fourier transform is firstly used for conducting the primary detection on a signal, then a binaryzation method is used for processing a primary detection result, phase position of the signal is kept in the processing, the fractional Fourier transform is used for detecting a signal after being restored by the short-time Fourier transform, by adopting multiple methods for combined processing, advantages of overcoming phenomenon that a strong signal side lobe presses a weak signal main lobe, improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the signal to be detected, and solving the problem of the large false alarm possibility which is caused by adopting traditional method to detect the signal at the low signal-to-noise ratio can be realized; and meanwhile, an image contrast method and a gradual elimination method are adopted, multiple strong signals and weak signals with different or identical frequency modulation rates can be detected by utilizing the space and power strength information of the signal, so that the detection probability and the calculation efficiency can be further improved, easiness in project realization is realized, and the method is worth of being adopted and popularized.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
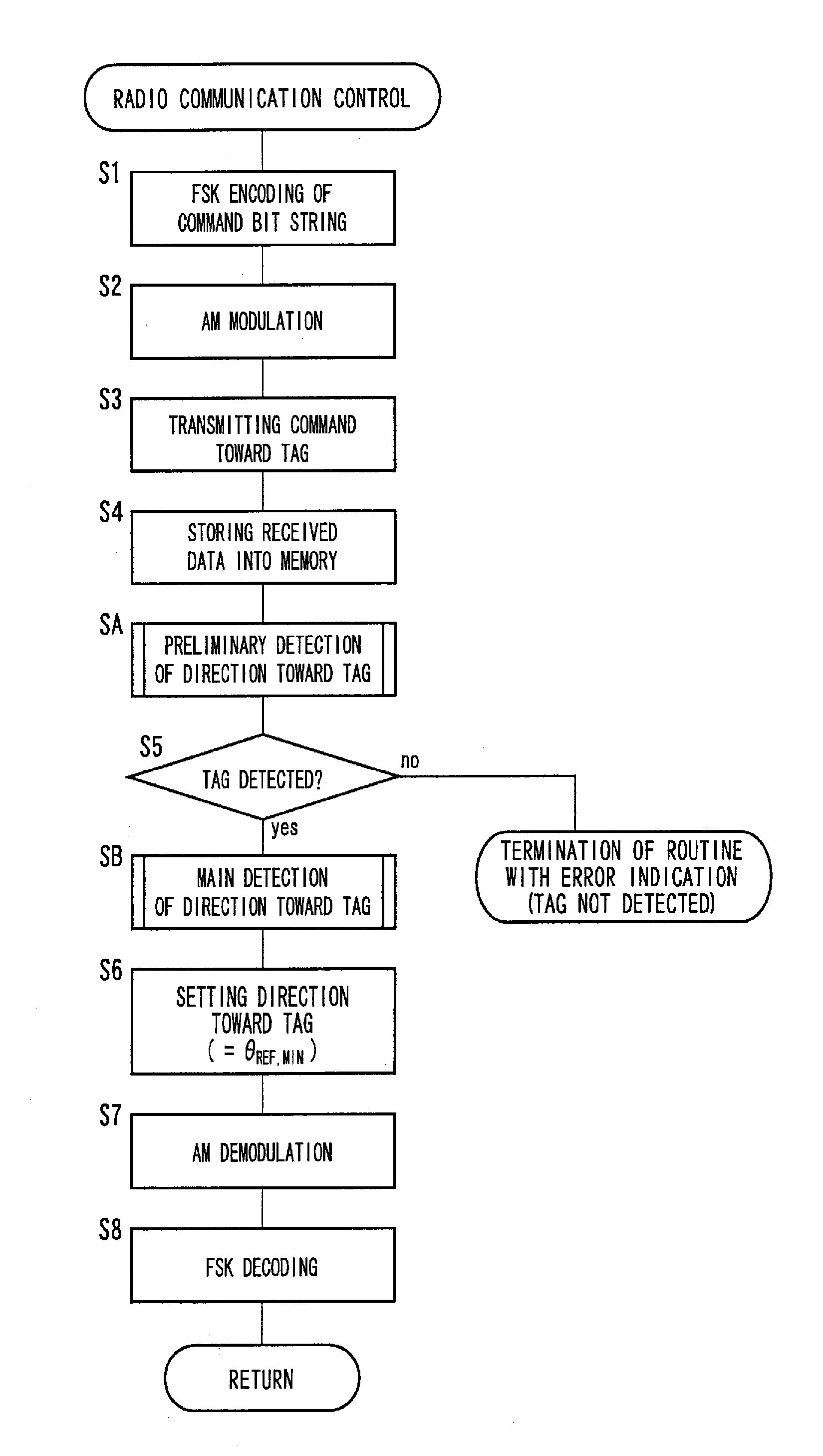
Radio-Frequency Device, And Radio-Frequency Tag Communication Device
ActiveUS20070279277A1Effective angular rangeSuitable for detectionRadio transmissionSubscribers indirect connectionImage resolutionEngineering
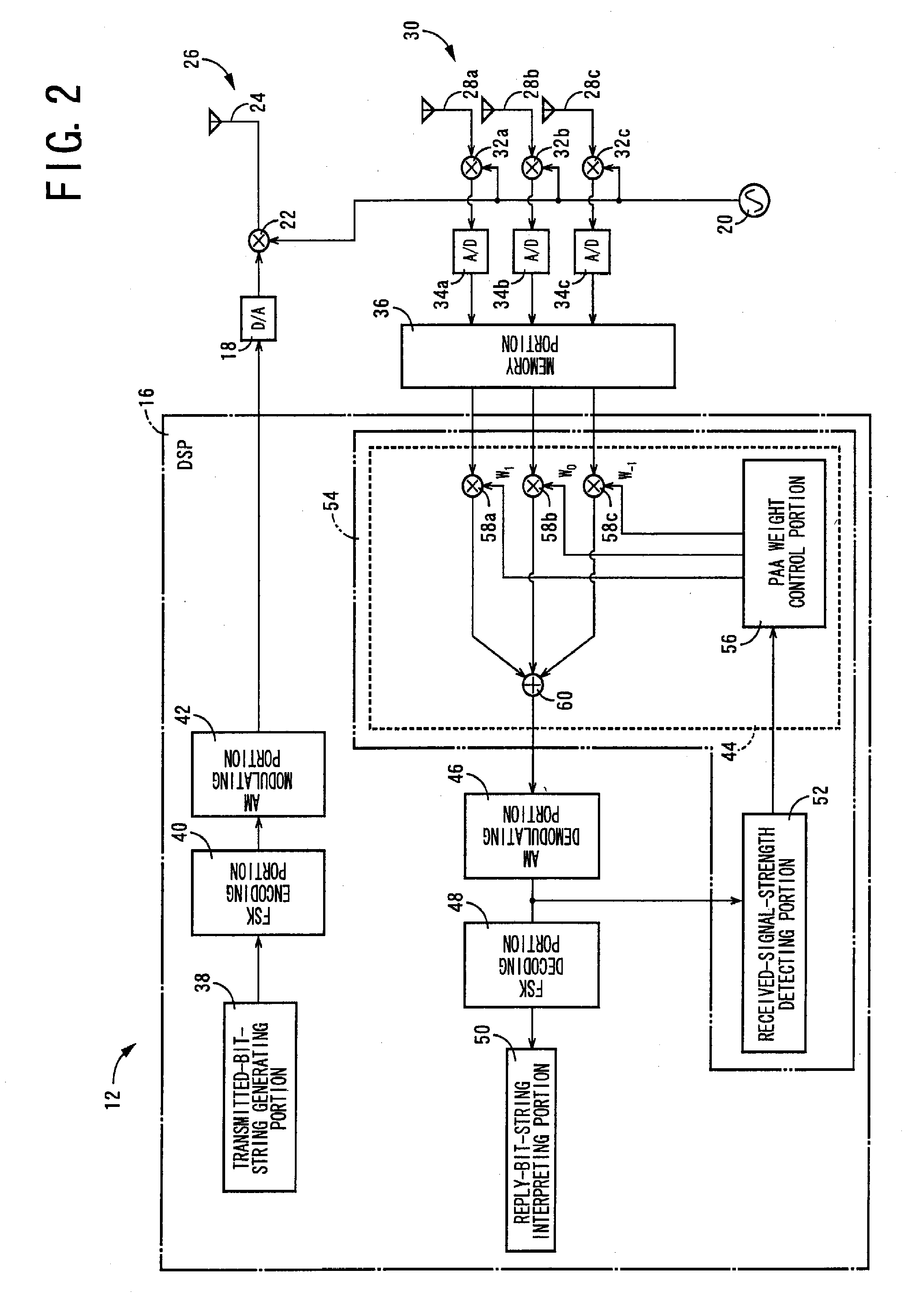
A radio-frequency device includes a PAA processing portion configured to control a directivity of reception of a receiver antenna device, a received-signal-strength detecting portion configured to detect a strength of the received signal received by the receiver antenna device, and a direction detecting portion configured to detect the direction toward the communication object, on the basis of a direction in which a higher one of two strength values of the received signal respectively detected in first and second maximum-reception-directivity directions of a predetermined angular difference established by the PAA processing portion is minimal. The direction detecting portion is operated based on a fact that the received signal strength is minimal at the bottom of a gain existing in an area of overlapping of two main lobes extending in the respective two directivity directions of the predetermined angular difference, so that the resolution of detection can be made higher than in the case based on the main lobe direction in which the sensitivity of communication with the radio-frequency tag is maximum. Accordingly, the direction toward the radio-frequency tag can be suitably detected.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Optical spot grid array printer
InactiveUS6897941B2High resolutionIncrease data rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusResistSide lobe
A high resolution and high data rate spot grid array printer system is provided, wherein an image is formed by scanning spot-grid array of optical beams across a substrate layered with a resist. High resolution is achieved by apodizing the optical beams to provide a narrower main lobe. Unwanted recordation of side lobes upon the substrate is prevented by assuring that the side lobes do not include energy above the threshold of the resist, using a memoryless resist, and by using a slanted and interleaved scan pattern adapted for use with the spot-grid array pattern and the memoryless characteristic of the resist.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
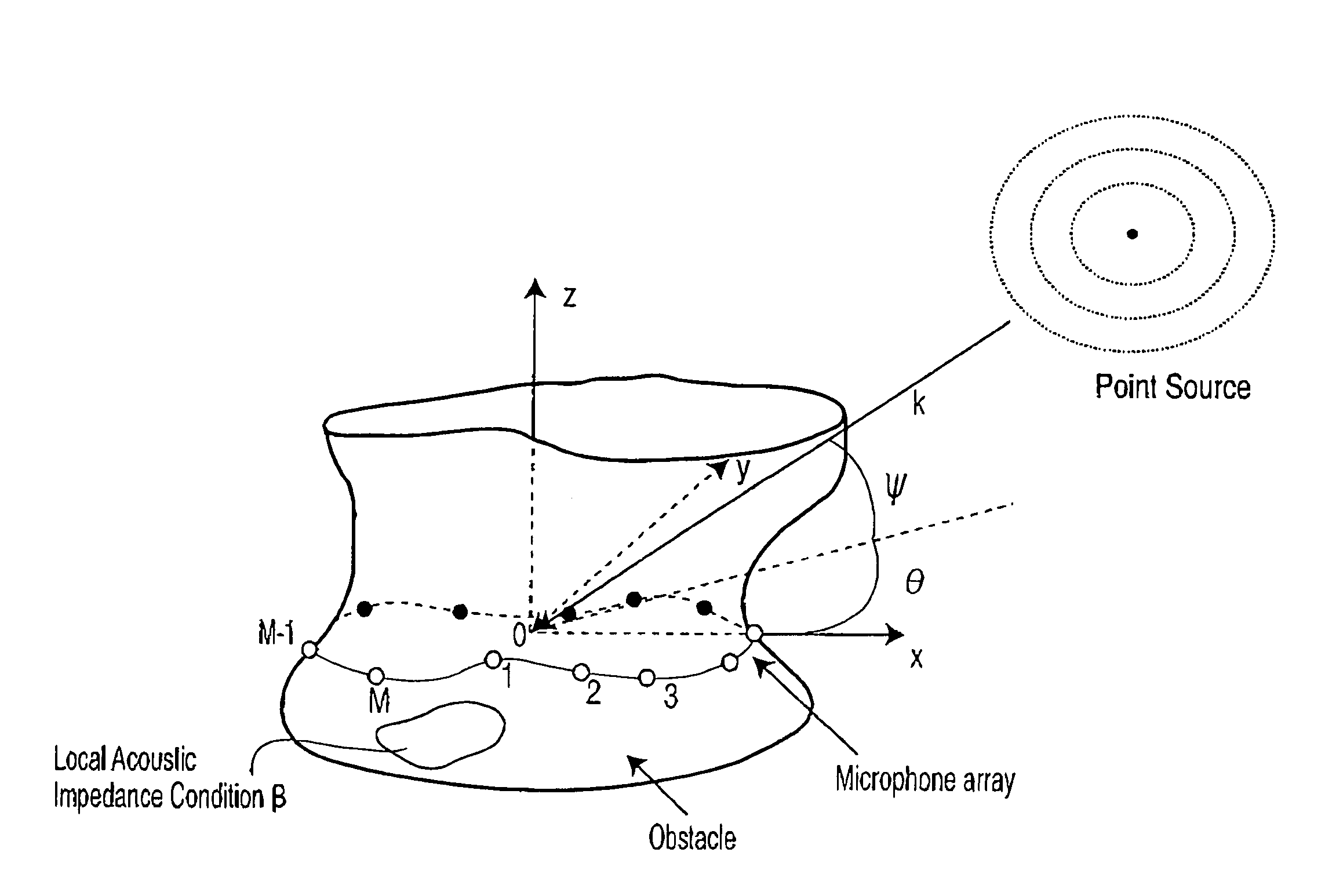
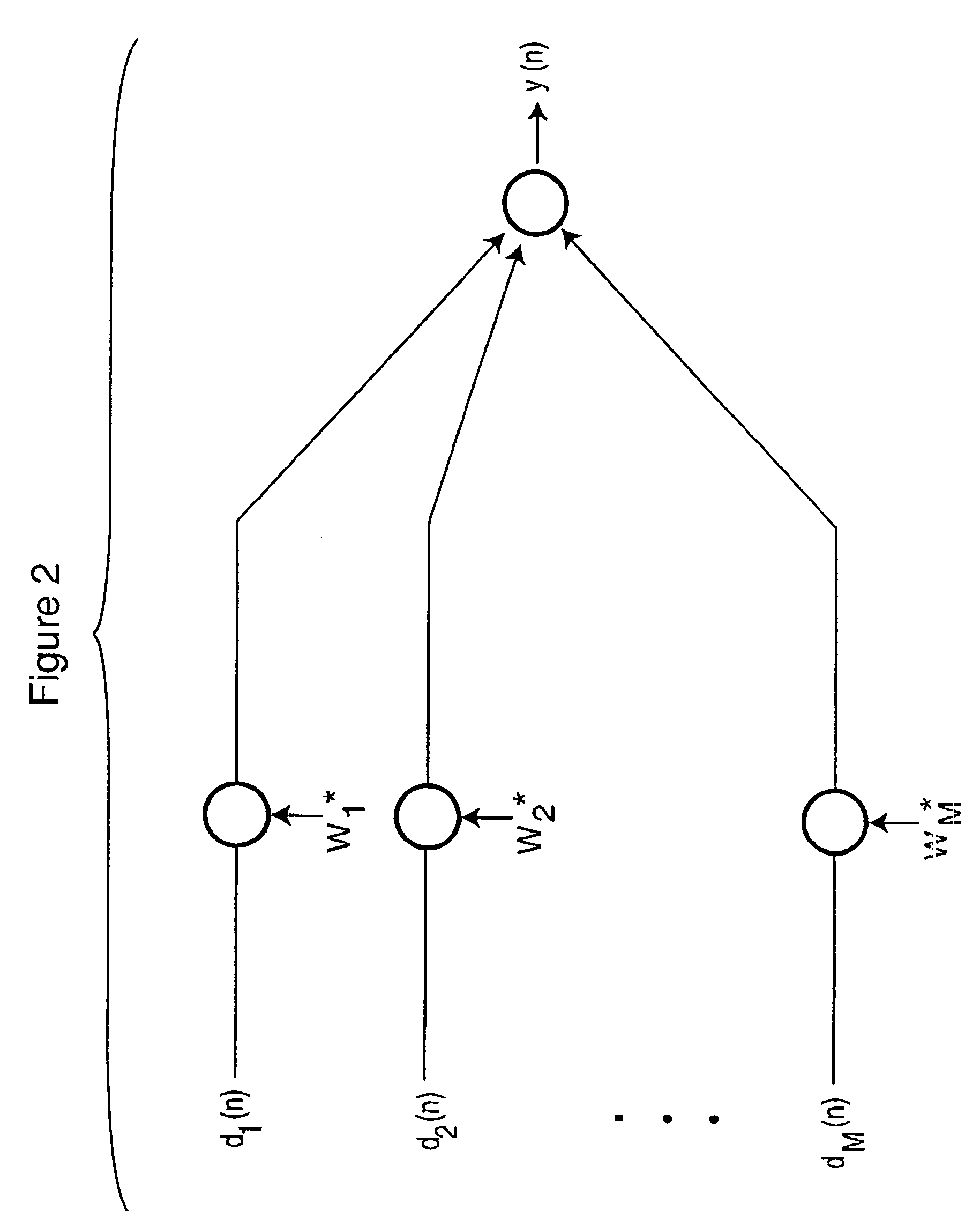
Method of broadband constant directivity beamforming for non linear and non axi-symmetric sensor arrays embedded in an obstacle
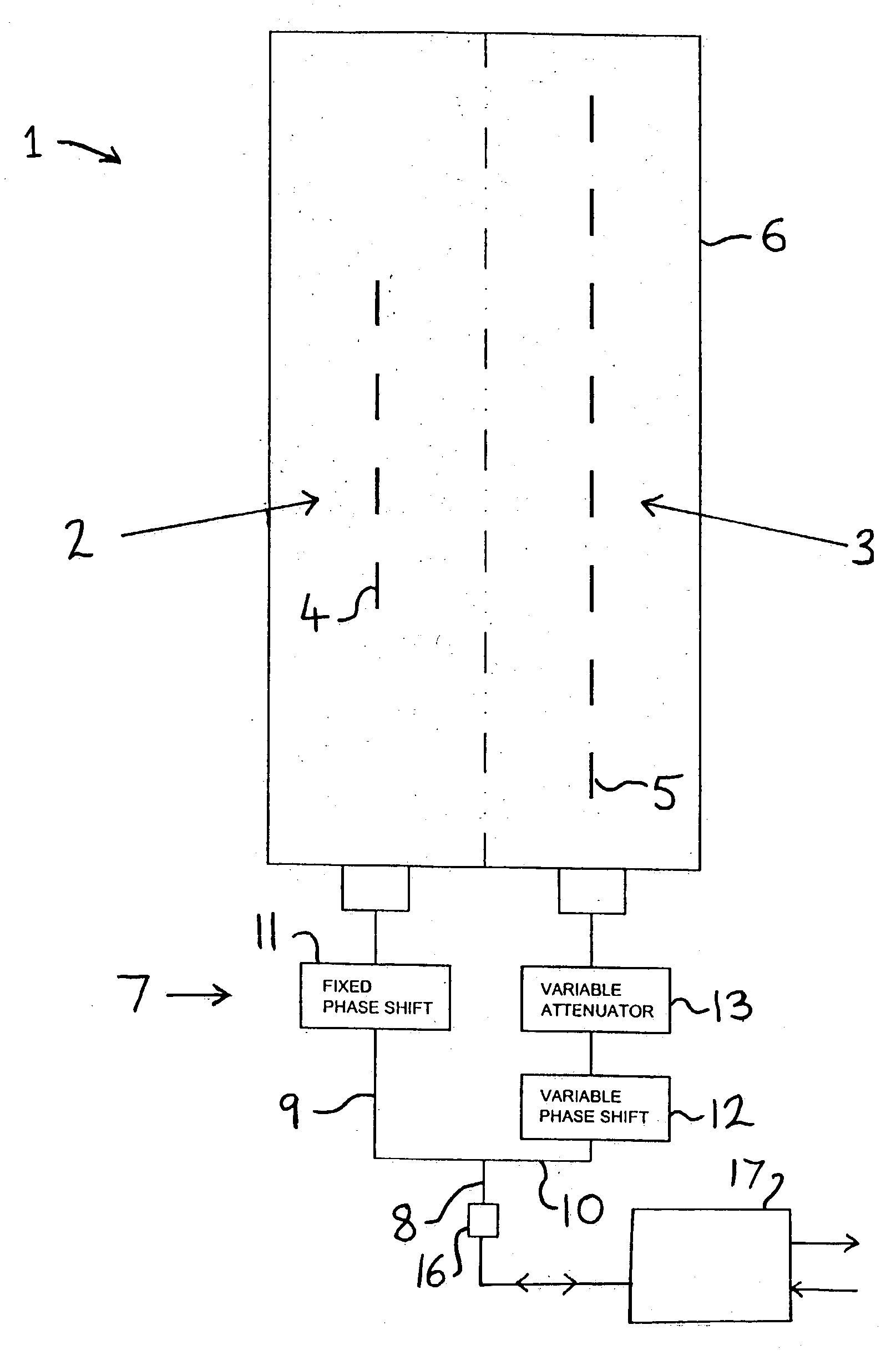
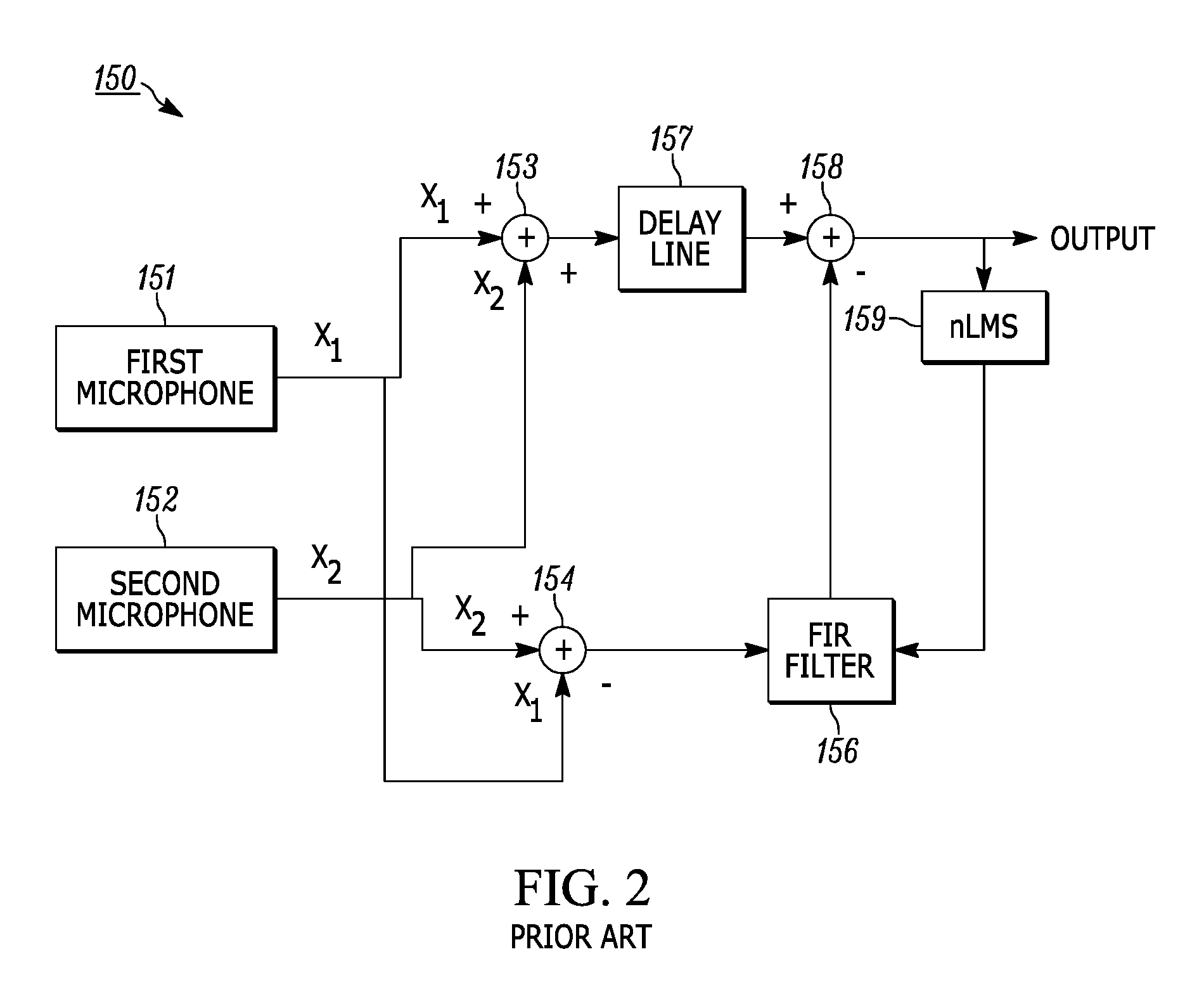
A method is provided for designing a broad band constant directivity beamformer for a non-linear and non-axi-symmetric sensor array embedded in an obstacle having an odd shape, where the shape is imposed by industrial design constraints. In particular, the method of the present invention provides for collecting the beam pattern and keeping the main lobe reasonably constant by combined variation of the main lobe with the look direction angle and frequency. The invention is particularly useful for microphone arrays embedded in telephone sets but can be extended to other types of sensors.
Owner:MITEL
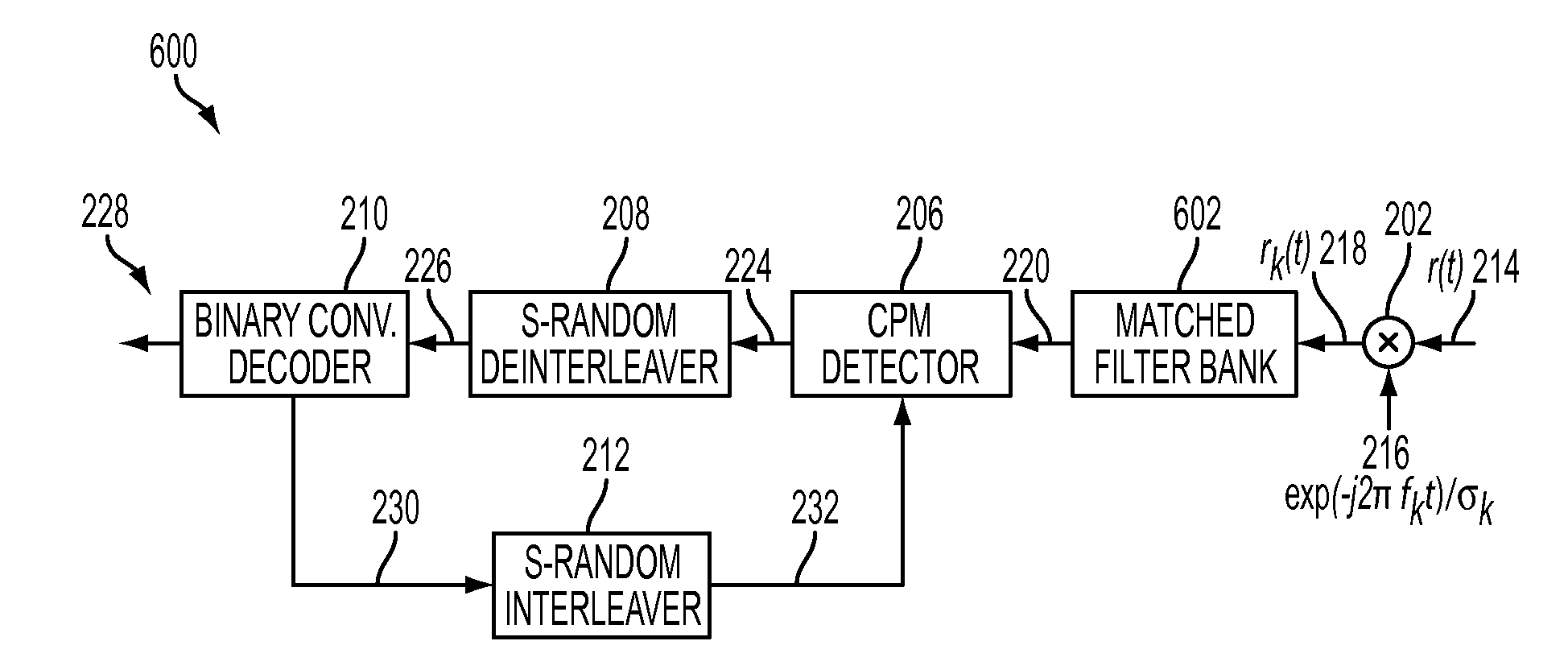
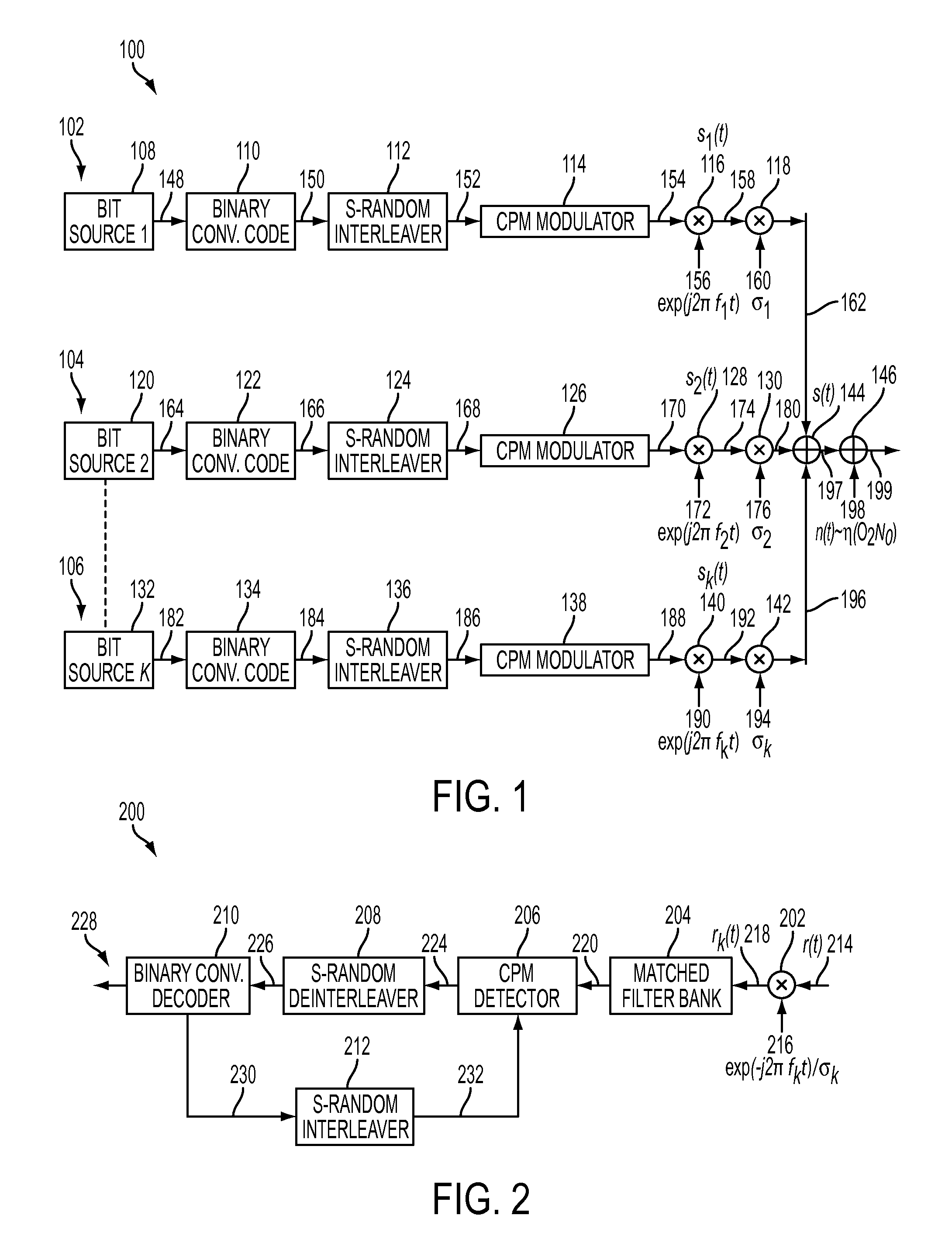
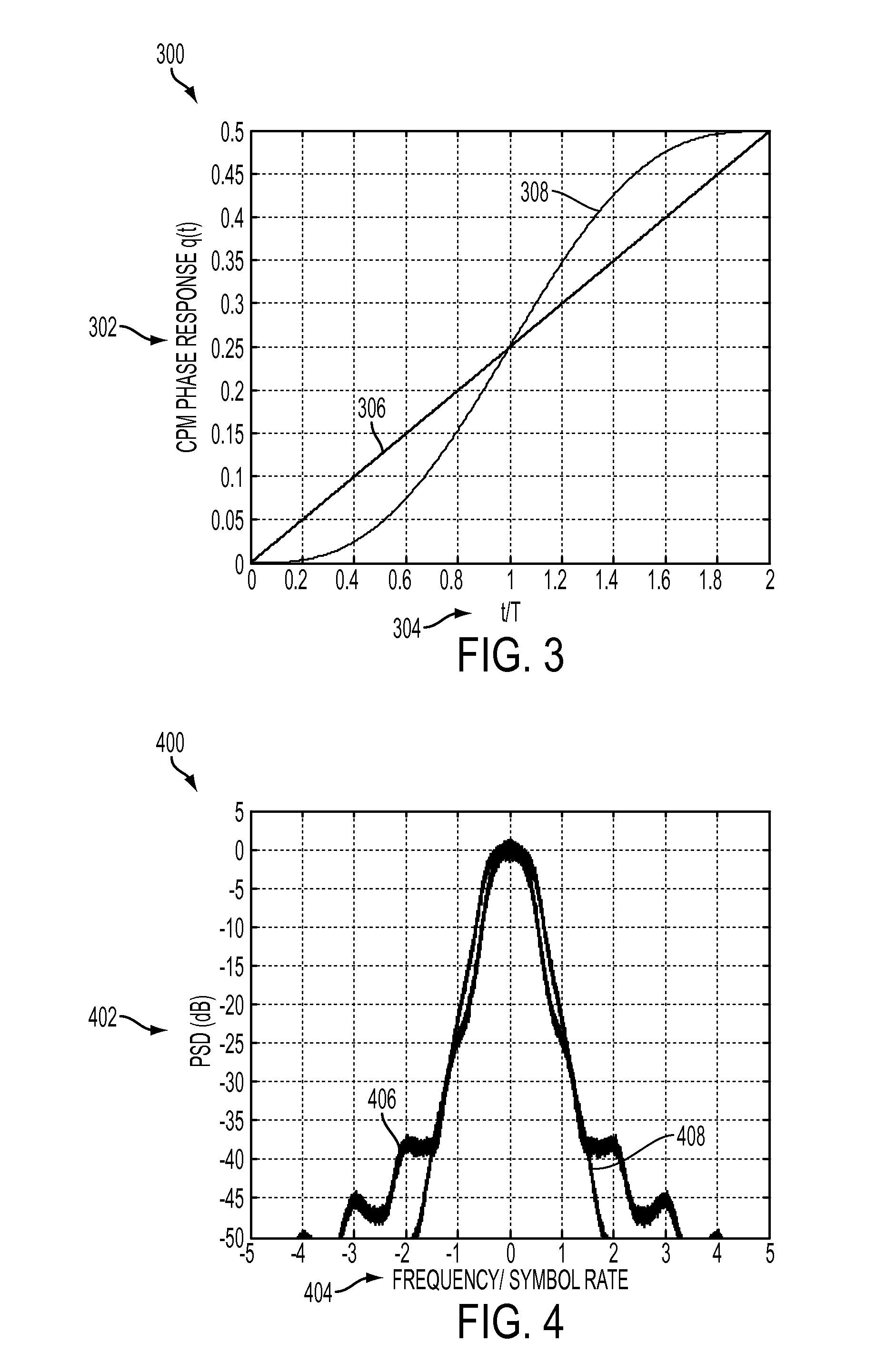
Phase pulse system and method for bandwidth and energy efficient continuous phase modulation
ActiveUS20110275338A1Improve performanceImprove bandwidth efficiencyError preventionAngle modulation detailsSide lobePulse shaping
A new pulse shape for CPM is introduced which is obtained by a linear combination of well-known RC and REC pulse shapes. The new pulse shape addresses the tradeoff between the width of the PSD main lobe and the rate of decay of the side lobe to improve the coded performance of multi-carrier systems affected by ACI. Also, a methodology is proposed to design and evaluate the performance of the new pulse shape for multi-carrier, coded systems based on the modulation constrained capacity. Furthermore, a binary convolutional code and the CPM modulator are concatenated using an S-random bit interleaver to lower the error floor. Finally, Laurent representation of the new pulse shape is suggested such that by retaining only the principal pulses at the receiver, complexity of the receiver can be reduced.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
Directional sound acquisition
ActiveUS7142677B2Reduce the impactEliminate the effects ofPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesElectrostatic transducer microphonesSignal processing circuitsDirectional sound
Directional sound acquisition is obtained by combining directional sensitivities in microphones with signal processing electronics to reduce the effects of noise received from unwanted directions. One or more microphones having directional sensitivity including a minor lobe pointing in the particular direction of interest and a major lobe pointing in a direction other than the particular direction are used. Signal processing circuitry reduces the effect of sound received from directions of a microphone major lobe.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Ultrasound transmit beamformer integrated circuit and method
ActiveUS20050033168A1Compact implementationLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsPulse envelopeSonification
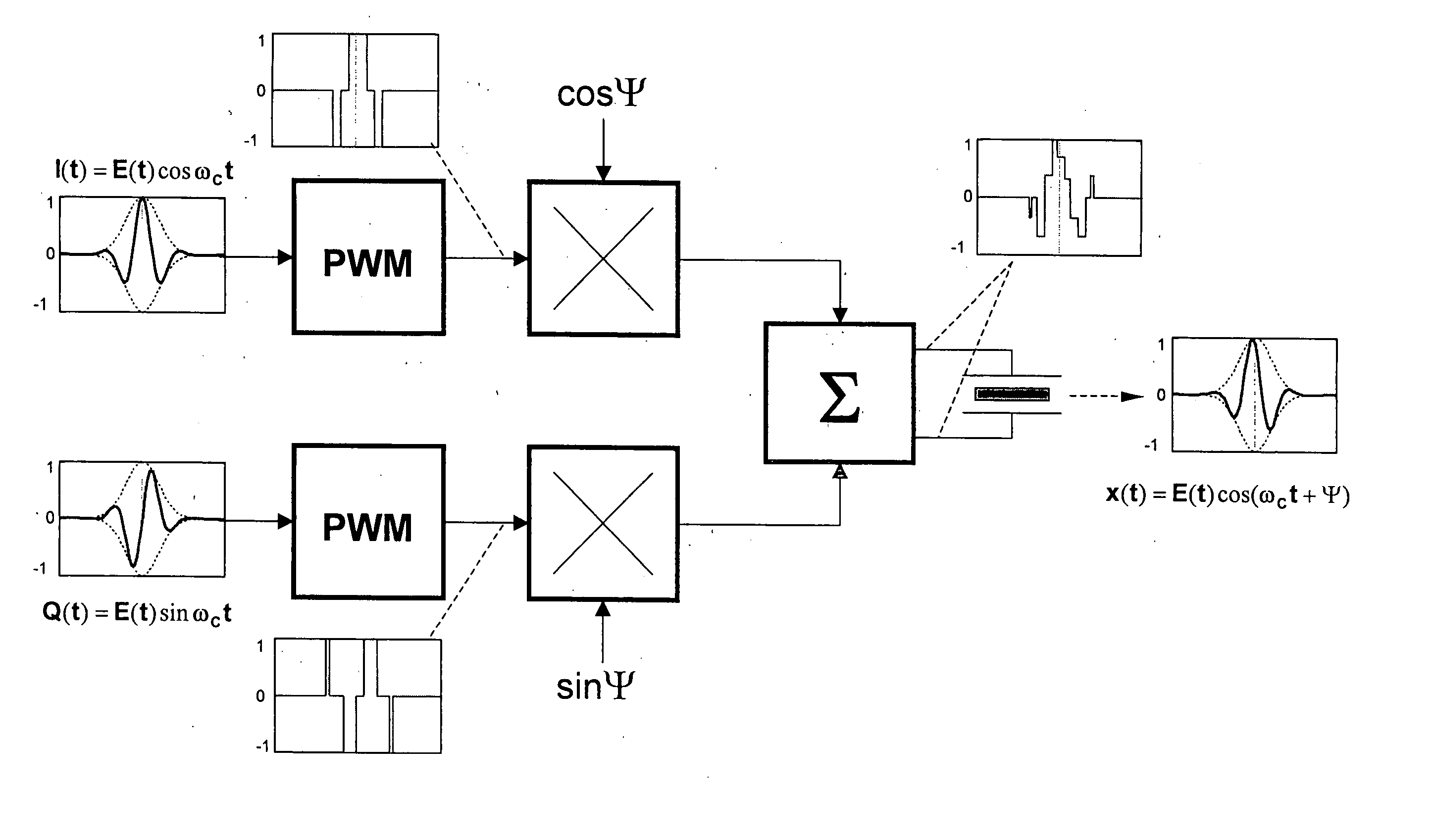
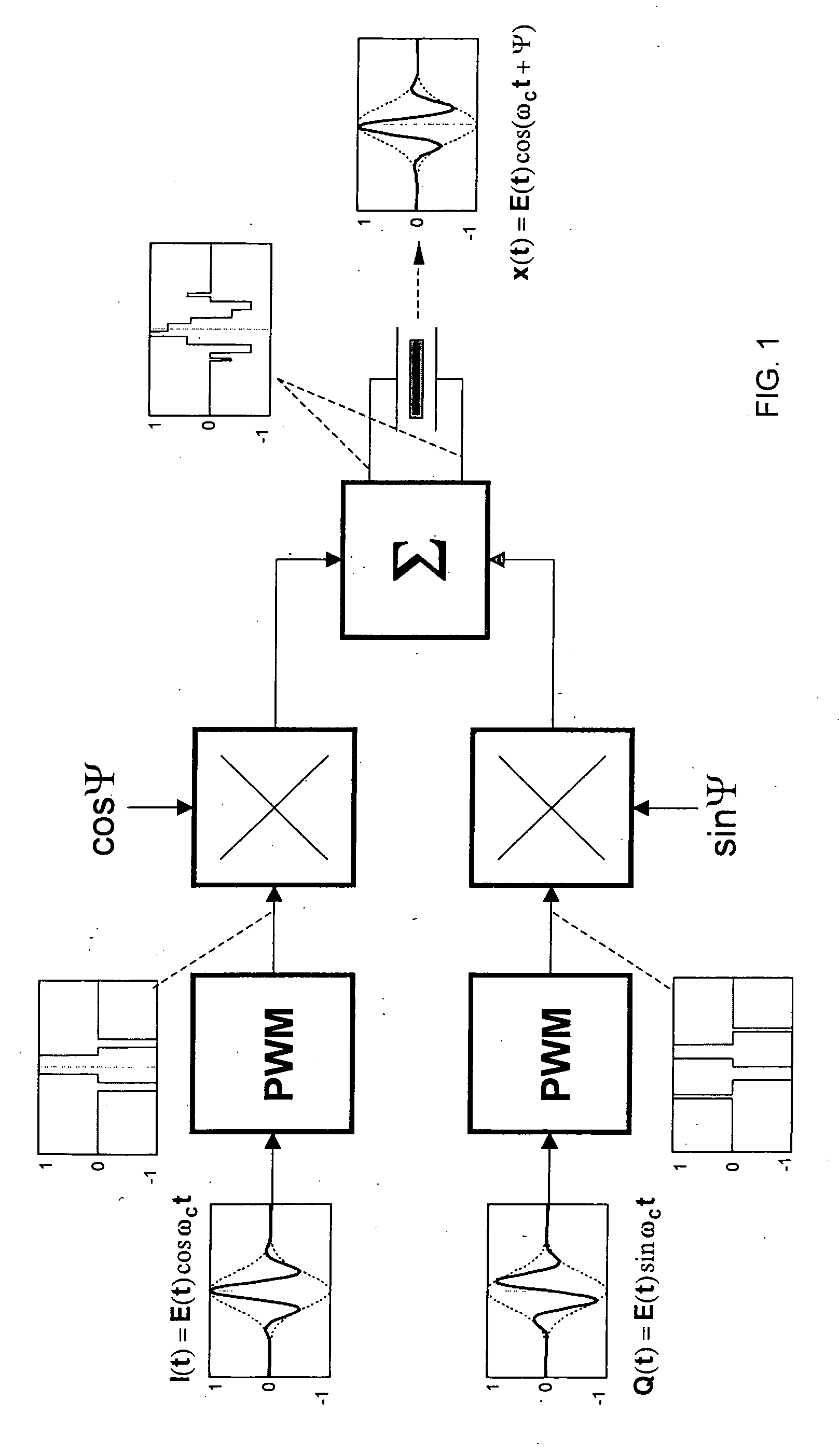
The invention provides a novel method of transmit beamforming, which allows compact analog implementation of complex digital algorithms without compromising their features. It is aimed to support envelope shaping, apodization, and phase rotation per channel and per firing. Each of three embodiments represents a complete transmit channel driven by pulse-width modulated (PWM) waveforms stored in a conventional sequence memory. PWM signals controls the transmit pulse envelope (shape) by changing the duty cycle of the carrier. Beamformation data are loaded prior to a firing via serial interface. Under the direction of a controller, the circuitry allows high precision (beyond sampling rate) phase rotation of the carrier. It also provides transmit apodization (aperture weighting), which maintains an optimal trade-off among low sidelobe level and widening of the mainlobe. Implementing such an IC, the manufacturing cost of a high-end ultrasound system can be reduced. Equally, the proposed solution makes the benefits of digital transmit beamformers available to midrange and entry-level machines since it merely requires a modified programming of the sequence memory.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
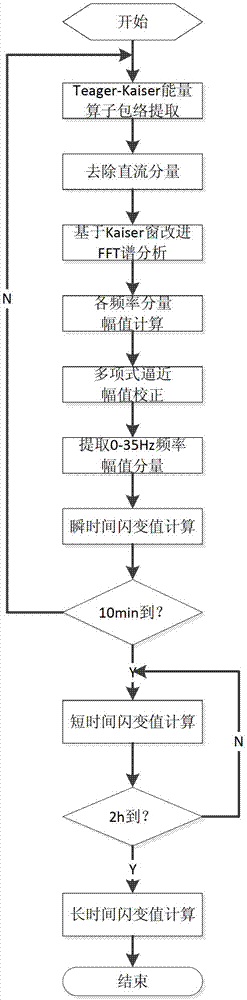
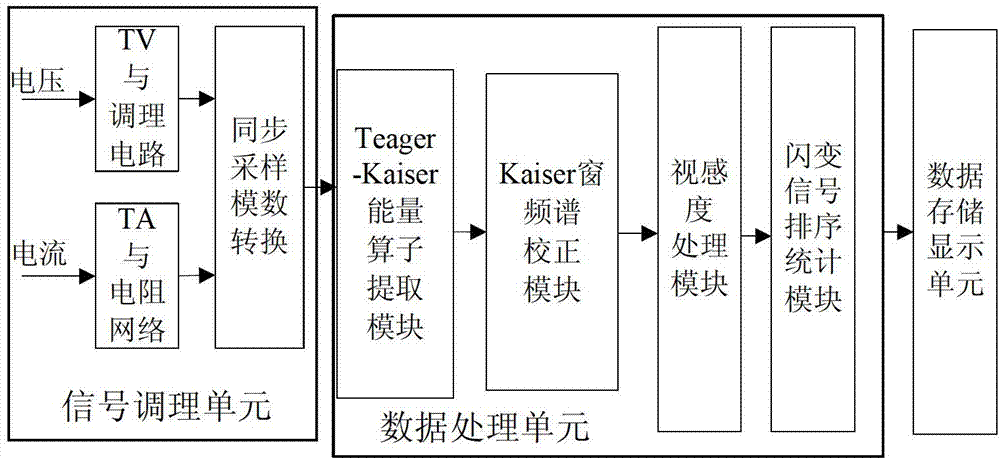
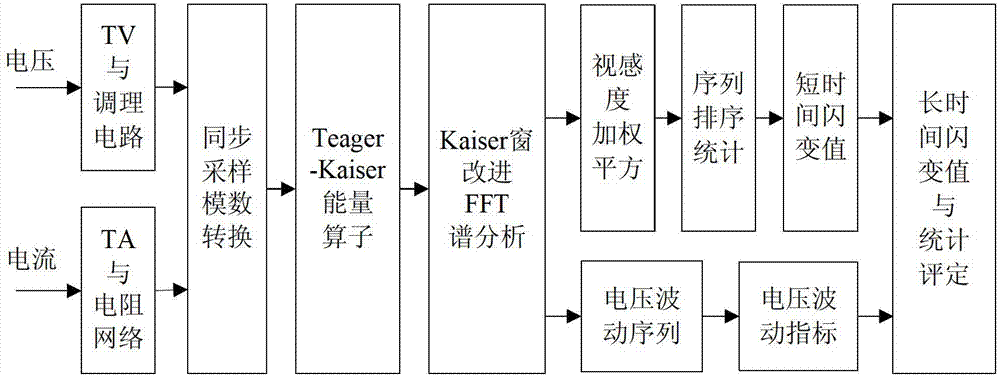
Method and device for detecting voltage fluctuation and flicker based on energy operator and spectrum correction
InactiveCN103116064AContinuous detectionLong-term detectionSpectral/fourier analysisMeasurement using digital techniquesFrequency spectrumEngineering
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting voltage fluctuation and flicker based on an energy operator and spectrum correction. The method comprises the steps of: extracting an envelope signal of a voltage flicker signal by utilizing a Teager-Kaiser energy operator, and speeding up an operational speed to overcome influences from change of parameters such as a signal frequency, a waveform, an amplitude value and a sampled data length during the extraction of the flicker envelope signal and realize rapid and real-time detection of the flicker signal; and performing improved FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) spectrum correction analysis on the voltage flicker signal by adopting a Kaiser window function with a freely selectable proportion of a width of a main lobe to a height of a side lobe, and exactly obtaining the frequency and the amplitude component of the voltage flicker signal when the frequency, the waveform and the amplitude value of the flicker signal are changed excessively. The device based on the method comprises a signal conditioning unit, a data processing unit and a data storage and display unit all of which are connected in order. The detecting method is convenient for rapid and in-time detection process of the signal; and the device has a simple structure and is easy to realize.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Light source unit, phase type optical element, and laser beam scanning device
ActiveUS20080019255A1Add depthImprove light utilization efficiencyInking apparatusRecord information storageLight beamSide lobe
A light source unit is disclosed. The light source unit includes a phase type optical element which modulates a phase distribution of laser beams emitted from a light source. The phase type optical element has a phase distribution so that a first ratio of the peak intensity of side lobe laser beams to the peak intensity of main lobe laser beams in a beam intensity profile at a focal position of the laser beam condensing element is greater than a second ratio of the peak intensity of side lobe laser beams to the peak intensity of main lobe laser beams in the beam intensity profile at the focal position of the laser beam condensing element when it is assumed that the phase type optical element is not disposed.
Owner:RICOH KK
Generating method for multi-user beam shaping emission value
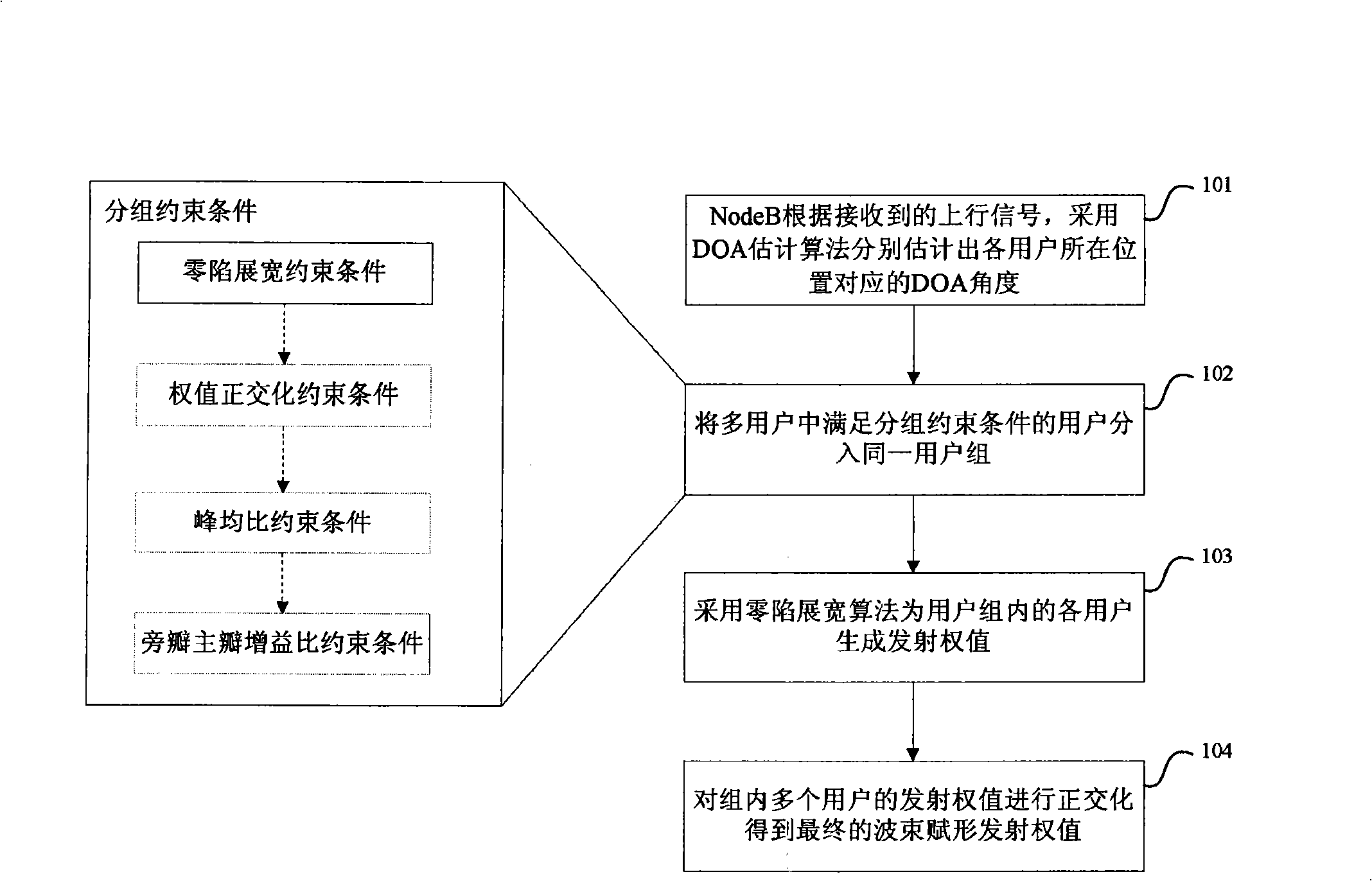
InactiveCN101340648AEffective multiplexingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationComputer scienceMain lobe
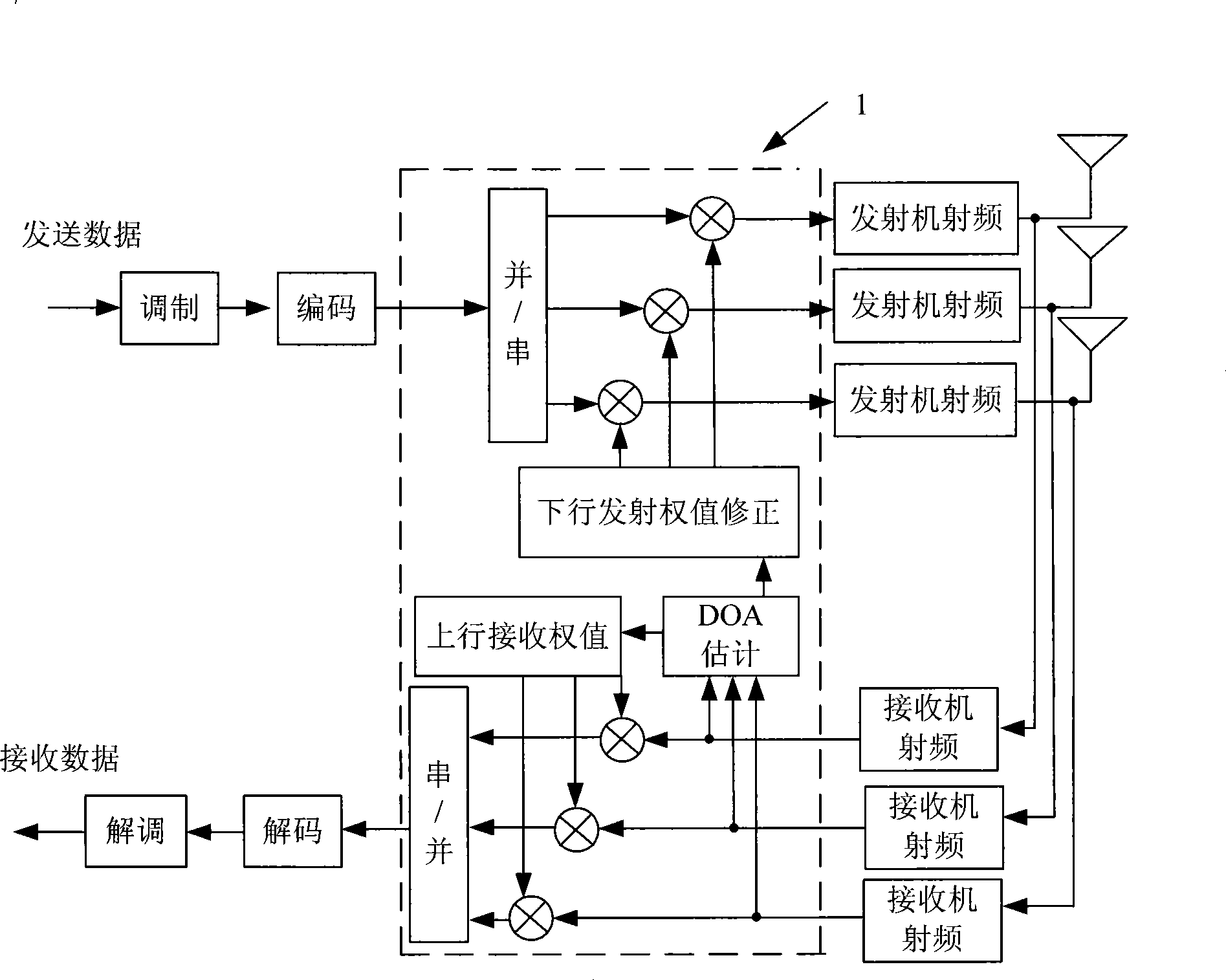
The invention relates to a method for generating multi-user beam-forming launch weight, which comprises steps that: a base station estimates the DOA angle of each user by DOA arithmetic according to a received up run signal; the base station distributes users who meet grouping constraints into the same user group. The grouping constraints include: as to two random users Uj and Uk, corresponding Theta and Theta is required to meet: the absolute value of (Theta minuses Theta) is larger than or equal to Sigma that is multiplied by Delta Theta; wherein, Sigma is larger than or equal to 0.5 and smaller than or equal to 2; Delta Theta is a null width value used by broadening null width algorithm; as to user U in the user group, Thetai is used as a main lobe direction and theta1, ... thetai-1, theta i+1, ... theta are used as the null directions; the launch weight of the U is generated by the broadening null width algorithm. In conclusion, without using a code, the method of the invention is used for generating the launch weight for multiple users, and at the same time, time, frequency and code resources effectively multiplexed by the multiple users with relatively small interference can be realized.
Owner:ZTE CORP
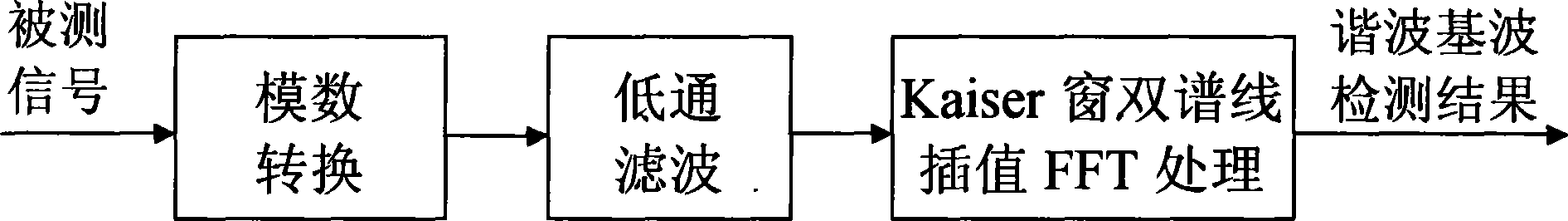
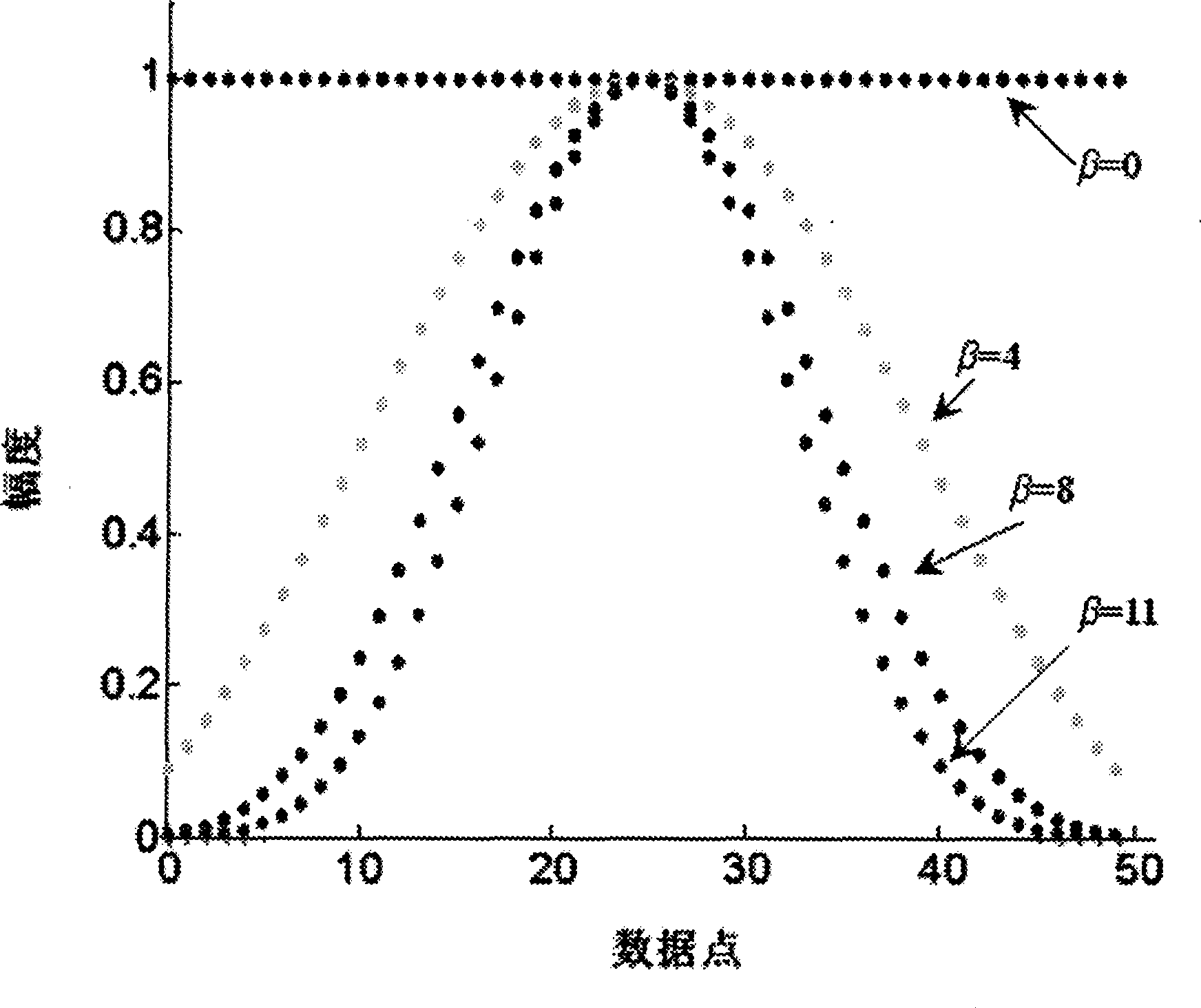
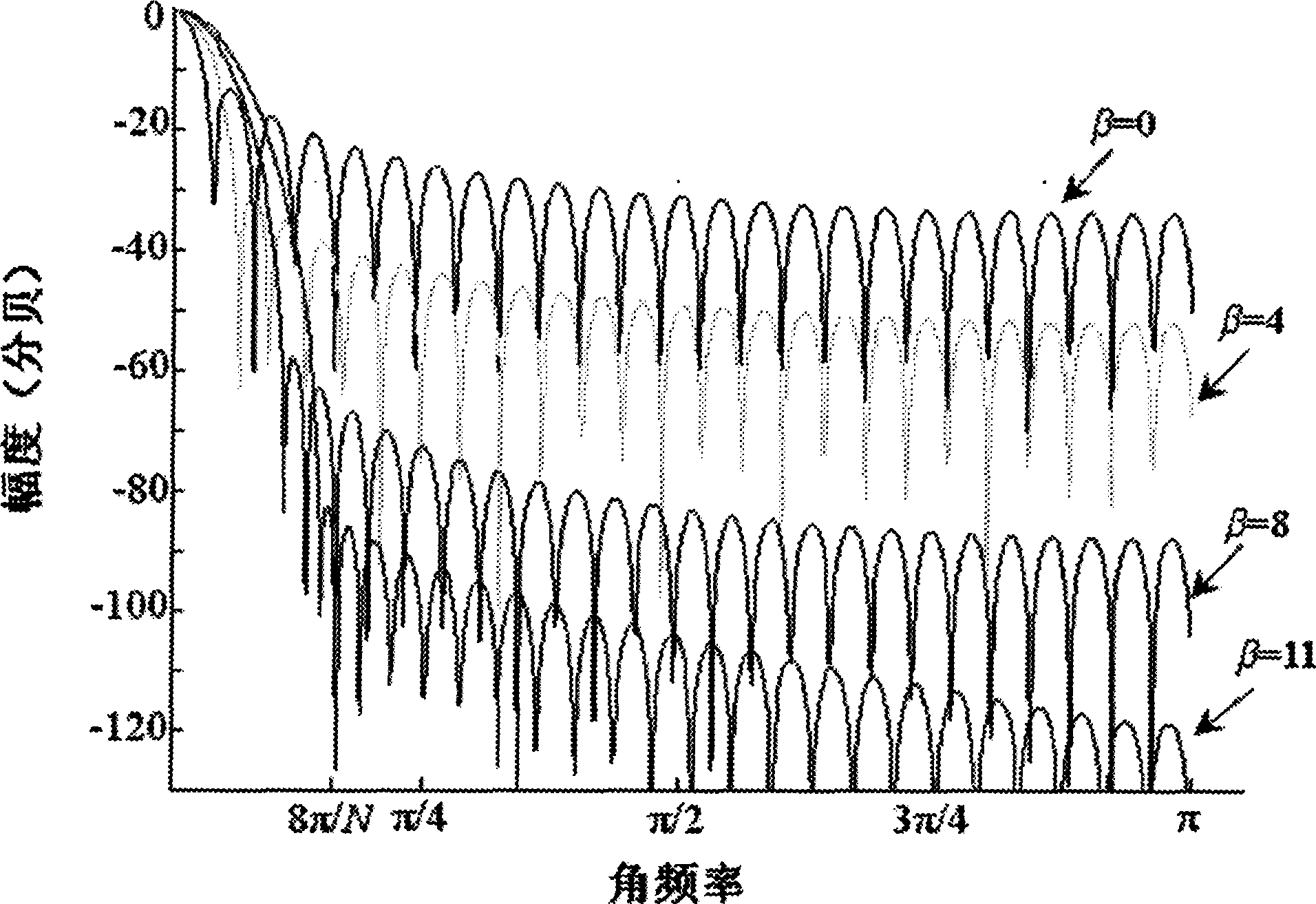
Base wave and harmonic detecting method based on Kaiser window double-line spectrum insert value FFT
InactiveCN101441233AOvercome the effects of frequency fluctuationsQuick checkSpectral/fourier analysisWave detectionHarmonic
The invention discloses a fundamental wave based on Kaiser Window bispectrum line interpolation FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) and a harmonic wave detection method. The method comprises the following steps: analog-to-digital conversion and low-pass filtration treatment is conducted on the signal to be detected; the Kaiser Window with free proportion selection between the attenuation of a main lobe and side lobes, flexible design realization, low side lobe level and quick attenuation speed is adopted to conduct windowing FFT operation on the signal; and bispectrum line interpolation algorithm is used for detecting base wave and harmonic quantities of the detected signal. The following aspects are included: (1) analog-to-digital conversion and low-pass filtration; (2) the FFT operation based on the Kaiser Window; (3) base wave and harmonic wave parameters derived by bispectrum line interpolation and polynomial fitting.
Owner:湖南海兴电器有限责任公司
Dual ridge horn antenna
The present invention provides apparatus and methods for a ridge horn antenna that exhibits improved directivity and main lobe of the radiation pattern at the high end of the frequency range for which its gain remains usably high, while providing a relatively low VSWR across the frequency range of operation.
Owner:ETS-LINDGREN
Antenna system
An antenna system including a coverage antenna (2) with a coverage beam pattern; and an auxiliary antenna (3) with an auxiliary beam pattern. The auxiliary beam pattern is arranged to perform sidelobe suppression, null steering, null addition, or null-fill. In the case where the auxiliary antenna is used to perform sidelobe suppression, the auxiliary beam pattern has a mainlobe with: an amplitude lower than an amplitude of a mainlobe of said coverage beam pattern; a width lower than a width of said mainlobe of said coverage beam pattern; a phase different to a phase of a sidelobe of said coverage beam pattern; and a direction which is selected so as to at least partially suppress said sidelobe.
Owner:ANDREW CORP
Millimeter band signal transmitting/receiving system having function of transmitting/receiving millimeter band signal and house provided with the same
InactiveUS7164932B1Easy to set upConvenient ArrangementTelevision system detailsSpatial transmit diversitySignal waveSide lobe
A millimeter band transmitter transmits one or more indirect path signal waves from the main lobe of a transmit antenna, and a direct path signal wave is transmitted in a side lobe of the transmit antenna. A receiver simultaneously receives each of the indirect and direct path signal waves if the receive antenna is unobstructed. If the direct line of sight path between the transmitter and receiver is blocked, the receiver only receives one or more of the indirect path signal waves.
Owner:SHARP KK
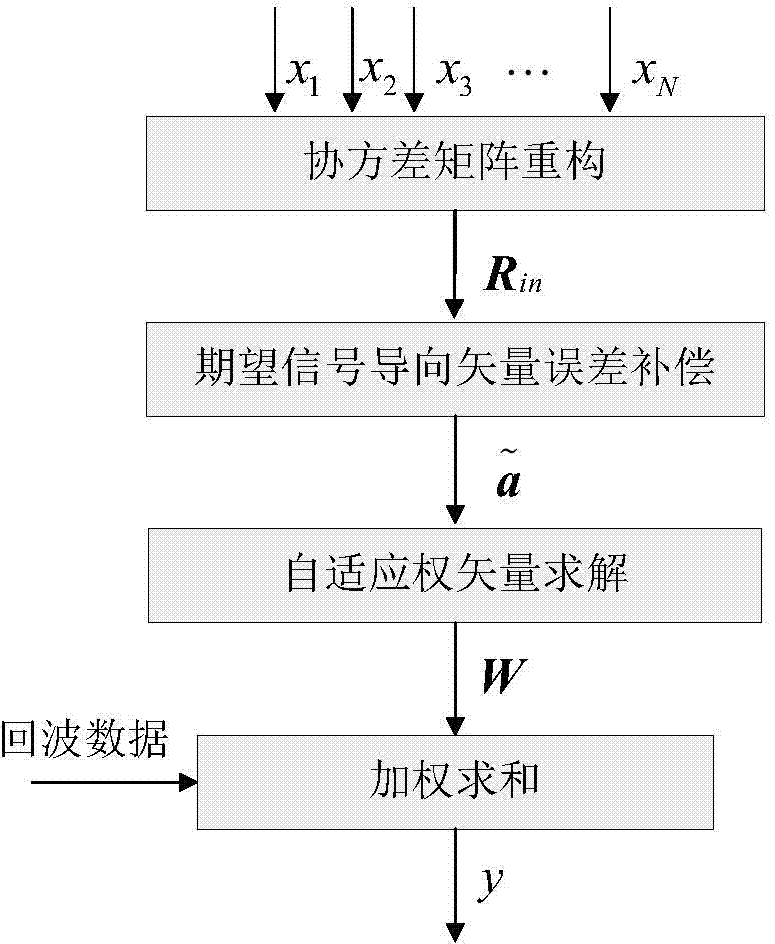
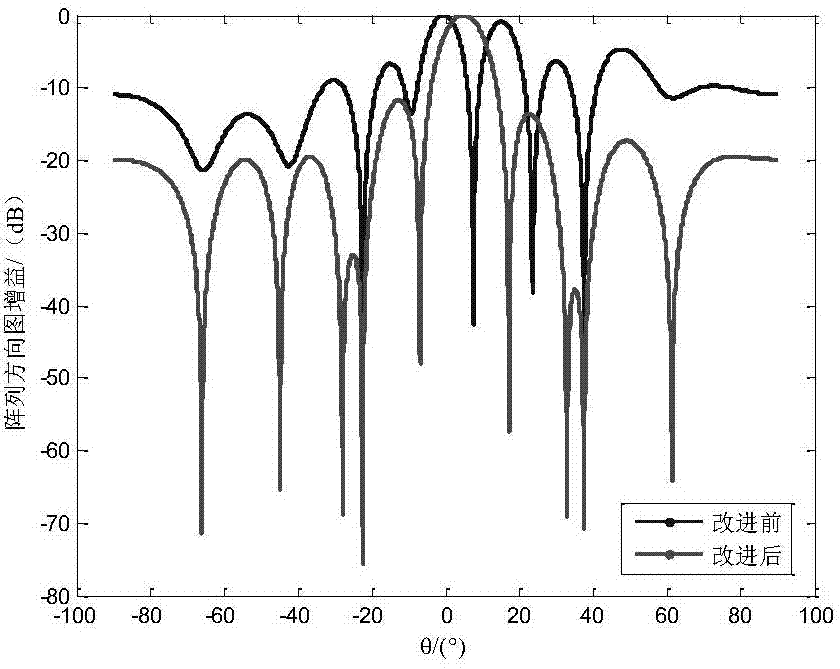
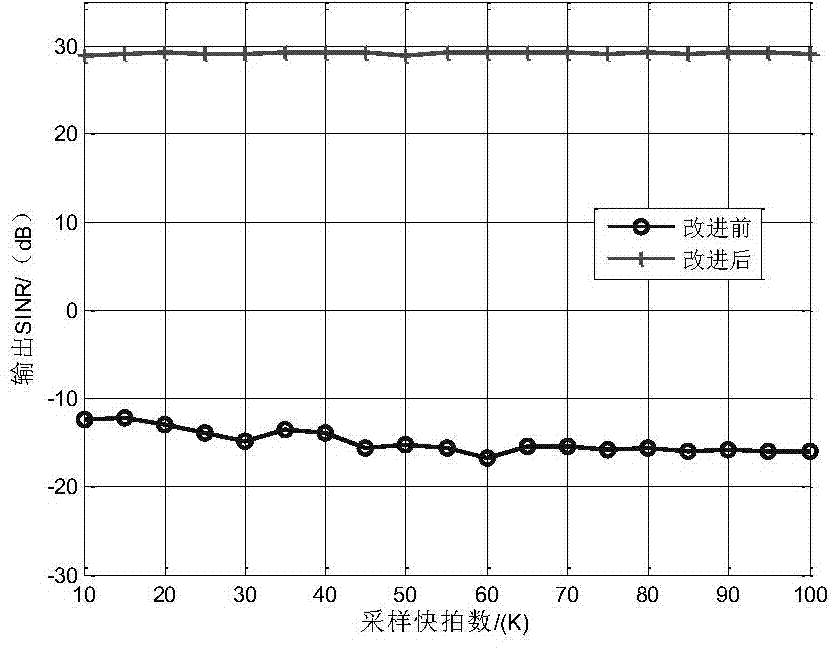
Self-adaptive beam forming method based on covariance reconstruction and guide vector compensation
InactiveCN104270179AAdaptive Beamforming EffectiveSuppress interferenceSpatial transmit diversityDecompositionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a self-adaptive beam forming method based on covariance reconstruction and guide vector compensation. According to the method, in the situation that desired signals exist in sampling snapshot and signal guide vectors are mismatched, interference can be effectively inhibited, main lobe shape preservation and side lobes of a self-adaptive directional diagram can be reduced, and high output SINR and quick convergence speed can be obtained. According to the method, eigenvalue decomposition is carried out on a sampling covariance matrix, noise sub space is estimated by means of an MDL criterion, the incident angle of a signal source is estimated in a Root-MUSIC method, the incident angle of the desired signals is judged, and then a new interference and noise covariance matrix is reconstructed; mismatching of the guide vectors of the desired signals is compensated by solving a quadratic programming problem with quadratic constraints; ultimately, a self-adaptive weight vector is solved by means of the reconstructed new interference and noise covariance matrix and the corrected guide vectors, a null is formed in the interference direction in a self-adaptive mode, and interference is effectively inhibited.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Transmit and receive phased array for automotive radar improvement
InactiveUS20130088393A1Reduce couplingReduced chip complexityAntennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSide lobeControl circuit
Examples of the present invention include methods and apparatus for phased array automotive radar which allow reductions in erroneous detections such as sidelobe clutter and ghost images. An example radar includes a steerable transmit antenna and a steerable receive antenna. Transmit and receive beams may be steered using an electronic control circuit so the main lobe of the transmit beam remains generally aligned with the main lobe of the receive beam, and the side lobe of the receive beam remains generally aligned with a null in the transmit beam.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR ENGINEERING & MANUFACTURING NORTH AMERICA
Downlink beam forming method
InactiveCN101364828APointing accuratelySimple structureSpatial transmit diversityComputer scienceMain lobe
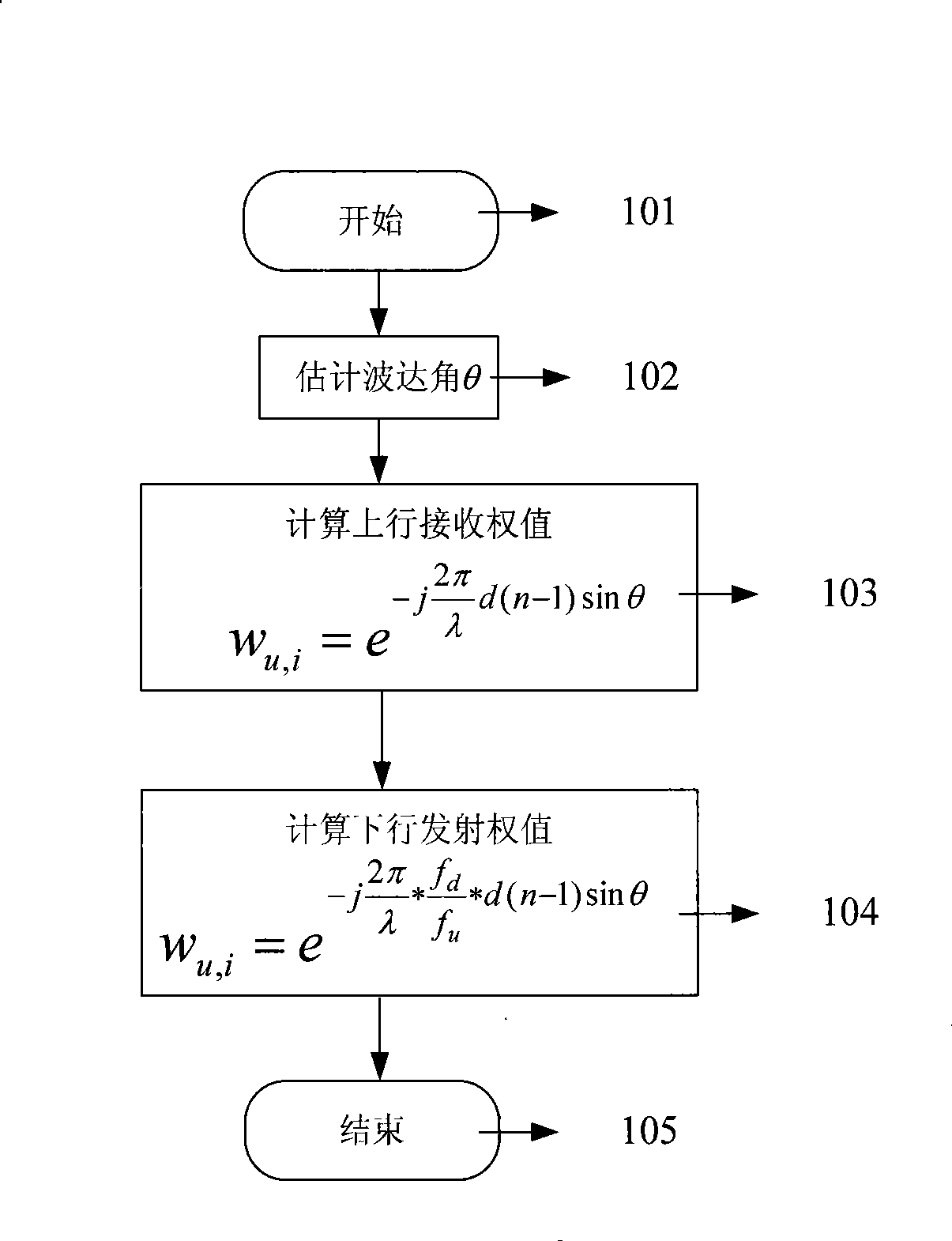
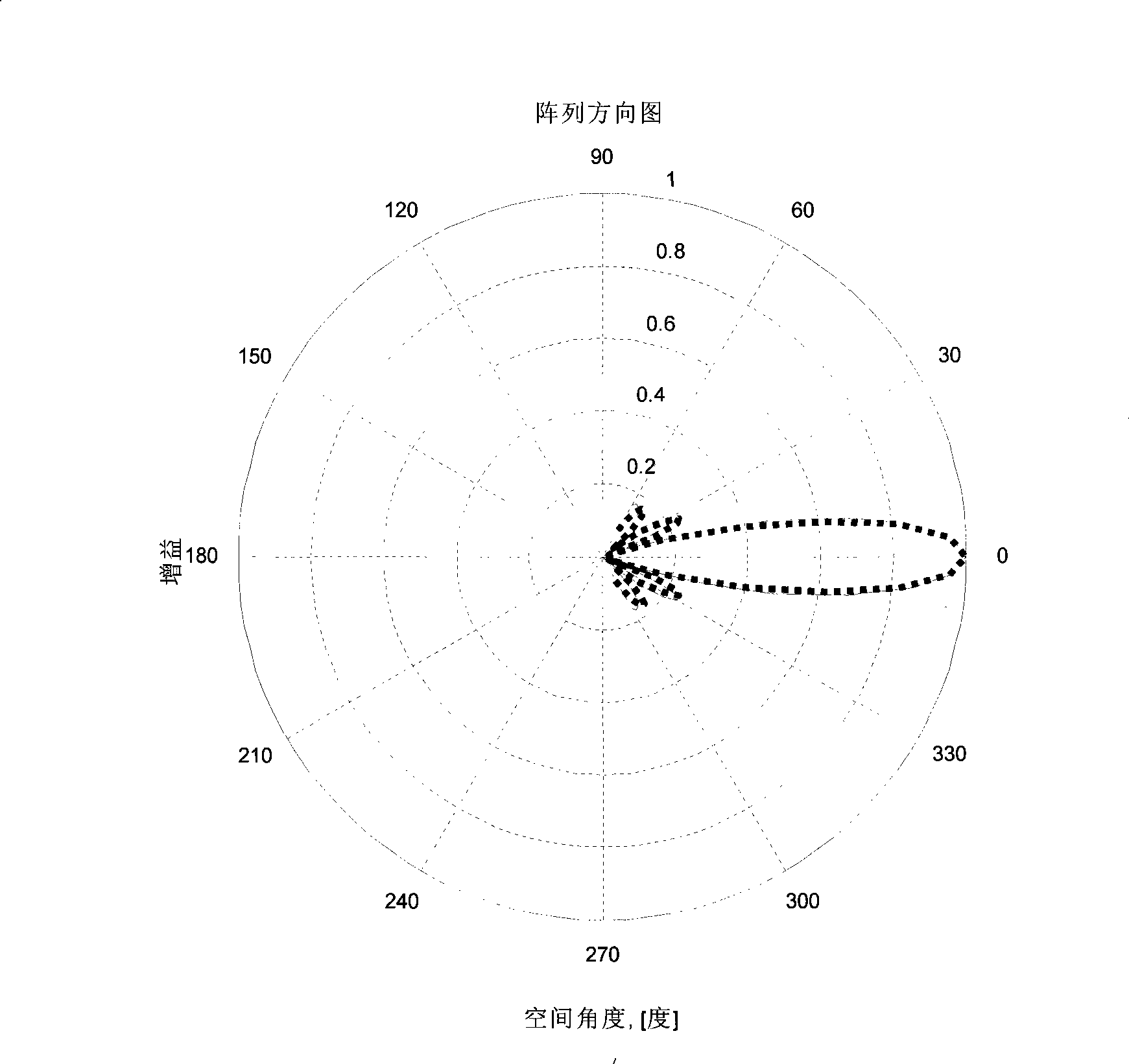
The invention relates to a downlink waveform forming method, which comprises the following steps: (1.1) estimating a direction-of-arrival angle theta of a mobile terminal; and (1.2) calculating a downlink transmission weight Wd,i according to the direction-of-arrival angle theta and a frequency correction factor fd / fu and shaping, wherein the formula is shown in the chart. The method can acquire direction-of-arrival angle theta by using an uplink reference signal and can eliminate the pointing error of waveform formation caused by the difference of uplink / downlink carrier frequency in an FDD mode through the frequency correction factor fd / fu, thereby ensuring the accurate pointing direction of the main lobe of a downlink wave.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method for calculating dielectric loss angle of compatible insulating device
ActiveCN103576002ASuppression of Spectrum Leakage EffectsSolve the measurement error of dielectric loss angleResistance/reactance/impedenceObservational errorFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a method for calculating the dielectric loss angle of a compatible insulating device in the technical field of monitoring. According to the technical scheme, firstly, a Blackman self-convolution window is constructed, current and voltage signals of a device to be detected are collected, and discrete sampling is performed on the current and voltage signals; secondly, windowing truncation is performed on a discrete signal sequence with the constructed Blackman self-convolution window, and a discrete spectrum function of discrete signals after the windowing truncation is obtained; thirdly, the discrete spectrum function of the discrete signals after the windowing truncation is analyzed, and a main lobe width and side lobe characteristics are obtained; finally, voltage and current fundamental wave signal phase angles are solved with the four spectral line interpolation amendment theory, and therefore the dielectric loss angle is solved. According to the method for calculating the dielectric loss angle of the compatible insulating device, the extremely good spectrum leakage restraining effect of the Blackman self-convolution window is used, frequency spectrum correction is performed with the four spectral line interpolation, dielectric loss angle measuring errors based on the FFT theory under asynchronous sampling are avoided, the measuring precision is high, and requirements for hardware are low.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Modeling method based on three-dimensional spatial domain multi-antenna MIMO (Multiple input and multiple output) statistical channel
ActiveCN103747456AImprove researchBroaden applicationSpatial transmit diversityNetwork planningMulti inputAlgorithm
The invention discloses a modeling method specific to an indoor 3D (Three-Dimensional) spatial statistical channel. The modeling method can be applied to a distributed multiple input and multiple output (MIMO) system. When a base station (BS) is designed with a directional antenna, important space-time channel parameters such as Doppler Power Spectrum (DS), space-time correlation and channel capacity are concluded by taking a Poda signal at an MS (Mobile Station) end as a basis; space-time model parameters and the mechanism relationship among included angles of directional antenna main lobes are resolved by using channel space-time feature parameters; meanwhile, the system transmission performance of an MIMO multi-antenna linear array and a circular array under a 3D spatial statistical channel model is researched, so that accurate, flexible diverse channel models are provided for an MIMO multi-antenna space-time processing algorithm and a simulation wireless communication system, and the research of the spatial statistical channel model is expanded.
Owner:南京洛仑通讯科技有限公司
MIMO angle estimation with simultaneous mainlobe jammer cancellation
ActiveUS20150323650A1Jam suppressionIncrease signal strengthCommunication jammingRadio transmissionRadar systemsAdaptive weighting
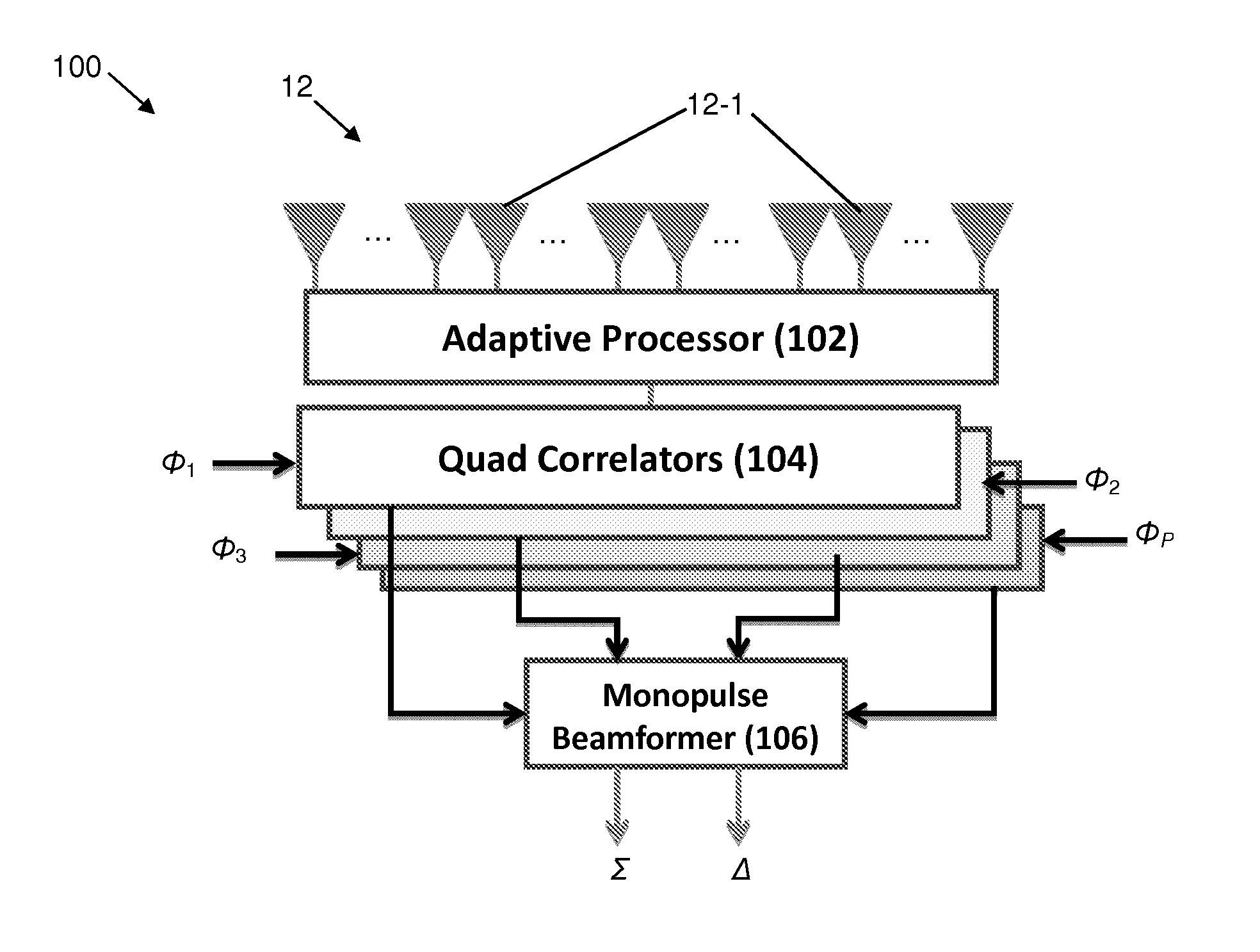
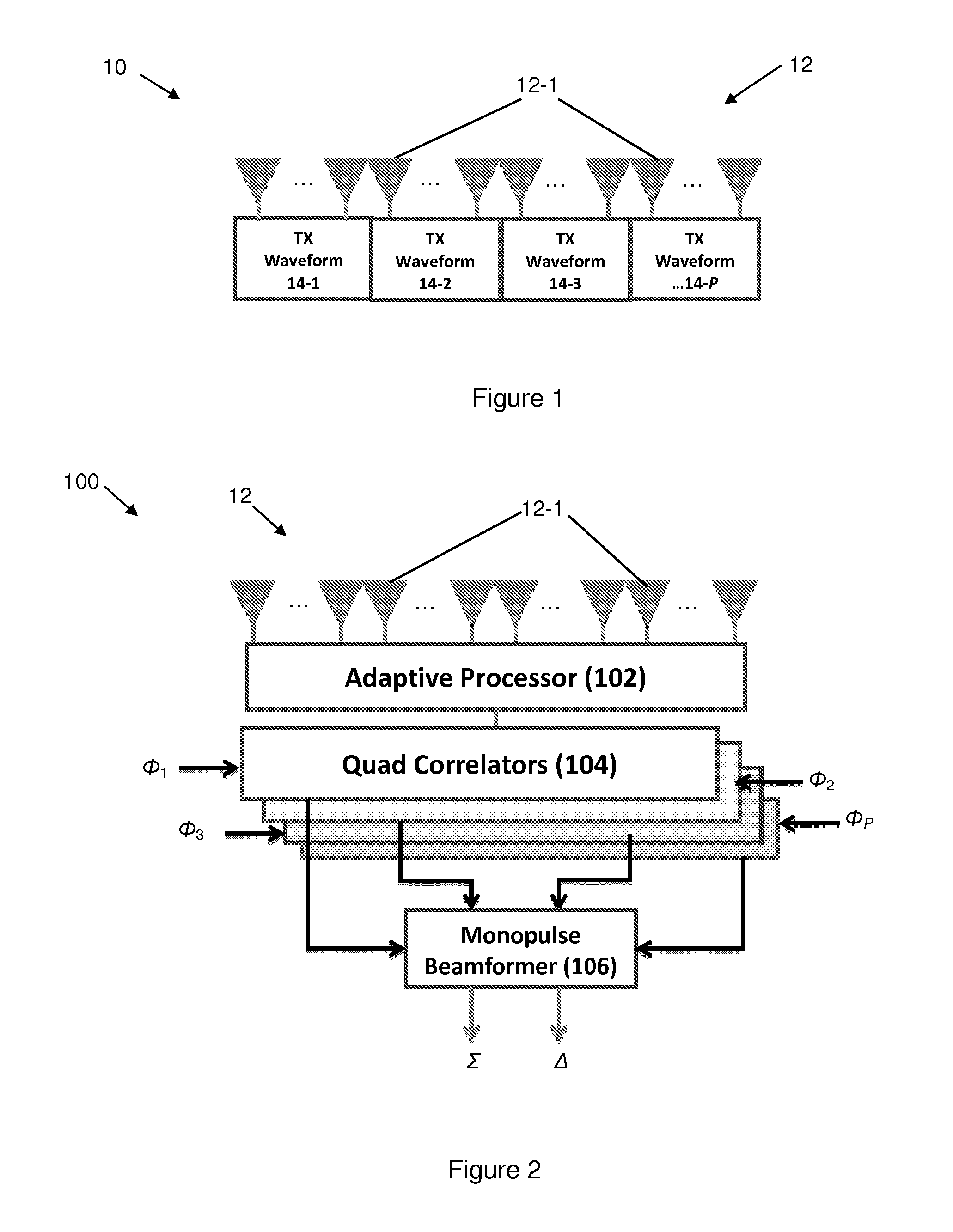
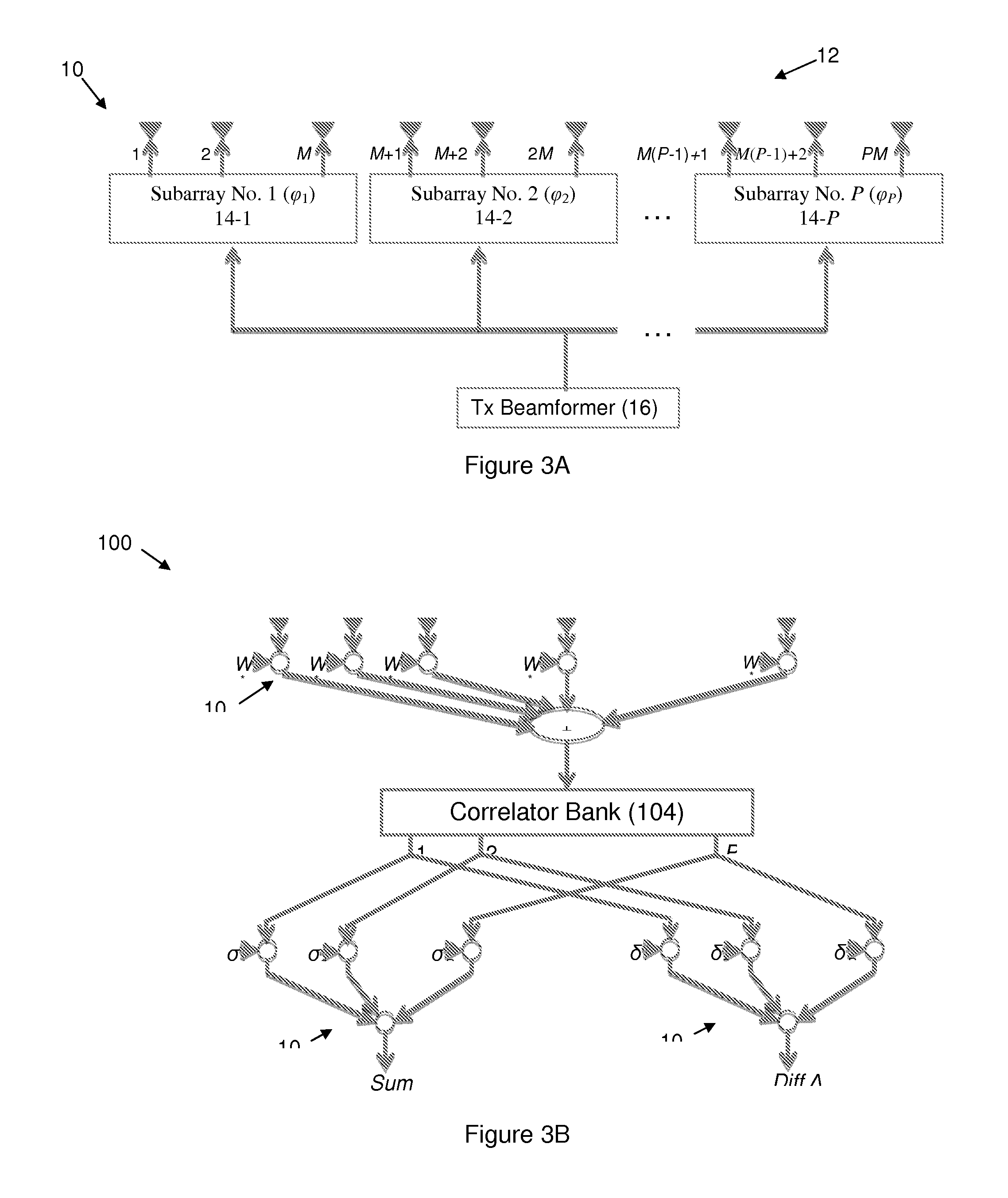
A radar system includes a transmit antenna array having subarrays disposed at predetermined positions. An orthogonal waveform signal is directed to a corresponding one of the subarrays. On receive, an adaptive processor derives a plurality of adaptive weight factors from a plurality of receive signals and applies them to the receive signals to obtain a jammer cancelled signal. That signal is separated into its orthogonal waveform components by passing it through a bank of correlators. The correlator system provides a plurality of unique receive signals substantially corresponding one-to-one to the unique transmit subarrays. The receive beamformer derives an angular estimate of at least one target relative to boresight from the unique receive signals.
Owner:SRC INC
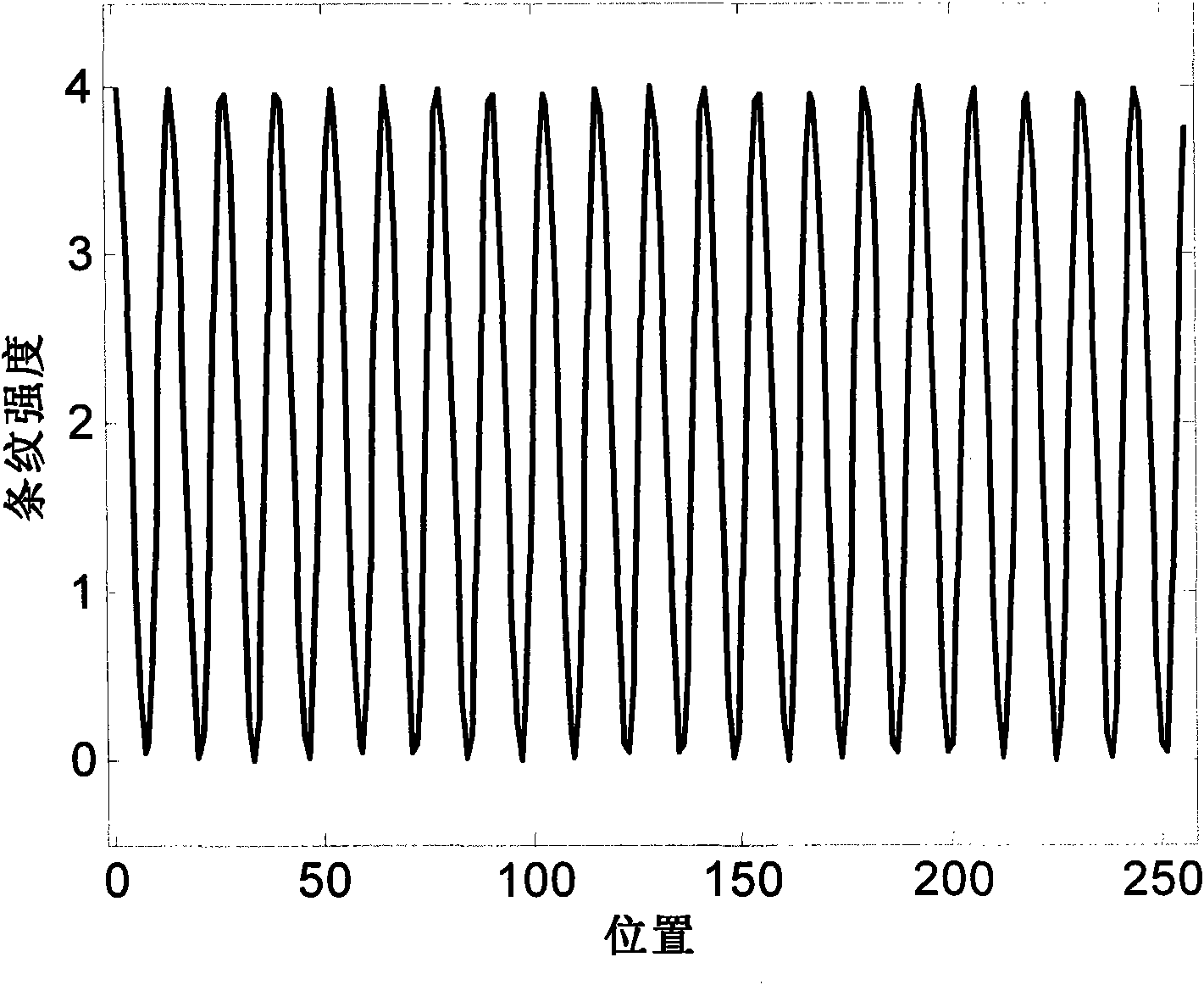
Method for analyzing digital interference fringe and device for detecting optical component surface shape
ActiveCN101650163AImprove estimation accuracySuppression of leakage effectsUsing optical meansFrequency spectrumSide lobe
The invention discloses a method for analyzing digital interference fringe and a device for detecting optical component surface shape. The main technical characteristic of the invention is that firstly a digital interference fringe image times a window function to expand the width of main lobe of interference fringe image spectrum and to inhibit side lobe of the interference fringe image spectrum;carrying out Fourier analysis on the digital interference fringe image; estimating space carrier frequency of the digital interference fringe by adopting an algorithmic method of a barycentric coordinates of a barycentric group; and the method is also used for the frequency shift of the digital interference fringe image, thus effectively inhibiting error to measurement by a hurdle effect. Besides, the device for detecting optical component surface shape constructed based on the method for analyzing digital interference fringe can carry out high-accuracy analysis on the interference fringe ofthe space carrier frequency when frequency sampling interval is not integral multiple, and has simple structure and good measuring instantaneity.
Owner:CHINA NORTH IND NO 205 RES INST
Method for measuring target azimuth by single-beam mechanical scanning radar
InactiveCN101887120AHigh measurement accuracyFlexible handlingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMeasurement precisionMain lobe
The invention discloses a method for measuring a target azimuth by single-beam mechanical scanning radar, which relates to the technical field of radar and communication and solves the problems of low angle measurement precision and large operation amount of the conventional single-beam mechanical scanning radar. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring echo signals by using the single-beam mechanical scanning radar, then performing phase coherence accumulation on the acquired echo signals to acquire a higher signal detection signal-to-noise ratio, taking an azimuth interval of any two echo pulses of a main lobe width of a radar antenna as two beams required for measuring an angle by the single-pulse technology after target information is detected, then calculating two-dimensional images, sum signal intensity and difference signal intensity of a target on two azimuths, and further calculating a sum-to-difference ratio k so as to acquire a target error deflection angle delta theta, wherein the target azimuth theta T is equal to theta i + theta k + delta theta. The method is suitable for radar angle measurement.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and system for adaptively cancelling clutter from the sidelobes of a ground-based radar
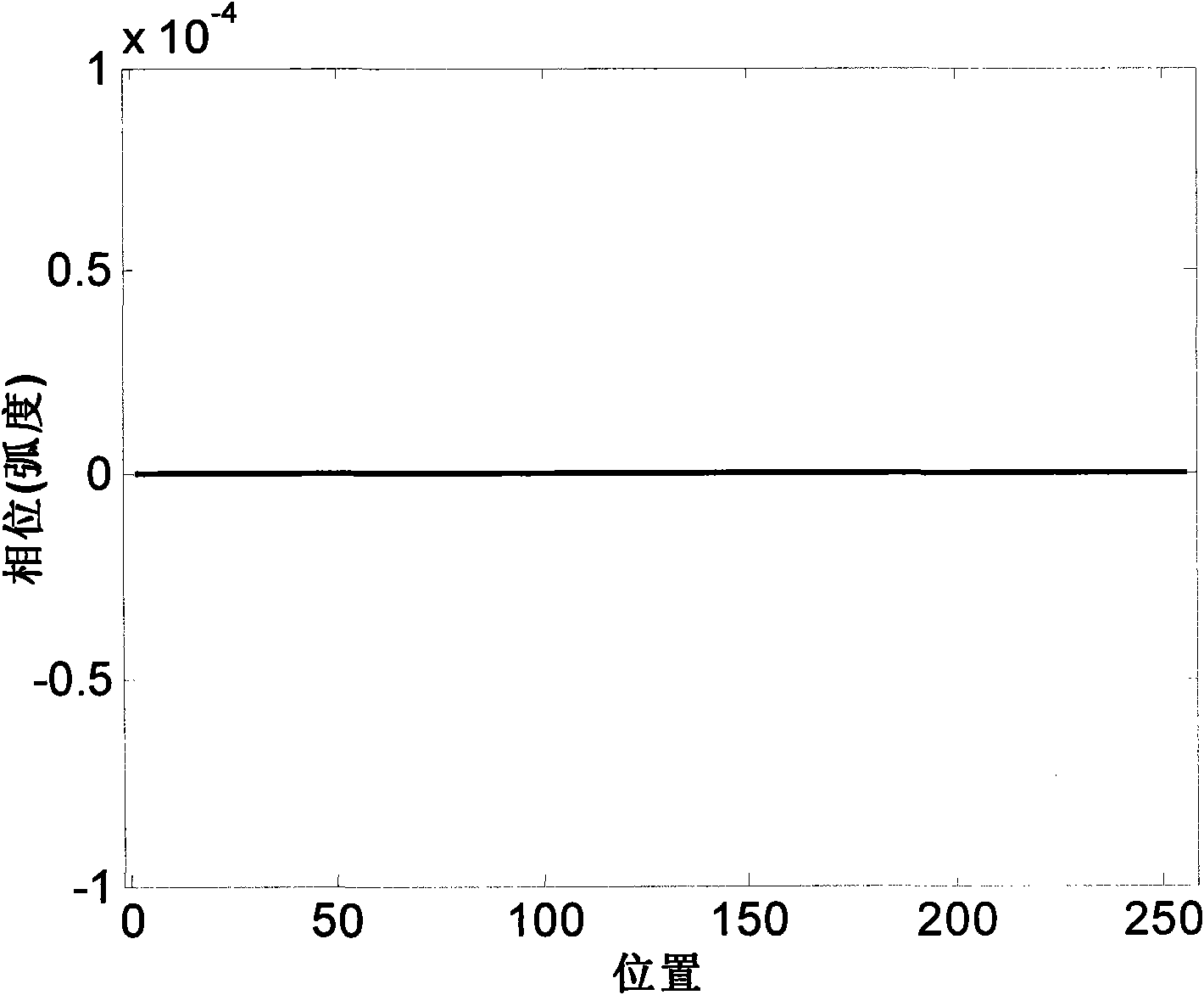
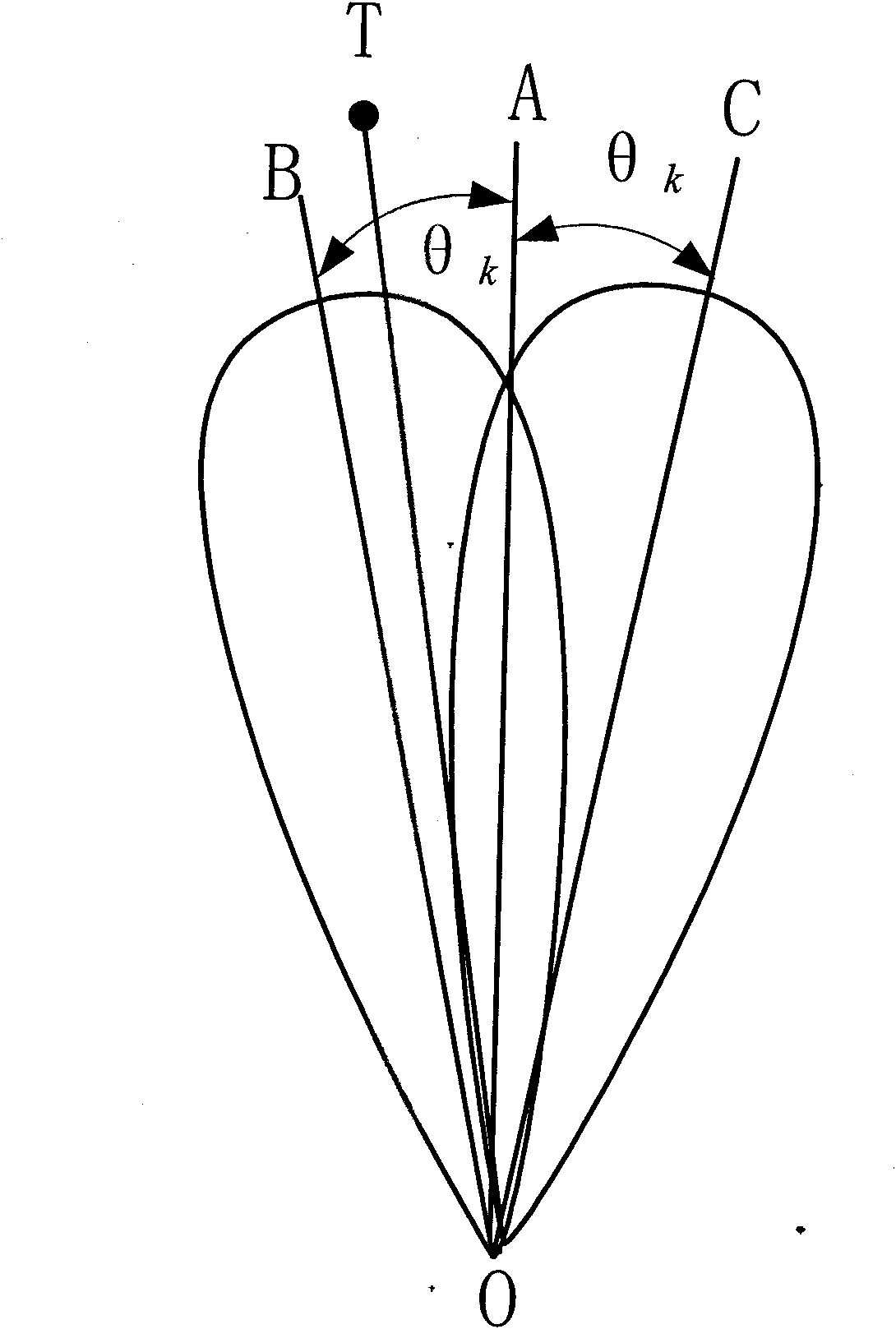
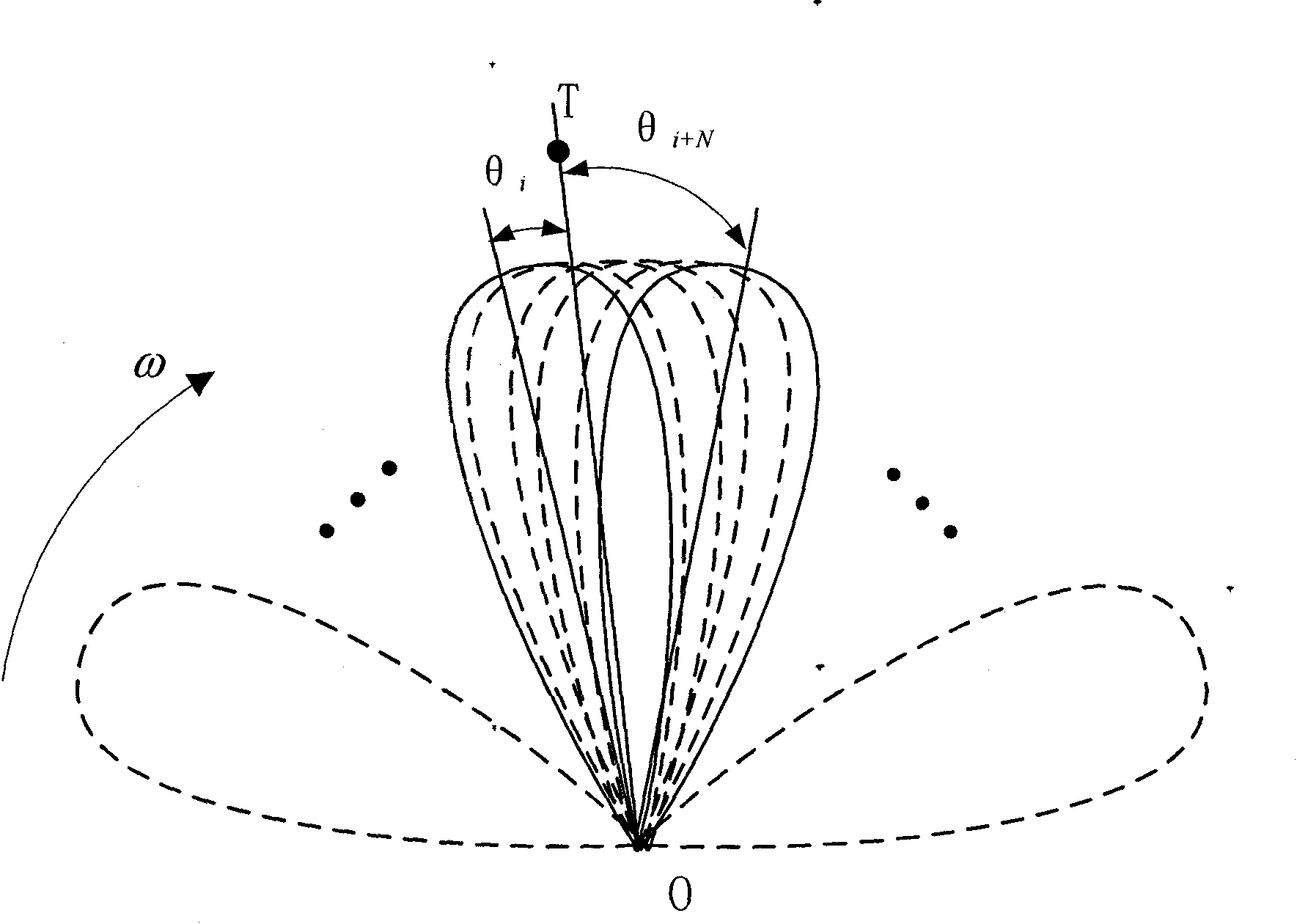
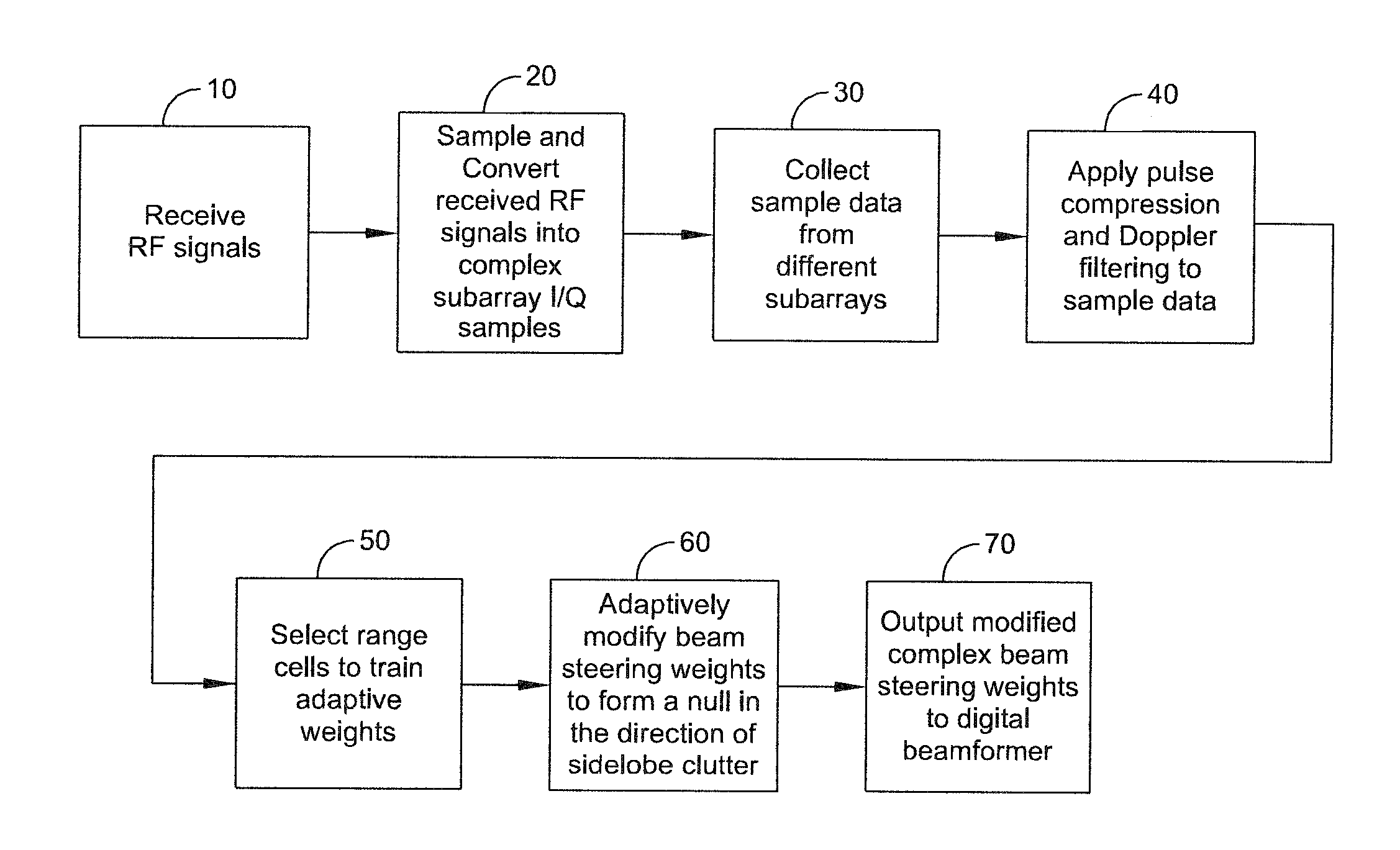
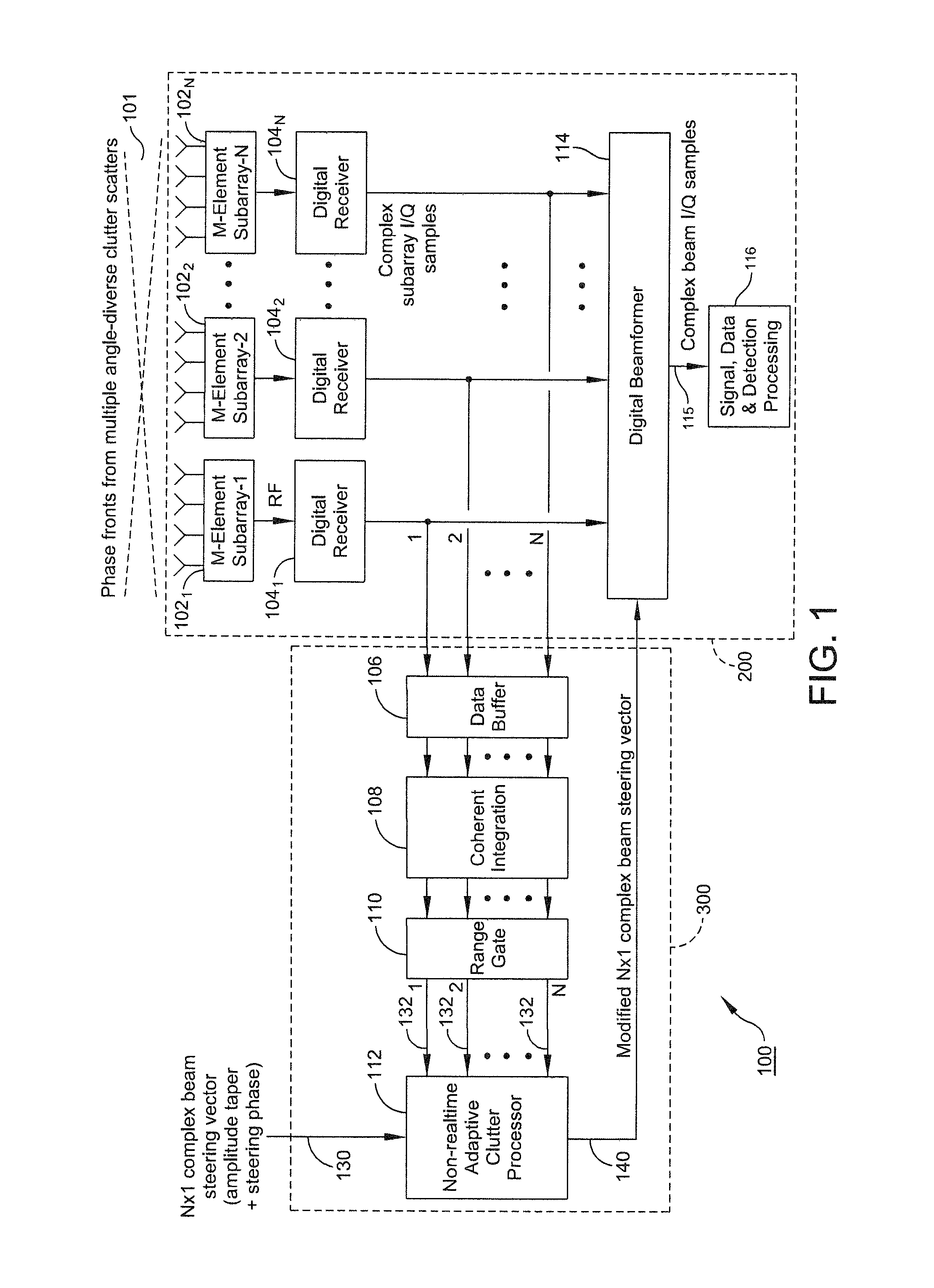
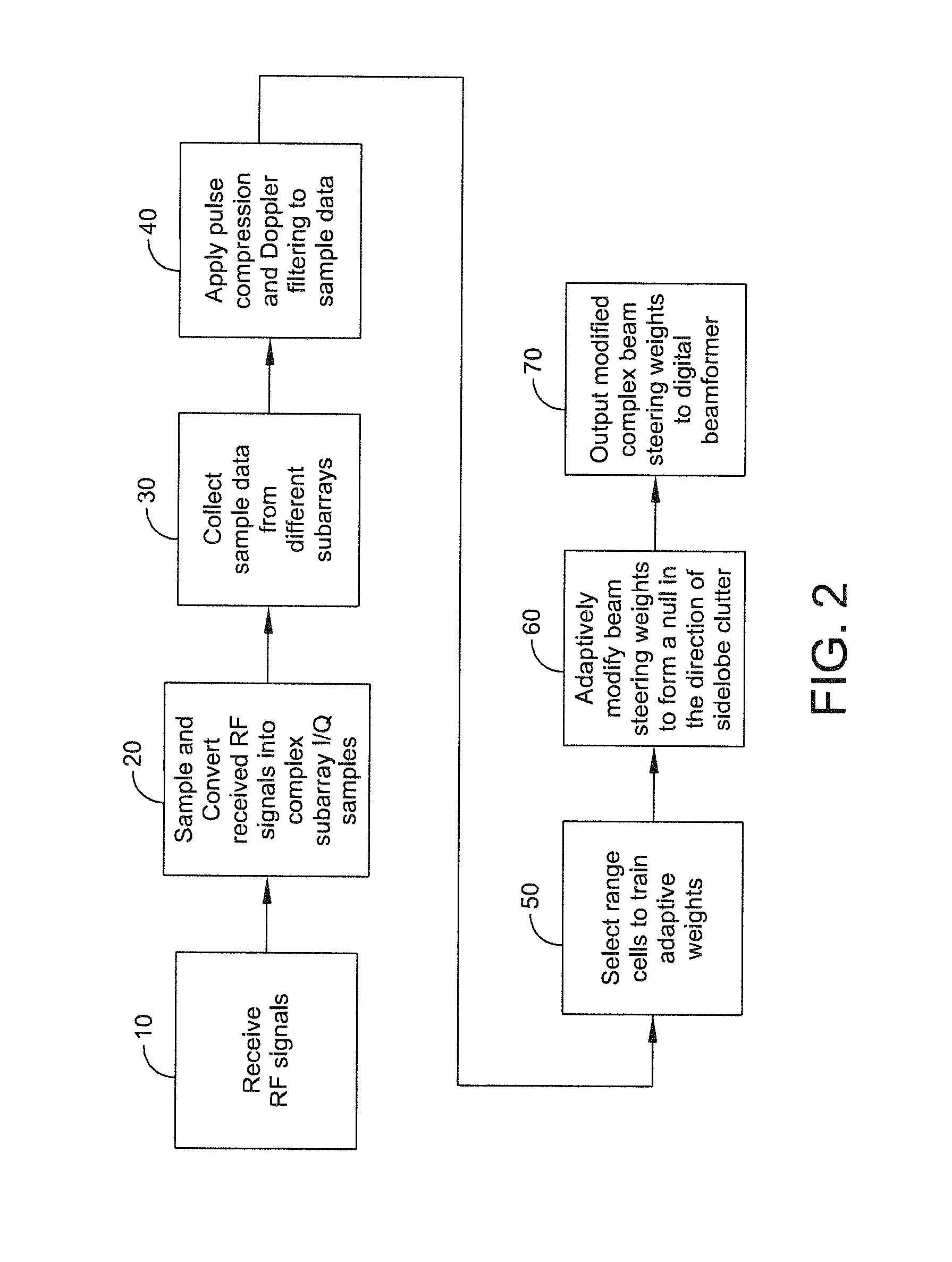
ActiveUS8947294B1Enhance clutter-to-noise ratioReduced sidelobe gainAntennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionGround based radarHorizon
A system and method of providing to a beamformer a modified complex beam steering vector includes collecting subarray I / Q samples from a plurality of subarrays receiving clutter, performing coherent integration of the subarray I / Q samples to increase the CNR, adaptively modifying a complex beam steering vector to form a null in the direction of the received clutter, and outputting to a beamformer the modified complex beam steering vector. The beamformer receives complex I / Q data samples representing a radar signal containing near-horizon clutter and applies the modified beam steering vector to generate a beamformed signal having an elevated mainlobe and a spatial sidelobe null in the direction of the received clutter.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Methods and apparatuses for performing null steering of adaptive microphone array
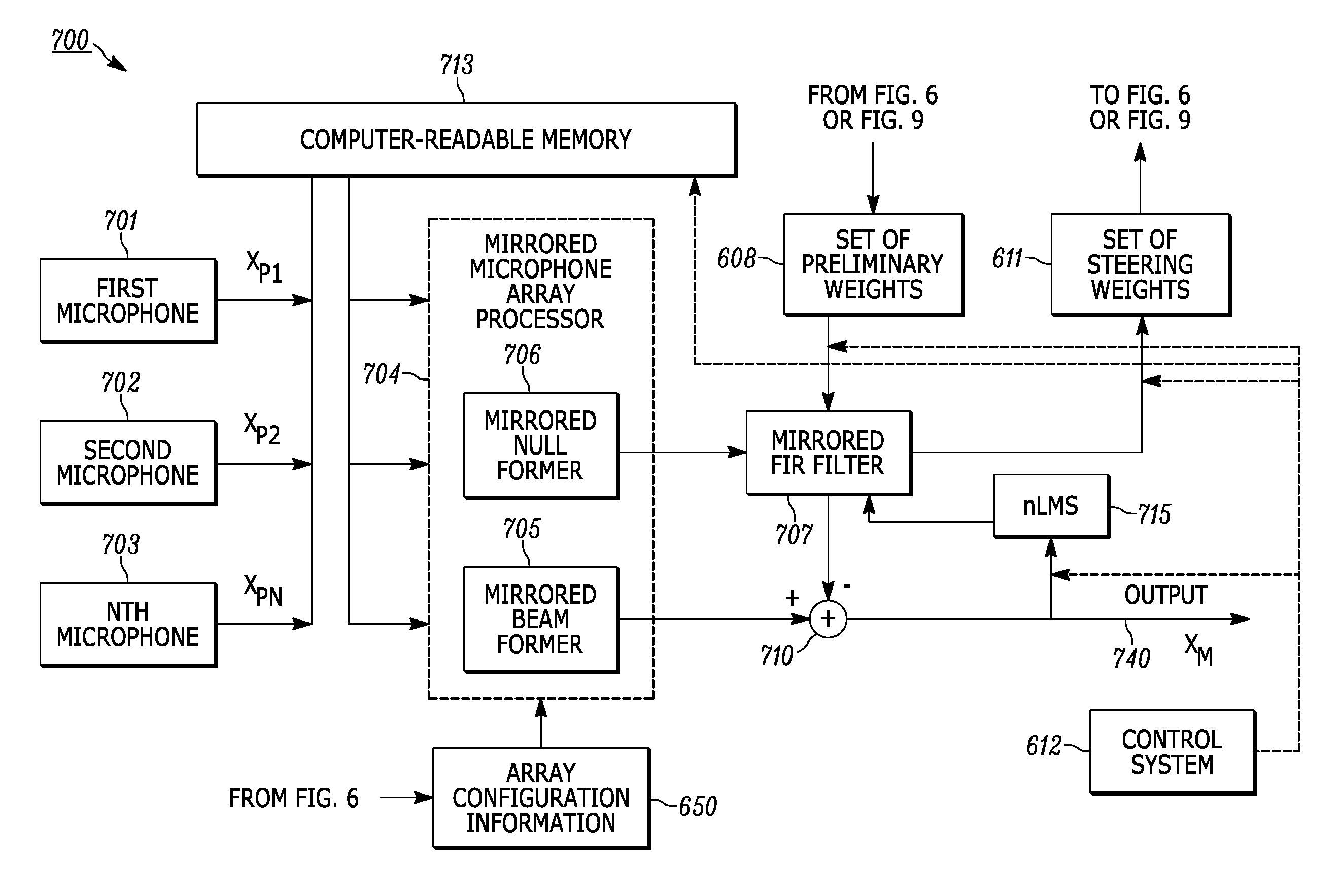
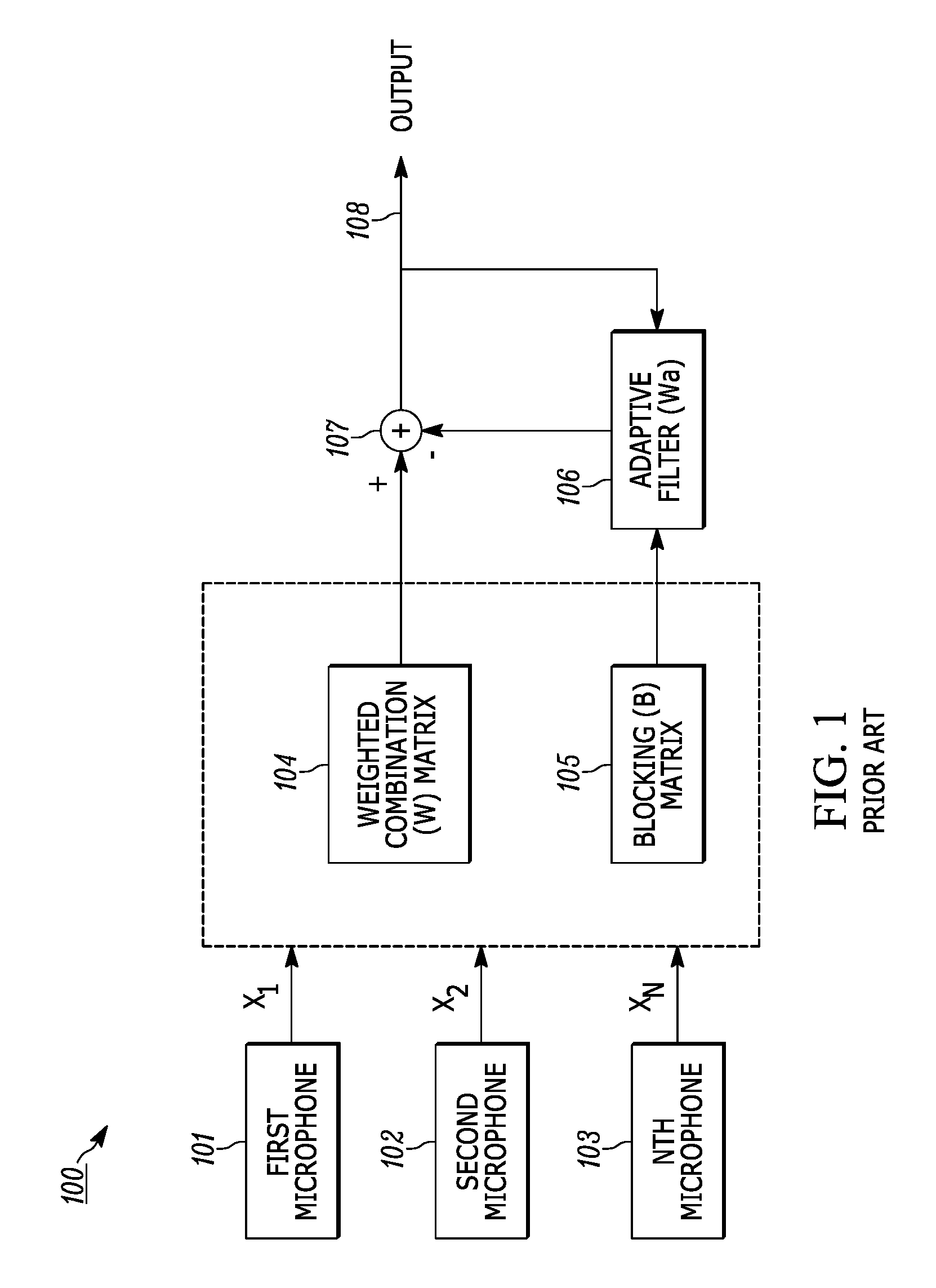
ActiveUS9479885B1Reduce distractionsMicrophonesSignal processingAmplitude responseAngular orientation
Configuring an adaptive microphone array to gather signals from a main lobe of the array, and configuring the array to reduce side interference gathered from sources that are not situated within the main lobe. A memory stores test signals gathered by the array at a plurality of predetermined angular bearings with reference to the array in an anechoic chamber. Signals gathered in real time are processed to provide a preliminary output and preliminary weights. The test signals are retrieved from memory. The preliminary weights are applied to the test signals to provide null steering weights. The null steering weights and the preliminary output are processed to reduce or minimize the amplitude response of the array at the angular orientation.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
A microstrip array antenna
InactiveCN101552380ARealize unequal amplitude feedReduce volumeAntenna arraysMicrostrip array antennaSide lobe
The invention discloses a microstrip array antenna and relates to an antenna capable of resolving problem of low main lobe gain and difficult side-lobe suppression of ETC array antenna. The microstrip array antenna includes a antenna array composed of more than two antenna array elements, the antenna matrix includes more than two antenna array elements in the same row with each the antenna array element connecting with each output terminal port of one multiplex power divider, and between the adjacent antenna array elements, that are in different distance from the central line of the antenna matrix, is connected by cascaded impedance transforming section. The invention is suitable for antennas in ETC system.
Owner:BEIJING WATCH DATA SYST
Space-time two-dimensional narrow band barrage jamming method
InactiveCN101533091AEasy to upgradeLow costWave based measurement systemsCurrent technologyMain lobe
The invention discloses a space-time two-dimensional narrow band barrage jamming method aiming at phased array radar. The conventional phased array radar controls the narrow band jamming by self adaptation, firstly learns the jamming data received by a radar receiver, and then forms zero point in a jamming direction. Such a conventional self-adaptive treatment method easily generates signal counteraction and is not suitable for motion jamming and fast-varied interstitial jamming, and the zero point depth and width are seriously influenced by the array error. The method for using ultra-low side lobe antenna can effectively resist jamming. But under the prior art and technological level, excessive side lobe requirements on phased array radar are unpractical. The invention comprises the steps of firstly estimating jamming parameters by a spatial spectrum estimation technique so as to obtain the jamming azimuth and frequency parameters, using relative parameter information to construct a space-time two-dimensional barrage matrix, multiplying the space-time two-dimensional barrage matrix by the received data so as to block the narrow band jamming with a specific frequency in the specific azimuth, and finally realizing space-time two-dimensional narrow band barrage jamming. The advantages of the invention are that the invention can be used for the phased array radar for resisting specific side lobe jamming and main lobe jamming, has small operand, and is easily realized and popularized.
Owner:PLA AIR FORCE RADAR COLLEGE
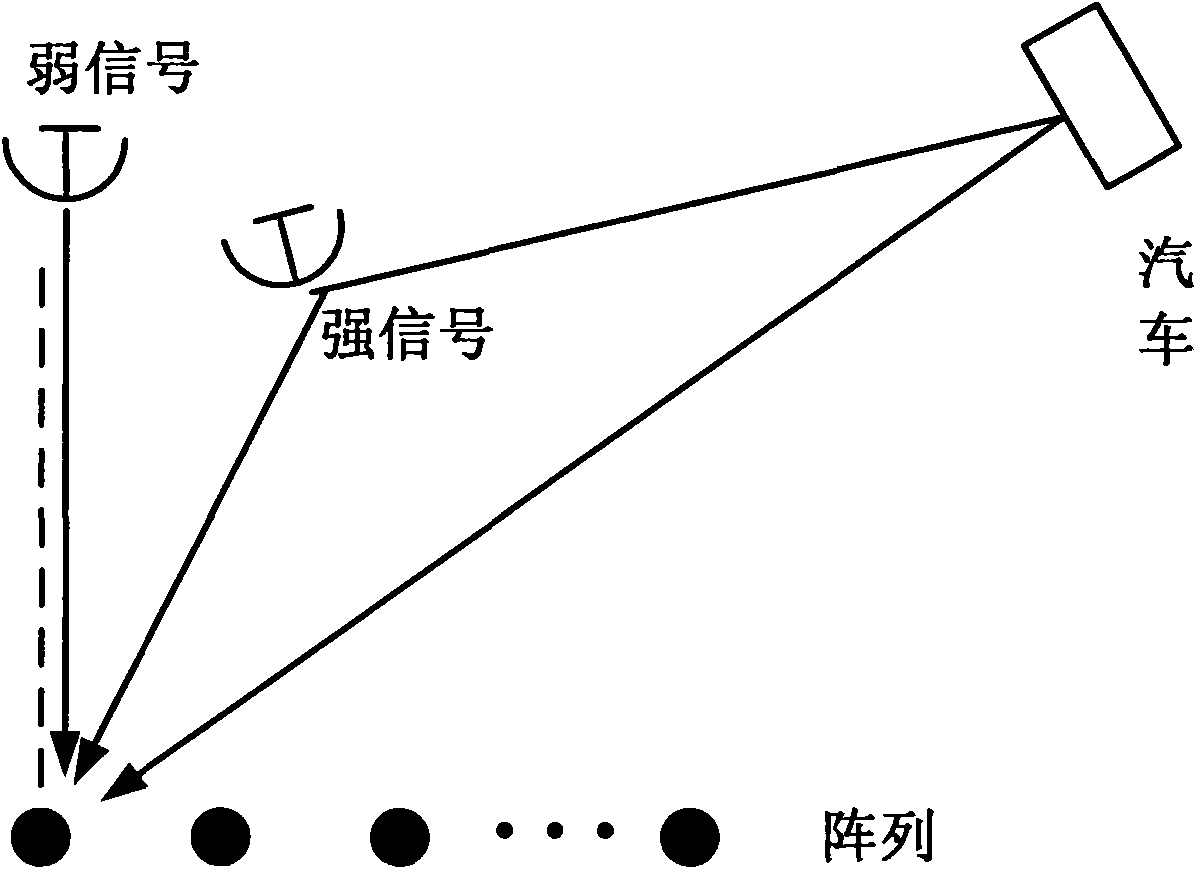
Method for estimating direction of arrival and information source number of strong and weak signals
ActiveCN101795150ASimple calculationReduce computationSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionRadarDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for estimating a direction of arrival and an information source number of strong and weak signals, which mainly solves the problem that the conventional method cannot accurately estimate the direction of arrival of the strong and weak signals when the information source number is unknown. The method comprises the following implementing processes: estimating a covariance matrix according to array receiving data; performing characteristic decomposition on the covariance matrix to acquire characteristic values arranged in a descending order and corresponding characteristic vectors; calculating spatial spectrums of characteristic beams in turn from the first characteristic vector; and estimating the direction of arrival and the information source number of each signal by comparing the difference between a maximum value of the spatial spectrums and an average value outside a main lobe beam width with a set threshold value. The method is simple and practical, can accurately estimate the direction of arrival and the information source number of the strong and weak signals when a plurality of strong and weak signals are coexistent, and can be used for extracting information or suppressing interference in numerous fields of radar, communication, navigation, measurement and control and electronic reconnaissance.
Owner:XIAN DAHENG TIANCHENG IT CO LTD
Adaptive beamformer for sonar imaging
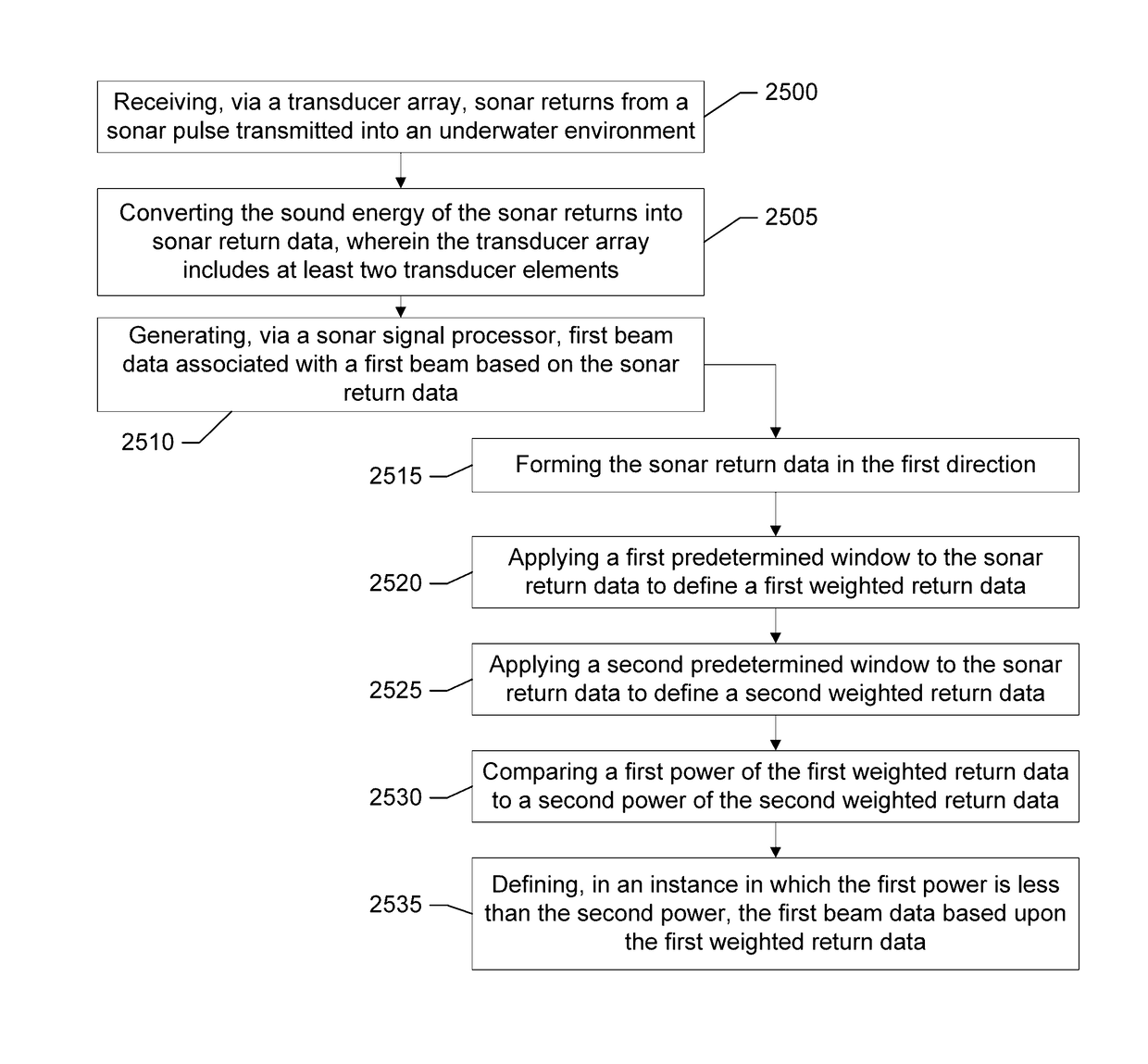
Provided are method, system, and computer program product for imaging an underwater environment. The method may include receiving sonar returns and converting the sound energy of the sonar returns into sonar return data, and generating first beam data associated with a first beam having at least one first main lobe oriented in a first direction. Generating the first beam data may include: forming the sonar return data in the first direction; applying a first predetermined window to the sonar return data to define a first weighted return data; applying a second predetermined window to the sonar return data to define a second weighted return data; comparing a first power of the first weighted return data to a second power of the second weighted return data; and defining, when the first power is less than the second power, the first beam data based upon the first weighted return data.
Owner:NAVICO HLDG
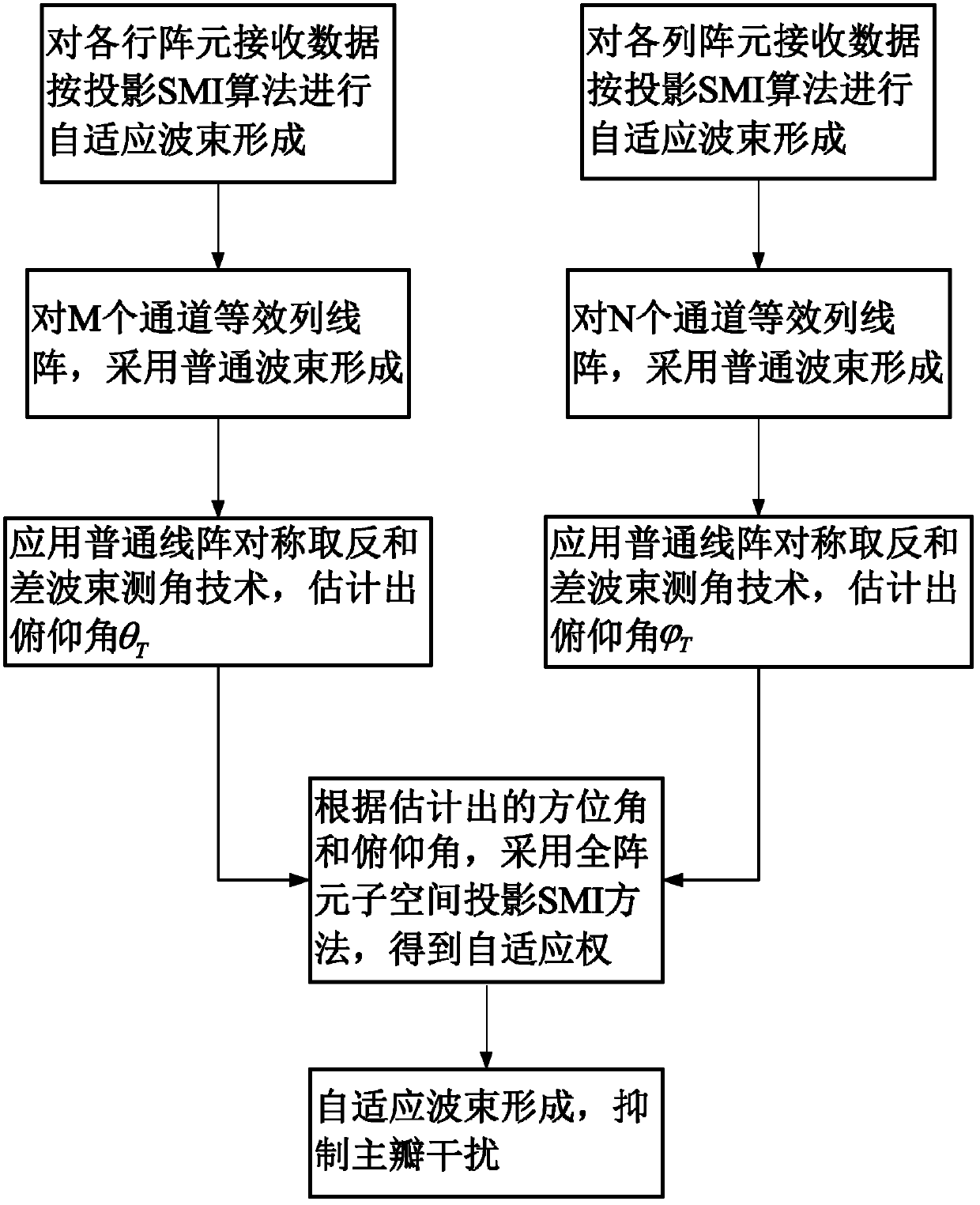
Self-adaptive sum-difference angle measurement method for plane phased array
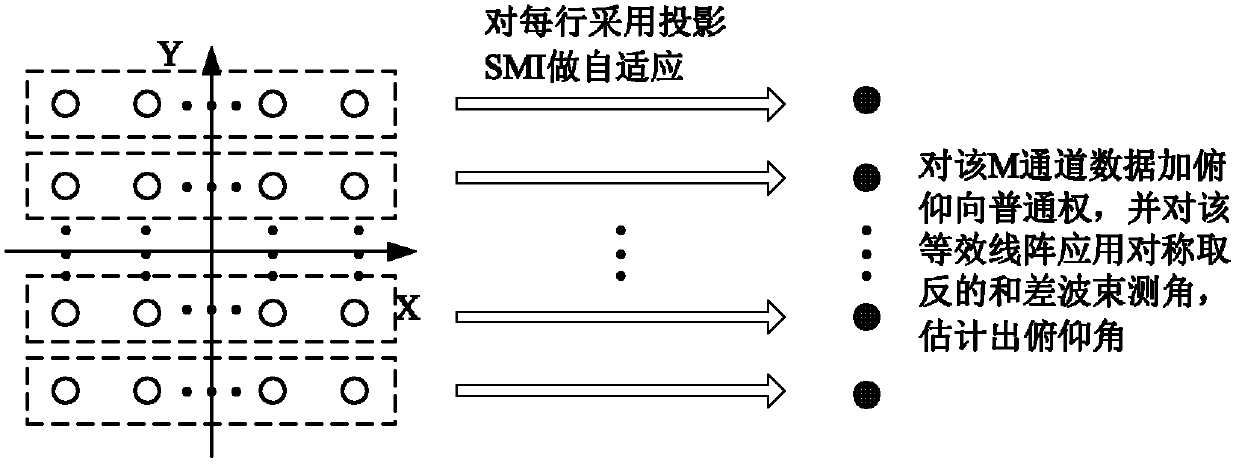
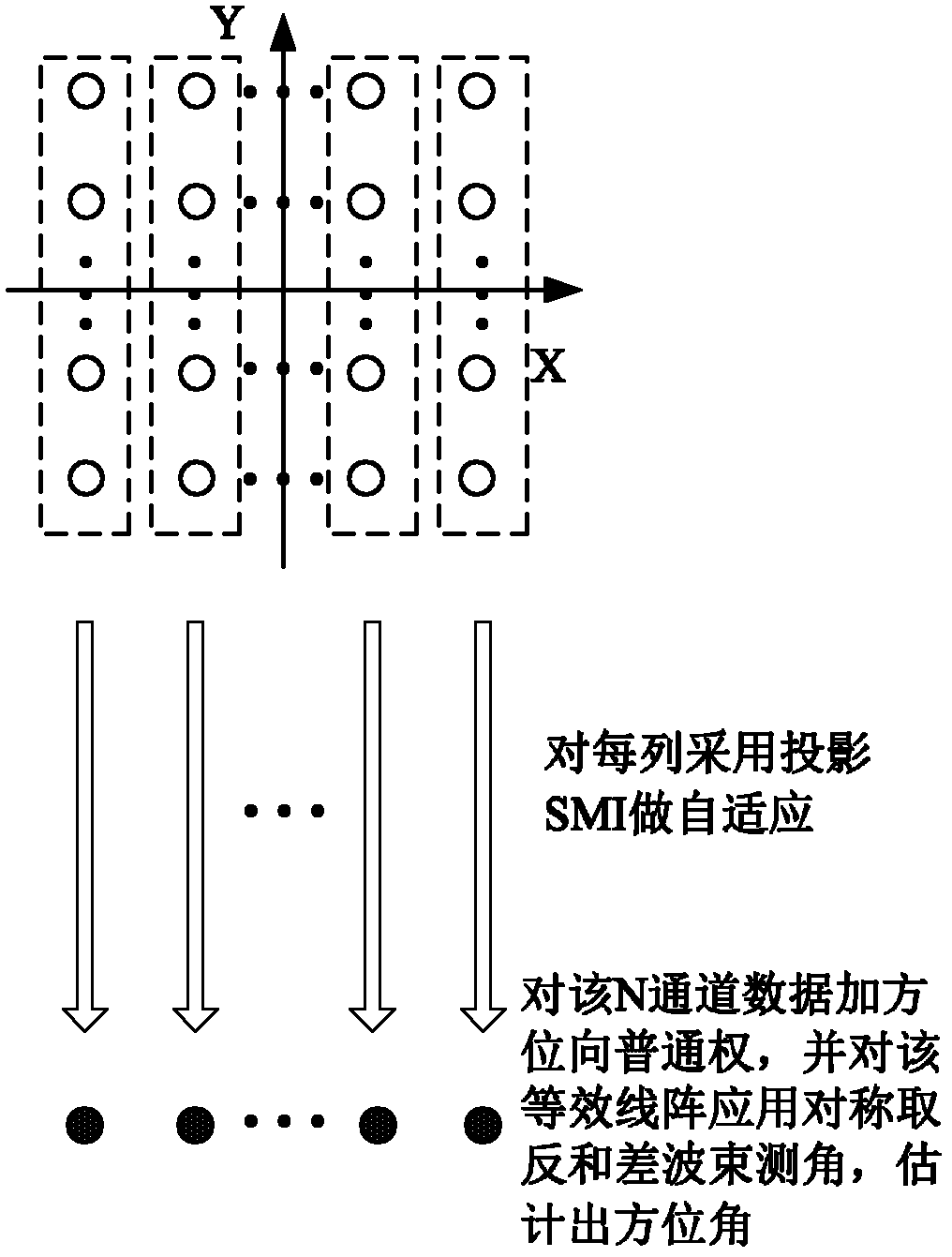
InactiveCN102565790AImprove angle measurement accuracyStrong interference abilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBeam angleClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a self-adaptive sum-difference angle measurement method for a plane phased array, which mainly solves the problem of the prior art that the target angle cannot be estimated accurately while the main lobe interference is restrained. The realization process is that the self-adaptive beam formation is performed for received data of array elements of all the lines, an equivalent linear array of the output of the beam formation is formed in the Y-direction, and the sum-difference beam formation in symmetry inversion is adopted to estimate the target pitching angle theta T; the self-adaptive beam formation is performed for the received data of the array elements of all the rows, an equivalent linear array of the output of the beam formation is formed in the X-direction, and the sum-difference beam formation in symmetry inversion is adopted to estimate the target azimuth angle; and the self-adaptive beam formation for all the received data of all the array elements can be performed through adopting the subspace projection SMI algorithm and based on the pitching angle theta T and the azimuth angle, so as to obtain an output signal for restraining the main lobe interference. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of excellent performance of restraining the main lobe interference, as well as accuracy in sum-difference beam angle measurement, and can be used for estimating the angle of the target and tracking the target on the premise that the main lobe interference exists.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com