Patents
Literature
1072results about "Circuit elements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
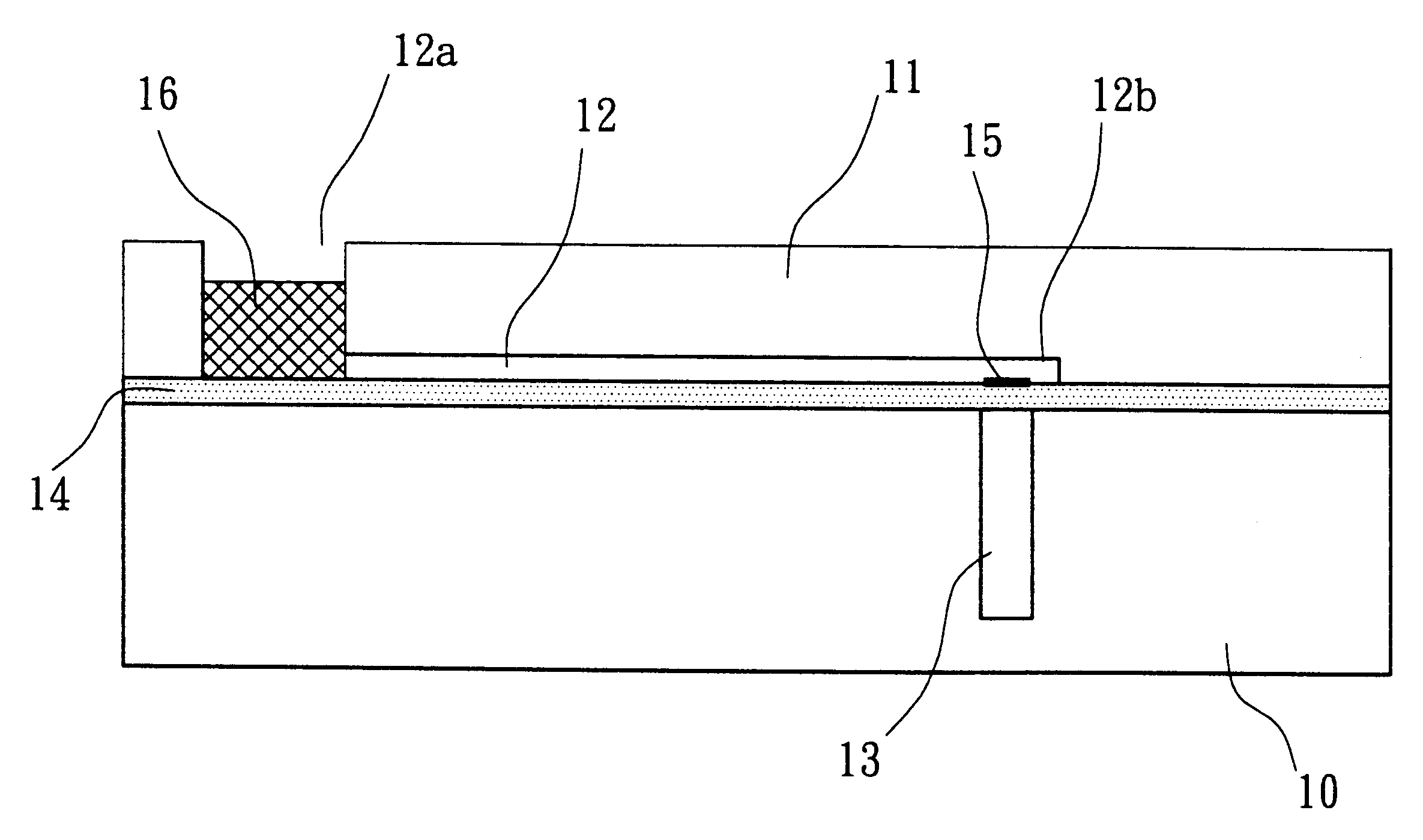
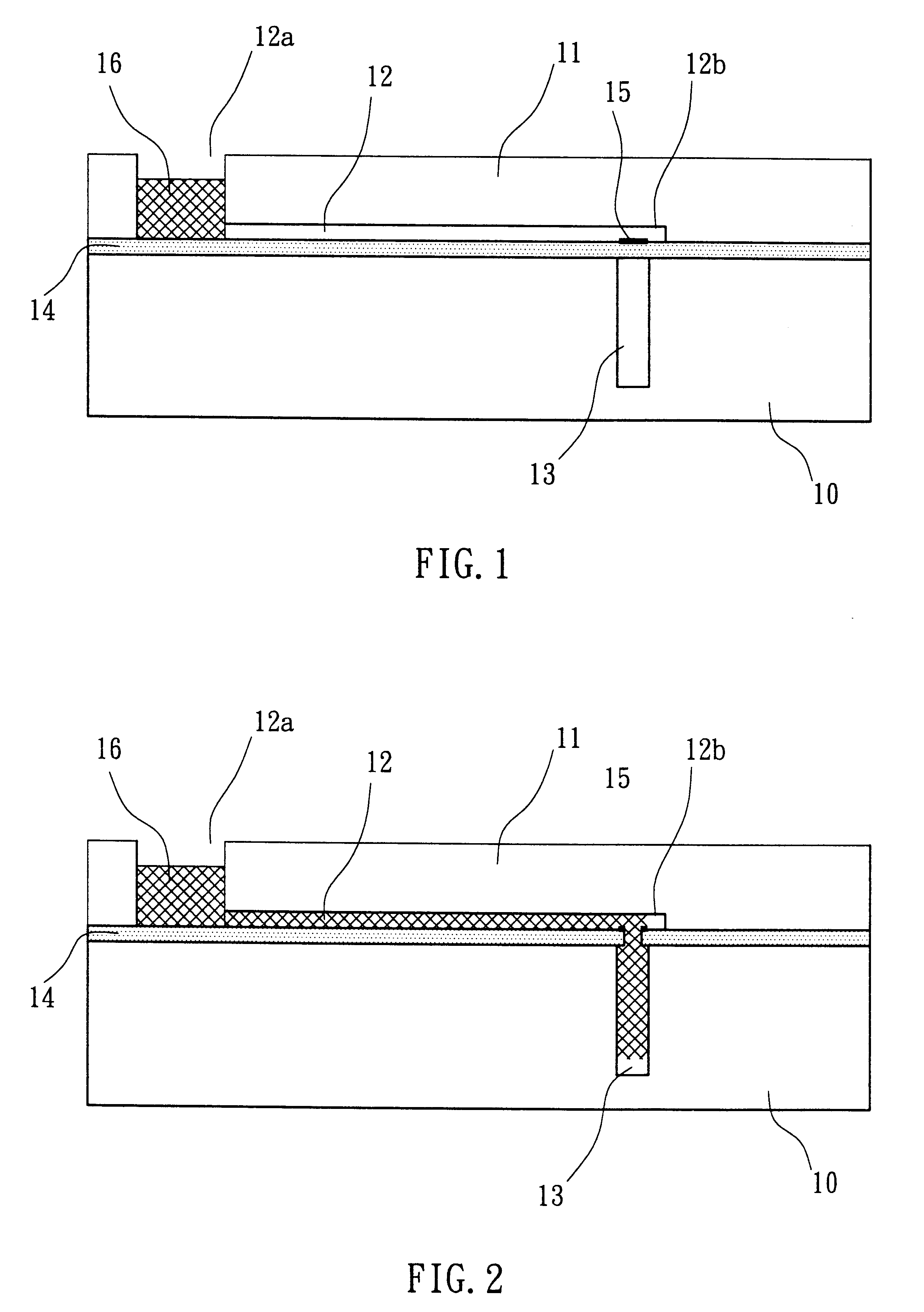
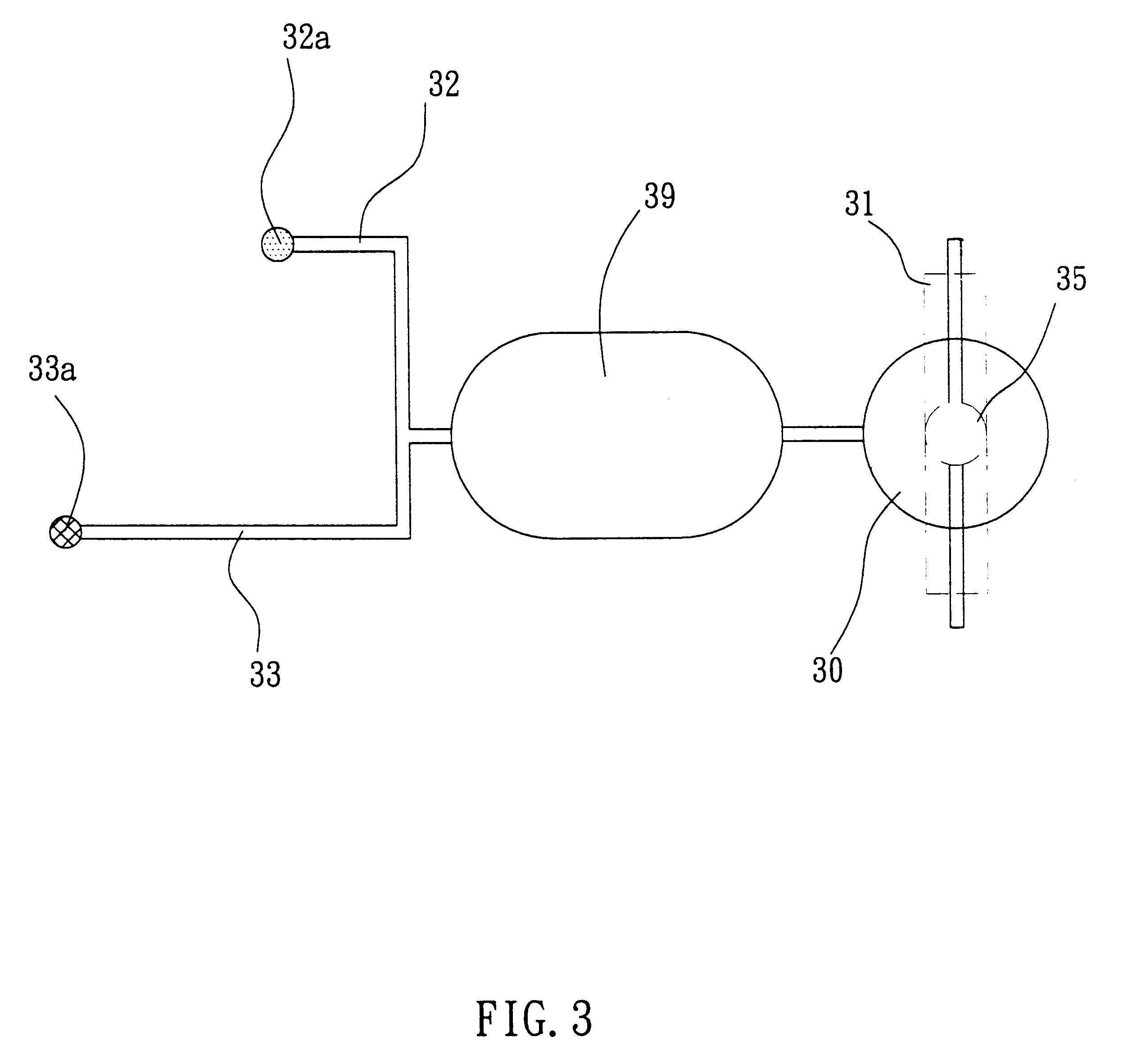
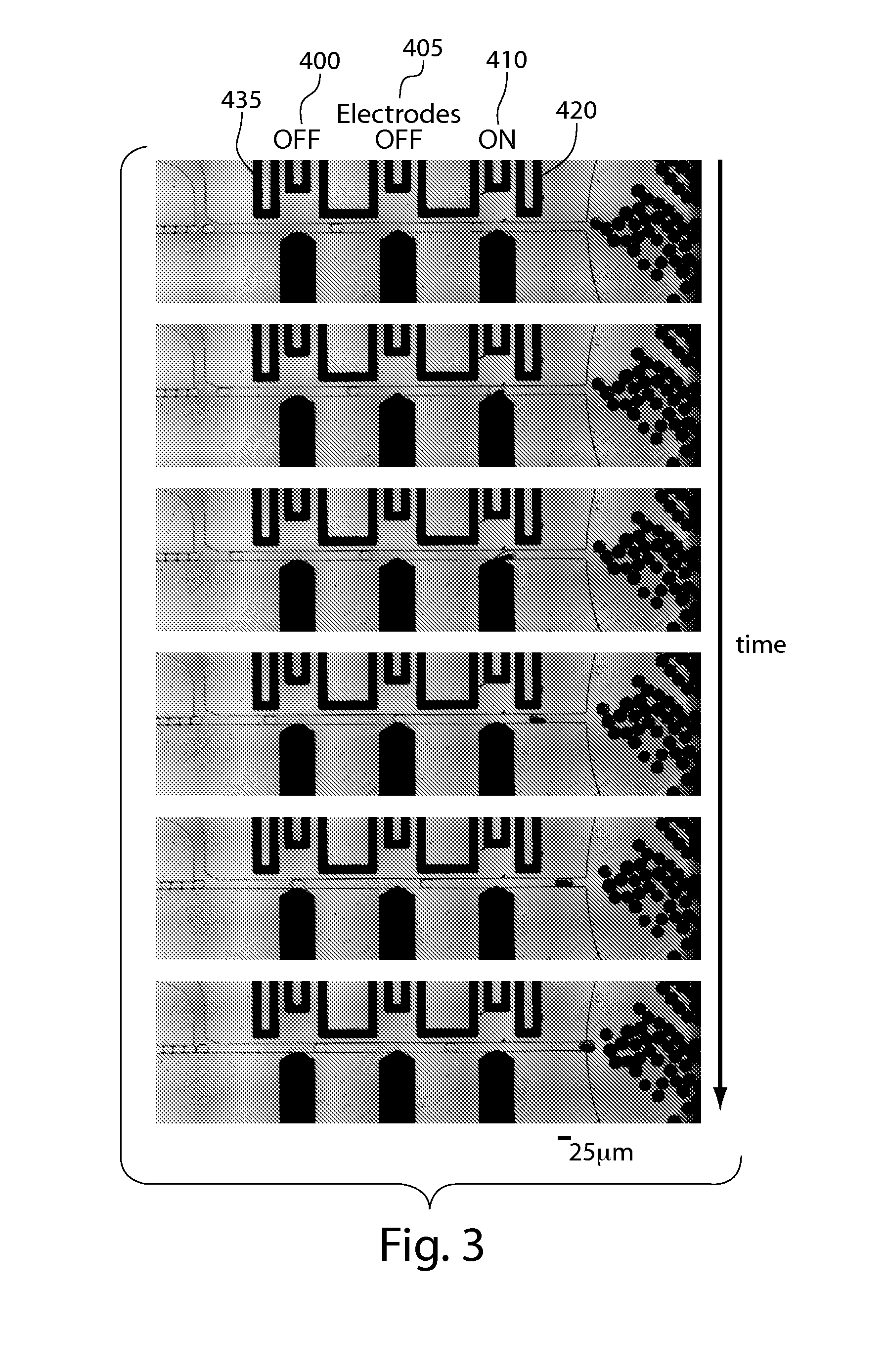
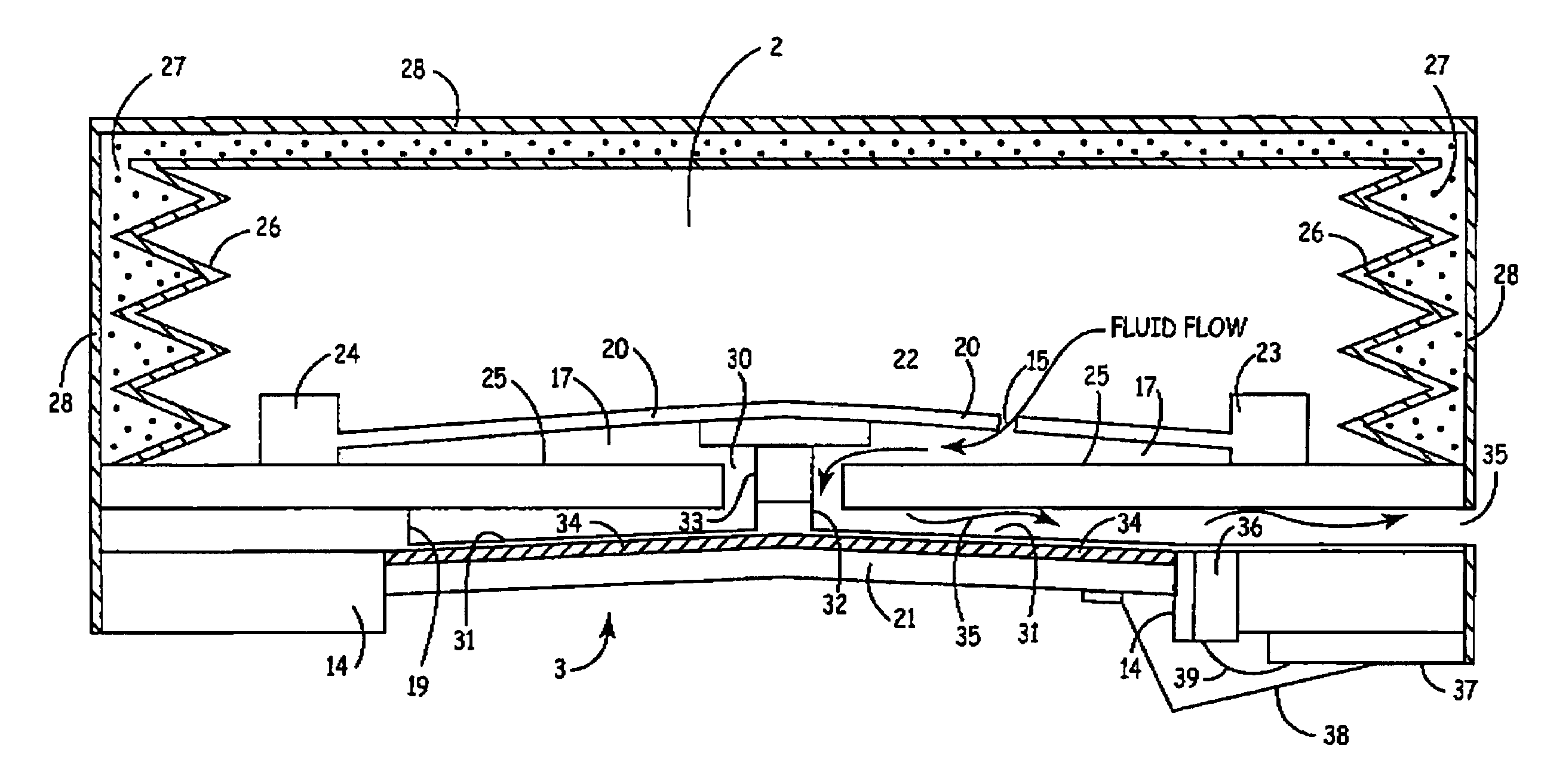
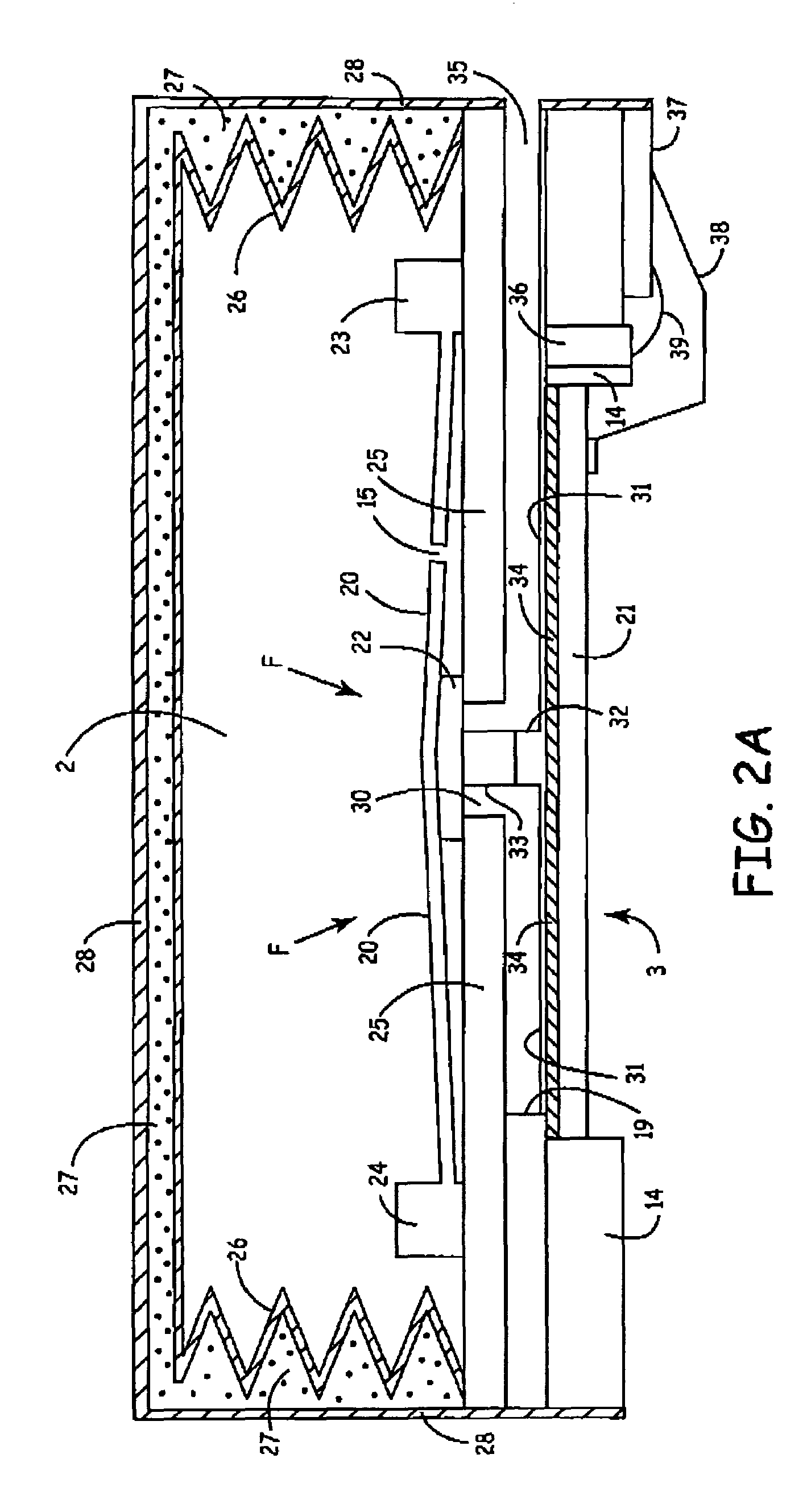
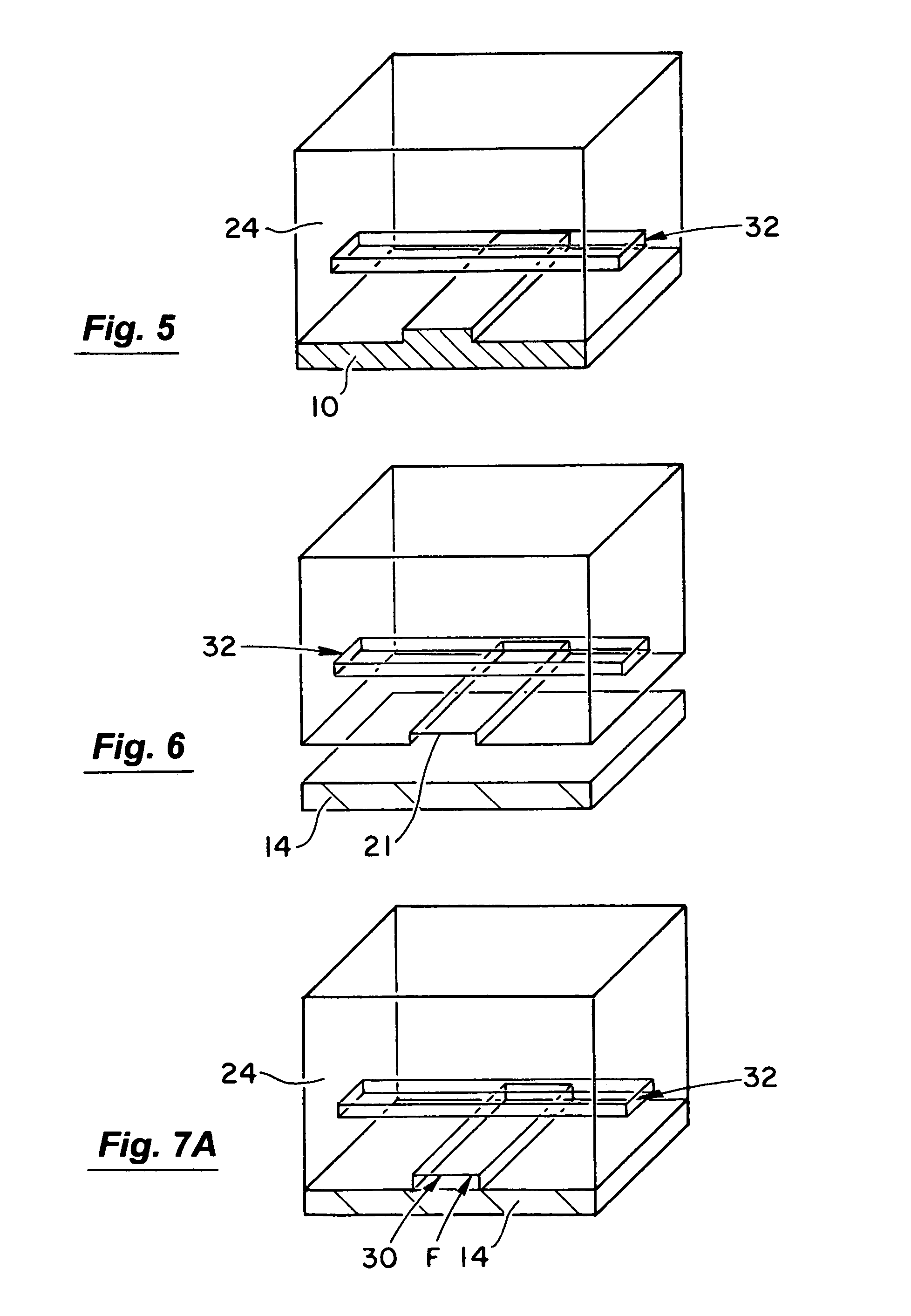
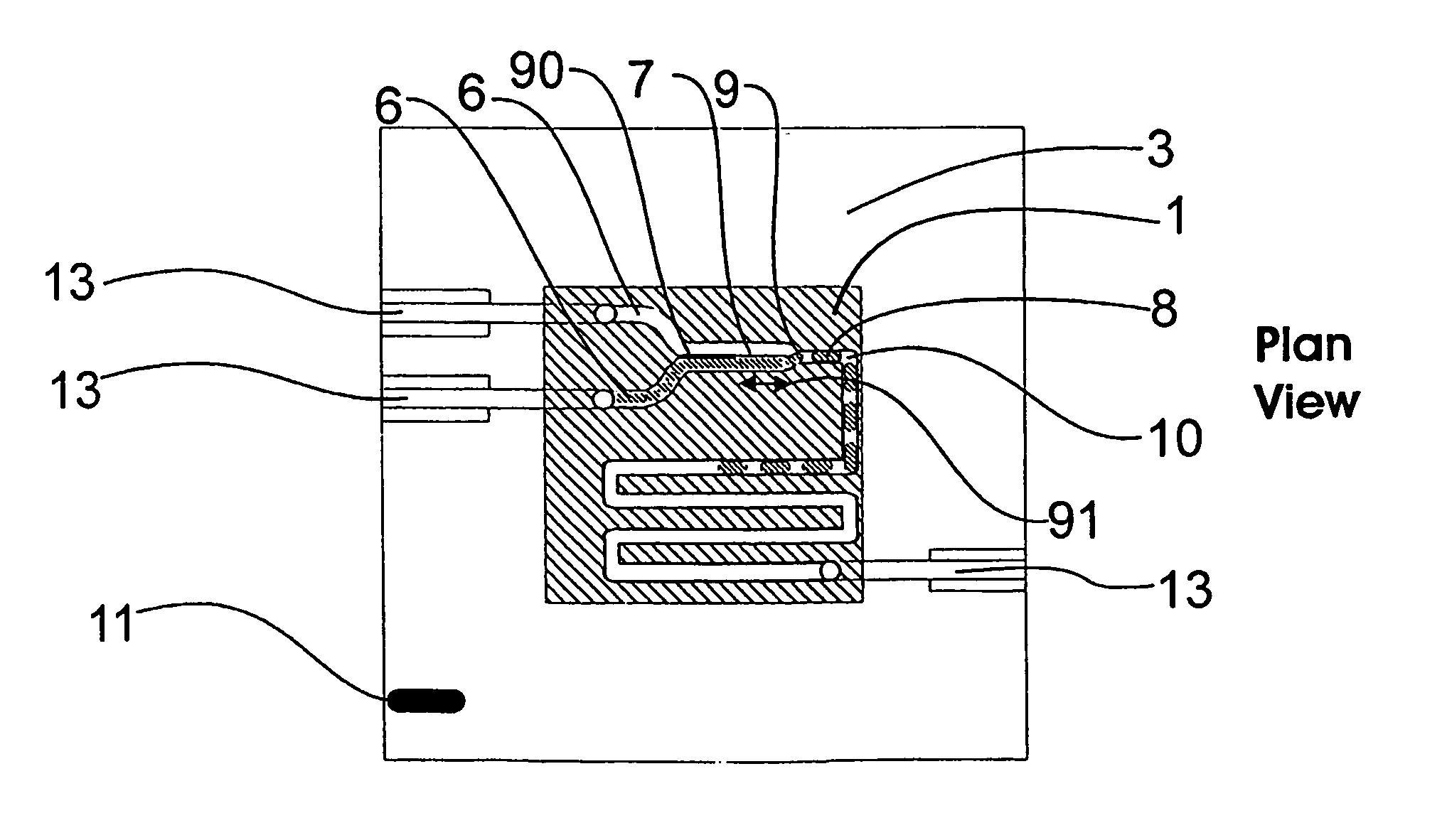
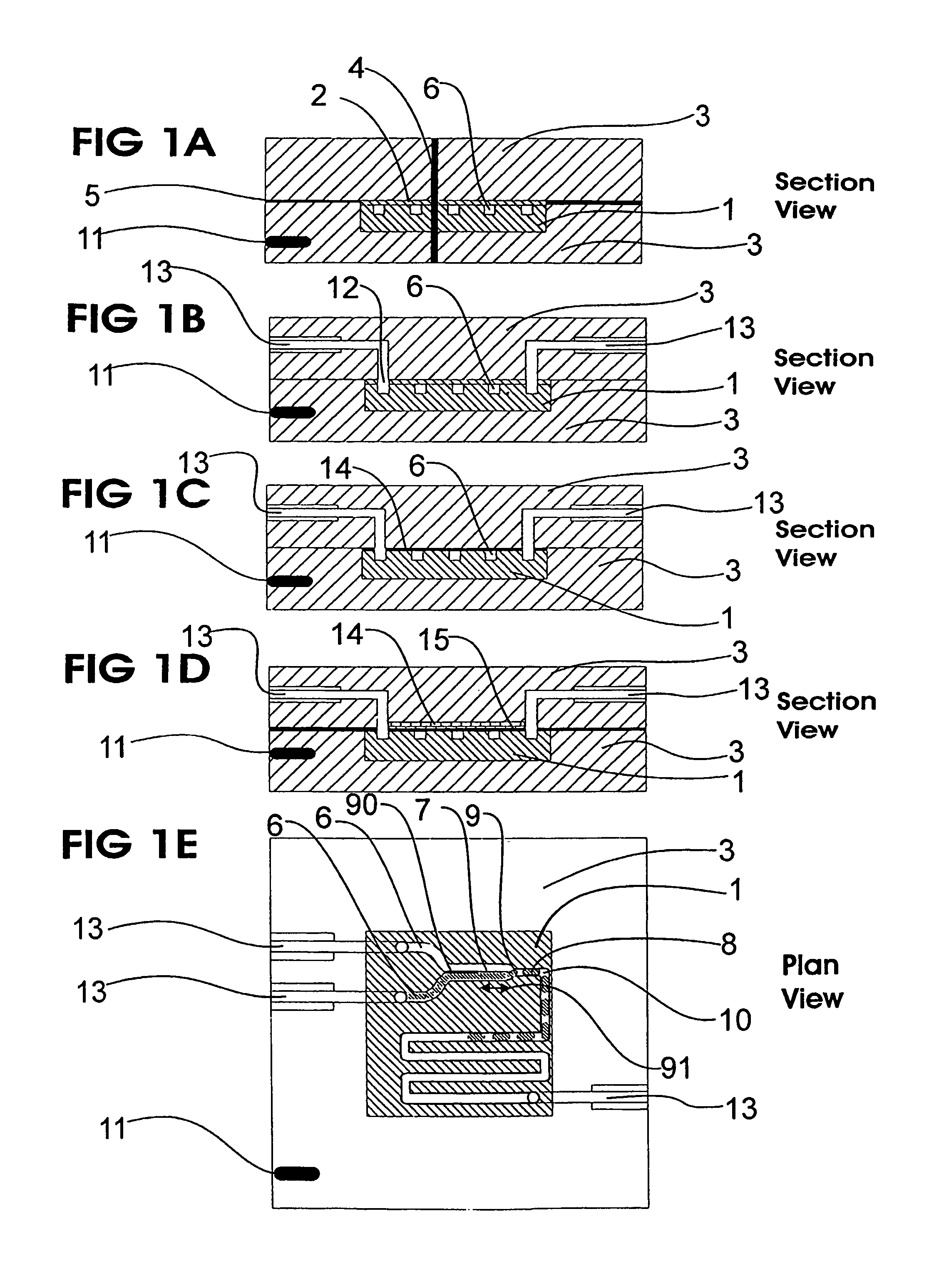
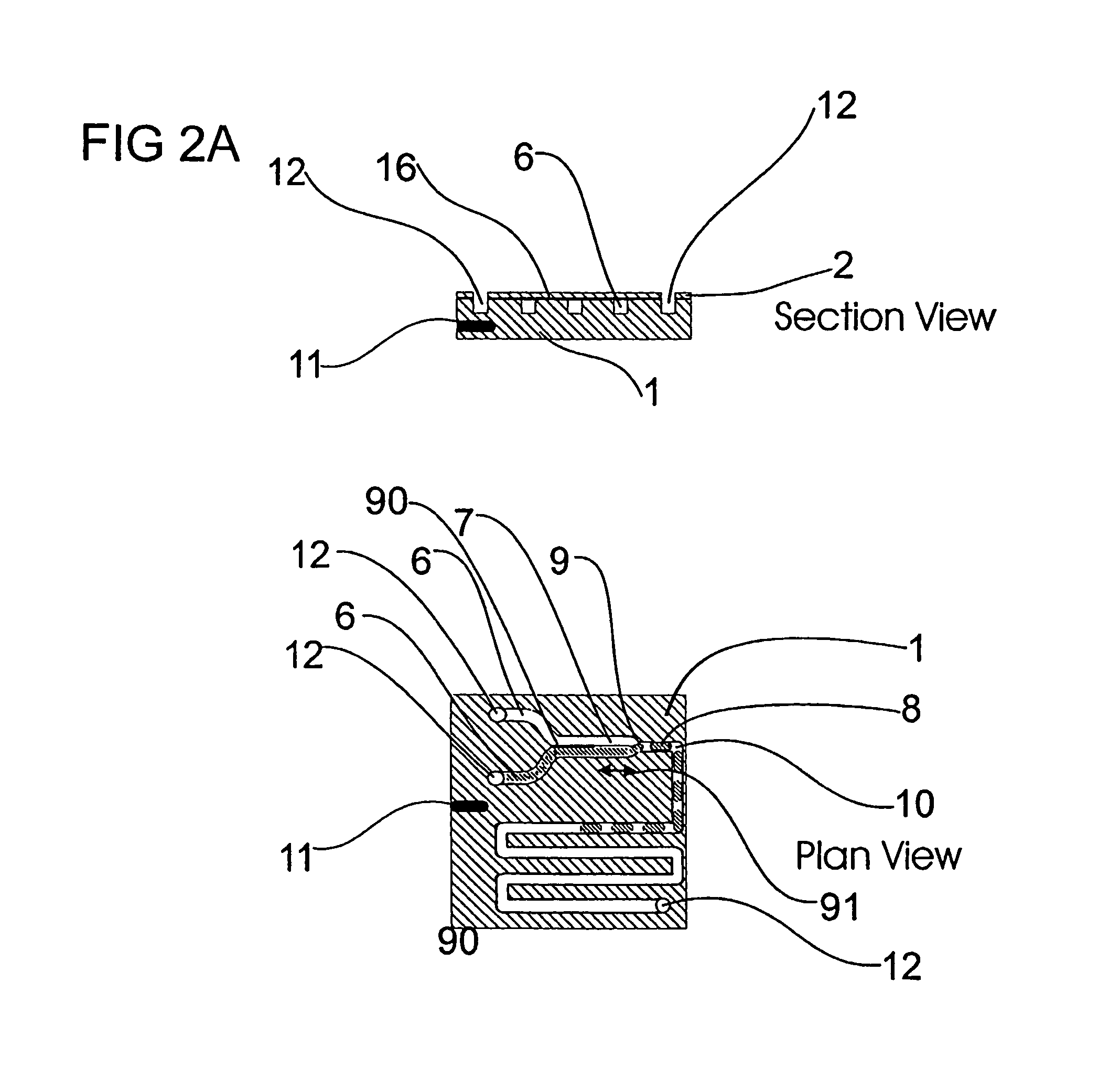
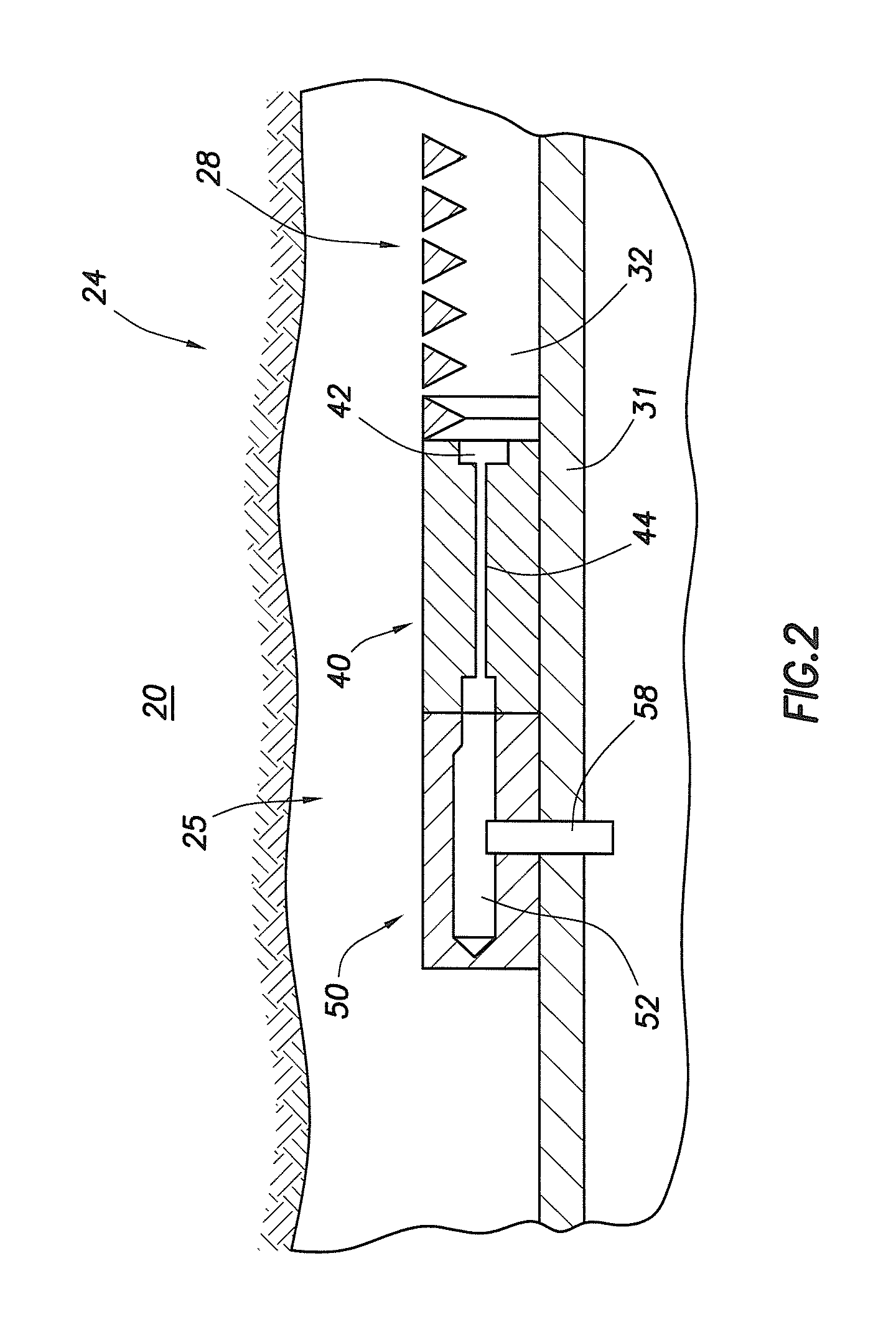
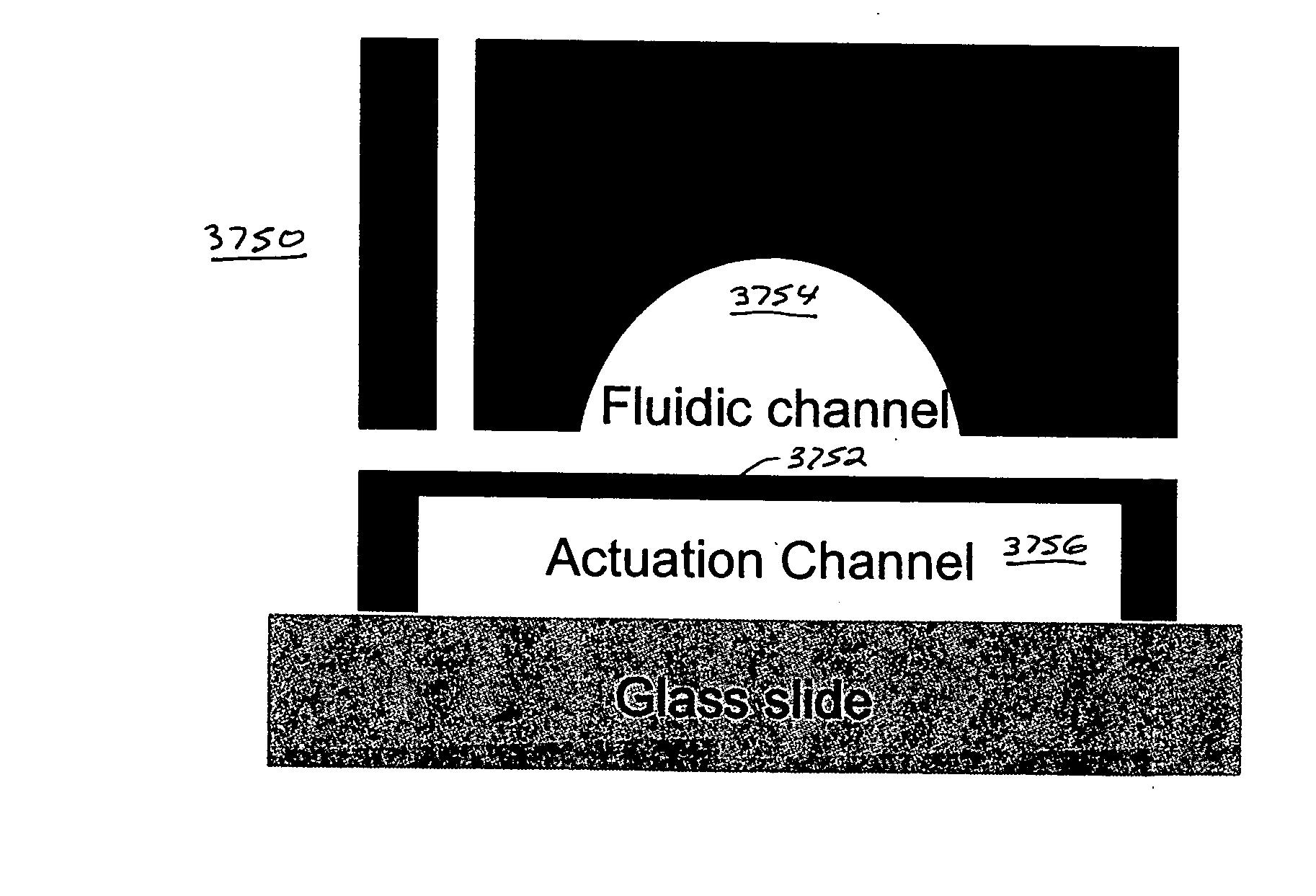
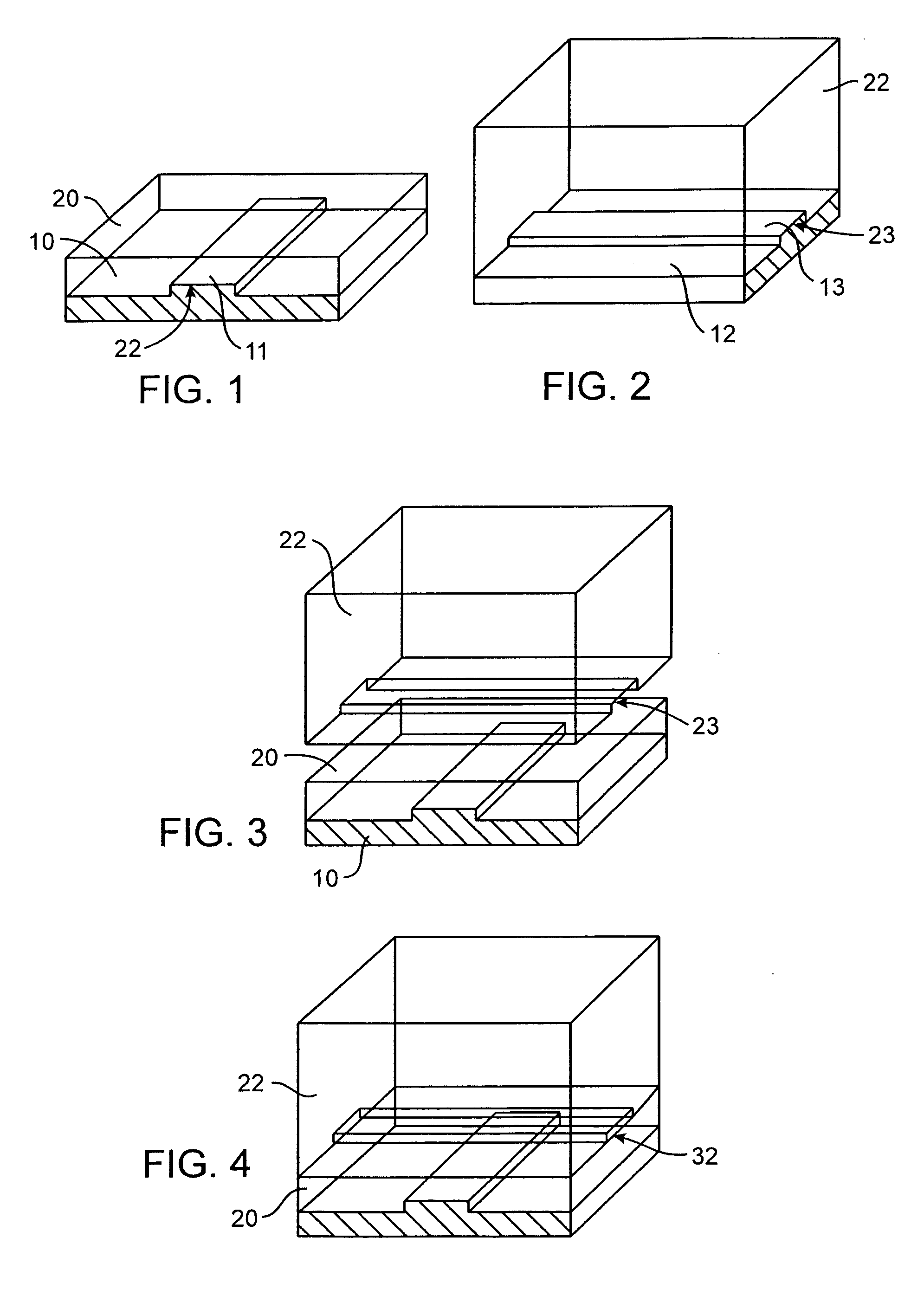
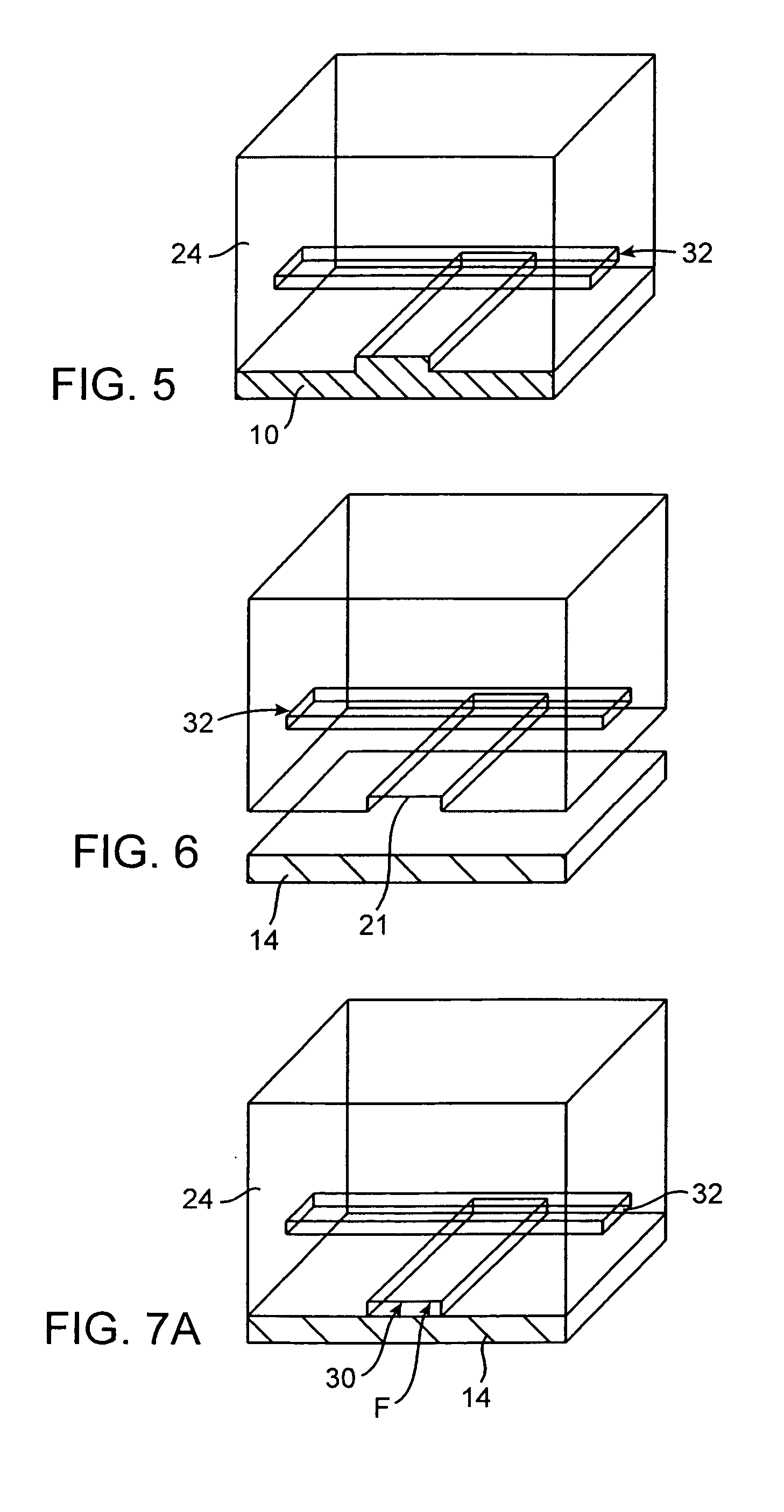
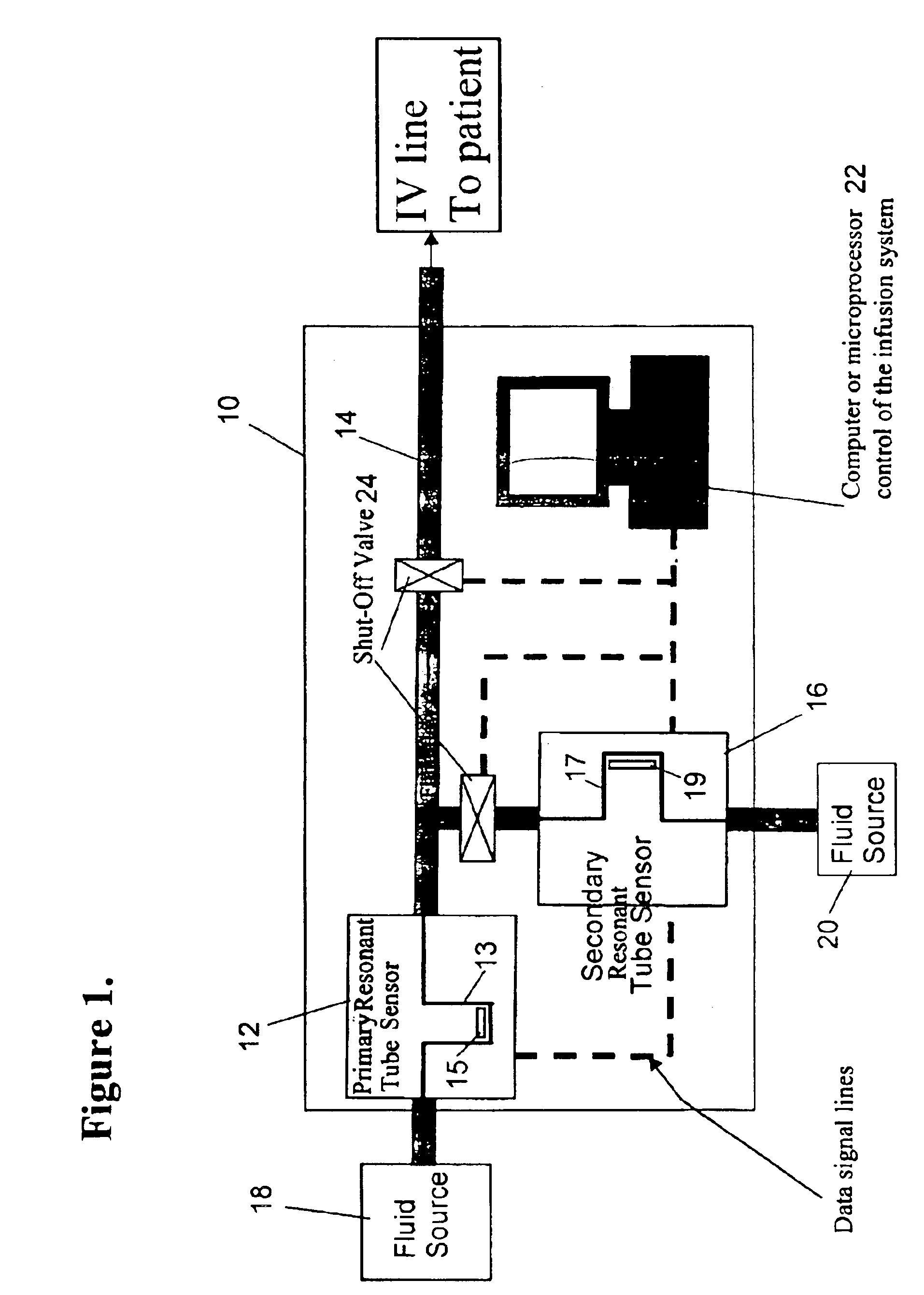
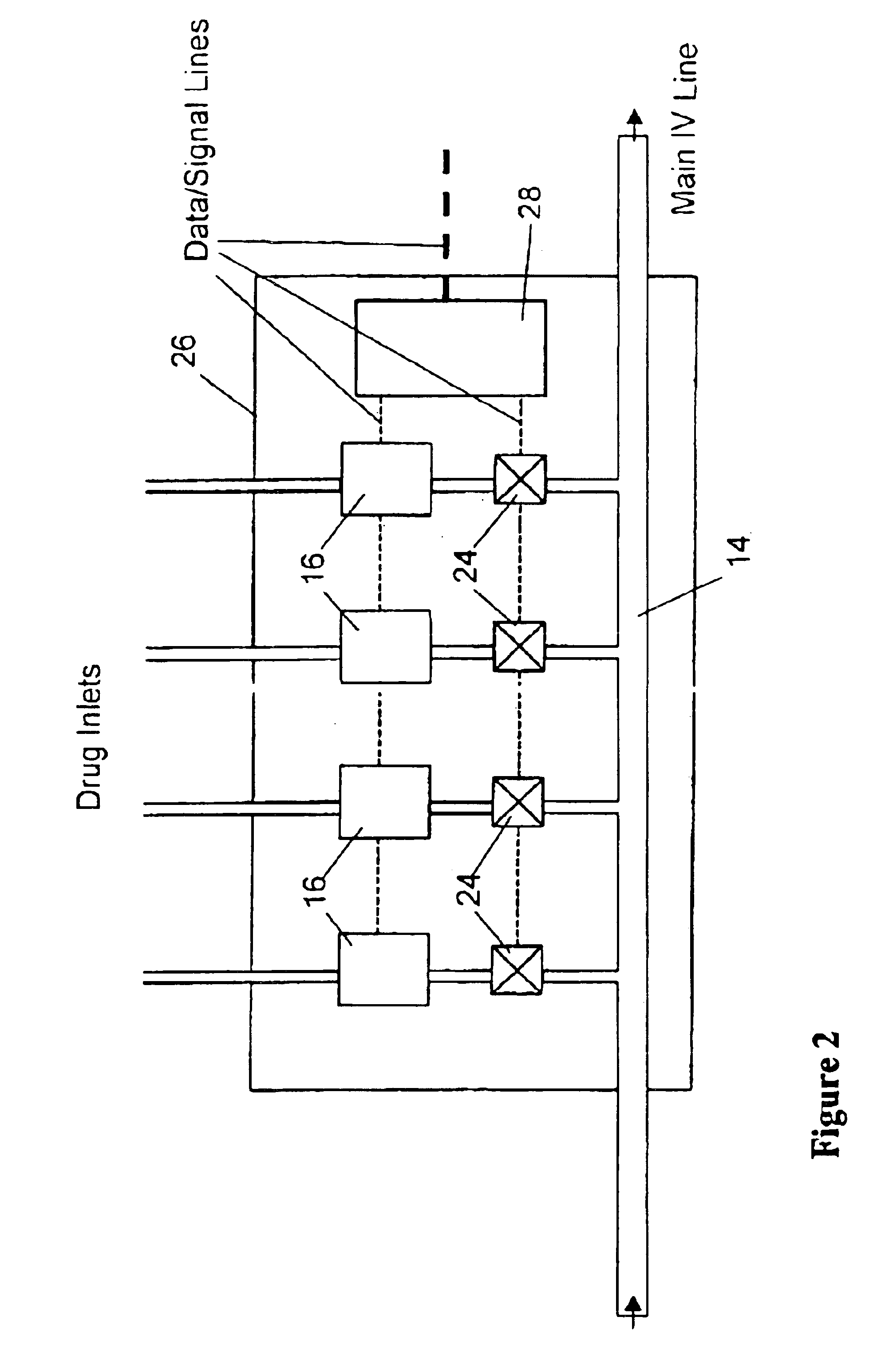
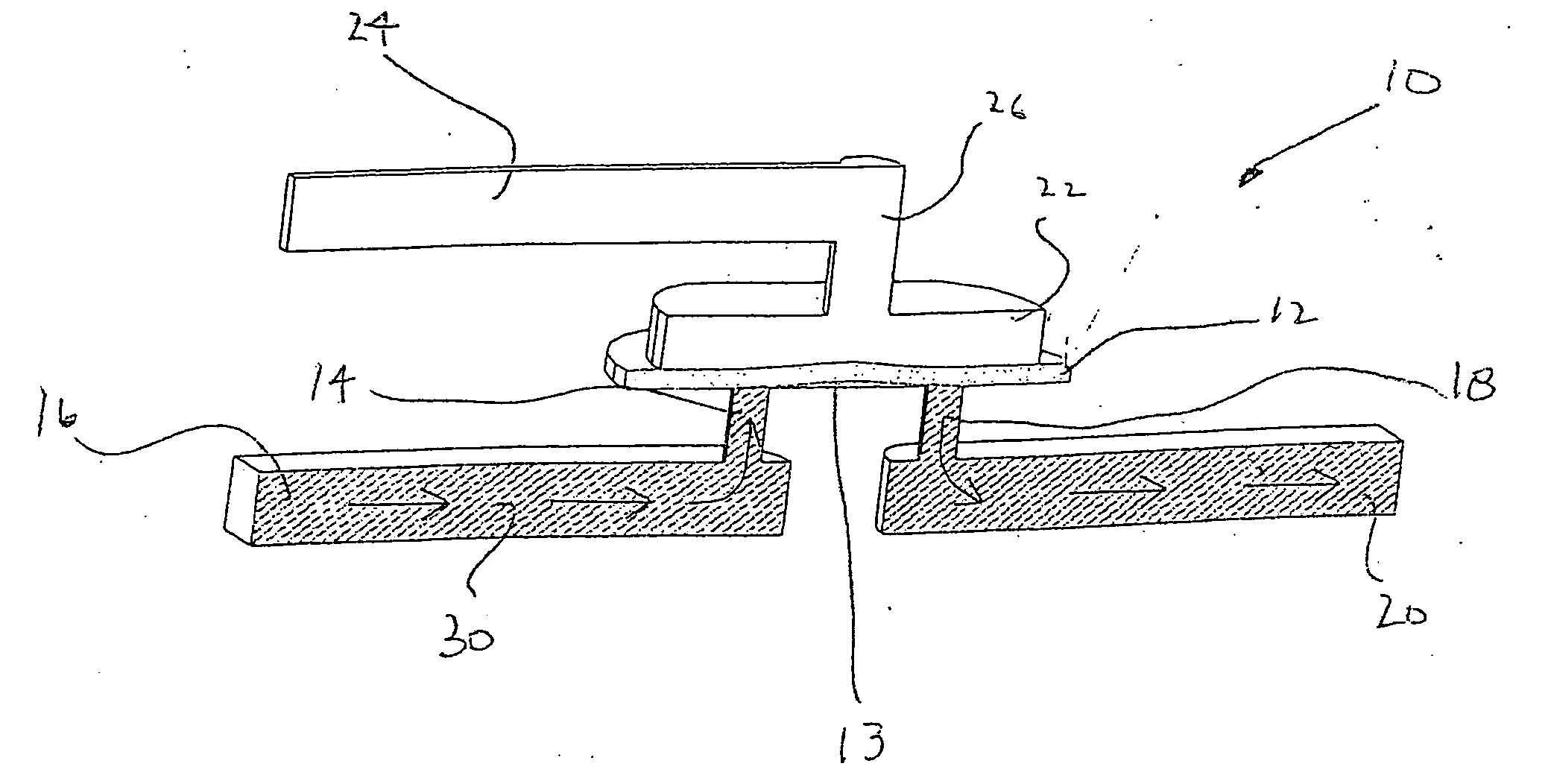
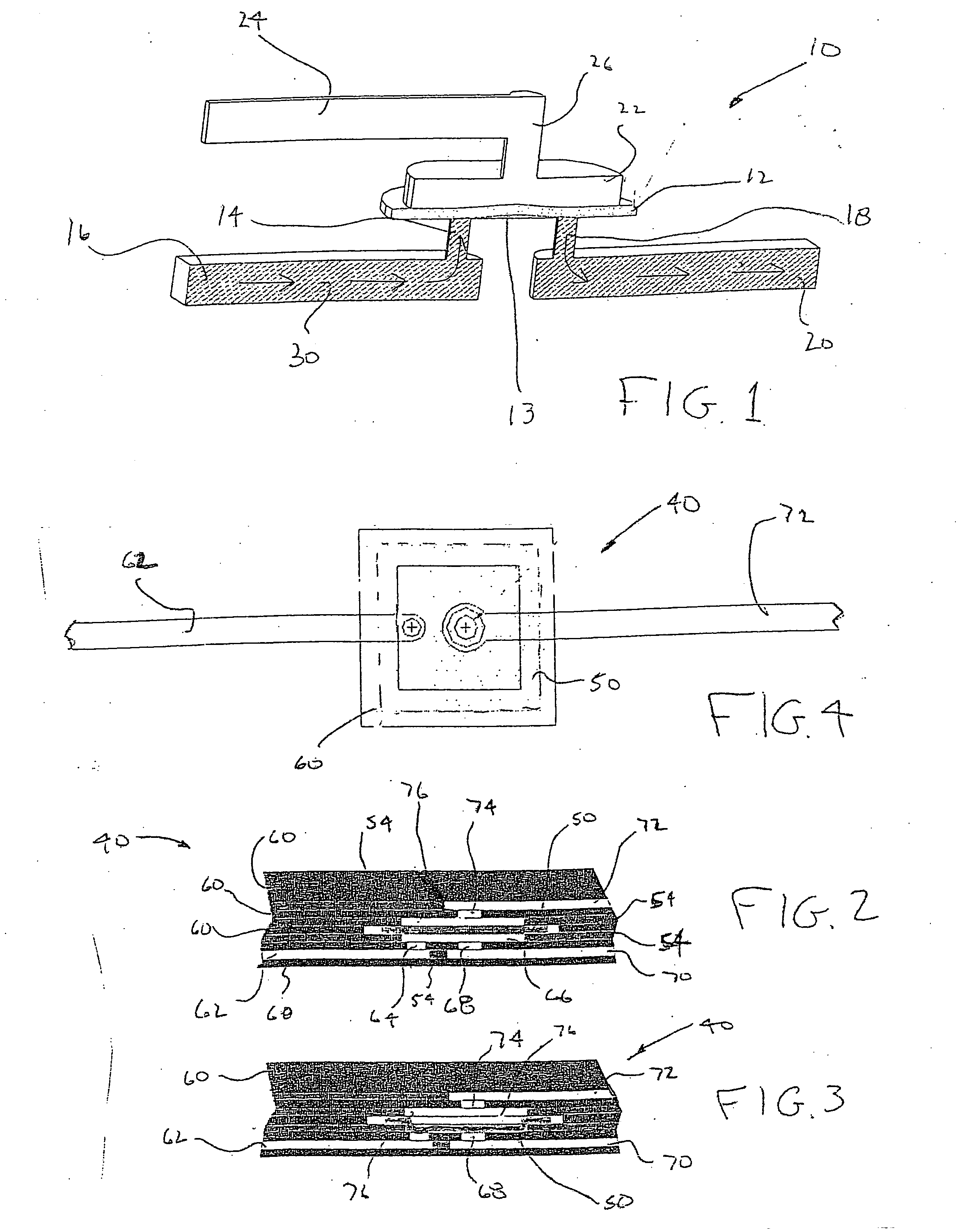
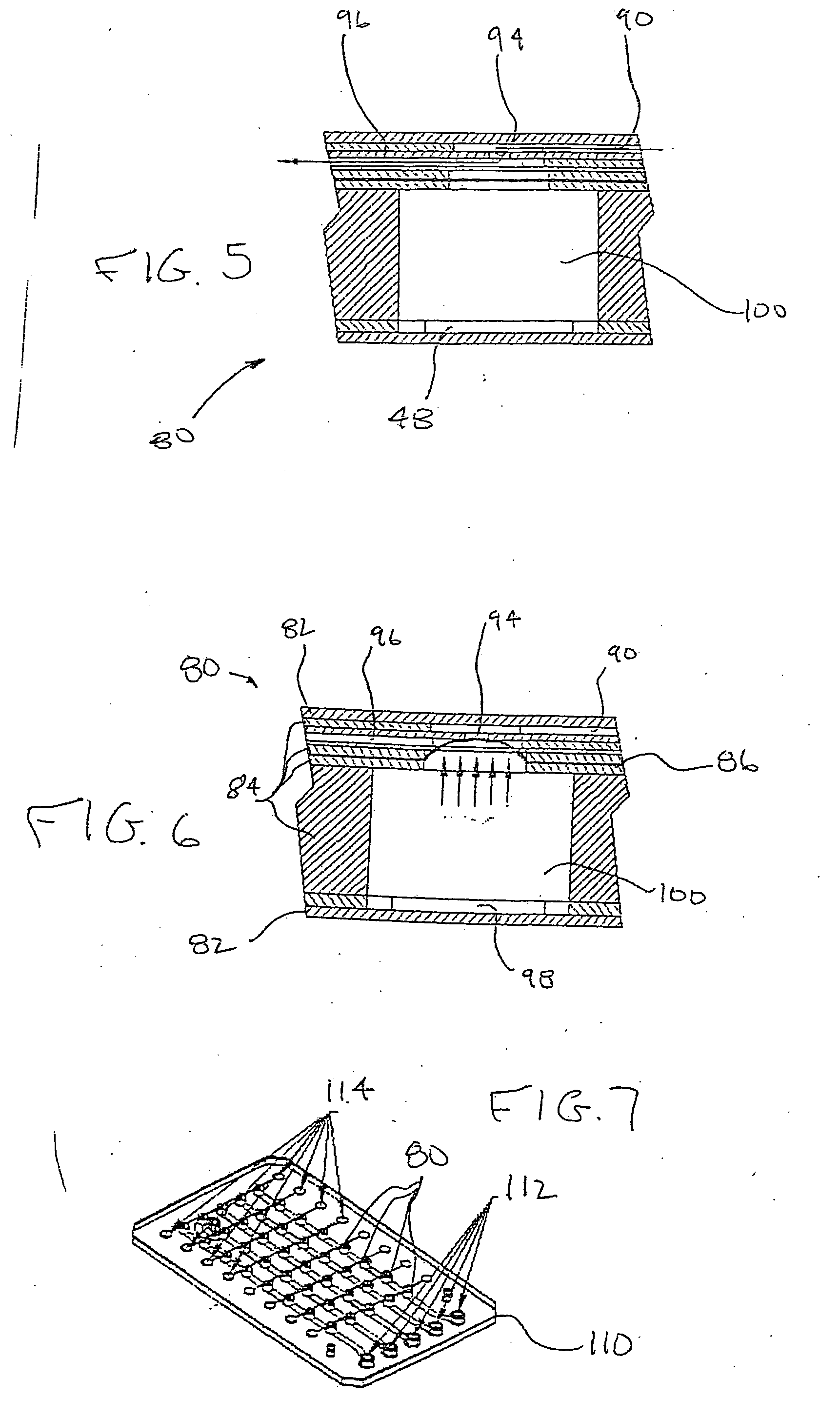
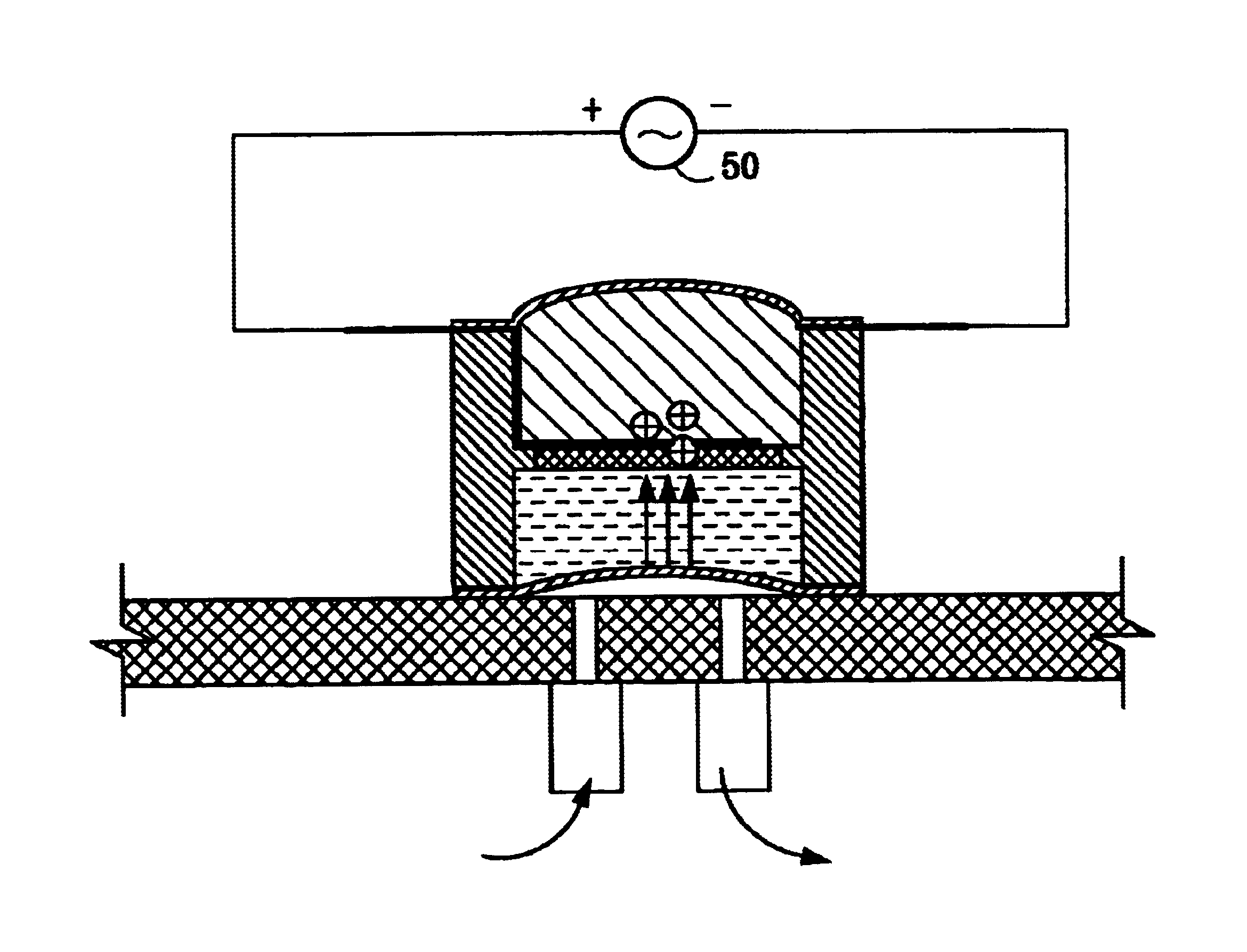
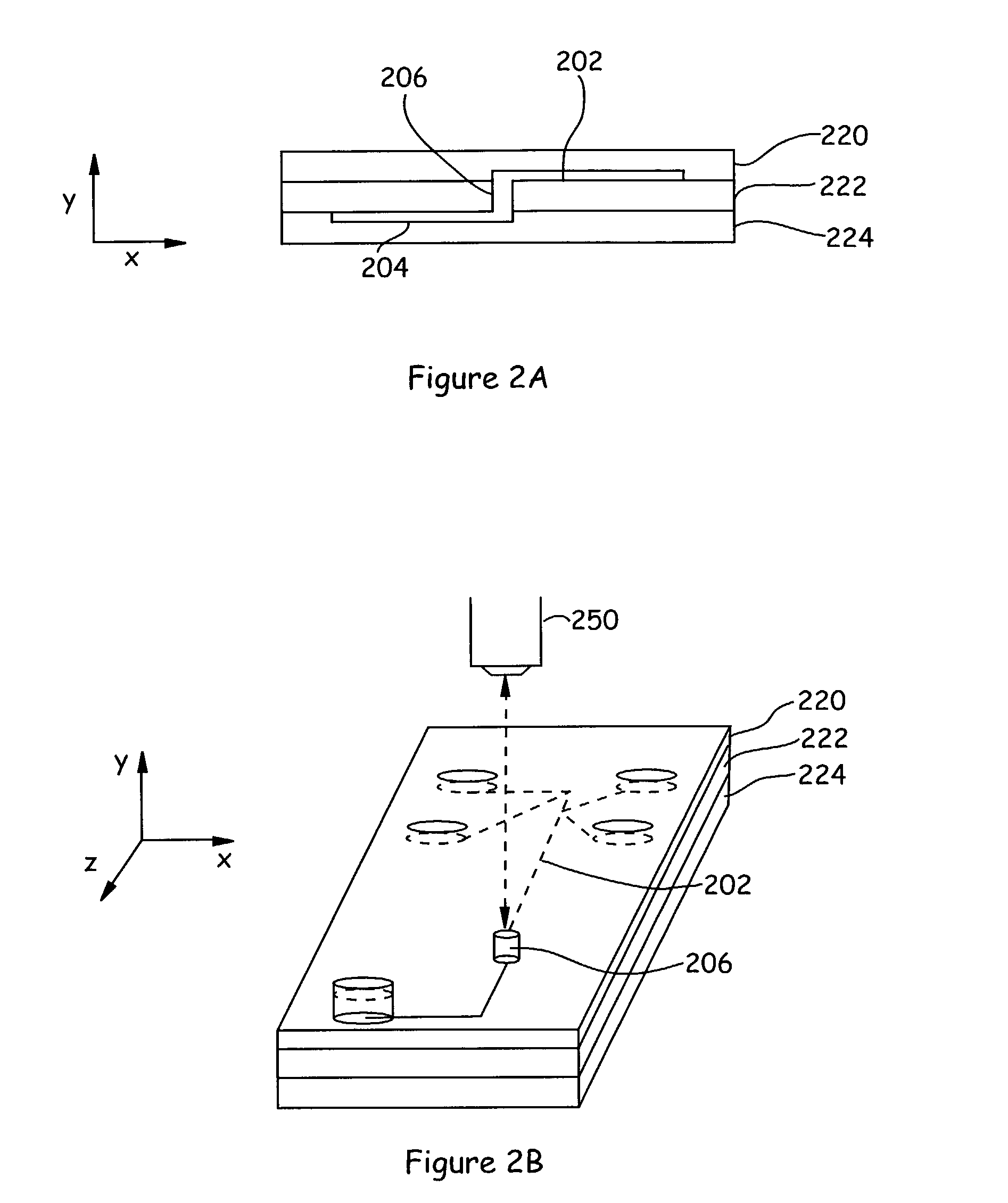
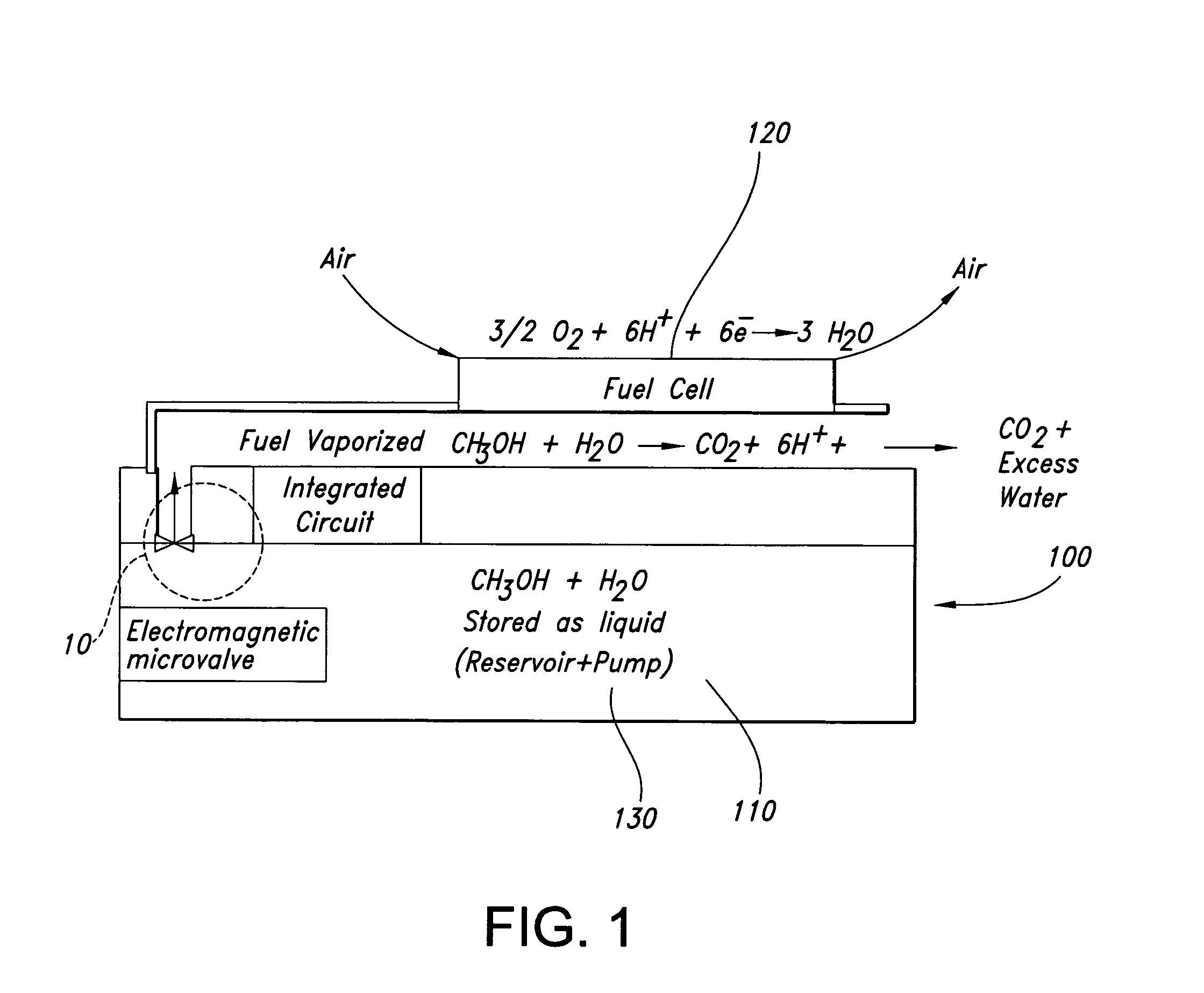
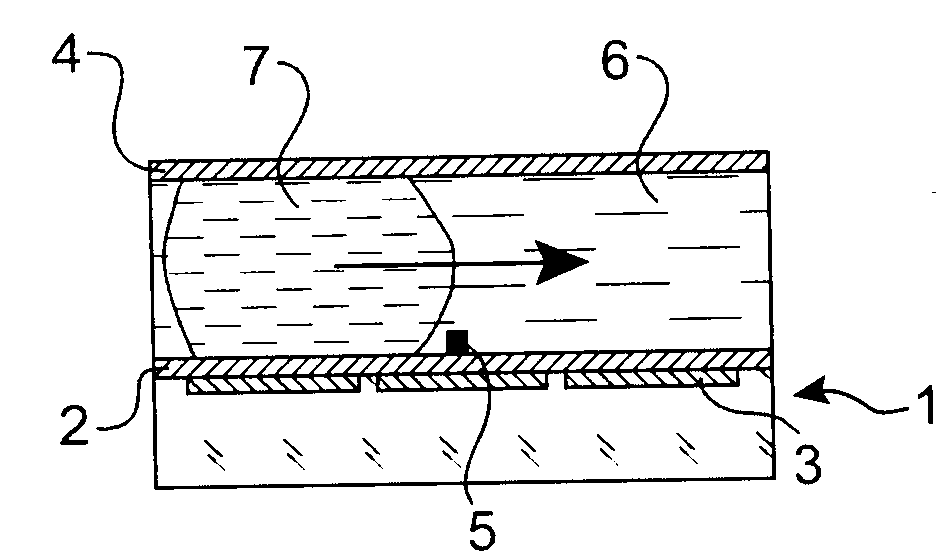
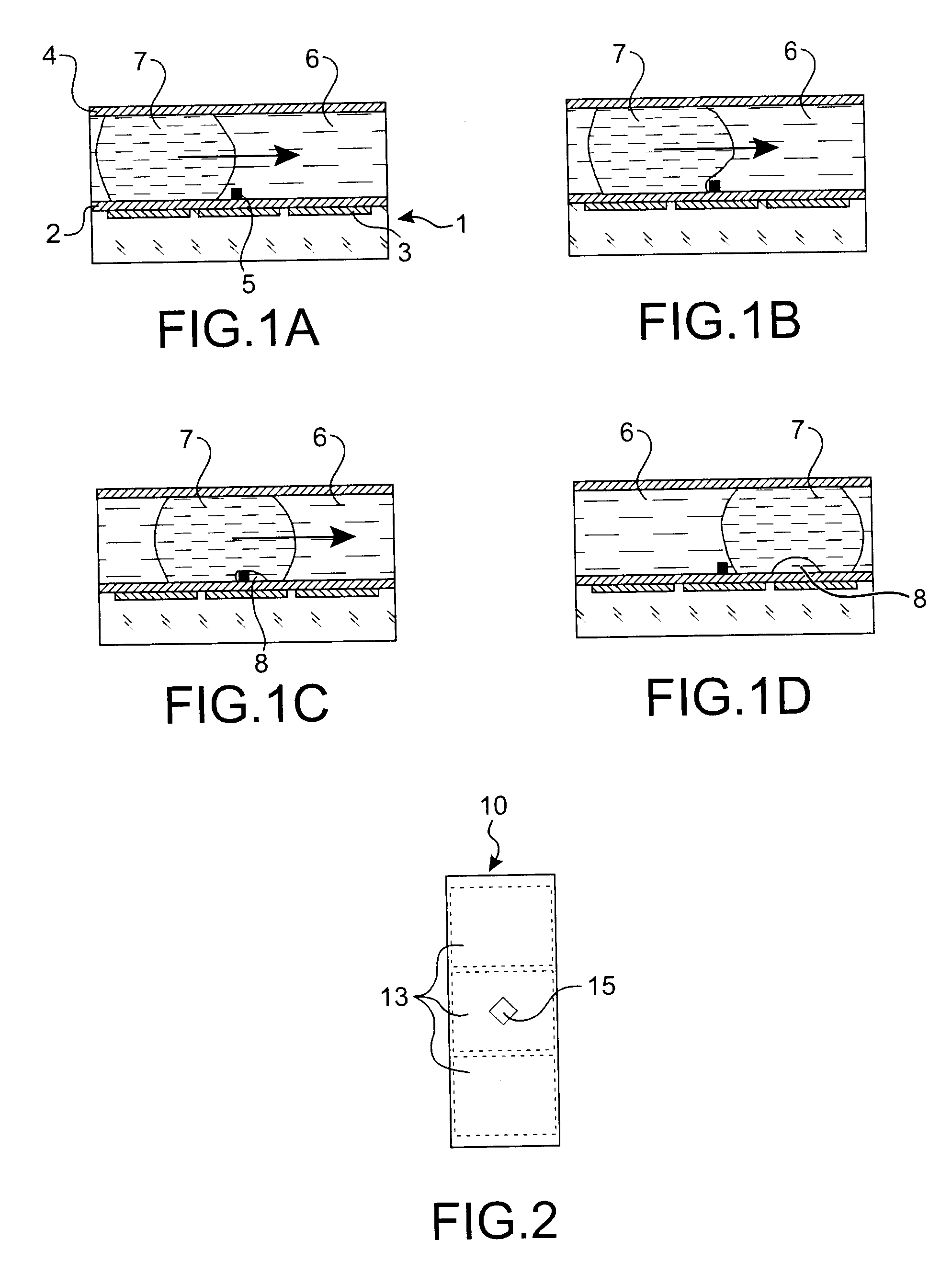
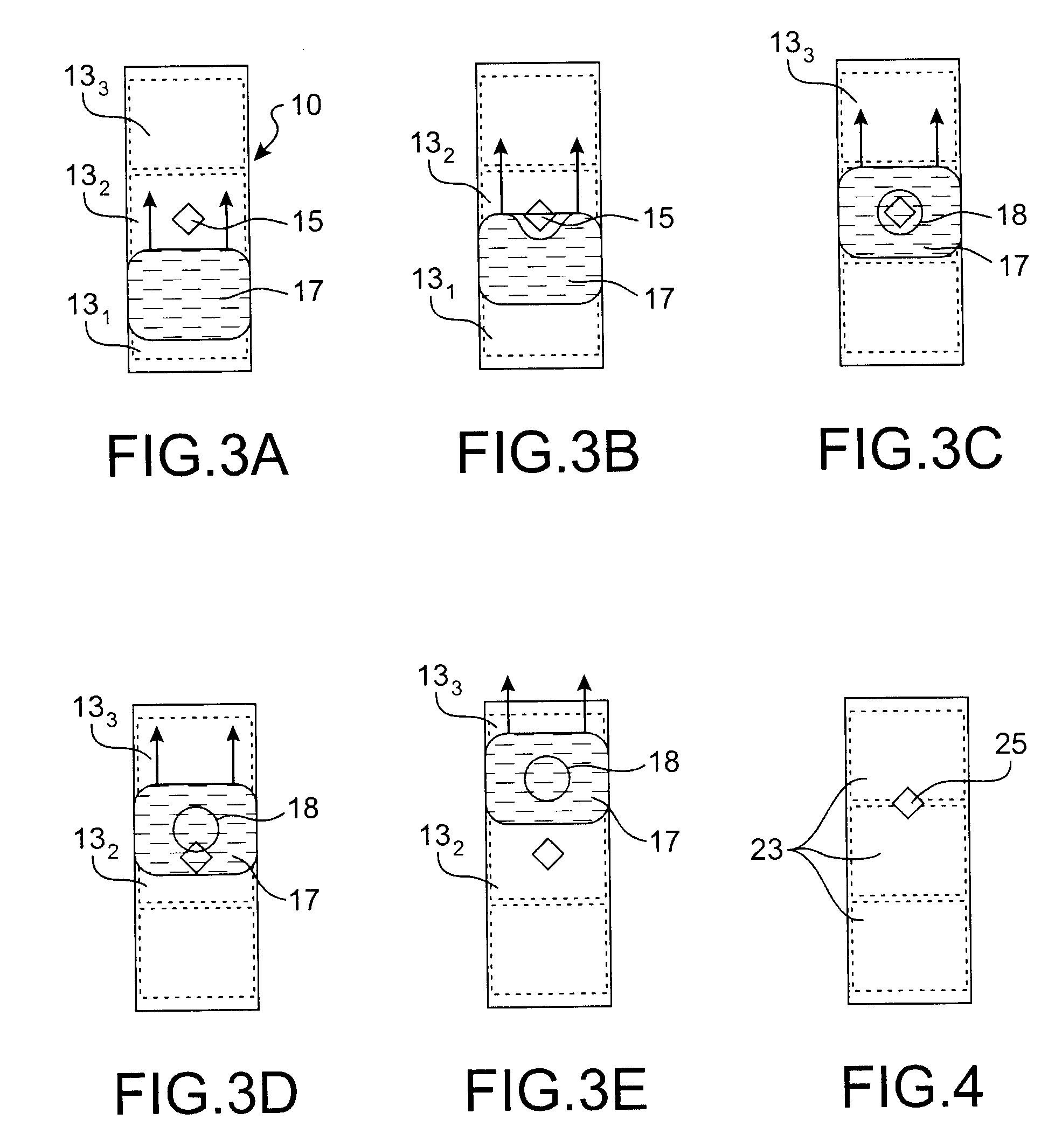
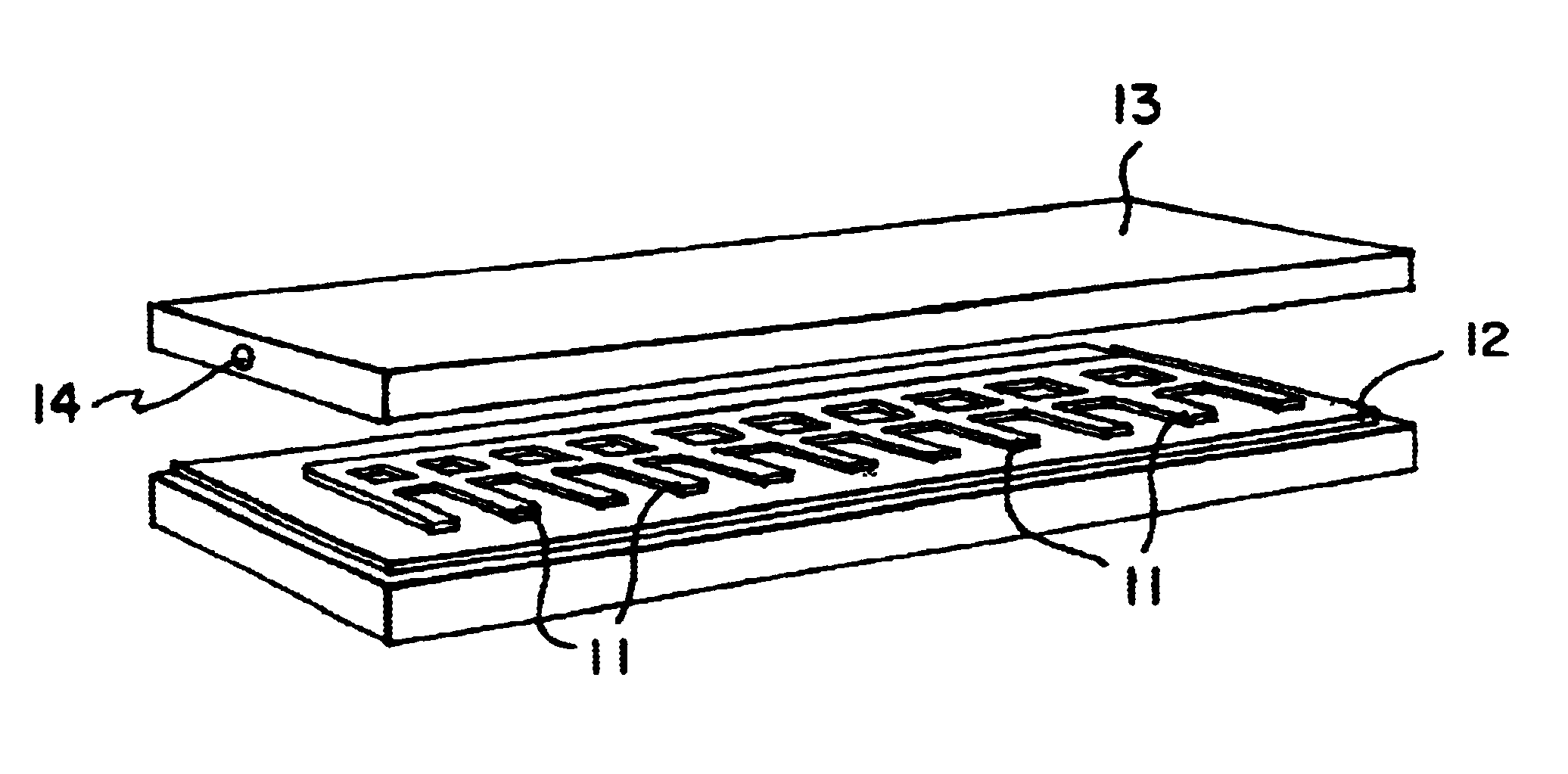
Microfluidic actuator
InactiveUS6521188B1Easy to prepareLow costCircuit elementsPressure pumpsEngineeringAtmospheric pressure
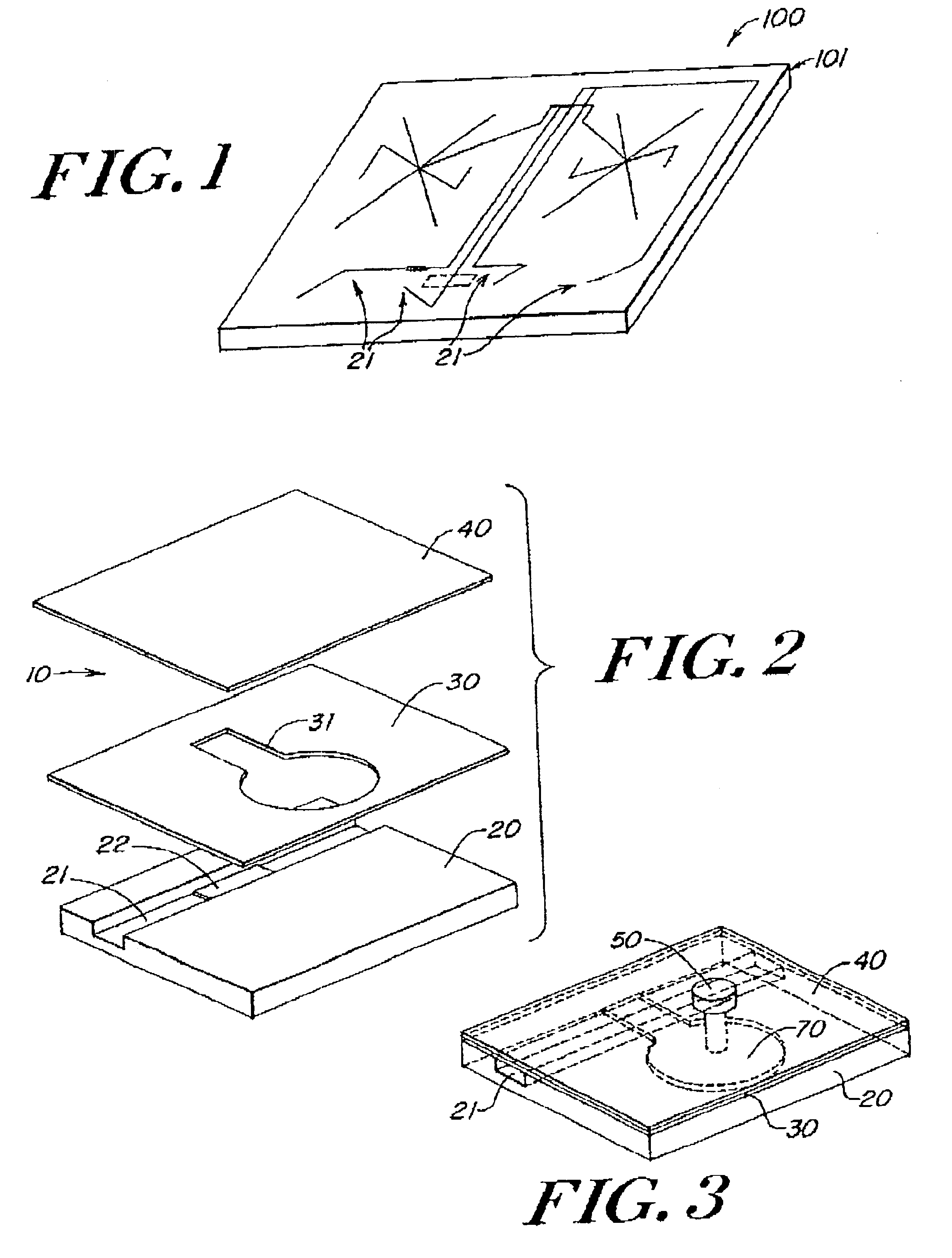
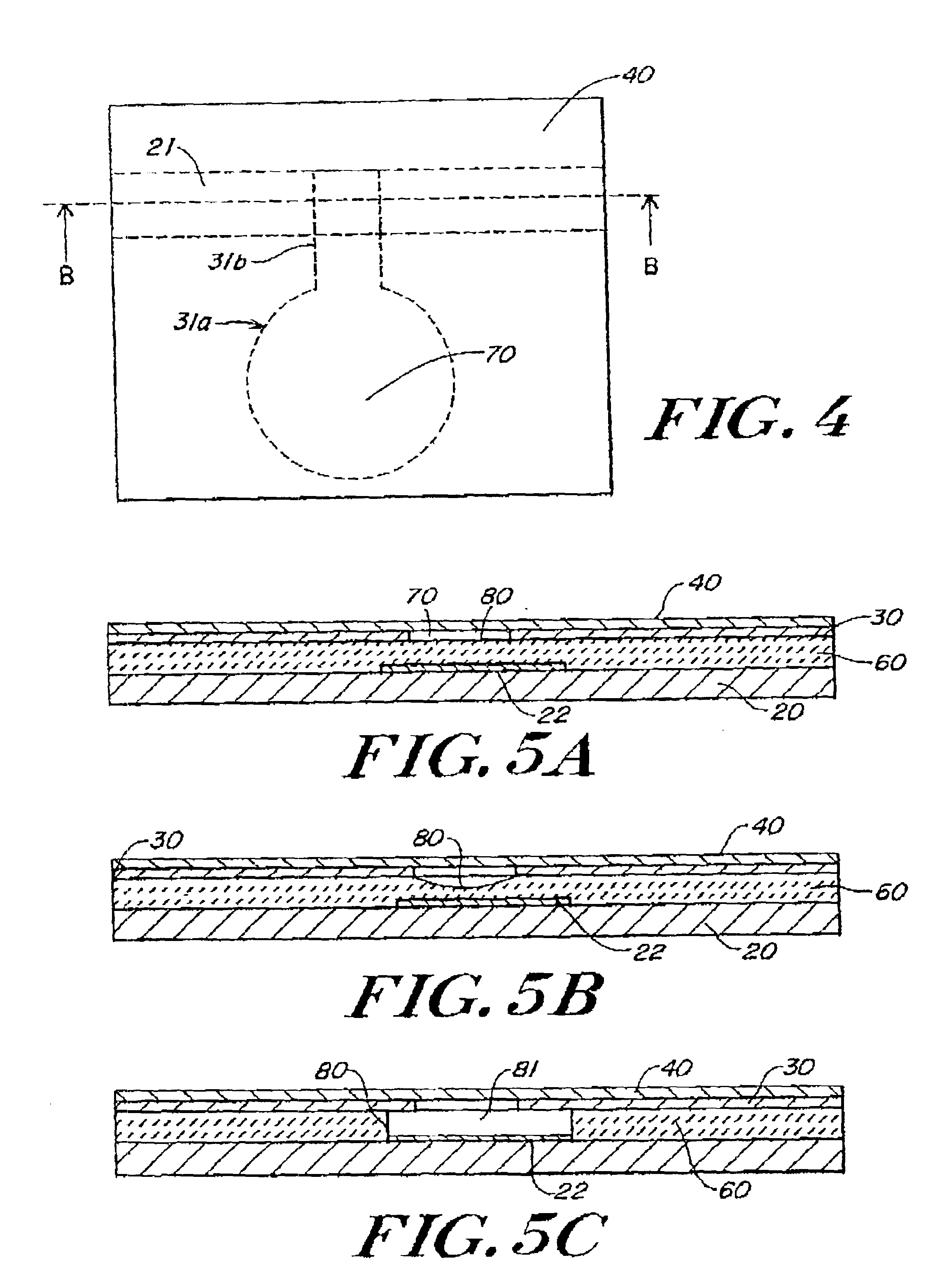
A simple microfluidic actuator includes a sealed vacuum chamber actuated by providing a current to a thin film heater, which in turn weakens and, under the atmospheric pressure differential, breaks a diaphragm sealing said vacuum chamber whereby the vacuum inside said chamber is released. By applying the microfluidic actuator to a microfluidic network the resulting pressure differential can be used to generate a pumping force with the microfluidic network. The chamber may be prepared in a silicon, glass, or plastic substrate. The diaphragm may be a metallic gas-impermeable film. A releasing member comprising a thin-film metallic heater is then microfabricated on the diaphragm. The assembly so prepared may be bonded to a glass or plastic substrate that contains a network of microchannels. The microfluidic actuator is suited for a microfluidic platform in generating driving powers for operations including pumping, metering, mixing and valving of liquid samples.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
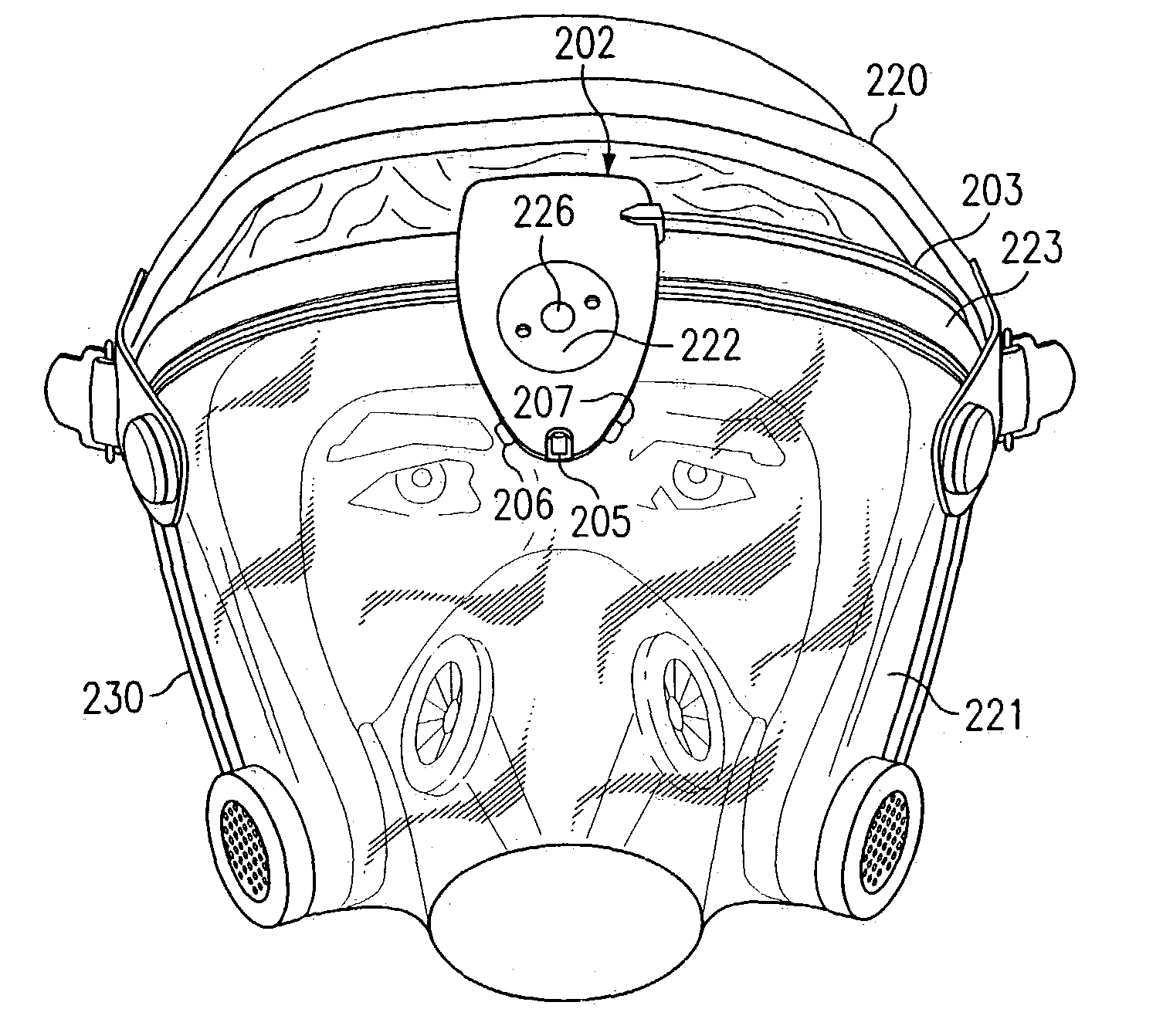
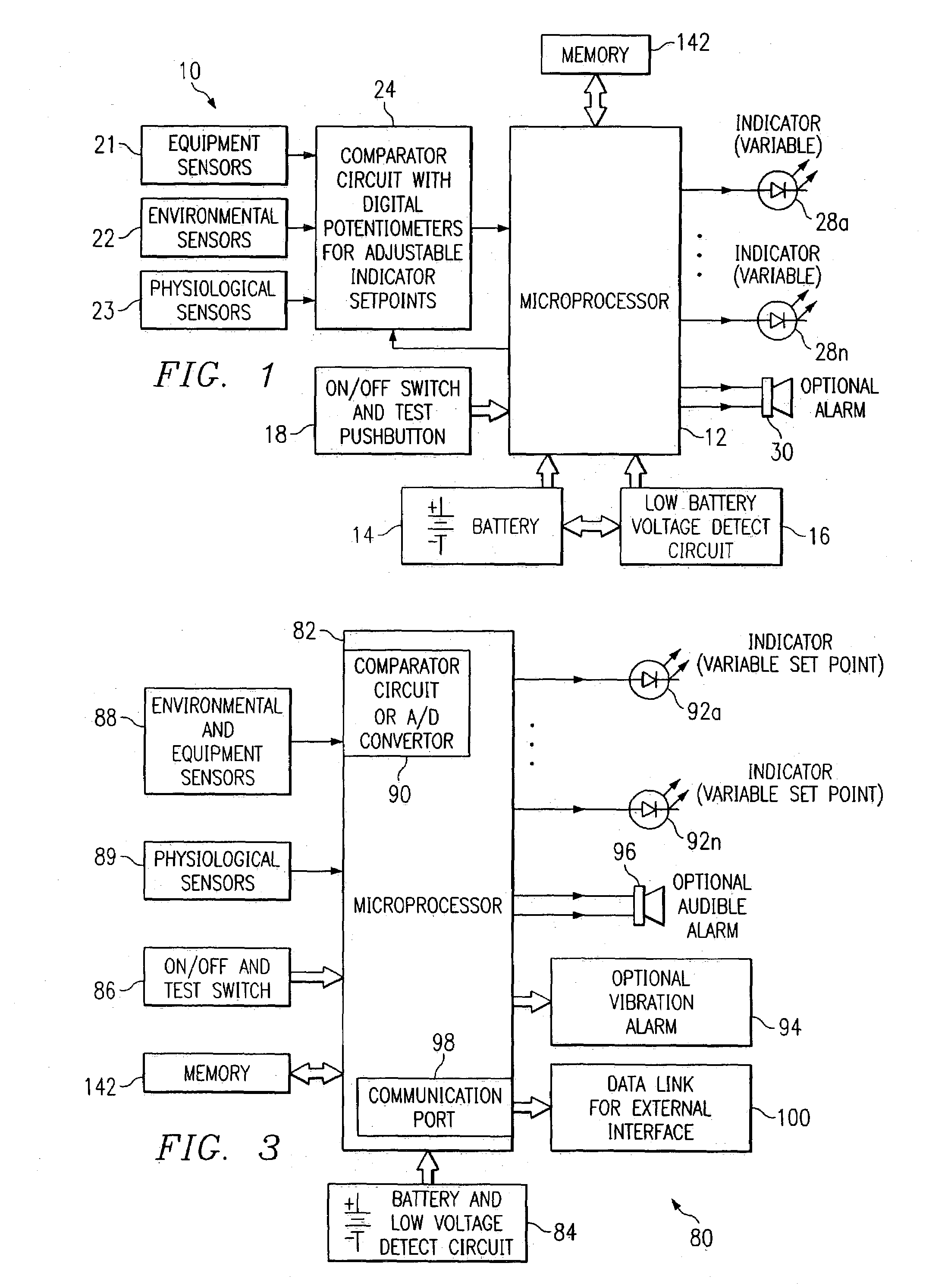
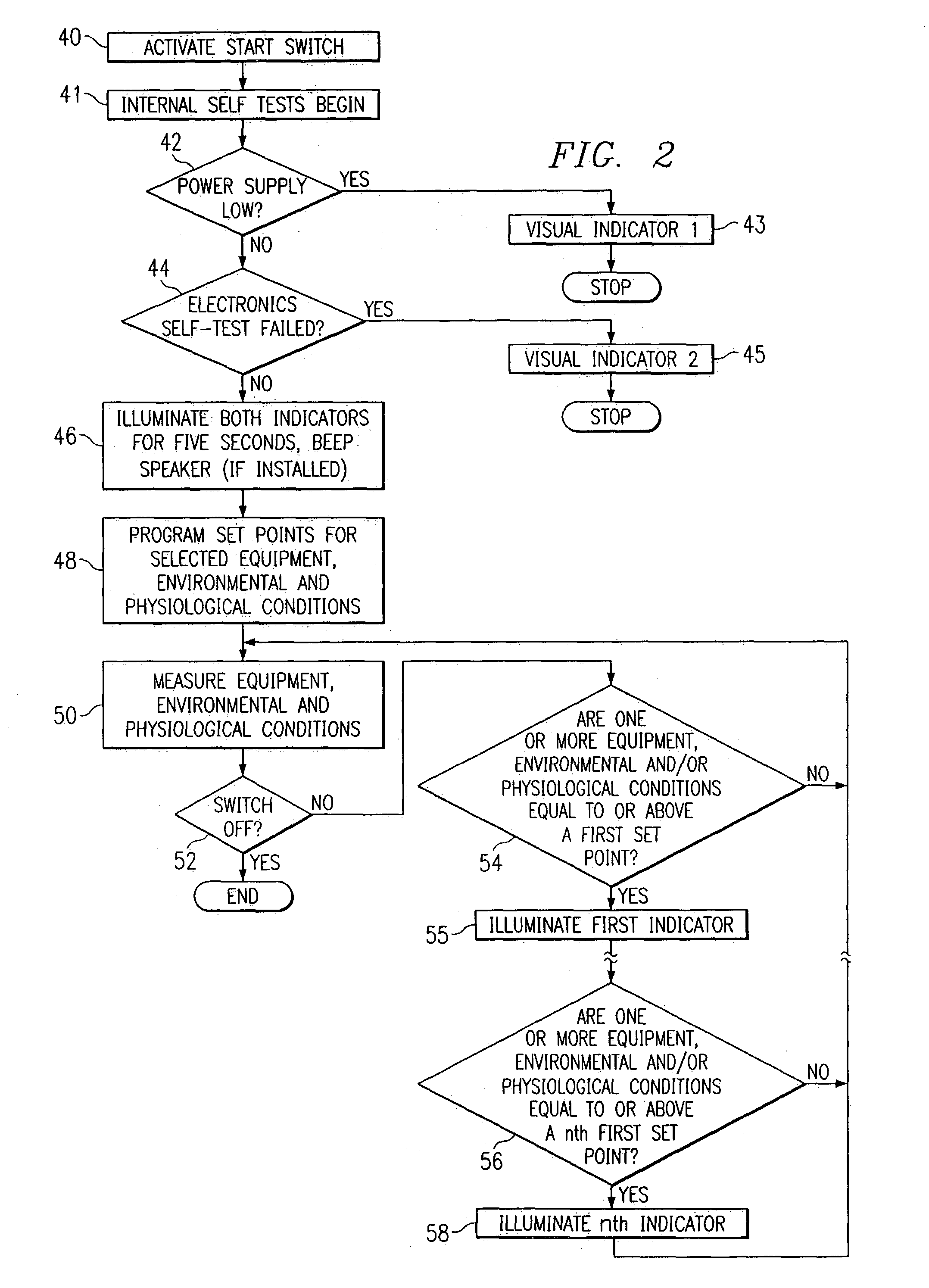
System and method for identifying, monitoring and evaluating equipment, environmental and physiological conditions
InactiveUS6995665B2Reduce in quantityAvoid injuryRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringHazard potential
A system and method are disclosed for identifying monitoring and evaluating hazardous or potentially hazardous conditions. The system may be worn by safety personnel to detect equipment conditions such as low power supply, environmental conditions such as ambient temperature and / or physiological conditions such as heart rate of a wearer. The system further includes a control unit having electronics operable to communicate signals associated with equipment, environmental and physiological conditions.
Owner:MINE SAFETY APPLIANCES CO
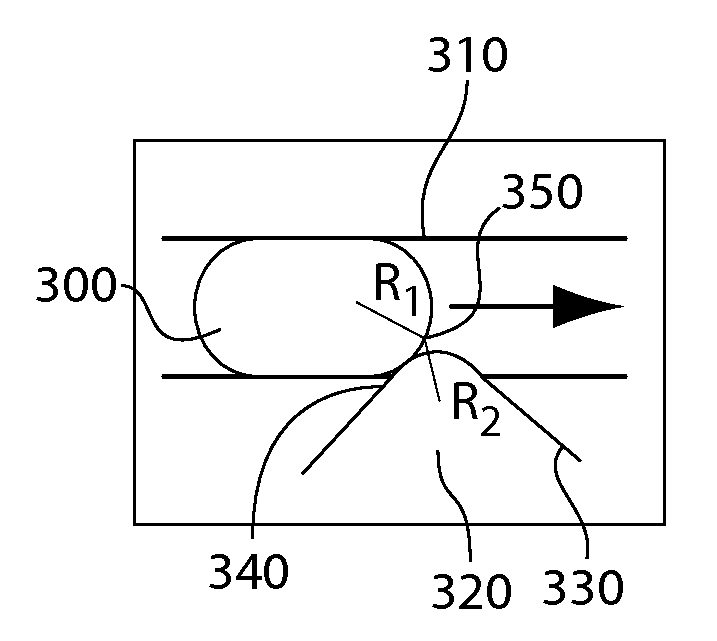
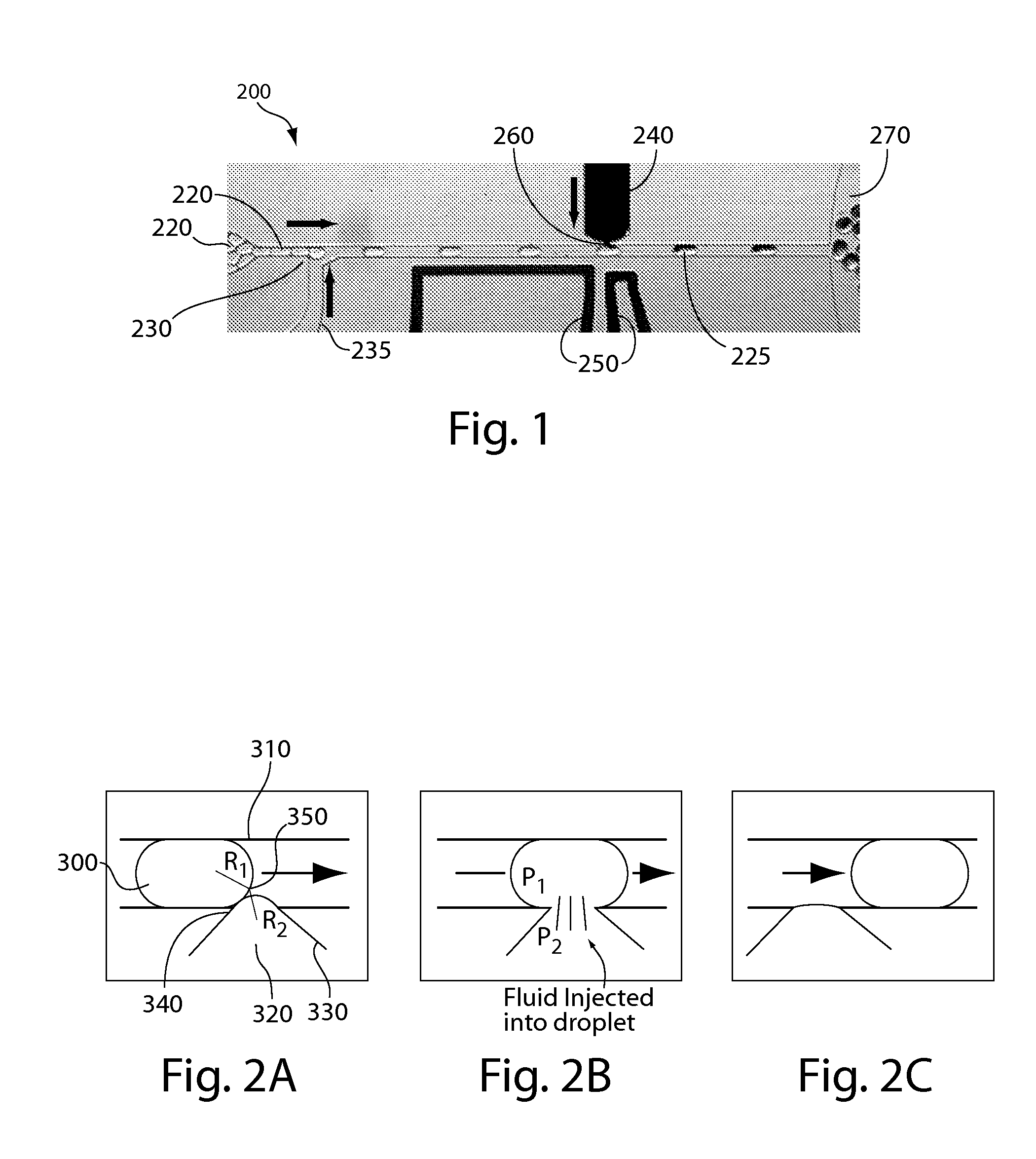
Fluid injection
ActiveUS20120132288A1Avoid enteringValve arrangementsFlow mixersBiomedical engineeringFluid injection
The present invention generally relates to systems and methods for the control of fluids and, in some cases, to systems and methods for flowing a fluid into and / or out of other fluids. As examples, fluid may be injected into a droplet contained within a fluidic channel, or a fluid may be injected into a fluidic channel to create a droplet. In some embodiments, electrodes may be used to apply an electric field to one or more fluidic channels, e.g., proximate an intersection of at least two fluidic channels. For instance, a first fluid may be urged into and / or out of a second fluid, facilitated by the electric field. The electric field, in some cases, may disrupt an interface between a first fluid and at least one other fluid. Properties such as the volume, flow rate, etc. of a first fluid being urged into and / or out of a second fluid can be controlled by controlling various properties of the fluid and / or a fluidic droplet, for example curvature of the fluidic droplet, and / or controlling the applied electric field.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Device, system, and method for depositing processed immiscible-fluid-discrete-volumes
ActiveUS20070039866A1Avoid pollutionFacilitates the downstream addition of aqueous reagents to the slugsValve arrangementsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalyteBiology
Various embodiments relate to systems and / or methods for sample preparation that can be used for biochemical and / or molecular biology procedures involving small volumes, for example, micro volumes or smaller. Methods and systems that can reduce sample size requirements and increase the number of samples on a substrate are provided. Samples can be applied to a plate or other appropriate substrate and can be used for, inter alia, sequencing reactions. In some embodiments, apparatuses, systems, and / or methods for charged analyte collection are provided. Charged analytes in a sample can be electrokinetically collected or extracted from a conduit through a hole formed in a sidewall of the conduit, by application of an electric field that causes the charged analytes to migrate in a direction that is transverse to the conduit.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Drive circuit having improved energy efficiency for implantable beneficial agent infusion or delivery device
InactiveUS7070577B1Valve arrangementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityEnergy recovery
An implantable beneficial agent infusion device featuring a unique energy recovery circuit and a deflectable energy storing member such as a piezo-electric membrane is disclosed. The circuit and deflectable energy storing member cooperate to permit electrical energy employed to activate the member to be at least partially recovered. In a preferred embodiment, the deflectable energy storing member is connected to a seal which is opened to permit the delivery or infusion of a pre-determined amount of a beneficial agent to a patient when the member is deflected or actuated through the application of a sufficiently high voltage thereacross. Charge stored on or in the deflectable energy storing member as a result of the voltage being applied thereacross is recovered by a novel circuit when the deflectable energy storing membrane is permitted to return to its non-actuated state or position.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Microfluidic large scale integration
ActiveUS7143785B2Easy to handleDiaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesHigh densityRandom access memory
High-density microfluidic chips contain plumbing networks with thousands of micromechanical valves and hundreds of individually addressable chambers. These fluidic devices are analogous to electronic integrated circuits fabricated using large scale integration (LSI). A component of these networks is the fluidic multiplexor, which is a combinatorial array of binary valve patterns that exponentially increases the processing power of a network by allowing complex fluid manipulations with a minimal number of inputs. These integrated microfluidic networks can be used to construct a variety of highly complex microfluidic devices, for example the microfluidic analog of a comparator array, and a microfluidic memory storage device resembling electronic random access memories.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC +1
Bistable microactuator with coupled membranes
InactiveUS6168395B1Improves pneumaticImproves liquid couplingCircuit elementsDecorative surface effectsMetallic electrodeCoupling
A bistable electrostatic actuator with pneumatic or liquid coupling. The actuator has enclosed metallic electrodes. It can be used for a microvalve or micropump. The actuator has buckled membrane sections in pairs and curved substrate electrodes, locally associated with said membrane sections.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
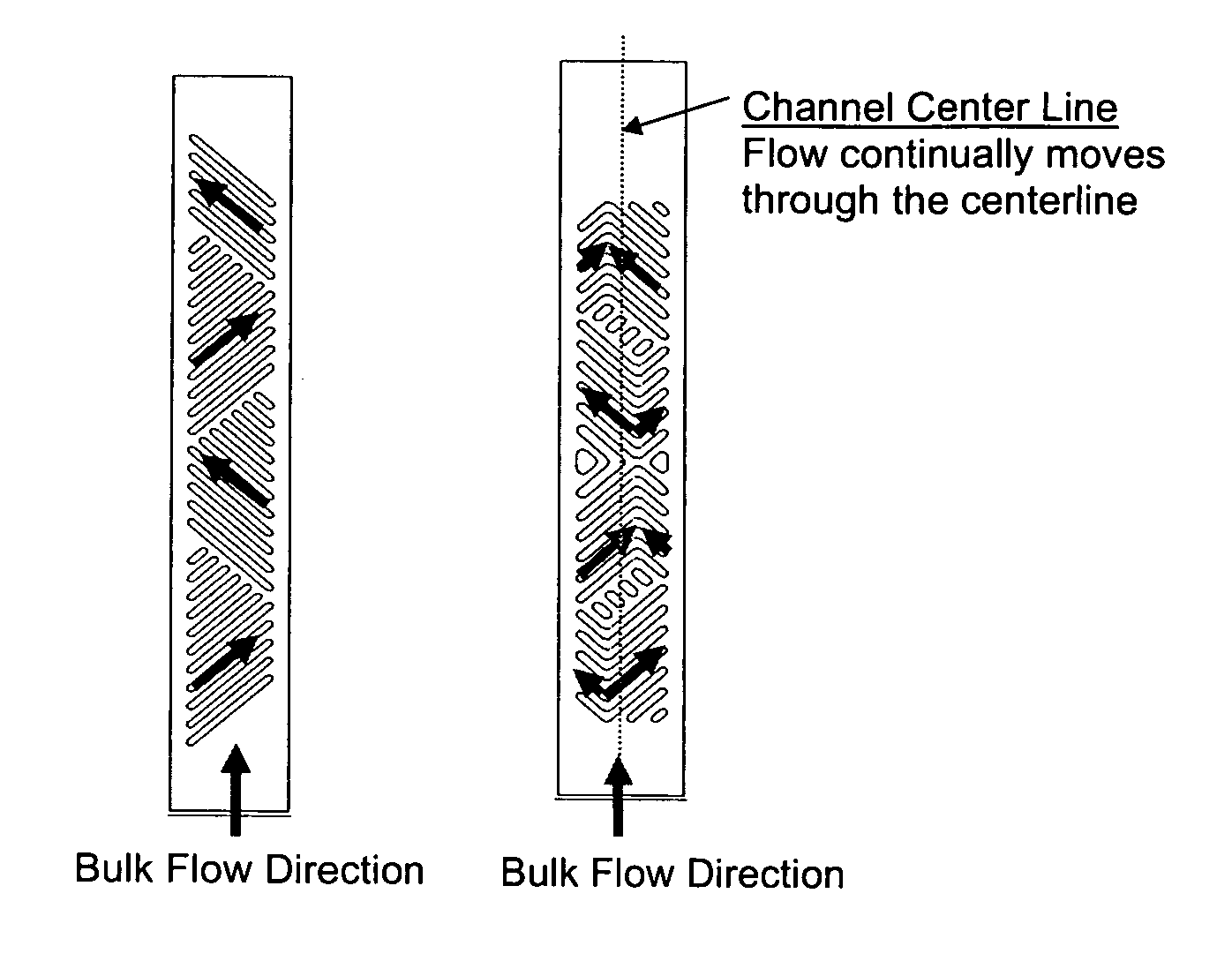
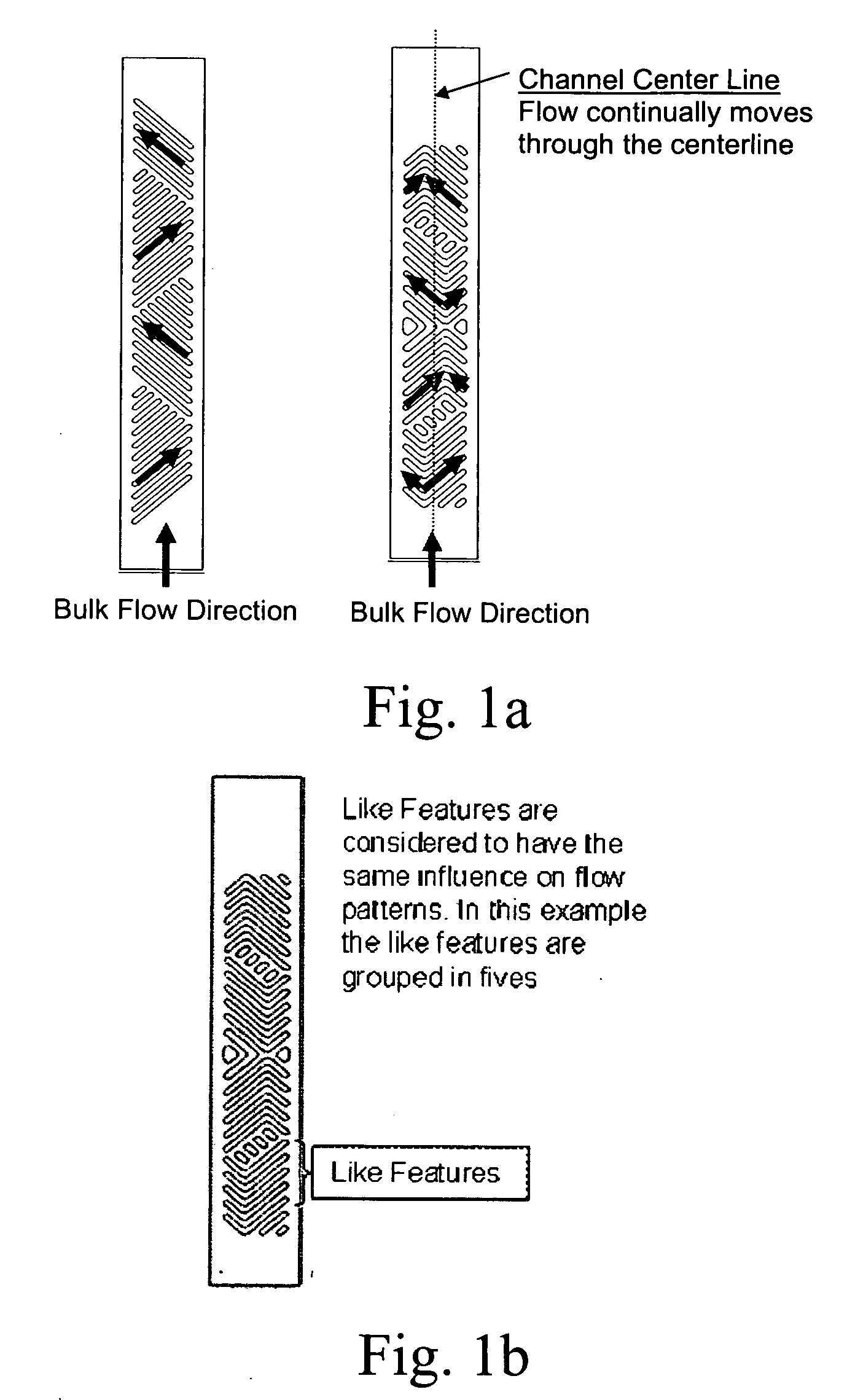
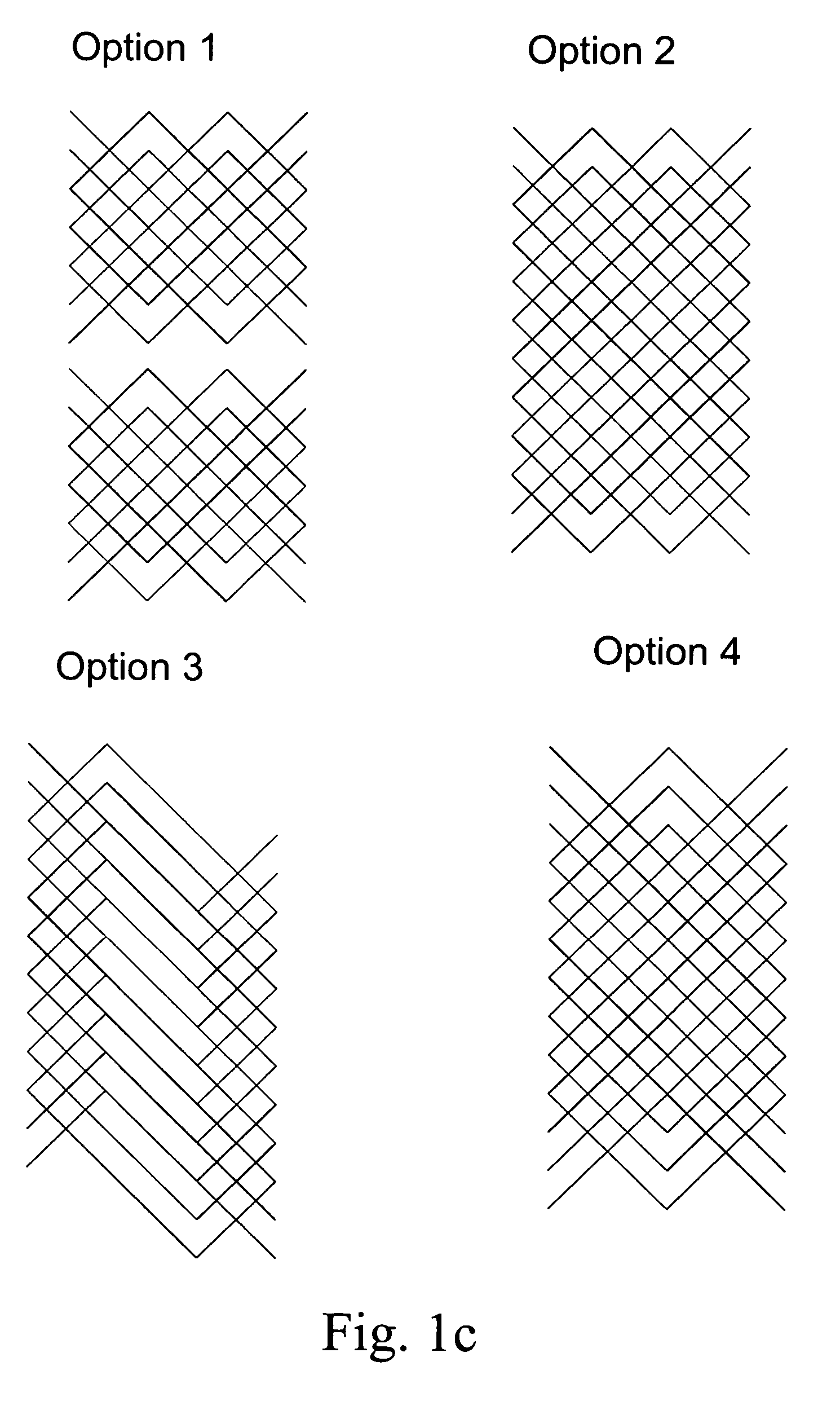
Microfluidic device and methods for construction and application
InactiveUS20060108012A1Considerable precisionEasy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyCircuit elementsEngineeringTwo fluid
A microfluidic device comprises first and second inlet passages (13) for respective immiscible fluids, these inlet passages merging into a third passage (8) along which the two fluids flow under parallel laminar flow conditions, the third passage being formed with a constriction or other discontinuity (9) causing the two fluids to form into a flow of alternate segments.
Owner:Q CHIP
Moving microdroplets
InactiveUS6911183B1Easy to assembleIncrease the degree of mixingMaterial nanotechnologyValve arrangementsElectrophoresisOptoelectronics
The movement and mixing of microdroplets through microchannels is described employing microscale devices, comprising microdroplet transport channels, reaction regions, electrophoresis modules, and radiation detectors. The discrete droplets are differentially heated and propelled through etched channels. Electronic components are fabricated on the same substrate material, allowing sensors and controlling circuitry to be incorporated in the same device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method and apparatus for autonomous downhole fluid selection with pathway dependent resistance system
An apparatus is described for controlling flow of fluid in a tubular positioned in a wellbore extending through a subterranean formation. A flow control system is placed in fluid communication with a main tubular. The flow control system has a flow ratio control system and a pathway dependent resistance system. The flow ratio control system has a first and second passageway, the production fluid flowing into the passageways with the ratio of fluid flow through the passageways related to the characteristic of the fluid flow. The pathway dependent resistance system includes a vortex chamber with a first and second inlet and an outlet, the first inlet of the pathway dependent resistance system in fluid communication with the first passageway of the fluid ratio control system and the second inlet in fluid communication with the second passageway of the fluid ratio control system. The first inlet is positioned to direct fluid into the vortex chamber such that it flows primarily tangentially into the vortex chamber, and the second inlet is positioned to direct fluid such that it flows primarily radially into the vortex chamber. Undesired fluids, such as natural gas or water, in an oil well, are directed, based on their relative characteristic, into the vortex primarily tangentially, thereby restricting fluid flow when the undesired fluid is present as a component of the production fluid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Continuous high-frequency oscillation breathing treatment apparatus
ActiveUS7191780B2Assist in mucus secretionSimply and inexpensively manufacturingRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInhalationBreathing treatments
Owner:COMEDICA INC
Microfluidic large scale integration
InactiveUS20050072946A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesCircuit elementsElastomerFlow resistivity
Using basic physical arguments, a design and method for the fabrication of microfluidic valves using multilayer soft lithography is presented. Embodiments of valves in accordance with the present invention feature elastomer membrane portions of substantially constant thickness, allowing the membranes to experience similar resistance to an applied pressure across their entire width. Such on-off valves fabricated with upwardly- or downwardly-deflectable membranes can have extremely low actuation pressures, and can be used to implement active functions such as pumps and mixers in integrated microfluidic chips. Valve performance was characterized by measuring both the actuation pressure and flow resistance over a wide range of design parameters, and comparing them to both finite element simulations and alternative valve geometries.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
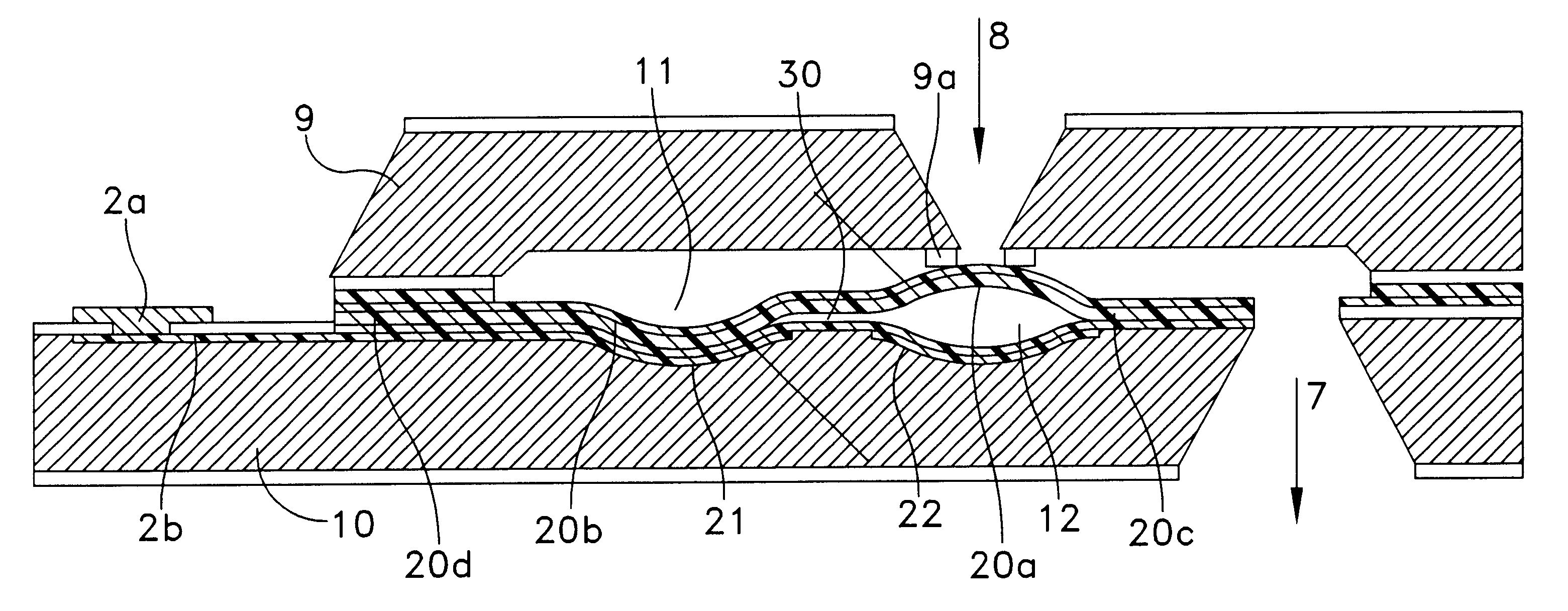
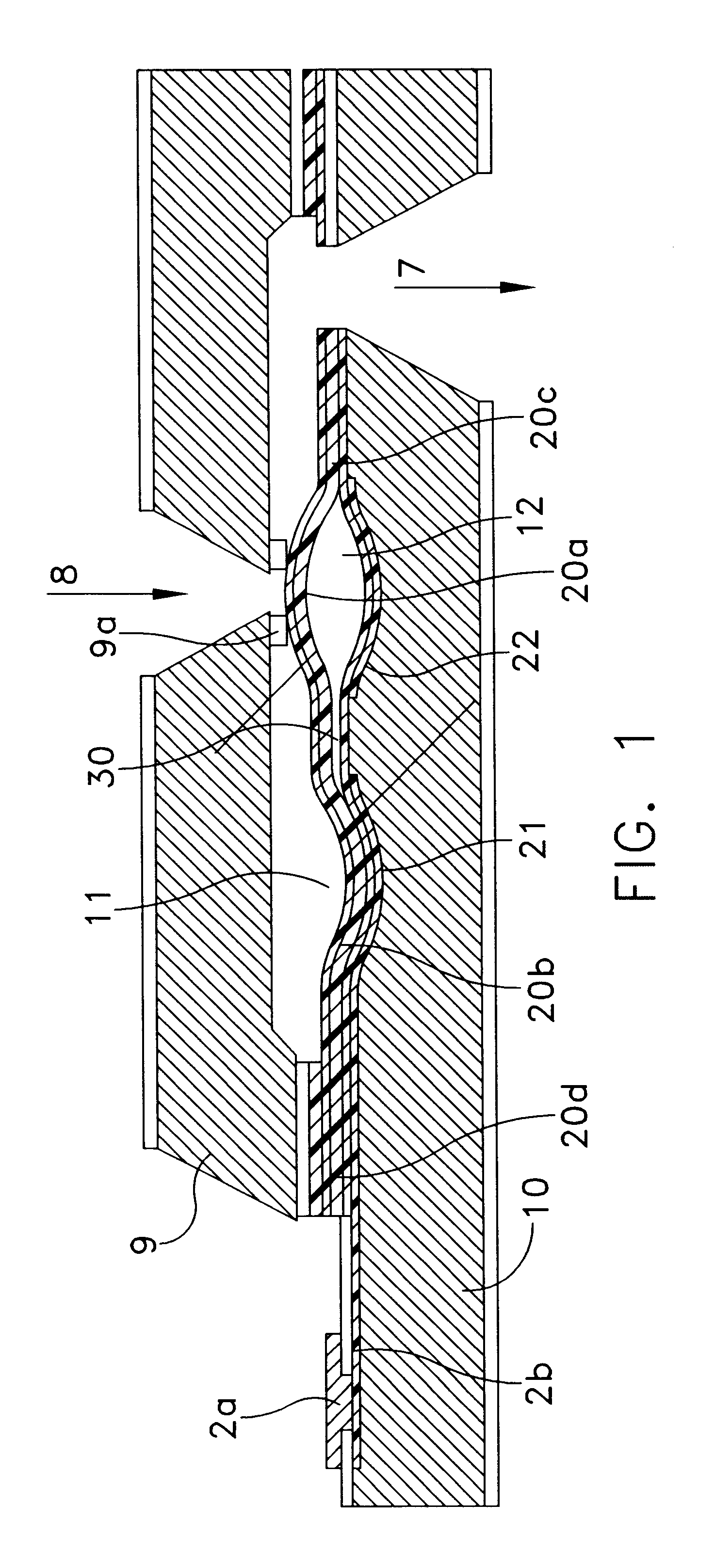
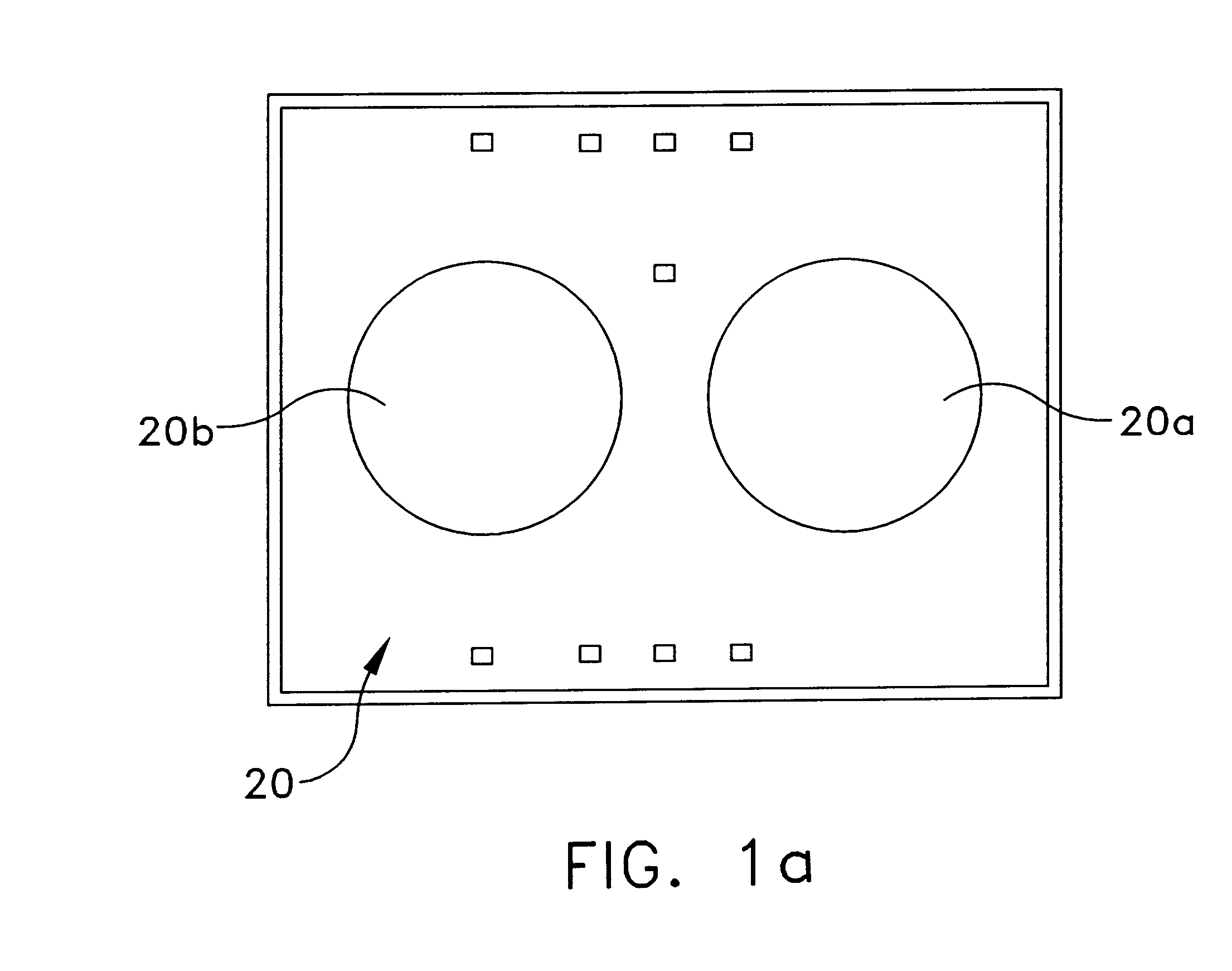
Microfluidic system including a bubble valve for regulating fluid flow through a microchannel
InactiveUS6877528B2Effective controlEnhanced on-off switchingValve arrangementsSludge treatmentEngineeringActuator
A microfluidic system includes a bubble valve for regulating fluid flow through a microchannel. The bubble valve includes a fluid meniscus interfacing the microchannel interior and an actuator for deflecting the membrane into the microchannel interior to regulate fluid flow. The actuator generates a gas bubble in a liquid in the microchannel when a sufficient pressure is generated on the membrane.
Owner:CYTONOMEST
Electrostatic valves for microfluidic devices
InactiveUS7232109B2Additive manufacturing apparatusOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElastomerPolyester
Valve structures formed in elastomer material are electrostatically actuated by applying voltage to a flexible, electrically conductive wire pattern. An actuation force generated between the patterned wire structure and an electrode result in closure of a flow channel formed in elastomer material underlying the wire. In one embodiment of a valve structure in accordance with the present invention, the wire structure is patterned by lithography and etching of a copper / polyimide laminate, with an underlying gold plate positioned on the opposite side of the flow channel serving as an electrode. In an alternative embodiment, a first wire structure is patterned by physically cutting out a first pattern of strips from an Aluminum / Mylar(®) laminate sheet. A second patterned wire structure serving as the electrode is formed by the same method, and positioned on the opposite side of a control channel. Application of an actuation force between the first and second patterned strips closes the control channel and an associated flow channel underlying the control channel.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
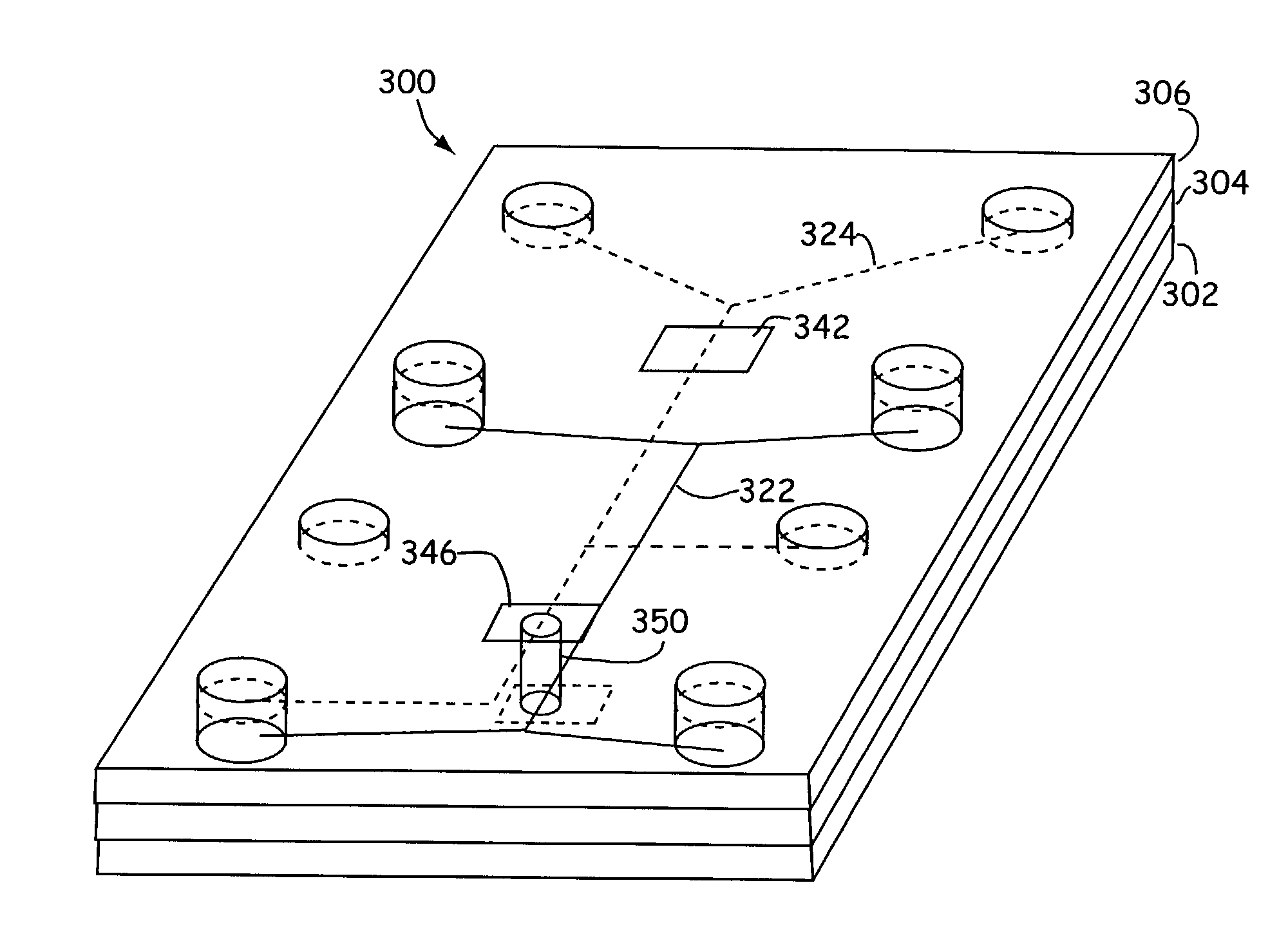
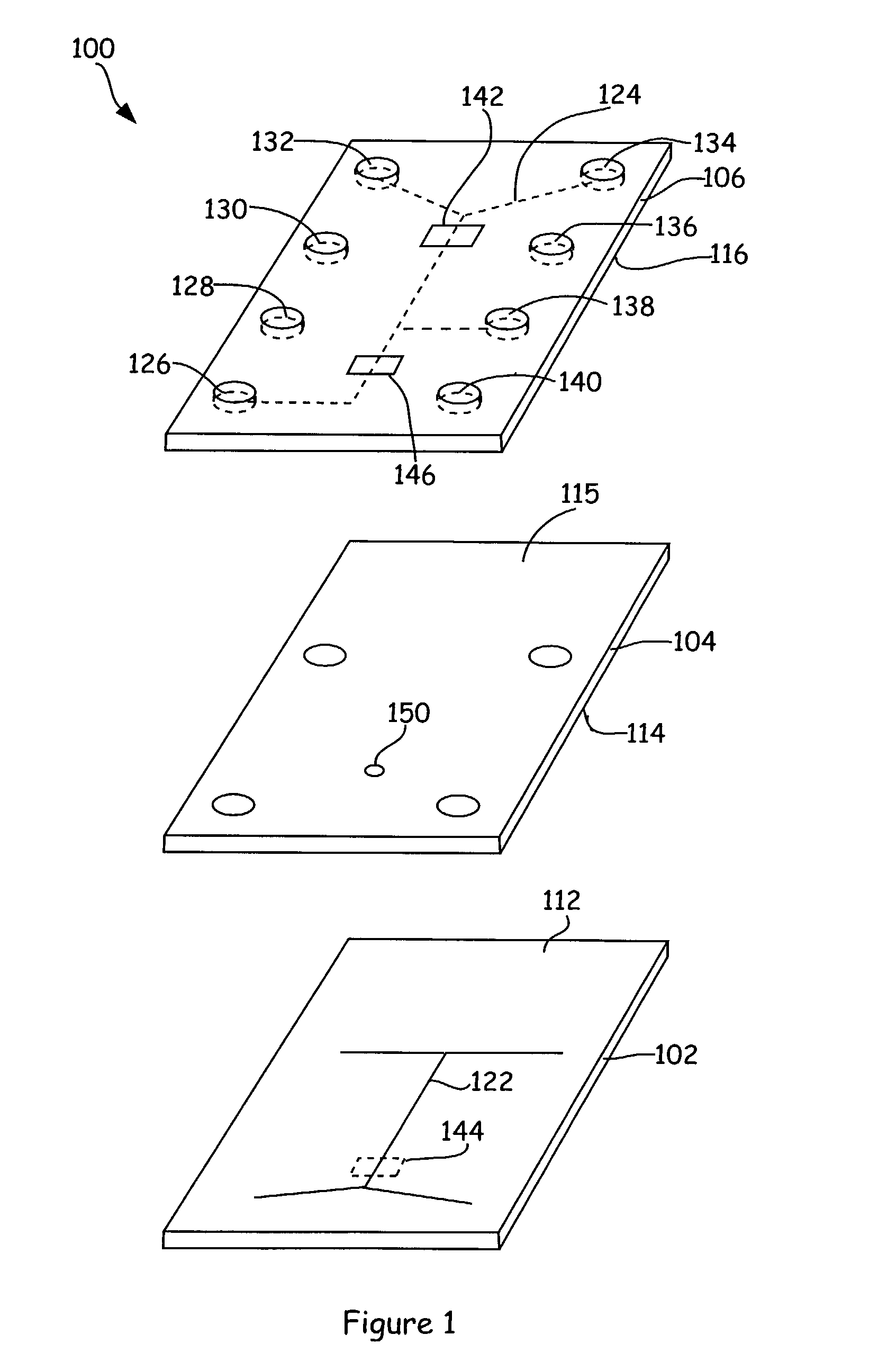
Microfluidic systems and components
Microfluidic systems and components. A microfluidic system includes one or more functional units or microfluidic chips, configured to perform constituent steps in a process and interconnected to form the system. A multi-layer microfluidic system includes a separate dedicated fluid layer and dedicated electromechanical layer connected via through-holes. Electromechanical components are formed on the electromechanical layer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
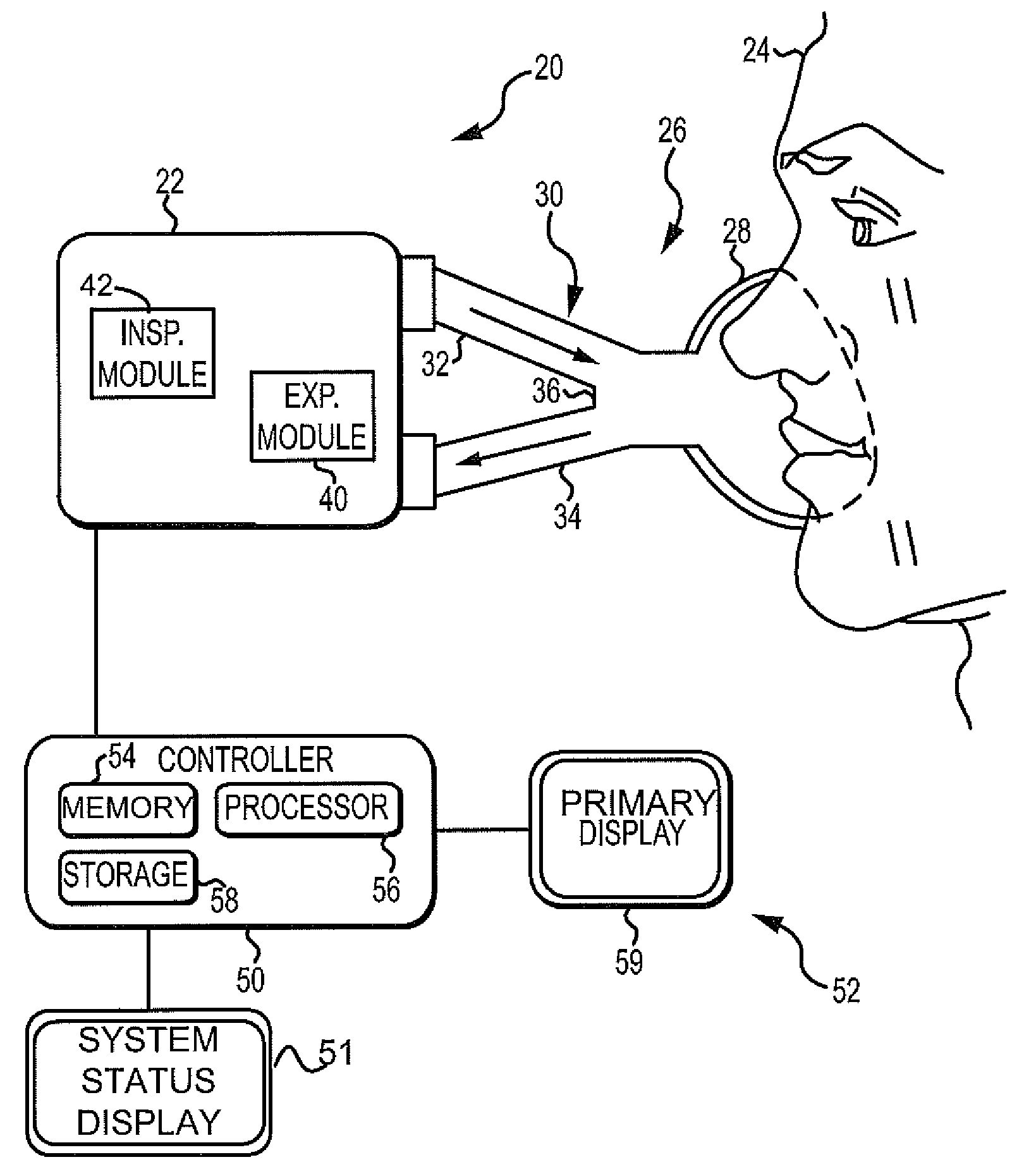
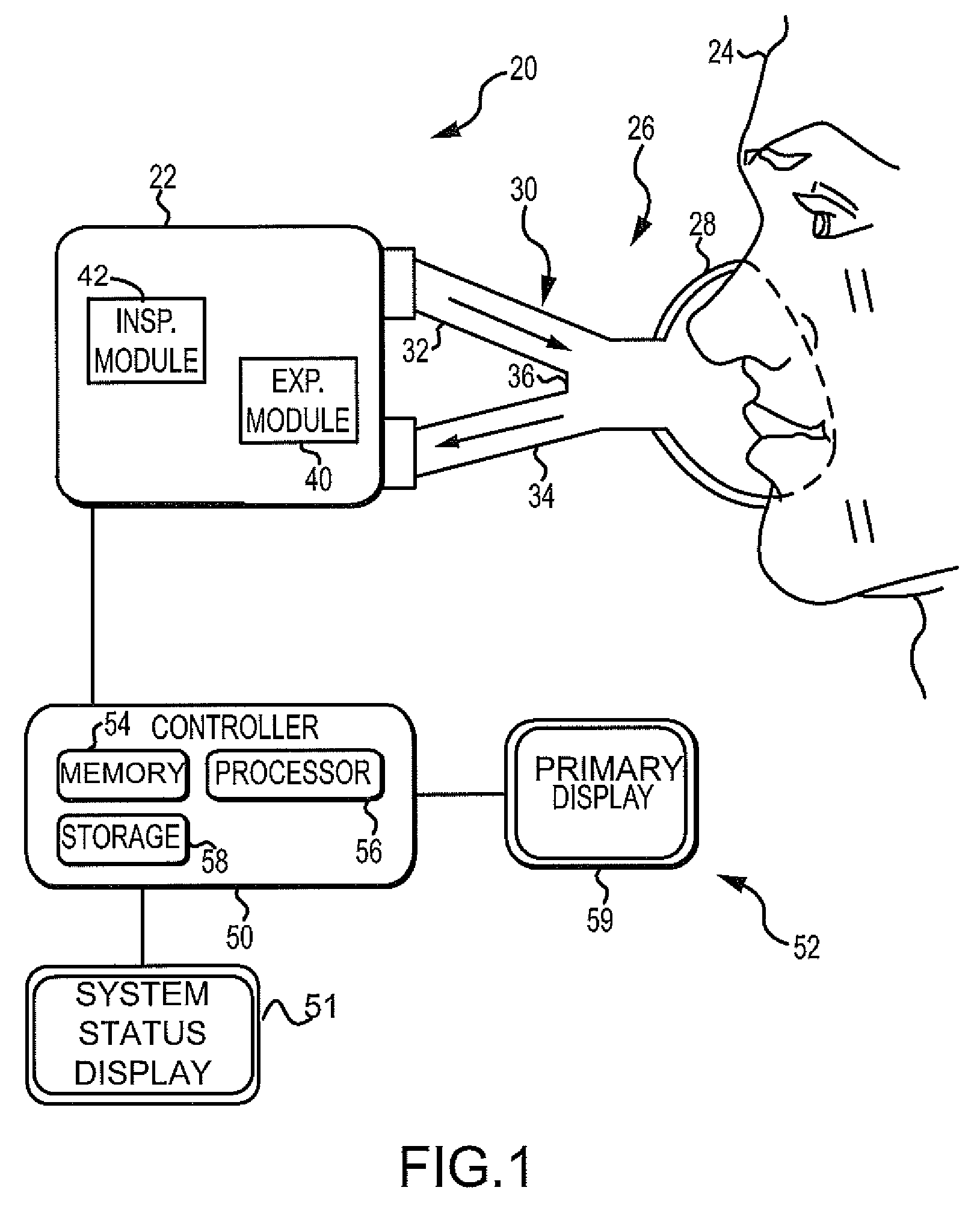
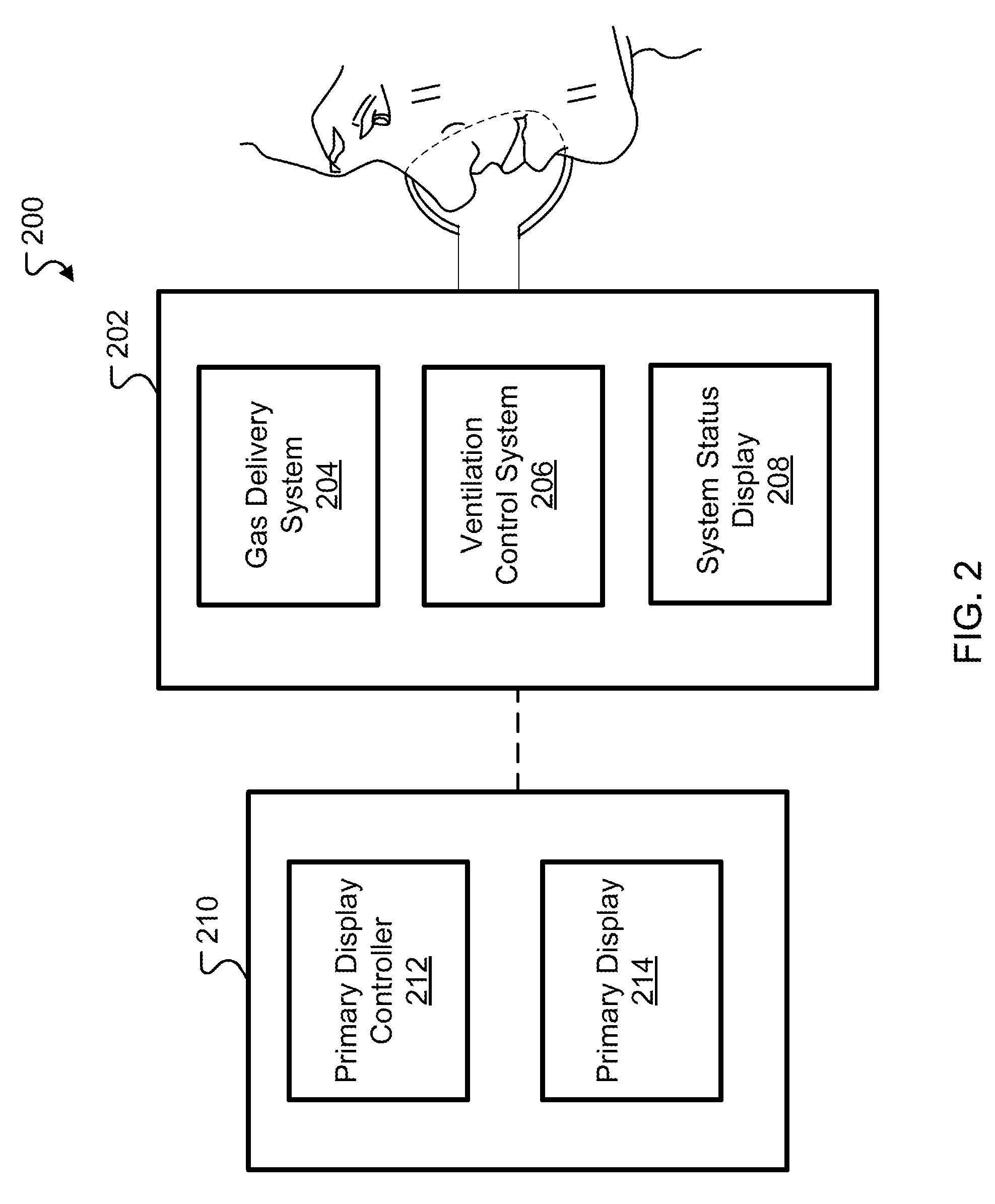
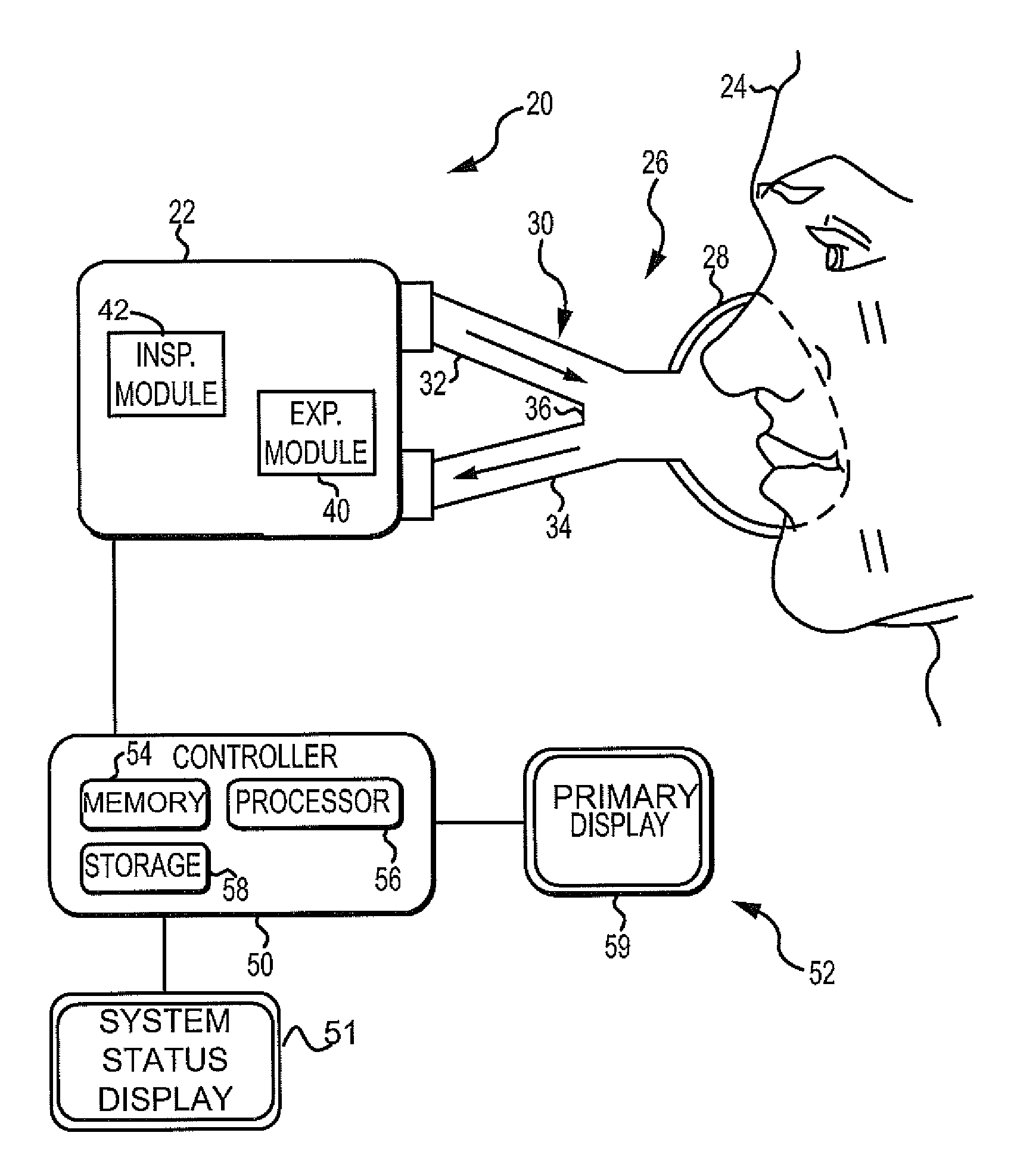
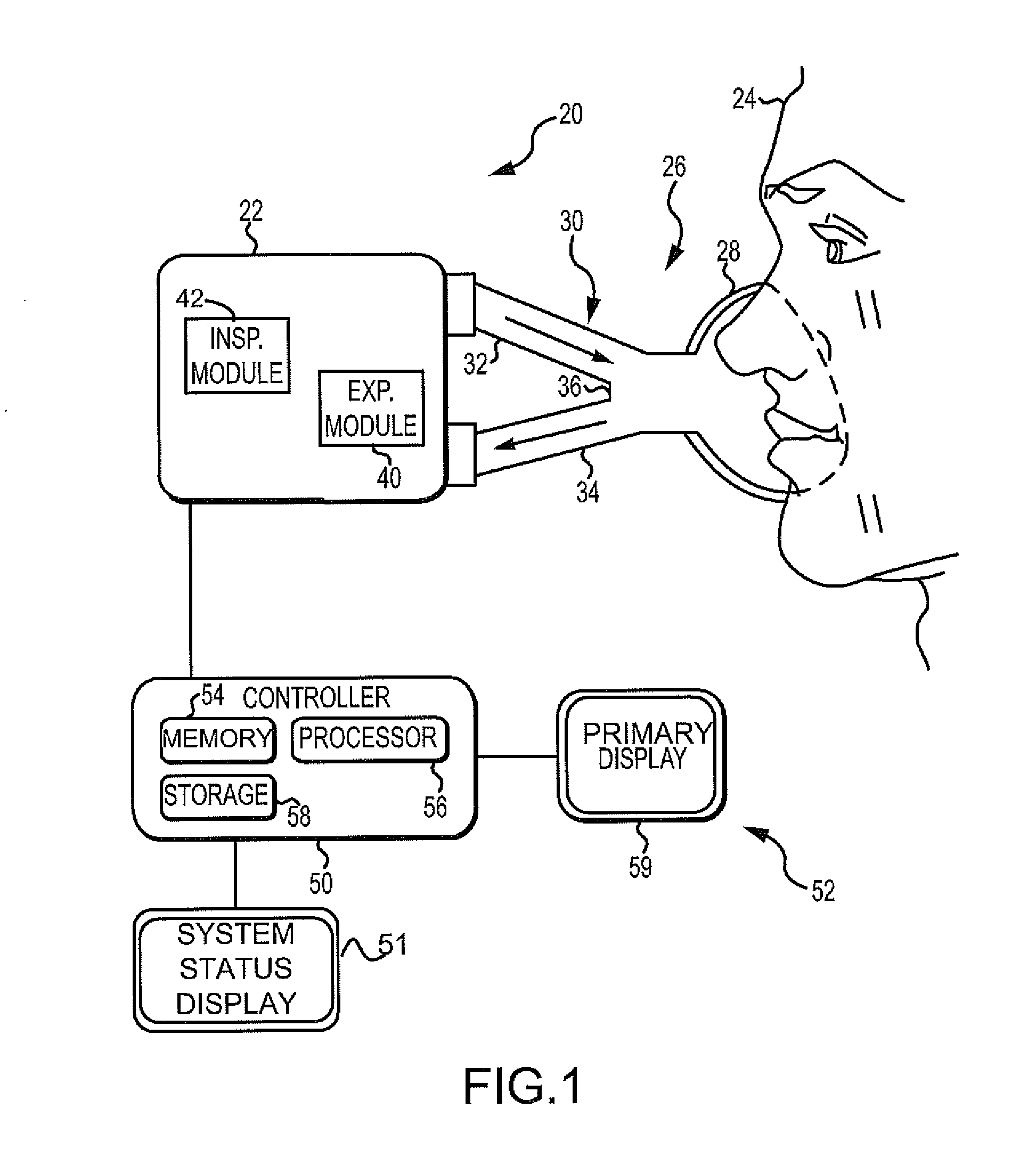
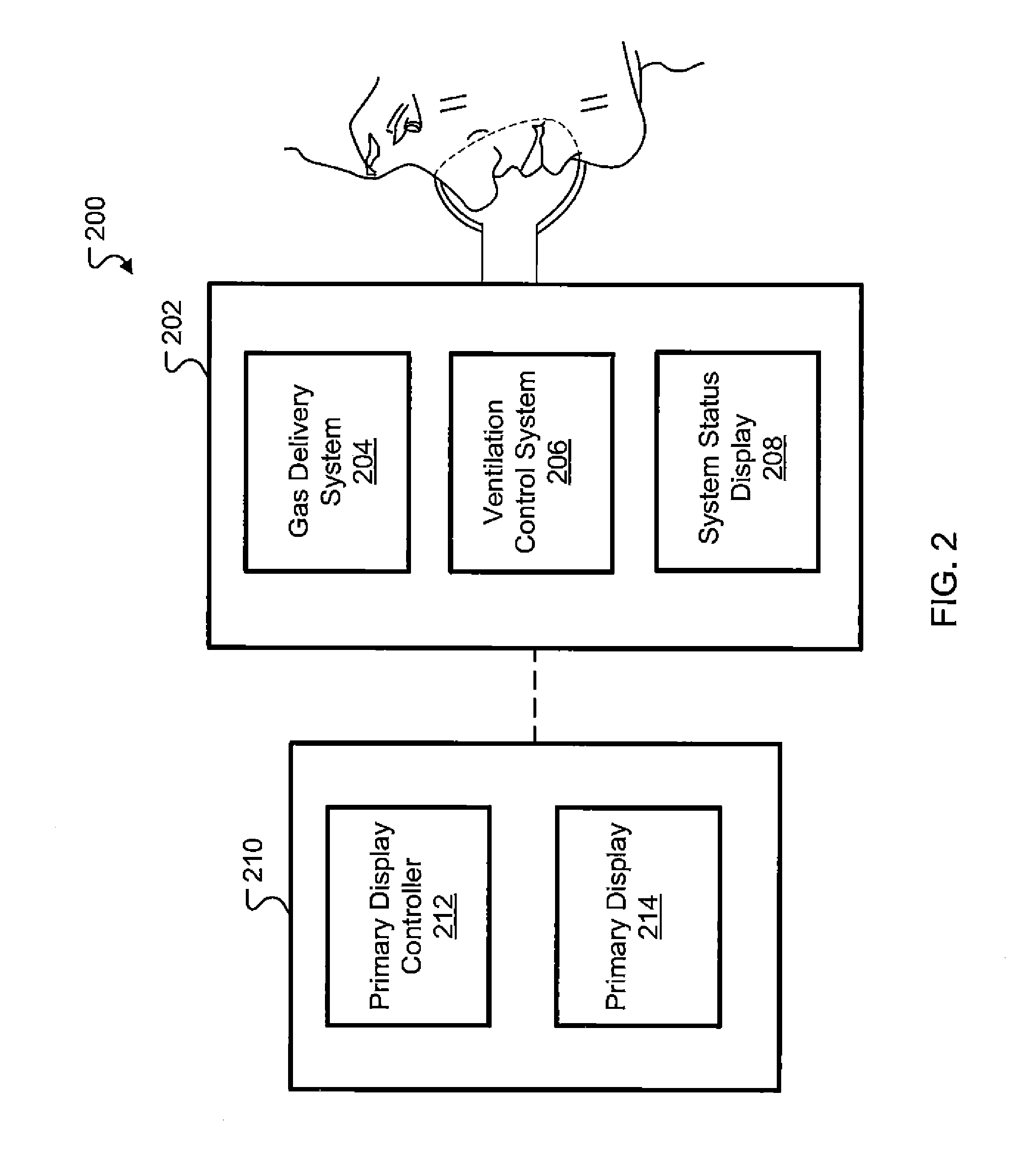
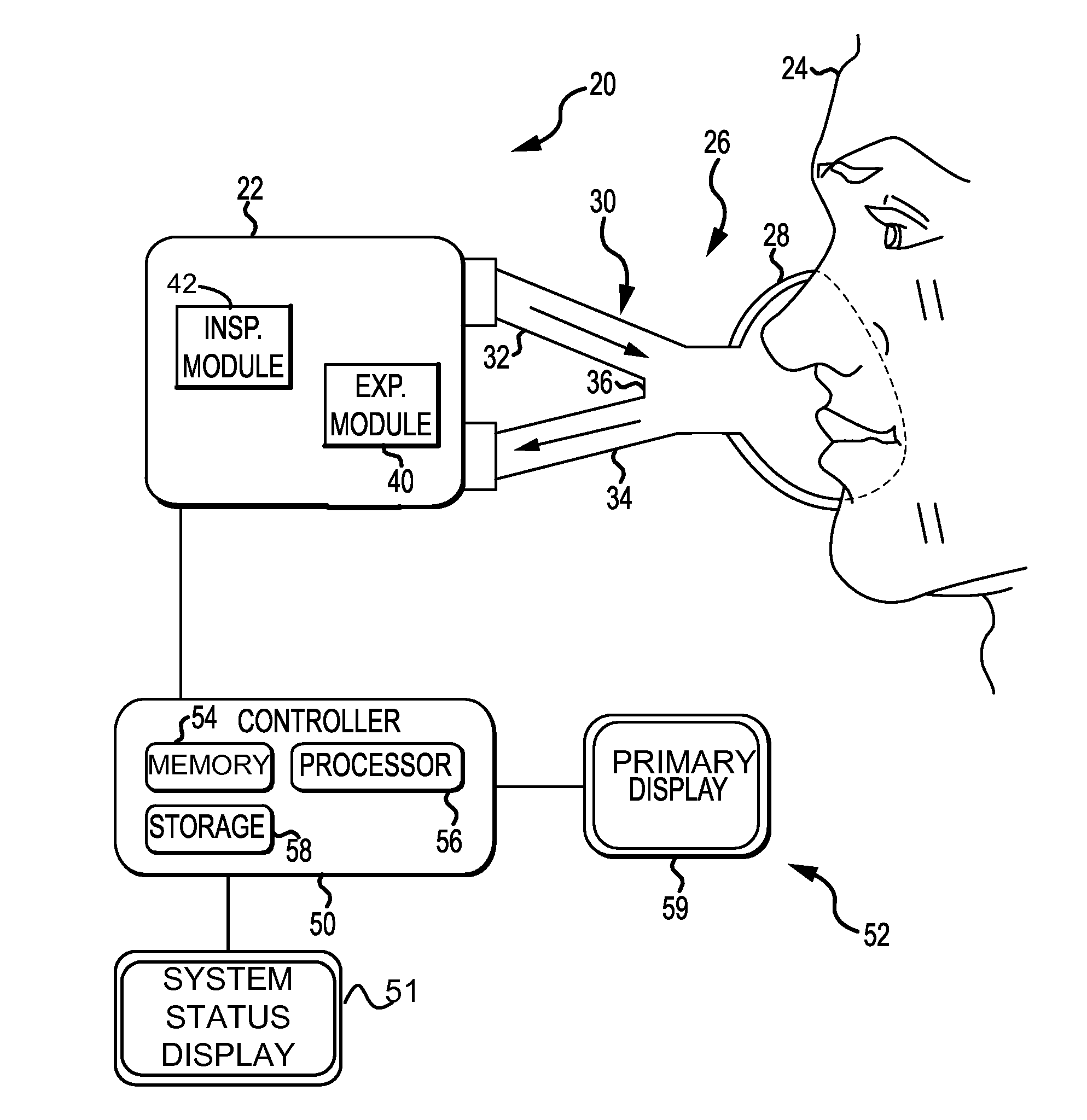
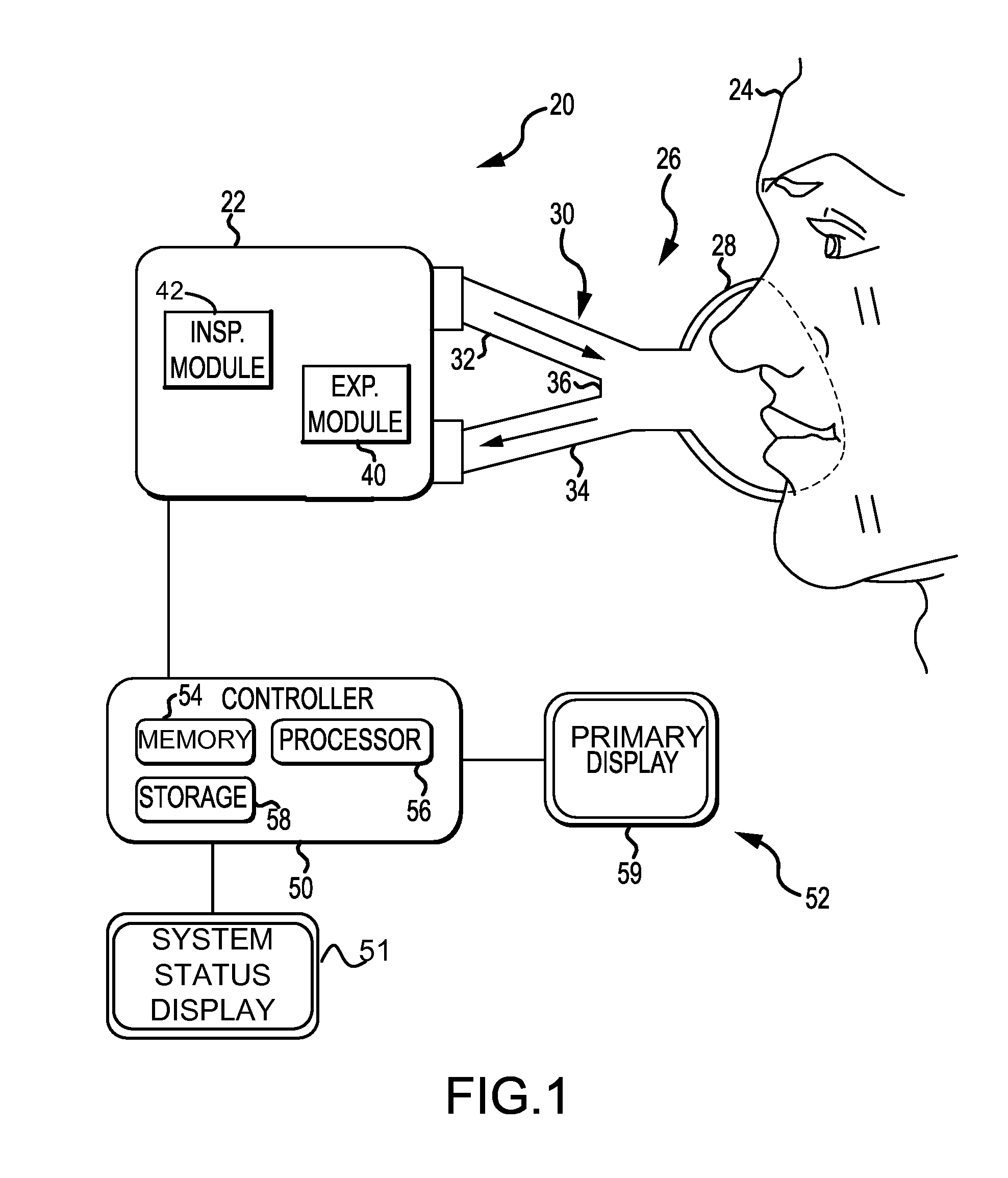
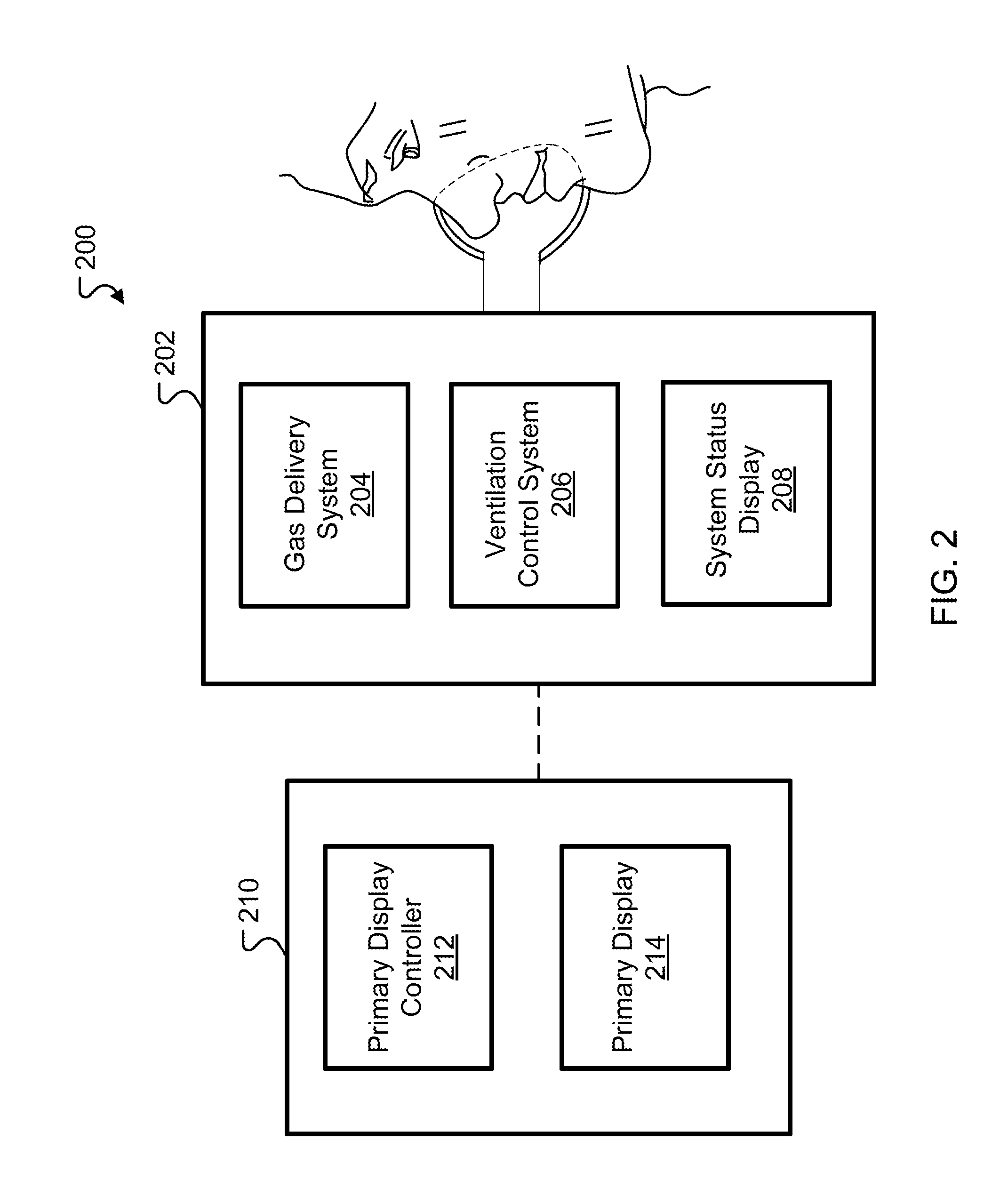
Ventilation System With System Status Display For Configuration And Program Information
ActiveUS20110259332A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesBreathing masksDisplay deviceEngineering
The disclosure describes a novel approach for displaying information on a ventilation system. The disclosure describes a novel respiratory system including a removable primary display and system status display. Further, the disclosure describes a novel method for displaying ventilator information and a novel method for controlling a ventilation system.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
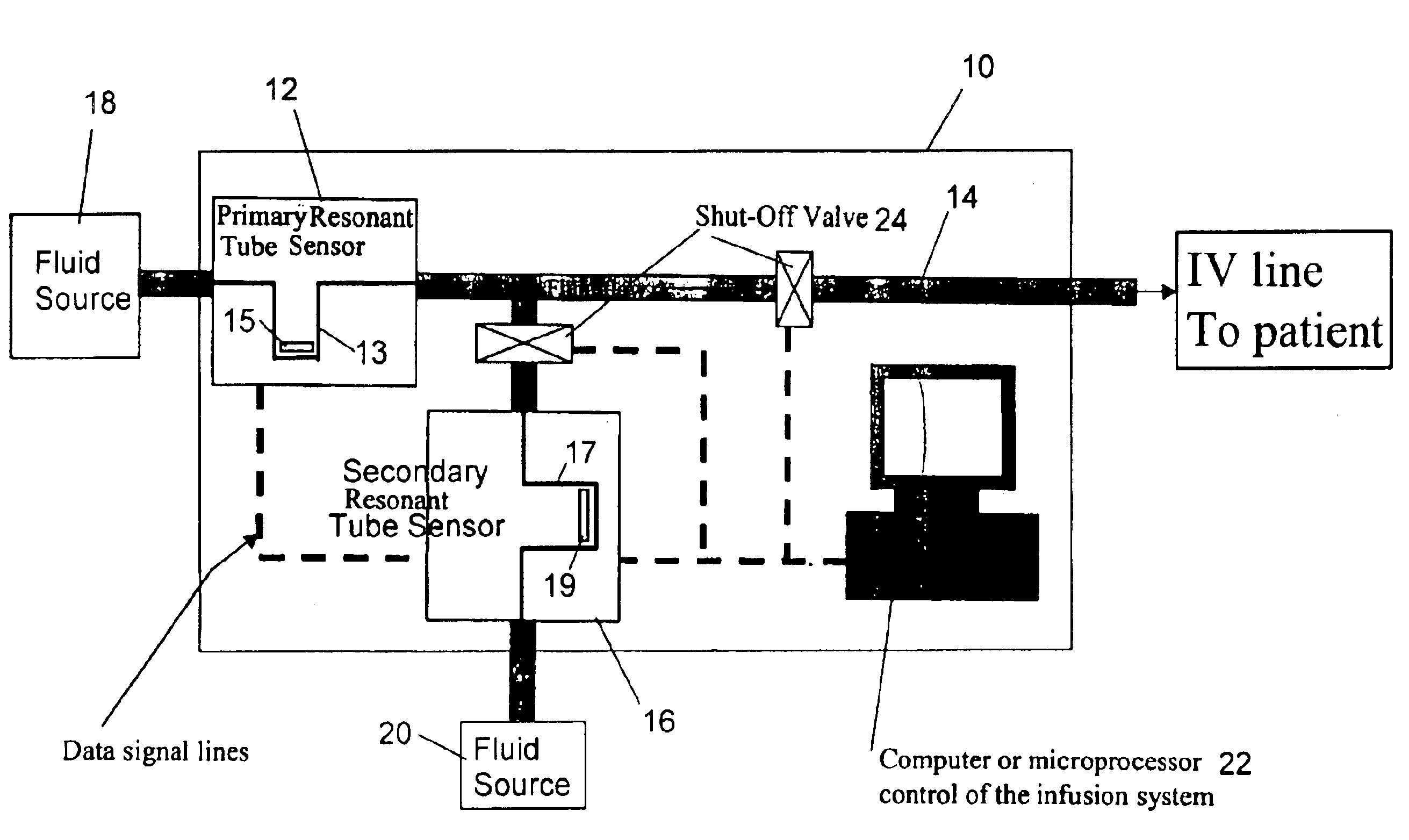
Fluid delivery system and method
InactiveUS6932114B2The right amountSafe deliveryCircuit elementsVolume measurement and fluid deliveryEngineeringDelivery system
A fluid delivery system capable of delivering a precise amount of fluid and monitor certain properties of the fluid so that the correct fluid is safely delivered to its intended destination. The system makes use of a flow sensor comprising a freestanding tube portion vibrated at a resonant frequency, wherein the resonant frequency corresponds to the density of the fluid flowing through the tube portion and the tube portion exhibits a degree of twist that varies with the mass flow rate of the fluid flowing therethrough. Movement of the tube portion is then sensed to produce a first output signal corresponding to the fluid density and a second output signal corresponding to the mass flow rate. The system is also equipped to measure elapsed time and to stop fluid flow in response to either of the first and second output signals.
Owner:INTEGRATED SENSING SYST INC
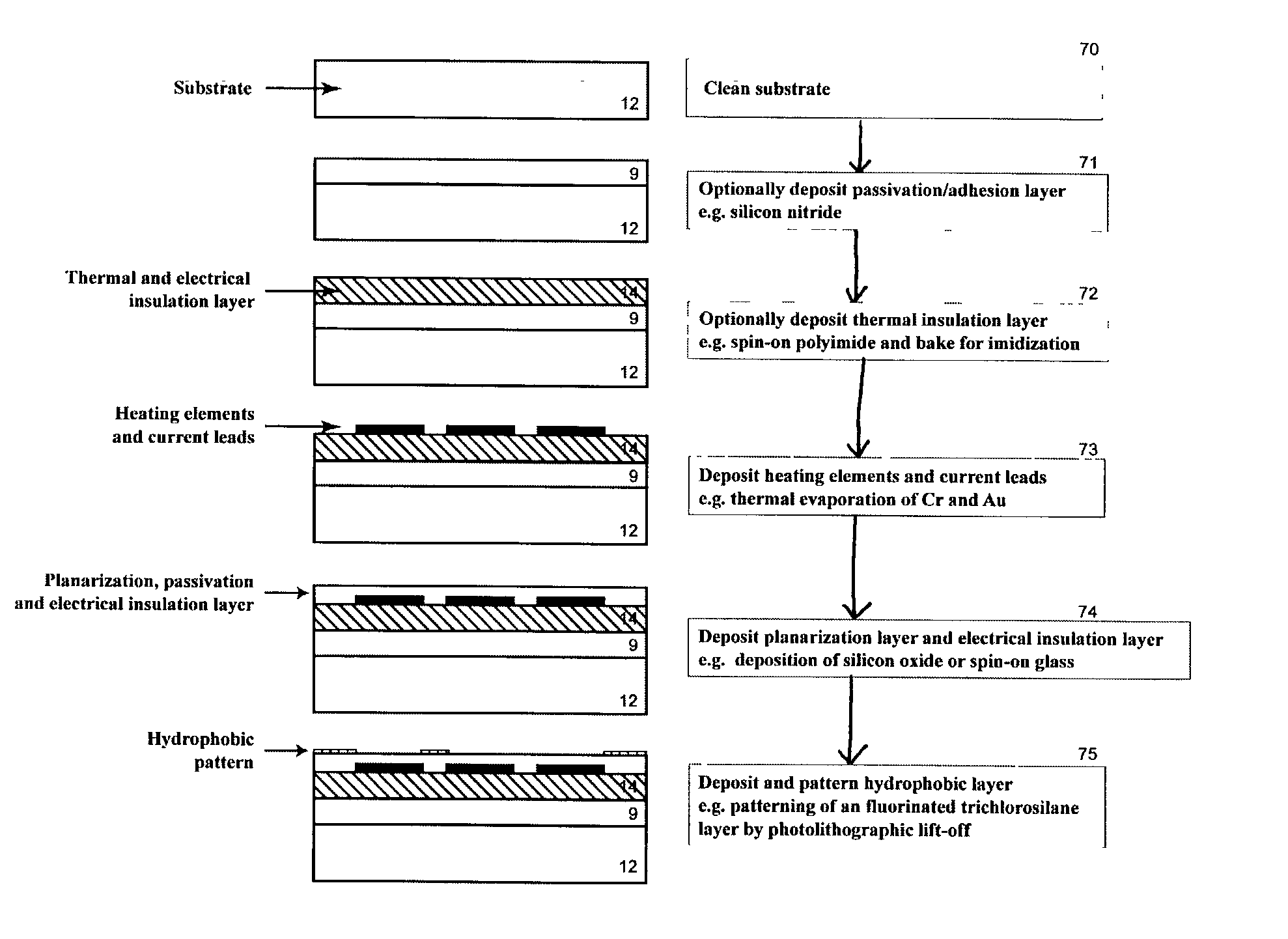
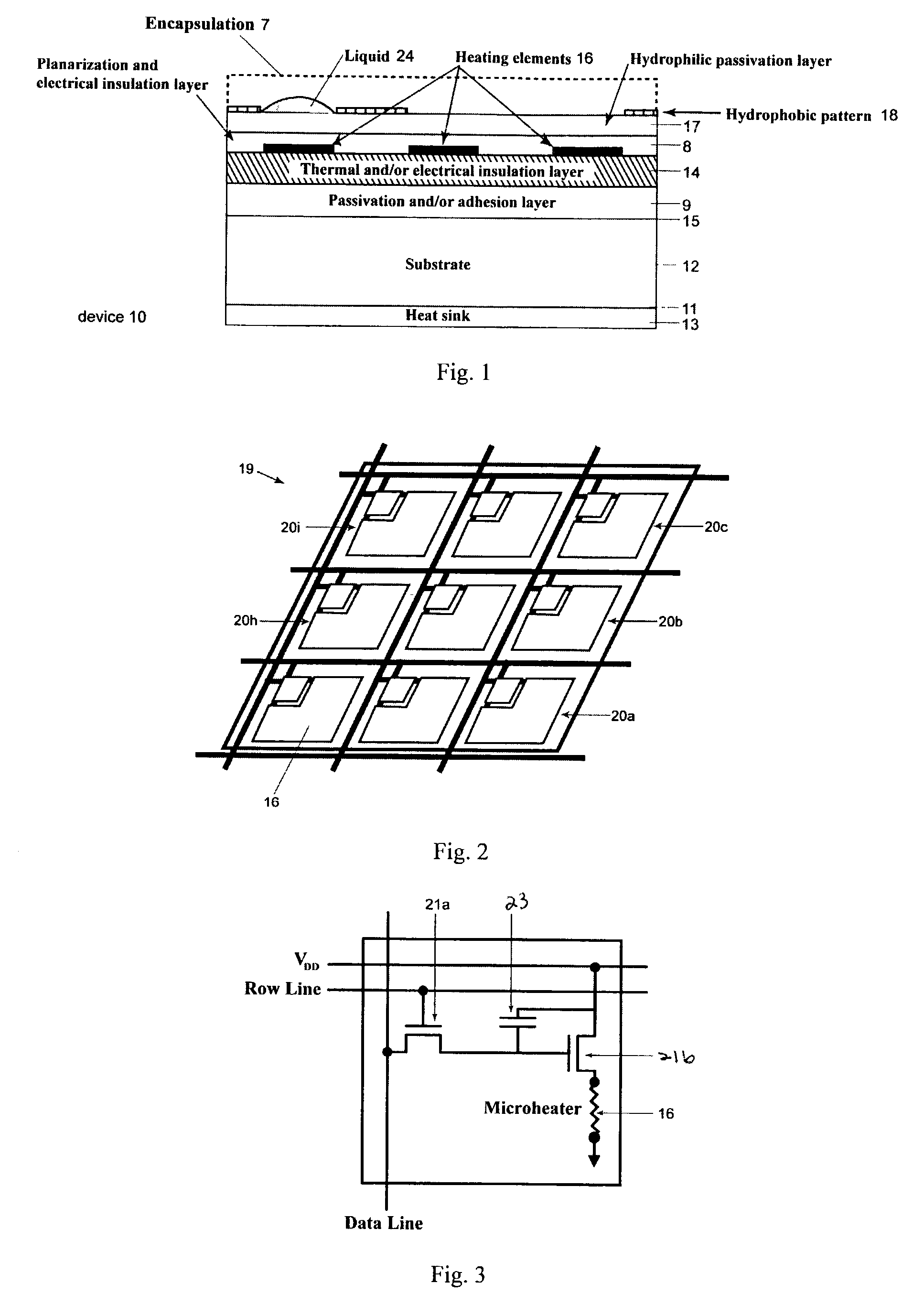
Method and device for controlling liquid flow on the surface of a microfluidic chip
The invention is directed to a method and device for routing, mixing, or reacting droplets or liquid microstreams along the surface of a flat substrate. The flow of liquid microstreams or microdroplets along designated pathways is confined by chemical surface patterning. Individually addressable heating elements, which are embedded in the substrate, can be used to generate flow via thermocapillary effects or to trigger or quench chemical reactions. The open architecture allows the liquid to remain in constant contact with the ambient atmosphere. The device can be used for microfluidic applications or as a surface reactor or biosensor, among other applications.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Pulsed laser triggered high speed microfluidic switch and applications in fluorescent activated cell sorting
ActiveUS20110030808A1Improve compatibilityValve arrangementsCircuit elementsFluorescenceFluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting
In certain embodiments this invention provides a pulsed-laser triggered microfluidic switching mechanism that can achieve a switching time of 70 μs. This switching speed is two orders of magnitude shorter than that of the fastest switching mechanism utilized in previous μFACS.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Pneumatic valve interface for use in microfluidic structures
A pneumatic valve for use in laminated plastic microfluidic structures. This zero or low dead volume valve allows flow through microfluidic channels for use in mixing, dilution, particulate suspension and other techniques necessary for flow control in analytical devices.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Actuator device utilizing a conductive polymer gel
InactiveUS6685442B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesCircuit elementsElastomerConductive polymer
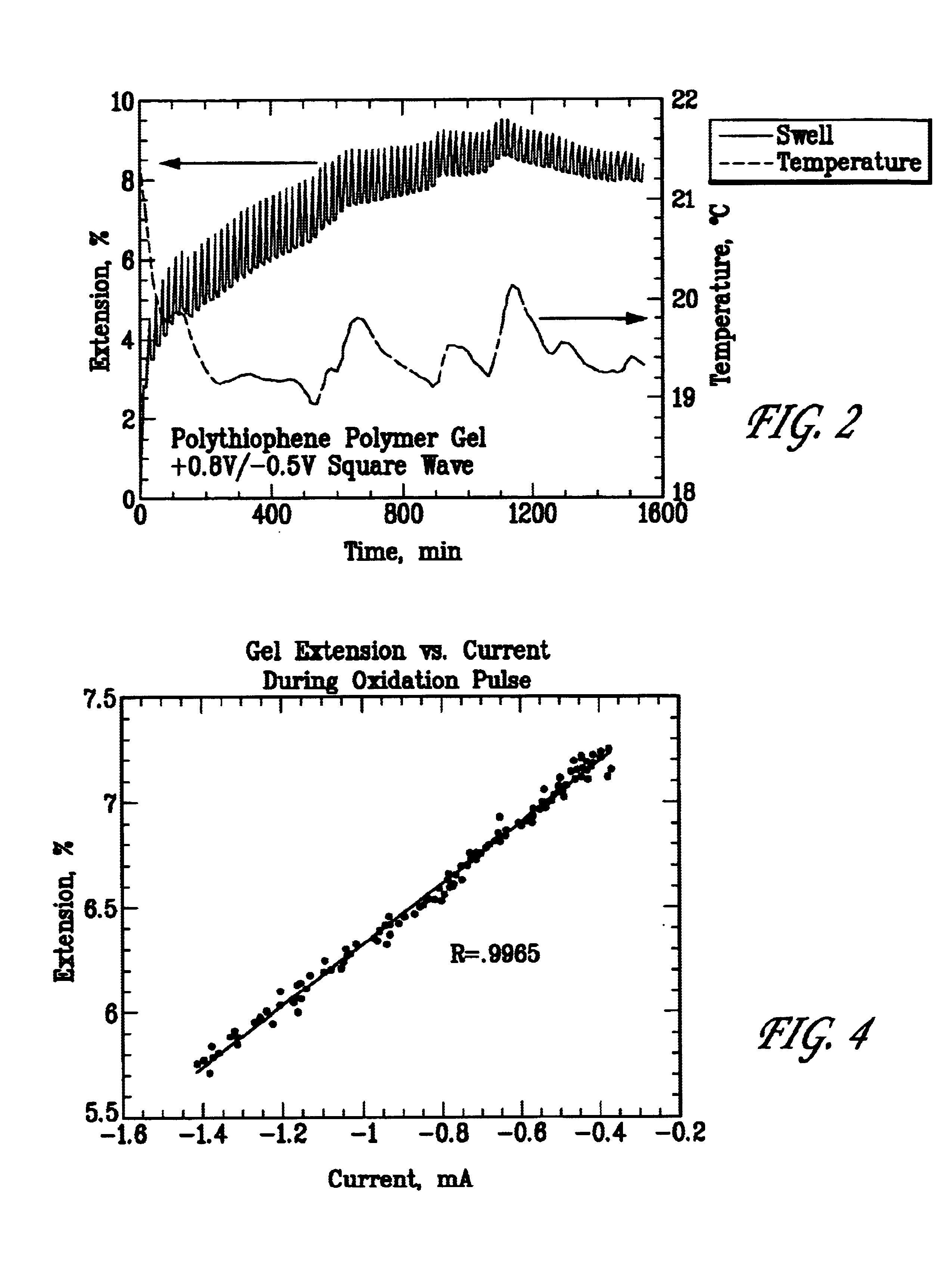
A valve actuator based on a conductive polymer gel is disclosed. A nonconductive housing is provided having two separate chambers separated by a porous frit. The conductive polymer is held in one chamber and an electrolyte solution, used as a source of charged ions, is held in the second chamber. The ends of the housing a sealed with a flexible elastomer. The polymer gel is further provide with electrodes with which to apply an electrical potential across the gel in order to initiate an oxidation reaction which in turn drives anions across the porous frit and into the polymer gel, swelling the volume of the gel and simultaneously contracting the volume of the electrolyte solution. Because the two end chambers are sealed the flexible elastomer expands or contracts with the chamber volume change. By manipulating the potential across the gel the motion of the elastomer can be controlled to act as a "gate" to open or close a fluid channel and thereby control flow through that channel.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Microfluidic devices and methods of their manufacture
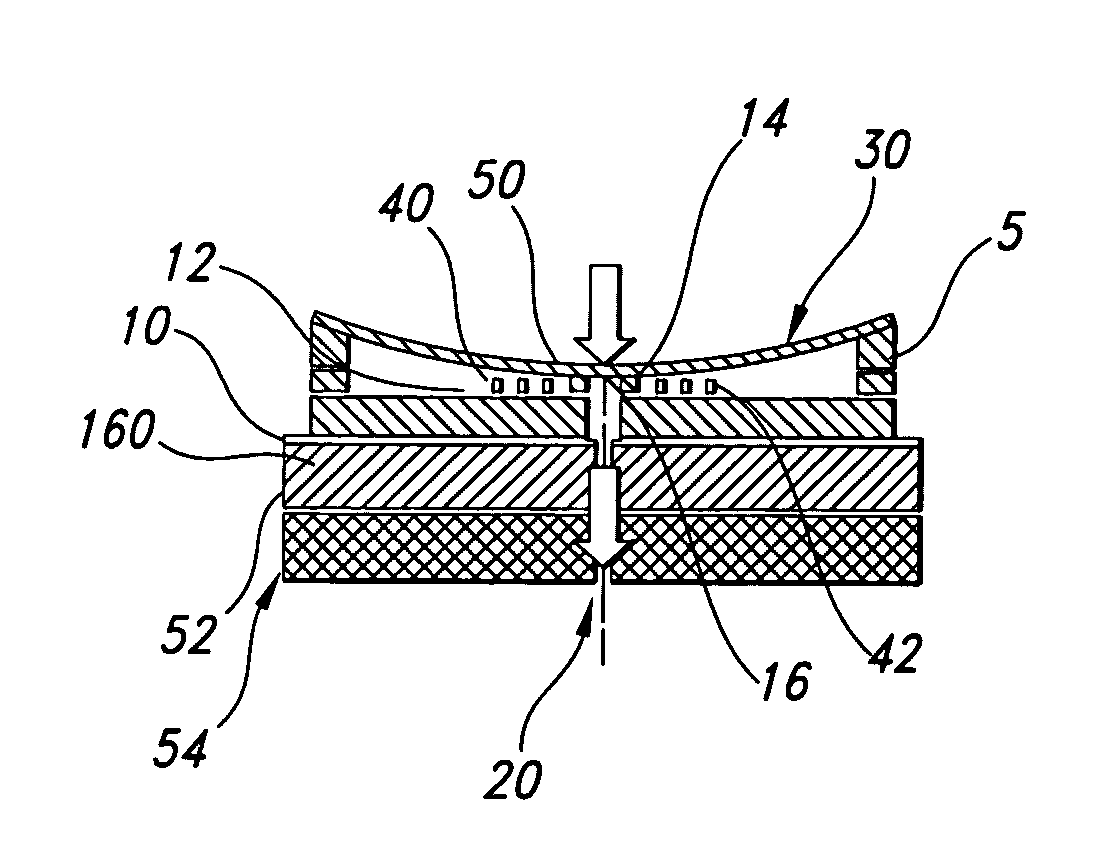
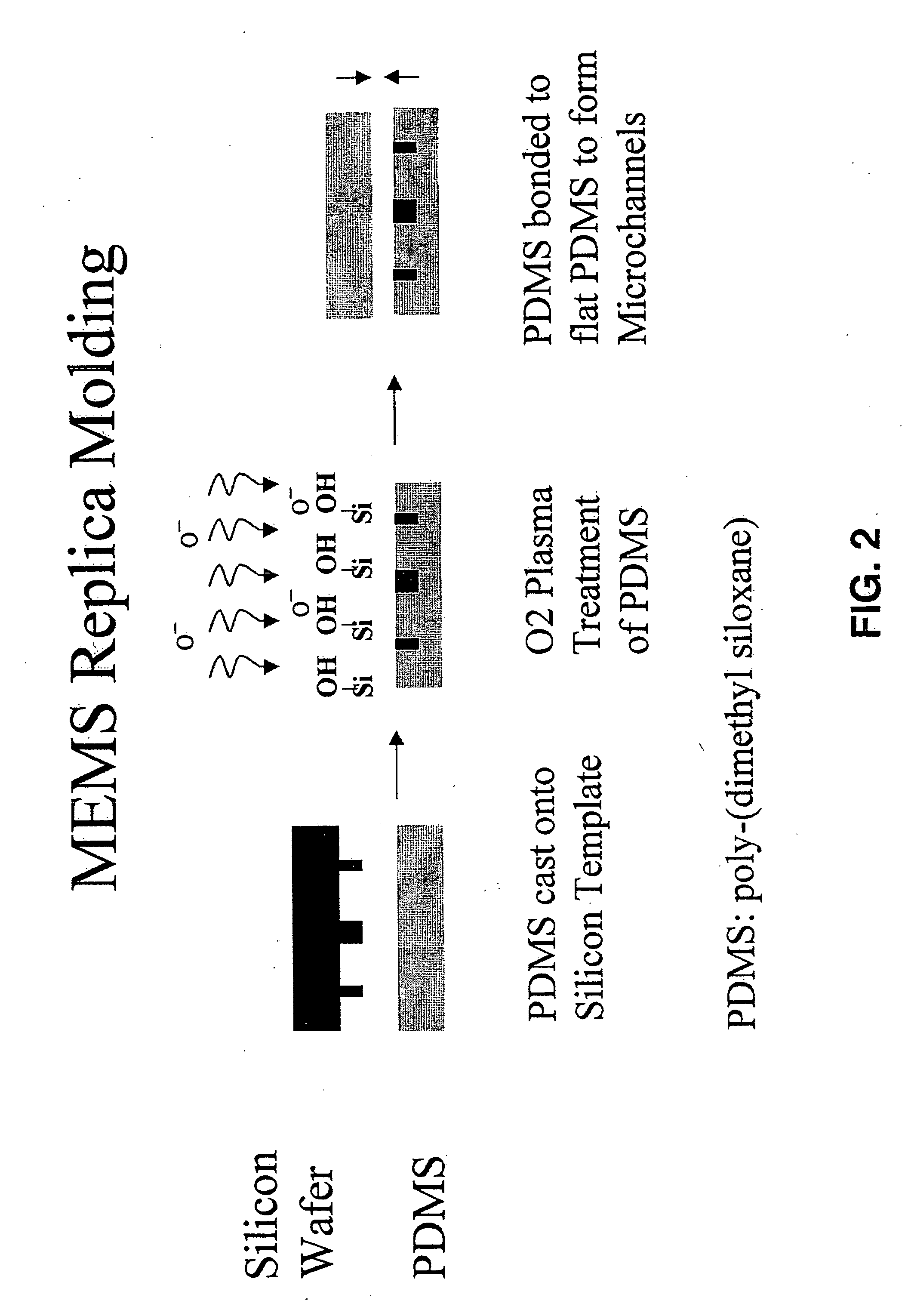
ActiveUS7069952B1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesCircuit elementsInterface layerAnodic bonding
The present invention provides multi-layered microfluidic devices comprising an interface layer between every two substrate layers. The interface layer simplifies the manufacturing process of the multi-layered devices because the interface may comprise a material suitable for etching whereby manufacturing of these devices is simplified to a great extent.The invention also provides methods of manufacturing the multi-layered devices wherein the devices may comprise substrates composed of non-similar materials that are bonded together by anodic bonding.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Surface features in microprocess technology
ActiveUS20070017633A1Enhance unit operationEasy to useFlow mixersCircuit elementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:VELOCYS CORPORATION
Ventilation System With System Status Display For Maintenance And Service Information
The disclosure describes a novel approach for displaying information on a ventilator system. The disclosure describes a novel respiratory system including a removable primary display and system status display. Further, the disclosure describes a novel method for displaying ventilator information and a novel method for controlling a ventilator system.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
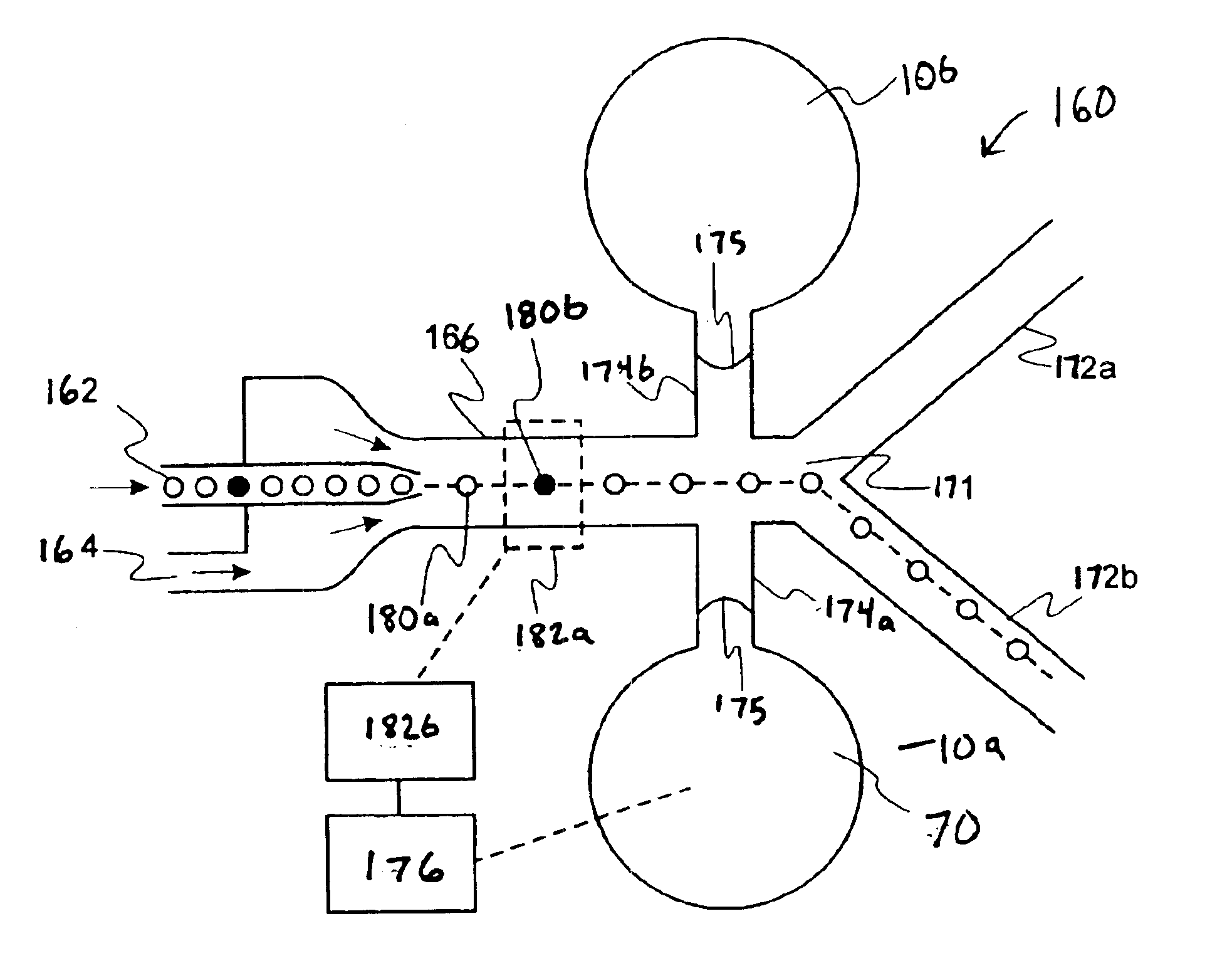
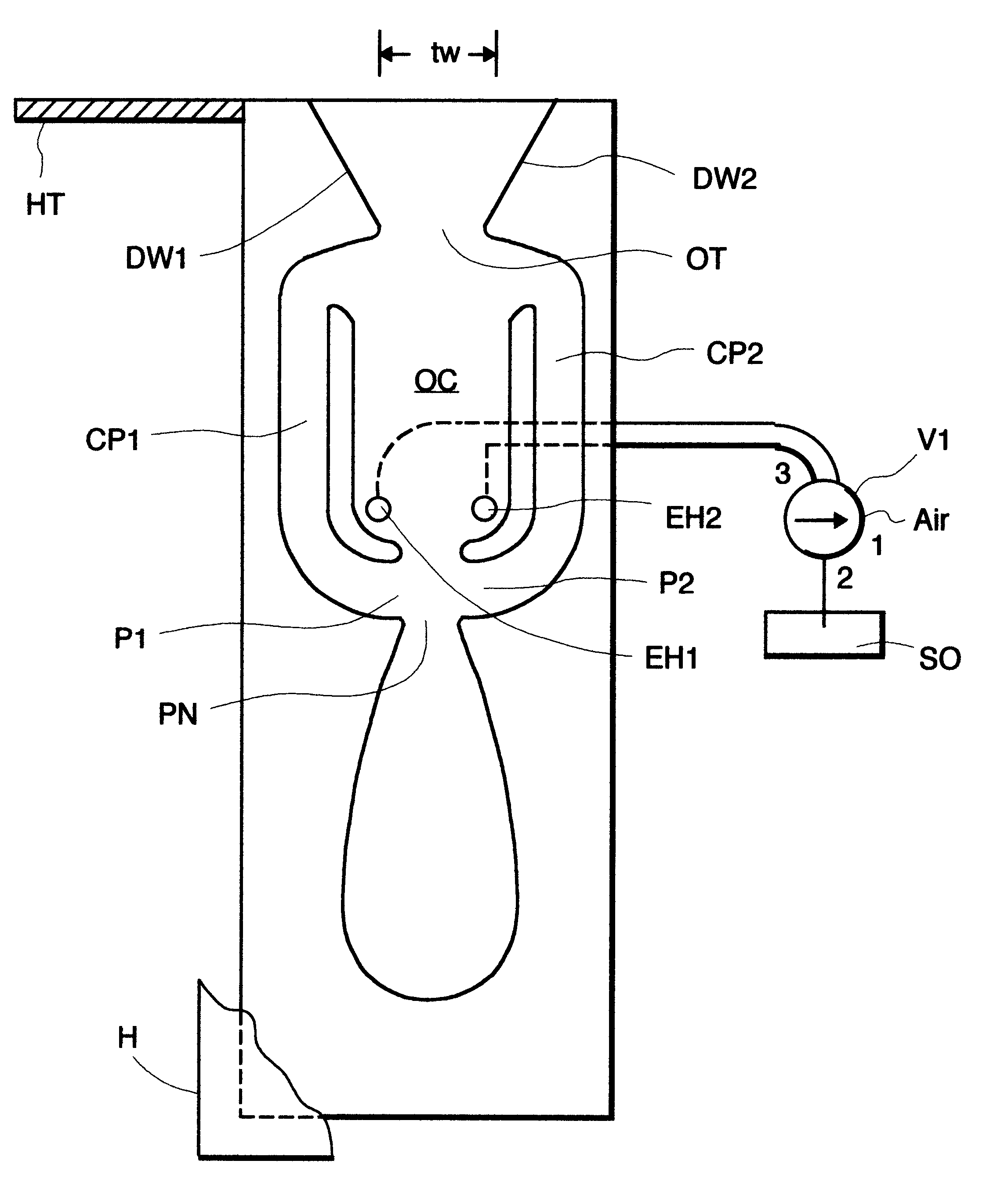
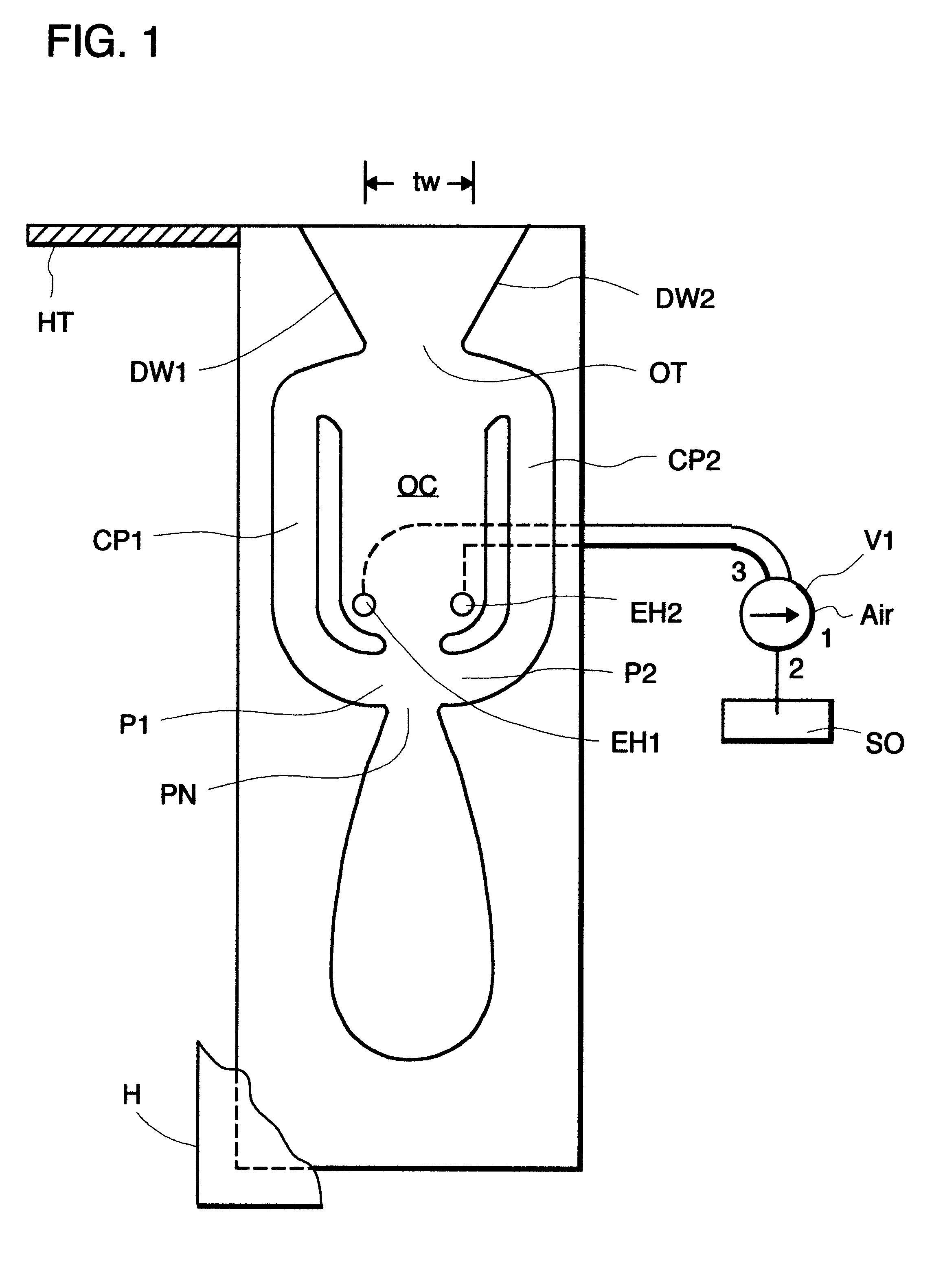
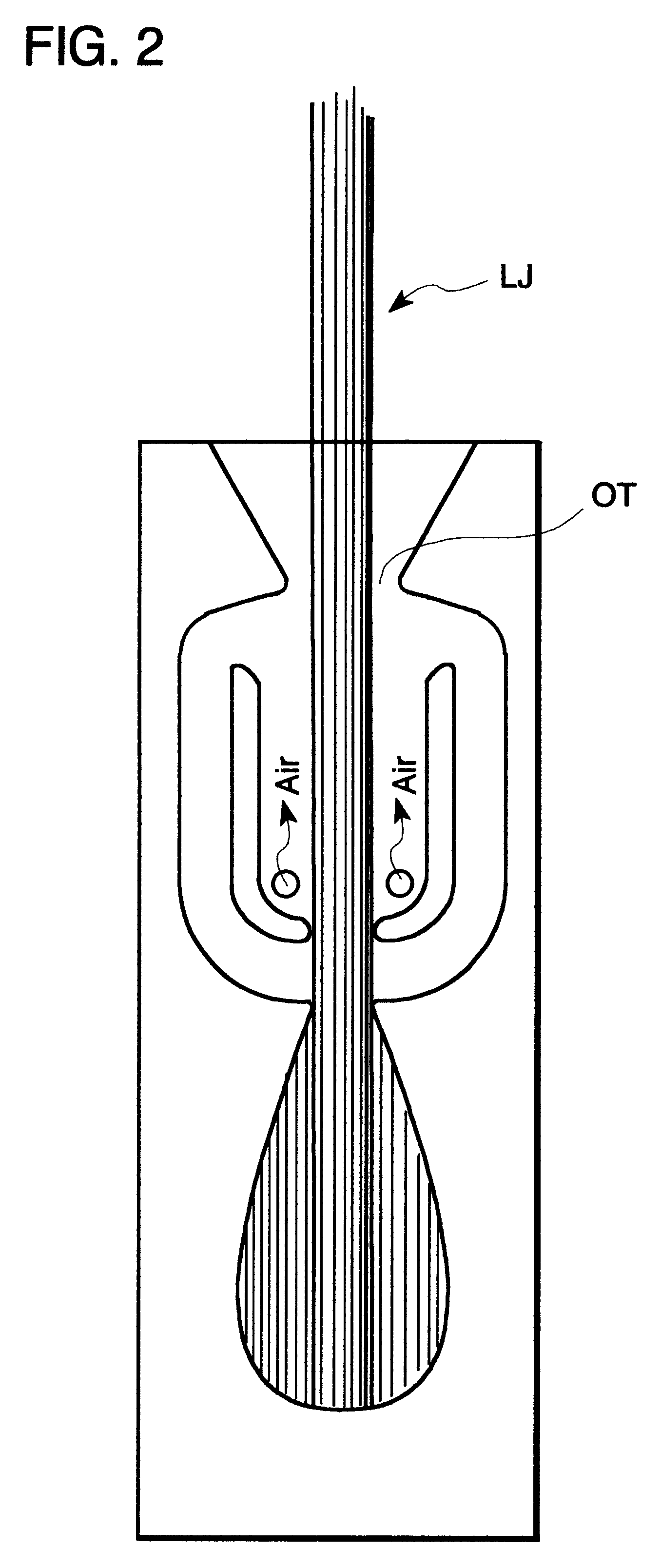
Fluidic nozzle with multiple operating modes
A fluidic nozzle having multiple operating modes comprising a fluidic oscillator circuit having an oscillation chamber having an upstream end and a downstream end and a power nozzle at the upstream end for introducing a jet of a liquid (water) into the oscillation chamber. An outlet throat at the downstream end has a width, which does not allow the oscillation circuit to fill up and start to oscillate without entrained liquid. A pair of control ports are at the upstream end of the oscillation chamber and a pair of feedback passages connect said control ports to downstream ends of said oscillation chamber adjacent said outlet throat. A pair of controllable entrainment holes are provided in the oscillation chamber at the upstream end and a valve opens and closes the entrainment holes, such that when the entrainment holes are open to air, air is entrained and the oscillator does not oscillate. Closing the air entrainment holes initiates oscillation and the issuance of a sweeping liquid jet through the outlet throat.
Owner:DLHBOWLES INC
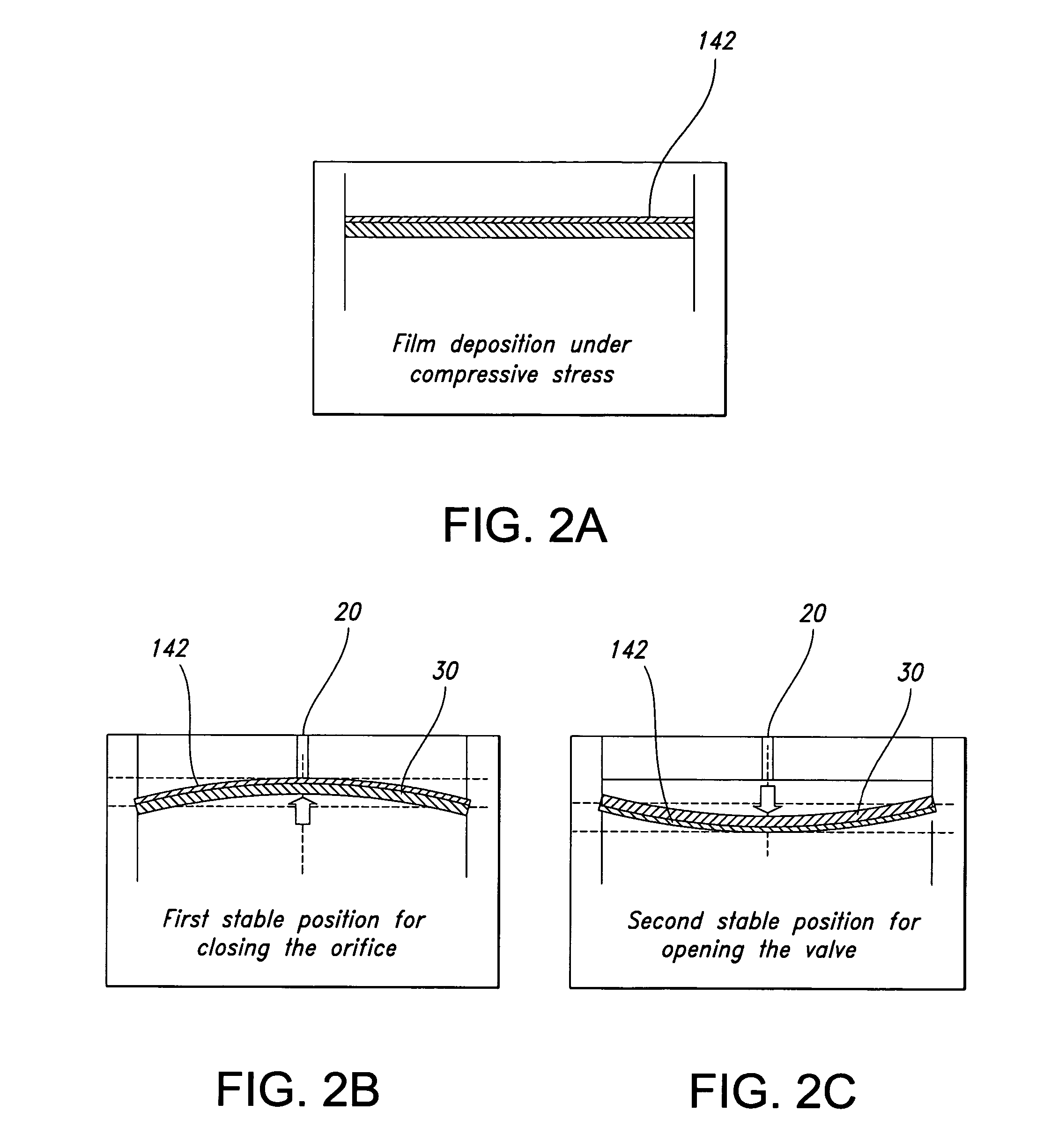
Single substrate electromagnetic actuator
InactiveUS20050116798A1Improve dynamic operation of valveLower average currentValve arrangementsAdditive manufacturing apparatusManufacturing technologyEngineering
A microvalve which utilizes a low temperature (<300° C.) fabrication process on a single substrate. The valve uses buckling and an electromagnetic actuator to provide a relatively large closing force and lower power consumption. A buckling technique of the membrane is used to provide two stable positions for the membrane, and to reduce the power consumption and the overall size of the microvalve. The use of a permanent magnet is an alternative to the buckled membrane, or it can be used in combination with the buckled membrane, or two sets of micro-coils can be used in order to open and close the valve, providing the capability for the valve to operate under normally opened or normally closed conditions. Magnetic analysis using ANSYS 5.7 shows that the addition of Orthonol between the coils increases the electromagnetic force by more than 1.5 times. At a flow rate of 1 mL / m, the pressure drop is <100 Pa. The maximum pressure tested was 57 kPa and the time to open or close the valve in air is under 100 ms. This results in an estimated power consumption of 0.1 mW.
Owner:AIR FORCE THE US SEC THE +1
Ventilation System With Removable Primary Display
ActiveUS20110132361A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDisplay deviceComputer science
The disclosure describes a novel approach for displaying information on a ventilator system. The disclosure describes a novel respiratory system including a removable primary display and system status display. Further, the disclosure describes a novel method for displaying ventilator information and a novel method for controlling a ventilator system.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
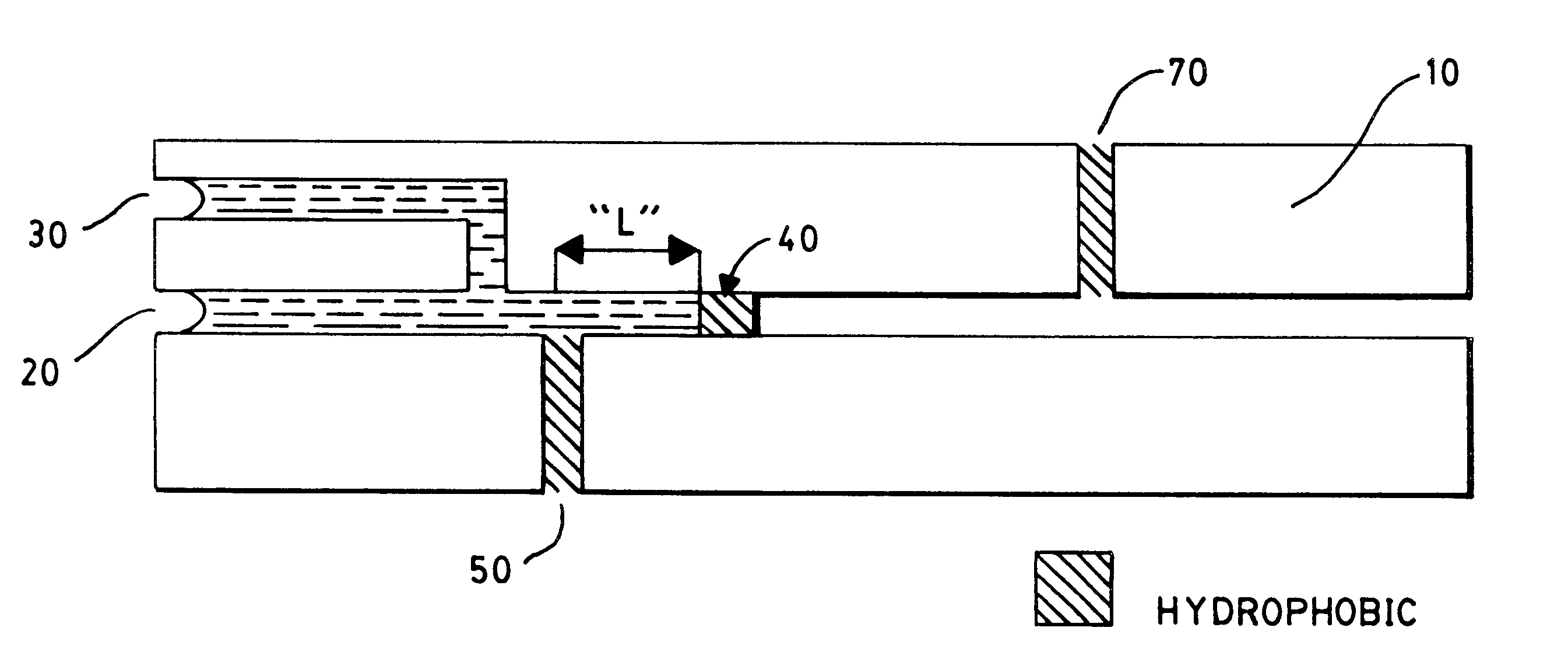
Making a two-phase liquid/liquid or gas system in microfluidics
The invention relates to a microfluidic device for making a liquid / liquid or gas biphasic system using a first liquid or a gas and a second liquid, non-miscible with each other, the device having a first hydrophobic surface for the second liquid, the first liquid forming a layer (6) on said first hydrophobic surface. The device comprises means for introducing a drop (7) of the second liquid into the layer of first liquid or gas and in contact with said first hydrophobic surface, and means for displacing the drop on said first hydrophobic surface along a determined path, the device having on the path of the drop, at least one wetting defect causing, upon passing of the drop over this defect, failure of the triple line of contact of the drop on the first hydrophobic surface and inclusion of first liquid (8) or gas into the drop.The invention also relates to the associated method.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method of setting and actuating a multi-stable micro valve and adjustable micro valve
InactiveUS6926246B2Less sensitive to blockageOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCircuit elementsShape-memory alloyEngineering
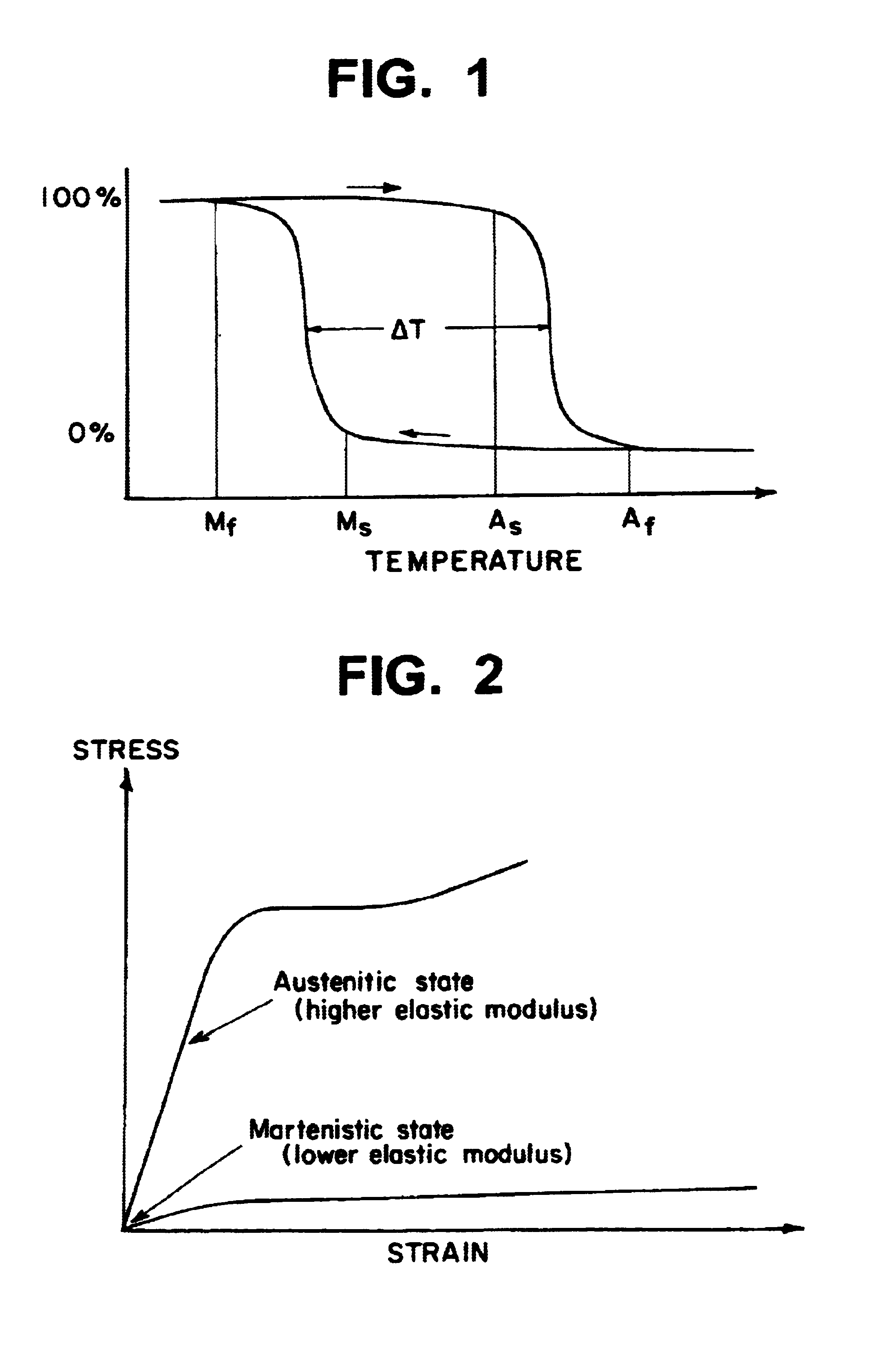
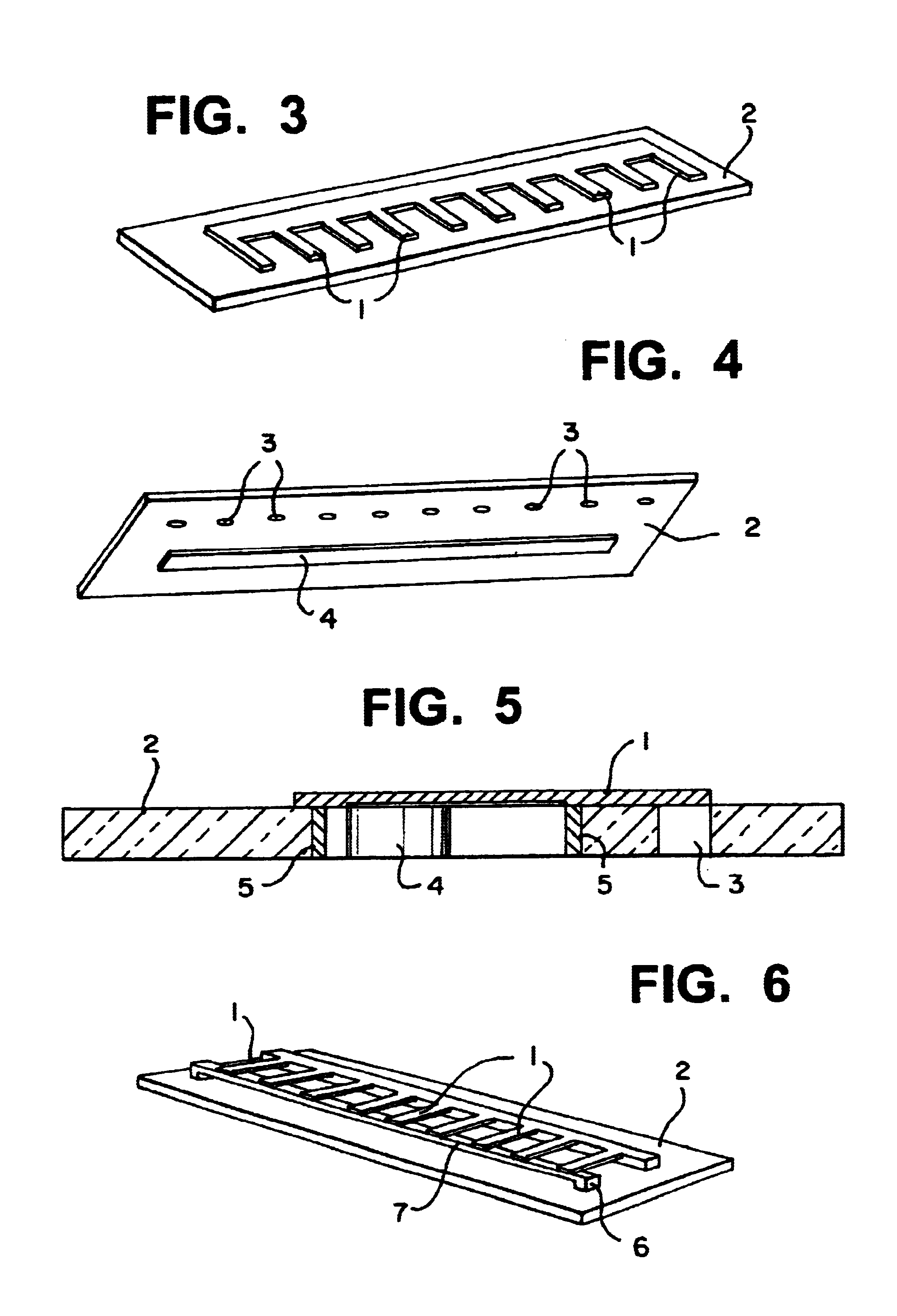
A micro valve and a method for setting or actuating a micro valve for use in fluidic applications includes cooling an array of actuating members made of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) material. The SMA material is cooled to a temperature equal to or below the temperature at which a transformation from austenitic to martensitic state occurs so that the entire array of SMA actuating members is either fully or partially in the martensitic state. At least one of the actuating member is selected to correspond to a pre-determined opening pressure or flow resistance. Each of the actuating members are heated individually, except the previously selected one, to a temperature equal to or above the temperature at which a transformation from the martensitic state to the austensitic state occurs.
Owner:MEDOS
Three dimensional construct for the design and fabrication of physiological fluidic networks
ActiveUS20060136182A1Increase cell densityIncrease the number ofMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusEngineeringSmall vessel
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com