Patents
Literature
1118 results about "Two fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
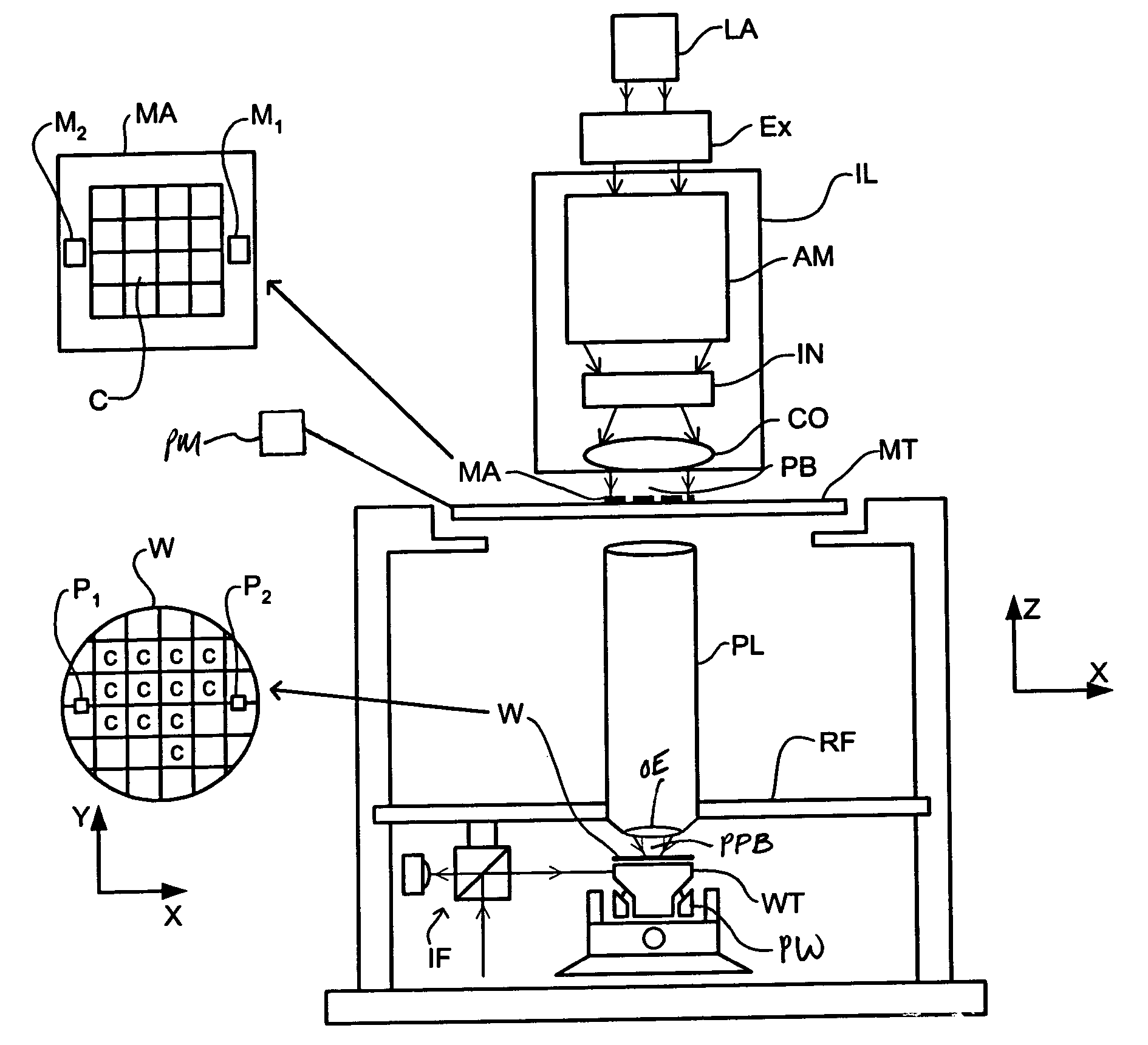
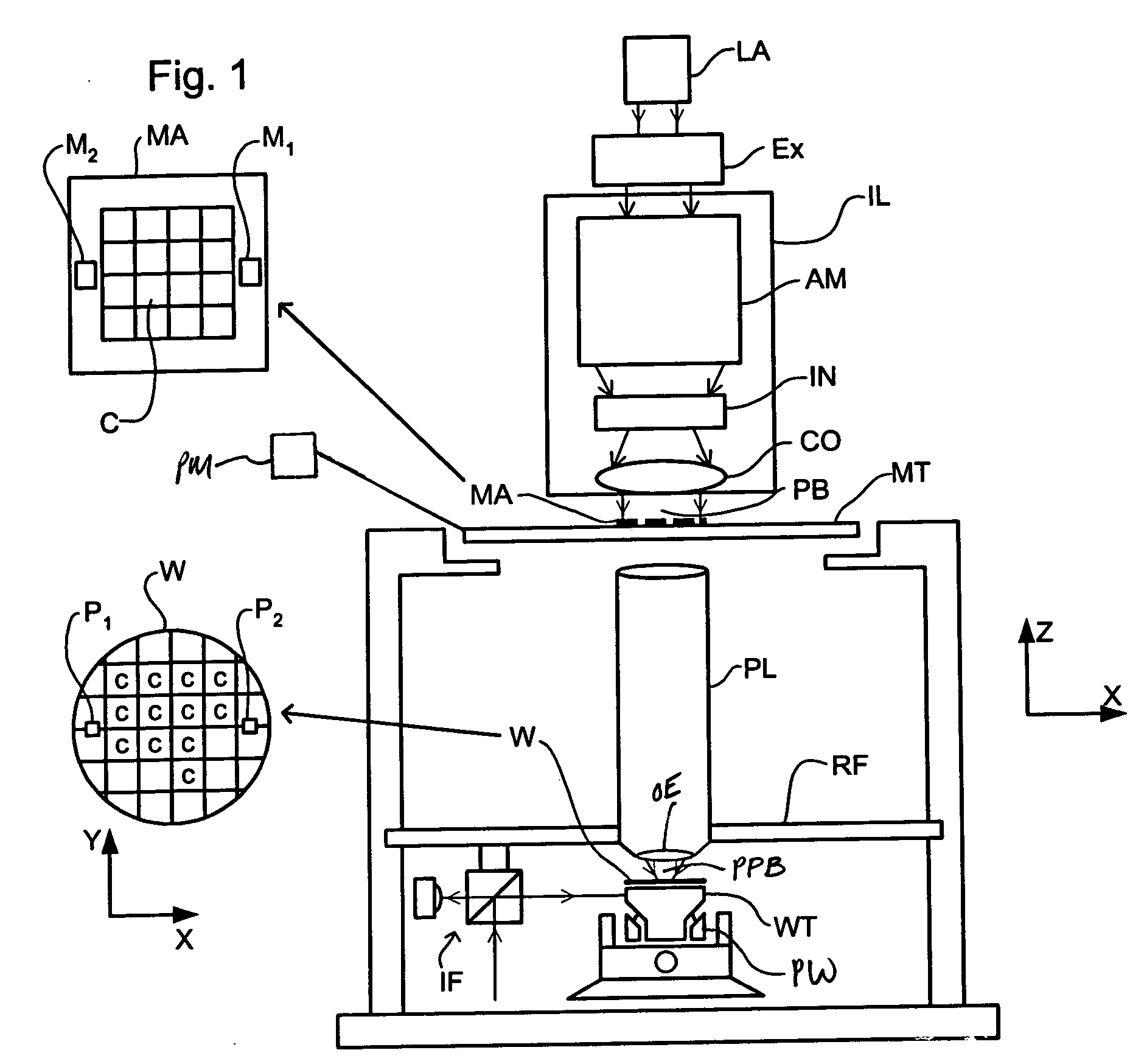
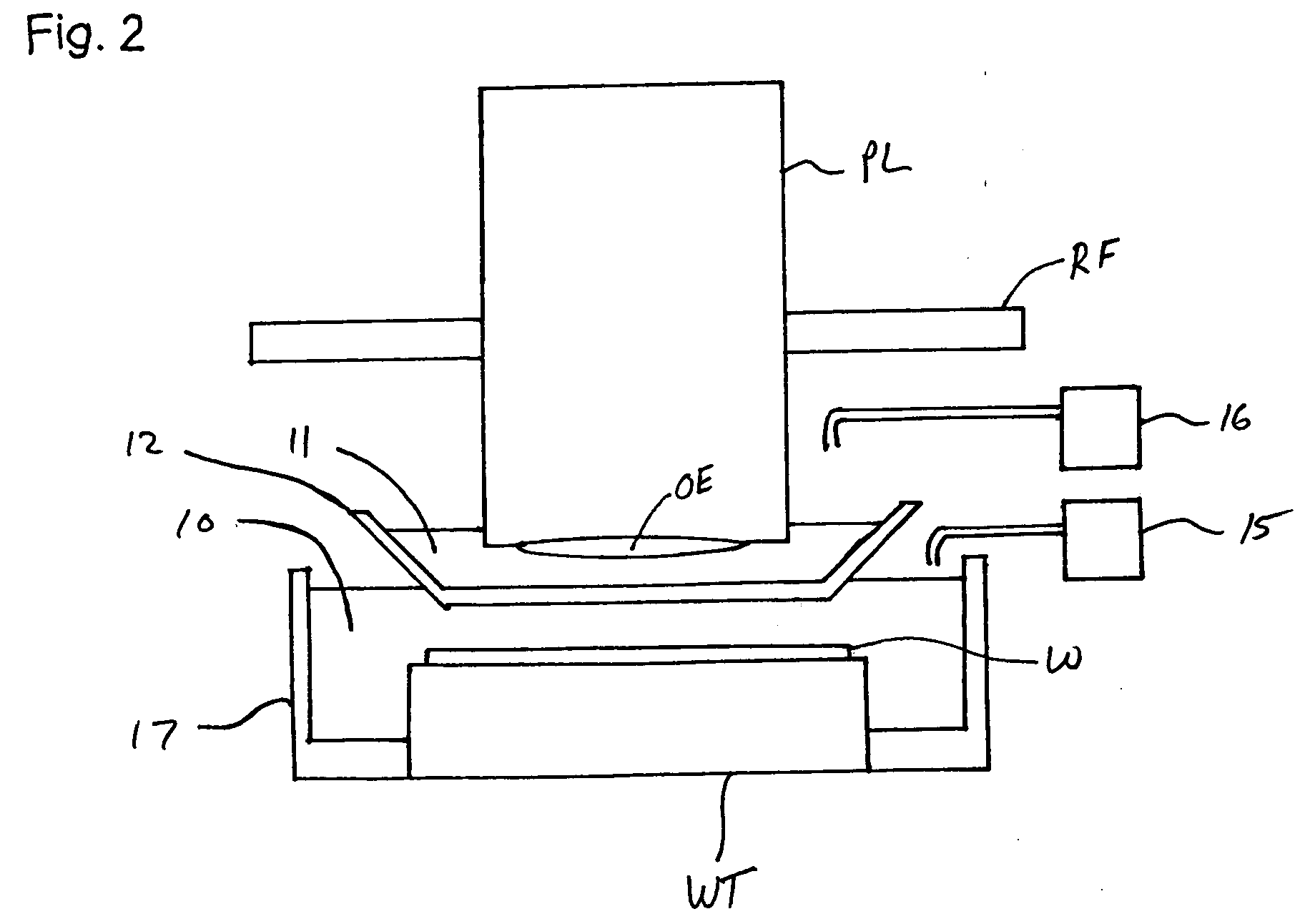
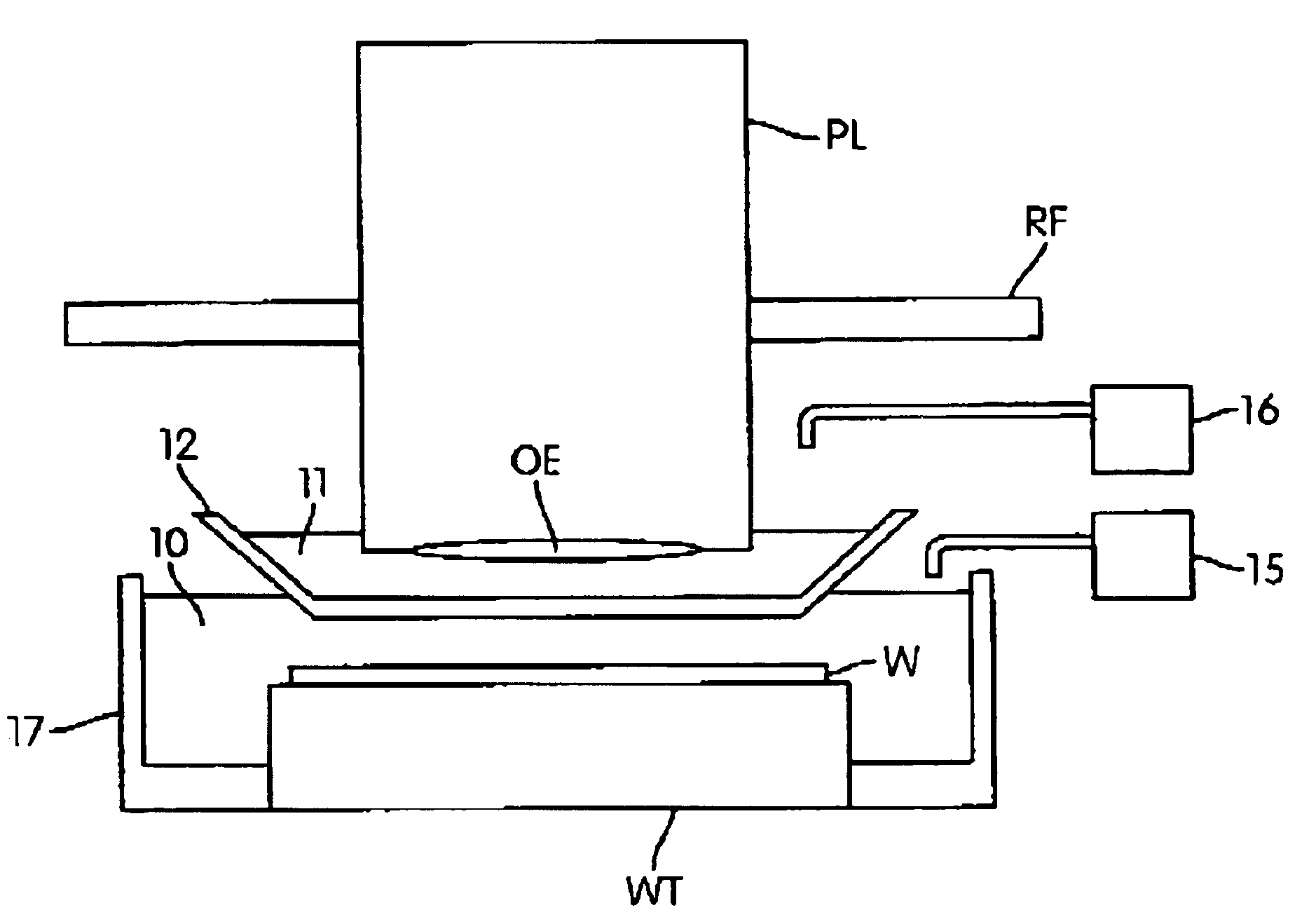
Gradient immersion lithography
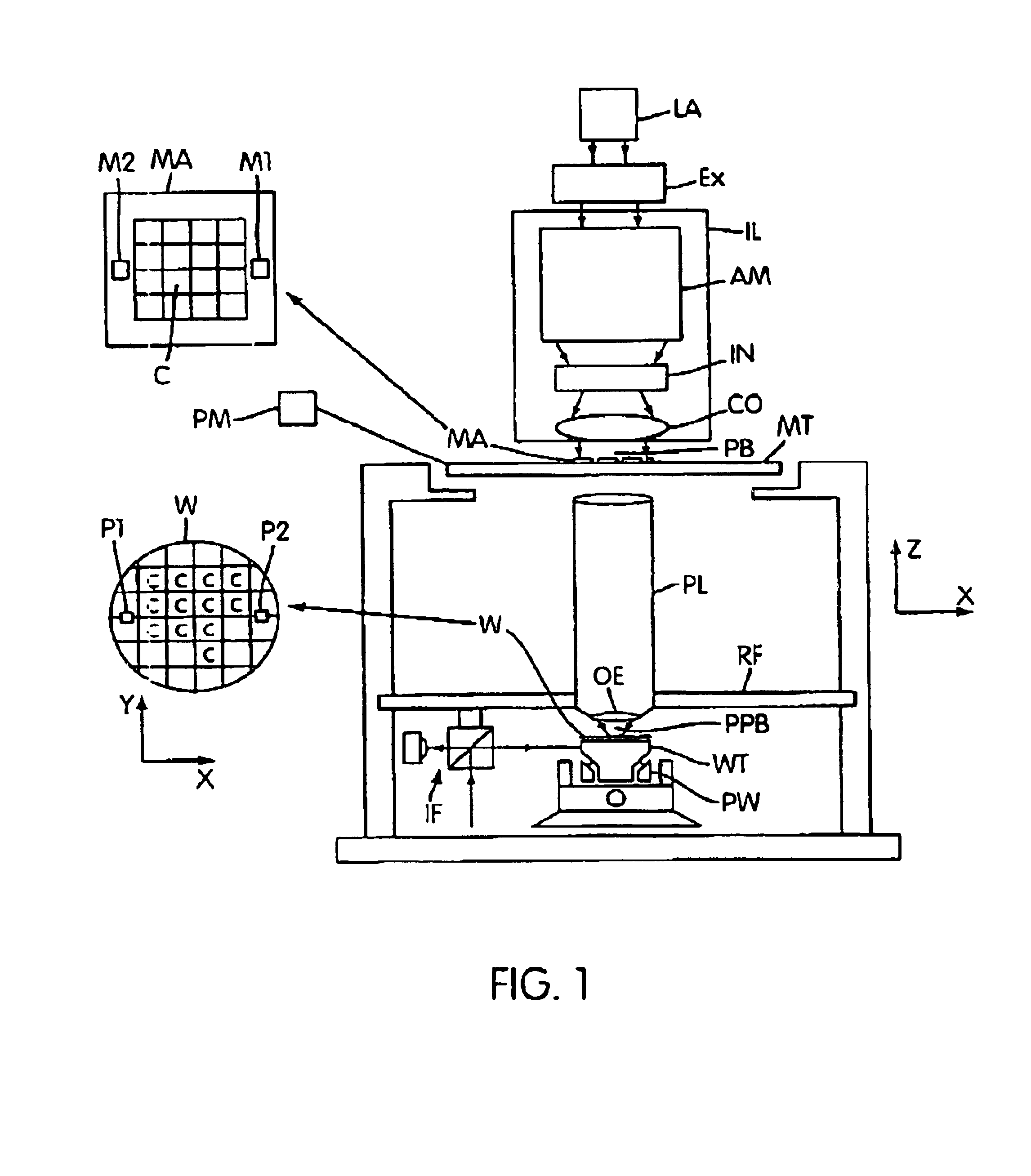
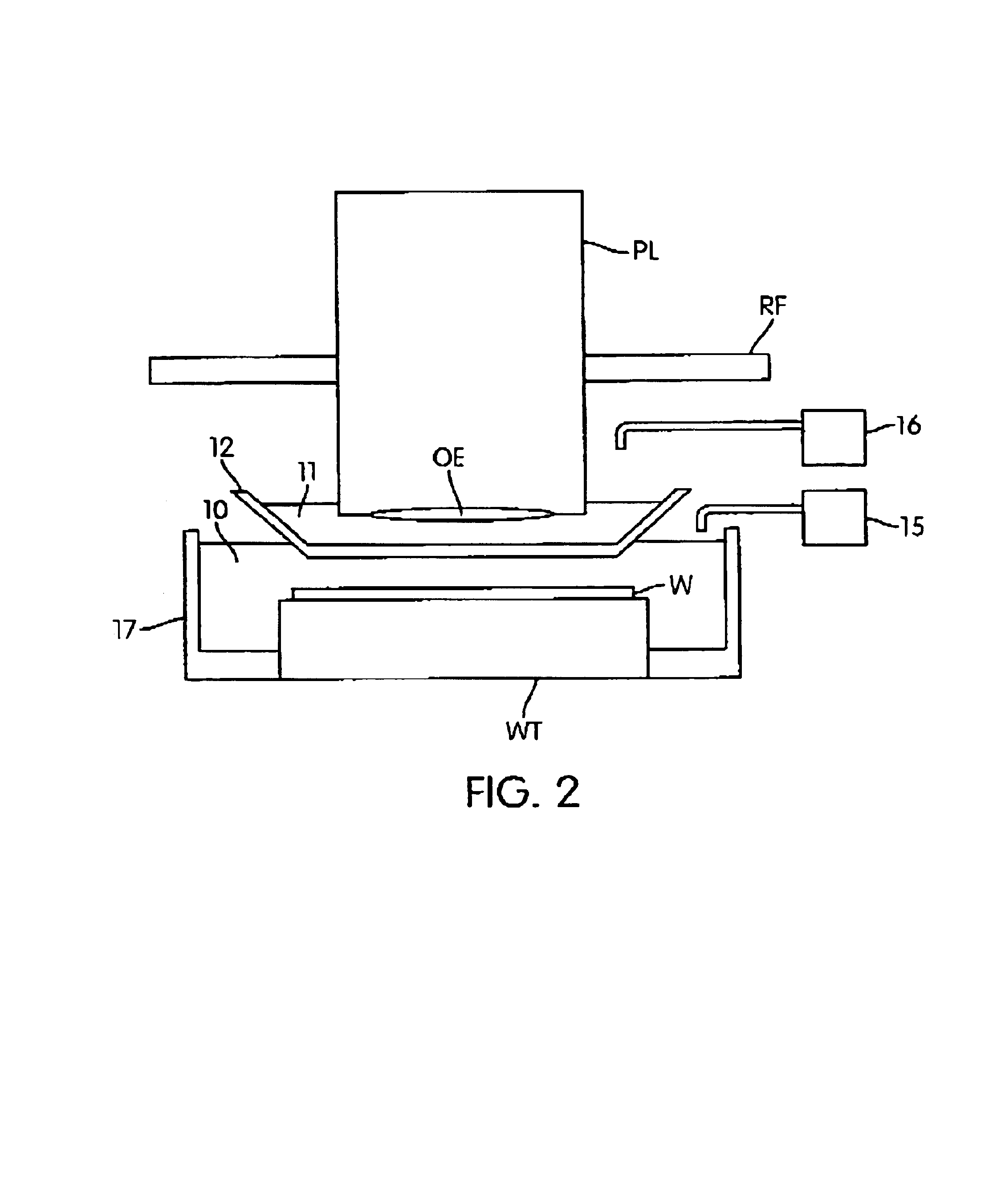
InactiveUS20050094116A1Increase the angle of incidenceReduce reflectionRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefractive indexProjection system
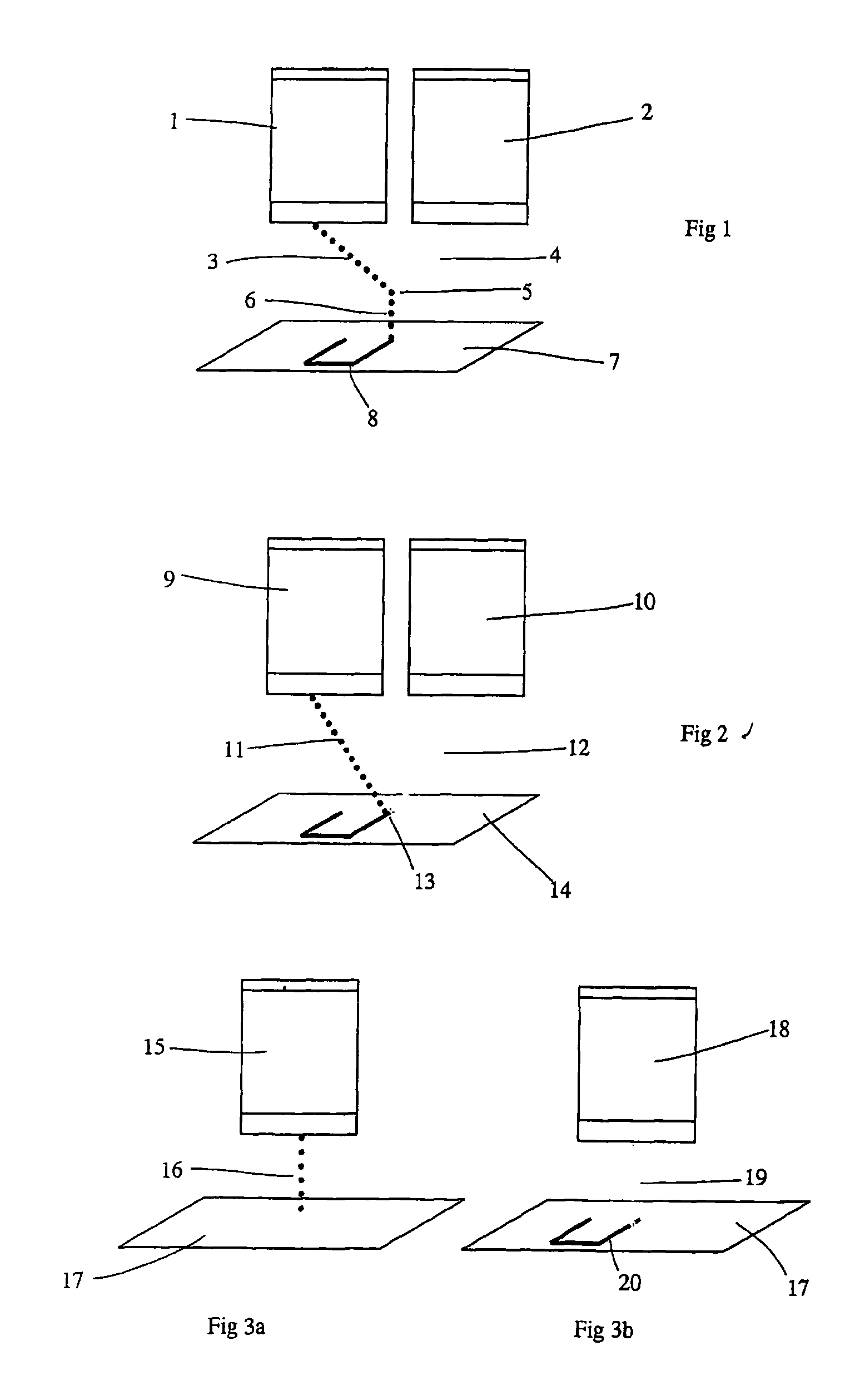
In a lithographic projection apparatus, a space between an optical element of a projection system is filled with a first fluid and a second fluid separated by a translucent plate. The first and second fluids have first and second indices of refraction, respectively, that are different from one another. The first fluid is provided in a space between a substrate and the translucent plate and preferably has an index of refraction similar to the index of refraction of the substrate. The second fluid is provided in a space between the translucent plate and the optical element and preferably has an index of refraction similar to the index of refraction of the optical element. The translucent plate has a third index of refraction between the first and second indices of refraction. The third index of refraction may be equal to the first index of refraction or the second index of refraction. A device manufacturing method includes filling a space between the optical element and the substrate with at least two fluids having different indices of refraction.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Gradient immersion lithography
InactiveUS6954256B2Increase the angle of incidenceReduce reflectionRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefractive indexImmersion lithography
In a lithographic projection apparatus, a space between an optical element is filled with a first fluid and a second fluid separated by a transparent plate. The first and second fluids have first and second indices of refraction, respectively, that are different from one another. The first fluid is provided between a substrate and the transparent plate and has an index of refraction similar to the index of refraction of the substrate. The second fluid is provided between the transparent plate and the optical element and has an index of refraction similar to the index of refraction of the optical element. The transparent plate has a third index of refraction between the first and second indices of refraction and may be equal to the first index of refraction or the second index of refraction. A device manufacturing method includes filling a space between the optical element and the substrate with at least two fluids having different indices of refraction.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
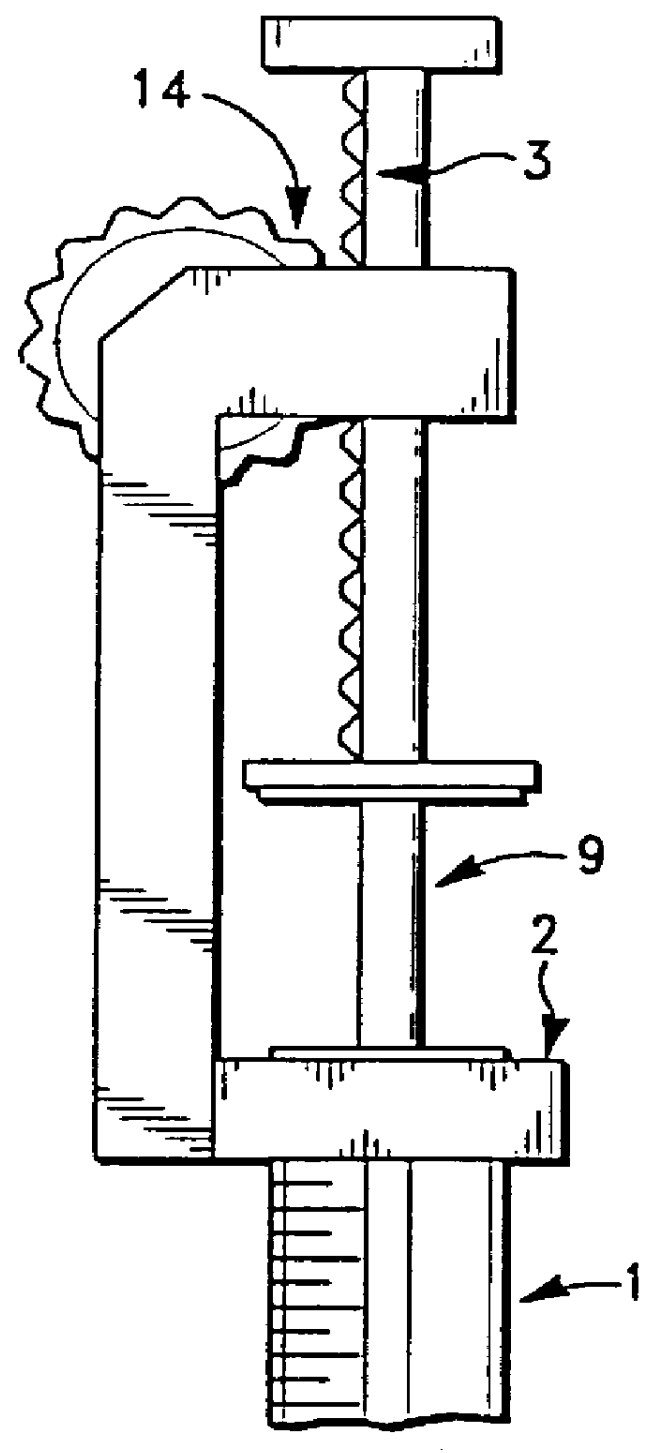
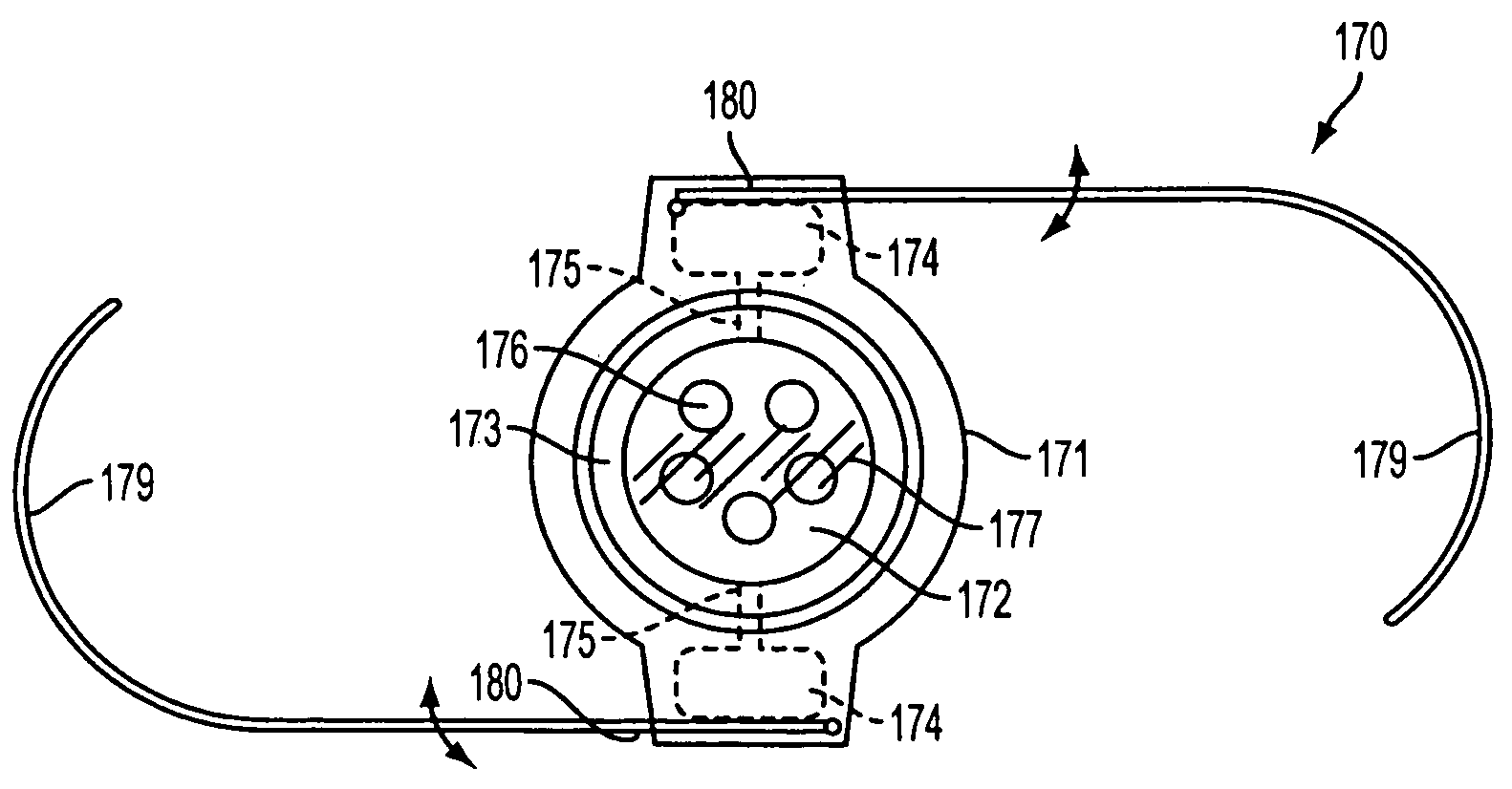
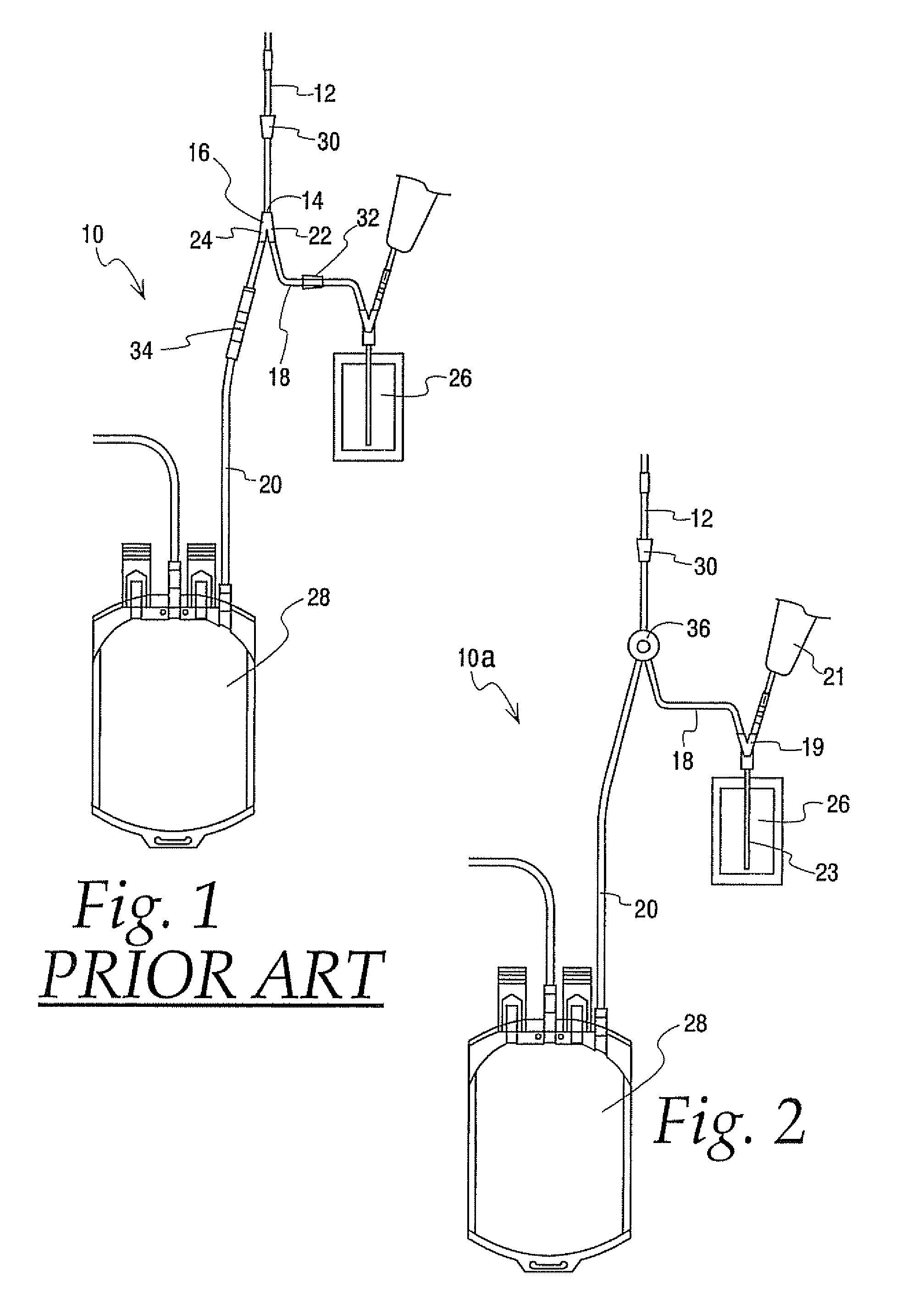
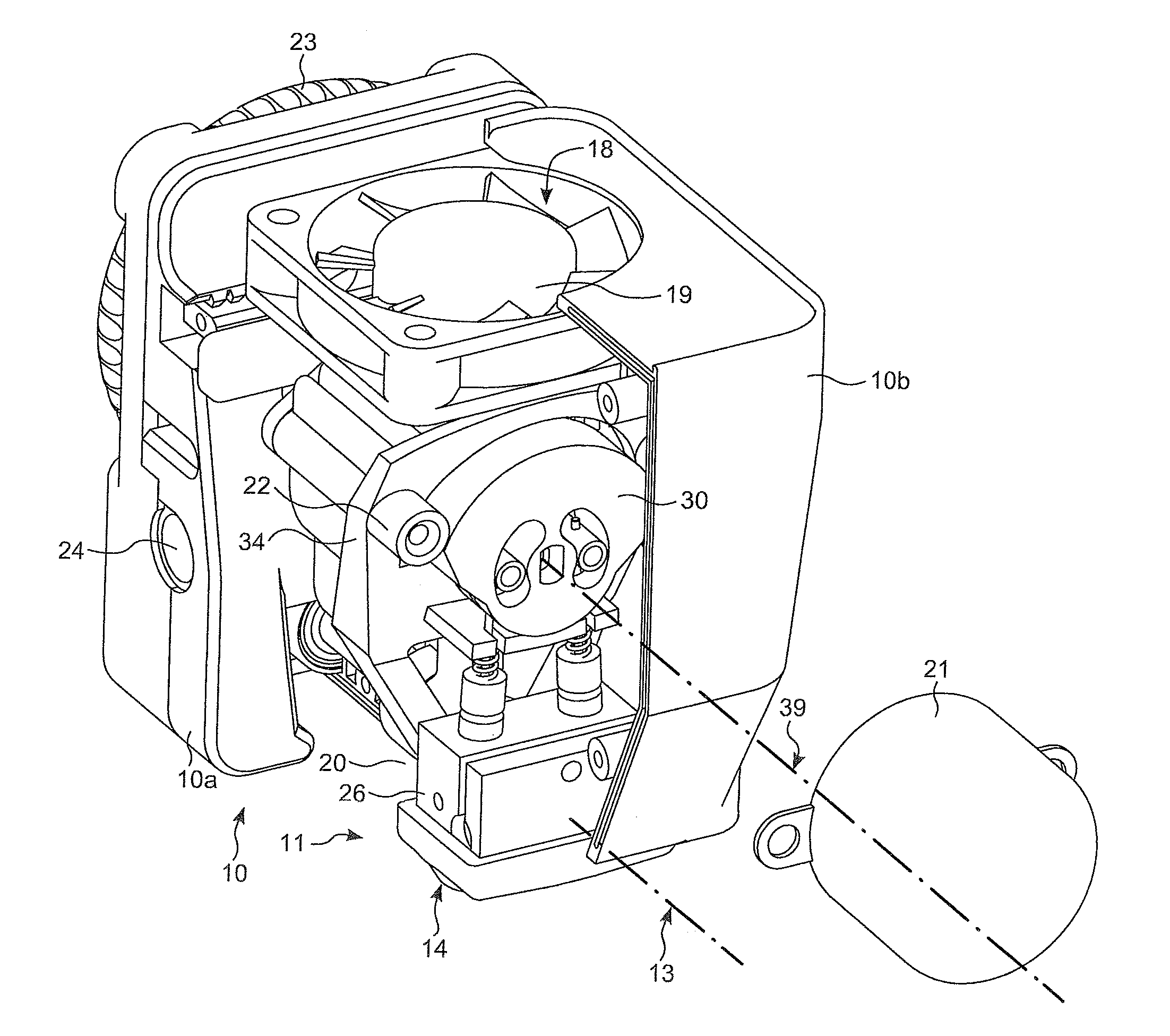
Apparatus for applying tissue sealant
InactiveUS6132396AEasy to fillEasy to assembleLiquid surface applicatorsSurgeryTissue sealantGear wheel
A device and method for applying a fibrinogen-based tissue sealant to seamlessly connect human or animal tissues or organ parts, to seal wounds, stop bleeding and the like by mixing fibrin or fibrinogen with blood clot-promoting coagulation factors are disclosed. The device includes two cylindrical compartments for separately containing the separate fluid components of the sealant preparation, which are simultaneously displaced from the respective compartments by plungers commonly depressable with the same effective strokes. The plungers may be depressed directly or by a common mechanism (e.g., rack and pinion) for accurately controlling the rate of dispensing fluid. The cylindrical compartments are of the same or different cross-sectional area and are arranged either concentrically or side-by-side. The device further includes structure for merging the two fluid components within an outer sleeve housing an inner needle. The sleeve and needle contain conduits for the flow of the two fluid sealant components as they are expressed from the respective compartments. Also disclosed are a convenient device for filling the two compartments, structure for mixing the fluid components, and for atomizing the effluent sealant fluid stream (i.e., spraying).
Owner:PLASMASEAL
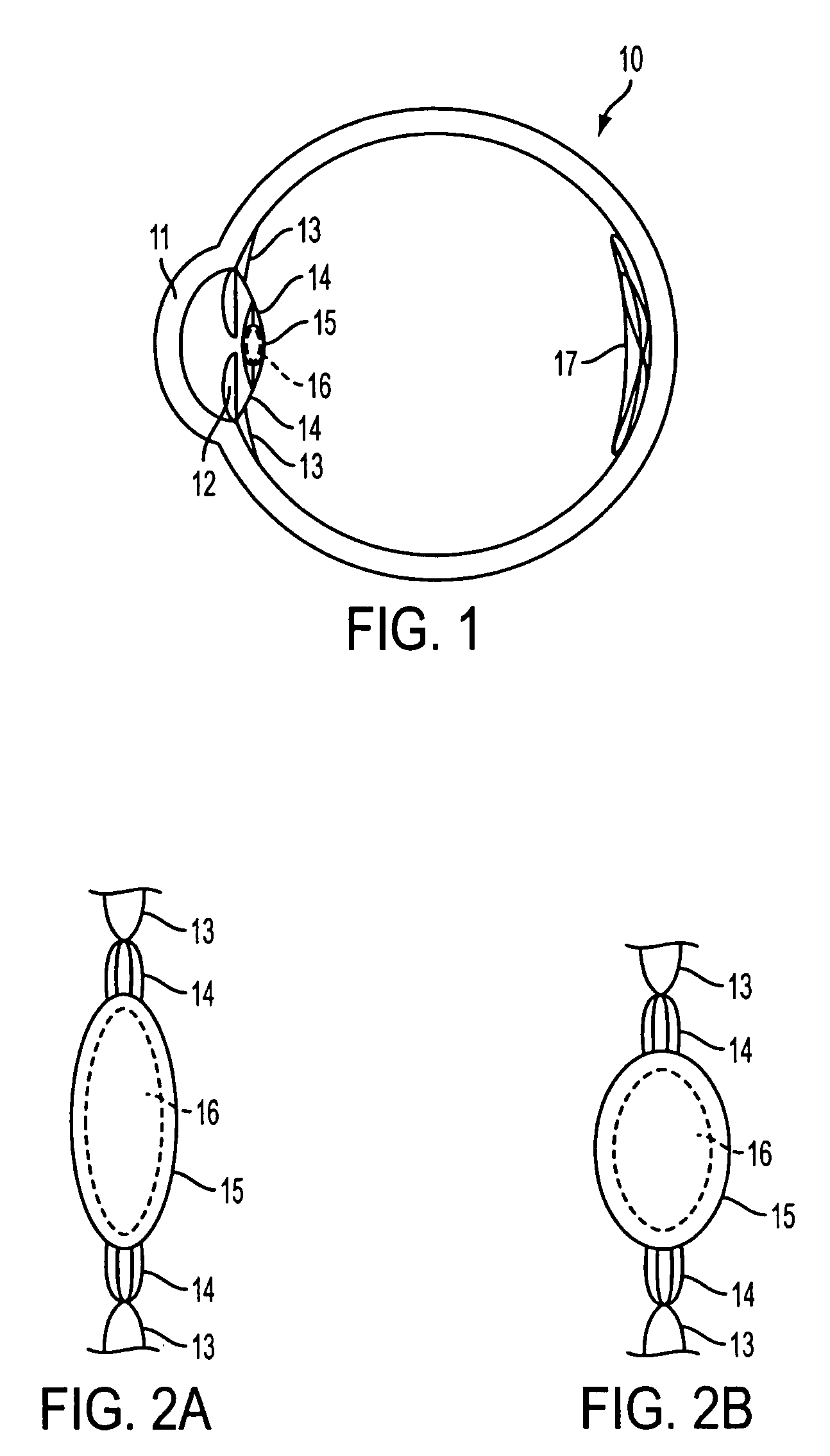
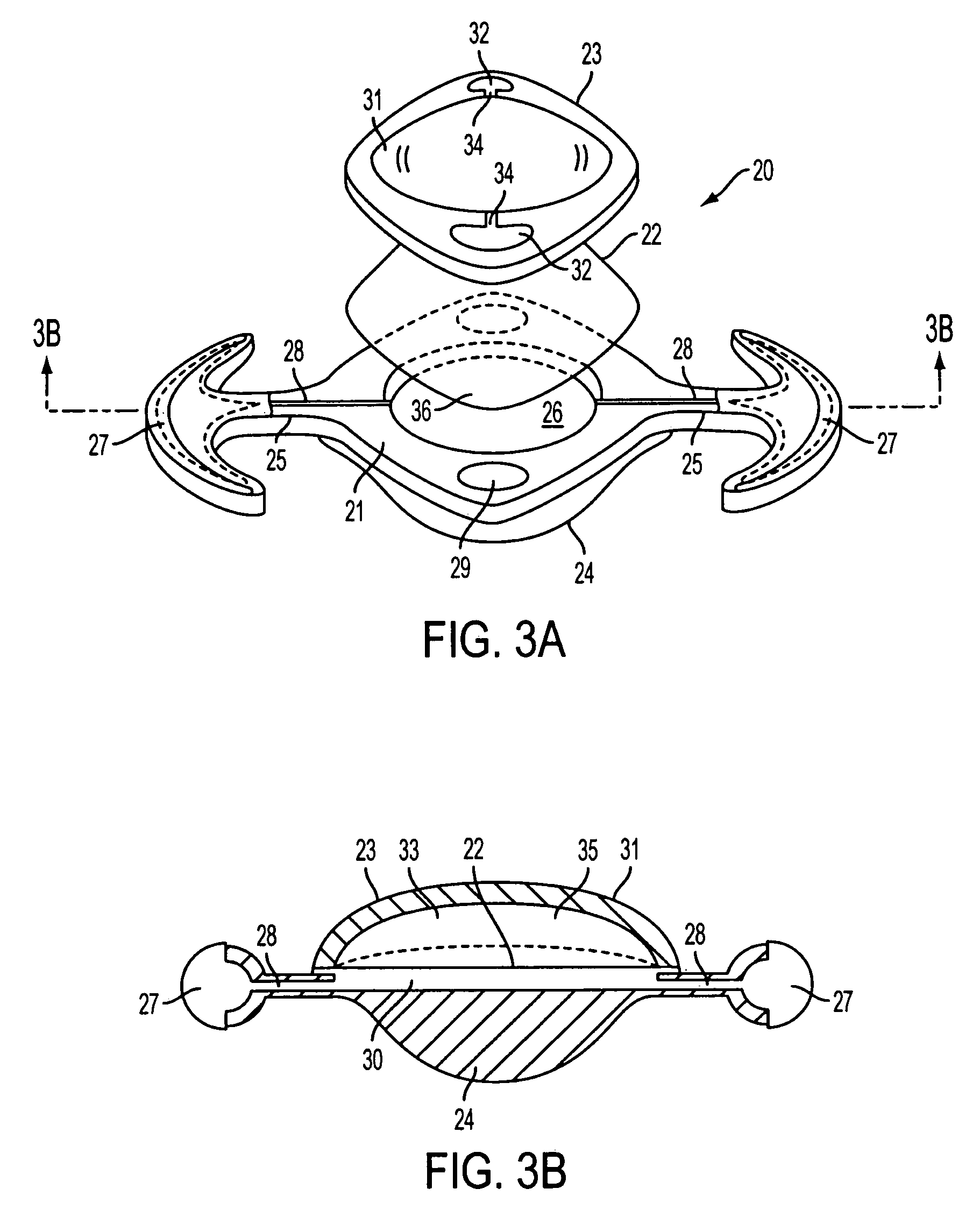
Accommodating intraocular lens system and method
ActiveUS7122053B2Great motionEfficiently manipulatedIntraocular lensOptical partsIntraocular lensRelative Volume
An accommodating intraocular lens is provided that having optical parameters that are altered in-situ using forces applied by the ciliary muscles, in which a lens body carries an actuator separating two fluid-filled chambers having either the same index of diffraction or different indices of refraction, actuation of the actuator changing the relative volumes of fluid within an optic element of the lens and altering the optical power of the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
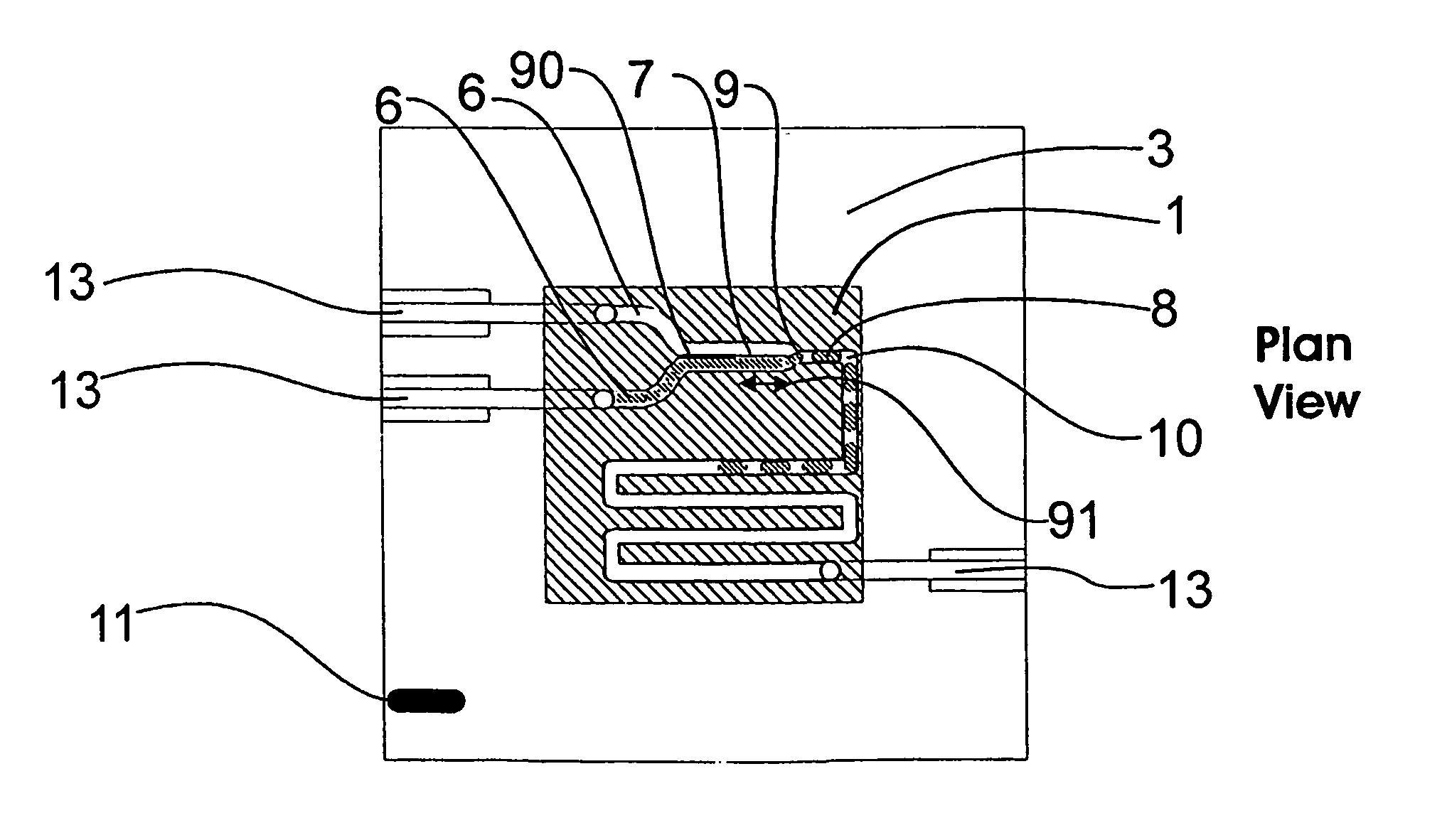
Microfluidic device and methods for construction and application
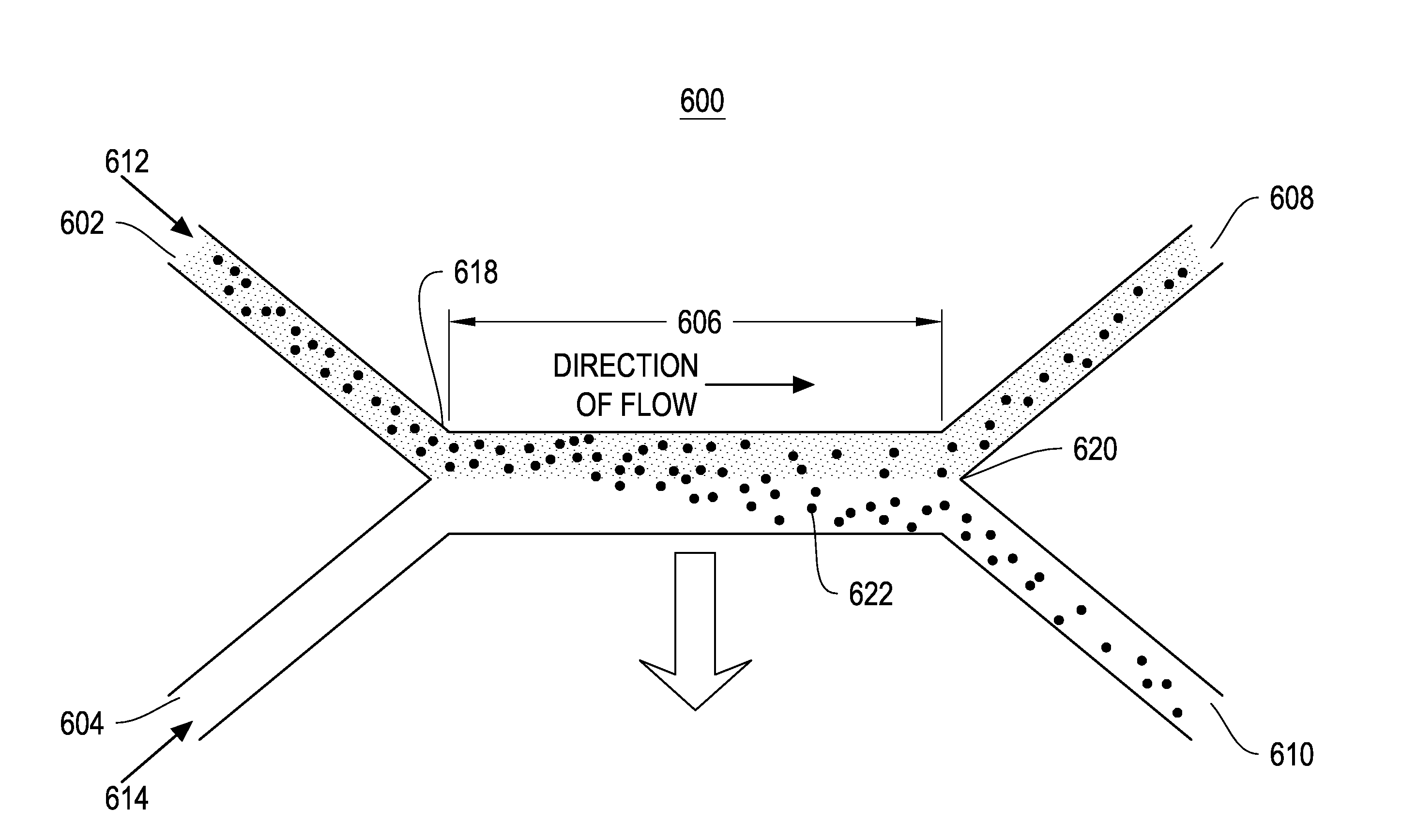
InactiveUS20060108012A1Considerable precisionEasy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyCircuit elementsEngineeringTwo fluid
A microfluidic device comprises first and second inlet passages (13) for respective immiscible fluids, these inlet passages merging into a third passage (8) along which the two fluids flow under parallel laminar flow conditions, the third passage being formed with a constriction or other discontinuity (9) causing the two fluids to form into a flow of alternate segments.
Owner:Q CHIP
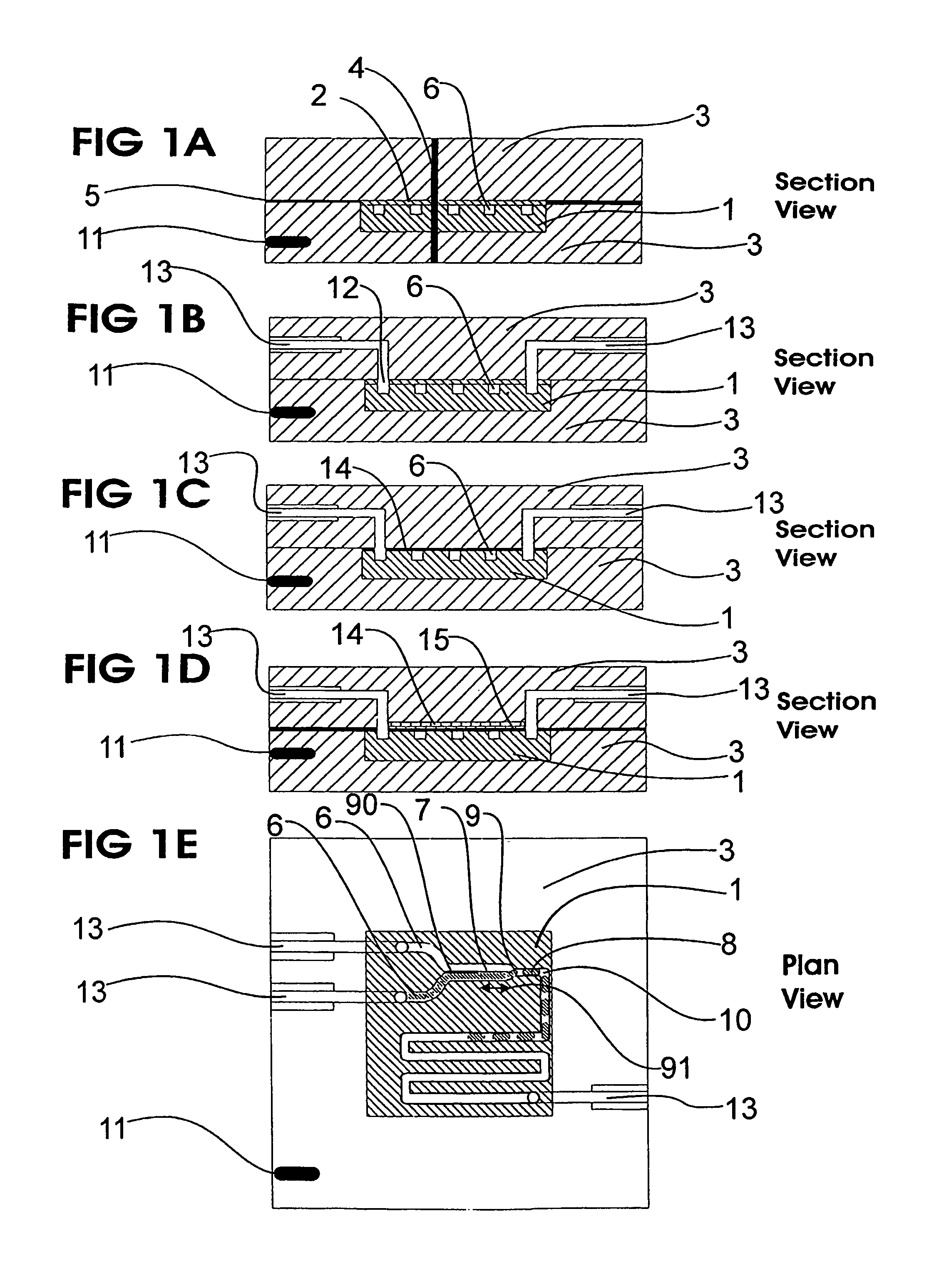
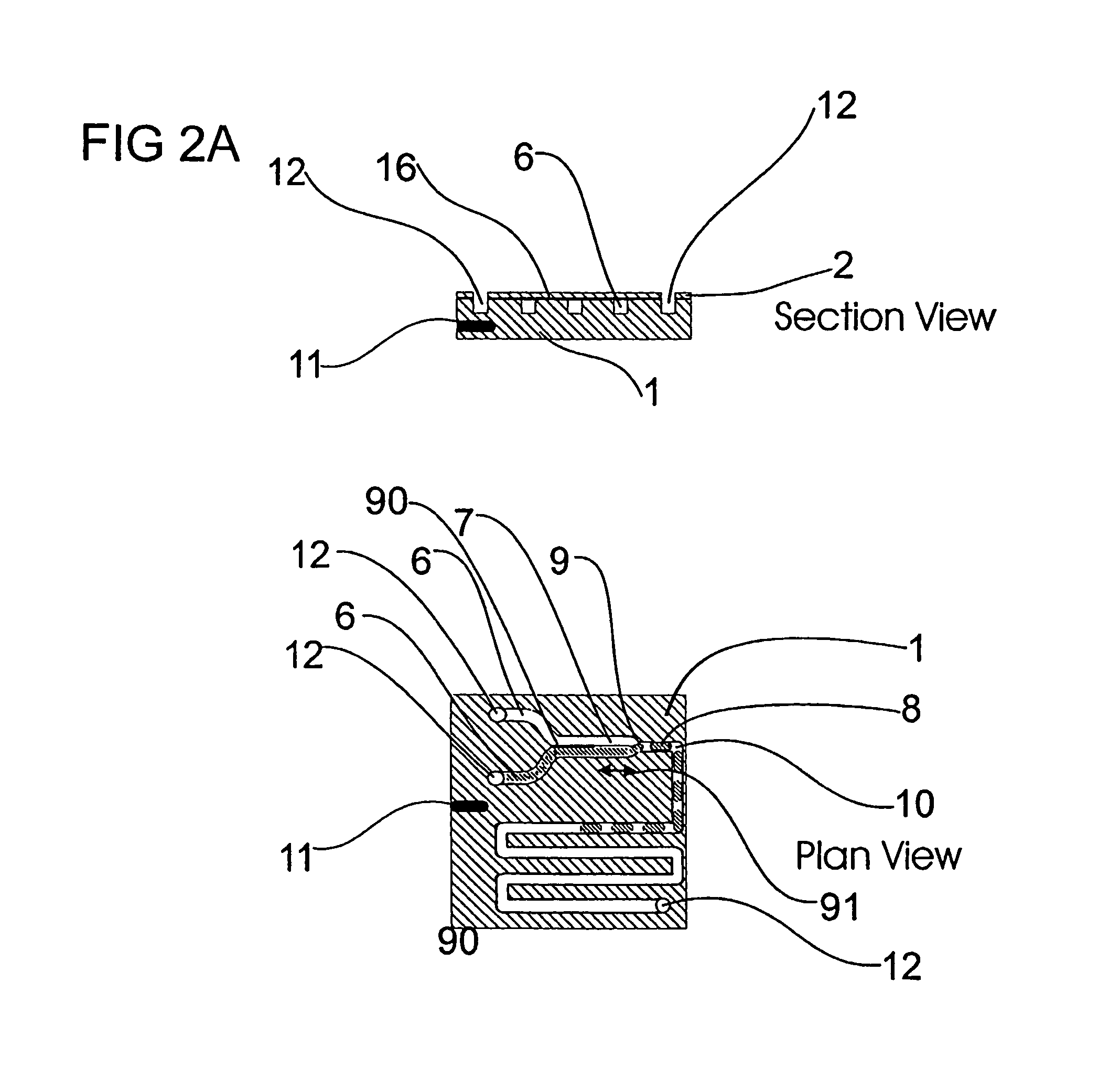
Interstitial microwave system and method for thermal treatment of diseases
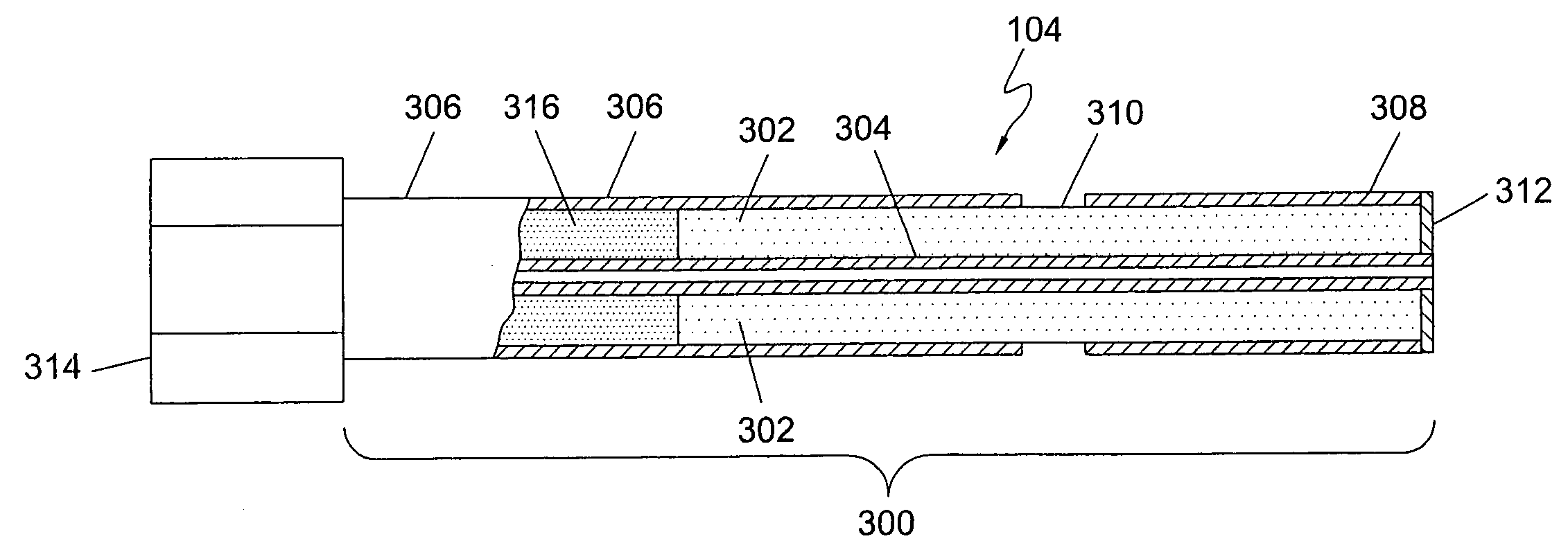
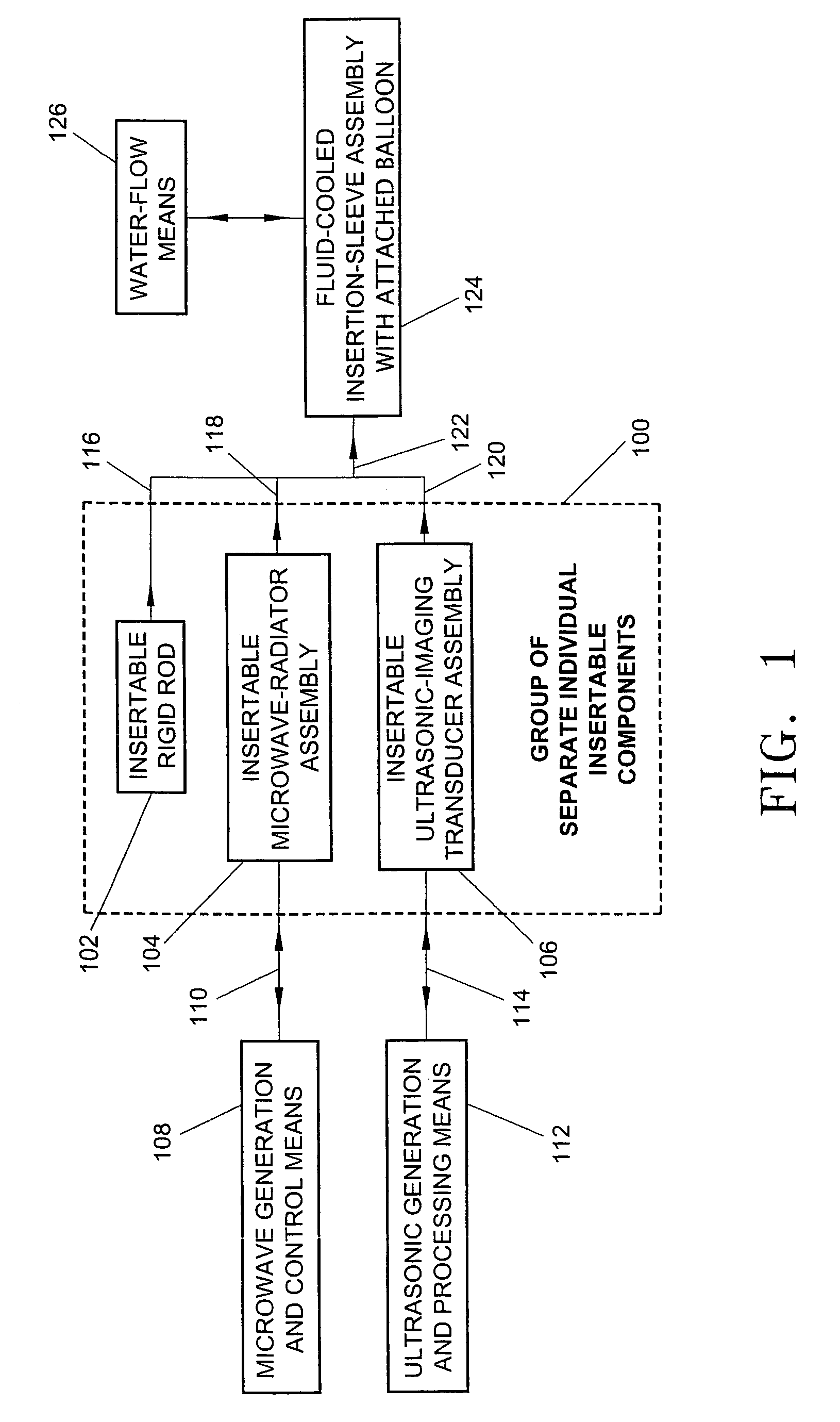
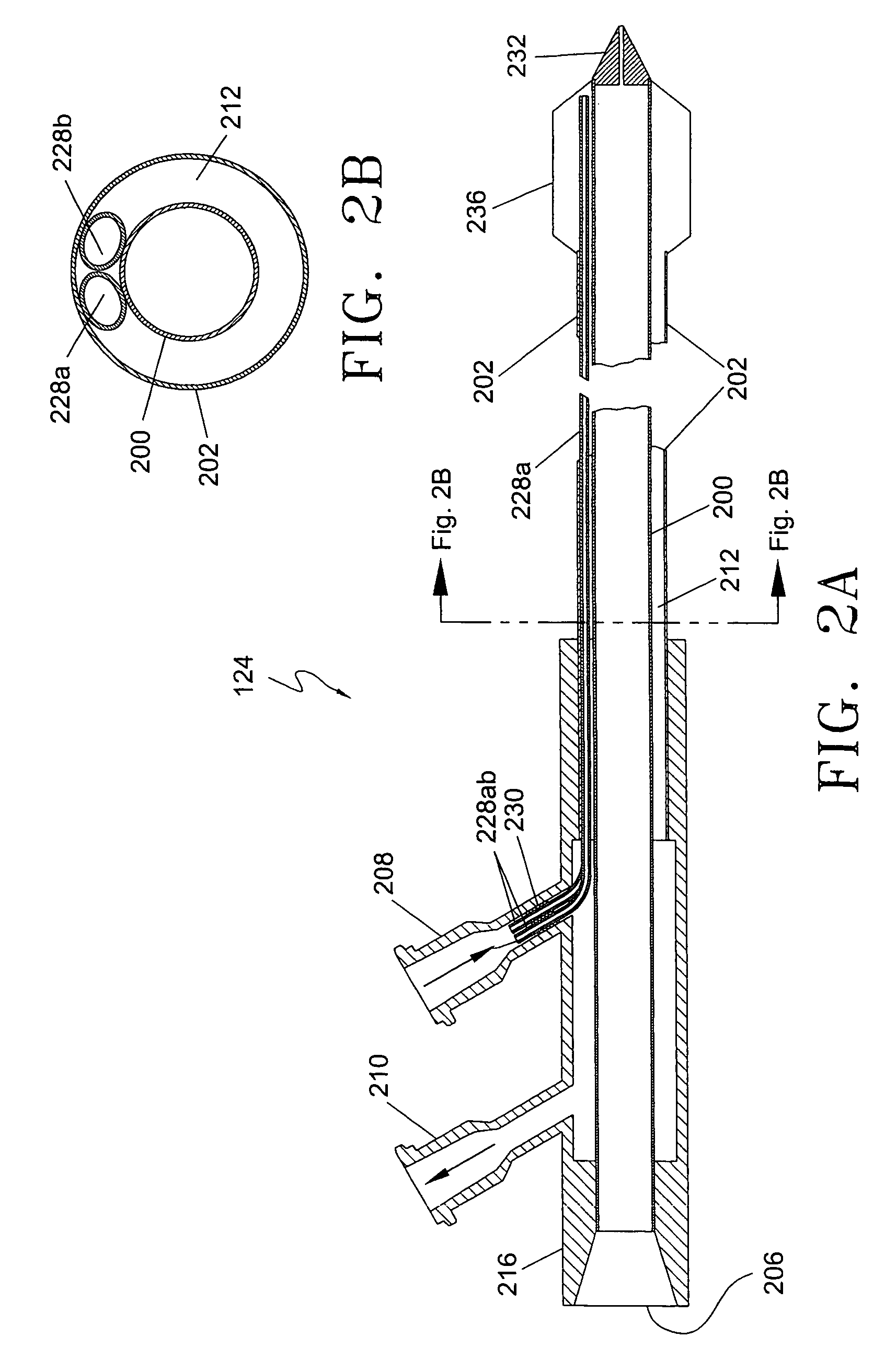
A minimally-invasive fluid-cooled insertion sleeve assembly, with an attached balloon and distally-located penetrating tip, into which sleeve any of a group comprising a rigid rod, a microwave-radiator assembly and an ultrasonic-imaging transducer assembly may be inserted, constitutes a probe of the system. The sleeve assembly comprises spaced inner and outer plastic tubes with two fluid channels situated within the coaxial lumen between the inner and outer tubes. The fluid coolant input flows through the fluid channels into the balloon, thereby inflating the balloon, and then exits through that coaxial lumen. An alternative embodiment has no balloon. The method employs the probe for piercing sub-cutaneous tissue and then ablating deep-seated tumor tissue with microwave-radiation generated heat.
Owner:MMTC LTD +1
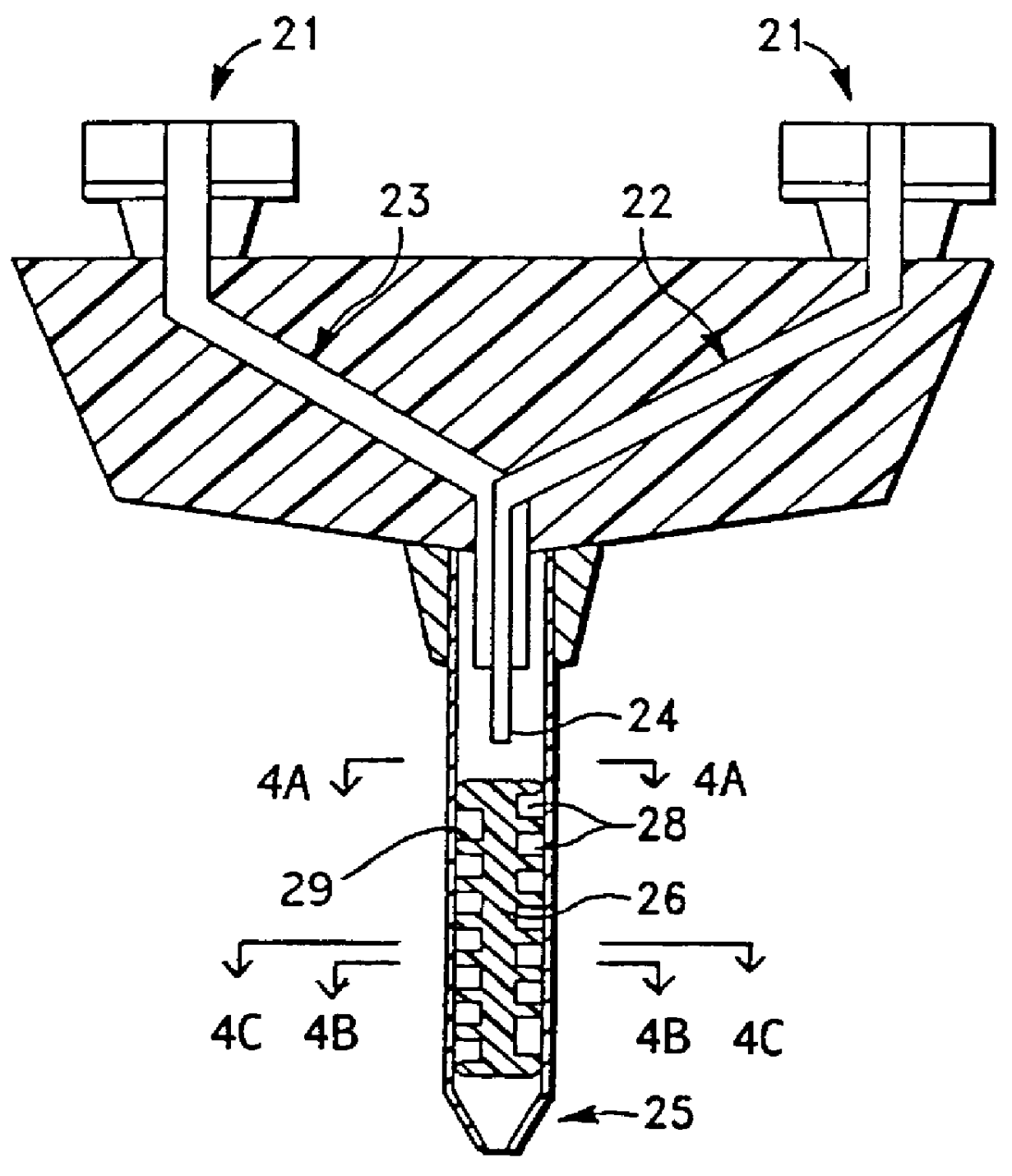
Apparatus and method for injection of fibrin sealant in spinal applications
ActiveUS20070191781A1Reduce the amount requiredGood pain reliefJet injection syringesMulti-lumen catheterMedicineBiomedical engineering
An apparatus for percutaneous delivery of a sealant comprising: at least two fluid reservoirs, an introducer needle having a distal tip that is in fluid communication with at least one reservoir, a fluid delivery tube that is in fluid communication with a second reservoir, wherein the fluid delivery tube has a tip and wherein the fluid delivery tube is configured so that the tip of the fluid delivery tube does not extend past the distal tip of the introducer needle during use.
Owner:PAUZA KEVIN
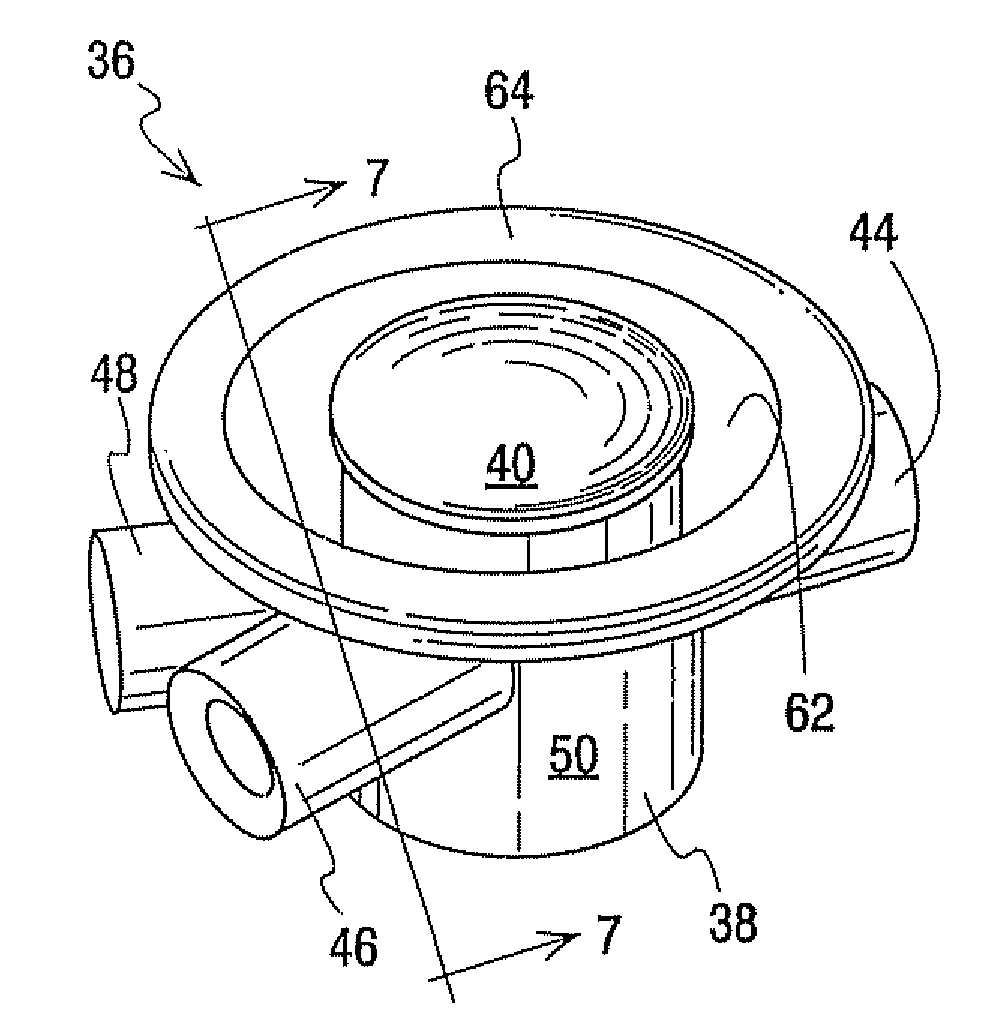
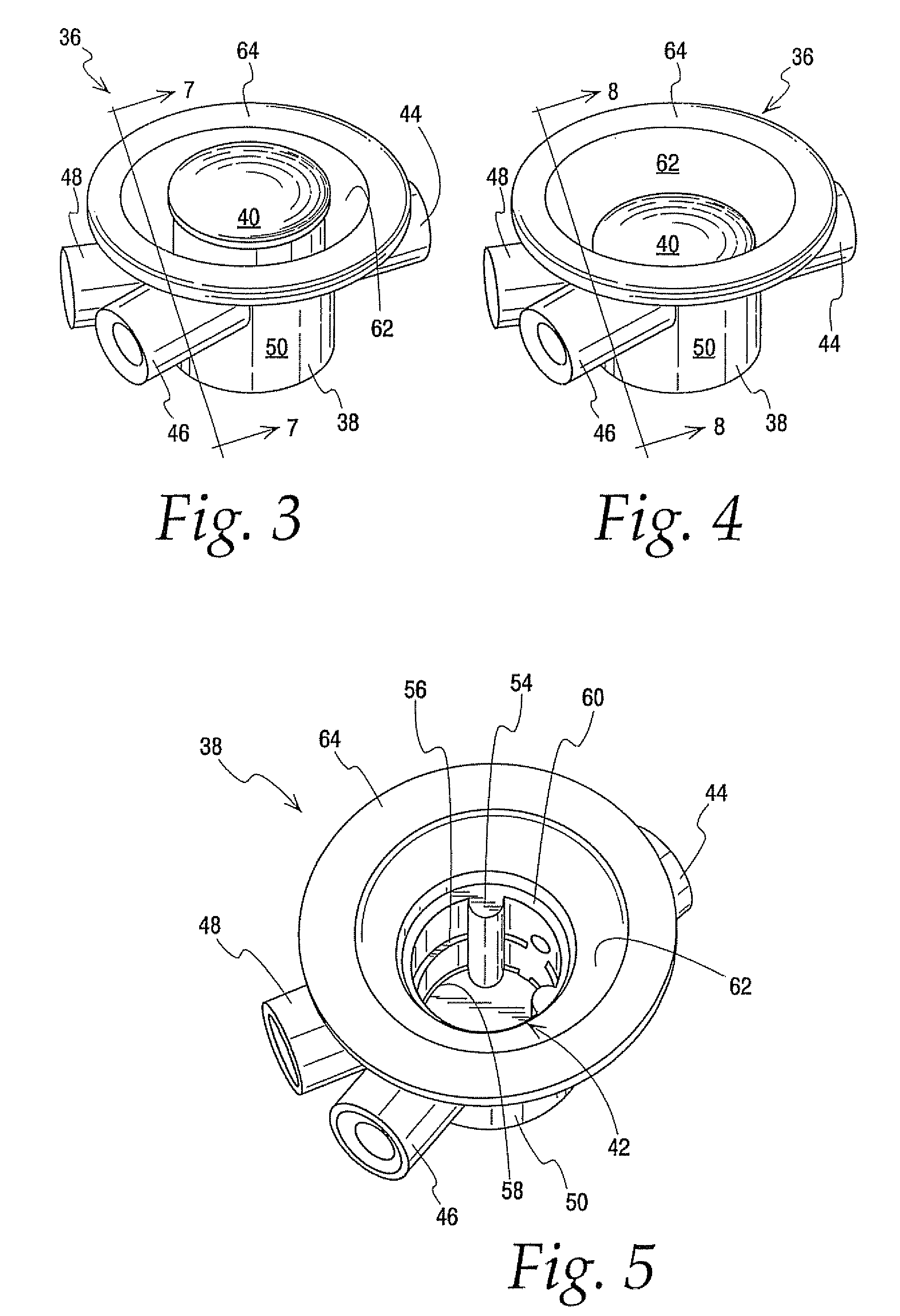
Flow Controllers
Flow controllers are provided for interconnecting a fluid source to two separate collection zones. The flow controllers include a body having a fluid inlet communicating with the source and two fluid outlets, each communicating with one of the collection zones. An actuator member received within a cavity of the body includes first and second flow paths. In a first position, the first flow path is aligned with the fluid inlet of the body to allow fluid communication with one of the fluid outlets and the associated collection zone. The actuator member is non-rotationally moved to a second position within the cavity to align the second flow path with the fluid inlet of the body, thereby halting flow through the first flow path and allowing fluid communication with the other collection zone. An optional safety feature prevents movement of the actuator member from the second position to the first position.
Owner:FENWAL
Fluid-dispensing head for a 3D printer
ActiveUS20140242208A1Readily switched into operationIncrease flexibilityConfectionerySweetmeatsInfill3d printer
A head assembly for an extrusion-based 3D printer includes: a fluid-dispensing head having a manifold and at least two fluid-dispensing nozzles, of different sizes, which are mounted in communication with a melt chamber in a manifold. Outlets of each nozzle are closed by respective valve members. A rocker serves both to pivot the nozzles to their lowermost nozzle-operating position and to actuate the valve members, for ready switching between the valves, such that the smaller nozzle can be used for high resolution work, and the larger nozzle can be used for bulk infill.
Owner:CEL TECH
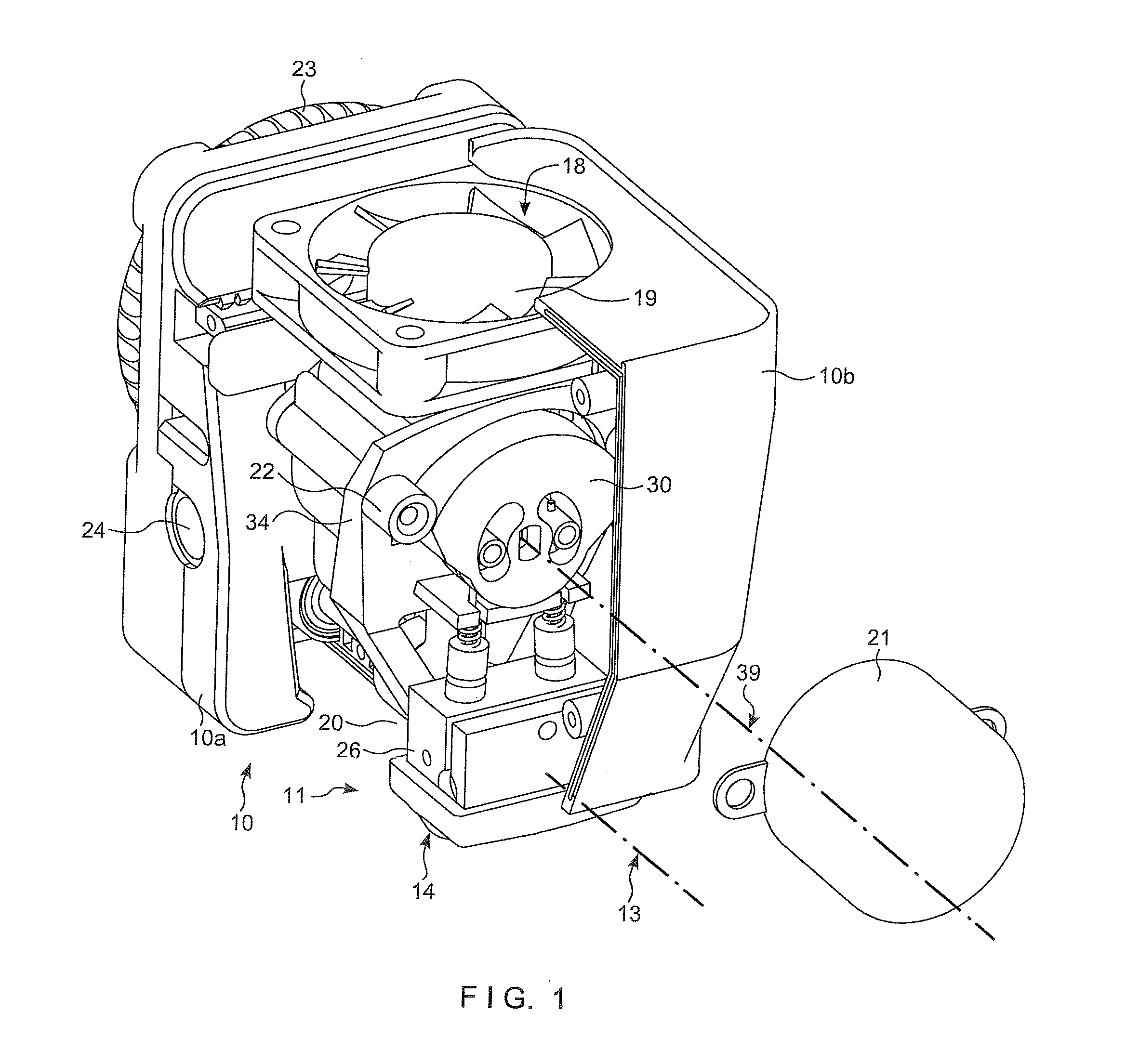
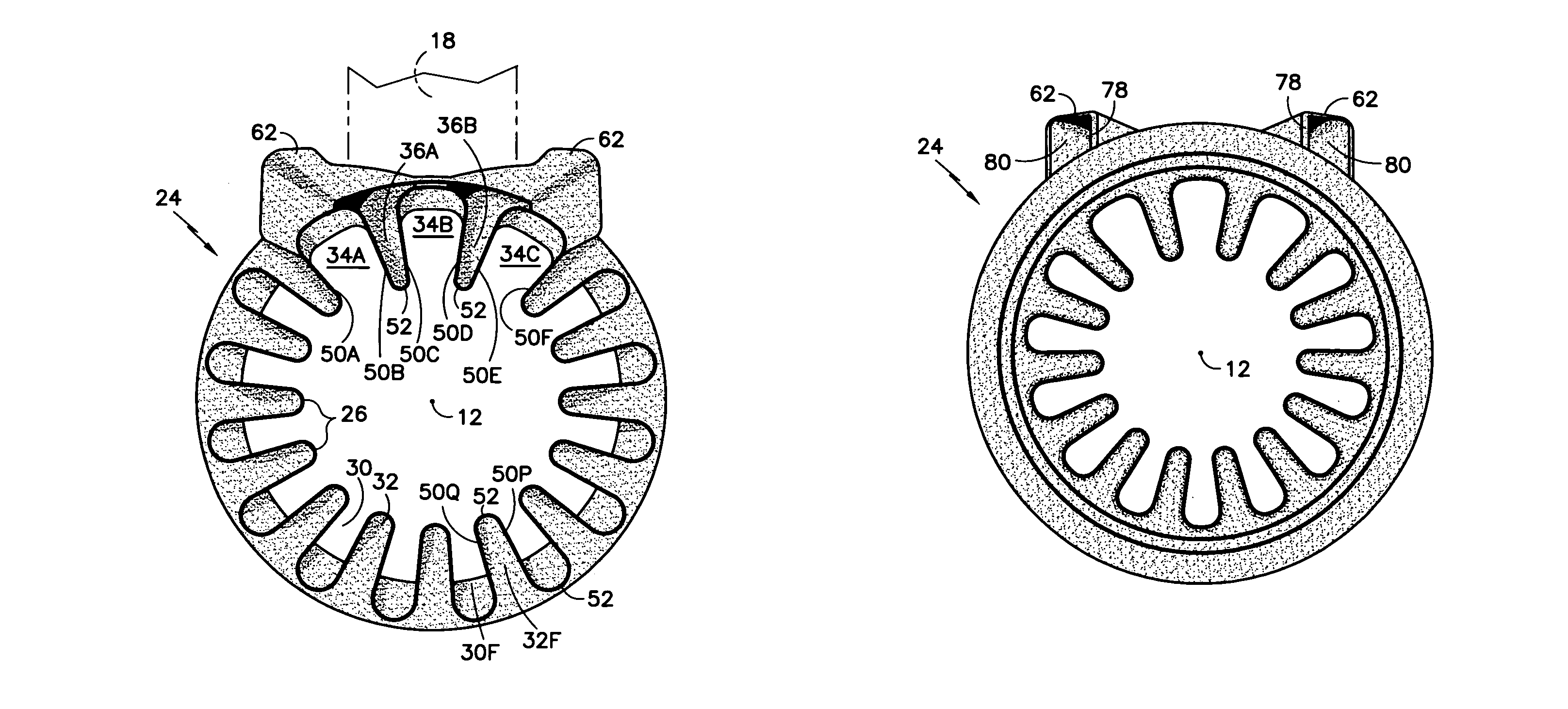
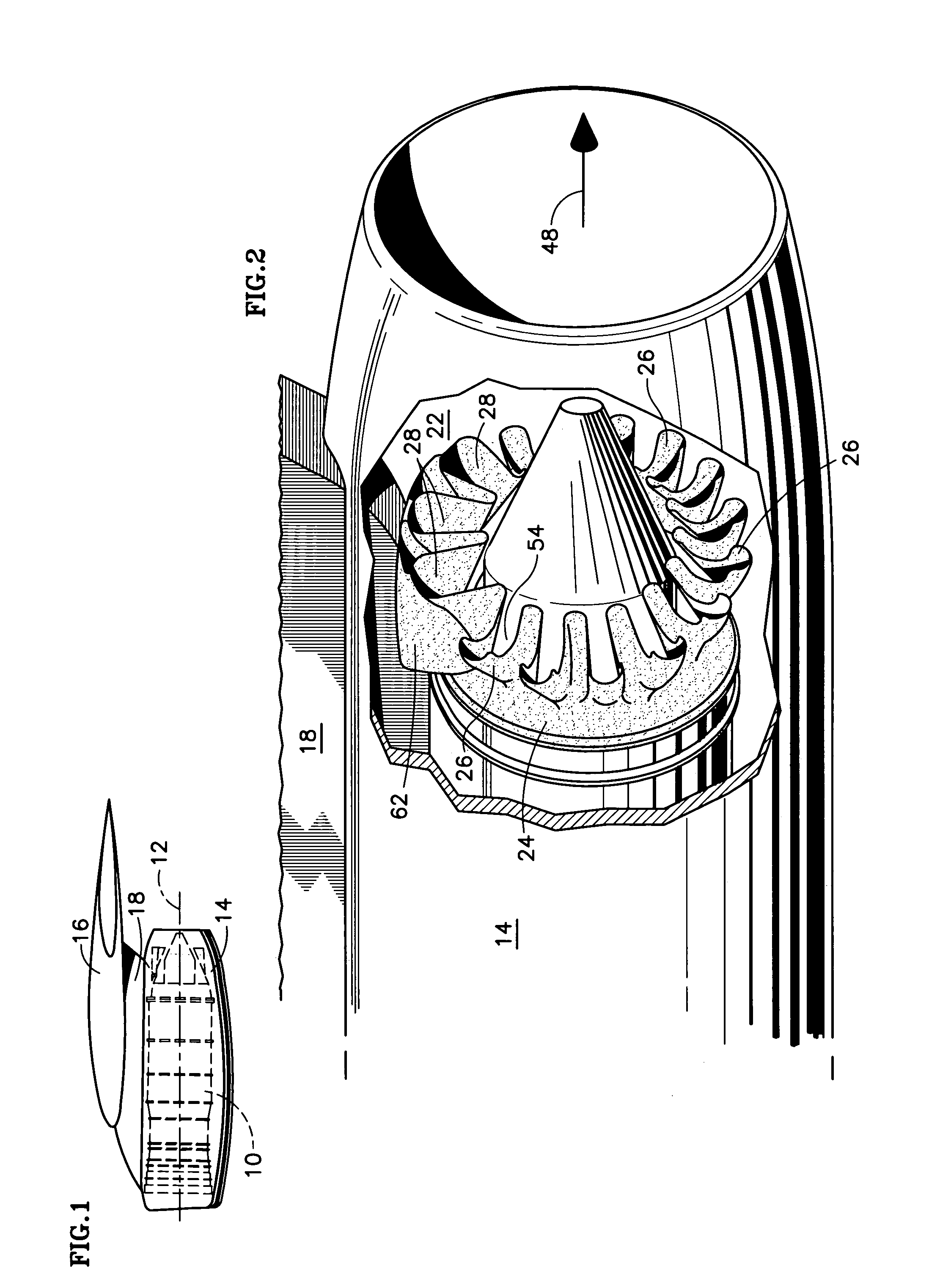
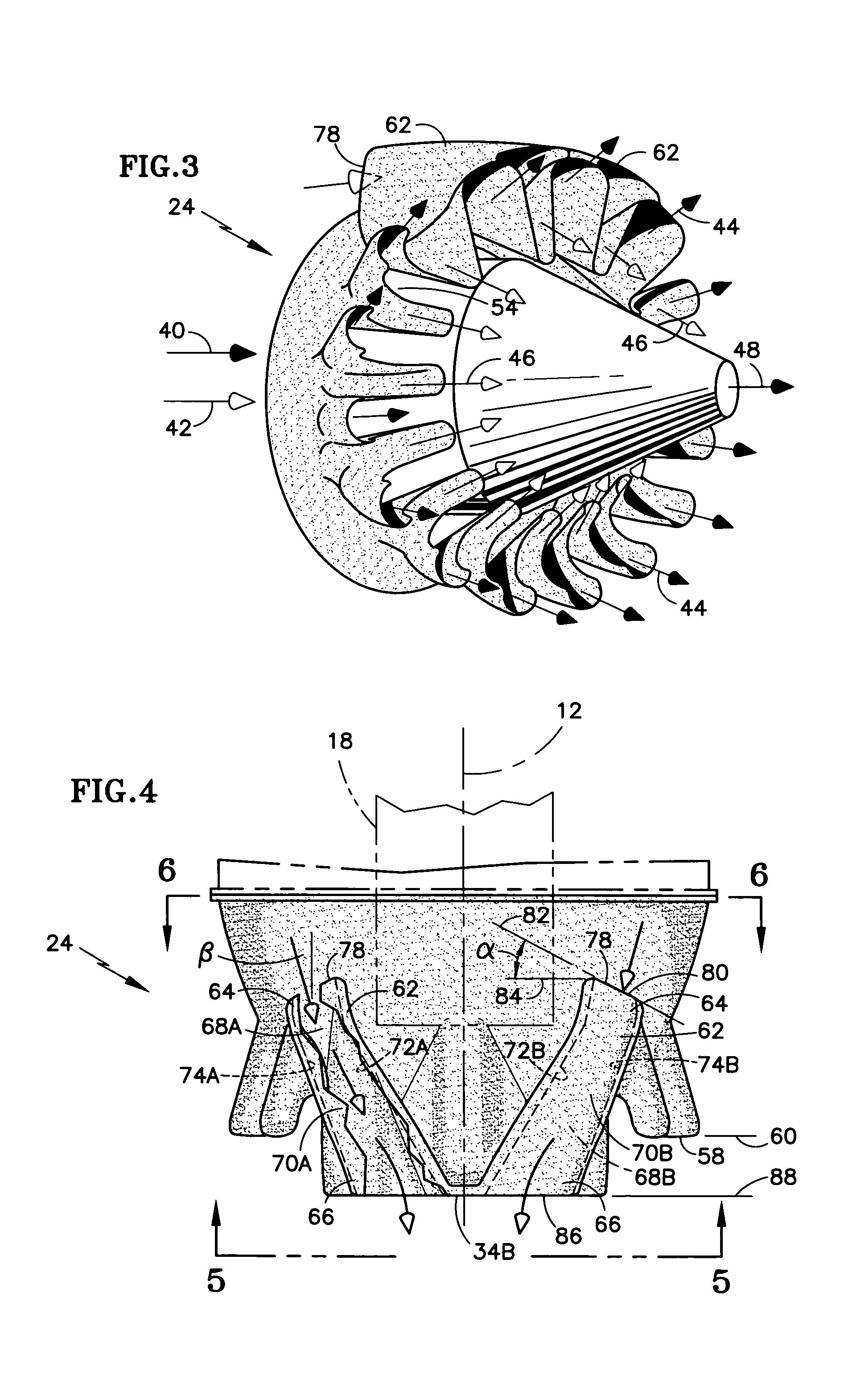
Fluid mixer with an integral fluid capture ducts forming auxiliary secondary chutes at the discharge end of said ducts
ActiveUS7434384B2Improve performanceEfficient capturePower plant exhaust arrangementsPower plant constructionEngineeringMain lobe
A fluid mixer for mixing two fluid streams 40, 42 includes a set of main lobes 26 defining alternating primary and secondary main chutes 30, 32, one or more auxiliary lobes 28 intermediate two of the main lobes, and an auxiliary fluid capture duct 62. The auxiliary lobes are defined, at least in part, by the discharge end of the duct. In operation, the duct conveys secondary fluid to secondary chutes 36 defined by the lobes thereby improving the performance of the mixer despite the presence of an obstruction 18 that would otherwise impede thorough mixing of two fluid streams.
Owner:RTX CORP
Apparatus and method for filter cleaning by ultrasound, backwashing and filter movement during the filtration of biological samples
InactiveUS8273253B2Minimises fouling and clogging of filterImprove overall efficiency and accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCyclic processVacuum pressure
The present application is directed to the separation of—a solid fraction from a fluid sample particularly a therapeutic cellular fraction from a biological sample such as a bone marrow sample by a porous filter (2) which separates a filtration unit (1) into an upper pre-filtration chamber (3) into which a fluid sample (4) requiring cell separation is introduced and a lower post-filtration chamber (5) into which a fluid (6) capable of transmitting an acoustic standing wave is introduced. An acoustic element (8) is coupled to a substrate (7) which is located within and at the bottom of the lower chamber (5) and which resonates in response to the acoustic generating element (8) and generates a standing wave through the two fluid phases and the filter to agitate the sample (4). Simultaneously, a cyclic process of vacuum draw (9). causes movement of the sample (4) downwards through the filter (2). Vacuum pressure, fluid flow rate and frequency of vibration are controlled from a remote unit housing appropriate pumps and valves.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Bio-interventional therapeutic treatments for cardiovascular diseases
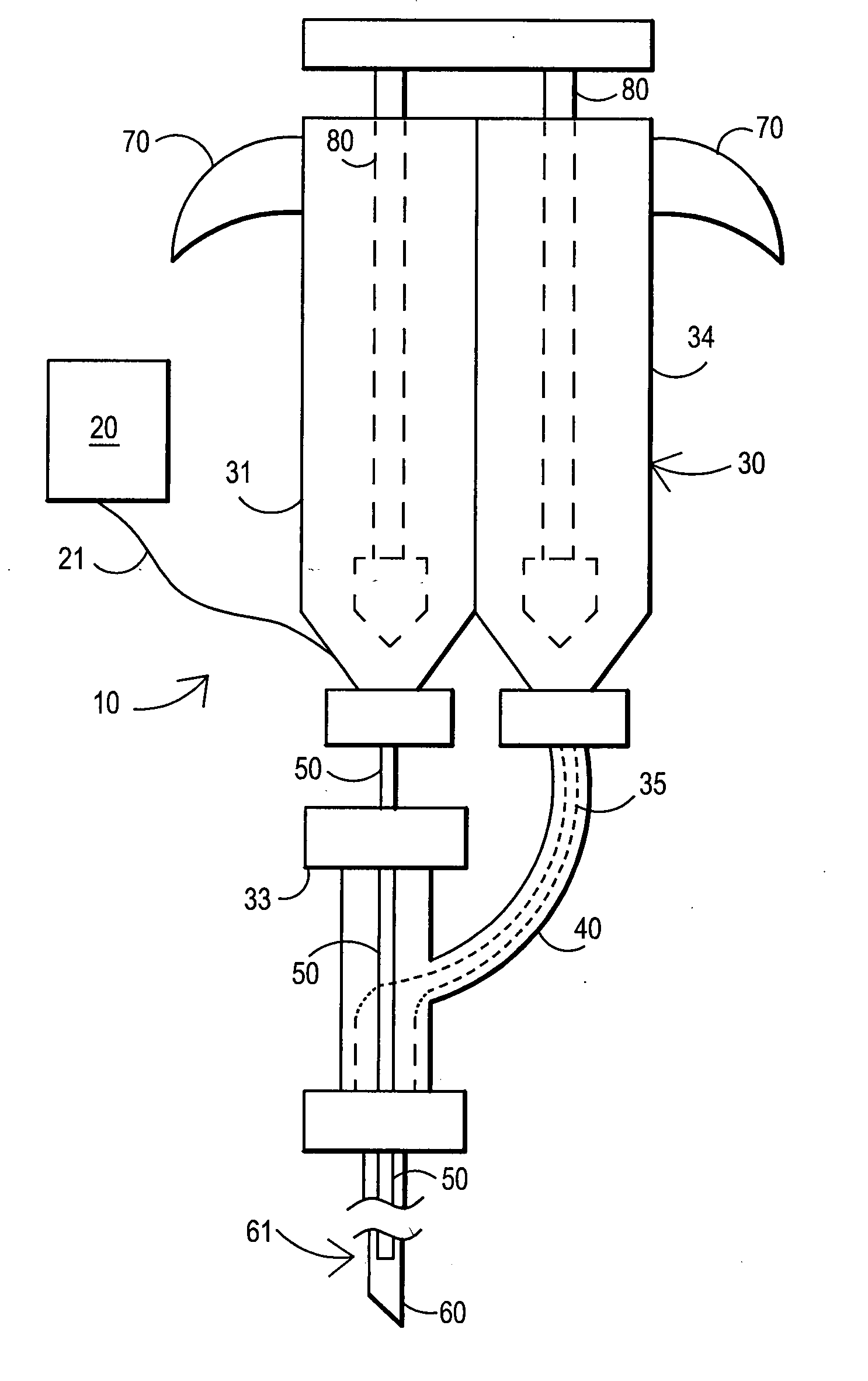
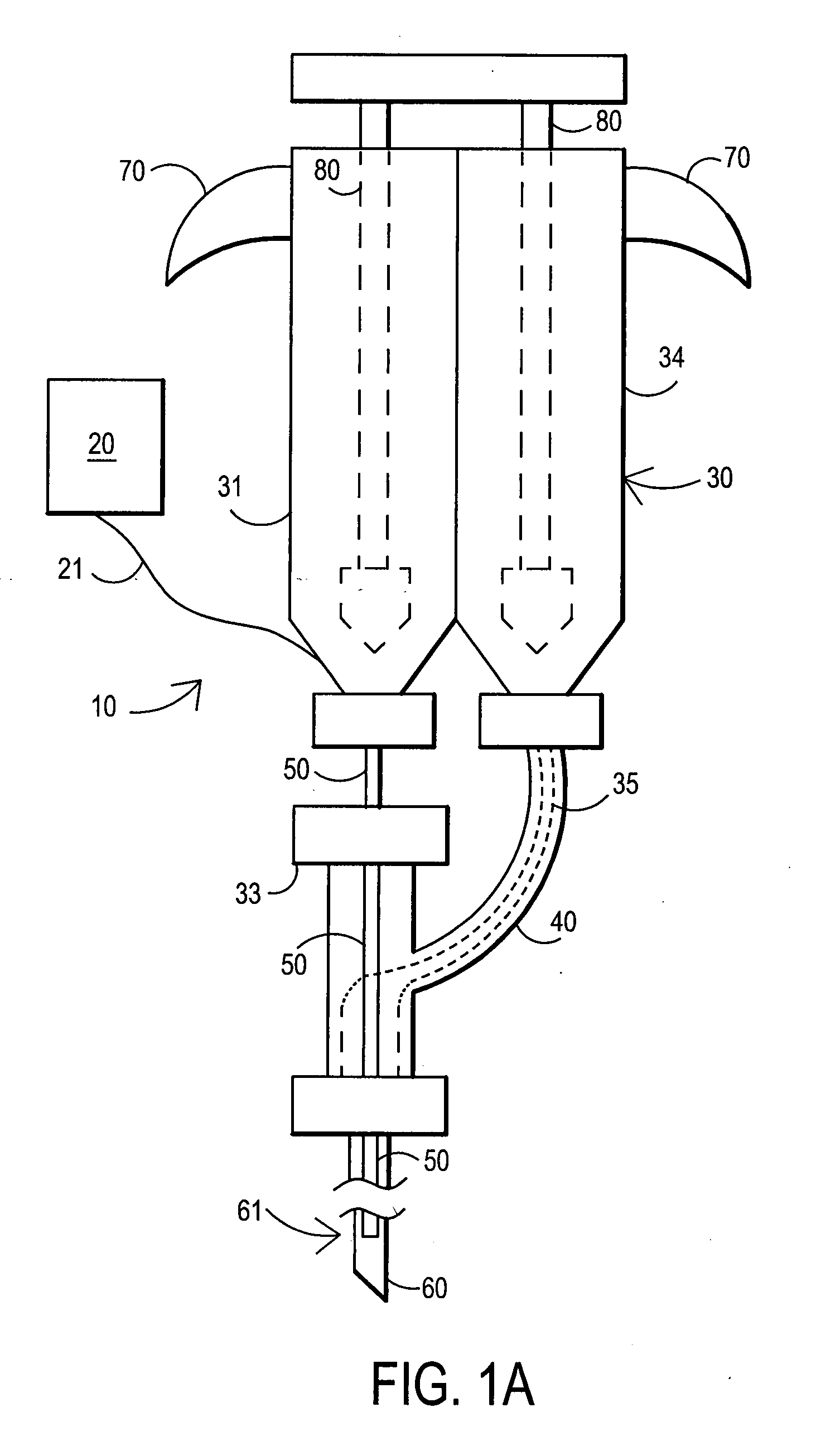
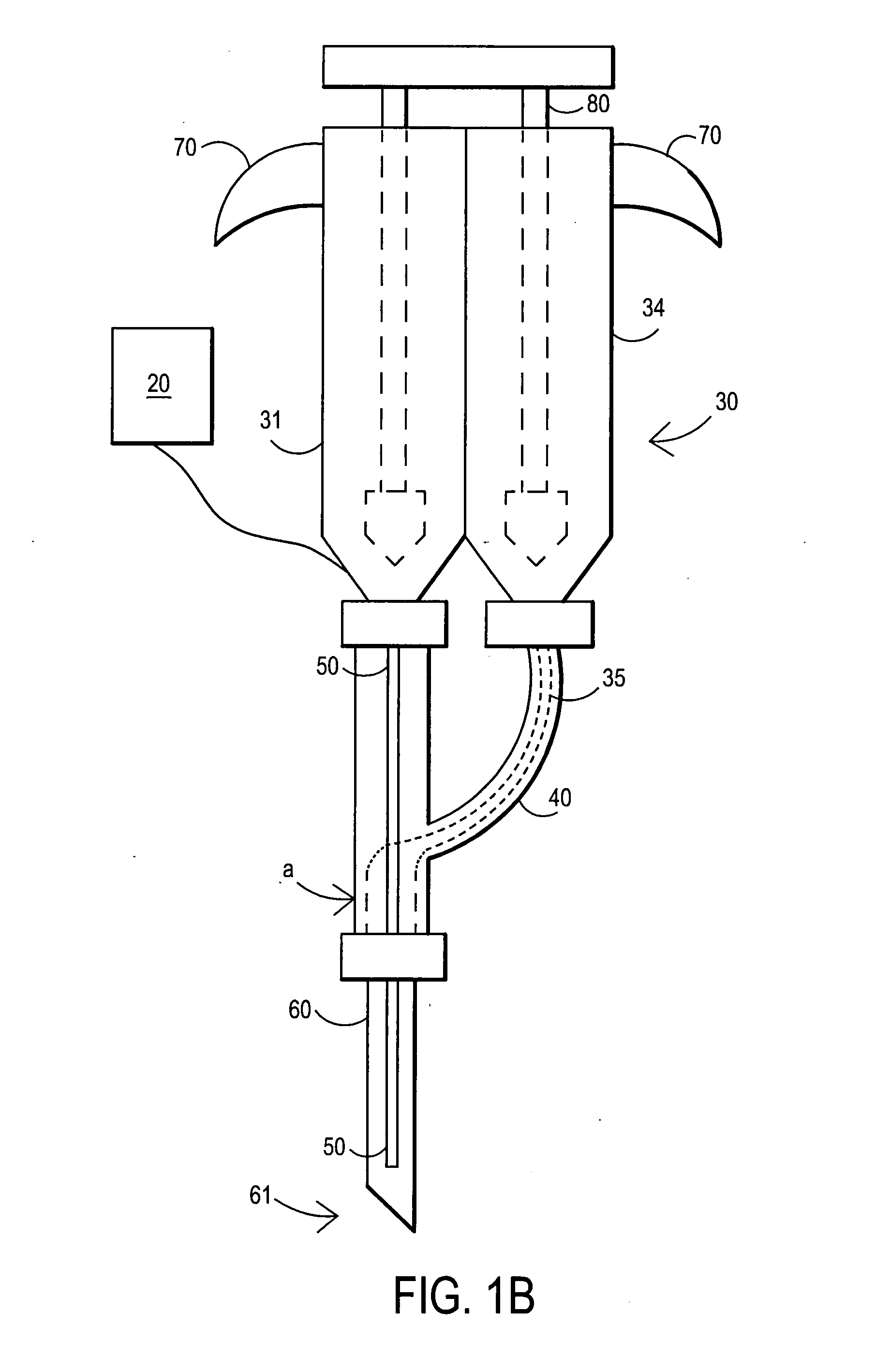
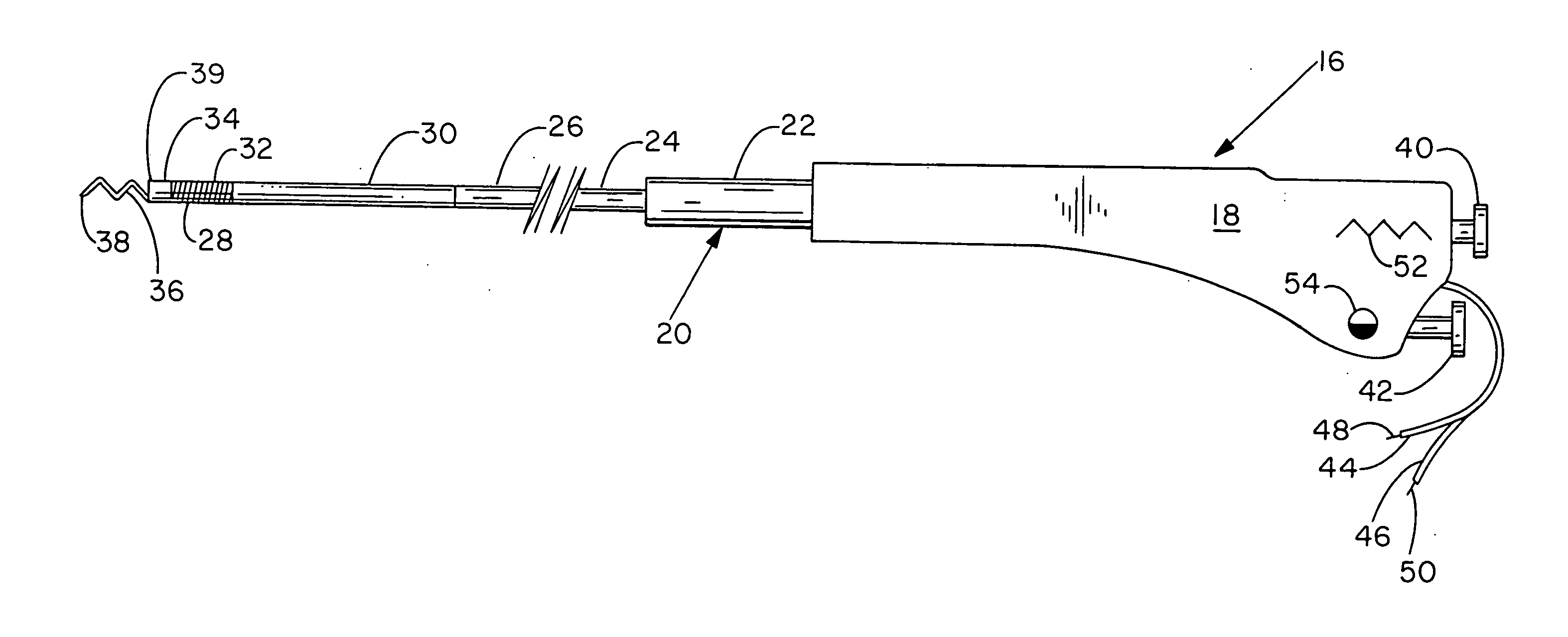
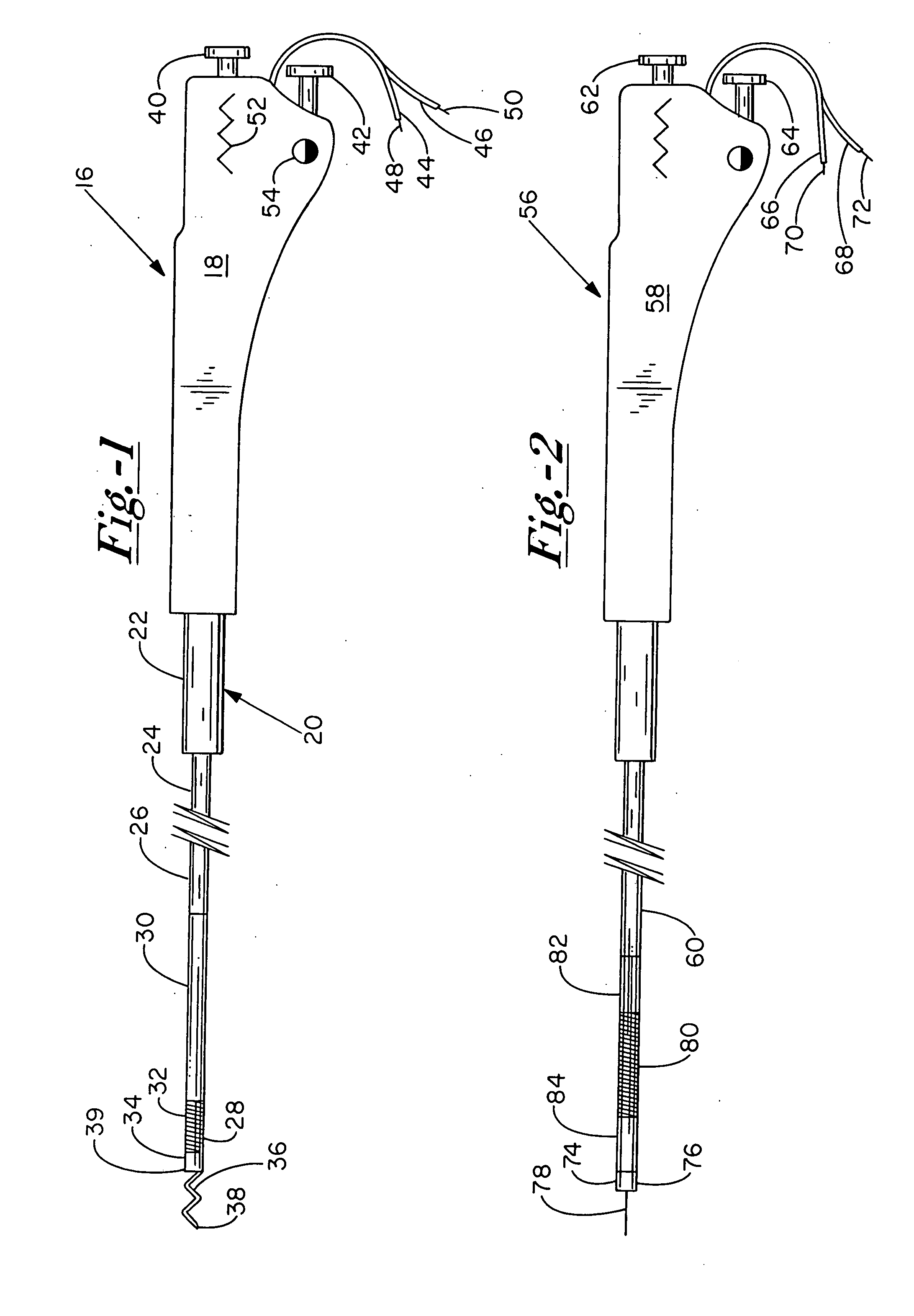
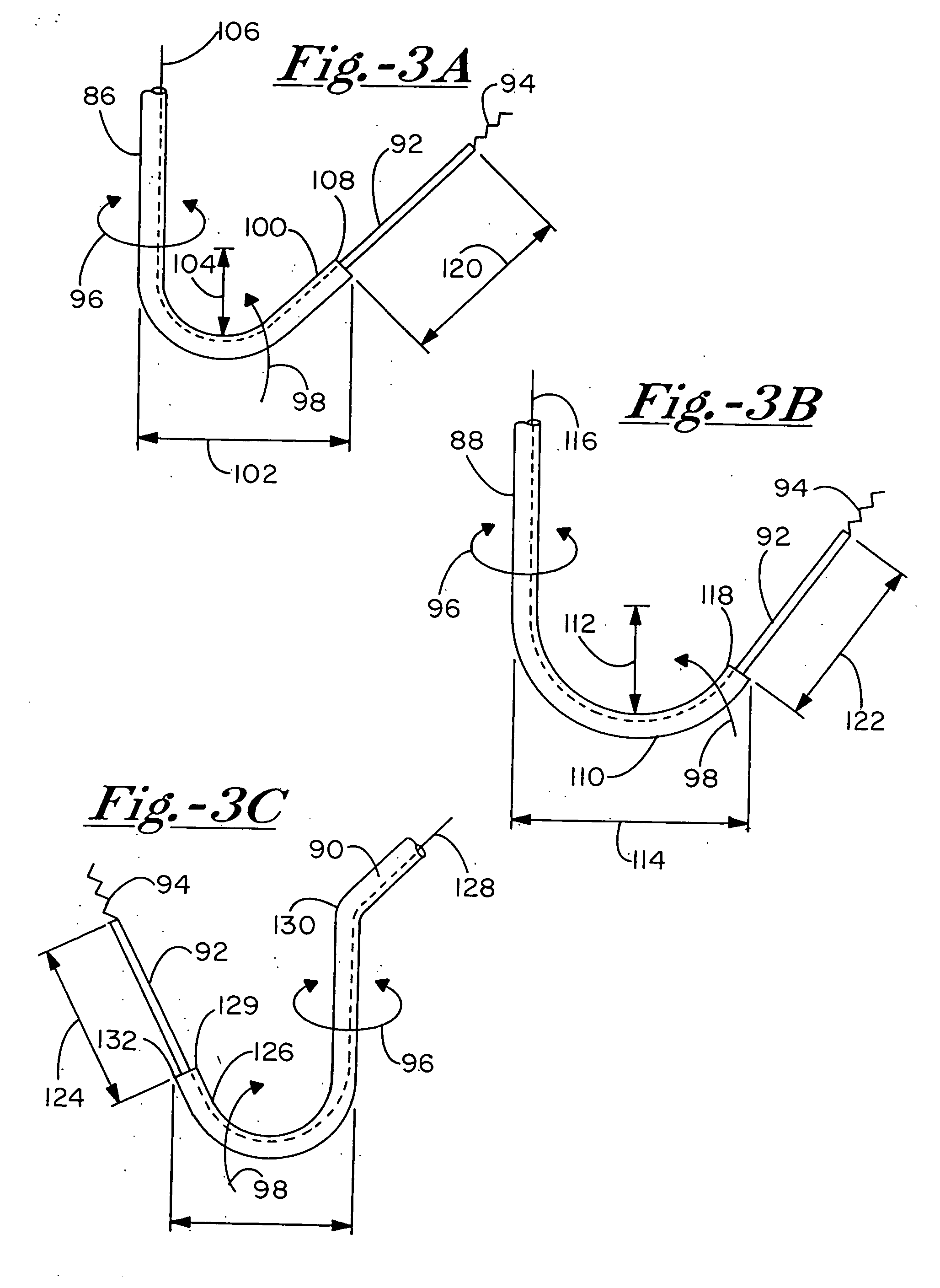
Catheter-based systems are disclosed for geometrically and temporally controlled deliveries of fluid agents to the heart. Each system includes an elongate catheter shaft, a helical, linear or curved tissue penetration element at the distal end of the shaft, and a handle at the proximal end of the shaft for manipulating the penetrating element through the catheter shaft. The penetrating element and a conductive coil near the shaft distal end provide a pair of electrodes for bipolar sensing of tissue electrical activity. One version of the system includes a fluid lumen through the penetrating element and a contrast fluid lumen open at the catheter shaft distal end. In other versions of the catheter system, the penetrating element contains two fluid lumens. These systems facilitate a variety of tissue mapping and therapeutic agent delivery protocols in which several agents can be simultaneously delivered at a depth within heart tissue, prevented from intermingling until they reach the tissue. Treatment and contrast agents can be delivered simultaneously or temporally spaced, directed to the same region in tissue or to different regions separated by intervening tissue.
Owner:BIOCARDIA
Depositing solid materials
InactiveUS20050174407A1High levelHigh yieldAdditive manufacturing apparatusLiquid surface applicatorsInk printerElectronic component
Material can be deposited directly onto a substrate by using a fluid applicator such as an inkjet printer to apply at least two fluids which react to give the desired material for a range of applications. Thus, multiples of a printing mechanism are used to deposit materials as reagents that react together to form products. The materials may also be advantageously deposited from multiple inkjet heads to prepare a wide range of reaction scenarios in the form of user-defined patterns which may be sequences of differing layers and possibly to build up thicker layers. Thus, a PCB could be printed by the inkjet printer by simply printing the metal salt and the reducing agent directly, instead of two colours from a conventional inkjet printer for example. To print a three dimensional article, a pair of fluids which react to give a precipate can be used instead. Repeated passes can then build up a desired shape. The two processes could be combined to produce composite devices such as electrical components.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Brush-seal and matrix for regenerative heat exchanger, and method of adjusting same
InactiveUS20090000762A1Avoid mixingCombustion processIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationEngineeringGuide tube
Disclosed is a regenerative heat exchanger including a brush-seal configuration to prevent mixing of fluid flows. The regenerative heat exchanger includes a regenerator, and at least two conduits, each conduit having a matrix end abutting a face of the regenerator matrix. The at least two conduits carrying at least two fluid flows, the fluid flows which pass through the regenerator matrix. The regenerative heat exchanger includes a plurality of brush-seals, each brush-seal located at a matrix end of each conduit without contacting the matrix, thereby sealing around a periphery of each conduit to prevent mixing of fluid flows. Also disclosed is a method for establishing a minimal gap between a regenerator matrix of a regenerative heat exchanger and a plurality of brush-seals.
Owner:WILSON SOLARPOWER CORP
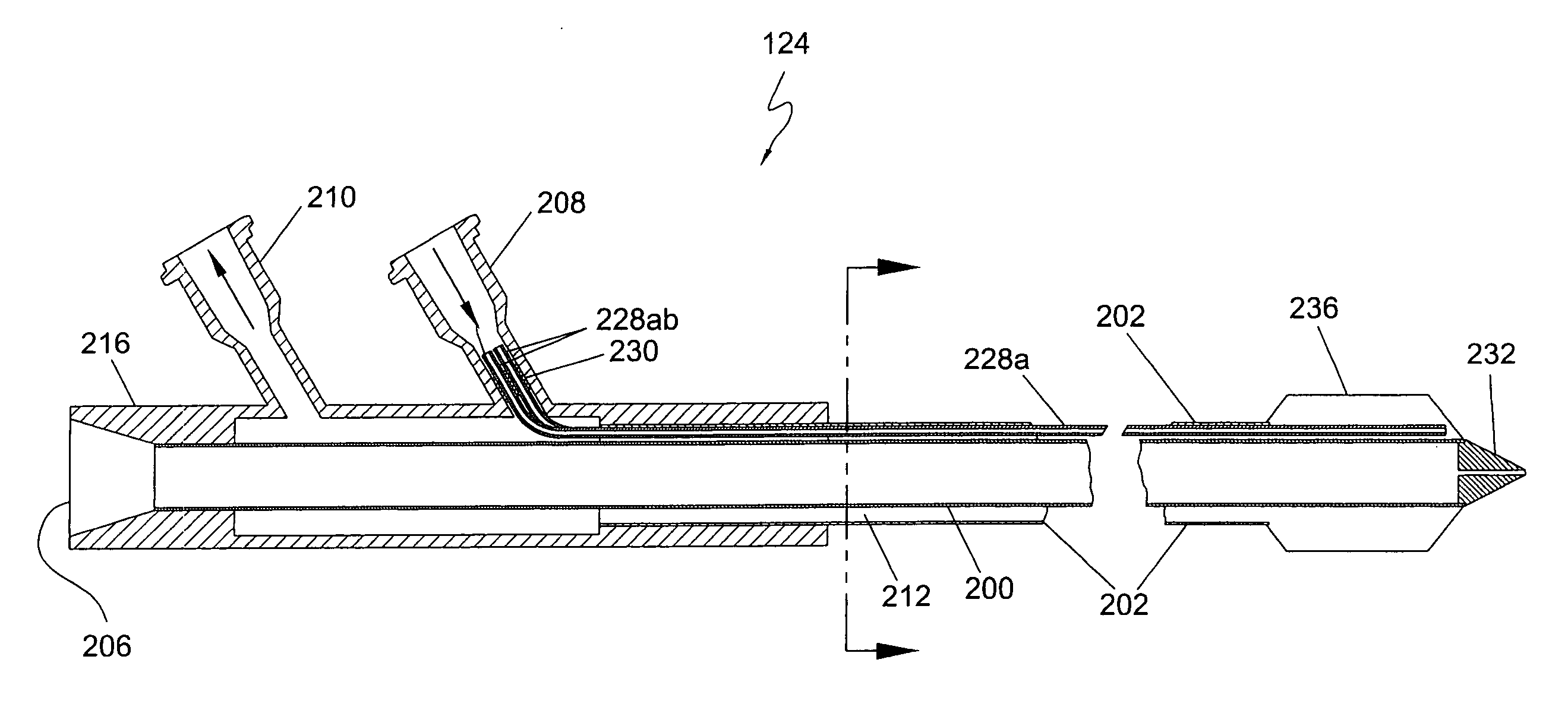
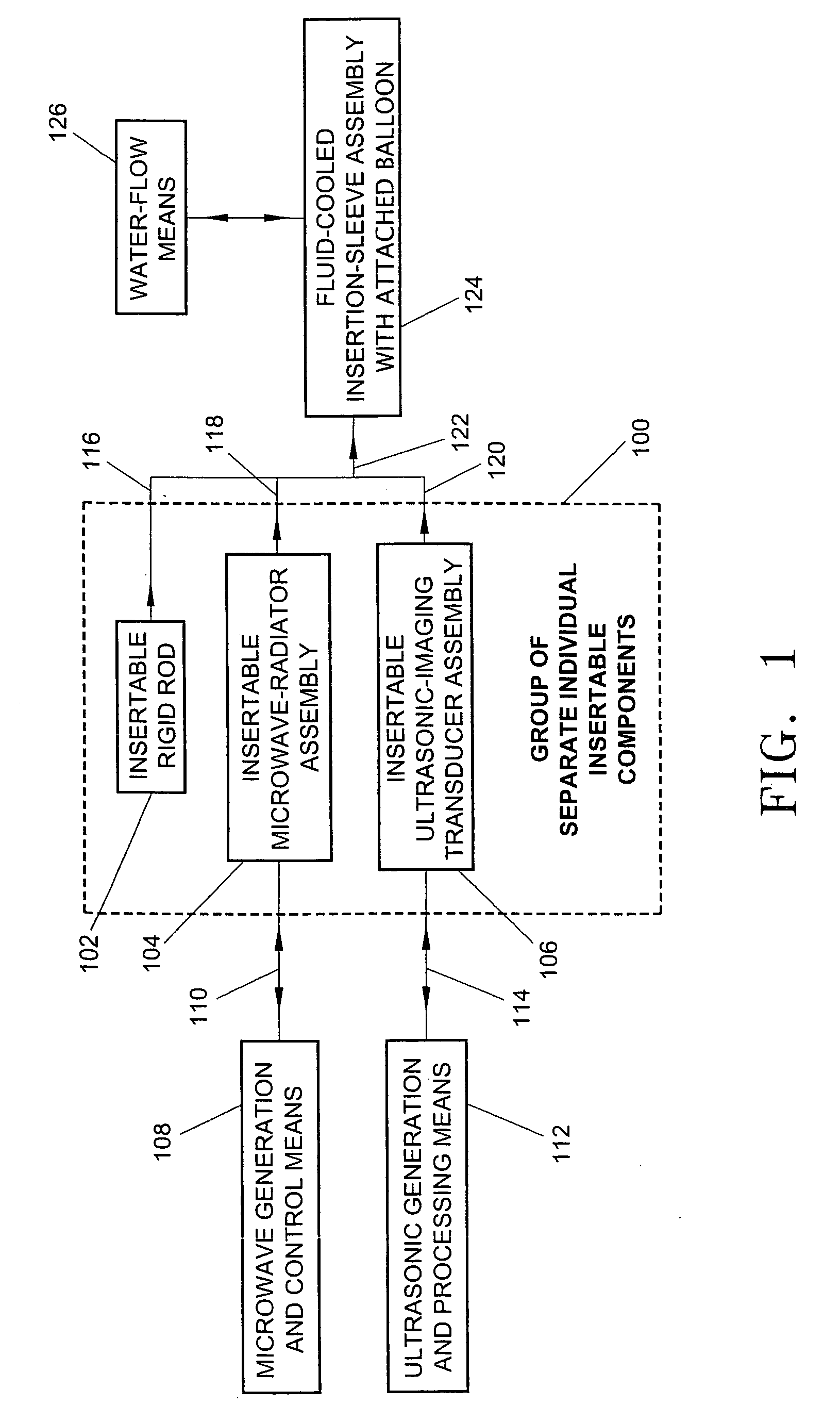
Interstitial microwave system and method for thermal treatment of diseases
A minimally-invasive fluid-cooled insertion sleeve assembly, with an attached balloon and distally-located penetrating tip, into which sleeve any of a group comprising a rigid rod, a microwave-radiator assembly and an ultrasonic-imaging transducer assembly may be inserted, constitutes a probe of the system. The sleeve assembly comprises spaced inner and outer plastic tubes with two fluid channels situated within the coaxial lumen between the inner and outer tubes. The fluid coolant input flows through the fluid channels into the balloon, thereby inflating the balloon, and then exits through that coaxial lumen. An alternative embodiment has no balloon. The method employs the probe for piercing sub-cutaneous tissue and then ablating deep-seated tumor tissue with microwave-radiation generated heat.
Owner:MMTC LTD +1
Multi-channel cross-flow porous device
InactiveUS20060090651A1Dispersed particle filtrationTransportation and packagingStream flowEngineering
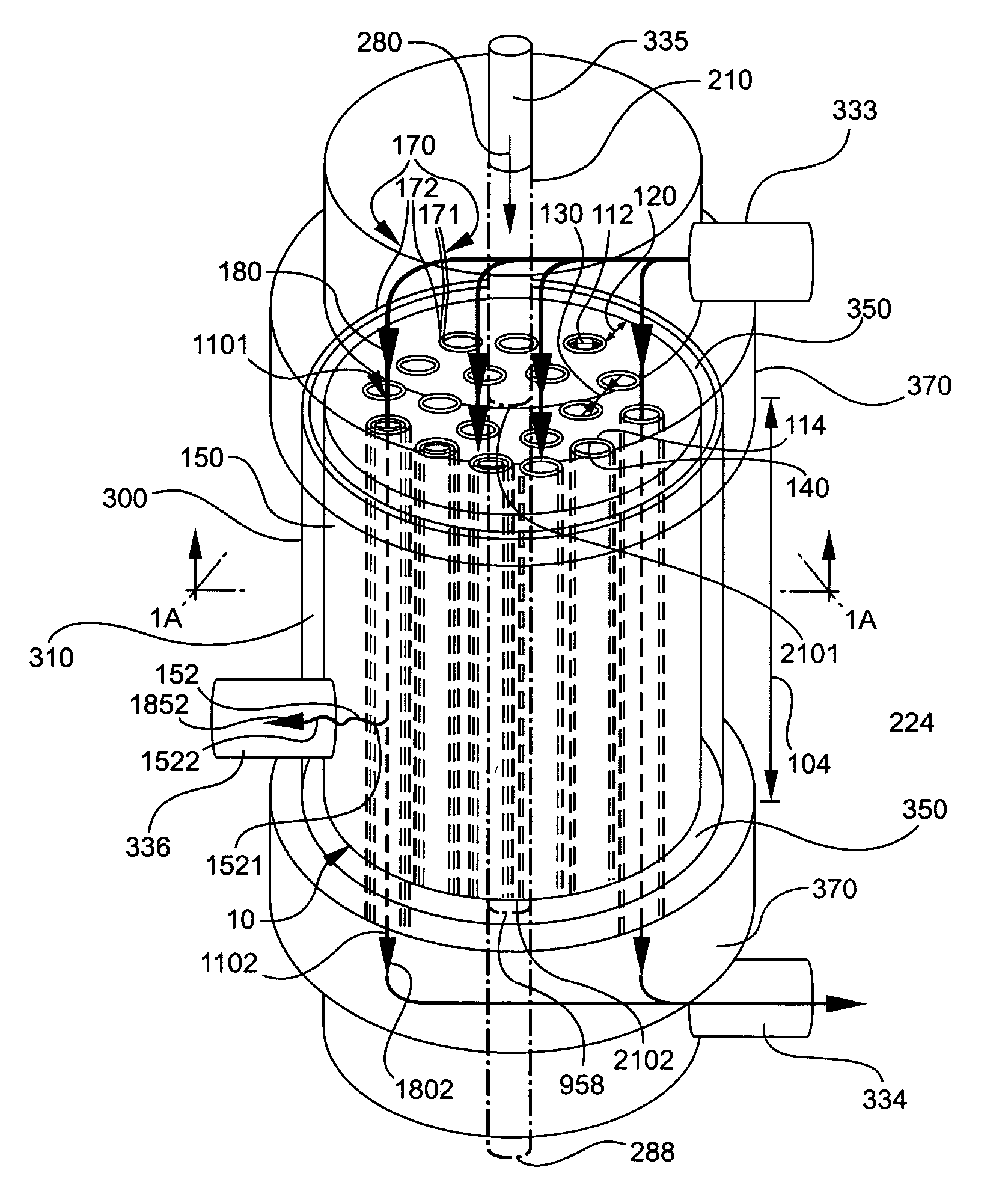
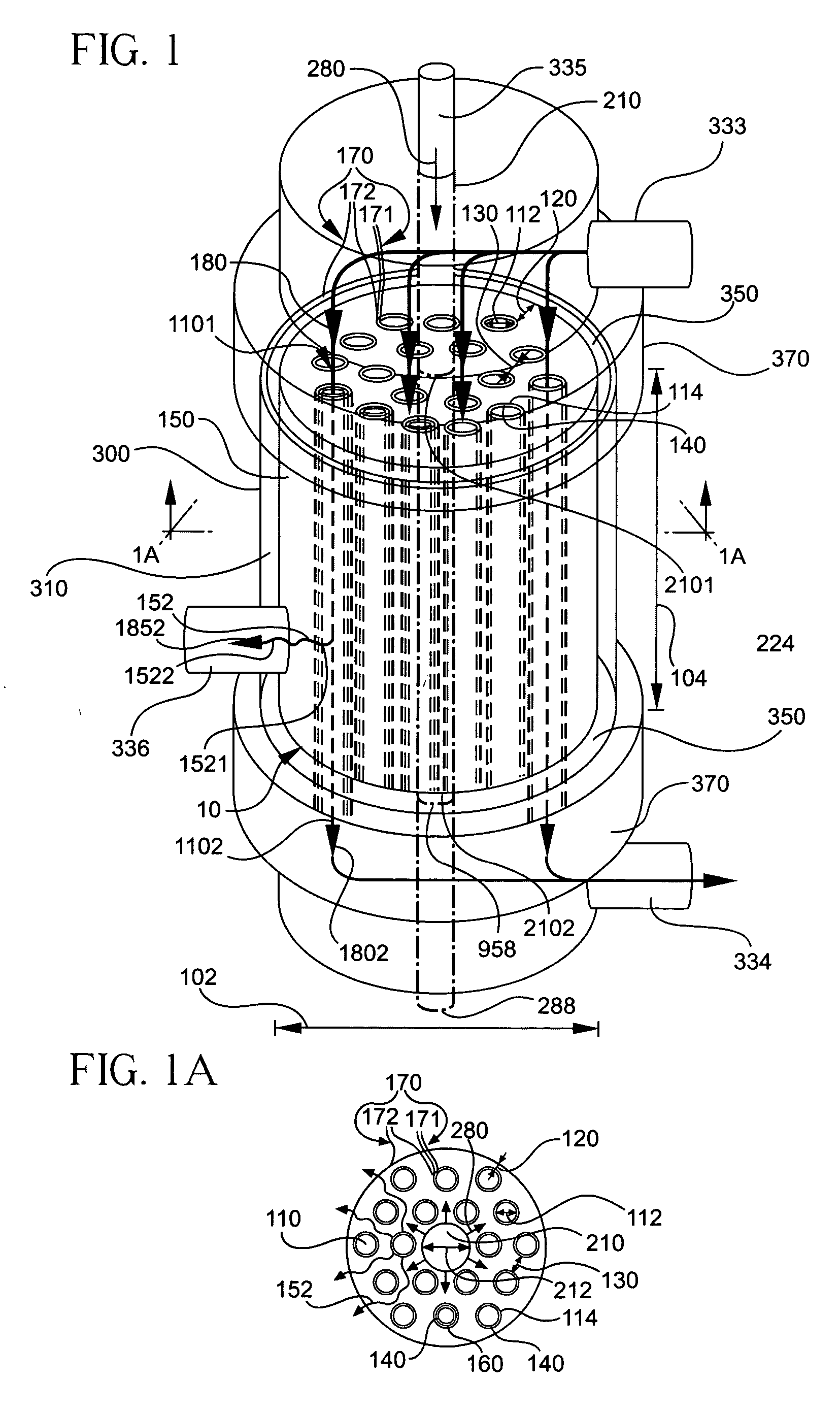
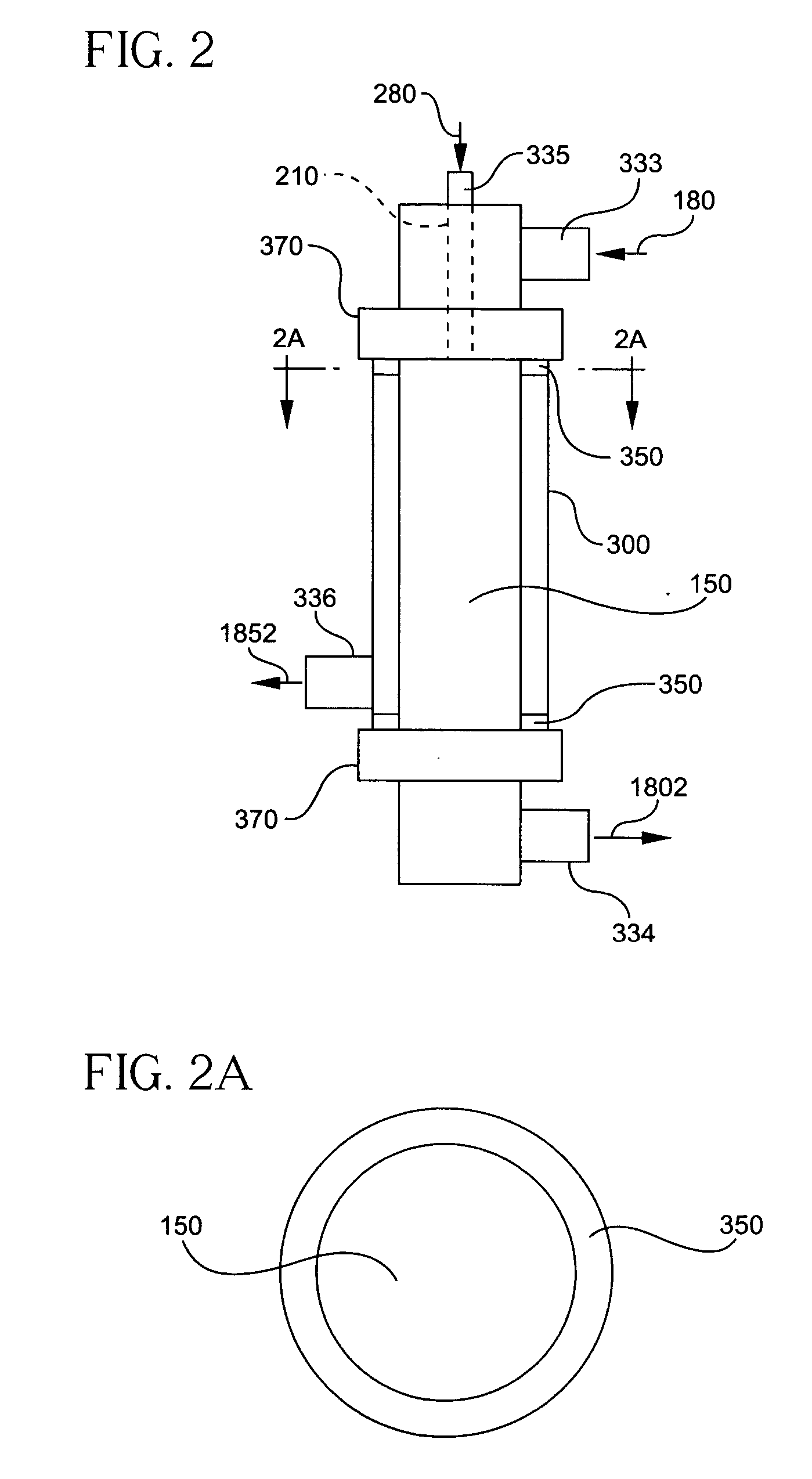
A multi-channel modular device (10) processes between two fluid streams of different compositions. The device (10) includes a porous body (150) having a first plurality of feed-flow pathways (110) disposed in the body (150) for transporting a first stream (180). A pathway wall (114) surrounds each of the first plurality of feed-flow pathways (110) for processing the first stream (180) into a first composition (1852) and a second composition (1802). At least one feed-flow inlet (1101) is disposed in the body (150) for introducing the first stream (180) into the first plurality of feed-flow pathways (110). At least one feed-flow outlet (1102) is disposed in the body (150) for discharging the remaining first stream containing the second composition (1802). At least one second pathway (210) is disposed in the body (150) for transporting a second stream (280) having a second inlet (2101) and a second outlet (2102). A networked plurality of fluid conduits (152) formed in the porous body (150) provides the flow-conduit for the second stream (280) to sweep the first composition (1852) from each of the first plurality of the feed-flow pathways (110) to the second outlet (2102). A vessel (300) ports the inlets (1101 and 2101) and outlets (1102 and 2102) to provide a second stream flow access and for spacing the body within and away from the inner surfaces of the vessel (300) to provide a gap (310) for access. A partition (350) is disposed in the gap between the body and the vessel for diverting the flow within the gap (310).
Owner:CORNING INC
Device and method for contacting picoliter volumes of fluid
InactiveUS20070099289A1Avoid adsorptionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteLysis
The invention features devices for mixing fluids, e.g., for lysing cells, and methods of use thereof. One device is based on the ability to control the flow of fluids, e.g., by contact angle and channel size. Fluids in this device can be divided to form segments of controlled volume, which are then brought together to initiate midxing. An exemplary use of the device is for the lysis of single cells. Another device is based on the ability to two mix two fluids in a channel and affinity capture of analytes. The devices can be integrated on the same chip with other devices, for example, for cell handling or analysis of DNA, rnRNA, and proteins released from the lysis of a cell.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Geometry of heat exchanger with high efficiency
ActiveUS20130206374A1Additive manufacturing apparatusRecuperative heat exchangersHigh energyEngineering
The present disclosure includes geometry of a two-fluid heat exchanger to provide higher energy efficiency than conventional heat exchangers. The geometry is based upon sequential branching of nearly circular passages in sets, followed by some deformation and twisting of the sequential branches that intermingle flow passages of one fluid with flow passages of another fluid. The flow passages gradually vary in dimension from larger branching at fluid entrance and exit to smaller branching in the middle section of the heat exchanger. The heat exchanger is substantially symmetric, with the sequential branching in the first half being mirrored as serial regrouping in the second half. The present disclosure also provides stacking methods and layered manufacturing methods for fabricating the three-dimensional geometry of the heat exchanger.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
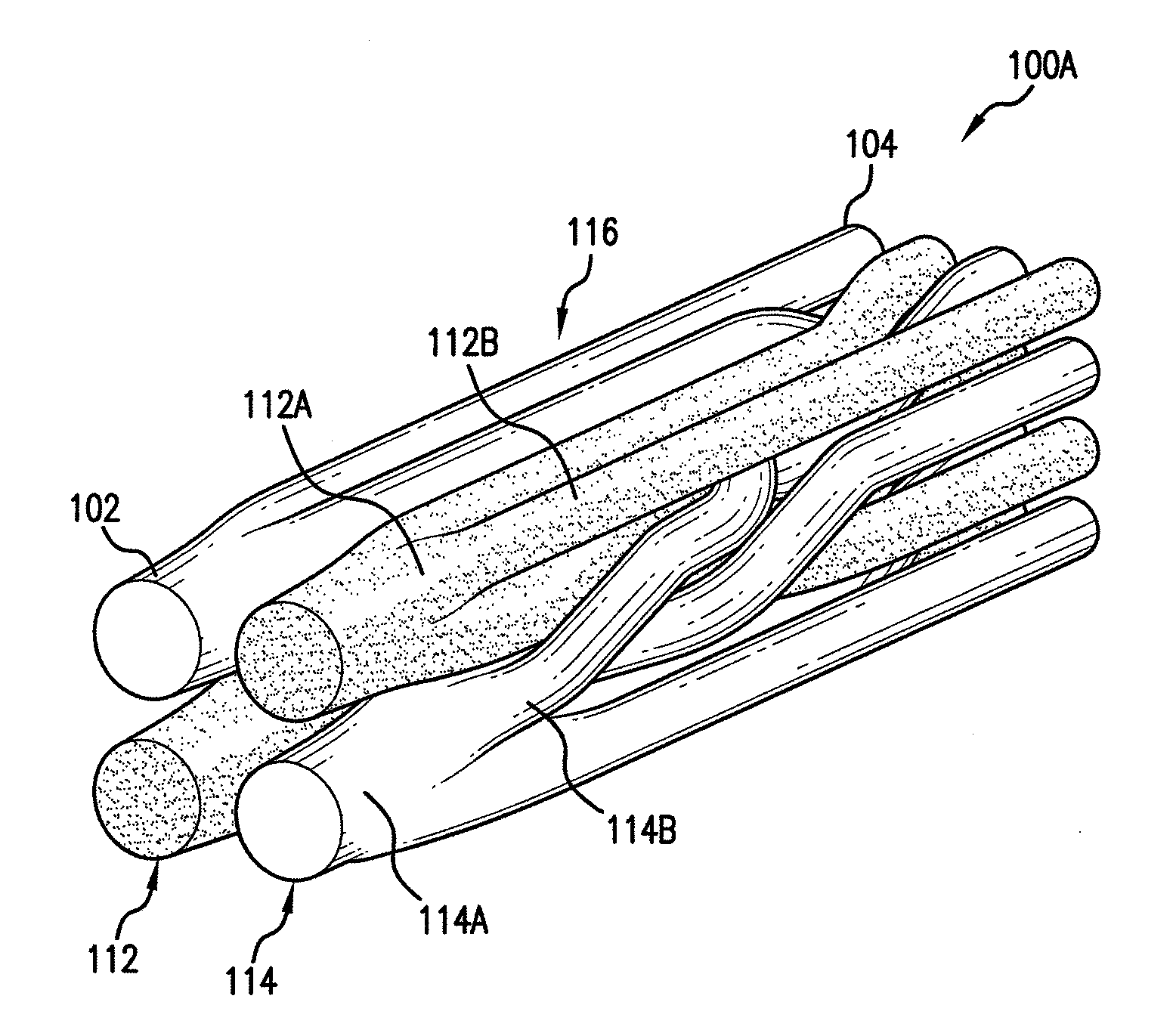
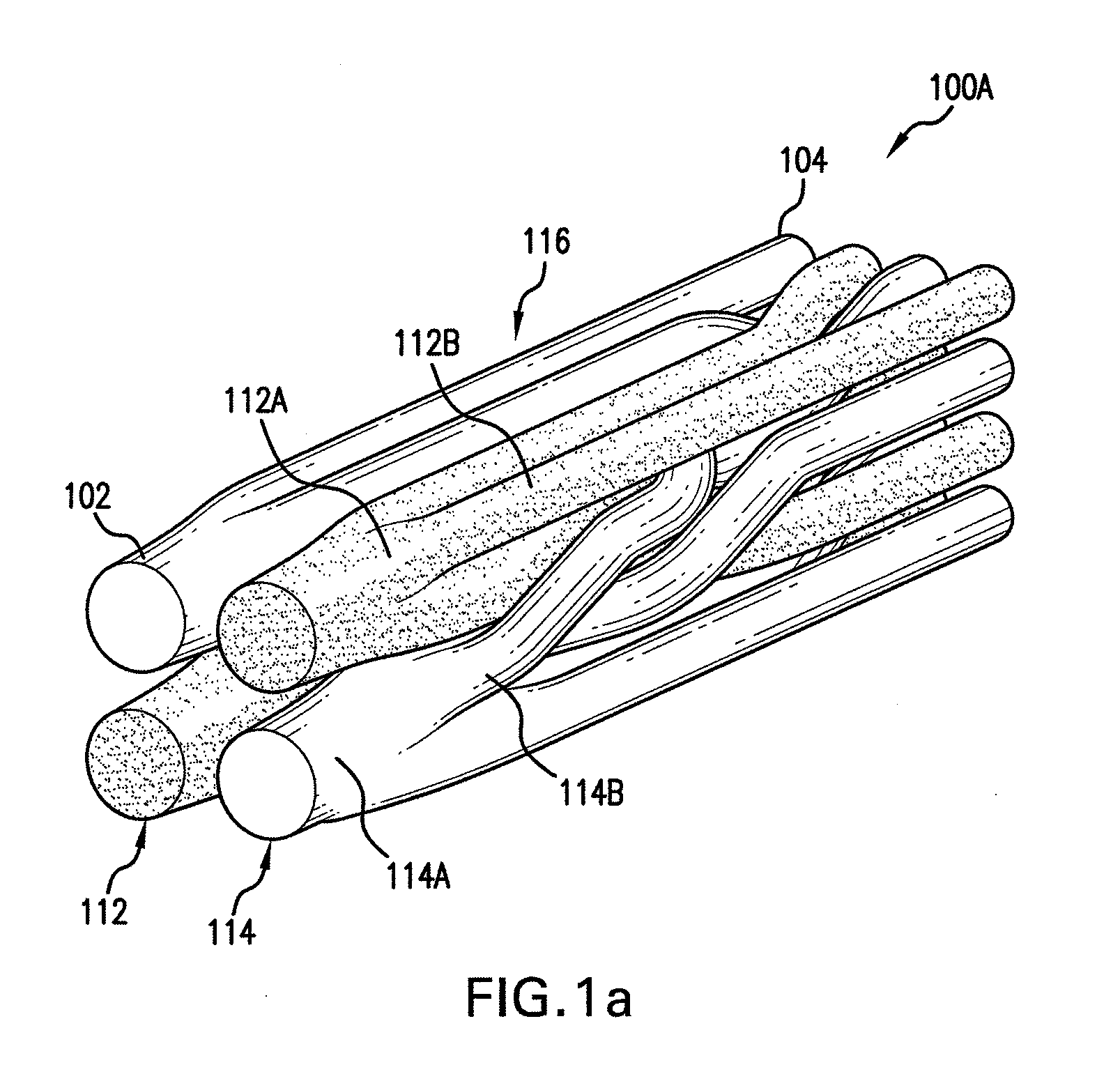
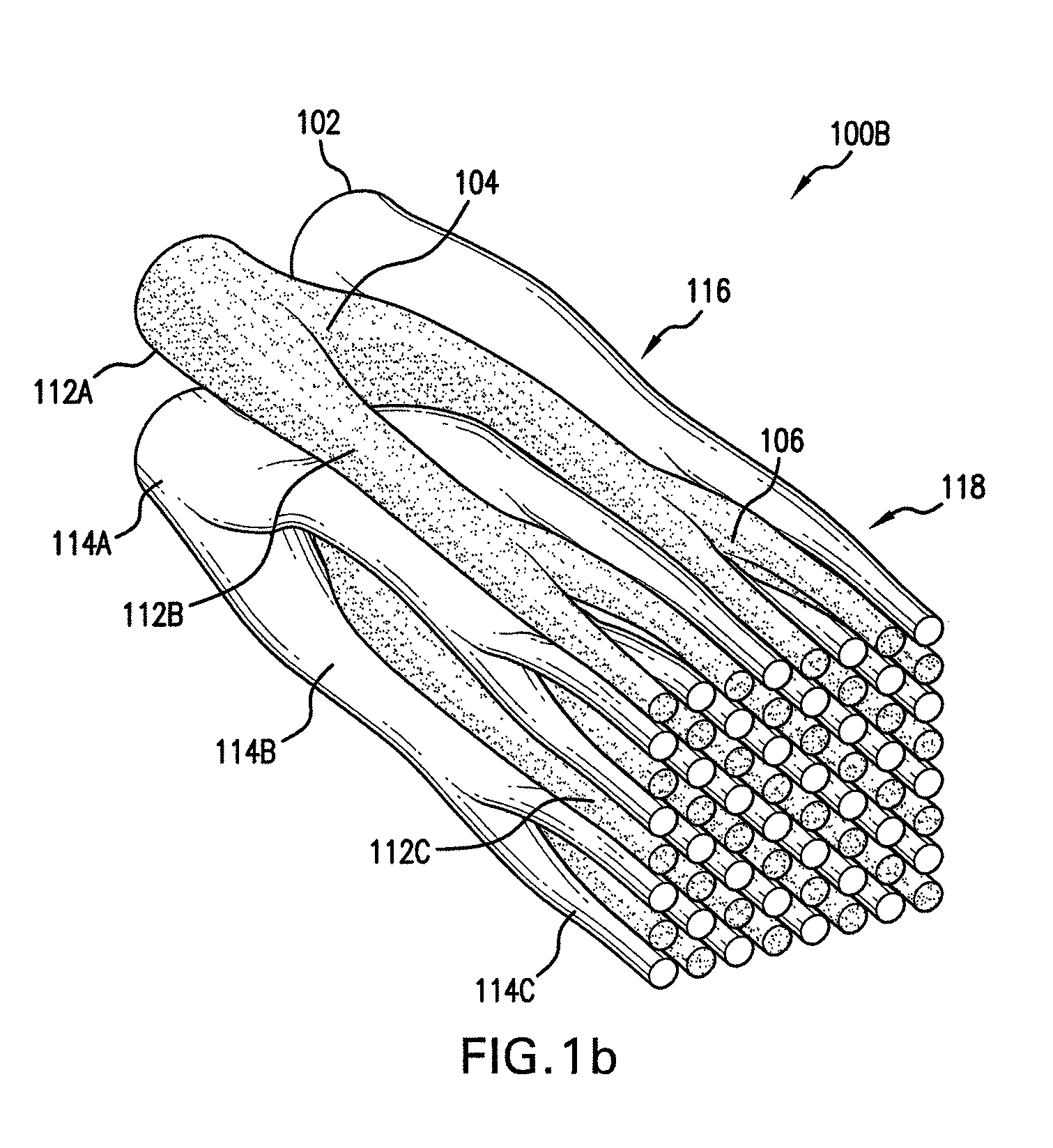
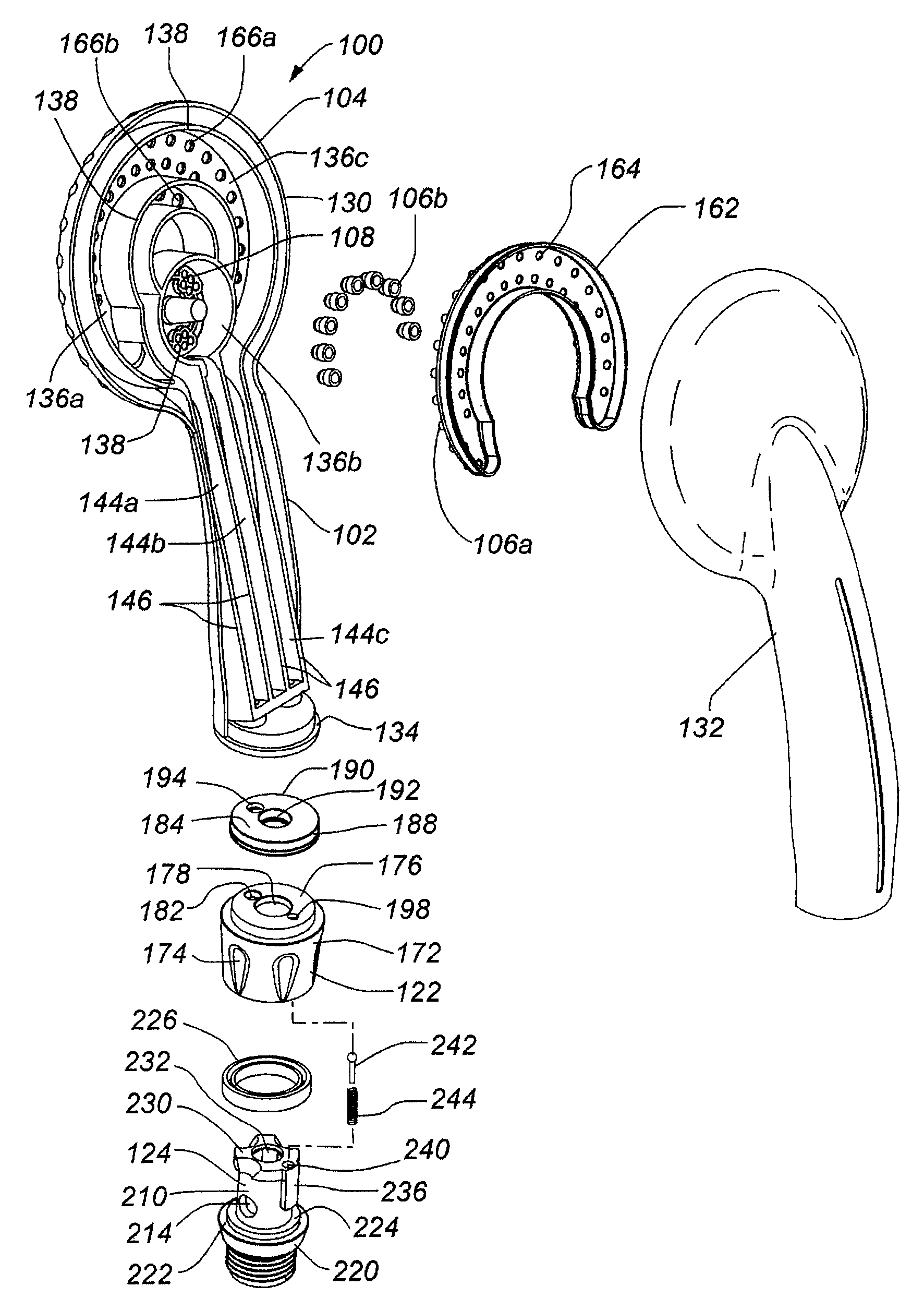
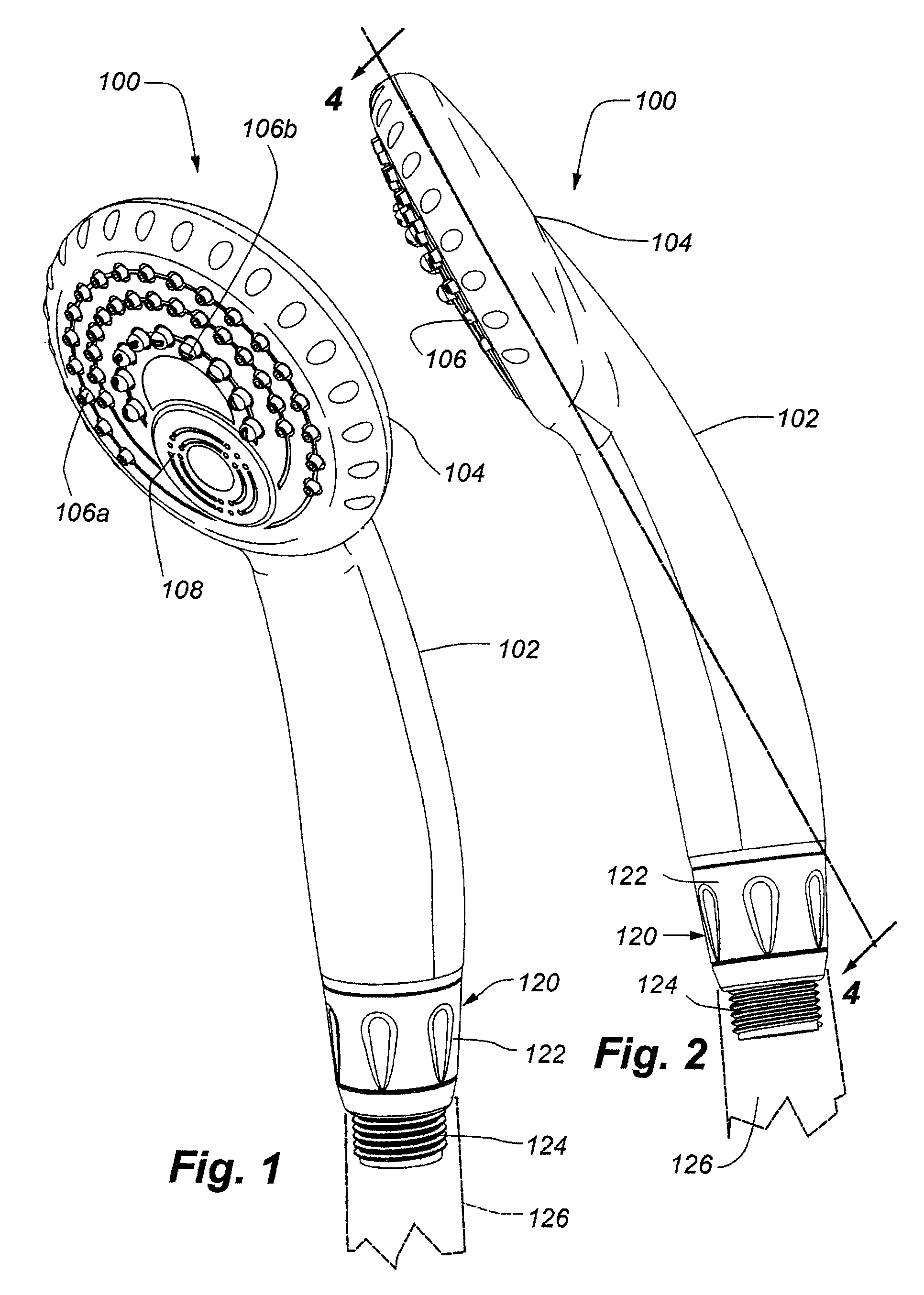
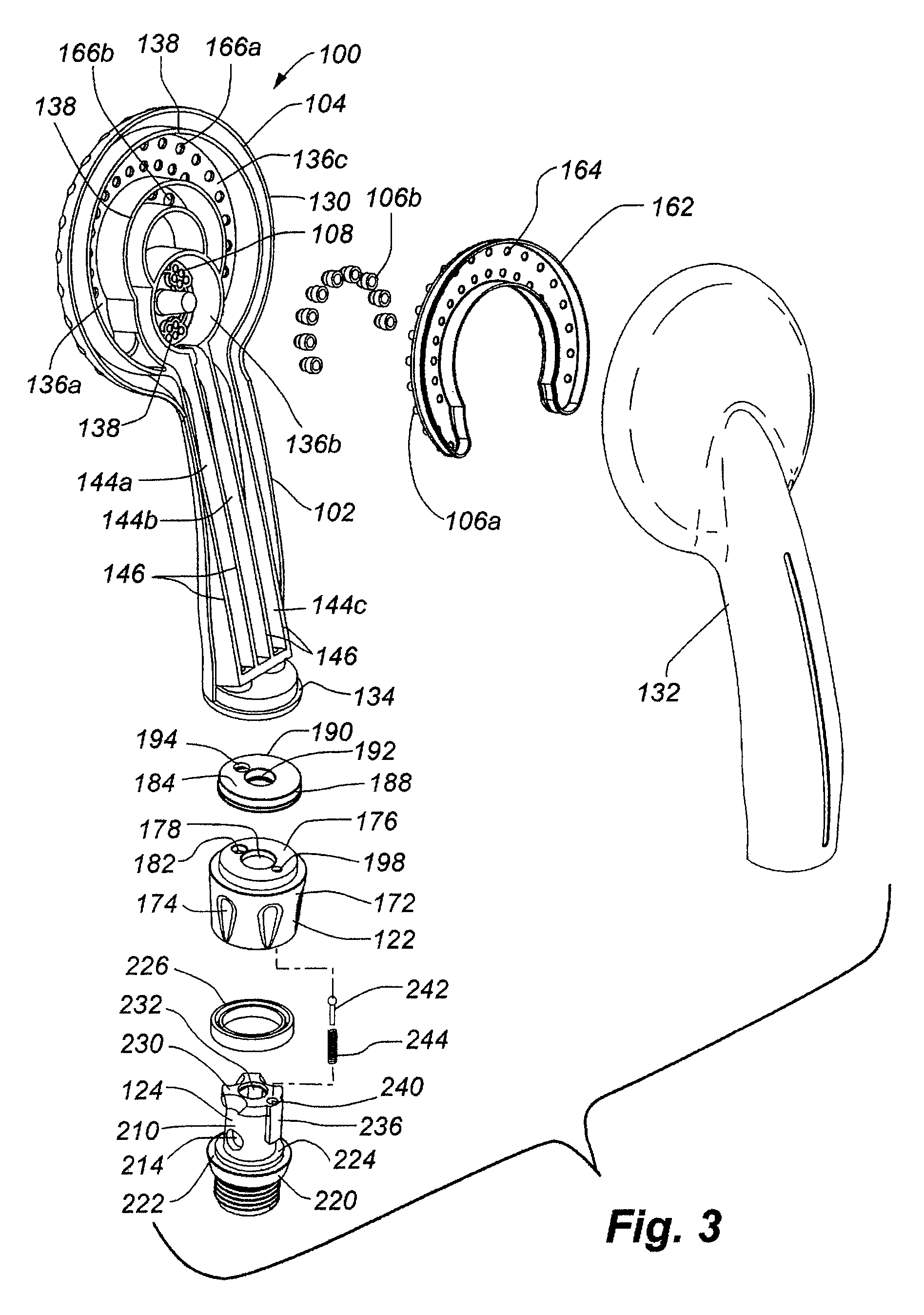
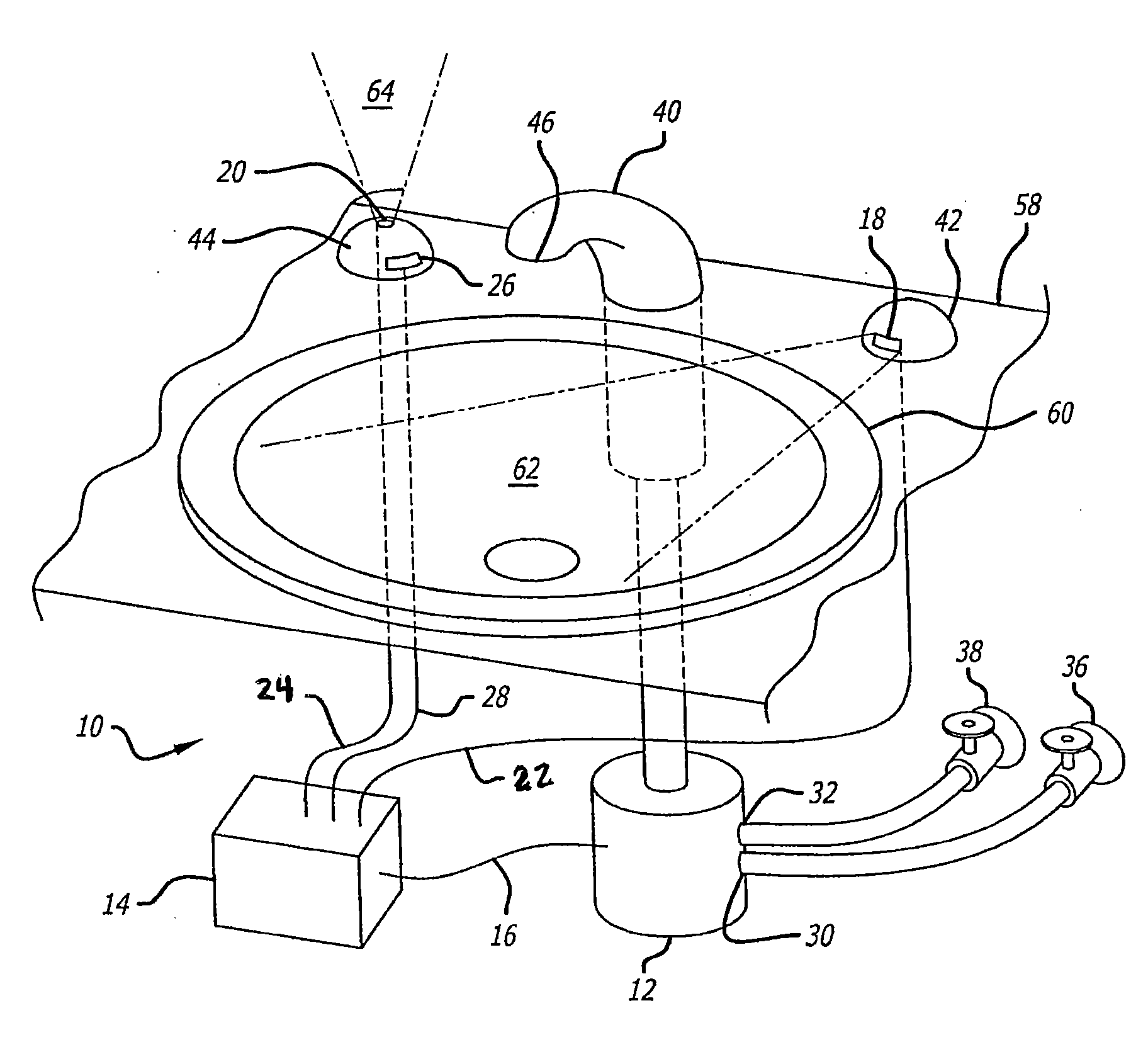
Handheld showerhead with mode control and method of selecting a handheld showerhead mode
A handheld showerhead with a showerhead portion and a handle portion. The showerhead portion may include at least two fluid channels. The handle portion may be operatively associated with the shower portion. The handle portion may include at least one fluid inlet or fluid passage. The handle portion may further include a movable mode selector. Movement of the mode selector may selectively place the fluid inlet or fluid passage in fluid communication with at least one of the two fluid channels in the showerhead portion.
Owner:WATER PIK INC
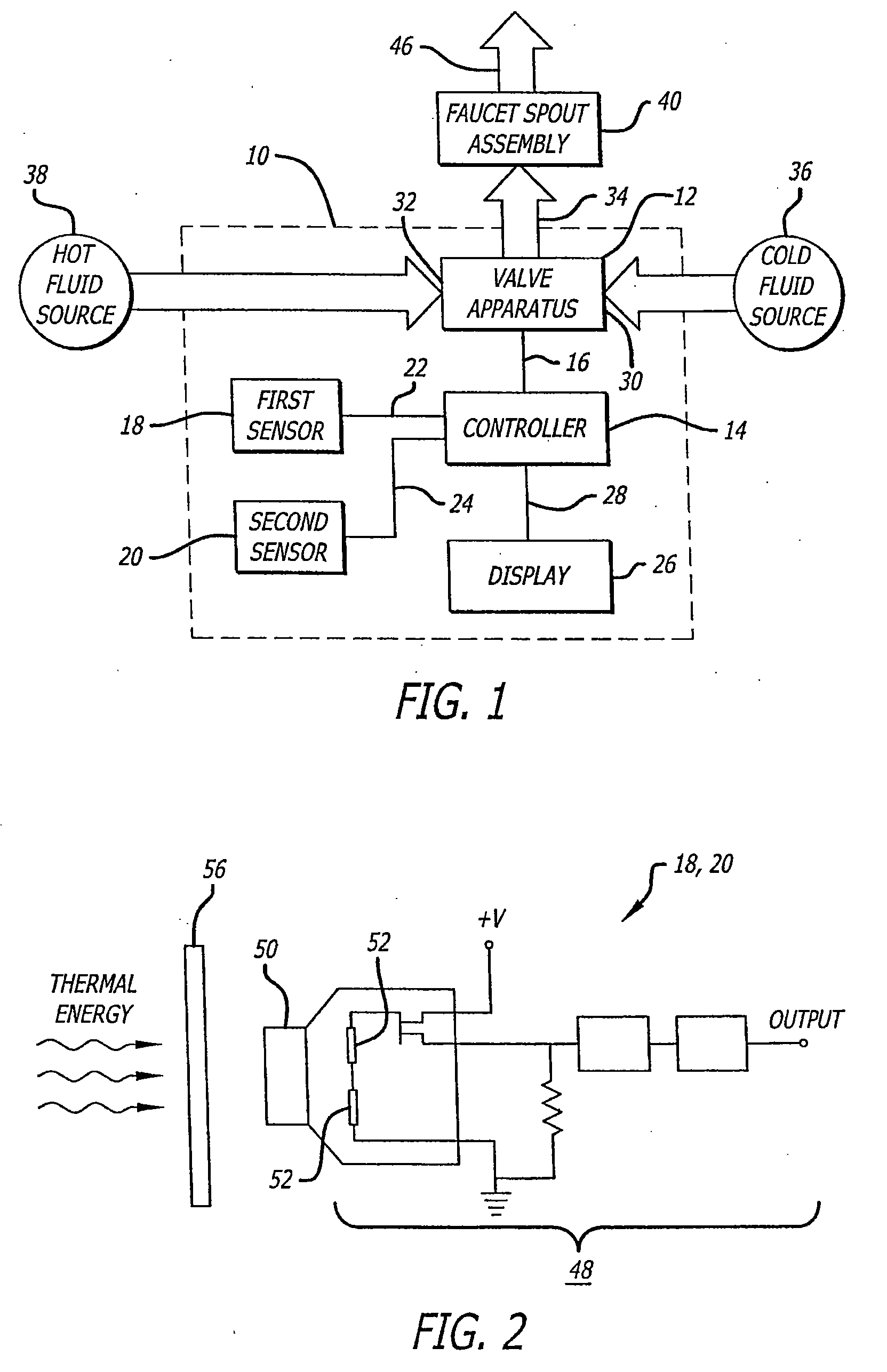
Faucet control system and method
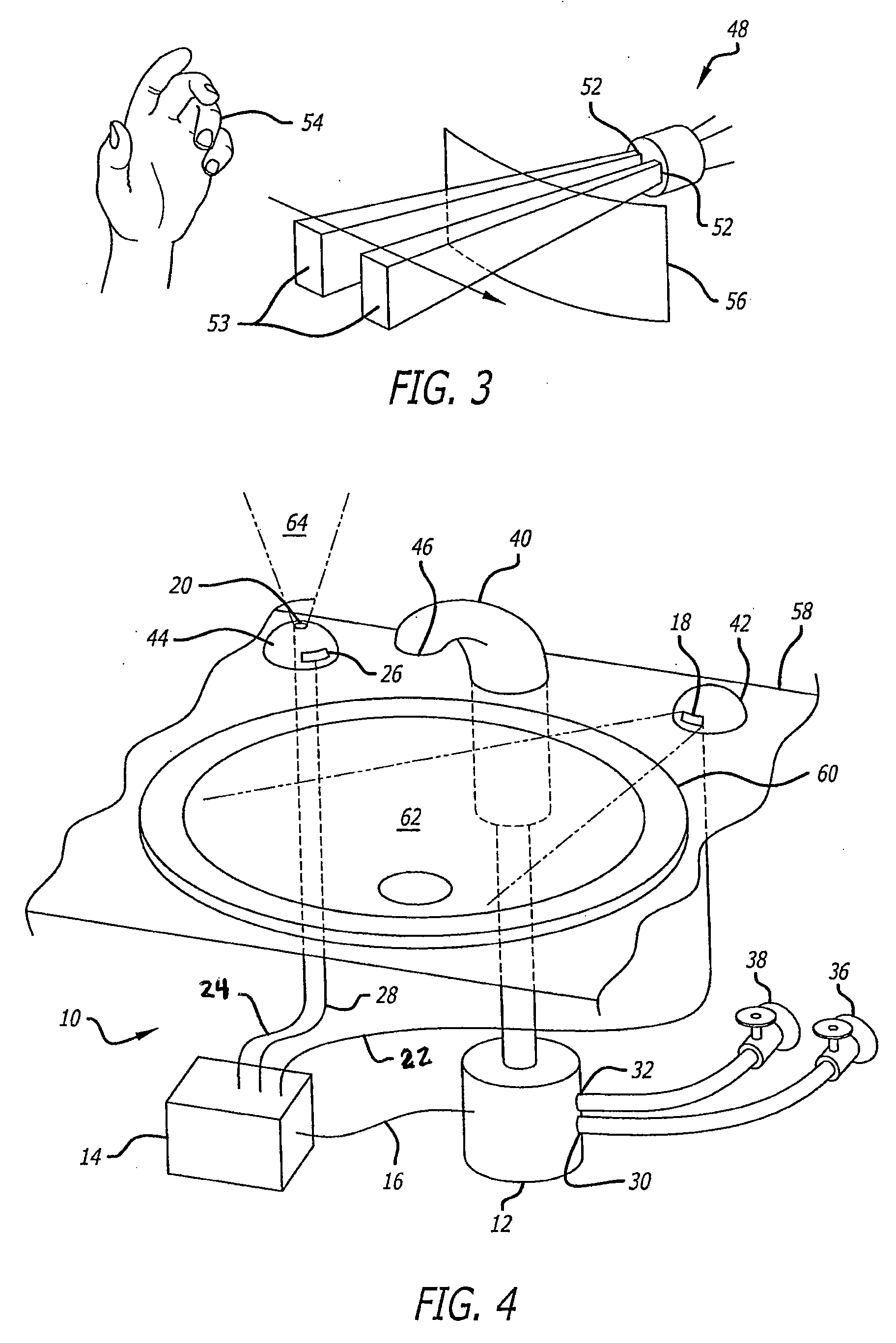
ActiveUS20080099088A1Avoid energy wasteWide temperature rangeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDomestic plumbingMotion detectorControl system
A faucet control system comprises a valve apparatus, sensors or a motion detector to be activated by a user, and a controller that controls the valve apparatus. A first sensor may start fluid flow and a second sensor may alter the proportion of fluids delivered from two fluid sources. The sensors may be activated without being touched and may include infrared and / or photodiode sensing elements. In a sink embodiment, when a user approaches the sink to wash hands, water flow is activated. Optionally, the initial water flow may be cold water, to prevent energy wastage. A second sensor may be placed elsewhere on the sink, such as on the left hand side of the faucet spout. Consequently, when the right hand, for example, is placed below the faucet spout, the water flow is activated with the first sensor. The left hand may be placed above a second sensor and, by waiving the left hand, the hand sensor will cause the hot valve to allow hot water to mix with cold water from the cold valve, should the user wish a warm temperature water flow. If the user wishes hot water, the user will then waive his or her hands over the second sensor, which will close the cold valve and open only the hot valve, thus allowing only hot water to flow from the spout.
Owner:BOEY KUM F
Electromagnetically controlled tissue cavity distending system
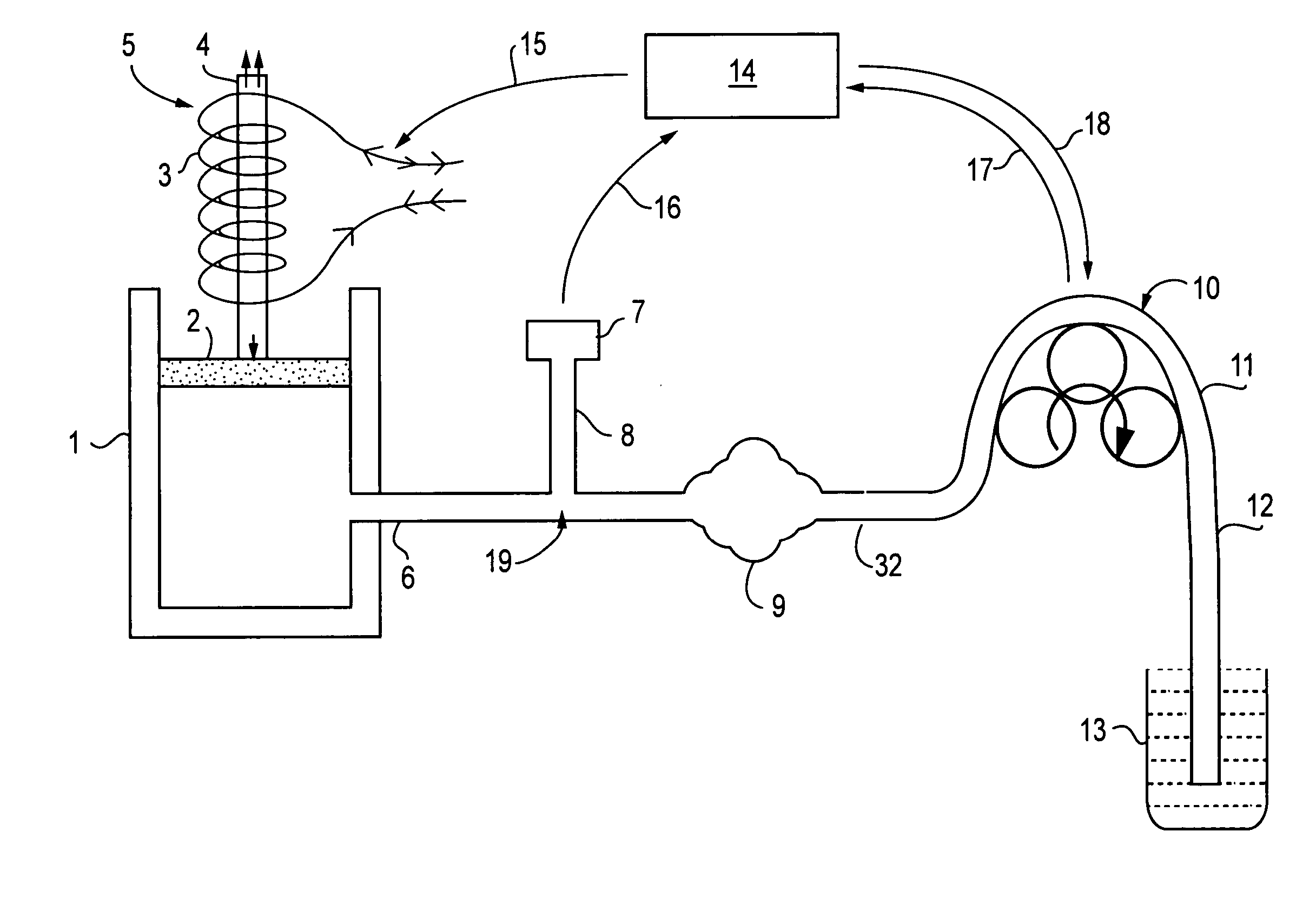
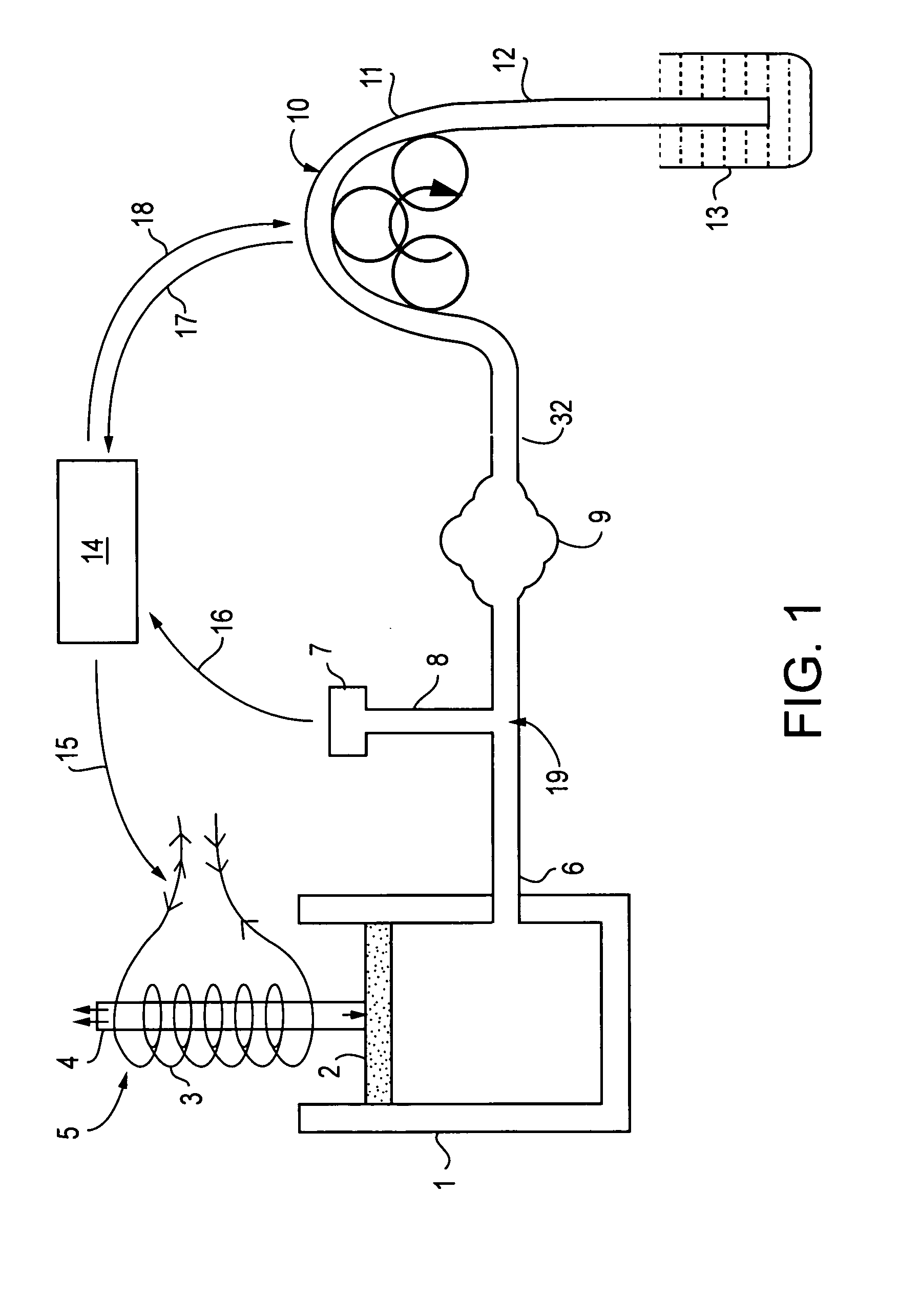
ActiveUS20060052666A1Accurate and reliable and simple mannerAltering valueJet injection syringesAutomatic syringesPeristaltic pumpEndoscopic Procedure
A system to minimize fluid turbulence inside a tissue cavity during endoscopic procedures. A body tissue cavity of a subject is distended by continuous flow irrigation using a solenoid operated pump on the inflow side and a positive displacement pump, such as a peristaltic pump, on the outflow side, such that the amplitude of the pressure pulsations created by the outflow positive displacement pump inside the said tissue cavity is substantially dampened to almost negligible levels. The present invention also provides a method for accurately determining the rate of fluid loss into the subject's body system during any endoscopic procedure without utilizing any deficit weight or fluid volume calculation, the same being accomplished by using two fluid flow rate sensors. The present invention also provides a system of creating and maintaining any desired pressure in a body tissue cavity for any desired cavity outflow rate.
Owner:KUMAR BV
Method and apparatus for separating particles, cells, molecules and particulates
InactiveUS20090078614A1Easy to makeLow costElectrostatic separationMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetic field gradientParticulates
A method and apparatus for continuously separating or concentrating particles that includes flowing two fluids in laminar flow through a magnetic field gradient which causes target particles to migrate to a waste fluid stream, and collecting each fluid stream after being flowed through the magnetic field gradient.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY +1
Heat exchangers for fluid media
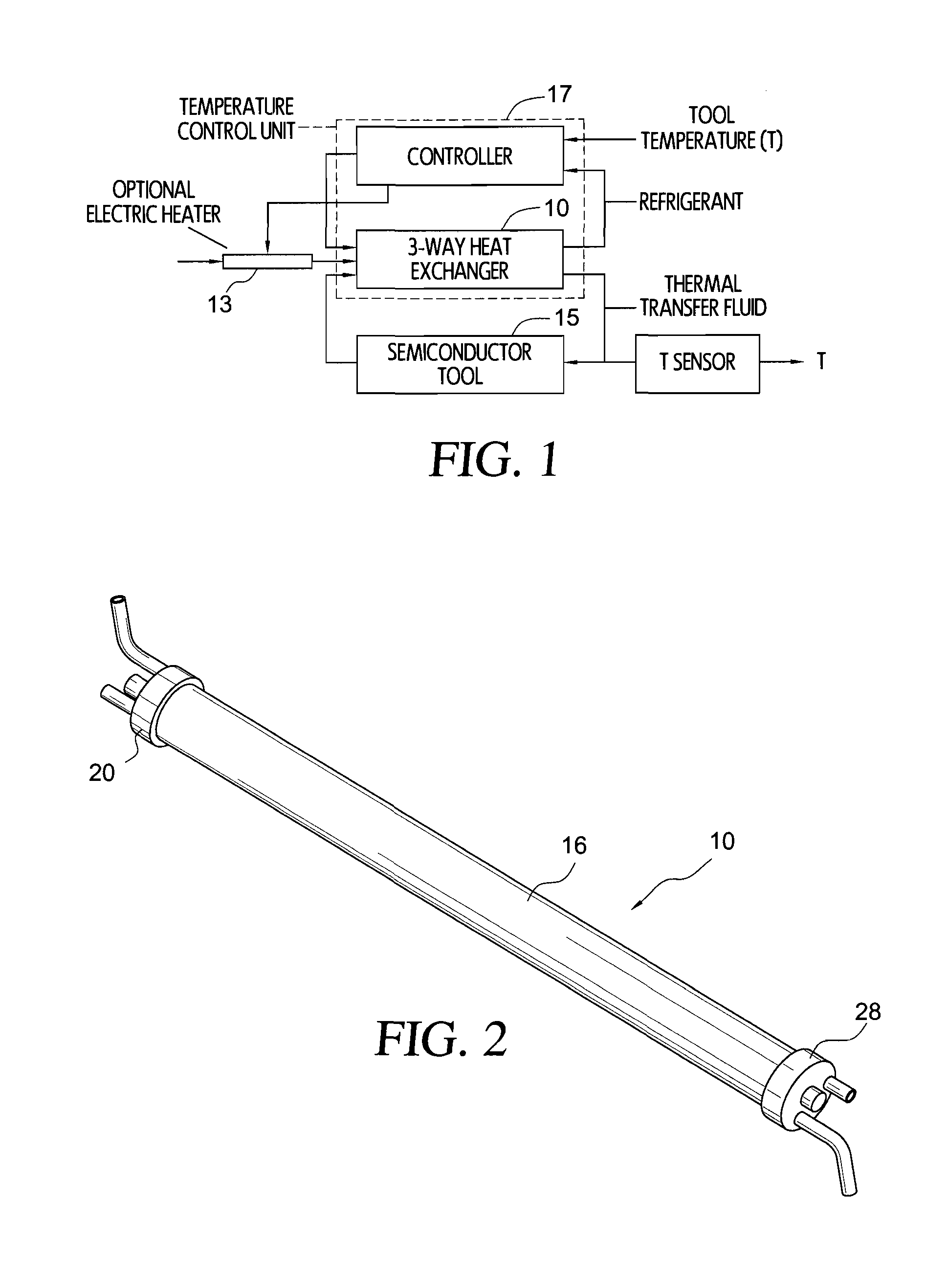
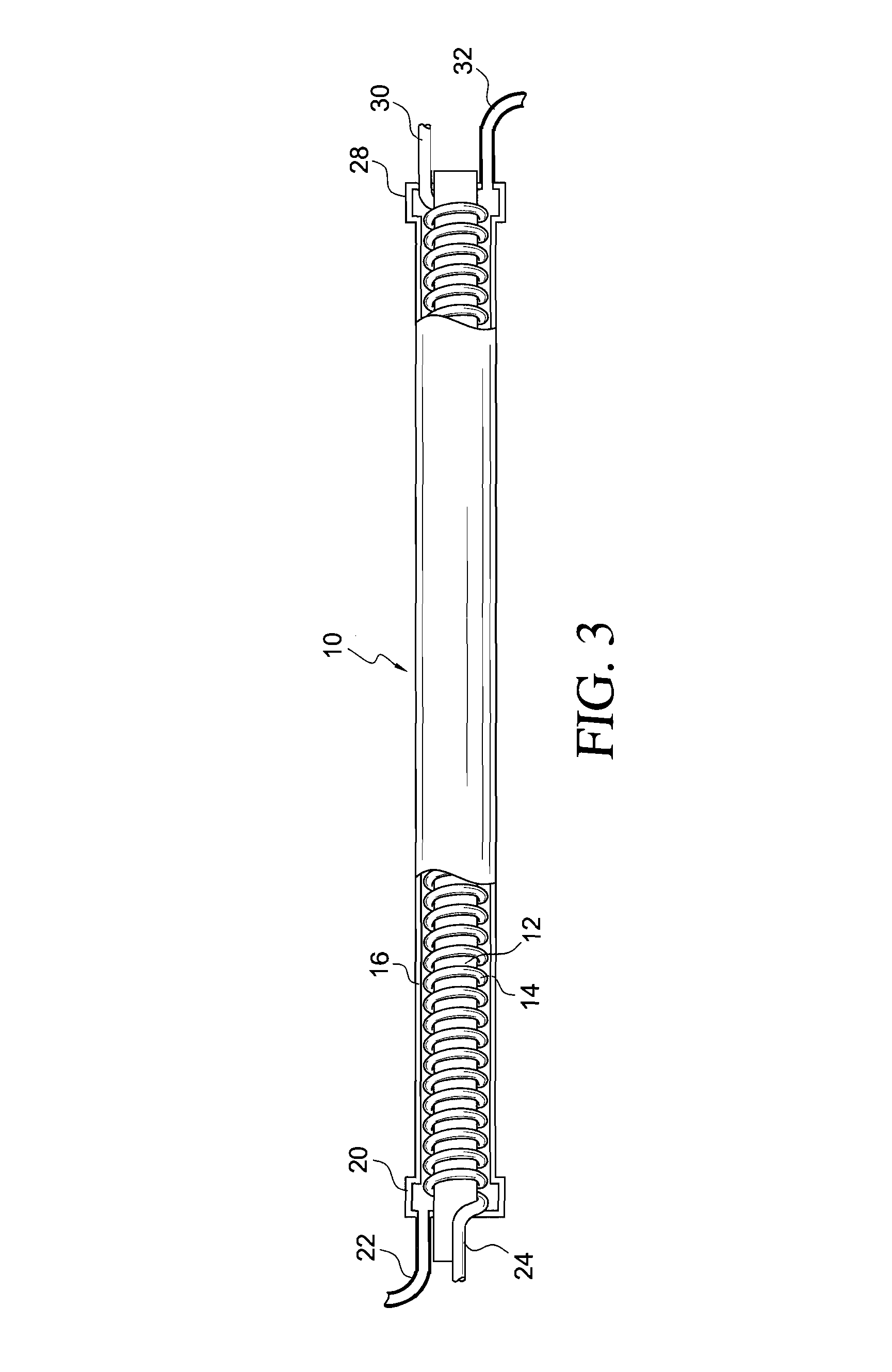
ActiveUS7661460B1Increase temperatureReduce system costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCompression machines with several evaporatorsThermal energyCold formed
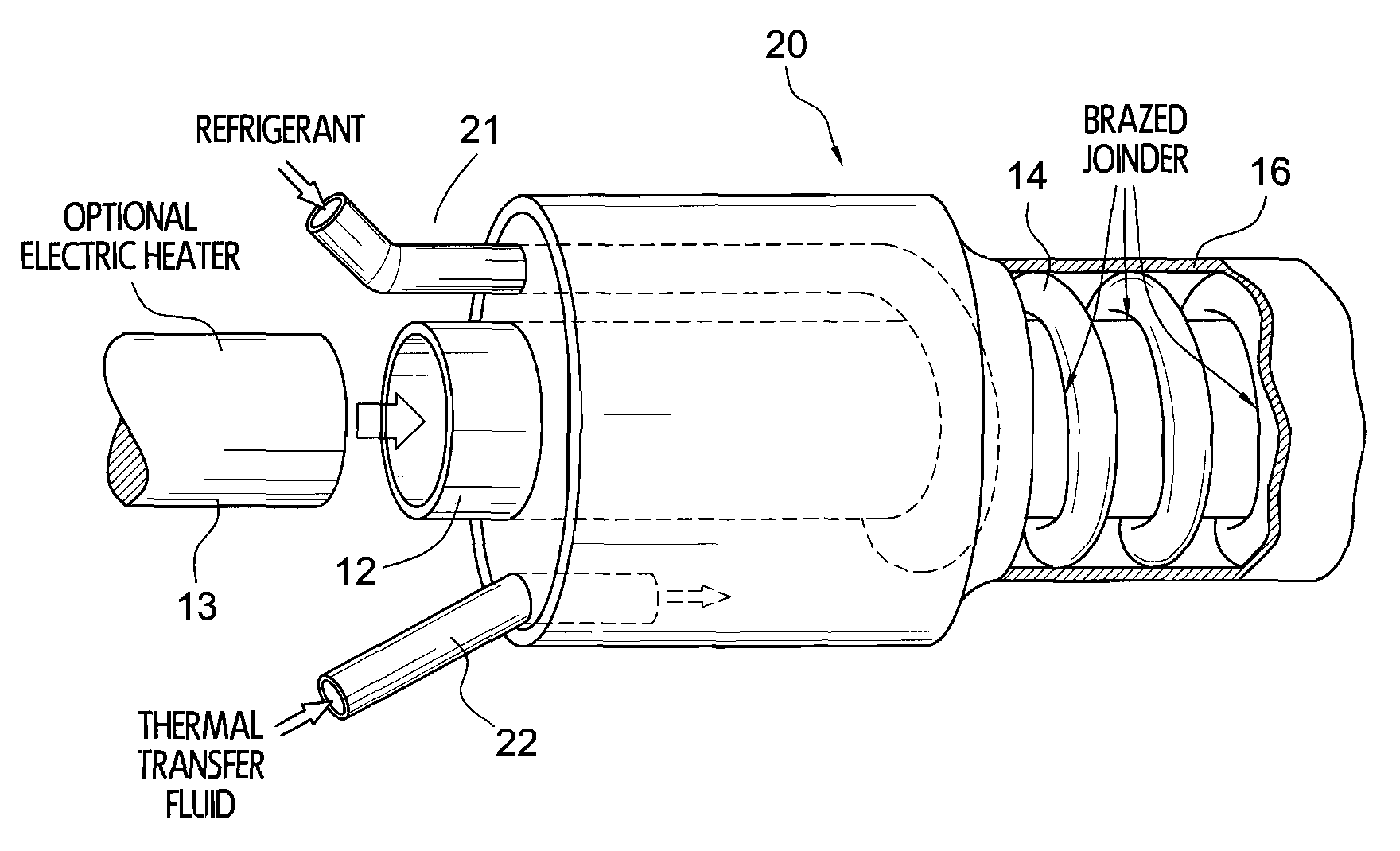
A compact heat exchanger for interchanging thermal energy between at least two fluids, one of which fluids may be a refrigerant in hot or cold form or in a liquid / vapor phase, and another of which fluids is a thermal transfer fluid. The heat exchanger may incorporate an internal heating element. The thermal transfer fluid is transported between two concentric metal tubes, while the refrigerant moves along a tubing helically wrapped about or between the tubes and is in thermal contact therewith.
Owner:BE AEROSPACE INCORPORATED
Microfluidic free interface diffusion techniques
InactiveUS20080182273A1Reduce concentrationFrom normal temperature solutionsFlow mixersFree interfaceCompetitive binding
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Cooling electronics via two-phase tangential jet impingement in a semi-toroidal channel
InactiveUS20060162365A1Domestic cooling apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEvaporationEngineering
A two-fluid-phase cooling device for absorbing high thermal flux from electronics devices and other thermally dissipating devices. It consists of a thermally conductive plate with thermally dissipating elements on one face and a semi-toroidal cavity in the opposite face with the cavity's axis perpendicular to the face of the plate, a liquid refrigerant supply tube ending in a thermodynamic cycle's refrigeration expansion valve that directs jets of liquid to impact the conical surface in the center region of the semi-toroidal cavity in a direction along the cavity's axis and tangent to the conical surface, a second plate with a semi-toroidal protrusion extending into the semi-toroidal cavity to form a thin, semi-toroidal channel between the two plates, and a seal between the liquid supply tube and the second semi-toroidal plate. In operation liquid refrigerant jets strike the conical surface generally tangential to the surface and flow at high velocity in a thin film on the surface of the semi-toroidal cavity from its center radially to the outer edge of the toroidal channel, absorbing heat and boiling as it does so. The high radial acceleration forces caused by the liquid film moving at high velocity on the cavity's concave surface force the liquid film against the surface and create a pressure gradient that biases evaporation toward the liquid / vapor interface. The vapor moves parallel to the liquid flow radially outwards between the liquid film and the surface of the semi-toroidal protrusion at very high velocity, causing extreme turbulence in the liquid film and highly augmented heat transfer between the heated plate and the liquid film, while the liquid film nevertheless remains intact and forced against the heated surface by radial acceleration and carried to a distance significantly greater than in conventional jet impingement systems. The device may also be composed of wedge-shaped sections of the semi-toroidal plates. It may further have two expansion valves in series in the liquid supply line, the first generating a small amount of vapor (increase in quality) so the resulting increase in flow volume greatly increases the velocity through the second expansion valve toward the heated surface to further enhance heat transfer.
Owner:HOANG TRIEM T +1
System and method for proportional mixing and continuous delivery of fluids
A system and method for mixing and delivering fluids such as contrast media and saline is disclosed including at least two fluid sources, a pump, a joining fluid path connecting the at least two fluid sources to an inlet to the pump, and a valve device in the fluid path upstream of the pump. The valve device includes an actuator adapted to restrict flow in at least one of respective fluid lines connecting the at least two fluid sources to the pump inlet. A patient interface device may be associated with an outlet of the pump. The valve device actuator is generally adapted to restrict the flow in at least one of the respective fluid lines such that an incremental positional change in valve device actuator position provides a substantially linear change in fluid mixture ratio of the fluids from the at least two fluid sources to the pump inlet.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
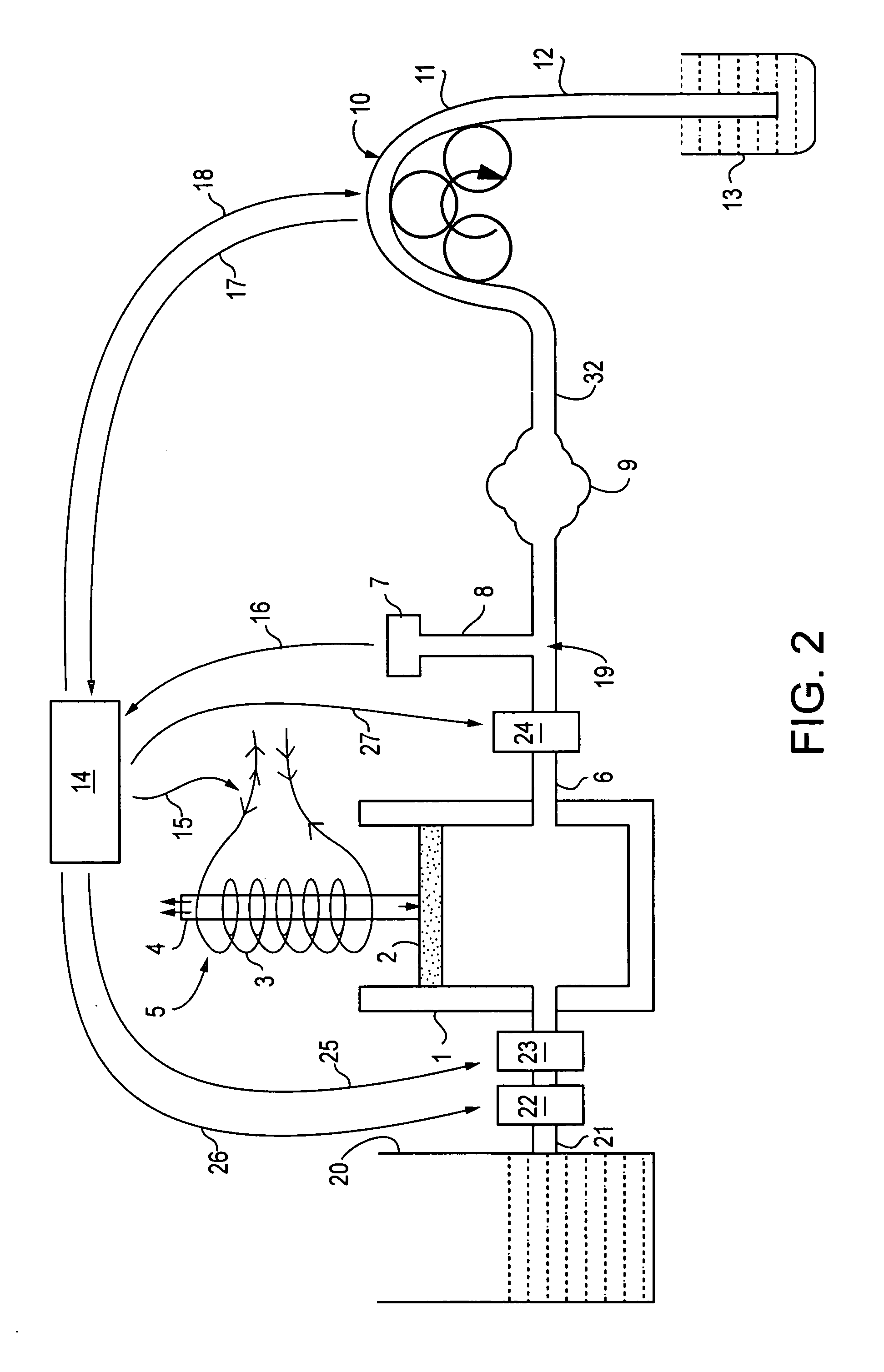
Low turbulence fluid management system for endoscopic procedures
ActiveUS20060122556A1Reduce cavity filling timeMinimize such riseEndoscopesMedical devicesPeristaltic pumpEndoscopic Procedure
The present invention provides a system and a method for distending a body tissue cavity of a subject by continuous flow irrigation by using two positive displacement pumps, such as peristaltic pumps, one pump on the inflow side and another pump on the outflow side, such that the amplitude of the pressure pulsations created by a the said positive displacement pumps inside the tissue cavity is substantially dampened to almost negligible levels. The present invention also provides a method of reducing the frequency of the said pressure pulsations. The present invention also provides a method for accurately determining the rate of fluid loss, into the subject's body system, during any endoscopic procedure without utilizing any deficit weight or fluid volume calculation, the same being accomplished by using two fluid flow rate sensors. The present invention also provides a system of creating and maintaining any desired pressure in a body tissue cavity for any desired cavity outflow rate. The system and the methods of the present invention described above can be used in any endoscopic procedure requiring continuous flow irrigation few examples of such endoscopic procedures being hysteroscopic surgery, arthroscopic surgery, trans uretheral surgery, endoscopic surgery of the brain and endoscopic surgery of the spine.
Owner:KUMAR BV
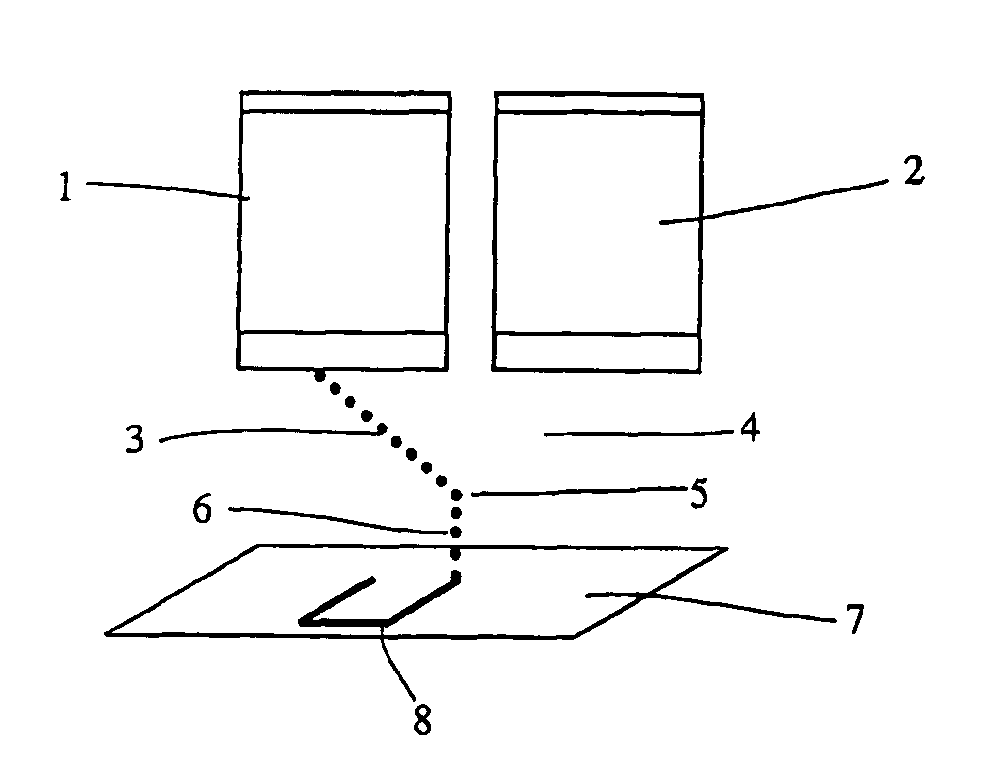
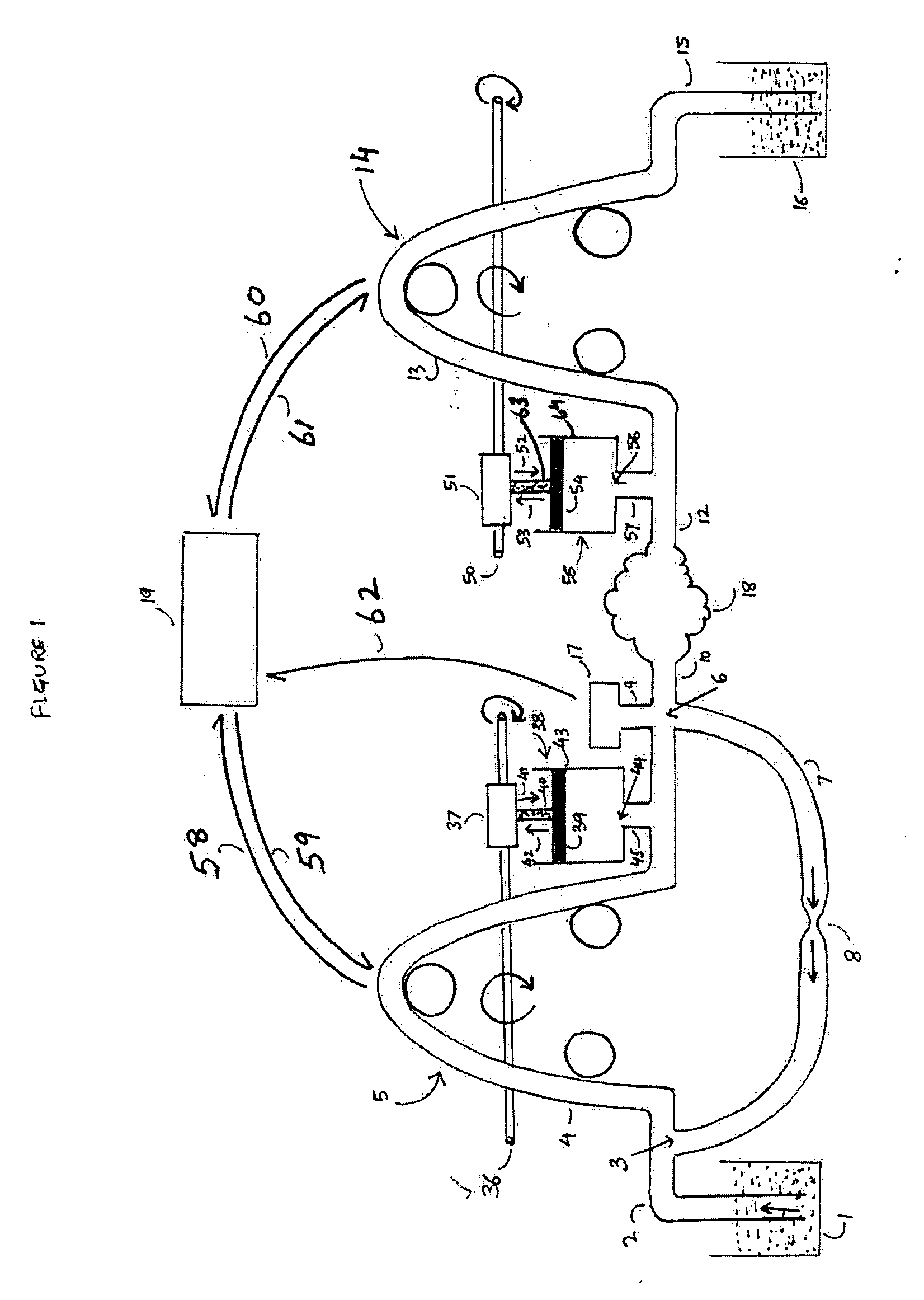
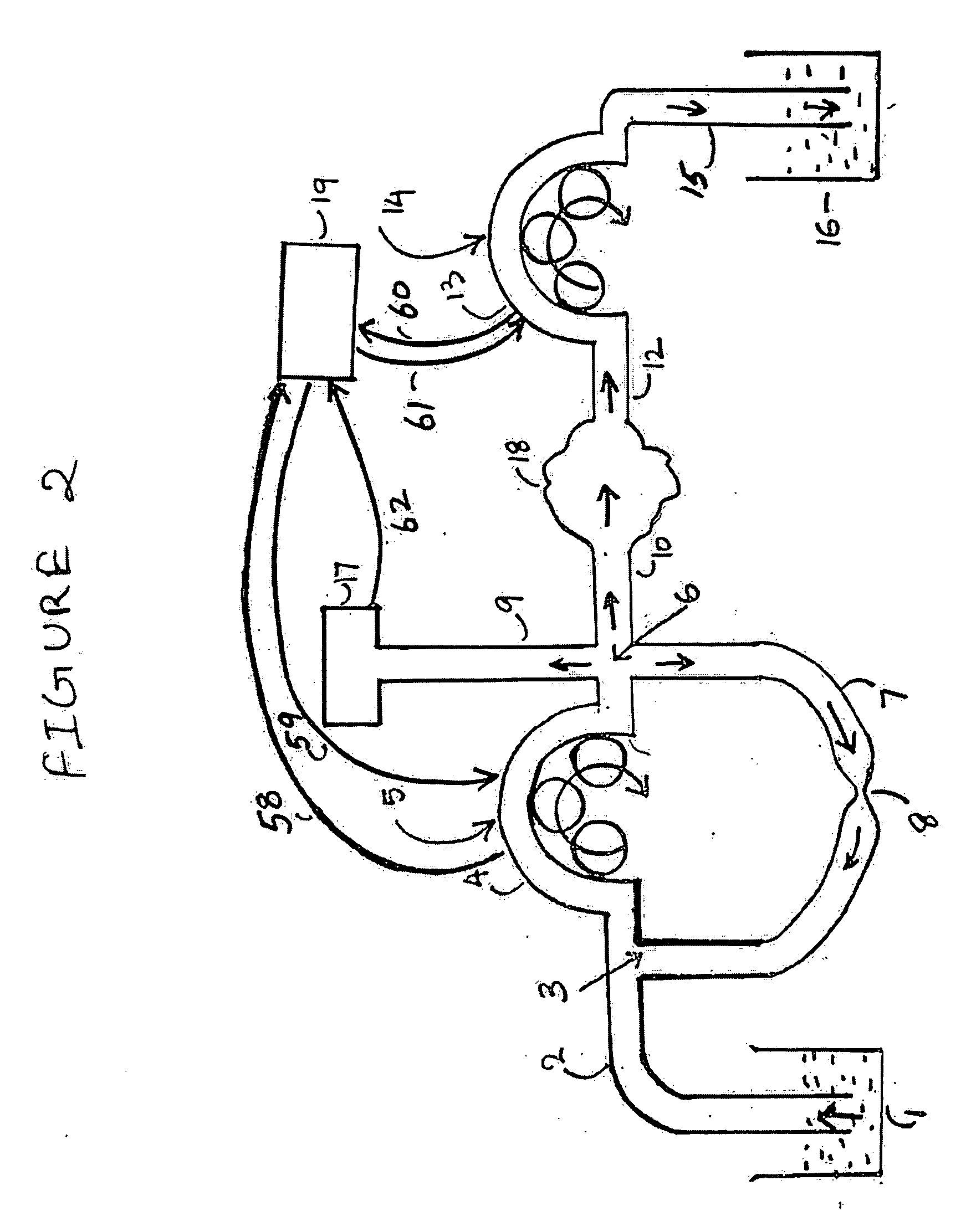
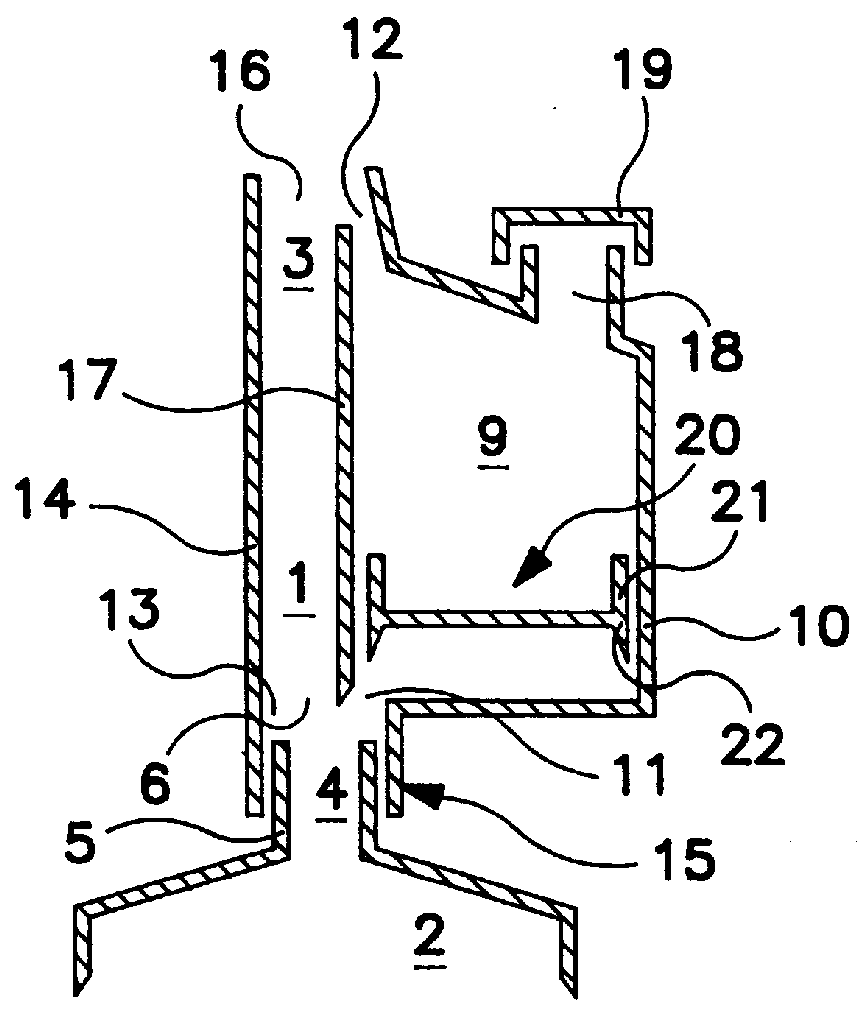
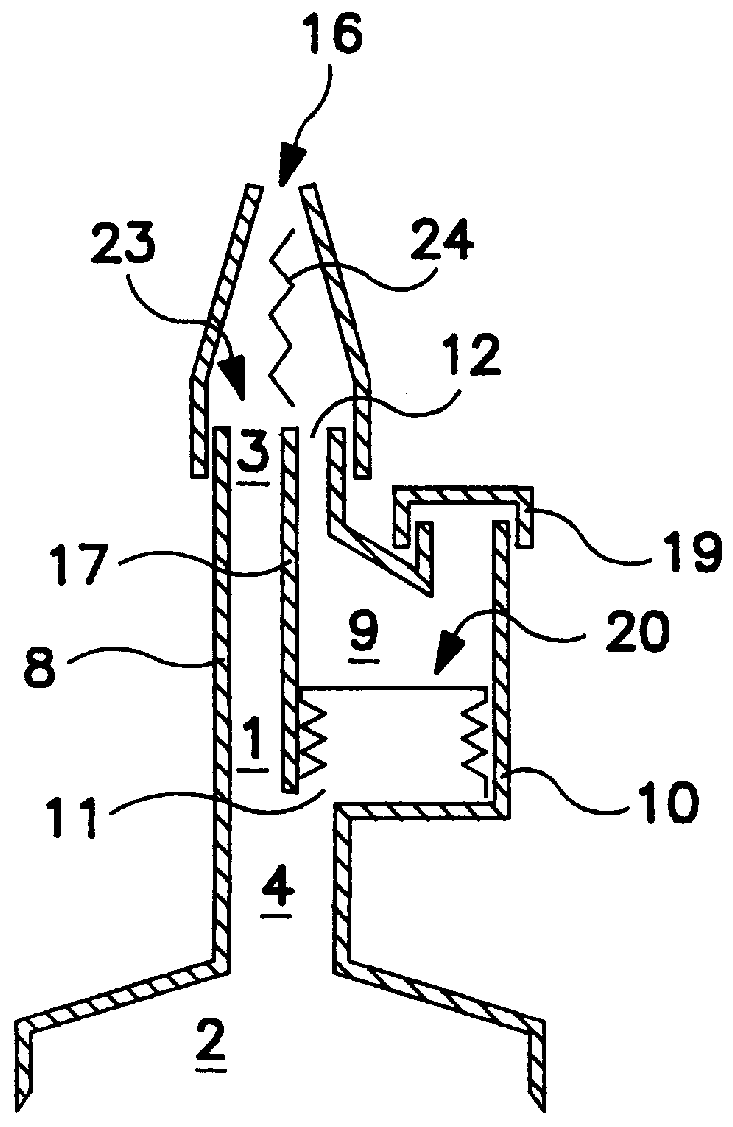
Method and device for combining at least two fluid media
PCT No. PCT / DE95 / 00462 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 5, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 5, 1996 PCT Filed Apr. 7, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO95 / 27558 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 19, 1995The invention is a device and a method for combining at least two fluid media. The device comprises a flow region (1) which is attached to and / or formed with an opening of a first chamber (2) and which is designed to accommodate the fluid medium coming from the first chamber and to transport it to the outlet (3) of the flow region (1) which is preferably followed by a mixing zone. A second chamber (9) designed to be filled with a second fluid medium is connected to the flow region and / or to the first chamber through at least one first opening element (inlet opening) (11) for diverting part of the first fluid medium from the first into the second chamber. The second chamber is provided with at least one second opening element (second opening) (12) opening into or adjoining the flow region (1) for discharging the second fluid medium displaced into it by the first fluid medium. Several first chambers (2) or second chambers (9) may be provided.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Gas inlets for wafer processing chamber
InactiveUS6500734B2Avoid mixingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSusceptorProduct gas
A system for supplying processing fluid to a substrate processing apparatus having walls, the inner surfaces of which define a processing chamber in which a substrate supporting susceptor is located. The system consists of a number of fluid storages, each which stores a separate processing fluid, at least two fluid conduits along which processing fluid flows from the fluid storages to the processing apparatus and a fluid inlet which connects the fluid conduits to the processing chamber. The inlet has a separate fluid passage, corresponding to each of the fluid conduits, formed along it. Each fluid passage opens at or near an inner surface of a wall to define a fluid mixing zone, so that fluid moving along one fluid passage is prevented from mixing with fluid moving along any other passage until reaching the mixing zone.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
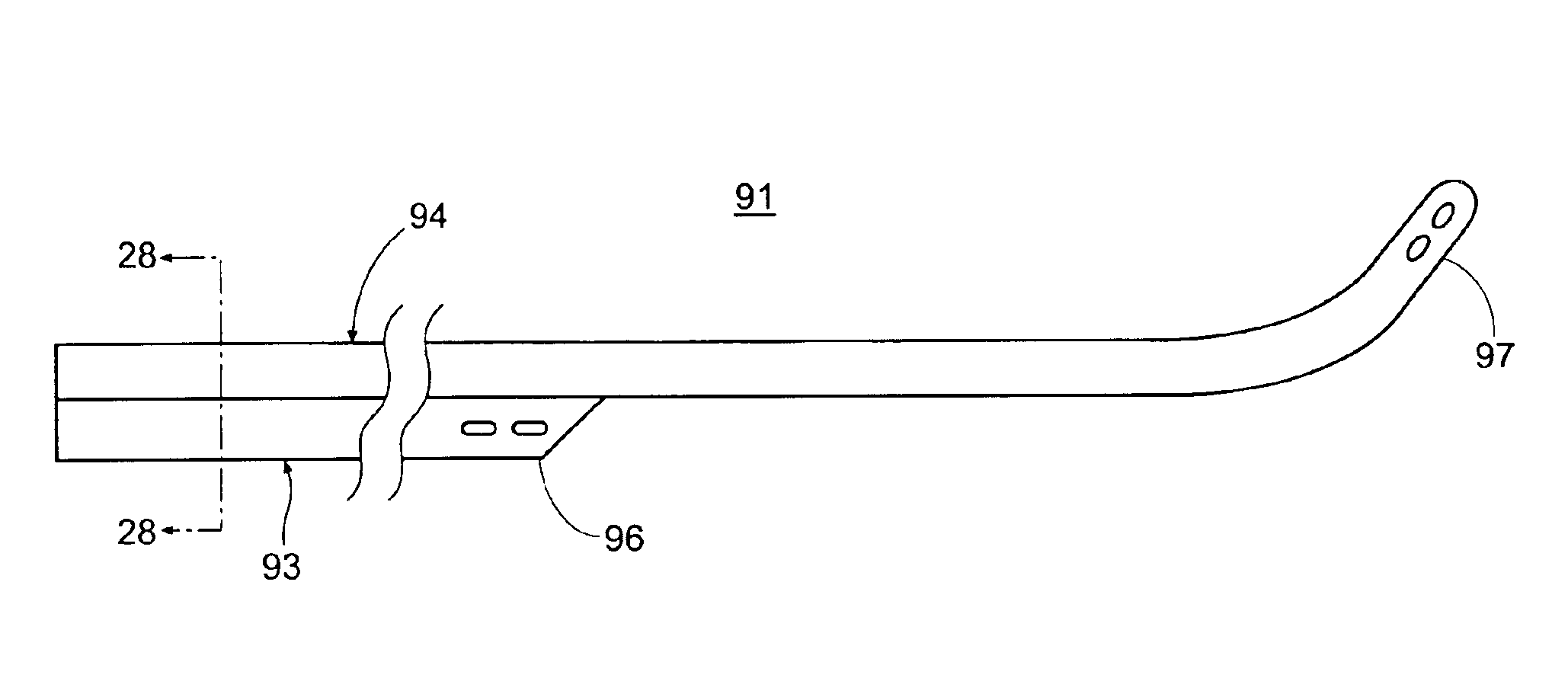
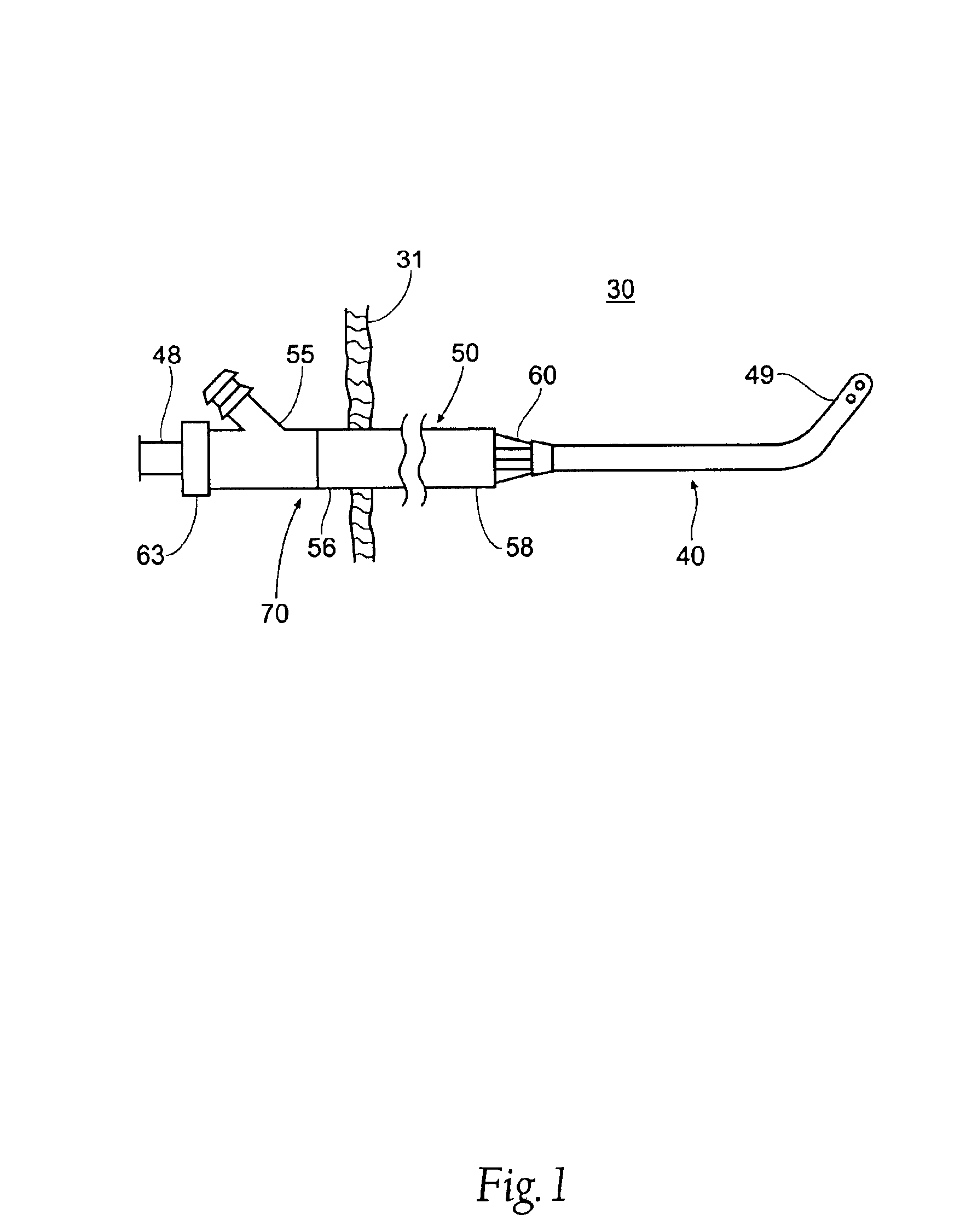
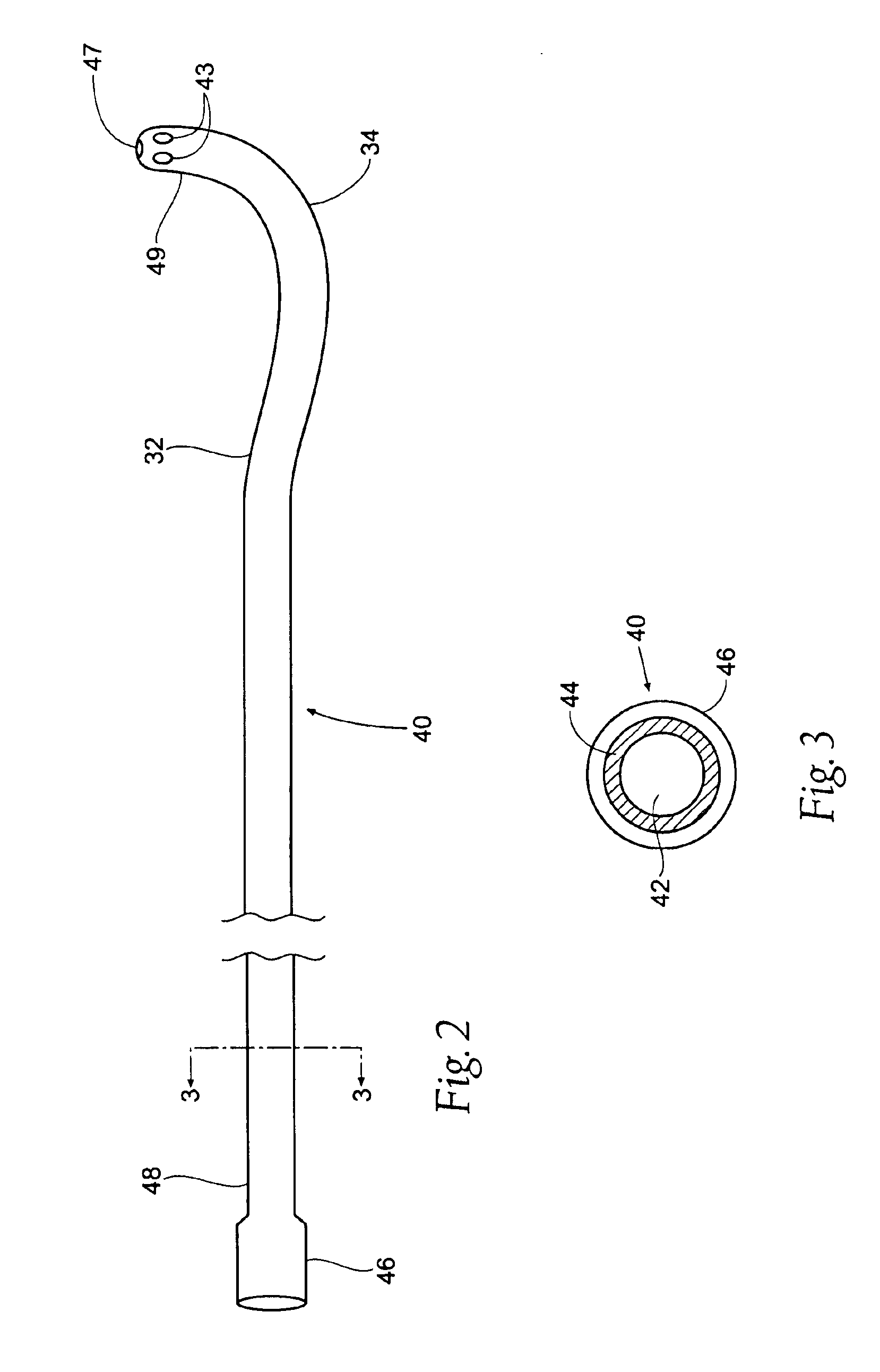
Intravascular cannulation apparatus and methods of use
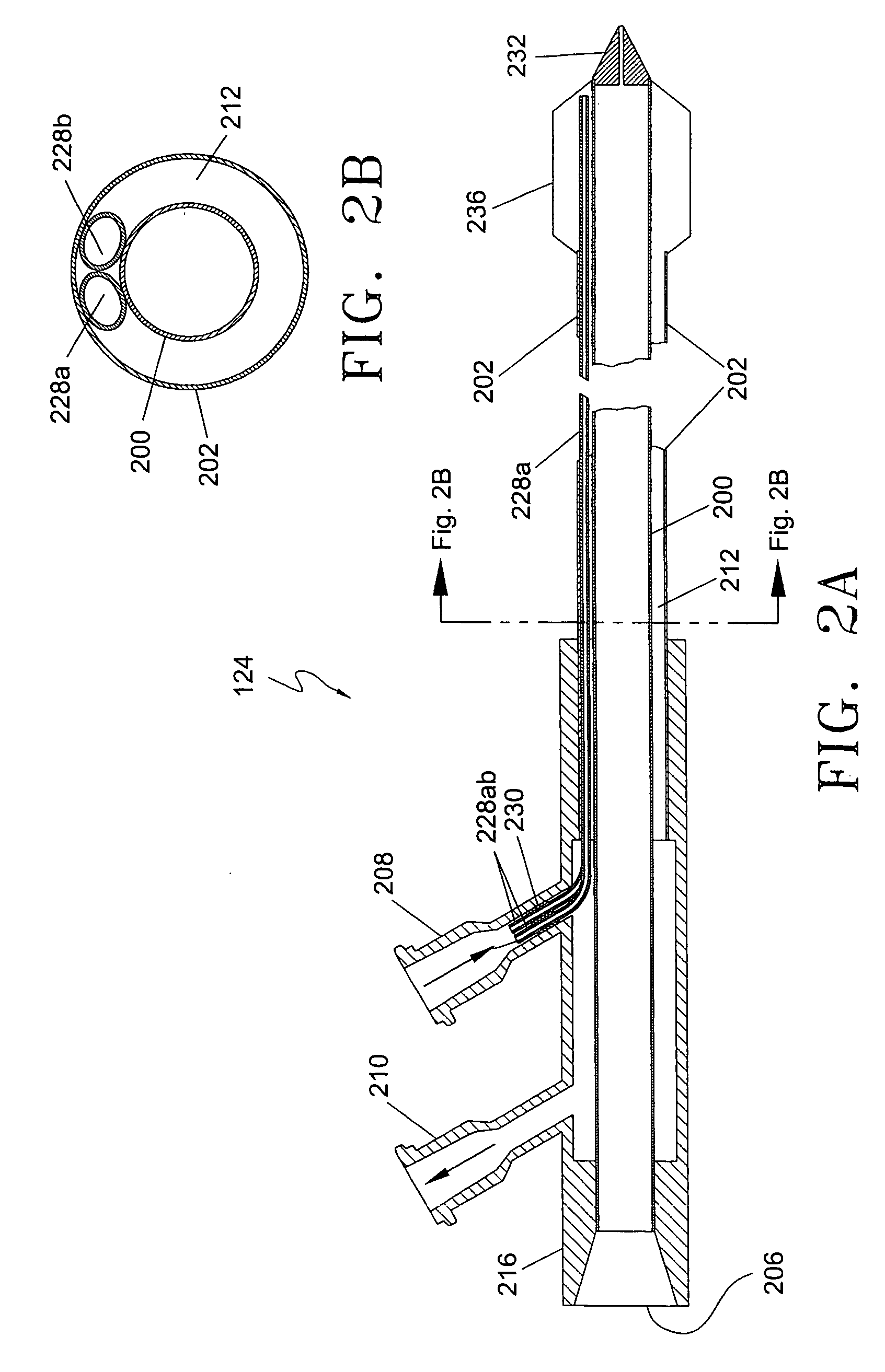
This invention is a cannulation apparatus, and related methods for providing indirect access to a surgical site within a patient. The cannulation apparatus includes at least two fluid flow paths that are slidable coupled (40) (50) to one another, and selectively positional within the patient. The first, the second flow path s may be advanced through a single incision disposed remotely from the surgical field to first, and second predetermined locations within the patient. Exemplary sites for the incision include the groin region or in the neck region of the patient. The cannulation apparatus, and method of the present invention are particularly suited for use in providing cardiopulmonary support during cardiac surgery, including coronary artery bypass graft surgery. The cannulation apparatus of the present invention also provides an entry site for one or more support devices used in the surgical procedure.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com