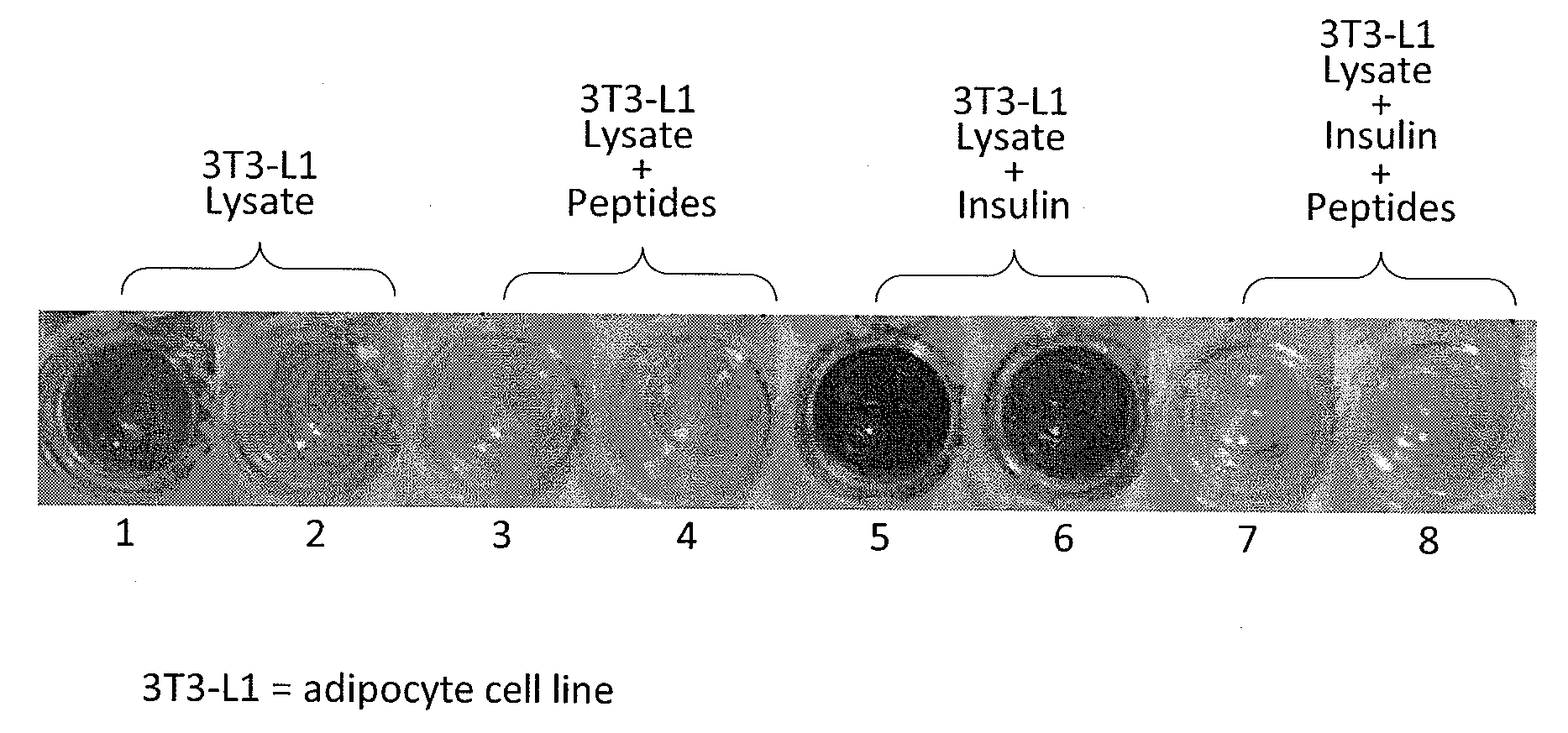
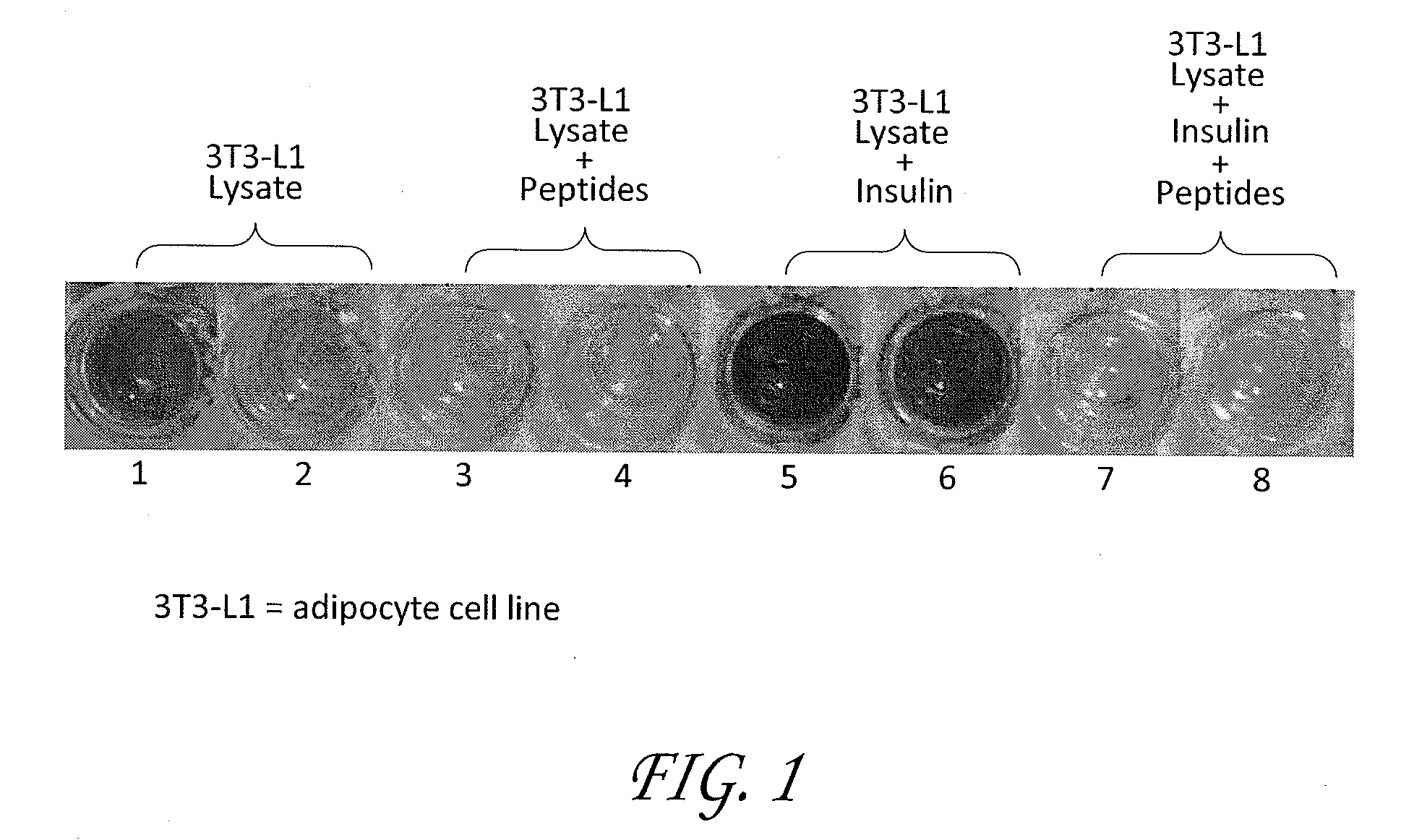
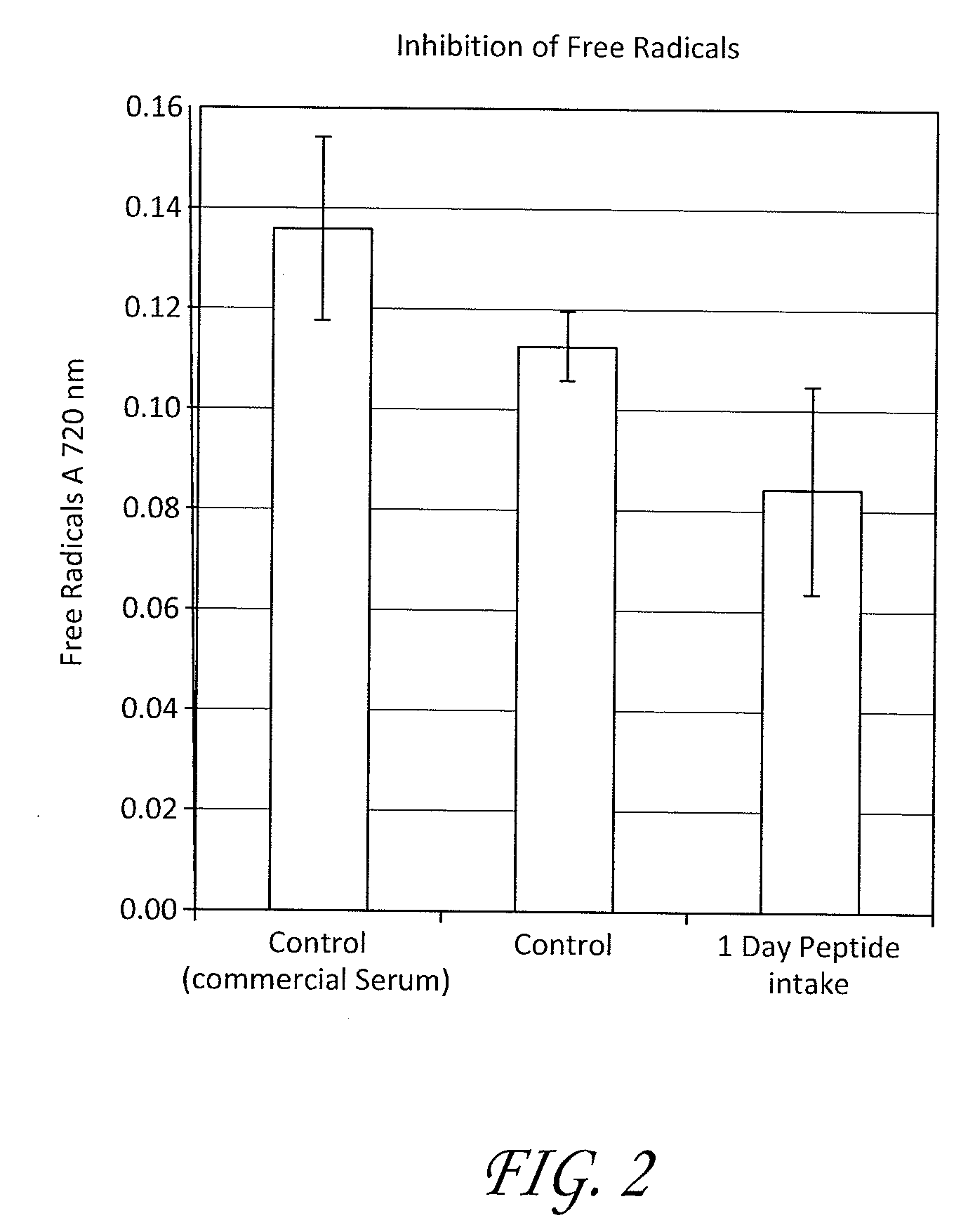
Patents
Literature
146 results about "Insulin receptor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
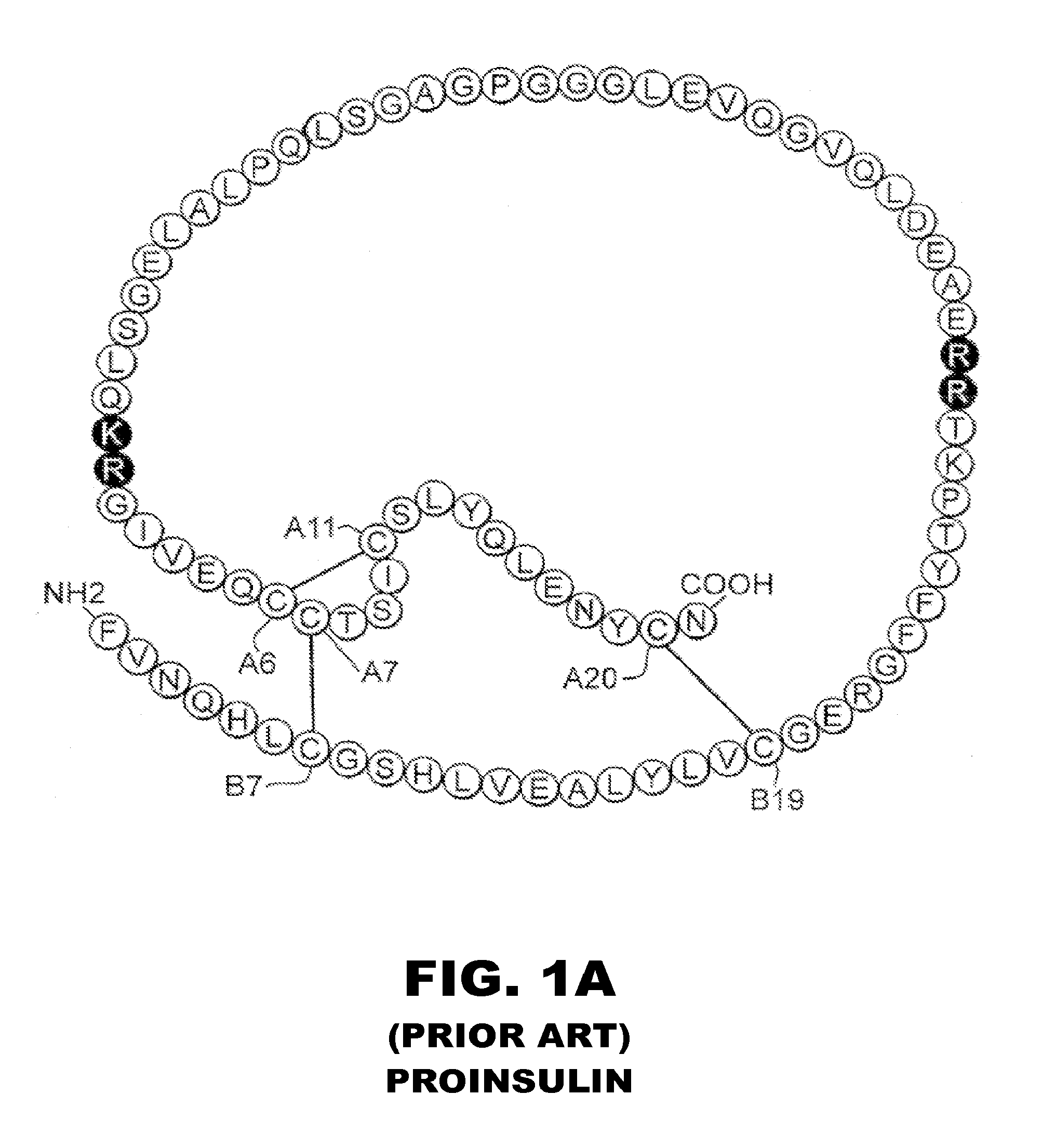
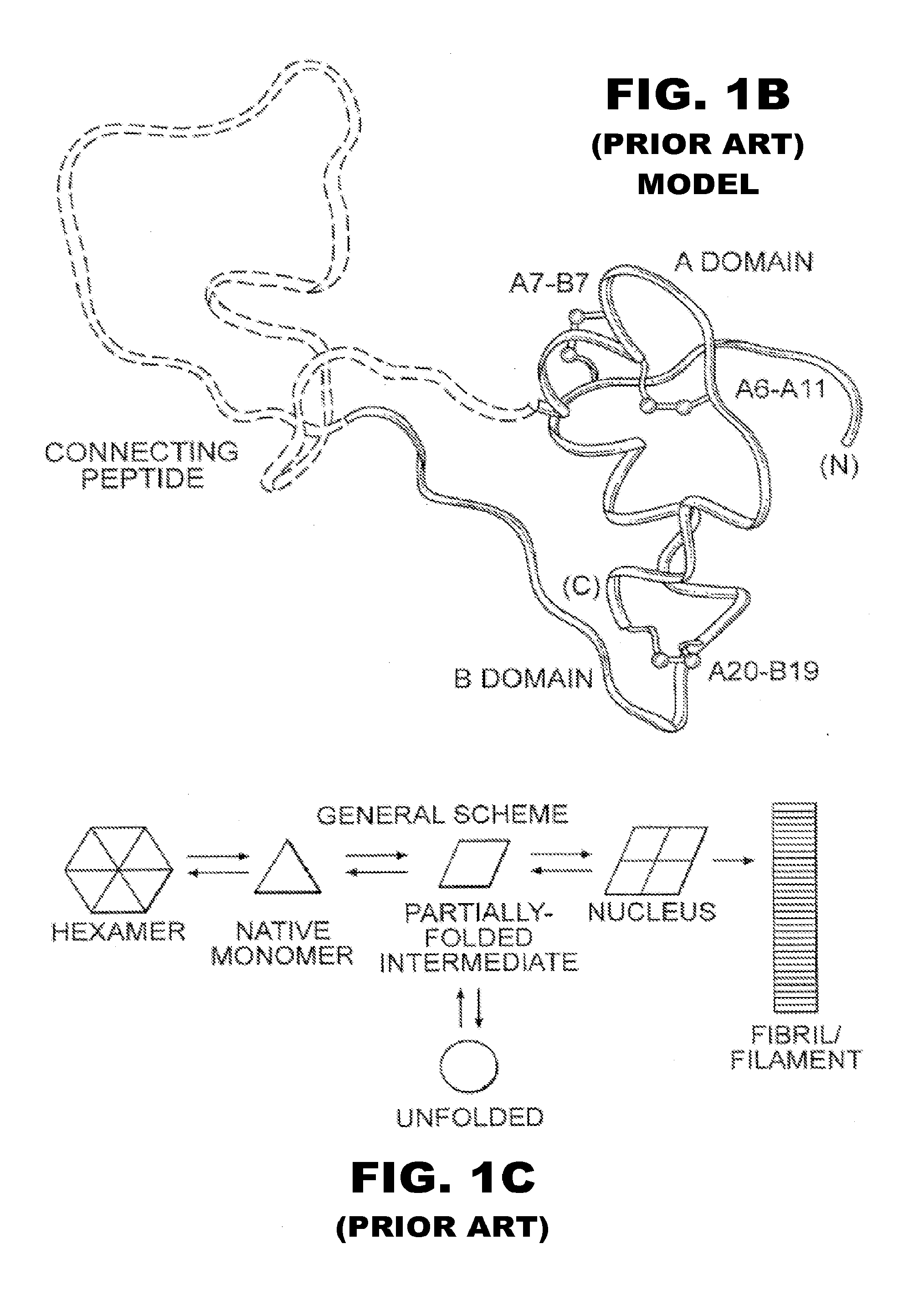
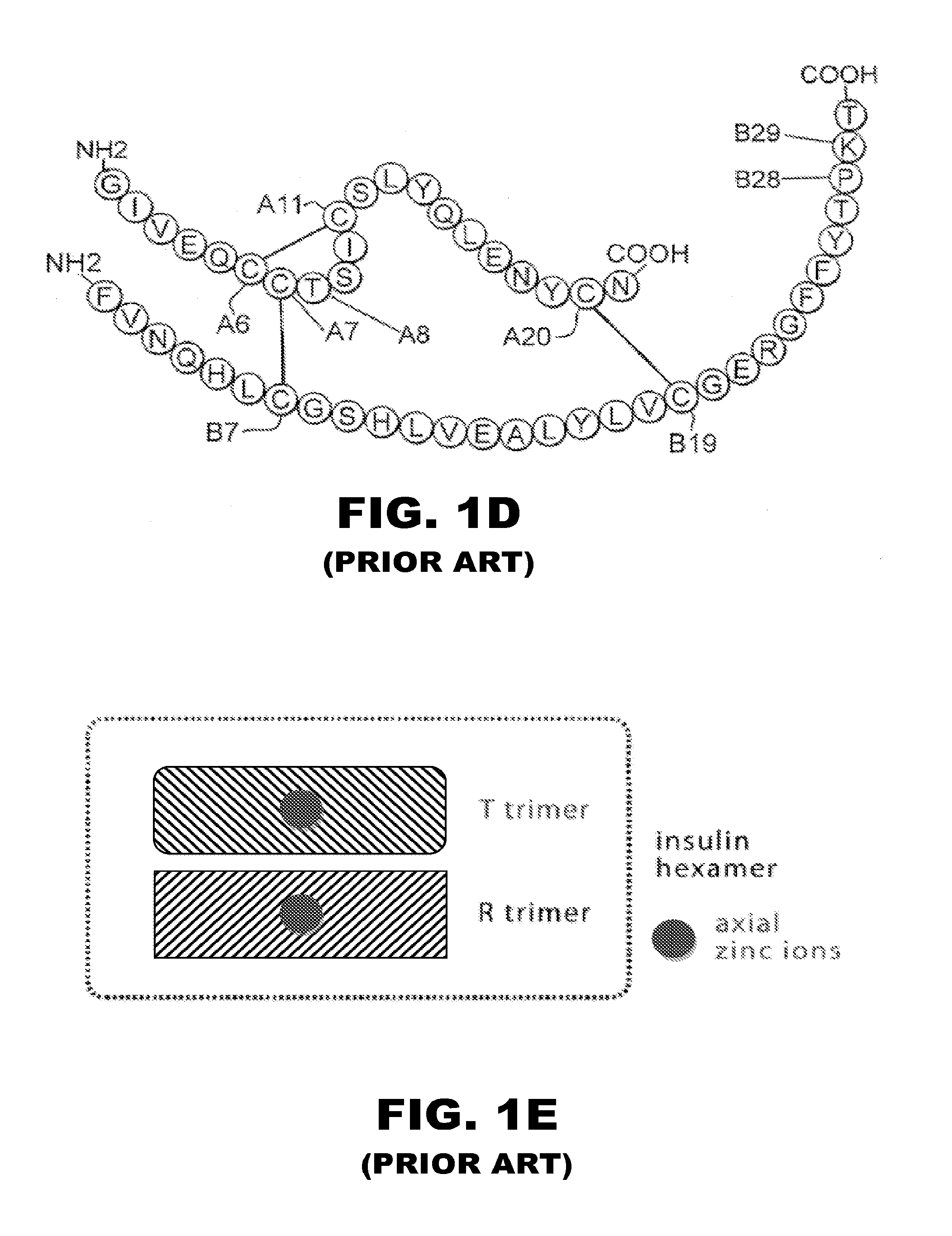
The insulin receptor (IR) is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by insulin, IGF-I, IGF-II and belongs to the large class of tyrosine kinase receptors. Metabolically, the insulin receptor plays a key role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis, a functional process that under degenerate conditions may result in a range of clinical manifestations including diabetes and cancer. Insulin signalling controls access to blood glucose in body cells. When insulin falls, especially in those with high insulin sensitivity, body cells begin only to have access to lipids that do not require transport across the membrane. So, in this way, insulin is the key regulator of fat metabolism as well. Biochemically, the insulin receptor is encoded by a single gene INSR, from which alternate splicing during transcription results in either IR-A or IR-B isoforms. Downstream post-translational events of either isoform result in the formation of a proteolytically cleaved α and β subunit, which upon combination are ultimately capable of homo or hetero-dimerisation to produce the ≈320 kDa disulfide-linked transmembrane insulin receptor.
Response element
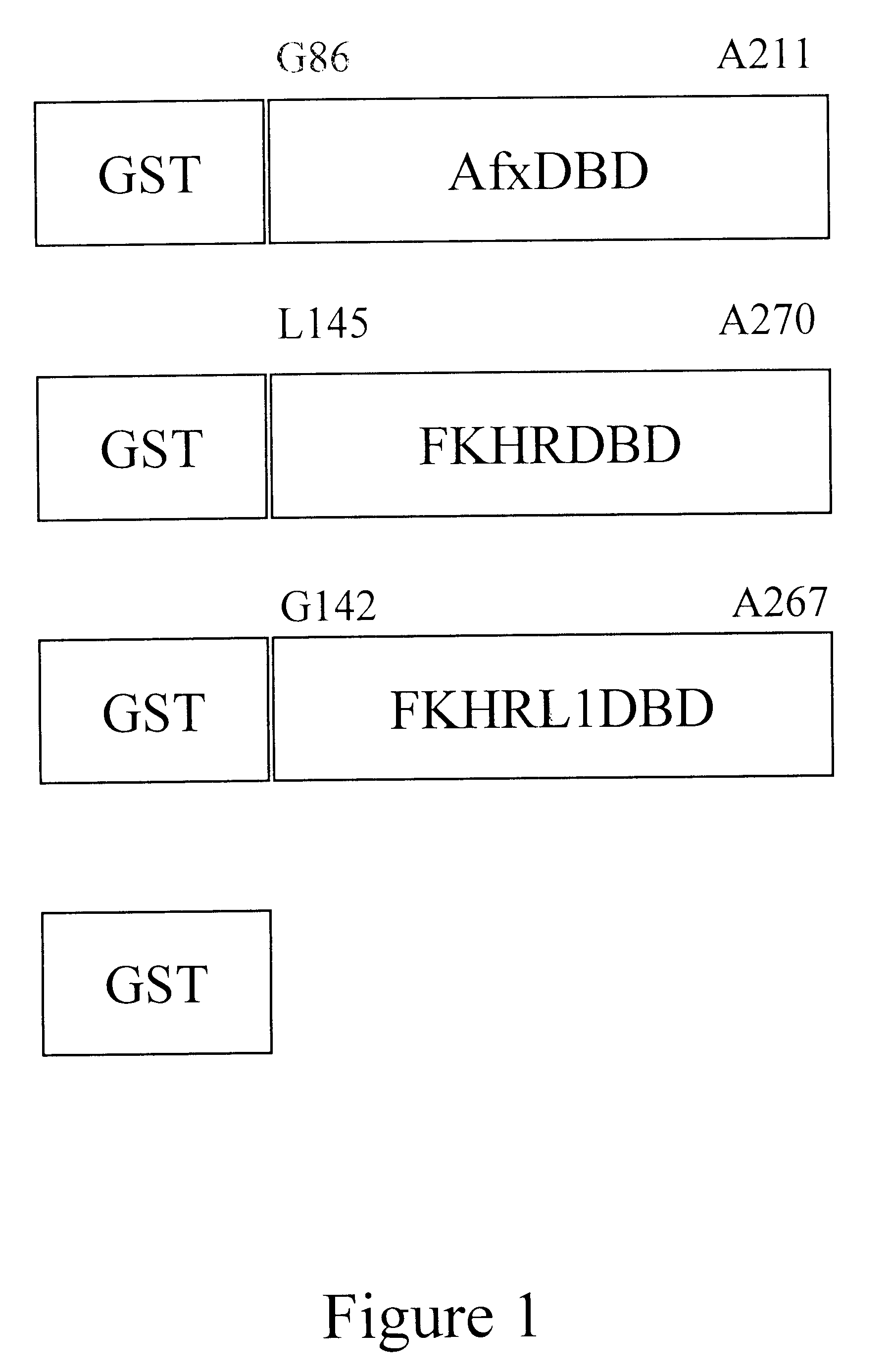
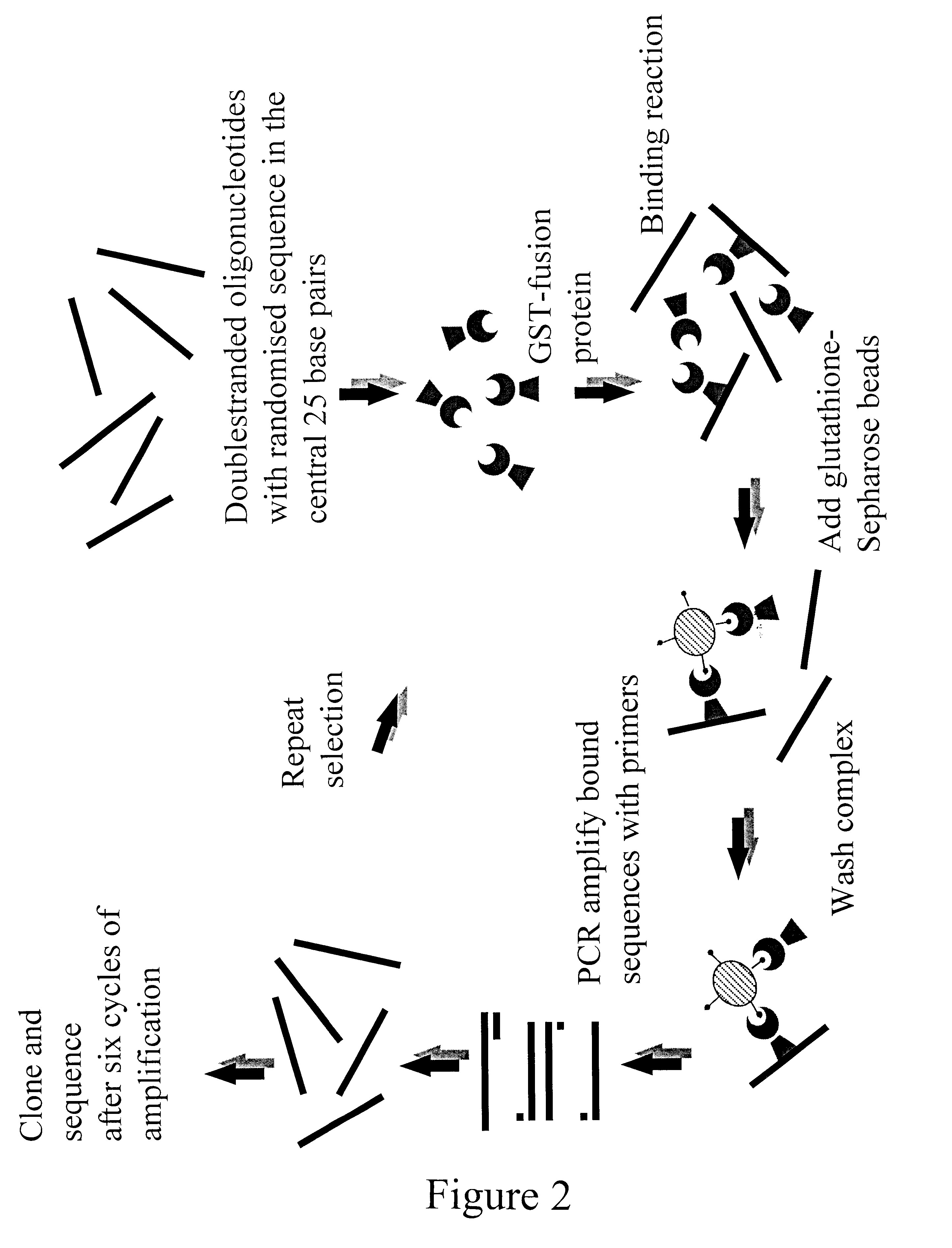
The present invention is directed to a novel Afx response element comprising the nucleotide sequence AACATGTT, said nucleotide sequence having a DNA binding site for the human fork head transkription factor Afx. The invention also relates to the use of the Afx response element in the screening for genes as diabetes drug targets and in the bioinformatic analysis of the human genome, said genes in turn being useful in other screening methods for compounds modifying the insulin receptor signaling pathway. A further aspect of the invention is a vector construct comprising the novel nucleotide sequence, a host cell transformed with said vector construct as well as the fusion protein expressed by said host cell.
Owner:BIOVITRUM AB (PUBL) +1
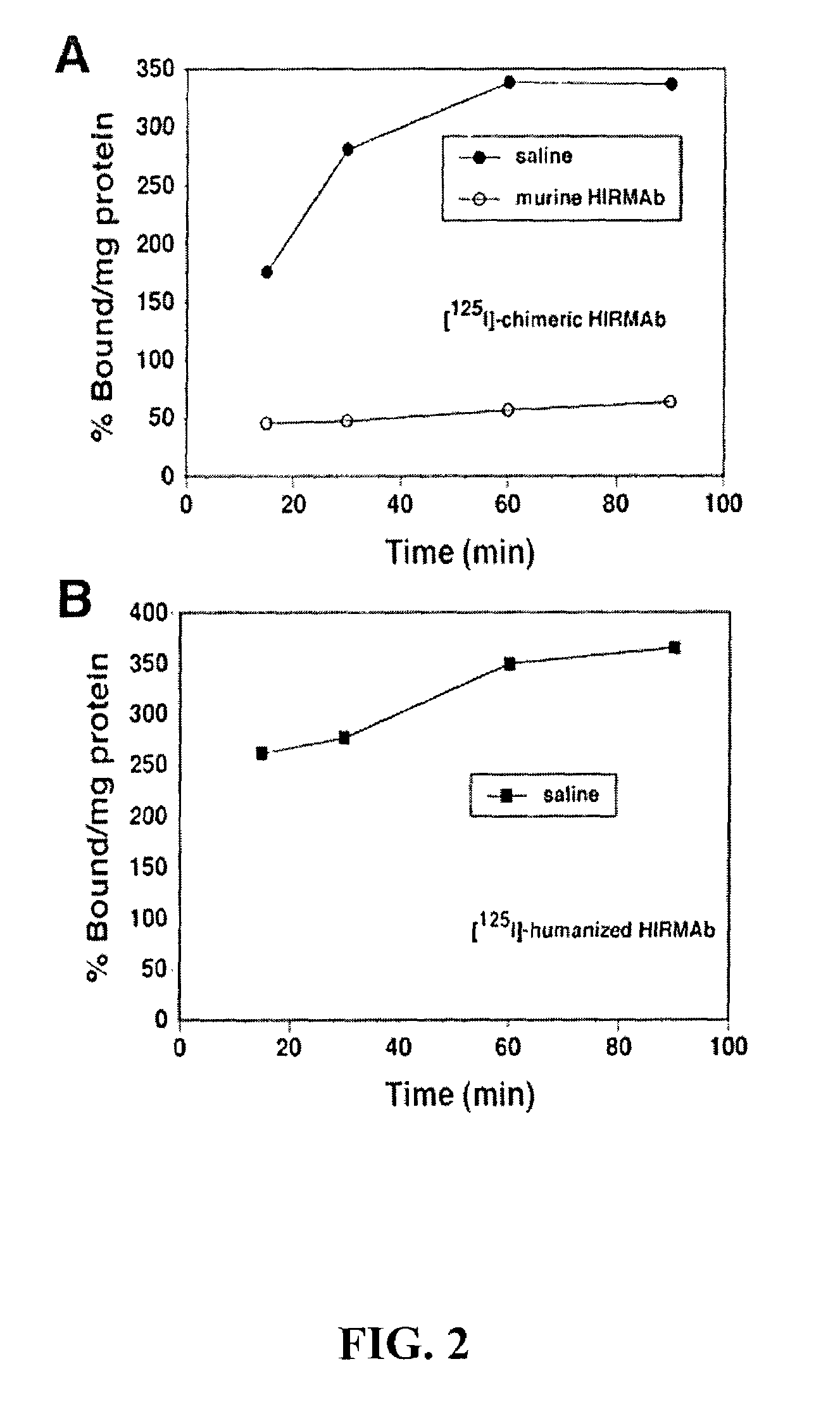
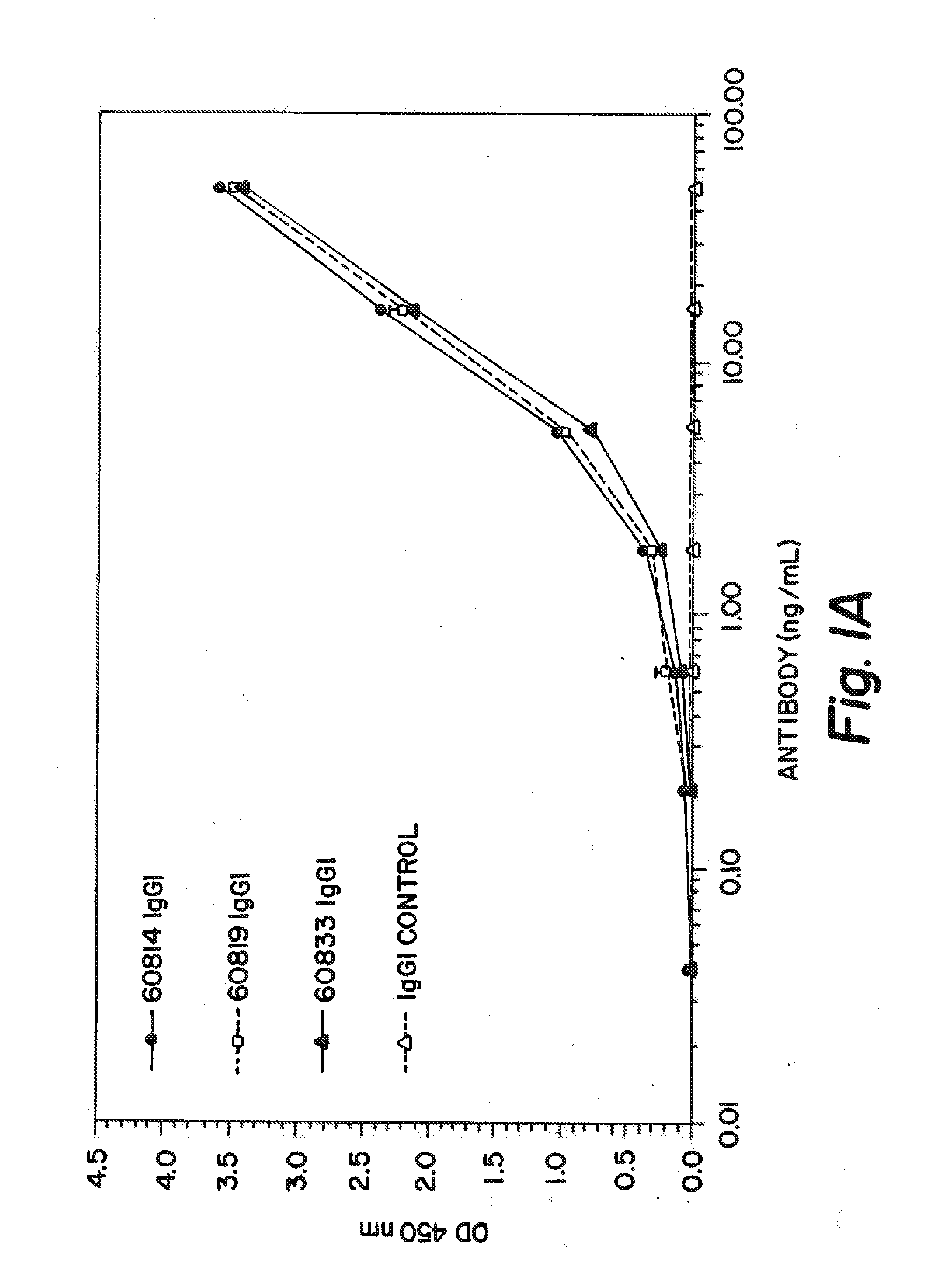
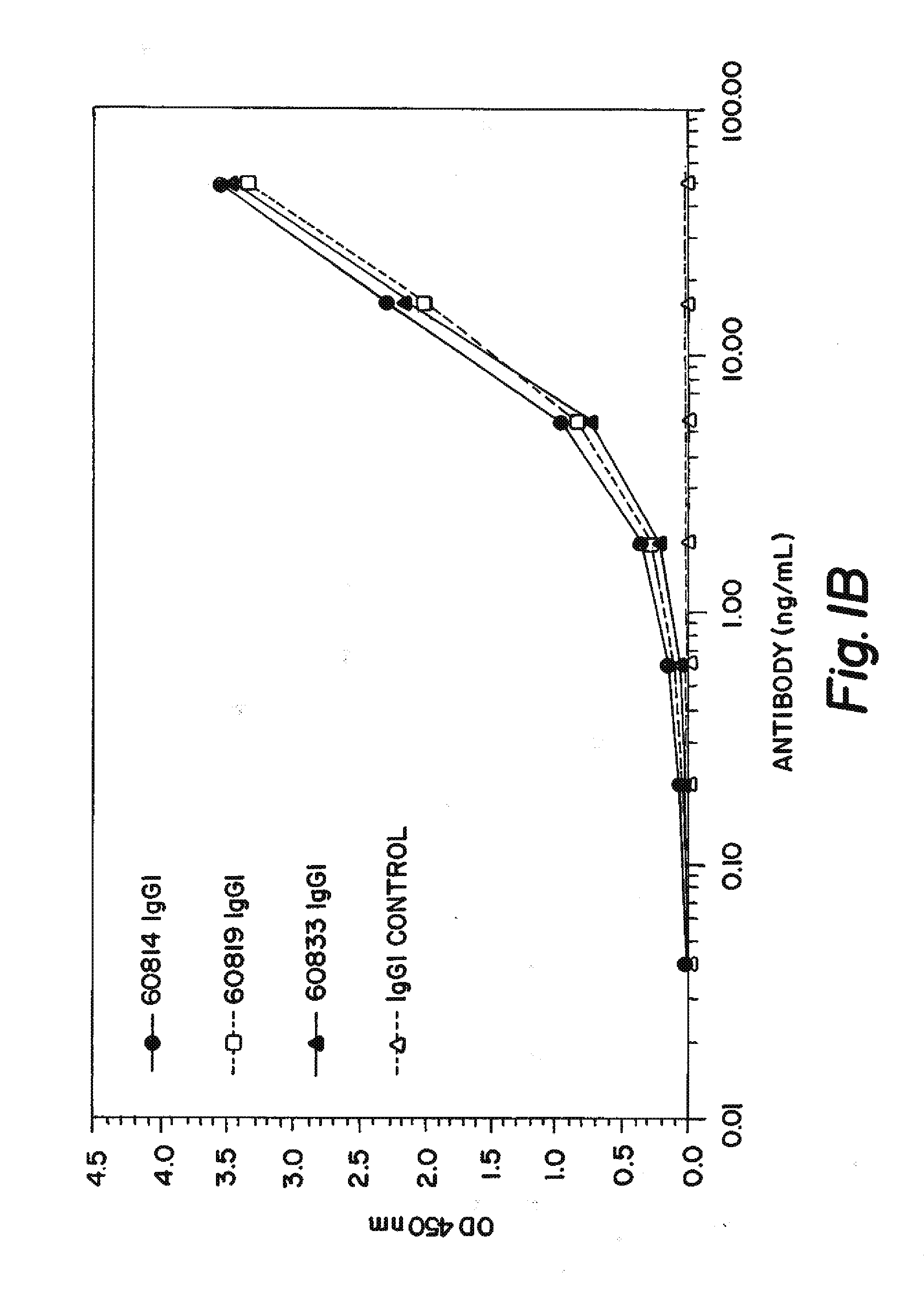
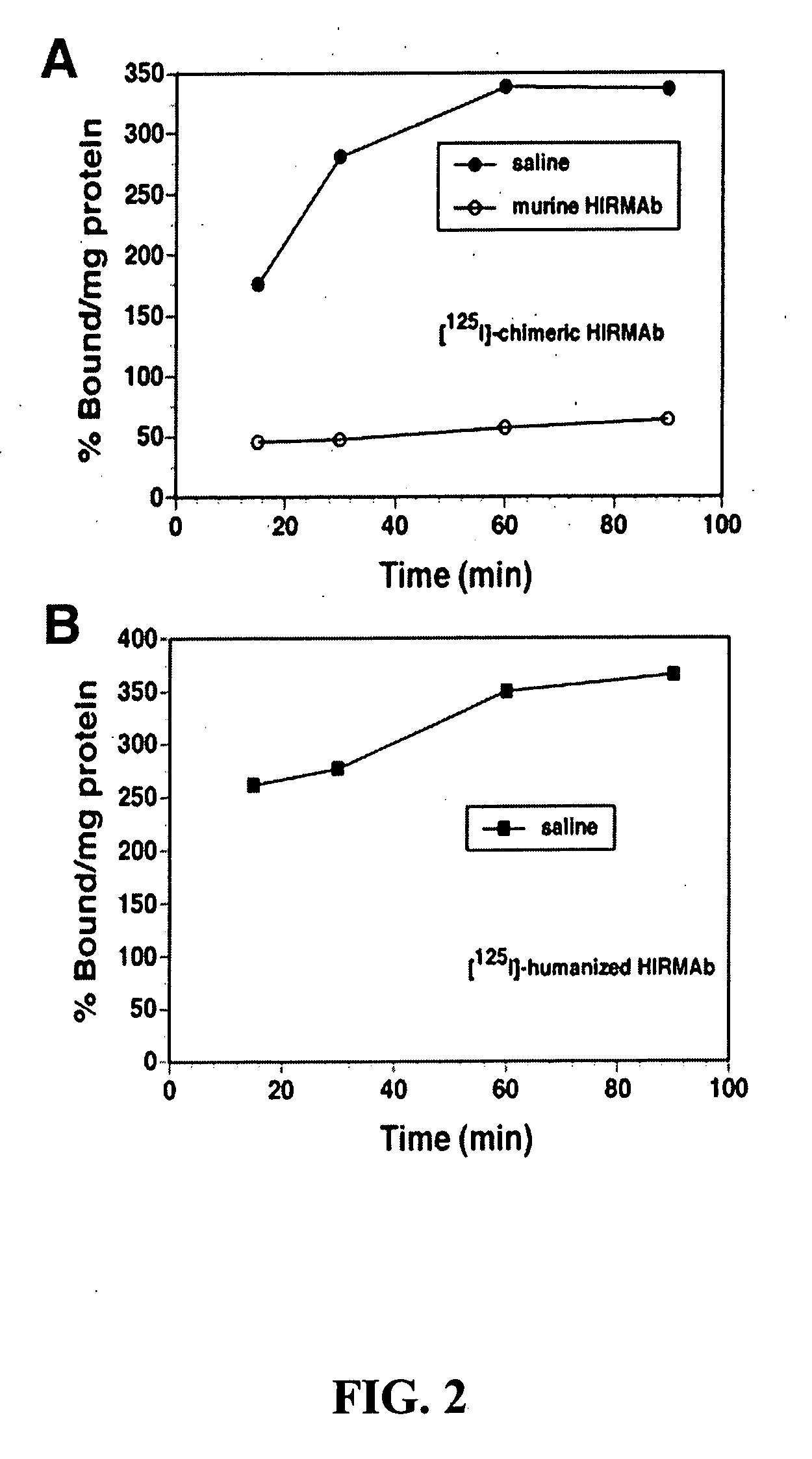
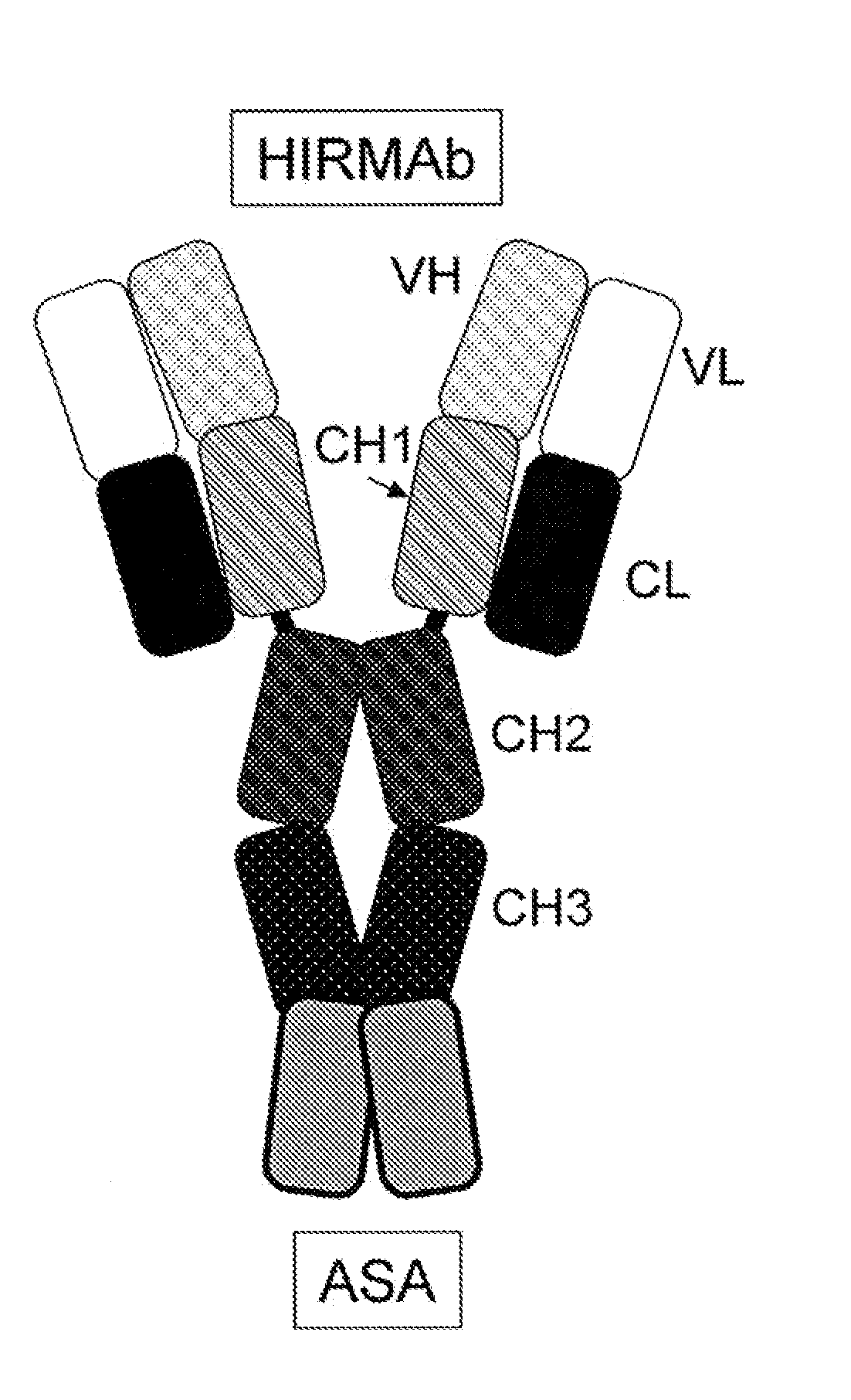
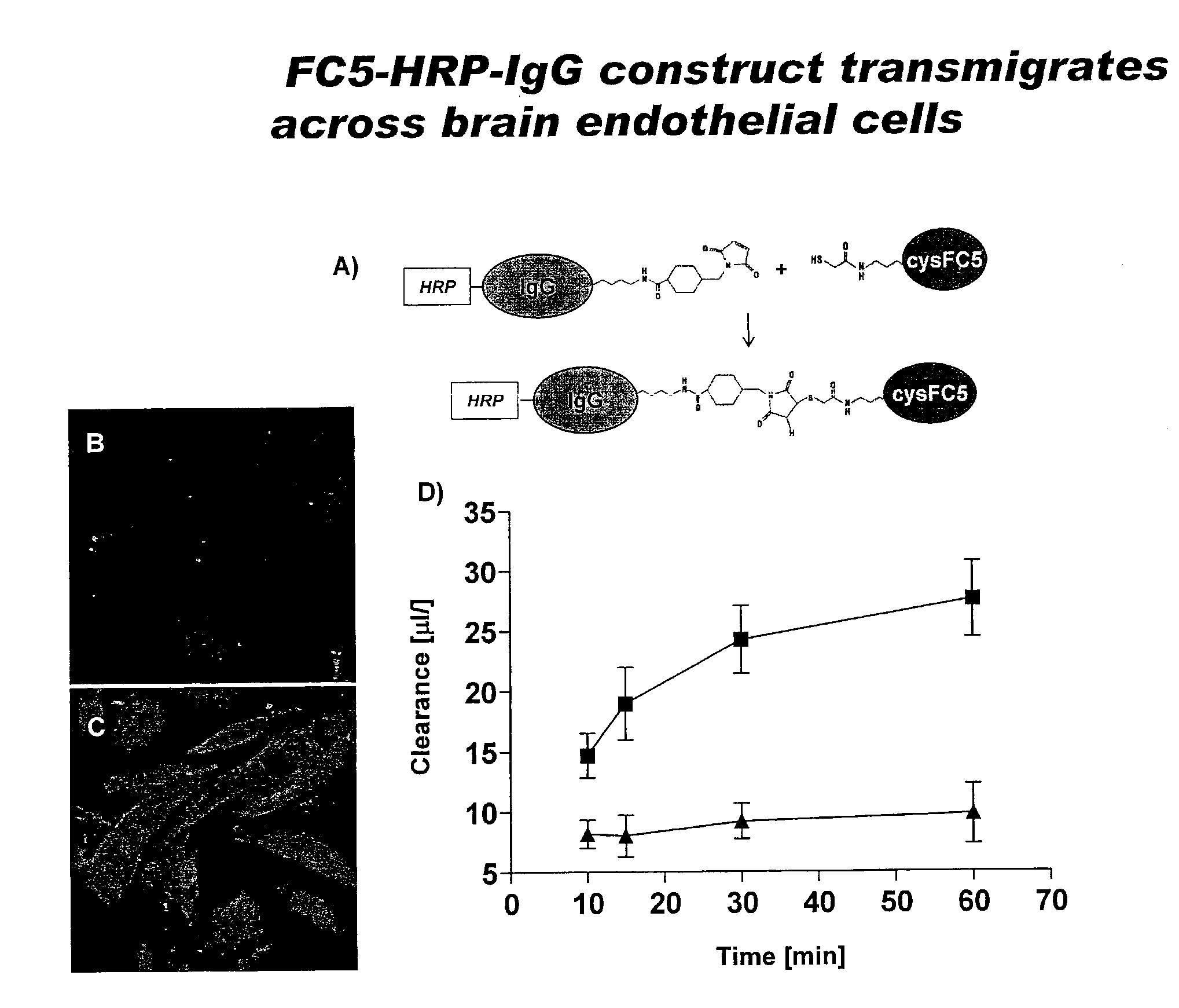
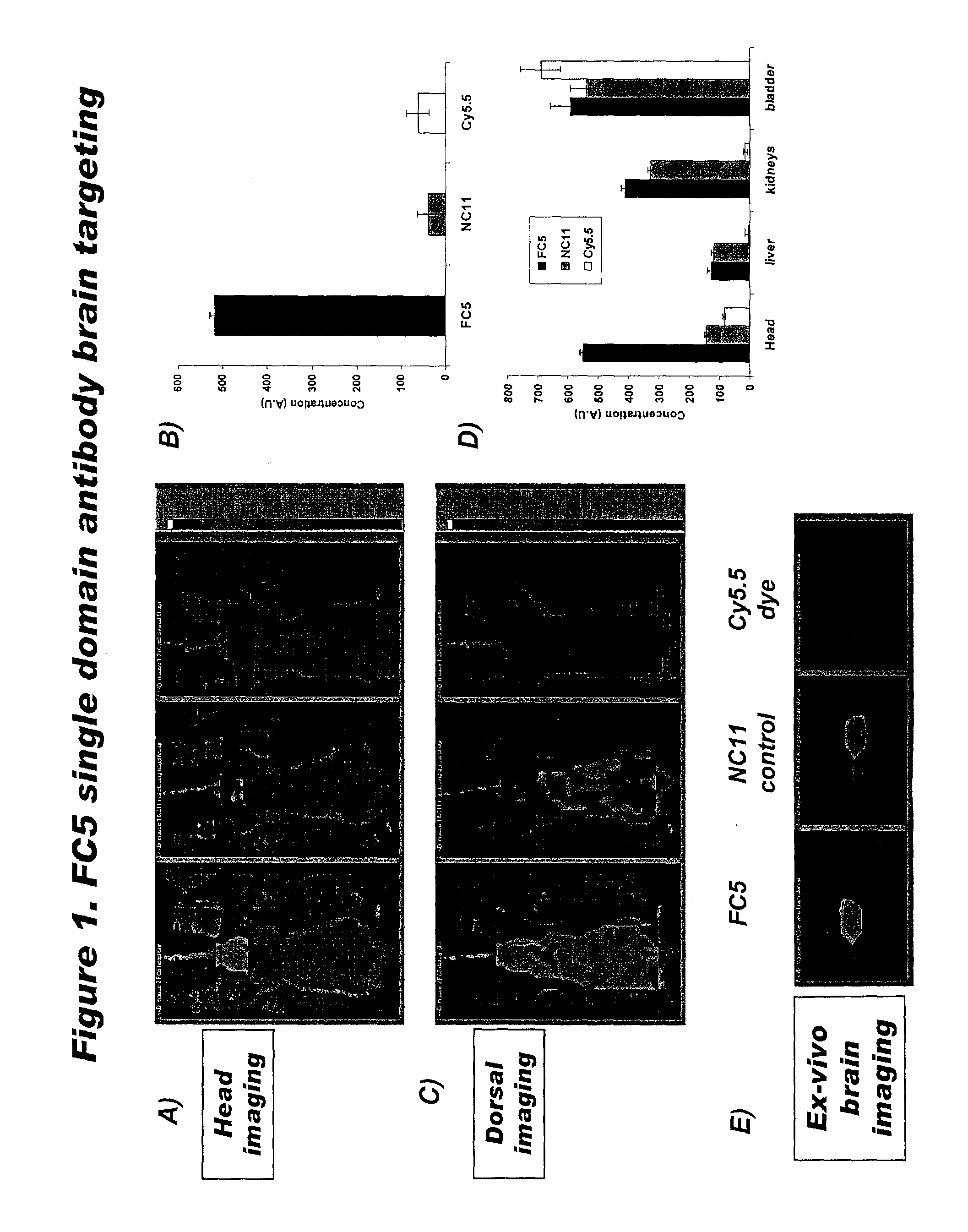
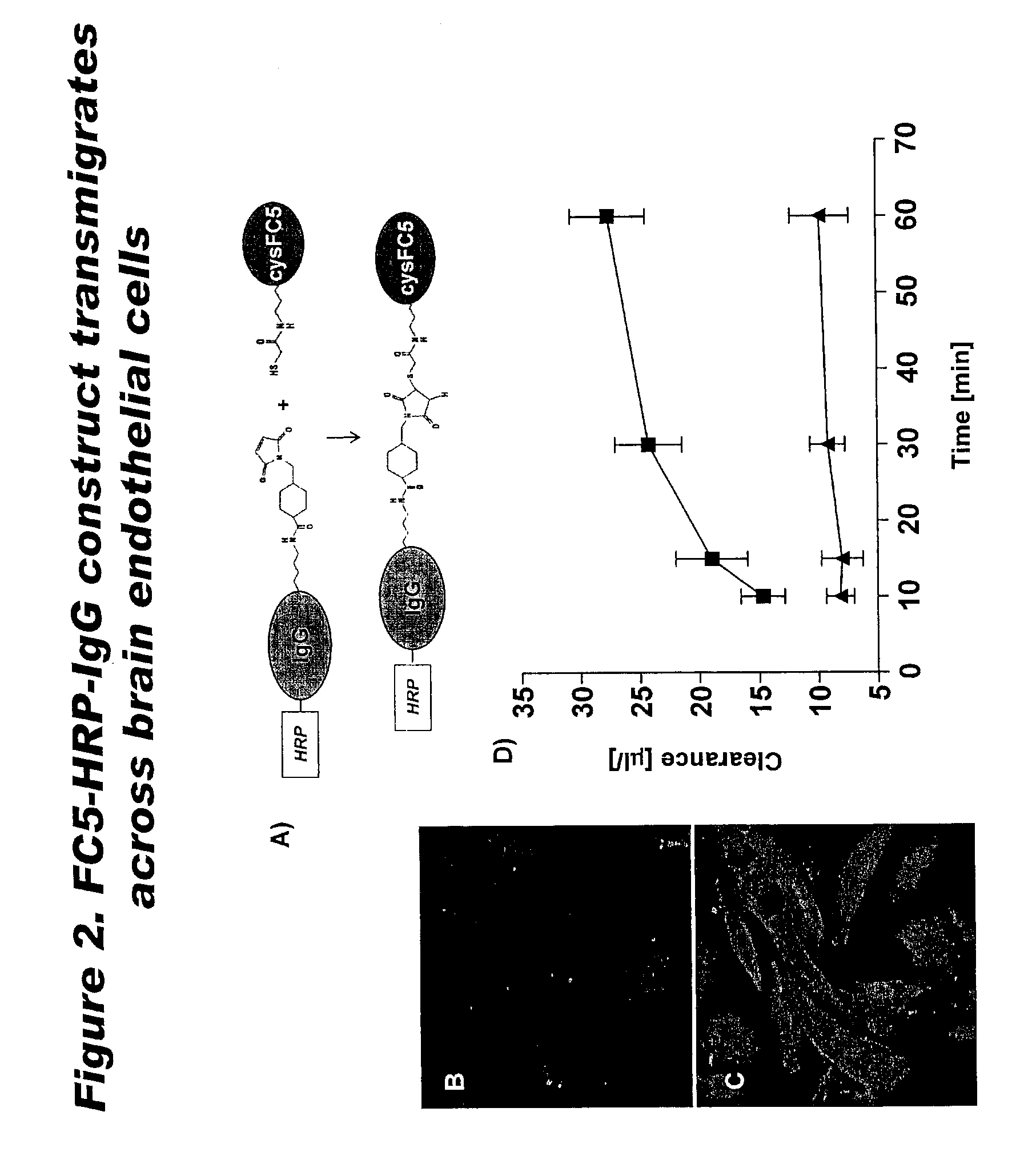
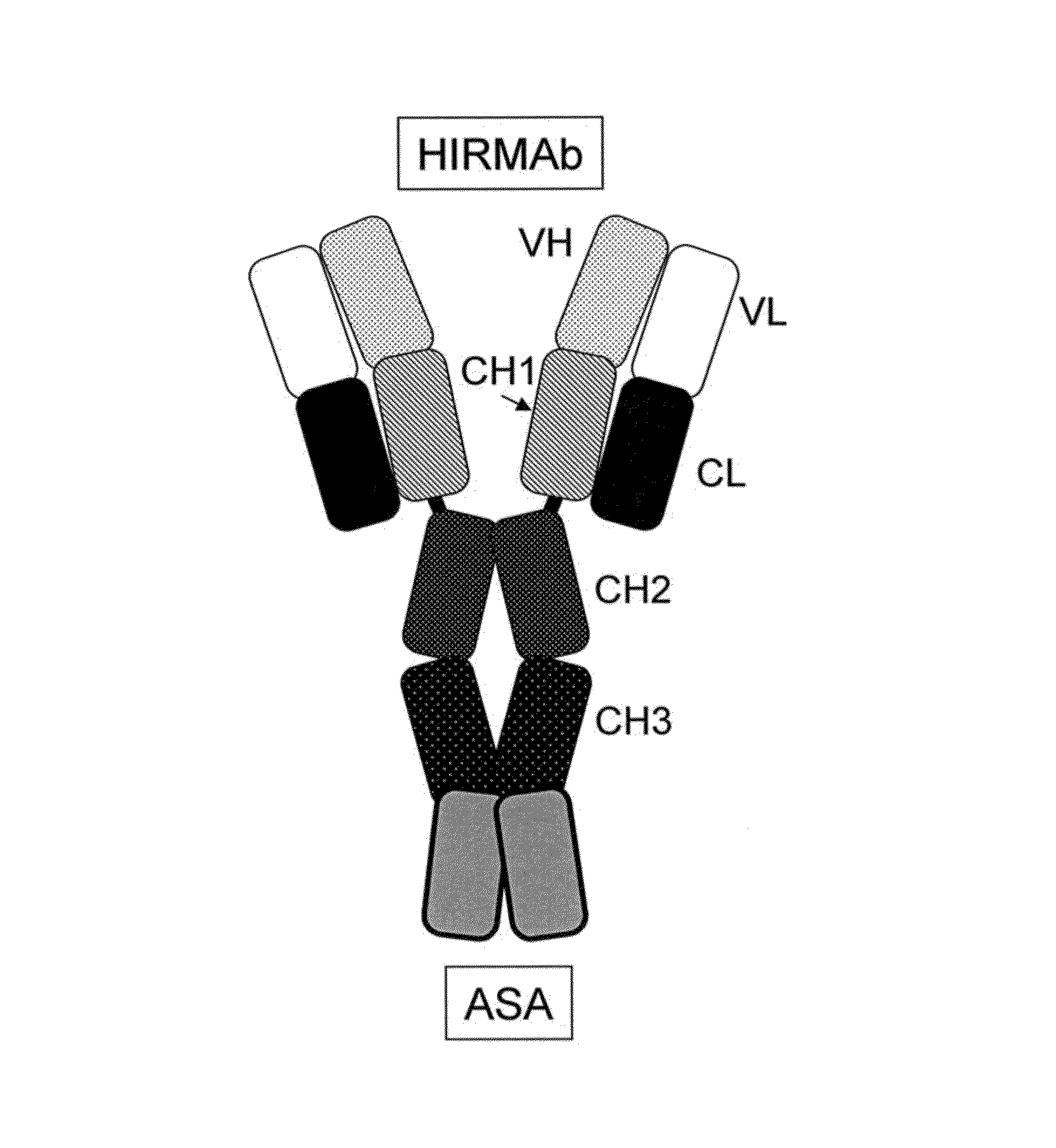
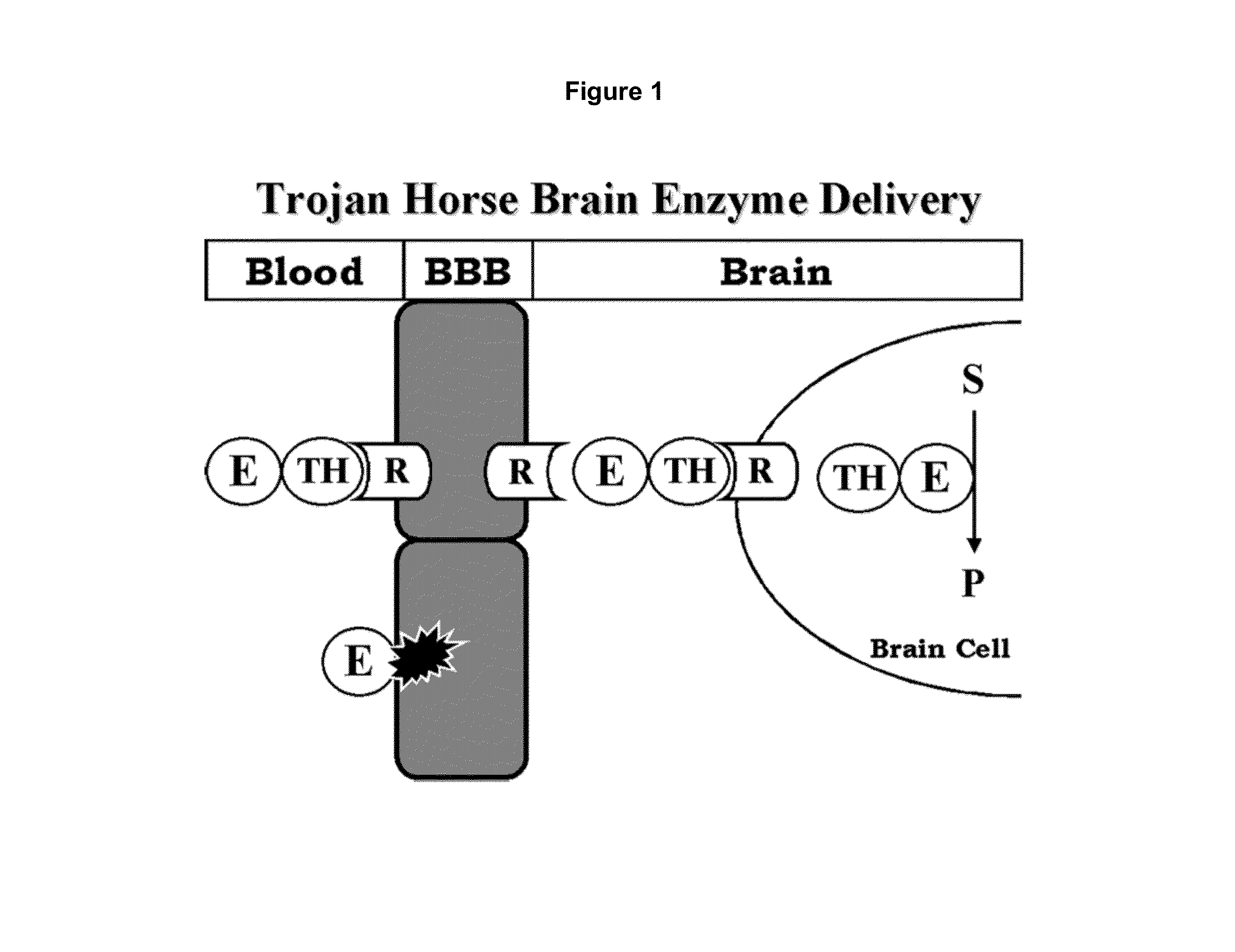
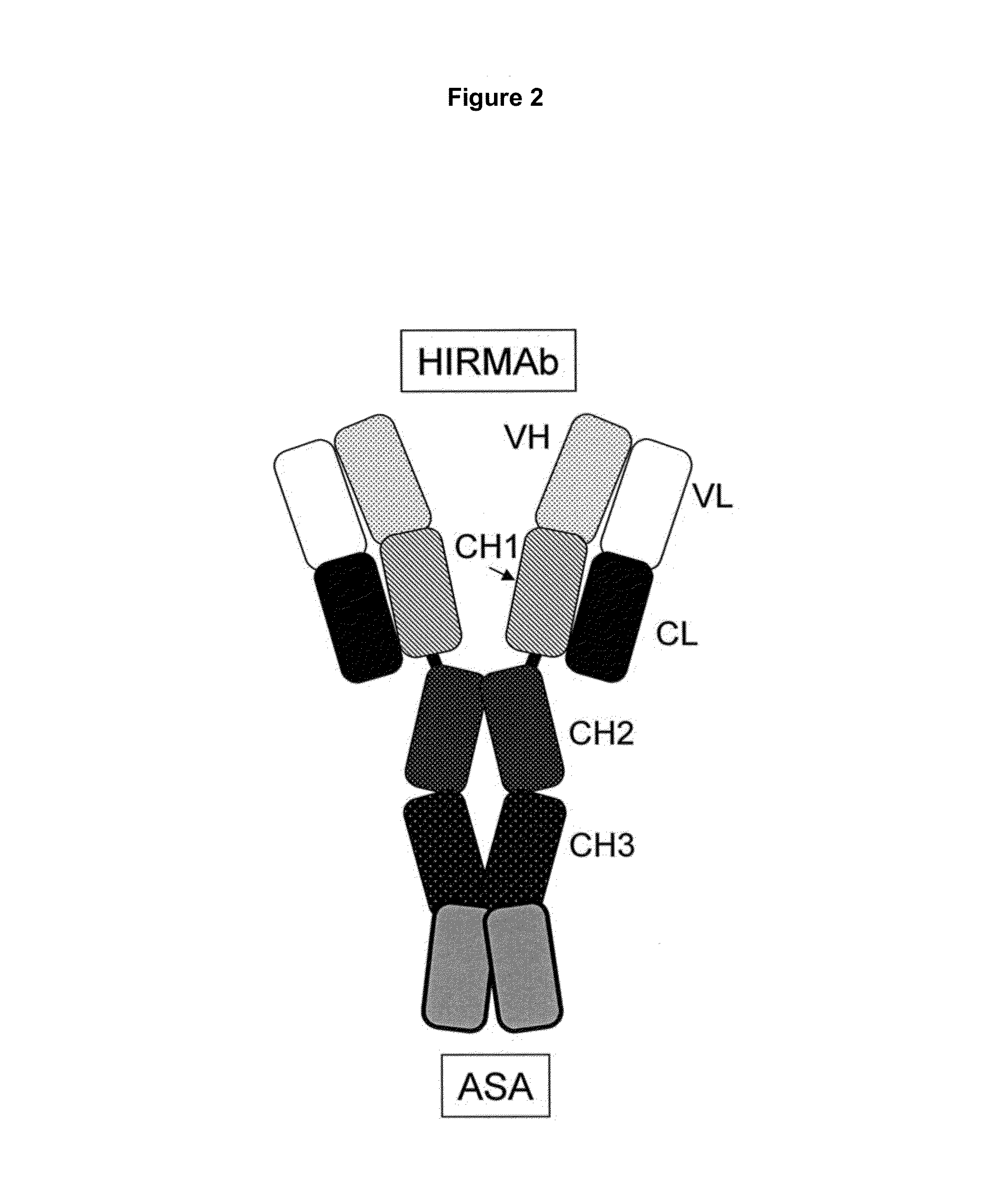
Delivery of pharmaceutical agents via the human insulin receptor
ActiveUS7388079B2Reduces immunogenic reactionNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMurine antibodyInsulin receptor
A humanized murine antibody is provided that binds to the human insulin receptor (HIR). The humanized murine antibody is suitable for use as a Trojan horse to deliver pharmaceutical agents to human organs and tissue that express the HIR. The humanized munne antibody is especially well suited for delivering neuropharmaceutical agents from the blood stream to the brain across the blood brain barrier (BBB). The humanized murine antibody may be genetically fused to the pharmaceutical agent or it may be linked to the pharmaceutical agent using an avidin-biotin conjugation system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Anti-igf antibodies
ActiveUS20100150940A1Organic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsDiseaseInsulin receptor
Antibody molecules, in particular fully human antibodies that bind to human IGF-1 and cross-react with IGF-2 such that binding of IGF-1 and IGF-2 to the IGF-1 receptor is prevented and IGF-1 receptor-mediated signaling is inhibited. The antibodies do not bind to insulin and thus do not affect the mitogenic properties of insulin that are mediated by its binding to the insulin receptors. The antibodies are useful for the treatment of hyperproliferative diseases, in particular cancer.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Delivery of pharmaceutical agents via the human insulin receptor
InactiveUS20080051564A1Reduces immunogenic reactionNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMurine antibodyInsulin receptor
A humanized murine antibody is provided that binds to the human insulin receptor (HIR). The humanized murine antibody is suitable for use as a Trojan horse to deliver pharmaceutical agents to human organs and tissue that express the HIR. The humanized murine antibody is especially well suited for delivering neuropharmaceutical agents from the blood stream to the brain across the blood brain barrier (BBB). The humanized murine antibody may be genetically fused to the pharmaceutical agent or it may be linked to the pharmaceutical agent using an avidin-biotin conjugation system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Novel Modulators
ActiveUS20110076284A1Reduces elevated HbA1c levelImproving impaired glucose toleranceMetabolism disorderDigestive systemAntiendomysial antibodiesMedicine
Owner:XOMA US
Method of designing agonists and antagonists to IGF receptor
InactiveUS7020563B1Inhibit bindingReduced activityOrganic chemistry methodsBiological material analysisAgonistInsulin receptor
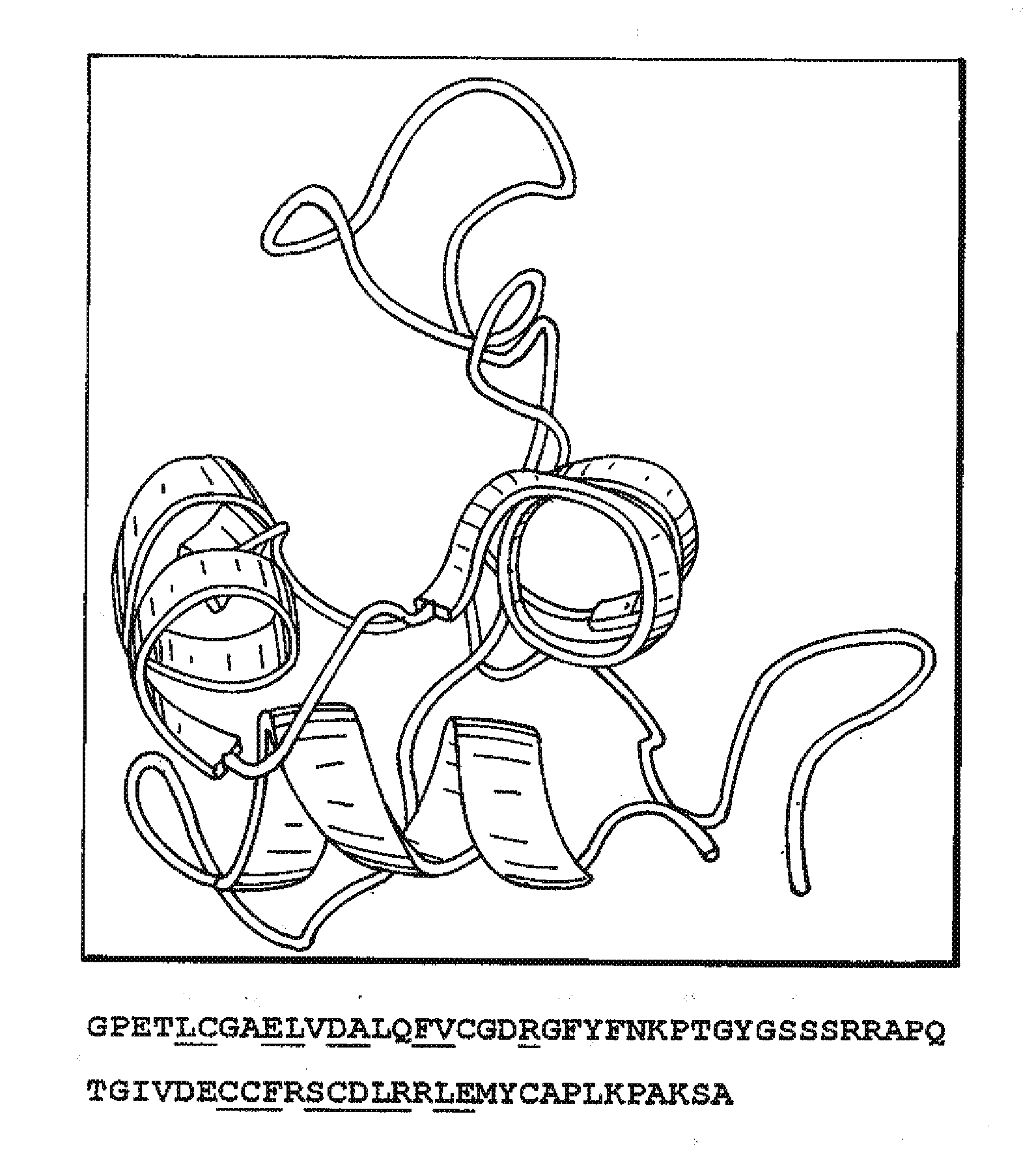
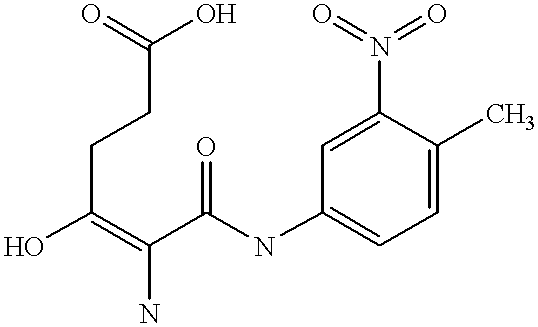
Identification of the human insulin receptor binding site sequence of certain spatial molecular structures conforming to such binding site and of certain insulinomimetic sequences including the binding site sequence are disclosed.
Owner:WALTER & ELIZA HALL INST OF MEDICAL RES
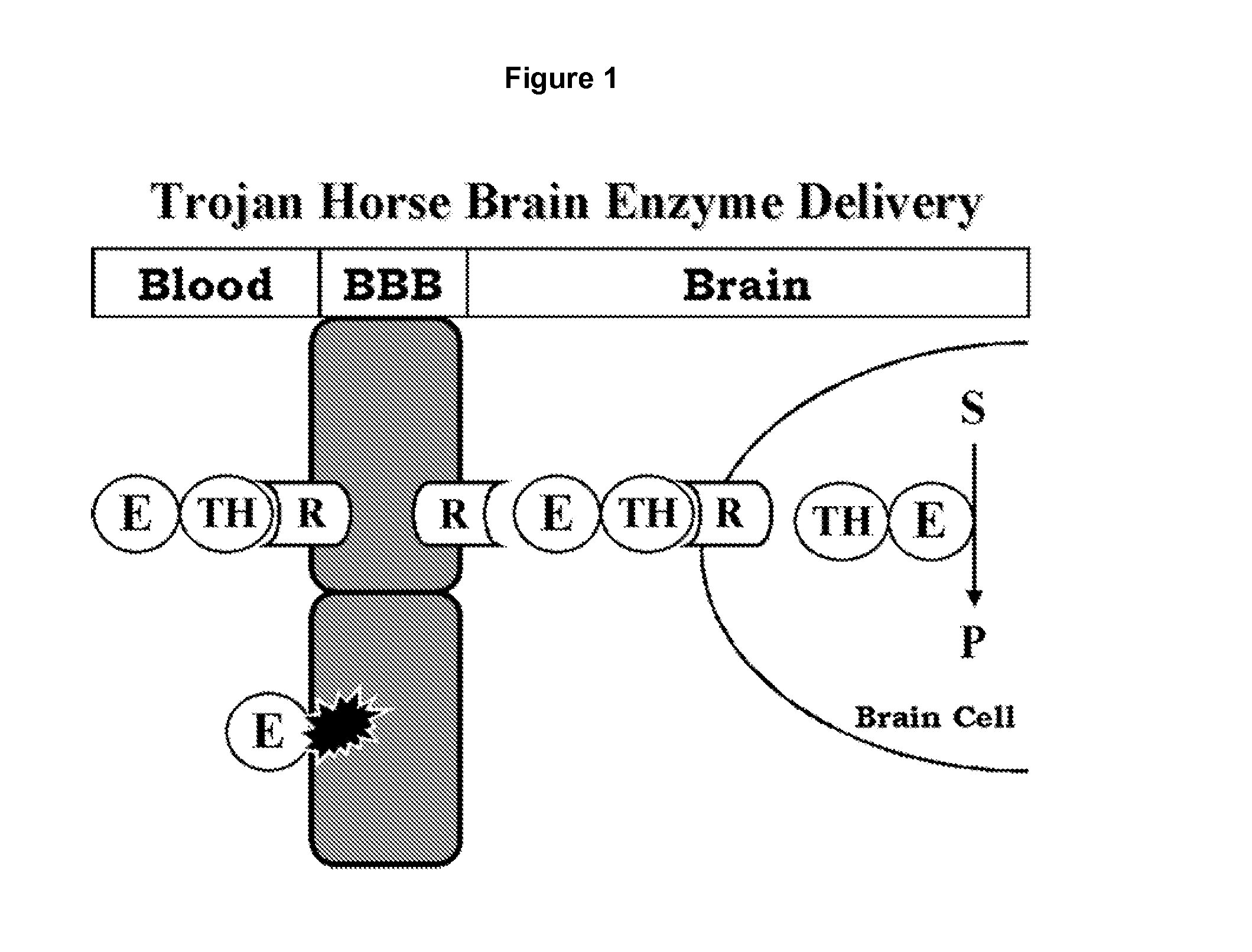
Methods and Compositions for Increasing Arylsulfatase A Activity in the CNS
ActiveUS20130142794A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderArylsulfatase A activityInsulin receptor
Provided herein are methods and compositions for treating a subject suffering from a deficiency in arylsulfatase A in the CNS. The methods include systemic administration of a bifunctional fusion antibody comprising an antibody to a human insulin receptor and an arylsulfatase A.
Owner:JCR PHARMA +1
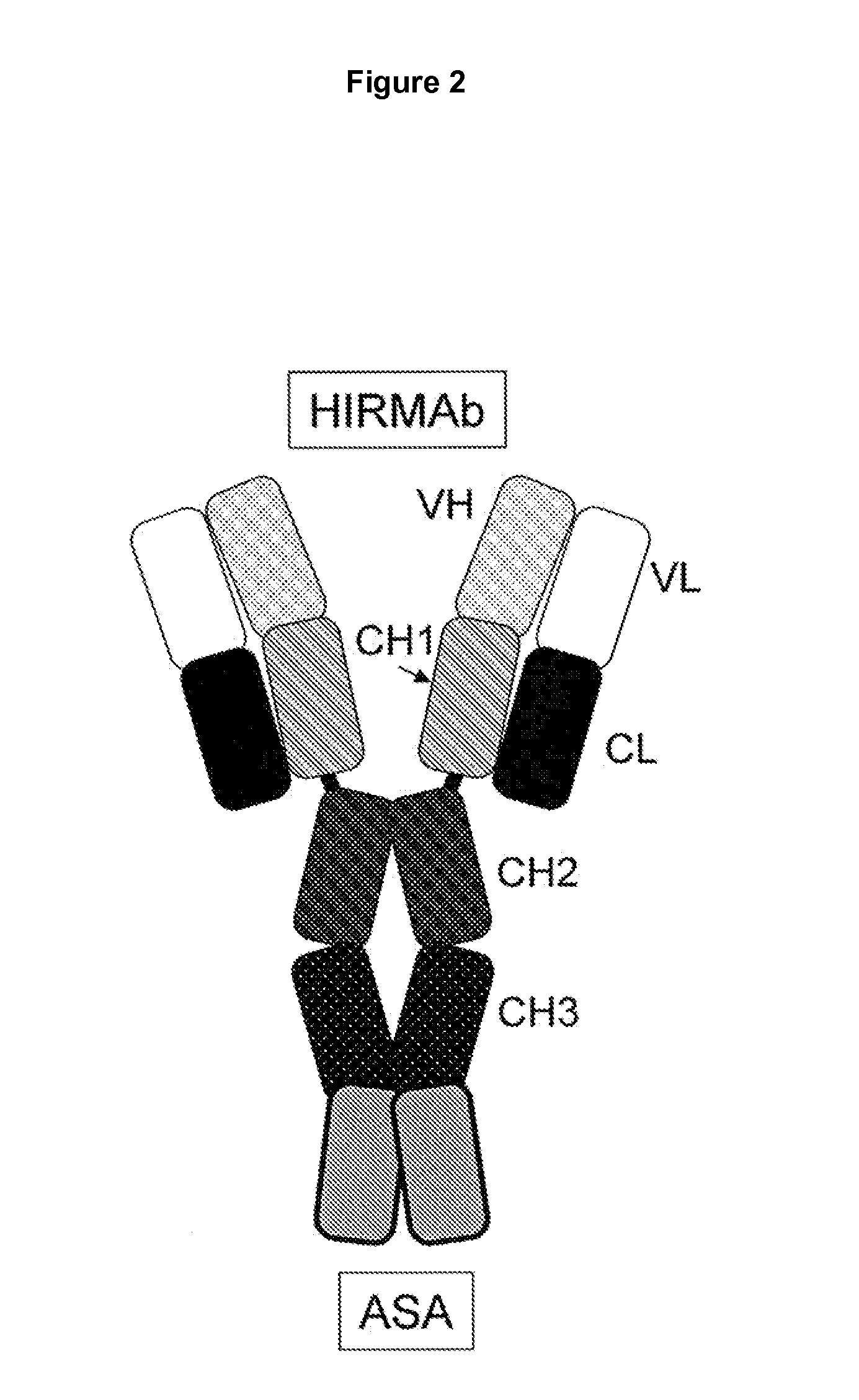
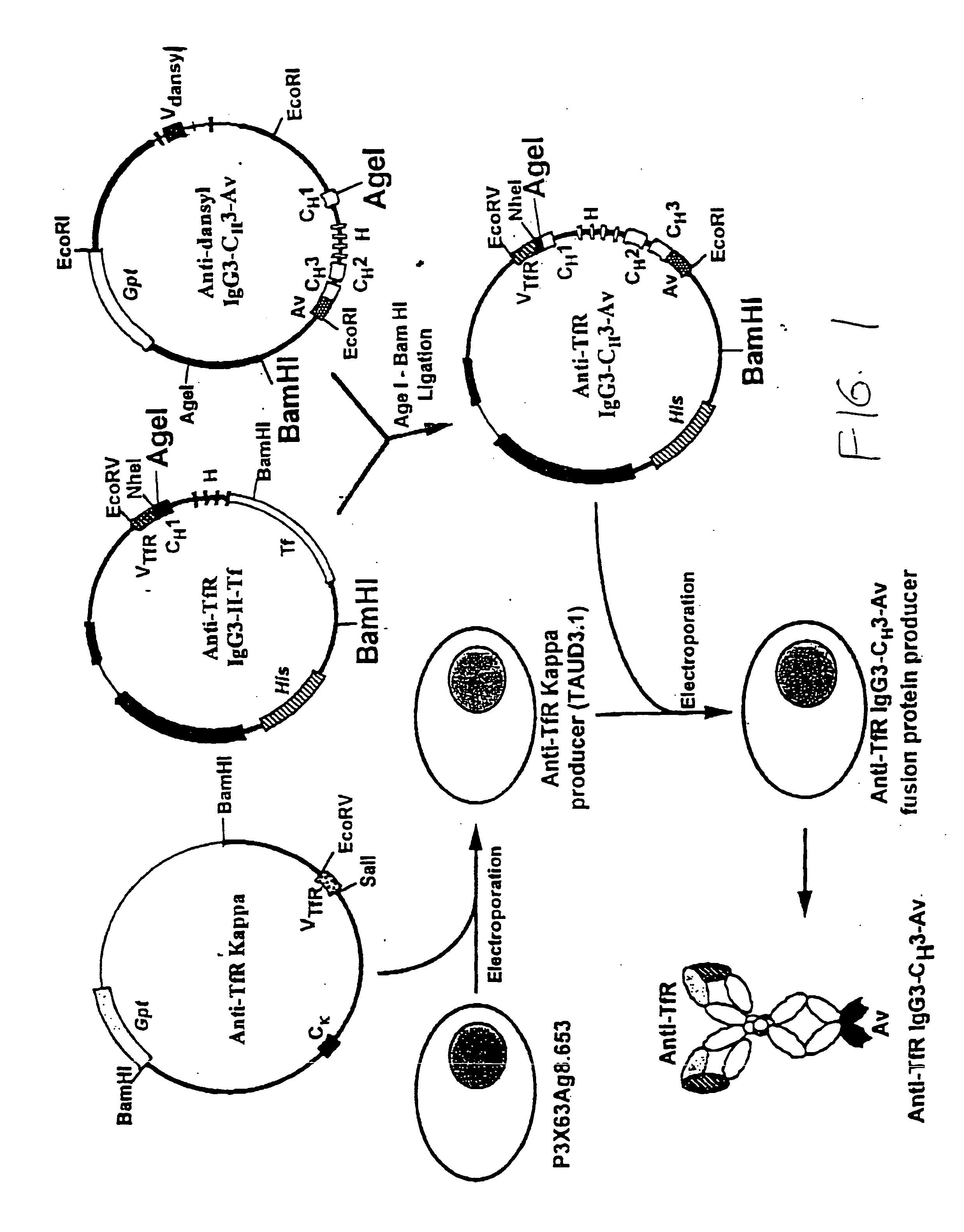
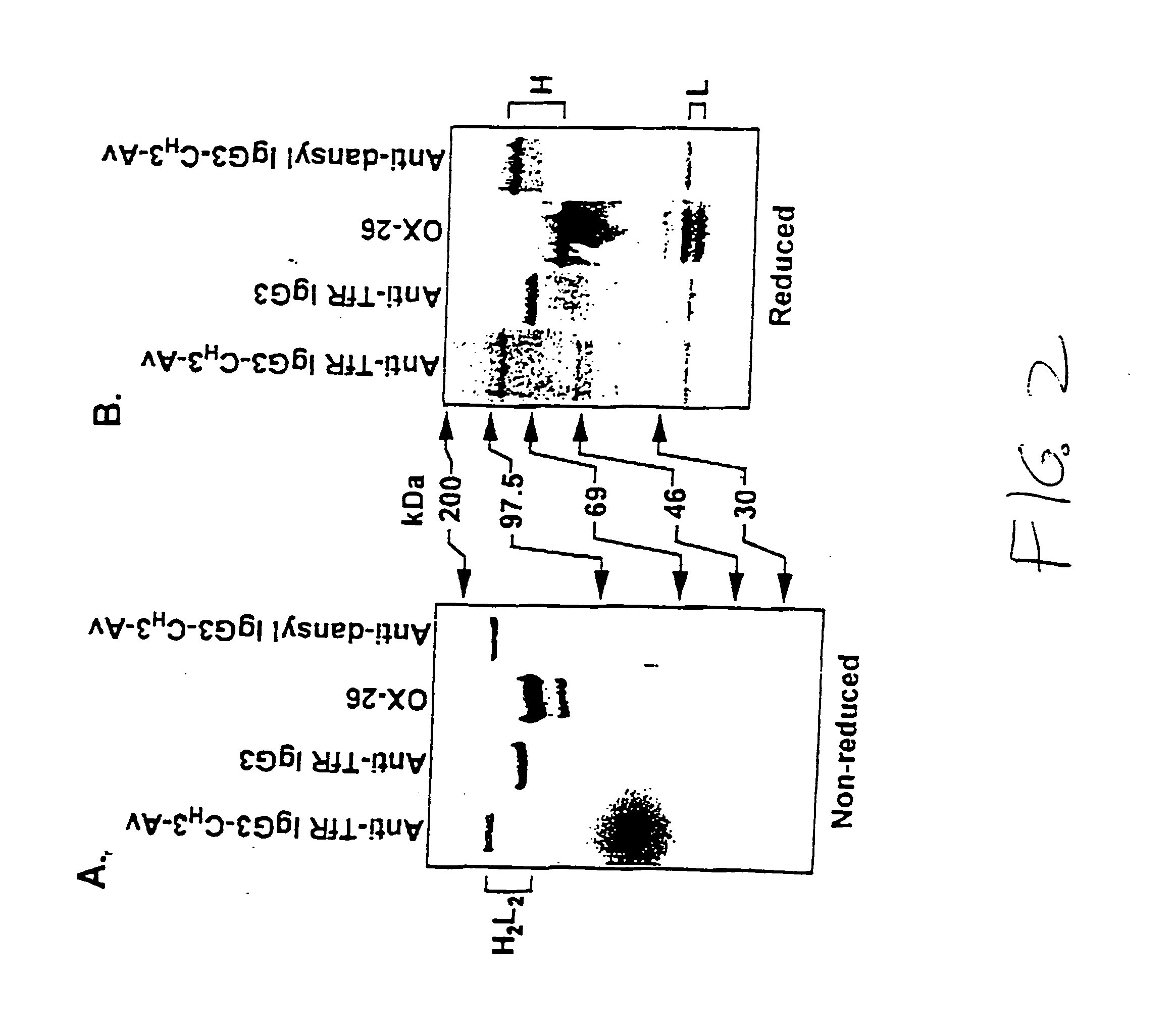
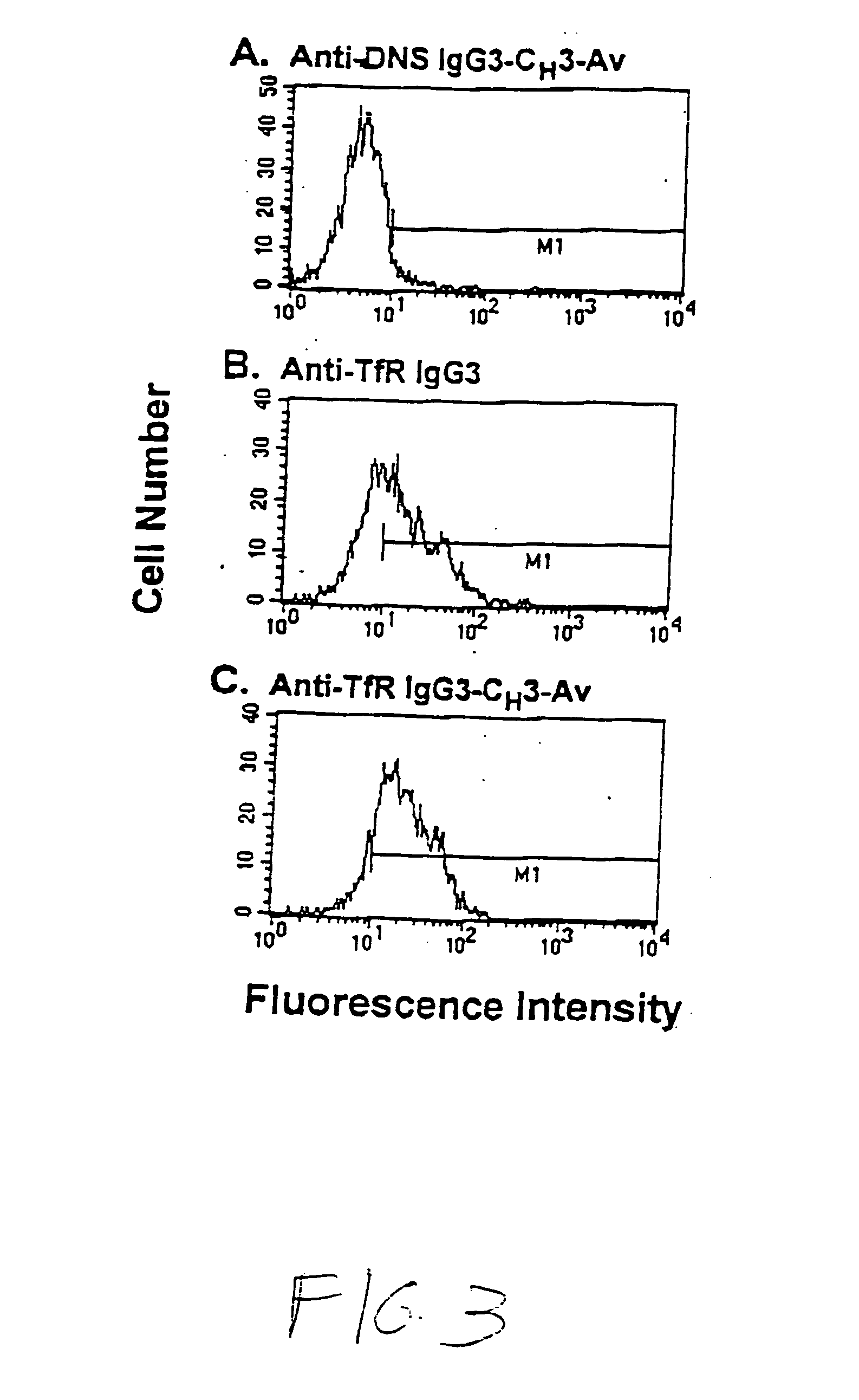
Anti-growth factor receptor avidin fusion proteins as universal vectors for drug delivery
A fusion protein for delivery of a wide variety of agents to a cell via antibody-receptor-mediated endocytosis comprises a first segment and a second segment: the first segment comprising a variable region of an antibody that recognizes an antigen on the surface of a cell that after binding to the variable region of the antibody undergoes antibody-receptor-mediated endocytosis, and, optionally, further comprises at least one domain of a constant region of an antibody; and the second segment comprising a protein domain selected from the group consisting of avidin, an avidin mutein, a chemically modified avidin derivative, streptavidin, a streptavidin mutein, and a chemically modified streptavidin derivative. Typically, the antigen is a protein. Typically, the protein antigen on the surface of the cell is a receptor such as a transferrin receptor-or an insulin receptor. The invention also includes an antibody construct incorporating the fusion protein that is either a heavy chain or a light chain together with a complementary light chain or heavy chain to form an intact antibody molecule. The invention further includes targeting methods and screening methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Modulators
ActiveUS8926976B2Reduce riskEasy to controlMetabolism disorderDigestive systemInsulin receptorAntibody
Owner:XOMA US
Medicinal agent for treating fatness, diabetes, and diseases associated with impaired glucose tolerance
InactiveUS20110008452A1Specific pharmacologicalImprove efficacyPowder deliveryEnergy modified materialsDiseaseIGT - Impaired glucose tolerance
The inventive medicinal agent comprises antibodies against beta-subunit of insulin receptor in an activated form produced by means of repeated serial dilution and an external action performed according to homeopathic technology. The inventive method for producing a solid medicinal formulation for perorally treating fatness, diabetes, and other diseases associated with impaired glucose tolerance, consists in mixing the effective amount of carrier, which is showered in a fluidised layer by a water-alcohol dilution of antibodies in the form active against the beta-subunit of the insulin receptor produced by combining the repeated serial dilution, thereby reducing the concentration of antibodies, and an external action according to homeopathic technology, and is dried at a temperature equal to or less than 35° C., with pharmaceutically acceptable additives and in subsequently pelleting the mixture thus obtained by means of direct dry compression.
Owner:EPSHTEIN OLEG ILIICH
Anti-IGF antibodies
ActiveUS8580254B2Sugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against growth factorsInsulin receptorInsulin humulin
Antibody molecules, in particular fully human antibodies that bind to human IGF-1 and cross-react with IGF-2 such that binding of IGF-1 and IGF-2 to the IGF-1 receptor is prevented and IGF-1 receptor-mediated signaling is inhibited. The antibodies do not bind to insulin and thus do not affect the mitogenic properties of insulin that are mediated by its binding to the insulin receptors. The antibodies are useful for the treatment of hyperproliferative diseases, in particular cancer.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
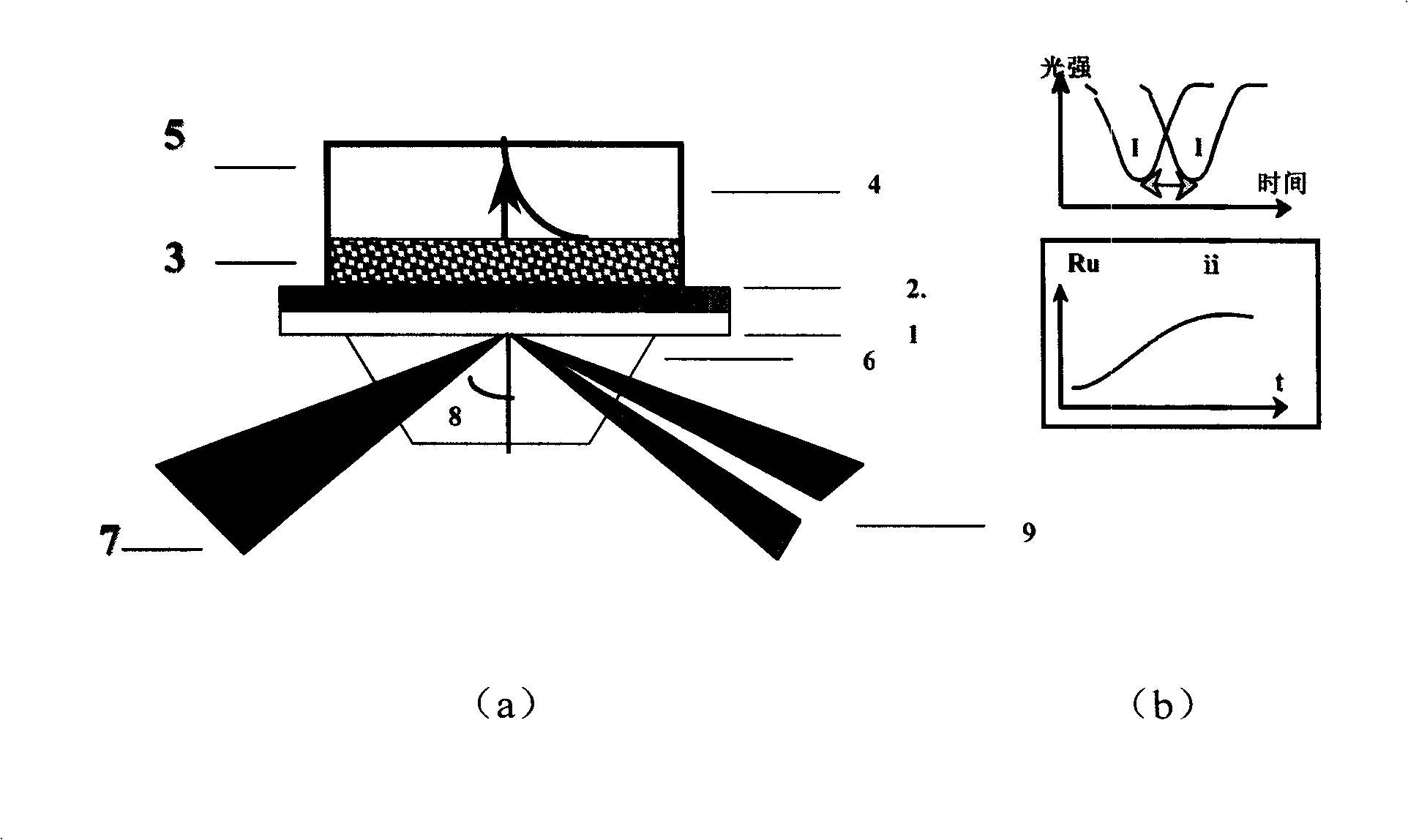
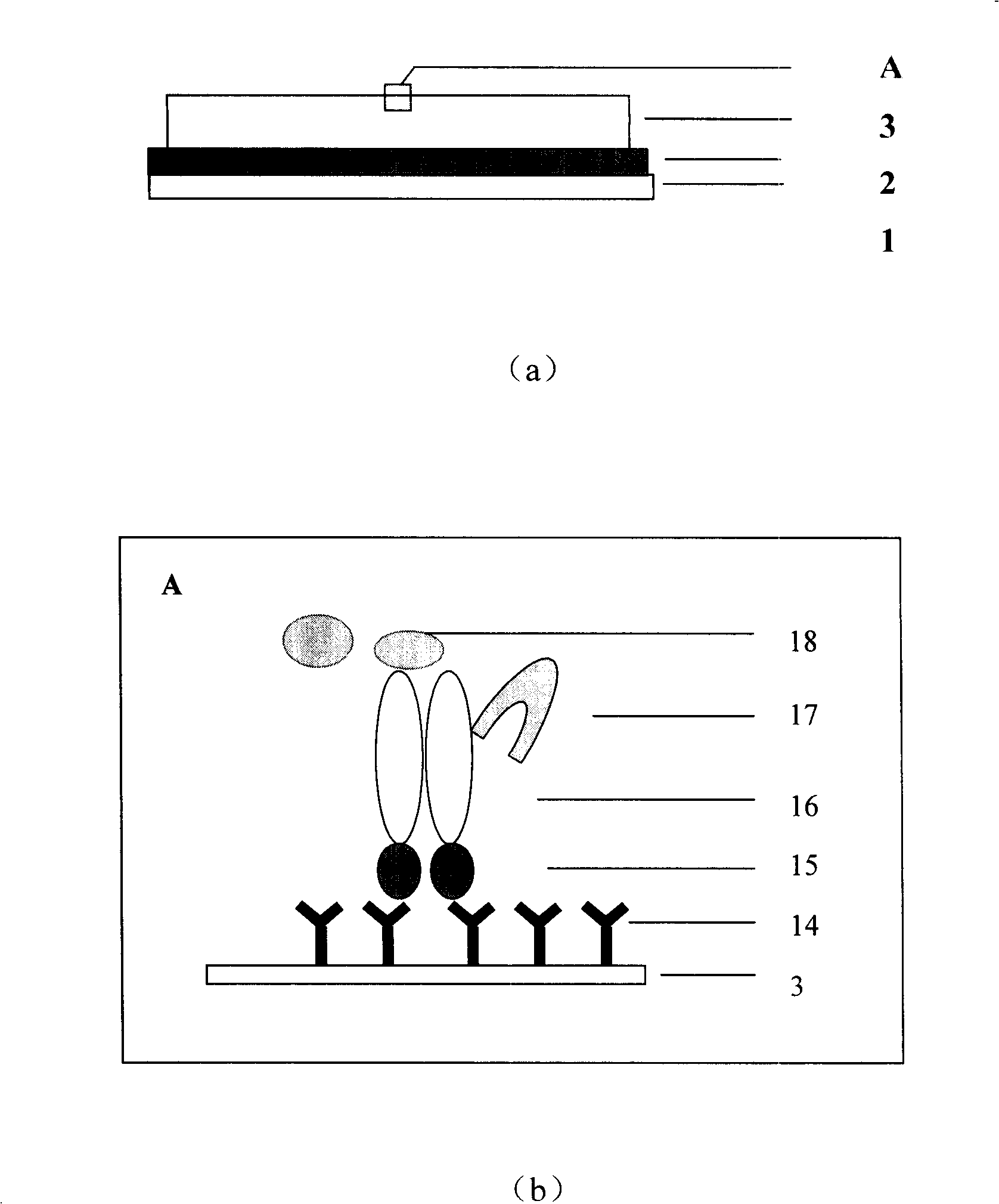
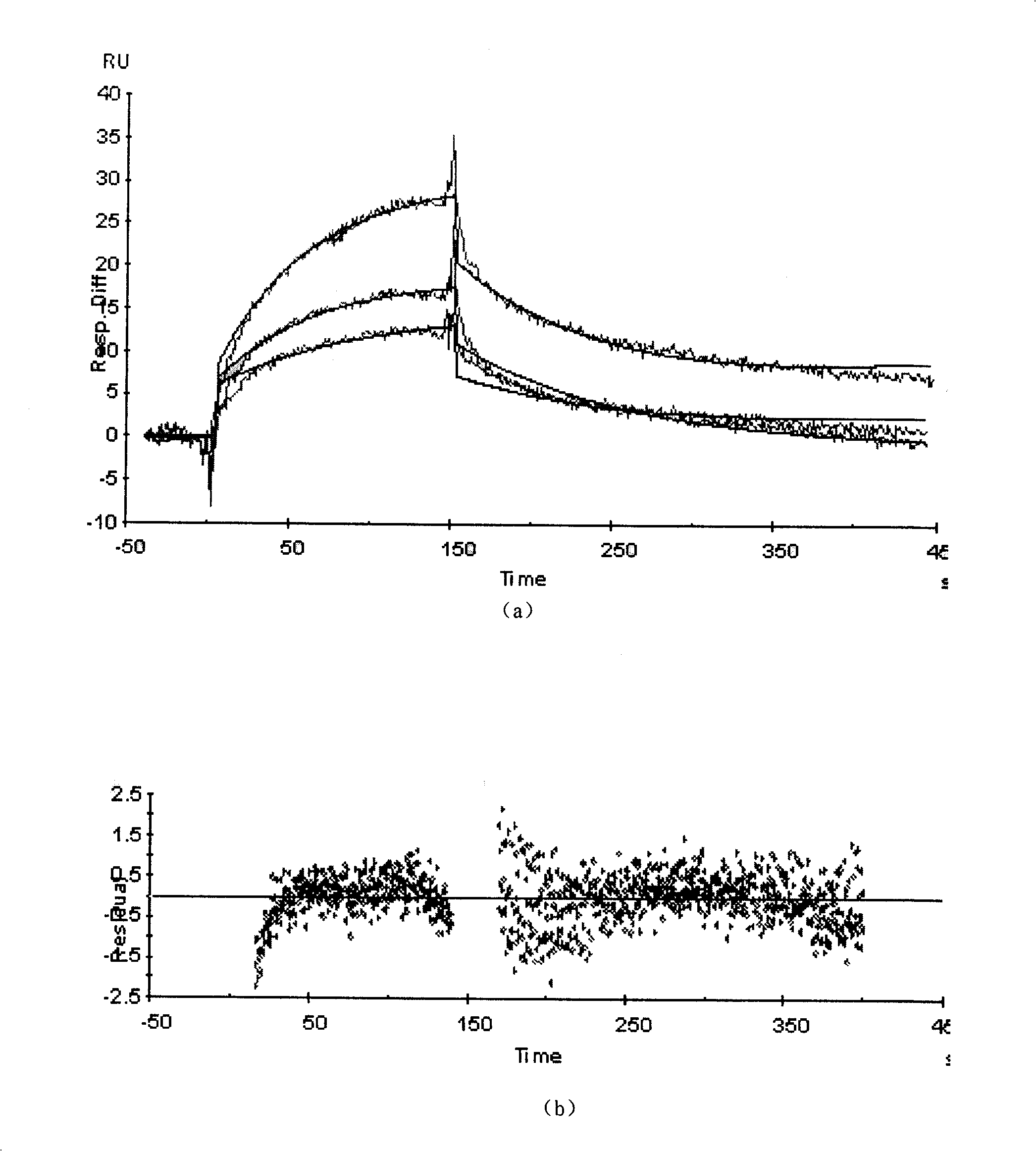
Biological chips of surface plasma resonating biological sensor, preparation and application
The invention relates to a cell surface receptor biochip based on a surface plasmon resonance biosensor, a preparation method and application thereof. The biochip is characterized in that the chip is provided with a gold surface coating at a glass substrate and the gold surface is fixed with a sephadex layer which is fixed with the monoclonal antibody of the Beta subunit of the receptors of anti para-insulin and surface receptors are fixed by antibody capture. The preparation method includes that the monoclonal antibody of the Beta subunit of the receptors of anti para-insulin adopts the method of antibody capture and is fixed on the surface of CM5 chip based on the surface plasmon resonance biosensor, so as to produce the protein chip of para-insulin receptors which is applicable to the mutual action between IGF-1R and IRS-1, SHC, PI3K or GRB2 and hopeful to be applied to screening cancer-fighting drugs.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Treatment of diabetes mellitus and insulin receptor signal transduction
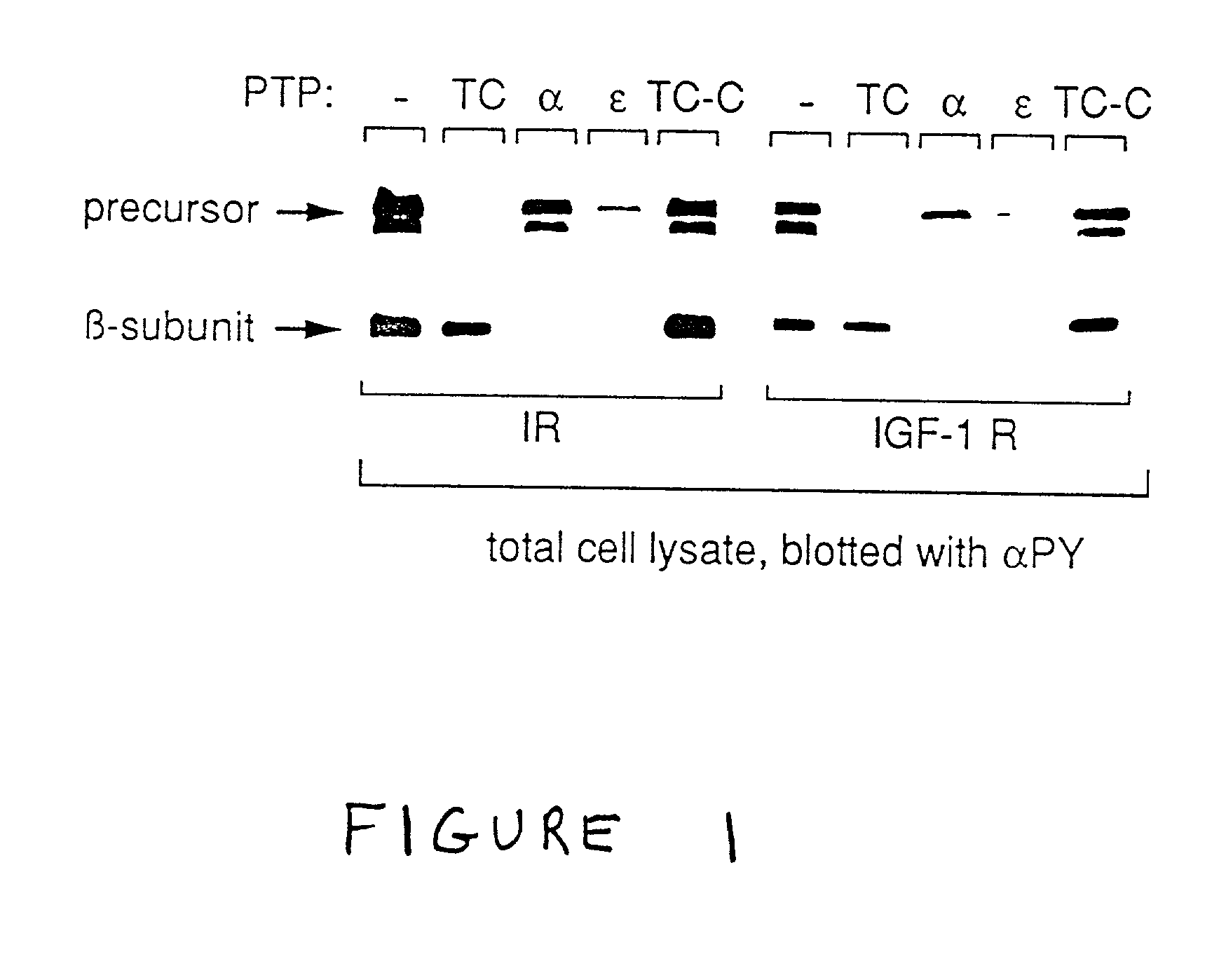
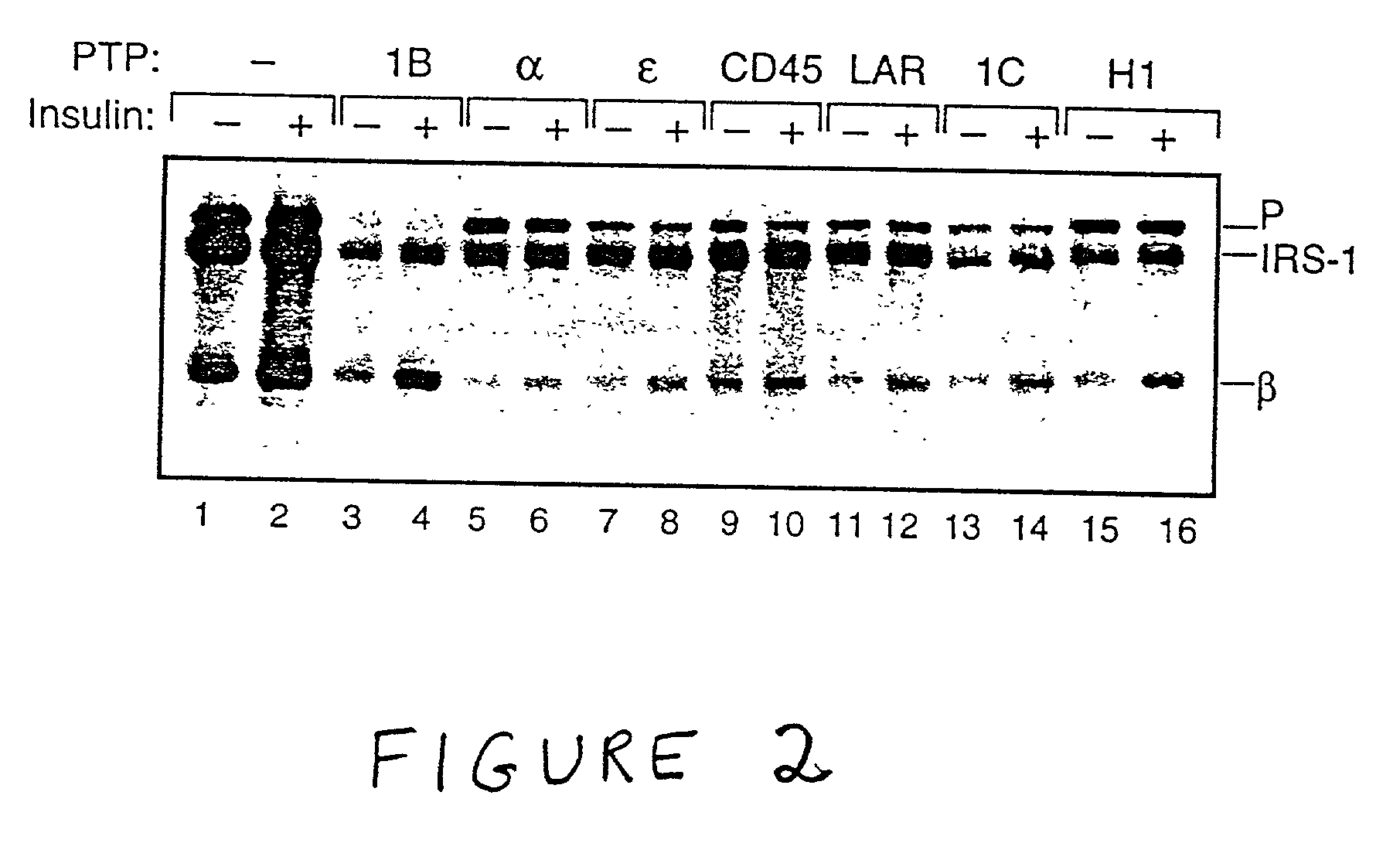
The present invention relates to novel modalities of treatment of diabetes, and other diseases caused by dysfunctional signal transduction by insulin receptor type tyrosine kinases (IR-PTK). Applicants discovered that IR-PTK activity may be modified by modulating the activity of a tyrosine phosphatase, and IR-PTK signal transduction may be triggered even in the absence of ligand. Methods for identifying compounds that, by modulating RPTPalpha or RPTPepsi activity, elicit or modulate insulin receptor signal transduction are also described.
Owner:ULLRICH AXEL +4
IGF antagonist peptides
Peptides are provided that antagonize the interaction of IGF-1 with its binding proteins, insulin receptor, and IGF receptor. These IGF antagonist peptides are useful in treating disorders involving IGF-1 as a causative agent, such as, for example, various cancers.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
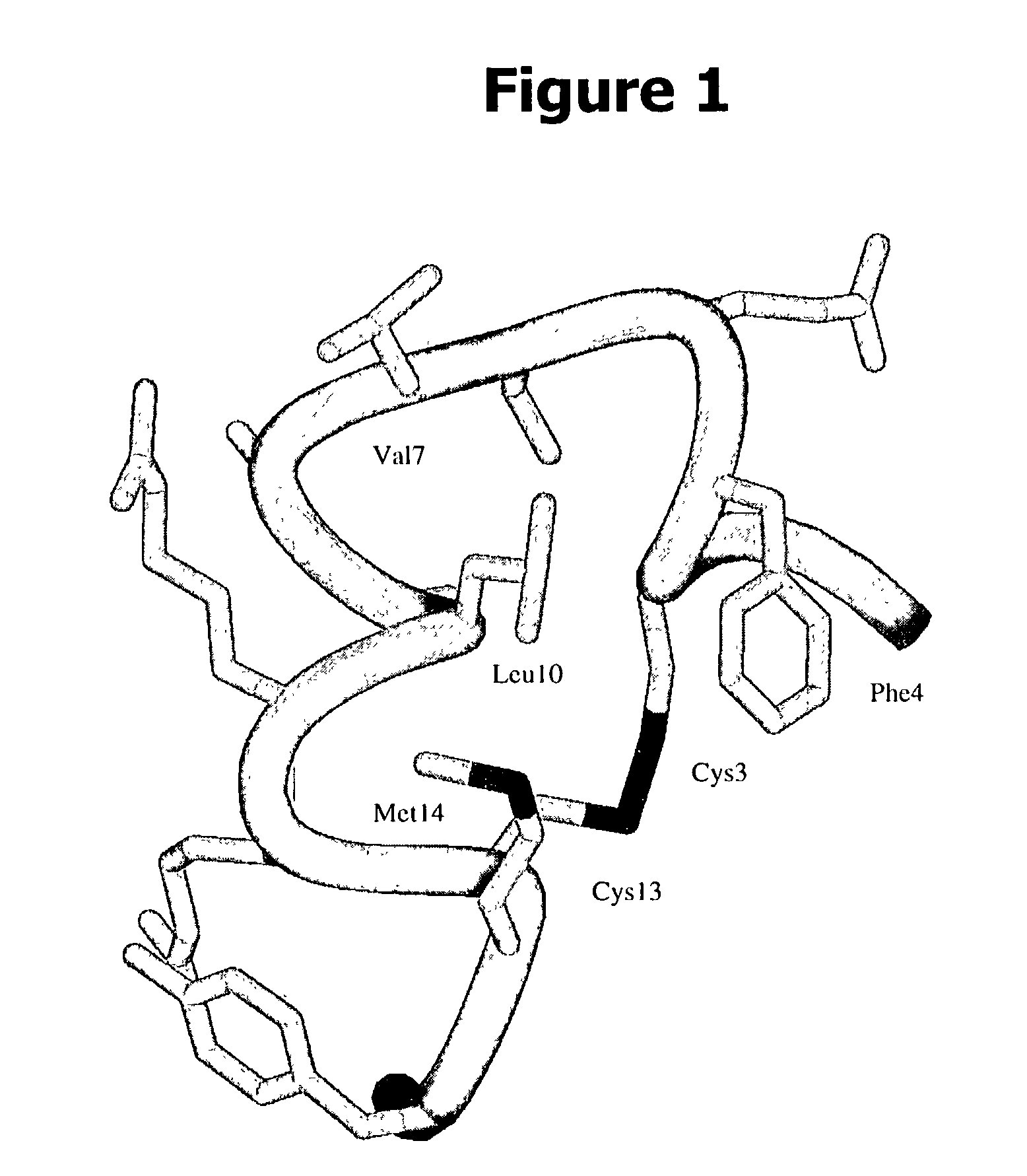
Blood-brain barrier epitopes and uses thereof
The invention features a method of identifying an agent and generating an antibody that can cross the blood bram barrier, through the use of novel antigen isoforms of transmembrane domain protein 30A (TMEM30A) This is useful in establishing mechanisms of transmigration across the blood-bram barrier. These antigens are enriched in bram endothelium compared to other endothelial cells and may have better selectivity and capacity for bram delivery compared to transferrin and insulin receptors One antigen is TMEM30A.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
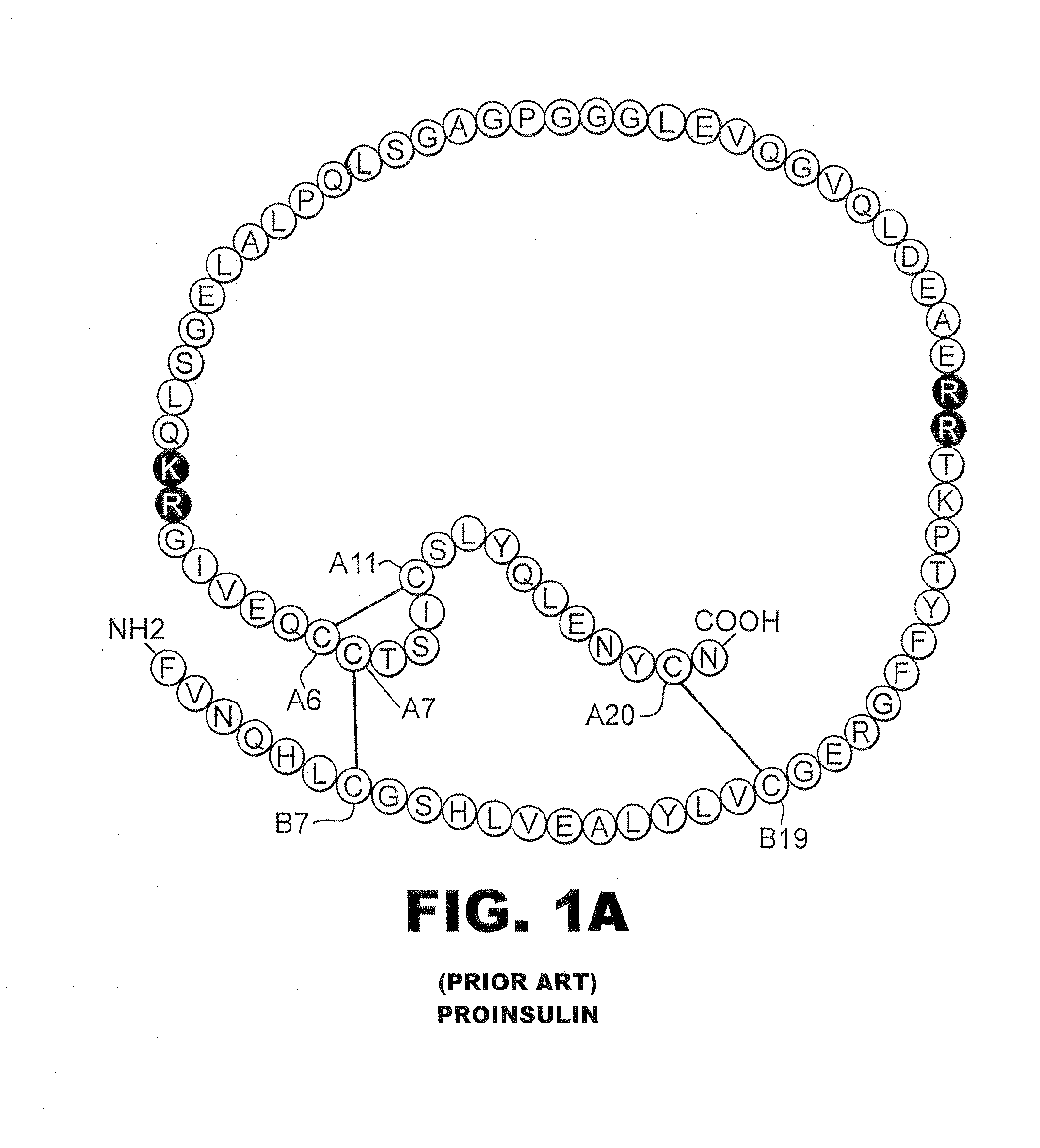
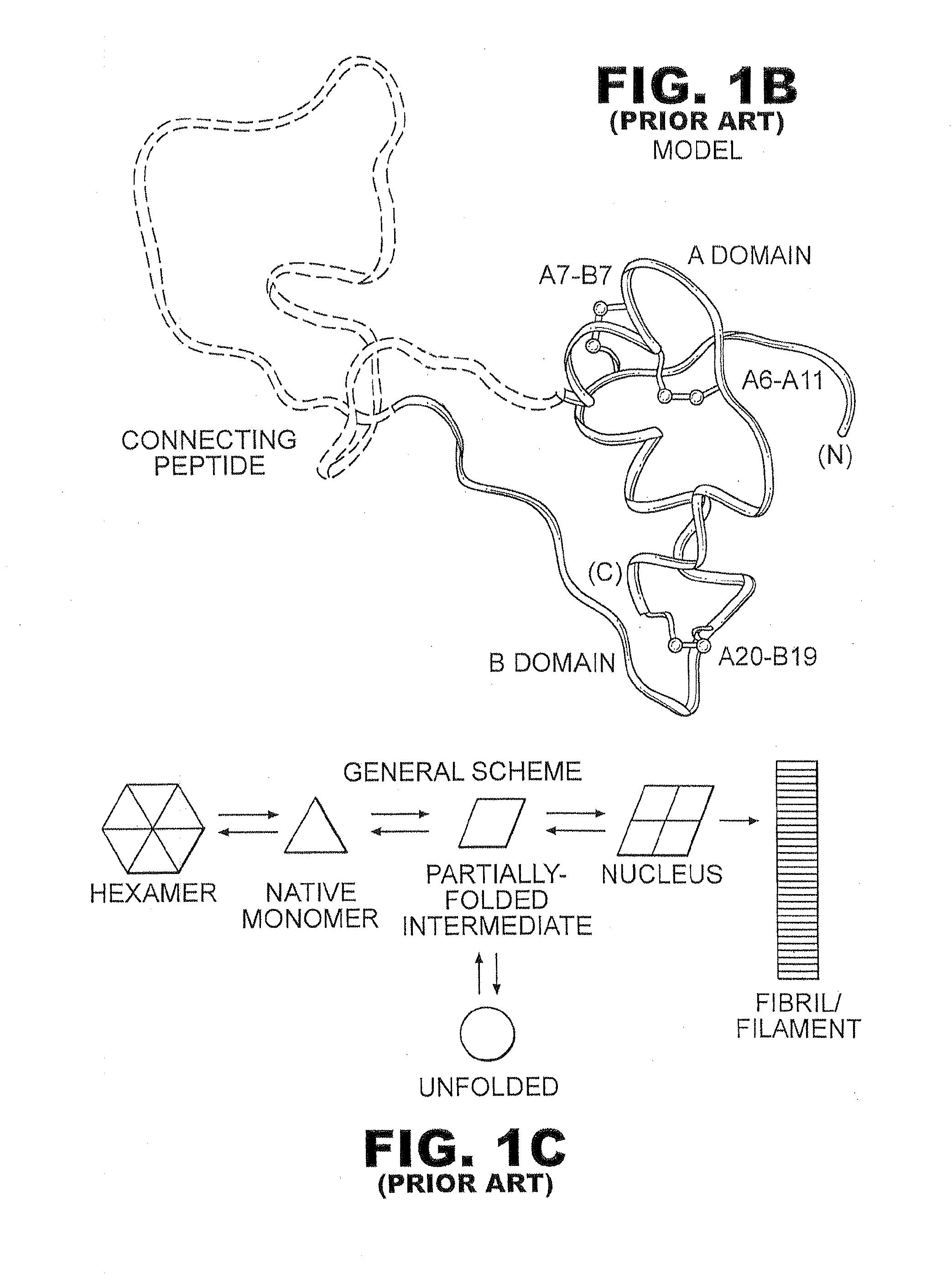
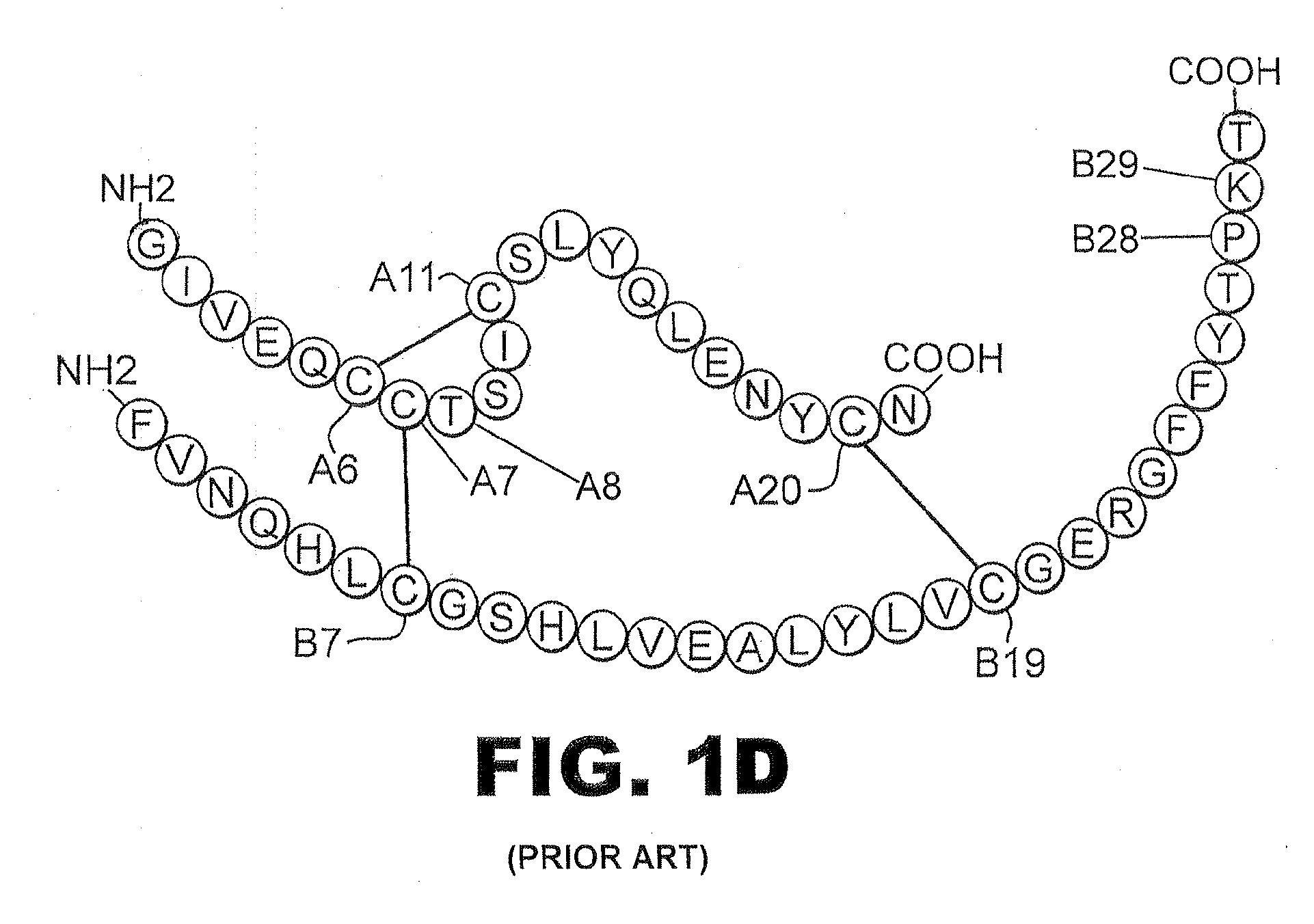
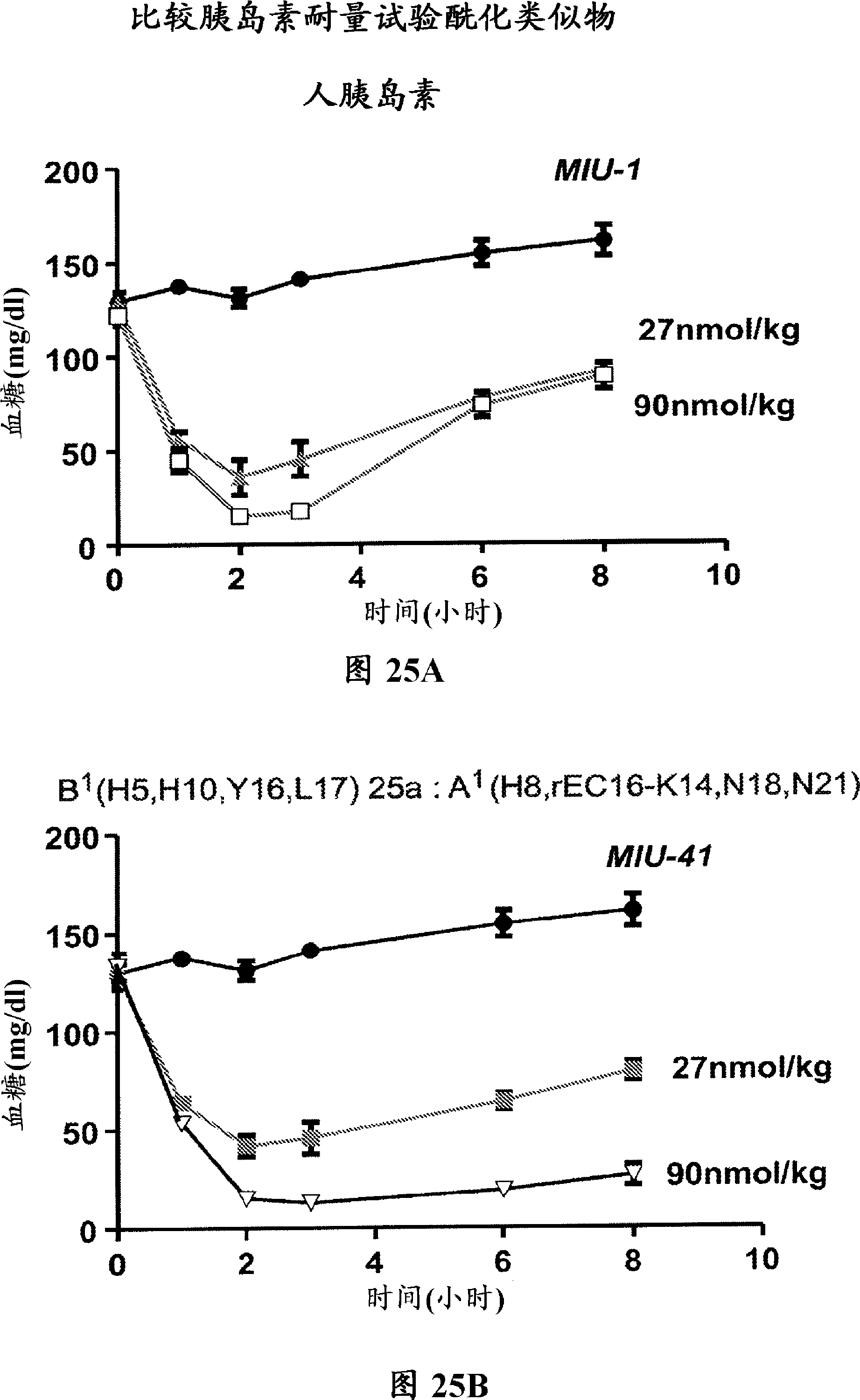
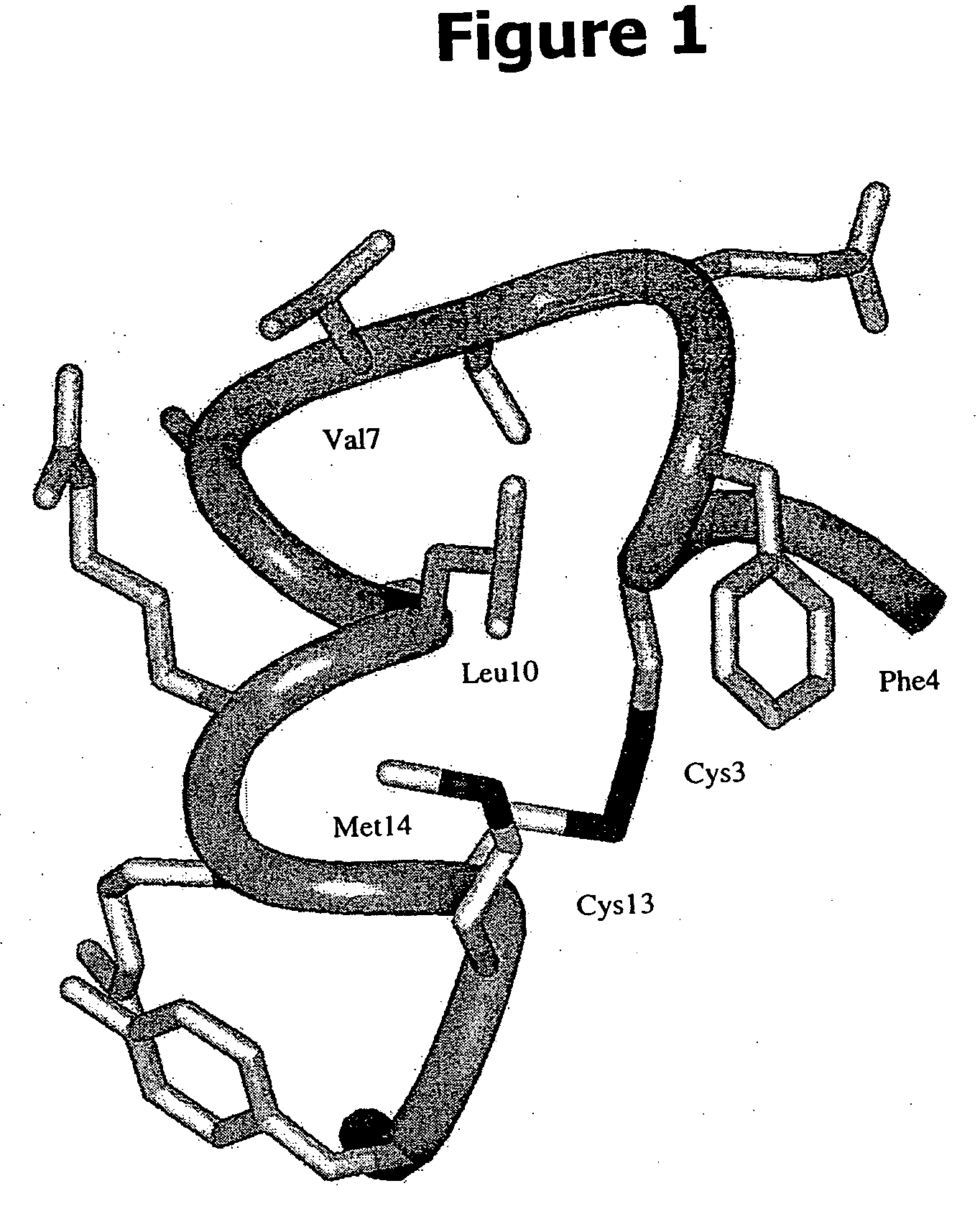
Insulin analogues of enhanced receptor-binding specificity
InactiveUS20120184488A1Good physical propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin A ChainArginine
A method of treating a patient includes administering a physiologically effective amount of an insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to the patient. The insulin analogue or physiologically acceptable salt thereof contains an insulin A-chain sequence modified at positions selected from the group consisting of A0, A1, A4, A8, and A21. The insulin analogue may exhibit decreased affinity for the IGF receptor in comparison to wild type insulin of the same species and at least 20% of the affinity of wild-type insulin for the insulin receptor of the same species. Position A0 may be arginine. Position A1 may be D-alanine, D-aspartic acid, or D-leucine. Position A8 may be histidine, lysine, or arginine. Optionally, an insulin B-chain analogue sequence comprises a histidine at position B1. A nucleic acid may encode such an insulin polypeptide.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Method of managing blood glucose levels, insulin levels and/or insulin receptor functionality in individuals with diabetes, polycystic ovarian syndrome and/or alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS20090054513A1Improve fertilitySimple processBiocideMetabolism disorderDiseaseAdditive ingredient
A combination of constituents for oral administration by women with polycystic ovarian syndrome includes α-lipoic acid, linolenic acid complex, biotin, and coenzyme Q-10. A preferred method of manufacture is by separate microencapsulation of one or more of the components followed by encapsulation of the individual components, for oral administration. Other methods of delivery include packaging in impermeable, disposable packets and mixing the formulations with food or a cold liquid. A combination of constituents for administration by either men or women to encourage increase in brain insulin levels and / or brain insulin receptor functionality also includes α-lipoic acid, linolenic acid complex, biotin, and coenzyme Q-10.
Owner:RESPONSE SCI
Methods and compositions for increasing arylsulfatase A activity in the CNS
ActiveUS8486399B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderArylsulfatase A activityInsulin receptor
Provided herein are methods and compositions for treating a subject suffering from a deficiency in arylsulfatase A in the CNS. The methods include systemic administration of a bifunctional fusion antibody comprising an antibody to a human insulin receptor and an arylsulfatase A.
Owner:JCR PHARMA +1
Anti-IGF antibodies
ActiveUS8318159B2Heavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsInsulin receptorInsulin humulin
Antibody molecules, in particular fully human antibodies that bind to human IGF-1 and cross-react with IGF-2 such that binding of IGF-1 and IGF-2 to the IGF-1 receptor is prevented and IGF-1 receptor-mediated signaling is inhibited. The antibodies do not bind to insulin and thus do not affect the mitogenic properties of insulin that are mediated by its binding to the insulin receptors. The antibodies are useful for the treatment of hyperproliferative diseases, in particular cancer.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
IGF antagonist peptides
Peptides are provided that antagonize the interaction of IGF-1 with its binding proteins, insulin receptor, and IGF receptor. These IGF antagonist peptides are useful in treating disorders involving IGF-1 as a causative agent, such as, for example, various cancers.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
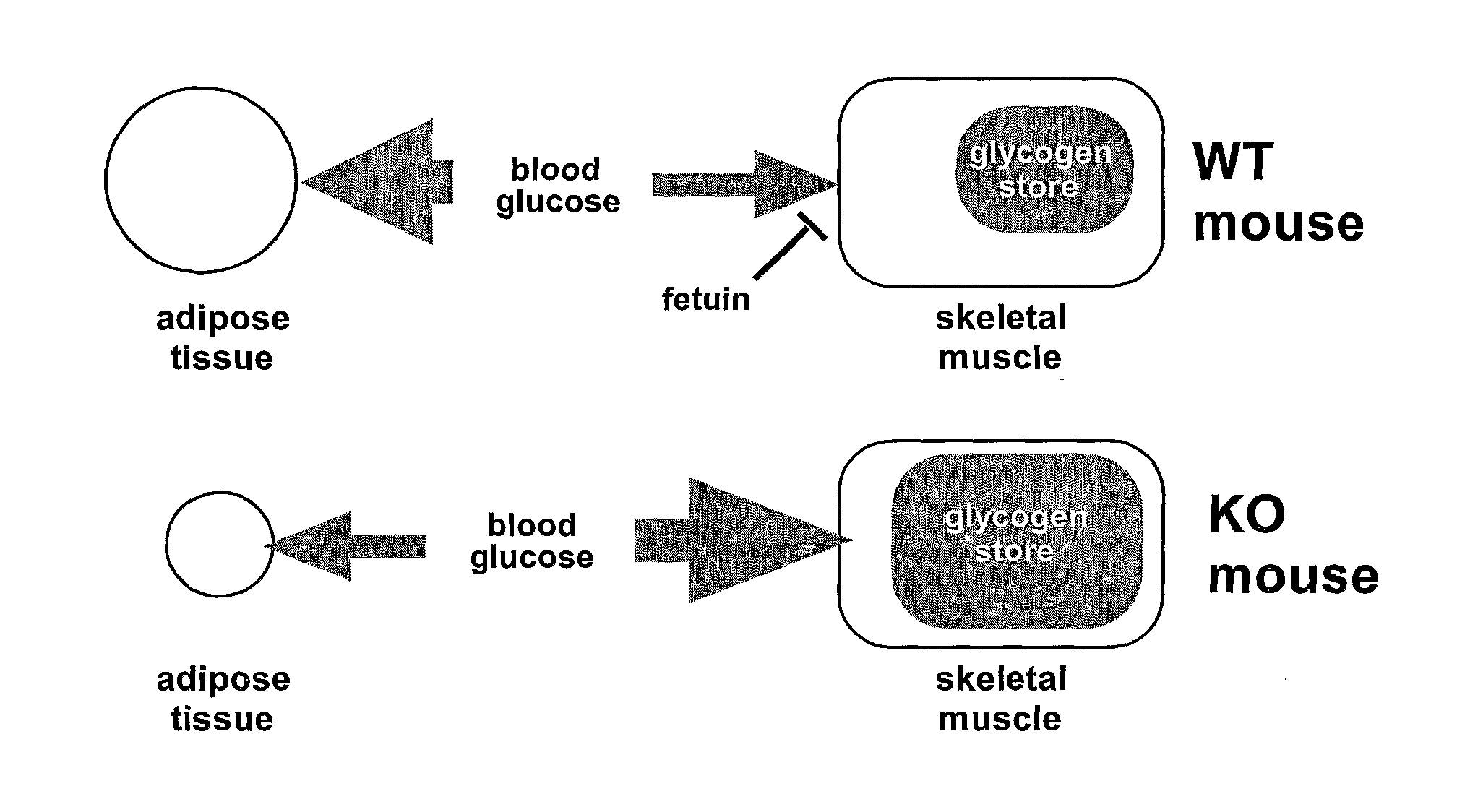
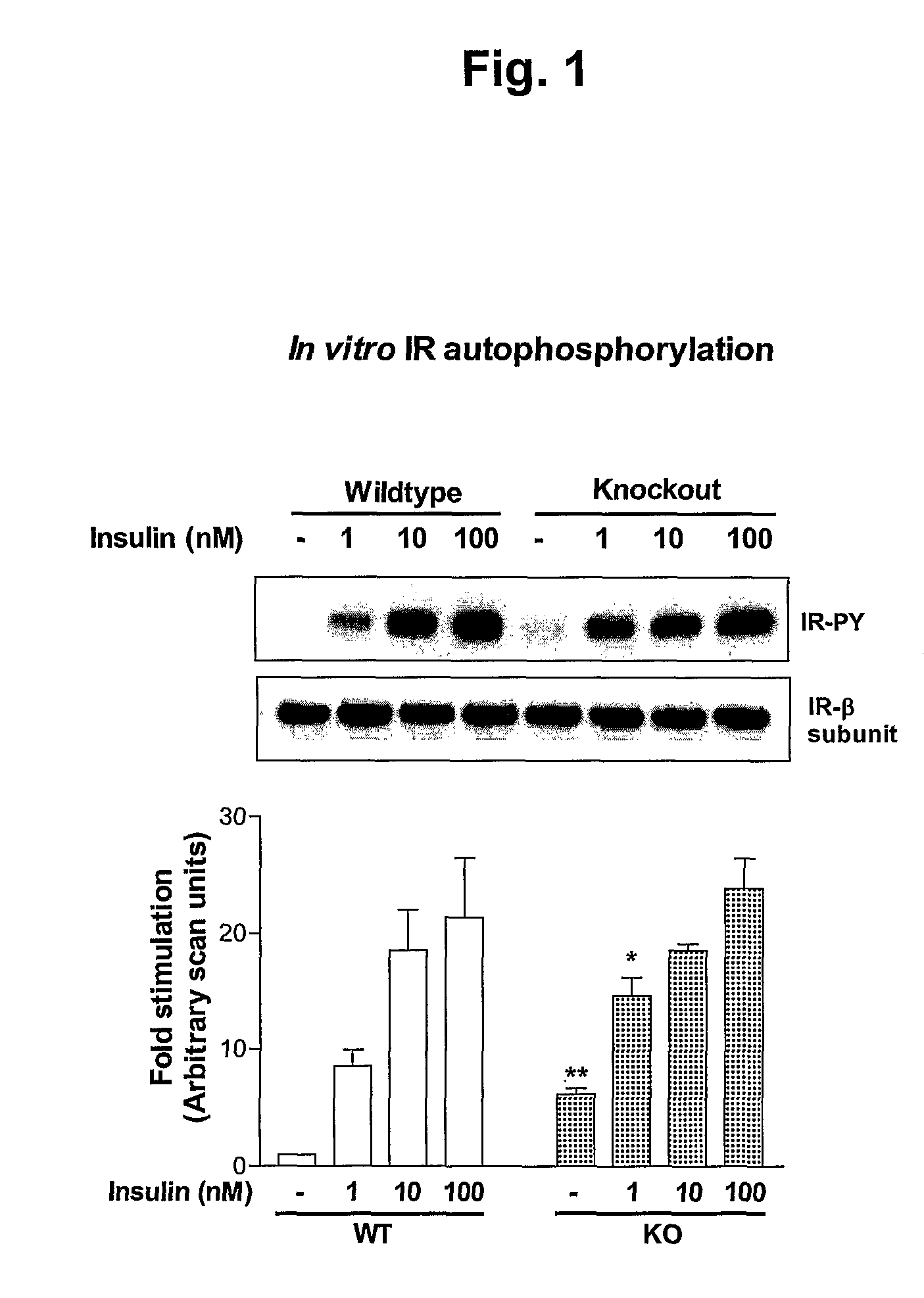
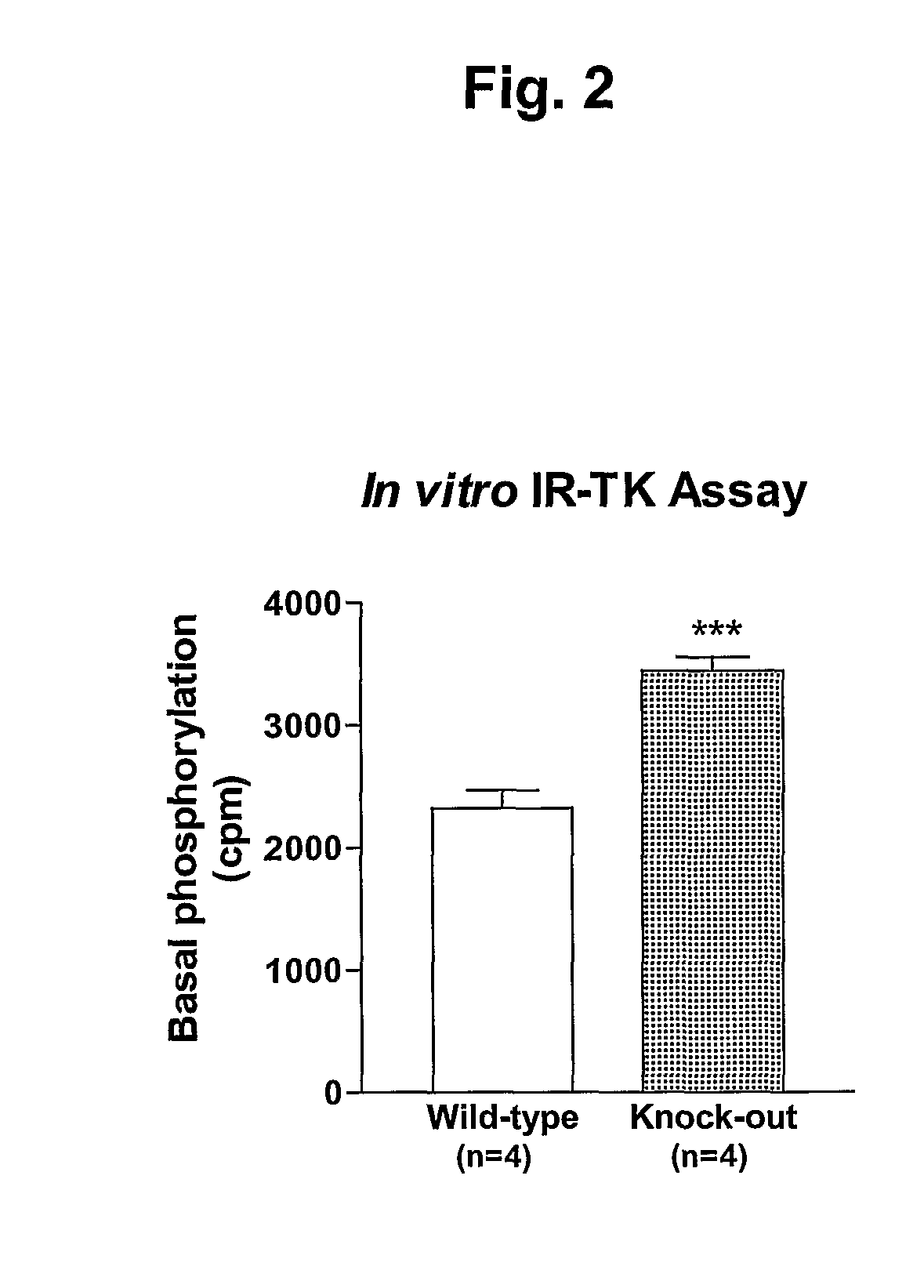
Inhibition of alpha-2 hs glycoprotein (AHSG/fetuin) in obesity and insulin control of glucose homeostasis
InactiveUS20080050372A1Reduce the amount requiredIncreased basalPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAlpha-2-HS-glycoproteinAnti-CEA Antibody
α2-Heremans Schmid Glycoprotein (AHSG) inhibits insulin-induced autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor (IR) and IR-tyroskine kinase (TK) activity; genetic ablation of the Ahsg gene enhances insulin signal transduction and increase whole-body insulin sensitivity. Therefor, AHSG and its gene(s) are useful targets for agents that inhibit the development or progression of Type II diabetes or any disease or disorder associated with increased insulin resistance. Provided herein is a method for inhibiting the biological activity of AHSG protein in a cell using compounds that inhibit phosphorylation of AHSG. Also disclosed is a method of augmenting the phosphorylation or IR-TK activity in a liver or muscle cell by providing a compound that lowers the amount of active AHSG or inhibits the biological activity of AHSG. Such effects may be achieved by delivering an antisense nucleic acid construct that hybridizes with AHSG encoding DNA. This invention includes a method (a) treating a subject that is susceptible to, or suffers from, obesity and insulin resistance or (b) increasing insulin sensitivity, and thereby preventing or treating insulin resistance in the subject. The method comprises lowering the amount of active AHSG or inhibiting the biological activity of AHSG in the subject, preferably in liver or muscle, by using AHSG antisense constructs or an anti-AHSG antibody. In a subject eating a high fat diet, the effect on body weight gain and / or insulin resistance is diminished, and total body fat content is lowered, by lowering the amount of active AHSG or inhibiting the action of the AHSG in the subject using the agents noted above.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
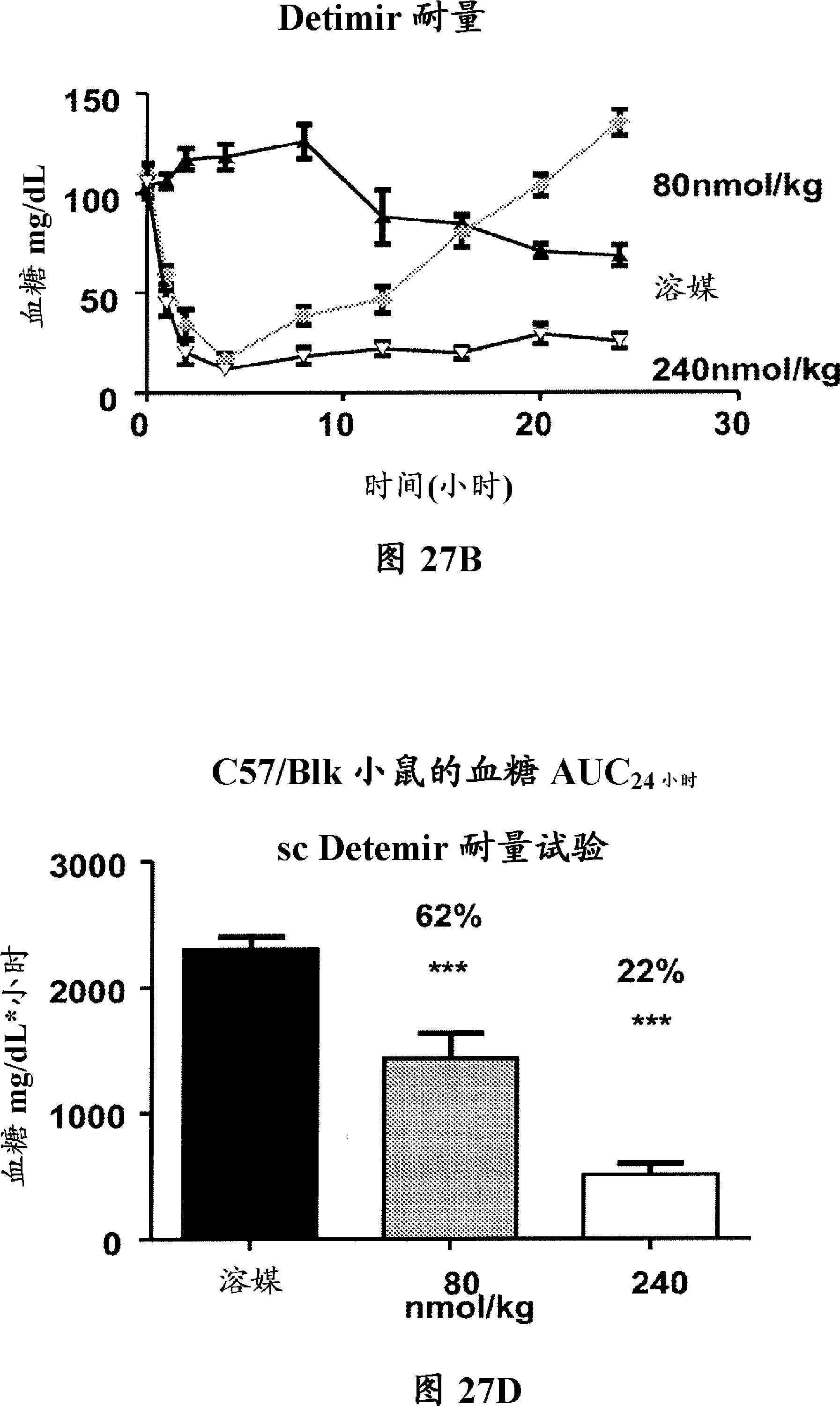
Long-acting insulin analogue preparations in soluble and crystalline forms
InactiveUS20130085101A1Enhances receptor-binding selectivityDecrease absolute affinity for IGF-1ROrganic active ingredientsBacteriaInsulin A ChainPharmaceutical formulation
A pharmaceutical formulation comprises an insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, wherein the insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof contains an insulin A-chain sequence that contains paired Histidine substitutions at A4 and A8, and optionally a substitution at A21. The formulation further contains a pharmaceutically acceptable buffer containing at least about 4 zinc ions per 6 insulin analogue molecules. The formulation forms a long-acting zinc-dependent subcutaneous depot upon subcutaneous injection. In a zinc-free formulation, the insulin analogue monomer exhibits decreased affinity for the Insulin-like Growth Factor receptor and at least 20% of the affinity for the insulin receptor of the same species, in comparison to an otherwise identical insulin or insulin analogue that does not contain the HisA4 and HisA8 substitutions.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
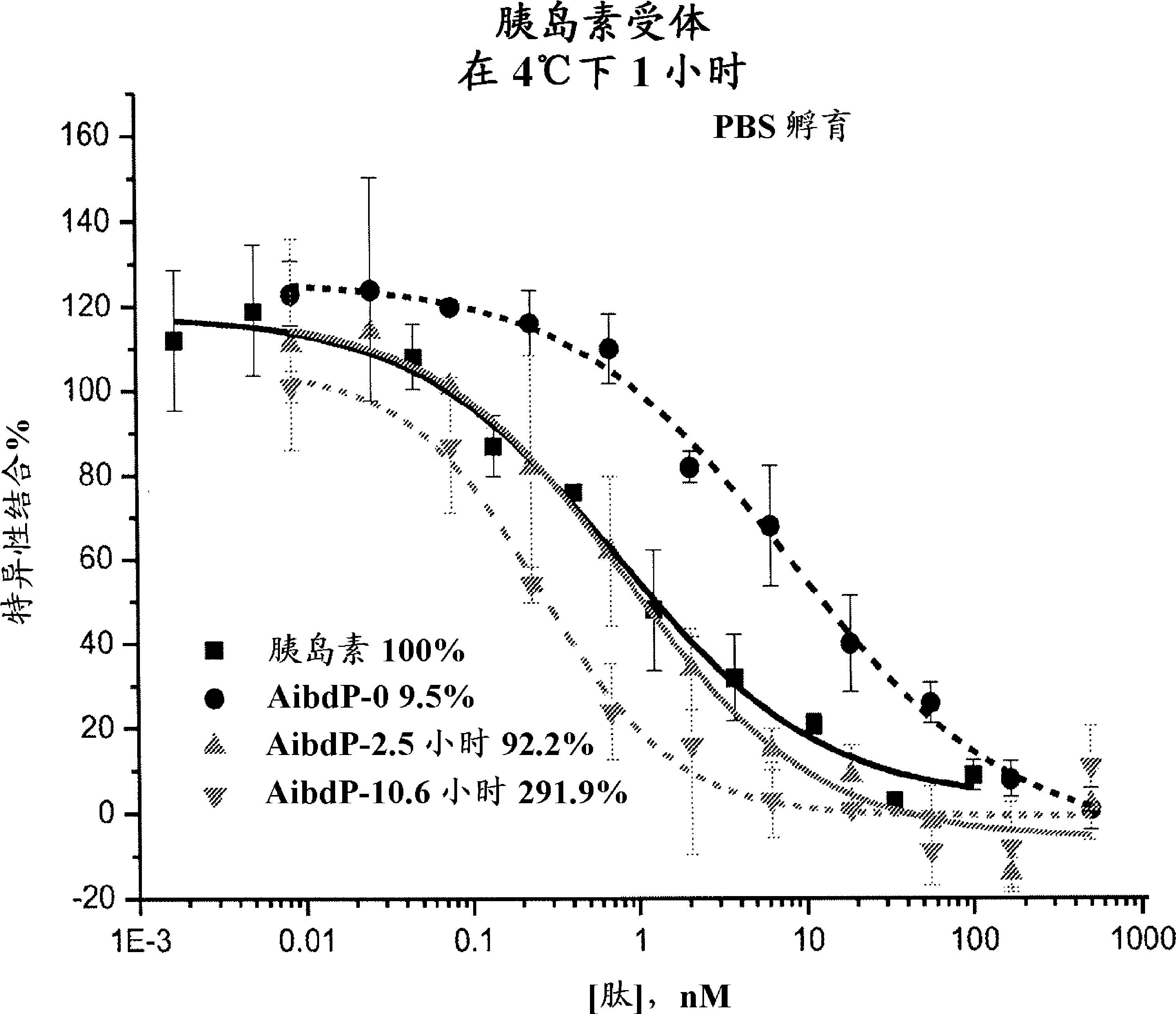
Methods for measuring the insulin receptor alpha subunit
ActiveUS20070059784A1Easy to collectEasy to synthesizeImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDisease diagnosisFree insulinInsulin Receptor alpha Subunit
Presence of free insulin receptor α-subunit in blood was discovered. Furthermore, methods for measuring the insulin receptor α-subunit was provided, the method comprising the steps of contacting the insulin receptor α-subunit in a blood sample with an antibody recognizing the insulin receptor α-subunit, and detecting the binding between the two. Measurement of the free insulin receptor α-subunit in the blood is useful for evaluating risk factors for diabetes. In addition, the measurement methods of the present invention showed that concentrations of the free insulin receptor α-subunit in the blood of diabetes or cancer patients are significantly high. Free insulin receptor α-subunit in blood is useful as a marker for diabetes or cancer.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD
CTP-based insulin analogs for treatment of diabetes
Insulin analogs comprising a non-native glycosylation site sequence are provided having high potency and specificity for the insulin receptor. In one embodiment a peptide sequence of greater than 18 amino acids is used as a linking moiety to link human insulin A and B chains, or analogs or derivatives thereof, to provide high potency single chain insulin analogs. In one embodiment the linking moiety comprises one or more glycosylation sites. Also disclosed are prodrug and conjugate derivatives of the insulin analogs.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Composition to enhance joint function and repair
InactiveUS20050113287A1Improve joint functionPromote repairBiocideDipeptide ingredientsMethylsulfonylmethaneSulfur containing
The present invention relates to a composition to enhance joint function, reduce inflammation and homocysteine levels, and repair cartilage. The present invention relates to a nutritional supplement comprising a glucosamine-containing constituent, a chondroitin-containing constituent, methylsulfonylmethane, and at least one sulfur-containing amino acid. A preferred sulfur-containing amino acid is taurine. The nutritional supplement can also include folic acid, vitamins B6, B12, C. The nutritional supplement can also include chromium and lipoic acid to improve insulin receptor sensitivity.
Owner:MOTION POTION
IGF antagonist peptides
Peptides are provided that antagonize the interaction of IGF-1 with its binding proteins, insulin receptor, and IGF receptor. These IGF antagonist peptides are useful in treating disorders involving IGF-1 as a causative agent, such as, for example, various cancers.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method of Judging Risk for Onset of Drug-Induced Granulocytopenia
InactiveUS20070264631A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGranulocytopeniasInsulin receptor
Means for determining the presence of the risk of drug-induced granulocytopenia in a human is provided. A method for assessing the risk of drug-induced granulocytopenia, including detecting a polymorphism of the human insulin receptor substrate-2 gene of a subject, and determining the presence of the risk of drug-induced granulocytopenia of the subject by use of the genetic polymorphism as an index.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
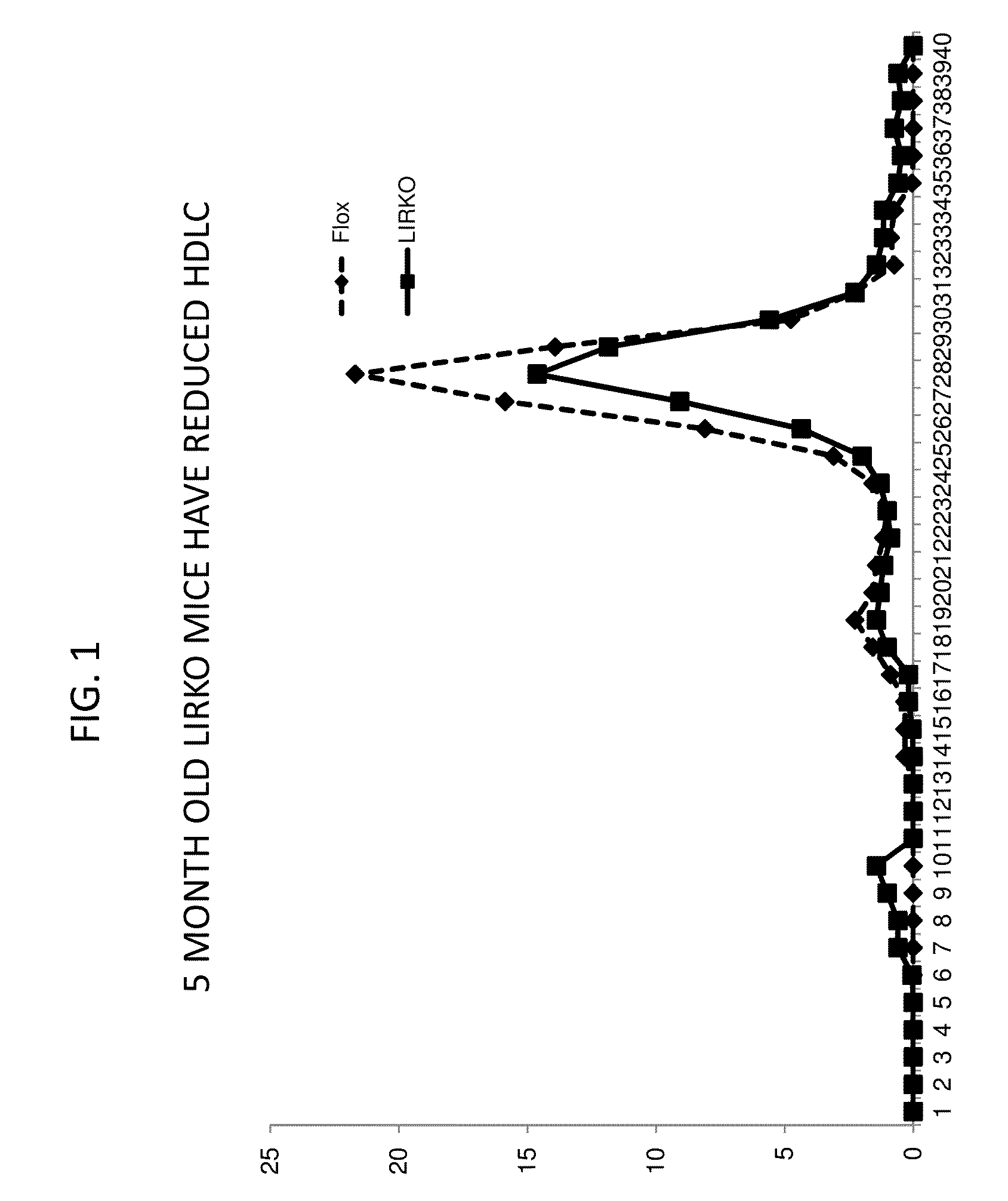
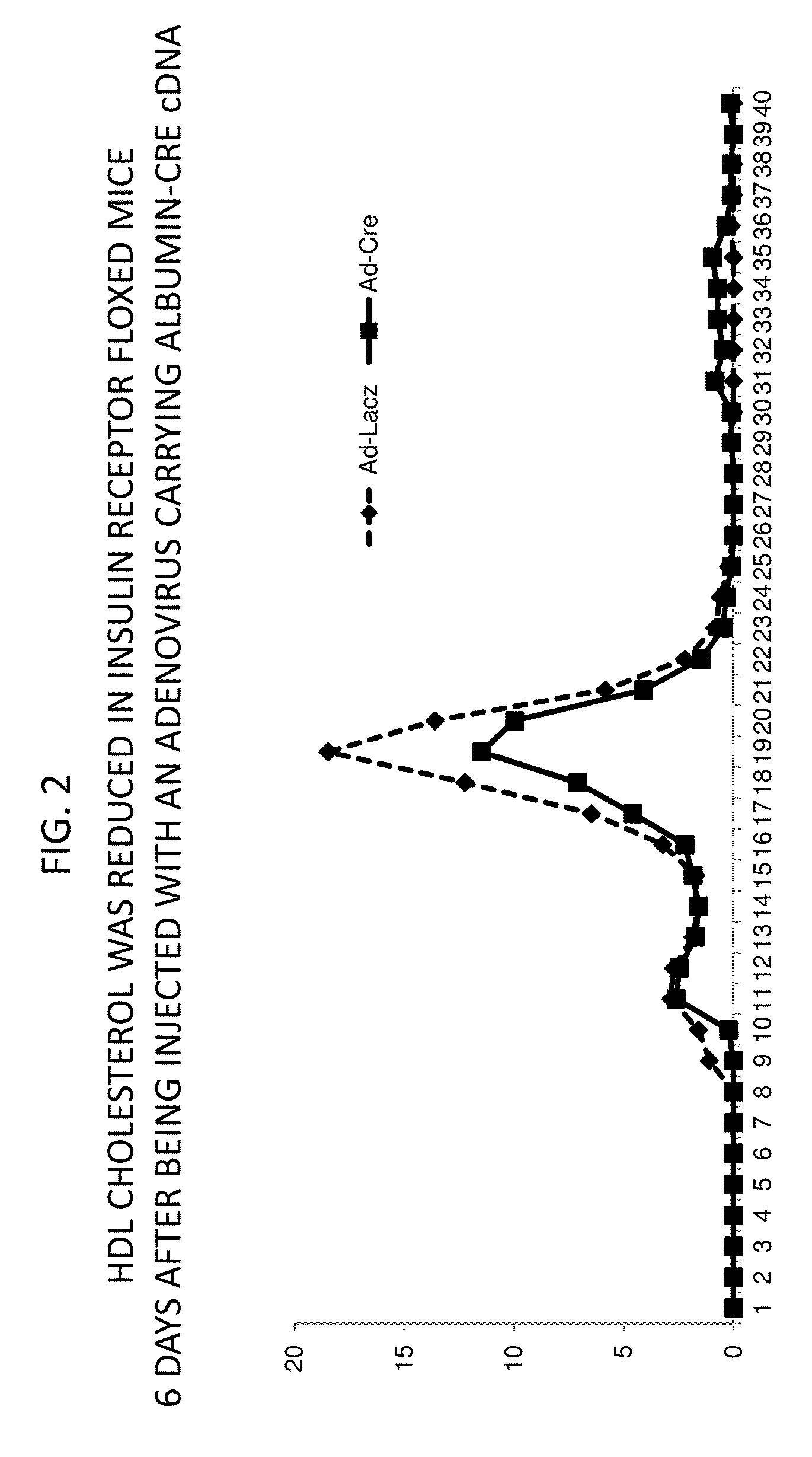
Methods For High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Regulation
InactiveUS20130017250A1Reduced insulin receptor expressionReduce biological activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsBlood plasma
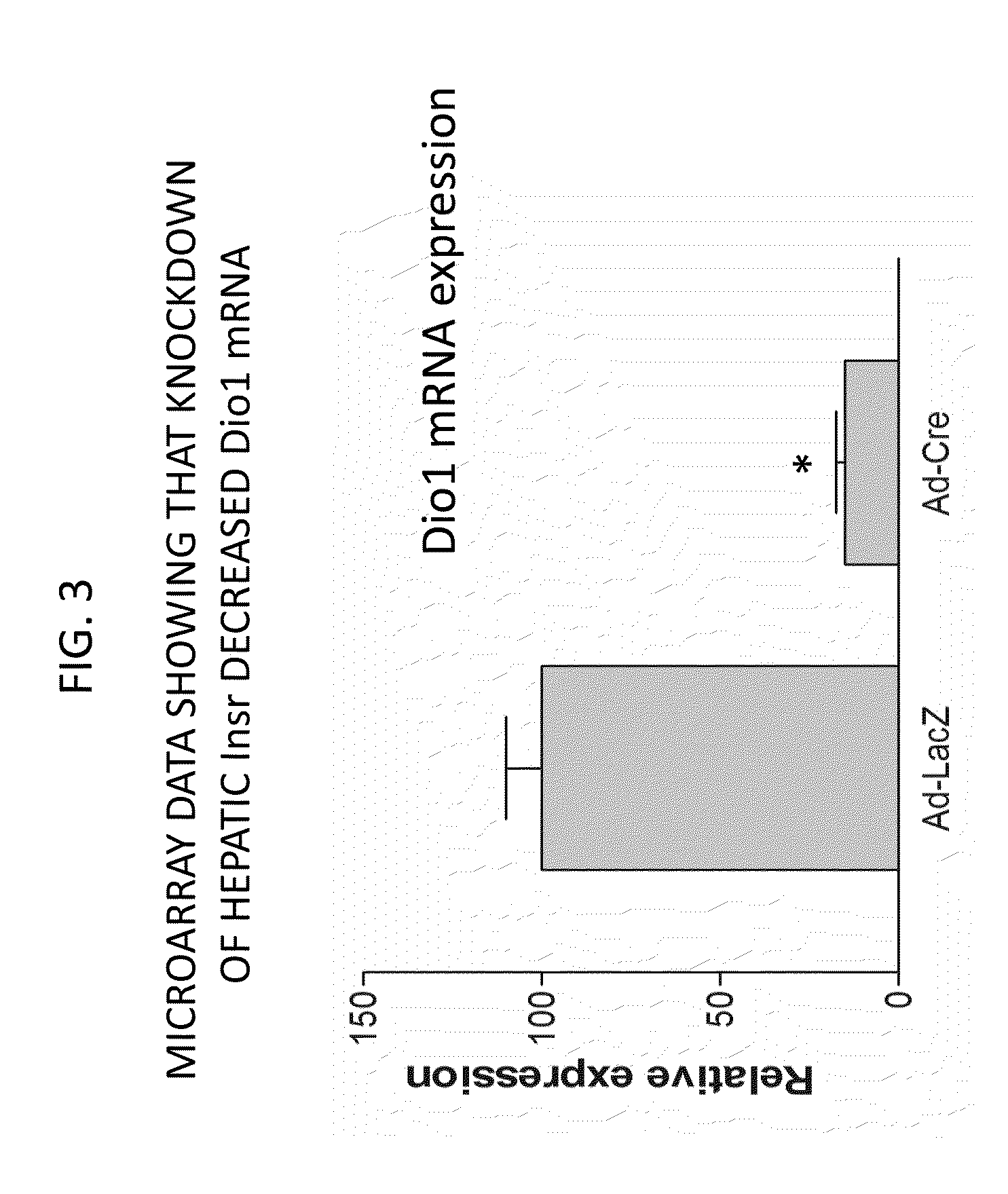
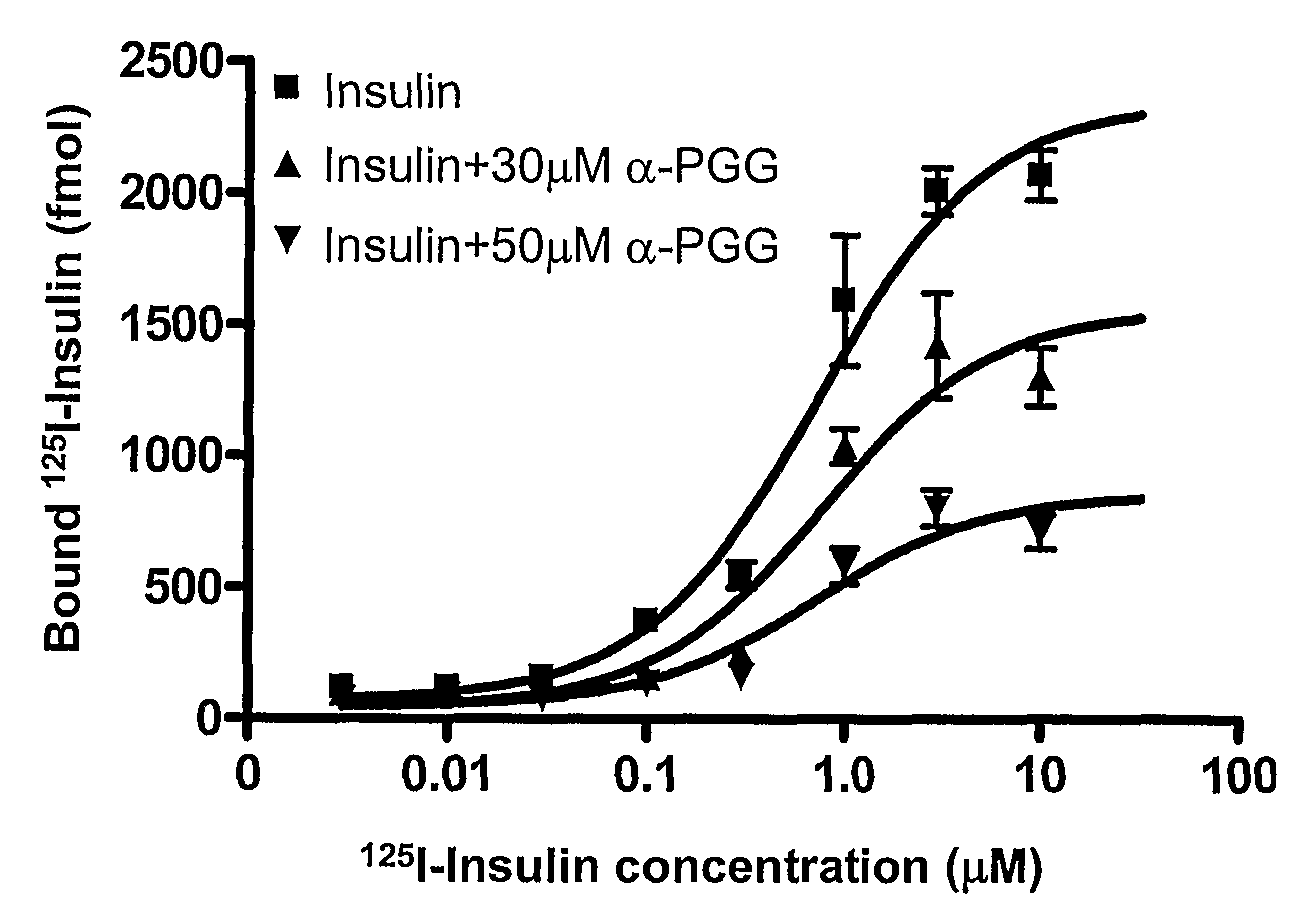
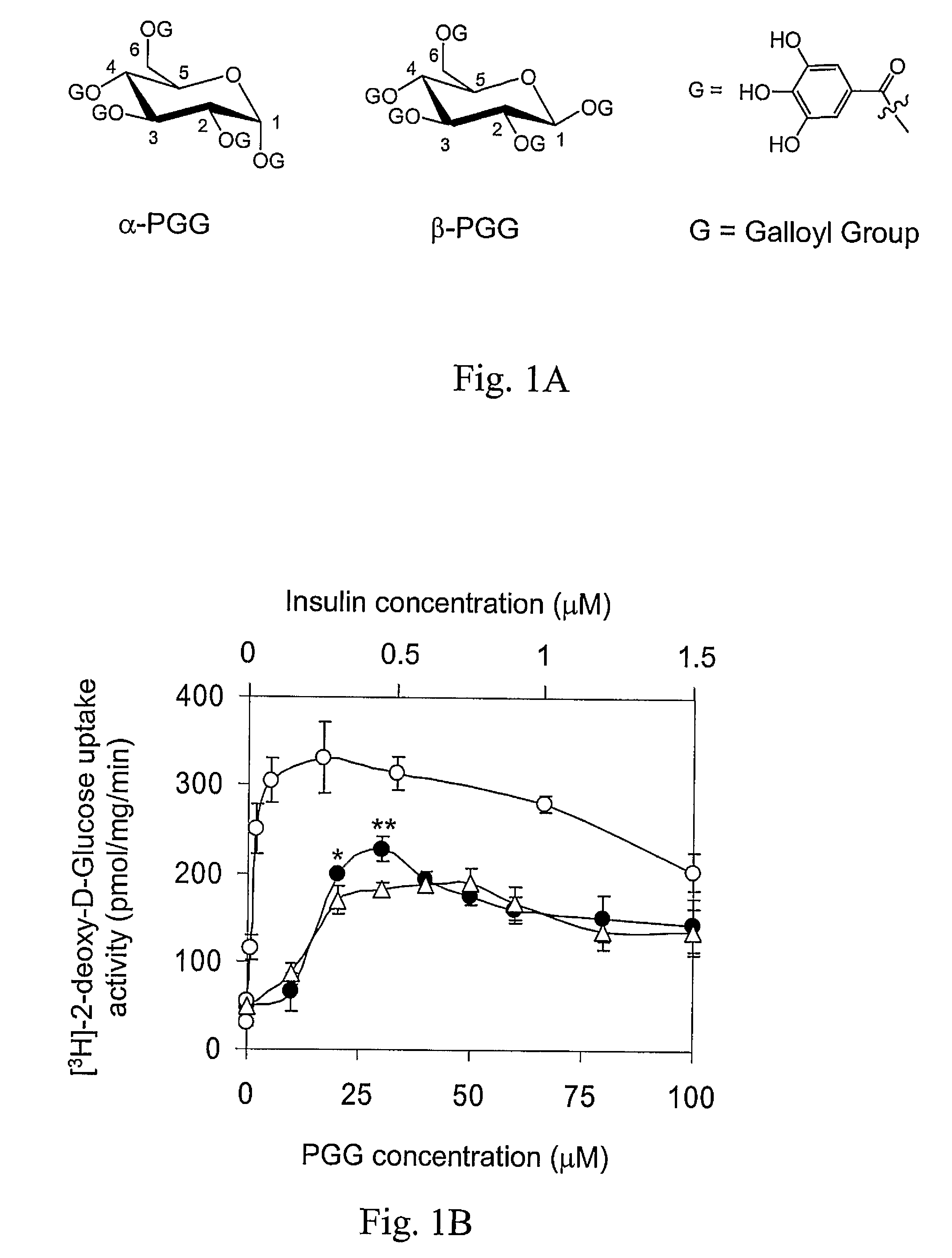
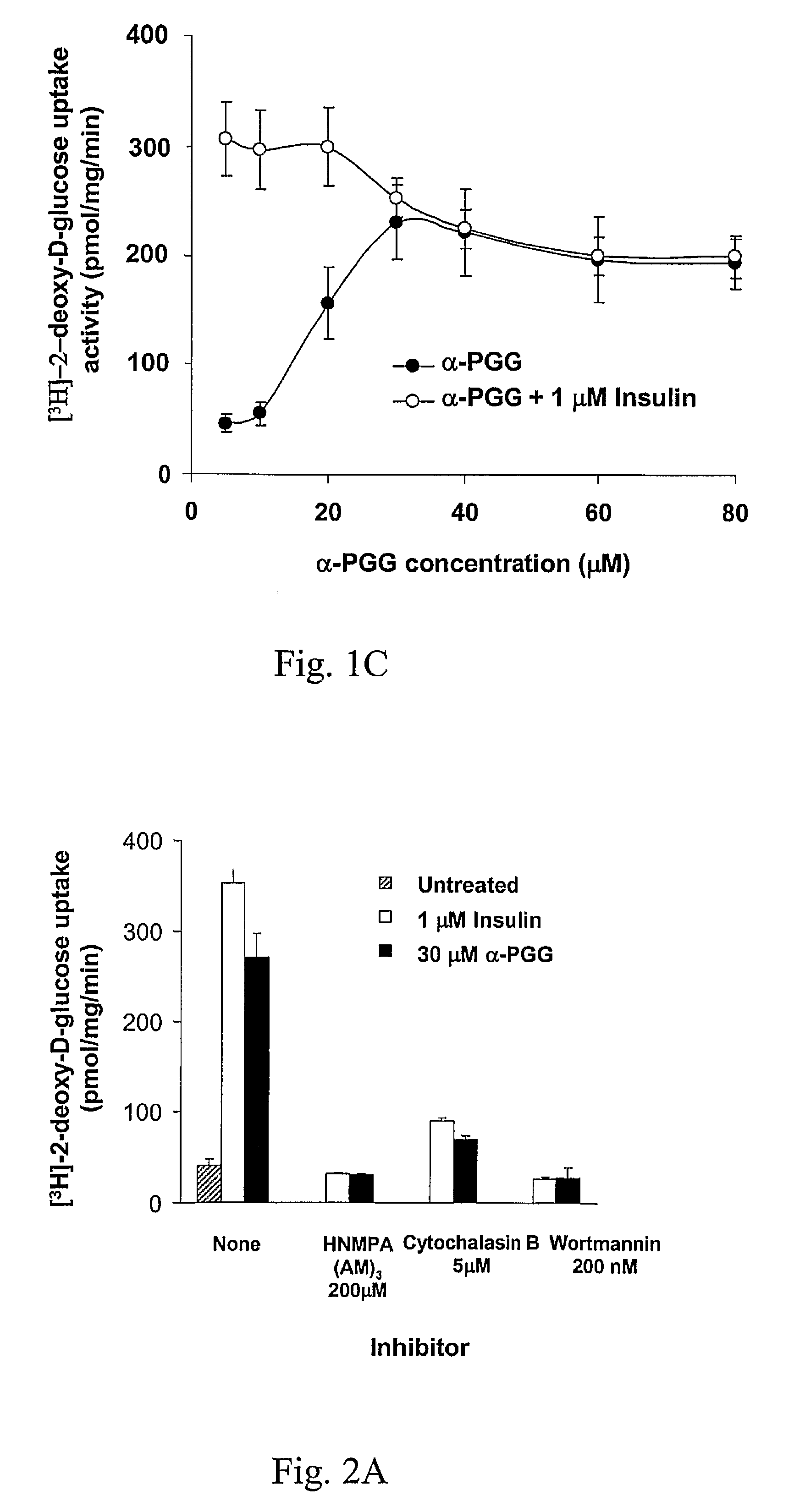
It was discovered that insulin binding to insulin receptors signals the upregulation of expression of the liver enzyme deiodinase 1 (Dio1), which in turn activates the ApoA-1 promoter, thereby thereby increasing ApoA-1 expression (primarily in the liver), that in turn raises the levels of plasma ApoA-1, the major and necessary protein in HDLC. Certain embodiments of the invention are directed to methods for increasing circulating HDLC levels in an animal by administering therapeutically effective amounts of Dio1, or by increasing the level of Dio1 through gene therapy.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods for identifying insulin mimetics
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Compositions and methods for increasing serum antioxidant concentrations, decreasing serum triglyceride levels, inhibiting insulin-receptor signaling activity, increasing serum ghrelin levels, and decreasing serum tnf-alpha levels
InactiveUS20100022442A1Improve concentrationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticAntioxidantSerum triglyceride levels
Compositions and methods are provided for increasing serum antioxidant levels, decreasing serum levels of oxidative chemical species, inhibiting insulin-receptor signaling activity, decreasing triglycerides levels, increasing serum ghrelin levels, and decreasing serum TNF-alpha levels. Compositions provided comprise a mixture of zinc-charged, fragmented proteins derived, for example, from serum or milk. Compositions are administered in a therapeutically effective amount to, for example, reduce oxidative stress levels in a mammalian subject.
Owner:AMBRYX BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com