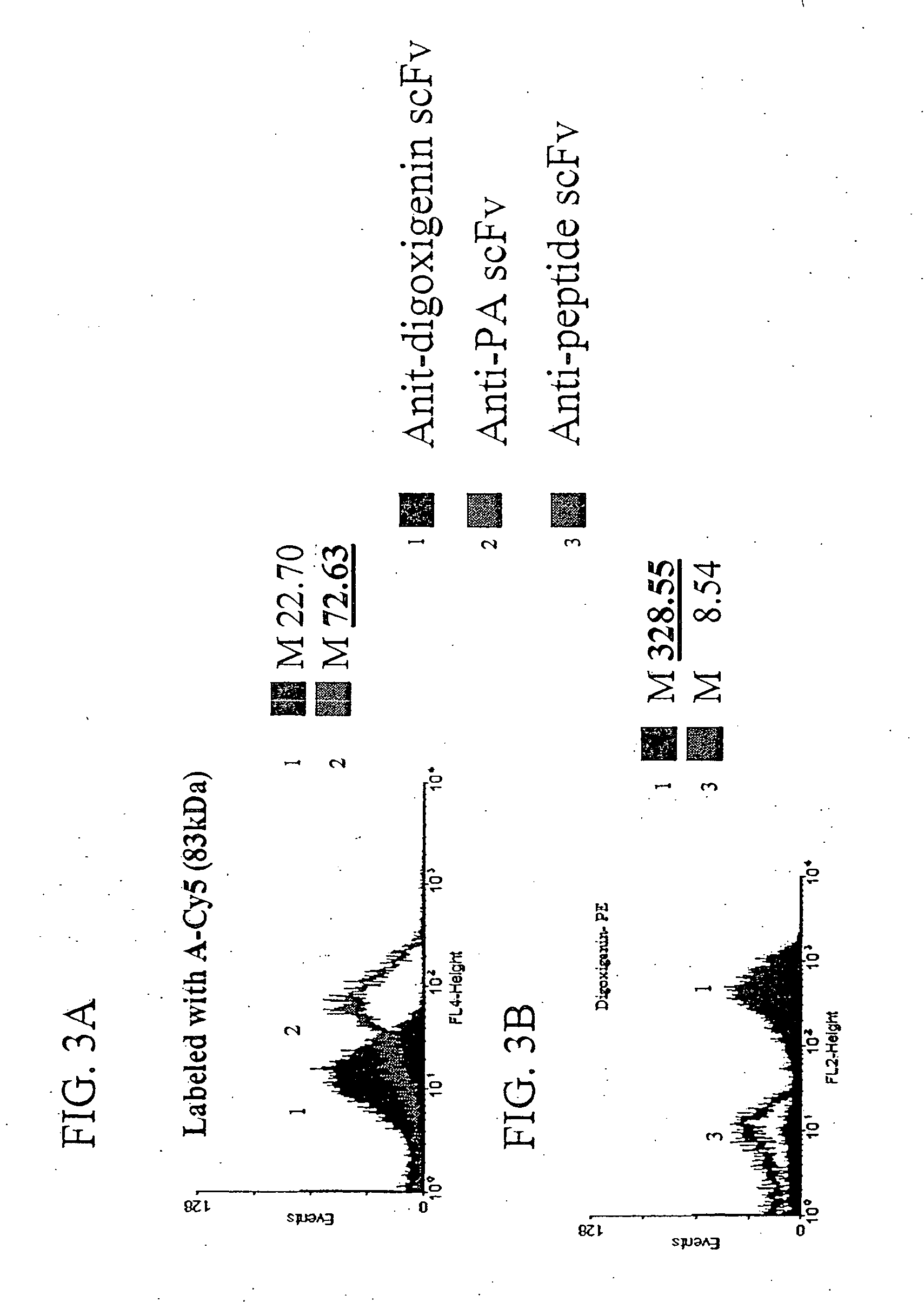
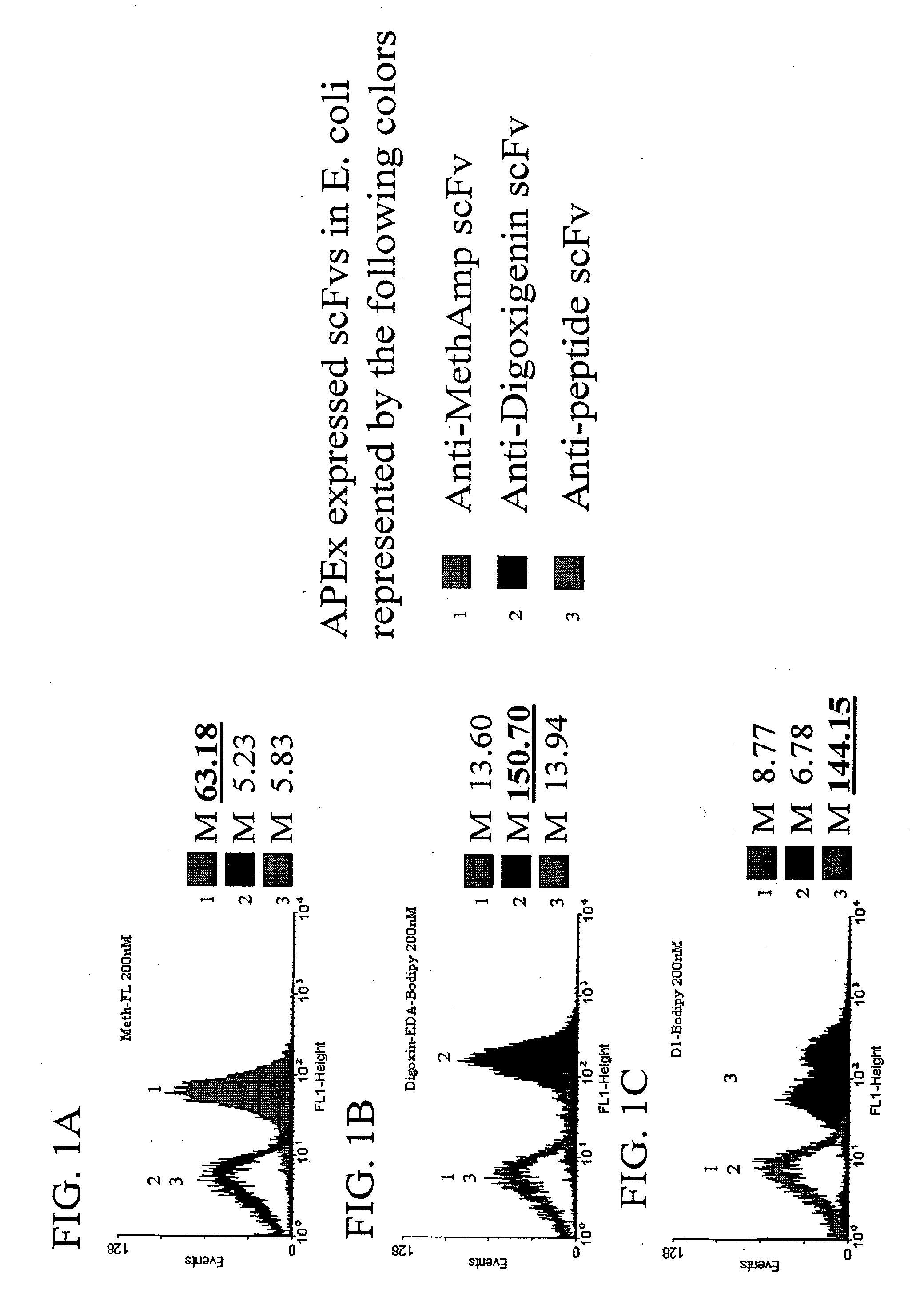
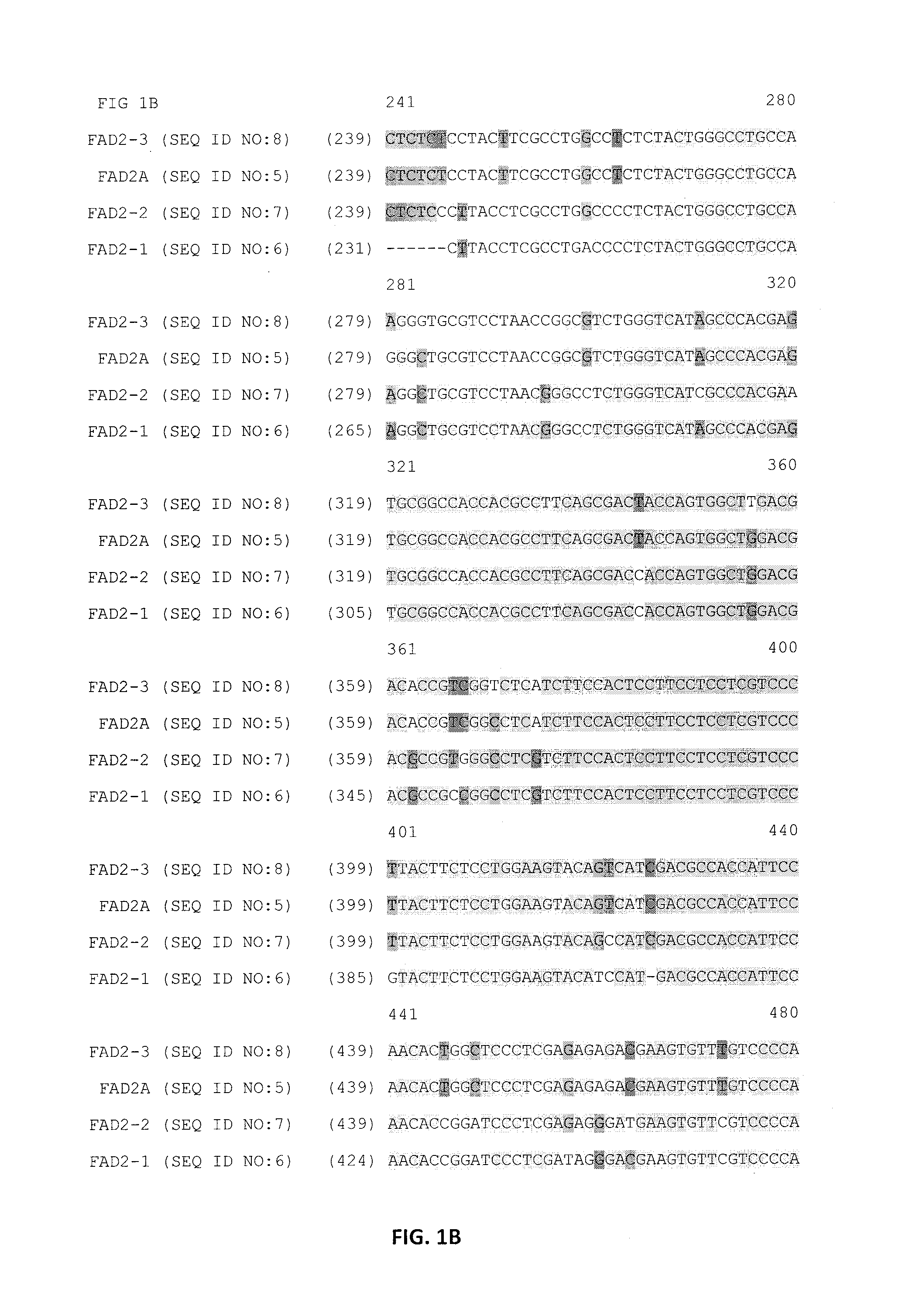
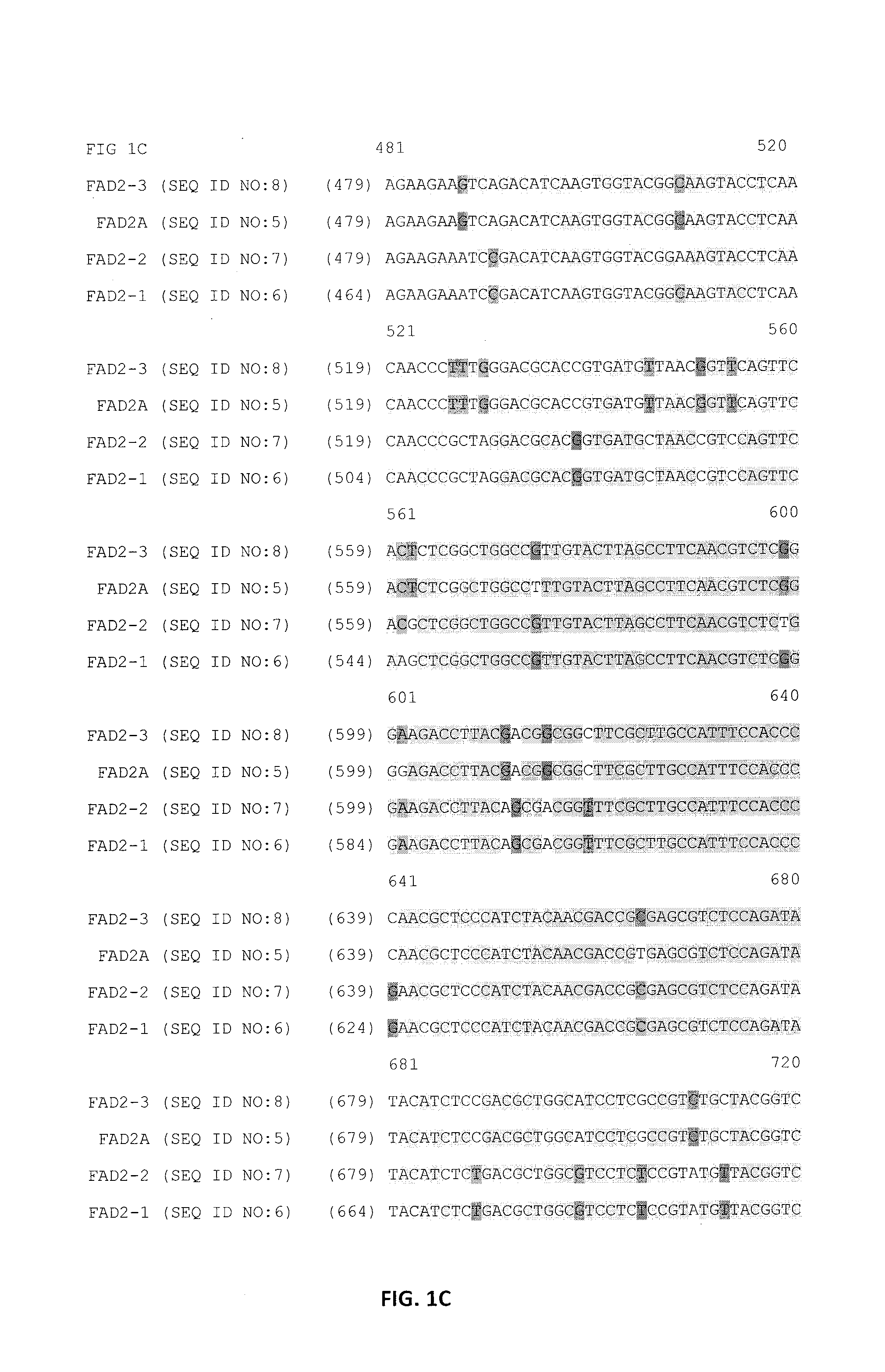
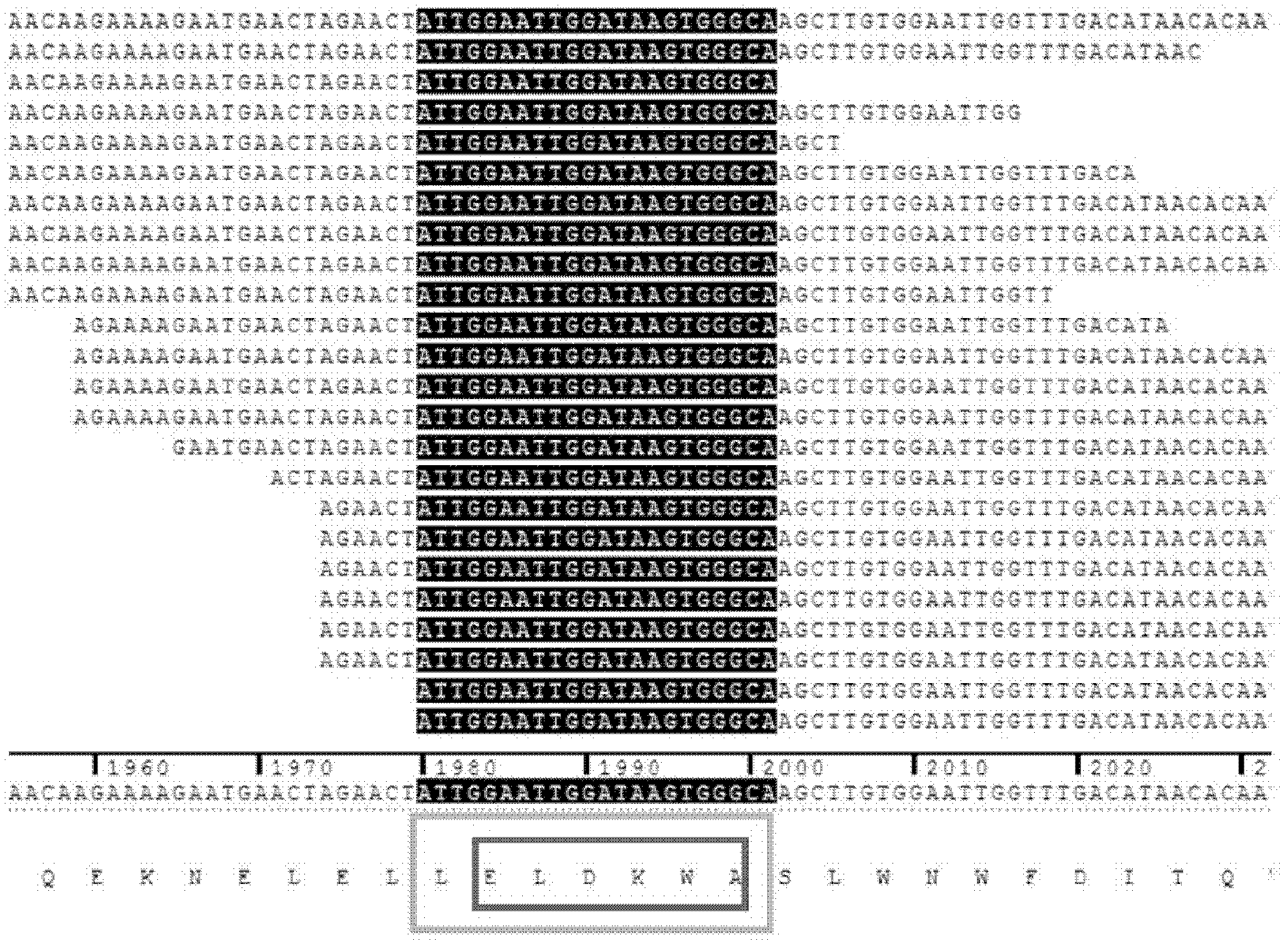Patents
Literature
51 results about "Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pulsed laser triggered high speed microfluidic switch and applications in fluorescent activated cell sorting
ActiveUS20110030808A1Improve compatibilityValve arrangementsCircuit elementsFluorescenceFluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting
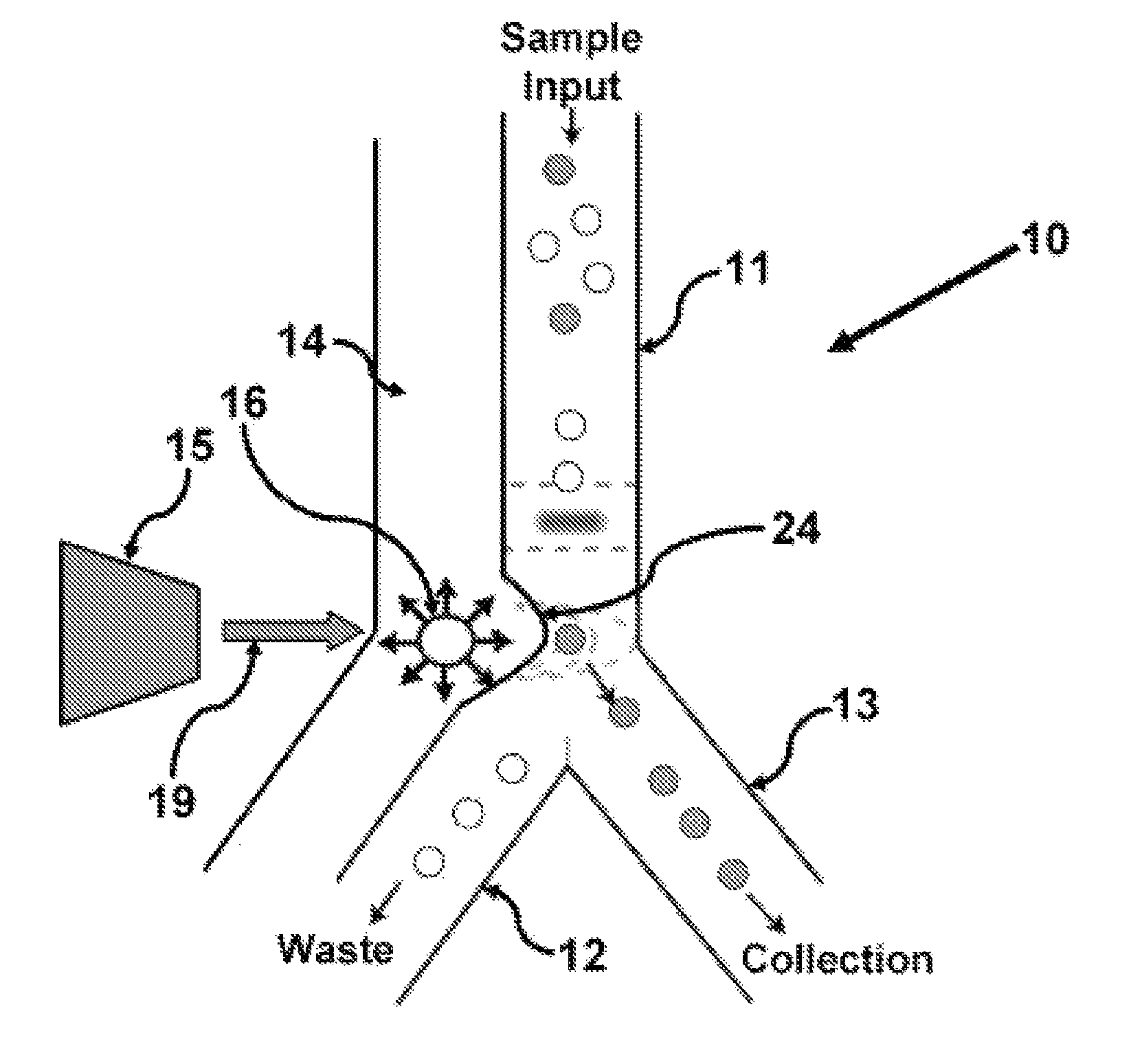
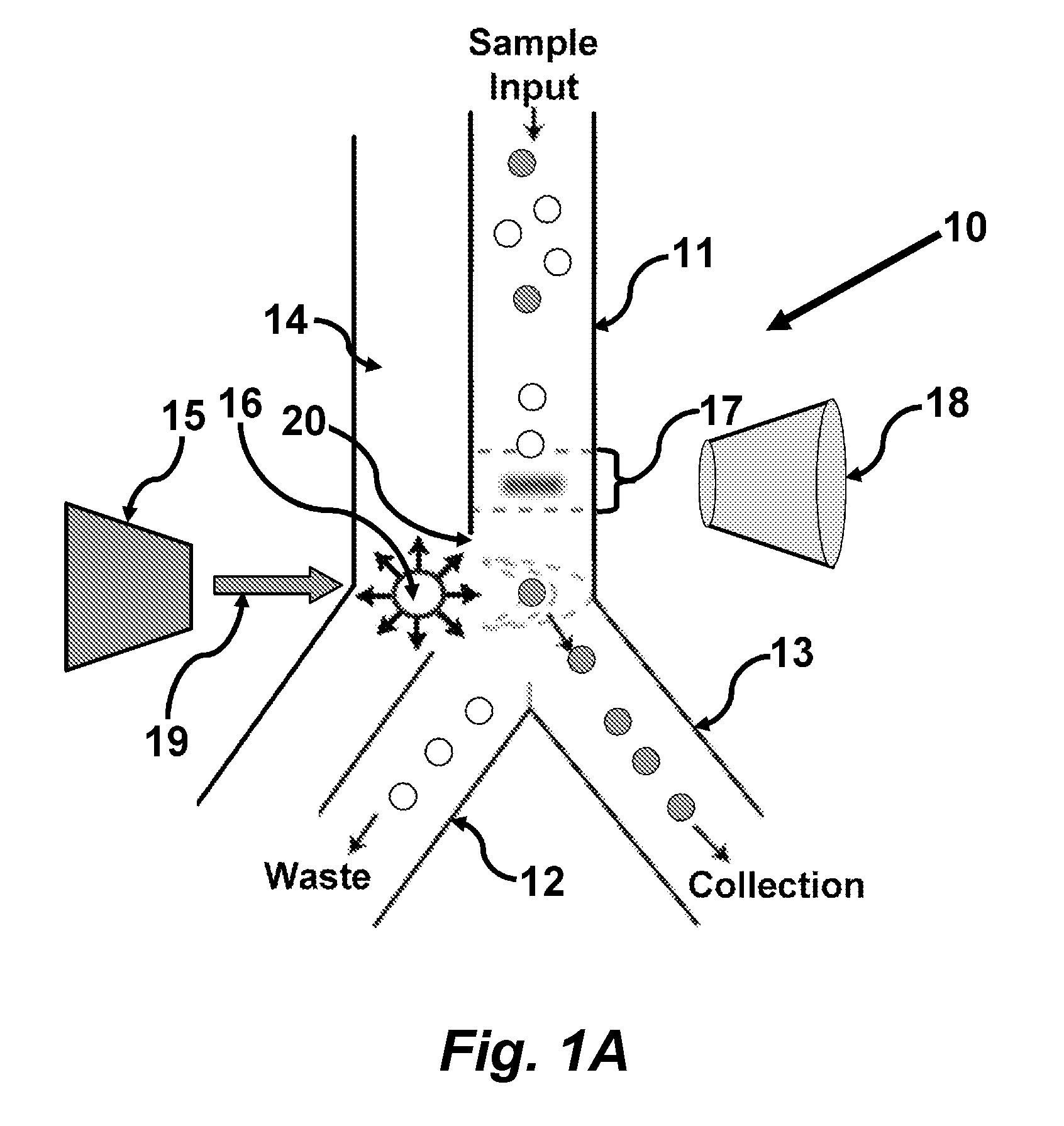
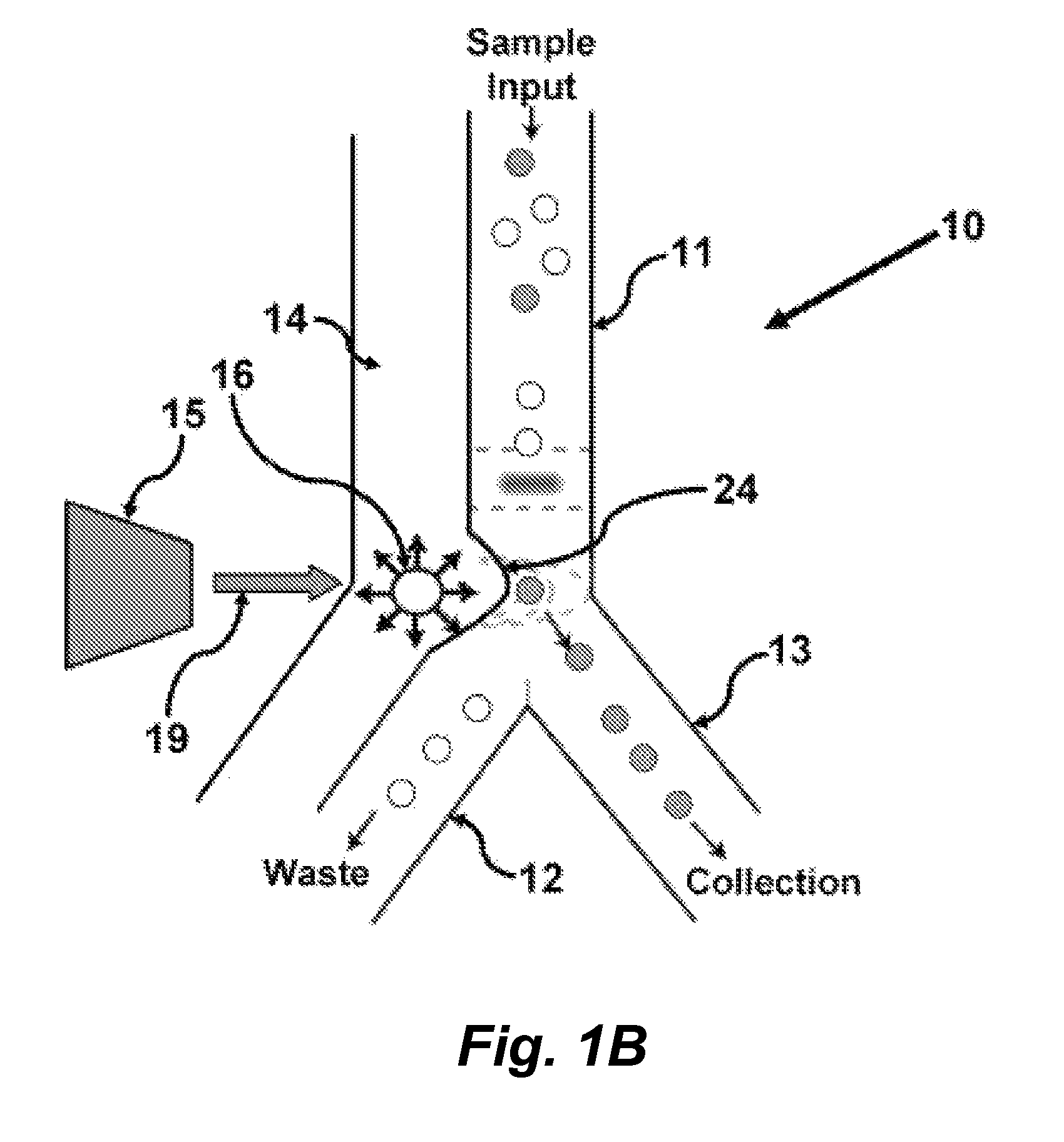
In certain embodiments this invention provides a pulsed-laser triggered microfluidic switching mechanism that can achieve a switching time of 70 μs. This switching speed is two orders of magnitude shorter than that of the fastest switching mechanism utilized in previous μFACS.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
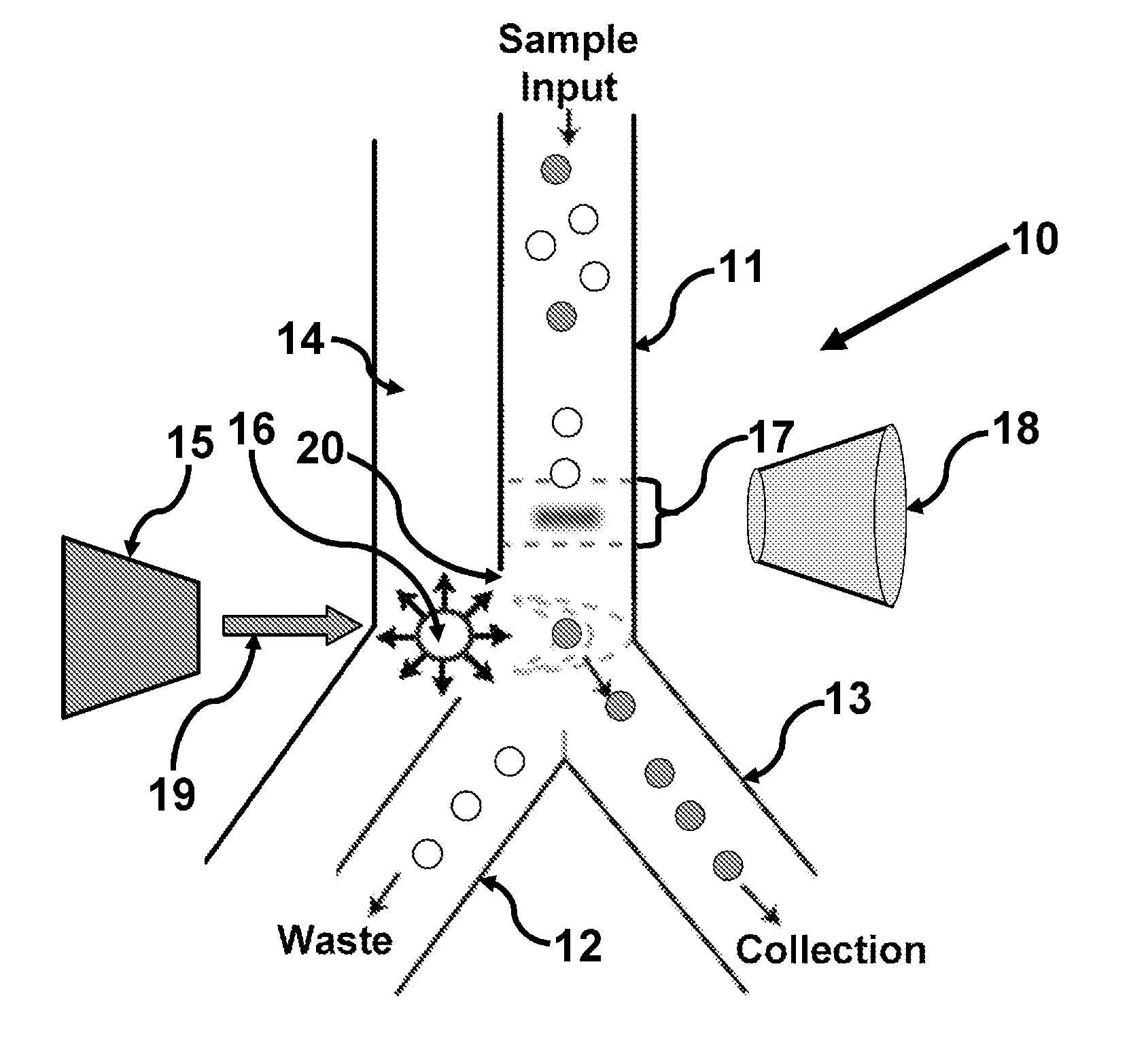
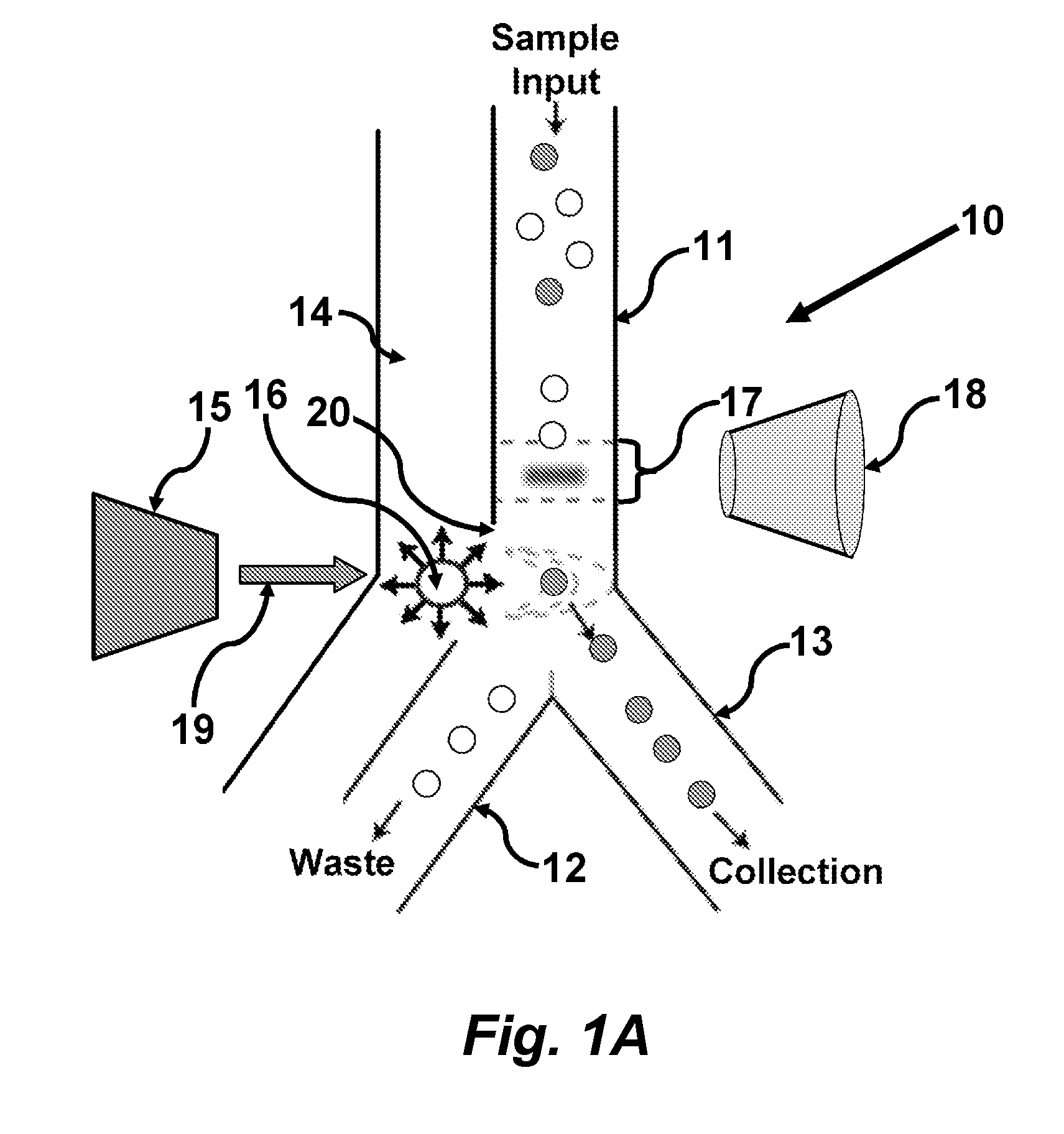
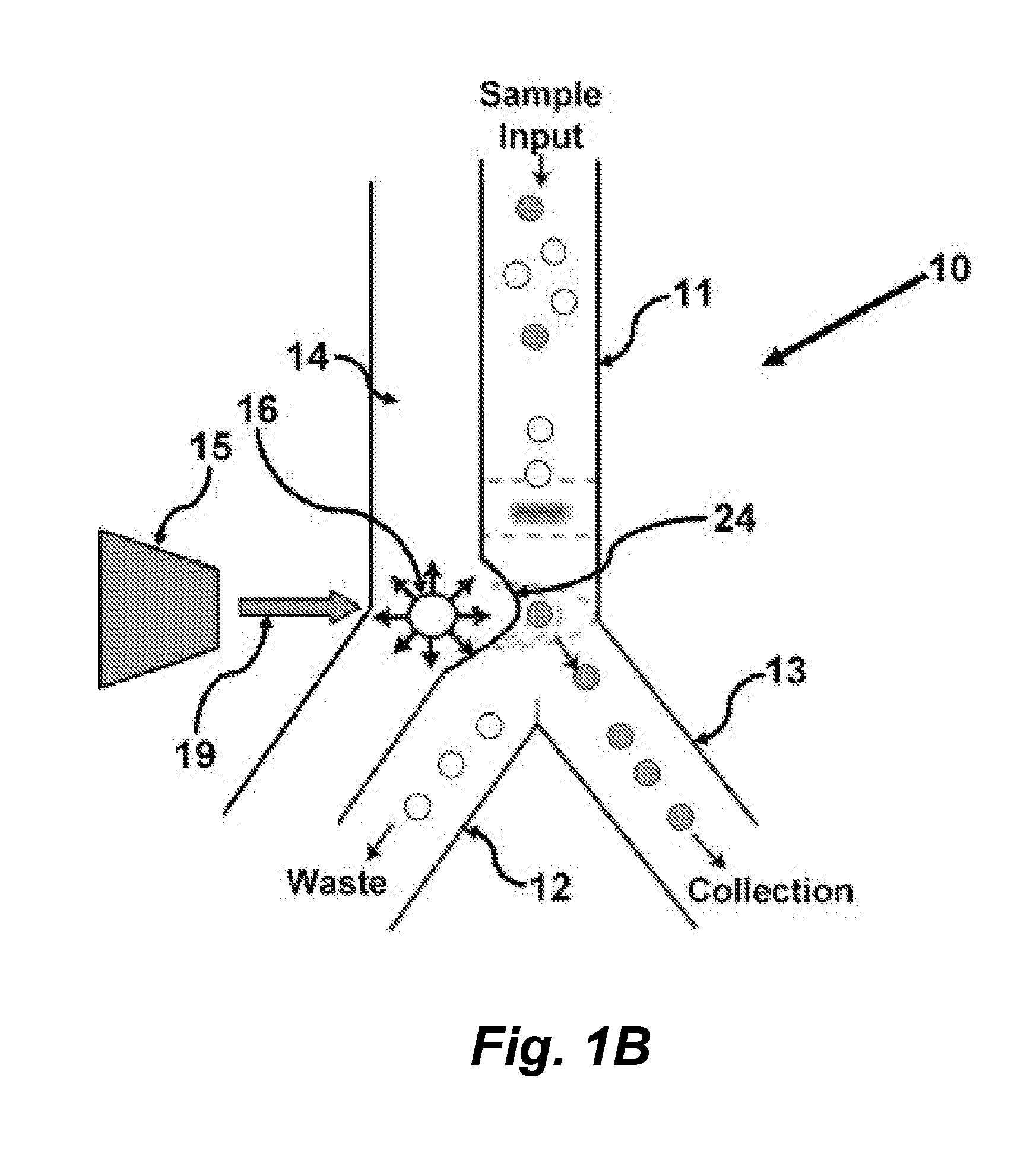
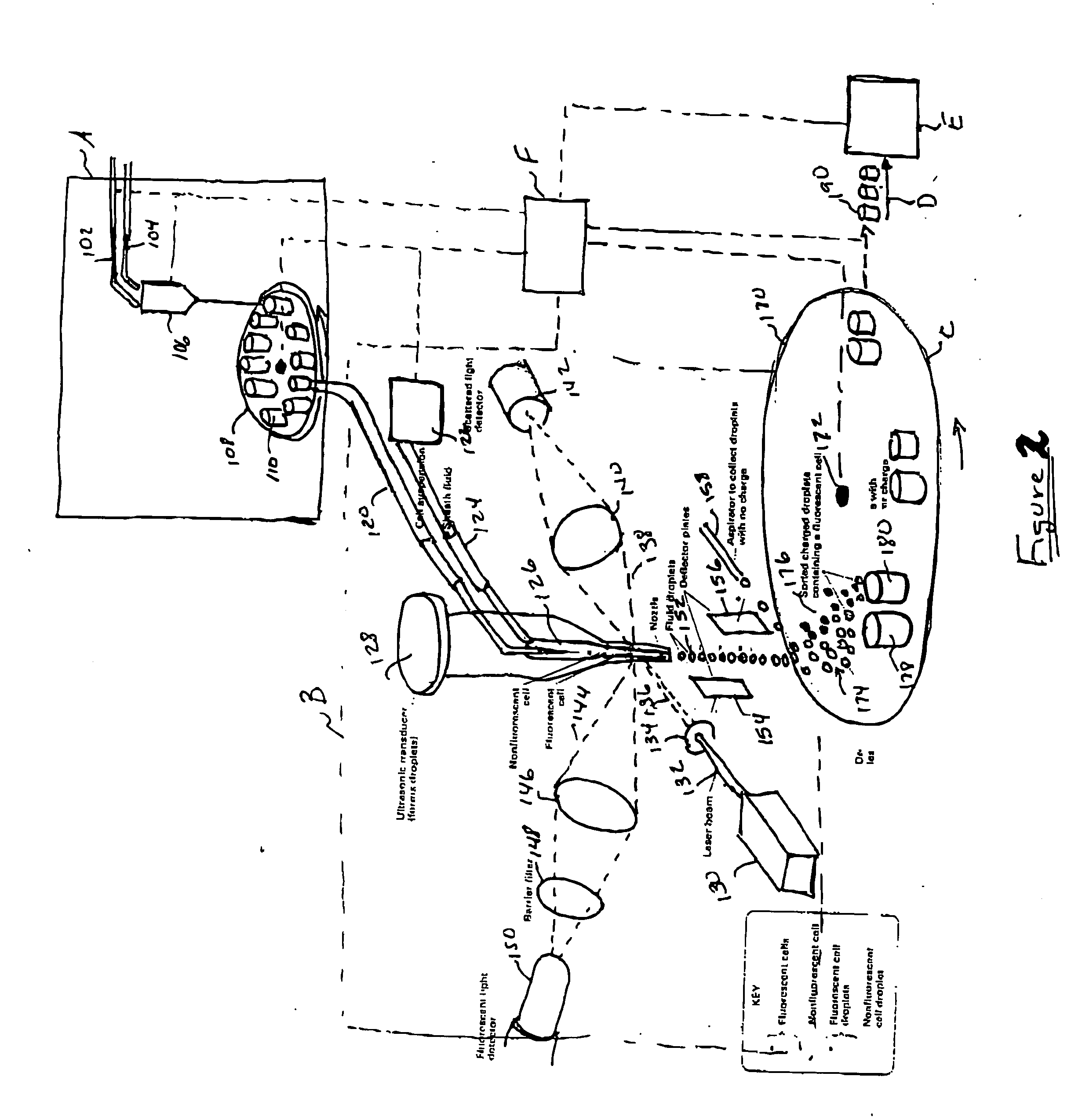
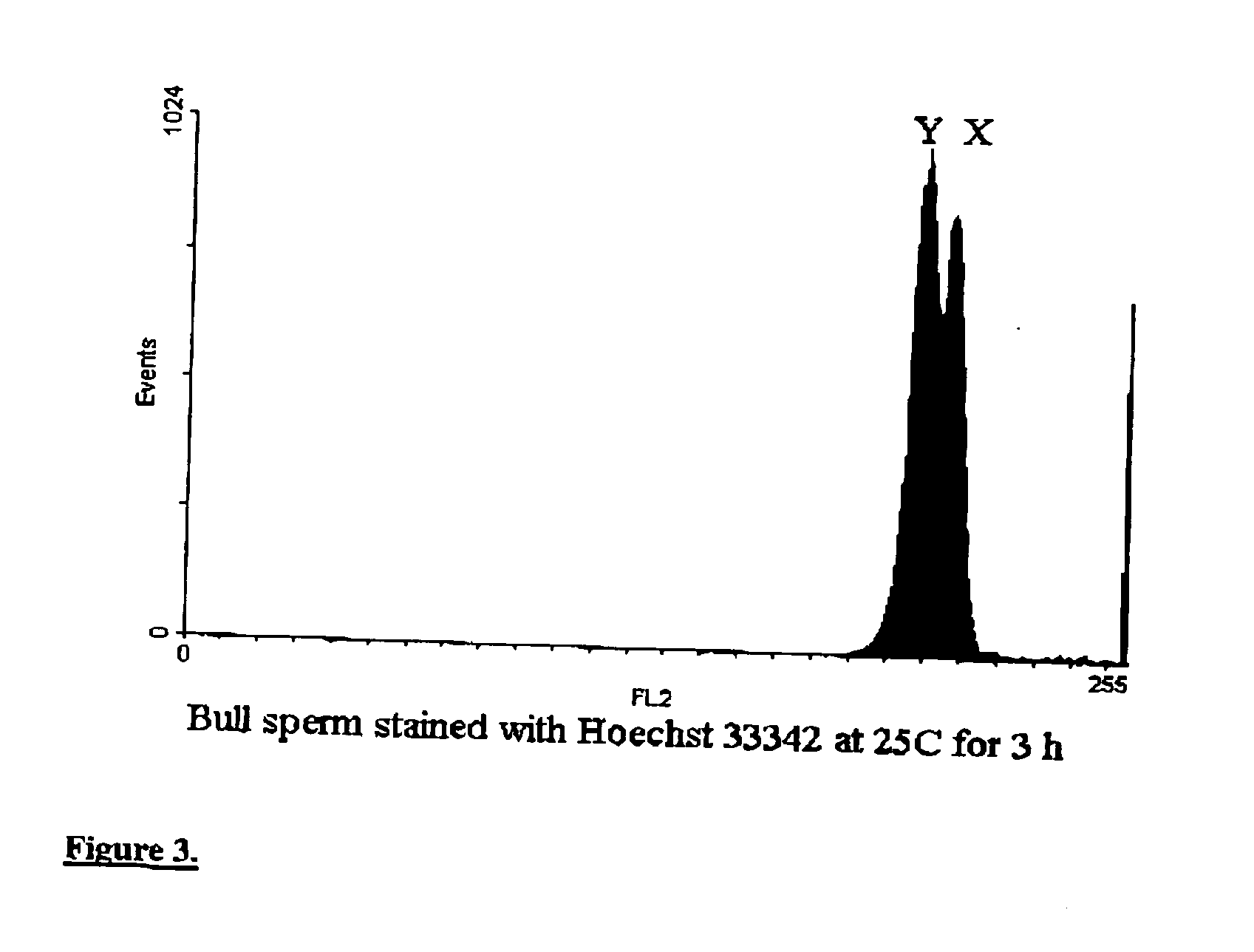
Methods and apparatus for producing gender enriched sperm
InactiveUS20050064383A1Shorten the time to eliminateIncrease temperatureMicrobiological testing/measurementMammal material medical ingredientsVital stainPhysiology
Sperm in semen are sorted by fluorescence-activated cell sorting into gender-enriched populations enriched in X-chromosome or Y-chromosome bearing sperm by use of a fluorescent quantitative DNA-binding vital stain.
Owner:BASHKIN JAMES K +2
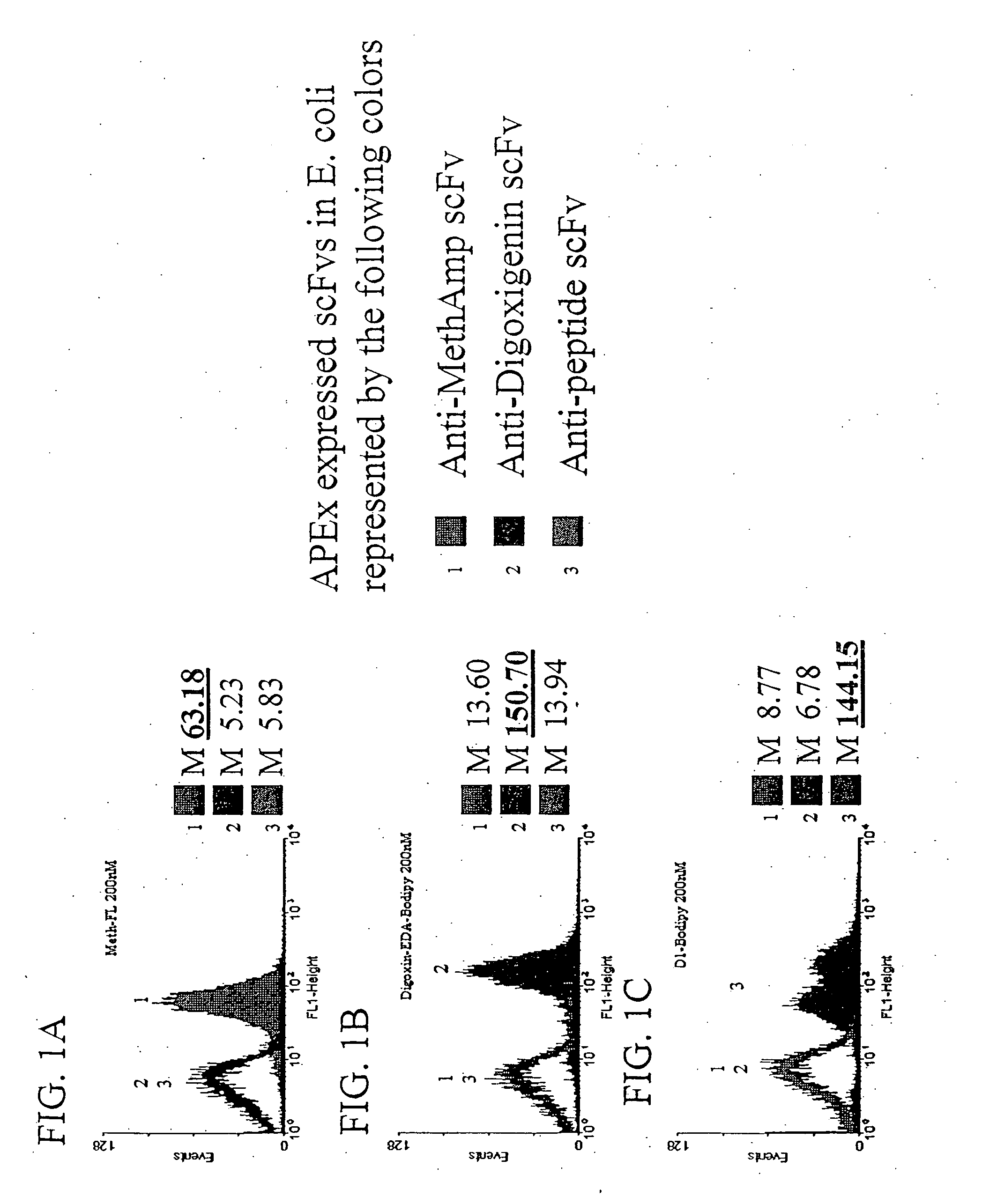
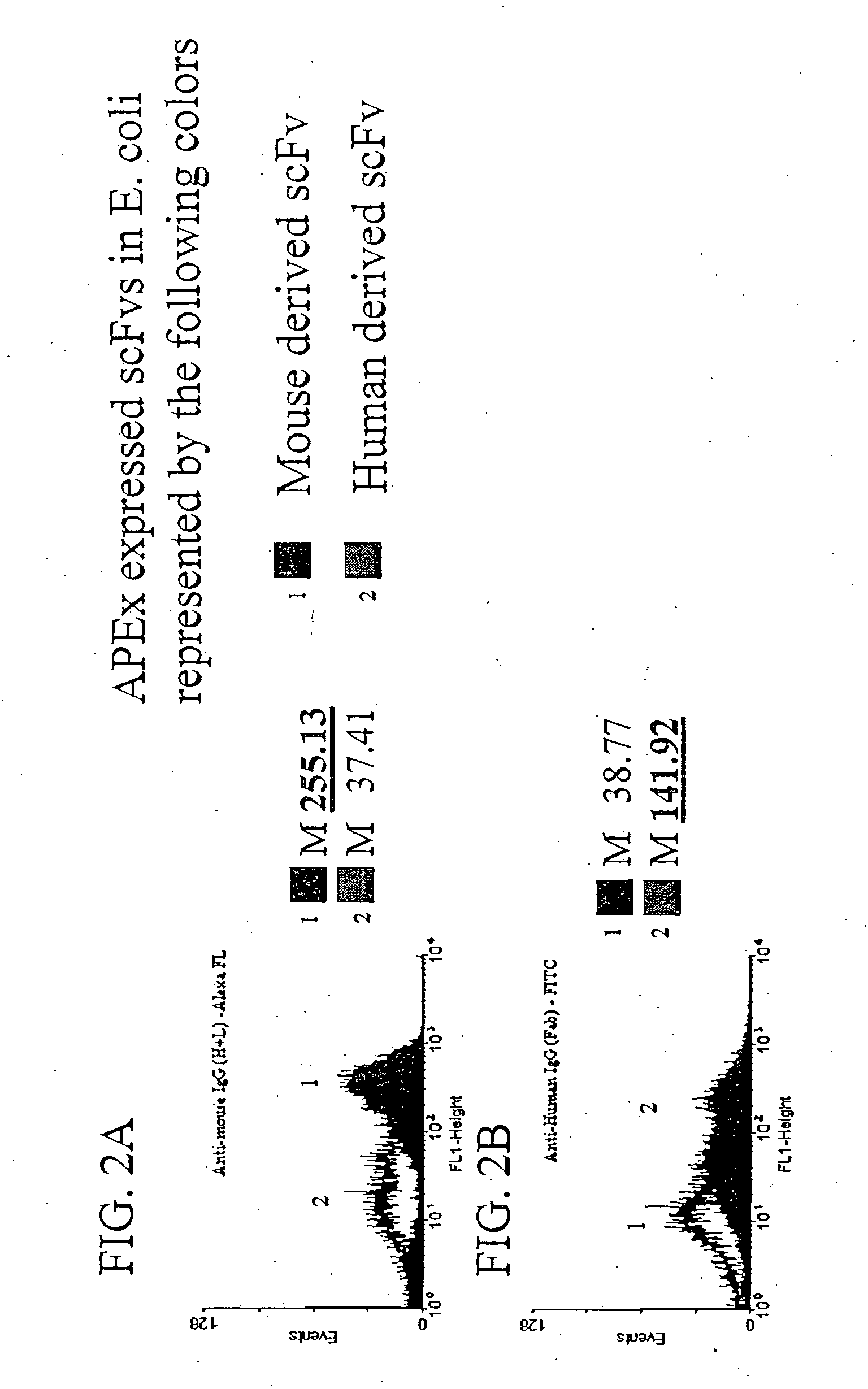
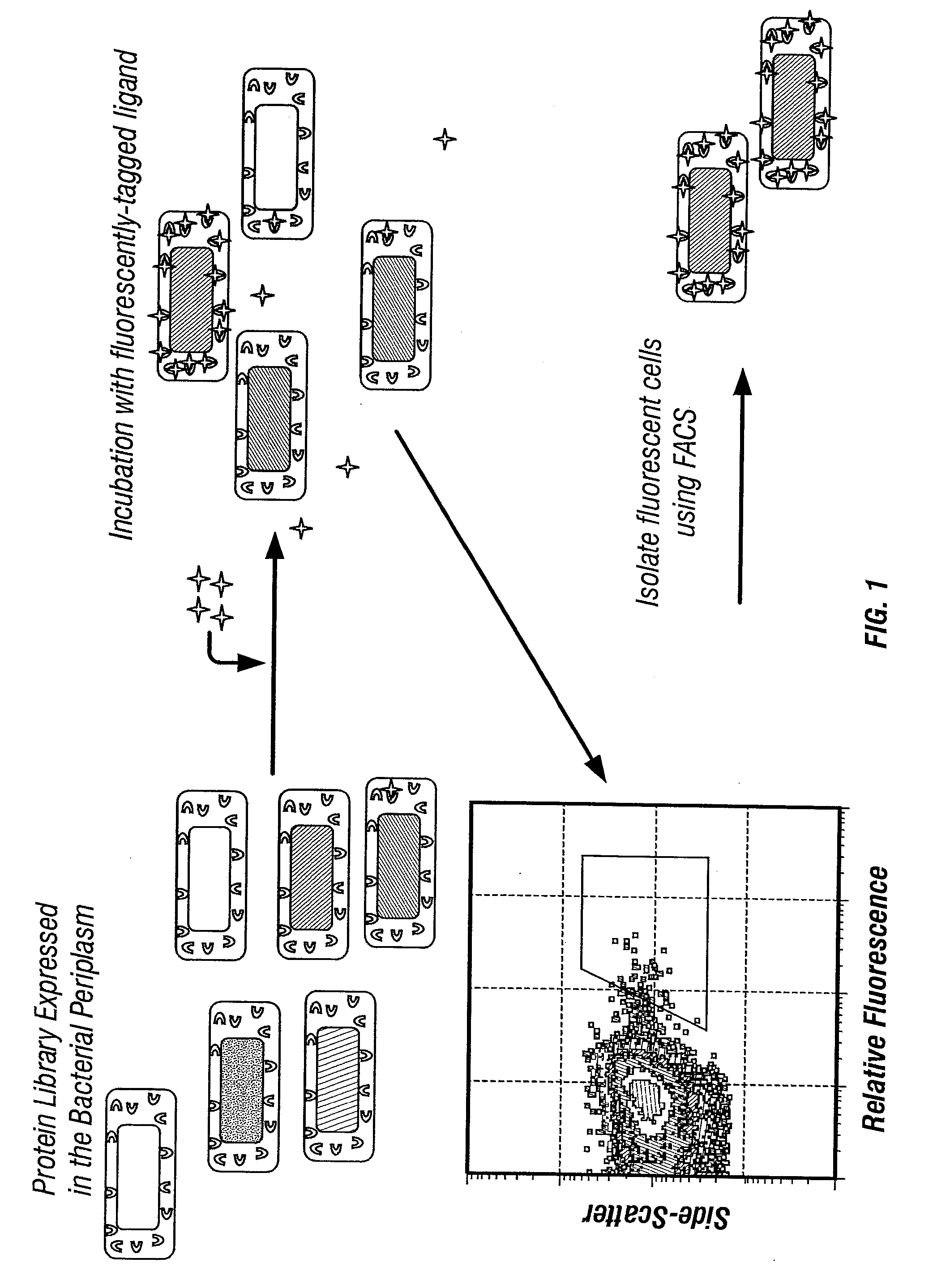
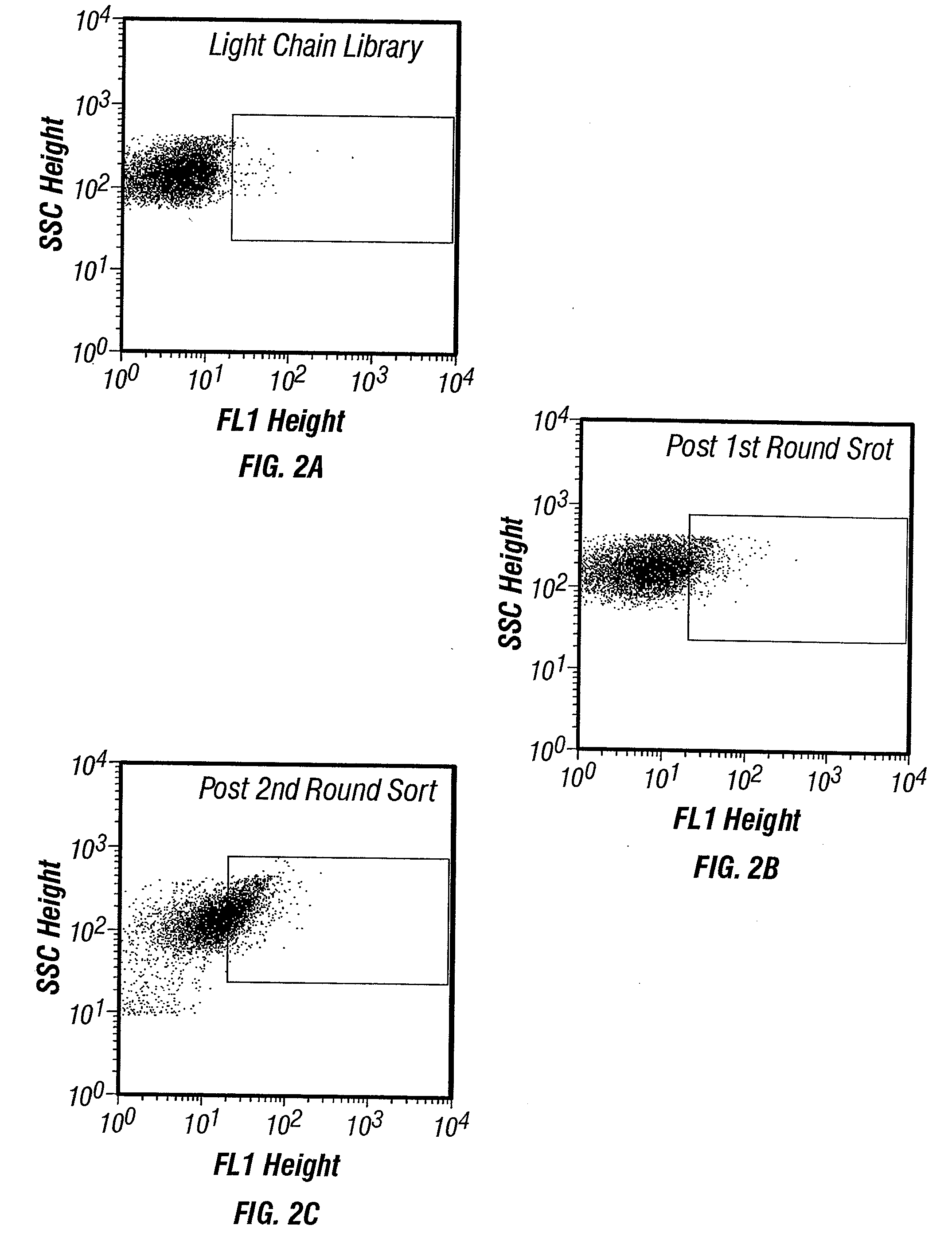
Combinatorial protein library screening by periplasmic expression
InactiveUS20060029947A1Improve breathabilityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaScreening techniquesSurface expression
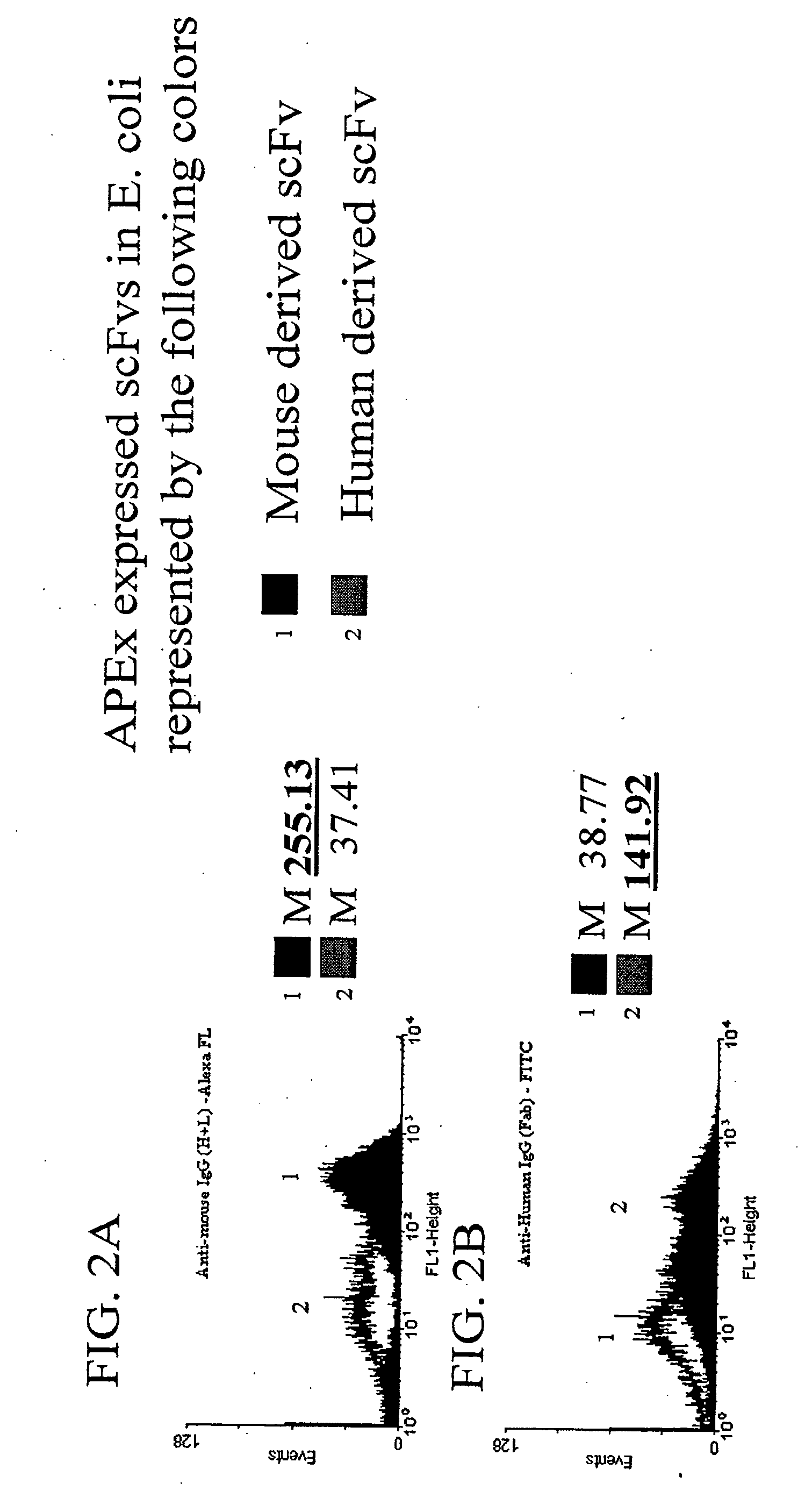
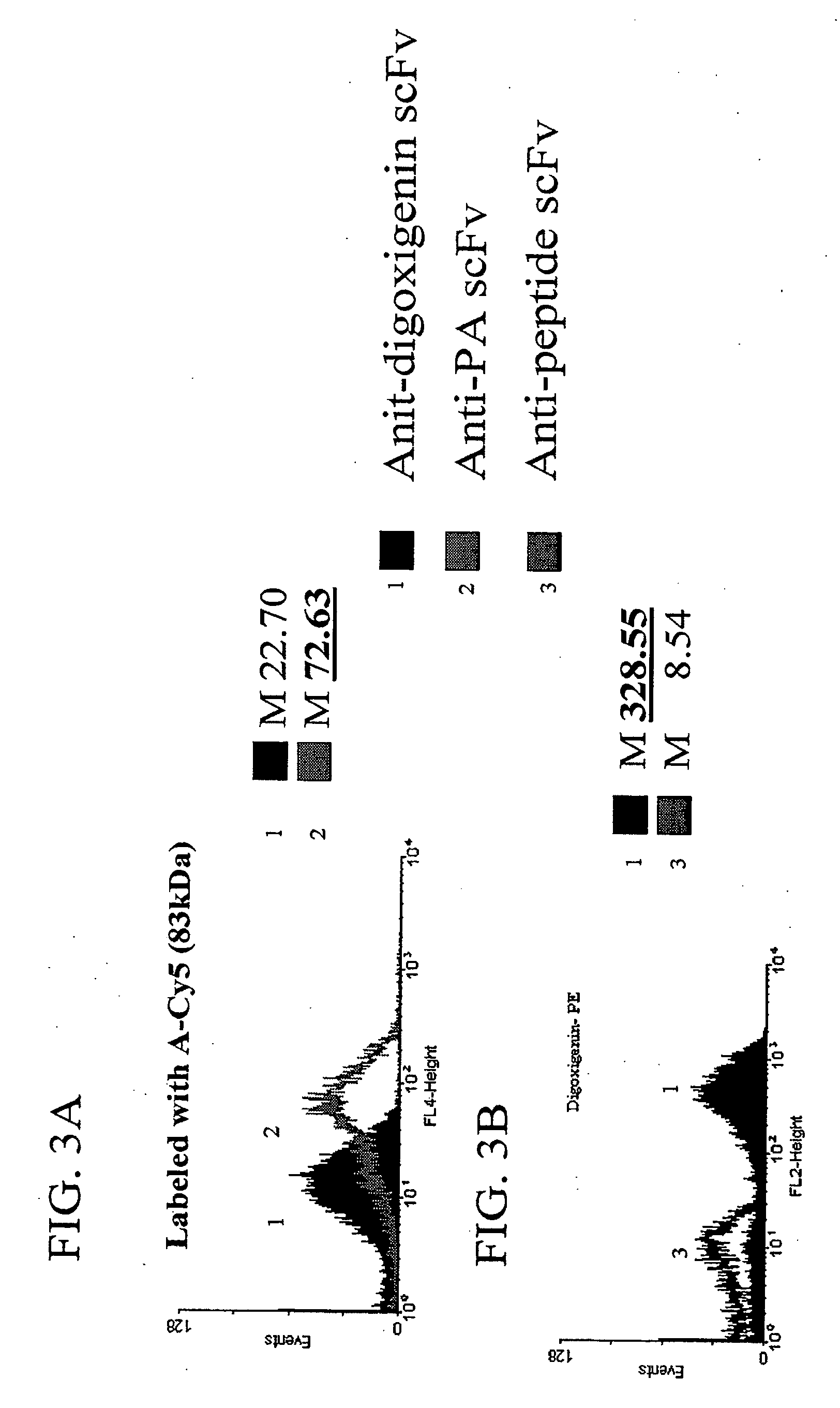
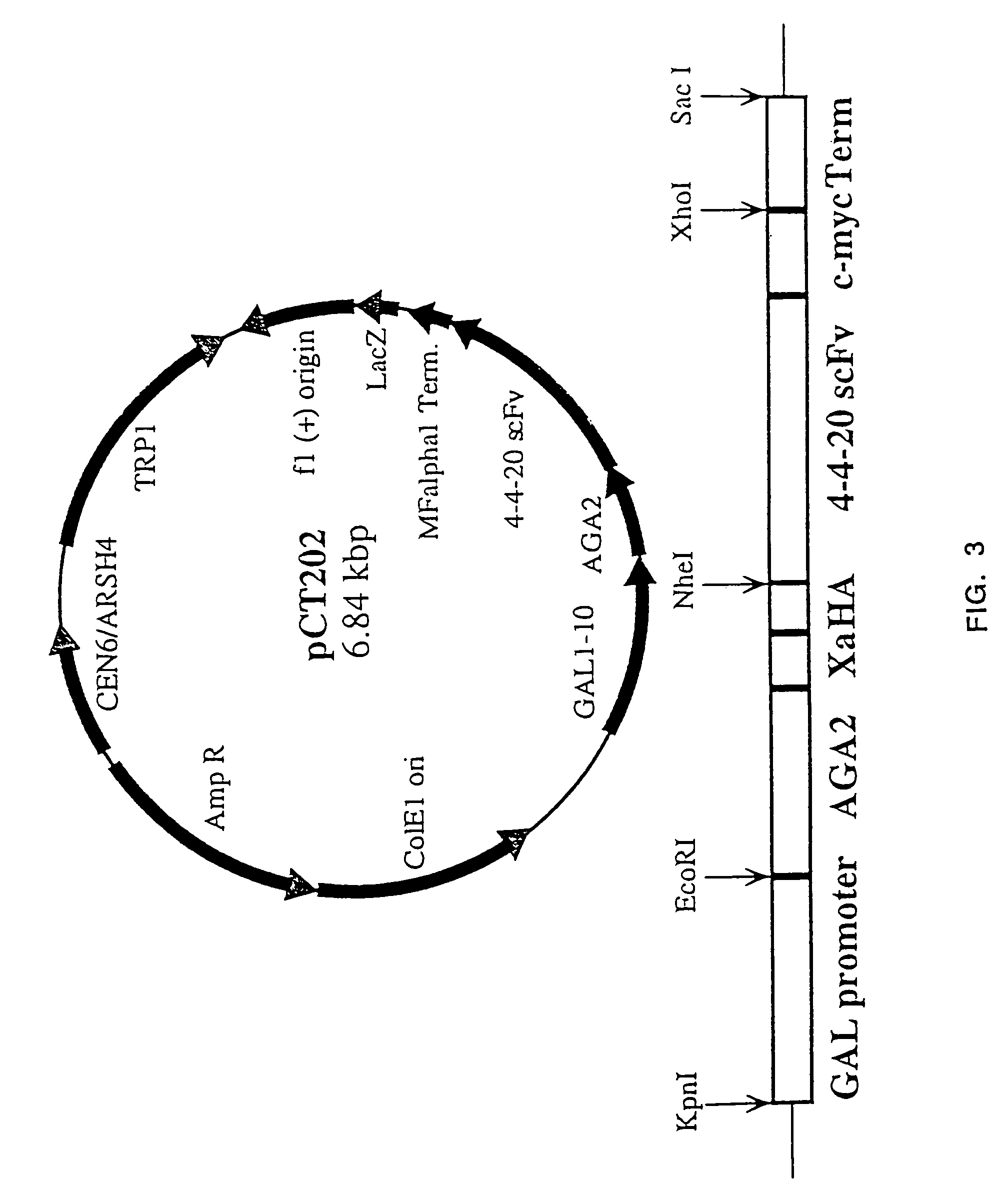
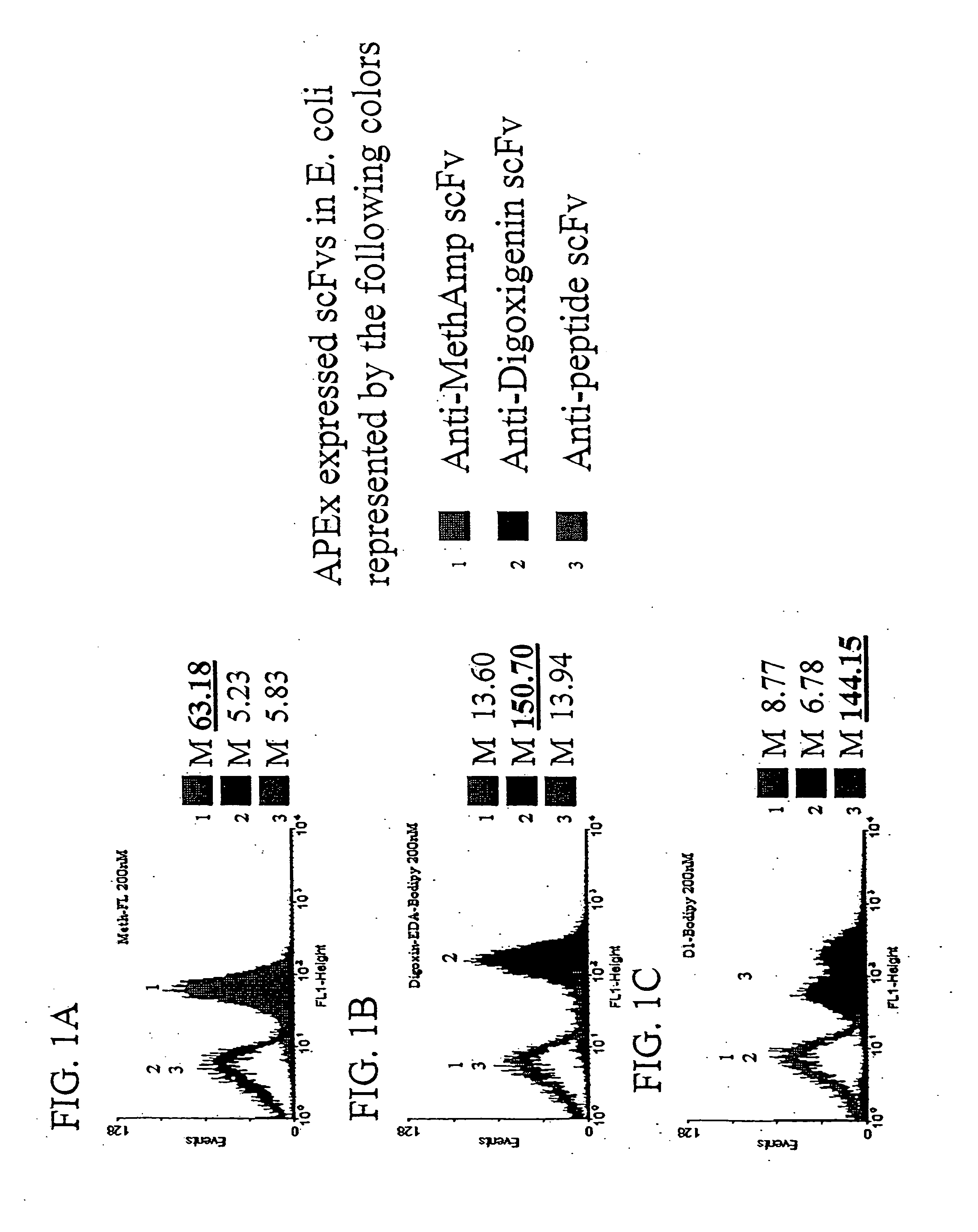
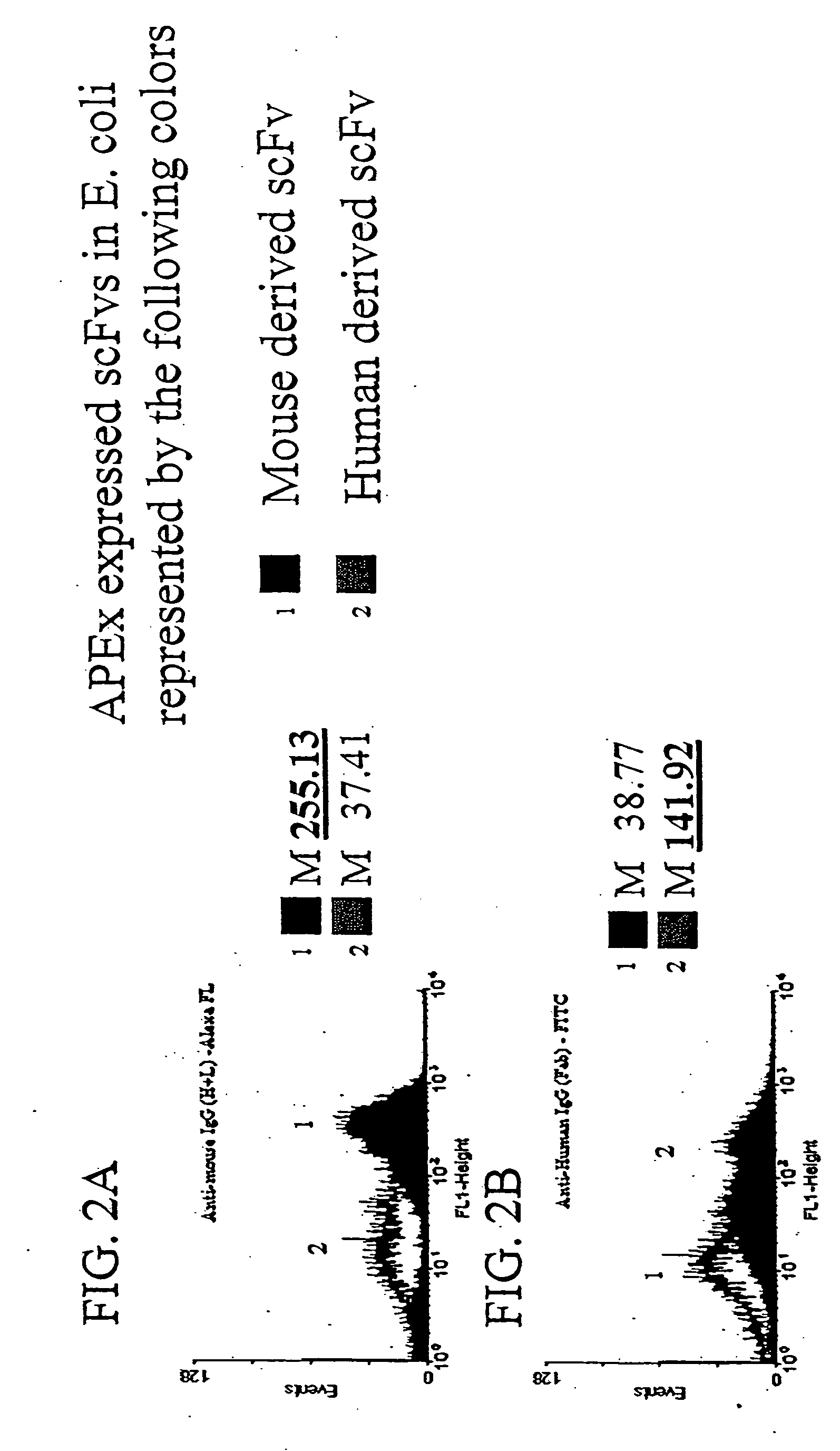
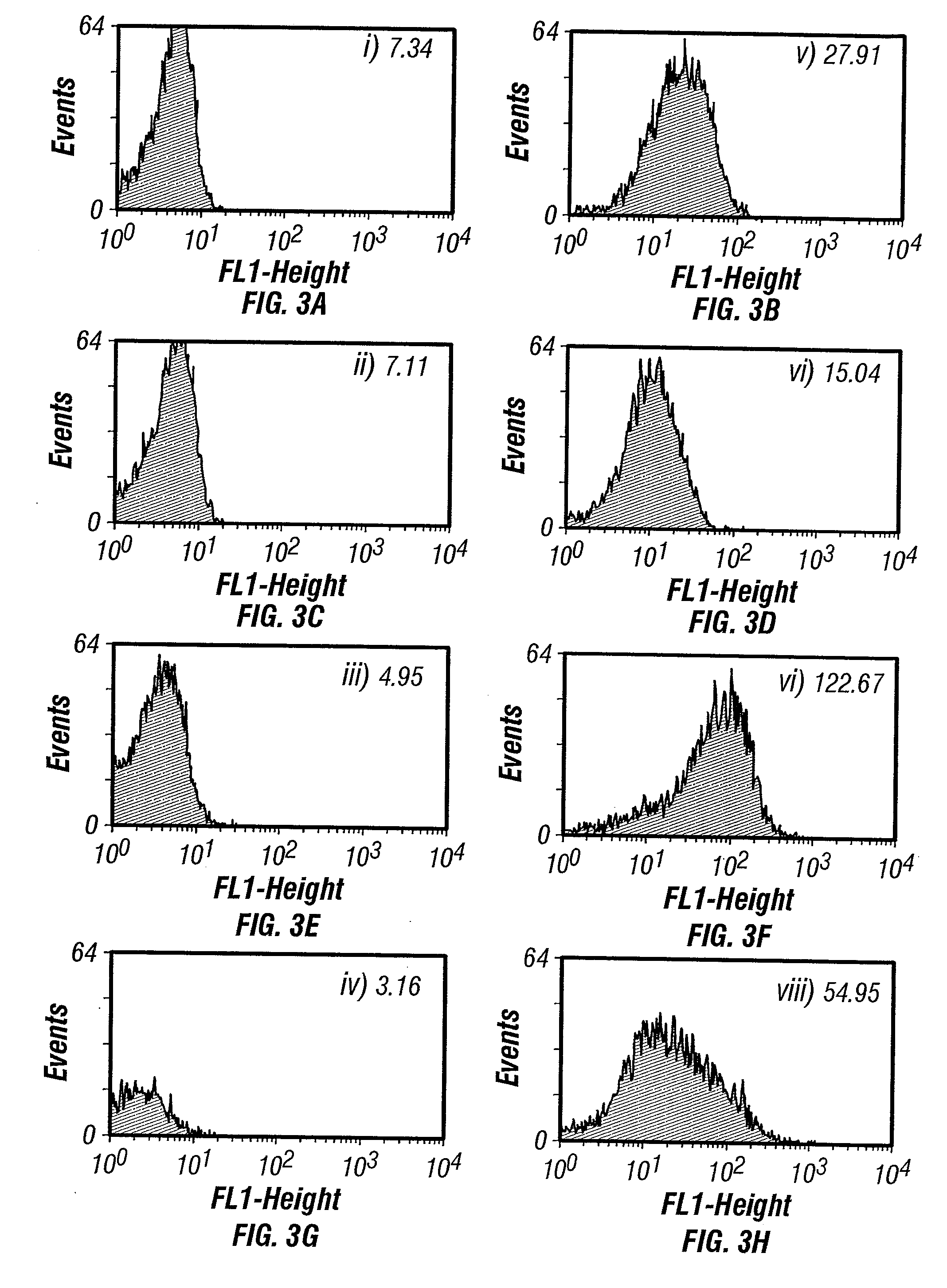
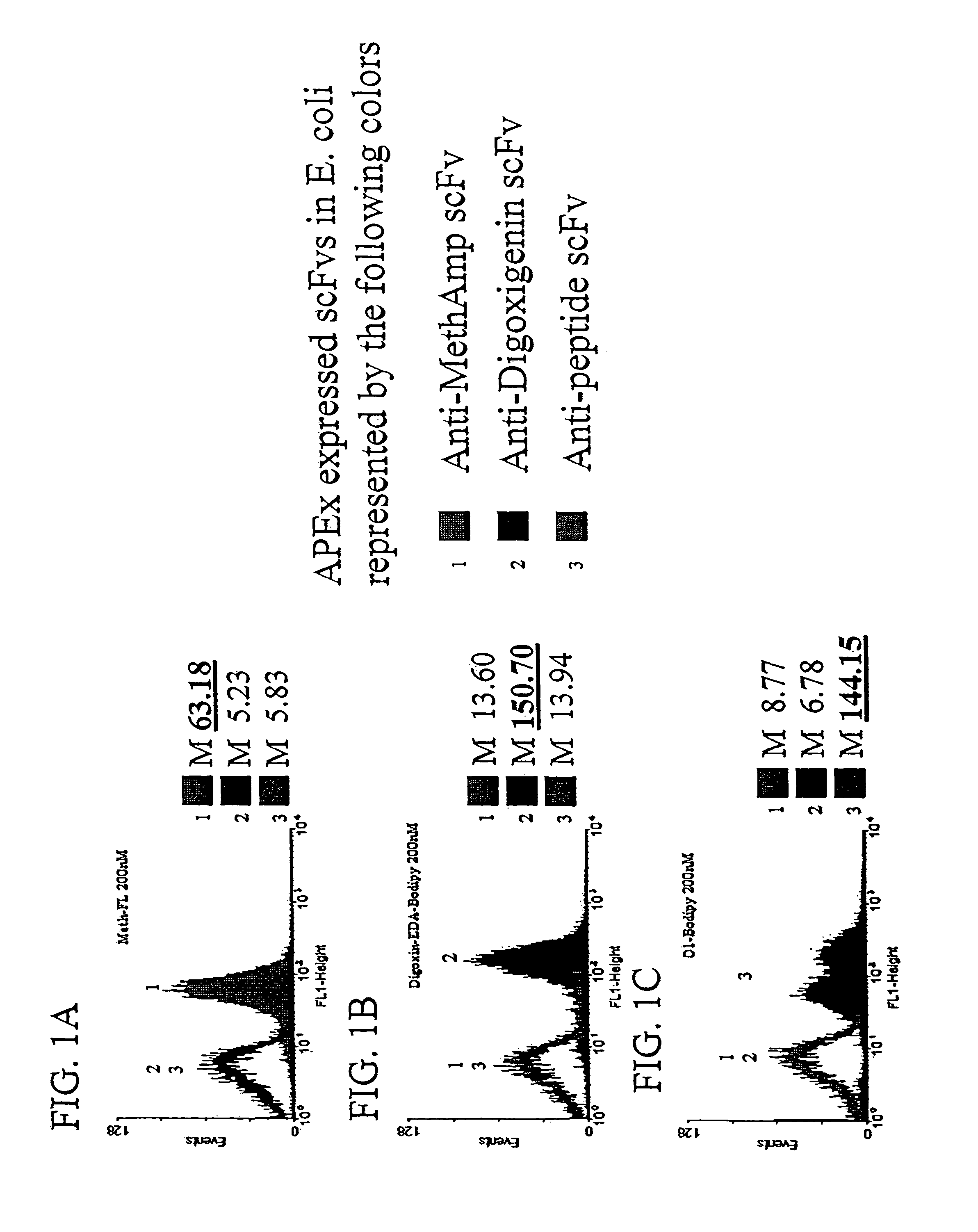
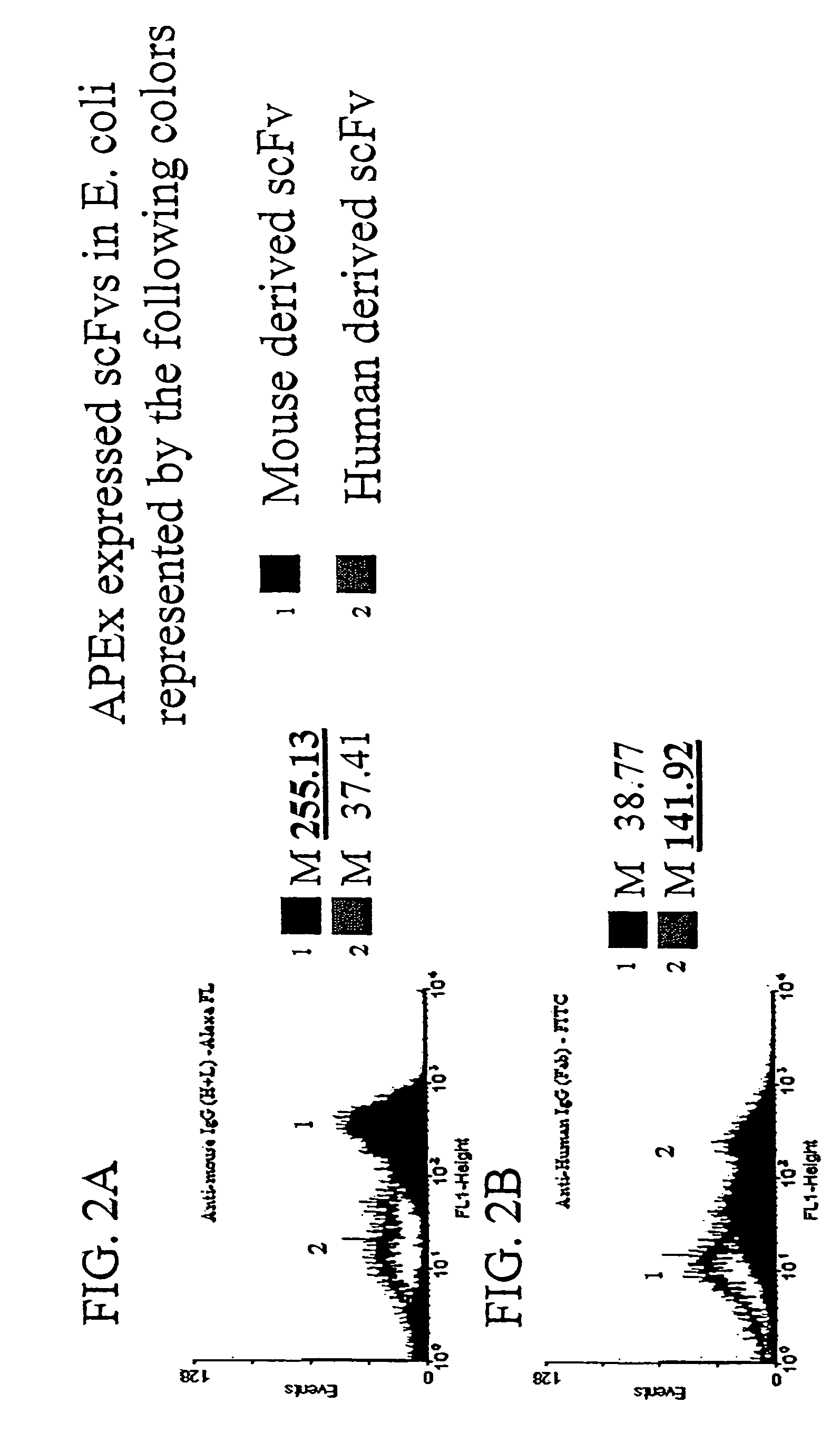
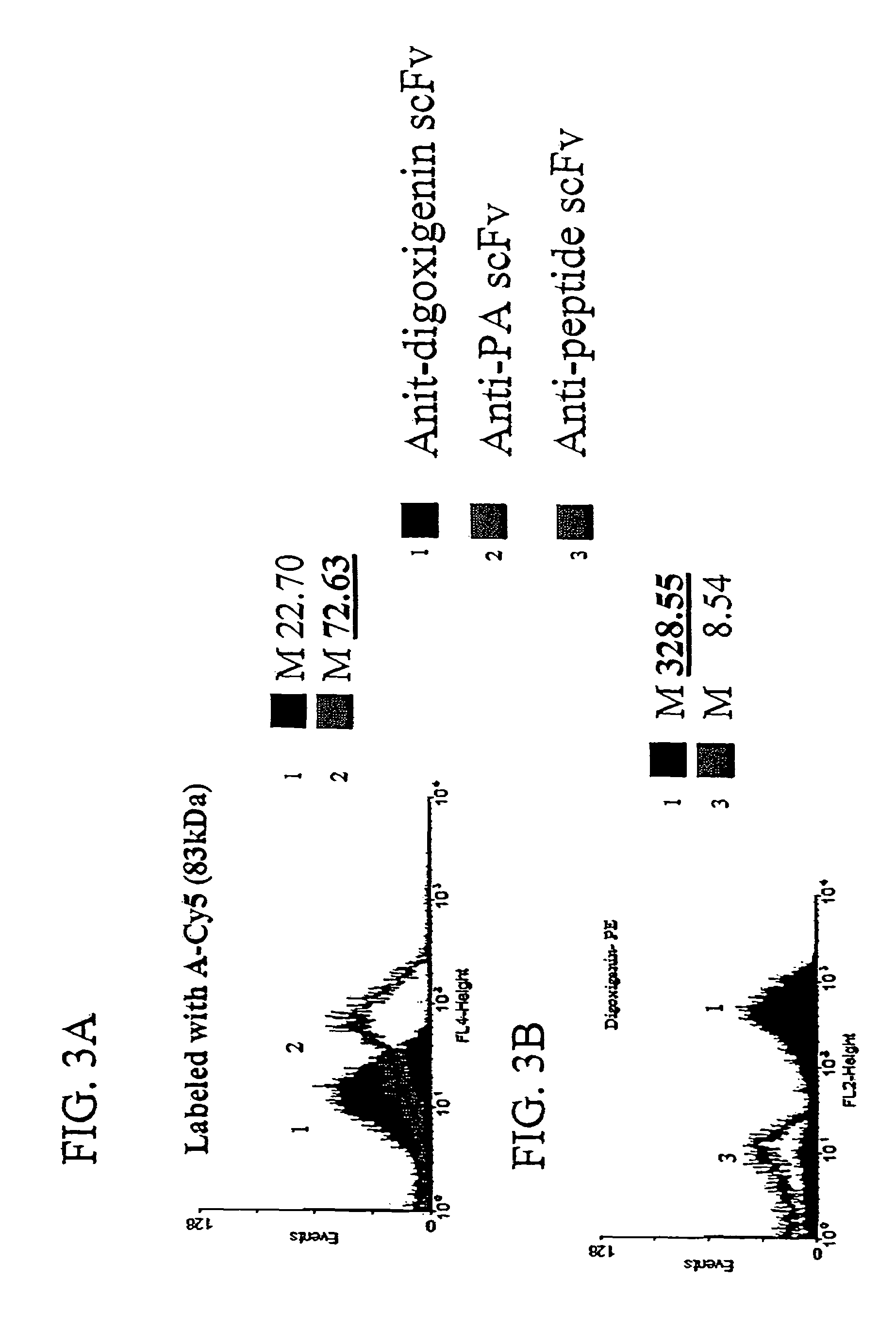
The invention overcomes the deficiencies of the prior art by providing a rapid approach for isolating binding proteins capable of binding small molecules and peptides. In the technique, libraries of candidate binding proteins, such as antibody sequences, may be expressed in the periplasm of gram negative bacteria with at least one target ligand. In clones expressing recombinant polypeptides with affinity for the ligand, the ligand becomes bound and retained by the cell even after removal of the outer membrane, allowing the cell to be isolated from cells not expressing a binding polypeptide with affinity for the target ligand. The target ligand may be detected in numerous ways, including use of direct fluorescence or secondary antibodies that are fluorescently labeled, allowing use of efficient screening techniques such as fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS). The approach is more rapid and robust than prior art methods and avoids problems associated with the outer surface-expression of ligand fusion proteins employed with phage display.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
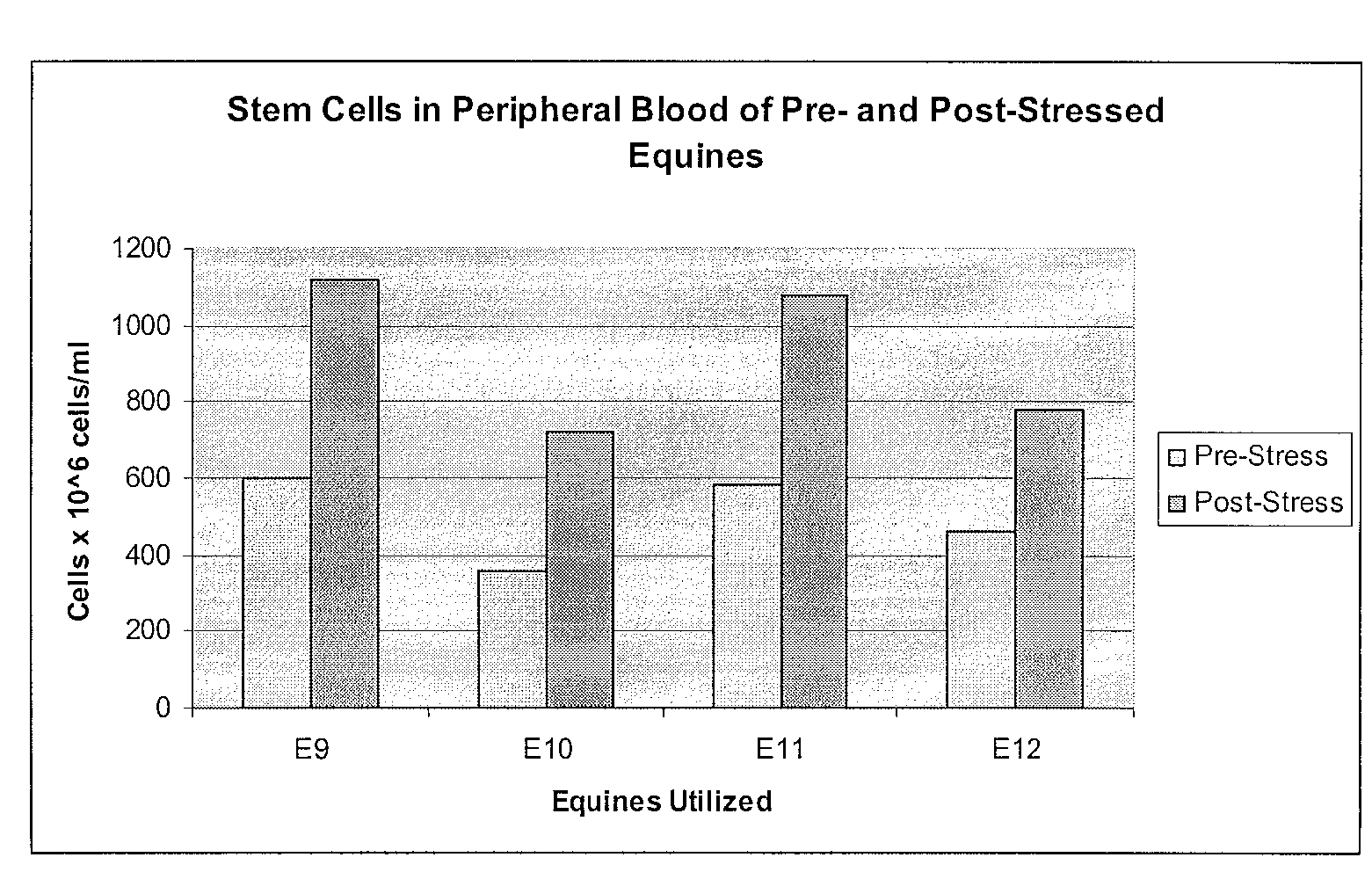
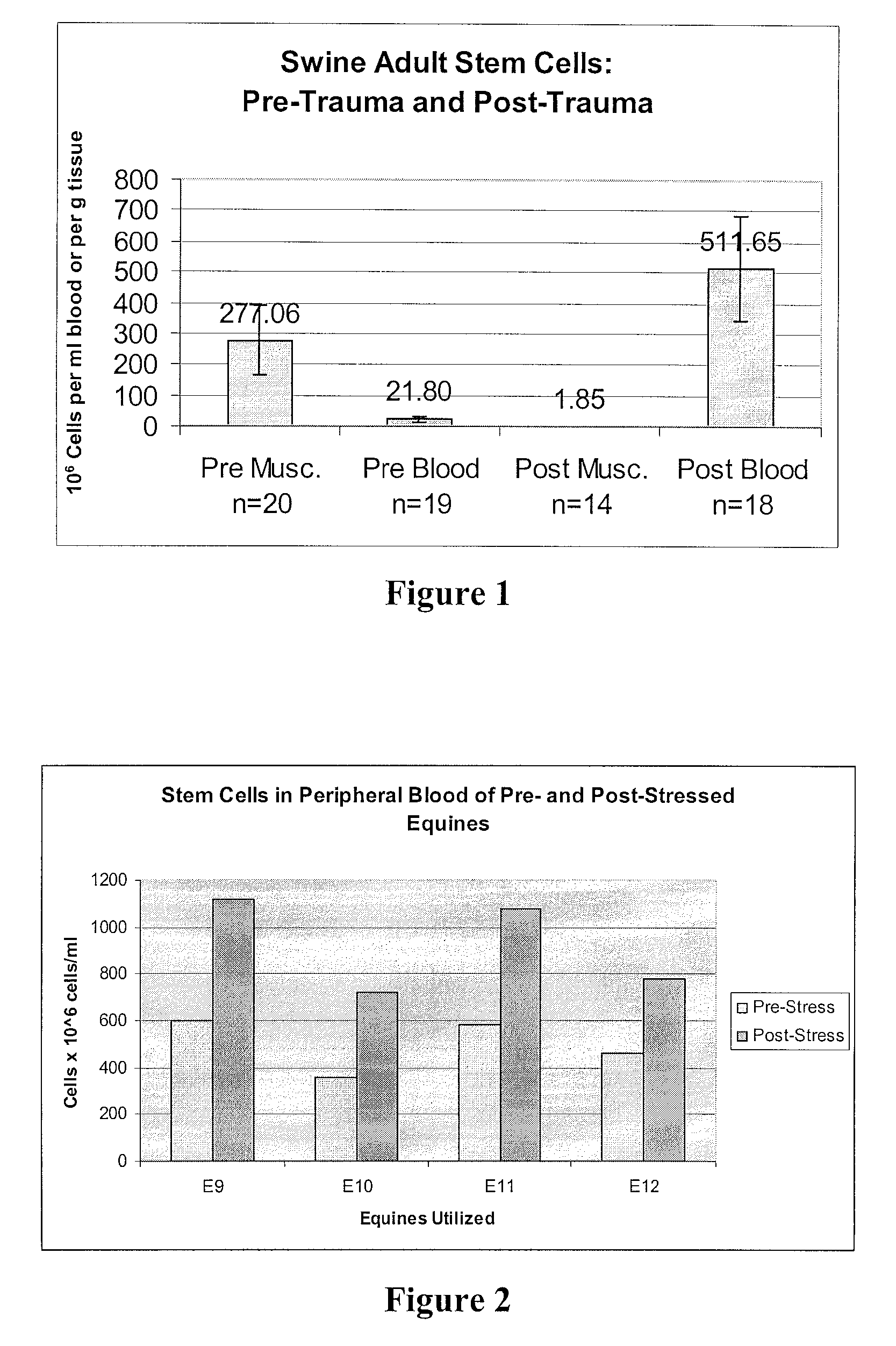
Mobilization of Stem Cells After Trauma and Methods Therefor
Methods are presented in which release of stem cells from skeletal muscle is quantitated and correlated with severity of a disease or trauma, a future treatment option, prognosis, and / or anticipated time to recovery. Most preferably, the stem cell is a BLSC and / or an ELSC, and the stem cell isolation for the cell count is performed using sedimentation or filtration as principal separation step, thereby avoiding commonly used complicated, expensive, and time-consuming processes such as antibody-based separation and fluorescence-activated cell sorting.
Owner:MORAGA BIOTECH CORP
Combinatorial protein library screening by periplasmic expression
The invention overcomes the deficiencies of the prior art by providing a rapid approach for isolating binding proteins capable of binding small molecules and peptides. In the technique, libraries of candidate binding proteins, such as antibody sequences, are expressed in the periplasm of gram negative bacteria and mixed with a labeled ligand. In clones expressing recombinant polypeptides with affinity for the ligand, the concentration of the labeled ligand bound to the binding protein is increased and allows the cells to be isolated from the rest of the library. Where fluorescent labeling of the target ligand is used, cells may be isolated by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS). The approach is more rapid than prior art methods and avoids problems associated with the outer surface-expression of ligand fusion proteins employed with phage display.
Owner:HARVEY BARRETT R +2
Yeast cell surface display of proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS7465787B2Improve the level ofEnhance level of cell surface expression of cellFungiDirected macromolecular evolutionSurface displayAgglutinin-B
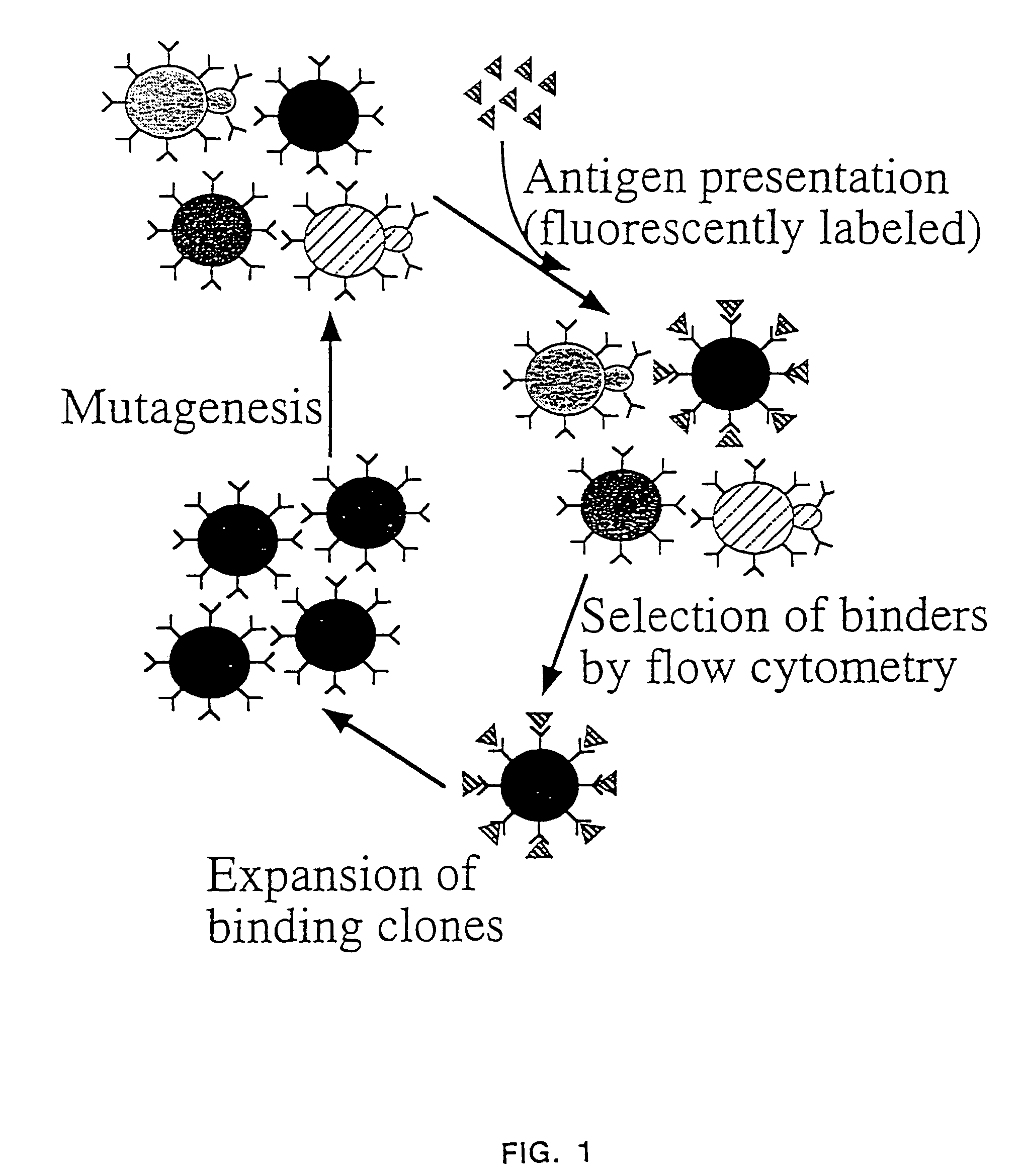
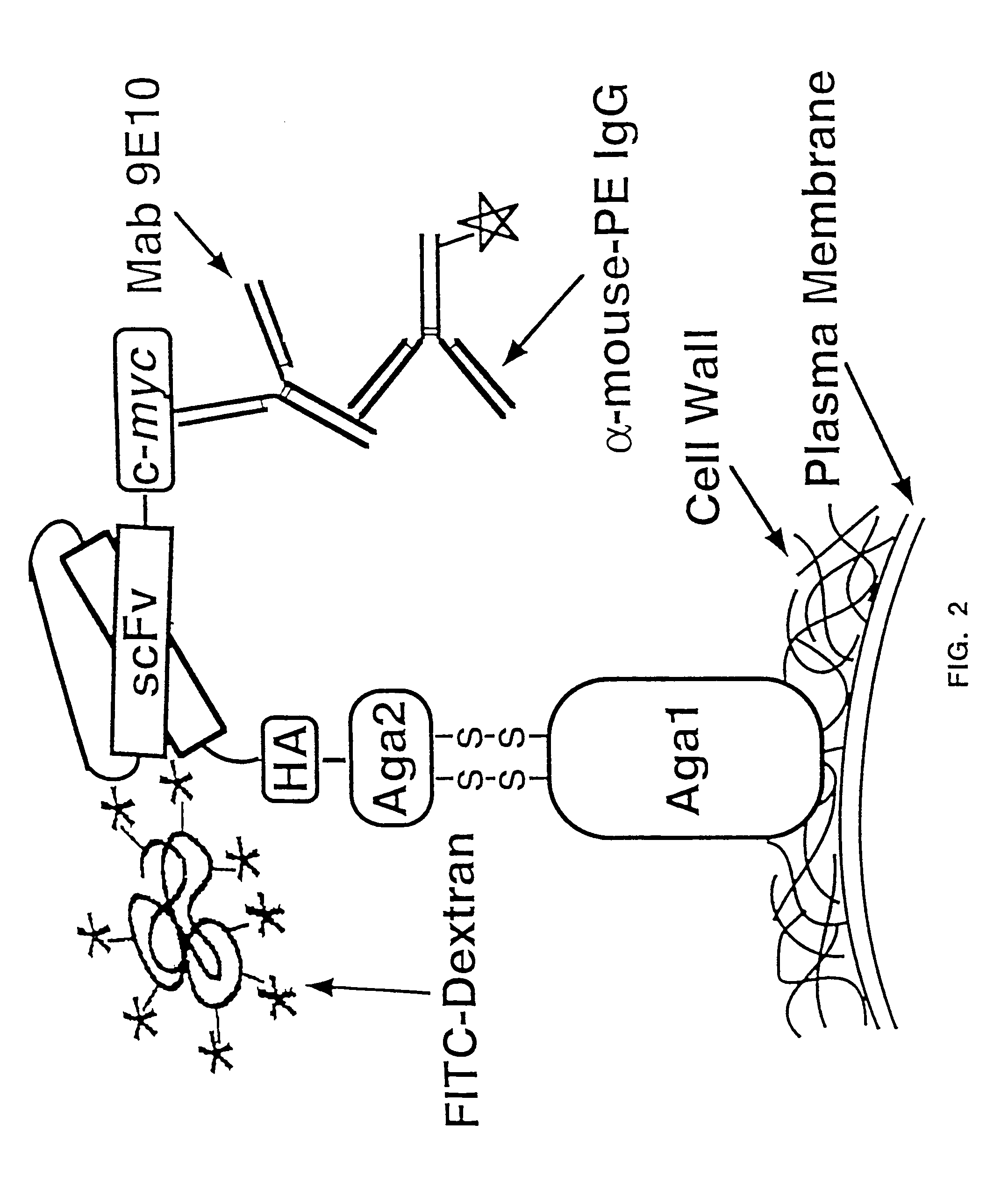
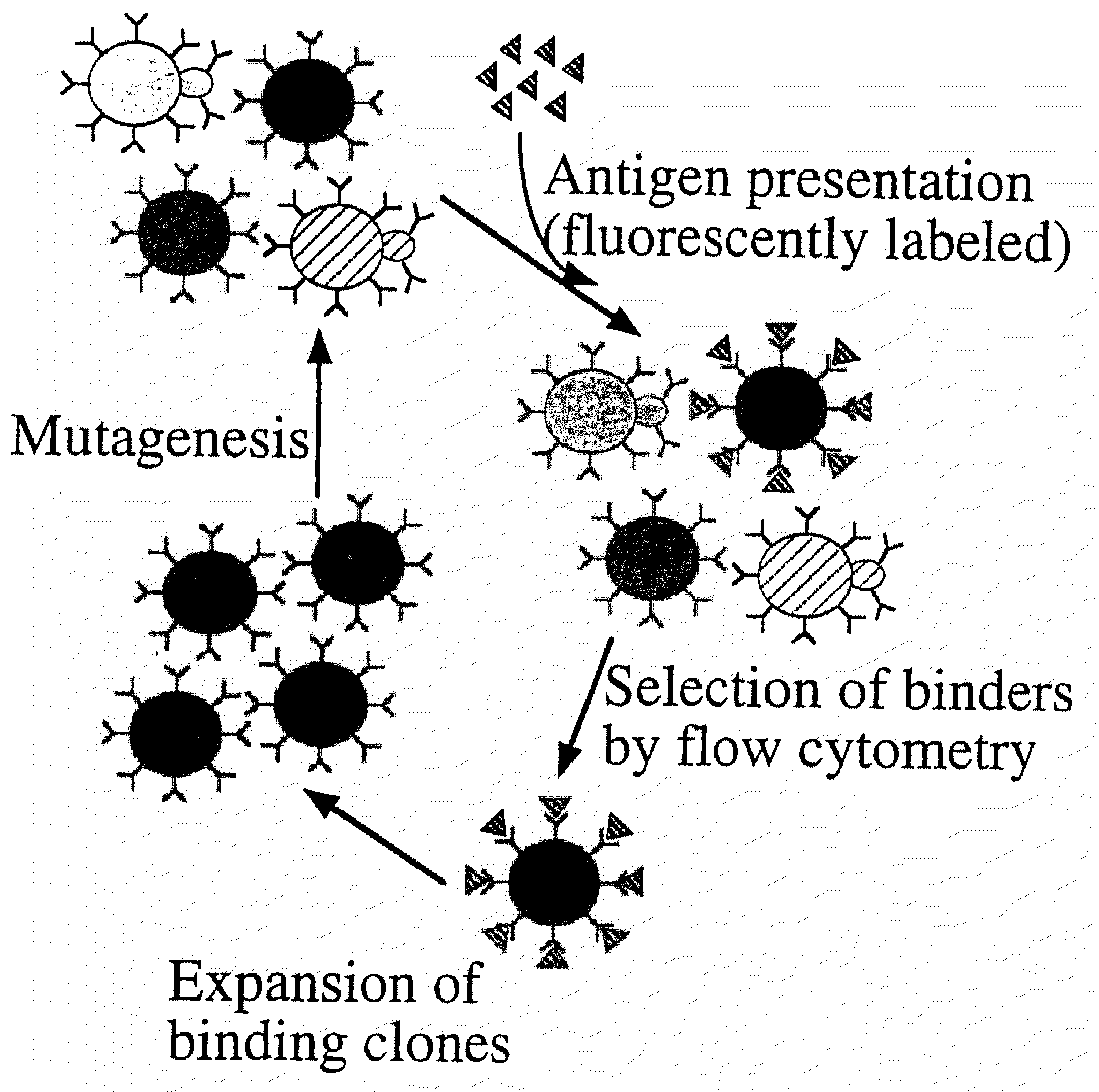
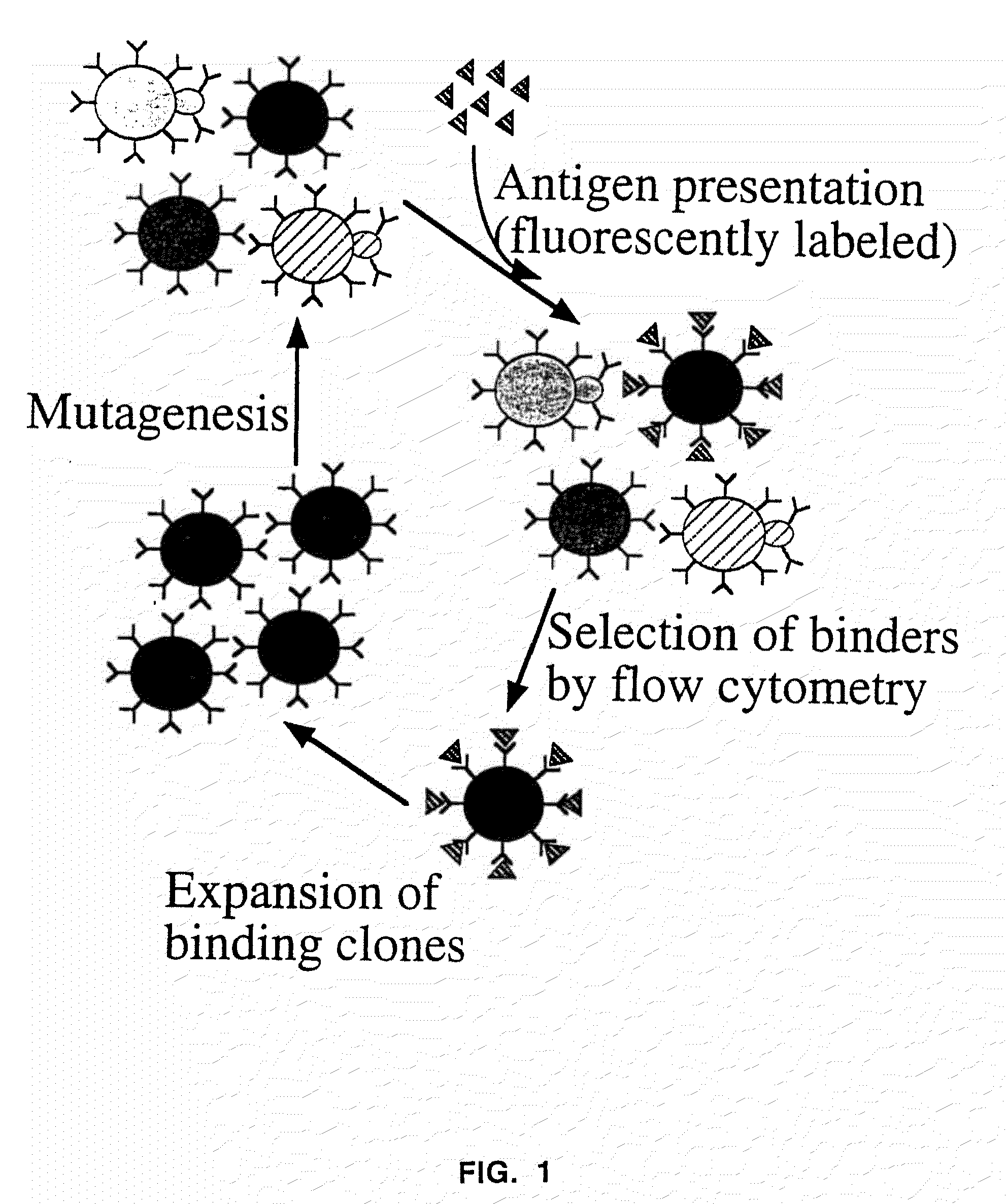
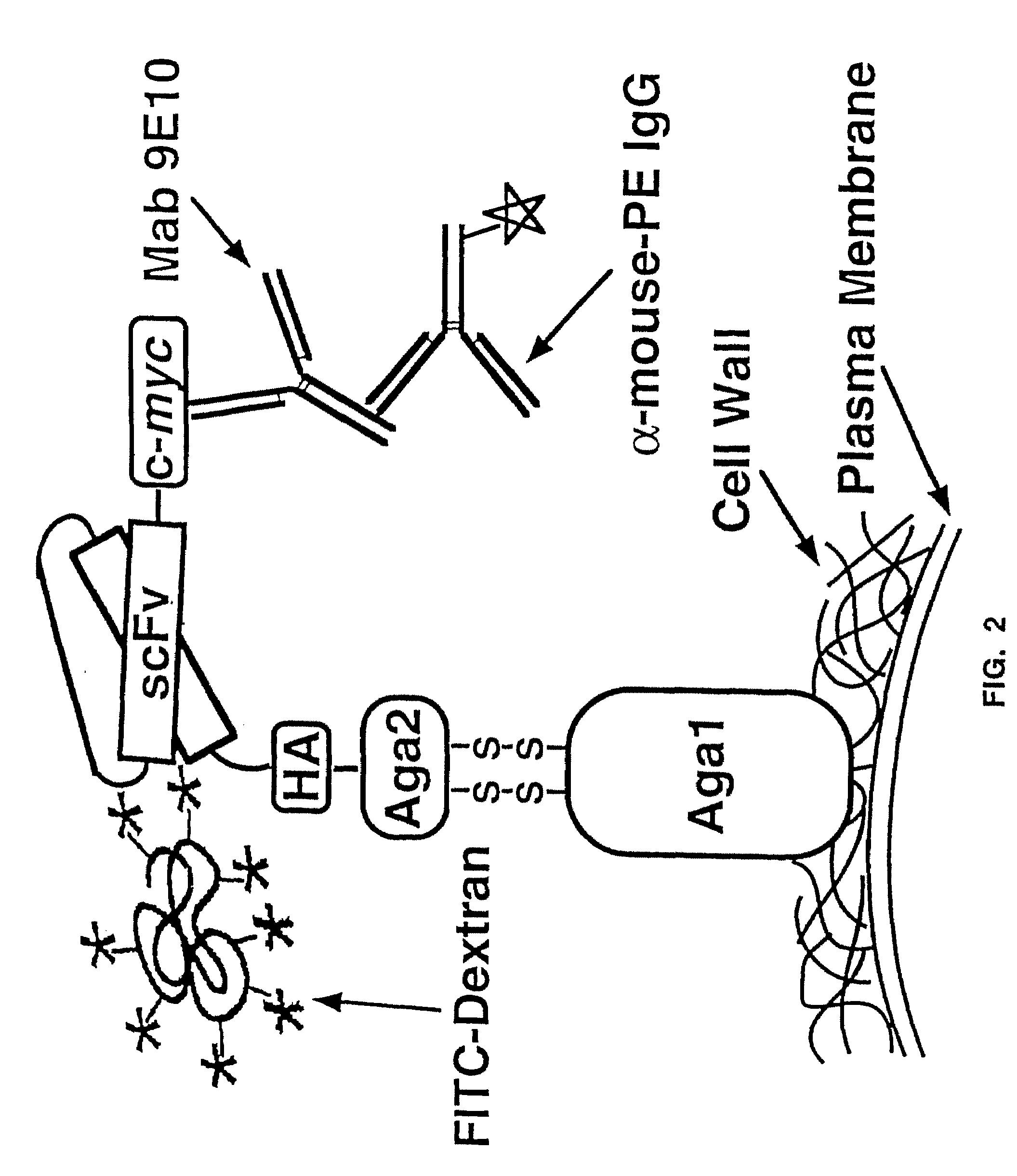
The present invention provides a genetic method for tethering polypeptides to the yeast cell wall in a form accessible for binding to macromolecules. Combining this method with fluorescence-activated cell sorting provides a means of selecting proteins with increased or decreased affinity for another molecule, altered specificity, or conditional binding. Also provided is a method for genetic fusion of the N terminus of a polypeptide of interest to the C-terminus of the yeast Aga2p cell wall protein. The outer wall of each yeast cell can display approximately 10 protein agglutinins. The native agglutinins serve as specific adhesion contacts to fuse yeast cells of opposite mating type during mating. In effect, yeast has evolved a platform for protein-protein binding without steric hindrance from cell wall components.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Selection of bacterial inner-membrane anchor polypeptides
InactiveUS20050260736A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaBacterial inner membraneHeterologous
The invention overcomes the deficiencies of the prior art by providing a rapid approach for isolating polypeptides capable of anchoring heterologous polypeptides to a bacterial inner membrane. In the technique, libraries of candidate anchor polypeptides are expressed as fusions with a heterologous polypeptide that is capable of being detected when bound to the inner membrane. In bacteria expressing a functional anchor sequence, the heterologous polypeptide becomes bound to outer face of the inner membrane. Bacteria with the functional anchor sequence can be identified by removing the outer membrane to remove non-anchored heterologous polypeptide followed by detection of anchored heterologous polypeptide. Such bacteria may be detected in numerous ways, including use of direct fluorescence or secondary antibodies that are fluorescently labeled, allowing use of efficient techniques such as fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS).
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
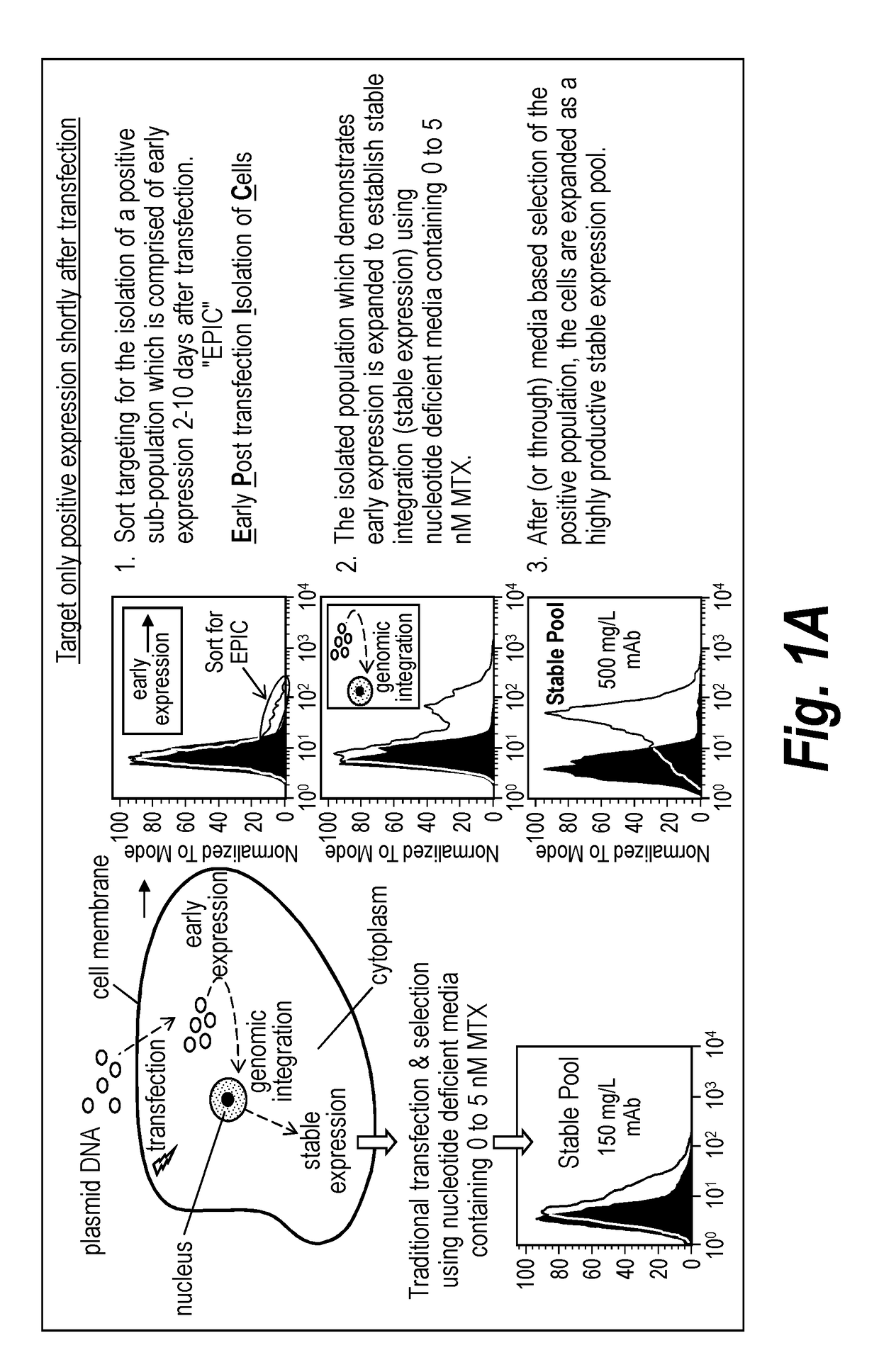
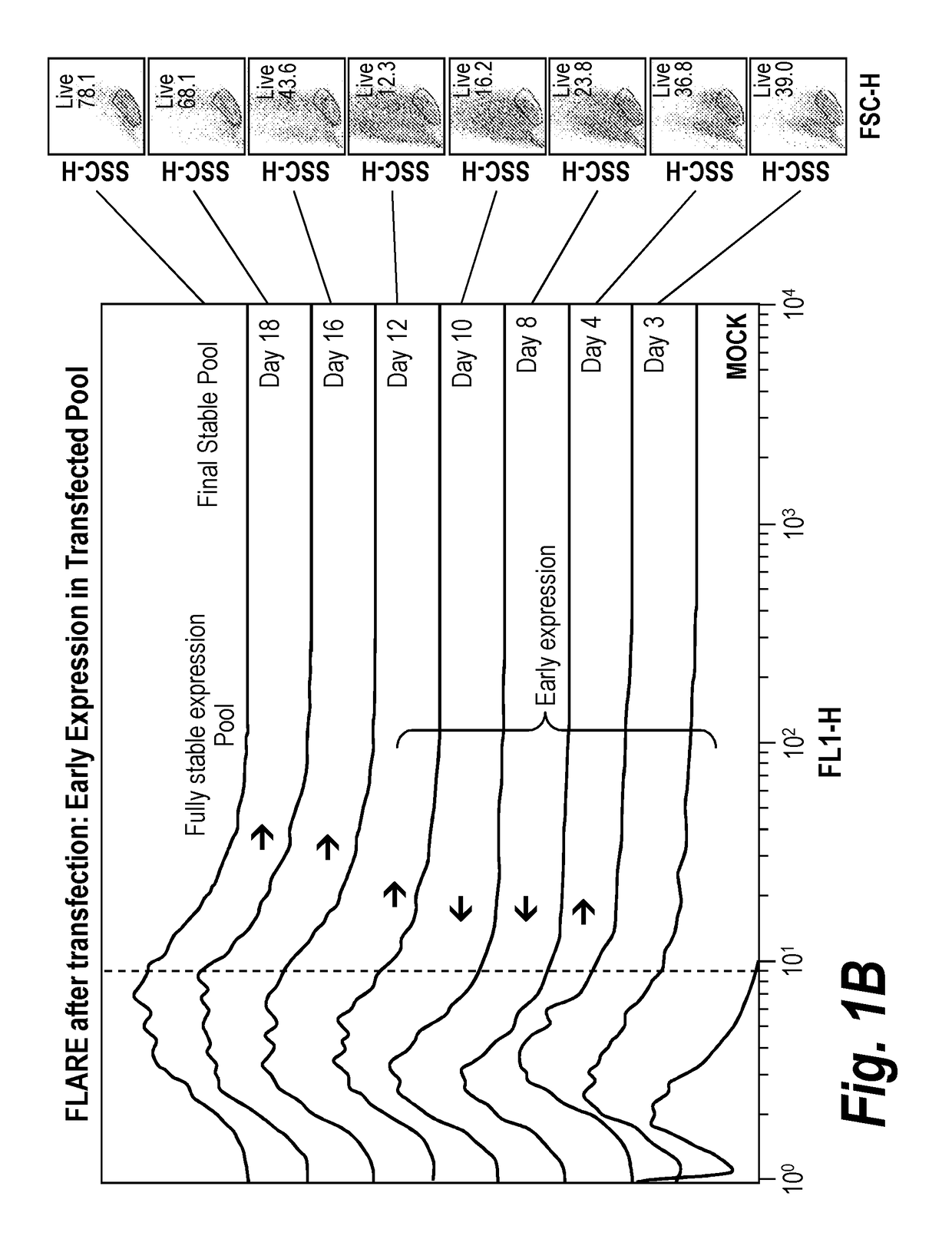
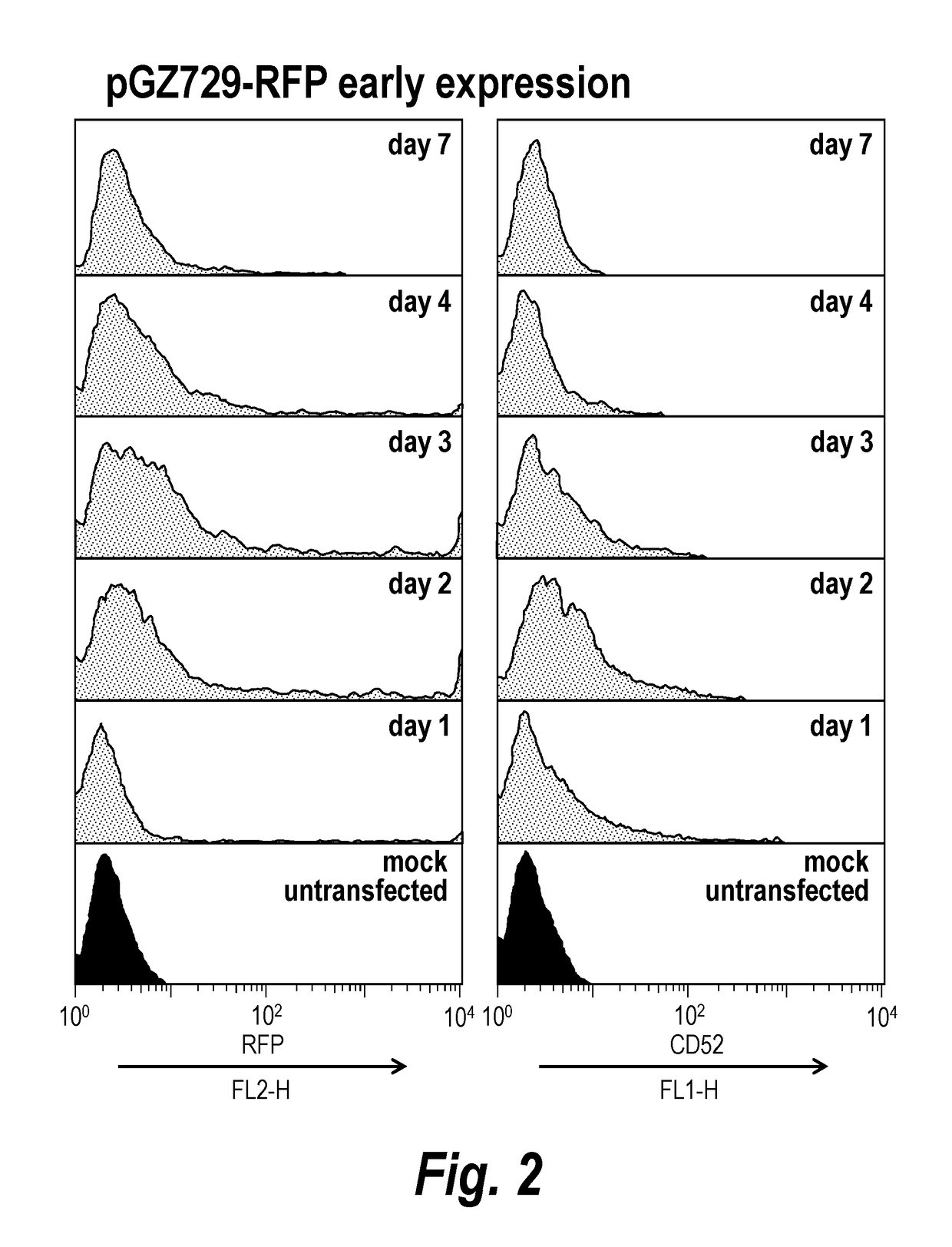
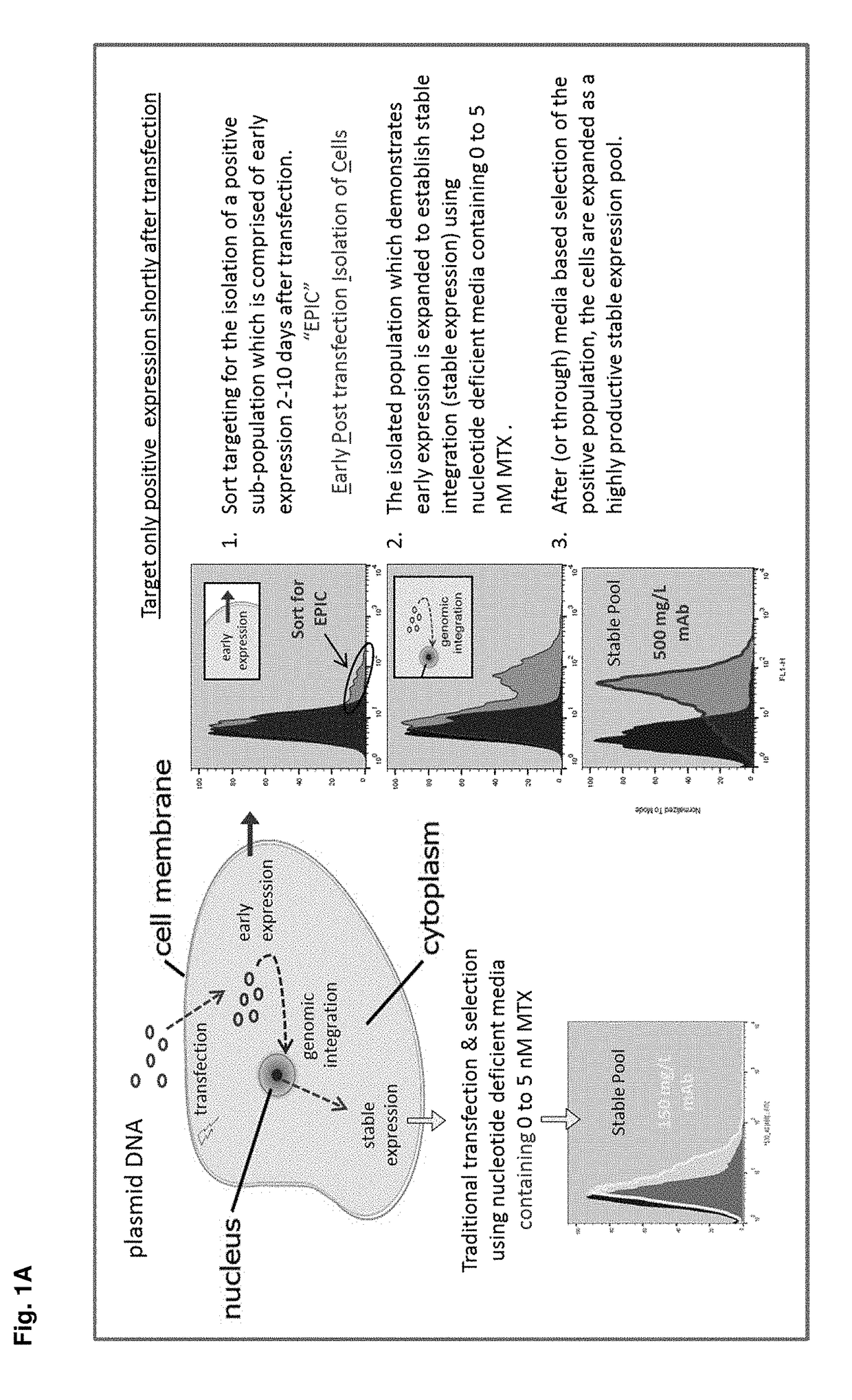
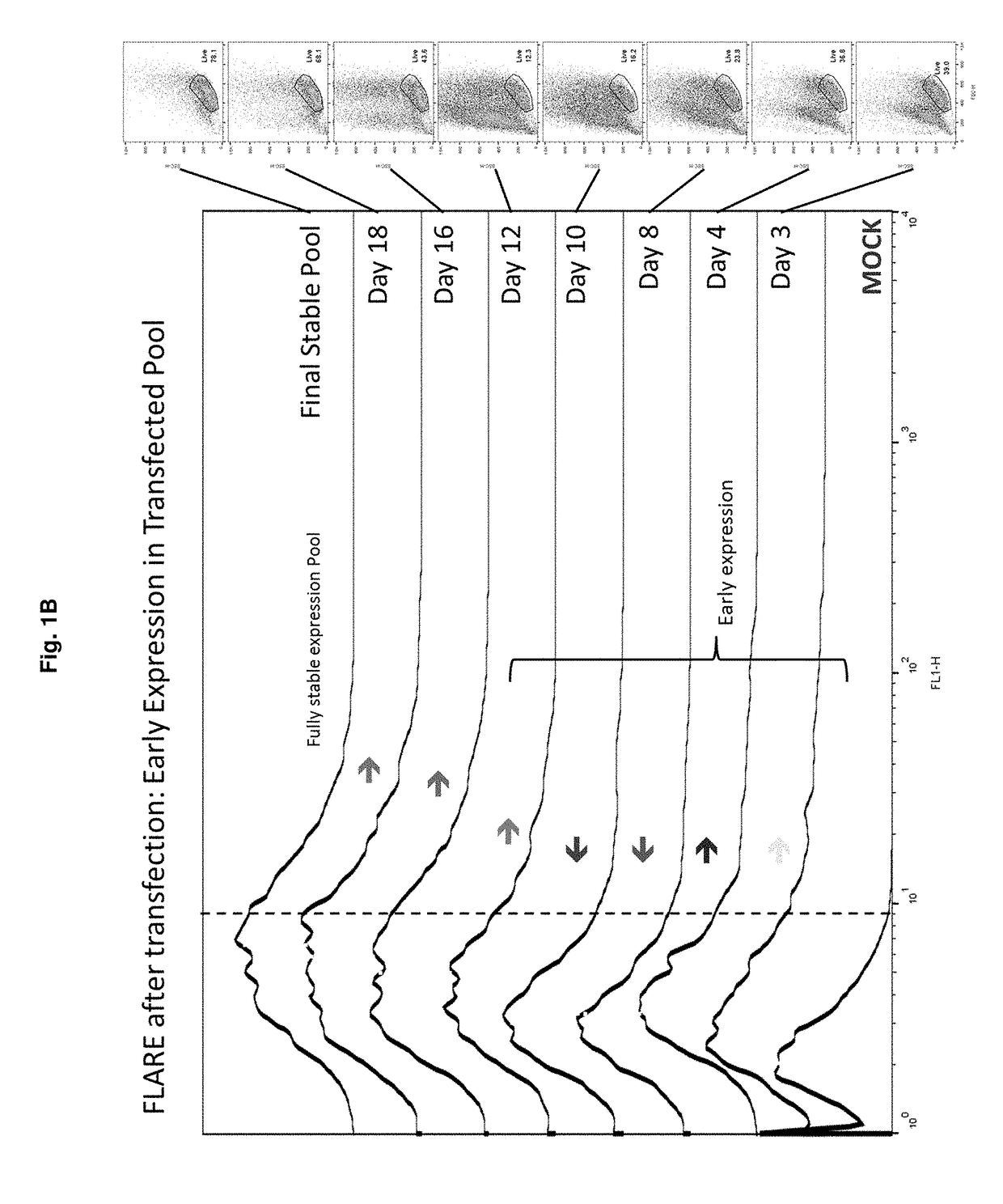
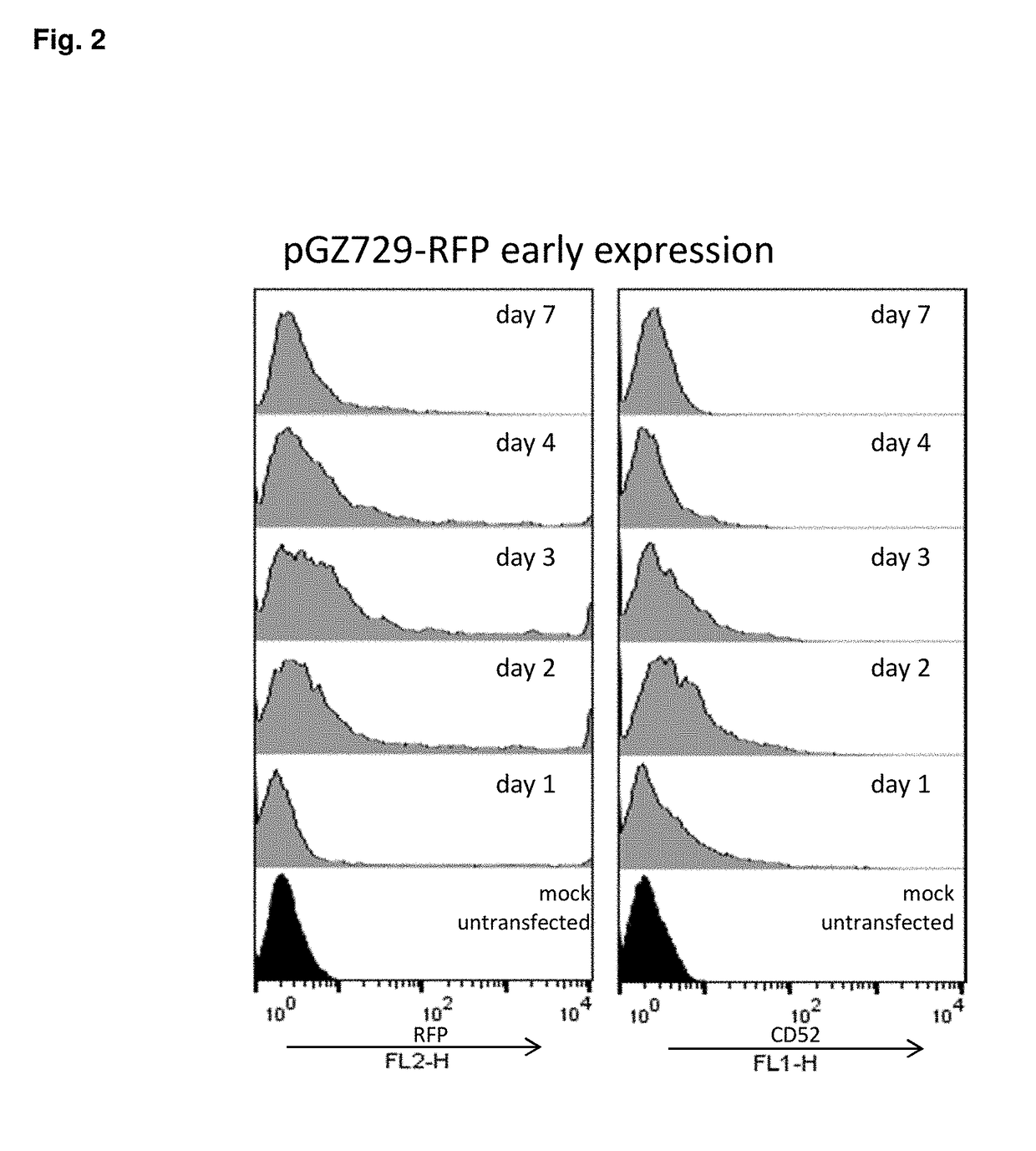
Early post-transfection isolation of cells (EPIC) for biologics production
ActiveUS20170121734A1Increase productionGenetically modified cellsBiological material analysisFluorescenceMagnetic-activated cell sorting
Provided herein are methods for selecting a population of cells expressing a target polypeptide. In some aspects, the disclosure provides methods for sorting and selecting populations of transfected host cells based on their early expression of a selectable polypeptide. In certain embodiments, the sorting is performed using fluorescence-activated cell sorting or magnetic-activated cell sorting based on the selectable polypeptide. Such selection methods can be further utilized to generate clonal populations of producer cells, e.g. for large-scale manufacturing of a target polypeptide of interest.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Isolation of binding proteins with high affinity to ligands
The invention overcomes the deficiencies of the prior art by providing a rapid approach for isolating binding proteins capable of binding small molecules and peptides via “display-less” library screening. In the technique, libraries of candidate binding proteins, such as antibody sequences, are expressed in soluble form in the periplasmic space of gram negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, and are mixed with a labeled ligand. In clones expressing recombinant polypeptides with affinity for the ligand, the concentration of the labeled ligand bound to the binding protein is increased and allows the cells to be isolated from the rest of the library. Where fluorescent labeling of the target ligand is used, cells may be isolated by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS). The approach is more rapid than prior art methods and avoids problems associated with the surface-expression of ligand fusion proteins employed with phage display.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Selection of bacterial inner-membrane anchor polypeptides
The invention overcomes the deficiencies of the prior art by providing a rapid approach for isolating polypeptides capable of anchoring heterologous polypeptides to a bacterial inner membrane. In the technique, libraries of candidate anchor polypeptides are expressed as fusions with a heterologous polypeptide that is capable of being detected when bound to the inner membrane. In bacteria expressing a functional anchor sequence, the heterologous polypeptide becomes bound to outer face of the inner membrane. Bacteria with the functional anchor sequence can be identified by removing the outer membrane to remove non-anchored heterologous polypeptide followed by detection of anchored heterologous polypeptide. Such bacteria may be detected in numerous ways, including use of direct fluorescence or secondary antibodies that are fluorescently labeled, allowing use of efficient techniques such as fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS).
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Yeast cell surface display of proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090280560A1Effectively mimickedHigh affinityFungiSaccharide peptide ingredientsSurface displayAgglutinin-B
The present invention provides a genetic method for tethering polypeptides to the yeast cell wall in a form accessible for binding to macromolecules. Combining this method with fluorescence-activated cell sorting provides a means of selecting proteins with increased or decreased affinity for another molecule, altered specificity, or conditional binding. Also provided is a method for genetic fusion of the N terminus of a polypeptide of interest to the C-terminus of the yeast Aga2p cell wall protein. The outer wall of each yeast cell can display approximately 104 protein agglutinins. The native agglutinins serve as specific adhesion contacts to fuse yeast cells of opposite mating type during mating. In effect, yeast has evolved a platform for protein-protein binding without steric hindrance from cell wall components. As one embodiment, attaching an scFv antibody fragment to the Aga2p agglutinin effectively mimics the cell surface display of antibodies by B cells in the immune system for affinity maturation in vivo. As another embodiment, T cell receptor mutants can be isolated by this method that are efficiently displayed on the yeast cell surface, providing a means of altering T cell receptor binding affinity and specificity by library screening.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
In Vitro Generation of Hepatocytes from Human Embryonic Stem Cells
Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells, such as human embryonic stem cells (hESC), into hepatocytes by in vitro methods is disclosed. The pluripotent stem cells are cultured in conditioned medium from the hepatocarcinoma cell line, HepG2. Specific growth factors and defined media may also be added to the medium for stage specific differentiation of the derived hepatocytes. Hepatocytes differentiated from human pluripotent stem cells may be characterized by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS), immunofluorescence analysis (IF), real time polymerase reaction (RT-PCR), and functional assays. The methods disclosed herein are able to differentiate high percentages of hepatocytes from human pluripotent stem cells using the disclosed methods. These differentiated cells may exhibit polygonal shape morphology, typical of hepatocytes, and may express hepatocyte specific genes. The differentiated cells may also be positive for definitive endoderm markers and hepatic markers.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Isolation of endothelial progenitor cell subsets and methods for their use
InactiveUS20060035290A1Artificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsFluorescenceAngiogenesis growth factor
A method is provided for the isolation of endothelial progenitor cells from a source of progenitor cells by isolating a population of lineage-negative cells and further isolating CD34+ cells from the lineage-negative population by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Isolated populations of endothelial progenitor cells and therapeutic compositions containing CD34+ cells for the induction of blood vessels, induction of angiogenic responses in surrounding blood vessels and the chemotaxis of inflammatory cells are also provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Pulsed laser triggered high speed microfluidic switch and applications in fluorescent activated cell sorting
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Determination of cell viability and phenotype
InactiveUS7018804B1Accurate and straightforward quantificationFurther processing may be delayedMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationFluorescenceBiology
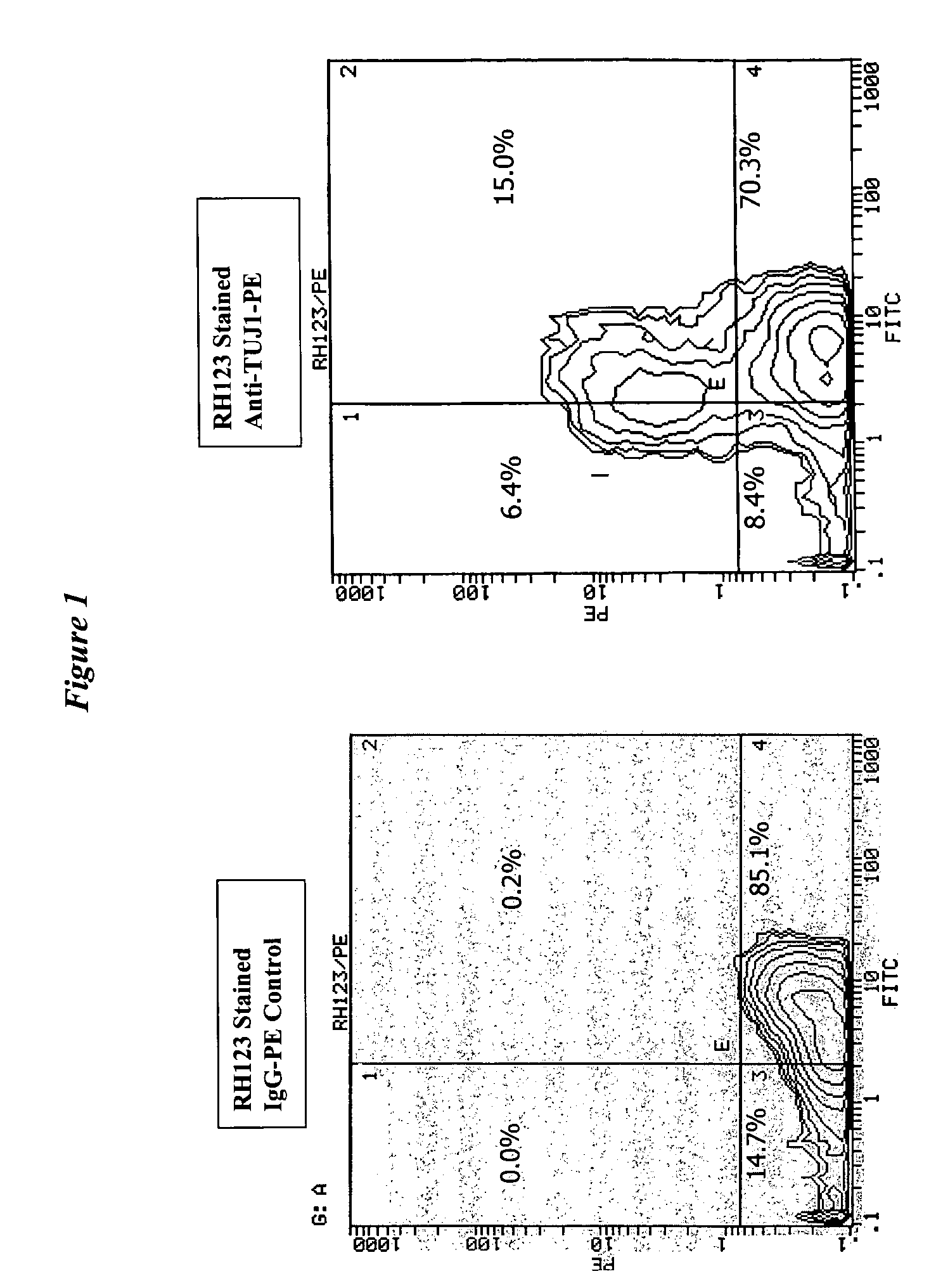
This invention provides methods to the determination of the viability of the cell by a first reagent and the phenotype of a cell by use of one or more second reagent. The first reagent is one that is detectable in viable, or living, cells even after they have been fixed such that they are no longer viable. The one or more second reagent is compatible for use in fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) including intracellular FACS. The invention thus provides methods of simultaneously identifying a cell as both viable and having a phenotype of interest. The invention also provides compositions for use in the disclosed methods.
Owner:ORION BIOSOLUTIONS
Method for analyzing epitope of monoclonal antibody by using yeast surface display system and application of method in vaccine development
InactiveCN102321146AEasy to displayThere are many ways to modifyFungiPeptide preparation methodsFluorescence-Activated Cell SortingProtein target
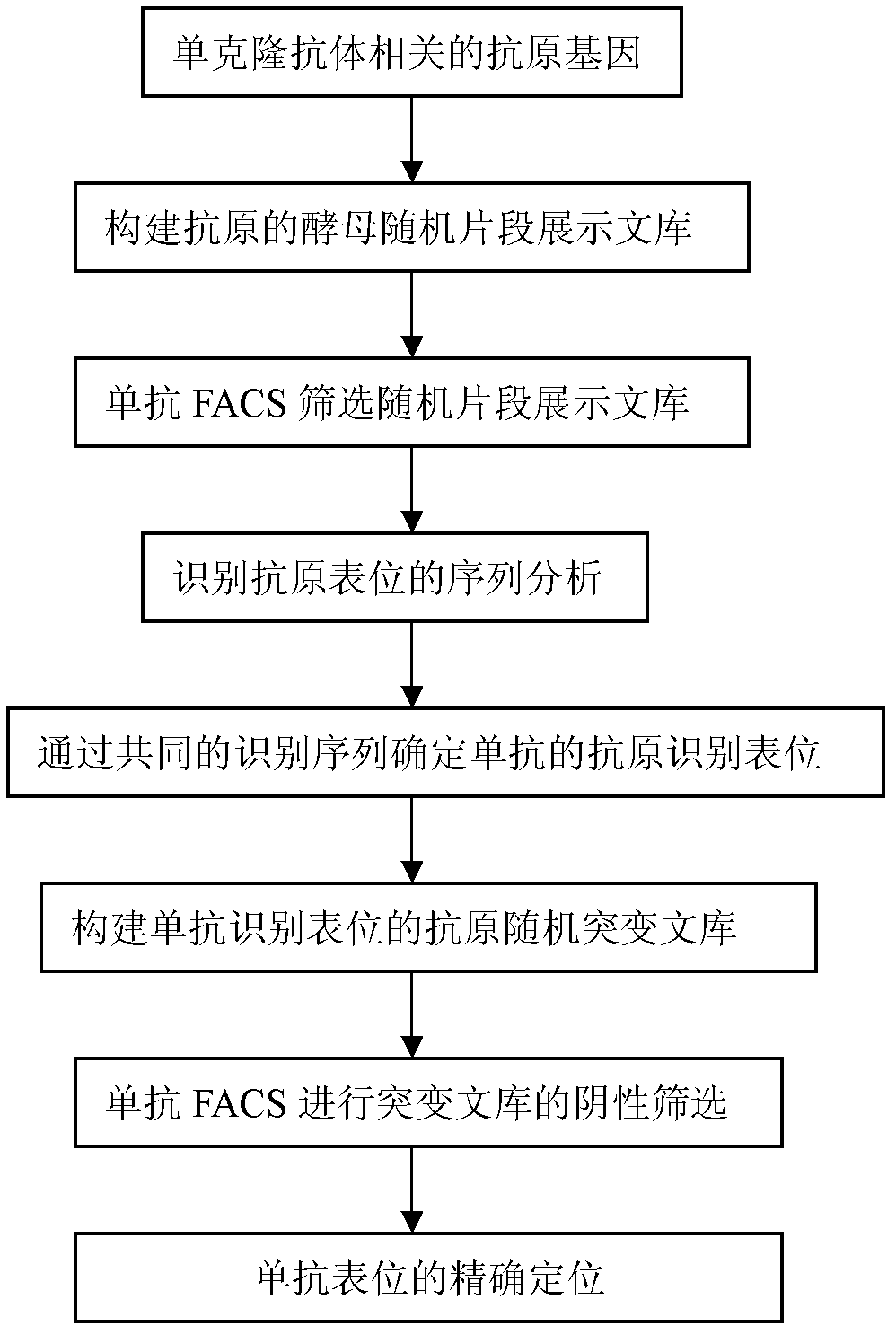
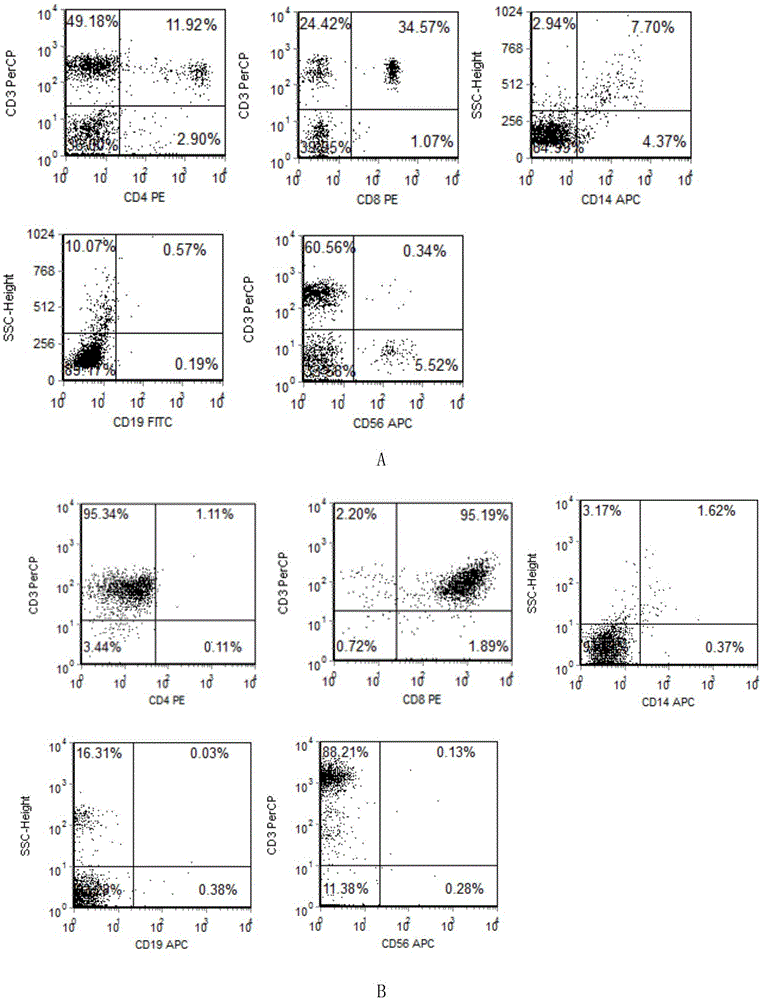
The invention discloses a method for analyzing epitope of monoclonal antibody by using a yeast surface display system and application of the method in vaccine development. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) constructing a DNA library of target protein; (2) displaying the DNA library on the surface of yeast to obtain a yeast display library; (3) mixing the monoclonal antibody of the target protein and a yeast display library A, and screening yeast combined with the monoclonal antibody; and (4) extracting plasmid of the screened yeast, sequencing, and analyzing the epitope of the target protein. Compared with the traditional method, the method has the advantages that: (1) ways of modifying the protein by yeast cells on are more, and high molecular weight and complicated protein can be displayed; (2) the yeast can be screened one by one by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS), and the accuracy and screening flux are improved; (3) the yeast can independently complete self growing and reproducing process, the operation is simple and convenient and interference factors are a few; and (4) the yeast is an immunologic adjuvant, and can check whether the epitope can induce the generation of antibody with similar activity again.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of HLA-A0201 restriction AFP antigen specific CTL
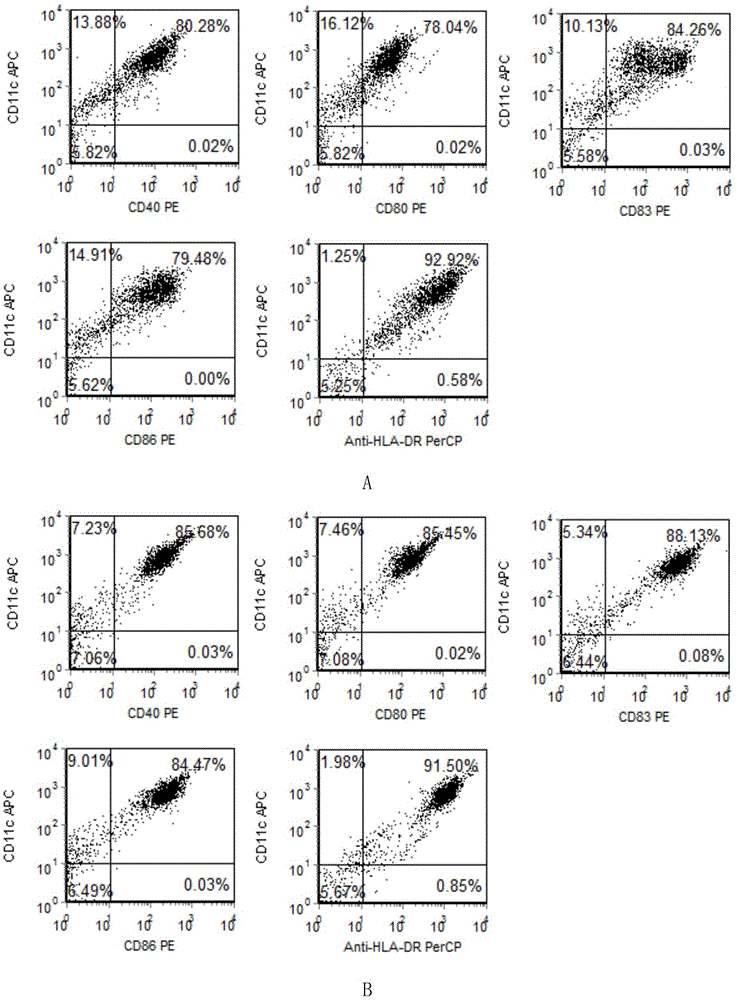
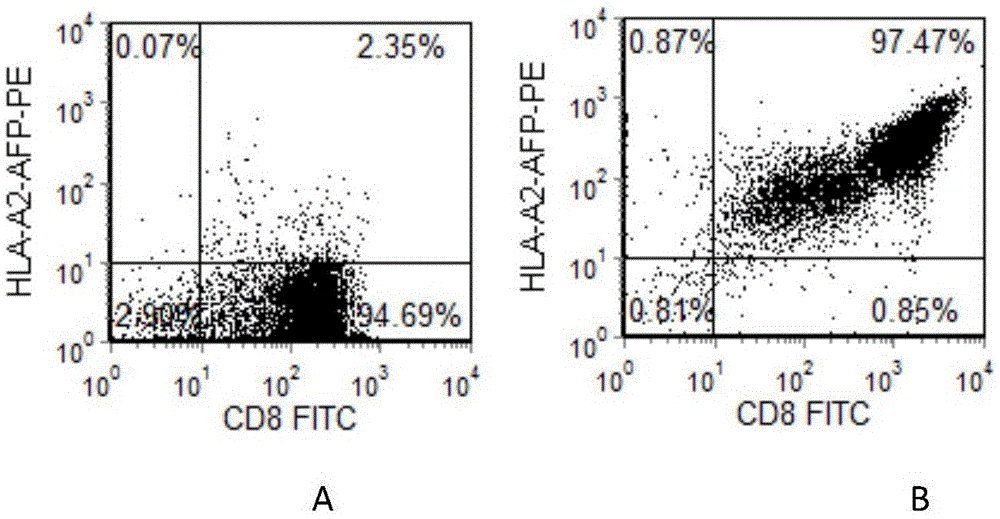
InactiveCN105524884AHigh purityImprove proliferative abilityBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsDendritic cellPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology development and application and discloses a preparation method of HLA-A0201 restriction AFP antigen specific CTL. The method is characterized in that peripheral blood mononuclear cells are collected through hemapheresis, and CD8+T lymphocytes are enriched and purified; mature dendritic cells loaded with HLA-A0201 restriction AFP antigen polypeptides are used to stimulate the CD8+T lymphocytes, and rhIL-2 and rhIL-7 are combined to promote the growth of the CD8+T lymphocytes; a Tetramer marking method and a fluorescence-activated cell sorting method are used to purify the target CTL; a solid-phase-coated anti-CD3 antibody and IL-2 are used to stimulate the growth of the target CTL; autologous PBMC irradiated by gamma rays is added to enhance the activation of the target CTL; rhIL-15 is added for culture amplification, and collection and identification are performed. The target CTL prepared by the method is high in purity, high in proliferation ability, high in killing activity, high in CTL-CM proportion, and applicable to immunological treatment of tumors and the like.
Owner:时宏珍
Method for analysis of multiple regions of DNA in single cells of uncultured microorganisms
InactiveUS20090186778A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismCulture cell
Described herein are methods for single cell sorting and DNA analysis which permit metabolic mapping of taxonomically diverse microbial cells. Methods described herein encompass procedures for single-cell separation of individual uncultured cells, such as aquatic microbial cells, by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS), subsequent single cell whole genome amplification (WGA), and downstream analyses of multiple regions of DNA.
Owner:BIGELOW LAB FOR OCEAN SCI
Fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) enrichment to generate plants
InactiveUS20140075593A1Other foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureFluorescenceBinding site
An Engineered Transgene Integration Platform (ETIP) is described that can be inserted randomly or at targeted locations in plant genomes to facilitate rapid selection and detection of a GOI that is perfectly targeted (both the 3′ and 5′ ends) at the ETIP genomic location. One element in the invention is the introduction of specific double stranded breaks within the ETIP. In some embodiments, an ETIP is described using zinc finger nuclease binding sites, but may utilize other targeting technologies such as meganucleases, TALs, CRISPRs, or leucine zippers. Also described are compositions of, and methods for producing, transgenic plants wherein the donor or payload DNA expresses one or more products of an exogenous nucleic acid sequence (e.g. protein or RNA) that has been stably-integrated into an ETIP in a plant cell. In embodiments, the ETIP facilitates testing of gene candidates and plant expression vectors from ideation through Development phases.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
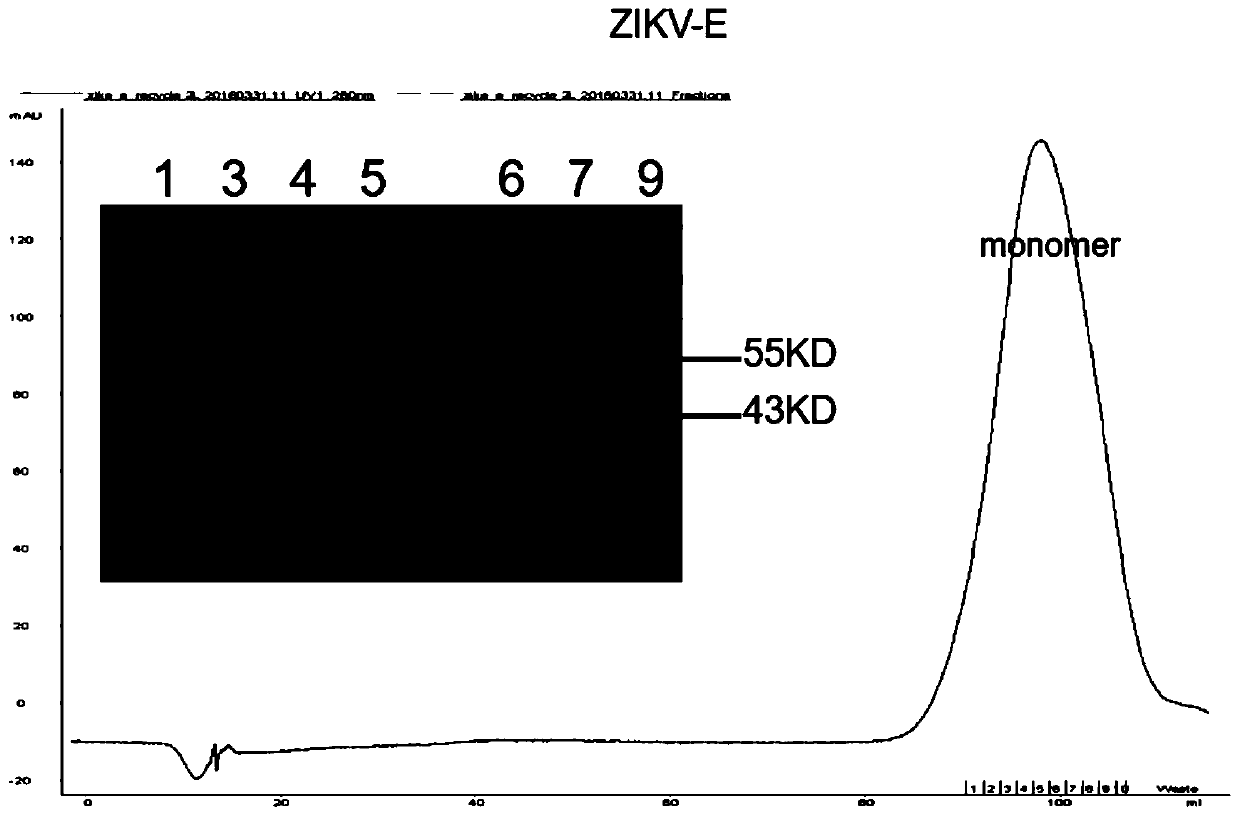
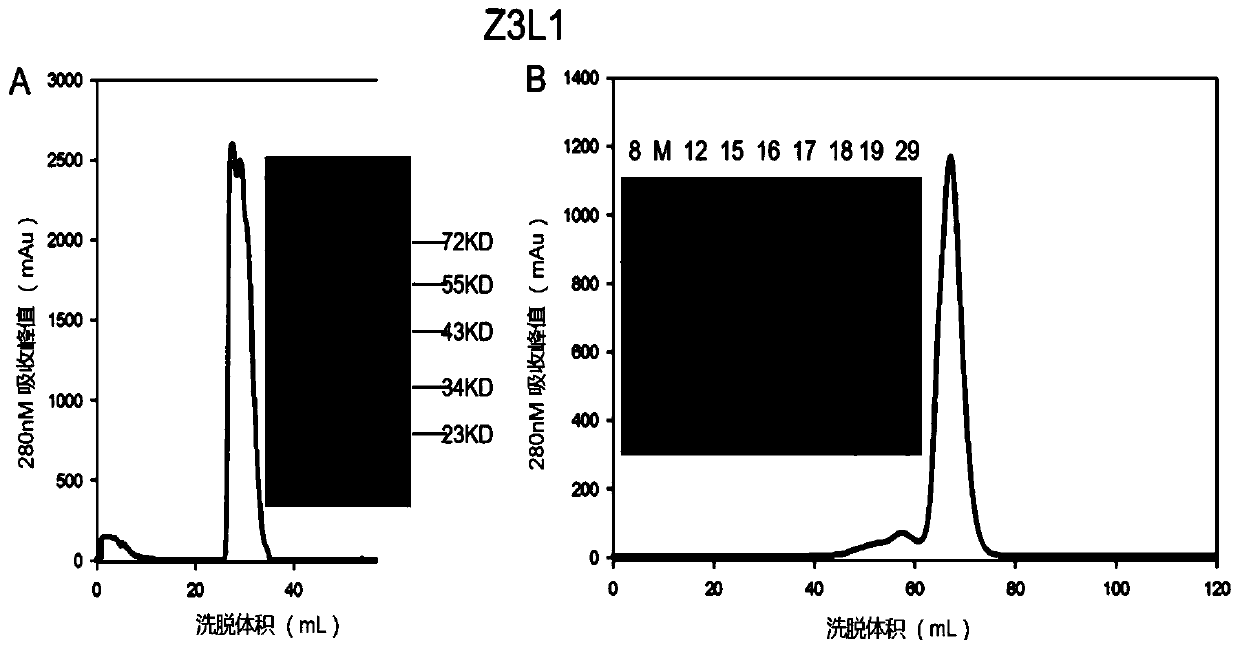
Specific Zika virus neutralizing antibodies and application thereof
ActiveCN110066333AFree from attackStrong neutralizing activityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsEscherichia coliAntigen
The invention discloses specific Zika virus neutralizing antibodies and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medicine. Zika E protein expressed by colibacillus serves as an antigen, through fluorescence-activated cell sorting, memory B cells capable of being specifically bound with the Zika E protein are screened in PBMCs of a Zika patient in the rehabilitation stage, the screened single B cells are subjected to a RT-PCR, the sequence and segments of the variable region of the antibody are obtained, and the variable region and the constant region are connected in an expression vector. After mammalian cell expression and purification, a series of function detection is conducted, such as the binding force of the ZIKE-E protein, the in-vitro neutralizing effect and the in-vivo protection capacity, and the three human monoclonal antibodies capable of completely protecting Zika virus infection are obtained.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
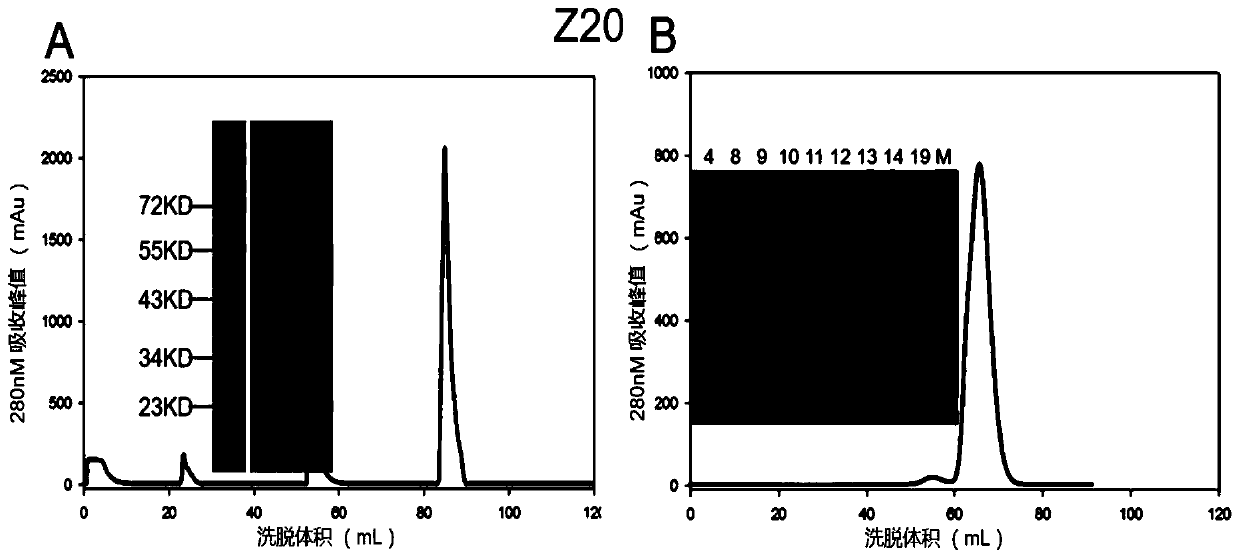
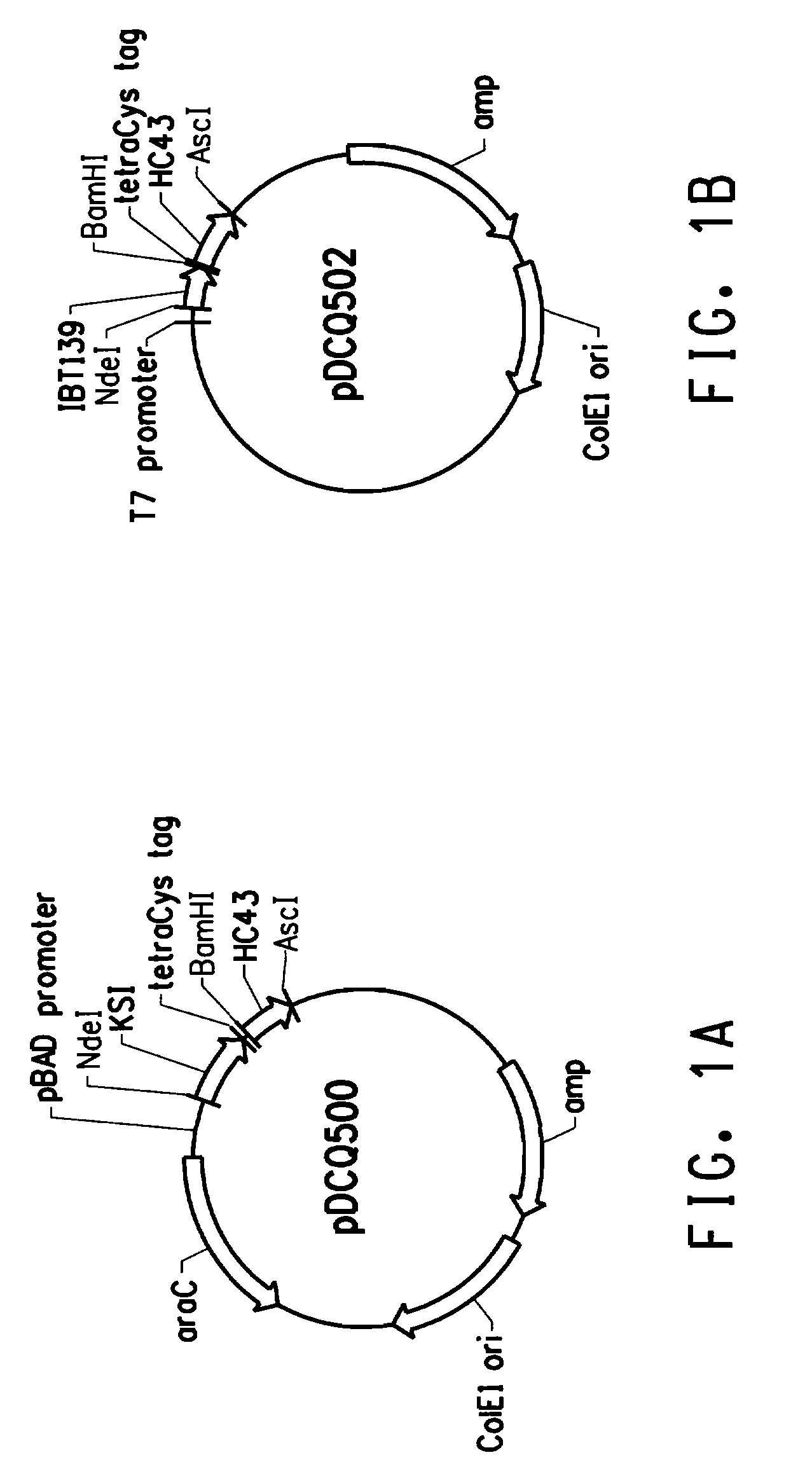
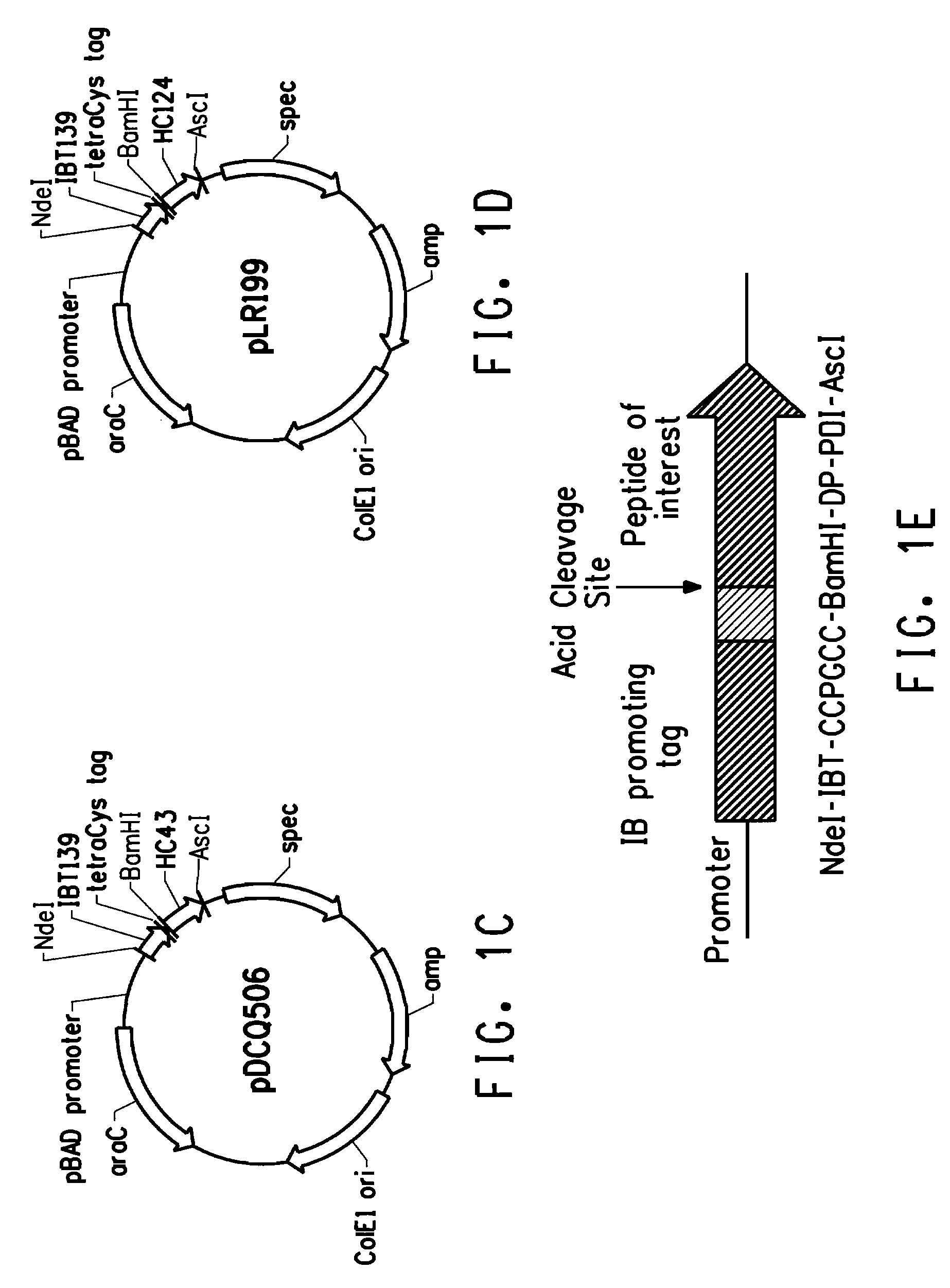
Use of tetracysteine tags in fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis of prokaryotic cells producing peptides or proteins
InactiveUS20090117609A1Efficient and fast detectionFast and efficient and selectionPeptide/protein ingredientsPolypeptide with affinity tagCell sorterIn vivo
A process of in vivo labeling and identifying recombinantly produced peptides or proteins within an unpermeabilized prokaryotic host cell. Recombinant prokaryotic cells expressing a fusion peptide comprising at least one tetracysteine tag were labeled in vivo using a biarsenical labeling reagent. A fluorescent activated cell sorter was used to identify and select subpopulations of fluorescent cells wherein the amount of fusion peptide in the cell was proportional to the amount of fluorescence detected.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
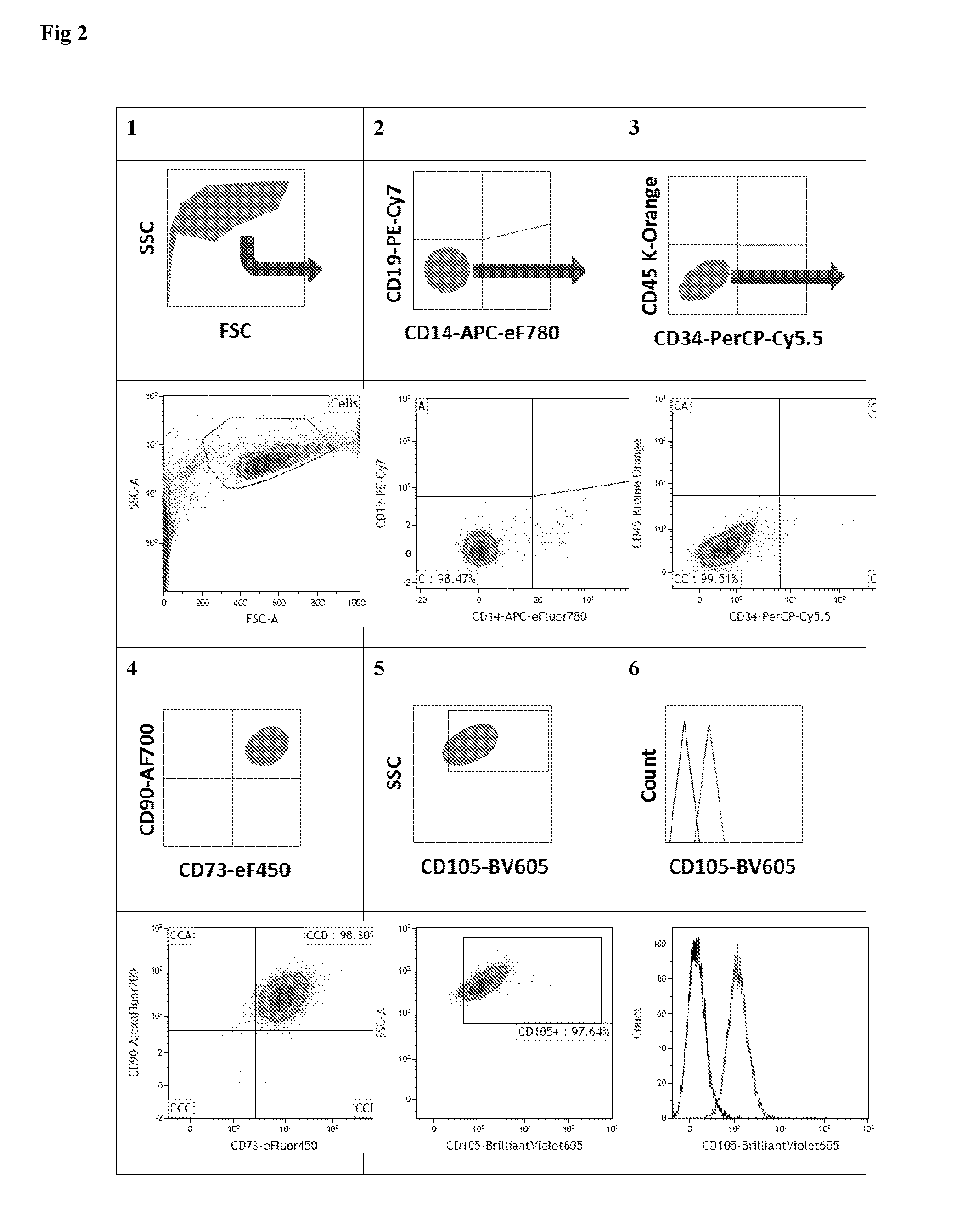
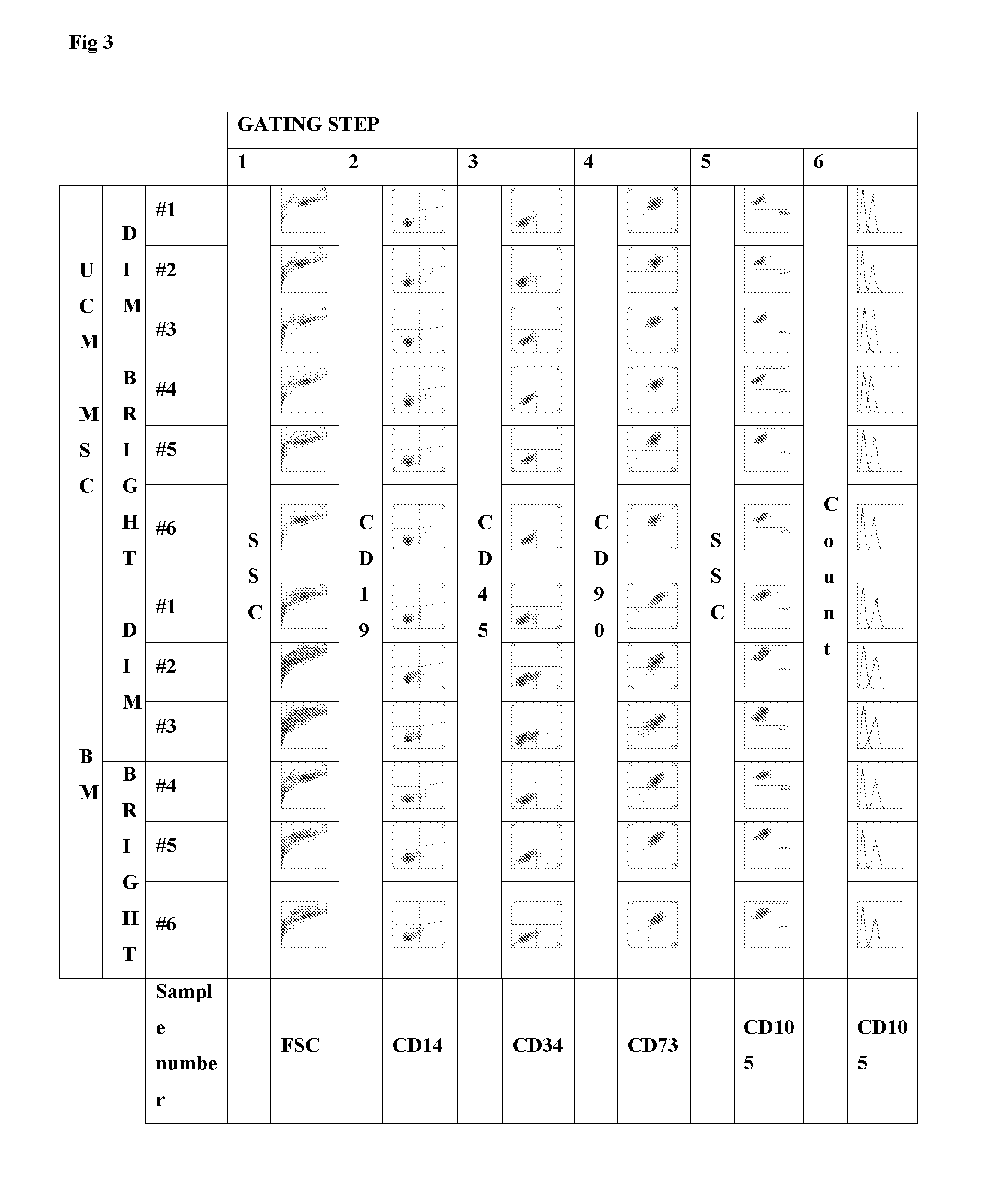
Multicolor flow cytometry method for identifying a population of cells, in particular mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveUS20160123980A1Improve accuracyHigh sensitivityPeptide librariesLibrary screeningMesenchymal stem cellCell type
This invention is in the field of the identification and even isolation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and other cell types by means of differential specific fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS).
Owner:CELL THERAPY LTD
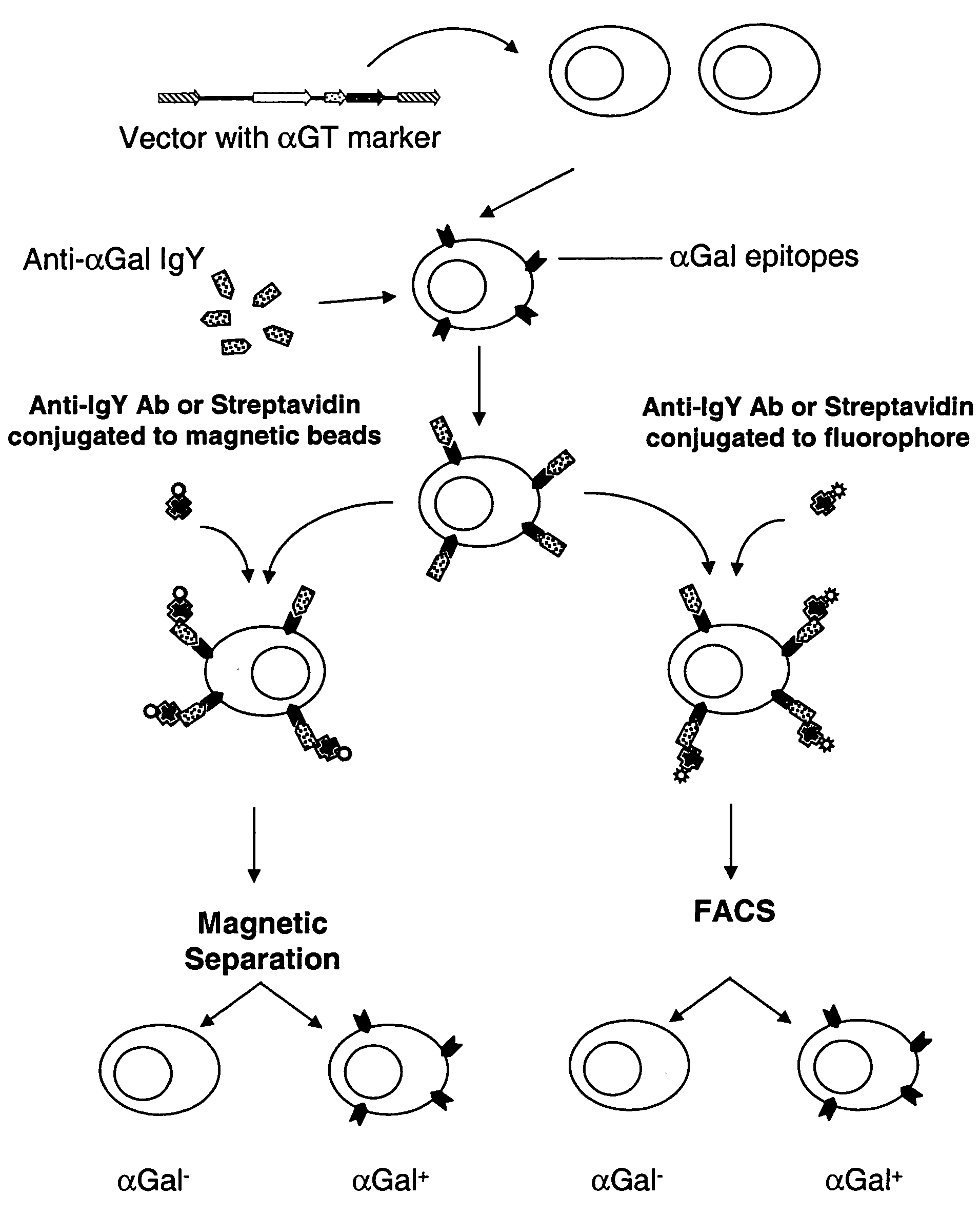
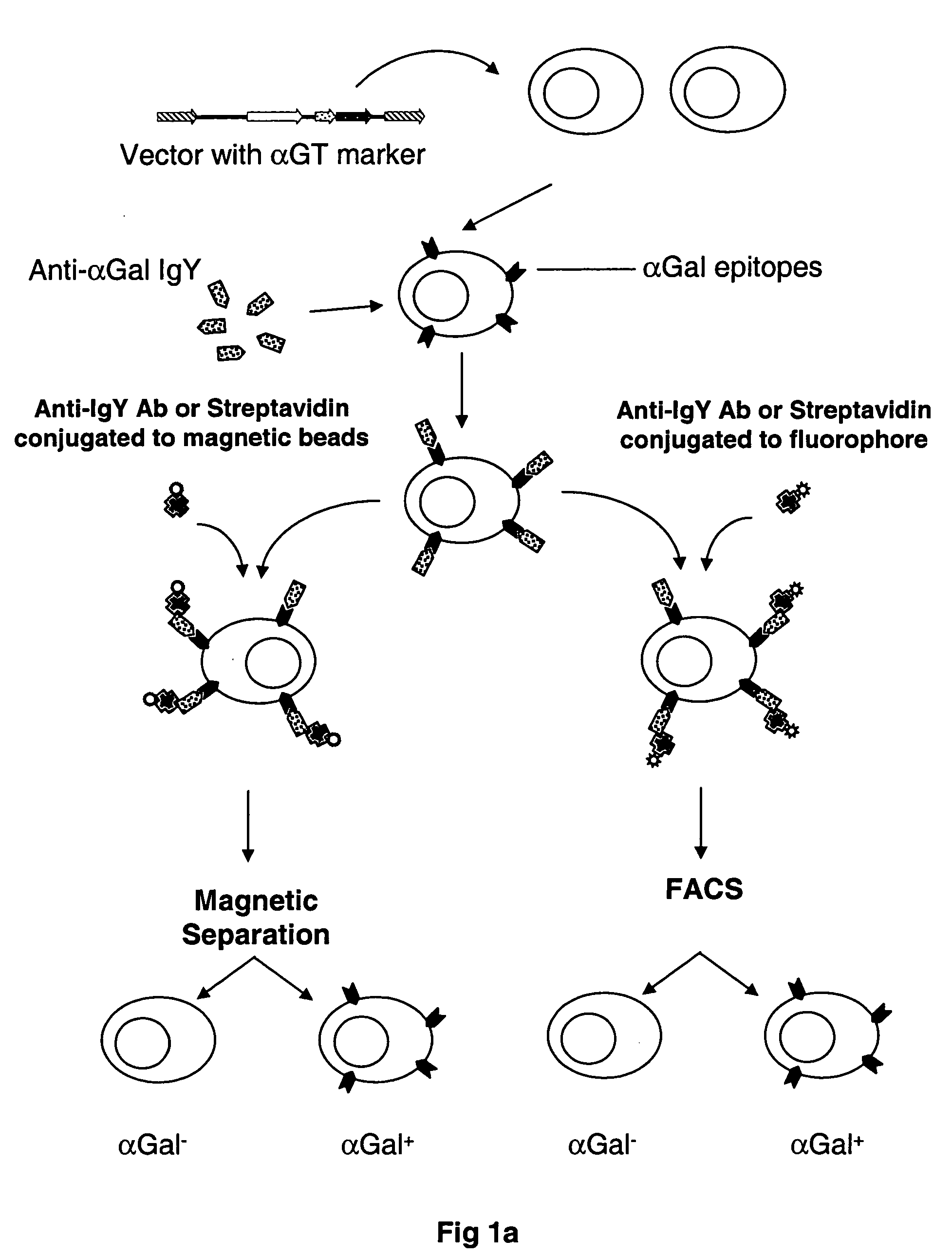
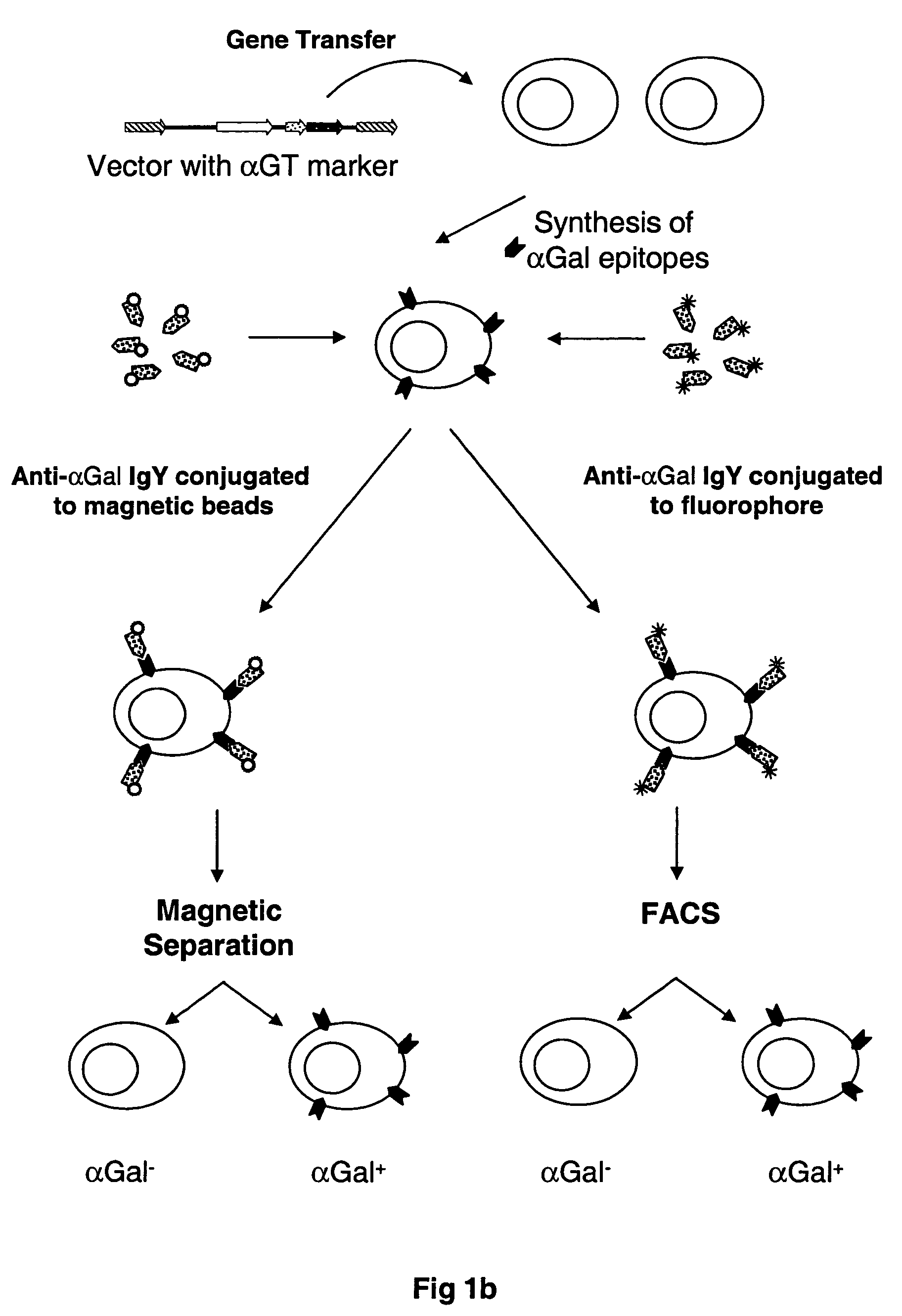
Selectable gene marker system based on expression of N-acetyllactosaminide 3-alpha galactosyltransferase
InactiveUS20050250107A1Facilitate functional studyImprove satisfactionEgg immunoglobulinsVirusesLipid formationFluorescence
A method is described for the rapid identification and isolation of cells based on the presence or absence of an ectopically-expressed N-acetyllactosaminide 3-α Galactosyltransferase (αGT) enzyme for the production of αGalactosyl-(1,3)Galactosyl (αGal) epitopes on the surface of αGal-negative cells. These cells which are genetically modified to express the αGT enzyme and αGal epitopes on glycosylated lipids and proteins of the cell surface are then labeled via an antibody composition which recognizes and binds the αGal epitopes on the cell surface. Cells labeled with the anti-αGal antibody can be isolated by sorting via fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS), or by magnetic panning techniques. This method is suitable for the rapid positive or negative selection of αGal-positive cells from within a population of αGal-negative cells without the need to expose cells to antibiotics for any period of time. In addition, the specification provides a method for the production and purification of anti-αGal antibodies from chicken egg yolk.
Owner:NEWLINK GENETICS
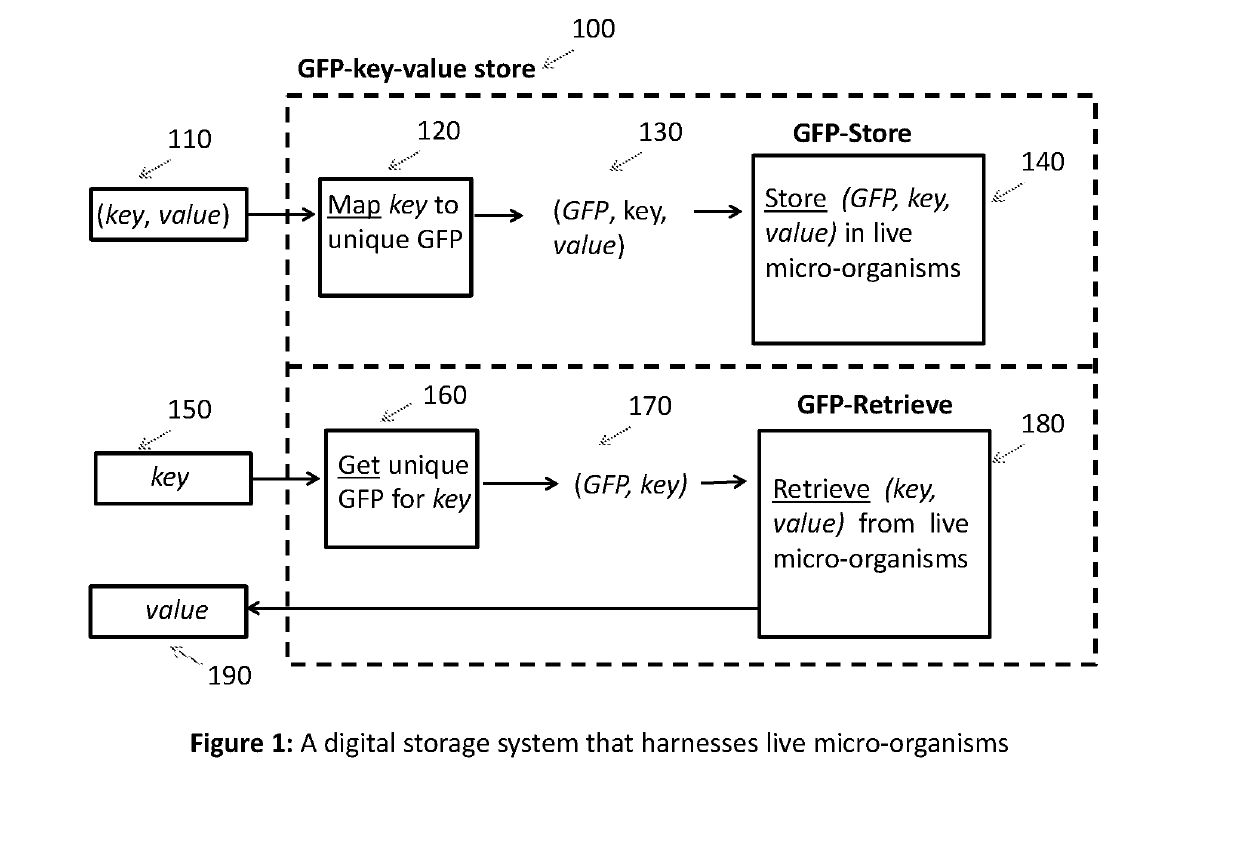
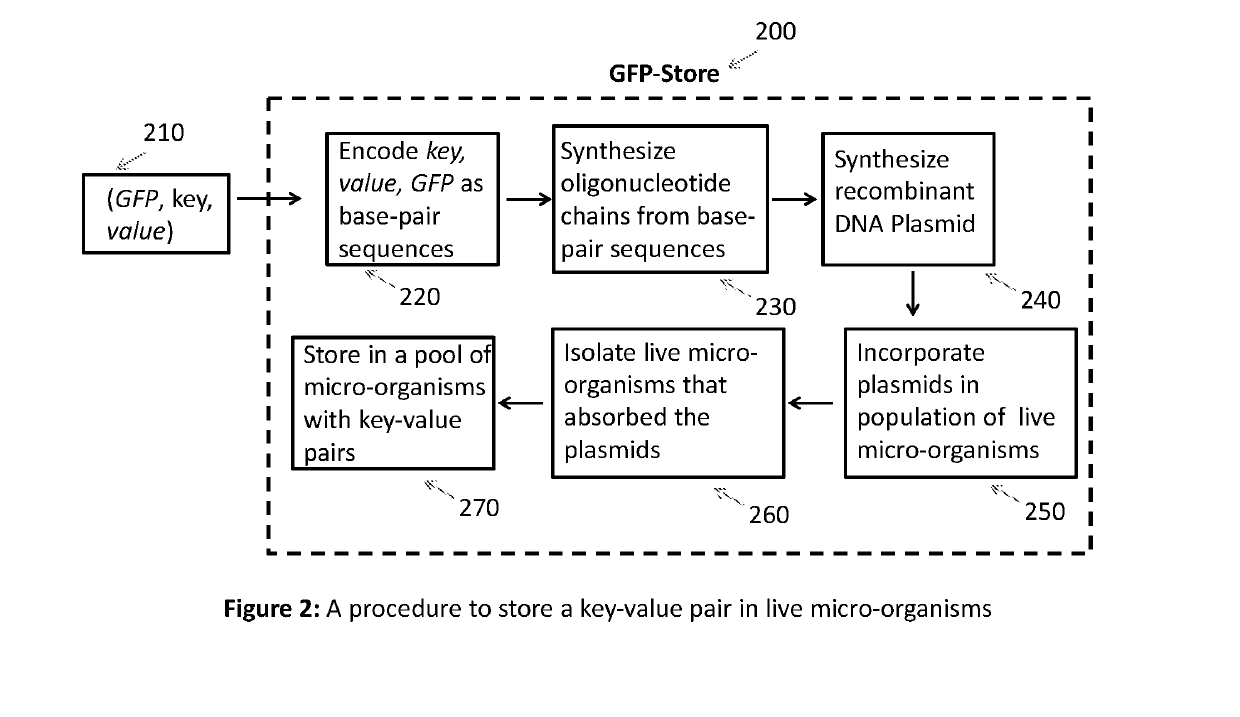
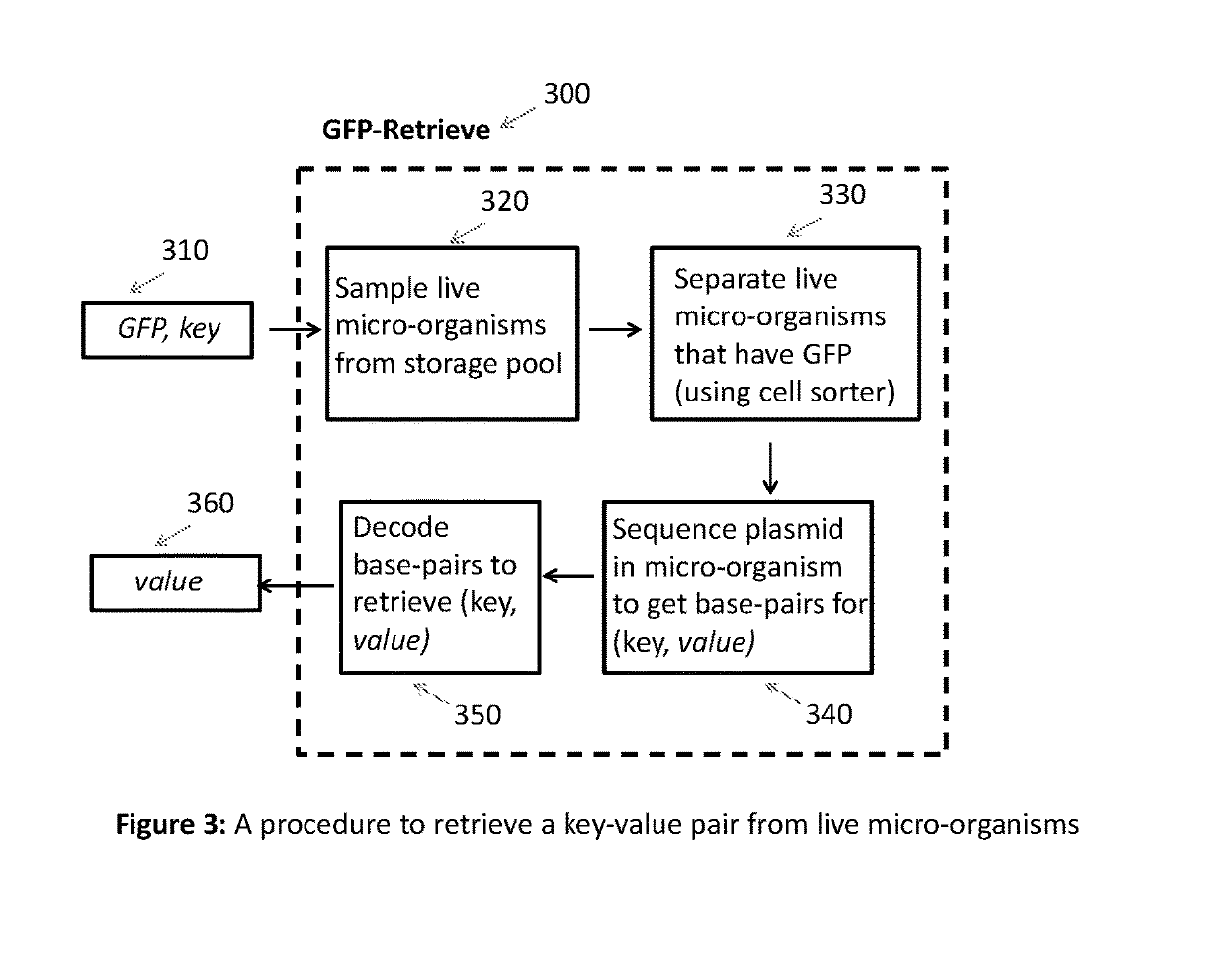
Key-value store that harnesses live micro-organisms to store and retrieve digital information
PendingUS20190194738A1Reduce storage costsReduce retrieval timeMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual particle analysisCell phenotypeCell sorter
A digital store comprising of a method to store digital data in live micro-organisms, and a method to selectively retrieve subsets of stored data, is disclosed. Digital data is represented as a plurality of key-value pairs. The proposed system stores copies of key-value pairs in a plurality of live micro-organisms. Upon presentation of a retrieval key, the proposed digital store retrieves the value associated with the retrieval key. Storage method for a key-value pair comprises of (a) mapping the key to a gene that expresses a unique fluorescent protein so that no two keys map to the same gene, (b) encoding the key-value pair as base-pair sequences, (c) synthesizing oligonucleotide chains from base-pairs for the key-value pair and the gene, (d) synthesizing recombinant DNA plasmids that have oligonucleotide chains for the key-value pair, the gene, and two primers, as foreign DNA inserts, (e) incorporation of recombinant DNA plasmids into live micro-organisms, (f) isolation of live micro-organisms that have absorbed the recombinant DNA plasmids, and (g) safe storage of population of live micro-organisms with embedded key-value pairs in a common pool. Retrieval of the value paired with a key comprises of (a) taking as input the retrieval key, and mapping the key to the specific gene for fluorescent protein, (b) taking a sample from the safe storage pool that contains live micro-organisms embedded with key-value pairs, (c) isolating the live micro-organisms that have expressed the gene by using high-speed fluorescence activated cell sorting or flow cytometry, (d) extracting DNA from the recombinant DNA plasmid in the isolated live micro-organisms, (d) selectively amplifying and sequencing only those DNA strands that contain the value for the key, and (e) decoding the base-pair sequence obtained after DNA sequencing to yield the value associated with the retrieval key.We also disclose two important variations. The first variation relates to the storage step. The recombinant DNA plasmid is constructed to include additional non-fluorescent oligonucleotides and genes so that during the data retrieval step, the live micro-organisms that have absorbed the said plasmid can be sorted by cell sorters based on parameters of individual cells such as cell size, cell complexity, cell phenotype, cell structure, cell function, and magnetic or electrical properties. The second variation relates to both storage and retrieval of key-value pairs with large values. To store such a key-value pair, the large value is split into smaller blocks so that a block can fit into a recombinant DNA plasmid, and a distinct pair of primers is used for each block. A block's primer pair is used to selectively amplify and sequence only the DNA that encodes the data in the block, thereby enabling the retrieval of a specific block of the value, as opposed to retrieving the entire value associated with a key.
Owner:CHAKRADHAR ANJALI
Method for generating high affinity antibodies
ActiveUS10752698B2High affinityEasy to manufactureGenetically modified cellsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsLymphocytic cellNucleic acid cloning
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Ultrahigh-flux screening method for phosphotriesterase
ActiveCN105218583AImprove retentionImprove hydrophilicityMicrobiological testing/measurementGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsHigh fluxScreening method
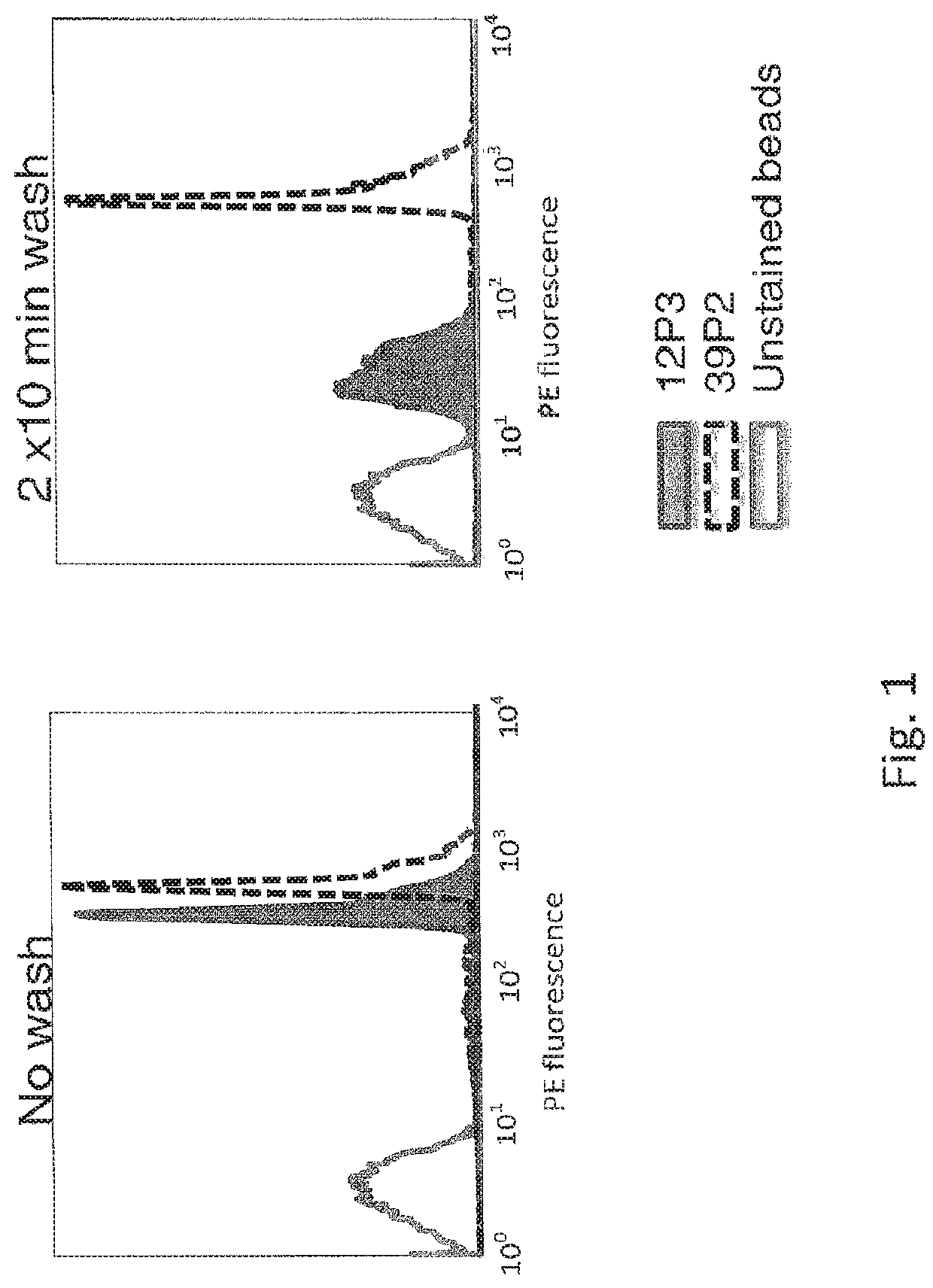
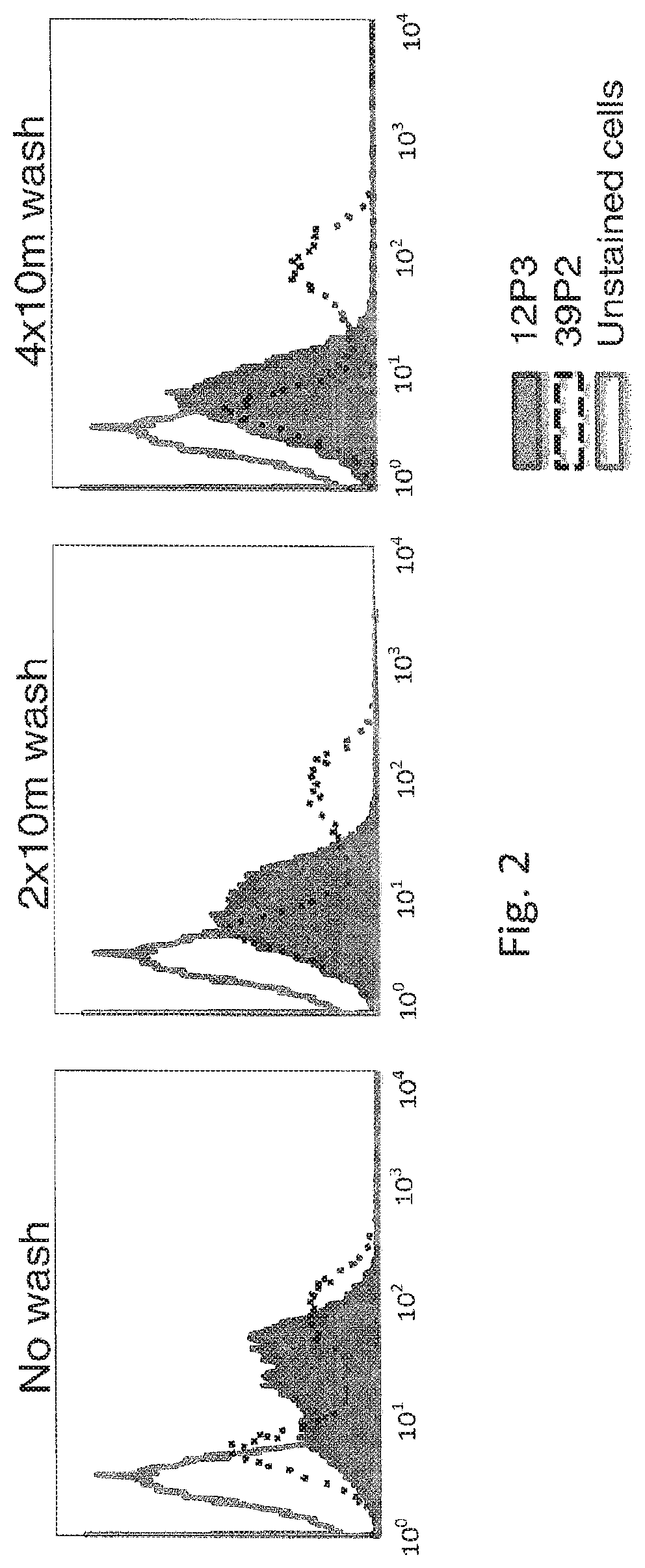
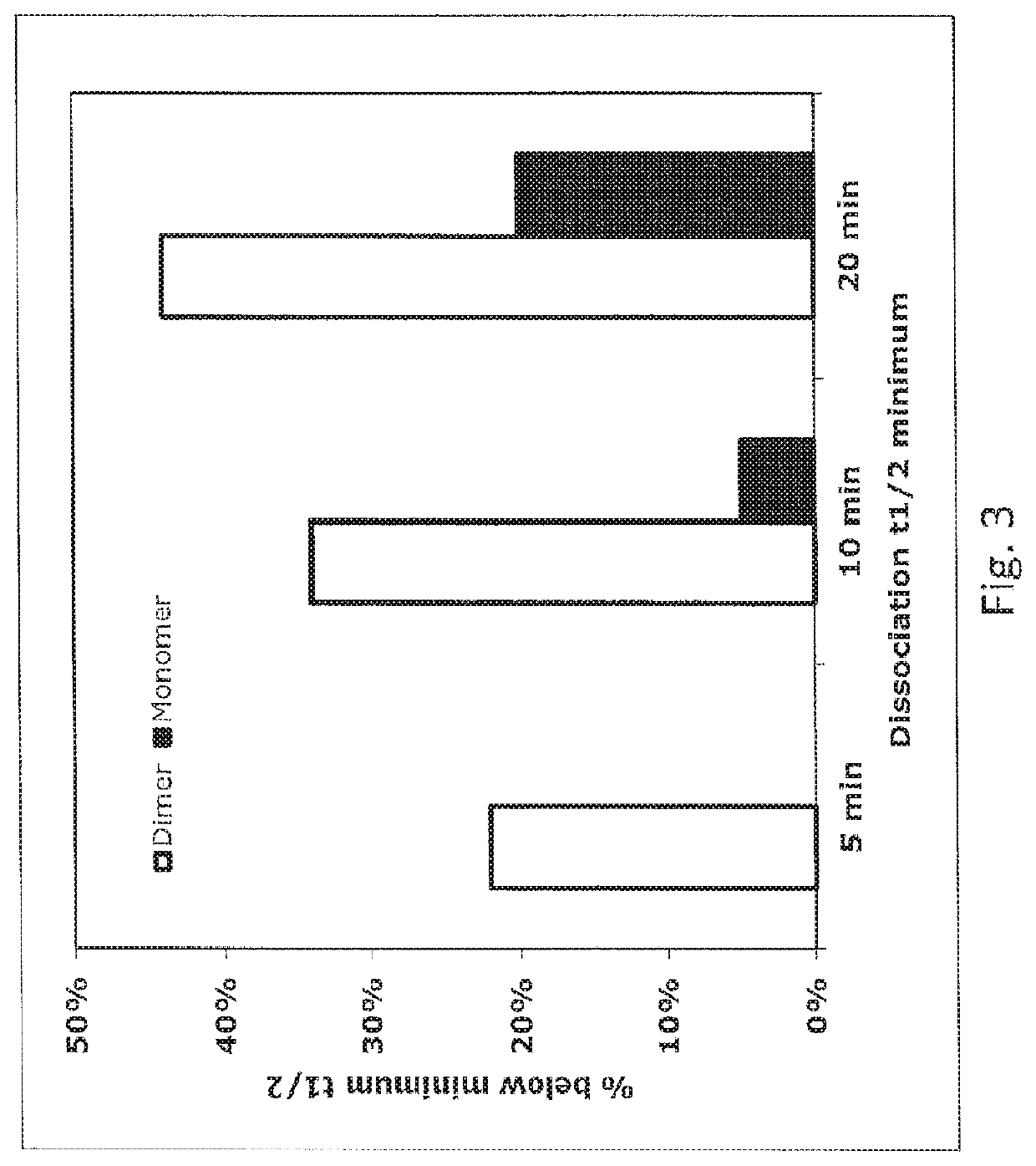
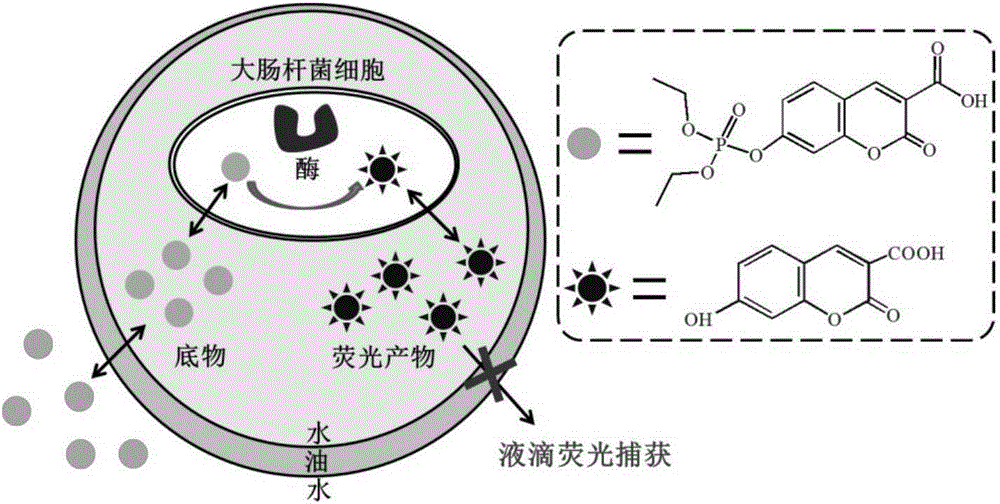
The invention belongs to the field of enzyme engineering and discloses a carboxyl coumarin based phosphotriesterase fluorogenic substrate and a substrate based high-flux screening method for phosphotriesterase. The method is an in vitro compartmentalization based fluorescence-activated cell sorting ultrahigh-flux screening technology for phosphotriesterase. According to the method, a reacted fluorescent product of the carboxyl coumarin based phosphotriesterase substrate has a very good droplet retention property and has the advantages of high sensitivity and accuracy in quantification in the quantifying and screening of enzymatic activity. Due to the hydrophilic difference between the substrate and a reaction product, the substrate can be added into an external water phase and seep through an oil phase for enzymatic reaction; and the produced product is retained in liquid droplets due to improved hydrophilicity, so that the effect of liquid droplet fluorescence capture is achieved, the reaction time is accurately controlled, the fluorescent background interference is lowered, and the accuracy of screening is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Methods of isolating hepatic progenitors
This invention relates to methods of isolating hepatoblasts utilizing panning techniques and fluorescence activated cell sorting. This invention further relates to isolated hepatoblasts and to a method of treating liver dysfunction as well as to methods of forming artificial livers.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
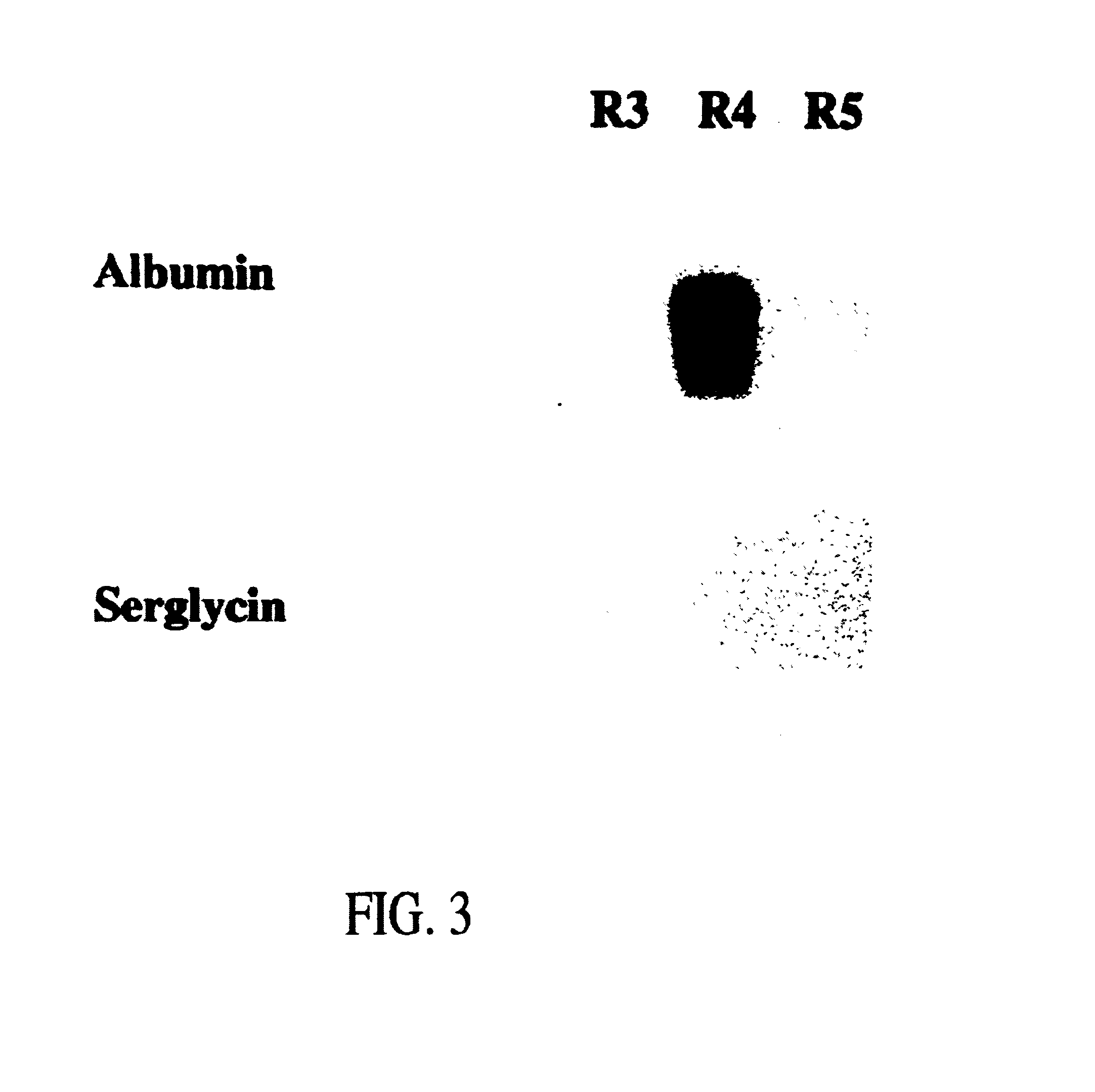
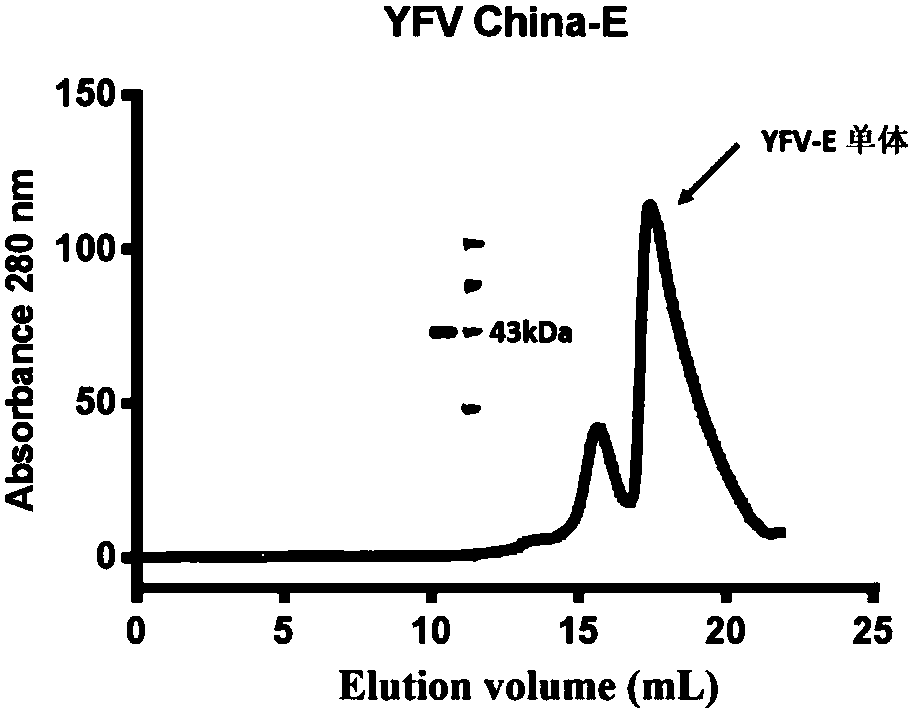
High-functional-activity yellow fever virus humanized monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN110343173AHigh affinityFree from attackBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against virusesEscherichia coliAntigen
The present invention discloses a high-functional-activity yellow fever virus humanized monoclonal antibody and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. A yellow fevervirus E protein expressed by escherichia coli is used as an antigen, memory B cells specifically combined with the yellow fever virus E protein are screened from PBMCs of a case of a convalescent patient through fluorescence-activated cell sorting, then the screened single B cells are subjected to RT-PCR and PCR amplification to obtain an antibody variable region segment, and the antibody variableregion segment is further connected with a constant region into an expression vector. After mammalian cell expression and purification, a series of function detections are carried out to obtain the humanized monoclonal antibody with a function of protecting from yellow fever virus infection. The antibody has affinity with the antigen at 0.588 nM, has strong yellow fever virus neutralization activity, has IC50 at 3.7ng / ml, can completely protect mice from being attacked by yellow fever viruses with a lethal dose, and has application values of clinical treatment and prevention of the yellow fever viruses.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Early post-transfection isolation of cells (EPIC) for biologics production
InactiveUS20180119192A1Increase productionCD52Individual particle analysisFluorescenceMagnetic-activated cell sorting
Provided herein are methods for selecting a population of cells expressing a target polypeptide. In some aspects, the disclosure provides methods for sorting and selecting populations of transfected host cells based on their early expression of a selectable polypeptide. In certain embodiments, the sorting is performed using fluorescence-activated cell sorting or magnetic-activated cell sorting based on the selectable polypeptide. Such selection methods can be further utilized to generate clonal populations of producer cells, e.g. for large-scale manufacturing of a target polypeptide of interest.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) enrichment to generate plants
InactiveCN104736712AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionFluorescenceBinding site
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com