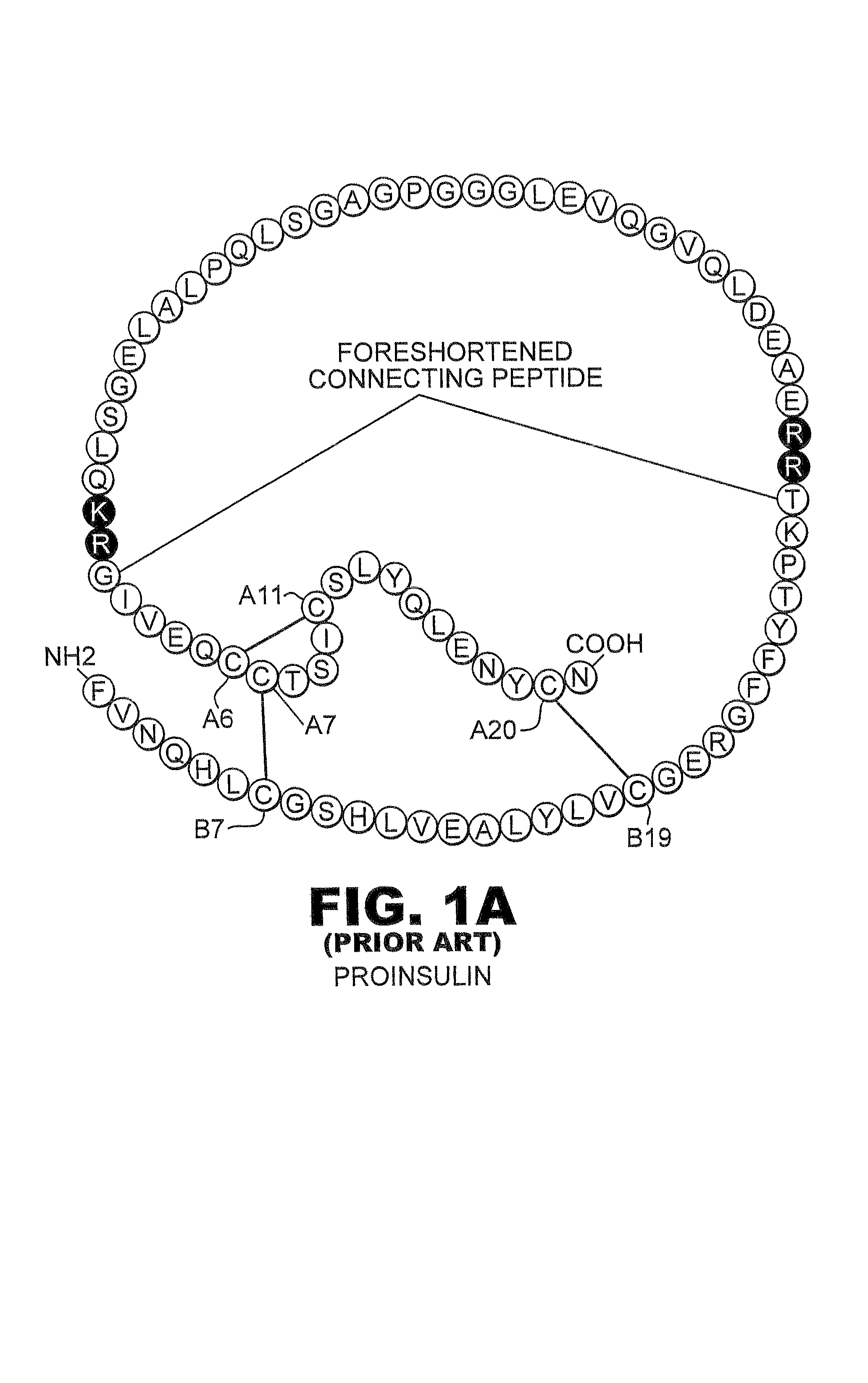
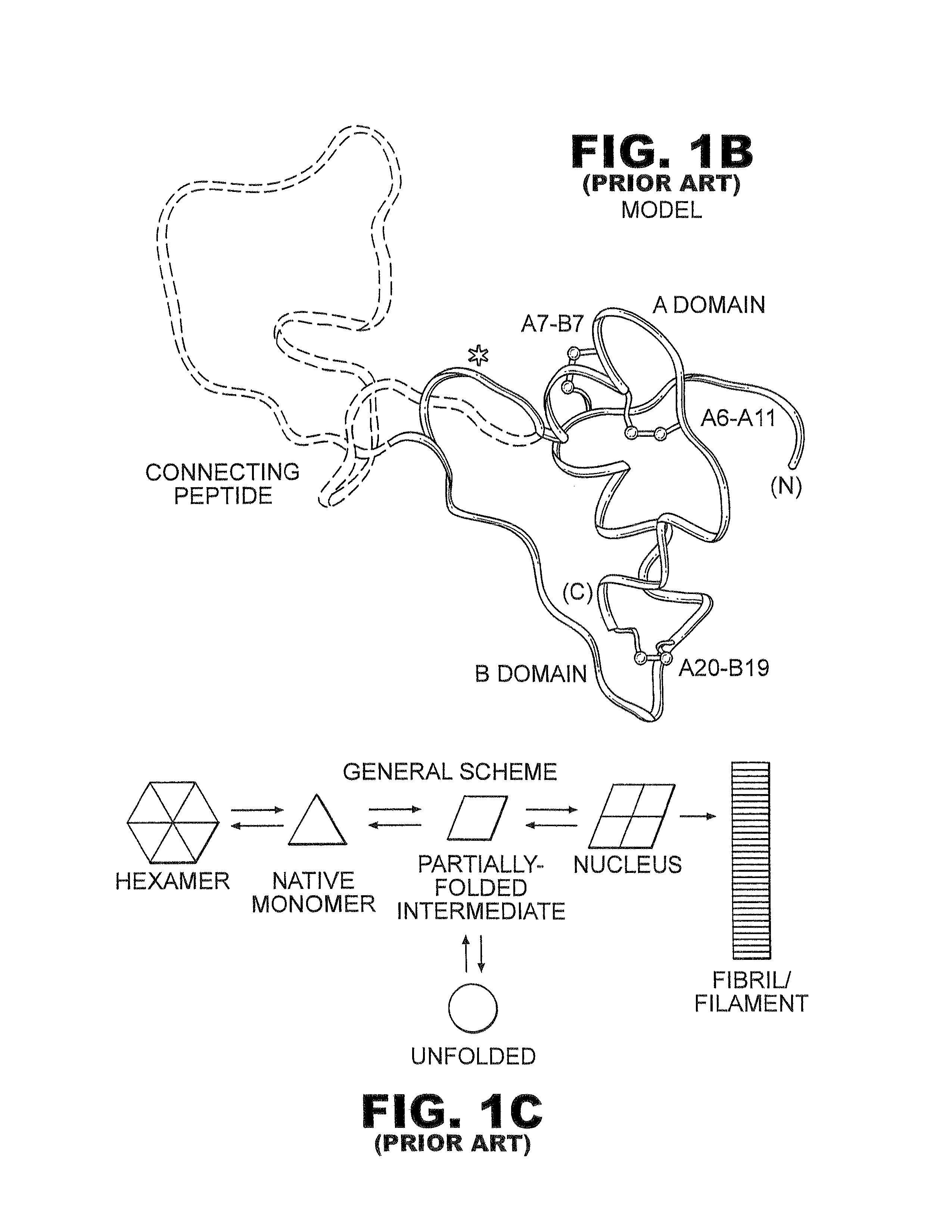
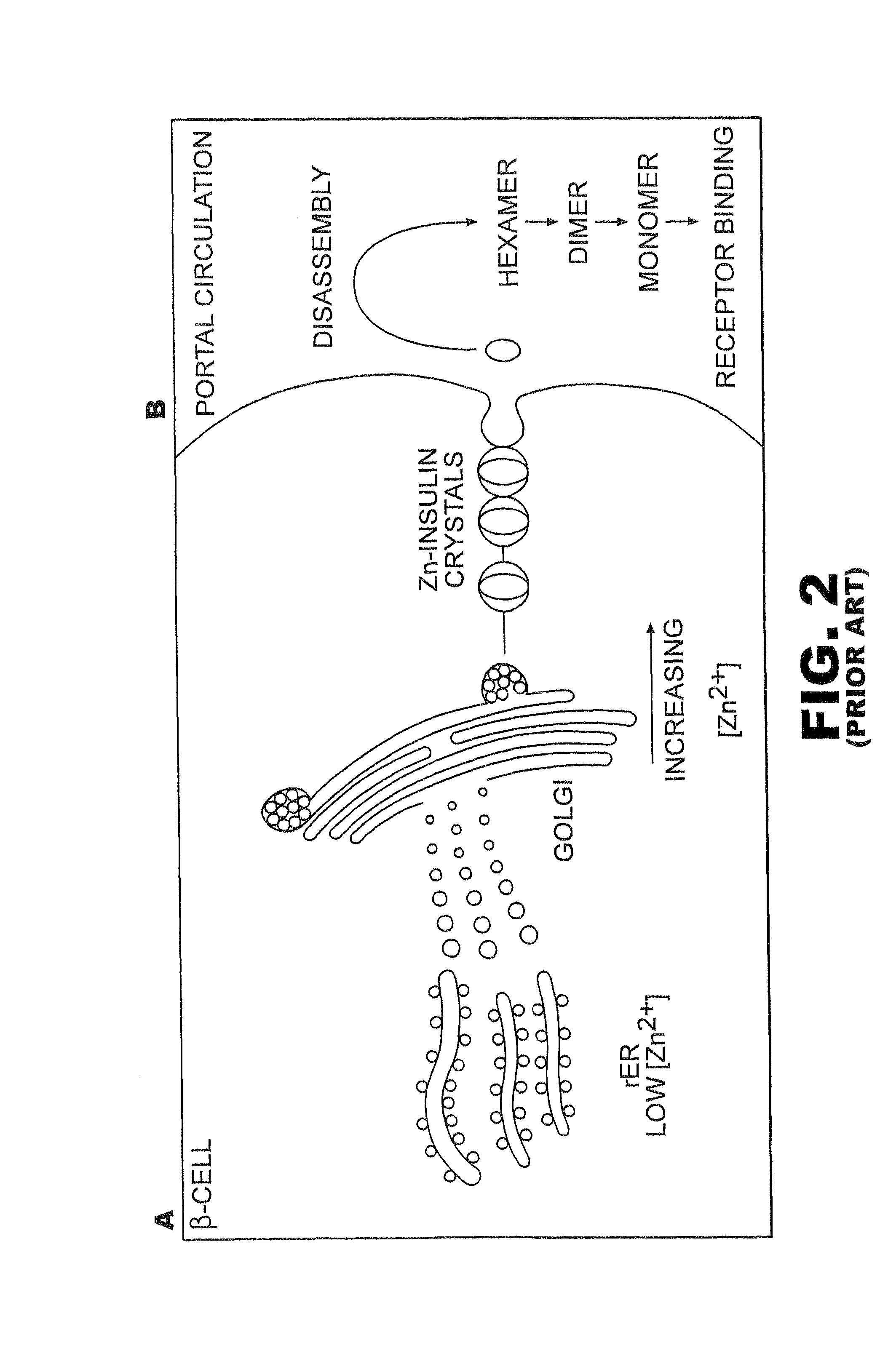
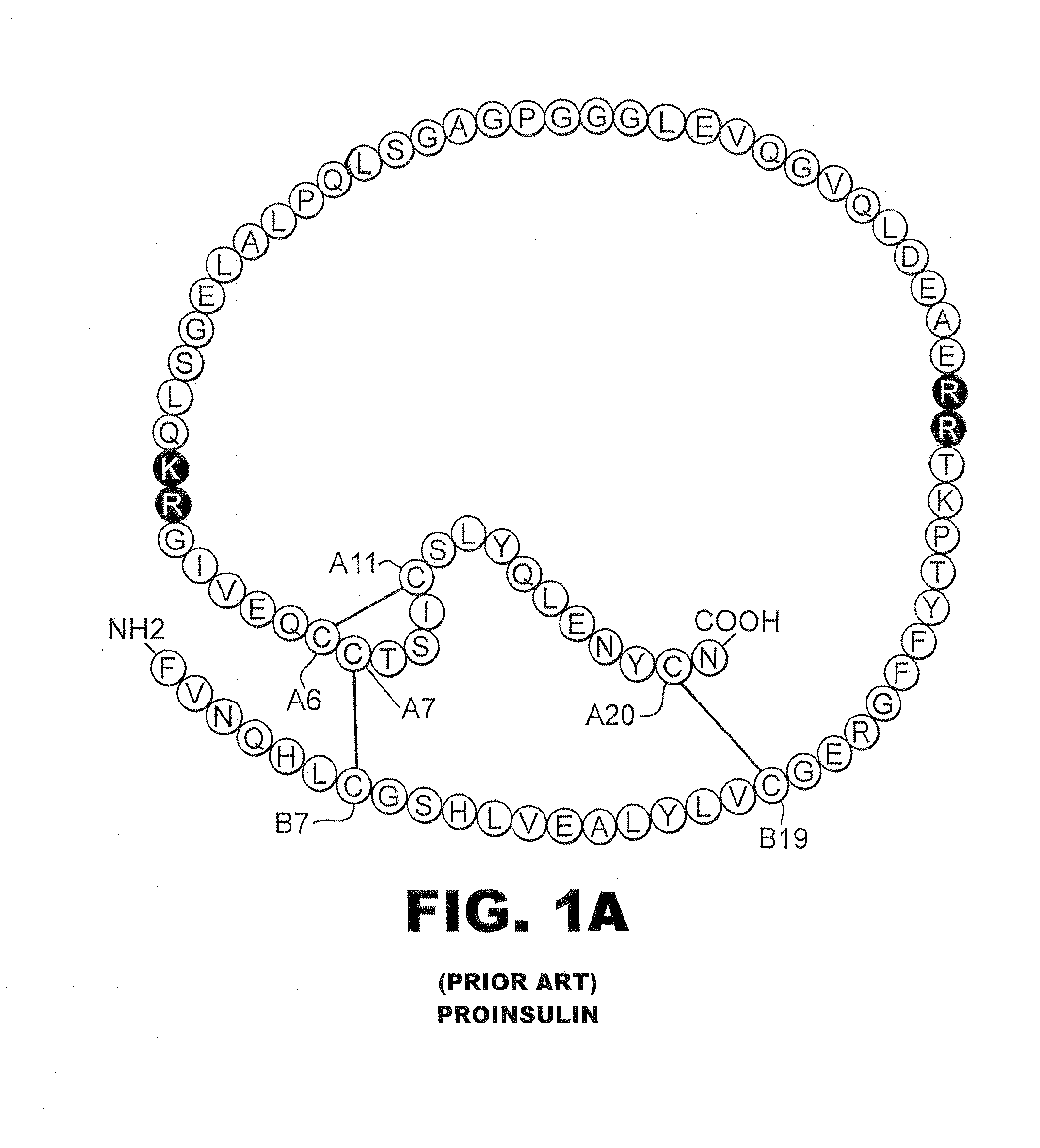
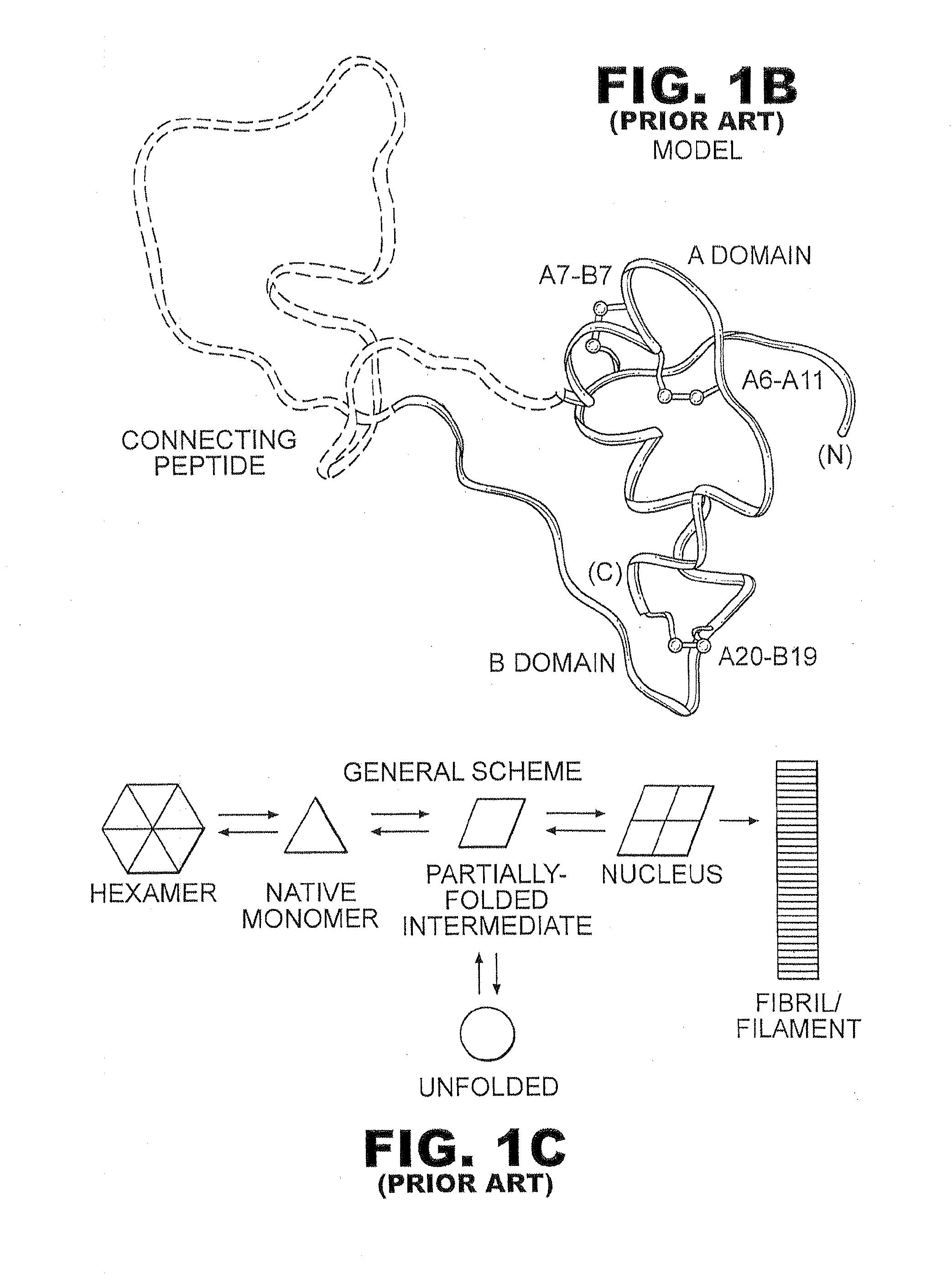
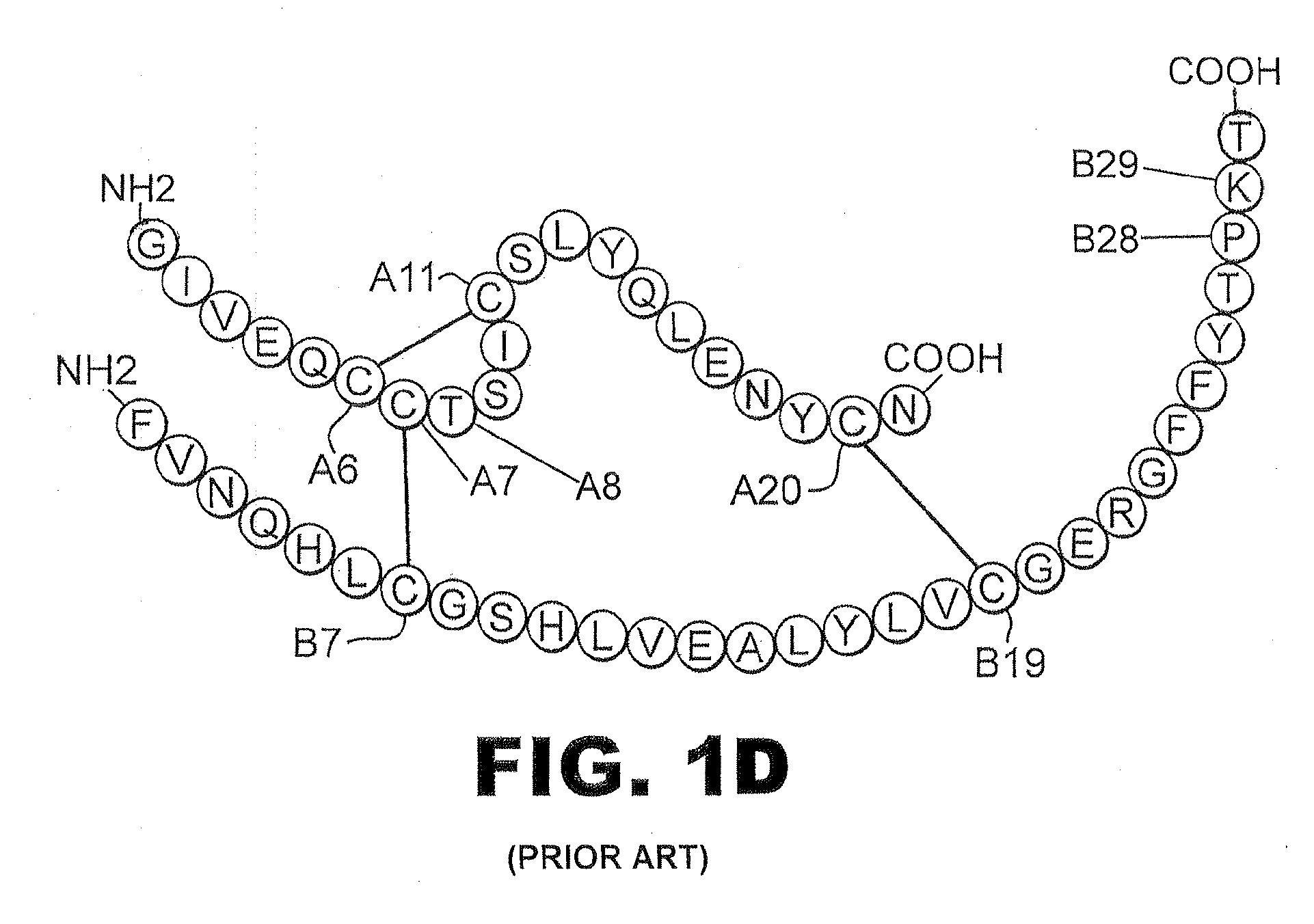
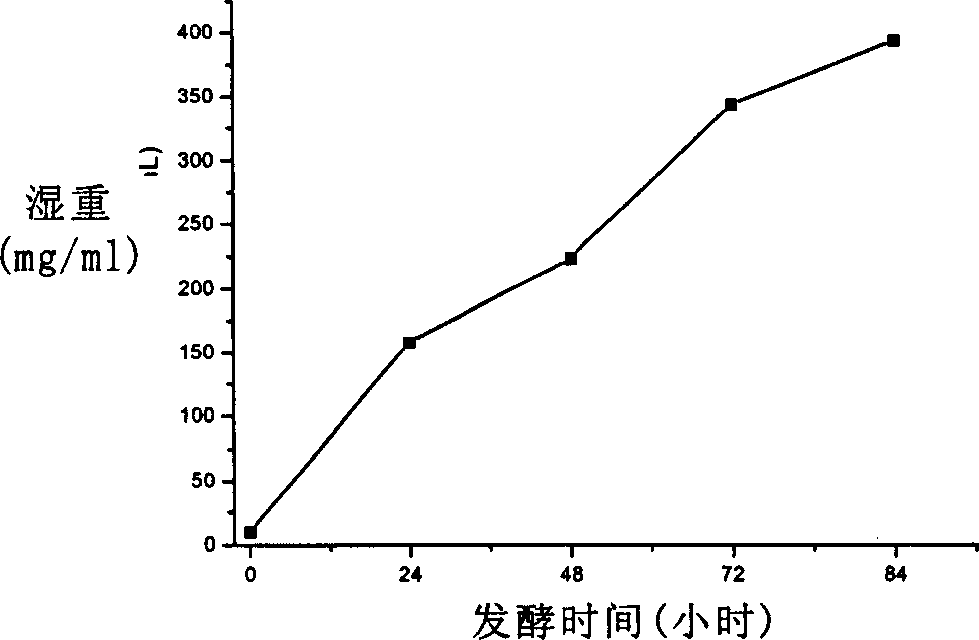
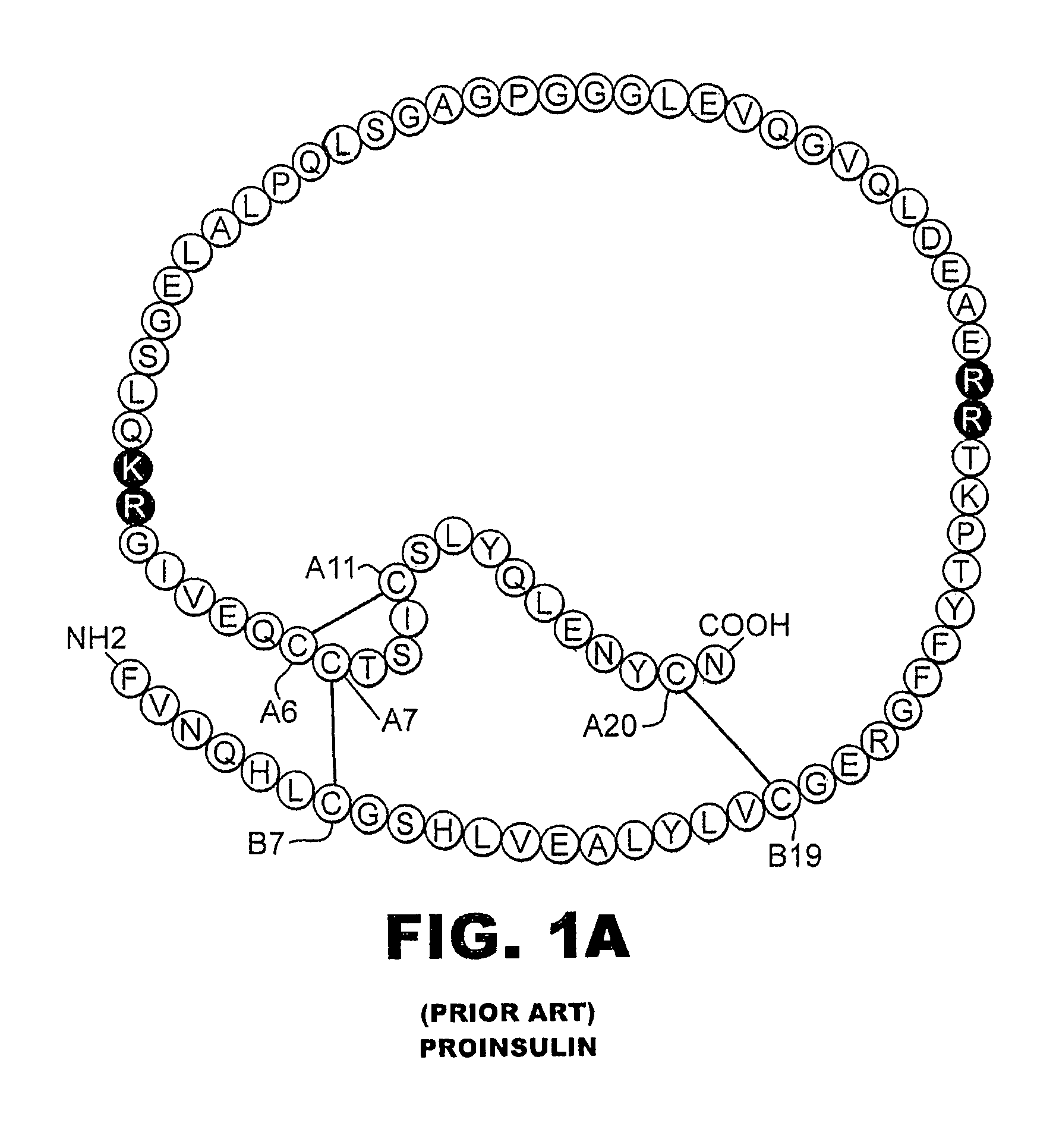
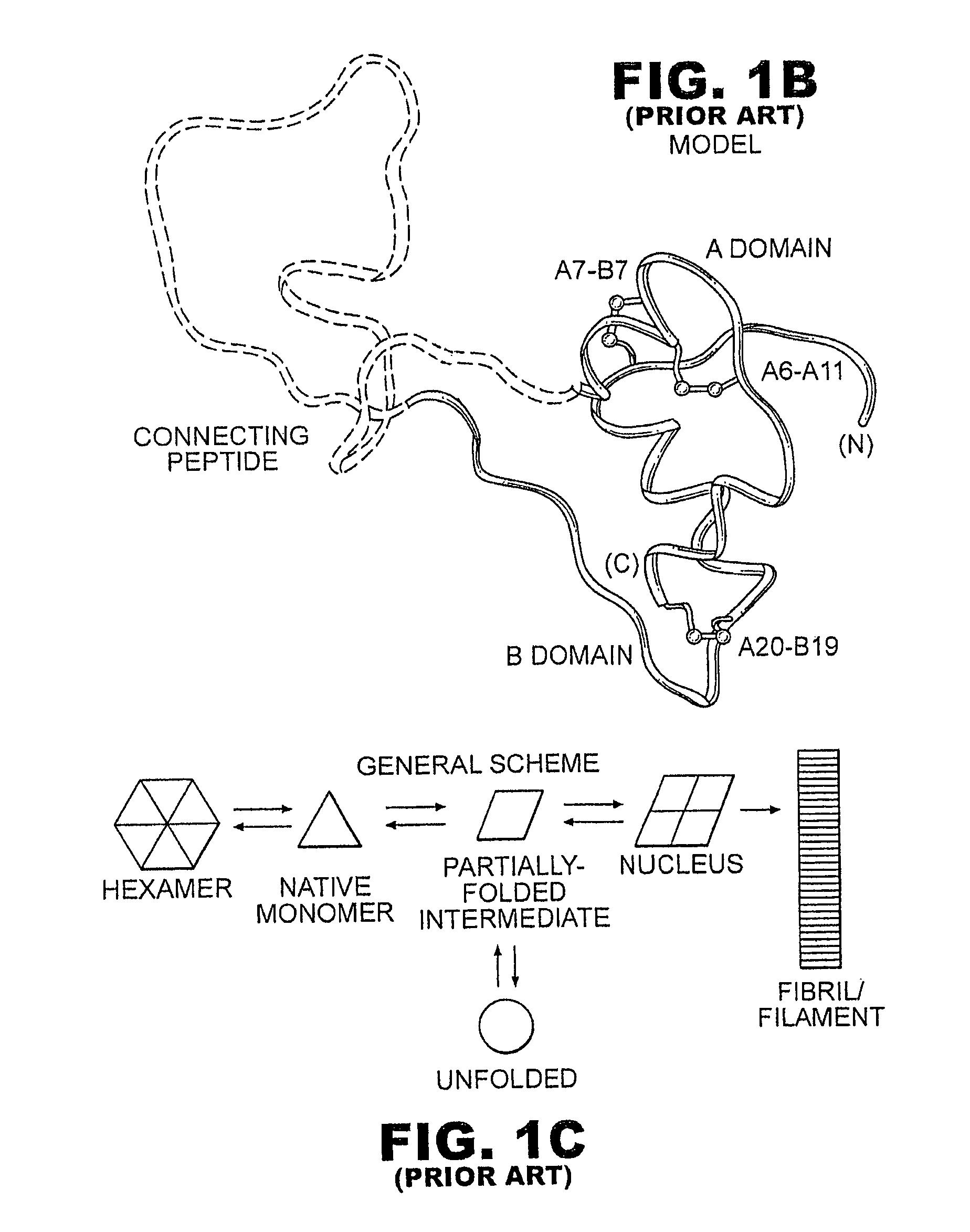
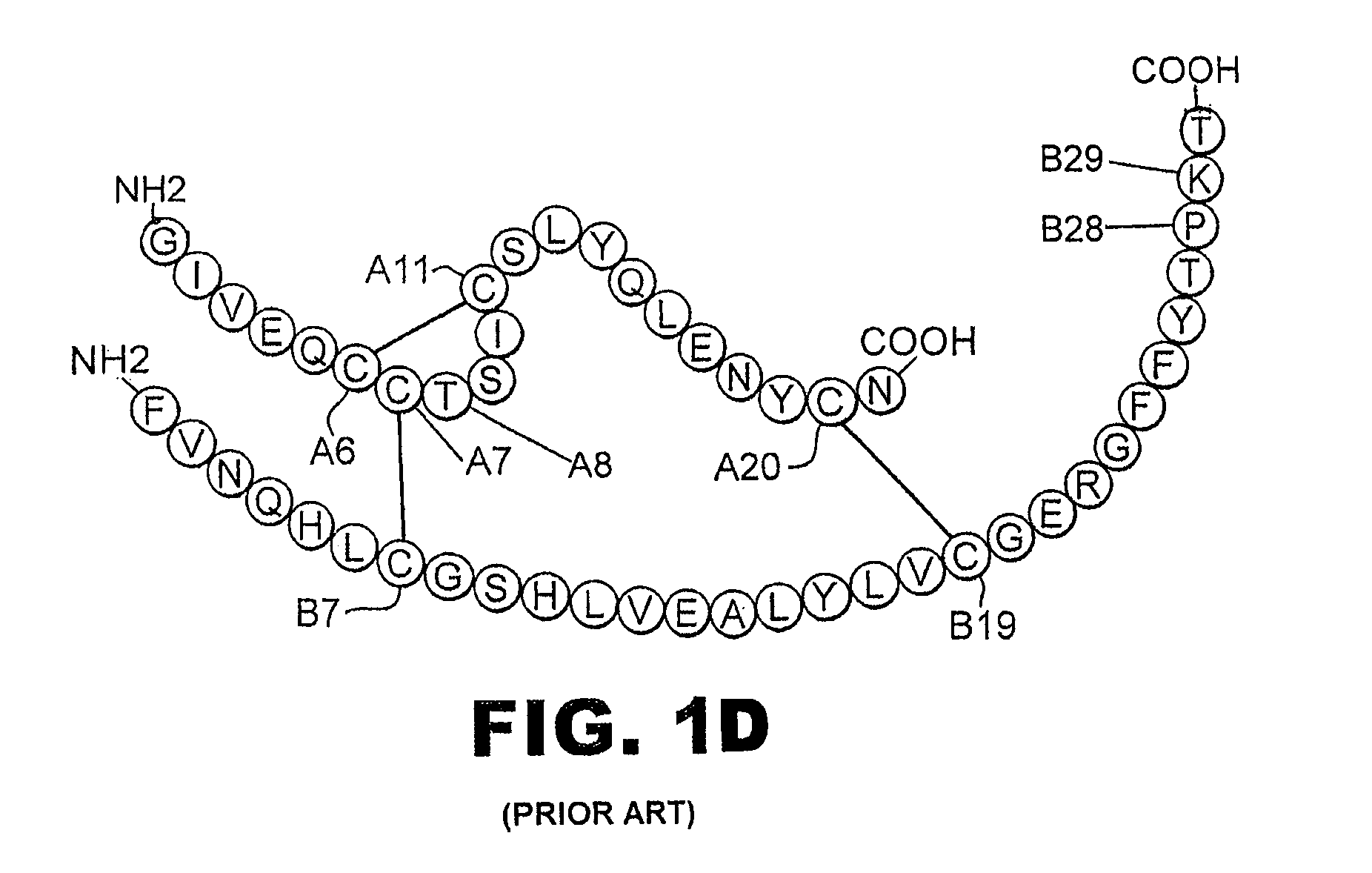
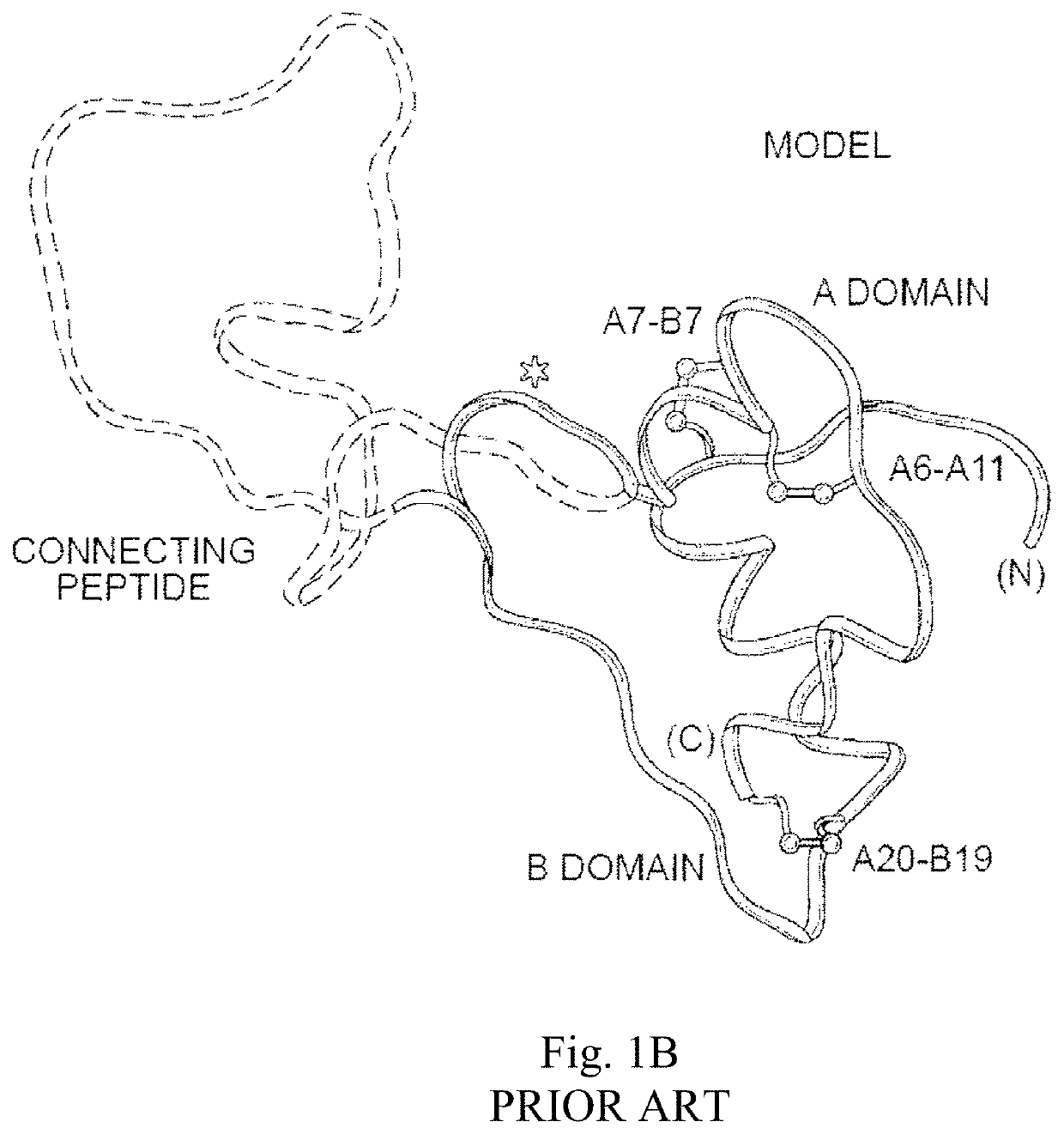
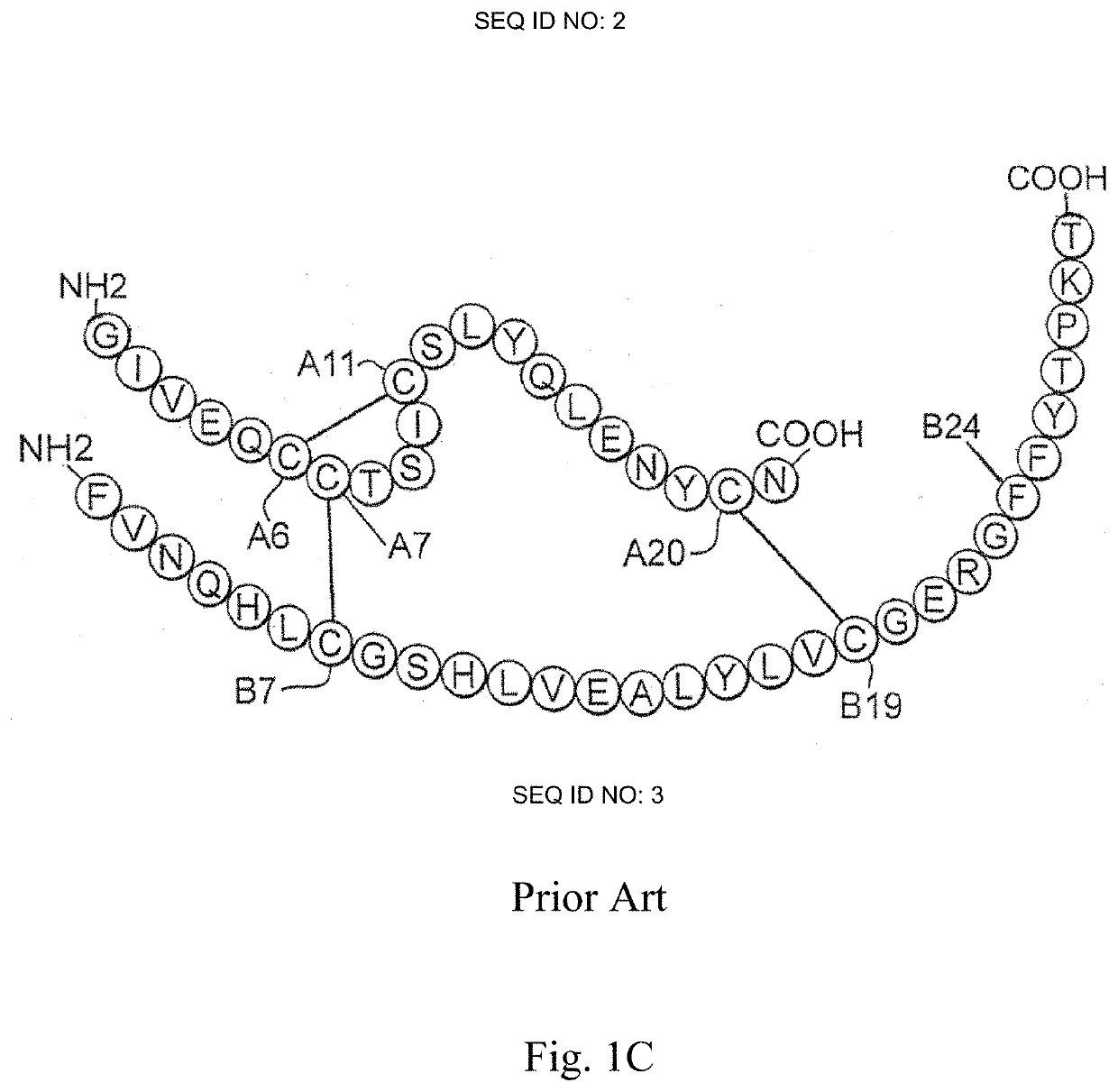
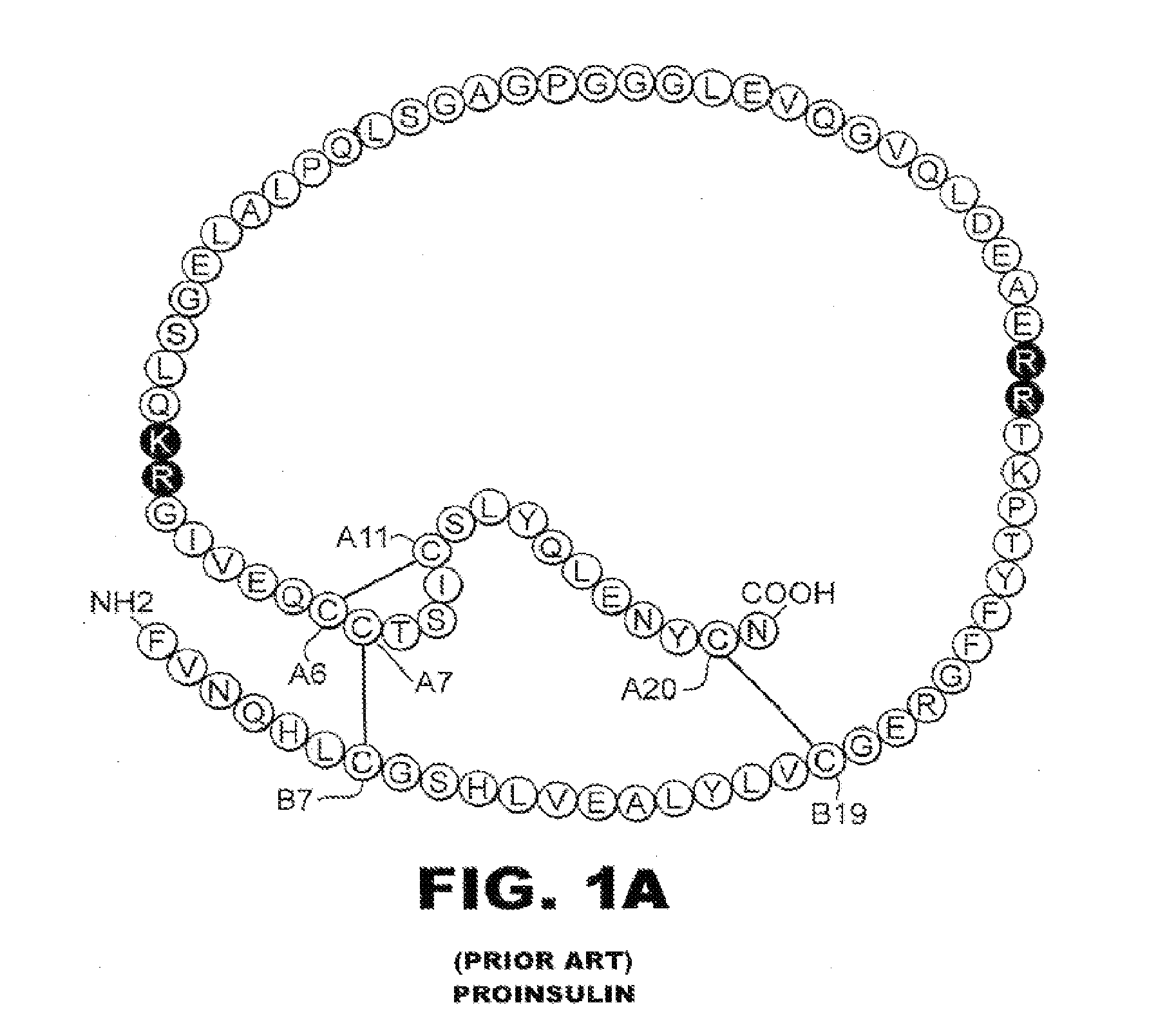
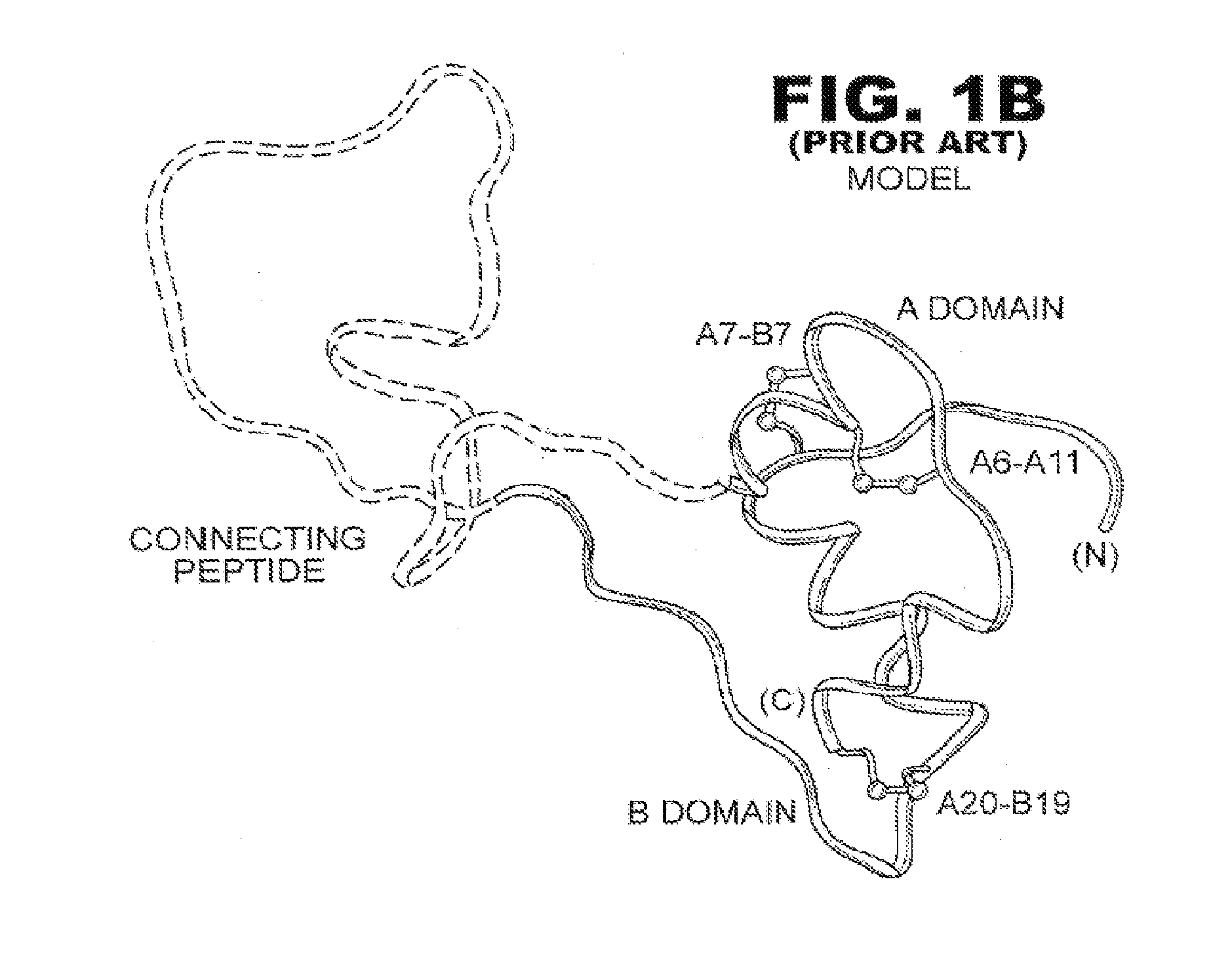
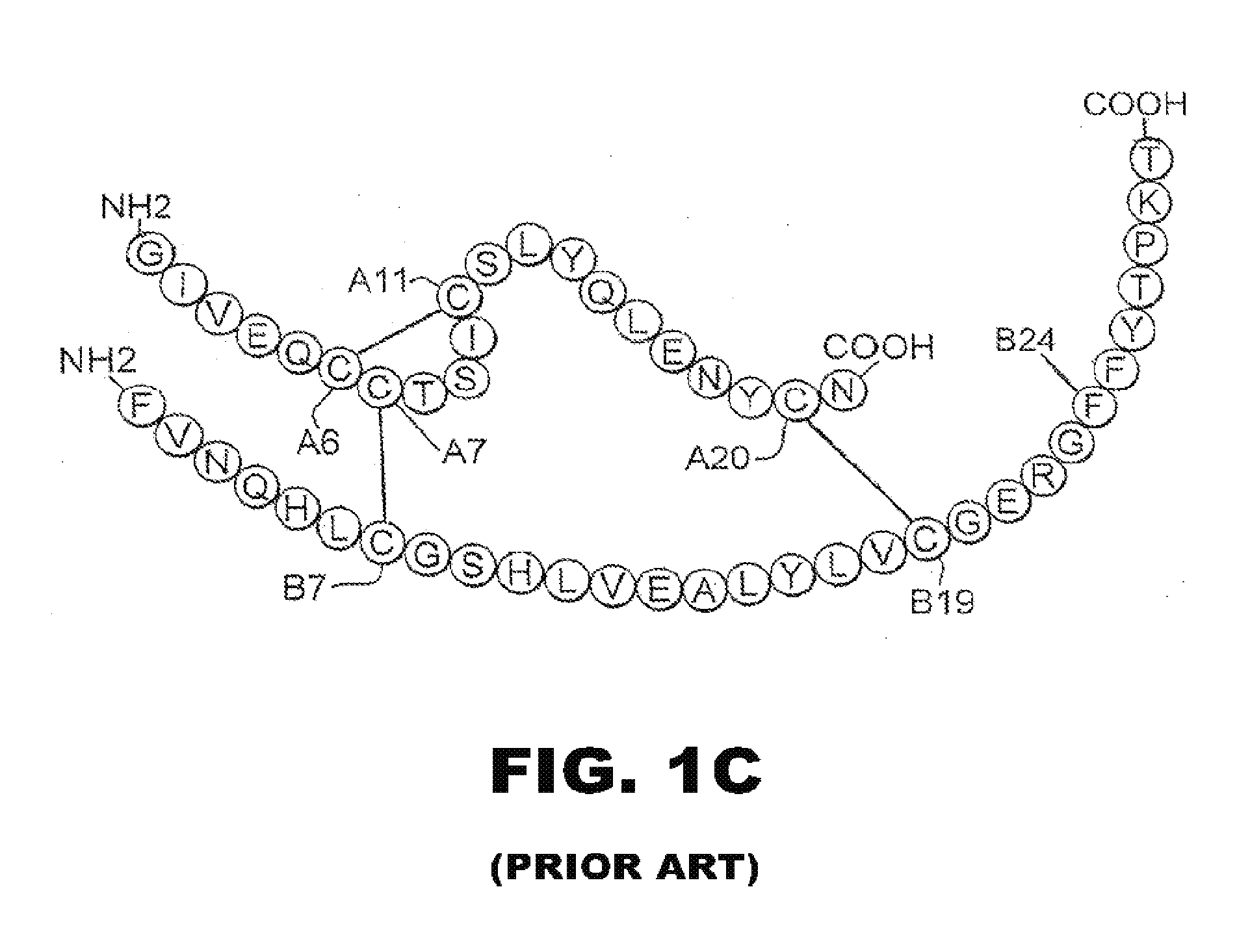
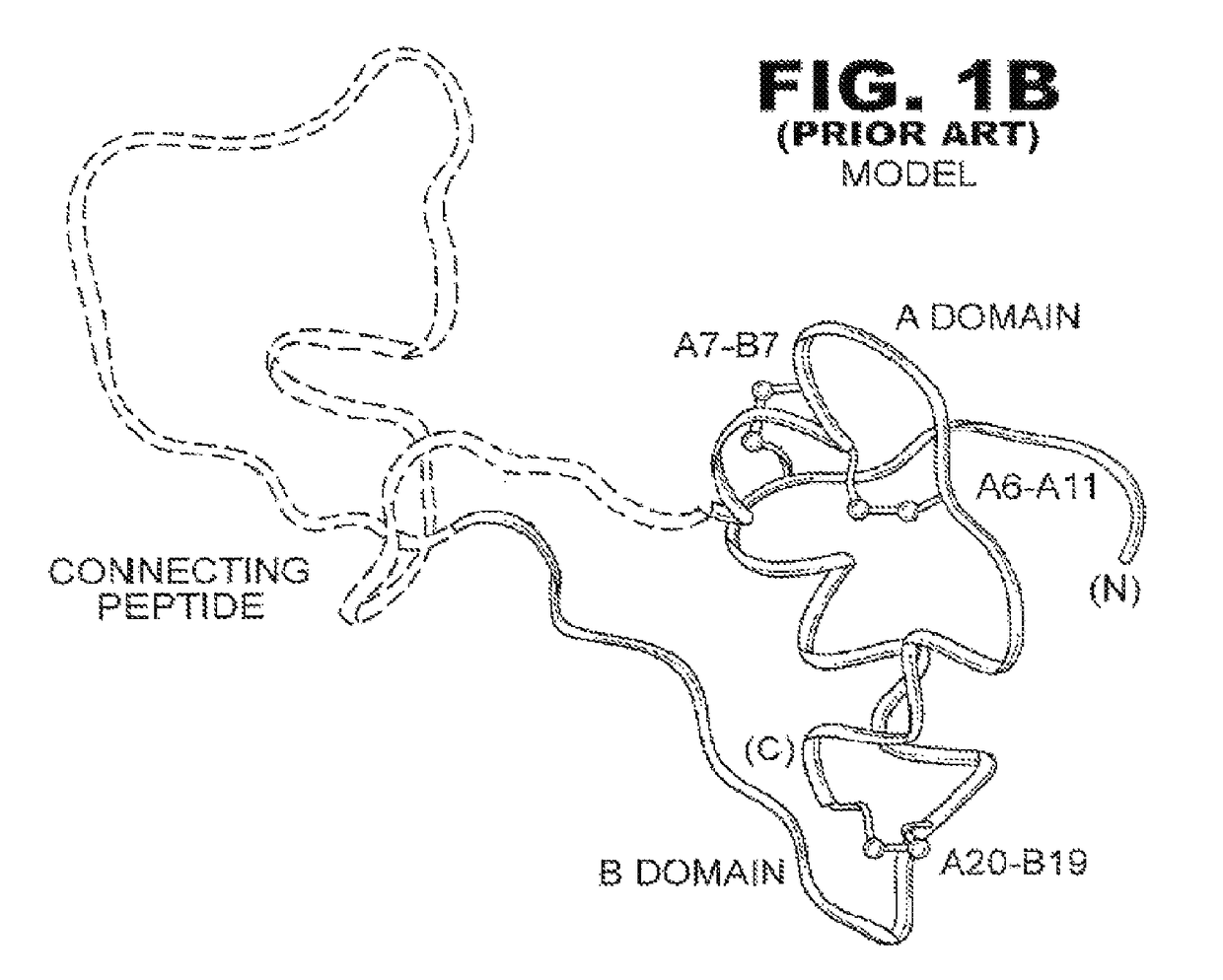
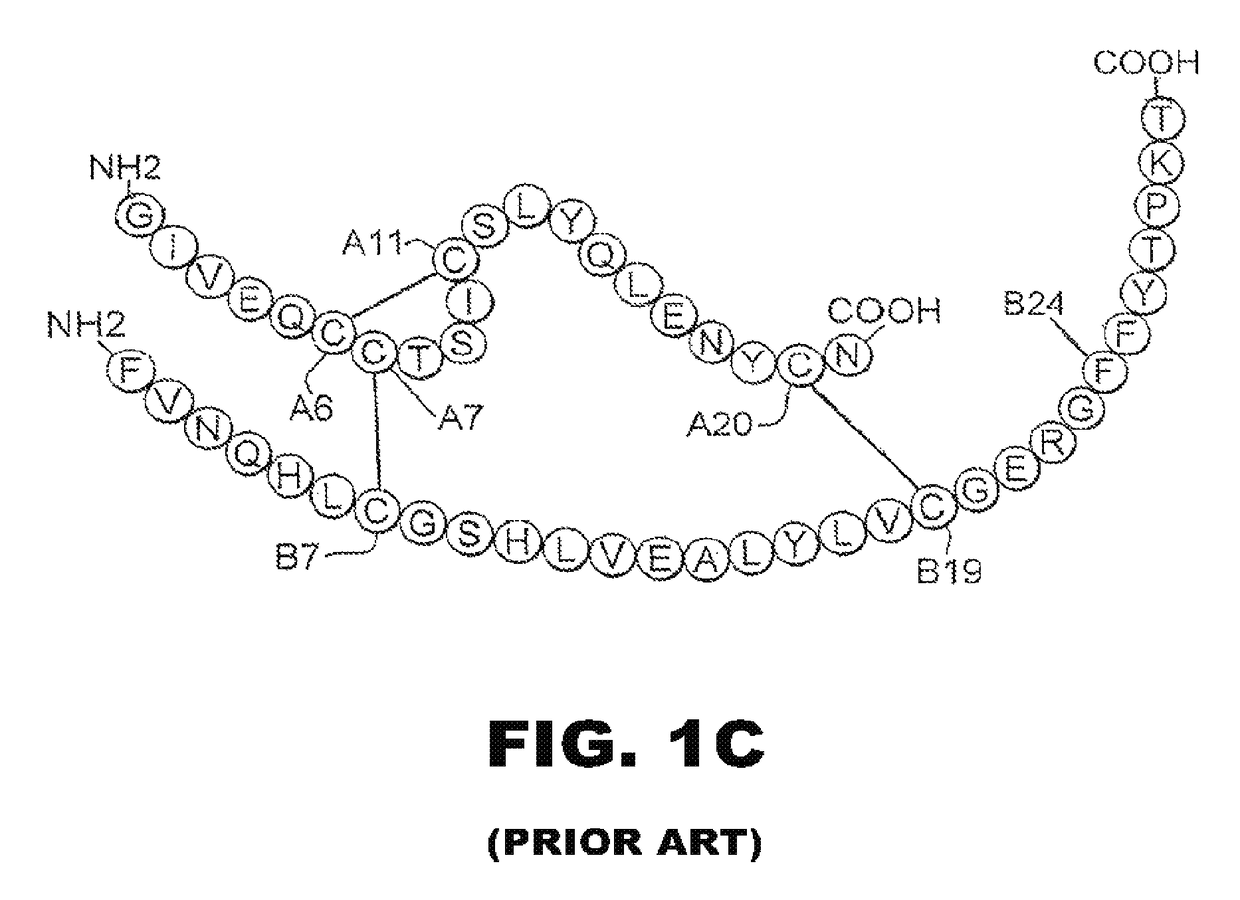
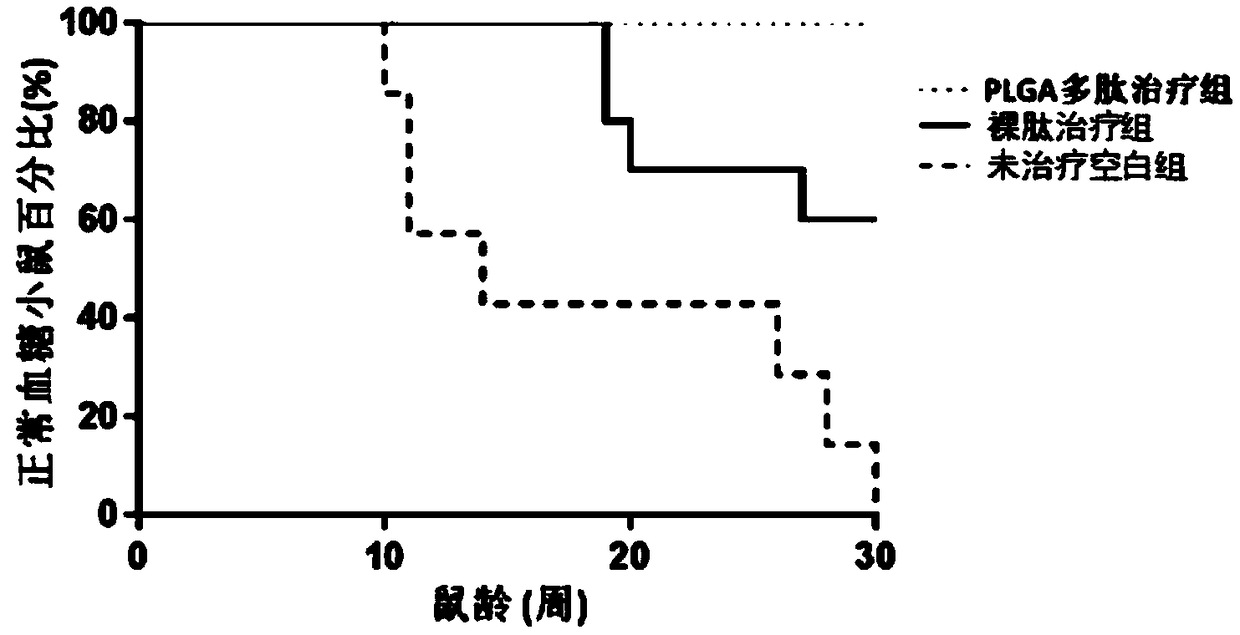
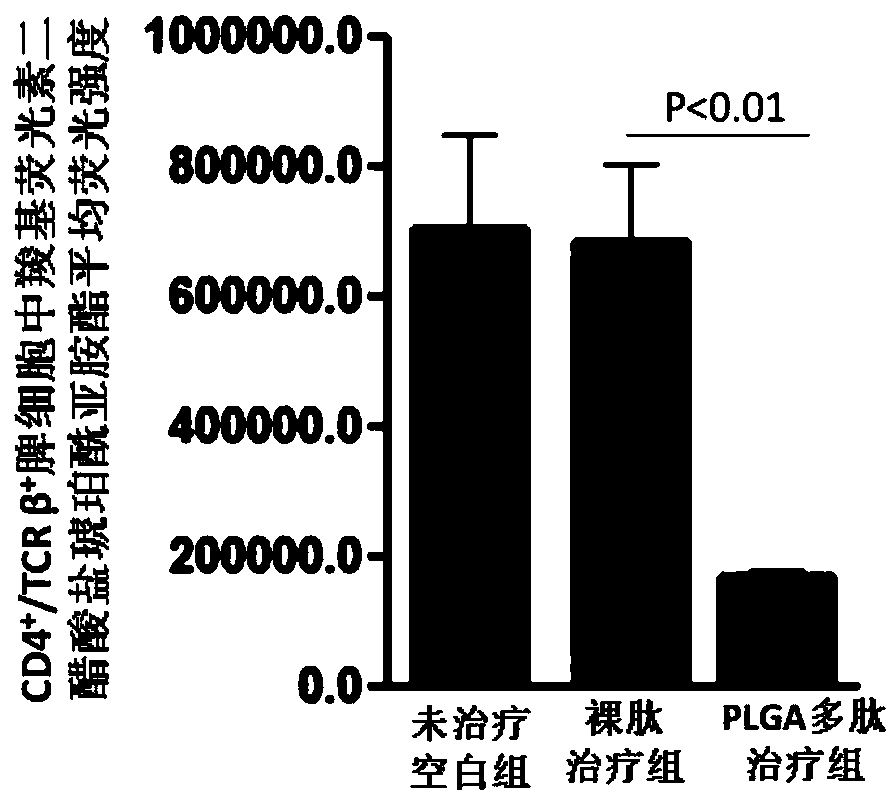
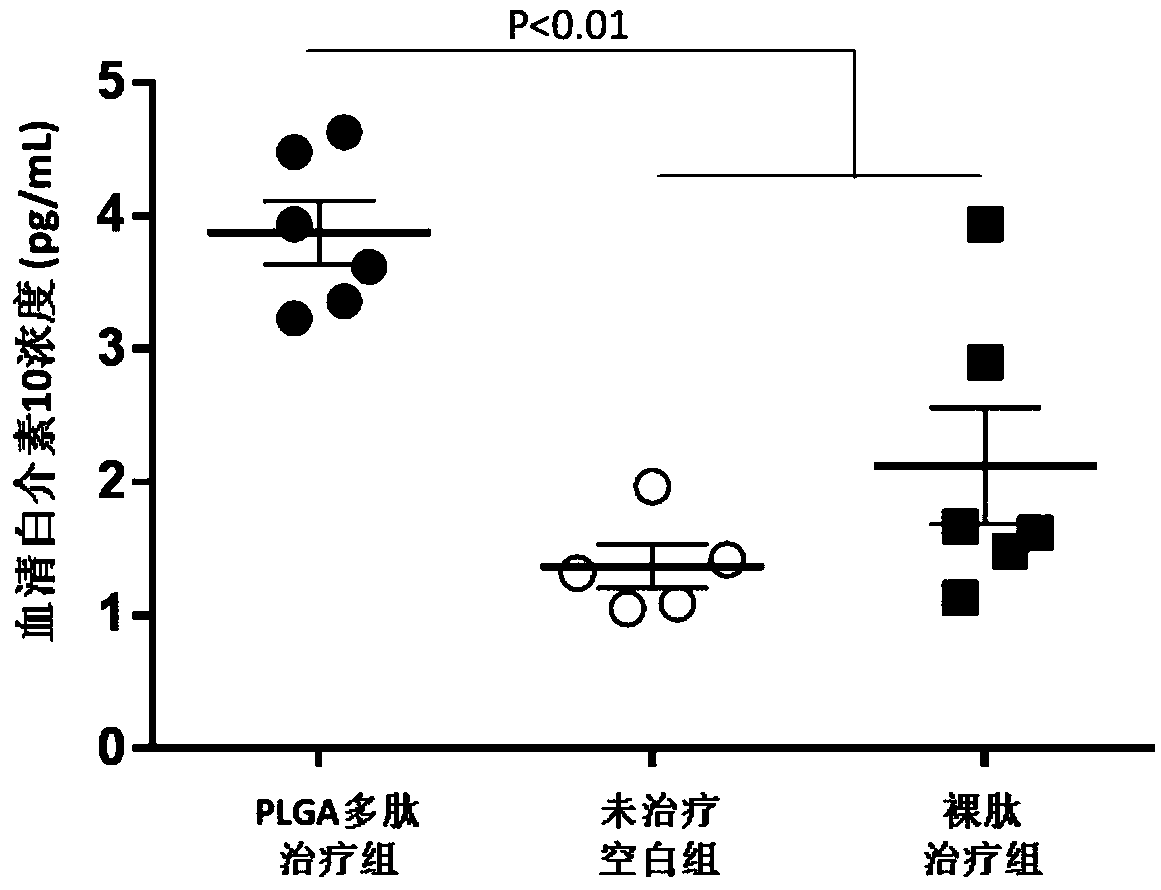
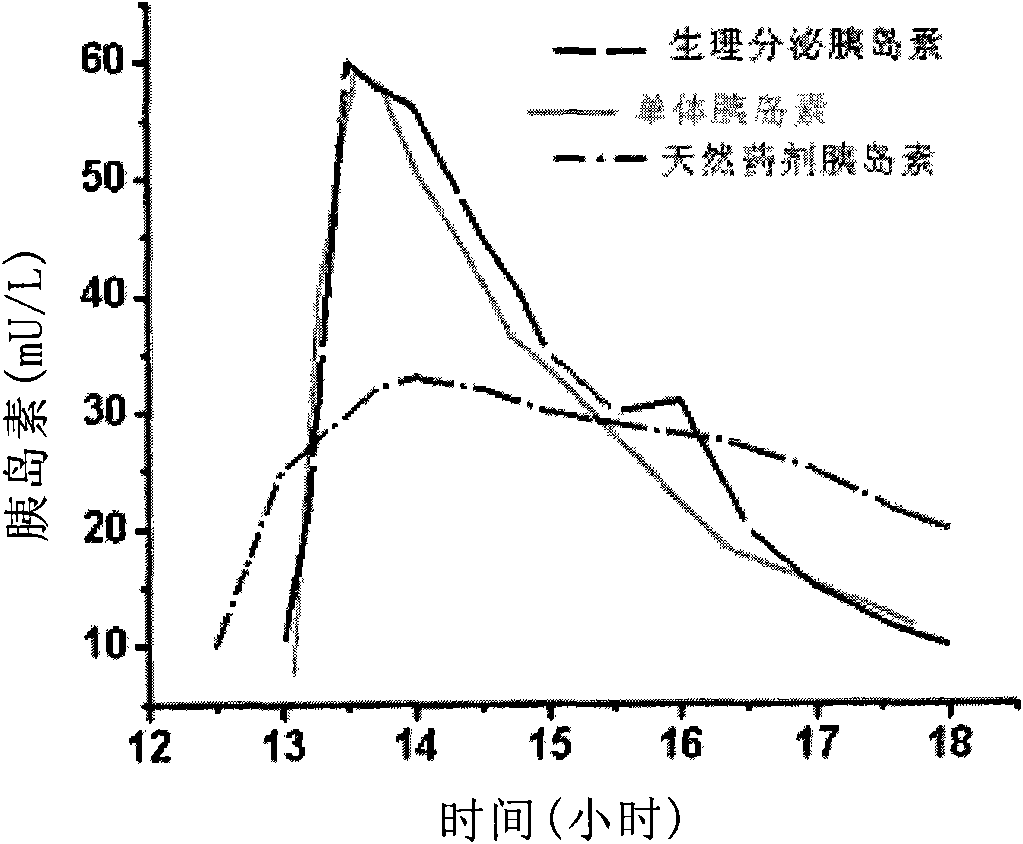
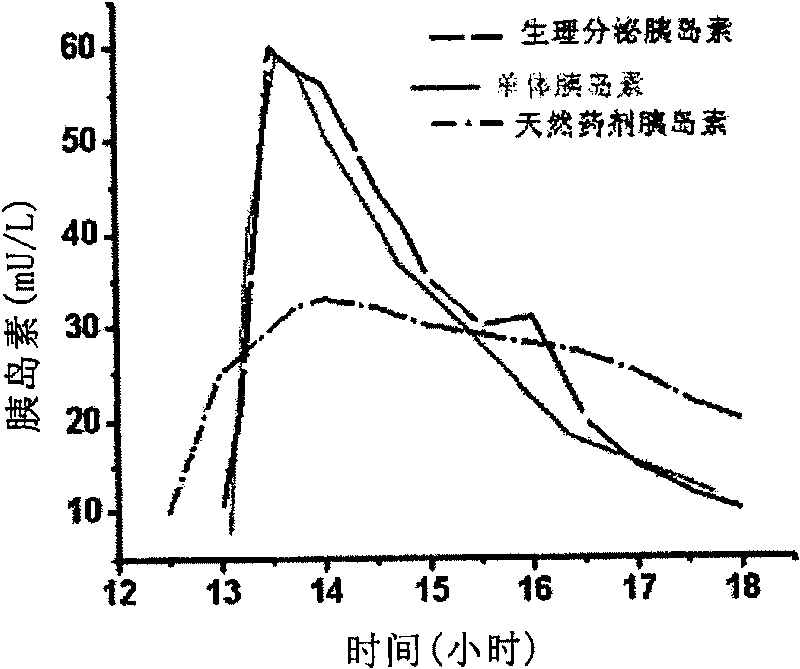
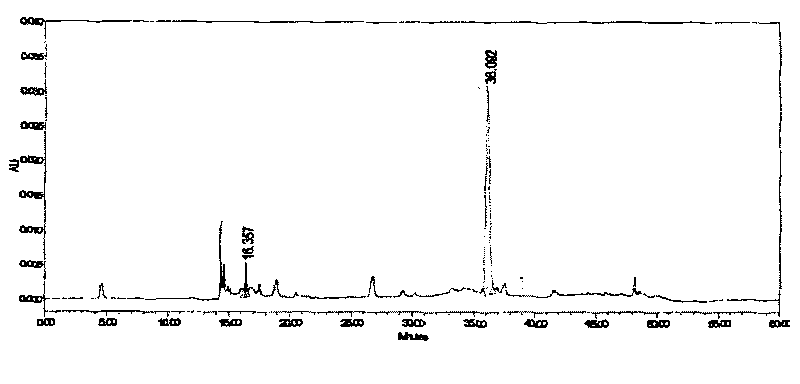
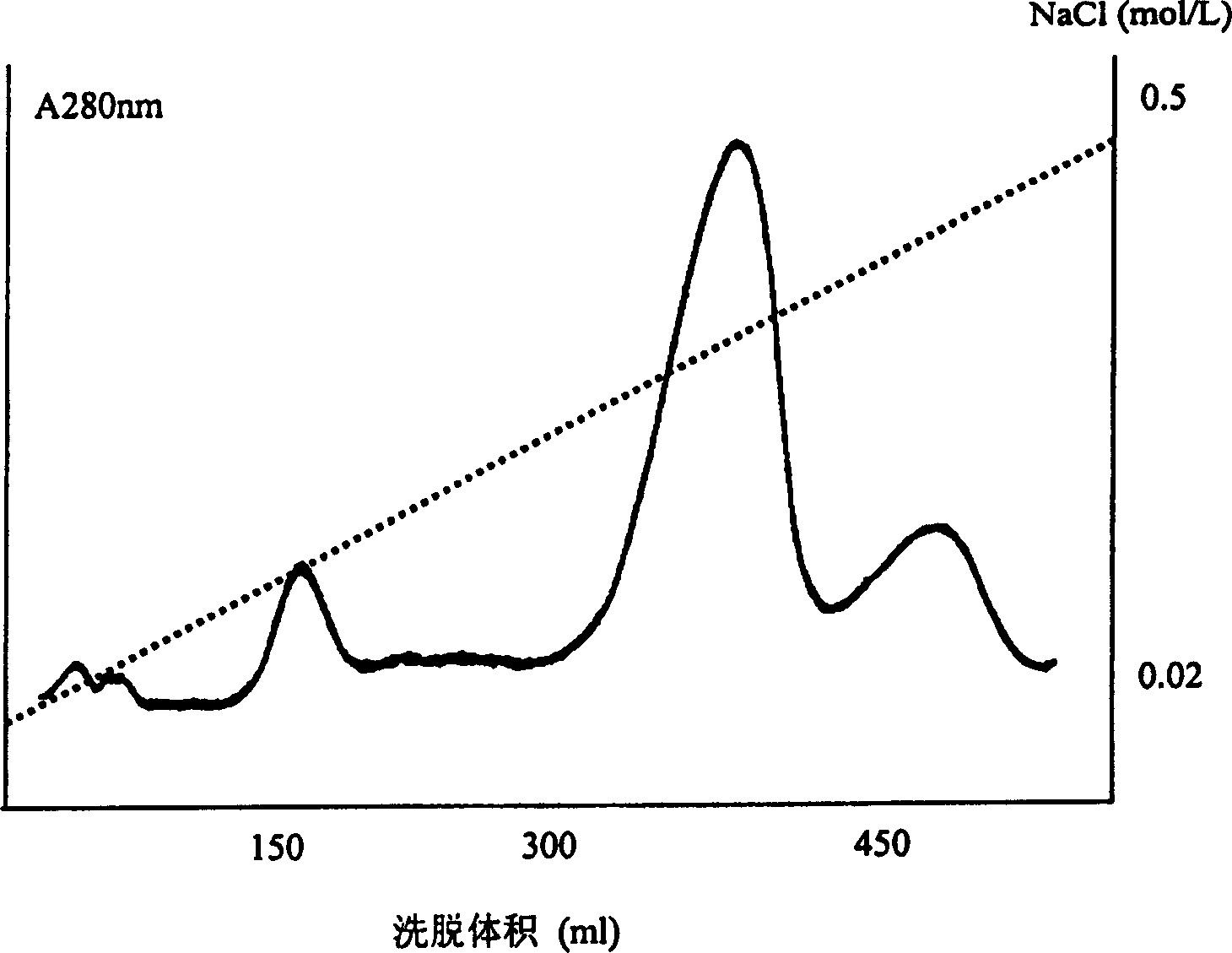
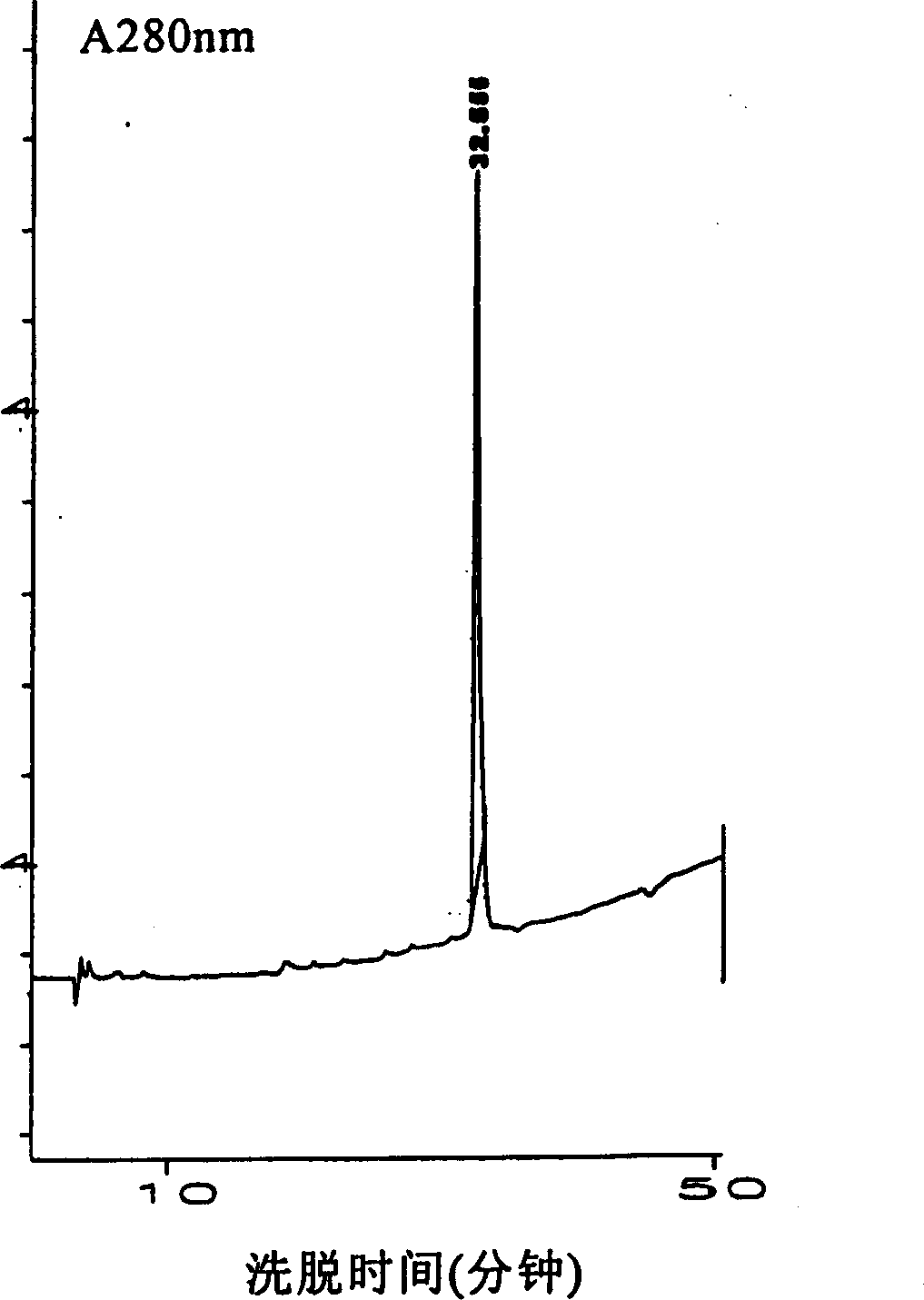
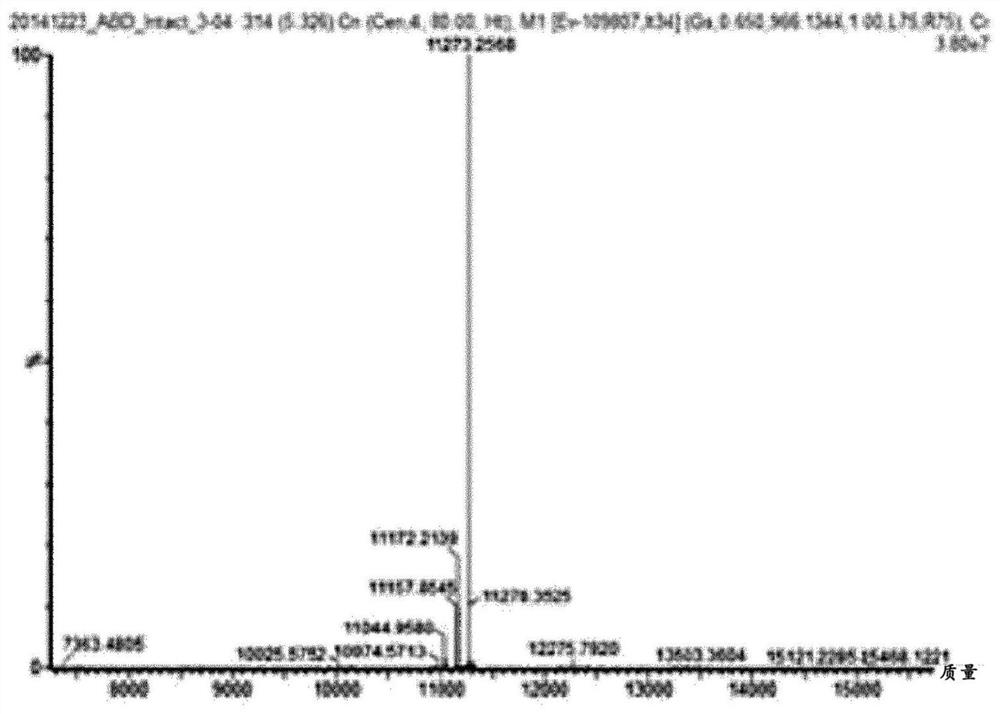
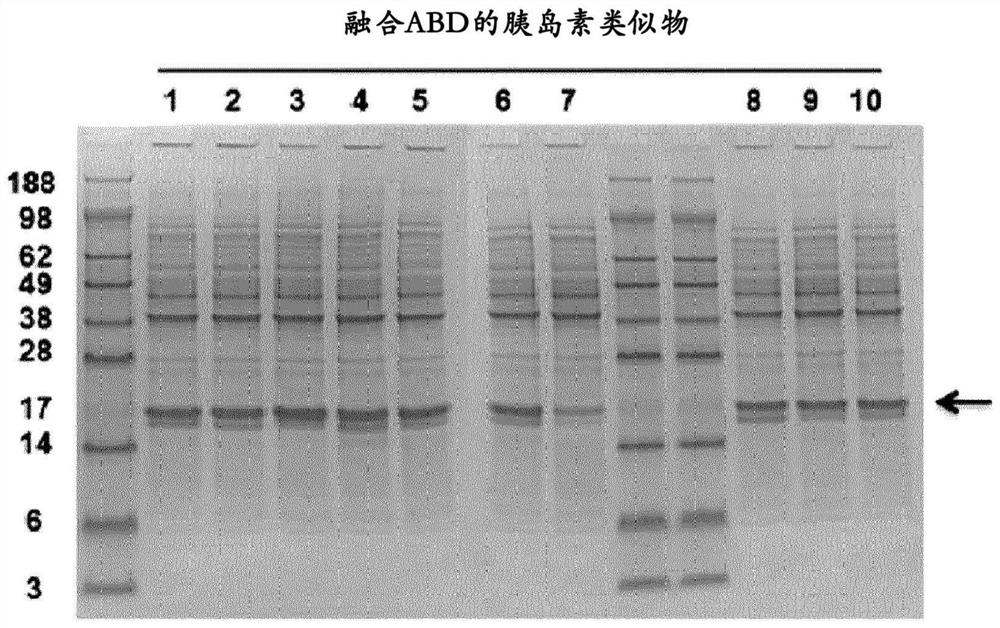
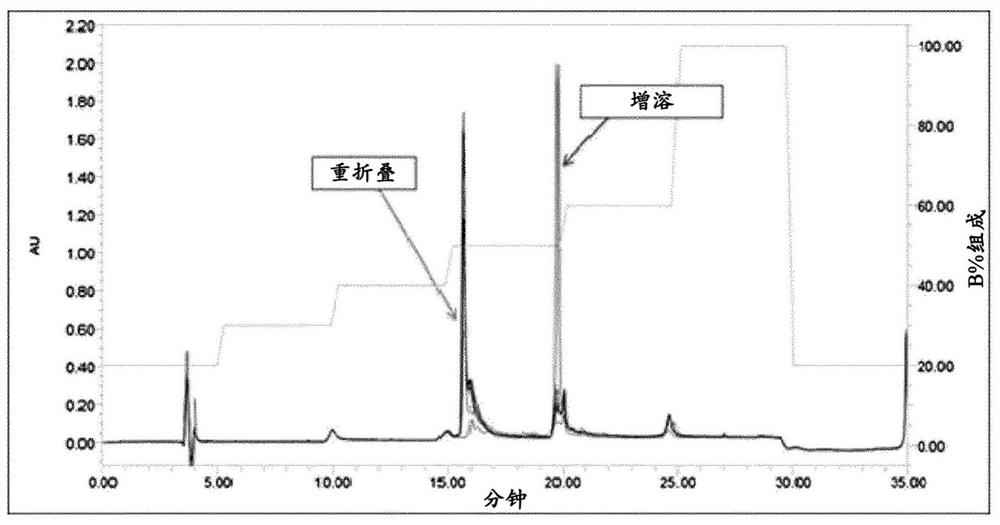
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Insulin B Chain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
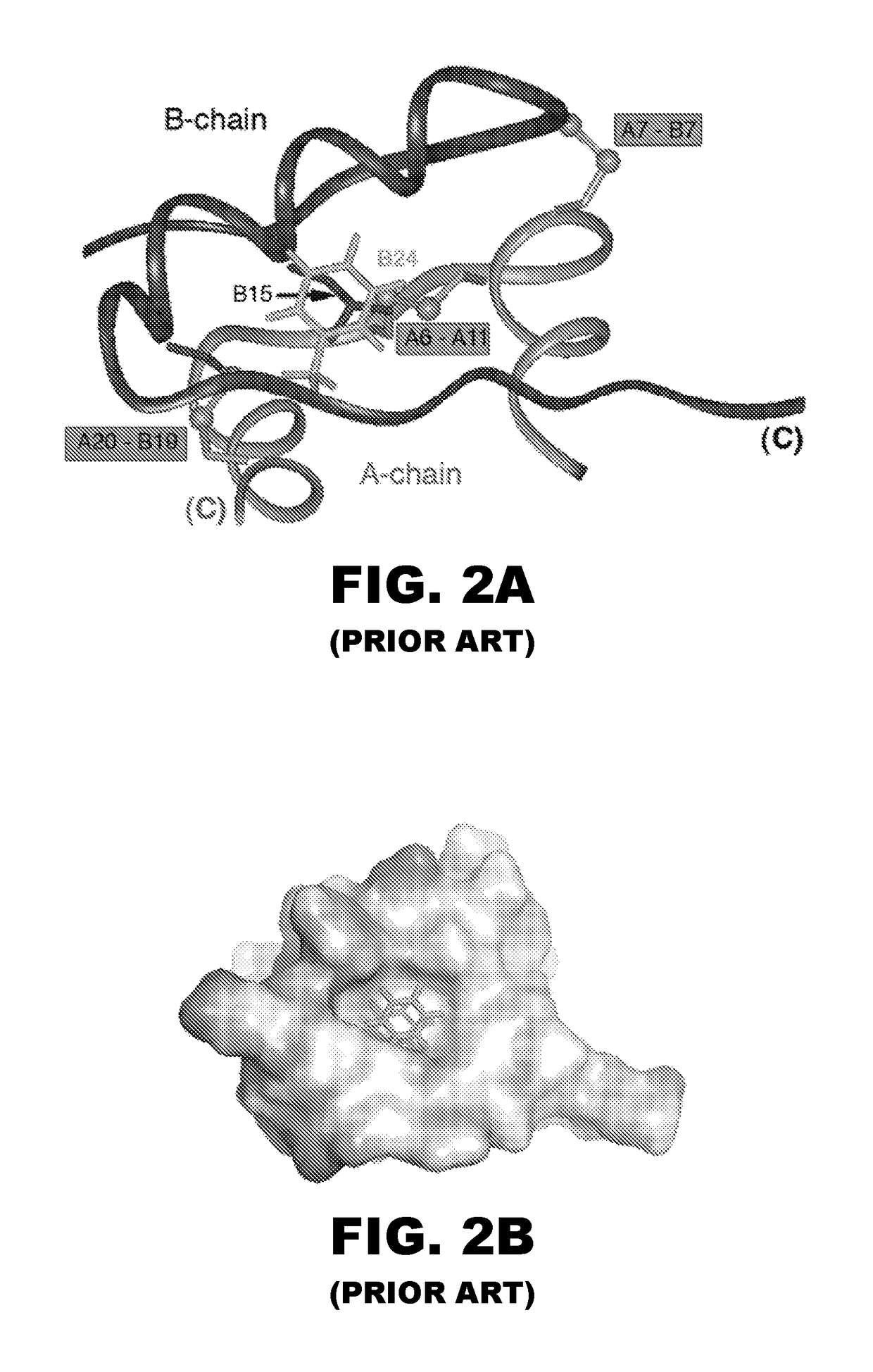
Fibrillation-resistant insulin and insulin analogues
InactiveUS8192957B2High thermodynamic stabilityMaintain biological activityBacteriaSugar derivativesInsulin A ChainNormal insulin
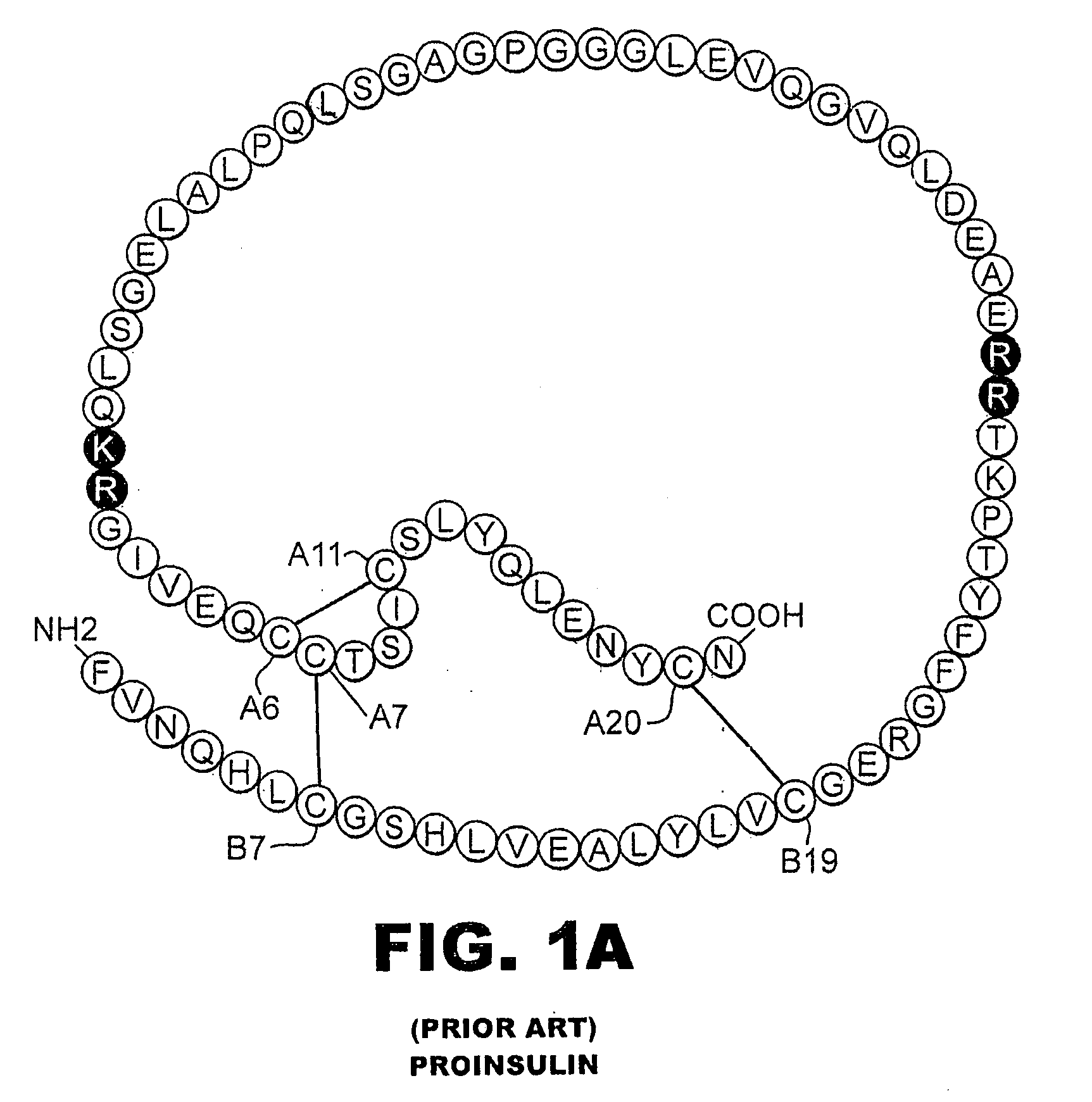
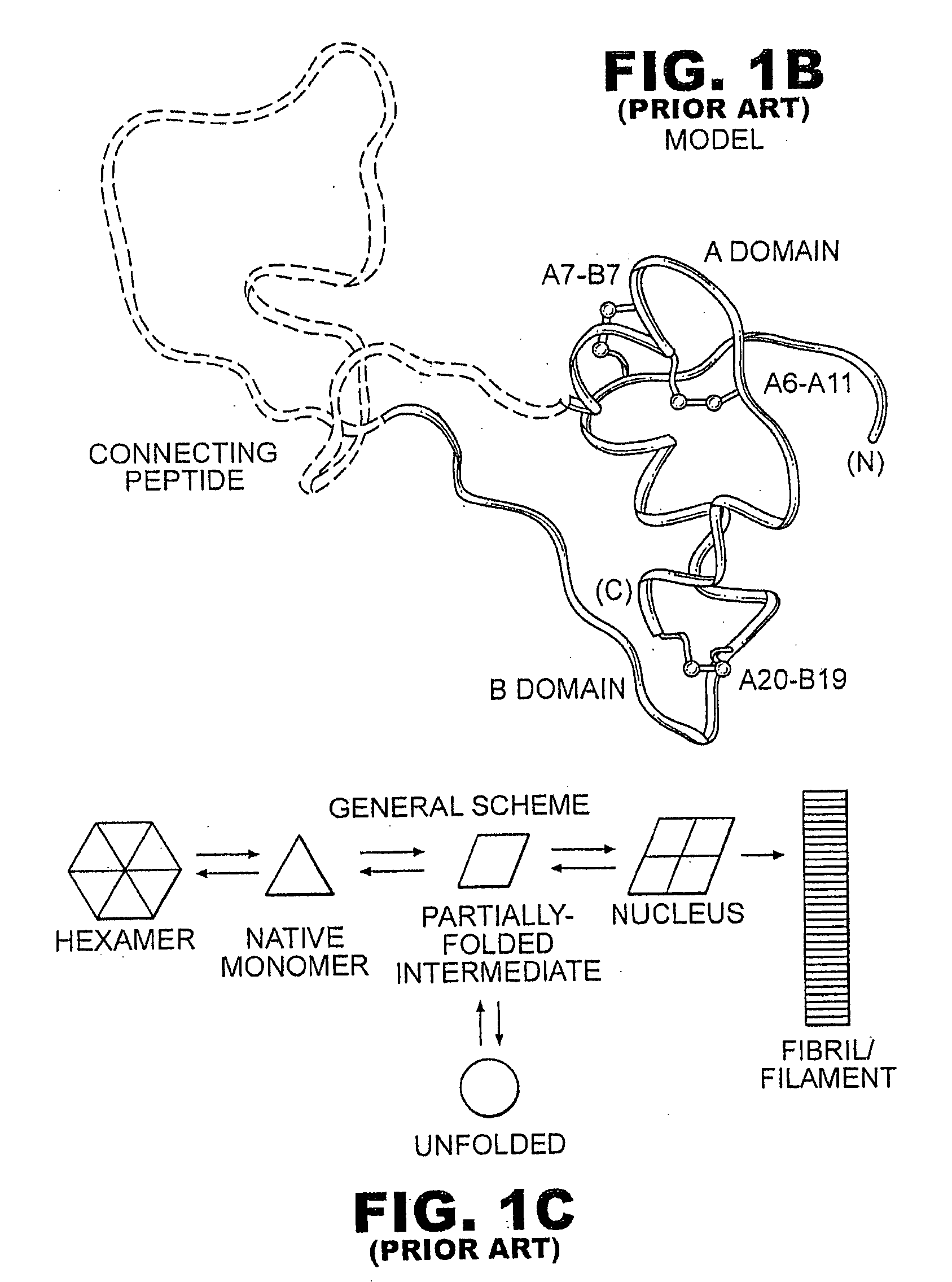
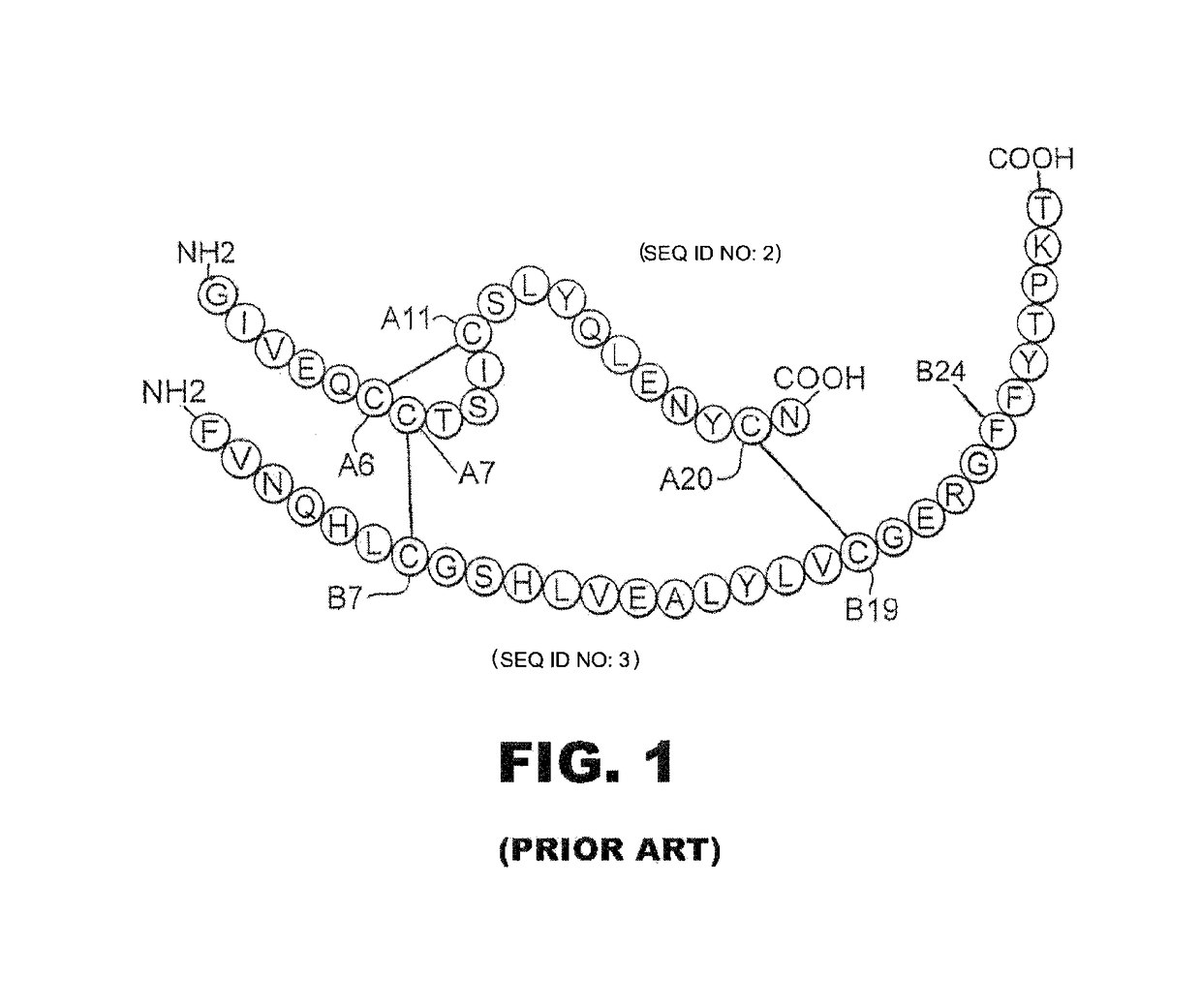
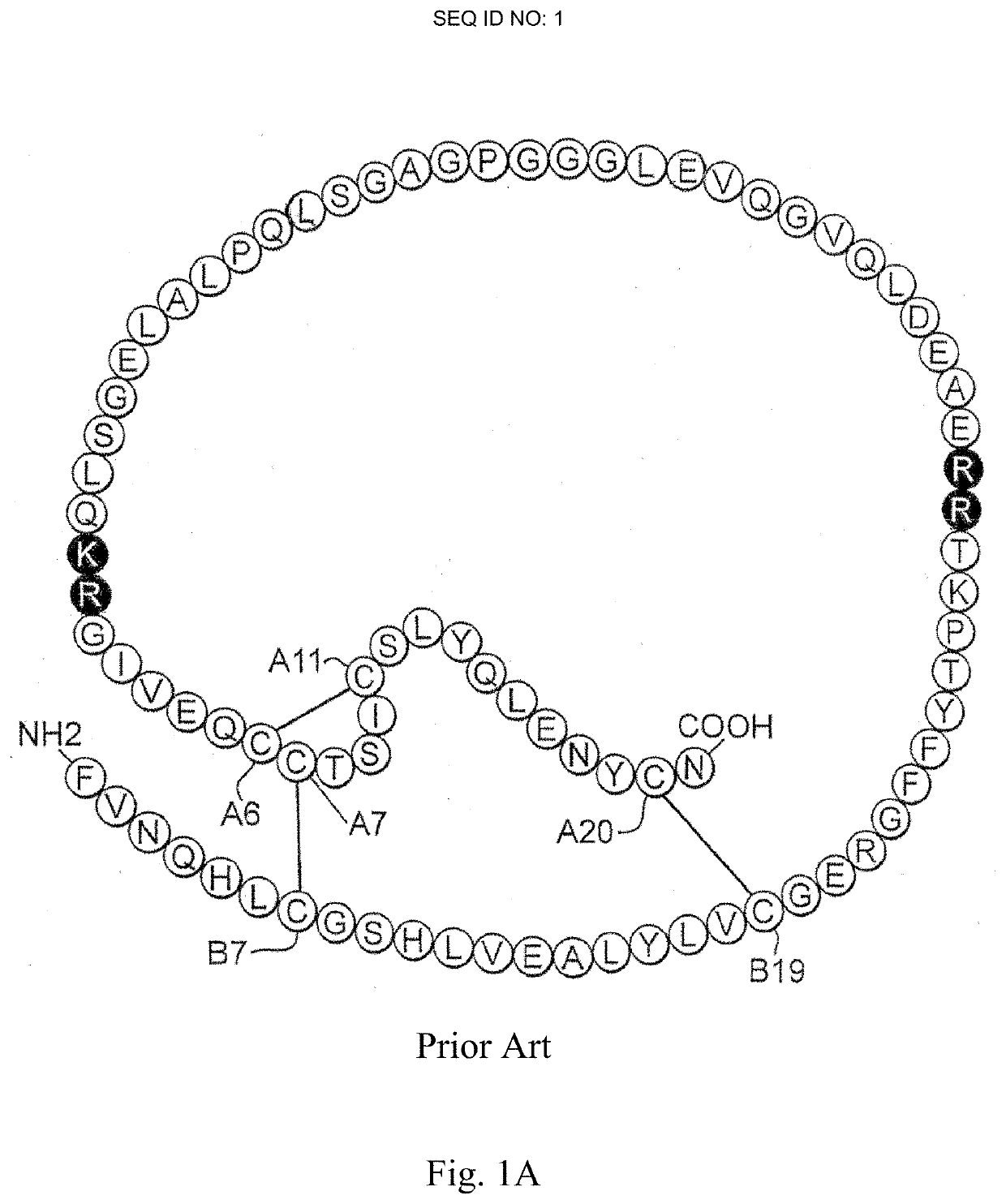
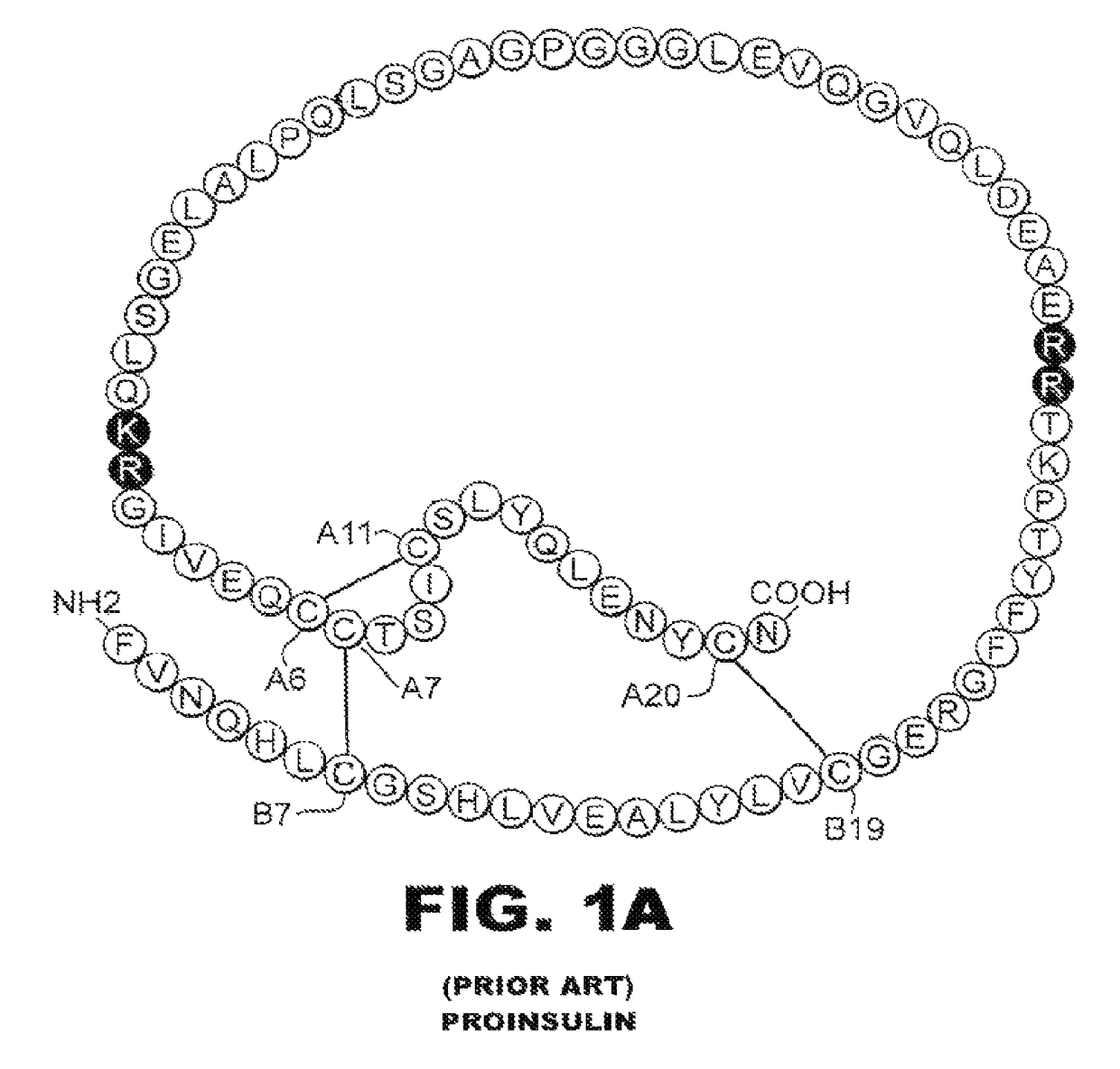
A fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue may be a single-chain insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, containing an insulin A chain sequence or an analogue thereof and an insulin B chain sequence or an analogue thereof connected by a polypeptide of 4-10 amino acids. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue preferably displays less than 1 percent fibrillation with incubation at 37° C. for at least 21 days. A single-chain insulin analogue displays greater in vitro insulin receptor binding than normal insulin while displaying less than or equal binding to IGFR than normal insulin. The fibrillation-resistant insulin may be used to treat a patient using an implantable or external insulin pump, due to its greater fibrillation resistance.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Insulin analogues of enhanced receptor-binding specificity
InactiveUS20120184488A1Good physical propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin A ChainArginine
A method of treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of an insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to the patient. The insulin analogue or physiologically acceptable salt thereof contains an insulin A-chain sequence modified at positions selected from the group consisting of A0, A1, A4, A8, and A21. The insulin analogue may exhibit decreased affinity for the IGF receptor in comparison to wild type insulin of the same species and at least 20% of the affinity of wild-type insulin for the insulin receptor of the same species. Position A0 may be arginine. Position A1 may be D-alanine, D-aspartic acid, or D-leucine. Position A8 may be histidine, lysine, or arginine. Optionally, an insulin B-chain analogue sequence comprises a histidine at position B1. A nucleic acid may encode such an insulin polypeptide.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Rapid Acting Insulin Analogues
InactiveUS20110021423A1Promote formationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineInsulin B Chain
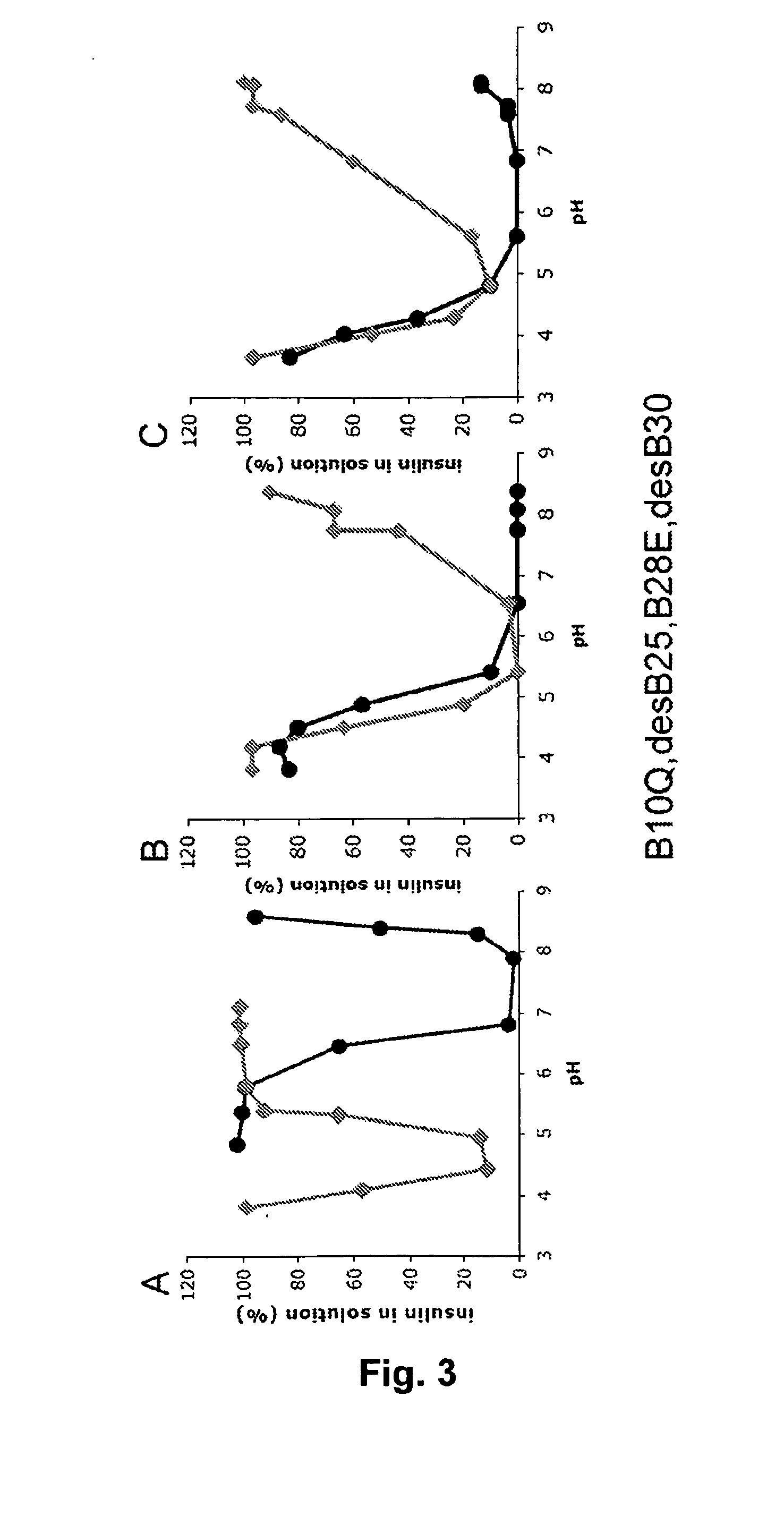
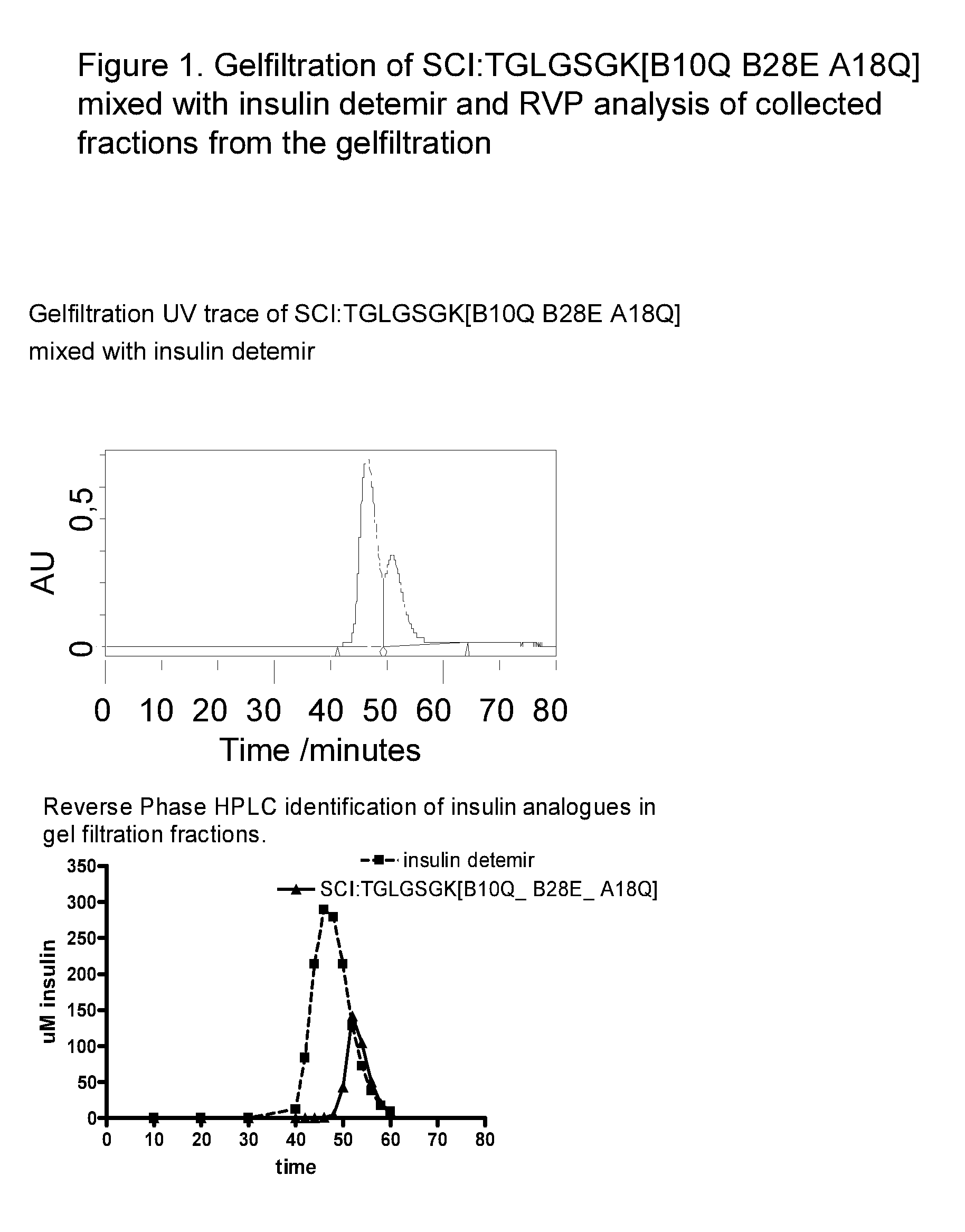
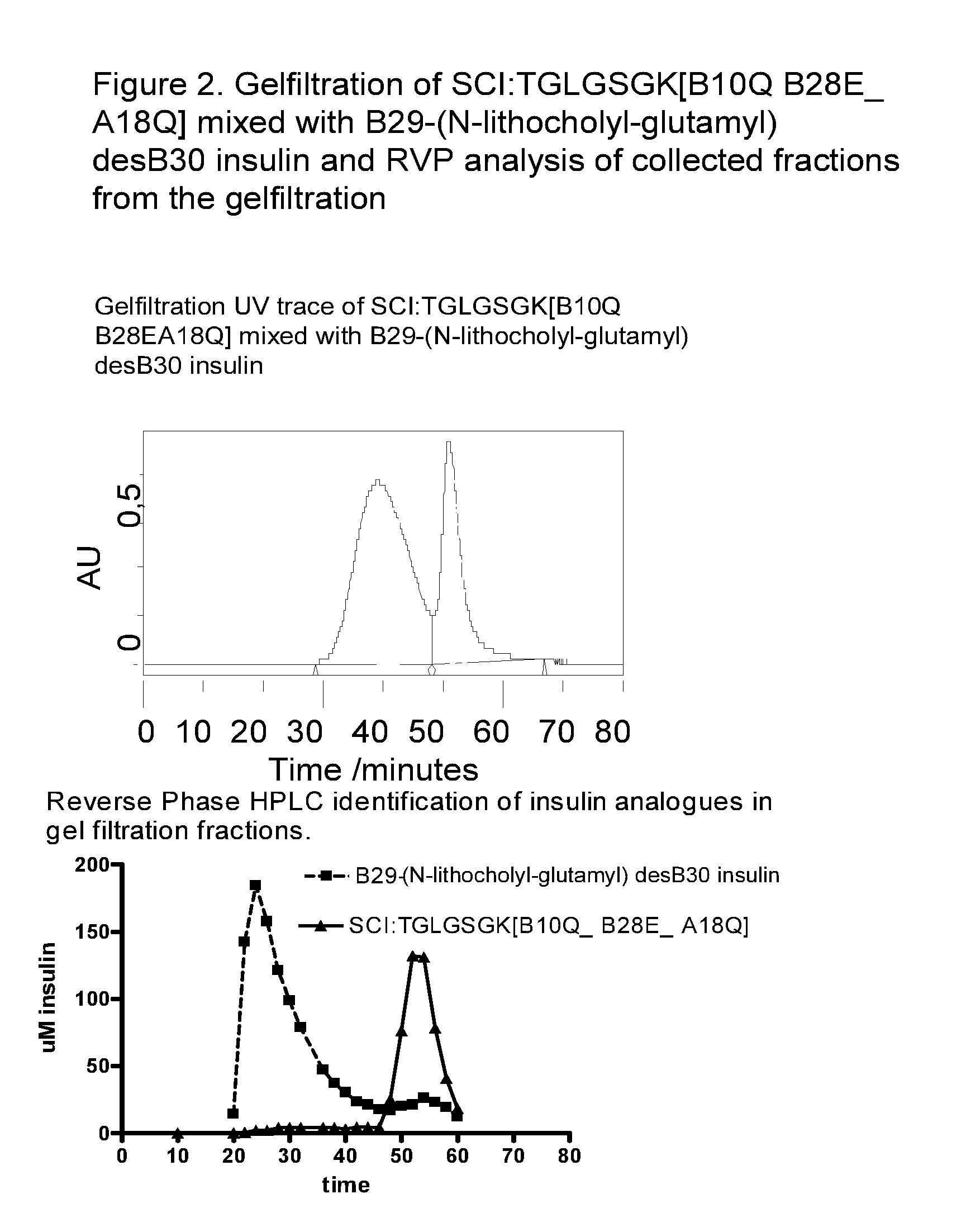
The invention is related to fast acting insulin analogues which can form soluble mix-tures (pre-mixed or self-mixed) with long acting insulin analogues. The fast action is achieved through monomerizing substitutions / deletions in the C-terminus of the B-chain of human insulin and the mixability with long acting insulin analogues is achieved through a substitution of the Zn-binding His in position B10 of human insulin with a Gln amino acid residue. In one embodiment the invention is related to fast acting insulin analogues in which at least one of the natural amino acid residues in position B22-B30 in the human B-chain has been substituted with another amino acid residue having the effect of promoting formation of the monomeric form of insulin, the His amino acid residue in position 10 in the B-chain is substituted with a Gln and wherein further one or more of the amino acid residues in position B22-B30 optionally have been deleted.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Meal-time insulin analogues of enhanced stability
InactiveUS20110059887A1Increase propensityImprove stabilitySugar derivativesBacteriaInsulin A ChainWild type
A method treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of a fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to the patient. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, contains an insulin A-chain sequence modified at position A8 and an insulin B-chain sequence or an analogue thereof. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue may exhibit thermodynamic stability similar to or exceeding that of wild-type human insulin and displays a susceptibility to fibrillation similar to or exceeding that of wild-type human insulin. An insulin analogue may display greater in vitro insulin receptor binding than normal insulin while displaying binding to IGFR less than twice that of normal insulin and less than that of fast-acting insulin analogs. The fibrillation-resistant insulin may be used to treat a patient by subcutaneous injection or by using an implantable or external insulin pump, due to its fibrillation resistance.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
High alkaline protease and use thereof
InactiveUS8153413B2Good alkali resistanceImprove the immunitySugar derivativesBacteriaSitus inversusAmino acid
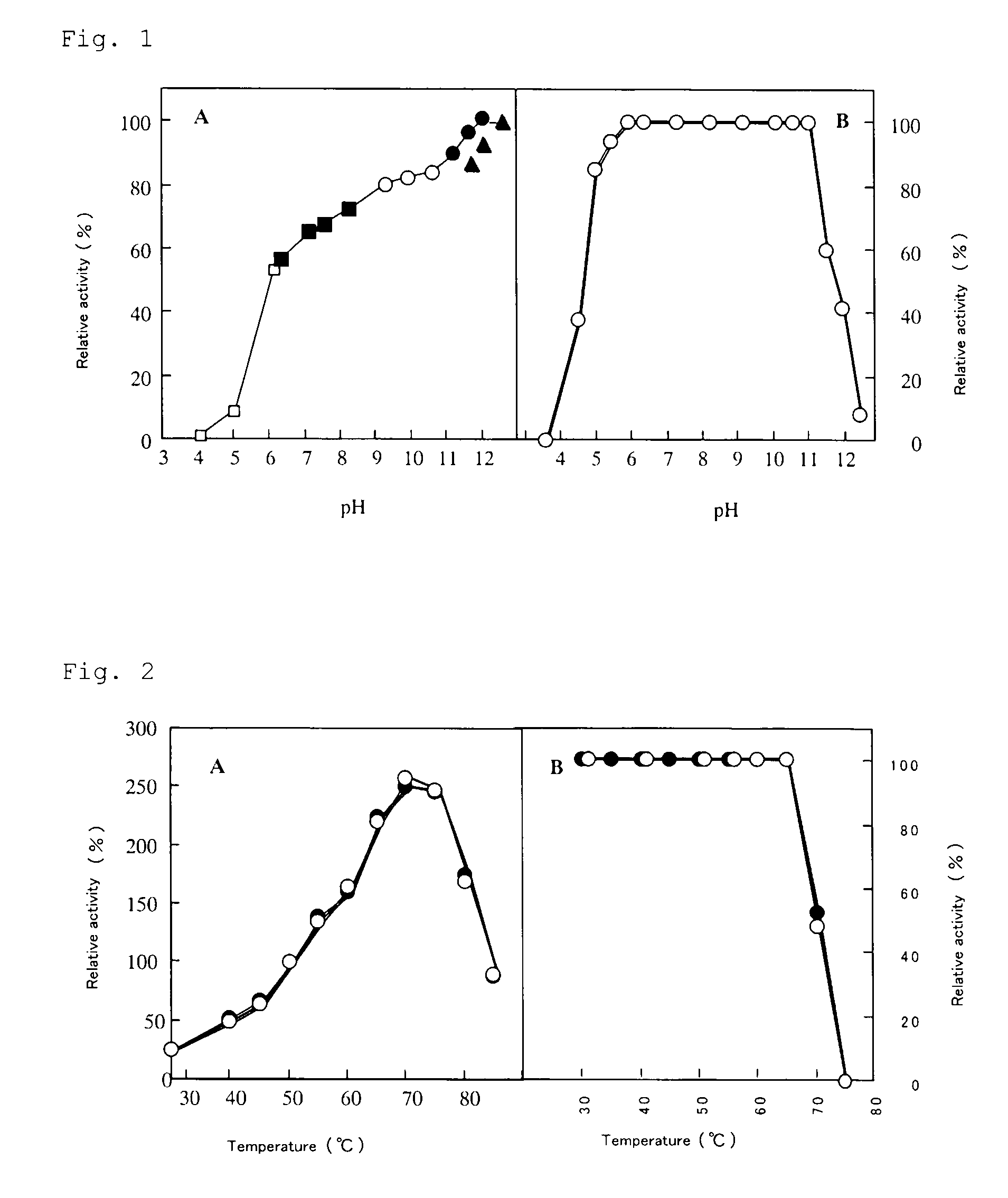
The invention aims to provide a novel alkaline protease having peculiar properties such as high alkali activity, resistance to surfactants and calcium-dependent thermostability and exhibiting excellent performance in highly alkaline detergents, and a gene coding for the amino acid sequence thereof. There is provided an alkaline protease with such properties that an active pH range is from 5 to 13, an optimum pH is approximately 12.6, an optimum temperature is 70° C., no activity drop by heating is observed up to 65° C. at pH 10 and the optimum temperature and the thermostability are not affected by Ca2+ ions. Specifically, there is provided, for example, an alkaline protease having an amino acid sequence constituting a mature enzyme as represented by SEQ ID NO: 3 or an amino acid sequence resulting from deletion, substitution, situs inversus arrangement, addition or insertion of a part of amino acids thereof, or derived from Alkaliphillus transvaalensis. The protease cleaves 26 peptide bonds among 29 peptide bonds of acidic insulin B-chain.
Owner:JAPAN AGENCY FOR MARINE-EARTH SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Novel process for genetic engineering preparation of insulin and insulin analogs
The invention provides a novel process for genetic engineering preparation of insulin and insulin analogs, which comprises enzyme cutting insulin precursor with parenzyme, then isolating insulin, wherein the insulin precursor comprises the following elements from amino end to carboxyl end, (1) spacing peptide element with formula (Xaa)mZ, (2) insulin B chain element, (3) joint peptide element with formula (Xaa)nZ, and (4) insulin A chain element.
Owner:费俭
Meal-time insulin analogues of enhanced stability
InactiveUS8993516B2Increase propensityImprove stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesInsulin A ChainWild type
A method treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of a fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to the patient. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, contains an insulin A-chain sequence modified at position A8 and an insulin B-chain sequence or an analogue thereof. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue may exhibit thermodynamic stability similar to or exceeding that of wild-type human insulin and displays a susceptibility to fibrillation similar to or exceeding that of wild-type human insulin. An insulin analogue may display greater in vitro insulin receptor binding than normal insulin while displaying binding to IGFR less than twice that of normal insulin and less than that of fast-acting insulin analogs. The fibrillation-resistant insulin may be used to treat a patient by subcutaneous injection or by using an implantable or external insulin pump, due to its fibrillation resistance.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Single-Chain Insulin Analogues and Pharmaceutical Formulations Thereof
InactiveUS20110009314A1Good physical and chemical stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin activityInsulin B Chain
The present invention is related to fast acting single-chain insulin comprising a modified B-chain and the A-chain of human insulin or an analogue thereof connected by a connecting peptide wherein one or more of the amino acid residues in position B25, B26 or B27 in the human B-chain are Glu or Asp or are deleted and / or B28 is Glu, Asp, Lys or is deleted, and the amino acid residue in position B10 in the human insulin B-chain is Gln, Ala, Val, Thr or Ser. The invention is also related to pharmaceutical compositions being a mixture of the rapid acting single-chain insulin and the protracted acylated insulin.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
New monomeric insulin and its medicinal composition and prepn process
InactiveCN1468864AEasy to makeSuitable for mass productionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderYeastInsulin activity
The present invention provides new insulin strand B, monomeric insulin containing strand B, medicinal composition containing the monomeric insulin and their preparation process and use. The insulin analog B27K-DTrI sample of high purity is obtained via enzymatic semi-synthesis process and is proved to have the property of monomeric insulin and overall insulin activity 80 % of that of normal insulin. The monomeric insulin precursor is secreted and expressed in yeast expressing system and enzyme cut to obtain B27K-DTrI, and the enzymatic peptide converting step is omitted to raise the final yield and suit for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI C A S SHENGLONGDA BIOTECH GRP
Ultra-concentrated rapid-acting insulin analogue formulations
InactiveUS20140323398A1Good chemical stabilityImprove physical stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSide chainPharmaceutical formulation
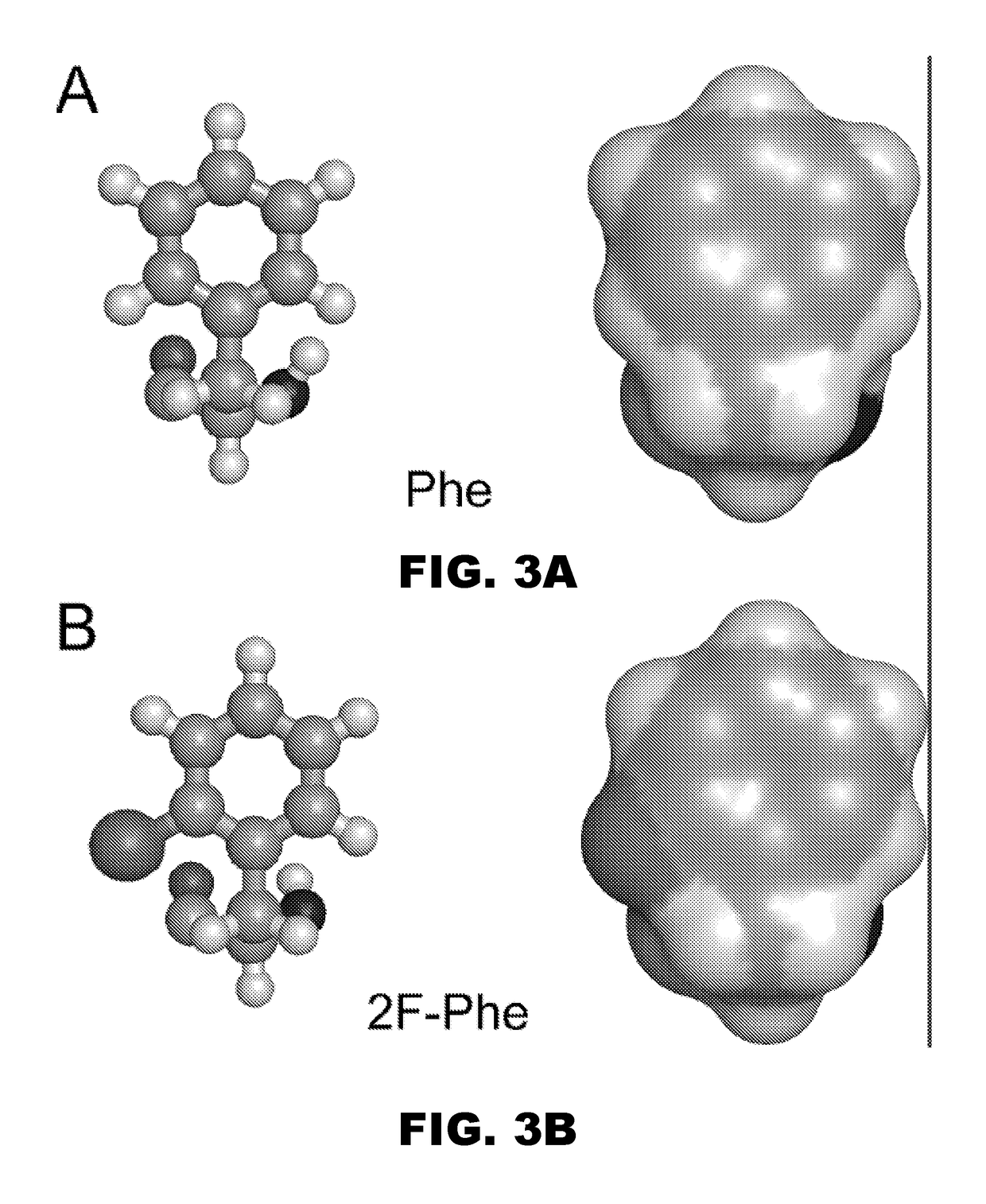
A pharmaceutical formulation comprises insulin having a variant insulin B-chain polypeptide containing an ortho-monofluoro-Phenylalanine substitution at position B24 in combination with a substitution of an amino acid containing an acidic side chain at position B10, allowing the insulin to be present at a concentration of between 0.6 mM and 3.0 mM. The formulation may optionally be devoid of zinc. Amino-acid substitutions at one or more of positions B3, B28, and B29 may additionally be present. The variant B-chain polypeptide may be a portion of a proinsulin analogue or single-chain insulin analogue. The insulin analogue may be an analogue of a mammalian insulin, such as human insulin. A method of lowering the blood sugar of a patient comprises administering a physiologically effective amount of the insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to the patient.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
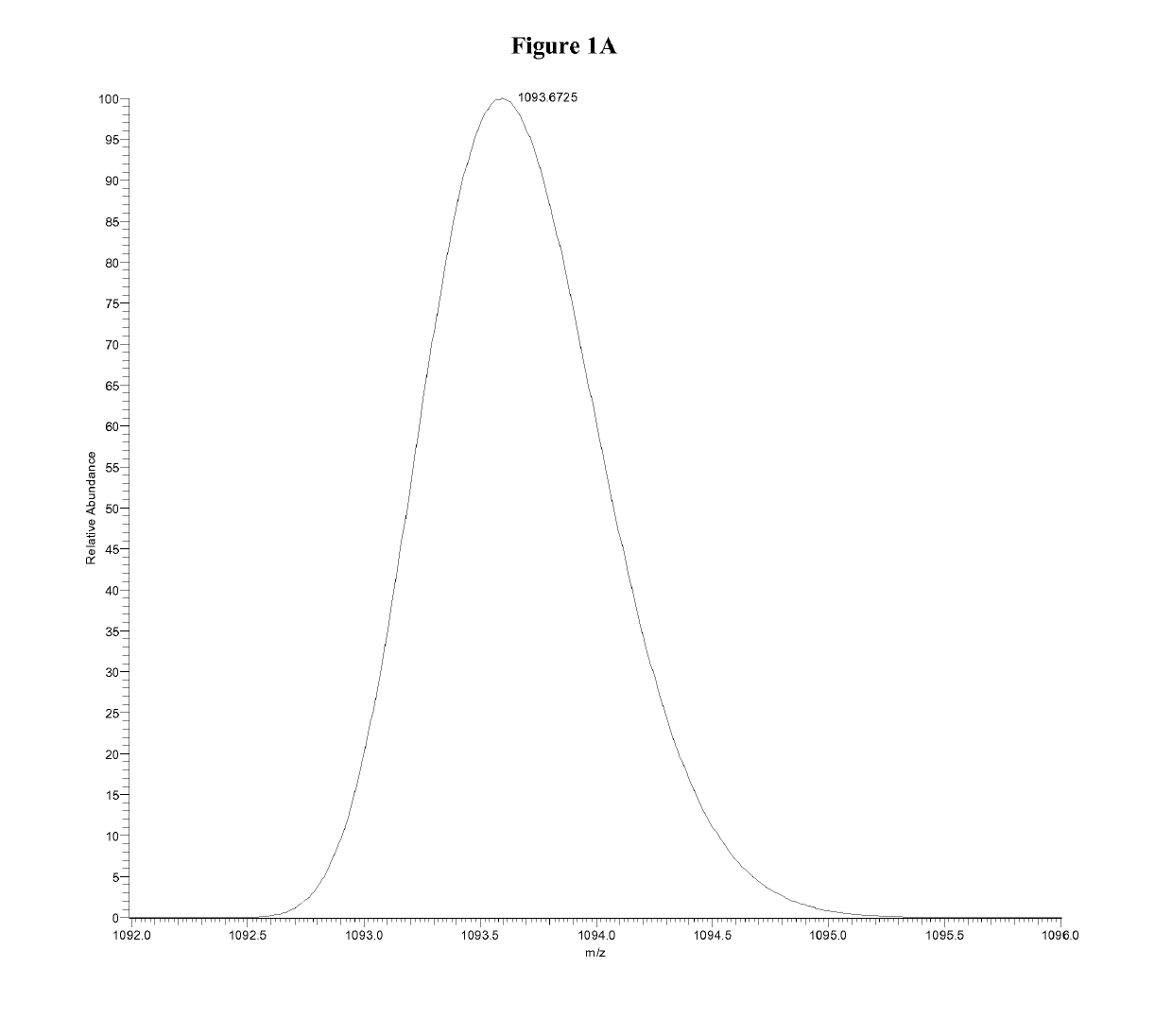
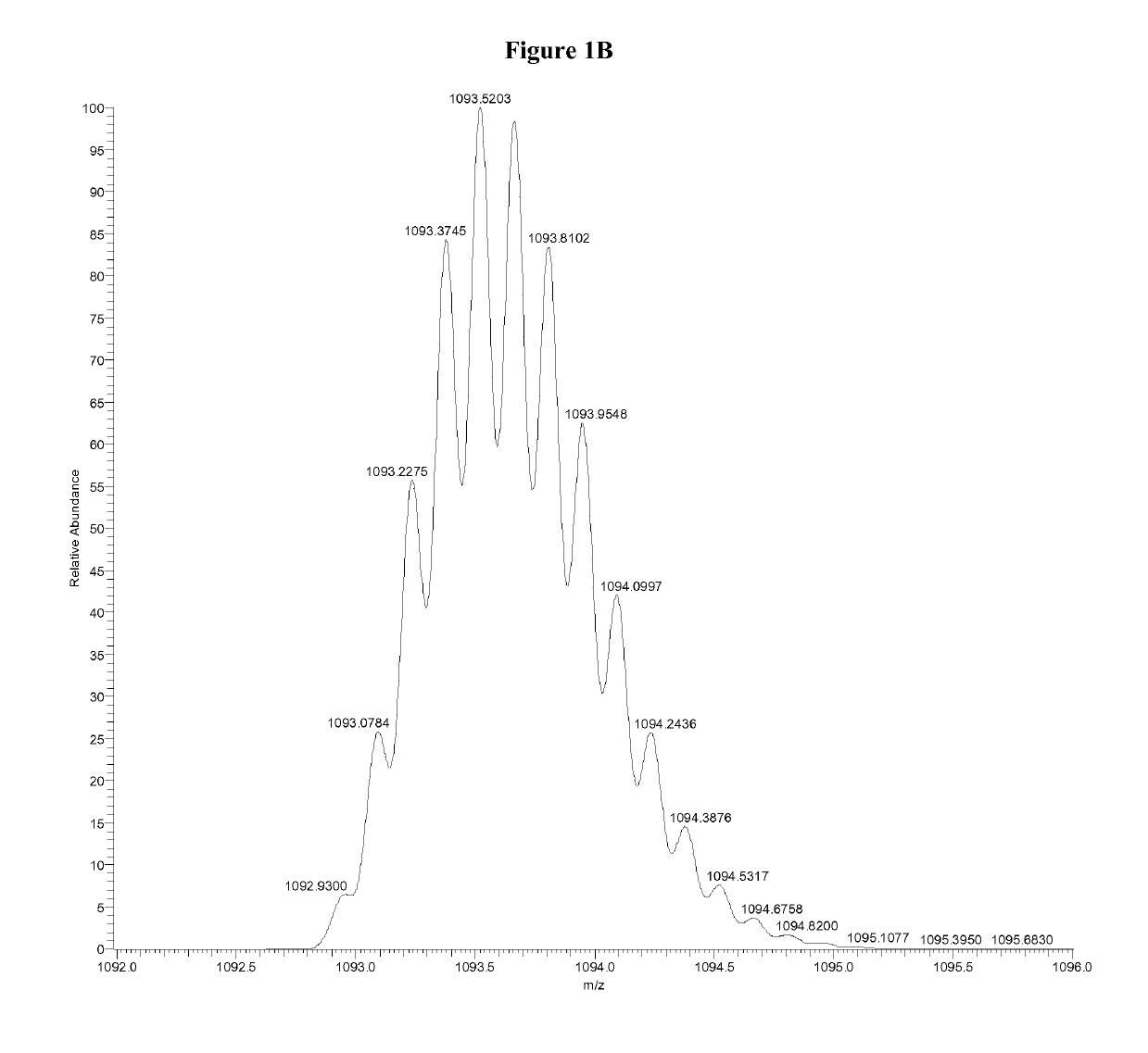
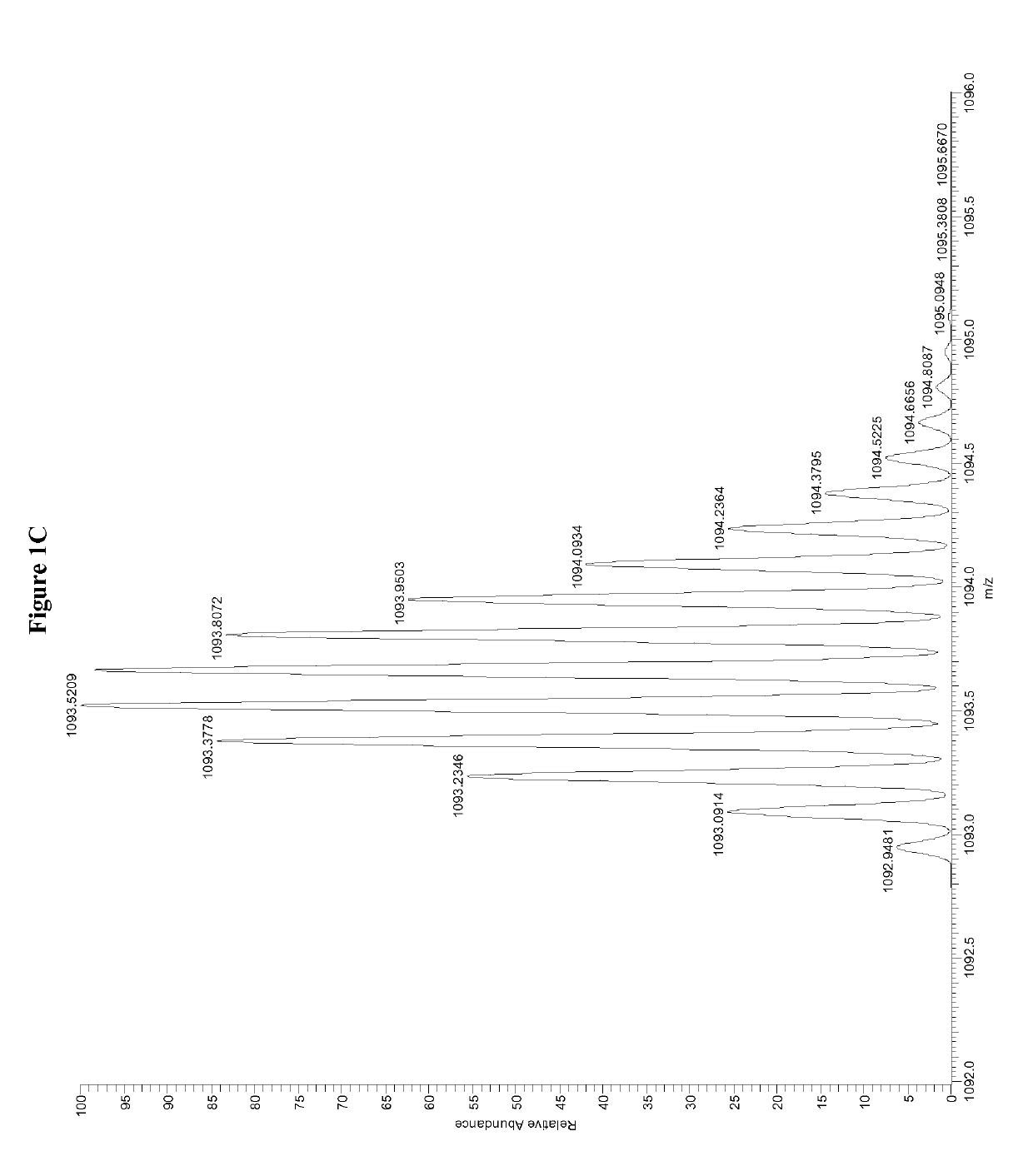
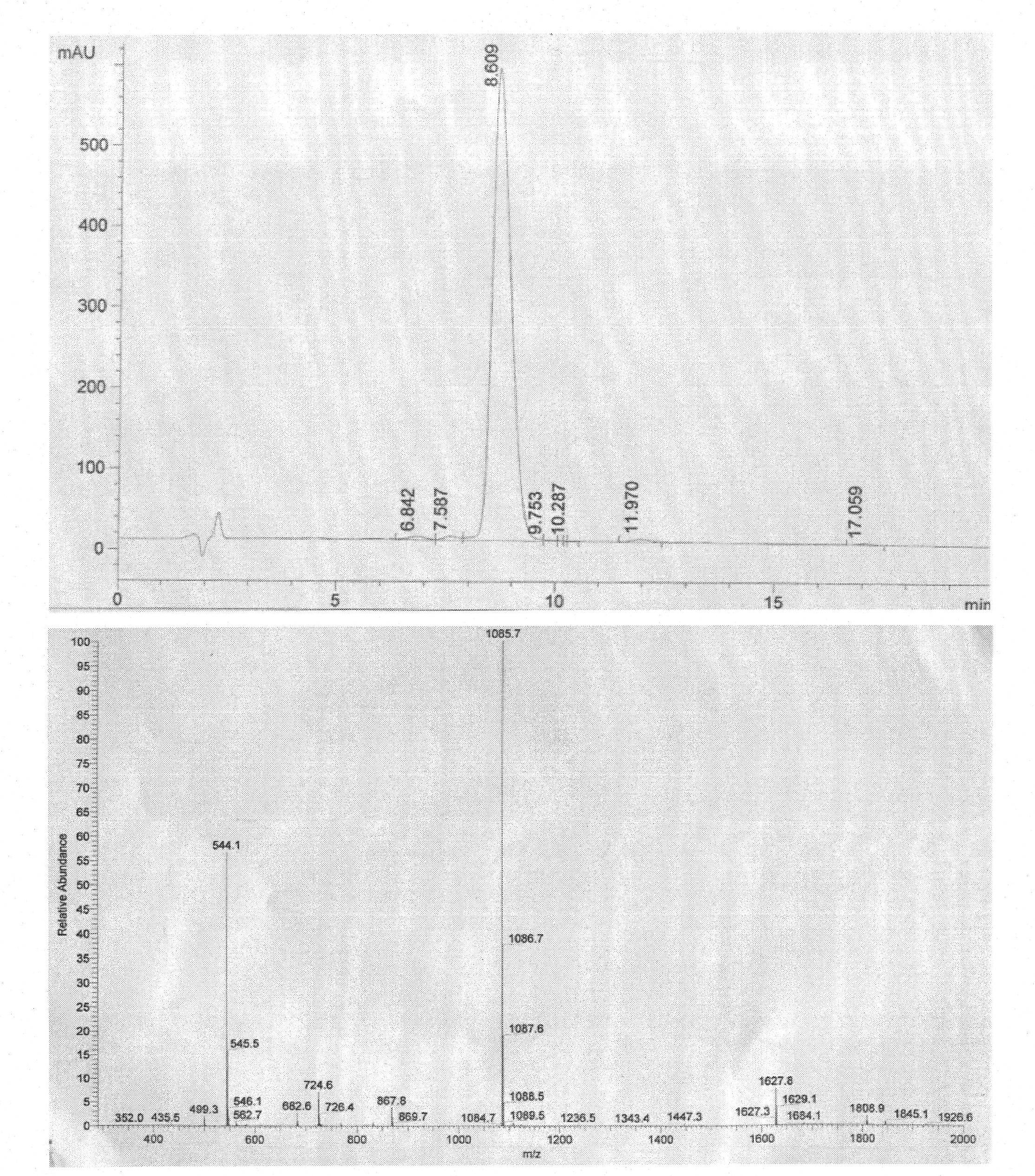
Quantitation of insulin by tandem mass spectrometry of insulin B chain
Methods are described for determining the amount of insulin in a sample. More specifically, mass spectrometric methods are described for detecting and quantifying insulin in a biological sample utilizing purification methods coupled with tandem mass spectrometric or high resolution / high accuracy mass spectrometric techniques.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Monomer quick-effective insulin and preparation method and usage thereof
InactiveCN101062948AStrong Monomer PropertiesWill not aggregatePeptide/protein ingredientsInsulinsInsulin B ChainMonomer
The invention discloses a new insuline B chain, monomer quick-effective insuline and medicinal composite. This invention also relates to preparing method and usage.
Owner:费俭
Insulin B chain HLA-A*0201 restrictive CTL epitope modified peptide ligand and acquisition method and application thereof
InactiveCN101974071AReduce workloadEasy to purifyMetabolism disorderPeptide preparation methodsCtl epitopePeptide ligand
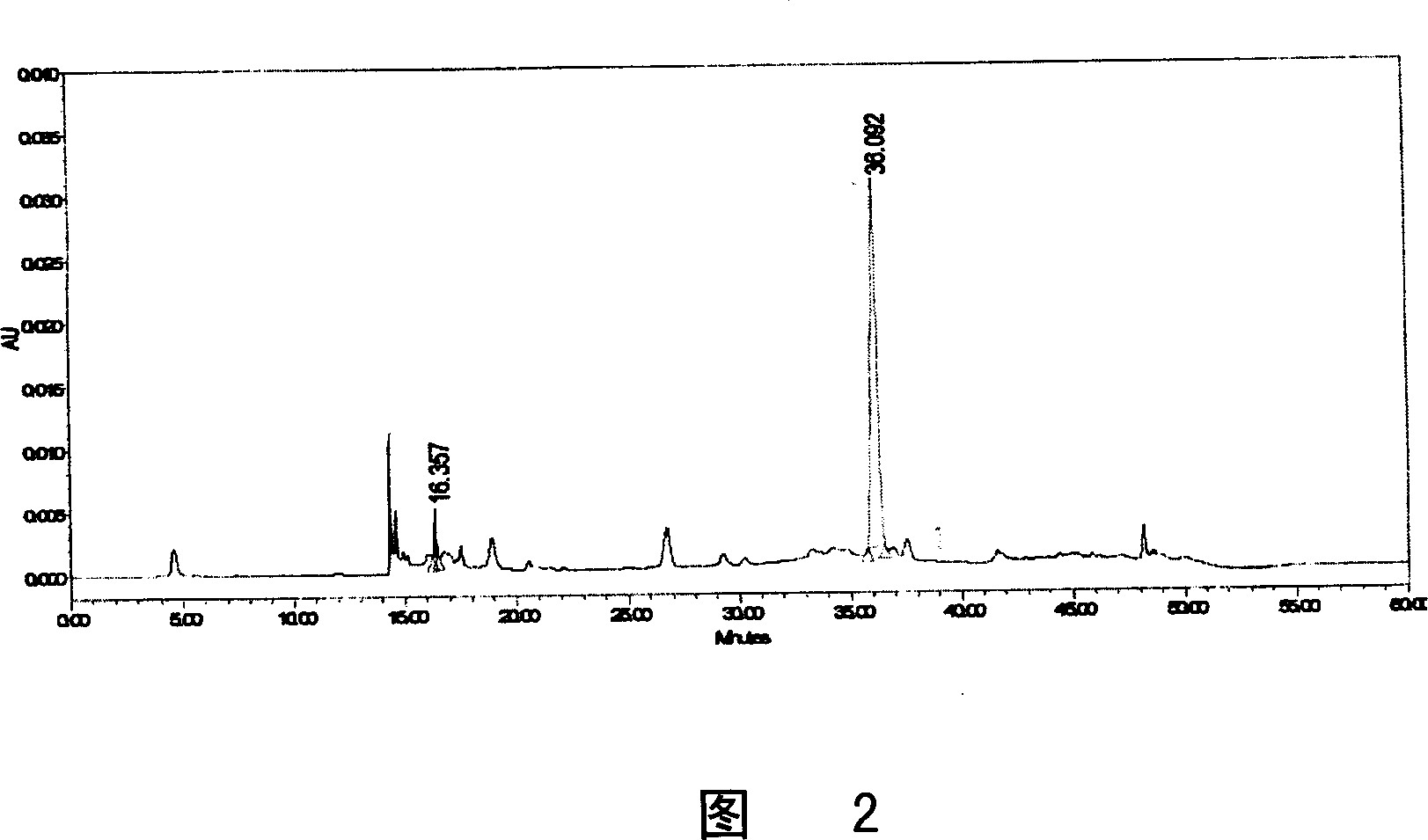
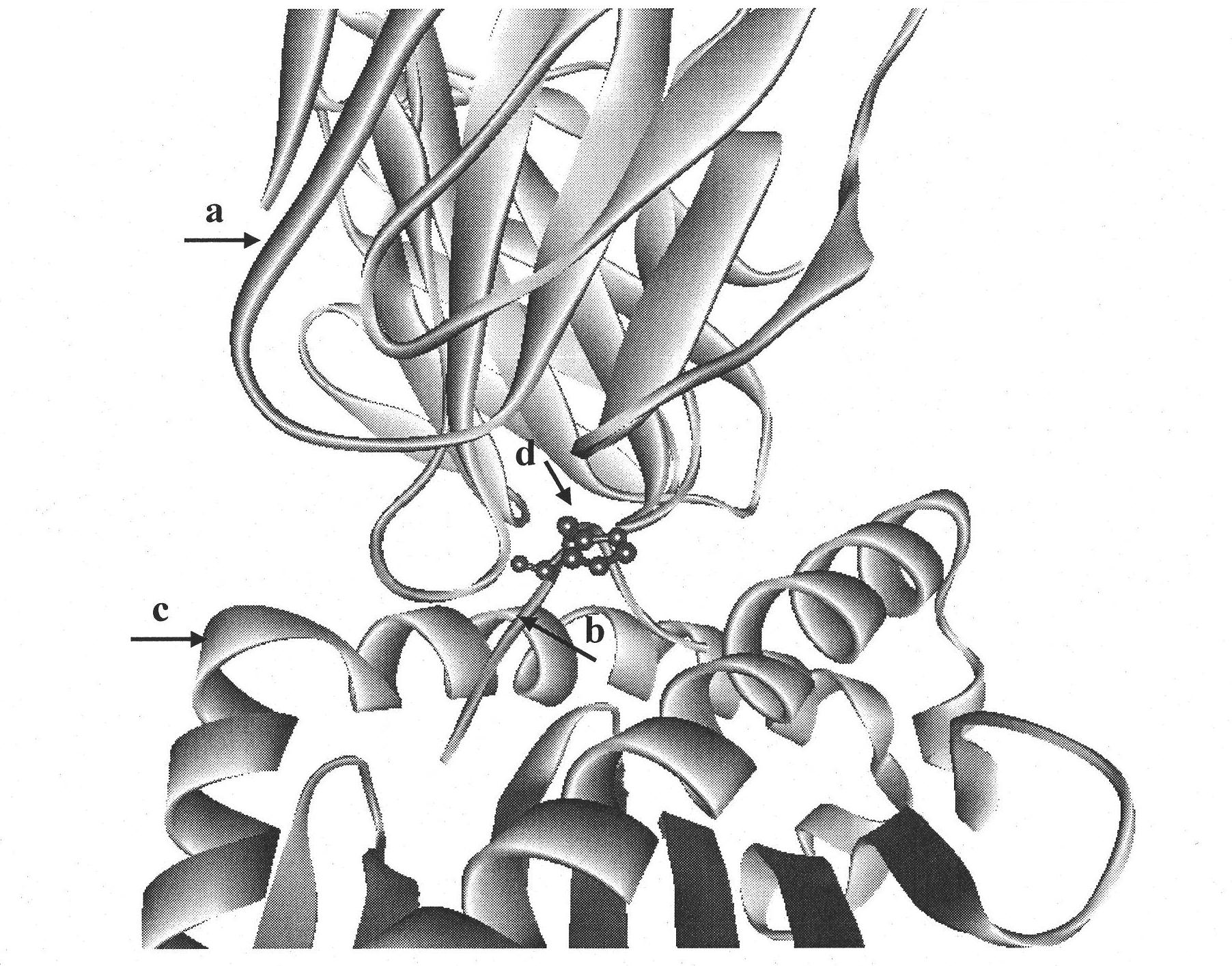
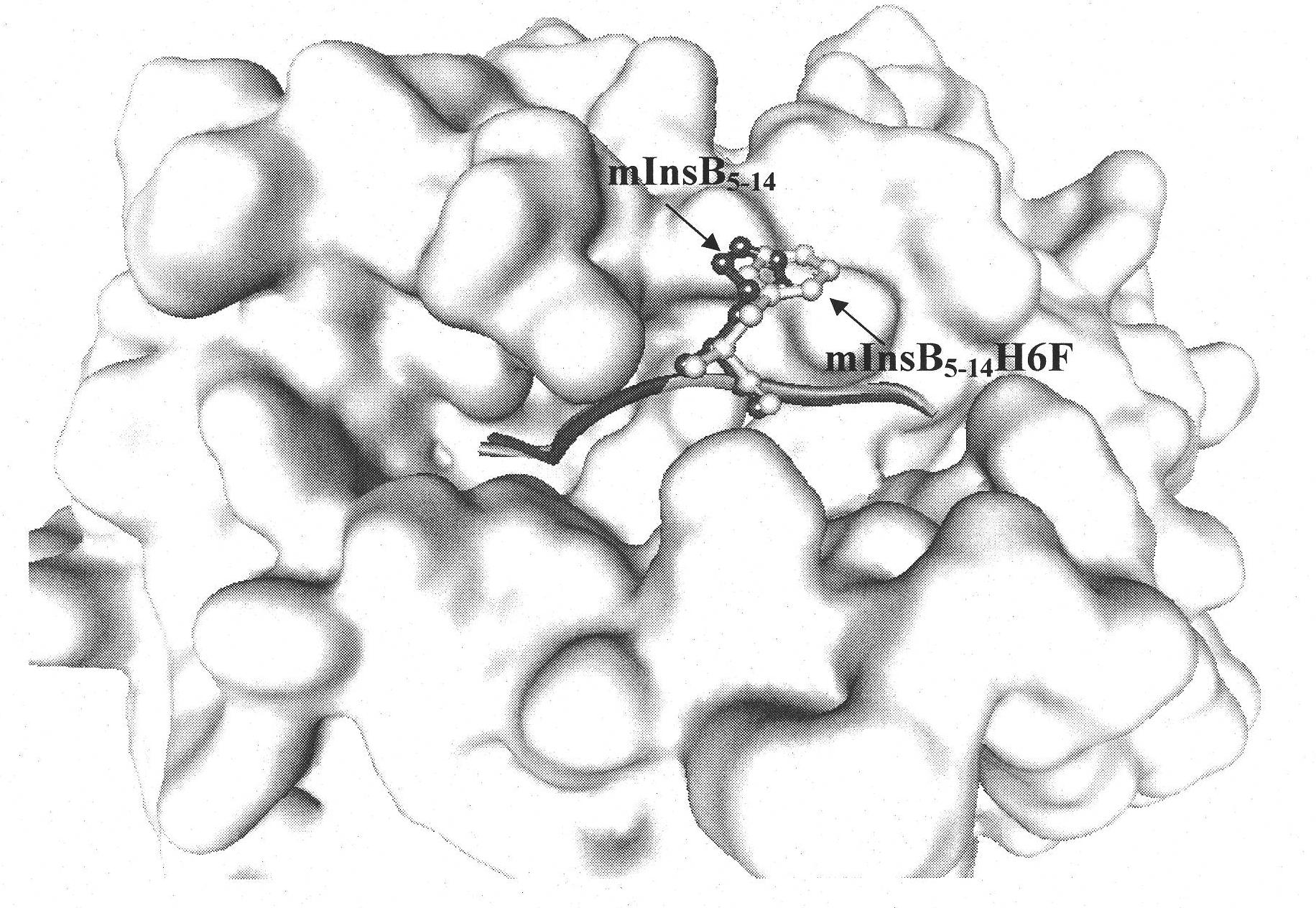
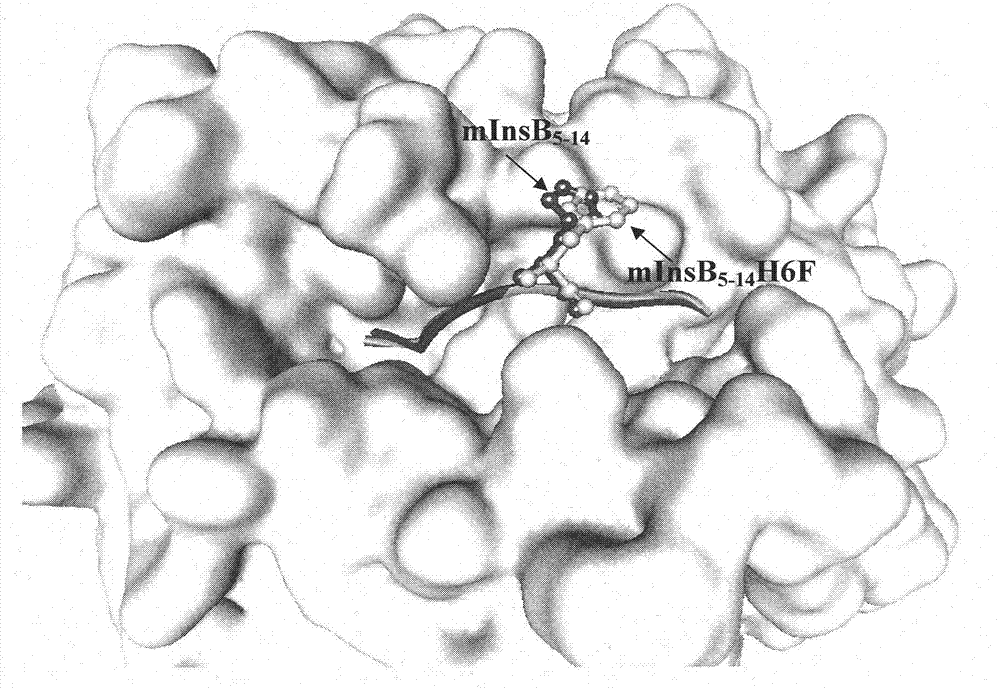
The invention discloses an insulin B chain HLA-A*0201 restrictive CTL epitope altered peptide ligand (APL) and an acquisition method and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the APL is HLCGPFLVEA, and is obtained by replacing the sixth position histidine of the natural epitope mInsB5-14 by phenylalanine. The acquisition method comprises the following steps of: establishing a TCR-HLA-A*0201-mInsB5-14 compound model, determining potential TCR acting loci in the mInsB5-14, performing monoamino acid mutation on the potential TCR acting loci, and screening candidate APL having higher affinity with the HLA-A*0201 molecules than the natural epitope and space conformation close to the natural epitope; and further identifying the APL capable of obviously reducing mInsB5-14 specificity CTL response level through cell function experiments. The APL of the invention can be used for preparing a type 1 diabetes treatment negative peptide vaccine.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Insulin B chain autoantigen composition
ActiveUS8652488B2Reduce incidenceHigh incidencePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAntigenHuman use
The invention features methods for the prevention or treatment of autoimmune disorders in humans. The methods include administering an autoantigen in combination with an oil-based carrier. Included are methods for the prevention and treatment of diabetes mellitus which include treating a patient with a diabetes type 1 autoantigen, e.g., human insulin B-chain or GAD65, and an oil-based carrier approved for human use. Also included are vaccines and kits for the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Owner:JOSLIN D ABETES CENTER INC
Ultra-concentrated rapid-acting insulin analogue formulations
InactiveUS9908925B2Improve stabilityModulates bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSide chainPhenylalanine
A pharmaceutical formulation comprises insulin having a variant insulin B-chain polypeptide containing an ortho-monofluoro-Phenylalanine substitution at position B24 in combination with a substitution of an amino acid containing an acidic side chain at position B10, allowing the insulin to be present at a concentration of between 0.6 mM and 3.0 mM. The formulation may optionally be devoid of zinc. Amino-acid substitutions at one or more of positions B3, B28, and B29 may additionally be present. The variant B-chain polypeptide may be a portion of a proinsulin analog or single-chain insulin analog. The insulin analog may be an analog of a mammalian insulin, such as human insulin. A method of lowering the blood sugar of a patient comprises administering a physiologically effective amount of the insulin analog or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to the patient.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Non-standard insulin analogues
ActiveUS20190382463A1Decreased hepatic insulin signalingAltered propertyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin A ChainInsulin B Chain
An insulin analogue comprises an insulin A-chain polypeptide and an insulin B-chain polypeptide. The A-chain polypeptide contains a Glu substitution at a position corresponding to position A8, and an Ala, Glu, Gln, His, Tyr, Phe or Trp substitution at a position A13, relative to wild type insulin. The B-chain polypeptide contains a cyclohexanylalanine substitution at position B24, relative to wild type insulin. The analogue may be an analogue of a mammalian insulin, such as human insulin. A nucleic acid encoding such an insulin analogue is also provided. A method of lowering the blood sugar of a patient comprises administering a physiologically effective amount of the insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to a patient.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
O-linked carbohydrate-modified insulin analogues
ActiveUS20150299287A1Improve the immunityRapid hexamer disassemblyPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsSide chainInsulin B Chain
An insulin analogue comprises an insulin B-chain polypeptide modified with an O-linked monosaccaride pyranoside adduct at the side chain of residue B27 or an O-linked monosaccaride pyranoside adduct at the side chain of residue B30, or both, where the positions are recited relative to human insulin. The monosaccaride may be a manopyranoside, an N-acetyl-galactopyranoside, or a glucopyranoside. The insulin analogue may additionally comprise containing a foreshortened B-chain polypeptide lacking residues B1-B3, an extension of 1 or 2 Glu residues on the carboxy terminal end of the B-chain polypeptide, an extension of ornithine at the carboxy-terminal end of the B-chain, the substitutions Lys at position B28 and Pro at position B29, an ornithine substitution at position B29, or combinations thereof. The analogue may be an analogue of a mammalian insulin, such as human insulin. A method of treating a patient comprises administering a physiologically effective amount of the insulin analogue.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Insulin modifier and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103467594AImprove securityFacilitate vertical sortingPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderHalf-lifeImmunogenicity
The invention discloses an insulin modifier, comprising insulin and a fatty acid chain which is connected to the tail end of an insulin B chain, wherein the insulin is swine insulin or dog insulin; alanine at the 30th bit of the insulin B chain is cut off; the insulin and the fatty acid chain are connected by an amido bond. The insulin modifier can form an oelophilic group to promote longitudinal sorting of insulin protein, so as to form an intermolecular force-dominant chain polyethylene polymer due to the hydrophobic effect of the long fatty acid chain after the insulin modifier enters the body. Compared with monomer insulin, the half-life period of the polyethylene polymer is greatly prolonged; the polyethylene polymer has a good slow-release effect; meanwhile, the insulin modifier does not contain other protein with immunogenicity, and is high in safety performance. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the insulin modifier.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Preparation for preventing or treating type i diabetes
ActiveUS20150238572A1Sufficient effectSuppression of of typeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulin A ChainInsulin B Chain
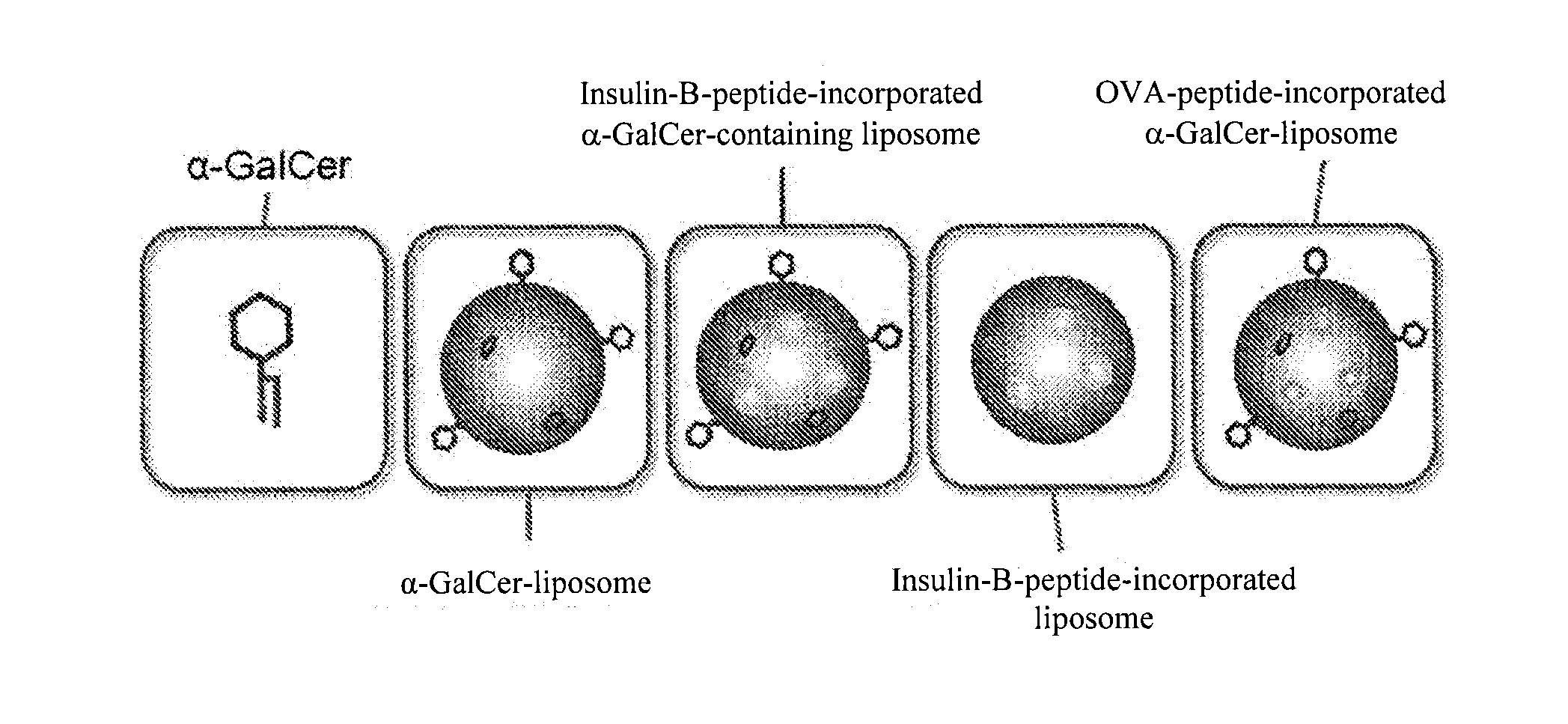
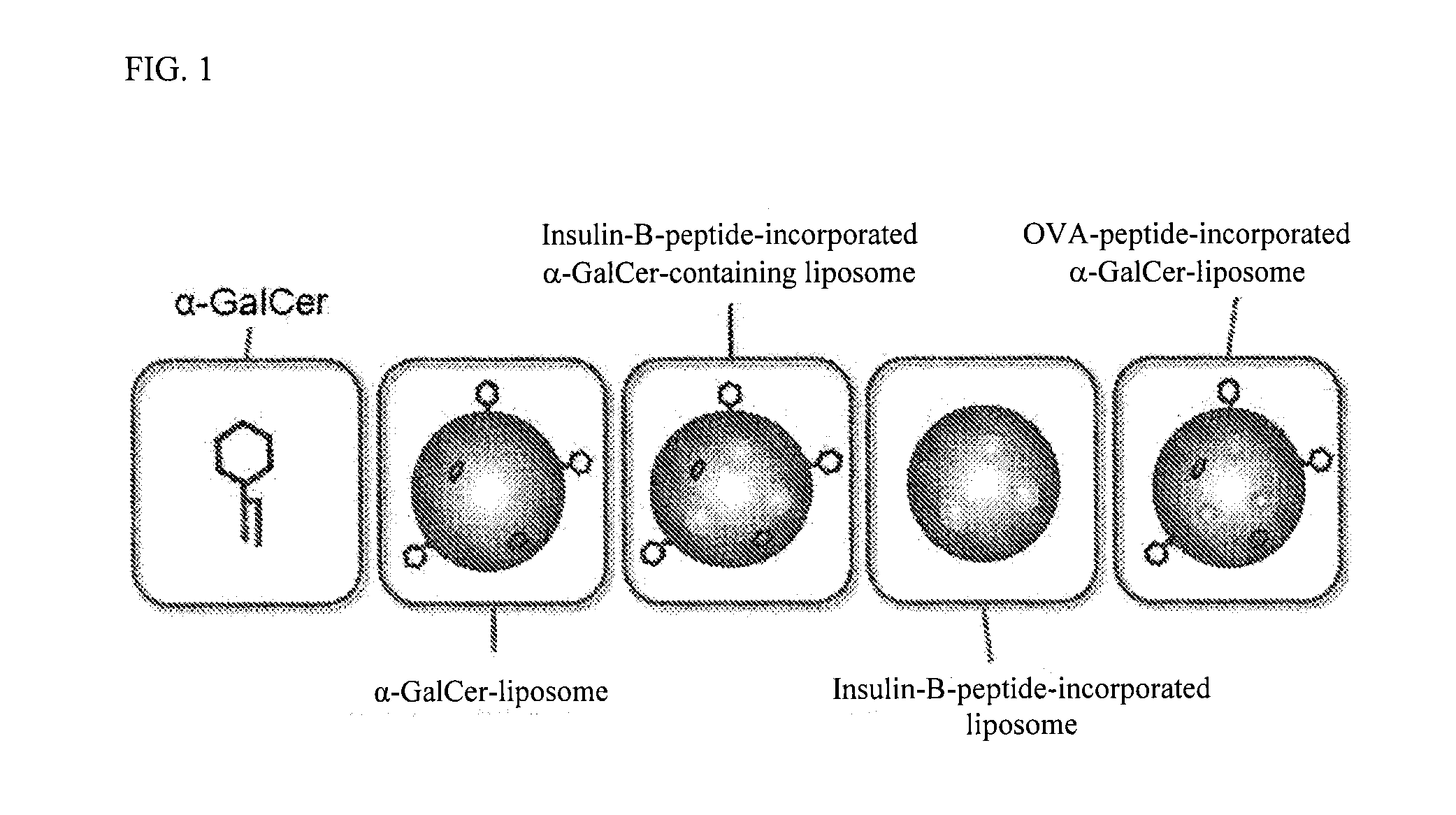
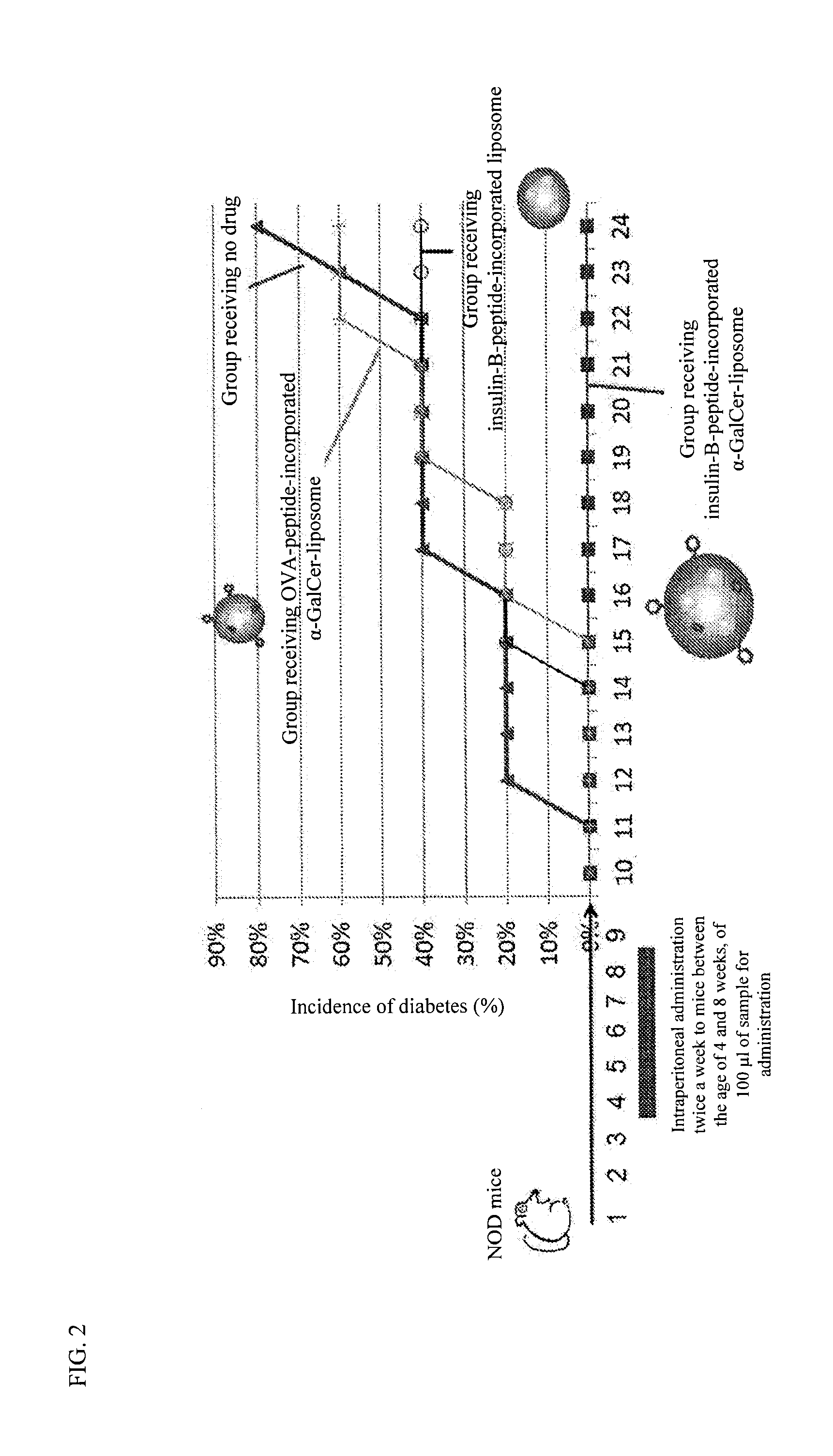
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a preparation for preventing or treating type I diabetes, said preparation exerting an excellent effect of preventing or treating type I diabetes, and a method for preventing or treating type I diabetes. The onset and symptoms of type I diabetes can be very remarkably relieved by dosing a combination of: (A) at least one member selected from the group consisting of proinsulin, insulin, insulin A chain, insulin B chain, fragments thereof and variants thereof; with (B) α-GalCer.
Owner:REGIMMUNE
O-linked carbohydrate-modified insulin analogues
ActiveUS9624287B2Improve the immunityRapid hexamer disassemblyPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulinsSide chainInsulin B Chain
An insulin analogue comprises an insulin B-chain polypeptide modified with an O-linked monosaccaride pyranoside adduct at the side chain of residue B27 or an O-linked monosaccaride pyranoside adduct at the side chain of residue B30, or both, where the positions are recited relative to human insulin. The monosaccaride may be a manopyranoside, an N-acetyl-galactopyranoside, or a glucopyranoside. The insulin analogue may additionally comprise containing a foreshortened B-chain polypeptide lacking residues B1-B3, an extension of 1 or 2 Glu residues on the carboxy terminal end of the B-chain polypeptide, an extension of ornithine at the carboxy-terminal end of the B-chain, the substitutions Lys at position B28 and Pro at position B29, an ornithine substitution at position B29, or combinations thereof. The analogue may be an analogue of a mammalian insulin, such as human insulin. A method of treating a patient comprises administering a physiologically effective amount of the insulin analogue.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
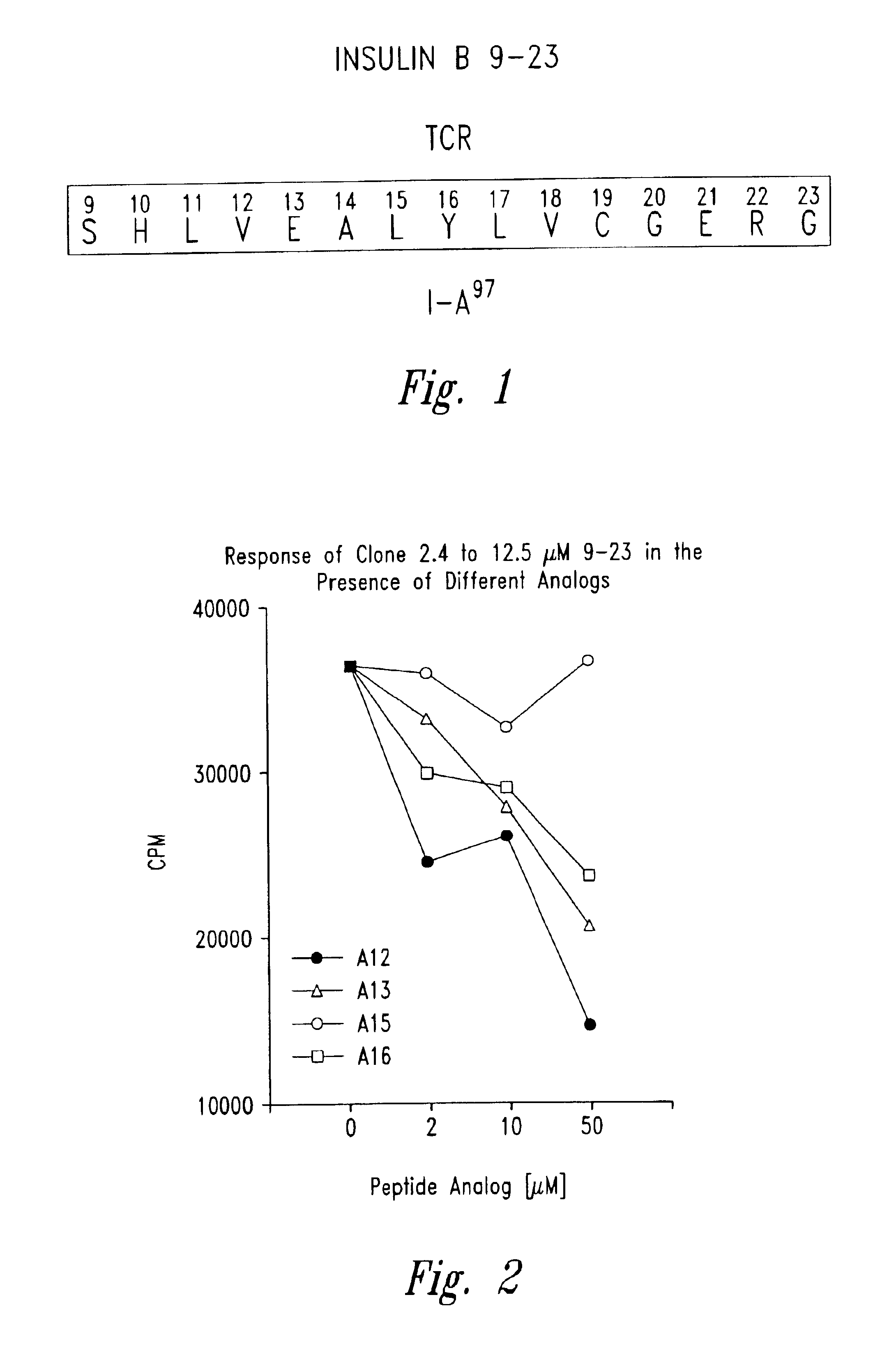
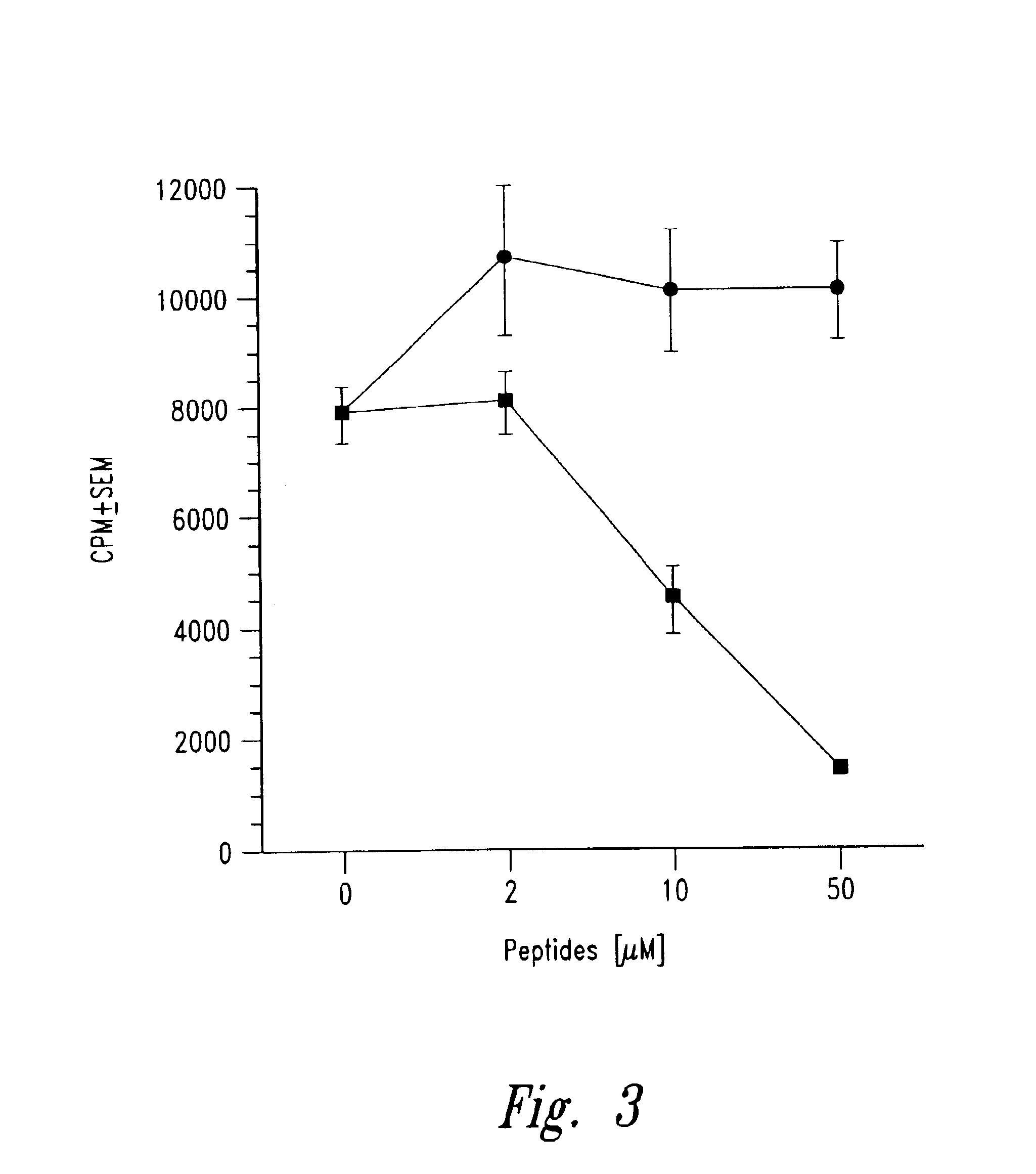
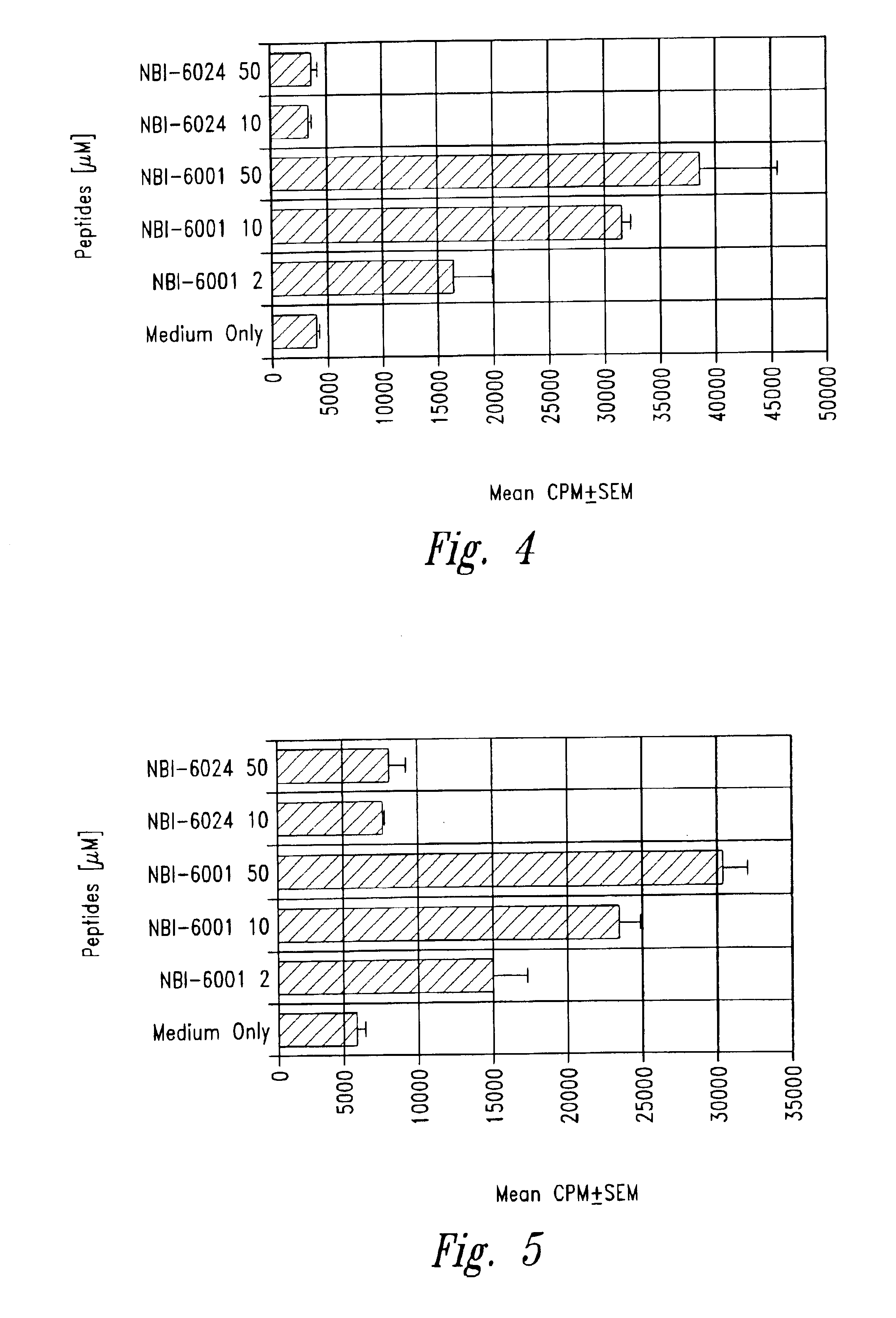
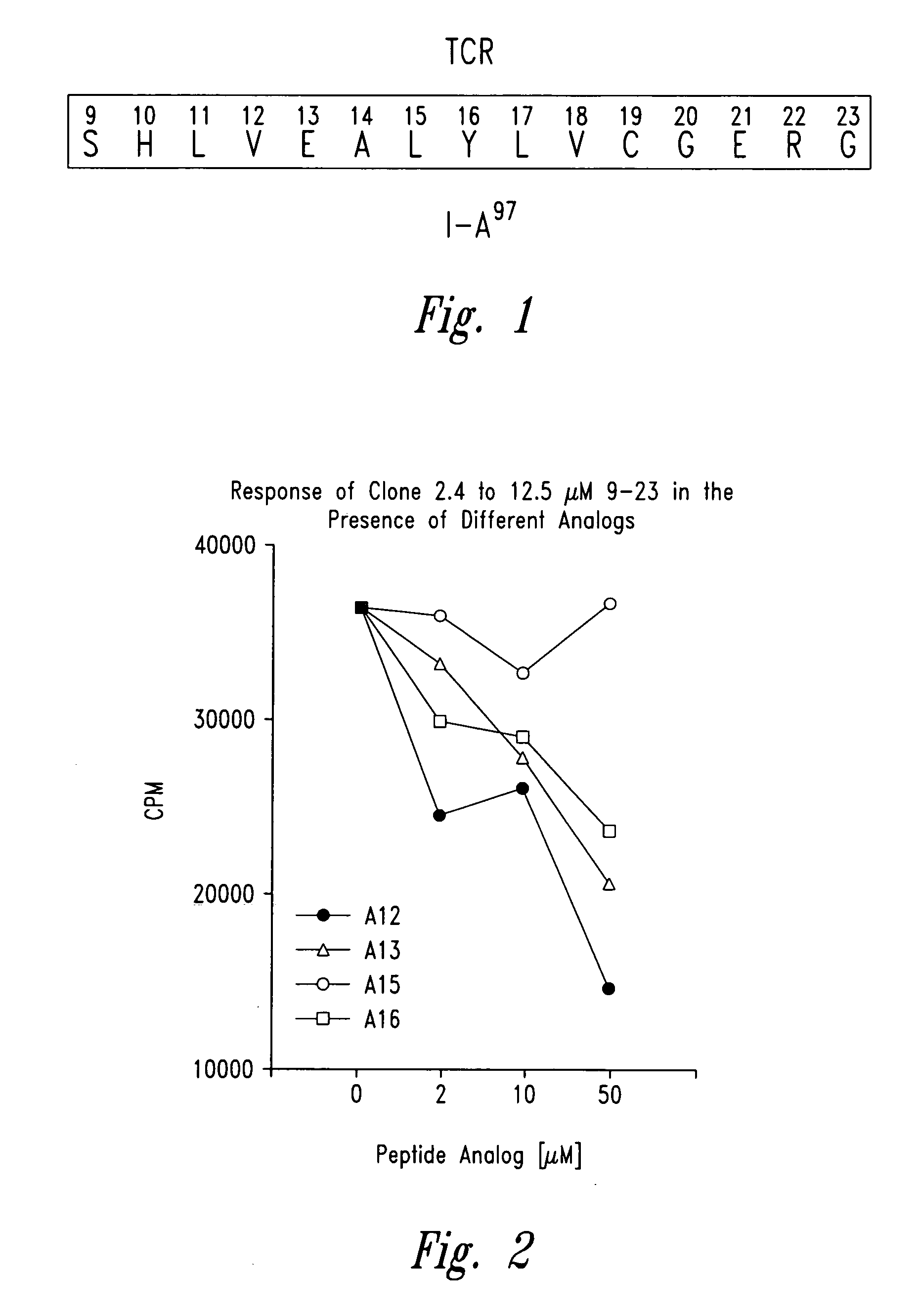
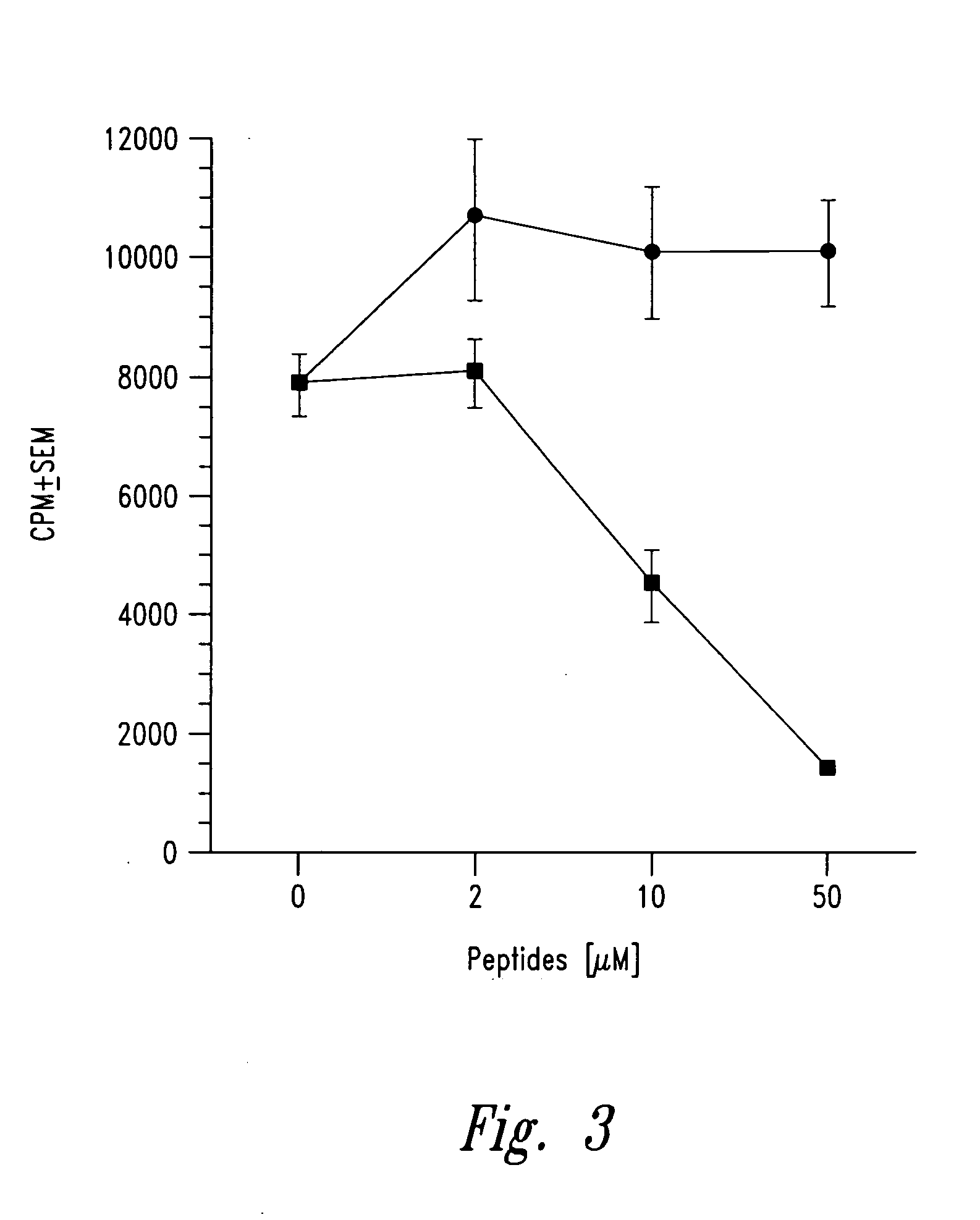
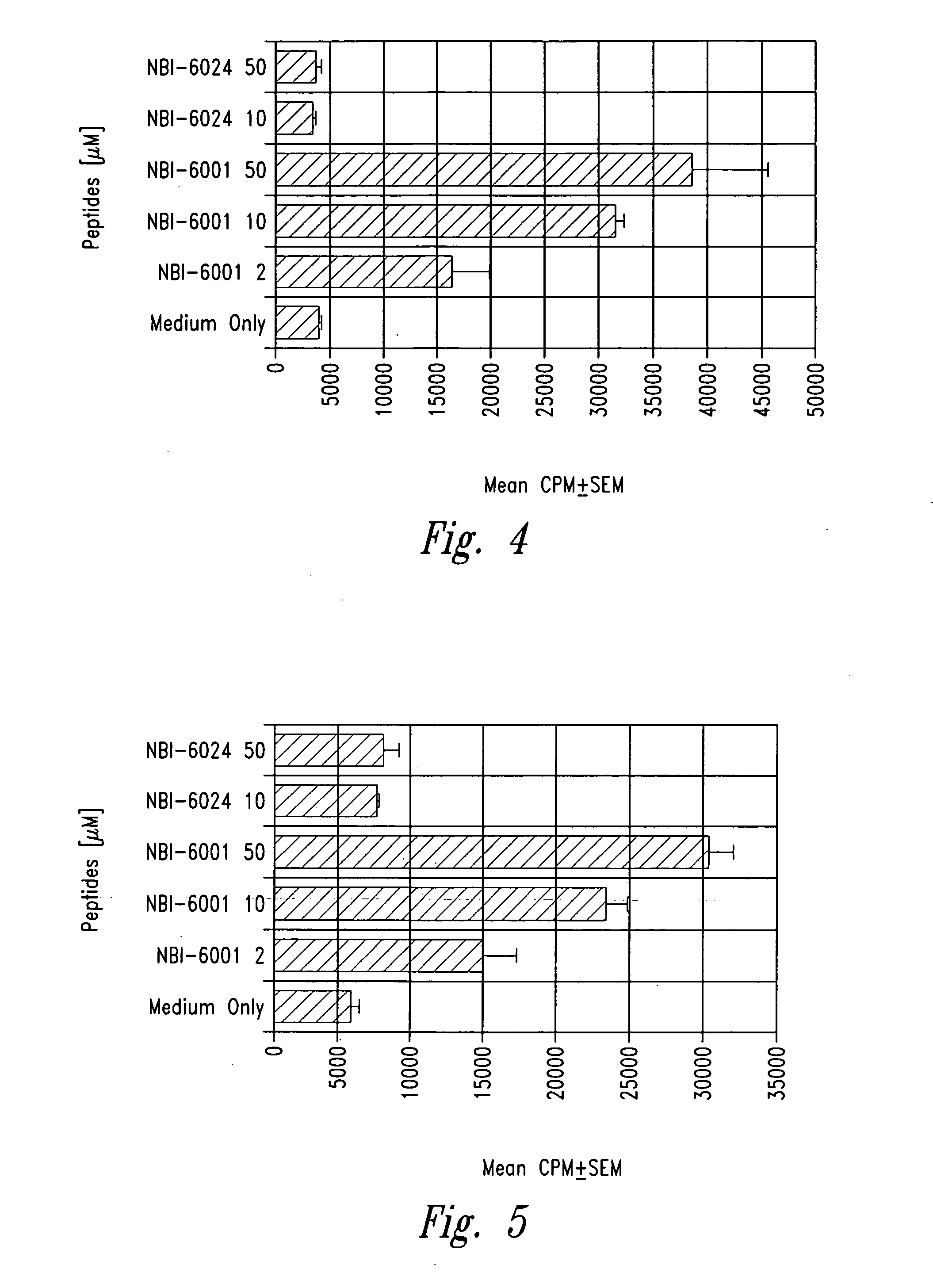
Methods for treatment of diabetes using a peptide analogues of insulin
The present invention is directed toward peptide analogues of insulin B chain that are generally derived from peptides comprising residues 9 to 23 of the native B chain sequence. The analogues are altered from the native sequence at position 12, 13, 15 and / or 16, and may be additionally be altered at position 19 and / or other positions. Pharmaceutical compositions containing these peptide analogues are provided. The peptide analogues are useful for treating and inhibiting the development of diabetes.
Owner:NEUROCRINE BIOSCI INC
Methods for treatment of diabetes using peptide analogues of insulin
InactiveUS20060040863A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiabetes mellitusInsulin B Chain
Owner:NEUROCRINE BIOSCIENCES INC
Vaccine adjuvant for treating autoimmune diseases and application thereof
InactiveCN108853492AReduced autoantibody titersLower titerMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDiseaseRegulatory T cell
The invention relates to a vaccine adjuvant for treating autoimmune diseases and application thereof, and particularly discloses application of a polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer to preparing drugs for treating autoimmune diseases by serving as a vaccine adjuvant. The polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer is produced to be microballoon spheres to load insulin B chain polypeptide B9-23 toserve as effective antigen, through hypodermic injection, the polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer can assist the function of the antigen and achieves the effect of an immunologic adjuvant, the auto-antibody titer in a mouse is reduced, accordingly the antigen can be more effectively assisted to activate proliferation and functions of regulatory T cells in vivo, immune tolerance is induced, andaccordingly attack of 1 type diabetes can be effectively prevented or delayed. In addition, because the 1 type diabetes belongs to the autoimmune diseases, the polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymercan serve as an adjuvant and applied to other autoimmune diseases.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Monomer quick-acting insulin as well as preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN101817878AStrong Monomer PropertiesWill not aggregatePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin B ChainMonomer
Owner:费俭
Preparation of sugar-responsive functionalized nano-composite micelle and application of sugar-responsive functionalized nano-composite micelle in insulin delivery
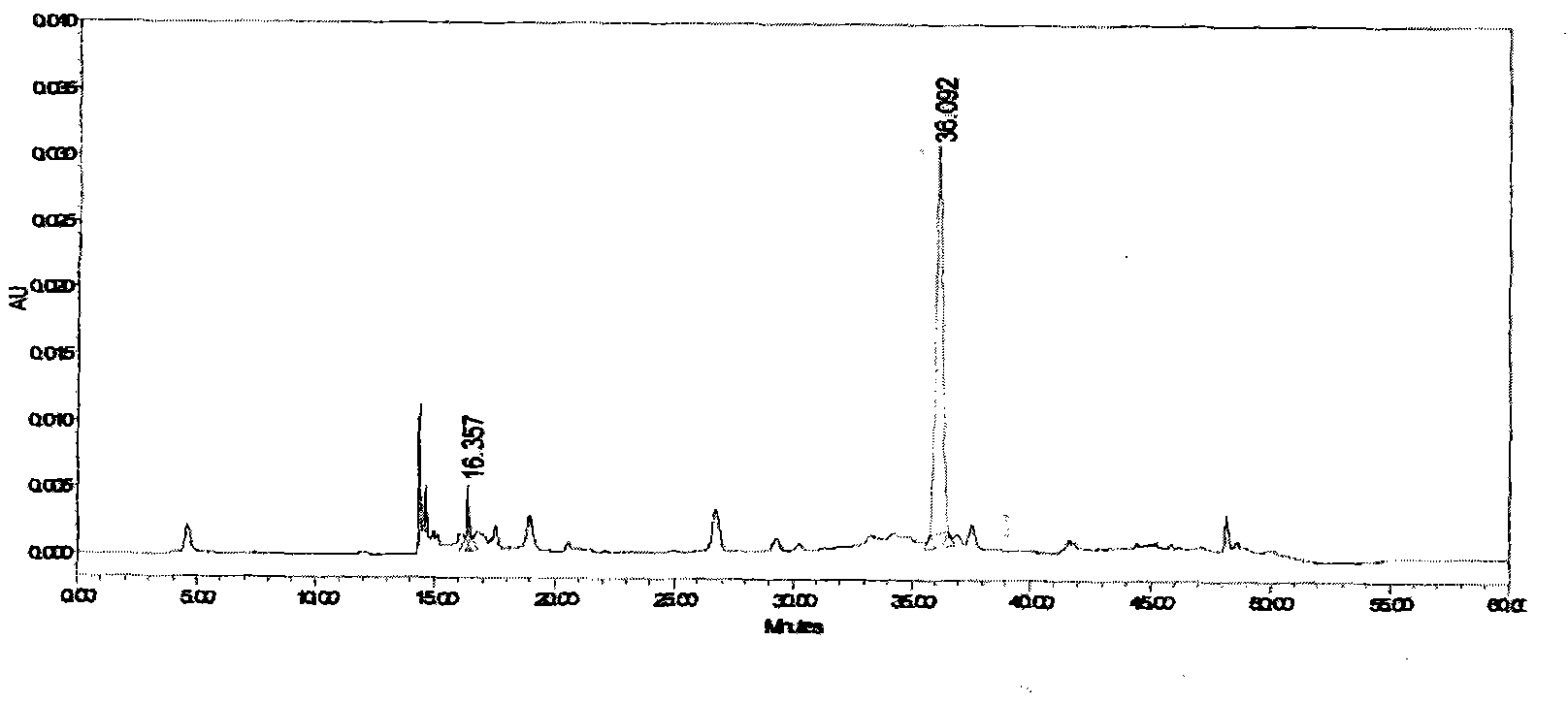
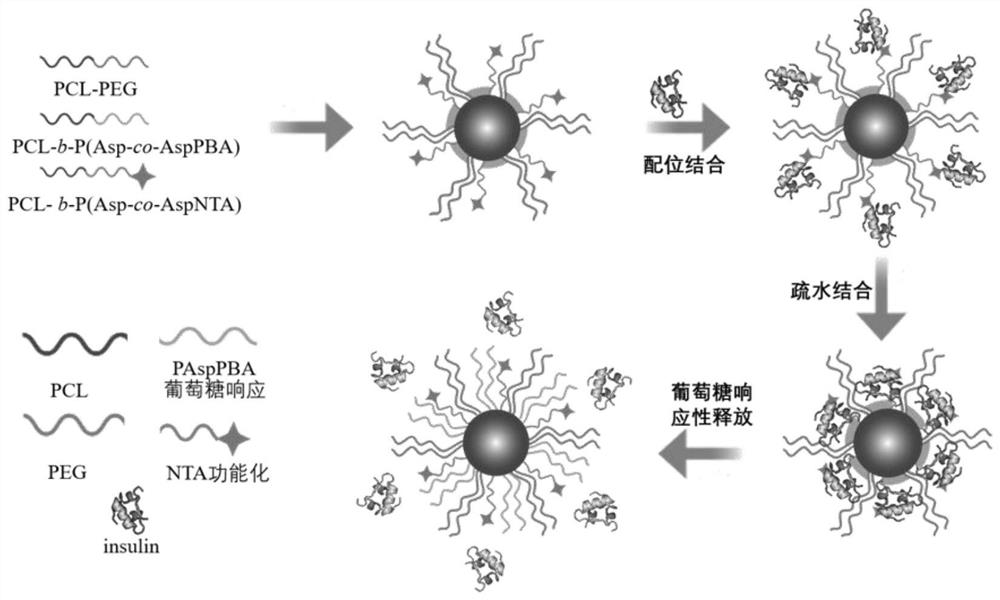
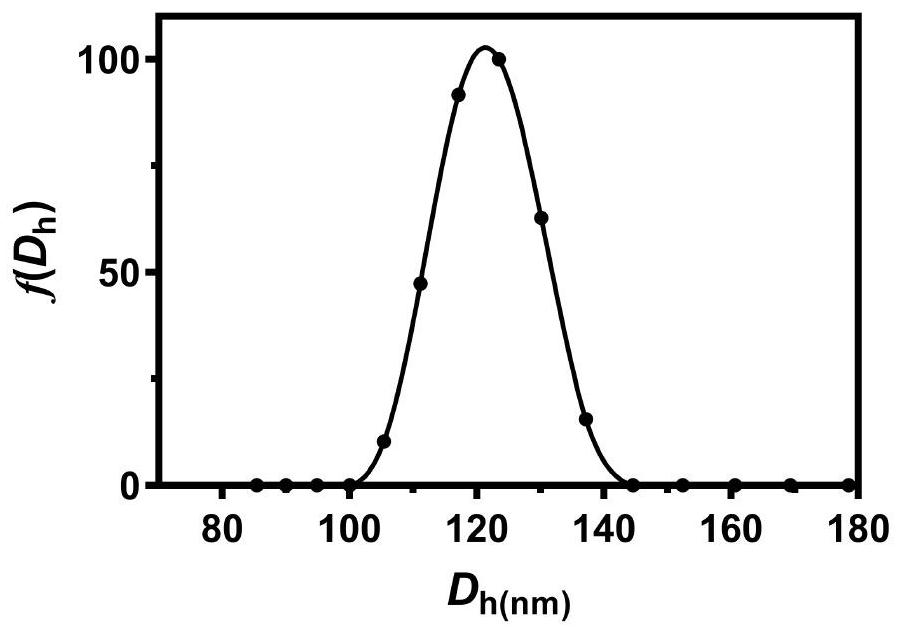
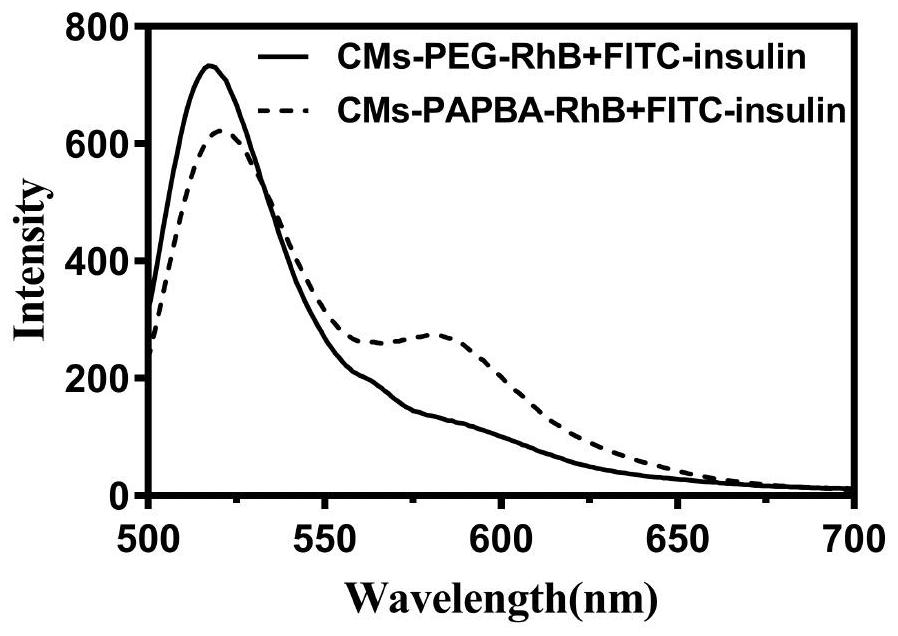
ActiveCN112870374AStrong loadProtective structurePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineInsulin B Chain
The invention relates to preparation of a sugar-responsive functionalized nano-composite micelle and application of the sugar-responsive functionalized nano-composite micelle in insulin delivery. Three block copolymers, namely PCL-b-PEG, PCL-b-P (Asp-co-AspPBA) and PCL-b-P (Asp-co-AspNTA), are self-assembled to form the composite micelle which takes PCL as a core and takes PEG / PAPBA / PANTA as a mixed shell layer. The NTA-modified chain segment PANTA is combined with Zn<2+> through chelation, and then insulin is captured by utilizing the coordination effect of Zn<2+> and histidine on an insulin B chain. The segment PAPBA with PBA forms a hydrophobic area under neutral or sugar-free conditions. The captured insulin is incubated for a period of time and then can be bound to a hydrophobic area, and the insulin is loaded to the composite micelle through the synergistic effect of coordination and hydrophobicity. Under the high-glucose condition, the hydrophobic area is changed from hydrophobic to hydrophilic, the acting force between the composite micelle and insulin is weakened, and the insulin is released to play a role.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Monomer quick-effective insulin and preparation method and usage thereof
InactiveCN101062948BStrong Monomer PropertiesWill not aggregatePeptide/protein ingredientsInsulinsInsulin B ChainMonomer
The invention discloses a new insuline B chain, monomer quick-effective insuline and medicinal composite. This invention also relates to preparing method and usage.
Owner:费俭
New monomeric insulin, its medicinal composition and prepn process
InactiveCN1247616CEasy to makeSuitable for mass productionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderYeastInsulin activity
The present invention provides new insulin strand B, monomeric insulin containing strand B, medicinal composition containing the monomeric insulin and their preparation process and use. The insulin analog B27K-DTrI sample of high purity is obtained via enzymatic semi-synthesis process and is proved to have the property of monomeric insulin and overall insulin activity 80 % of that of normal insulin. The monomeric insulin precursor is secreted and expressed in yeast expressing system and enzyme cut to obtain B27K-DTrI, and the enzymatic peptide converting step is omitted to raise the final yield and suit for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI C A S SHENGLONGDA BIOTECH GRP
Method for preparation of active form of long-acting insulin analogue conjugate by using clostripain
The present invention relates to a method for preparation of an active form of a long-acting insulin analog conjugate, wherein the amino acid at position 22 on the insulin B chain is changed from arginine (Arg) to lysine (Lys) whereby the insulin can be converted to an active form without cleaving the insulin B chain even though reacting with clostripain. The preparation method according to the present invention surmounts the problem with a conventional method using trypsin in converting proinsulin to an active form that it is difficult to convert a long-acting insulin analog conjugate to an active form due to the cleavage of the albumin binding domain. Thus, the method of the present invention can be advantageously used for producing a long-acting therapeutic agent for diabetes.
Owner:DAEWOONG PHARM CO LTD
A fusion gene, it expressed protein and producing process thereof
InactiveCN100471955CHigh activityRelieve painFermentationHybrid peptidesTreatment effectInsulin B Chain
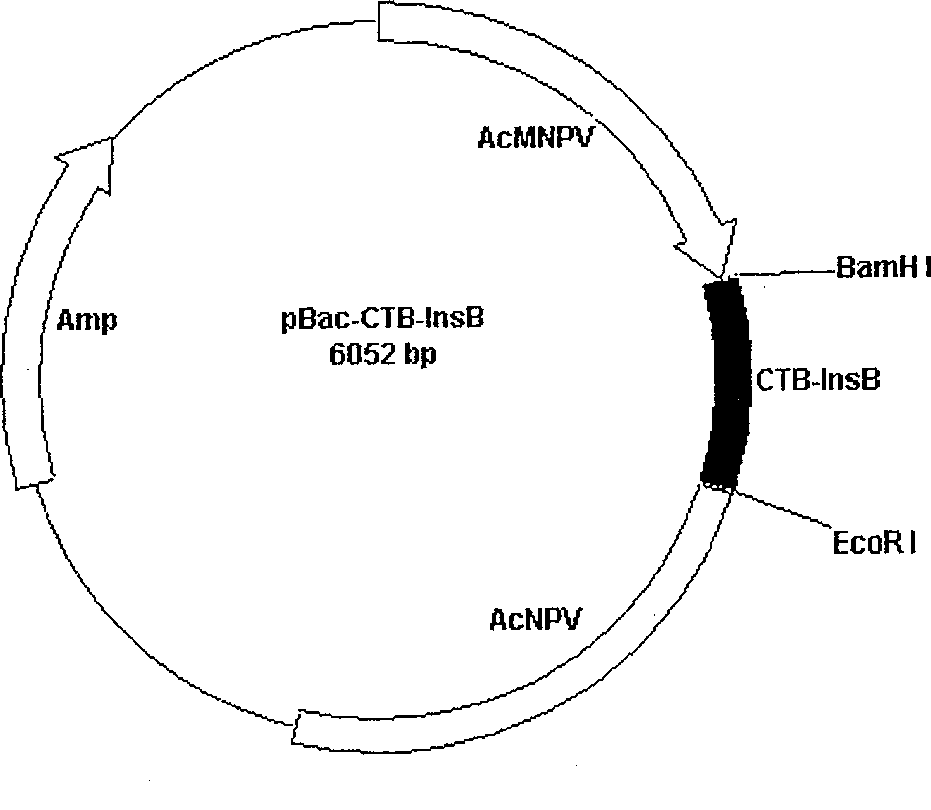
This invention belongs to polypeptide drug producing skill by genetic engineering of biological technique pharmaceutical engineering. It constitutes fusion gene of CTB and human insulin B chain. It also has a high-efficient CTB and human insulin B chain fusion gene expression in silkworm larvae, pupae and strawberry. By animal orally test, it has obvious inhibition effect on diabetes for mice and becomes a kind of new method of producing anti-I type diabetes drugs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Insulin B chain HLA-A*0201 restrictive CTL epitope modified peptide ligand and acquisition method and application thereof
The invention discloses an insulin B chain HLA-A*0201 restrictive CTL epitope altered peptide ligand (APL) and an acquisition method and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the APL is HLCGPFLVEA, and is obtained by replacing the sixth position histidine of the natural epitope mInsB5-14 by phenylalanine. The acquisition method comprises the following steps of: establishing a TCR-HLA-A*0201-mInsB5-14 compound model, determining potential TCR acting loci in the mInsB5-14, performing monoamino acid mutation on the potential TCR acting loci, and screening candidate APL having higher affinity with the HLA-A*0201 molecules than the natural epitope and space conformation close to the natural epitope; and further identifying the APL capable of obviously reducing mInsB5-14 specificity CTL response level through cell function experiments. The APL of the invention can be used for preparing a type 1 diabetes treatment negative peptide vaccine.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com