Recovery process for valuable metals in tungsten residues
A technology for valuable metals and tungsten slag, which is applied in the recovery process of valuable metals in tungsten slag, can solve the problems of large environmental pollution and high energy consumption in pyrometallurgy, and achieves a reduction in recycling costs, good environmental benefits and low costs. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
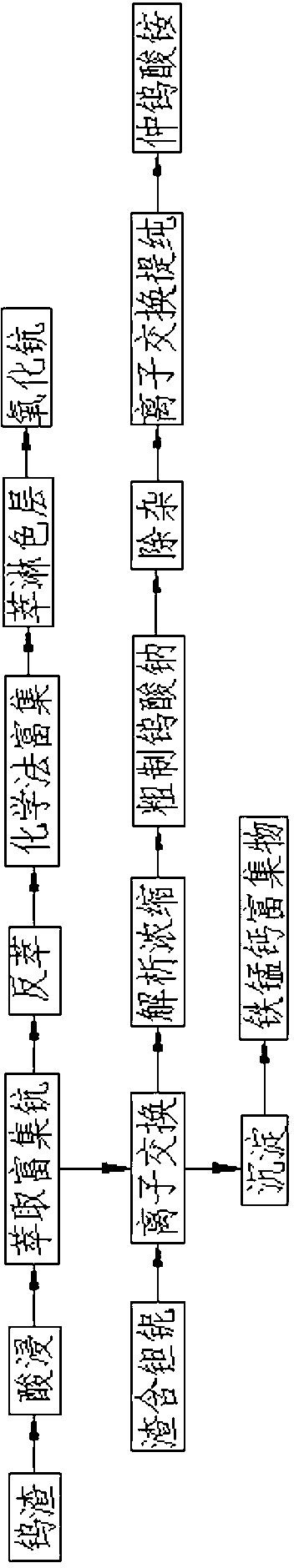
[0037] Such as figure 1 Shown, the present invention comprises the steps:
[0038] 1) Preparation of tungsten
[0039] 1) Solvent material
[0040] First add hydrochloric acid with a calculated concentration of 15~25% into the tank, heat to 60°C, slowly add black and white mixed tungsten slag under stirring, after adding black and white mixed tungsten slag, then add about 0.2 times of % hydrochloric acid, after heating and boiling, add 20kg / T NaF, 10kg / T NaNO3; when the pH value reaches about 1.0, add 0.4~0.5 times the amount of 15~25% hydrochloric acid, make S:L=1:4.5, boil Stop heating when the mud turns reddish brown, continue to stir, add water 2T / T, stir for 0.5h;
[0041] 2) Press filter
[0042] When the temperature of the material liquid prepared in step 1) is below 80°C, plate-and-frame filter press can be carried out. After the filter press, add water to wash, and blow dry; put the filtrate in the storage tank and let it stand for at least 12 hours, and then fine...
Embodiment 2
[0087] 1) Preparation of tungsten
[0088] 1) Solvent material
[0089] Add tungsten slag to the tank body with water or acid leaching and filtered washing water under slow stirring, and the liquid-solid ratio is 1:1; steam is heated to 60°C and then added according to the mass ratio of tungsten slag and sulfuric acid 1:1.2 8% sulfuric acid, keep the reaction temperature for 1.5 hours, then add 15%-25% HCl 0.25 times the amount of sulfuric acid, heat to boil, then add 20kg / T NaF, 10kg / T NaNO 3 ;When the pH value reaches about 1.0, put in 15~25% hydrochloric acid of 0.4~0.5 times the amount of sulfuric acid to make S:L=1:4.5, boil until the mud turns reddish brown, stop heating, continue stirring, add water 2T / T, stirring for 0.5h; when the temperature of the feed liquid reaches 80°C, put the feed liquid into a filter for filtration while stirring, then wash and dry it, put the filtrate in a storage tank and let it stand for at least 12 hours, and then finely filter it.
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0136] Except for the 7) W extraction step in the 1) preparation step of tungsten, the other steps are the same as those in Example 1 and will not be repeated here. The specific operation of the extraction step of this embodiment is as follows:
[0137] After reducing the finely filtered filtrate produced in step 2), put it into the extraction tank according to O / A=1 / 20-30, stir for 2 minutes, add citric acid or stearic acid with a concentration of 0.01%, grade 4 Countercurrent extraction, then add water according to the ratio O / A=1 / 1, stir for 3 minutes, and wash in 6 stages; then add hot 2mol / L NaOH solution according to the ratio O / A=2 / 1, stir for 15~20 Minutes; 3-stage reverse extraction and countercurrent, filter the stripping solution; then add water to backwash according to O / A=1 / 3~5, stir for 5~10 minutes, clarify, and return the water phase to alkali dissolution; then press the comparison O / A=3~5 / 1 Add 6M hydrochloric acid to acidify, stir for 3~5 minutes. Adding or...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com