Patents
Literature
1059 results about "Metal recycling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Treatment method for waste of positive electrode material of lithium battery
InactiveCN106505272AHigh recovery rateGuaranteed purityWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementPhysical chemistryManganese
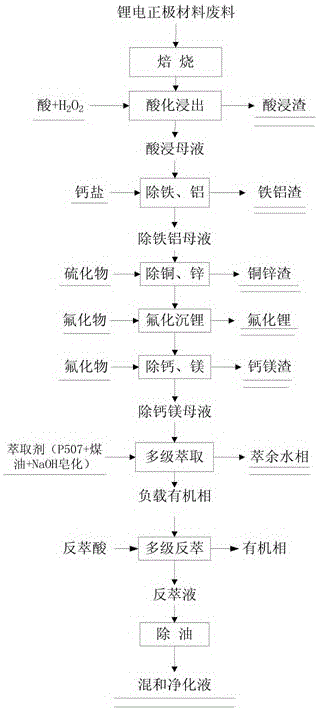
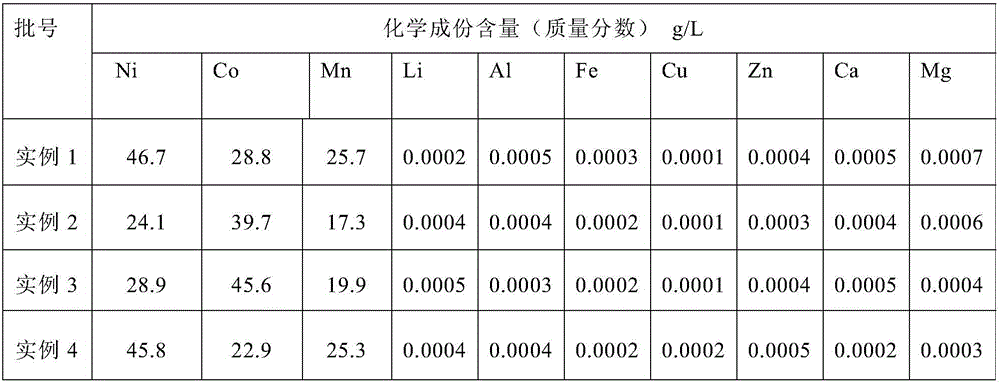
The invention discloses a treatment method for waste of a positive electrode material of a lithium battery. The method comprises the steps of (A) roasting; (B) acidifying and leaching; (C) iron and aluminum removal; (D) copper and zinc removal; (E) fluorinating lithium deposition; (F) calcium and magnesium removal; (G) multi-stage extraction; and (H) oil removal. According to the treatment method for the waste of the positive electrode material of the lithium battery, multiple valuable metals of lithium, cobalt, manganese, nickel and the like contained in the positive electrode material of the lithium battery can be comprehensively recovered; the treatment method has the advantages that the metal recovery rate is high, the obtained lithium product is good in quality and the treatment method is friendly to environment, low in production cost and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:GANFENG LITHIUM CO LTD
Method for preparing ethylenediamine modified chitosan composite magnetic microspheres and application thereof
InactiveCN102079823AWide variety of sourcesEasy to makeOther chemical processesMagnetic liquidsMicrosphereWastewater
The invention relates to a method for preparing ethylenediamine modified chitosan composite magnetic microspheres and application thereof. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: mixing acidic aqueous solution of chitosan and a water-based magnetofluid first, then crosslinking by using glutaraldehyde, then adjusting the pH value to form a gelatinous precipitate, then modifying by using ethylenediamine and epichlorohydrin, and washing and drying to obtain a final product. The product has good absorption effect on radionuclide aranium and metal ions such as heavy metal Pb, Cr and the like; the removal rate reaches over 95 percent when the initial concentration of various ions is within the range of 200mg / L; and the product has quick absorption rate and good regeneration performance. The ethylenediamine modified chitosan composite magnetic microspheres can be used for metal recovery and pollution remediation in mines, radioactive waste water, smelteries, electronics factories and waste water of electroplating factories.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
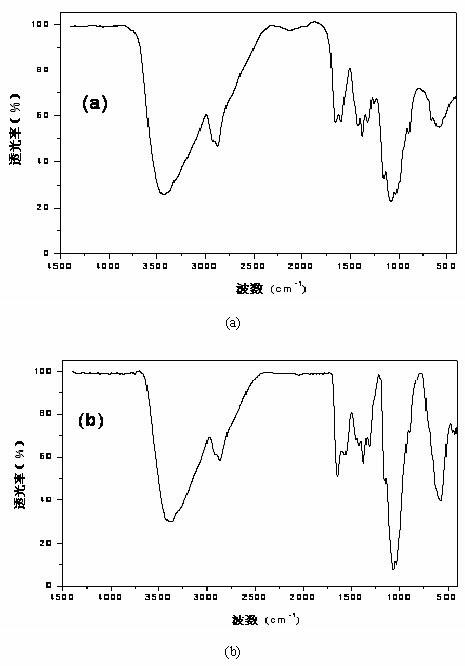
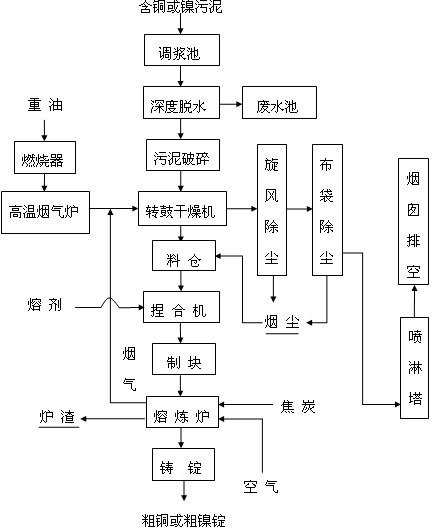
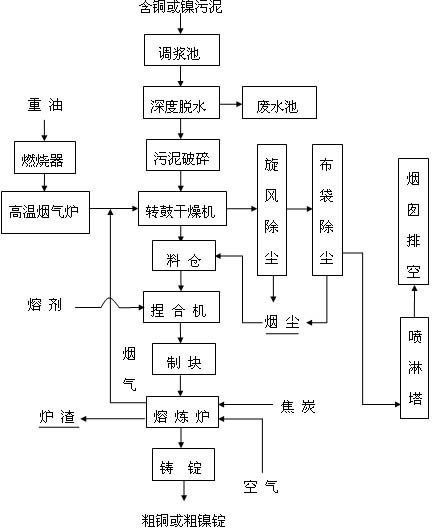
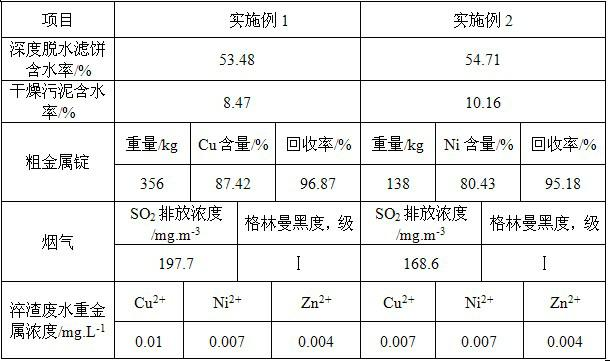
Heavy metal sludge recycling and innocent treatment method
ActiveCN102433437AImprove usabilityHigh recovery rateSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningProcess efficiency improvementSocial benefitsAdhesive
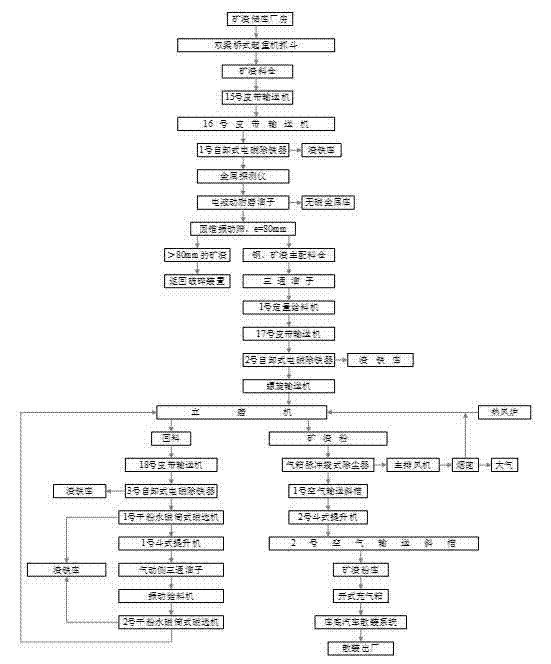
The invention relates to a heavy metal sludge recycling and innocent treatment method. The treatment method comprises the following steps of: deeply dehydrating sludge until the water content is less than 55 percent and the weight of the dehydrated sludge is reduced to be 33 to 56 percent of the original weight; crushing the dehydrated sludge and drying the crushed sludge in a sludge dryer until the water content is 6 to 12 percent; mixing the dried sludge, a flux and an adhesive, and preparing blocks or balls; and smelting coke and the block material or ball-shaped material in a smelting furnace. The method has the advantages of high material utilization rate, short process flow, high metal recovery rate, simple operation of equipment, low investment and low production cost, and has goodeconomic and social benefits.
Owner:惠州TCL环境科技有限公司
Method of recovery copper, nickel and noble metal in waste water and slag by combined technology of wet method and fire method
A process for recovering the copper, Ni and noble metals from the sewage and dregs by the combination of wet method and fire method includes the wet process including extracting, Cu-Ni separation, removing Fe, extracting, and refining nickel carbonate, and the fire process including sintering and smelting to produce nickel matte and black copper. Its advantages are high recovery rate of Ni, Cu, Au, Ag and Pd, and no secondary pollution.
Owner:孙涛 +1
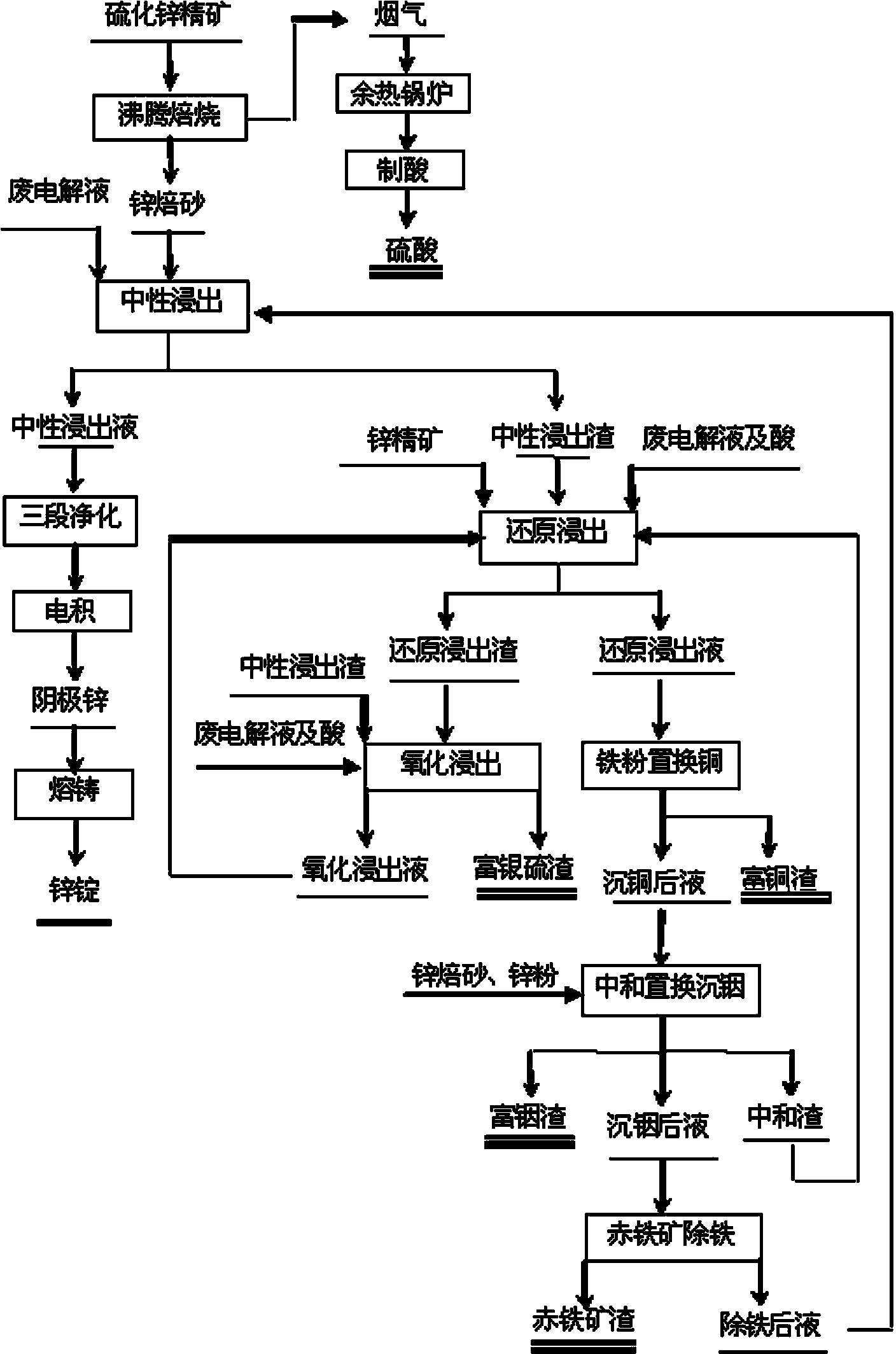
Method for individually processing high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate
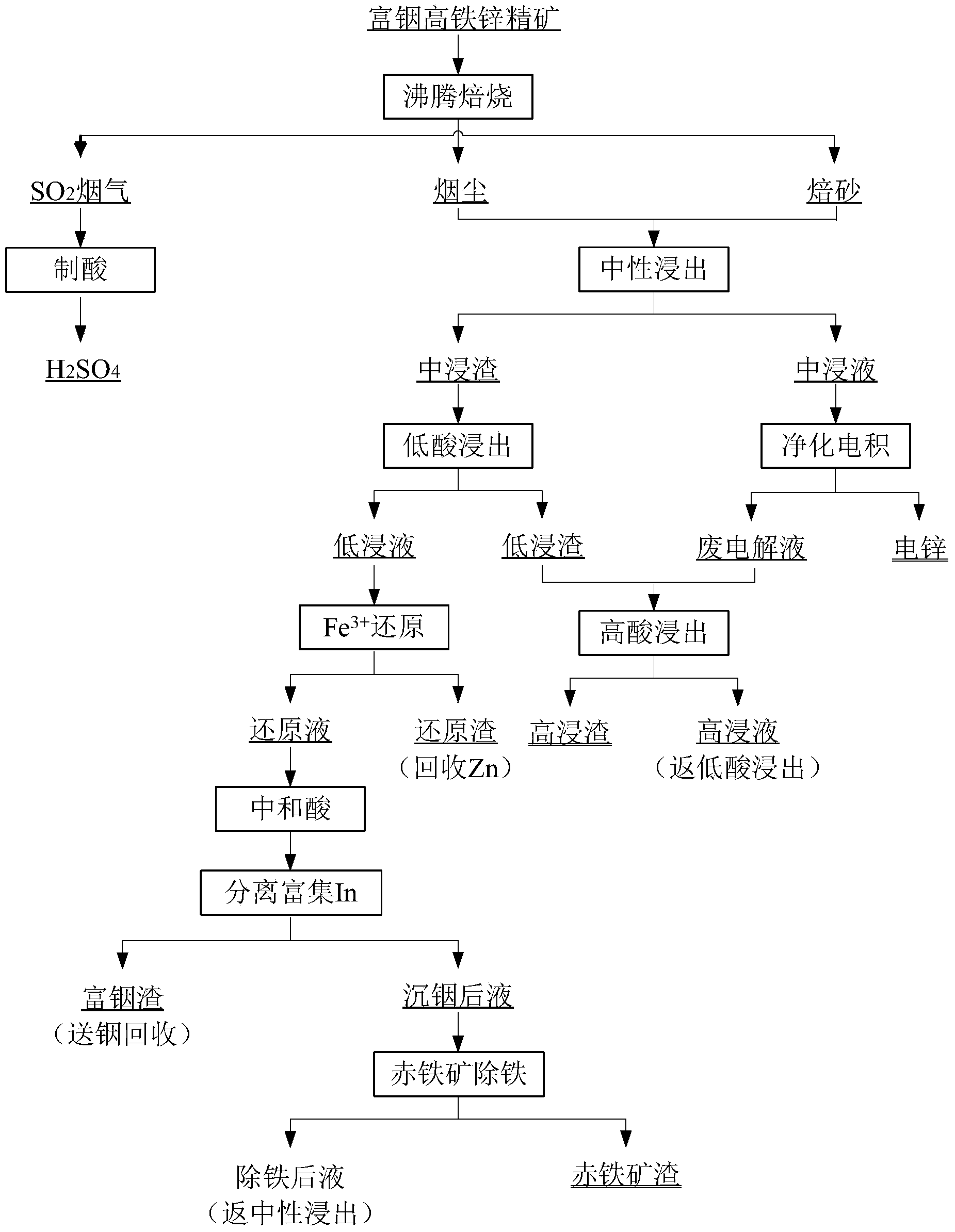
ActiveCN103409622AThe process is highly targetedHigh enrichment ratioProcess efficiency improvementIndiumHydrometallurgy
The invention belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy, and particularly relates to a method for individually processing high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate. The method comprises a step of subjecting the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate to calcination in a fluidized bed combustion boiler to obtain zinc calcine; a step of subjecting the zinc calcine to neutral leaching to produce neutral leaching solution and neutral leaching residue; a step of, after the neutral leaching residue and the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate are mixed, successively performing reduction leaching and oxidation leaching, and circulating oxidation leaching solution to the reduction leaching to produce reduction leaching solution and silver-rich sulfur residue; a step of replacing the reduction leaching solution by using iron powder to precipitate copper and to produce copper-rich slag and solution after copper precipitation; a step of subjecting the solution after copper precipitation to pre-neutralization by using the zinc calcine, and then replacing by using zinc powder to precipitate indium and to produce indium-rich slag and solution after indium precipitation; and a step of bubbling oxygen into the solution after indium precipitation, heating and removing iron to obtain iron removal solution and hematite slag. The hematite slag can be utilized as a raw material for ironmaking. The method has strong pertinence, short technological process and high metal recovery yield, and the method is clean, efficient, energy-saving and environmental friendly. Separation and comprehensive utilization of zinc, indium, copper and iron are achieved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH TECH IND SALES MANAGEMENT
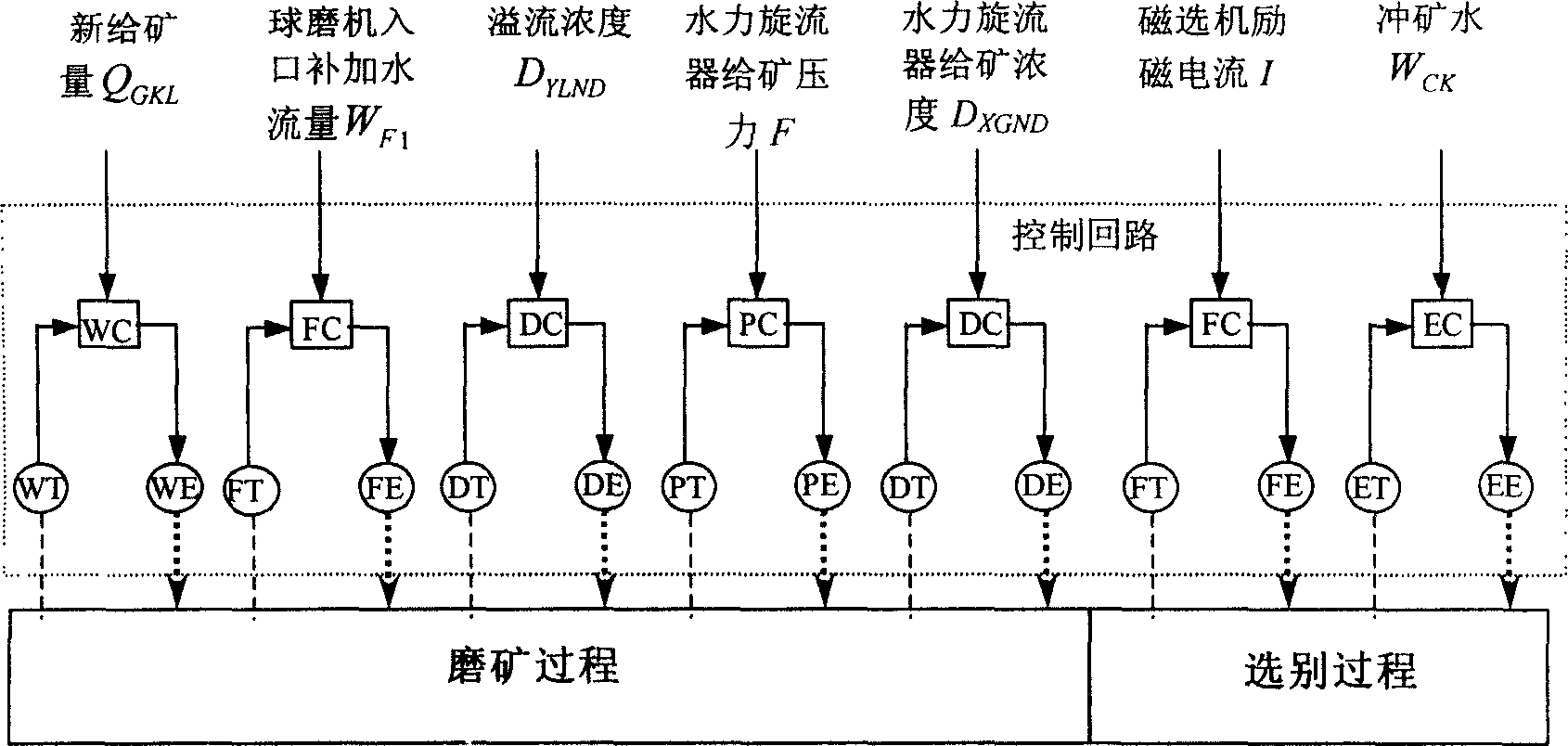
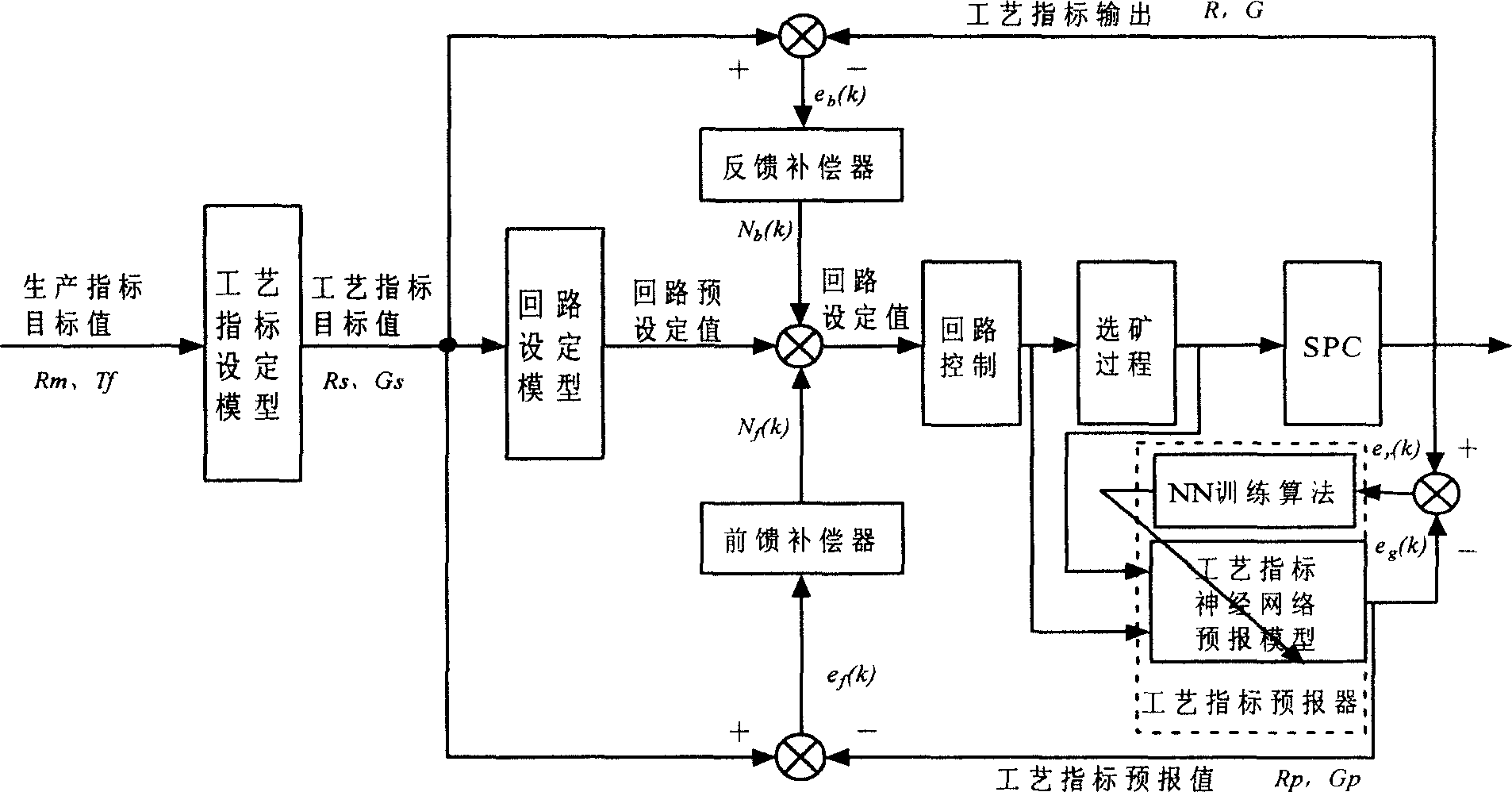
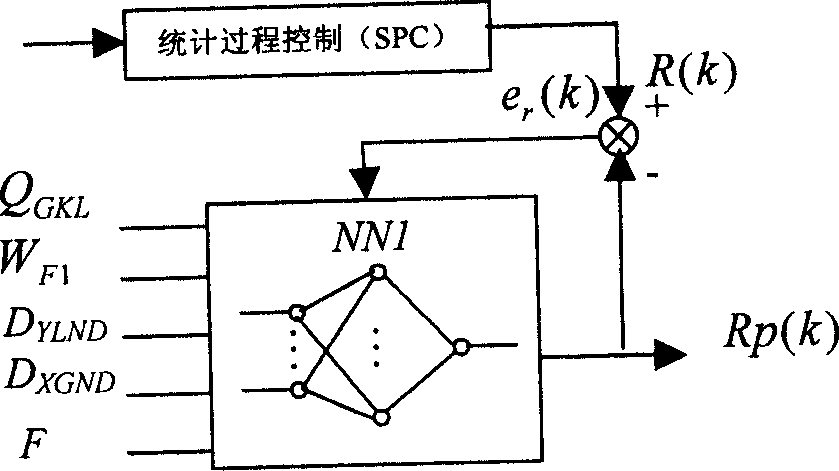
Intelligent optimized control method for comprehensive production index in ore dressing process
InactiveCN1749891AHigh recovery rateComputer controlSpecial data processing applicationsAutomatic controlNerve network
The present invention belongs to the field of automatic control technology. The intelligent optimized control process for comprehensive production indexes in ore dressing process includes the steps of: setting technological indexes, setting control loop, controlling statistical process, predicting technological indexes with the nerve network, feedback compensation, feedforward compensation, etc. The present invention is superior in that based on the requirement of the ore dressing process in concentrate grade and metal recovering rate and through the said control process, the optimized set values for ore grinding work section and selecting work section are given and the loop setting values are then given to realize comprehensive production index optimization in the ore dressing process.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
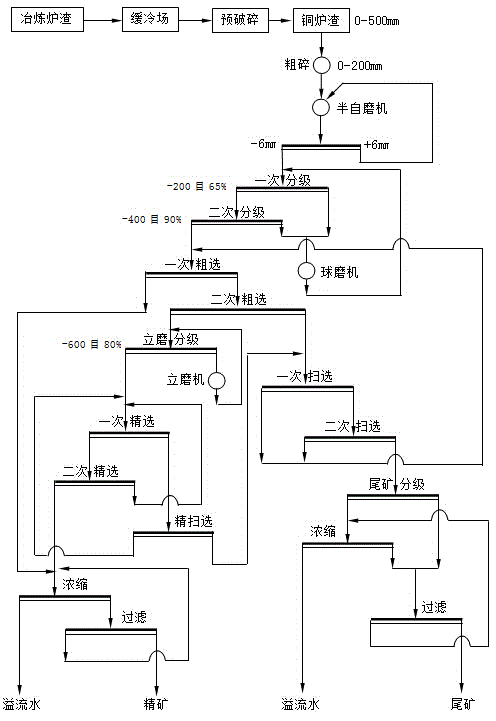
Copper furnace slag mineral processing process
InactiveCN104399573AExtend slow cooling timeIncrease collisionFlotationGrain treatmentsSlagEngineering
The present invention provides a copper furnace slag mineral processing process. According to the copper furnace slag mineral processing process, the slow cooling mode adopts centralized natural slow cooling for 12 h and spraying slow cooling for 60 h so as to prolong the slow cooling time of the slag ladle at a temperature of 1000-1250 DEG C, increase the opportunity of collision and growth of the copper matte particles, and easily achieve the crystallization development of the copper crystal, such that the recovery rate of the subsequent flotation operation is easily increased; the disseminated grain size of the copper sulfides in the furnace slag is fine, and for complete dissociation of the useful minerals, the stirring mill is adopted to carry out mineral grinding, ie., the crude concentrate is graded with a cyclone device, the setting sand after the grading is subjected to mineral grinding by adopting the stirring mill, the overflow after the grading is subjected to fine selection twice by adopting the flotation column, and the selected concentrate is directly adopted as the final concentrate, wherein the tailings being subjected to the one fine selection through the flotation column is sorted by adopting the flotation machine, and the tailings being subjected to the double fine selection through the flotation column cyclically returns. According to the present invention, the flotation machine, flotation column and vertical stirring mill combined process combining the machine, the column and the mill is adopted, such that the useful minerals with various particle sizes are easily recovered, and the metal recovery rate is efficiently increased.
Owner:广西金川有色金属有限公司
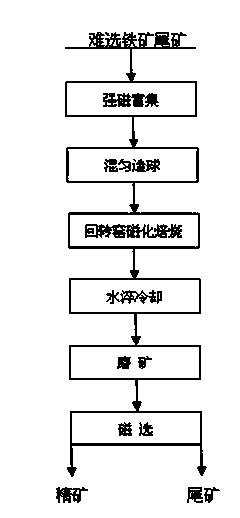
Difficult-separation iron ore tailing pelletizing rotary kiln magnetic roasting treatment technology
The invention provides a difficult-separation iron ore tailing pelletizing rotary kiln magnetic roasting treatment technology. The technology mainly comprises the following technological steps: 1, carrying out magnetic separation enrichment of iron ore tailing by a strongly-magnetic magnet separator having a field intensity of 0.6-1.2T; 2, uniformly mixing an obtained enriched tailing with coal dust and a binder according to a ratio of 100:0.5-2:1-3, drying, carrying out damp milling treatment, and pelletizing; 3, drying pellets obtained in step 2; 4, carrying out the magnetic roasting of dried pellets by adopting a rotary kiln; 5, cooling the magnetically-roasted pellets in a water quenching mode; 6, milling the cooled pellets; and 7, carrying out magnetic separation of ground ore powder to obtain iron ore concentrate. The technology allows the iron ore concentrate having a TF2 grade of about 56% can be obtained, increases the metal recovery rate to above 75% from original 65-70%, improves the resource utilization rate and reduces the environmental pollution.
Owner:GANSU JIU STEEL GRP HONGXING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method to improve recovery of gold from double refractory gold ores
ActiveUS20090071295A1Liberation of additionalReducing gold lossBlast furnace detailsFlotationSulfideGold ore
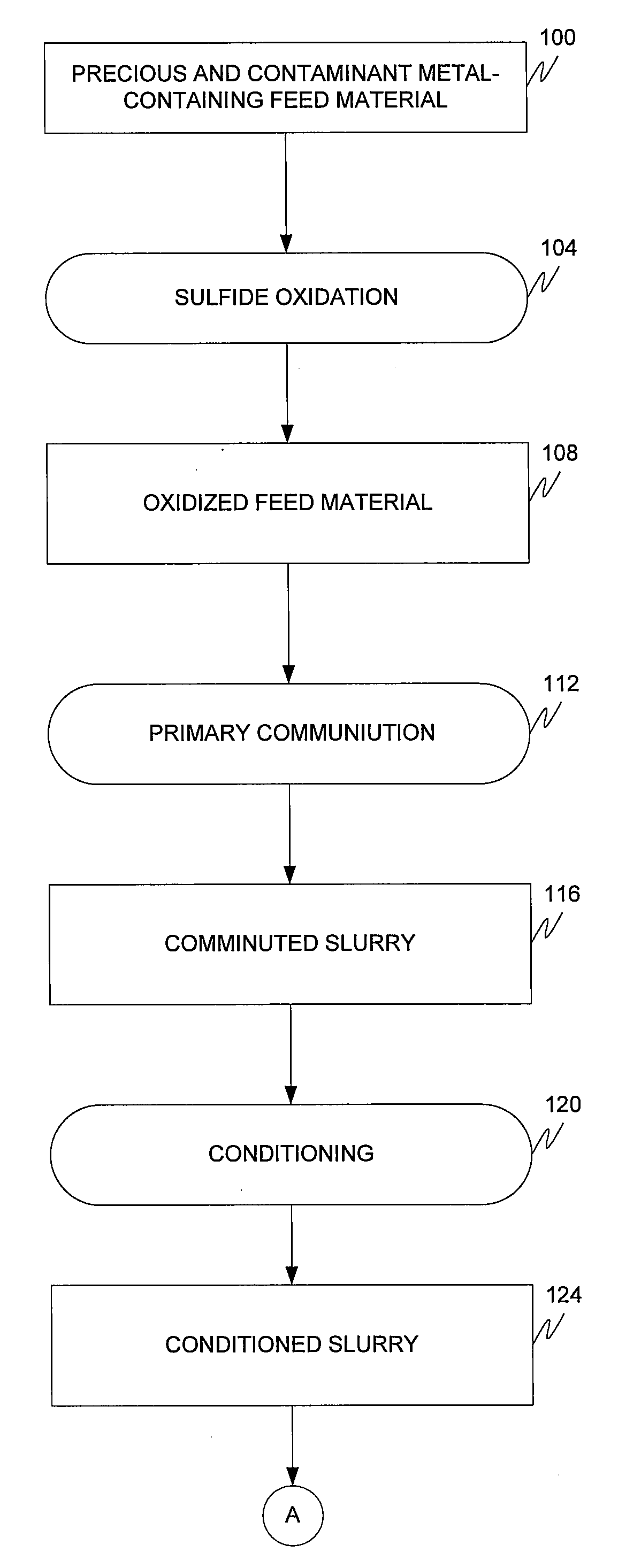
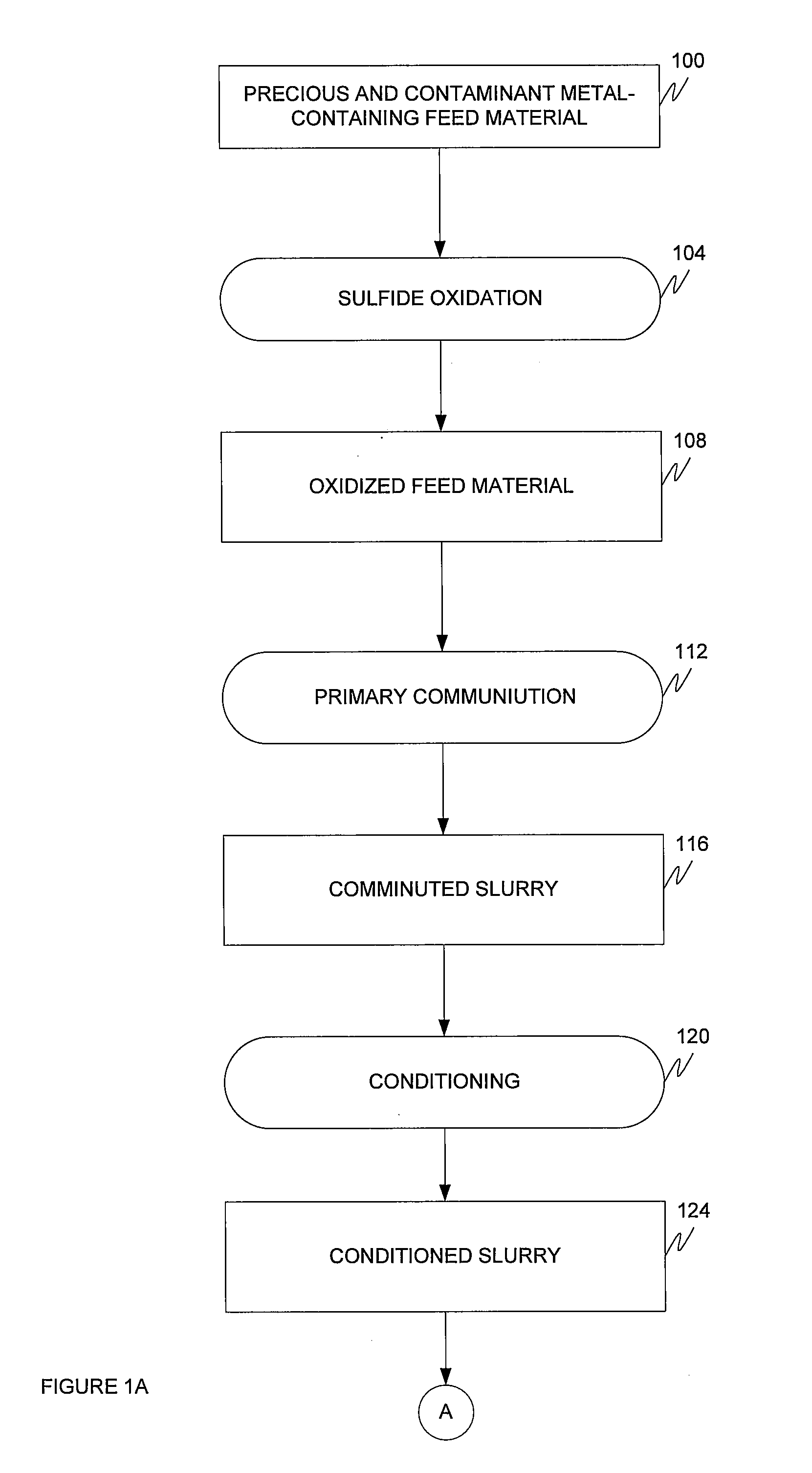
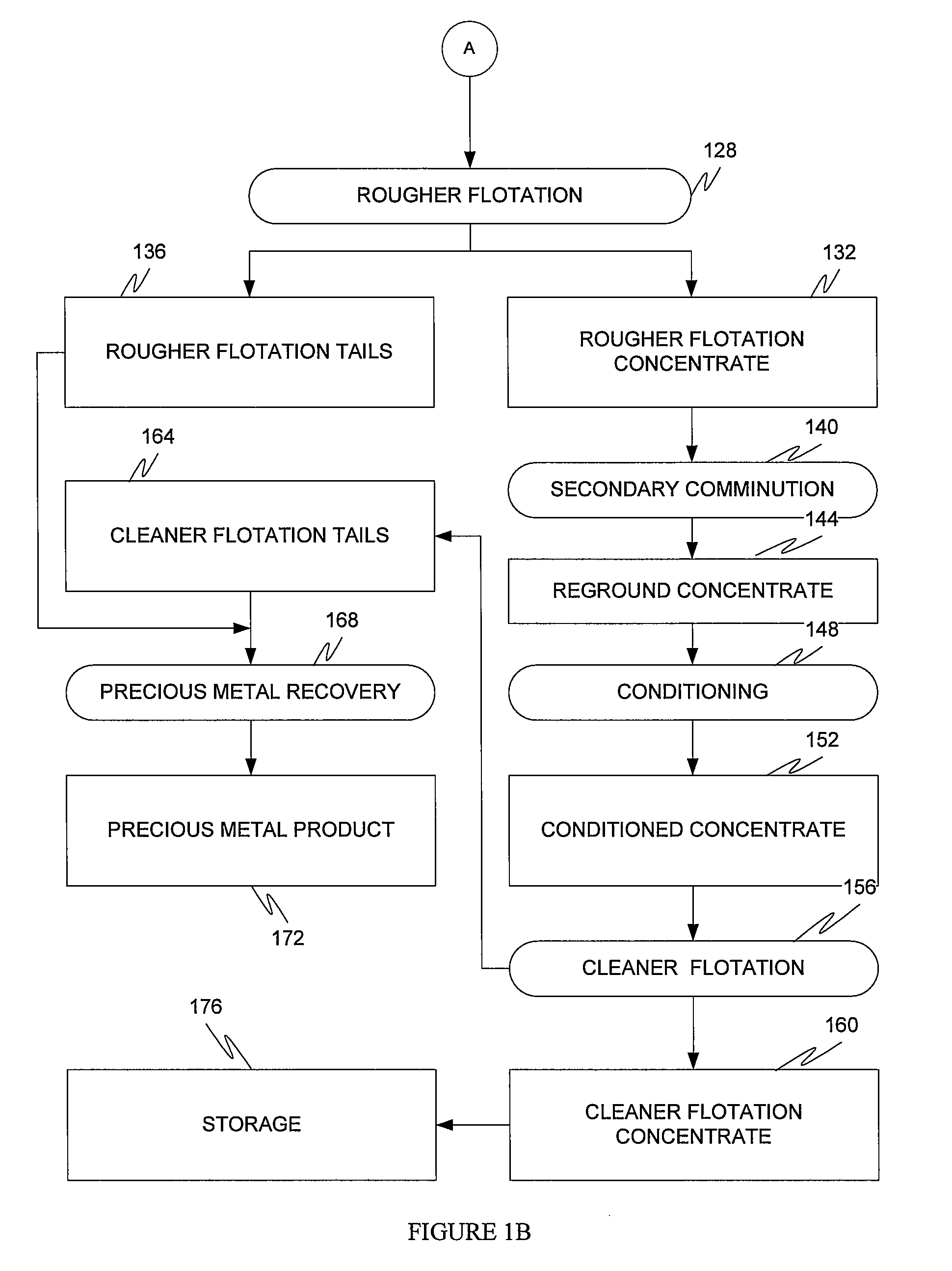
The present invention is directed to a precious metal recovery process in which carbonaceous material, such as preg robbing carbon, is floated after sulfide oxidation to separate the carbonaceous material from the precious metal.
Owner:BARRICK GOLD
Method for extracting and refining platinum group metal in automobile tail gas three-way catalyst
InactiveCN107604165AReduce lossesHigh recovery ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementHydrazine compoundDissolution
The invention relates to a method for extracting and refining platinum group metal in an automobile tail gas three-way catalyst. The method comprises the procedures of conducting extraction through apyrogenic method recycling process and conducting refining through a platinum group metal refining process. The extraction procedure comprises the steps of 1, pulverizing the waste catalyst, and conducting material compounding; 2, conducting smelting; 3, conducting blowing; 4, conducting atomization; and 5, obtaining a mixture of copper, platinum, palladium and rhodium through leaching. The refining procedure comprises the steps that 1, pretreatment is conducted; 2, a platinum refining process comprises the sub-steps of solution production, oxidation, repeated precipitation and calcination; 3,a palladium refining process comprises the sub-steps of conducting dissolution through ammonium hydroxide and precipitation, conducting acidification to precipitate the palladium, and conducting reduction through hydrazine hydrate; and 4, a rhodium refining process comprises the steps of conducting matching through sodium nitrite, conducting precipitation through ammonium chloride, conducting dissolution, and conduction reduction. According to the method for extracting and refining the platinum group metal in the automobile tail gas three-way catalyst, the platinum group metal is gathered through copper obtained through the pyrogenic method process; and the platinum group metal in the waste catalyst can be gathered through the copper at the low temperature and in weak reducing atmosphere.The method is high in treatment capacity; a small amount of waste water and a small amount of waste gas are generated; and in addition, the recycling rate of the platinum group metal is high.
Owner:XINGUANG RECYCLING SHANGHAI
Clean and environment-friendly comprehensive novel recycling process by virtue of high-indium high-iron zinc concentrate
ActiveCN103526024AHigh recovery rateEasy to separateFerric oxidesProcess efficiency improvementIndiumResource utilization
The invention discloses a clean and environment-friendly comprehensive recycling method by virtue of high-indium high-iron zinc concentrate, and relates to a method for comprehensively recycling zinc, indium and iron by taking the high-indium high-iron zinc concentrate as a raw material by using a hydrometallurgy method. The method is characterized in that in a comprehensive recycling process, Fe3+ in a zinc calcine thermal acid leaching liquid is reduced into Fe2+ by using a reducing agent, In / Fe is separated in two-stage process, indium is further recycled from high-indium slag, iron is removed from liquid by a hematite process after In / Fe is separated, iron slag which can be utilized as iron concentrate can be obtained, and the liquid after iron is removed is fed back to subject to neutral leaching. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and short in procedure, thorough in separation of zinc, indium and iron metals, high in metal recycling rate and environment-friendly, and resource utilization of iron slag is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY +1
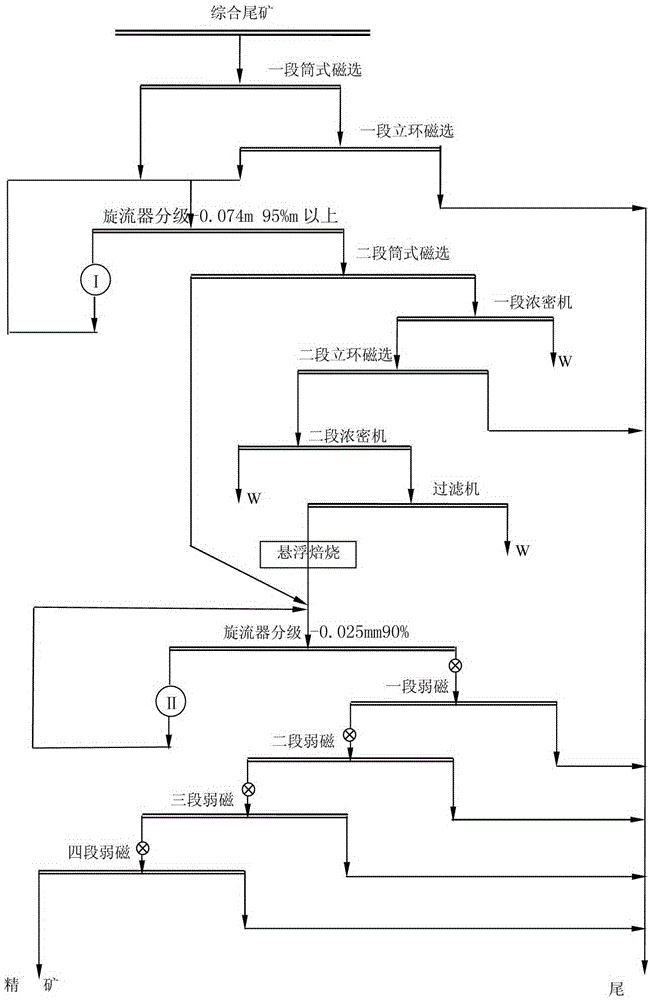
Tailing recovery process adopting preconcentration-roasting-regrinding and magnetic separation method
ActiveCN105233976AEfficient recyclingReduce the processing volume of subsequent grinding and sorting operationsMagnetic separationProcess efficiency improvementMagnetic separatorReducing atmosphere
The invention relates to a tailing recovery process adopting a preconcentration-roasting-regrinding and magnetic separation method. The tailing recovery process is characterized by comprising the following steps: concentrate extraction and tailing discarding are carried out by virtue of a preconcentration process which sequentially comprises first-section drum magnetic separation, first-section vertical ring magnetic separation, ore grinding, second-section drum magnetic separation and second-section vertical ring magnetic separation, so that a rough concentrate grade is increased, and a subsequent operation treatment amount is reduced; suspension roasting is adopted, so that a rotational-flow suspension state of rough concentrate materials in a suspension magnetization roasting furnace under the conditions of a high temperature of 500 DEG C and a reducing atmosphere can be ensured, and micro-and fine-grained hematite, siderite and limonite in the rough concentrate materials are converted to magnetic iron minerals; and meanwhile, multi-section continuous fine separation is carried out by virtue of a regrinding and fourth-section low-intensity magnetic separation machine, thus the good indexes of a concentrate grade of more than 65% and a metal recovery rate of 48-55% are obtained.
Owner:ANSTEEL GRP MINING CO LTD
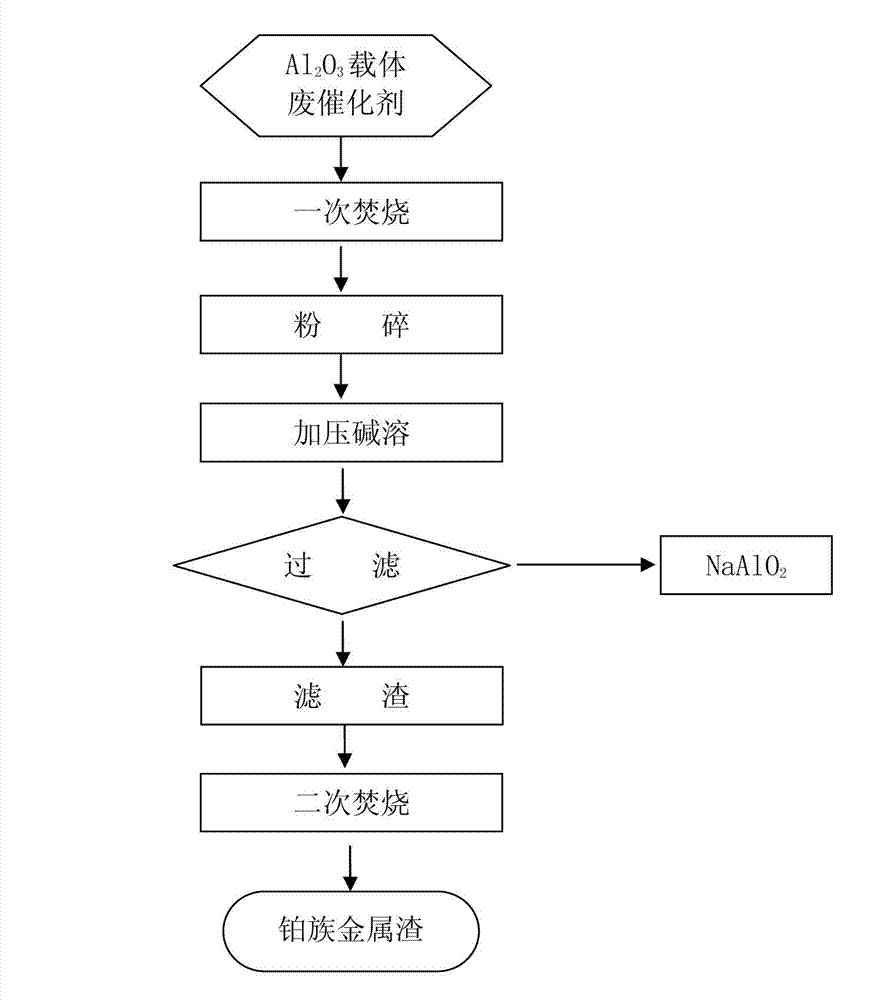
Method for concentrating platinum group metals from alumina-based waste catalyst
ActiveCN103194606AImprove dissolution rateGood for dissolving carrierProcess efficiency improvementPtru catalystSlag
The invention relates to the field of extraction of platinum group metals, particularly relates to a method for concentrating platinum group metals from an alumina-based waste catalyst, and the method overcomes the defects of the prior art. The method is suitable for a wide range of materials; and based on the method, the carrier dissolution effect is good, the platinum group metal concentration rate is high, the content of platinum group metals in concentrated slag is high, the recovery rate of platinum group metals is high, and the equipment corrosion degree is low. The method for concentrating platinum group metals from an alumina-based waste catalyst comprises the steps of: (A) primary incineration; (B) crushing; (C) pressure alkali dissolution; (D) filtering; and (E) secondary incineration. The method is suitable for a wide range of materials; the dissolution ratio of aluminum oxide is more than 95 percent; the concentration degree of platinum group metals is 80-120, and the concentration effect is good; the content of platinum group metals in slag is in the range of 10-14 percent, thereby being beneficial for the post procedure of refining platinum group metals; and the recovery rate of platinum group metals in concentration technology is more than 99 percent; and the equipment corrosion degree is low.
Owner:GUIYAN RESOURCE YIMEN
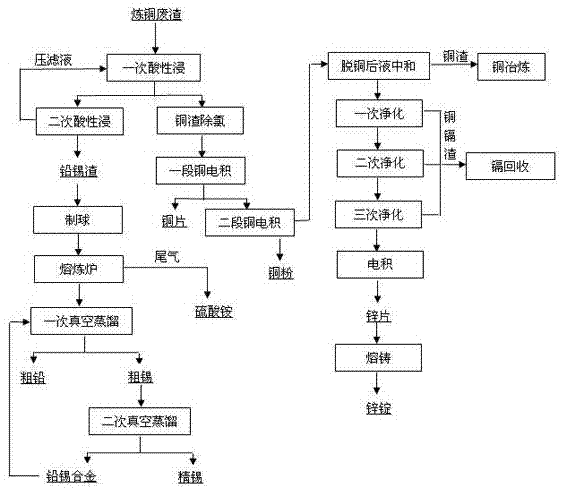
Metallurgical process for recovering metal copper, lead, zinc and tin from copper refining waste slag
ActiveCN102409180APhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSulfate zincElectrolysis
The invention discloses a metallurgical process for recovering metal copper, lead, zinc and tin from copper refining waste slag, which uses waste liquid of zinc electrolysis with sulfuric acid or waste liquid of zinc electrolysis to perform the acid leaching; more than 95% of the zinc and copper are in the solution, the Fe 2+ in the solution is less than or equal to 1.5g / L; then the copper slag is used for removing chlorine; when the Cl- in the solution is less than or equal to 1.0g / L, the solution is sent to a copper electro-deposition; the electro-deposition decopperization can produce copper piece or copper powder; the decopperization neutralization is to add calcine or zinc oxide for neutralizing acid when the Cu2+ in the solution is less than or equal to 1.0g / L; lime is used for adjusting the pH value to 5.2-5.4; after purifying and removing residue of the zinc sulfate solution, the solution is sent to the zinc electro-deposition for producing zinc piece; the lean and tin pyrometallurgical purification is that, after more than 98% of lead and tin is sent to the acid leaching residue, the material of the acid leaching residue is balled and sent to a smelting furnace, so as to produce lead-tin alloy; the lead-tin alloy is directly sent to a vacuum fractionation furnace for purifying the lead and tin product; sulfur dioxide in the tail gas is absorbed by ammonia, so as to obtain ammonium sulphate product. The process is to extract copper and zinc joint wet process and to purify lead and tin by pyrometallurgical method; the process flow is effectively shortened, the metalrecovery rate and the resource utilization rate are both largely increased, and there is no secondary pollution in the process.
Owner:CHENZHOU FENGYUE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
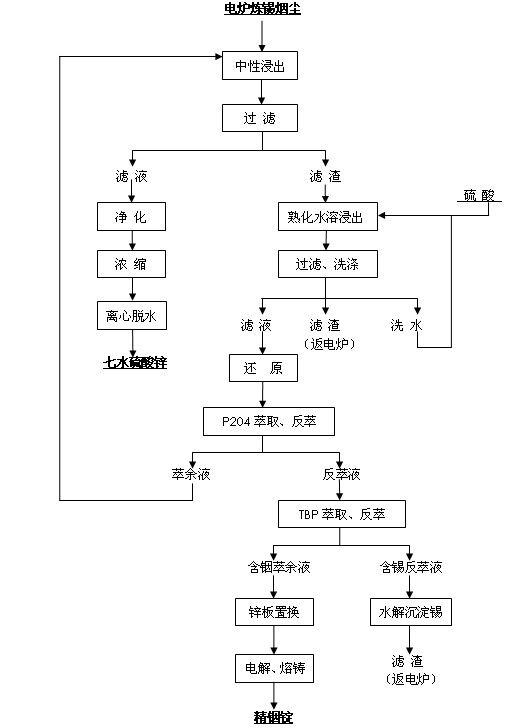
Multi-metal recycling method of electric furnace tin-smelting dust
InactiveCN102140580AImprove leaching rateEfficient extractionProcess efficiency improvementHigh concentrationIndium
The invention discloses a multi-metal recycling method of electric furnace tin-smelting dust. The method comprises the following steps: electric furnace tin-smelting dust is placed in a reaction kettle, sulfuric acid or / and raffinate are added to perform neutral leaching so that metals such as zinc are leached in the neutral solution and indium, tin and lead are left in residues; the neutral residues are placed in a reaction kettle, concentrated sulfuric acid is added for cure leaching, cleaning solution is added after the reaction to ensure that indium and a part of tin are leached in the solution and most of tin and lead are left in residues; extractant P204 is used to extract the indium and tin of the leachate and separate indium and tin from zinc, hydrochloric acid is used to perform backextraction to the extract so that tin and indium can be separated from the organic phase through backextraction and high concentration indium-tin mixed backextraction solution can be obtained; tributyl phosphate (TBP) extractant is used to extract tin to obtain material solution with indium and material solution with tin; and the material solution with indium is replaced by using a zinc plate and casted to obtain crude indium, the crude indium is electrolyzed and purified to obtain a refined indium product. The method combines the mature concentrated acid curing technology, extraction technology and other technologies into a whole, solves the separation problem of indium and tin and ensures that various high-value metals in the electric furnace dust can be recycled efficiently, continuously and largely; and the actual indium yield is more than 80% and the purity of the refined indium is more than 99.93%.
Owner:刘辉 +1
Production method for grinding steel-iron slag powder, mineral slag powder and steel slag powder by using vertical mill
ActiveCN104291714AImprove uniformitySimplify production stepsManufacturing cost reductionIron powder
The invention relates to a production method for grinding steel-iron slag powder, mineral slag powder and steel slag powder by using a vertical mill. The innovation points comprise that the same vertical mill is employed for independently grinding steel-iron slag powder, mineral slag powder and steel slag powder, steel slag tailings obtained in the steel-slag processing and metal recovery processing step and mineral slag obtained in the mineral-slag metal-removal pretreatment step are sent into the vertical mill according to the ratio of 2-4:8-6, and then a step of using the vertical mill to grind steel and iron slag powder and a step of performing magnetic separation on a recycled material of the vertical-mill ground steel and iron slag powder to remove iron and performing closed cycling are executed, so that the technology of using the vertical mill to grind steel and iron slag powder is realized. The method helps to simplify conventional production steps of steel and iron slag powder, improve the uniformity of the steel and iron slag powder and reduce production energy consumption and cost. The production method is capable of realizing sharing of most of equipment while realizing recovery and reutilization of resource by using the same vertical mill to respectively grind steel and iron slag powder, mineral powder and steel slag powder, so that the utilization rate of equipment and resource are substantially improved, and the manufacturing cost is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU RONGDA NEW MATERIAL
Wet-method process for reclaiming zinc from zinc leaching residue
InactiveCN1837380AIncrease loadReduce the amount of acid used for leachingProcess efficiency improvementKeroseneSlag
This invention relates to wet process of recovering zinc from leach slag containing zinc. It belongs to a wet process for zinc ore, in particular to a process for slag containing zinc produced from the systerm of wet zinc metallurgy. This method comprises the following steps: washing residue with water or diluted acid to get slag, selecting P204 as extractant and coal oil as thinner to extract them to water phase, configuring the solution containing zinc and sulfuric acid, eluting the impurity loaded in organic phase, back extracting the load organic phase with depleted electrolyte and sulfuric acid, transferring zinc in organic phase to water phase, deoiling all water phases which contact with organic phase, finally, taking the liquid which has been back extracted as fresh liquid, and adding it into zinc electrodeposition systerm. The invention has high metal recovery ratio, and can recovery zinc from leach slag containing zinc, save resource, avoid environmental contamination. And it perfectly joins with the process of wet processing of zinc oxide ore, decreases the consumption of acid in the leaching of zinc oxide, and reduces the cost.
Owner:YUNNAN XIANGYUNFEILONG RESOURCES RECYCLING TECH CO LTD +1
Method for extracting vanadium and chromium from vanadium chromate mixed solution
InactiveCN106893877AReduce processing costsEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementBarium saltSlag
The invention relates to a method for extracting vanadium and chromium from a vanadium chromate mixed solution. The method has the characteristics that the vanadium in the vanadium chromate mixed solution is separated and recycled through the crystallization precipitation method or the hydrolysis precipitation method or the calcium salt precipitation method at first, then the chromium in the enrichment solution is separated through the copper salt precipitation method or the barium salt precipitation method, an obtained chromium precipitation enrichment product is then transformed into chromium enrichment liquid, the chromium enrichment liquid is further processed into products of chromic acid and chromate, and production of vanadium-chromium reducing slag and ammonia-nitrogen wastewater in the separation and recycling process of the vanadium and the chromium in the solution is effectively avoided. The method for extracting the vanadium and the chromium from the vanadium chromate mixed solution has the advantages of being good in vanadium and chromium separation effect, short in technological process, high in metal recycling rate, easy and convenient to operate, low in production cost, environmentally friendly and the like and is suitable for industrial production and application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
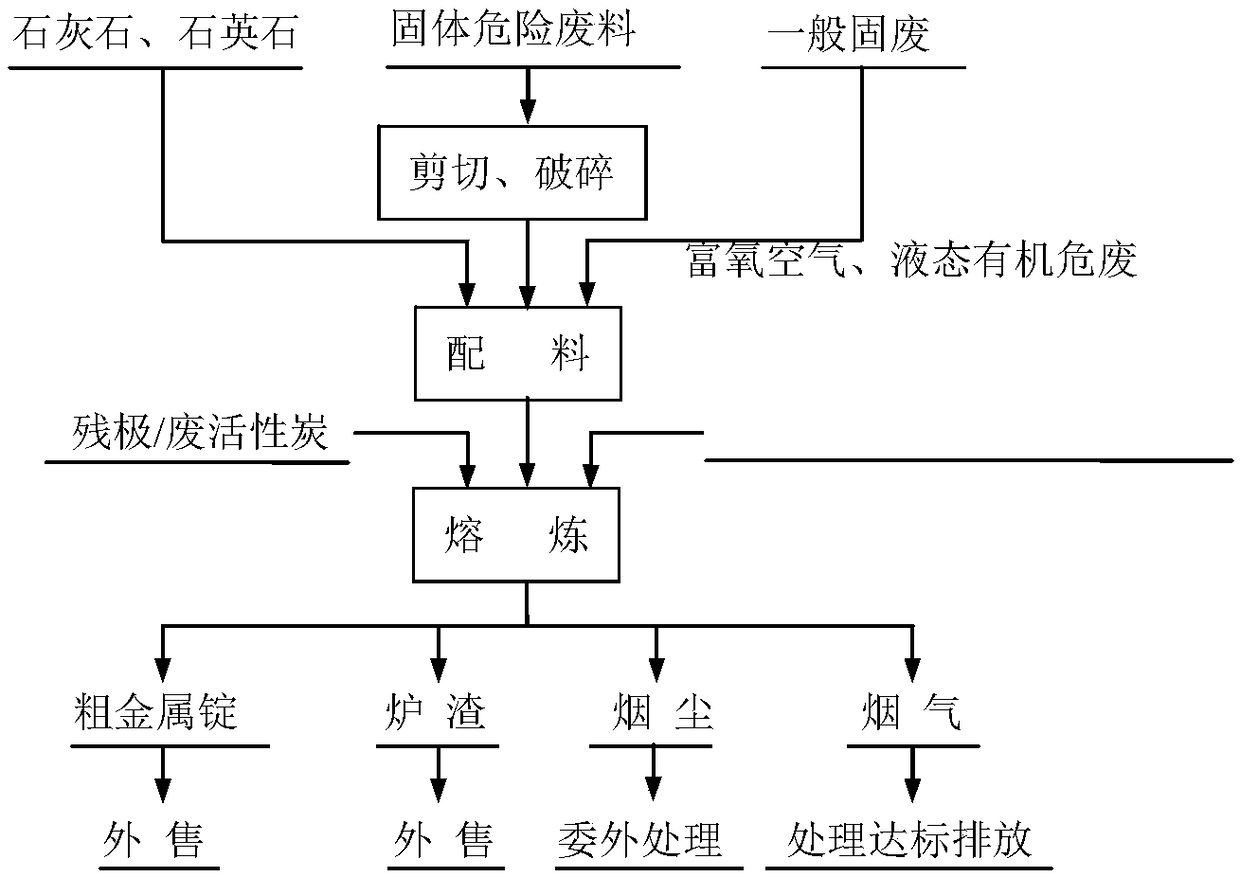
Resource regeneration method for hazardous waste
The invention discloses a resource regeneration method for hazardous waste. According to the method, fire melting is conducted in an oxygen-enriched side blown converter by taking metal-containing solid hazardous waste as a raw material, taking organic liquid hazardous waste as auxiliary fuel, taking hazardous waste such as waste activated carbon or residual electrodes as a reducing agent and adopting a fluxing agent in a matched mode, organic matter in the materials generates heat through oxygen-enriched combustion pyrolysis, copper, nickel, precious metals and the like are fused and reducedinto crude metal melt at high temperature, low-melting-point metals such as lead, zinc and tin are volatilized for smoke dust recovery, metals such as iron, aluminum and calcium and silicon take participation in a slagging reaction to generate slag, and flue gas is fully combusted, treated and then exhausted after reaching the standard. The crude metal melt and the slag settle and are separated inan oxygen-enriched side blown converter hearth, cast ingots of the crude metal melt are discharged from an alloy port arranged at the bottom of the hearth, crude metal ingots are generated, the slagis discharged from a slag port over the alloy port, and water-quenched slag is generated through water quenching. The resource regeneration method for the hazardous waste has the advantages of being wide in application range, capable of saving energy, environmentally friendly, good in operation condition and high in metal recycling rate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENLIAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION GRP CO LTD
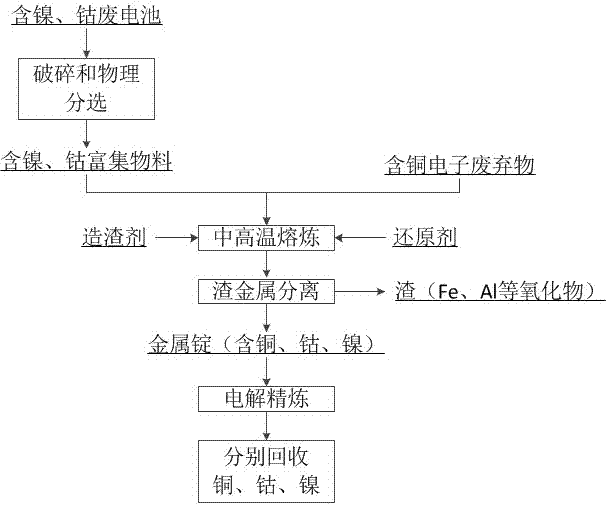
Synergetic metal recycling method for nickel and cobalt containing waste batteries and copper containing electronic waste
InactiveCN107012332AHigh purityAvoid efficiencyPhotography auxillary processesWaste accumulators reclaimingElectrolysisElectrical battery
Owner:SINO SCI PROCESS BEIJING SCI&TECH CO LTD
Method for reclaiming zirconium oxide and yttrium oxide from zirconium-containing solid waste
A method to recycle zirconium oxide and yttrium oxide from solid waste containing zirconium comprises the steps of screening of solid solution waste and milling, adding solvent and latent solvent to the milled powder, sintering and conversion, dipping and washing sinters with dilute acid and removing impurity, leaching of acid pickling materials in high temperature and high acid, concentrating and cooling of leaching liquid containing zirconium and yttrium and precipitation of zirconium oxychloride crystal, purifying and burning the crystal to obtain zirconium oxide, purifying, neutralizing and precipitating mother solution after zirconium is separated out, dissolving and purifying yttrium slug with a large amount of yttrium in acid solution and extracting yttrium oxide. The method of recycling zirconium oxide and yttrium oxide from solid waste containing zirconium is characterized by short technique process, low production cost and high recycling rate of metals, etc., thus effectively realizing the reclamation and the cyclic utilization of the solid waste.
Owner:李树昌
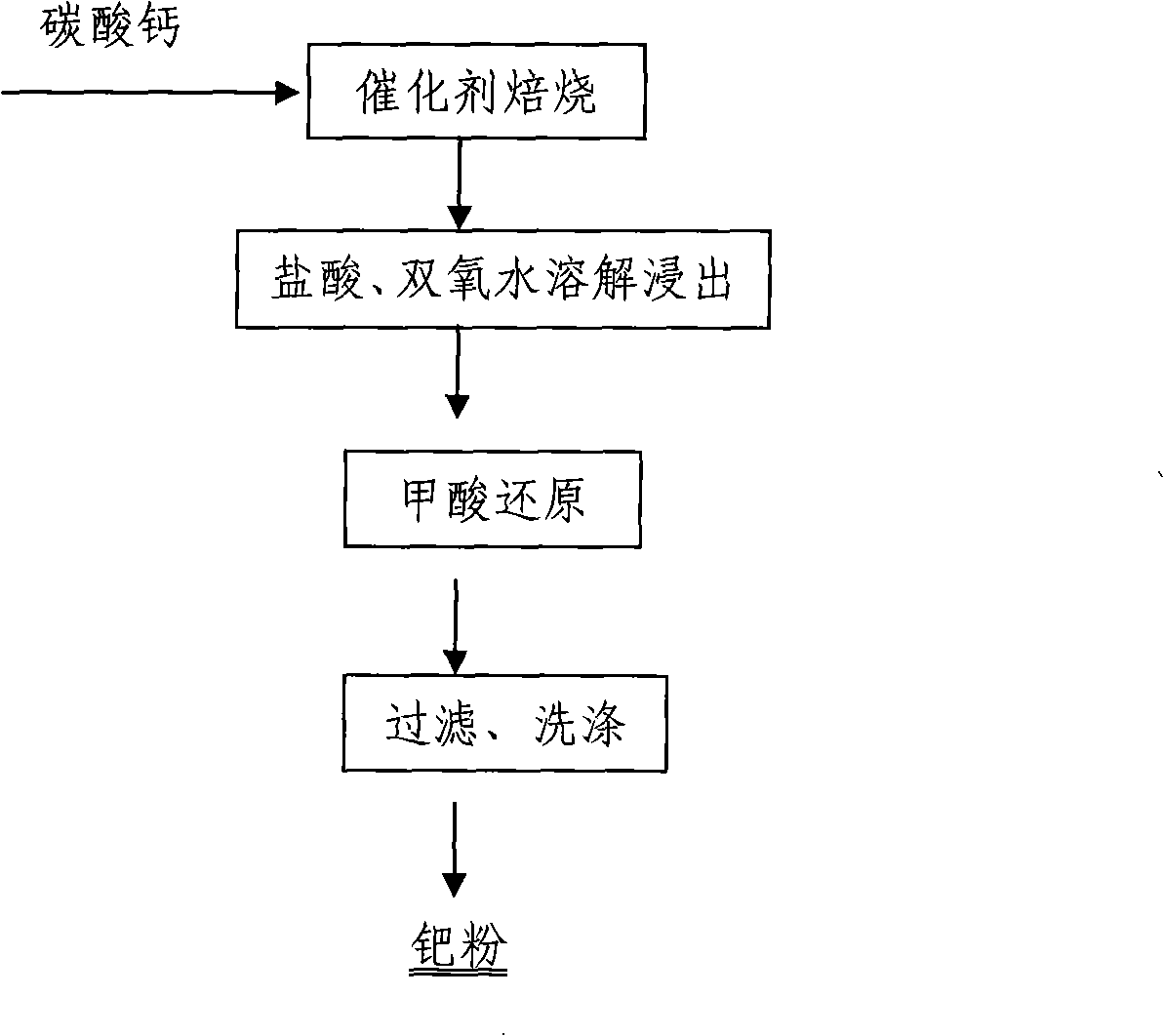
Method for recovery of palladium from waste palladium-carbon catalyst
InactiveCN101280363AHigh recovery rateOptimum Process ParametersProcess efficiency improvementMetal recyclingPalladium
The invention discloses a method for recycling palladium from the waste palladium carbon catalyst, which relates to a method for recycling the palladium from the waste palladium carbon catalyst by dissolving noble metal directly. The method is characterized in that the recycling procedure comprises the steps that waste palladium carbon catalyst and cineration agent calcium carbonate are mixed to slurry uniformly and then perform the roasting, to ensure that organism and carbon in the waste catalyst are oxidized, the roasting residue is boiled by using chlorhydric acid and then is added into hydrogen peroxide to be boiled and then filtered, then the filter residue is washed, and the filter liquor and the cleaning liquor are combined to adjust the pH value to be 6.5 to 7.5, and then crude palladium powder can be obtained by using the formic acid to reduce. In the method of the invention, the method of dissolving the noble metal is adopted directly to recycle the palladium in the waste palladium carbon catalyst, and a novel process for recycling the palladium powder is proposed. Compared with the traditional art, the method has the advantages that the process is short, the environment is friendly, and the metal recycling rata is high. Because the optimal process parameter is given, the palladium recycling rata is more than 99.50 percent.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
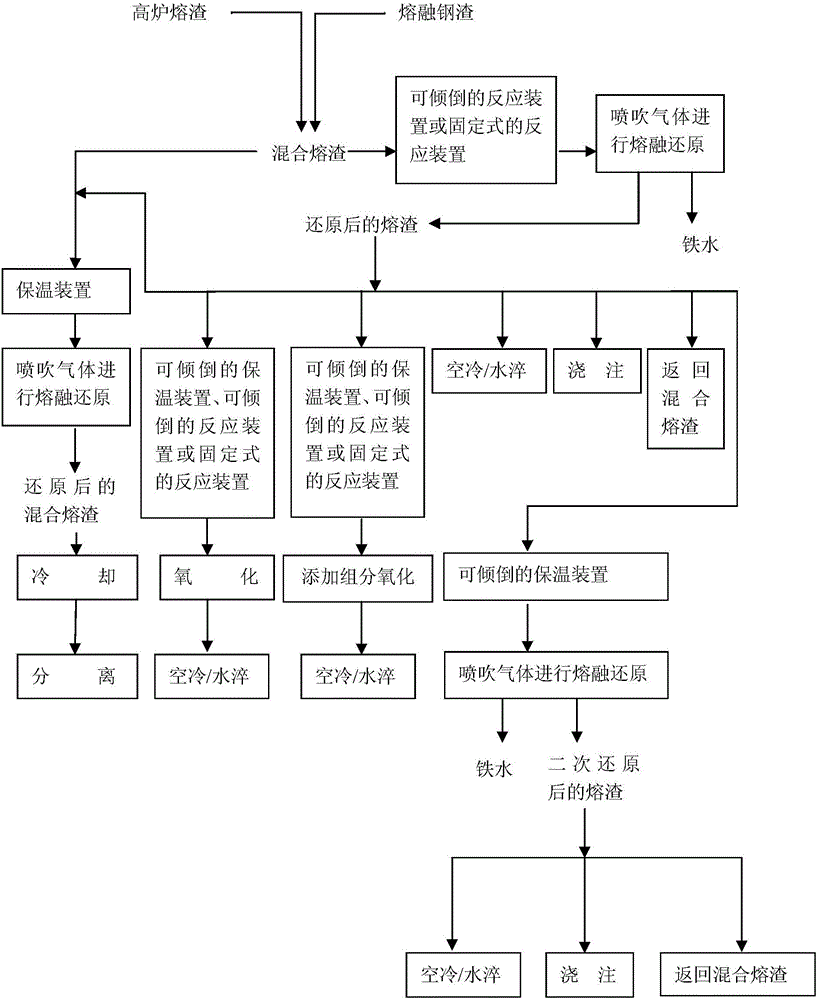
Method for mixed slag smelting reduction recycling and thermal refining
ActiveCN106048109ARealize smelting reduction ironmakingEasy to removeCement productionRecycling and recovery technologiesThermal energyEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a method for mixed slag smelting reduction recycling and thermal refining, and belongs to the field of non-blast furnace iron making and comprehensive utilization of resources. With the method, pig iron or steel and a phosphorus-rich phase are recycled from mixed slag, and slag thermal refining is carried out. The method comprises the following steps that (1) blast furnace slag and molten steel slag are mixed; (2) gas blowing is carried out to carry out smelting reduction; and (3) separation and recycling are carried out. According to the method, blast furnace slag and the molten steel slag are mixed, then, oxidizing gas is blown to carry out molten reduction iron making, the iron in the mixed slag is recycled, phosphorus-rich phase recycling and slag thermal refining are achieved, and the reduced slag can serve as slag cement or a cement regulator or an additive in cement production or cement clinker, or be used for producing high-value-added cement clinker. The method for mixed slag smelting reduction recycling and thermal refining is short in reaction time, high in metal recycling rate, low in production cost, high in material adaptability, high in handling capacity, friendly to the environment, high in economic benefit, and capable of effectively achieving the purpose of high-efficiency recycling of metallurgical resources and thermal energy, and is a new smelting reduction technology.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
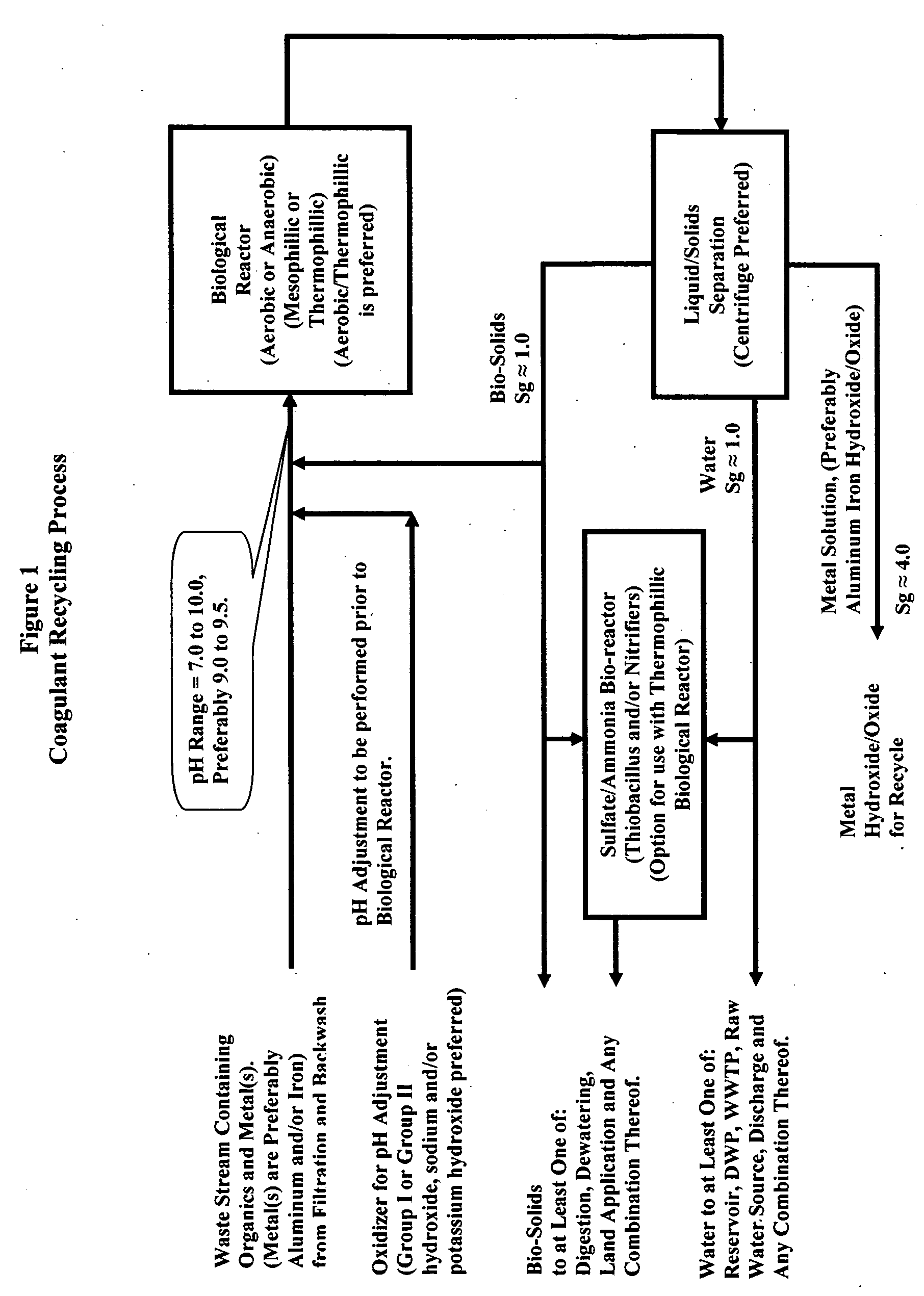
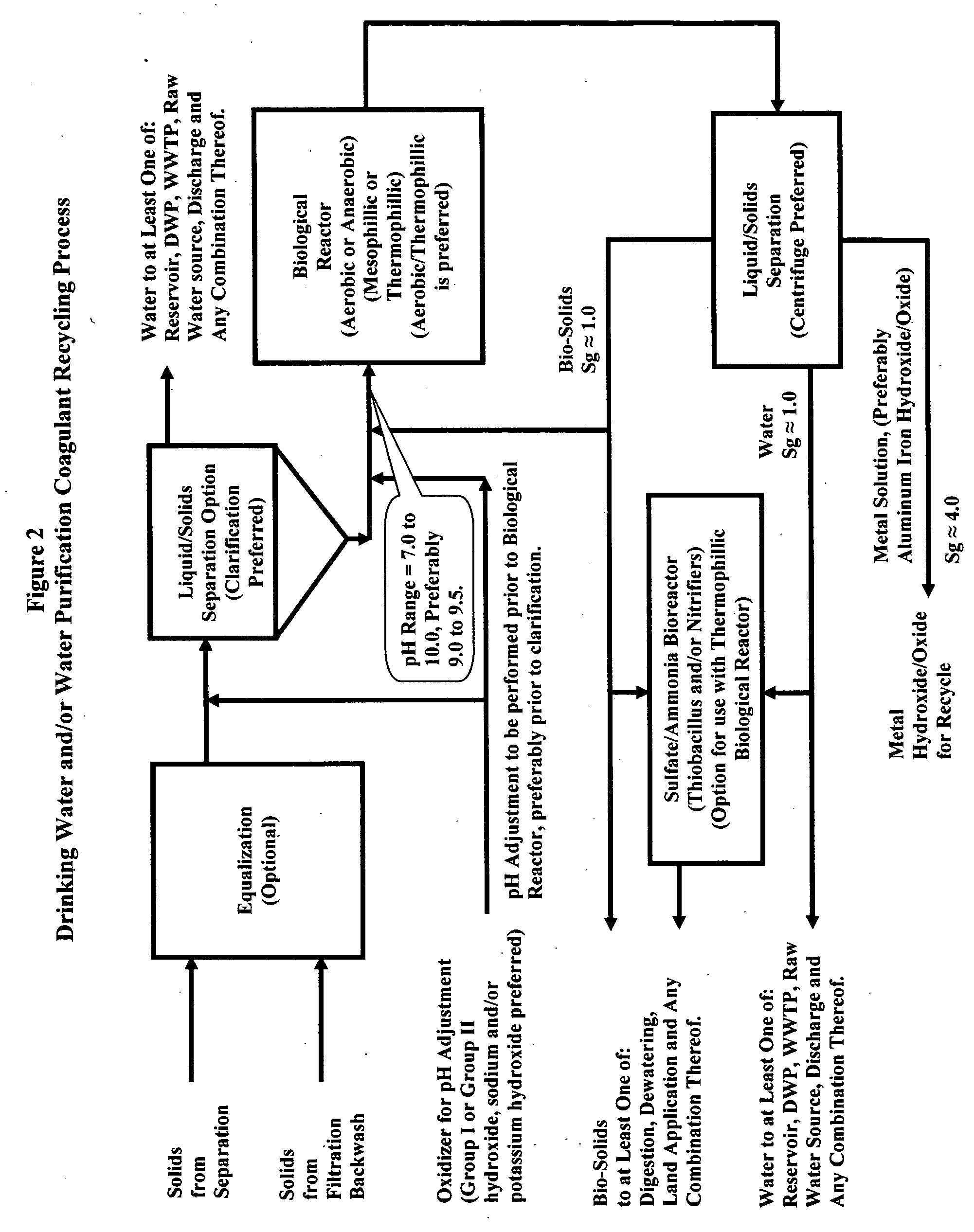
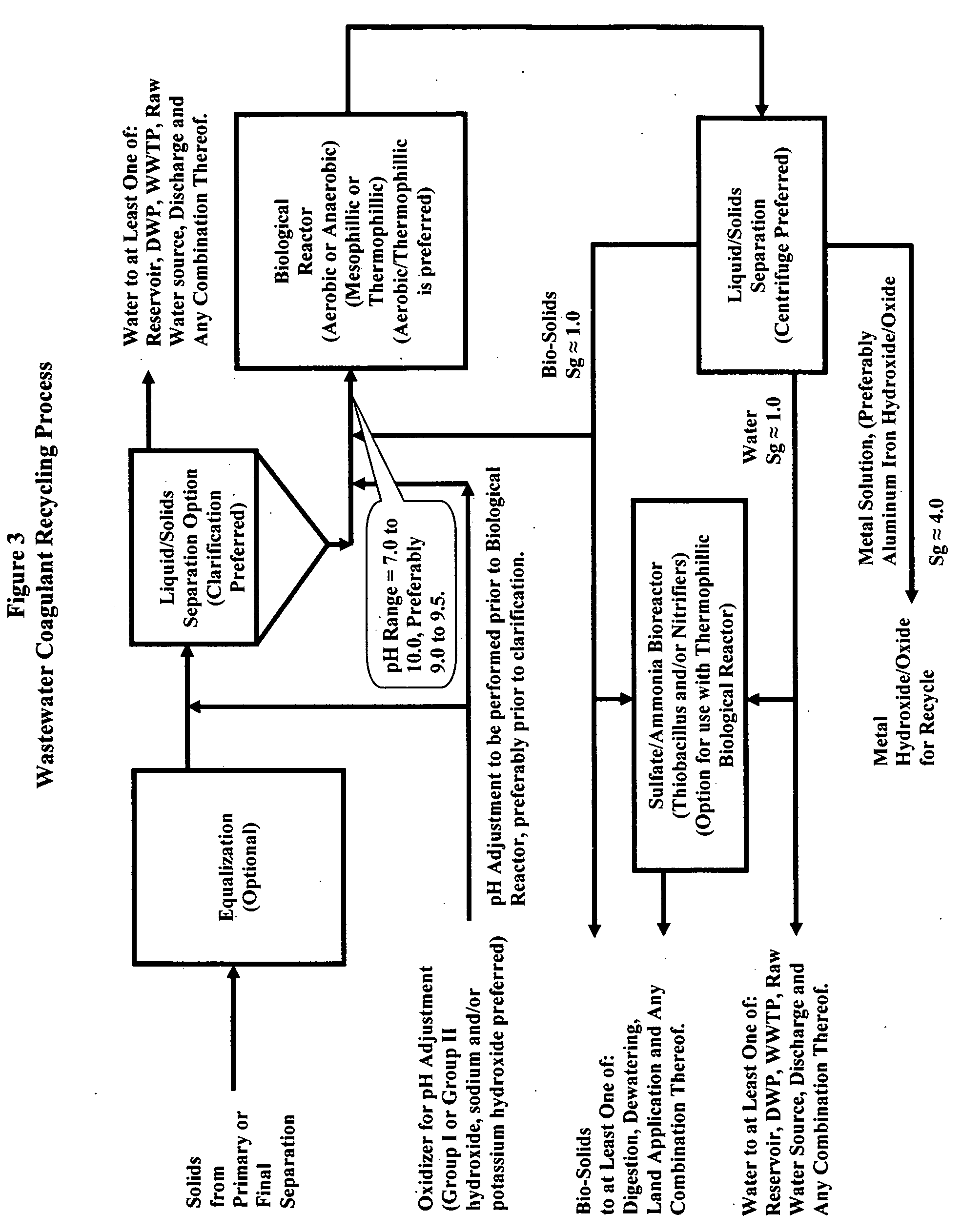
Waste metals recycling-methods, processed and systems for the recycle of metals into coagulants
InactiveUS20050112740A1Efficient and effective processWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationBacteriaPresent methodWaste stream
This invention presents chemical and biological methods, processes and systems for purifying, reclaiming and / or recycling metal(s) in aqueous solution. This invention presents methods, processes and systems for purifying, reclaiming and / or recycling: waste sludge from water purification plants, waste catalyst form polymer manufacturing plants and other waste aqueous metal streams, wherein said waste stream(s) contains at least one metal in concert with BOD and / or TOC and / or COD. Removal of at least one of: BOD, TOC, COD and any combination therein is accomplished via a biological reactor, wherein it is most preferred that an operating pH of 9.25+ / −0.50 is maintained to maximize the insoluble oxide and / or hydroxide form of the metal, while minimizing the ionic form, toxic form, of the metal, thereby providing an environment which is conducive to biological activity. Post biological reaction, metal(s) are removed from aqueous solution with liquid / solids separation. Post biological reaction bacteria are removed from aqueous solution with liquid / solids separation. In the most preferred embodiment, the metals from liquid / solids separation are recycled into coagulant manufacture.
Owner:CLEARVALUE TECH
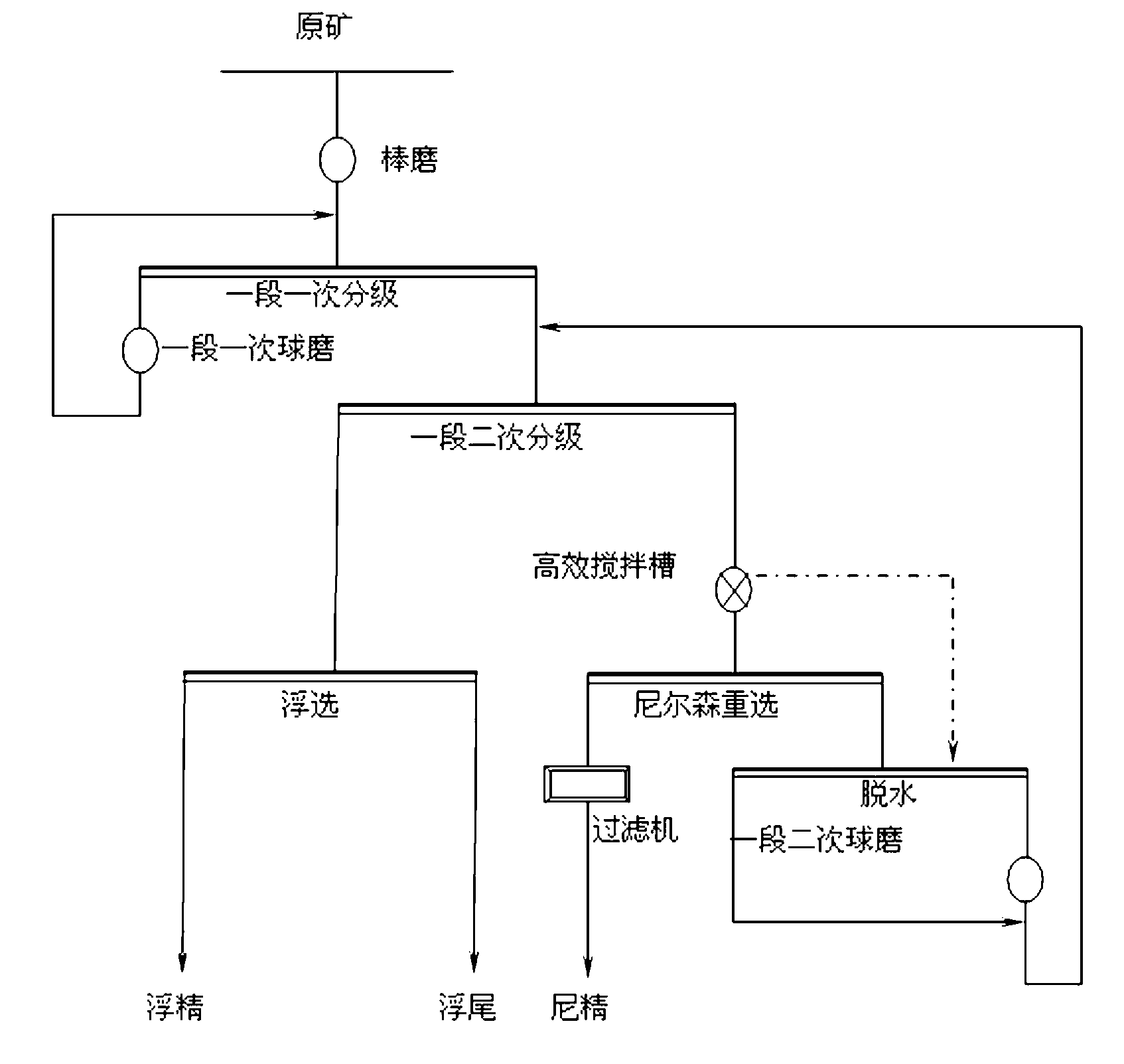
Method for improving recovery rate of copper nickel associated precious metals
The invention provides a method for improving the recovery rate of high copper nickel associated precious metal. A Nielsen centrifugal ore separator is utilized for a section of secondary grading sand setting and a section of secondary ball milling ore discharge to recover sperrylite separated in a monomer mode and ore containing the precious metals such as gold and silver. The technical principles include that in a high power strengthened gravity field, the gravity difference of ores large in specific gravity and ores small in specific gravity is enormously amplified so as to enable separation between the heavy oars and the light oars to be easier than that in a natural gravity field, and therefore ore particles sorted according to specific gravities is realized. A part of precious metals are enriched and recovered in advance, and ore concentrate after ore dressing directly enters an alloy vulcanizing oven to be processed, and therefore the recovery rate of the gold, the silver and other precious metals is improved by a large margin, and normal production and stable operation of an original production system can be ensured. Compared with the indexes of the original production system, concentrate grades of precious metals aurum and platinum are respectively improved by 1.1g / t and 2.0g / t, and recovery rates of the precious metals aurum and platinum are respectively improved by 5% and 10%.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
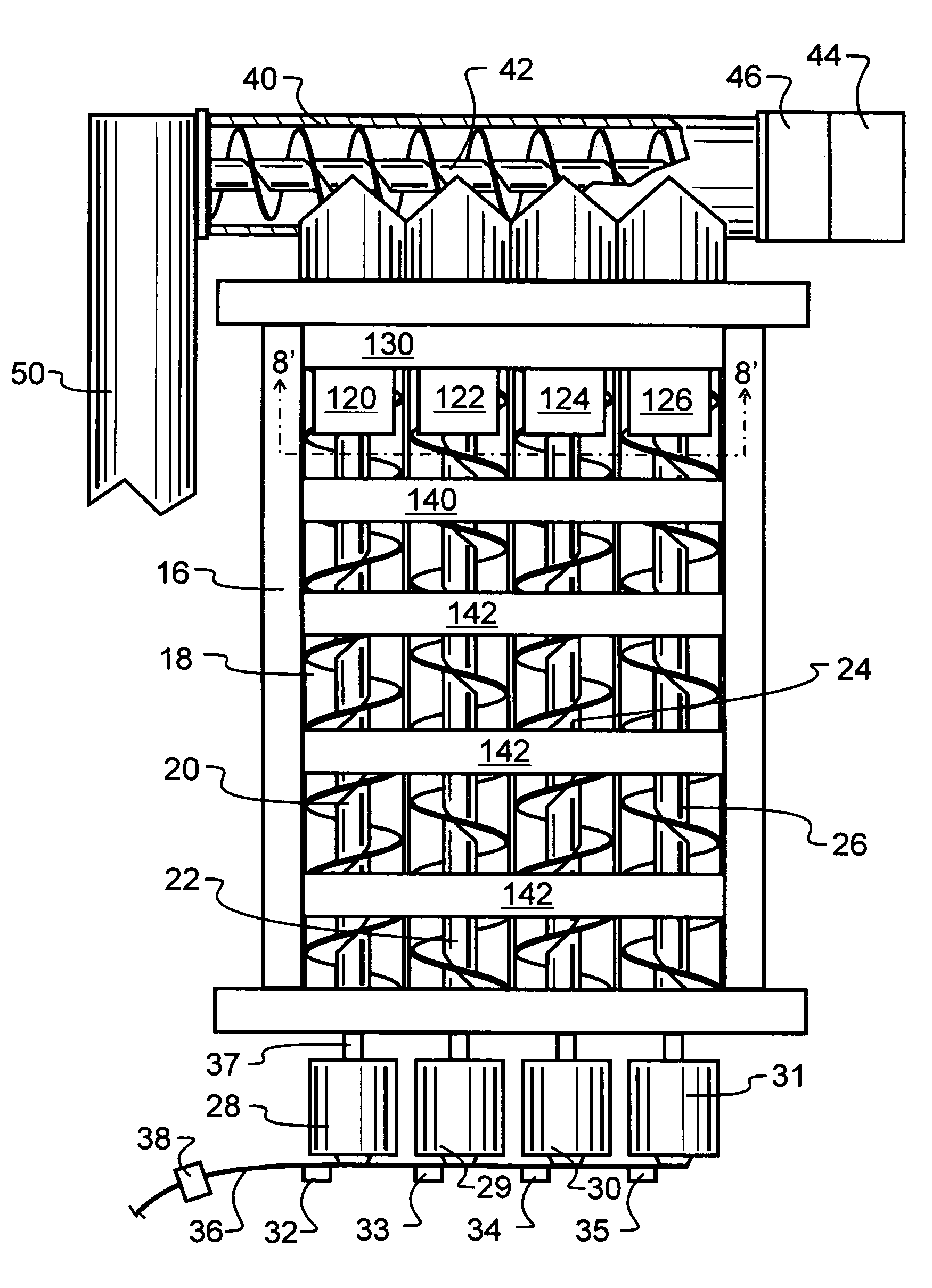
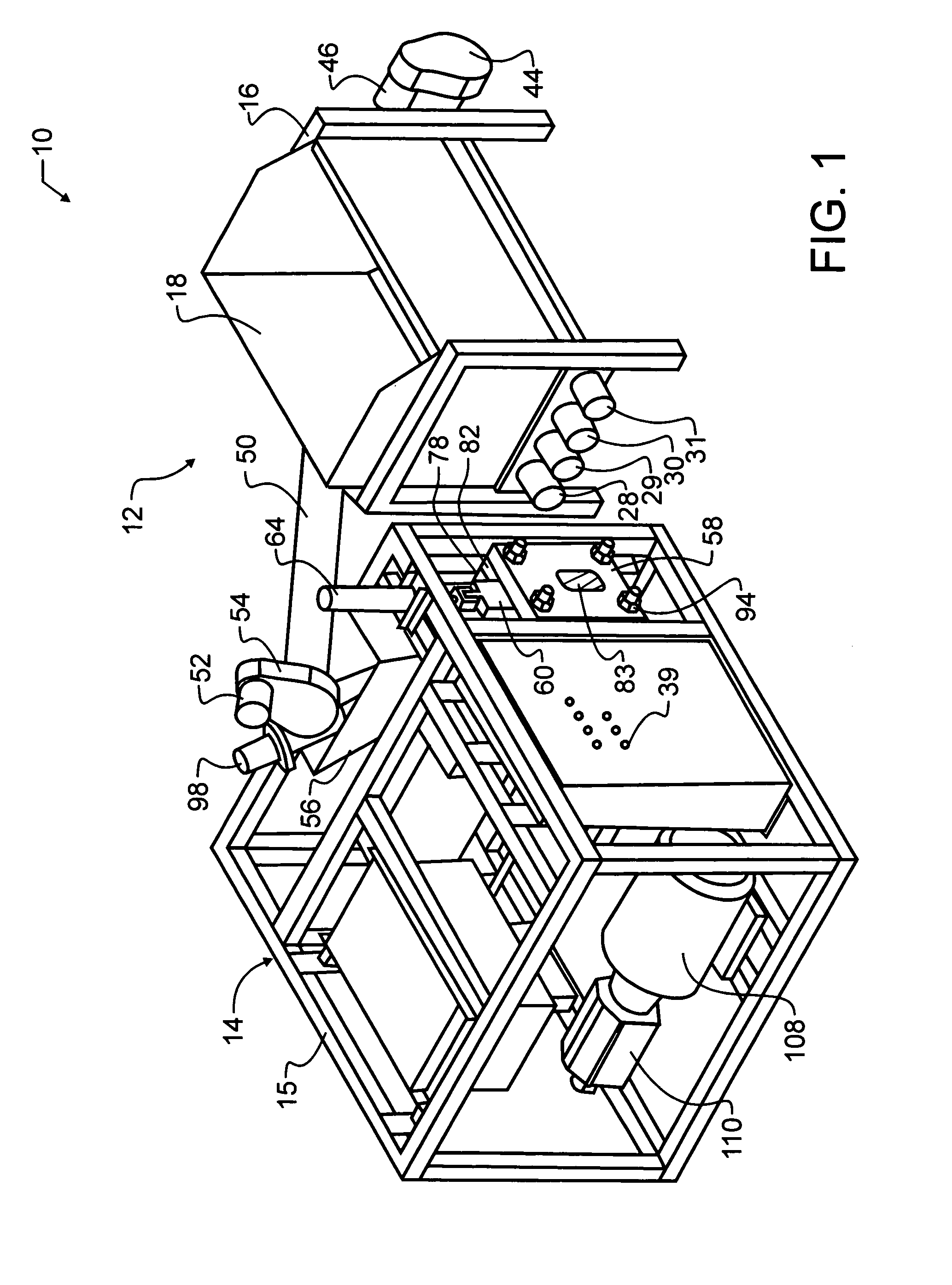
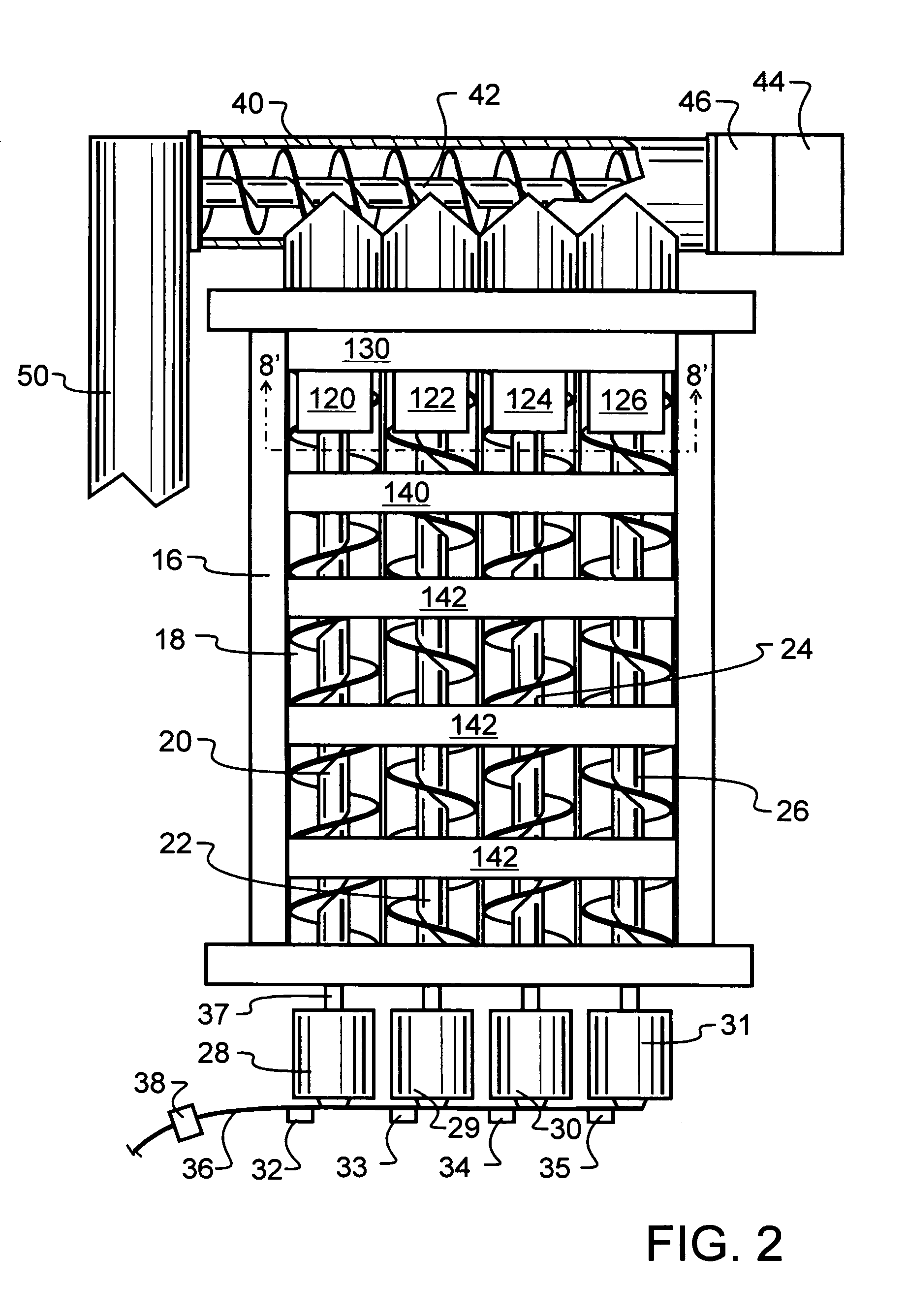
Compacting apparatus
InactiveUS7028610B1Efficient and economical recyclingEasy to removeGrain huskingGrain polishingControlled drainageMetal recycling
A machining waste metal recycling machine has an in-feed hopper. The hopper uses paired augers to move the waste metal through the hopper to a cutting and transporting auger. The hopper augers are powered independently from each other, and may be individually reversed or reversed as a group to clear jams. In the event a jam is not cleared through one or more reversal cycles, the remaining augers may be operated to clear the hopper, thereby avoiding the need for manual unloading. Within the hopper are one or more shear bars that are provided to sever bunches or bundles of machining waste and thereby clear tangles which might otherwise jam the augers. The cutting and transporting augers ultimately feed a reciprocating compactor having a movable gate with one or more grooves for controlled drainage of machining oil and other liquid, as the machining waste metal is compressed into pellets.
Owner:RALICKI DANIEL J
Multi-metal recovery processing technique of waste liquid generated in germanium producing process
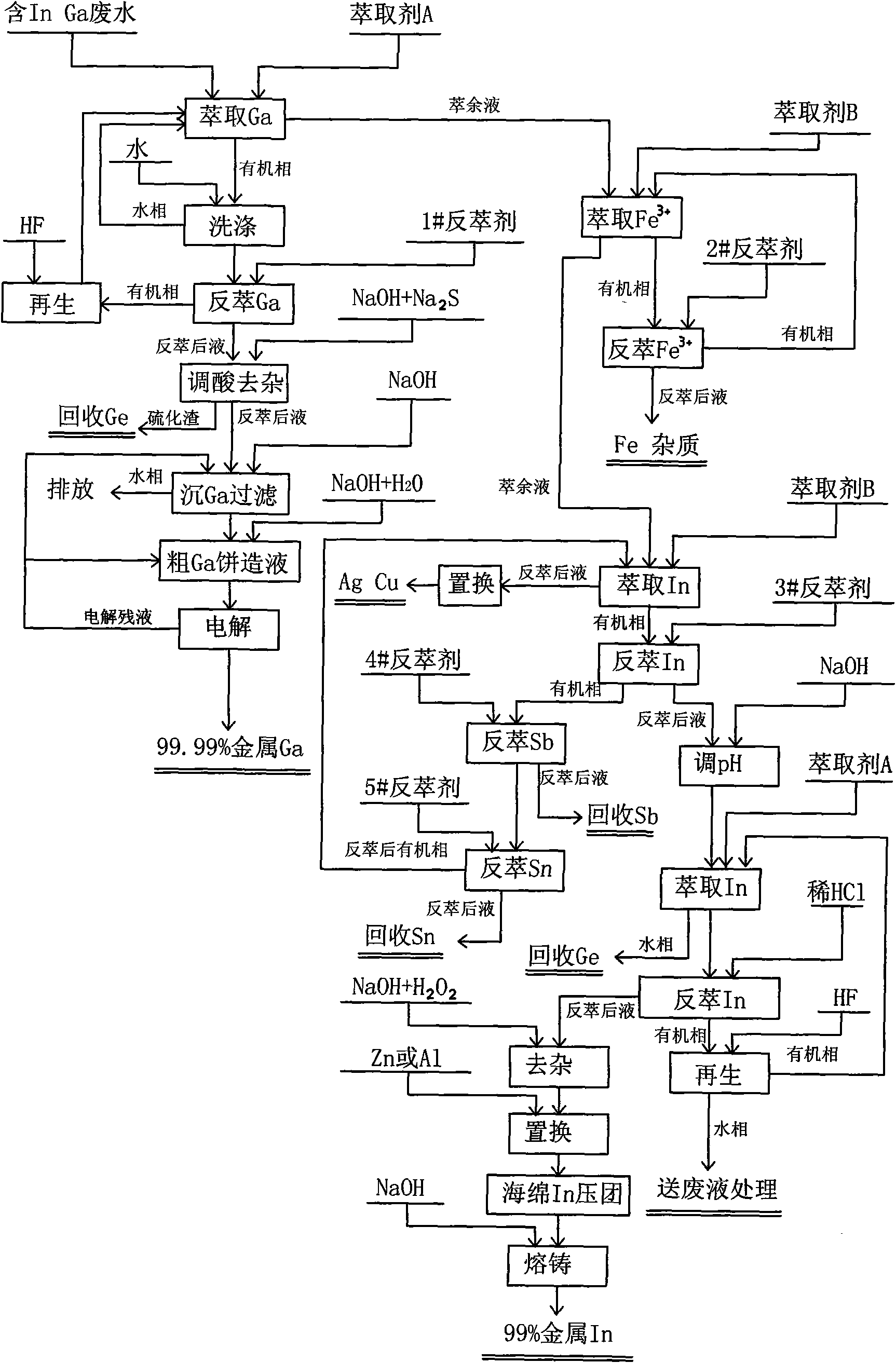
InactiveCN101671777AReduce corrosionLow pricePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementLiquid wasteIndium
The invention relates to a multi-metal recovery processing technique of waste liquid generated in a germanium producing process, belonging to the technical field of non-ferrous metal wet method metallurgy. The multi-metal recovery processing technique comprises the following steps: extracting germanium from the waste liquid generated in the germanium producing process by an extractant A and a kerose diluent, washing, carrying out back-extraction, removing impurities, purifying, depositing the germanium and electrolyzing to obtain the metal germanium with the purity of 99.99%; firstly extracting iron and partial impurities from the residual waste liquid after extracting the germanium by an extractant B and the kerose diluent, and extracting indium from the residual waste liquid after extracting the iron by the same organic extractant B, adjusting the pH, extracting the indium by the extractant A, carrying out the back-extraction, neutralizing, oxidizing, removing the impurities and replacing to obtain spongy indium, and then briquetting and casting to obtain 99% metal indium. The invention has the advantages of short process flow, small occupied area, few investment, fast implementation and good working conditions, solves the problems that the valuable metal in the waste acid solution can not be recovered and has higher value of the resource comprehensive utilization. Furthermore, the metal recovery rate is larger than 92%; the purity of the obtained product, metal germanium, is 99.99%, and the purity of the metal indium is 99%.
Owner:湖南福欣锗业科技有限公司
Complete-set device for recycling metal in waste lithium battery
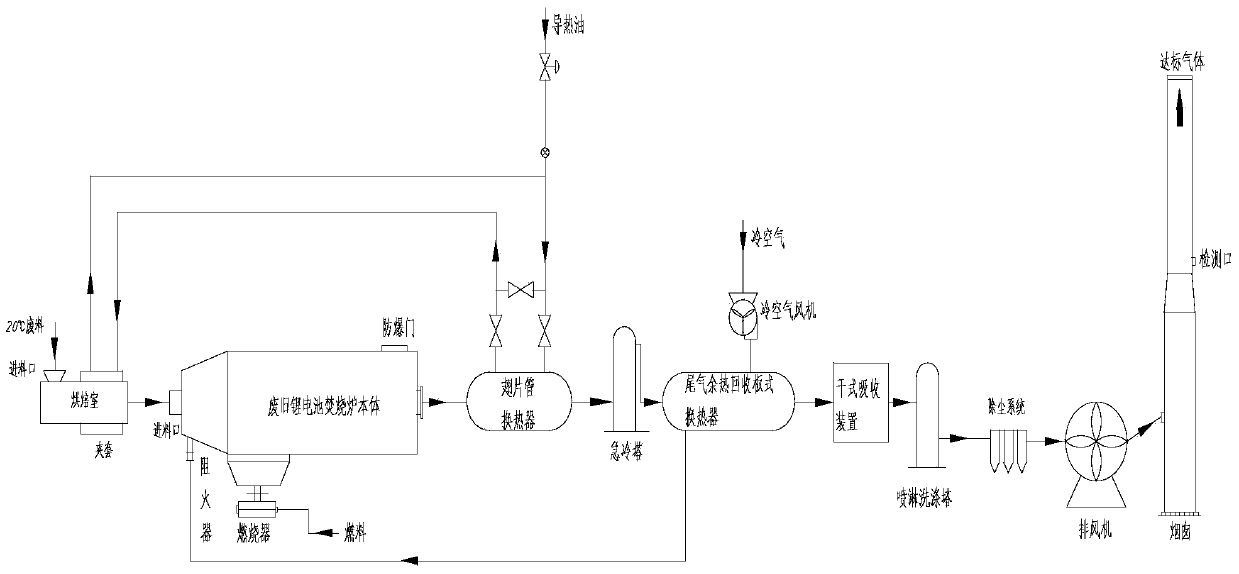
InactiveCN103515668AThe method is simple and clearAdaptableWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementEnvironmental resistanceRare earth
The invention provides a complete-set device for recycling metal in a waste lithium battery and belongs to the technical field of environmental protection. Materials such as lithium, cobalt, copper, nickel and light rare earth can be extracted from the waste lithium battery; the lithium battery recycling has huge potential commercial value and a broad prospect. According to the design, crushing pre-treatment is performed on the waste lithium battery firstly, feeding is performed, the waste lithium battery enters into a baking room for first baking, and then enters into a rotary incinerator for secondary combustion, three-time cooling is performed continuously and tail gas purification is performed, and smoke is discharged into air after reaching standards finally. During the process of smoke discharging, a rapid cooling device is used to enable the tail gas to be cooled so as to prevent dioxin from being produced. The heat quantity of a plate-type heat exchanger is adopted for recycling, and the purpose of recycling can be achieved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
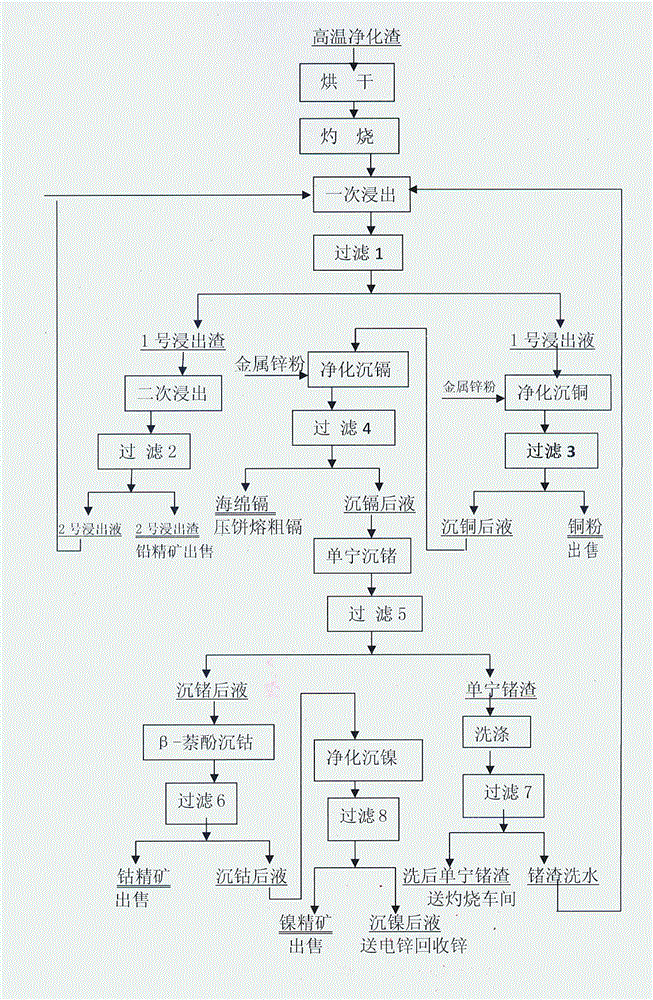
Method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from zinc hydrometallurgy high-temperature purification slags
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from zinc hydrometallurgy high-temperature purification slags. The method comprises the following steps: (1) drying and firing of the high-temperature purification slags; (2) first leaching; (3) second leaching; (4) purification and deposition of copper; (5) purification and deposition of cadmium; (6) deposition of tannin germanium; (7) deposition of cobalt; and (8) deposition of nickel and recovery of zinc by returning liquid obtained by deposition of nickel to a zinc hydrometallurgy system. The invention provides a method for leaching the zinc hydrometallurgy high-temperature purification slags twice after drying and firing to obtain the produced leaching slags, namely silver lead ore concentrate for sales, and comprehensively recovering copper, cadmium, germanium, cobalt, nickel and zinc from filtering liquid subjected to first leaching; the method is easy to carry out and simple in process; the recovery rate of the valuable metals is high, as the recovery rate of lead, silver, copper, cadmium, germanium, cobalt, nickel and zinc respectively reaches 98.50-99.50 percent, 99.10-99.70 percent, 94.40-97.80 percent, 95.10-96.90 percent, 93.50-96.70 percent, 94.70-95.70 percent, 94.80-96.80 percent, and 96.00-97.00 percent; moreover, the recovery of the valuable metals is more comprehensive, scientific and reasonable; waste water, waste gas and waste slags are avoided, and the requirement on national circular economy and sustainable development is met.
Owner:YUNNAN LUOPING ZINC & ELECTRICITY
Method for recycling valuable metals in waste lithium ion batteries
ActiveCN104611566AThe preparation process is matureReduce constructionWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementElectrical batterySlag
The invention discloses a method for recycling valuable metals in waste lithium ion batteries. The method comprises the following steps: mixing waste lithium ion batteries with carbon powder, feeding into a rotary kiln for low-temperature reduction roasting, and controlling the roasting temperature to be less than 900 DEG C during low-temperature reduction roasting, so as to obtain a roasting product, wherein the amount of the carbon powder is not greater than 30% of that of the waste lithium ion batteries; mixing the roasting product with a slag former, so as to obtain a mixed material, wherein the mass of the roasting product accounts for at least 10% of that of the mixed material; feeding the mixed material into an electric furnace for smelting, so as to obtain an alloy with valuable metals and slag with CaO and SiO2. The method has the remarkable advantages of simple equipment, low investment operation cost, easiness in popularization, remarkable process energy consumption reduction, high valuable metal recycling rate and the like.
Owner:CHANGSHA RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com