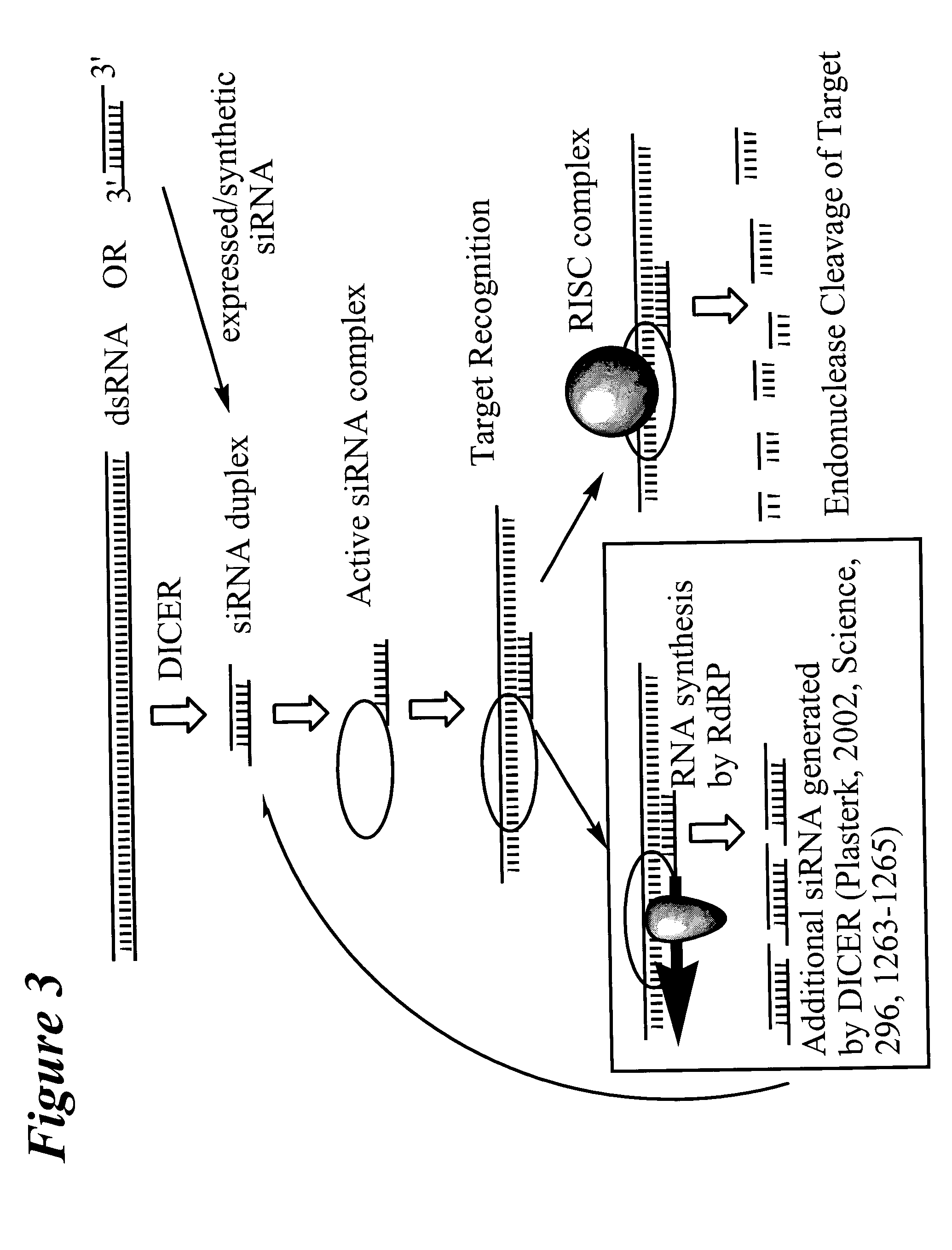
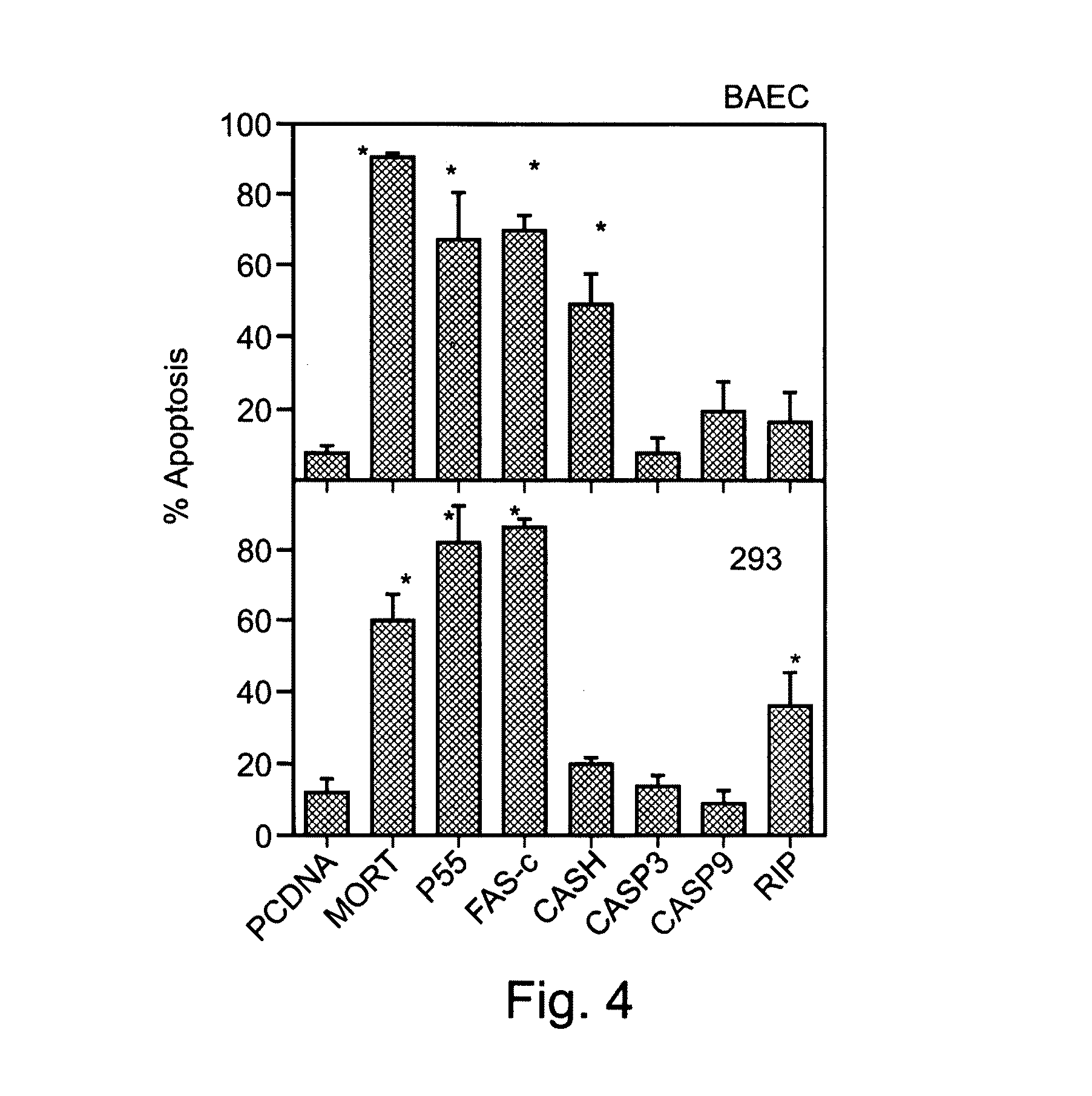
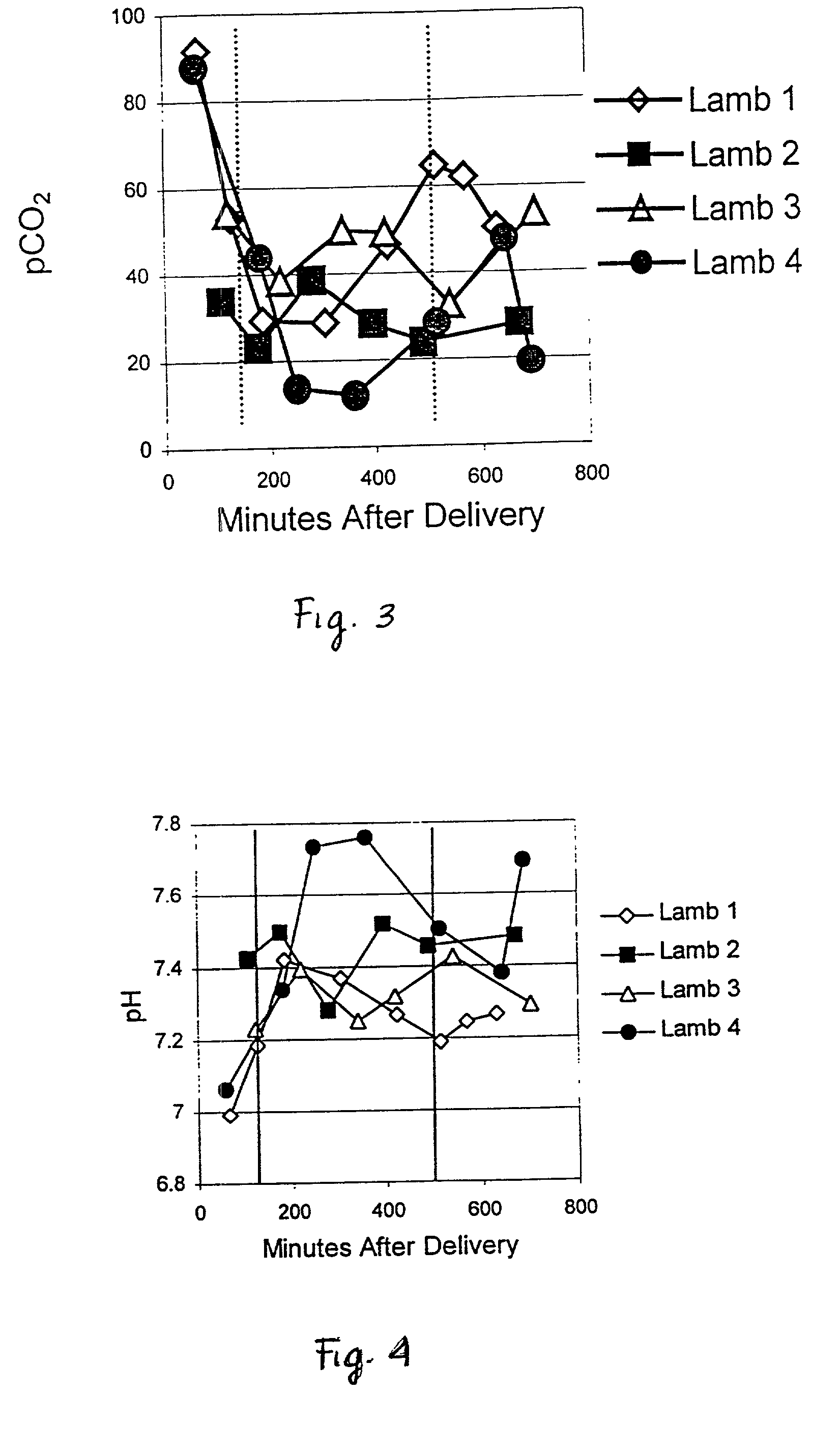
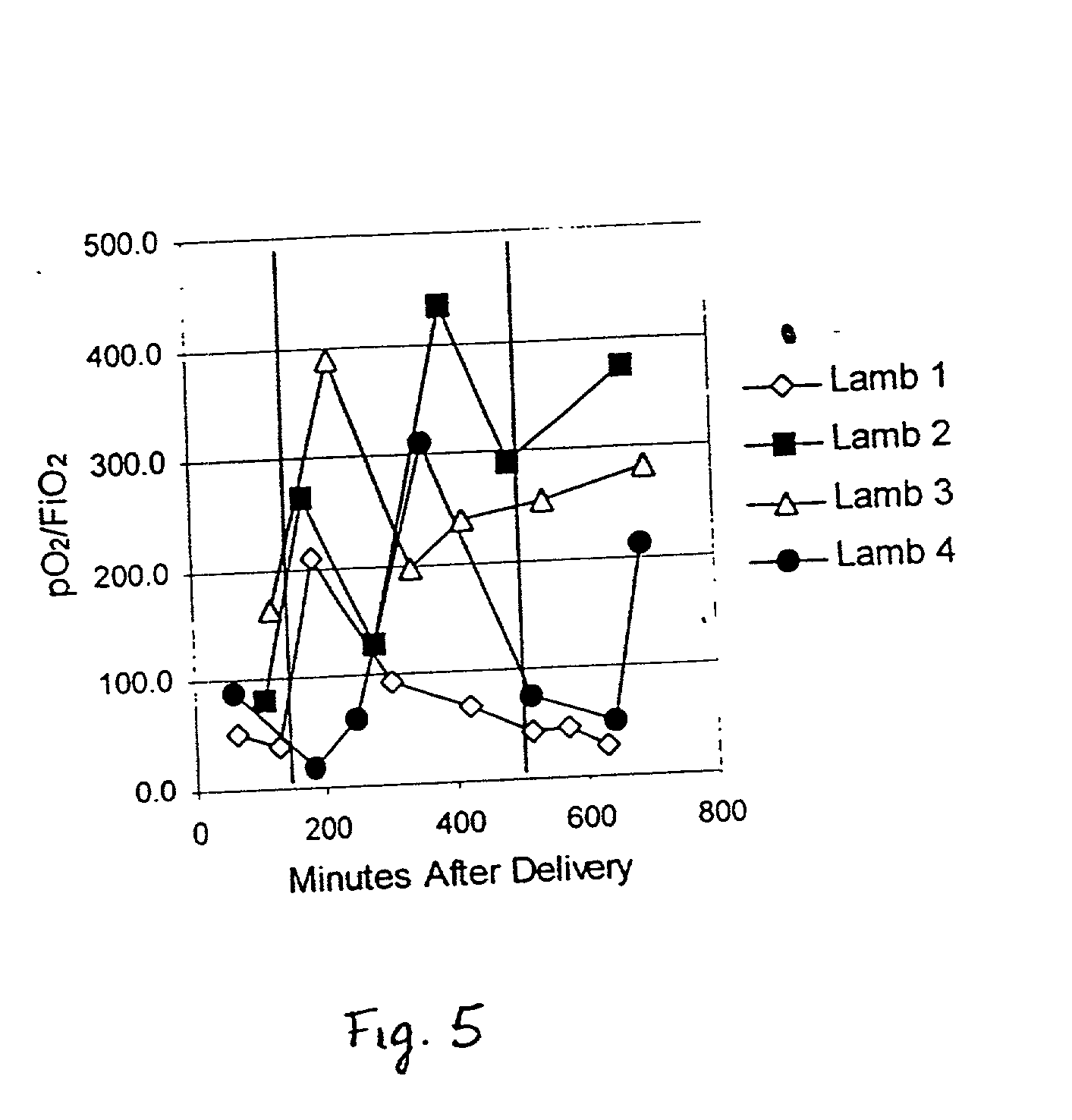
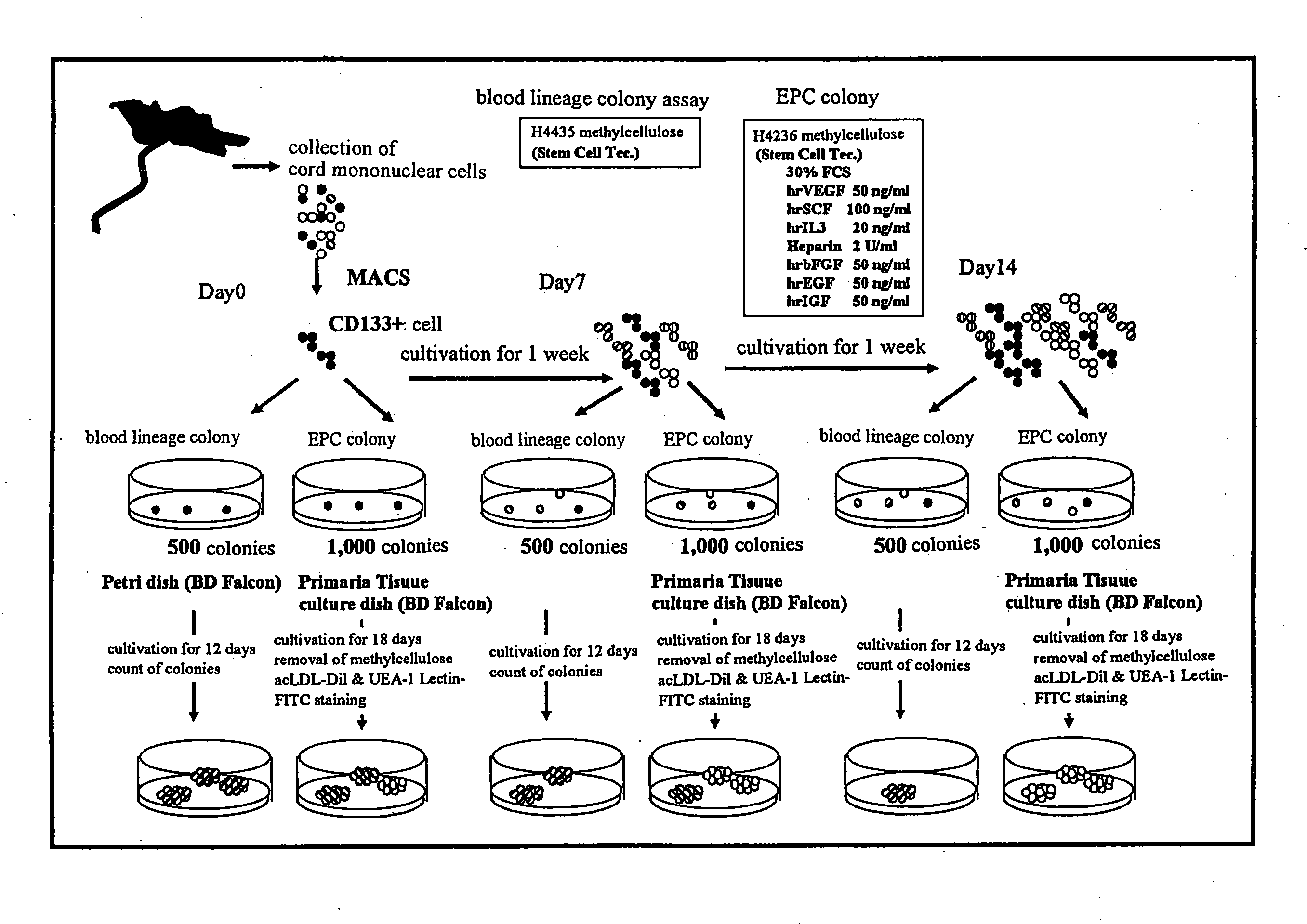
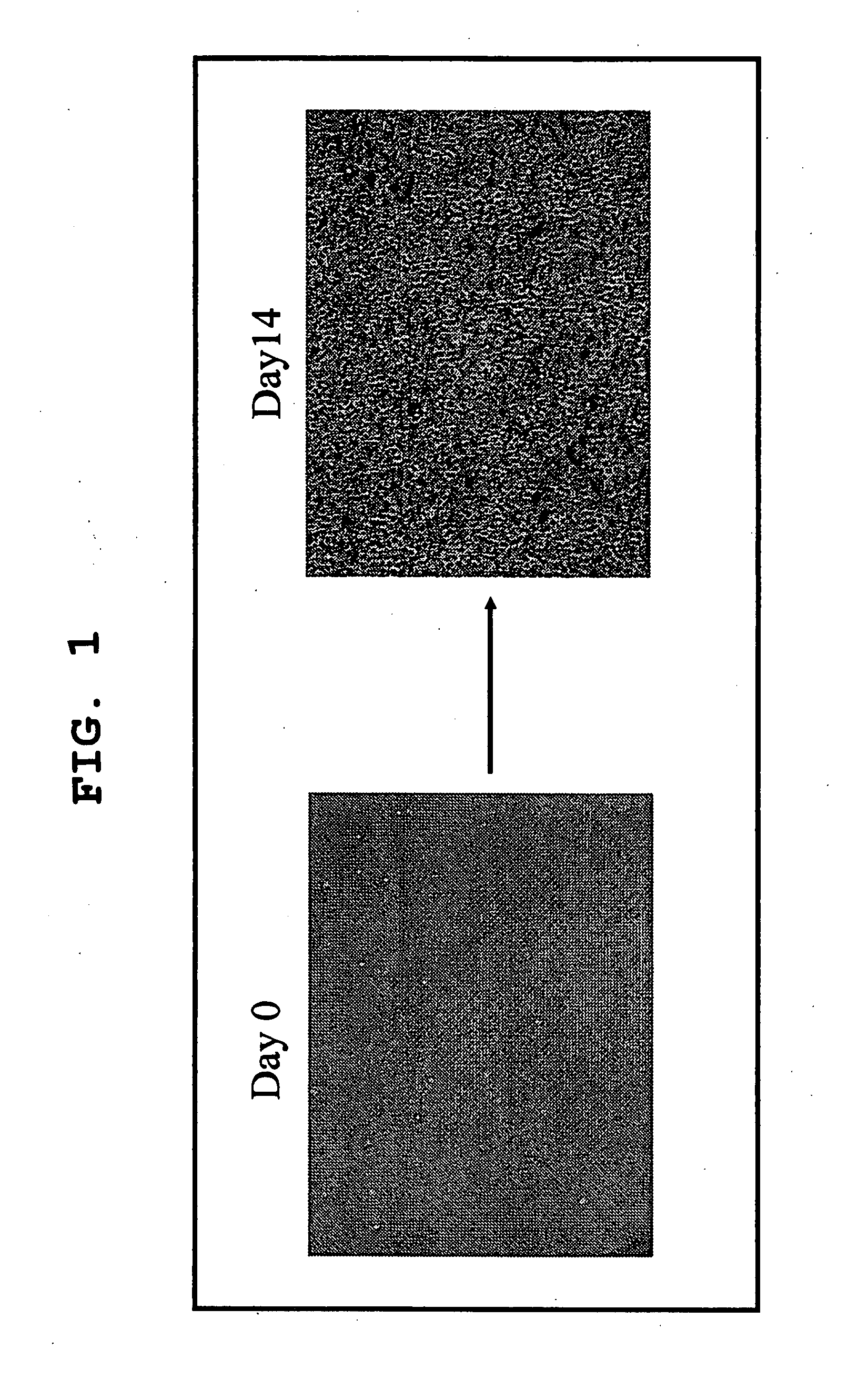
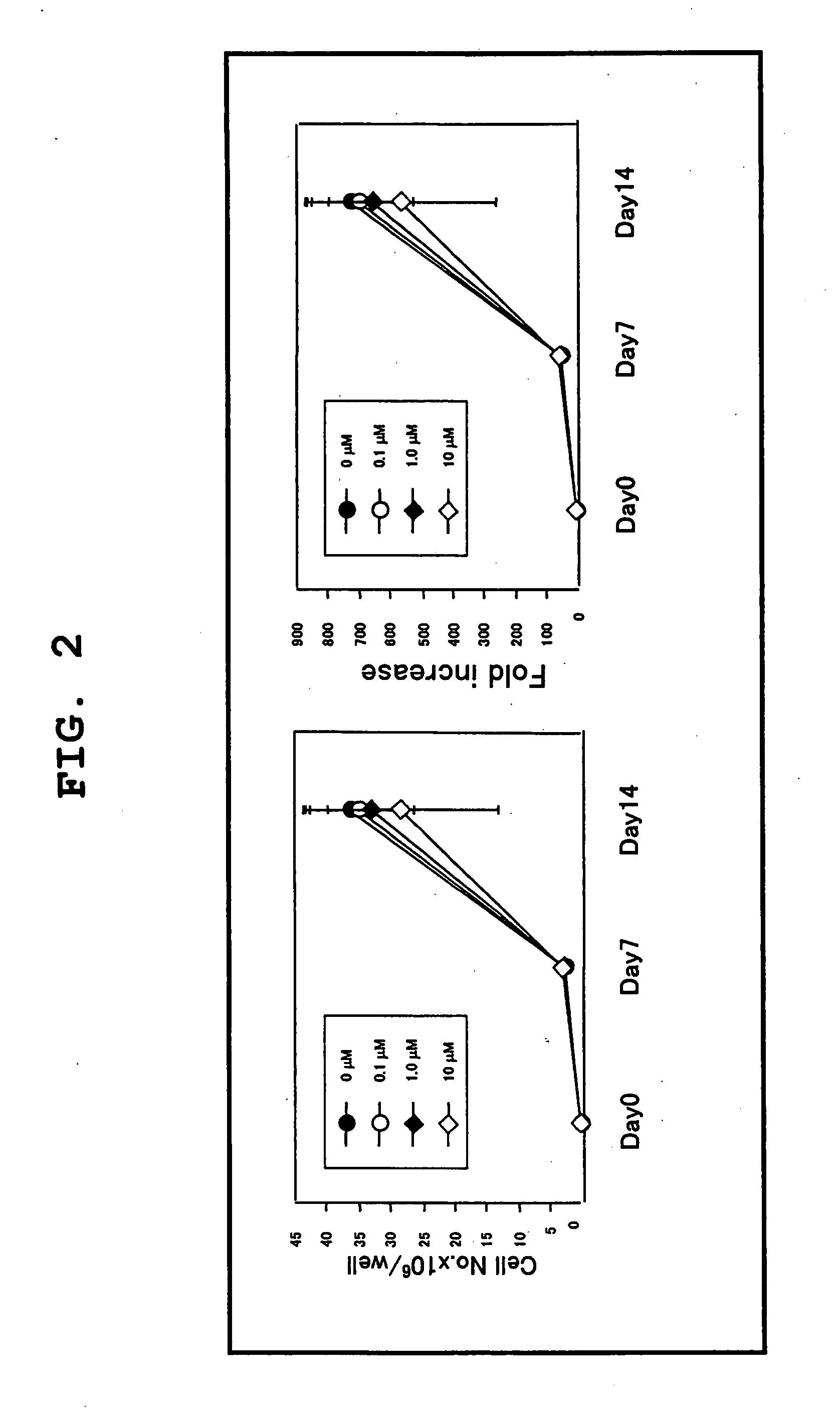
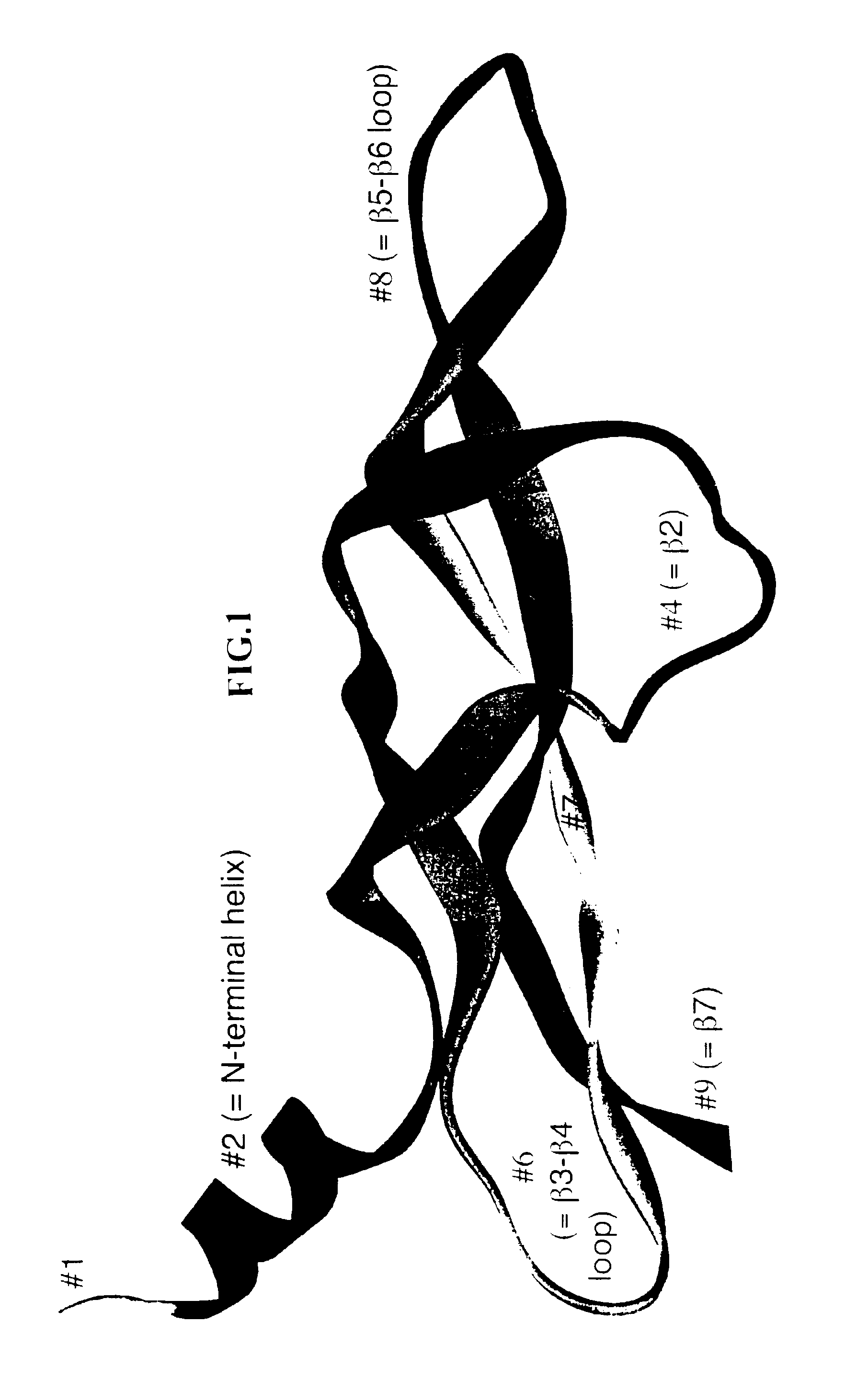
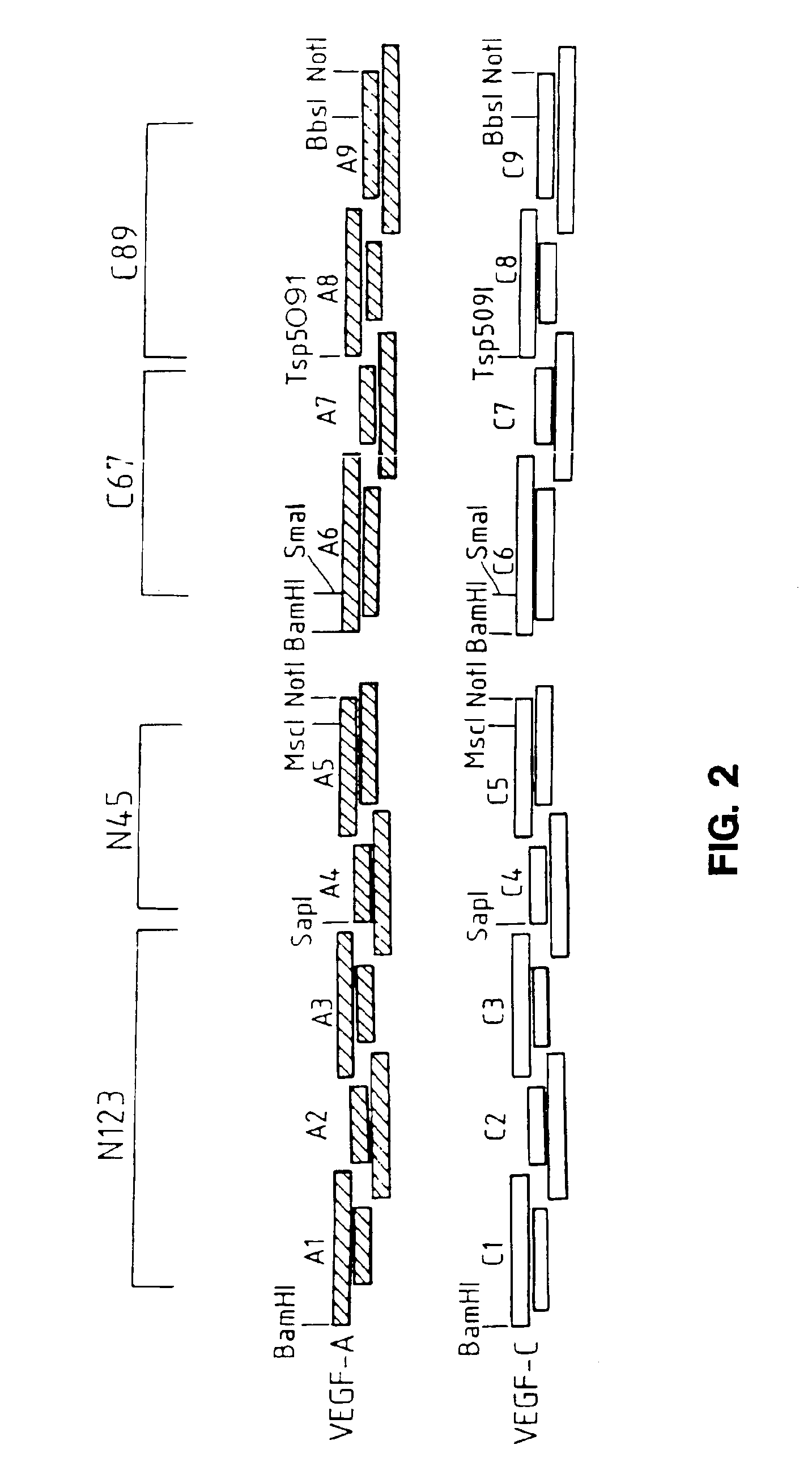
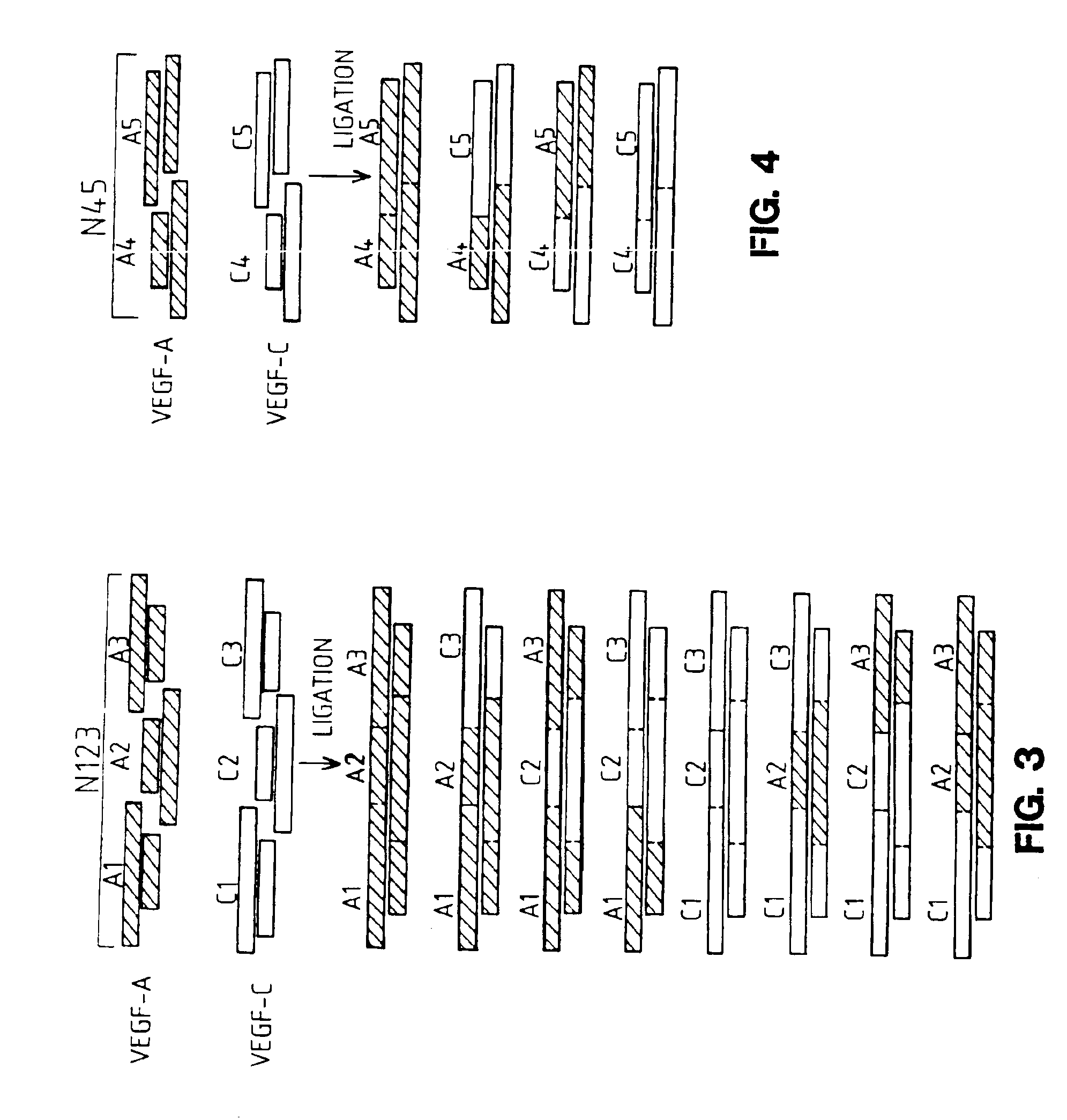
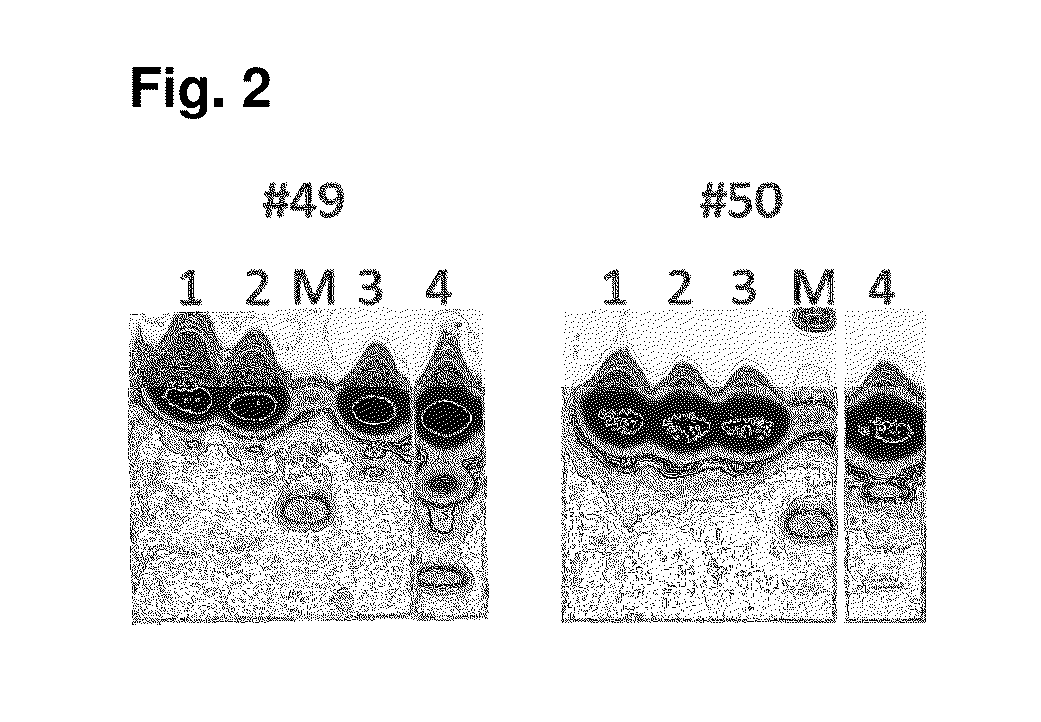
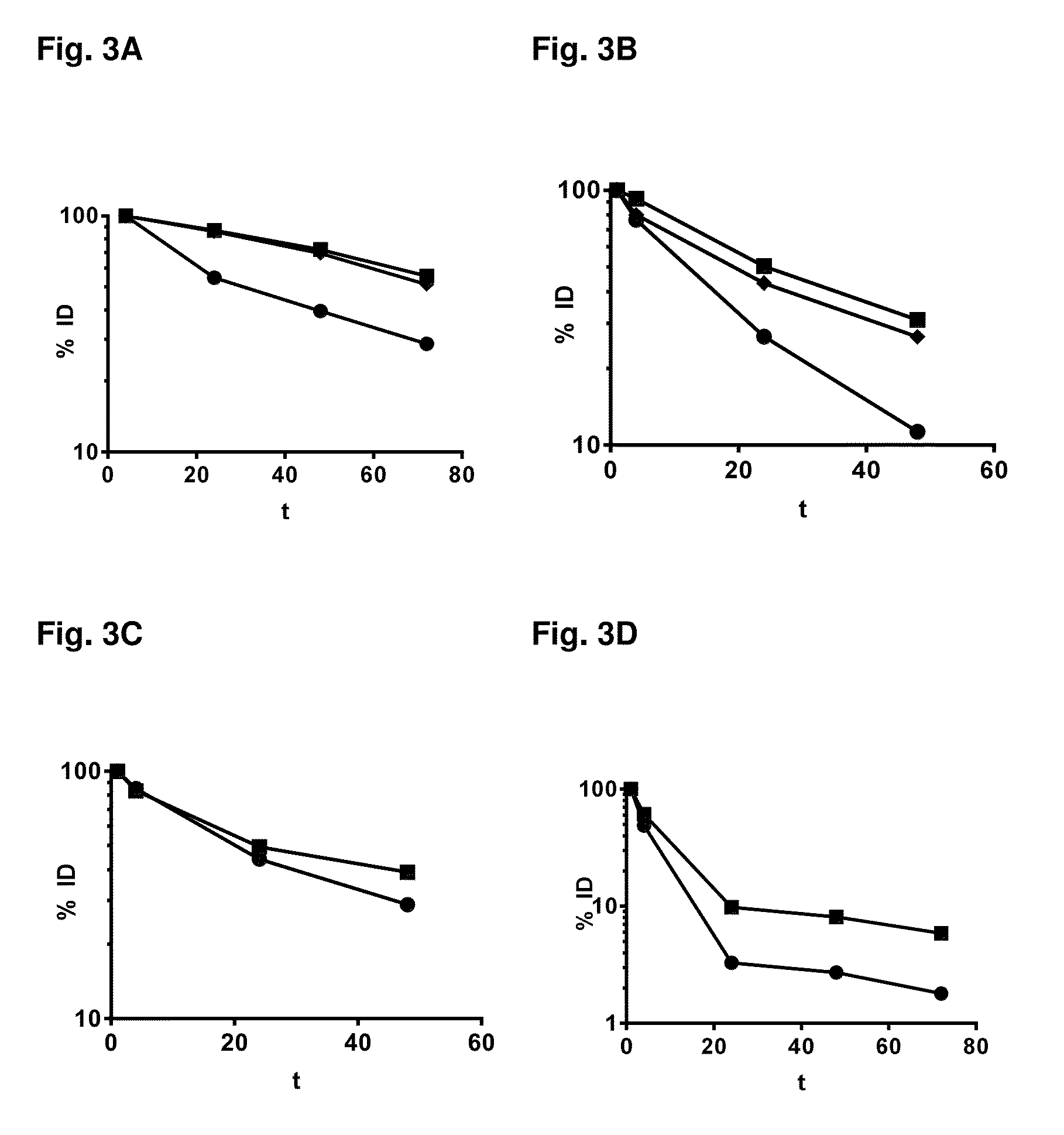
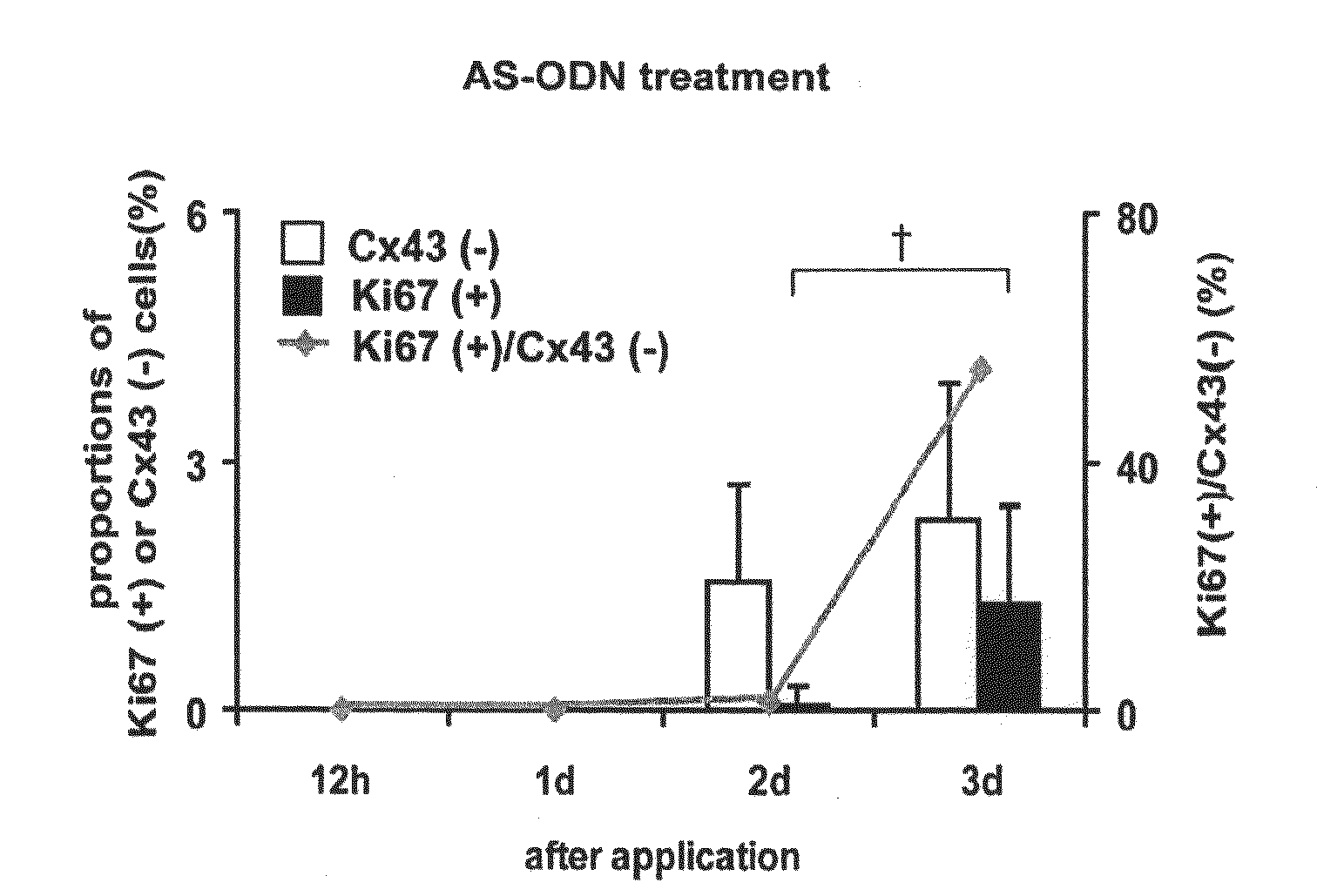
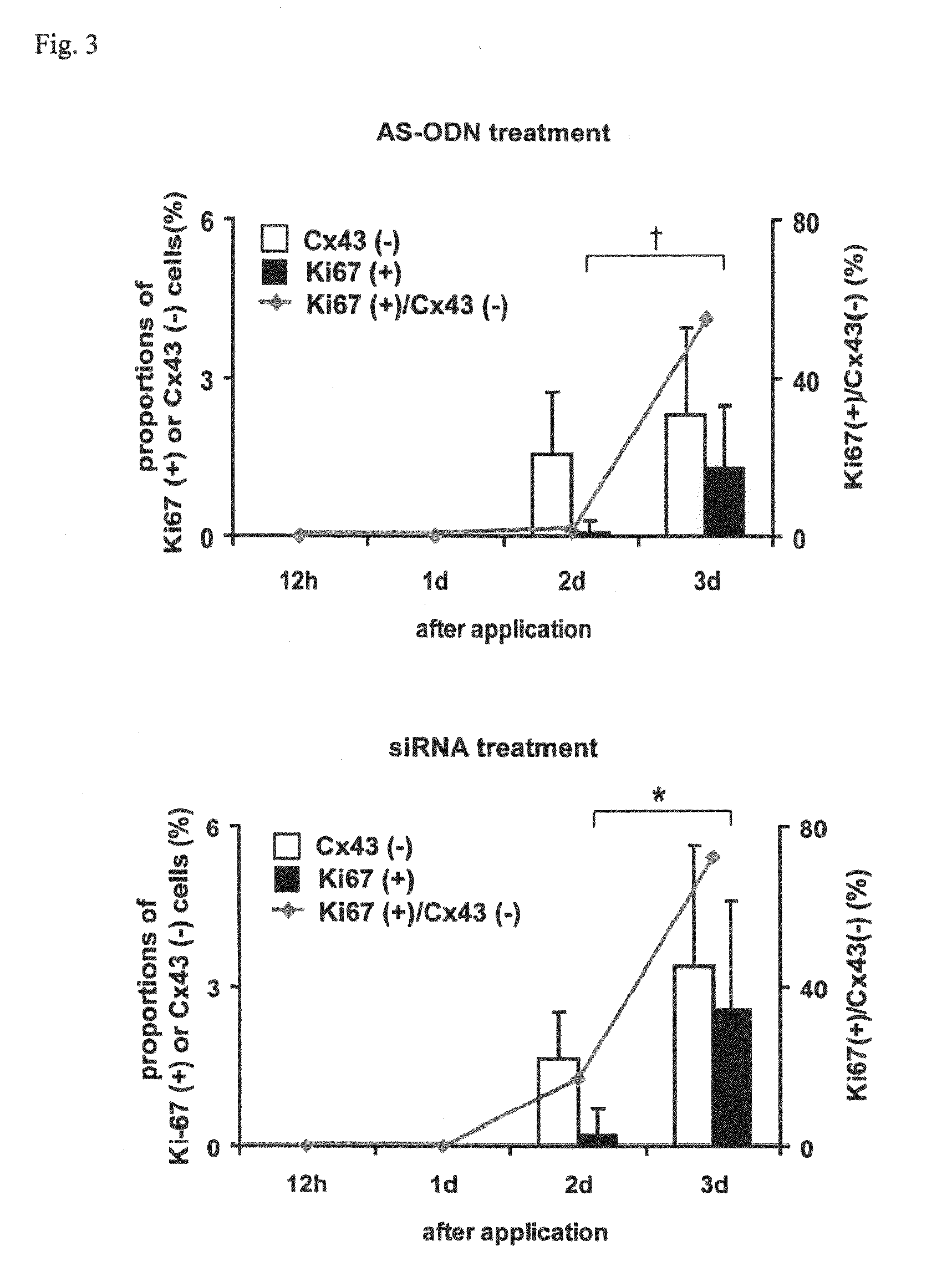
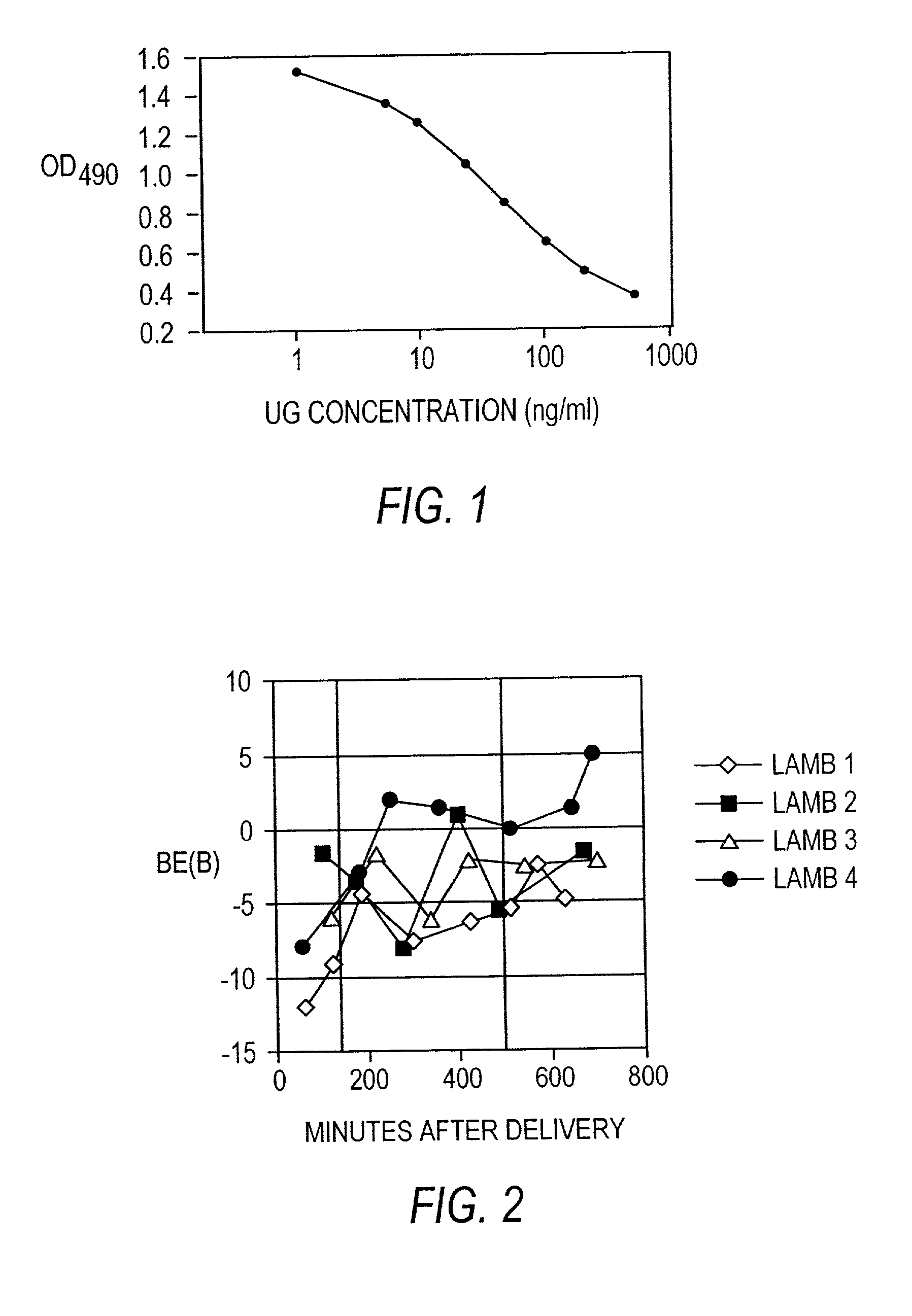
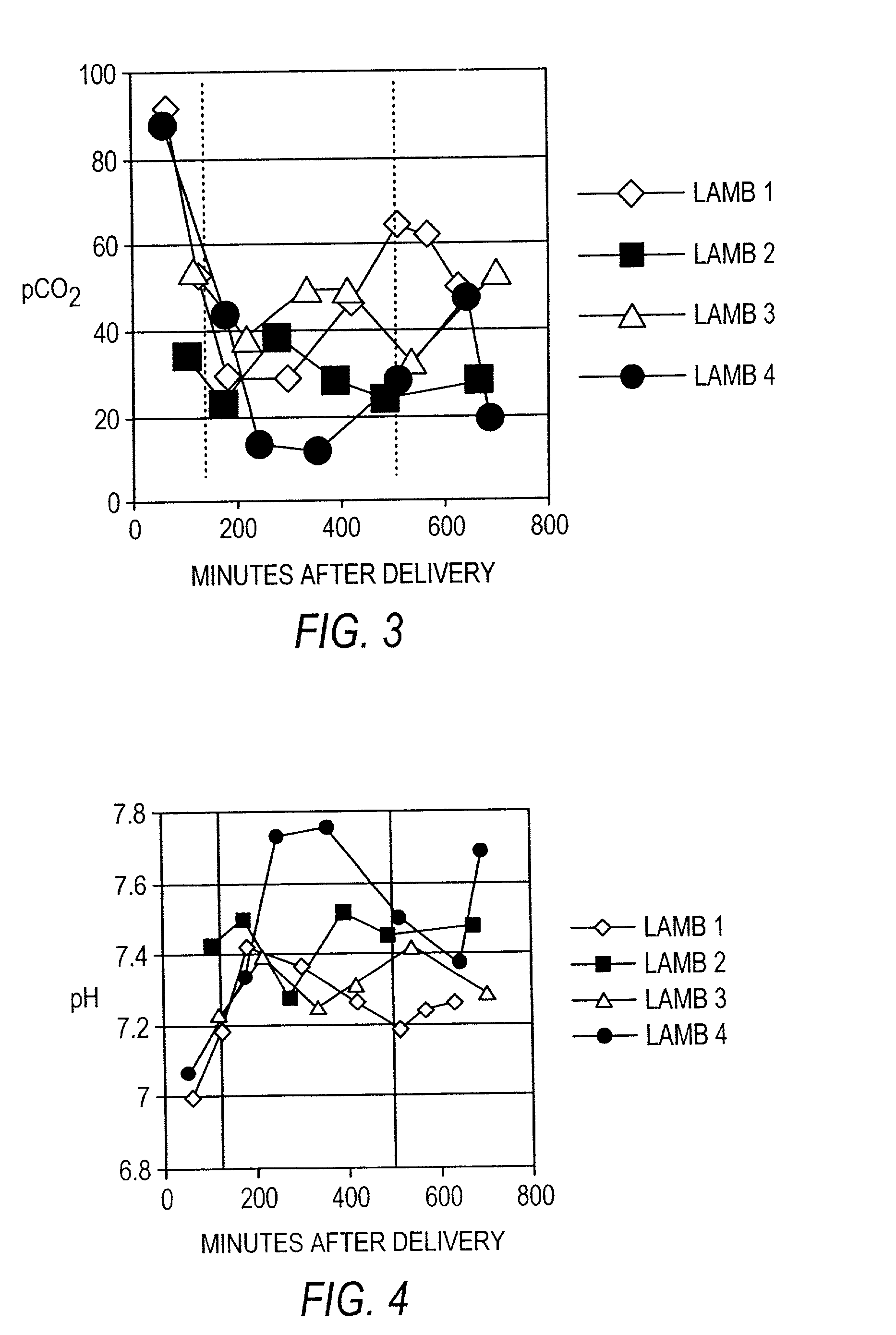
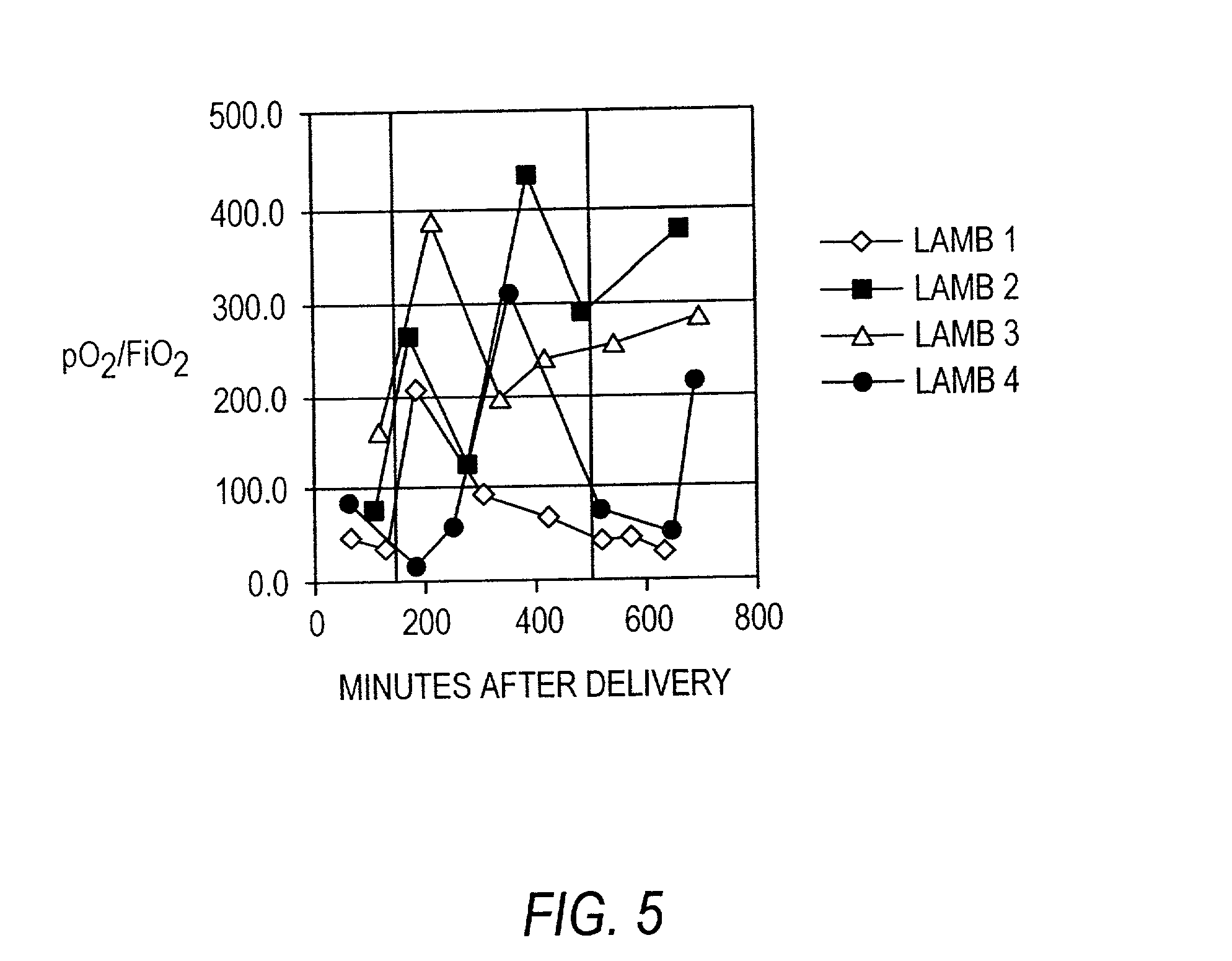
Patents
Literature
401 results about "Endothelial NOS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Endothelial NOS (eNOS), also known as nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3) or constitutive NOS (cNOS), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS3 gene located in the 7q35-7q36 region of chromosome 7. This enzyme is one of three isoforms that synthesize nitric oxide (NO), a small gaseous and lipophilic molecule that participates in several biological processes. The other isoforms include neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), which is constitutively expressed in specific neurons of the brain and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), whose expression is typically induced in inflammatory diseases. eNOS is primarily responsible for the generation of NO in the vascular endothelium, a monolayer of flat cells lining the interior surface of blood vessels, at the interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the remainder of the vessel wall. NO produced by eNOS in the vascular endothelium plays crucial roles in regulating vascular tone, cellular proliferation, leukocyte adhesion, and platelet aggregation. Therefore, a functional eNOS is essential for a healthy cardiovascular system.
Tumour necrosis factor antibodies
InactiveUS6451983B2Enhance or inhibit TNF alpha activityInduction of endothelial procoagulant activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman tumorSingle-Chain Antibodies
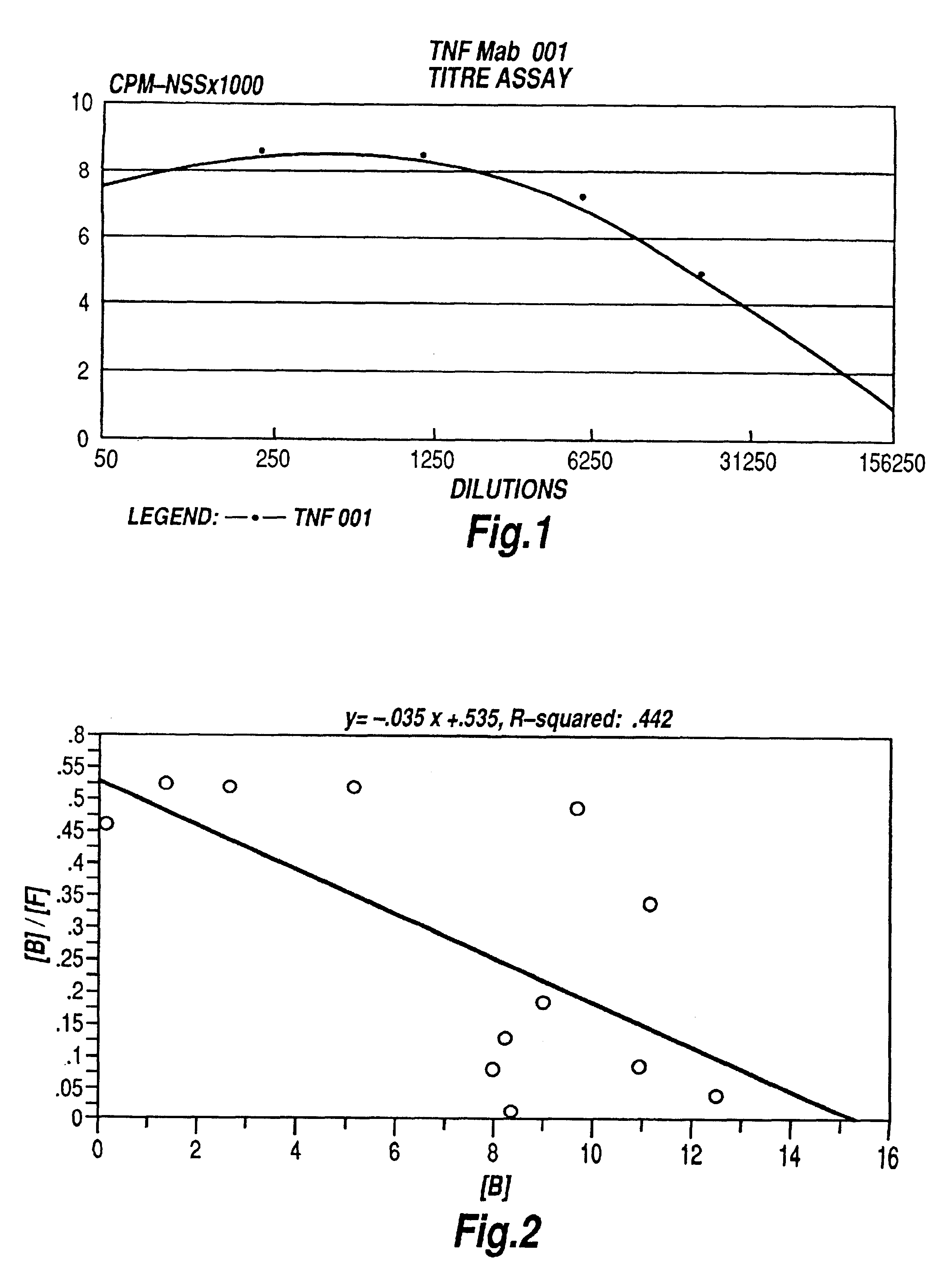
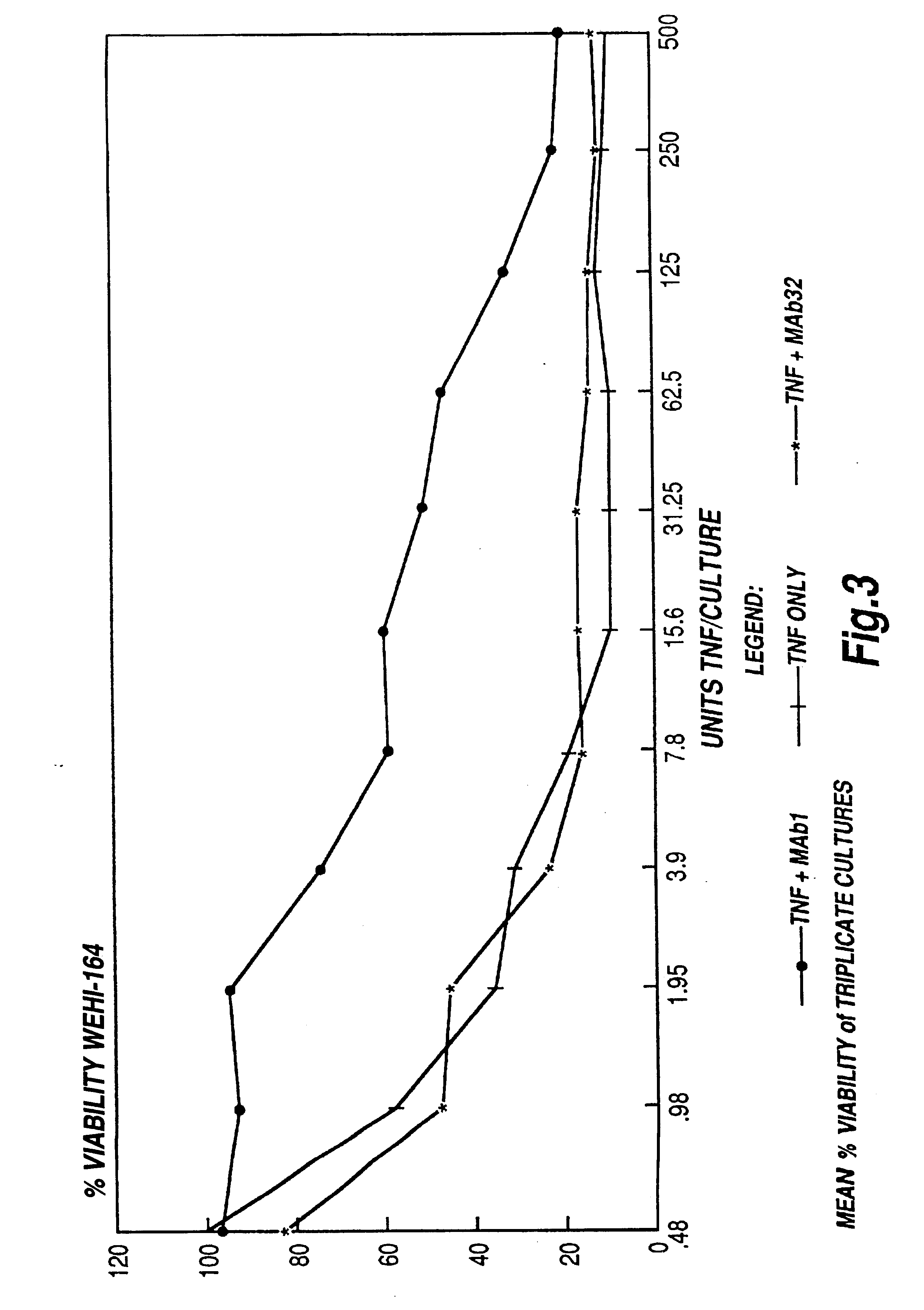
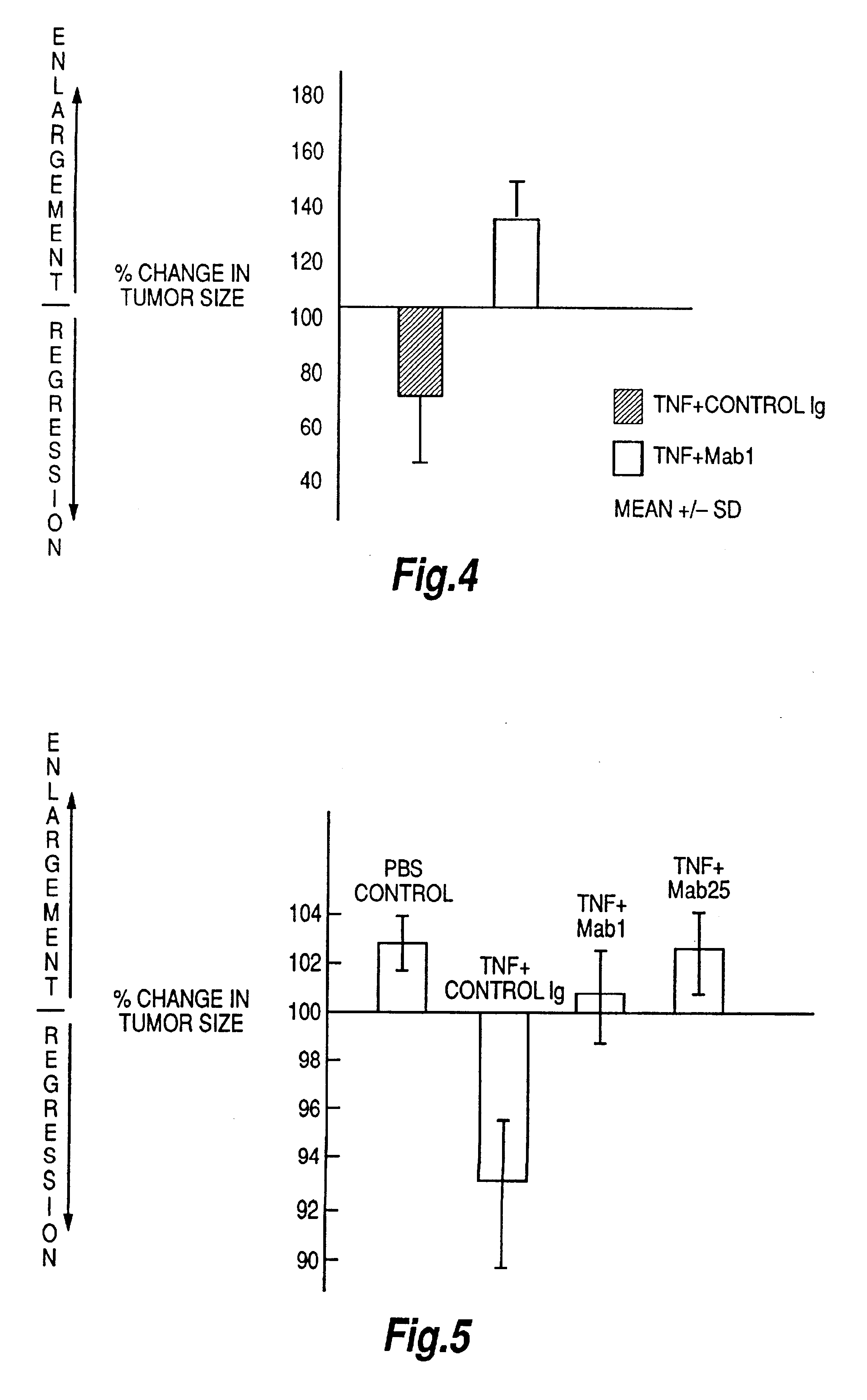
The present invention relates to ligands which bind to human tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) in a manner such that upon binding of these ligands to TNF the biological activity of TNF is modified. In preferred forms the ligand binds to TNF in a manner such that the induction of endothelial procoagulant activity of the TNF is inhibited; the binding of TNF to receptors on endothelial cells is inhibited; the induction of fibrin deposition in the tumor and tumor regression activities of the TNF are enhanced; and the cytotoxicity and receptor binding activities of the TNF are unaffected or enhanced on tumor cells. The ligand is preferably an antibody, F(ab) fragment, single domain antibody (dABs) single chain antibody or a serum binding protein. It is preferred, however, that the ligand is a monoclonal antibody or F(ab) fragment thereof.
Owner:CEPHALON AUSTRALIA
RNA interference mediated inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050171039A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityBiocideSugar derivativesDiseaseFactor ii
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF, VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D) and / or vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (e.g., VEGFR1, VEGFR2 and / or VEGFr3) gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against VEGF and / or VEGFr gene expression and / or activity. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, proliferative diseases, and any other disease or condition that responds to modulation of VEGF and / or VEGFr expression or activity.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
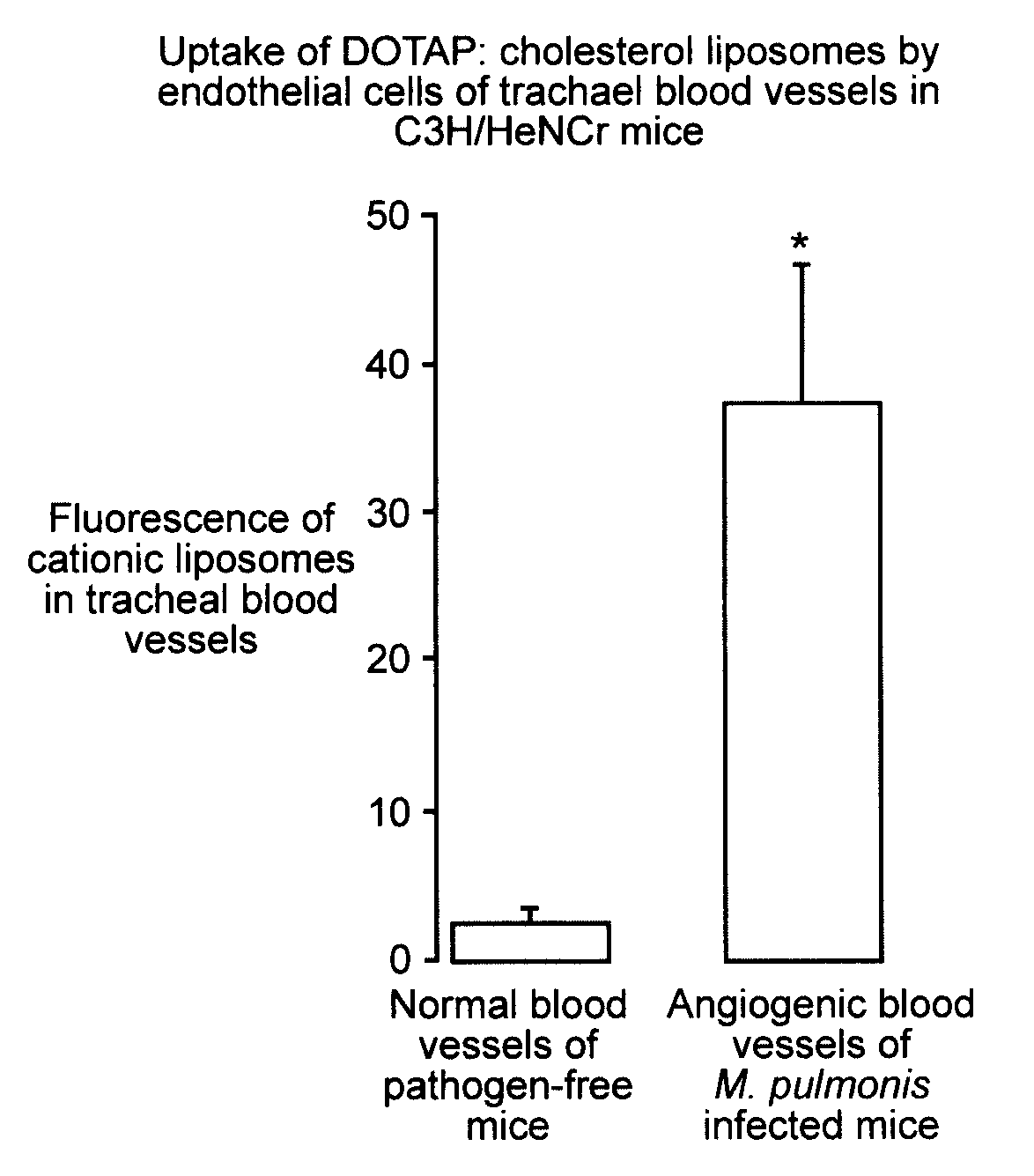
Cationic lipid compositions targeting angiogenic endothelial cells
Angiogenic endothelial cells are selectively targeted with lipid / DNA complexes or cationic liposomes containing a substance which affects the targeted cells by inhibiting or promoting their growth. A site of angiogenesis can be precisely located by administering cationic liposomes containing a detectable label. The complexes may comprise nucleotide constructs which are comprised of promoters which are selectively and exclusively activated in the environment of an angiogenic endothelial cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Treatment and diagnosis of cancer
InactiveUS7163680B2Effective diagnosisEffective treatmentBiological material analysisNanomedicineAntigenVascular endothelium
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
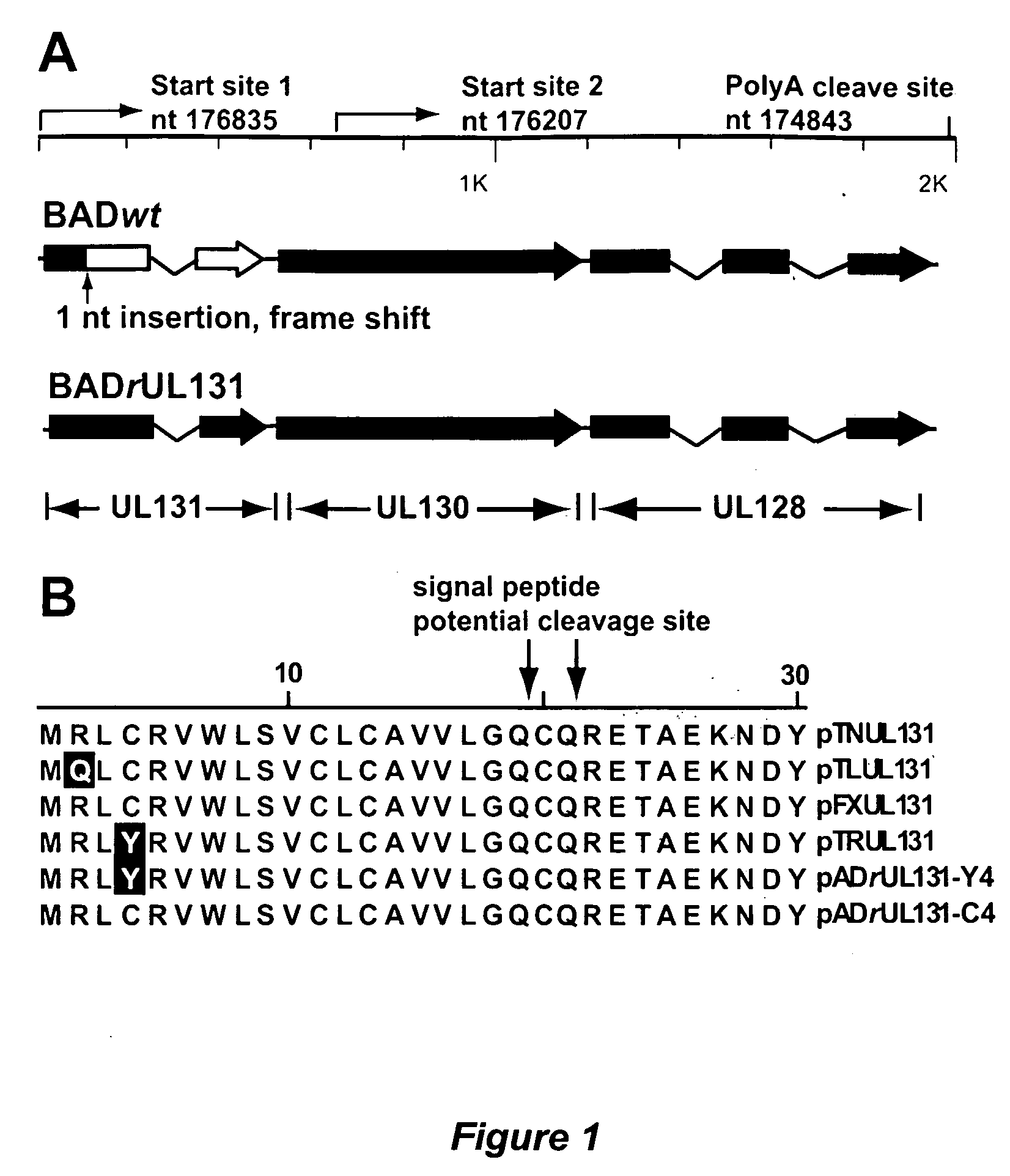
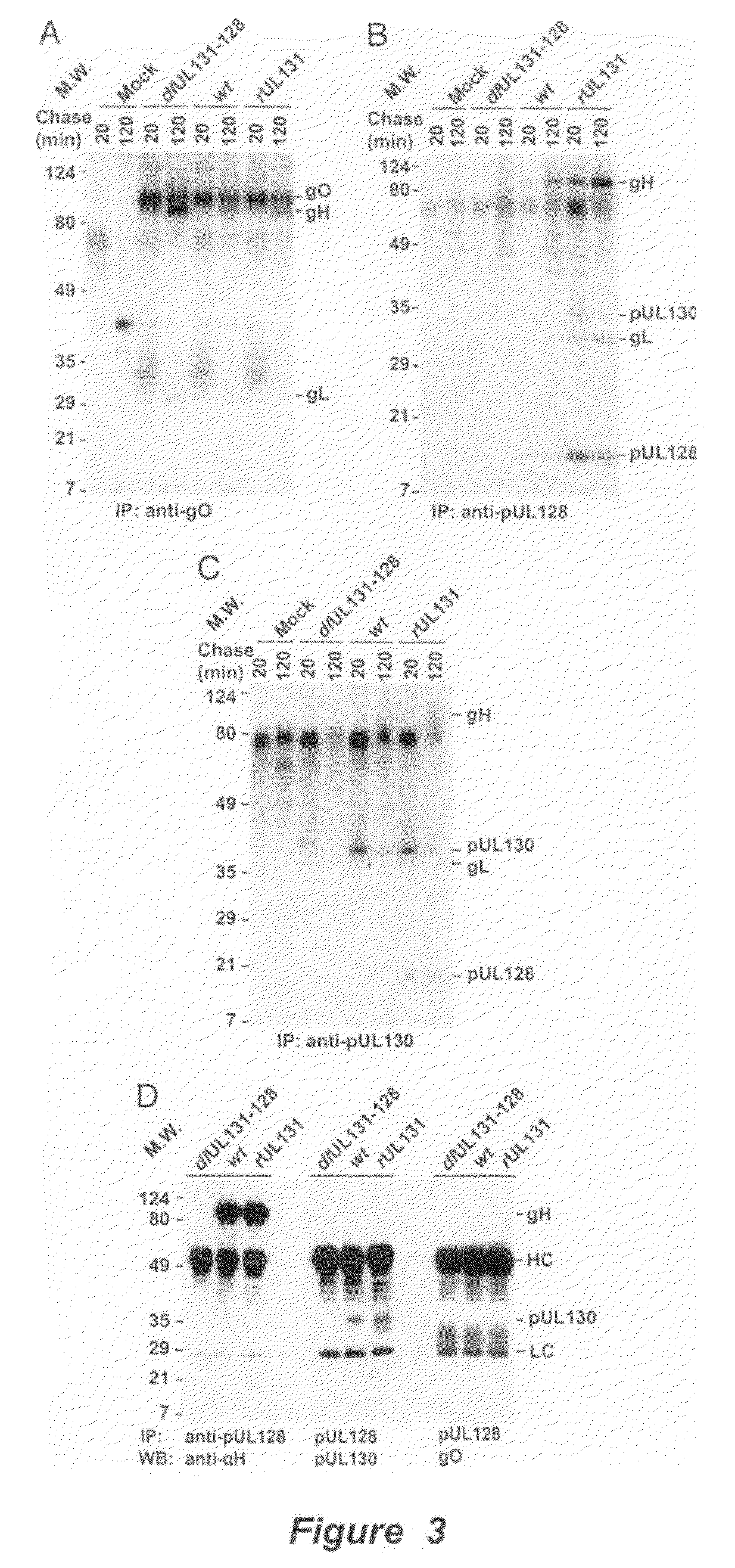
Cytomegalovirus surface protein complex for use in vaccines and as a drug target
Immunogenic compositions and prophylactic or therapeutic vaccines for use in protecting and treating against human cytomegalovirus (CMV) are disclosed. Subunit vaccines comprising a human CMV protein complex comprising pUL128 or pUL130, and nucleic acid vaccines comprising at least one nucleic acid encoding a CMV protein complex comprising pUL128 or pUL130 are described. Also disclosed are therapeutic antibodies reactive against a CMV protein complex comprising pUL128 or pUL130, as well as methods for screening compounds that inhibit CMV infection of epithelial and endothelial cells, methods for immunizing a subject against CMV infection, methods for determining the capability of neutralizing antibodies to inhibit human CMV infection of cell types other than fibroblasts, and methods of diminishing an CMV infection.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Methods and compositions for the treatment and diagnosis of vascular inflammatory disorders or endothelial cell disorders
InactiveUS20080199426A1Inhibition effectLow release rateOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsVasculitisMedicine
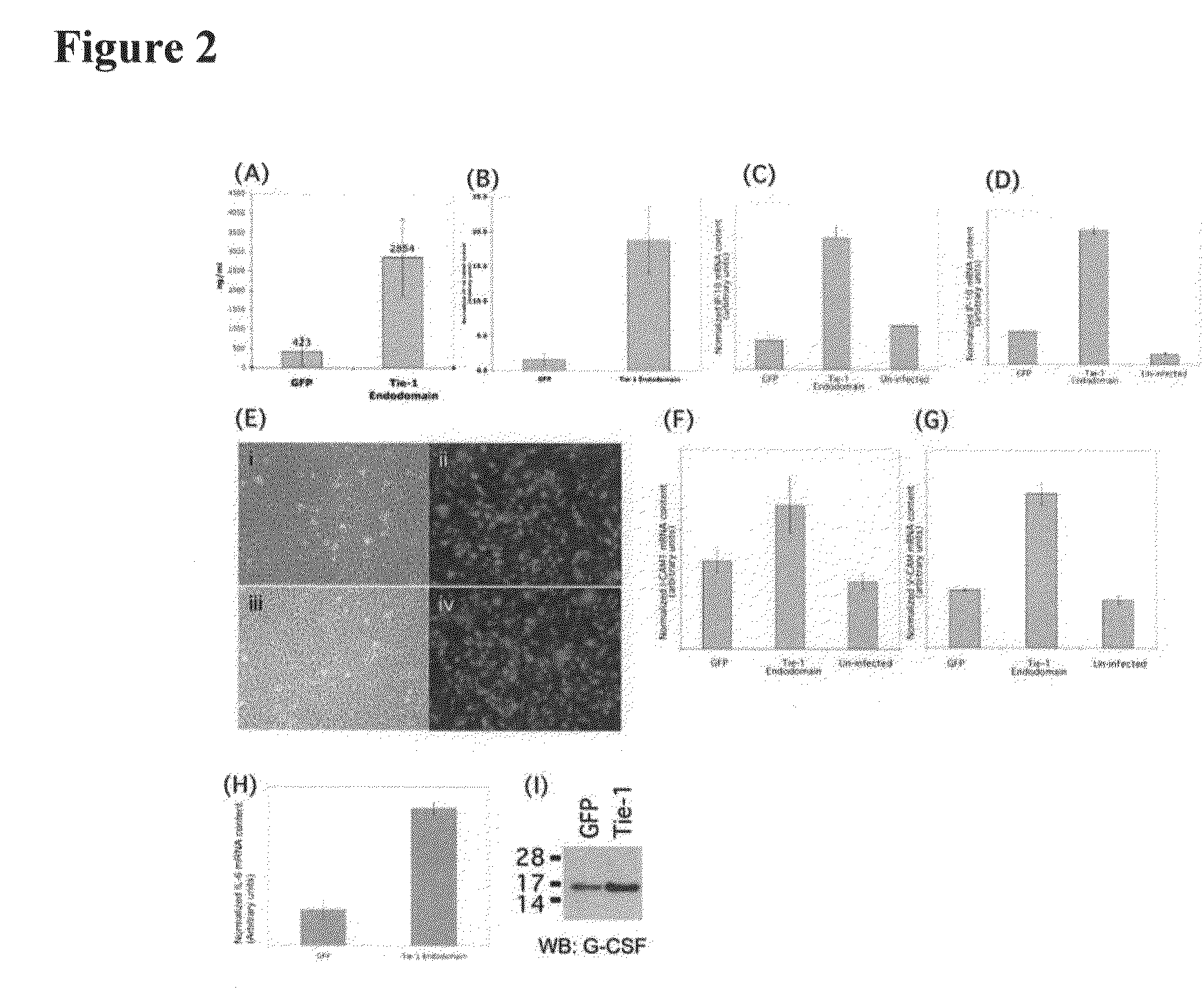
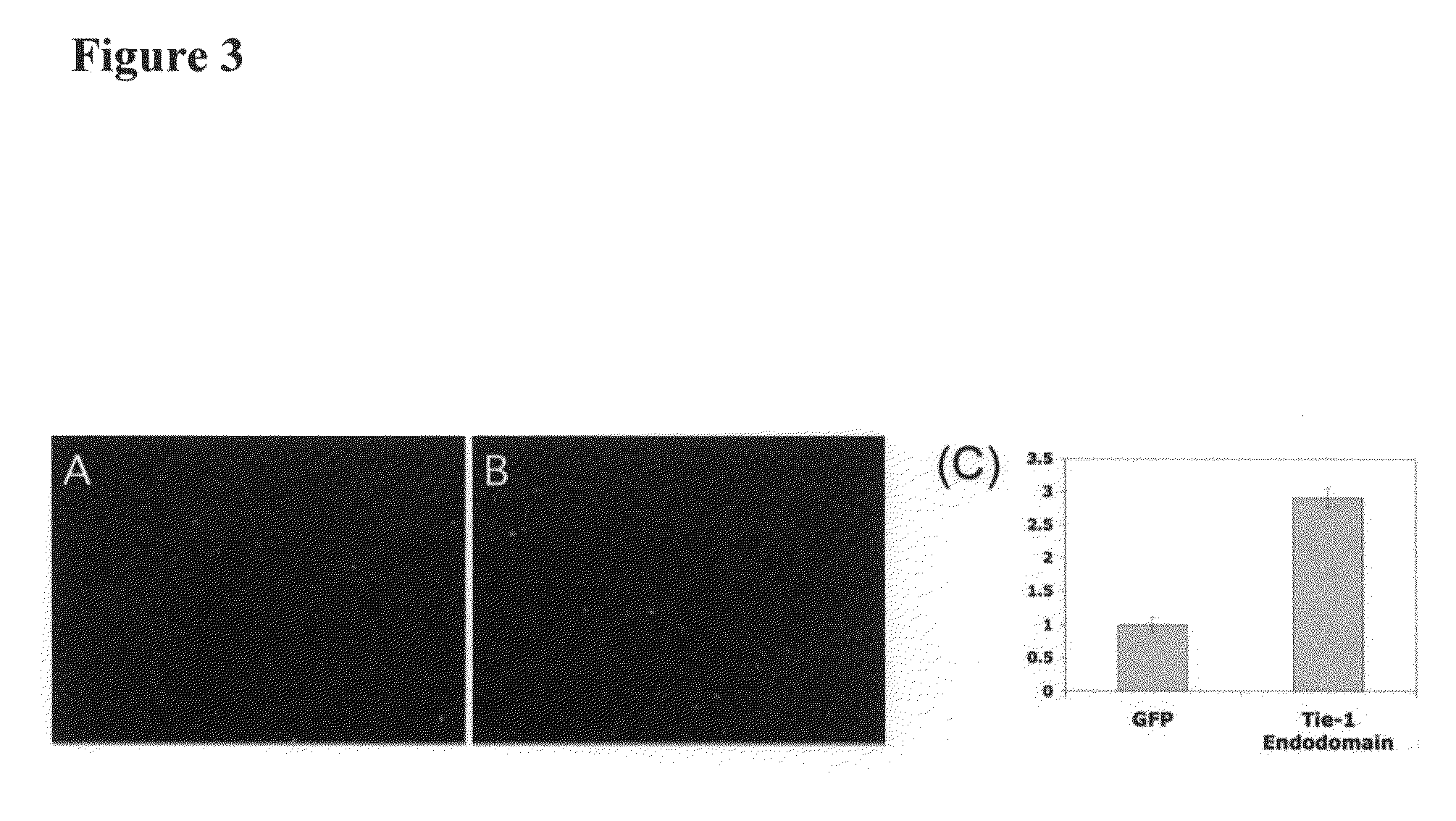
Disclosed herein are methods for treating a vascular inflammatory disorder or endothelial cell disorder using inhibitor compounds that inhibit the expression or biological activity of Tie-1, Tie-1 endodomain, thrombin, VEGFR2, VEGFR2 endodomain, EphA2, and any of the cytokines or kinases that are upregulated by activation of Tie-1 or thrombin, as provided herein. Also disclosed are the use of combinations of inhibitor compounds or the use of an eNOS activator compound in combination with any one or more of the inhibitor compounds. Also disclosed are methods for inhibiting the pro-coagulant activity of thrombin using a Tie-1 or Tie-1 endodomain inhibitor compound or an EphA2 inhibitor compound. Methods for diagnosing and monitoring vascular inflammatory disorders or endothelial cell disorders that include the measurement of any of the polypeptides or nucleic acid molecules of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
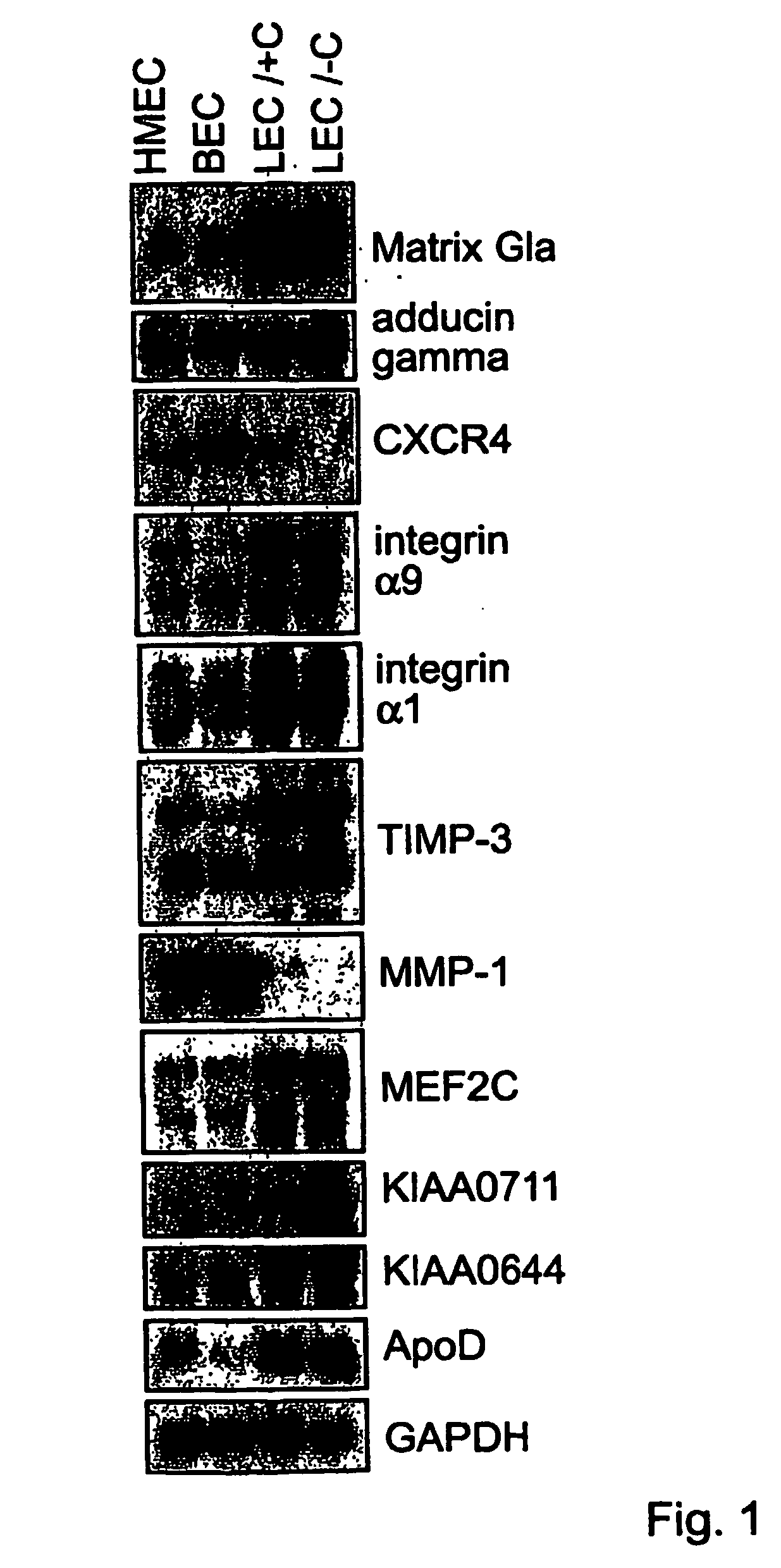
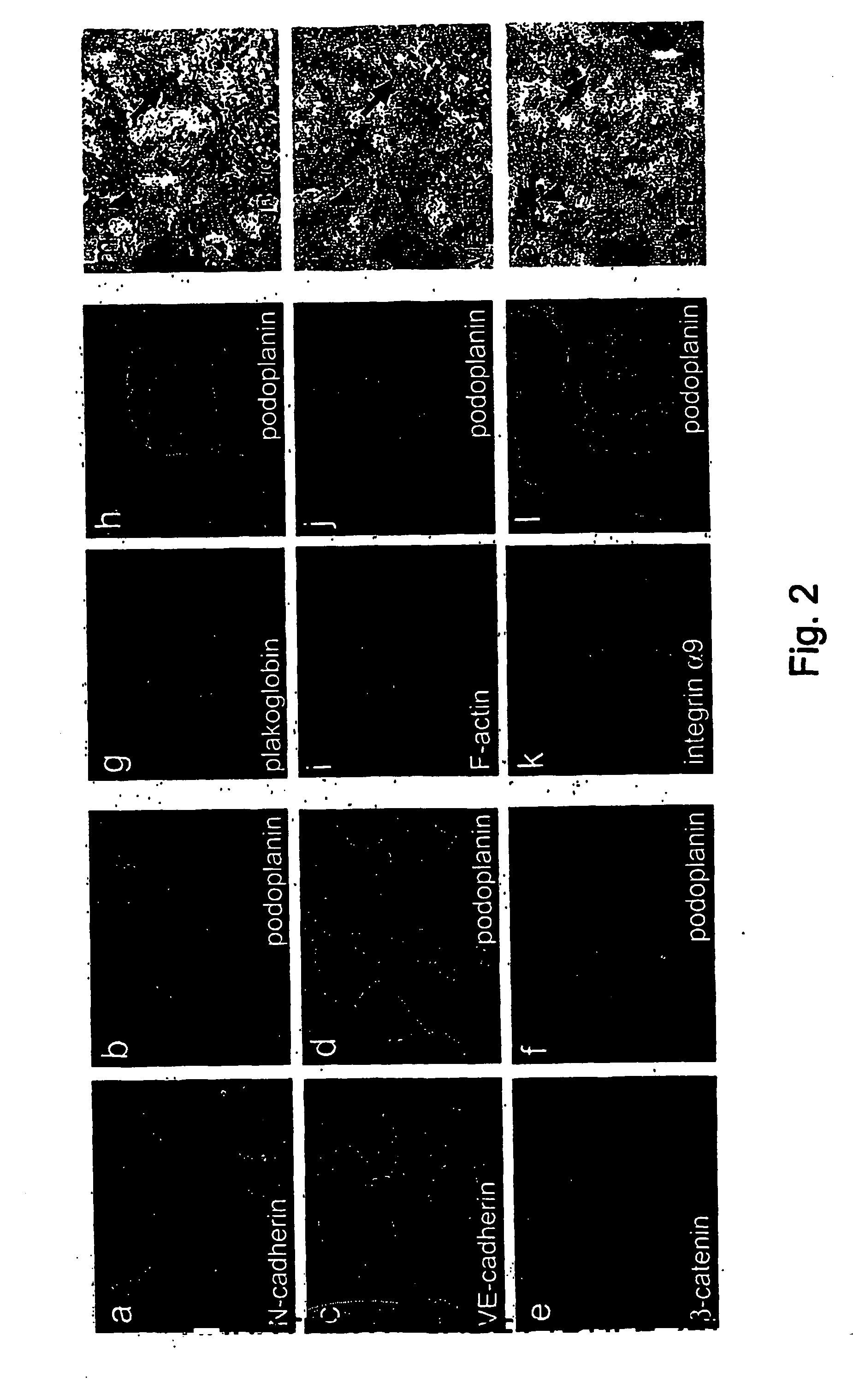
Lymphatic and blood endothelial cell genes
The invention provides polynucleotides and genes that are differentially expressed in lymphatic versus blood vascular endothelial cells. These genes are useful for treating diseases involving lymphatic vessels, such as lymphedema, various inflammatory diseases, and cancer metastasis via the lymphatic system.
Owner:VEGENICS PTY LTD
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods to vaccinate against candidiasis
InactiveUS20030124134A1Treat prevent alleviateToxic reductionPeptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsHospitalized patientsVirulent characteristics
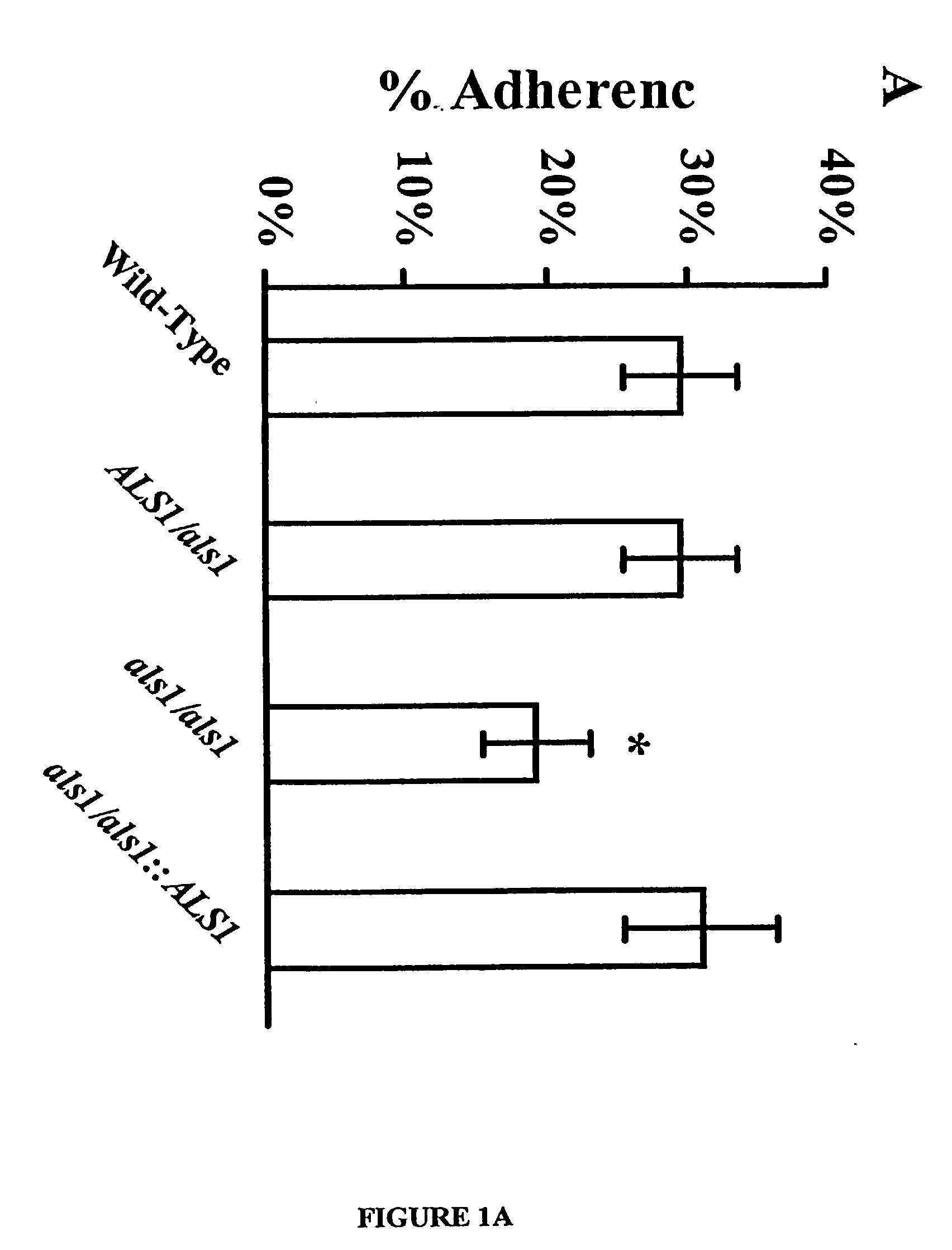
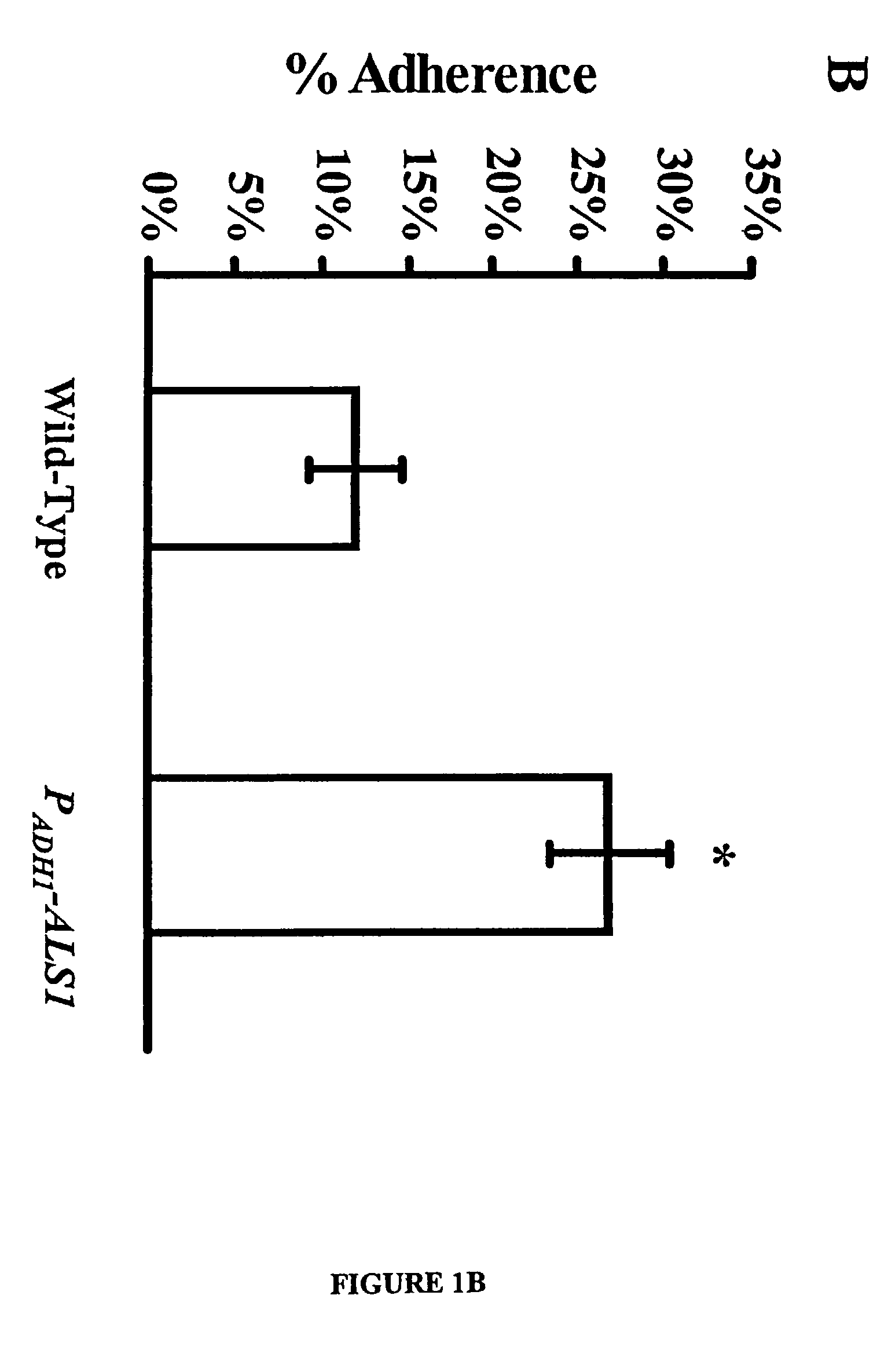
A Candida albicans bloodstream infections cause significant morbidity and mortality in hospitalized patients. Filament formation and adherence to host cells are critical virulence factors of C. albicans. Multiple filamentation regulatory pathways have been discovered, however the downstream effectors of these regulatory pathways remain unknown. The cell surface proteins in the ALS group are downstream effectors of the filamentation regulatory pathway. Particularly, Als1p mediates adherence to endothelial cells in vitro and is required for virulence. The blocking of adherence by the organism is described resulting from the use of a composition and method disclosed herein. Specifically, a pharmaceutical composition comprised of a gene, gene product, or specific antibody to the ALS gene family is administered as a vaccine to generate an immune response capable of blocking adherence of the organism.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT UCLA HARBOR MEDICAL CENT +1
Use of integrin antagonists to inhibit angiogenesis
InactiveUS7074408B2Inhibit biological activityInhibit cell migrationAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseaseIntegrin antagonist
The present invention provides methods and compositions for inhibiting the biological activity of integrins, for inhibiting endothelial cell migration. and for inhibiting angiogenesis. In particular, the invention provides compositions comprising ADAM disintegrin domains and methods for using said compositions. In preferred embodiments the methods and compositions of the invention are used to inhibit angiogenesis and to treat diseases or conditions mediated by angiogenesis.
Owner:IMMUNEX CORP
Multipotent stem cells derived from placenta tissue and cellular therapeutic agents comprising the same
InactiveUS20070243172A1Negative immunological responseBiocideArtificial cell constructsGerm layerDisease
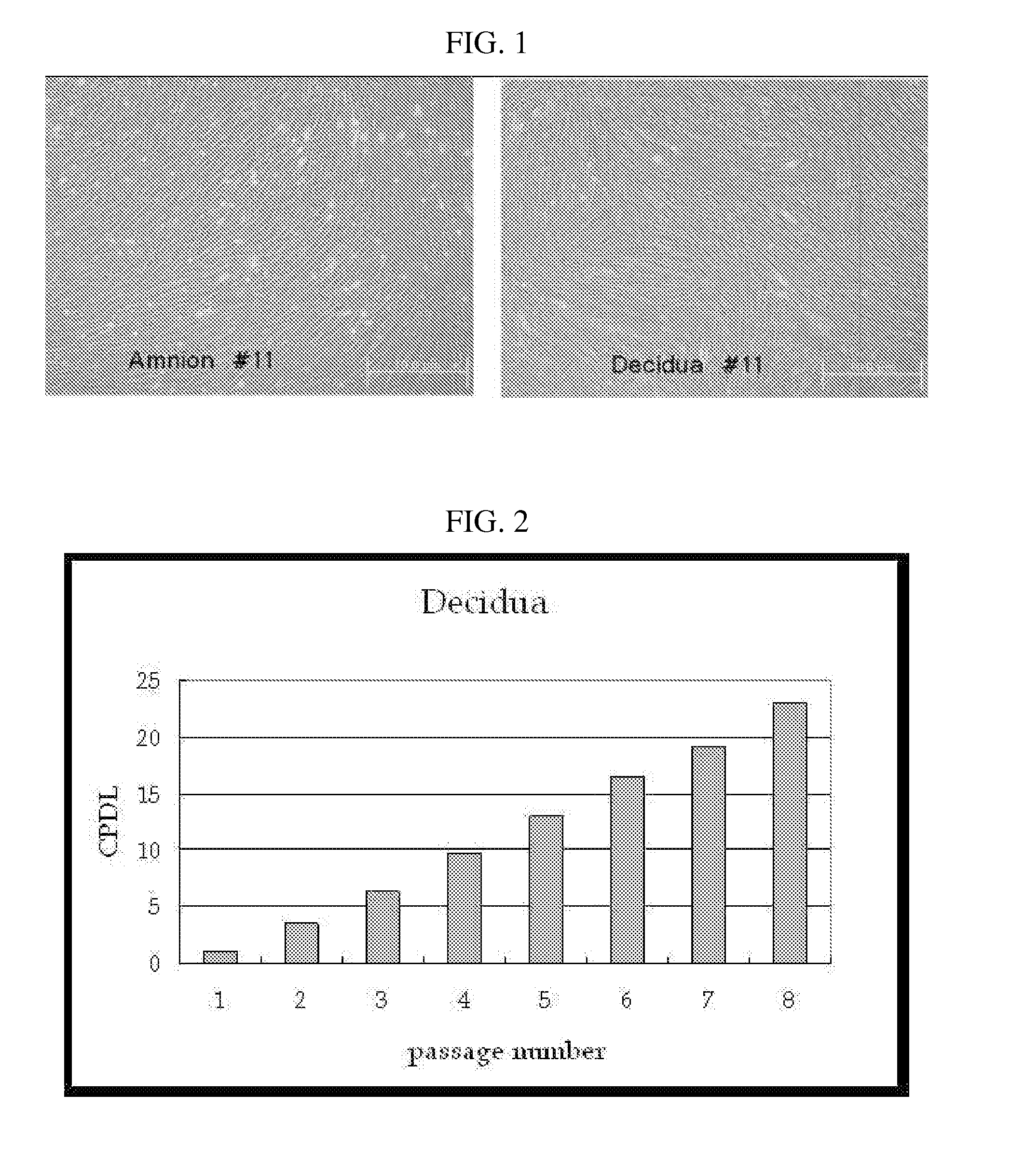
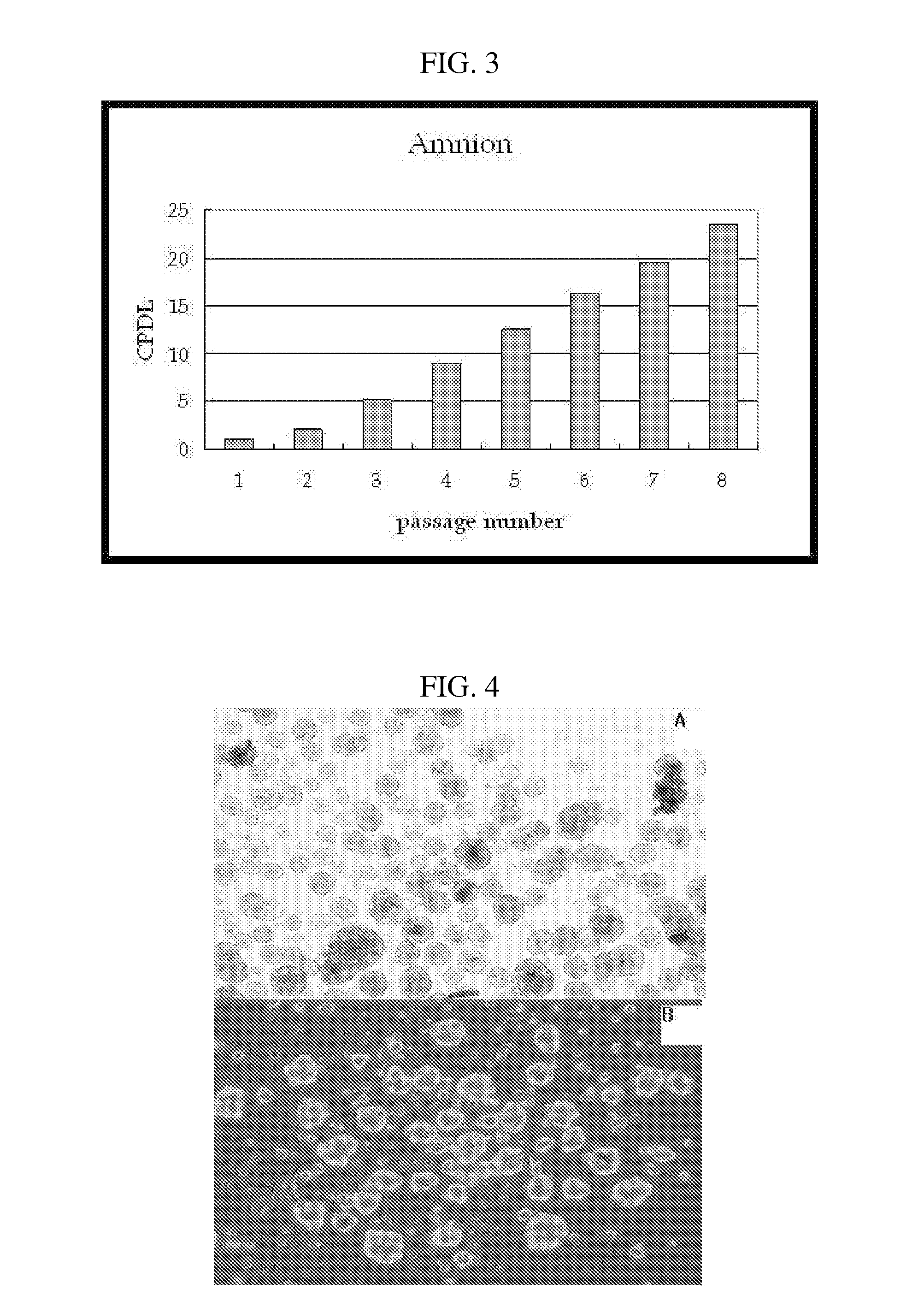
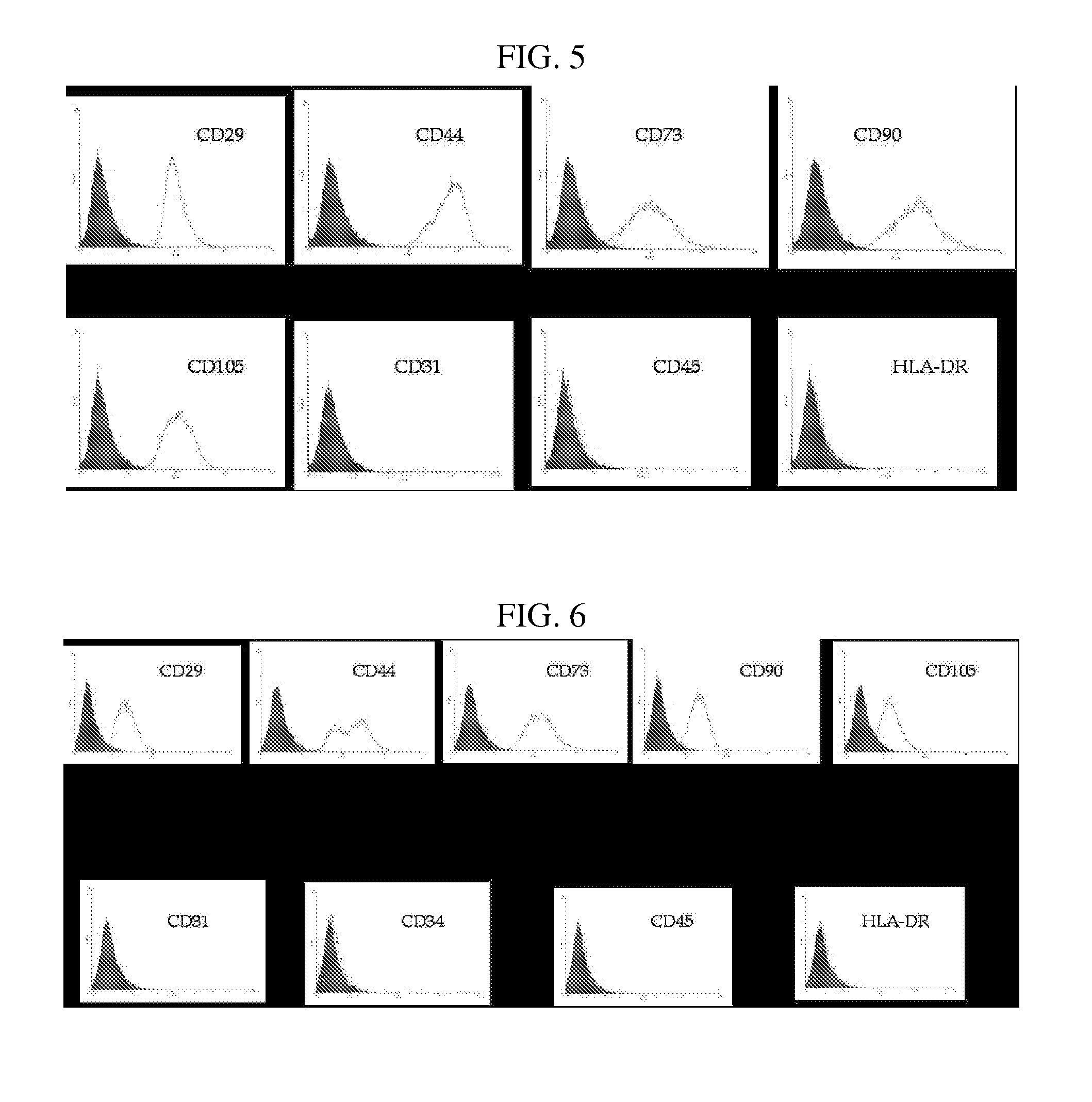
The present invention relates to placenta tissue-derived multipotent stem cells and cell therapeutic agents containing the same. More specifically, to a method for producing placenta stem cells having the following characteristics, the method comprising culturing amnion, chorion, decidua or placenta tissue in a medium containing collagenase and bFGF and collecting the cultured cells: (a) showing a positive immunological response to CD29, CD44, CD73, CD90 and CD105, and showing a negative immunological response to CD31, CD34, CD45 and HLA-DR; (b) showing a positive immunological response to Oct4 and SSEA4; (c) growing attached to plastic, showing a round-shaped or spindle-shaped morphology, and forming spheres in an SFM medium so as to be able to be maintained in an undifferentiated state for a long period of time; and (d) having the ability to differentiate into mesoderm-, endoderm- and ectoderm-derived cells. Also the present invention relates to placenta stem cells obtained using the production method. The inventive multipotent stem cells have the ability to differentiate into muscle cells, vascular endothelial cells, osteogenic cells, nerve cells, satellite cells, fat cells, cartilage-forming cells, osteogenic cells, or insuline-secreting pancreatic β-cells, and thus are effective for the treatment of muscular diseases, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, nervous diseases, diabetes and the like, and are useful for the formation of breast tissue.
Owner:RNL BIO
Medicinal agent for treating erectile dysfunction
A medicament based on antibodies contains an activated form of ultra-low doses of monoclonal, polyclonal, or natural antibodies to endothelial nitric oxide synthase (NO synthase), the activated form being prepared by multiple consecutive dilutions and exposure to external factors, preferably according to the homeopathic technology. A method of treating erectile dysfunctions and vegetative disturbances of male climax by regulating the level of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in the cavernous bodies on sexual stimulation, the method being characterized by the use of activated forms of ultra-low doses of antibodies to the entire molecule of the endothelial NO synthase or to its polypeptide fragments, activated forms being prepared by multiple consecutive dilutions and exposure to external factors.
Owner:EPSHTEIN OLEG I
Inhibition of neovascularization with a soluble chimeric protein comprising VEGF FLT-1 and KDR domains
ActiveUS8216575B2Reduce neovascularizationImprove acuitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsChimerin ProteinsEndothelial NOS
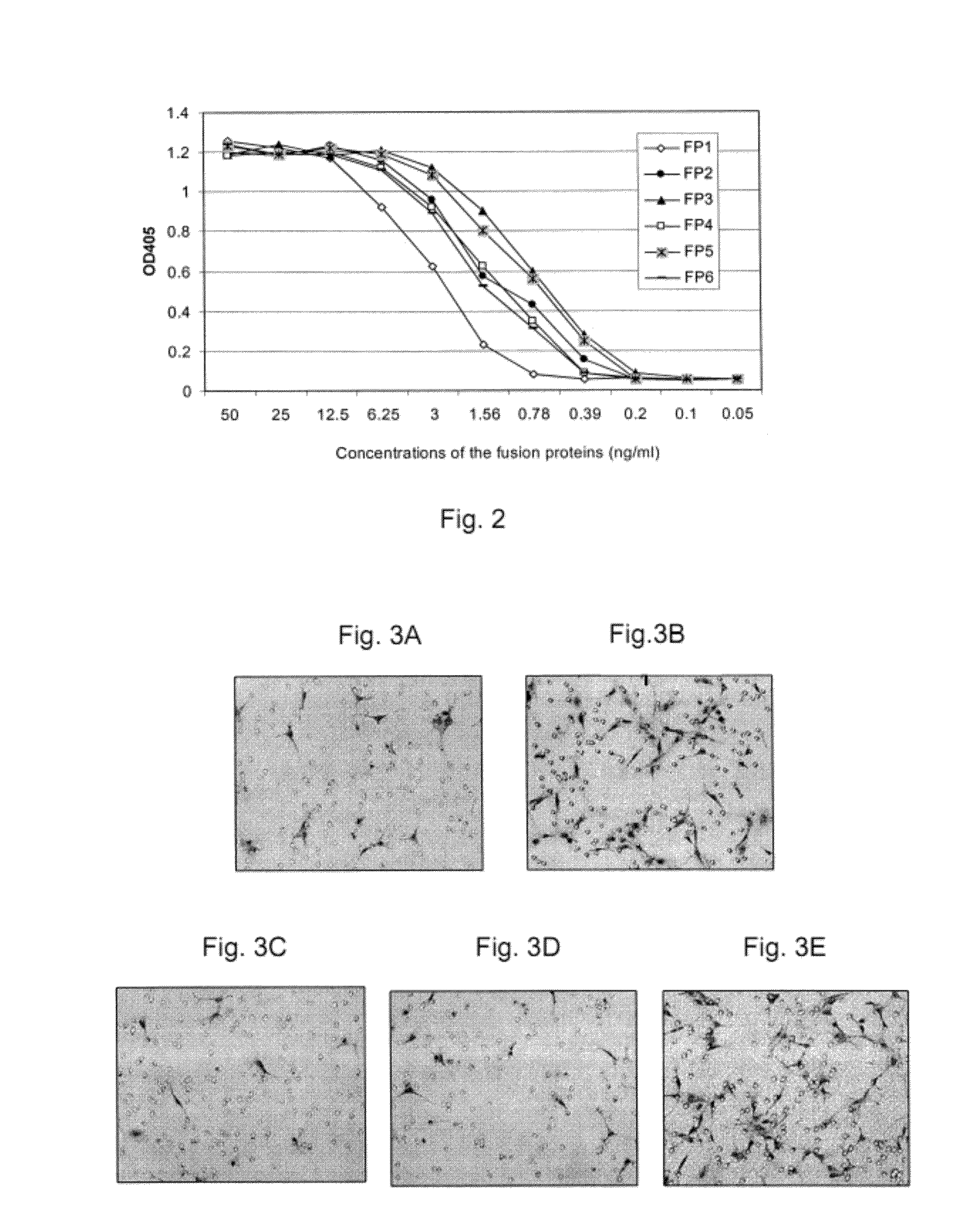
Described herein are novel soluble chimeric fusion proteins comprising amino acid sequences derived from the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors flt-1 and KDR, including domain 4 of KDR. The claimed chimeric fusion proteins antagonize the endothelial cell proliferative and angiogenic activity of VEGF and are useful in the treatment of neovascularization-related disease.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHONG BIOTECH
Use of Opioid Antagonists to Attenuate Endothelial Cell Proliferation and Migration
ActiveUS20080274119A1Avoid problemsAvoid confusionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderOpioid antagonistAngiogenesis growth factor
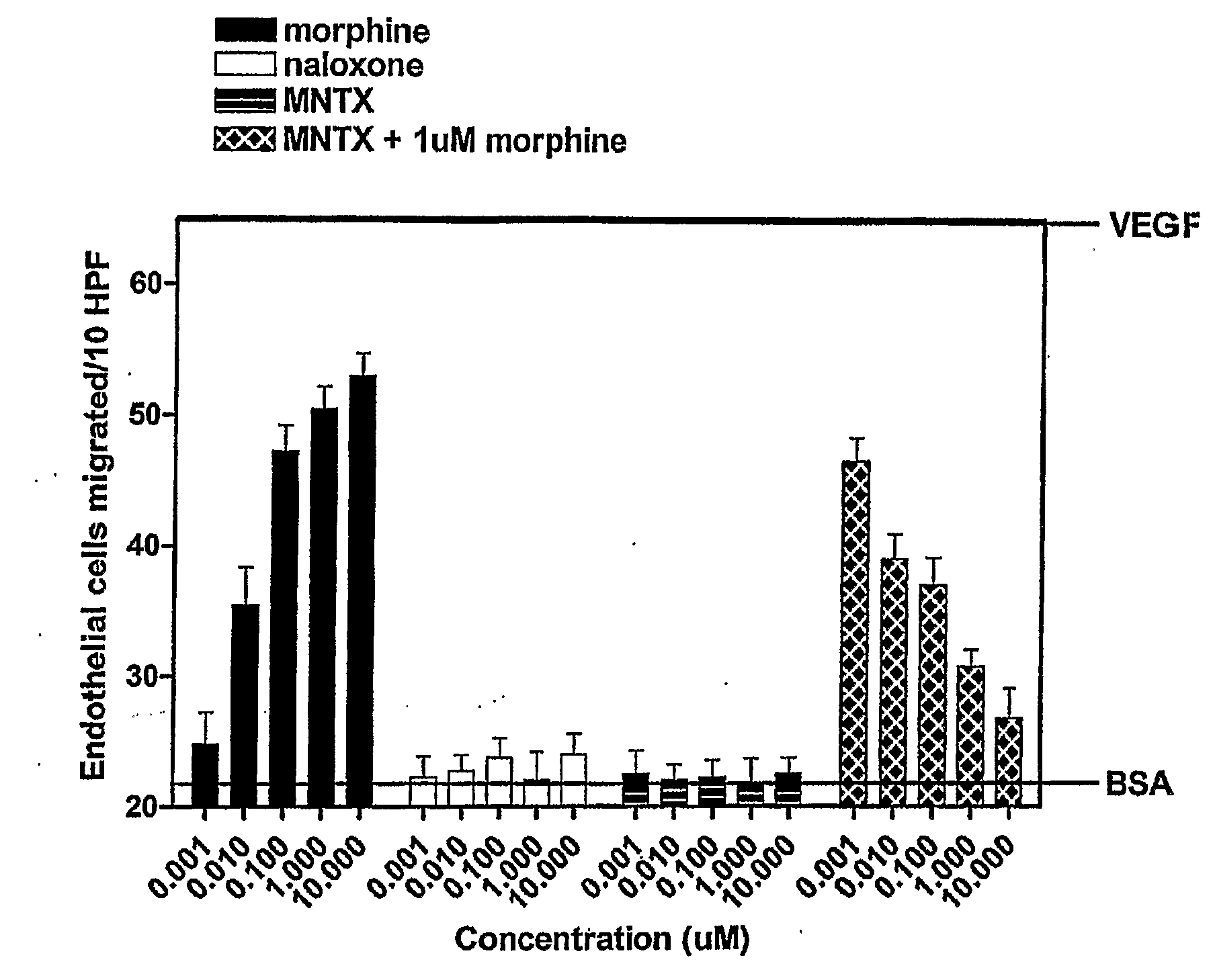
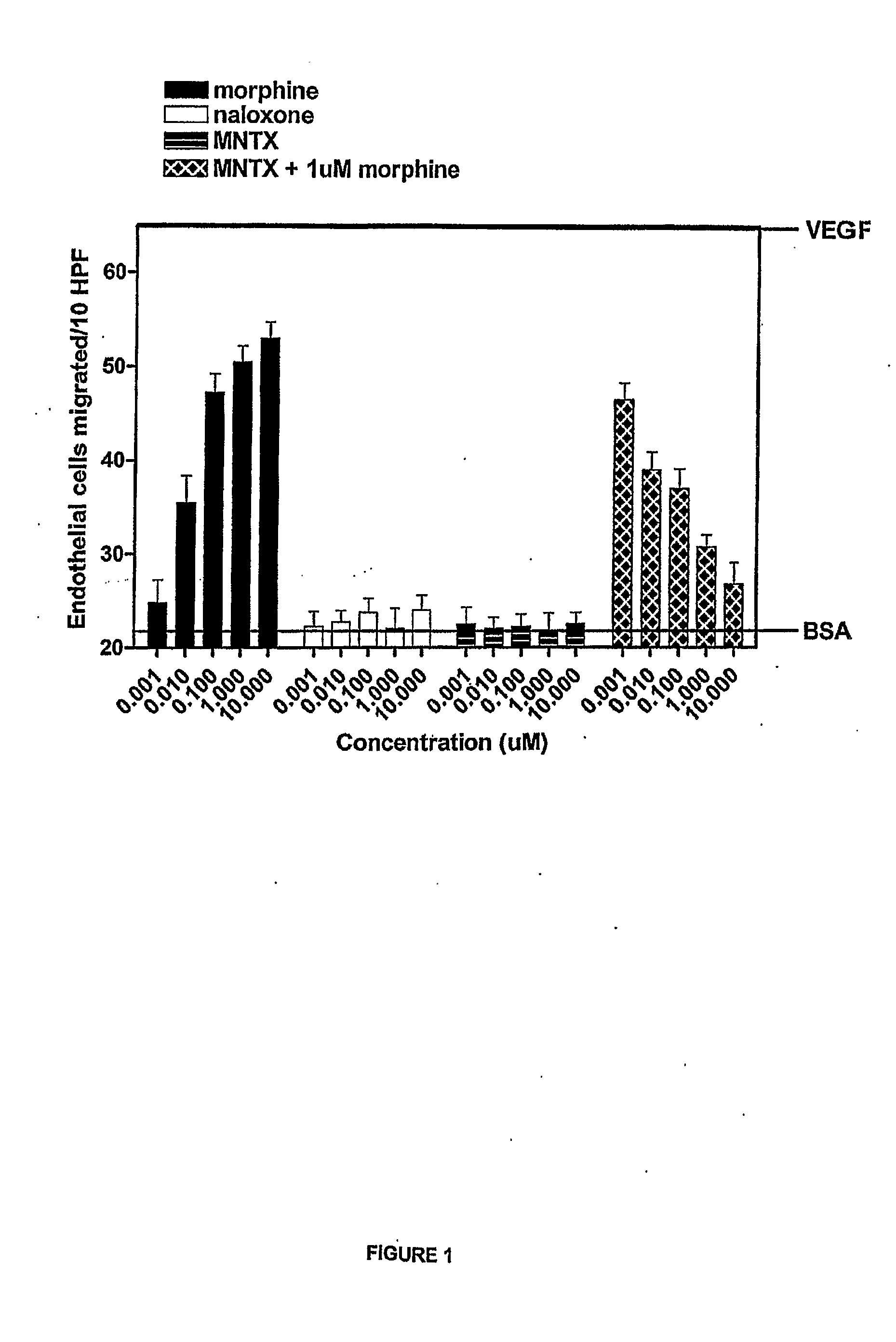
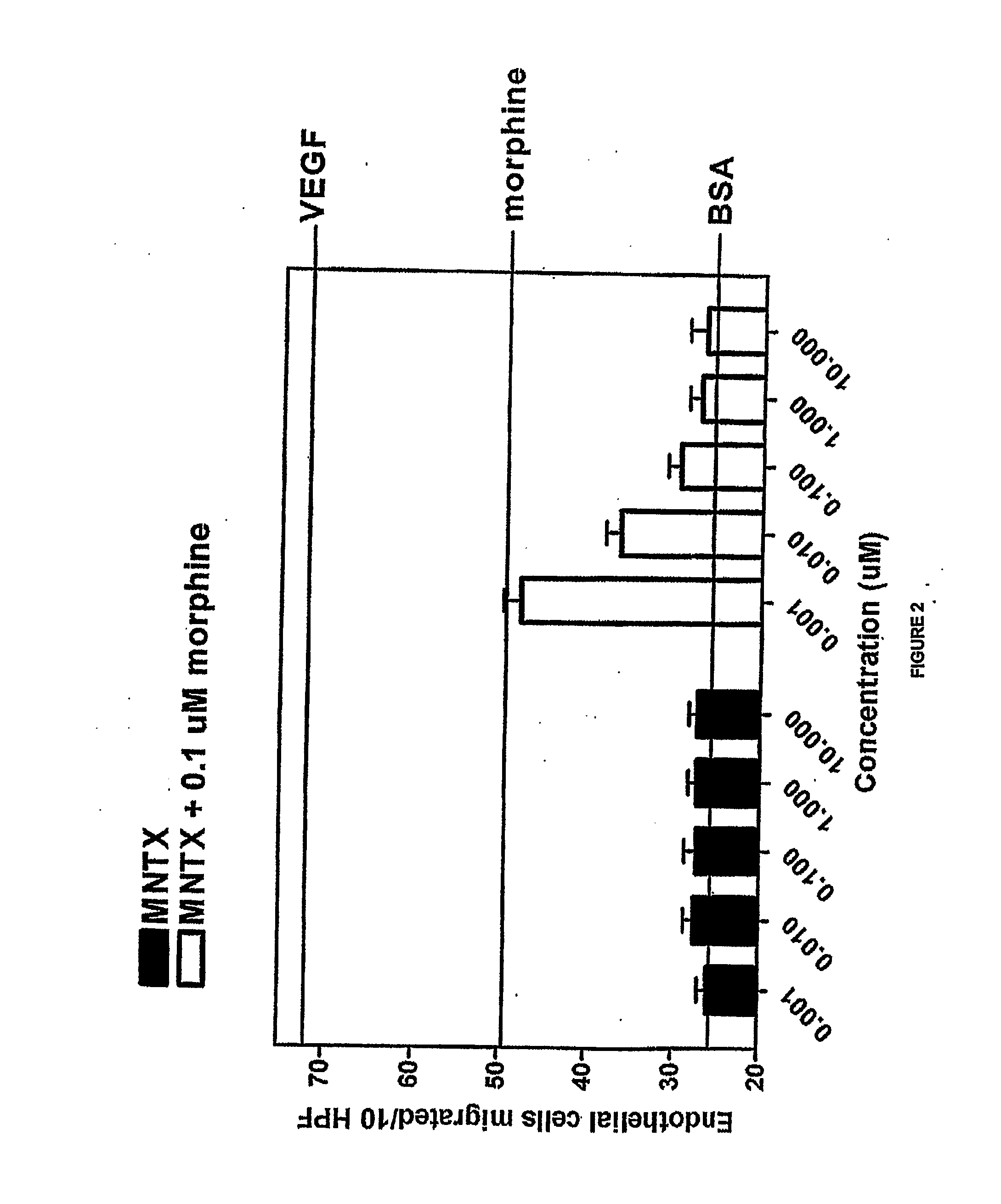
The invention provides methods of attenuating, e.g., inhibiting or reducing, cellular proliferation and migration, particularly endothelial cell proliferation and migration, including that associated with angiogenesis, using opioid antagonists, including, but not limited to, those that are peripherally restricted antagonists.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Methods and compositions for targeting agents into and across the blood-barrier and other endothelial cell microvascular barriers
InactiveUS8026209B2Improve permeabilityHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMammalBiology
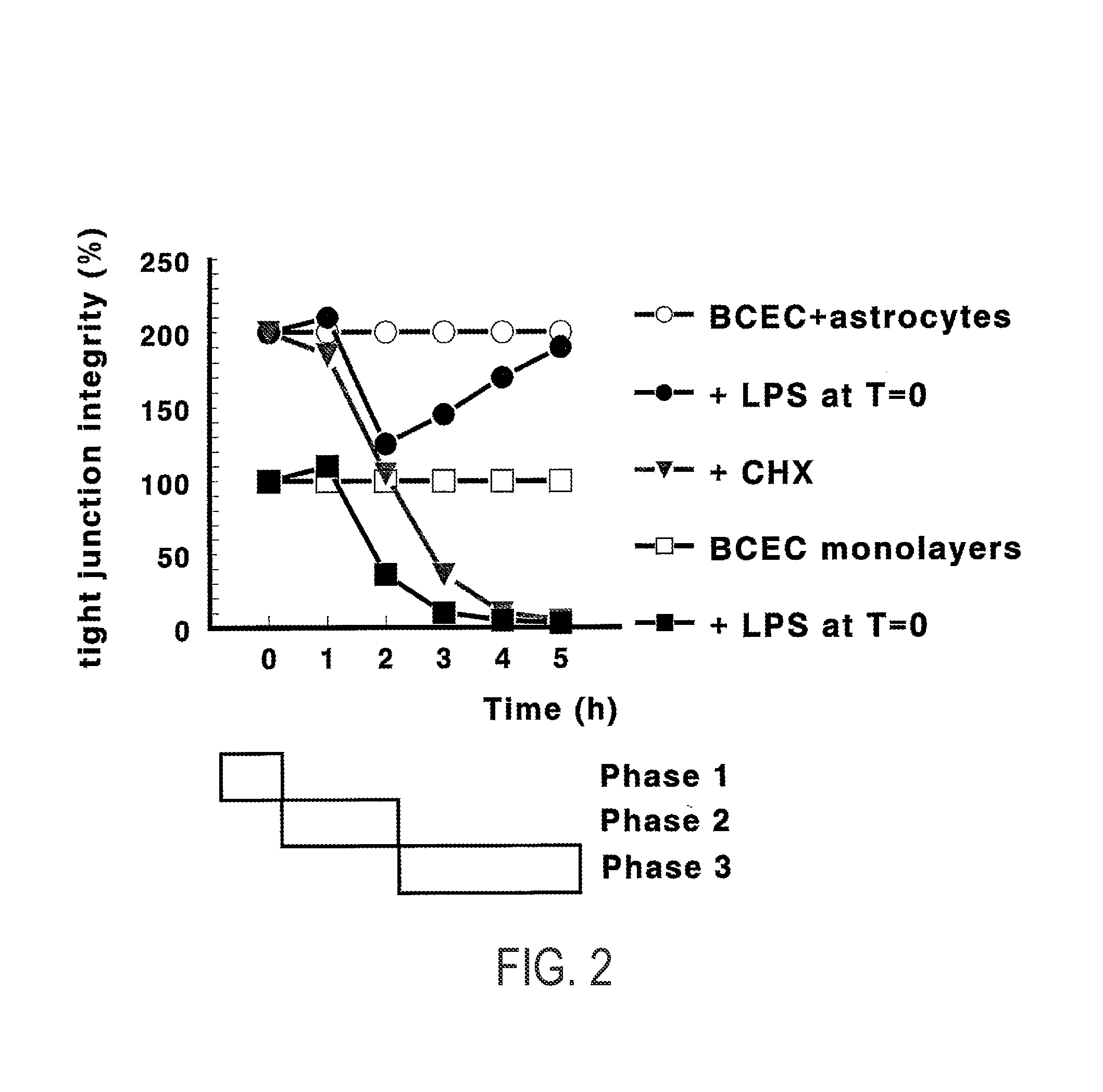
The present invention relates to nucleic acids and polypeptides encoded thereby, whose expression is modulated in brain microvascular endothelial cells undergoing early dynamic inflammation-induced changes in blood-brain barrier functionality. Such polypeptides are referred to as lipopolysaccharide-sensitive (LPSS) polypeptides herein. These nucleic acids and polypeptides may be useful in methods for controlling blood-brain barrier properties in mammals in need of such biological effects. This includes the diagnosis and treatment of disturbances in the blood-brain / retina barrier, brain (including the eye) disorders, as well as peripheral vascular disorders. Additionally, the invention relates to the use of anti-LPSS polypeptide antibodies or ligands as diagnostic probes, as blood-brain barrier targeting agents or as therapeutic agents as well as the use of ligands or modulators of expression, activation or bioactivity of LPSS polypeptides as diagnostic probes, therapeutic agents or drug delivery enhancers.
Owner:2 BBB MEDICINES BV
RNA interference mediated inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050148530A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityBiocideSugar derivativesDiseaseFactor ii
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF, VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D) and / or vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (e.g., VEGFR1, VEGFR2 and / or VEGFr3) gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (mRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against VEGF and / or VEGFr gene expression and / or activity. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, proliferative diseases, and any other disease or condition that responds to modulation of VEGF and / or VEGFr expression or activity.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Promoters exhibiting endothelial cell specificity and methods of using same for regulation of angiogenesis
Isolated polynucleotide sequences exhibiting endothelial cell specific promoter activity, novel cis regulatory elements and methods of use thereof enabling treatment of diseases characterized by aberrant neovascularization or cell growth are disclosed.
Owner:VASCULAR BIOGENICS
Endothelial cell expression patterns
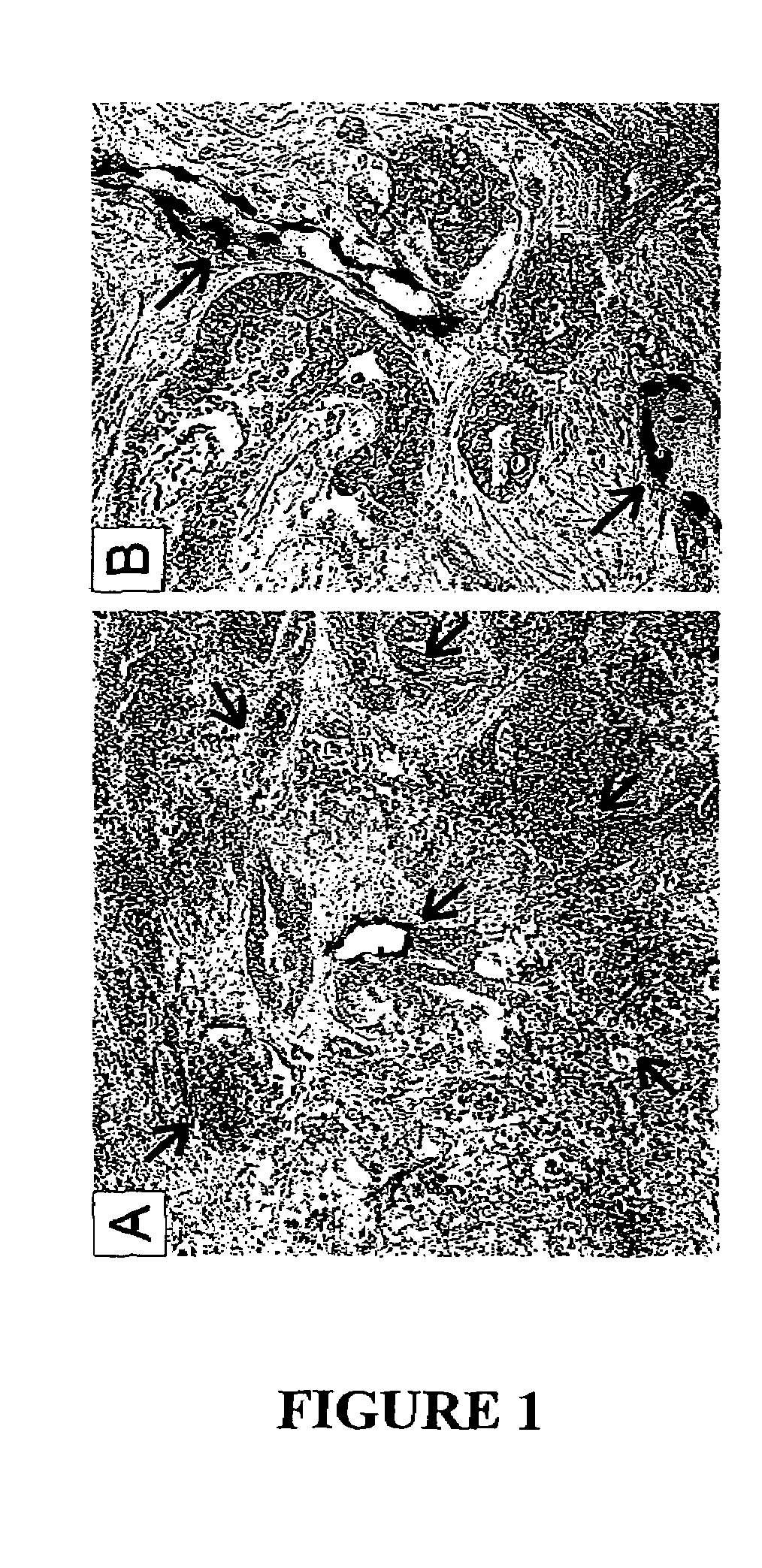
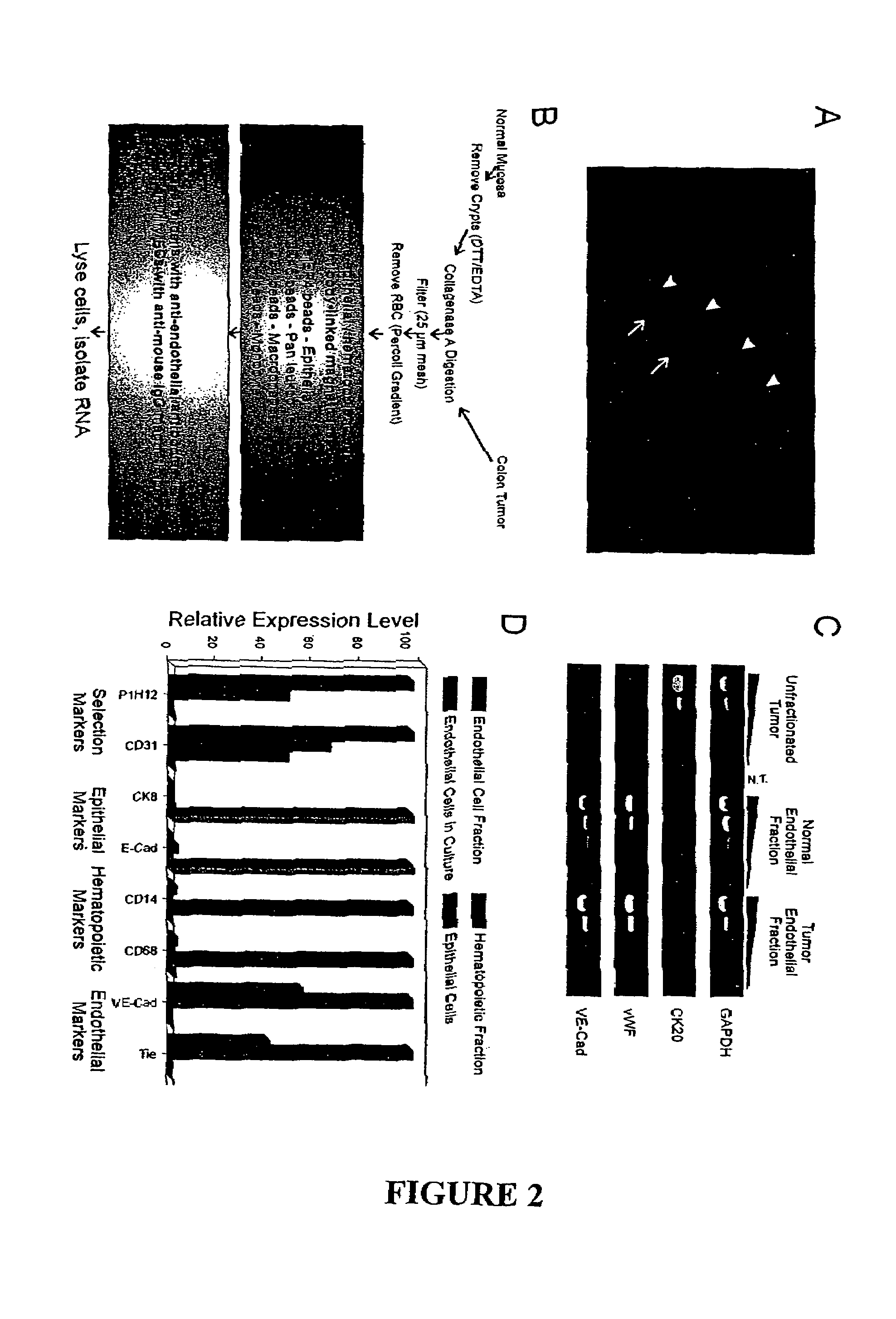
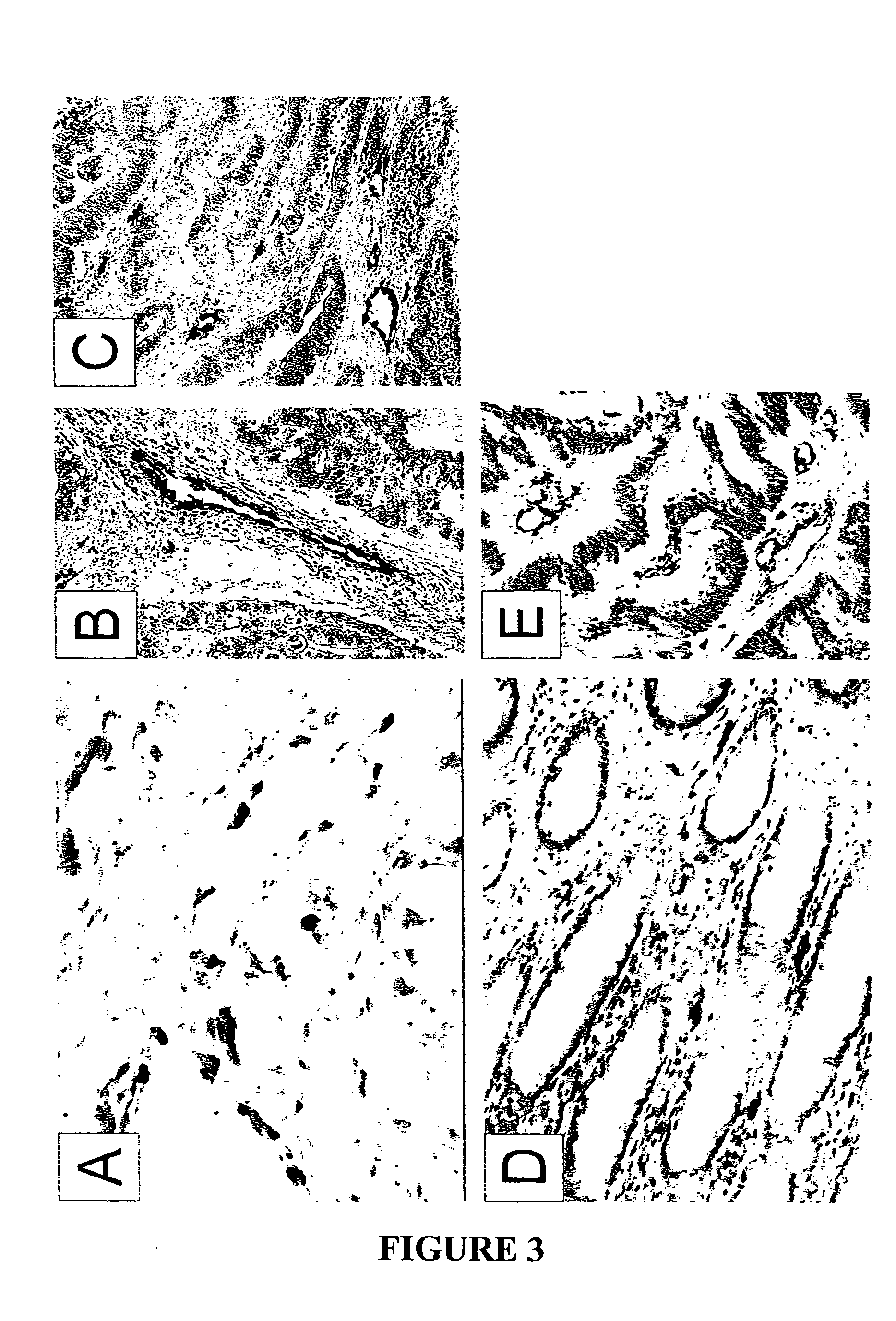
To gain a better understanding of tumor angiogenesis, new techniques for isolating endothelial cells (ECs) and evaluating gene expression patterns were developed. When transcripts from ECs derived from normal and malignant colorectal tissues were compared with transcripts from non-endothelial cells, over 170 genes predominantly expressed in the endothelium were identified. Comparison between normal- and tumor-derived endothelium revealed 79 differentially expressed genes, including 46 that were specifically elevated in tumor-associated endothelium. Experiments with representative genes from this group demonstrated that most were similarly expressed in the endothelium of primary lung, breast, brain, and pancreatic cancers as well as in metastatic lesions of the liver. These results demonstrate that neoplastic and normal endothelium in humans are distinct at the molecular level, and have significant implications for the development of anti-angiogenic therapies in the future.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D) antibodies and vectors, and methods of use
InactiveUS7122654B2Promote blood circulationImprove in gaseous exchangeFungiSenses disorderBlood vesselAntagonist
VEGF-D, a new member of the PDGF family of growth factors, which among other things stimulates endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis and increases vascular permeability, as well as nucleotide sequences encoding it, methods for producing it, antibodies and other antagonists to it, transfected or transformed host cells for expressing it, pharmaceutical compositions containing it, and uses thereof in medical and diagnostic applications.
Owner:VEGENICS PTY LTD
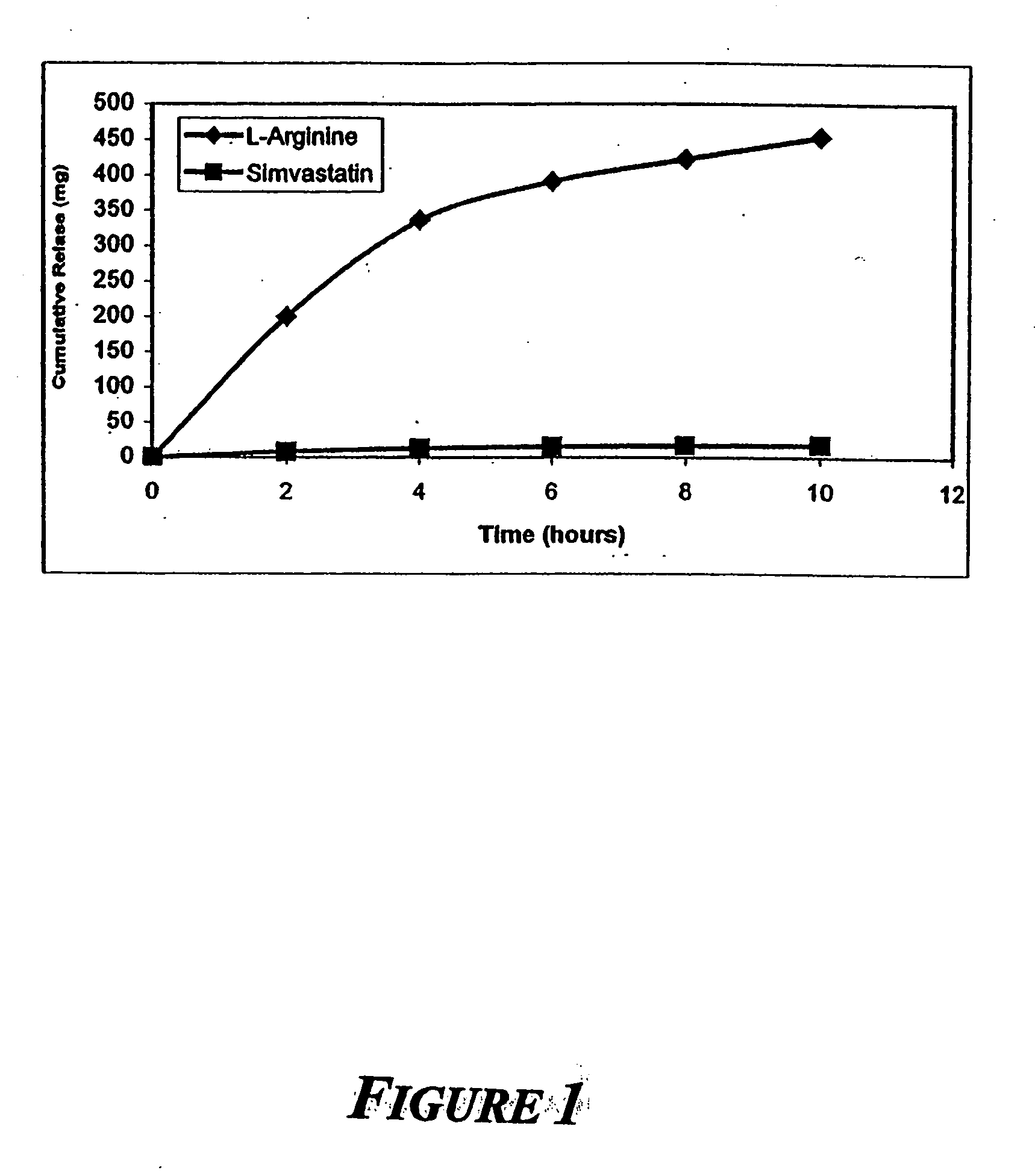
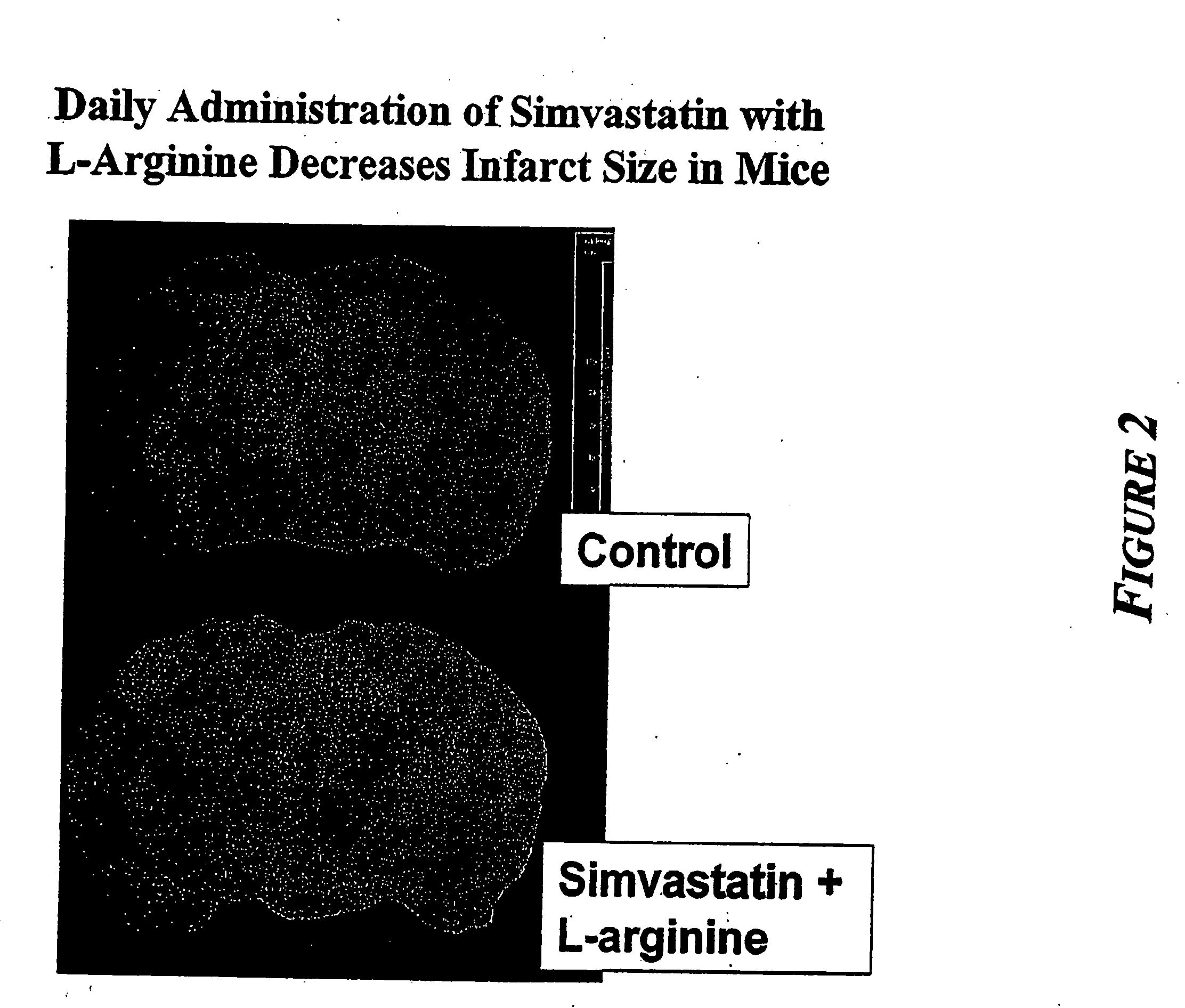
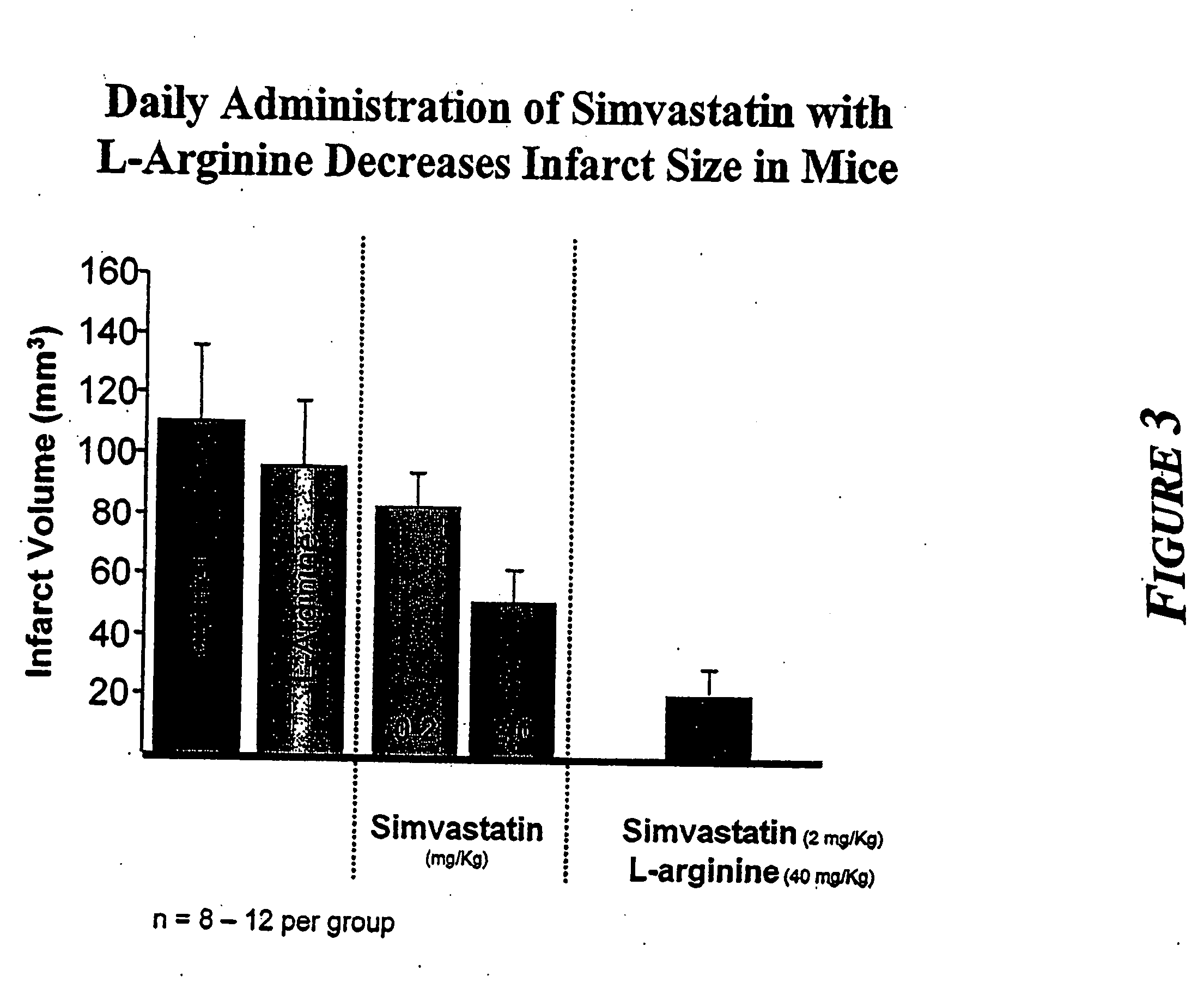
Sustained release L-arginine formulations and methods of manufacture and use
InactiveUS20050287210A1Easy to compressReduce cholesterolOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHMG-CoA reductaseArginine
The present invention provides methods and formulations for the treatment and prevention of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases and disorders. The present invention is based, at least in part, on the discovery that administering to a subject a formulation comprising an agonist of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), such as an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, and a formulation comprising a precursor of NO, such as L-arginine, may be used to treat or prevent cerebrovascular and / or cardiovascular diseases or disorders.
Owner:PALMETTO PHARMA
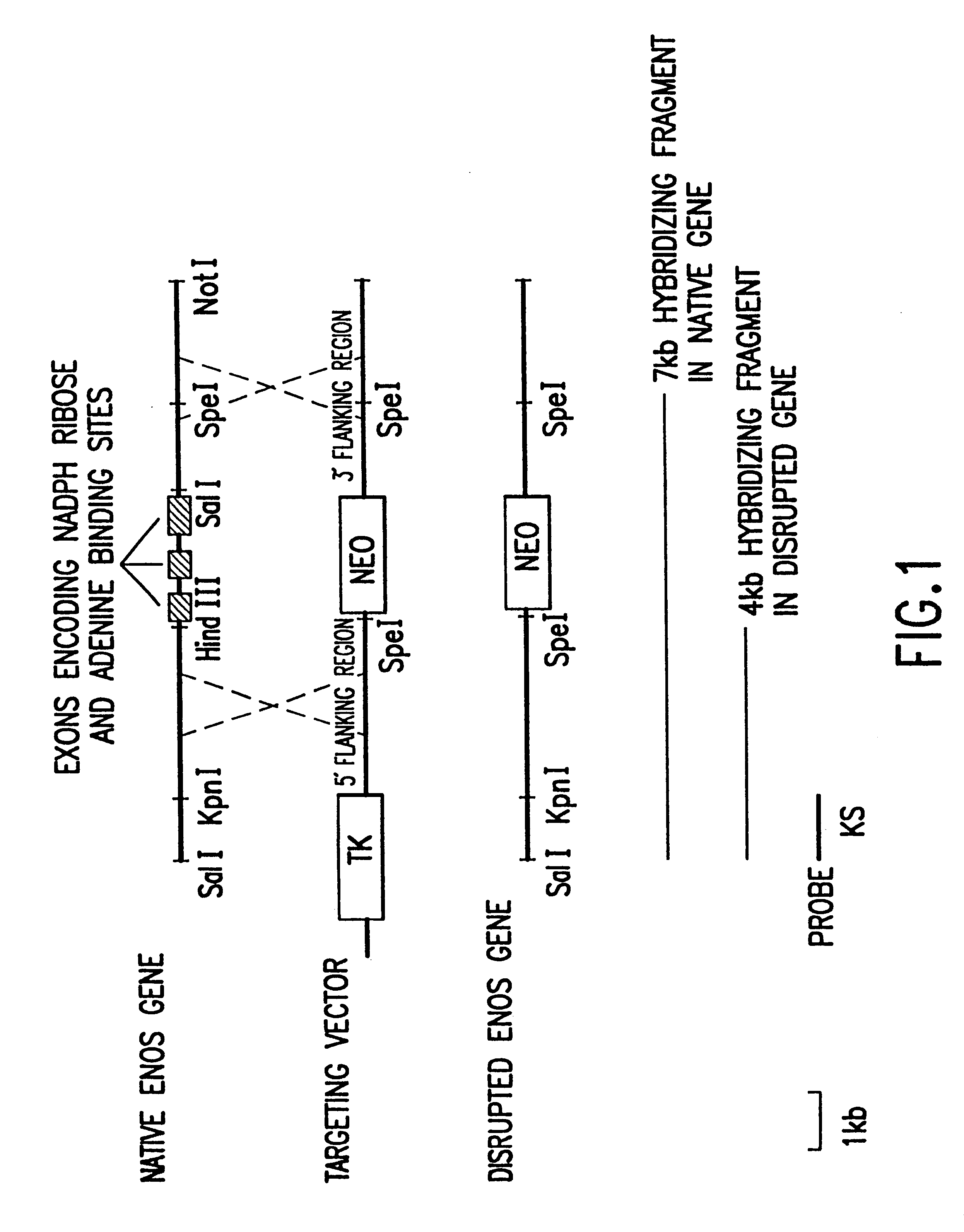
Endothelial NOS knockout mice and methods of use
This invention relates to transgenic non-human animals comprising a disrupted endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene. These animals exhibit abnormal wound-healing properties and hypertension. This invention also relates to methods of using the transgenic animals to screen for compounds having a potential therapeutic utility for vascular endothelial disorders, such as hypertension, cerebral ischemia or stroke, atherosclerosis and wound-healing activities. Moreover, this invention also relates to methods of treating a patient suffering from hypertension and wound-healing abnormalities with the compounds identified using the transgenic animals, and methods of making the transgenic animals. A method of treating a wound using nitroglycerin is also provided.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Methods and compositions for the treatment of fibrotic conditions & impaired lung function & to enhance lymphocyte production
InactiveUS20030008816A1Improve complianceFunction increaseAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsCell adhesionPulmonary compliance
The present invention provides methods and compositions to treat fibrotic conditions, to increase lymphocyte production in vivo, and to improve and / or normalize lung function, pulmonary compliance, blood oxygenation, and blood pH to inhibit inflammatory processes to stimulate or inhibit pro-inflammatory and immune cells, and to inhibit migration of vascular endothelial cells. The invention contemplates the administration of human uteroglobin, native or recombinant, as a means of achieving these ends. Specifically, it has been found that uteroglobin inhibits cell adhesion to fibronectin, increases lymphocyte production in vivo, and improves and / or normalizes lung function, pulmonary compliance, blood oxygenation, and blood pH, and inhibits inflammatory process. In addition it has been found that uteroglobin can stimulate or inhibit pro-inflammatory and immune cells and inhibitor migration of vascular endothelial cells.
Owner:CC10 SWEDEN +4
Method for Amplification of Endothelial Progenitor Cell in Vitro
ActiveUS20080166327A1Function increaseImprove heart functionBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsInterleukin 6Fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 3
The present invention provides a method for expanding an endothelial progenitor cell in vitro. More particularly, the present invention provides a method for culturing a hemangioblast comprising incubating a hemangioblast in a serum-free culture medium containing one or more factors selected from the group consisting of stem cell growth factor, interleukin-6, FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 and thrombopoietin, and a vascular endothelial cell produced by the method; and a serum-free culture medium containing one or more factors selected from the group consisting of stem cell growth factor, interleukin-6, FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 and thrombopoietin, and a kit for the preparation of the serum-free culture medium and the like.
Owner:STEMMED +1
Materials and methods involving hybrid vascular endothelial growth factor DNAs and proteins
InactiveUS6965010B2Improve purification effectExtended half-lifeOrganic active ingredientsFungiNucleotideVascular endothelium
The present invention provides polypeptides that bind cellular receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor polypeptides; polynucleotides encoding such polypeptides; compositions comprising the polypeptides and polynucleotides; and methods and uses involving the foregoing. Some polypeptides of the invention exhibit unique receptor binding profiles compared to known, naturally occurring vascular endothelial growth factors.
Owner:VEGENICS PTY LTD
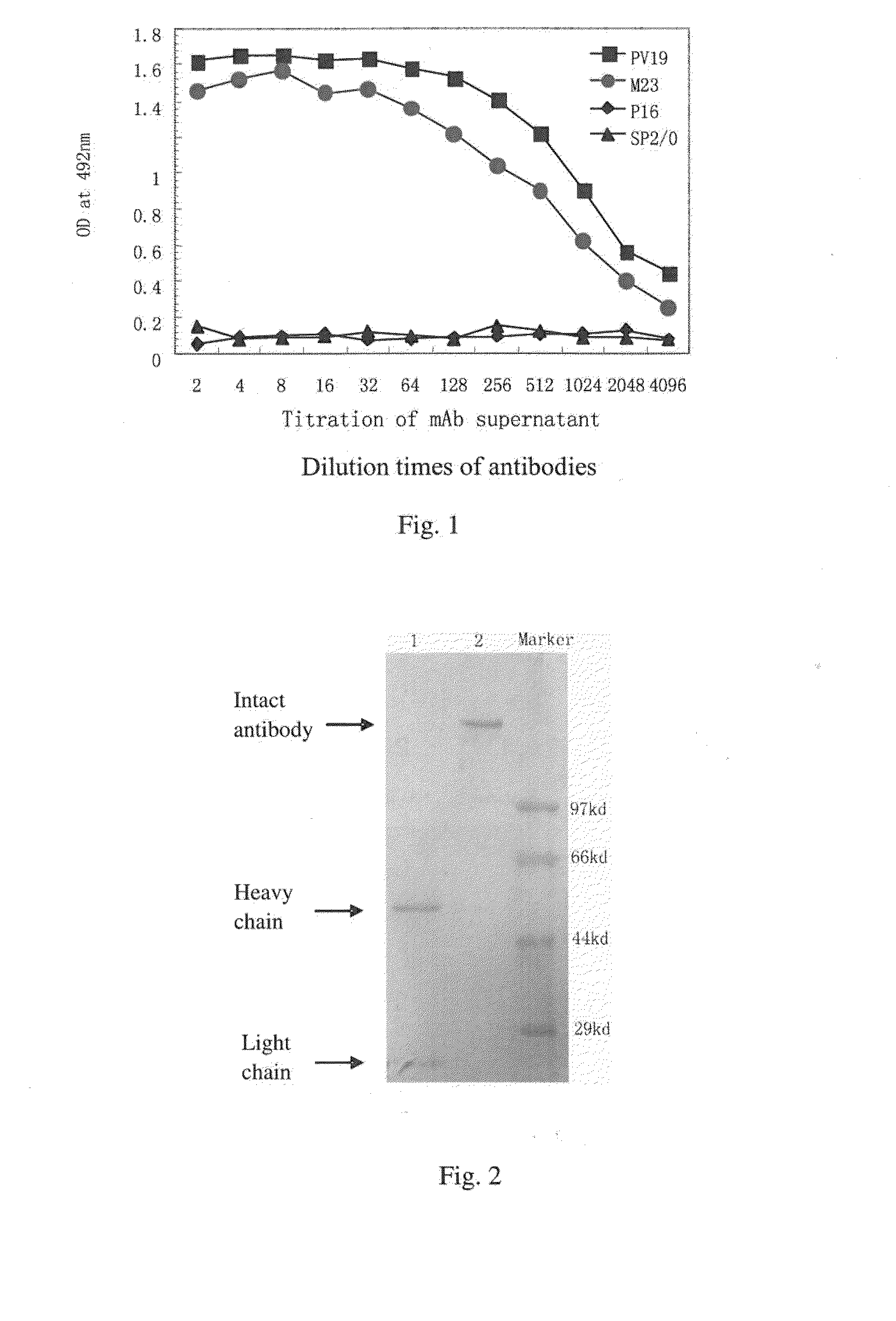
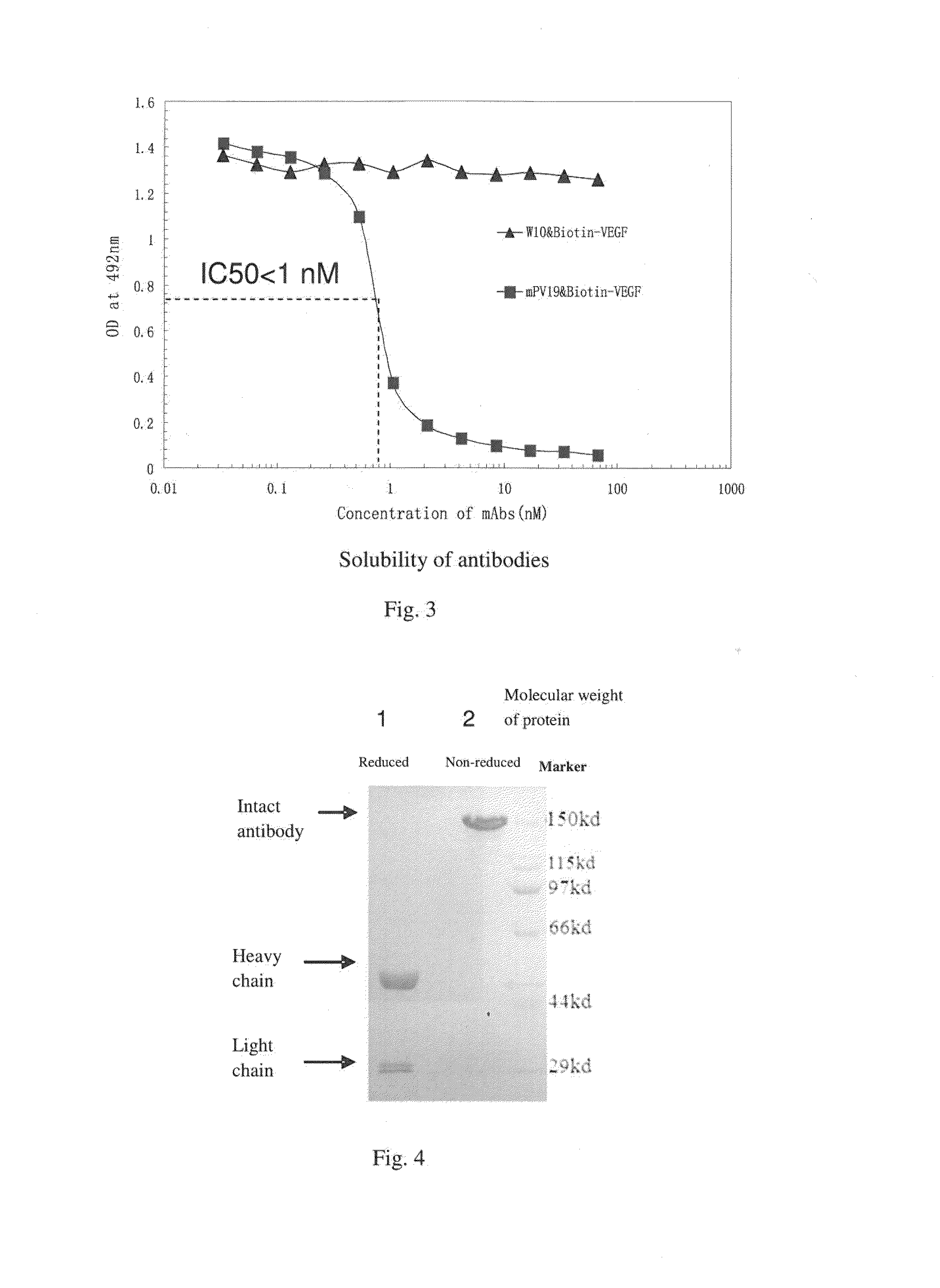
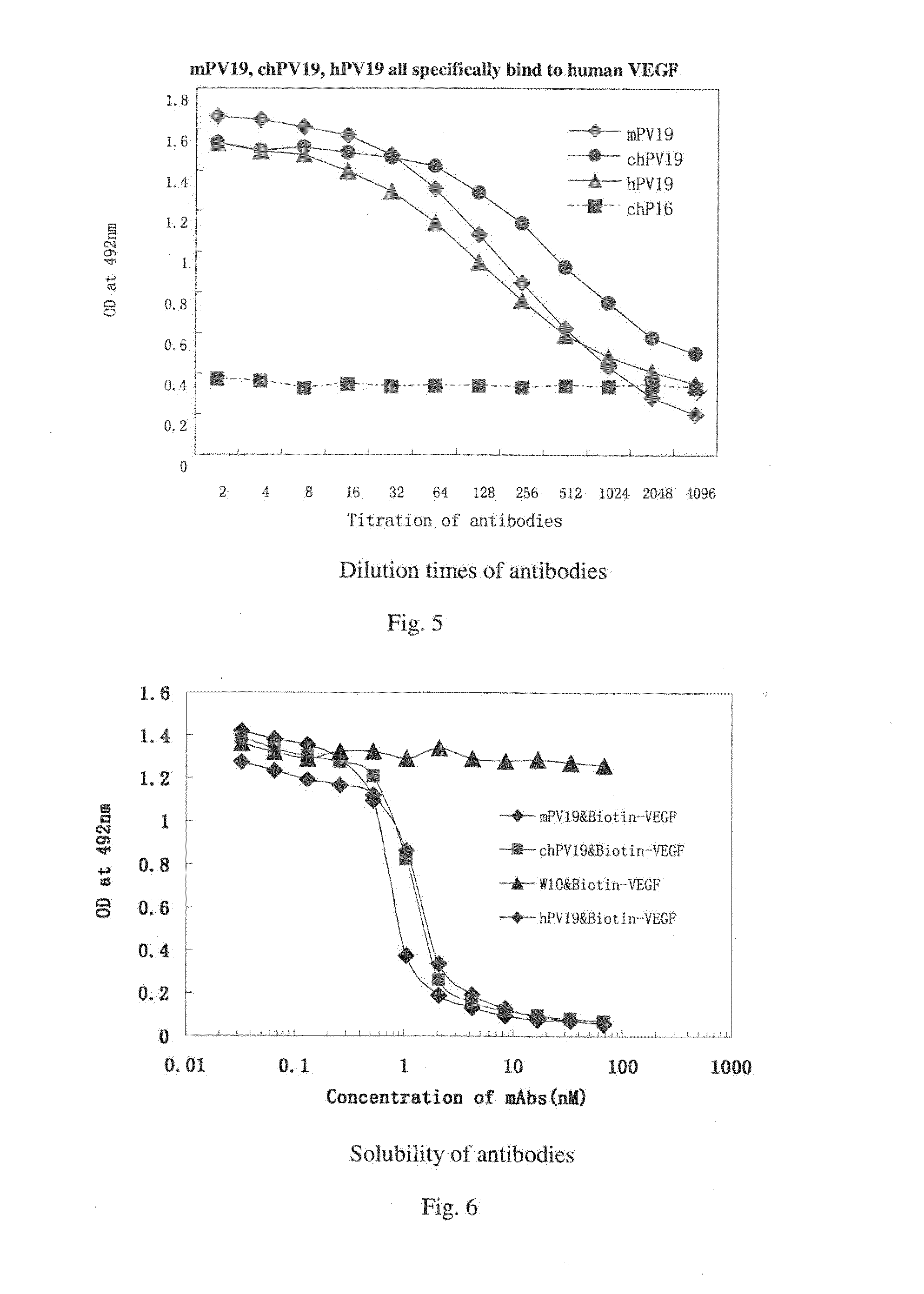
Monoclonal antibody for antagonizing and inhibiting binding of vascular endothelial cell growth factor and its receptor, and coding sequence and use thereof
ActiveUS20160039921A1Reduce the impactAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHumanized antibodyMouse monoclonal antibody
A mouse monoclonal antibody for antagonizing and inhibiting binding of a vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGF-R), and a heavy chain variable region and light chain variable region amino acid sequence thereof. Also disclosed are a humanized preparation process of the antibody and a heavy chain variable region and light chain variable region amino acid sequence of the humanized antibody. The humanized antibody or its derivative can act as an ingredient of a pharmaceutical composition or be prepared into a suitable pharmaceutical preparation, is administered alone or in combination with a chemotherapy drug or other treatment means, and is used in broad-spectrum treatment of various solid tumors such as colon cancer, breast cancer and rhabdomyosarcoma.
Recombinant proteins that simultaneously bind HGF, VEGF-A and serum albumin, comprising ankyrin repeat domains
ActiveUS9458211B1Good storage stabilitySenses disorderNervous disorderSerum protein albuminAnkyrin Repeat Protein
New designed ankyrin repeat domains with binding specificity for serum albumin, recombinant binding proteins comprising at least two designed ankyrin repeat domains with binding specificity for serum albumin, as well as recombinant binding proteins comprising at least one designed ankyrin repeat domain with binding specificity for hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), at least one designed ankyrin repeat domain with binding specificity for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A), and at least two designed ankyrin repeat domain with binding specificity for serum albumin are described, as well as nucleic acids encoding such designed ankyrin repeat domains and recombinant binding proteins, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such designed ankyrin repeat domains, recombinant binding proteins or nucleic acids and the use of such designed ankyrin repeat domains, recombinant binding proteins, nucleic acids or pharmaceutical compositions in the treatment of diseases.
Owner:MOLECULAR PARTNERS AG
Therapeutic Agent for Corneal Diseases
InactiveUS20090163432A1Maintain transparencyLittle abilityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCorneal diseasePharmacology
The present invention relates to a treatment agent for a disease or a disorder caused by a reduction in corneal endothelial cells, comprising as an active component at least one nucleic acid molecule inhibiting the expression of a connexin 43 gene.
Owner:KANSAI TLO KK
Cationic liposome delivery of taxanes to angiogenic blood vessels
InactiveUS7112338B2Precise deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationCell selectivity
Angiogenic endothelial cells are selectively targeted with lipid / DNA complexes or cationic liposomes containing a substance which affects the targeted cells by inhibiting or promoting their growth. A site of angiogenesis can be precisely located by administering cationic liposomes containing a detectable label. The complexes may comprise nucleotide constructs which are comprised of promoters which are selectively and exclusively activated in the environment of an angiogenic endothelial cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Drug for treating states related to the inhibition of angiogenesis and/or endothelial cell proliferation
Owner:IBCC HLDG
Methods and compositions for the treatment of fibrotic conditions & impaired lung function & to enhance lymphocyte production
InactiveUS20020169108A1Improve complianceFunction increaseCosmetic preparationsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsCell adhesionVascular endothelium
The present invention provides methods and compositions to treat fibrotic conditions, to increase lymphocyte production in vivo, and to improve and / or normalize lung function, pulmonary compliance, blood oxygenation, and blood pH to inhibit inflammatory processes to stimulate or inhibit pro-inflammatory and immune cells, and to inhibit migration of vascular endothelial cells. The invention contemplates the administration of human uteroglobin, native or recombinant, as a means of achieving these ends. Specifically, it has been found that uteroglobin inhibits cell adhesion to fibronectin, increases lymphocyte production in vivo, and improves and / or normalizes lung function, pulmonary compliance, blood oxygenation, and blood pH, and inhibits inflammatory process. In addition it has been found that uteroglobin can stimulate or inhibit pro-inflammatory and immune cells and inhibitor migration of vascular endothelial cells.
Owner:CC10 SWEDEN
Medicinal agent and method for curing erectile dysfunction
A medicament based on antibodies contains an activated form of ultra-low doses of monoclonal, polyclonal, or natural antibodies to endothelial nitric oxide synthase (NO synthase), the activated form being prepared by multiple consecutive dilutions and exposure to external factors, preferably according to the homeopathic technology. A method of treating erectile dysfunctions and vegetative disturbances of male climax by regulating the level of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in the cavernous bodies on sexual stimulation, the method being characterized by the use of activated forms of ultra-low doses of antibodies to the entire molecule of the endothelial NO synthase or to its polypeptide fragments, activated forms being prepared by multiple consecutive dilutions and exposure to external factors.
Owner:EPSHTEIN OLEG I
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com