Patents
Literature
2847 results about "Flux control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
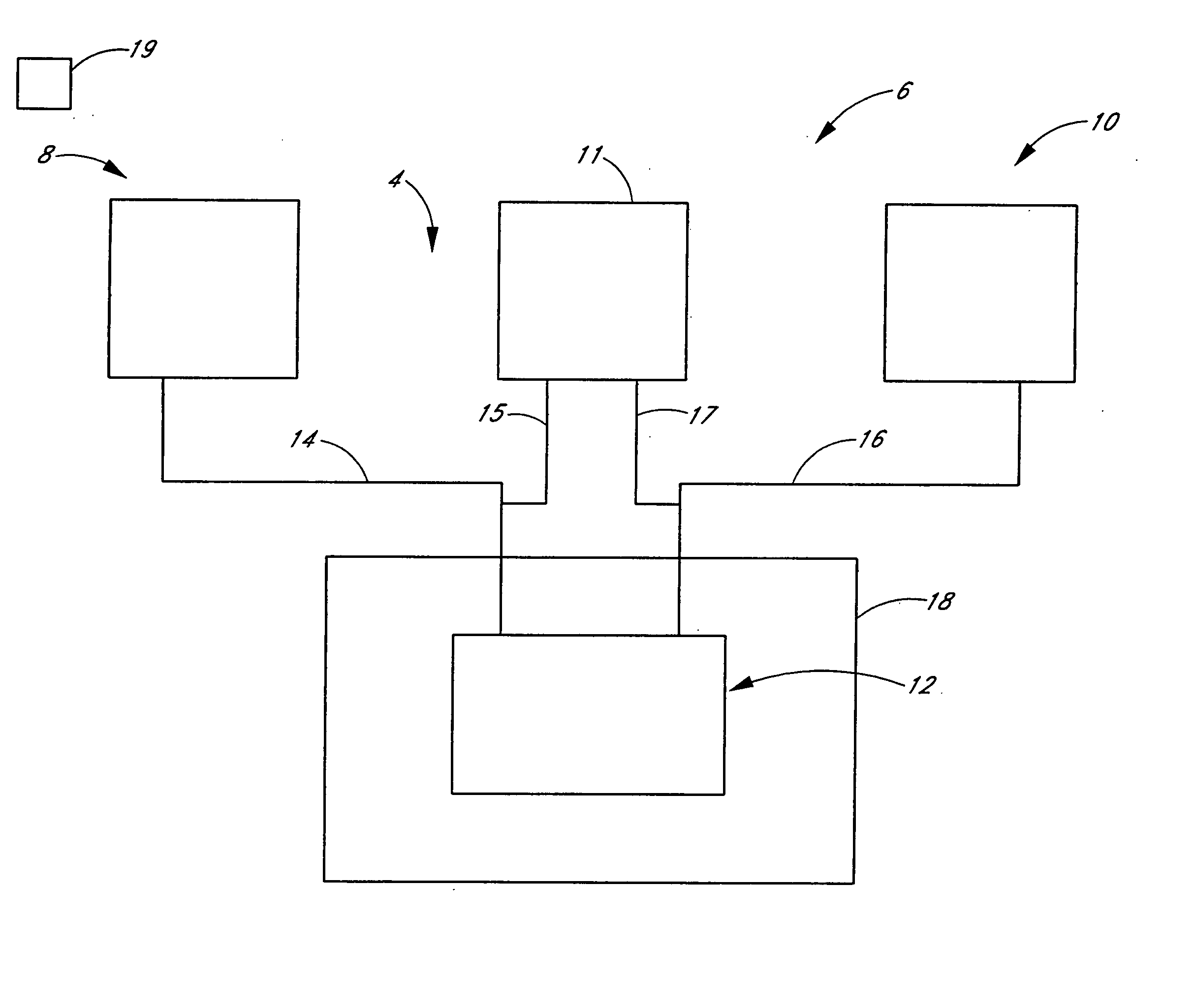
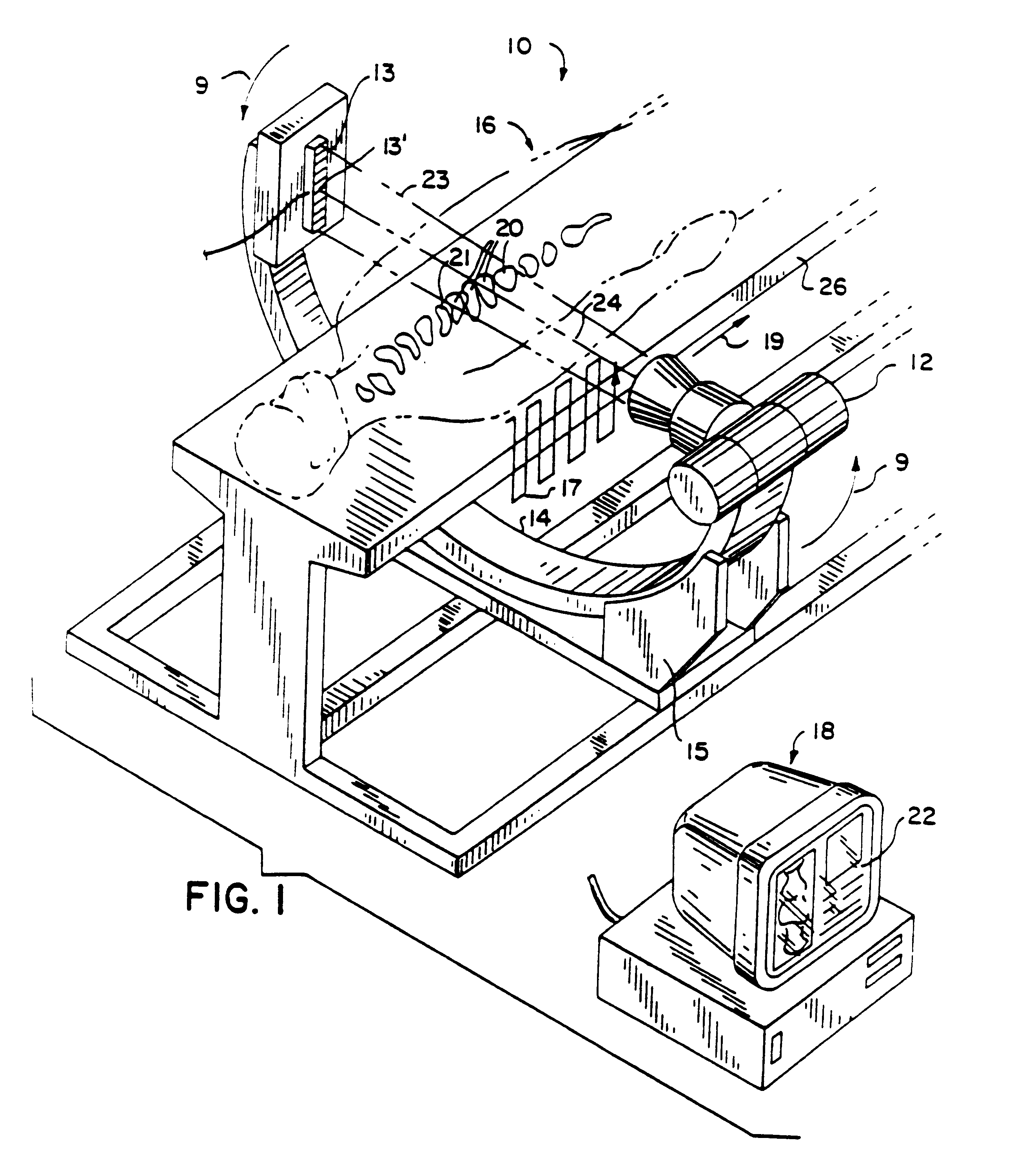
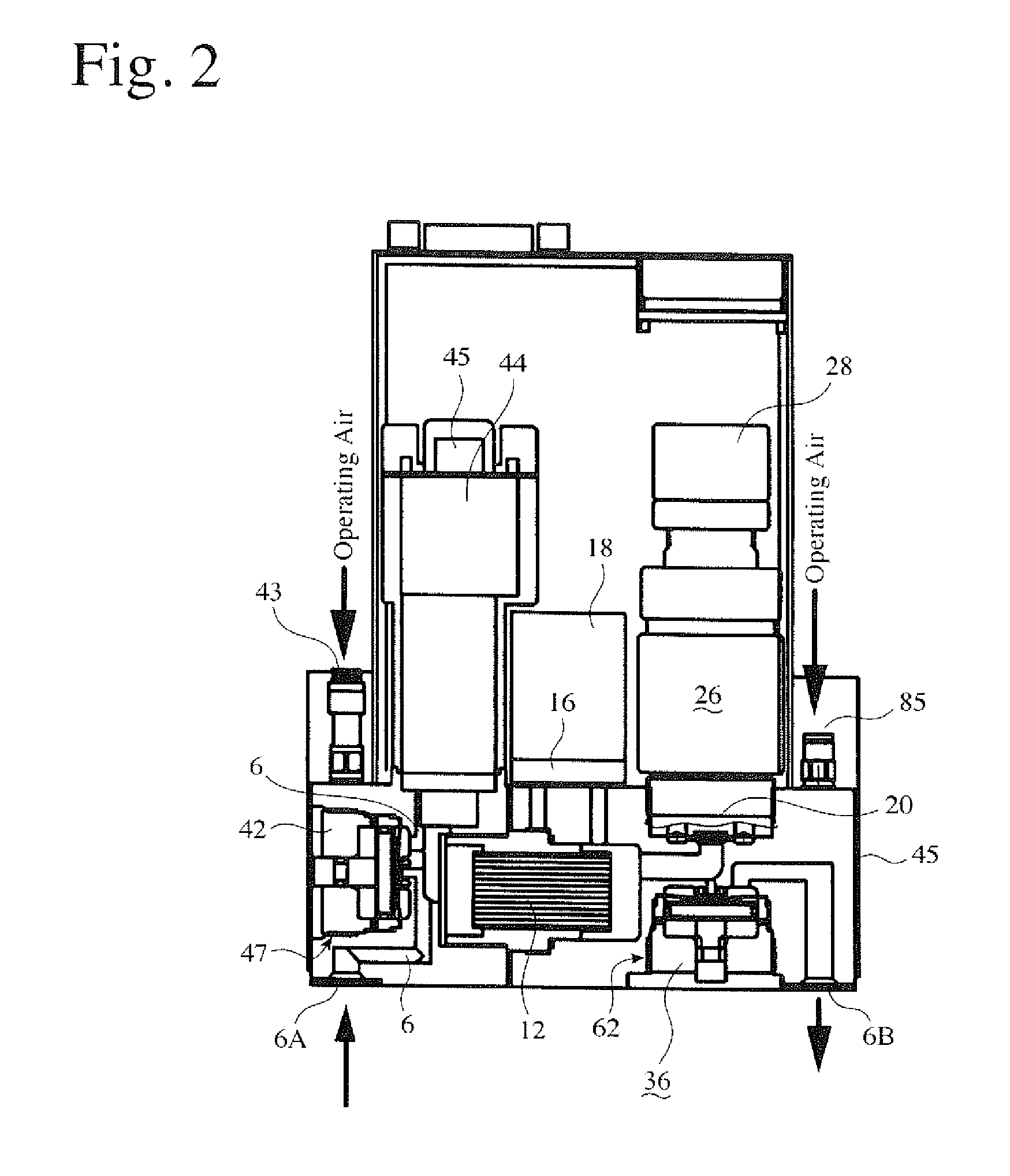
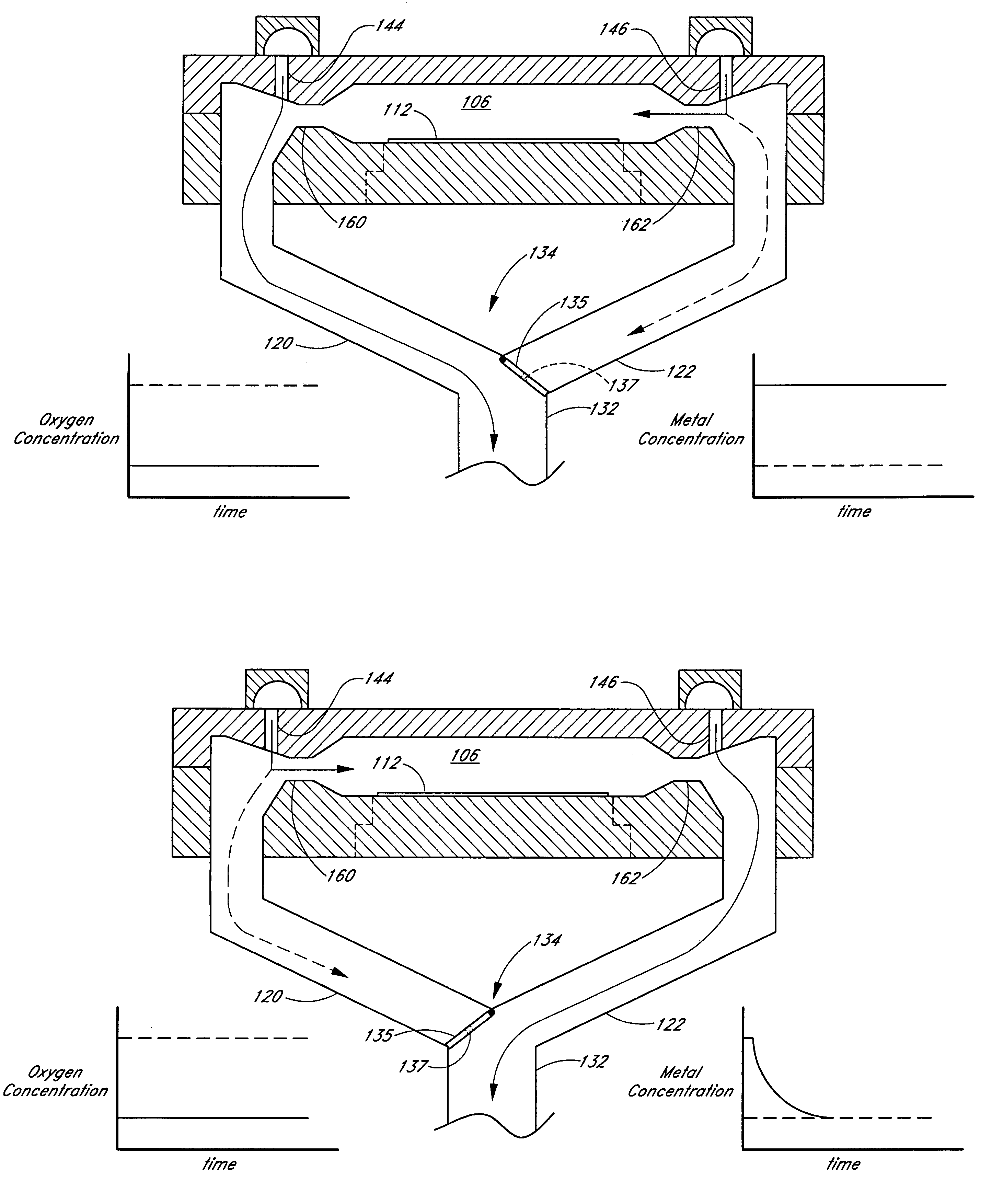
Reaction system for growing a thin film
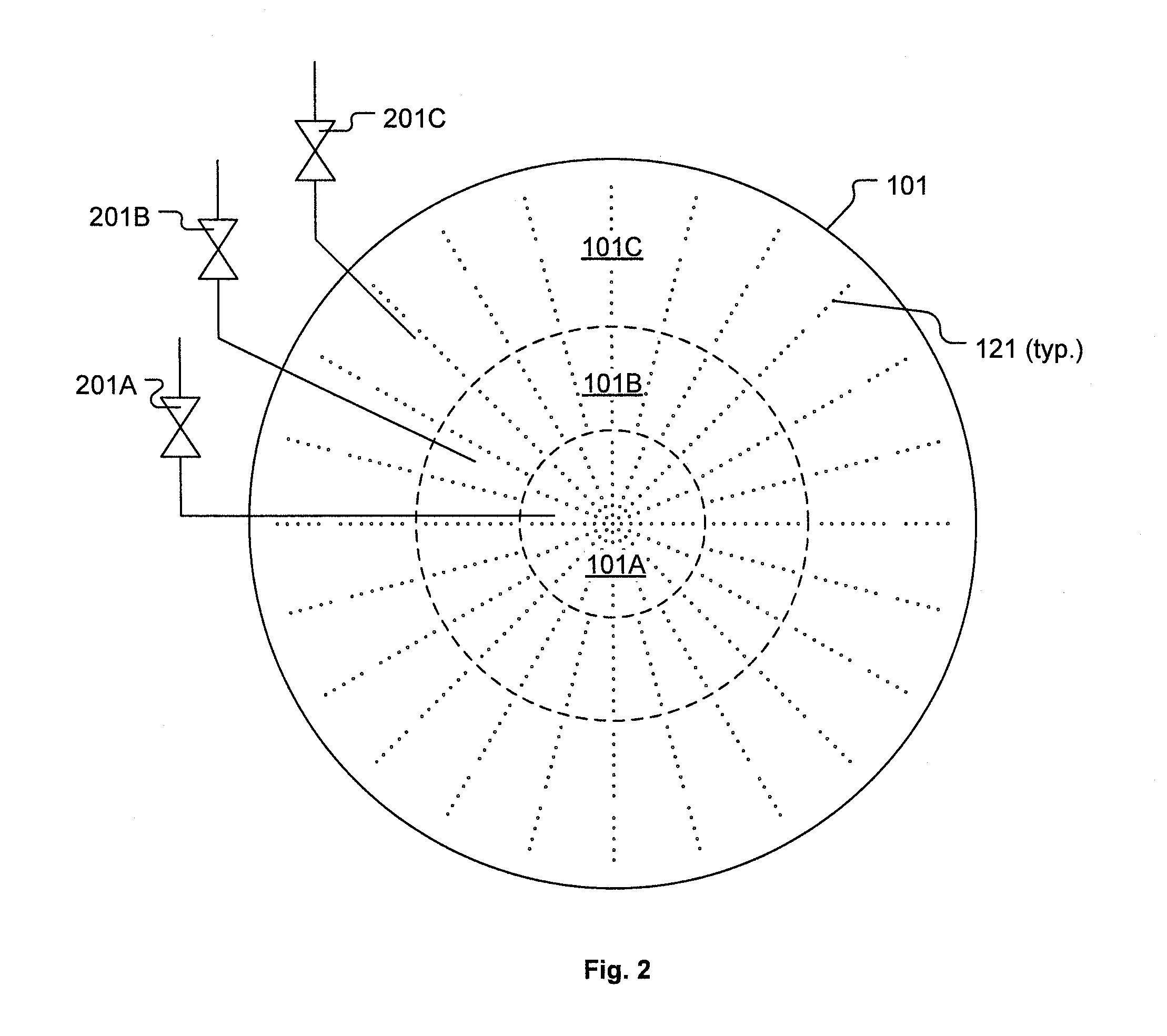
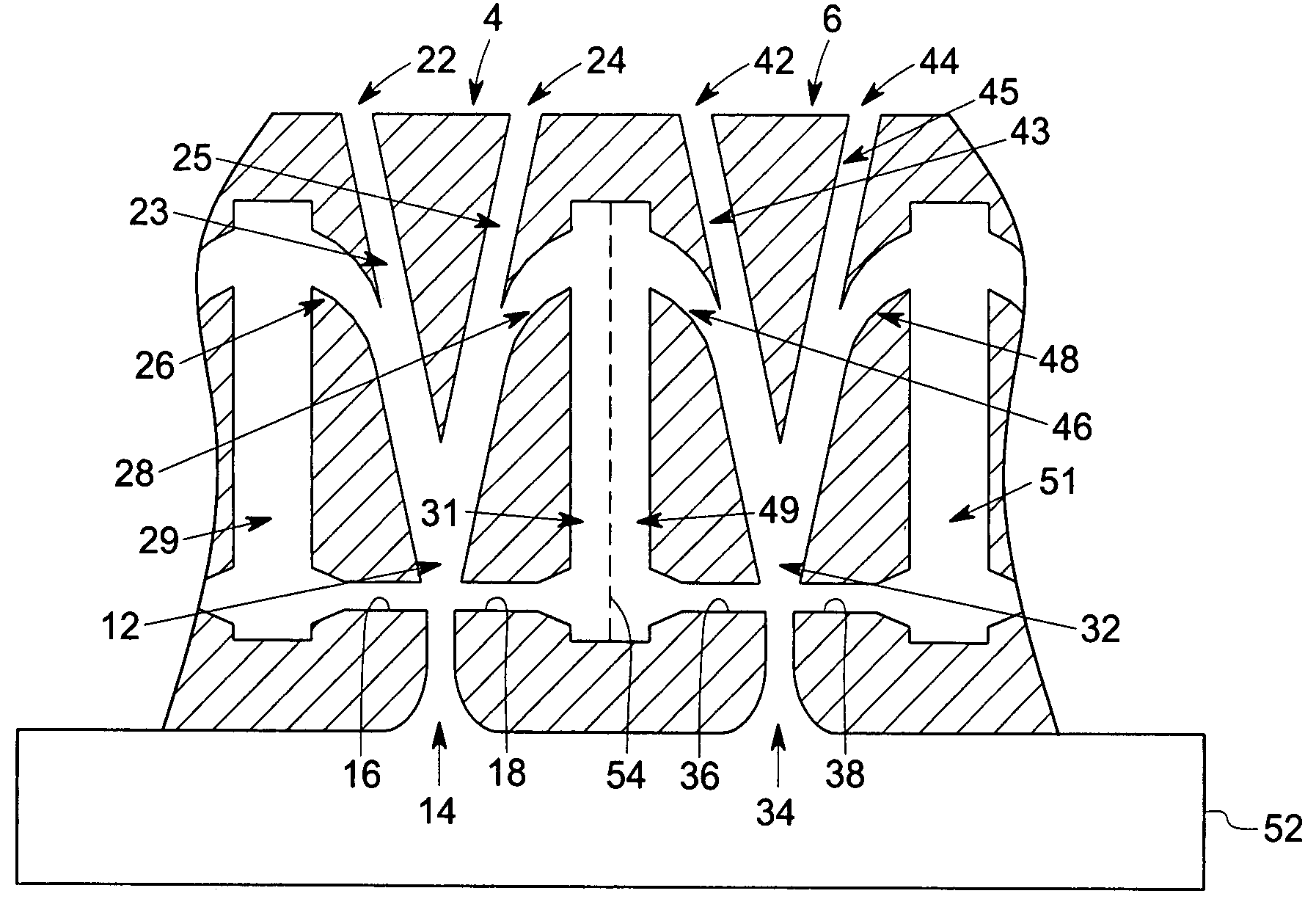
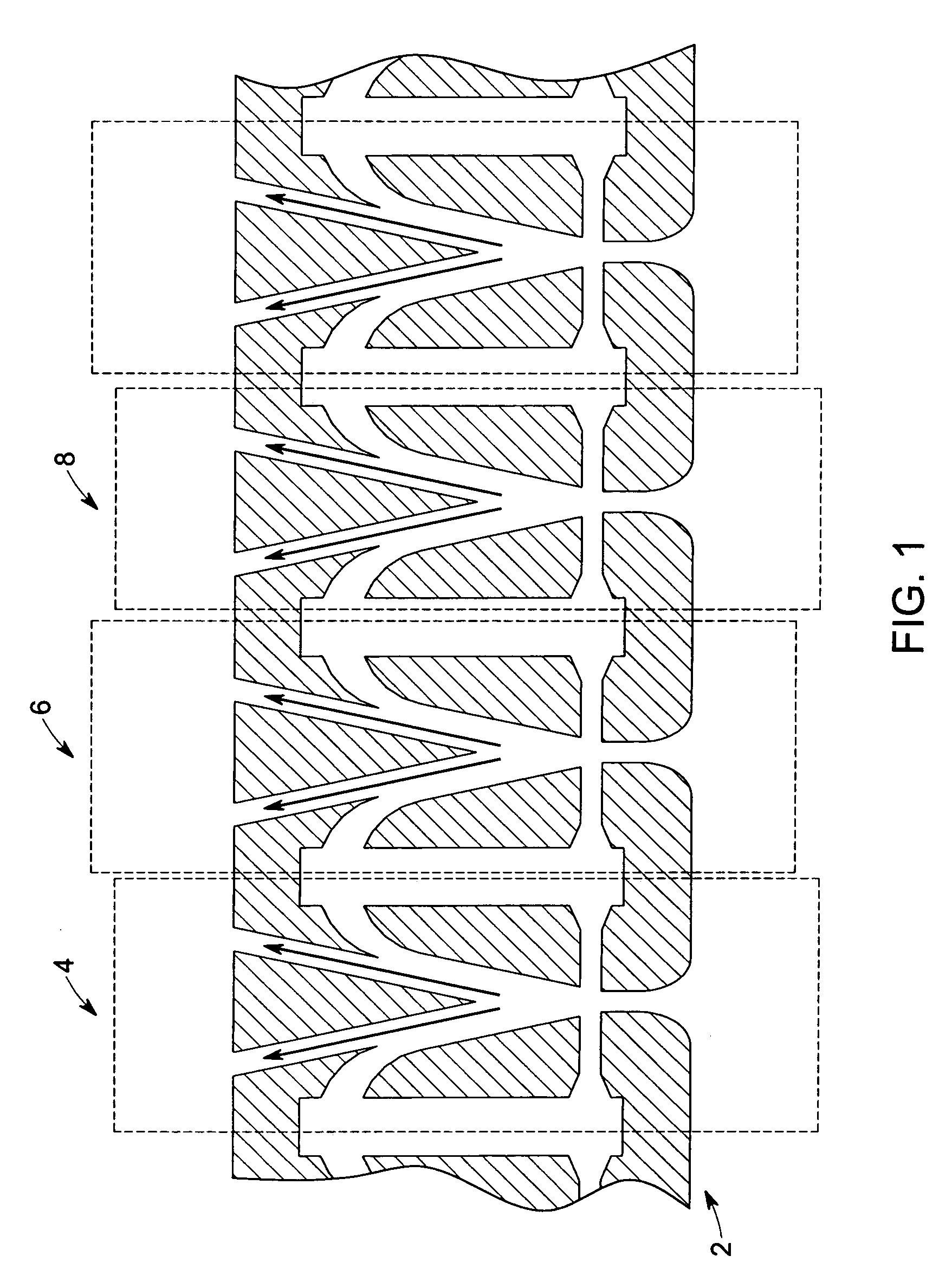
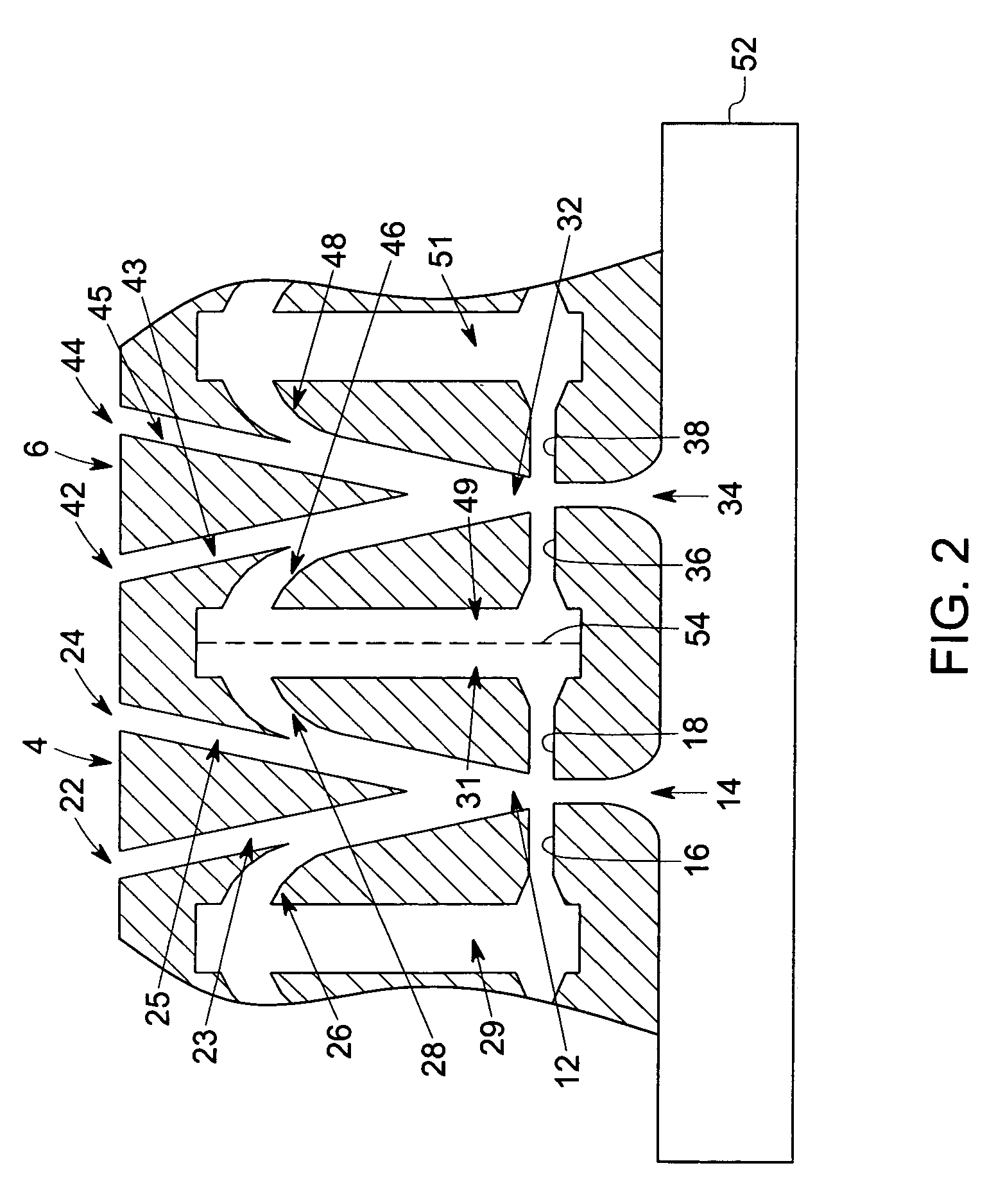
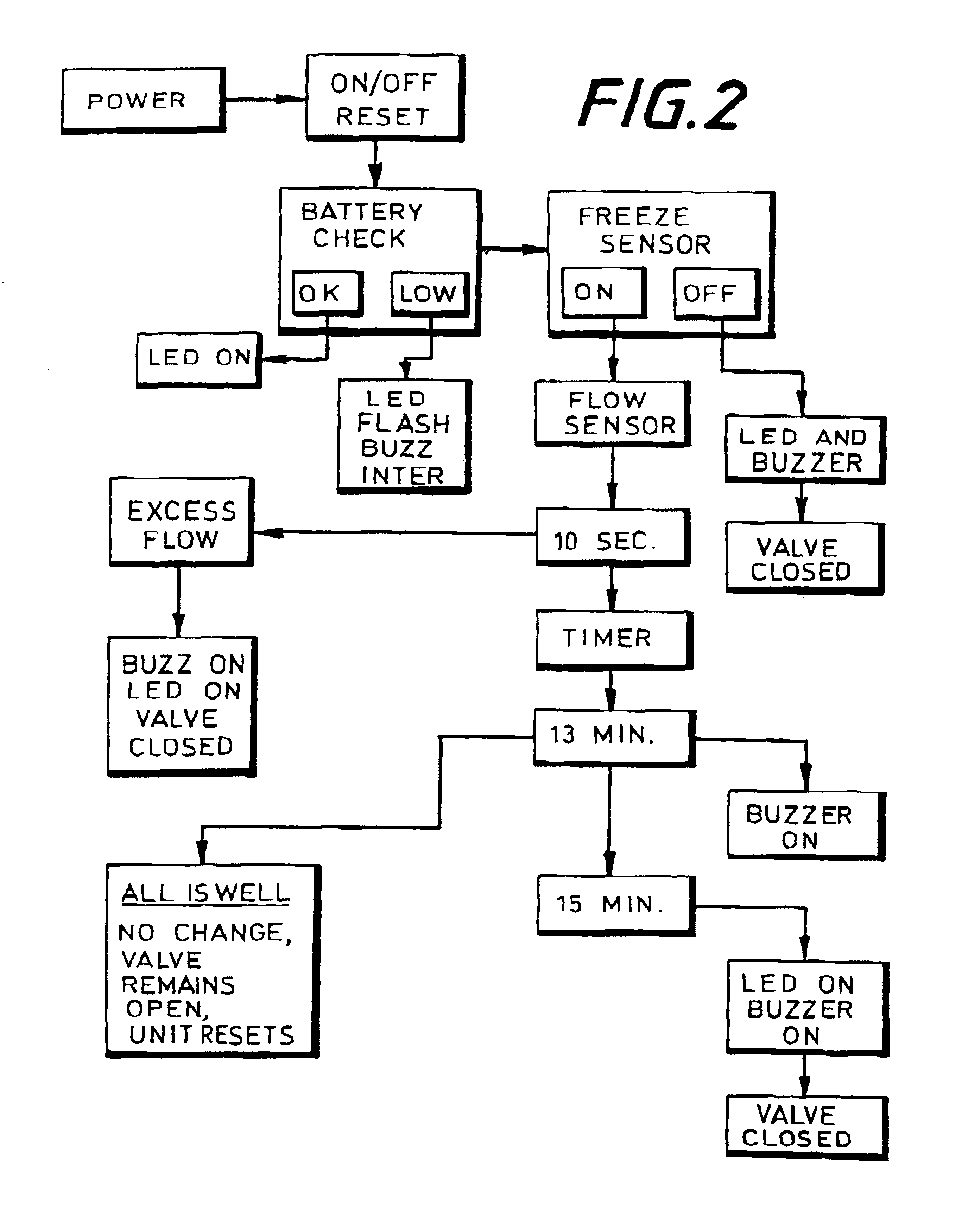
ActiveUS20050241176A1Extension of timeLong stepDrying using combination processesDrying solid materials with heatControl systemDiffusion barrier
A reactor defines a reaction chamber for processing a substrate. The reactor comprises a first inlet for providing a first reactant and to the reaction chamber and a second inlet for a second reactant to the reaction chamber. A first exhaust outlet removes gases from the reaction chamber. A second exhaust outlet removes gases from the reaction chamber. A flow control system is configured to alternately constrict flow through the first and second exhaust outlets. The reactor chamber is configured to for a diffusion barrier within the reaction chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Vapor flow control apparatus for atomic layer deposition
A device for performing ALD includes a housing having a vacuum chamber that surrounds a horizontal flow reactor. The device further includes a gas distribution system for delivering gases to the reactor. The gas distribution system includes at least one of a high temperature valve and a high temperature filter disposed inside the vacuum chamber. The high temperature valve (and / or filter) controls (and / or filters) a supply of a precursor / reactant gas, inert gas, or precursor / reactant and inert gas mixture before it enters the horizontal flow reactor.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Dual Plasma Volume Processing Apparatus for Neutral/Ion Flux Control
ActiveUS20120031559A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesGas supplySemiconductor
A semiconductor wafer processing apparatus includes a first electrode exposed to a first plasma generation volume, a second electrode exposed to a second plasma generation volume, and a gas distribution unit disposed between the first and second plasma generation volumes. The first electrode is defined to transmit radiofrequency (RF) power to the first plasma generation volume, and distribute a first plasma process gas to the first plasma generation volume. The second electrode is defined to transmit RF power to the second plasma generation volume, and hold a substrate in exposure to the second plasma generation volume. The gas distribution unit includes an arrangement of through-holes defined to fluidly connect the first plasma generation volume to the second plasma generation volume. The gas distribution unit also includes an arrangement of gas supply ports defined to distribute a second plasma process gas to the second plasma generation volume.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
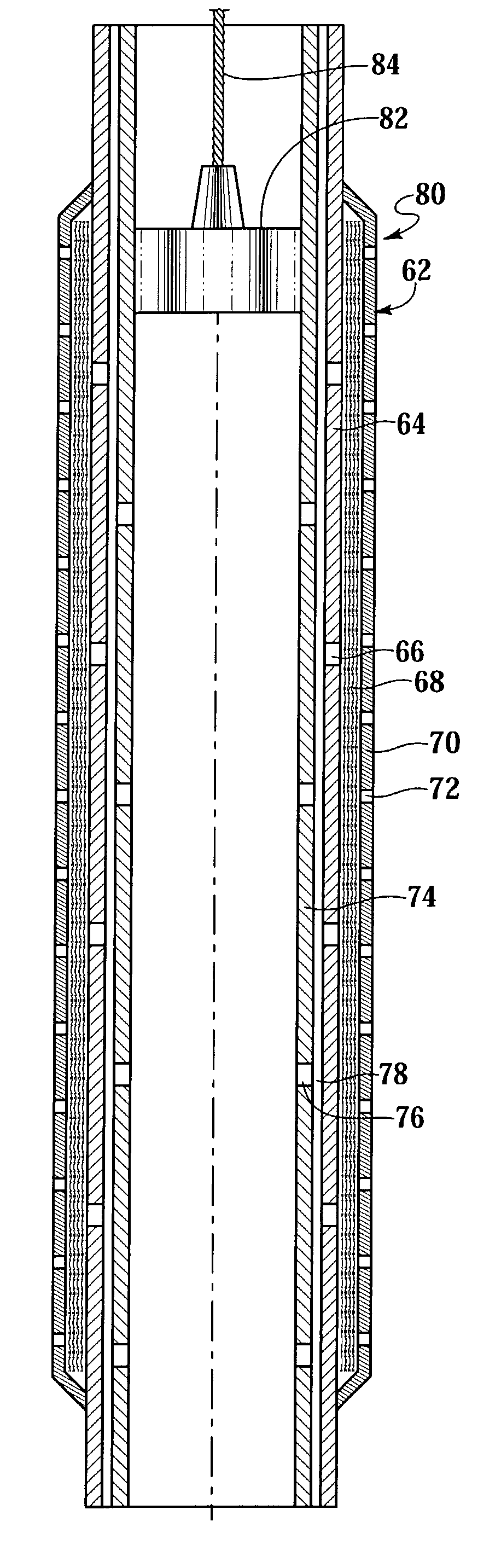
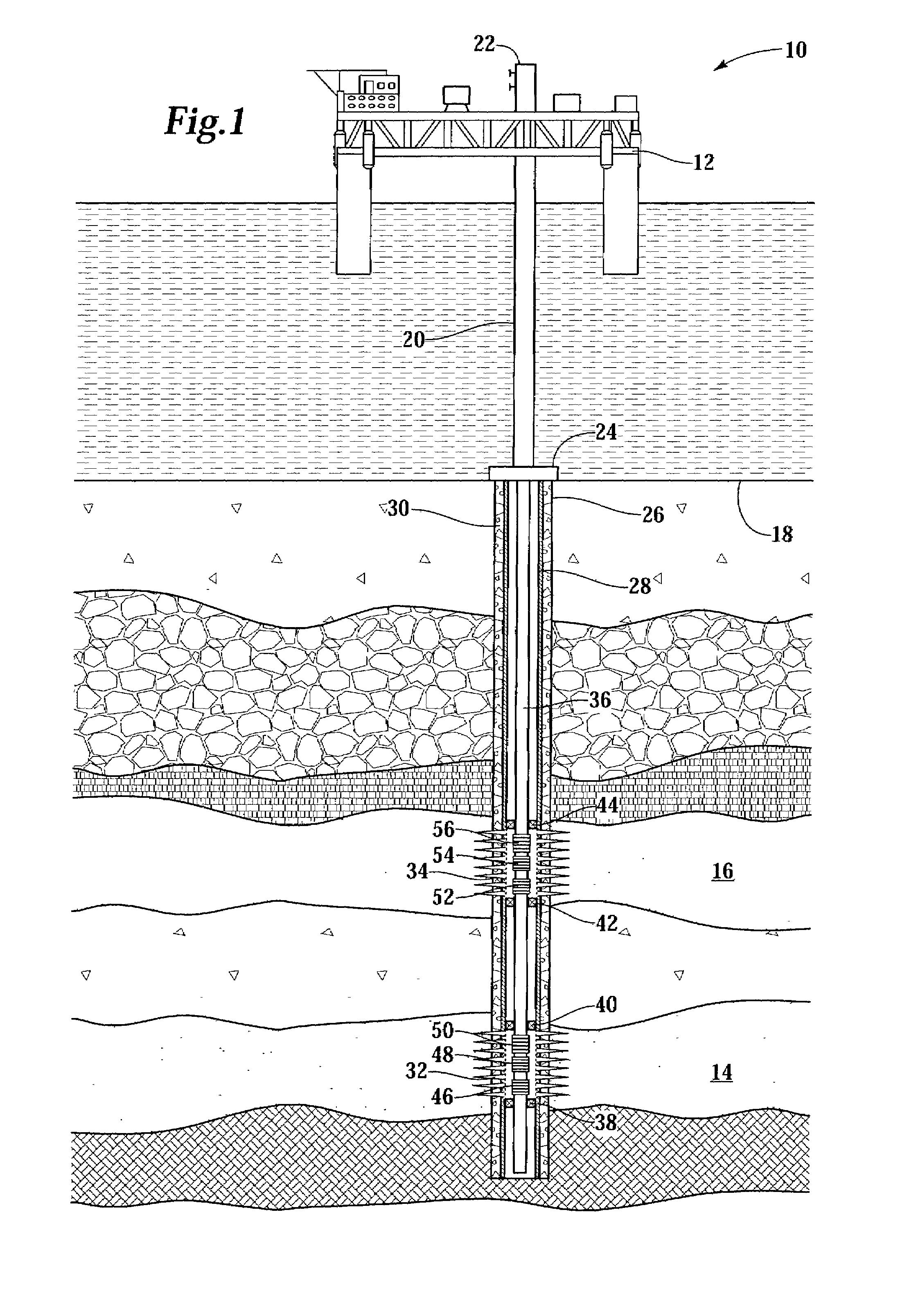
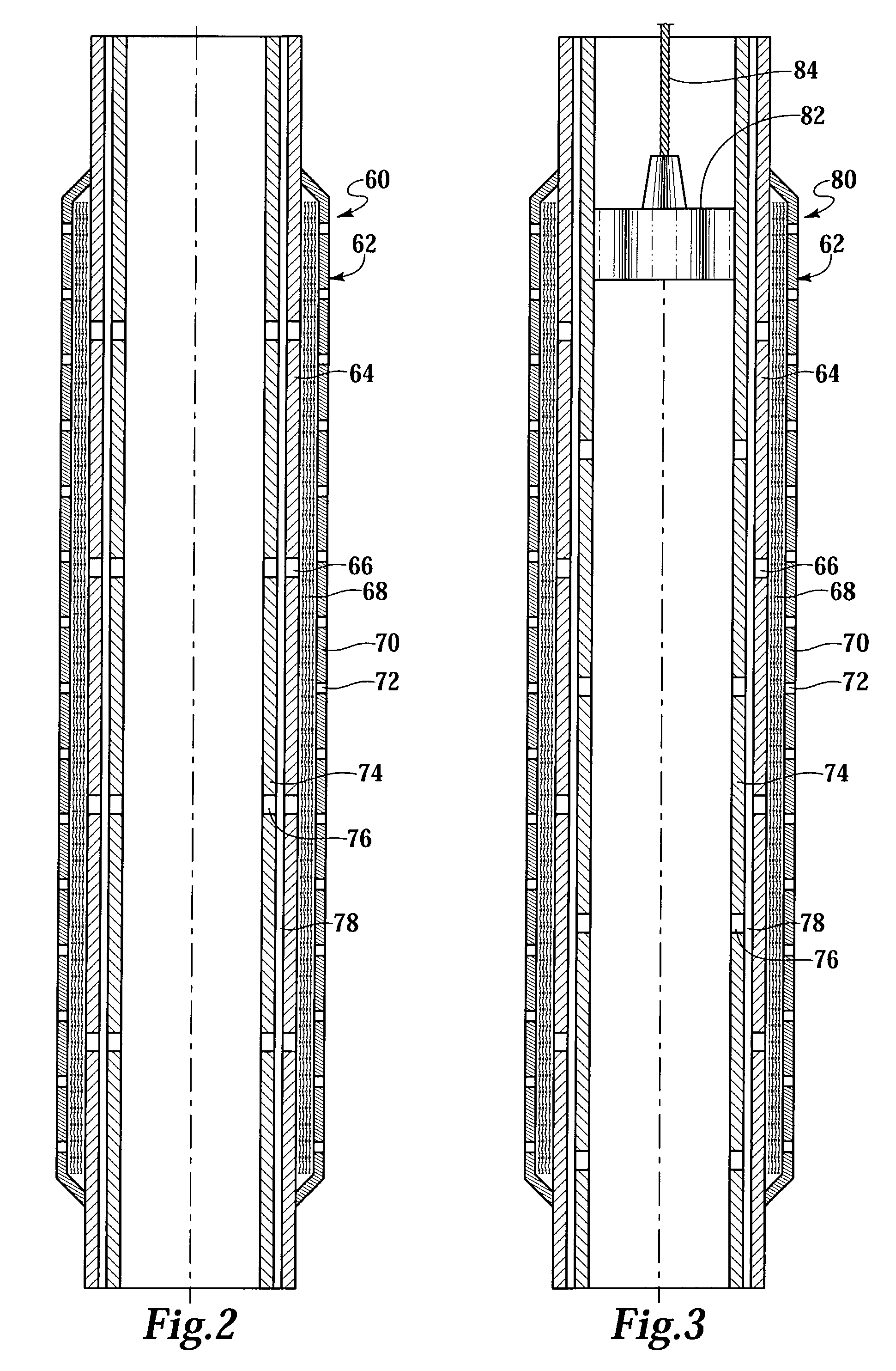
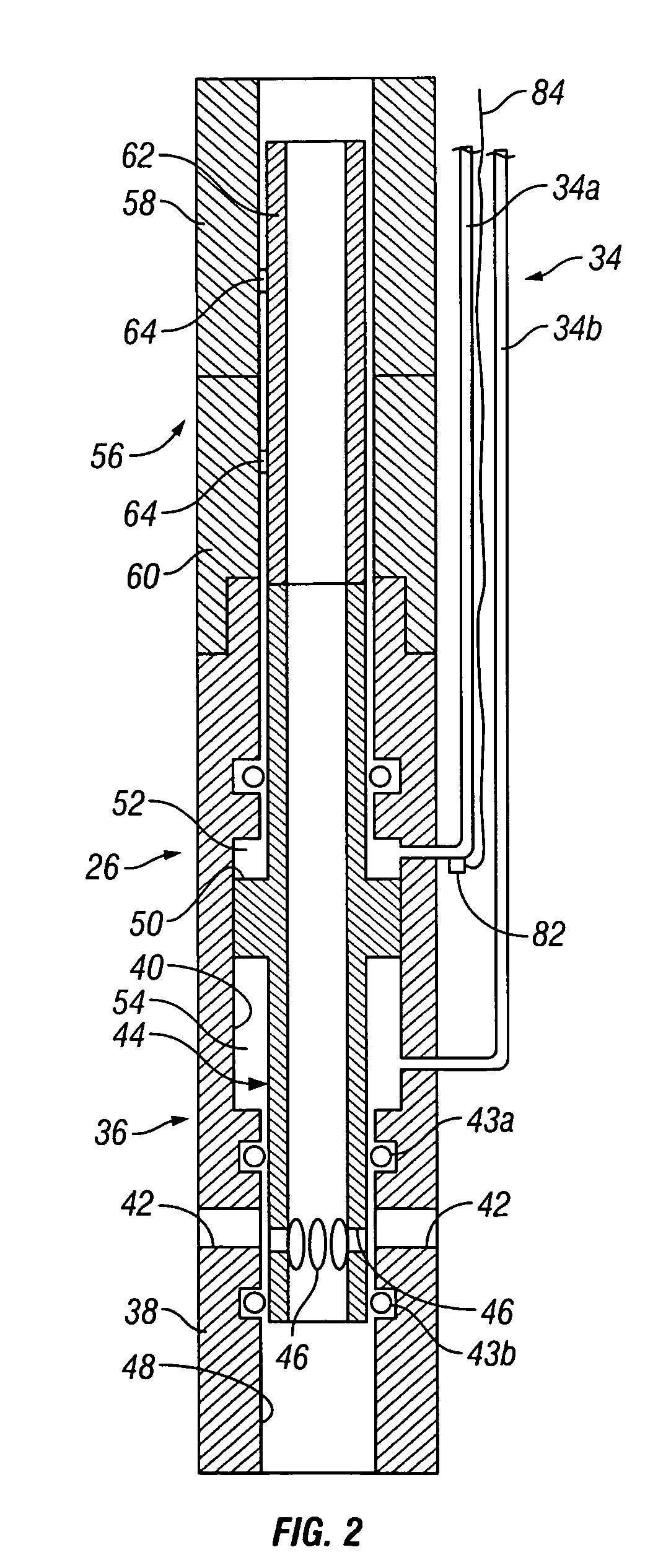
Fluid flow control device and method for use of same
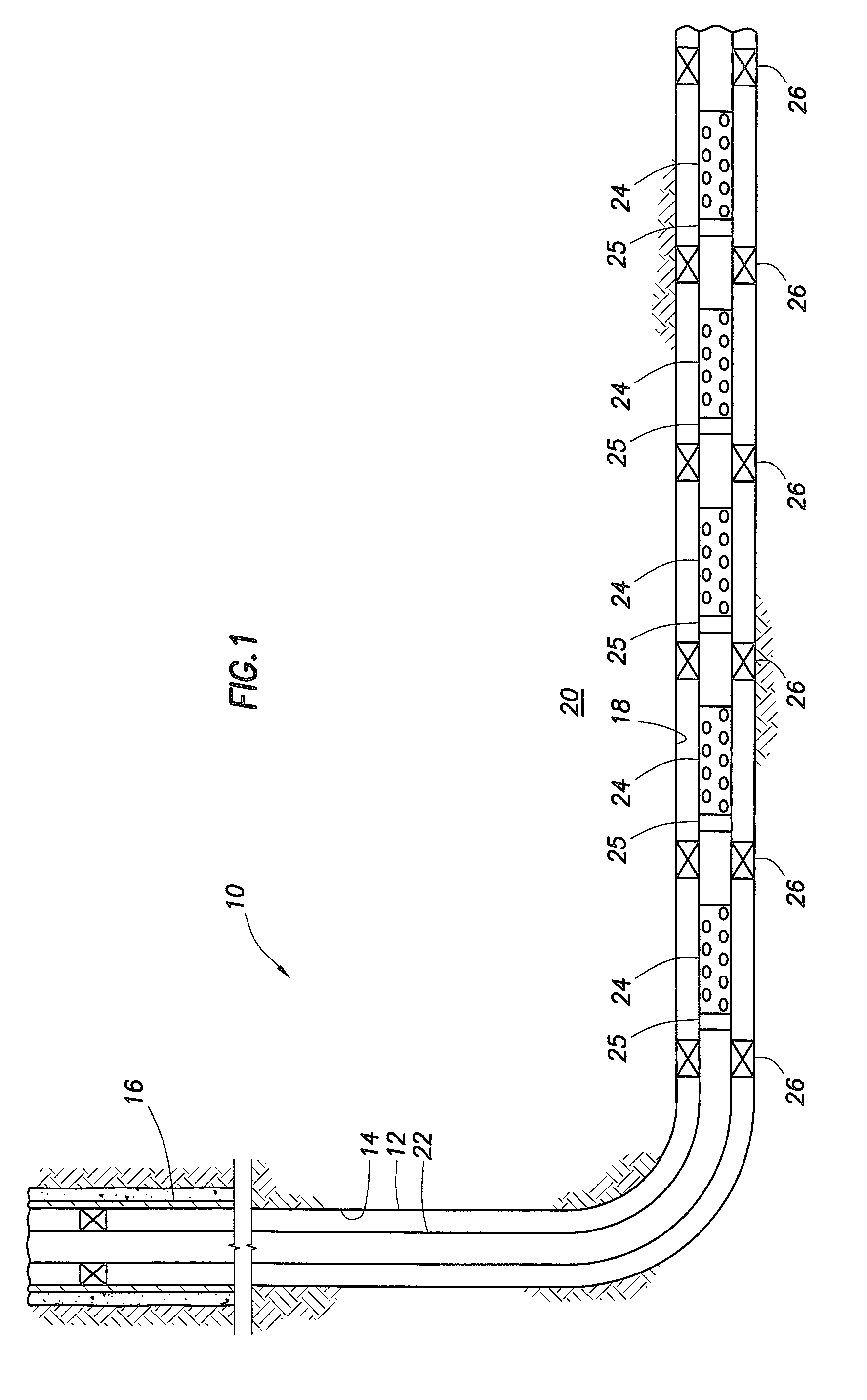
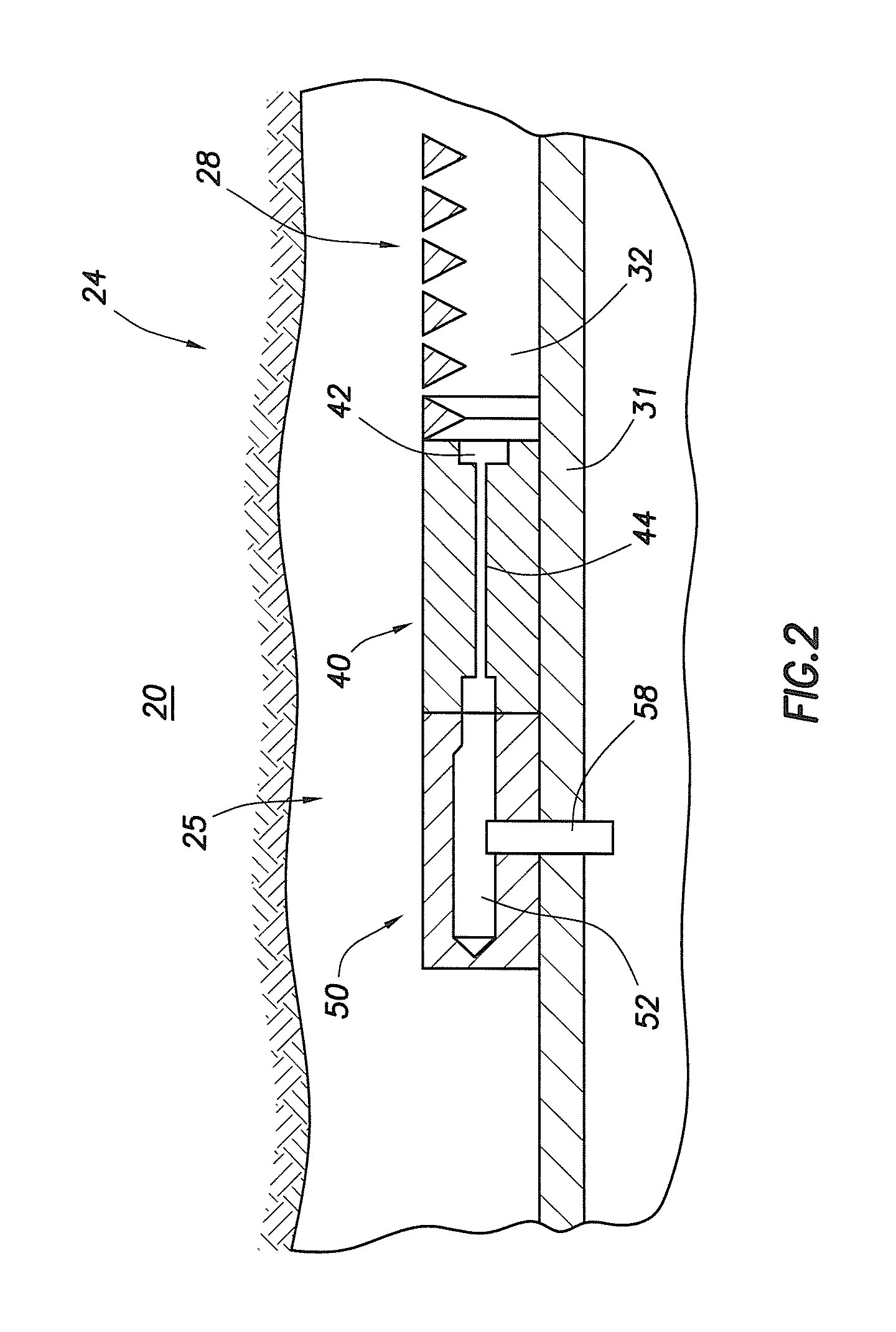
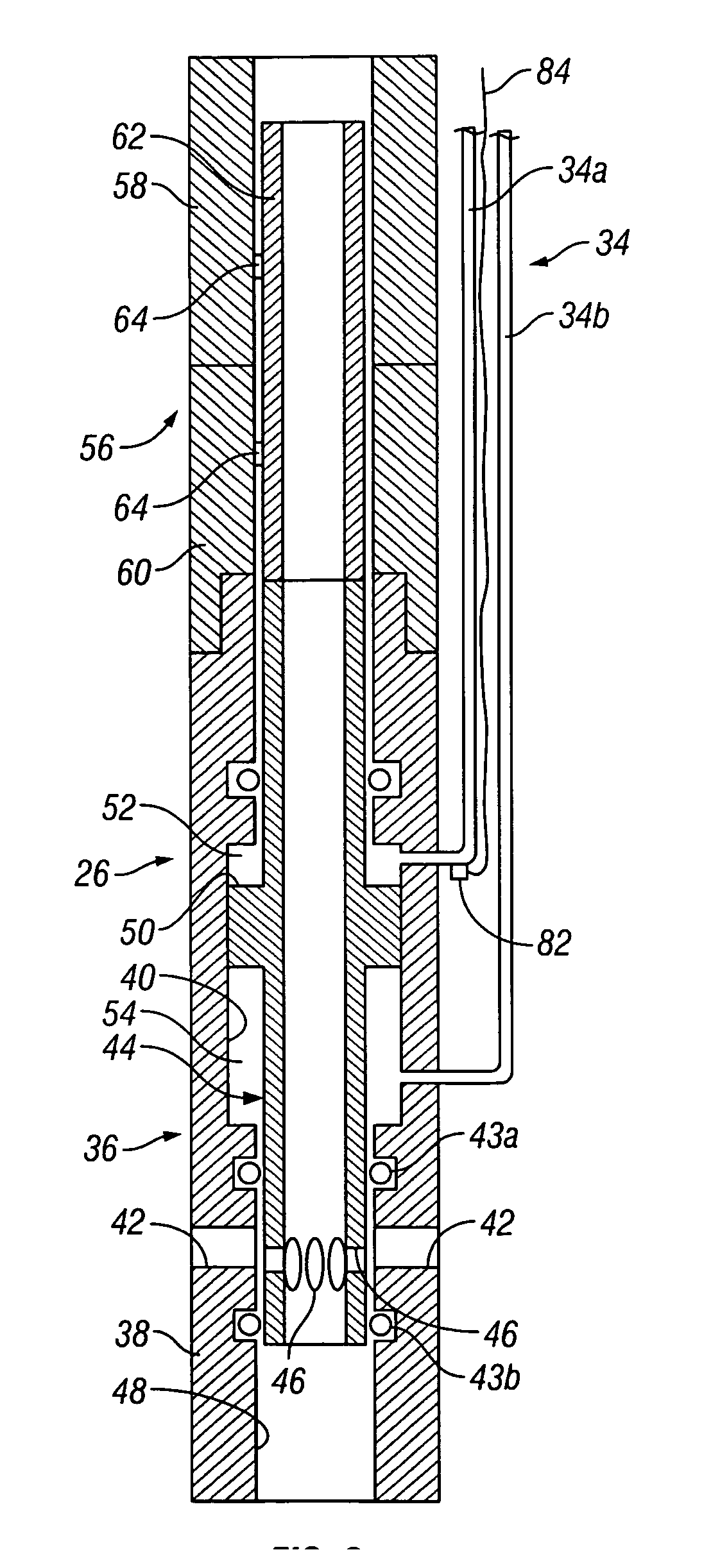
InactiveUS7055598B2Not difficult and expensive to manufactureIncrease pressureSurveyFluid removalStream flowEngineering
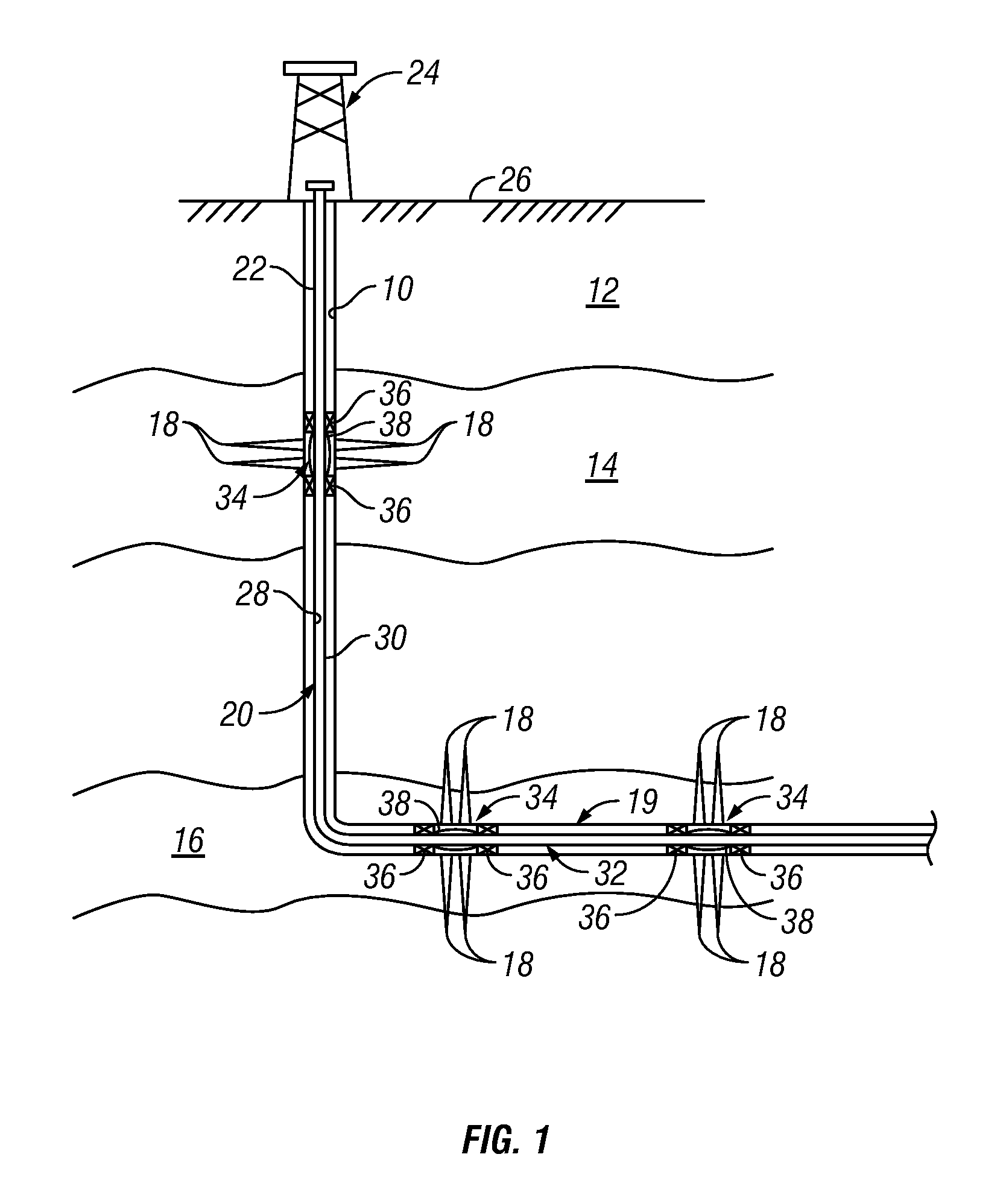
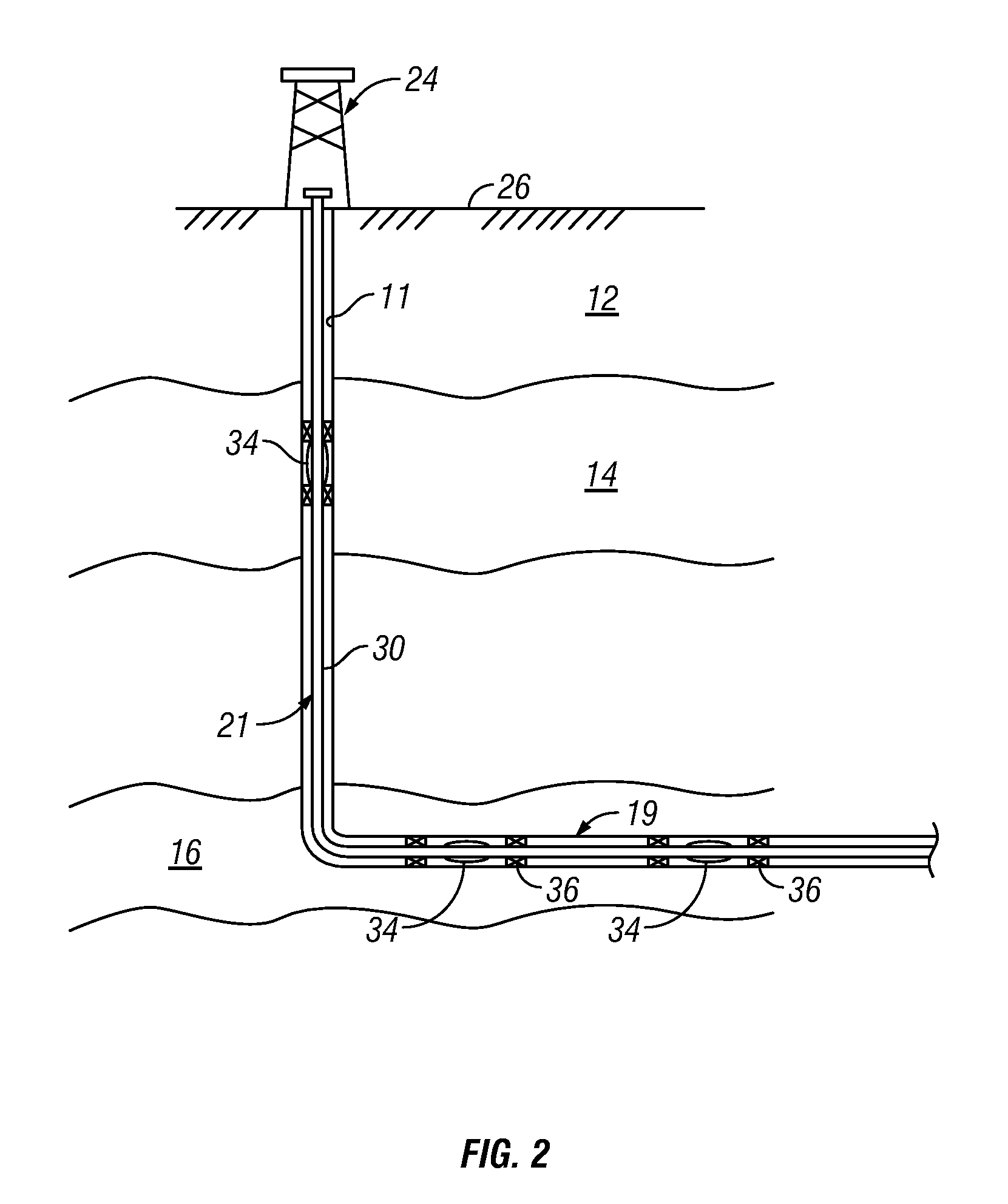
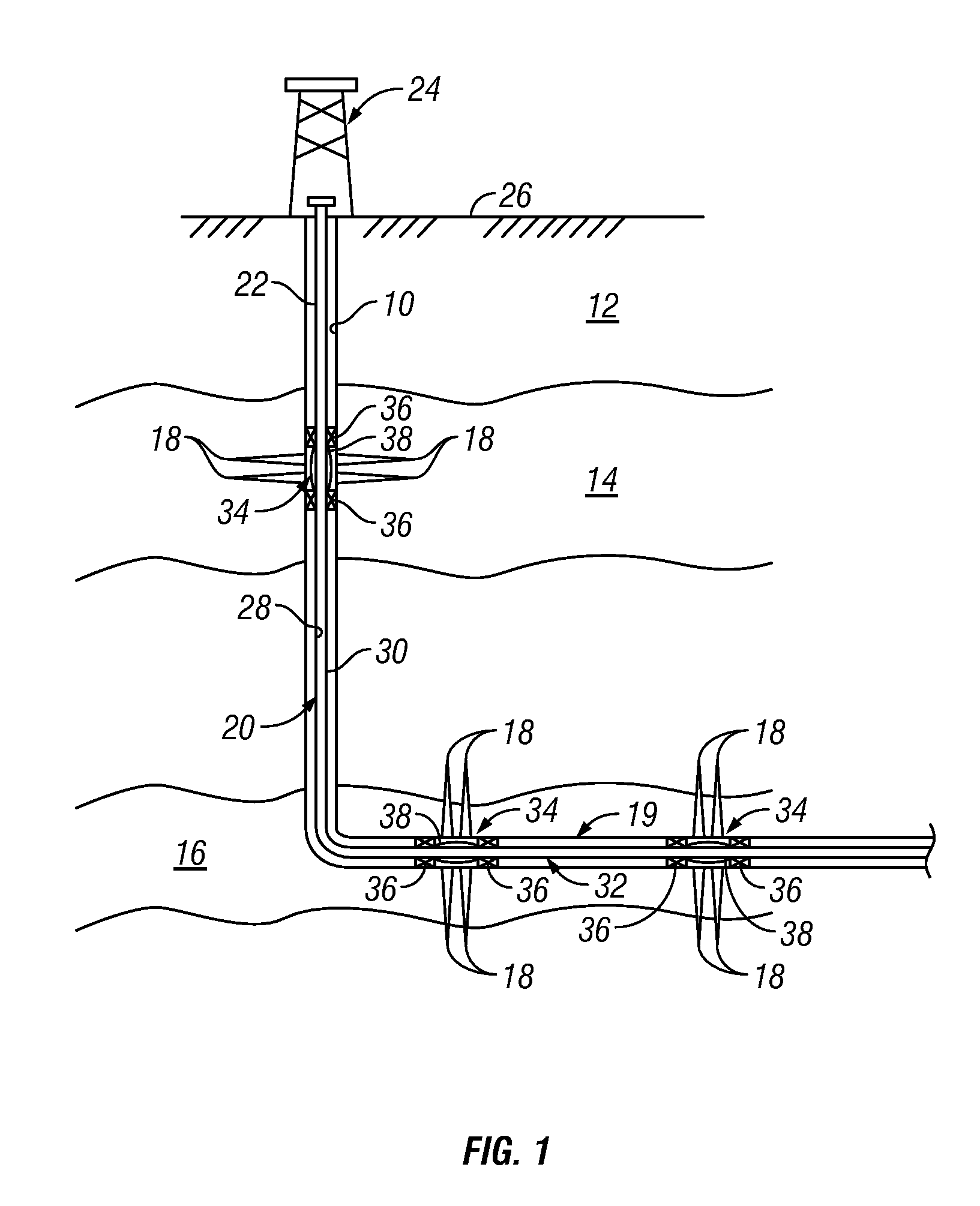
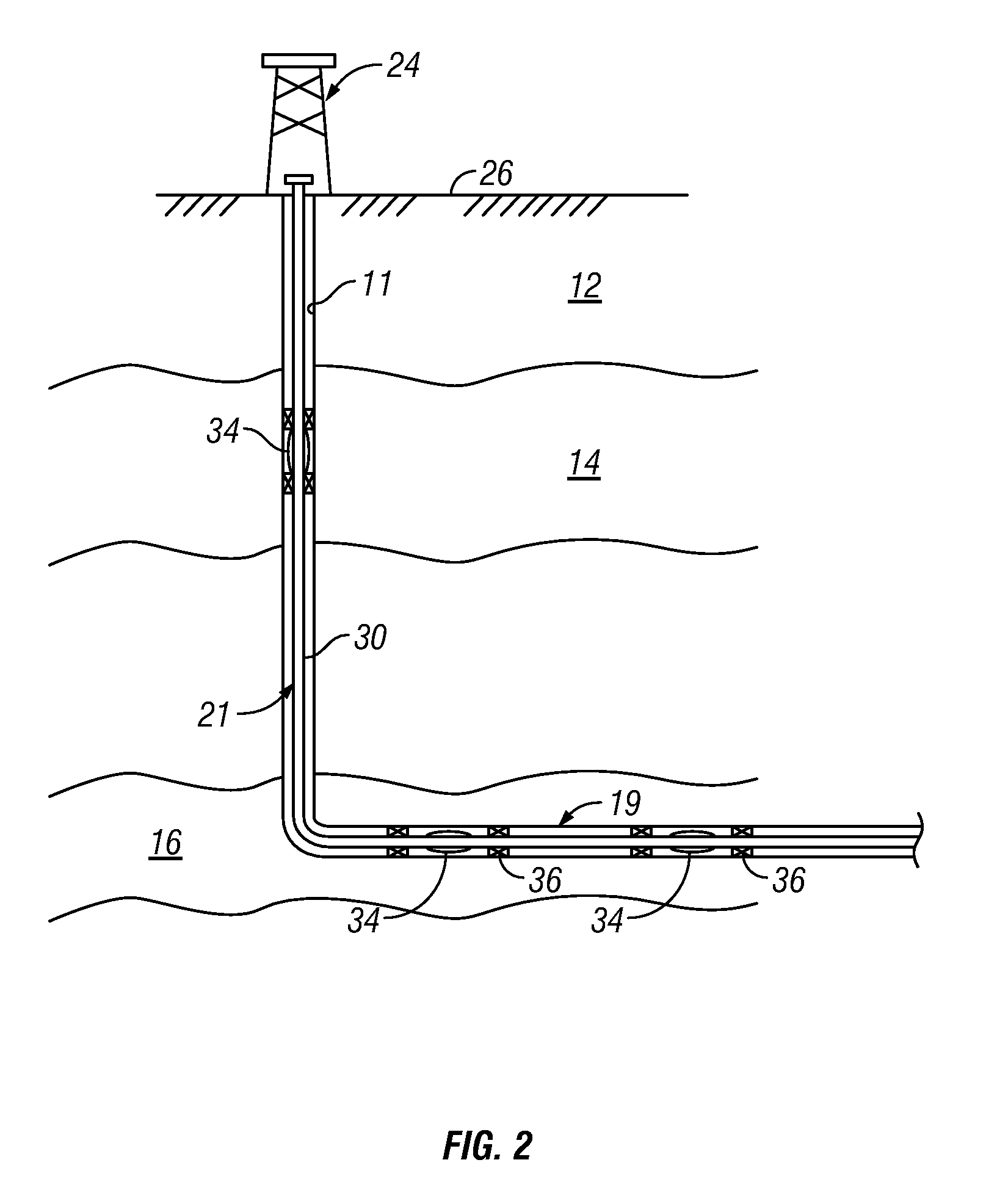
A fluid flow control device (60) for use in a wellbore to control the inflow of production fluids comprises a sand control screen (62) having a base pipe (64) with a first set of openings (66) that allows the production fluids to flow therethrough and a sleeve (74) coaxially disposed adjacent to the base pipe (64). The sleeve (74) has a second set of openings (76) that allows the production fluids to flow therethrough. The sleeve (74) is selectively positionable relative to the base pipe (64) such that a pressure drop in the production fluids is selectively controllable by adjusting an alignment of the first set of openings (66) relative to the second set of openings (76).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
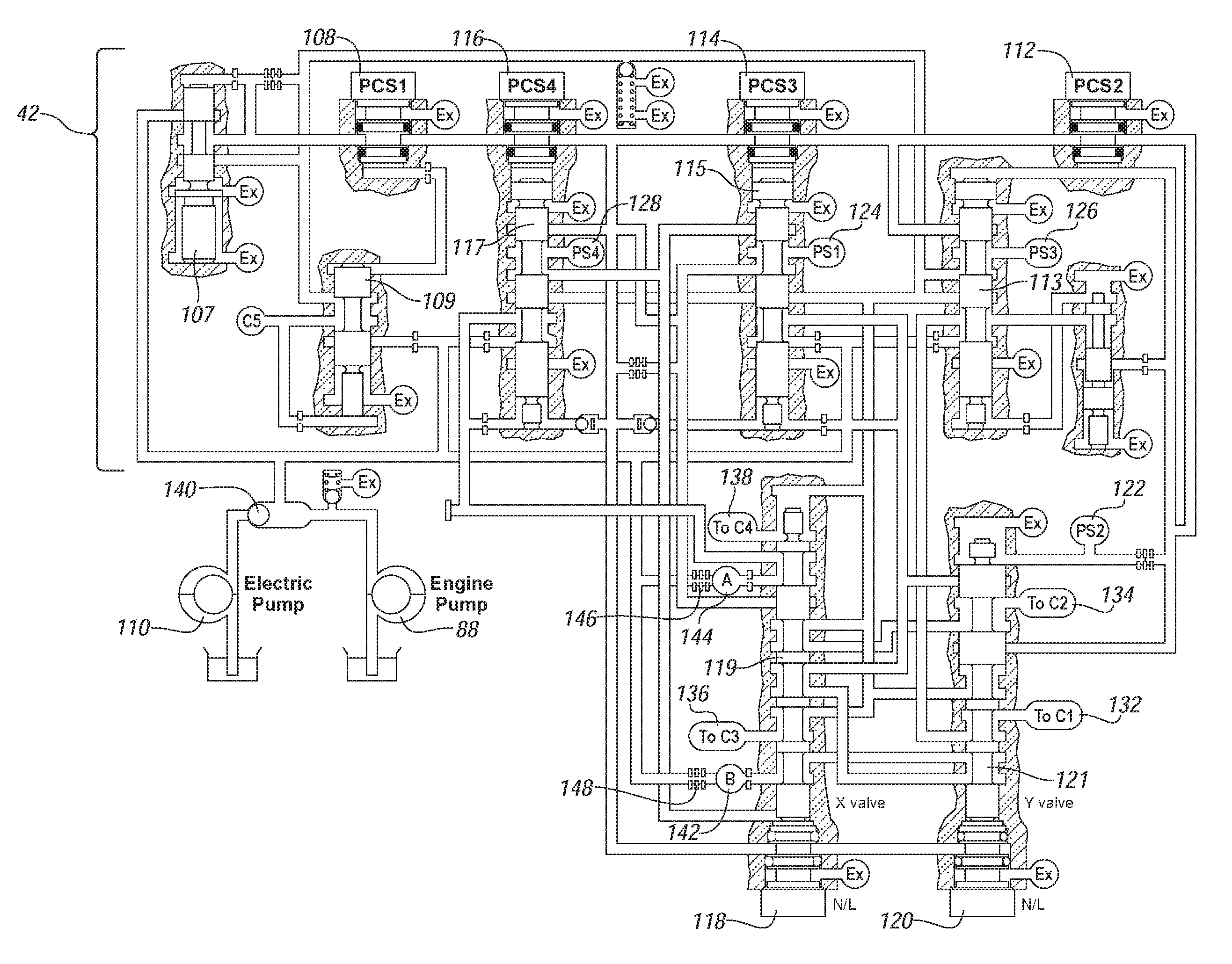
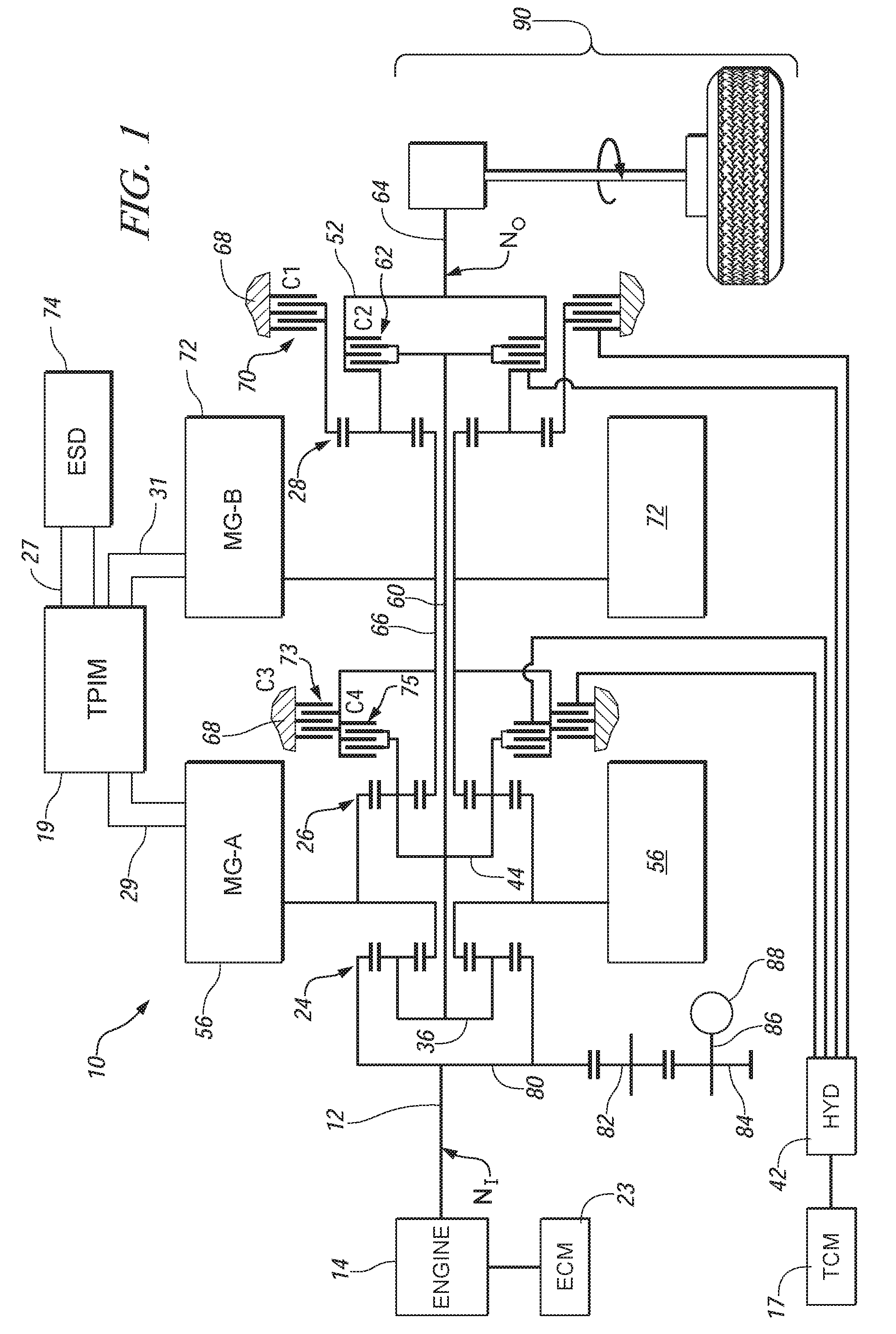
Method and apparatus to monitor devices of a hydraulic circuit of an electro-mechanical transmission
A method and an apparatus are provided to control operation of an electro-mechanical transmission device selectively operative in one of a plurality of fixed gear modes and two continuously variable modes. The method comprises controlling the flow control devices of the electro-hydraulic control circuit, and monitoring a plurality of pressure monitoring devices in the electro-hydraulic control circuit. A fault is identified in the electro-hydraulic control circuit when a signal output of one of the pressure monitoring devices does not correspond to an expected signal output for the pressure monitoring device after an elapsed time period.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Water Sensitive Adaptive Inflow Control Using Couette Flow To Actuate A Valve
An apparatus for controlling fluid flow into a wellbore tubular includes a flow control member that selectively aligns a port with an opening in communication with a flow bore of the wellbore tubular. The flow control member may have an open position wherein the port is aligned with the opening and a closed position wherein the port is misaligned with the opening. The flow control member moves between the open position and closed position in response to a change in drag force applied by a flowing fluid. A biasing element urges the flow control member to the open or the closed position. The apparatus may include a housing receiving the flow control member. The flow control member and the housing may define a flow space that generates a Couette flow that causes the drag force. In embodiments, the flow space may include a hydrophilic and / or water swellable material.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Scanning densitometry system with adjustable X-ray tube current
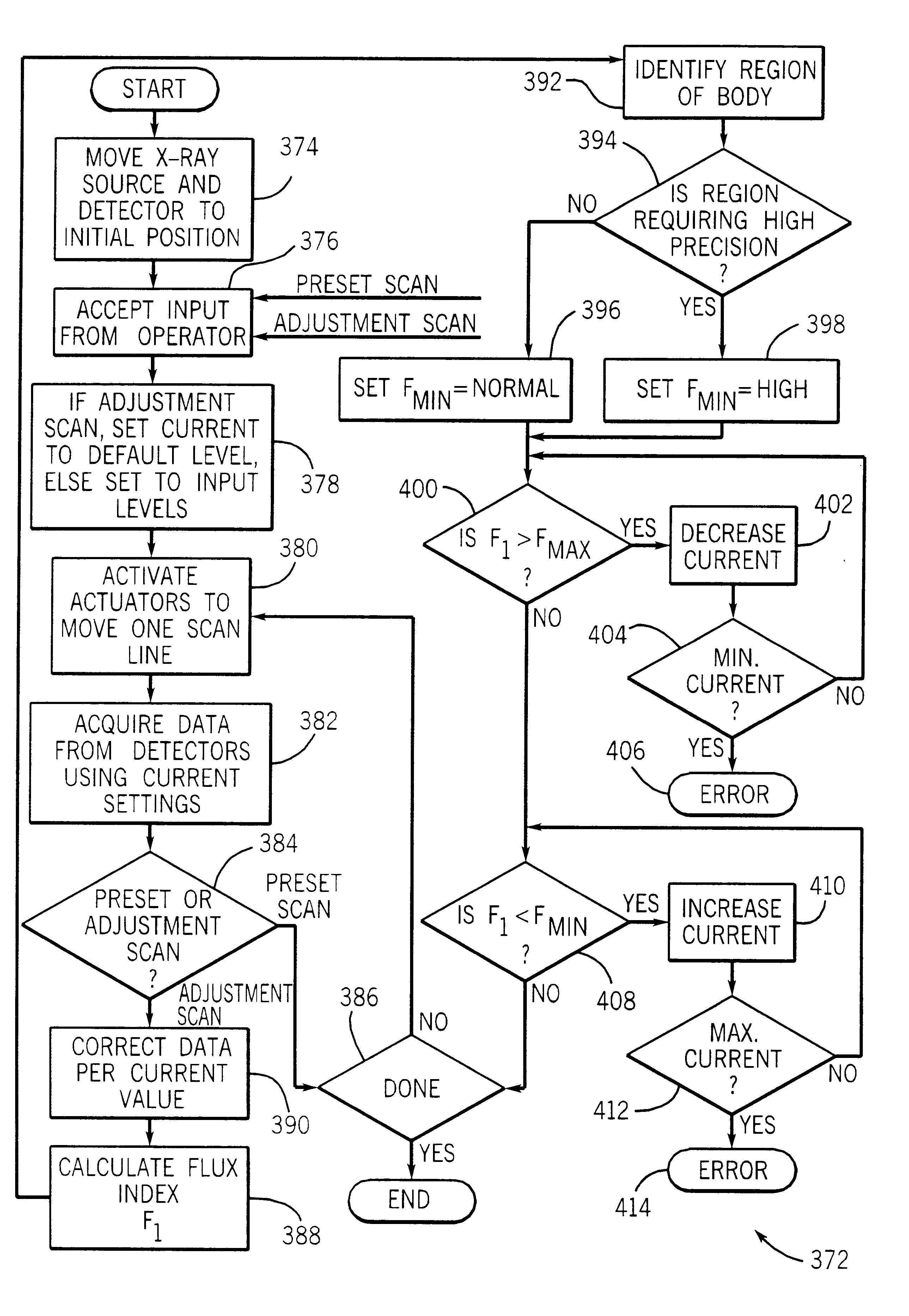
InactiveUS6438201B1Effectively continuous adjustmentEffective regulationImage enhancementImage analysisBone densityX-Ray Tube Current
A dual energy scanning densitometry system for imaging and measuring bone density maintains acceptable flux by adjusting the x-ray current or scan speed according to preceding scan line data. The amount of acceptable flux is maintained within limits modified by information about the region of the body being scanned so that different precisions may be maintained for different body regions. Scan speed and current may be controlled so that scan speed is maximized within the current limits. Essentially continuous flux control can be achieved.
Owner:LUNAR CORP
Inflow control device with passive shut-off feature
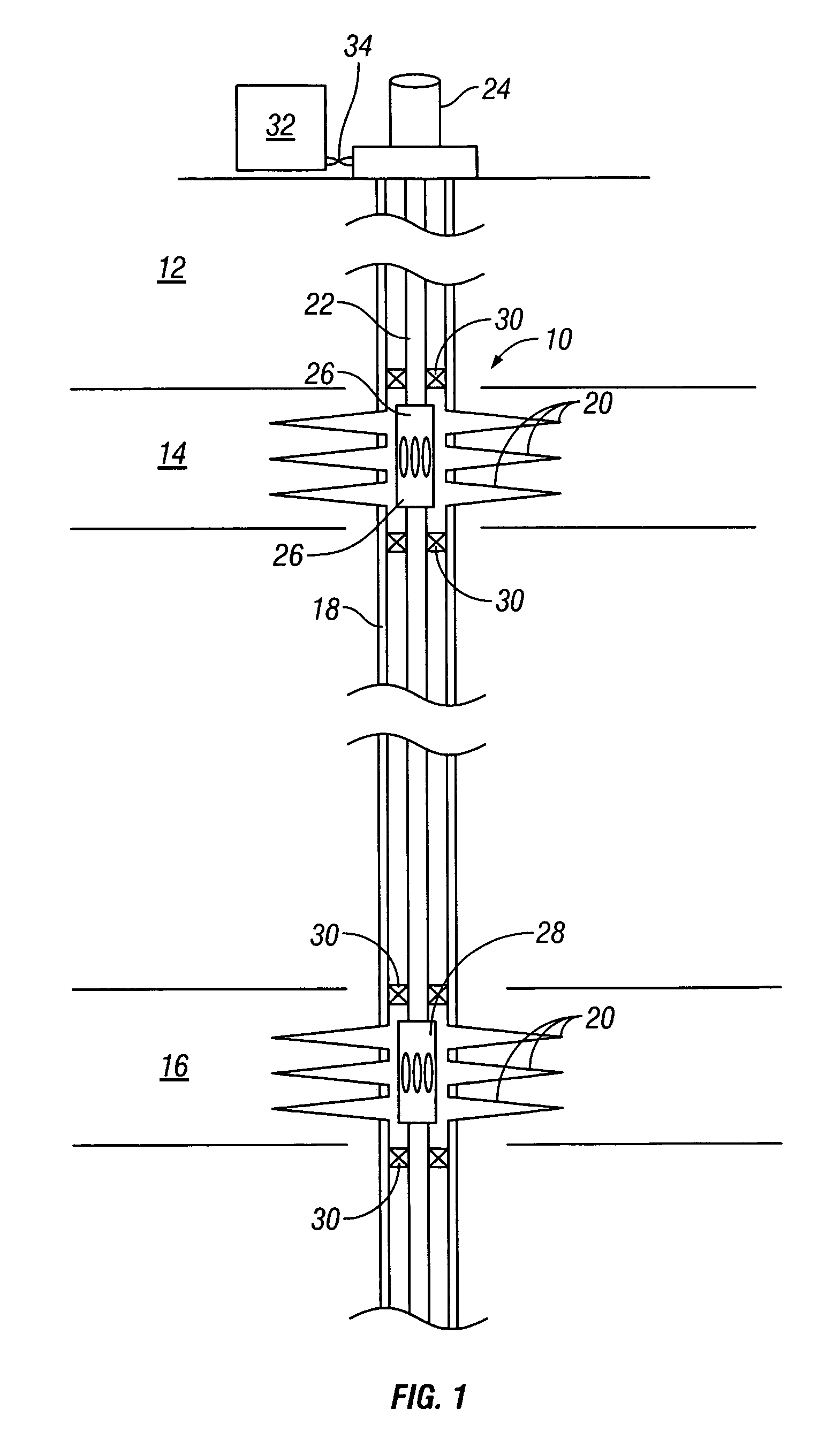
InactiveUS20060076150A1Reduce gas flowConsistent service lifeSurveyConstructionsControl flowStream flow
Devices and methods for control flow of formation fluids respect to one or more selected parameter relating to the wellbore fluid. In one embodiment, a flow control device for controlling fluid flow into the production tubular uses a flow restriction member that is actuated by a character change of the formation fluid, such as liquid to gas or oil to water. The flow restriction member can be sensitive to a change in density of the formation fluid. The flow restriction member is passive, self-regulating and does not need any power source or control signal to control fluid flow. In one embodiment, the flow control device automatically rotates into a predetermined orientation upon being positioned in the wellbore. A seal disposed on the flow control devices expands into sealing engagement with an enclosure after the flow control device assumed the desired predetermined position.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
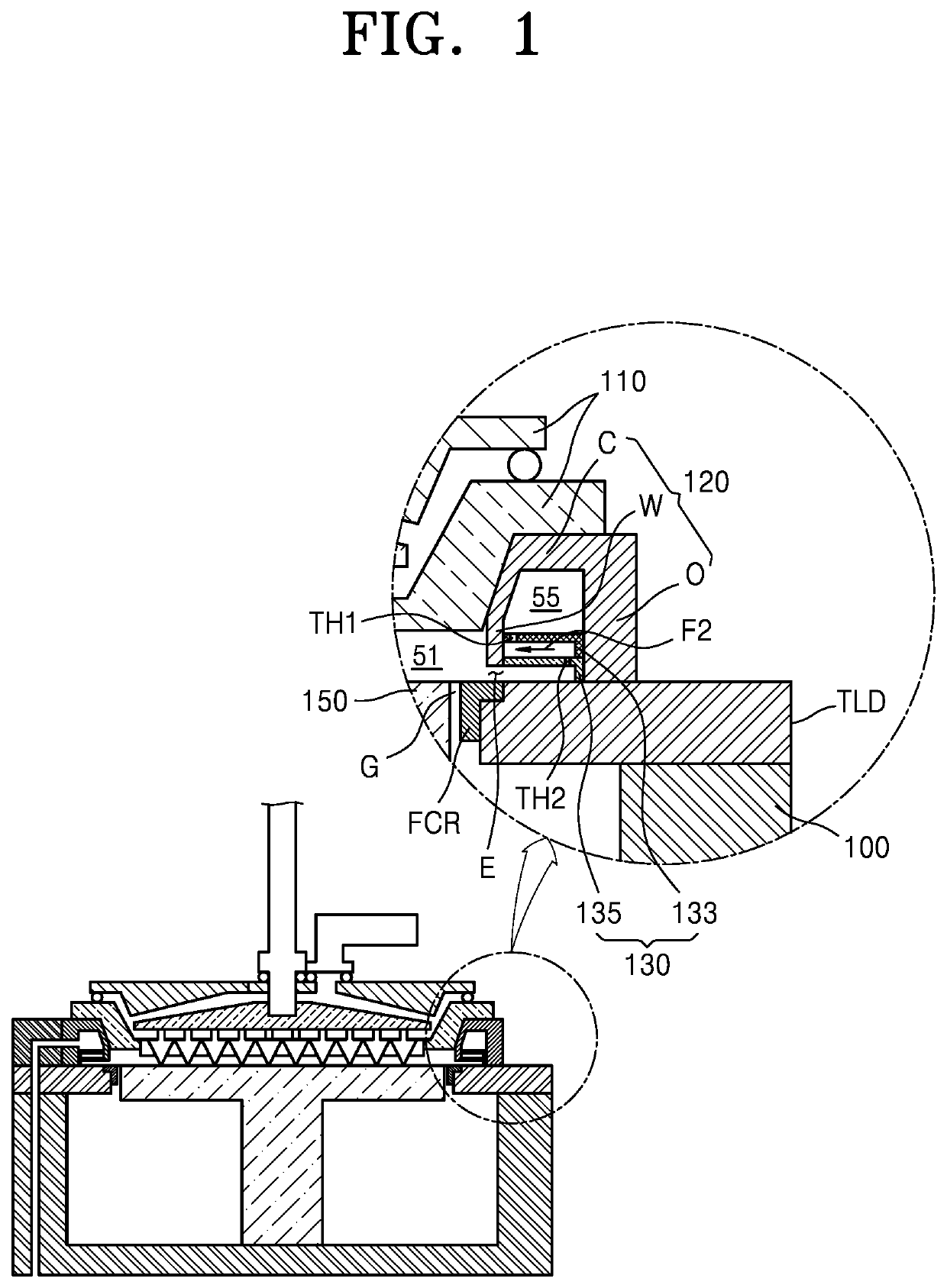
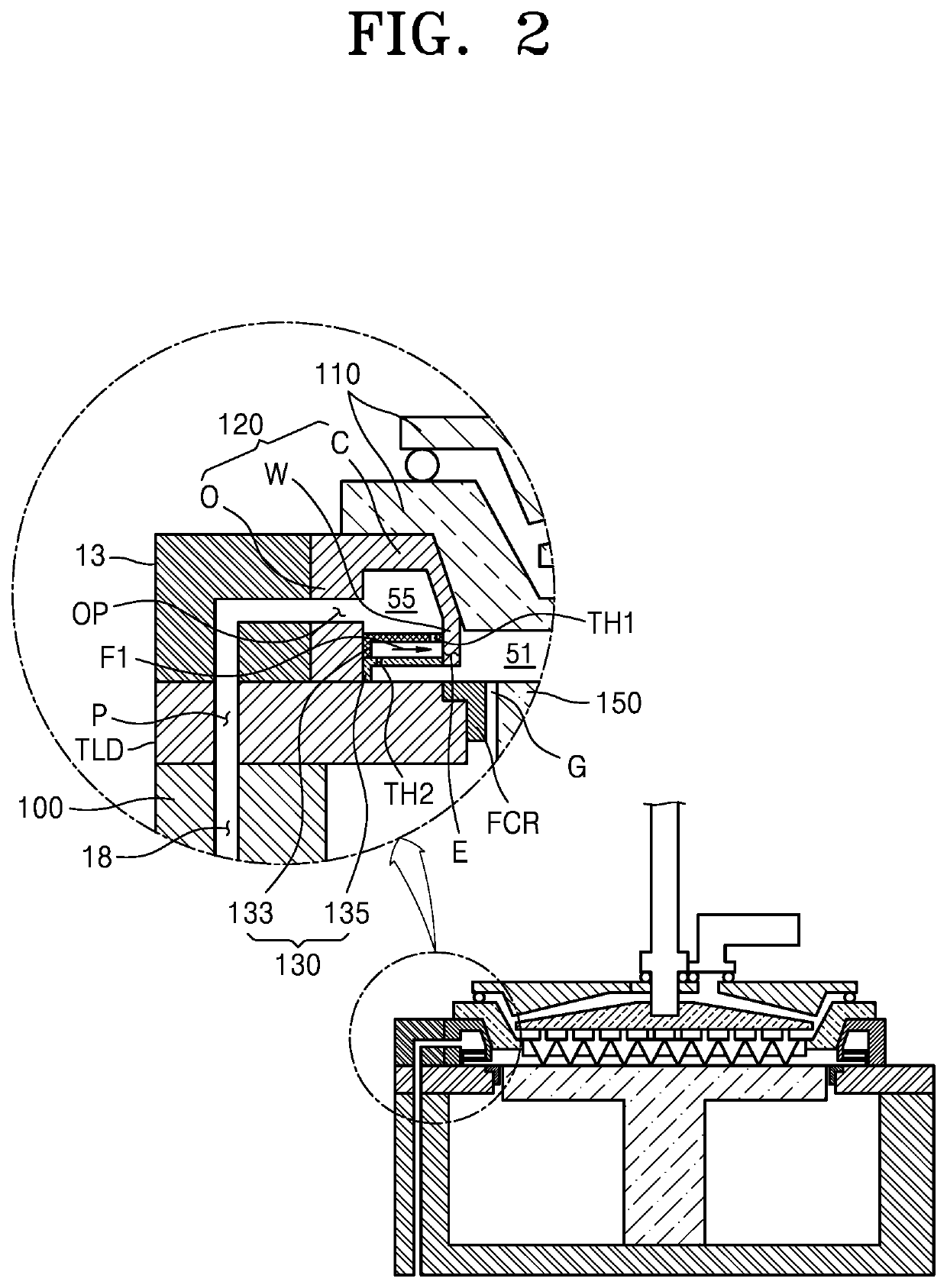
Substrate processing apparatus
ActiveUS20210156024A1Avoid skewElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingMechanical engineeringFlux control
A substrate processing apparatus capable of preventing deflection of exhaust flow which may occur when an asymmetric exhaust structure is introduced includes: an exhaust unit providing an exhaust space surrounding a reaction space; an exhaust port connected to the exhaust unit; and a flow control unit disposed in the exhaust space, wherein the exhaust port is arranged asymmetrically with respect to the reaction space, and the flow control unit may include: an upper flow control plate including a plurality of first through holes; and a lower flow control plate disposed below the upper flow control plate and including a plurality of second through holes.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
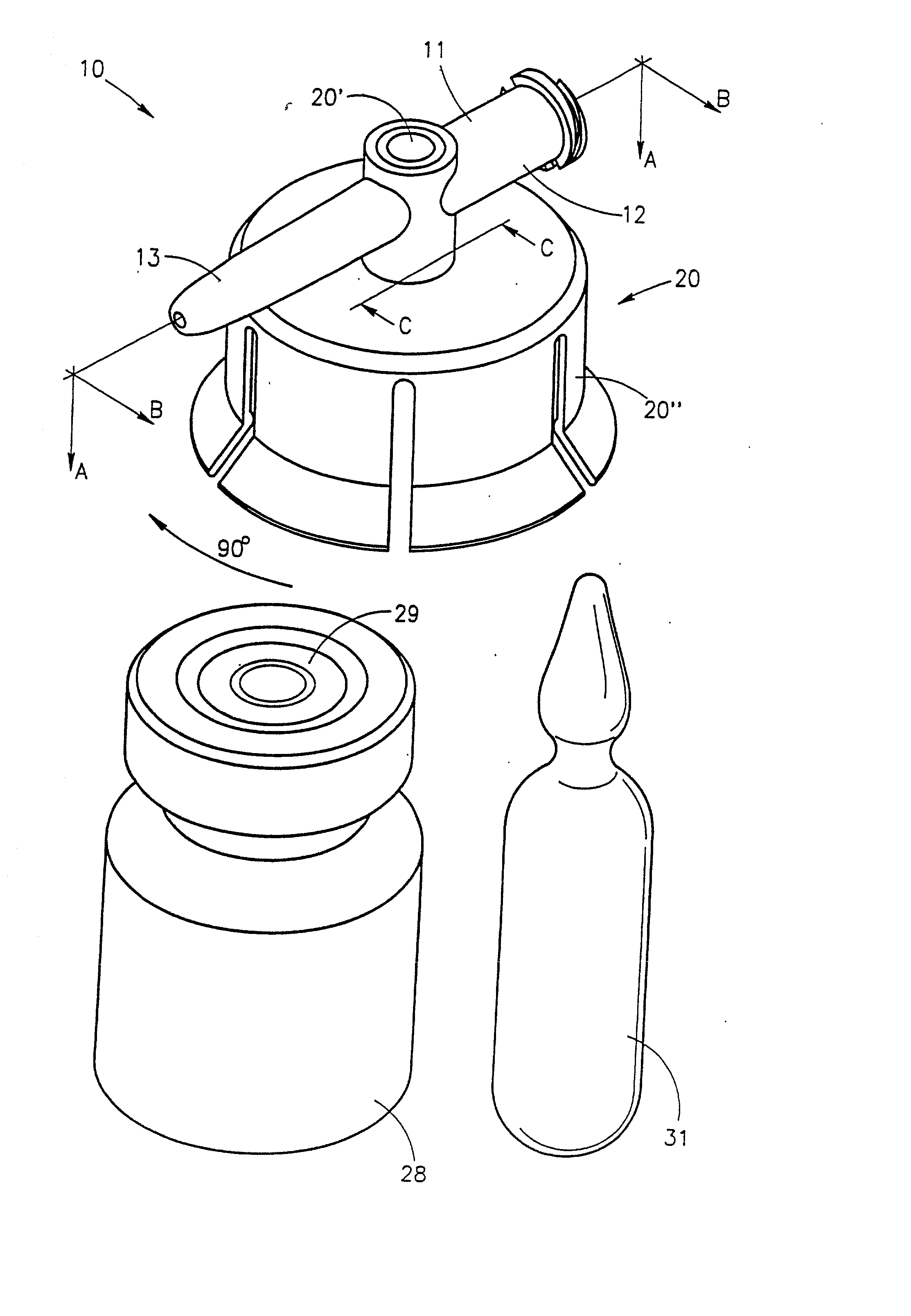
Fluid control device
A fluid ducting assembly for enabling flow communication between a syringe and either one of a vessel and a dispenser for dispensing a fluid contained, a priori in the syringe or in the vessel. The fluid ducting assembly includes a base having a first member, a second member, and a third member for connection to and providing flow communication with the syringe, the vessel and the dispenser, respectively. The fluid ducting assembly further includes a flow controller within the base enabling any one of a flow path between the first member and the second member and a flow path between the first member and the third member. The flow controller has either a first operative position in which the flow path between the first member and the second member is enabled or a second operative position in which the flow path between the first member and the third member is enabled. The flow controller being readily switchable from its first operative position to its second operative position but not readily switchable from its second operative position to its first operative position.
Owner:MEDIMOP MEDICAL PROJECTS
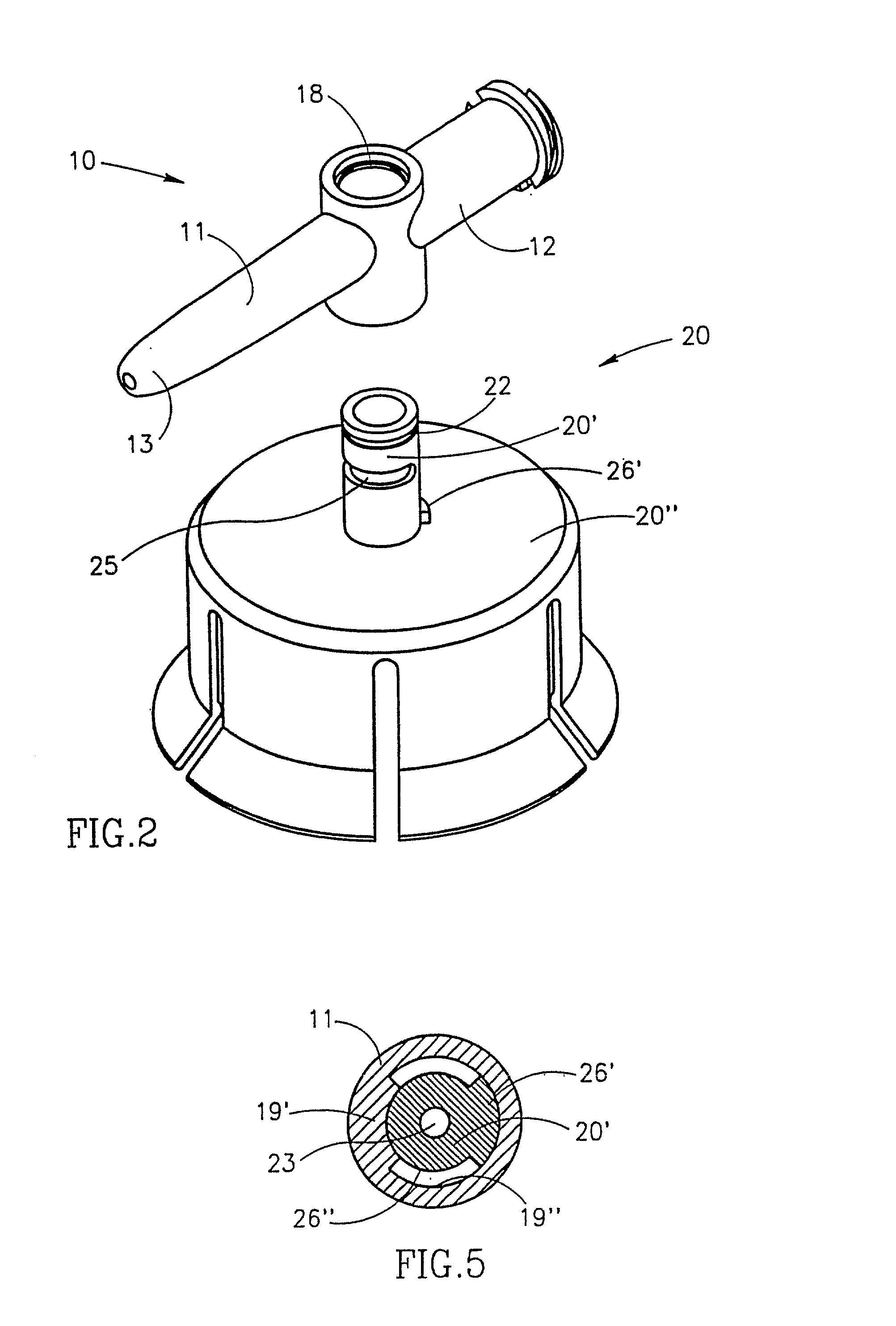
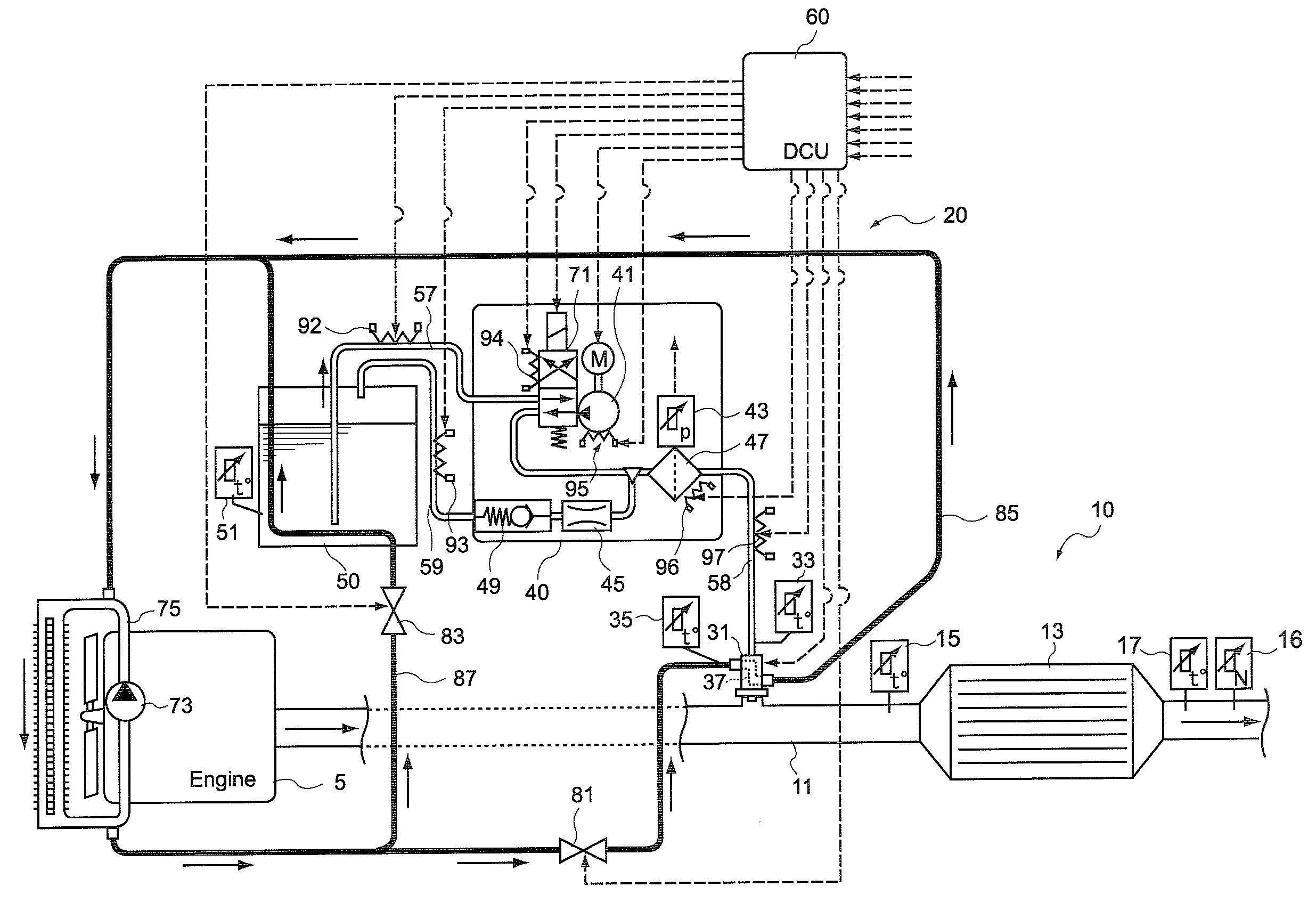
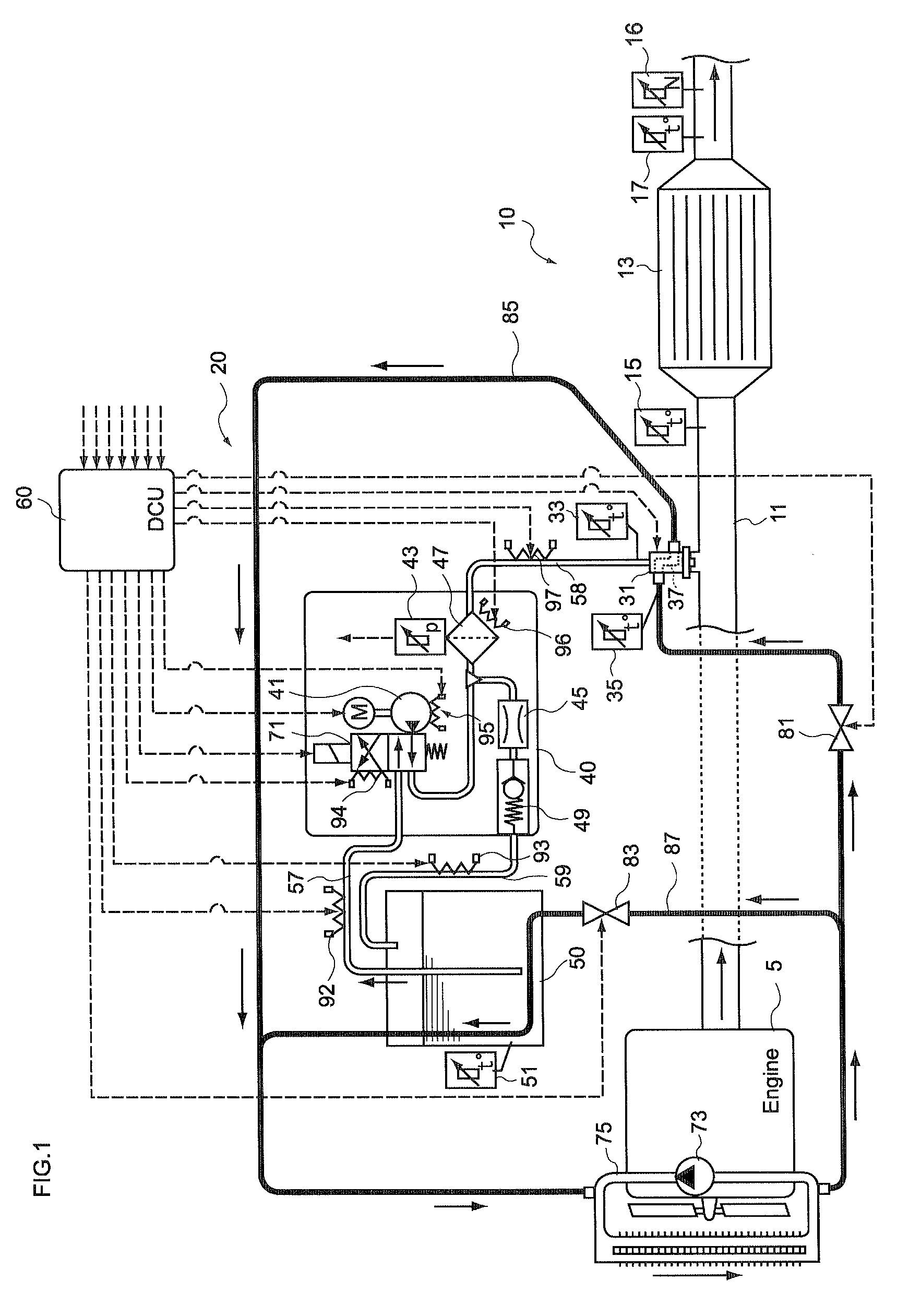
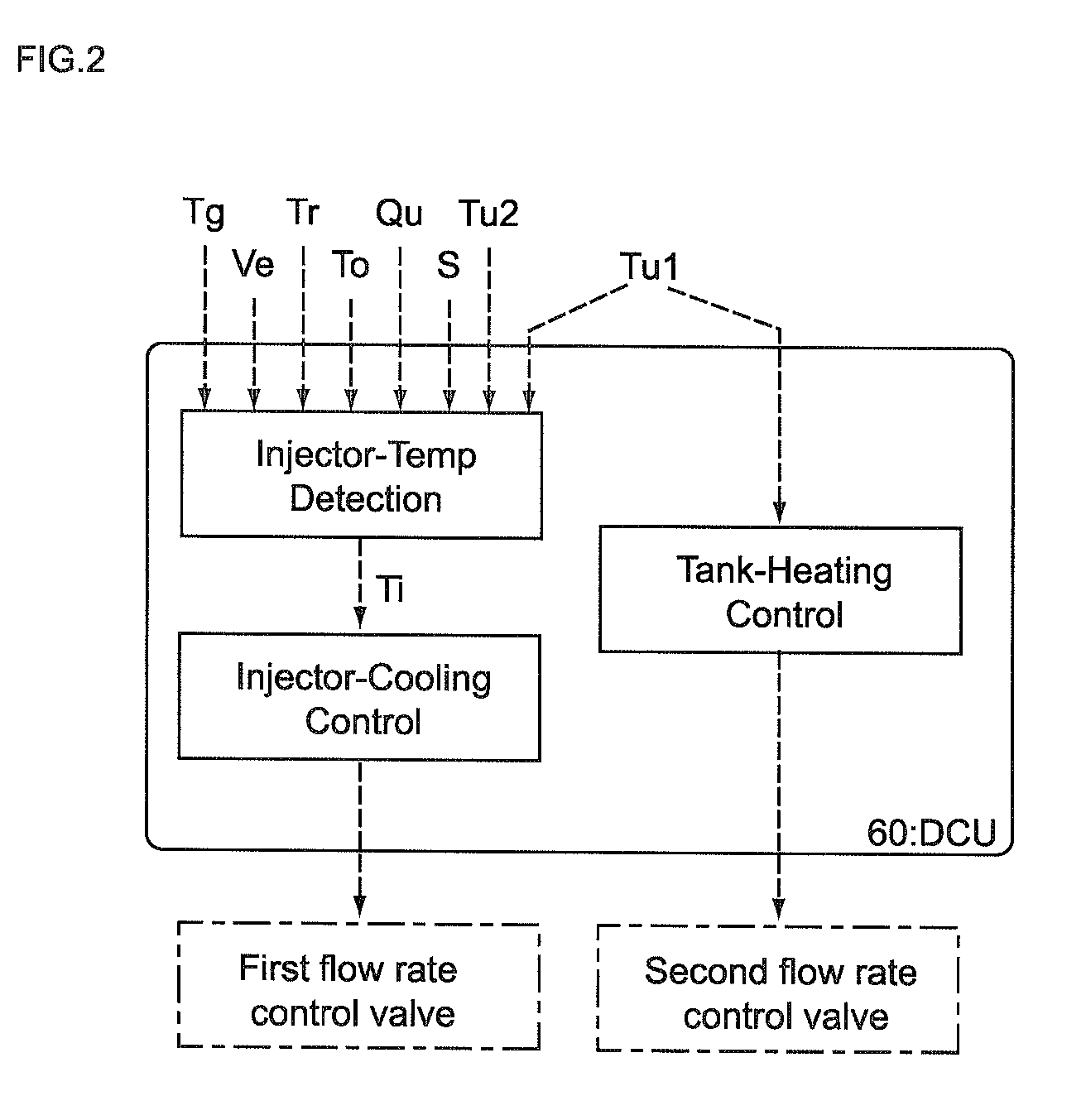
Control unit and control method for reductant supply device
InactiveUS20100242439A1Prevent overcoolingImprove cooling effectLiquid coolingInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringWater circulation
There are provided a reductant supply device and a control method for the reductant supply device, which can prevent heat damage of a reductant injection valve, and also prevent crystallization of urea solution due to excessive cooling of the solution reductant.The reductant supply device which is used in an exhaust gas purification device that injects and supplies, as a reductant, a urea solution to an exhaust gas upstream side of a reduction catalyst disposed in an exhaust gas passage of an internal combustion engine, and that reduces and purifies nitrogen oxides contained in exhaust gas using the reduction catalyst, the reductant supply device having a reductant injection valve that is fixed to an exhaust pipe on the exhaust gas upstream side of the reduction catalyst, includes: a cooling water circulation passage that circulates at least part of cooling water of the internal combustion engine to cool the reductant injection valve; flow rate control means for adjusting a flow rate of cooling water flowing through the cooling water circulation passage; temperature detection means for detecting a temperature of the reductant injection valve; and control means for controlling the flow rate control means based on the temperature of the reductant injection valve.
Owner:BOSCH CORP
Method and system for flow control with fluidic oscillators
A system for control of a fluid flow. The system includes an array of fluidic oscillators. Each fluidic oscillator carries an oscillating flow of the fluid and includes a throat, an input port connected to the throat, two control ports connected to the throat and two output ports extending from the throat. A feedback line is connected to each of the two output ports and each of the two control ports. The system further includes a plenum connected to the input ports of the fluidic oscillators to supply the fluid to the fluidic oscillators and a feedback chamber disposed along each feedback line of each fluidic oscillator to provide a feedback path for the control fluid to cause oscillatory fluid motion between the first output port and the second output port, the frequency of which may be modulated by adjusting the volume of the feedback chamber.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Water Sensing Devices and Methods Utilizing Same to Control Flow of Subsurface Fluids
InactiveUS20090101354A1Contributions to the art may be appreciatedFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
An apparatus for controlling fluid flow in a wellbore includes a reactive element that reacts when exposed to a fluid and a flow control device configured to control a flow of the fluid. The flow control device may be actuated by a reaction of the reactive element to the fluid. In embodiments, the reactive element reacts by exhibiting a change in a material property. The reaction of the reactive element may be reversible. In embodiments, the reactive element may be a shape memory polymer. The flow control device may include an actuating element operably coupled to the reactive element. The reaction of the reactive element to a given fluid releases the actuating element to actuate the flow control device.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Dual volume shower head system
InactiveUS20060219822A1The implementation process is simpleSpray nozzlesFire rescueEngineeringFlow limitation
Owner:ALSONS CORP
Multiple zone gas distribution apparatus for thermal control of semiconductor wafer
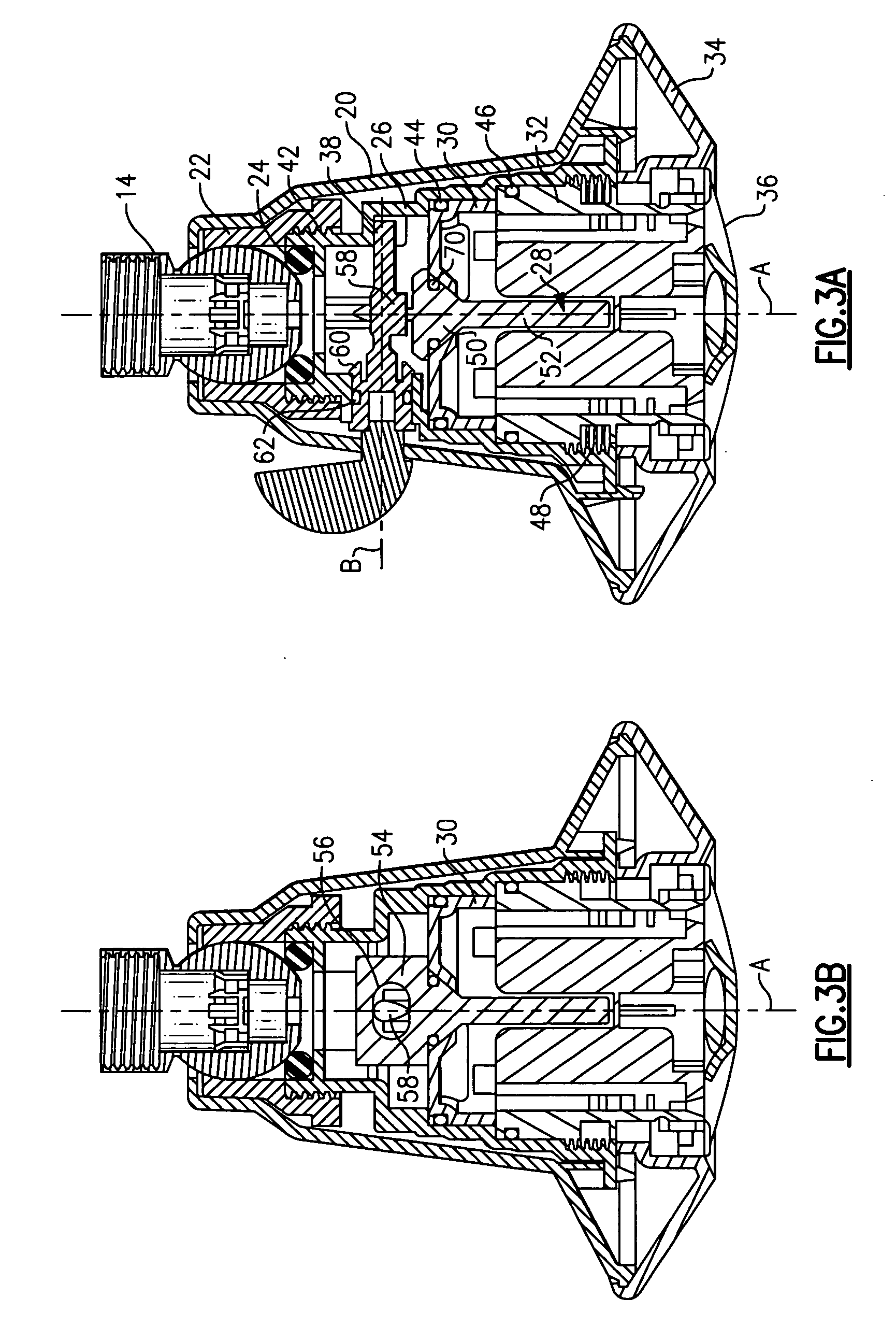
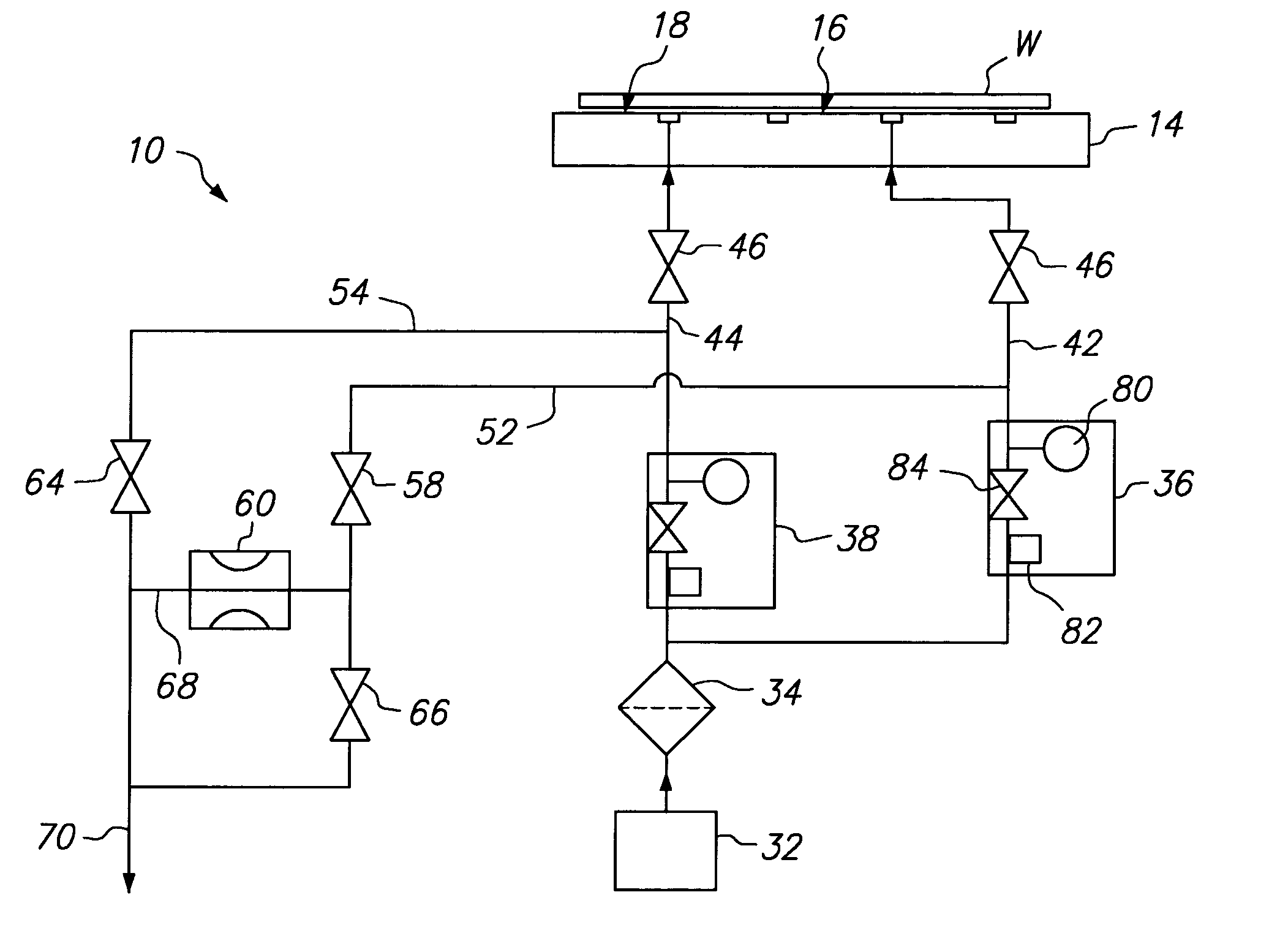
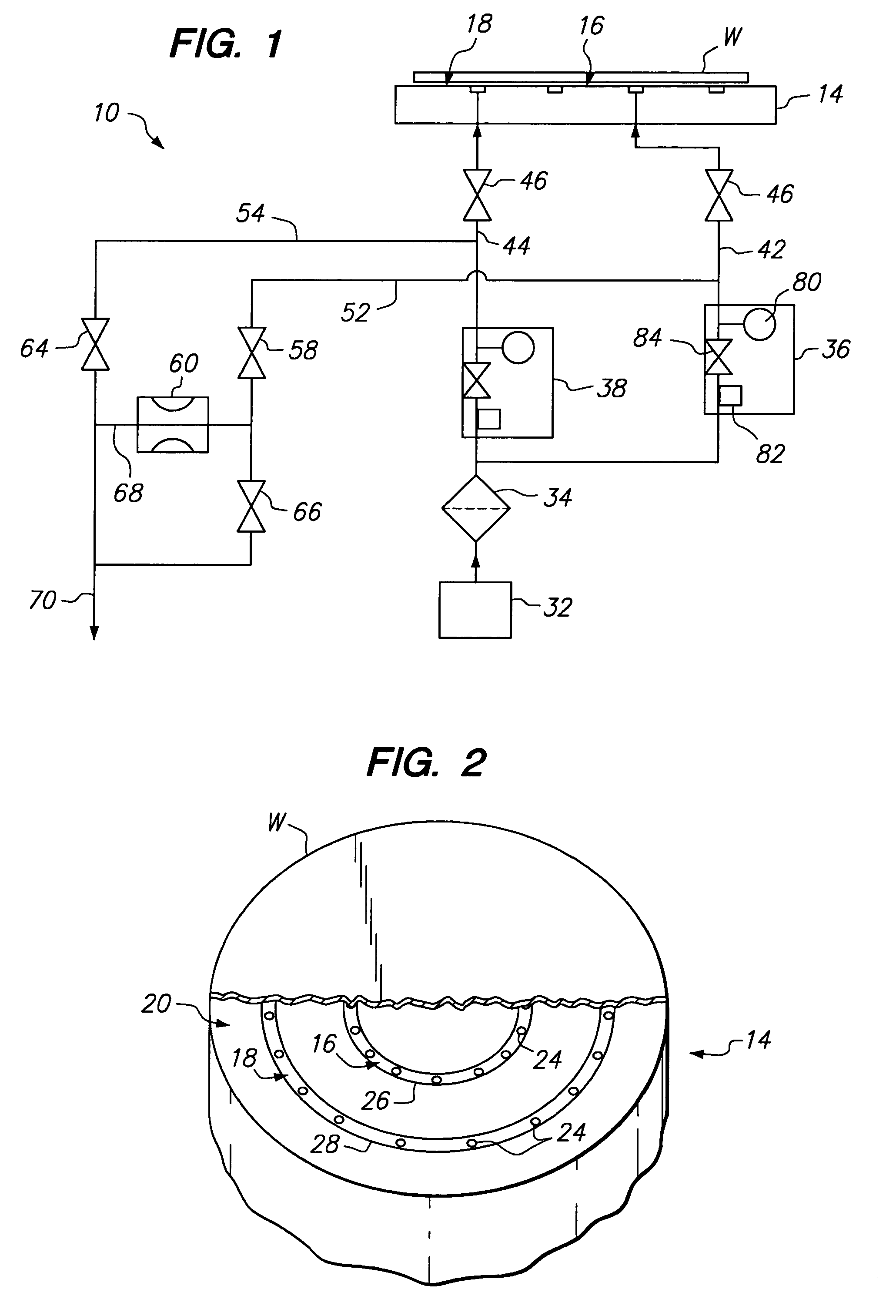
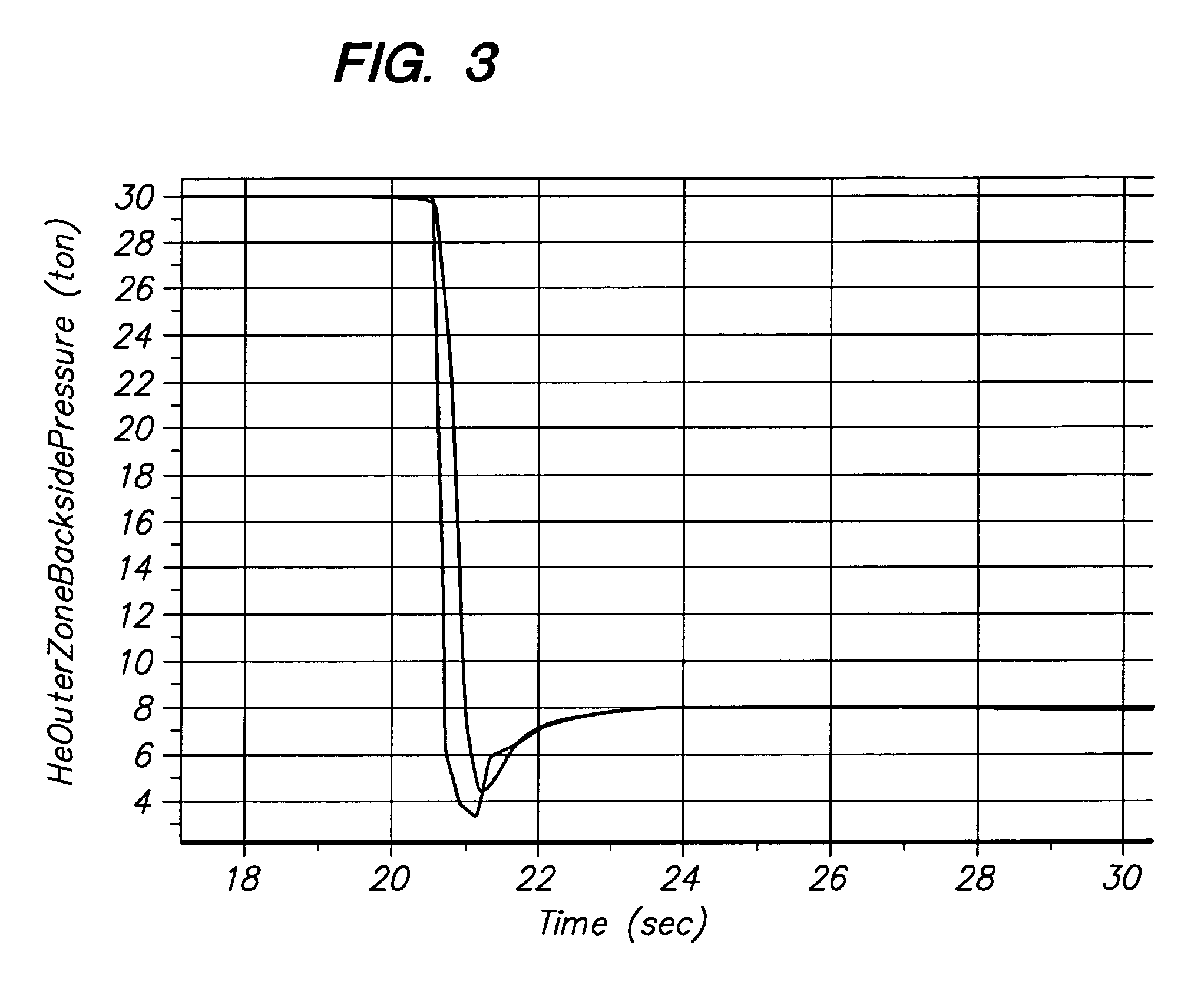
ActiveUS7156951B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingControl systemProduct gas
A gas distribution apparatus delivers a coolant gas, such as helium, to an upper surface of a chuck for controlling a temperature of a wafer placed on the chuck. The gas distribution apparatus allows first and second zones, such as an inner zone and an outer zone of the chuck, to be supplied with a coolant gas at different pressures for control of the temperature across the wafer. The gas distribution apparatus includes a pressure and flow control system for supplying the coolant gas at selected pressures and bleed lines which provide the dual function of allowing rapid evacuation of the inner and outer zones and preventing excess pressure from one zone from migrating to another zone.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Electromagnetic actuator and integrated actuator and fluid flow control valve
InactiveUS20040025949A1Rapid responseLow driving energyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPipeline systemsMagnetic polesEngineering
A magnetic device is formed from a permanent magnet generating magnetic flux, an armature which can occupy two positions between four poles and an electromagnet winding to which current can be supplied to produce a magnetic flux in one direction or the other, the flux from the winding causing the armature to move into one position and continue to remain in that position after the current flow ceases. The device can be incorporated into a fluid valve to act as a drive for opening and closing the valve. It may also serve as the drive for opening and closing electrical contacts. Monostable operation can be achieved by locating a magnetic flux shunt at one end of the armature travel. A holding solenoid may be incorporated. A pivoting armature in a fluid tight chamber comprises a fluid flow controlling device. It can adopt either of two home positions in contact with two magnetic poles and is retained by magnetic flux from a permanent magnet. Fluid can flow into and out of the chamber via a first passage. A second passage extends through one of the poles to an opening in the pole face which is covered by the armature when the latter occupies one home position but is uncovered when the armature occupies its other home position. A third fluid passage extends through and leads to a second opening in another pole, which is covered when the armature occupies its said other home position. Passages in the poles house energy storing springs each of which is compressed as the armature approaches the pole. A push rod can extend through a passage in one of the poles for conveying armature movement externally of the device.
Owner:CAMCOM
Flow control device and method of controlling flow
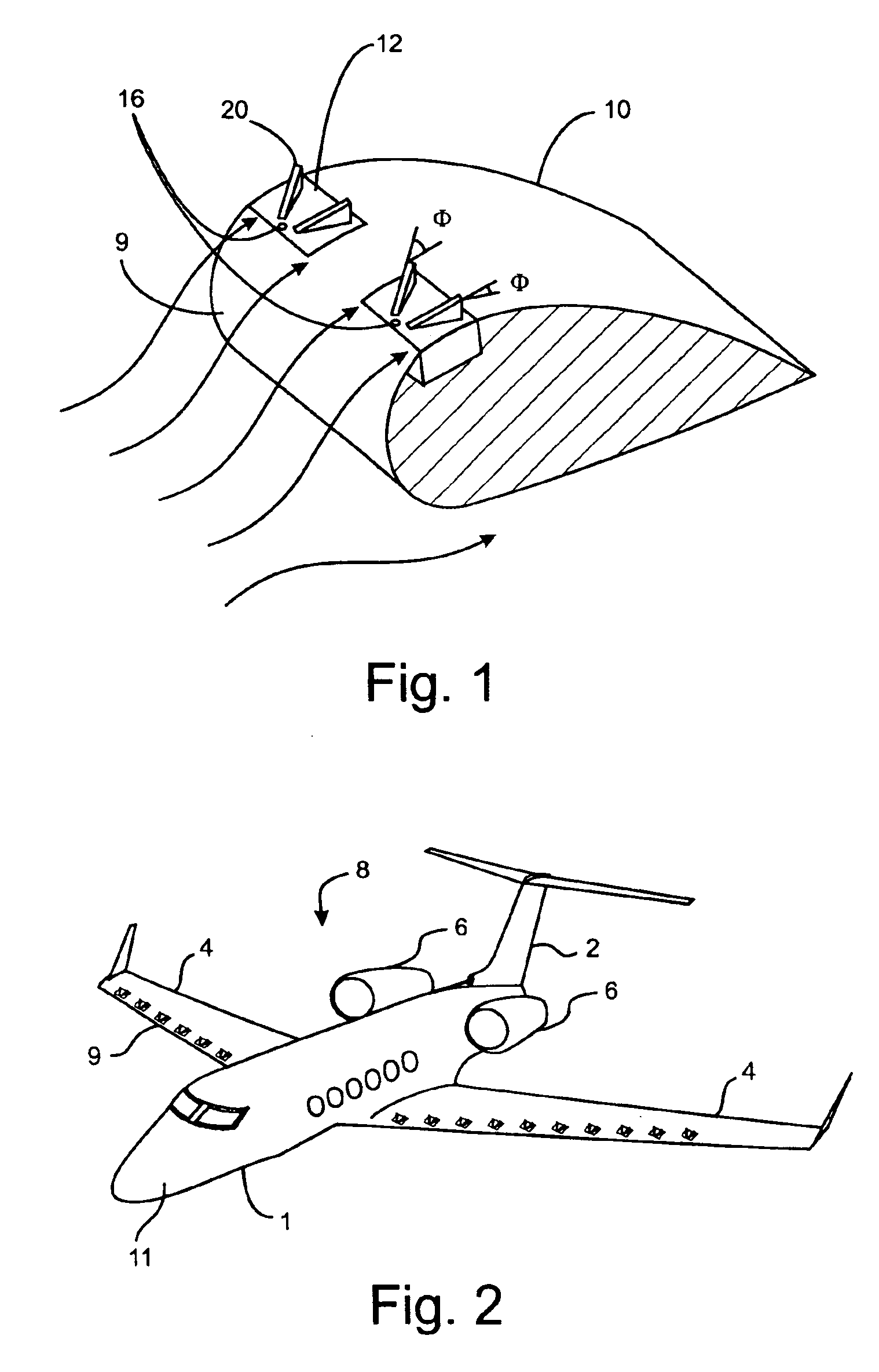
The present invention relates to a flow control device and more particularly to reactive modular flow control device with deployable flow effectors. The present invention further relates to a method of operating the flow control device. One embodiment of the present invention includes a method of controlling air flow across a surface of an aircraft under certain flight conditions comprising the steps of sensing fluid separation from the surface by measuring the pressure on the surface; determining a standard deviation of the pressure measurements over a period of time; and deploying a flow of effector in response to the standard deviation of the pressure measurements exceeding a predetermined threshold number.
Owner:ORBITAL RES
Mass flow rate control apparatus, its calibration method and semiconductor-producing apparatus
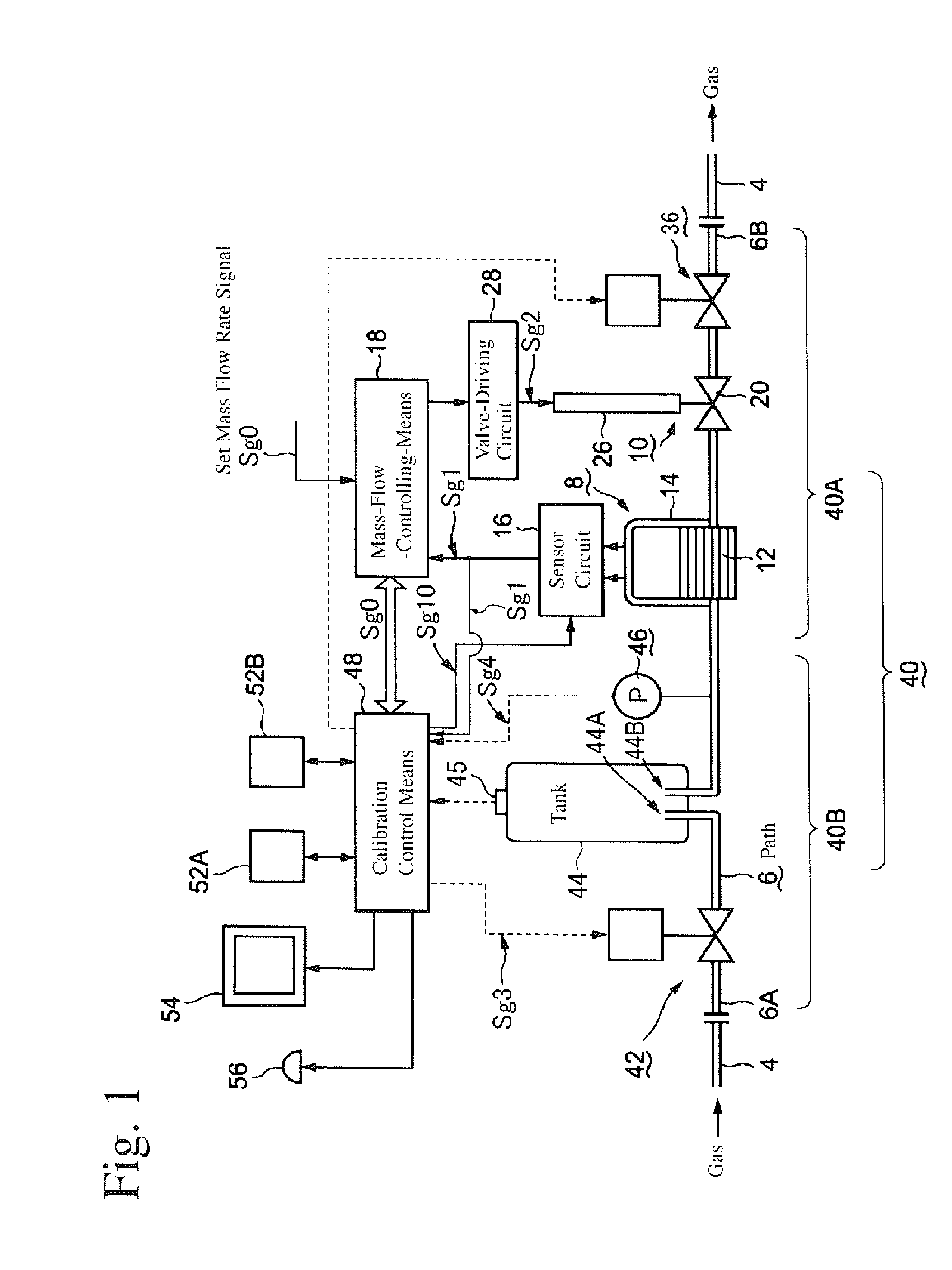
ActiveUS20070233412A1Improve accuracyTesting/calibration apparatusVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringControl valves
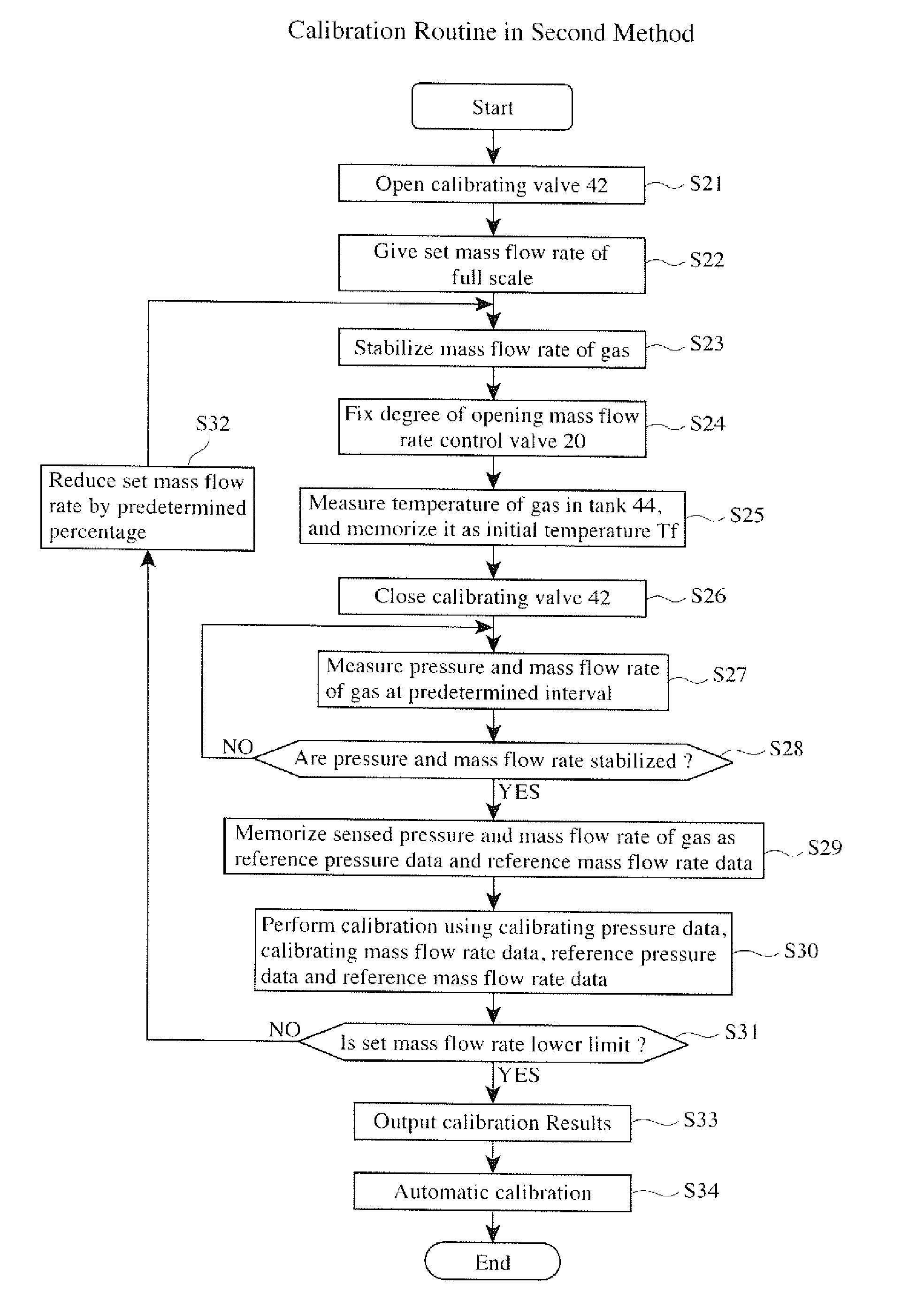
A method for calibrating a mass flow controller comprising a calibrating valve disposed on the most upstream side of a path, a mass flow rate control valve mechanism, a tank provided at the path on the upstream side of the mass flow rate control valve mechanism, a mass-flow-rate-sensing means, a pressure-sensing means, a means for controlling the mass flow rate control valve mechanism, and a mass flow rate calibration control means, the method comprising the steps of (1) permitting a fluid at a set mass flow rate to flow through the path, (2) setting the mass flow rate control valve mechanism at a degree of opening that the mass flow rate of the fluid is equal to the set mass flow rate, (3) closing the calibrating valve, (4) measuring the pressure and mass flow rate of the fluid after a fluid flow from the tank is stabilized, (5) determining a variation ratio of the pressure and mass flow rate to reference pressure and mass flow rate measured by the same procedures in an initial state, is and (6) performing calibration depending on the variation ratio.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Permeable Medium Flow Control Devices for Use in Hydrocarbon Production
An in-flow control device controls fluid flow into a wellbore tubular using a permeable medium positioned in a flow space. The permeable medium induces a predetermined pressure differential in the flow space. The permeable medium may include separate elements having interstitial spaces and / or solid porous members. In arrangements, a filtration element may be positioned upstream of the flow space. In arrangements, the flow space may be formed in a plug member associated with the housing. In certain embodiments, a flow restriction element, such as a check valve, in the housing may provide parallel fluid communication with the bore of the wellbore tubular. Additionally, an occlusion body may be positioned in the flow space and configured to disintegrate upon exposure to a preset condition. The occlusion body temporarily seals the flow space so that a bore of the tubular may be pressurized.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
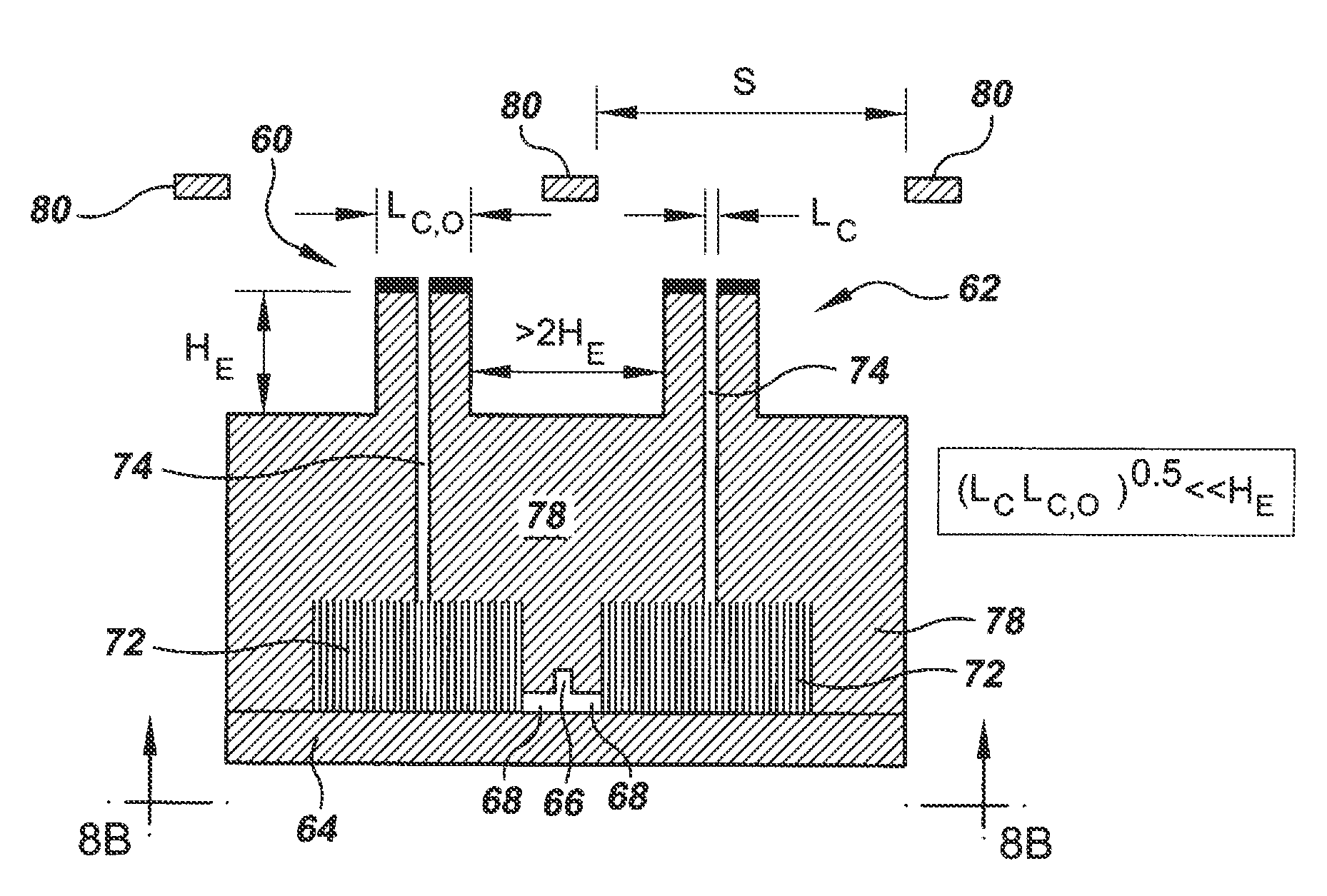
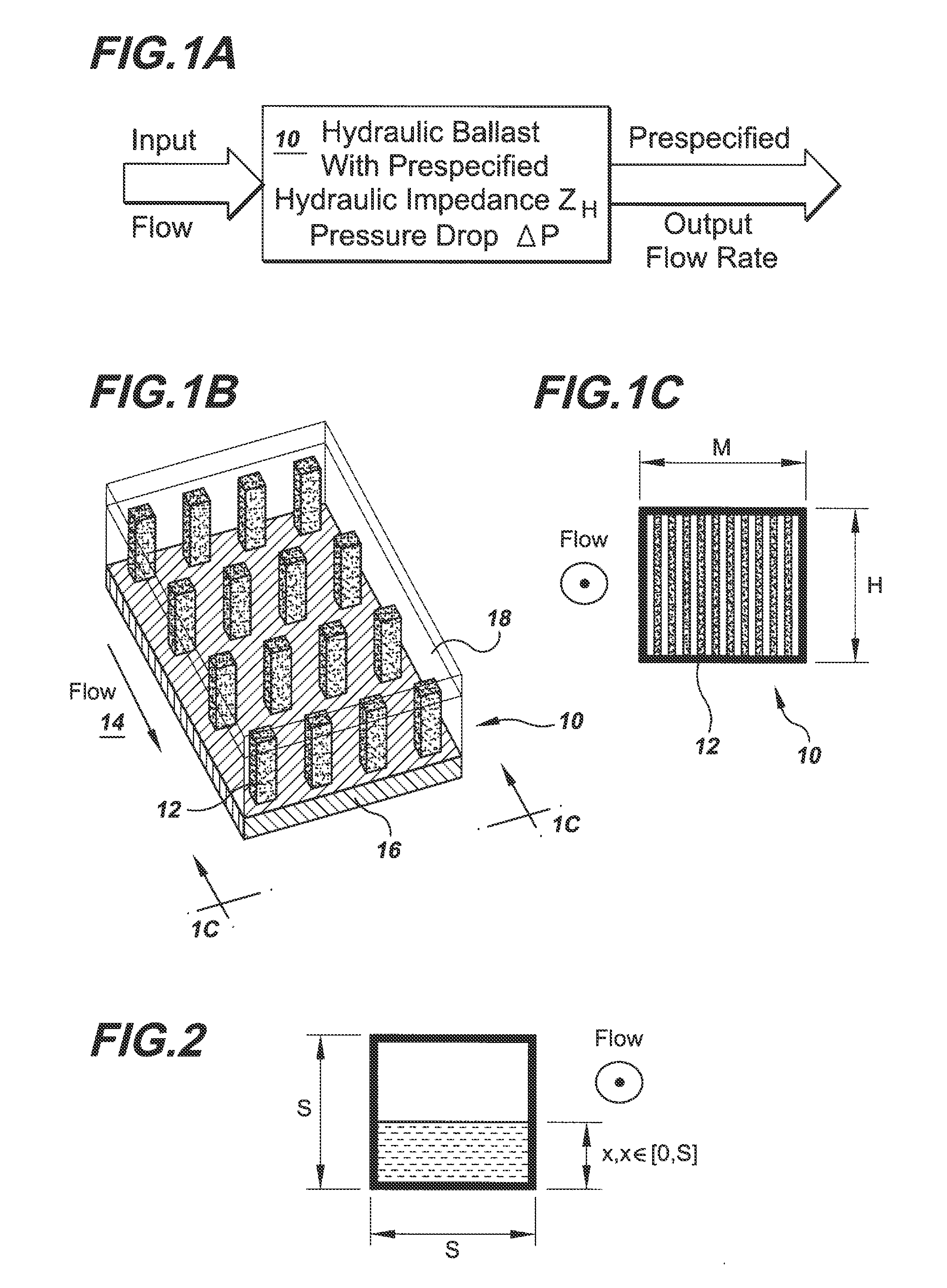
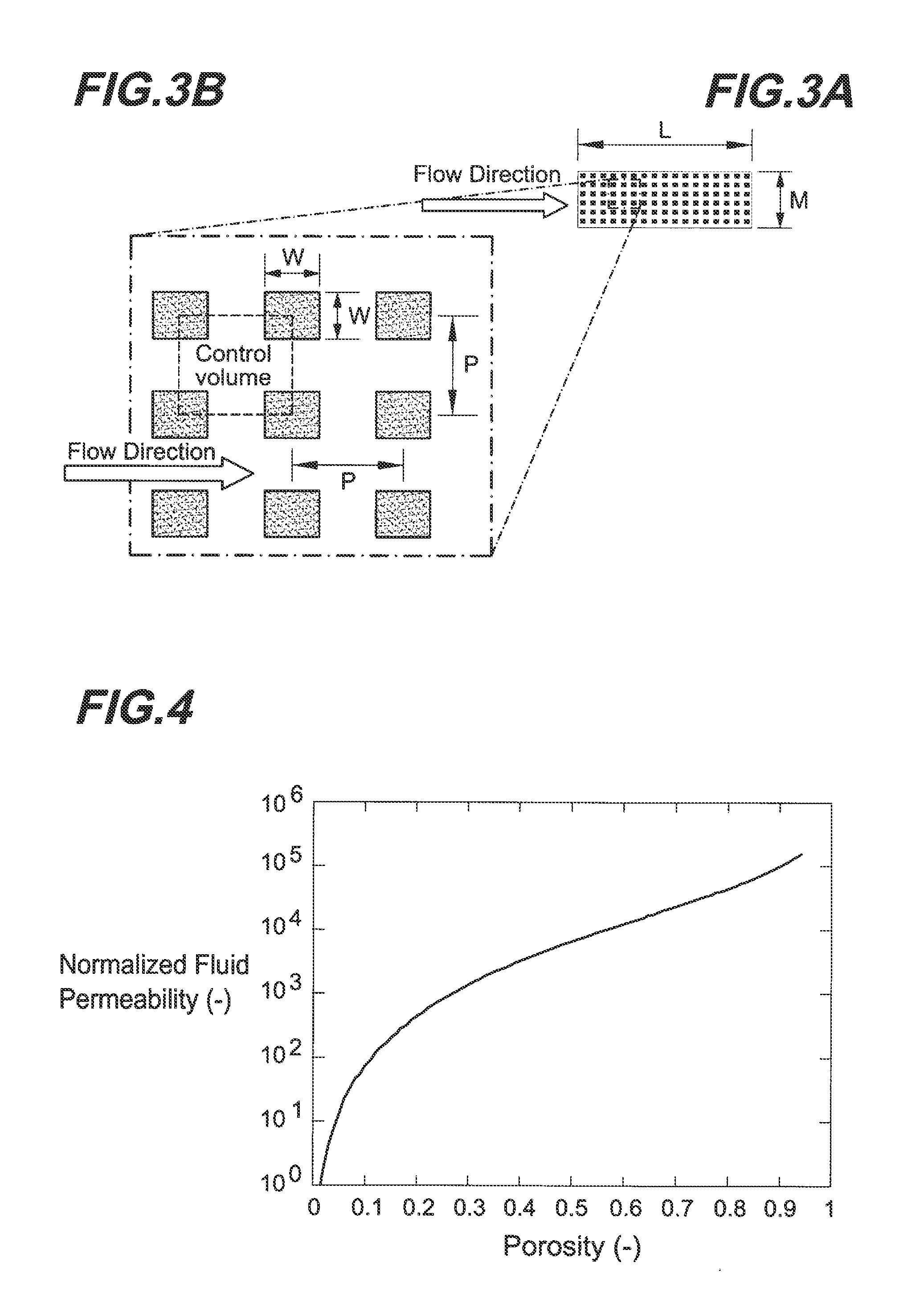
Microstructures For Fluidic Ballasting and Flow Control
InactiveUS20110126929A1Pipe supportsReactant parameters controlElectrical ballastControl engineering
In one example hydraulic ballast of the invention there is provided an input port and an output port through which a prespecified output flow rate is required. There is provided between the input and output ports a ballasting array of columns having a cross-sectional column extent, W, a column pitch, P, and an array length, L, selected based on the required output flow rate, to produce a prespecified pressure drop that enforces the required output flow rate.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Controlling pressure in adjustable restriction devices
ActiveUS20090216255A1Reduce restrictionsStrengthen restrictionsDiaphragm valvesEngine diaphragmsPressure controlled ventilationPressure control
Methods and devices are provided for regulating a hydraulic restriction system. In general, the methods and devices can allow for non-invasive pressure control using a flow control mechanism. The flow control mechanism can be disposed between an implantable restriction device and a fluid source and include an adjustable, variably-sized fluid communication member in fluid communication with the restriction device and the fluid source. The geometry of the fluid communication member can control a rate of fluid flow between the restriction device and the fluid source, thereby also regulating a rate at which a pressure of fluid within the restriction device changes. Alternatively, the fluid flow control mechanism can include a biasing mechanism that can control the rate of fluid flow between the restriction device and the fluid source.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
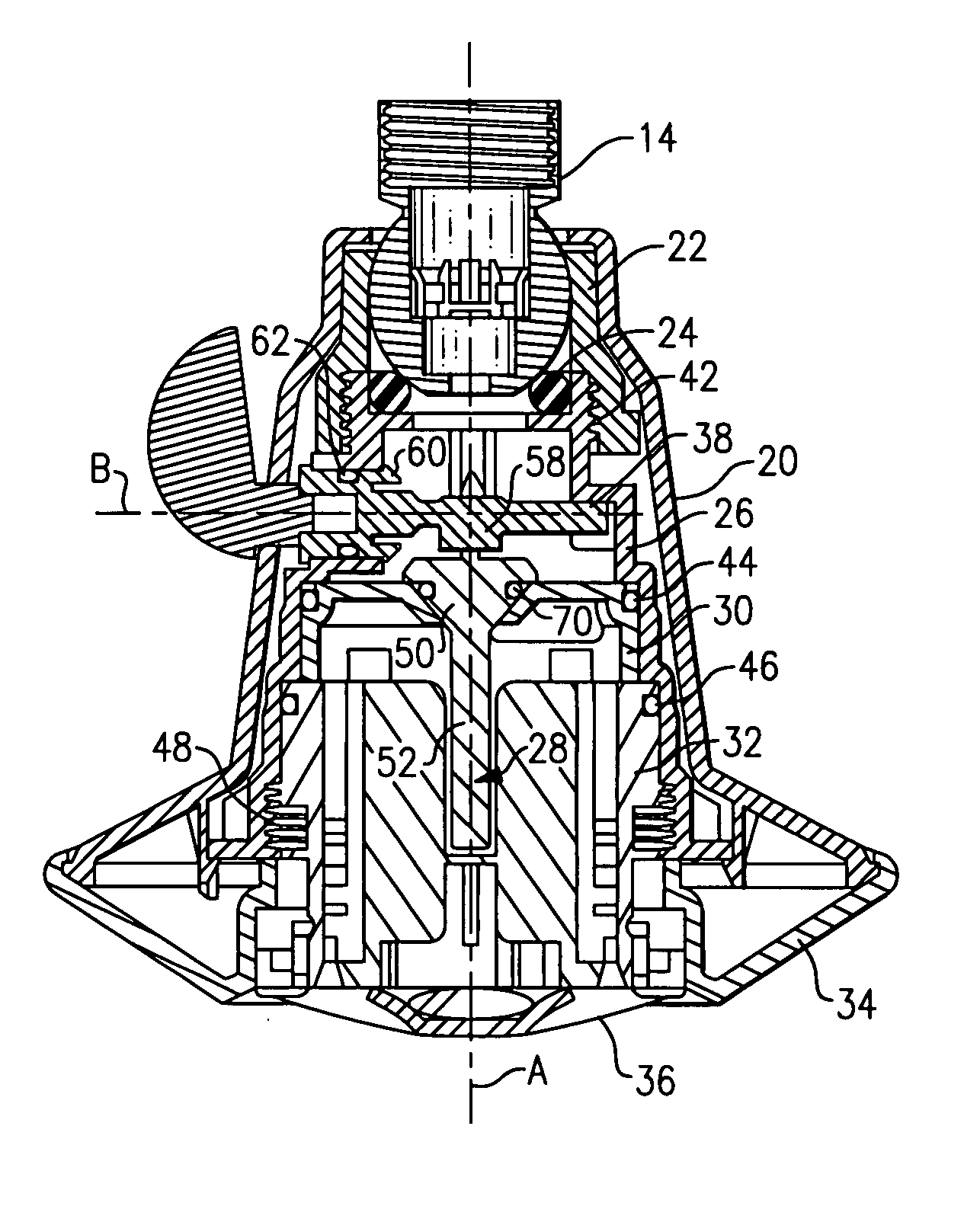
Liquid flow control valve
InactiveUS6837271B1Minimise water wastageReduce wasteMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringControl valves
A liquid flow control valve has a valve body 10 in which is mounted a valve member 41 moveable between valve open and closed positions. A turbine 15 senses liquid flow through the valve body 10 and generates electrical pulses which are counted by a control circuit, over a pre-set period. An electro-magnet 54,55 controls operation of the valve member 41 and is driven by the control circuit so as to close the valve in the event that flow continues for longer than the pre-set period or the flow is greater than at a pre-set rate. The valve may also be closed should the temperature fall to about 0° C.
Owner:SAINT WILLIAM HENRY
Aircraft and missile afterbody flow control device and method of controlling flow
ActiveUS7070144B1Reduce dragEasy to operateAutonomous decision making processInfluencers by generating vorticesAirplaneMissile
The present invention relates to an afterbody flow control system and more particularly to aircraft or missile flow control system for enhanced maneuverability and stabilization. The present invention further relates to a method of operating the flow control system.In one embodiment, the present invention includes a missile or aircraft comprising an afterbody and a forebody; at least one activatable flow effector on the missile or aircraft afterbody; at least one sensor each having a signal, the at least one sensor being positioned to detect forces or flow conditions on the missile or aircraft afterbody; and a closed loop control system; wherein the closed loop control system is used for activating and deactivating the at least one activatable flow effector based on at least in part the signal of the at least one sensor.
Owner:ORBITAL RES
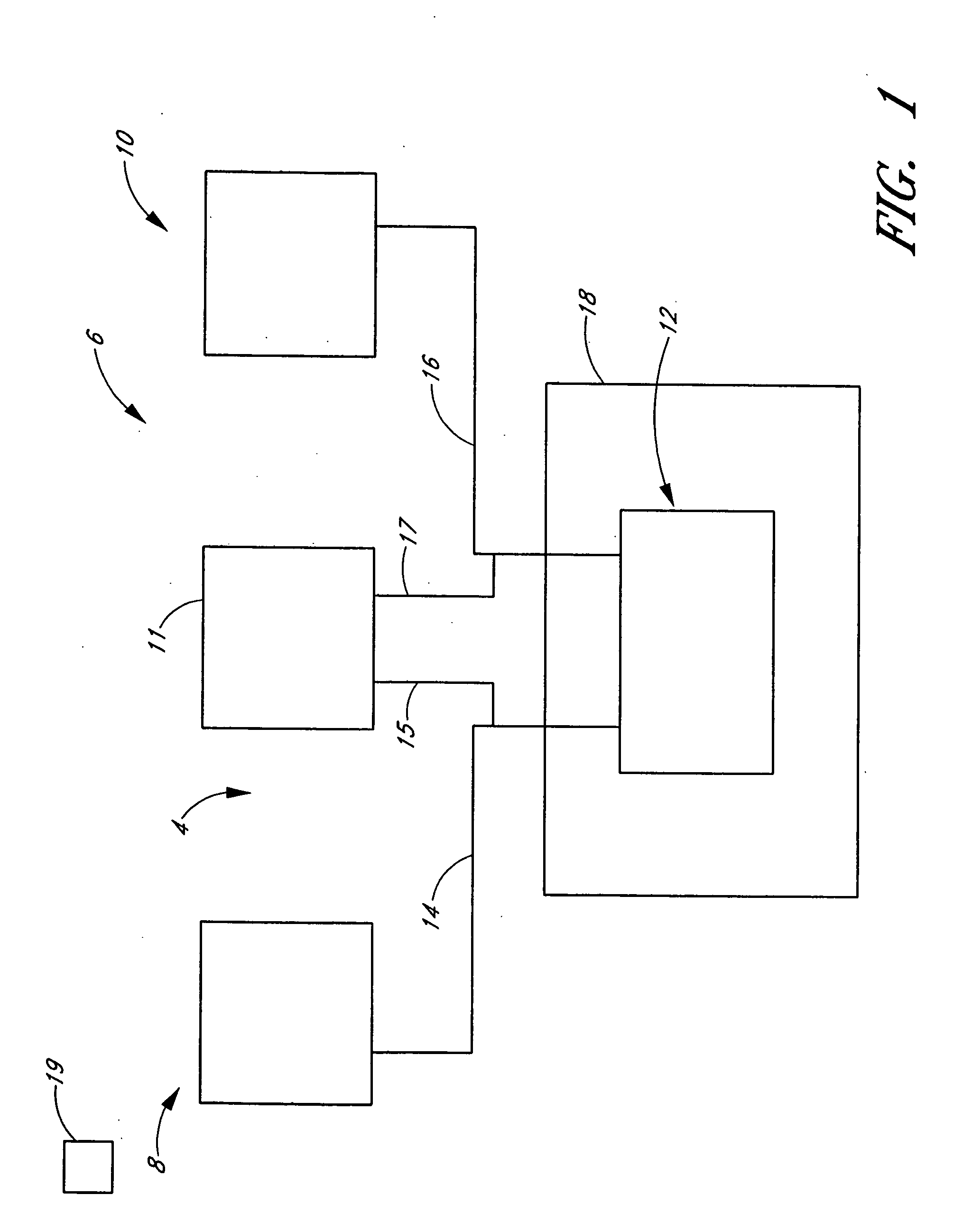
Reaction system for growing a thin film
ActiveUS7020981B2Extension of timeLong stepDrying using combination processesDrying solid materials with heatControl systemPhysical chemistry
A reactor defines a reaction chamber for processing a substrate. The reactor comprises a first inlet for providing a first reactant and to the reaction chamber and a second inlet for a second reactant to the reaction chamber. A first exhaust outlet removes gases from the reaction chamber. A second exhaust outlet removes gases from the reaction chamber. A flow control system is configured to alternately constrict flow through the first and second exhaust outlets. The reactor chamber is configured to for a diffusion barrier within the reaction chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
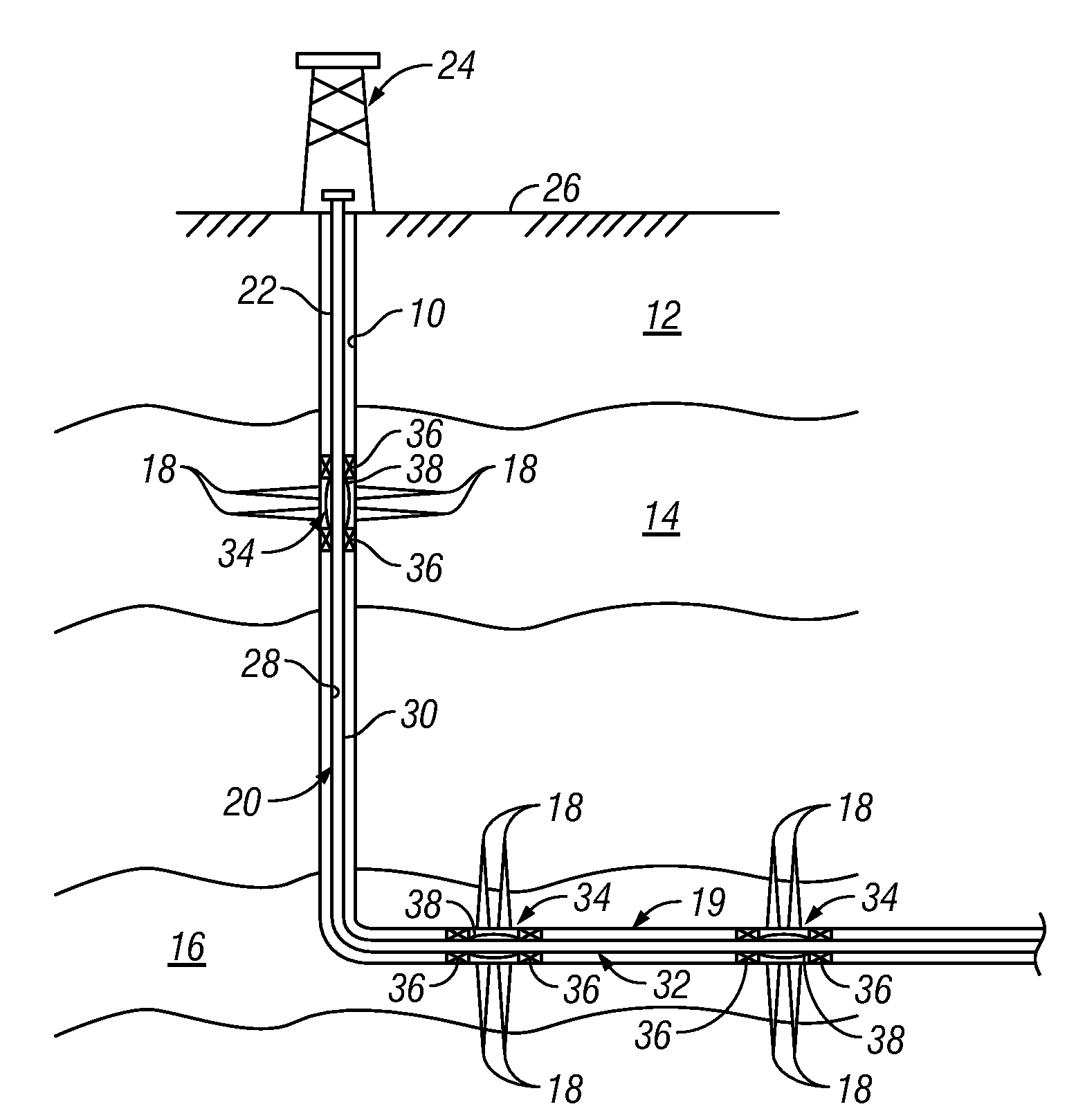
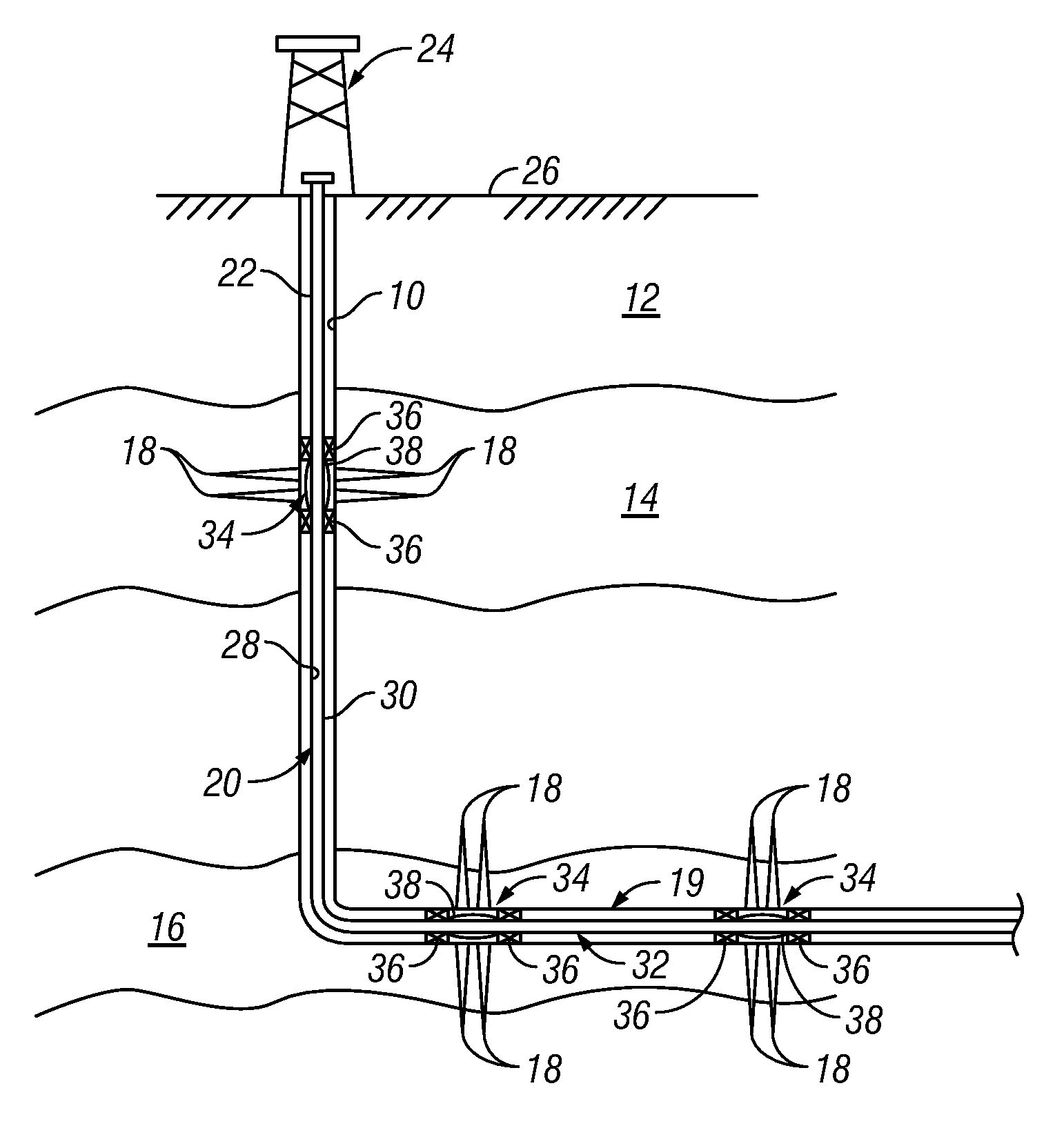
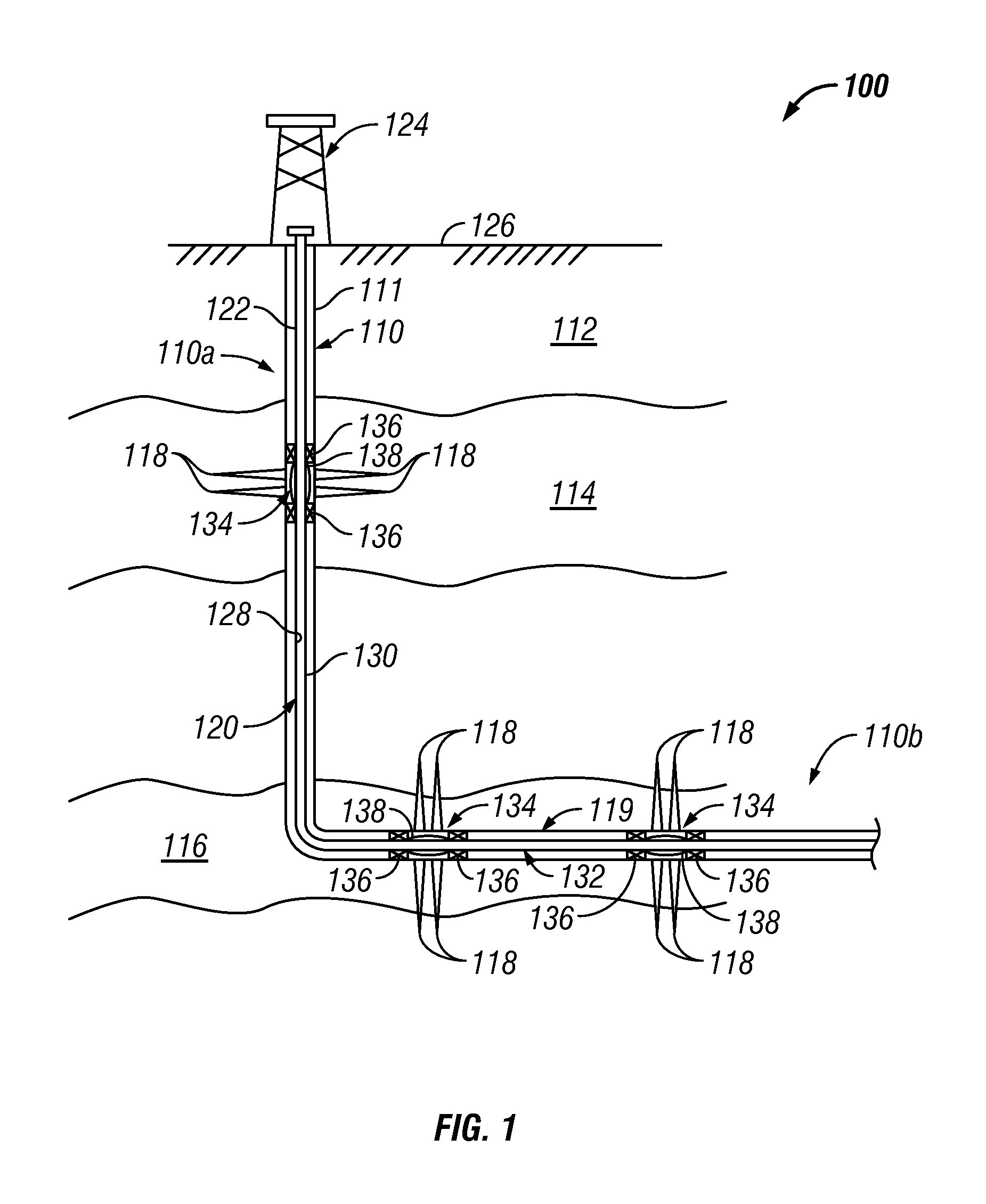
Method and apparatus for autonomous downhole fluid selection with pathway dependent resistance system
An apparatus is described for controlling flow of fluid in a tubular positioned in a wellbore extending through a subterranean formation. A flow control system is placed in fluid communication with a main tubular. The flow control system has a flow ratio control system and a pathway dependent resistance system. The flow ratio control system has a first and second passageway, the production fluid flowing into the passageways with the ratio of fluid flow through the passageways related to the characteristic of the fluid flow. The pathway dependent resistance system includes a vortex chamber with a first and second inlet and an outlet, the first inlet of the pathway dependent resistance system in fluid communication with the first passageway of the fluid ratio control system and the second inlet in fluid communication with the second passageway of the fluid ratio control system. The first inlet is positioned to direct fluid into the vortex chamber such that it flows primarily tangentially into the vortex chamber, and the second inlet is positioned to direct fluid such that it flows primarily radially into the vortex chamber. Undesired fluids, such as natural gas or water, in an oil well, are directed, based on their relative characteristic, into the vortex primarily tangentially, thereby restricting fluid flow when the undesired fluid is present as a component of the production fluid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Pressure monitoring of control lines for tool position feedback
A flow control device for use in a wellbore to allow flow of formation fluid into the wellbore comprises a valve member adapted to move when disposed in the wellbore. A fluid line supplies a working fluid under pressure to move the valve member to allow the fluid to flow into the wellbore. A sensor in the wellbore, and associated with the fluid line, provides an indication of a position of the valve member. A method of determining a state of a flow control tool within a wellbore comprises supplying fluid under pressure to the flow control tool to move a flow control member of the tool into the state. Pressure of the supplied fluid is detected downhole. The state of the flow control device is determined from the detected pressure of the supplied fluid.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
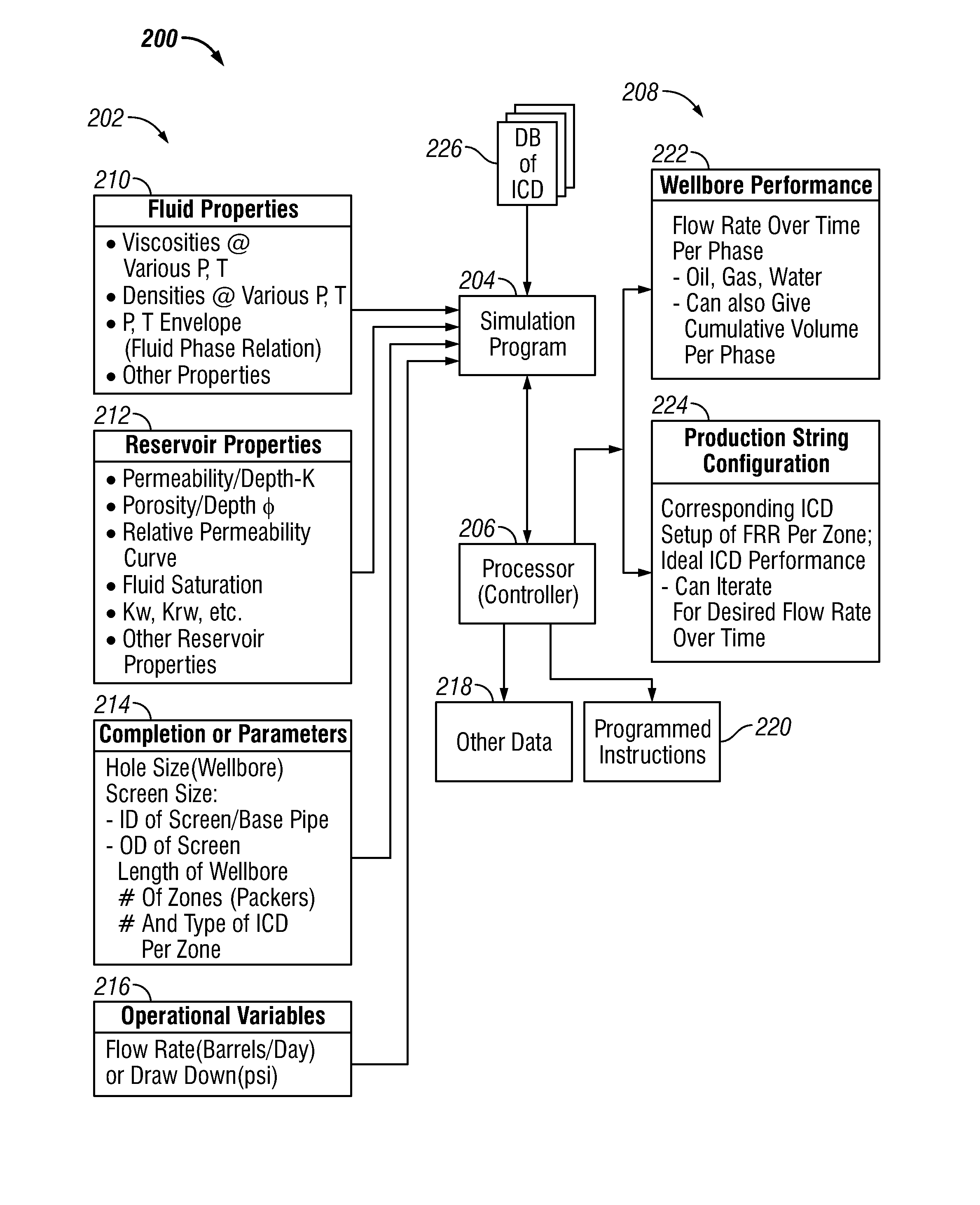
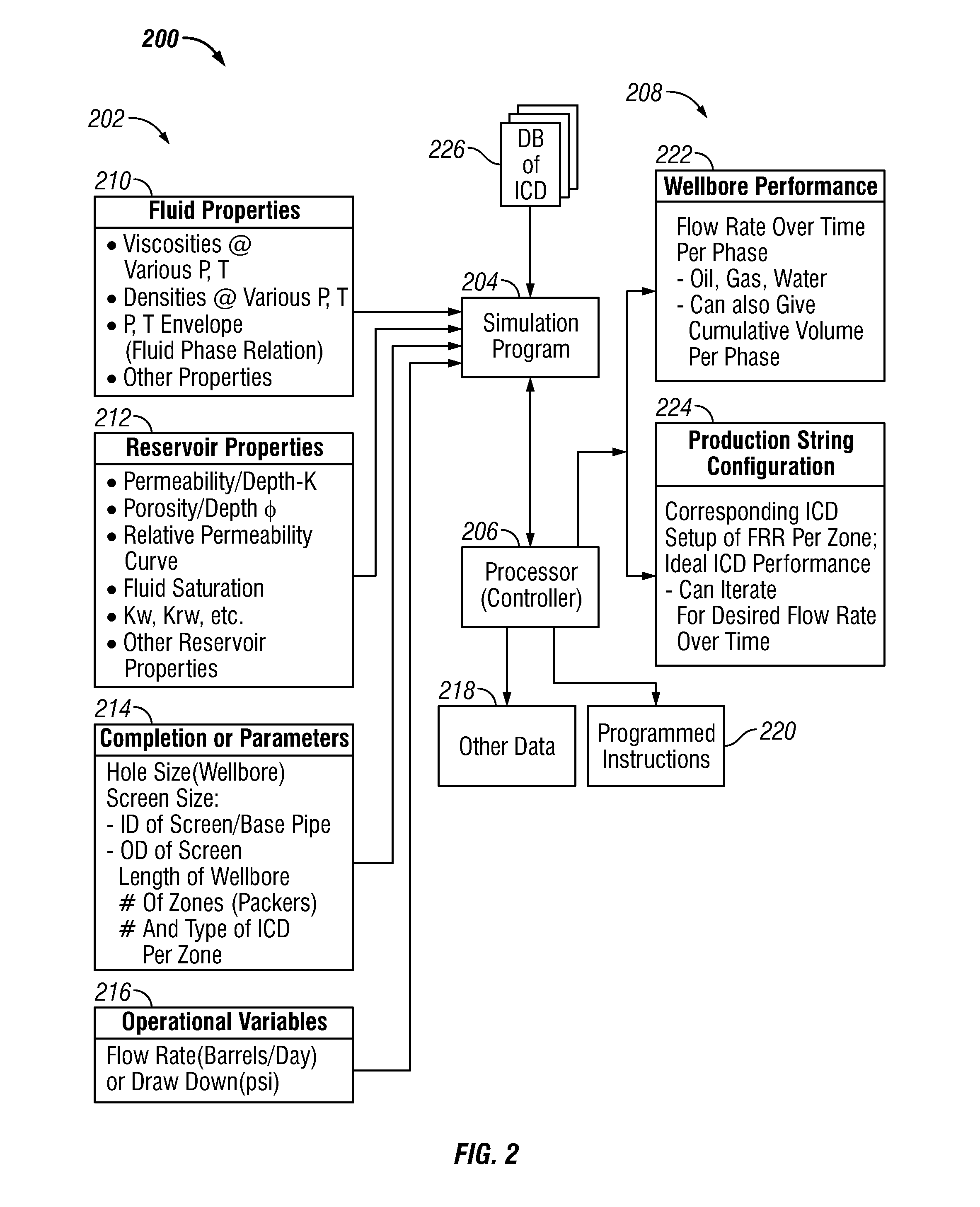
Method of Providing Flow Control Devices for a Production Wellbore
A method of providing a production string for a wellbore formed in a formation is disclosed. The method, in one embodiment may include: defining a performance criterion for flow of a fluid from a formation into a wellbore; performing a simulation using a processor, a simulation program, a parameter of the fluid, a parameter of the formation and a parameter of the wellbore to determine a first flow characteristic of the flow of the fluid from the formation into the wellbore corresponding to an initial set of flow control devices arranged in the wellbore; performing one or more additional simulations using the processor, the simulation program and the parameters of formation, fluid and wellbore to determine a new flow characteristic of the flow of the fluid from the formation into the wellbore for a new set of flow control devices until a new determined characteristic of the flow of the fluid from the formation into the wellbore meets the performance criterion; and storing results of simulation results relating to the flow control devices in a suitable storage medium.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Flow control for on-board inert gas generation system
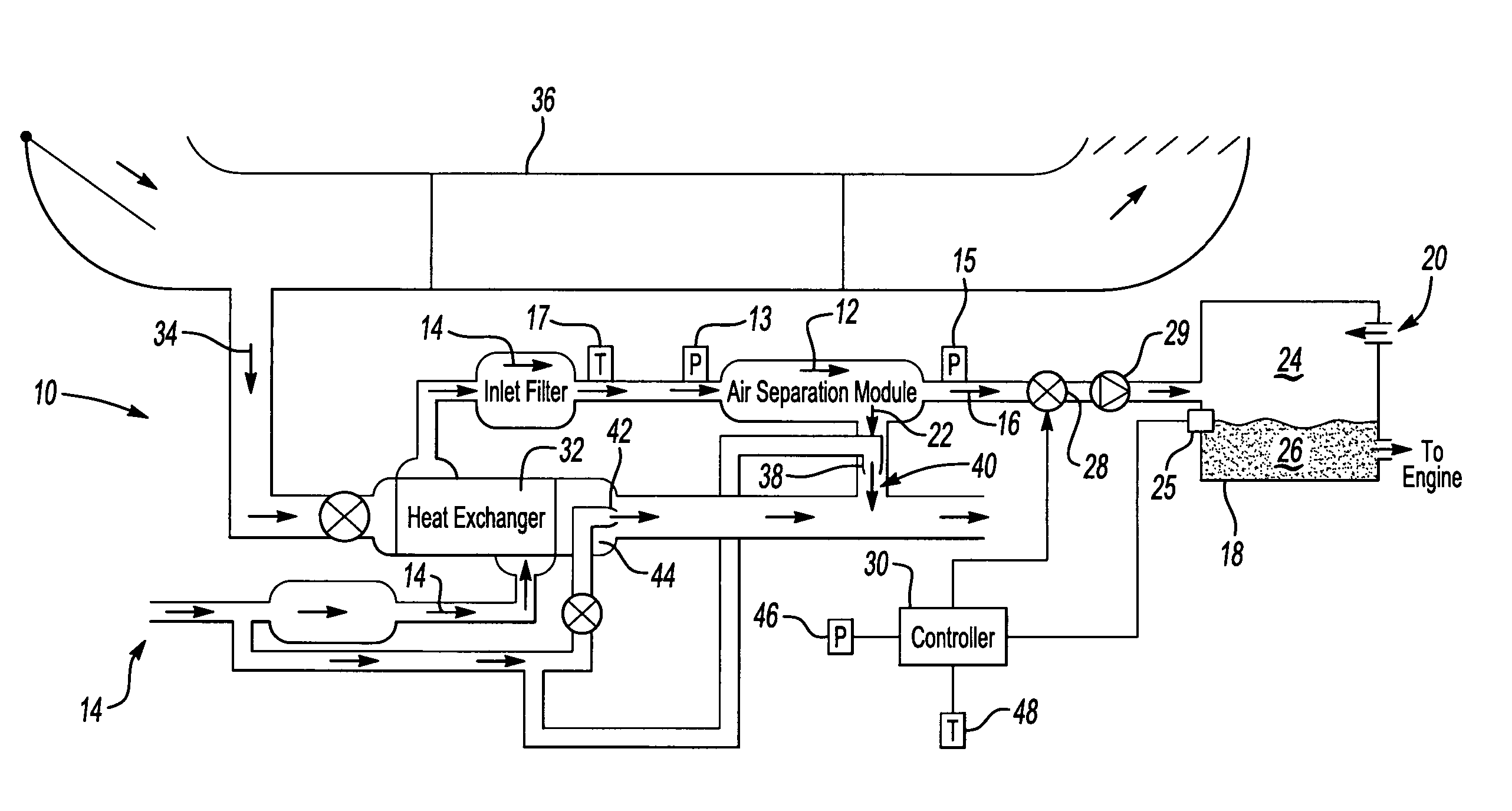
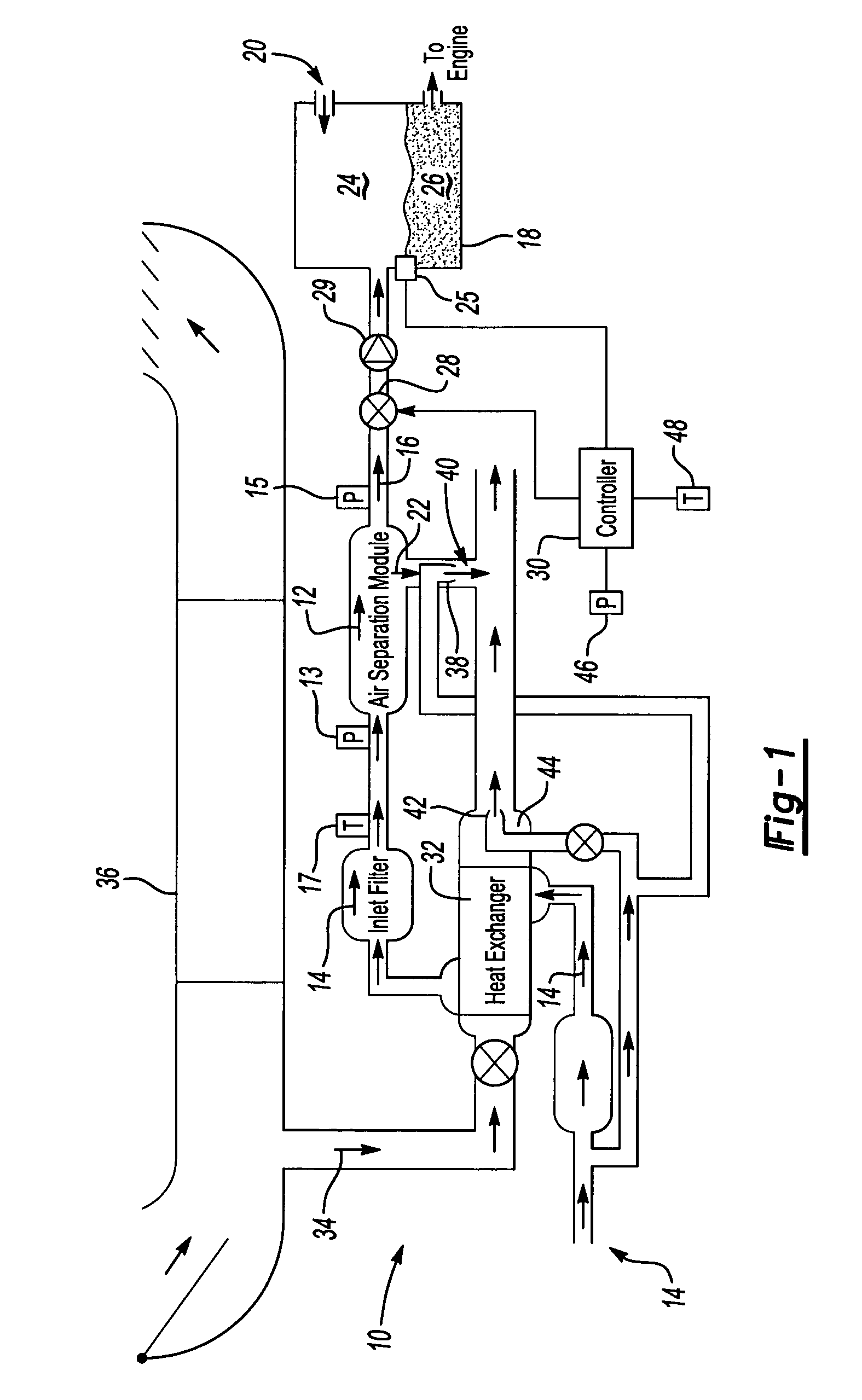
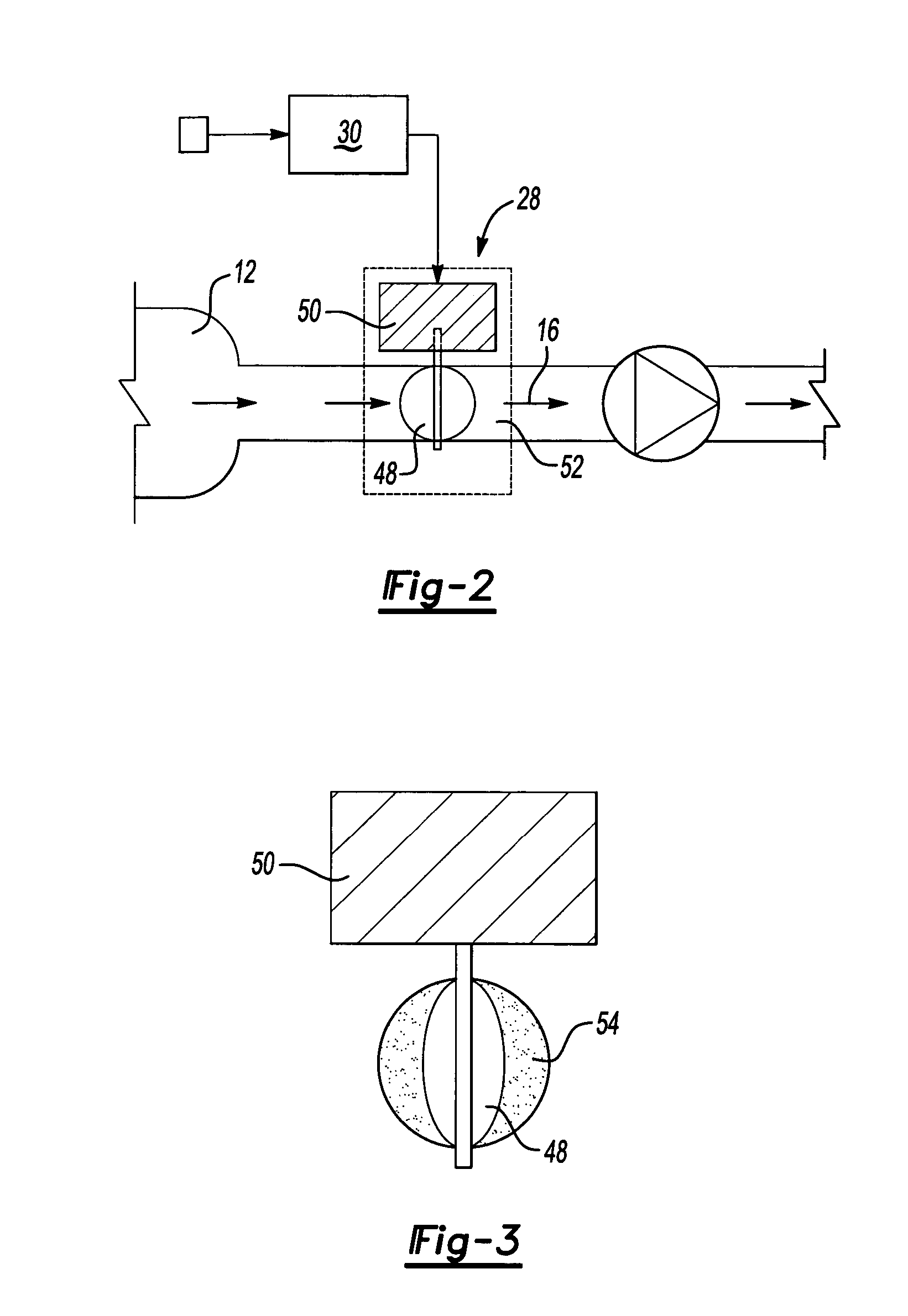
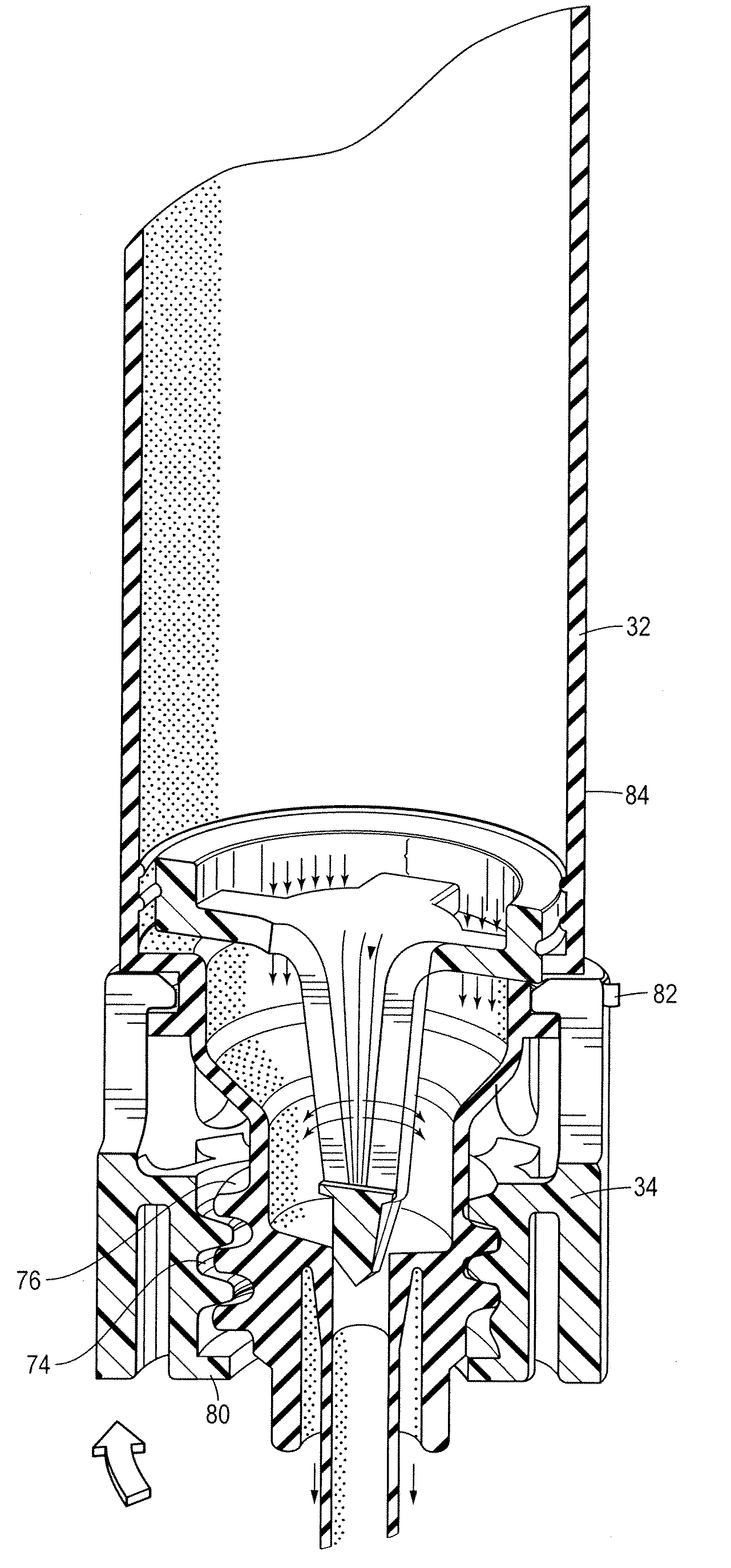
An on-board inert gas generating system includes a flow control valve modulated according to changes in ambient conditions to minimize changes to oxygen content within a fuel tank. The quality of the nitrogen-enriched air stream that is provided by the air separation module varies in response to flow. Higher flow rates through the air separation module removes less oxygen relative to lower flow rates. The amount of flow through the air separation module that produces the least amount of oxygen within the fuel tank is determined for an ambient pressure and provided by modulating the flow control valve.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Drip chamber with flow control
ActiveUS20110125103A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesFlow monitorsControl systemStreamflow
A flow control system includes a drip chamber having lower and upper wall sections and a collapsible wall extending between the lower and upper wall sections, a downwardly depending valve seat attached to the lower wall section, and a valve member disposed in the drip chamber, attached to the upper wall section and having a valve surface engageable with the valve seat. The system also includes a driver rotatably engaged to the lower and upper wall sections. Upon rotation of the driver in a first direction, the collapsible wall of the drip chamber moves between a collapsed condition in which the valve seat is sealingly engaged with the valve surface and an extended condition in which the valve seat is sufficiently spaced from the valve surface to form a flow passageway between the valve surface and the valve seat and permit flow through the opening of the drip chamber.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
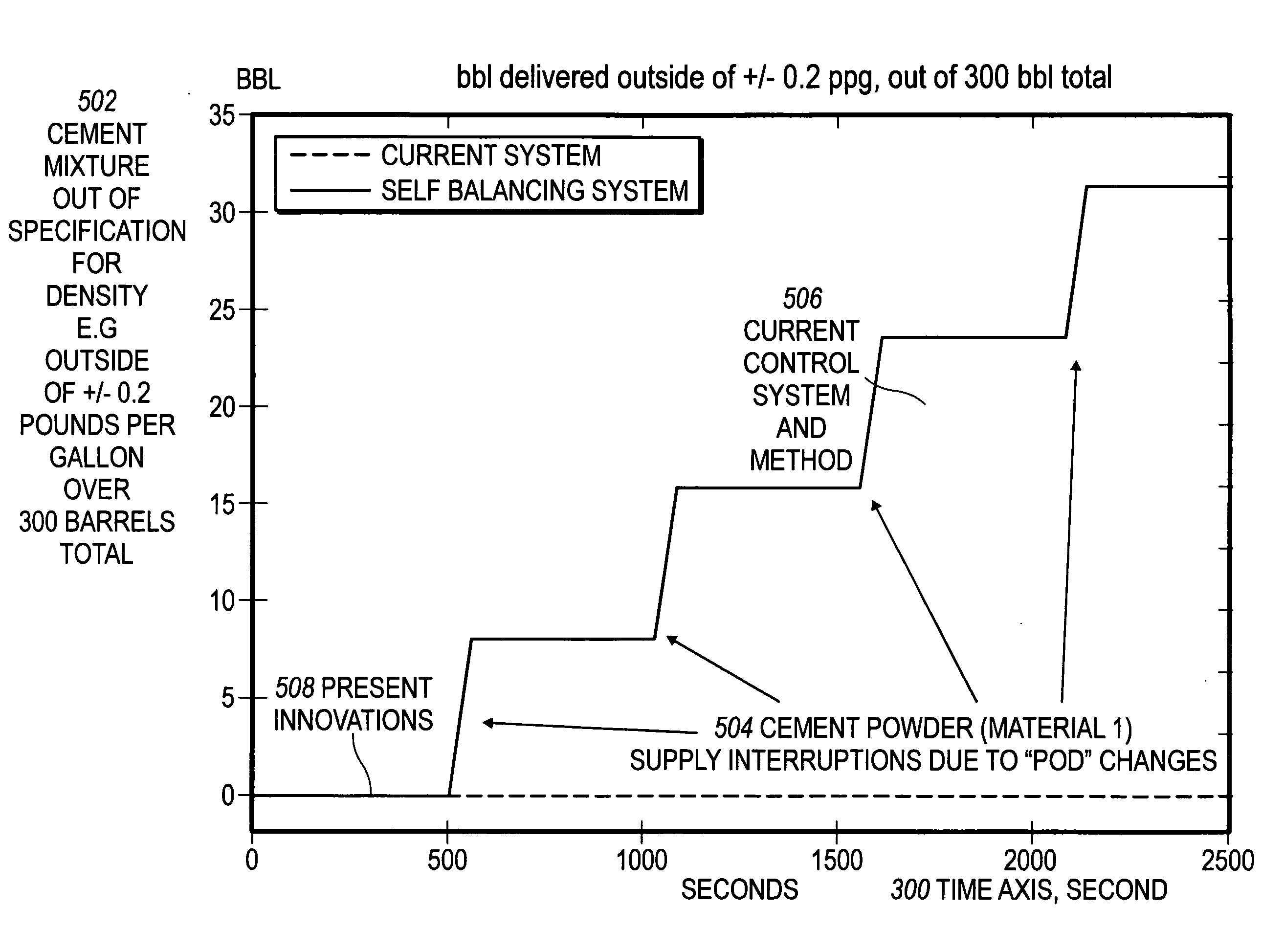
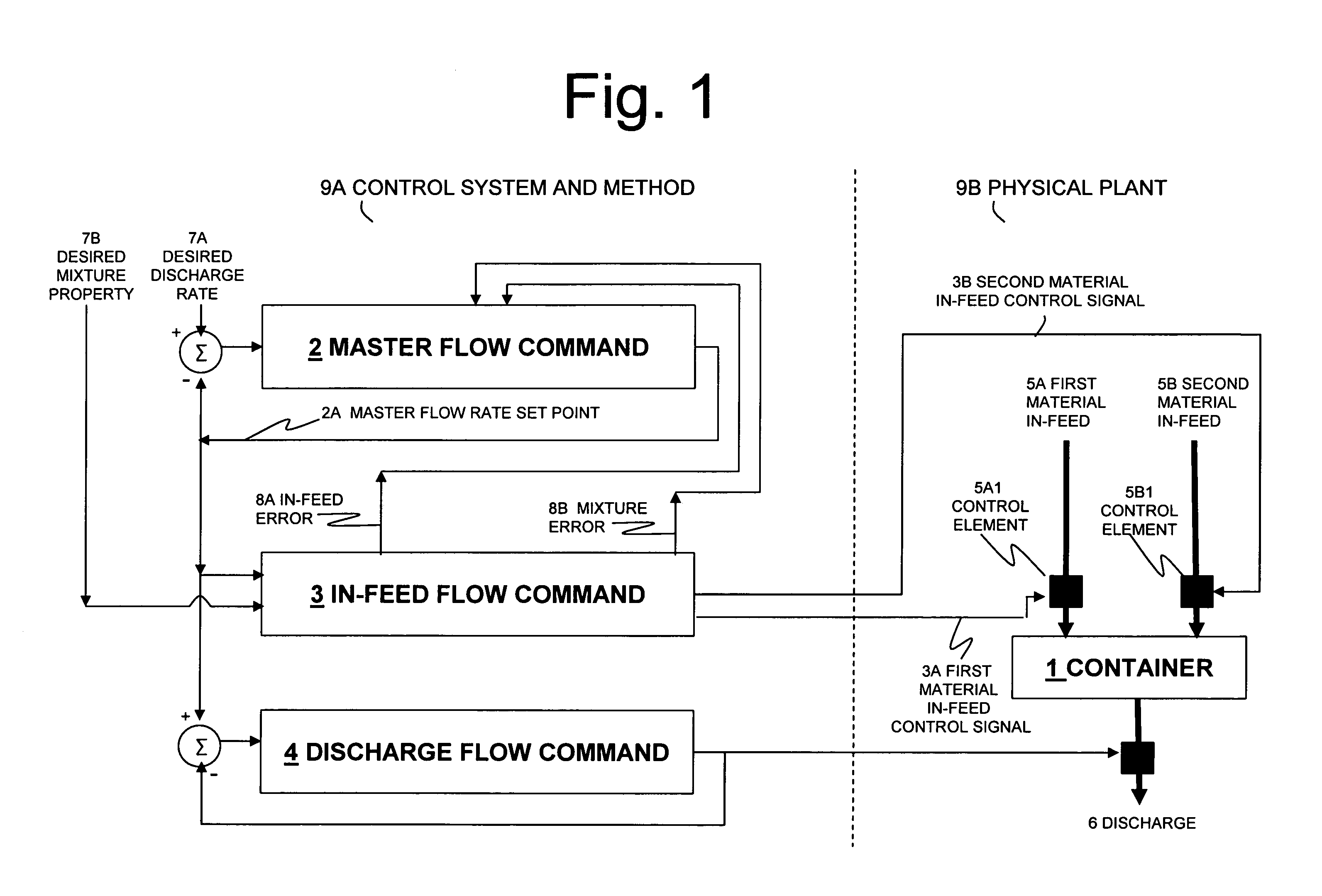
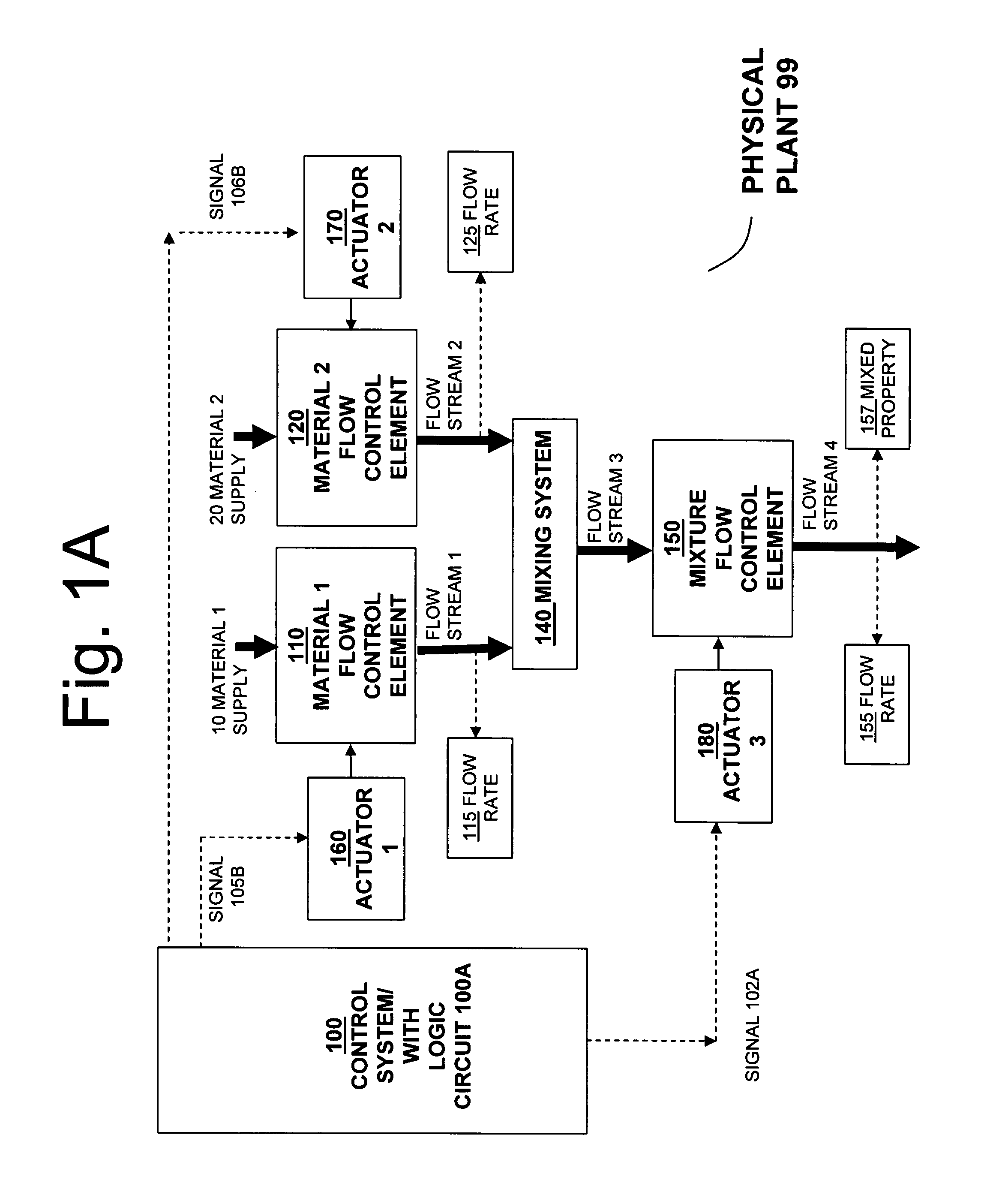
Systems for self-balancing control of mixing and pumping
ActiveUS20080165613A1Reduce needImprove consistencySampled-variable control systemsControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsControl signalControl system
Systems for controlling the in-feed and discharge rates of materials flowing into and out of a mixing process where one priority is to achieve a target mixture flow rate from the mixing process and another priority can be to achieve a target value for a mixture property. Actuators can be operated to control material in-feed rates, the mixture composition, and discharge rate, and can maintain a hold-up of the mixture in the mixing process. A total flow rate controller provides a control signal to a controller acting on the discharge rate and a controller acting on the in-feed rates. The mixture discharge flow rate can be automatically reduced from its desired target when the commanded rate of at least one of the materials exceeds its available supply rate as inferred from an inability to maintain the targeted value for the mixture property.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com