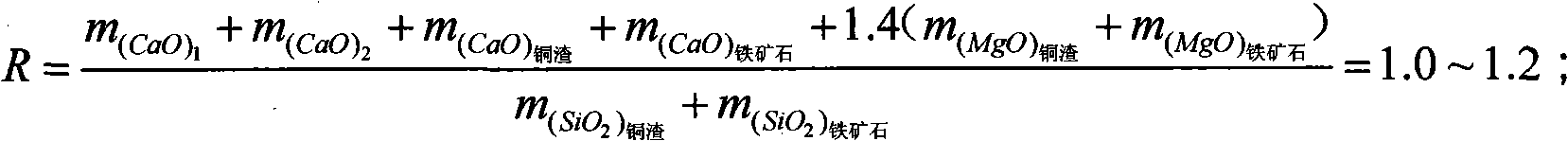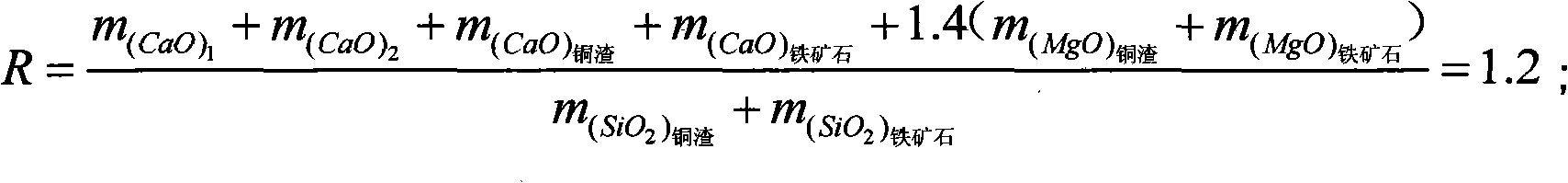Patents
Literature
824 results about "Copper slag" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
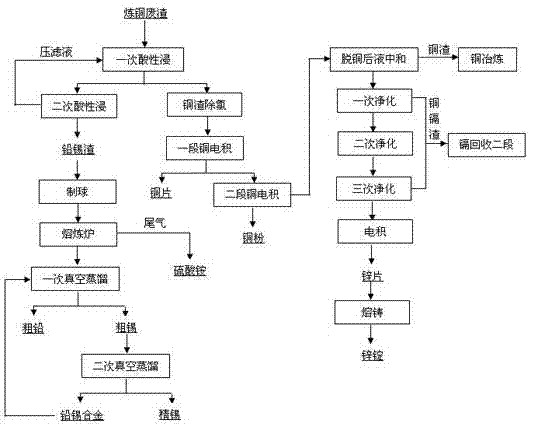
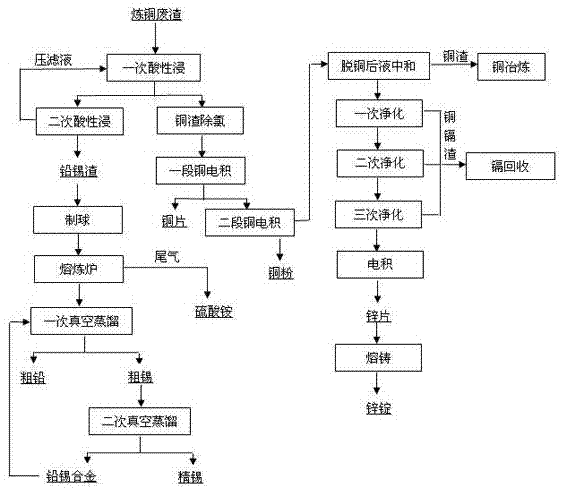
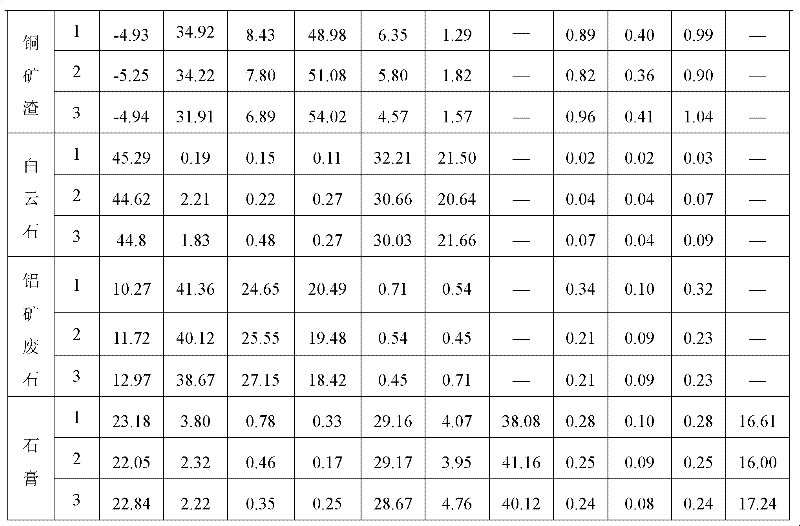
Copper slag is a by-product of copper extraction by smelting. During smelting, impurities become slag which floats on the molten metal. Slag that is quenched in water produces angular granules which are disposed of as waste or utilized as discussed below.
Burning-free block brick prepared from bulky industrial waste residues
The invention relates to a burning-free block brick prepared from bulky industrial waste residues. The burning-free block brick is characterized in that the block brick comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight or volume: 10-80 parts of at least one of tailing, magnesium slag, basic slag, mountain flour, cinder, fly ash, coal gangue, oil shale waste and sulfuric acid slag, 0-80 parts of at least one of gravel, waste sand, construction waste, garbage to be burnt, steel slag, mineral slag, copper slag, iron slag with gold, ardealite, phosphorous slag and carbide slag, 0-50 parts of active cementing material, 0-30 parts of cement clinker, 2-15 parts of cement and a defined amount of water. The preparation method of all types of burning-free and steaming-free standard bricks, perforated bricks, hollow blocks, paving tiles, road edge bricks and fence railings which have low cost and high strength, is as follows: proportioning, stirring for 1-6 minutes, adding a defined amount of water to stir, placing in moulds to form in a machine and performing natural curing for 7-28 days. The burning-free block brick has high raw material selectability, simple technology and wide development and application prospects, and is environmental-friendly.
Owner:司密花 +2
Method for separating valuable metals from copper slag
InactiveCN104404260AReduce consumptionAchieve recyclingProcess efficiency improvementFayaliteAdhesive
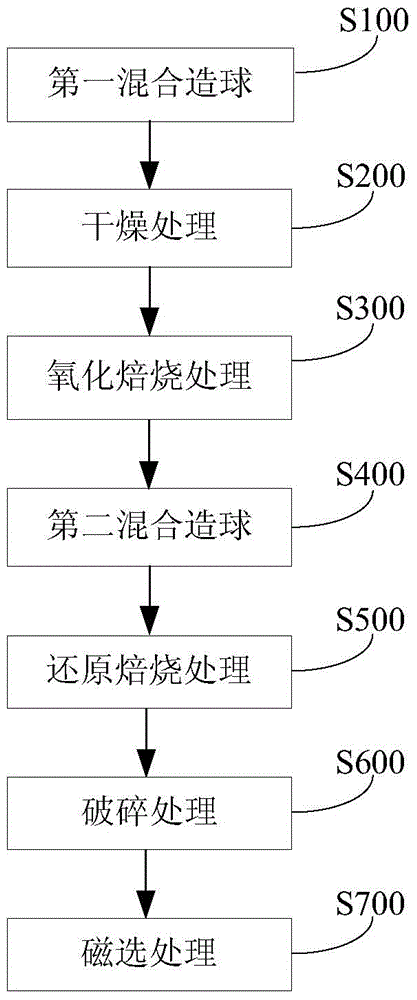
The invention discloses a method for separating valuable metals from copper slag. The method comprises the steps: (1) performing primary mixing palletizing on the copper slag and an adhesive to obtain copper slag pellets; (2) performing drying treatment on the copper slag pellets; (3) performing oxidation roasting treatment on the dried copper slag pellets so as to convert fayalite in the copper slag into ferric oxide; (4) performing secondary mixing palletizing on the copper slag pellets subjected to oxidization roasting and a mixture containing a reducing agent, an additive and an adhesive to obtain a pellet material; (5) performing reducing roasting on the pellet material so as to obtain reduced pellets and smoke containing zinc oxide and lead oxide; (6) smashing the reduced pellets to obtain a mixture containing metal iron powder and tailings; (7) performing magnetic separation on the mixture containing the metal iron powder and the tailings to respectively obtain the metal iron powder and the tailings. According to the method disclosed by the invention, iron, zinc and lead can be effectively separated from the copper slag, and the grade of obtained metal iron is higher.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
Method for smelting lead-containing material
InactiveCN101768670ANo explosion hazardAdaptableProcess efficiency improvementLead smeltingSmelting process
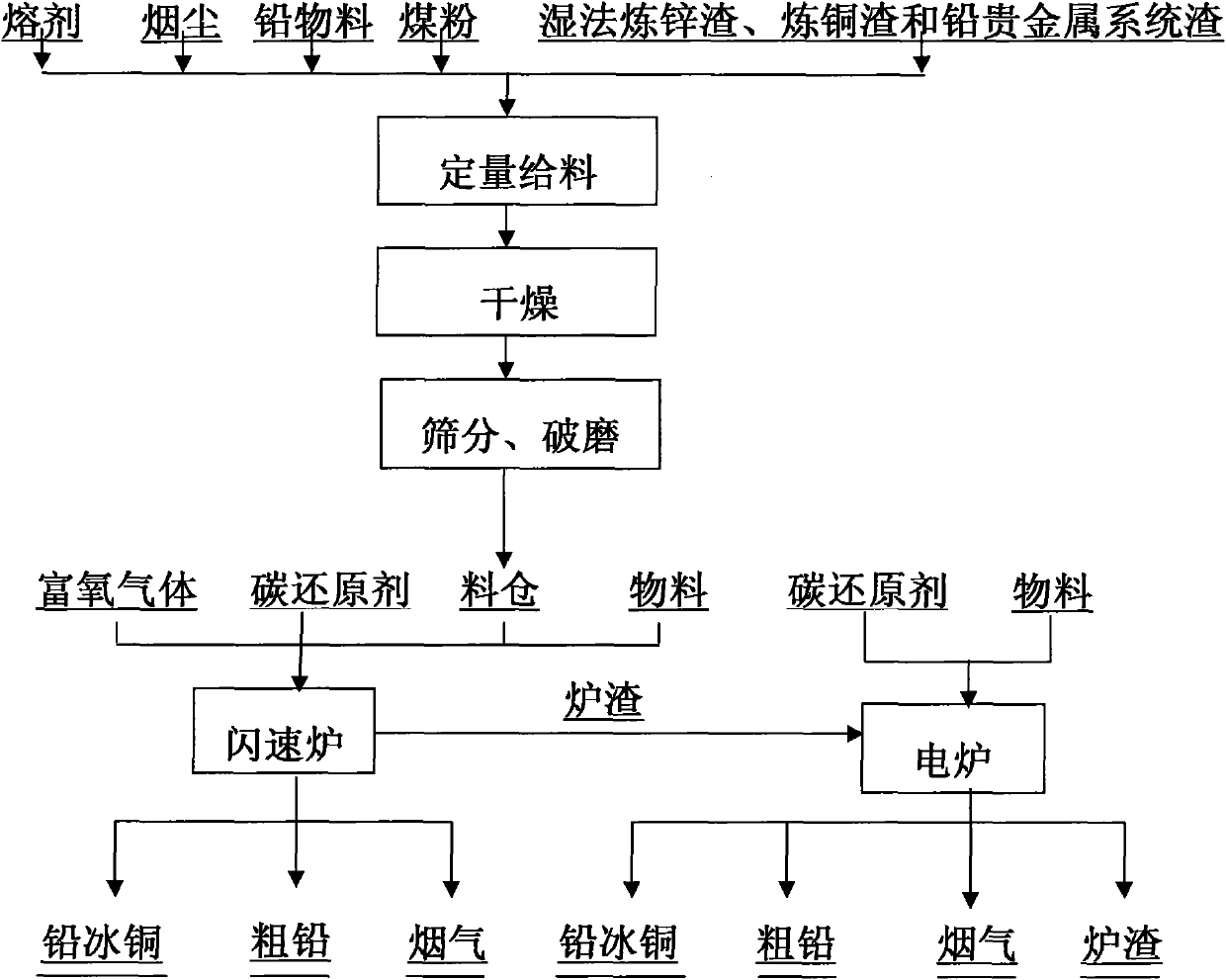
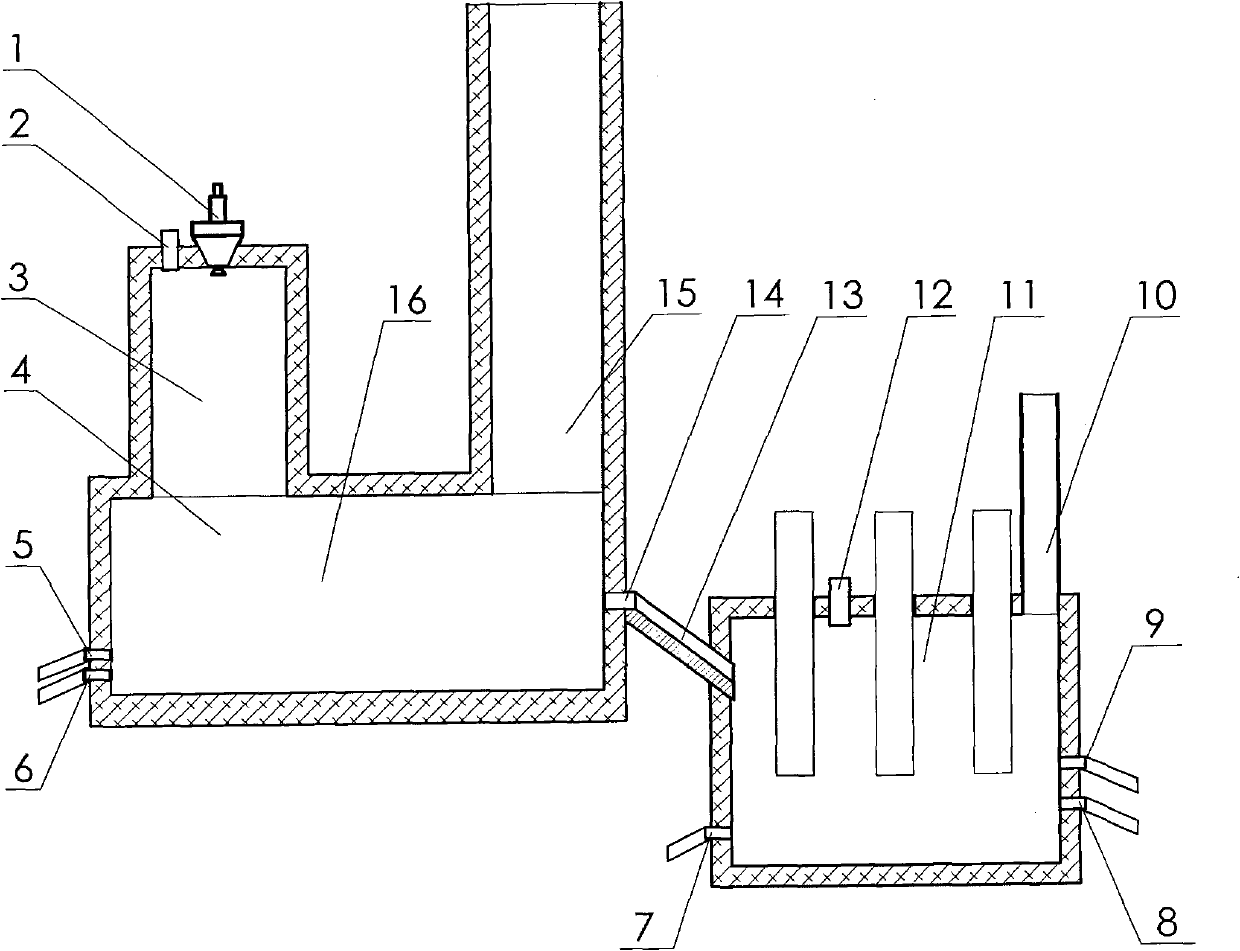
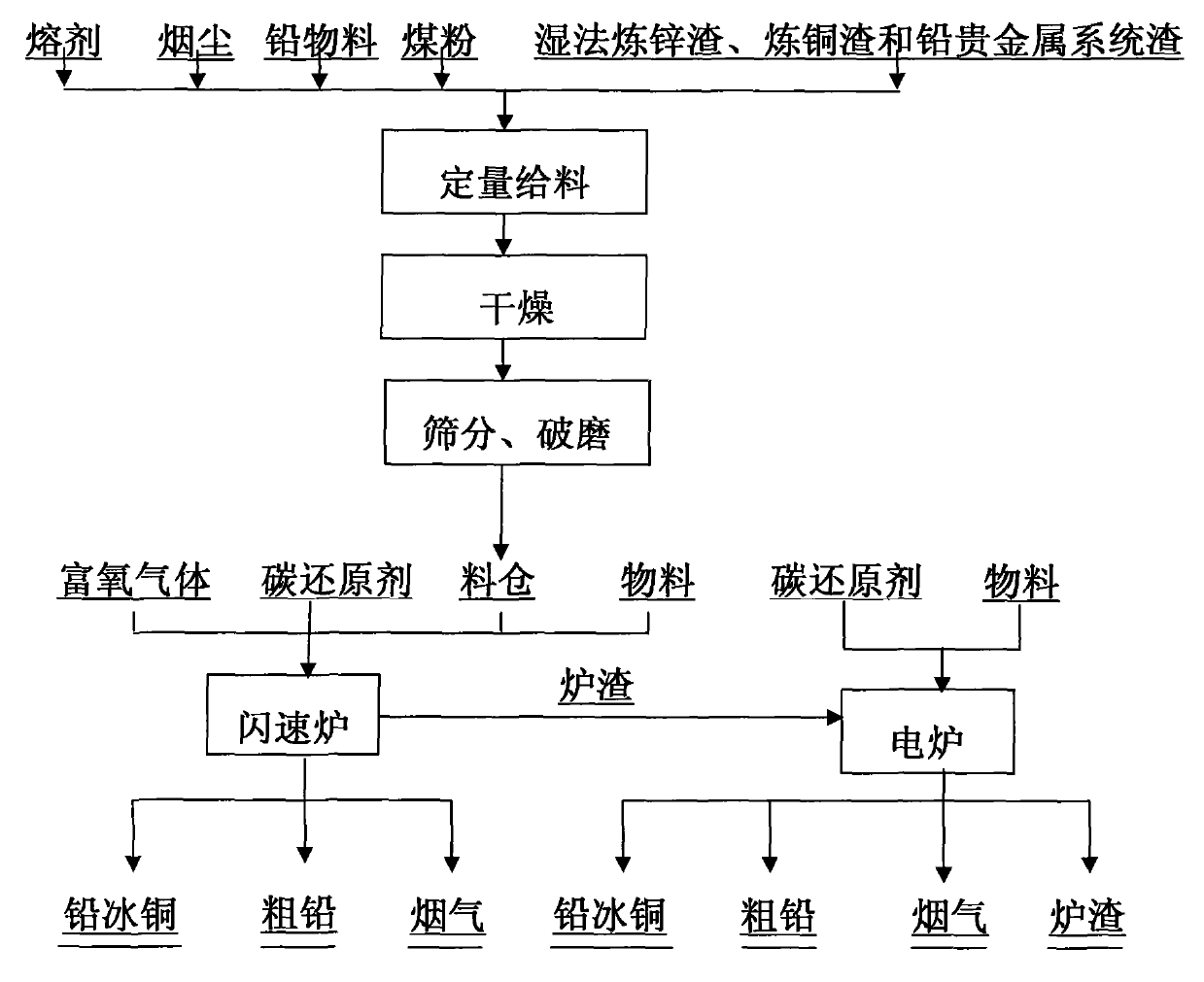
The invention discloses a method for smelting a lead-containing material, relating to the technological process for processing complex lead materials by utilizing a smelting method. The method is characterized in that a flash furnace and a depletion furnace are combined for smelting during the smelting process. The method of the invention has the advantages of short and continuous flow, energy saving, large capacity, efficient source utilization, environment protection, good safety and good industrial hygiene, no danger of foam slag exploration and safe production. The lead smelting process with high smelting strength and various advantages realizes single-step lead smelting, and has stronger adaptability on materials. The process is not only suitable for treating lead ore with complex components, but also suitable for treating wet smelting zinc slag, wet smelting copper slag and lead noble metal system slag, can do complementation of lead, zinc and copper and has more advantages over lead, zinc and copper jointed enterprises. The recovery rates of lead and concomitant valuable metals of copper, zinc and noble metals are higher.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY +1
Method for directly restoring and recovering copper iron from smelting copper slag
ActiveCN102952952AMeet the requirements of energy saving and emission reductionEfficient recyclingProcess efficiency improvementGas emission reductionMolten stateOxygen
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy, and particularly relates to a method for directly restoring and recovering copper iron from smelting copper slag. The method comprises the following steps of: transferring high-temperature molten state copper slag to a high-temperature reducing furnace by a tundish, jetting oxygen to previously desulfurize, adding slagging constituent to keep temperature, jetting natural gas to carry out smelting reduction, slowly cooling to 1096 DEG C at the speed of 1.5-2 DEG C / min, and keeping the temperature for 1h to obtain 7.3at% Cu-Fe copper alloy melt and gamma pig iron, or slowly cooling to 850 DEG C at the speed of 1.5-2 DEG C / min, and keeping the temperature for 1h to obtain 2.7at% Cu-Fe copper alloy melt and gamma pig iron. According to the method provided by the invention, the total recovery use of valuable components, i.e. copper, iron and the like, can be realized, and the alloy melt obtained by the reduction smelting is slowly cooled and separated to obtain copper-rich alloy and low-sulfur gamma pig iron, so that separation of copper and iron is realized and the additional values of products can be improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
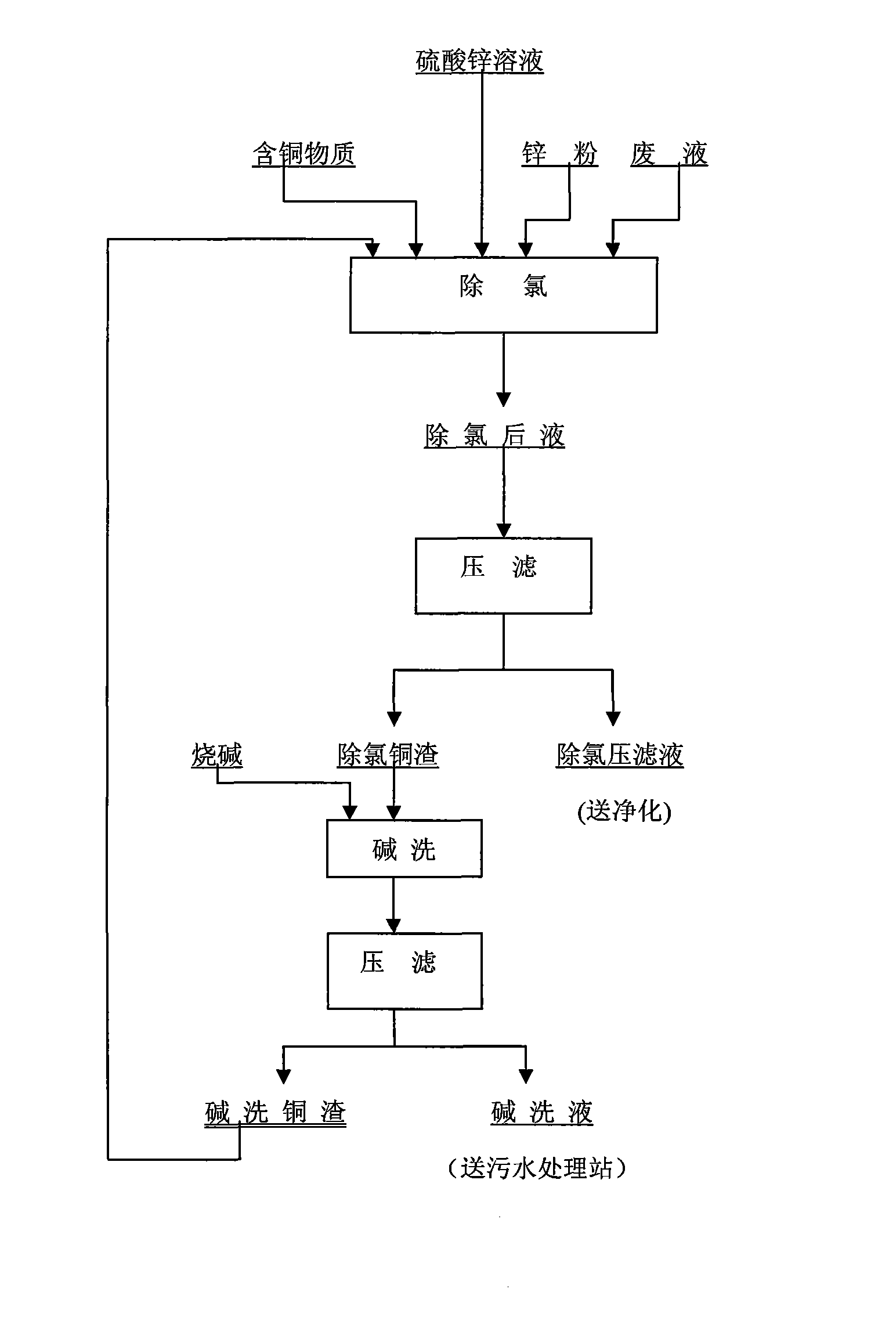
Method for circularly removing chlorine in zinc sulphate solution by copper slag
InactiveCN101633982ATake advantage ofReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementZincCopper sulfate
The invention relates to a method for circularly removing chlorine in a zinc sulphate solution by copper slag. The method comprises the following steps: copper ions, zinc powders and a zinc sulphate solution are added into a continuous reaction groove and react in a stirring state to obtain the zinc sulphate solution containing Cl<-> equal to or less than0.3g / l, and a CuCl precipitate generated in the reaction enters slag; a mixture of the zinc sulphate solution and the slag are treated by liquid-solid separation to obtain a dechlorinated zinc sulphate solution and copper slag; the separated copper slag is washed with alkali to remove chlorine ions; the copper slag after being washed with the alkali is returned to the continuous reaction groove for carrying out a circular reaction; and when the copper ions are deficient, a certain copper sulfate is added at proper time for replenishment. The invention utilizes the zinc powders as a reducer for reacting with the copper ions in the zinc sulphate solution to generate a CuCl copper slag precipitate, Cl<-> is eluted with the alkali, Cu2O is also obtained and is returned to react with the Cl<-> in the solution for circular dechlorination, copper sulfate does not need to be added or a little copper sulfate is only added in the dechlorination process, the consumption of raw materials is little, and the cost is low; compared with a method that the copper slag which can be changed is added continuously, the interference of external factors to a dechlorination technique is little, the process is easy to control, and the dechlorination effect is stable and reliable.
Owner:蒙自矿冶有限责任公司
Preparation method of calcium oxide expansion agents
The invention relates to a preparation method of calcium oxide expansion agents. The method comprises the following steps: mixing and grinding lime stone and composite mineralizer to obtain raw material, calcining at 1100-1300 DEG C to obtain calcium oxide expansion agent chamotte, and mixing and grinding the chamotte with disperse carrier to obtain the calcium oxide expansion agents, wherein composite mineralizer is composed of 50-70wt% of gypsum and 30-50wt% of copper slag, the weight ratio of composite mineralizer to lime stone is 5:95-10:90, and the weight ratio of calcium oxide expansion agent chamotte to disperse carrier is 75:25-90:10. The calcining heat of the calcium oxide expansion agents of the invention is relatively lower, calcium oxide is not easy to overheat; the water requirement of hydrated product is small, the expansion efficiency is high, the expansion rate is high; and cement concrete can realize effective expansion in dry environment.
Owner:JIANGSU SOBUTE NEW MATERIALS
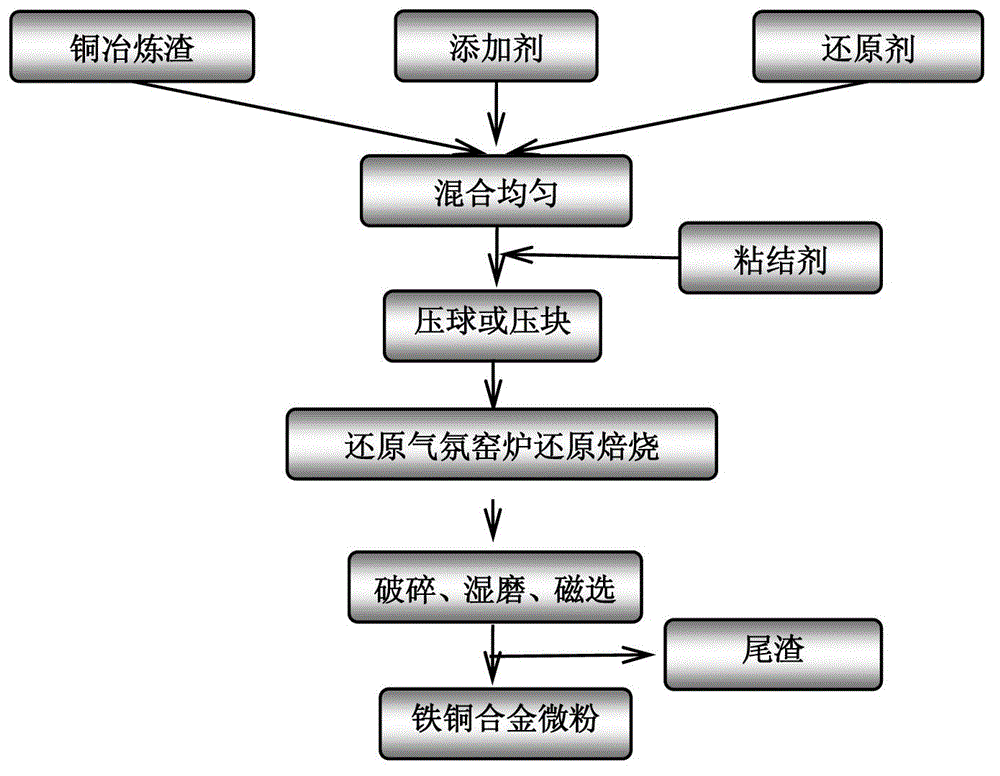
Method for rapidly reducing copper slags to produce iron-copper alloys in kiln in reducing atmosphere
ActiveCN102719676AIncrease added valueAchieve restorationProcess efficiency improvementSilicic acidReducing atmosphere
A method for rapidly reducing copper slags to produce iron-copper alloys in a kiln in a reducing atmosphere is characterized by including the steps: proportionally mixing the copper slags, reducing agents and additives, crushing or levigating the mixture to 200 meshes to obtain 20%-40% of residues on sieve; doping agglomerants and water occupying 5-20% of all materials on a dry mass basis, uniformly mixing, producing the uniformly mixed mixture to pellets with the diameters ranging from 15mm to 30mm and small cylindrical briquettes with all the heights ranging from 15mm to 30mm by a pellet press or a briquetting machine, and drying the pellets or small cylindrical briquettes; flatly laying the dried pellets or small cylindrical briquettes at the bottom of the kiln, wherein the material layer thickness ranges from 20mm to 45mm, the material layer reducing temperature ranges from 1250 DEG C to 1450 DEG C, and the reducing time is 10-40min; and subjecting the reduced pellets or the briquettes to cooling, crushing, wet grinding and wet separation so that iron-copper alloy powder with the iron recovery rate of 85%-99% is obtained. According to the method, iron in a great quantity of silicate iron in the copper slags, which cannot be separated out by the traditional technology, is extracted and turns into the iron-copper alloy micro powder with high added value so that iron and copper in the copper slags are extracted and used simultaneously, and physical and chemical heat energy in strong reducing waste gas can be completely recovered during rapid depth reduction.
Owner:TONGLING NON FERROUS METAL GROUP CORP +1
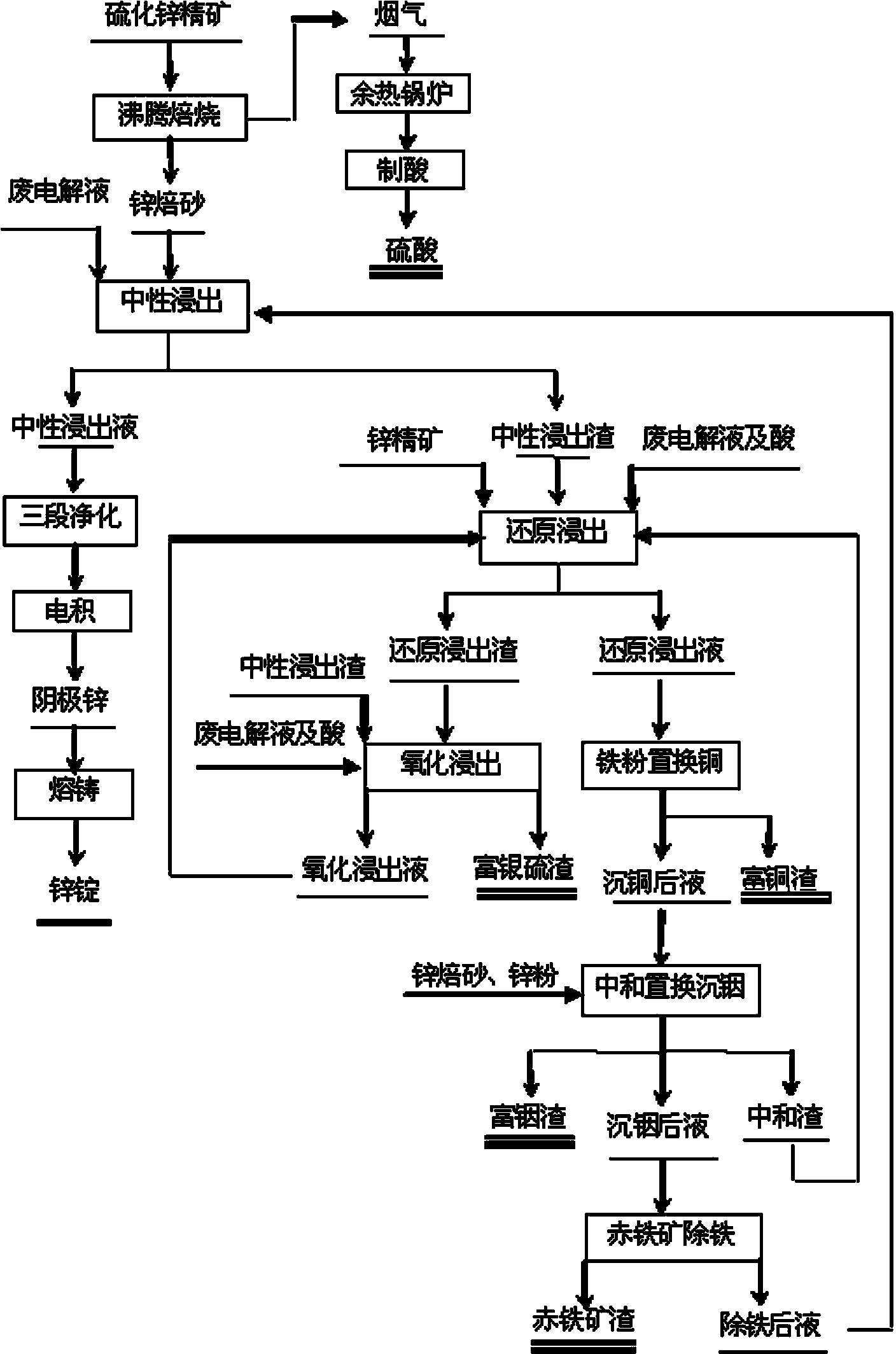
Method for individually processing high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate
ActiveCN103409622AThe process is highly targetedHigh enrichment ratioProcess efficiency improvementIndiumHydrometallurgy
The invention belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy, and particularly relates to a method for individually processing high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate. The method comprises a step of subjecting the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate to calcination in a fluidized bed combustion boiler to obtain zinc calcine; a step of subjecting the zinc calcine to neutral leaching to produce neutral leaching solution and neutral leaching residue; a step of, after the neutral leaching residue and the high-iron zinc sulfide concentrate are mixed, successively performing reduction leaching and oxidation leaching, and circulating oxidation leaching solution to the reduction leaching to produce reduction leaching solution and silver-rich sulfur residue; a step of replacing the reduction leaching solution by using iron powder to precipitate copper and to produce copper-rich slag and solution after copper precipitation; a step of subjecting the solution after copper precipitation to pre-neutralization by using the zinc calcine, and then replacing by using zinc powder to precipitate indium and to produce indium-rich slag and solution after indium precipitation; and a step of bubbling oxygen into the solution after indium precipitation, heating and removing iron to obtain iron removal solution and hematite slag. The hematite slag can be utilized as a raw material for ironmaking. The method has strong pertinence, short technological process and high metal recovery yield, and the method is clean, efficient, energy-saving and environmental friendly. Separation and comprehensive utilization of zinc, indium, copper and iron are achieved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH TECH IND SALES MANAGEMENT
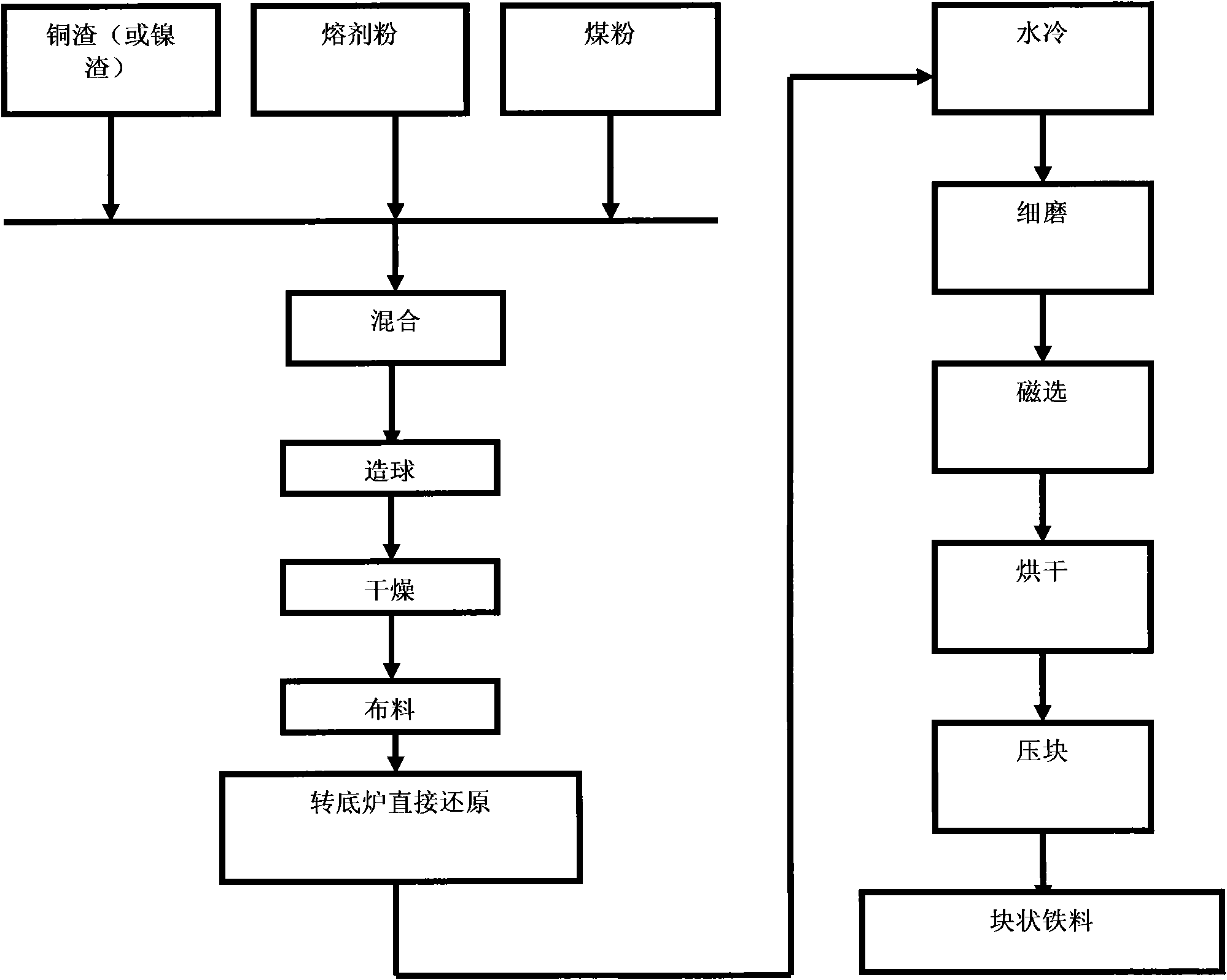
Iron making method using direct reduction-grinding screening to treat copper slag and nickel slag
The invention discloses an iron making method using direct reduction-grinding screening to treat copper slag and nickel slag, which comprises the following steps: firstly mixing a proper amount of coal, copper slag or nickel slag and a fusing agent to make balls; drying the balls; distributing the green balls in a rotary hearth furnace; heating the green balls to 1,100 to 1,350 DEG C; keeping the temperature for 15 to 40 minutes; directly delivering 600 to 1,100 degree centigrade high temperature reducing iron material into water for cooling; performing fine grinding screening; and drying the fine grinding-screened iron material with high temperature oxygen-losing waste gas and briquetting to form blocky iron materials. The method is simple in process, short in flow, high in efficiency, free from coking coal needs and suitable for treating the copper slag and the nickel slag.
Owner:吴道洪
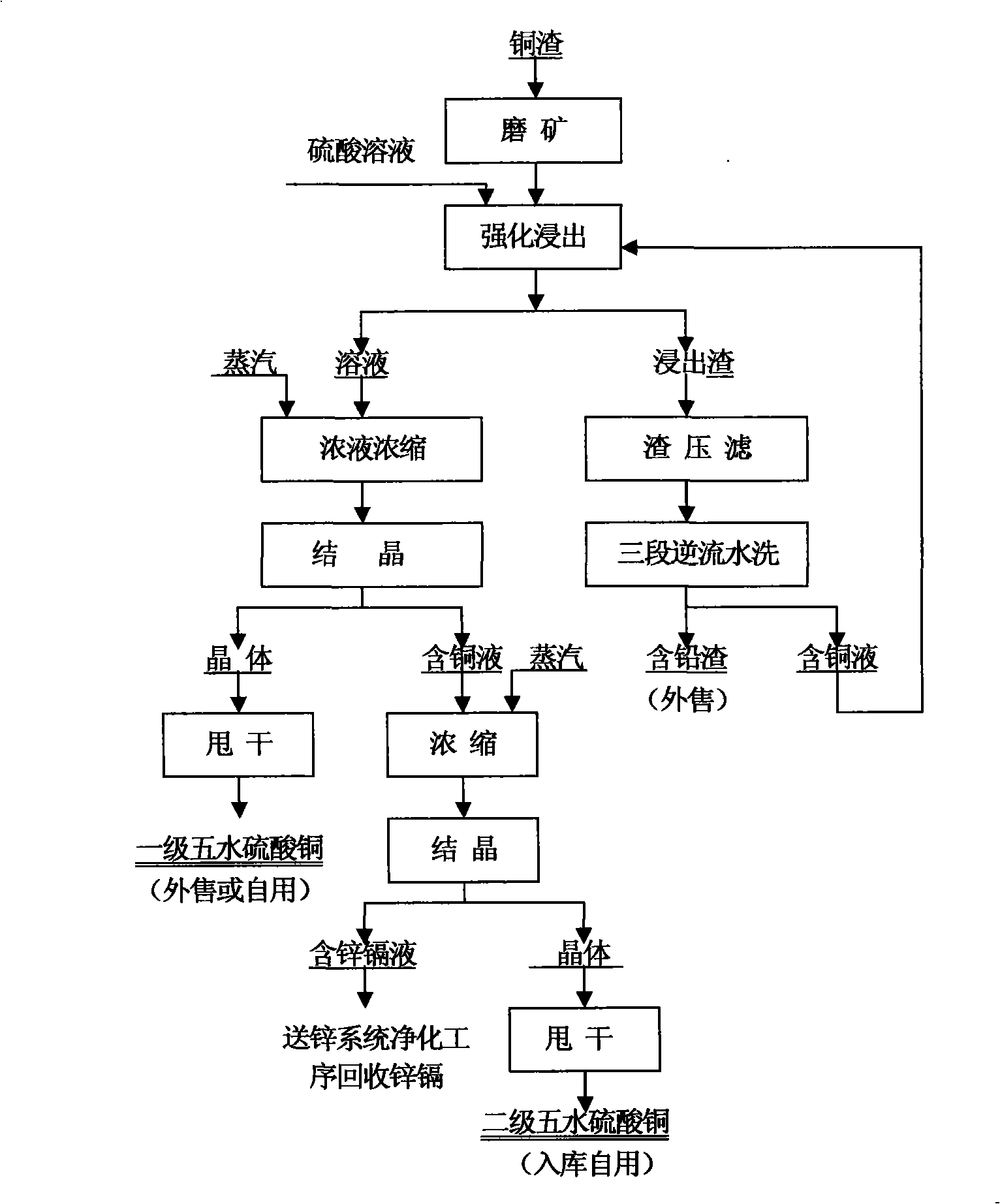
Process method for producing copper sulfate by intensified leaching of copper-containing materials
InactiveCN101538646AImprove leaching rateImprove product qualityProcess efficiency improvementHigh energyNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention relates to a process method for producing copper sulfate by intensified leaching of copper-containing materials, which has short production flow, low energy consumption, good environment and high metal recovery rate and belongs to the technical field of integrated recovery and utilization of nonferrous metal smelting slag. The process method is mainly characterized in that the copper slag is directly intensifiedly leached, and the oxidation roasting process of the copper slag is replaced by intensified leaching, thereby solving the problems of high energy consumption, great environmental pollution and long process flow of the copper slag during the oxidation roasting process. As the process method intensifies the leaching conditions, the leaching rate of copper is improved to be more than 94 percent, and the leaching time is reduced to 2 hours from the conventional 24 hours, thereby greatly improving the production efficiency of the copper sulfate, effectively reducing the production cost, reducing the production flow of the copper sulfate by one third, and greatly improving the metal recovery rate.
Owner:YUNNAN CHIHONG ZINC & GERMANIUM
Preparation method for manufacturing building board by utilizing mine tailing residue
The invention discloses a preparation method for manufacturing building board by utilizing mine tailing residue. The following raw materials are used by weight ratio: 30-75% of tailing residue and 25-70% of additive; brine with the weight percent concentration of 25-28% is utilized to stir the material into paste, the paste is placed into a mould to be rolled and moulded, and the tailing residue is one or more than one of gold slag, copper slag and ferrum slag. The invention utilizes tailing residue to produce building board, massive tailing residue is consumed, pollution harm of tailing discharge is solved, the produced building board has low cost and high strength, tailing residue can be made into various building boards by utilizing the technology, and various building section bars, stone pillar, brick and lattice prism used for historic building restoration as well as modern city sculpture, roman column pendant, external decorative wall, leisure chair, rail and sidewalk lattice brick can be cast.
Owner:王琦 +3
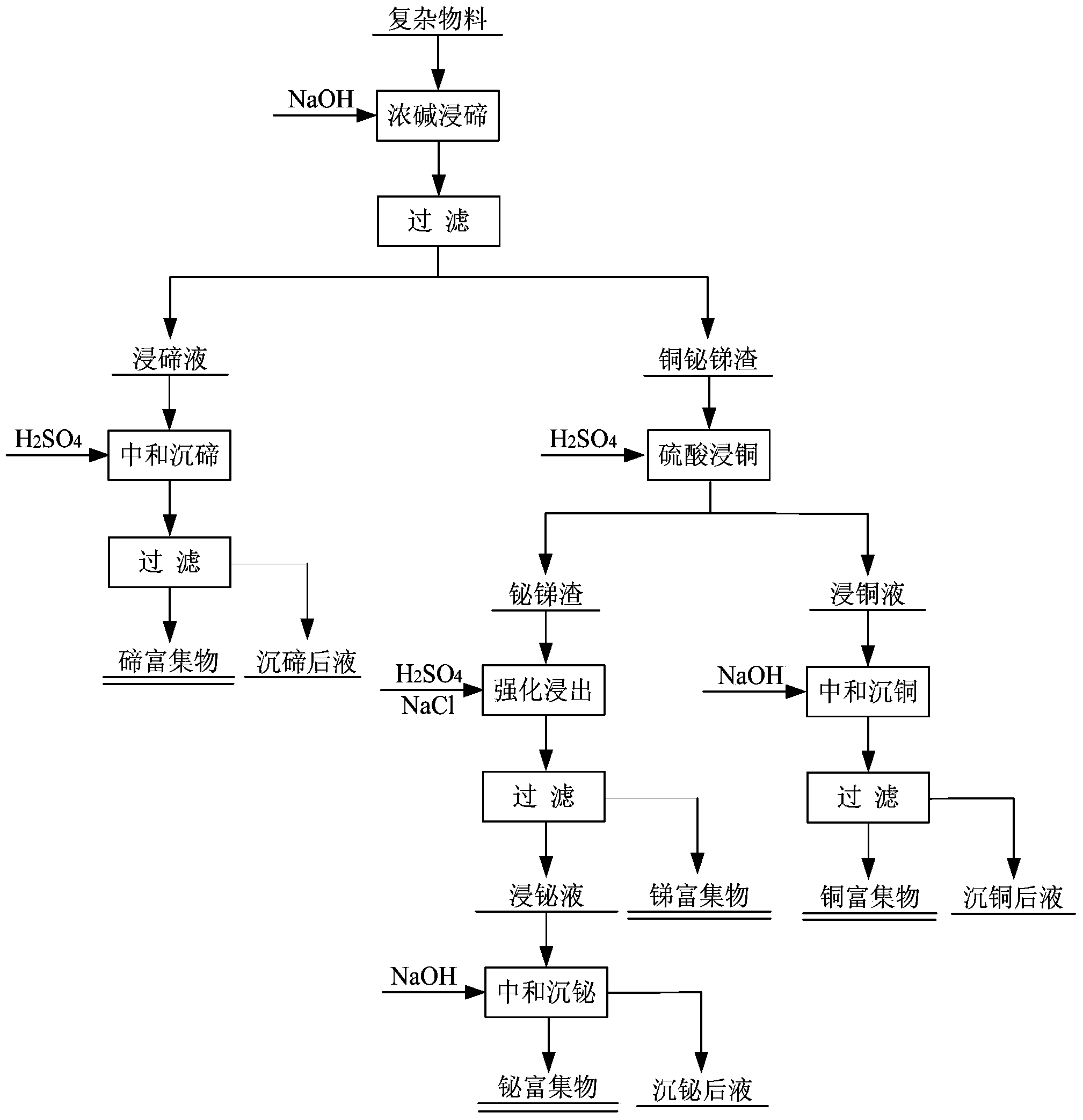
Method for recovering tellurium, bismuth, antimony, and copper from complex material
The invention aims at providing a method for recovering tellurium, bismuth, antimony, and copper from a complex material. The method comprises the steps that: the complex material is added into a sodium hydroxide solution according to a solid-liquid ratio; a temperature and a stirring time are controlled; when a reaction is finished, bismuth, antimony and copper slag and tellurium leaching liquid are obtained; the pH of the tellurium leaching liquid is regulated by adding dilute sulfuric acid; the mixture is settled and is subjected to solid-liquid separation, such that tellurium enrichment is obtained; the bismuth, antimony and copper slag is added into a dilute sulfuric acid solution according to a solid-liquid ratio; a reaction is sufficiently carried out, such that bismuth and antimony slag and copper leaching liquid are obtained; the solution temperature of the copper leaching liquid is controlled, and NaOH is added for precipitating copper; according to a solid-liquid ratio, the bismuth and antimony slag is added into a mixed solution of sulfuric acid and sodium chloride; the mixture is violently stirred, such that bismuth-antimony separation is realized; NaOH is used for regulating solution pH value and for precipitating bismuth; when the reaction is completed, bismuth enrichment and bismuth-precipitated liquid are obtained. With the technical scheme provided by the invention, tellurium, bismuth, antimony, and copper valuable metals can be comprehensively recovered from the complex material, such that waste is turned into valuable matters.
Owner:JIANGXI COPPER
Method for treating copper slag
InactiveCN105039728AAchieve recyclingReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementProduct containing ironMixed materials
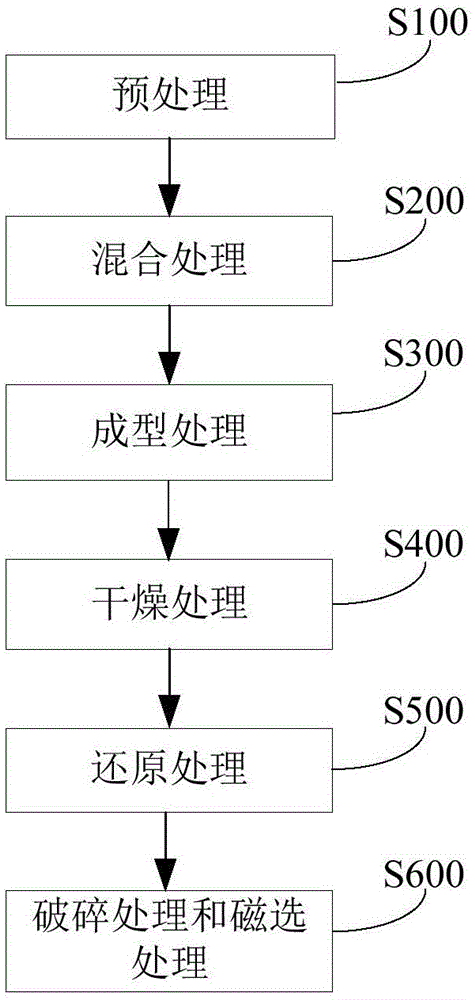
The invention discloses a method for treating copper slag. The method includes the steps that (1) the copper slag, a reducing agent and additives are pre-treated respectively; (2) the pre-treated copper slag, the pre-treated reducing agent and the pre-treated additives are mixed so that a mixed material can be obtained; (3) the mixed material is formed so that copper slag pellets can be obtained; (4) the copper slag pellets are dried so that the dried copper slag pellets can be obtained; (5) at the temperature of 1,350-1,550 DEG C, the dried copper slag pellets are reduced so that a solid reduced product containing iron-copper alloy particles and smoke containing lead and zinc can be obtained; and (6) the solid reduced product containing the iron-copper alloy particles is broken and magnetically separated so that the iron-copper alloy particles and tailings can be obtained respectively. According to the method, multiple metal elements in the copper slag can be comprehensively recycled, and the higher recovery rate is achieved.
Owner:SHENWU TECH GRP CO LTD
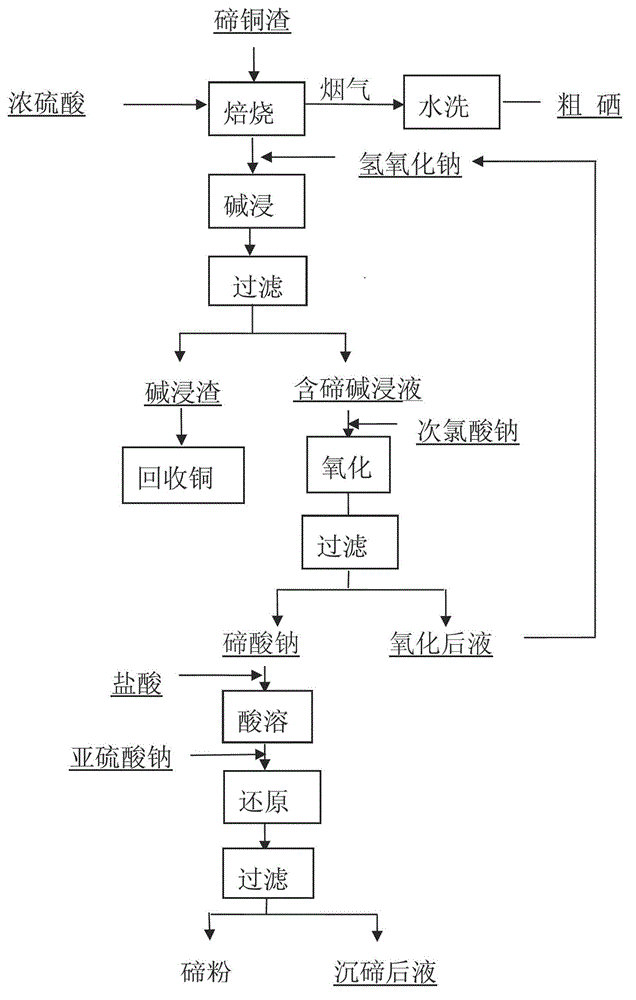
Method for extracting tellurium from tellurium copper slags
ActiveCN102745657AEasy to separateAchieve separationProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumAcid dissolutionCalcination
The invention provides a method for extracting tellurium from tellurium copper slags. The method includes the following steps of (1) sulfating calcination at a high temperature, grinding the tellurium copper slags, mixing ground tellurium copper slags with a concentrated sulfuric acid to calcine, enabling the mass ratio between the concentrated sulfuric acid and the tellurium copper slags to be (1.2-1.5):1, maintaining the calcination temperature in a range from 450 DEG C to 600 DEG C and maintaining the calcination time in a range from 3 hours to 5 hours; (2) alkaline leaching to separate the tellurium, leaching obtained calcination slags by a sodium hydroxide alkaline liquor, and then filtering to obtain a tellurium containing alkali leaching liquid and alkali leaching slags; (3) oxidizing the alkali leaching liquid, oxidizing the tellurium containing alkali leaching liquid by sodium hypochlorite of an oxidant and then filtering to obtain sodium tellurate filtered slags; and (4) acid dissolution reduction, dissolving the sodium tellurate filtered slags by a chloridion containing acidic system, adding a reducing agent to achieve reduction and then filtering to obtain tellurium powders. According to the method for extracting the tellurium from the tellurium copper slags, a complete separation of copper, selenium and tellurium can be fully achieved, a comprehensive recovery of the copper, selenium and tellurium can be achieved, the technological process is simple, tellurium dioxide of an intermediate product is not required, the tellurium powders with a high purity can be directly produced, and the tellurium powders can serve as raw materials of 6N high purity tellurium.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
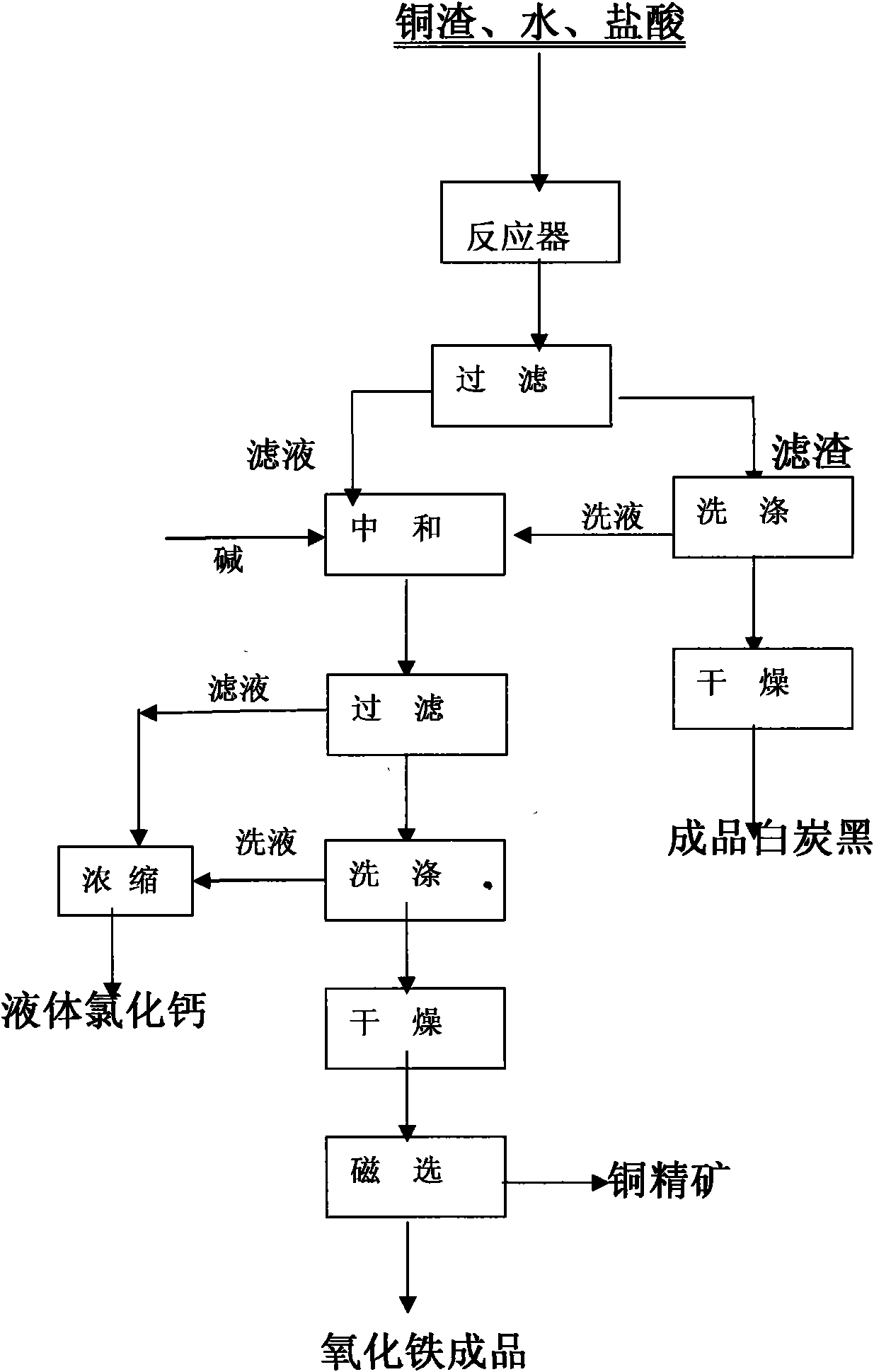
Method for comprehensively recovering Fe, Cu and Si from copper smelting slag
InactiveCN101555551AImprove resource utilizationImprove product added valueSilicaCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesSilicon dioxideMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering iron, copper and silicon dioxide from copper smelting slag. The method takes copper smelting slag as a raw material, and comprehensively recovers Fe, Cu and Si in copper slag by adopting wet chemistry metallurgical technology. A muriatic acid and an inorganic acid are mainly adopted for leaching the copper smelting slag, the leaching acid concentration, the solid to liquid ratio, the leaching temperature and the leaching time are selected according to the quality requirement of silicon dioxide products under certain conditions, and silicon dioxide is firstly separated through filtering and drying to prepare silica pigment; the leaching filtered liquid is counteracted, settled, filtered, dried and ground, and ferric oxide phase and copper-bearing phase are selectively separated by adopting a conventional mineral processing method.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for treating arsenic-containing waste copper slag
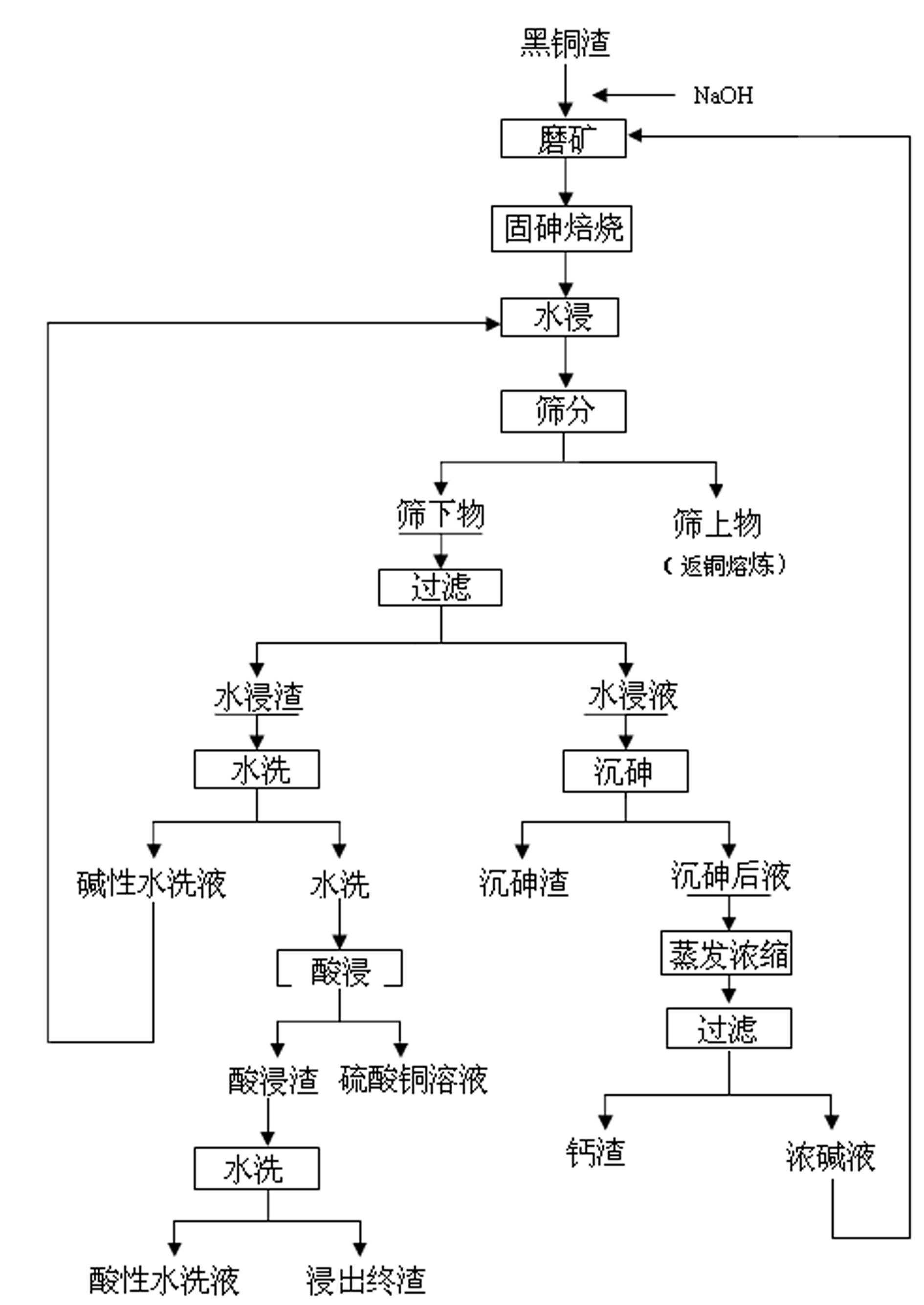
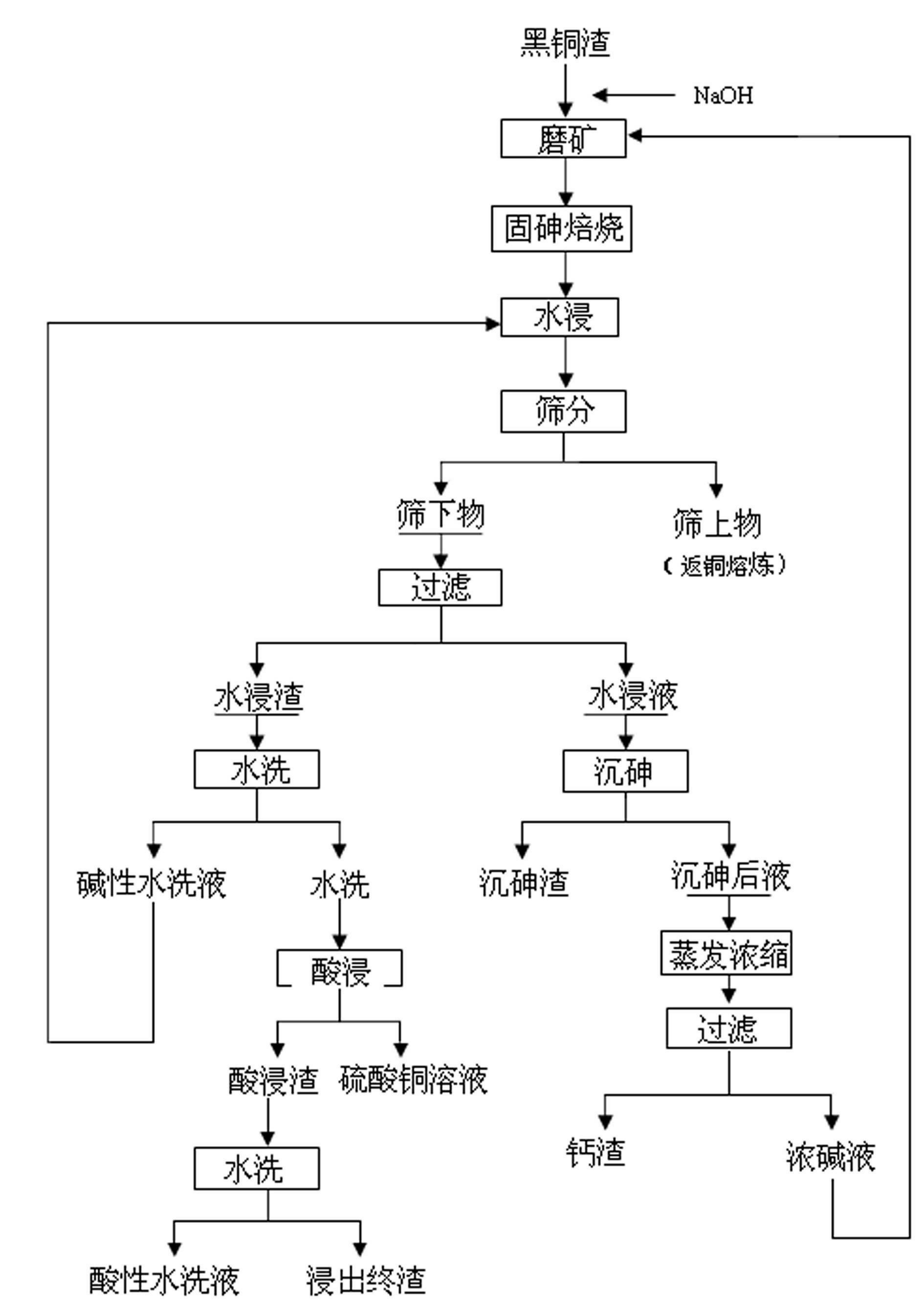
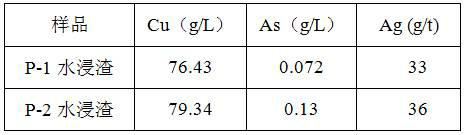
InactiveCN102634672ASolve the open circuit problemHigh enrichment ratioProcess efficiency improvementArsenateEnvironmental engineering
The invention provides a method for treating arsenic-containing waste copper slag. The method comprises the following steps of: adding alkali and arsenic fixation roasting on the arsenic-containing waste copper slag from a copper electrolysis purification procedure to convert the arsenic into low-toxicity, water-soluble and nonvolatile arsenate, leaching the roasting slag into water to remove the arsenic, recovering copper and enriching antimony bismuth silver by virtue of acid leaching, and embedding calcium arsenate sediment converted from the arsenic in the water leaching solution; and comprehensively recovering valued metals such as copper, silver, antimony and bismuth in the black copper slag. The method is a safe and effective wet smelting method for recovering the valued metals in the black copper slag, and the arsenic and the copper are leached separately; the recovery rate of the copper in the black copper slag reaches 99.6 percent, and the removal rate of the arsenic reaches over 98 percent; over 95 percent of antimony and over 98 percent of bismuth enter the slag, and over 98 percent of silver also enters the acid leaching slag by adding trace chlorine radicals during acid leaching, so that the antimony, the bismuth and the silver are comprehensively recovered; and the method has the advantages of low equipment investment, short flow, low running cost and safe and reliable operating environment.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
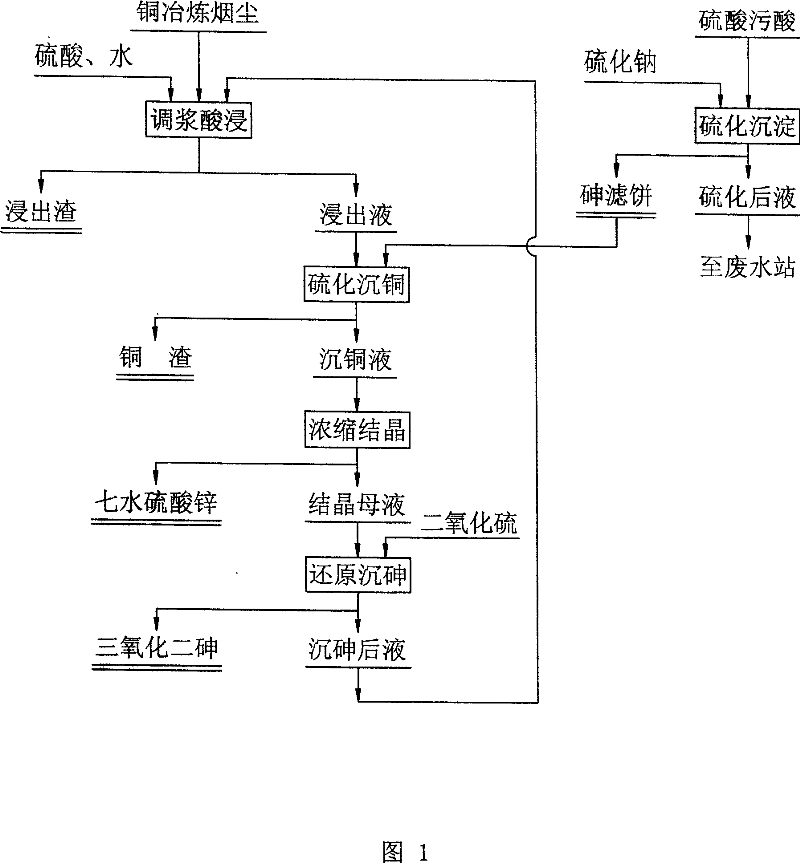
Method for treating arsenic pollution of copper smelt industry
InactiveCN101037725AAchieve separationProcess efficiency improvementWater/sewage treatment by oxidationArsenic pollutionZINC SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE
The invention provides a method for controling arsenic pollution in the copper metallurgy industry, is characterized in that arsenic acid filtering case is added as vulcanized agent in sulphuric acid extract of copper metallurgy smoke to precipitate copper, copper slag and the solution containing copper are obtain by separation; the solution containing copper is contracted to 60-100 g / l of arsenical concentration and then cooled to the room temperature, heptahydrate zinc sulphate and crystal mother liquor are obtained after separation; sulfur dioxide is added to crystal mother liquor, thereby arsenic is dissolved out in the form of arsenic trioxide, arsenic trioxide and the solution after precipitating arsenic are obtained after separation, the solution after precipitating arsenic is back to smoke extract. The separature of the main component such as copper, arsenic, zinc and cadmium is performed in sulphuric acid extract of copper metallurgy smoke and arsenic acid filtering case with an objective for controling arsenic pollution economically and effectively, while provided with an advantage for further recycling valent metal synthetically.
Owner:朱永文
Method for producing low-sulfur molten iron in one step by smelting and reducing copper slag
InactiveCN101824505ALower oxygen potentialReduce sulfur contentFluidised-bed furnacesMelting tankCyclone
The invention discloses a method for producing low-sulfur molten iron in one step by melting and reducing copper slag. The method is characterized in that the method includes the following processing steps that: the high-temperature molten copper slag is first reduced by reducing agent in a high-temperature reduction furnace, wherein, when the reduction reaction of iron is nearly finished, a certain amount of additive, which is theoretically calculated, is added in a melting bath based on the existing slag system in the reduction furnace, a jet gun is inserted into a slag-iron interface to blow carbon monoxide into the melting bath when the additive is completely molten, the blowing time is 30min to 40min, and desulphurization reaction is almost finished. The melting bath is kept still, and when slag and iron are completely separated, the high-temperature low-sulfur molten iron and the slag are respectively discharged out of a tap hole and a slag hole. In addition, after high-temperature flue gas passes through a secondary combustion chamber, a residual heat boiler recovers residual heat from the flue gas, dust is collected from the flue gas by cyclone, and the flue gas is washed. By sufficiently utilizing the high desulphurization of the refined slag and blowing the carbon monoxide, the invention solves the defect that the content of sulfur in the molten iron produced by melting and reducing the copper slag for ironmaking is high; the processing flow is short, the emission of pollutant is less, and moreover, the applicability is high.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing low-copper molten iron by mixed melting reduction of copper slag and iron ore
InactiveCN101886154AHigh copper concentrationOvercome the disadvantage of higher concentrationFluidised-bed furnacesGranularityCoal
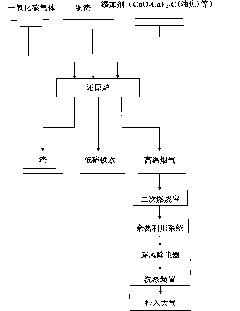
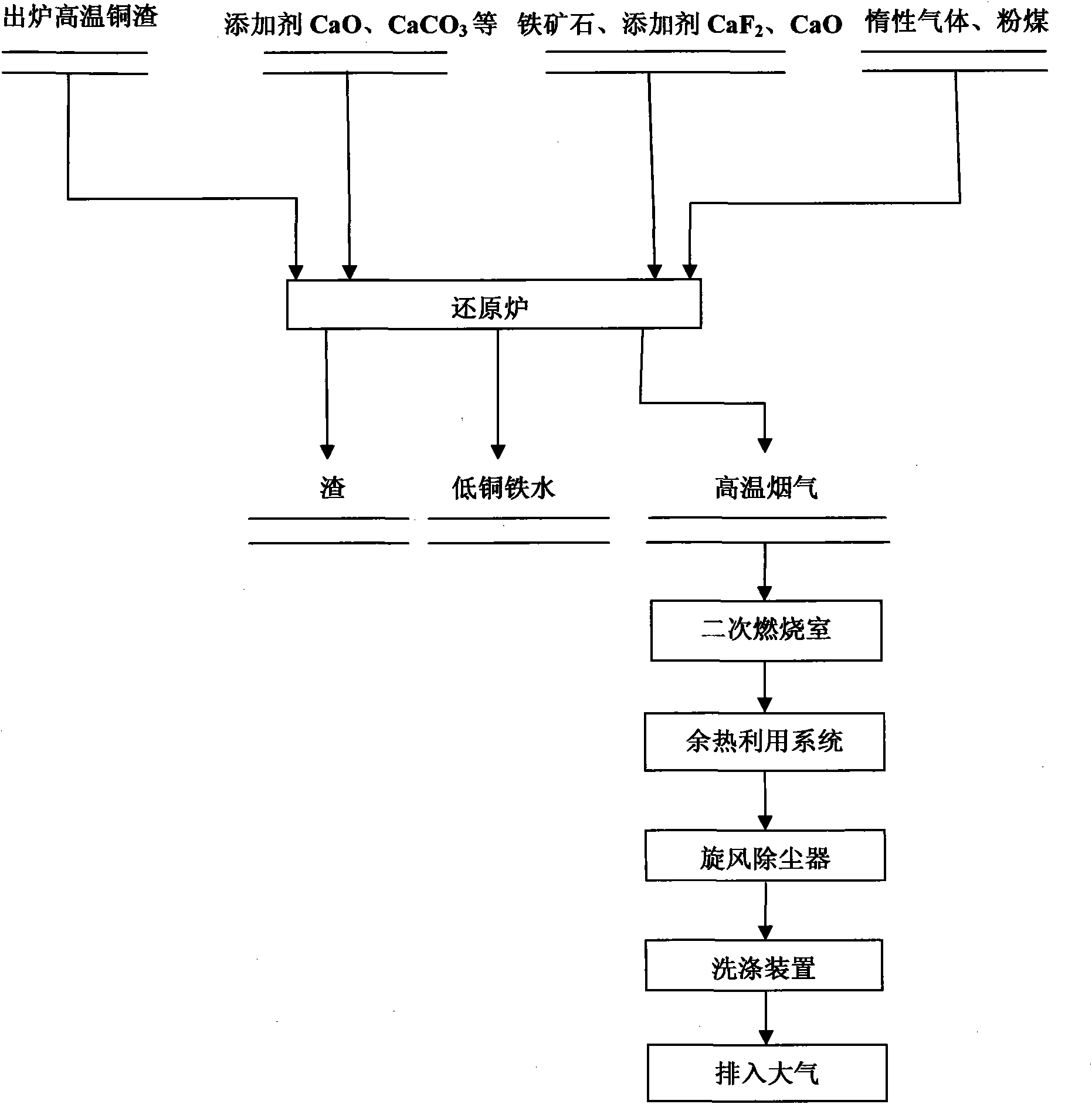
The invention discloses a method for preparing low-copper molten iron by mixed melting reduction of copper slag and iron ore. The method comprises the following processes of: putting the high-temperature molten copper slag into a reduction furnace, grinding a certain amount of slag forming agent CaO, CaCO3 and the like into certain granularity, adding the ground slag forming agent into the reduction furnace, fully melting the mixture, and standing the molten pool for 10 minutes; grinding the iron ore, quantitative additive CaF2 and CaO into certain granularity respectively, then uniformly mixing the iron ore, the CaF2 and the CaO, adding the mixture into the reduction furnace, raising the temperature of the furnace to between 1,600 and 1,700 DEG C, fully melting the materials in the furnace, and then standing the molten pool for 20 minutes; and crushing a coal reducing agent to certain granularity, spraying the crushed coal reducing agent to the molten pool by using inert gas as carrier gas through a spray gun, and performing mixed melting reduction reaction of the copper slag and the iron ore. The method greatly reduces the defect of high copper in the molten iron obtained by single copper slag melting reduction by fully using the mutual coupling effect of the components among the copper slag, the iron ore and the additive and the diluting effect of the molten iron obtained by iron ore reduction on high copper content of the molten iron obtained by copper slag reduction, and has wide applicability.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mine whole-tailing alkali binding material bond filling material
The invention discloses a mine whole-tailing alkali binding material bond filling material, which is formed by mixing an alkali exciting agent, industrial waste residues containing glass bodies, cement, whole tailings and water, a mass ratio of the alkali exciting agent, the industrial waste residues containing glass bodies, the cement, the whole tailings to water is (10-30): (10-70): (0-20): (880-980): (150-350). According to the invention, the alkali exciting agent enables silicon aluminum in industrial waste residue powder containing glass bodies and natural silicon aluminum mineral powder in the whole tailings to be subjected to depolymerization, migration and repolymerization, so that the filling body strength can be greatly improved, then the mixing amount of the cement is substantially reduced or the requirement of the mine filling material performance can be met without mixing cement, therefore, the cost of the filling material is lowered; and meanwhile, the industrial waste residues containing the glass bodies such as granulated blast furnace slag powder, steel slag powder, copper slag powder, coal ash and the like can be fully utilized, so that the waste materials are changed into things of value, the waste residue pollution is reduced, and the environment protection is facilitated.
Owner:郑州工大高新材料科技有限公司
Method for directly drilling blind hole by laser using carbon dioxide
The invention provides a method used for directly drilling blind holes by using CO2 laser; two or more different diaphragms are used to carry out direct laser boring, which is also called dual-diaphragm or multi-diaphragm mode; the method comprises the steps: 1) according to the diameter of the hole to be processed, a diaphragm is selected, the dimension of laser pulse dot is controlled, a pulse is used for ablating the copper layer on the surface of the processing plate so as to lead the copper layer to form an opening; 2) another diaphragm is selected, the dimension of the laser pulse dot is changed and less than that of the laser pulse dot in the step 1); one or more pulses are used to ablate the medium layer below the opened copper layer on the surface of the processing plate, thus forming a blind hole on the processing plate. The method can generate good laser hole shape, reduces copper slag at the circumference of hole, increases the taper of the hole, avoids the defects in electroplating process, is especially applicable to electroplating hole filling process after boring, and leads the electroplating liquid medicine easy to be replaced and the fovea to be reduced; furthermore, after electroplating, no hollow defects are generated, the preparation process is simple and the cost is low.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEADVILLE SCI & TECH +1
Metallurgical process for recovering metal copper, lead, zinc and tin from copper refining waste slag
ActiveCN102409180APhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSulfate zincElectrolysis
The invention discloses a metallurgical process for recovering metal copper, lead, zinc and tin from copper refining waste slag, which uses waste liquid of zinc electrolysis with sulfuric acid or waste liquid of zinc electrolysis to perform the acid leaching; more than 95% of the zinc and copper are in the solution, the Fe 2+ in the solution is less than or equal to 1.5g / L; then the copper slag is used for removing chlorine; when the Cl- in the solution is less than or equal to 1.0g / L, the solution is sent to a copper electro-deposition; the electro-deposition decopperization can produce copper piece or copper powder; the decopperization neutralization is to add calcine or zinc oxide for neutralizing acid when the Cu2+ in the solution is less than or equal to 1.0g / L; lime is used for adjusting the pH value to 5.2-5.4; after purifying and removing residue of the zinc sulfate solution, the solution is sent to the zinc electro-deposition for producing zinc piece; the lean and tin pyrometallurgical purification is that, after more than 98% of lead and tin is sent to the acid leaching residue, the material of the acid leaching residue is balled and sent to a smelting furnace, so as to produce lead-tin alloy; the lead-tin alloy is directly sent to a vacuum fractionation furnace for purifying the lead and tin product; sulfur dioxide in the tail gas is absorbed by ammonia, so as to obtain ammonium sulphate product. The process is to extract copper and zinc joint wet process and to purify lead and tin by pyrometallurgical method; the process flow is effectively shortened, the metalrecovery rate and the resource utilization rate are both largely increased, and there is no secondary pollution in the process.
Owner:CHENZHOU FENGYUE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
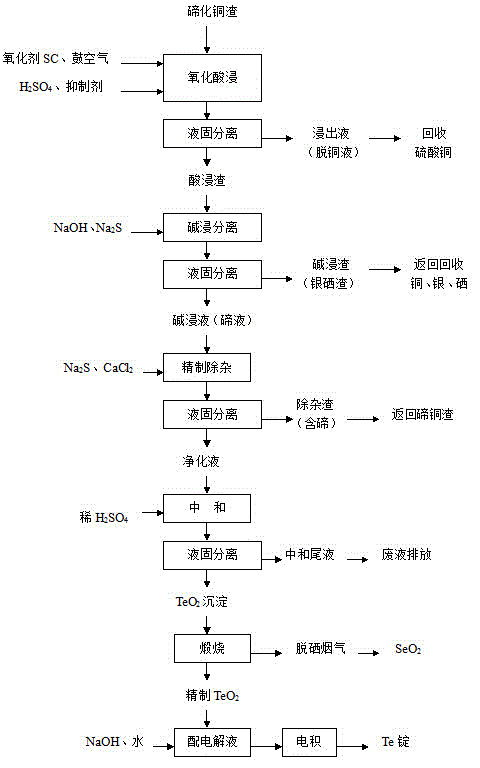
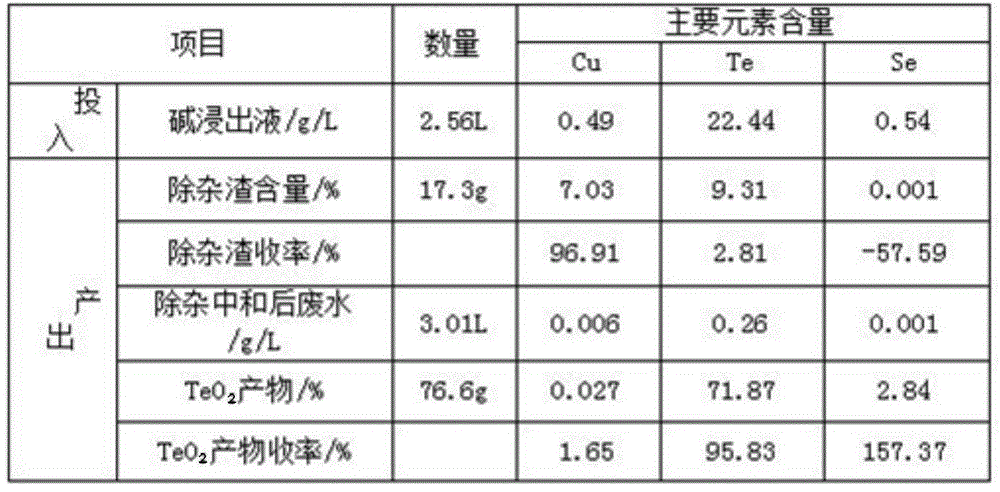
Method for comprehensively recycling silver, selenium, tellurium and copper from telluride copper slag
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recycling silver, selenium, tellurium and copper from telluride copper slag. The method comprises the following steps of (1), oxidizing acid leaching, wherein the telluride copper slag is added into a sulfuric acid solution containing an oxidizing agent to be heated and stirred so as to be leached, after filtering, copper sulfate leaching liquid and acidic leaching residues are obtained, and the leaching liquid is conveyed to a furnace for copper recycling; and (2) alkali leaching separation, wherein the acidic leaching residues are added into sodium hydroxide solutions to be leached, sodium tellurite solutions and basic leached residues are obtained, the basic leached residues are sent to the KALDO furnace for smelting, so that the silver and the selenium are recycled, and after purification, tellurium deposition, forging and electrolysis of the alkali leaching liquid, refined tellurium is obtained. According to the method, the recycling rate of the silver, the selenium, the tellurium and the copper is high, the silver, the selenium, the tellurium and the copper are not lost, the concentration ratio is high, the silver, the selenium, the tellurium and the copper can be separated from other impurities well, the pollution to the environment is small, the technology is simple, and needed equipment cost is low.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
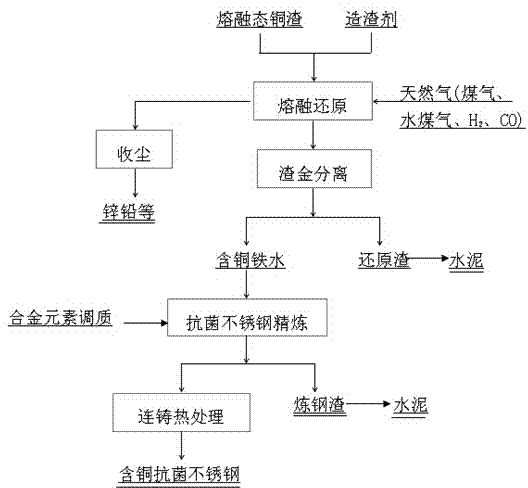
Method for directly smelting copper-bearing antibacterial stainless steel by utilizing copper slag for reducing molten iron
ActiveCN104120351AAchieve high valueRealize slag-free cleaning processSteelmakingRefining (metallurgy)
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy, and particularly relates to a method for directly smelting copper-bearing antibacterial stainless steel by utilizing copper slag for reducing molten iron. According to the method, high-temperature molten-state copper slag is directly transferred and injected into a high-temperature reduction furnace, oxygen is sprayed and blown into the furnace to perform oxidation impurity removing pretreatment on the molten copper slag, then, slagging constituents are added in the furnace, inert gas and natural gas are sprayed and blown into the furnace for smelting reduction to obtain copper-bearing molten iron, the copper-bearing molten iron is conveyed to the steelmaking process, copper-bearing mother steel liquor is obtained, continuous casting is performed on the molten steel mother liquor obtained by refining to obtain a steel billet, hot rolling and annealing treatment are performed on the steel billet, and the antibacterial stainless steel is obtained. According to the method, the production cost of the antibacterial stainless steel is greatly reduced, and meanwhile the comprehensive utilization added value of valuable elements of the copper slag is greatly improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
A kind of treatment method of waste copper sulfate electrolyte
InactiveCN102260879AReduce copper contentImprove direct yieldPhotography auxillary processesWater contaminantsElectrolysisBismuth
A method for treating waste copper sulfate electrolyte relates to a method for removing copper and removing impurities such as arsenic, antimony and bismuth from waste copper sulfate electrolyte in a copper electrolysis process. It is characterized in that the steps of its treatment process include: (1) electrowinning and decoppering the waste copper sulfate electrolyte to obtain standard cathode copper; (2) performing deep electrowinning and decoppering the solution after step (1) decoppering; 3) Electrodeposition and removal of impurities from the solution after deep electrowinning copper removal in step (2). The method of the invention can efficiently separate copper from waste copper sulfate electrolyte, produce standard cathode copper, and can effectively remove impurities such as arsenic, antimony and bismuth. Compared with the traditional induced decopper method, it can greatly reduce the amount of black copper slag, reduce the copper content in black copper slag, increase the direct recovery rate of copper, reduce the production cost of copper, and significantly improve the economic and environmental benefits of the enterprise.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Method for treating waste copper slag
ActiveCN102994765AEfficient recyclingEliminate and reduce negative impactsSolid waste managementProcess efficiency improvementBrickEconomic benefits
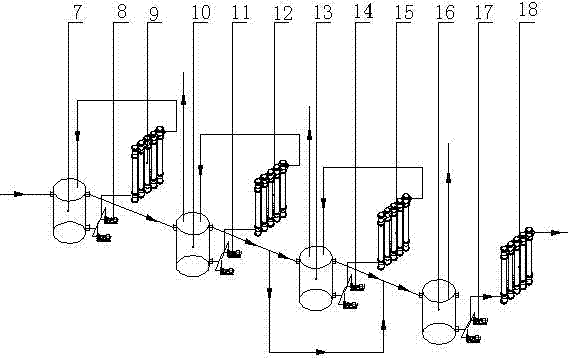
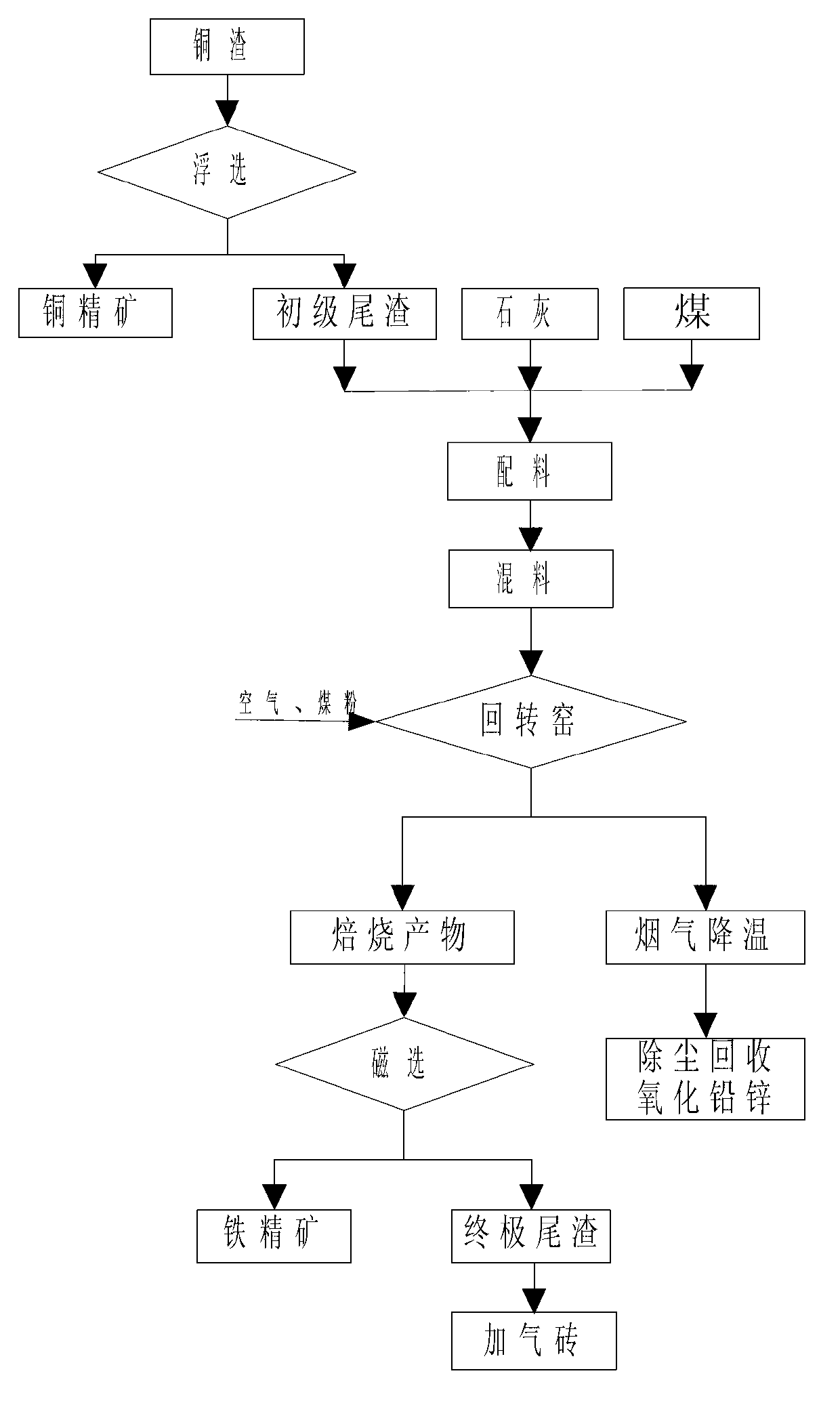
The invention provides a method for treating waste copper slag. The method is characterized by respectively obtaining copper concentrate, ferrum concentrate and waste materials containing lead and zinc smoke and capable of being used for air-entrapping bricks according to the process route of floatation, reduction-oxidation roasting of a rotary kiln and magnetic separation in sequence; according to the process scheme, the method comprises the following steps: a. floating 90% of 200-mesh waste copper slag with fine grinding size of smaller than 74mu m to obtain the copper concentrate and primary tailings; b. conducting reduction-oxidation roasting to the primary tailings in the rotary kiln, recovering lead and zinc through smoke, conducting magnetic separation on the roasted product to obtain the ferrum concentrate and the final tailings; and c. taking the final tailings as raw materials of aerated concrete products to produce air-entrapping bricks. The method has the advantages of being clean, environment-friendly and zero-emission in waste copper slag treatment process, not only realizing the effective recovery of resources, and reducing environmental pollution, but also obtaining good economic benefits.
Owner:北京中冶设备研究设计总院有限公司
Method for extracting iron from copper smelting waste residue
The invention relates to a method for extracting iron from copper smelting waste residue. The method comprises the following steps: pulverizing copper slag, a reductant which is a mixture comprising one or more of anthracite, graphite, petroleum coke and coke, calcium oxide or calcium carbonate into a certain granularity, fully mixing the materials, carrying out mineralogical reconstruction and carbothermal reduction under high temperature to convert fayalite in the residue into iron oxide and then reduce the iron oxide into iron, and recovering the iron by magnetic separation, wherein, nonmagnetic products can be taken as raw materials for burning cement.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Stabilizing treatment method for sulfide arsenic-removed dregs
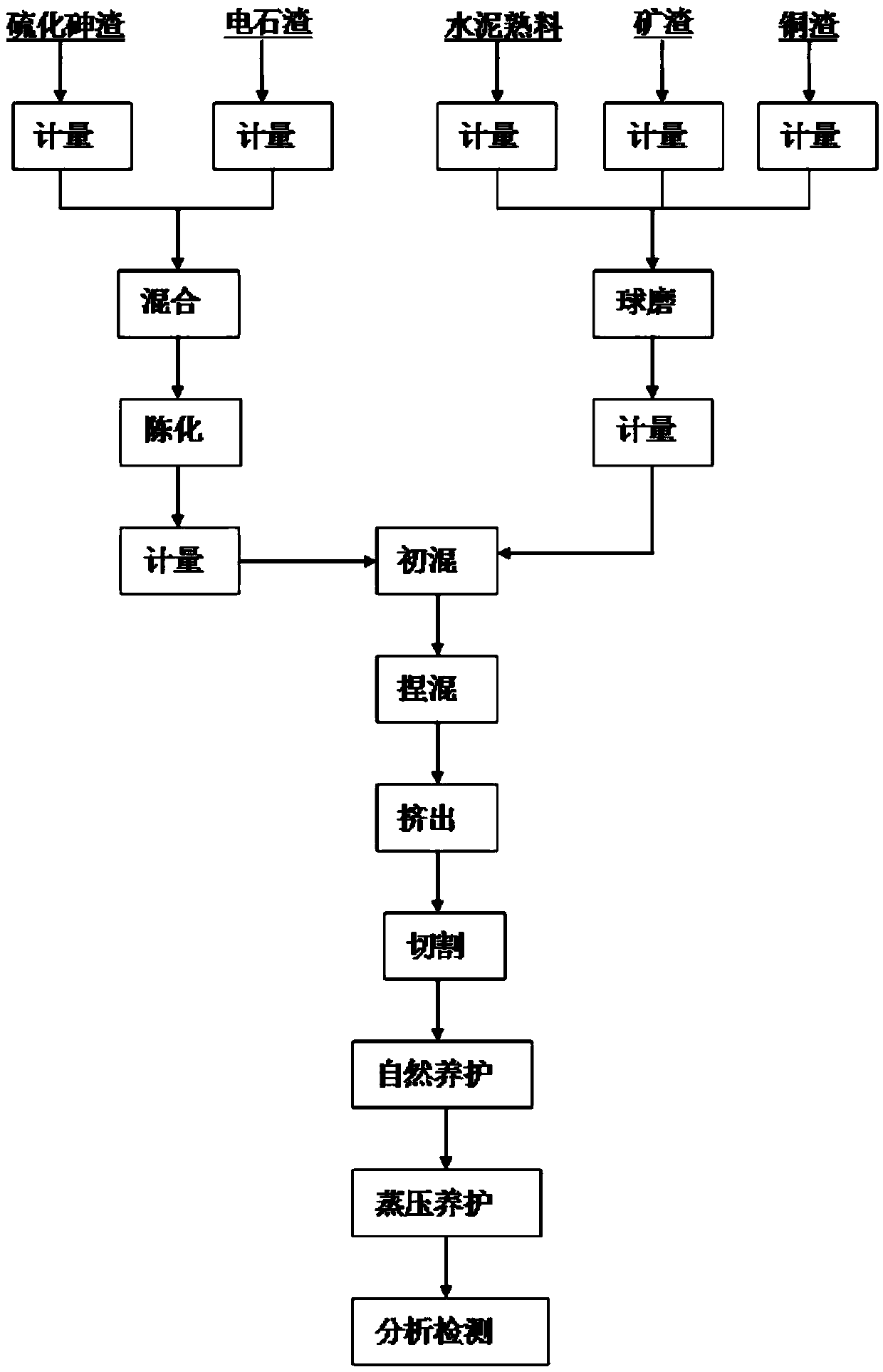
The invention discloses a stabilizing treatment method for sulfide arsenic-removed dregs. The stabilizing treatment method comprises the following steps: mixing cement clinker, mineral slag and copper slag in a ratio of parts by mass being (25-30) to (60-70) to (5-10), carrying out ball-milling on the materials, and enabling the materials to pass through a 180-mesh square hole sieve with weight of screen residues being 5wt%, thereby preparing a gel material; mixing arsenic sulfide slag and carbide slag in a dry-weight mass ratio being 1 to (1.0-1.2), and ageing and pre-treating the arsenic sulfide slag and carbide slag for 24 hours; preparing the pre-treated arsenic sulfide slag and the self-made gel material in a ratio of parts by mass being (25-35) to (65-75), adding calcium chloride with gel material amount being 0.4-0.5wt% or a mixture of calcium chloride and sodium chloride as an additive, controlling moisture content of materials to be 20-22wt%, mixing the materials on a horizontal type stirrer to macroscopically homogenize the materials, putting the homogenized materials into a continuous kneading extruder to forcibly mix, extrude, cut, naturally cure and carry out steam curing for 10 hours under pressure of 0.8-1.0MPa, and carrying out a toxicity leaching test on a solidified body according to GB5085.3-2007 to enable the solidified object to meet stock-piling or filling requirements.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for purifying zinc sulfide solution
InactiveCN103194600AEfficient recyclingReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisAntimony trioxide
A method for purifying zinc sulfide solution comprises the following steps of: firstly, removing suspended solids from zinc sulfide solution by using a sean filter at a normal temperature; secondly, adding zinc powder by 120% of solution copper metal weight, stirring for 90 minutes at normal temperature for removing copper, and filtering; thirdly, adding zinc powder by 120-150% of solution cadmium metal weight, stirring for 60 minutes at a normal temperature for removing cadmium, and filtering; fourthly, increasing the temperature of the solution to the range of 82-94 DEG C, adding zinc powder in a proportion of 1 g / L of solution, and simultaneously adding some antimonous oxide, stirring for 50-70 minutes, removing cobalt and nickel impurities, and filtering; and finally, removing few suspended solids from the filtered solution by the sean filter. The method provided by the invention is capable of directly producing copper slag and sponge cadmium product; and the solution is capable of meeting the quality standard requirements of fresh electrolyte even though no extra zinc powder is added to the solution to remove residual cadmium; therefore, the consumption of the zinc powder is effectively reduced.
Owner:吴鋆
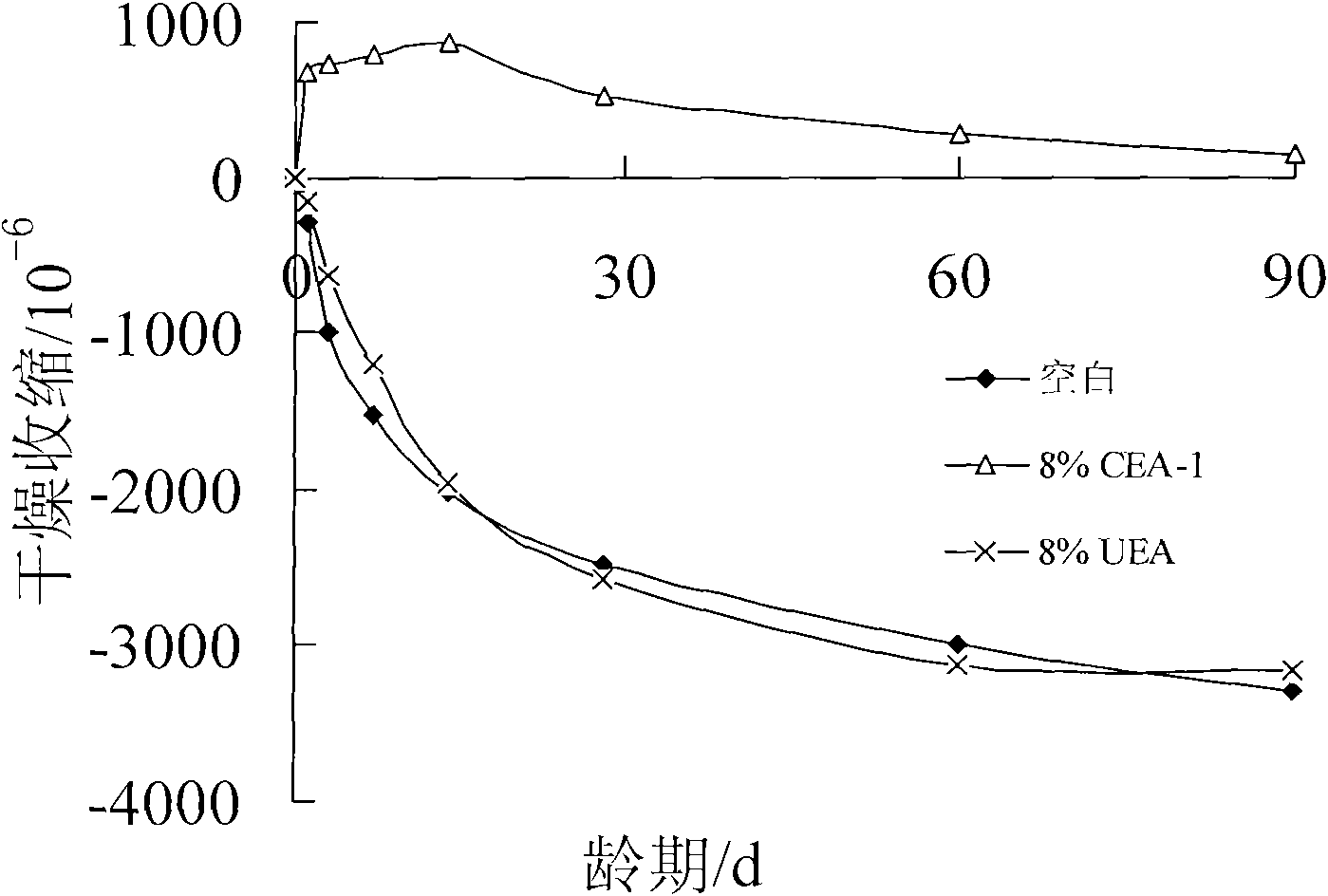
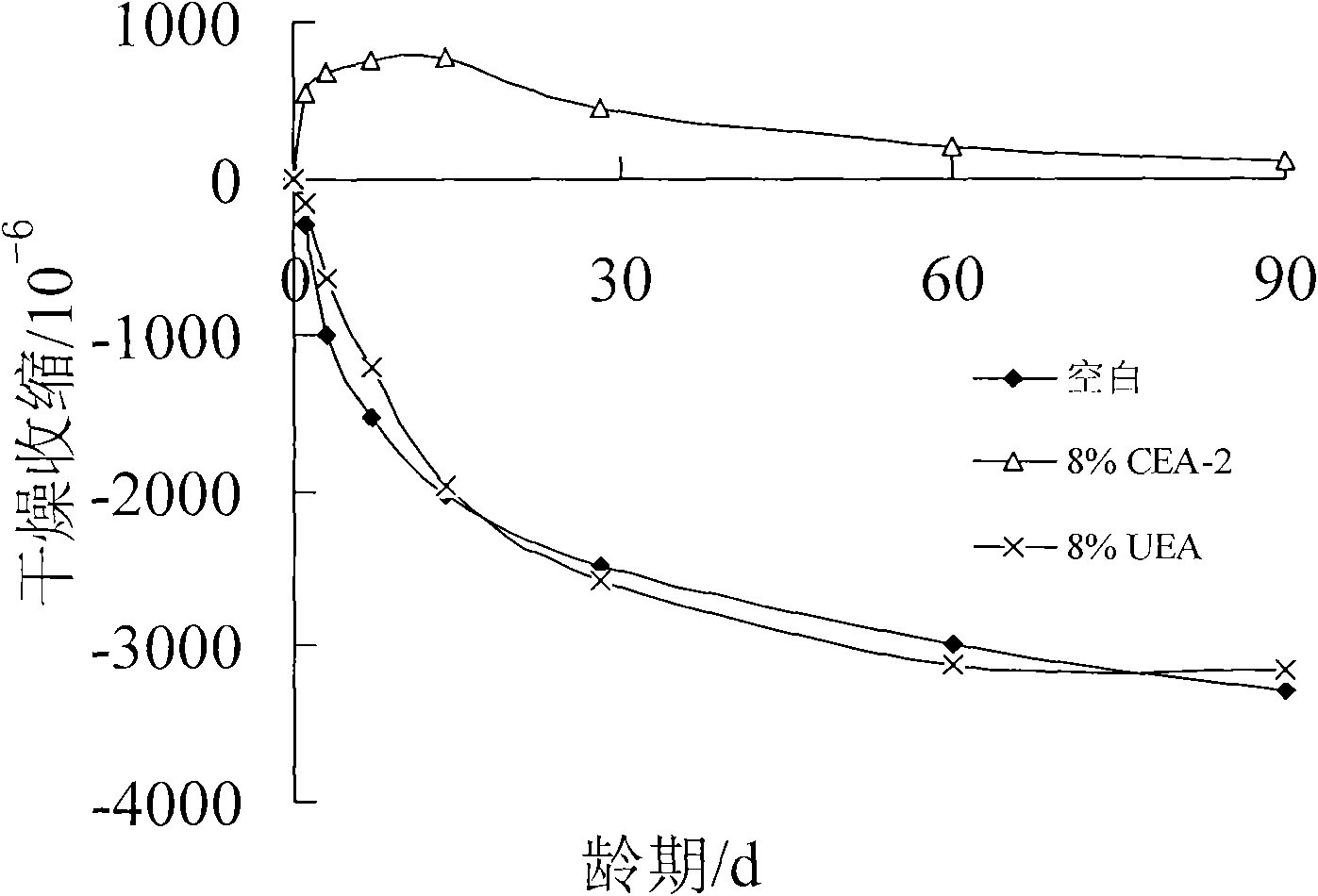
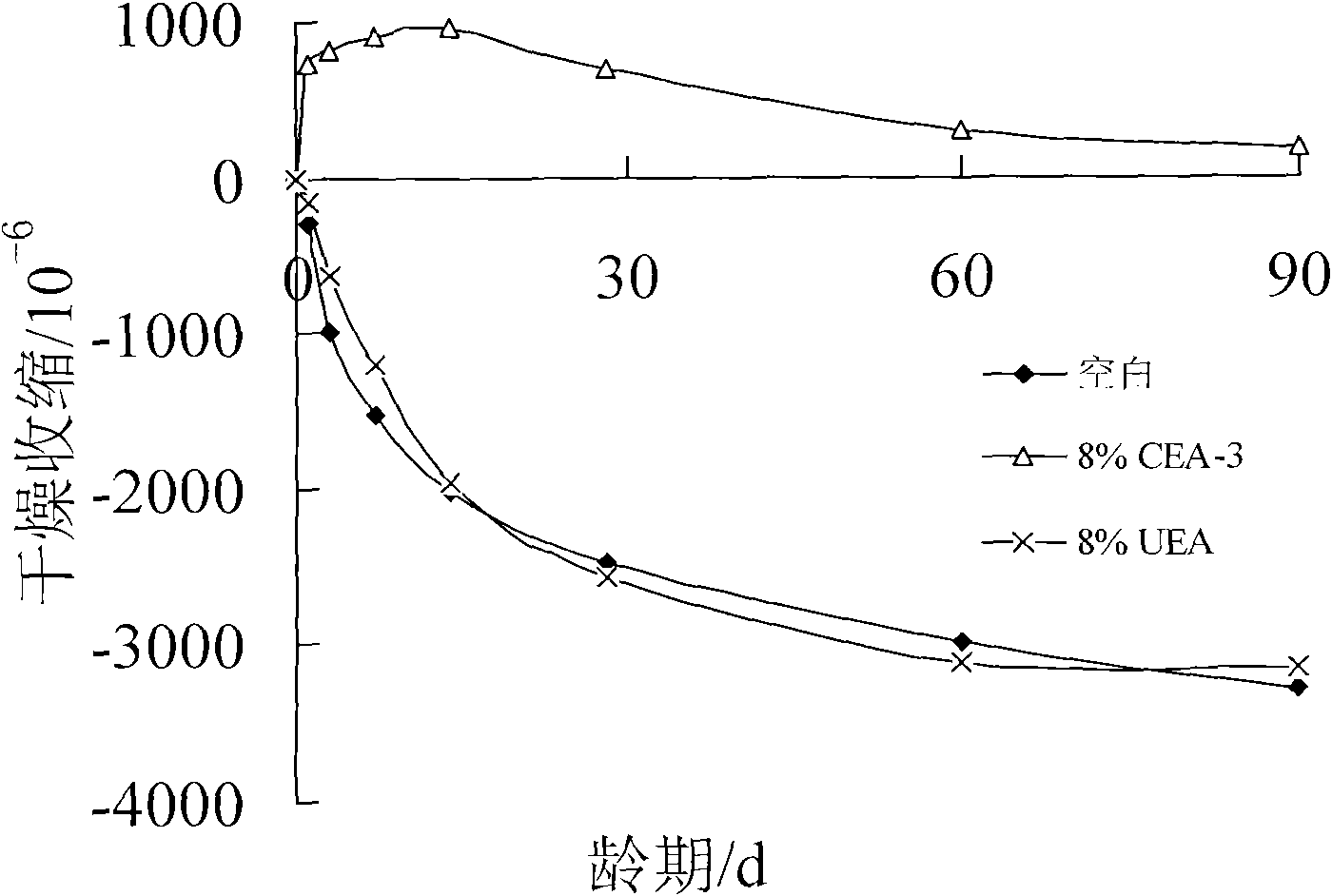
Low-alkali expansive moderate heat silicate cement and production method thereof
ActiveCN102249568ASmall shrinkageLow alkali contentClinker productionCement grindingToxic industrial waste
The invention discloses low-alkali expansive moderate heat silicate cement and a production method thereof, and belongs to the field of cement. The invention provides the low-alkali expansive moderate heat silicate cement. A calcareous raw material, a clayey raw material, a magnesium raw material, aluminum ore barren rock and copper slag are taken as raw materials, and are subjected to raw material milling, clinker calcination and cement milling to form the low-alkali expansive moderate heat silicate cement. The low-alkali expansive moderate heat silicate cement is prepared by the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 67 to 80 percent of calcareous raw material, 8 to 15 percent of clayey raw material, 7 to 13 percent of magnesium raw material, 0.5 to 5 percent of aluminum ore barren rock and 4 to 9 percent of copper slag. The moderate heat silicate cement has the alkali content of less than or equal to 0.50 percent, the 3-day heat of hydration of less than or equal to 231kJ / kg and the 7-day heat of hydration of less than or equal to 273kJ / kg. The industrial waste slag of copper slag is used as an iron corrective raw material, and the aluminum ore barren rock is used as an aluminum corrective raw material, so that the pollution of solid waste gas on the environment is avoided, the waste is changed into treasure, and the performance of the moderate heat cement is improved.
Owner:SICHUAN ESHENG CEMENT GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com