Patents
Literature
132 results about "Relative Volume" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Relative Volume (often times called RVOL) is an indicator that tells traders how current volume is compared to past trading volumes over a given period. It is kind of a like a radar for how “in-play” a stock is.
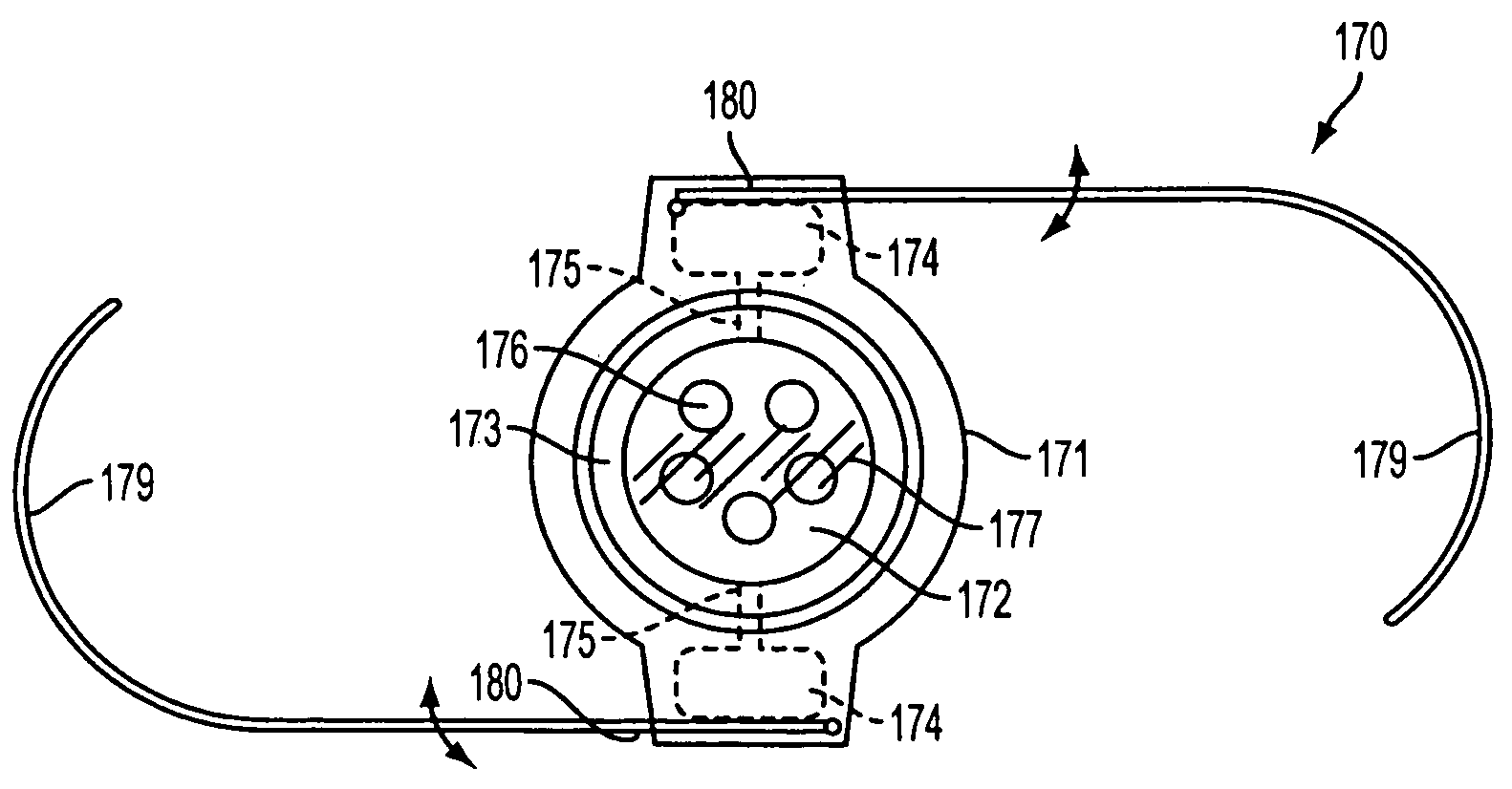
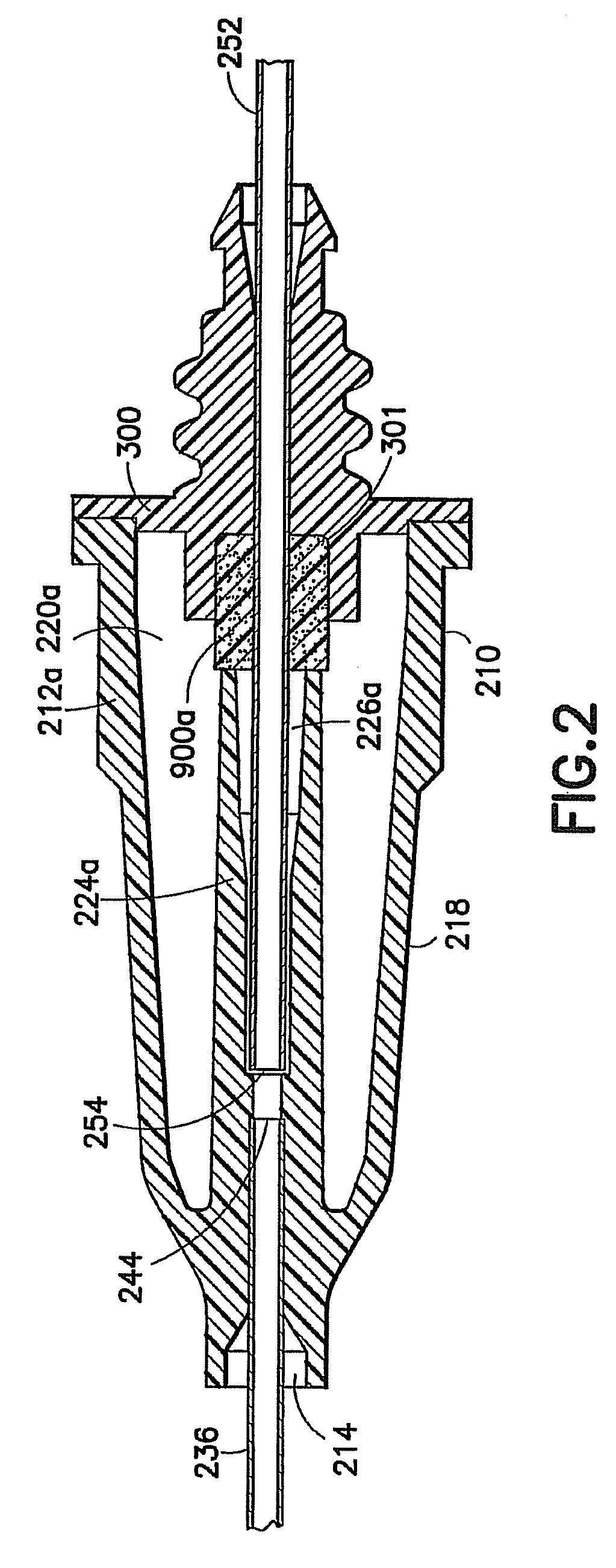
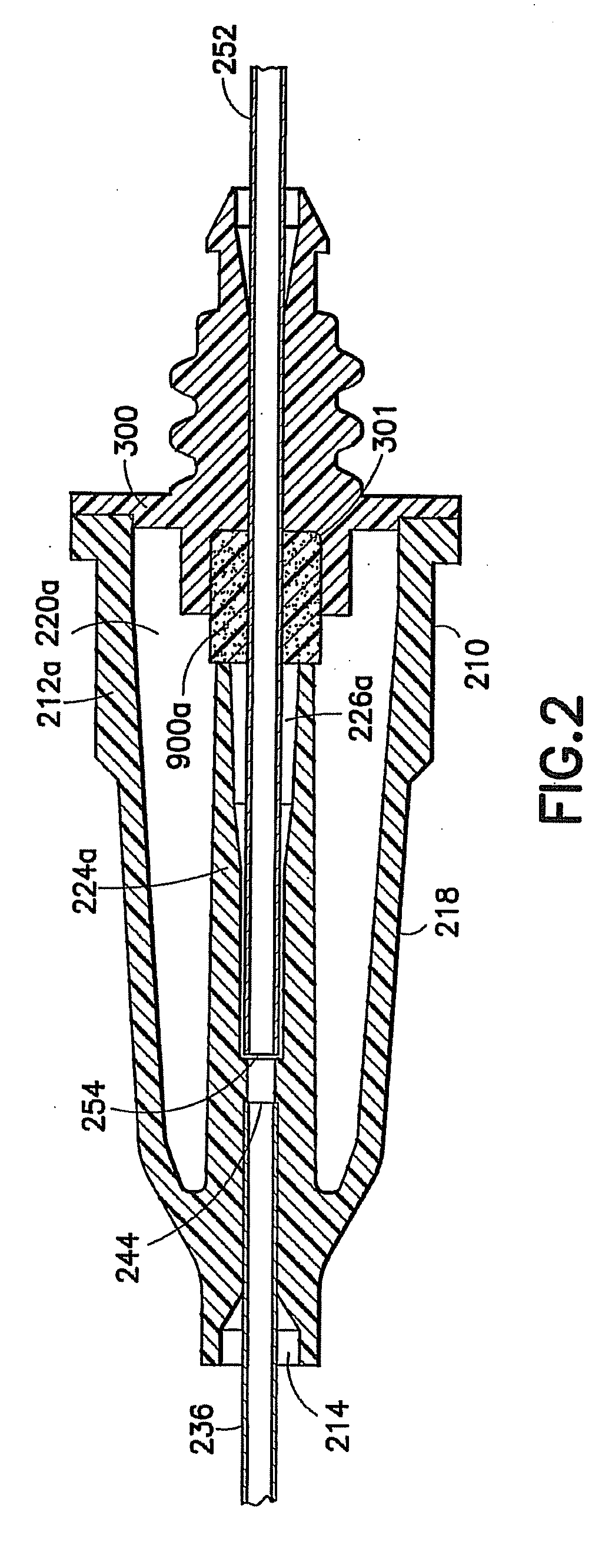
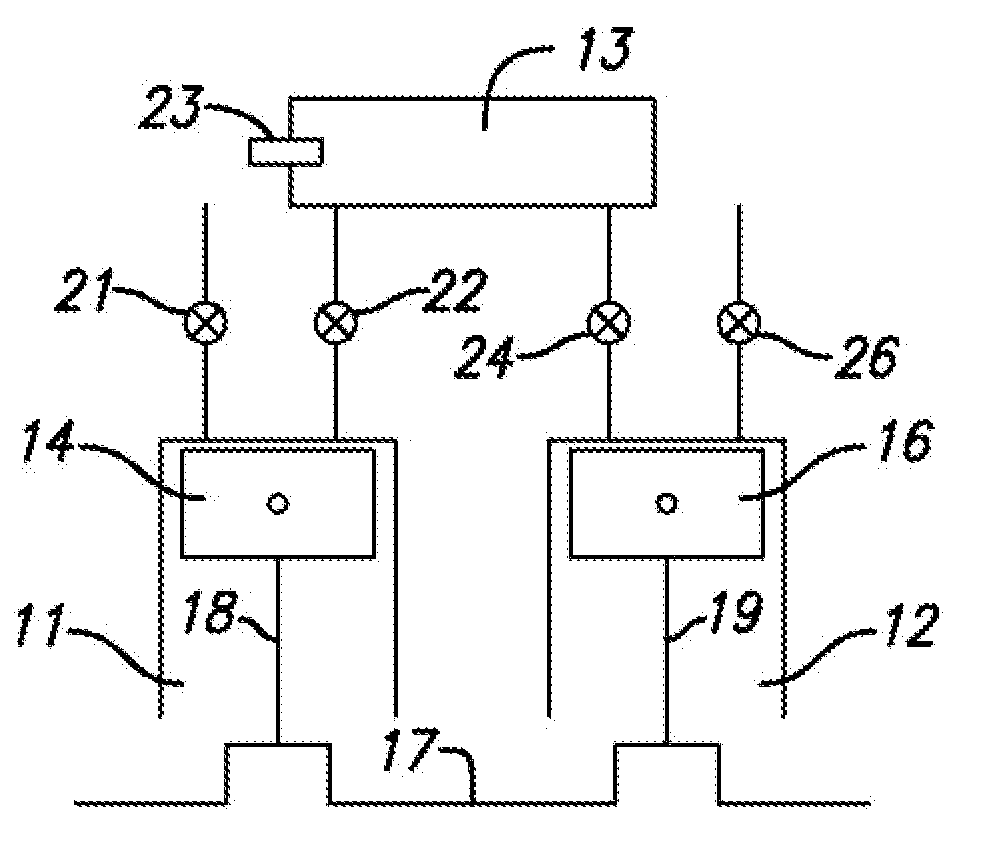
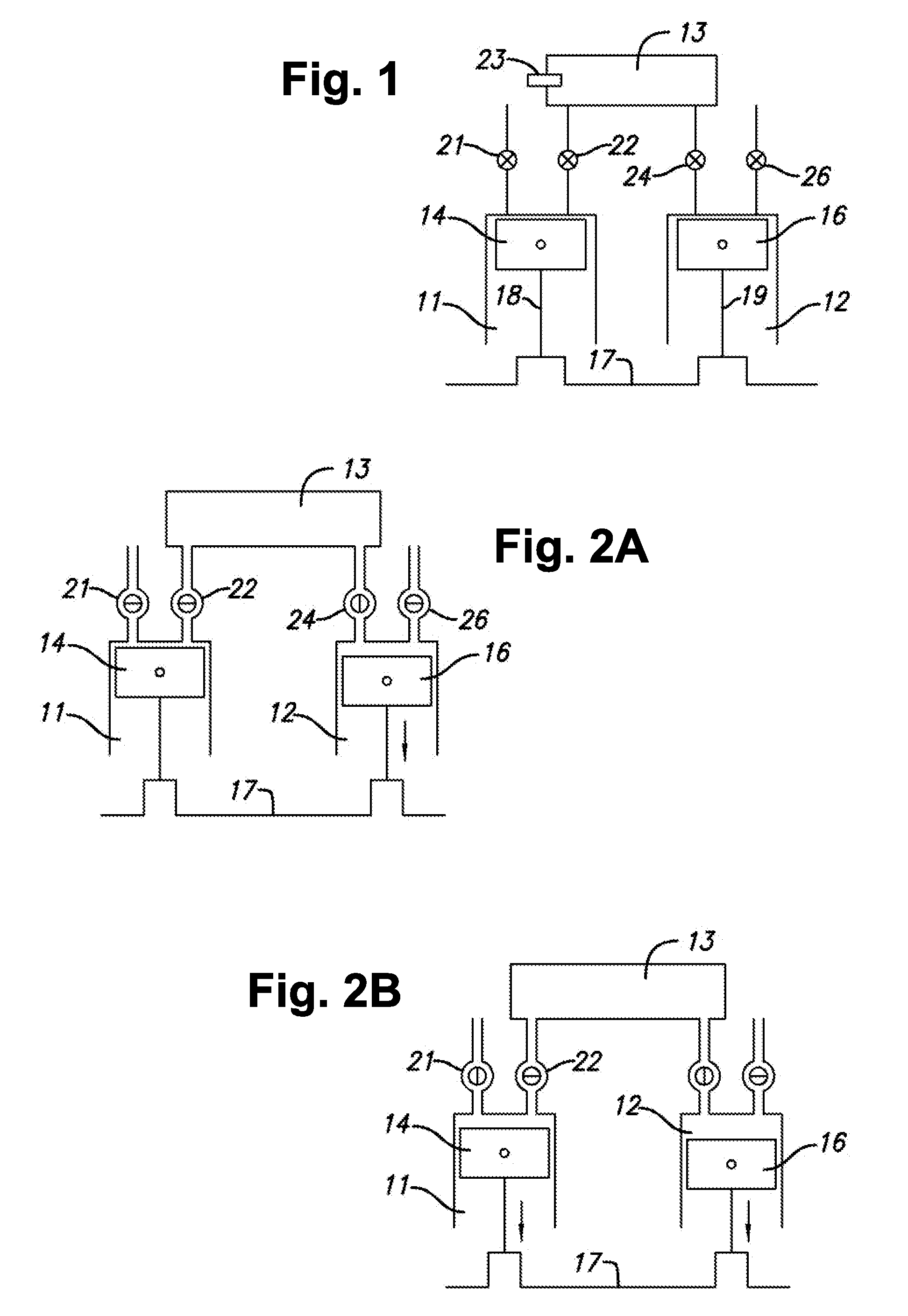
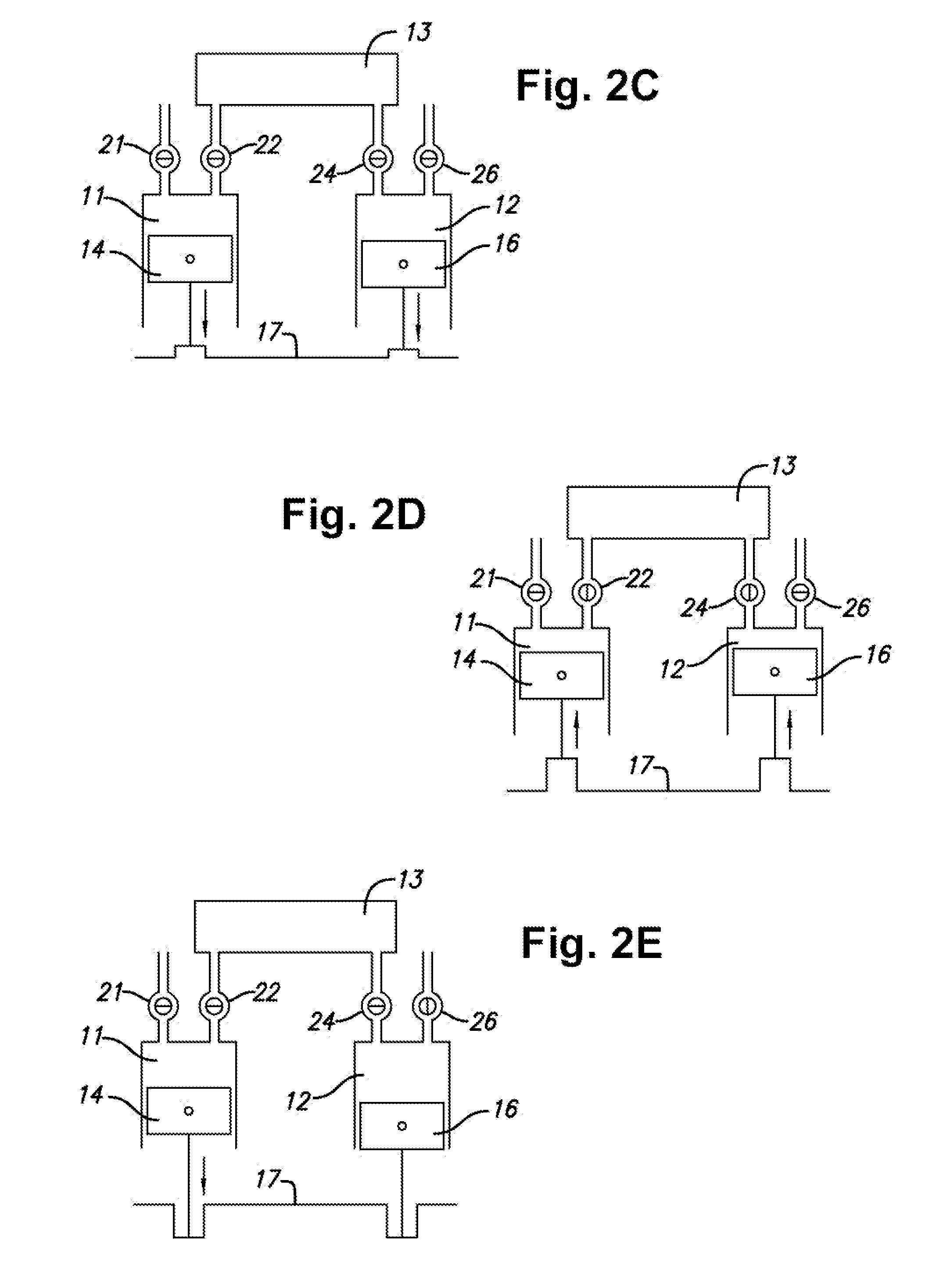
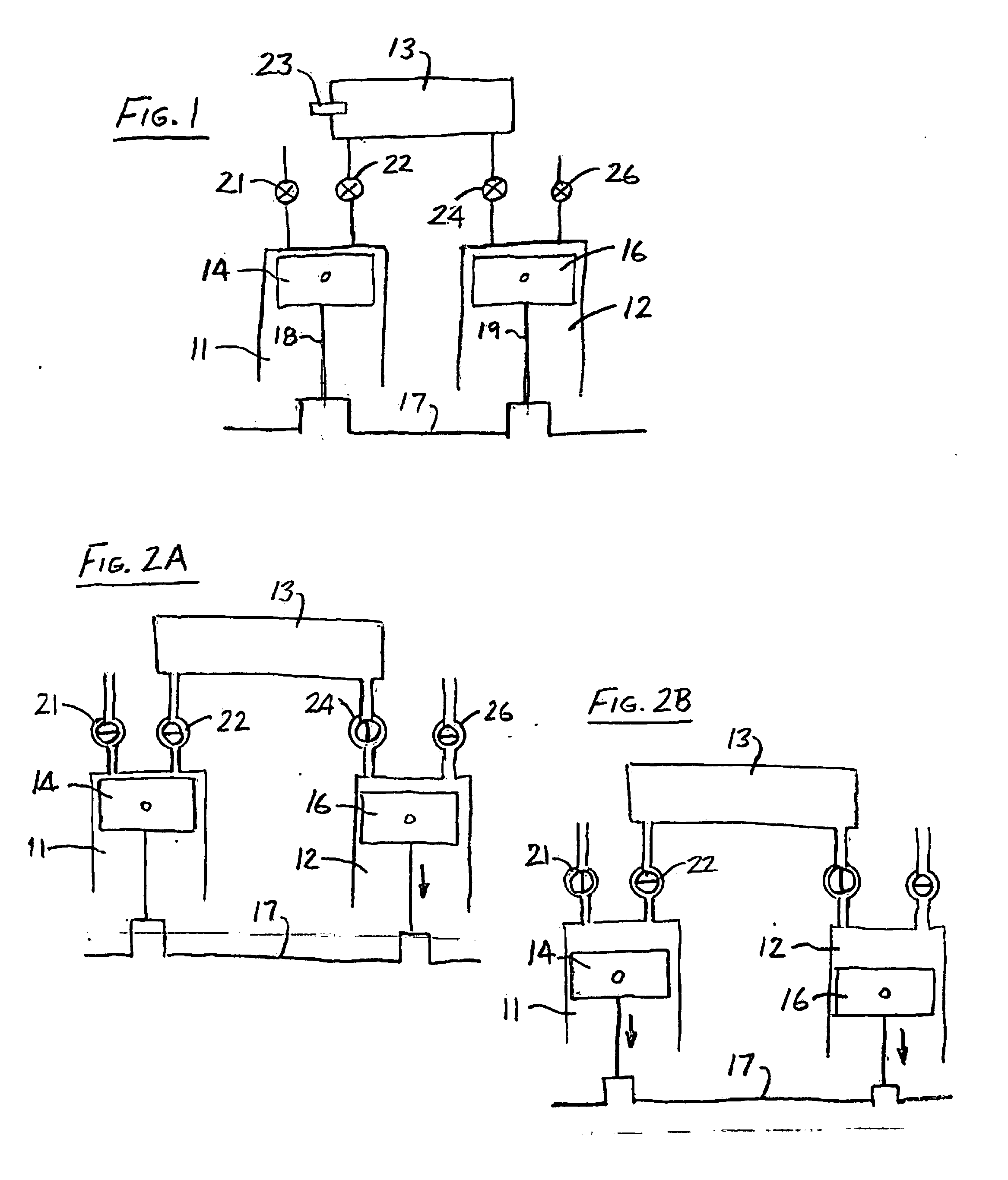
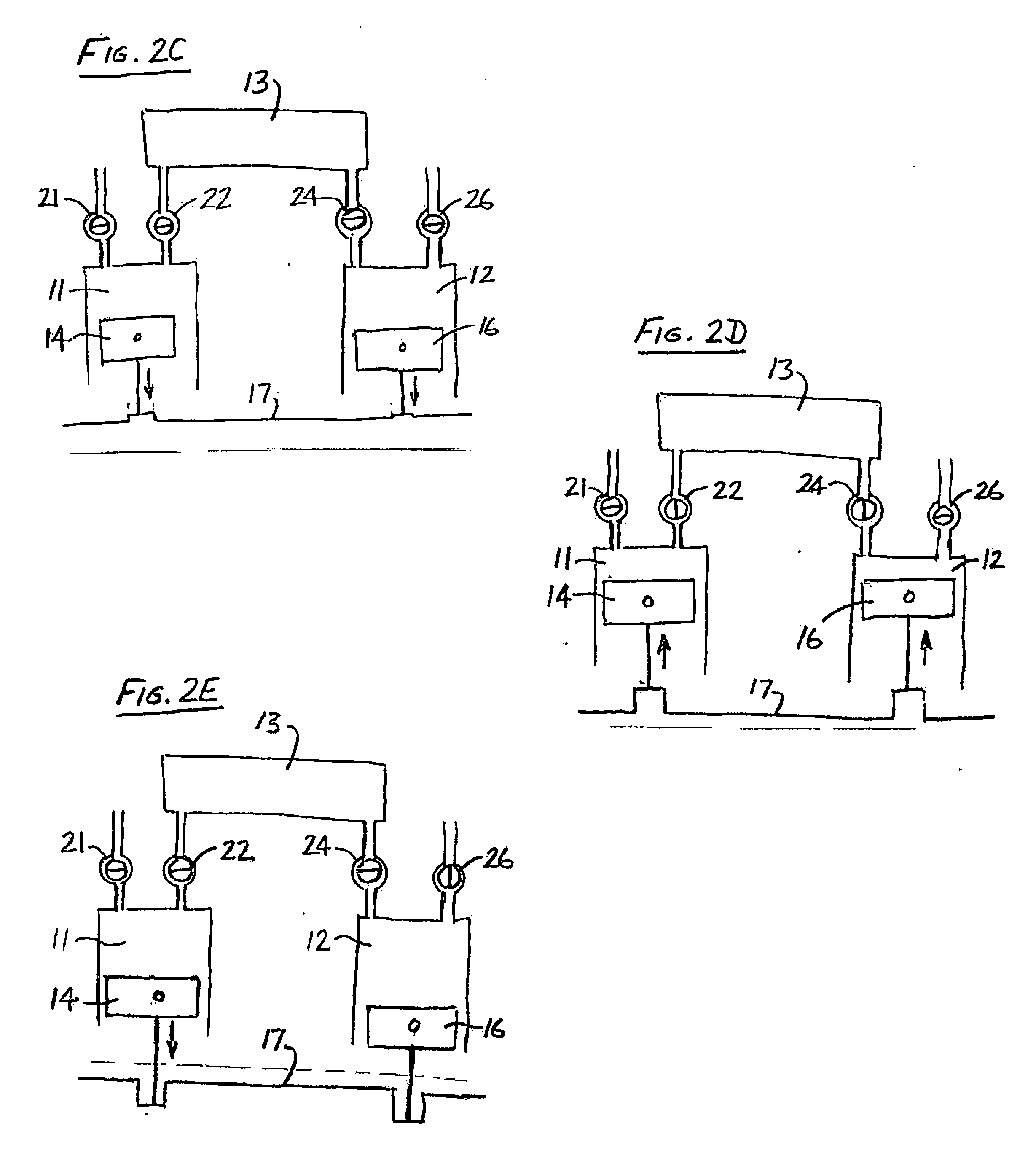
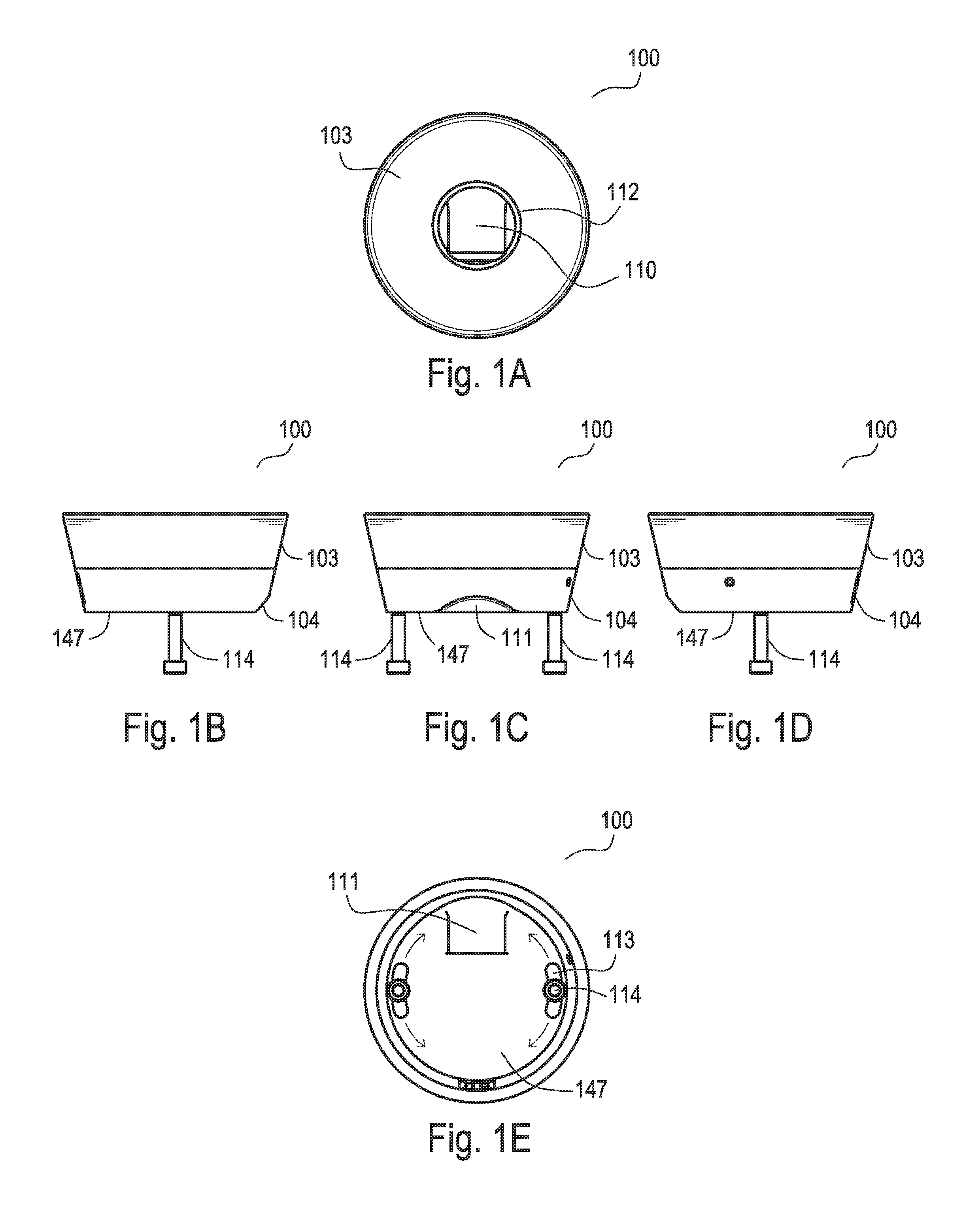
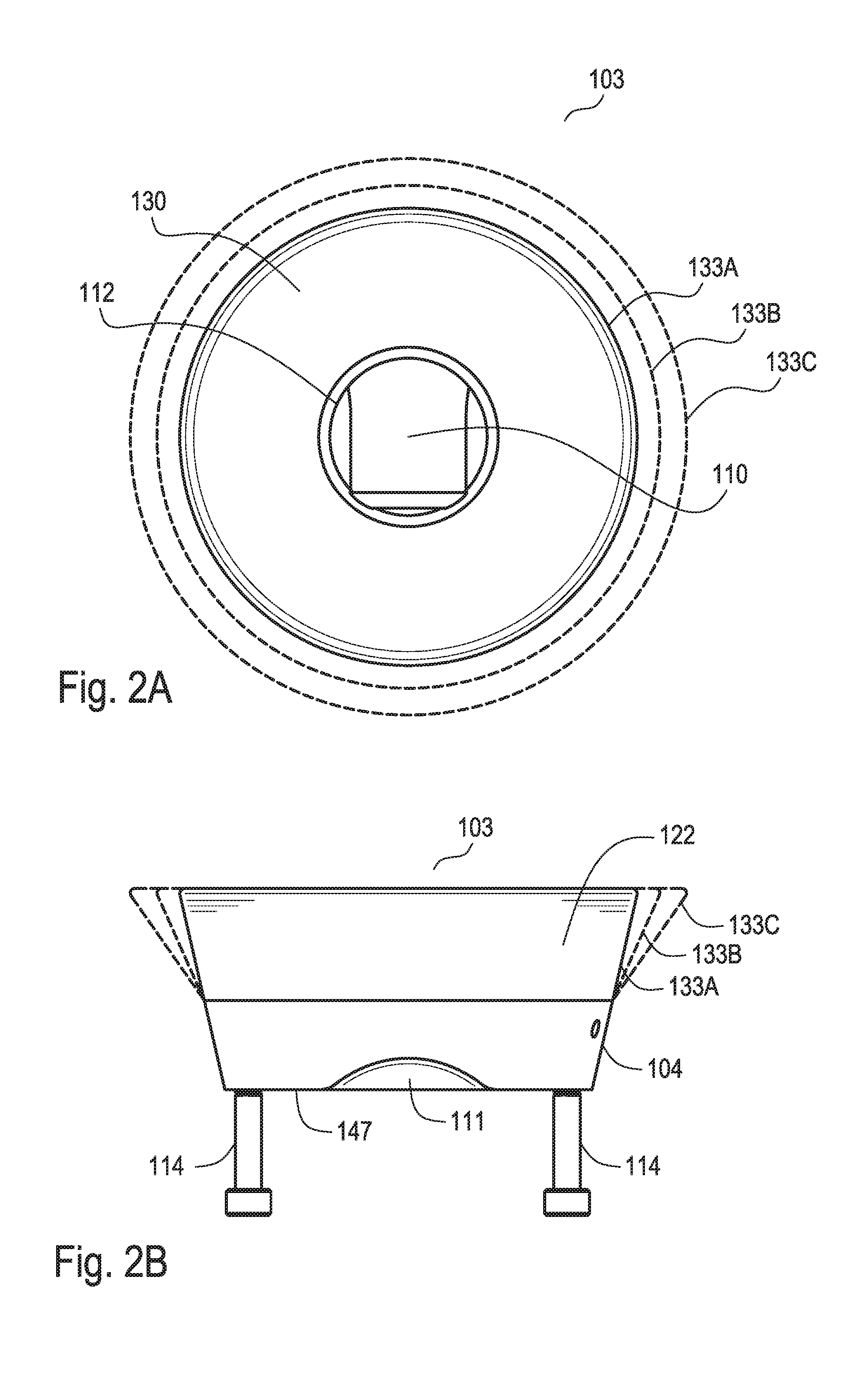
Accommodating intraocular lens system and method
ActiveUS7122053B2Great motionEfficiently manipulatedIntraocular lensOptical partsIntraocular lensRelative Volume
An accommodating intraocular lens is provided that having optical parameters that are altered in-situ using forces applied by the ciliary muscles, in which a lens body carries an actuator separating two fluid-filled chambers having either the same index of diffraction or different indices of refraction, actuation of the actuator changing the relative volumes of fluid within an optic element of the lens and altering the optical power of the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
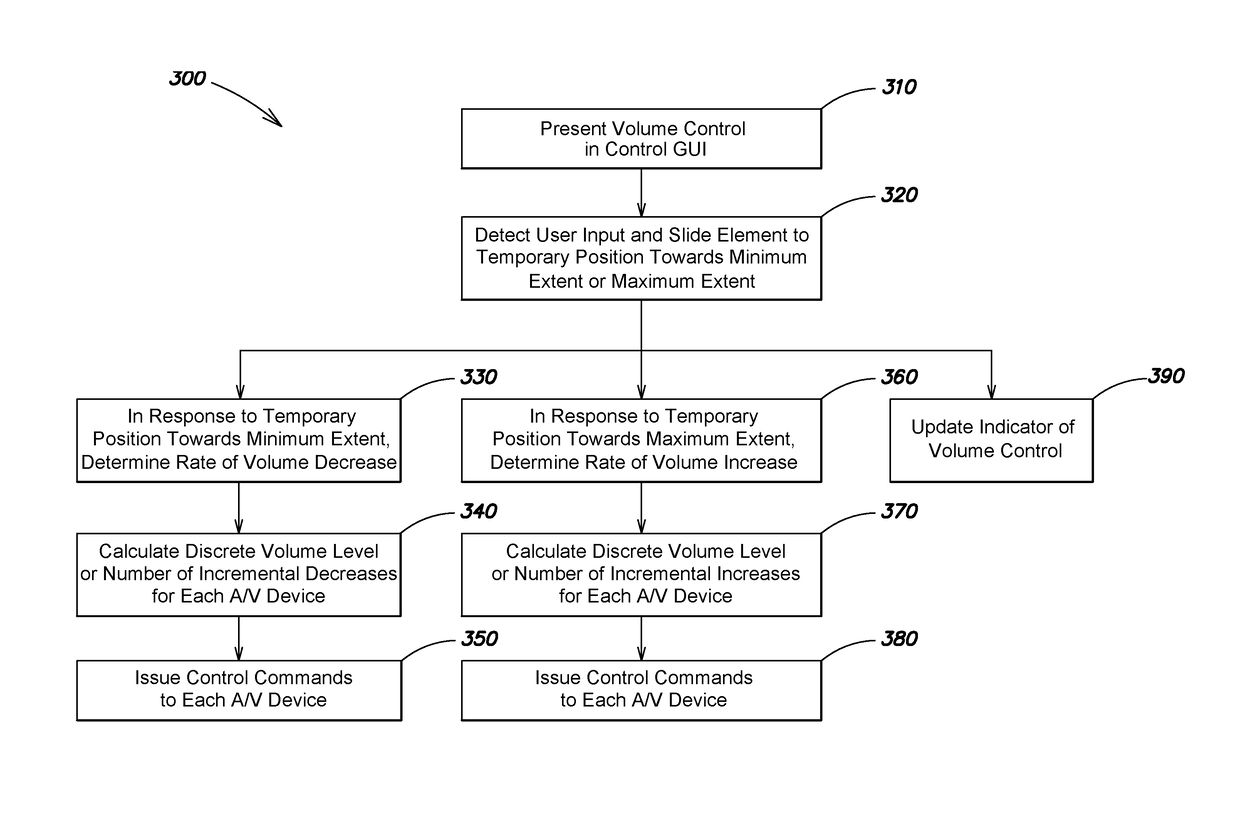
Volume control for audio/video devices
ActiveUS20170134872A1Easy volume controlLower the volumeSignal processingPublic address systemsRelative VolumeUser input
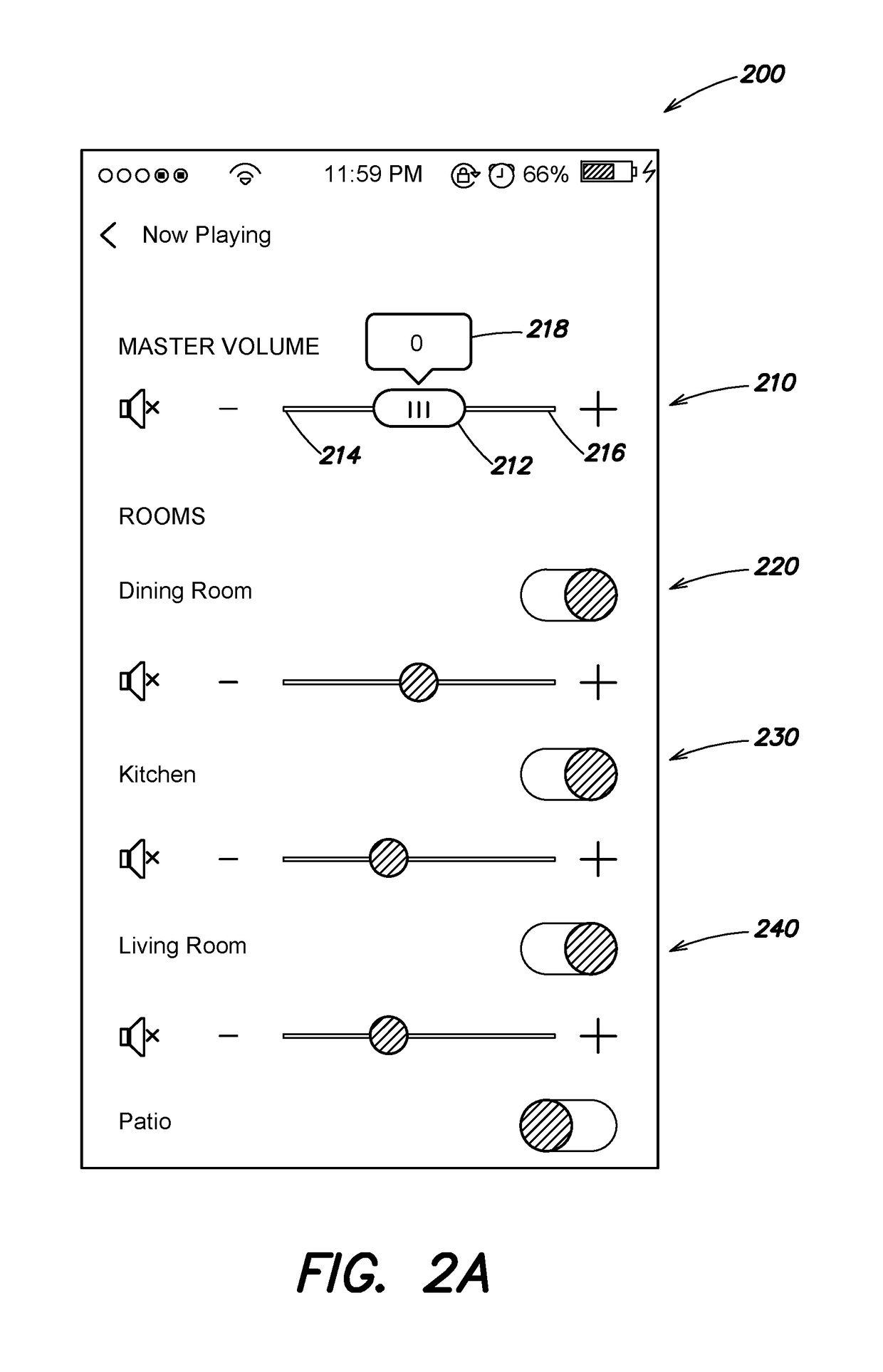
Example techniques are provided for controlling volume of A / V devices using an improved volume control. The volume control may be implemented as a slider, where the sliding element is temporarily slid in response to user input (e.g., touched and dragged by the user), but then automatically “snaps” back to the center of the slider's range when the user input ends (e.g., is released by the user). Movement of the element from the center is interpreted as a relative volume adjustment, with the rate of volume change being proportional to the distance between the center of the range and the temporary position of the element. An indicator is provided indicating the rate, to provide user feedback. The volume control may be utilized as a master volume control in a home automation system.
Owner:SAVANT SYST INC
Flashback blood collection needle
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
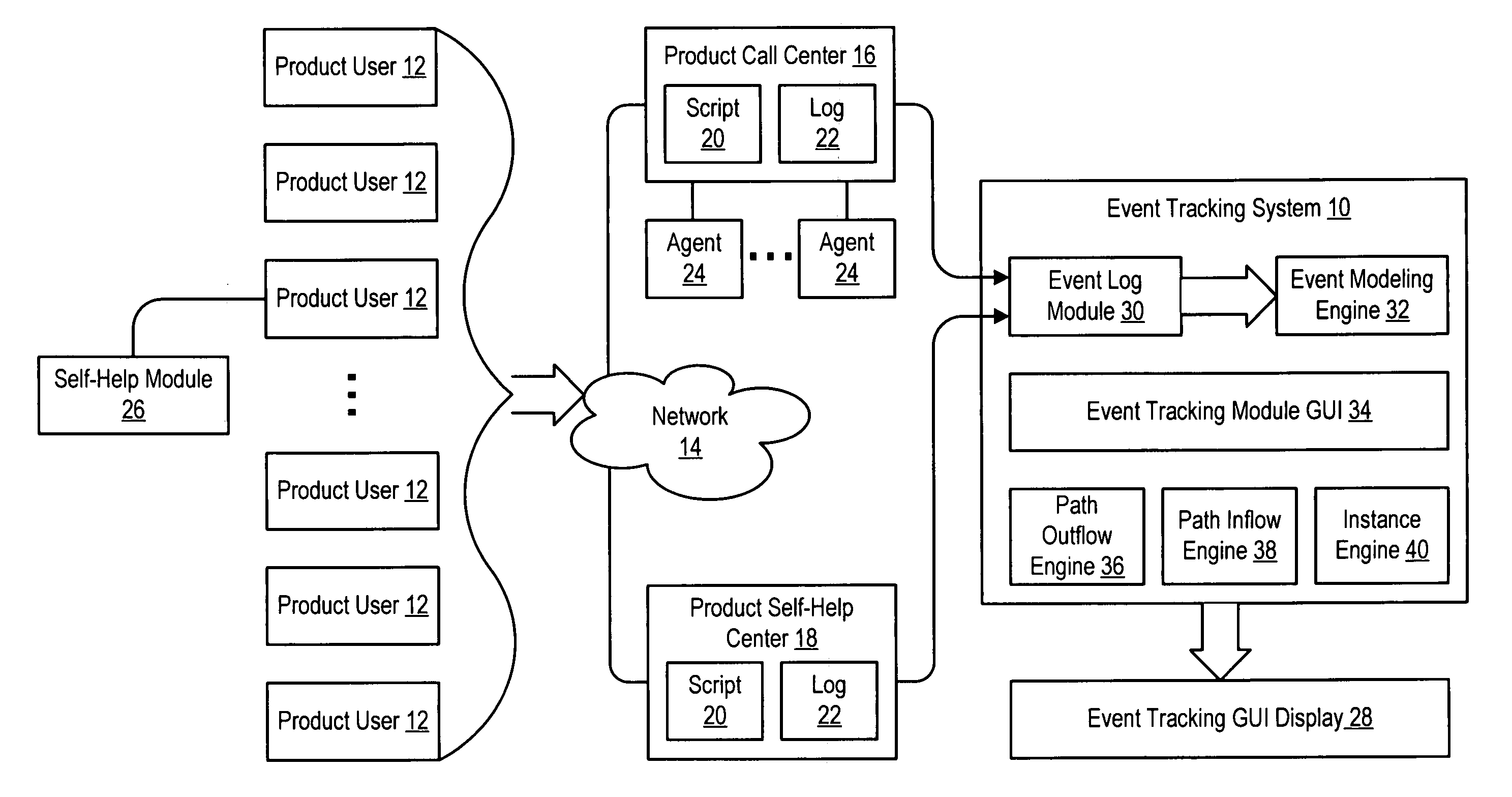
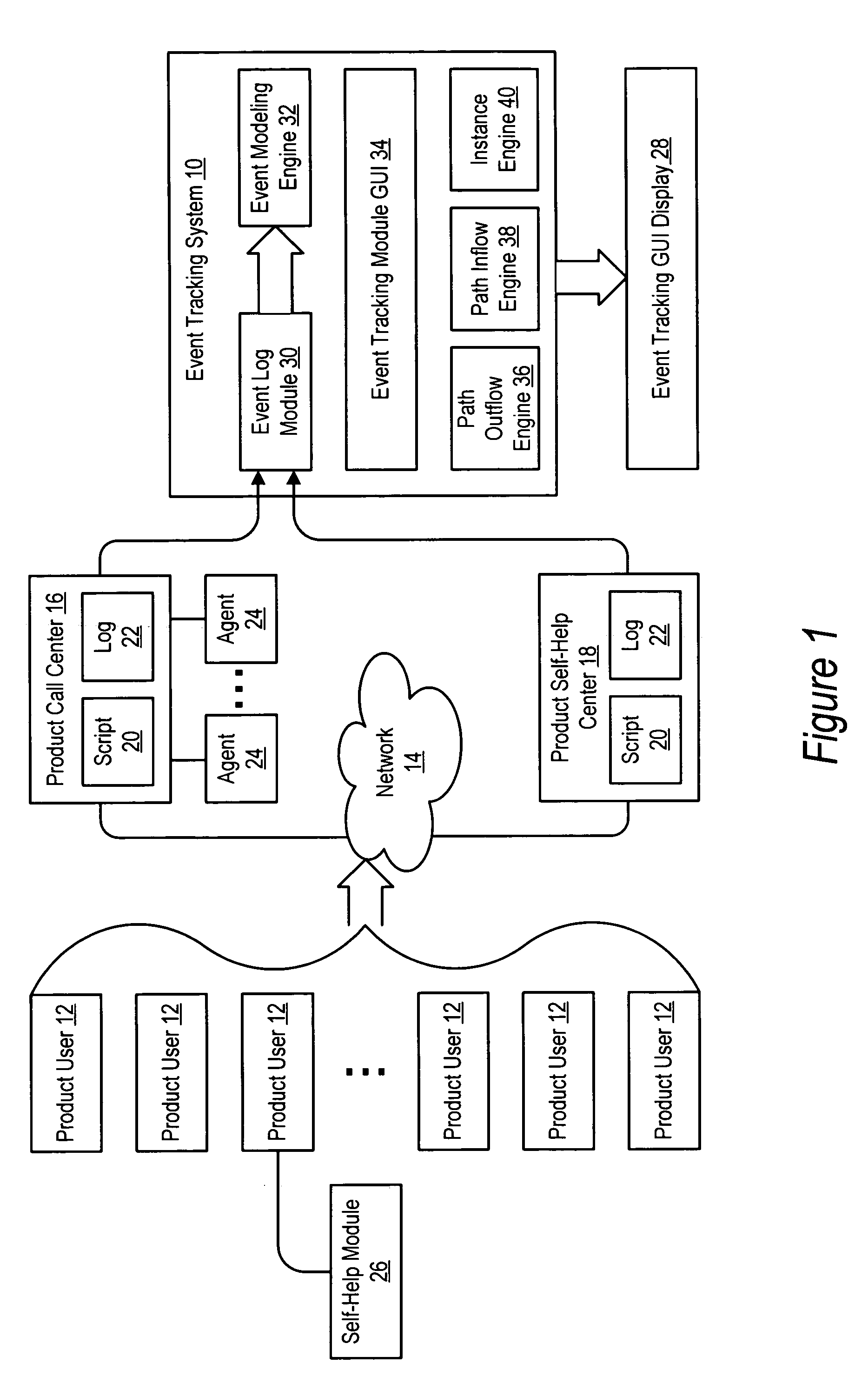
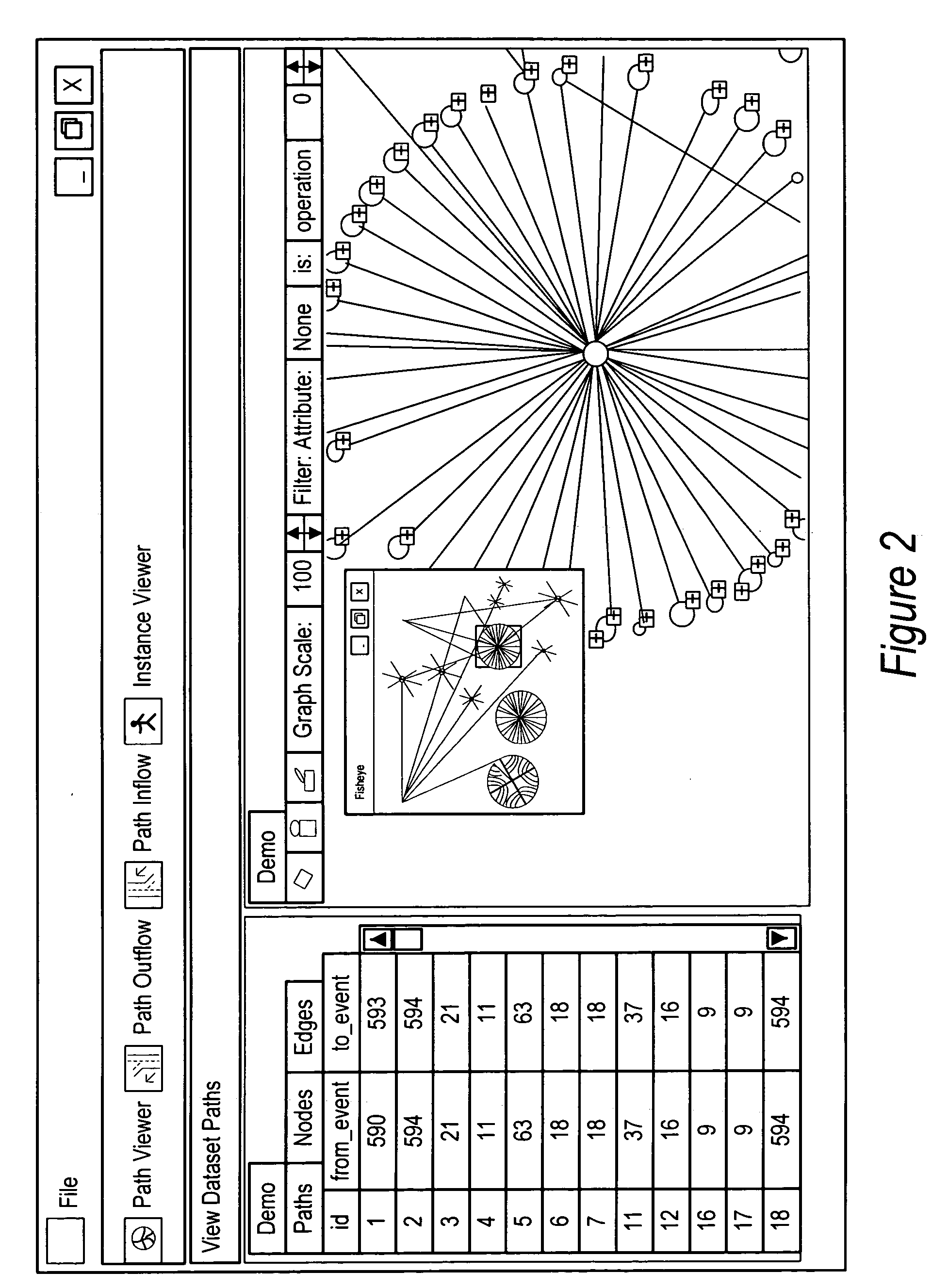
System and method for event tracking across plural contact mediums
InactiveUS20050125276A1Improve customer interactionReduce disadvantagesMarketingSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsDirected graph
An event tracking system tracks customer interactions to obtain product information that are made across plural contact mediums and displays an intuitive directed graph for analysis of the customer interactions. Each customer interaction is logged at each contact medium with a labeled reference associated with the content of the interaction, a time stamp and an identifier for the product or product user. An event modeling engine analyzes the log to identify contact sessions as contacts by the same identifier within a predetermined time so that an event tracking graphical user interface module prepares each contact session for display as a path of nodes interconnected by edges. Selected directed graph characteristics are highlighted, such as transitions from one contact medium to another or contact session volumes associated with an edge that have a relative volume compared with other contact sessions.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Flashback blood collection needle
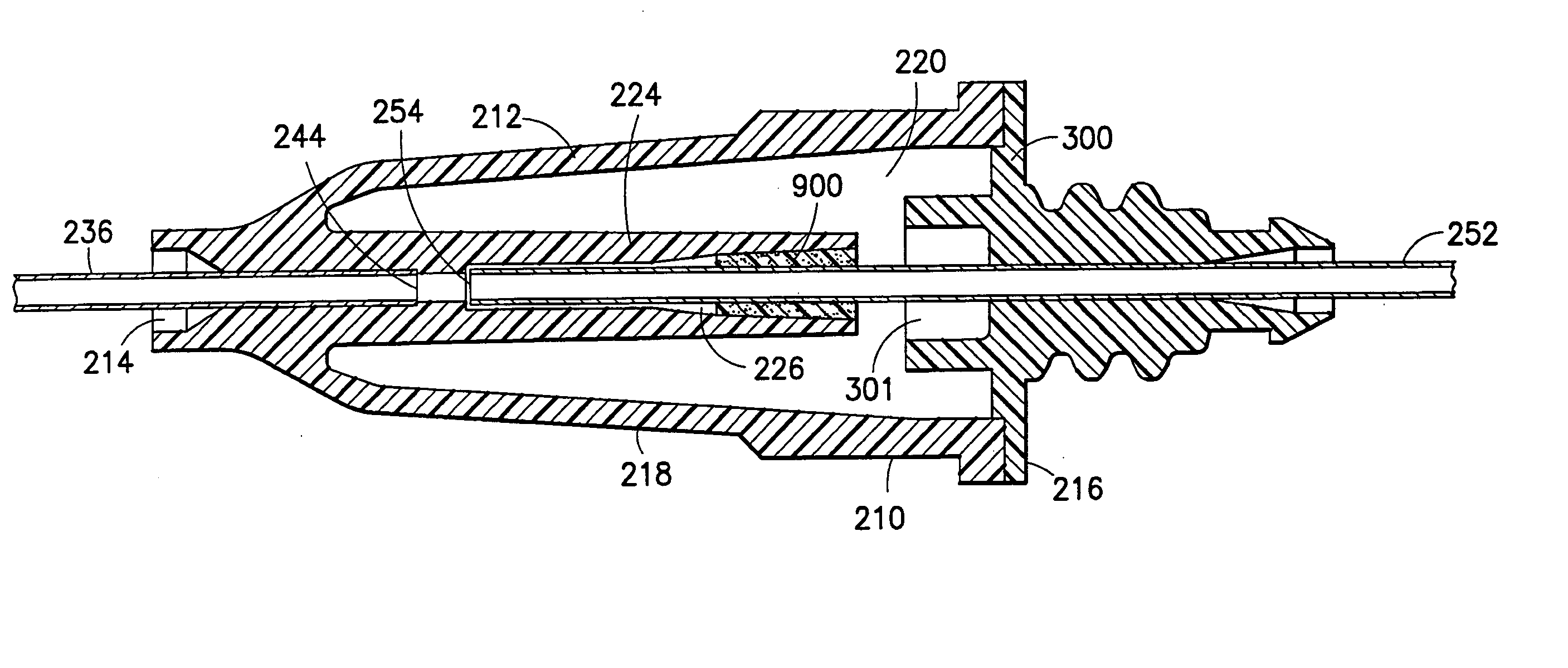
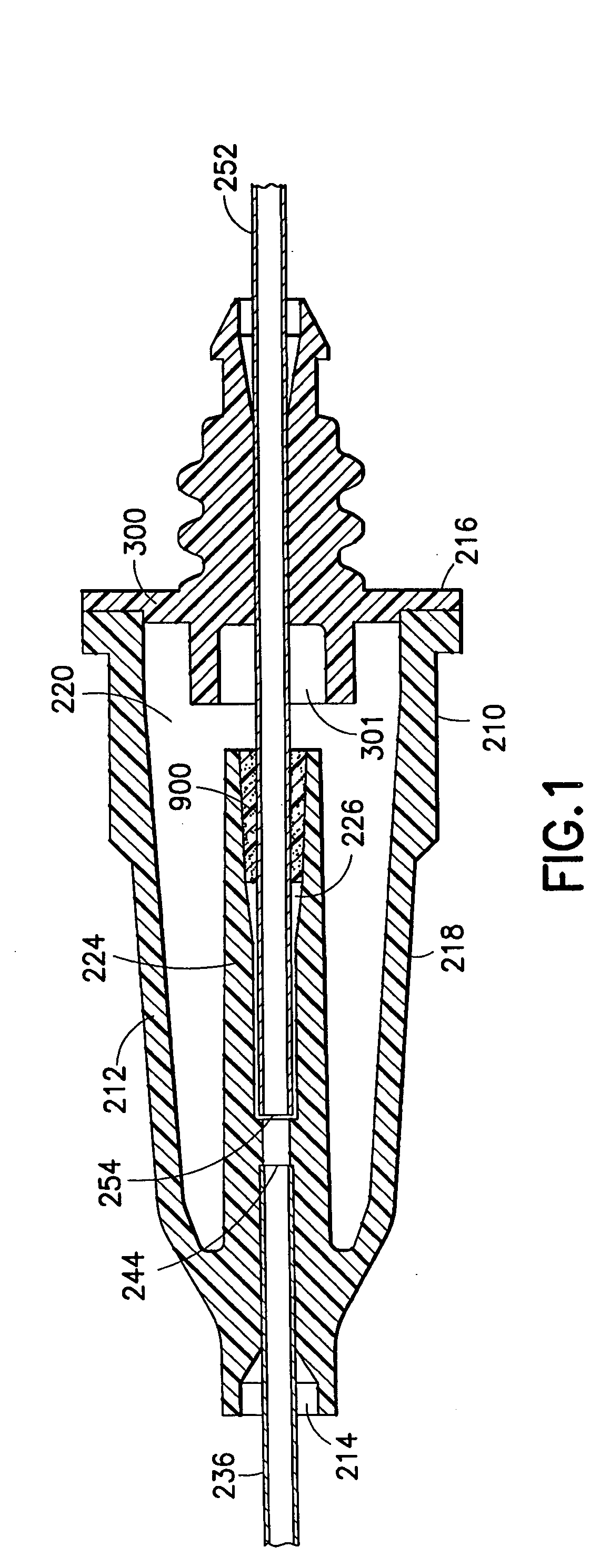
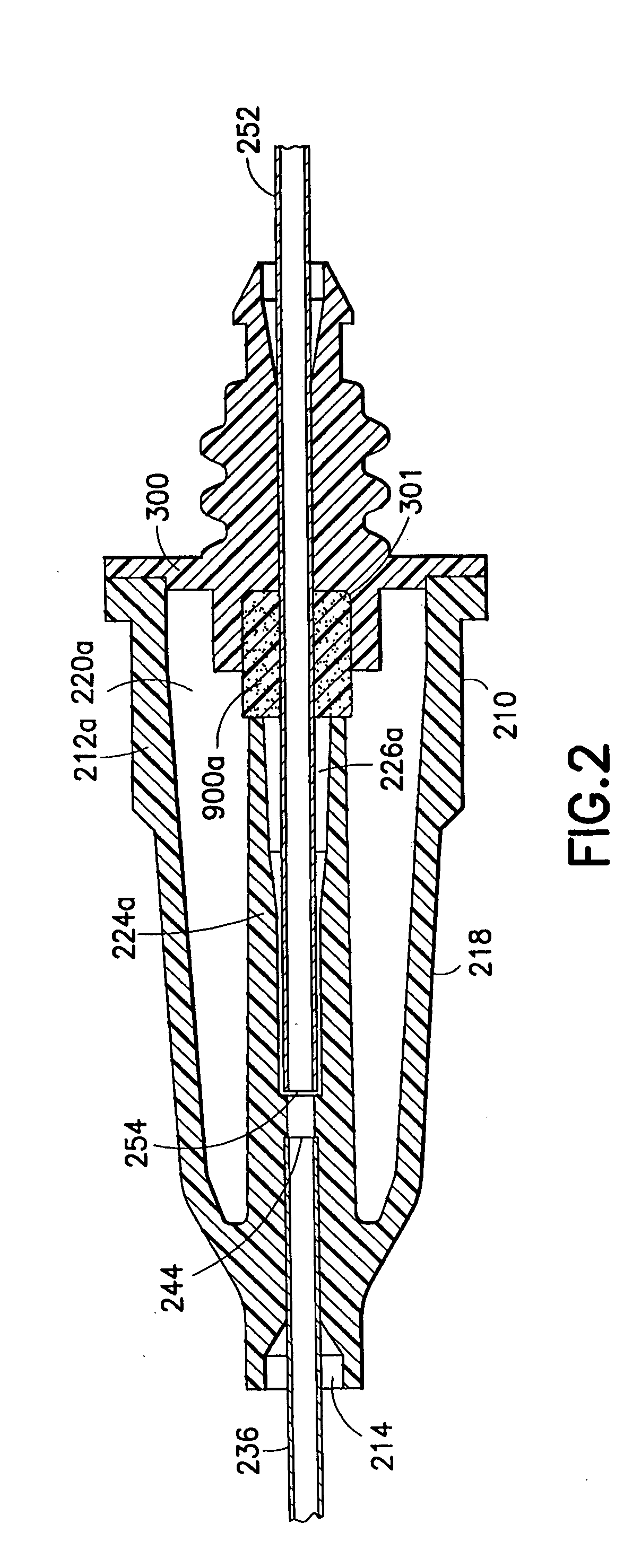
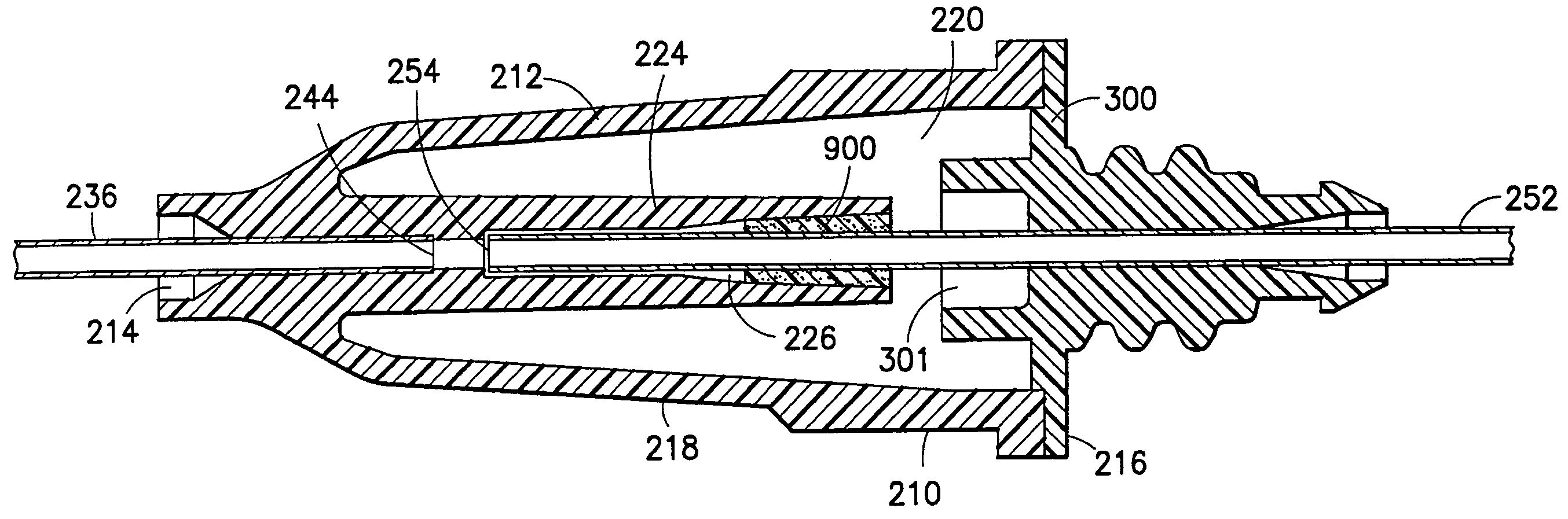
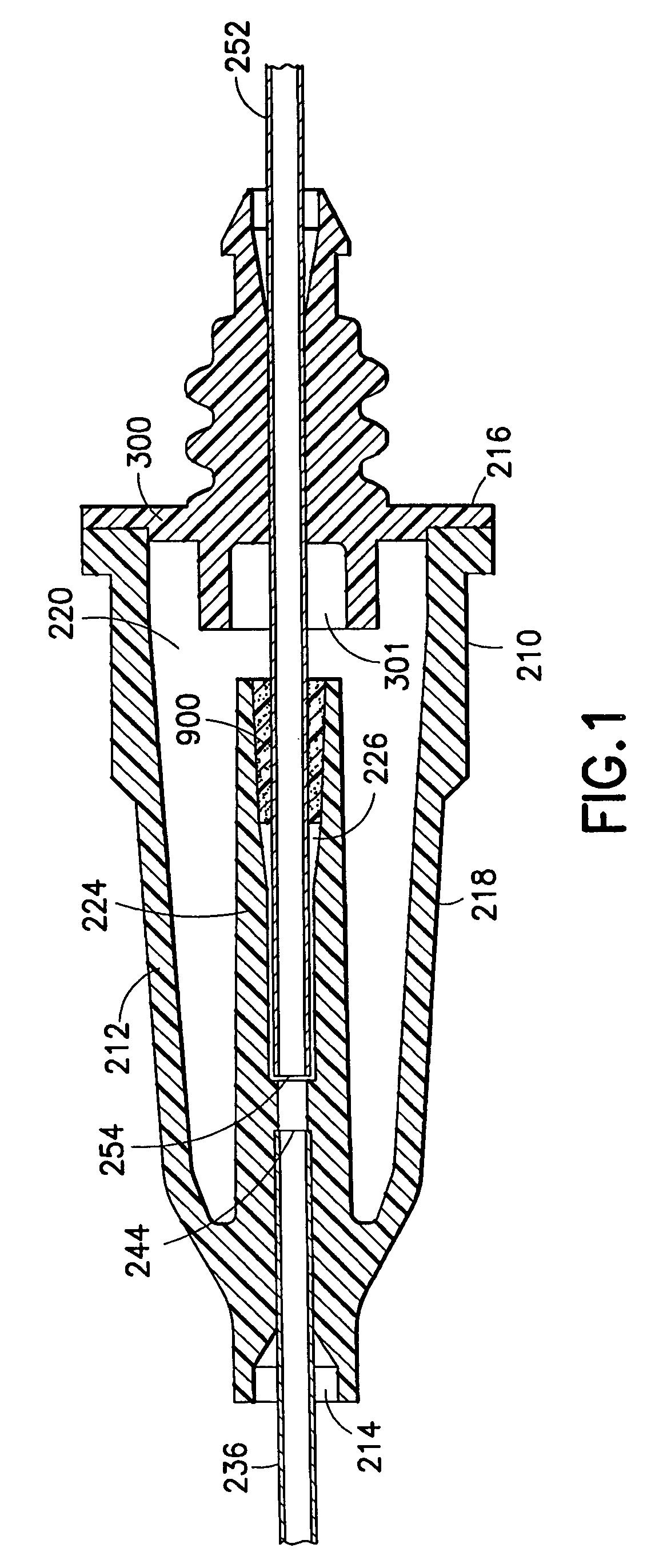
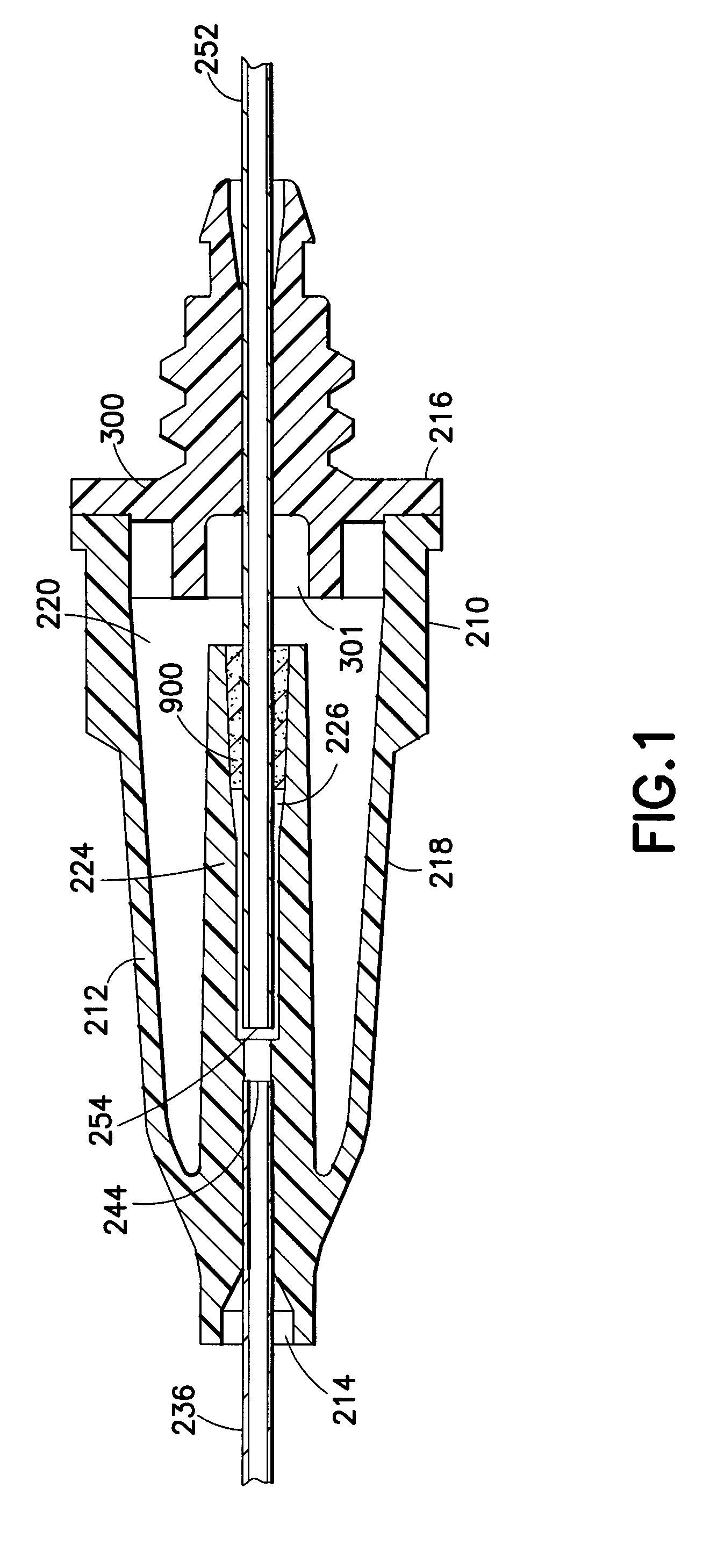
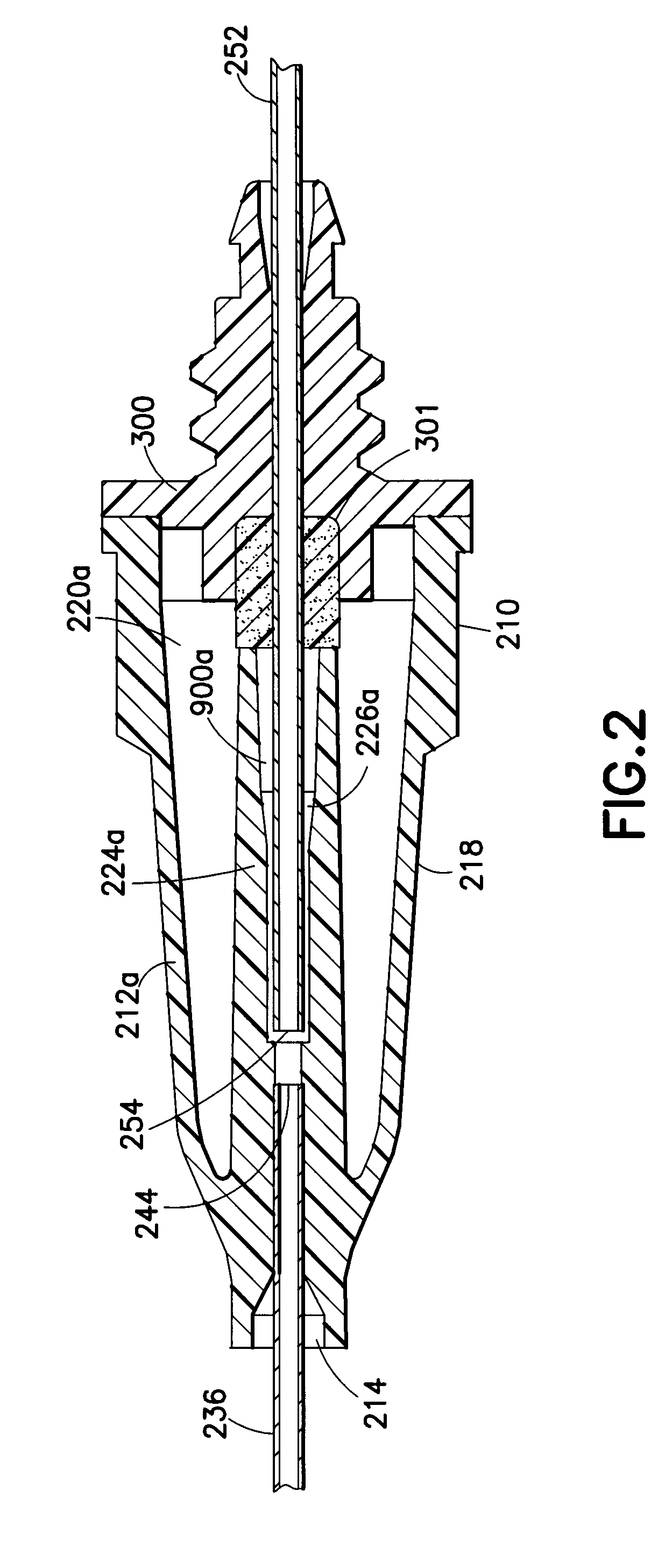
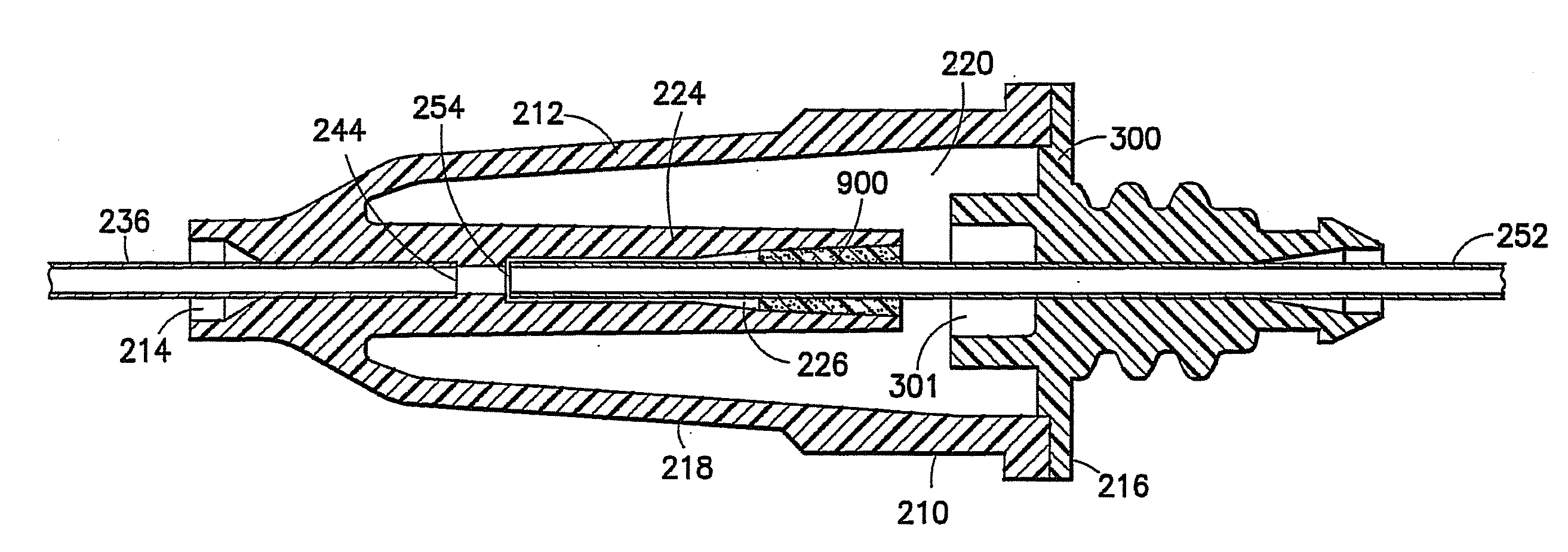
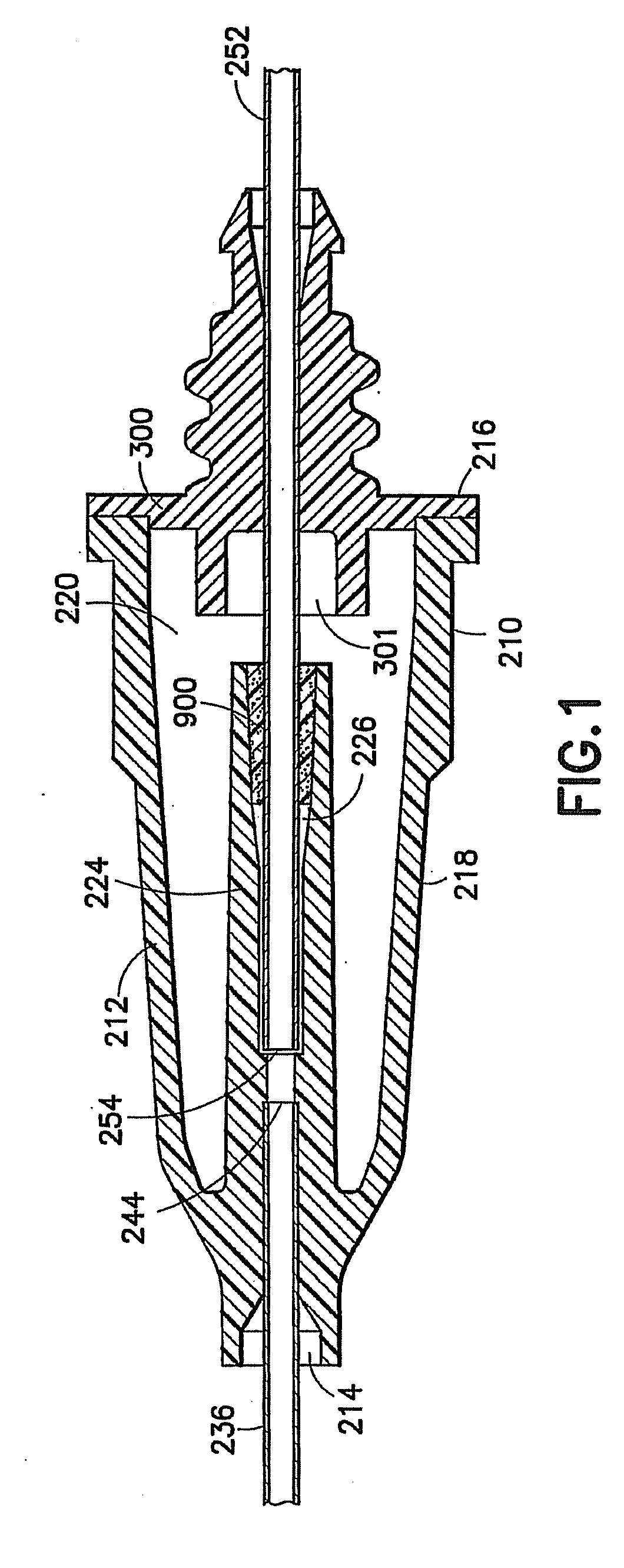
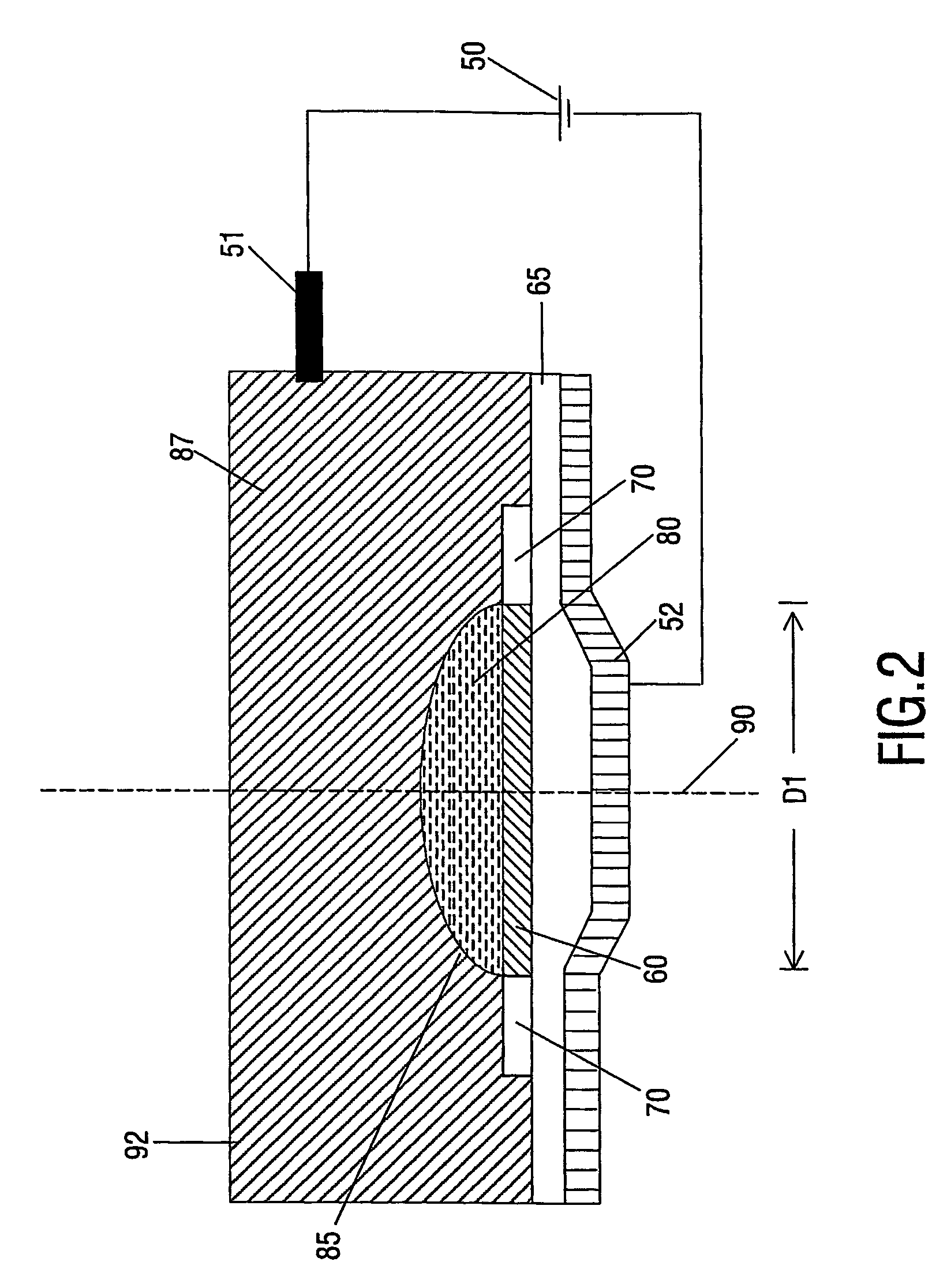
A needle assembly includes a transparent or translucent housing with a fluid inlet end, a fluid outlet end, a flashback chamber and a venting mechanism therebetween. Substantially axially aligned inlet and outlet cannulas extend from the housing and communicate with the chamber. A sealable sleeve covers the external end of the outlet cannula. Relative volumes of the cannulas, the chamber and the sleeve are selected to provide rapid reliable flashback indicative of venous entry with an internal vent plug over the outlet of the flashback chamber to inhibit leakage of blood from the needle on withdrawal from the patient.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
User-controlled selective overlay in a streaming media
InactiveUS8341662B1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesRelative VolumeUser input
A method and system for tailoring a multimedia presentation of an event on a computerized multimedia system to meet a user's desires. In a preferred embodiment, a set of video streams and a set of audio streams for the event are provided to the user via a network coupled to the multimedia system. From the set of available video streams for the event, one or more video streams are selected for presentation to the user. From the set of available audio streams for the event, one or more audio streams are selected for presentation to the user. Furthermore, the relative volumes of the different audio streams may be adjusted. In response to user input, the selected video and audio streams are assigned to respective portions of video and audio output devices. The event is presented to the user according to the selected video stream assignments.
Owner:IBM CORP
Flashback blood collection needle
A needle assembly includes a transparent or translucent housing with a fluid inlet end, a fluid outlet end, a flashback chamber and a venting mechanism therebetween. Substantially axially aligned inlet and outlet cannulas extend from the housing and communicate with the chamber. A sealable sleeve covers the external end of the outlet cannula. Relative volumes of the cannulas, the chamber and the sleeve are selected to provide rapid reliable flashback indicative of venous entry with an internal vent plug over the outlet of the flashback chamber to inhibit leakage of blood from the needle on withdrawal from the patient.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Drop volume measurement and control for ink jet printing
A system and method is presented for measuring the volume of an ink-jet droplet or the relative volumes of a plurality of ink-jet droplets using their electrical properties. In a preferred embodiment a single small capacitor or an array of capacitors is used to measure the dielectric properties of ink-jet droplets and the absolute drop volumes are derived. In an alternative preferred embodiment the relative differences in drop volumes are determined. A feedback circuit, such as one using lock-in technique, may be used to automatically adjust subsequent drop volumes.
Owner:DOLYA HOLDCO 5 LTD
Flashback Blood Collection Needle
ActiveUS20110178427A1External profile can be decreasedPrevent leakageDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVeinBlood collection
A needle assembly includes a transparent or translucent housing with a fluid inlet and outlet end, a flashback chamber, and a venting mechanism therebetween. The venting mechanism includes a blocking member to control the fluid flow in the venting mechanism so that it flows along the longest path through the vent. Substantially axially aligned inlet and outlet cannulas extend from the housing and communicate with the chamber. A sealable sleeve covers the external end of the outlet cannula. Relative volumes of the cannulas, the chamber, and the sleeve are selected to provide rapid reliable flashback indicative of venous entry with an internal vent positioned within the housing to divide the interior into first and second chambers, with the second chamber being adapted to maintain a negative pressure therein relative to the external environment so as to inhibit leakage of blood from the needle tip on withdrawal from the patient.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Flashback Blood Collection Needle
ActiveUS20090227896A1External profile can be decreasedAvoid blood leakageSensorsPackagingBlood collectionVein
A needle assembly includes a transparent or translucent housing with a fluid inlet end, a fluid outlet end, a flashback chamber, and a venting mechanism therebetween. Substantially axially aligned inlet and outlet cannulas extend from the housing and communicate with the chamber. A sealable sleeve covers the external end of the outlet cannula. Relative volumes of the cannulas, the chamber, and the sleeve are selected to provide rapid reliable flashback indicative of venous entry with an internal vent positioned within the housing so as to divide the interior into first and second chambers, with the second chamber being adapted to maintain a negative pressure therein relative to the external environment so as to inhibit leakage of blood from the needle on withdrawal from the patient.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Flashback Blood Collection Needle
A needle assembly includes a transparent or translucent housing with a fluid inlet end, a fluid outlet end, a flashback chamber, and a venting mechanism therebetween. Substantially axially aligned inlet and outlet cannulas extend from the housing and communicate with the chamber. A sealable sleeve covers the external end of the outlet cannula. Relative volumes of the cannulas, the chamber, and the sleeve are selected to provide rapid reliable flashback indicative of venous entry with an internal vent positioned within the housing so as to divide the interior into first and second chambers, with the second chamber being adapted to maintain a negative pressure therein relative to the external environment so as to inhibit leakage of blood from the needle on withdrawal from the patient.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
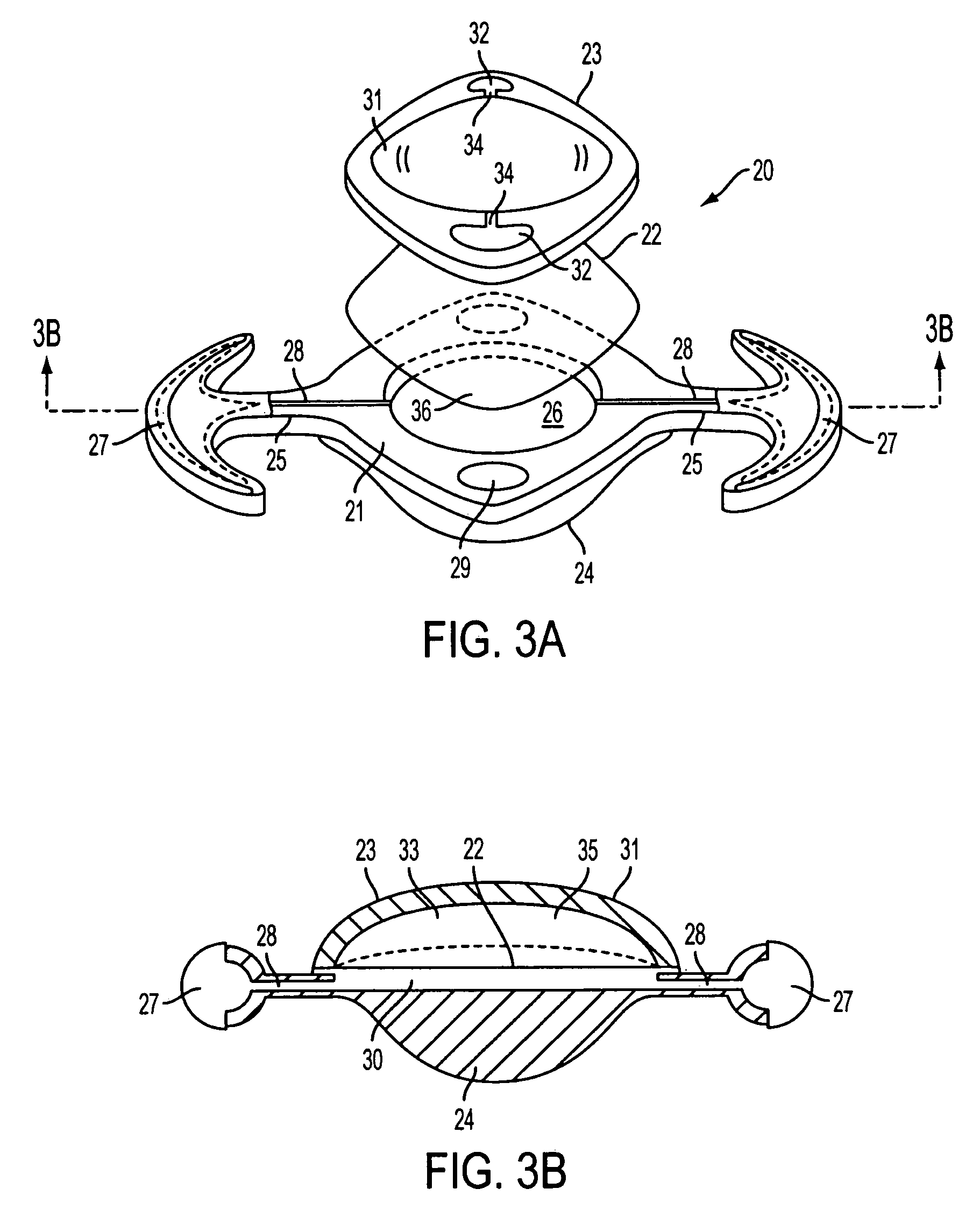
Methods of adjusting the power of an intraocular lens
ActiveUS20070010880A1Efficiently manipulatedAltering the optical parametersIntraocular lensSuction devicesIntraocular lensRelative Volume
An accommodating intraocular lens is provided, in which optical parameters are altered in-situ using forces applied by the ciliary muscles, and in which a lens body carries an actuator separating two fluid-filled chambers having either the same index of diffraction or different indices of refraction. The actuator causes the relative volumes of fluid within an optic element of the lens to change, thereby altering the optical power of the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
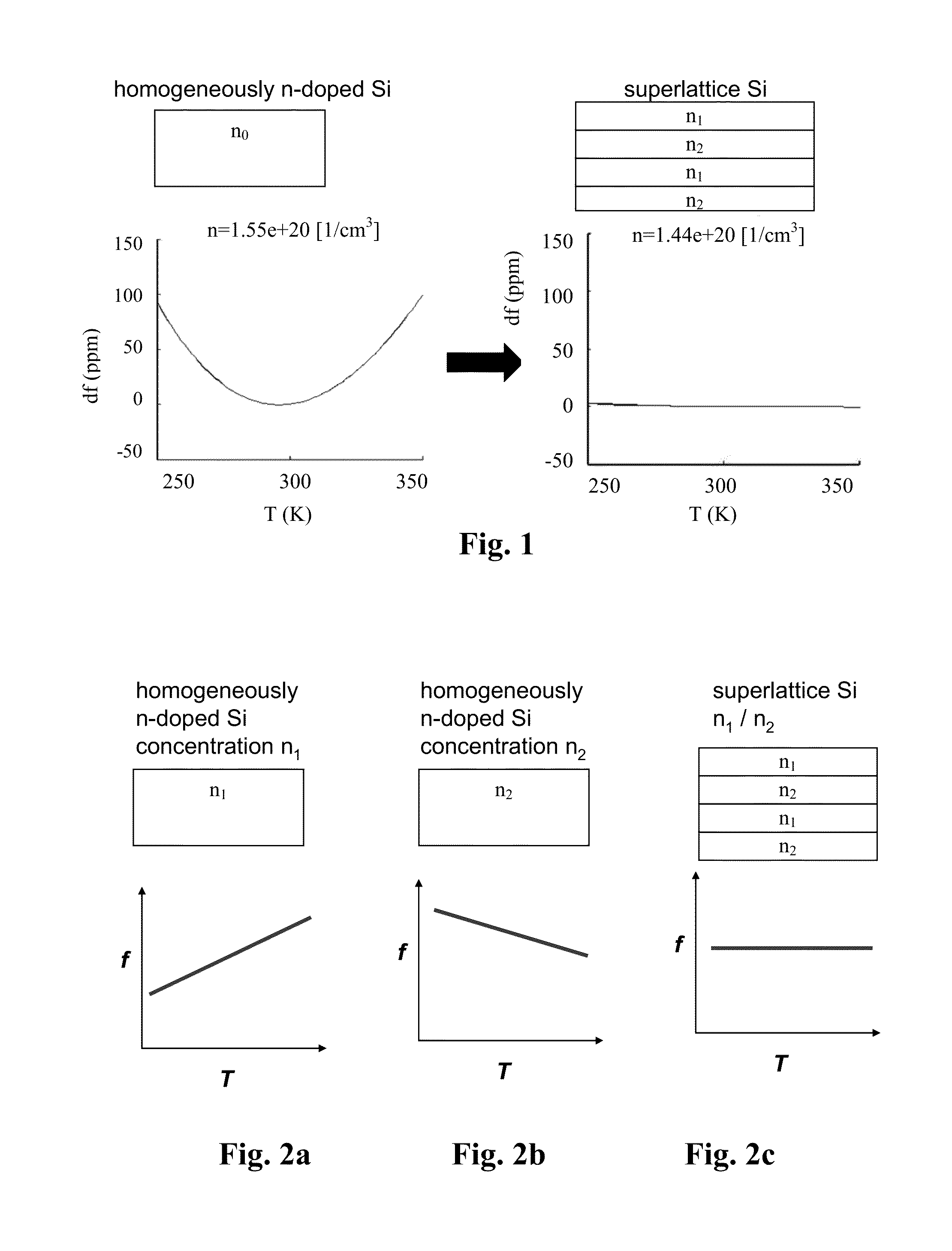
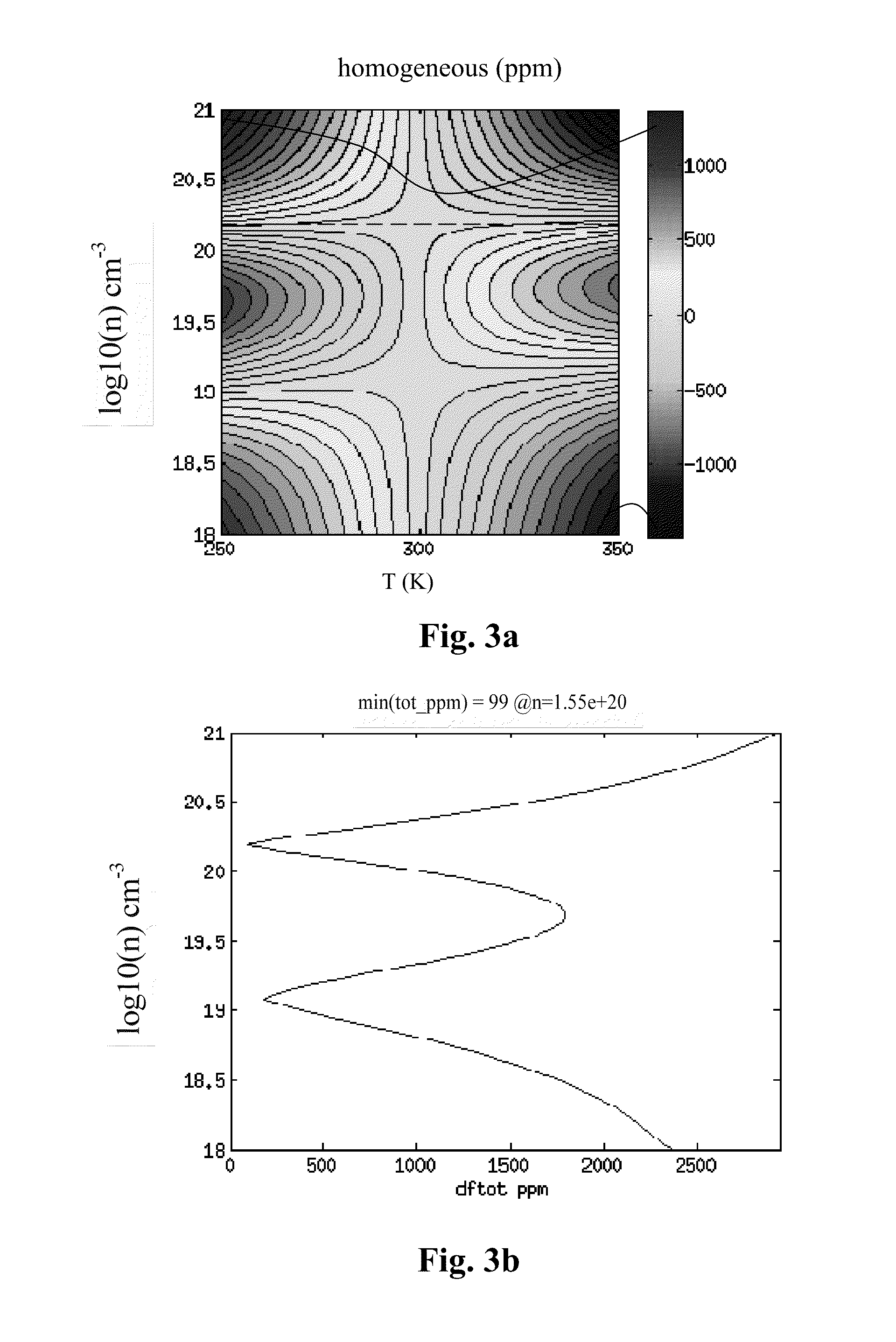
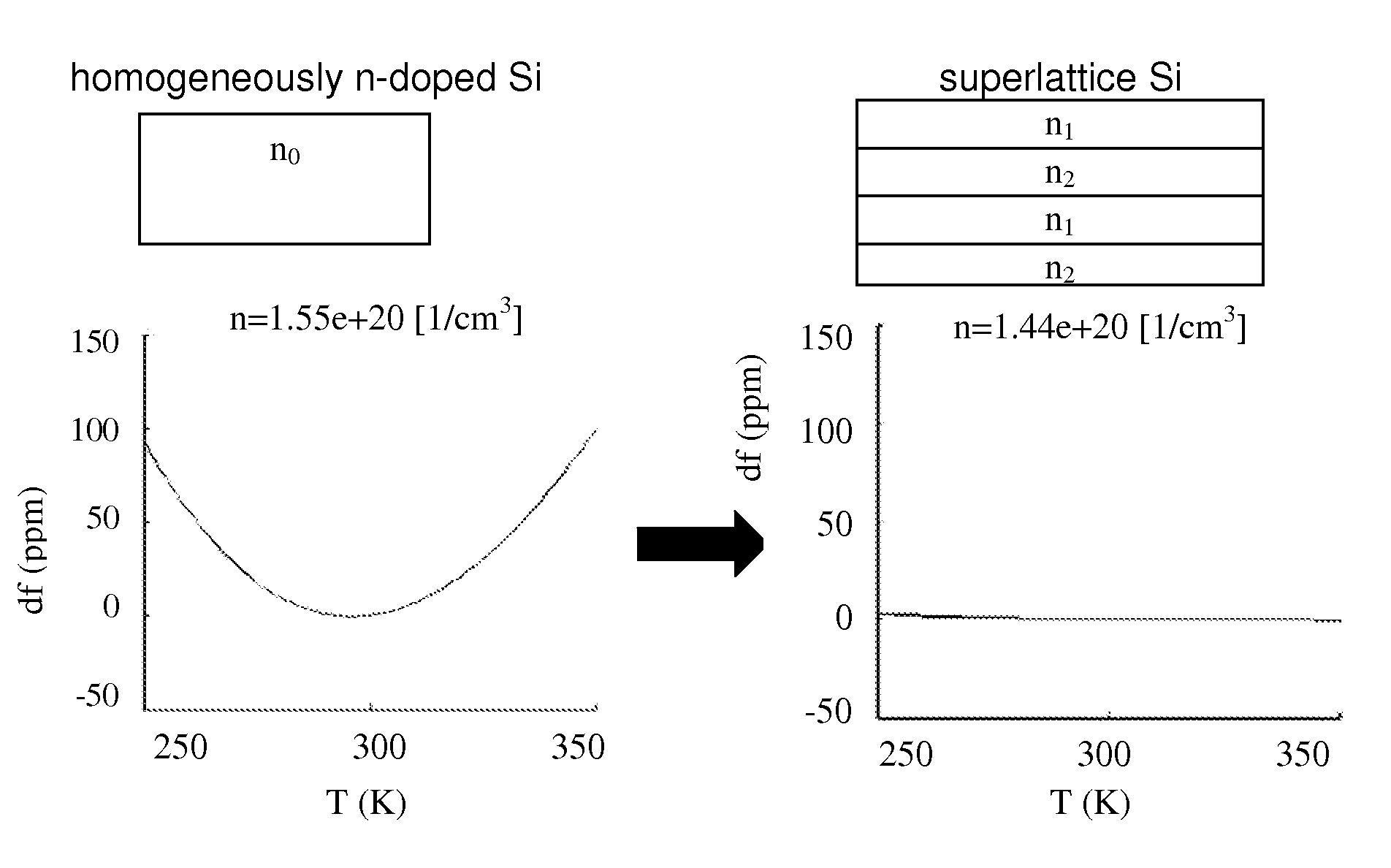
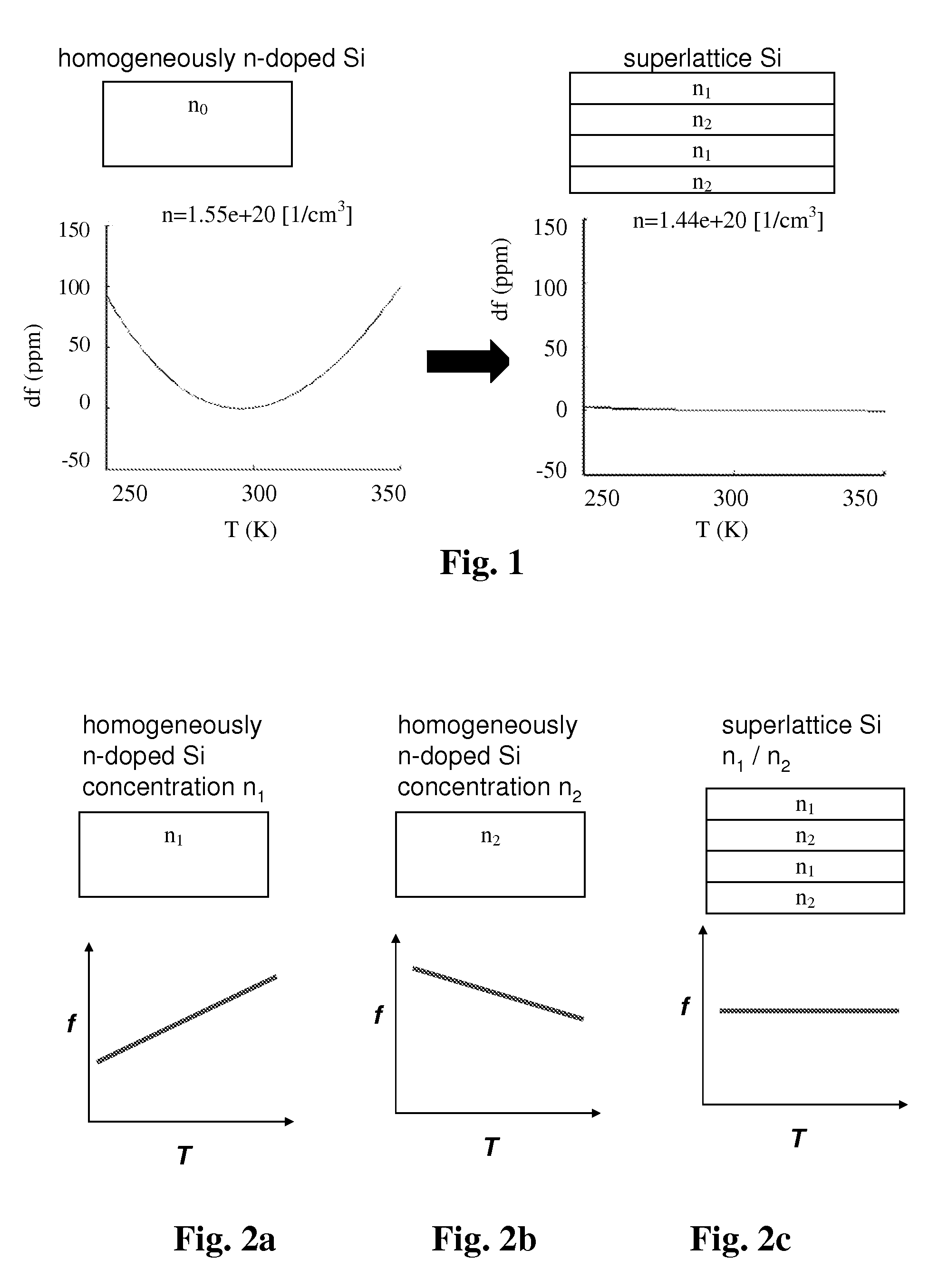
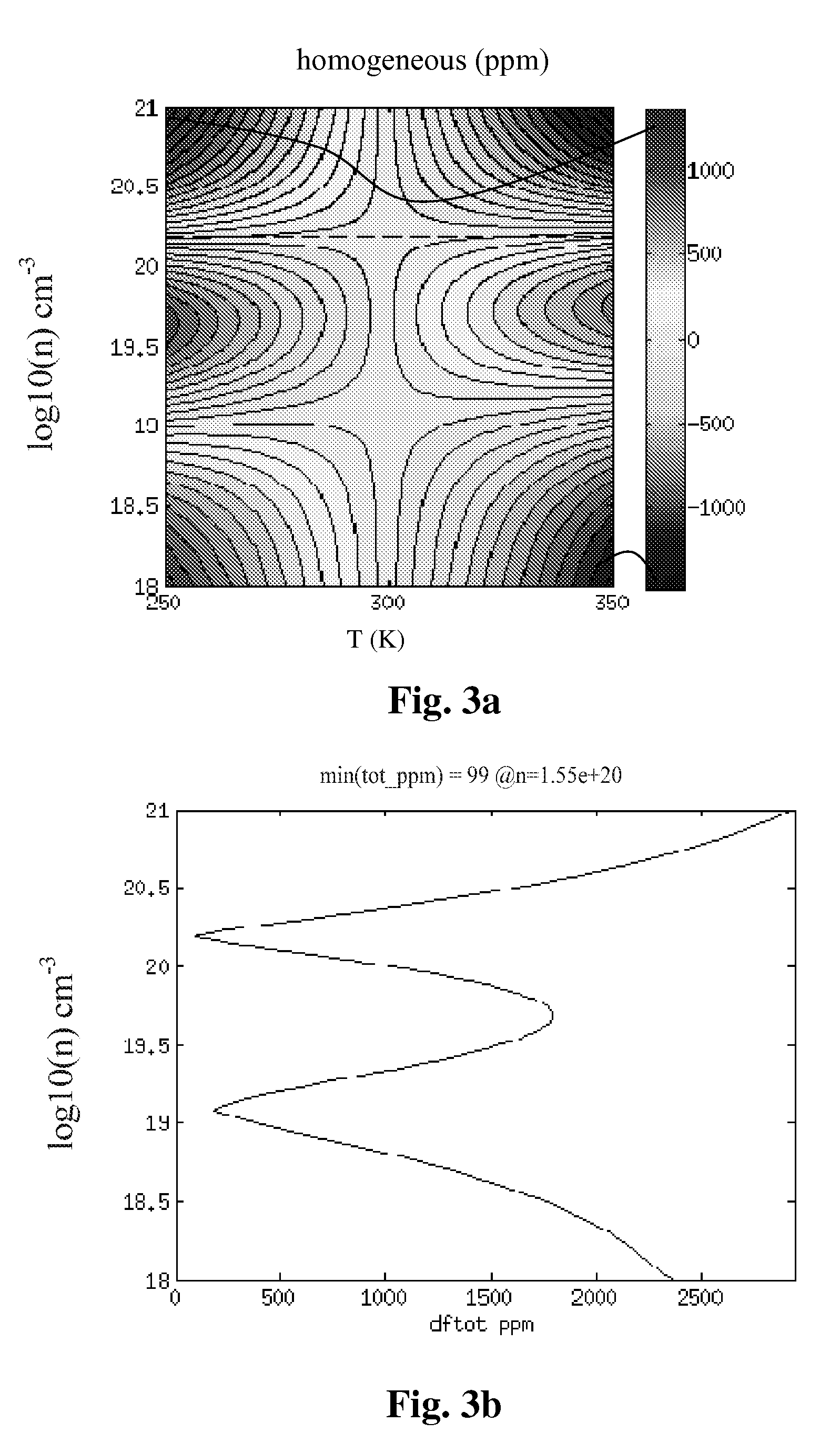
Micromechanical device including N-type doping for providing temperature compensation and method of designing thereof
The invention relates to a micromechanical device comprising a semiconductor element capable of deflecting or resonating and comprising at least two regions having different material properties and drive or sense means functionally coupled to said semiconductor element. According to the invention, at least one of said regions comprises one or more n-type doping agents, and the relative volumes, doping concentrations, doping agents and / or crystal orientations of the regions being configured so that the temperature sensitivities of the generalized stiffness are opposite in sign at least at one temperature for the regions, and the overall temperature drift of the generalized stiffness of the semiconductor element is 50 ppm or less on a temperature range of 100° C. The device can be a resonator. Also a method of designing the device is disclosed.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Micromechanical device and method of designing thereof
The invention relates to a micromechanical device comprising a semiconductor element capable of deflecting or resonating and comprising at least two regions having different material properties and drive or sense means functionally coupled to said semiconductor element. According to the invention, at least one of said regions comprises one or more n-type doping agents, and the relative volumes, doping concentrations, doping agents and / or crystal orientations of the regions being configured so that the temperature sensitivities of the generalized stiffness are opposite in sign at least at one temperature for the regions, and the overall temperature drift of the generalized stiffness of the semiconductor element is 50 ppm or less on a temperature range of 100° C. The device can be a resonator. Also a method of designing the device is disclosed.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Flashback blood collection needle
ActiveUS8603009B2External profile can be decreasedPrevent leakageInfusion syringesIntravenous devicesVeinBlood collection
A needle assembly includes a transparent or translucent housing with a fluid inlet and outlet end, a flashback chamber, and a venting mechanism therebetween. The venting mechanism includes a blocking member to control the fluid flow in the venting mechanism so that it flows along the longest path through the vent. Substantially axially aligned inlet and outlet cannulas extend from the housing and communicate with the chamber. A sealable sleeve covers the external end of the outlet cannula. Relative volumes of the cannulas, the chamber, and the sleeve are selected to provide rapid reliable flashback indicative of venous entry with an internal vent positioned within the housing to divide the interior into first and second chambers, with the second chamber being adapted to maintain a negative pressure therein relative to the external environment so as to inhibit leakage of blood from the needle tip on withdrawal from the patient.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Audio mixer
An audio mixer system is described for producing coded output in which at least a left audio signal, a right audio signal and a surround audio signal are encoded in two output channels so that the surround signal can be decoded from the difference of the two output channels. The system comprises means for generating position data designating a desired position for a sound source in a 360 degree sound field. Logic is provided for determining the relative volume of the sound source in the left, right and surround audio signals from the position data. A signed continuity factor is maintained so that the sign of the continuity factor is changed in response the desired position crossing a nominal position of the surround signal in the sound field and logic is provided for encoding the sound source data into the two output channels in accordance with the determined relative volume of the sound source in at least two of the left, right and surround signals each multiplied by the continuity factor. This reduces audible artifacts associated with phase discontinuities in the output signals either side of the surround speaker nominal position.
Owner:IBM CORP
Constant temperature internal combustion engine and method
InactiveUS20070289562A1Easy to operateReduce the amount requiredInternal combustion piston enginesGas turbine plantsCombustion chamberExhaust valve
Internal combustion engine and method with compression and expansion chambers of variable volume, a combustion chamber, a variable intake valve for controlling air intake to the compression chamber, a variable outlet valve for controlling communication between the compression chamber and the combustion chamber, means for introducing fuel into the combustion chamber to form a mixture of fuel and air which burns and expands in the combustion chamber, a variable inlet valve for controlling communication between the combustion chamber and the expansion chamber, a variable exhaust valve for controlling exhaust flow from the expansion chamber, means for monitoring temperature and pressure conditions, and a computer responsive to the temperature and pressure conditions for controlling opening and closing of the valves and introduction of fuel into to the combustion chamber to optimize engine efficiency over a wide range of engine load conditions. In some disclosed embodiments, the relative volumes of the compression and expansion chambers and the timing of the valves are such that the pressure in the combustion chamber remains substantially constant throughout the operating cycle of the engine, and exhaust pressures are very close to atmospheric pressure regardless of the load on the engine. In others, the temperature within the combustion chamber is maintained at a substantially constant level throughout the operating range of the engine, and the power produced by the engine is determined by the amount of air passing through the engine. The engine runs so quietly and burns so cleanly that in some applications it may not require a muffler and / or a catalytic converter.
Owner:ZAJAC OPTIMUM OUTPUT MOTORS
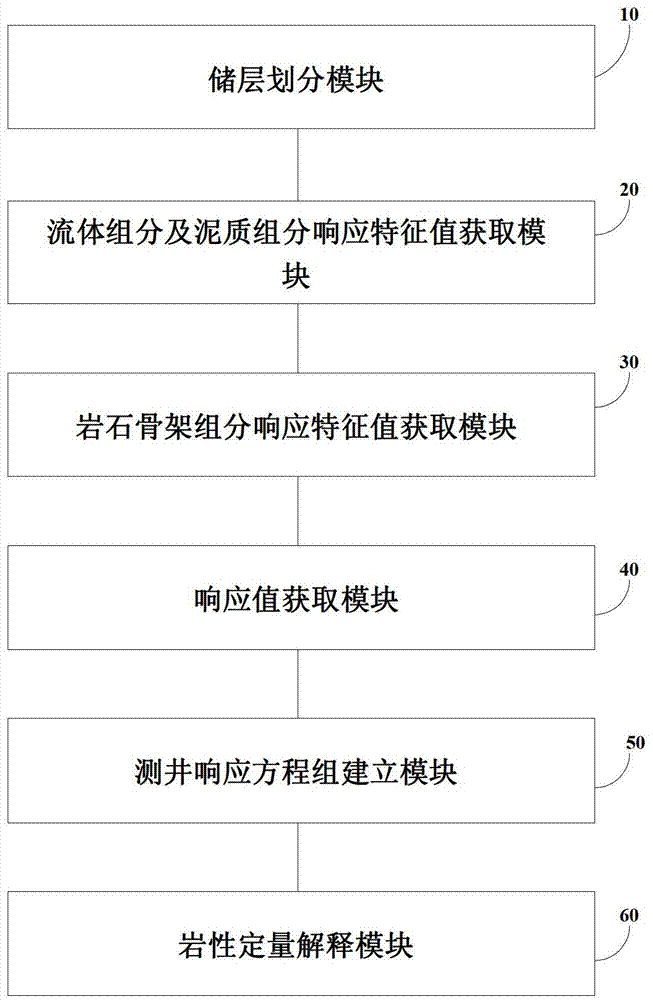
Method and device for performing fitting inversion by utilizing plurality of pieces of data to realize complex lithologic interpretation
InactiveCN103485758AAccurate calculation of relative contentThe principle of the method is simpleSurveyLithologyRelative Volume
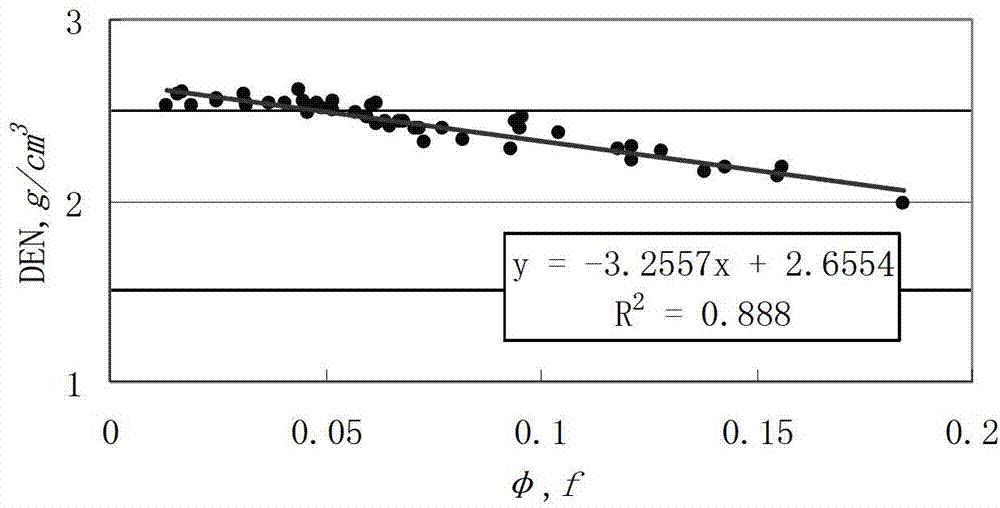
The invention discloses a method and a device for performing fitting inversion by utilizing a plurality of pieces of data to realize complex lithologic interpretation. The method comprises the following steps of dividing a reservoir into fluid components, muddy components and rock matrix components according to the geological condition of a research work area; setting a fluid component response characteristic value and a muddy component response characteristic value; determining the types and the number of the rock matrix components in the research work area and a rock matrix component response characteristic value according to logging data by utilizing methods of oilfield on-site coring, geologic description, physical property analysis and laboratory thin section authentication; acquiring a conventional logging response value and the element content of the stratum of the research work area by utilizing a logging instrument; establishing a logging response equation set by combining a conventional logging curve and an elemental capture spectroscopy logging curve; performing joint inversion to obtain the optimal relative volumes of the fluid components, the muddy components and the rock matrix components in the stratum of the research work area by utilizing the logging response equation set and householder transformation and conjugate gradient optimization algorithms, and drawing lithologic analysis results.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method and system for quantitatively fast level testing flow
InactiveCN1786712AHigh sensitivityReduce box-to-box variancePreparing sample for investigationBiological testingFiltrationDifferential pressure
The invention relates to quantitative fast horizontal side flow method and system. It includes the following steps: practicing each detecting item for liquid state biological specimen on biochemical reaction platform; using filtration to separate cell from liquid state biological specimen to reach the need liquid volume; the biochemical reaction platform is made up test strip and testing cassete shell; the biological specimen is added at any one of the application of sample port of the shell; forming effective capillary chromatography differential pressure to make the filtered liquid and the dissolved measured matter do orientation flow on the platform; judging detecting result according to optical density. Thus the invention can do quantitative fast detection for whole blood or other cell biology, and realize relative volume non dependence of detecting result to ensure its accuracy.
Owner:RELIA BIOTECH SHENZHEN LTD
Elastomer and/or composite based material for thermal energy storage
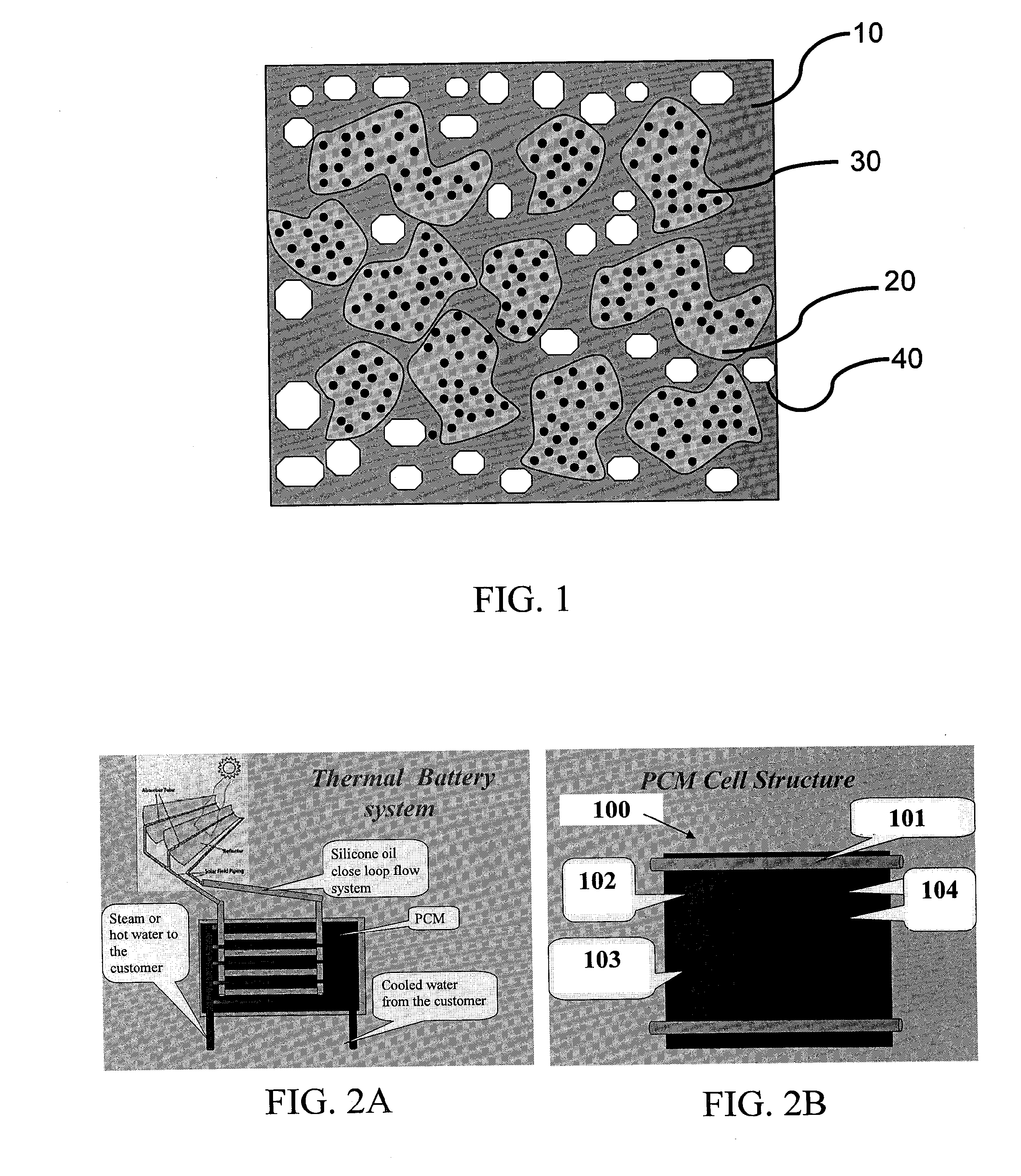
A composite material for storing thermal energy at various temperatures (30° C. to 450° C.) formed by an elastomer matrix into which a phase change material such as an inorganic salt is encapsulated. The material is characterized by a high volumetric thermal conductivity, a low density, a highly interconnected porosity and a relatively high modulus of elasticity. The significant properties of the matrices are: a large amount of energy involved in full melting / crystallization, a fairly low relative volume expansion upon melting and fairly low sub-cooling. The main advantages of the resulting composites are a very high energy density, a relatively low volume expansion, highly enhanced heat transfer, thermo adaptability, stability and insignificant hysteresis.
Owner:ENRAD
Internal combustion engine and method
InactiveUS20060243229A1Easy to operateReduce the amount of fuelInternal combustion piston enginesGas turbine plantsCombustion chamberEngine efficiency
Internal combustion engine and method with compression and expansion chambers of variable volume, a combustion chamber, a variable intake valve for controlling air intake to the compression chamber, a variable outlet valve for controlling communication between the compression chamber and the combustion chamber, means for introducing fuel into the combustion chamber to form a mixture of fuel and air which burns and expands in the combustion chamber, a variable inlet valve for controlling communication between the combustion chamber and the expansion chamber, a variable exhaust valve for controlling exhaust flow from the expansion chamber, means for monitoring temperature and pressure conditions, and a computer responsive to the temperature and pressure conditions for controlling opening and closing of the valves and introduction of fuel into to the combustion chamber to optimize engine efficiency over a wide range of engine load conditions. The relative volumes of the compression and expansion chambers and the timing of the valves are such that the pressure in the combustion chamber remains substantially constant throughout the operating cycle of the engine, and exhaust pressures are very close to atmospheric pressure regardless of the load on the engine. The engine runs so quietly and burns so cleanly that in some applications it may not require a muffler and / or a catalytic converter.
Owner:ZAJAC OPTIMUM OUTPUT MOTORS
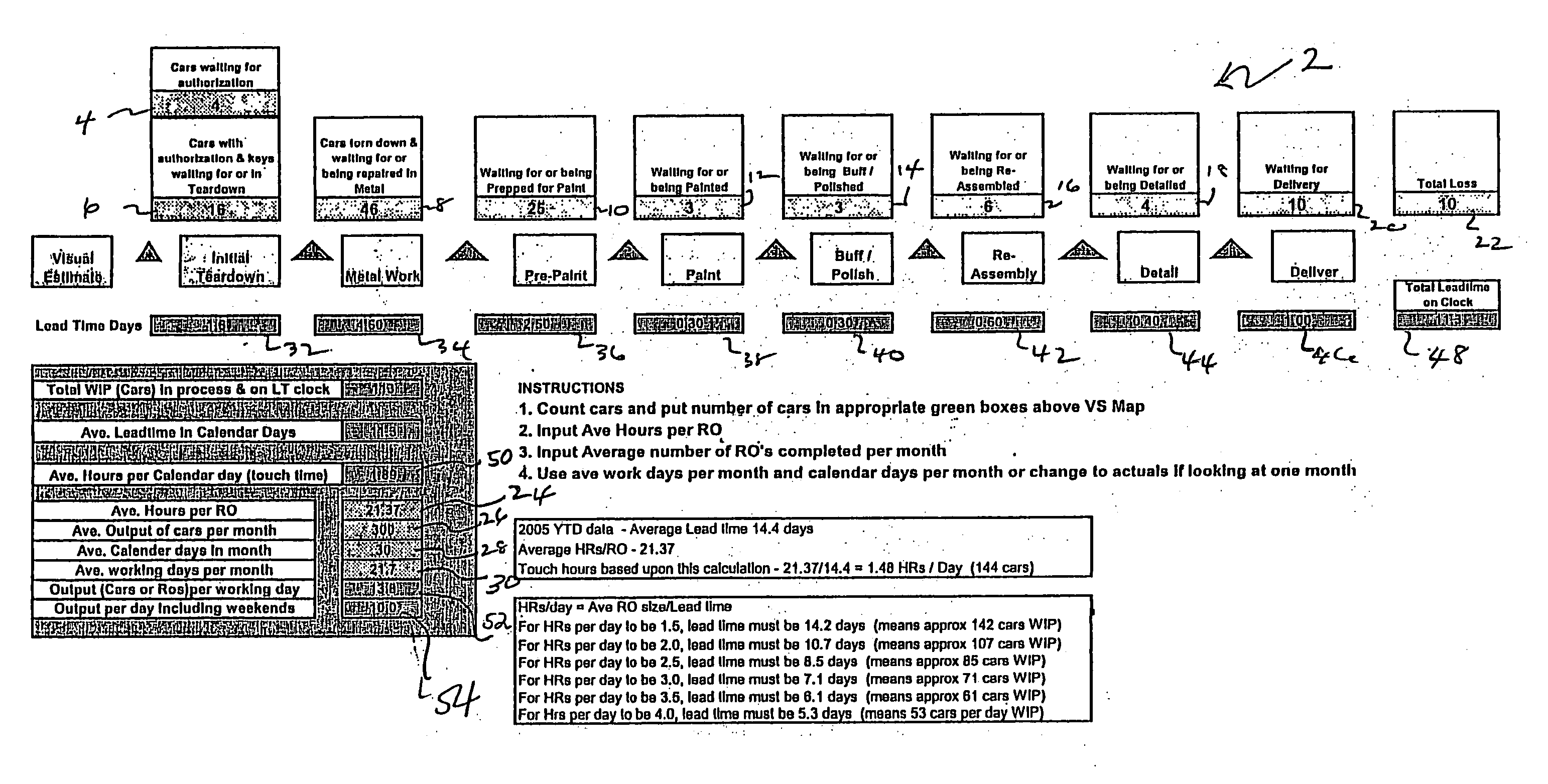
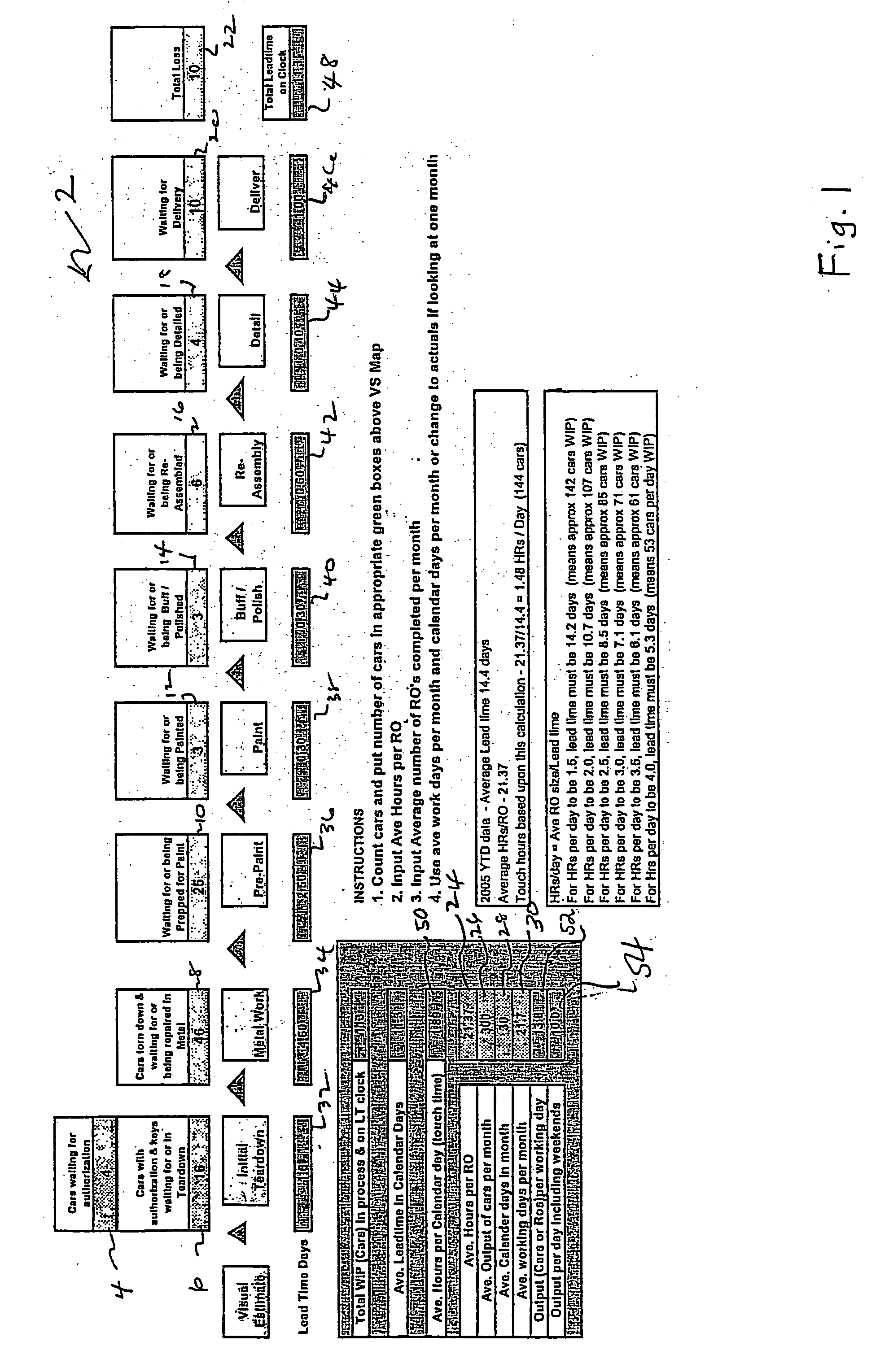
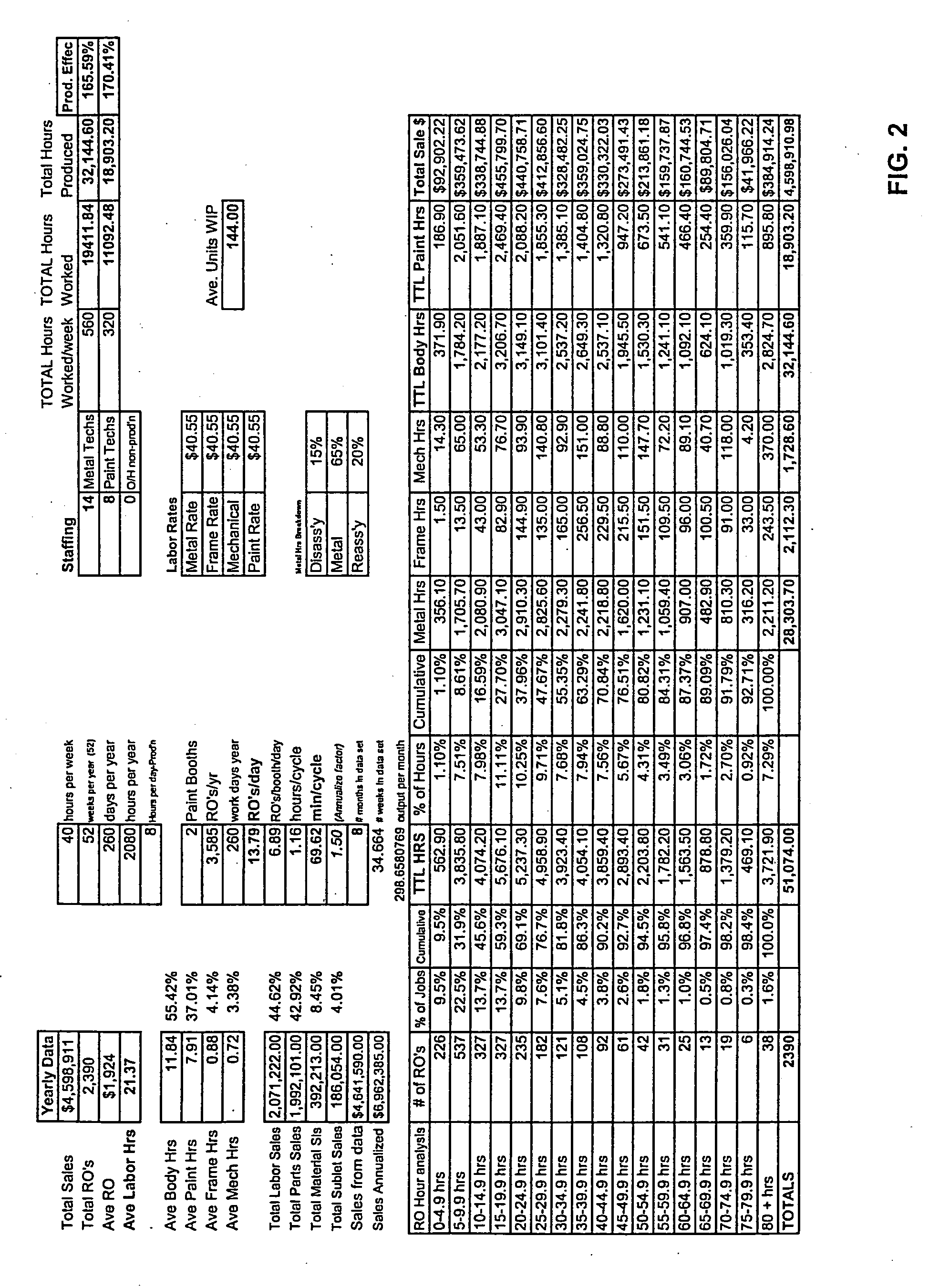
Method of improving throughput performance of an automotive repair shop
InactiveUS20070203777A1Improve throughputSpeed up the flowMultiprogramming arrangementsResourcesRepair shopRelative Volume
A method of improving the throughput of an automotive collision repair shop is disclosed comprising the steps of conducting a market analysis of a collision repair shop to determine a potential value of sales by the repair shop; analyzing the relative volume of sales by severity of repair needed for a period of time; analyzing the existing facilities for conducting repairs; and identifying changes in operating procedures and facilities of the repair shop based on the market analysis, relative volume of sales by repair severity and facilities analysis, wherein the identified changes improve the efficiency of the repair shop.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Flashback blood collection needle
ActiveUS8795198B2External profile can be decreasedPrevent leakageSensorsPackagingVeinBlood collection
A needle assembly includes a transparent or translucent housing with a fluid inlet end, a fluid outlet end, a flashback chamber, and a venting mechanism therebetween. Substantially axially aligned inlet and outlet cannulas extend from the housing and communicate with the chamber. A sealable sleeve covers the external end of the outlet cannula. Relative volumes of the cannulas, the chamber, and the sleeve are selected to provide rapid reliable flashback indicative of venous entry with an internal vent positioned within the housing so as to divide the interior into first and second chambers, with the second chamber being adapted to maintain a negative pressure therein relative to the external environment so as to inhibit leakage of blood from the needle on withdrawal from the patient.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Variable shape lens
ActiveUS7436598B2Easy to shapeRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansCamera lensRelative Volume
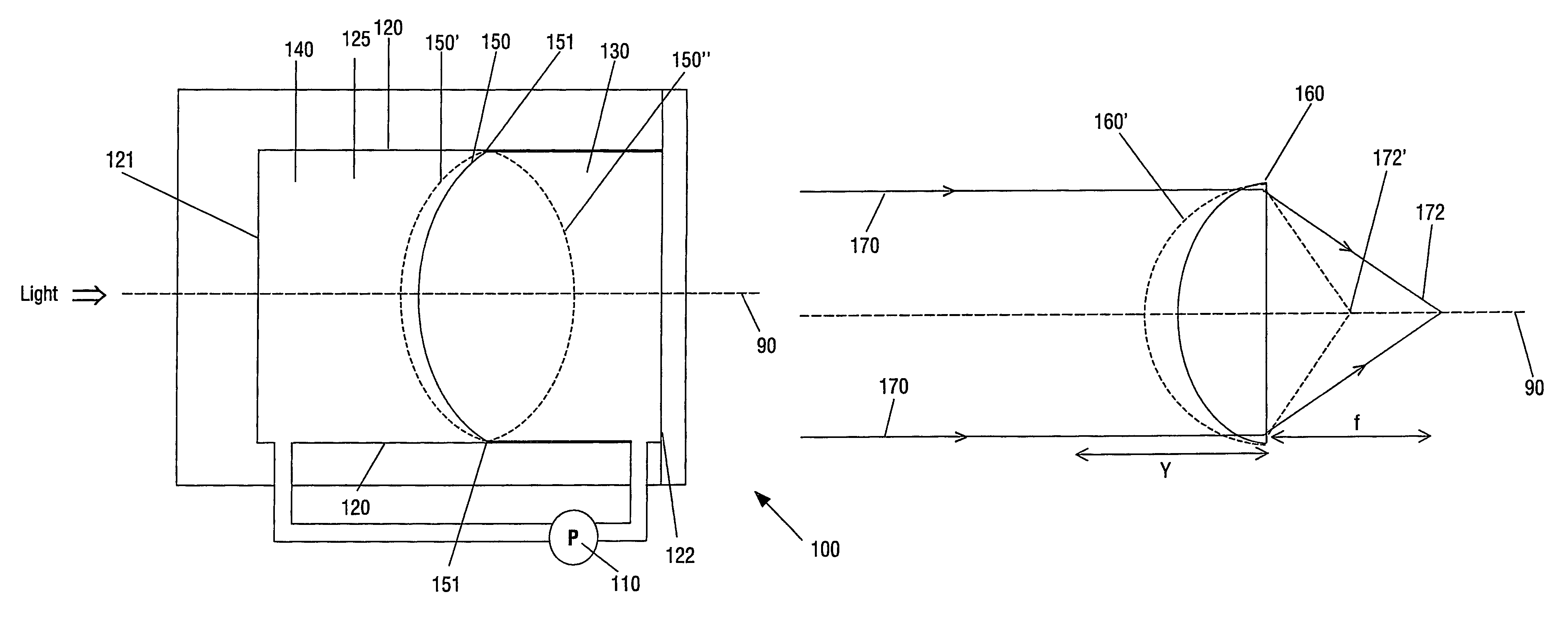
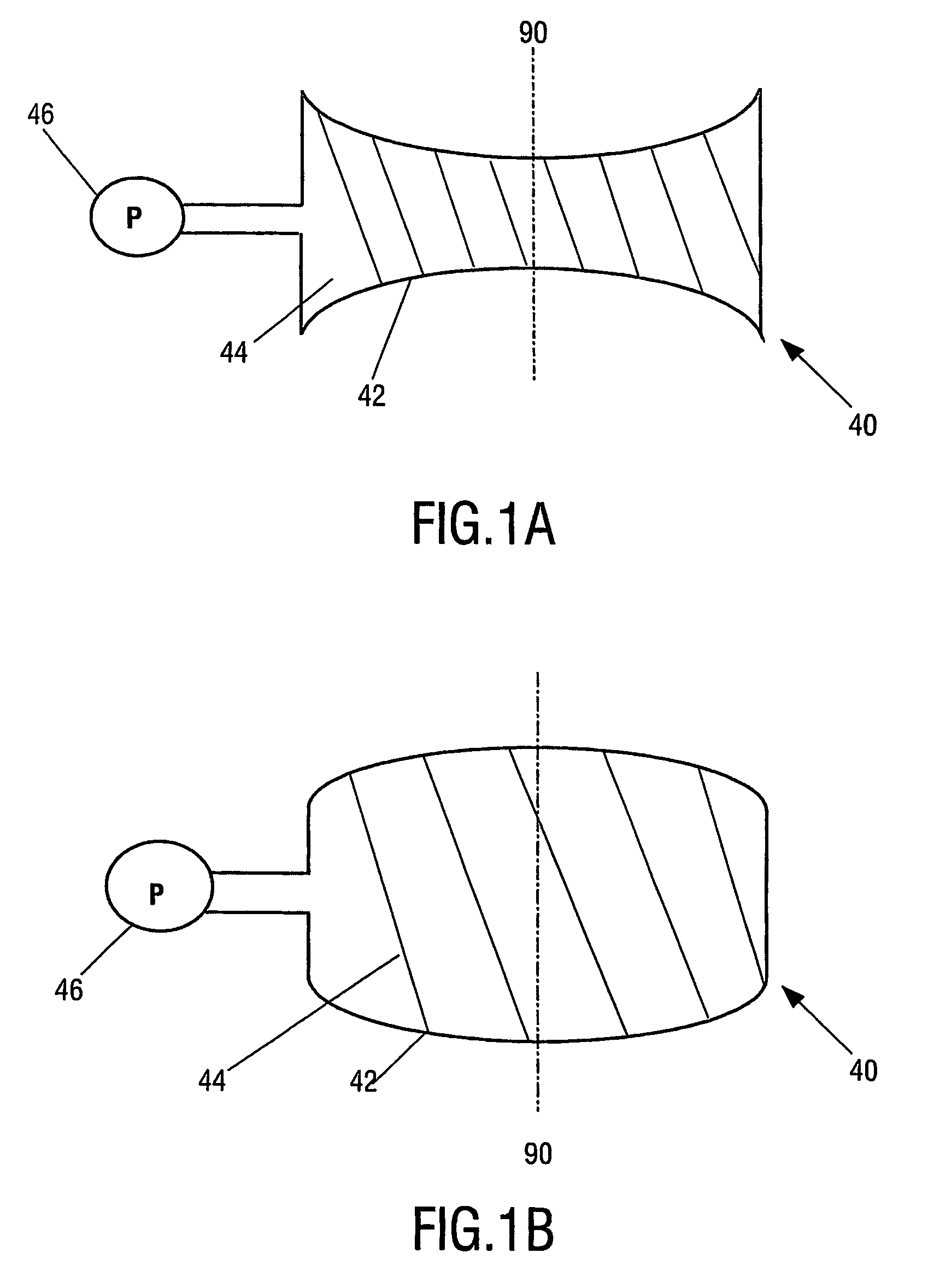
A variable lens system includes a chamber with an optical axis extending through the chamber. The chamber contains a first fluid and a second fluid in contact over a meniscus extending transverse the optical axis. The perimeter of the meniscus is fixedly located on an internal surface of the chamber. The fluids are substantially immiscible and have different indices of refraction. A pump is arranged to controllably alter the shape of the meniscus by altering the relative volume of each of the fluids contained within the chamber.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
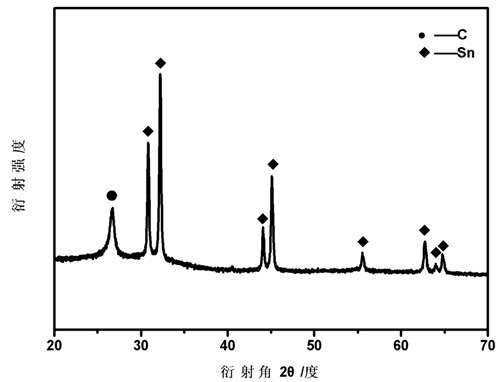
Preparation method of tin carbon composite material for negative electrode of lithium ion batteries
ActiveCN102185135AReduce relative volume changeImprove cycle performanceCell electrodesCarbon compositesKrypton
The invention discloses a preparation method of a tin carbon composite material for negative electrode of lithium ion batteries. The preparation method comprises the following steps: the method that a medium is adopted to block discharge plasma for assisting high-energy ball milling is adopted to ball mill the mixed powder of tin and graphite for 2.5h to 20h, thus obtaining the tin carbon composite powder; and then the tin carbon composite powder is made into an lithium ion electrode plate which is then assembled into batteries, wherein the mass of a graphite raw material accounts 30 to 70 percent of the total mass of the mixed powder; during the ball milling process, the mass ratio of the grinding balls to the ball powder of the tin and graphite mixed powder is 30:1 to 70:1; and the medium adopts an inert gas which is not reacted with Sn, such as helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon or nitrogen. The preparation method can effectively improve ball-milling efficiency, keep lamellar integrity of graphite, improve first reversible capacity and cycle life, and refine Sn particles to enable the relative volume change of a working electrode in the charging and discharging process to be reduced and improve the cycle performance of the lithium batteries.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Variable lens
ActiveUS7301708B2Effective positioningDifferent refractive indexRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansCamera lensOptical axis
A variable lens includes a chamber defined by at least one side wall and has an optical axis extending longitudinally through the chamber. The chamber contains a first fluid and a second fluid contact over a meniscus extending transverse the optical axis. The perimeter of the meniscus is constrained by the side walls. The fluids are substantially immiscible, and have different indices of refraction. At least one pump is arranged to controllably alter the position of the meniscus along the optical axis by altering the relative volume of each of the fluids contained within the chamber.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
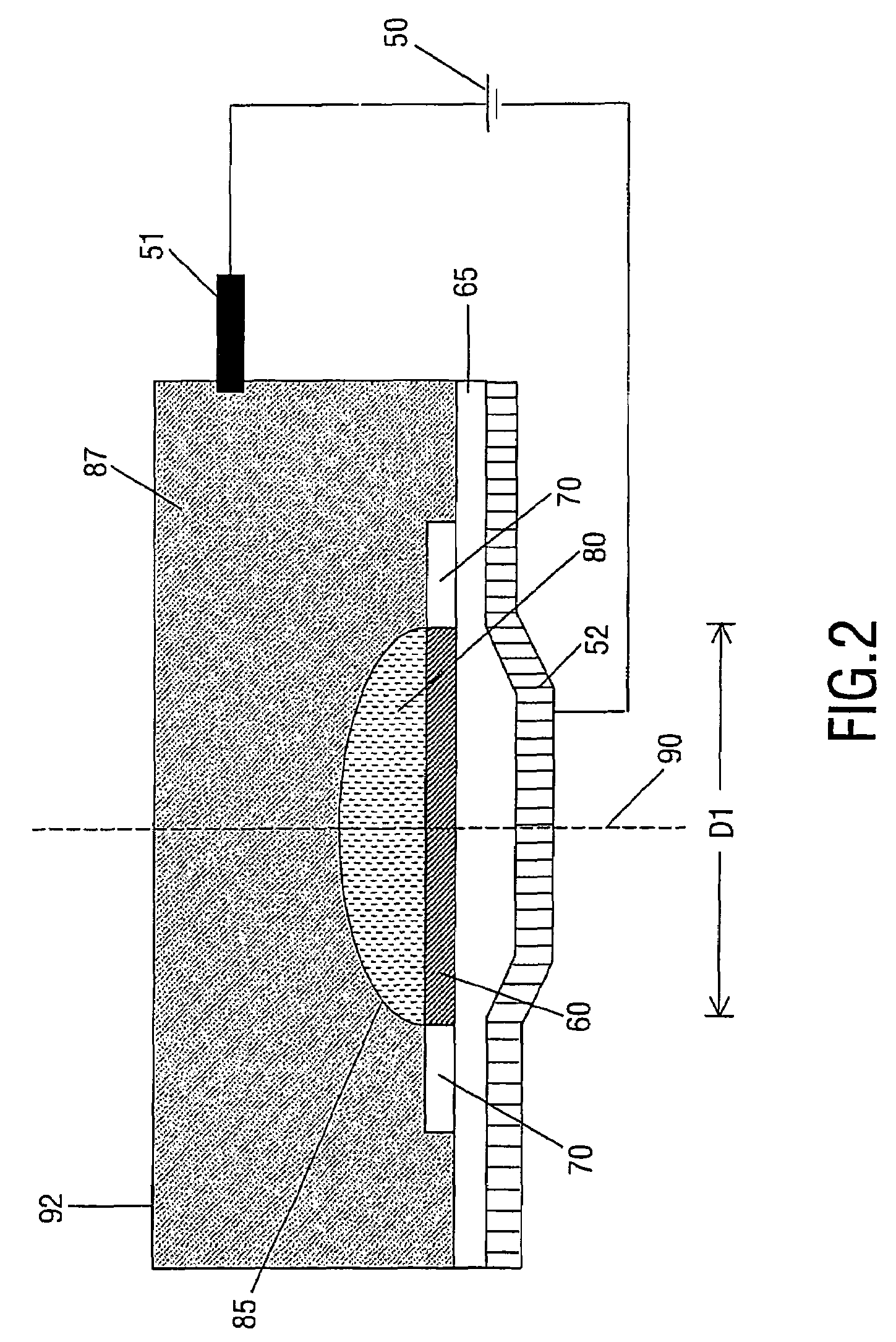
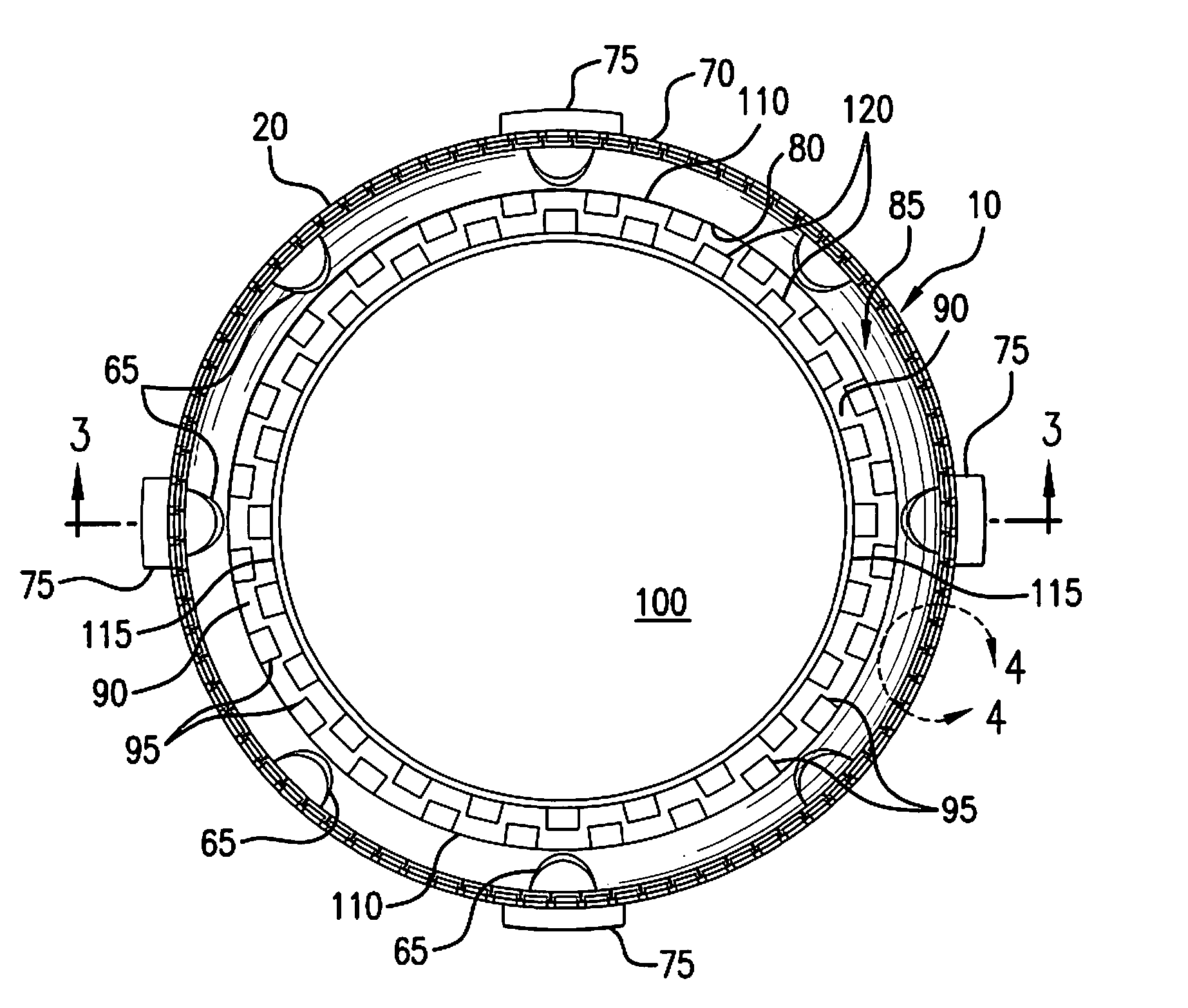
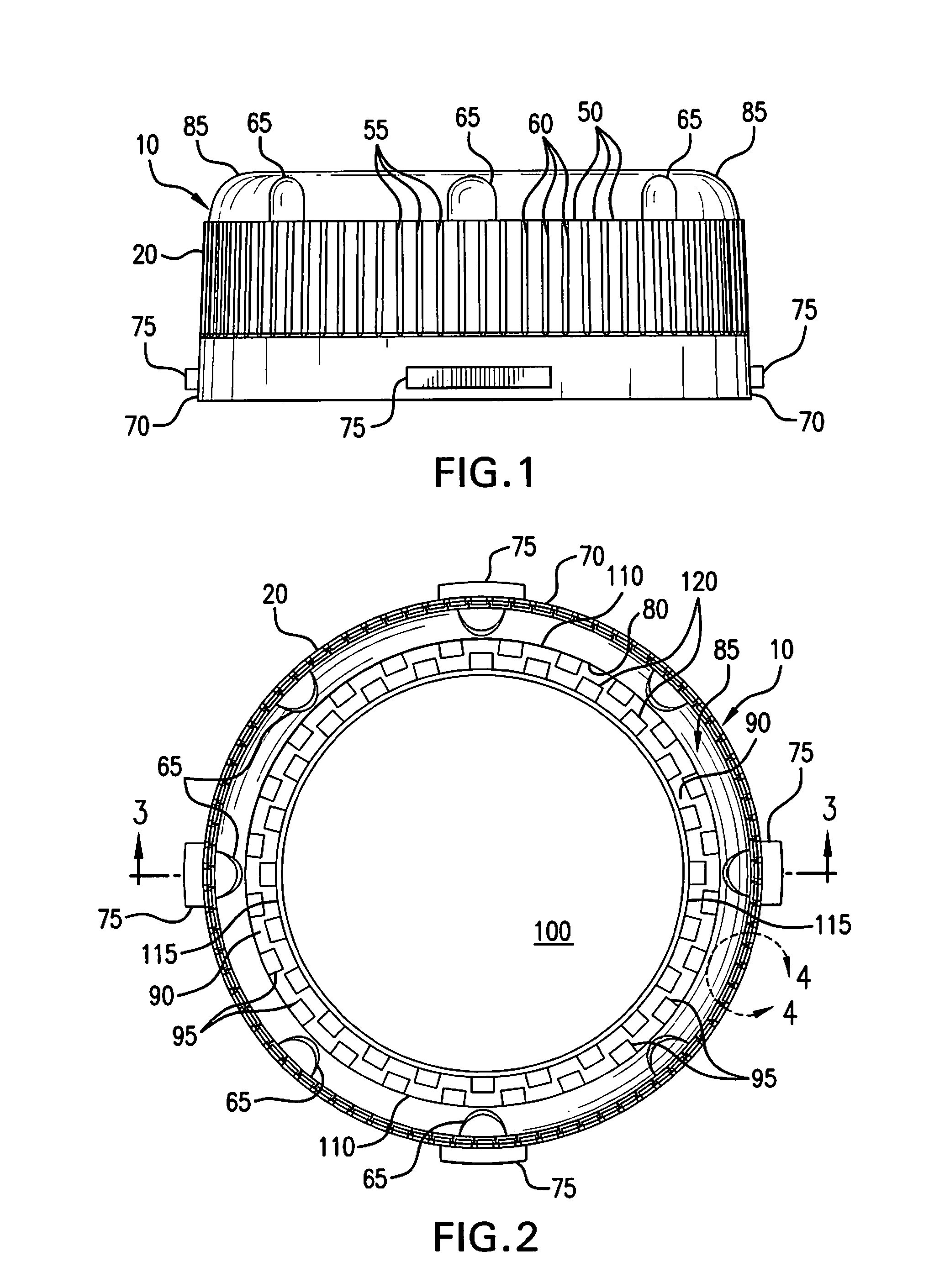
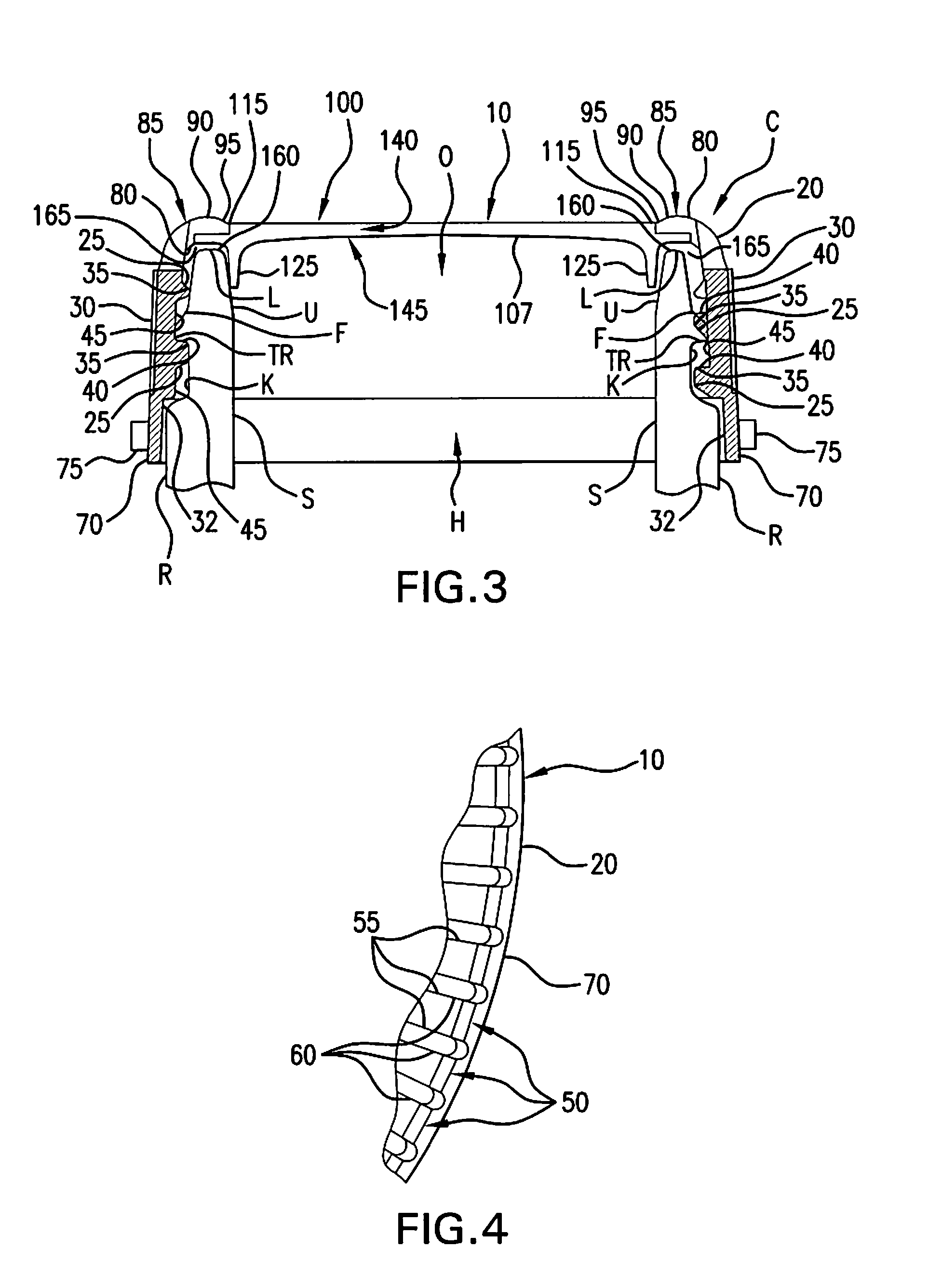
Retortable Closures and Containers
InactiveUS20100176134A1Improve sterilityLess to manufactureClosure capsSealingRelative VolumeEngineering
A retortable container (C) or a retortable closure (10) for use with the container (C). A receptacle (R) is included that may incorporate fasteners (F) attaching the closure (10). The closure (10) includes a retainer (20) received with a sealing barrier (100) formed from a polymeric material. The sealing barrier (100) includes a heat transfer material such as powdered metal in a volume that is between about 25% and about 65% of the closure (10) and an an oxygen barrier material such as a nanocompound or other barrier material having a relative volume of approximately between 10% and 60%. Variations of the closure (10) may incorporate seal layer of a thermoplastic elastomeric vulcanizate such as a santoprene and the heat transfer material may be an economically attractive powdered and / or oxide material such as zinc, aluminum, copper, nanotube, or similarly available material, which preferably is diffused throughout the closure (10).
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Cotton seed delinting process method and drying device special for method
ActiveCN101911876ARelatively smallLow costSeed and root treatmentDrying machines with non-progressive movementsRelative VolumePulp and paper industry
The invention discloses a cotton seed delinting process method and a drying device special for the method. The process method mainly comprises the processes of acid liquid preparation, quantitative acid application, drying and frictional delinting. The process method is characterized in that the drying is performed in the following special device that: the device comprises a drying roller (6) and a drying roller transmission mechanism (15); the end of the drying roller (6) is provided with at least one feeding hole, and a seal cover is arranged on the feeding hole; and the lower part of the drying roller (6) is provided with a heating device (13), and meanwhile, the drying roller (6) is also provided with a turnover lifting device (12) capable of turning over the drying roller (6) towards the direction of the feeding hole. Compared with the prior art, the drying roller is heated outside an acid stirring drying roller, and acid-spraying stirring can be performed on the cotton seeds in the drying roller when the drying roller is heated, so the drying operation time is shortened, the relative volume of the drying roller can be small, the cost of a drying device is reduced, and the drying device has low energy consumption and dries the cotton seeds uniformly.
Owner:SHIHEZI DEV ZONE TIANZUO SEED MACHINERY
Variable elastic modulus cushion disposed within a distal cup of a prosthetic socket
A cushion for a distal cup of a prosthetic socket has a total volume that includes a solid thermoplastic composition volume and a void volume. A ratio of the solid composition relative volume to the total volume yields a relative thermoplastic elastomer fill volume that is correlated with an elastic modulus of the cushion. The relative thermoplastic elastomer fill volume can vary regionally within the cushion in a customized manner, and accordingly, so can the elastic modulus and the durometer. Varying the elastic modulus or durometer regionally within a cushion, such as by 3D printing the cushion, provides therapeutic and prophylactic benefits in the application of the cushion to articles that interface with the body, such as a cushion disposed in the distal portion of a prosthetic socket for a residual limb of an amputee.
Owner:LIM INNOVATIONS
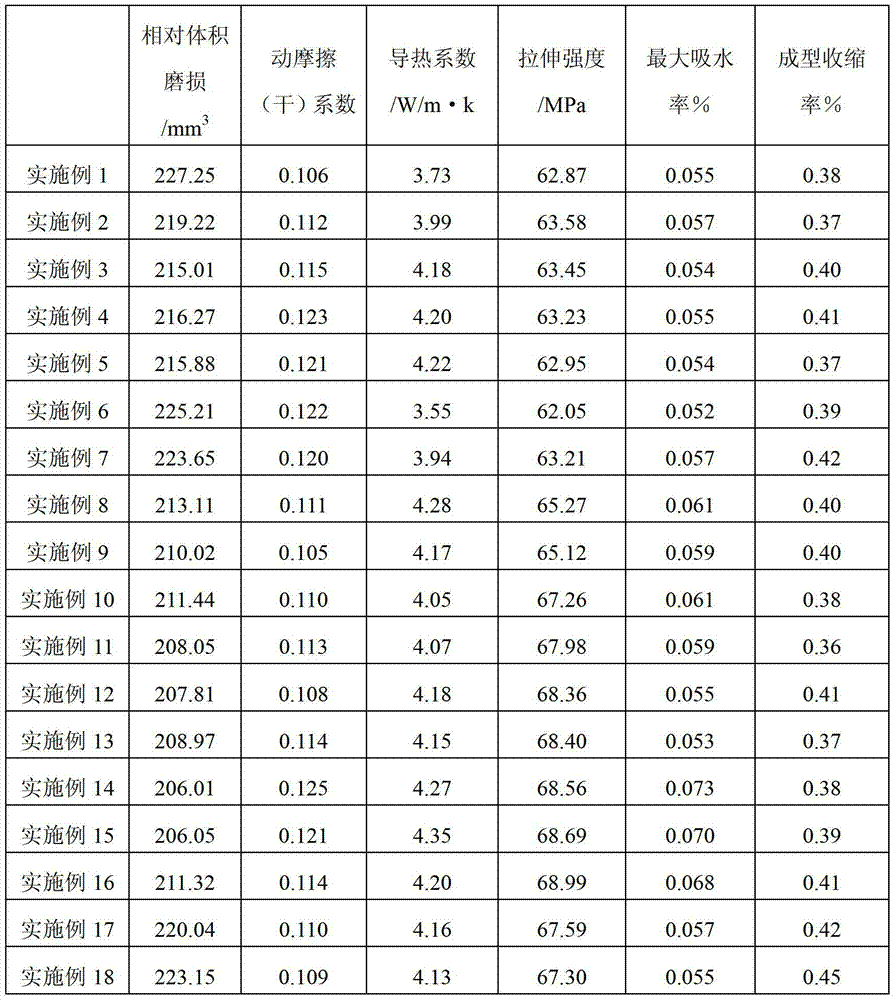
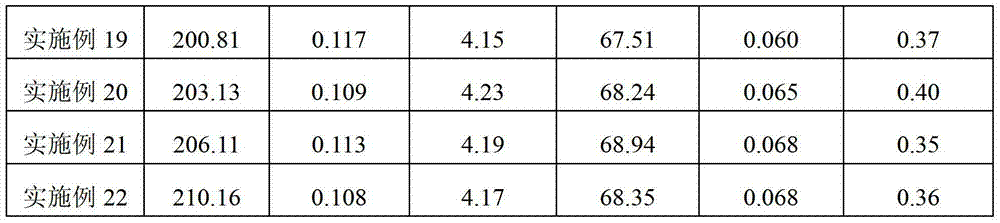
Low-water-absorptivity heat-conducting wear-resistant polymer alloy, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of polymer alloy materials, and discloses a low-water-absorptivity heat-conducting wear-resistant polymer alloy, and a preparation method and application thereof. The low-water-absorptivity heat-conducting wear-resistant polymer alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 20-80% of PP / PA66 (polypropylene / polyamide 66) alloy phase, 5-30% of graphite powder and 10-50% of carbon fiber. The PP / PA66 alloy phase comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 20-70% of PP, 25-70% of PA66 and 5-25% of compatilizer. The low-water-absorptivity heat-conducting wear-resistant polymer alloy disclosed by the invention has excellent properties: the weight is lowered by 50%, the relative volume abrasion is lower than 250 mm<3>, the dynamic friction (dry) coefficient is less than 0.15, the maximum water absorptivity is lower than 0.1%, the heat conductivity coefficient is up to 4.35 W / m.k, the tensile strength is greater than 60 MPa, and the service life is prolonged by 100%.
Owner:肇庆市端州区广德润机电有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com