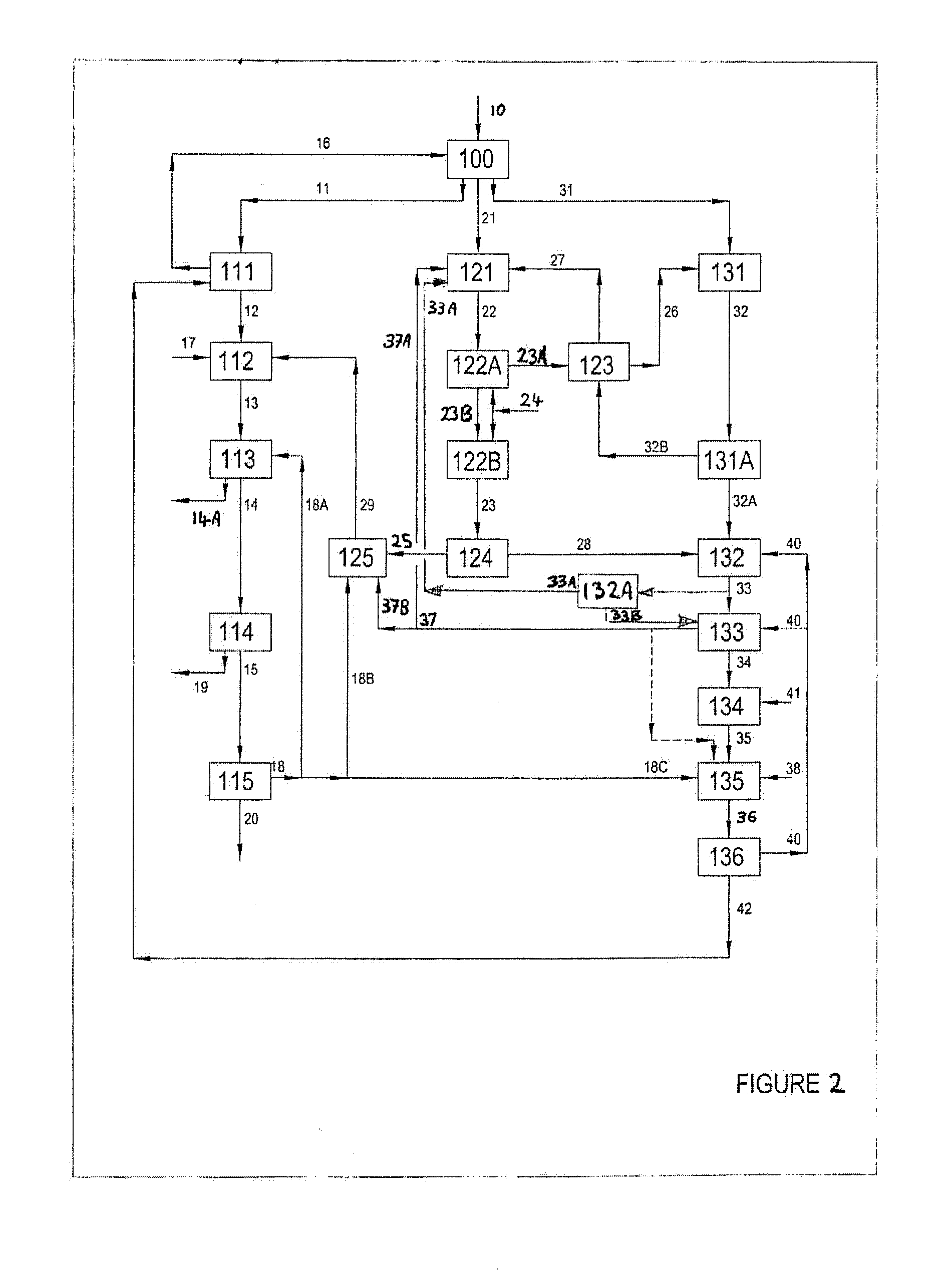
Patents
Literature
342 results about "Pyrometallurgy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pyrometallurgy is a branch of extractive metallurgy. It consists of the thermal treatment of minerals and metallurgical ores and concentrates to bring about physical and chemical transformations in the materials to enable recovery of valuable metals. Pyrometallurgical treatment may produce products able to be sold such as pure metals, or intermediate compounds or alloys, suitable as feed for further processing. Examples of elements extracted by pyrometallurgical processes include the oxides of less reactive elements like iron, copper, zinc, chromium, tin, and manganese.
Comprehensive recovery method of complex polymetal sulphide ore containing copper, lead and zinc
InactiveCN101643857AHigh recovery rateSimple processSulfur preparation/purificationFlotationRecovery methodLead smelting
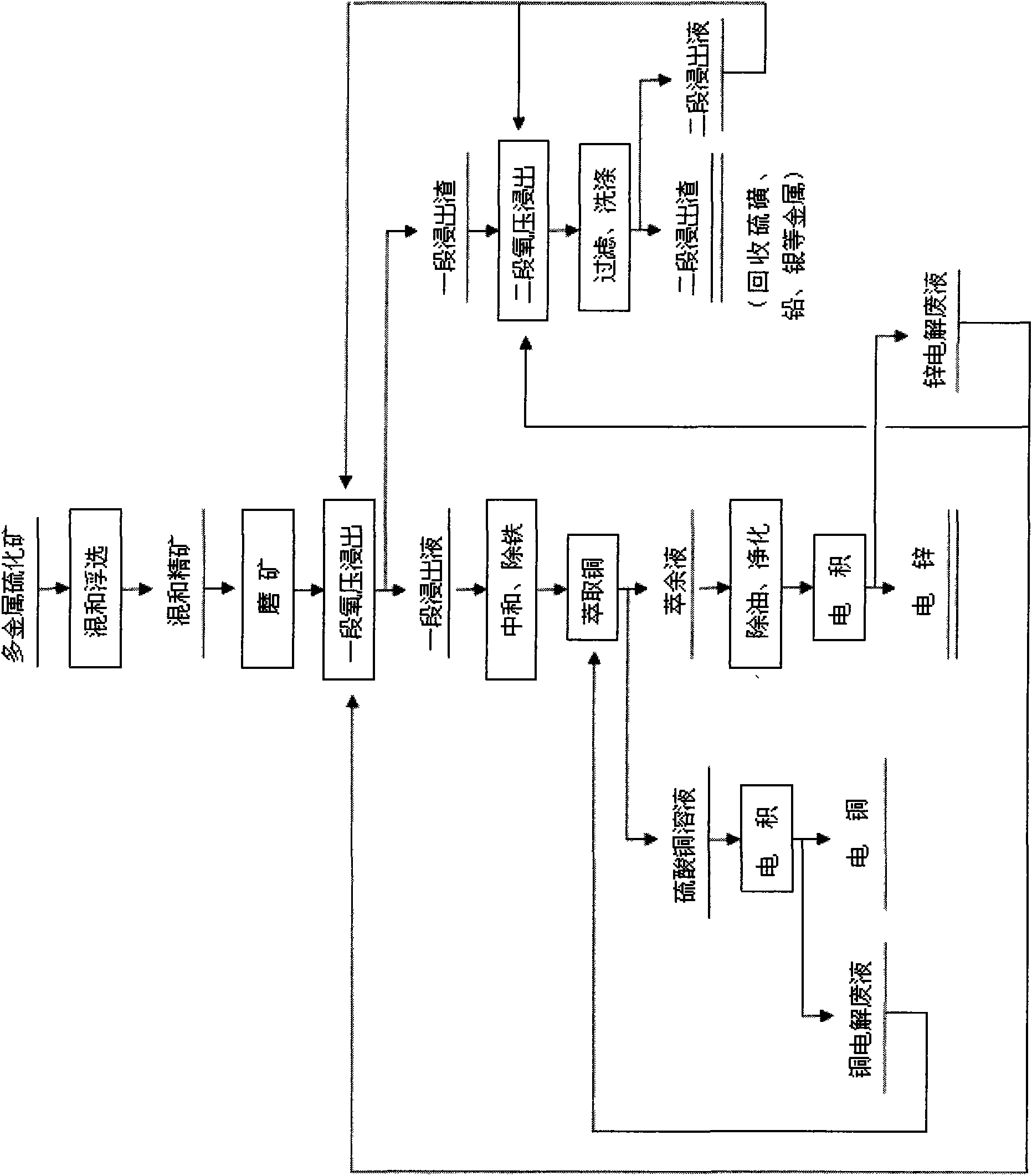
The invention discloses a comprehensive recovery method of complex polymetal sulphide ore containing copper, lead and zinc and adopts dressing-metallurgy combination method and hydrometallurgy-pyrometallurgy combination method to recover metals. The recovery method comprises the following steps: first performing bulk flotation to the complex polymetal sulphide ore, fine grinding the obtained concentrate, leaching by using two-step counter flow oxygen pressure leaching process, extracting and separating copper and zinc from the obtained leachate, electrodepositing the strip liquor of copper-loaded organic phase to obtain cathode copper, cleaning the obtained raffinate and electrodepositing to obtain cathode zinc; pressurizing leaching residue to perform flotation separation and obtain sulfur concentrate and lead silver residue, distilling sulfur concentrate to obtain sulfur; performing lead smelting process to lead silver residue to obtain electrolytic lead product and lead anodic slime; and comprehensively recovering noble metals such as gold, silver and the like from lead anodic slime. The method can greatly improve the metal recovery rate, resource utilization and the economic efficiency of mines and generate a lot of sulfur so as to obviously reduce the sulfur dioxide pollution to the atmosphere.
Owner:WESTERN MINING CO LTD
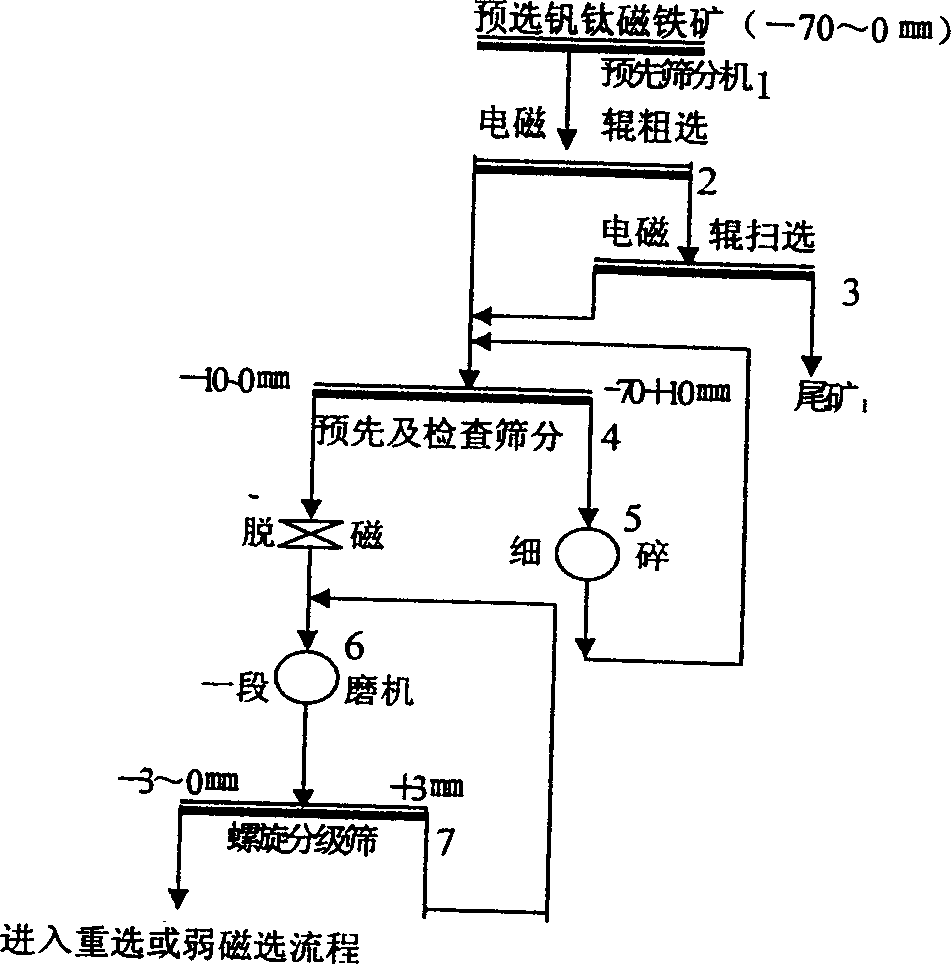
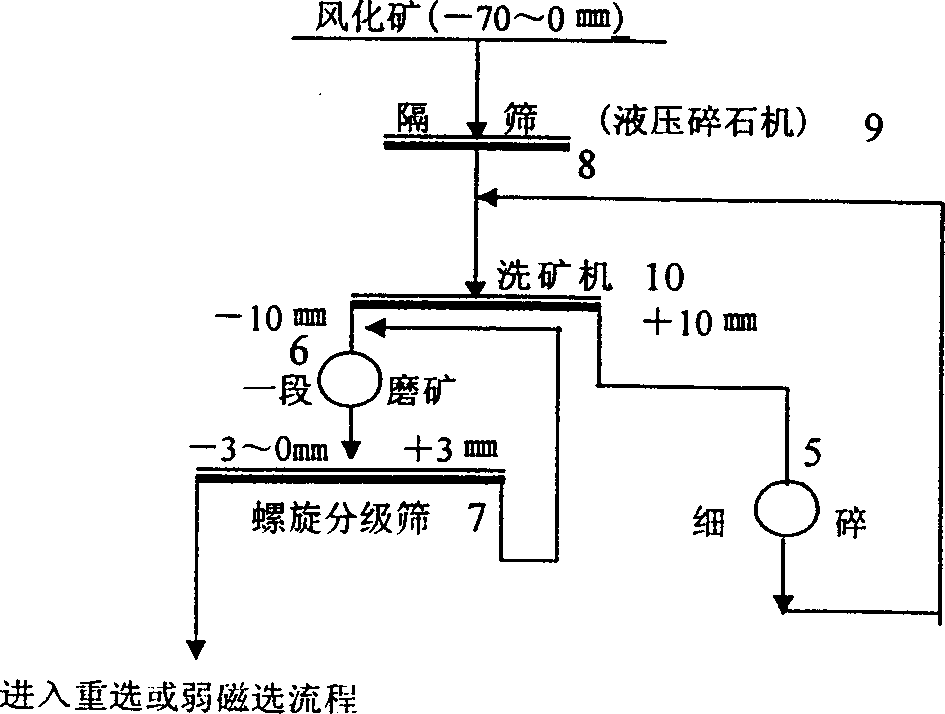
Method of producing titanium enriched material using titanium mineral
InactiveCN1429919AEfficient recyclingImprove resource utilization efficiencyMagnetic separationAdhesiveMagnetite
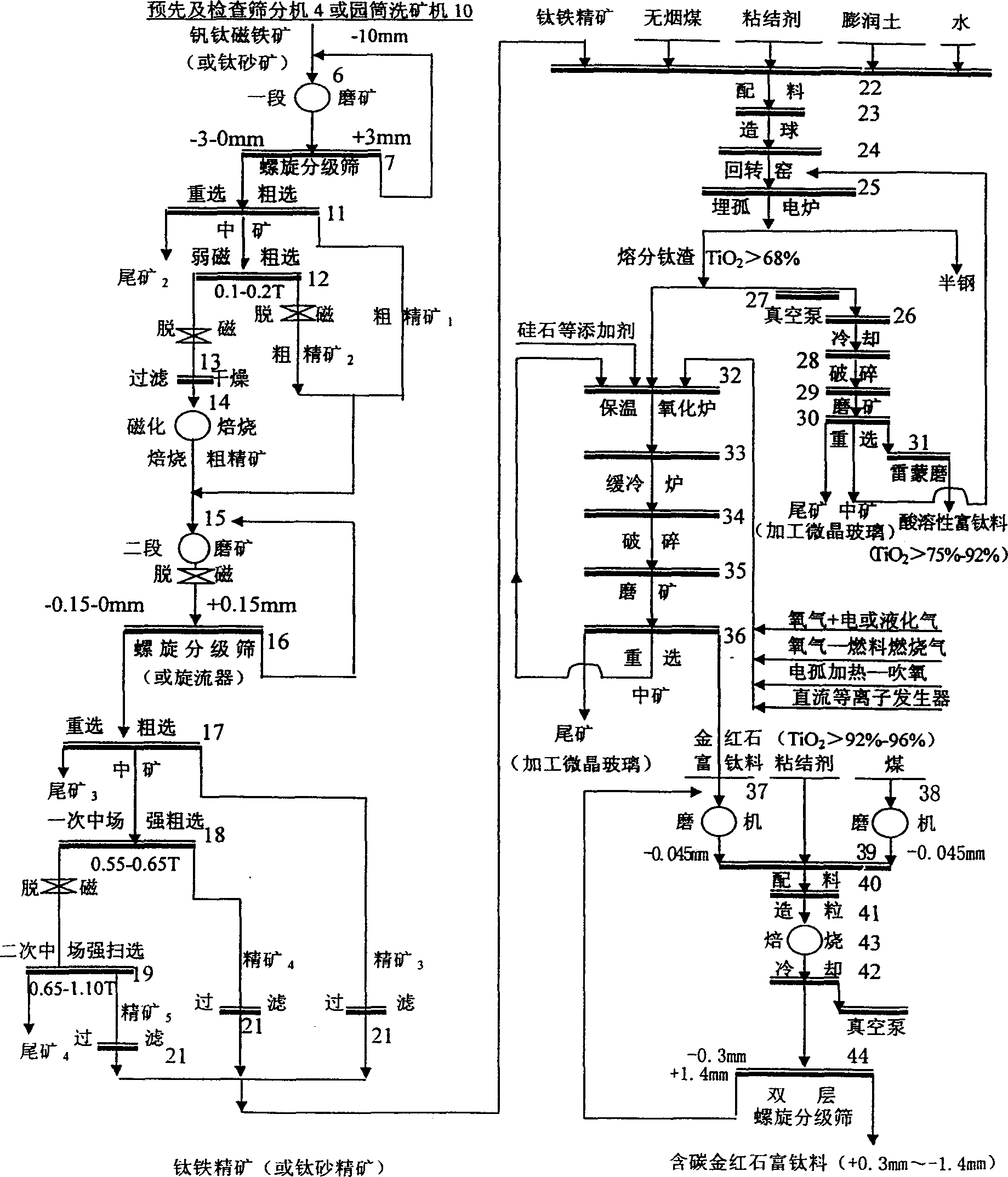
A process for preparing Ti-enriched material from V-Ti magnetite through preseparating to obtain Ti-Fe ore concentrate, proportionally mixing it with V-Ti-Fe core concentrate, adhesive and carbon reducer, smelting to obtain high-Ti slag and semi-steel, blowing V-Cr to melten alloy iron to obtain V-Cr contained steel slag, separating V and Cr, fire metallurge of high-Ti slag to obtain artificial rutile and microcrystal glass, ball grinding of artificial rutile and coal while adding adhesive to obtain C-contained Ti particles, calcining, cooling and classifying.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Integrated hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical processing of base-metal sulphides
InactiveUS20080173132A1Maximize recoveryChemical efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementSulfideCopper
The present invention relates to the recovery of base metals, in particular but not exclusively copper, via integrated hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical processing of base-metal sulphides, in particular but not exclusively iron-containing base-metal sulphides.
Owner:AUSENCO SERVICES PTY LTD
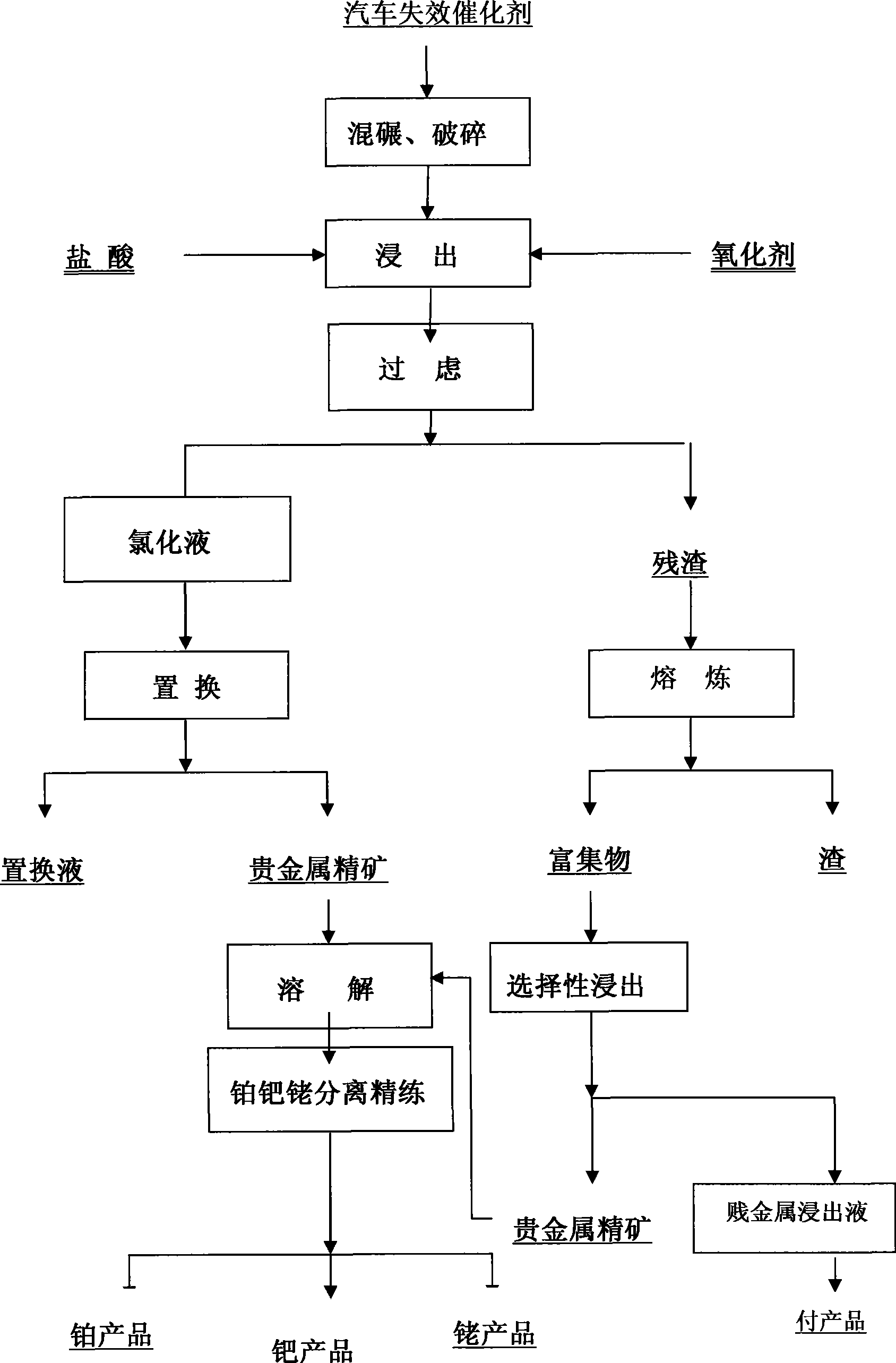
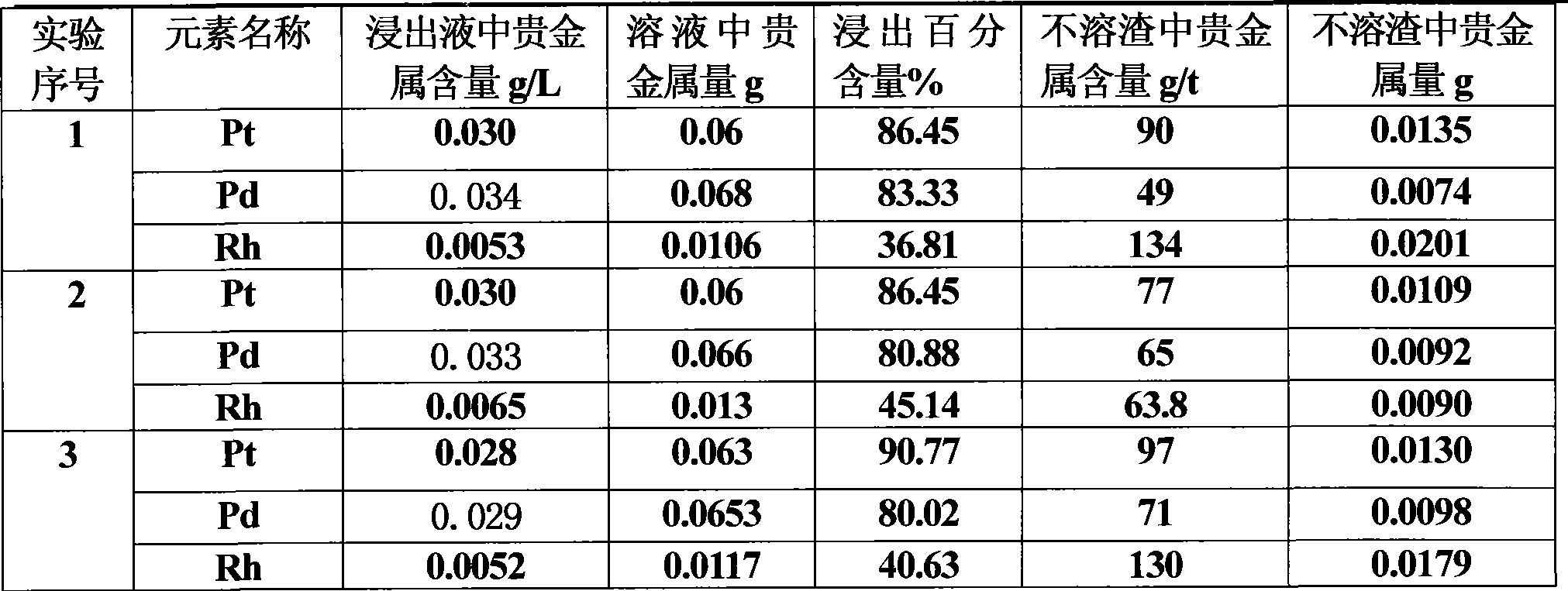
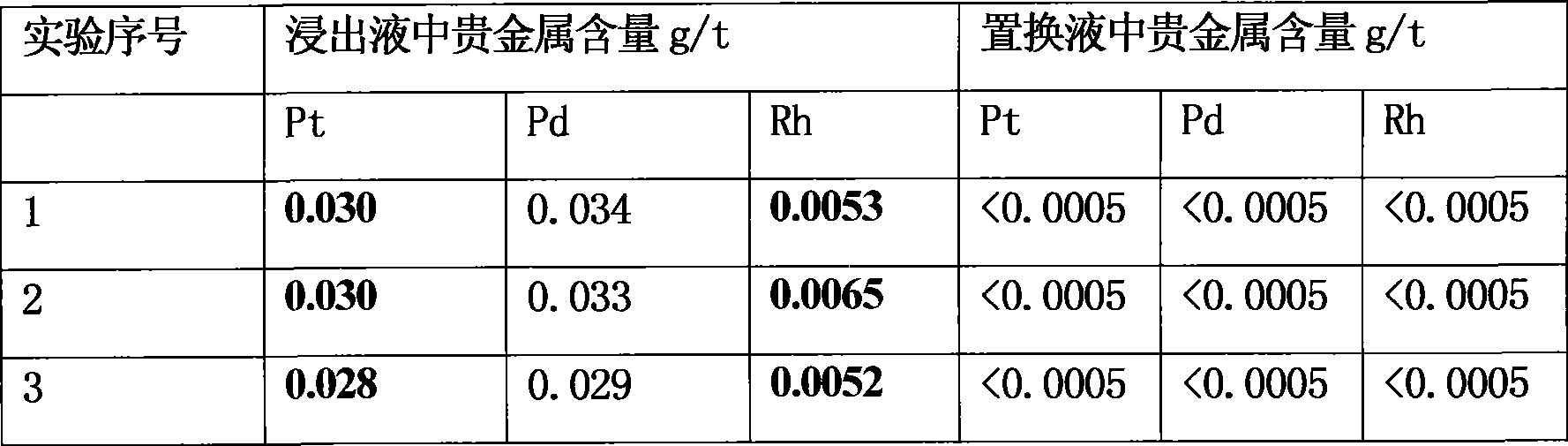
Method for extracting precious metal from auto-exhaust catalyst by hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy complex process
InactiveCN101519725ALoose process conditionsImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionPlatinum
The invention relates to a method for extracting precious metal from a disabled auto-exhaust catalyst, which comprises the following steps: 1. lixiviating precious metal from the disabled auto-exhaust catalyst by a hydrometallurgy process and obtaining precious metal concentrates after permuting lixivium; 2. lixiviating slag, collecting precious metal of the slag by a pyrometallurgy process to obtain a precious metal phase and selectively lixiviating base metal in the precious metal phase to obtain precious metal concentrates; and 3 combining the precious metal concentrates obtained in the first two steps and refining the precious metal concentrates to produce platinum, palladium and rhodium products. The invention compensates the deficiency that the percent recovery of the precious metal is low by simply treating the disabled auto-exhaust catalyst with the hydrometallurgy process and has the advantages that the contents of platinum, palladium and rhodium in the waste slag are smaller than 1g / t and the product purity reaches 99.95 percent.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
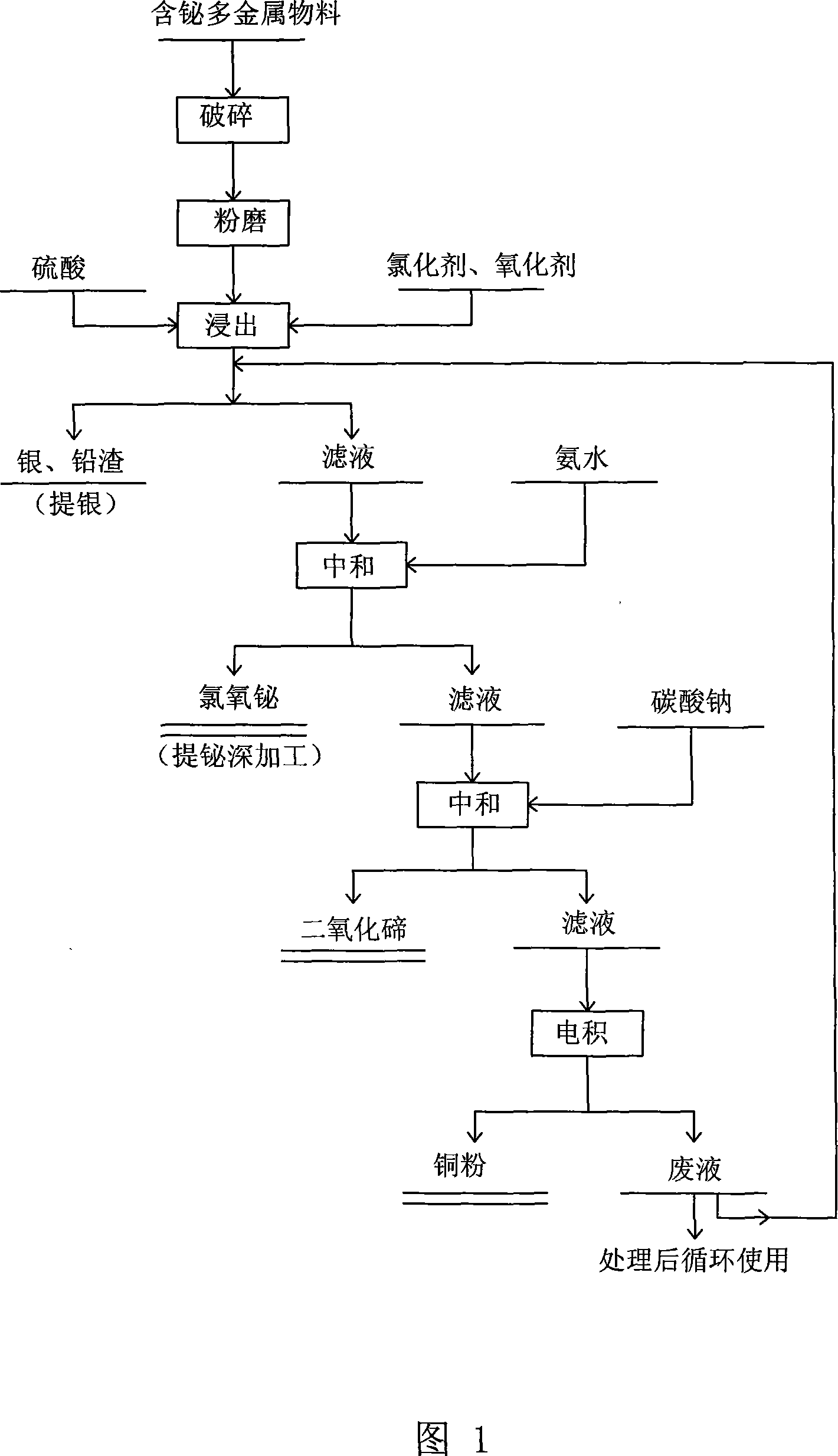
Comprehensive extraction of valent metal from bismuth-containing polymetallic material
InactiveCN101029353AHigh recovery rateImprove product added valuePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSesquioxideTe element
A method for extracting metal from bismuth-contained multi-metal material is carried out by leaching out copper and tellurium from bismuth-contained multi-metal by sulfuric acid, adding into chlorinating agent and oxidant to leach out metal bismuth, extracting silver from leaching-out slag with AgCl, PbSO4 and PbC12, adding ammonia water into leaching-out liquid, adjusting pH value to 1.5 to obtain bismuth oxychloride slag with 70% bismuth content, smelting into coarse bismuth by firing method or machining to obtain high-purity bismuth sesquioxide, adjusting pH value to 4.5 by Na2CO3, depositing tellurium to obtain tellurium dioxide and copper-contained solution, and electrically depositing to obtain copper powder with copper-contained content90%. It adopts wetting and firing metallurgical technology, has higher metal recovery rate and excellent leaching-out separation effect and effluent circulating utilization and no environmental pollution.
Owner:HUNAN JINWANG BISMUTH
Method for recycling valuable metals in manganese series waste batteries
ActiveCN102569838AEfficient recyclingStrong ability to useReclaiming serviceable partsProcess efficiency improvementResource utilizationLithium metal
The invention discloses a method for recycling valuable metals in manganese series waste batteries. In the method, the manganese, iron, zinc and lithium metal resources in a waste zinc-manganese dry battery, a waste alkaline-manganese battery and a waste lithium-manganese primary battery and a waste lithium ion battery taking lithium manganate or lithium manganate derivative as a positive electrode material are comprehensively utilized by pyrometallurgy and made into products such as manganese-iron alloy and zinc oxide, wherein the total mass of manganese and iron in the prepared manganese-iron alloy reaches over 90%, and the manganese-iron alloy can be applied to steel enterprises and stainless steel enterprises; and the total mass of zinc and lithium in zinc oxide reaches over 40%, and zinc oxide can be applied to wet refining of zinc and lithium. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high resource utilization and recovery rate, simple technology and high recovery value.
Owner:GUANGDONG BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +1
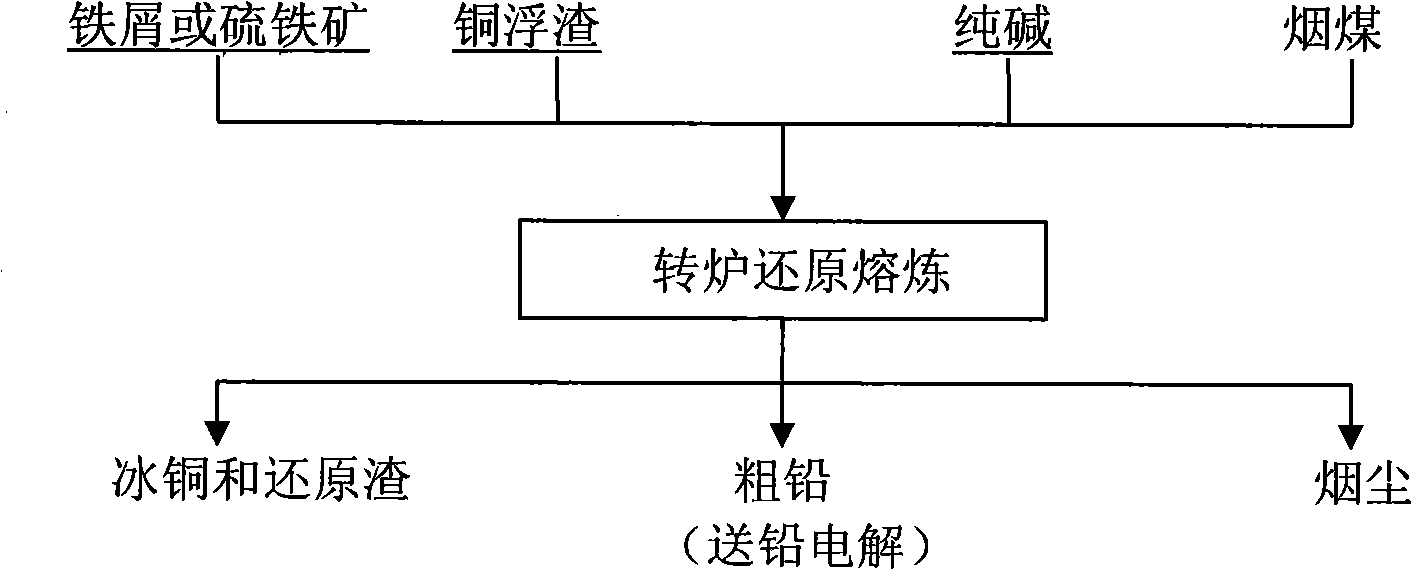
Method for treating copper scum using converter
The invention relates to a method for processing copper dross slag by using a converter, which belongs to the technical field of thermometallurgy. Copper dross slag, calcined soda, scrap iron or sulfurous iron ore and soft coal are proportioned in proportion and then are added into a converter for retailoring. The temperature is controlled within the range of from 700 DEG C to 800 DEG C, the smelting lasts for 1.5 hours to 2 hours, so that lead in the metal form in the copper dross slag is separated from copper; then the temperature is increased to the slag overtemperature of 1100 DEG C to 1250 DEG C, the smelting lasts for 2.5 hours to 3 hours, so that lead compound is deoxygenated to produce metal lead, and the copper becomes copper matte to realize the separation of copper and the lead. The dross slag on the copper matte and the wet lead are fished out to obtain the copper matte and the wet lead. Because the operation process of the invention is carried out in the converter, the separation of copper and lead is more complete. The method can solve the problems of high energy consumption, heavy environmental pollution, low metal recovery ratio, high production cost and the like in the prior copper dross slag processing.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
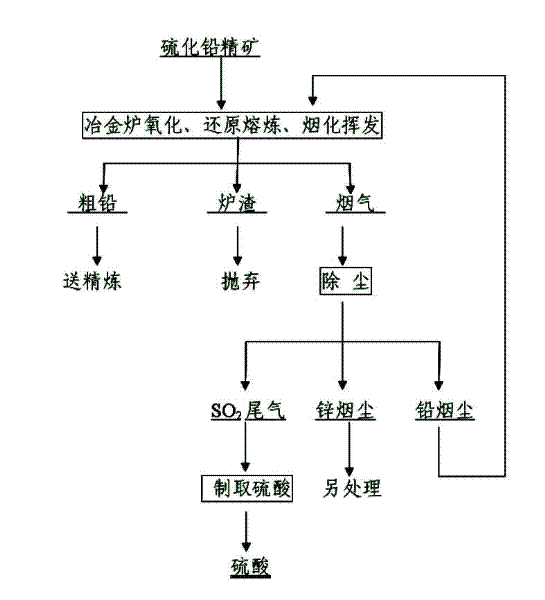
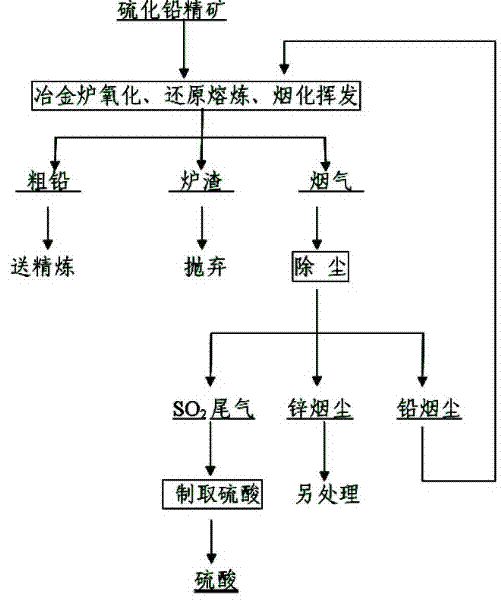
One-step oxidation smelting, reduction smelting and slag fuming and volatilization methods for lead sulfide concentrate
The invention relates to non-ferrous metal metallurgy technology, in particular to the pyrometallurgy technology of lead sulfide concentrate. The process method is to successively carry out three smelting processes of oxidation smelting, reduction smelting and fuming volatilization in the same metallurgical furnace to smelt lead sulfide concentrate, and smelt crude lead, zinc fume and discardable slag in one step. In the oxidation smelting stage, after the feed reaches the set amount, the lead oxide slag is not released, and the high-temperature liquid slag is directly used in the furnace to transfer to the reduction stage of the lead oxide slag, and the smoke generated by oxidation smelting and reduction smelting is returned to the furnace for smelting. After the reduction is completed, all the crude lead is released, and the high-temperature liquid slag remains in the furnace, and it enters the slag fuming stage, and the zinc fume dust from the slag fuming is recovered and enters the next smelting cycle. The heat of the slag in the invention is fully utilized, and the energy-saving effect is obvious. The raw material preparation of the method is simple, the reducing agent only needs ordinary anthracite, and part of the fuel that needs to be supplemented in the reducing section and the fuming section is pulverized coal, which is low in value and easy to obtain.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN GROUP HLDG
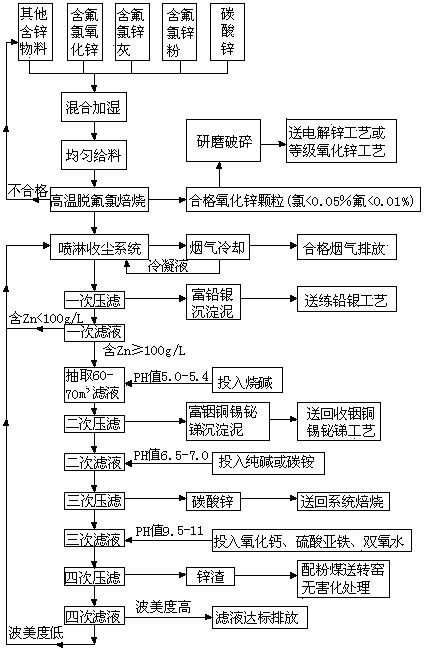
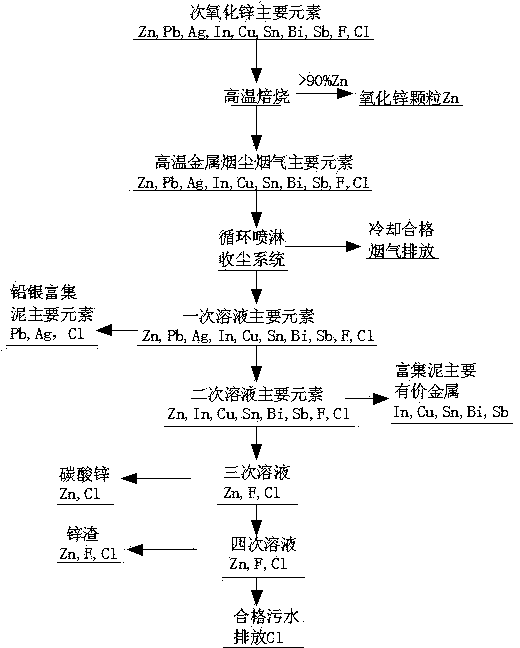
Smelting method for removing fluorine and chlorine out of fluorine-and-chlorine-containing inferior zinc oxide and enriching valuable metals
InactiveCN103924091AReduce water consumptionEasy to handleProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgySoot
The invention discloses a smelting method of removing fluorine and chlorine out of fluorine-and-chlorine-containing inferior zinc oxide and enriching valuable metals and relates to the technical field of hydrometallurgy and thermometallurgy of nonferrous metals such as zinc. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: oxidizing and roasting inferior zinc oxide in a rotary kiln at a high temperature so as to remove fluorine and chlorine and generate high-purity zinc oxide particles; meanwhile, volatilizing valuable metals in form of high-temperature soot and smoke, circularly spraying and washing so that valuable metals enter a spraying solution or precipitate to be enriched; further separating valuable metals in the solution; and finally, treating the sewage containing fluorine and chlorine and discharging the sewage reaching the standard or reusing the sewage by the system. Therefore, the inferior zinc oxide is purified in a primary continuous multi-sectional process to reach the technical index of conventional zinc-making raw materials, and the valuable metals are enriched by 5-20 times. The zinc making enterprises can widely use various types of inferior zinc oxide as the raw material, so that the production process is unified, the production cost is lowered, various valuable metals are comprehensively recovered, and discharge of sewage is reduced.
Owner:何宇波
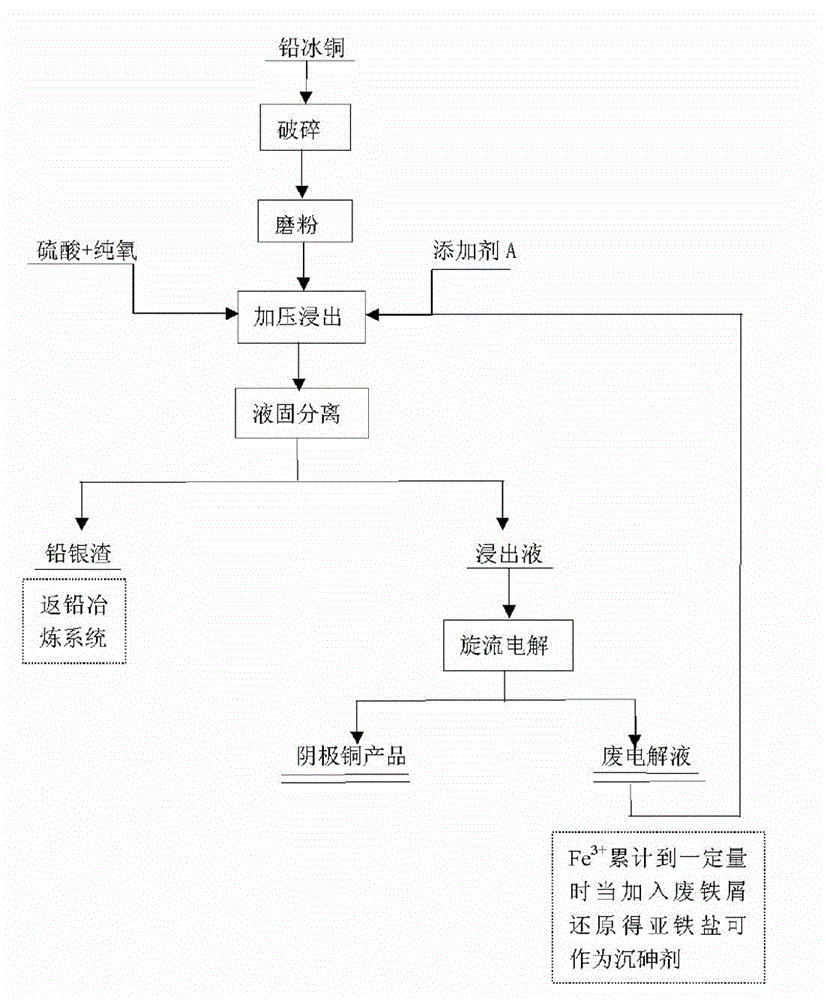
Process for selective efficient copper extraction and comprehensive recovery from lead copper matte
ActiveCN104789783ANo pollution to the environmentNo pollution in the processPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementCycloneElectrolysis
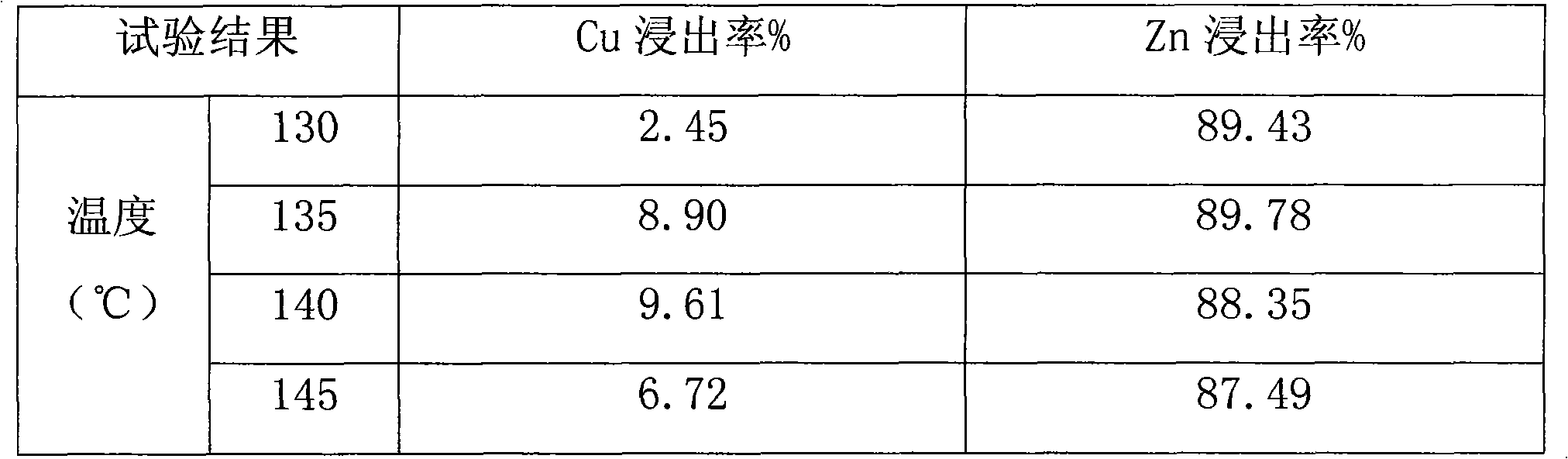
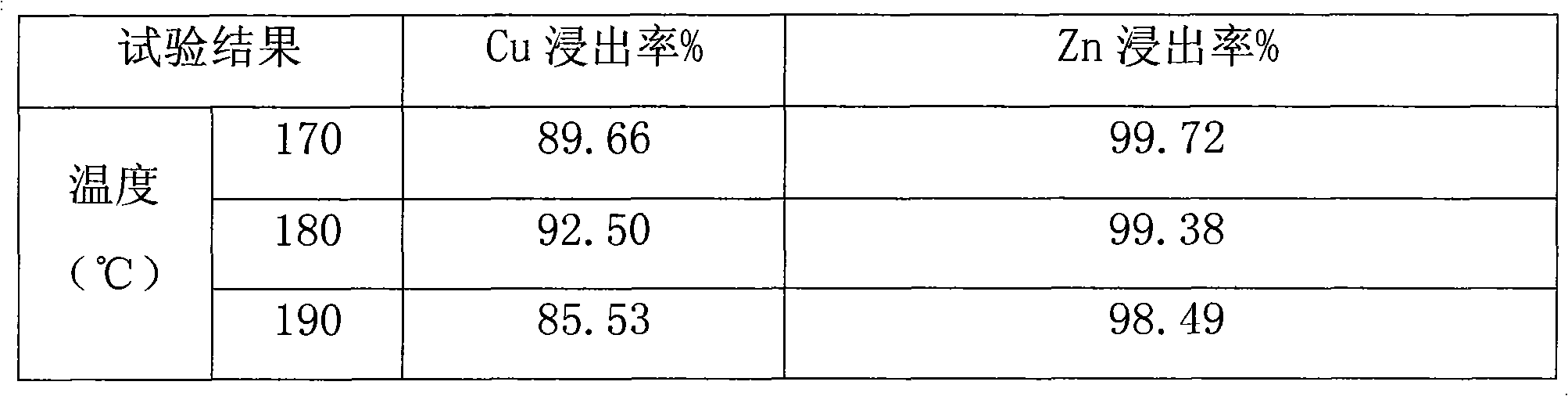
The invention discloses a process for selective efficient copper extraction and comprehensive recovery from lead copper matte and belongs to the field of wet processes of non-ferrous metal metallurgy. According to the process disclosed by the invention, the lead copper matte is taken as a raw material, and the process comprises the following steps: crushing, grinding and screening the lead copper matte, performing pulp conditioning on the lead copper matte after screening and sulfuric acid (or a waste electrolyte), then pouring into a high-pressure kettle, performing leaching, adding an adjusting agent A and introducing pure oxygen; controlling technical conditions, oxidizing sulfur in the lead copper matte to elemental sulfur in the oxidization and leaching processes, and transferring into slag; oxidizing copper to enable the copper to enter a solution in the form of copper ions and enabling lead to leave in the slag in the form of lead sulfate with gold and silver; and enabling most of iron to enter into the slag in the forms of hematite and yellow calcium iron vitriol under high-temperature, high-pressure and high-acid conditions. After the completion of the leaching process, liquid-solid separation is performed to realize primary separation of the copper and other valuable elements; after acid adjustment of a leachate, cyclone electrolysis is directly performed to extract the copper in the leachate, and then a cathode copper product which is in line with a national standard can be obtained; and leaching residues are sent into a lead pyrometallurgy system for comprehensively recovering Pb, Ag, Au and other valuable elements.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
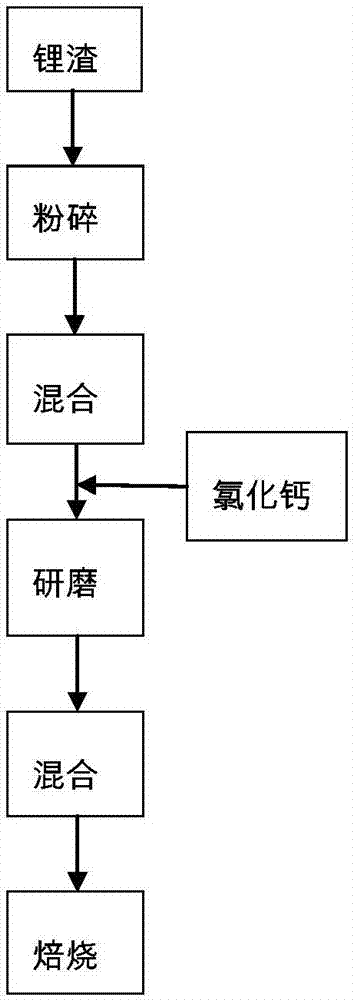
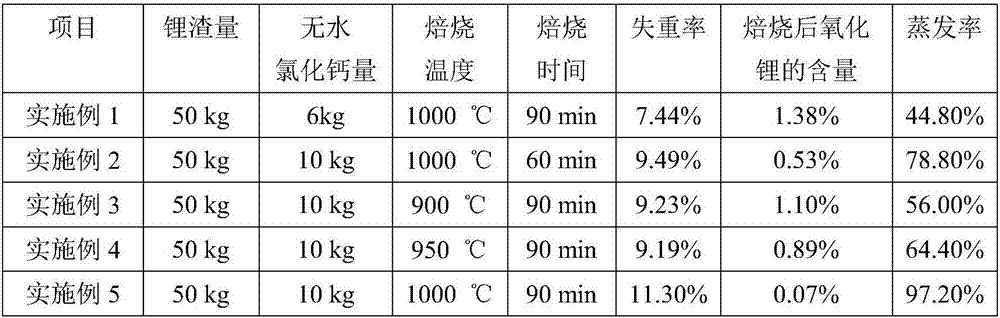
Method for recycling lithium in waste lithium battery slags through chloridizing roasting and evaporation
ActiveCN107964593AHigh purityWon't happenProcess efficiency improvementMetal chlorideLithium chloride
The invention provides a method for recycling lithium in waste lithium battery slags through chloridizing roasting and evaporation and belongs to the field of resource recycling. The method comprisesthe following steps: uniformly mixing pulverized lithium slags with a certain quantity of metal chloride; and then, roasting mixed lithium slag and metal chloride at high temperature, and transferringlithium in the lithium slags into a gas-phase removing system in the form of lithium chloride. The problem that the lithium in the waste lithium batteries is difficult to recycle by thermometallurgytreatment is solved. The molar ratio of chlorine in the metal chloride and the lithium in the lithium slags is 1: 1 to 2:1, and the roasting temperature is 800-1200DEG C. The method is simple to operate, causes small pollution, and is high in economical benefit and suitable for industrial popularization.
Owner:安徽惠宏科技有限公司
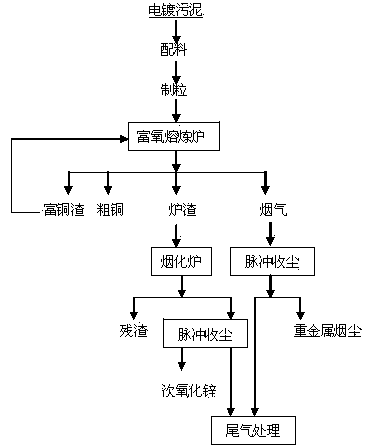
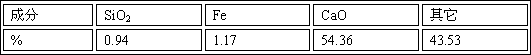
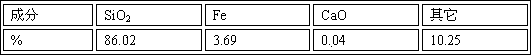
Method for comprehensive recovery of valuable metals from electroplating sludge and innocent treatment of electroplating sludge
InactiveCN103667714AWide adaptabilityEfficient separationRotary drum furnacesCrucible furnacesSludgeMetal recycling
The invention discloses a method for comprehensive recovery of valuable metals from electroplating sludge and innocent treatment of electroplating sludge. The method comprises the steps of burdening, pelletizing, smelting, blowing, dust collection, fuming, tail gas treatment and the like. According to the invention, thermometallurgy is adopted, the adaptation of the raw material is broad, the smelting and the blowing are completed in one furnace, equipment is simple to operate, and the metal recovery rate is high; through strong reduction smelting at high temperature, harmful chromium<6+> is reduced to harmless chromium<3+>, so that innocent treatment of electroplating sludge is completed; as the main component of electroplating sludge is metallic oxides, reduced and smelted smoke contains microscale sulfur dioxide only, and desulfuration is not needed for the reduced and smelted smoke; technological waste water is not generated, and pollution to the environment is less; valuable metals can be effectively recovered from electroplating sludge, and innocent treatment of electroplating sludge is realized.
Owner:CHENZHOU FENGYUE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
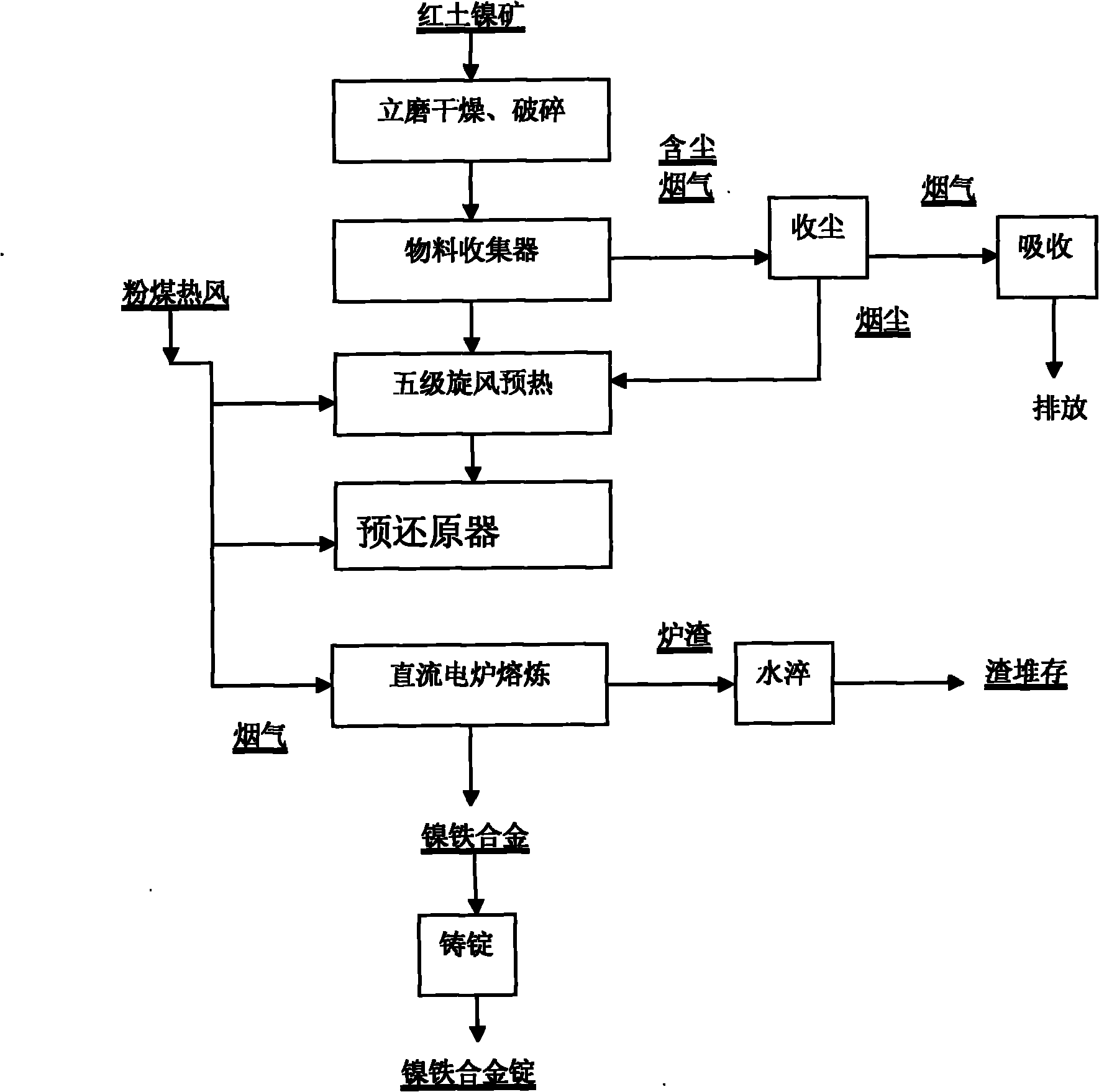
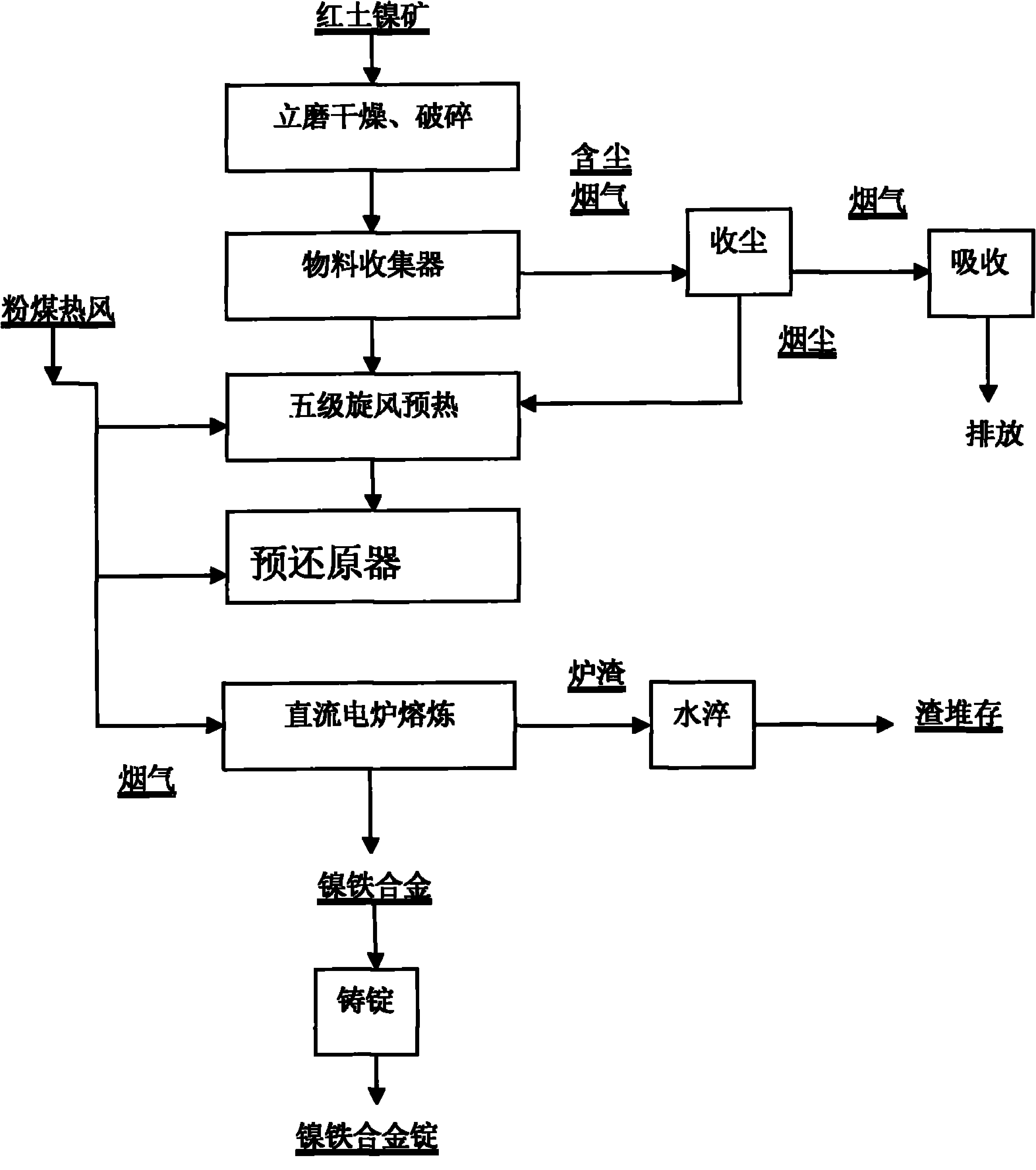
Method for smelting ferronickel or nismatte with laterite-nickel ore
The invention relates to a laterite nickel ore smelting process, in particular to a method for smelting ferronickel or nismatte with laterite-nickel ore, which comprises the following steps: crushing the laterite-nickel ore with a vertical mill until the particle size is less than 1mm, feeding the crushed laterite-nickel ore into various levels of suspension, drying and calcinating devices and a pre-reduction device in sequence, and guiding flue gas generated by the various levels of suspension, drying and calcinating devices into the vertical mill; spraying bituminous coal powder into the pre-reduction device for reduction and calcination of the materials in a suspension state, directly guiding the exhaust of the pre-reduction device into the the last level of drying and calcinating device, and smelting hot materials after pre-reduction in a DC furnace to produce the ferronickel or nismatte. The invention has the advantages of simple process, easy operation, low investment and high thermal efficiency, and can solve the problems of high energy consumption and high smelting cost in the traditional pyrometallurgy of the laterite-nickel ore.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN GROUP HLDG +1
Lead matte pyrogenic process treatment technology
The invention relates to a lead matte pyrogenic process treatment technology, which belongs to the field of pyrometallurgy. According to the lead matte pyrogenic process treatment technology, coke is used as a reducer and sodium carbonate is used as a mixed reactant, the major elements of lead and copper in lead matte are recovered by using the principle that the carbon in the coke reacts with sulfides of lead and copper in the lead matte to produce a lead copper alloy; since sodium sulfide is produced by the reaction, the melting point of the slag is reduced, and the slag is more completely separated from the lead copper alloy; meanwhile, other impurity metals such as zinc and iron in the lead matte are also subjected to similar reaction to be reduced into the lead copper alloy, and the impurity metals entering the lead copper alloy are separated with ease subsequently and have an extremely small effect on the entire lead matte pyrogenic process treatment technology; the sulfur in the lead matte is completely converted into the sodium sulfide so as to prevent environmental pollution, realize green production and meet the environmental protection requirements.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Method for recovering valuable metals from copper anode mud flotation tailings
InactiveCN105483384ASettle the lossHigh removal rateSelenium/tellurium compundsProcess efficiency improvementSootAntimony
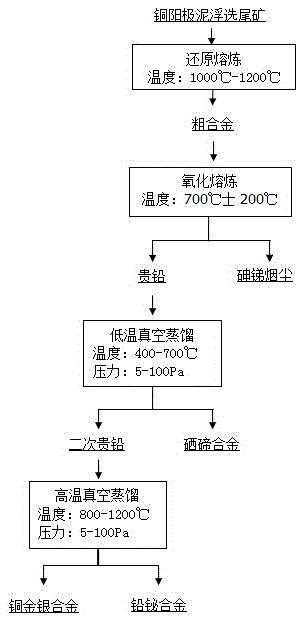
The invention relates to a method for recovering valuable metals from copper anode mud flotation tailings and belongs to the technical field of thermometallurgy. The method comprises: firstly, performing retailoring on the copper anode mud flotation tailings to obtain a reduction product, and then performing oxidative blowing on the reduction product to obtain rich lead and arsenic and antimony containing soot; first-stage low-temperature vacuum distillation: performing primary low-temperature vacuum distillation on the obtained rich lead under the conditions of a temperature of 400-700 DEG C and a pressure of 1-100Pa for 1-3h, thereby obtaining secondary rich lead and a selenium-tellurium alloy; and second-stage high-temperature vacuum distillation: performing primary high-temperature vacuum distillation on the obtained secondary rich lead under the conditions of a temperature of 800-1200 DEG C and a pressure of 1-100Pa for 1-3h, thereby obtaining a lead-bismuth and a copper-gold-silver alloy. The method for recovering valuable metals from copper anode mud flotation tailings is safe and controllable in whole process flow, simple and convenient to operate, simple in equipment needed, free from three-waste emissions, and environment-friendly.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for processing tin refining sulfur slag
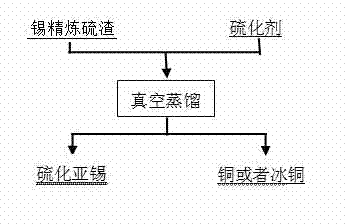
InactiveCN103589870ANo pollution in the processSimple processProcess efficiency improvementCopperPyrometallurgy
The invention relates to a method for processing tin refining sulfur slag and belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metal pyrometallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, uniformly mixing the tin refining sulfur slag and a vulcanizing agent according to a molar ratio of Sn to S of 1:(1 to 2.5) to obtain mixed materials; then placing the mixed materials into a vacuum furnace and performing the reaction for 1 to 50 min under a pressure of 1 to 100 Pa and a temperature of 700 to 1,200 DEG C so as to obtain copper or copper matte and solid stannous sulfide on a condenser. According to the method, a vacuum distillation process is adopted and tin reacts with the vulcanizing agent under the vacuum high temperature condition to obtain the stannous sulfide and the copper matte so as to implement separation and recovery of tin and copper in the tin refining sulfur slag; the method adopts the simple process, has a safe and controllable process, is convenient to operate, has a tin direct recovery rate of over 98 percent, has a copper removal rate of over 96 percent and has no pollution to the environment.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
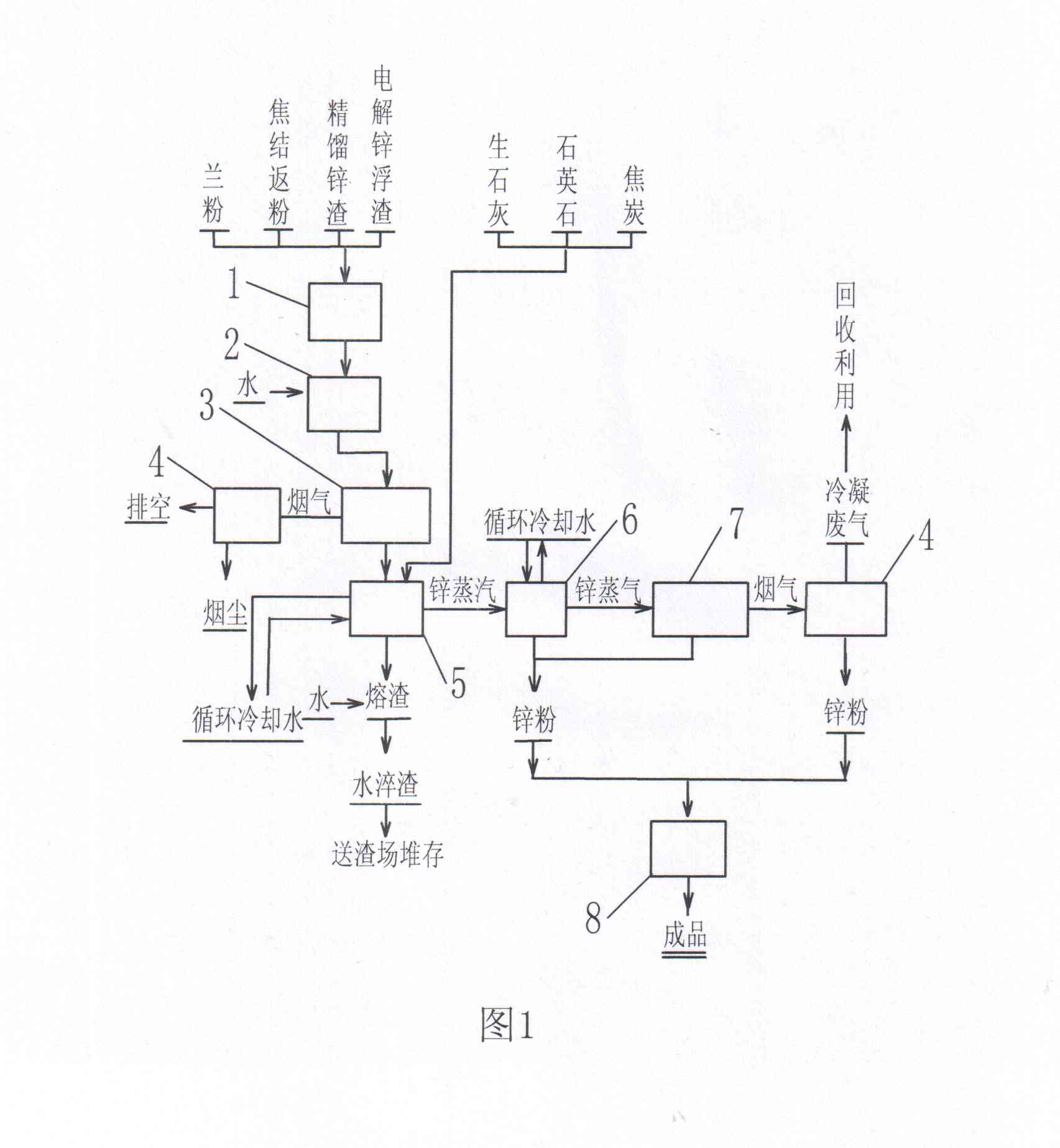
Method for producing zinc powder by treating zinc-containing miscellaneous material through electric furnace
InactiveCN102181663AReduce sootWith defluorinationProcess efficiency improvementElectric arc furnaceHydrometallurgy
The invention relates to a method for producing zinc powder by treating a zinc-containing miscellaneous material through an electric furnace. The zinc powder is prepared by the zinc-containing miscellaneous material through a zinc-containing miscellaneous material quantitatively-batching process, a zinc-containing miscellaneous material mixture pelletizing process, a zinc-containing miscellaneousmaterial particle roasting process, a roasted flue gas dust collection process, an electric furnace smelting process, a zinc powder condensation process and a smelted flue gas dust collection process. In the method, the zinc powder is produced by the zinc-containing miscellaneous material generated by zinc pyrometallurgy or zinc hydrometallurgy, so that useful zinc powder can be extracted and recycled from the zinc-containing miscellaneous material. The zinc-containing miscellaneous material can be completely utilized; and the method has the advantages of removing fluorine and chlorine and completely recycling condensed waste gas, along with extremely low content of impurities such as iron and the like in raw materials and low yield of waste residues of a device, and is suitable to be applied to the production of the zinc powder prepared by recycling the zinc-containing miscellaneous material. The obtained zinc powder can be used for a replacement reduction process of hydrometallurgy.
Owner:HULUDAO ZINC IND CO LTD
Method for recycling valuable elements from blast furnace flocculated dust
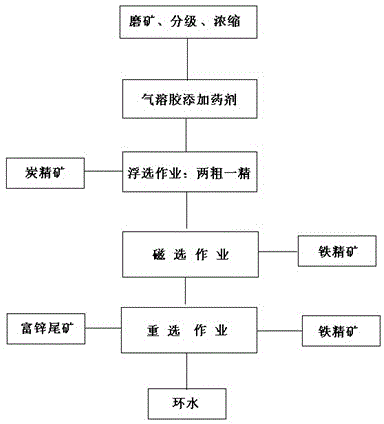
InactiveCN103551244AReduce lossesEliminate the effects of smeltingWet separationMining engineeringProcess engineering
A method for recycling valuable elements from blast furnace flocculated dust adopts a process integrating flotation, magnetic separation and reselection to treat low-grade blast furnace flocculated dust with a 2 to 8 percent zinc content and recycle the valuable elements in the low-grade blast furnace flocculated dust, and comprises the following specific steps: firstly, conducting ore grinding on blast furnace cloth bag dust, sieving the blast furnace cloth bag dust with a fine screen for fineness classification, conducting ore grinding on coarse graded products on the fine screen, returning the coarse graded products for classification, placing the blast furnace flocculated dust on the fine screen directly for classification, returning products on the fine screen to a grinding machine, mixing and then concentrating products under the fine screen after classification, adding a medicament into the concentrated product, carrying out flotation including twice roughing and once fine screening, and carrying out classification to obtain carbon ore concentrate, iron ore concentrate and final tailing serving as a raw material in pyrometallurgy of zinc oxide. The method has the advantages that the process is simple; the energy consumption and the manufacturing cost are low; the comprehensive recycle effect is good; the selected carbon ore concentrate can serve as injection coal of steel enterprises; the selected iron ore concentrate can return to a pelletizing process directly; the final tailing (a zinc-rich material) is used for pyrometallurgy to extract zinc oxide.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Wet process for treating lead copper matte
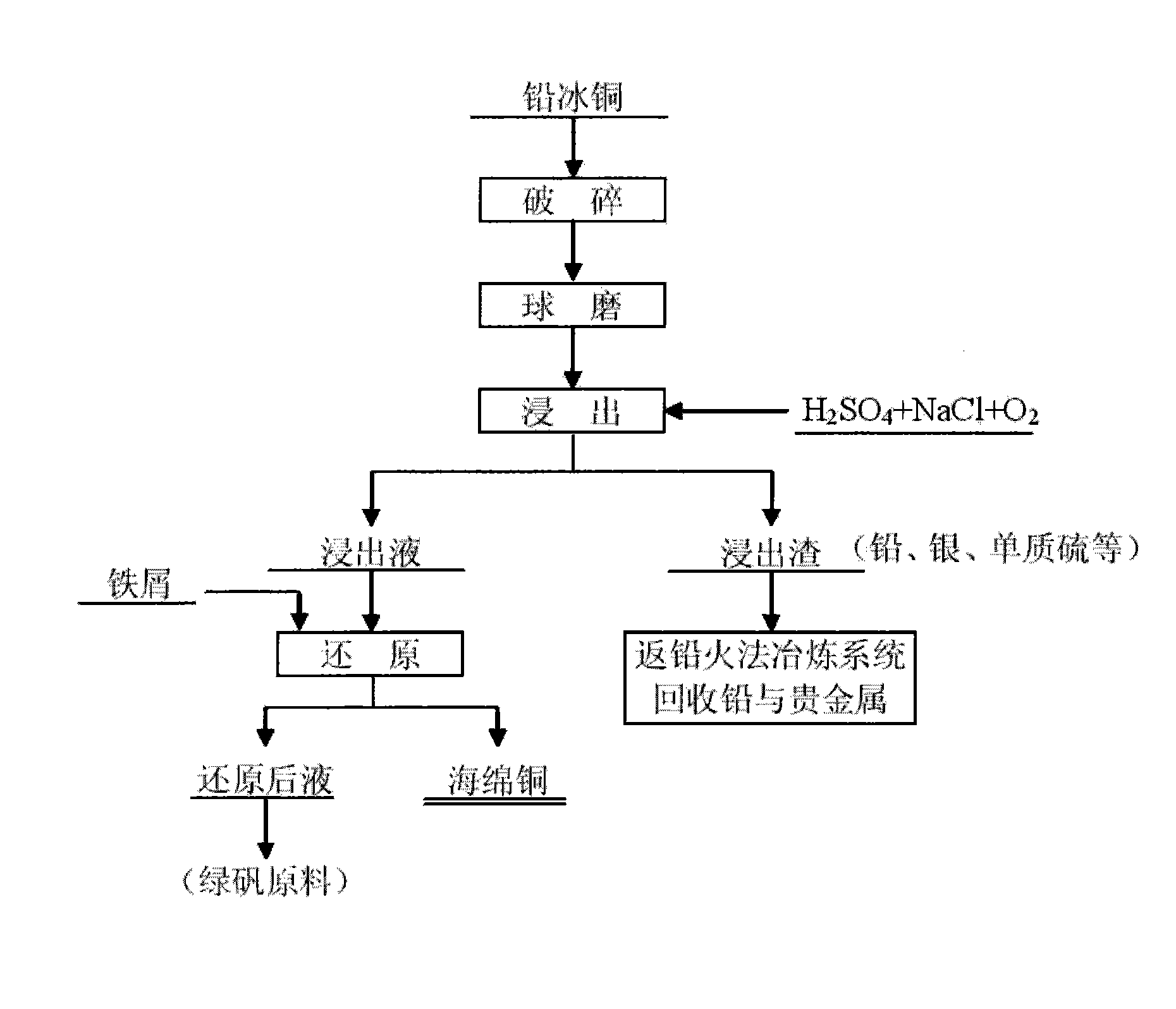
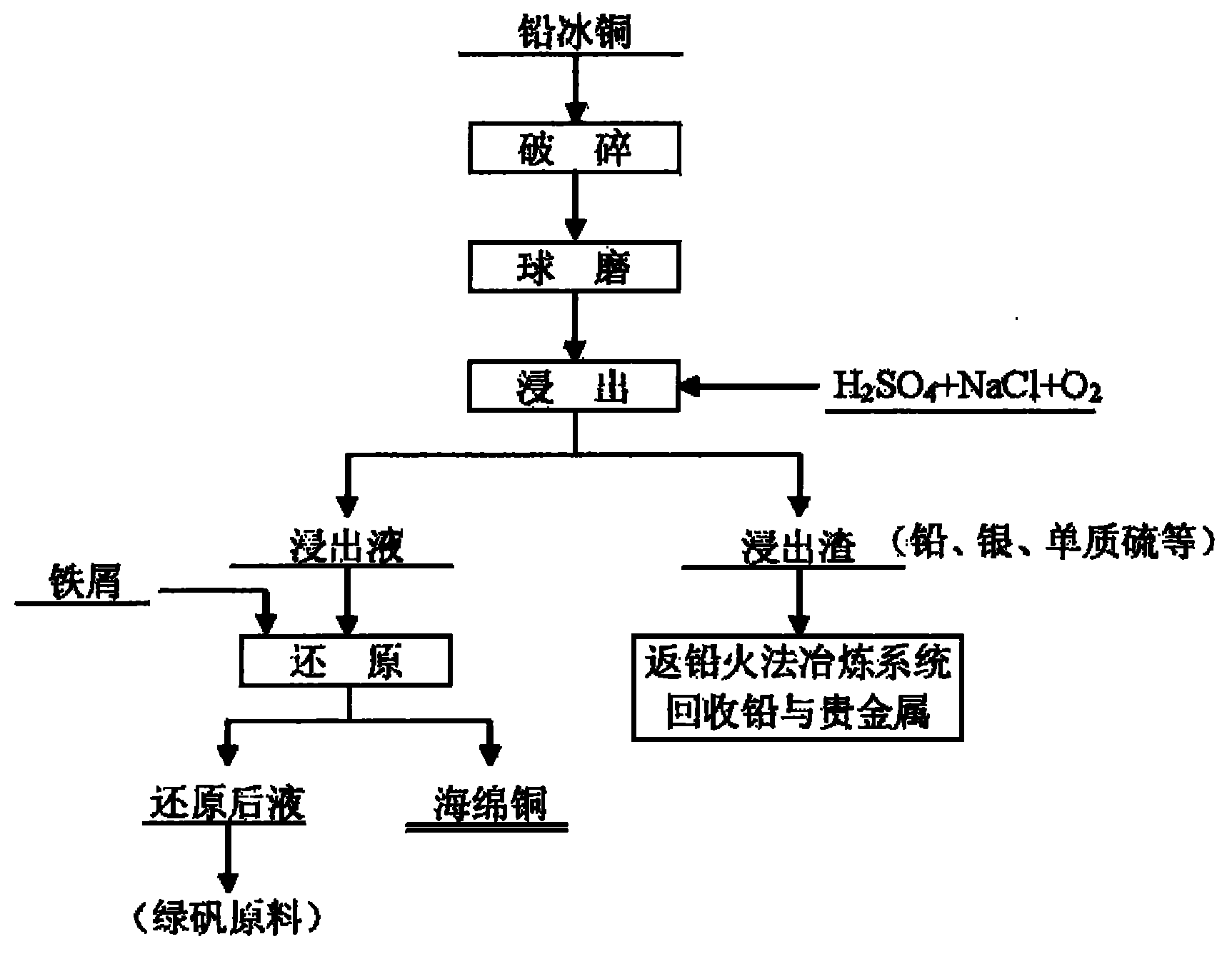
The invention relates to a wet process for treating lead copper matte, and belongs to the field of non-ferrous metal hydro-metallurgy. In the process, the lead copper matte is treated by a normal-pressure leaching wet process; and the lead copper matte is leached by sulfuric acid and sodium oxide, and oxygen is continuously introduced in the leaching process, wherein copper is leached, and the lead in forms of lead sulfate and lead chloride is retained in residue. After the leaching process is finished, liquid-solid separation is carried out and primary separation of metals is implemented; copper-containing leachate is reduced by scrap iron to form copper sponge, and solution after reduction serves as a raw material for recycling iron; and the leaching residue returns to a lead pyrometallurgy system, and valuable elements such as lead, silver, simple sulfur substance and the like are recycled. In the wet process, solution is not discharged, the environment is protected, and the wet process belongs to clean metallurgy; the process is simple and practicable, and is convenient to operate; and the cost is low and the comprehensive recoverability is high.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Aluminum-magnesium light castable and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102010216AGood medium and low temperature performancePrevent over-sinteringSilicon oxideActivated Aluminum Oxide
The invention relates to an aluminum-magnesium light castable and a preparation method thereof. The technical scheme comprises the following steps: using 60 to 85 wt% of aluminum-magnesium porous ceramic particles as the skeletal material, and using 10 to 35 wt% of corundum fines, 0 to 0.3 wt% of silicon oxide micropowder, 1 to 6 wt% of magnesium oxide micropowder and 2 to 8 wt% of activated aluminum oxide micropowder as the host material; premixing 1 to 3 wt% of water reducer with the host material additionally based on the total weight of the skeletal material and the host material, adding the premixed host material into the skeletal material, and adding 8 to 20 wt% of water additionally based on the total weight of the skeletal material and the host material; and stirring uniformly, pouring, vibration-moulding, and drying the body after the moulding for 6 to 36 hours under the temperature of 110 to 150 DEG C. The product provided by the invention has the characteristics of low silicon content, is cement-free, and has high porosity, small average pore size, high fire resistance, large high temperature strength, low thermal conductivity, good thermal shock stability and strong medium erosion resistance such as the slag and the like. The castable provided by the invention can be used as the energy saving working lining material of the industrial furnace in pyrometallurgy and the like, which can contact with the medium such as the high temperature slag and the like in a long term.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
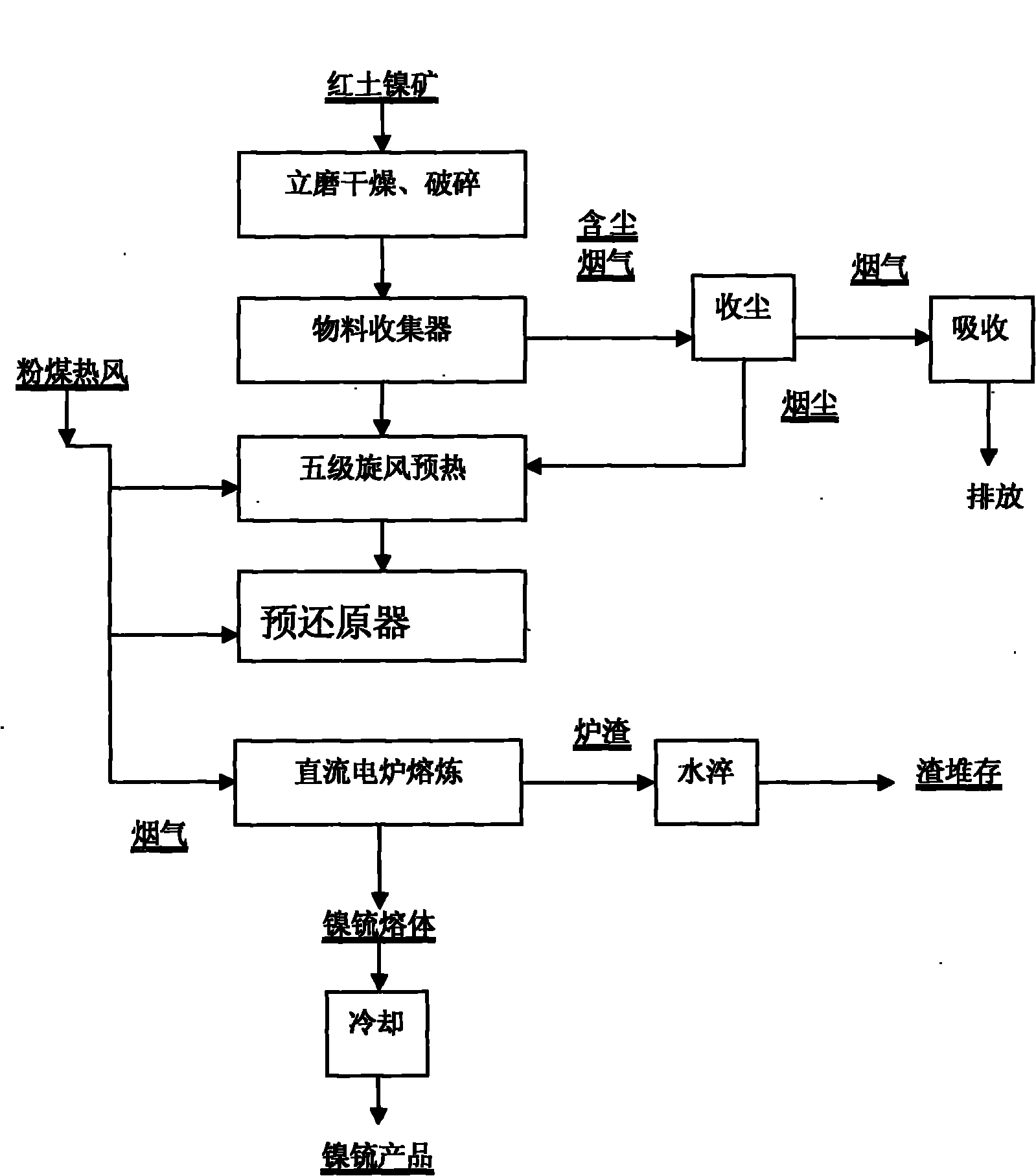
Copper-nickel sulfide ore concentrate smelting method through pyrometallurgy
InactiveCN103725896AStir wellFast adjustmentRotary drum furnacesCrucible furnacesNickel sulfideCobalt
The invention relates to a copper-nickel sulfide ore concentrate smelting method through the pyrometallurgy and particularly relates to improvement of the process for smelting the copper-nickel sulfide ore concentrate through the pyrometallurgy. According to the invention, during the process of transferring smelting slag to a sedimentation electric furnace from a smelting furnace, the reduction slagging reaction of magnetic iron oxide is completed in a chute, so that oxides of nickel, copper and cobalt in the slag are vulcanized and converted into sulphonium. The method provided by the invention has the advantages as follows: the depletion of smelting slag and adjustment of slag types can be completed in the reaction chute, so that the operation of the sedimentation electric furnace is facilitated, and the waste slag discharged from the electric furnace contains less valuable metal, and the metal recovery rate is increased; the smelting slag flows through the reaction chute to adjust the types of slag, so that the smelting slag, which does not contain high magnetic iron oxides or copper-nickel oxides, can be subjected to the smelting process so as to product high-grade sulphonium; the separation of iron and copper nickel is completed during the process of smelting, the blowing of white matte is non-slag smelting, so that the low-air pollution is not caused, and the difficulties of treatment of blowing slag are avoided.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Method for extracting zinc from non-ferrous metal waste residue
InactiveCN102776384AAchieve recyclingGreat tasteProcess efficiency improvementEnvironmental engineeringPyrometallurgy
The invention discloses a method for extracting zinc from non-ferrous metal waste residue. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of pyrometallurgy, acid leaching, zinc depositing, reduction smelting and the like. Firstly, a fire system is utilized to obtain smoke phase secondary zinc oxide products under specific smelting conditions to enable the zinc in the non-ferrous metal waste residue to enter a secondary zinc oxide phase as far as possible, so that good raw material foundation is laid for improving zinc quality; secondly, according to characteristics of the metal zinc, a wet process is utilized to recover the zinc under a certain process condition; and finally, the reduction smelting is performed on the obtained crude zinc to obtain refined zinc. By utilizing a fire-wet combination process to recover the zinc, the recovery rate of the zinc is high, the zinc quality is good, and cyclic utilization of the waste residue is achieved. The existing resources are further recovered, and pollution of the valuable metal to the environment is avoided, so that the method is safe and environment-friendly. Besides, the method is simple in principle, reasonable in flow path and low in cost.
Owner:HANYUAN GUANGCHAO NON FERROUS METALS COMPREHENSIVE RECOVER
Mixed treatment technology of copper and lead anode slime
InactiveCN107574300ASolve the problem of large amount of waste waterAchieve recyclingSelenium/tellurium compundsElectrolysisSoot
The invention provides a mixed treatment technology of copper and lead anode slime. The mixed treatment technology comprises the technical steps that crude selenium and calcine are obtained after copper anode slime is subjected to sulfatizing roasting, a selenium dioxide product is obtained after crude selenium is subjected to oxidation, calcine is rinsed, and copper is removed; decoppering slagsare mixed with lead anode slime after being dried, a mixture of the decopper slags and lead anode slime is subjected to reduction smelting through a bullion lead furnace, soot, slags and primary bullion lead are obtained, and antimony is recycled from soot and the slags; primary bullion lead enters an antimony removing furnace, antimony is removed, antimony soot and secondary bullion lead are obtained, antimony is recycled from antimony soot, and secondary bullion lead is subjected to oxidation refining through a silver-smelting furnace; bismuth slags, tellurium slags, soot and a silver anodeplate are obtained through oxidation refining of the silver-smelting furnace, bismuth is recycled from the bismuth slags, tellurium is recycled from the tellurium slags, soot returns to a pyrometallurgy system to be treated, and the silver anode plate is subjected to silver electrolysis; and silver powder and black gold dust are generated through silver electrolysis, gold is recycled from black gold dust, silver powder is molten, and silver ingots are generated through pouring. According to the technology, mixed treatment of copper and lead anode slime and comprehensive recovery of various valuable metals like gold, silver, copper, lead, selenium, antimony, bismuth, tellurium are mainly achieved, and the problem that the quantity of wastewater generated in a traditional copper anode slimetreatment technology is effectively solved.
Owner:SHANDONG HUMON SMELTING
Method for smelting nickel ore concentrate by using smelting furnace
The invention relates to a method for smelting nickel ore concentrate by using a smelting furnace, belonging to the field of non-ferrous metallurgy. A refractory lining is needed for high-temperature smelting of a general pyrometallurgical furnace, but the refractory lining is prevented from being used above the melting bath surface of an Ausmelt furnace and the nickel ore concentrate is directlysmelt by adopting a slag-hanging operation technology of a cooper water jacket; and for the general pyrometallurgical furnace, a refractor brick is required to be lined outside the copper water jacket which plays roles of cooling the refractor brick and prolonging the service life of the refractor brick. In the method, the refractor brick is arranged below the nickel matte surface of the melting bath and is prevented from being used above the nickel matte surface, so that the production cost of the smelting furnace is greatly reduced and the considerable economic benefit is obtained.
Owner:JILIN JIEN NICKEL IND
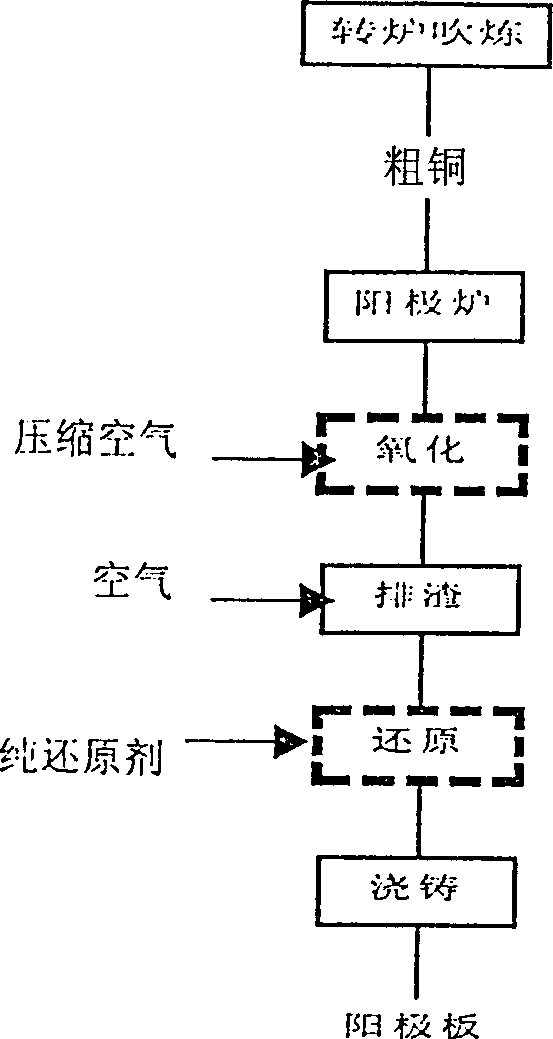
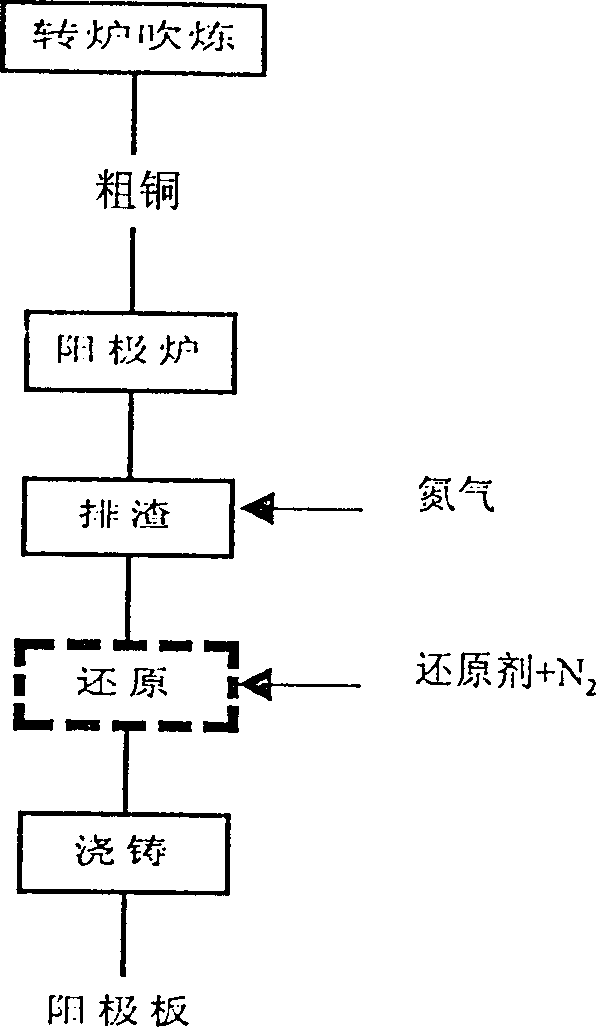
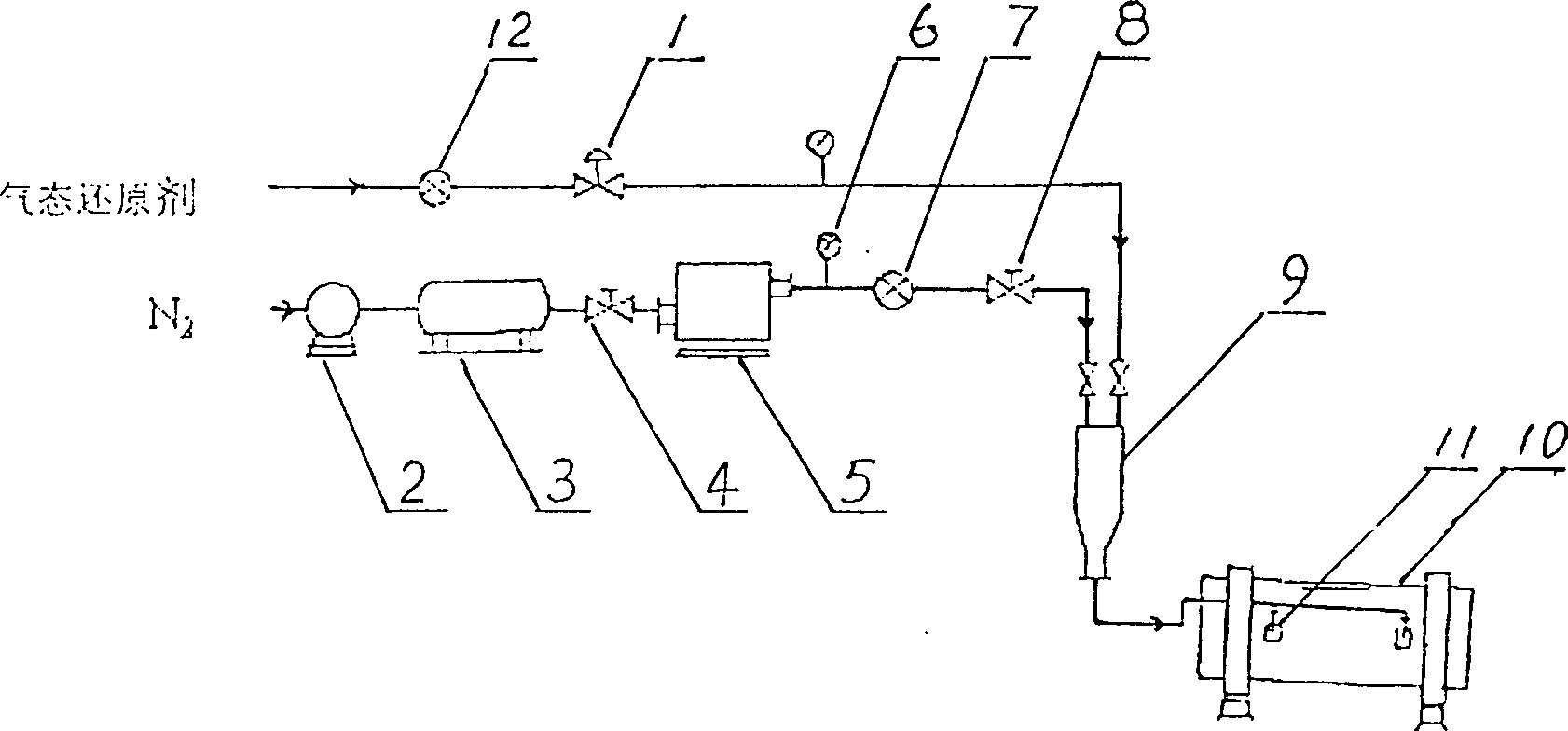
Process for refining raw copper bynon-oxidizing nitrogen-doping reducing pyrometallurgy
A technology for refining crude copper features that at the blowing stage in converter, the contents of S and O in discharged copper are reasonably controlled, the nitrogen instead of air is used for discharge slags, and at reducing stage the nitrogen gas is proportionally added to reducer. Its advantages are simple operation, short period, high productivity, less energy consumption and no smoke pollution.
Owner:JINLONG COPPER
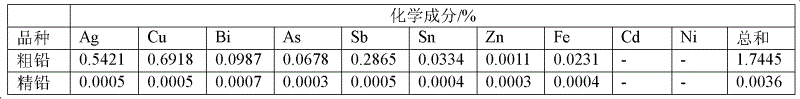
Method for direct electrolytic refining of crude lead
ActiveCN102618883AImprove solubilityImprove conductivityPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisEconomic benefits
The invention relates to a method for direct electrolytic refining of crude lead, and belongs to the technical field of lead refining. According to the method, the crude lead prepared by pyrometallurgy is casted into a crude lead anode, wherein the crude lead anode is sleeved inside an anode bag; and electrolysis is performed in an additive-containing perchloric acid-lead perchlorate solution electrolyte to electrically deposit the lead in the anode on the cathode, such that the high purity electrolyzed lead and the anode mud are respectively obtained from the cathode and the anode. With the present invention, the lead without a pre-refining treatment can be directly subjected to electrolytic refining to obtain the pure lead with the purity more than 99.99% and the anode mud doped with noble metals, such that the recovery rate of the noble metals can be substantially improved so as to provide greater economic benefits.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
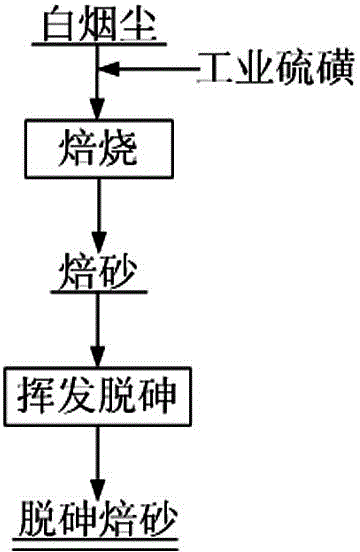
Method for removing arsenic from white smoke
InactiveCN103952563AHigh calcining rateSimple arsenic removal conditionsProcess efficiency improvementCopperPyrometallurgy
The invention belongs to the technical field of thermometallurgy, and particularly relates to a method for removing arsenic from white smoke generated in copper smelting. The method comprises the steps of mixing the white smoke generated in copper smelting with sulfur for industrial use by a weight ratio of 1:(0.3-0.5); roasting at 330-370DEG C firstly; then volatilizing the obtained roasted product at 600-660DEG C, so as to lower the content of arsenic in the final roasted product to be 0.6-2%. The method has simple conditions in removing the arsenic, has a short technological process, can thoroughly remove the arsenic in the white smoke, and has high roasting rate of valuable metals; and the content of arsenic and iron cake can be greatly lowered after the white smoke with the arsenic removed is leached through a wet process.
Owner:云南锡业研究院有限公司研究设计院 +1
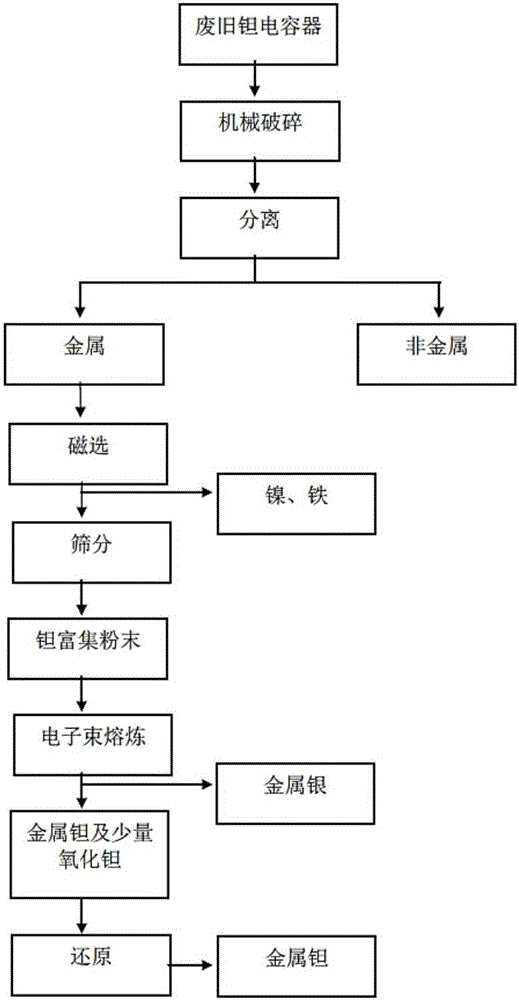
Method for recovering tantalum, silver, nickel and iron from waste tantalum capacitor
ActiveCN106048231AAvoid pollutionRealize resource utilizationMagnetic separationTantalum capacitorResource utilization
The invention relates to a method for recovering tantalum, silver, nickel and iron from a waste tantalum capacitor. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, the waste tantalum capacitor is mechanically crushed, and metal and nonmetal are separated to obtain a metal material; then, the metal material is magnetically separated to separate out a nickel-iron magnetic material; then, a residue is screened to obtain silver-contained tantalum-enriched powder; then, the electronic beam smelting is performed for the tantalum-enriched powder, and metal silver is separated out through evaporation-condensation; and finally, a residual metal tantalum material (containing less tantalum oxide) is reduced to obtain high-purity metal tantalum. The method is simple, generates no poisonous gas and waste liquid in the whole process, prevents the environmental pollution caused by traditional thermometallurgy and hydrometallurgy, and realizes the resource utilization of the waste tantalum capacitor under environment-friendly condition.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
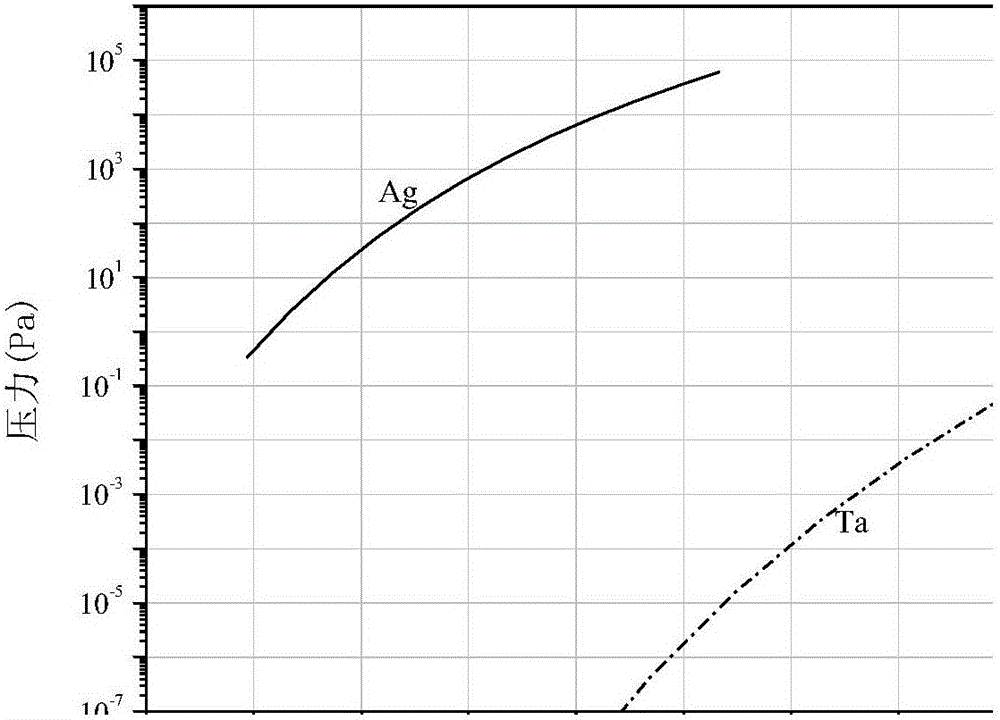
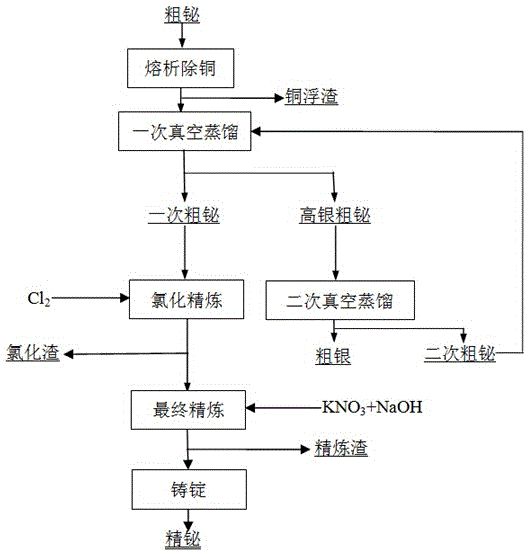
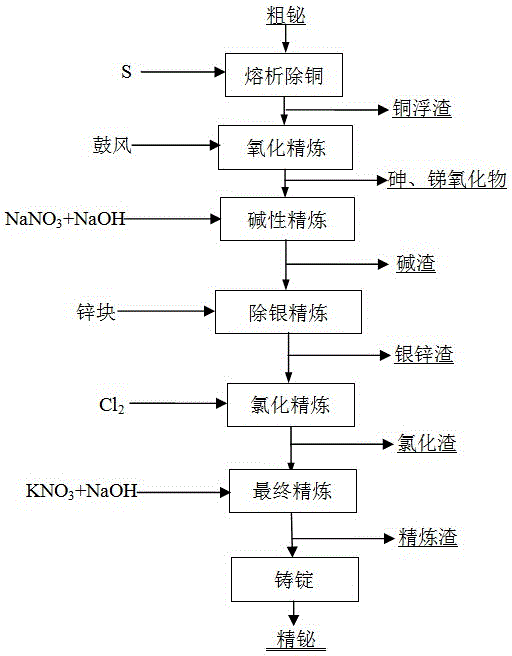
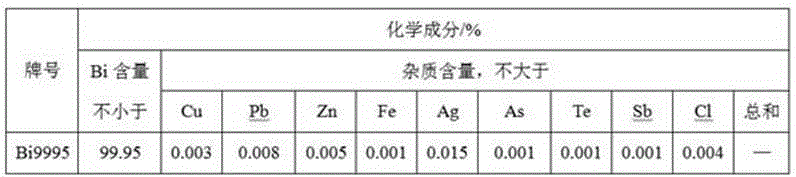
Fire-refining method of crude bismuth
The invention relates to a fire-refining method of crude bismuth, and belongs to the technical field of fire metallurgy. The fire-refining method comprises the following steps: liquating a crude-bismuth melt so as to remove copper; performing vacuum distillation again on the liquated crude-bismuth melt so as to remove impurities, such as lead and silver; performing chlorination refining; and finally performing refining so as to obtain refined bismuth. According to the fire-refining method disclosed by the invention, a vacuum distillation technique is adopted for replacing a procedure that zinc is added in a refining kettle so as to remove silver, and partial lead, antimony, tellurium and arsenic are removed, so that the labor strength of workers is reduced; through secondary vacuum distillation, crude silver with a high silver content can be directly collected in a vacuum furnace, and generated secondary crude bismuth can be recycled, so that the cost is greatly reduced; a subsequent zinc removing procedure is also omitted, and the amount of chlorine gas for subsequent chlorination refining is greatly reduced, so that harm to environment is reduced to a great extent, and the direct recovery rate of bismuth is increased; the whole technological process is safe and controllable, the operation is convenient, adopted equipment is simple, the universality of raw materials is high, the direct recovery rate of bismuth is high, and the slag yield is low.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Energy-saving and high-efficiency rare earth ore concentrate sulfuric acid stepped roasting method
InactiveCN104561539AGuaranteed liquidityReduce unit consumptionProcess efficiency improvementHydrofluoric acidWater vapor
The invention relates to an energy-saving and high-efficiency rare earth ore concentrate sulfuric acid stepped roasting method, and belongs to the technical field of wet metallurgy and thermometallurgy. The energy-saving and high-efficiency rare earth ore concentrate sulfuric acid stepped roasting method comprises the following steps: mixing rare earth ore concentrate with sulfuric acid with the mass concentration of more than or equal to 92.5% according to weight ratio of 1 : (1.0-1.3); pelletizing, and charging particles into a first-section roasting kiln to roast, so that fluorine ions and water in the rare earth ore concentrate are completely volatilized; condensing the gasified fluorine ions and water, recovering hydrofluoric acid, roasting defluorinated dry ore particles, and charging the roasted particles into a second-section roasting kiln to separate; washing and absorbing separated sulfuric acid gas during roasting, recovering sulfuric acid, and directly leaching roasted ores to obtain a sulfuric acid rare earth solution. According to the energy-saving and high-efficiency rare earth ore concentrate sulfuric acid stepped roasting method, after the stepped roasting process is utilized, waste gas generated in pelletizing step is water vapor and can be directly discharged; compared with the prior art, the stepped roasting method has the advantages that a waste gas washing and absorbing system is reduced to more than 70% and the environmental protection input is reduced to more than 80%.
Owner:包头市锦园化工科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com