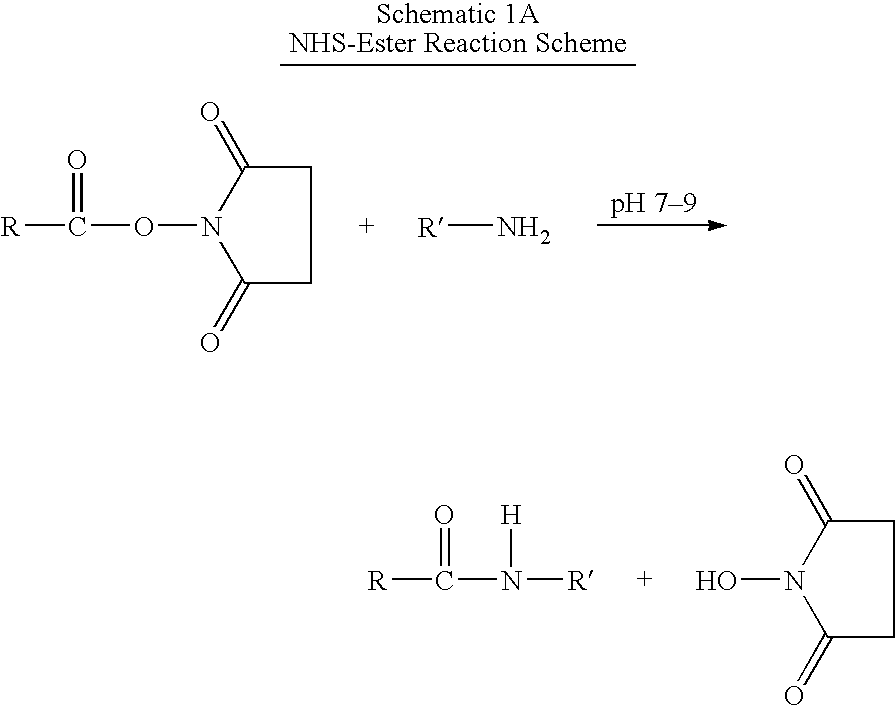
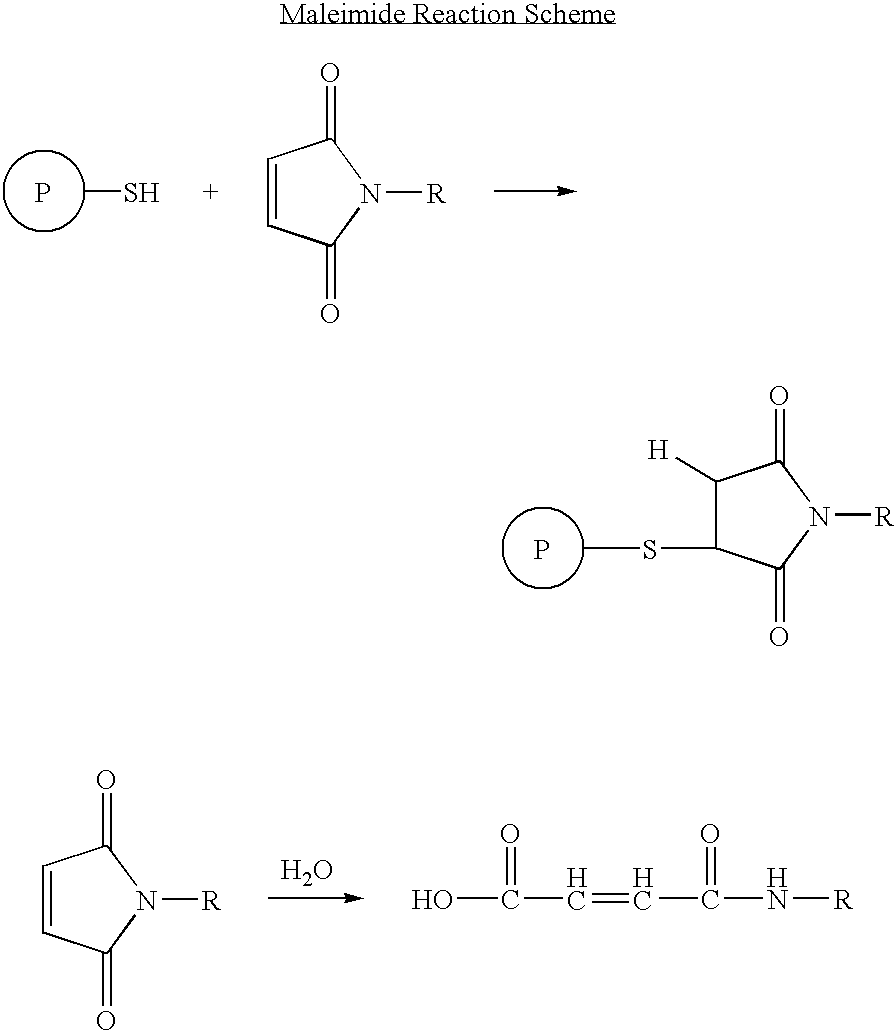
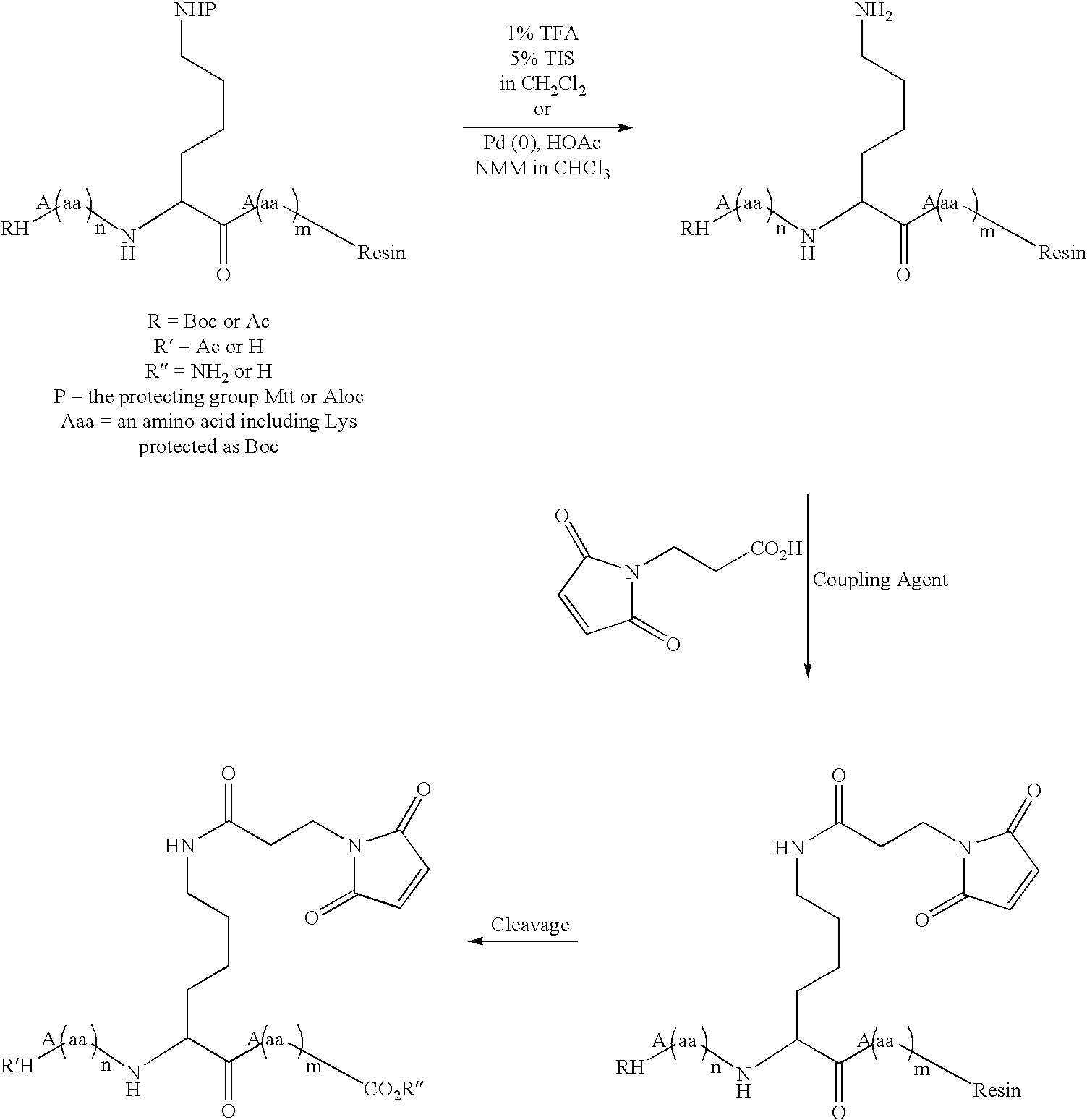
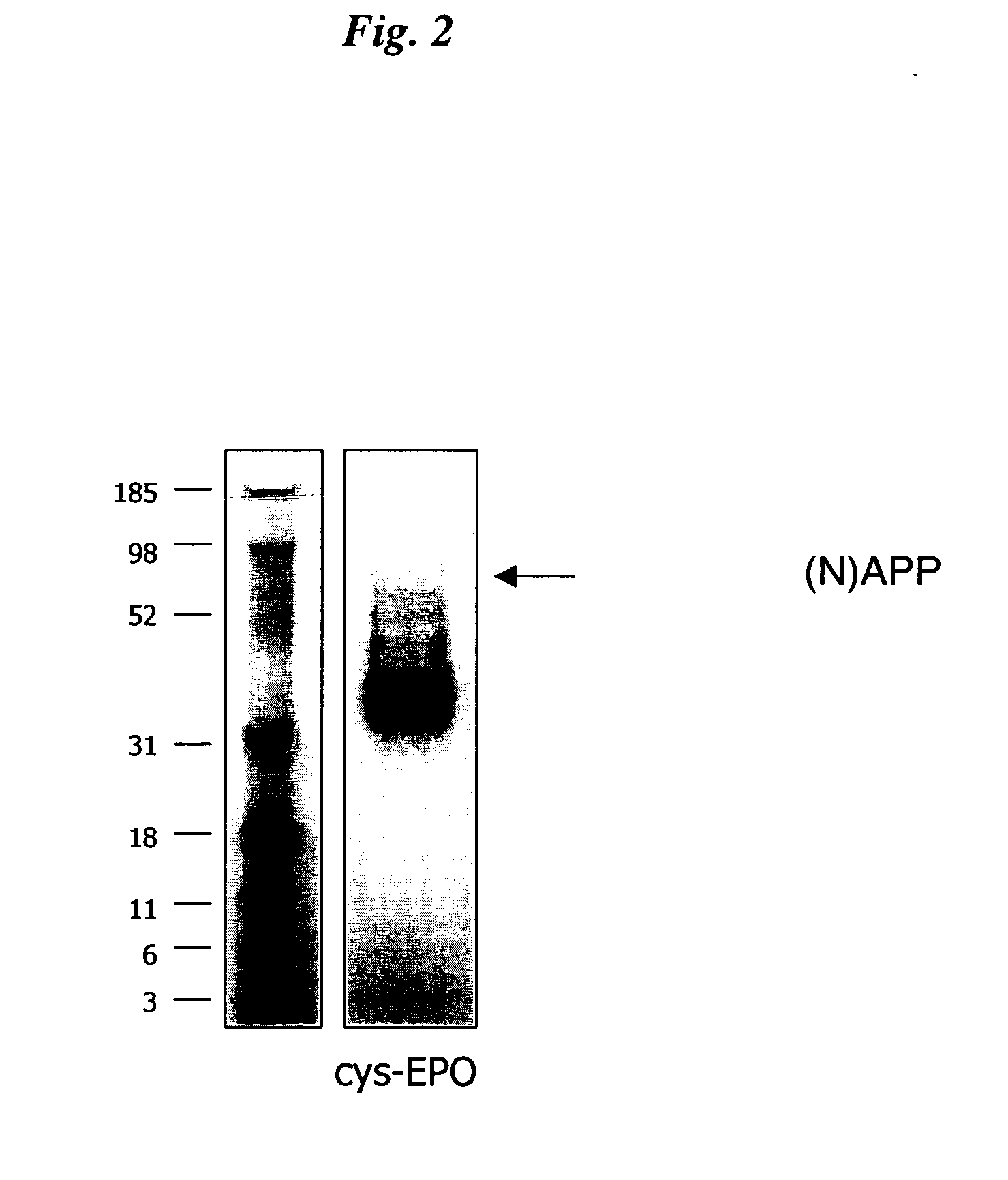
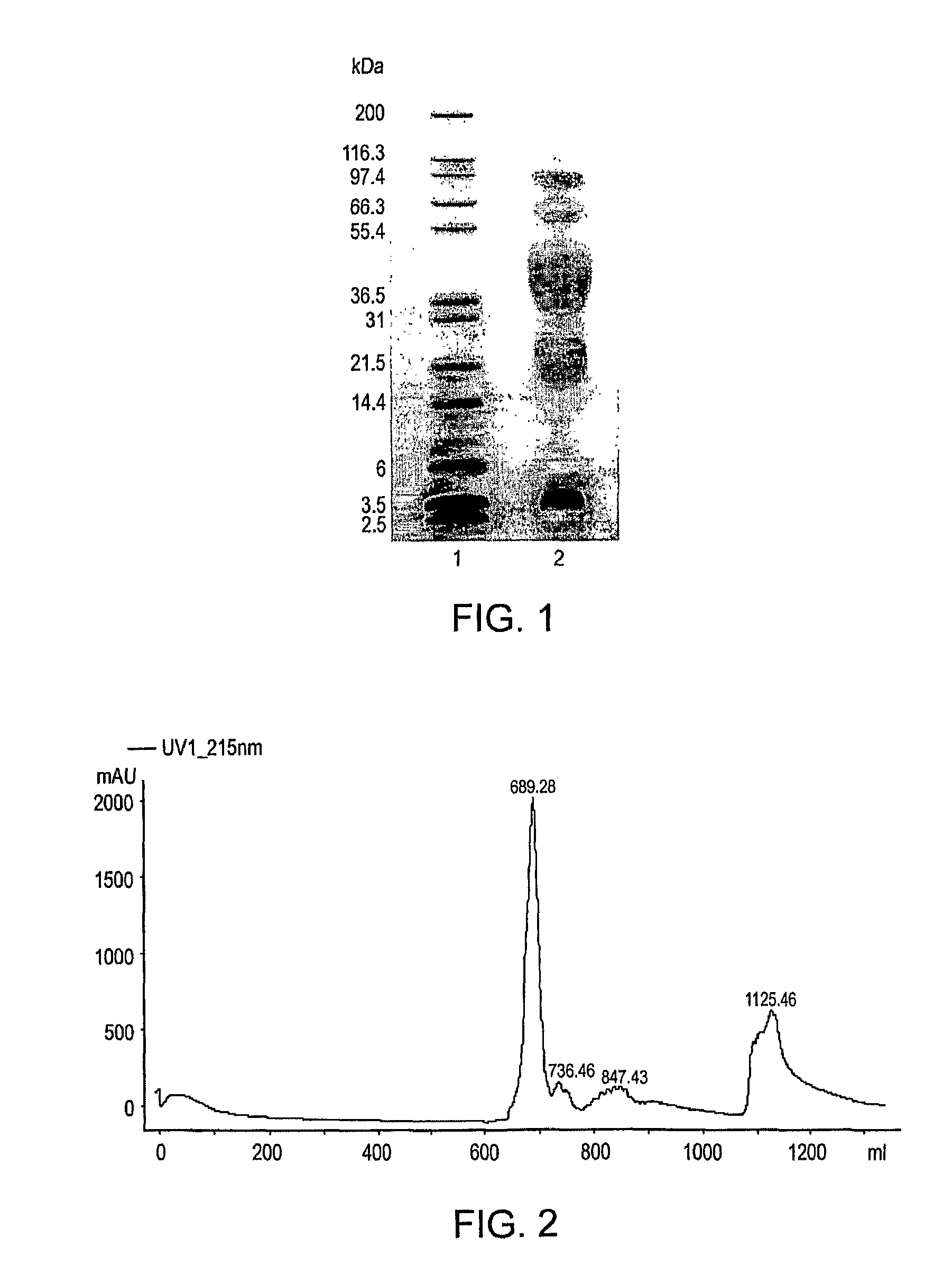
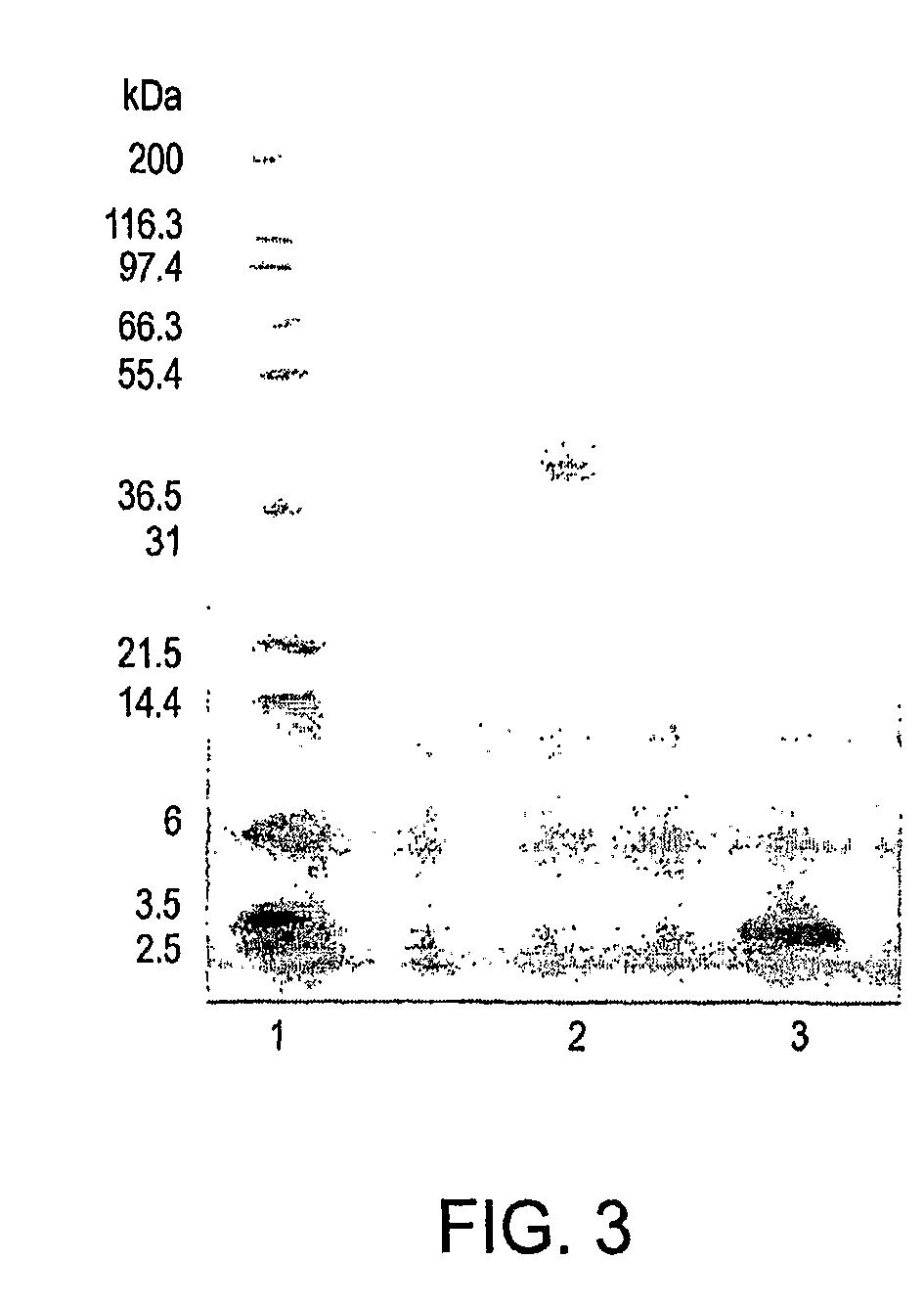
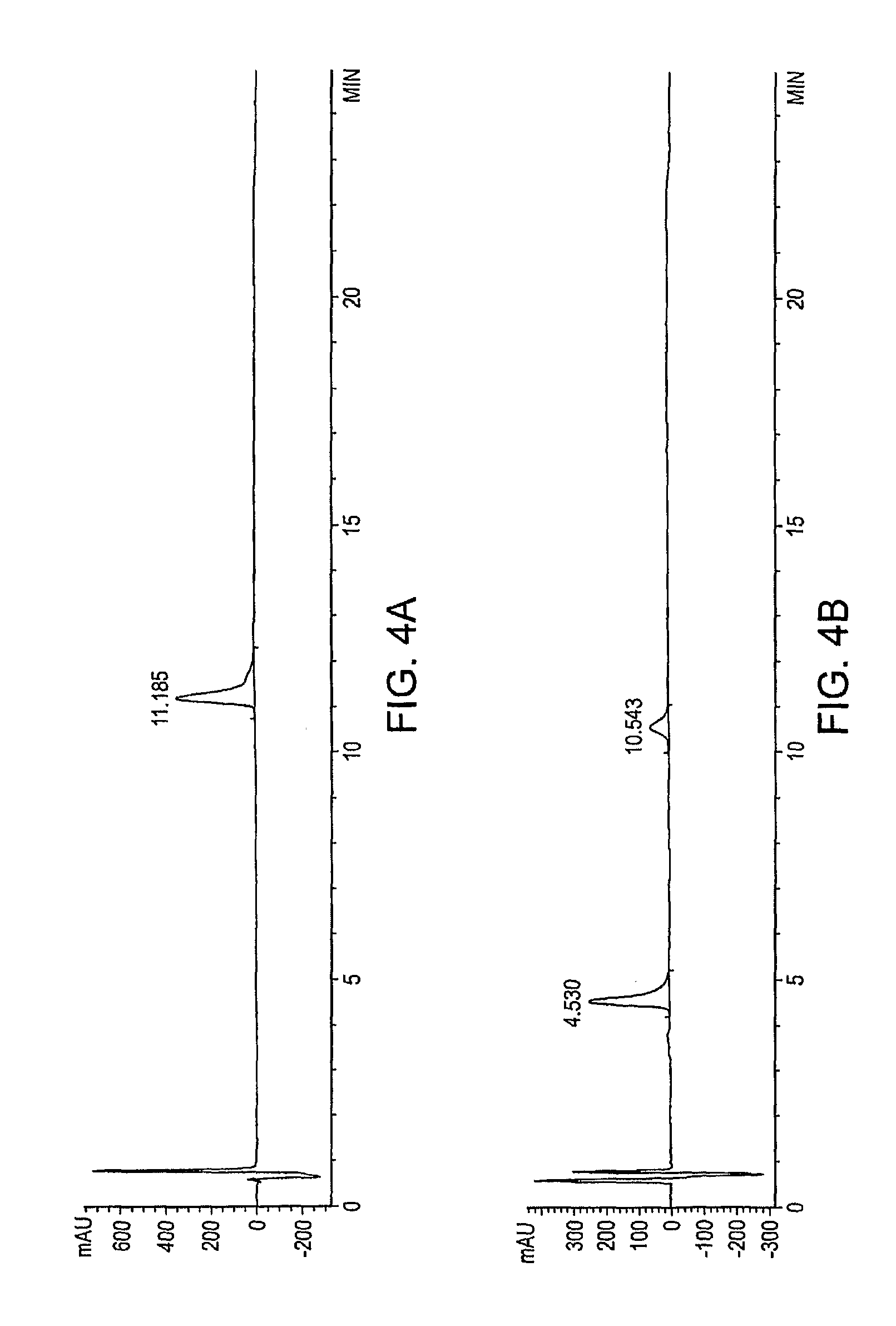
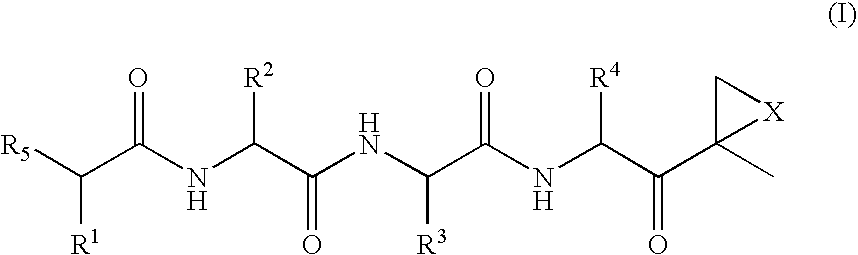
Patents
Literature
721 results about "N-terminus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH₂-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide referring to the free amine group (-NH₂) located at the end of a polypeptide. Normally the amine group is bonded to another carboxylic group in a protein to make it a chain, but since the end of a protein has only 1 out of 2 areas chained, the free amine group is referred to the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right in LTR languages. This correlates the translation direction to the text direction (because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus - amino acids are added to the carbonyl end).
Protection of endogenous therapeutic peptides from peptidase activity through conjugation to blood components
InactiveUS6887470B1Easy to testPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBlood componentCombinatorial chemistry
A method for protecting a peptide from peptidase activity in vivo, the peptide being composed of between 2 and 50 amino acids and having a C-terminus and an N-terminus and a C-terminus amino acid and an N-terminus amino acid is described. In the first step of the method, the peptide is modified by attaching a reactive group to the C-terminus amino acid, to the N-terminus amino acid, or to an amino acid located between the N-terminus and the C-terminus, such that the modified peptide is capable of forming a covalent bond in vivo with a reactive functionality on a blood component. In the next step, a covalent bond is formed between the reactive group and a reactive functionality on a blood component to form a peptide-blood component conjugate, thereby protecting said peptide from peptidase activity. The final step of the method involves the analyzing of the stability of the peptide-blood component conjugate to assess the protection of the peptide from peptidase activity.
Owner:CONJUCHEM
Novel recombinant proteins with N-terminal free thiol
InactiveUS20050170457A1Extended half-lifeIncreases circulating serum half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureCysteine thiolateHalf-life
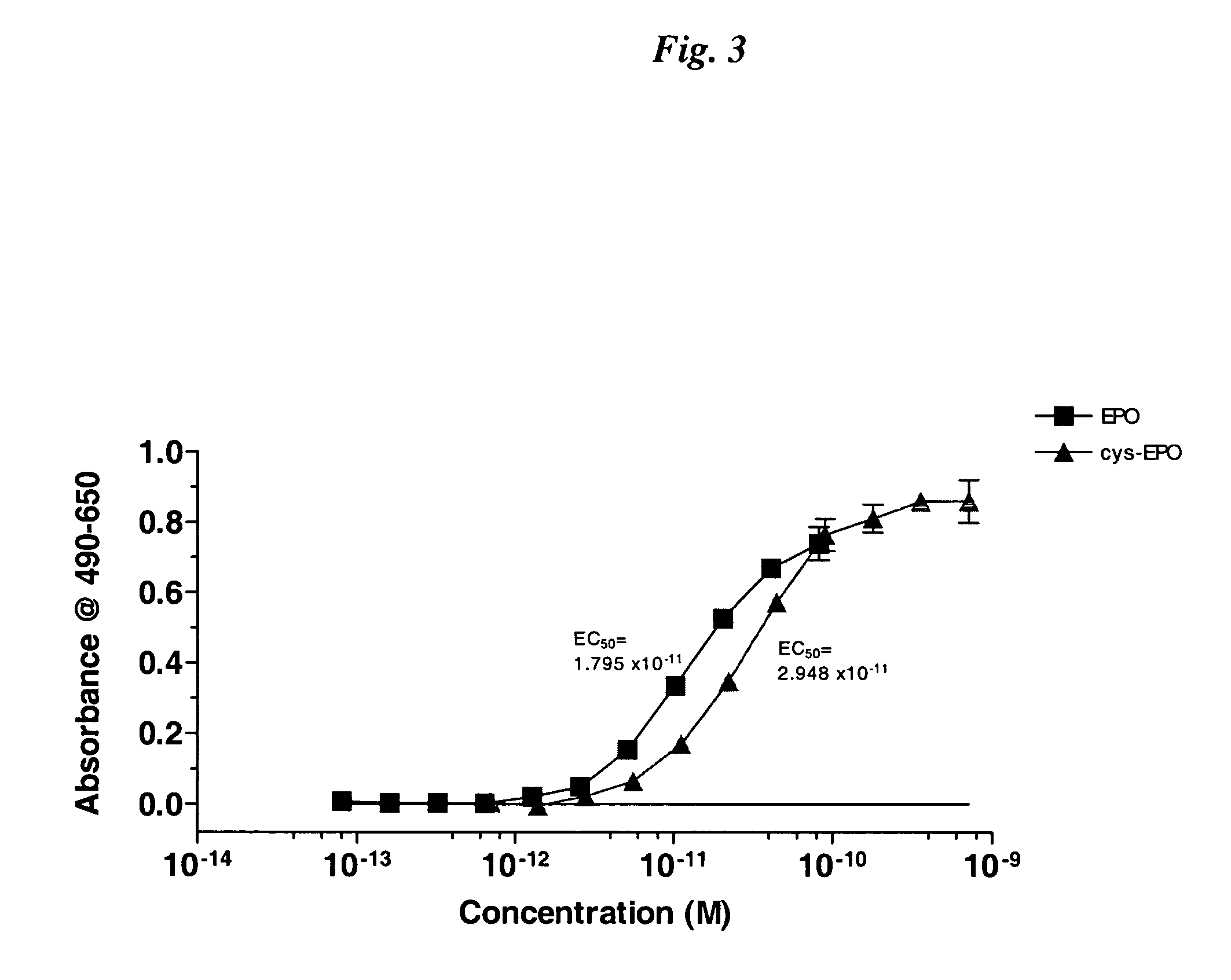
The present invention relates to novel modified proteins having N-terminal free thiols that can be produced by recombinant methods and are ready for further chemical derivatization. In particular, the invention relates to erythropoietin conjugate compounds having altered biochemical, physiochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. More particularly, one embodiment of the invention relates to erythropoietin conjugate compounds of the formula: (M)n-X-A-cys-EPO (I) where EPO is an erythropoeitin moiety selected from erythropoietin or an erythropoietin variant having at least one amino acid different from the wild-type human EPO, or any pharmaceutical acceptable derivatives thereof having biological properties of causing bone marrow cells to increase production of red blood cells; cys represents the amino acid cysteine and occurs at position −1 relative to the amino acid sequence of the erythropoietin moiety; A indicates the structure of the residual moiety used to chemically attach X to the thiol group of −1Cys; X is a water soluble polymer such as a polyalkylene glycol or other polymer; M is an organic molecule (including peptides and proteins) that increases the circulating half-life of the construct; and N is an integer from 0 to 15.
Owner:CENTOCOR
Compounds for enzyme inhibition
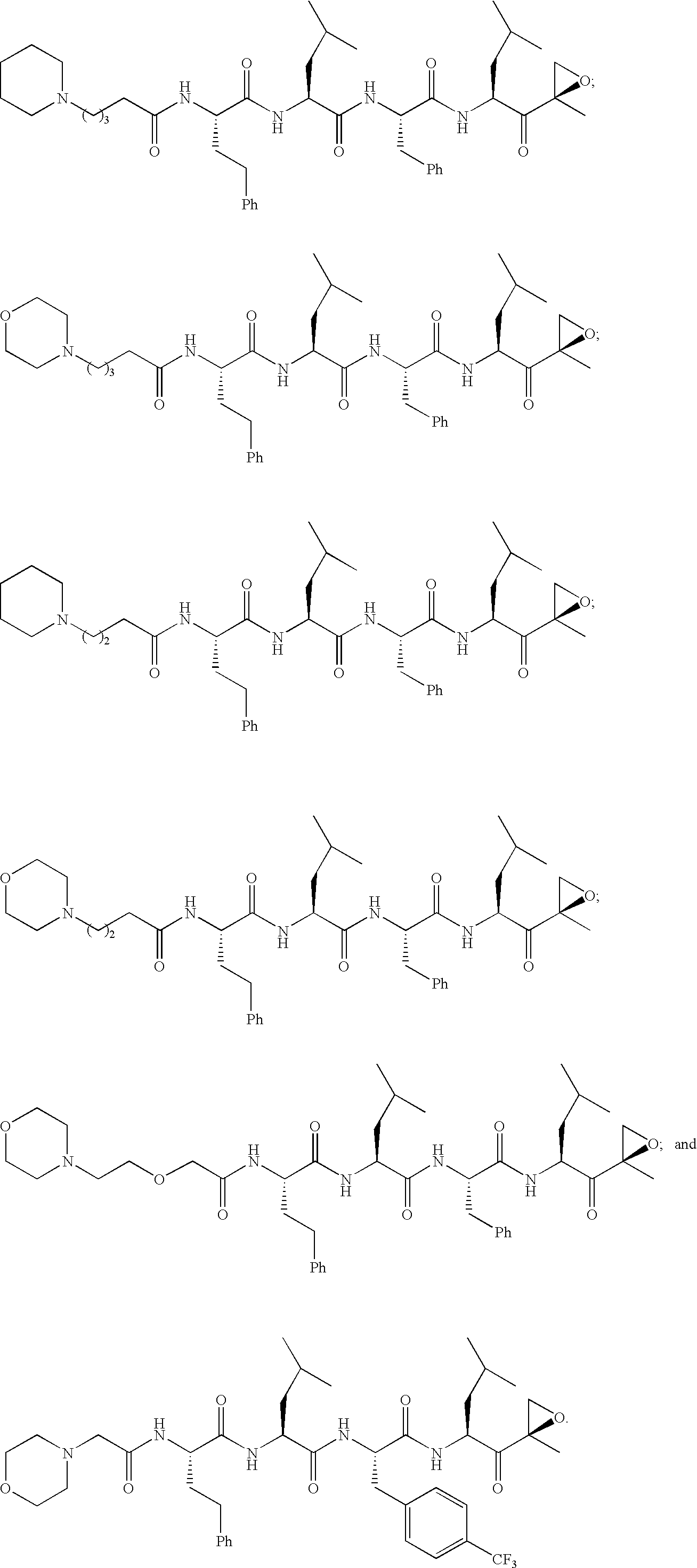
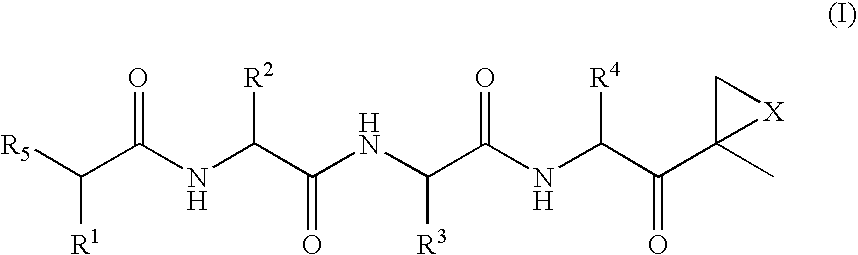
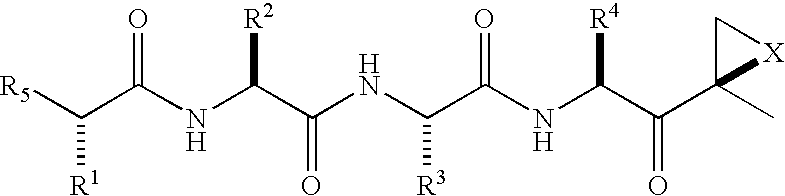
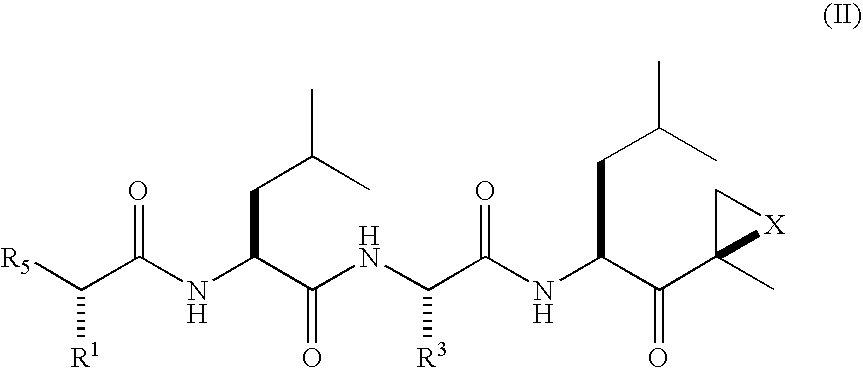
ActiveUS20050245435A1Inhibiting and reducing HIV infectionAffecting levelBiocideNervous disorderEnzyme inhibitionAziridine
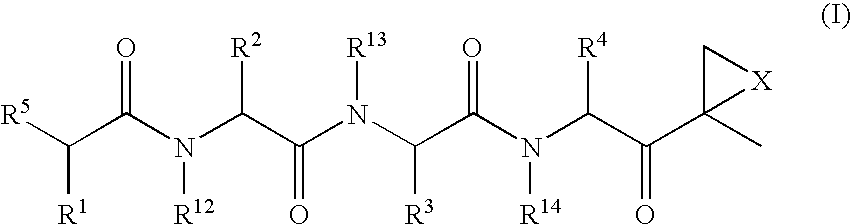
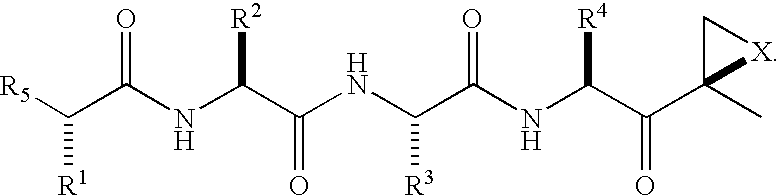
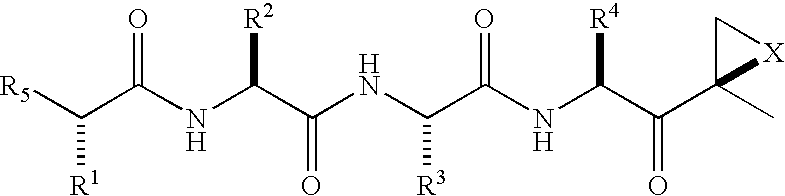
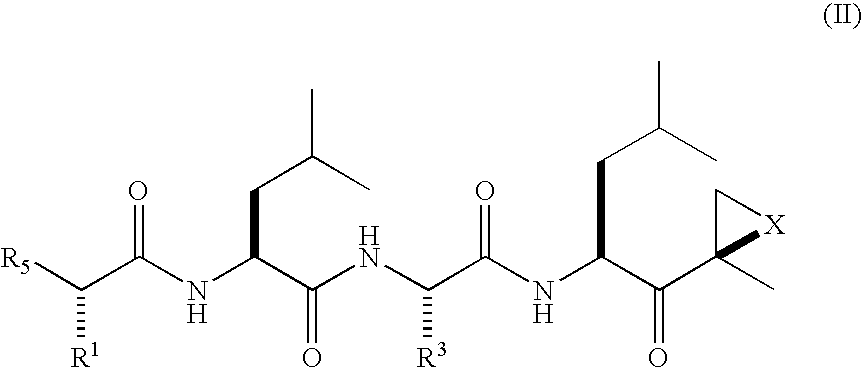
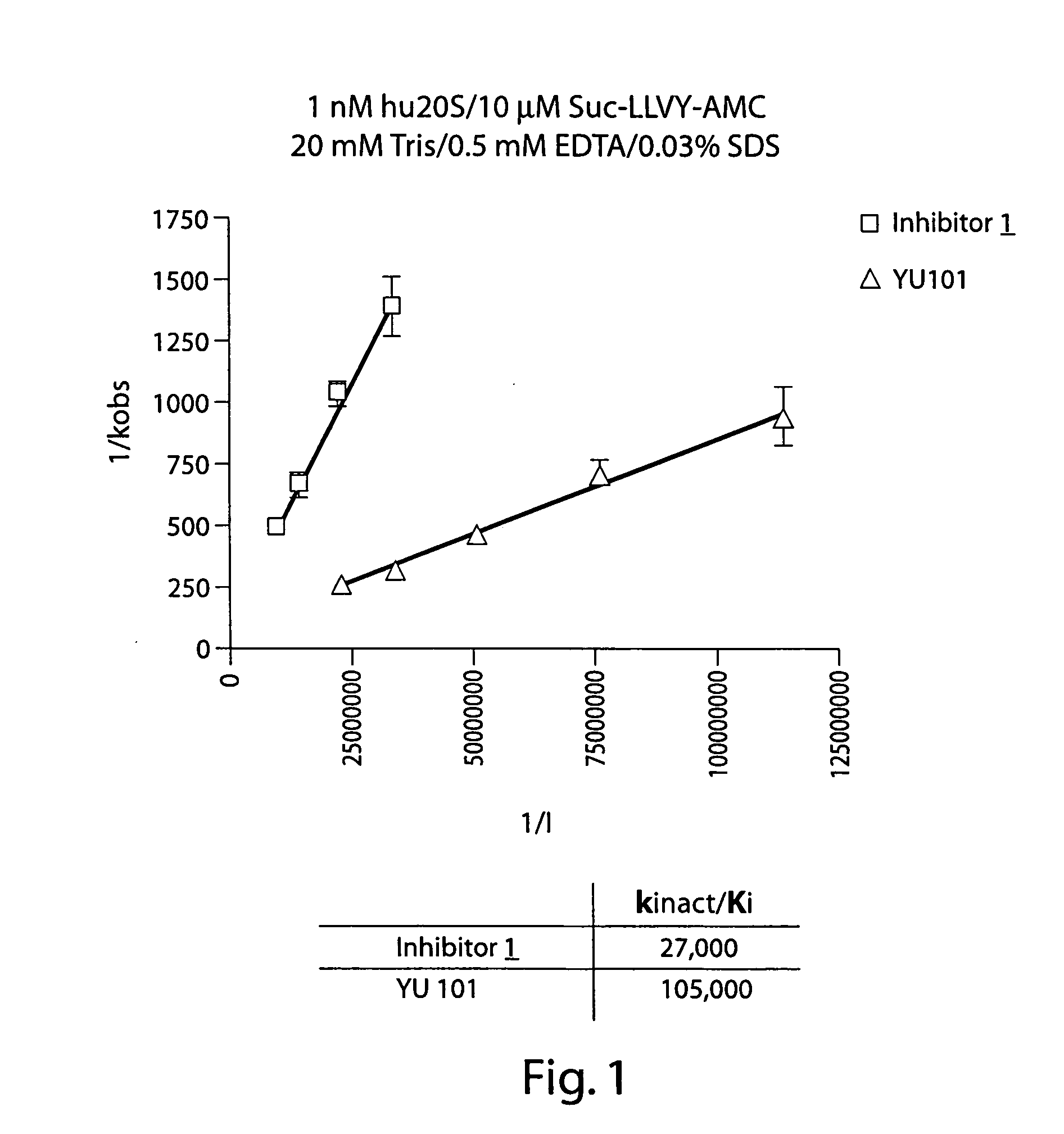
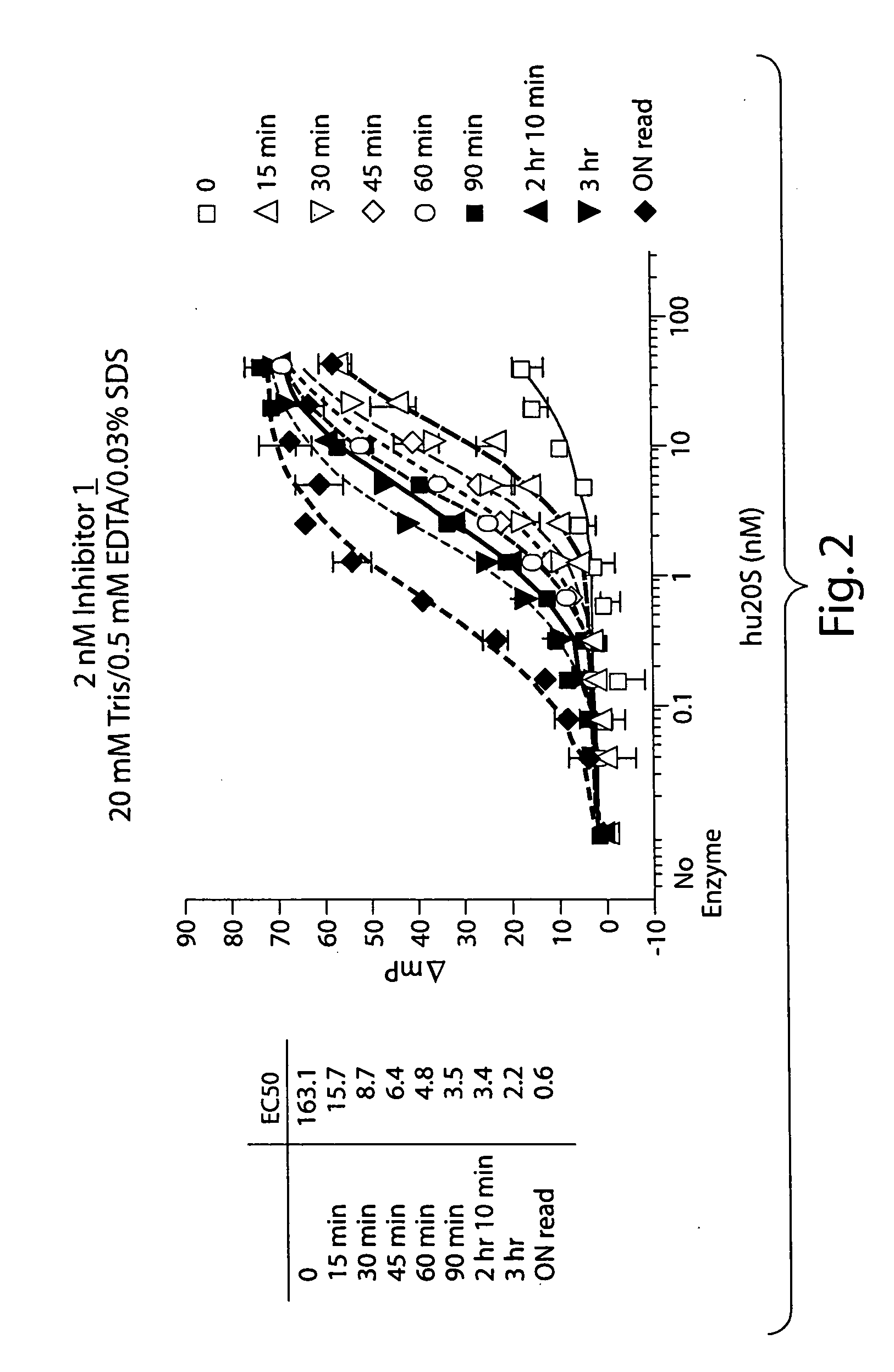
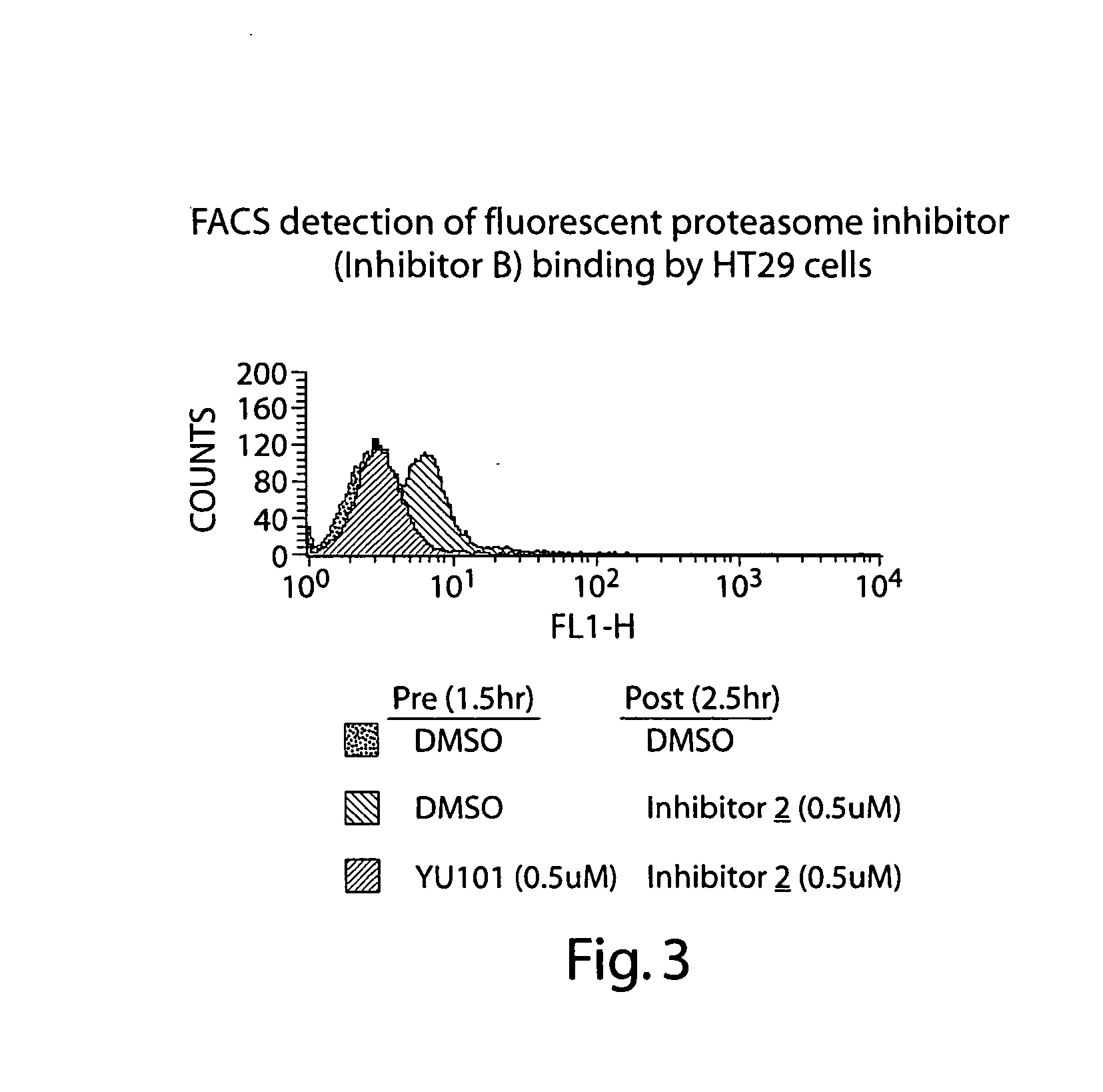
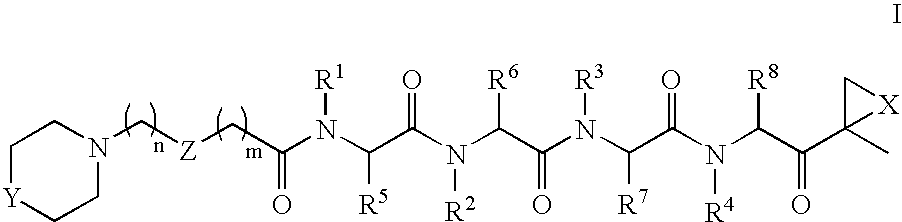
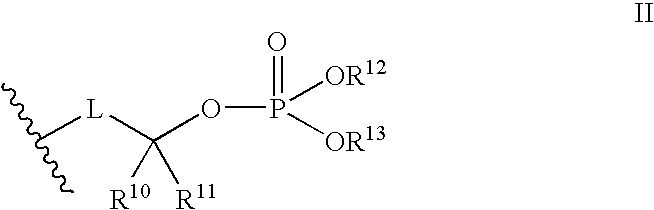
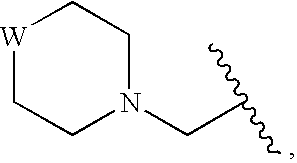
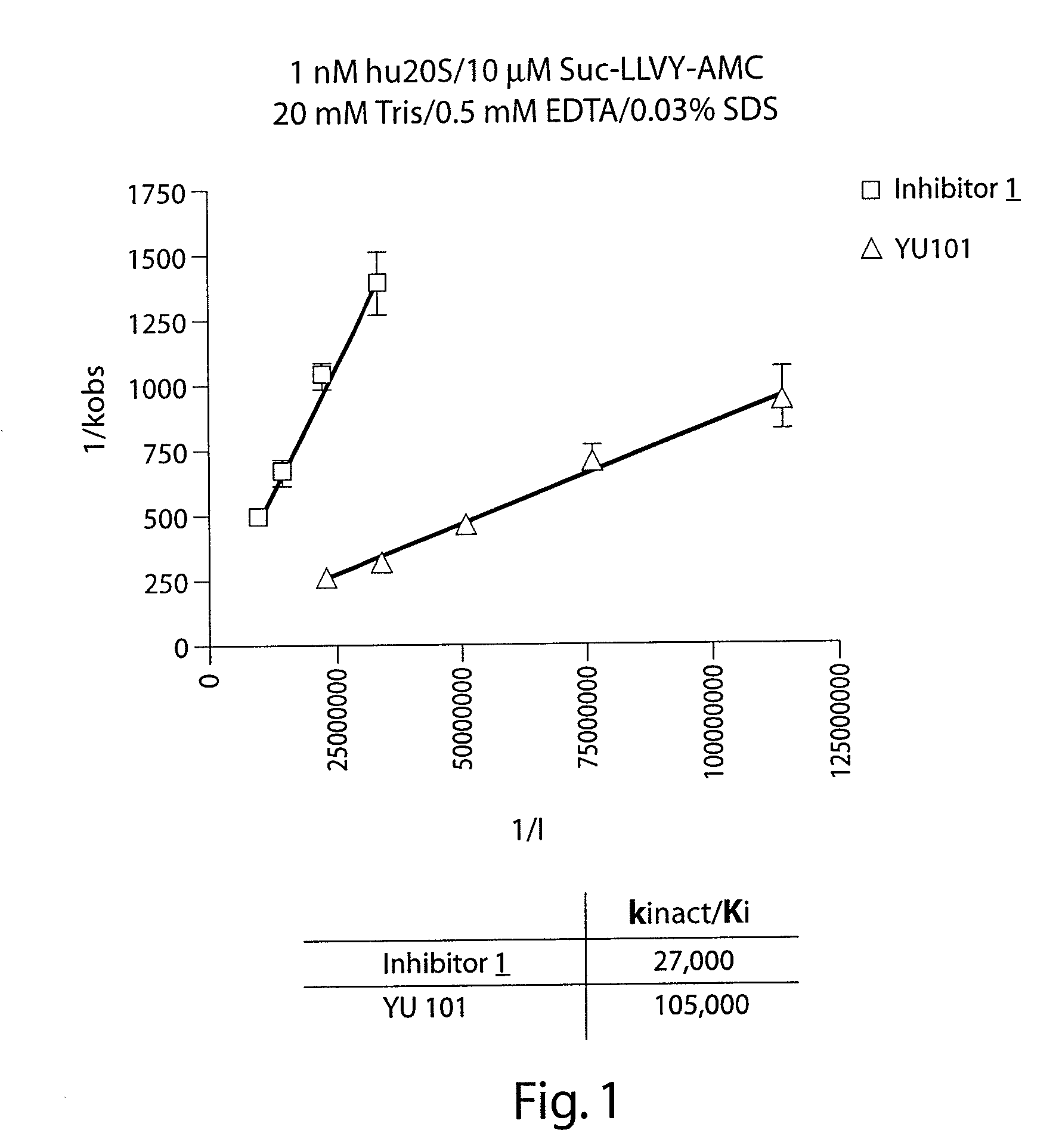
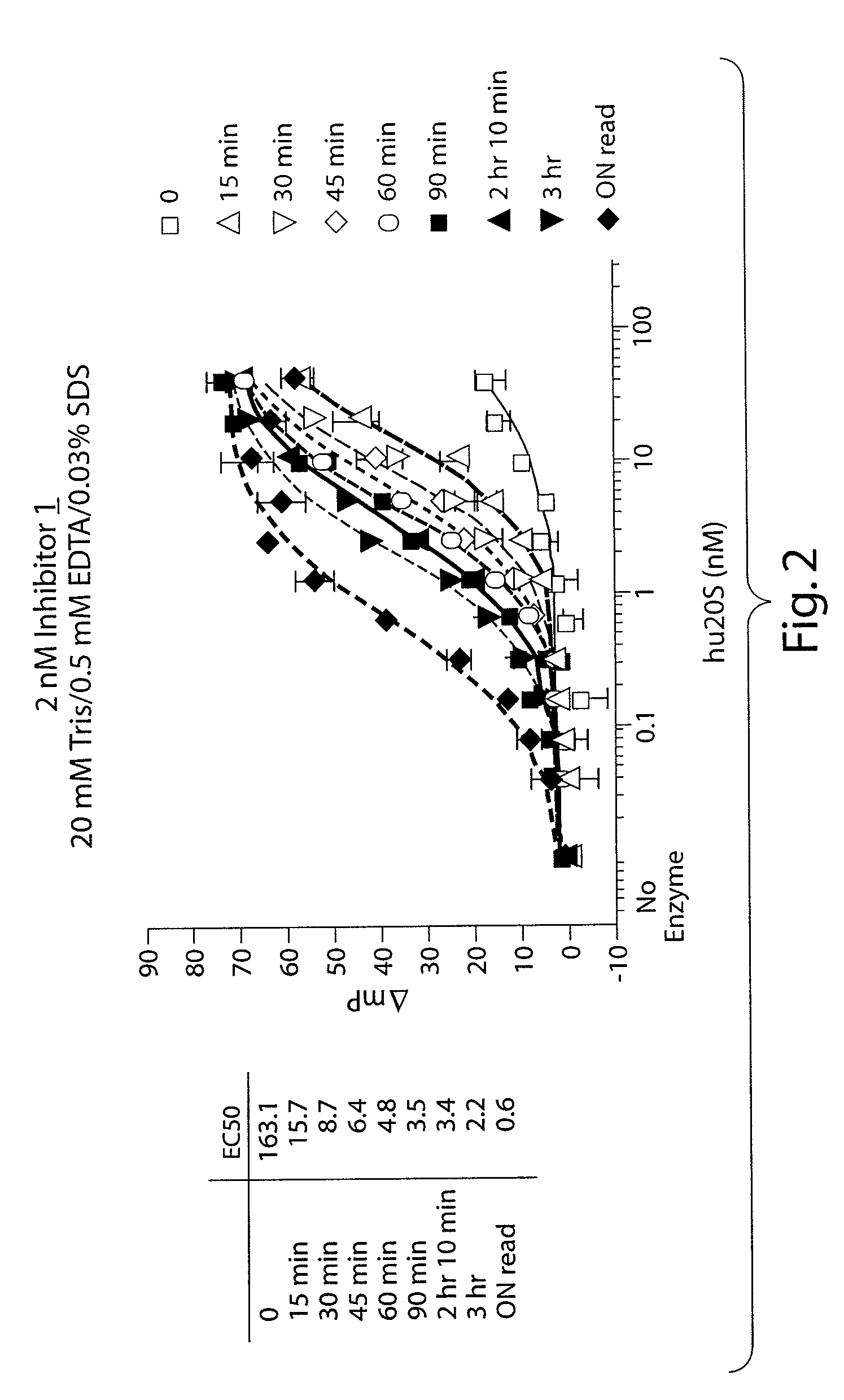
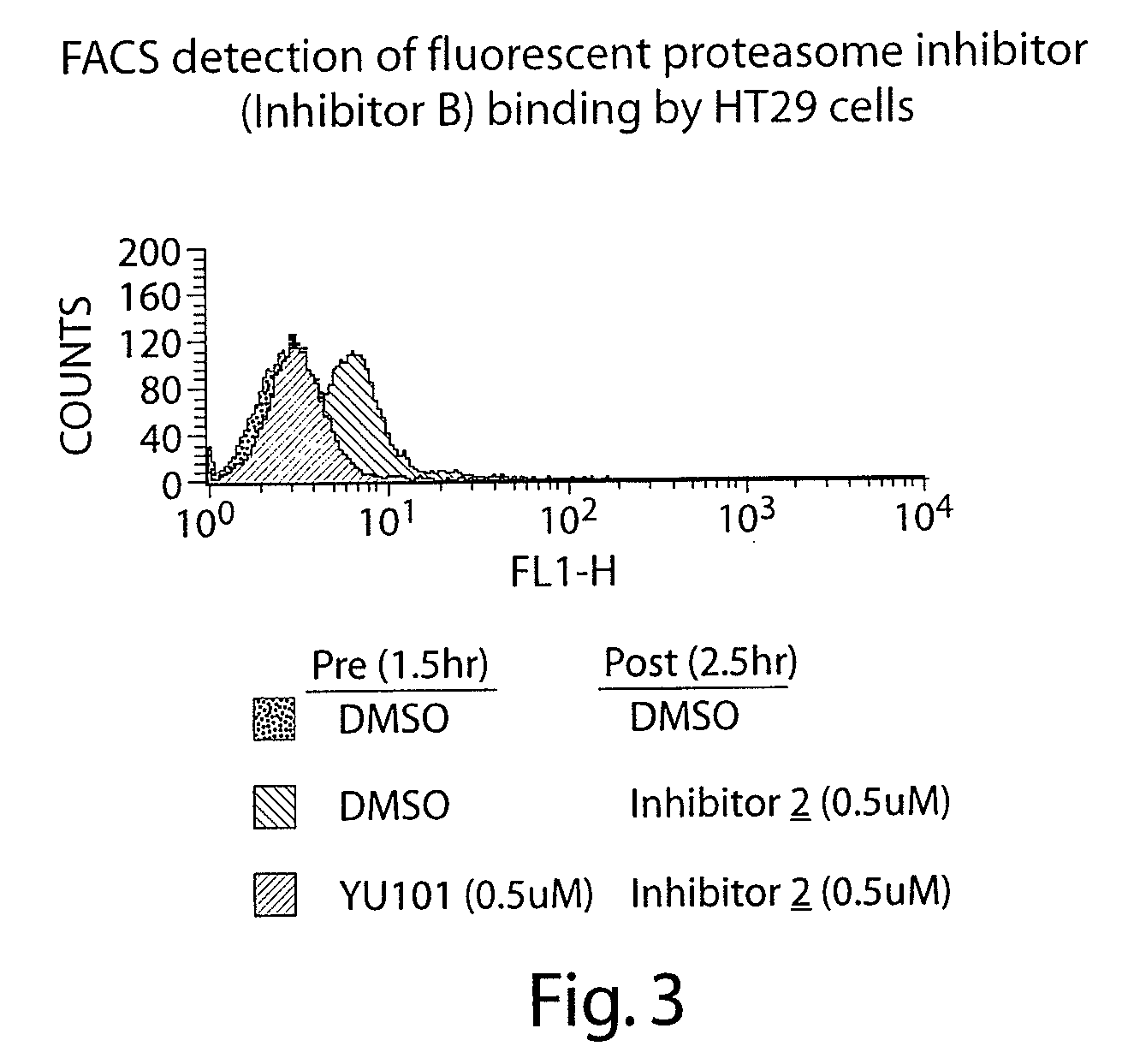
Peptide-based compounds including heteroatom-containing, three-membered rings efficiently and selectively inhibit specific activities of N-terminal nucleophile (Ntn) hydrolases. The activities of those Ntn having multiple activities can be differentially inhibited by the compounds described. For example, the chymotrypsin-like activity of the 20S proteasome may be selectively inhibited with the inventive compounds. The peptide-based compounds include at least three peptide units, an epoxide or aziridine, and functionalization at the N-terminus. Among other therapeutic utilities, the peptide-based compounds are expected to display anti-inflammatory properties and inhibition of cell proliferation.
Owner:ONYX THERAPEUTICS
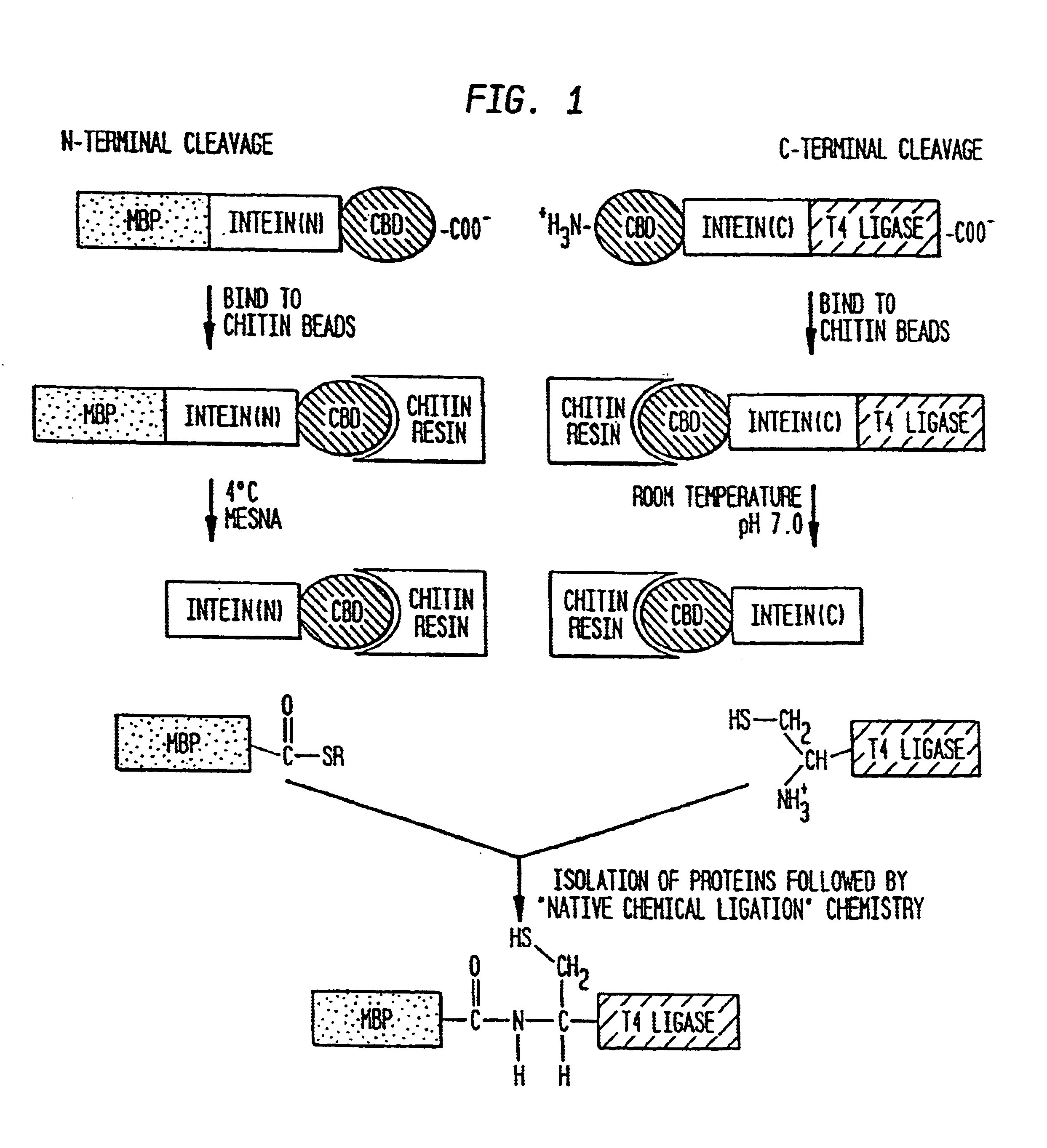
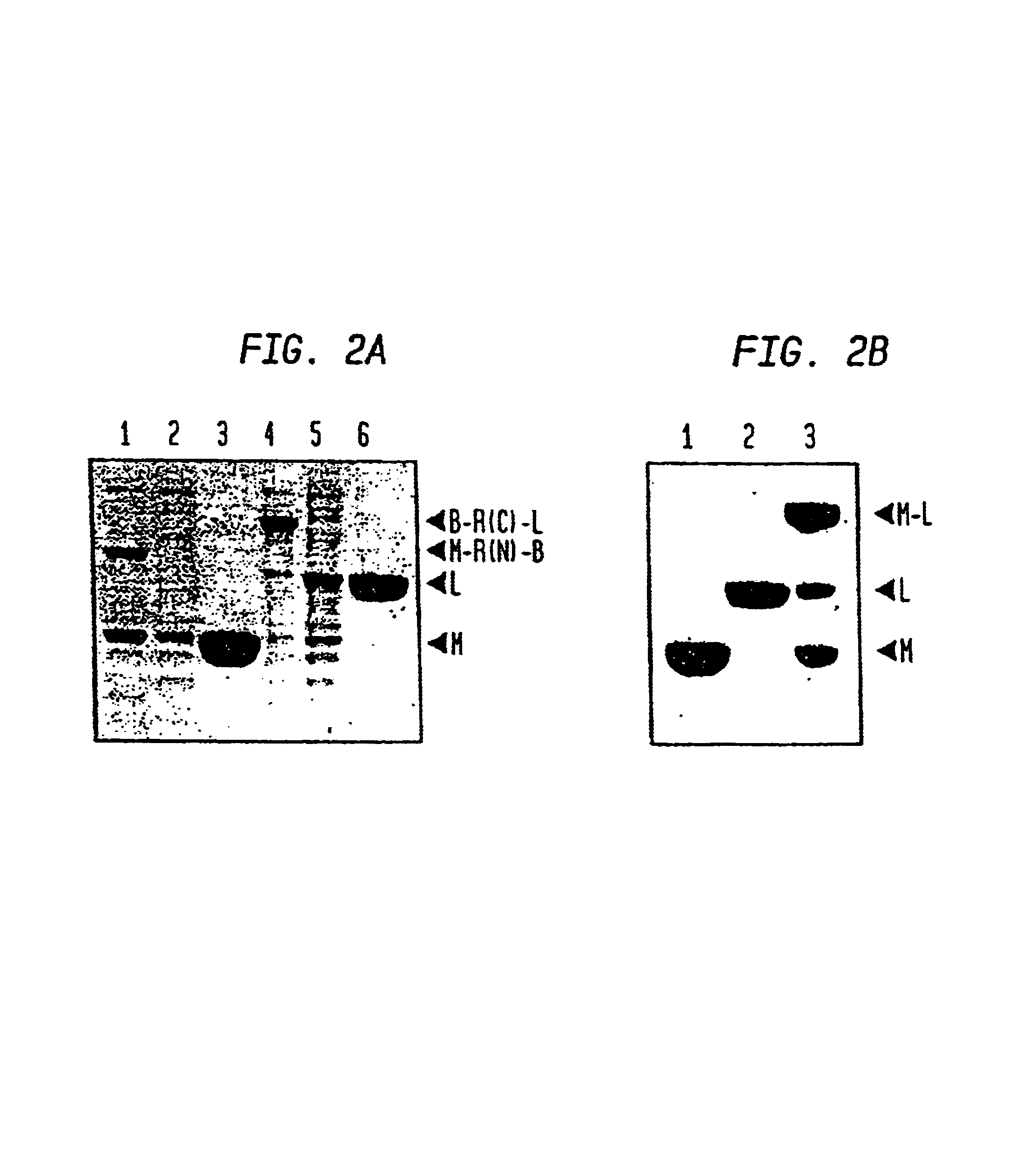
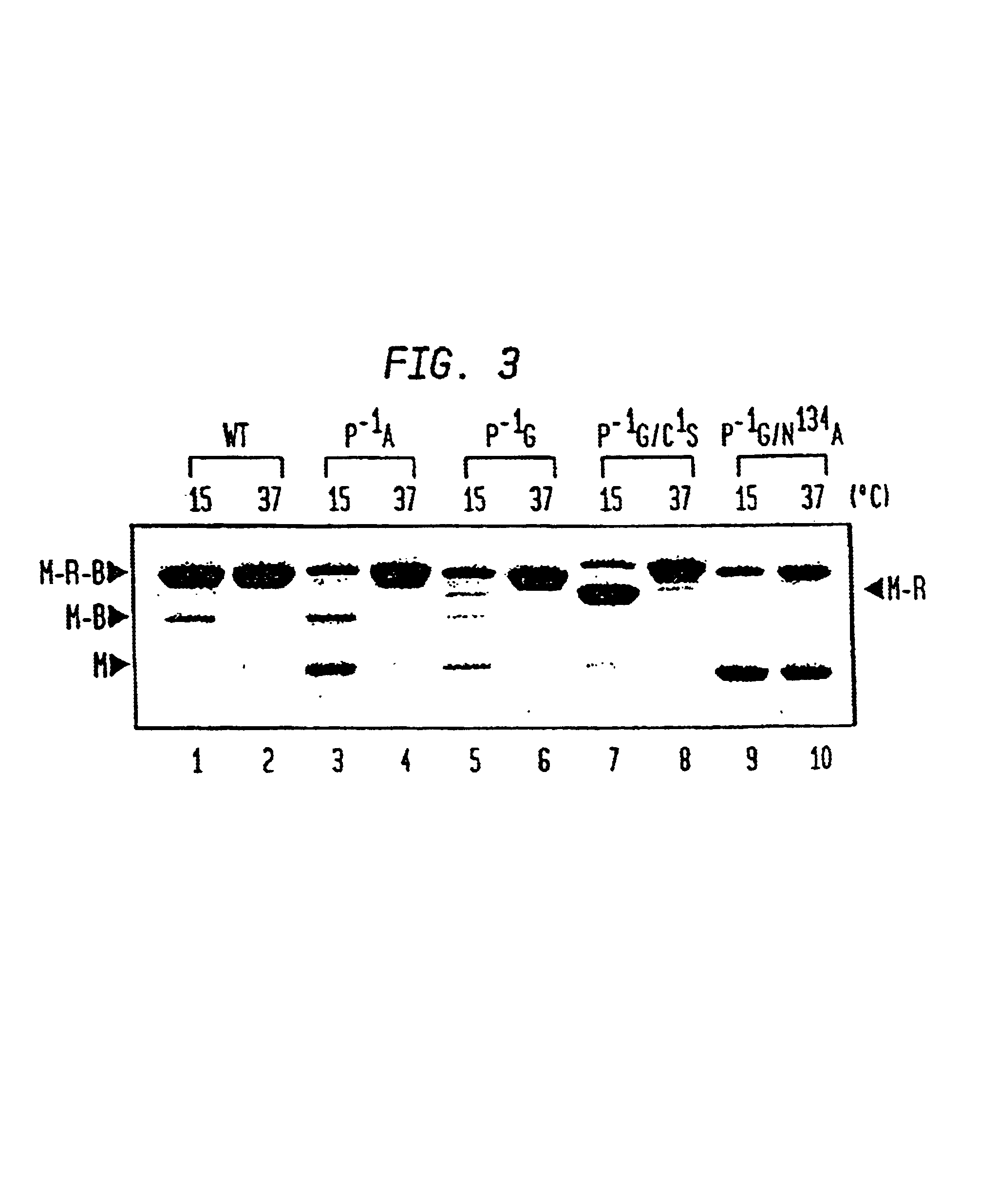
Intein-mediated protein ligation of expressed proteins
InactiveUS6849428B1Eliminate needBacteriaFusion with post-translational modification motifProtein targetIntein
A method for the ligation of expressed proteins which utilizes inteins, for example the RIR1 intein from Methanobacterium thermotrophicum, is provided. Constructs of the Mth RIR1 intein in which either the C-terminal asparagine or N-terminal cysteine of the intein are replaced with alanine enable the facile isolation of a protein with a specified N-terminal, for example, cysteine for use in the fusion of two or more expressed proteins. The method involves the steps of generating a C-terminal thioester-tagged target protein and a second target protein having a specified N-terminal via inteins, such as the modified Mth RIR1 intein, and ligating these proteins. A similar method for producing a cyclic or polymerized protein is provided. Modified inteins engineered to cleave at their C-terminus or N-terminus, respectively, and DNA and plasmids encoding these modified inteins are also provided.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Pegylated interleukin-10
InactiveUS7052686B2Minimize disruptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticInterleukin 10White blood cell
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) conjugated via a linker to one or more polyethylene glycol (PEG) molecules at a single amino acid residue of the IL-10, and a method for preparing the same, are provided. The method produces a stable mono-pegylated IL-10, which retains IL-10 activity, where pegylation is selective for the N-terminus on one subunit of IL-10 with little or no formation of monomeric IL-10. The method also provides a substantially homogenous population of mono-PEG-IL-10.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Modified therapeutic peptides with extended half-lives in vivo
A method for protecting a peptide from peptidase activity in vivo, the peptide being composed of between 2 and 50 amino acids and having a C-terminus and an N-terminus and a C-terminus amino acid and an N-terminus amino acid is described. In the first step of the method, the peptide is modified by attaching a reactive group to the C-terminus amino acid, to the N-terminus amino acid, or to an amino acid located between the N-terminus and the C-terminus, such that the modified peptide is capable of forming a covalent bond in vivo with a reactive functionality on a blood component. In the next step, a covalent bond is formed between the reactive group and a reactive functionality on a blood component to form a peptide-blood component conjugate, thereby protecting said peptide from peptidase activity. The final step of the method involves the analyzing of the stability of the peptide-blood component conjugate to assess the protection of the peptide from peptidase activity.
Owner:CONJUCHEM
Single chain recombinant T cell receptors
InactiveUS7569664B2Improve stabilityUseful purposeCompound screeningApoptosis detectionExtracellularC-terminus
A single chain T cell receptor (scTCR) comprising an a segment constituted by a TCR α chain variable region sequence fused to the N terminus of a TCR α chain constant region extracellular sequence, a β segment constituted by a TCR β chain variable region fused to the N terminus of a TCR β chain constant region extracellular sequence, and a linker sequence linking the C terminus of the α segment to the N terminus of the β segment, or vice versa, the constant region extracellular sequences of the α and β segments being linked by a disulfide bond, the length of the linker sequence and the position of the disulfide bond being such that the variable region sequences of the α and β segments are mutually orientated substantially as in native αβ T cell receptors. Complexes of two or more such scTCRs, and use of the scTCRs in therapy and in various screening applications are also disclosed.
Owner:IMMUNOCORE LTD +1
Peptide having cell membrane penetrating activity
InactiveUS20130129726A1Prominent penetrating efficiencyTargeting of drugs is required high efficientlyPeptide/protein ingredientsDrug compositionsHistamine releasing factorProtein transduction domain
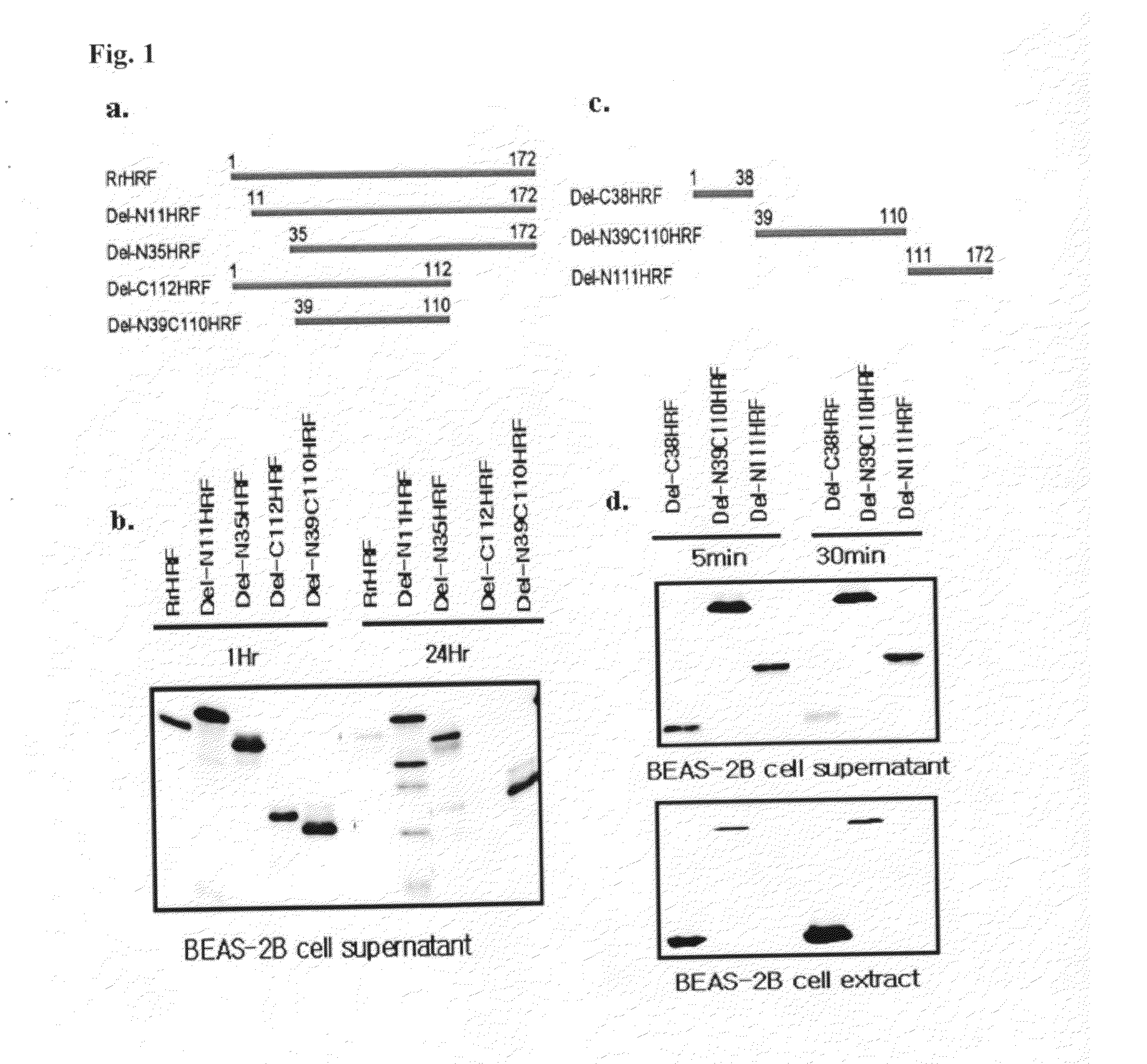
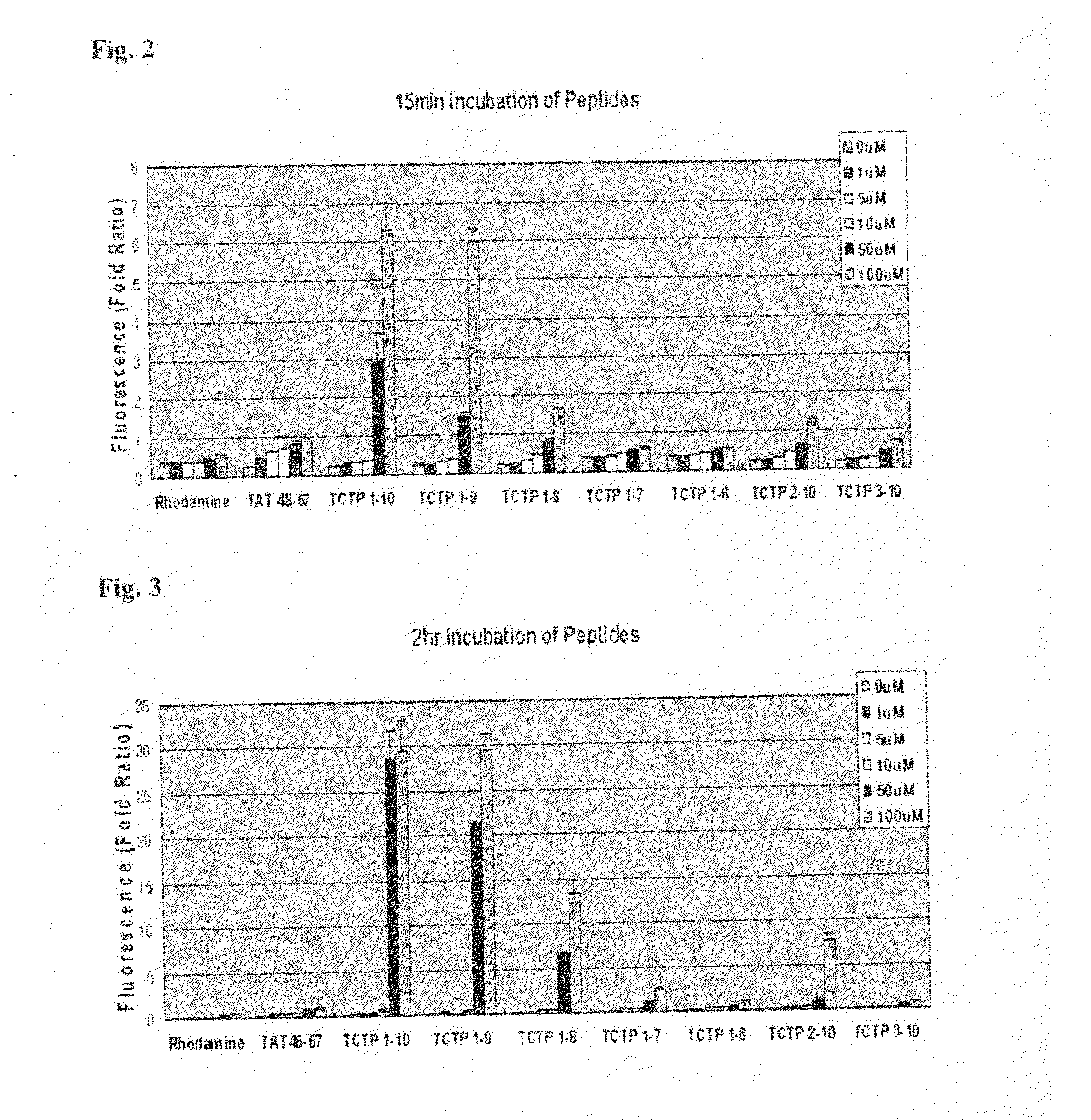
Provided are transmembrane complexes that contain a protein transduction domain (PTD) from the N-terminus of IgE-dependent histamine-releasing factor (HRF) and a target substance that is to be delivered into a cell. Also provided are nucleic acid molecules encoding the transmembrane complex, and methods of delivering the target substance into a cell interior by contacting the transmembrane complex with a cell. Also provided are transfection kits containing the PTD and the target substance.
Owner:EWHA UNIV IND COLLABORATION FOUND
Pegylated interleukin-10
InactiveUS20060210534A1Minimize disruptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticInterleukin 10White blood cell
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) conjugated via a linker to one or more polyethylene glycol (PEG) molecules at a single amino acid residue of the IL-10, and a method for preparing the same, are provided. The method produces a stable mono-pegylated IL-10, which retains IL-10 activity, where pegylation is selective for the N-terminus on one subunit of IL-10 with little or no formation of monomeric IL-10. The method also provides a substantially homogenous population of mono-PEG-IL-10.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Compounds for enzyme inhibition
InactiveUS20070105786A1Inhibiting and reducing HIV infectionAffecting levelBiocideNervous disorderEnzyme inhibitionAziridine
Peptide-based compounds including heteroatom-containing, three-membered rings efficiently and selectively inhibit specific activities of N-terminal nucleophile (Ntn) hydrolases associated with the proteasome. The peptide-based compounds include an epoxide or aziridine, and functionalization at the N-terminus. Among other therapeutic utilities, the peptide-based compounds are expected to display anti-inflammatory properties and inhibition of cell proliferation. Oral administration of these peptide-based proteasome inhibitors is possible due to their bioavailability profiles
Owner:ONYX THERAPEUTICS
Follicle stimulating hormones
Heterodimeric polypeptide conjugates exhibiting FSH activity, comprising a dimeric polypeptide comprising an FSH-.alpha. subunit and an FSH-.beta. subunit, wherein at least one of the FSH-.alpha. and FSH-.beta. subunits differs from the corresponding wildtype subunit in that at least one amino acid residue acid residue comprising an attachment group for a non-polypeptide moiety has been introduced or removed, and having at least one non-polypeptide moiety bound to an attachment group of at least one of said subunits are provided. Preferably, at least one attachment group, e.g., an N- or O-glycosylation site or an attachment site for a polymer molecule such as polyethylene glycol, has been introduced, e.g., at an N-terminal. The polypeptide conjugates exhibit improved properties, in particular an increased half-life, compared to human FSH.
Owner:MAXYGEN
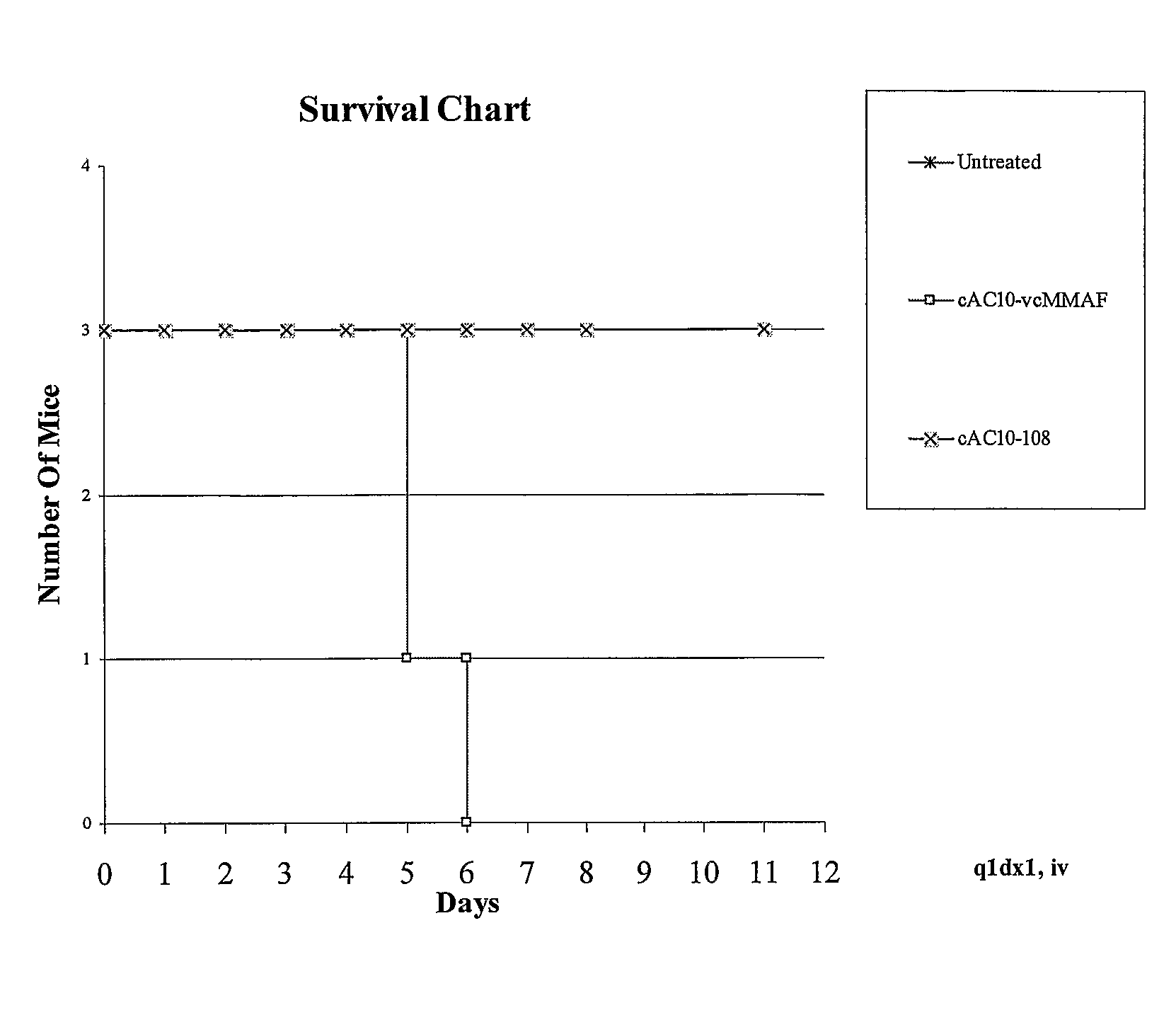
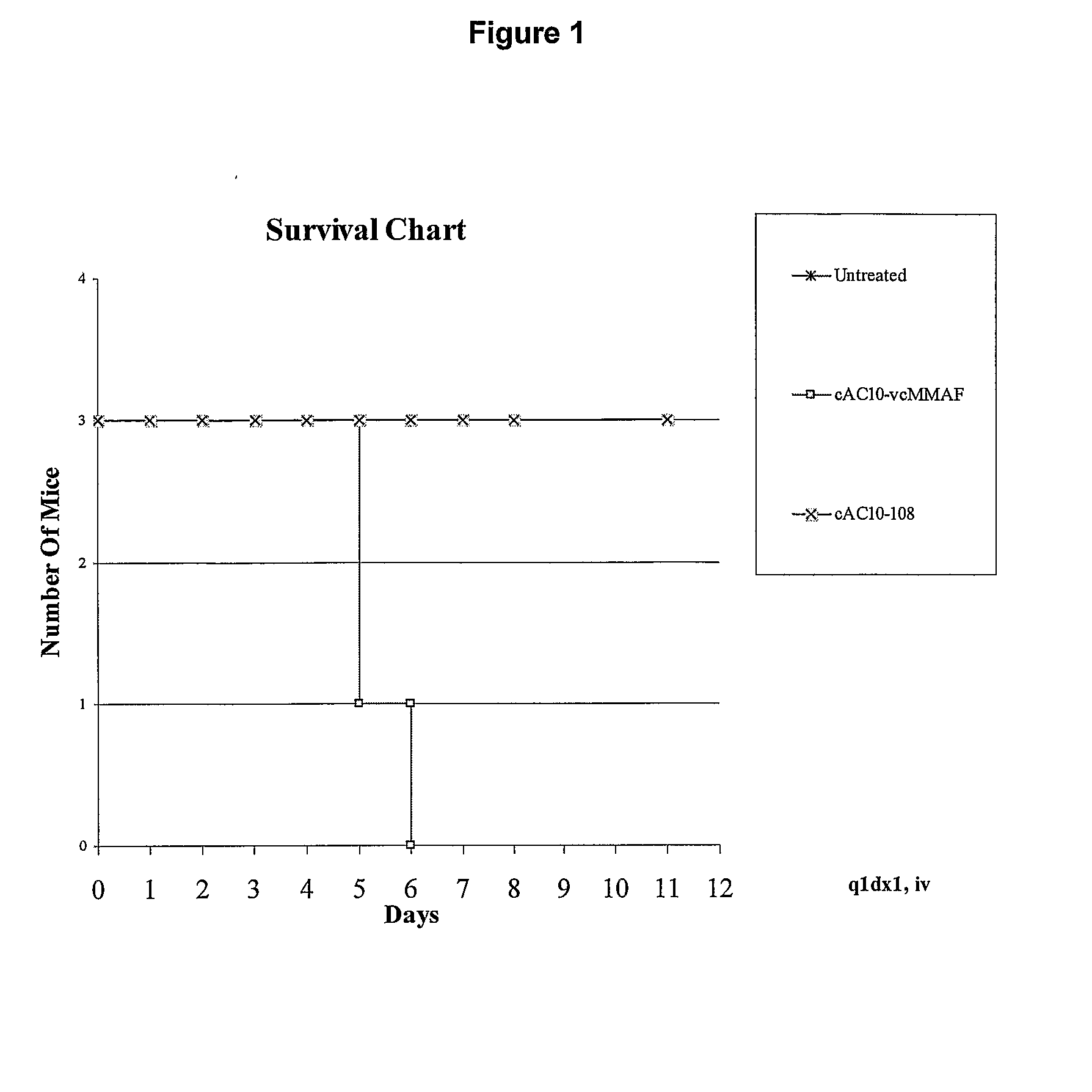
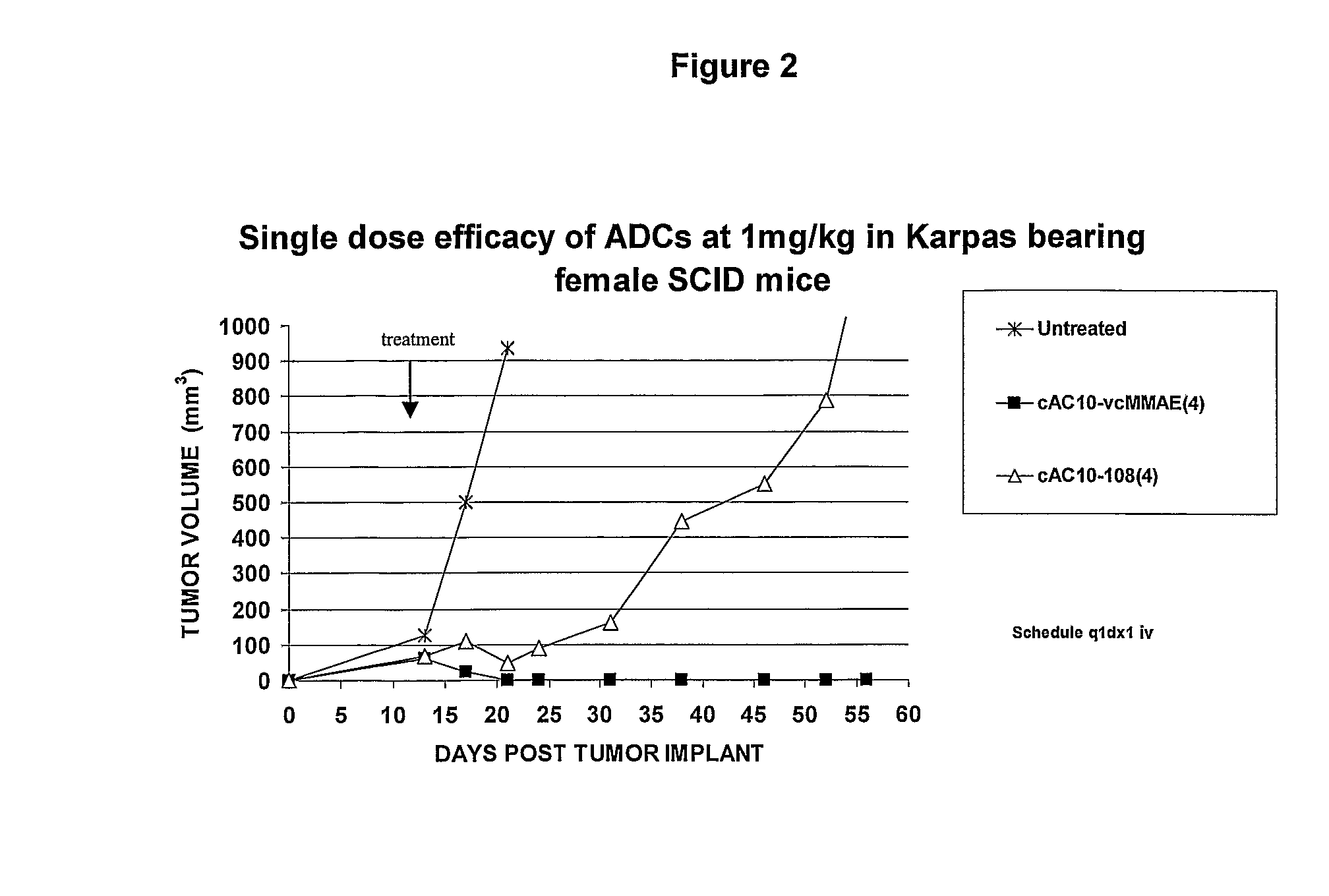
Auristatins Having an Aminobenzoic Acid Unit at the N Terminus
Owner:SEAGEN INC
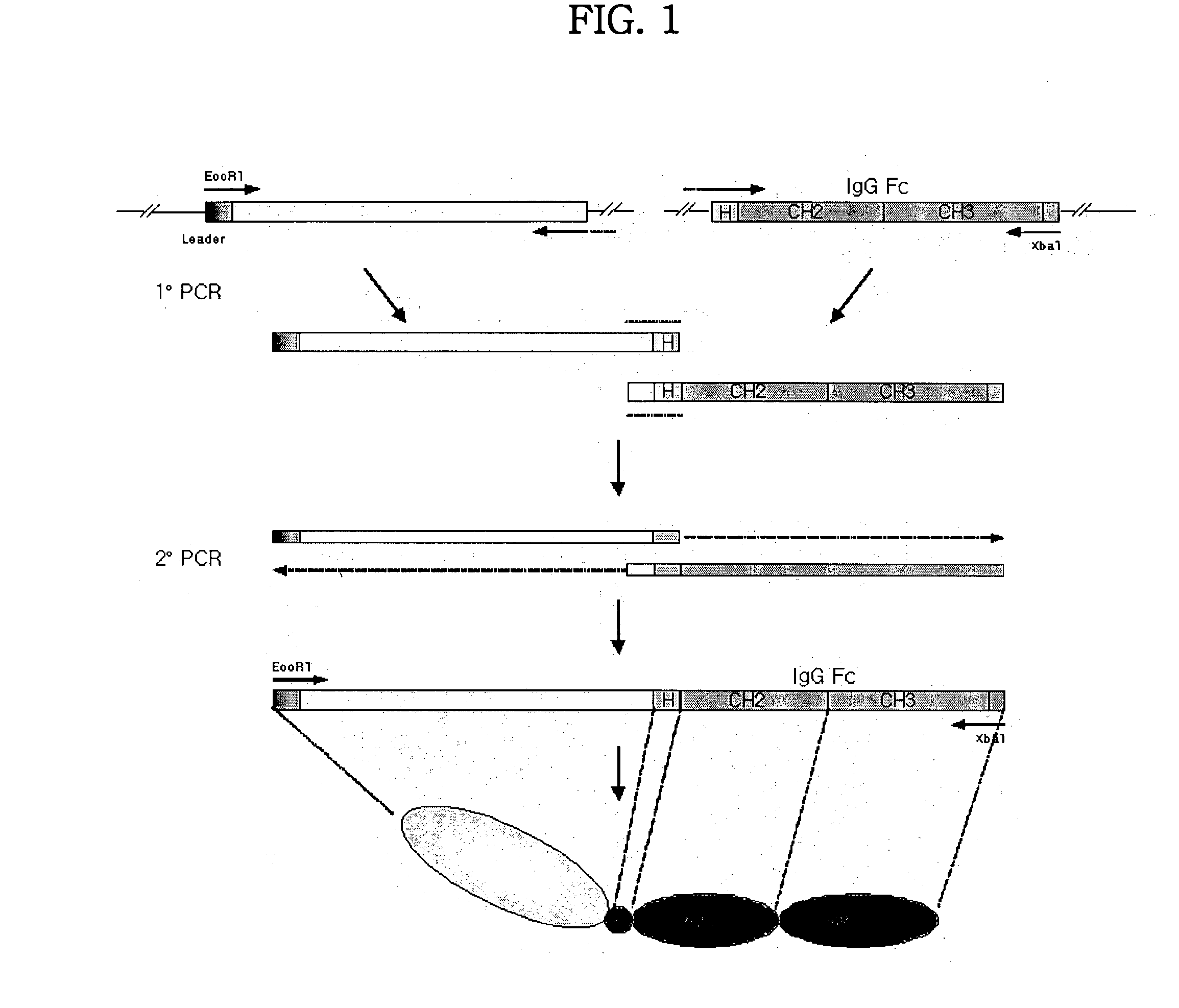
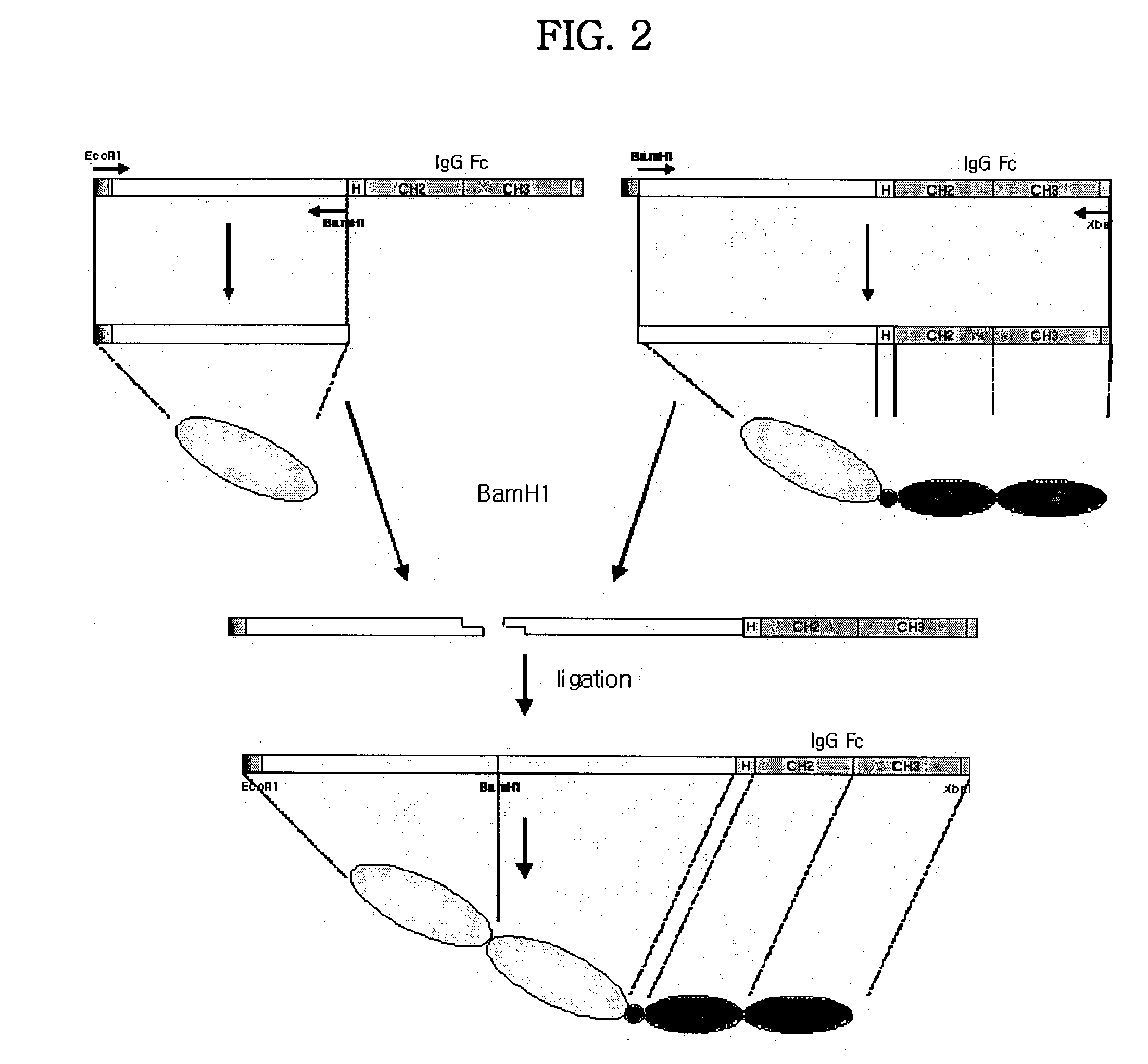
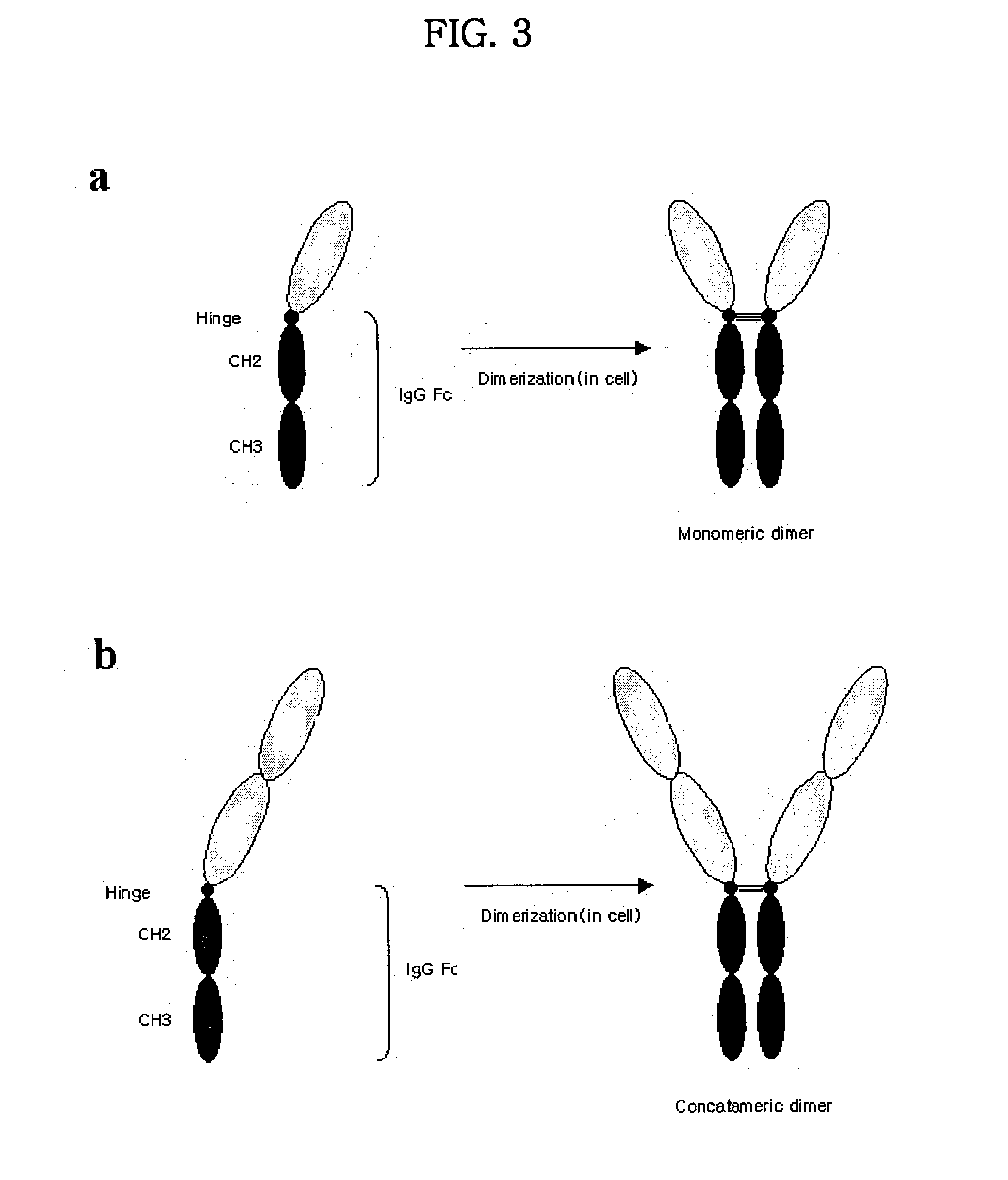
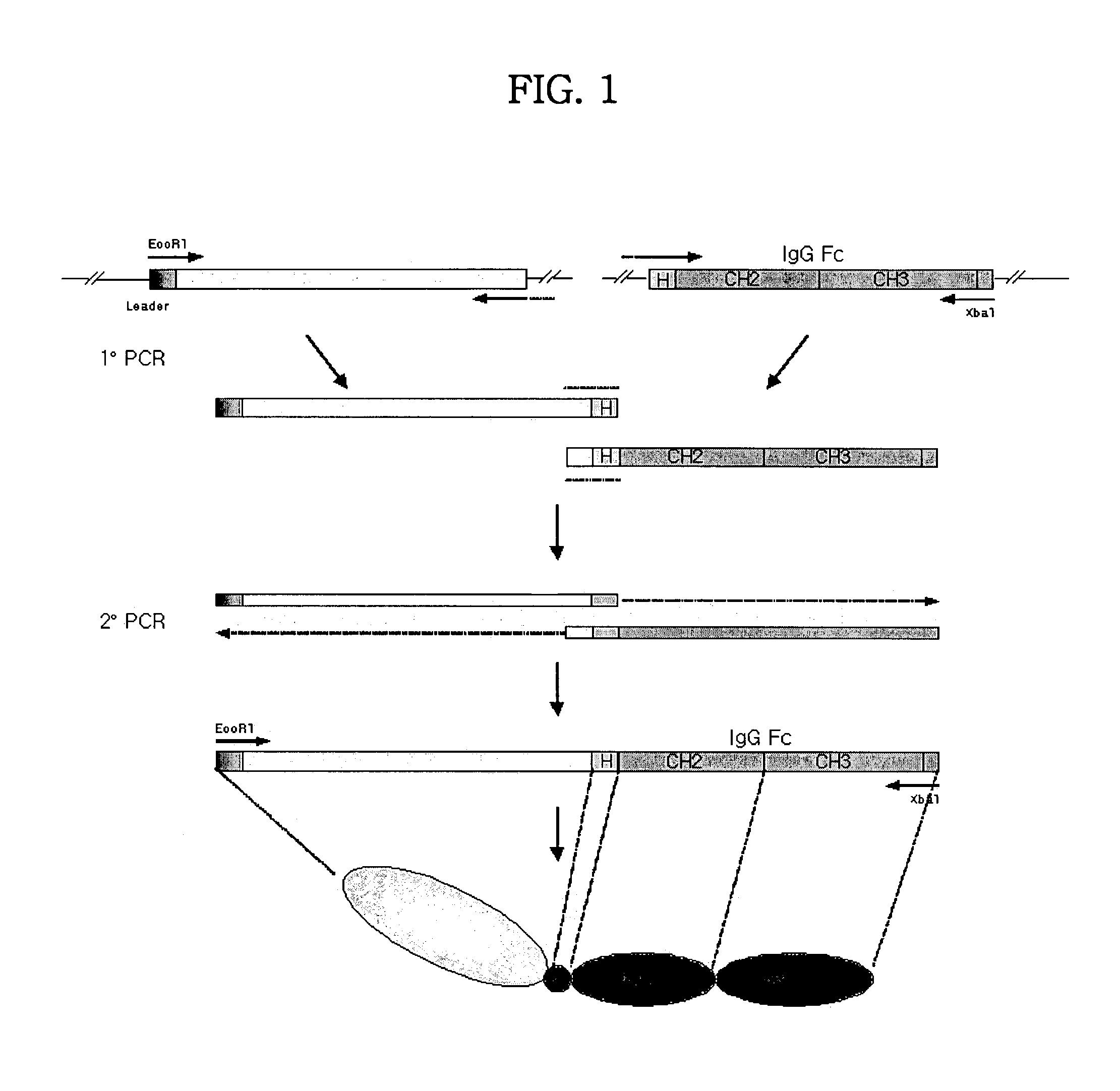
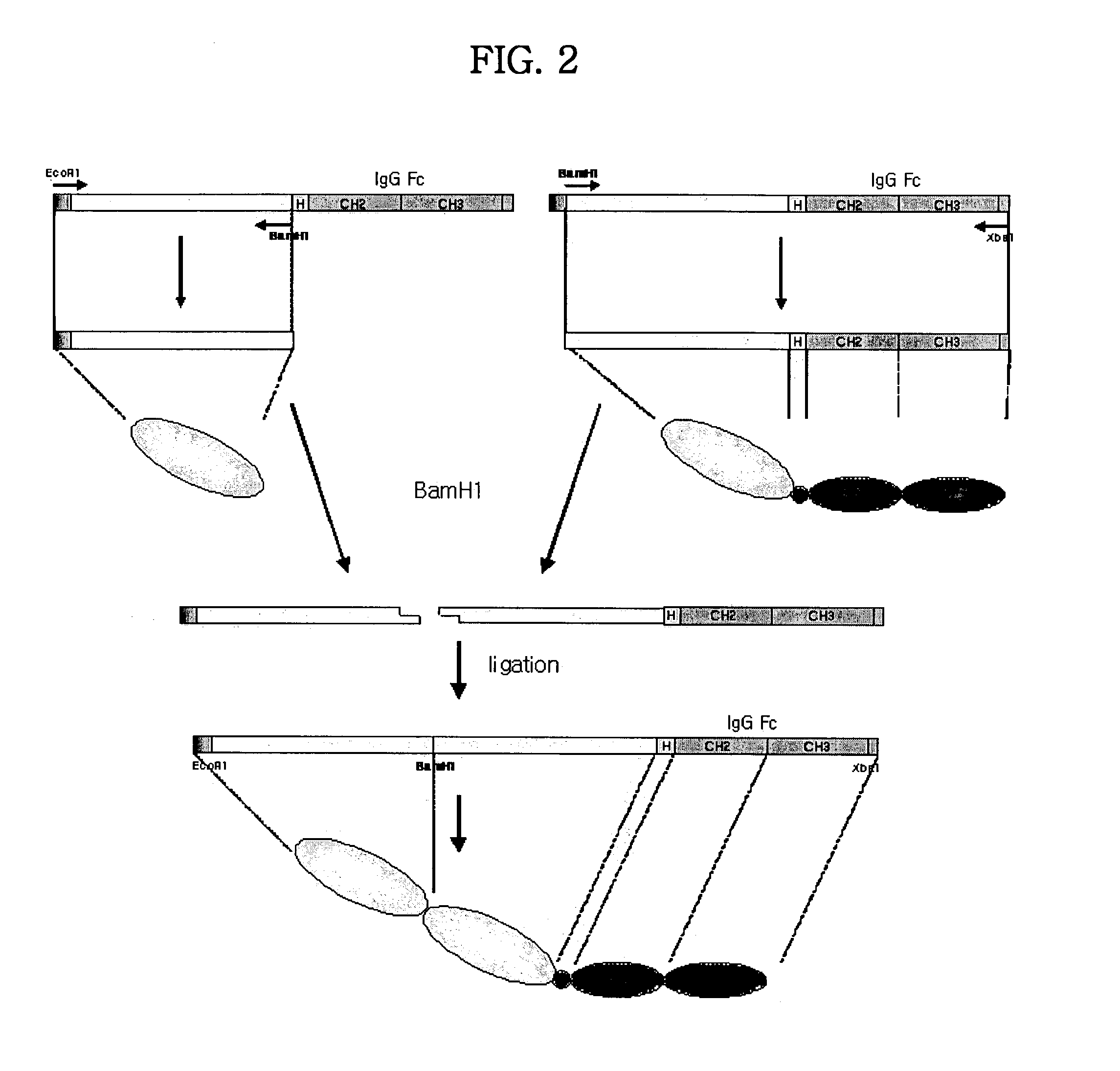
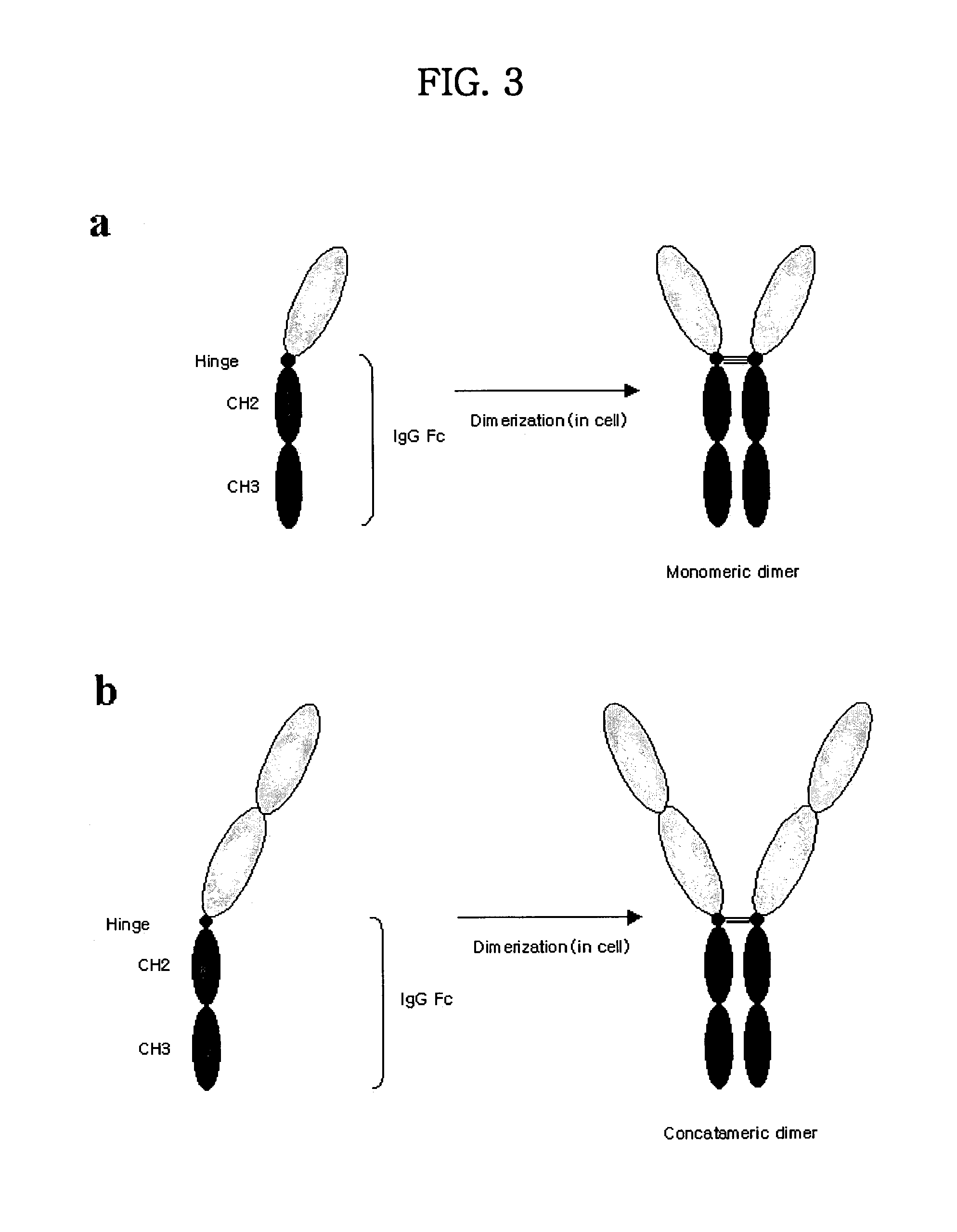
Concatameric immunoadhesion
ActiveUS20030195338A1Improve efficacyImprove stabilityAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA constructActive protein
Disclosed are concatameric proteins comprising two soluble domains, in which the C-terminus of a soluble domain of a biologically active protein is linked to the N-terminus of an identical soluble domain or a distinct soluble domain of a biologically active protein. Also, the present invention discloses dimeric proteins formed by formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds at the hinge region of two monomeric proteins formed by linkage of a concatamer of two identical soluble extracellular regions of proteins involving immune response to an Fc fragment of an immunoglobulin molecule, their glycosylated proteins, DNA constructs encoding the monomeric proteins, recombinant expression plasmids containing the DNA construct, host cells transformed or transfected with the recombinant expression plasmids, and a method of preparing the dimeric proteins by culturing the host cells. Further, the present invention discloses pharmaceutical or diagnostic compositions comprising the dimeric protein or its glycosylated form.
Owner:MEDEXGEN
Short peptide carrier system for cellular delivery of agent
InactiveUS7176185B2Promote sportsPowder deliveryMicrobiological testing/measurementDipeptideActive agent
A dipeptide or tripeptide carrier system for active agent delivery to cells has an N-terminus natural amino acid and an active agent covalently bonded to a side chain of one of the remaining amino acid bases. The system is amenable to formulation as an oral administrant. The active agent being a therapeutic, a fluorescent dye, or contrast agent where the active agent has a molecular weight of less than 500 atomic mass units. An optional linker is provided intermediate between the active agent and the linking side chain.
Owner:TSRL
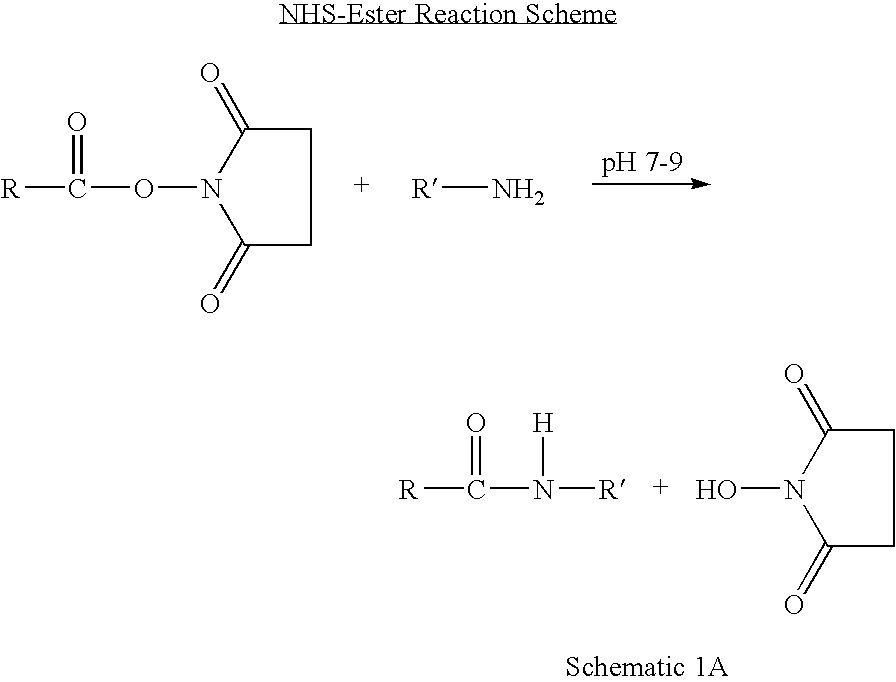
Site-specific labelling of proteins
InactiveUS7449558B2Hydrolysed protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsThioester synthesisCombinatorial chemistry
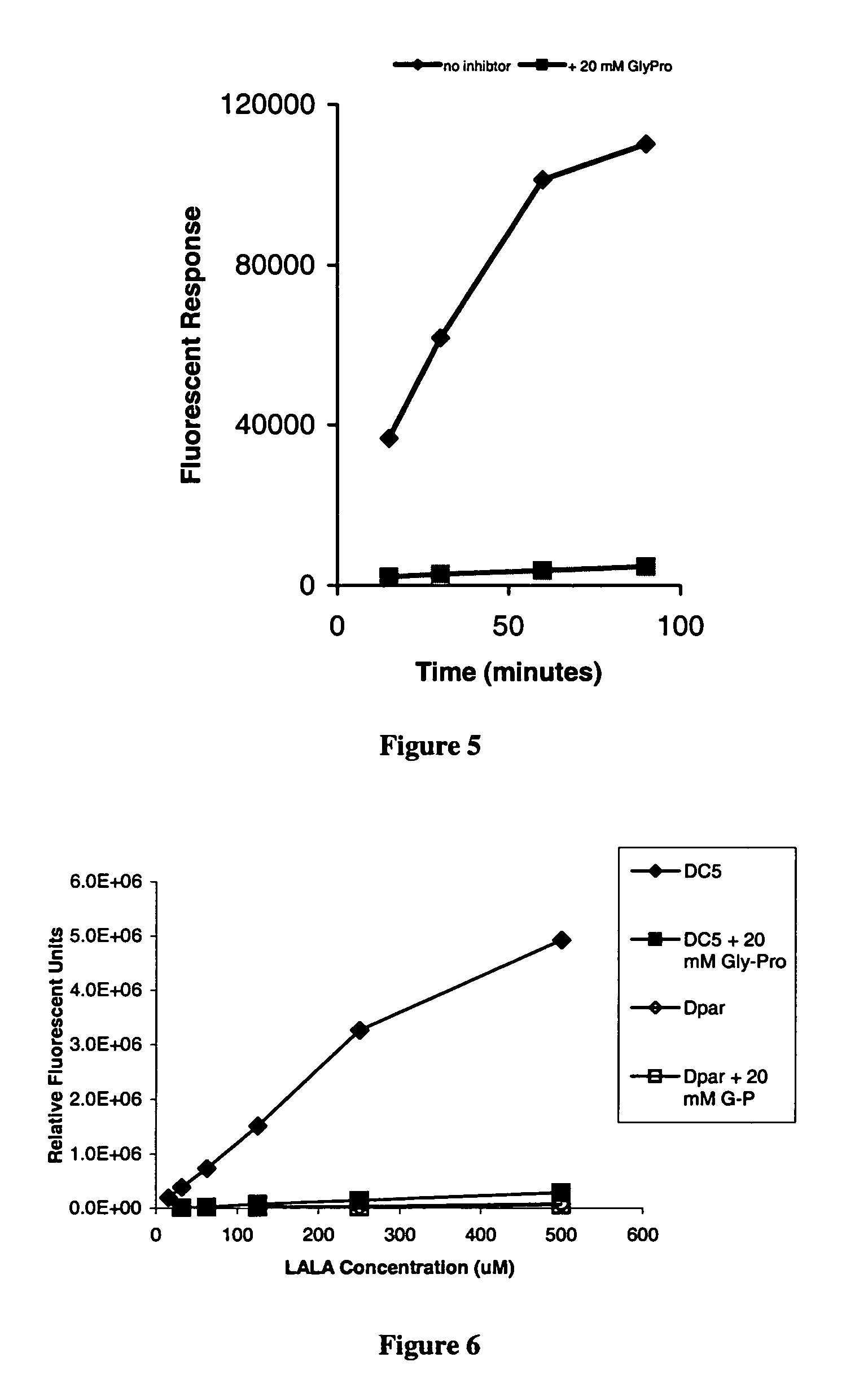
An in vivo method for labelling a protein having an N-terminal cysteine is disclosed. A probe comprising a thioester group and a detectable label is introduced into a cell expressing the N-terminal cysteine protein, allowing for the N-terminal cysteine to cleave the thioester bond and resulting in the label being covalently attached to the N-terminus of the protein by an amide bond.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Polymer conjugates of GLP-1
ActiveUS8293869B2Rapid clearanceGood release effectMetabolism disorderSaccharide peptide ingredientsWater solubleMethyl group
Conjugates of a GLP-I moiety may be covalently attached to one or more water-soluble polymers. For instance, a GLP-I polymer conjugate may include a GLP-I moiety releasably attached at its N-terminus to a water-soluble polymer. The GLP-I polymer conjugate may include a GLP-I moiety covalently attached to a water-soluble polymer, wherein the GLP-I moiety possesses an N-methyl substituent. The GLP-I polymer conjugate may include a GLP-I moiety covalently attached at a polymer attachment site to a water-soluble polymer, wherein the GLP-I moiety is glycosylated at a site separate from the polymer attachment site.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Compounds For Enzyme Inhibition
InactiveUS20080090785A1Inhibiting and reducing HIV infectionAffecting levelAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEnzyme inhibitionAziridine
Peptide-based compounds including heteroatom-containing, three-membered rings efficiently and selectively inhibit specific activities of N-terminal nucleophile (Ntn) hydrolases. The activities of those Ntn having multiple activities can be differentially inhibited by the compounds described. For example, the chymotrypsinlike activity of the 20S proteasome may be selectively inhibited with the inventive compounds. The peptide-based compounds include an epoxide or aziridine, and functionalization at the N-terminus. Among other therapeutic utilities, the peptide-based compounds are expected to display anti-inflammatory properties and inhibition of cell proliferation.
Owner:ONYX THERAPEUTICS
Compounds for enzyme inhibition
Peptide-based compounds including heteroatom-containing, three-membered rings efficiently and selectively inhibit specific activities of N-terminal nucleophile (Ntn) hydrolases. The activities of those Ntn having multiple activities can be differentially inhibited by the compounds described. For example, the chymotrypsin-like and PGPH activities of the 20S proteasome can be selectively inhibited with the inventive compounds. The peptide-based compounds include at least three peptide units, an epoxide or aziridine, and functionalization at the N-terminus, such as a detectable label. Along with therapeutic utilities, these peptide based compounds can be used in assays useful for screening, monitoring, diagnostic and / or dosing purposes.
Owner:PROTEOLIX INC
Chimeric fibroblast growth factor 23 proteins and methods of use
ActiveUS20140243260A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsChimera ProteinFibroblast growth factor 23
The present invention relates to an isolated chimeric protein. The isolated chimeric protein includes an N-terminus coupled to a C-terminus, where the N-terminus includes an N-terminal portion from a fibroblast growth factor (“FGF”) 23 molecule and the C-terminus includes a C-terminal portion from an FGF19 molecule. The present invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition including an isolated chimeric protein and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The isolated chimeric protein includes an N-terminus coupled to a C-terminus, where the N-terminus includes an N-terminal portion from a fibroblast growth factor (“FGF”) 23 molecule and the C-terminus includes a C-terminal portion from an FGF19 molecule, and a pharmaceutically-acceptable carrier. Yet another aspect of the present invention relates to a method for treating a subject suffering from a disorder. This method includes selecting a subject suffering from the disorder and administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a chimeric protein according to the present invention.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Compounds for enzyme inhibition
ActiveUS20060030533A1Inhibiting and reducing HIV infectionAffecting levelOrganic active ingredientsBiocideEnzyme inhibitionAziridine
Peptide-based compounds including heteroatom-containing, three-membered rings efficiently and selectively inhibit specific activities of N-terminal nucleophile (Ntn) hydrolases. The activities of those Ntn having multiple activities can be differentially inhibited by the compounds described. For example, the chymotrypsin-like activity of the 20S proteasome may be selectively inhibited with the inventive compounds. The peptide-based compounds include an epoxide or aziridine, and functionalization at the N-terminus. Among other therapeutic utilities, the peptide-based compounds are expected to display anti-inflammatory properties and inhibition of cell proliferation.
Owner:ONYX THERAPEUTICS INC
Compounds for enzyme inhibition
InactiveUS8088741B2Inhibiting and reducing HIV infectionAffecting levelAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEnzyme inhibitionAziridine
Peptide-based compounds including heteroatom-containing, three-membered rings efficiently and selectively inhibit specific activities of N-terminal nucleophile (Ntn) hydrolases. The activities of those Ntn having multiple activities can be differentially inhibited by the compounds described. For example, the chymotrypsinlike activity of the 20S proteasome may be selectively inhibited with the inventive compounds. The peptide-based compounds include an epoxide or aziridine, and functionalization at the N-terminus. Among other therapeutic utilities, the peptide-based compounds are expected to display anti-inflammatory properties and inhibition of cell proliferation.
Owner:ONYX THERAPEUTICS INC
Tetravalent etanercept
ActiveUS7229962B2Improve efficacyImprove stabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntipyreticDNA constructEtanercept
Disclosed are concatameric proteins comprising two soluble domains, in which the C-terminus of a soluble domain of a biologically active protein is linked to the N-terminus of an identical soluble domain or a distinct soluble domain of a biologically active protein. Also, the present invention discloses dimeric proteins formed by formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds at the hinge region of two monomeric proteins formed by linkage of a concatamer of two identical soluble extracellular regions of proteins involving immune response to an Fc fragment of an immunoglobulin molecule, their glycosylated proteins, DNA constructs encoding the monomeric proteins, recombinant expression plasmids containing the DNA construct, host cells transformed or transfected with the recombinant expression plasmids, and a method of preparing the dimeric proteins by culturing the host cells. Further, the present invention discloses pharmaceutical or diagnostic compositions comprising the dimeric protein or its glycosylated form.
Owner:MEDEXGEN
Monoclonal Antibody And Use Thereof
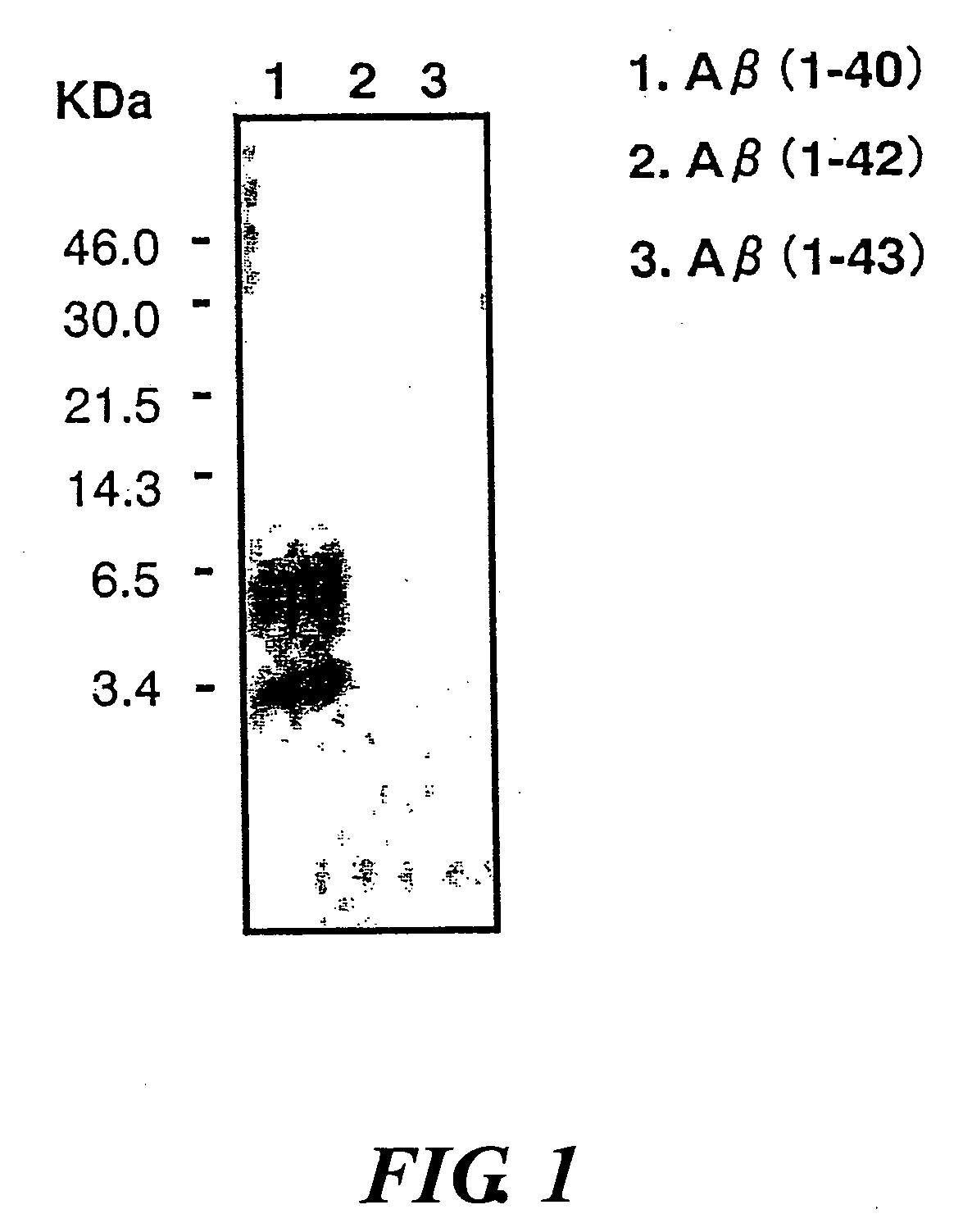
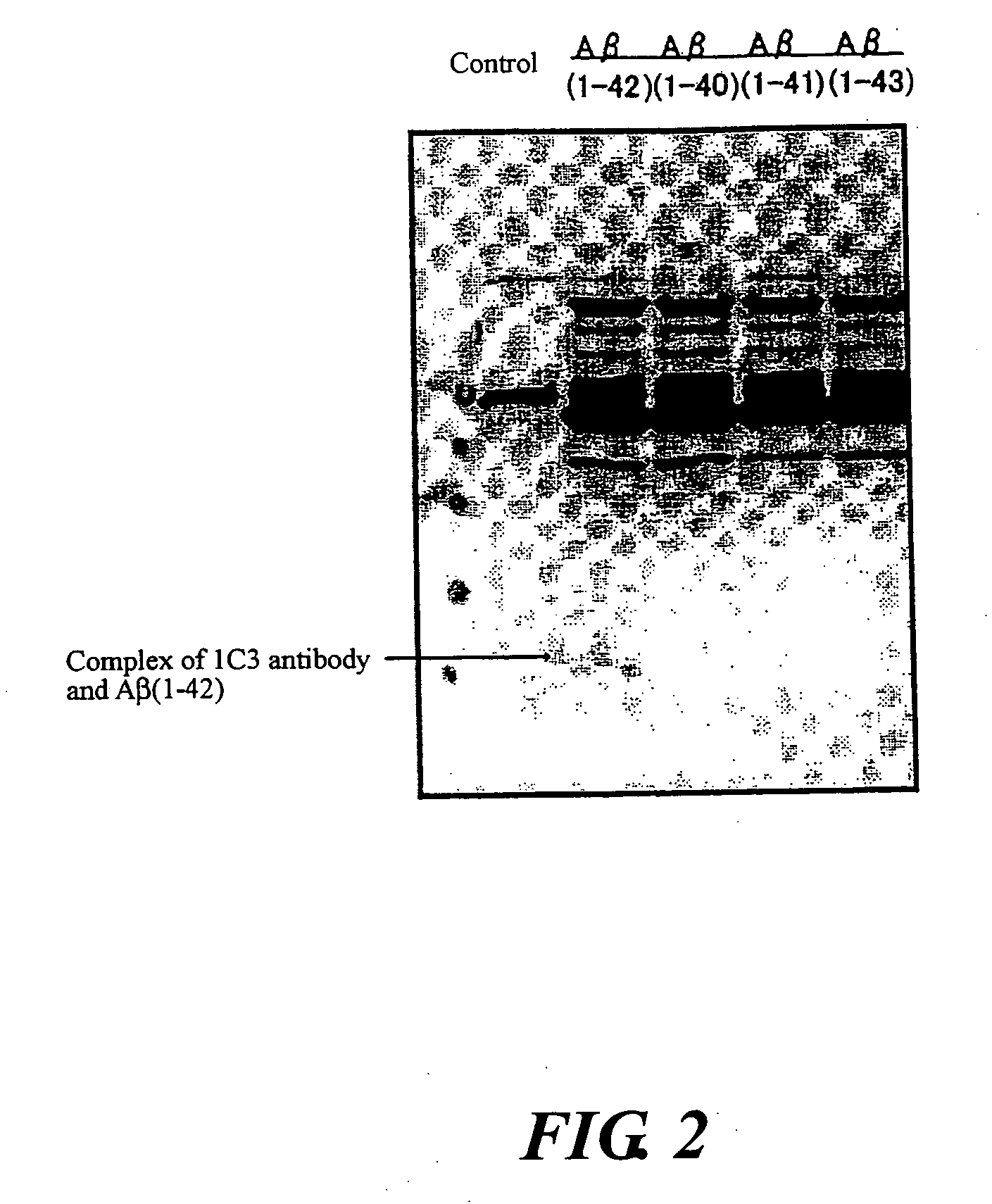
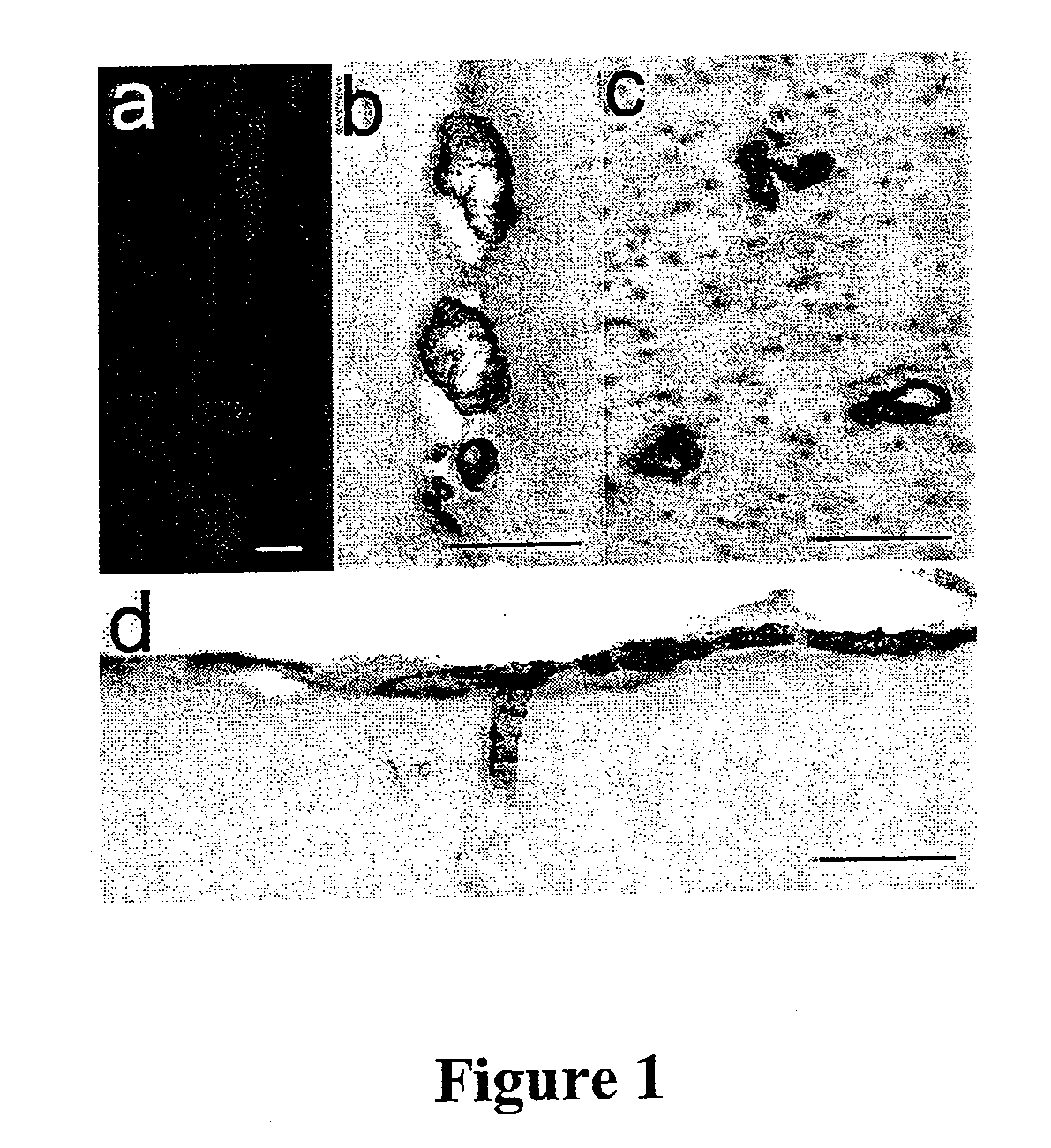
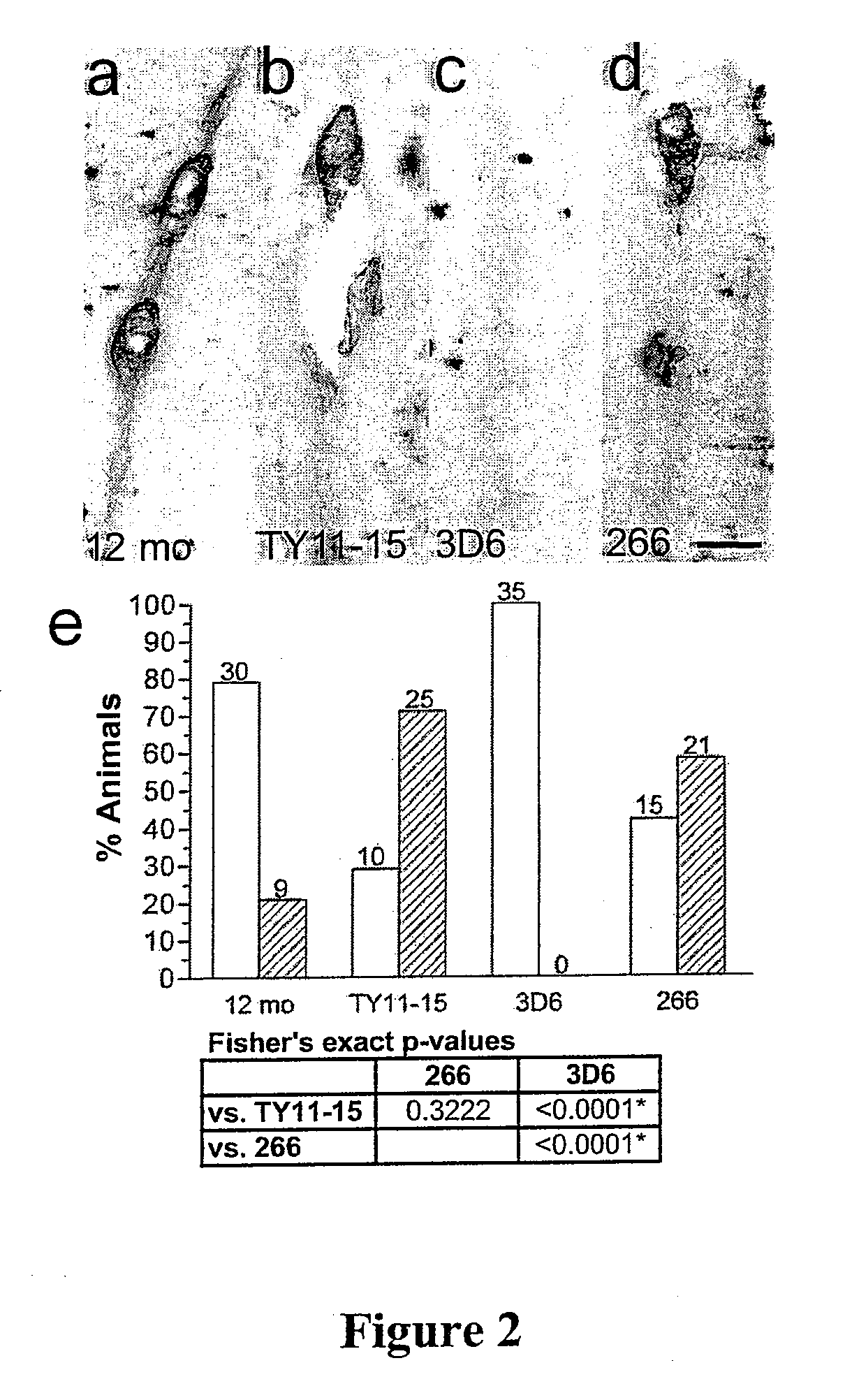
InactiveUS20080025988A1Treatment safetySuppress deposition of amyloidNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDiseaseAmyloid
An antibody capable of recognizing amyloid β while not recognizing amyloid β precursor proteins, and a method for using the same.A monoclonal antibody characterized by being capable of recognizing the N-terminus peptide of amyloid β while not recognizing amyloid β precursor proteins, an amyloid β assay kit, a therapeutic agent of Alzheimer's disease, and a method for treating Alzheimer's disease using the monoclonal antibody.
Owner:COLLATERAL AGENTS
Nucleic acids encoding non aggregating fluorescent proteins and methods for using the same
Nucleic acid compositions encoding non-aggregating chromo / fluoroproteins and mutants thereof, as well as the encoded proteins, are provided. The proteins of interest are polypeptides that are non-aggregating colored and / or fluorescent proteins, where the non-aggregating feature arises from the modulation of residues in the N-terminus of the protein and the chromo and / or fluorescent feature arises from the interaction of two or more residues of the protein. Also provided are fragments of the subject nucleic acids and the peptides encoded thereby, as well as antibodies to the subject proteins and transgenic cells and organisms. The subject protein and nucleic acid compositions find use in a variety of different applications. Finally, kits for use in such applications, e.g., that include the subject nucleic acid compositions, are provided.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
Compounds for Enzyme Inhibition
InactiveUS20090203698A1Inhibiting and reducing HIV infectionAffecting levelBiocideNervous disorderEnzyme inhibitionAziridine
Peptide-based compounds including heteroatom-containing, three-membered rings efficiently and selectively inhibit specific activities of N-terminal nucleophile (Ntn) hydrolases associated with the proteasome. The peptide-based compounds include an epoxide or aziridine, and functionalization at the N-terminus. Among other therapeutic utilities, the peptide-based compounds are expected to display anti-inflammatory properties and inhibition of cell proliferation. Oral administration of these peptide-based proteasome inhibitors is possible due to their bioavailability profiles.
Owner:ONYX THERAPEUTICS INC
Single chain recombinant t cell receptors
InactiveUS20060166875A1Improve stabilityUseful purposeCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDisulfide bondingExtracellular
A single chain T cell receptor (scTCR) comprising an a segment constituted by a TCR α chain variable region sequence fused to the N terminus of a TCR α chain constant region extracellular sequence, a β segment constituted by a TCR β chain variable region fused to the N terminus of a TCR β chain constant region extracellular sequence, and a linker sequence linking the C terminus of the a segment to the N terminus of the β segment, or vice versa, the constant region extracellular sequences of the α and β segments being linked by a disulfide bond, the length of the linker sequence and the position of the disulfide bond being such that the variable region sequences of the α and β segments are mutually orientated substantially as in native αβ T cell receptors. Complexes of two or more such scTCRs, and use of the scTCRs in therapy and in various screening applications are also disclosed.
Owner:IMMUNOCORE LTD +1
Compounds for enzyme inhibition
Peptide-based compounds including heteroatom-containing, three-membered rings efficiently and selectively inhibit specific activities of N-terminal nucleophile (Ntn) hydrolases. The activities of those Ntn having multiple activities can be differentially inhibited by the compounds described. For example, the chymotrypsin-like and PGPH activities of the 20S proteasome can be selectively inhibited with the inventive compounds. The peptide-based compounds include at least three peptide units, an epoxide or aziridine, and functionalization at the N-terminus, such as a detectable label. Along with therapeutic utilities, these peptide based compounds can be used in assays useful for screening, monitoring, diagnostic and / or dosing purposes.
Owner:ONYX THERAPEUTICS INC
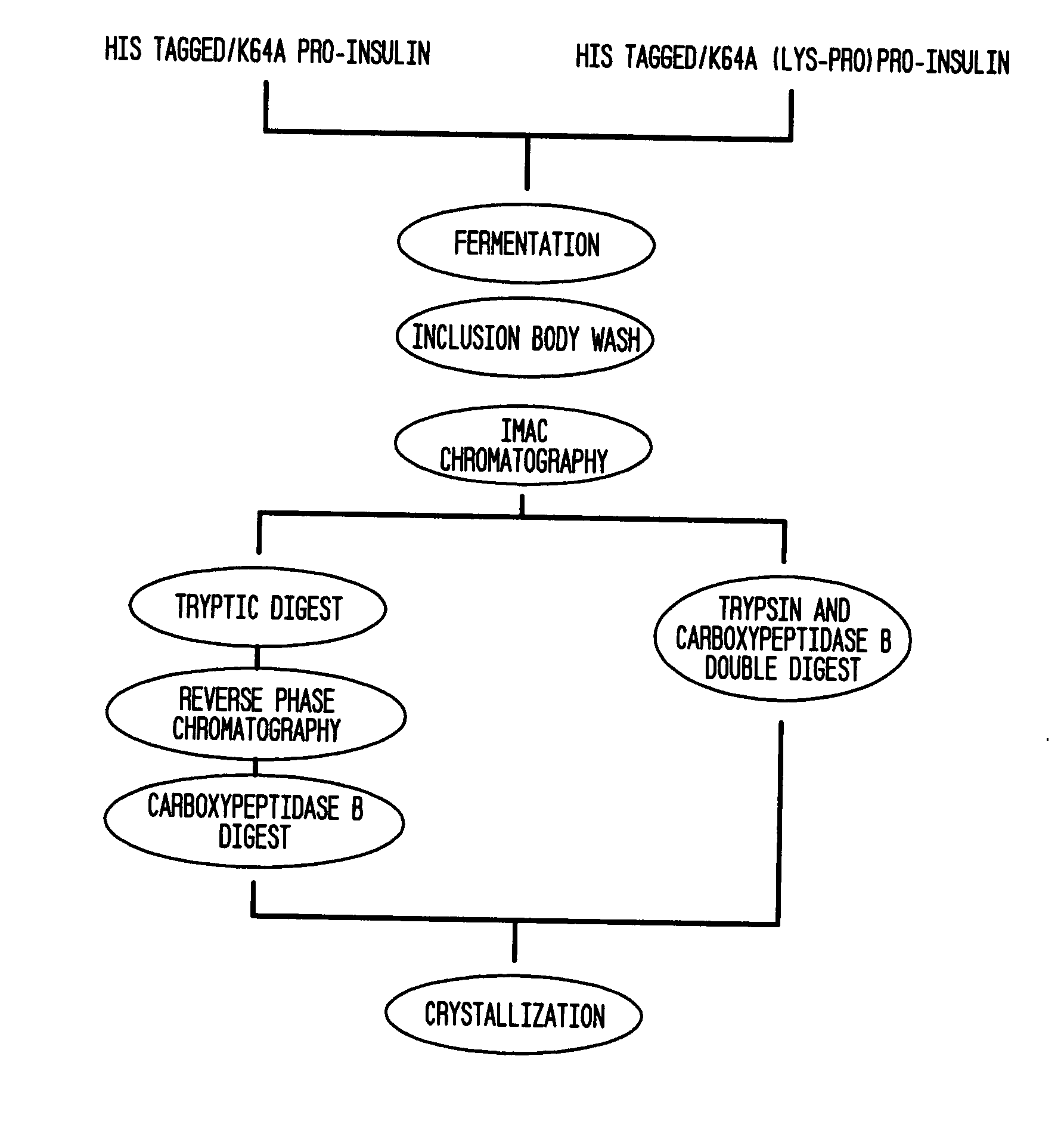
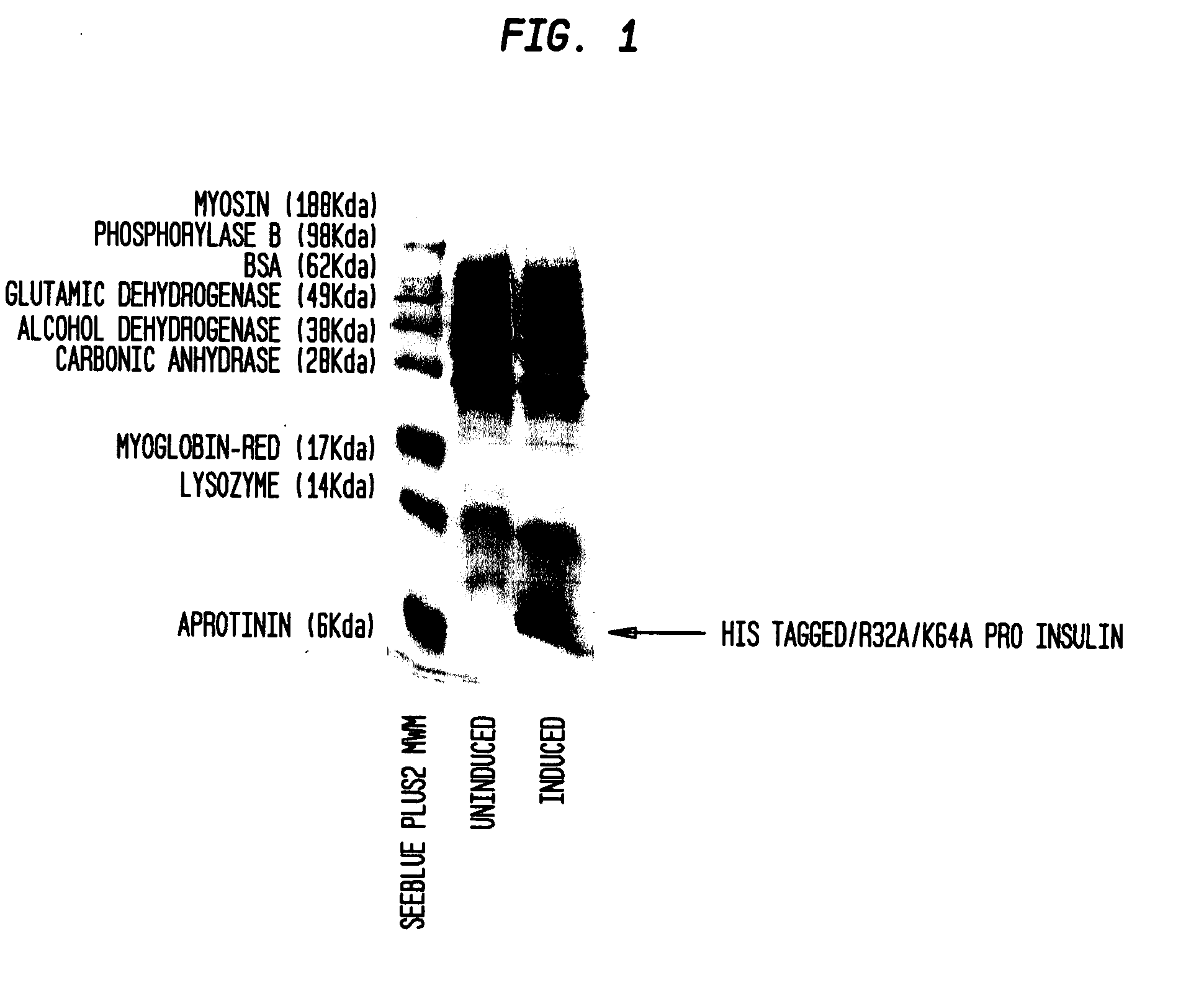
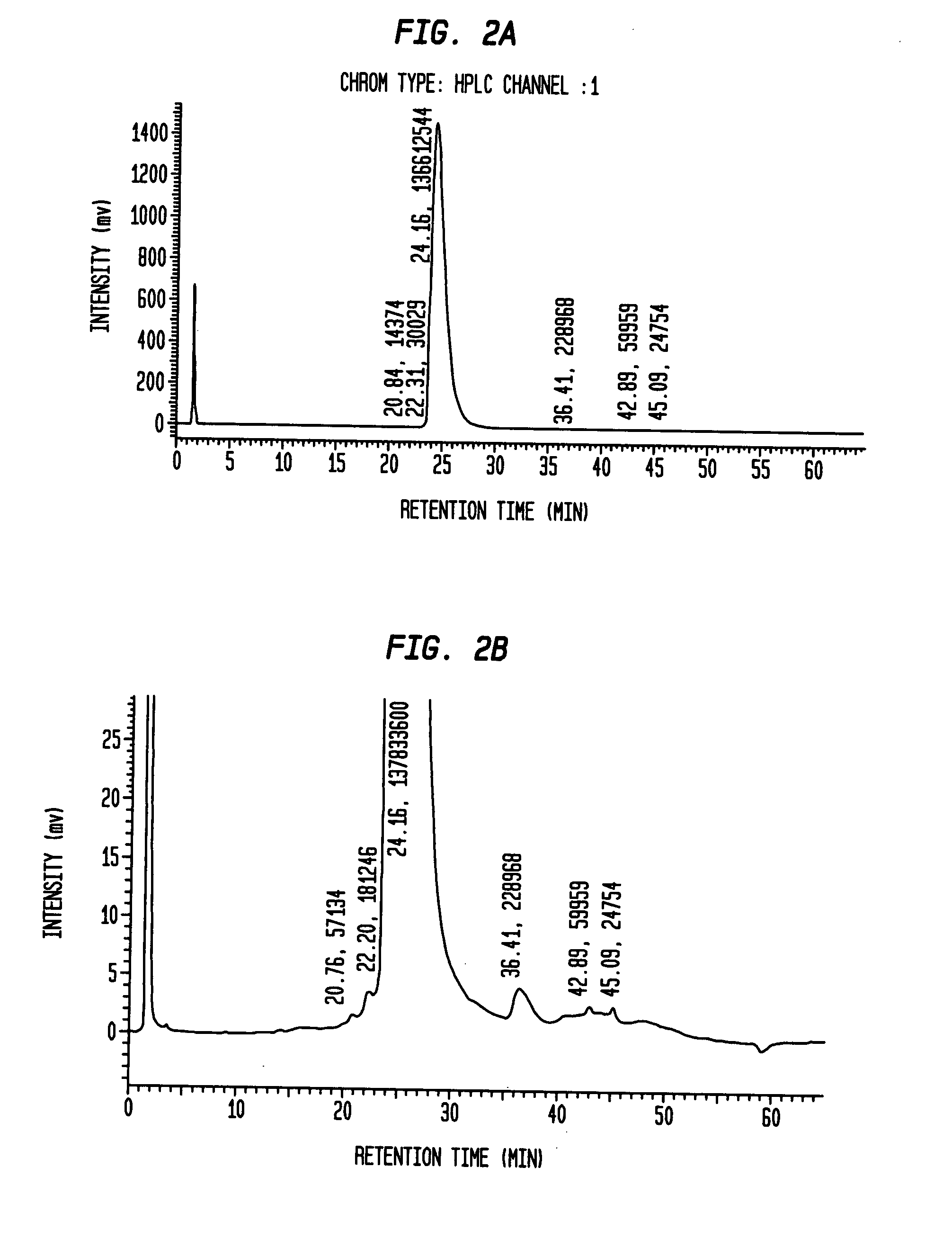
Insulin production methods and pro-insulin constructs
InactiveUS20080146492A1Reduce eliminateImprove efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesInsulin activityImproved method
Novel pro-insulin having specific amino acid and / or nucleic acid modifications suitable for improved methods of insulin production are provided. Novel and highly efficient processes for preparing the pro-insulin preparations and preparations containing them are also disclosed. The novel pro-insulin preparations may be converted into human insulin useful in therapeutic preparations. Novel peptides of the C-peptide, and N terminus, including RREAEALQVGQVELGGGPGAGSLQPLALEGSLQAR (SEQ ID NO: 32), and MHHHHHHGGR (SEQ ID NO: 2) respectively are provided, as well as the unique nucleic acid molecules encoding them.
Owner:AGILA BIOTECH PVT LTD
Prevention and treatment of cerebral amyloid angiopathy
InactiveUS20080292625A1Reduces and inhibits vascular amyloidogenic pathologyMinimizes microhemorrhageNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAmyloid angiopathyDisease cause
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) and methods to effect prophylaxis of CAA. The methods can treat CAA concurrently with Alzheimer's disease or separately. The methods can effect prophylaxis of CAA concurrently with Alzheimer's disease or separately. The methods involve administering antibody that is specific for the N-terminus of Aβ or an agent that can induce such an antibody.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY +1
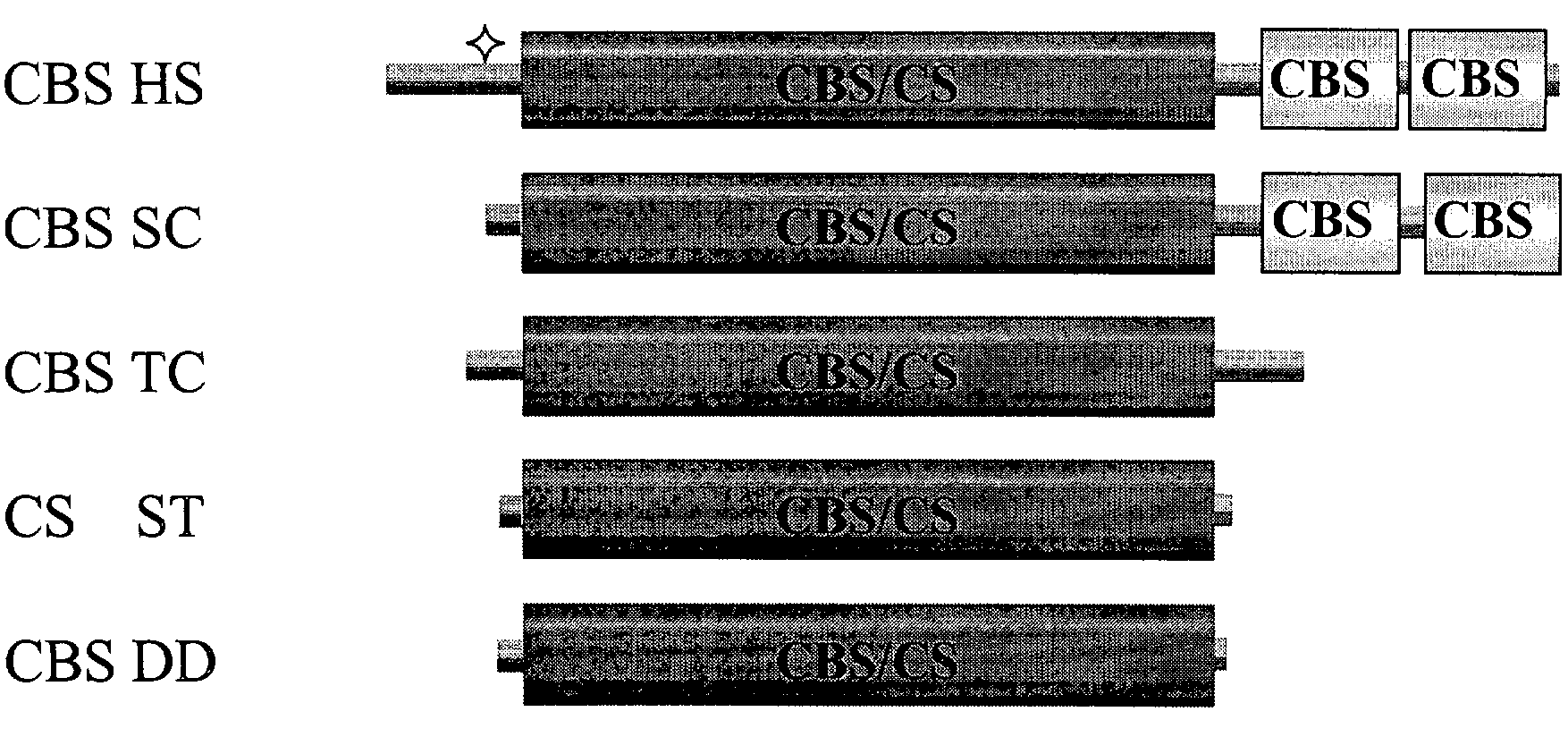
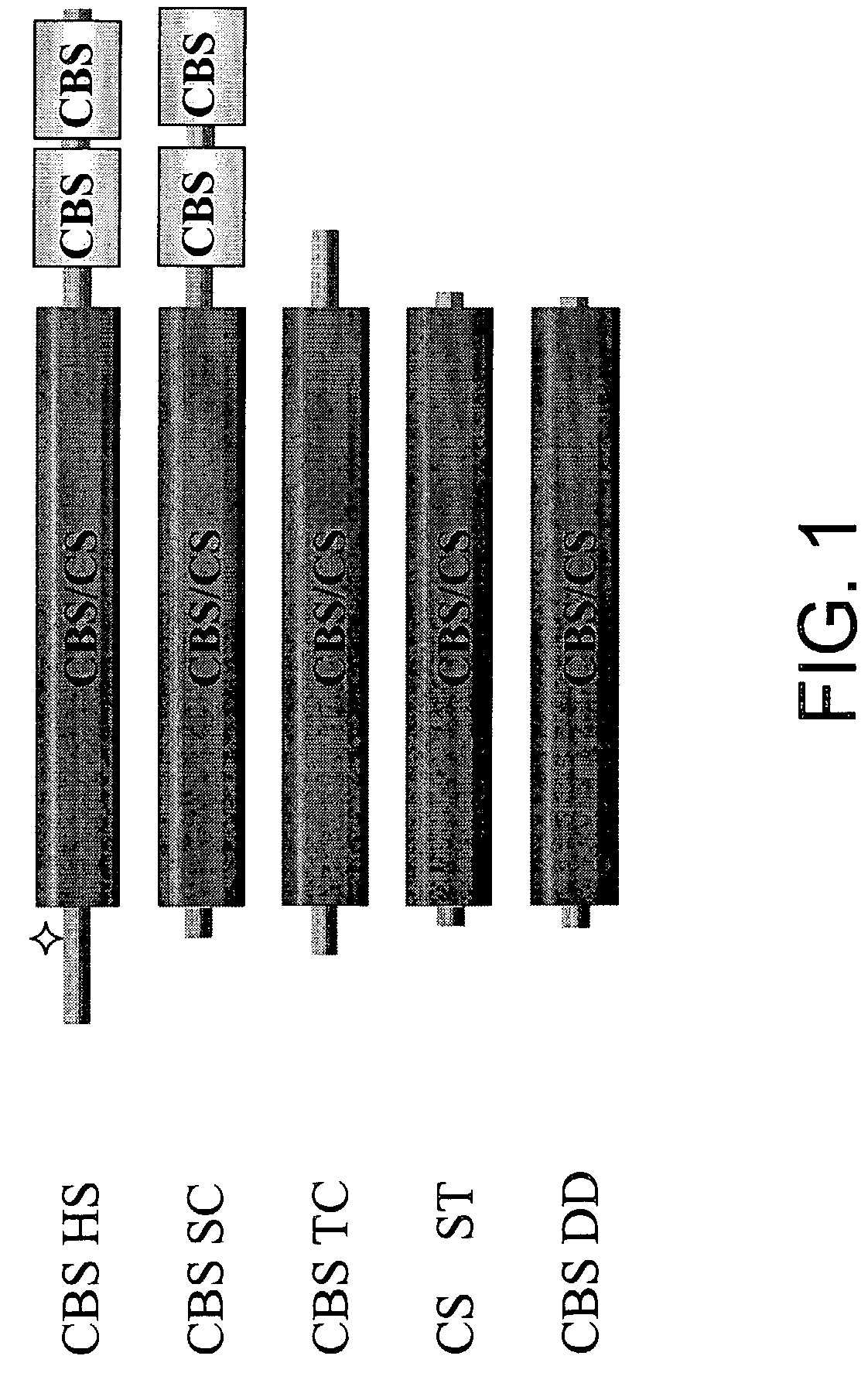
Human cystathionine beta-synthase variants and methods of production thereof
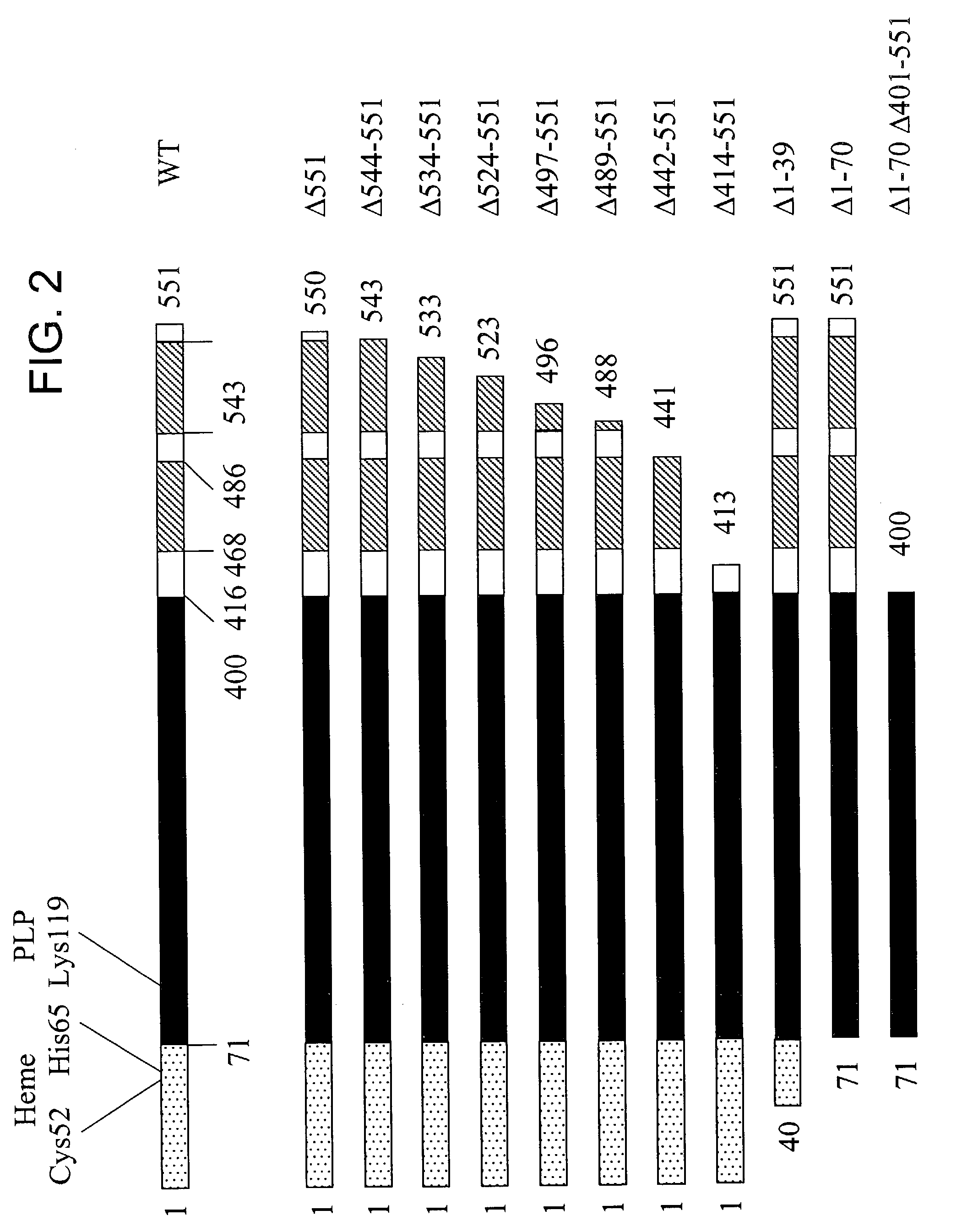
Human cystathionine β-synthase variants are disclosed, as well as a method to produce recombinant human cystathionine β-synthase and variants thereof. More particularly, the role of both the N-terminal and C-terminal regions of human CBS has been studied, and a variety of truncation mutants and modified CBS homologues are described. In addition, a method to express and purify recombinant human cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) and variants thereof which have only one or two additional amino acid residues at the N-terminus are described.
Owner:COLORADO UNIV OF RGT THE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com