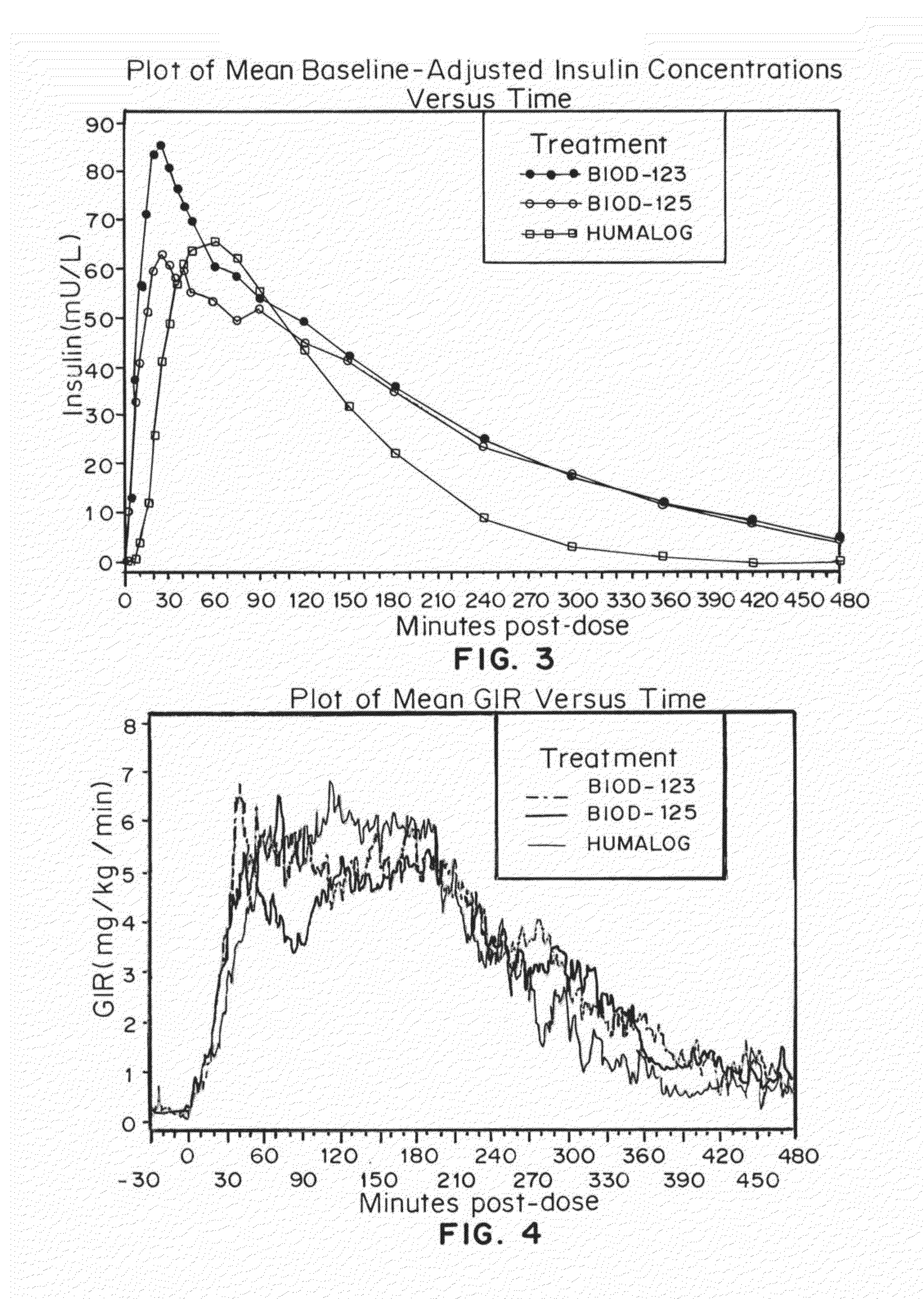
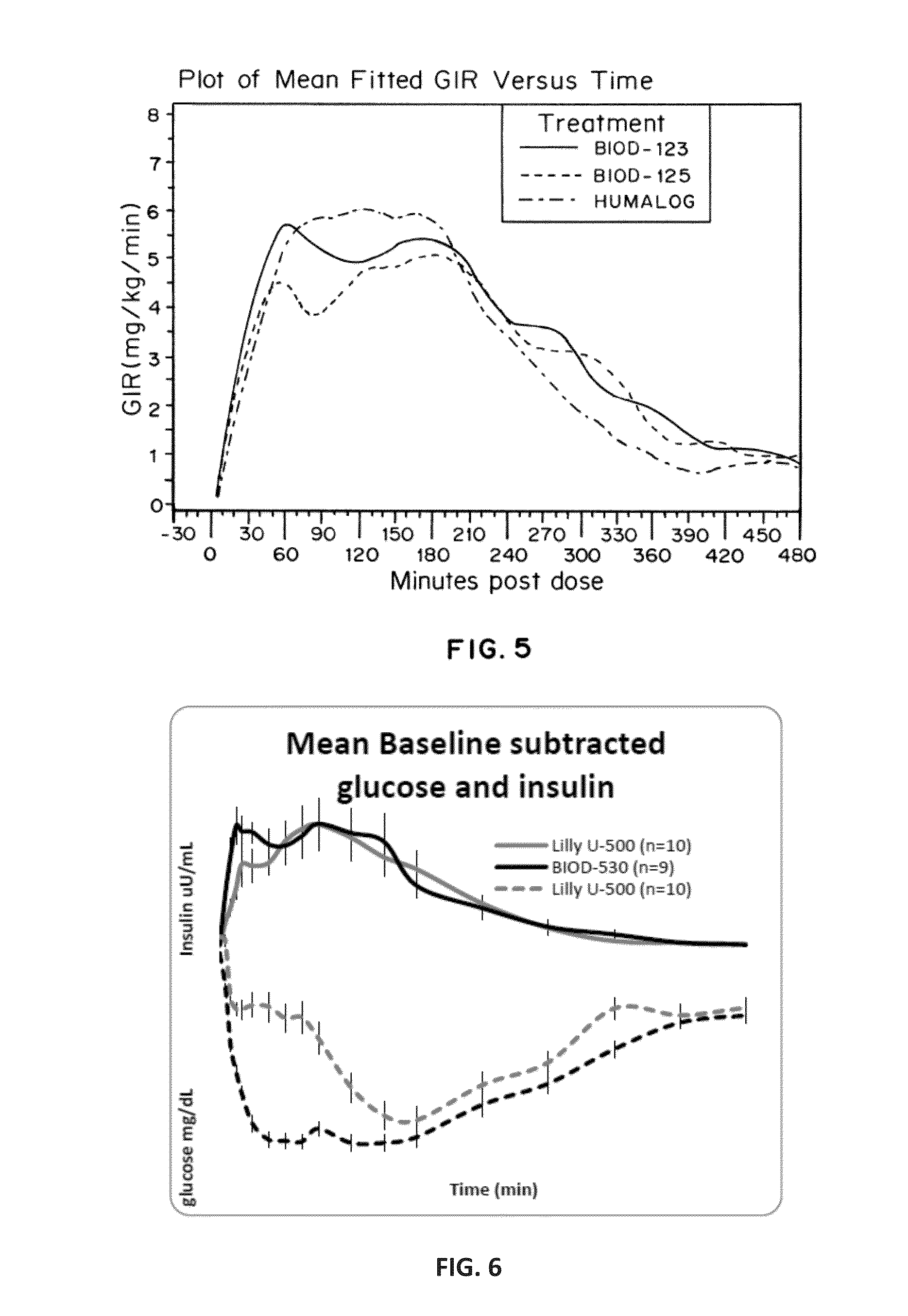
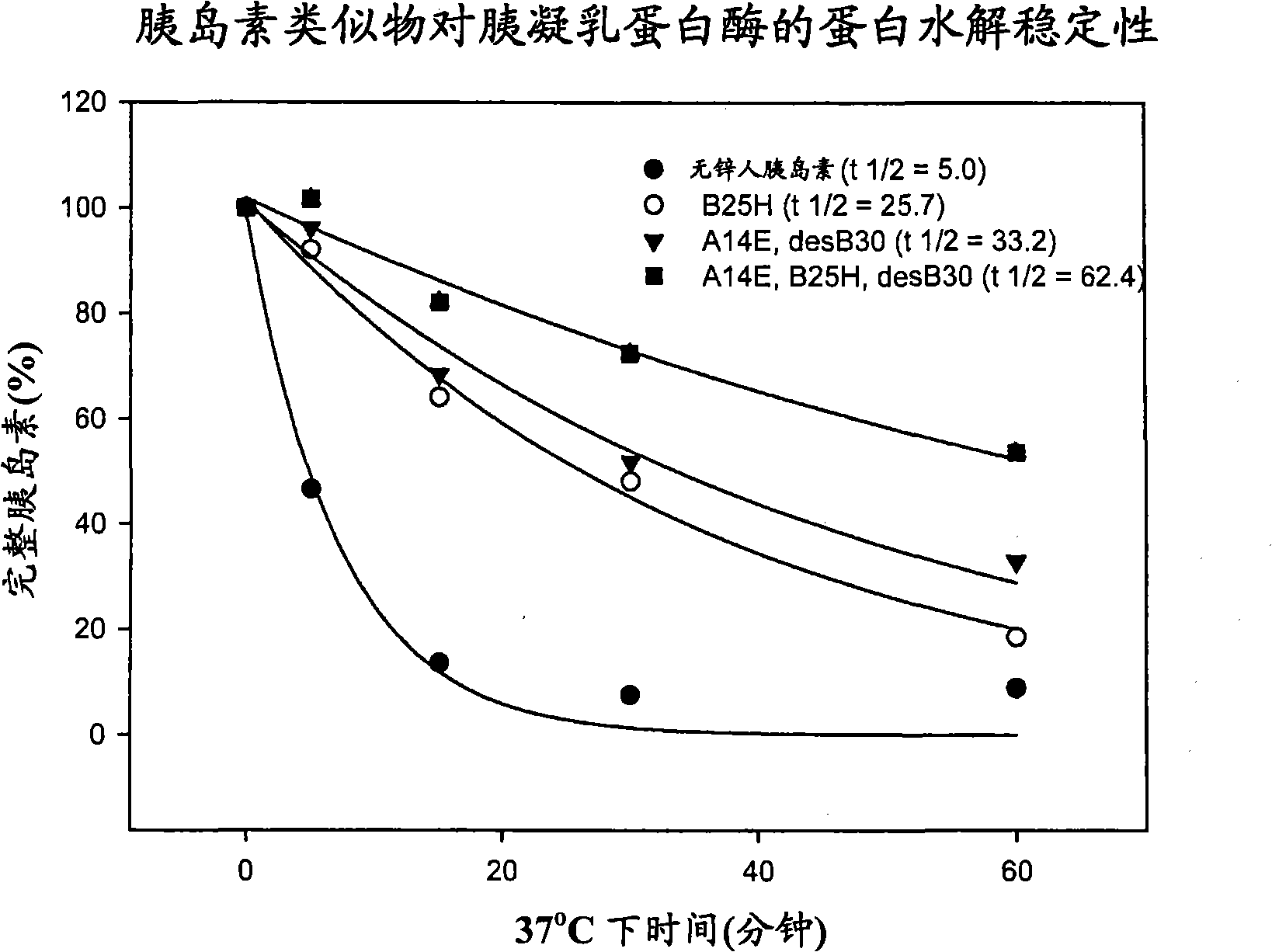
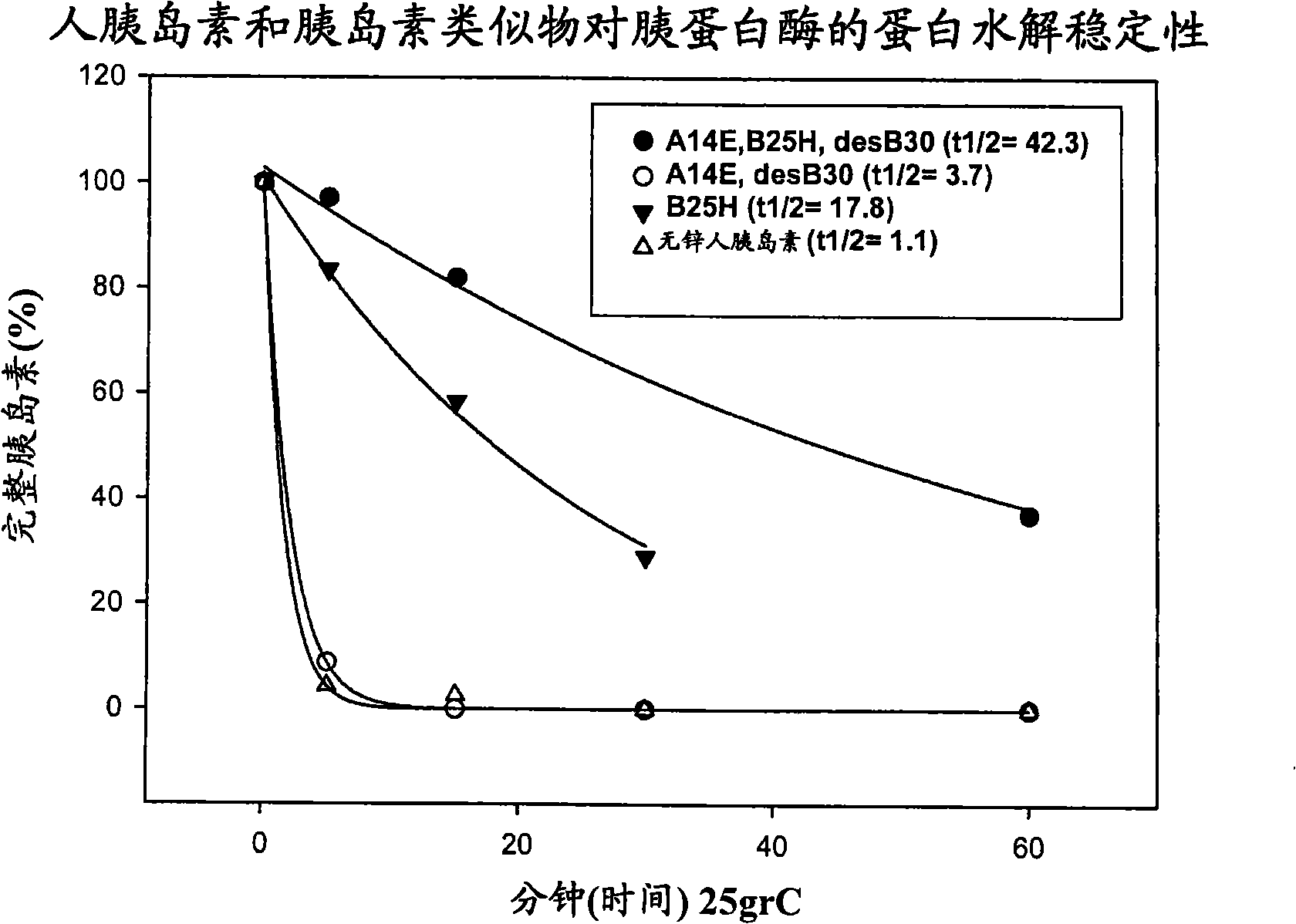
Patents
Literature
119 results about "INSULIN PREPARATIONS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quickly compare key characteristics of insulin preparations with the MIMS insulins table. The table lists the species from which the insulin is derived (human, porcine or bovine), along with the available presentations (vials, cartridges and prefilled pens) and compatible delivery devices.
Stabilized insulin formulations
InactiveUS6852694B2Easy to separateBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsINSULIN PREPARATIONSEndocrinology
The present invention is directed to stabilized insulin composition comprising a mixture of insulin species such as insulin and an insulin analog. As disclosed herein, insulin compositions comprising a mixture of insulin and insulin analog species form heterodimeric complexes having a greater stability than the homodimeric complexes formed in compositions comprising single insulin species. Consequently, the present invention provides methods for stabilizing insulin molecules, methods for identifying stable heterodimeric insulin complexes and stabilized insulin compositions.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Methods of evaluating protein formulation stability and surfactant-stabilized insulin formulations derived therefrom
InactiveUS6737401B2Improve physical stabilityReliable timePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCell AggregationsProtein aggregation
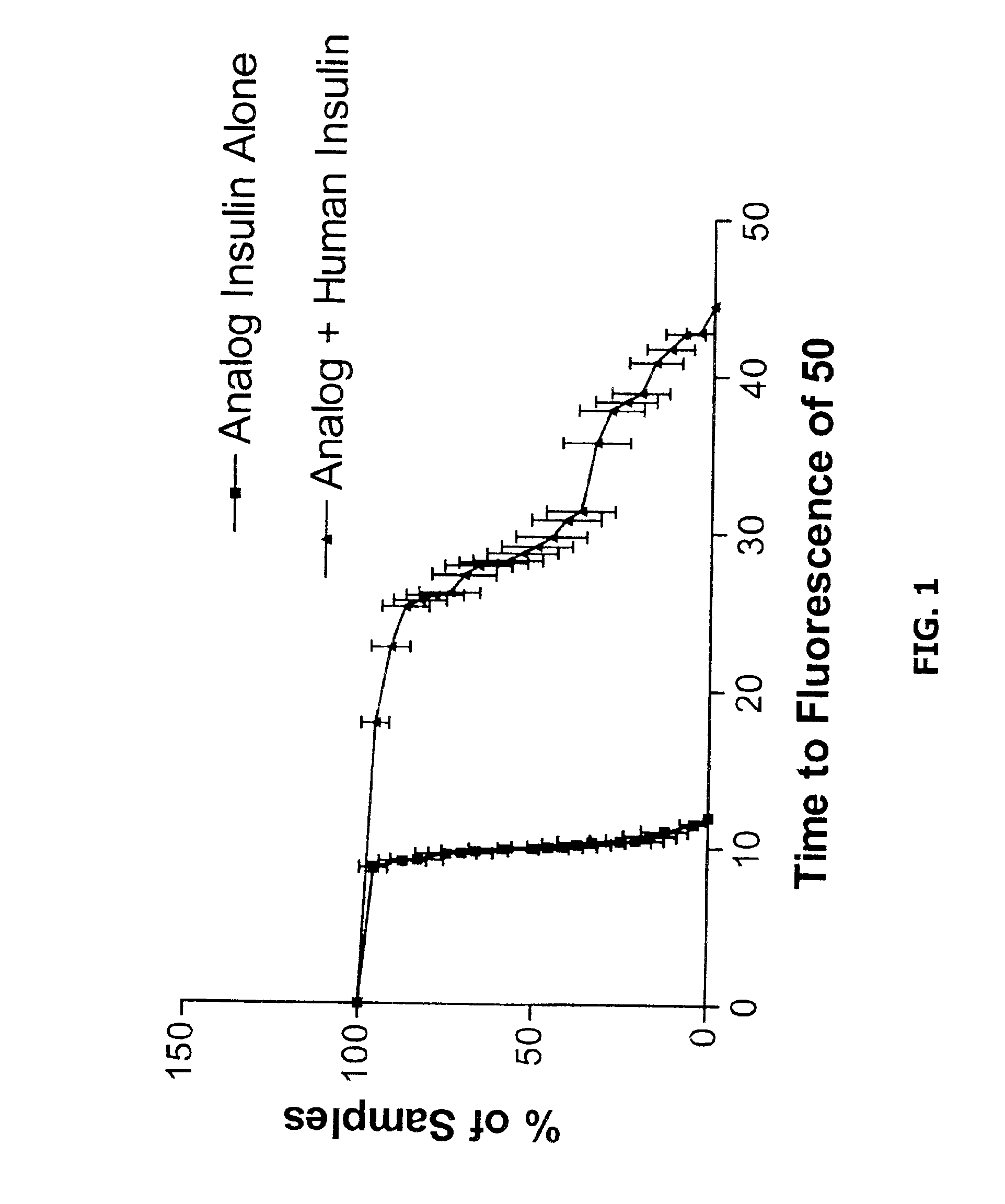
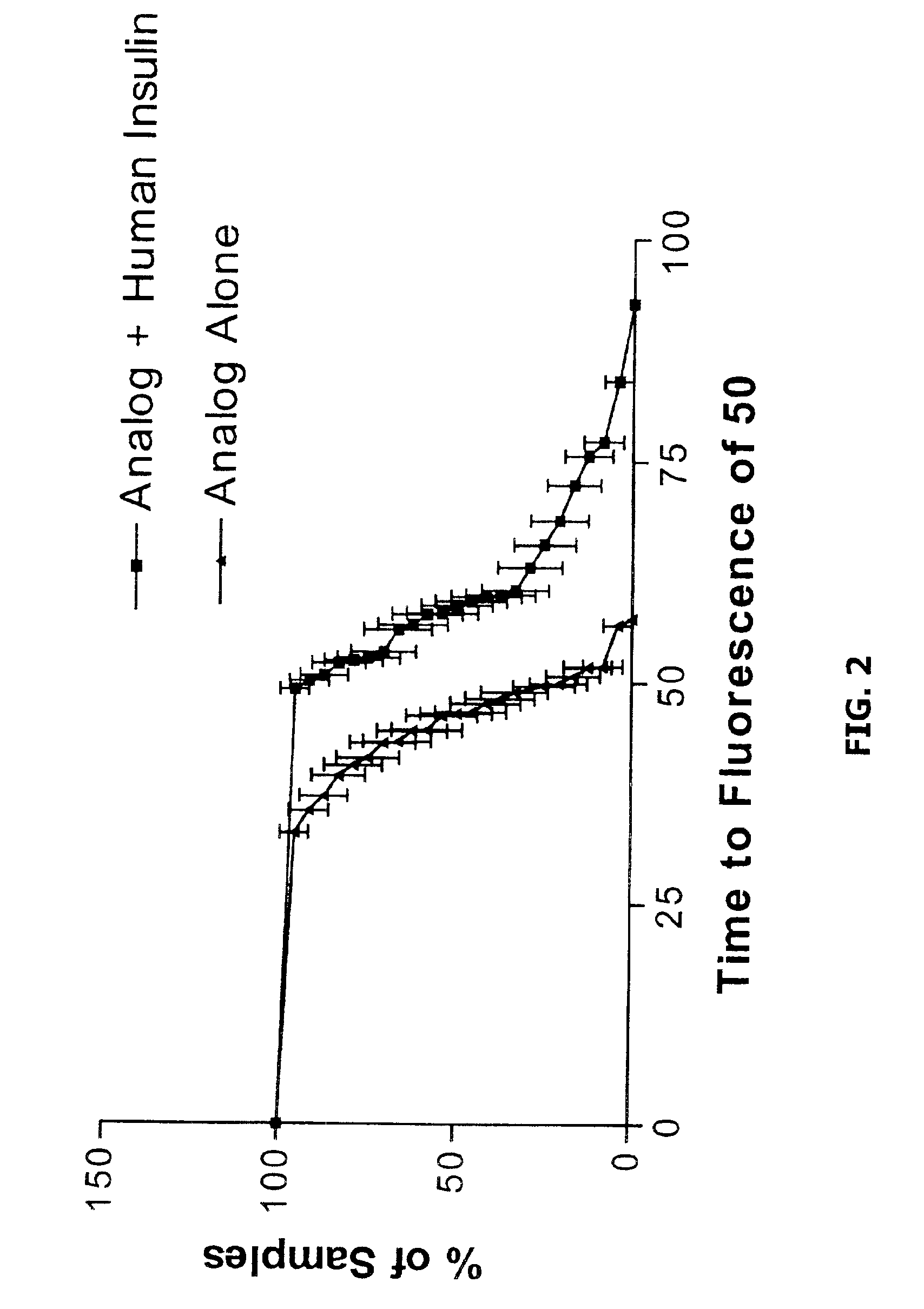
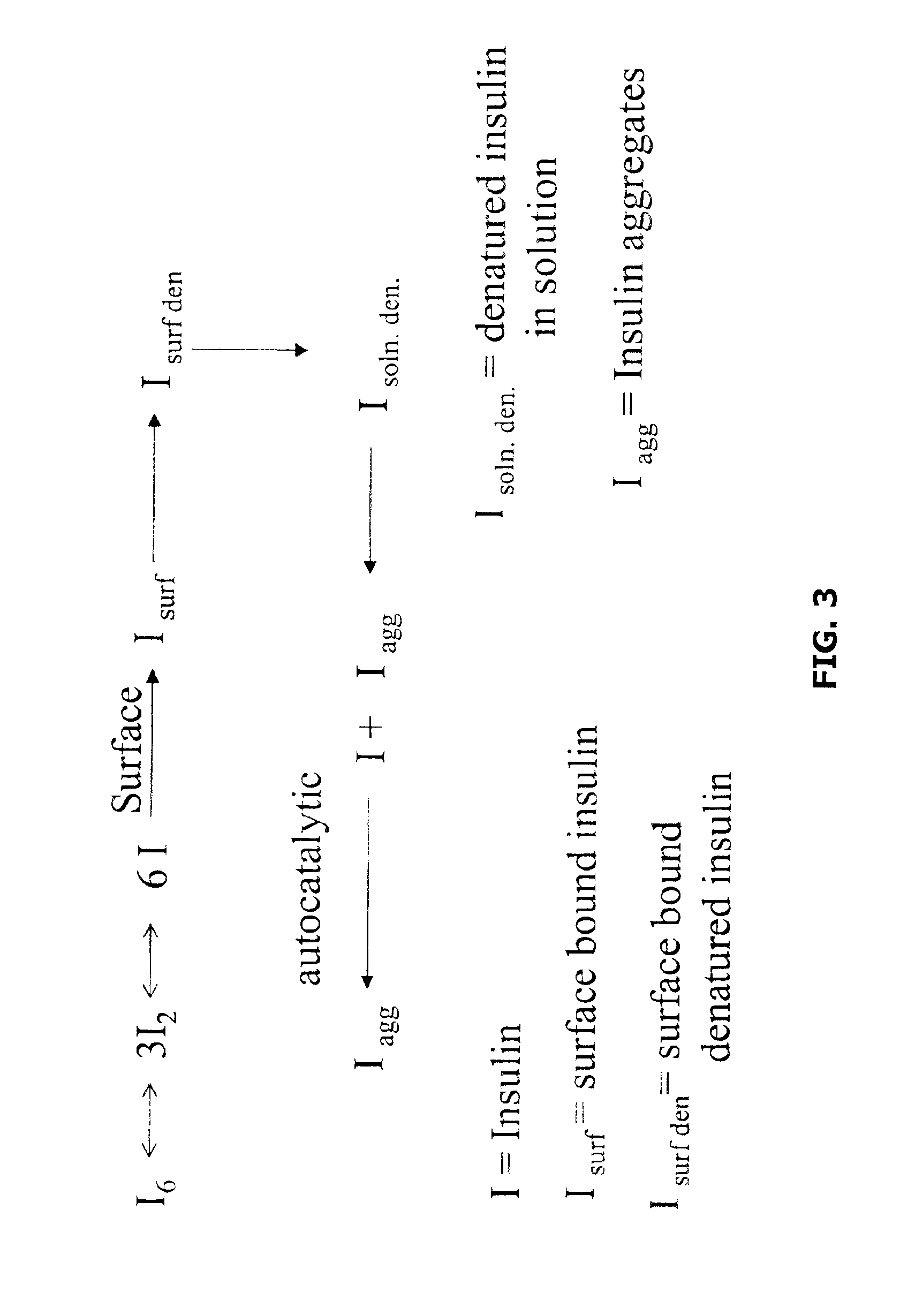
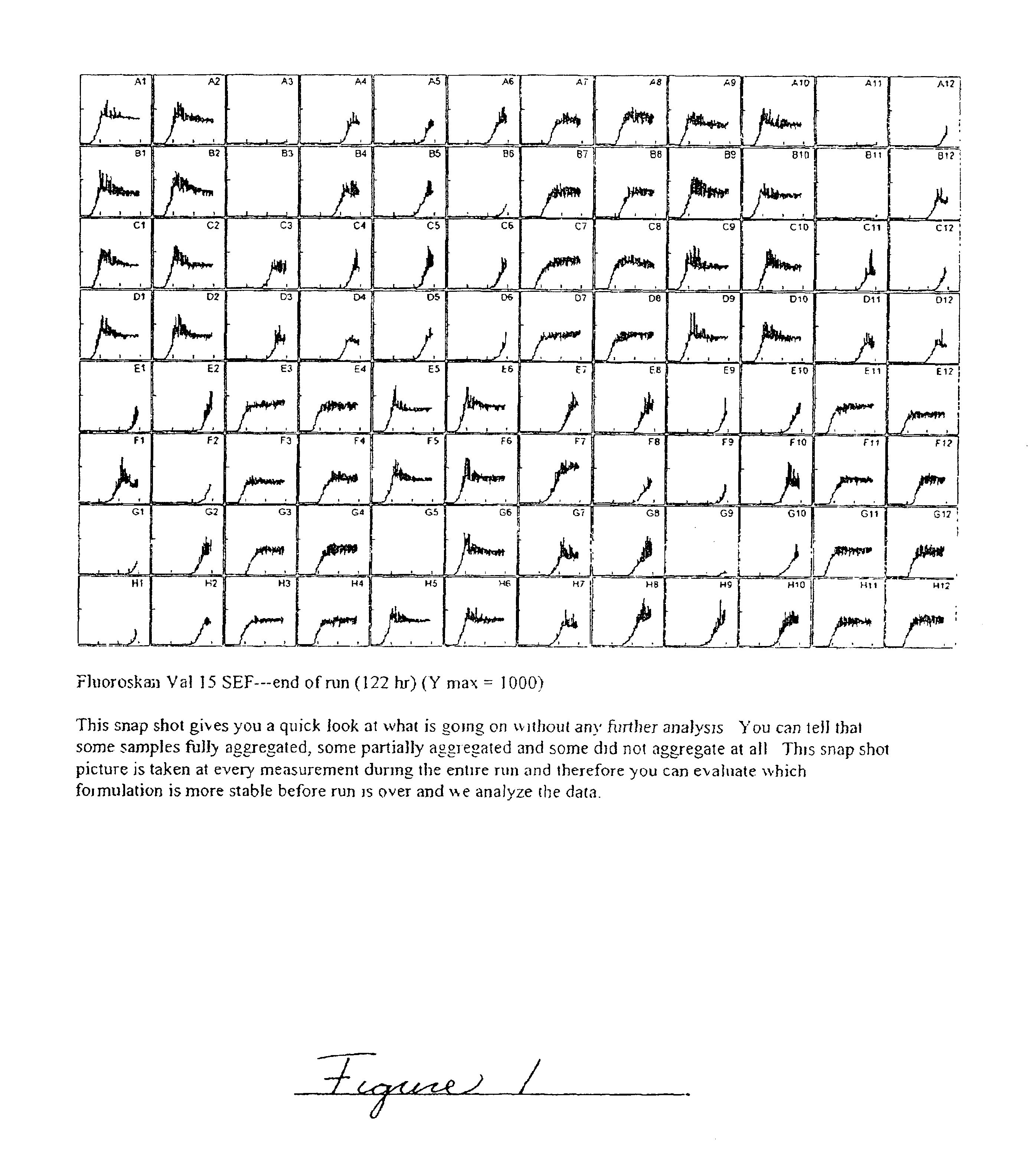
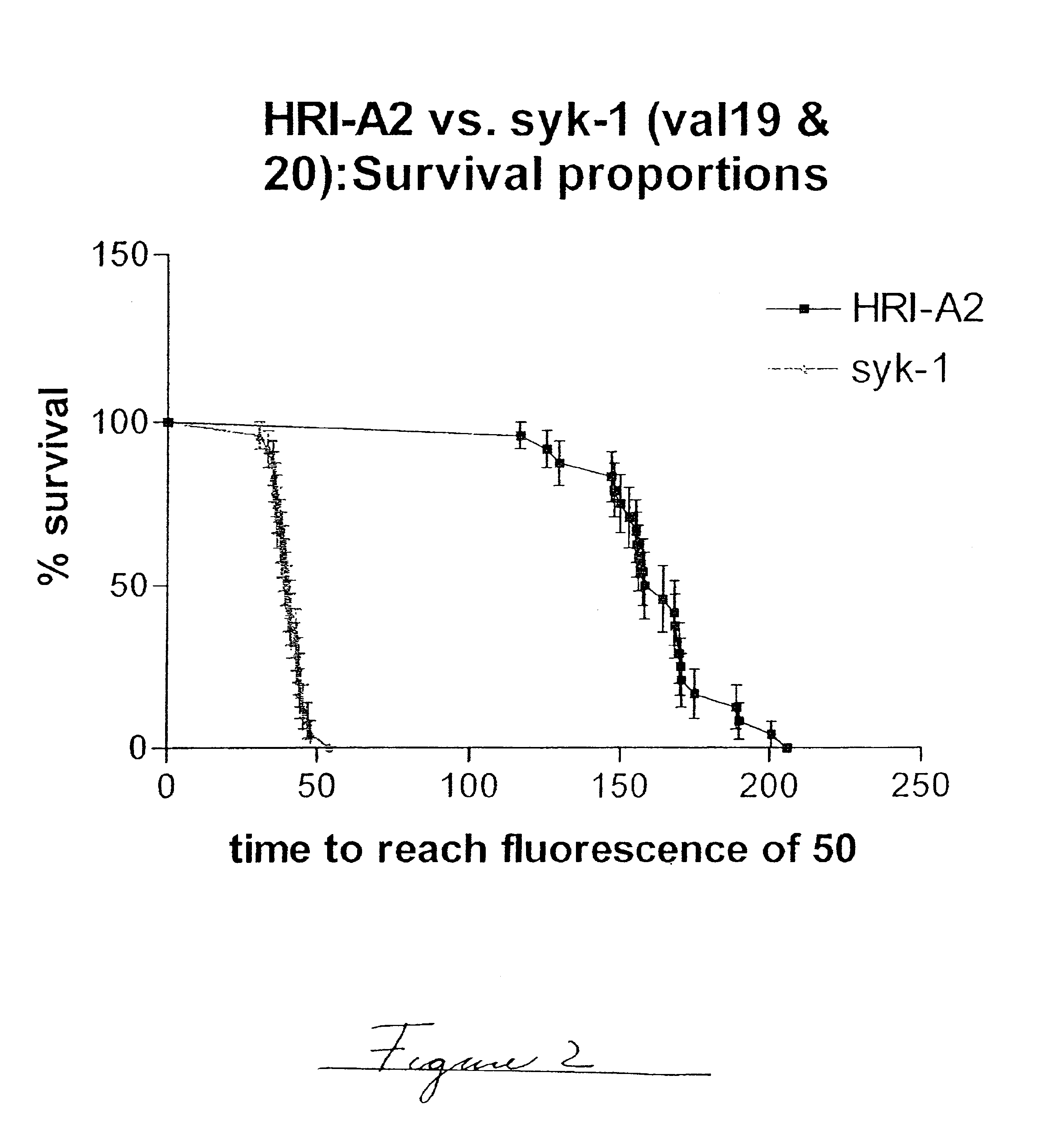
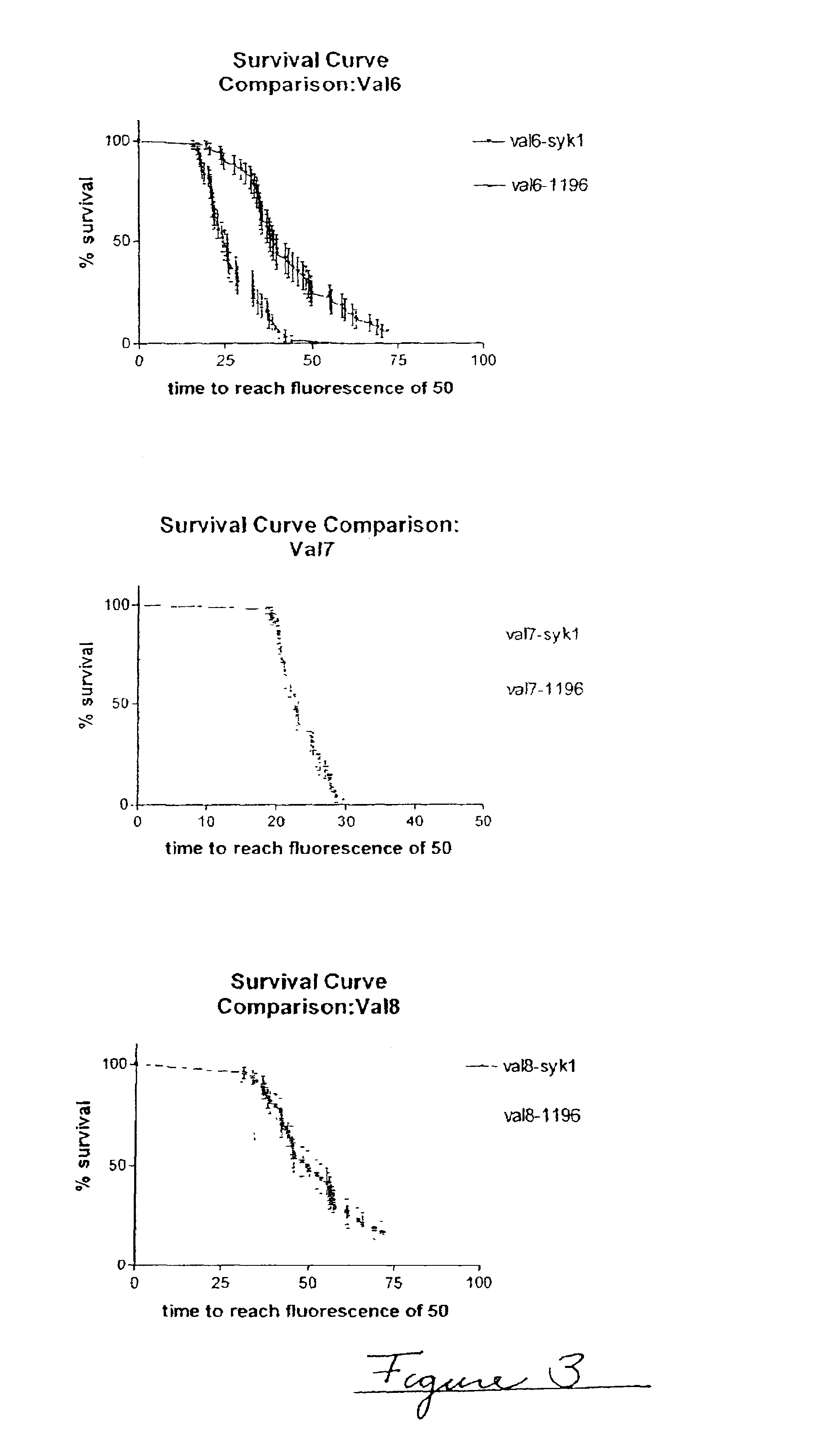
Embodiments of the invention are directed to a method of estimating the physical stability of a protein formulation. A particular embodiment of the invention places the protein formulation under an agitational stress that causes the protein to aggregate at an accelerated rate. In one embodiment, the change in protein aggregation is monitored spectroscopically using Thioflavin-T. Embodiments of the invention then utilize a survival curve analysis to ascertain the relative physical stability of the different protein formulations under study. This method was used to develop novel surfactant-stabilized insulin formulations in a rapid, cost efficient manner, thus illustrating the utility of the inventive method to the discovery and development of pharmaceutical protein formulations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Biologically active oral preparation that can be site-specific released in colon
InactiveUS6949258B2Reduce probabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesINSULIN PREPARATIONSDrug biological activity
The invention is directed to an oral biological preparation for specific delivery in colon, especially an oral insulin preparation for specific delivery in colon.
Owner:HAO ZHANG
Polypeptide formulations and methods for making, using and characterizing them
ActiveUS20060183178A1Improve performancePeptide/protein ingredientsComponent separationGlucose sensorsDiabetes management
Embodiments of the invention include polypeptide formulations and methods for making, using and characterizing them. Embodiment of the invention include stabilized polypeptide formulations, for example stable glucose oxidase formulations that can be used with glucose sensors used in the management of diabetes. Another embodiment of the invention includes methods to characterize the concentration of nonionic surfactants in stabilized polypeptide formulation for example stable insulin formulations that can be used in the treatment of diabetes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Polypeptide formulations and methods for making, using and characterizing them
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Acidic insulin preparations having improved stability
ActiveUS7476652B2Improve stabilityHigh stressOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMetabolitePreservative
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical formulation comprising a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of insulin, an insulin metabolite, an insulin analog, an insulin derivative and combinations thereof; a surfactant or combinations of two or more surfactants; optionally a preservative or combinations of two or more preservatives; and optionally an isotonicizing agent, buffers or further excipients or combinations thereof, the pharmaceutical formulation having a pH in the acidic range.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Insoluble compositions for controlling blood glucose
InactiveUS6531448B1Easy to controlReduce rateBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineDivalent metal
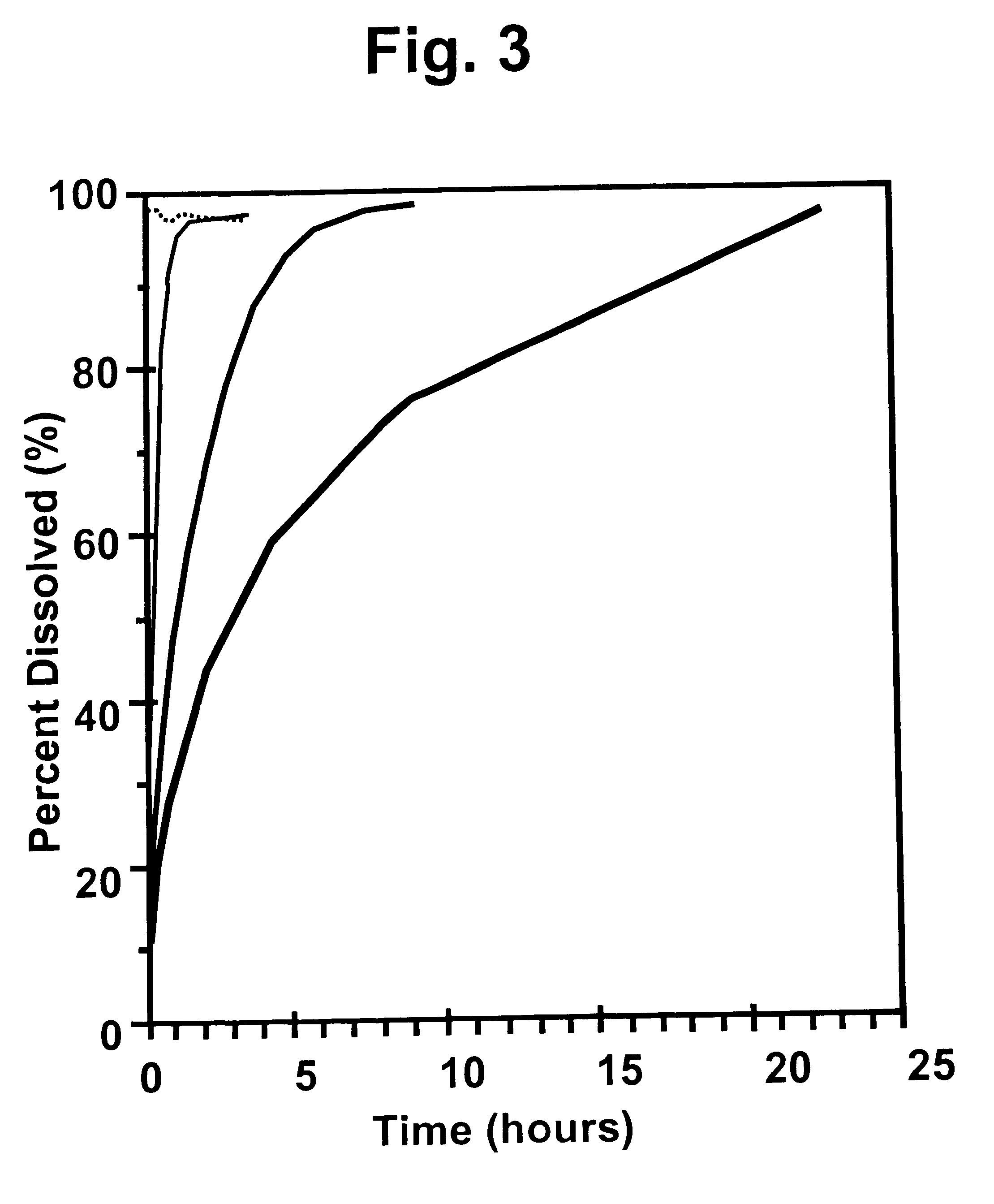
The present invention relates to insoluble compositions comprising a protein selected from the group consisting of insulin, insulin analogs, and proinsulins; a derivatized protein selected from the group consisting of derivatized insulin, derivatized insulin analog, and derivatized proinsulin; a complexing compound; a hexamer-stabilizing compound; and a divalent metal cation. Formulations of the insoluble composition are suitable for both parenteral and non-parenteral delivery for treating hyperglycemia and diabetes. Microcrystal forms of the insoluble precipitate are pharmaceutically analogous to the neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin crystal form. Surprisingly, it has been discovered that suspension formulations of such insoluble compositions possess unique and controllable dissolution properties that provide therapeutically advantageous glucodynamics compared with insulin NPH formulations.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
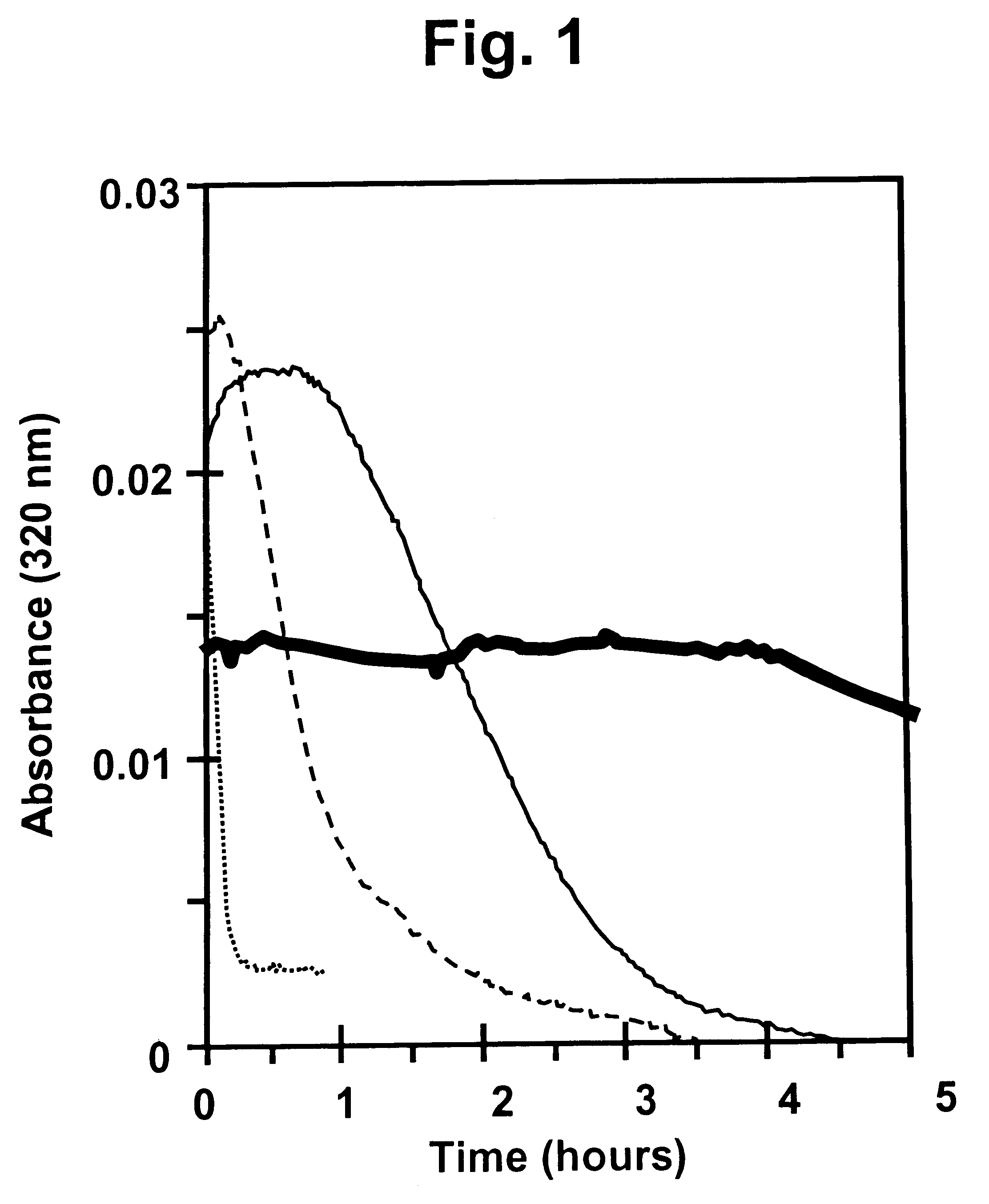
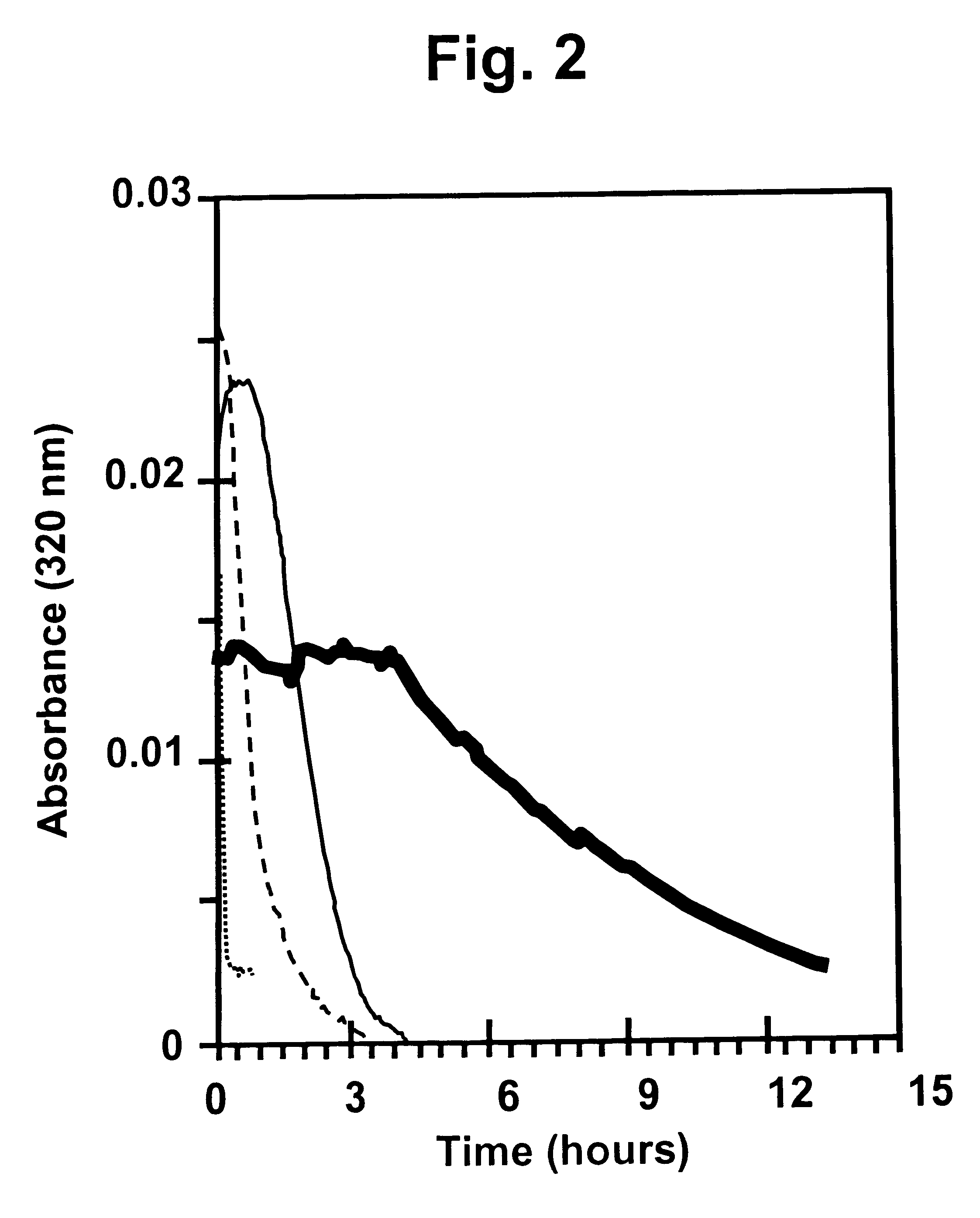
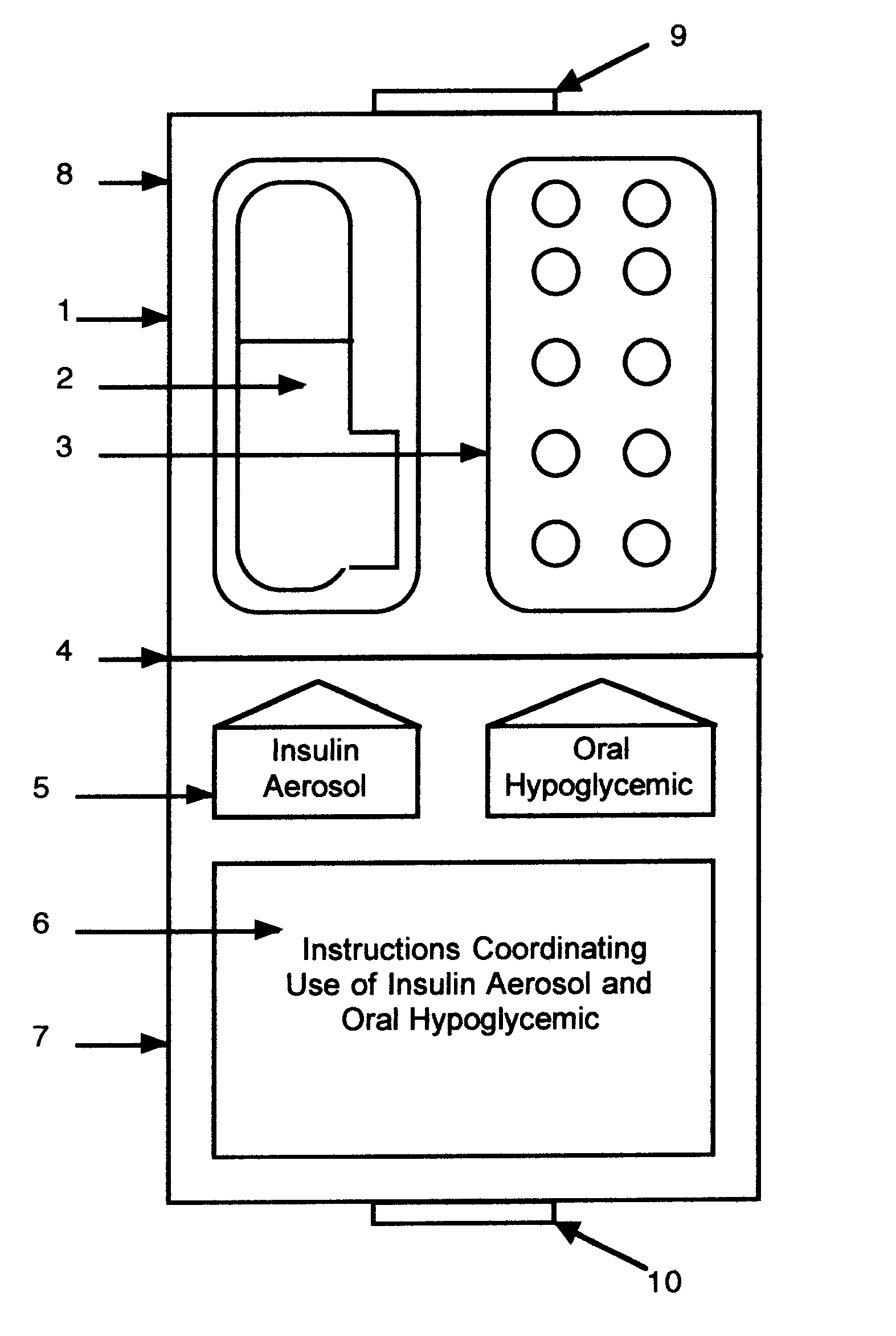
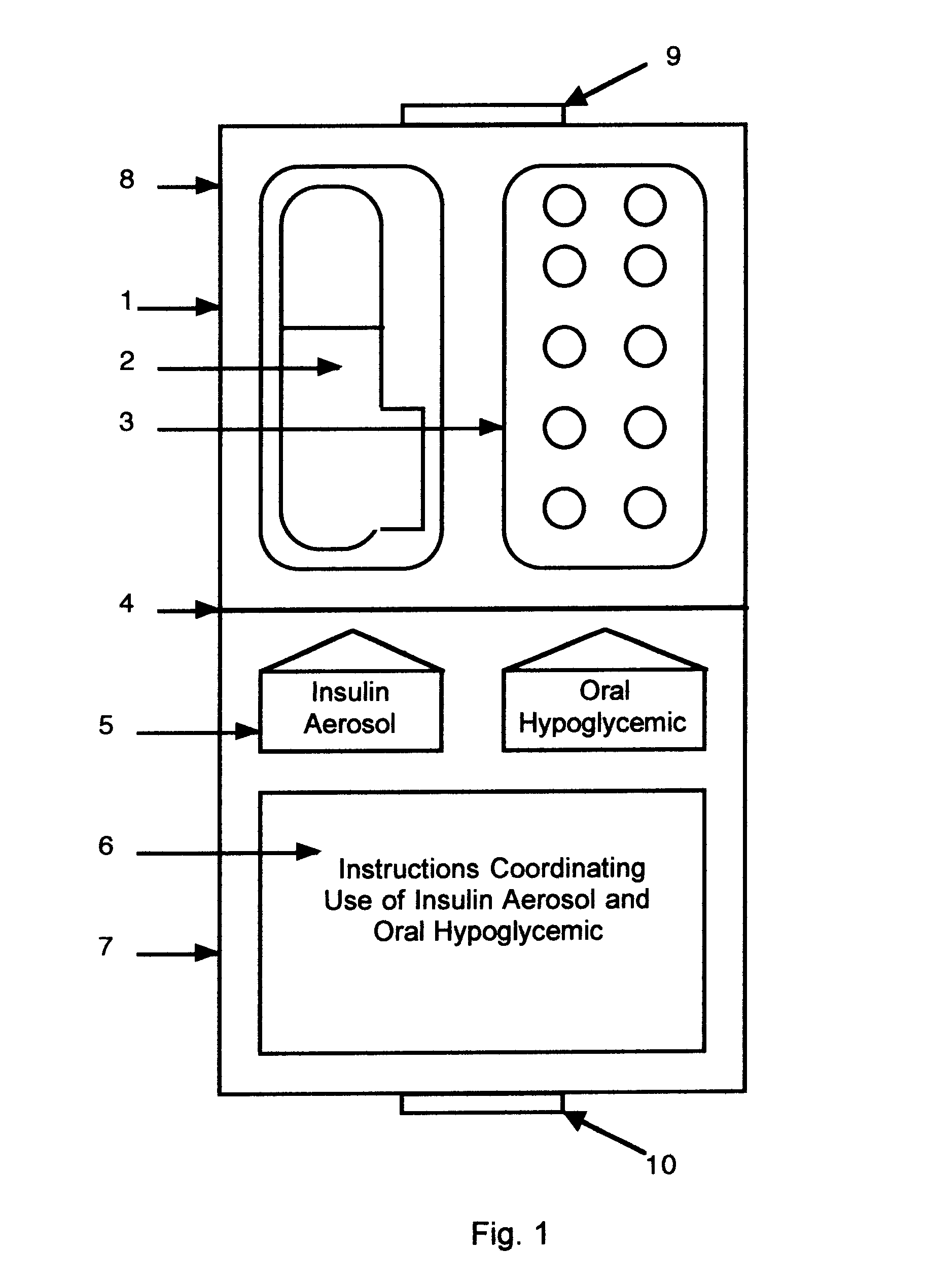
Method and device for facilitating combined aerosol and oral treatments for diabetes mellitus
InactiveUS6187291B1Improve convenienceImprove organizationPowder deliveryAerosol deliveryOral treatmentINSULIN PREPARATIONS
A dispensing container which incorporates an aerosolizable topical insulin preparation, at least one oral hypoglycemic agent, and indicia and instructions for their coordinated use as a single therapeutic regimen for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in a human, and a method for treating diabetes mellitus which employs such a device.
Owner:WEINSTEIN ROBERT E +1
Amylin formulations
InactiveUS20080248999A1Reduce in quantityAct quicklyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderGLP-1 MimeticsBefore Breakfast
A combined insulin and amylin and / or GLP-1 mimetic formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the insulin is decreased so that the amylin and / or GLP-1 remains soluble when mixed together with the insulin. In the preferred embodiment, a bolus insulin is administered by injection before breakfast, providing adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, without producing hypoglycemia after the meal. This can be combined with an adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of the insulin and amylin and / or GLP-1 mimetic combination. A GLP-1 mimetic may be combined with either rapid acting or basal insulin formulations. As a result, a patient using the combination formulation therapy may only need to inject half as many times per day.
Owner:BIODEL INC
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS20080039368A1Increase speedReduce the amount of solutionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
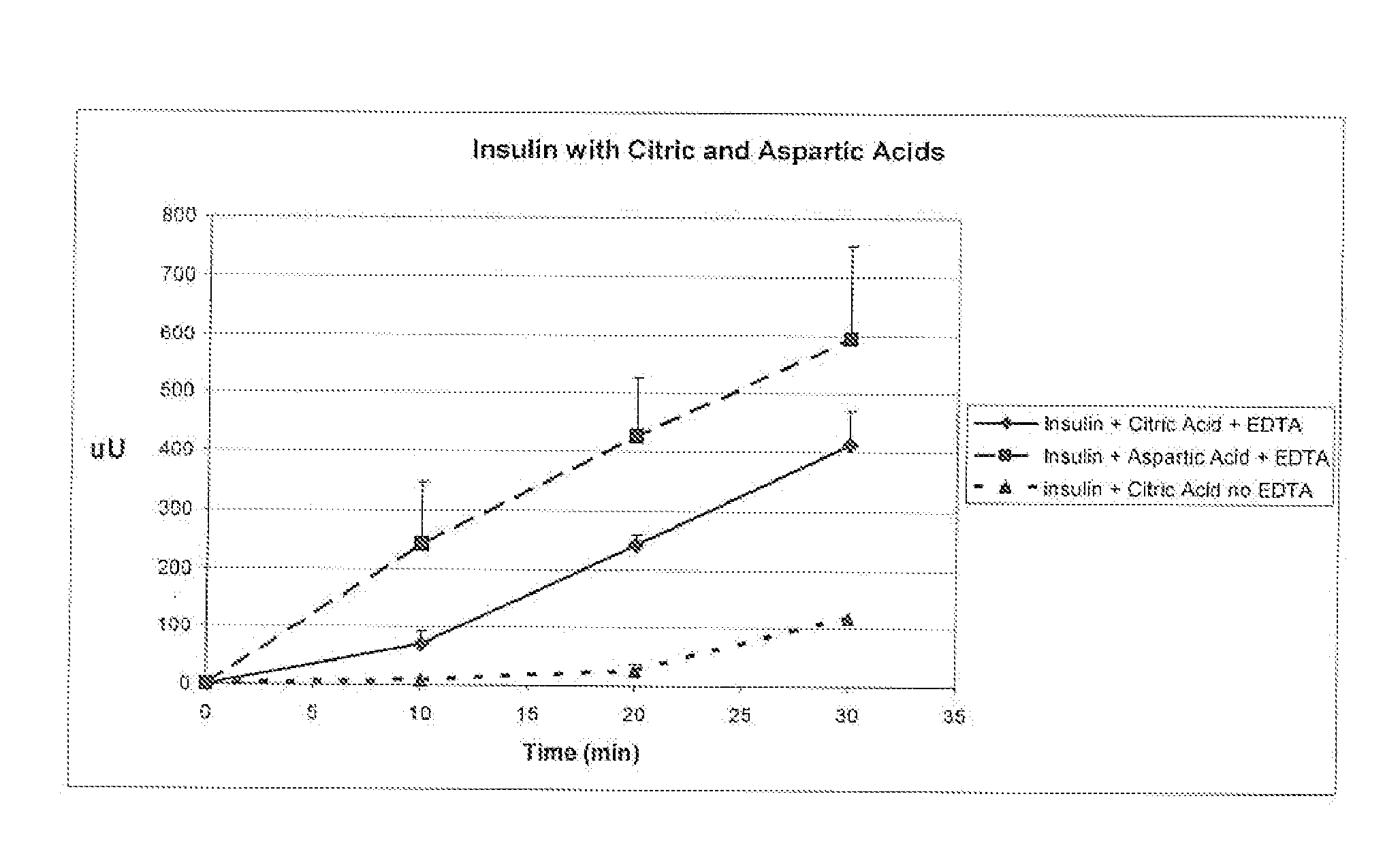
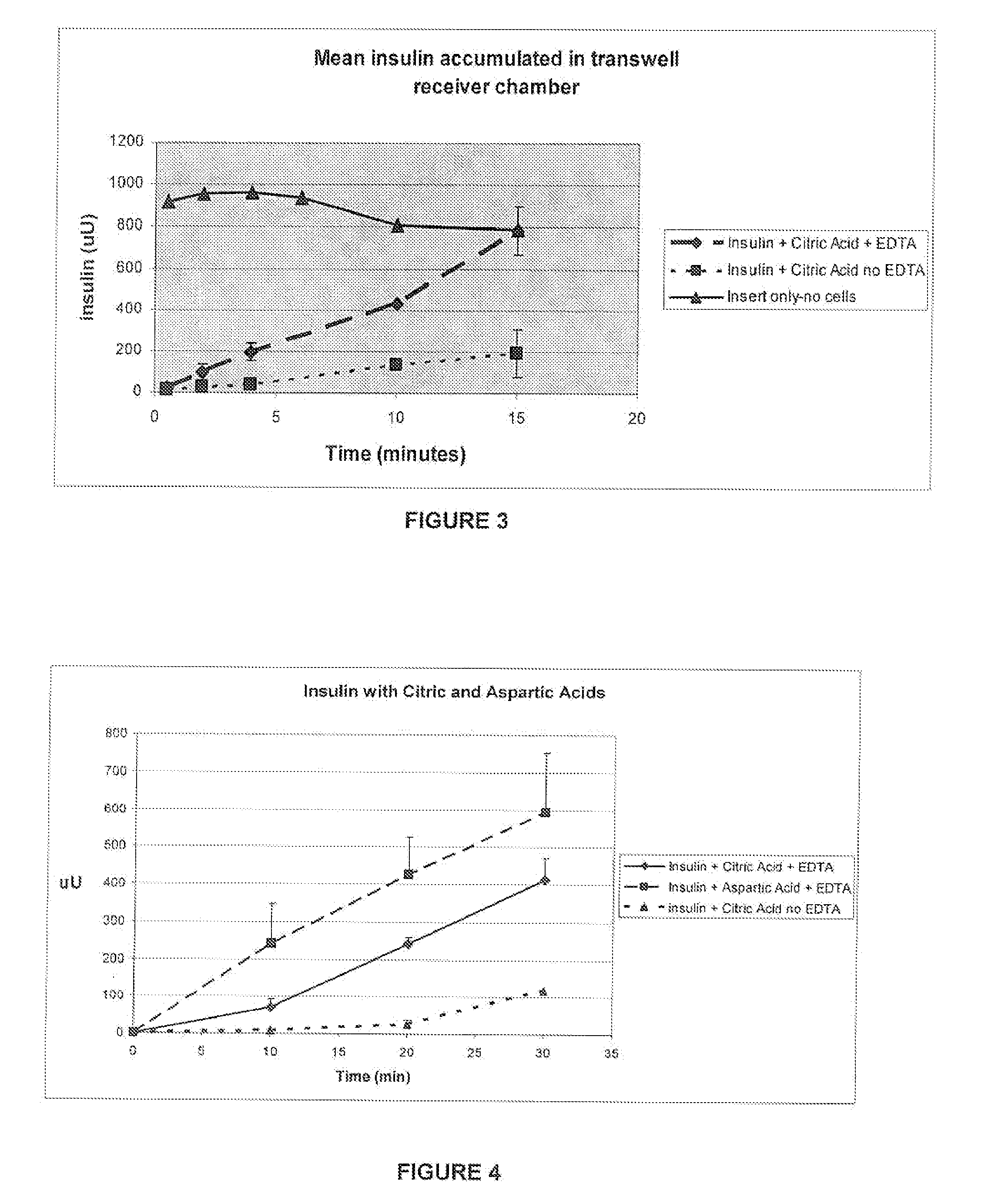
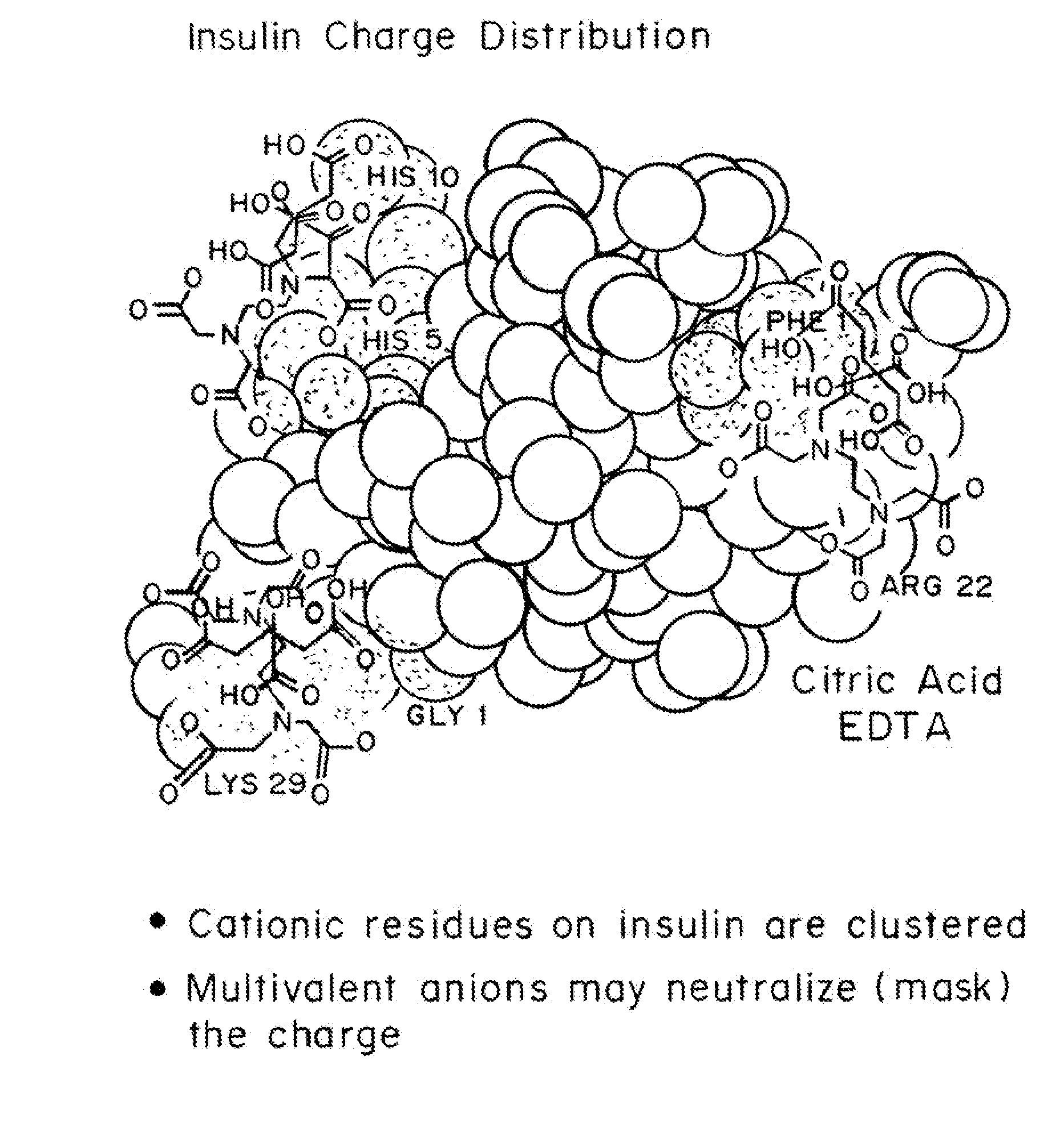
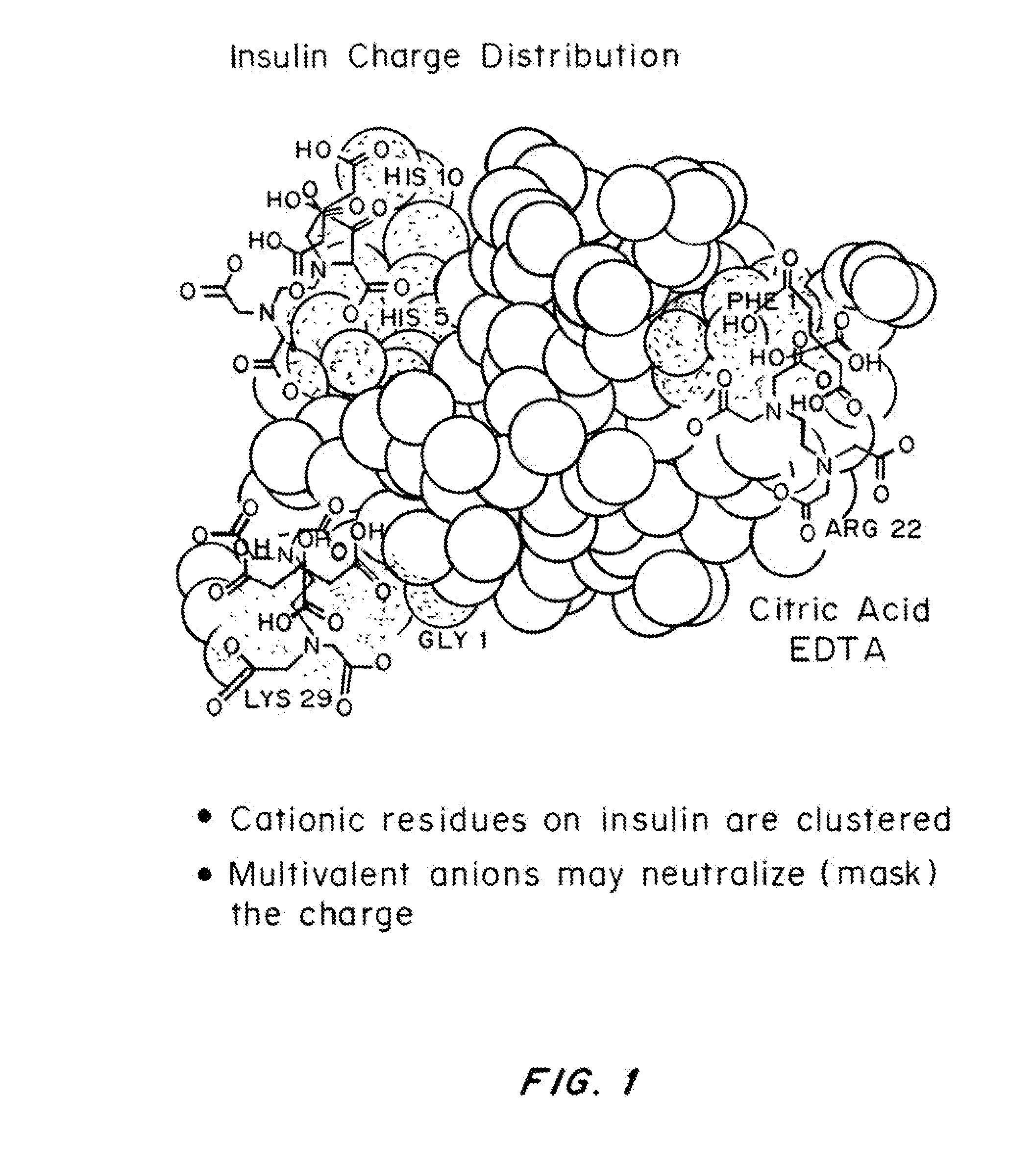
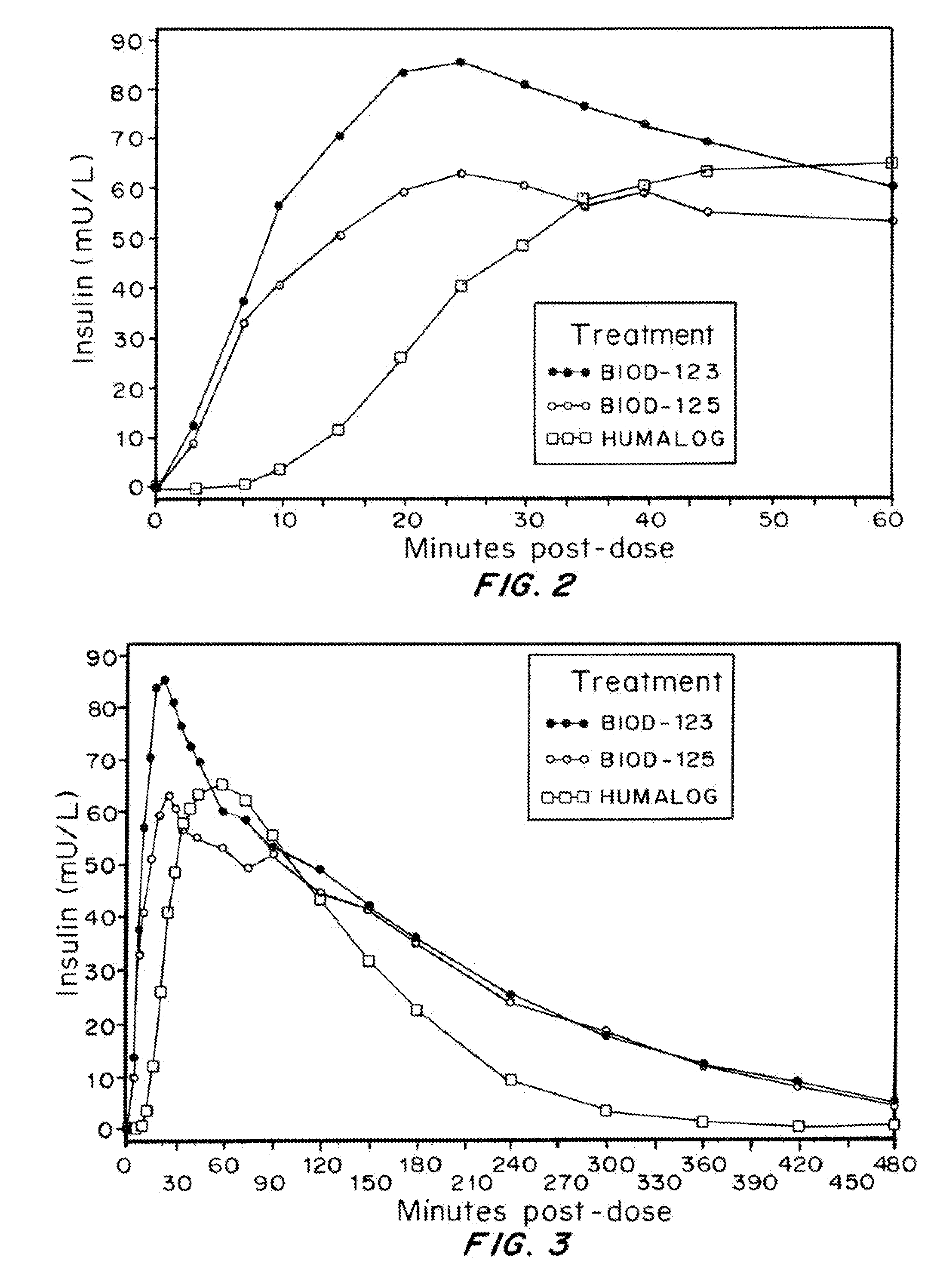
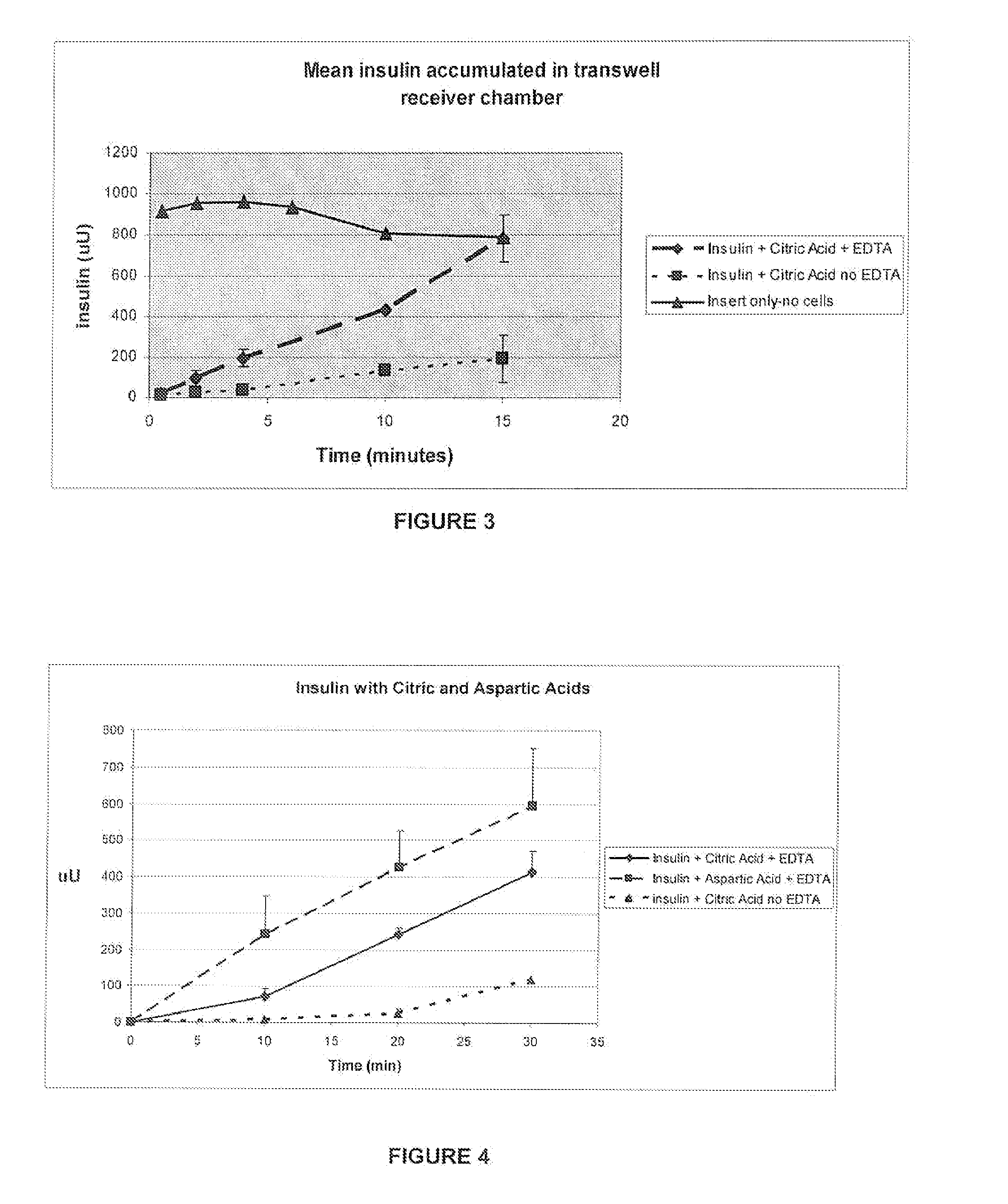
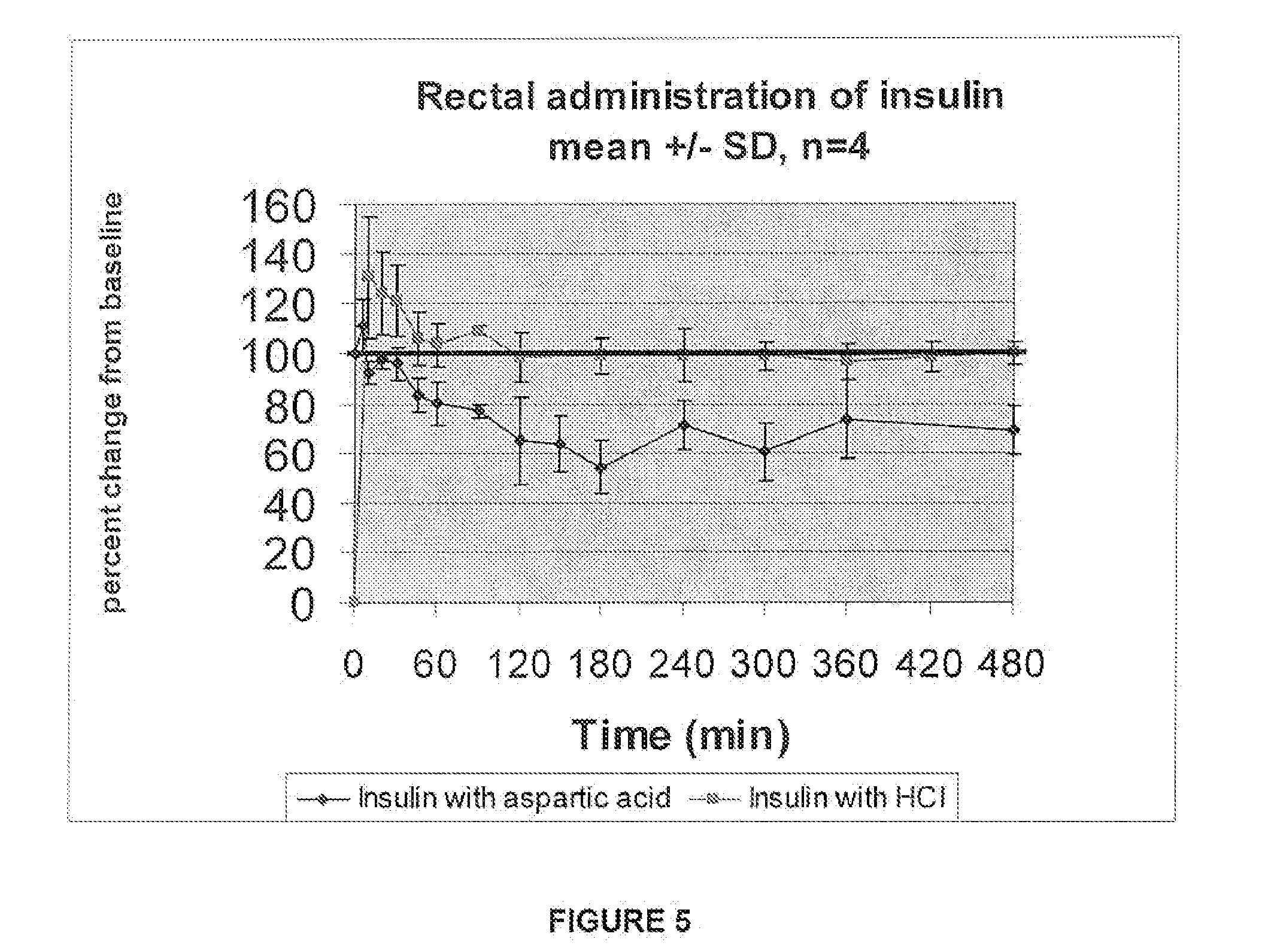
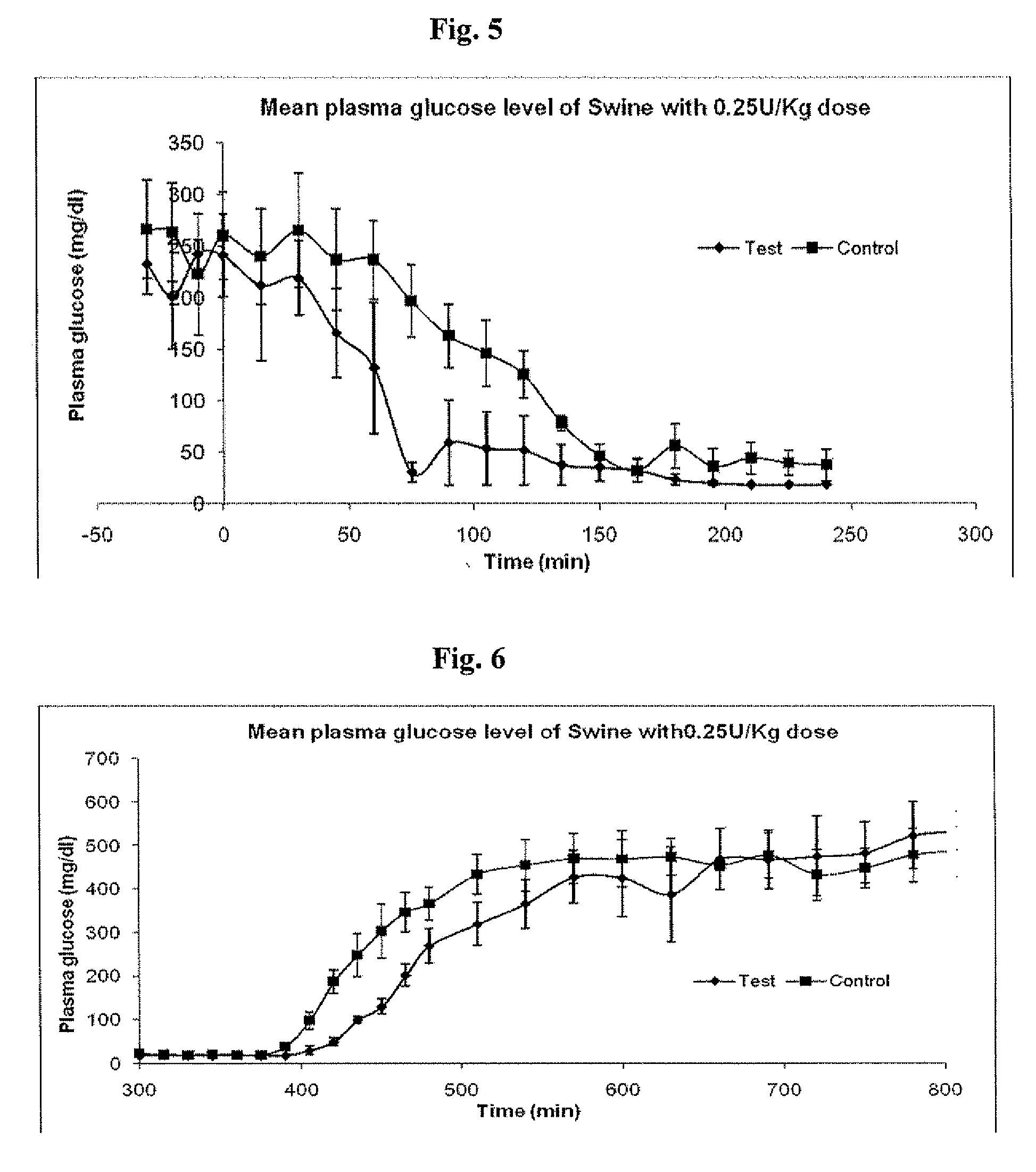
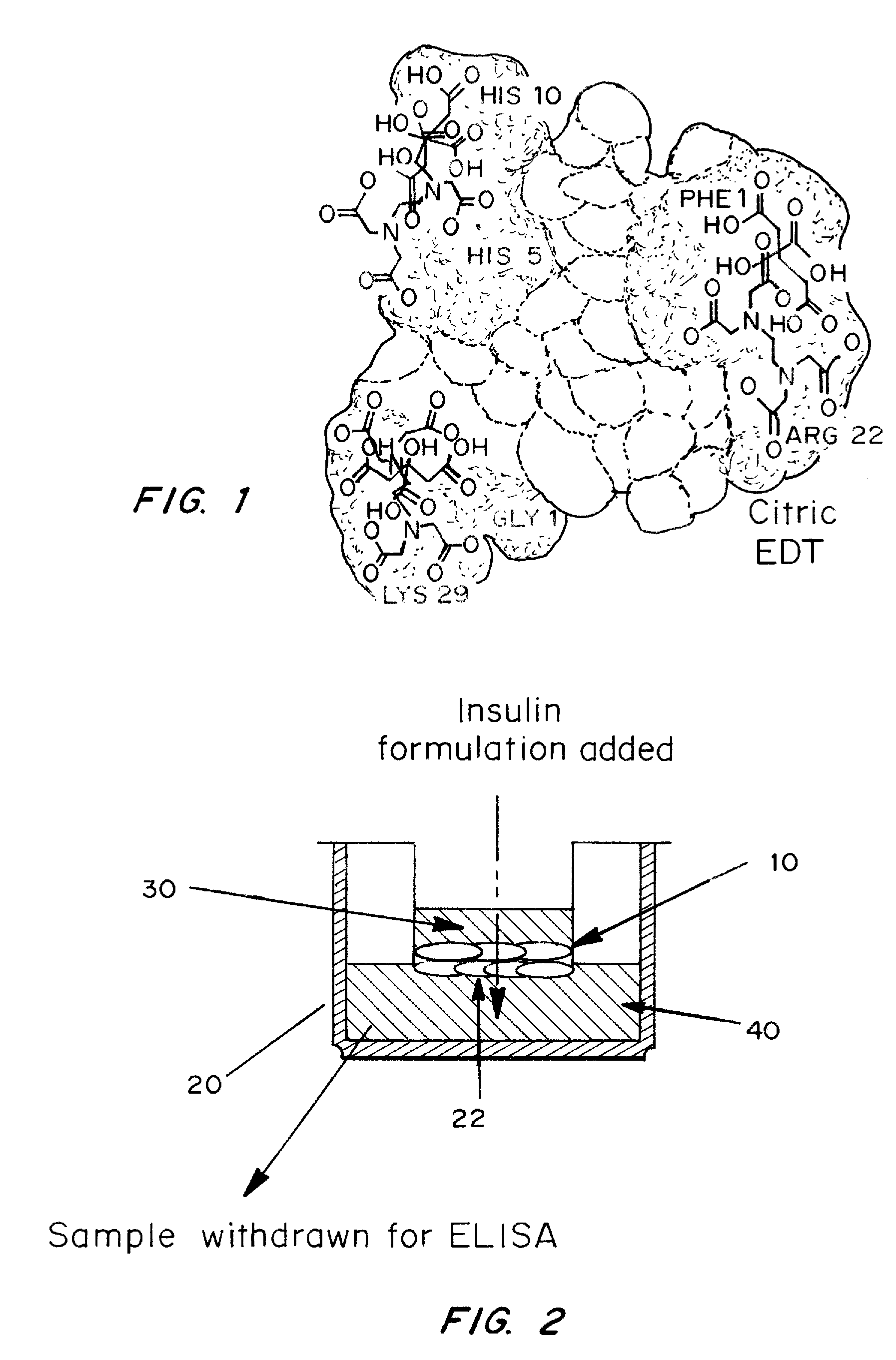
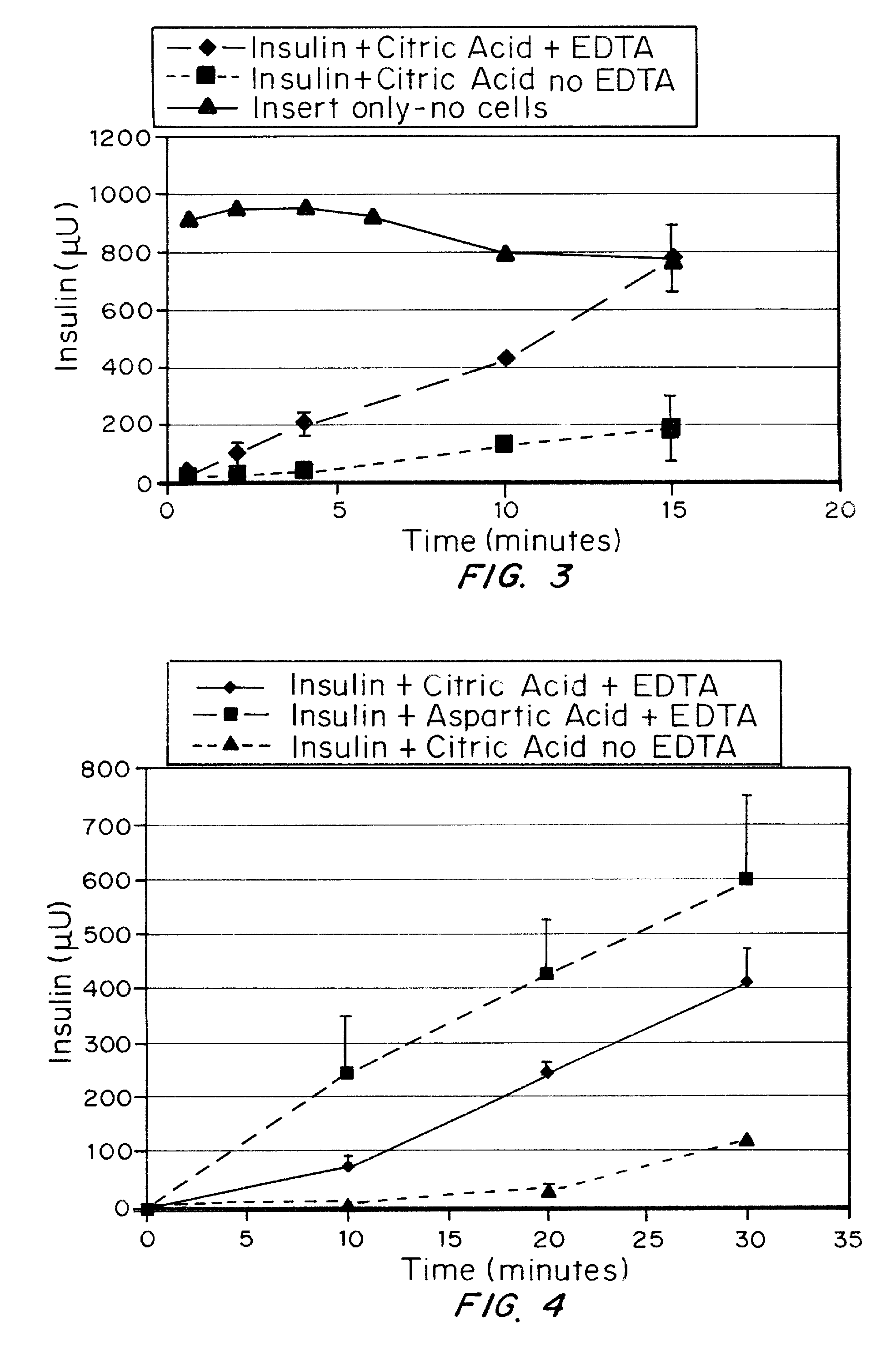
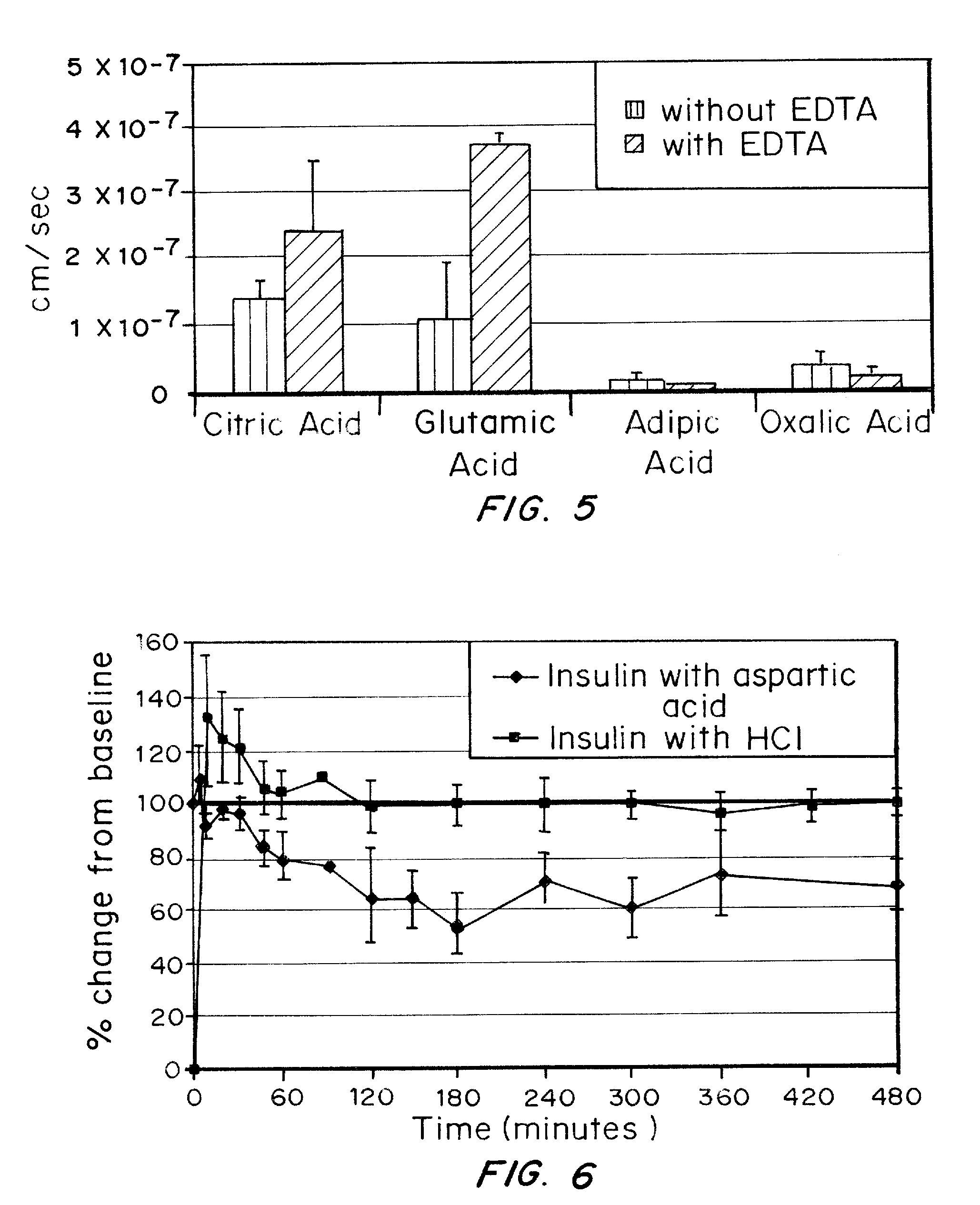
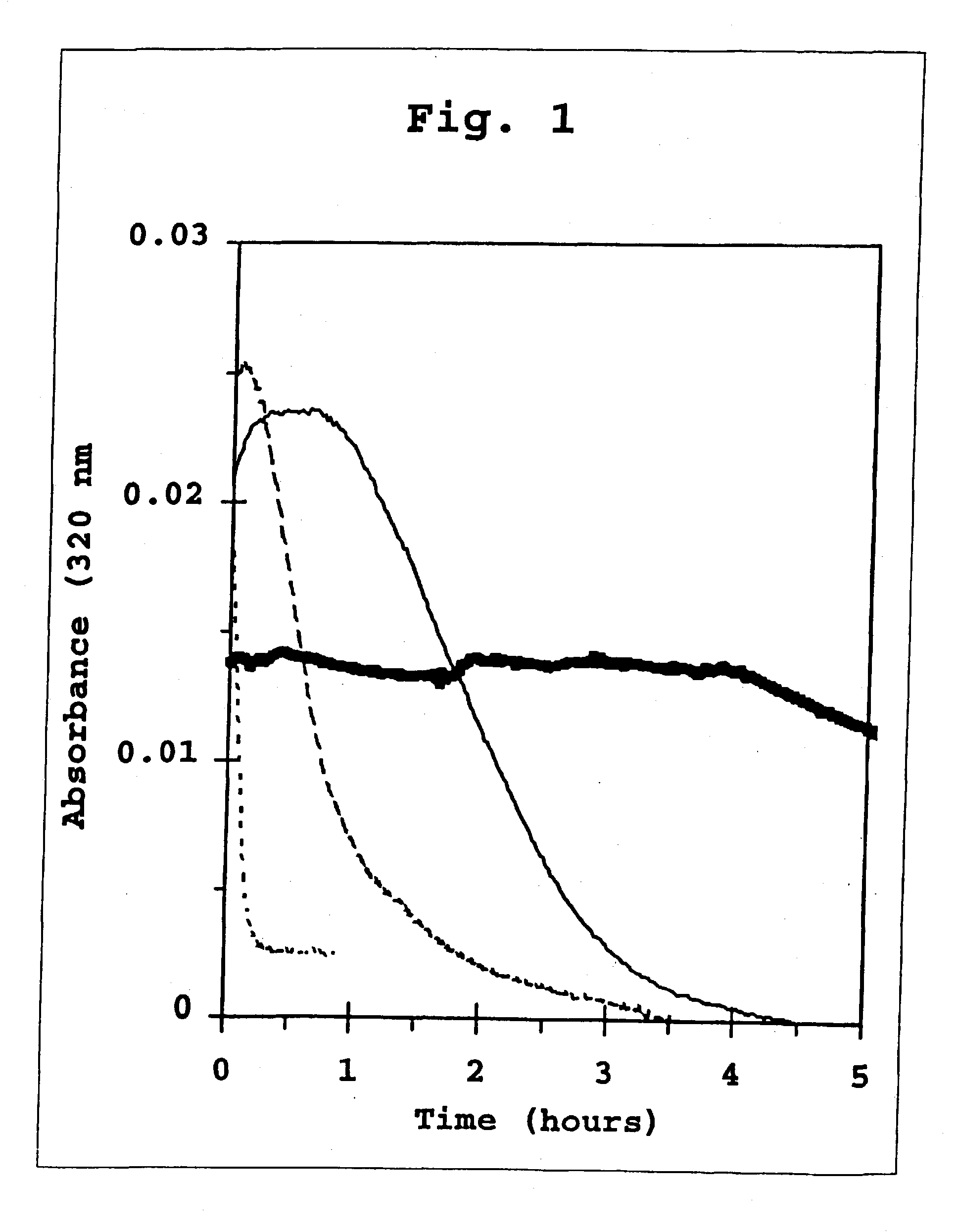
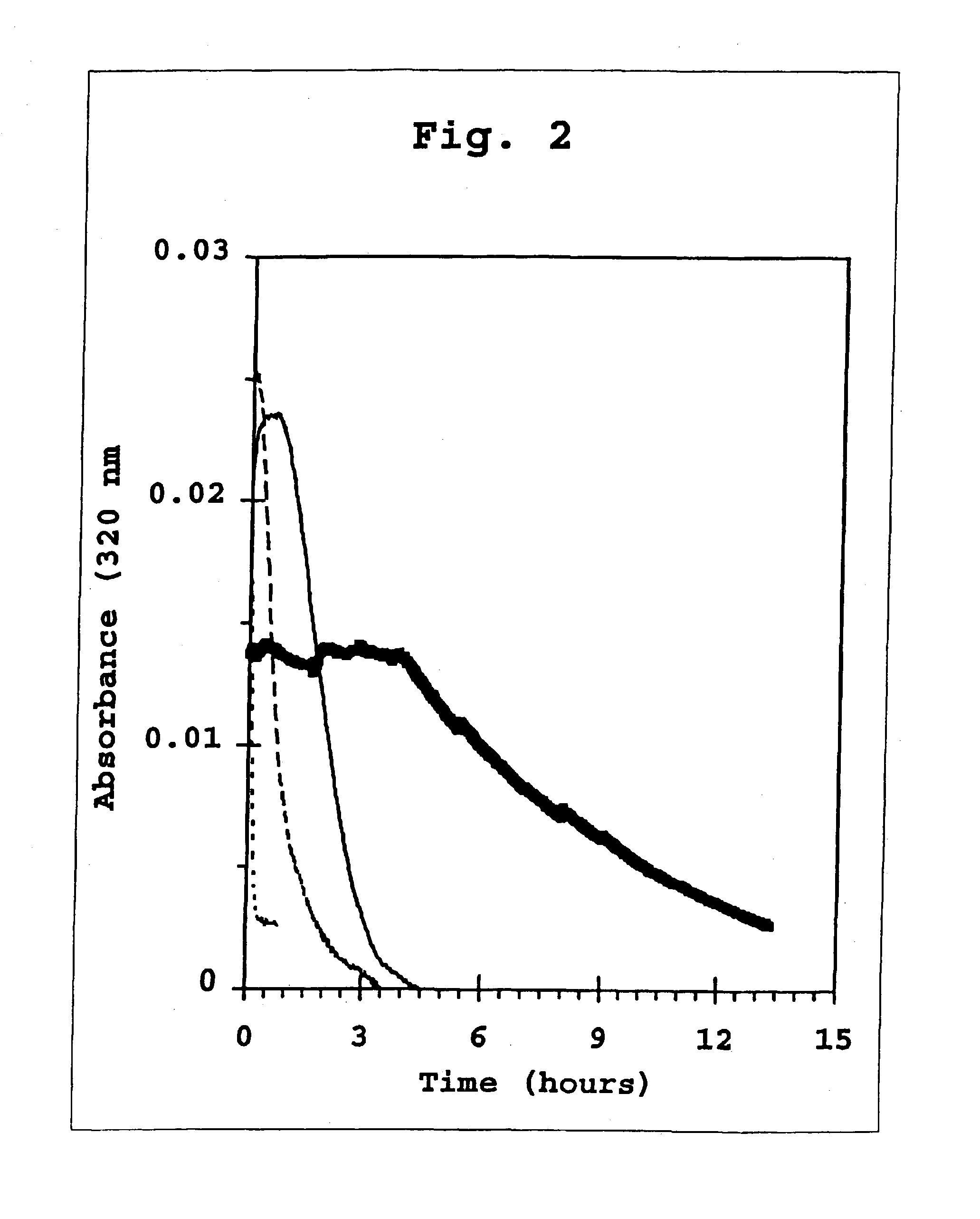
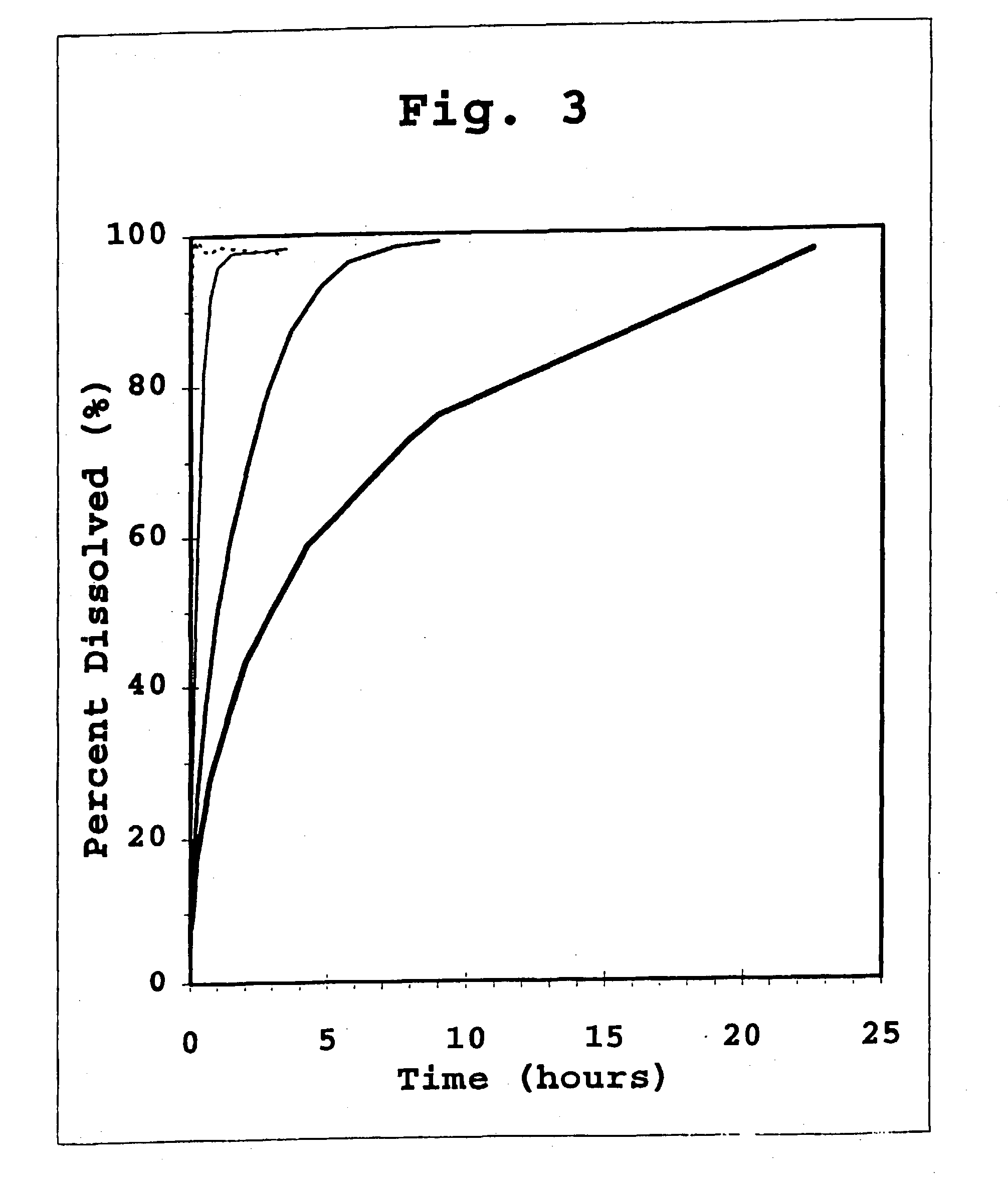
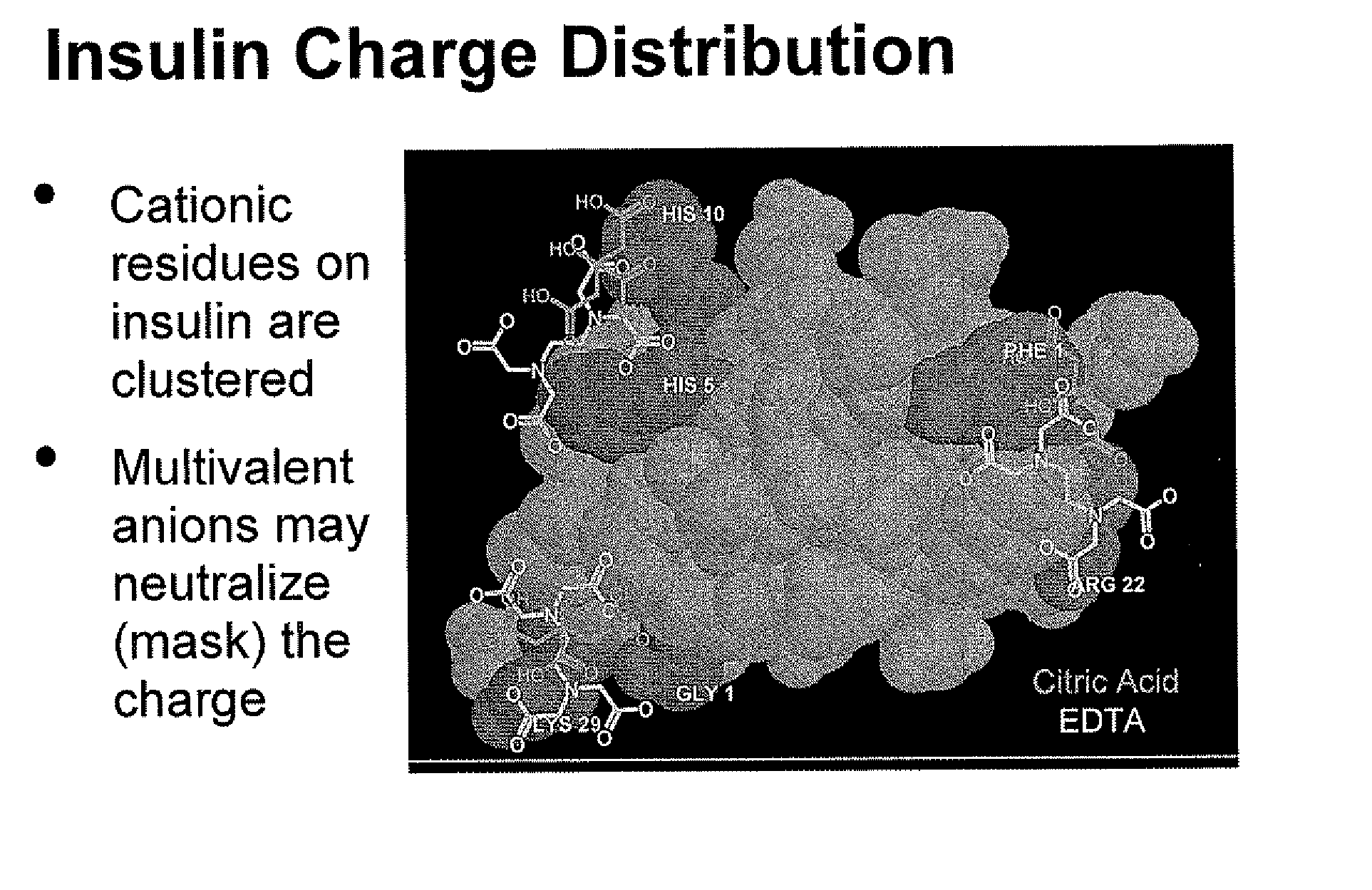
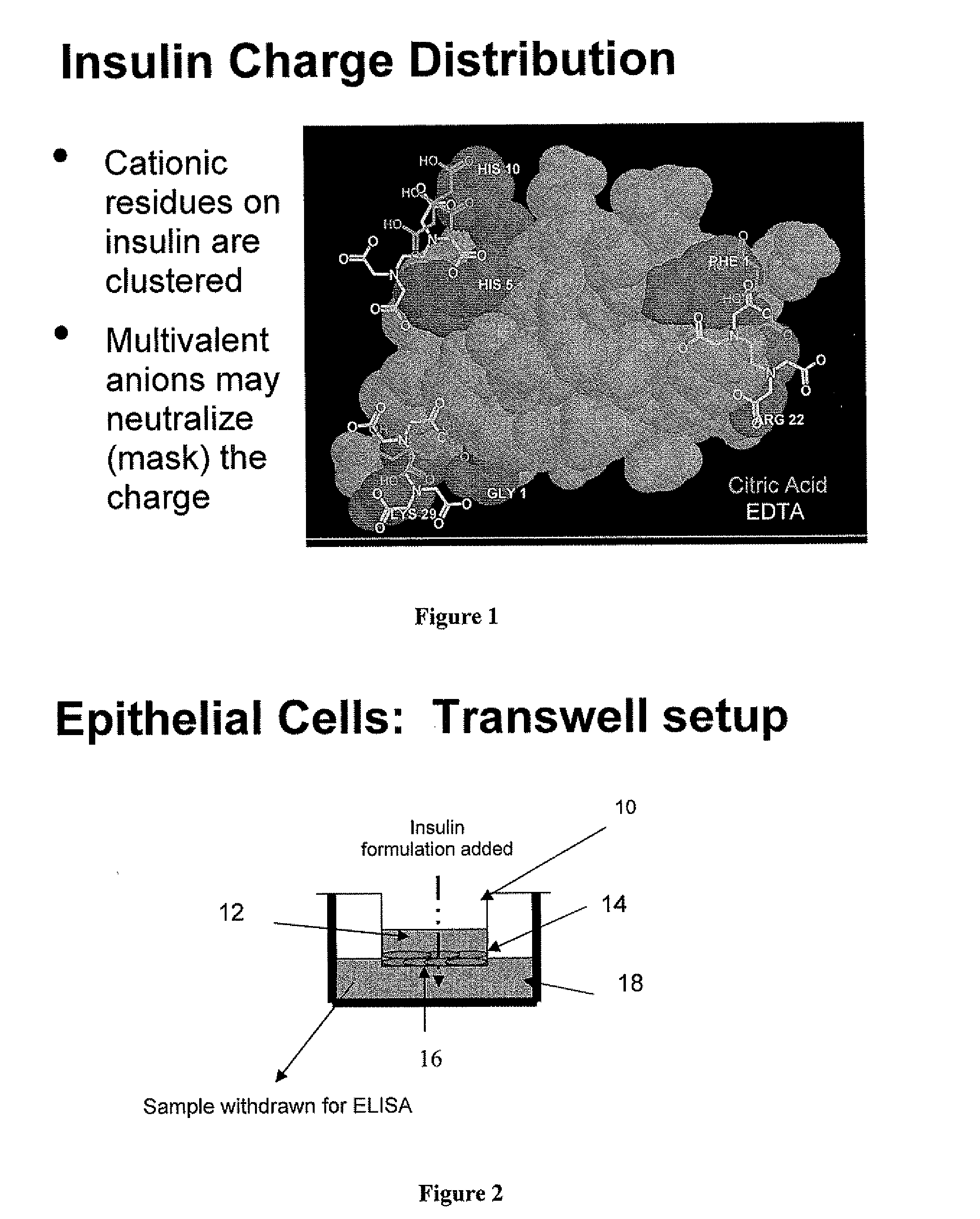
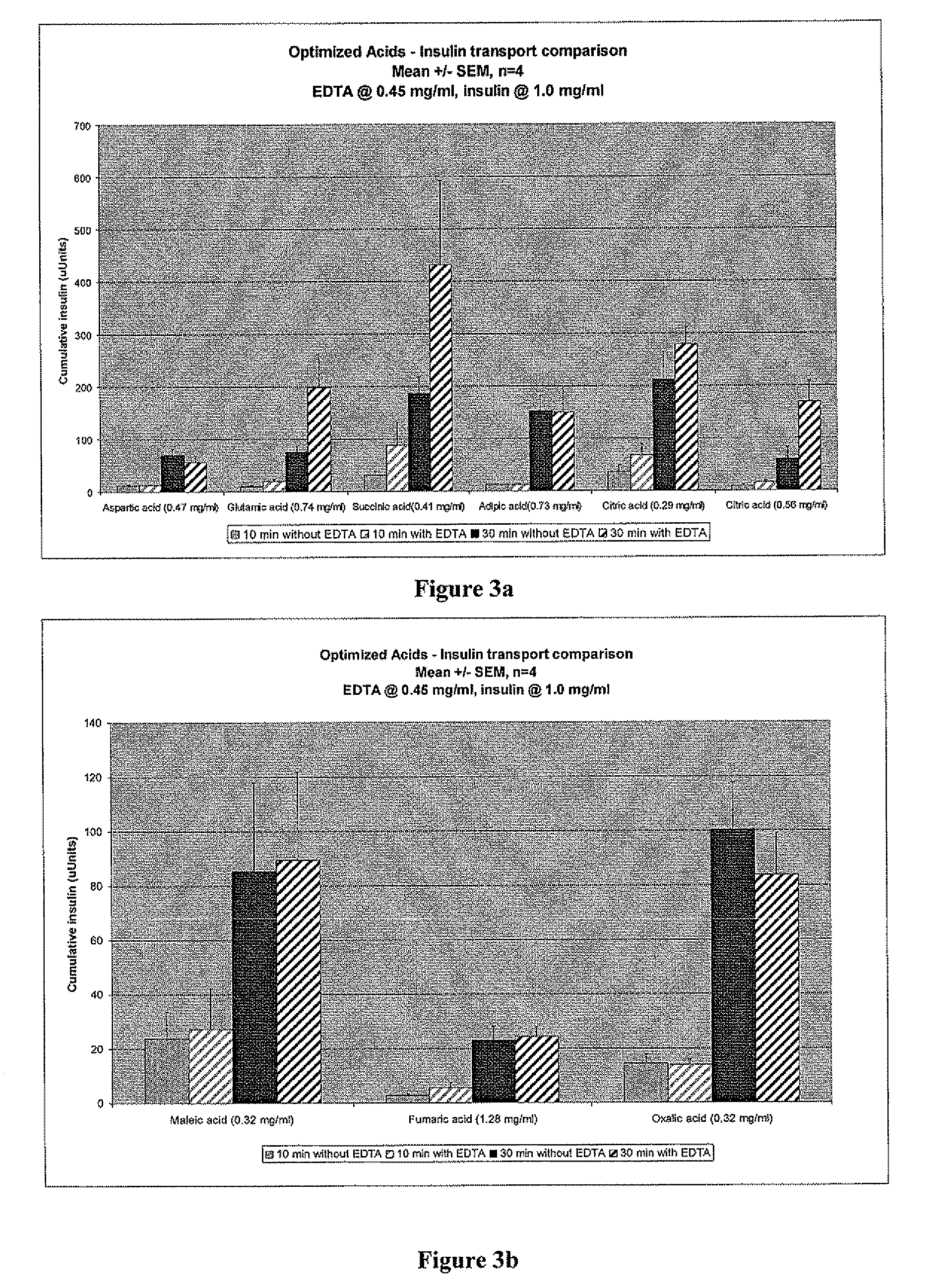
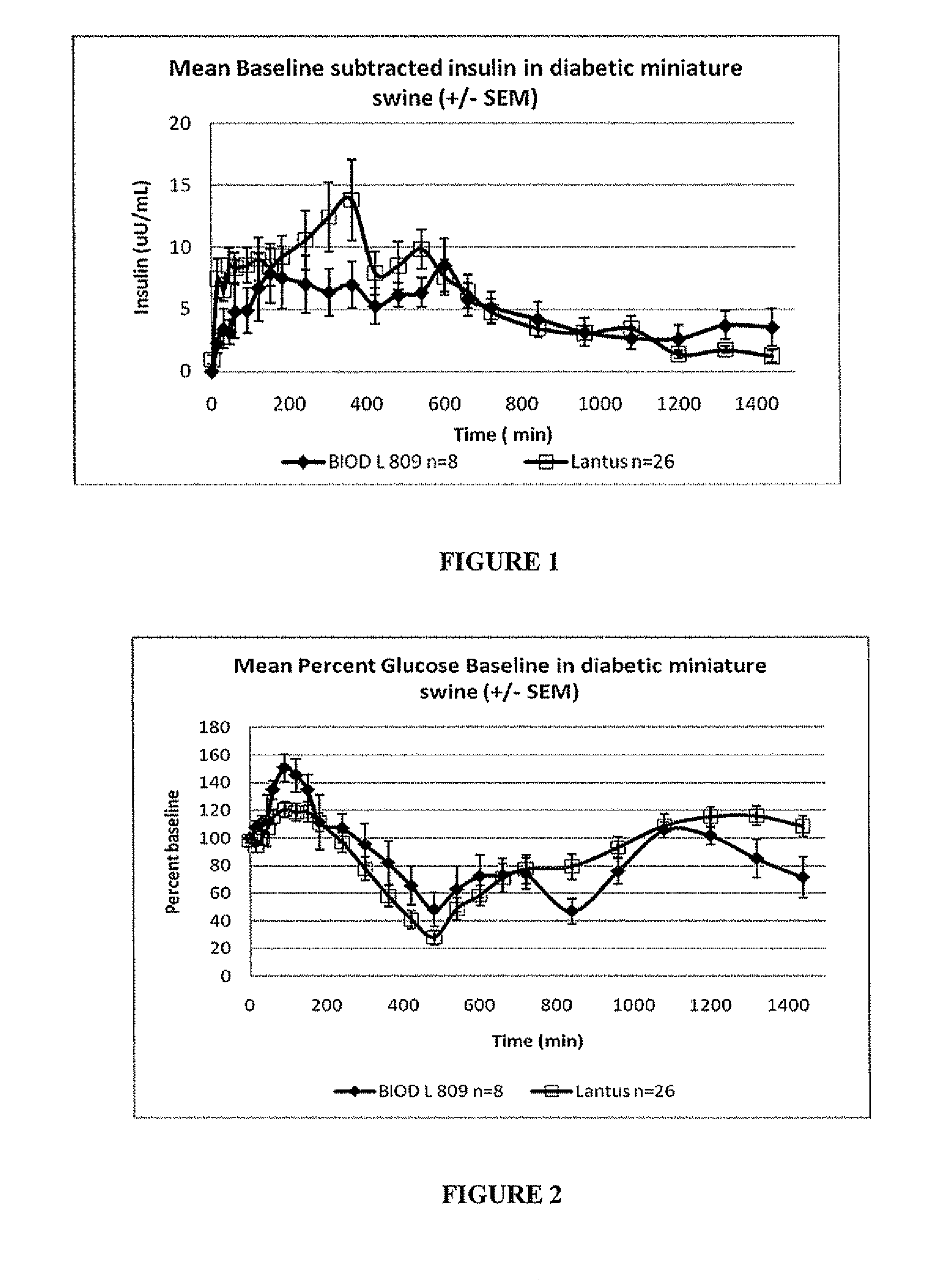
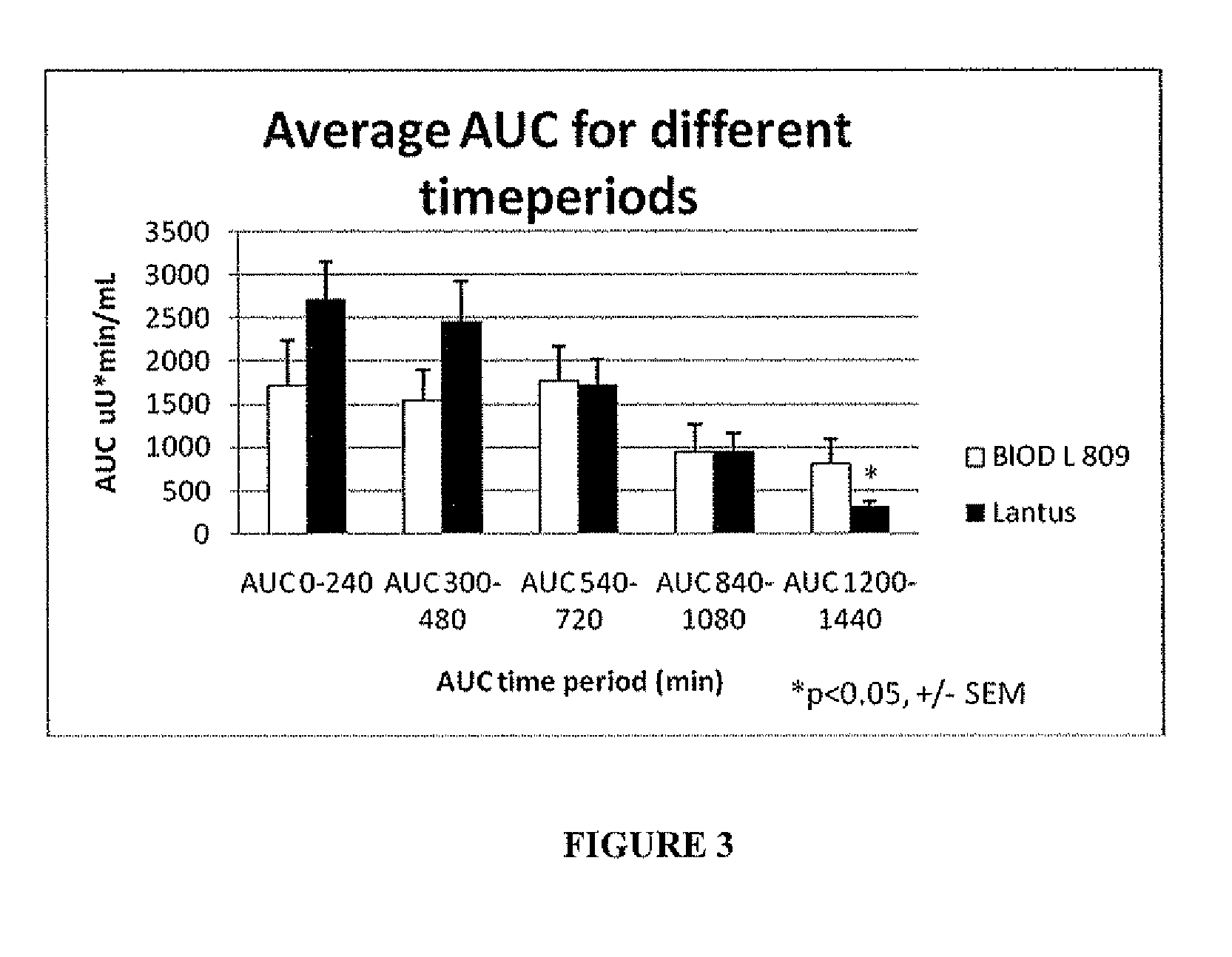
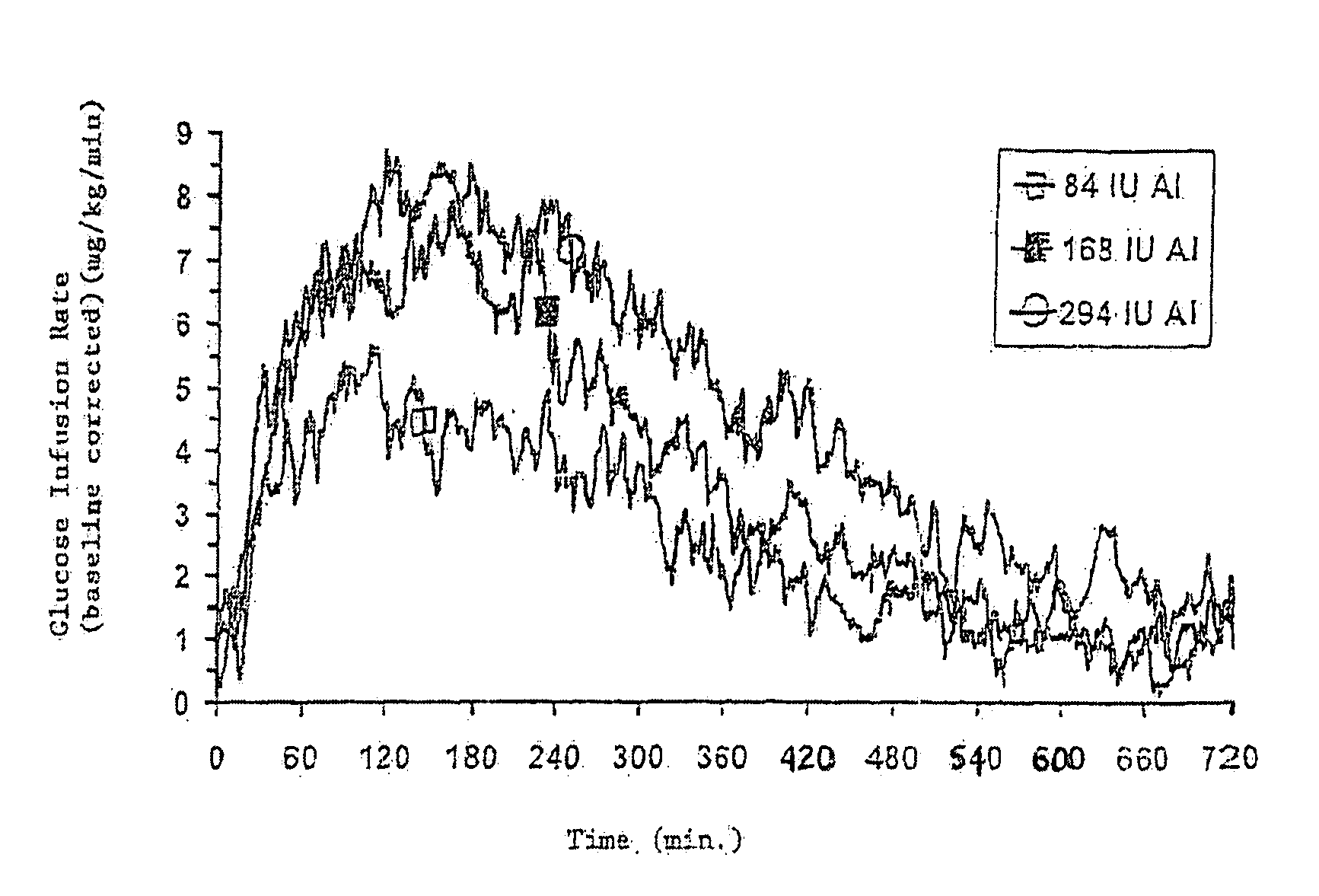
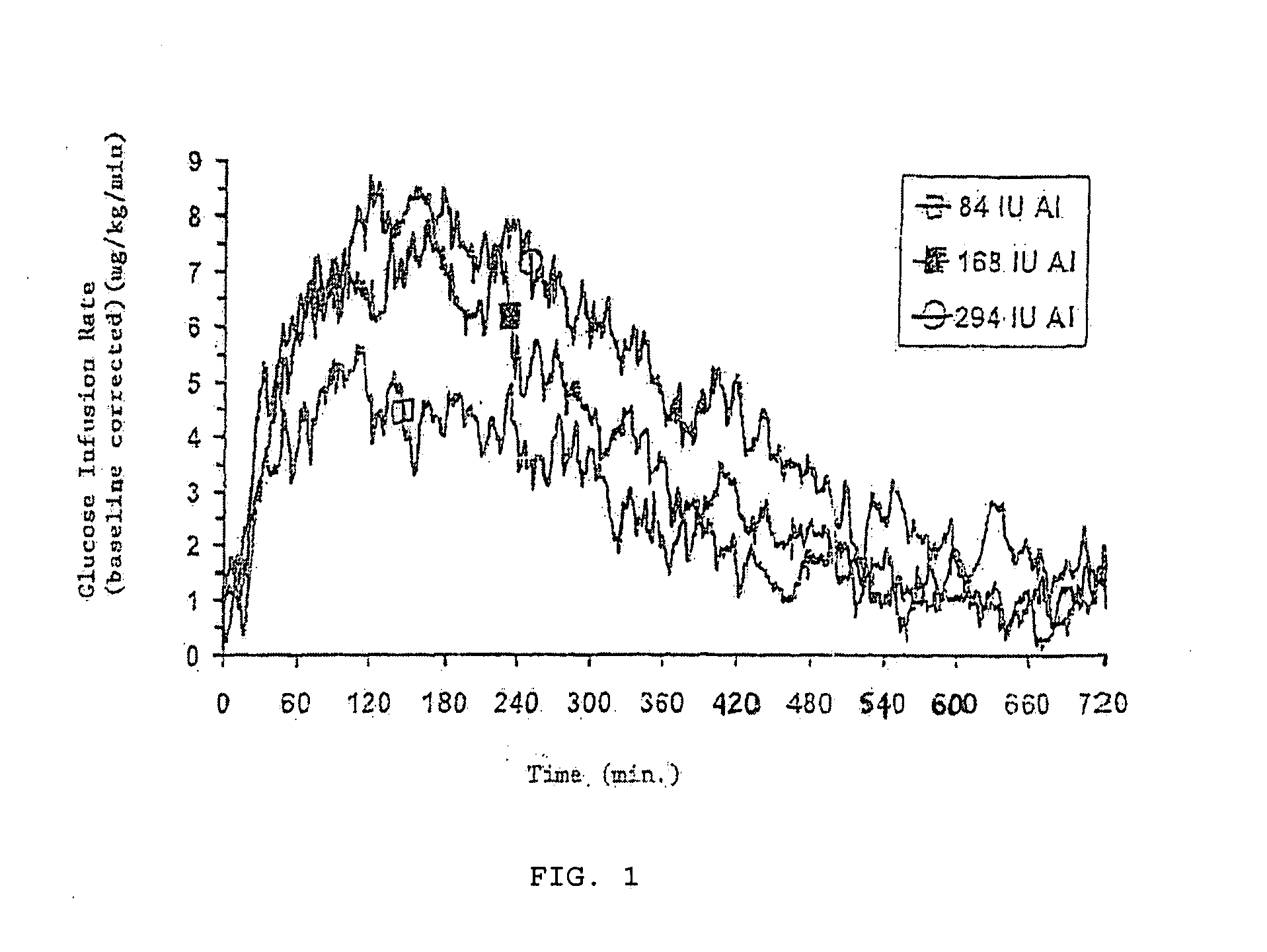
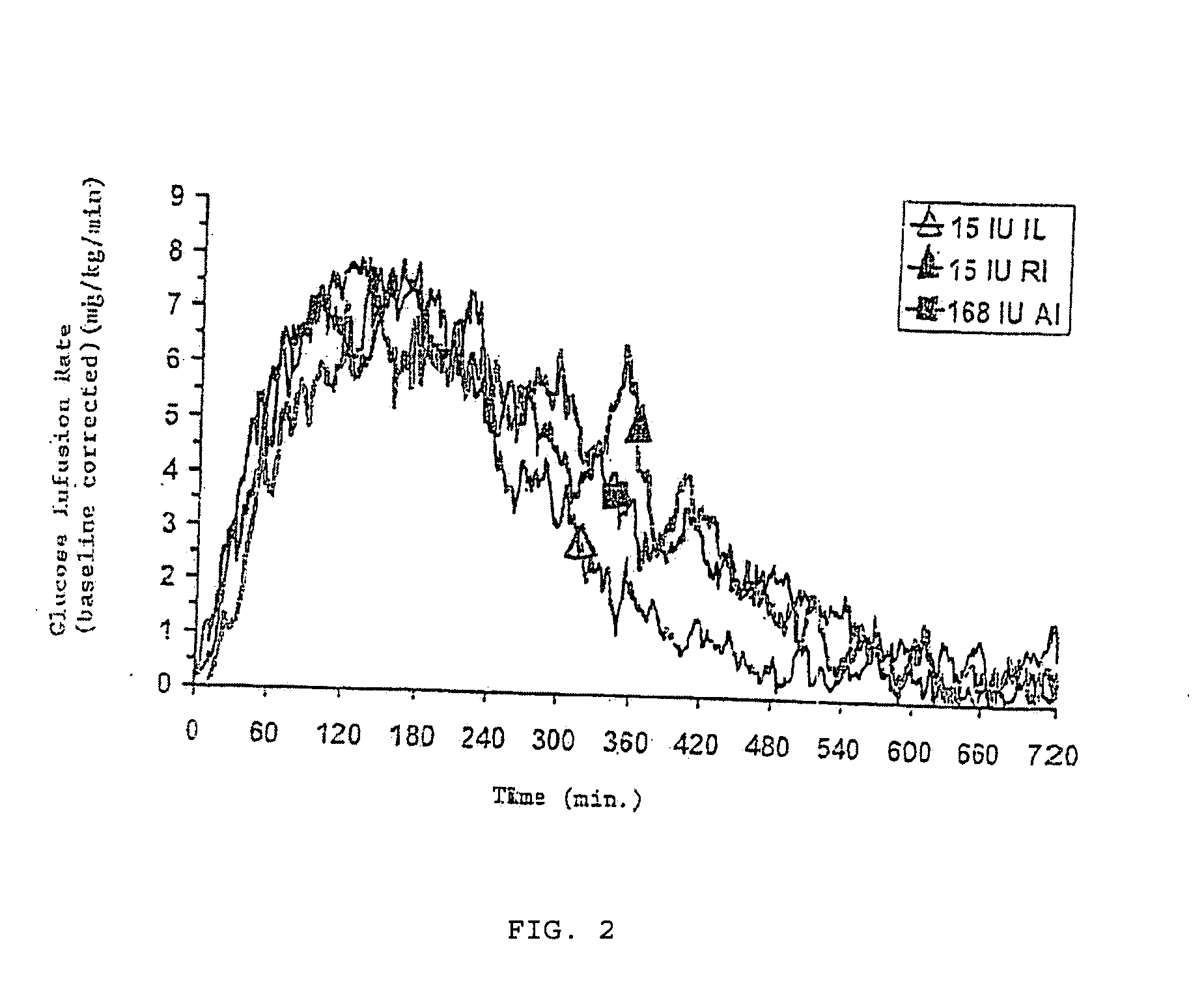
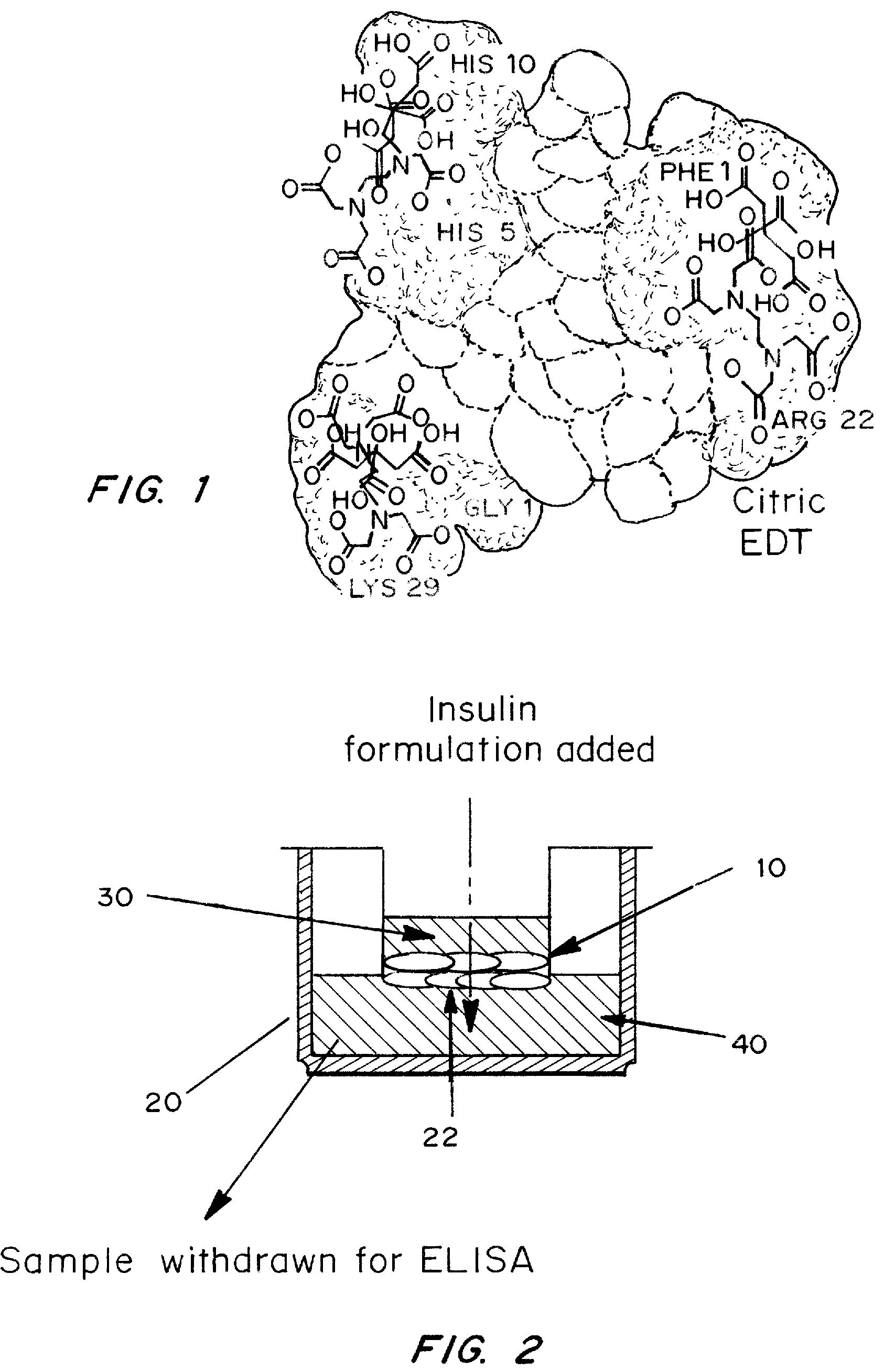
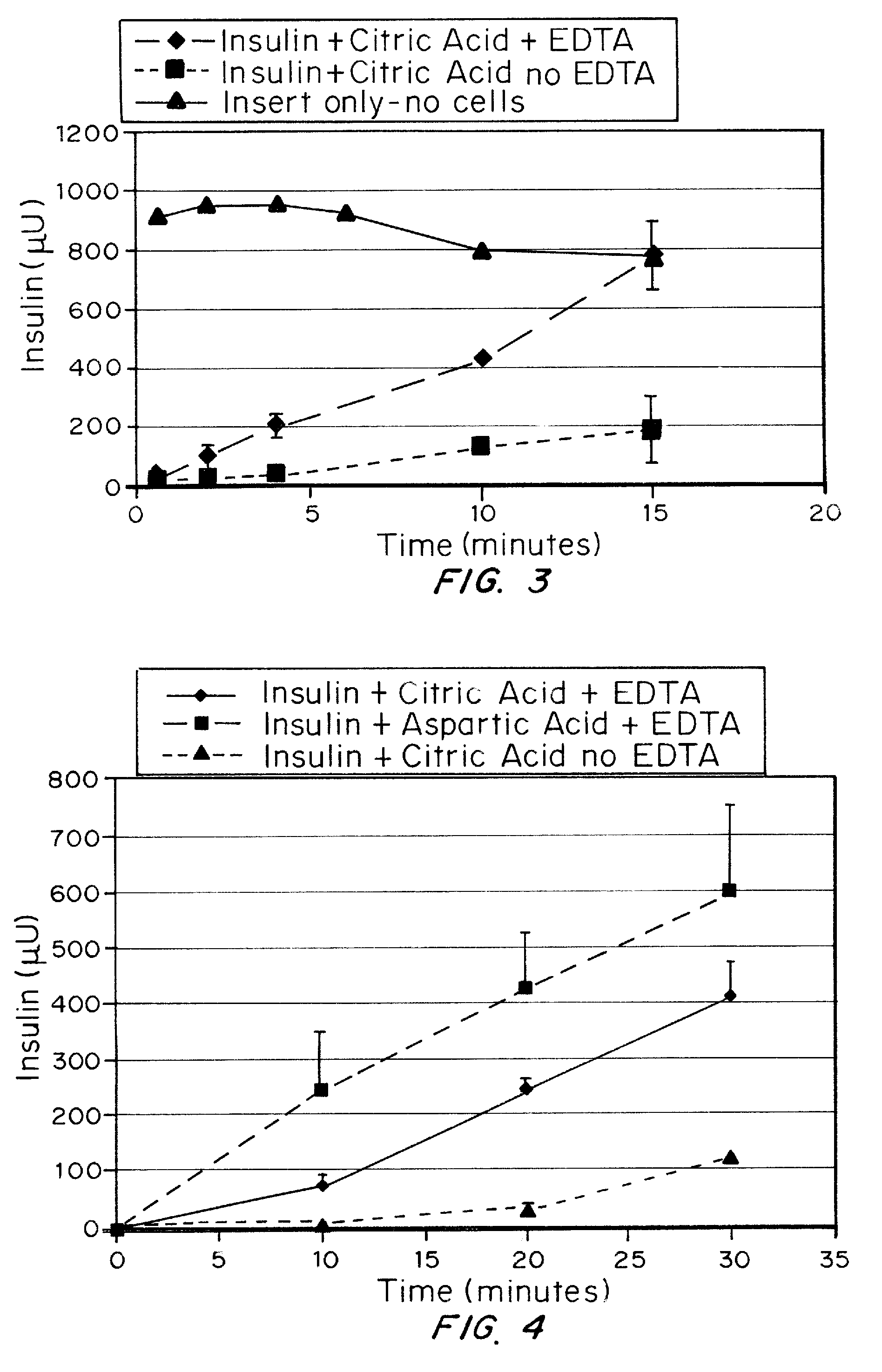
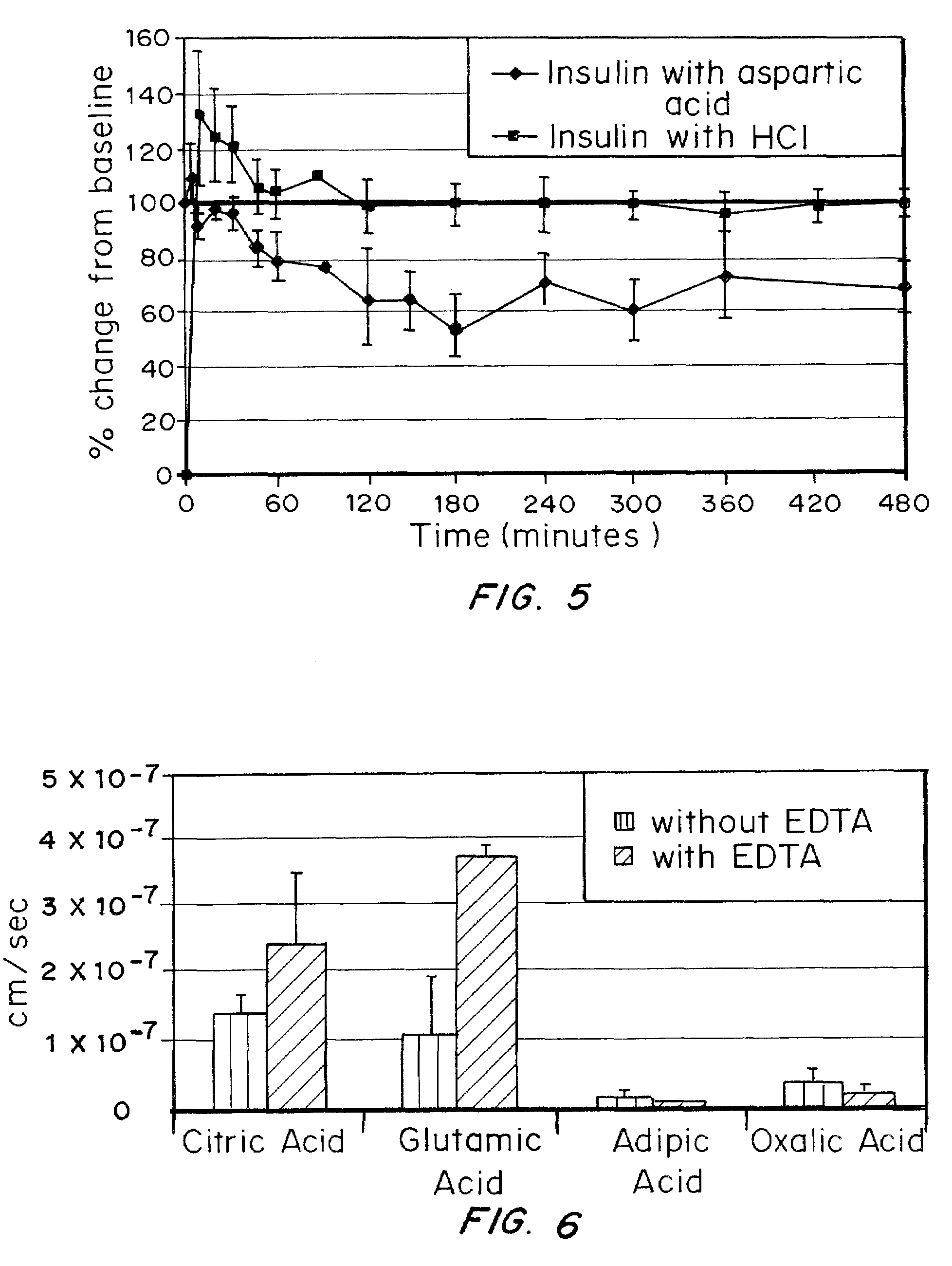
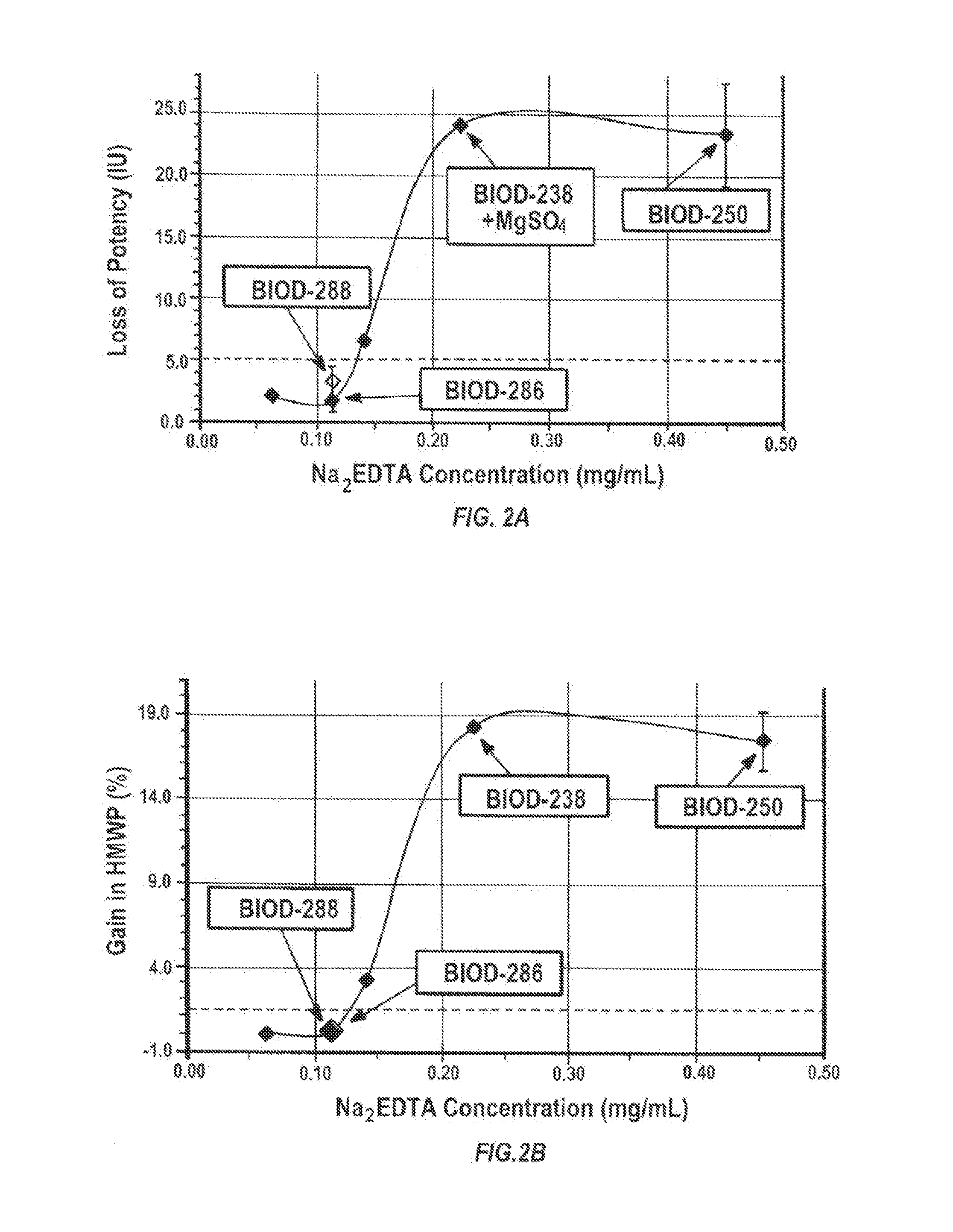
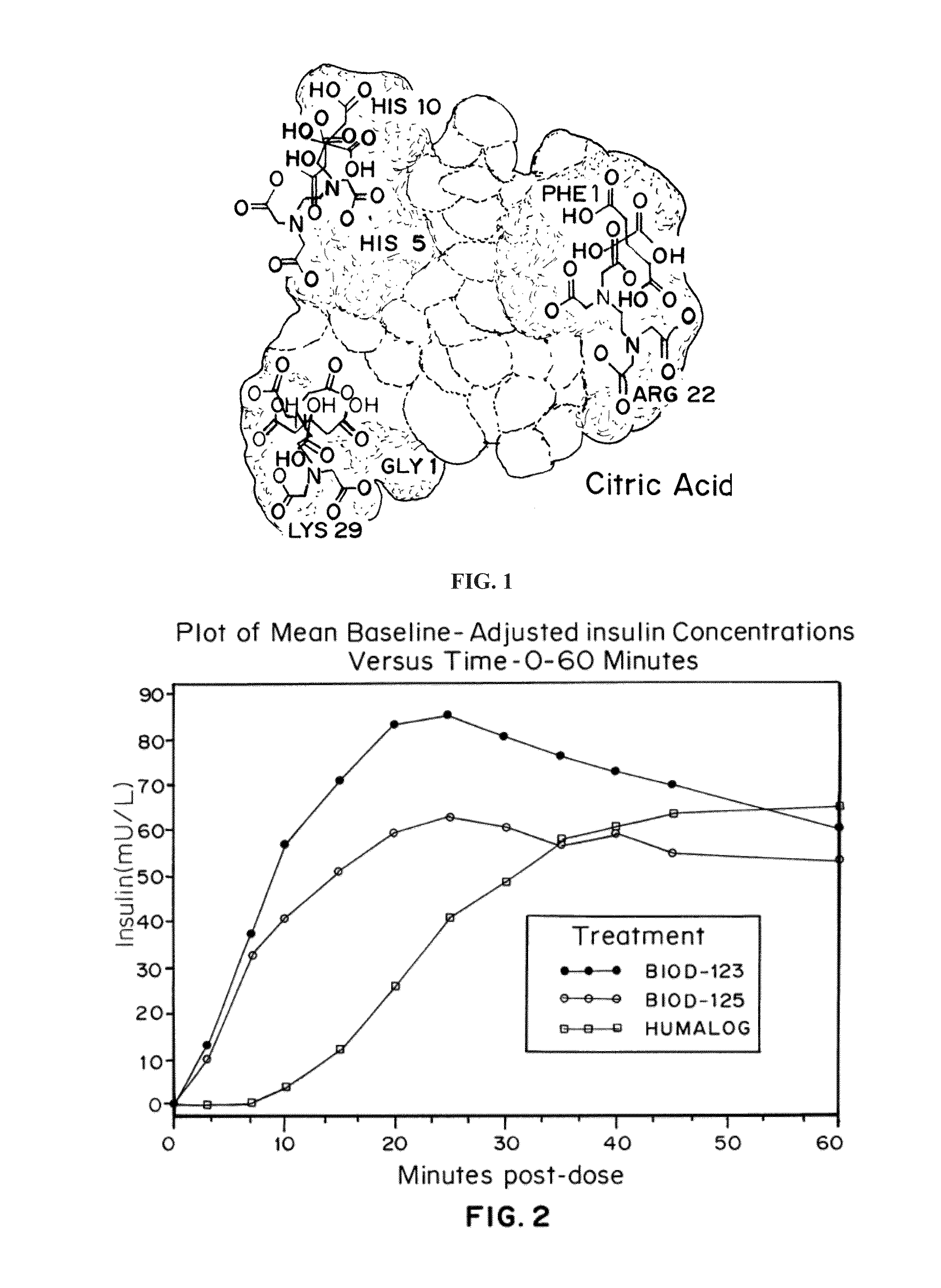
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day. Experiments have been performed to demonstrate, the importance of the addition of specific acids to hexameric insulin to enhance speed and amount of absorption and preserve bioactivity following dissociation into the monomeric form by addition of a chelator such as EDTA. As shown by the examples, the preferred acids are aspartic, maleic, succinic, glutamic and citric acid. These are added in addition to a chelator, preferably ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The results show that the citric acid formulation was more effective at dropping the blood glucose rapidly than the identical rapid acting formulation prepared with HCl in swine. Charge masking by the polyacid appears to be responsible for rapid insulin absorption. EDTA was not effective when used with adipic acid, oxalic acid or HCl at hastening the absorption of insulin. These results confirm the results seen in clinical subjects and patients with diabetes treated with the rapid acting insulin in combination with citric acid and EDTA.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Method of use of monomeric insulin as a means for improving the reproducibility of inhaled insulin
The need for the delivery of insulin by injection can be reduced or eliminated by delivering an aerosolized monomeric insulin formulation. Repeatability of dosing and more particularly the repeatability of the blood concentration versus time profile is improved relative to regular insulin. The blood concentration versus time profile is substantially unaffected by specific aspects of the patient's breathing maneuver at delivery. Further, the rate at which blood glucose is lowered is increased by the use of monomeric insulin. Particles of insulin and in particular monomeric insulin delivered to the surface of lung tissue will be absorbed into the circulatory system. The monomeric insulin may be a dry powder but is preferably in a liquid formulation delivered to the patient from a hand-held, self-contained device which automatically releases an aerosolized burst of formulation. The device includes a sensor which is preferably electronic which measures inspiratory flow and volume which measurement can be used to control the point of drug release.
Owner:ARADIGM
Magnesium Compositions for Modulating the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Insulin and Insulin Analogs, and Injection Site Pain
ActiveUS20140113856A1Improved injection site tolerabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderEthylenediamineMagnesium salt
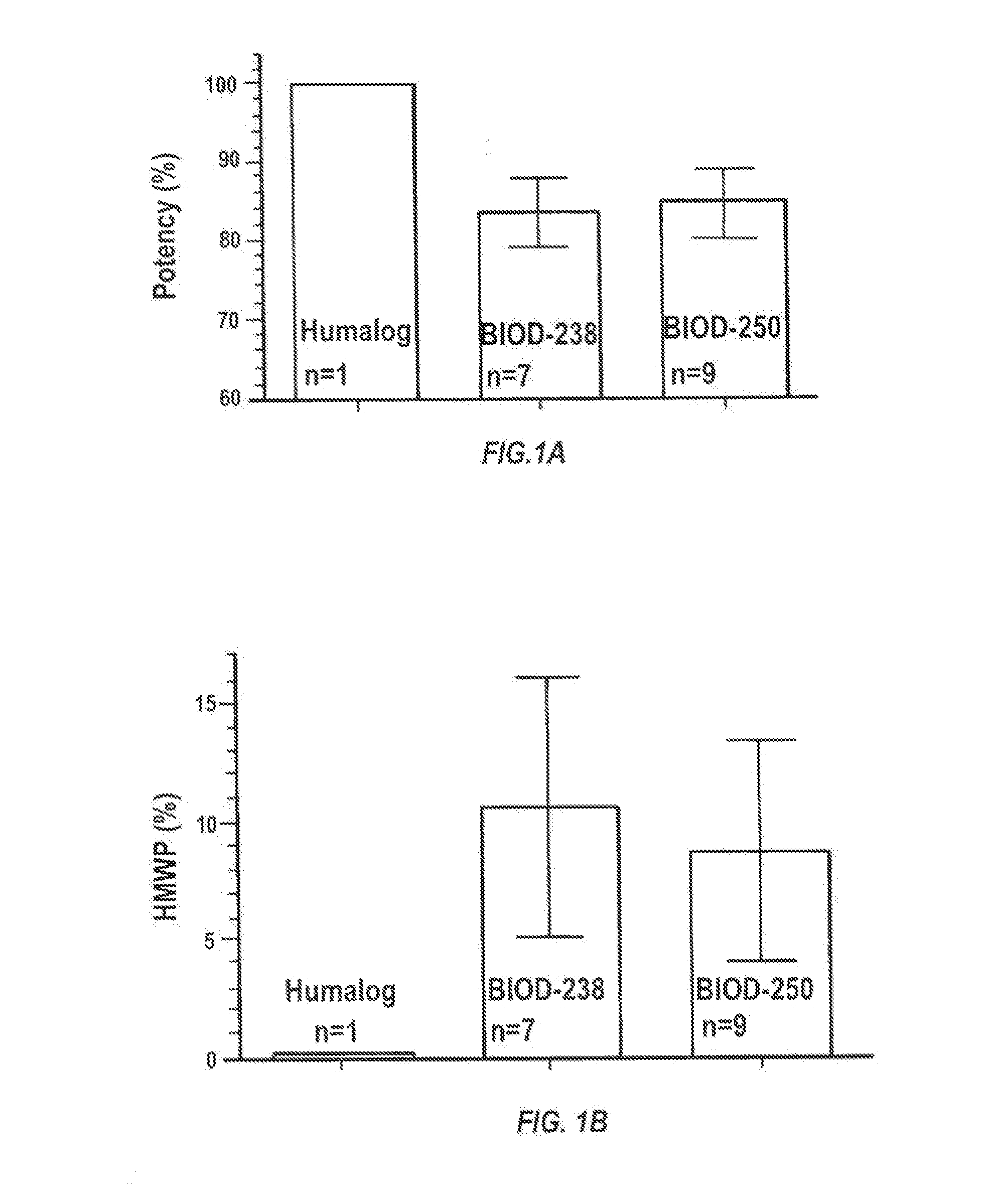
Compositions and methods for modulating injection site pain associated with rapid acting injectable insulin formulations have been developed for subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain insulin in combination with a zinc chelator such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (“EDTA”), a dissolution / stabilization agent such as citric acid, a magnesium salt, and, optionally, additional excipients. New presentations include rapid acting concentrated insulin formulations and a way to enhance the absorption of commercially available rapid acting analog formulations by mixing them with a vial containing dry powder excipients that accelerate their absorption. Devices for mixing excipient and insulin together at the time of administration, while minimizing residence time of the mixture, are also described.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Rapid Acting and Long Acting Insulin Combination Formulations
InactiveUS20080039365A1Promote absorptionAct quicklyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is decreased so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day. Experiments have been performed to demonstrate the importance of the addition of specific acids to hexameric insulin to enhance speed and amount of absorption and preserve bioactivity following dissociation into the monomeric form by addition of a chelator such as EDTA. As shown by the examples, the preferred acids are aspartic, glutamic and citric acid. These are added in addition to a chelator, preferably ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The results show that the citric acid formulation was more effective at dropping the blood glucose rapidly than the identical rapid acting formulation prepared with HCl in swine. Charge masking by the polyacid appears to be responsible for rapid insulin absorption. EDTA was not effective when used with adipic acid, oxalic acid or HCl at hastening the absorption of insulin. These results confirm the results seen in clinical subjects and patients with diabetes treated with the rapid acting insulin in combination with citric acid and EDTA.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
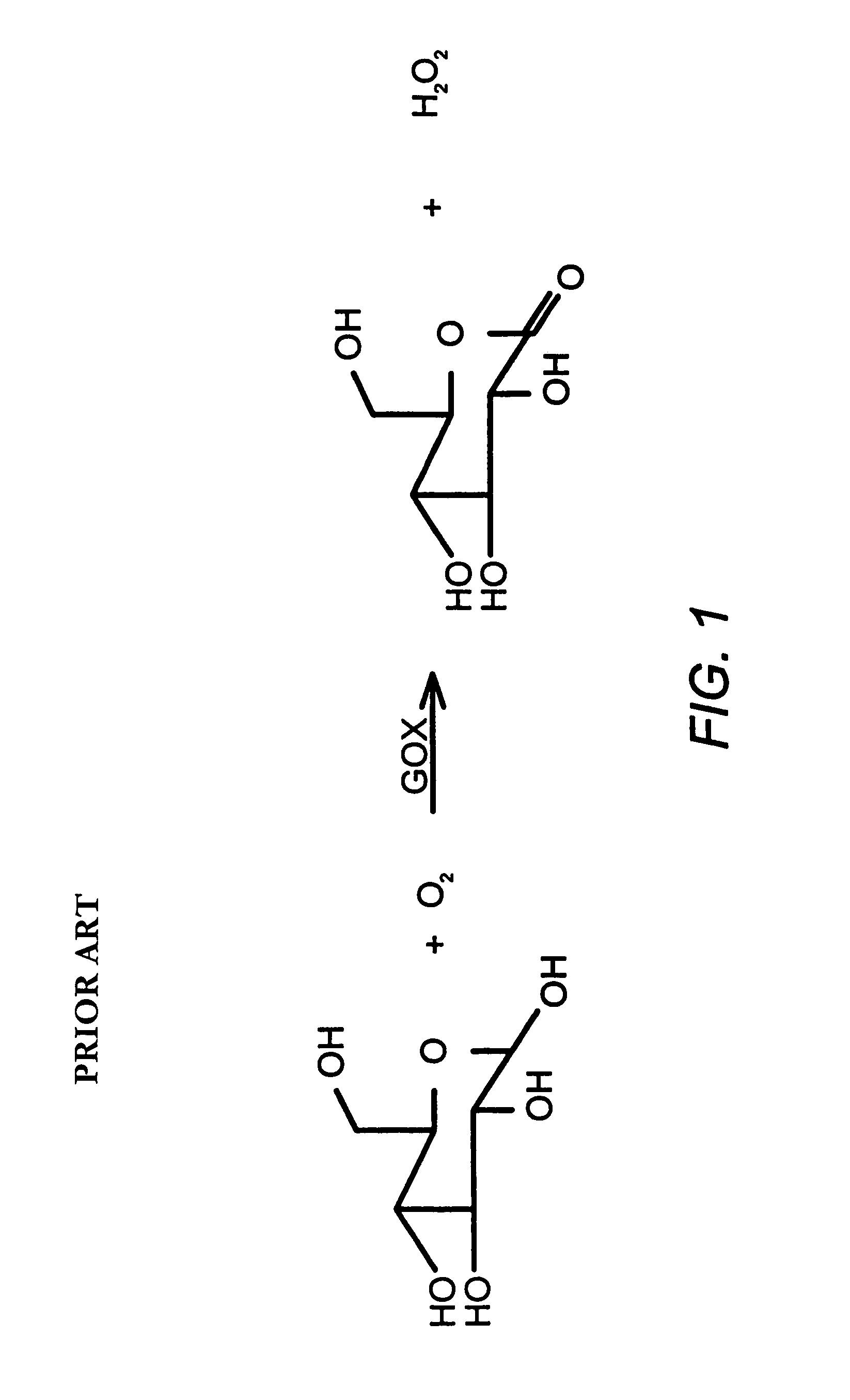
Insulin formulations for insulin release as a function of tissue glucose levels
InactiveUS20090175840A1Reduce productionRaise the pHPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInjections insulinReducing agent
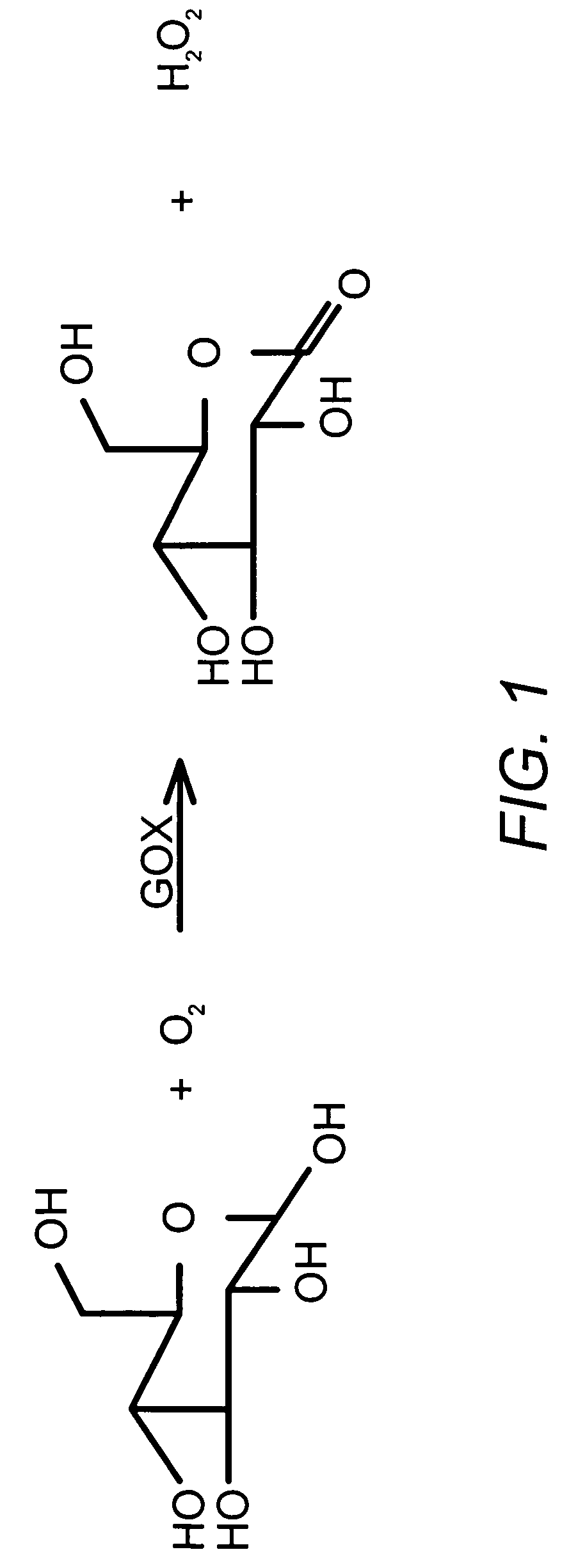
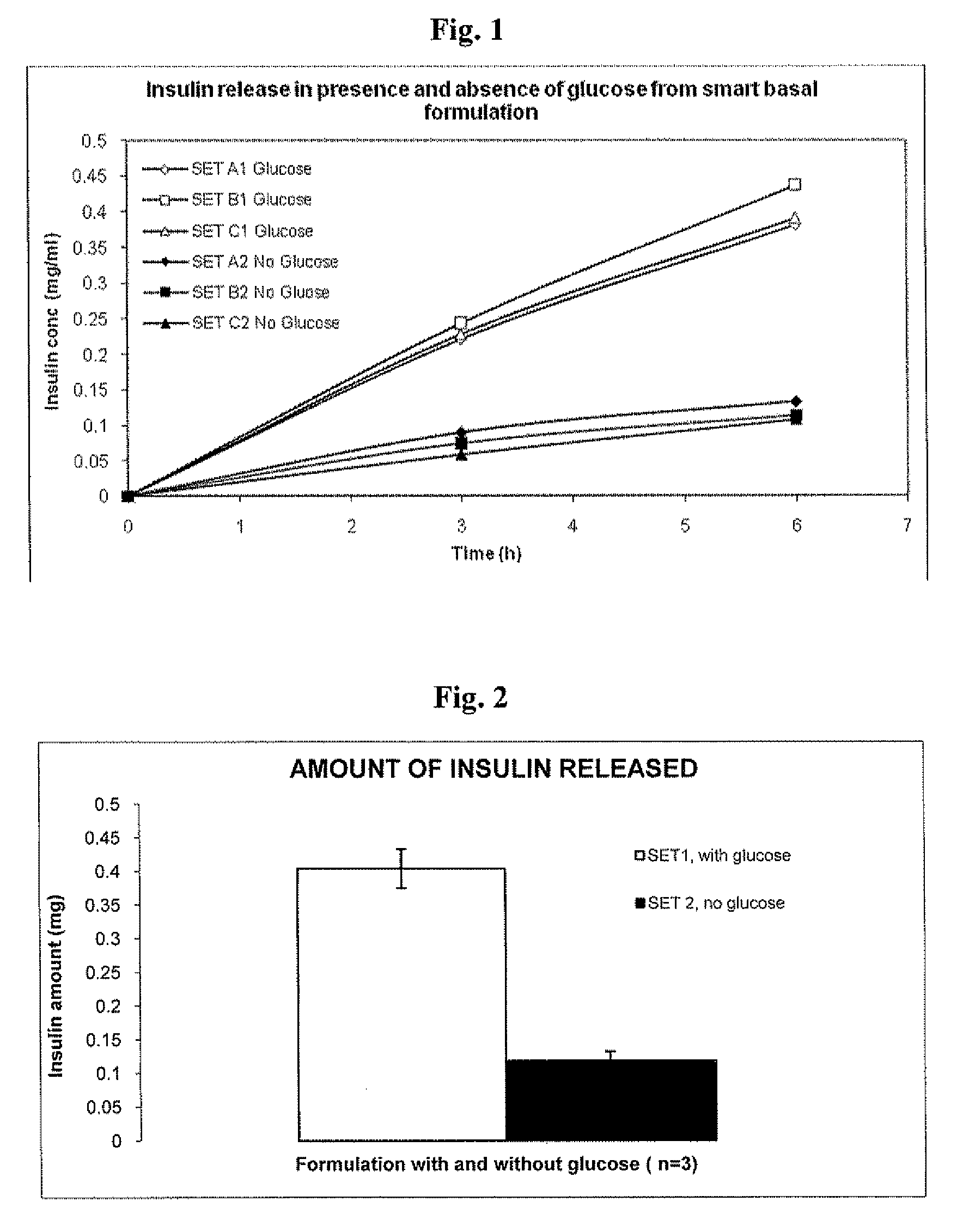
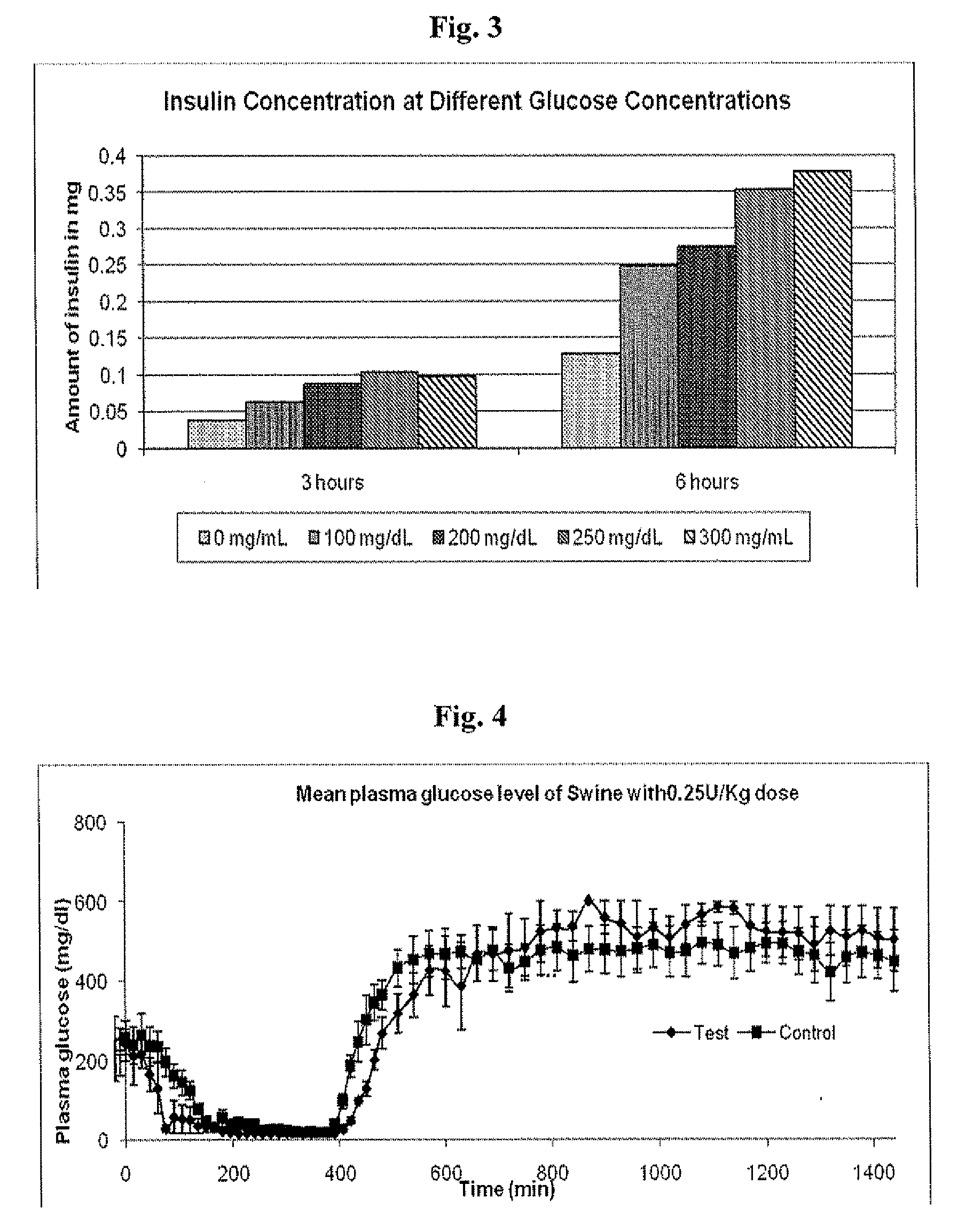
Injectable insulin formulations that are capable of modifying the amount of insulin released based on the patient's tissue glucose levels, methods for making and using these formulations are described herein. The formulation may be administered via subcutaneous, intradermal or intramuscular administration. In one preferred embodiment, the formulations are administered via subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain insulin, an oxidizing agent or enzyme and a reducing agent or enzyme, a diluent and optionally one or more thickening agents. If a thickening agent is present in the formulation, the thickening agent increases the viscosity of the formulation following administration. Preferably the formulation contains an insulin, a diluent, glucose oxidase and peroxidase. Following administration to a patient, the insulin is released from the formulations as a function of the patient's tissue glucose level, which in turn maintains the patient's blood glucose level within an optimum range. The formulation is often referred to as a “smart” formulation since it modifies its release rate of insulin according to the patient's needs at a particular time. In a preferred embodiment, the formulation is designed to release insulin into the systemic circulation over time with a basal release profile following injection in a patient. In another embodiment, the formulation is designed to release insulin into the systemic circulation over time with a non-basal release profile following injection in a patient, such as a regular human insulin release profile or a prandial release profile.
Owner:BIODEL
Insulin production methods and pro-insulin constructs
InactiveUS20080146492A1Reduce eliminateImprove efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesInsulin activityImproved method
Novel pro-insulin having specific amino acid and / or nucleic acid modifications suitable for improved methods of insulin production are provided. Novel and highly efficient processes for preparing the pro-insulin preparations and preparations containing them are also disclosed. The novel pro-insulin preparations may be converted into human insulin useful in therapeutic preparations. Novel peptides of the C-peptide, and N terminus, including RREAEALQVGQVELGGGPGAGSLQPLALEGSLQAR (SEQ ID NO: 32), and MHHHHHHGGR (SEQ ID NO: 2) respectively are provided, as well as the unique nucleic acid molecules encoding them.
Owner:AGILA BIOTECH PVT LTD
Amylin Formulations
InactiveUS20090192075A1Reduce in quantityAct quicklyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderGLP-1 MimeticsBefore Breakfast
A combined insulin and amylin and / or GLP-1 mimetic formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the insulin is decreased so that the amylin and / or GLP-1 remains soluble when mixed together with the insulin. In the preferred embodiment, a bolus insulin is administered by injection before breakfast, providing adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, without producing hypoglycemia after the meal. This can be combined with an adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of the insulin and amylin and / or GLP-1 mimetic combination. A GLP-1 mimetic may be combined with either rapid acting or basal insulin formulations. As a result, a patient using the combination formulation therapy may only need to inject half as many times per day.
Owner:BIODEL INC
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS7718609B2Increase speedReduce the amount of solutionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed in which the pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Insoluble compositions for controlling blood glucose
InactiveUS20030144181A1Easy to controlReduce ratePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineDivalent metal
The present invention relates to insoluble compositions comprising a protein selected from the group consisting of insulin, insulin analogs, and proinsulins; a derivatized protein selected from the group consisting of derivatized insulin, derivatized insulin analog, and derivatized proinsulin; a complexing compound; a hexamer-stabilizing compound; and a divalent metal cation. Formulations of the insoluble composition are suitable for both parenteral and non-parenteral delivery for treating hyperglycemia and diabetes. Microcrystal forms of the insoluble precipitate are pharmaceutically analogous to the neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin crystal form. Surprisingly, it has been discovered that suspension formulations of such insoluble compositions possess unique and controllable dissolution properties that provide therapeutically advantageous glucodynamics compared with insulin NPH formulations.
Owner:BRADER MARK LAURENCE
Rapid Acting Injectable Insulin Compositions
InactiveUS20080090753A1Improve stabilityQuick effectPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDissolutionExcipient
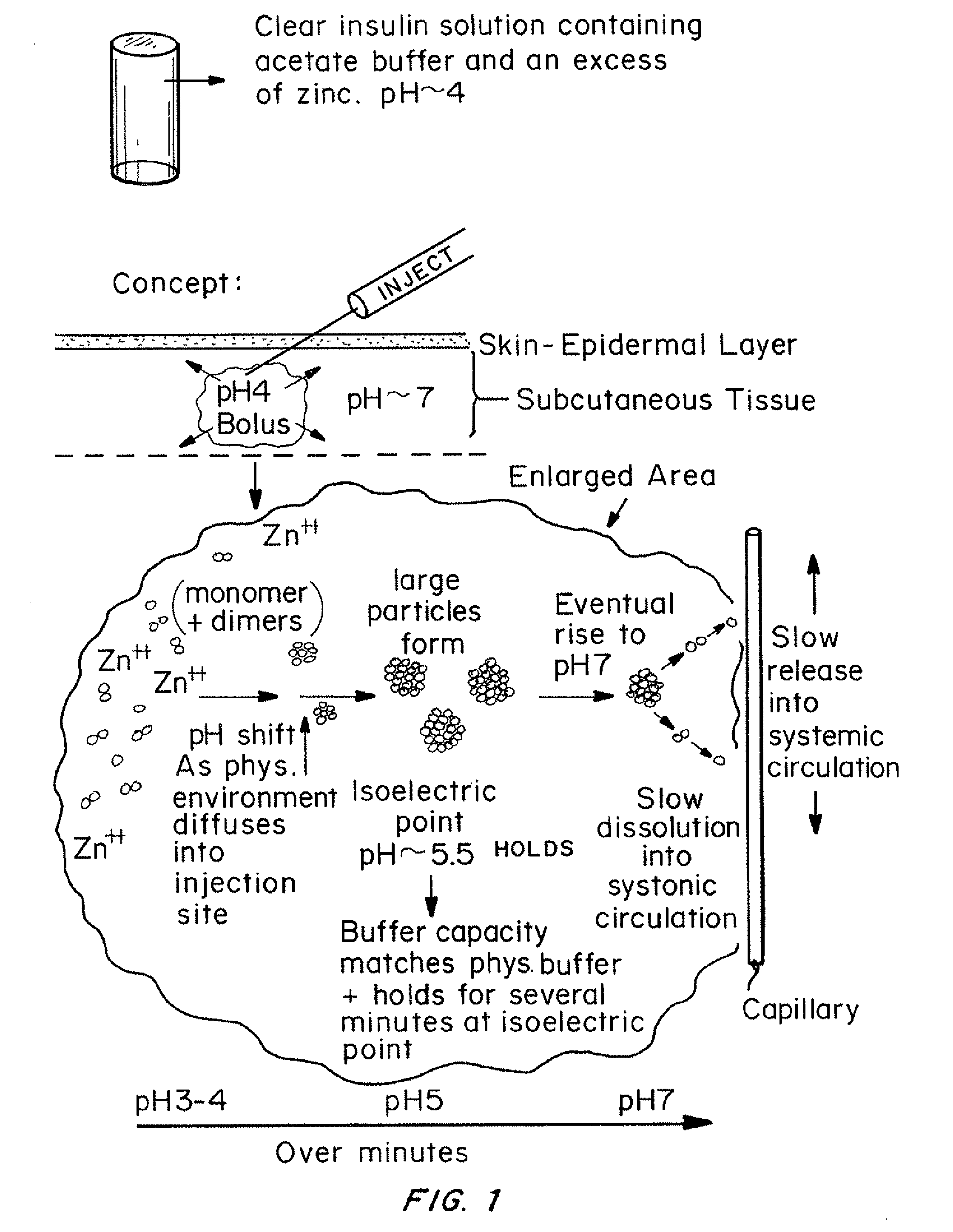
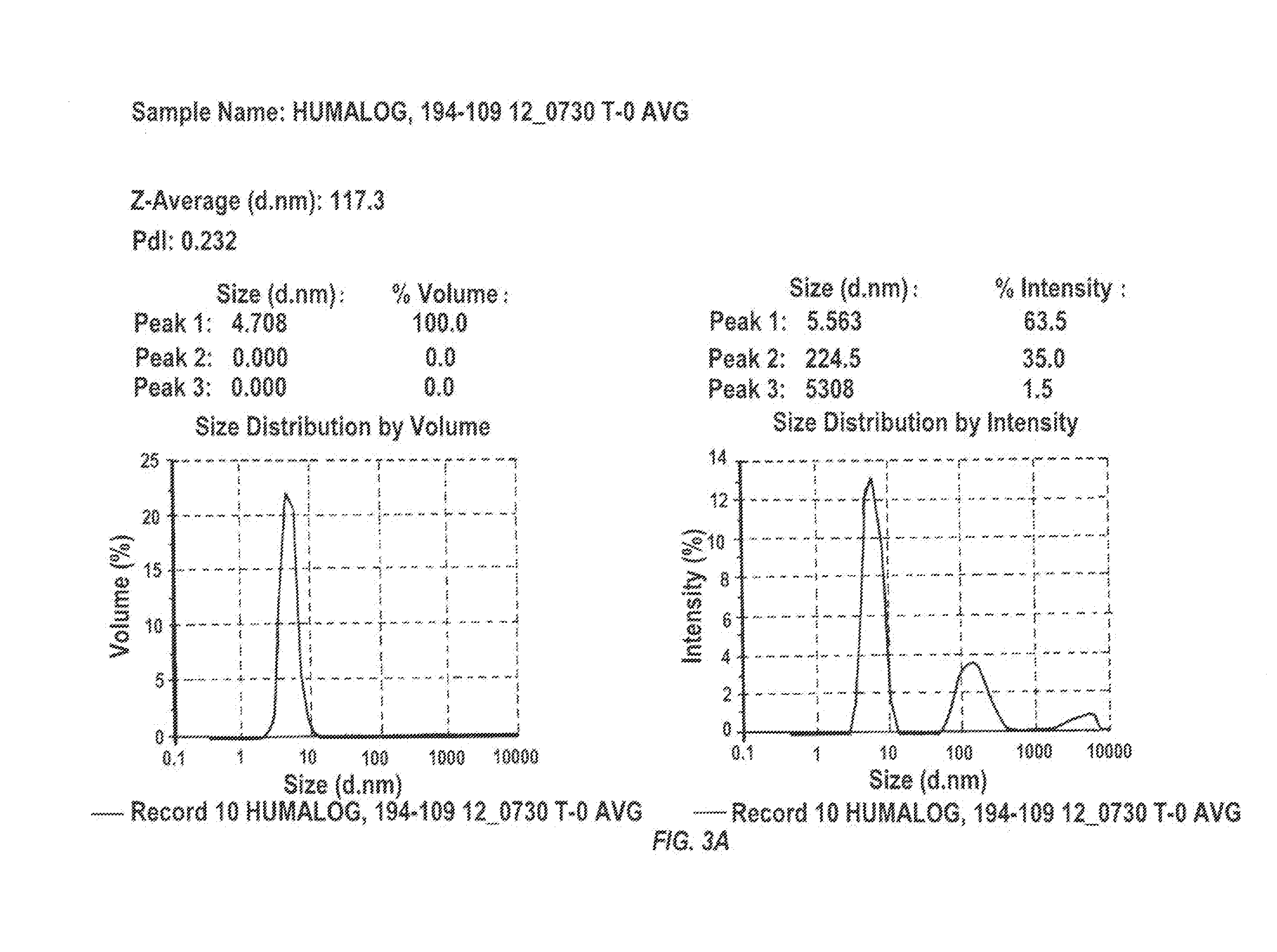
Injectable insulin formulations with improved stability and rapid onset of action are described herein. The formulations may be for subcutaneous, intradermal or intramuscular administration, In the preferred embodiment, the formulations are administered via subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain insulin in combination with a chelator and dissolution agent, and optionally additional excipients. In the preferred embodiment, the formulation contains human insulin, a zinc chelator such as EDTA and a dissolution agent such as citric acid. These formulations are rapidly absorbed into the blood stream when administered by subcutaneous injection. In the preferred embodiment, the insulin is provided as a dry powder in a sterile vial. This is mixed with a diluent containing a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, such as water, a zinc chelator such as EDTA and a dissolution agent such as citric acid shortly before or at the time of administration. In another embodiment, the insulin is stored as a frozen mixture, ready for use upon thawing.
Owner:BIODEL
Insulin with a stable basal release profile
ActiveUS20110281790A1Accelerated precipitationLess solublePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin glargineZinc
A basal insulin formulation composed of insulin, preferably insulin glargine, injectable zinc and injectable iron compounds as precipitating and / or stabilizing agents has been developed for subcutaneous, intradermal or intramuscular administration. The formulation is designed to form a precipitate of insulin following injection, creating a slow releasing “basal insulin” over a period of 12 to 24 hours.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Particles for inhalation having rapid release properties
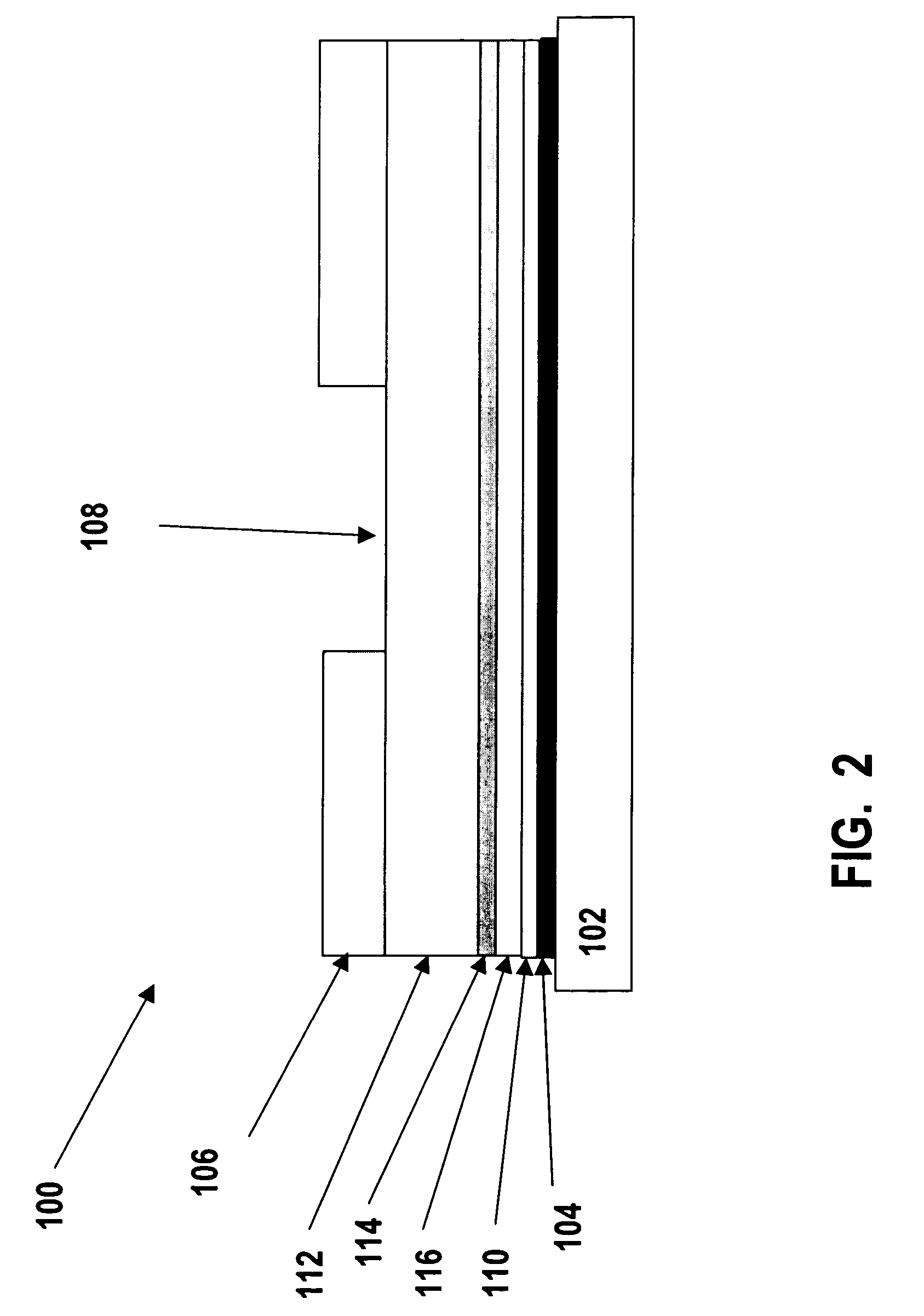
InactiveUS20080226730A1Facilitated releaseShorten the timePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsActive agentPhospholipid
The invention generally relates to formulations having particles comprising phospholipids, bioactive agent and excipients and the pulmonary delivery thereof. Dry powder inhaled insulin formulations are disclosed. Improved formulations comprising DPPC, insulin and sodium citrate which are useful in the treatment of diabetes are disclosed. Also, the invention relates to a method of for the pulmonary delivery of a bioactive agent comprising administering to the respiratory tract of a patient in need of treatment, or diagnosis an effective amount of particles comprising a bioactive agent or any combination thereof in association, wherein release of the agent from the administered particles occurs in a rapid fashion.
Owner:CIVITAS THERAPEUTICS
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
InactiveUS7713929B2Rapid acting insulin isPromote absorptionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed in which the pH of the rapid acting insulin is decreased so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Insulin with a basal release profile
InactiveUS20100069292A1Not possibleAvoid the needPeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsBuffering agentINSULIN PREPARATIONS
A clear basal insulin formulation composed of insulin (preferably human recombinant insulin), buffering agents, precipitating agents, and / or stabilizing agents for subcutaneous, intradermal or intramuscular administration. The formulation is designed to form a precipitate of insulin following injection, creating a slow releasing “basal insulin” over a period of 12 to 24 hours, which can be varied by compositional changes to tailor the release profile to the needs of the individual diabetic patient
Owner:BIODEL
Stabilized ultra-rapid-acting insulin formulations
InactiveUS20150273022A1Quick effectPromote absorptionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsZinc compoundsMagnesium salt
Compositions and methods for enhancing the stability of rapid acting injectable insulin formulations have been developed for subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain insulin in combination with a zinc chelator such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (“EDTA”), a dissolution / stabilization agent such as citric acid, a magnesium salt, a zinc compound and, optionally, additional excipients. New presentations include rapid acting concentrated insulin formulations and a way to enhance the absorption of commercially available rapid acting analog formulations while maintaining insulin stability.
Owner:ALBIREO PHARMA INC
Formulations of insulin
InactiveUS7387996B2Superior long-term physical stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBiochemistryINSULIN PREPARATIONS
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Acidic insulin preparations with improved stability
ActiveUS20050171009A1Improve long-term stabilityIncrease pressureBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMetaboliteMedicine
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical formulation comprising a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of insulin, an insulin metabolite, an insulin analog, an insulin derivative and combinations thereof; a surfactant or combinations of two or more surfactants; optionally a preservative or combinations of two or more preservatives; and optionally an isotonicizing agent, buffers or further excipients or combinations thereof, the pharmaceutical formulation having a pH in the acidic range.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Magnesium Compositions for Modulating the Pharmacokinetics and Injection Site Pain of Insulin
ActiveUS20140357554A1Peptide/protein ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsMagnesium saltDissolution
Compositions and methods for modulating injection site pain associated with rapid acting injectable insulin formulations have been developed for subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain insulin in combination with a zinc chelator such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (“EDTA”), a dissolution / stabilization agent such as citric acid, a magnesium salt, and, optionally, additional excipients. New presentations include rapid acting concentrated insulin formulations and a way to enhance the absorption of commercially available rapid acting analog formulations by mixing them with a vial containing dry powder excipients that accelerate their absorption. Devices for mixing excipient and insulin together at the time of administration, while minimizing residence time of the mixture, are also described.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Protease resistant insulin analogues
PendingCN101541830APeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPancreatic hormoneProtease resistant
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Protease-stabilized insulin analogues
InactiveUS20110092419A1Proteolytic stability is enhancedRetained biological insulin activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsINSULIN PREPARATIONSInsulin Analogue
The present invention relates to novel insulin analogues comprising mutations at position A14 in the A chain and at positions B27, B28, B29 and B30 in the B chain and exhibiting resistance towards protease; a method for the preparation of such insulin analogues; insulin preparations containing the insulin analogues of the invention; and, a method of treating diabetes mellitus using these insulin analogues.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Measurement of Glucose in an Insulin Delivery Catheter by Minimizing the Adverse Effects of Insulin Preservatives
ActiveUS20160354542A1Avoid VulnerabilityLow costFiltering accessoriesMedical devicesFiltrationPharmaceutical formulation
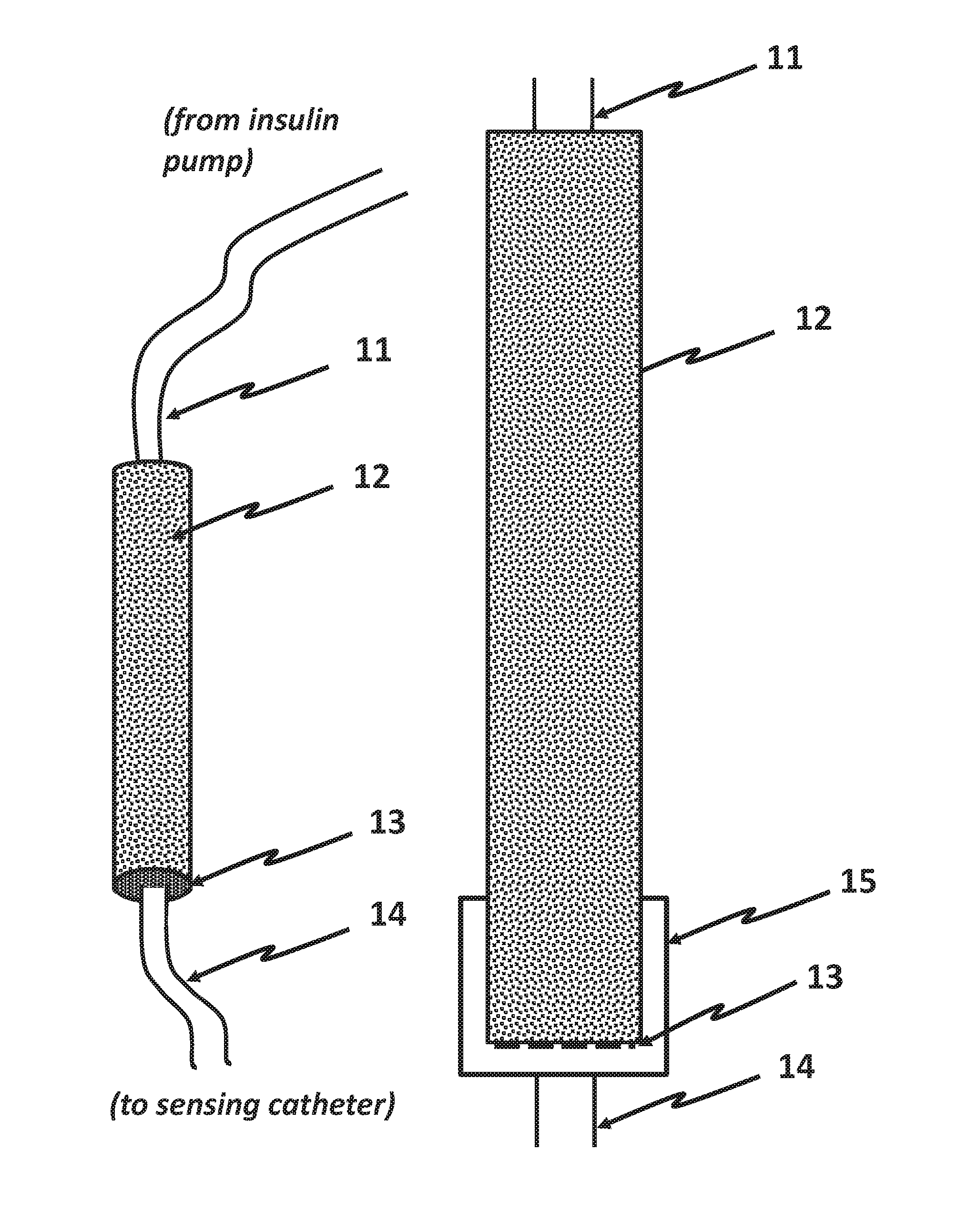
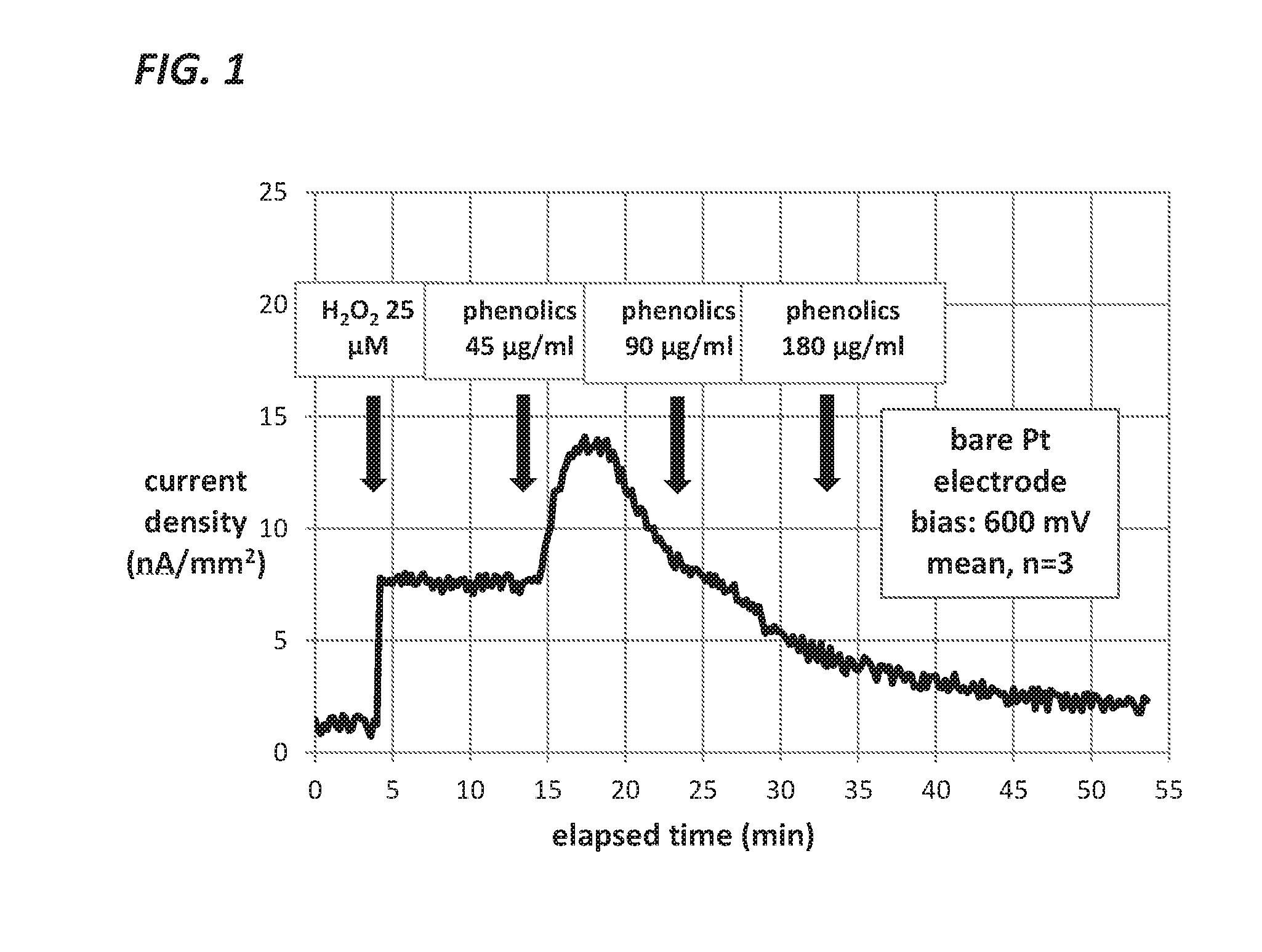
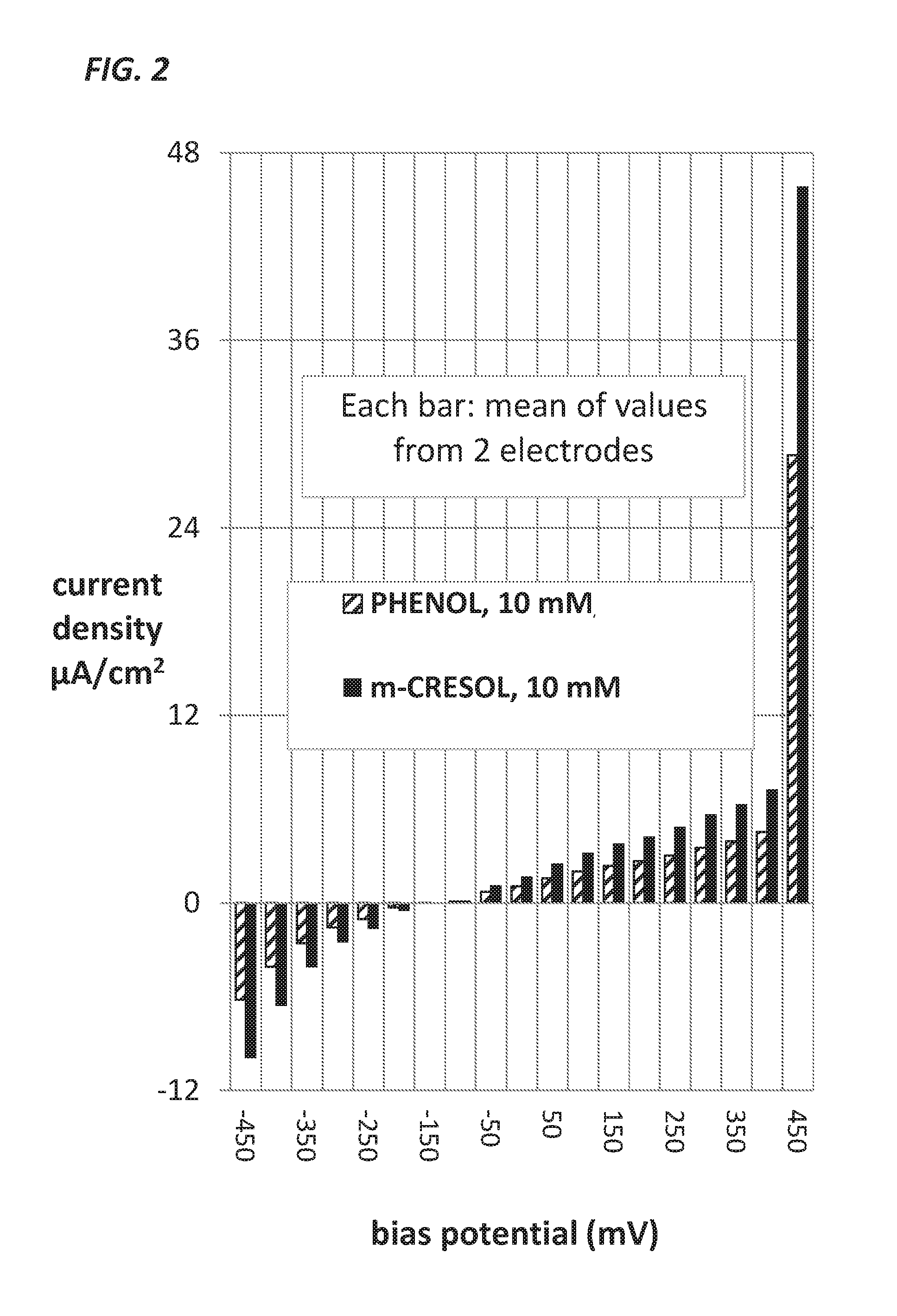
This disclosure teaches the concept, and method of creating, a dual use device intended for persons who take insulin. In one embodiment, the novel device is an insulin delivery cannula, the outer wall of which contains electrodes, chemical compounds and electrical interconnects that allow continuous glucose sensing and delivery of data to a remote device. Heretofore, the main problem in attempting to sense glucose at the site of insulin delivery has been the high current resulting from oxidation by the sensor of the preservatives in the insulin formulations. One means of eliminating these interferences is to poise the indicating electrode(s) of the sensor at a bias sufficiently low to avoid the signal from oxidation of the preservatives. One way of obtaining a glucose signal at a low bias is to use an osmium-ligand-polymer complex instead of conventional hydrogen peroxide sensing. Another is to use a size exclusion filter located in line with the insulin delivery tubing in order to remove the smaller phenolic preservative molecules while allowing the larger insulin molecules to pass unimpeded. These filtration concepts can also be more broadly applied, that is, the general concept of removal of unwanted drug formulation excipients from a drug delivery system.
Owner:PACIFIC DIABETES TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com