Patents
Literature
440 results about "Krypton" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Krypton (from Ancient Greek: κρυπτός, romanized: kryptos "the hidden one") is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is often used with other rare gases in fluorescent lamps. With rare exceptions, krypton is chemically inert.
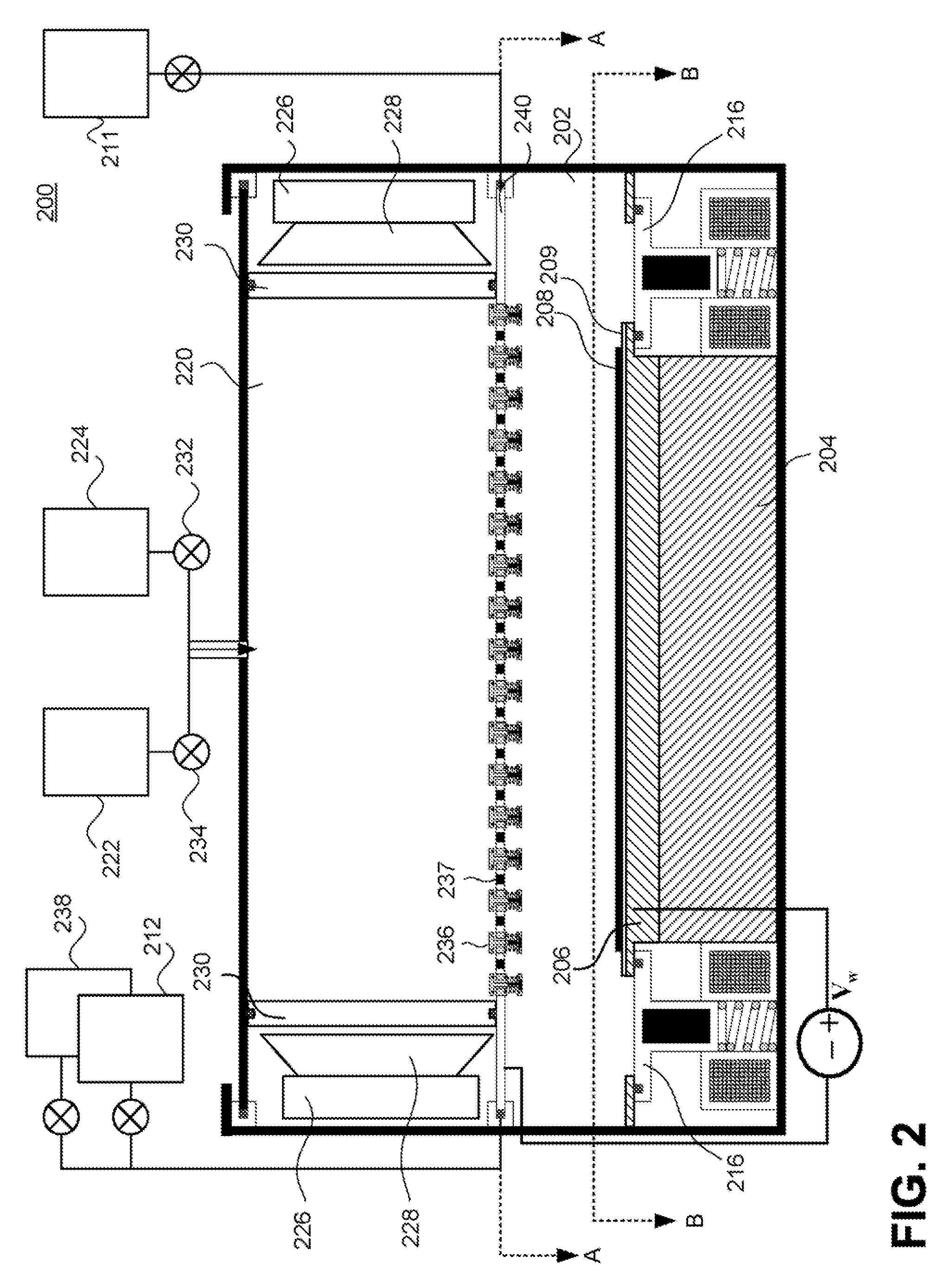
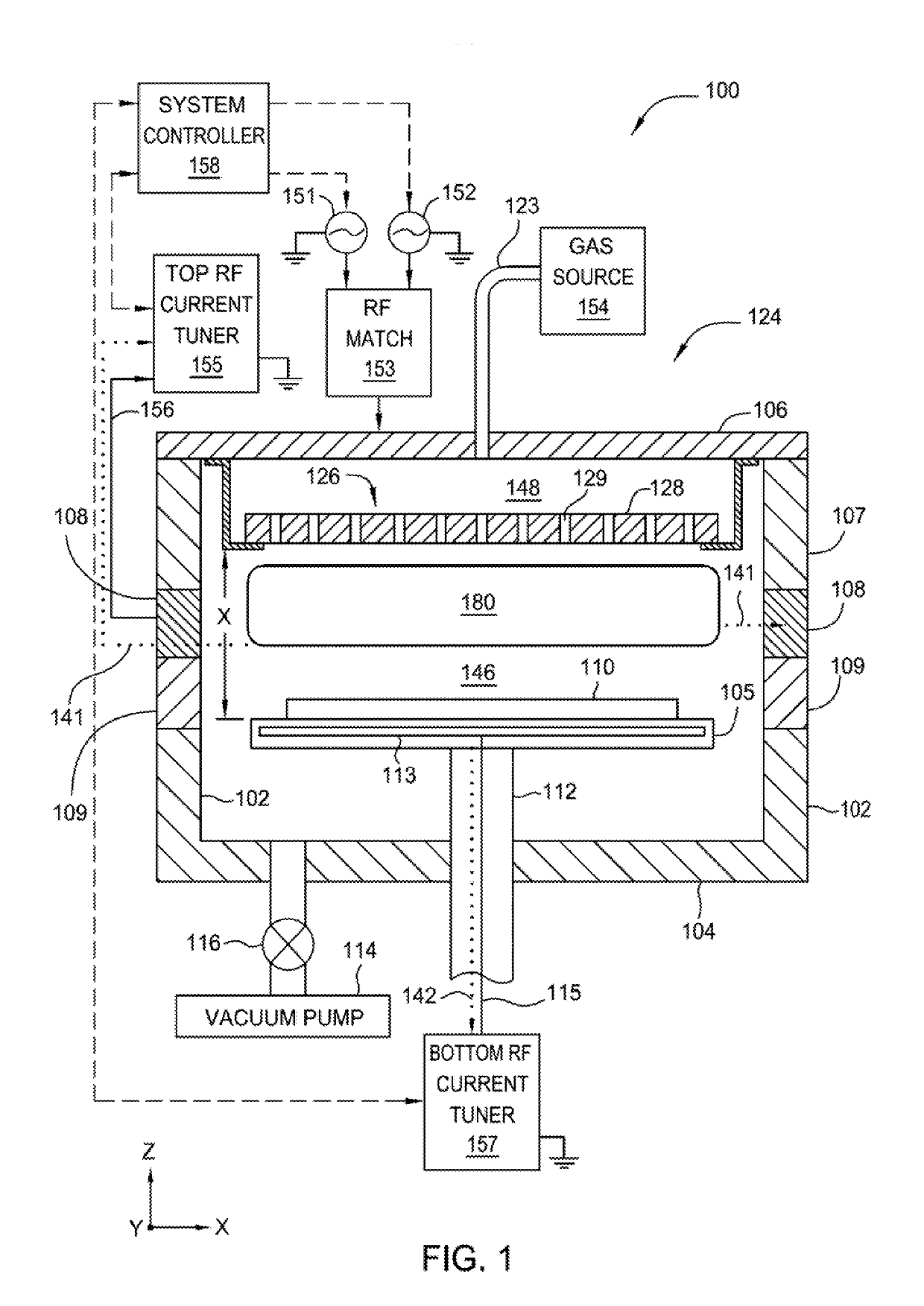
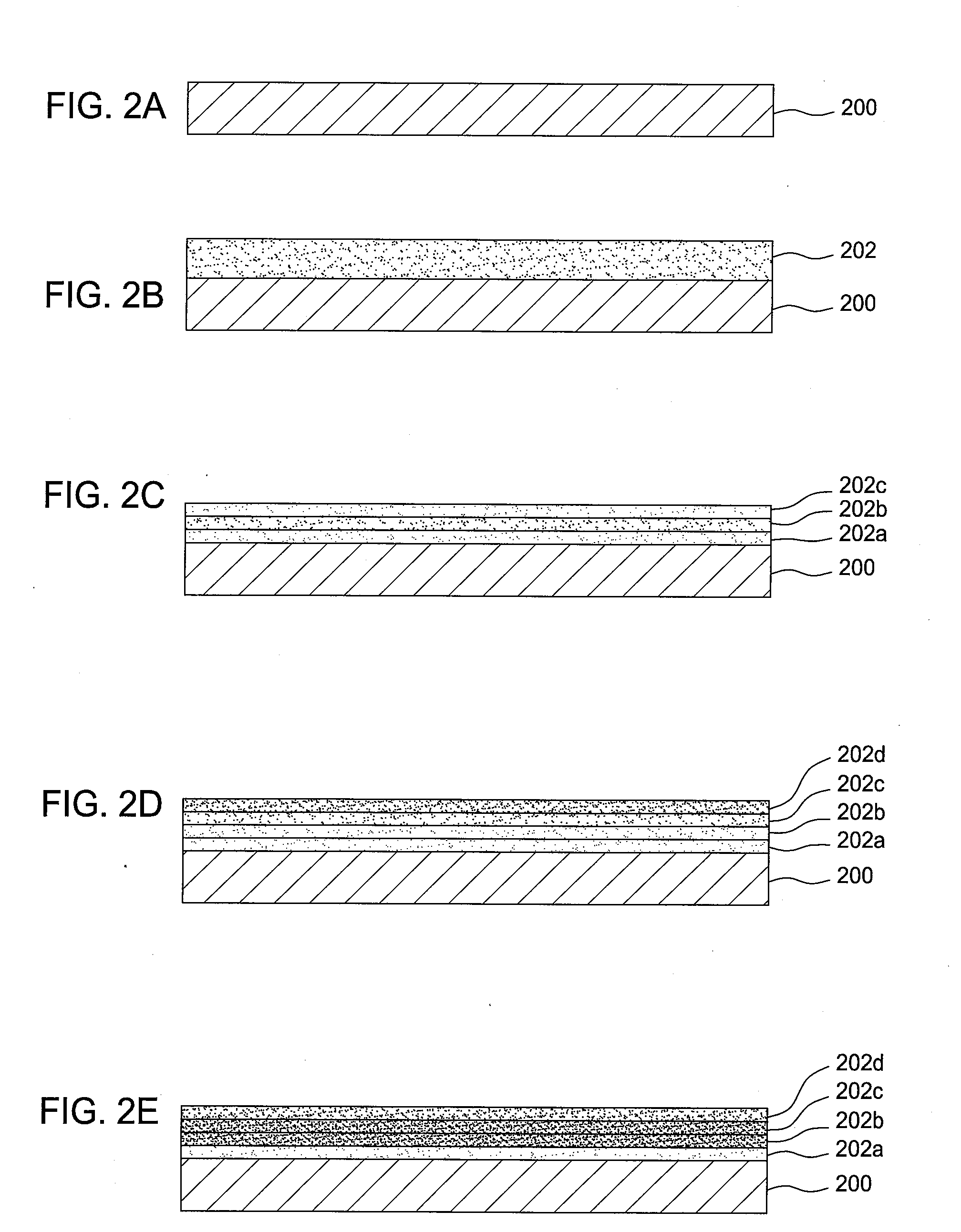
Method For Depositing an Amorphous Carbon Film with Improved Density and Step Coverage
ActiveUS20080003824A1High densityLower thermal budgetPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbon layerKrypton
A method for depositing an amorphous carbon layer on a substrate includes the steps of positioning a substrate in a chamber, introducing a hydrocarbon source into the processing chamber, introducing a heavy noble gas into the processing chamber, and generating a plasma in the processing chamber. The heavy noble gas is selected from the group consisting of argon, krypton, xenon, and combinations thereof and the molar flow rate of the noble gas is greater than the molar flow rate of the hydrocarbon source. A post-deposition termination step may be included, wherein the flow of the hydrocarbon source and the noble gas is stopped and a plasma is maintained in the chamber for a period of time to remove particles therefrom.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of forming a layer and method of forming a capacitor of a semiconductor device having the same
InactiveUS20060063346A1Improve reliabilityLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsKryptonDevice material
In a method of forming a layer using an atomic layer deposition process, after a substrate is loaded into a chamber, a reactant is provided onto the substrate to form a preliminary layer. Atoms in the preliminary layer are partially removed from the preliminary layer using plasma formed from an inert gas such as an argon gas, a xenon gas or a krypton gas, or an inactive gas such as an oxygen gas, a nitrogen gas or a nitrous oxide gas to form a desired layer. Processes for forming the desired layer may be simplified. A highly integrated semiconductor device having improved reliability may be economically manufactured so that time and costs required for the manufacturing of the semiconductor device may be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Atomic Layer Deposition of Oxides Using Krypton as an Ion Generating Feeding Gas
InactiveUS20070281105A1Improve abilitiesImprove efficiencyChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueKryptonHigh density
An atomic layer deposition system and method utilizing radicals generated from a high-density mixed plasma for deposition is disclosed. A high-quality oxide or oxynitride can be deposited by exposing a substrate to a first precursor which is adsorbed onto the substrate during a first phase of one deposition cycle. After purging the deposition chamber, the substrate is exposed to a second precursor which includes oxygen radicals and krypton ions formed from the high-density mixed plasma. The ions and radicals are formed by introducing a radical generating feed gas (e.g., O2) and an ion generating feed gas into a plasma chamber and exciting the gases to form the high-density mixed plasma. The radicals and ions are then introduced to the substrate where they react with the first precursor to deposit a layer of the desired film. Krypton is preferably used as the ion generating feed gas because the metastable states of krypton lead to an efficient dissociation of oxygen into oxygen radicals when compared with other inert gases.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
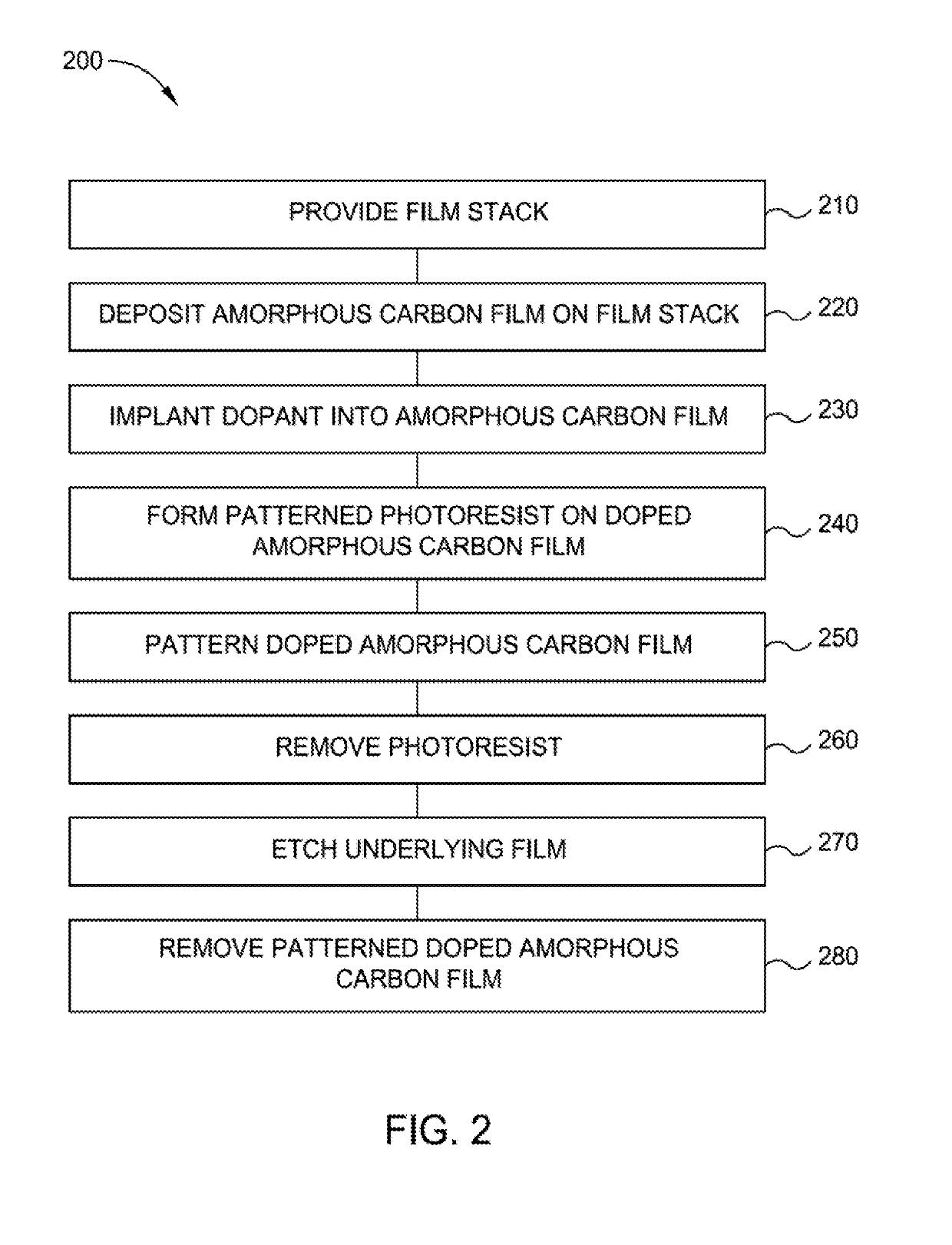
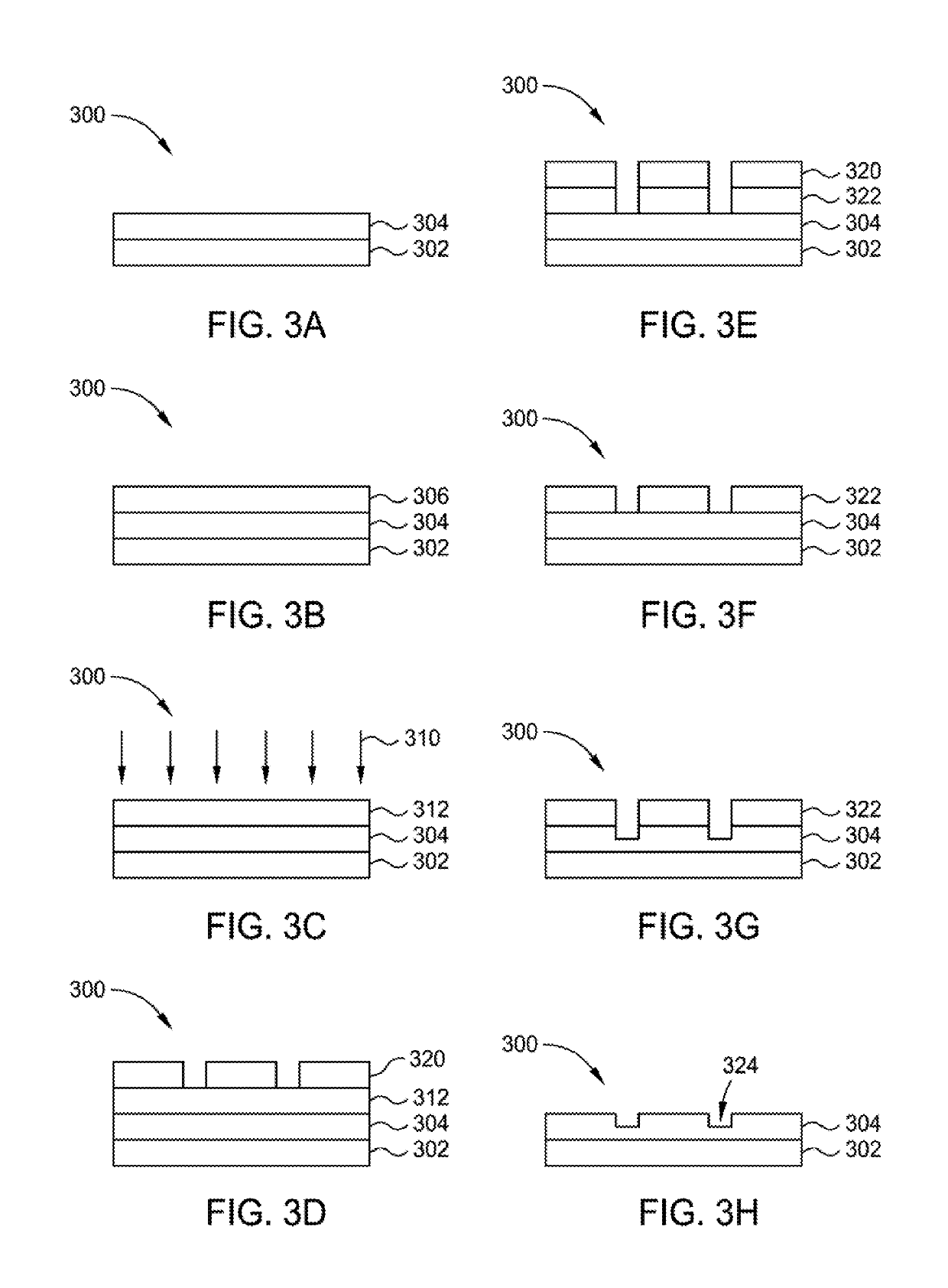
Highly etch selective amorphous carbon film
ActiveUS20190172714A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingKryptonDopant
Implementations described herein generally relate to the fabrication of integrated circuits. More particularly, the implementations described herein provide techniques for deposition of amorphous carbon films on a substrate. In one implementation, a method of forming an amorphous carbon film is provided. The method comprises depositing an amorphous carbon film on an underlayer positioned on a susceptor in a first processing region. The method further comprises implanting a dopant or inert species into the amorphous carbon film in a second processing region. The dopant or inert species is selected from carbon, boron, nitrogen, silicon, phosphorous, argon, helium, neon, krypton, xenon or combinations thereof. The method further comprises patterning the doped amorphous carbon film. The method further comprises etching the underlayer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Structure and method for manufacturing MOSFET with super-steep retrograded island
InactiveUS20060068555A1Reduce morbidityReduce diffuseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingKryptonDopant
The present invention comprises a method for forming a semiconducting device including the steps of providing a layered structure including a substrate, a low diffusivity layer of a first-conductivity dopant; and a channel layer; forming a gate stack atop a protected surface of the channel layer; etching the layered structure selective to the gate stack to expose a surface of the substrate, where a remaining portion of the low diffusivity layer provides a retrograded island substantially aligned to the gate stack having a first dopant concentration to reduce short-channel effects without increasing leakage; growing a Si-containing material atop the recessed surface of the substrate; and doping the Si-containing material with a second-conductivity dopant at a second dopant concentration. The low diffusivity layer may be Si1-x-yGexZy, where Z can be carbon (C), xenon (Xe), germanium (Ge), krypton (Kr), argon (Ar), nitrogen (N), or combinations thereof.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
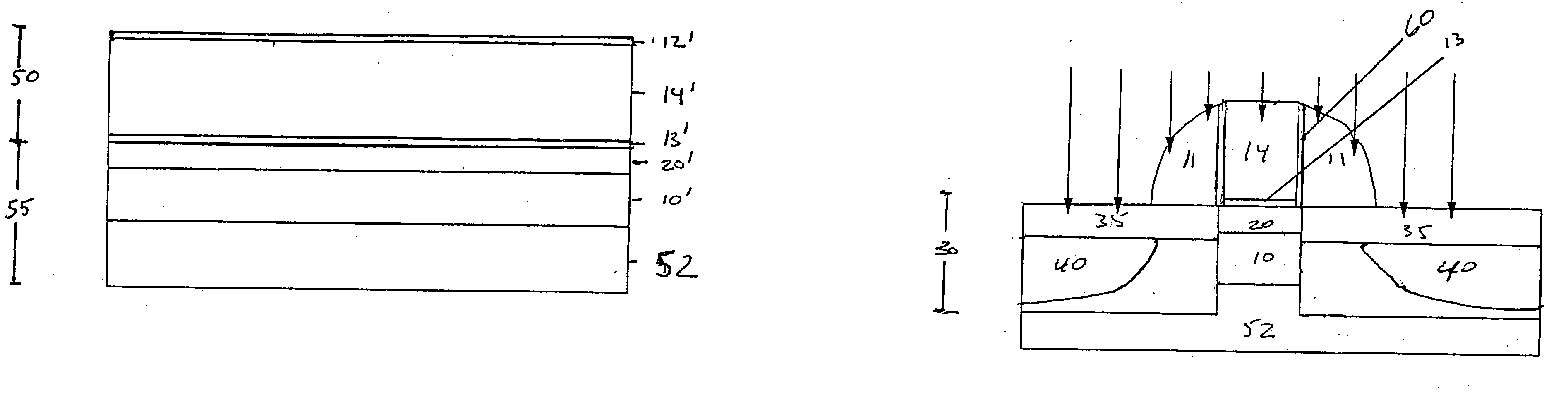
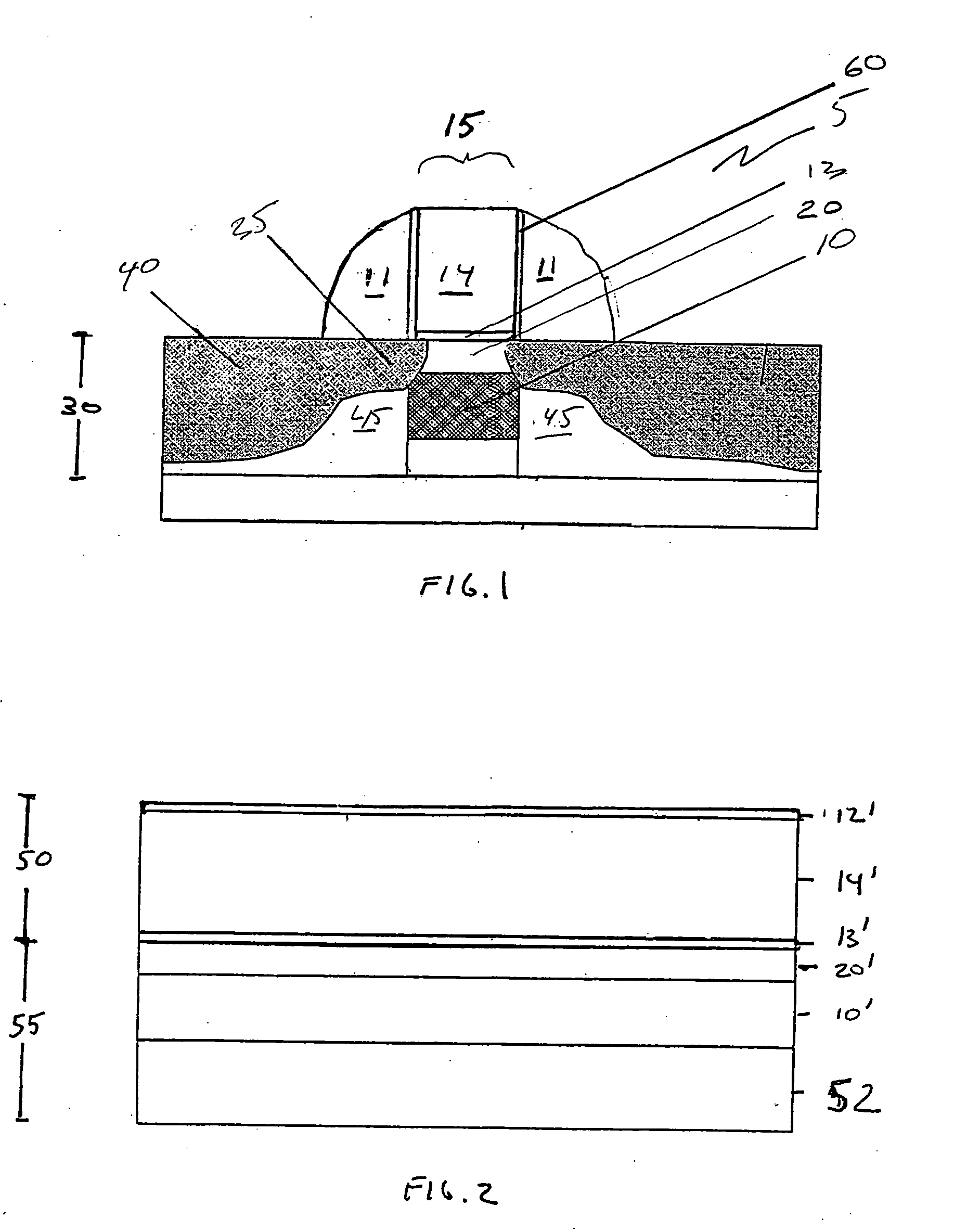
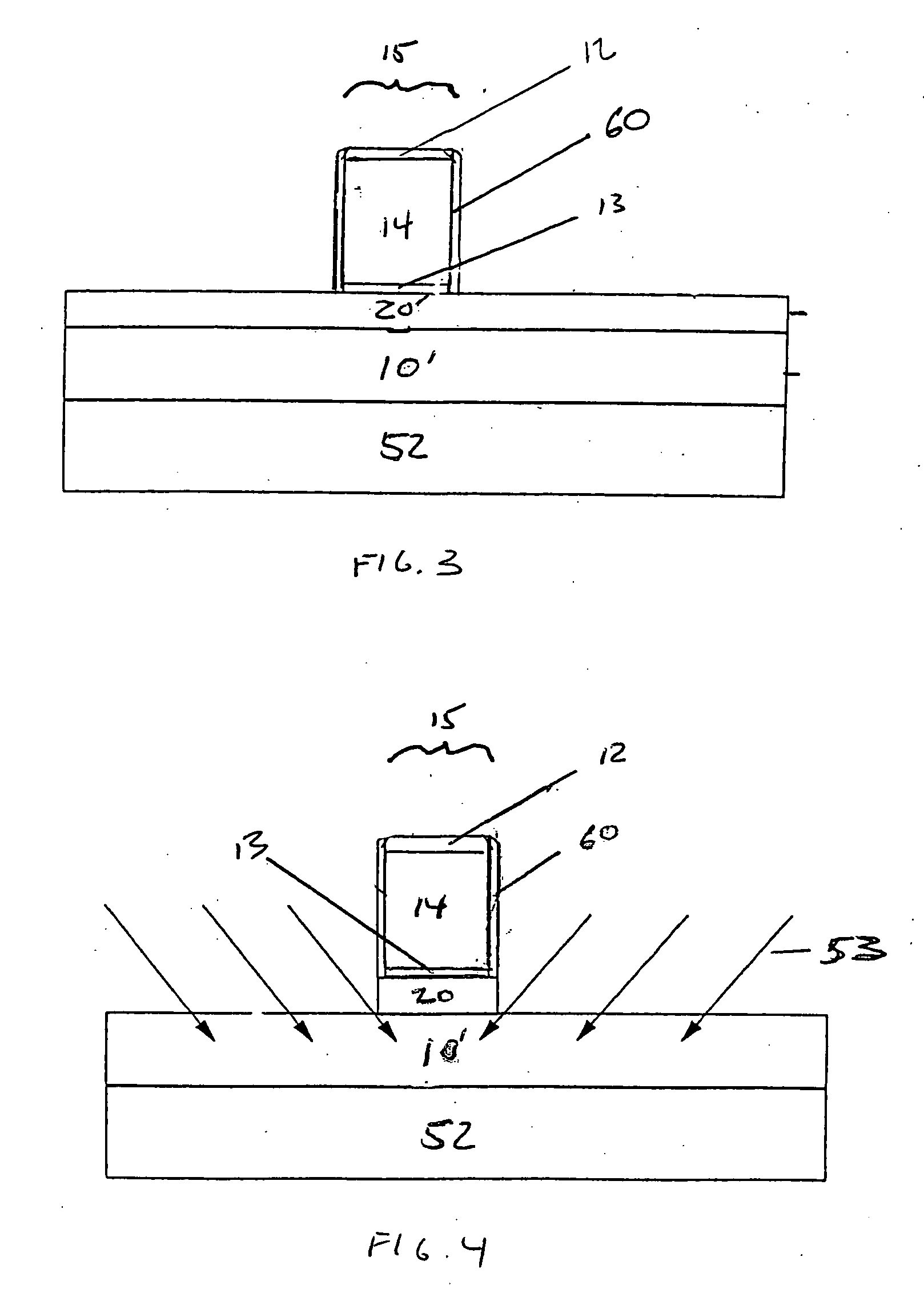
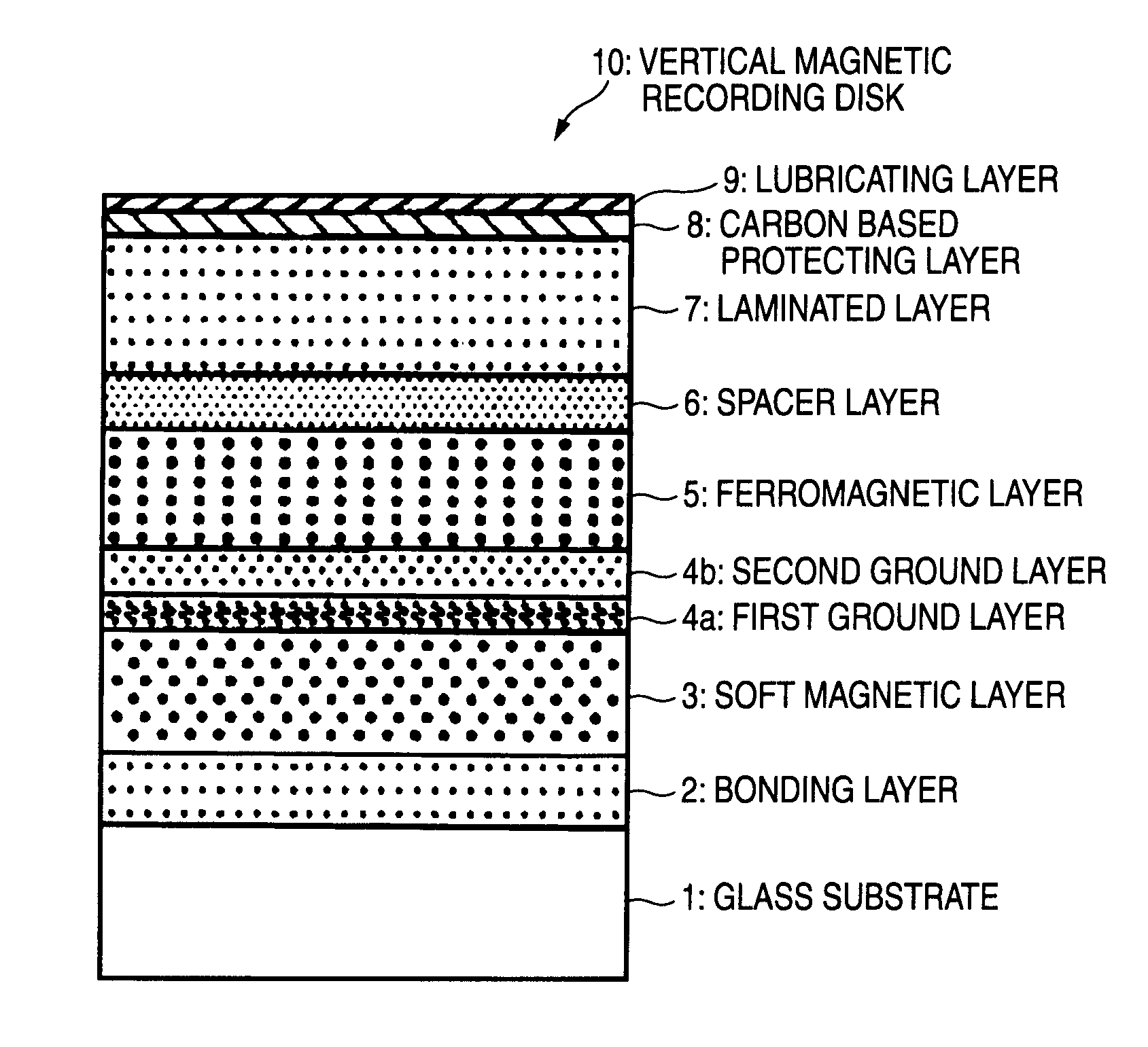
Vertical magnetic recording disk manufacturing method and vertical magnetic recording disk
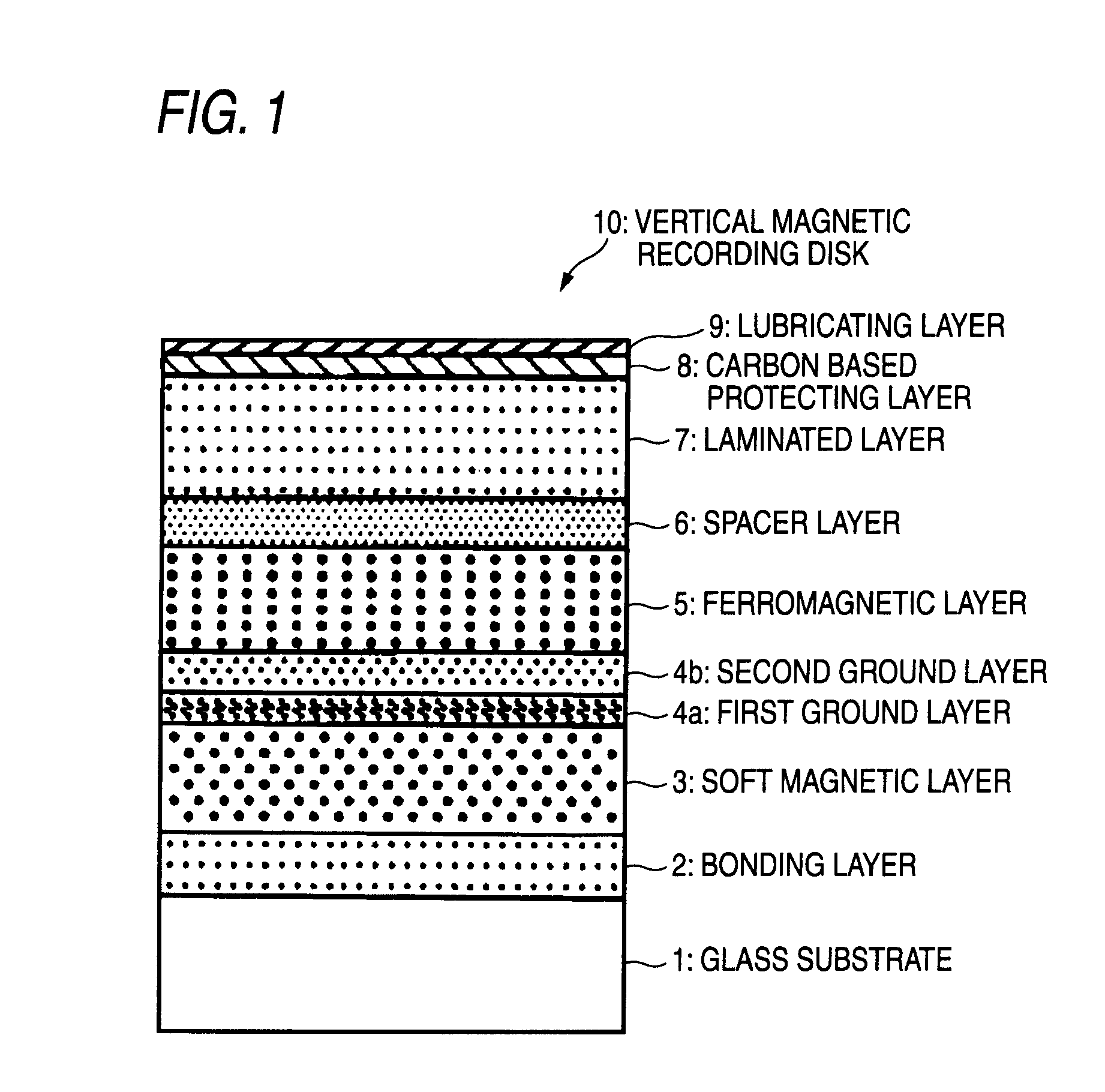
ActiveUS20090202866A1Improve magnetic propertiesImprove recording densityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingKryptonSputtering
In a method of manufacturing a magnetic disk including at least a magnetic recording layer on a substrate 1 and used for vertical magnetic recording, in a step of forming, on the substrate 1, the magnetic recording layer composed of a ferromagnetic layer 5 having a granular structure and an exchange energy control layer 7 constituted by a laminated layer formed on the ferromagnetic layer 5, at least the exchange energy control layer 7 is formed through sputtering in an atmosphere of a rare gas having a greater mass than an argon gas. The rare gas having a greater mass than the argon gas is a krypton (Kr) gas, for example. The exchange energy control layer 7 is a laminated layer composed of a first layer containing Co or a Co-alloy and a second layer containing palladium (Pd) or platinum (Pt), for example.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Treatment of effluent gases
A method is described for recovering a noble gas, such as xenon or krypton, from a first gas mixture comprising a plurality of components, one of which is the noble gas and the others are typically helium and / or nitrogen, argon, and relatively light fluorocarbons. The gas mixture is first conveyed to a gas chromatography column for separating the noble gas from the other components of the gas mixture. As the noble gas travels relatively slowly through the column, the other components are exhaust from the column before the relatively slow noble gas. Following the exhaust of these other components, a purge gas is supplied to the column to flush the noble gas therefrom. A second gas mixture comprising the noble gas and the purge gas is conveyed from the column to a membrane separator to separate the second gas mixture into a noble gas-rich gas stream and a purge gas-rich gas stream, which may be recirculated back to the column for re-use.
Owner:THE BOC GRP PLC
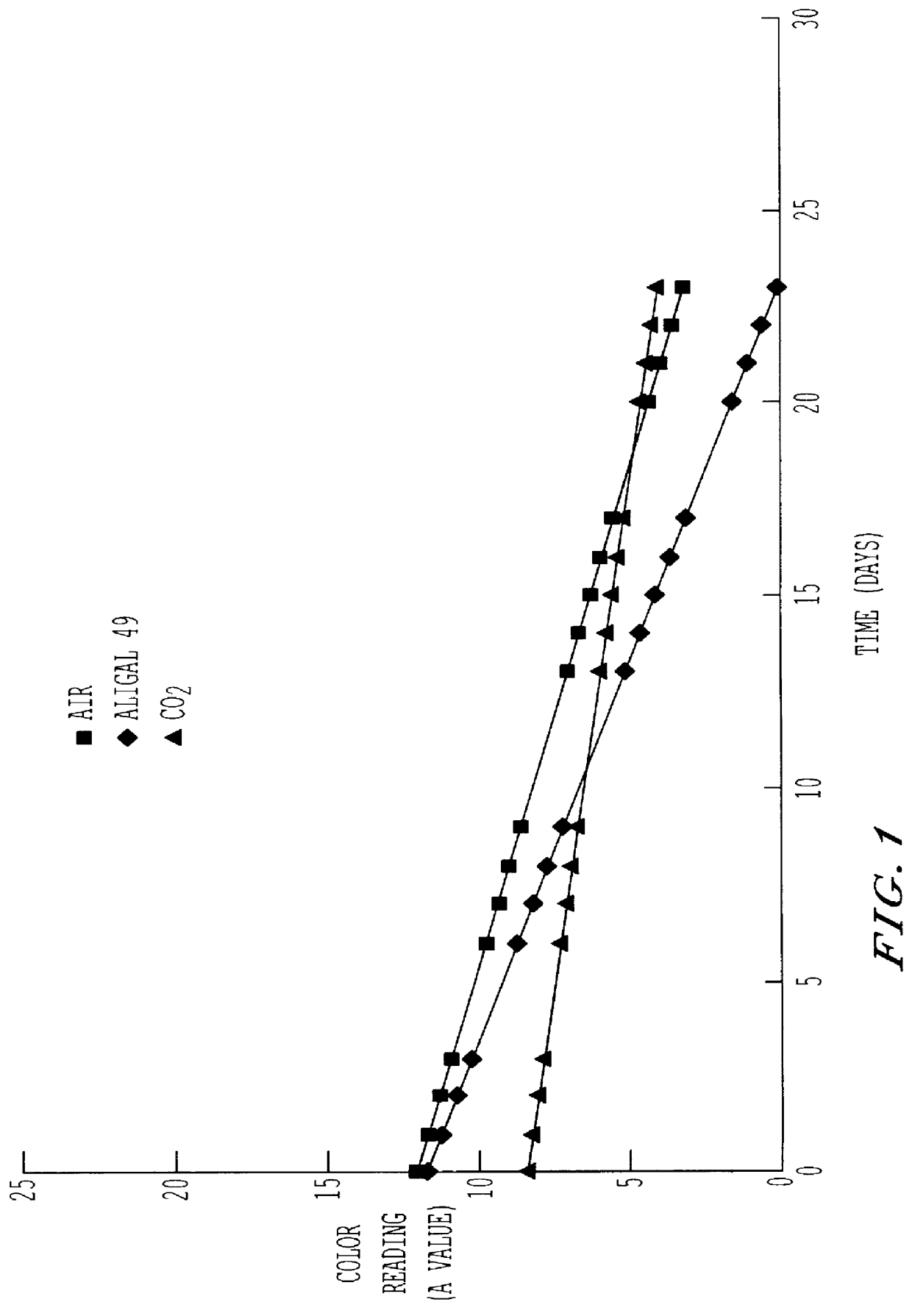
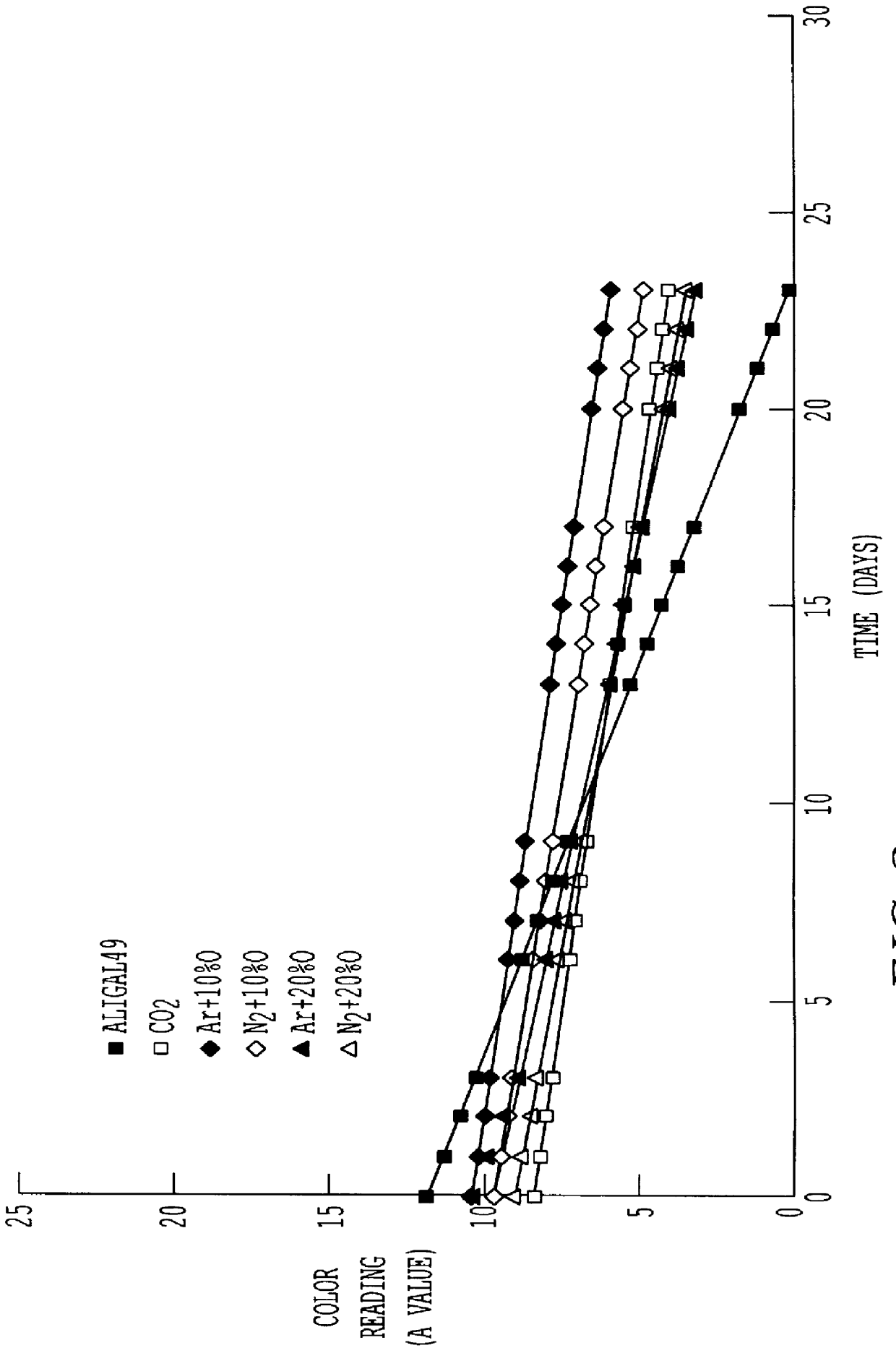
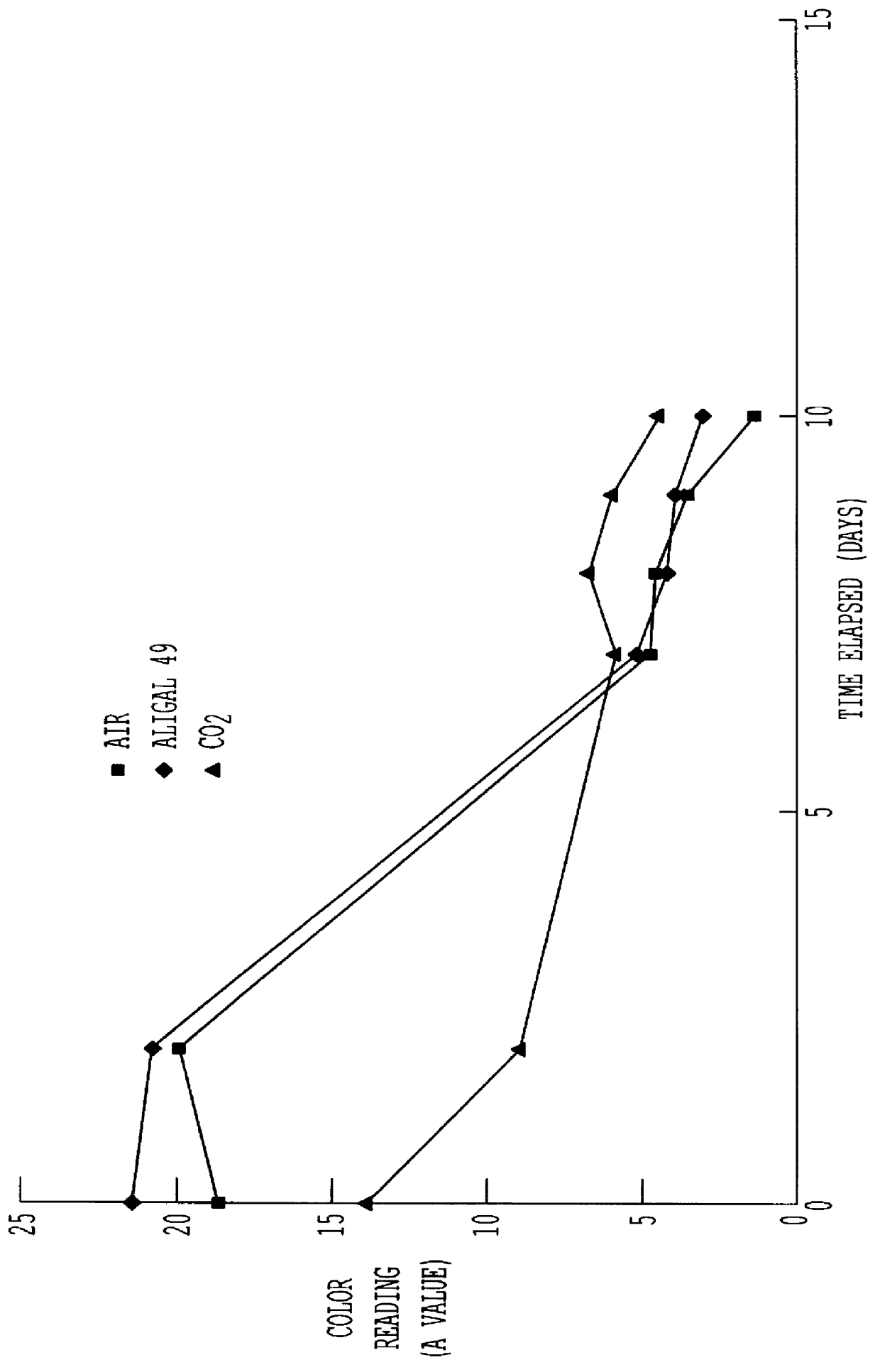
Preservation of color of stored meat using noble gases
A process for preserving the color of red meat, which entails contacting the meat with an effective amount of an atmosphere selected from the group consisting of a noble gas, a mixture of noble gases and a mixture containing at least one noble gas and a carrier gas, the noble gas in the mixture with the carrier gas being selected from the group consisting of argon, neon, xenon an krypton and being present in said mixture in an amount of greater than about 10% by volume.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC
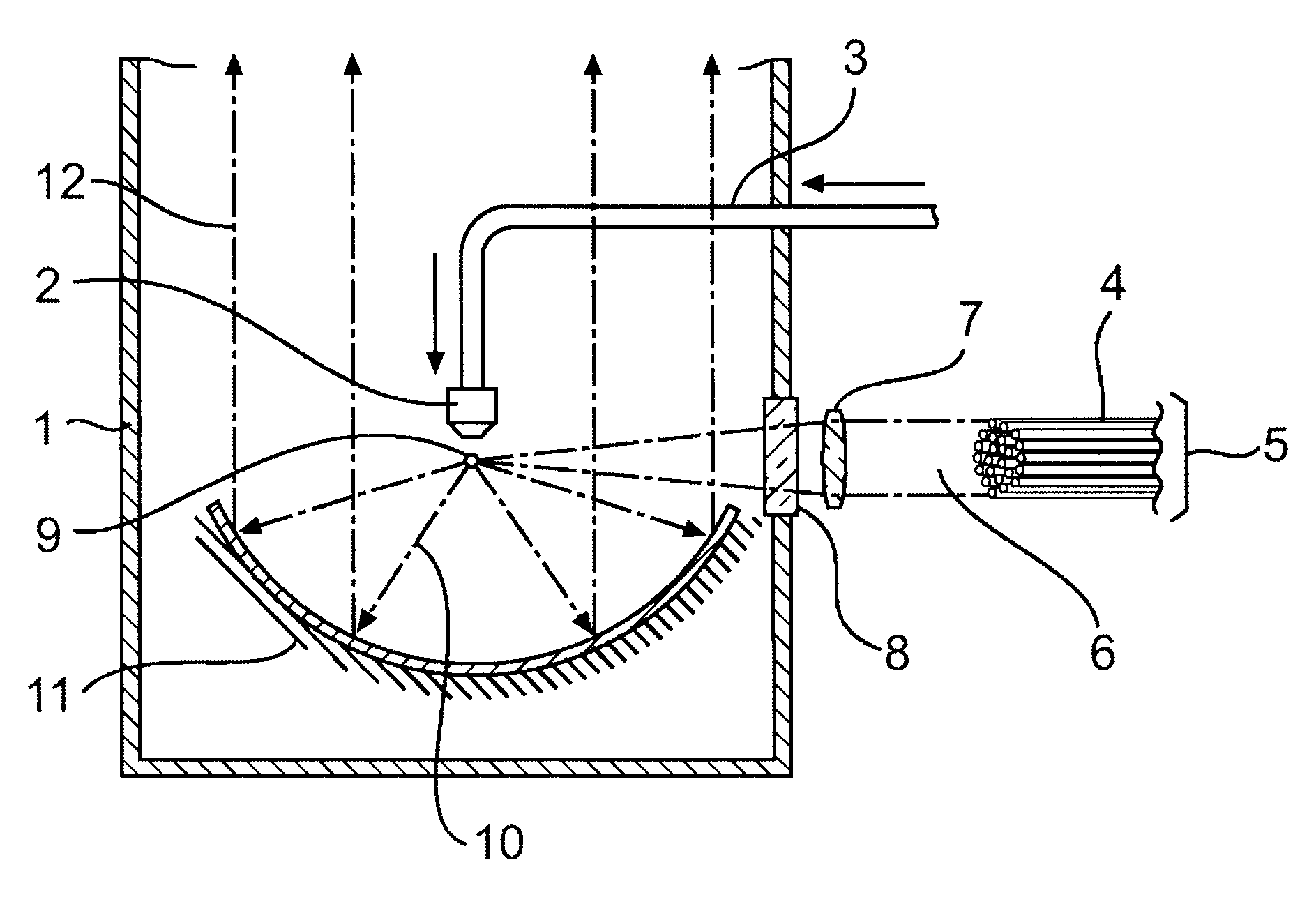
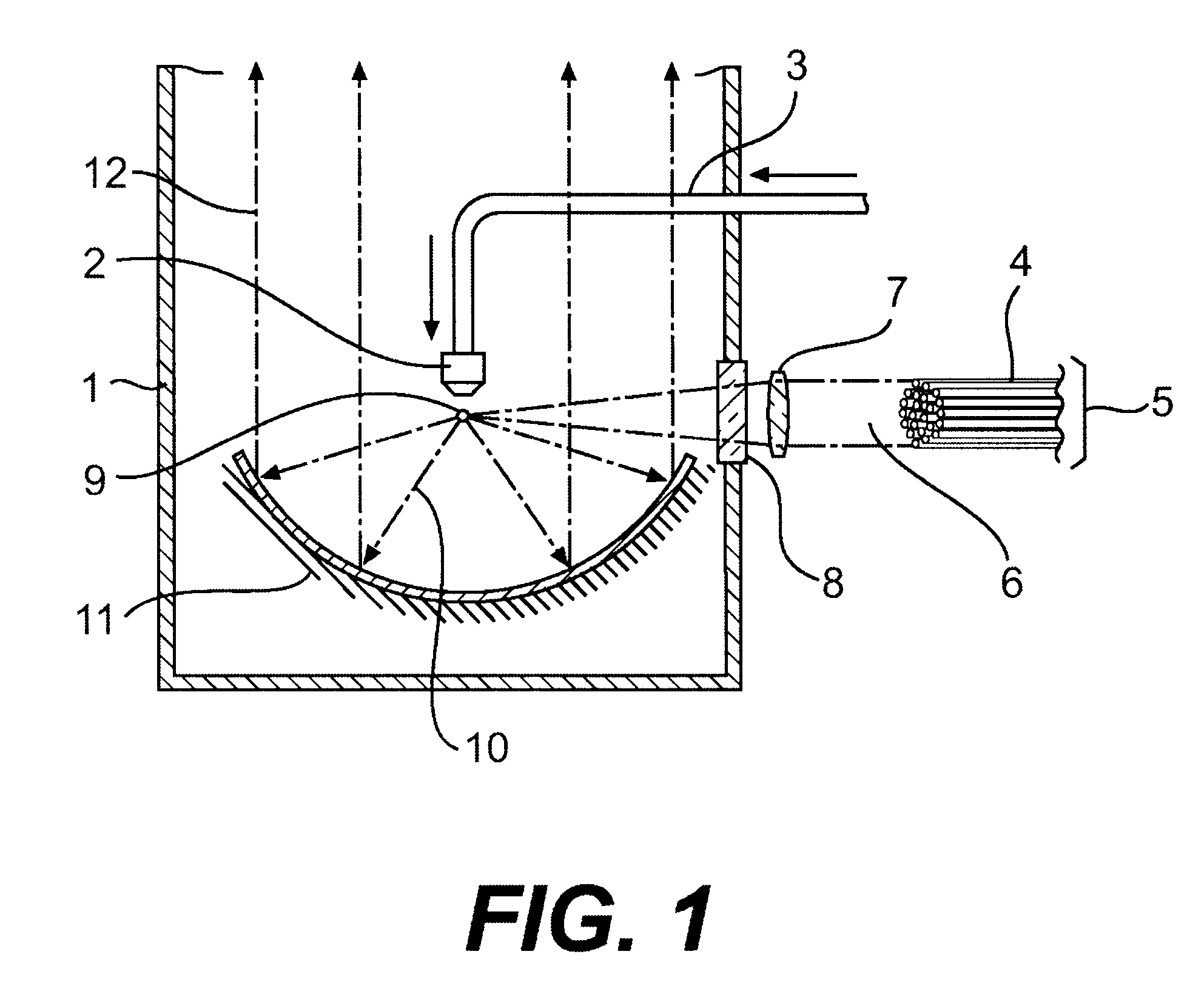
Soft x-ray light source device
A high-pressure krypton gas is supplied to the interior of a vessel from a gas introduction pipe. Light emitted from an optical fiber group formed by bundling together optical fibers constituting the output ends of fiber amplifiers or fiber lasers passes through a lens and exciting laser light introduction window, and is focused on the krypton gas jetting from the tip end of the nozzle. As a result, the krypton gas is excited as a plasma and soft X-rays are generated. The soft X-rays are reflected by a rotating multi-layer coat parabolic mirror and are emitted to the outside as a parallel beam of soft X-rays. Since light from fiber amplifiers is used as exciting light, and since numerous optical fibers are bundled together to form a light source, a large quantity of soft X-rays can easily be obtained.
Owner:NIKON CORP
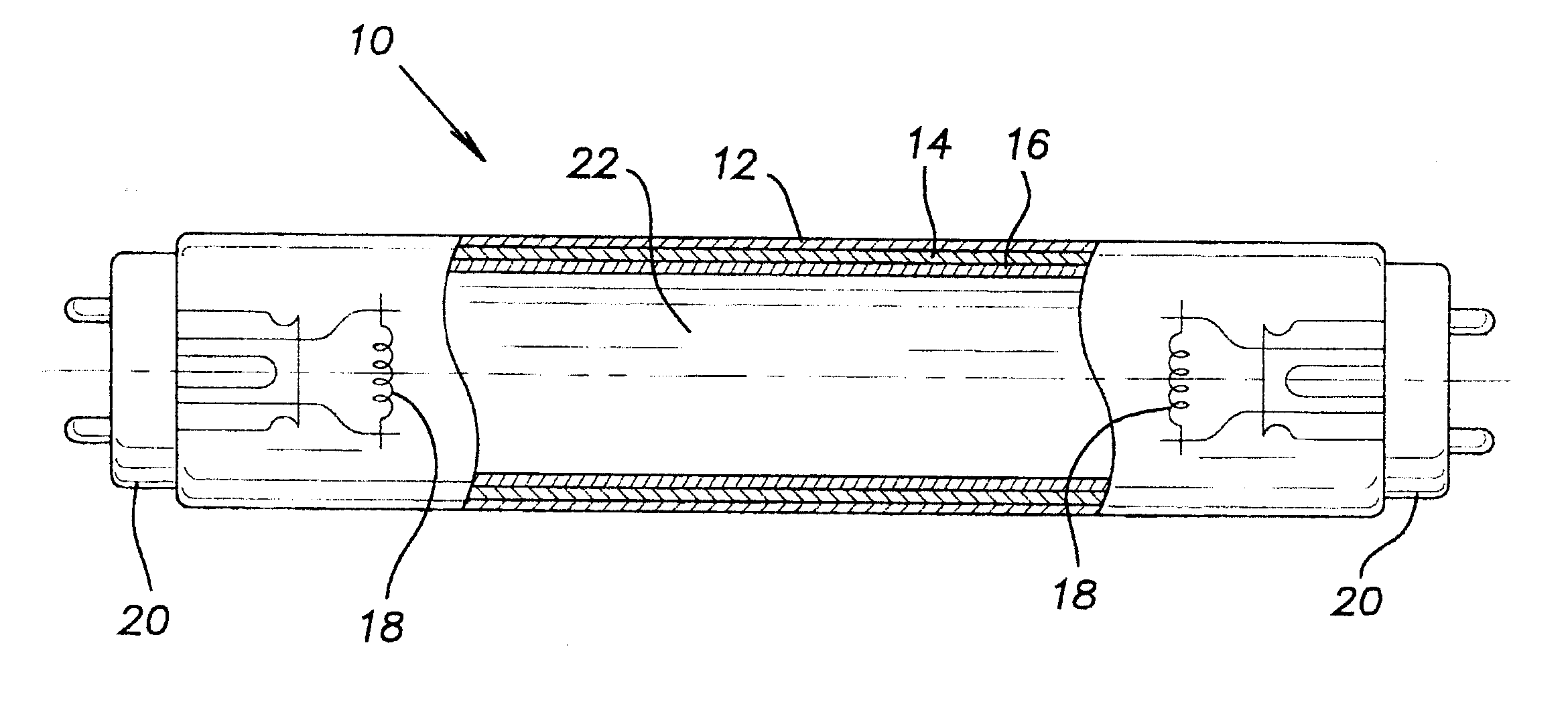
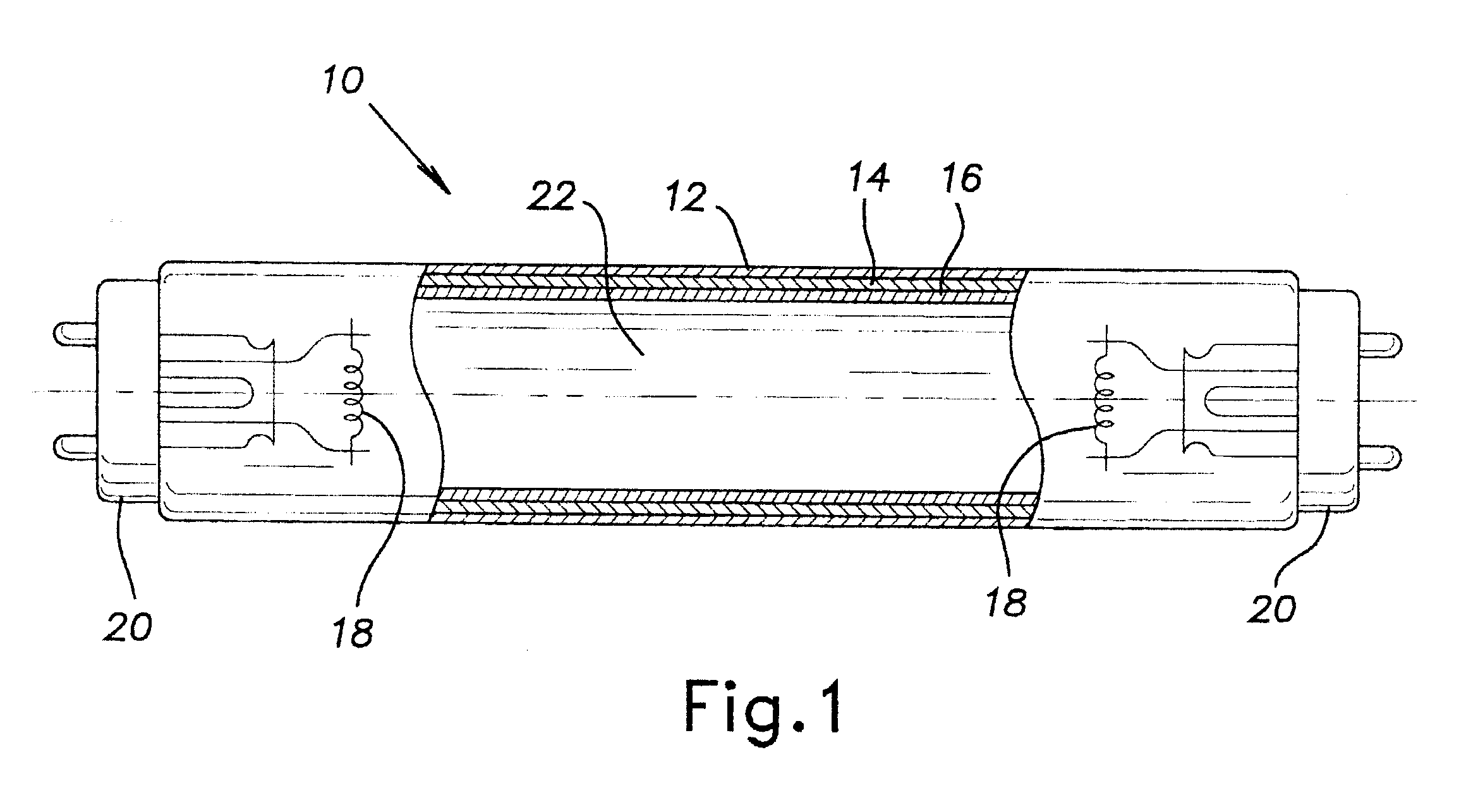
Low wattage fluorescent lamp
InactiveUS6400097B1Less energyIncrease coating weightDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectric lighting sourcesKryptonPhosphor
A low-wattage mercury vapor discharge fluorescent lamp is provided for use with existing 110V high frequency electronic ballasts. The lamp has a discharge sustaining fill gas of mercury vapor and an inert gas that does not require a starting aid. The inert gas has 40-100 vol. % krypton, balance argon, and the fill gas has a total pressure of 0.5-3 torr. The phosphor layer has a coating weight of 2.3-4.3 mg / cm2.
Owner:SAVANT TECH LLC
Method of patterning lead zirconium titanate and barium strontium titanate
In an embodiment of the present invention, a method is provided of patterning PZT layers or BST layers. For example, a PZT layer or a BST layer is plasma etched through a high-temperature-compatible mask such as a titanium nitride (TiN) mask, using a plasma feed gas comprising as a primary etchant boron trichloride (BCl3) or silicon tetrachloride (SiCi4). Although BCl3 or SiCl4 may be used alone as the etchant plasma source gas, it is typically used in combination with an essentially inert gas. Preferably the essentially inert gas is argon. Other potential essentially inert gases which may be used include xenon, krypton, and helium. In some instances O2 or N2, or Cl2, or a combination thereof may be added to the primary etchant to increase the etch rate of PZT or BST relative to adjacent materials, such as the high-temperature-compatible masking material. A TiN masking material can easily be removed without damaging underlying oxides. The selectivity of PZT or BST relative to TiN is very good, with the ratio of the etch rate of the PZT film to the etch rate of the TiN mask typically being better than 20:1. In addition, the etch rate for PZT using a BCl3-comprising plasma source gas is typically in excess of 2,000 Å per minute. A substrate bias power is applied to direct ions produced from the BCl3 or SiCl4 toward the surface to be etched. The bias power is controlled to avoid sputtering of a conductive layer or layers in contact with the PZT layer, so that the surface of the etched PZT is not contaminated by a conductive material, which can cause the semiconductor device which includes the patterned PZT to short out.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
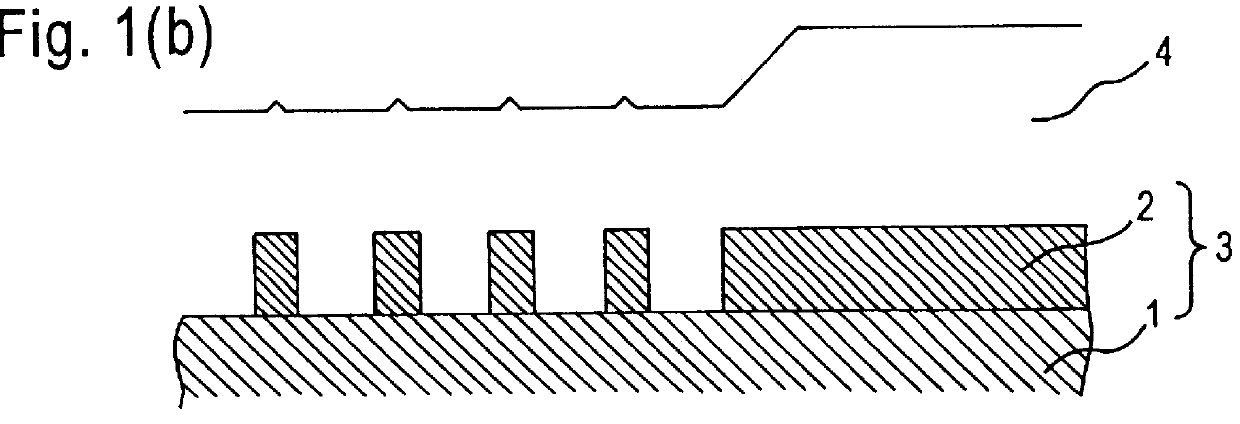
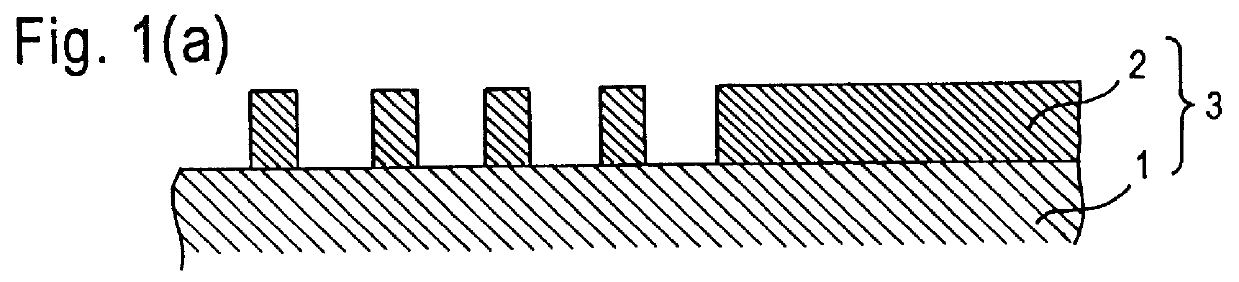
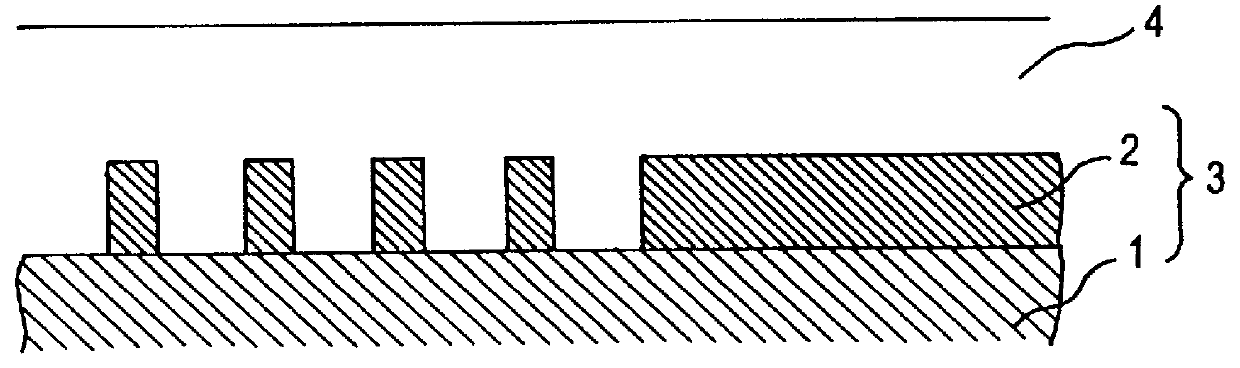
Dry etching method and photonic crystal device fabricated by use of the same
InactiveUS20050155951A1Minimize surface roughnessReduce roughnessElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsKryptonPhotonic crystal
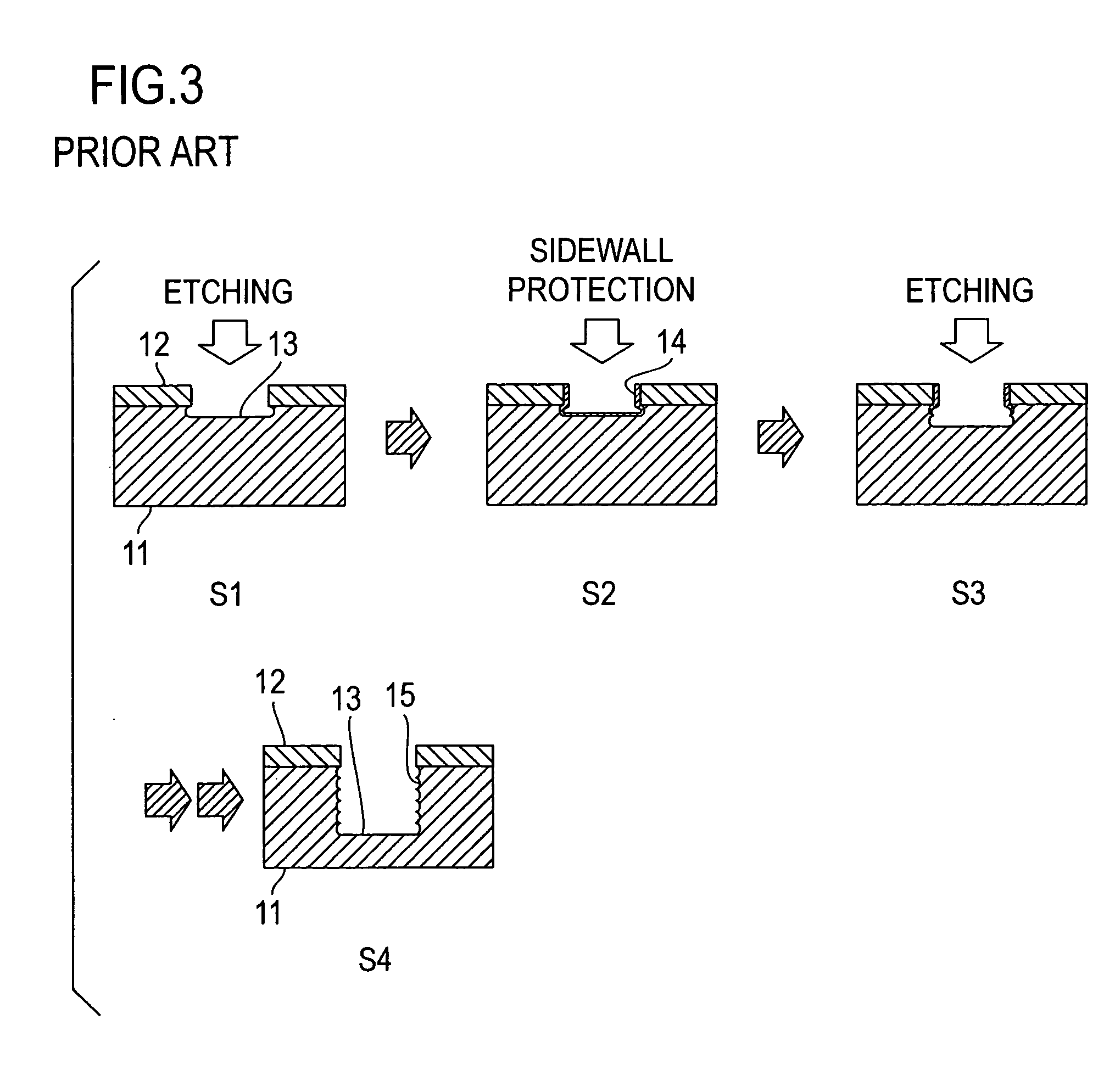
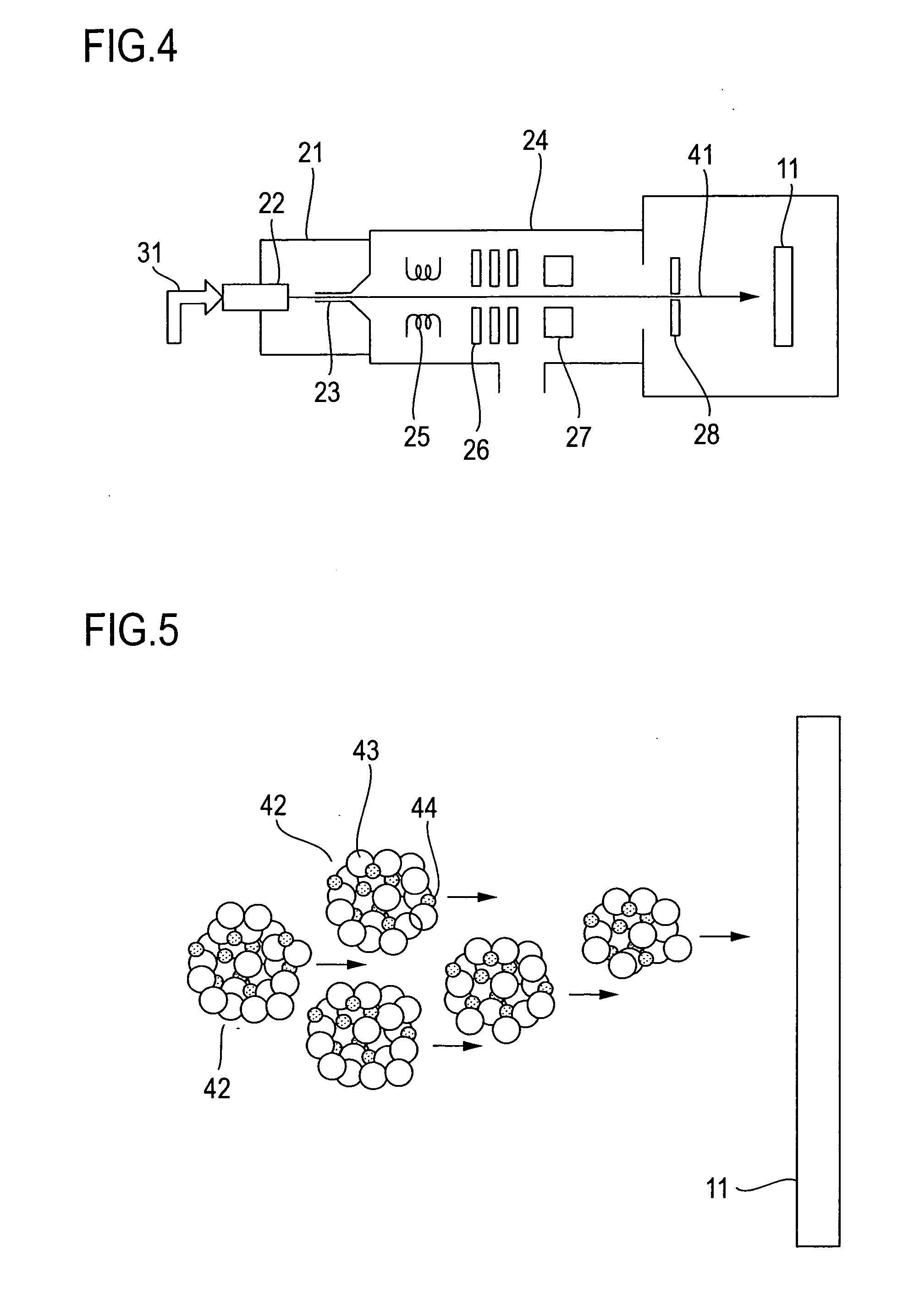
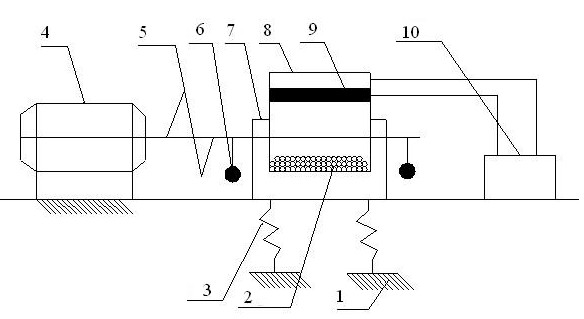
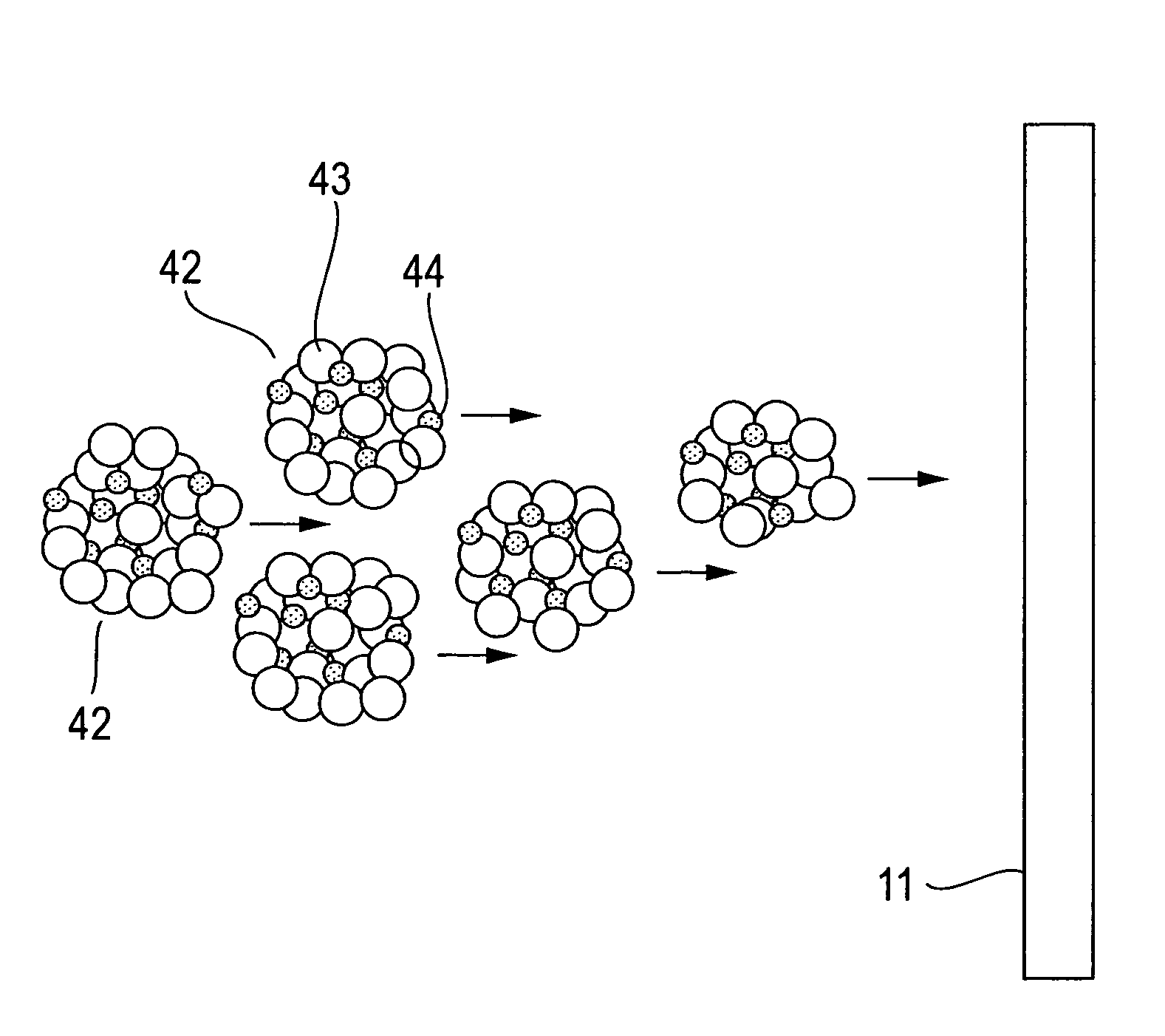
In a dry etching method in which clusters formed by agglomeration of atoms or molecules are ionized and accelerated as a cluster ion beam for irradiation of an object surface to etch away therefrom its constituent atoms, the clusters are mixed clusters 42 formed by agglomeration of two or more kinds of atoms or molecules, and the mixed clusters 42 contain atoms 43 of at least one of argon, neon, xenon and krypton, and a component 44 that is deposited on the object surface to form a thin film by reaction therewith. With this method, it is possible to provide an extremely reduced sidewall surface roughness and high vertical machining accuracy.
Owner:JAPAN AVIATION ELECTRONICS IND LTD
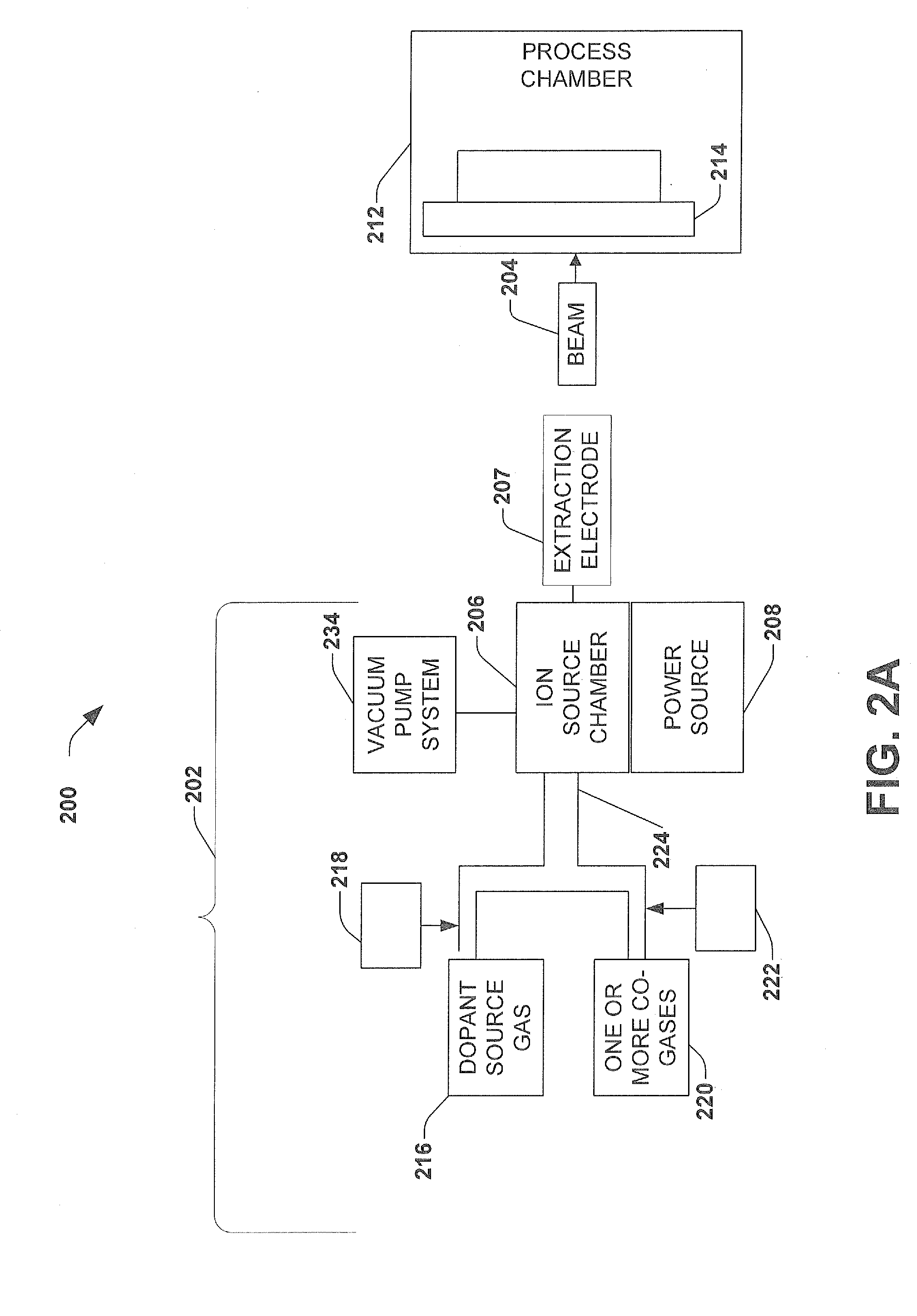
Implementation of CO-Gases for Germanium and Boron Ion Implants
ActiveUS20120119113A1Reduce harmIncrease ion source lifetimeElectric discharge tubesRadiation therapyKryptonHydrogen
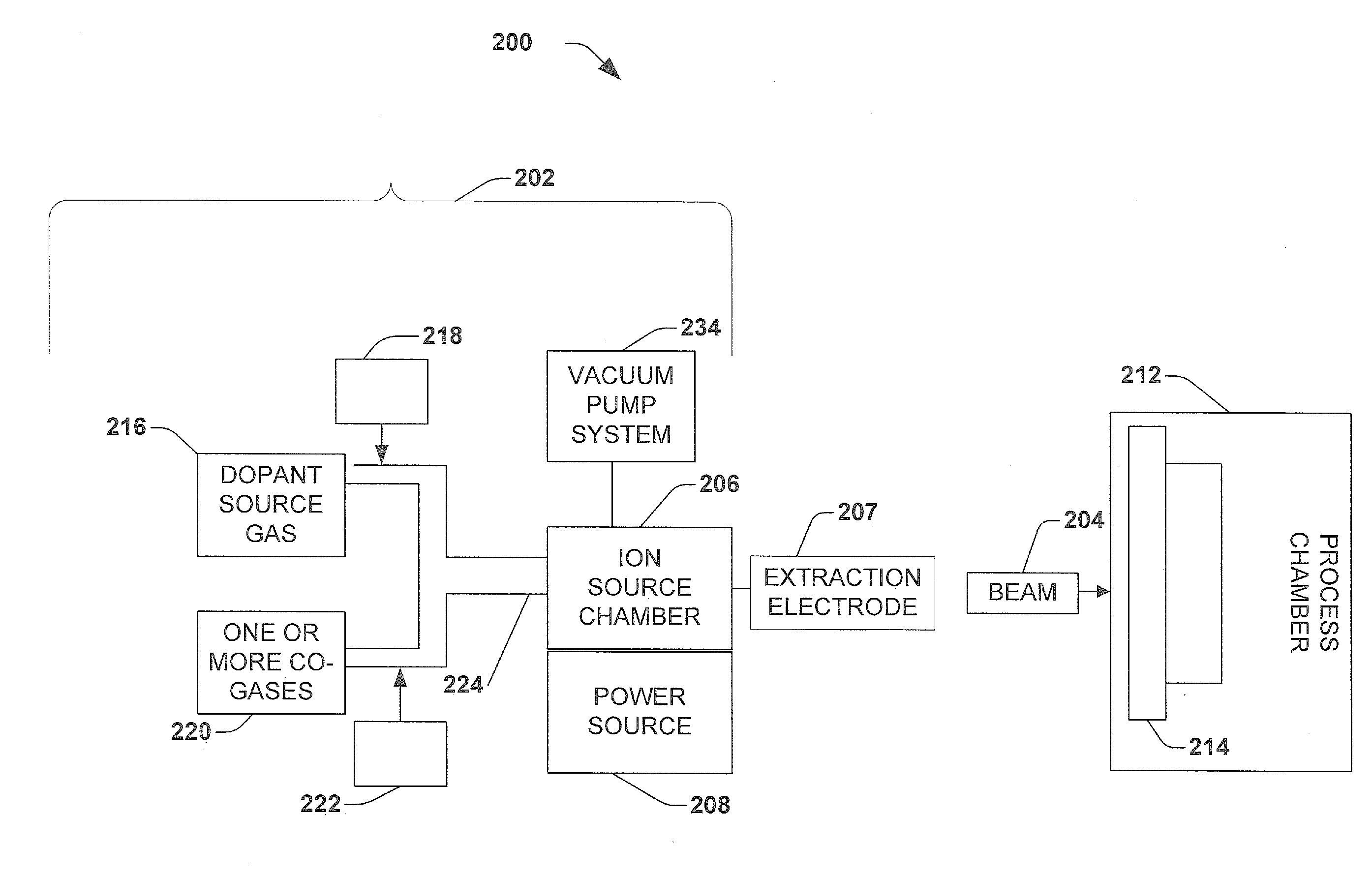
An ion implantation system for improving performance and extending lifetime of an ion source is disclosed. A fluorine-containing dopant gas source is introduced into the ion chamber along with one or more co-gases. The one or more co-gases can include hydrogen or krypton. The co-gases mitigate the effects caused by free fluorine ions in the ion source chamber which lead to ion source failure.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
Active gases and treatment methods
InactiveUS20120064016A1Optimise populationNegative side effectCosmetic preparationsBiocideKryptonNoble gas
A method of making an active gas by generating a glow discharge, non-thermal plasma, in a gas mixture of a carrier gas and a more readily ionisable gas. The gas mixture is exposed to water vapour at or downstream from the generator to form the active gas. The gas mixture includes helium as the carrier gas and up to 40% by volume of at least one noble gas such as argon, krypton, or xenon as the more readily ionisable gas. The gas mixture is ejected at a temperature between 5° C. to 42° C. The active gas may be used for oral treatment such as cosmetic whitening of teeth, medical or non-clinical cleaning of teeth or for cleaning laundry or dishwashing items.
Owner:LINDE AG
Process For Preserving Biological Materials For Extended Periods Of Time
The present invention provides for a process for preserving biological material. The process comprises subjecting the biological material to a fixation process and then packaging the biological material in a container under a controlled atmosphere of noble gas. In the process, the controlled atmosphere of noble gas utilized comprises one or more noble gases selected from argon, xenon, helium, neon, krypton and radon. The process optionally also utilizes one or more additional gases selected from nitric oxide, hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and oxygen. This process allows for the long term storage of the biological material.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE HEALTHCARE AMERICA CORP +1
High pressure processing of a substance utilizing a controlled atmospheric environment
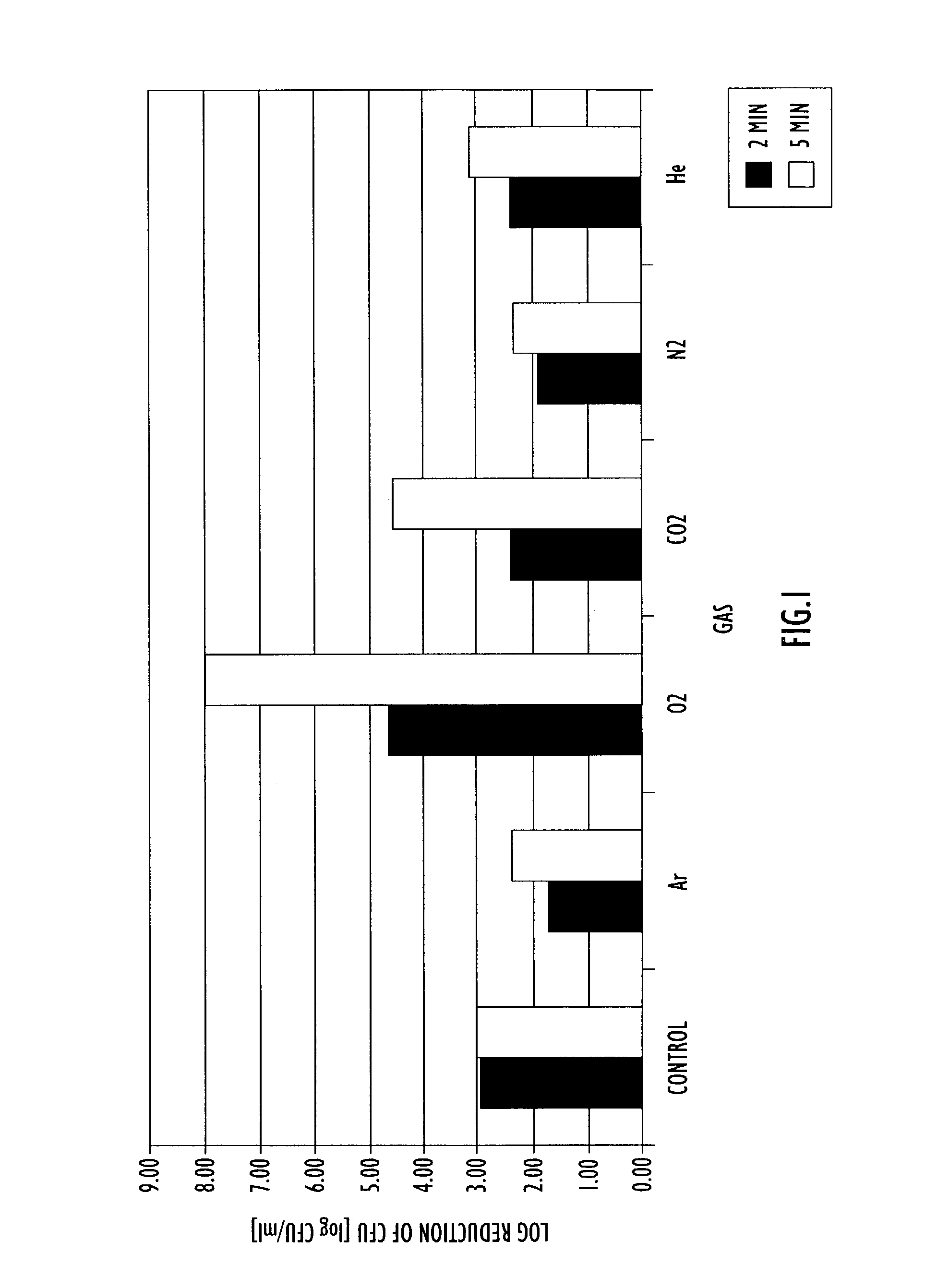
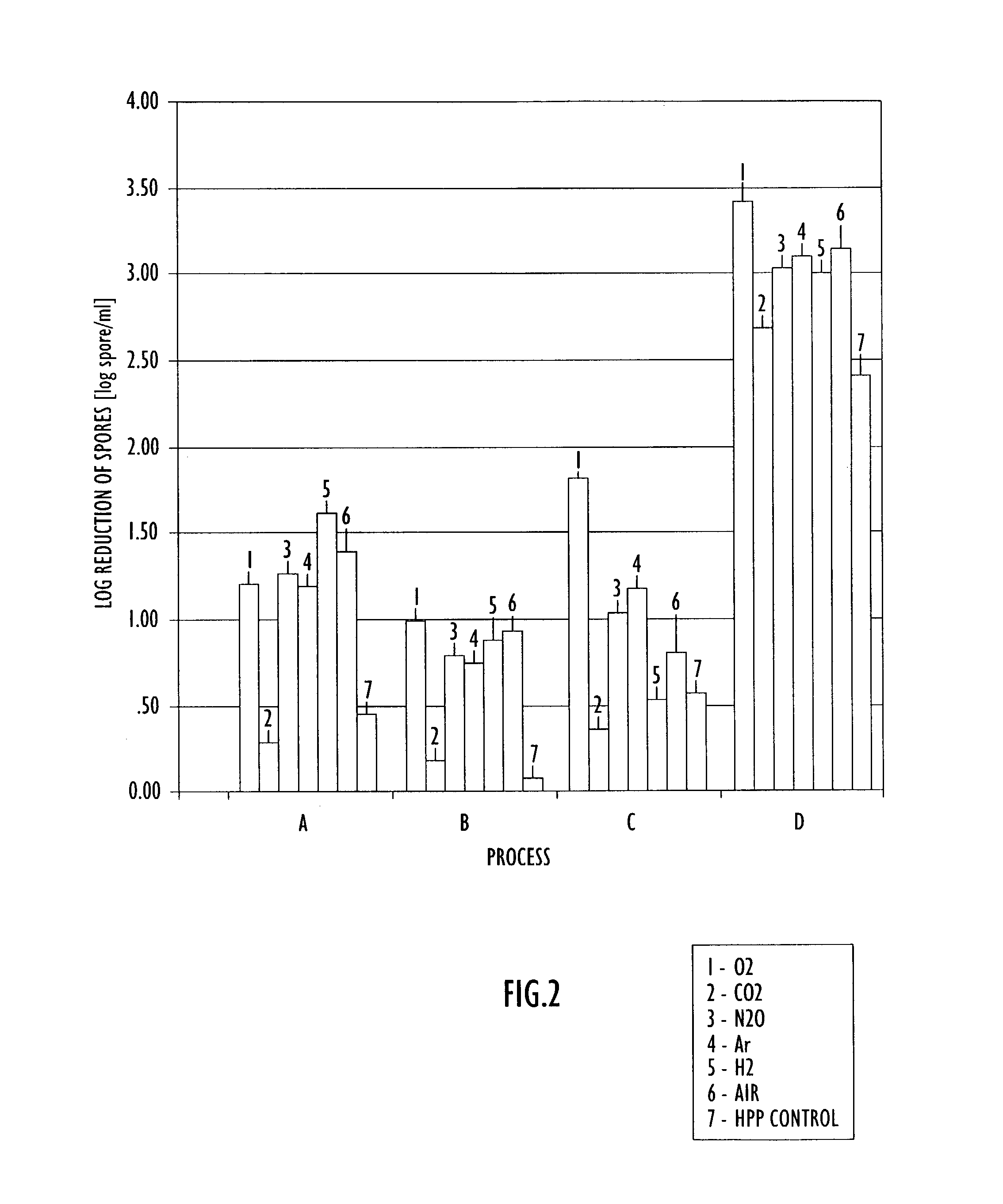
InactiveUS20030170356A1Slow growth ratePrevent spoilageFatty acid hydrogenationFood preservationKryptonNitric oxide
A method of processing a substance, such as a food item, utilizing high pressure processing includes providing an enclosed environment including the substance and one or more of the following gases: carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, nitric oxide, nitrous oxide, hydrogen, oxygen, helium, argon, krypton, xenon and neon. The enclosed environment including the substance and at least one gas is subjected to high pressure processing and sealed in a container. The high pressure processing may occur prior to or after sealing the substance in the container. Control of the amount and type of gases in the enclosed environment including the substance enhances the biocidal efficacy of high pressure processing as well as ensuring desirable sensory qualities of the substance during storage.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC +1
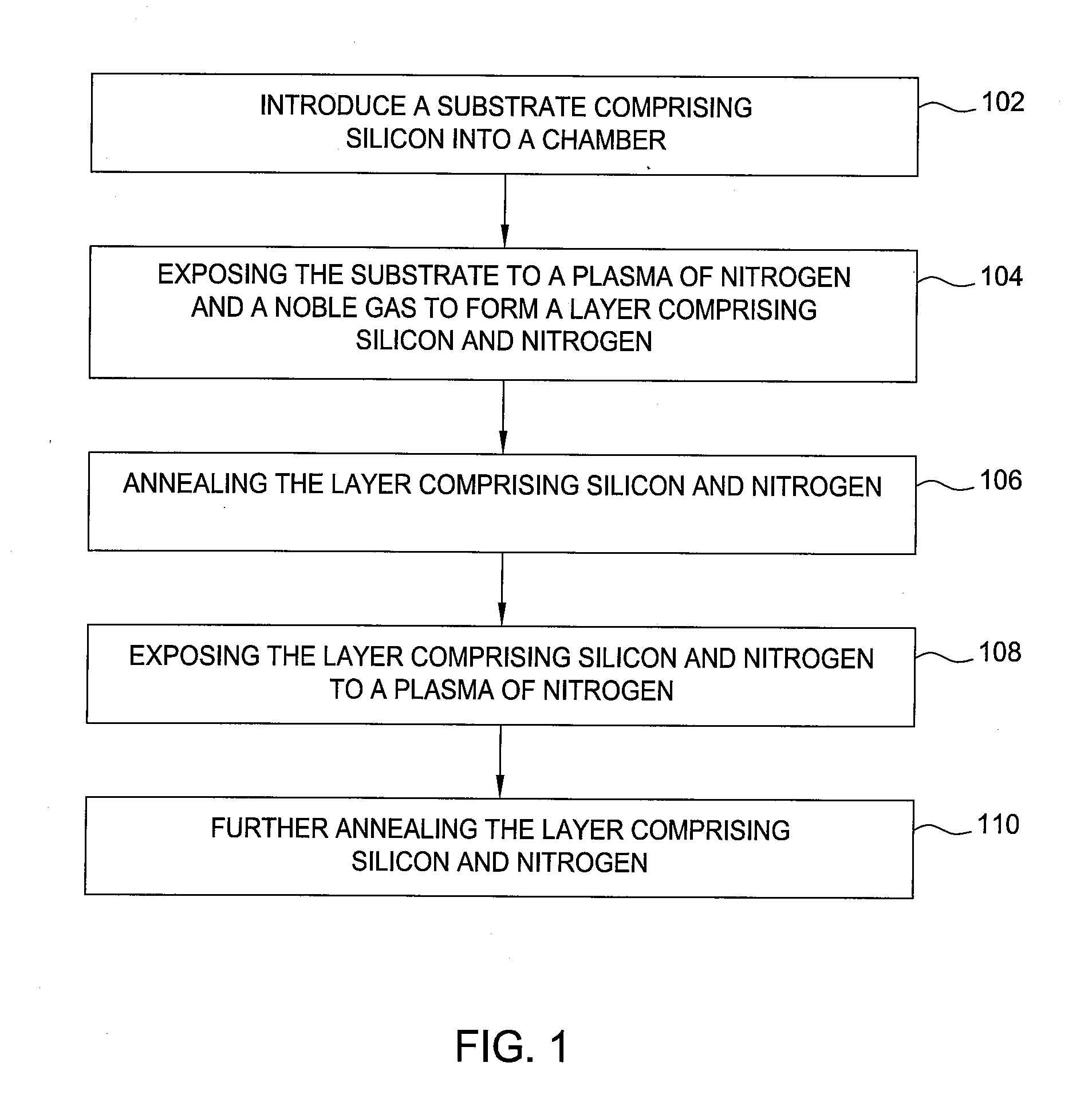
CMOS sion gate dielectric performance with double plasma nitridation containing noble gas
A method of forming a layer comprising silicon and nitrogen on a substrate is provided. The layer may also include oxygen and be used as a silicon oxynitride gate dielectric layer. In one aspect, forming the layer includes exposing a silicon substrate to a plasma of nitrogen and a noble gas to incorporate nitrogen into an upper surface of the substrate, wherein the noble gas is argon, neon, krypton, or xenon. The layer is annealed and then exposed to a plasma of nitrogen to incorporate more nitrogen into the layer. The layer is then further annealed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor device having improved insulation film and manufacturing method thereof
A semiconductor device which has an interlayer insulating film comprised of molecules with silicon-oxygen bonds and silicon-fluorine bonds and contains a rare gas in concentration higher than 1011 atoms per cm2. The interlayer insulating film is preferably a fluorine-containing silicon oxide film which contains a rare gas. In a manufacturing process, an interlayer insulating is formed by a chemical vapor deposition from a material gas including a silicon-containing gas, a fluorine compound gas, a rare gas, and oxygen. The silicon-containing gas is preferably SiH4 gas, and the fluorine compound gas is preferably SiF4 gas. The flow rate of the rare gas is greater than three times the total flow rate of the SiH4 gas and SiF4 gas. The rare gas is at least one type of gas selected from neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), and xenon (Xe).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
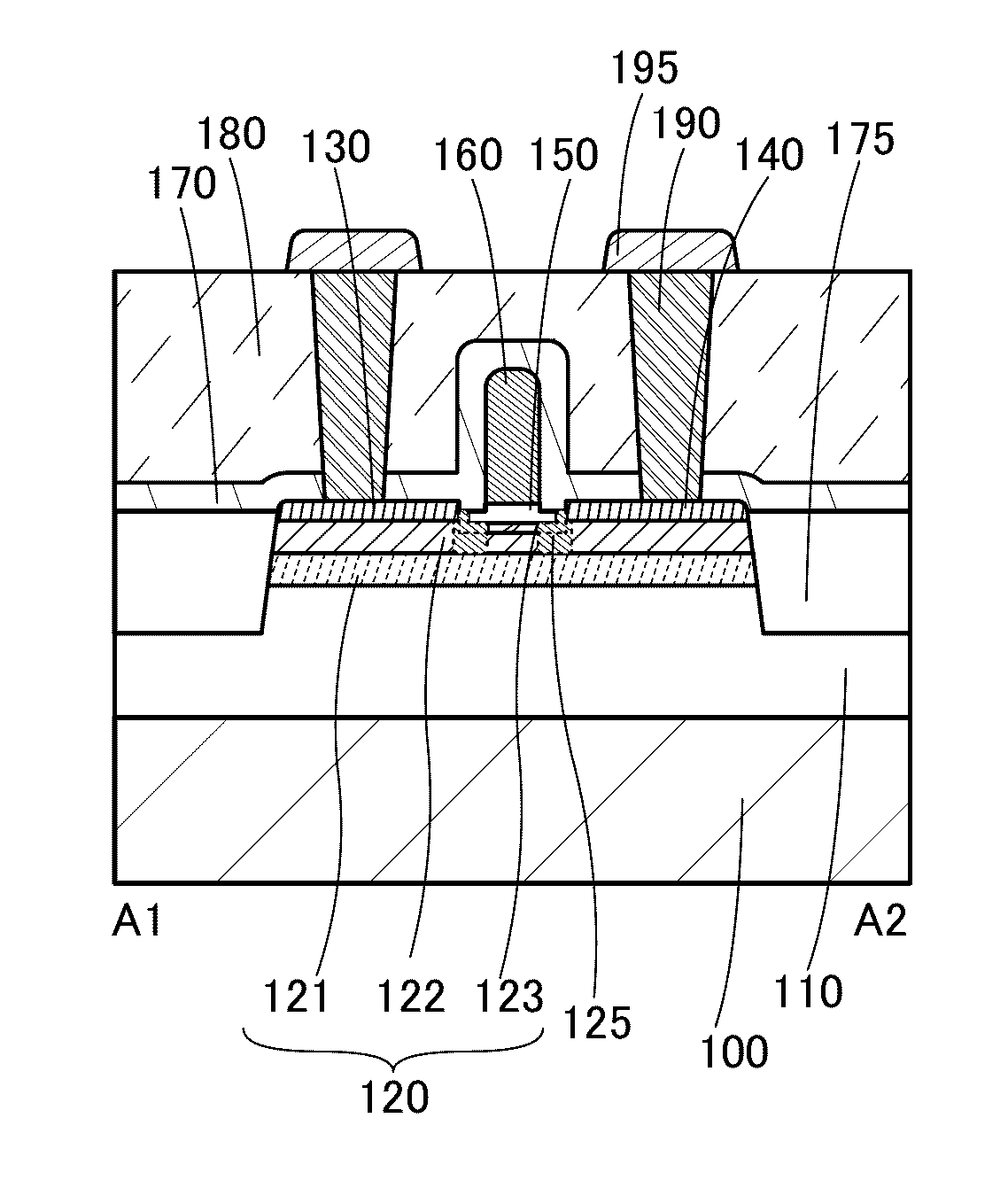
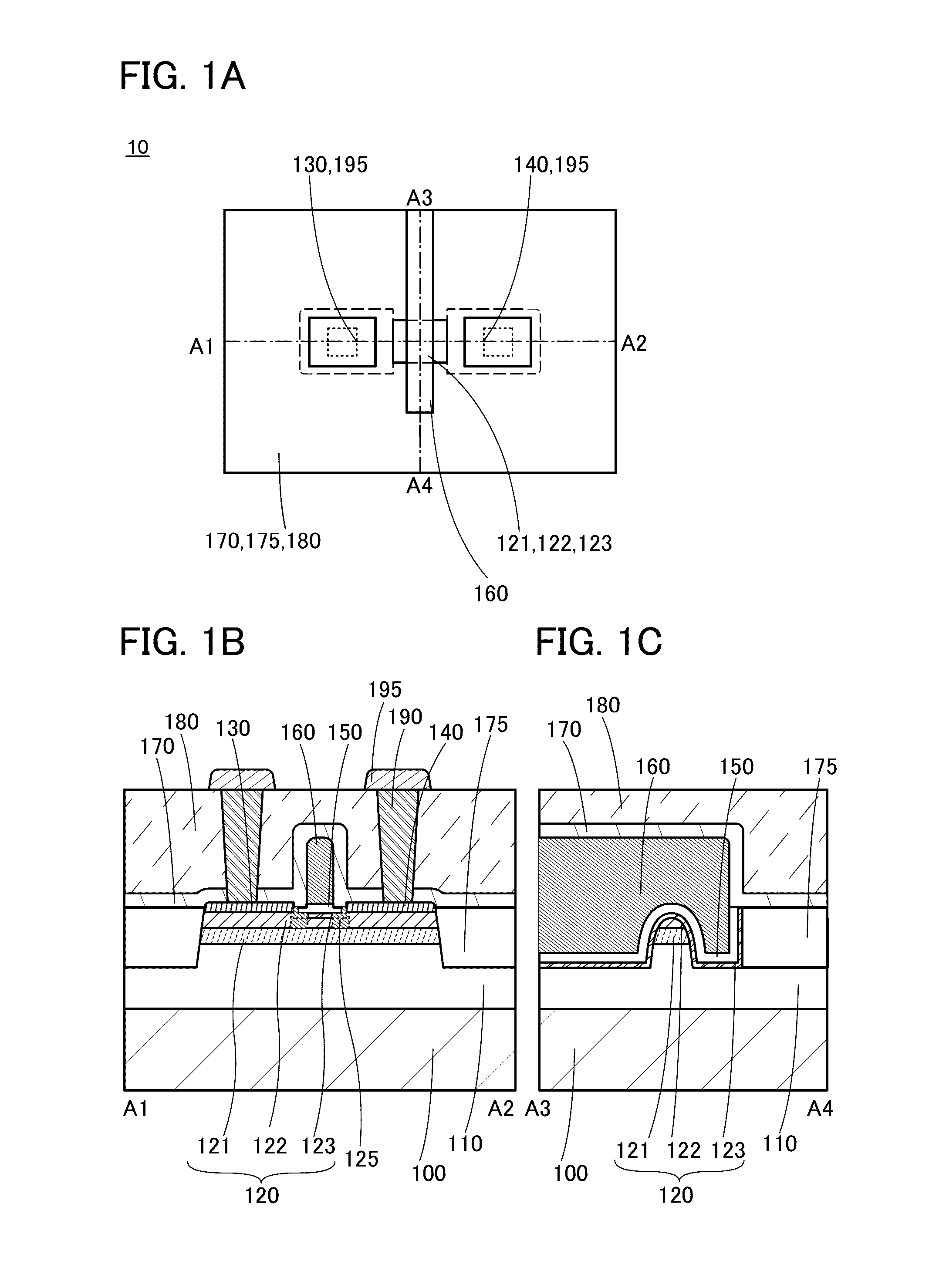
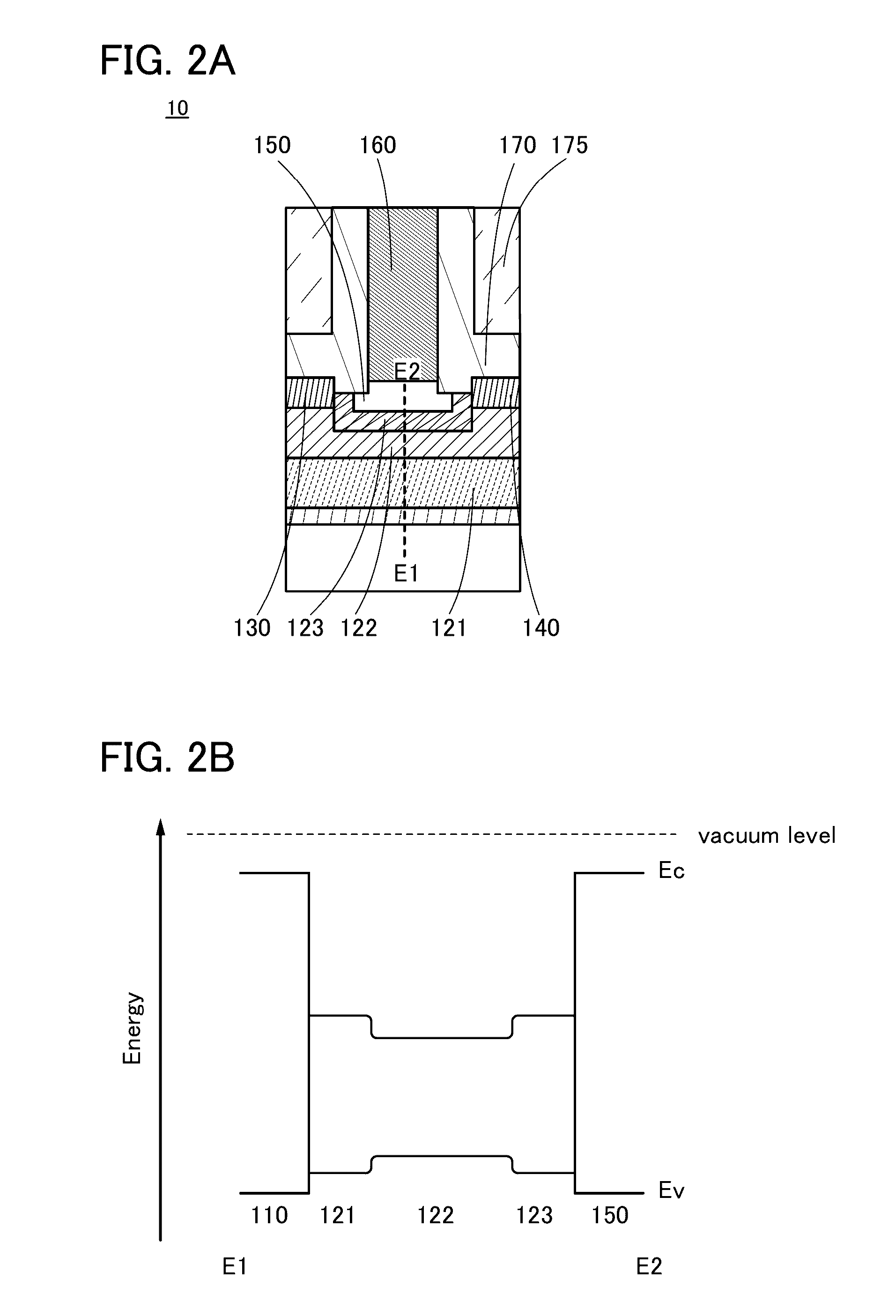
ActiveUS20160284859A1ResponsivenessReduced responsivenessTransistorSolid-state devicesKryptonSemiconductor device modeling
A semiconductor device with low parasitic capacitance is provided. The semiconductor device includes a first oxide insulator, an oxide semiconductor, a second oxide insulator, a gate insulating layer, a gate electrode layer, source and drain electrode layers and an insulating layer. The oxide semiconductor includes first to fifth regions. The first region overlaps with the source electrode layer. The second region overlaps with the drain electrode layer. The third region overlaps with the gate electrode layer. The fourth region is between the first region and the third region. The fifth region is between the second region and the third region. The fourth region and the fifth region each contain an element N (N is hydrogen, nitrogen, helium, neon, argon, krypton, or xenon). A top surface of the insulating layer is positioned at a lower level than top surfaces of the source and drain electrode layers.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Grade-C halogen lamp
InactiveCN102082066BIncrease contentReduce volatilityIncandescent lamp energy savingGas filling substancesX-ray shieldKrypton
The invention discloses a grade-C halogen lamp. 75 to 85 percent of krypton gas, 6 to 15 percent of dibromomethane, 3 to 7 percent of nitrogen gas and 3 to 7 percent of argon gas are charged into a quartz glass bulb shell, and the charge pressure in the bulb shell is 2.5 to 3.5 atmospheres. Through an optimal halogen gas ratio and an optimal formula of auxiliary gases, the luminous flux of the lamp bulb, under the same conditions (the same voltage and constant lamp filament specifications, shape and size), can be improved by about 15 percent, the actually consumed power of the lamp bulb can be reduced by 5 to 8 percent, the actual life of the lamp bulb can be improved by 30 to 50 percent, and the X-ray shielding capacity of the lamp bulb can be improved by 20 percent. According to the data, under the same conditions, the light efficiency of the lamp can be improved considerably, energy can be saved and radiation can be reduced, so the lamp contributes to environment protection and health of human body.
Owner:LIANYUNGANG HENGYANG LIGHTING
Working medium for heat cycle, composition for heat cycle system, and heat cycle system
ActiveCN107614652AFully playLow greenhouse potentialHeat-exchange elementsCompression machinesKryptonEngineering
This working medium for a heat cycle contains trifluoroethylene and a first component comprising at least one substance selected from carbon dioxide, fluoromethane, trifluoroiodomethane, methane, ethane, propane, helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, nitrogen, and ammonia.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Structure and method for manufacturing MOSFET with super-steep retrograded island
InactiveUS7268049B2Reduce morbidityReduce diffuseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingKryptonDopant
The present invention comprises a method for forming a semiconducting device including the steps of providing a layered structure including a substrate, a low diffusivity layer of a first-conductivity dopant; and a channel layer; forming a gate stack atop a protected surface of the channel layer; etching the layered structure selective to the gate stack to expose a surface of the substrate, where a remaining portion of the low diffusivity layer provides a retrograded island substantially aligned to the gate stack having a first dopant concentration to reduce short-channel effects without increasing leakage; growing a Si-containing material atop the recessed surface of the substrate; and doping the Si-containing material with a second-conductivity dopant at a second dopant concentration. The low diffusivity layer may be Si1-x-yGexZy, where Z can be carbon (C), xenon (Xe), germanium (Ge), krypton (Kr), argon (Ar), nitrogen (N), or combinations thereof.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Non-aqueous method for separating chemical constituents in spent nuclear reactor fuel
InactiveUS20060233685A1Reduce riskIncrease ratingsNuclear energy generationPlutonium oxides/hydroxidesKryptonGas phase
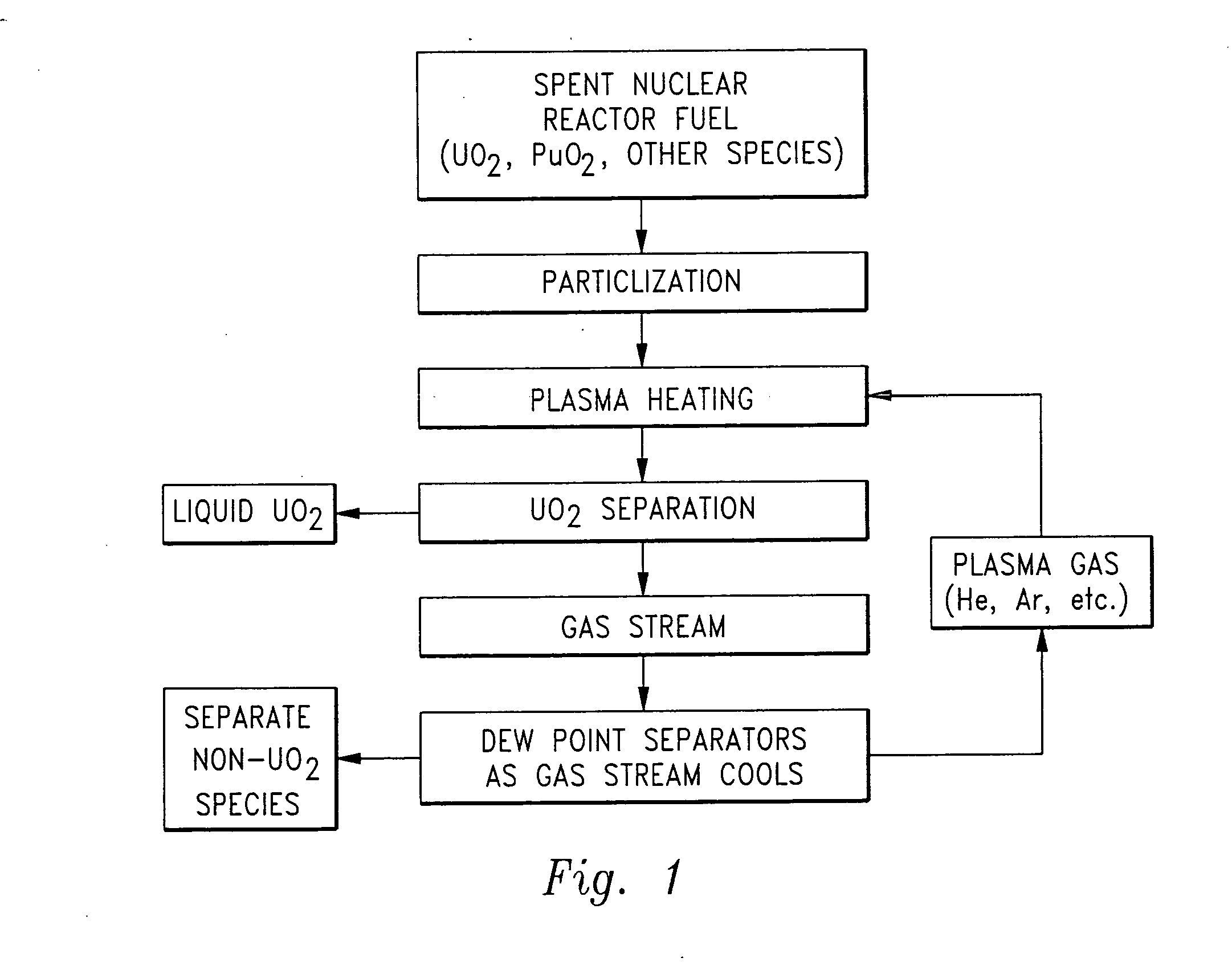
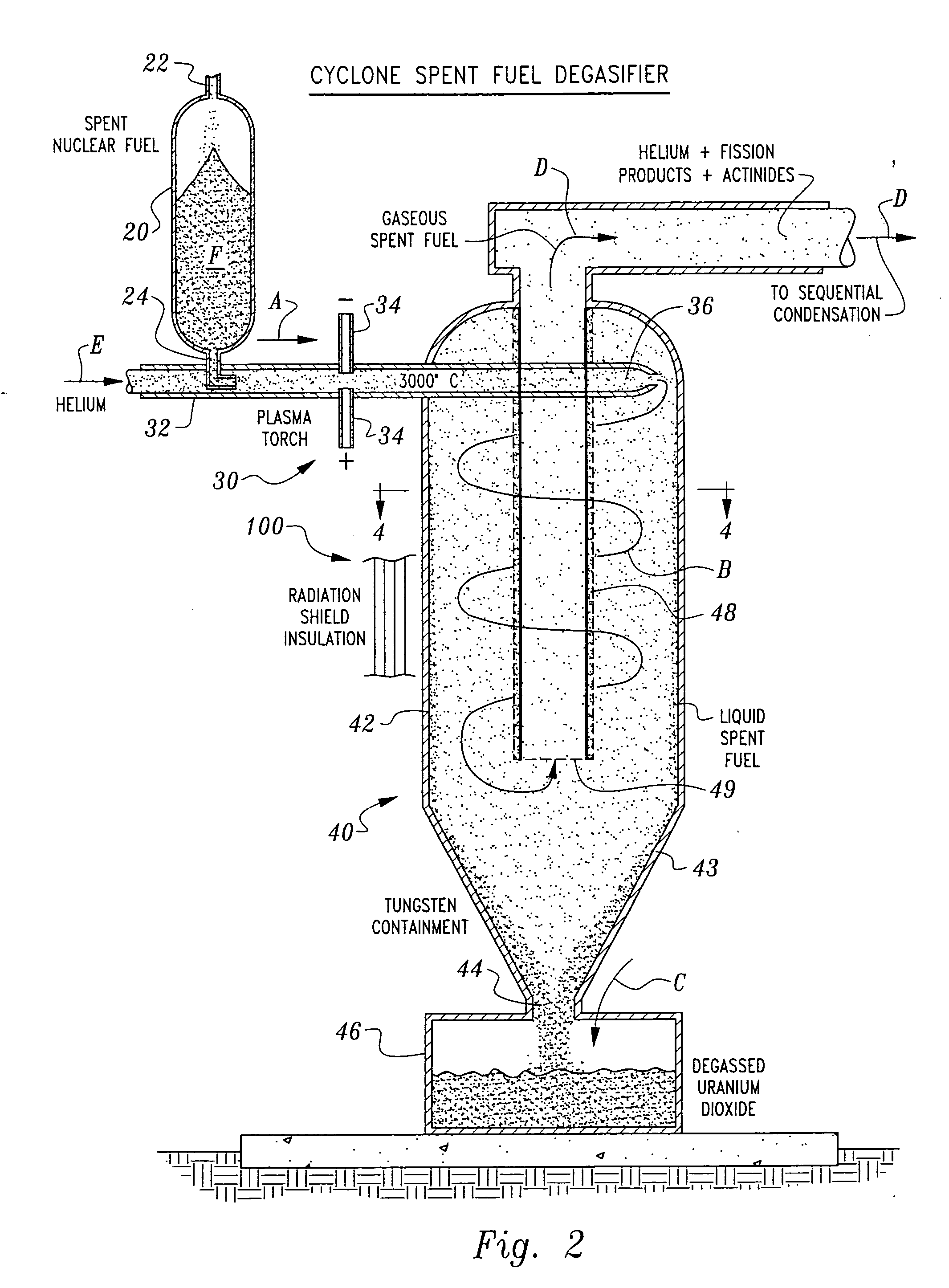
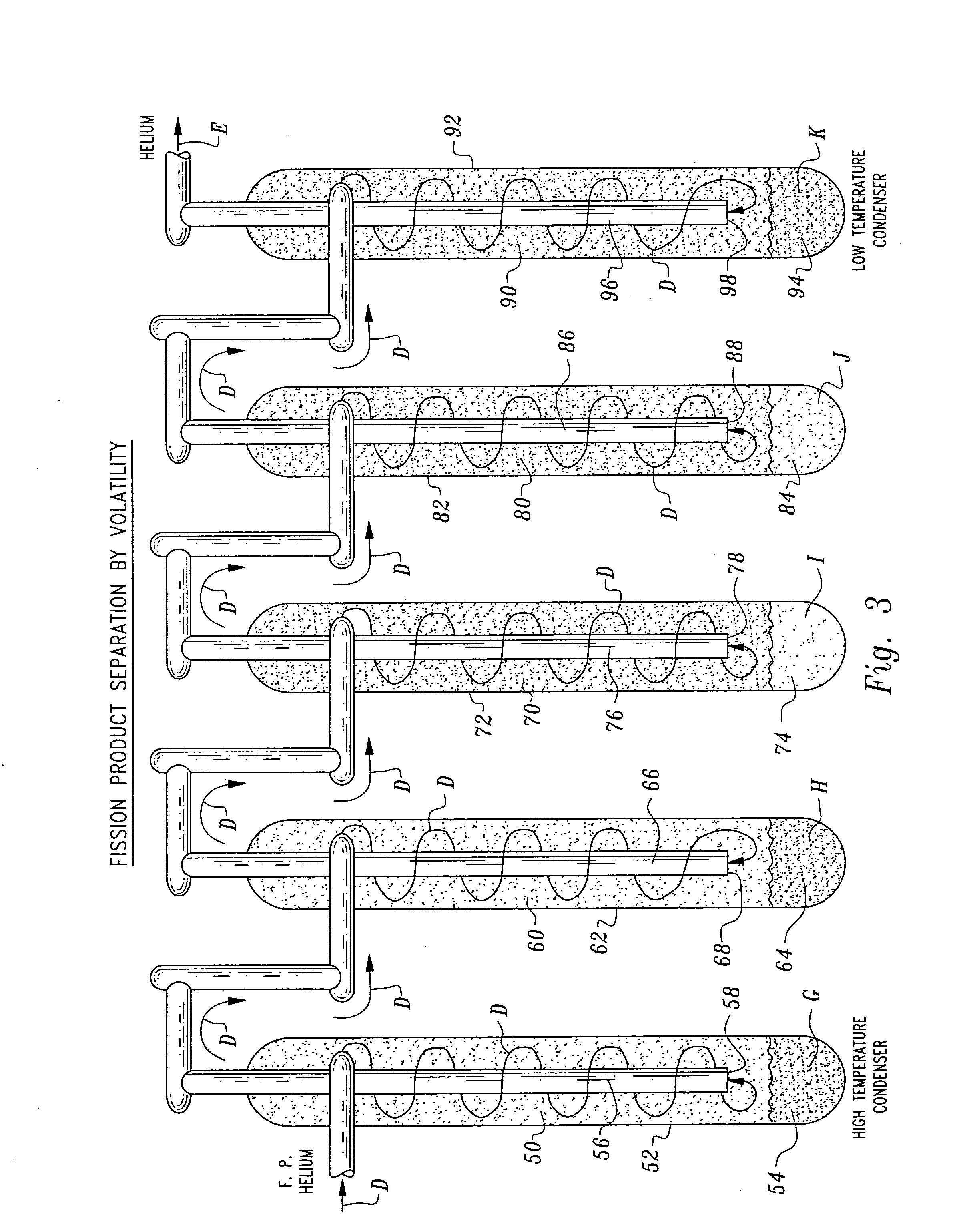
Herein is a method of segregating chemical species contained in spent nuclear reactor fuel without employing conventional acid dissolution. Particularly, pellets of spent fuel are ground to talc sized particles. Heat is added. The preferred heating is by flow through a plasma arc producing micron sized liquid drops suspended in helium flow. The vapor pressure of the chemical species is significantly greater than uranium dioxide. the ultra volatile chemical species evolve from the drops into the helium flow. The gas phase is separated from the mist by a gas / liquid separator (demister). Heavy mist drops of UO2 impact the walls, coalesce and flow down to the separator drain, becoming legally transportable. Helium flow exhausts from the separator vertically. The gaseous chemical species will condense in sequentially cooler stages and separate from the helium down to the cryogenic temperatures of liquid radioactive xenon and krypton. Non-condensed helium is recycled.
Owner:JANES CLARENCE W
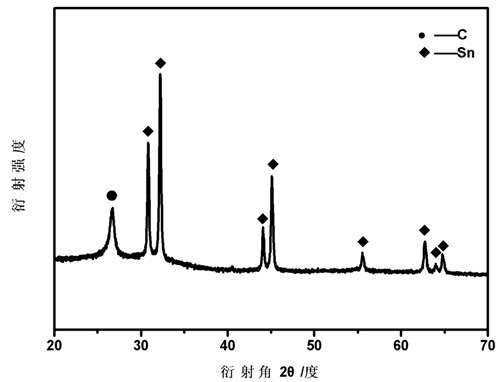
Preparation method of tin carbon composite material for negative electrode of lithium ion batteries
ActiveCN102185135AReduce relative volume changeImprove cycle performanceCell electrodesCarbon compositesKrypton
The invention discloses a preparation method of a tin carbon composite material for negative electrode of lithium ion batteries. The preparation method comprises the following steps: the method that a medium is adopted to block discharge plasma for assisting high-energy ball milling is adopted to ball mill the mixed powder of tin and graphite for 2.5h to 20h, thus obtaining the tin carbon composite powder; and then the tin carbon composite powder is made into an lithium ion electrode plate which is then assembled into batteries, wherein the mass of a graphite raw material accounts 30 to 70 percent of the total mass of the mixed powder; during the ball milling process, the mass ratio of the grinding balls to the ball powder of the tin and graphite mixed powder is 30:1 to 70:1; and the medium adopts an inert gas which is not reacted with Sn, such as helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon or nitrogen. The preparation method can effectively improve ball-milling efficiency, keep lamellar integrity of graphite, improve first reversible capacity and cycle life, and refine Sn particles to enable the relative volume change of a working electrode in the charging and discharging process to be reduced and improve the cycle performance of the lithium batteries.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method and Apparatus for Pressure Swing Adsorption
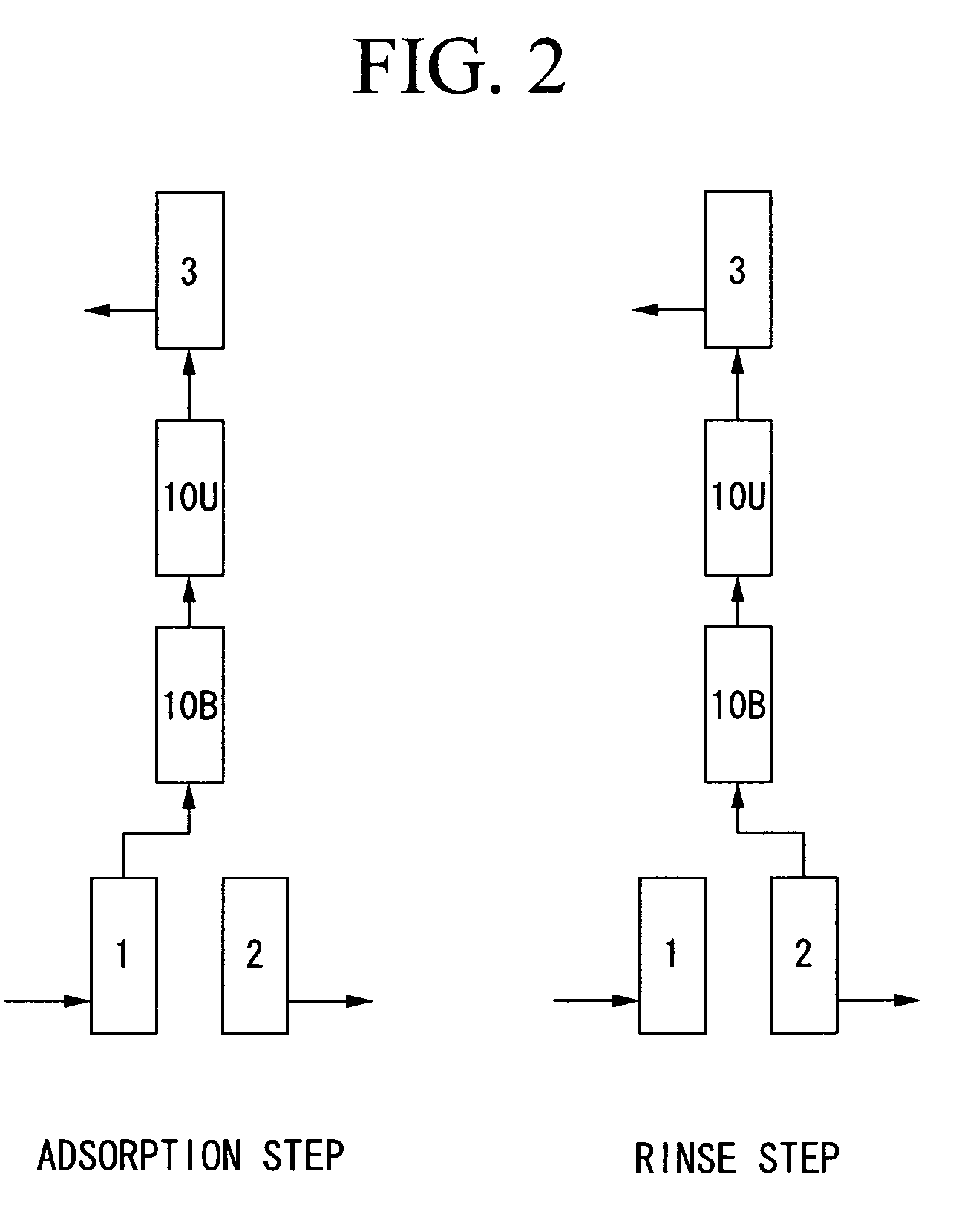
ActiveUS20090107331A1High recovery rateLow costGas treatmentIsotope separationHigh concentrationKrypton
In order to provide a new PSA method which can concentrate simultaneously a strong adsorbate such as xenon and a weak adsorbate such as nitrogen in a high concentration with a high recovery percentage when highly valuable gas such as xenon and krypton contained in the exhaust gas from a semiconductor manufacturing equipment, etc. is recovered in a high concentration with a high recovery percentage, the present invention provides a new PSA method in which the method uses a separation apparatus comprising a lower column and a upper column which are filled with an adsorbent, a material gas storage tank for storing the material gas to be introduced into the lower column, a strong adsorbate storage tank for storing a main component which is easily adsorbed by the adsorbent, and a compressor, and the strong adsorbate which is easily adsorbed by the adsorbent and the weak adsorbate which is not readily adsorbed by the adsorbent are recovered, wherein the method comprises an (a) adsorption step, (b) rinse step, (c) low column depressurization step, (d) upper column depressurization step, and (e) purge step sequentially repeated based on a predetermined sequence.
Owner:NIPPON SANSO CORP
Laser system utilizing sorbent-based gas storage and delivery system
A laser system utilizing a fluid as the excitatory medium for stimulated light emission, wherein the fluid is supplied from a sorbent-based fluid storage and dispensing system coupled in fluid-supplying relationship with the laser apparatus. The laser may be an excimer laser utilizing as the laser working fluid a rare gas halide compound such as fluorides and / or chlorides of krypton, xenon and argon, as well as fluorine and / or chlorine per se. The laser system may alternatively be a far infrared gas laser utilizing a gas such as CO2, N2O, CD3OD, CH3OD, CH3OH, CH3NH2, C2H2F2, HCOOH, CD3I, CH3F, and C13H3F. Laser systems of the present invention may be utilized in applications such as materials processing, measurement and inspection, reading, writing, and recording of information, holography, communications, displays, spectroscopy and analytical chemistry, remote sensing, surveying, marking, and alignment, surgical and medical applications, plasma diagnostics, laser weaponry, laser-induced nuclear fusion, isotope enrichment and atomic physics.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Dry etching method and photonic crystal device fabricated by use of the same
InactiveUS7563379B2Reduce roughnessHigh precision machiningElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsKryptonPhotonic crystal
In a dry etching method in which clusters formed by agglomeration of atoms or molecules are ionized and accelerated as a cluster ion beam for irradiation of an object surface to etch away therefrom its constituent atoms, the clusters are mixed clusters 42 formed by agglomeration of two or more kinds of atoms or molecules, and the mixed clusters 42 contain atoms 43 of at least one of argon, neon, xenon and krypton, and a component 44 that is deposited on the object surface to form a thin film by reaction therewith. With this method, it is possible to provide an extremely reduced sidewall surface roughness and high vertical machining accuracy.
Owner:JAPAN AVIATION ELECTRONICS IND LTD
Nanoporous articles and methods of making same
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Method for quickly structurizing water molecules of fresh-cut fruits and fresh-cut vegetables under ultrahigh pressure to preserve fresh-cut fruits and vegetables with low cost
InactiveCN101700055AMaintain sensory propertiesMaintain nutritional valueFruit and vegetables preservationNutritive valuesKrypton
The invention relates to a method for quickly structurizing the water molecules in fresh-cut fruits and the fresh-cut vegetables under ultrahigh pressure to preserve the fresh-cut fruits and the fresh-cut vegetables with low cost, belonging to the filed of the fruit and the vegetable preserving technology. After the raw fruits and the raw vegetables are peeled and cut, any two of the nonpolar gases including argon gas, krypton gas, nitrogen and carbon dioxide, which are at the proportion of 1:1, are fed in the fruits and the vegetables, then the fruits and the vegetables are packaged and sealed by PET / PE composite film packaging bags which have the pressureproof density of 98-110 g / cm and the pressureproof thickness of 72+ / -2 Mum, and the fruits and the vegetables are put in a superhigh-pressure container to be pressurized to 300-400 MPa at 10-15 DEG C for 20-30 min with the pressurizing speed being controlled at 50 MPa / s and the depressurizing speed being controlled at 100 MPa / s. The method can quickly structurize the water in the surfaces and the tissues of fresh-cut fruits and the fresh-cut vegetables which are processed at superhigh pressure on the basis of keeping the original nutritional value and sensory quality of the fruits and the vegetables so as to reduce the activity of the water molecules in the fresh-cut fruits and the fresh-cut vegetables, inhibit the enzymatic reaction and the microbial action of the tissues in the fresh-cut fruits and the fresh-cut vegetables and prolong the shelf lives of the fresh-cut fruits and the fresh-cut vegetables to 10-15 days.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High-flux electrodeless vacuum ultraviolet light source
InactiveCN101567297APrevent thermal deformationStable physical and chemical propertiesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectric discharge lampsKryptonRadio frequency
The invention discloses a high-flux electrodeless vacuum ultraviolet light source, which consists of a radio frequency power supply, a radio frequency tuned matching device, a gas distribution system, a gas cushion chamber, an electromagnetic induction coil, an inert gas excitation tube and a magnesium fluoride lens window sheet. The excited gas is inert gas of helium, neon, argon, krypton gas, xenon and the like or certain proportion of mixed gas thereof. The interfaces of a magnesium fluoride lens, the inert gas excitation tube and the gas cushion chamber are sealed by using fluorinated O-ring, and the method is simple and convenient, and can be repeatedly demounted and randomly replace damaged parts of a lamp body. The light source mainly outputs 8 to 10.5 eV of continuous vacuum ultraviolet light.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com