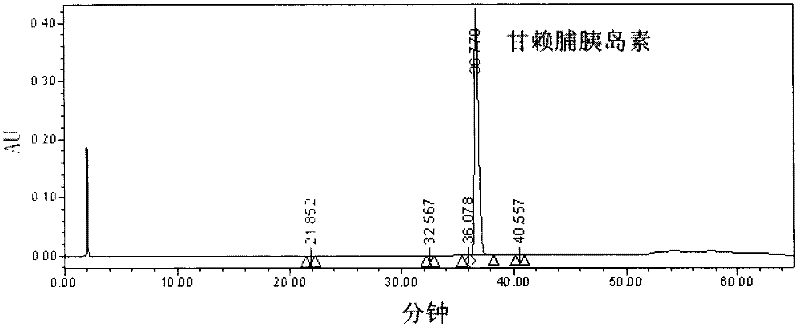
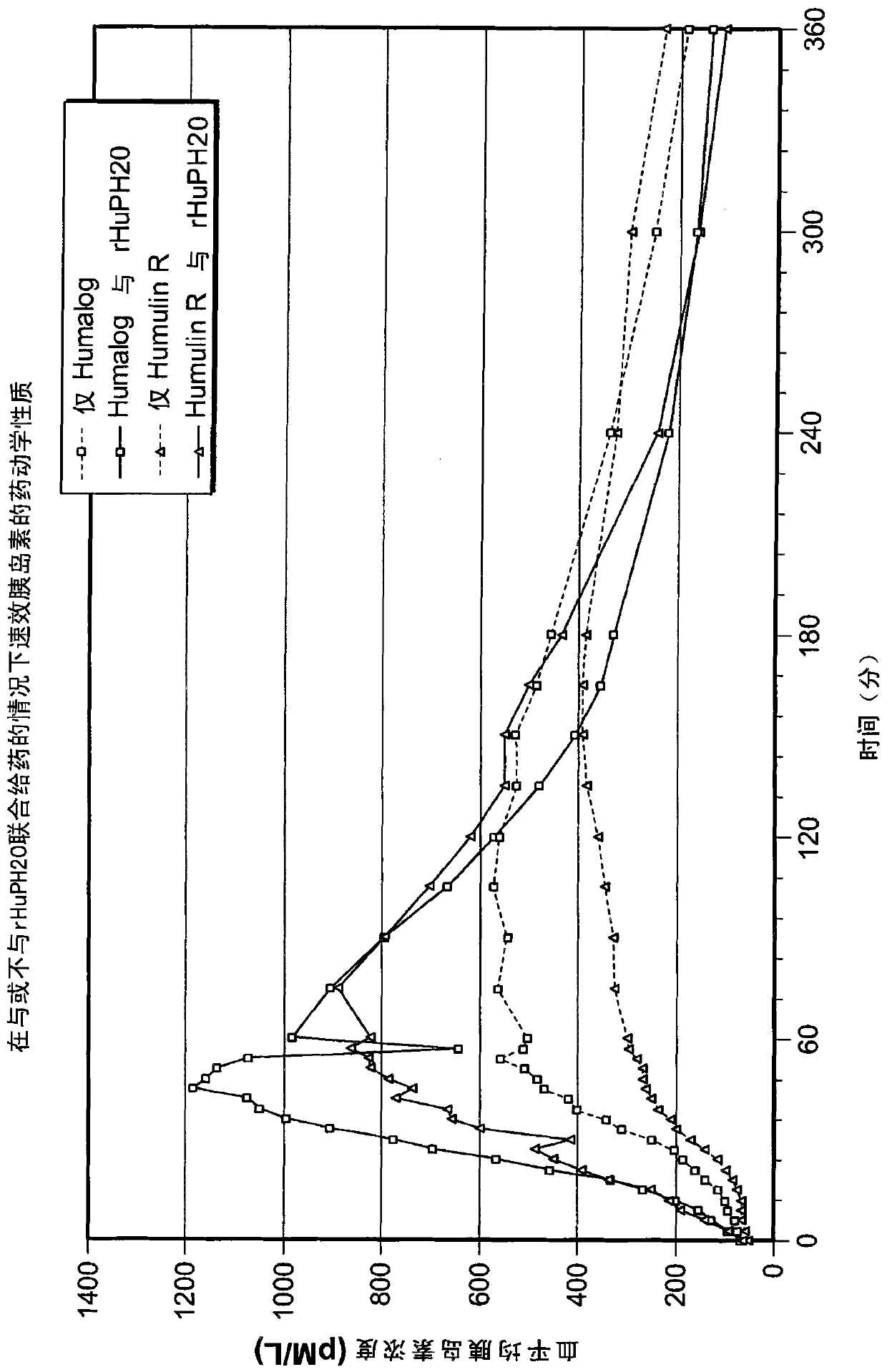
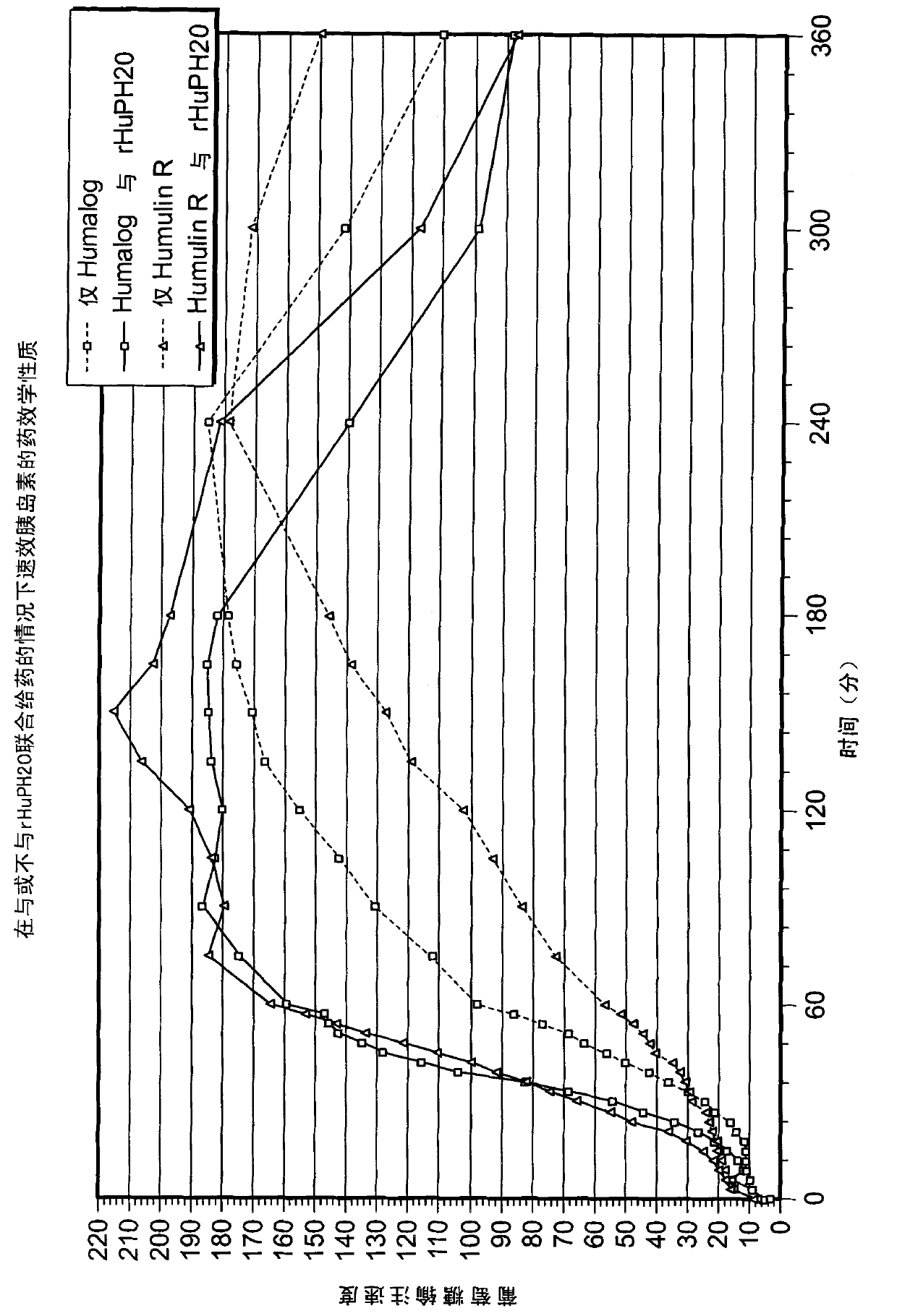
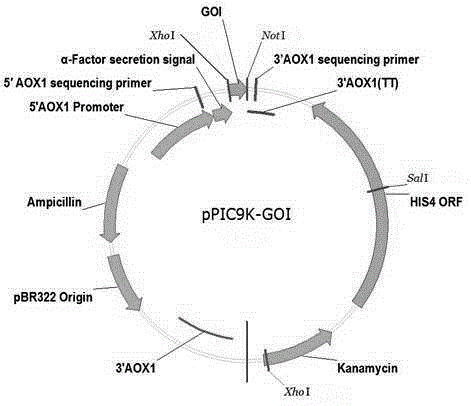
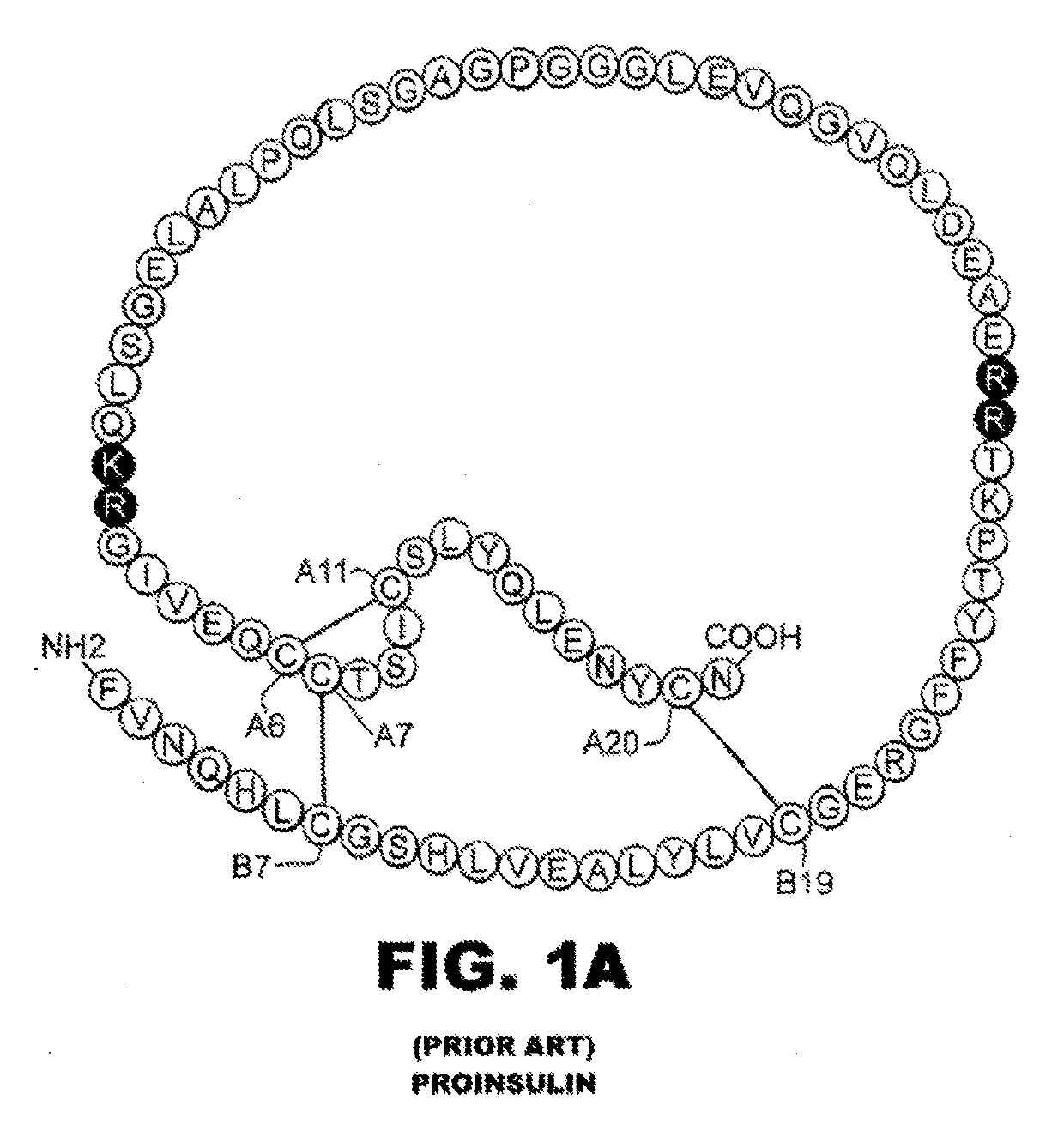
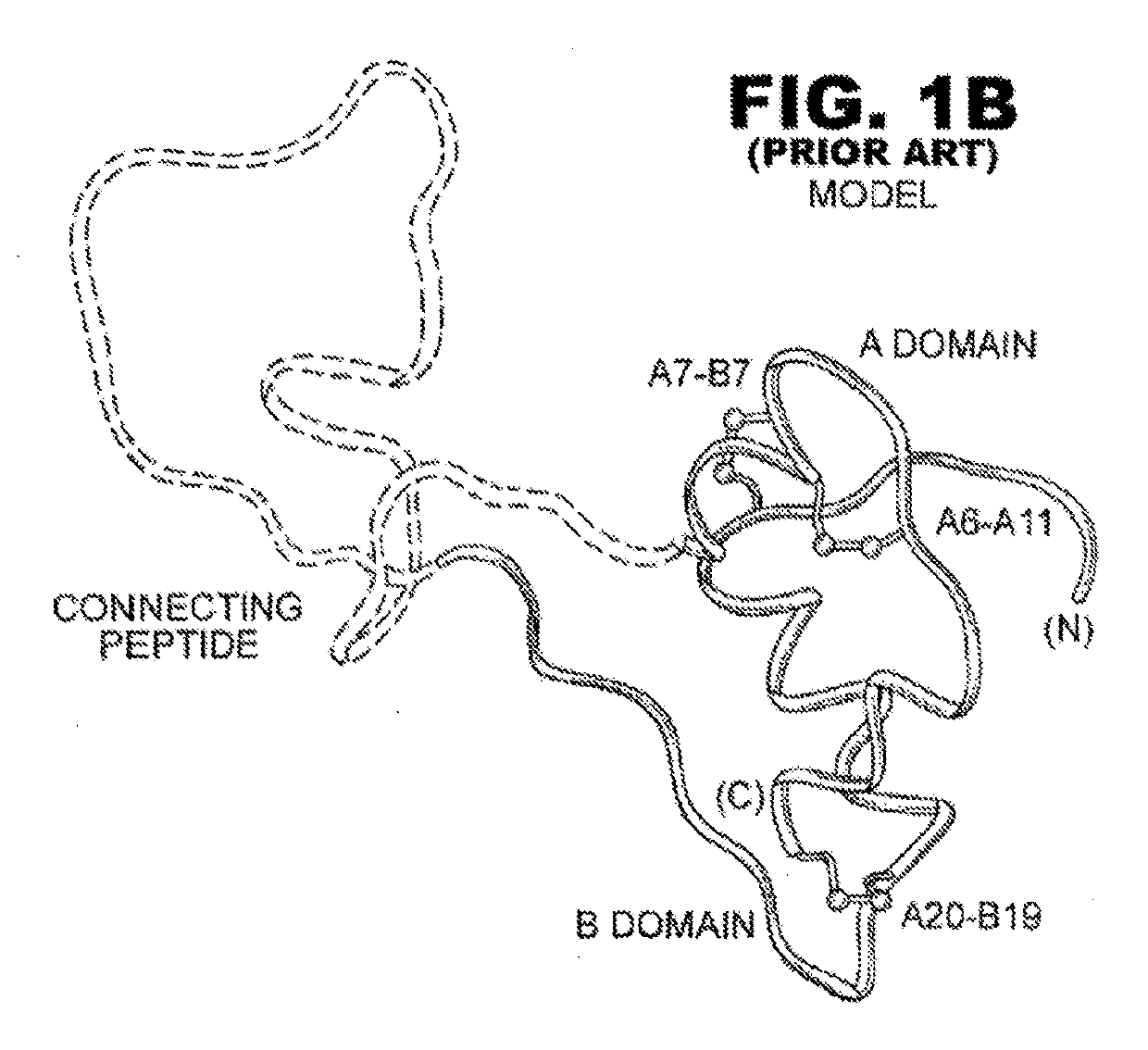
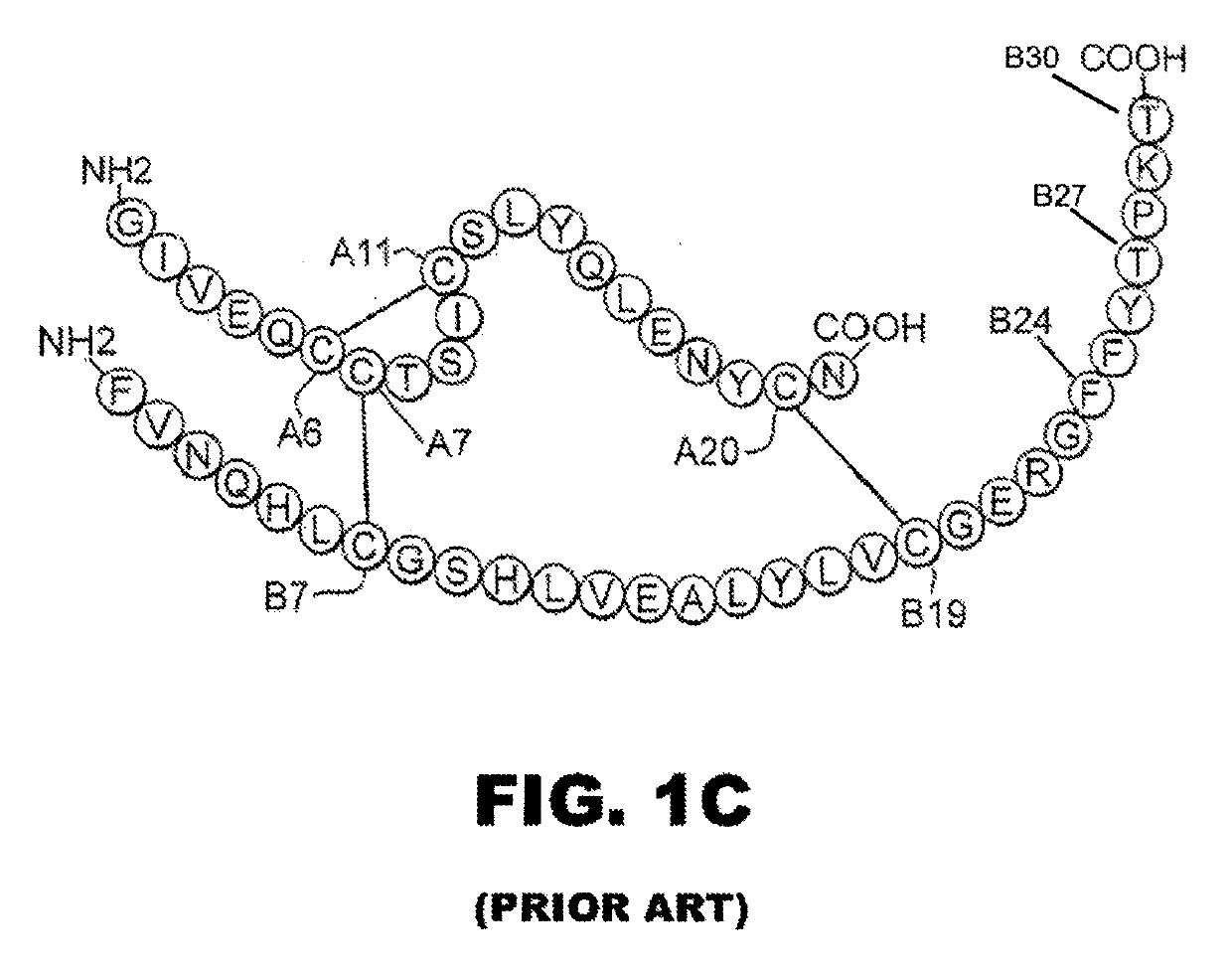
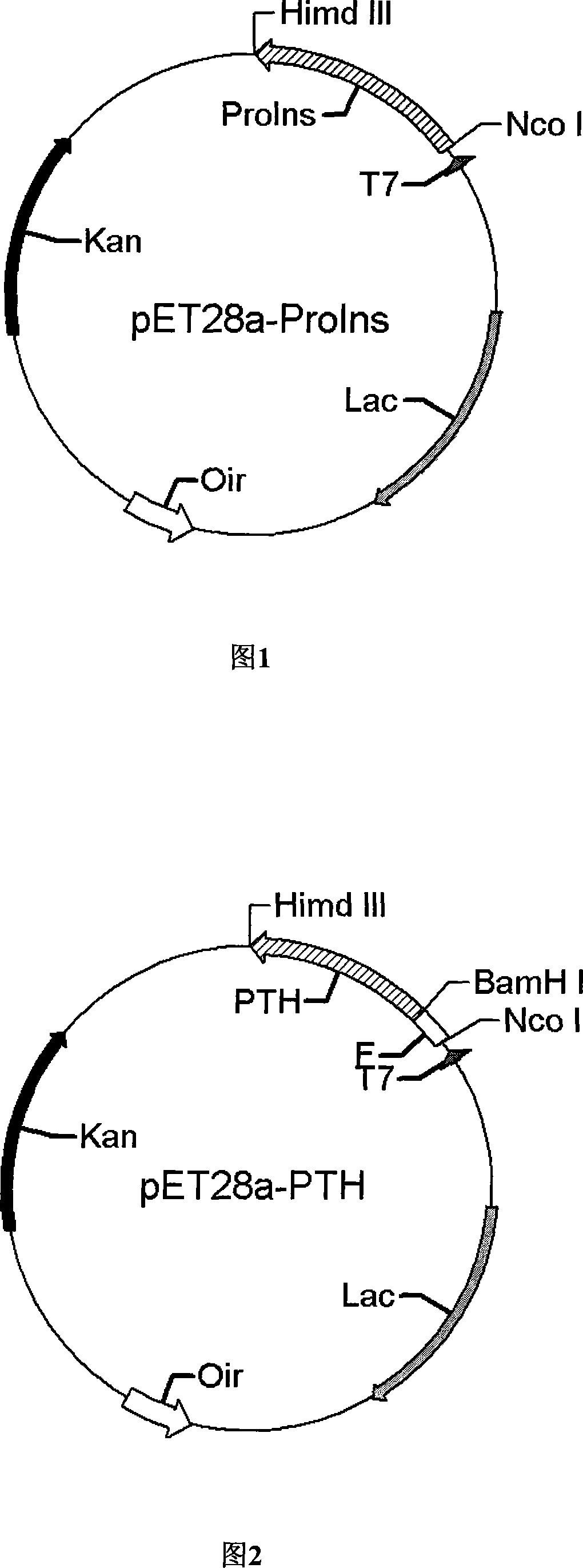
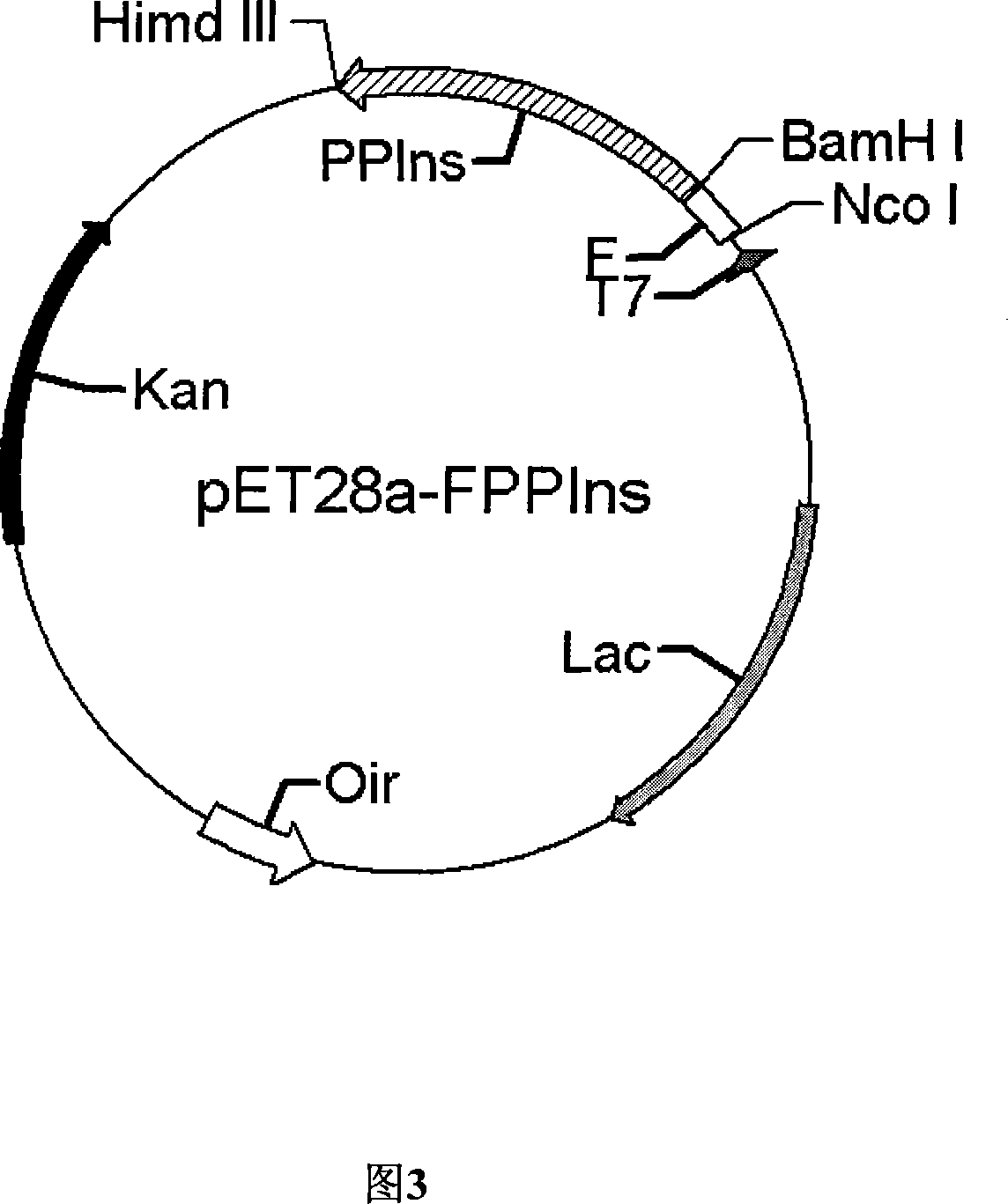
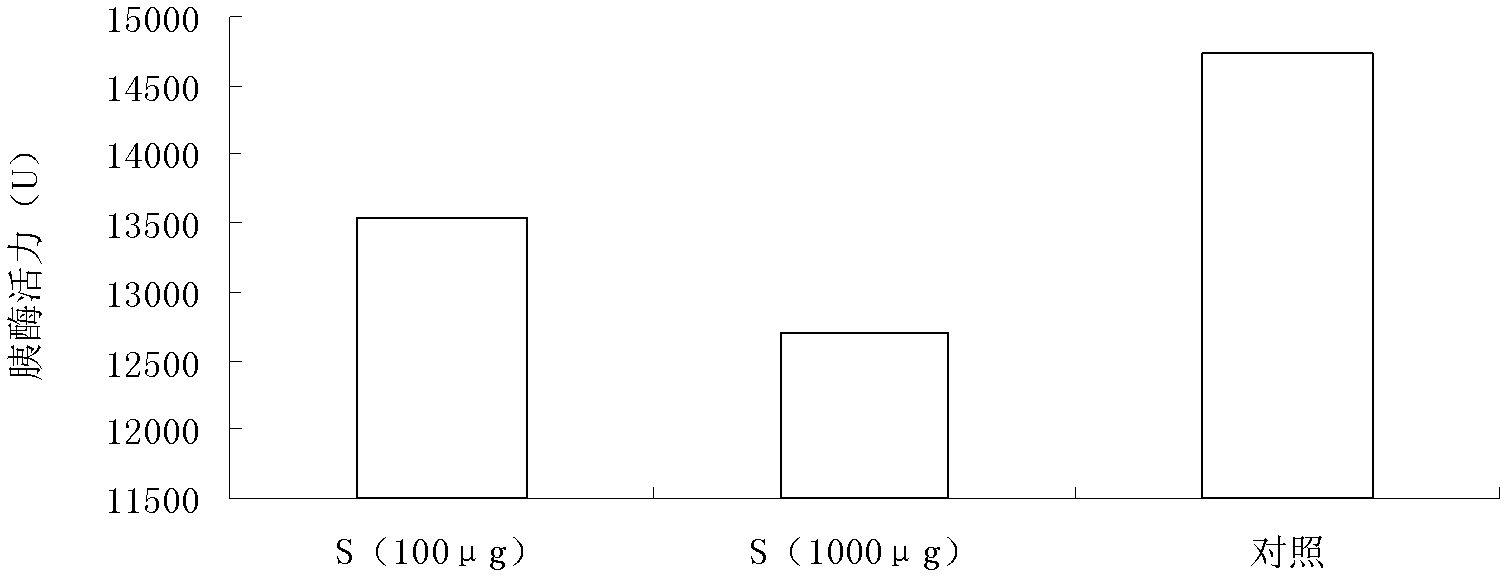Patents
Literature
51 results about "Rapid-acting insulin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
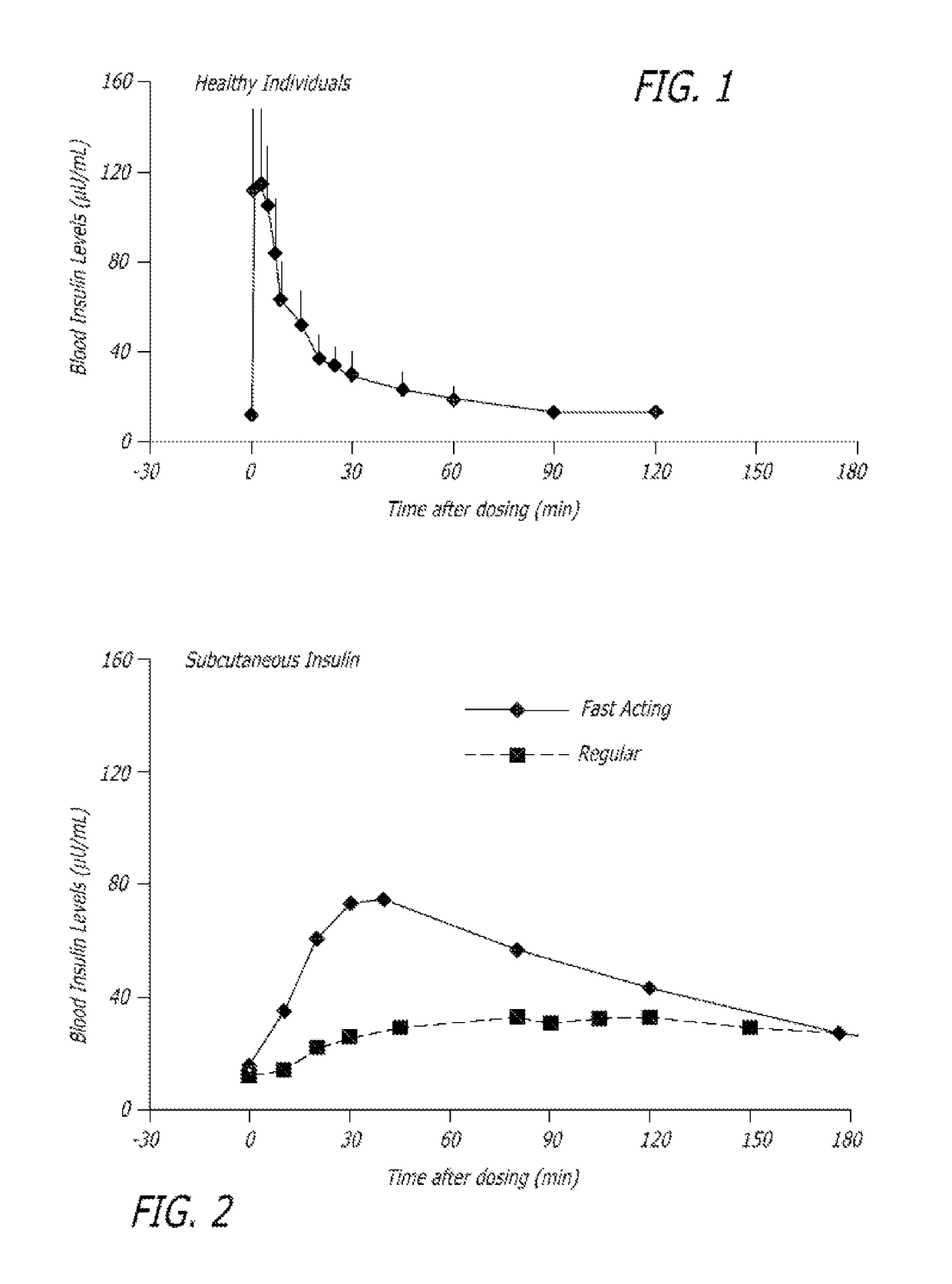
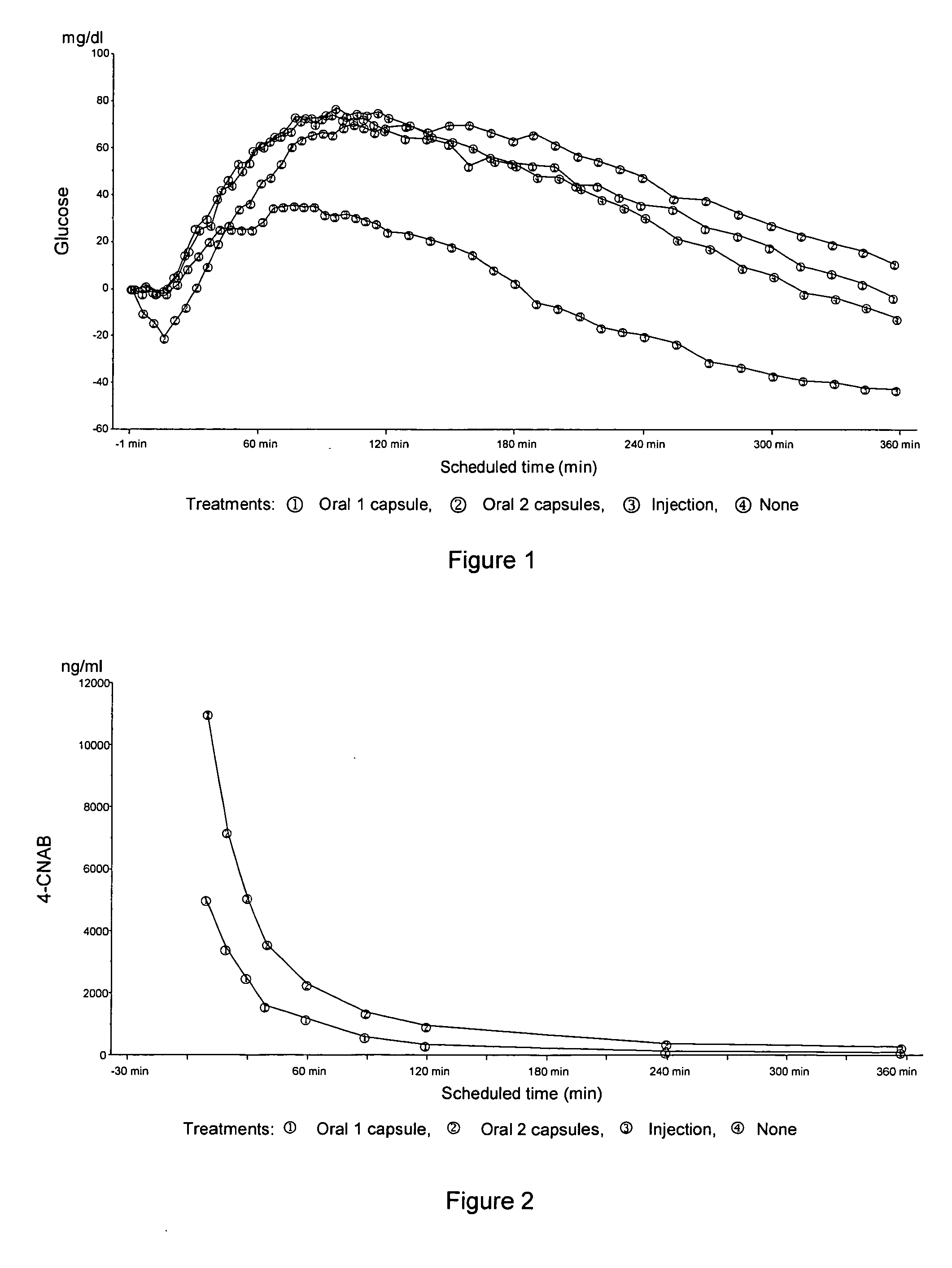
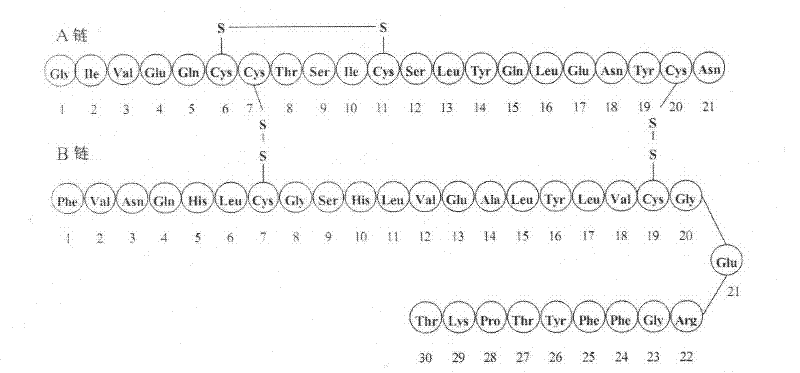
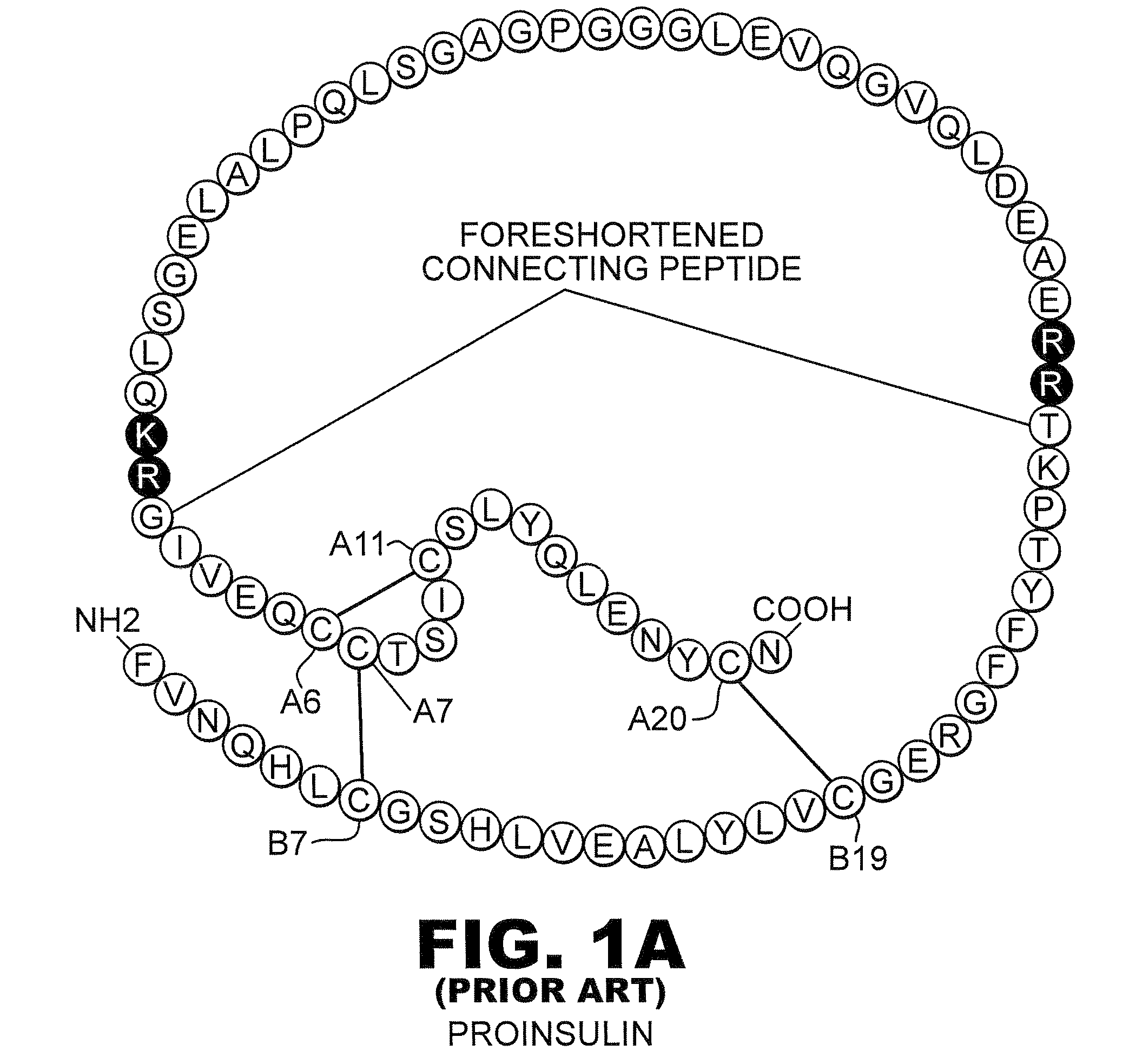
Rapid acting insulin is typically an analogue insulin. Rapid acting insulins are usually taken just before or with a meal. They act very quickly to minimise the rise in blood sugar which follows eating.
Remedy for Diabetes
ActiveUS20080319077A1Good secretion effectGood hypoglycemic effectBiocideMetabolism disorderAgonistDiabetic patient
The present invention relates to a therapeutic agent for diabetes with sulfonylurea secondary failure, which contains a GPR40 agonist. According to the present invention, a therapeutic agent for diabetes with sulfonylurea secondary failure that affords a superior insulin secretion effect and a superior hypoglycemic effect even in diabetic patients for whom a sulfonylurea compound or a fast-acting insulin secretagogue fails to provide an insulin secretion effect and therefore, fails to provide a sufficient hypoglycemic effect can be provided.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Method of treating diabetes type 2 by metformin and an ultrarapid acting insulin
Disclosed herein are improved methods of treating hyperglycemia with a combination of an ultrarapid acting insulin and insulin glargine comprising prandial administration of the ultrarapid insulin, and administration of a first dose of insulin glargine within 6 hours of waking for a day.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
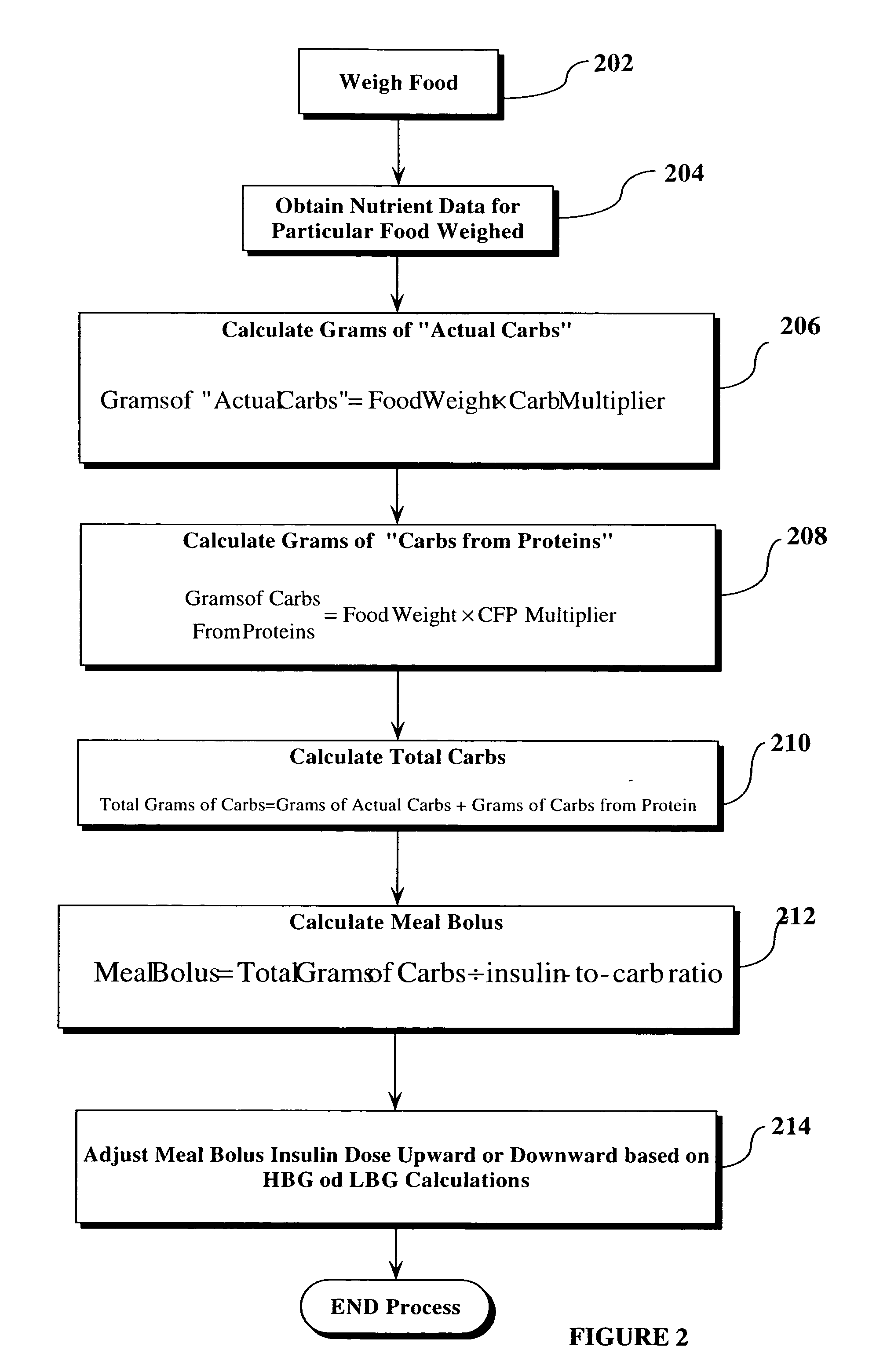
Method, system, and computer program for performing carbohydrate/insulin calculation based upon food weight
InactiveUS20050187749A1Computation using non-contact making devicesAnalogue computers for chemical processesAdditive ingredientElectron
A technique is disclosed by which a weight scale, having electronic output, is couplable to a processing device such as a computer, and preferably, a hand-held computer, PDA, cell phone or the like. The processing device is configured to receive weight inputs from the weight scale and identification information of the food or food ingredients being weighed, and then convert the gram weight of the food into grams of carbohydrate and protein for that food. For diabetes applications, the process also converts the carbohydrate and protein information into rapid-acting insulin dosages which can then be used to determine manually the amount of insulin to be dosed to the person with diabetes. In a preferred embodiment, the calculated insulin dosages information is automatically provided to a insulin pump or other automatic means of dosing insulin to a patient to thereby automatically dose the patient properly.
Owner:SINGLEY JUDY
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS20080039368A1Increase speedReduce the amount of solutionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
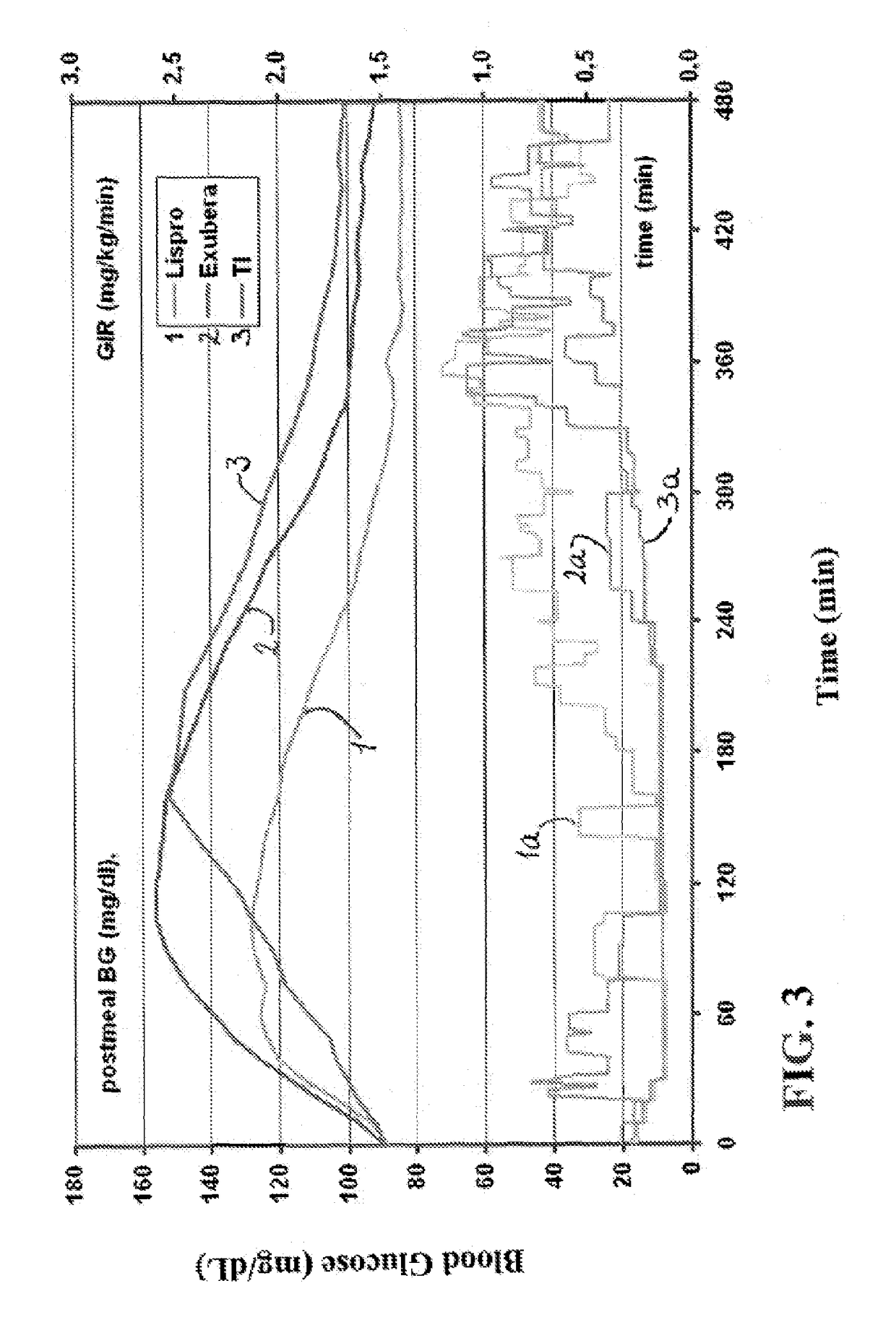
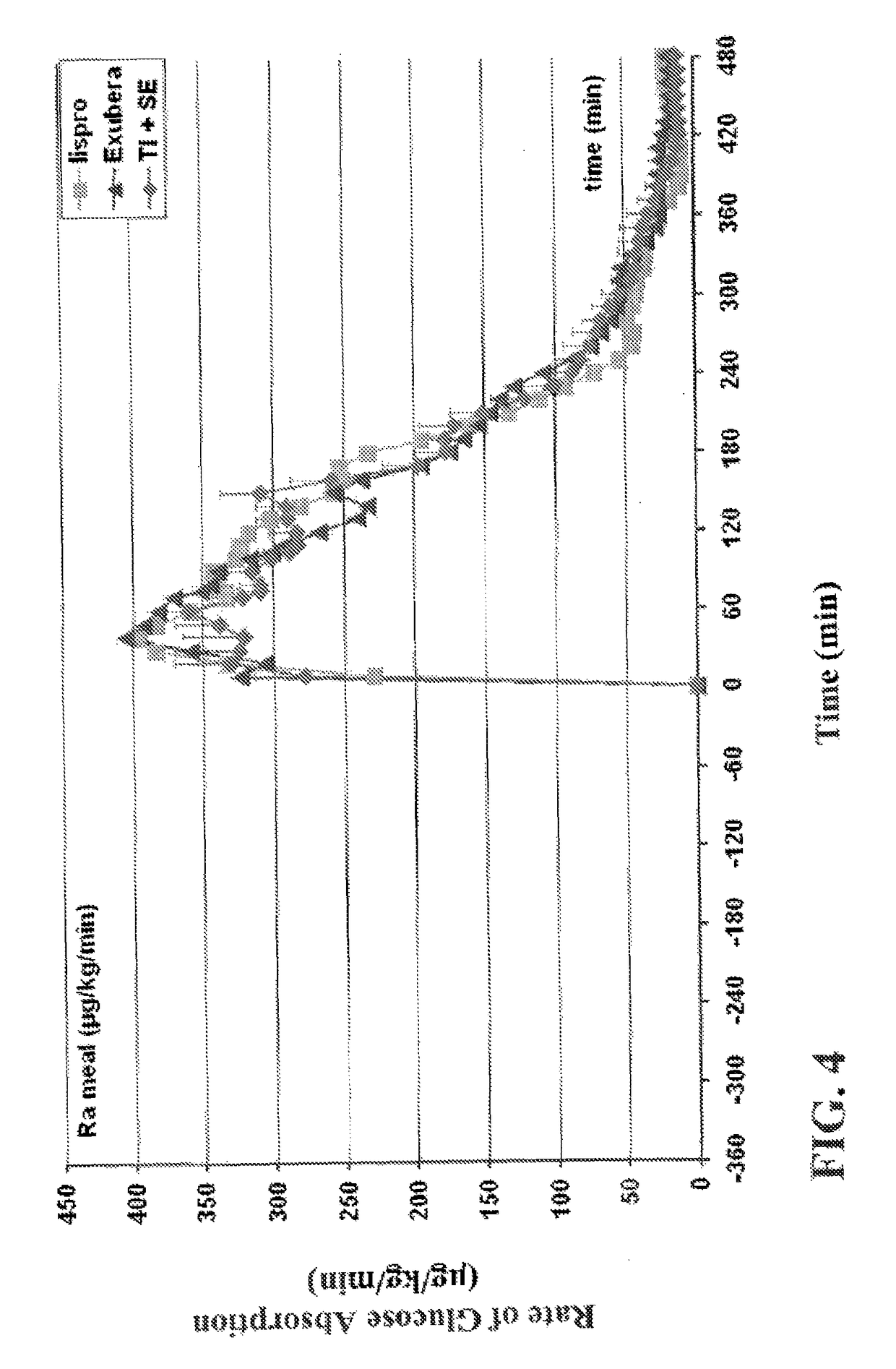
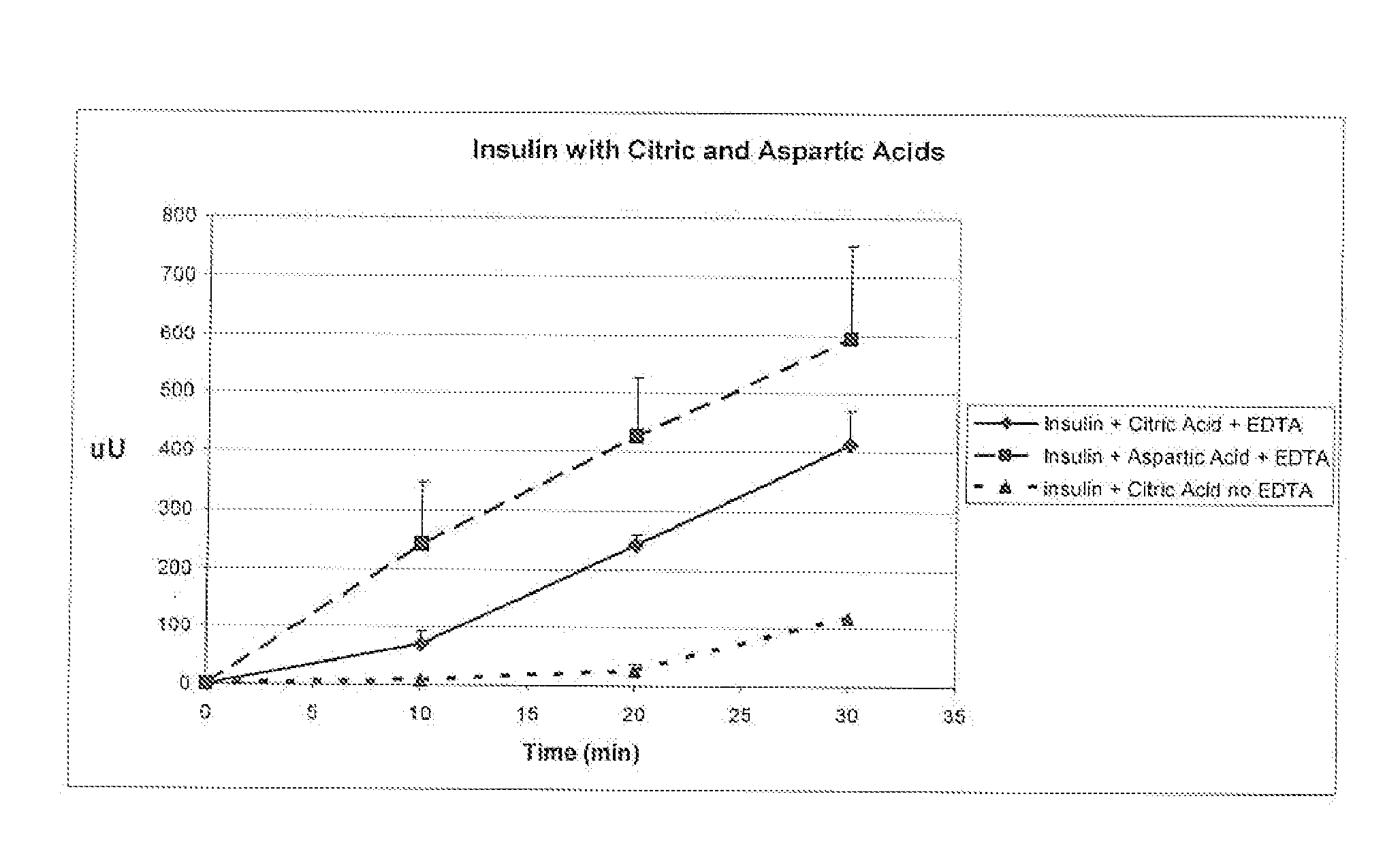
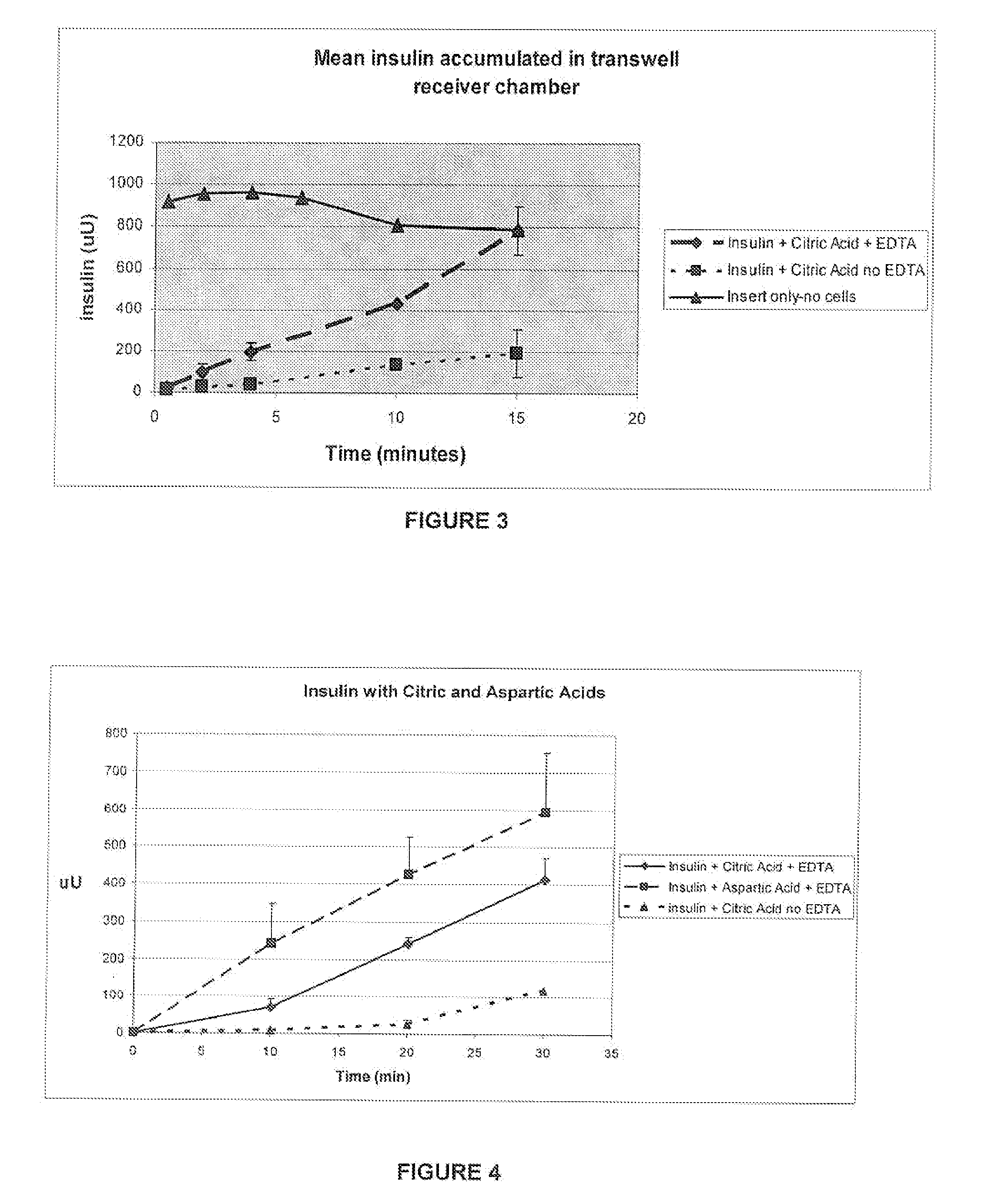
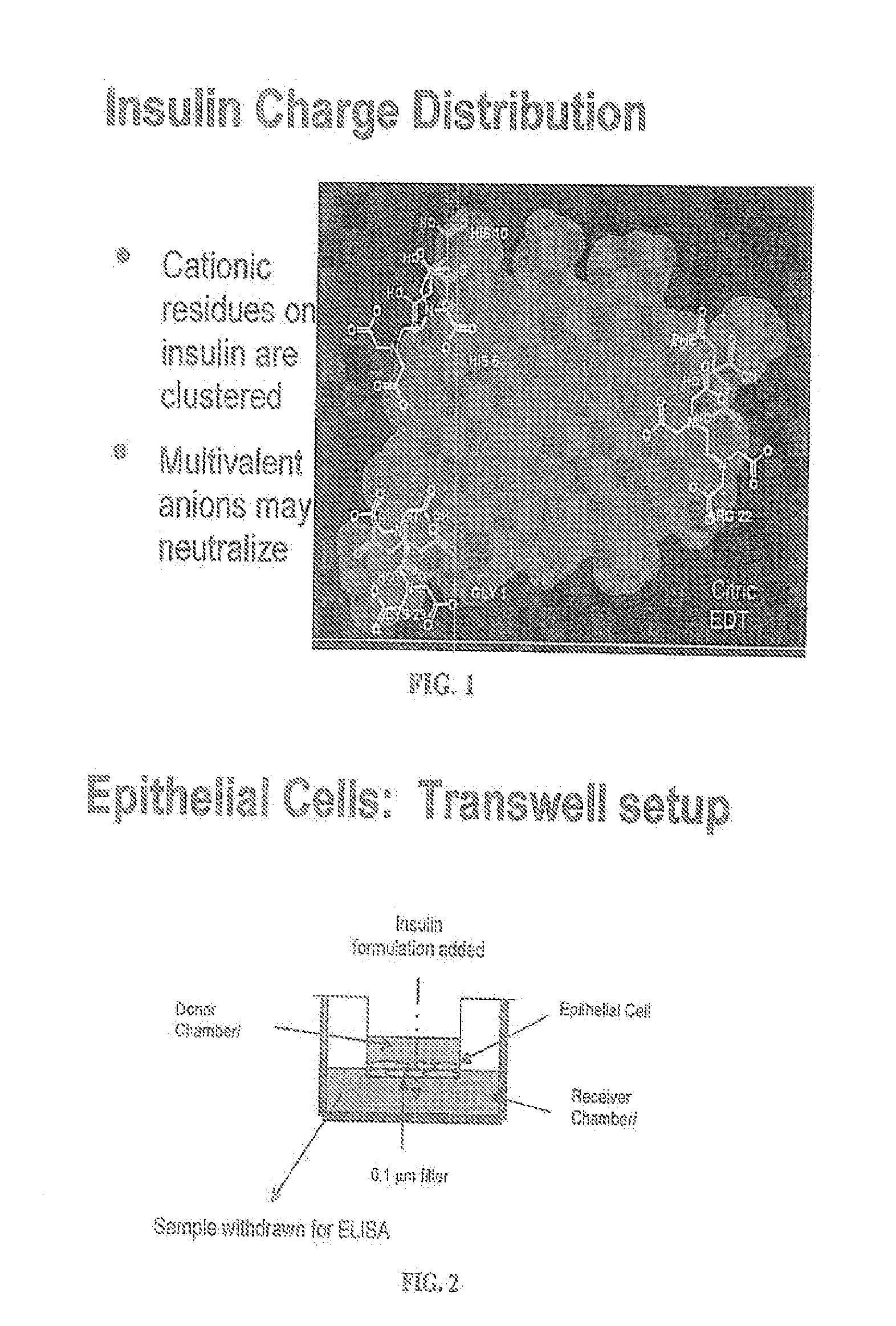
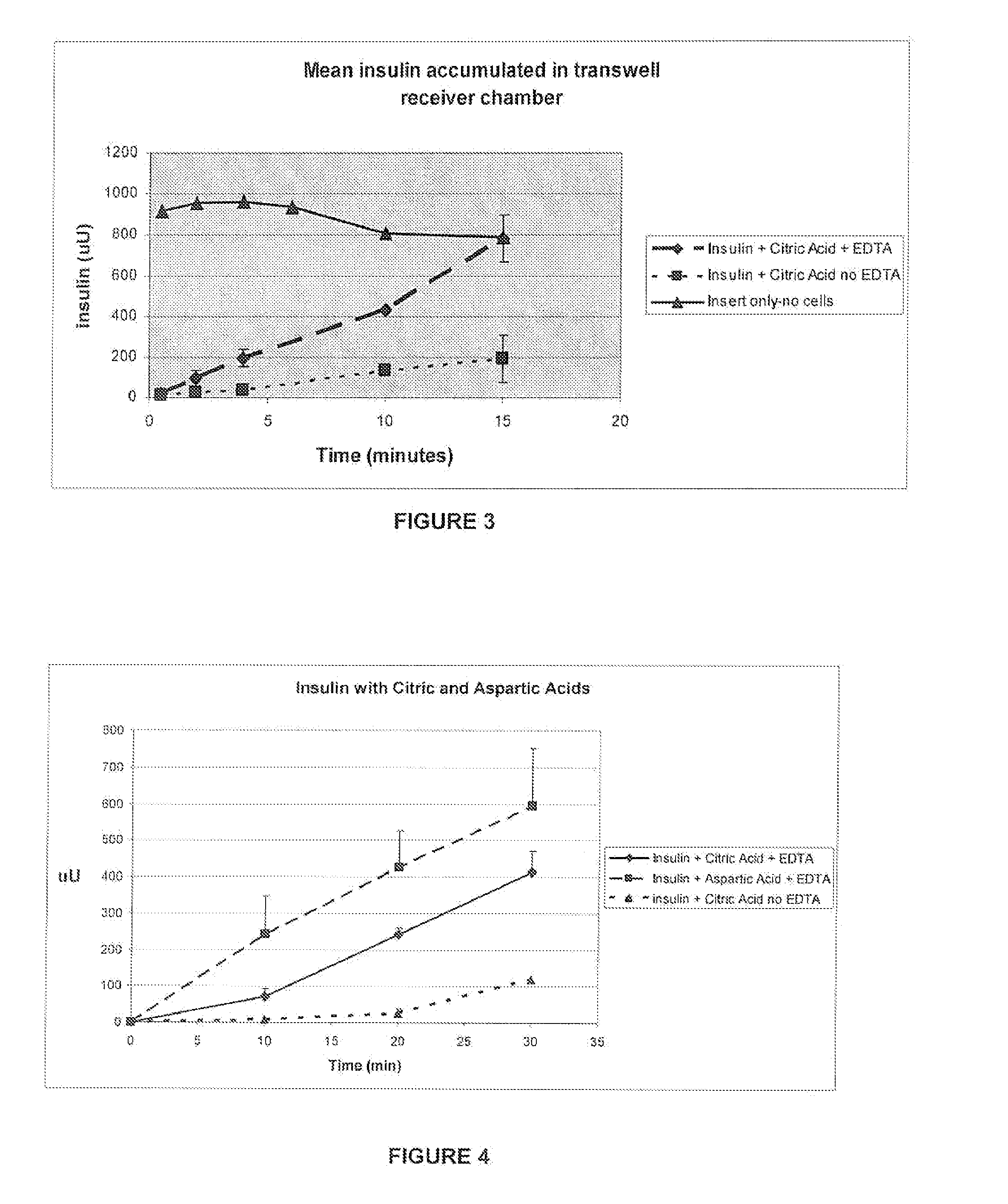
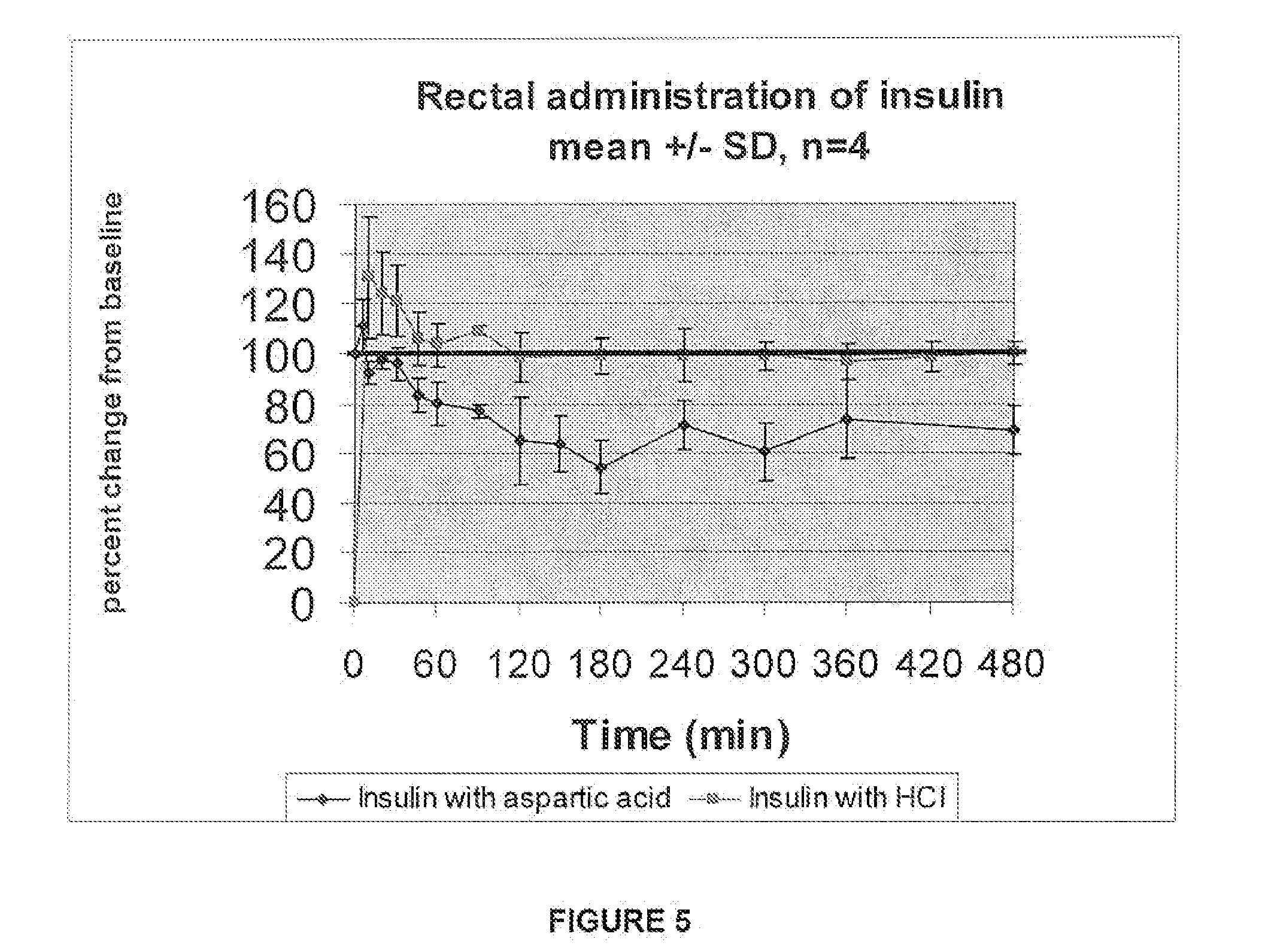
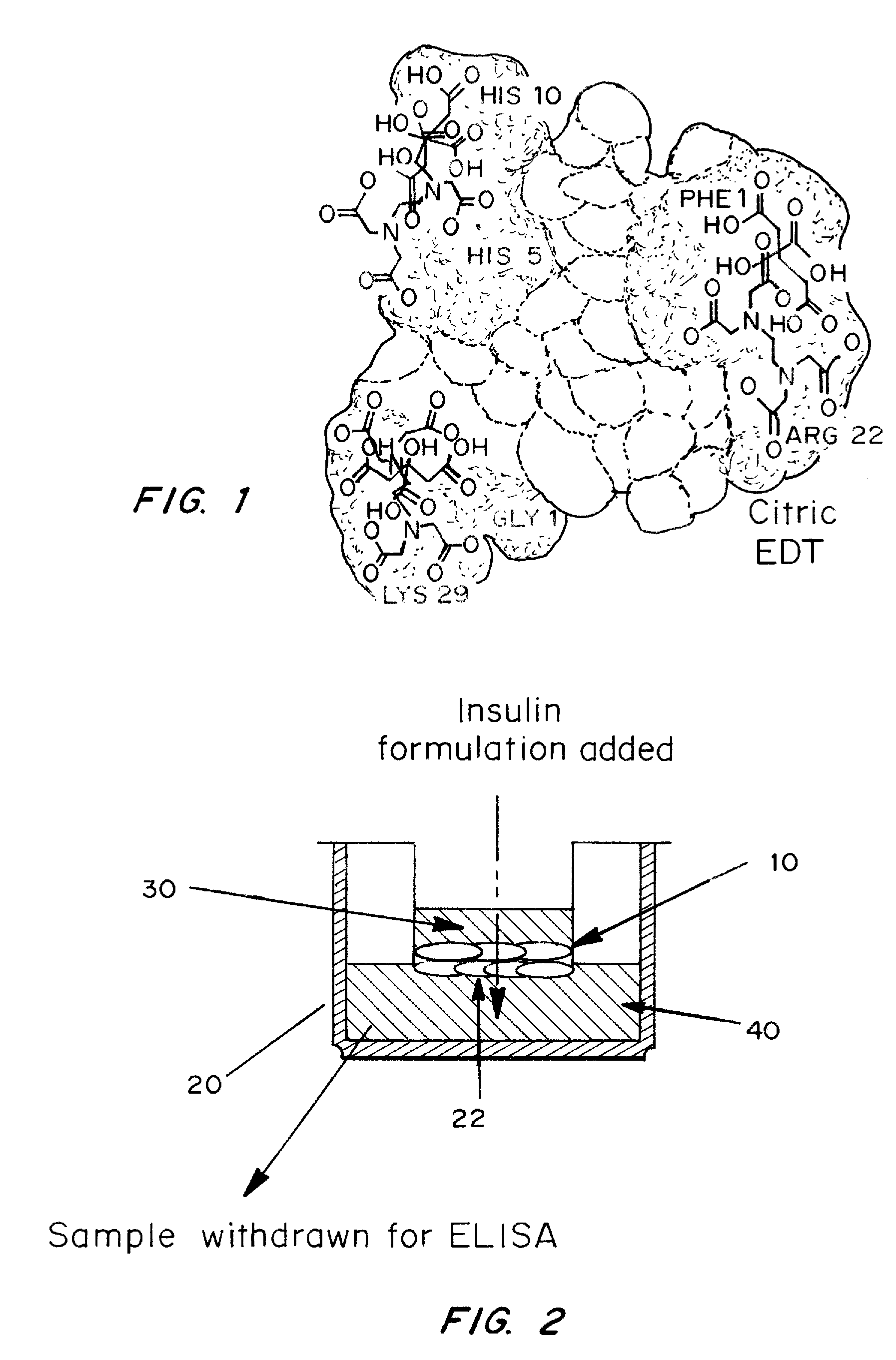
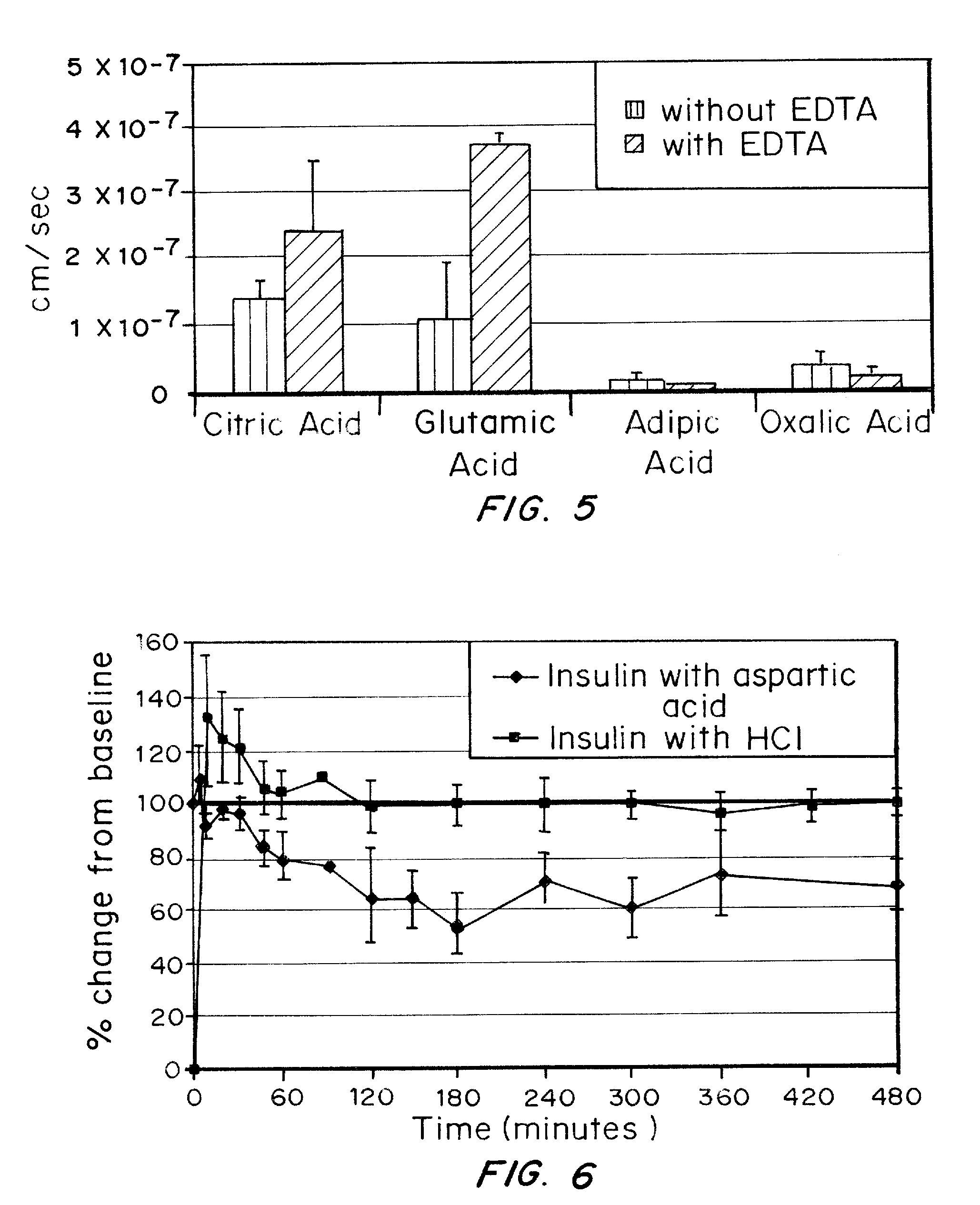
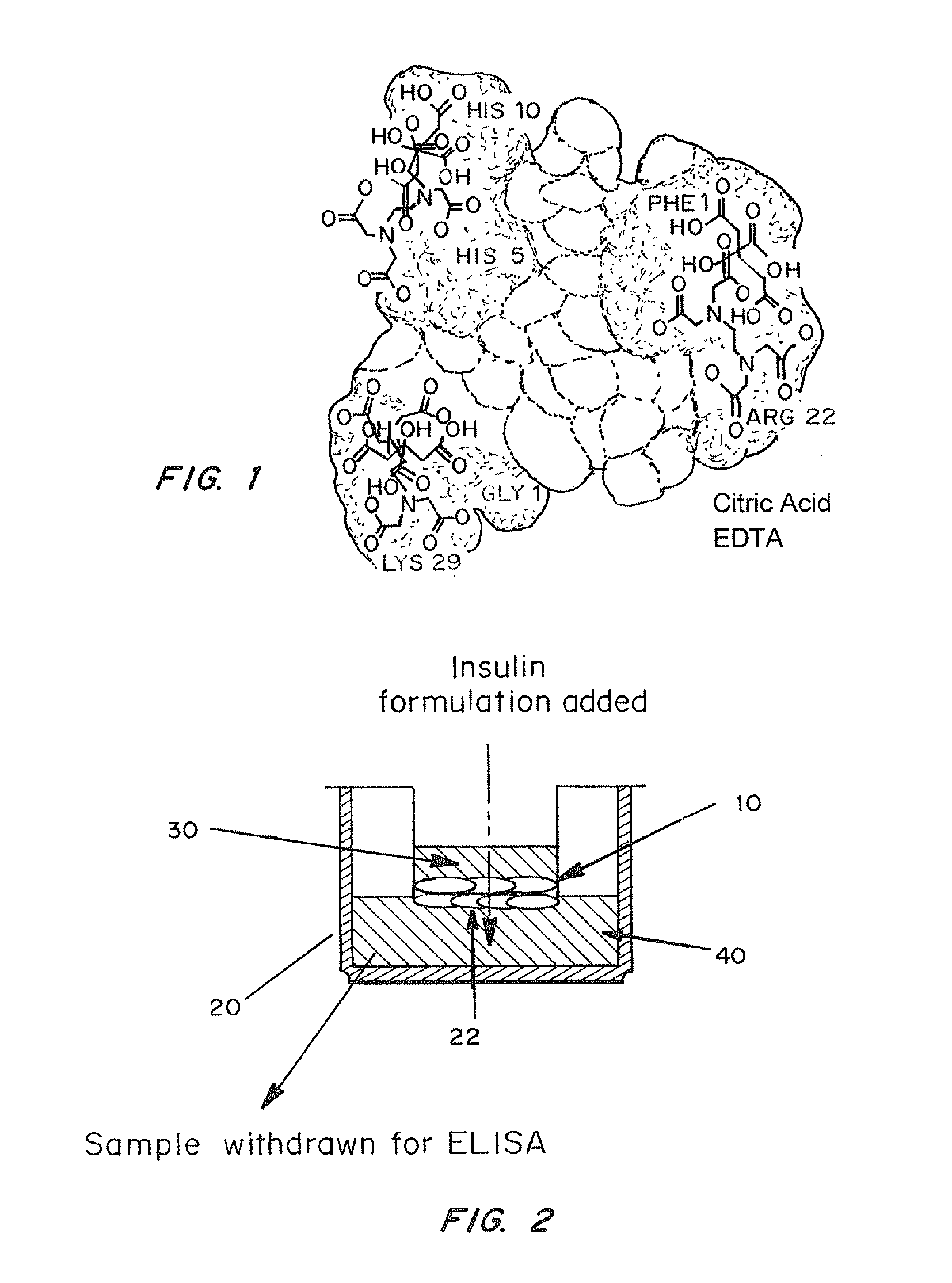
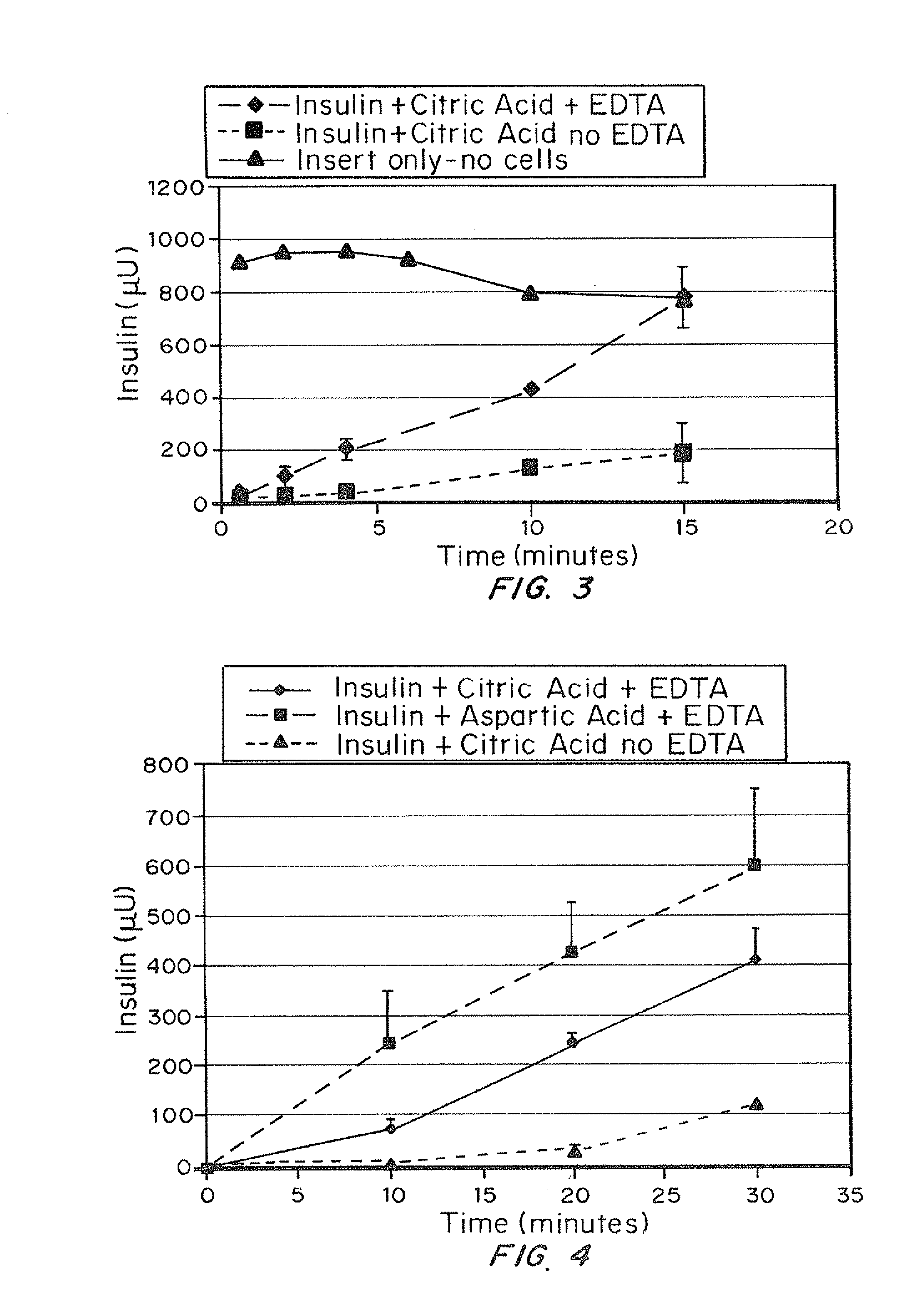
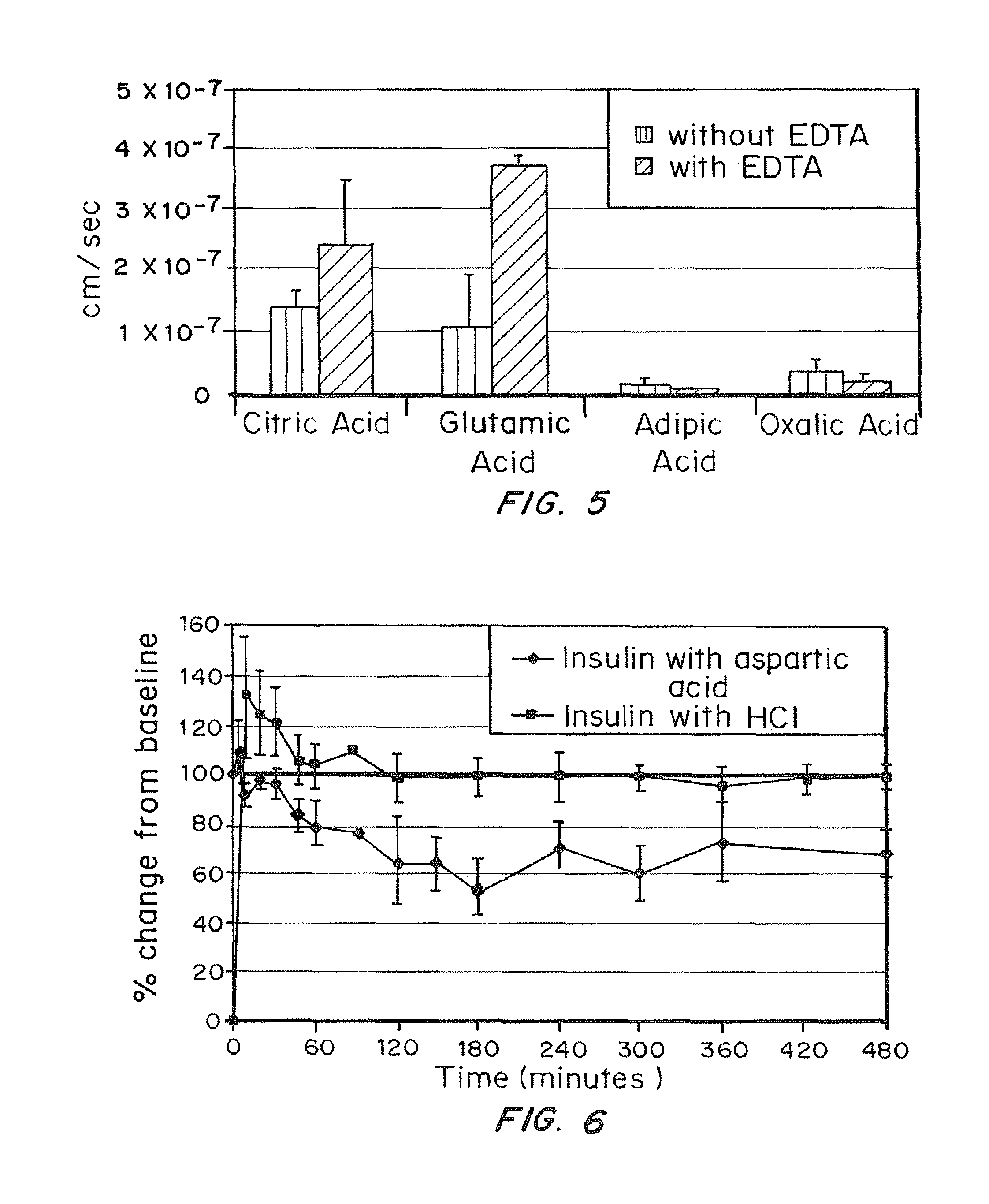
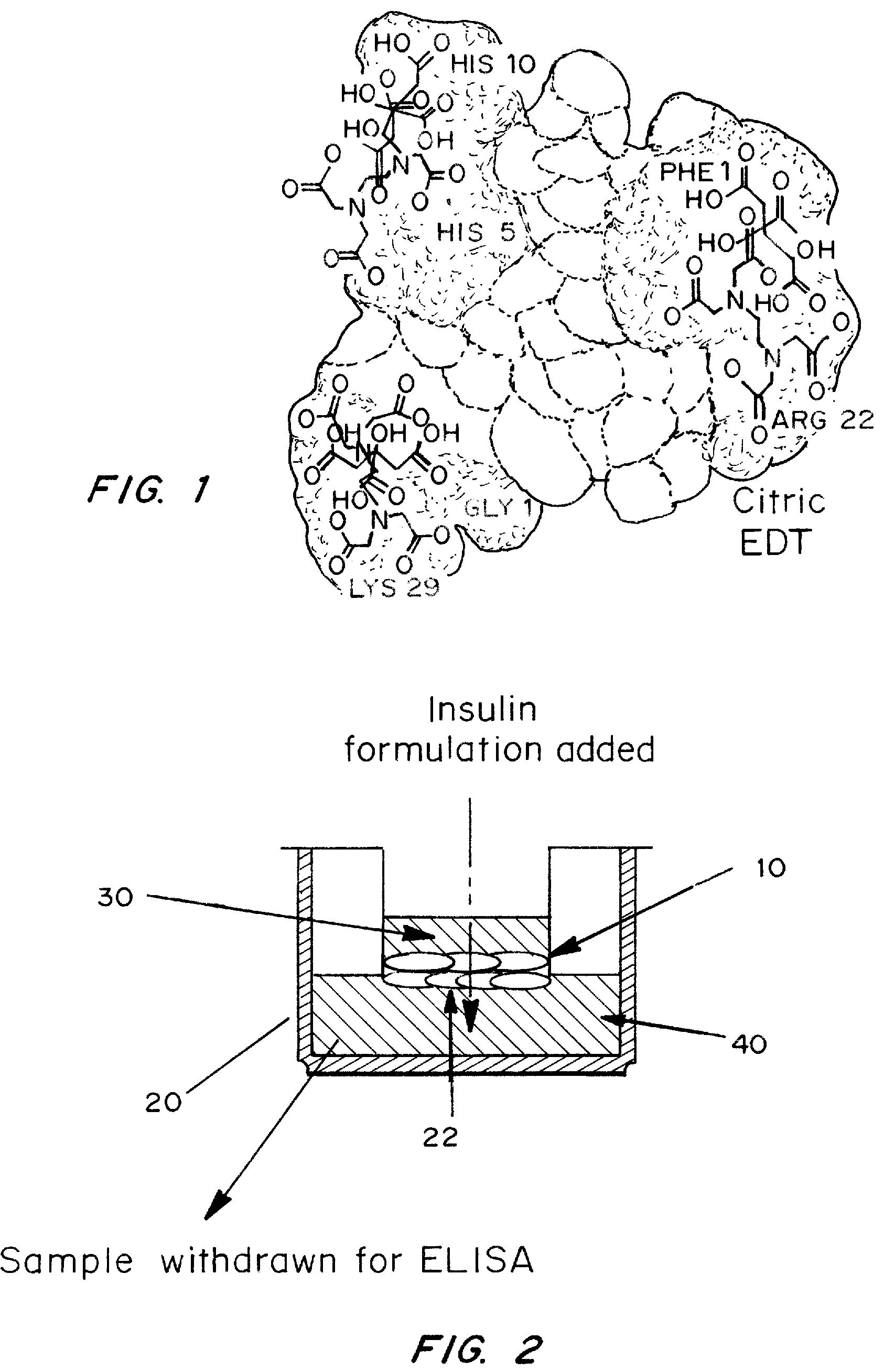
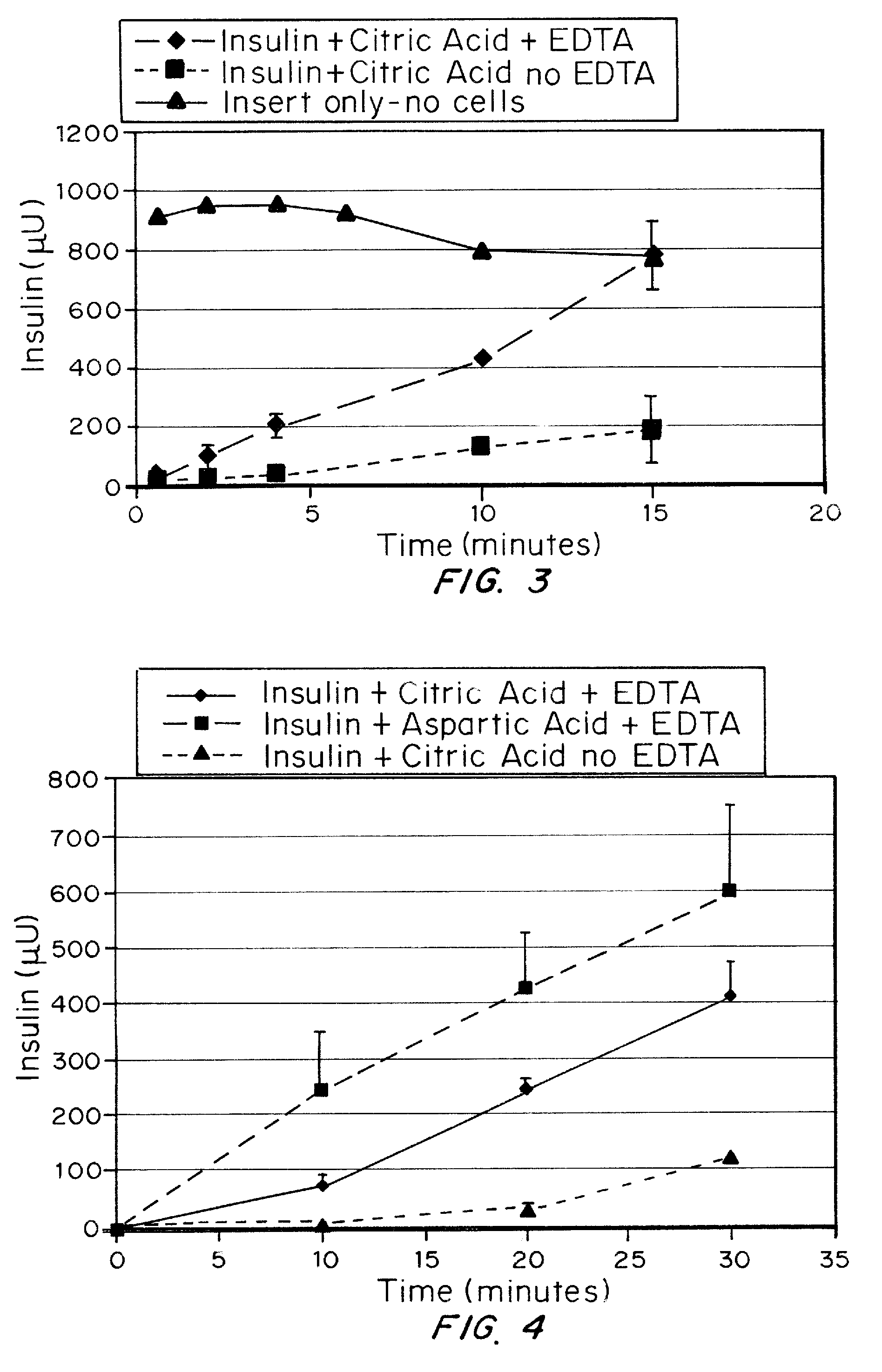
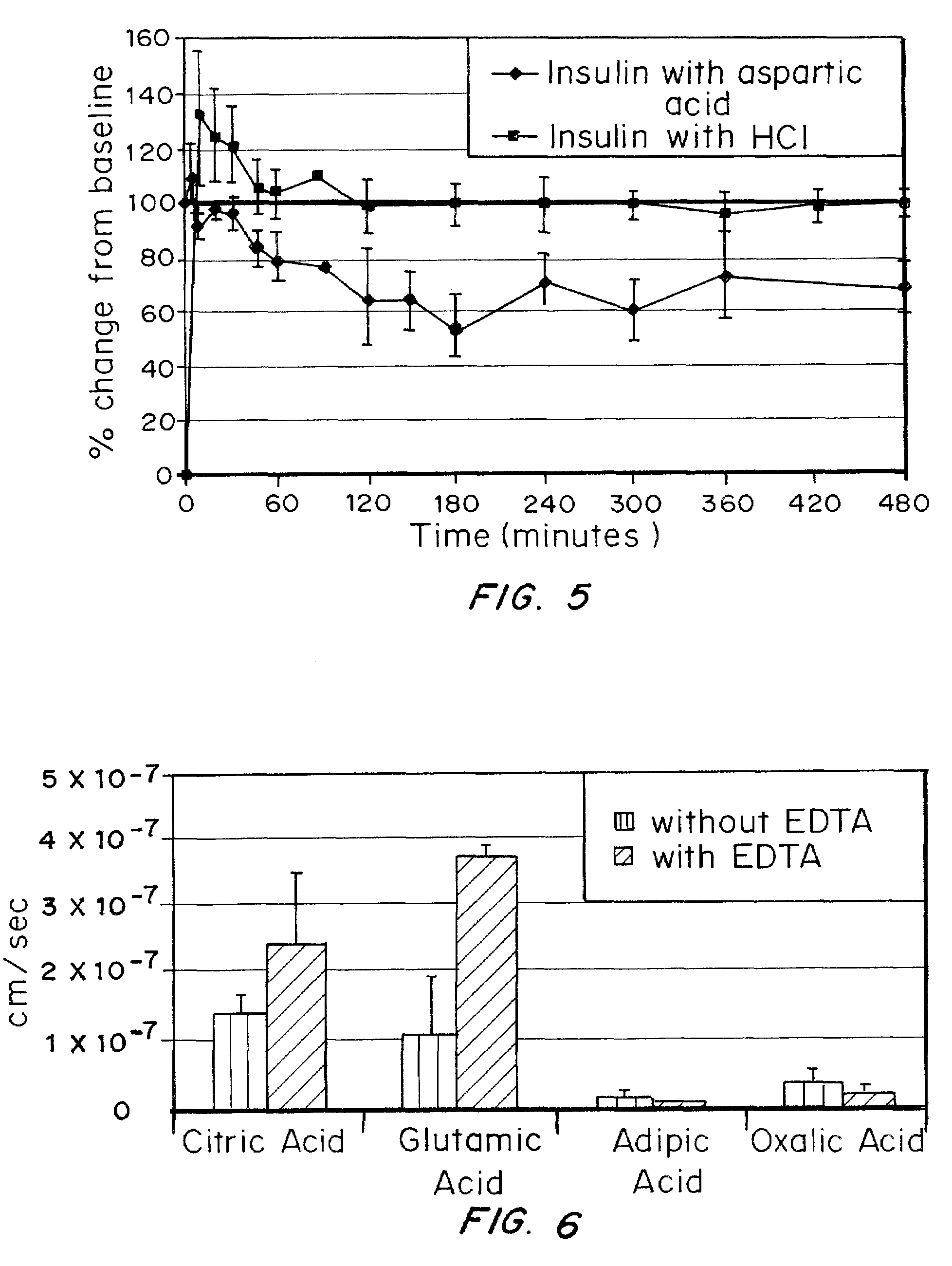
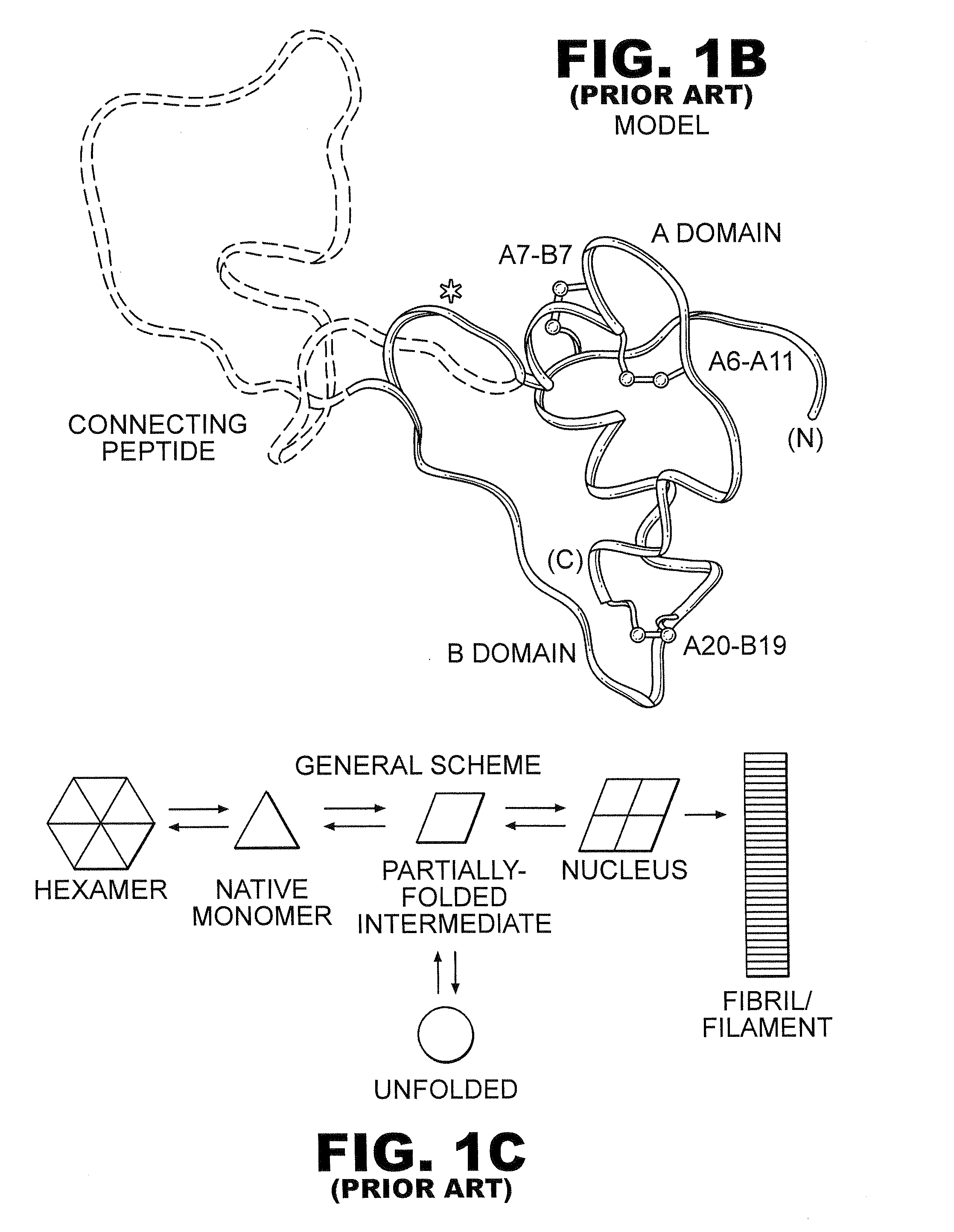
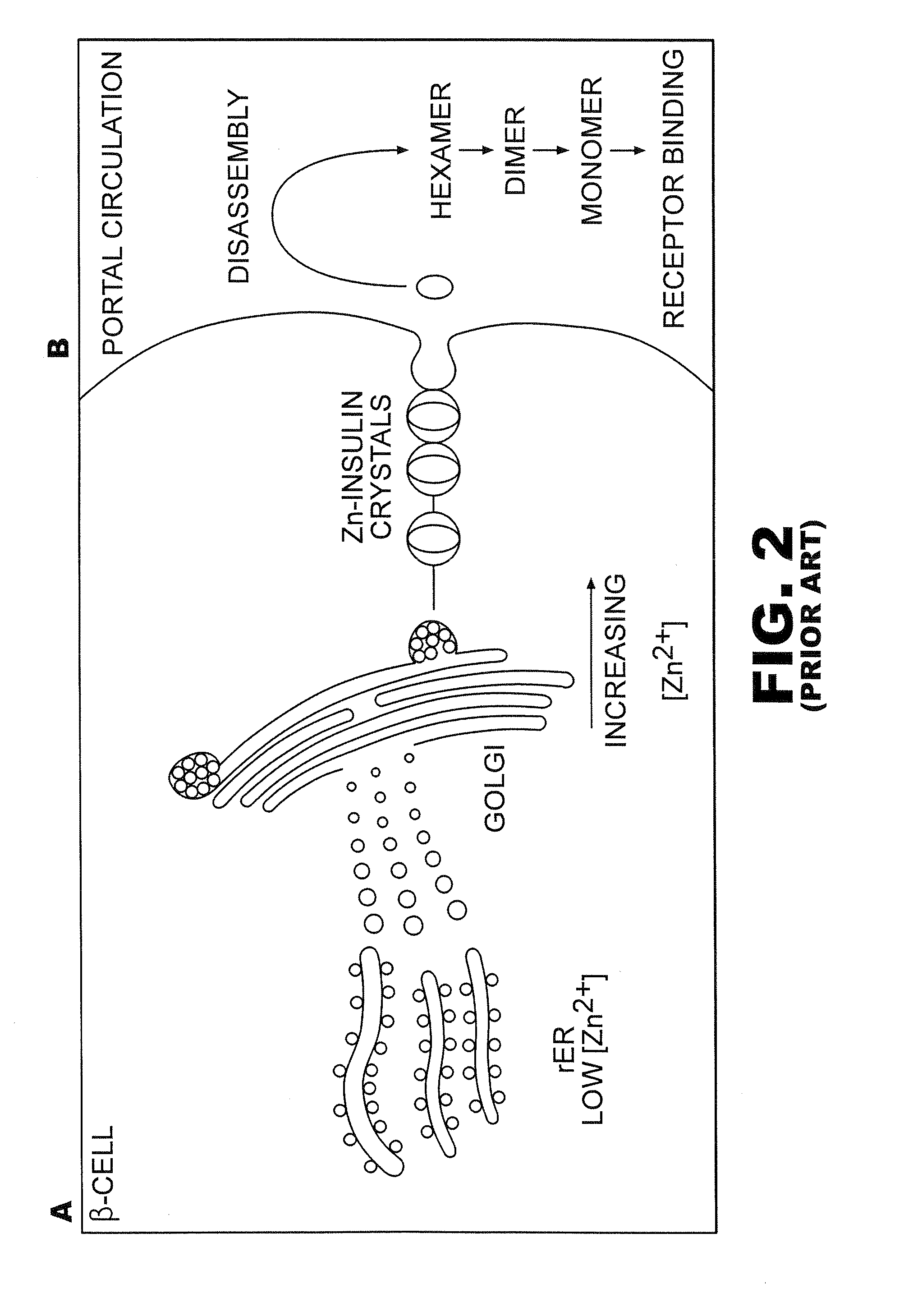
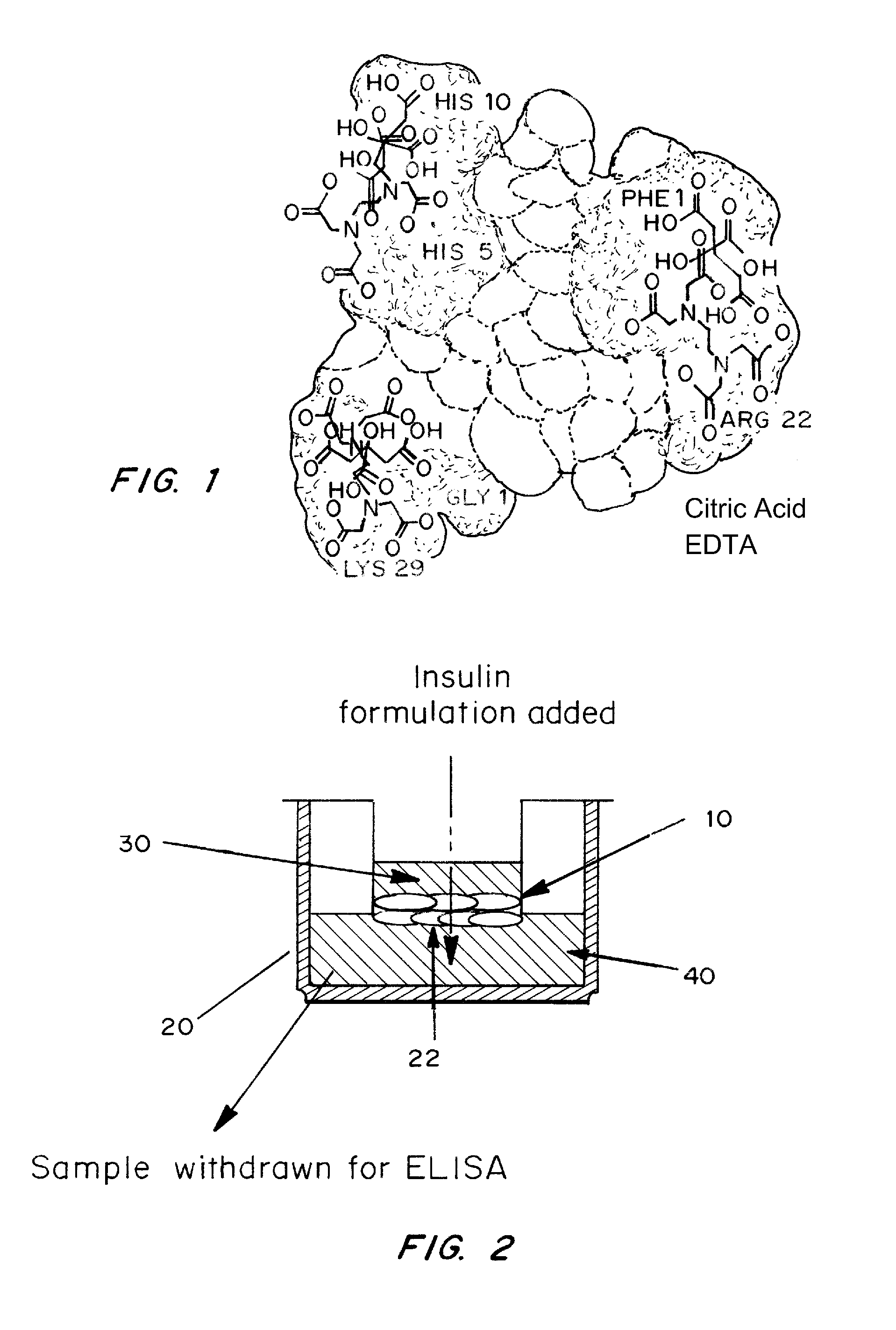
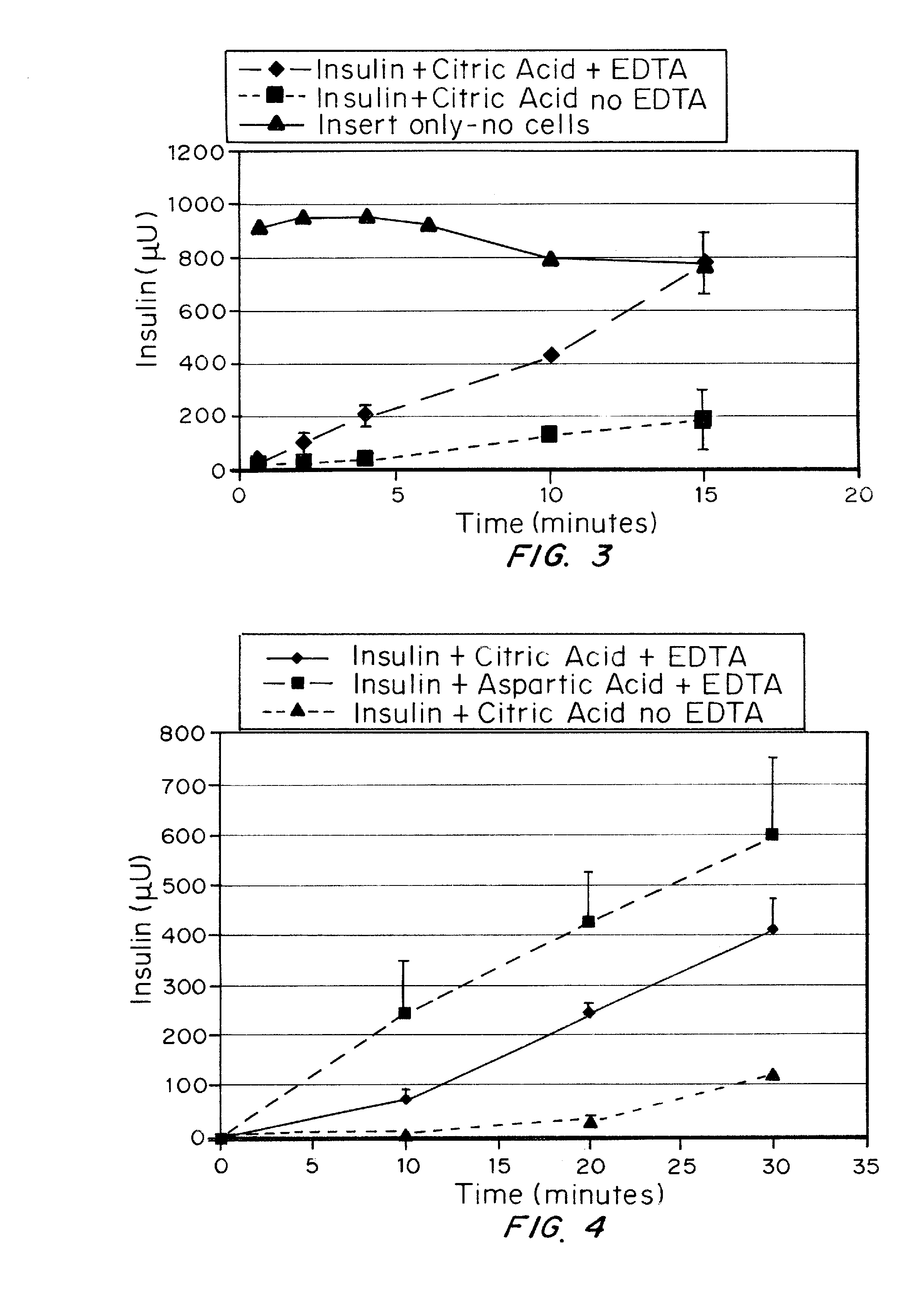
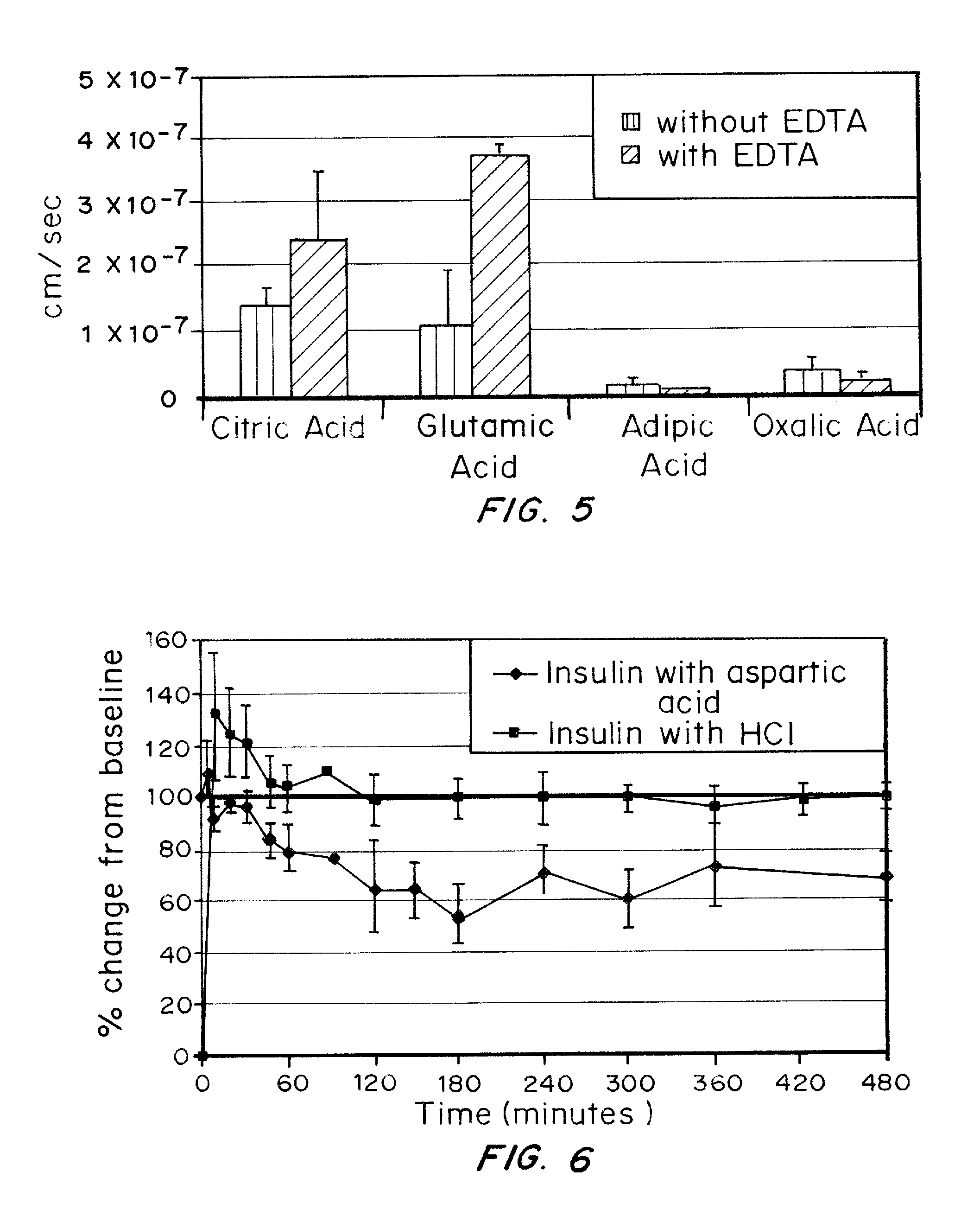
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day. Experiments have been performed to demonstrate, the importance of the addition of specific acids to hexameric insulin to enhance speed and amount of absorption and preserve bioactivity following dissociation into the monomeric form by addition of a chelator such as EDTA. As shown by the examples, the preferred acids are aspartic, maleic, succinic, glutamic and citric acid. These are added in addition to a chelator, preferably ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The results show that the citric acid formulation was more effective at dropping the blood glucose rapidly than the identical rapid acting formulation prepared with HCl in swine. Charge masking by the polyacid appears to be responsible for rapid insulin absorption. EDTA was not effective when used with adipic acid, oxalic acid or HCl at hastening the absorption of insulin. These results confirm the results seen in clinical subjects and patients with diabetes treated with the rapid acting insulin in combination with citric acid and EDTA.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Agent for treating diabetes
InactiveUS20070072810A1Excellent insulin-secretingGood hypoglycemic effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDipeptidyl peptidaseDipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitors
An agent for treating diabetes with sulfonylurea secondary failure which comprises a dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor. The agent of the present invention is an agent for treating diabetes with sulfonylurea secondary failure showing excellent insulin-secreting and hypoglycemic effects on even diabetic patients on whom a sulfonylurea compound or a fast-acting insulin secretagogue has no insulin-secreting effect and therefore no sufficient hypoglycemic effect.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
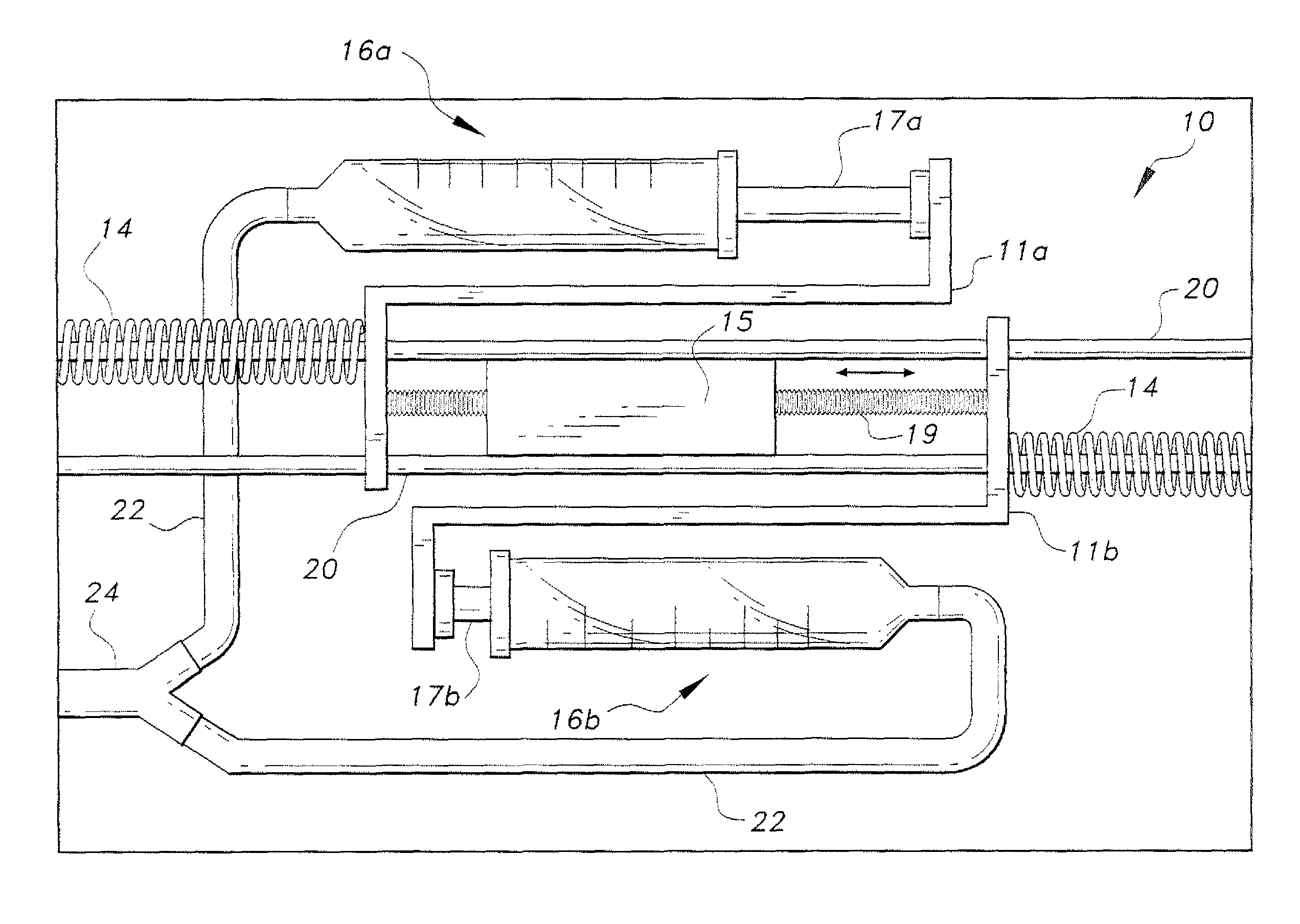
Piezoelectric dual-syringe insulin pump
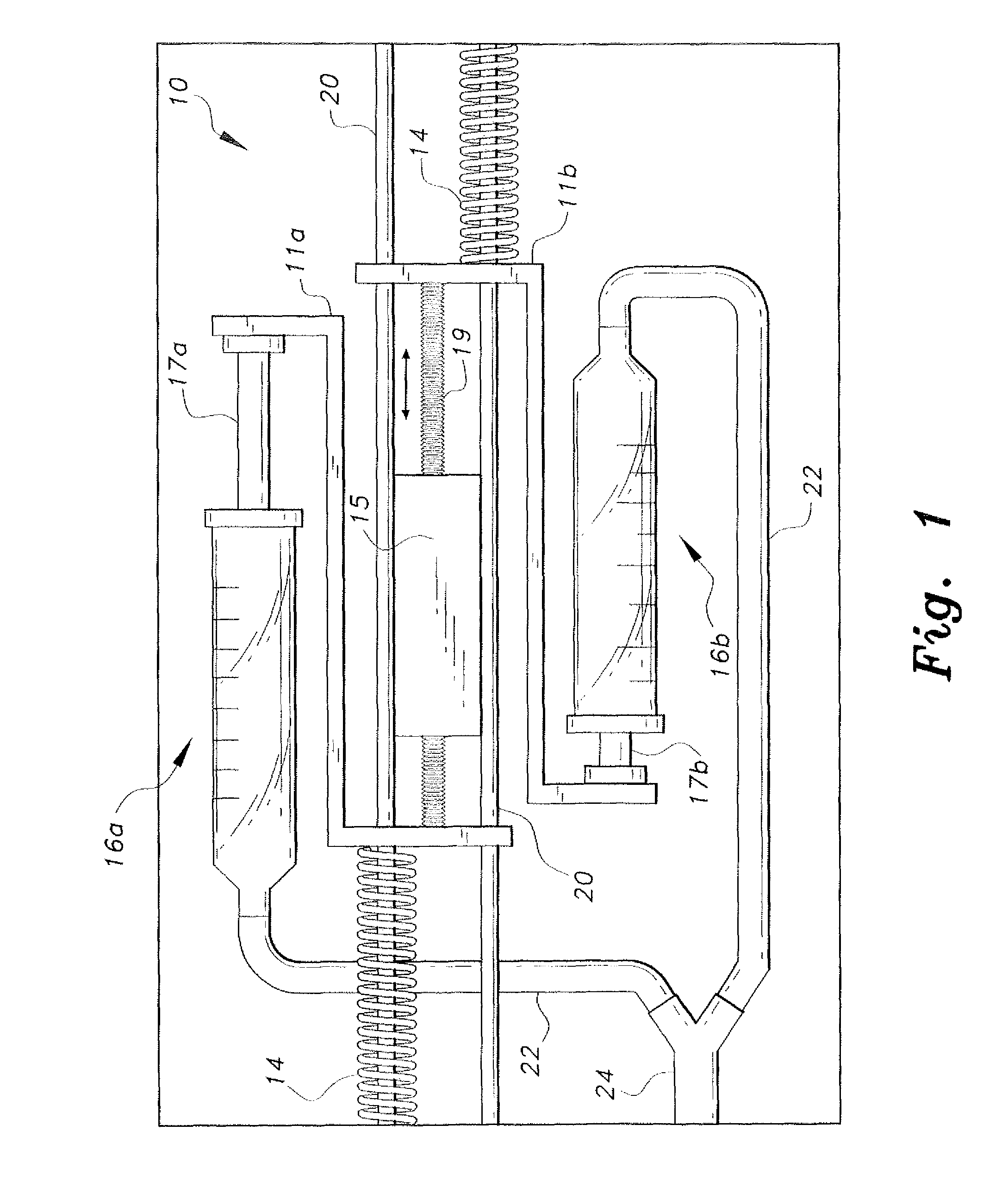
The piezoelectric dual-syringe insulin pump includes a single piezoelectric motor configured to pump insulin. The pump is controlled by a single controller. The pump uses two insulin reservoirs (in the form of two syringes), one of which is filled with a rapid-acting insulin, the other reservoir being filled with slow-acting insulin (providing the basal function). Both syringes are alternately actuated by a single PZT linear motor (particularly, a squiggle motor), depending upon polarity of the voltage applied to the motor, and feed into a common infusion line to the patient. The device includes an LCD display, audio alarm, controller, keypad, USB port, and a micro-energy harvesting circuit for recharging an on-board battery.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
Multifunctional analyte testing device and method thereof
Methods, systems and devices for detecting an analyte sample, determining an analyte concentration associated with the detected analyte sample, retrieving stored one or more dose determination information and associated analyte concentration associated with the retrieved one or more dose determination information, and determining a current dose level based at least in part on the determined analyte concentration and the retrieved prior dose determination information, where the determined current dose level includes a predetermined type of medication classification are provided. For example, dosage determination of fast or rapid acting insulin, long acting insulin, intermediate acting insulin, or one or more combinations may be provided to assist in the management of diabetes and related conditions.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Rapid Acting and Long Acting Insulin Combination Formulations
InactiveUS20080039365A1Promote absorptionAct quicklyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is decreased so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day. Experiments have been performed to demonstrate the importance of the addition of specific acids to hexameric insulin to enhance speed and amount of absorption and preserve bioactivity following dissociation into the monomeric form by addition of a chelator such as EDTA. As shown by the examples, the preferred acids are aspartic, glutamic and citric acid. These are added in addition to a chelator, preferably ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The results show that the citric acid formulation was more effective at dropping the blood glucose rapidly than the identical rapid acting formulation prepared with HCl in swine. Charge masking by the polyacid appears to be responsible for rapid insulin absorption. EDTA was not effective when used with adipic acid, oxalic acid or HCl at hastening the absorption of insulin. These results confirm the results seen in clinical subjects and patients with diabetes treated with the rapid acting insulin in combination with citric acid and EDTA.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS7718609B2Increase speedReduce the amount of solutionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed in which the pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS8084420B2Short durationImprove blood sugar controlPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastInsulin injection
An injectable formulation containing a rapid acting insulin and a long acting insulin has been developed. The pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting insulin, remains soluble when they are mixed together. Preferably, the formulation is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal and basal insulin for up to 24 hours, and does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast, rapid, or very rapid acting insulin. Alternatively, by adjusting the ratio of rapid to long acting insulin, the long acting insulin may be shortened to a 12 hour formulation, and re-administered to the patient at dinner time, providing a safe and effective basal insulin level until morning. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
InactiveUS7713929B2Rapid acting insulin isPromote absorptionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed in which the pH of the rapid acting insulin is decreased so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Stabilized ultra-rapid-acting insulin formulations
InactiveUS20150273022A1Quick effectPromote absorptionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsZinc compoundsMagnesium salt
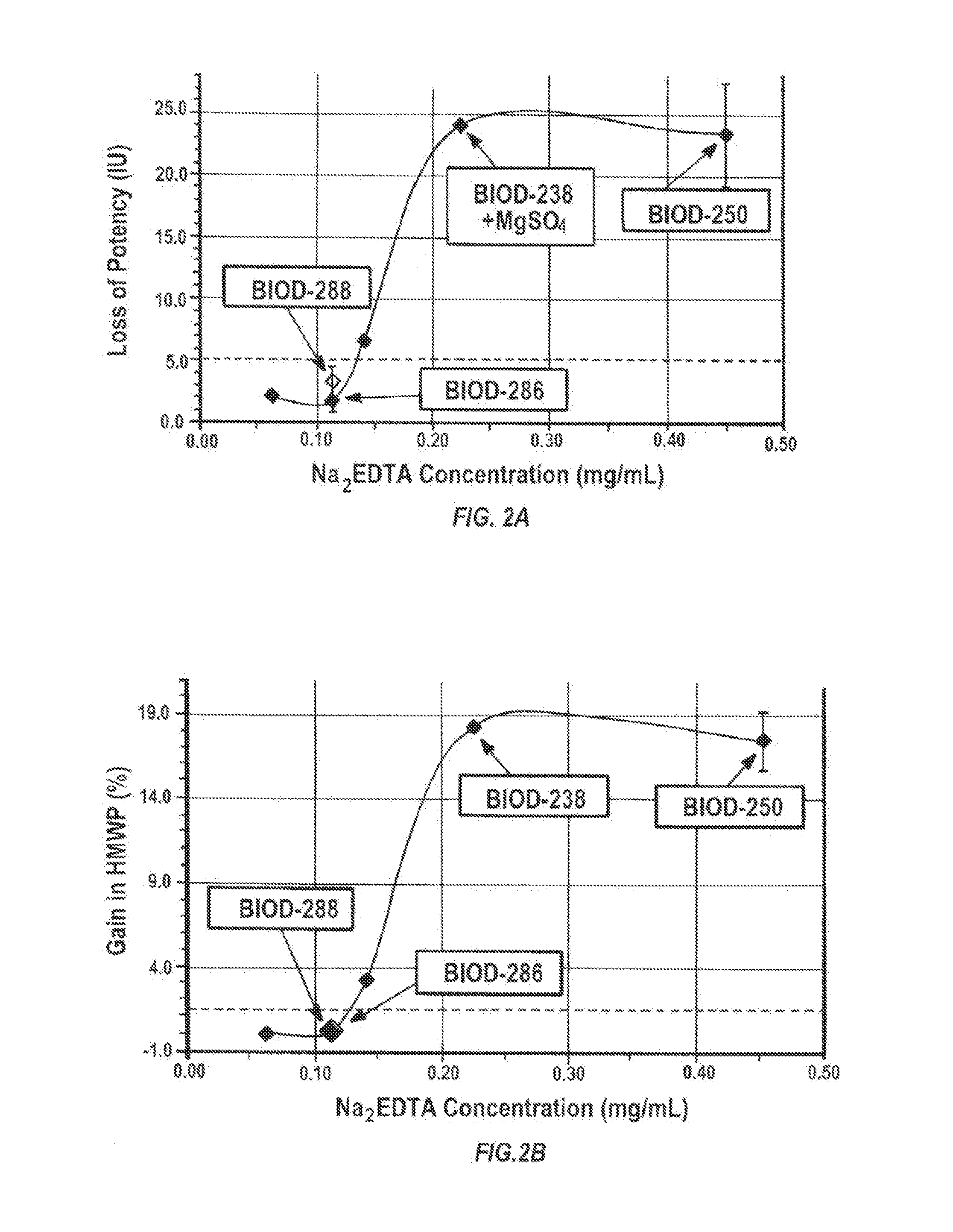
Compositions and methods for enhancing the stability of rapid acting injectable insulin formulations have been developed for subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain insulin in combination with a zinc chelator such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (“EDTA”), a dissolution / stabilization agent such as citric acid, a magnesium salt, a zinc compound and, optionally, additional excipients. New presentations include rapid acting concentrated insulin formulations and a way to enhance the absorption of commercially available rapid acting analog formulations while maintaining insulin stability.
Owner:ALBIREO PHARMA INC
Oral insulin therapies and protocol
InactiveUS20050203001A1Good treatment effectPositive therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsLate onset diabetesHypoglycemia
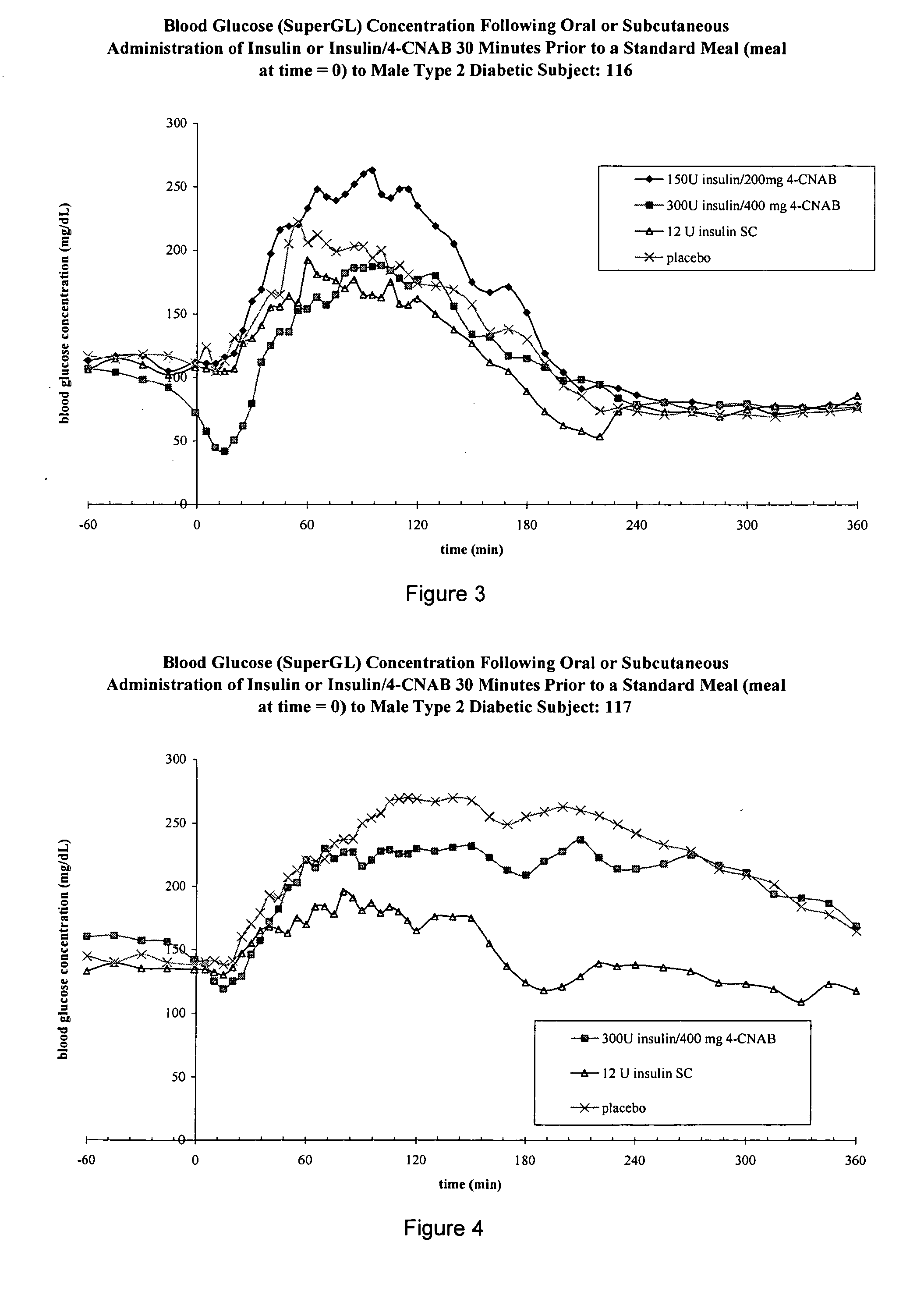
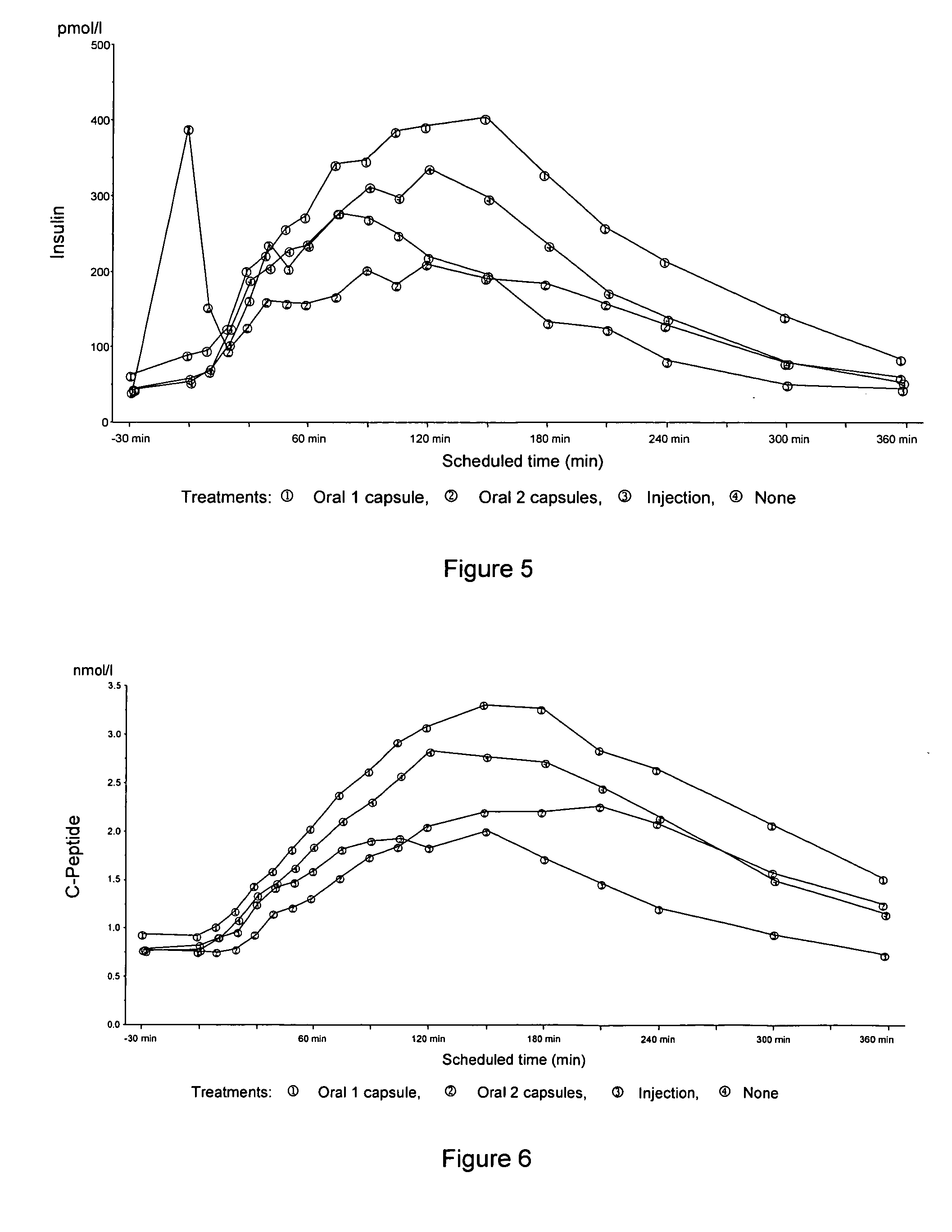
Methods for treating impaired glucose tolerance and early and late stage diabetes in mammals, for prophylactically sparing β-cell function, aiding in preventing β-cell death, preventing the onset of overt diabetes in a mammal with type 2 diabetes, treating the current level of glycemic control dysfunction of a mammal with impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes, comprising orally administering insulin and a delivery agent that facilitates insulin absorption from the gastrointestinal tract at the time of or shortly before mealtime, e.g., within about 10 minutes prior to ingestion of a meal, on a chronic basis. The methods also comprise, in addition to administering a rapid-acting insulin to provide a first insulin peak, administering a slow acting insulin to provide a second insulin peak occurring at a later time but of a longer duration. These methods achieve improved glycemic control without the risks of hypoglycemia, hyperinsulinemia and weight gain and the need for frequent blood glucose monitoring that are normally associated with insulin therapy.
Owner:EMISPHERE TECH INC
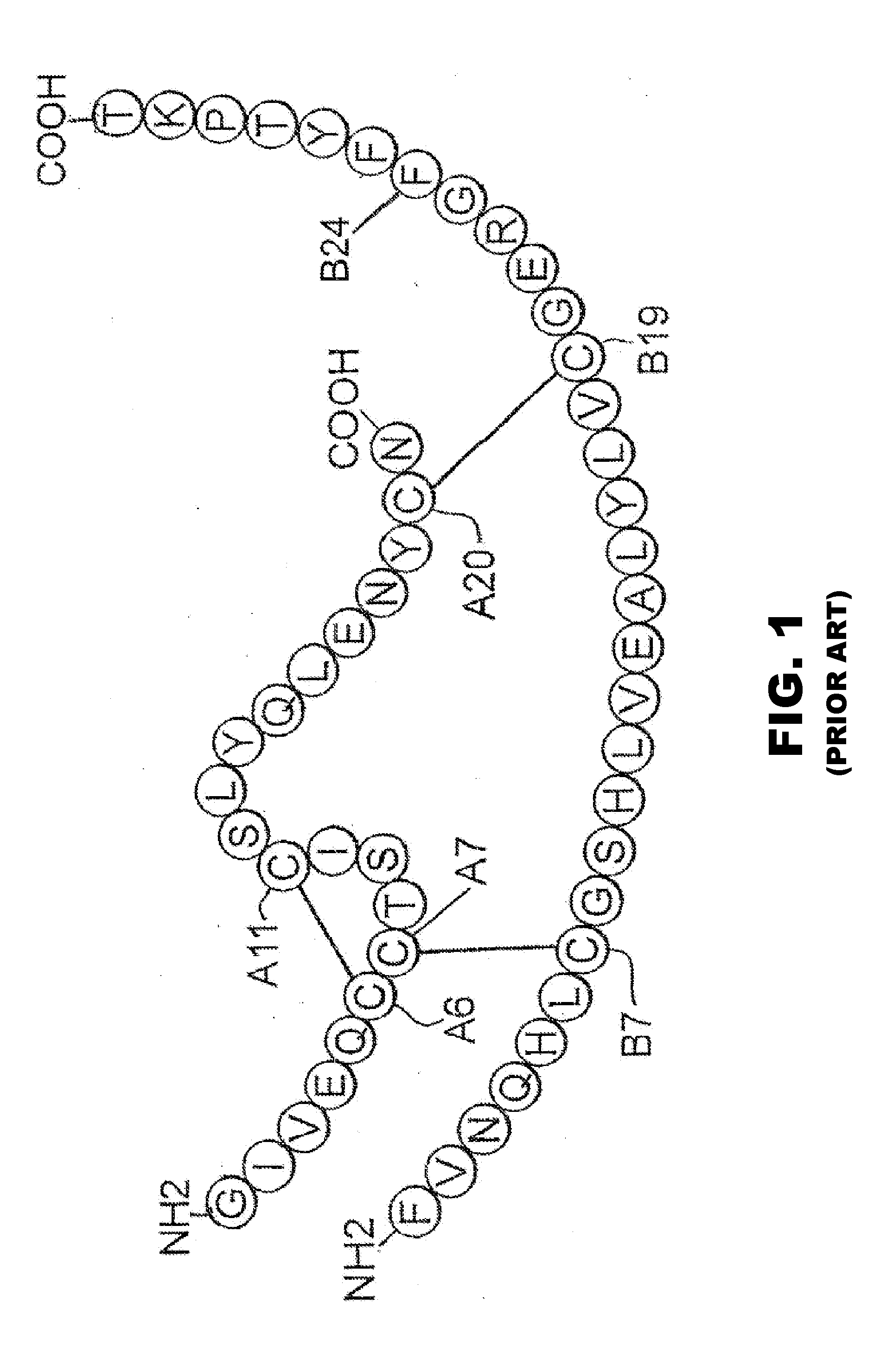
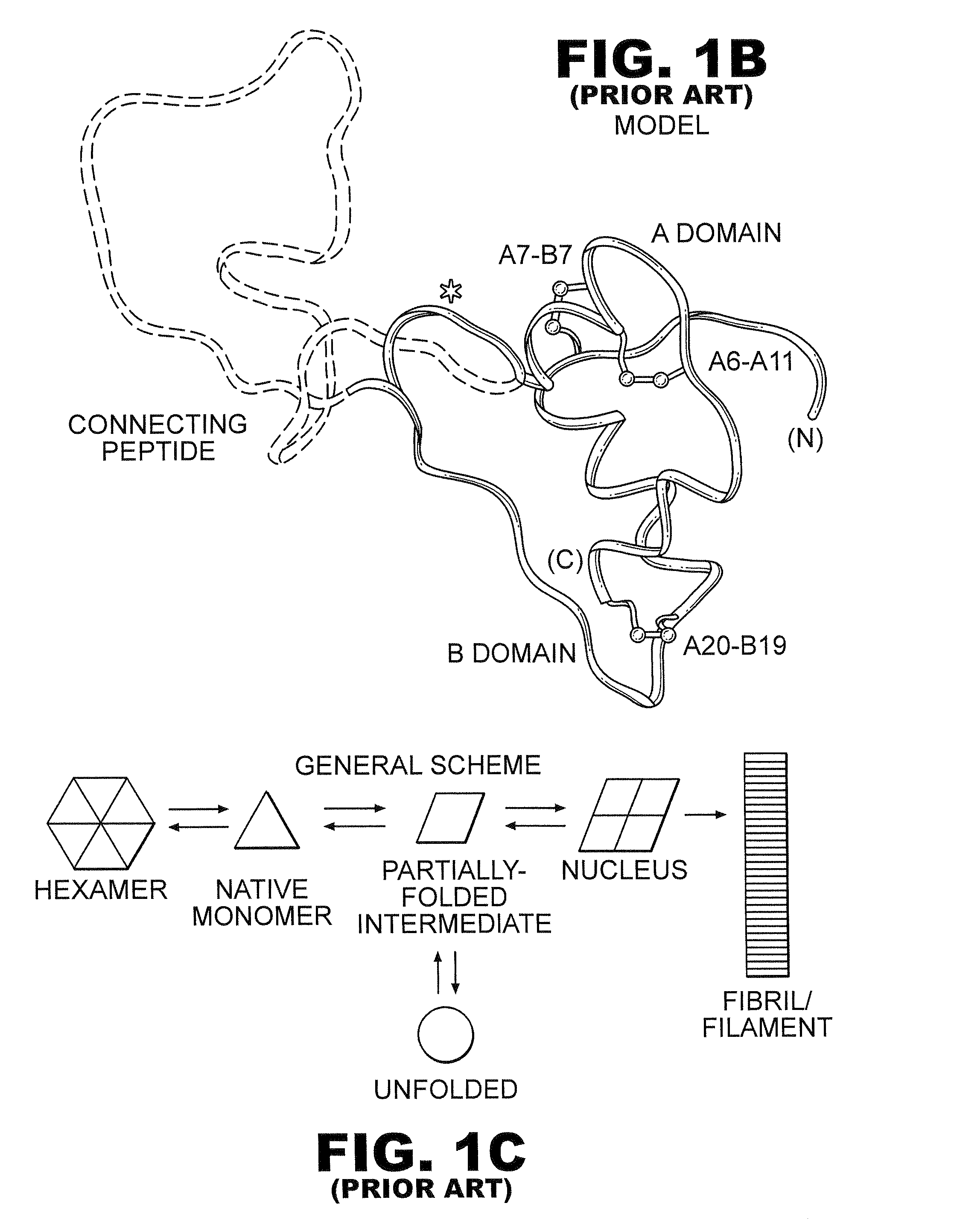
Fibrillation resistant proteins
ActiveUS20090304814A1Improve the immunityIncreased susceptibilityBiocideFungiFibrillationHistidine residue
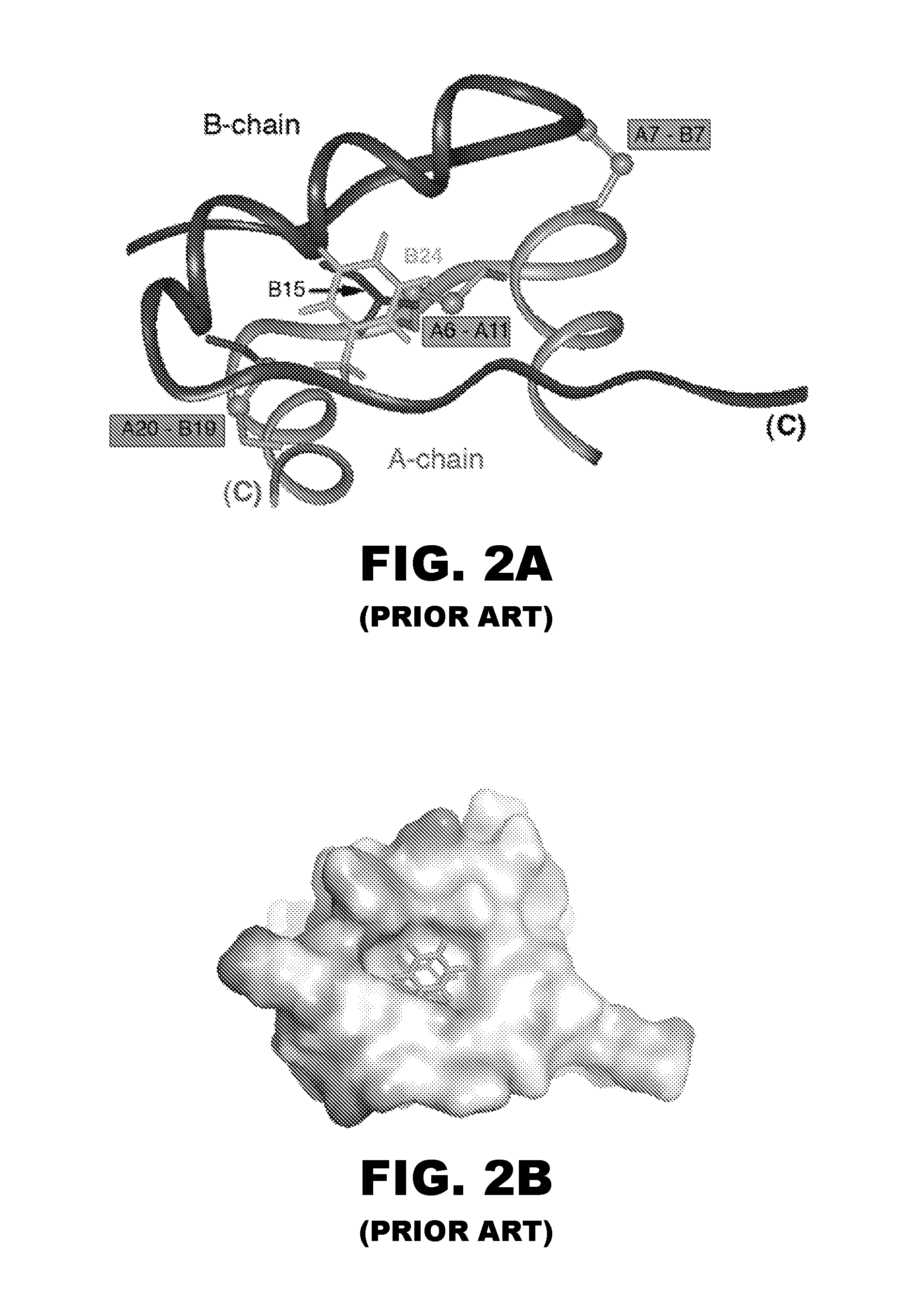
Protection of proteins against fibrillation may be afforded by introduction of certain histidine substitutions into the protein, such that a pair of histidines are present with sufficient spacing as to allow the histidines to coordinate with zinc. In the case of insulin, introduction of histidine residue substitutions at residues A4 and A8 together or a histidine residue substitution at residue B1, provides increased resistance to fibrillation while maintaining at least a majority of the activity of the insulin analogue. Introduction of a histidine residue substitution at residue A8 restores at least a portion of fibrillation resistance that may have been harmed by substitutions present on the B-chain such as those present in fast-acting insulins. Proteins protected by such histidine substitutions may be used to provide a pharmaceutical composition. A method of treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of the pharmaceutical composition to the patient.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS20090137455A1Short durationImprove blood sugar controlPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
An injectable formulation containing a combination of a rapid acting insulin and a long acting insulin has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting insulin, e.g. insulin glargine, remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for up to 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. Alternatively, through adjustment of the ratio of rapid acting insulin to long acting insulin, the long acting insulin may be shortened to a 12 hour formulation. This rapid and long acting blend is re-administered to the patient at dinner time, providing a safe and effective basal insulin level until morning. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Rapid Acting Insulin Analogues
InactiveUS20110021423A1Promote formationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineInsulin B Chain
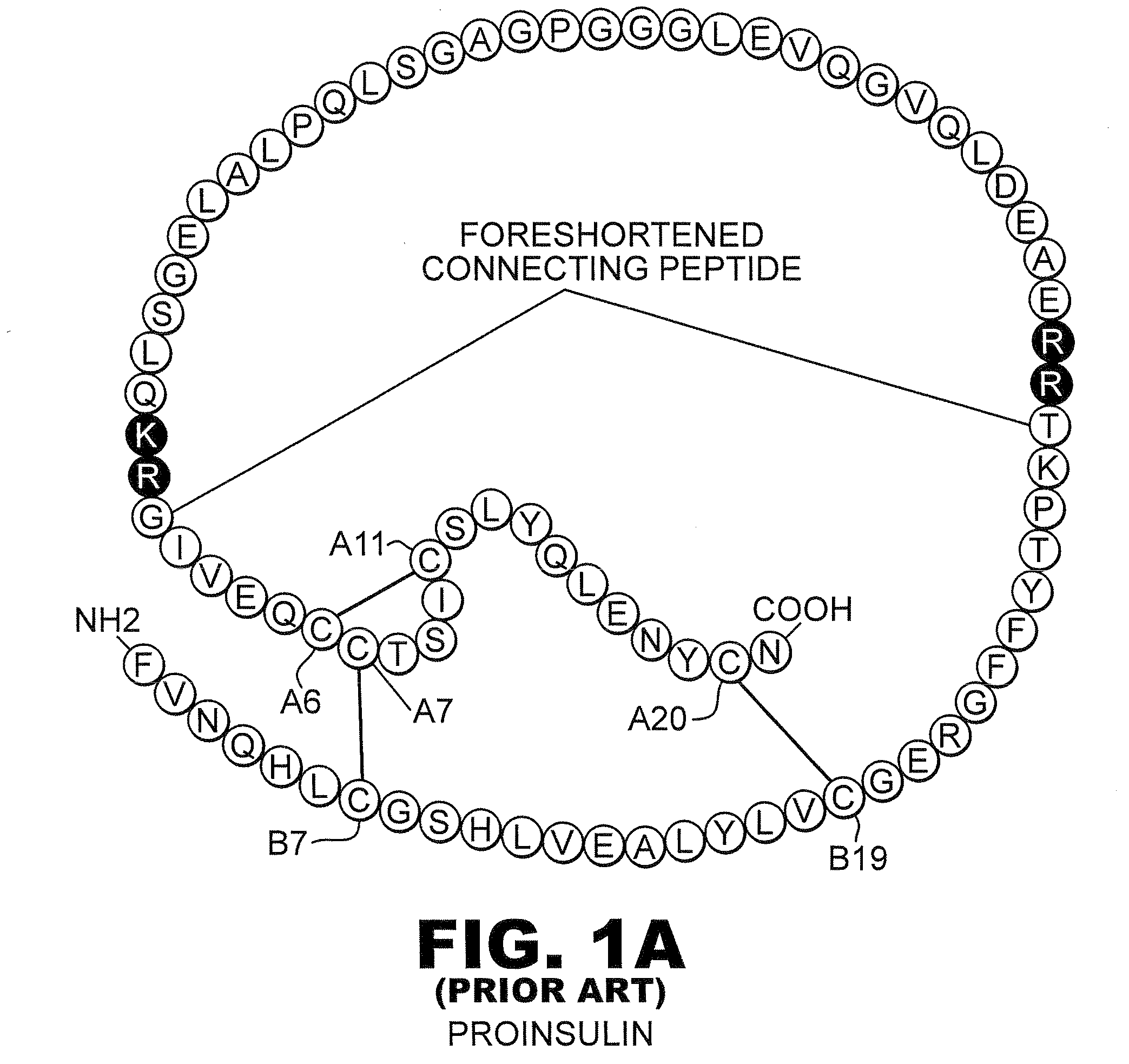
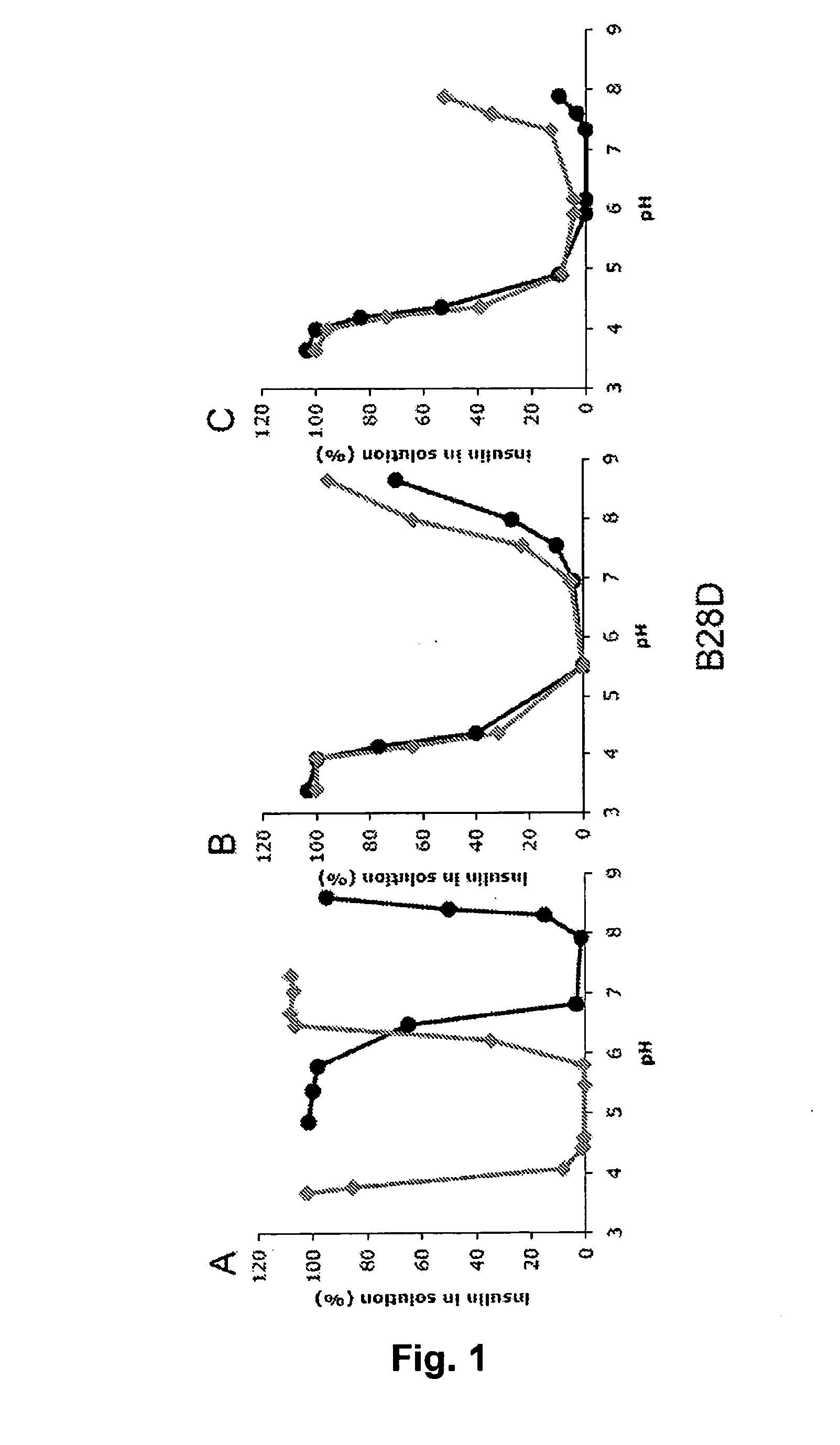
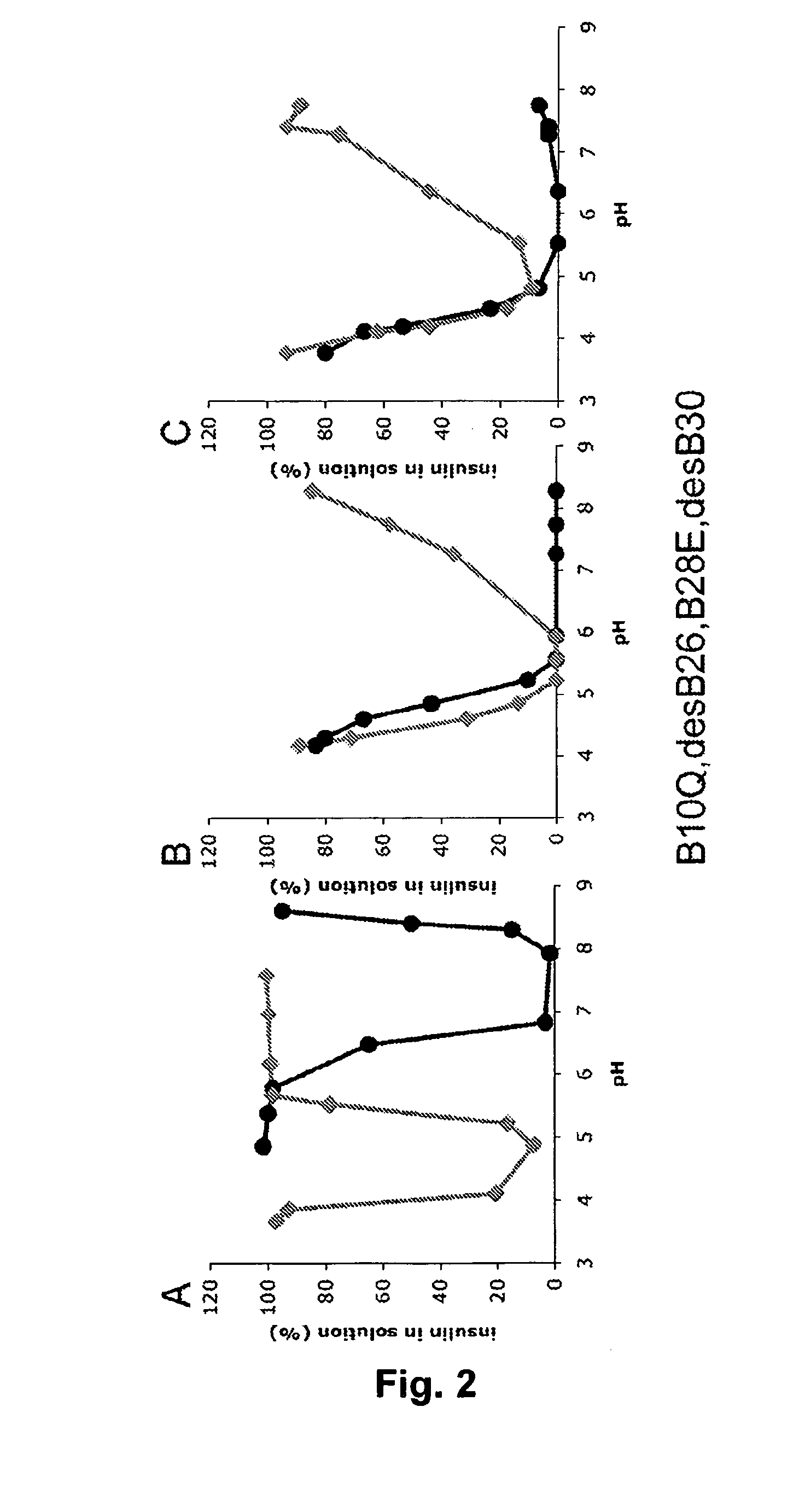
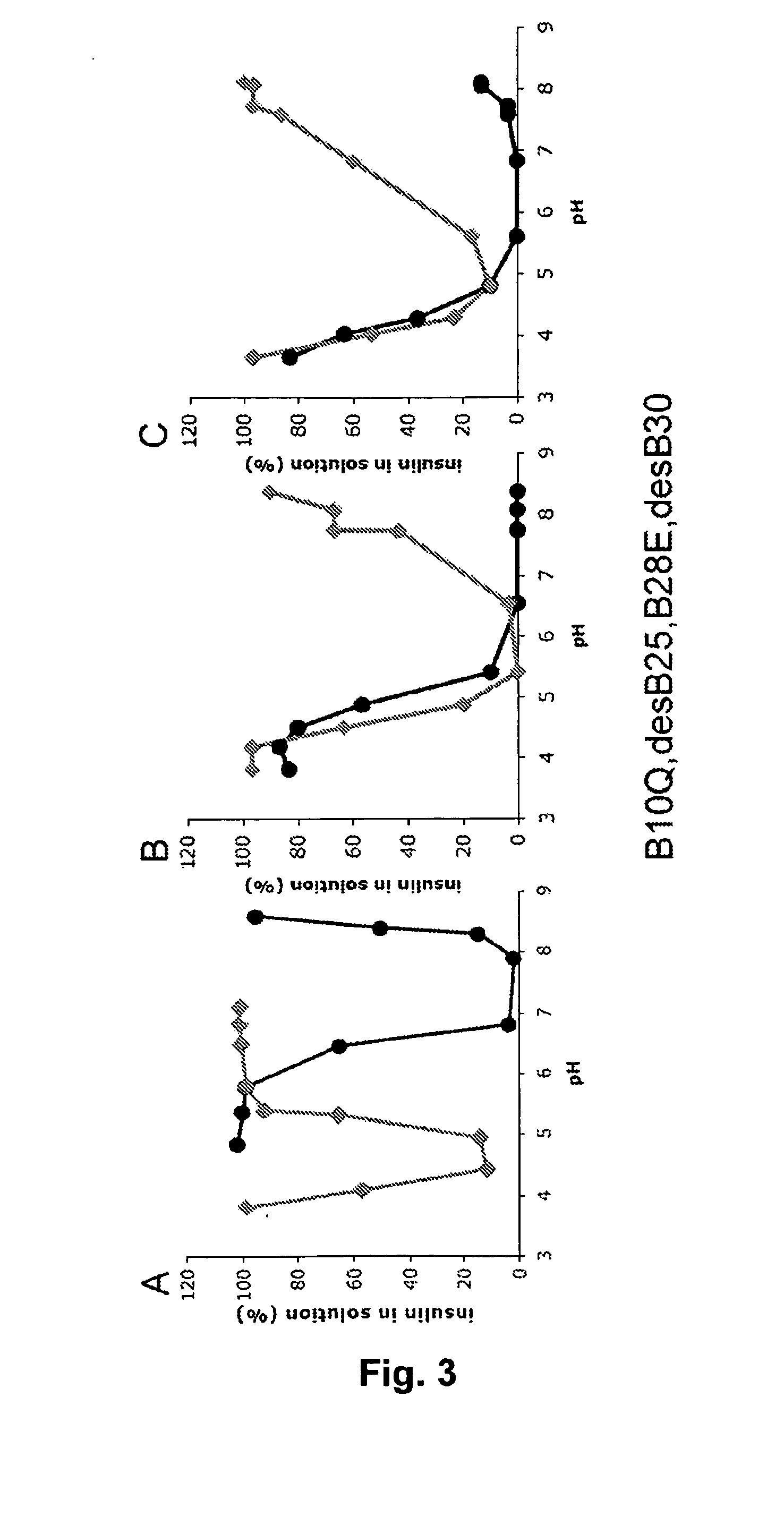
The invention is related to fast acting insulin analogues which can form soluble mix-tures (pre-mixed or self-mixed) with long acting insulin analogues. The fast action is achieved through monomerizing substitutions / deletions in the C-terminus of the B-chain of human insulin and the mixability with long acting insulin analogues is achieved through a substitution of the Zn-binding His in position B10 of human insulin with a Gln amino acid residue. In one embodiment the invention is related to fast acting insulin analogues in which at least one of the natural amino acid residues in position B22-B30 in the human B-chain has been substituted with another amino acid residue having the effect of promoting formation of the monomeric form of insulin, the His amino acid residue in position 10 in the B-chain is substituted with a Gln and wherein further one or more of the amino acid residues in position B22-B30 optionally have been deleted.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Insulin compositions and method of making a composition
InactiveUS20090074882A1High molecular weightBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsZinc atomInsulin Analogue
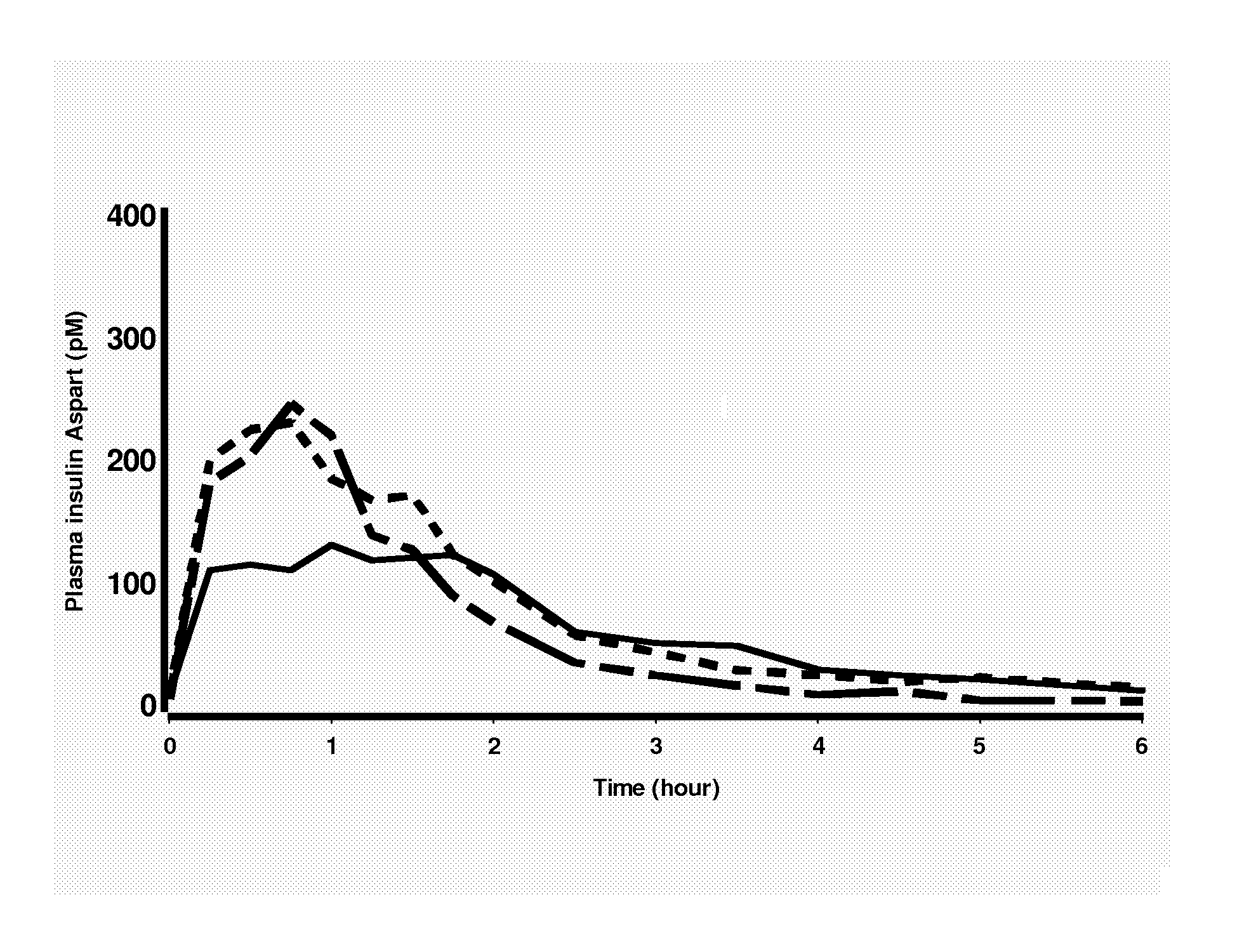
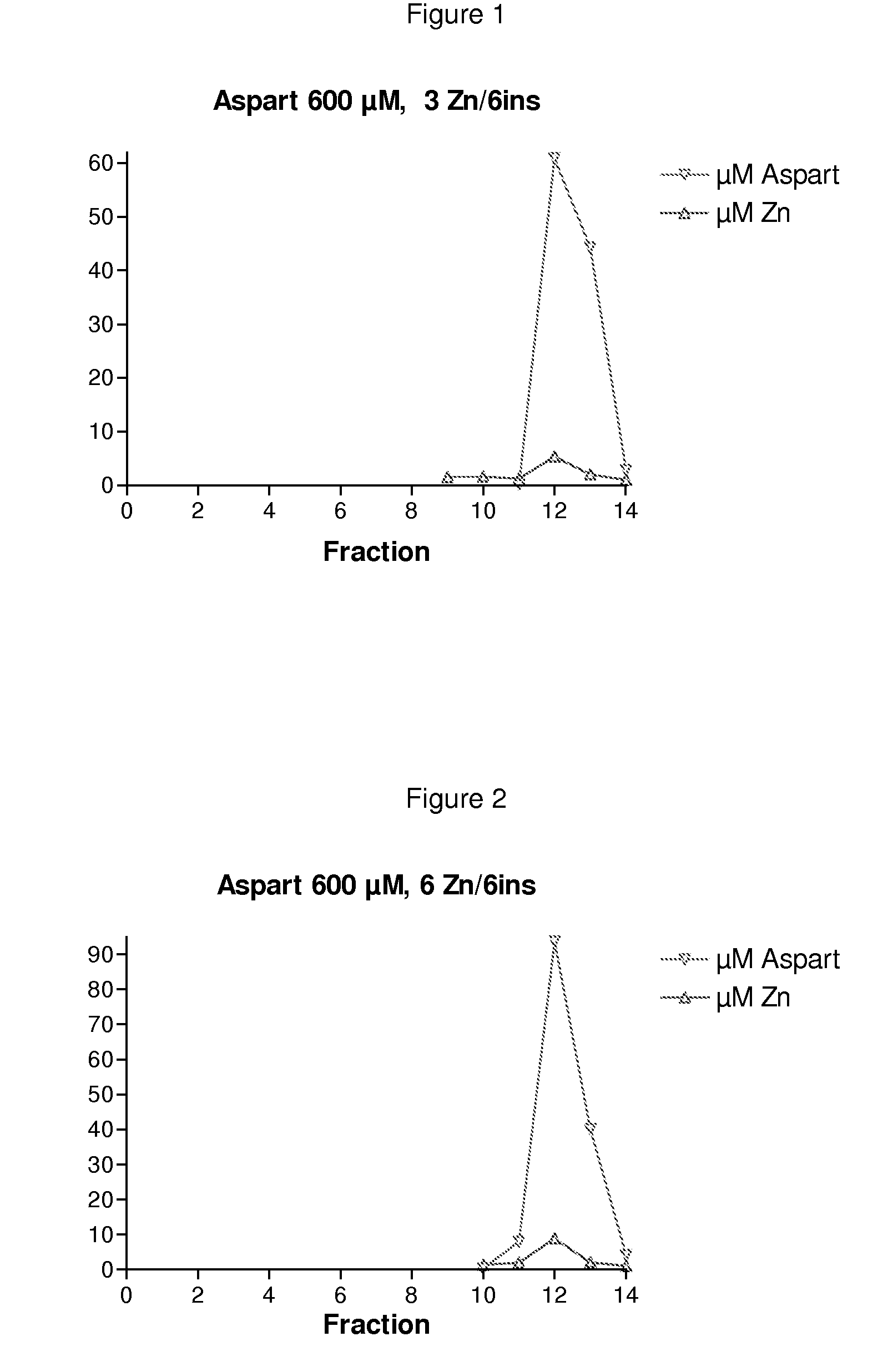
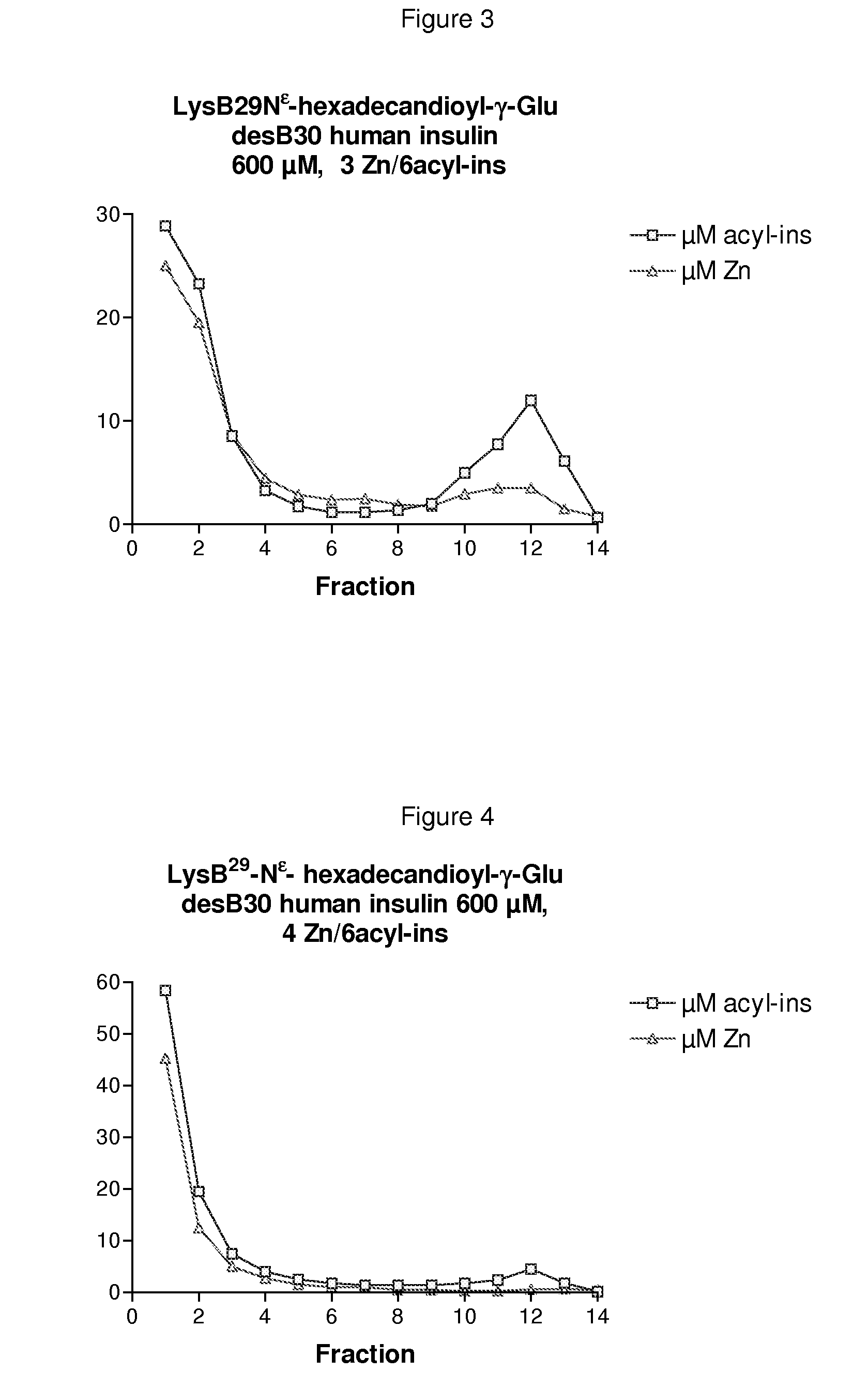
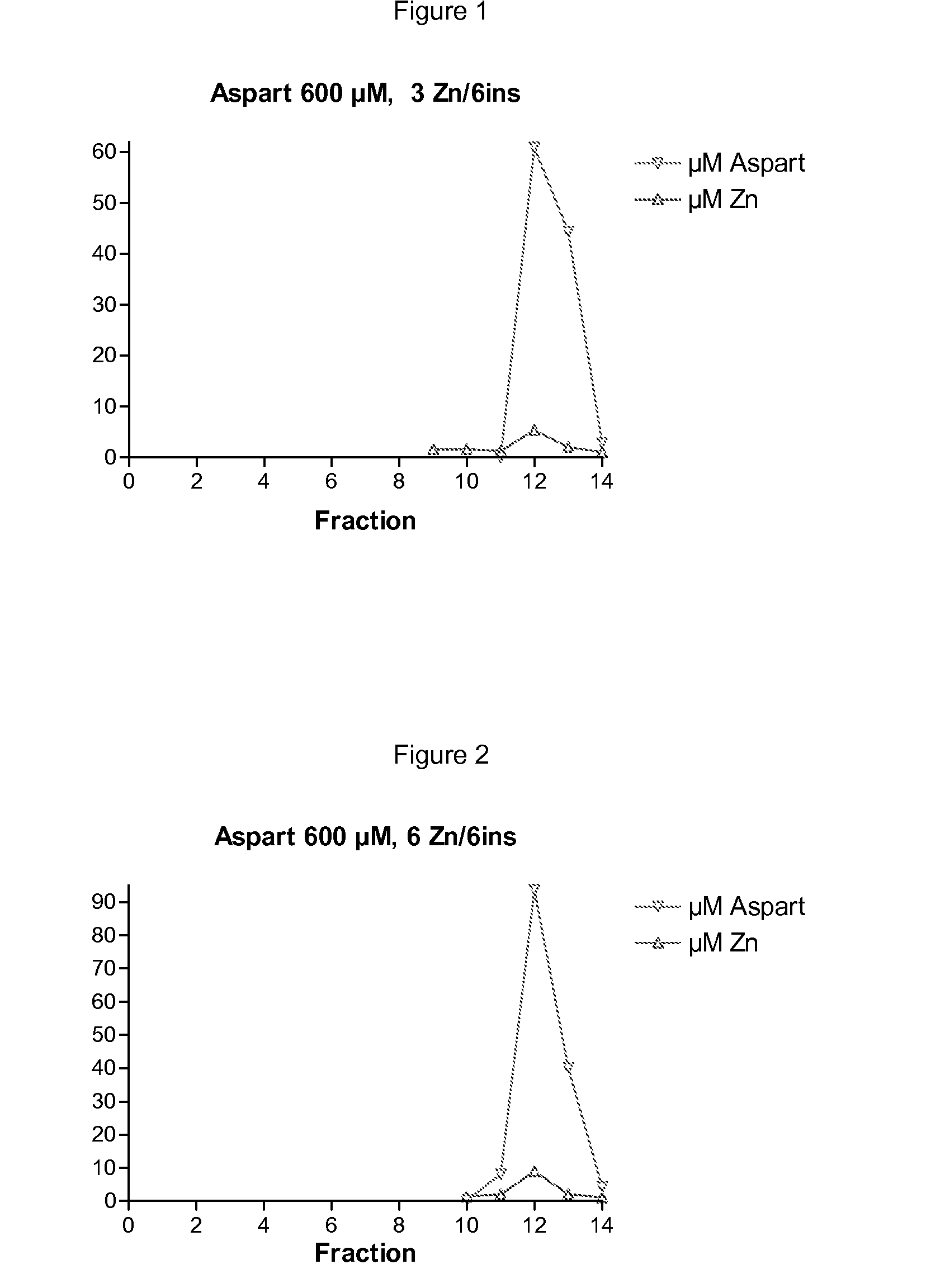
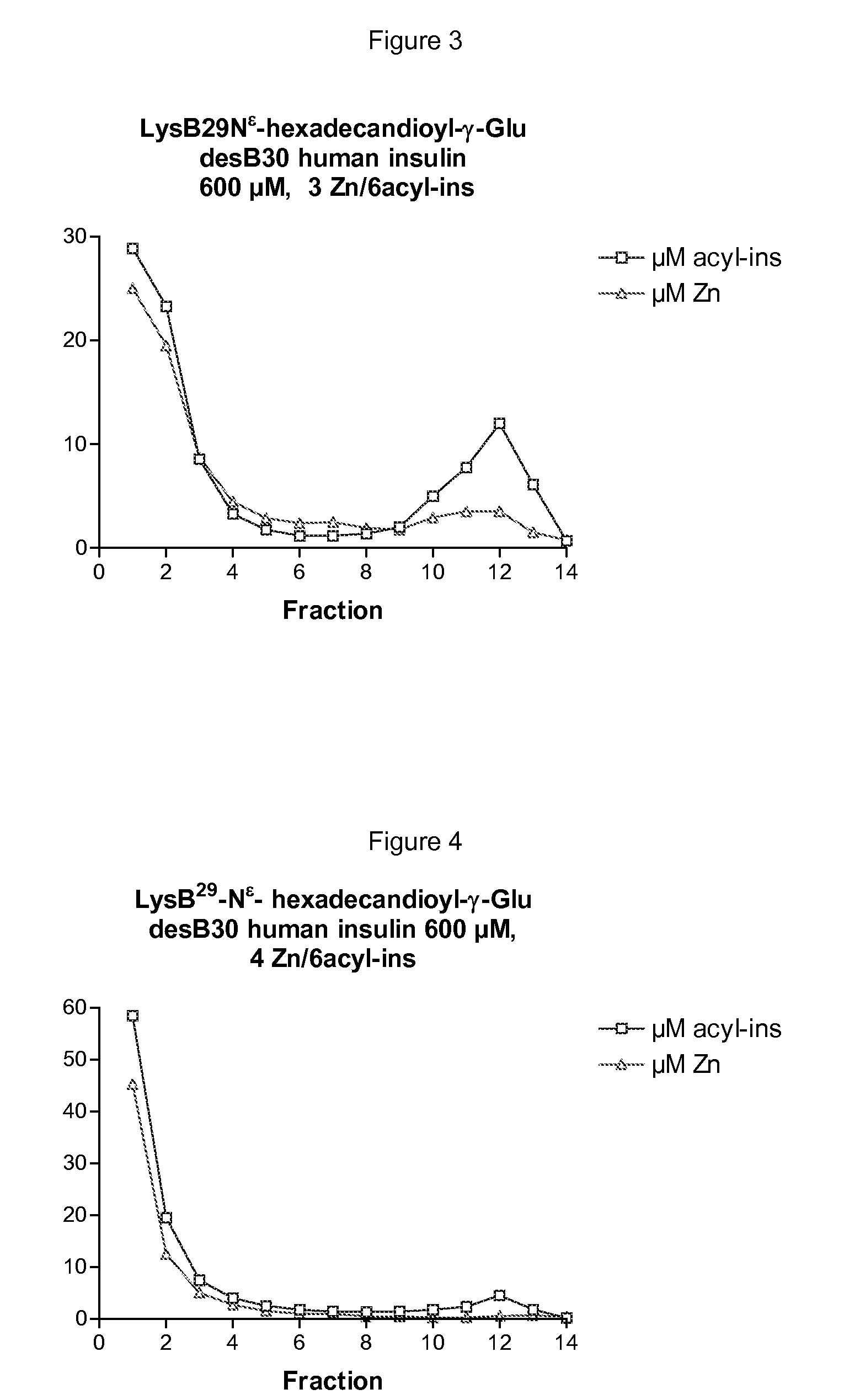
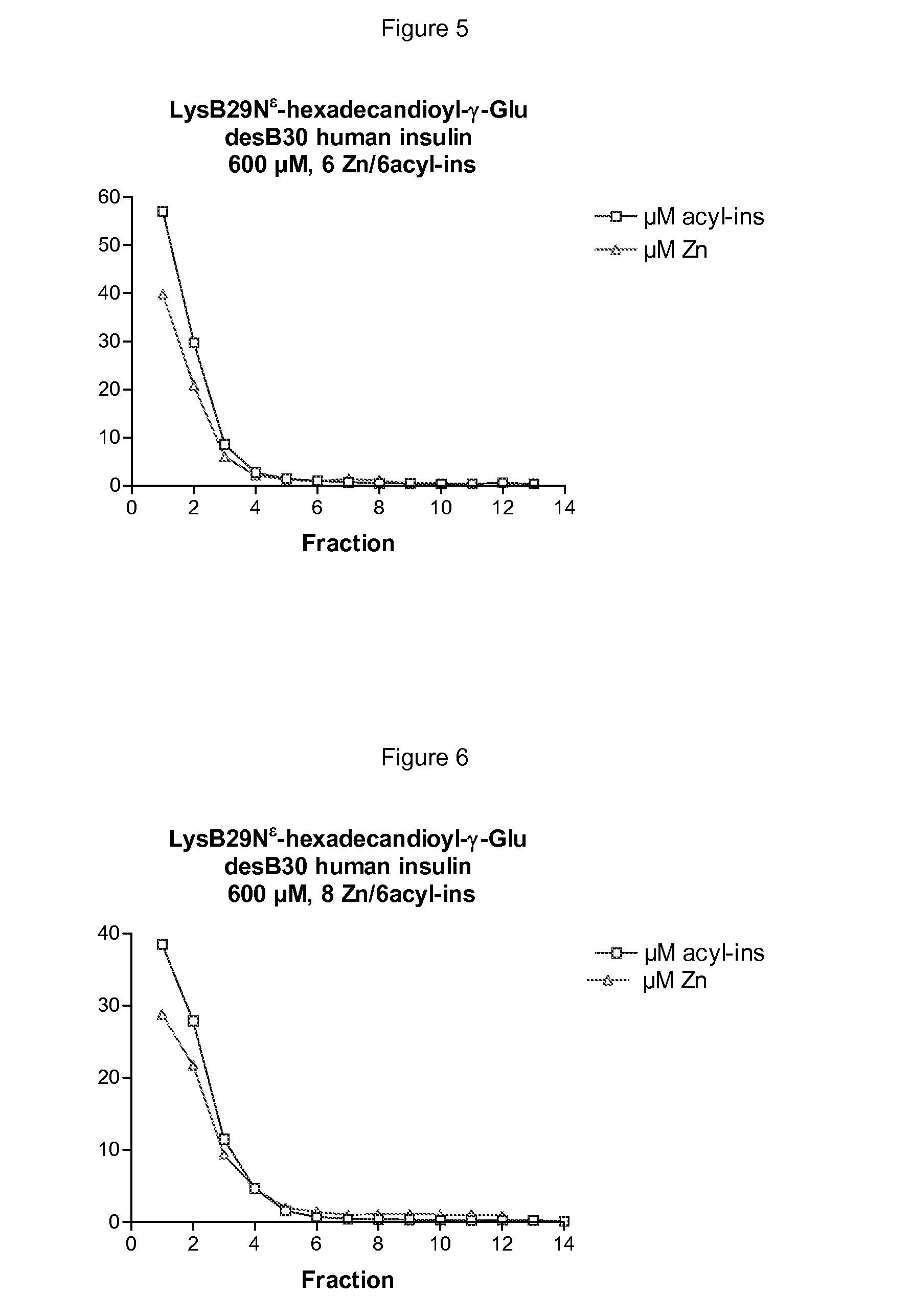
The invention is related to insulin compositions with a high content of zinc atoms per six molecules of acylated insulin. The insulin is an acylated insulin and may be mixed with a further insulin analogue such as the rapid acting insulin Asp B28 human insulin.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Insulin compositions and method of making a composition
The invention is related to insulin compositions with a high content of zinc atoms per six molecules of acylated insulin. The insulin is an acylated insulin and may be mixed with a further insulin analogue such as the rapid acting insulin Asp B28 human insulin.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Insulin analogue having quick response and stability under acidic condition and preparation thereof
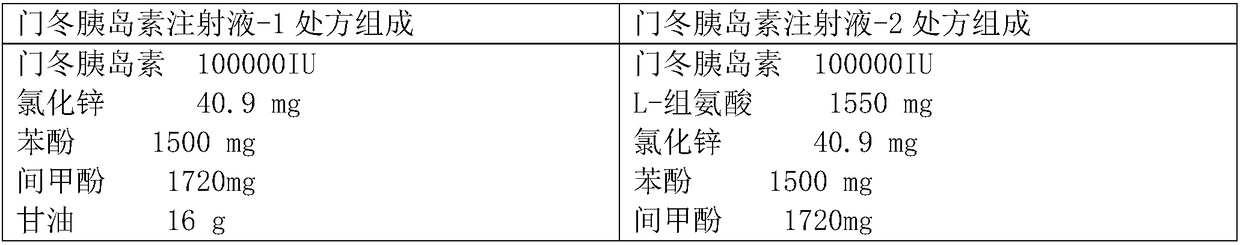
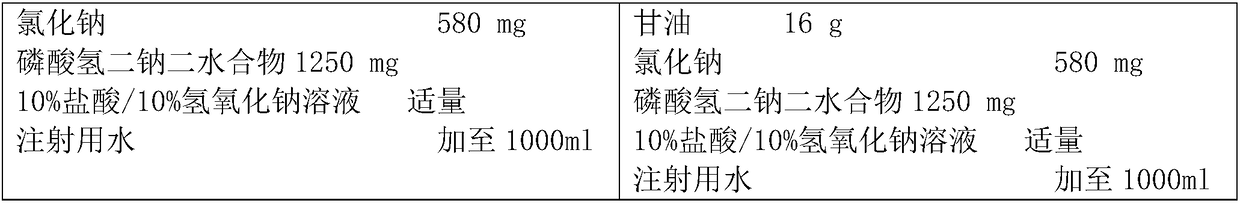
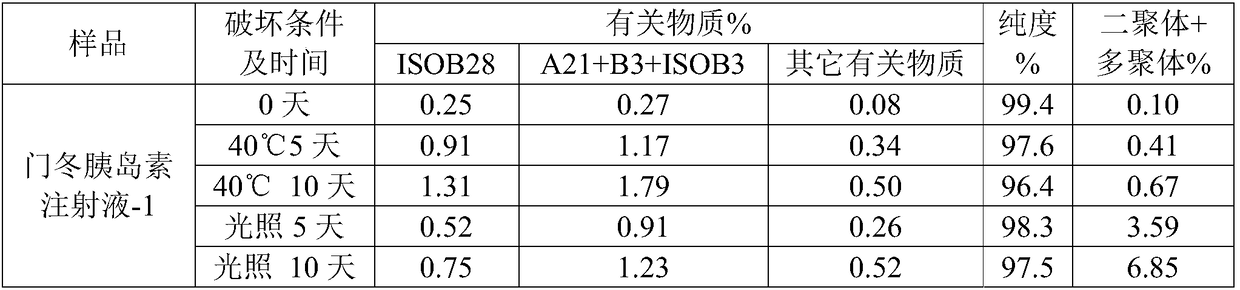
ActiveCN102199206AQuick effectProtect capillariesPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical formulationInsulin Analogue
The invention relates to an isulin analogue having quick response and stability under acidic condition, and a medicinal composition and a medicinal preparation thereof. Asparagine (Asn) at the A 21 position of the chain A of the isulin analogue is mutated into glycine (Gly), the isulin analogue can be mixed with a long-acting isulin analogue such as insulin glargine to form a premixed preparationwith two functions of quick-acting sugar reduction and stable long-acting sugar reduction, and the problems that the conventional natural insulin (of pigs, cows and human) and quick-acting isulin analogues are unstable in the acidic environment, and the conventional isulin premixed preparation is not clarified and needed to be introduced with a foreign protein (such as protamine) serving as a slow release preparation so as to easily cause immune reaction, and is needed to be injected twice each day, namely in the morning and evening are solved, so that the safety of the preparation is higher.
Owner:GAN&LEE PHARMA
Super fast-acting insulin compositions
Provided are combinations, compositions and kits containing an fast-acting insulin composition and a hyaluronan degrading enzyme composition formulated for parenteral administration. Such products can be used in methods of treating insulin- treatable diseases or conditions. Also provided are methods for administration of a fast-acting insulin and a hyaluronan degrading enzyme.
Owner:HALOZYME
Quick-acting insulin aspart precursor protein and preparation method for quick-acting insulin
InactiveCN105418755AHigh expressionStable structureFungiMicroorganism based processesInsulin aspartInsulin Precursor
The invention provides an insulin aspart precursor. The amino acid sequence is Z1(XY)nZ2Z3Z4-B(1-29)-C1C2C3-A(1-21), wherein Z1, X and Z2 are Asp or Glu respectively, Y is Ala or Gly, n is an integer from 1-10, Z3 is Pro, Glu or Asp, Z4 and C3 are Lys or Arg respectively, C1 and C2 are Glu, Asp, Ala or Gly respectively, B(1-29) is insulin aspart B chain 1-29 bit amino acid, and A(1-21) is insulin aspart A chain 1-21 bit amino acid. The invention also provides a coding gene, a cloning vector or an expression vector containing the coding gene, a transformant, and a method for preparing quick-acting insulin by utilization of the quick-acting insulin aspart precursor protein. The expression level of the product is high, the fermentation expression product purity is high, the extraction method is simple and the yield is high.
Owner:ZHUHAI JINBAIKANG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
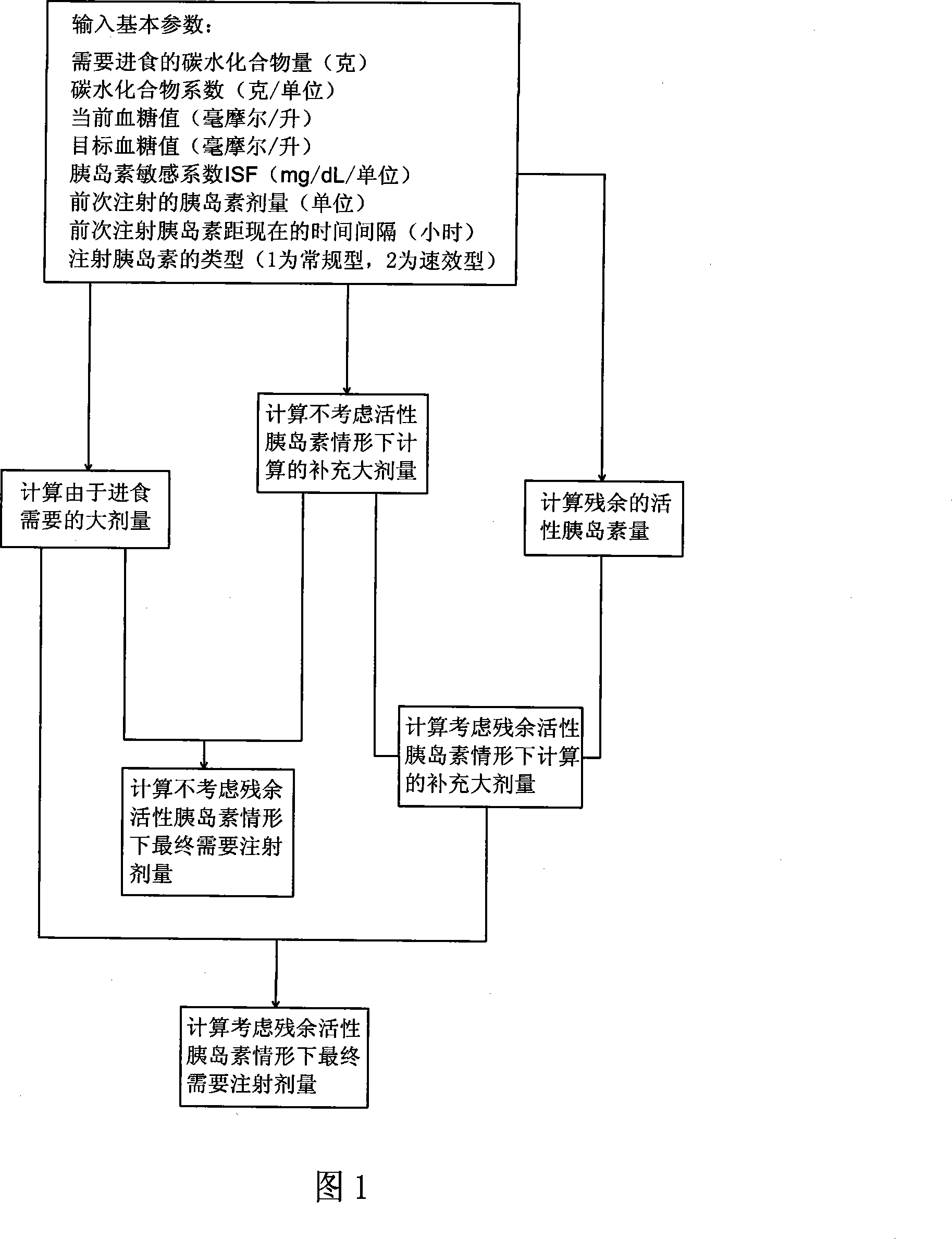
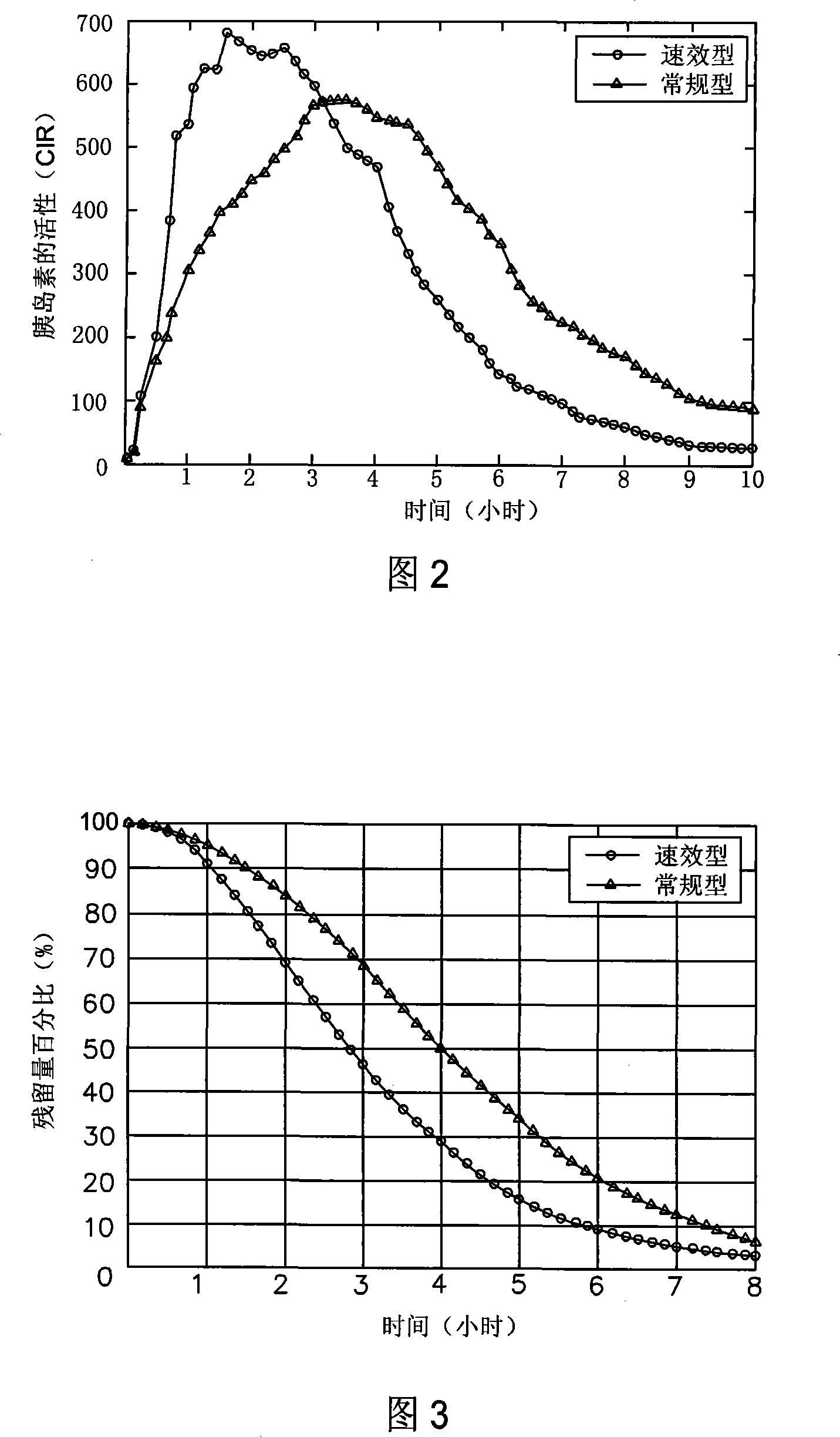
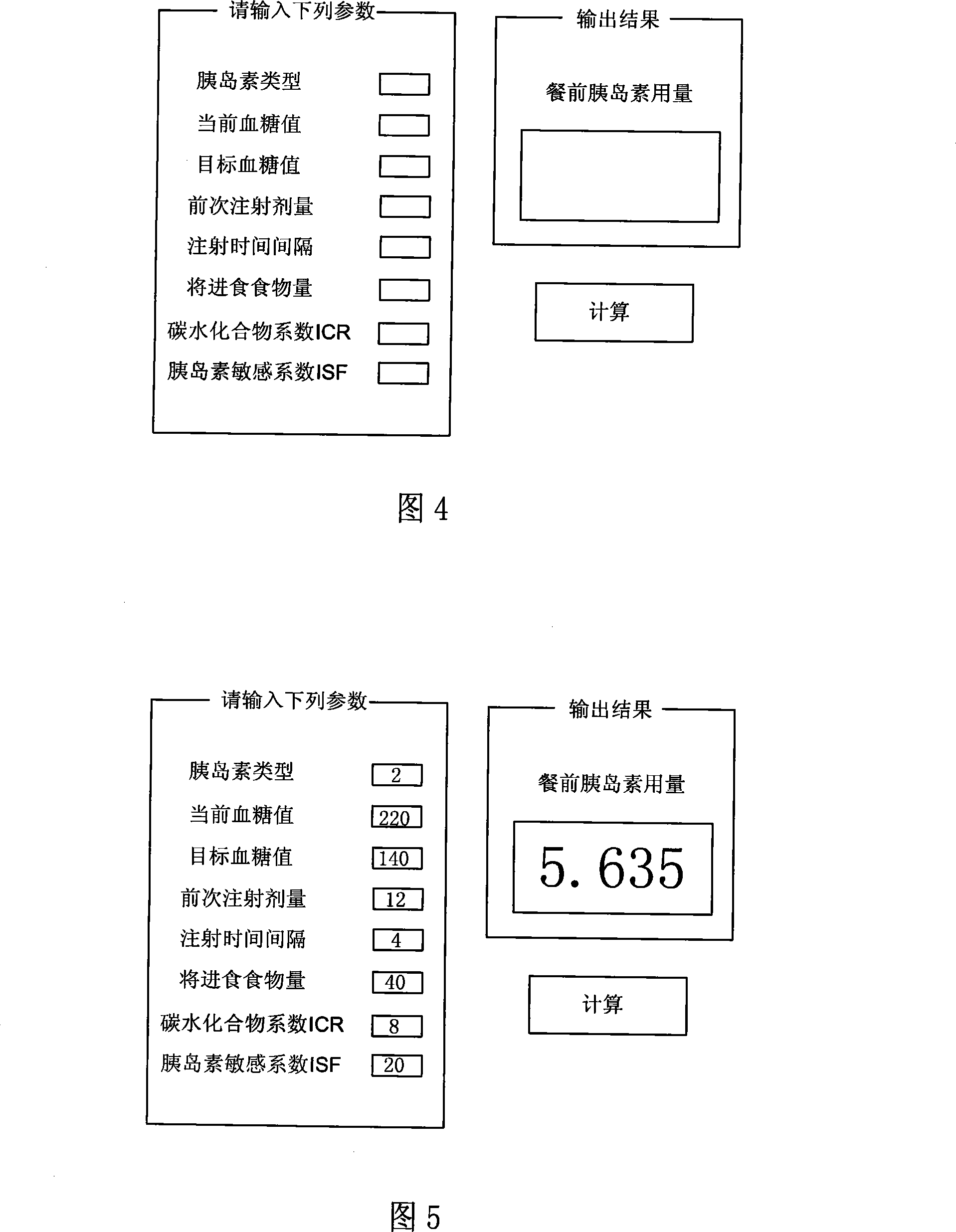
Pre-meal insulin dosage control method
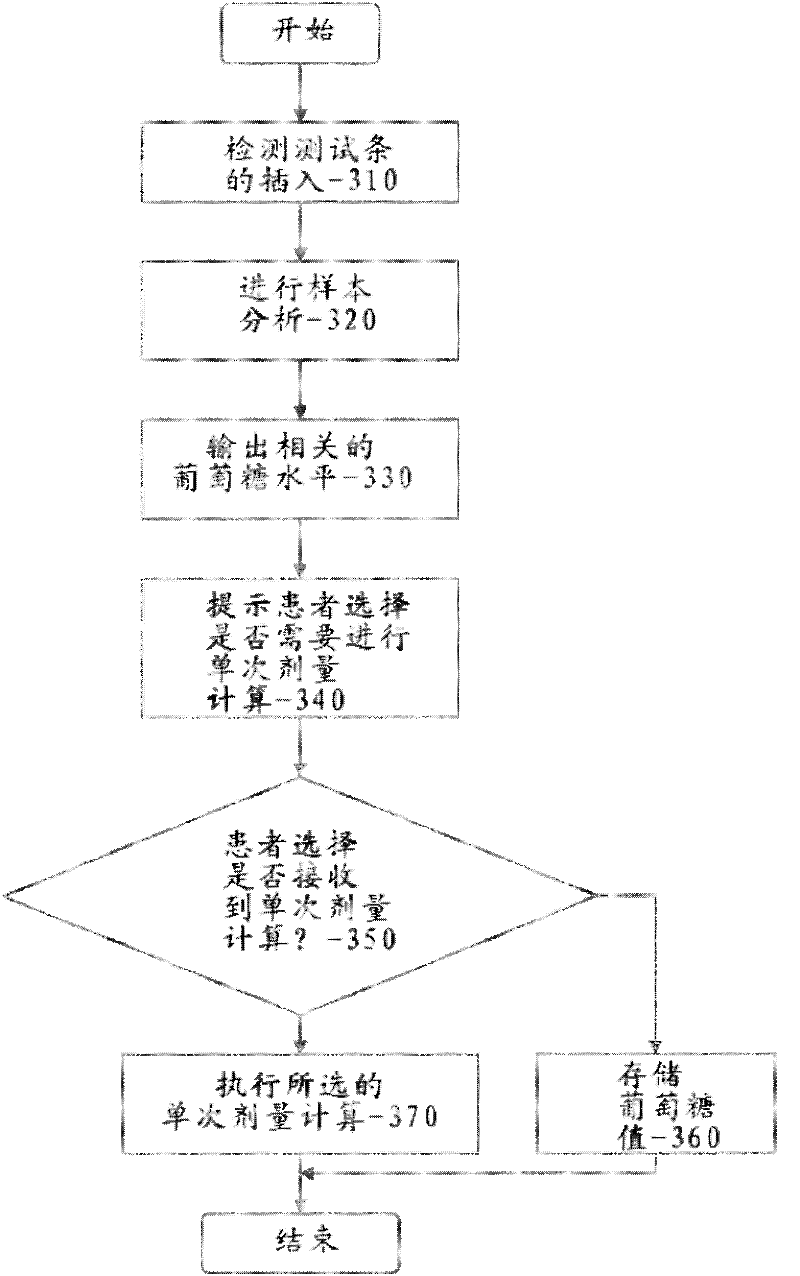
ActiveCN101214373AReduce high/low blood sugarPrecise and safe treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAcute hyperglycaemiaActrapid insulin
The present invention relates to a method of controlling the amount of insulin before meal. The present invention confirms whether the action of residual active insulin is taken into account by judging whether conventional or rapid-acting insulin is injected within a certain period of time. When taking the action of residual active insulin into account, the method of interpolation and numerical integration is adopted to accurately measure the residual amount of in vivo active insulin according to insulin pharmacodynamical data, thus more accurately measuring the insulin amount required before meal. The present invention can effectively reduce hyperglycemia / hypoglycemia caused by improper insulin amount, thus making the treatment more accurate and safer. In addition, the concept and method of measuring insulin amount provided by the present invention is also applicable to the measurement of insulin amount not before meal, which deserves promotion and application.
Owner:珠海福尼亚医疗设备有限公司
Ultra-concentrated rapid-acting insulin analogue formulations
InactiveUS20140323398A1Good chemical stabilityImprove physical stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSide chainPharmaceutical formulation
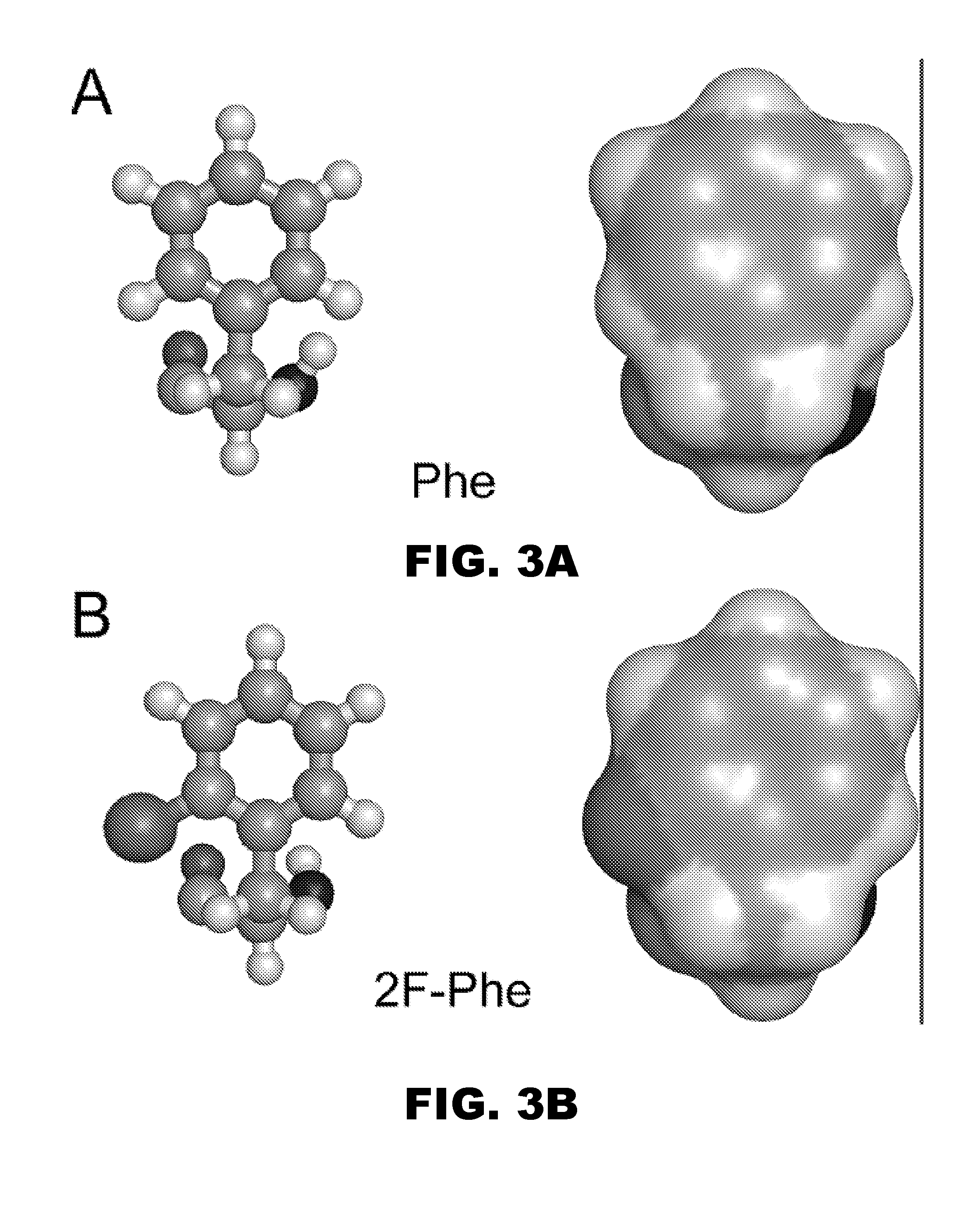
A pharmaceutical formulation comprises insulin having a variant insulin B-chain polypeptide containing an ortho-monofluoro-Phenylalanine substitution at position B24 in combination with a substitution of an amino acid containing an acidic side chain at position B10, allowing the insulin to be present at a concentration of between 0.6 mM and 3.0 mM. The formulation may optionally be devoid of zinc. Amino-acid substitutions at one or more of positions B3, B28, and B29 may additionally be present. The variant B-chain polypeptide may be a portion of a proinsulin analogue or single-chain insulin analogue. The insulin analogue may be an analogue of a mammalian insulin, such as human insulin. A method of lowering the blood sugar of a patient comprises administering a physiologically effective amount of the insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to the patient.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Fibrillation resistant proteins
ActiveUS8343914B2Improve the immunityEnhanced susceptibility to fibrillationBiocideBacteriaADAMTS ProteinsFibrillation
Protection of proteins against fibrillation may be afforded by introduction of certain histidine substitutions into the protein, such that a pair of histidines are present with sufficient spacing as to allow the histidines to coordinate with zinc. In the case of insulin, introduction of histidine residue substitutions at residues A4 and A8 together or a histidine residue substitution at residue B1, provides increased resistance to fibrillation while maintaining at least a majority of the activity of the insulin analogue. Introduction of a histidine residue substitution at residue A8 restores at least a portion of fibrillation resistance that may have been harmed by substitutions present on the B-chain such as those present in fast-acting insulins. Proteins protected by such histidine substitutions may be used to provide a pharmaceutical composition. A method of treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of the pharmaceutical composition to the patient.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
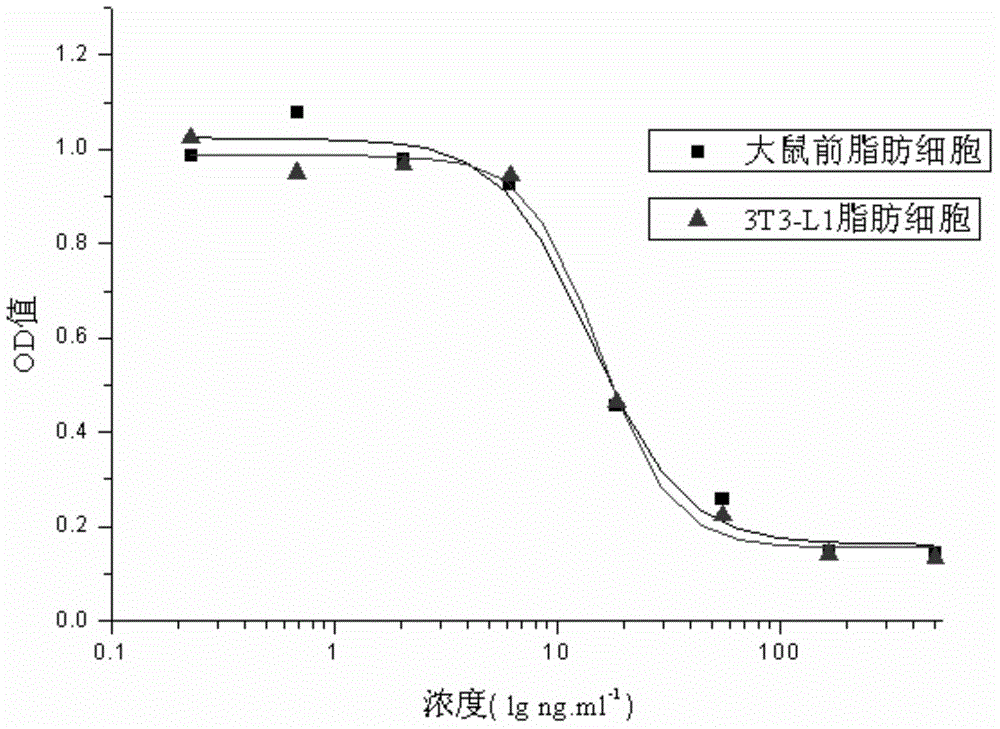
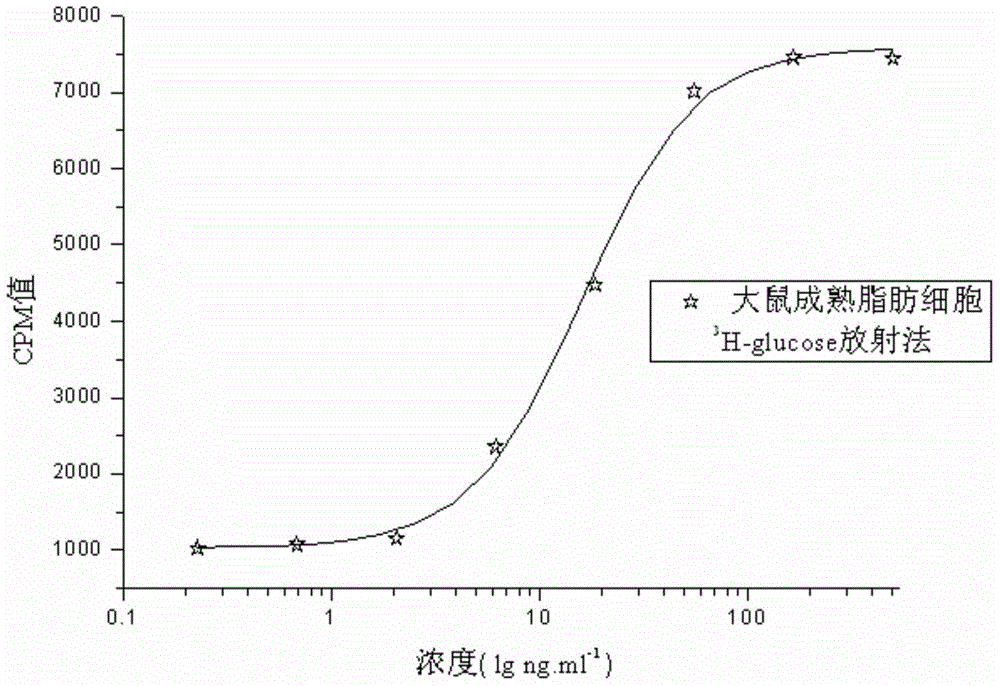
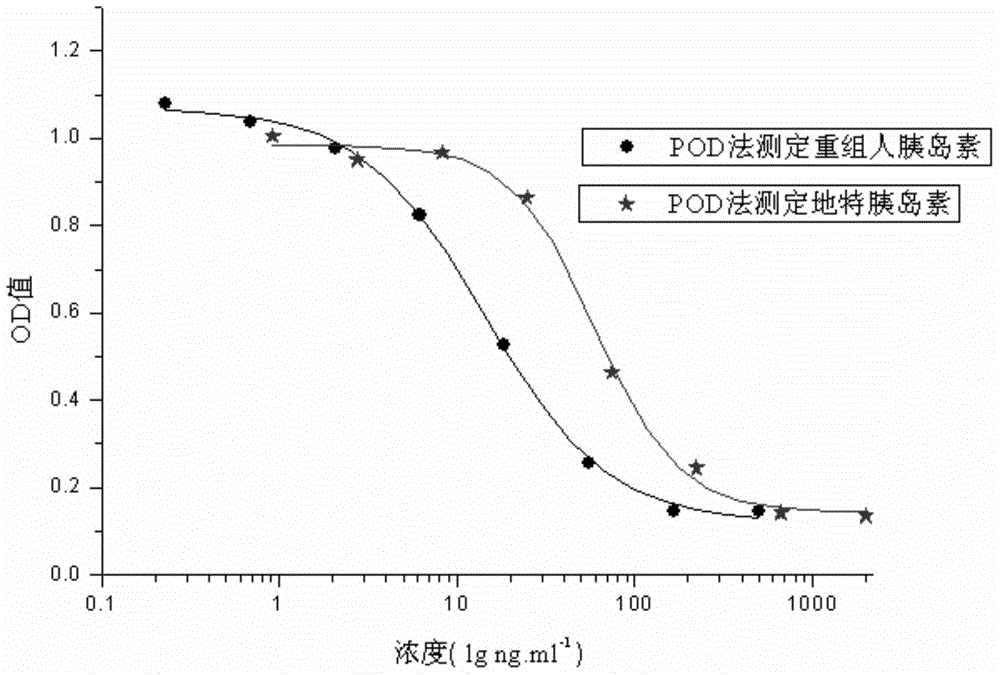
External biological activity determination method for human insulin and analog or conjugate
ActiveCN105092490AGood repeatabilityEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsPEGylated insulinDrug biological activity
The invention relates to a human insulin and analog including rapid-acting insulin (e.g. Insulinaspart, InsulinLispro, and InsulinGlulisine), long-acting insulin (e.g. Insulinglargine, InsulinDetemir, and InsulinDegludec), and modified conjugate (e.g. PEG-Insulin and PEG conjugatedinsulin lispro ), and also relates to the biological value determination method for the cell culture in vitro of PEG-Insulin and application thereof. The external biological activity determination method for human insulin and analog or conjugate is induced in vitro into adipocyte by using preadipocyte of male rat, and measure the glucose consumption after insulin reacting in the adipocyte nutrient solution by using glucose oxidase method to calculate the corresponding insulin biological value.
Owner:CHONGQING PEG BIO BIOTECH CO LTD
Fast-acting insulin preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108096185AImprove antioxidant capacityReduced deamidationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAntioxidantColor changes
The invention discloses application of L-histidine and pharmaceutically-acceptable derivatives thereof in improvement of stability of fast-acting insulin preparation. The fast-acting insulin preparation is Insulin Aspart. Shown by experiments, the L-histidine and the pharmaceutically-acceptable derivatives thereof serve as a stabilizer and an antioxidant in injections, deamidization, peptide chaincracking and polymerization reactions of the Insulin Aspart are reduced, the oxidation resistance of Insulin Aspart injections is improved, and the Insulin Aspart injections are prevented from oxidated destruction even liquid medicine color change during storage. The preparation process is simple and convenient and is applicable to industrial and big production.
Owner:ZHUHAI JINBAIKANG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Application of Safenour cyclopeptide in oral insulin medicine for treating diabetes
InactiveCN103169946AImprove thermal stabilityReduce oral doseMetabolism disorderCyclic peptide ingredientsTreatment effectPepsin
The invention discloses an application of Safenour cyclopeptide in an oral insulin medicine for treating diabetes, which comprises the following steps: 1) Safenour cyclopeptide and insulin are combined to have a protection effect; 2) after combining Safenour with insulin, the anti gastrointestinal tract acidic environment and digestive enzyme such as pepsin and trypsin after oral administration of insulin can be degraded; 3) absorption of intestinal tract on insulin can be promoted after combining Safenour with insulin; and 4) the administration is carried out after combining Safenour with insulin, the Safenour cyclopeptide has obvious diabetes and hpyerglycemic treatment effect. The security is high, the Safenour preparation is simple, and the problems that oral administration of insulin is easily degraded, so that unable oral administration and inconvenient carrying are provided can be solved. The oral insulin preparation which takes Safenour as an auxiliary material is easily carried, the usage is convenient, the problems of instability of natural insulin and quick-acting insulin analogues under acidic environment, twice injection on morning and evening everyday can be solved, and the Safenour cyclopeptide can be used for treating diabetes, and has good hpyerglycemic effect. The anti gastrointestinal tract degradating effect of the oral administration of insulin is good, and the Safenour cyclopeptide enables large scale production.
Owner:武汉光谷世傲生物科技有限公司
Rapid-acting insulin analogues of enhanced stability
ActiveUS20190322719A1High thermodynamic stabilityDecreased self-associationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiabetes mellitusFree solution
A two-chain insulin analogue contains a modified A-chain polypeptide and a modified B-chain polypeptide. The A-chain polypeptide comprises one or more of: a His or Glu substitution at position A8, a Glu substitution at position A14; and a Gln or Arg substitution at positon A17. The B-chain polypeptide comprises one or more of: a deletion of the amino acids at position B1, B1-B2, B1-B3, B30 or a combination thereof; an Ala or Glu substitution at position B2; a Glu substitution at position B3. The analogue exhibits thermodynamic stability in a zinc-free solution, decreased self-association, maintains biological potency, and no increased mitogenicity. The analogue exhibits resistance to chemical degradation and physical degradation. A method of treating a patient with diabetes mellitus or obesity comprises administering a physiologically effective amount of the insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to a patient.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
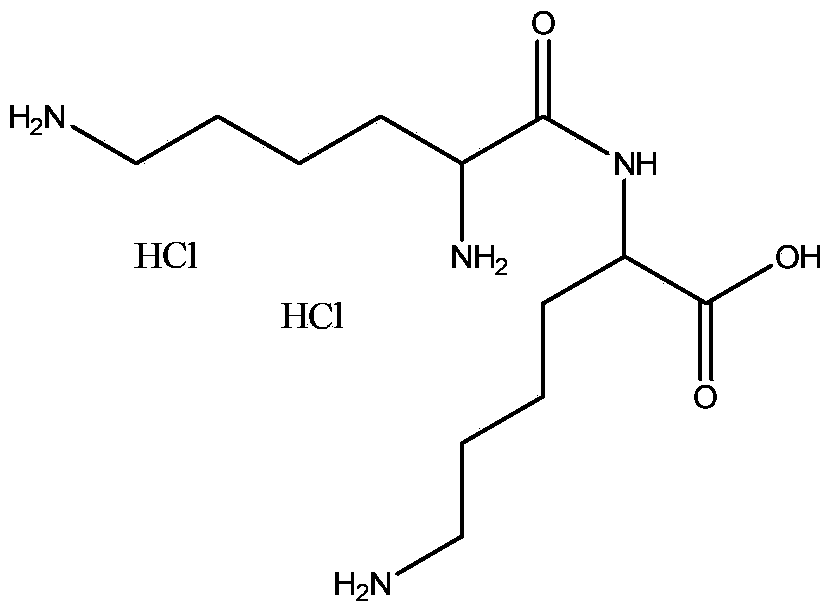
Preparation method of human insulin analogue and usage thereof
InactiveCN101157725ANot easy to formLow self-integrationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDipeptideBio engineering
The present invention pertains to the field of human medicine, which relates to a drug for the treatment of type I and type II diabetes and provides a preparation method and the usage of a human insulin analogue. The human insulin analogue of the present invention is characterized in that the human insulin analogue has the form as the right formula, wherein, R1 is any one amino acid residue of Pro, Ala, Gly, Ser, Val and Leu; R2 is any needed amino acid residue which can be encoded genetically; R3 is n paragraphs of R2-R1-dipeptide fragment, n is any one number of 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4. The human insulin analogue of the present invention is prepared by using a biological engineering method, the active insulin analogue has the advantages that the human insulin analogue is not easy to from the dimer and mainly exists by a monomer form after the subcutaneous injection, the local absorption is faster, the onset time is shorter, and the pharmacokinetics characteristics are more in line with the change spectra of physiological insulin and blood glucose.
Owner:江苏未名生物医药有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com