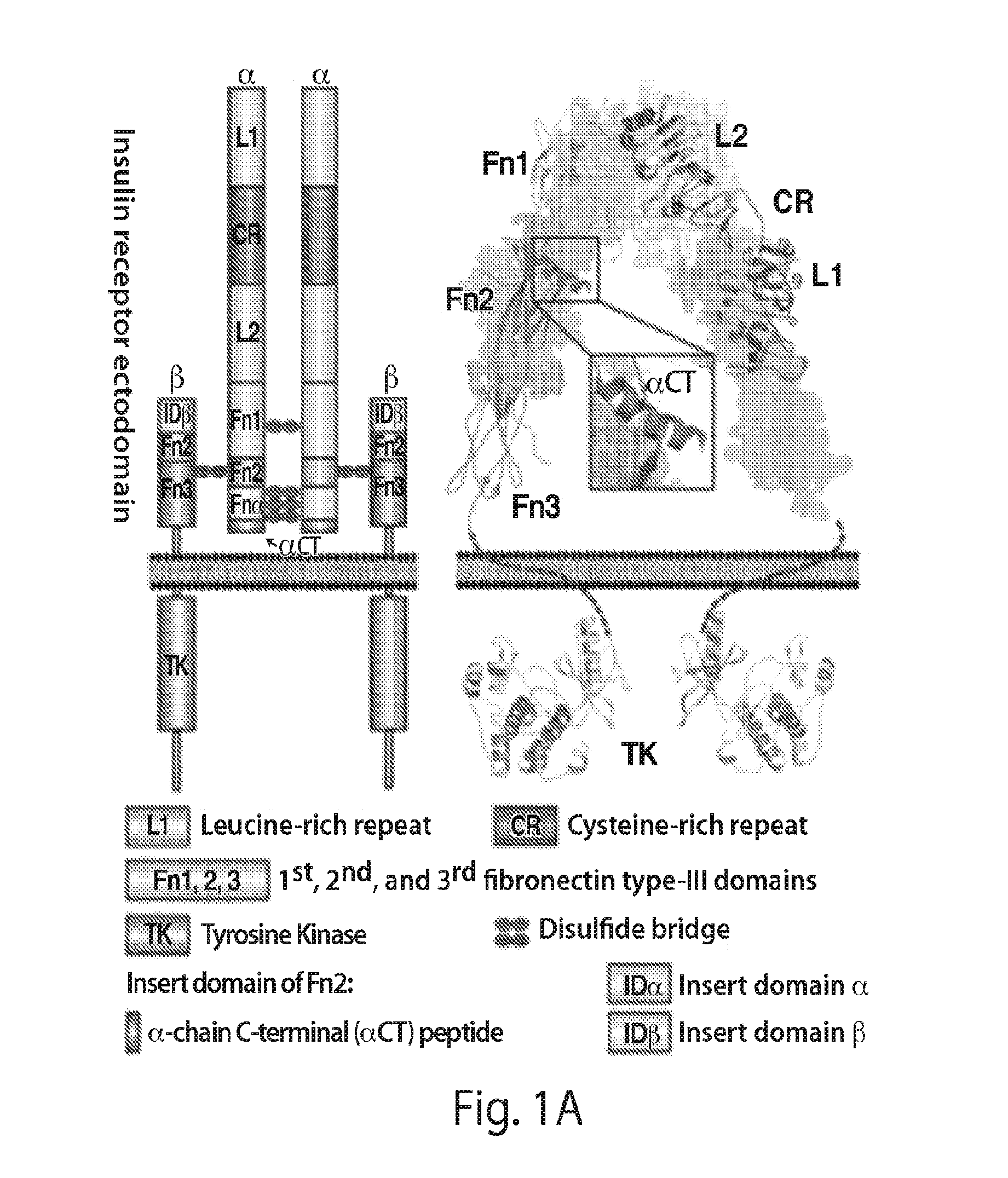
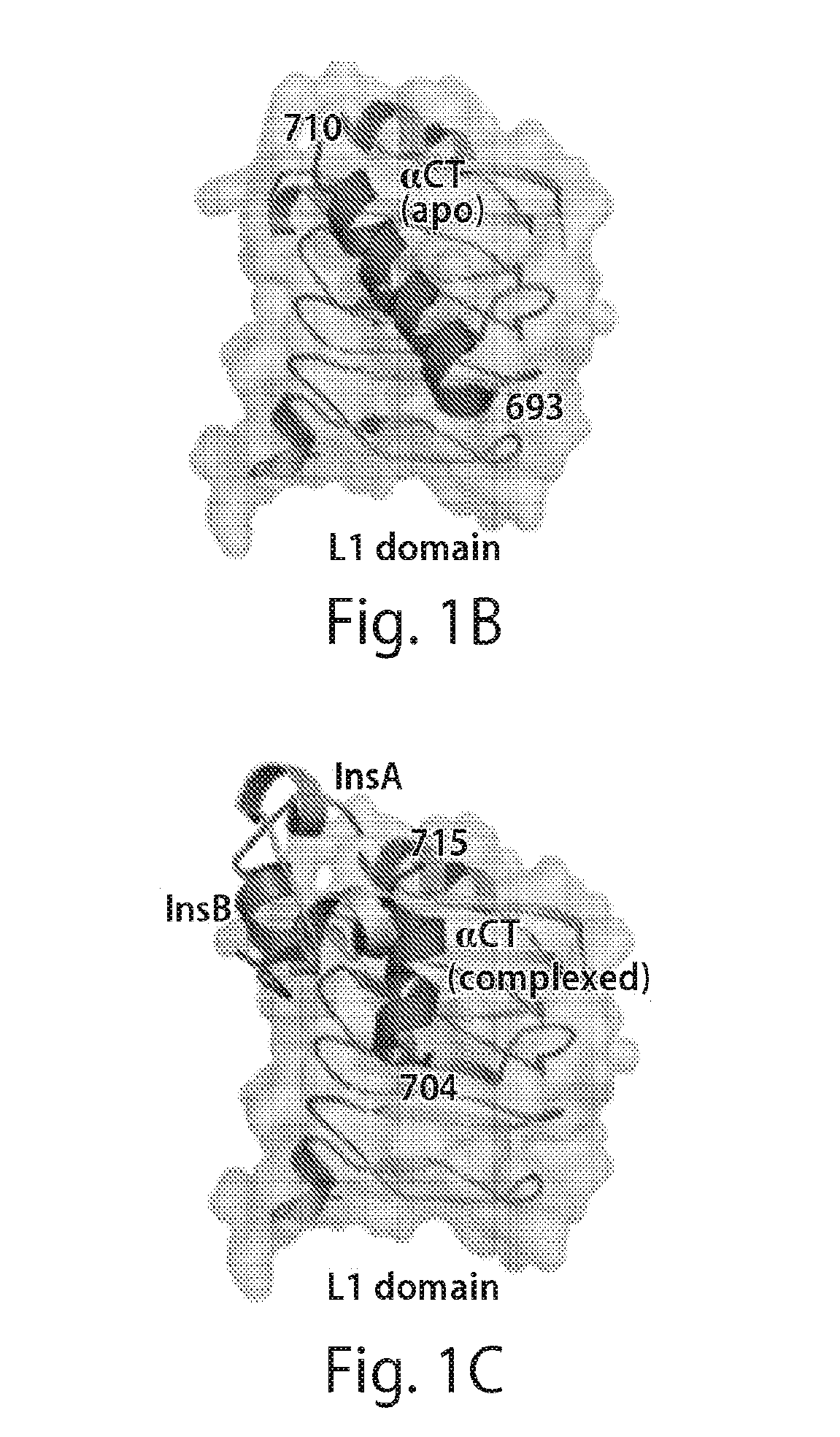
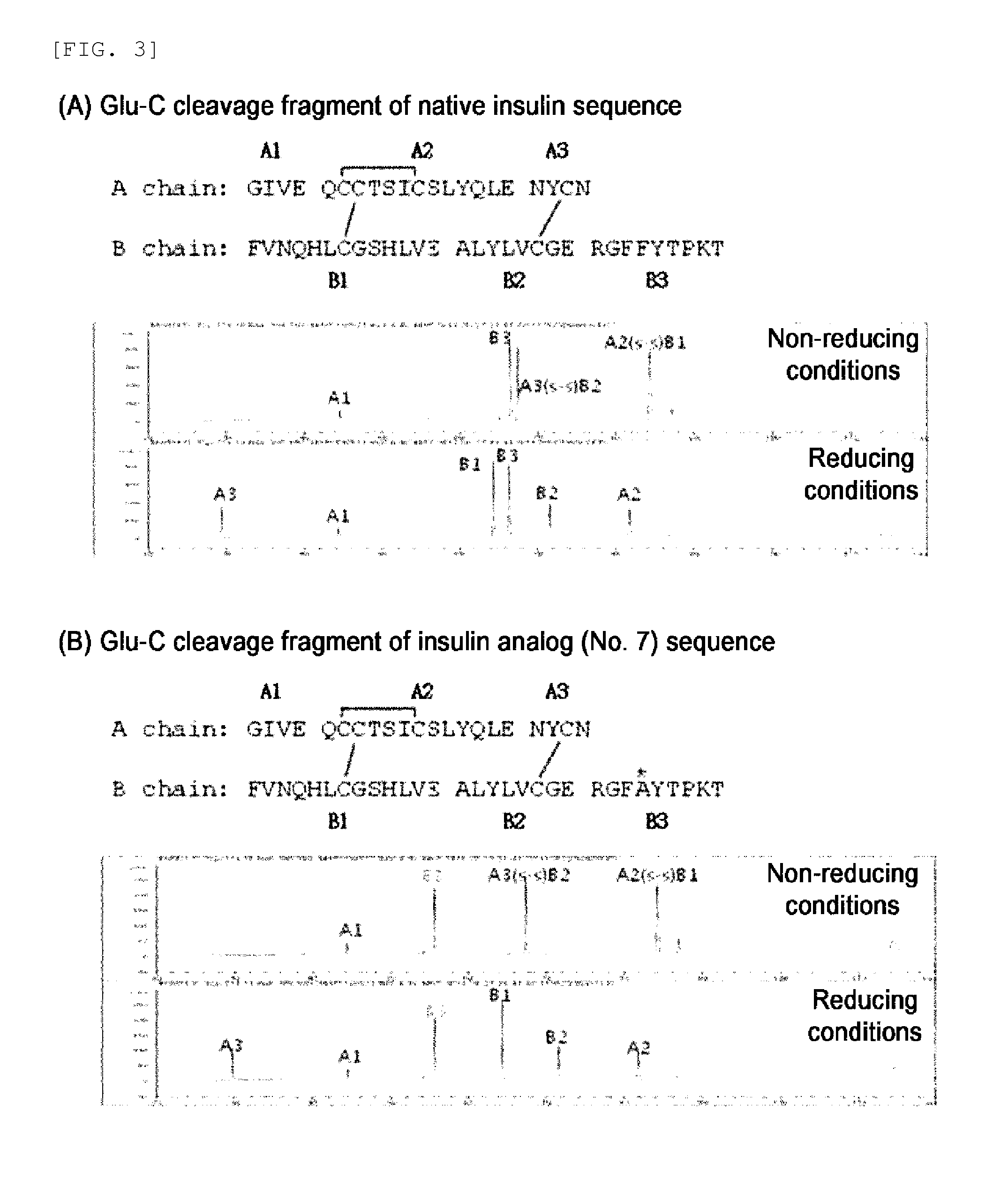
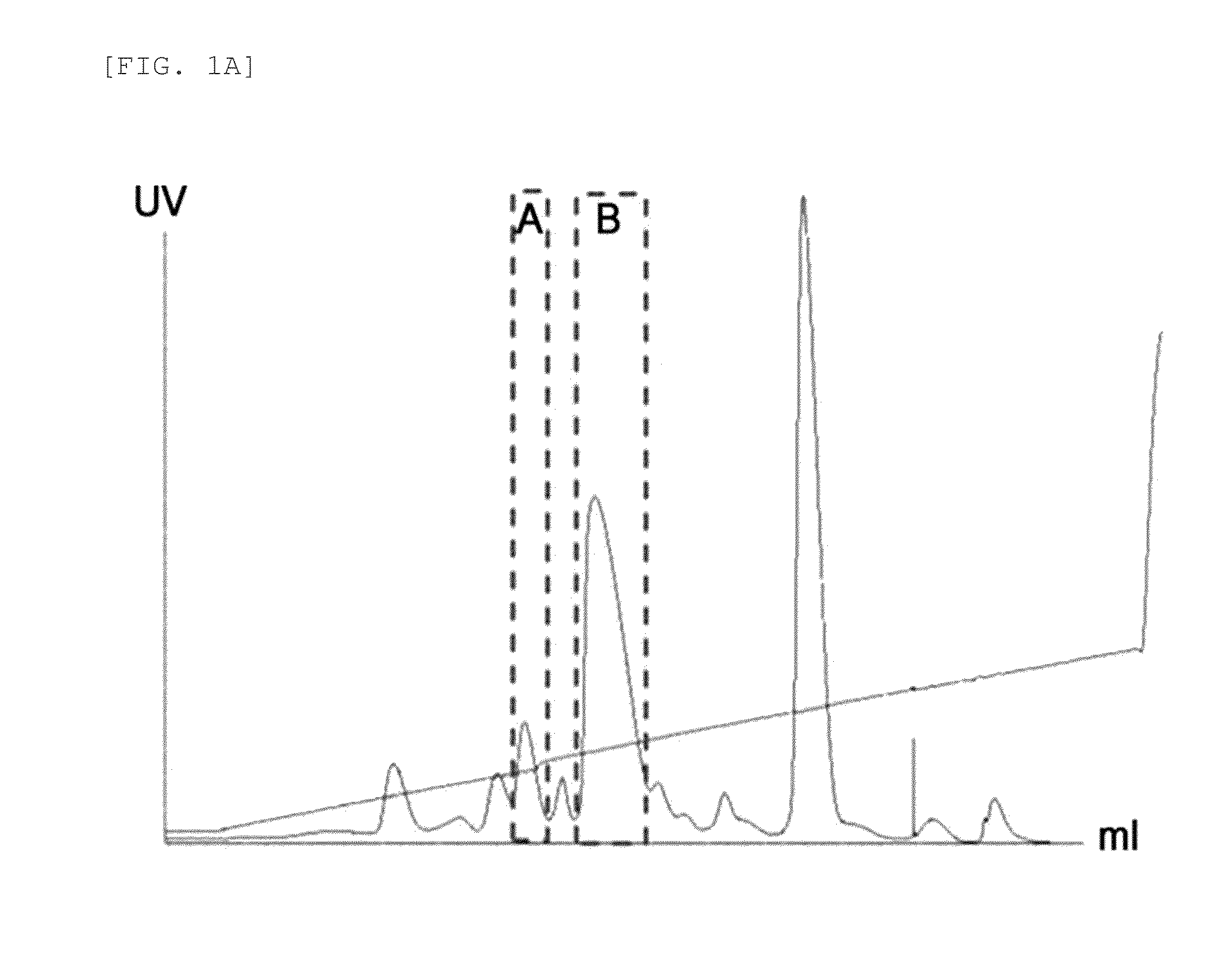
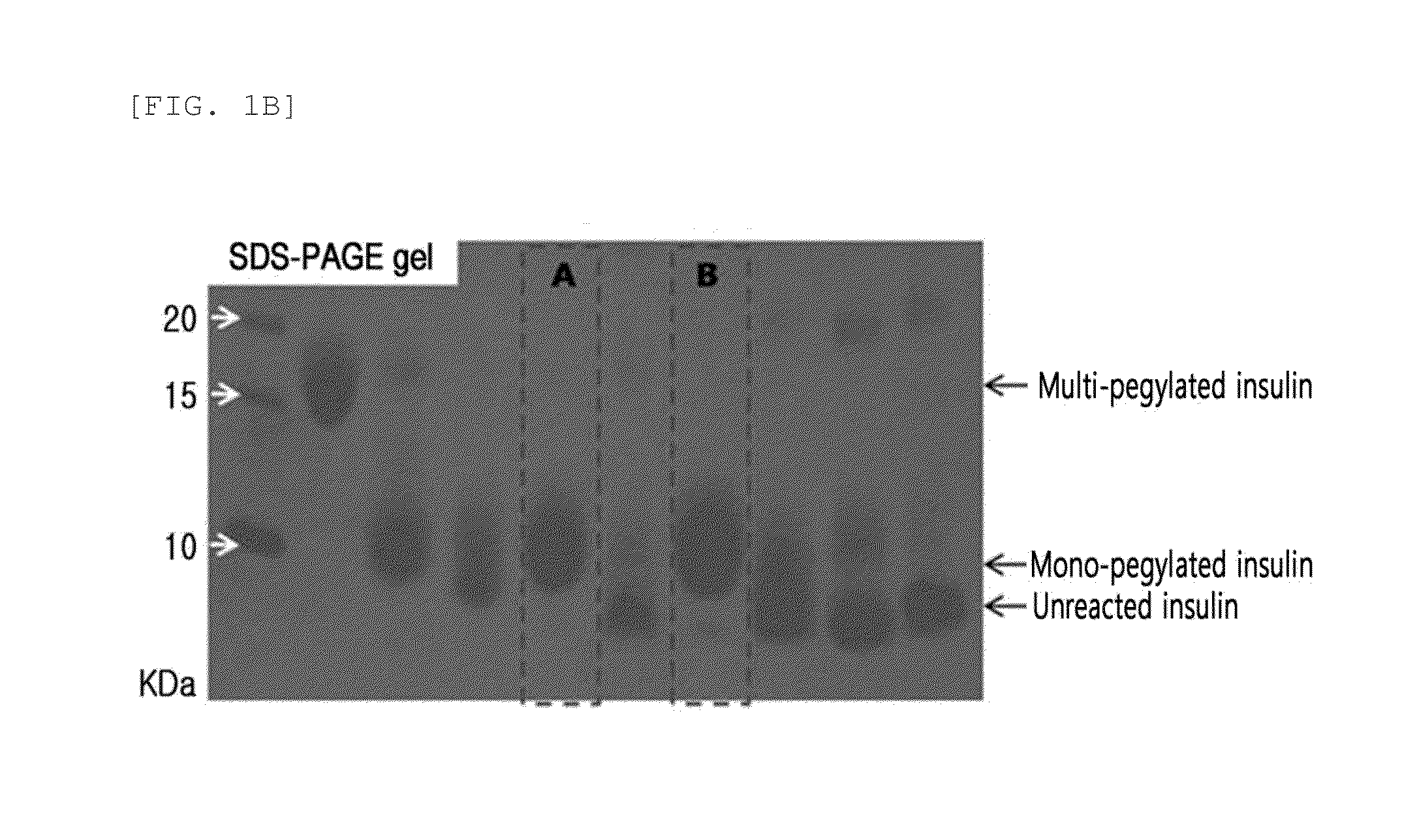
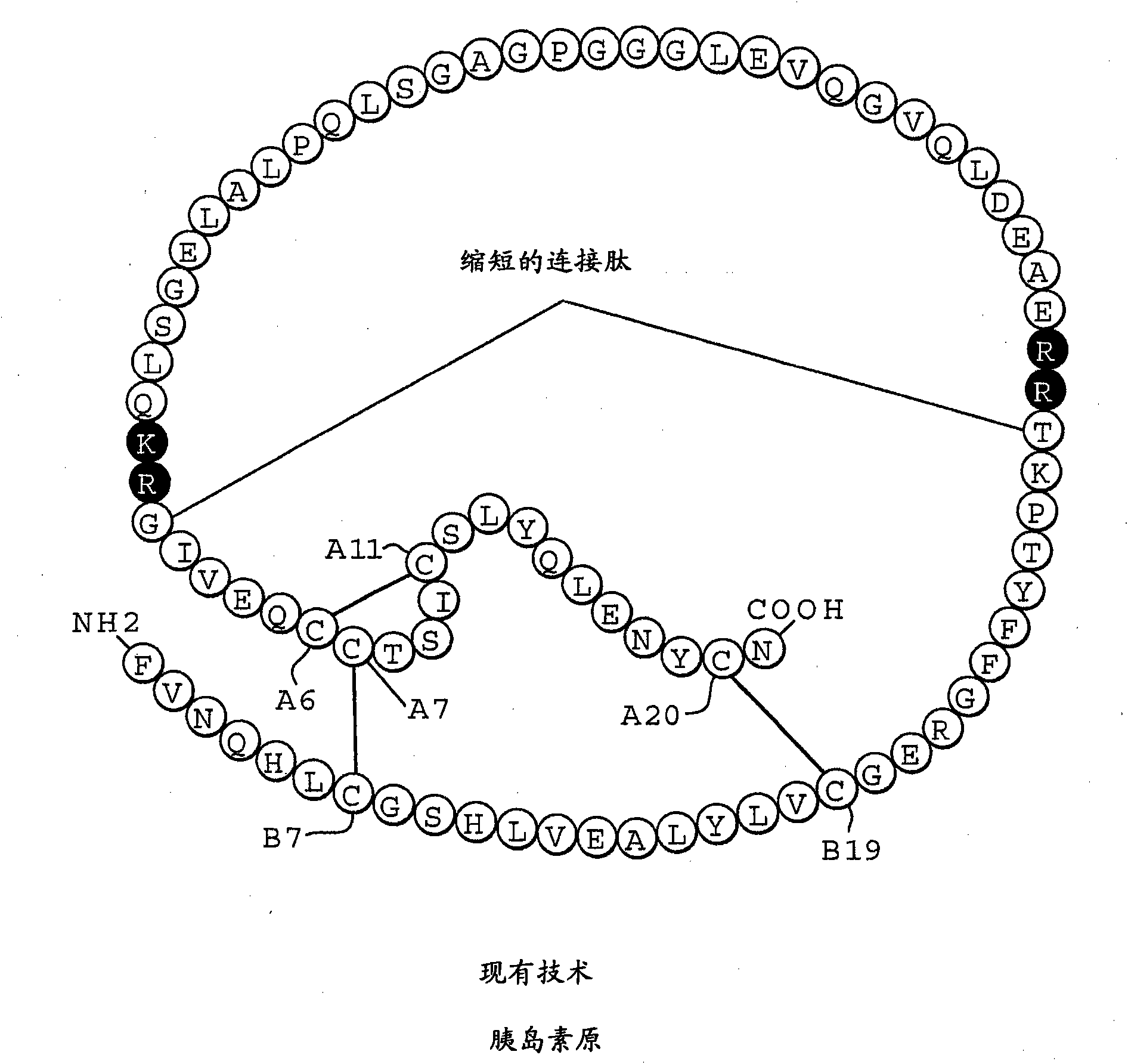
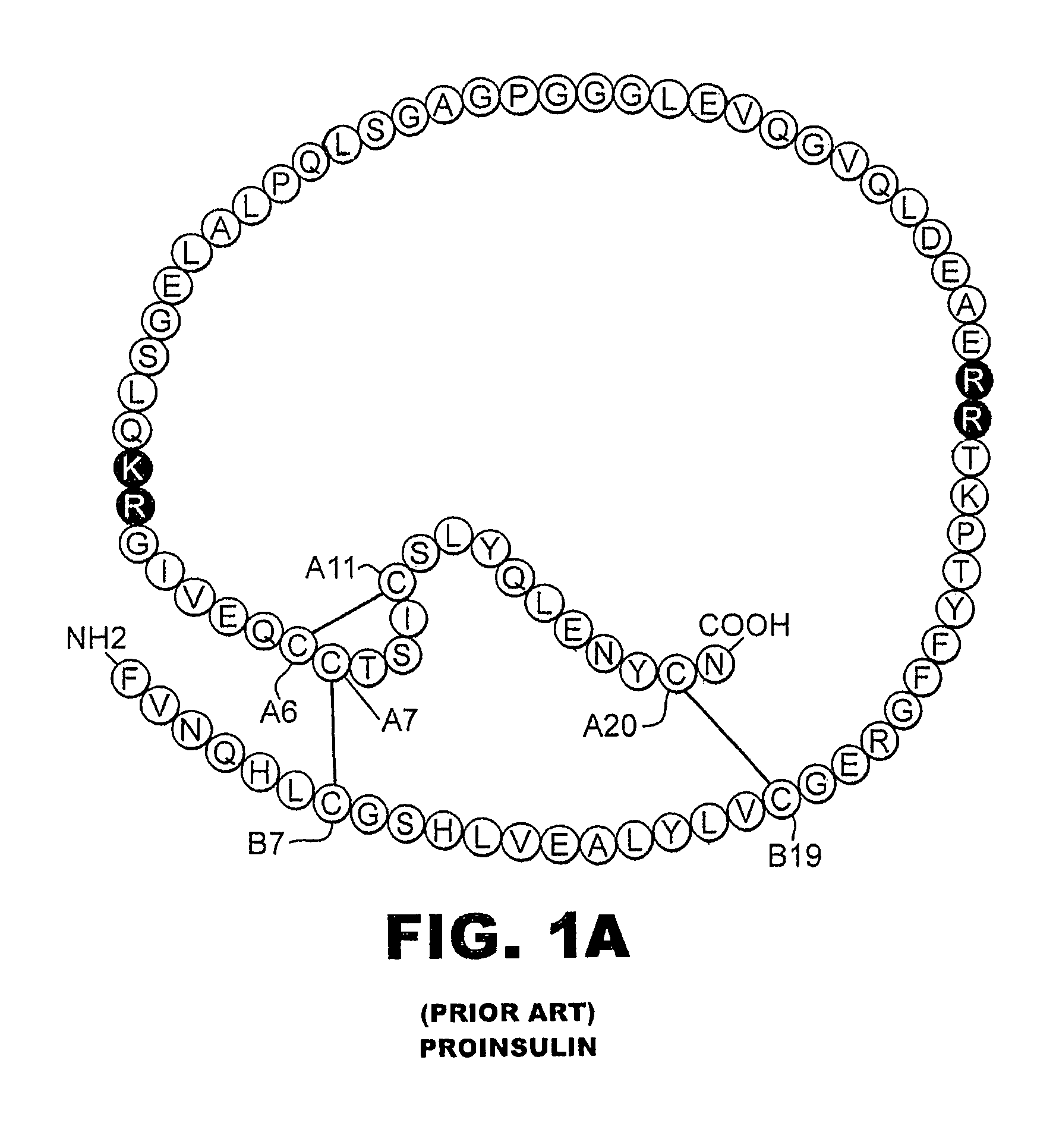
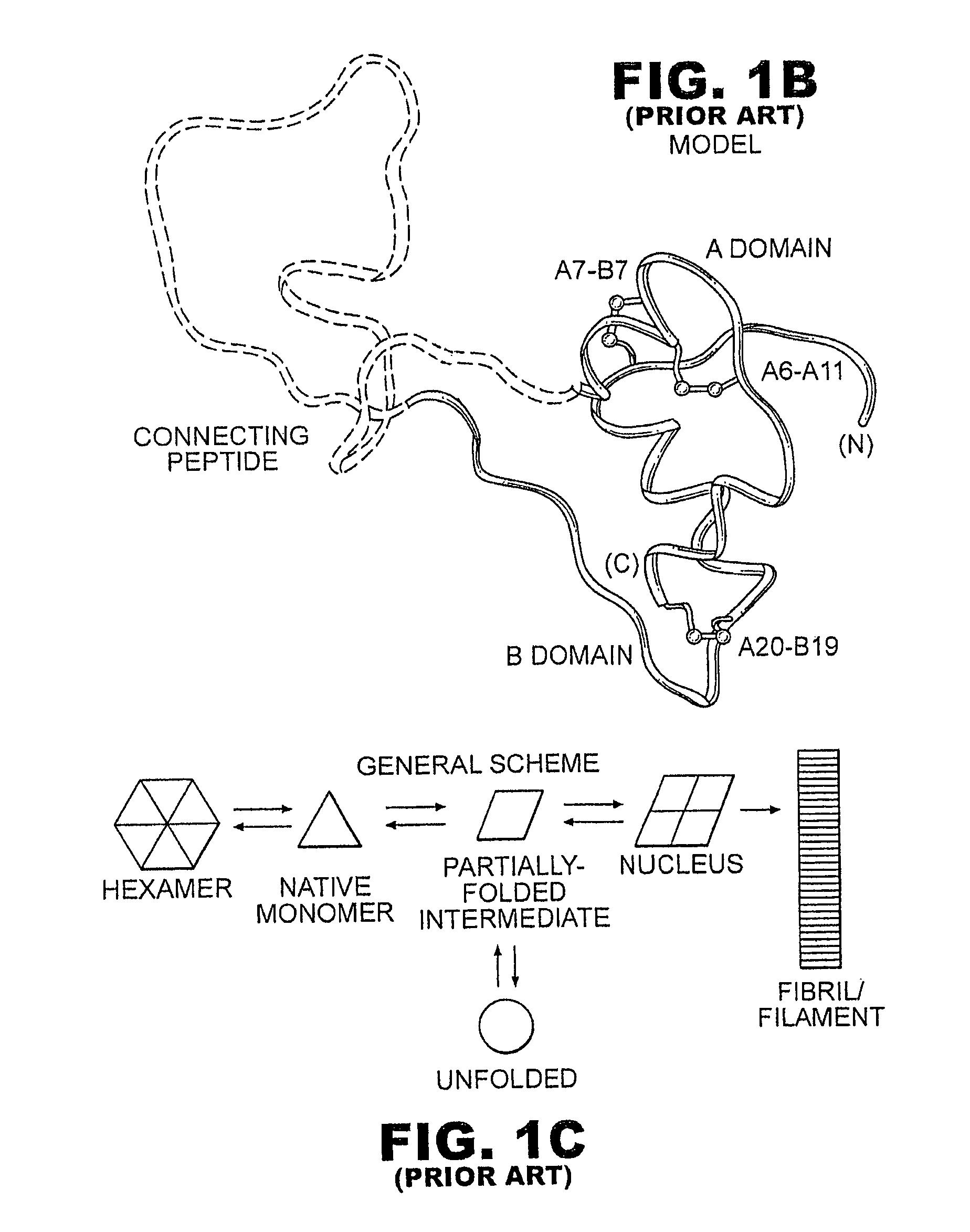
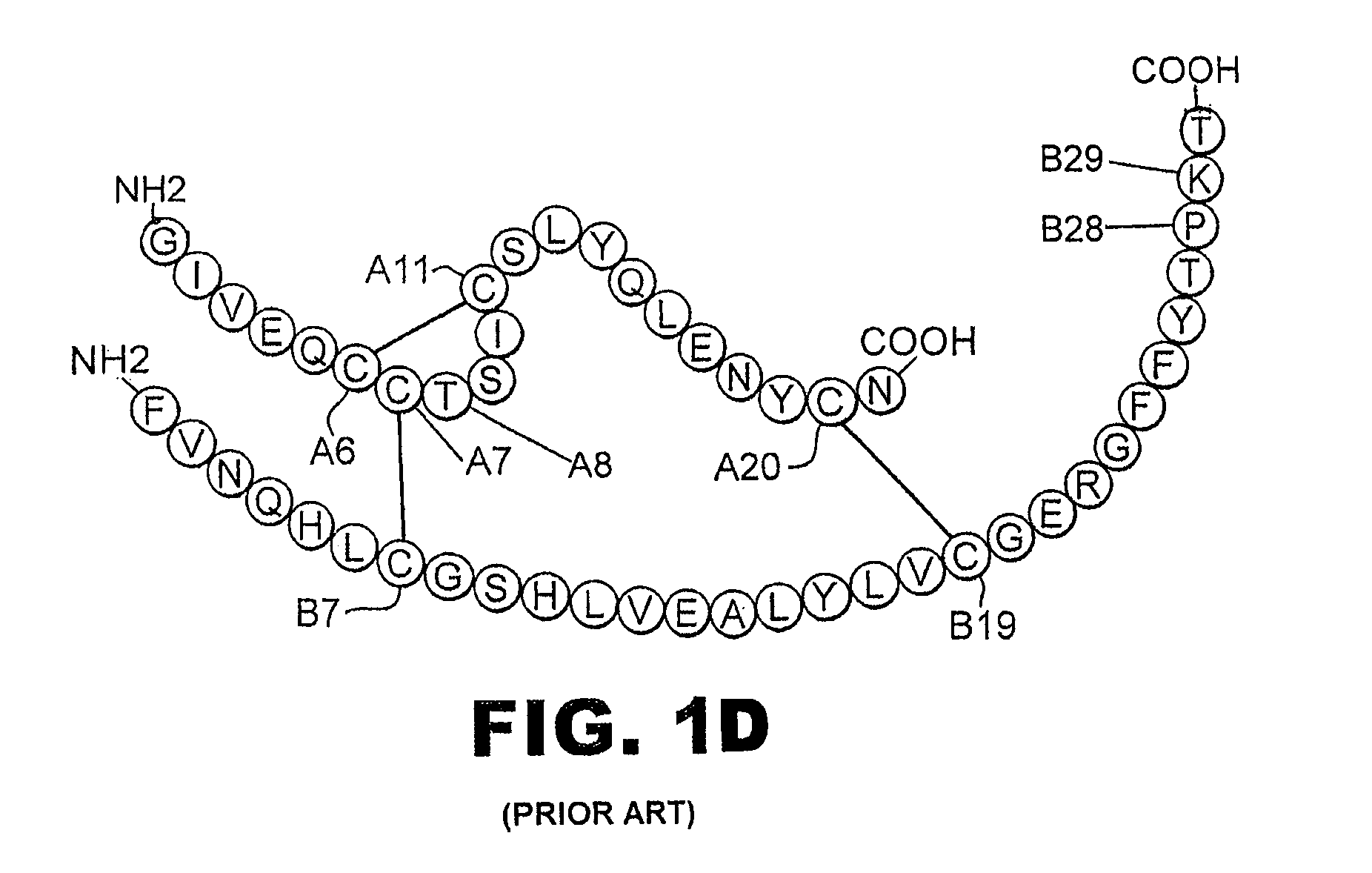
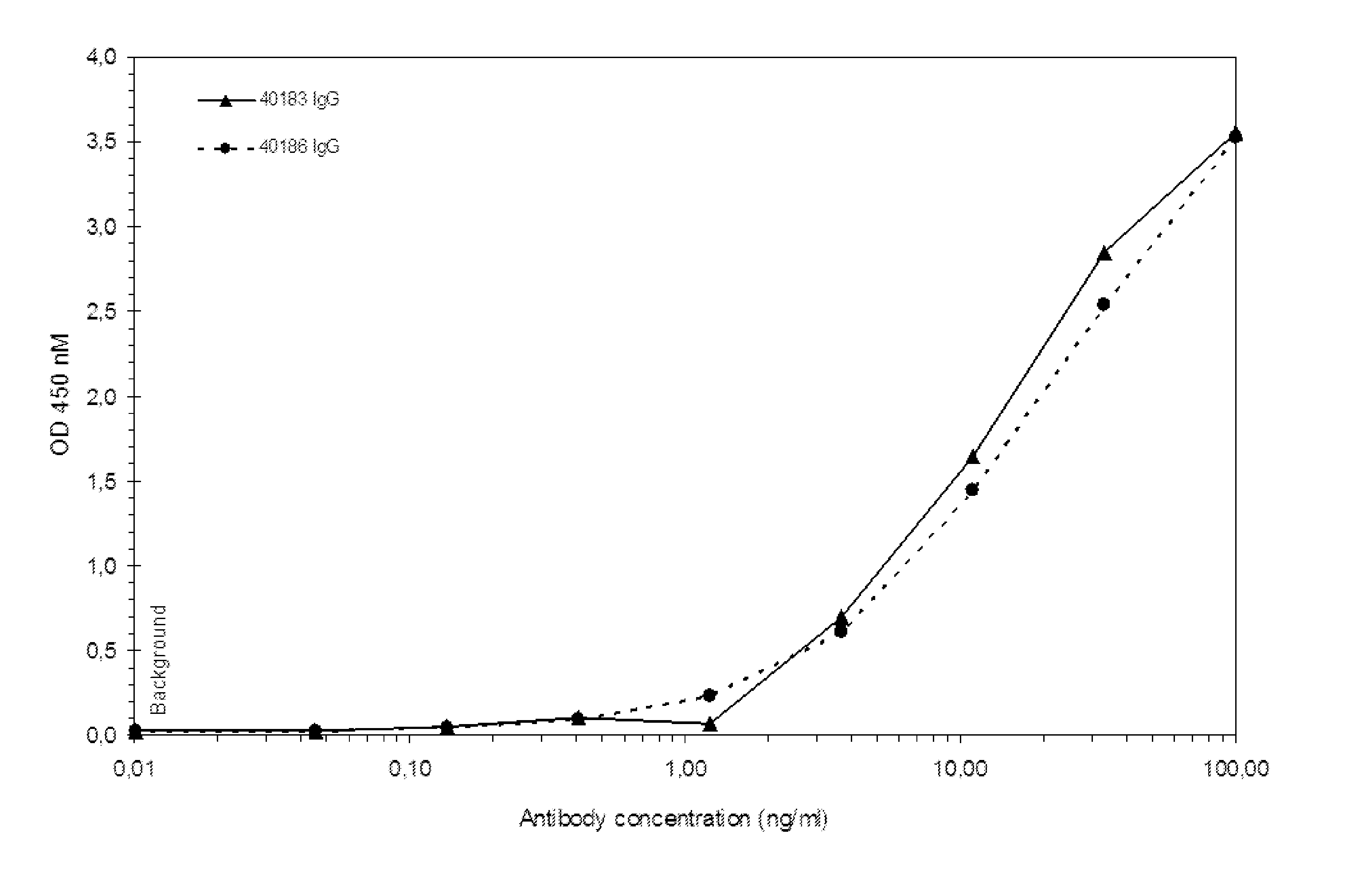
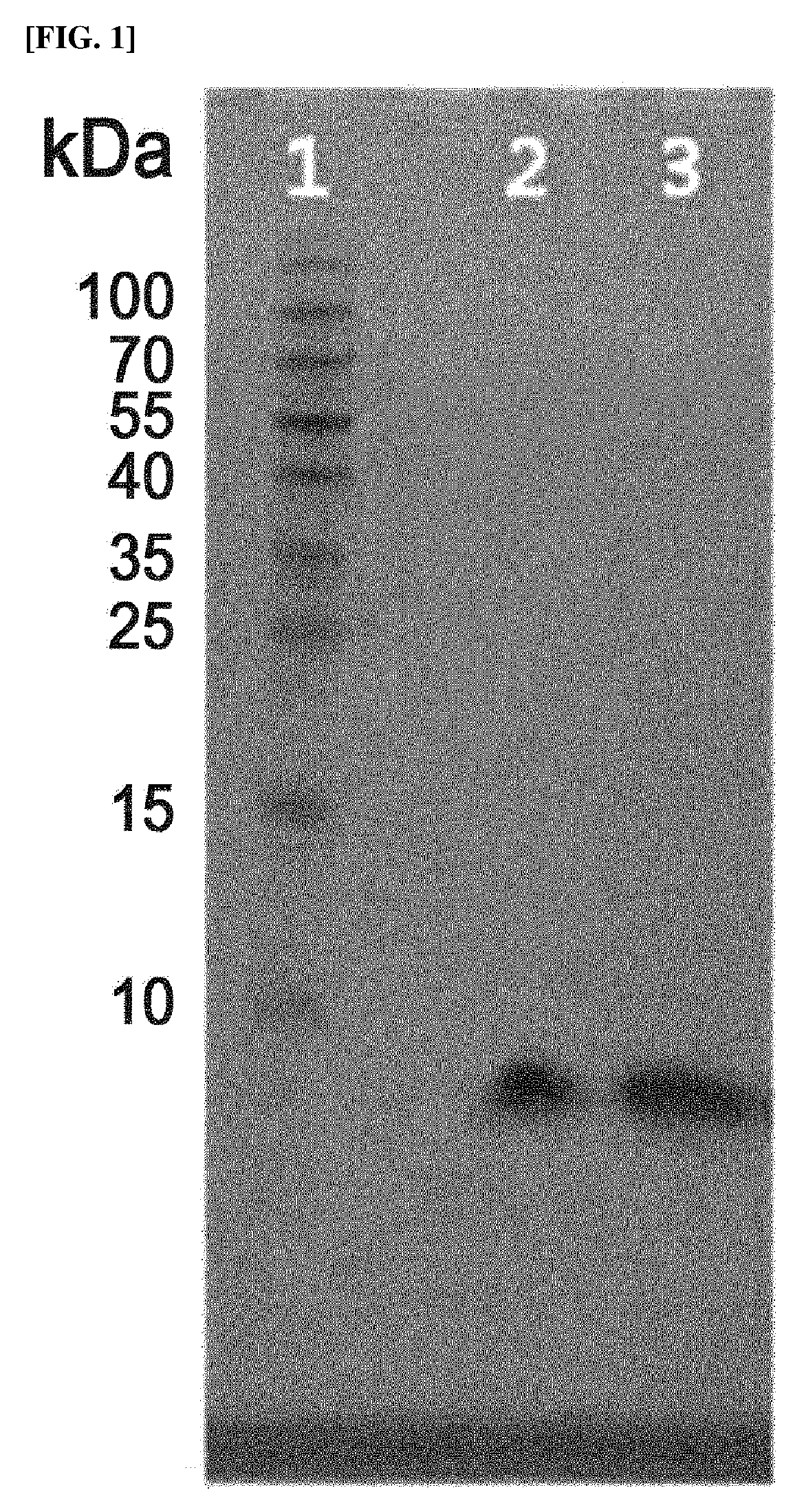
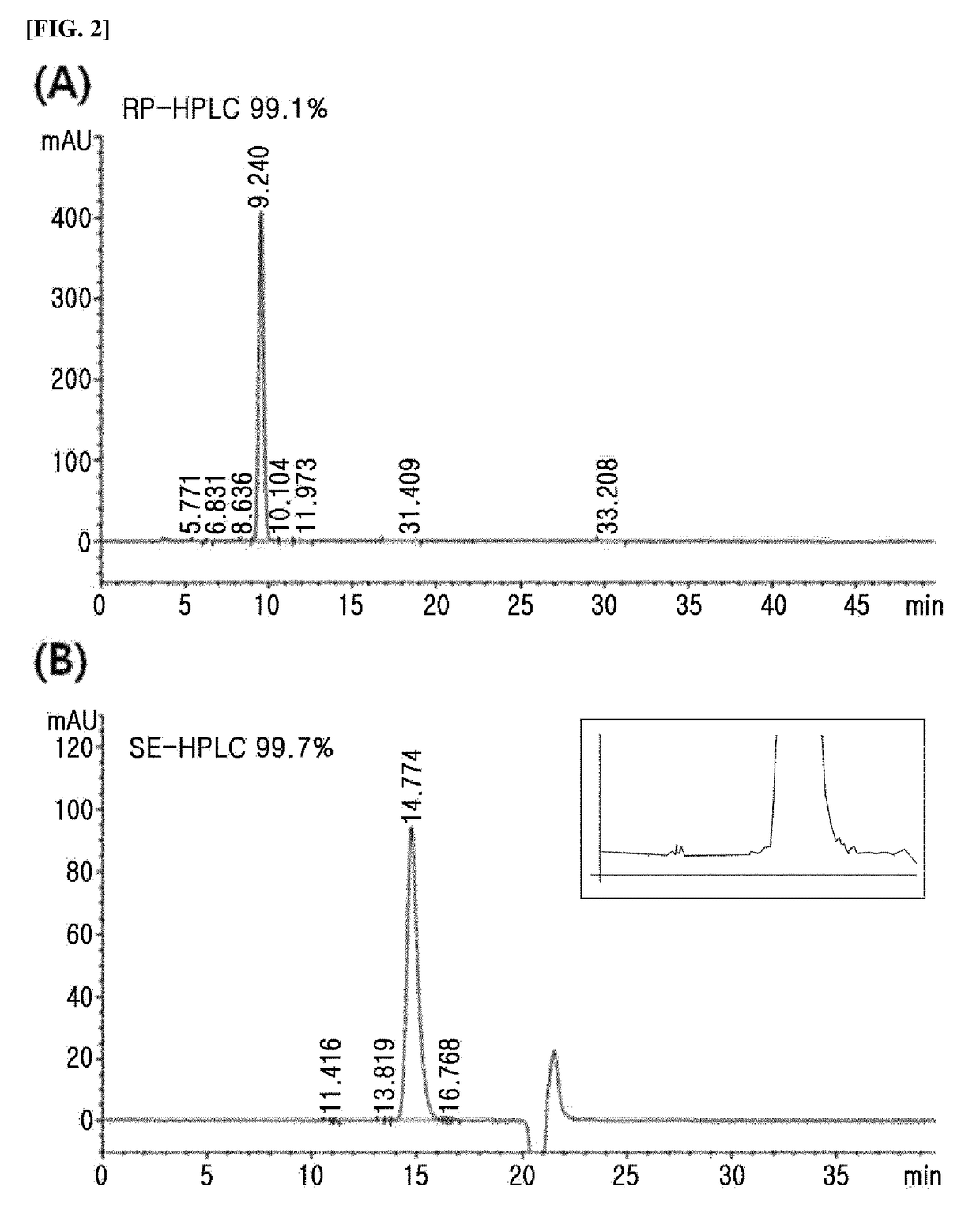
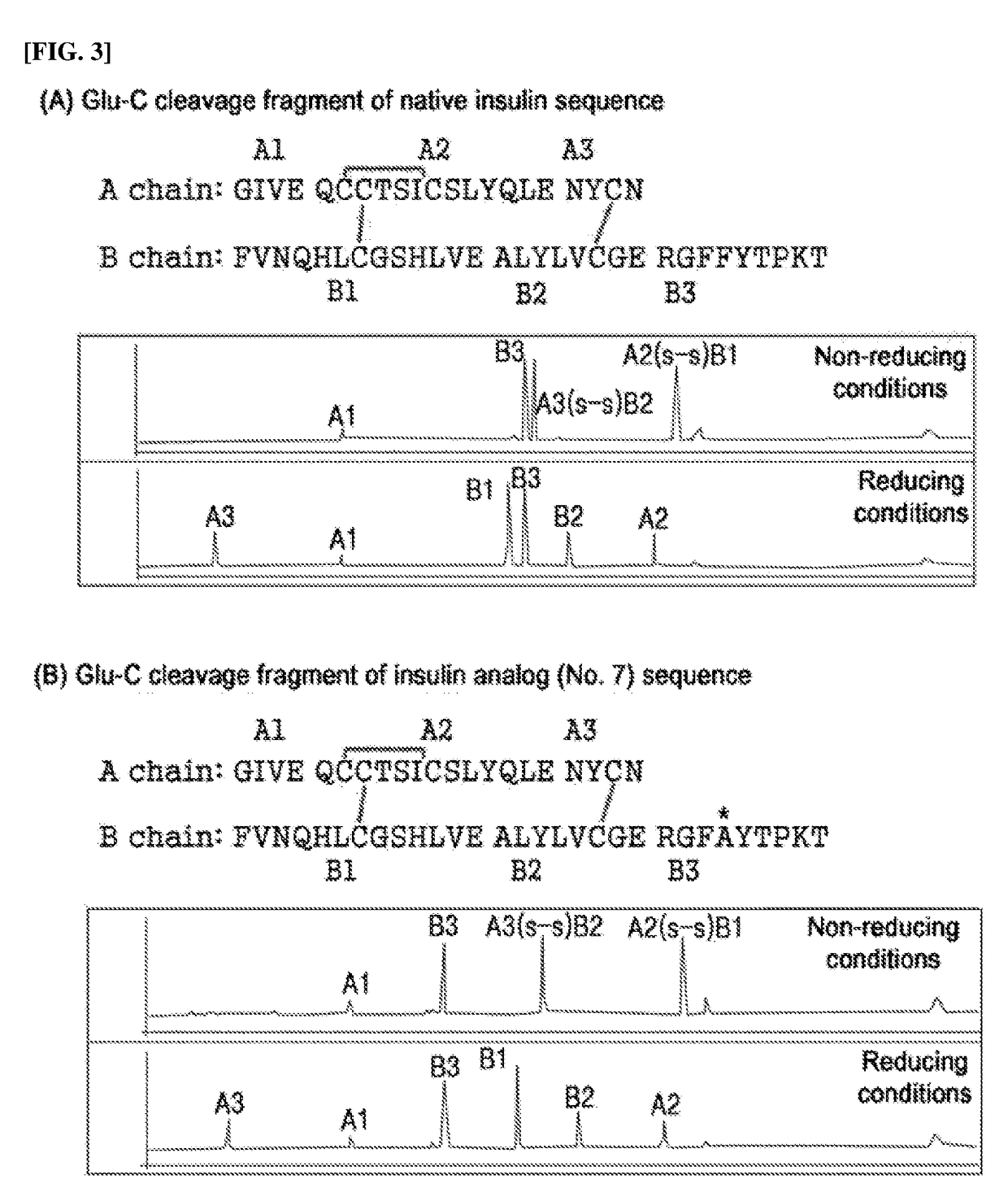
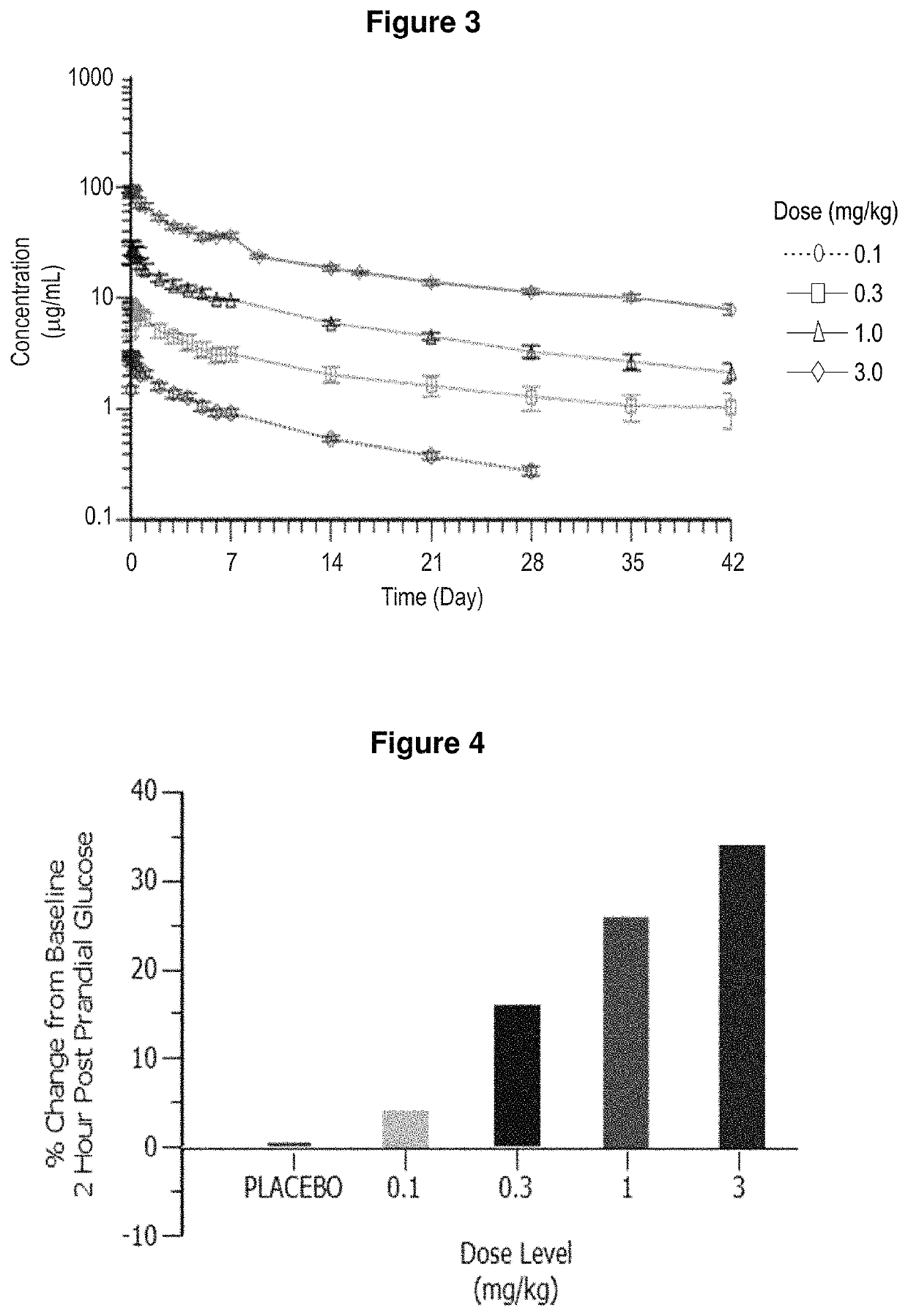
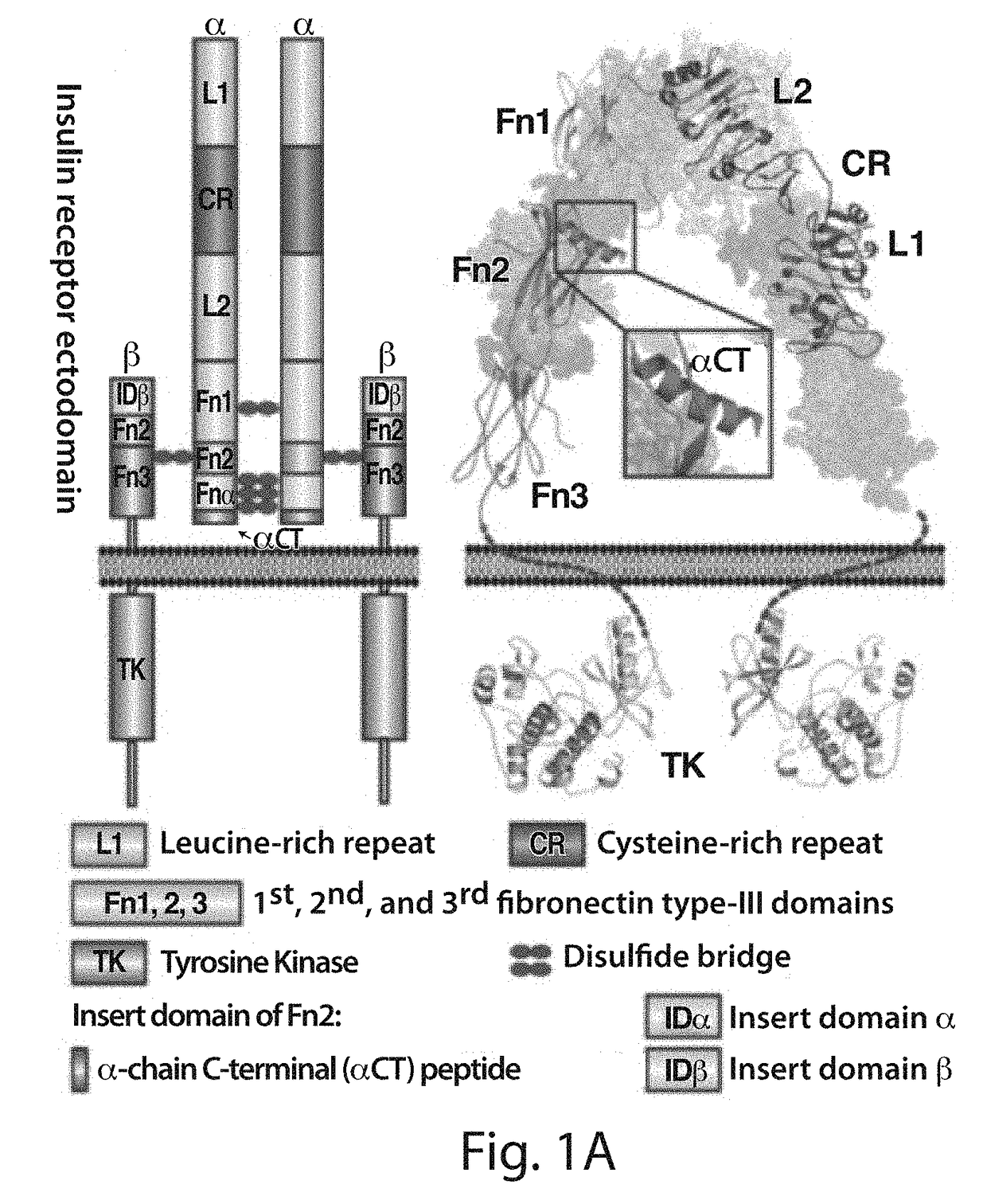
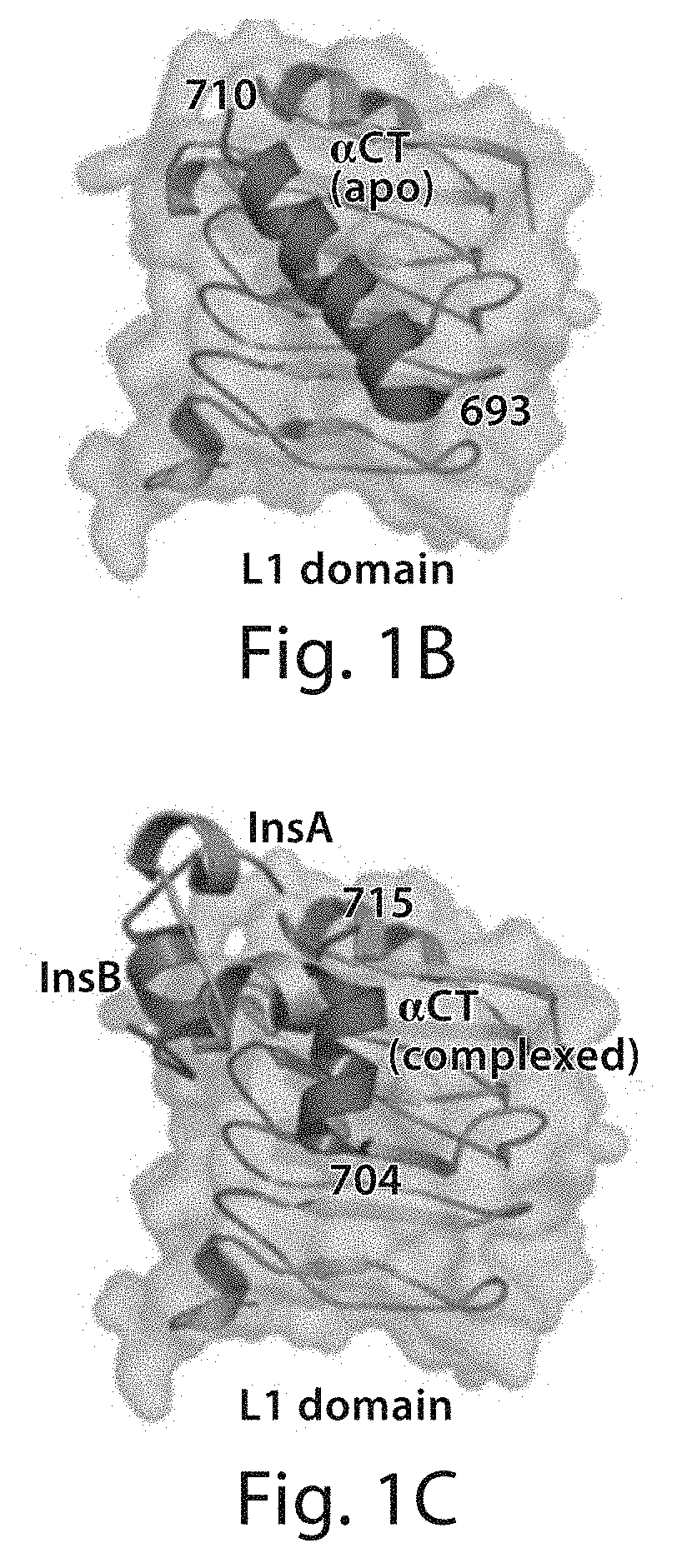
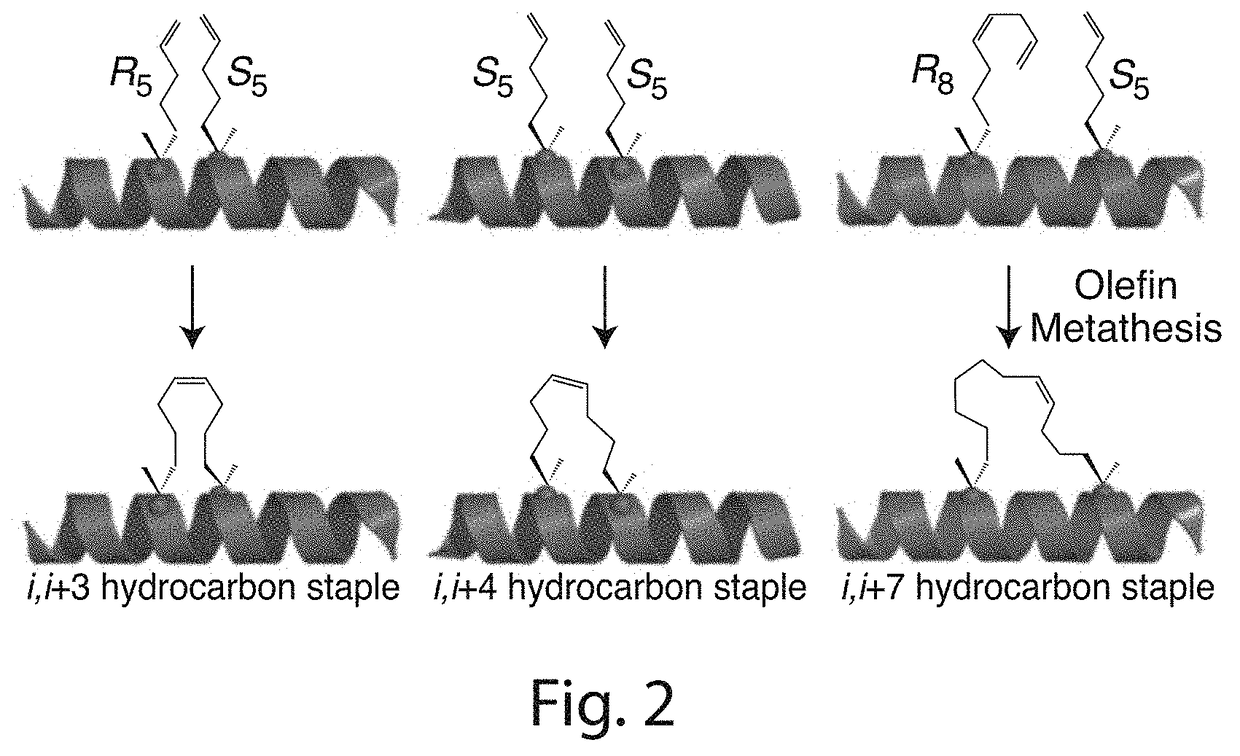
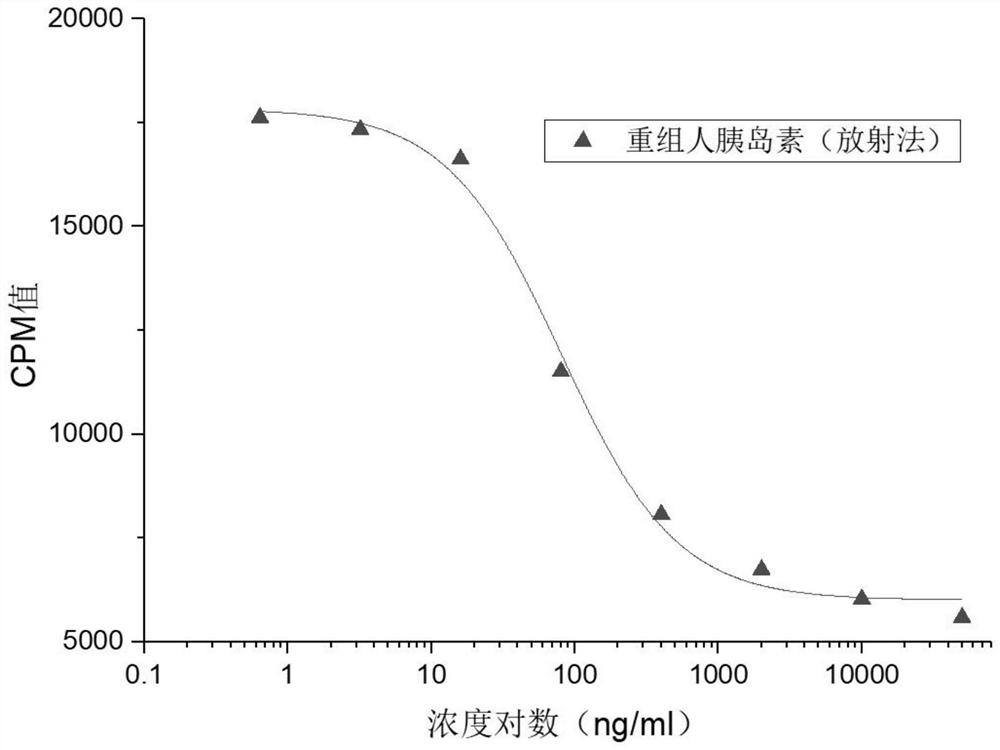
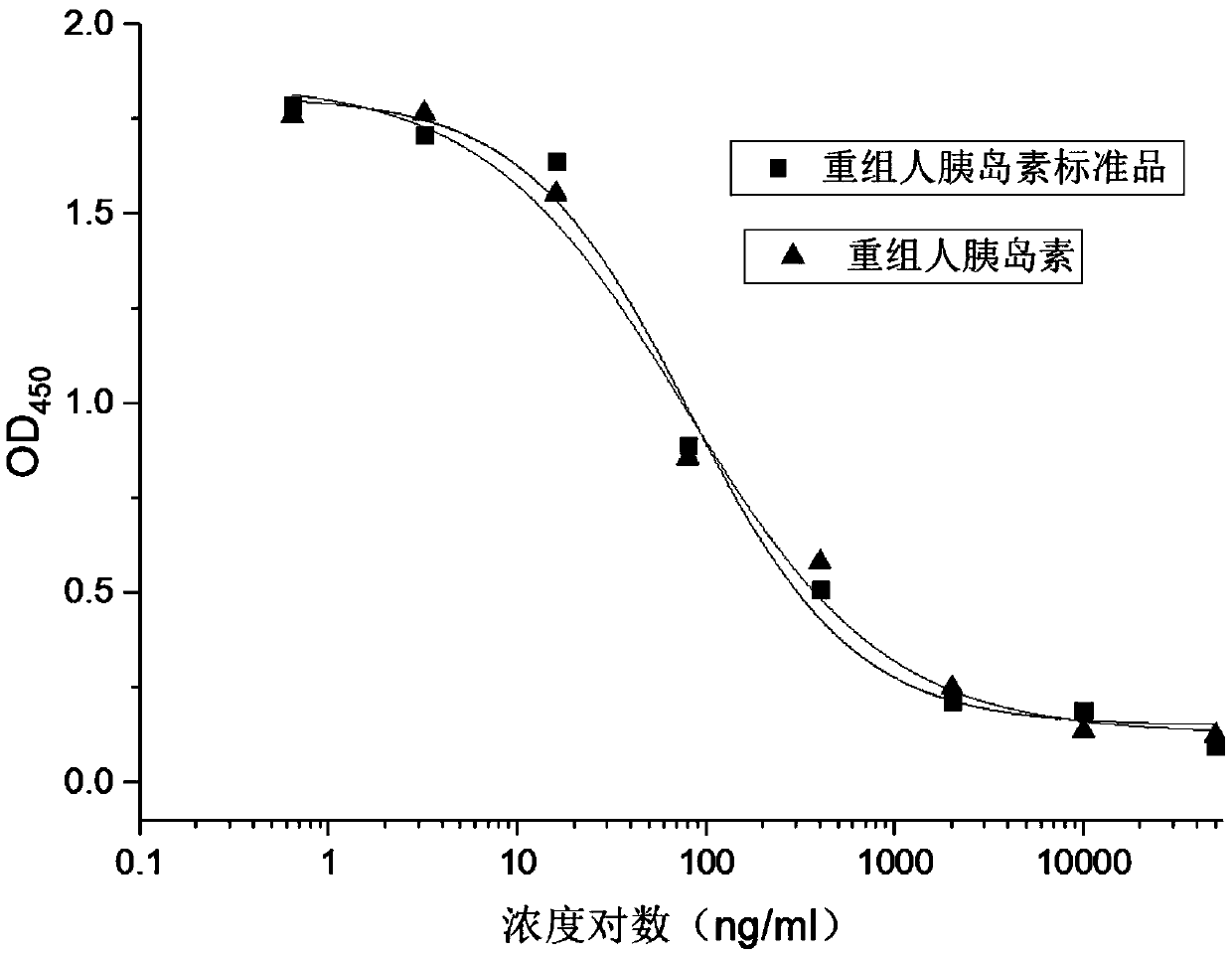
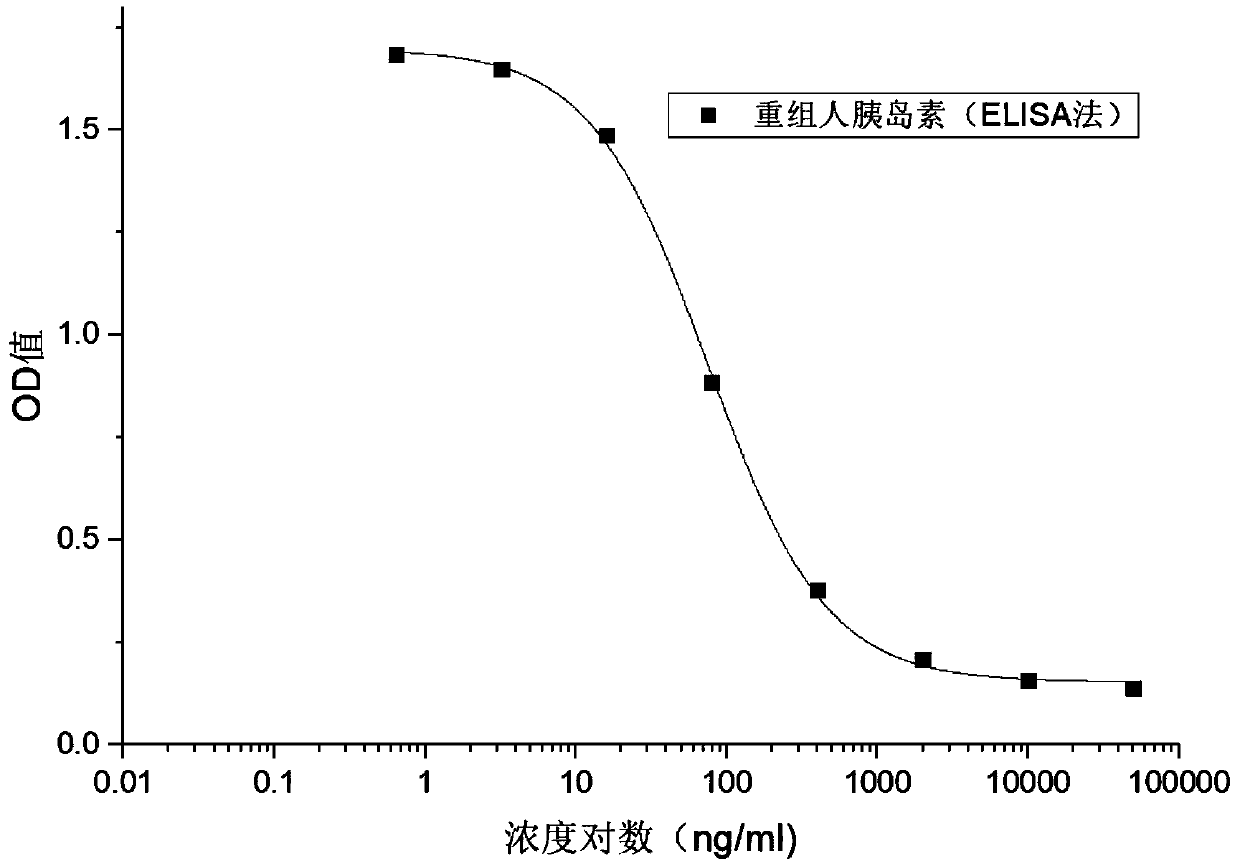
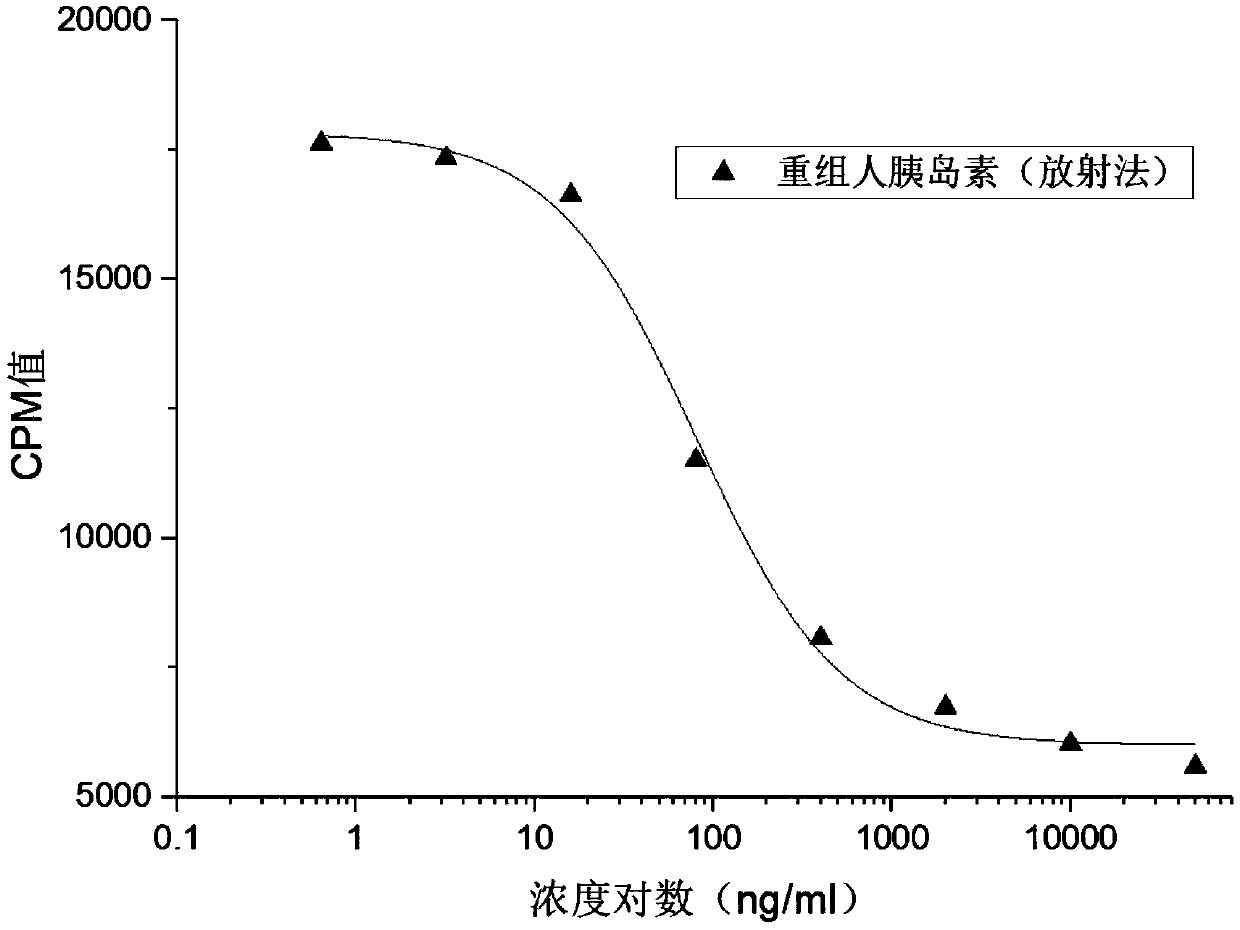
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Insulin receptor binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with the insulin receptor. [GOC:ai]
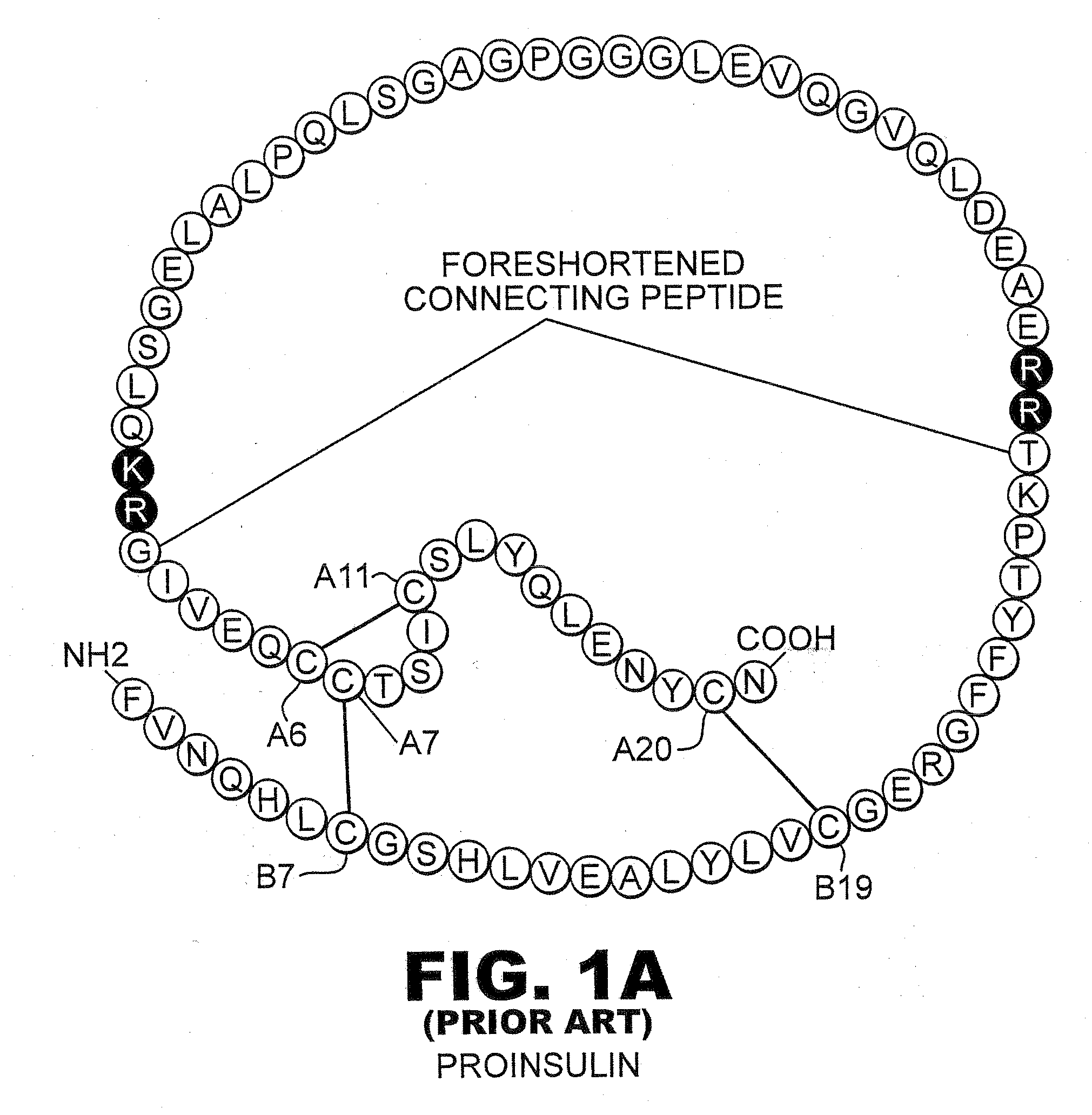
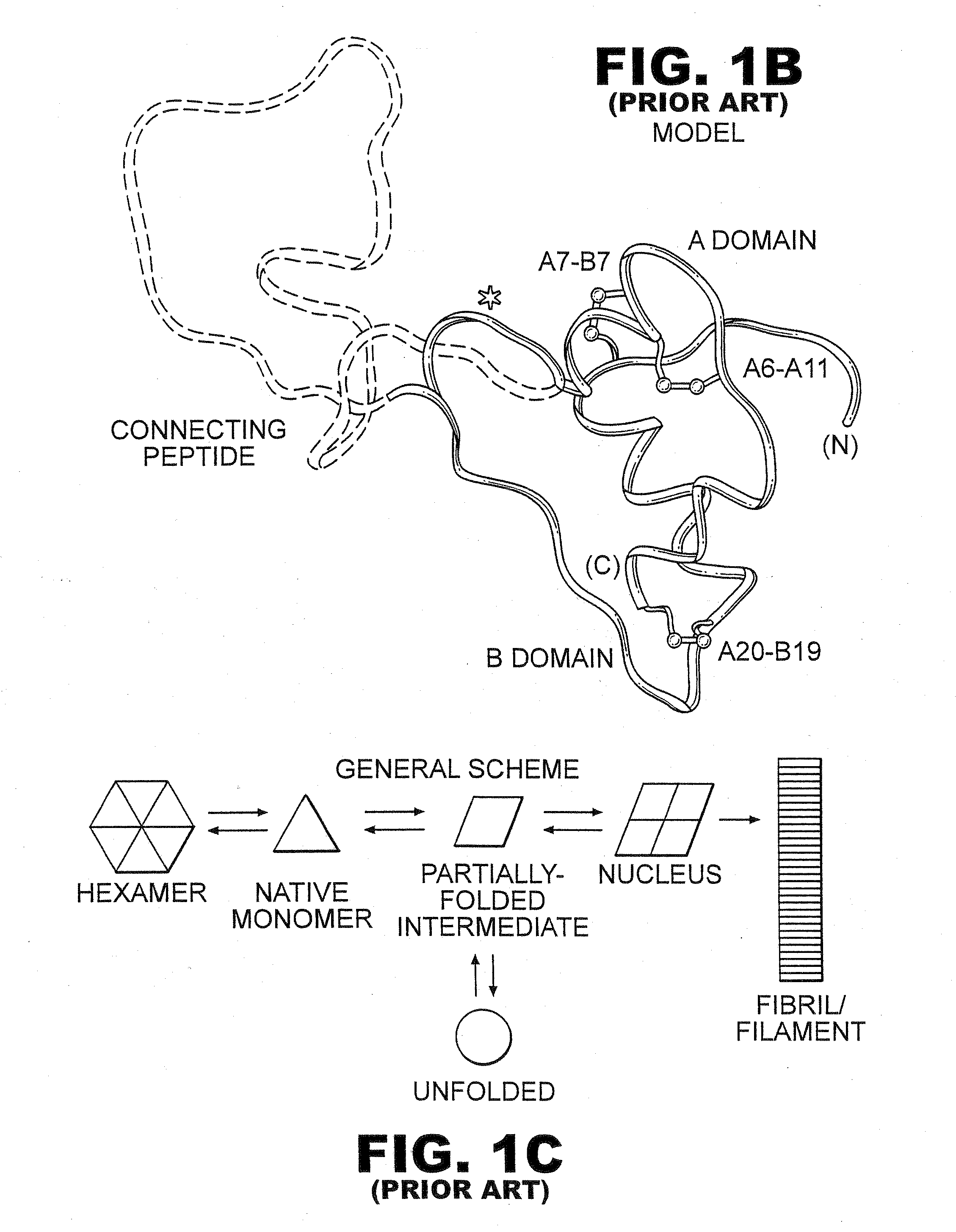
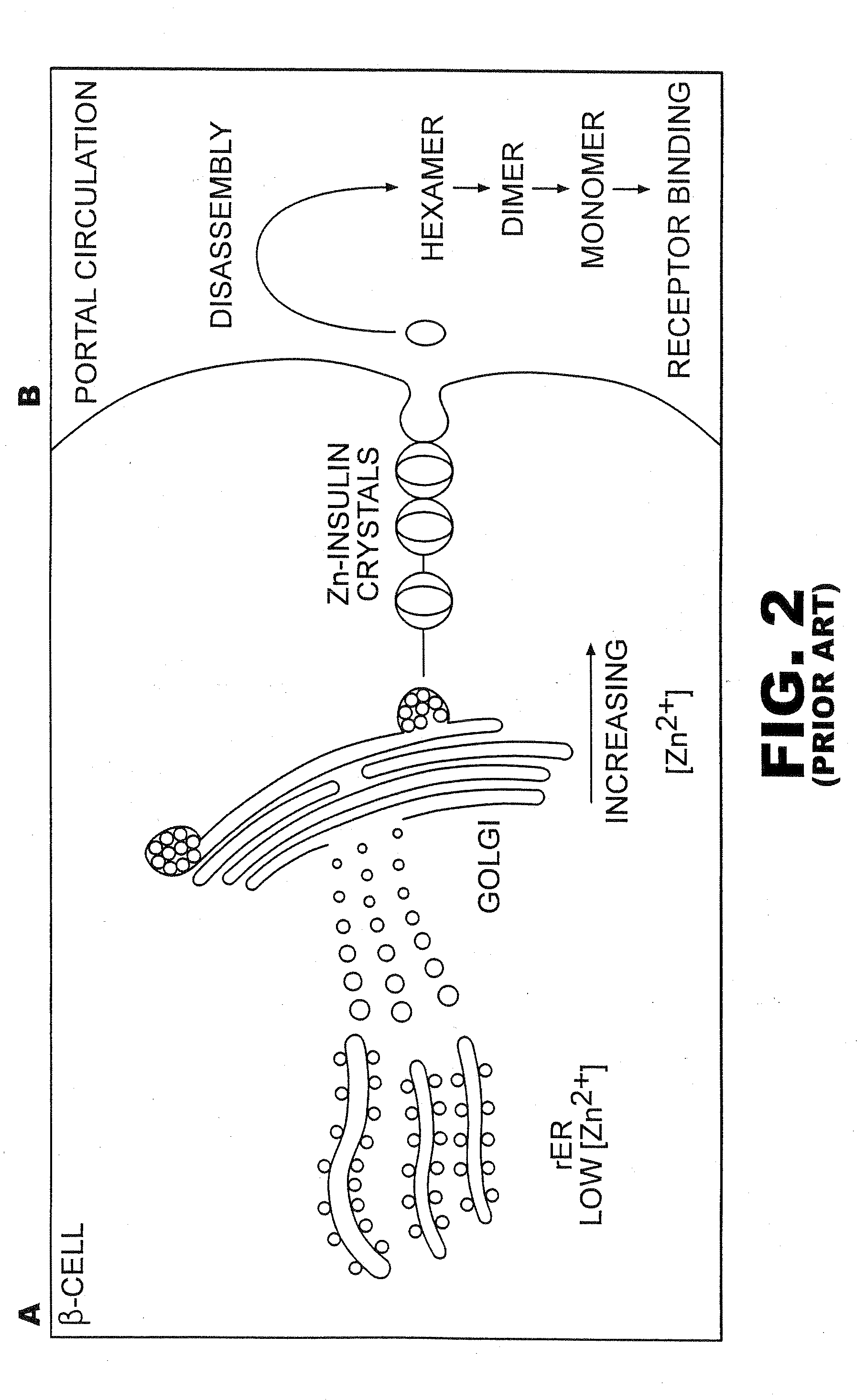
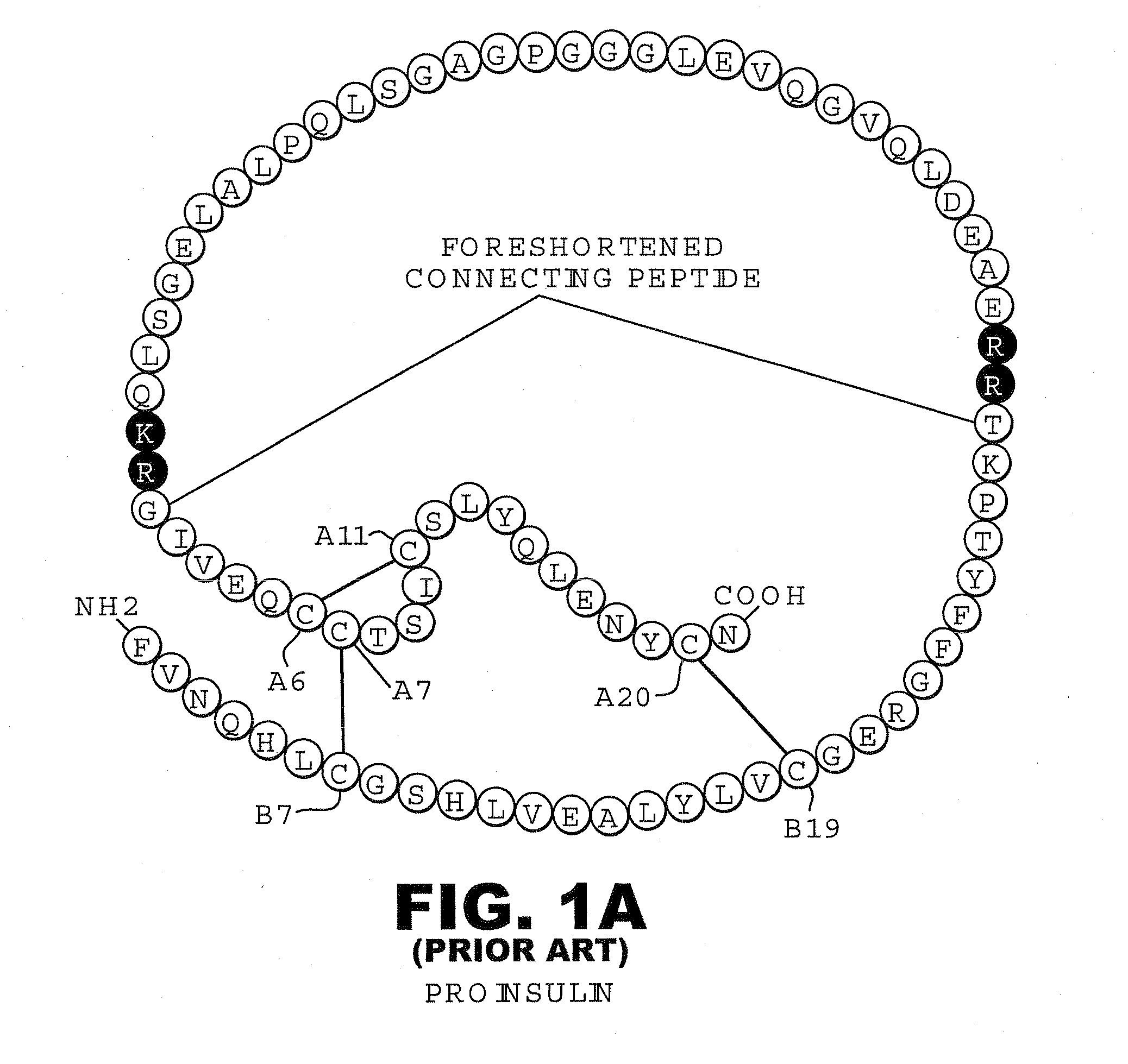
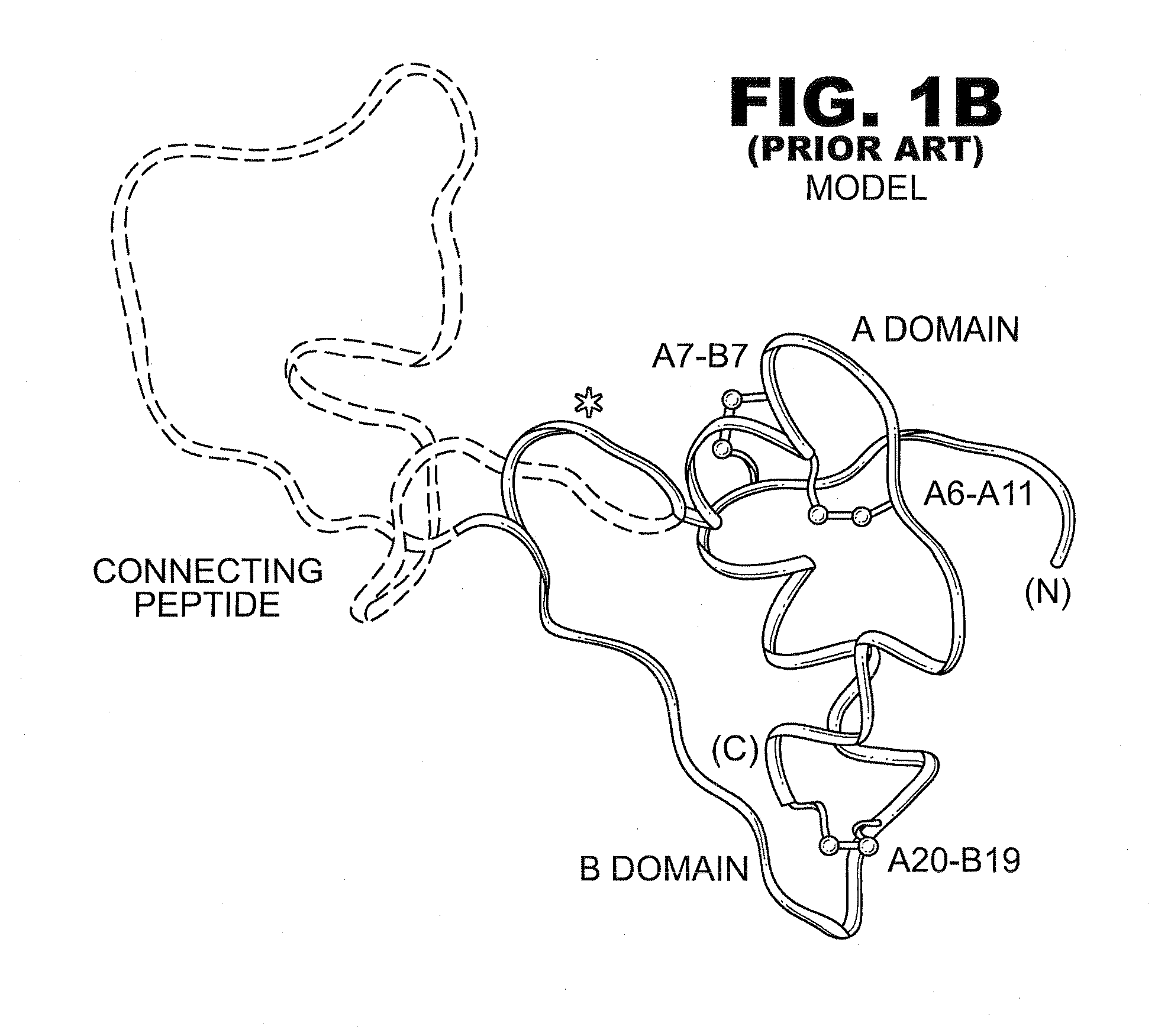
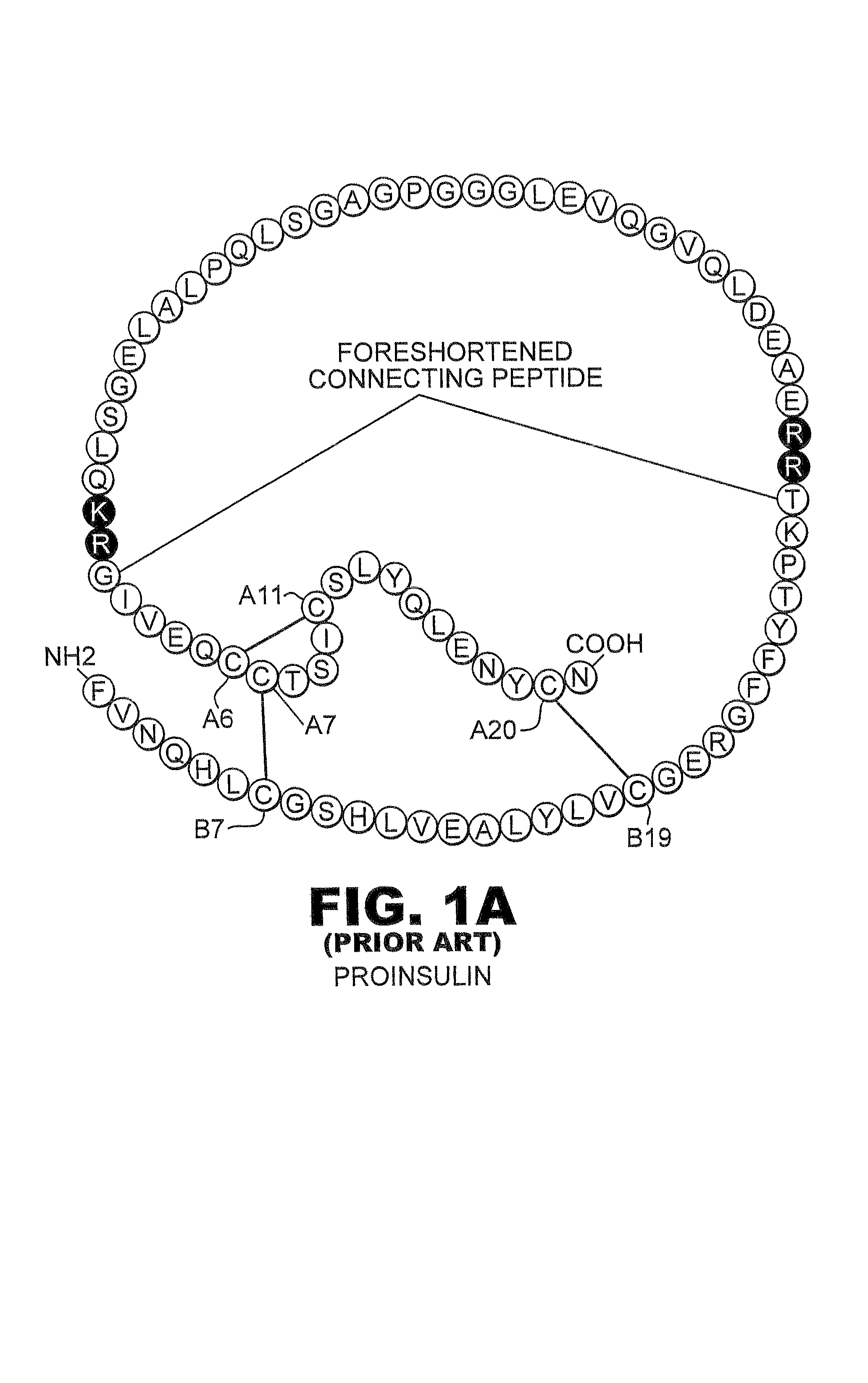
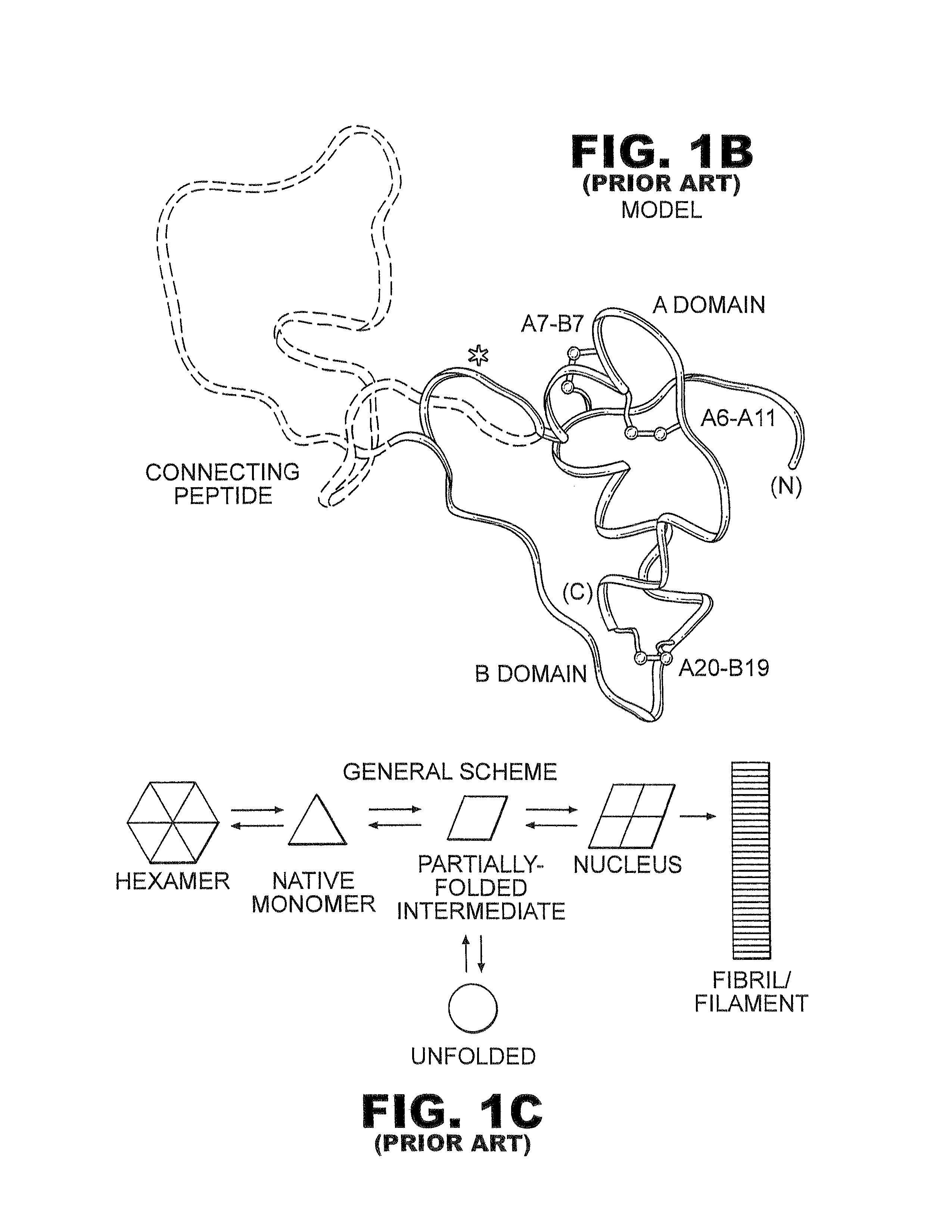
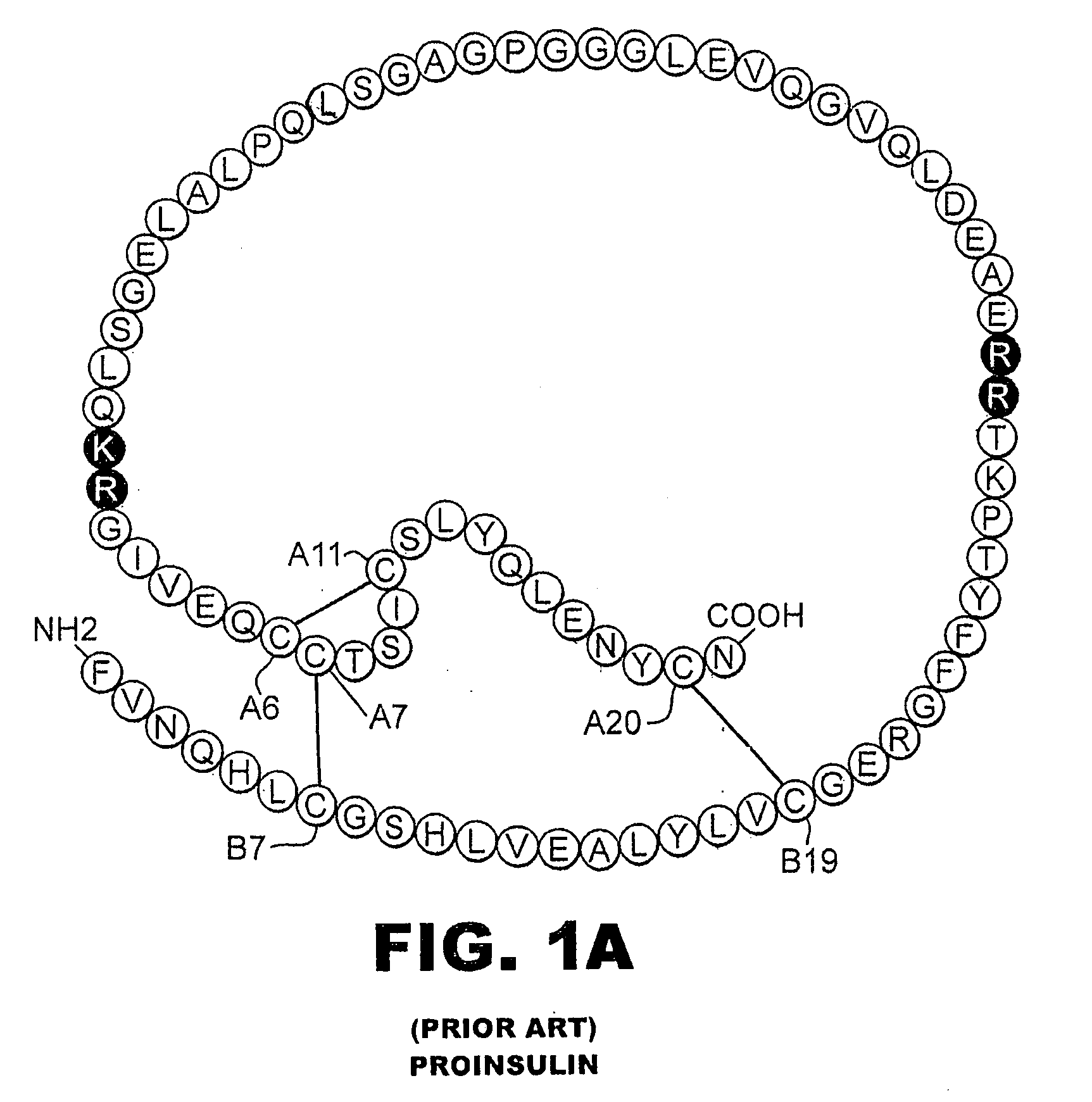
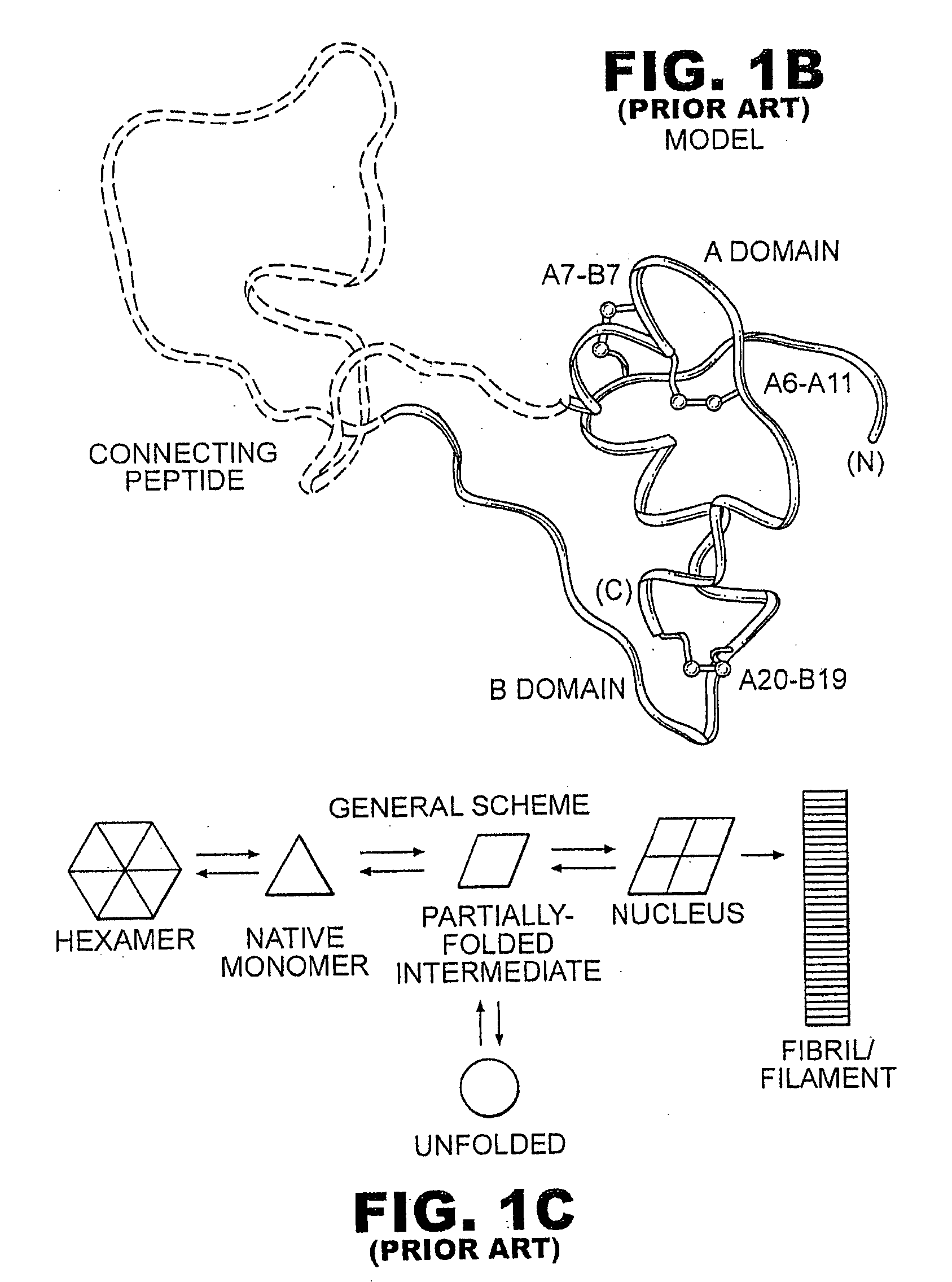
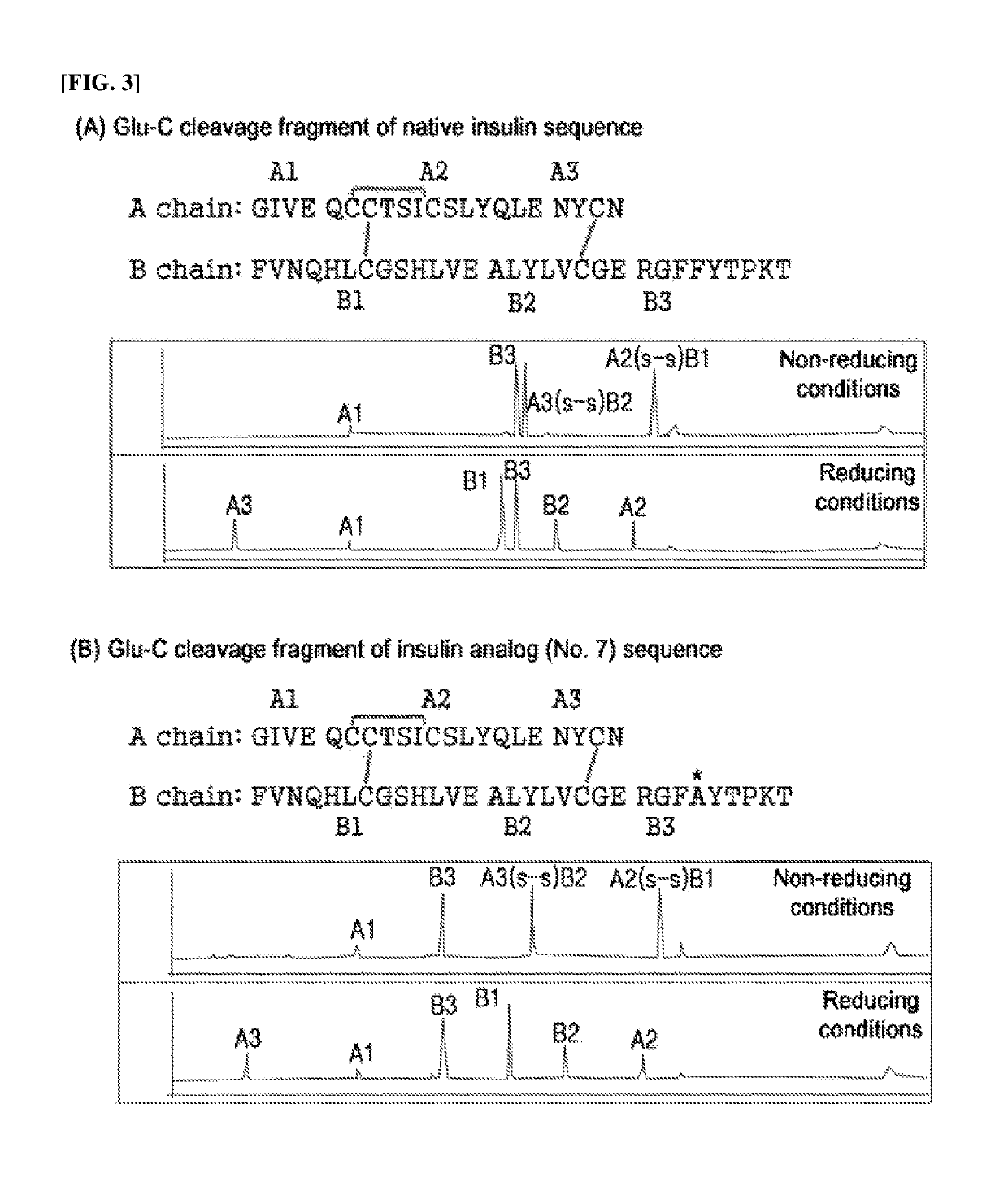
Fibrillation-resistant insulin and insulin analogues
InactiveUS20100099601A1Promote absorptionRapidity of absorptionFungiSugar derivativesInsulin pumpInsulin receptor binding
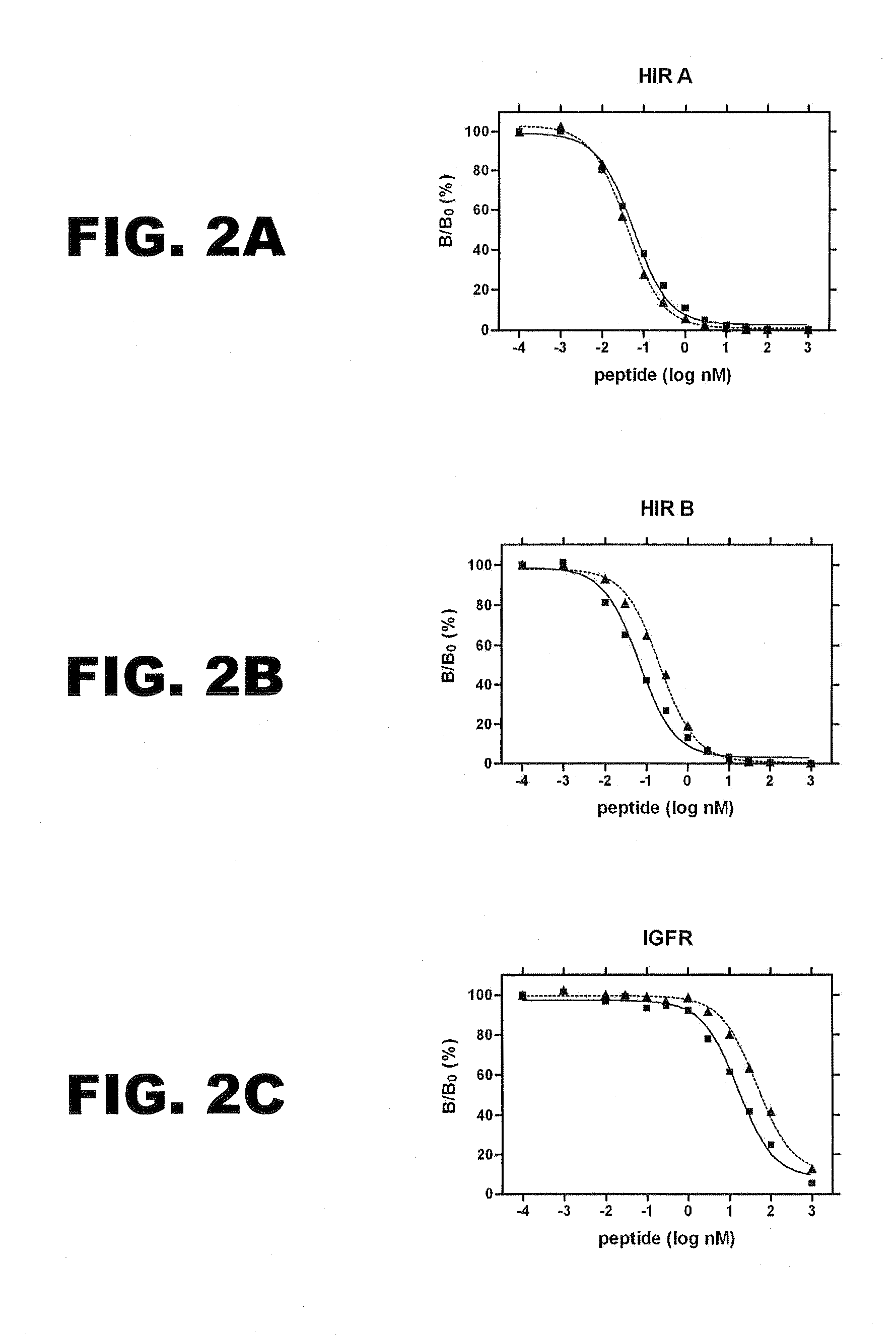
A fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue may be a single-chain insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, containing an insulin A chain sequence or an analogue thereof and an insulin B chain sequence or an analogue thereof connected by a polypeptide of 4-10 amino acids. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue preferably displays less than 1 percent fibrillation with incubation at 37° C. for at least 21 days. A single-chain insulin analogue displays greater in vitro insulin receptor binding than normal insulin while displaying less than or equal binding to IGFR than normal insulin. The fibrillation-resistant insulin may be used to treat a patient using an implantable or external insulin pump, due to its greater fibrillation resistance.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Isoform-specific insulin analogues
InactiveUS20110195896A1Improve stabilitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNormal insulinInsulin Analogue
A method treating a mammal by administering a physiologically effective amount of an insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof where the insulin analogue displays more than twofold greater binding affinity to insulin receptor isoform A (IR-A) than insulin receptor isoform B (IR-B). The insulin analogue may be a single-chain insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, containing an insulin A-chain sequence or an analogue thereof and an insulin B-chain sequence or an analogue thereof connected by a polypeptide of 4-13 amino acids. A single-chain insulin analogue may display greater in vitro insulin receptor binding to IR-A but lower binding to IR-B than normal insulin while displaying less than or equal binding to IGFR than normal insulin.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Fibrillation-resistant insulin and insulin analogues
InactiveUS8192957B2High thermodynamic stabilityMaintain biological activityBacteriaSugar derivativesInsulin A ChainNormal insulin
A fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue may be a single-chain insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, containing an insulin A chain sequence or an analogue thereof and an insulin B chain sequence or an analogue thereof connected by a polypeptide of 4-10 amino acids. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue preferably displays less than 1 percent fibrillation with incubation at 37° C. for at least 21 days. A single-chain insulin analogue displays greater in vitro insulin receptor binding than normal insulin while displaying less than or equal binding to IGFR than normal insulin. The fibrillation-resistant insulin may be used to treat a patient using an implantable or external insulin pump, due to its greater fibrillation resistance.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Stabilized polypeptide insulin receptor modulators
InactiveUS20150225471A1Increase helix stabilizationIncreased target affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsReceptors for hormonesDiabetes mellitusCross-link
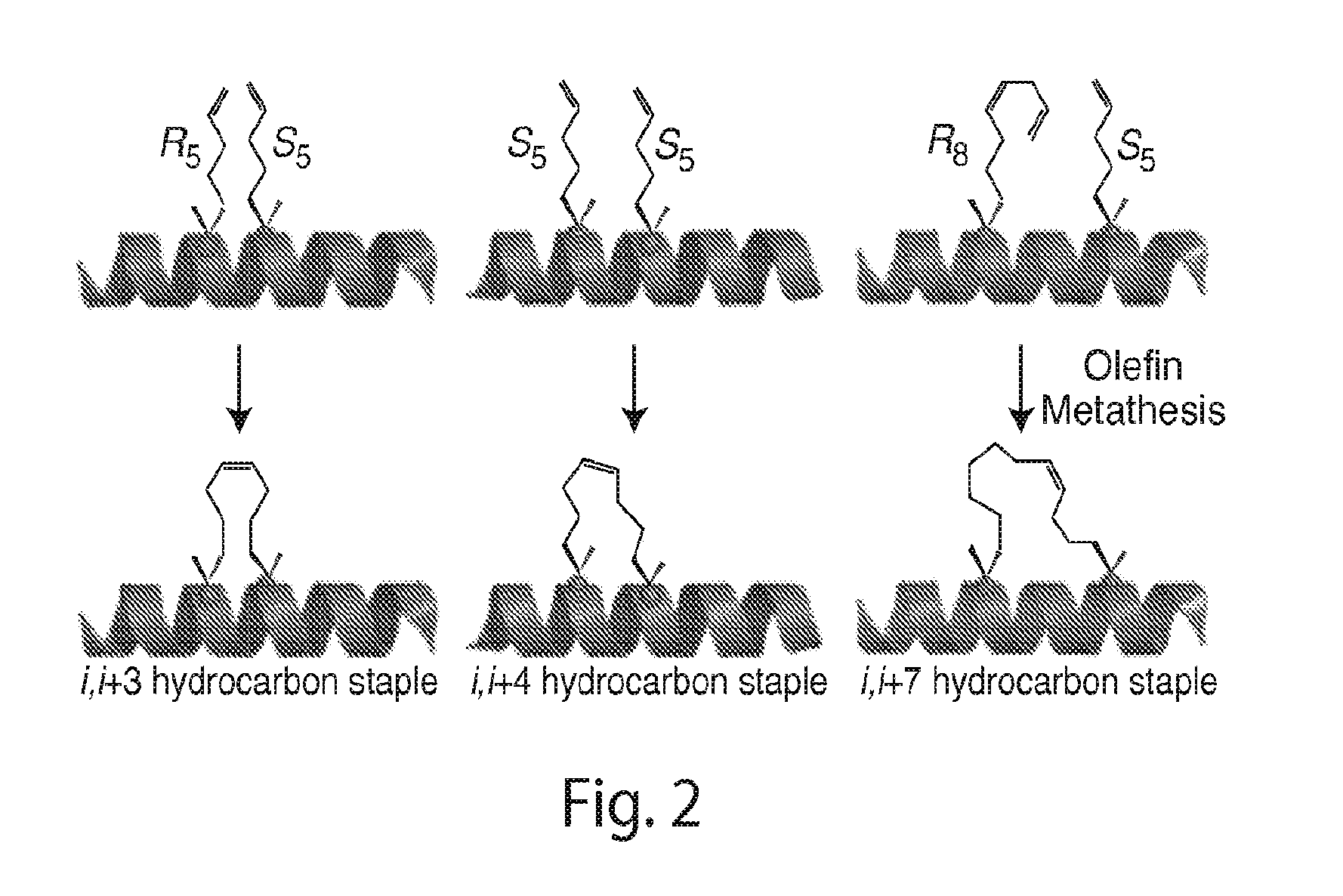
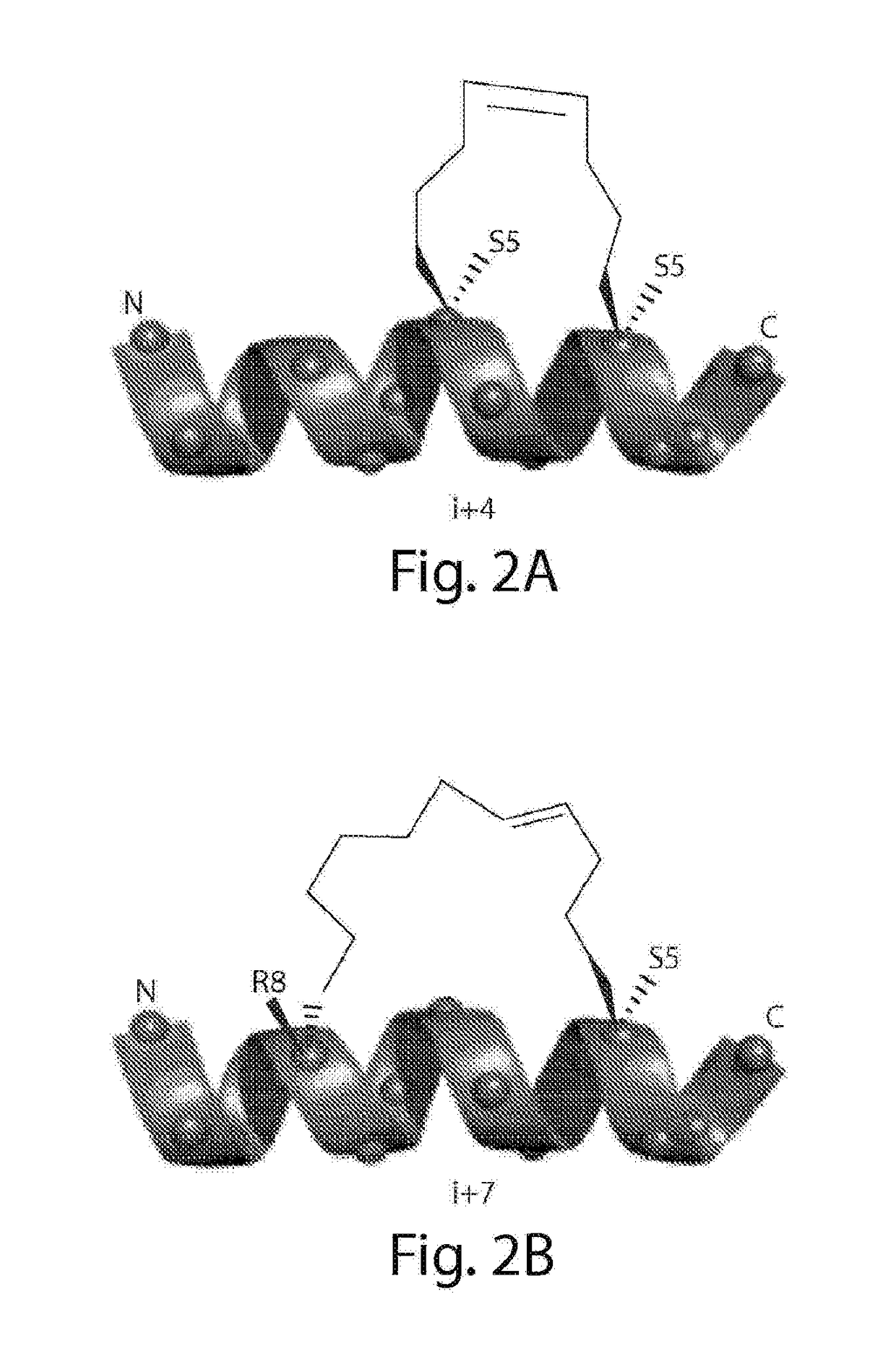
Provided herein are stapled or stitched polypeptides comprising an alpha-helical segment, wherein the polypeptide binds to the insulin receptor, and wherein the polypeptide comprises at least two cross-linked amino acids as shown in Formula (iii), or at least three cross-linked amino acids as shown in Formula (iv). Further provided are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the stapled or stitched polypeptides, methods of use, e.g., methods of treating a diabetic condition or complications thereof. Precursor “unstapled” polypeptides useful in the preparation of stapled and stitched polypeptides are also described.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Stabilized polypeptide insulin receptor modulators
InactiveUS20160215036A1Increase helix stabilizationIncreased target affinitySenses disorderNervous disorderPharmaceutical drugPancreatic hormone
Provided herein are stabilized α-CT polypeptides comprising an alpha-helical segment, and wherein the polypeptide is of Formula (I-1) or Formula (I-2): Rf—[XAA]s—XA1—XA2—XA3—XA4—XA5—XA6—XA7—XA8—XA9—XA10—XA11—XA12—XA13—XA14—[XAA]t—Re (I-1) Rf—[XAA]s—XC1—XC2—XC3—XC4—XC5—XC6—XC7—XC8—XC9—XC10—XC11—XC12—XC13—XC14—XC15—XC16—XC17—XC18—XC19—XC20—[XAA]t—Re (I-2) wherein the α-CT polypeptide binds to the insulin receptor, and wherein the α-CT polypeptide includes at least one staple (i.e. two cross-linked amino acids) and / or at least one stitch (i.e. three cross-linked amino acids). Further provided are insulin analogues including the stapled or stitched α-CT polypeptides, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, methods of use, e.g., methods of treating a diabetic condition or complications thereof.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Meal-time insulin analogues of enhanced stability
InactiveUS20110059887A1Increase propensityImprove stabilitySugar derivativesBacteriaInsulin A ChainWild type
A method treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of a fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to the patient. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, contains an insulin A-chain sequence modified at position A8 and an insulin B-chain sequence or an analogue thereof. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue may exhibit thermodynamic stability similar to or exceeding that of wild-type human insulin and displays a susceptibility to fibrillation similar to or exceeding that of wild-type human insulin. An insulin analogue may display greater in vitro insulin receptor binding than normal insulin while displaying binding to IGFR less than twice that of normal insulin and less than that of fast-acting insulin analogs. The fibrillation-resistant insulin may be used to treat a patient by subcutaneous injection or by using an implantable or external insulin pump, due to its fibrillation resistance.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Novel insulin analog and use thereof
InactiveUS20160008483A1Avoids in vivo clearance mechanismReduced receptor binding affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin humulinInsulin receptor binding
The present invention relates to an insulin analog that has a reduced insulin titer and a reduced insulin receptor binding affinity compared to the native form for the purpose of increasing the blood half-life of insulin, a conjugate prepared by linking the insulin analog and a carrier, a long-acting formulation including the conjugate, and a method for preparing the conjugate.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Site-specific insulin conjugate
ActiveUS20160000931A1Extended durationImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderIn vivoInsulin humulin
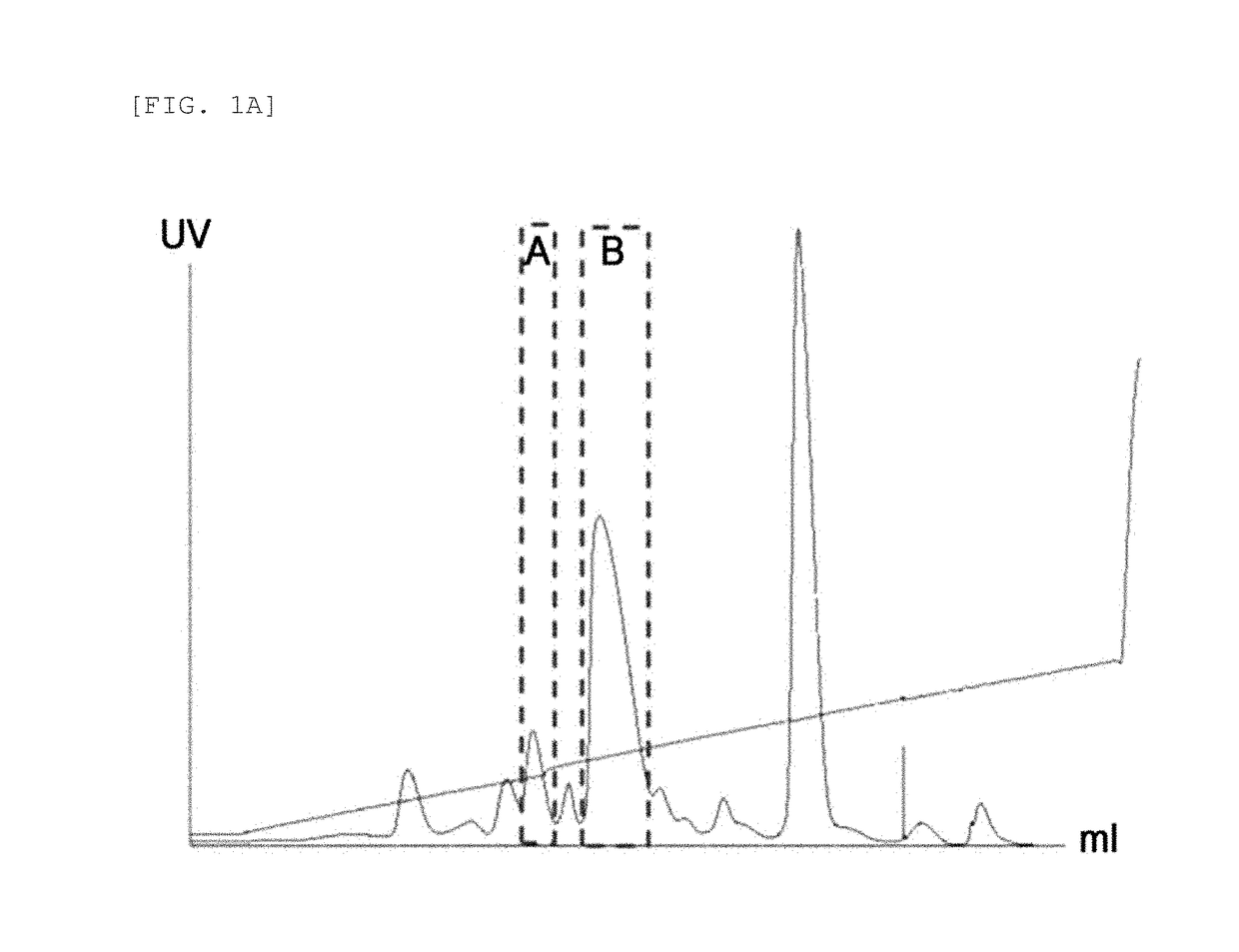
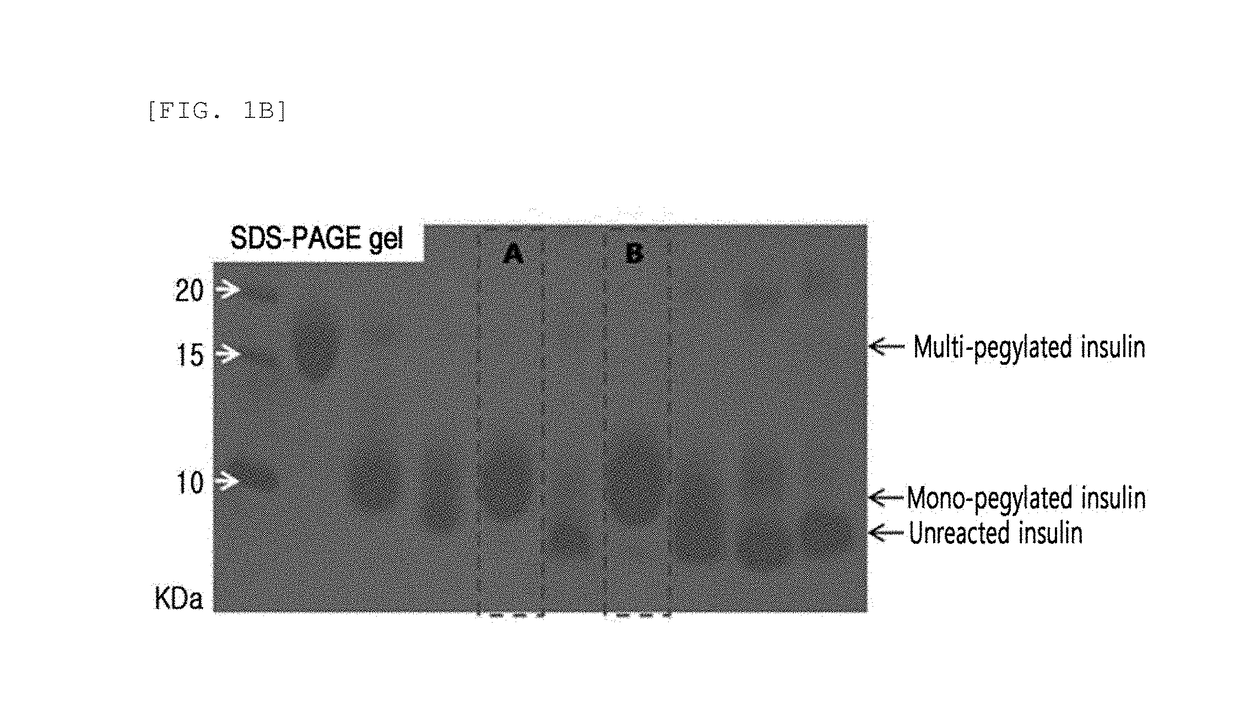
Provided are an insulin conjugate having improved insulin receptor binding affinity and increased activity, in which a non-peptidyl polymer and an immunoglobulin Fc region are site-specifically linked to an amino acid residue of the insulin beta chain excluding the N-terminus thereof via a covalent bond, a long-acting formulation including the same, and a preparation method thereof. The insulin conjugate of the present invention is used to provide an insulin formulation which exhibits a remarkably increased in vivo activity of the peptide.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Isoform-specific insulin analogues
A method treating a mammal by administering a physiologically effective amount of an insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof where the insulin analogue displays more than twofold greater binding affinity to insulin receptor isoform A (IR-A) than insulin receptor isoform B (IR-B). The insulin analogue may be a single-chain insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, containing an insulin A-chain sequence or an analogue thereof and an insulin B-chain sequence or an analogue thereof connected by a polypeptide of 4-13 amino acids. A single-chain insulin analogue may display greater in vitro insulin receptor binding to IR-A but lower binding to IR-B than normal insulin while displaying less than or equal binding to IGFR than normal insulin.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Human insulin/analogue conjugate with continuous blood sugar reduction function and high rate of combination with receptor
ActiveCN102675452AUnderstand clearlyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin activityHigh rate
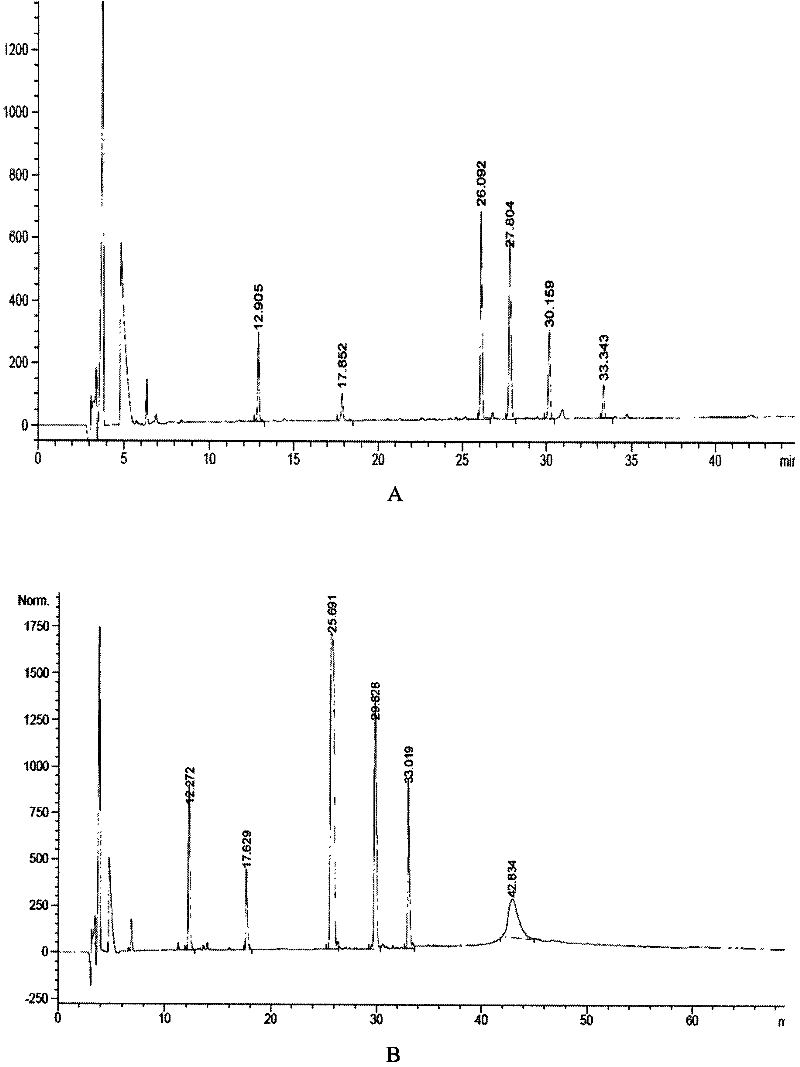
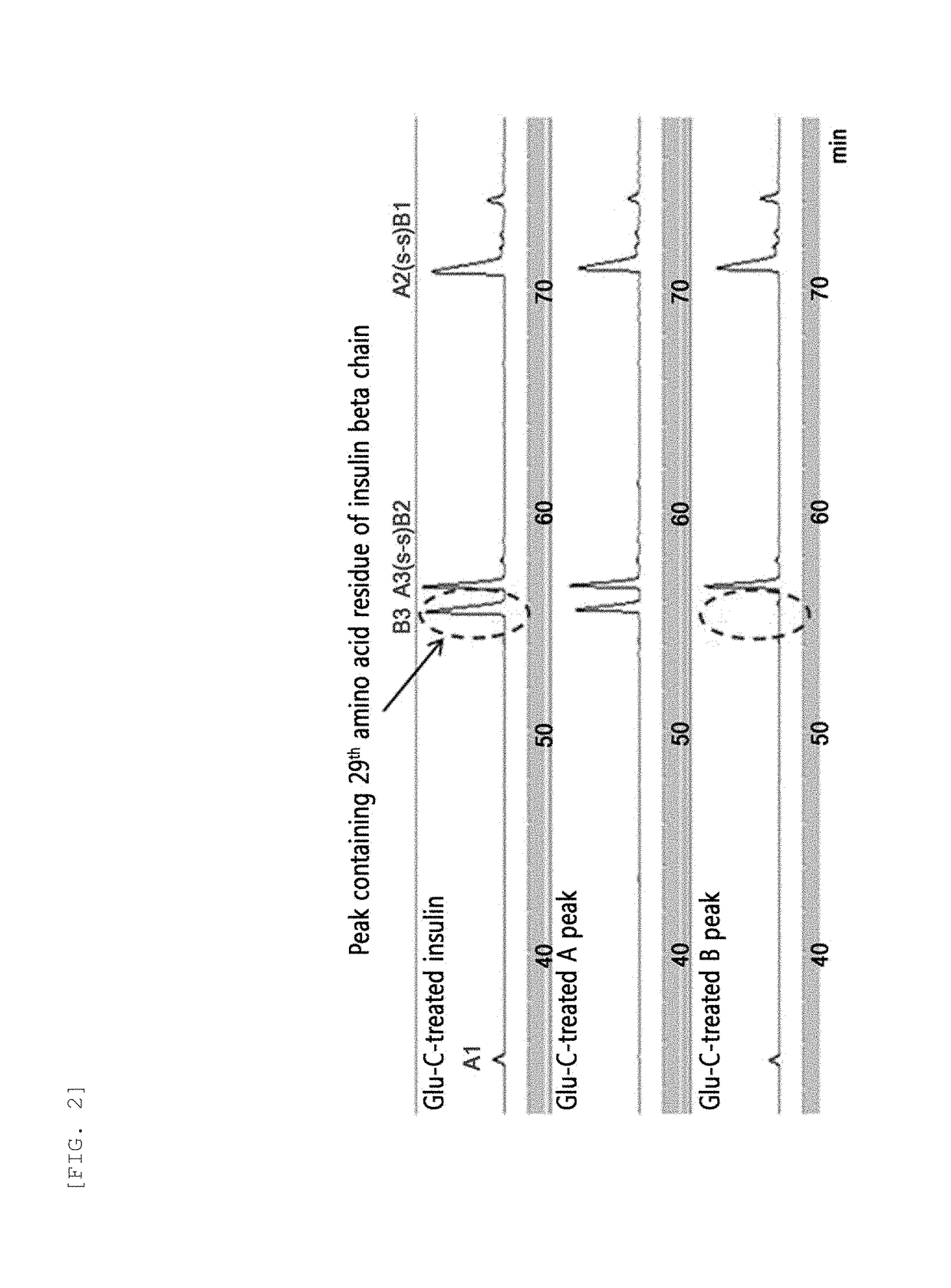
The invention relates to a human insulin / analogue conjugate with a continuous blood sugar reduction function and a high rate of combination with a receptor, and discloses a method for preparing a reconstructed human insulin / analogue conjugate by reconstructing a human insulin precursor by utilizing a methylotrophic yeast expression, performing purification, enzyme digestion, chromatography or synthesis to prepare a reconstructed human insulin and a DesB30 analogue thereof and coupling a side chain amino group of a 29th-bit lysine of a B chain of the reconstructed human insulin precursor and a polyethyleneglycol acetamide bond. The prepared reconstructed human insulin conjugate has the characteristics of high rate of combination with the insulin receptor, remarkable continuous blood sugar reduction effects and long in-vivo half-life period, and is applied to the treatment of I-type and II-type diabetes.
Owner:CHONGQING FAGEN BIOMEDICAL +1
Site-specific insulin conjugate
ActiveUS10046061B2Extended durationImprove stabilityHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsIn vivoPolymer
Provided are an insulin conjugate having improved insulin receptor binding affinity and increased activity, in which a non-peptidyl polymer and an immunoglobulin Fc region are site-specifically linked to an amino acid residue of the insulin beta chain excluding the N-terminus thereof via a covalent bond, a long-acting formulation including the same, and a preparation method thereof. The insulin conjugate of the present invention is used to provide an insulin formulation which exhibits a remarkably increased in vivo activity of the peptide.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Meal-time insulin analogues of enhanced stability
InactiveUS8993516B2Increase propensityImprove stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesInsulin A ChainWild type
A method treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of a fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to the patient. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, contains an insulin A-chain sequence modified at position A8 and an insulin B-chain sequence or an analogue thereof. The fibrillation-resistant insulin analogue may exhibit thermodynamic stability similar to or exceeding that of wild-type human insulin and displays a susceptibility to fibrillation similar to or exceeding that of wild-type human insulin. An insulin analogue may display greater in vitro insulin receptor binding than normal insulin while displaying binding to IGFR less than twice that of normal insulin and less than that of fast-acting insulin analogs. The fibrillation-resistant insulin may be used to treat a patient by subcutaneous injection or by using an implantable or external insulin pump, due to its fibrillation resistance.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Anti-igf antibodies
Antibody molecules, in particular fully human antibodies that bind to human IGF-1 and cross-react with IGF-2 such that binding of IGF-1 and IGF-2 to the IGF-1 receptor is prevented and IGF-1 receptor-mediated signaling is inhibited. The antibodies do not bind to insulin and thus do not affect the mitogenic properties of insulin that are mediated by its binding to the insulin receptors. The antibodies are useful for the treatment of hyperproliferative diseases, in particular cancer.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Stabilized polypeptide insulin receptor modulators
InactiveUS20180057565A1Improve stabilityHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsReceptors for hormonesCross-linkDiabetes mellitus
Provided herein are stapled or stitched polypeptides comprising an alpha-helical segment, wherein the polypeptide binds to the insulin receptor, and wherein the peptide comprises at least two cross-linked amino acids as shown in Formula (iii), or at least three cross-linked amino acids as shown in Formula (iv). Further provided are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the stapled or stitched polypeptides, methods of use, e.g., methods of treating a diabetic condition or complications thereof. Precursor “unstapled” polypeptides useful in the preparation of stapled and stitched polypeptides are also described.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Protein and protein conjugate for diabetes treatment, and applications thereof
ActiveUS20200002397A1Maximum efficacyReduce dosePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderReceptorEfficacy
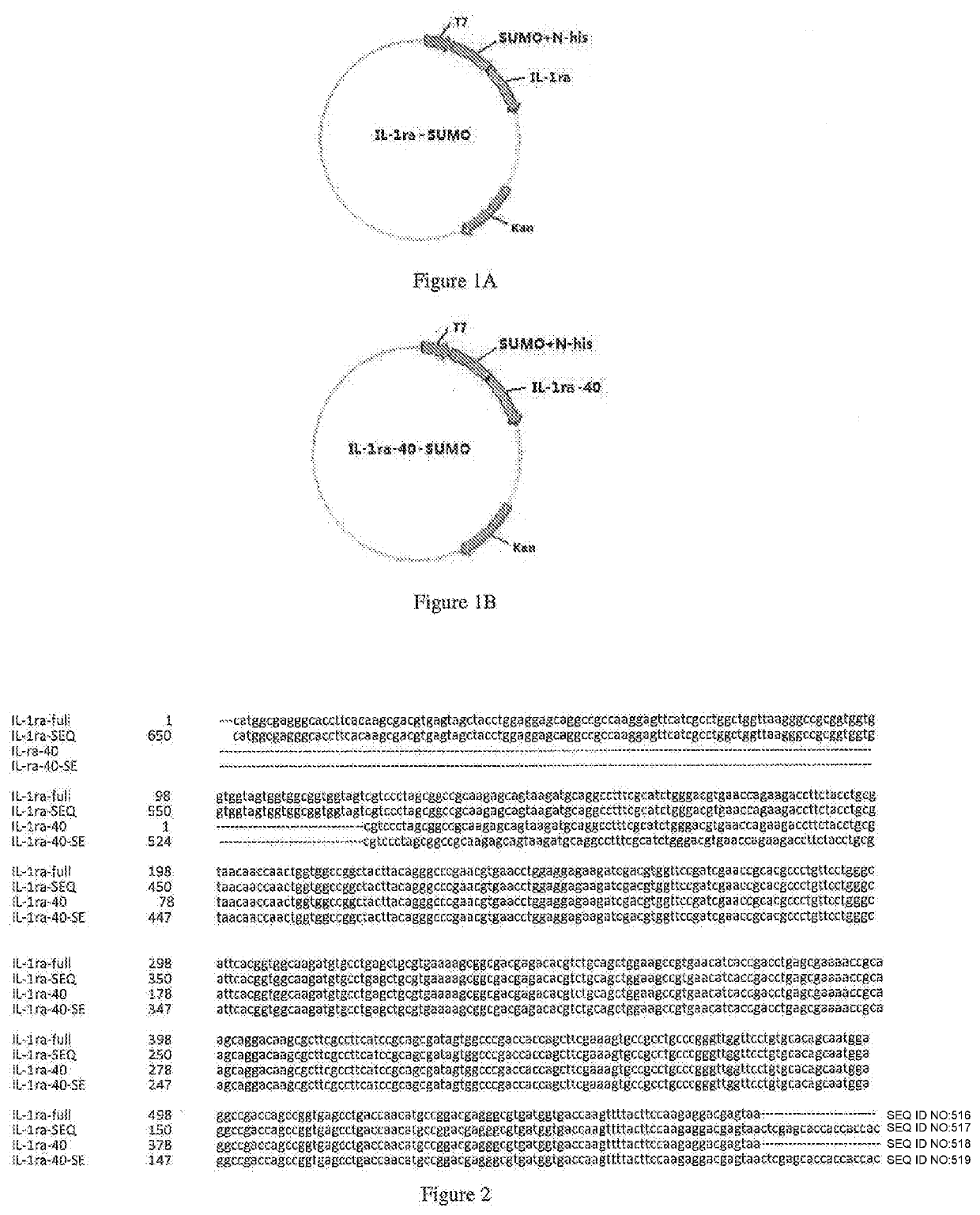
The present invention relates to the field of biopharmaceuticals, and in particular to a protein, a protein conjugate, a pharmaceutical composition and its use for treating diabetes. The fusion protein of the present invention is obtained by linking two polypeptides, wherein one polypeptide is an interleukin-1 receptor antagonistic protein or an analogue thereof, and another polypeptide is GLP-1 receptor binding polypeptide or an analogue thereof, or an insulin receptor binding polypeptide or an analogue thereof, or a GIP receptor binding polypeptide or an analogue thereof. The fusion proteins of the present invention and conjugates thereof have a significant efficacy in treating diabetes, and can be used in a lower dose, resulting in marked reduction in side effects.
Owner:ADDA BIOTECH
Long-acting insulin and use thereof
ActiveUS20170101455A1Improve convenienceExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHalf-lifeInsulin humulin
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Functional nutritional powder composition suitable for patients with diabetes mellitus type II
The invention relates to a functional nutritional powder composition suitable for patients with diabetes mellitus type II. The functional nutritional powder composition is prepared from the following raw materials by weight percent: 20-50% of soybean protein, 1-10% of whey protein, 15-35% of skim milk powder, 8-30% of konjac flour, 10-40% of beer yeast, 5-30% of resistant maltodextrin and sucralose. The functional nutritional powder composition can provide high-quality and complete protein, complete B-vitamin group, fourteen life-bound high-quality minerals, trace elements and high-quality functional dietary fibers. The functional nutritional powder composition supplements the nutritional components needed by special groups, controls the intake of carbohydrate, increases satiety, balances dietary structure and reduces kidney burden; the functional nutritional powder composition has the effects of adjusting blood glucose as well as preventing and treating early and middle stage of diabetes mellitus type II by repairing pancreas islets function and insulin receptor binding ability.
Owner:长沙一加一生物科技有限公司
Long-acting insulin and use thereof
ActiveUS10253082B2Improve convenienceExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderINSULIN USEInsulin humulin
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Protein and protein conjugate for diabetes treatment, and applications thereof
ActiveUS10472404B2Eliminate side effectsMaximum efficacyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSide effectInterleukin-1 receptor
The present invention relates to the field of biopharmaceuticals, and in particular to a protein, a protein conjugate, a pharmaceutical composition and its use for treating diabetes. The fusion protein of the present invention is obtained by linking two polypeptides, wherein one polypeptide is an interleukin-1 receptor antagonistic protein or an analogue thereof, and another polypeptide is GLP-1 receptor binding polypeptide or an analogue thereof, or an insulin receptor binding polypeptide or an analogue thereof, or a GIP receptor binding polypeptide or an analogue thereof. The fusion proteins of the present invention and conjugates thereof have a significant efficacy in treating diabetes, and can be used in a lower dose, resulting in marked reduction in side effects.
Owner:ADDA BIOTECH
Polypeptides, nucleic acid molecule encoding polypeptides, and uses of polypeptides
ActiveUS8697649B2Reducing blood sugarReducing glycated hemoglobinPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsDiseaseBlood sugar
A polypeptide, a nucleic acid molecule encoding the polypeptide and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the polypeptide are provided. The polypeptide is as defined in the description, can bind to insulin receptors, and is effective in reducing blood sugar, reducing glycated hemoglobin, and ameliorating hepato-renal disorders caused by diabetes.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY(TW)
Treatment of post-prandial hyperinsulinemia and hypoglycemia after bariatric surgery
ActiveUS10711067B2Preventing post-prandial hypoglycemiaPrevent post-prandial hypoglycemiaPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsLow glucoseExtracorporeal bypass
The present disclosure relates, in general, to methods of treating or preventing post-prandial hypoglycemia after gastric bypass surgery using a negative modulator antibody that binds to the insulin receptor and modulates the action of insulin at the insulin receptor.
Owner:XOMA US
Stabilized polypeptide insulin receptor modulators
InactiveUS10227390B2Improve stabilityHigh affinitySenses disorderNervous disorderPharmaceutical drugPancreatic hormone
Provided herein are stabilized α-CT polypeptides comprising an alpha-helical segment, and wherein the polypeptide is of Formula (I-1) or Formula (I-2): Rf—[XAA]s—XA1—XA2—XA3—XA4—XA5—XA6—XA7—XA8—XA9—XA10—XA11—XA12—XA13—XA14—[XAA]t—Re (I-1) Rf—[XAA]s—XC1—XC2—XC3—XC4—XC5—XC6—XC7—XC8—XC9—XC10—XC11—XC12—XC13—XC14—XC15—XC16—XC17—XC18—XC19—XC20—[XAA]t—Re (I-2) wherein the α-CT polypeptide binds to the insulin receptor, and wherein the α-CT polypeptide includes at least one staple (i.e. two cross-linked amino acids) and / or at least one stitch (i.e. three cross-linked amino acids). Further provided are insulin analogs including the stapled or stitched α-CT polypeptides, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, methods of use, e.g., methods of treating a diabetic condition or complications thereof.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Insulin-like growth factor-i receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20090311783A1Inhibit cell proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsApoptosisSignal transduction
The present invention relates to IGF-I variants that bind to the Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor I (IGF-IR) but do not initiate signal transduction and the subsequent metabolic, growth and anti-apoptotic activities associated with this molecule and the progression of cancer. These novel variants act to block the binding of the cognate ligands but do not bind to the insulin receptor.
Owner:MOLECULAR LOGIX INC
Novel insulin analog and use thereof
InactiveUS20180256731A1Extended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin humulinInsulin receptor binding
An insulin analog has a reduced insulin titer and a reduced insulin receptor binding affinity compared to the native form for the purpose of increasing the blood half-life of insulin. A conjugate is prepared by linking the insulin analog and a carrier. A long-acting formulation includes the conjugate.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Insulin analogs having reduced insulin receptor binding affinity
Provided herein are insulin analogs comprising at least one mutation relative to the parent insulin, wherein the insulin analogs comprise a mutation at position B16 which is substituted with a hydrophobic amino acid and / or a mutation at position B25 which is substituted with a hydrophobic amino acid.
Owner:SANOFI SA
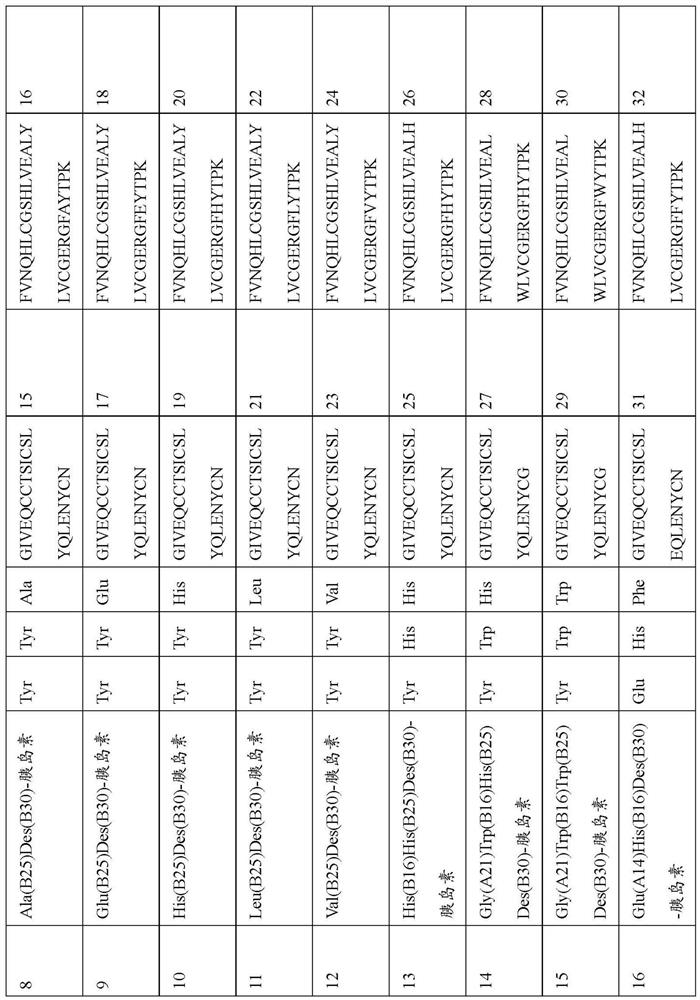
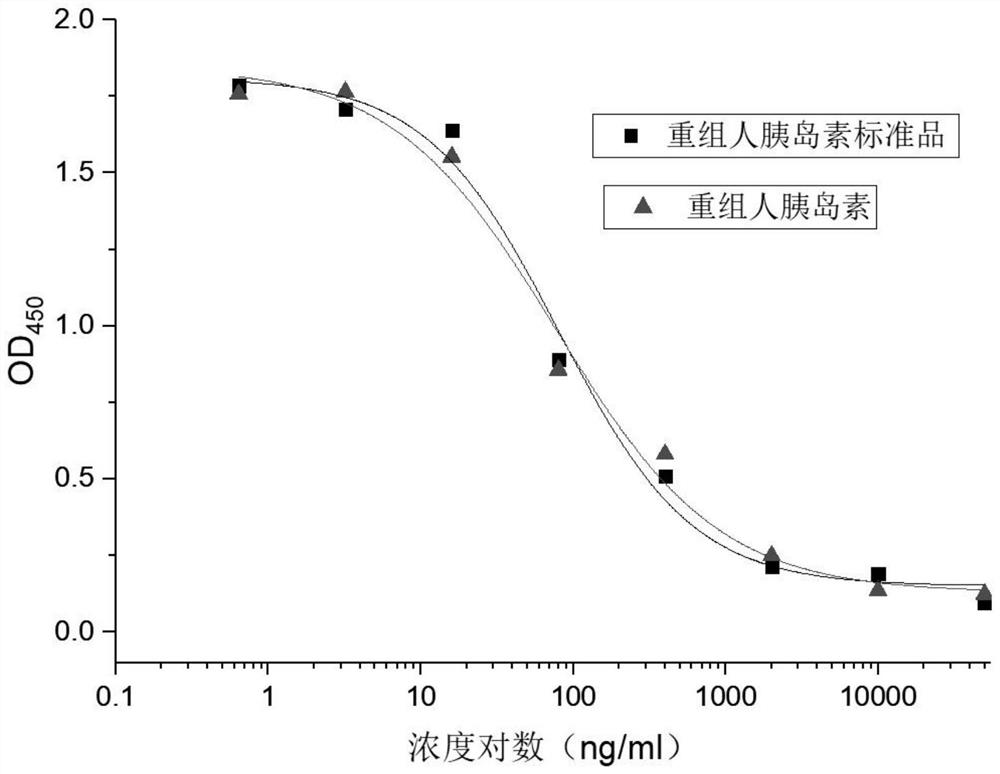
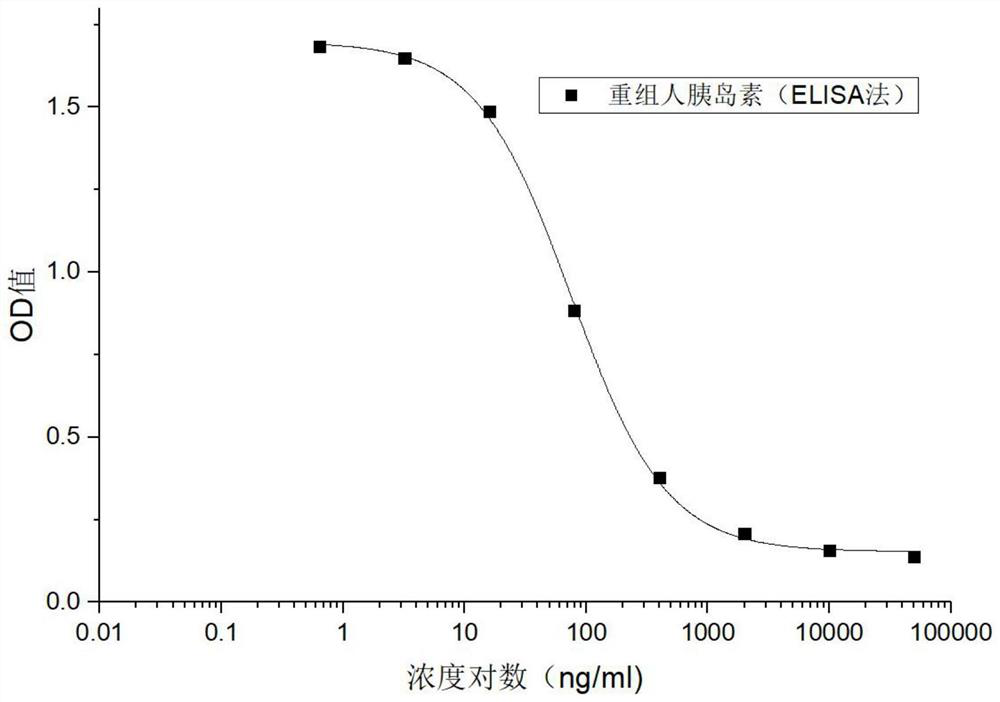
A method for analyzing the binding rate of recombinant human insulin and its analogs or conjugates to insulin receptors
ActiveCN109682963BEasy receptor bindingNo radioactive contaminationBiological material analysisAntiendomysial antibodiesBound insulin
The invention discloses a method for analyzing the binding rate of human insulin and its analogs or conjugates to insulin receptors. First, the insulin receptors are transfected onto HEK-293 cells; antibodies to human insulin receptors are coated on enzyme labels On the plate, the insulin receptor antibody binds to the insulin receptor, human insulin and its analogs or conjugates compete with biotin-labeled insulin for binding to the insulin receptor, avidin binds to biotin, and the receptor binding rate is determined by HRP chromogenicity. The present invention utilizes the principles of antigen-antibody binding, ligand-receptor binding, and biotin binding to avidin to accurately measure the change in insulin receptor binding rate. No pollution, low cost, high accuracy and other requirements.
Owner:CHONGQING PEG BIO BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for analyzing binding rate of recombinant human insulin and analogue or conjugate thereof with insulin receptor
ActiveCN109682963AEasy receptor bindingNo radioactive contaminationBiological material analysisInsulin activityBiotin-binding proteins
The invention discloses a method for analyzing the binding rate of recombinant human insulin and an analogue or conjugate thereof with an insulin receptor. The method comprises the steps that the insulin receptor is transfected to an HEK-29 cell firstly; an enzyme label plate is wrapped with the antibody of the insulin receptor, the insulin receptor is combined with the insulin receptor, the humaninsulin and the analogue or conjugate thereof and a biotin labeled insulin are competitively bound with the insulin receptor, an avidin is bound with the biotin, and the receptor binding rate is determined through HRP developing. The method has the advantages that the variation of the binding rate of insulin receptors can be accurately measured through the principals of antigen and antibody binding, ligand and receptor binding and the capability of binding avidin of the biotin, and the demands of being simple and convenient in operation steps, pollution free, low in cost high in accuracy andthe like of a measuring method of biological product receptor binding experiments are met.
Owner:CHONGQING PEG BIO BIOTECH CO LTD
Insulin receptor protein expression cell strain and application thereof
PendingCN114686437AImprove standardizationGood repeatabilityMicroorganism based processesReceptors for hormonesPhosphorylationReceptor
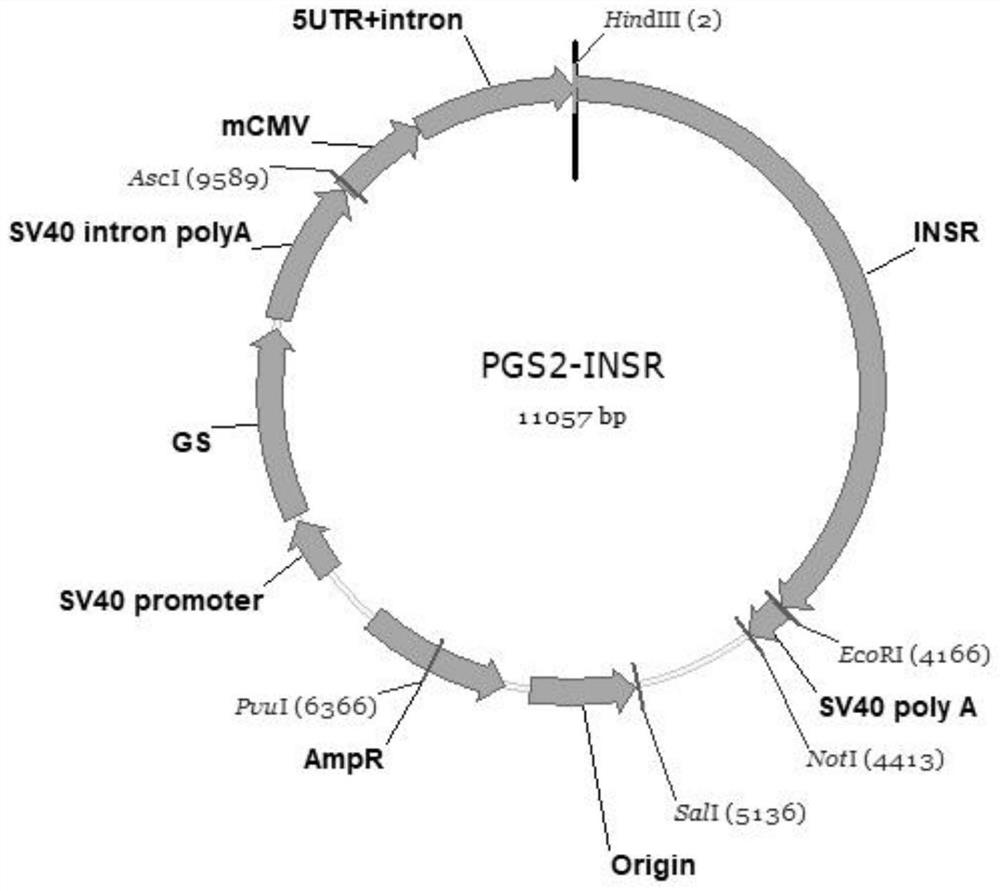
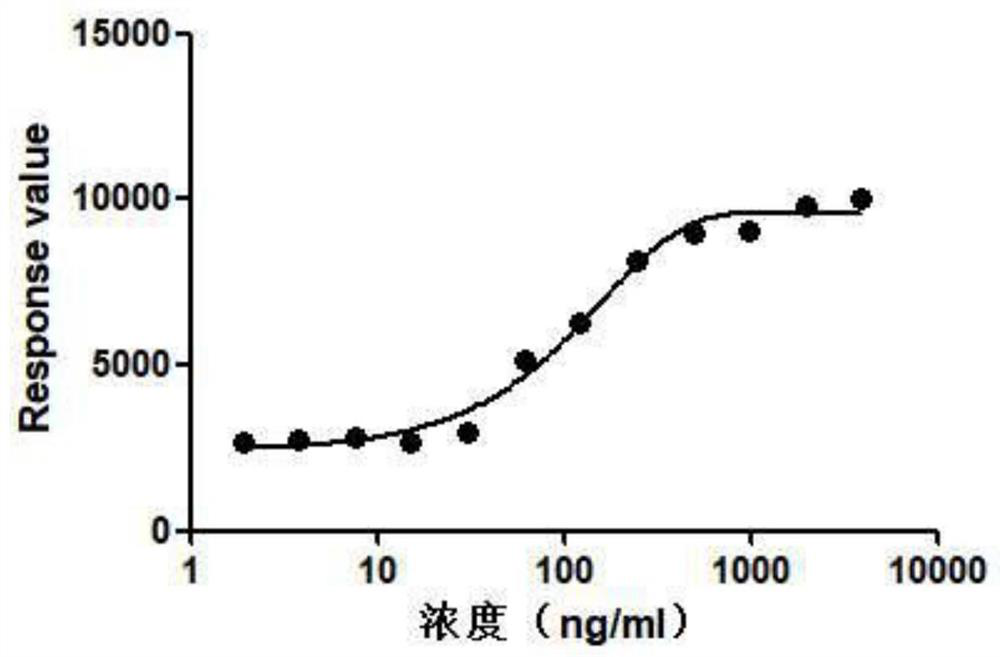
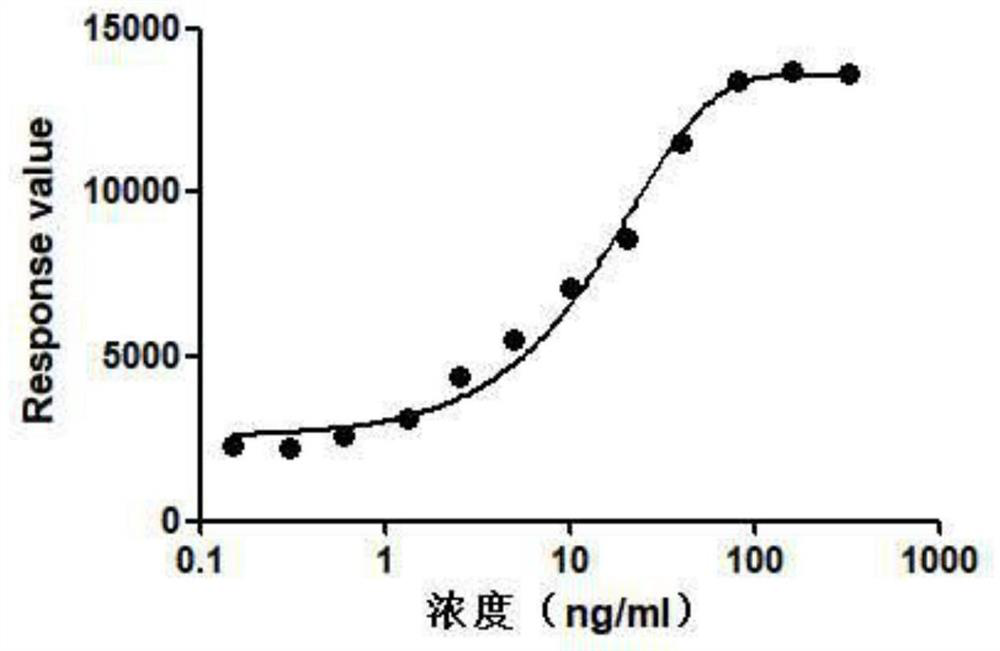
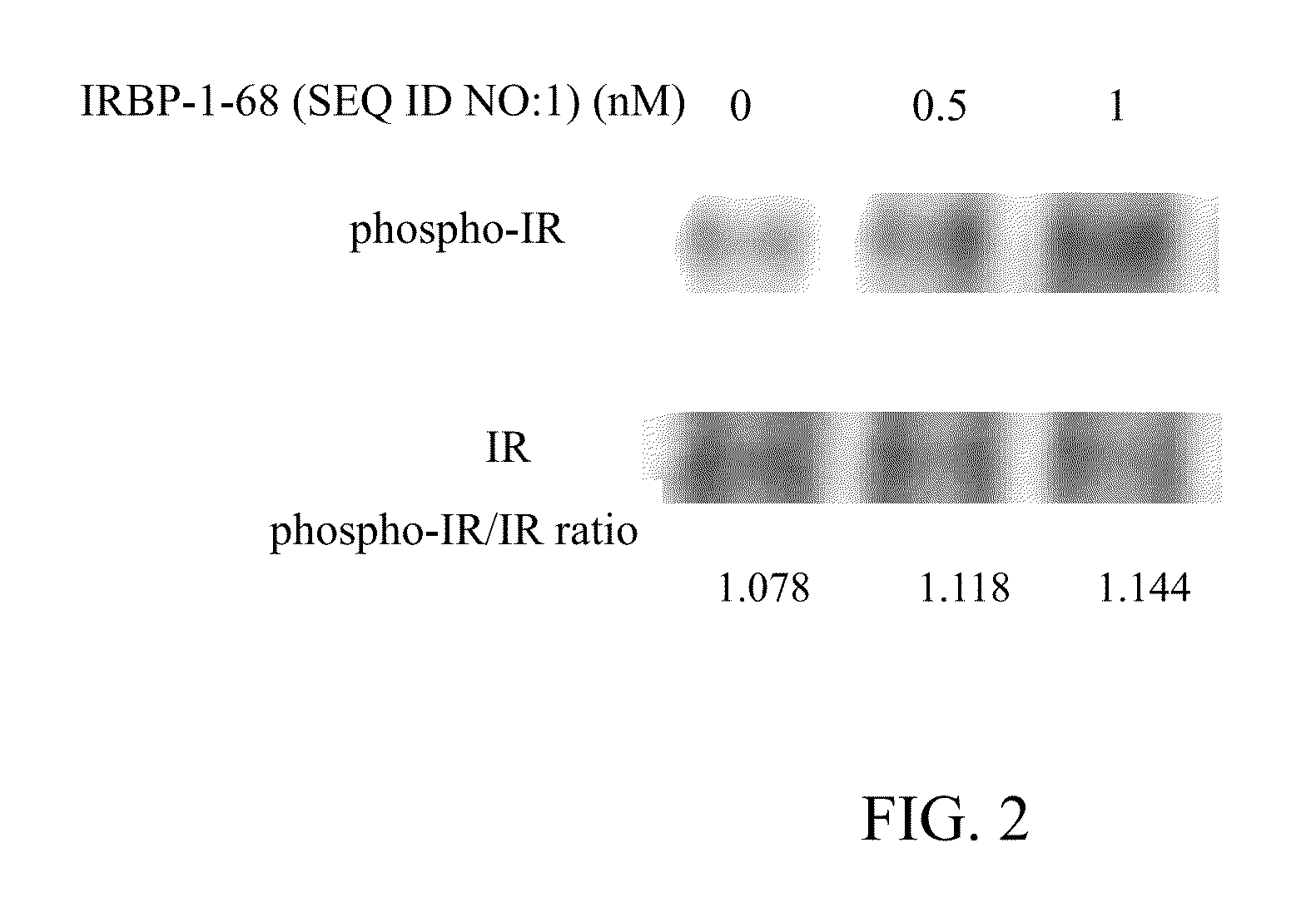
The invention belongs to the technical field of drug biological activity detection, and particularly relates to establishment of a genetic engineering cell strain of insulin receptor protein and a detection method for determining insulin biological activity based on change of insulin receptor phosphorylation level after the cell strain is stimulated by insulin. Specifically, the cell strain expressing the INSR protein is CHO-K1-INSR-6B3, after insulin is combined with an insulin receptor, the insulin receptor is phosphorylated, the activity of the insulin and the amount of the phosphorylated receptor have a dose-effect relationship, and the activity of the insulin can be quantitatively detected by detecting the phosphorylation level of the insulin receptor. The detection method is easy to standardize and good in repeatability, and has the characteristics of low cost, convenience and accuracy, thereby having a good application prospect.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Polypeptides, nucleic acid molecule encoding polypeptides, and uses of polypeptides
ActiveUS20130310313A1Reducing blood sugarReducing glycated hemoglobinPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsBlood sugarHepato-renal
A polypeptide, a nucleic acid molecule encoding the polypeptide and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the polypeptide are provided. The polypeptide is as defined in the description, can bind to insulin receptors, and is effective in reducing blood sugar, reducing glycated hemoglobin, and ameliorating hepato-renal disorders caused by diabetes.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY(TW)
Conjugates of human insulin and analogues with sustained hypoglycemia and high receptor binding
ActiveCN102675452BUnderstand clearlyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderReceptorPolyethylene glycol
Disclosed is a recombinant human insulin or analog conjugate thereof. Said conjugate is formed by connecting the µ-amino group of lysine 29 of the B chain to activated polyethylene glycol by means of an amide bond. Further disclosed is a method of preparing said conjugate, a pharmaceutical compound, and a use for said conjugate in preparing medication for treating Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
Owner:CHONGQING FAGEN BIOMEDICAL +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com