Patents
Literature
937 results about "Acid dissolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
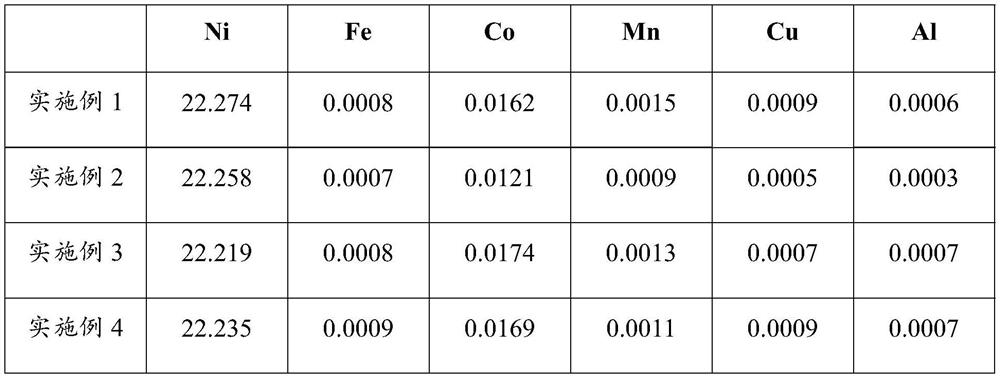
Method for recovering cobalt, nickel and manganese from waste lithium cells
ActiveCN101871048ANo pollution in the processReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodAlkaline earth metal
The invention discloses a method for recovering cobalt, nickel and manganese from waste lithium cells. Most of the conventional recovery methods can hardly guarantee the product quality. The technical scheme adopted by the invention is as follows: (1) the anode materials of waste lithium cells are immerged in low-concentration alkali solution, and because the anode materials do not react with the alkali solution, the anode materials shed from aluminum sheets to become black powder; (2) for the black powder, dilute sulfuric acid is first adopted for low-acid dissolution, Na2SO5 or Na2SO3 or Fe powder added with concentrated sulfuric acid is then adopted for reduction and dissolution, and finally, 3 to 6mol / L of sulfuric acid is adopted for high-acid dissolution; (3) solid-liquid separation is carried out on the substance obtained in step 2; (4) reagent is adopted for precipitating and deeply removing alkaline earth impurities. The method has the advantages of simple operation, low auxiliary material consumption, high product purity, high metal yield and no environment pollution, and is an ideal method for recovering cobalt, nickel and manganese from waste lithium cells.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAYOU COBALT +1
High-strength ceramsite proppant and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a high-strength ceramsite proppant and a process for preparation, wherein the agent comprises (by weight percentage) Al2O3 74-80%, SiO2 5.5-10.5%, TiO2 2.5-3.5%, Fe2O3 4-9%, other adjuvant 0-3%, the agent also contains SiO2, TiO2, Fe2O3, MnO2, K2O, Na2O, CaO, MgO. The preparation consists of mixing the components into mixed powder, rolling into balls through aerial fog, and finally obtaining the end product through high-sintering.
Owner:渑池县方圆陶粒砂厂
Preparation method for red mud-based iron-series catalyst and application of red mud-based iron-series catalyst in hydrogen production through cracking of methane
InactiveCN105478120AWell-developed pore structureIncrease contentHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsDispersityRed mud
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method for recovering rare-earth waste material
ActiveCN102643992AHigh recovery rateReduce recycling stepsProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementDecomposition
The invention relates to a method for recovering a rare-earth waste material. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) adding a decomposition auxiliary agent and fluxing agent powder into the rare-earth waste material, and evenly mixing to obtain mixed material, wherein the dosage of the decomposition auxiliary agent is 20-200wt% of the total weight of the rare-earth waste material, and the dosage of the fluxing agent powder is 1-20 wt% of the total weight of the rare-earth waste material; (2) roasting the mixed material obtained in the step (1) for 1-6 hours at the temperature of 600-1400 DEG C; (3) adding an acid solution into the roasted product obtained in the step (2) for acid dissolution, filtering and separating to obtain acid leaching liquor which mainly contains rare-earth elements and acid leaching residue; and (4) separating the rare-earth elements from other metal elements in the acid leaching liquor. The method provided by the invention realizes the cyclic utilization of the rare-earth waste material, is simple to operate, high in recovery rate of valuable elements in the waste material and low in reagent cost, saves energy, reduces emission and is low in environment harmfulness, and has important significance in the aspects of ecological protection and economic development promotion.
Owner:CHINA MINMETALS BEIJING RES INST OF RE
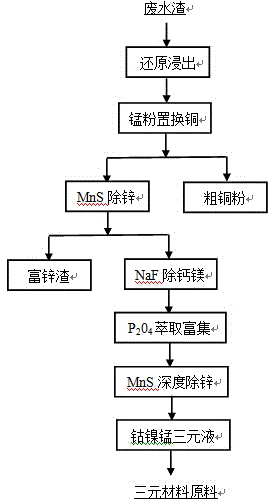
Cobalt nickel metallurgy wastewater sludge recycling method
ActiveCN104480317AEmission reductionHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementSludgeAcid dissolution
The invention provides a cobalt nickel metallurgy wastewater sludge recycling method, and belongs to the field of waste recycling. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out acid dissolution reduction on cobalt nickel metallurgy wastewater sludge to leach out valuable metals in the wastewater sludge, displacing copper by using manganese powder to recover copper, precipitating zinc by using manganese sulfide to recover zinc, using a fluoride to remove calcium and magnesium from the obtained zinc removed solution, carrying out advanced impurity removal and cobalt nickel manganese enrichment by using a P2O4 extractant, and carrying out advanced impurity removal on the obtained solution rich in cobalt, nickel and manganese by using manganese sulfide to obtain a solution for preparing an NCM ternary precursor. The method allows nickel, cobalt, manganese, zinc, copper and other metals to be completely recovered and the obtained cobalt, nickel and manganese solution to be used to prepare the NCM ternary precursor as a raw material, avoids cobalt, nickel and manganese separation, and also has the advantages of simple process, substantial improvement of the metal recovery rate, low cost, harmlessness to environment, and industrialization prospect.
Owner:SHAOXING KEQIAO DRAINING
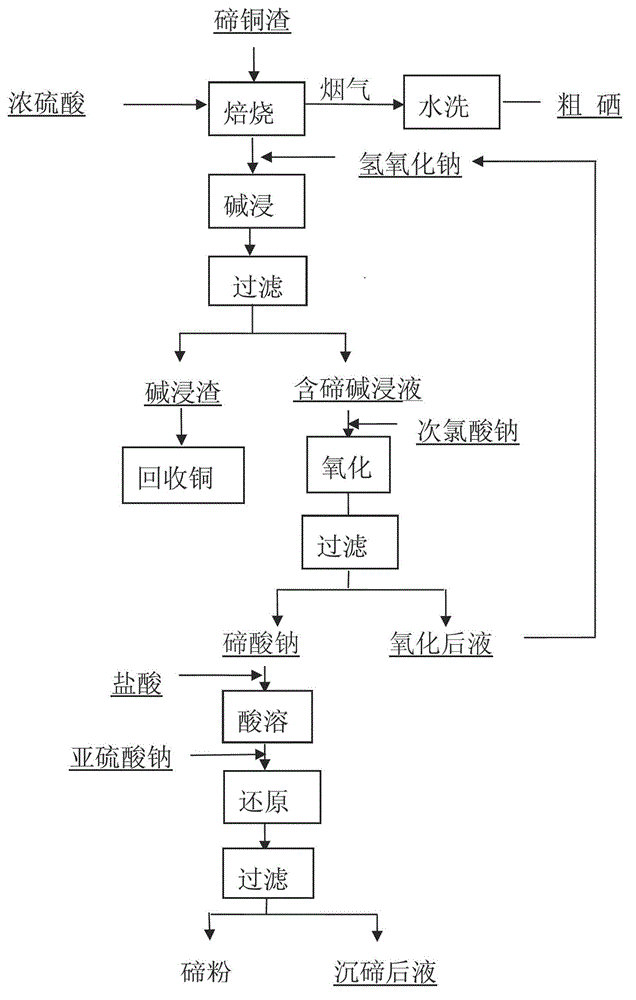
Method for extracting tellurium from tellurium copper slags
ActiveCN102745657AEasy to separateAchieve separationProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumAcid dissolutionCalcination
The invention provides a method for extracting tellurium from tellurium copper slags. The method includes the following steps of (1) sulfating calcination at a high temperature, grinding the tellurium copper slags, mixing ground tellurium copper slags with a concentrated sulfuric acid to calcine, enabling the mass ratio between the concentrated sulfuric acid and the tellurium copper slags to be (1.2-1.5):1, maintaining the calcination temperature in a range from 450 DEG C to 600 DEG C and maintaining the calcination time in a range from 3 hours to 5 hours; (2) alkaline leaching to separate the tellurium, leaching obtained calcination slags by a sodium hydroxide alkaline liquor, and then filtering to obtain a tellurium containing alkali leaching liquid and alkali leaching slags; (3) oxidizing the alkali leaching liquid, oxidizing the tellurium containing alkali leaching liquid by sodium hypochlorite of an oxidant and then filtering to obtain sodium tellurate filtered slags; and (4) acid dissolution reduction, dissolving the sodium tellurate filtered slags by a chloridion containing acidic system, adding a reducing agent to achieve reduction and then filtering to obtain tellurium powders. According to the method for extracting the tellurium from the tellurium copper slags, a complete separation of copper, selenium and tellurium can be fully achieved, a comprehensive recovery of the copper, selenium and tellurium can be achieved, the technological process is simple, tellurium dioxide of an intermediate product is not required, the tellurium powders with a high purity can be directly produced, and the tellurium powders can serve as raw materials of 6N high purity tellurium.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
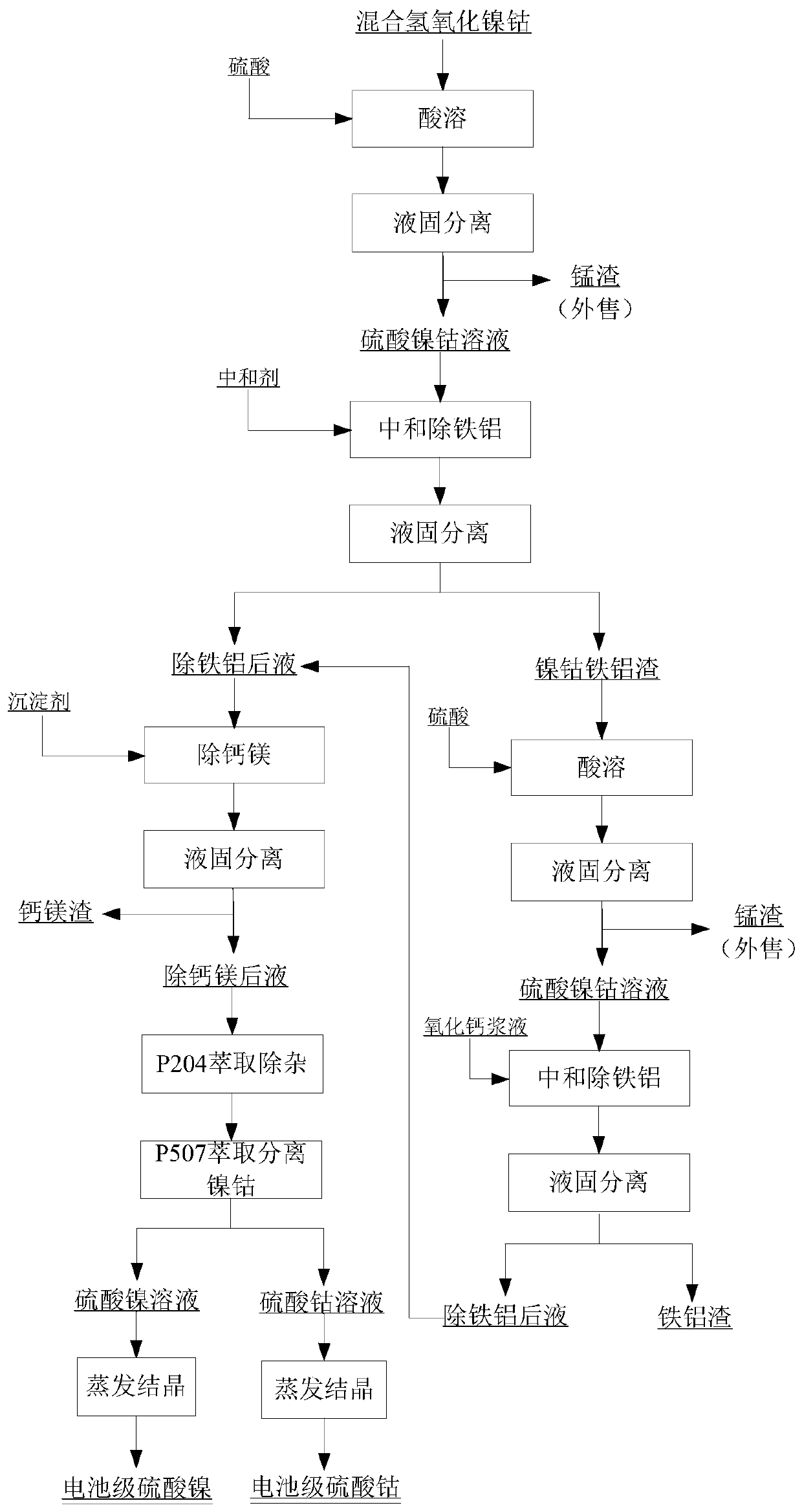
Method for preparing battery-grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate from mixed nickel cobalt hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing battery-grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate from mixed nickel cobalt hydroxide, and belongs to the technical field of nickel cobalt hydrometallurgy.The method comprises the following steps that the mixed nickel cobalt hydroxide is leached by using sulfuric acid, iron and aluminum in the solution are removed by using a nickel / cobalt / manganese-based neutralizer, liquid-solid separation is carried out to obtain iron-removed slag, nickel and cobalt are recycled through acid dissolution, a precipitator (one or more of nickel fluoride, and cobalt fluoride and manganese fluoride) is added into iron-removed liquid to remove calcium and magnesium ions in the system. Impurities such as Mn, Cu and Zn are removed from the calcium and magnesium removed liquid by using a saponified P204 extractant, nickel and cobalt are separated from the P204 raffinate by using a saponified P507 extractant to obtain battery-grade nickel sulfate and a cobalt sulfate solution, and evaporative crystallization is carried out to obtain a product. According to the method, the use amount of calcium oxide is greatly reduced, the amount of calcium ions introduced intothe system and the corresponding nickel-cobalt loss are greatly reduced, the influence of calcium sulfate crystallization on extraction is avoided, the P507 extraction operation amount is reduced, andthe purification cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING MINING & METALLURGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD
Method for simultaneously measuring elements of silicon, aluminum, calcium and barium
InactiveCN101344487AAccurate measurementReduce pollutionPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationRelative standard deviationAcid dissolution
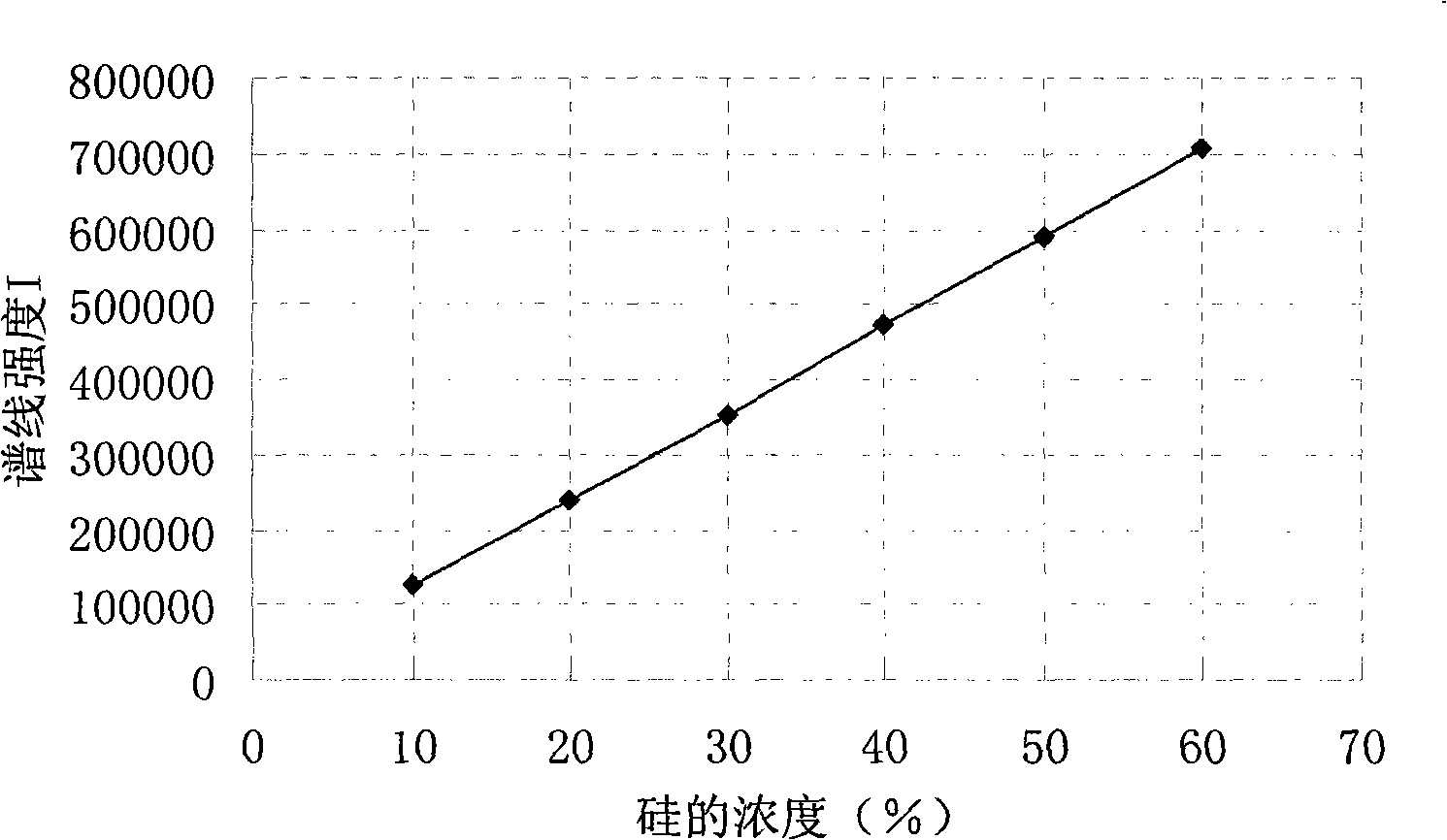
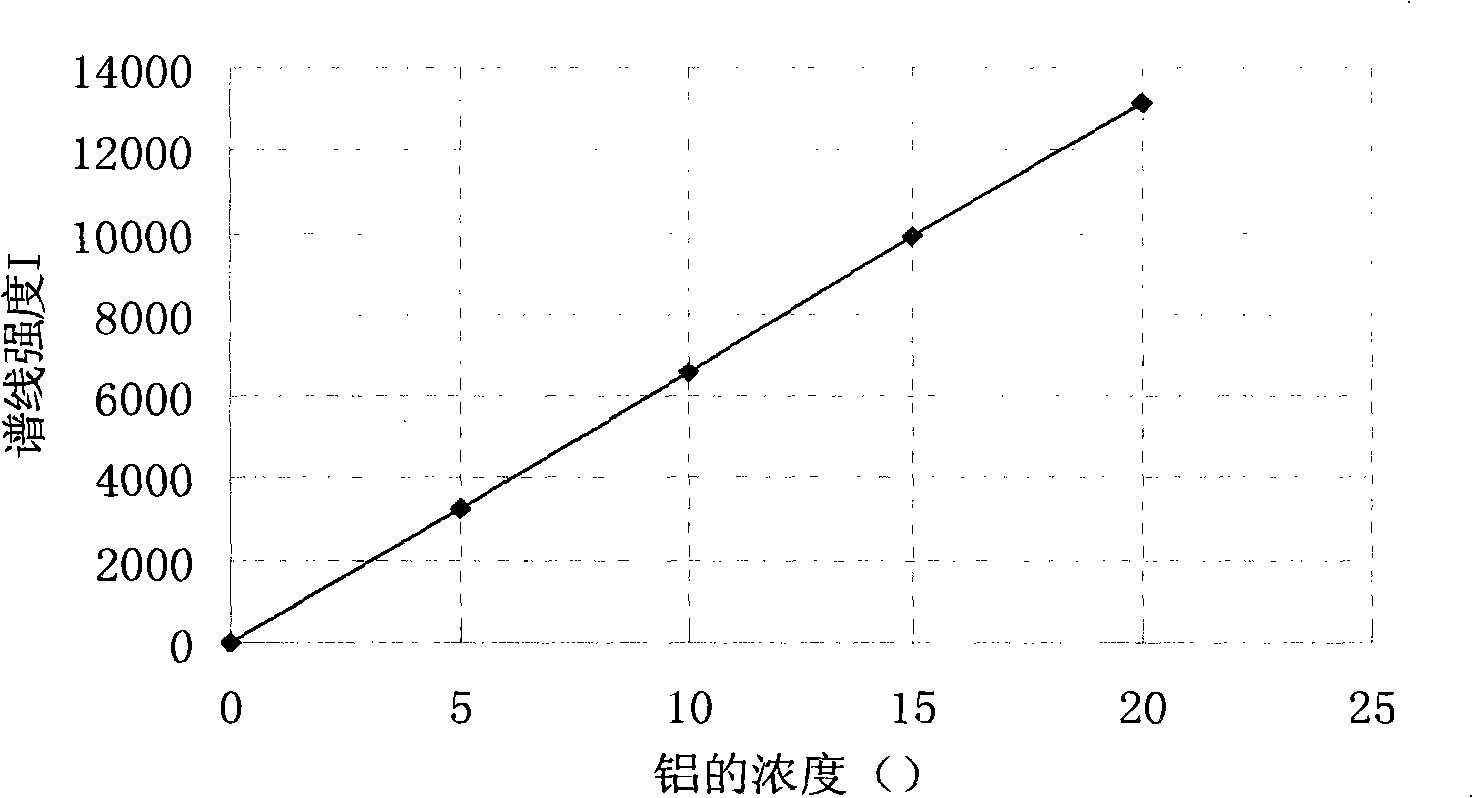
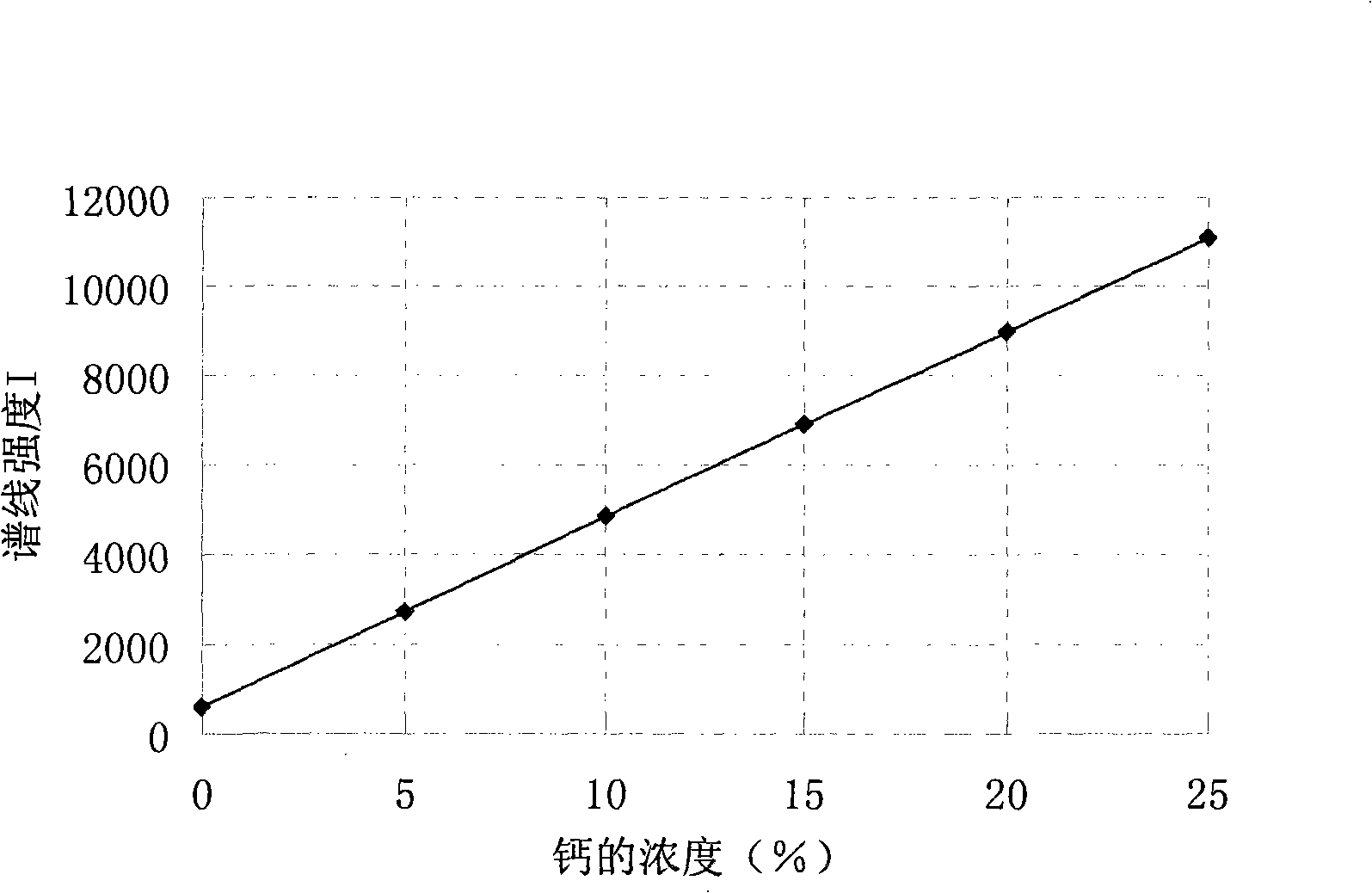
The invention discloses a method that can simultaneously analyze various elements, aims at solving the defects that currently the analysis of various elements cannot be finished at one time, and consequently the analysis time is long and the reagent usage is large, and discloses a method that can simultaneously measure the elements of silicon, aluminum, calcium and barium and comprises the following steps: a test sample is preprocessed through the acid dissolution method, microwave-digested, naturally cooled, and then placed into a volumetric flask with scales, diluted and shaken until well distributed, a solution with a standard working curve is prepared, an atomic emission spectrograph of inductance coupled plasmas is started and led to reach the measurement requirement, a plasma torch is lighted, the relative standard deviation of the plasma torch is led to be less than 5 percent, wavelength of each element is chosen, the working curves are plotted, and the content of each element is computed. The method combines the microwave digesting sample dissolution technique with the atomic emission spectrograph of inductance coupled plasmas, can simultaneously analyze nine elements including silicon, etc., is accurate and quick, has greatly reduced reagent usage, and reduces the environmental pollution that is caused by chemical reagents.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Acidum folicum production method without sewerage discharge
The invention discloses a production method of folacin without sewage discharge and a technological process thereof comprises crude product production, acid dissolution process, alkali dissolution process and refining process. The sewage discharge is reduced to zero, meeting the requirements of national environment protection and saving water and cost. The production method of the invention leads the yield of crude products to be increased from the original 80 percent to present 85 percent, thus improving product yield so as to decrease waste and improve the rate of production.
Owner:JIHENG PHARMA HENGSHUI CITY
Harmless extraction process for poultry manure prepared agricultural biochemical fulvic acid
ActiveCN102816332ATo achieve the extraction effect of separationEliminate hidden dangersOrganic chemistryFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologyAcid dissolution
The invention relates to a harmless extraction process for poultry manure prepared agricultural biochemical fulvic acid. The process includes an acid dissolution extraction technology of fulvic acid and a Fenton oxidative degradation technology. The acid dissolution extraction technology of fulvic acid consists of: making a suspending solution from a group A acid dissolution extracting agent that has a pH value of less than or equal to 2 and contains 0.1%-2.5% of ferrous sulfate as well as 1%-2.5% of sulfuric acid and fermented poultry manure in a ratio of 1:5-15, and conducting stirring for 30min-60min at room temperature, thus obtaining dissolved fulvic acid containing a chelate of an organic acid and ferrous ions. The Fenton oxidative degradation technology consists of: mixing a material subjected to the acid dissolution extraction with a group B acid dissolution extracting agent that has a pH value of less than or equal to 2 and contains 15% of hydrogen peroxide and 1%-2.5% of sulfuric acid, controlling the content of hydrogen peroxide in the material at 0.5%-3.0%, when the two groups of materials are mixed, catalyzing the hydrogen peroxide with the ferrous ions, thus generating a Fenton oxidative degradation reaction. Therefore, residual antibiotics, hormones, pesticides and pathogenic bacteria, rot-causing bacteria and helminth eggs can be rapidly degraded and their hazards can be eliminated, thereby reaching a harmless extraction effect.
Owner:FUJIAN CHAODA GROUP
Gelled acid used for acid fracturing of high-temperature fractured-vuggy type carbonate reservoir
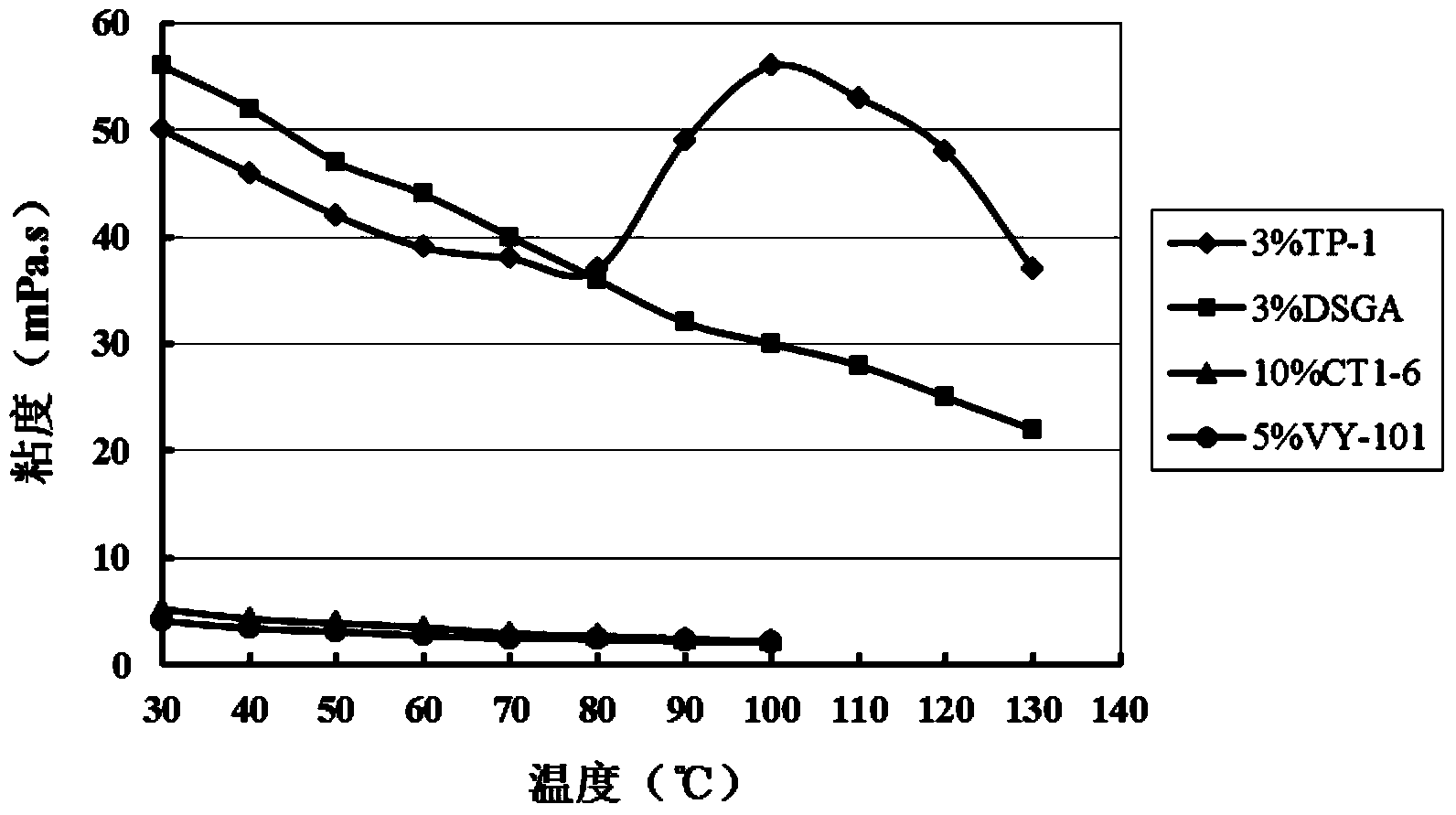
InactiveCN103820100AGood compatibilityGood filter loss reduction effectDrilling compositionAcid fracturingFiltration
The invention relates to gelled acid used for acid fracturing of a high-temperature fractured-vuggy type carbonate reservoir. The gelled acid comprises components in percentage by weight as follows: 20% of hydrochloric acid (HCl), 3% of a gelling agent (TP-1), 2% of a corrosion inhibitor (MC50), 1.5% of a ferric ion stabilizer (FL4-7), 0.05% of a demulsifying agent (PRJ), 1.5% of a discharge aiding agent (AD12) and the balance of water. The gelled acid can resist a temperature of 130 DEG C, and has an excellent rheological property and shearing resistance, good compatibility and filtration reduction performance and low frictional resistance; compared with common acid (20% of HCl), the acid-rock reaction speed can be reduced by 52%; under the condition of high temperature, the processing depth of the gelled acid to the stratum is enlarged, acidulating efficiency and success rate are increased, and pipe column corrosion and formation damage can be effectively reduced simultaneously, the gelled acid is prone to flowback and has a capacity of carrying solid-phase particles, the acid dissolution time of the gelling agent is short, so that field preparation is facilitated, and the gelled acid is very suitable for acid fracturing improvement of the high-temperature fractured-vuggy type carbonate reservoir.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for production of high purity manganese sulfate by using pyrolusite as raw material
ActiveCN103011297AImprove controllabilityGood reproducibilityManganese sulfatesPyrolusiteAcid dissolution
The invention relates to a production method for high purity manganese sulfate. The production method is characterized in that pyrolusite is used as a raw material and is reduced by using a carbon fire method, then an acid is added for leaching, a vulcanizing agent is used to remove heavy metals consisting of cobalt and nickel, a fluoride is employed to remove calcium and magnesium, then filtering is carried out, ammonium bicarbonate or ammonium carbonate is added into a filtrate for deposition of manganese to realize separation of potassium and sodium, an obtained filtrate is used for recovery of the by-product ammonia sulfate for usage as an additive for metal manganese, the filter residue manganese carbonate is washed and then subjected to acid dissolution so as to obtain a manganese sulfate solution, and then crystallization is carried out to obtain a high purity manganese sulfate product, wherein mother liquor can be returned to a high purity system for reutilization. With the method provided by the invention, the high purity manganese sulfate product in which MnSO4 content is more than 99.8% and respective content of impurities consisting of Ca, Mg, K and Na is lower than 10 ppm is produced.
Owner:DAXIN MANGANESE MINE BRANCH OF CITIC DAMENG MINING IND
Process for processing, recycling and reusing chromic slag and waste water
The invention discloses a process for processing, recycling and reusing chromic slag and waste water; the chromic slag is dissolved by acid, and then hex-valent chromium specific treating agent is added so as to thoroughly remove chromic slag pollution and extract the substance from the chromic slag to directly make the substance into other substance series product. The 'three wastes' emissions and secondary pollution are avoided in the chromic slag processing process. The chromic slag processing capacity is high, the cost is low, the rate of multipurpose utilization is high; the product obtained by the chromic slag processing and recycling process is good in quality, high in value, and the demanded amount in market is large; in this way, the process has good economic benefit and social benefit and is cable of greatly prompting the development of circular economy.
Owner:唐翔
Three-element determination method of nickel-cobalt-manganese ternary material
ActiveCN104316643AImprove measurement accuracyHigh precisionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical analysis using titrationMurexideAcid dissolution
The invention relates to a three-element determination method of a nickel-cobalt-manganese ternary material. The method comprises the following steps: determining the total quantity of cobalt, nickel and manganese ions by EDTA titration and recording titration consumption volume; sampling to an alkaline medium of ammonia chloride and ammonium to form nickel amine, oxidizing cobalt by utilizing hydrogen peroxide, complexing with ammonium to form a trivalent cobalt ammonia complex to generate manganese dioxide precipitate, filtering out the precipitate to obtain the filter liquid, titrating the filter liquid by utilizing EDTA in the presence of murexide serving as an indicator to determine the content of nickel, and recording the titration consumption volume; enabling the ammonia gas to escape from the solution after the nickel is determined through titration under the alkaline and heating condition and generating cobalt hydroxide precipitate at the same time, dissolving the cobalt hydroxide precipitate by utilizing acid, measuring the content of cobalt through EDTA titration, and recording the titration consumption volume; and calculating the respective content of the three elements according to the EDTA consumption volume in each step, the concentration of EDTA and the sample mass. The method is accurate in detection, high in detection efficiency, safe, environment-friendly and applicable to the detection of content of three elements in an anode material.
Owner:JINGMEN GEM NEW MATERIAL +1
Process for producing composite coagulant polymeric aluminium chloride ferrum
InactiveCN1463929AFreely adjust the ratioWide range of raw materialsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationArsenicAcid dissolution
The aluminum iron chloride polymer as composite coagulant is produced with aluminum-containing material and iron-containing material and through acid dissolution, oxidation with chlorate, neutralization with calcium aluminate powder and polymerization. Compared with available technology, the present invention has the advantages of low production cost, capability of being used as drinking water purifying agent, simple usage, and wide application range.
Owner:曹万印
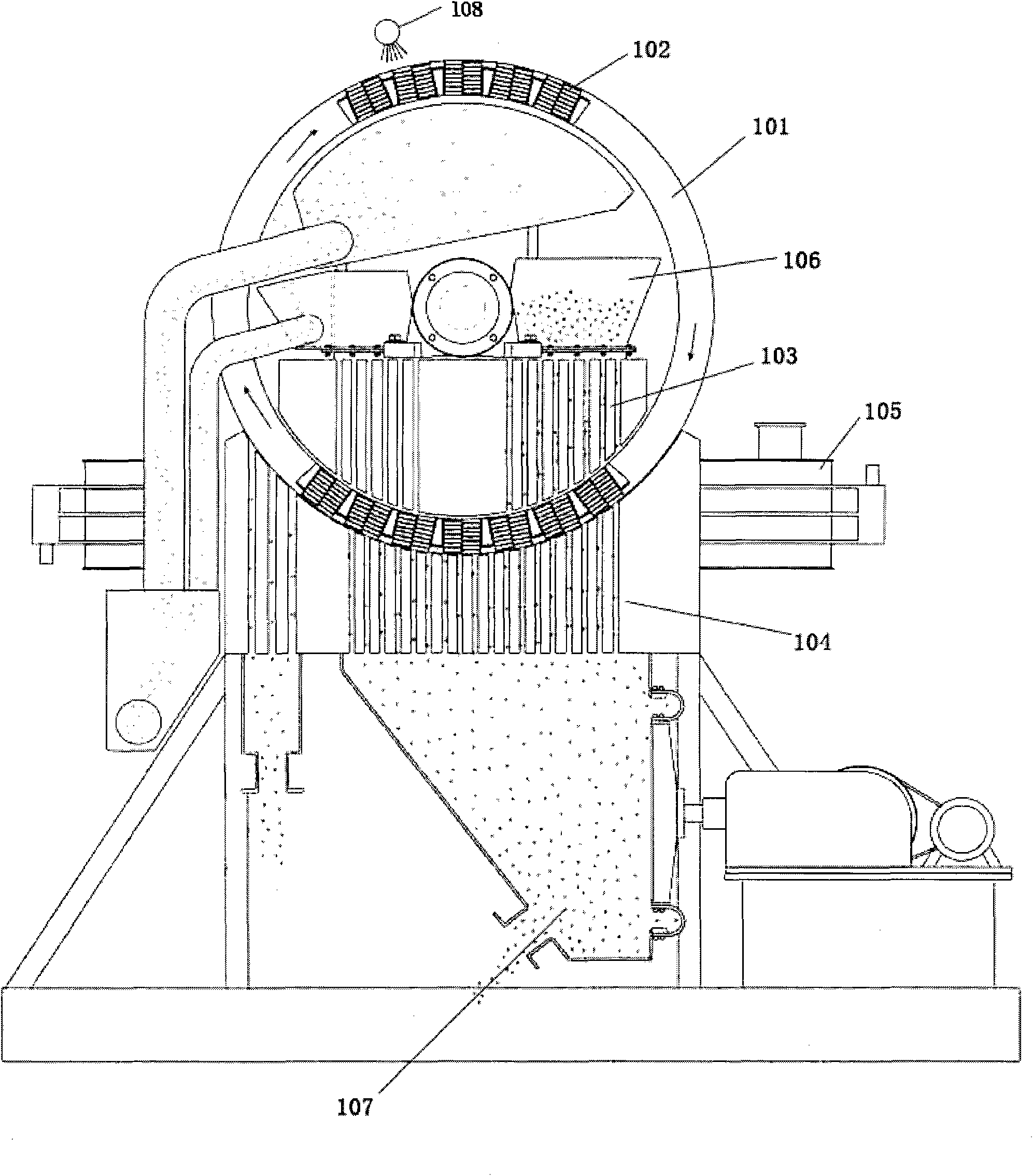
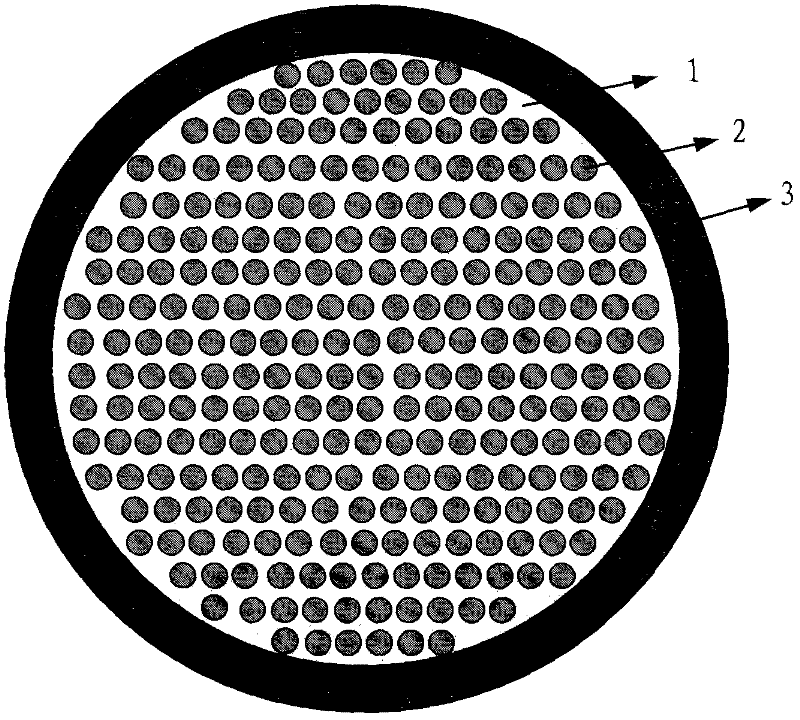
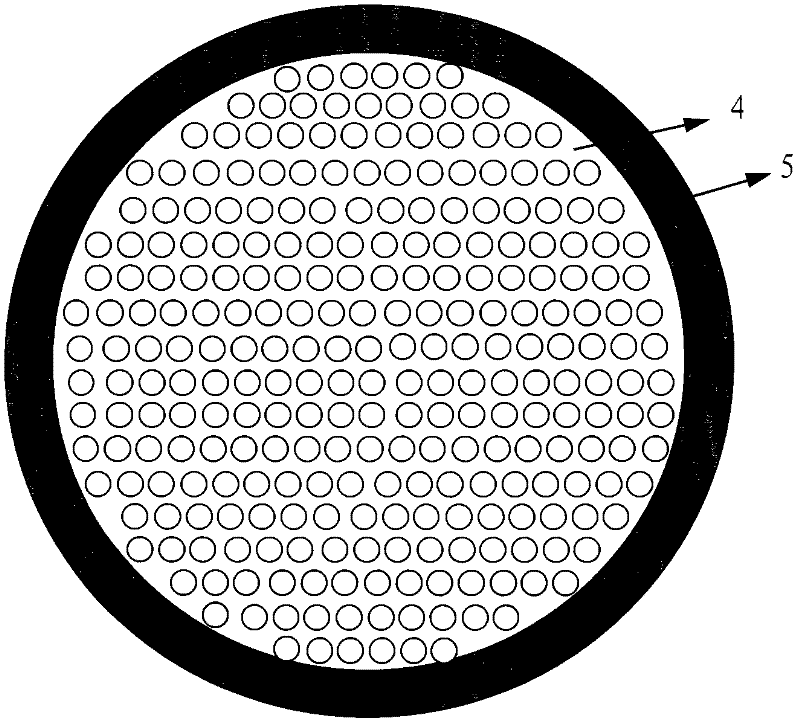
Production method of small section flexible optical fibre bundle for transmitting image using acid soluble method
InactiveCN1828348AMeet the design requirementsLarge effective light transmission areaGlass making apparatusBundled fibre light guideCrucibleAcid dissolution
The disclosed method comprises: with the core glass, cladding glass and acid-dissolved as raw material, heating in a crucible simultaneously to melt and manufacture the monofilament; arranging the monofilament to manufacture multifilament; then, obtaining the target product after acid dissolution. This bundle has core section as 40-50% and super effective permeance.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HONSUN OPTOELECTRONICS +1
Recovery process for valuable metals in tungsten residues
ActiveCN103290224AReduce recycling costsLow costProcess efficiency improvementAmmonium paratungstateFiltration
The invention provides a recovery process for valuable metals in tungsten residues. The tungsten residue treatment method comprises the following steps of: boiling tungsten residues and 15%-25% of hydrochloric acid for acid dissolution, further adding NaF and sodium nitrate, and filtering to obtain filtrate after the end of the reaction; then extracting tungsten from the filtrate by adopting N235, and evaporating, crystallizing and drying a stripping solution to obtain APT (ammonium paratungstate); and performing alkali dissolution on filtration residues, and performing pressure filtration to directly recover Ta, Nb and Sn valuable metals. Tungsten, scandium, iron, manganese, tin, copper, tantalum and niobium valuable elements and the like in the tungsten residues can be comprehensively recovered, thus the recovery cost is reduced. The recovery process disclosed by the invention further has the advantages of good environmental benefits and low cost. According to the recovery process disclosed by the invention, the acid is adopted for dissolving the tungsten residues, the tungsten and the scandium are recovered under acid conditions, the other elements are simultaneously recovered, and the process is simple.
Owner:北京恒泰岩磊科技有限公司
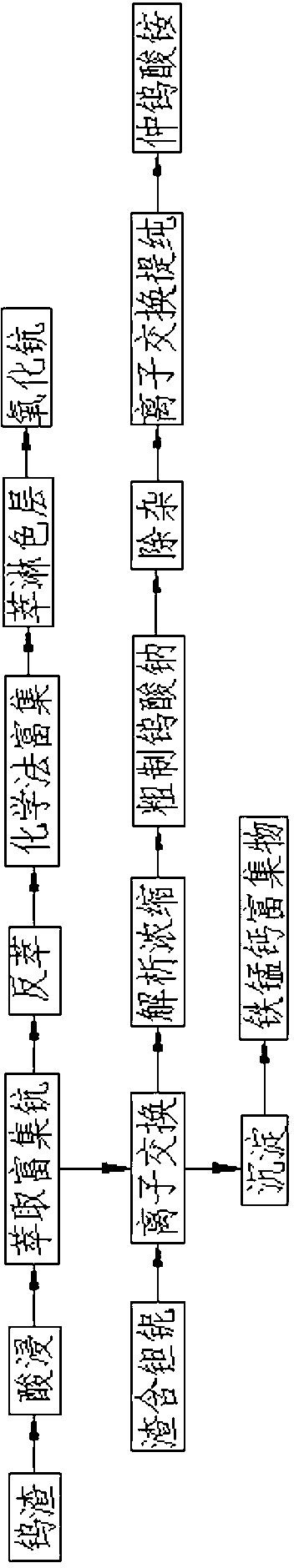
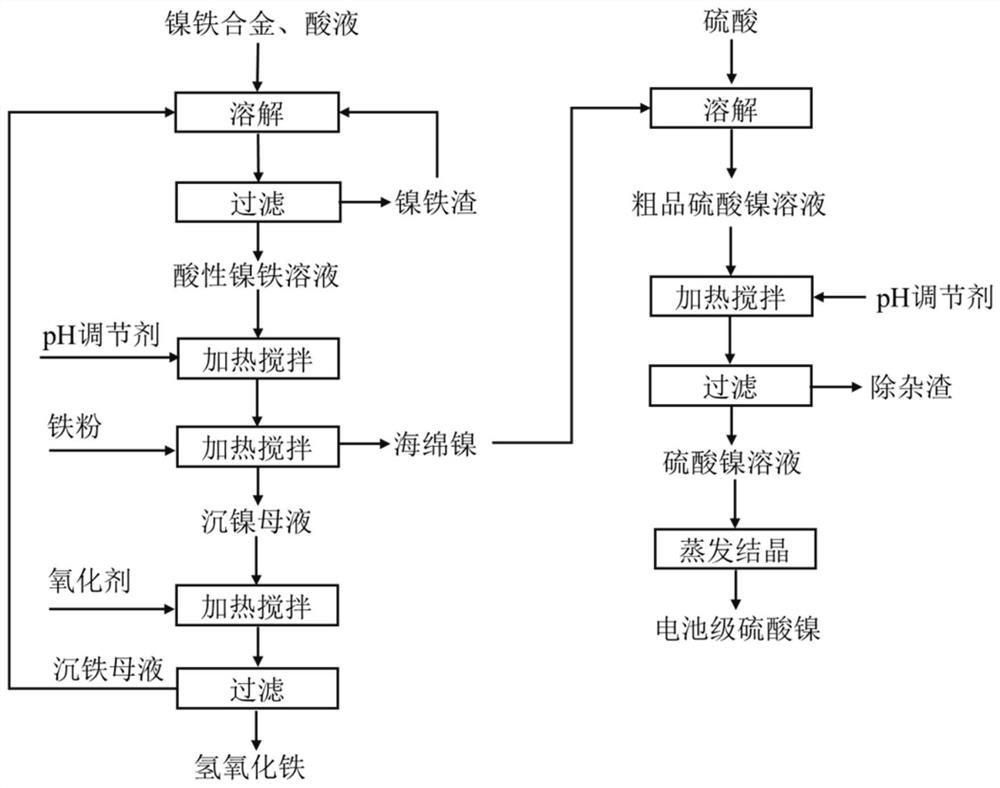
Method for separating nickel and iron from nickel-iron alloy and application
ActiveCN112941314AAchieve separationHas economic valueIron oxides/hydroxidesNickel sulfatesFerric hydroxideIron powder
The invention belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy, and discloses a method for separating nickel and iron from a nickel-iron alloy and application. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving the nickel-iron alloy in an acid solution, filtering, and taking filtrate to obtain an acidic nickel-iron solution; adjusting the pH value of the acidic nickel-iron solution, heating, stirring, adding iron powder, and continuously heating and stirring to obtain sponge nickel and nickel precipitation mother liquor; enabling the nickel precipitation mother liquor to be subjected to oxidation iron precipitation to obtain ferric hydroxide slag and iron precipitation mother liquor; and dissolving sponge nickel into sulfuric acid, filtering, collecting filtrate, heating, and adjusting the pH value to obtain a nickel sulfate solution; According to the method, after the nickel-iron alloy is dissolved by using the acid liquor, nickel in the solution is replaced by iron powder to obtain sponge nickel, the nickel precipitation mother liquor is oxidized to generate ferric hydroxide, the nickel content is lower than 0.4%, the iron precipitation mother liquor can be returned to a leaching section, and the sponge nickel is subjected to acid dissolution, impurity removal and evaporative crystallization to obtain a battery-grade nickel sulfate product.
Owner:HUNAN BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +2
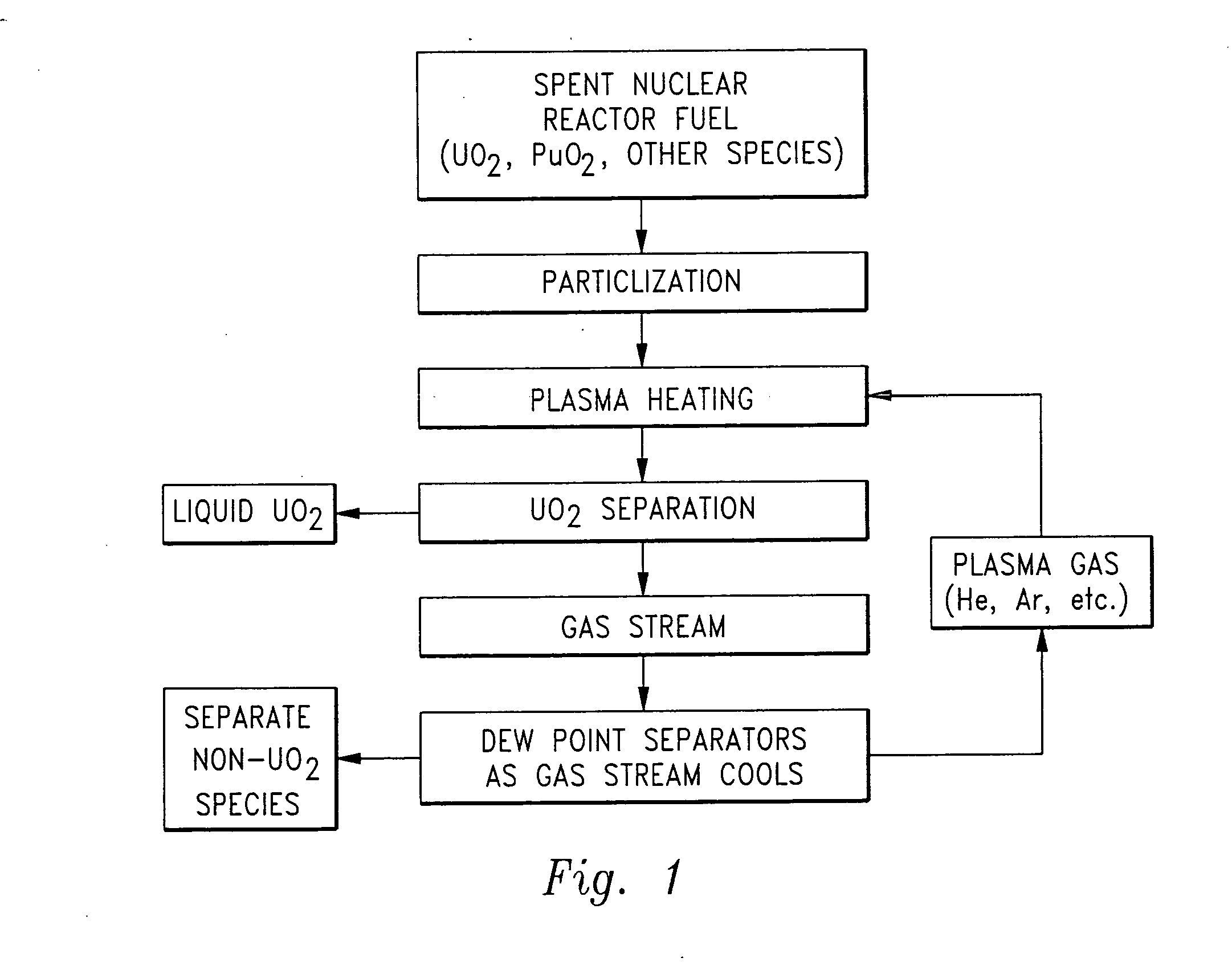
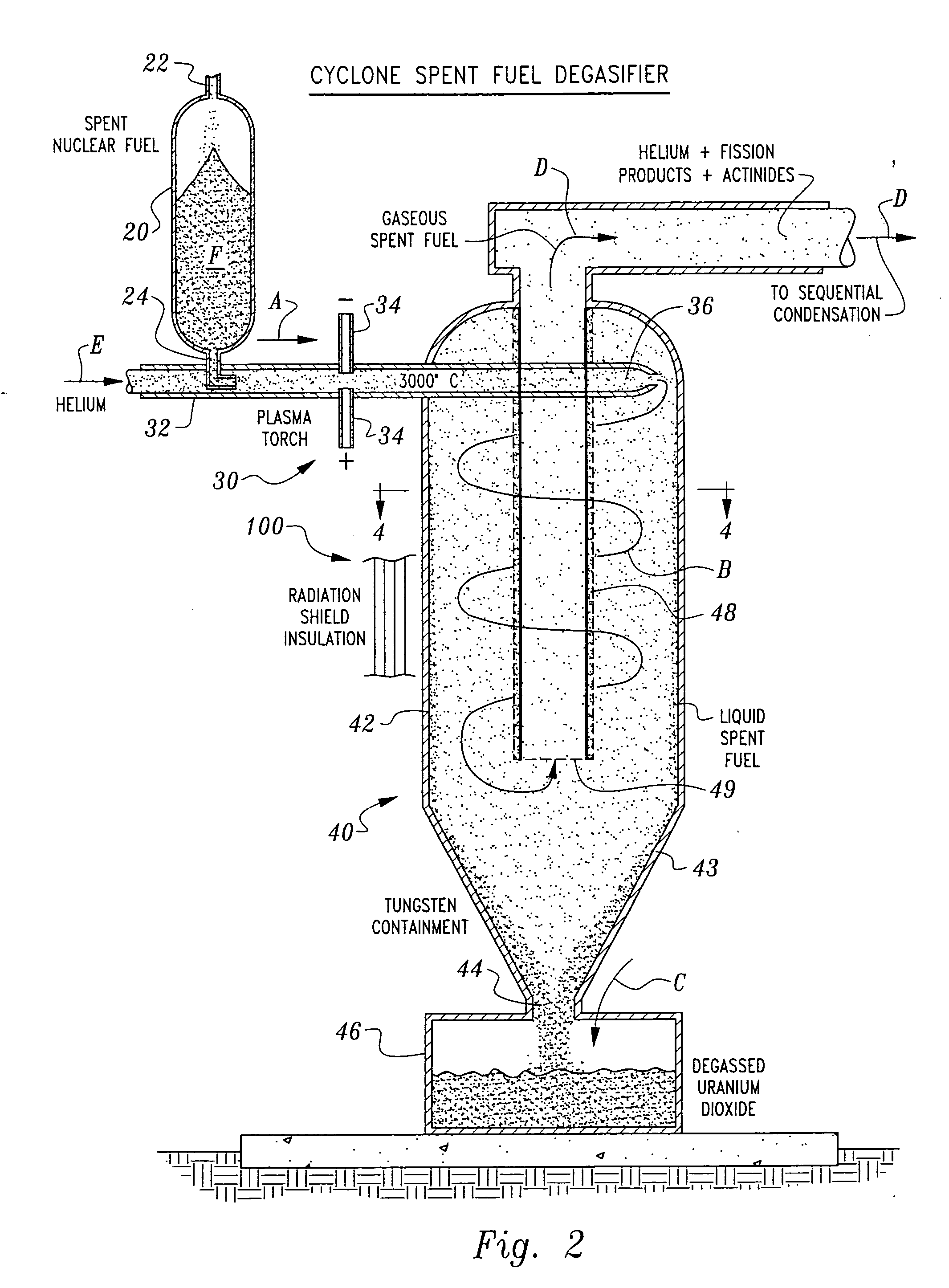
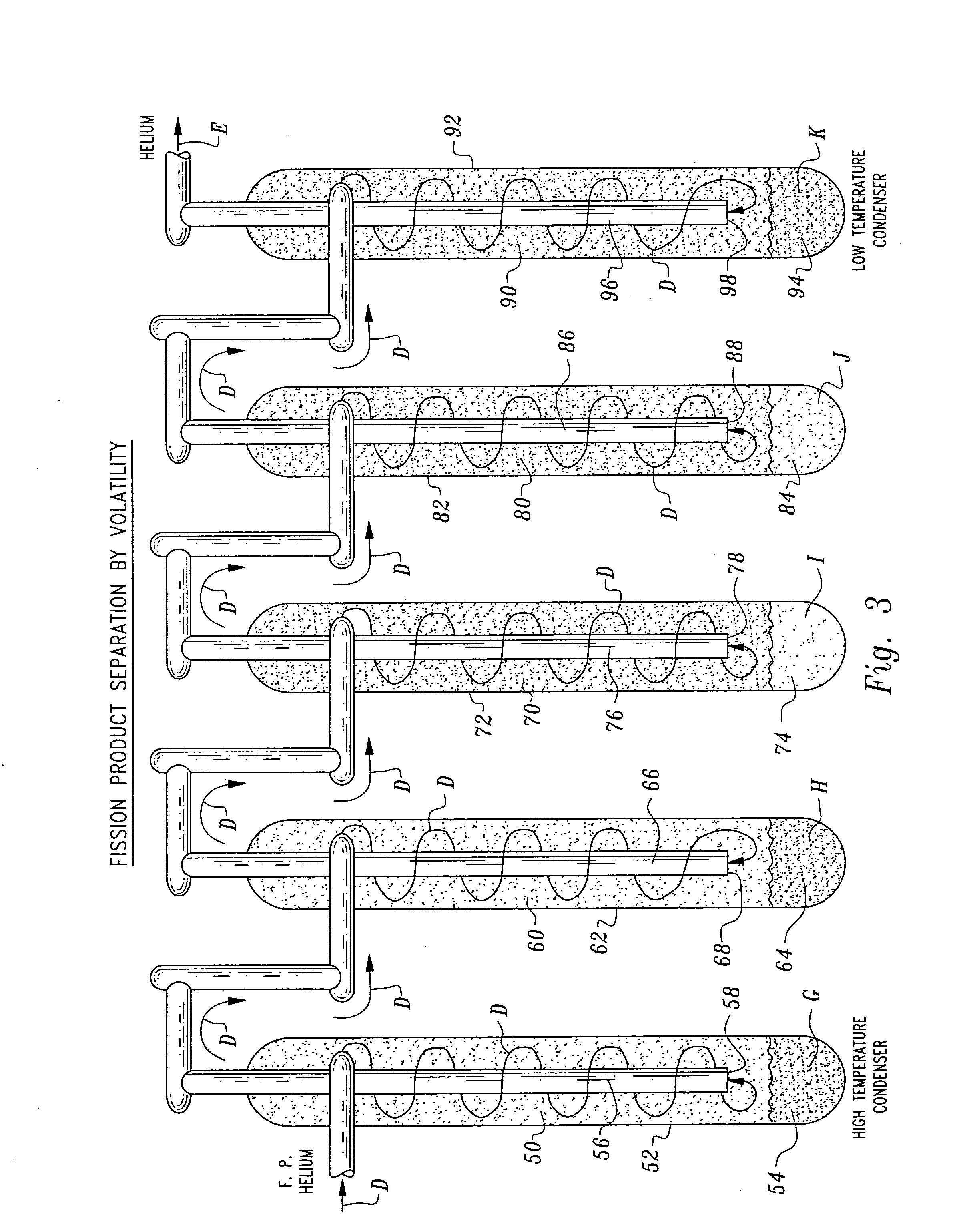
Non-aqueous method for separating chemical constituents in spent nuclear reactor fuel
InactiveUS20060233685A1Reduce riskIncrease ratingsNuclear energy generationPlutonium oxides/hydroxidesKryptonGas phase
Herein is a method of segregating chemical species contained in spent nuclear reactor fuel without employing conventional acid dissolution. Particularly, pellets of spent fuel are ground to talc sized particles. Heat is added. The preferred heating is by flow through a plasma arc producing micron sized liquid drops suspended in helium flow. The vapor pressure of the chemical species is significantly greater than uranium dioxide. the ultra volatile chemical species evolve from the drops into the helium flow. The gas phase is separated from the mist by a gas / liquid separator (demister). Heavy mist drops of UO2 impact the walls, coalesce and flow down to the separator drain, becoming legally transportable. Helium flow exhausts from the separator vertically. The gaseous chemical species will condense in sequentially cooler stages and separate from the helium down to the cryogenic temperatures of liquid radioactive xenon and krypton. Non-condensed helium is recycled.
Owner:JANES CLARENCE W
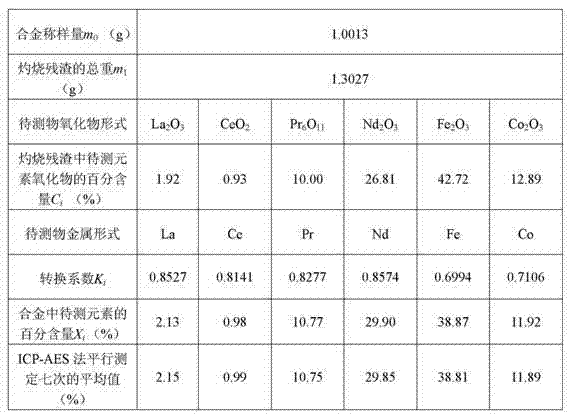
Metal alloy XRF spectrometry utilizing new sample preparation technology
InactiveCN102207475AHigh melting pointSolve the problem that cannot be detected by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationCarbonizationAcid dissolution
The invention provides a metal alloy XRF spectrometry utilizing a new sample preparation technology. The technology comprises the following steps: 1) acid dissolution: dissolving a metal alloy with inorganic acid; 2) precipitation: adjusting the above dissolved sample solution to be alkaline to precipitate elements to be measured, and filtering the precipitation with ashless filter paper; 3) calcination: placing the filtered filter residues together with the filter paper in a porcelain crucible calcined to a constant weight, conversing the filter residues into metal oxides through steps of drying, carbonization, ashing, calcination, etc, and calculating a weight of calcined filter residues; 4) sheet melting: preparing the above calcined filter residues into a sample sheet by a fusion sample preparation method for detection by an XRF spectrometer, and obtaining contents of elements to be measured in the metal alloy through conversion of obtained data. The invention enables the XRF spectrometry to be applied to detections of some special metal alloys which have a high melting point, a high hardness and is easily oxidized.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF XIAMEN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
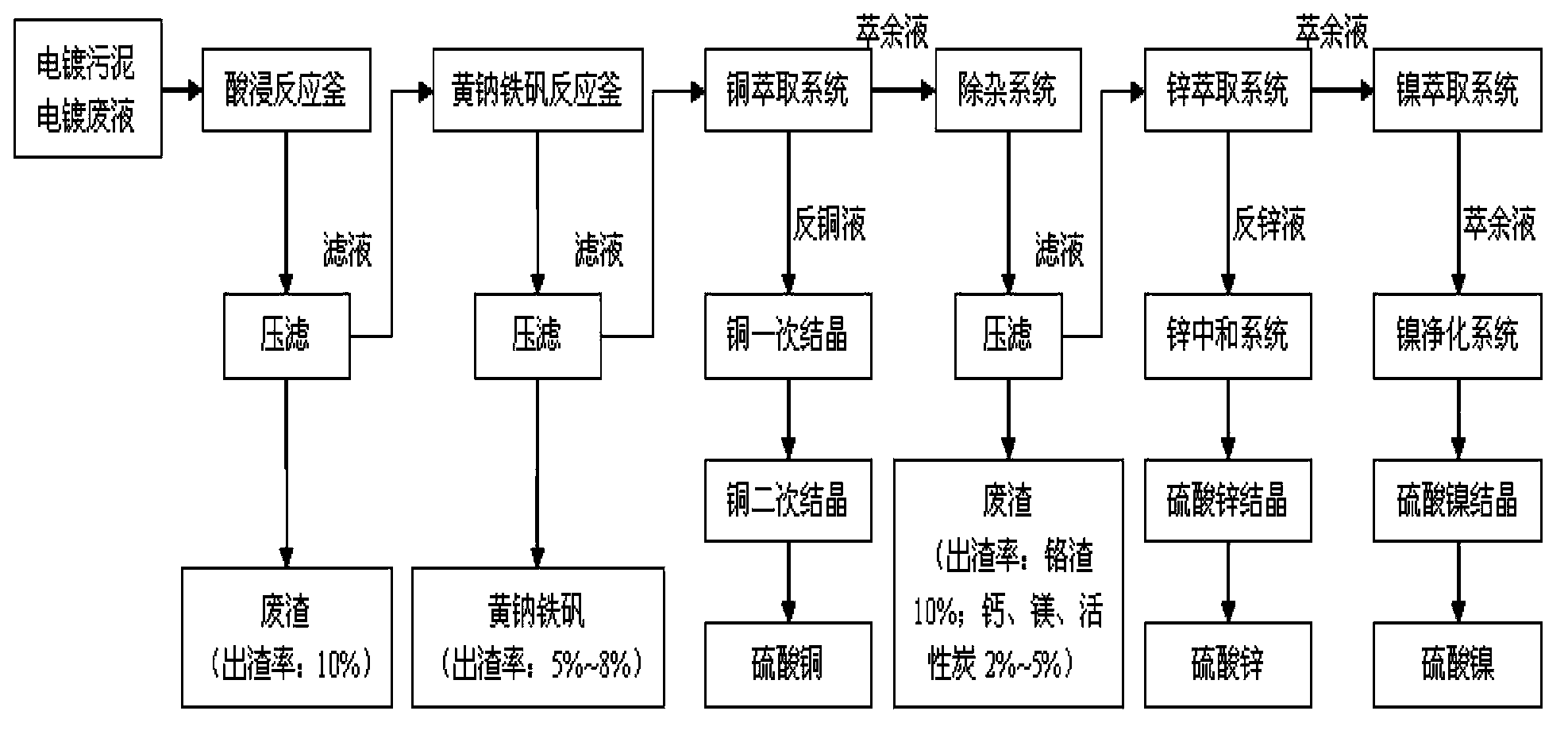
Electroplating sludge recycling technology
InactiveCN104099474AReduce dosageGuaranteed leaching rateZinc sulatesSludge treatmentLiquid wasteSludge
The invention discloses an electroplating sludge recycling technology. The technology comprises the steps of acid dipping, iron removal, copper extraction, impurity removal, zinc extraction, nickel extraction, low acid leaching and high acid leaching, tailings are washed with water, the iron removal step is carried out through a sodium jarosite process, copper extraction adopts two stage extraction, two stage water washing, four stage back extraction, and second stage extraction is carried out after first stage extraction, precipitation, washing and acid dissolution. The technology has the advantages of technological period shortening, guarantee of the product purity through multiple stage extraction, effective use of the waste resource, and reduction of the emission of a waste liquid.
Owner:ZHENJIANG HUAKE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
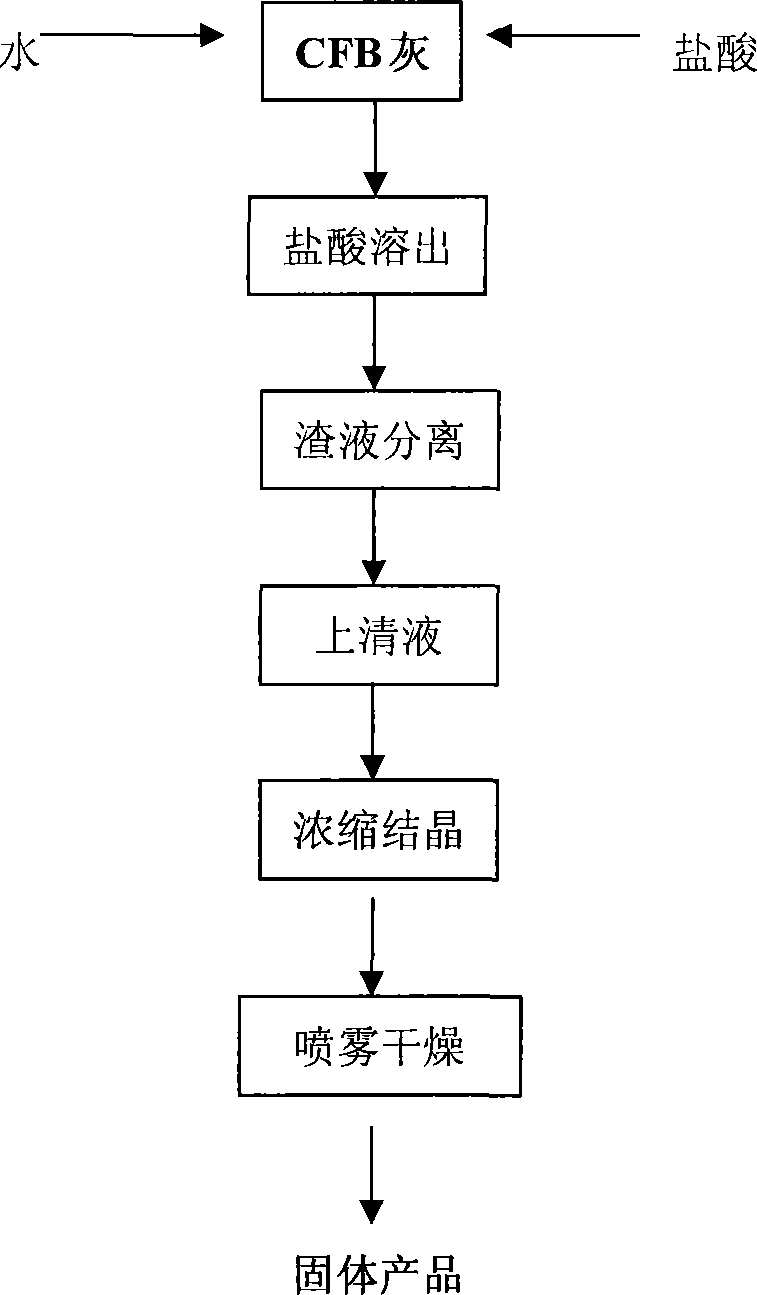
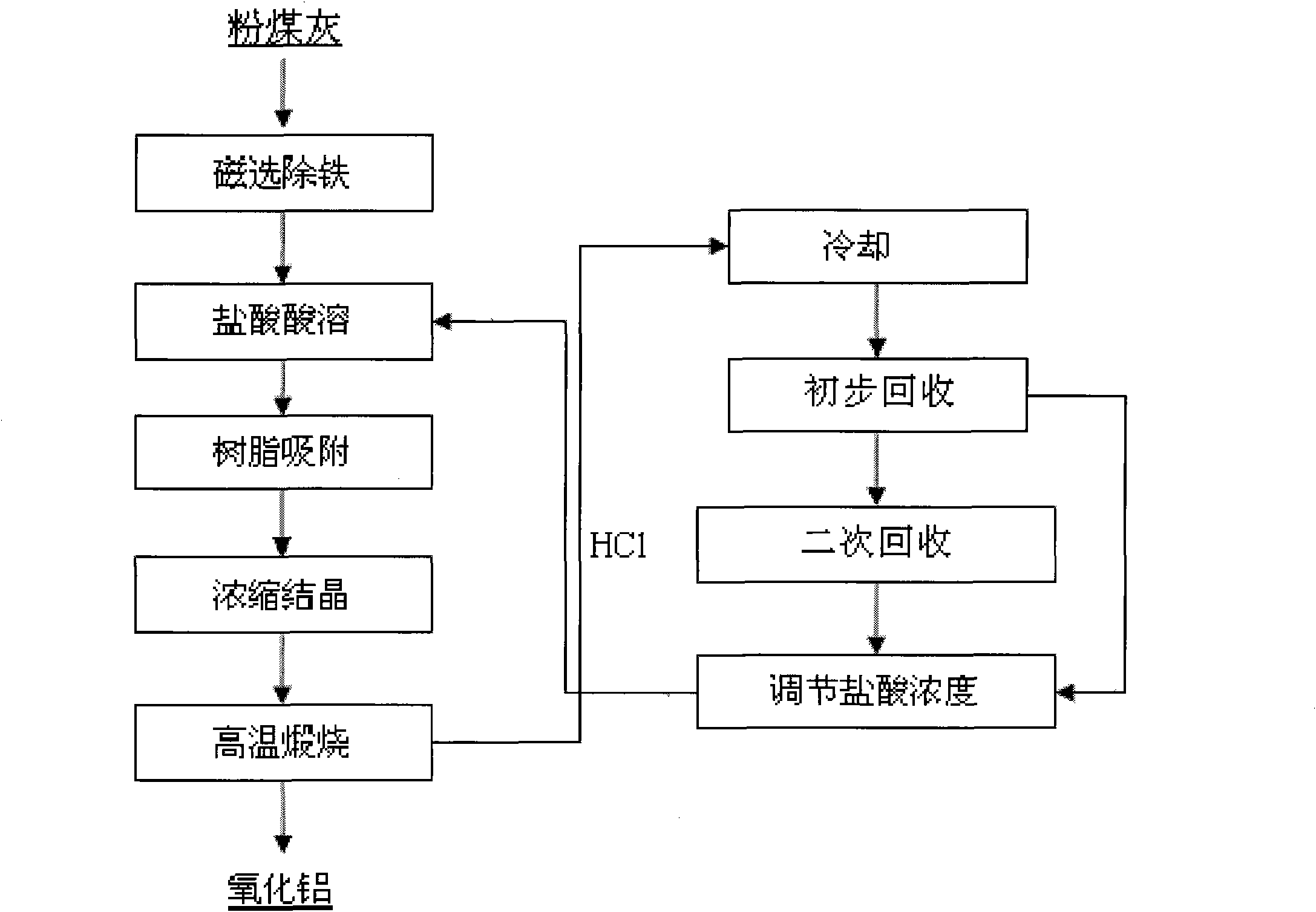
Method of preparing crystal aluminum chloride from circulation fluid bed fly ash
The present invention relates to a preparation method for crystalloid aluminum chlorate, in particular to a preparation method for crystalloid aluminum chlorate by using the circulating fluidized bed fly ash as raw material. By means of the better chemical activity of the aluminum contained in the circulating fluidized bed fly ash, the aluminum chlorate solution is obtained from the circulating fluidized bed fly ash by a direct acid dissolution process, and then the supernatant is obtained by separating the slag from the liquid in a setting tank, and the supernatant is concentrated and crystalled, finally, the solid crystalloid aluminum chlorate is obtained after spray drying. The present invention has a wide range of raw material, a low cost, a simple manufacturing process, quality product, less energy consumption, and meets the circular economy conception.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for reclaiming indium from waste mercury-free basic zinc-manganese battery
InactiveCN101104890AHigh and stable recoveryHigh purityPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementIndiumElectrolysis
The invention discloses a method for recycling indium from waste Hg-free alkaline zinc manganese dioxide battery, which comprises the following steps: separating and extracting the cathode material from waste Hg-free alkaline zinc manganese dioxide battery, dissolving with an acid, adding a reducing agent to replace sponge indium, and smelting the sponge indium to obtain indium ingots, the filtrate being used for electrolytic zinc process; or alternatively adjusting the pH value of the solution to 5 with a base solution after acid dissolution to allow the precipitation of In(OH)3, filtering to separate the filtrate used for electrolytic zinc process and the precipitate used as electrolyte after acid dissolution, and electrolyzing to obtain pure indium. Based on the existing state of indium in the waste Hg-free alkaline zinc manganese dioxide battery and the practical recovery of waste Hg-free alkaline zinc manganese dioxide battery, the invention realizes the recycle of indium and has the advantages of simple process, easy application, high and stable recovery rate of indium, less use of chemical additives in the recycle process, no secondary pollution, and high purity of extracted metal indium. Therefore, the invention realizes the cyclic regeneration of cathode material of waste alkaline zinc manganese dioxide battery and is better in economic benefit and environment-protection value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Wastewater treatment device with coupled Electro-Fenton and electrocatalytic oxidation without solid waste generation
ActiveCN105884091AAchieve recyclingOvercome the disadvantages of polluting the environmentWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentFenton reactionAcid dissolution
The invention relates to a wastewater treatment device with coupled Electro-Fenton and electrocatalytic oxidation without solid waste generation. The wastewater treatment device comprises a raw water pump, a first diaphragm electrolytic cell, a second diaphragm electrolytic cell, a Fenton reaction tank, a coagulating sedimentation tank and an iron cement dissolving tank which are connected in sequence, wherein the anode chambers of the first diaphragm electrolytic cell and the second diaphragm electrolytic cell are adopted for electrocatalytic oxidation reaction to dissolve organic pollutants; Fe<+3> generated after Fenton reaction is reduced into Fe<+2> in the cathode chamber of the first diaphragm electrolytic cell; H2O2 is generated through electrochemical synthesis in the cathode chamber of the second diaphragm electrolytic cell; the reduced Fe<+2>, the newly generated H2O2 and wastewater are fed into the reaction tank for Fenton reaction; the effluent is subjected to iron cement separation in the coagulating sedimentation tank; treated water is discharged; the sedimentary iron cement is Fe<+3> which is fed into the iron cement dissolving tank; after acid dissolution, the sedimentary iron cement is fed into the cathode chamber of the first diaphragm electrolytic cell and is circulated after electrochemical reduction; and therefore, solid waste production and emission are avoided.
Owner:南京赛佳环保实业有限公司
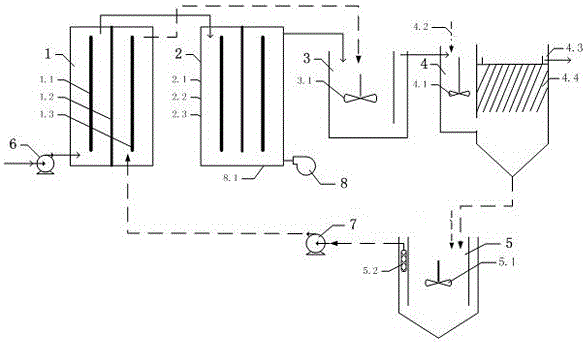
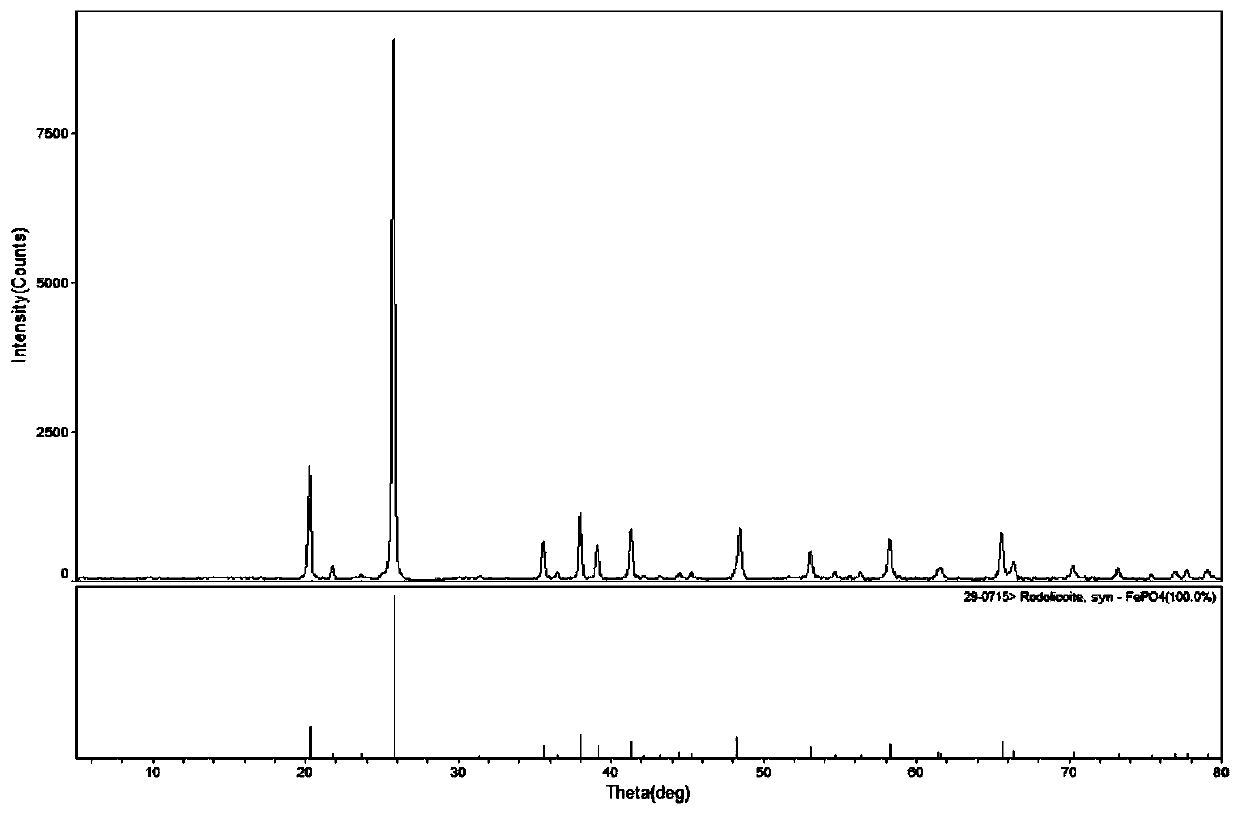
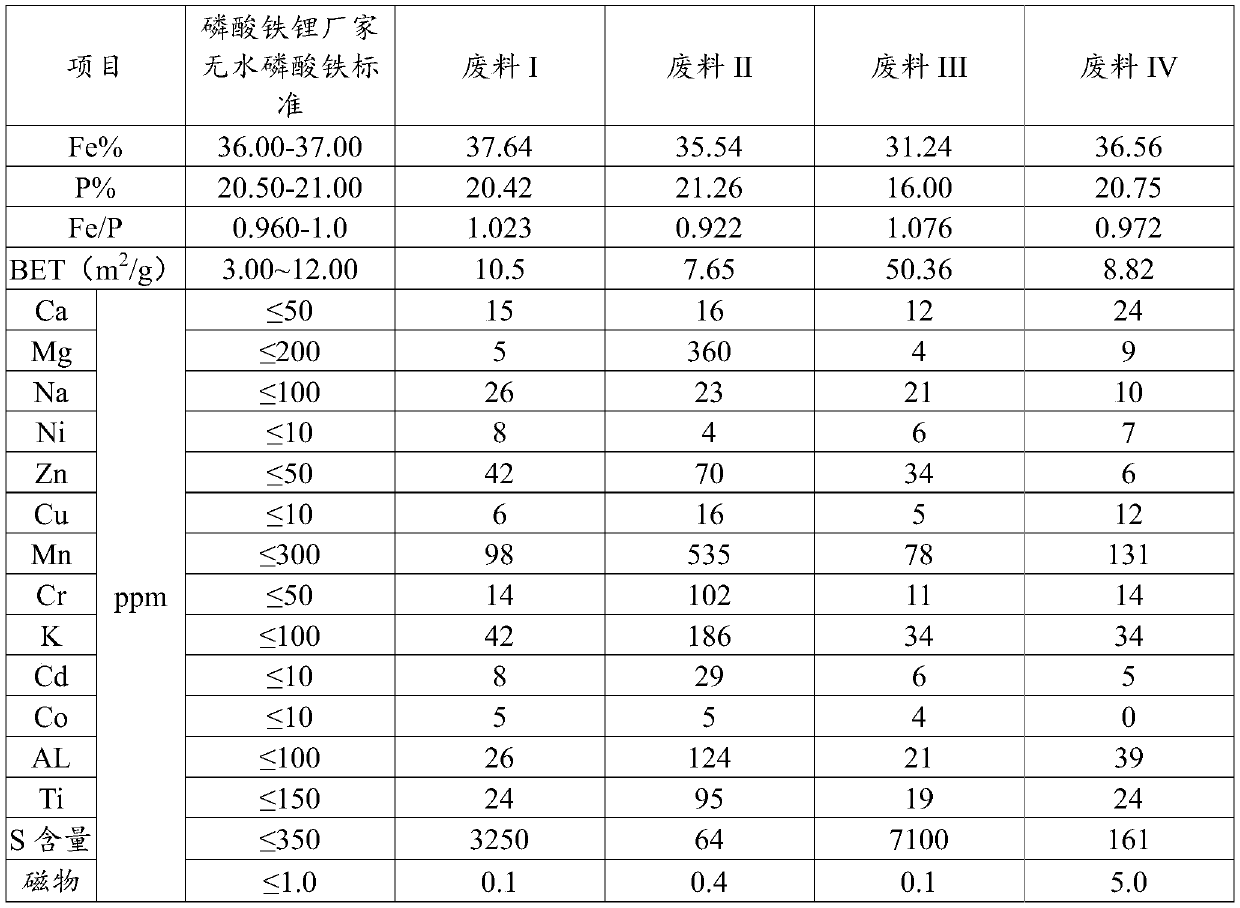
Method for regenerating iron phosphate waste
The invention discloses a method for regenerating an iron phosphate waste. The method comprises the following steps: S1, performing acid dissolution on the iron phosphate waste, and performing filtering so as to obtain a solution with iron and phosphorus; S2, detecting the ratio of iron to phosphorus in the solution A, controlling the ratio of iron to phosphorus in the solution A to 1:(0.9-1.02),so as to obtain a solution B; S3, adding an alkaline solution to the solution B under stirring, adjusting the pH value to 2.0-2.5, performing a reaction at (85-100) DEG C for (0.2-2) hours, performingsolid-liquid separation, and washing filter cakes so as to obtain amorphous iron phosphate intermediate filter cakes; and S4, pulping the amorphous iron phosphate intermediate filter cakes, adding phosphoric acid, performing a reaction under a stirring and heating condition, performing solid-liquid separation, washing the filter cakes so as to obtain crystalline iron phosphate filter cakes, and performing calcining, so as to obtain battery grade anhydrous iron phosphate. By adopting the scheme of the invention, not only are resource recycling and reuse achieved, but also economic benefits ofenterprises are increased, and the method has great significances for producers of iron phosphate.
Owner:HUNAN YACHENG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
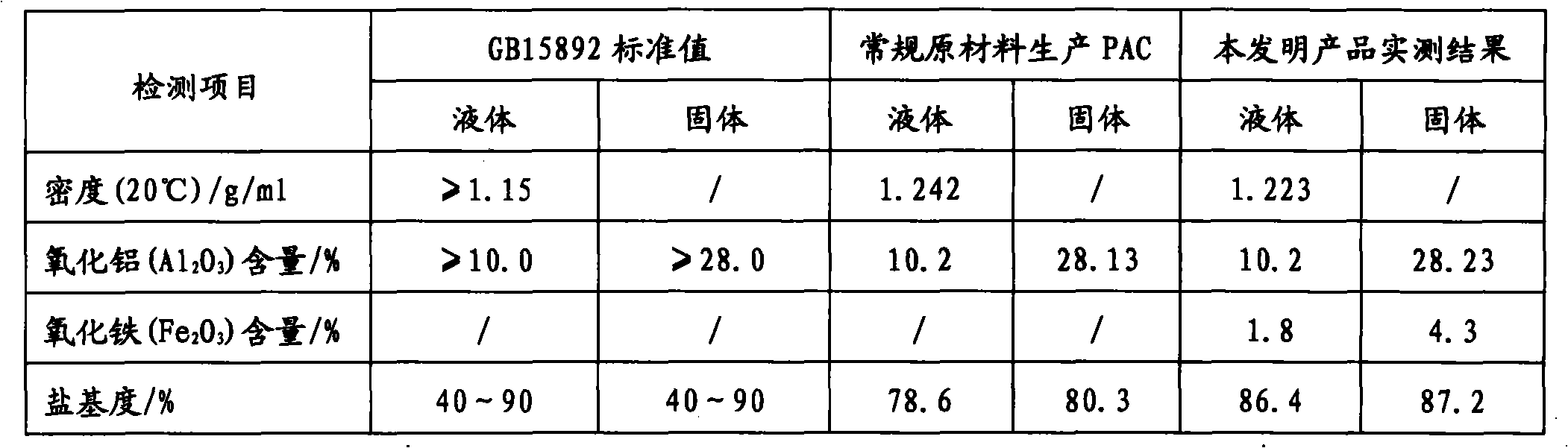
Method for preparing poly-aluminum ferric chloride sulfate and product thereof
ActiveCN101786667ALow costSimple preparation processIron compoundsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationAluminum IonSulfate
The invention relates to a method for preparing poly-aluminum ferric chloride sulfate and a product thereof. The method comprises the following steps: adding water into a reaction kettle with a stirring device, starting stirring, adding hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, then adding ferrous hydrargillite powder, heating to 90-100 DEG C, and maintaining the temperature to be subject to the reaction under the normal pressure for 2-4 hours; and filtering the feed solution after the reaction, taking and adding the mother solution to an acidproof steam-heating polyreaction vessel, adding calcium aluminate powder into the mother solution, adding water to regulate the density of the feed solution to be more than or equal to 1.20g / ml, adding synergist, heating, and controlling the temperature to be subject to the reaction for 3-5 hours to obtain the liquid poly-aluminum ferric chloride sulfate. Compared with the prior art, aluminum ions and iron ions are extracted by adopting the ferrous hydrargillite as the raw material, the extracting process adopts the sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid dissolving mode, and the poly-aluminum ferric chloride sulfate is obtained by carrying out the polyreaction on the calcium aluminate powder. Thus, the invention has the advantages of lower cost of each raw material and more simple preparation process. Besides, since the synergist is added in the polyreaction, the basicity of the product can be improved.
Owner:蓝保(厦门)水处理科技有限公司
Highly crystalline silver powder and production method of highly crystalline silver powder
InactiveUS20090116998A1High yieldLarge crystallite diameterTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusOrganic acidSilver particles
Object of the present invention is to provide a production method of a highly crystalline silver powder containing powder particles in fine particle region and having a good particle size distribution as well as the highly crystalline silver powder obtained by the production method. In order to achieve the object, the present invention adopts a production method characterized in that the method comprises preparation of a first aqueous solution in which gelatin, silver nitrate and nitric acid are dissolved in water, preparation of a second aqueous solution in which L-sorbic acid and / or ascorbic acid and a water-soluble organic acid are dissolved, adding of the second aqueous solution slowly to mix with the first aqueous solution, stirring of the mixture to grow the silver particles after finishing the mixing, keeping of the mixture still to settle the silver particles, discarding of the supernatant, filtration and rinsing to obtain the highly crystalline silver powder.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
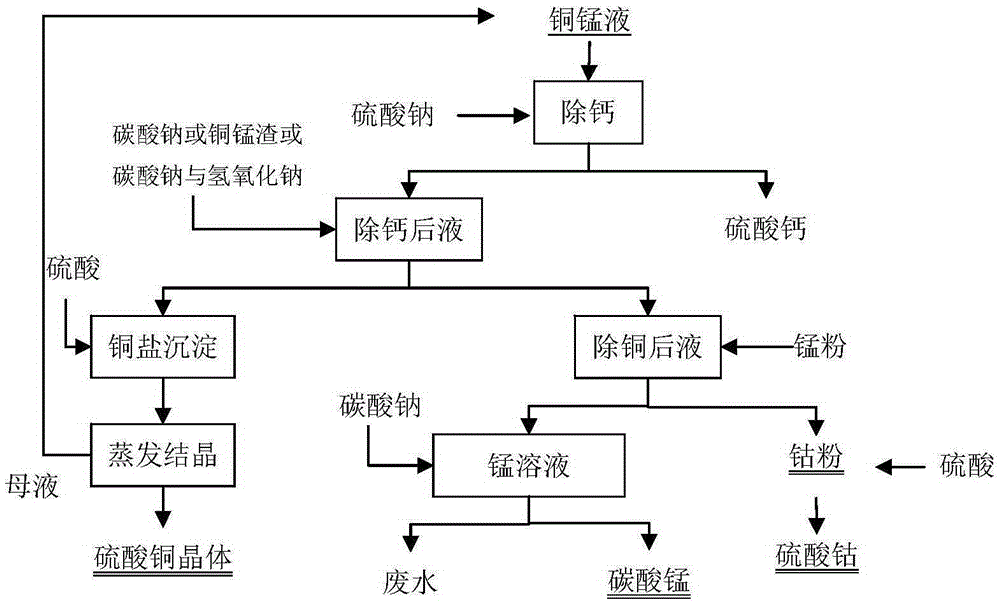
Method for separating copper, cobalt and manganese from cupric chloride manganese-cobalt-calcium-zinc impurity removal solution
ActiveCN105296754AShort processLow costRotary drum furnacesCrucible furnacesManganese(II) carbonateSulfate
The invention relates to a method for separating copper, cobalt and manganese from a cupric chloride manganese-cobalt-calcium-zinc impurity removal solution. The method comprises the steps that sodium sulfate is added to the cupric chloride manganese-cobalt-calcium-zinc solution, and calcium sulfate is removed by filtration; then sodium carbonate is added to a solution obtained in step one, a pH value is adjusted to 4.0-6.0 to allow copper ions in the solution to be precipitated, and copper precipitates are obtained by filtration separation; the copper precipitates are dissolved with sulfuric acid and are subjected to evaporation crystallization to form copper sulfate crystals; manganese powder is added to a solution after copper removal to allow cobalt ions to be reduced to cobalt powder to be precipitated, and cobalt powder is obtained after the filtration separation and is dissolved with acid to form a cobalt solution; and a solution after cobalt removal contains manganese and a little zinc and calcium, manganese is precipitated through the evaporation crystallization or by adding sodium carbonate, and manganese salts such as rough manganese carbonate are obtained. With the adoption of the method, three main valuable metals, namely copper, cobalt and manganese, can be separated and extracted economically and conveniently.
Owner:长沙百汇新材料科技有限公司
Method for recycling acid in process of producing alumina from fly ash by acid method
InactiveCN101863498ASimple processEasy to controlChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideSolid waste disposalIron removalAcid dissolution
The invention relates to a method for recycling acid in the process of producing alumina from fly ash by an acid method. The method comprises the following steps of magnetic separation and iron removal of the fly ash, acid dissolution, resin adsorption and iron removal, condensation crystallization, calcination, cooling, primary recycle of hydrogen chloride gas, secondary recycle of hydrogen chloride gas, regulation of concentration of recycled hydrochloric acid and application of the obtained hydrochloric acid to the step of acid dissolution. The method has the advantages of simple process, easily controlled production process, low production cost and recyclable adsorbed hydrogen chloride product.
Owner:CHINA SHENHUA ENERGY CO LTD +1
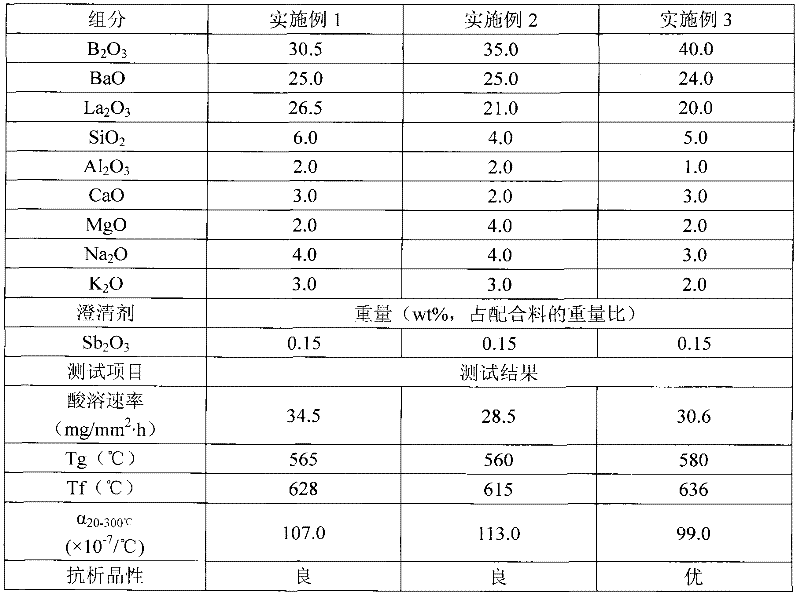
High-acid-dissolution-rate core material glass component for microchannel plate
InactiveCN102515515AHigh acid dissolution rateGood chemistryAcid dissolutionMicrochannel plate detector
The invention discloses a high-acid-dissolution-rate core material glass component for a microchannel plate. The glass component comprises 30-40wt% of B2O3, 20-30wt% of BaO, 20-30wt% of La2O3, 5-10wt% of SiO2, 1-5wt% of Al2O3, 5-10wt% of MgO and CaO and 5-10wt% of Na2O and K2O. The invention provides a new microchannel plate core glass system. The glass system is high in acid dissolution rate, has good compatibility with a microchannel slab glass system in chemical and thermal properties, and can be used for preparing a small-bore microchannel plate, a conductive glass microchannel plate and a thick bending microchannel plate.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com