Patents
Literature
1719 results about "Liquid ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Liquid ratio is a thermodynamic ratio of a liquid obtained by dividing boiling point by melting point of a substance in absolute temperature scales (in kelvin or rankine scales). This ratio is used for defining range of kinetic stability of its liquid state.
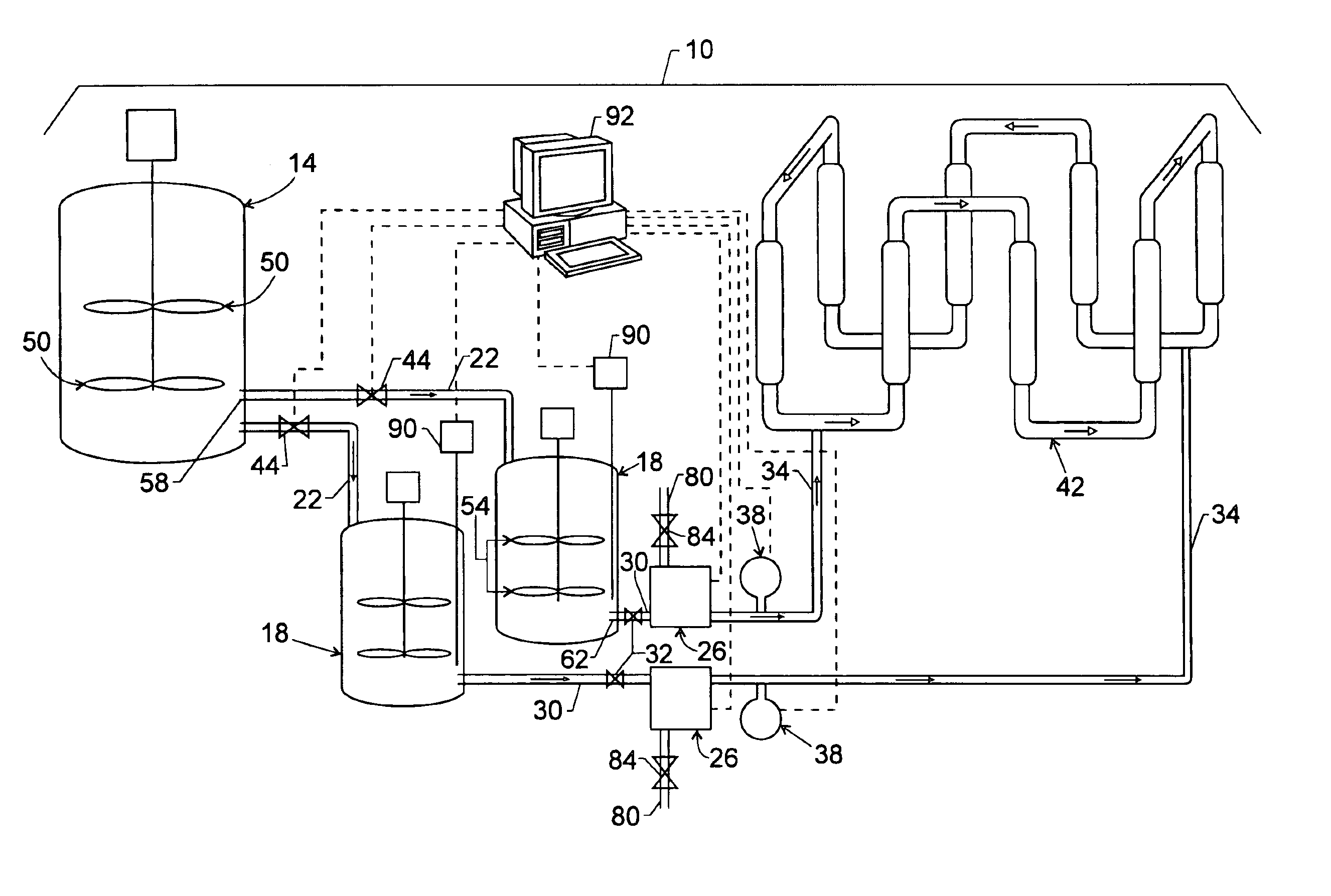
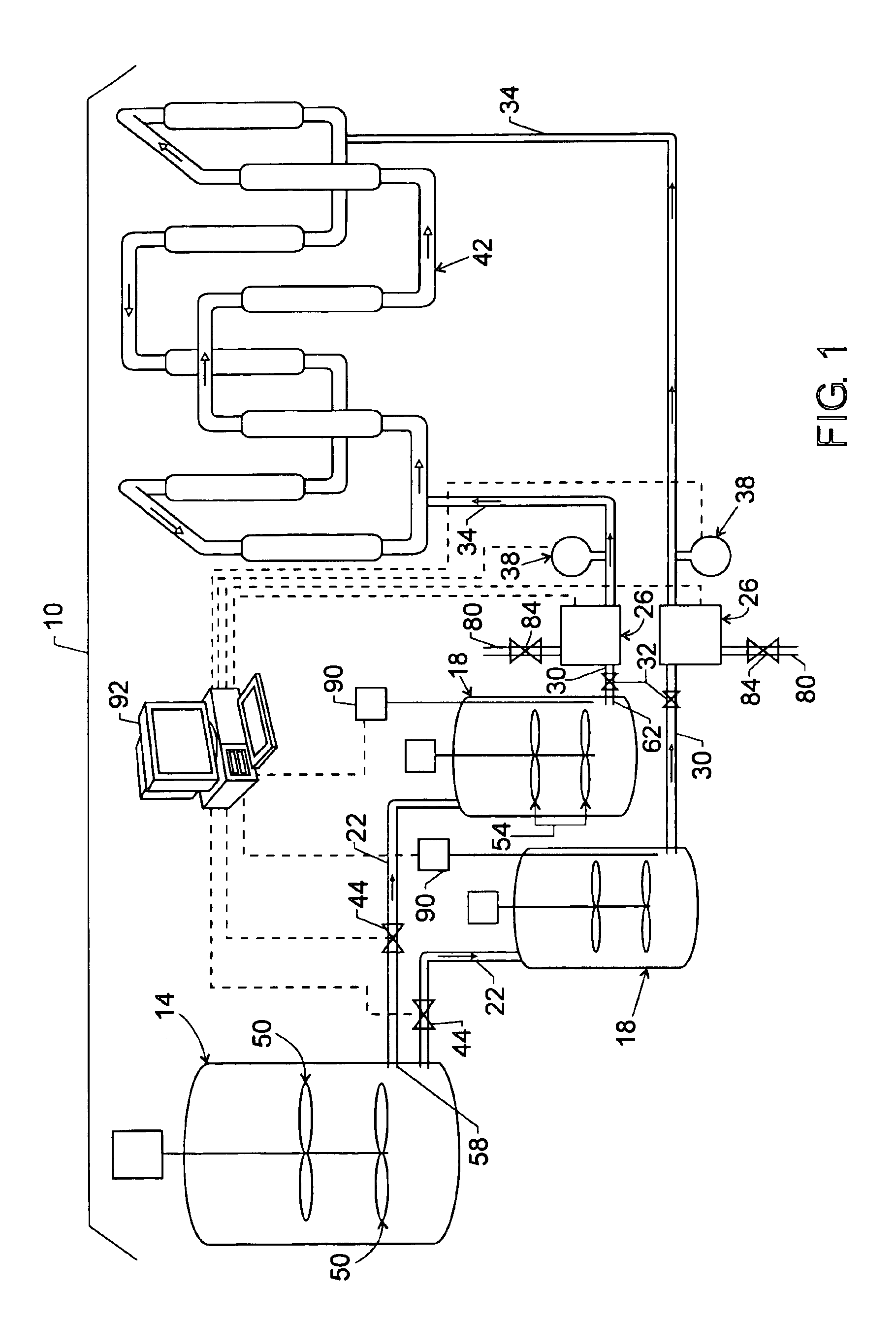
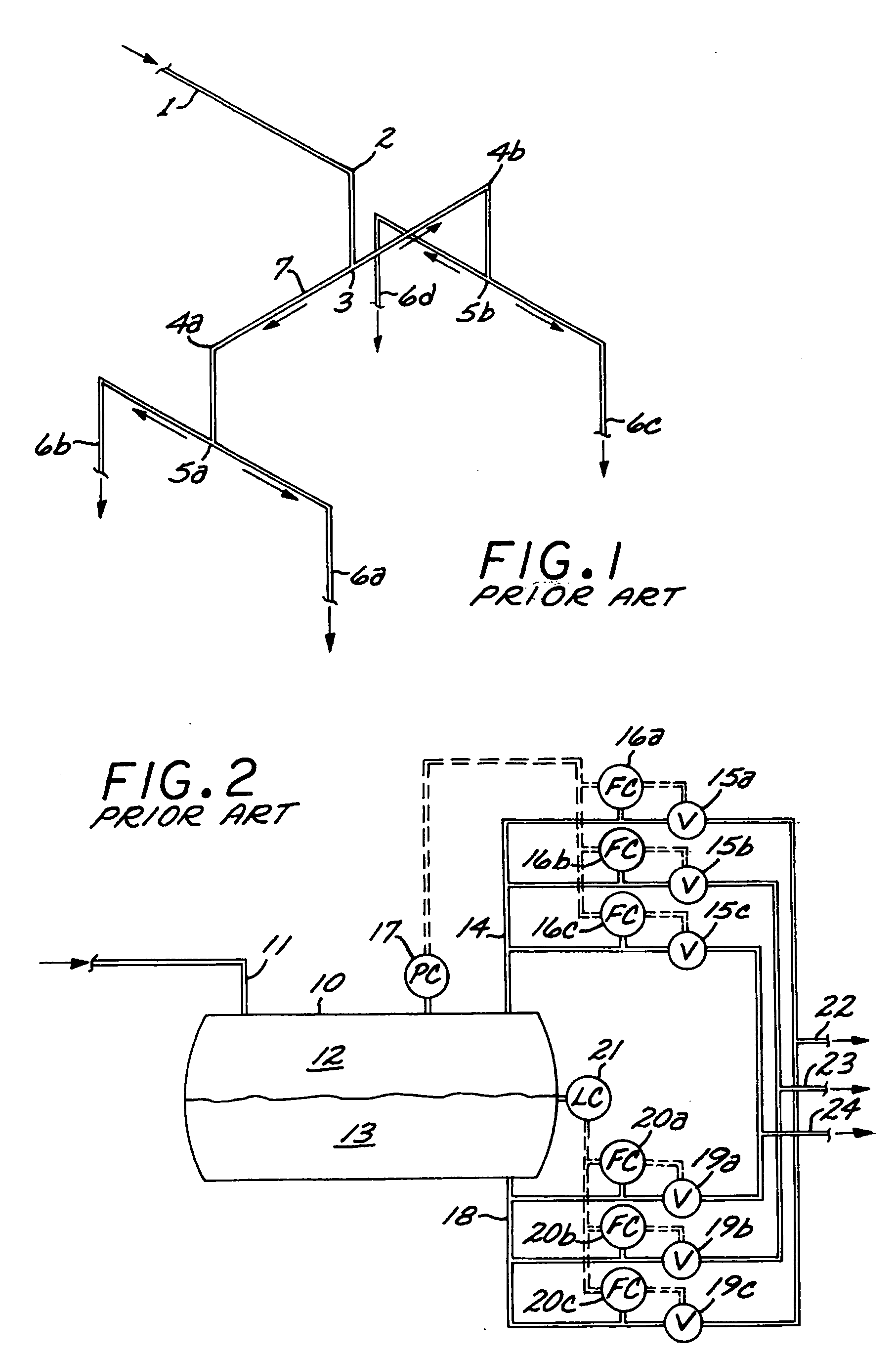
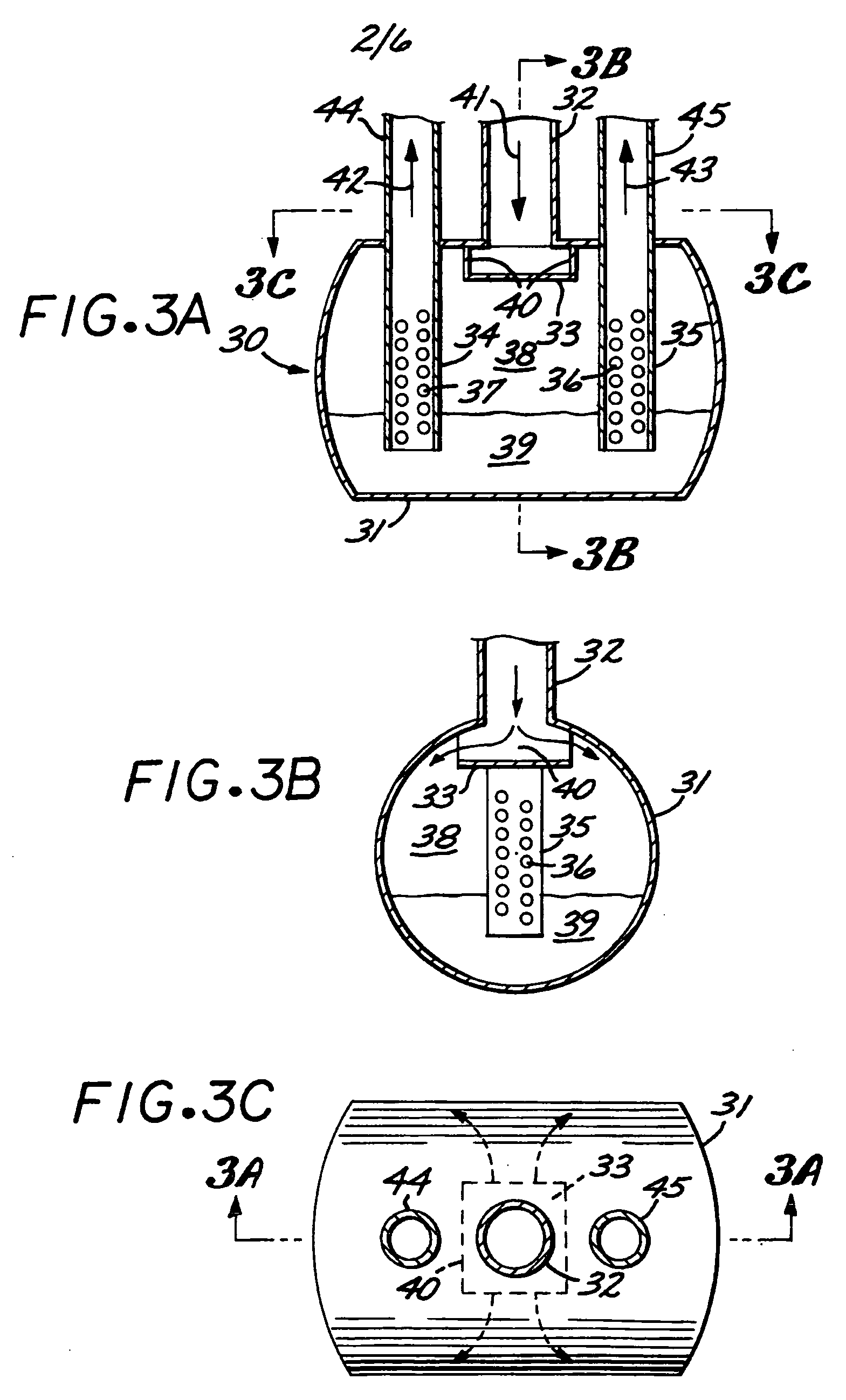
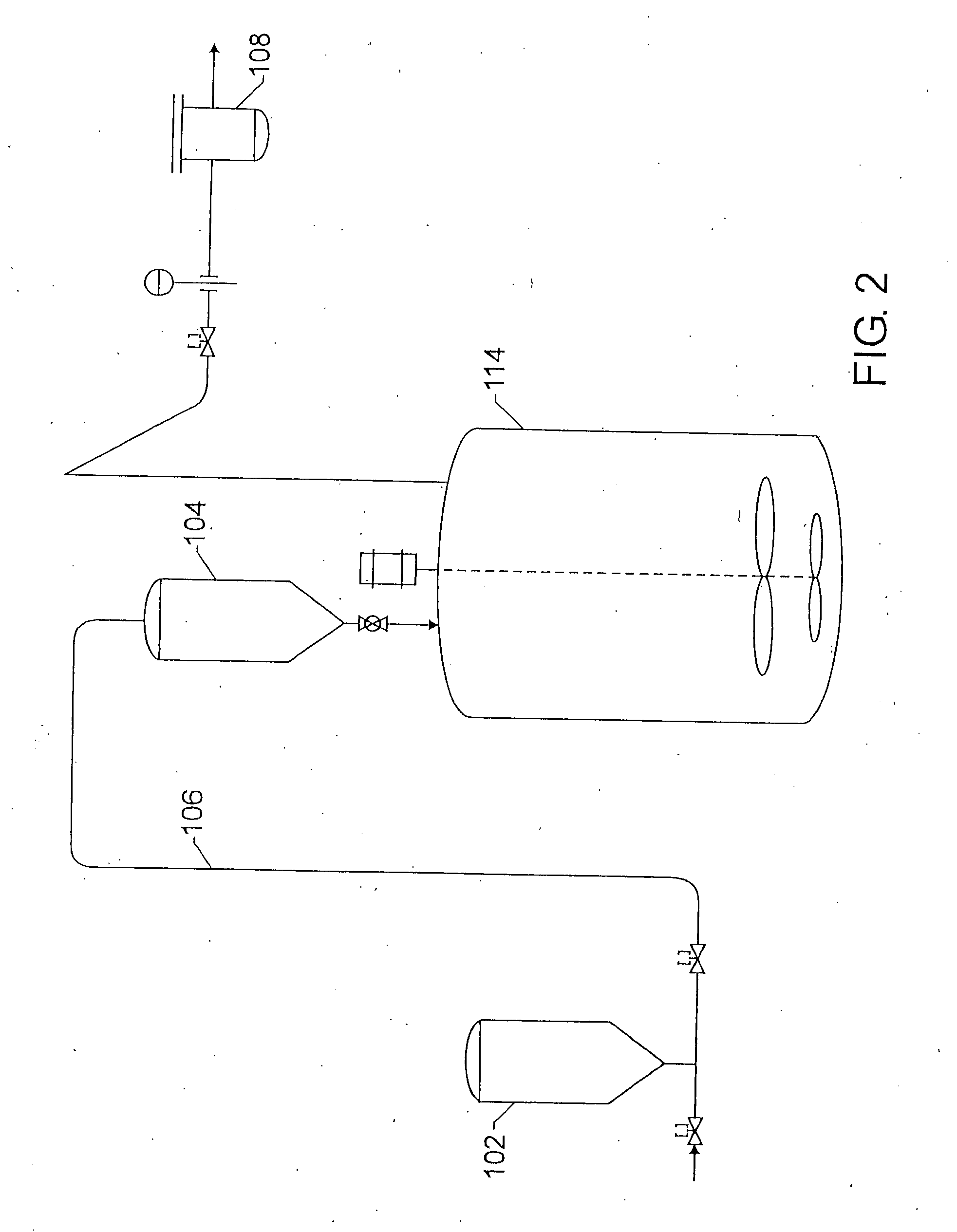
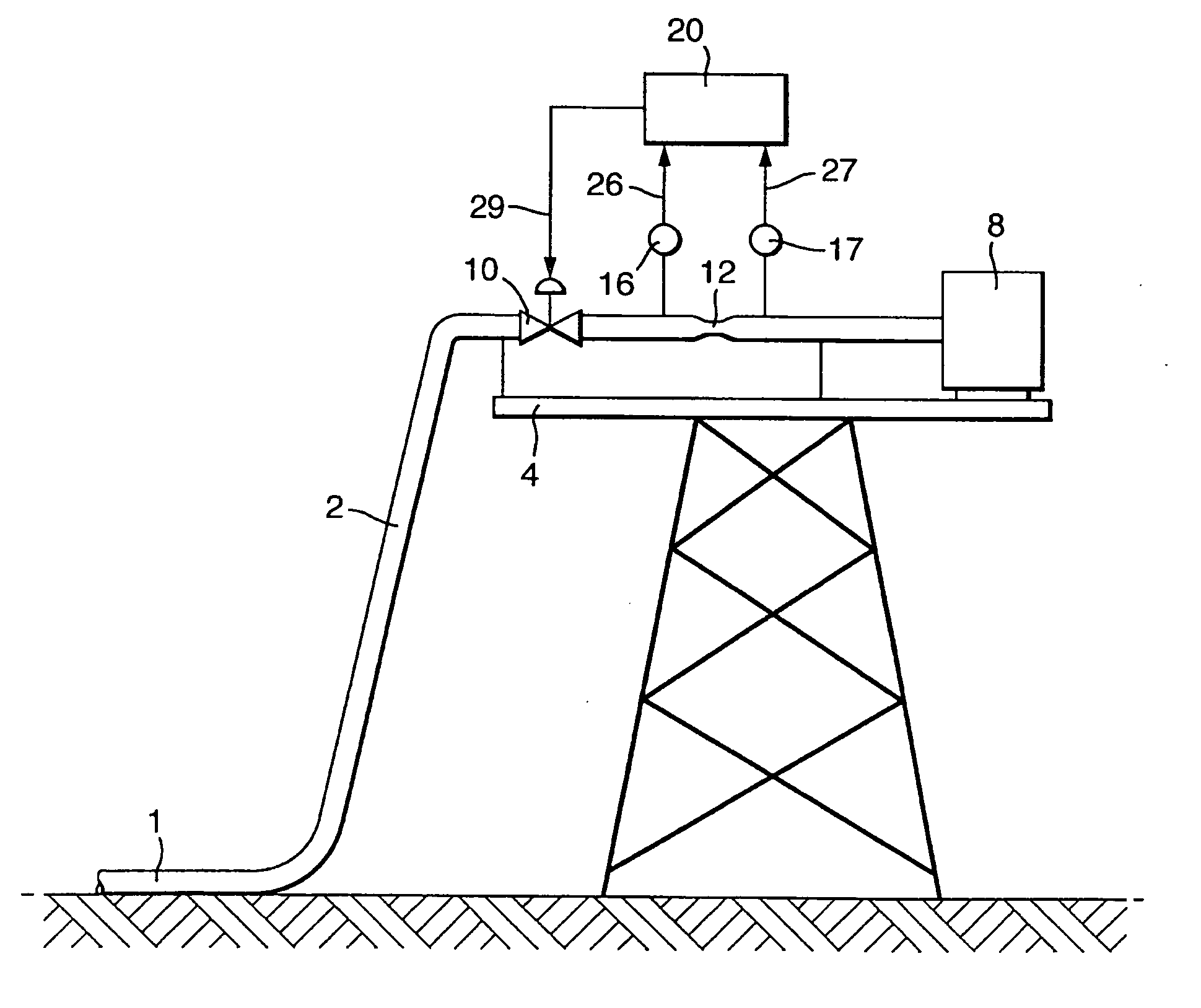
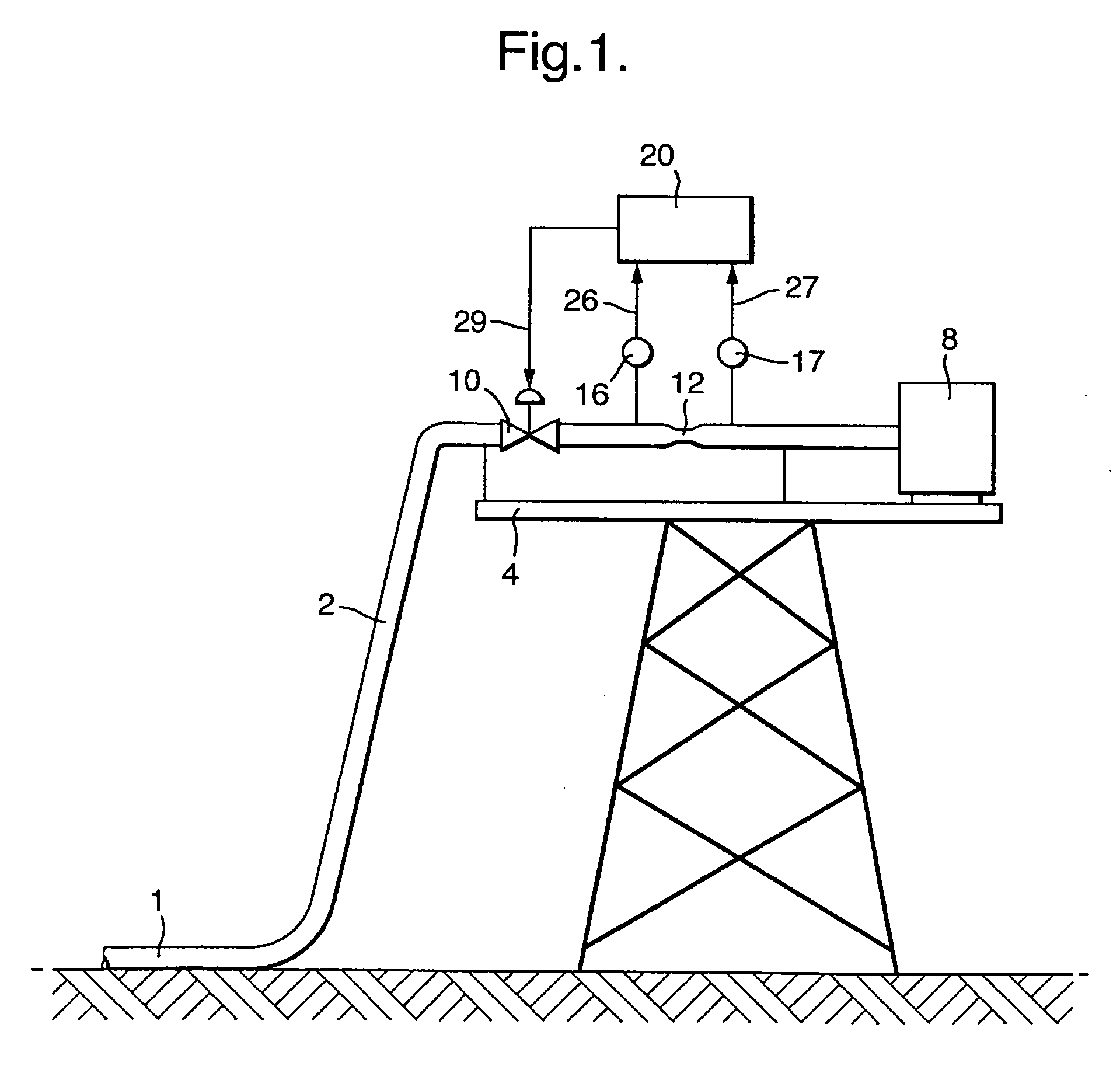
Catalyst slurry feeding assembly for a polymerization reactor
ActiveUS6908971B2Increase heightAvoid necessityChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsFlow controlLiquid ratioSlurry
A catalyst slurry for a polymerization reactor can be prepared in a mixing tank and the catalyst slurry fed to one or more storage tanks. The storage tanks can include agitators so that the catalyst slurry is maintained at an essentially homogeneous solids-to-liquid ratio. From the storage tank(s), the catalyst slurry can be pumped to the polymerization reactor along a fluid passage having a flow meter. The flow of the catalyst slurry can be continuous and / or adjusted based on a measured parameter. The catalyst slurry may be continuously and reliability fed to the polymerization reactor.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Device for splitting a two-phase stream into two or more streams with the desired vapor/liquid ratios
ActiveUS20050000572A1Simple and robust designReduce maintenancePressure pumpsDispersed particle separationLiquid ratioEngineering
Owner:MORTEN MULLER LTD APS
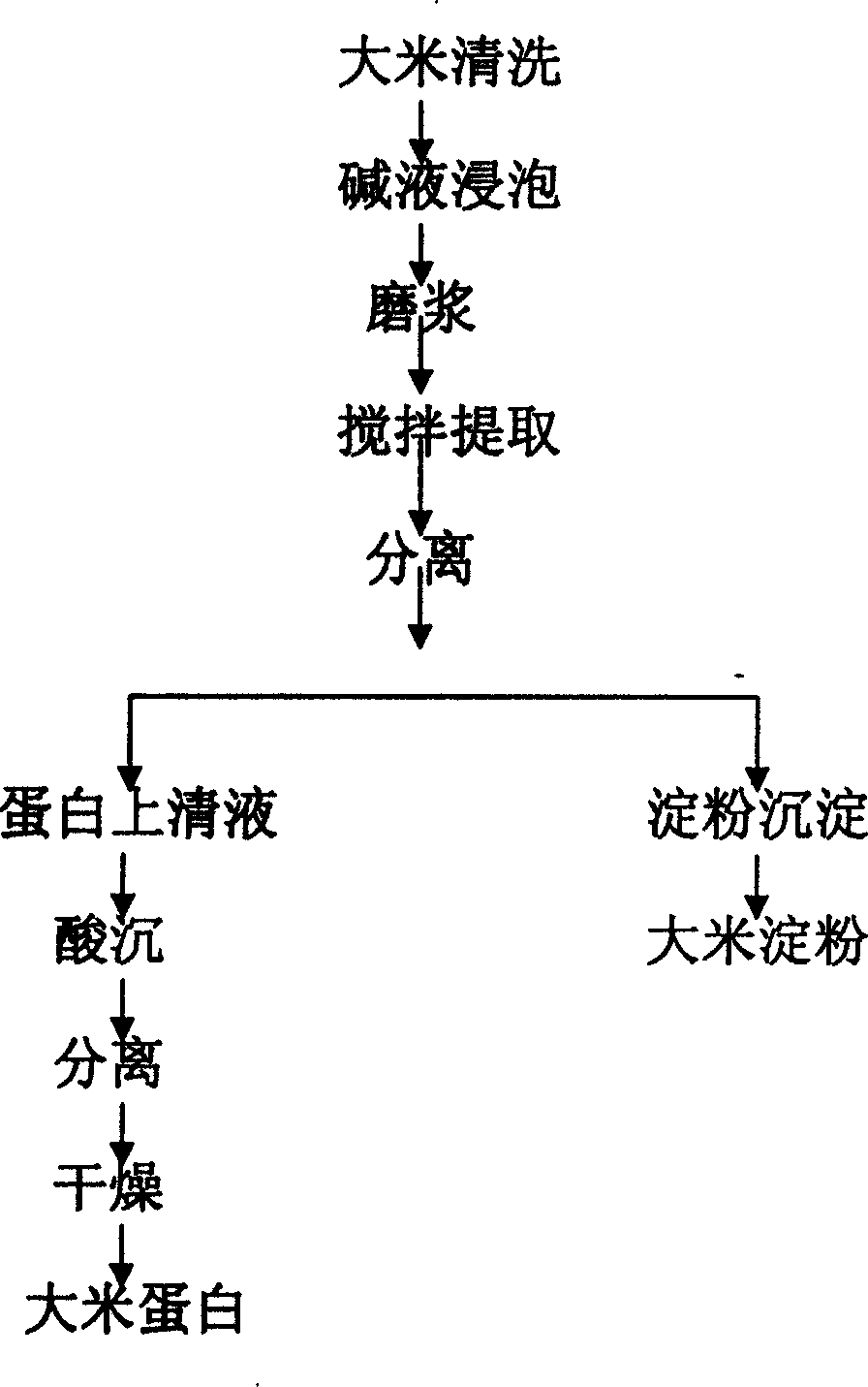
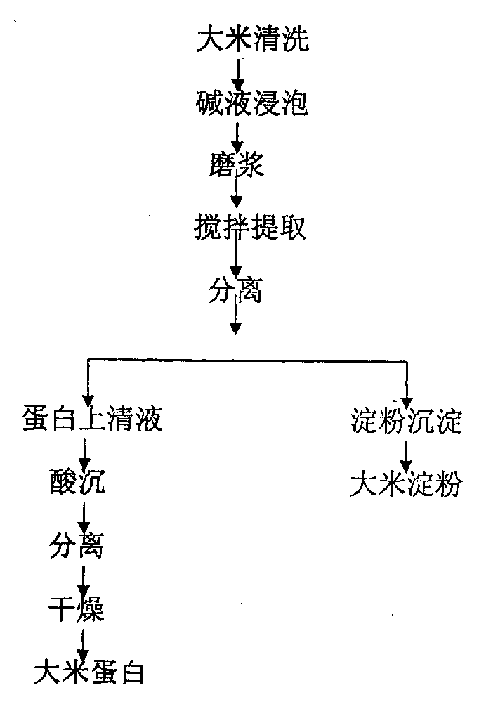
Method for extracting rice protein by alkaline process
InactiveCN1528786ASignificant advantagesSignificant positive effectPeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesLiquid ratioSlurry
Owner:GAEA GEM RICE
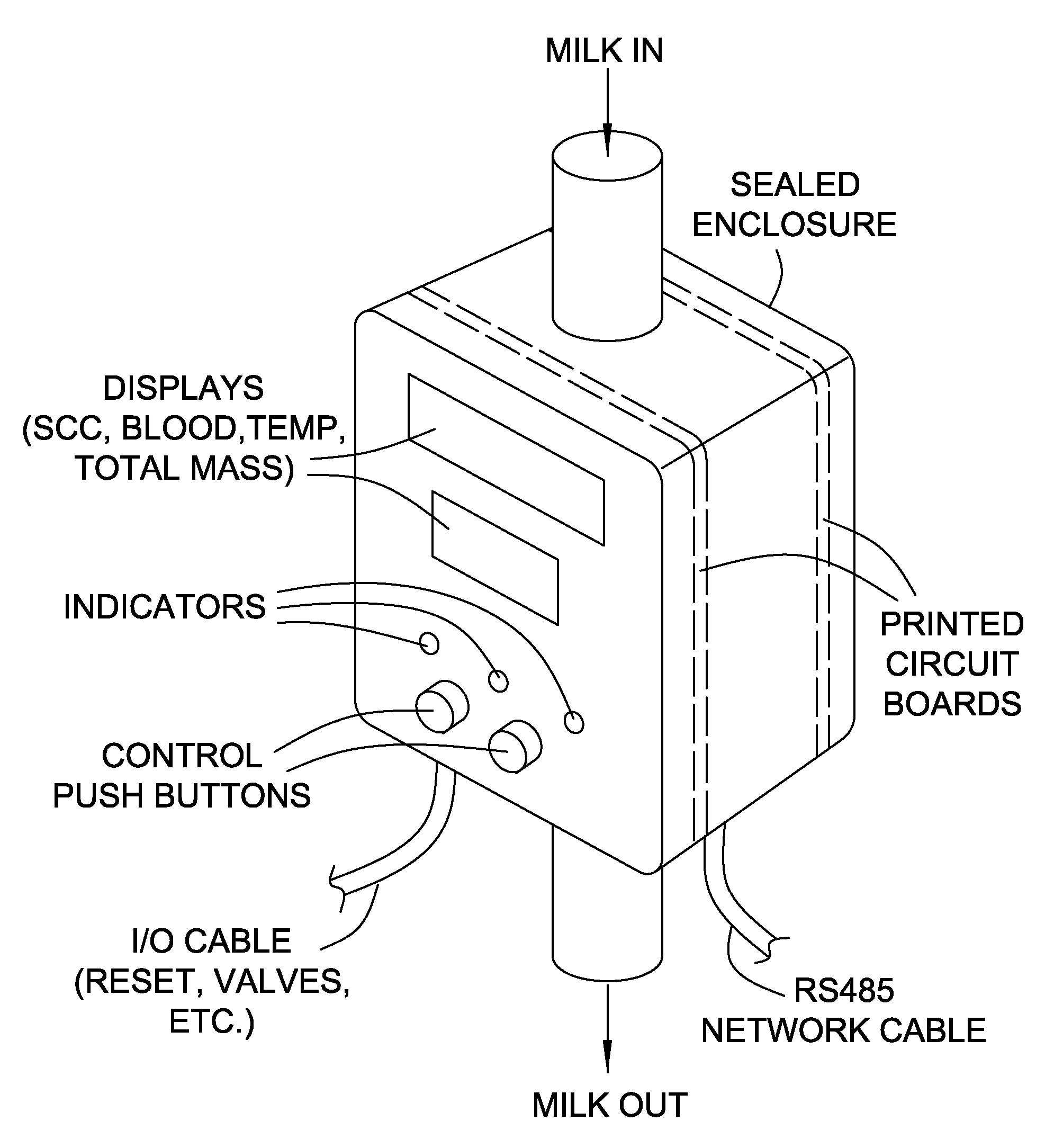
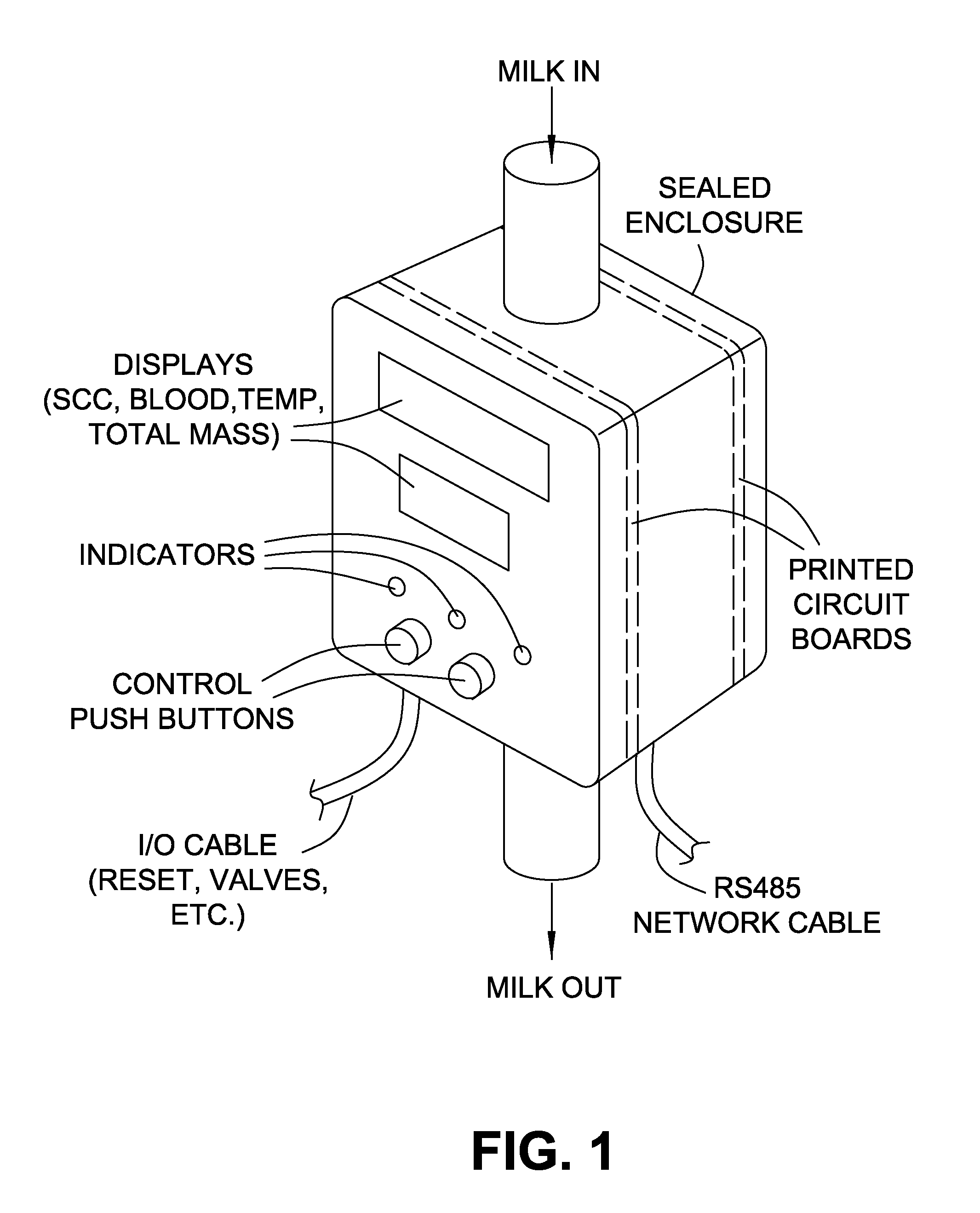
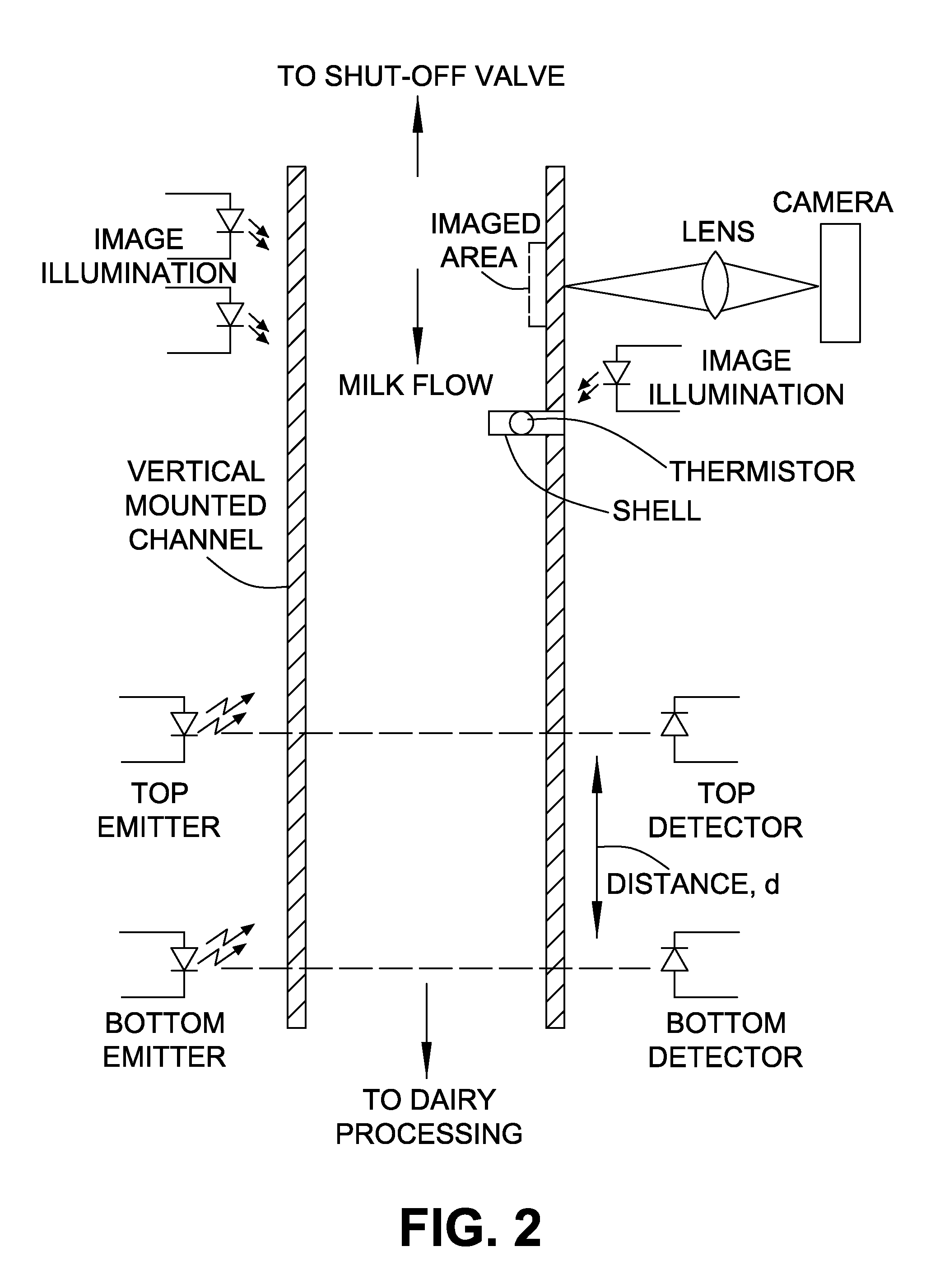
In-line apparatus and real-time method to determine milk characteristics
An apparatus and related methods using photographic imaging and the interactions between light beams and dairy milk to provide in-line monitoring, analysis, and display of the quality of milk collected from dairy animals. The apparatus is robust in that it is reliable, simple to install, relatively small in size, cost effective, easily cleaned, and low maintenance. The apparatus can be installed directly in-line with the milk collection apparatus for each animal so as to measure the entire milk yield produced by that animal at flow rates typically used in milking parlours without requiring any unusual tube fittings or non-standard equipment. The apparatus is capable of handling analysis of a flow having mixed densities, air / liquid ratios, temperature variations, or any other similar variation of physical characteristics.
Owner:DAIRY CONTROLS INT
Modified chitosan material capable of absorbing heavy metal ions and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102161781AEasy to makeEasy to recycleOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionLiquid ratioMass ratio
The invention discloses a modified chitosan material capable of absorbing heavy metal ions and a preparation method thereof. The modified chitosan material is prepared by a method comprising: dissolving the chitosan and sodium alga acid in water respectively to prepare chitosan solution at a concentration of 1.5 mass percent and sodium alga acid solution at a concentration of 2 mass percent; mixing the chitosan solution and sodium alga acid solution uniformly according to a mass ratio of the chitosan and the sodium alga acid of (8-10):1 under a room temperature condition, and dripping calcium chloride solution at a concentration of 1.5 mass percent according to a solid to liquid ratio of the sodium alga acid to the calcium chloride solution of 1:37 with stirring; fully stirring after dripping is finished; regulating the pH value of the solution to 7.2+-0.2 till solid floccules appear; standing till solid gel appears; and filtering, and drying the gel at 35 DEG C to obtain the modified chitosan material.
Owner:INST OF ANALYSIS GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI (CHINA NAT ANALYTICAL
Compact and portable low-field pulsed NMR dispersion analyzer
ActiveUS7417426B2Small and portableLow costAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientLiquid ratio
A compact and integrated portable device is provided for the analysis of dispersions by low-field pulsed NMR including: an NMR probe module, a means for generating radio frequency and magnetic field gradient pulses, a signal processor, and a master controller. Also provided are methods for using the device to measure one or more characteristics of phases or particles comprising a dispersion such as surface area, solid / liquid ratio, particle size, and elemental analysis.
Owner:XIGO NANOTOOLS
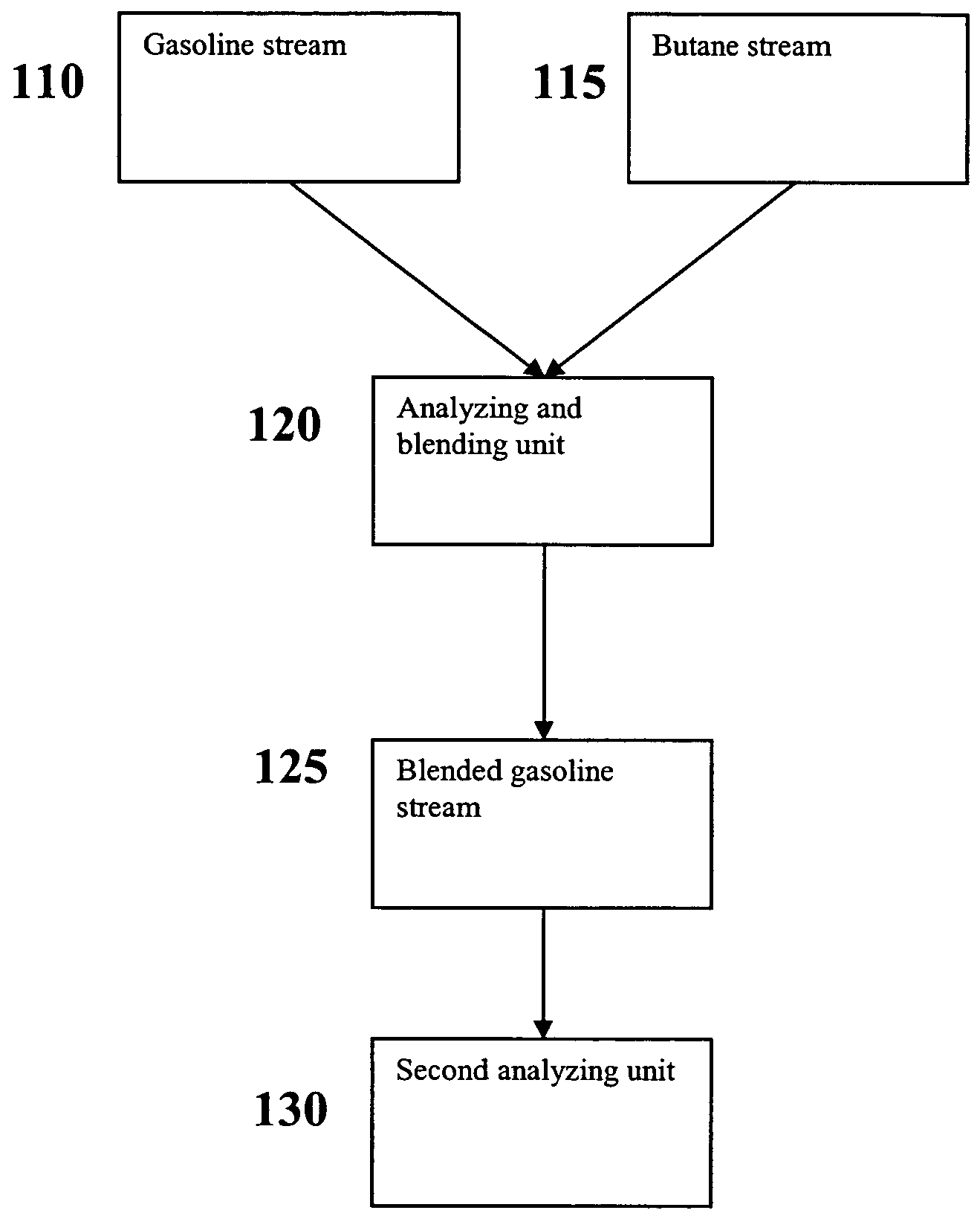
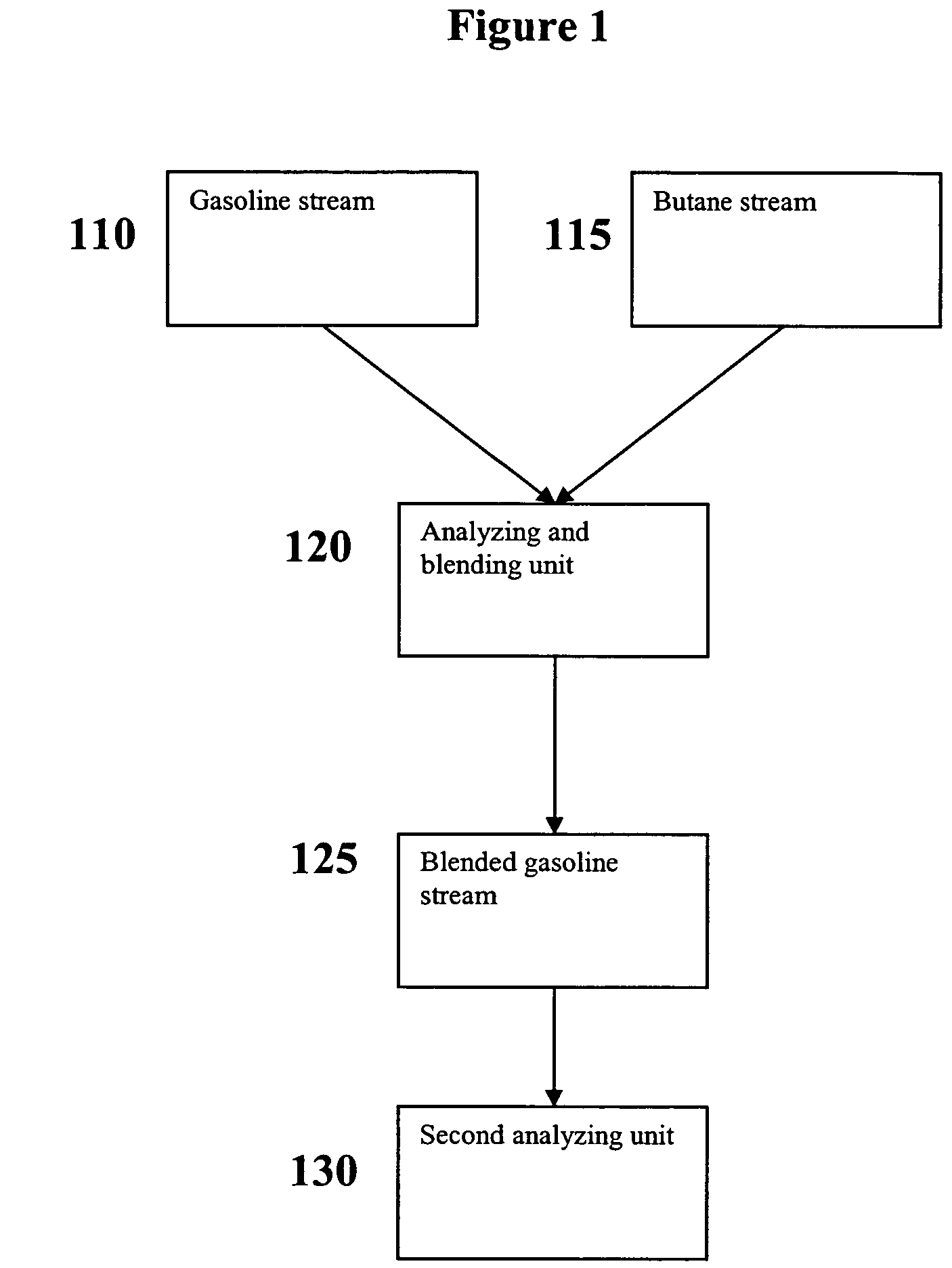
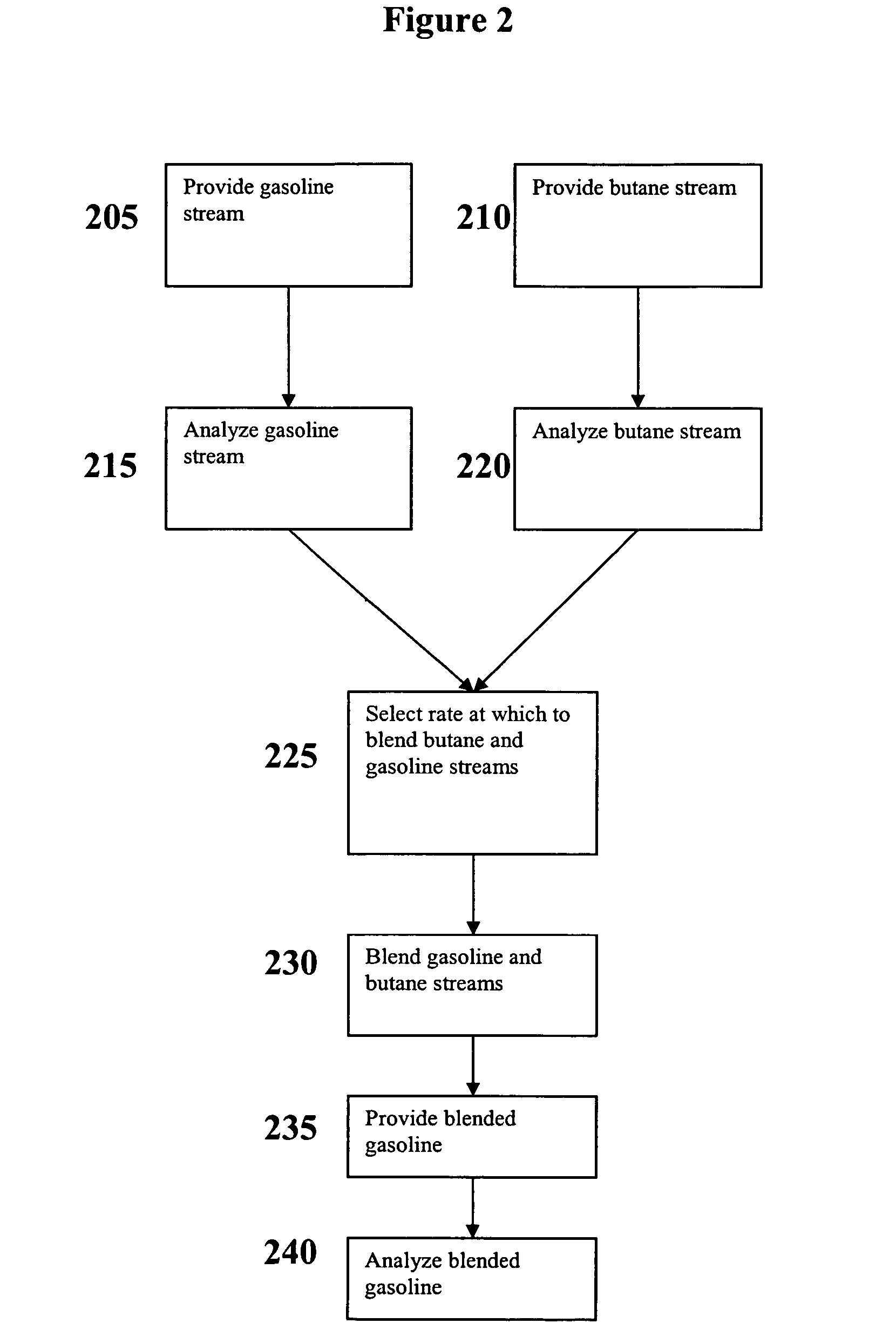
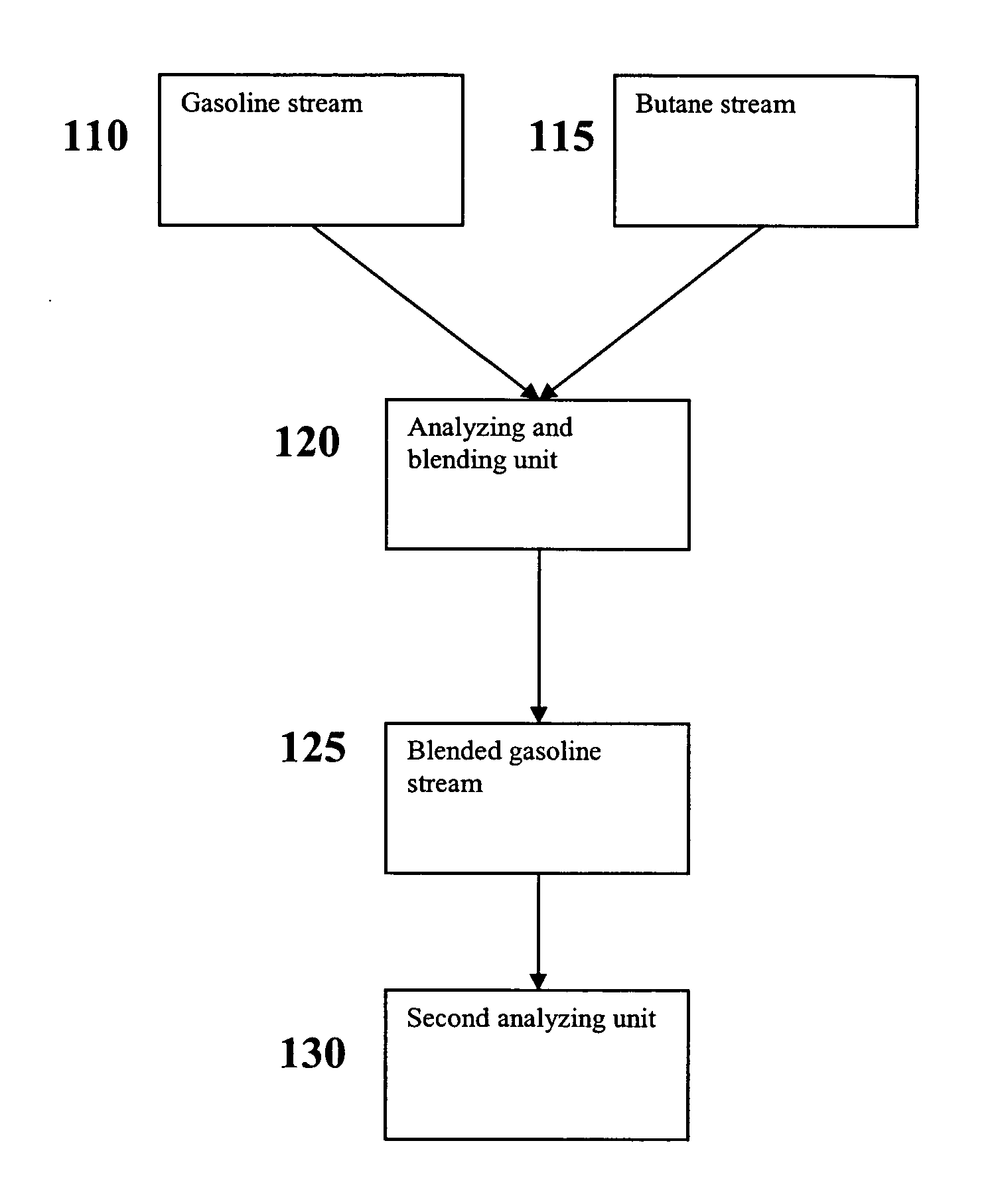
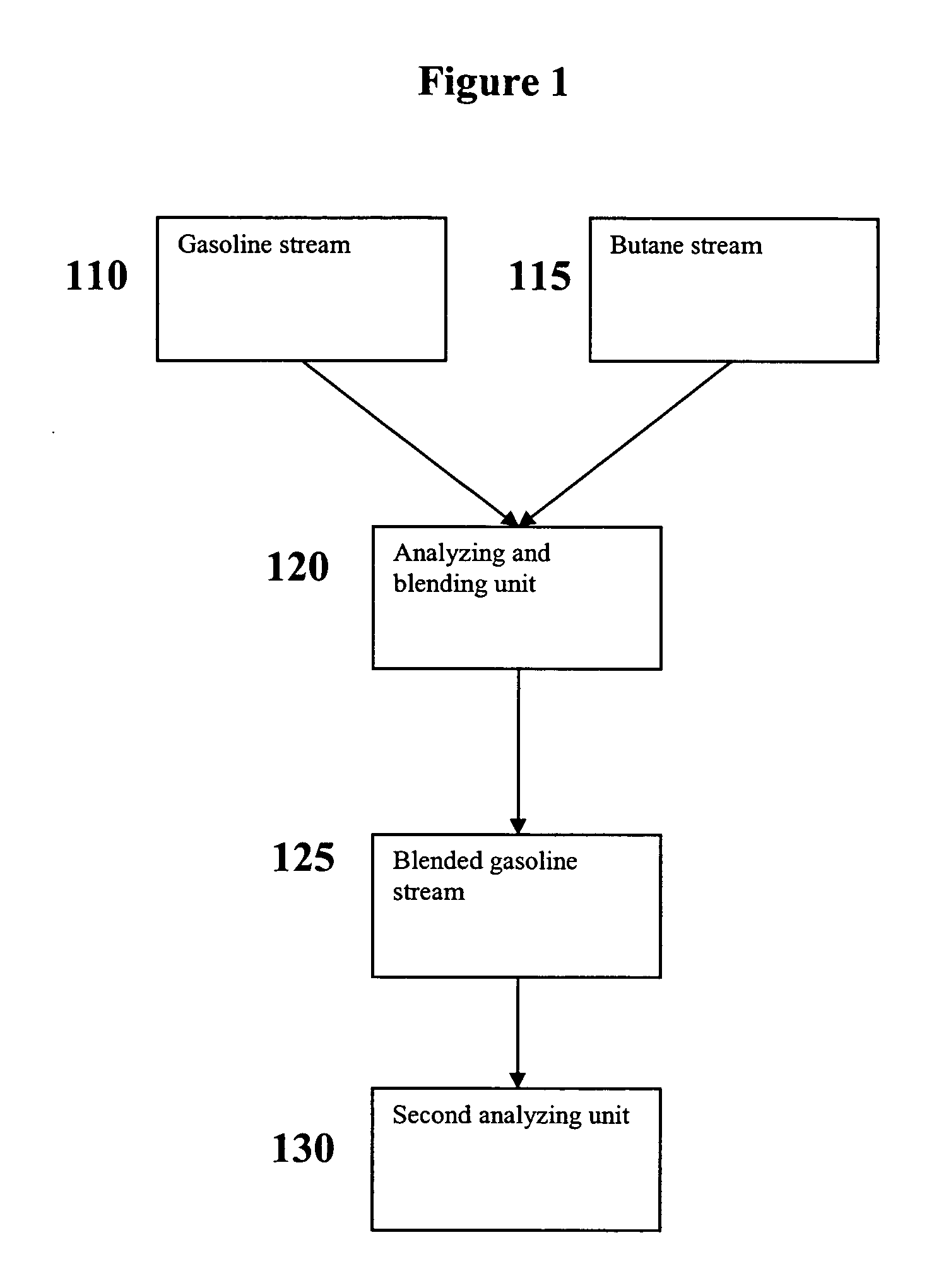
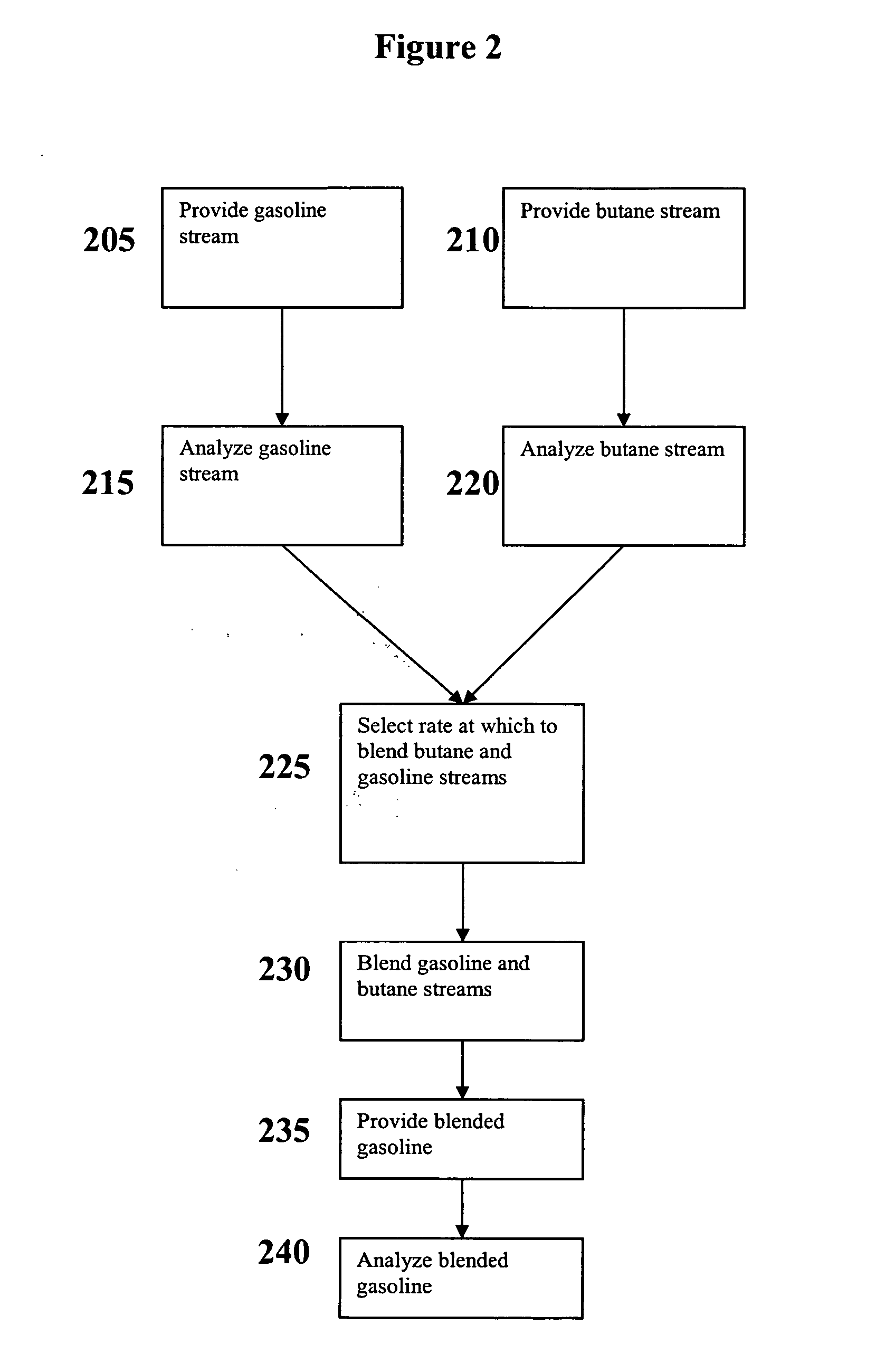
Versatile systems for continuous in-line blending of butane and petroleum
ActiveUS7631671B2Surprising versatilityGreat advantageProgramme controlLiquid fillingLiquid ratioGasoline
A system and method are provided for in-line processes of blending butane into gasoline streams, and for blending butane into a gasoline stream at any point along a petroleum pipeline. The invention additionally provides a method for measuring the vapor pressure and vapor to liquid ratio of the gasoline, both upstream and downstream of the blending operation, as well as the sulfur content of the butane entering the blending operation. The blending operation can be controlled to ensure that the blended gasoline meets EPA requirements for vapor pressure and sulfur content of gasoline. The invention further provides a method for accessing and monitoring the operation off-site.
Owner:SUNOCO PARTNERS MARKETING & TERMINALS LP
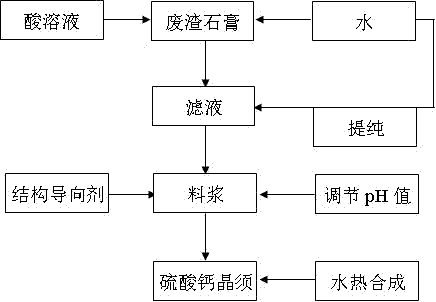
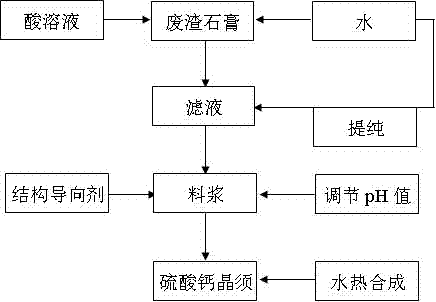
Method for preparing calcium sulfate crystal whisker from many kinds of industrial waste residue gypsum serving as raw materials
InactiveCN102212884AIncrease added valueTo achieve the purpose of turning waste into treasurePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsSolubilityLiquid ratio
The invention relates to a method for preparing a high-quality calcium sulfate crystal whisker, which comprises the following steps of: purifying industrial waste residue gypsum serving as a raw material by utilizing the characteristic of the obvious change of the solubility of calcium sulfate in specific acid solution with temperature, adjusting the solid-to-liquid ratio and pH value of purified filter liquor, and synthesizing the high-purity and high-whiteness calcium sulfate crystal whisker in a hydrothermal mode under the action of a structural guiding agent. In a process for preparing the calcium sulfate crystal whisker from many kinds of industrial waste residue gypsum, the bottleneck problem of the large-scale industrial utilization of complex varieties of waste residue gypsum impurities is solved fundamentally, and the aims of saving energy, reducing emission and recycling waste materials are fulfilled, and the method has a bright application and market prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Preparation and use method of microbial immobilized material for remedying polluted soil
InactiveCN101372688AHigh affinityHigh immobilization efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationOn/in organic carrierHectareIn situ bioremediation
The invention discloses a method for preparing and using a microbial immobilized material for repairing contaminated soil. The method comprises the following steps: (1) after being dried by air, the waste biomass raw material is pulverized or ground into 1-20mm of particles; (2) the biomass particles are carbonized and sterilized at the temperature of 150-450 DEG C and under limited oxygen condition for 0.5-6 hours to prepare a carrier material; (3) the carrier material is put into bacterium suspension for enrichment culture according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 0.5-2mL / g, then the microbial immobilized material is produced; (4) the produced microbial immobilized material is added to organic contaminated soil according to the proportion of 1-500 tons per hectare soil, 0-30cm of topsoil is ploughed to cause the microbial immobilized material to be mixed evenly in the soil, simultaneously, the contaminated soil is biologically repaired and safe agricultural products are produced. The method has the advantages that the carrier material contains abundant lignin structures, carbon and nutrient elements, which provides more suitable matrix for microbial growth; and the immobilized material has strong affinity, high immobilization efficiency, strong adsorption capacity and good resistance against the pollutants in the environment; and the immobilized material is a soil fertilizer, and is suitable for large-scale in-situ biological repair of the contaminated soil.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Versatile systems for continuous in-line blending of butane and petroleum
ActiveUS20060278304A1Surprising versatilityStrict controlProgramme controlLiquid fillingLiquid ratioGasoline
A system and method are provided for in-line processes of blending butane into gasoline streams, and for blending butane into a gasoline stream at any point along a petroleum pipeline. The invention additionally provides a method for measuring the vapor pressure and vapor to liquid ratio of the gasoline, both upstream and downstream of the blending operation, as well as the sulfur content of the butane entering the blending operation. The blending operation can be controlled to ensure that the blended gasoline meets EPA requirements for vapor pressure and sulfur content of gasoline. The invention further provides a method for accessing and monitoring the operation off-site.
Owner:SUNOCO PARTNERS MARKETING & TERMINALS LP
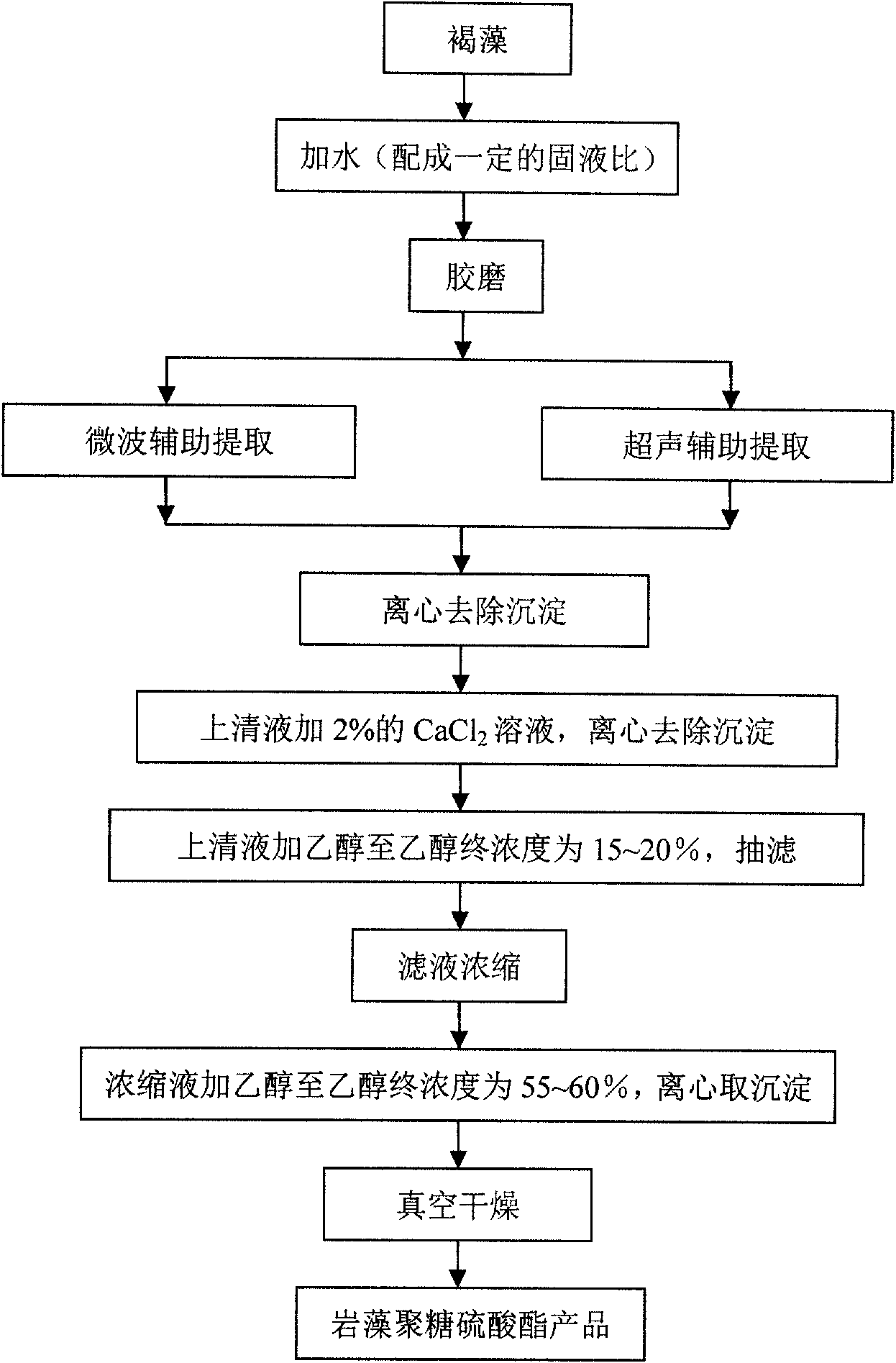
Method for preparing fucoidan
InactiveCN101993501AComprehensive utilization value has no impactComprehensive utilization value impactFood additiveLiquid ratio
The invention provides a method for preparing fucoidan, relating to the field of production and application of food additives. The method comprises the following steps of: adding distilled water according to a material to liquid ratio of 1:40-4:80 g / mL with brown algae, such as kelps, undaria pinnatifida, and the like as raw materials; treating by a colloid mill and then carrying out microwave-assisted extraction or ultrasonic wave-assisted extraction, wherein, in the microwave-assisted extraction process, the microwave time lasts 20-40min, the microwave extraction temperature is 60-80 DEG C, and the microwave power is 400-500W; and in the ultrasonic wave-assisted extraction process, the ultrasonic power is 800-100W, the microwave time lasts 20-40min, and the extraction temperature is 60-90 DEG C; and centrifuging an extracting solution, adding a proper amount of 2% CaCl2 solution into a supernatant, stirring, keeping constant temperature for 20-30h at 35-40 DEG C, centrifuging, adding 50-100% ethanol into the supernatant until the ethanol concentration of the solution is 15-20%, stirring, filtering, concentrating, adding 90-100% ethanol into a concentrated solution until the ethanol concentration of the solution is 55-60%, centrifuging again and drying a precipitate in vacuum to obtain white or yellow-white fucoidan powder.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Foaming agent with low gas liquid ratio foam for common heavy oil reservoir and injection method thereof
InactiveCN101580705AReduce interfacial tensionHigh interface activityFluid removalDrilling compositionFoaming agentLiquid ratio
The invention provides a foaming agent for low gas liquid ratio foam flooding for improving recovery ratio of common heavy oil reservoir and an injection method thereof. The foaming agent is prepared from a nonionic-anionic surfactant, a betaine type amphoteric surfactant and water, wherein the nonionic-anionic surfactant accounts for 0.01 to 0.03 weight percent of the total weight; the betaine type amphoteric surfactant accounts for 0.05 to 0.3 weight percent of the total weight; and the balance is oil field injection water. The foaming agent has good foaming tendency, can reduce the interfacial tension of oil and water to the lowest under the condition of not adding alkali, and can give full play to the foam flooding and the improvement of conformance factor and displacement efficiency. On the basis of the foaming agent, when the gas liquid ratio is between 0.1:1 and 0.3:1 (volume ratio), the generated foam can improve the recovery ratio by over 10 percent, and the technology with low cost and good effect for improving the recovery ratio of the heavy oil reservoir is realized.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
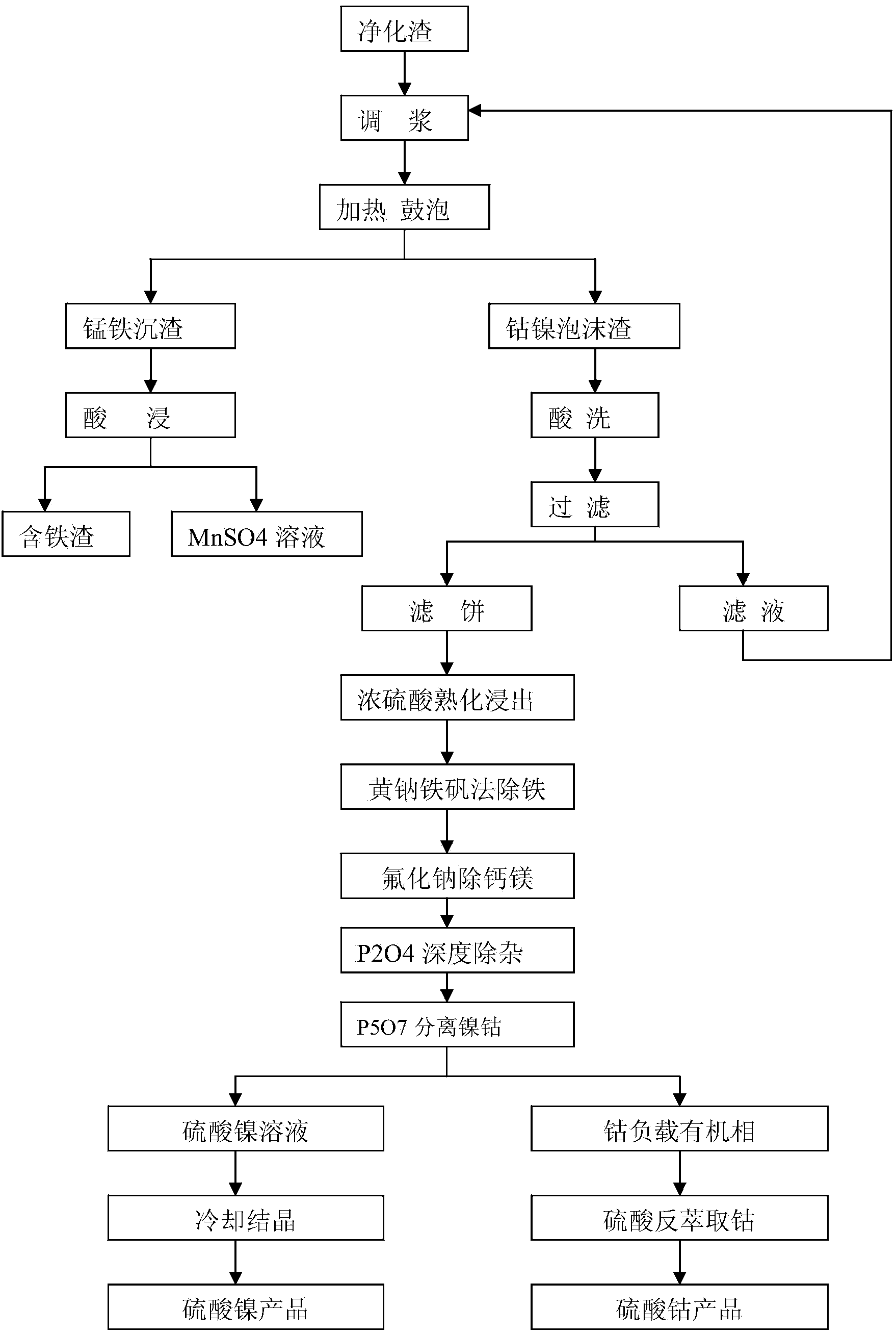
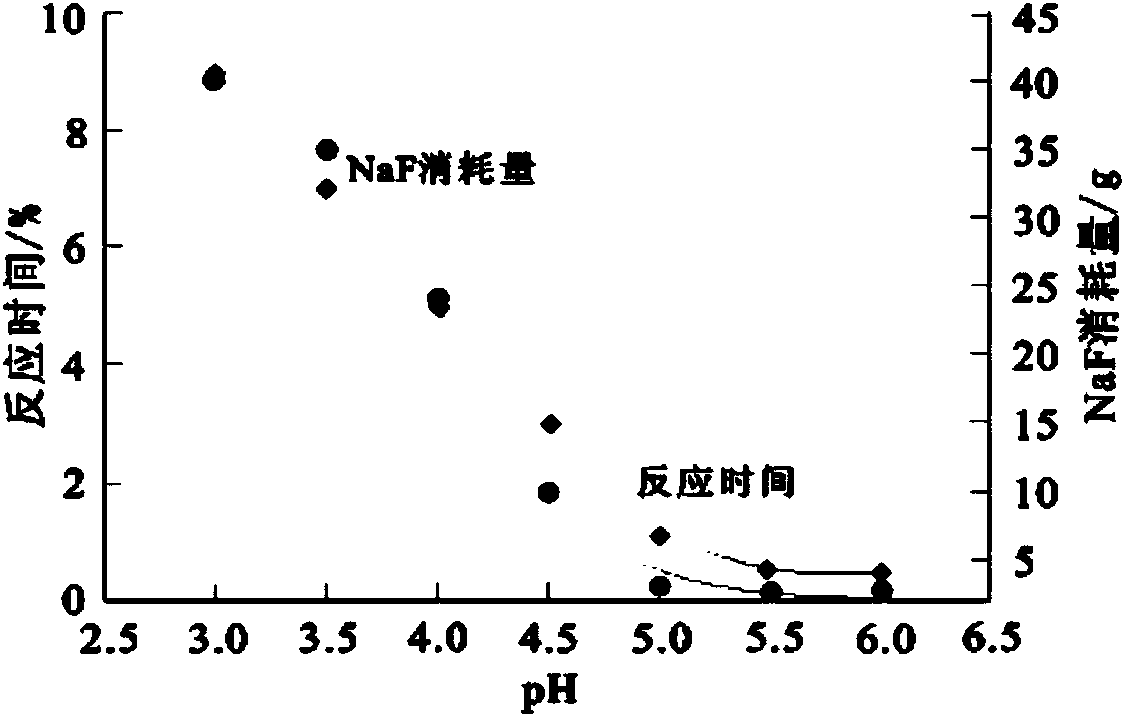
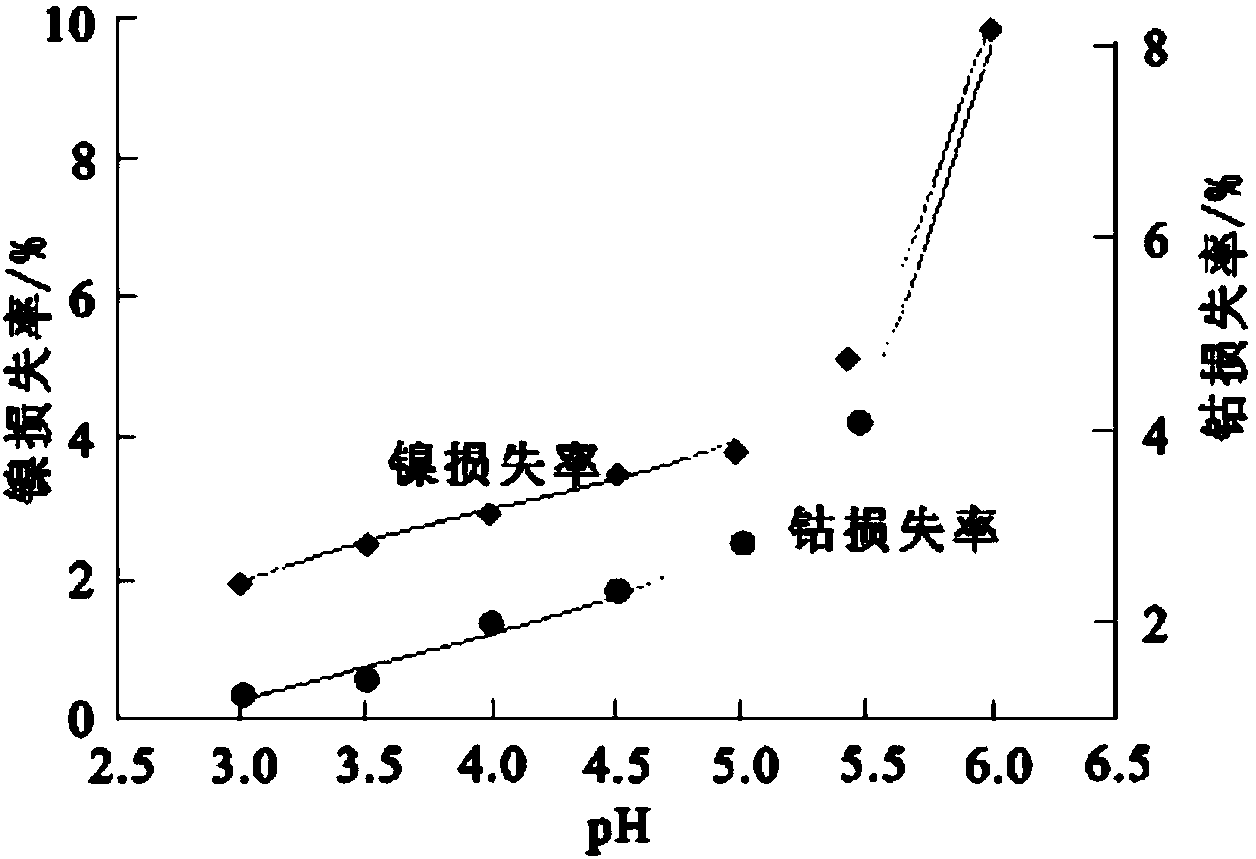
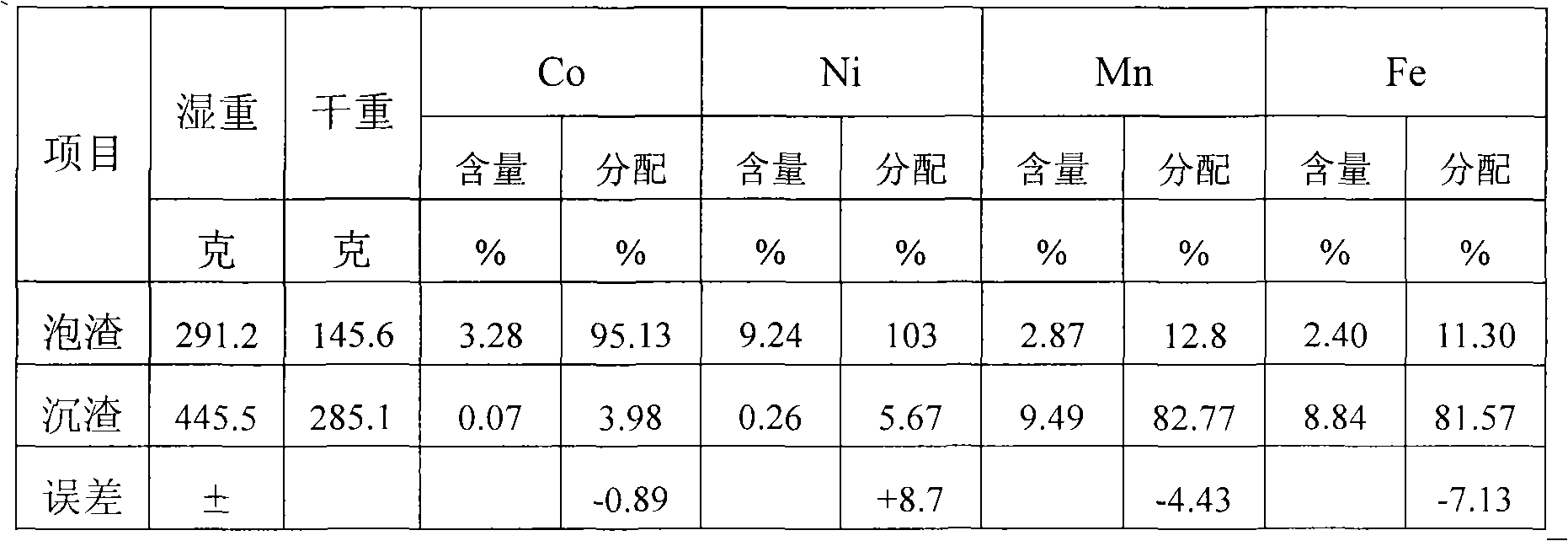
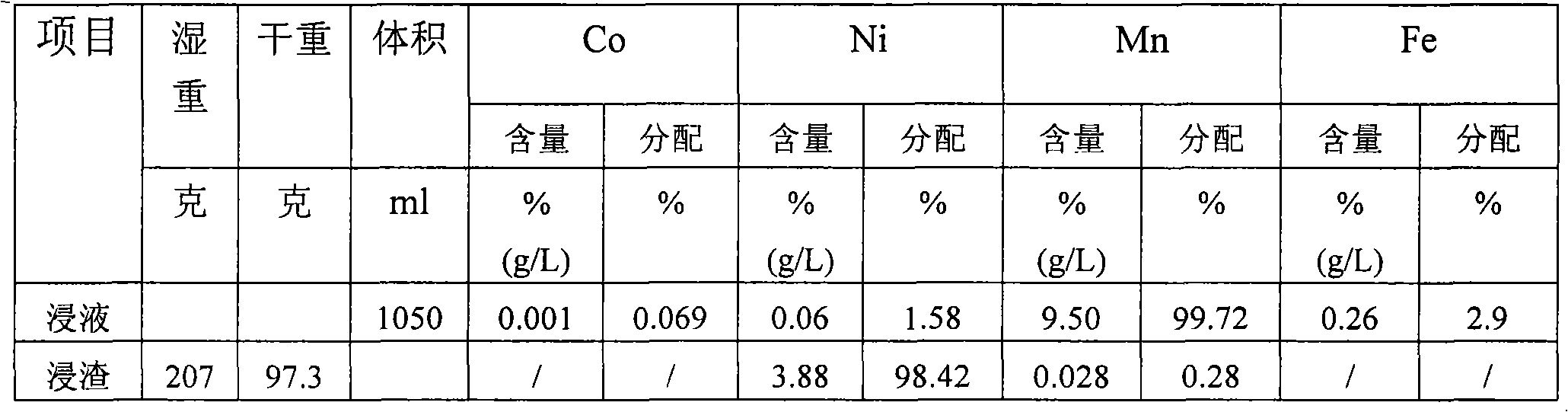
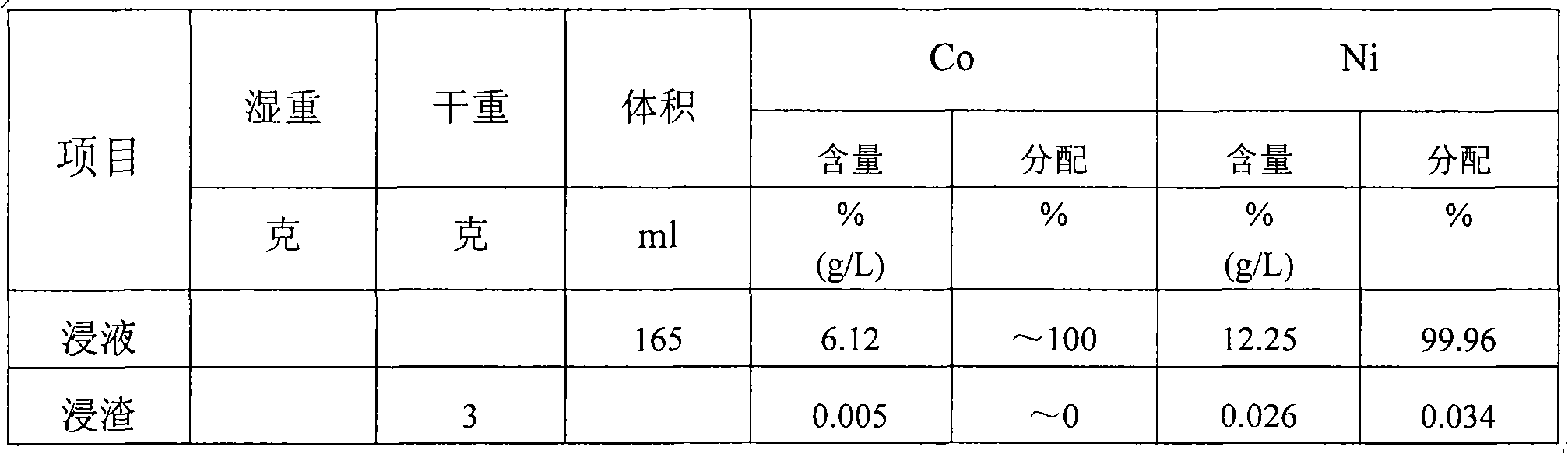
Method for extracting cobalt and nickel from manganese, cobalt and nickel waste residue
ActiveCN103773961AHigh recovery rateReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementLiquid ratioSlag
The invention discloses a method for extracting cobalt and nickel from a manganese, cobalt and nickel waste residue. The method sequentially comprises the following steps: a) adding water into the manganese, cobalt and nickel waste residue in a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:(2-5) to size, and heating and bubbling under stirring to obtain cobalt and nickel foaming slags and ferromanganese sediments; b) heating, pickling and filtering the cobalt and nickel foaming slags to obtain a cobalt and nickel filter cake; c) curing and leaching the cobalt and nickel filter cake by concentrated sulfuric acid to obtain cobalt and nickel liquor; d) removing impurities in the cobalt and nickel liquor to remove impurities such as copper, iron, calcium, magnesium, manganese and zinc, wherein the mass concentration of impurities in the liquor is reduced to below 0.01g / L; e) extracting and separating the cobalt and nickel liquor without impurities by a P507 extractant to obtain nickel sulfate liquor and a cobalt-loaded organic phase; and f) cooling and crystallizing the nickel liquor, and recovering a nickel sulfate product, and carrying out reverse extraction on the cobalt-loaded organic phase by sulfuric acid to obtain cobaltous sulfate liquor. According to the invention, the production condition is relatively simple, efficient grouping is realized, and the recovery rate of cobalt and nickel is high.
Owner:GUANGXI NON FERROUS METALS GROUP HUIYUANMENGYE
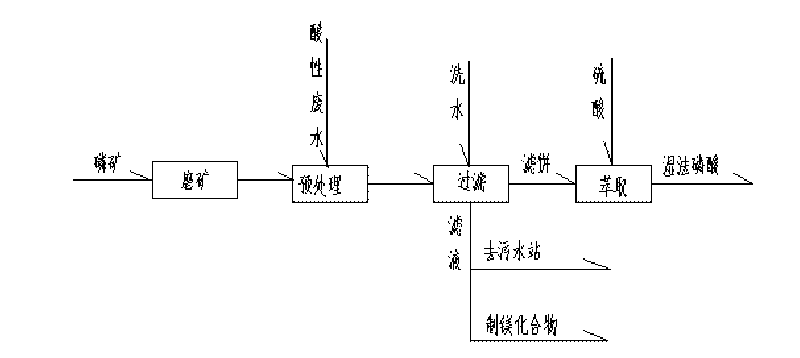
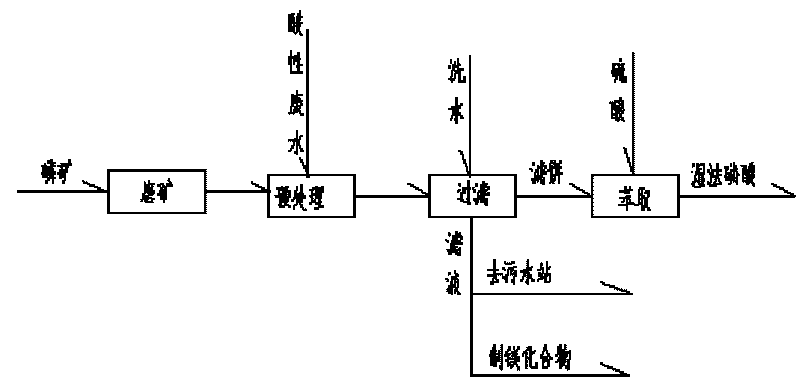
Method for pre-treating phosphorite by using acidic waste water in the production process of titanium pigment
ActiveCN101759166AReduce processing costsControl the strength of sulfuric acidPhosphoric acidPhosphoric acidSlurry
The invention discloses a method for pre-treating phosphorite of wet process phosphoric acid by using acidic waste water in the production process of titanium pigment, which comprises the following steps: (1), collecting the acidic waste water into an acidic waste water storage groove, controlling the acid degree to be 2 to 5 percent and the total iron concentration to be 0.3 to 0.5 percent; (2), adding the acidic waste water and the milled phosphorite in a solid-to-liquid ratio of 2-5:1 into a reaction groove for reaction; and (3), performing solid-liquid separation on the slurry which is obtained in the step (2) to obtain a solid phase, namely the required phosphorite. The content of magnesium in the phosphorite which is treated by the method is reduced by over 70 percent, the loss ratio of the phosphorus is controlled to be within 1 percent; when the phosphorite which is treated by the process is used for producing the phosphoric acid by a wet method, the consumption of the sulfuric acid for mine per ton is reduced by about 10 percent; and the acidic waste water pretreats phosphorite and then is delivered to a sewage station for treatment, the consumption of lime or other alkaline substance is reduced by 60 percent compared with the mode of directly delivering the waste water to the sewage station, so the economical efficiency of the process is high.
Owner:SICHUAN LOMON TITANIUM IND CO LTD
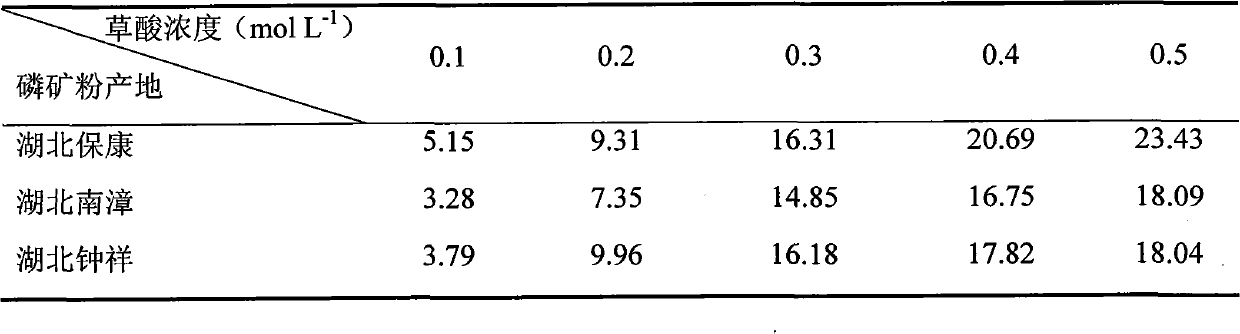
Passivator for controlling pollutions of heavy metals copper, lead and cadmium on soil and applications thereof
InactiveCN102559198ADoes not destroy physical and chemical propertiesPassivation is effectiveContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSoil heavy metalsMaterials science
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil heavy metal pollution control and particularly relates to a passivator which is suitable for the in-situ control of the pollutions of heavy metals copper, lead and cadmium on soil and applications thereof. The passivator uses middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore powder as the main raw material and the heavy metal passivator is prepared to passivate heavy metals in soil. The preparation method of the passivator comprises the following steps: smashing the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore of which P2O5 content is 20-30%, sieving with a 100 meshes of screen to obtain phosphate ore powder, mixing the phosphate ore powder with 0.1-0.7mol / L of oxalic acid according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:1-1:20, activating at 28 DEG C for 6 days, and then drying at 50 DEG C for 20-24h to obtain the passivator. 3.97g of the prepared passivator is applied in 1kg of soil which is polluted by heavy metals; and the lettuce which grows for 120 days is harvested, and sampling is performed to measure the content of various forms of heavy metals in soil and the plant absorption amount. The passivator fully utilizes the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore resource which is difficult in use in China; and the passivator has the characteristics that the investment is low, the engineering quantity is low, the physicochemical properties of soil can not be damaged and secondary pollution can not be caused.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Catalyst slurry feeding assembly for a polymerization reactor
ActiveUS20050186126A1Increase heightAvoid necessityExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusLiquid ratioSlurry
A catalyst slurry for a polymerization reactor can be prepared in a mixing tank and the catalyst slurry fed to one or more storage tanks. The storage tanks can include agitators so that the catalyst slurry is maintained at an essentially homogeneous solids-to-liquid ratio. From the storage tank(s), the catalyst slurry can be pumped to the polymerization reactor along a fluid passage having a flow meter. The flow of the catalyst slurry can be continuous and / or adjusted based on a measured parameter. The catalyst slurry may be continuously and reliability fed to the polymerization reactor.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
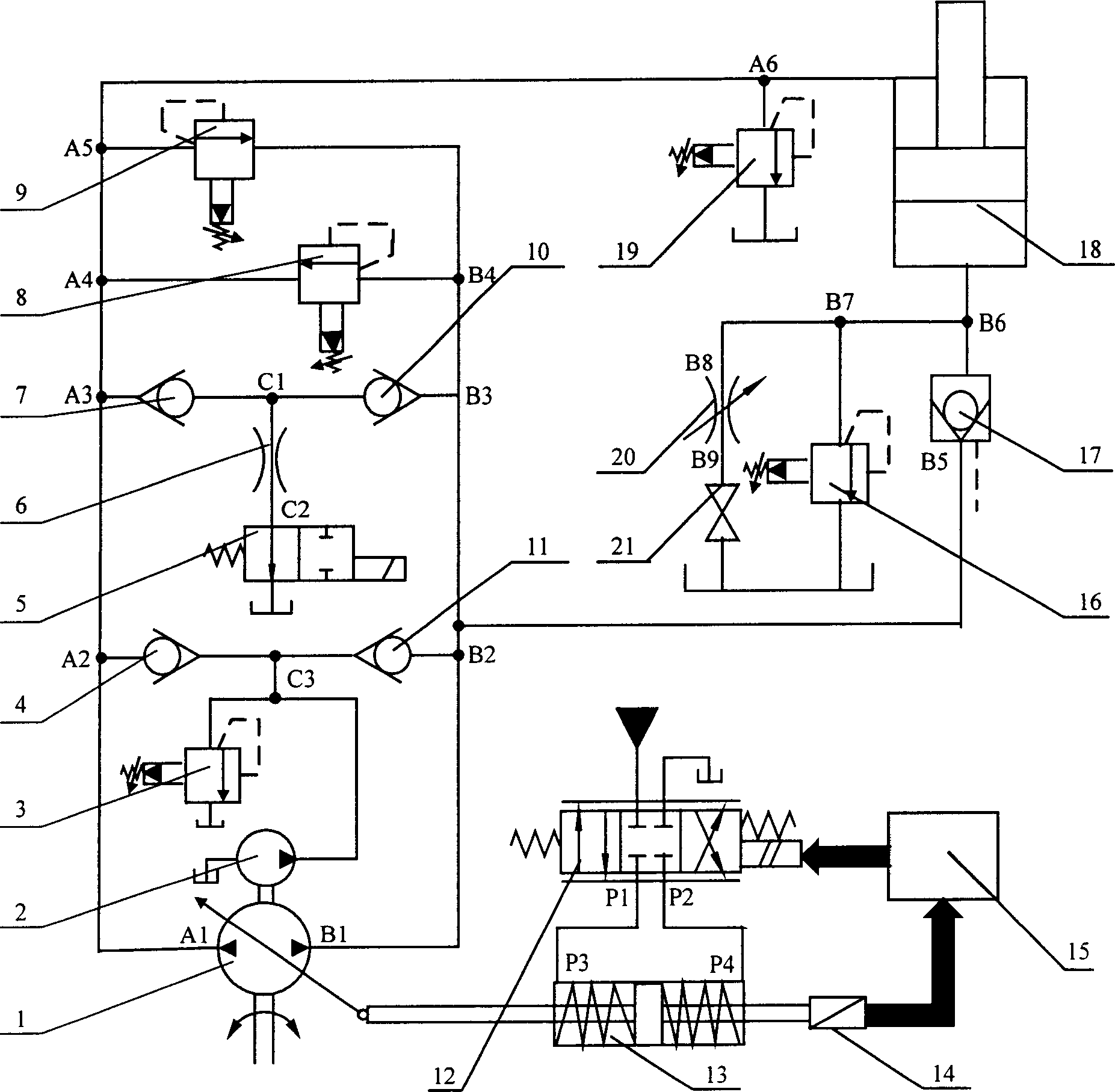
Asymmetric cylinder closed-loop speed system controlled by electro-hydraulic proportional pump
The invention relates to a control system of electric liquid ratio pump control asymmetry cylinder. Wherein, the oil gate A1 of electric liquid ratio pump (1) with closed-loop flux control system is connected to the single valve (4) oil gate A2, the single valve (7) oil gate A3, the overflow valve (8) oil gate A4, the overflow valve (9) oil gate A5, the flux division overflow valve (19) oil gate A6 and the asymmetry oil cylinder (18) rod chamber; the oil gate B1 of electric liquid ratio pump (1) is connected to the single valve (11) oil gate B2, the single valve (10) oil gate B3, the overflow valve (8) oil gate B4, the overflow valve (9) oil gate B4, and the liquid control single valve (17) oil gate B5; and the oil gate B6 of liquid control single valve (17) is connected to the non-rod chamber of asymmetry oil cylinder (18) and the maintenance-safety circuit. The oil feeding circuit, main pump zero flux unload circuit and pressure-limited circuit are arranged between the non-rod chamber and the rod chamber oil pip.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
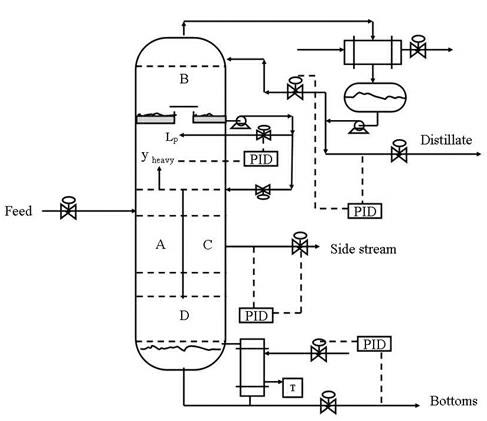
Method for controlling dividing-wall distillation column
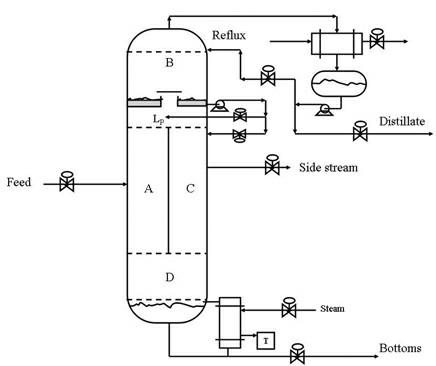
ActiveCN102631791ADistillation regulation/controlDistillation purification/separationLiquid ratioControl engineering
The invention discloses a method for controlling a dividing-wall distillation column. The method adopts four control loops, namely, an overhead distillate composition control loop which controls overhead reflux through overhead distillate component concentration; a siding distillate composition control loop which controls siding reflux through sliding distillate component concentration; a column bottom distillate composition control loop which controls column bottom thermal load through column bottom distillate component concentration; and a pre-distillation section top gas-phase composition control loop which controls a fractional liquid ratio of the interior of the dividing-wall distillation column through pre-distillation section top gas-phase component concentration. All the control loops are preferably a PID (proportion-integration-differentiation) control loop. The control method disclosed by the invention can realize stable control of the entire column when feeding flux or feeding component concentration changes, and further ensure the produce quality and ensure the energy consumption of the entire column to be within an optimum range.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
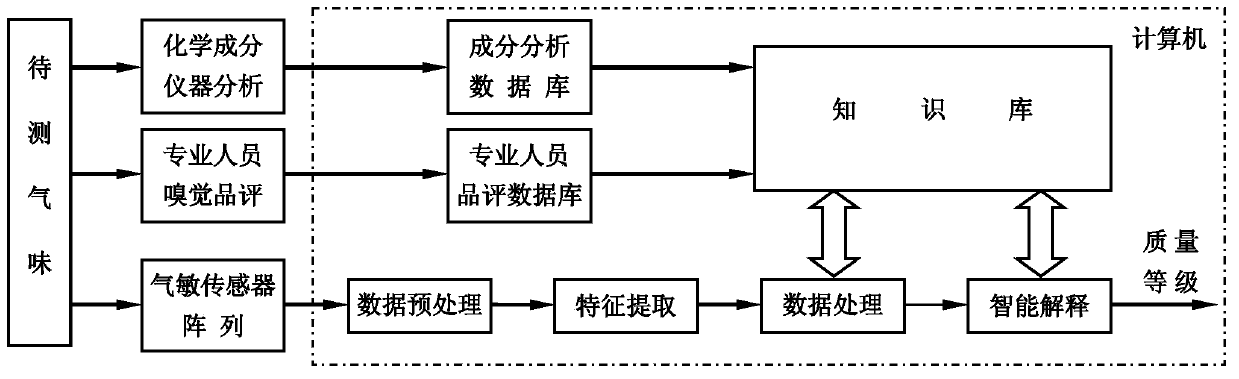
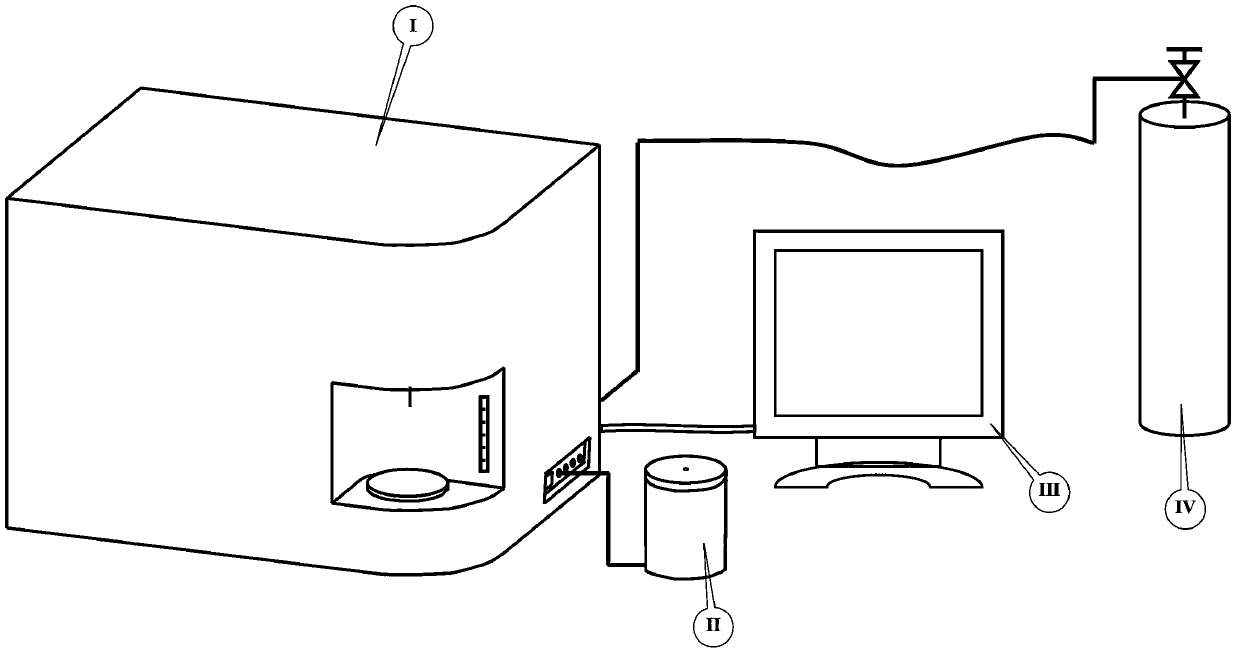
Olfactory analog instrument and on-site analysis method for odor grade of specific substance
ActiveCN103472094AHigh degree of integrationHigh constant temperatureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSensor arrayVegetable oil
The invention provides an olfactory analog instrument and an on-site analysis method for the odor grade of a specific substance. The invention has the following characteristics: 1, a gas sensor array constant temperature operation room, a computer and an autoinjection system are integrated in a test box; 2, utilization of a sample bottle with a volume of 250 ml and 25 ml of a to-be-tested sample enables a gas-liquid ratio to be 9: 1; 3, parallel resistance wires respectively wind in a semi-circle manner to generate 45-W power, so the sample and headspace volatilized gas are heated to a temperature of 80 DEG C in only 8 min and maintained at the temperature for 30 min; 4, 25 ml of an aqueous ethanol solution with a concentration of 100 ppm is used to generate standard reference gas in the sample bottle with a volume of 250 ml, and correction on gas sensors are carried out based on the generated standard reference gas; 5, headspace sampling flow is 500 ml / min, sampling time is 30 s, and gas sensor response signals undergo lowpass filtering and dimensionality reduction pretreatment; and 6, a database is established, and the olfactory analog instrument carries out on-site detection and grade prediction and identification on the odor of specific substances consisting of an adhesive, petroleum wax, leather, glycerin and edible vegetable oil.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
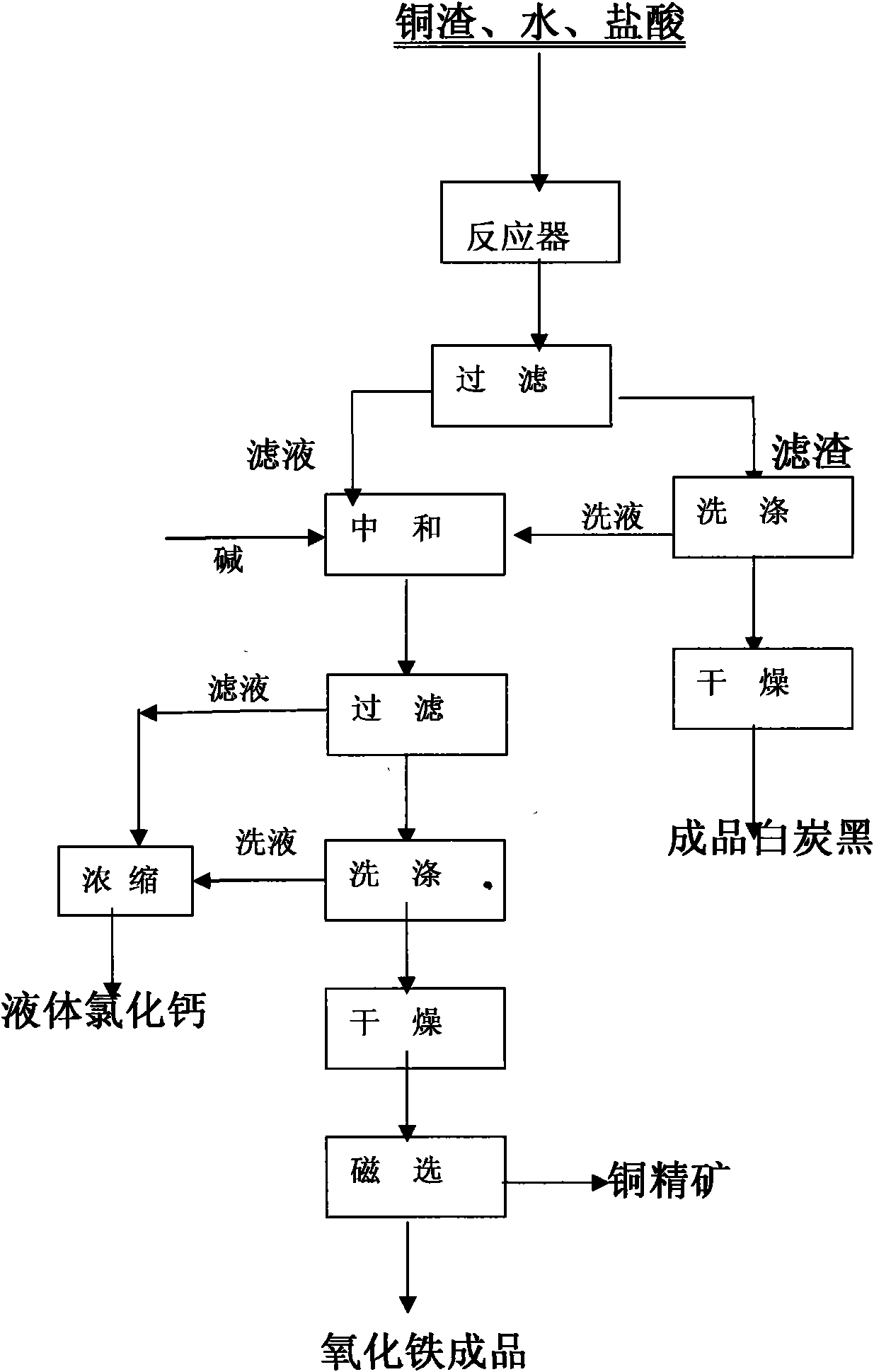
Method for comprehensively recovering Fe, Cu and Si from copper smelting slag
InactiveCN101555551AImprove resource utilizationImprove product added valueSilicaCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesSilicon dioxideMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering iron, copper and silicon dioxide from copper smelting slag. The method takes copper smelting slag as a raw material, and comprehensively recovers Fe, Cu and Si in copper slag by adopting wet chemistry metallurgical technology. A muriatic acid and an inorganic acid are mainly adopted for leaching the copper smelting slag, the leaching acid concentration, the solid to liquid ratio, the leaching temperature and the leaching time are selected according to the quality requirement of silicon dioxide products under certain conditions, and silicon dioxide is firstly separated through filtering and drying to prepare silica pigment; the leaching filtered liquid is counteracted, settled, filtered, dried and ground, and ferric oxide phase and copper-bearing phase are selectively separated by adopting a conventional mineral processing method.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
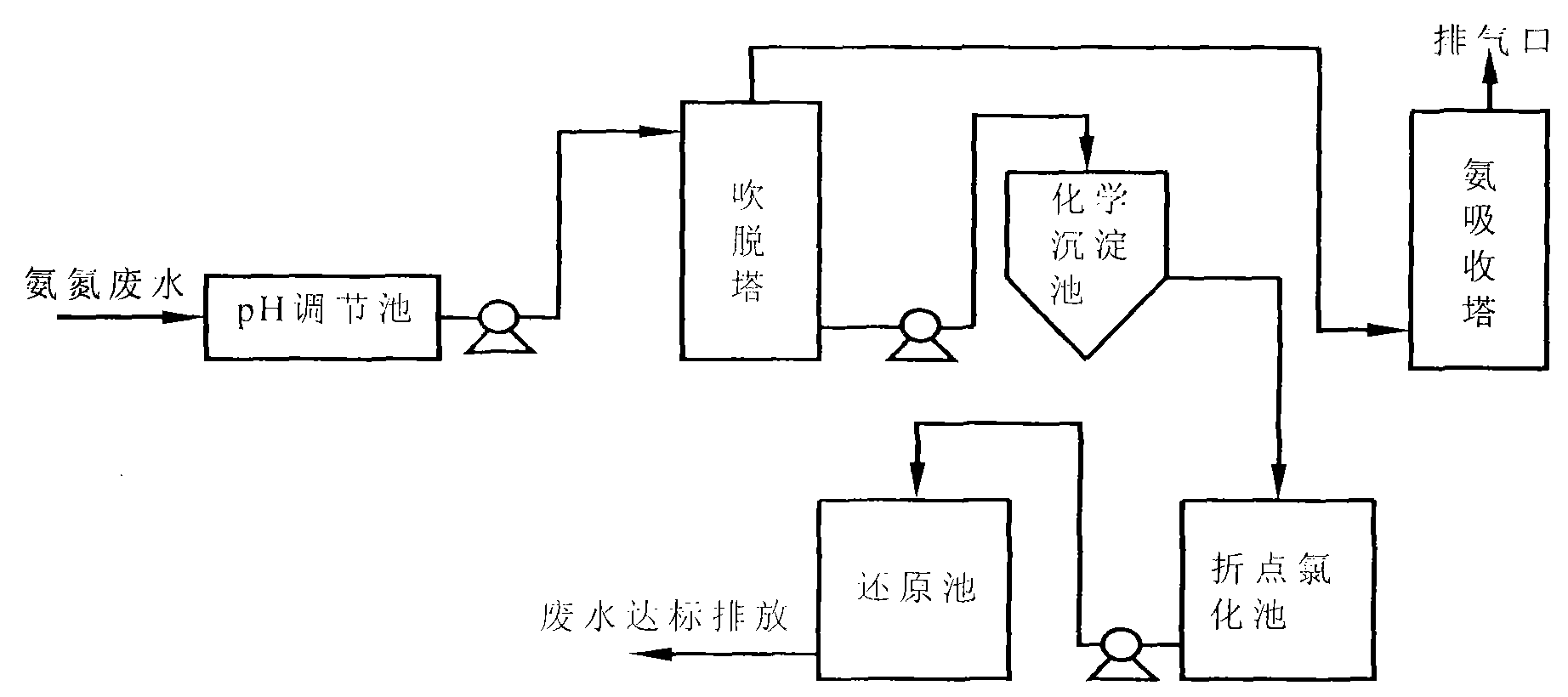
Method for treating highly concentrated ammonian wastewater with poor biodegradability by using a multiple-technique combination
InactiveCN101555077AShort processing cycleEasy to operateMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationMagnesium saltEmission standard
The invention relates to a method for treating highly concentrated ammonian wastewater with poor biodegradability by using a multiple-technique combination, which belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The method is characterized in that: the ammonian wastewater primarily enters a pH adjusting tank for adjusting the pH value to be 11-12.5 and enters a blow-off tower for blowing off with the gas-liquid ratio being 3000-4500, the blown-off wastewater enters a chemical precipitation tank, magnesium salts and phosphates are added according to the mol ratio of Mg : N : P being 1.4-1.7:1:1 for reacting with the wastewater to generate ammonium magnesium phosphate precipitate for removing ammonian, yielding water enters a break point chlorination tank, chlorine-containing oxide is added according to the weight ratio Cl / N being 9-12:1 of active chlorine and ammonian, the wastewater is transferred to a reducing tank after the reaction, reducing agent is added according to 1-1.1 times of theoretical mol value of the yielding water completely reacting with residual chlorine, and the wastewater can be directly discharged after the reaction. The treatment method has simple operation, high reaction speed and low wastewater treatment cost, and can lead ammonian to be recovered without secondary pollution to environment; and the yielding water can reach primary emission standard.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing whey protein gel-like emulsion
InactiveCN101878904AGreat tasteImprove stabilityAnimal proteins working-upFood preparationLiquid ratioVegetable oil
The invention discloses a method for producing a whey protein gel-like emulsion. The method comprises the following steps of: dispersing a whey protein condensate or a whey protein isolate in distilled water in a solid-liquid ratio of 0.8-1.5:10, and fully hydrating the mixture for 6 to 12 hours to obtain protein dispersion liquid; heating the protein dispersion liquid for 0.3 to 1 hour at the temperature of between 70 and 75 DEG C, stirring and mixing the whey protein dispersion liquid with plant oil in a volume ratio of 8-4:2-6 and performing proper high-speed homogenization treatment to obtain a rough protein emulsion; and finally, performing high pressure micro-jet homogenization treatment on the rough protein emulsion to obtain a milk white gel-like emulsion product. The method for producing the whey protein gel-like emulsion has the advantages of simple process, low cost, safety and environmental protection; and the produced emulsion product can be widely applied to various nutritious foods and functional (health-care) foods, and can also be used as an embedding carrier for fat soluble medicaments.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
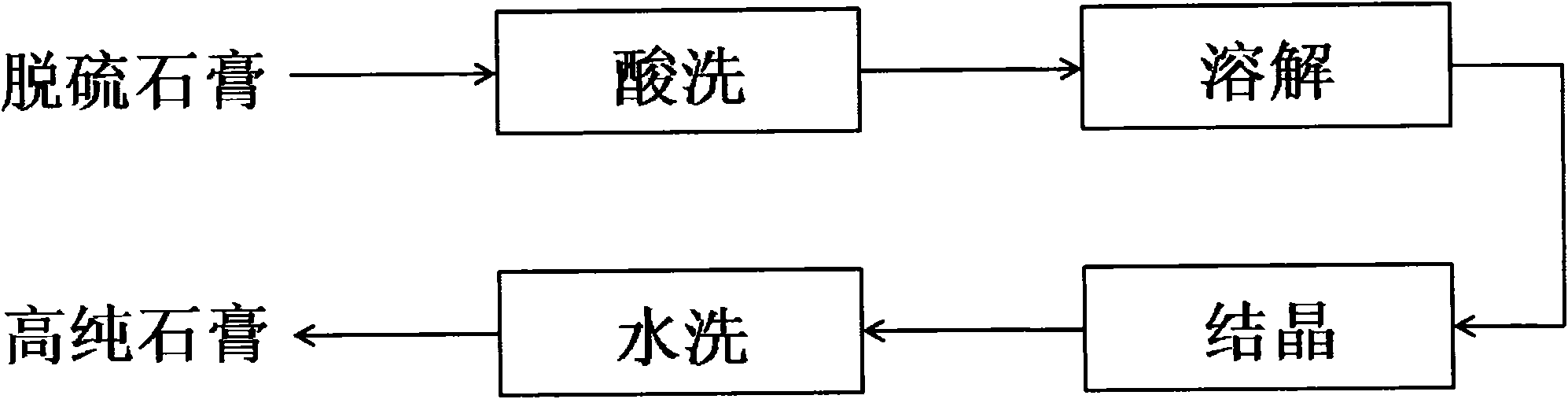
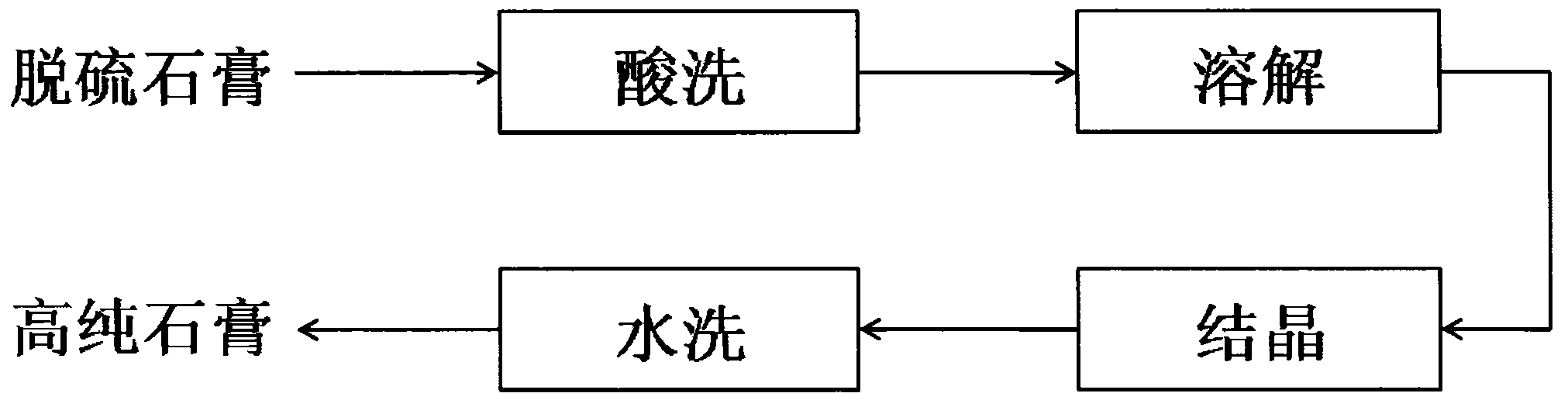
Method for recrystallizing and purifying desulphurized gypsum
InactiveCN101870494AHigh whitenessHigh purityCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesSolubilityAcid washing
The invention provides a method for recrystallizing and purifying desulphurized gypsum, which mainly comprises the four steps of acid-washing, dissolution, crystallization and washing, and specifically comprises the following steps of: removing impurities, reacted with acids, in the desulphurized gypsum by the aid-washing, dissolving calcium sulphate in the desulphurized gypsum into the acid solution at a relatively higher temperature by utilizing the characteristic that the solubility of the calcium sulphate in the specific acid solution is remarkably changed with the temperature, performing solid-liquid separation to remove undissolved solid-phase impurities at the high temperature, performing cooling recrystallization and the solid-liquid separation on a liquid phase at a relatively lower temperature, and washing and drying a filter cake to obtain high-purity gypsum, wherein the liquid phase in the dissolution and recrystallization processes can be reused. Through the method provided by the invention, the gypsum with relatively higher purity and whiteness can be prepared by selecting a proper solid-to-liquid ratio, proper temperatures and proper acid concentration and performing dissolution and crystallization for a certain time, and the performance of the desulphurized gypsum is remarkably improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method, system, controller and computer program product for controlling the flow of a multiphase fluid
ActiveUS20060150749A1Respond effectivelyMaximize productionFluid removalPipeline systemsLiquid ratioEngineering
A method, system, controller and computer program product, for controlling the flow of a multiphase fluid comprising gas and liquid in a conduit, which conduit is provided at a downstream side with a flow restriction and a valve having a variable aperture, which method comprises the steps of selecting a flow parameter of the multiphase fluid in the conduit as a function of a pressure difference over the flow restriction; selecting a setpoint for the flow parameter; allowing the multiphase fluid to flow at a selected setpoint of the aperture of the variable valve; determining the pressure difference over the flow restriction and determining an actual value of the flow parameter from the pressure difference, without using a measurement of another variable in order to determine an actual gas / liquid ratio pertaining to the pressure difference at the flow restriction; controlling the flow of the multiphase fluid by determining a deviation of the flow parameter from its setpoint, determining an updated setpoint for the aperture of the valve which is dependent on the deviation, and manipulating the aperture of the valve accordingly.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Method for reclaiming cobalt from manganese cobalt slag
The invention discloses a method for recycling cobalt and nickel from manganese and cobalt slag, comprising the following steps of: adding water into the manganese and cobalt slag according to a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1: 2 to 5 so that the manganese and cobalt slag becomes slurry, heating, bubbling and stirring to obtain cobalt-nickel foaming slag and ferromanganese sediment, heating the cobalt-nickel foaming slag to a temperature of 80 DEG C to 85 DEG C, washing the cobalt-nickel foaming slag with 0.5 to 2 mol / L of H2SO4 and controlling the pH value of the cobalt-nickel foaming slag to be at 1.5 to 2.5, filtering and then obtaining cobalt-nickel filter cake, curing and leaching with concentrated sulfuric acid on a base that the ratio of cobalt-nickel filter cake (dry-substrate weight) to concentrated sulfuric acid (volume) equals to 1:0.5 to 1.5 so as to obtain a cobalt-nickel solution and finally deeply purifying and extracting according to traditional technology to separate cobalt and nickel. The method can effectively separate Co and Ni from Mn, Fe in manganese and cobalt slag and recycle economic cobalt and nickel from manganese and cobalt slag; the extraction ratio of cobalt and nickel in manganese and cobalt slag is more than 95 percent.
Owner:广西冶金研究院有限公司
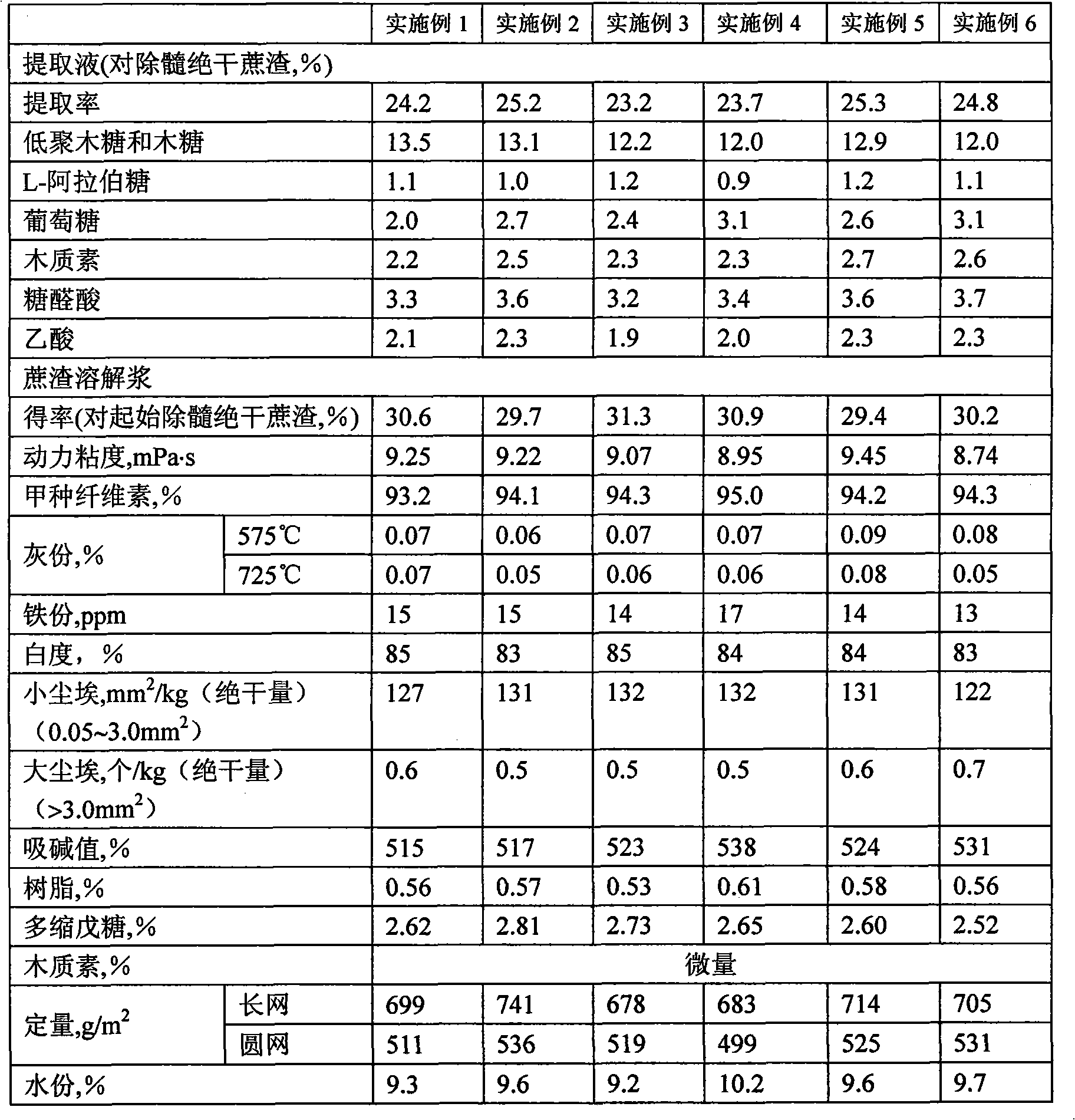
Method for preparing bagasse dissolving pulp and pre-extracting hemicellulose and product thereof
InactiveCN101613970AHigh extraction rateReduce the content of non-sugar organic debrisSugar derivativesPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsLiquid ratioDissolving pulp
The invention relates to a method for preparing bagasse dissolving pulp and pre-extracting hemicellulose and products thereof; the method comprises the following steps: bagasse preparation which comprises the steps of depithing and washing; prehydrolysis which is carried out in a globe digester or a hydrolysis boiler; wherein, the process conditions are as follows: in the process for depithing and oven-drying bagasse, the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:0.4-8.0, the hydrolysis temperature is 100-200 DEG C, the hydrolysis time is 15-240min, the pH value of the end point of hydrolysis is 2-5; in the process of the solid-to-liquid separation and washing, the filtrate is collected to prepare extracting solution; dissolving pulp is prepared by residue alkali method. By adopting the method, bagasse dissolving pulp and bagasse extracting solution which is used to prepare oligosaccharides are obtained. Most of pentosan in bagasse can be extracted by controlling the process conditions of the prehydrolysis, the technical route and the process conditions have strong pertinence so that the reactivity and the uniformity of bagasse dissolving pulp can be improved; by improving the traditional dissolving pulp alkali method for pulping, bagasse biorefinery based on dissolving pulp pulping can be realized in engineering so that the production costs for preparing bagasse dissolving pulp and pre-extracting hemicellulose are reduced.
Owner:上海士林纤维材料有限公司
Vanadium-containing non-magnesium hard alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a nonmagnetic hard alloy material and a preparation method thereof. The alloy comprises (wt %) tungsten carbide 75-90, nickel powder 8-20, chromium carbide 0.5-3.0, and vanadium carbide 0.3-2.5. The preparation method comprises compounding, wet grinding, drying, pressing, sintering and checking, wherein in the wet grinding step, a nonmagnetic alloy lining board wet grinder is used, alcohol or acetone is added as grinding medium, nonmagnetic hard alloy balls is used as grinding material, the ratio of grinding medium to material is 5:1, the solid-to-liquid ratio is 350ml / Kg, and the wet grinding time is 48-56 hours; and pressure sintering is adopted. In the inventive nonmagnetic hard alloy material, fine-particle tungsten carbide powder (1.0-1.5 mum) is used as hard phase, so as to improve the hardness and abrasion resistance of the alloy. The nickel is used as binder, and a small amount of chromium carbide and vanadium carbide are added as tungsten carbide grain growth inhibitor, so as to refine tungsten carbide crystal grains, and further improve the hardness and abrasion resistance of the alloy. The pressure sintering technique accelerates densification speed during sintering process, effectively reduces porosity of the alloy, and remarkably improves the strength of the alloy.
Owner:ZHUZHOU JINGGONG CEMENTED CARBIDE
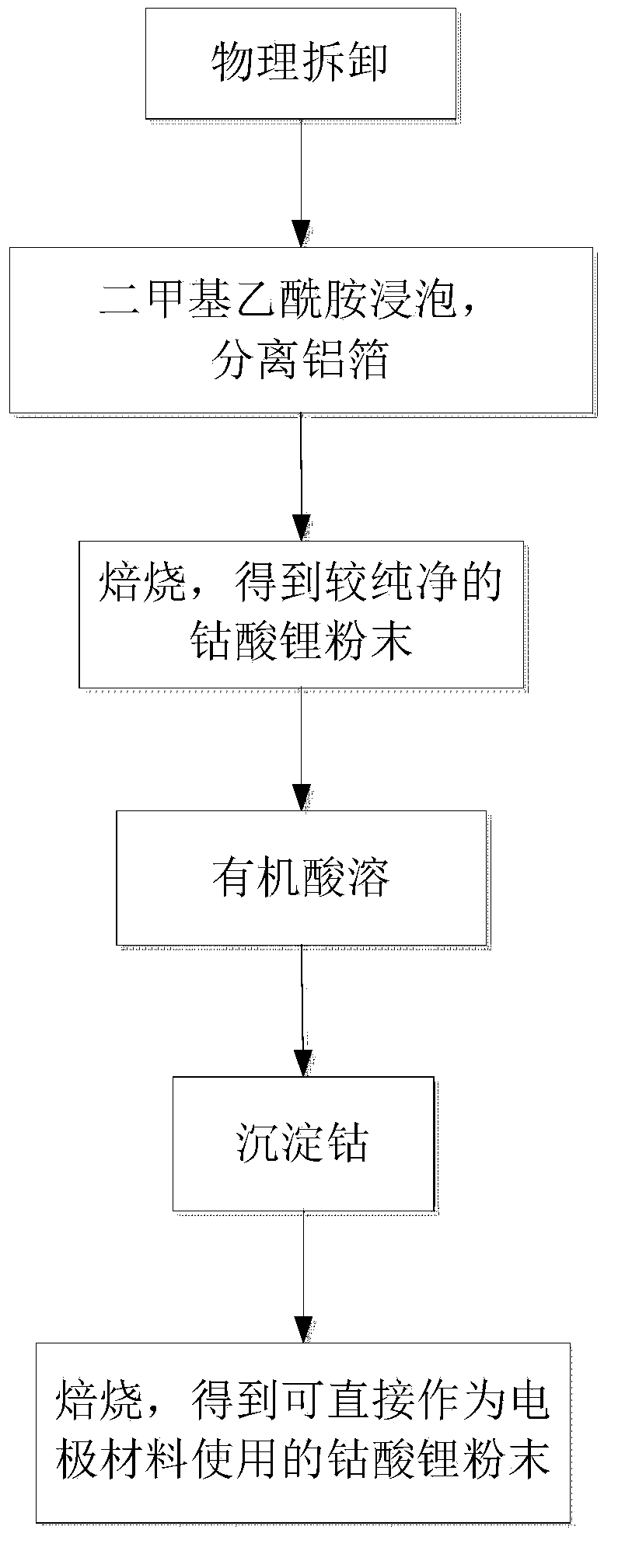
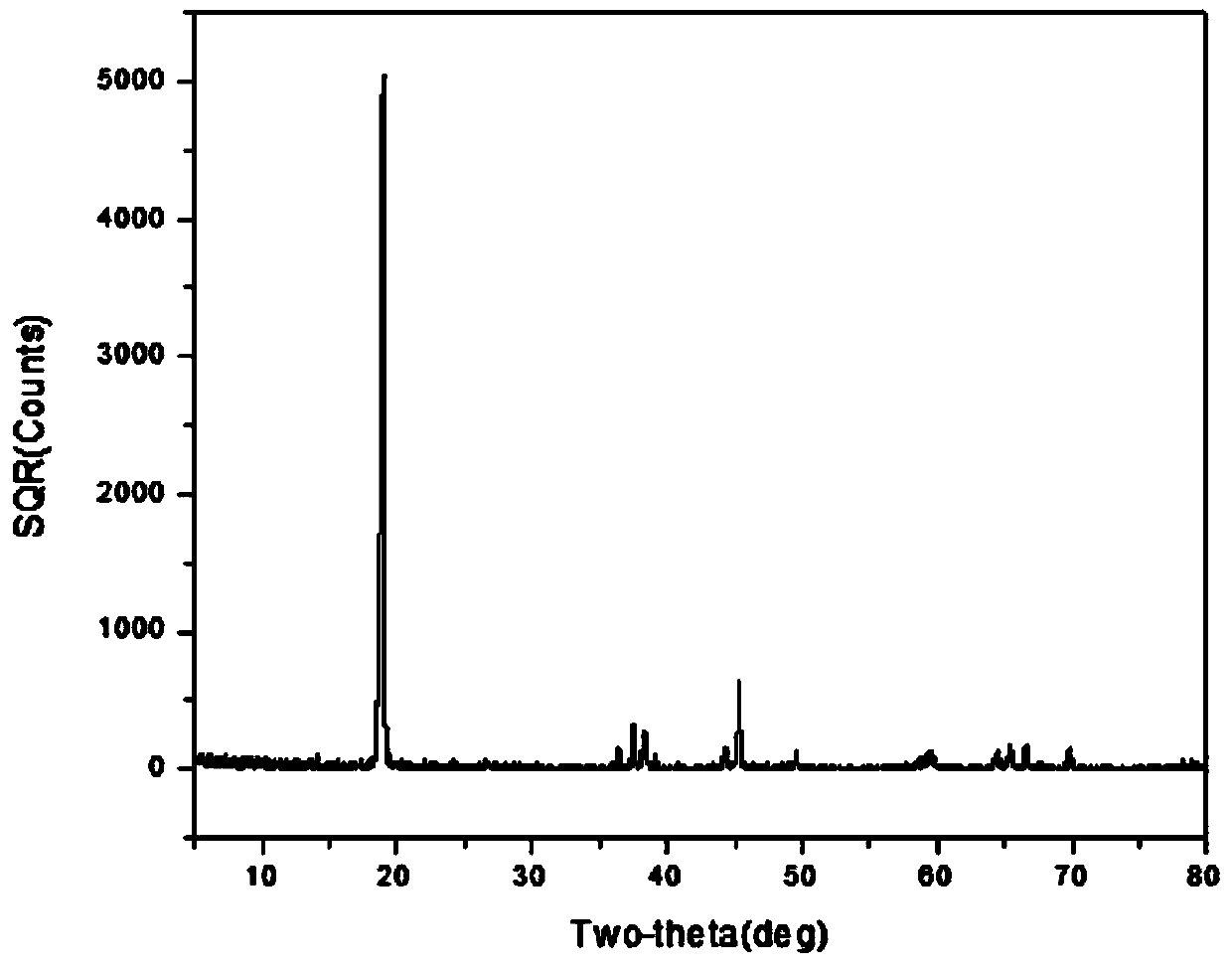
Method for recovering cobalt from lithium battery anode material
ActiveCN103474718AHigh recovery rateLow powder impurity contentWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingSolid matterAmmonium oxalate
The invention discloses a method for recovering cobalt from a lithium battery anode material. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) removing aluminum foil from the anode material, obtaining a black solid matter containing lithium cobalt oxide, roasting the black solid matter to form lithium cobalt oxide powder, (2) weighing and adding the lithium cobalt oxide powder into 119-240g / L of citric acid according to a solid-to-liquid ratio of (20-30):1g / L, adding hydrogen peroxide at a mass fraction of 30% according to a mole ratio of 2:(1-1.05), performing stirring leaching for 5-7h at 80-90 DEG C, filtering to form filtrate containing the cobalt, (3) adding an ammonium oxalate solution into the filtrate to form a cobalt oxalate precipitate, and (4) after drying the cobalt oxalate precipitate, adding lithium carbonate powder according to a mole ratio (1:(1-1.05)) of the cobalt to lithium, grinding uniformly, roasting for 6-8h at 800-850 DEG C, and obtaining lithium cobalt oxide powder capable of directly serving as the electrode material. The method is easy to operate and high in recovery rate, equipment is simple, waste liquid is easy to treat, and the pollution of waste lithium batteries to an environment can be effectively reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH WUCHANG BRANCH
Catalytic cracking catalyst
The present invention relates to a cracking catalyst. Its composition contains (by wt%) 10%-50% of high rare earth ultrastable Y-type molecular sieve, 10%-40% of aluminium oxide adhesive and 10%-70% of clay. The preparation method of described high rare earth ultrastable Y-type molecular sieve includes the following steps: fully mixing ultrastable Y-type zeolite and acid solution whose equivalent concentration is 0.01N-2N according to the solid-liquid ratio of 20:4 at temperature range of 20deg.C-100deg.C, stirring them for 10min-300min, then washing, filtering, adding rare earth salt solution to make rare earth ion exchange, after the exchange washing, filtering and drying so as to obtain the high rare earth ultrastable Y-type molecutar sieve.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for removing sulfur dioxide from flue gas
InactiveCN1883764AFast absorption of sulfur dioxideGood effectDispersed particle separationElectrolysisManganese
The invention relates to a process for removing sulfur dioxide in flue gas, which belongs to the field of environmental protection, characterized by mixing manganese dioxide and sulfur dioxide-containing flue gas to give sulfur trioxide and manganese sulfate at the temperature of 1 to 1300 DEG C in a solid-liquid ratio of 1:(0-40), wherein manganese dioxide is used as oxidant, and further processing the manganese sulfate solution to produce crystalline manganese sulfate, manganese carbide, or electrolytic manganese metal. In the present invention, the product is provided with quick absorption rate and of sulfur dioxide and low cost.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com