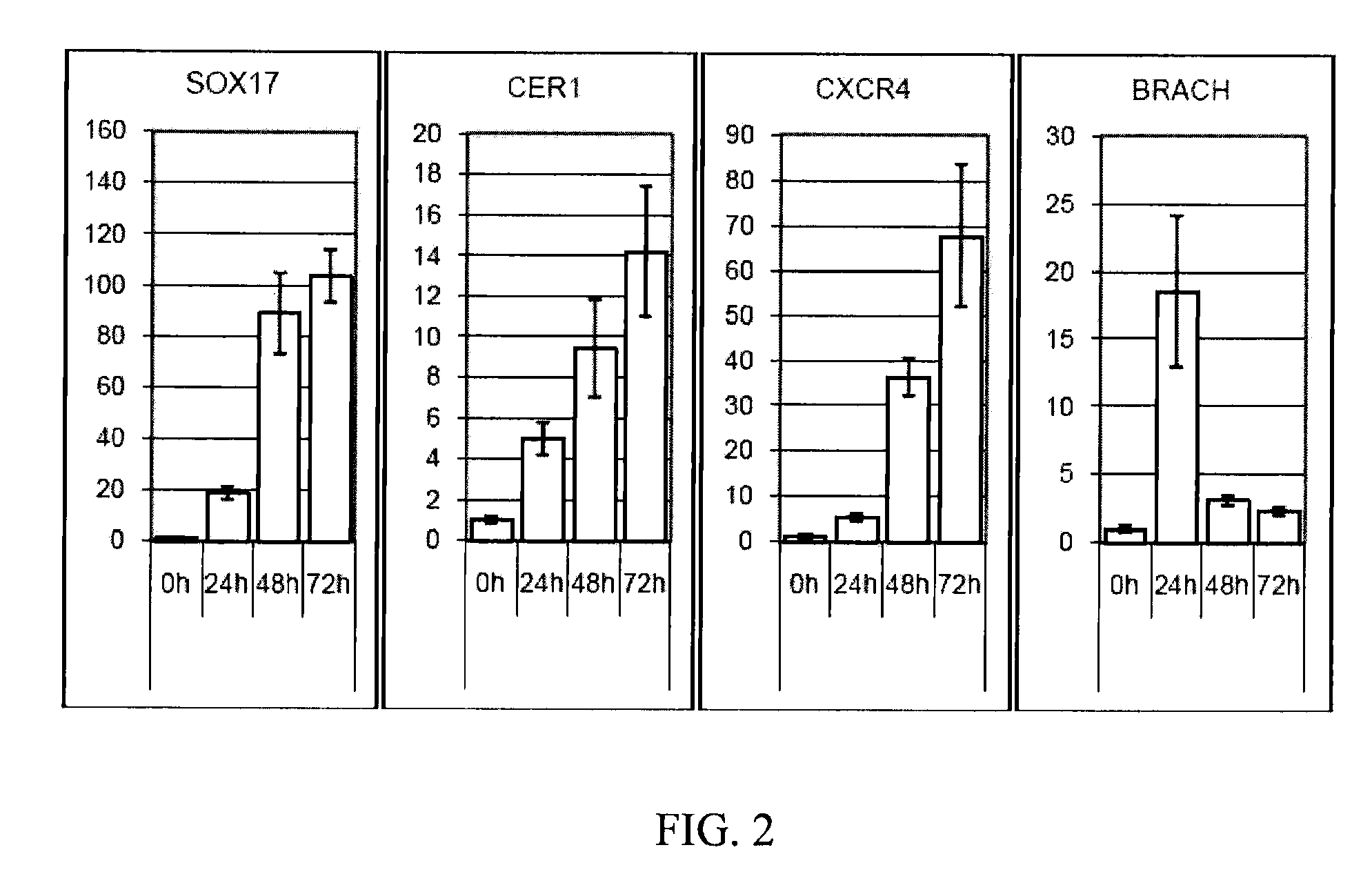
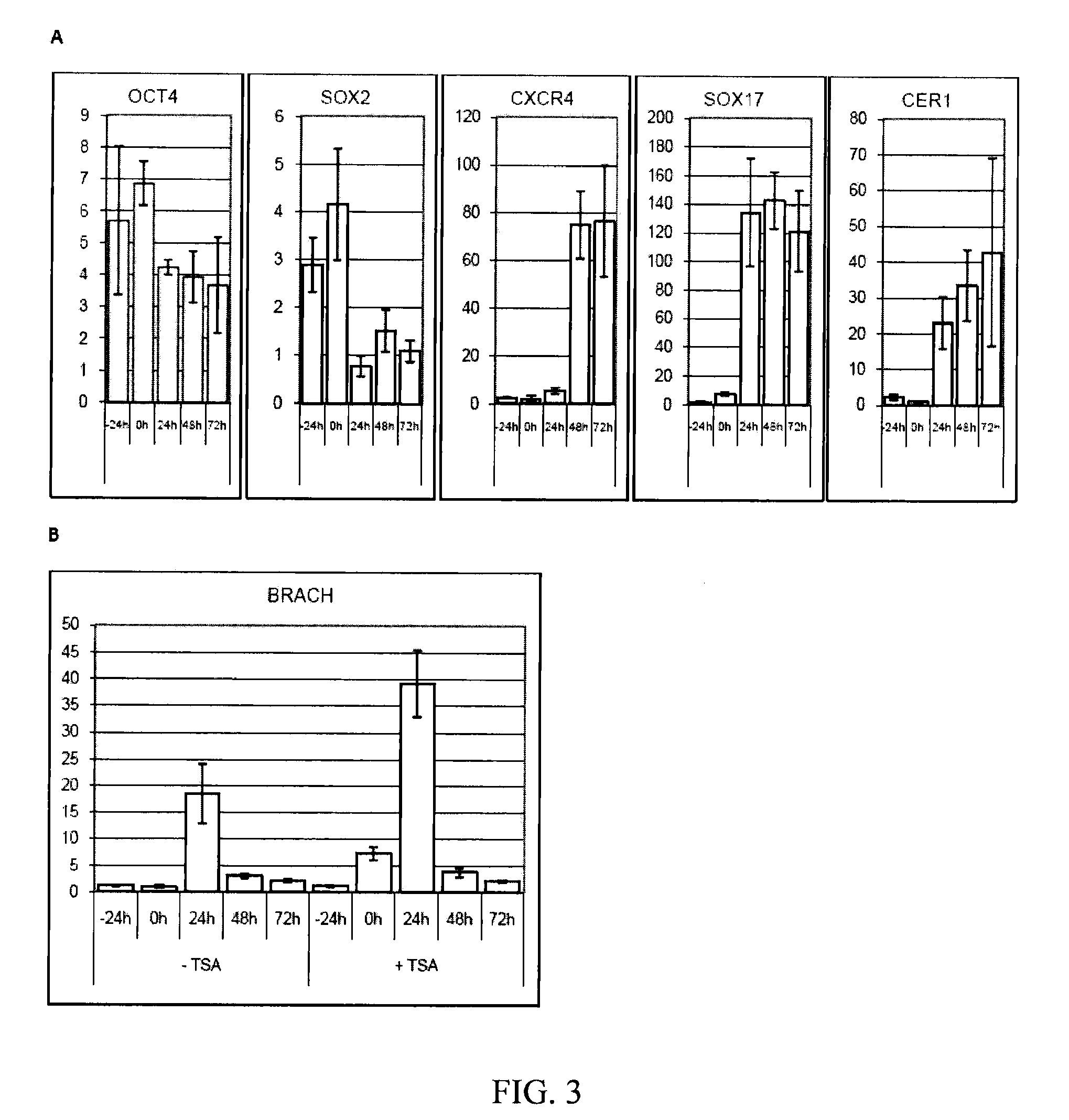
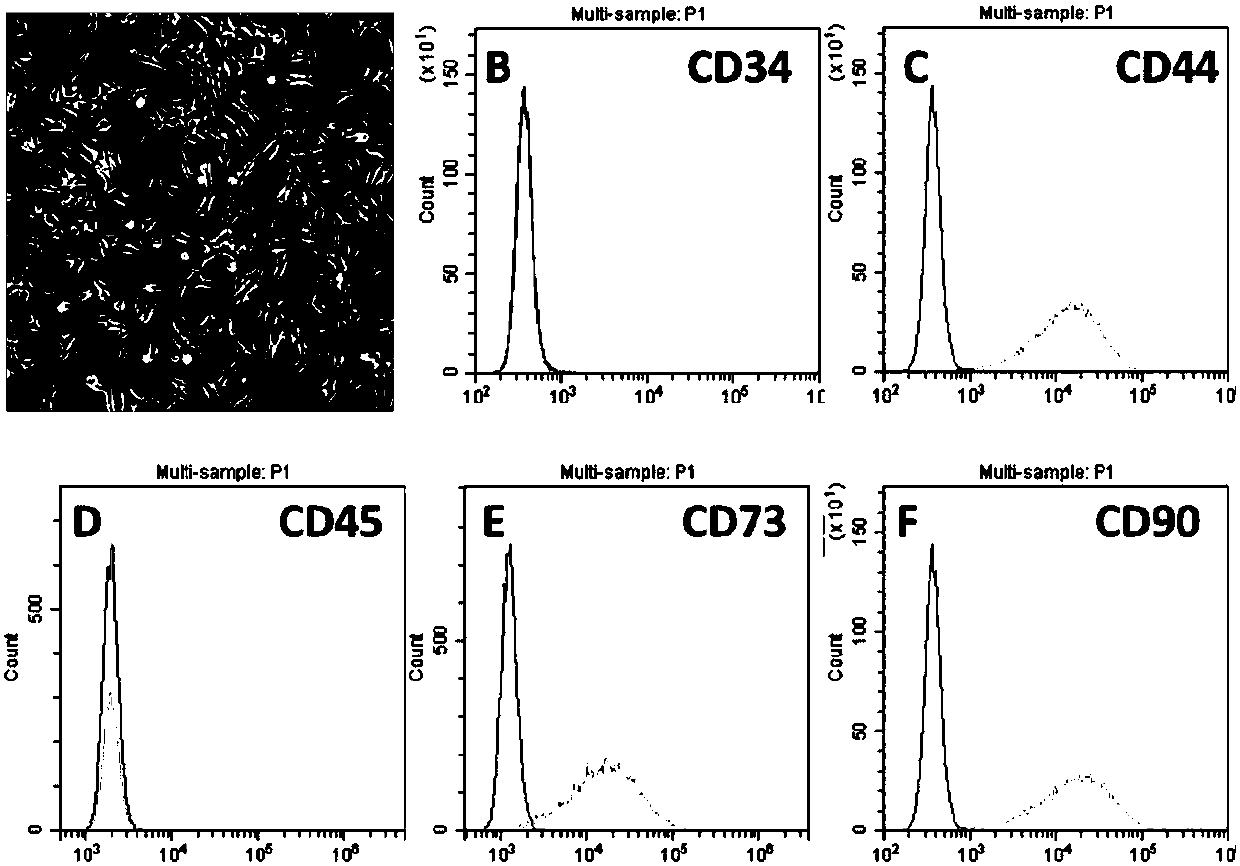
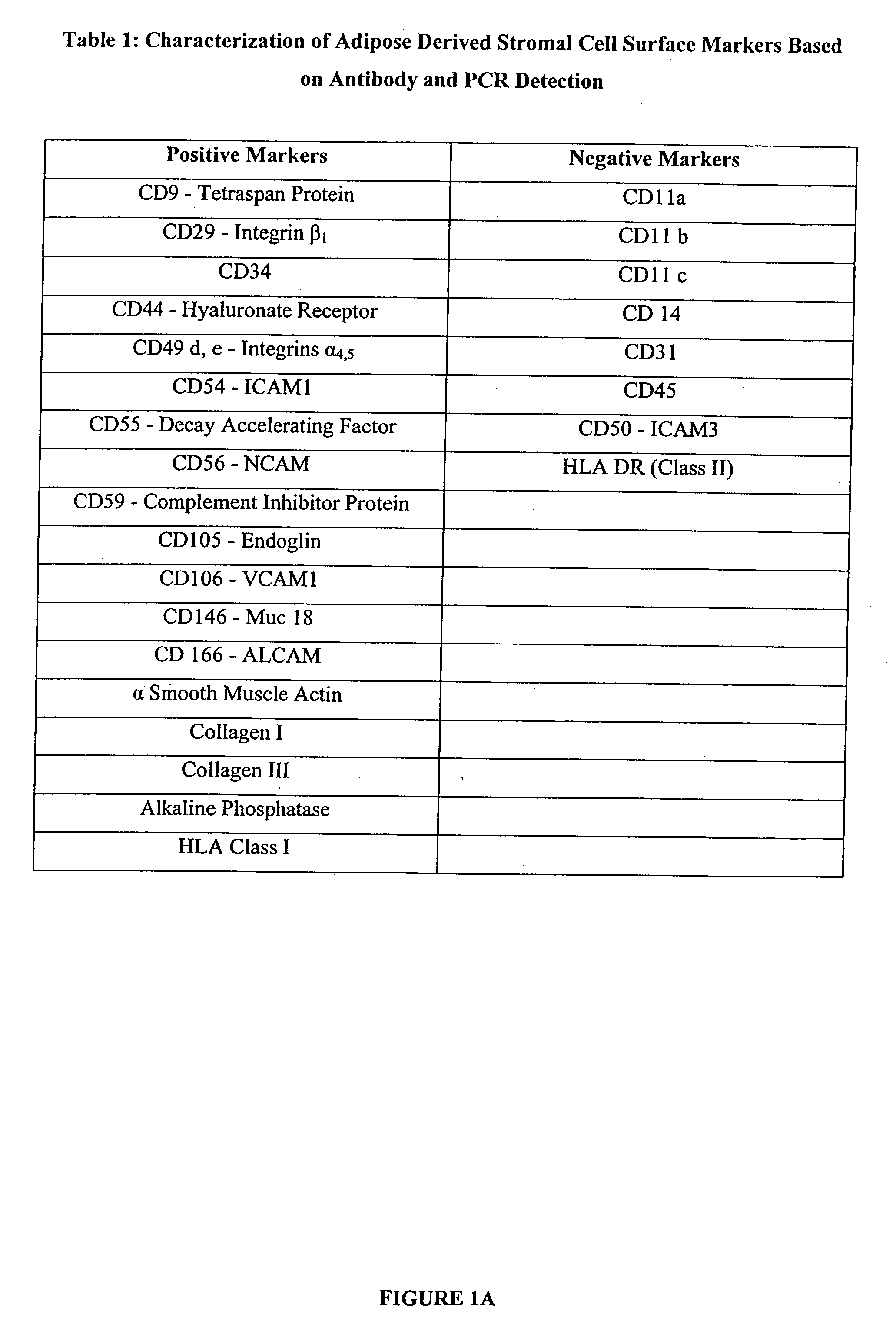
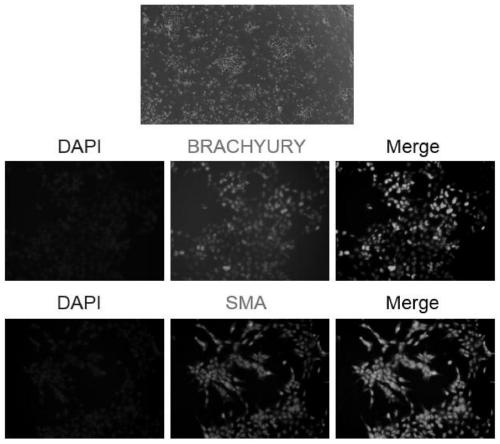
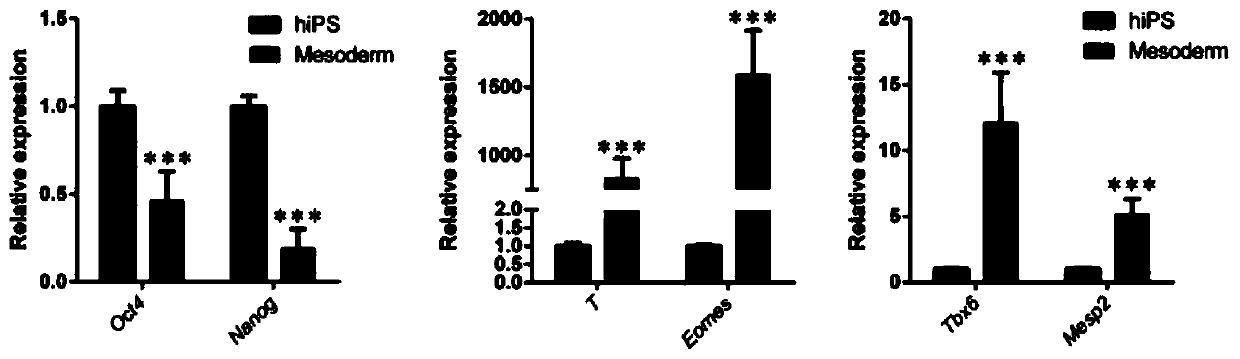
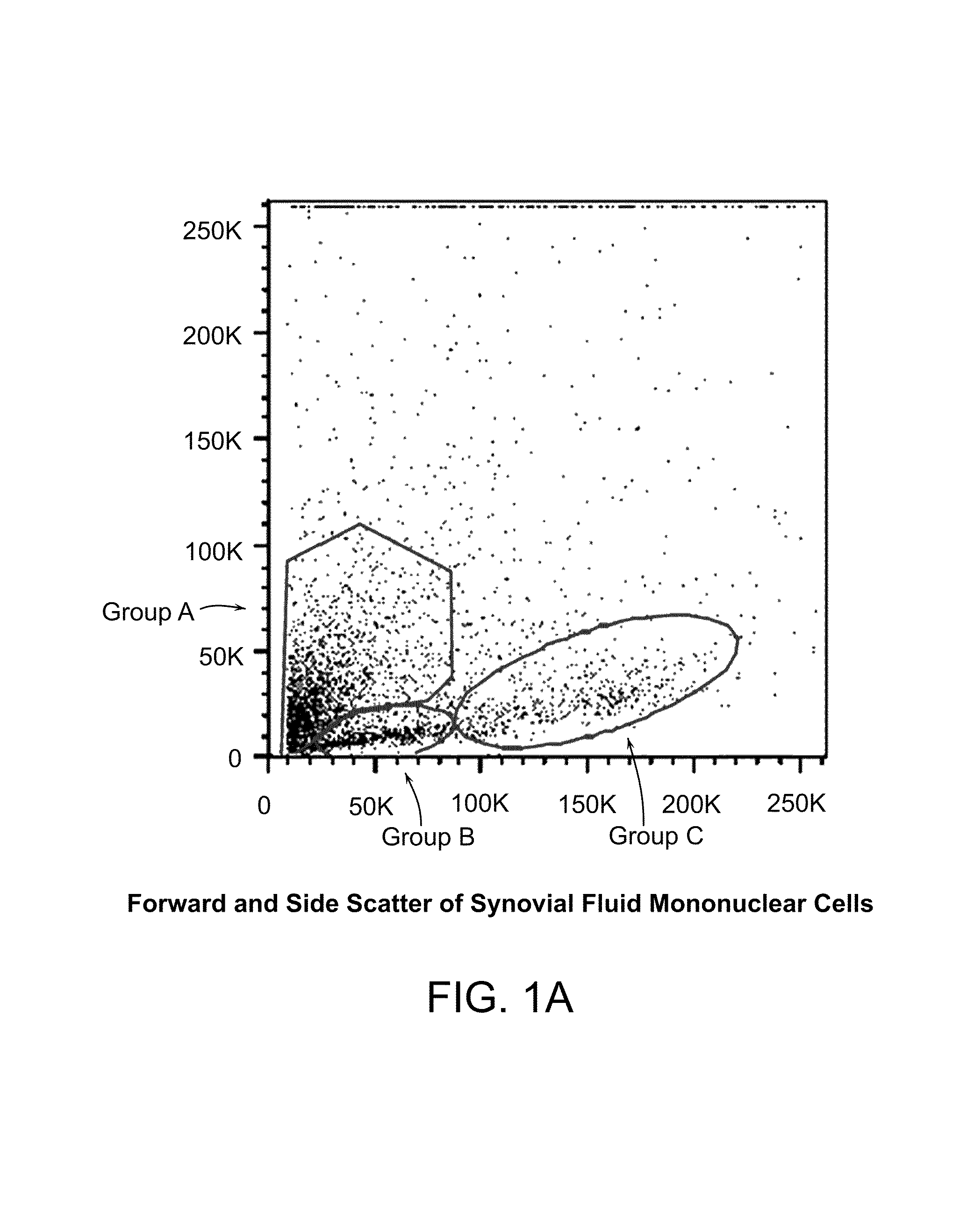
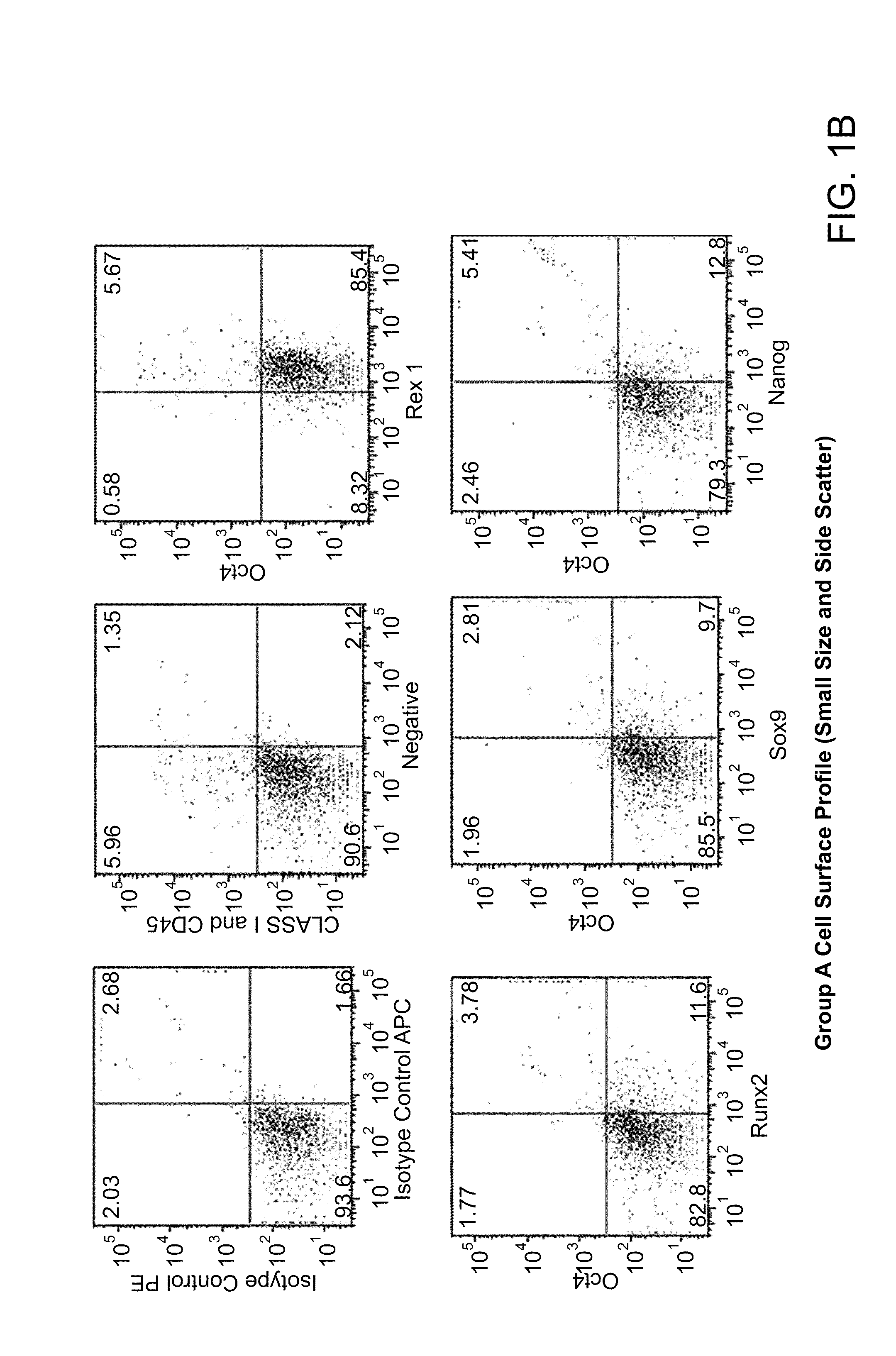
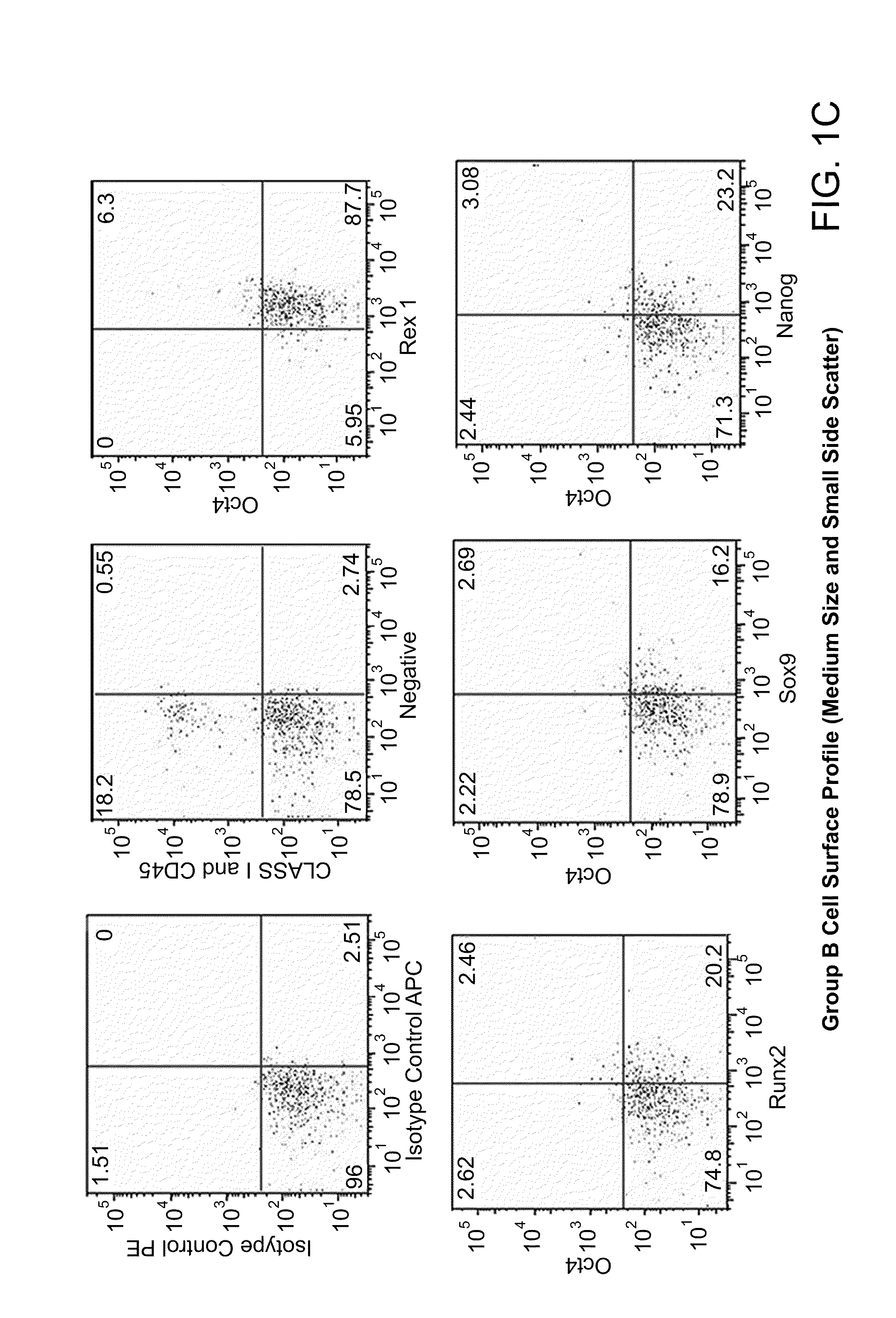
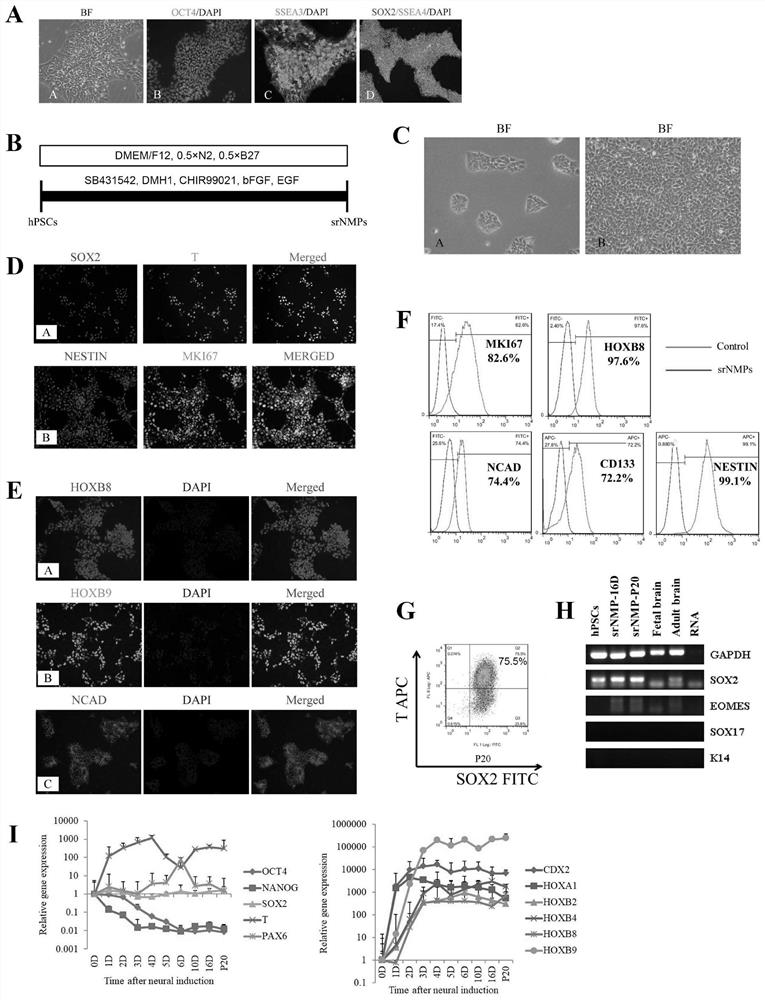
Patents
Literature
134 results about "Mesoderm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
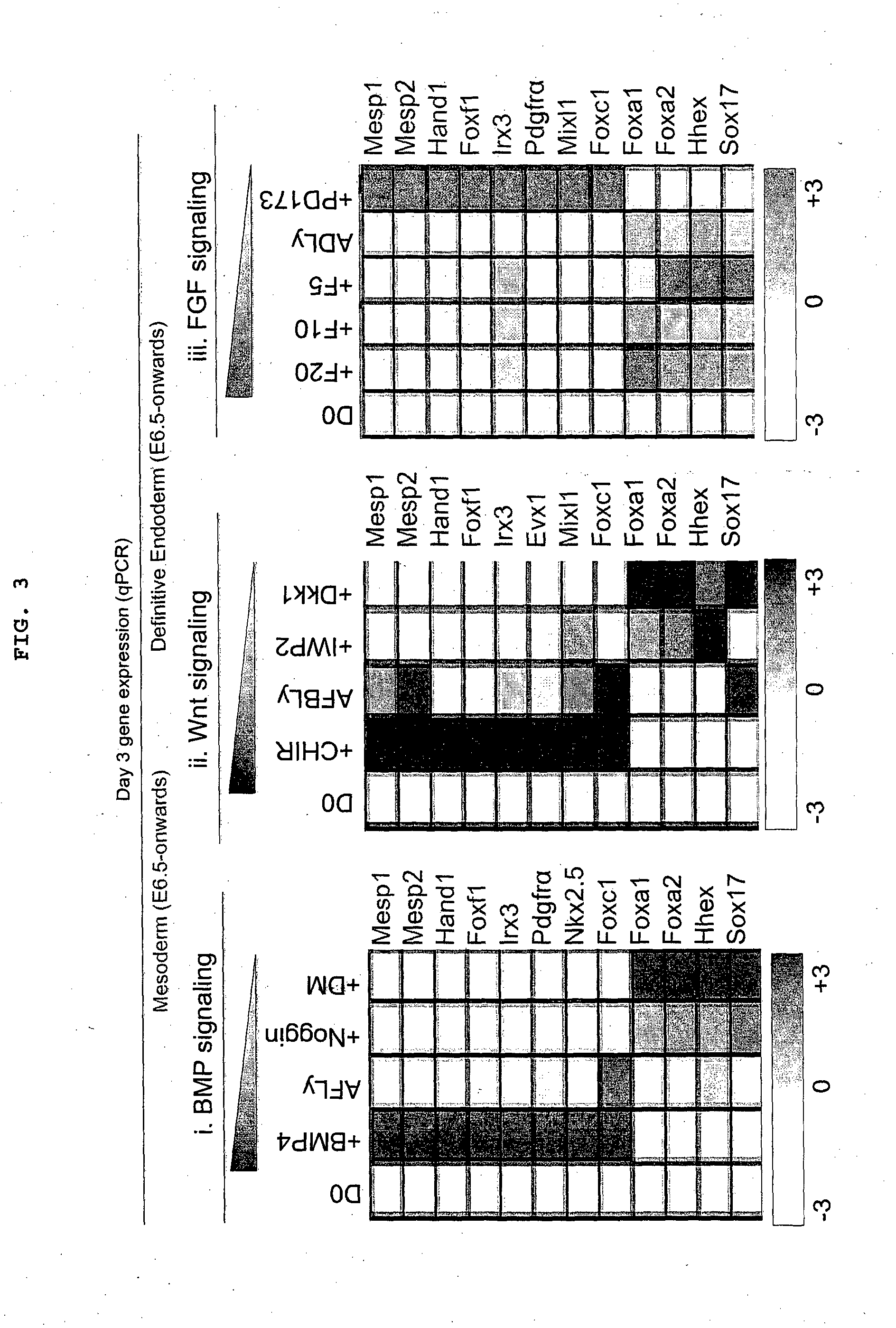
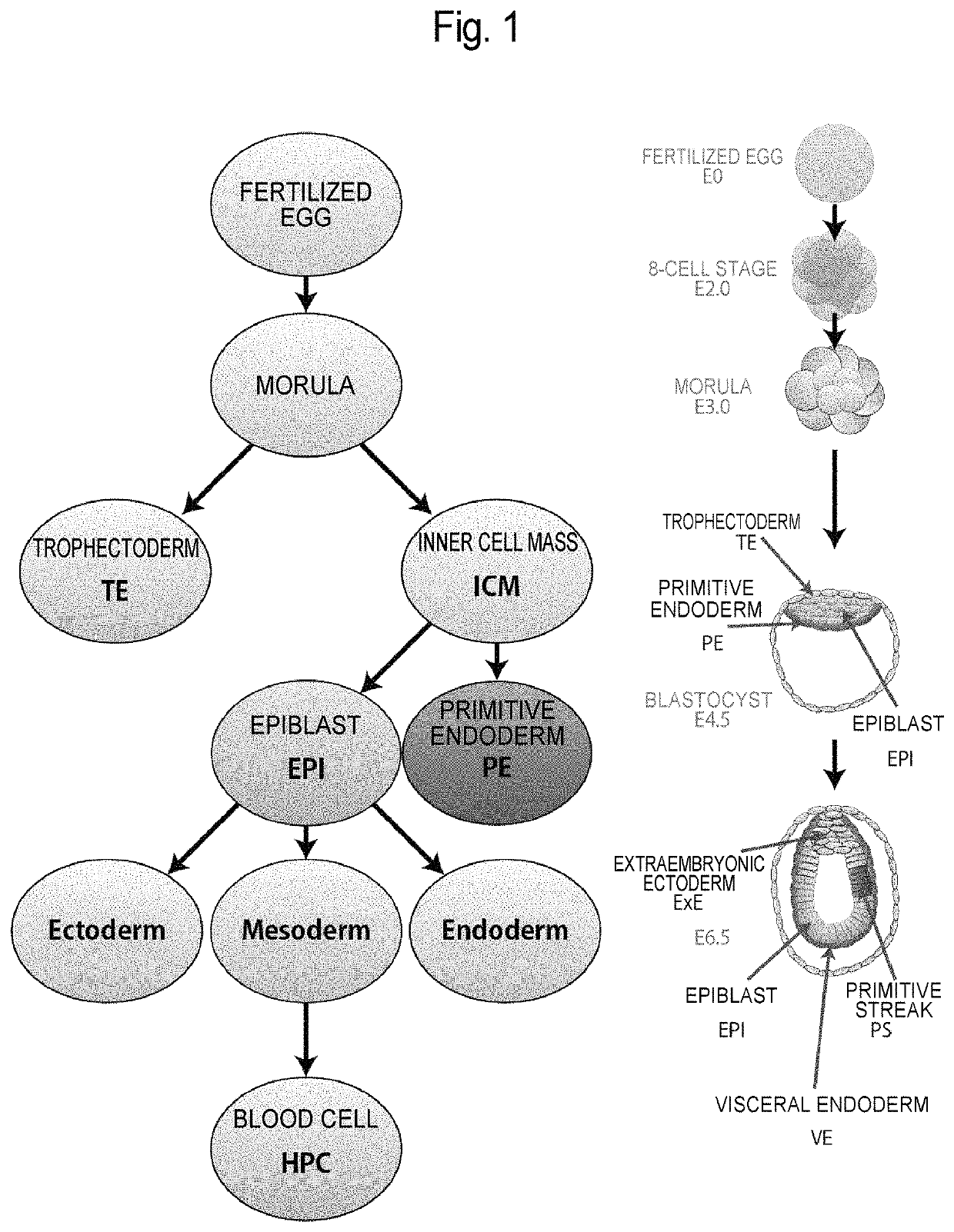
In all bilaterian animals, the mesoderm is one of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and endoderm (inside layer), with the mesoderm as the middle layer between them.
Multipotent amniotic fetal stem cells
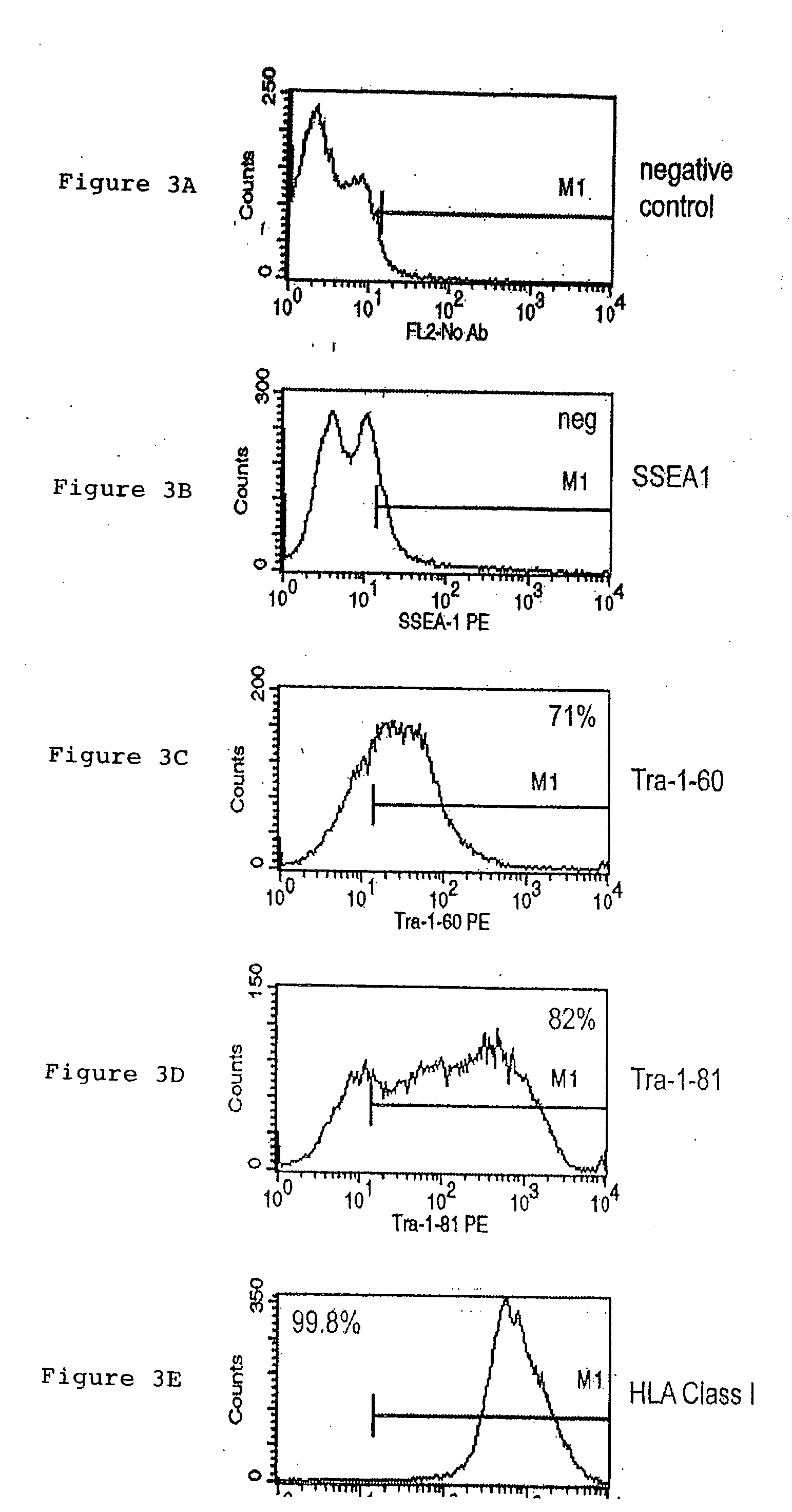
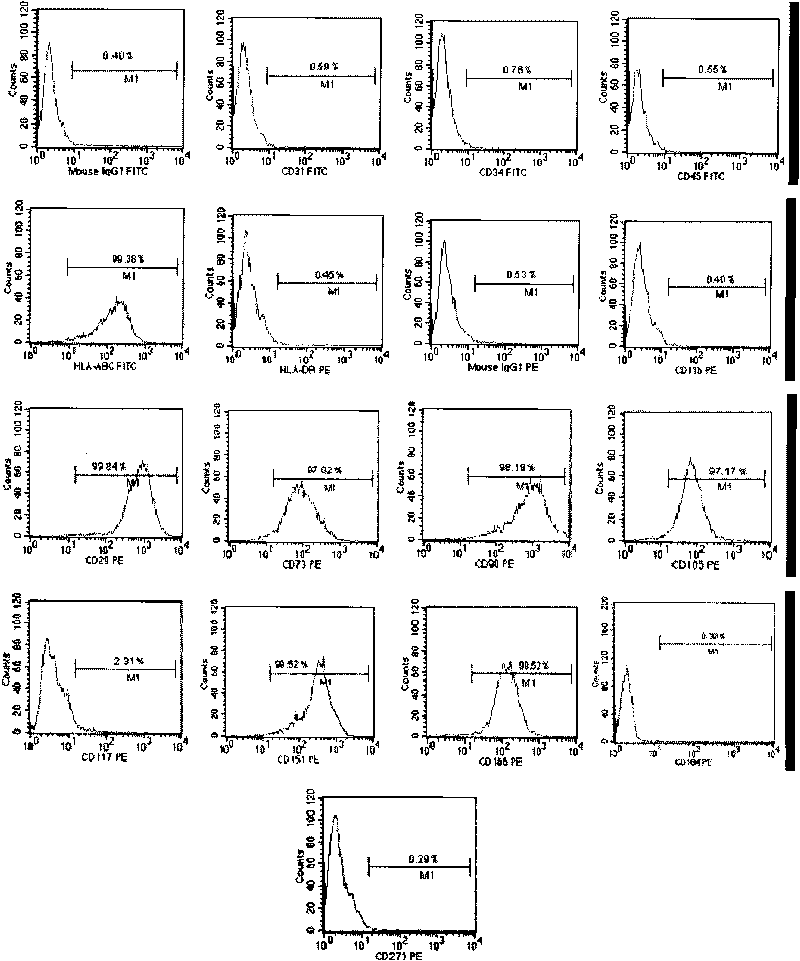
A source of multipotent amniotic fluid / fetal stem cells (MAFSCs) is disclosed. MAFSC are of fetal origin and have a normal diploid karyotype. These cells are characterized by the following cell surface markers: SSEA3, SSEA4, Tra-1-60, Tra-1-81, Tra-2-54, HLA class I, CD13, CD44, CD49b, CD105 and are distinguished by the absence of the antigen markers CD34, CD45, and HLA Class II, but are distinguished from mouse embryonic stem cells in that these cells do not express the cell surface marker SSEA1. MAFSC express the stem cell transcription factor Oct-4. MAFSC cells can be propagated for an indefinite period of time in continuous culture in an undifferentiated state. The MAFSCs have the ability to differentiate in culture in a regulated manner, into three or more subphenotypes. Cells can then be differentiated into endodermal, mesodermal and ectodermal derived tissues in vitro and in vivo. A method for isolating, identifying, expanding and differentiating MAFSCs is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Pluripotent stem cells derived without the use of embryos or fetal tissue
InactiveUS20030113910A1New breed animal cellsArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
Owner:STEMA
Pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells, compositions, methods and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050255588A1Avoid developmentInhibit progressBone marrow stroma cellsGenetic material ingredientsGerm layerIn vivo
The present invention relates to pluripotent stem cells, particularly to pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells. The invention further relates to methods of purifying pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells and to compositions, cultures and clones thereof. The present invention also relates to a method of transplanting the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention in a mammalian host, such as human, comprising introducing the stem cells, into the host. The invention further relates to methods of in vivo administration of a protein or gene of interest comprising transfecting a pluripotent stem cell with a construct comprising DNA which encodes a protein of interest and then introducing the stem cell into the host where the protein or gene of interest is expressed. The present also relates to methods of producing mesodermal, endodermal or ectodermal lineage-committed cells by culturing or transplantation of the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention.
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY
Induction of pluripotent stem cells into mesodermal lineages
InactiveUS20080038820A1Promotes commitment and survivalGenetic material ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProgenitorGerm layer
The present invention provides a method of inducing mesoderm derived cells from pluripotent stem cells. In contrast to methods known in the art that are often designed to replicate in vivo events of mesoderm induction, the present invention provides a unique, yet simple, method whereby pluripotent stem cells are mesodermally primed in the presence of factors that concomitantly inhibit the spontaneous differentiation of endoderm and ectoderm during expansion and suspension steps. Exposure and / or adherence of primed aggregates to a extracellular matrix that promotes the commitment and survival of induced mesoderm progenitors, followed by exposure to various mesoderm associated factors, allows for the subsequent induction of such cells into terminally differentiated lineages, such as cardiomyocytes. End products of this induction system will ultimately provide an unlimited source of mesoderm-derived cell types for therapeutic and pharmacological purposes.
Owner:RUDY REIL DIANE ELIZABETH DR +1
Pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells, compositions, methods and uses thereof
The present invention relates to pluripotent stem cells, particularly to pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells. The invention further relates to methods of purifying pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells and to compositions, cultures and clones thereof. The present invention also relates to a method of transplanting the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention in a mammalian host, such as human, comprising introducing the stem cells, into the host. The invention further relates to methods of in vivo administration of a protein or gene of interest comprising transfecting a pluripotent stem cell with a construct comprising DNA which encodes a protein of interest and then introducing the stem cell into the host where the protein or gene of interest is expressed. The present also relates to methods of producing mesodermal, endodermal or ectodermal lineage-committed cells by culturing or transplantation of the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention.
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY
Pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells derived from corneal limbus, methods of isolation and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060216821A1Increase telomerase activityCulture processNervous system cellsGerm layerDisease
The present disclosure describes mammalian pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells (ELSCs) isolated from corneal limbal tissue, a non-embryonic tissue. The ELSCs of the present disclosure are capable of proliferating in an in vitro culture, maintain the potential to differentiate into cells of endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm lineage in culture, and are capable of forming embryoid-like bodies when placed in suspension culture. Thus, these cells possess multi-lineage differentiation potential and self-renewing capability. ELSCs may be a promising therapeutic tool, and may provide new therapeutic alternatives for various diseases, conditions, and injuries.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Pluripotent stem cells, method for preparation thereof and uses thereof
Human pluripotent stem cells which are isolated from cut human umbilical cord or placenta and characteristic of cell surface marker CD151+, OCT4+ and CD184−, can adhere to tissue culture plastic and have the potential to differentiate into three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. Methods of isolating, purifying and culturally expanding of a population of human pluripotent stem cells and uses for treating diseases caused by cell damage or cell aging, and as a kind of carrier cells in gene therapy are provided.
Owner:BEIJING HEALTH & BIOTECH (H&B) CO LTD
Mesoderm and definitive endoderm cell populations
InactiveUS20080226558A1Genetic material ingredientsMuscular disorderEndoderm cellDefinitive endoderm
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Non-Embryonic Totipotent Blastomere-Like Stem Cells And Methods Therefor
Non-embryonic blastomere-like totipotent stem cells are disclosed. Most preferably, such cells are obtained from various tissues of postnatal mammals (e.g., using tissue biopsied from the mammal), are smaller than 1 μm, have normal karyotype, and do not spontaneously differentiate in serum-free medium without differentiation inhibitors. These non-embryonic blastomere-like totipotent stem cells typically express CD66e, CEA-CAM-1 and telomerase, but do not typically express CD10, SSEA-1, SSEA-3, and SSEA-4. Such blastomere-like totipotent cells can be differentiated into ectodermal, mesodermal, or endodermal tissues, including placental tissues and germ cells. Moreover, when implanted into a mammal, such cells will not be teratogenic.
Owner:MORAGA BIOTECH CORP
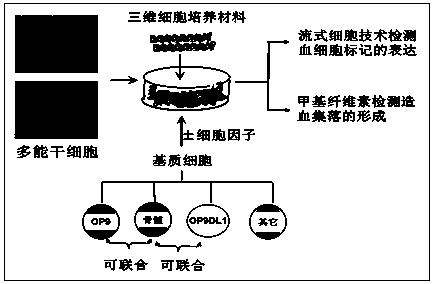
Method for obtaining hemopoietic stem cell by using three-dimensional induction system
ActiveCN103937743ABlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsInduced pluripotent stem cellBone marrow cell
The invention provides a method for obtaining a hemopoietic stem cell by using a three-dimensional induction system. A three-dimensional cell culture medium or cell culture bracket, such as a three-dimensional cell culture system made of the materials such as hydrogel, seaweed and the like is utilized, and / or combined with matrix cells such as bone marrow cell, mouse bone marrow cell lines OP9, OP9DL1 and the like, and / or combined with a plurality of factors including mesoderm induction factors, hematopoietic growth factor and the like to induce multipotent stem cells to differentiate into hemopoietic stem cells. A new method for obtaining the hemopoietic stem cells is built. The system for efficiently inducing the multipotent stem cells to differentiate into the hemopoietic stem cells by using a three-dimensional induction system and / or combining with matrix cells such as bone marrow cell and the like and / or a plurality of factors is built for the first time. Theoretical basis and a technology platform are provided for obtaining clinically available hemopoietic stem cells, and a new method and a new concept are developed for application of hematopoietic cells derived from multipotent stem cells in the fields such as disease mechanism exploration, drug screening and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
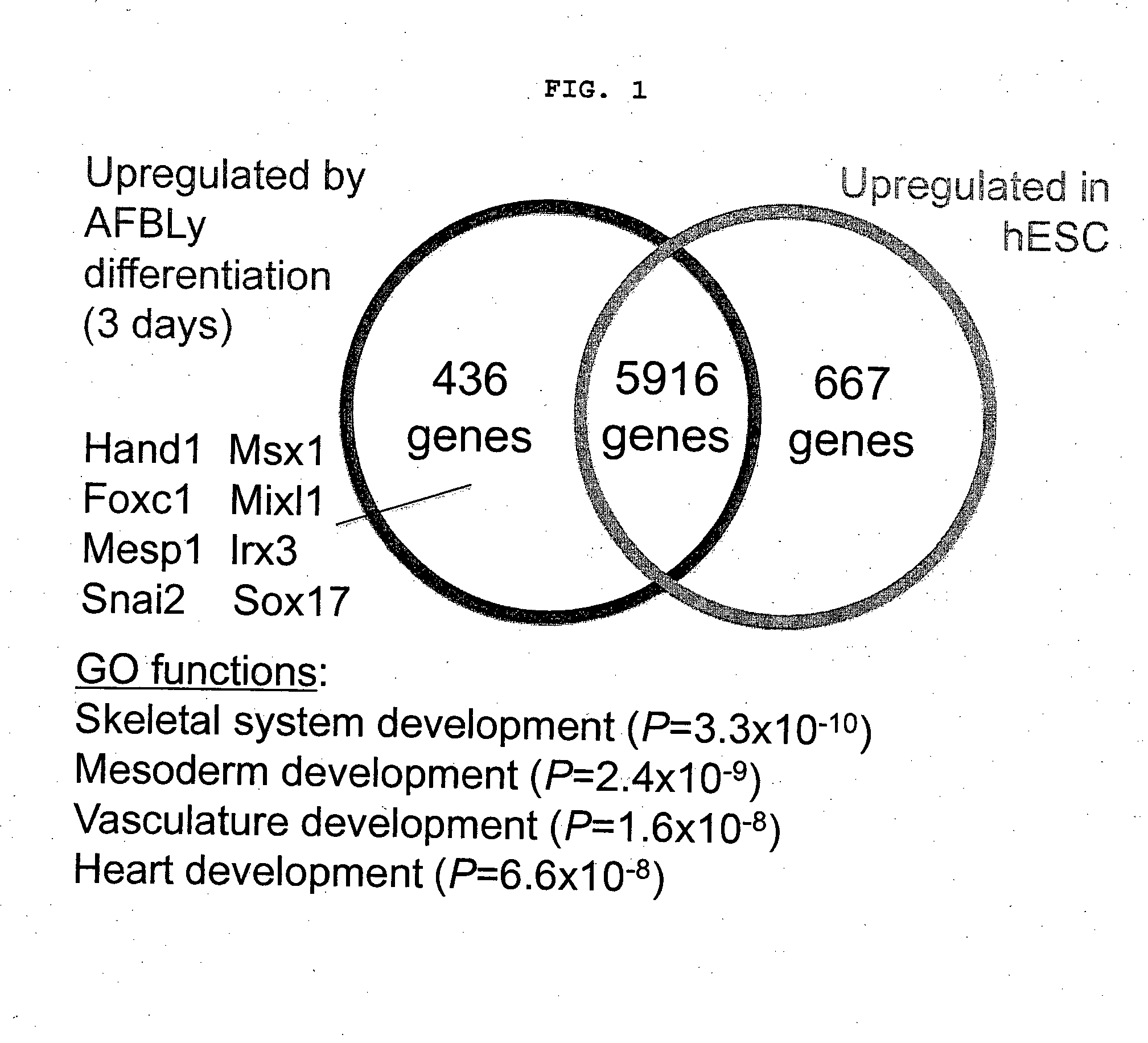
Methods of differentiating stem cells into one or more cell lineages
The present disclosure provides an understanding of the regulation of the developmental phases of stem cells and their induction into relevant cell lineages, such as primitive streak, endoderm, mesoderm, or subterrotories of endoderm's. In particular, the present disclosure provides methods, culture medium and kits for the maintenance and differentiation of stem cells into relevant cell lineages.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Sub totipotential stem cell and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a method for preparing a population of?human pluripotent stem cells and the application thereof. The preparation of stem cells is characterized by comprising the following steps: CD151<+>, CD31<->, Sox<2+> pluripotent stem cells are separated and collected from human umbilical cord and or placenta tissues; the cells adhere to grow in a culture vessel under a predetermined condition and expand through passage 20 or above to be still stable in gene expression. The population of cells of this invention do not form teratoma after injection into animals. The human pluripotent stem cells highly express CD151, OCT4 and Sox-2 as specific markers of embryonic stem cells, as well as specific markers of epidermic cells, endothelial cells, thrombocytes, dendritic cells, while lack expression of CD31, CD34, CD45 and HLA-II. The pluripotent stem cells are also characterized as being able to adhere to tissue culture plastic and having the potential to differentiate into three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. These pluripotent stem cells are able to be used as carrier cells of gene therapy and for the treatment of diseases caused by cell damage or cell aging. The present invention provides a method of isolating, purifying and culturally expanding of a population of human pluripotent stem cell for preparing the high purity injection preparation. The preparation of stem cells has a good therapeutic effect on the treatment of diseases caused by cell damage or cell aging in animal and human clinical trials. The preparation also has no toxic side effect and no immune rejection.
Owner:BEIJING HEALTH & BIOTECH (H&B) CO LTD
Multipotent stem cells and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110070205A1Easily attainable embryonic-likePromote wound healingBiocideNervous disorderGerm layerMHC class I
The invention provides a quiescent stem cell having the capacity to differentiate into ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, and which does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105 CD90, CD66A, CD66E, CXCR4, CD133 or an SSEA. The invention further provides a proliferative stem cell, which expresses genes including Oct-4, Nanog, Sox2, GDF3, P16INK4, BMI, Notch, HDAC4, TERT, Rex-1, TWIST, KLF-4 and Stella but does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105, CD90, CD66A, CD66E, CXCR4, CD133 or an SSEA. The cells of the invention can be isolated from adult mammals, have embryonic cell characteristics, and can form embryoid bodies. Methods for obtaining the stem cells, as well as methods of treating diseases and differentiated the stem cells, are also provided.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Methods for developing endothelial cells from pluripotent cells and endothelial cells derived
PendingUS20120301443A1Maintain abilityExpanding ECs in cell populationBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsGerm layerStable Populations
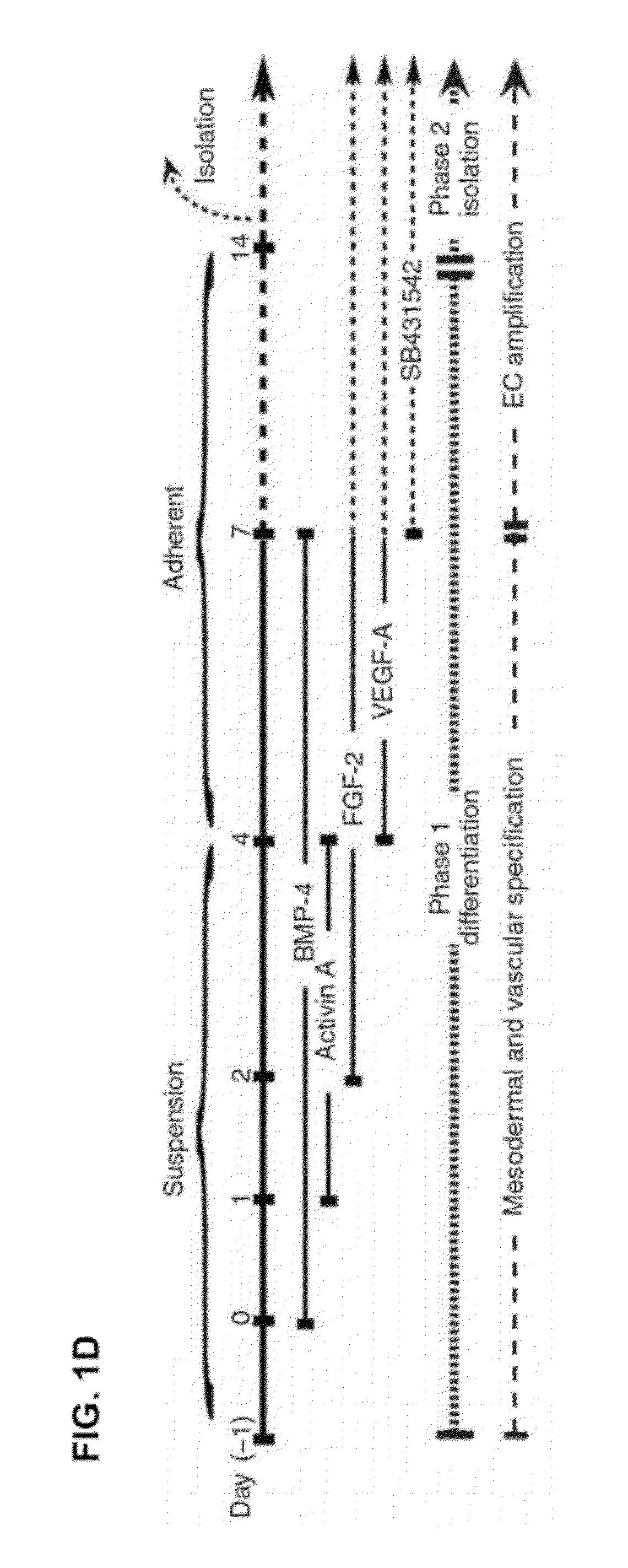
Disclosed herein is a method for developing human endothelial cells (ECs) from human embryonic stem cells (ESCs). The method is based on inhibition of TGF signaling following mesoderm induction and during vascular differentiation of hESC-derived cells. Also disclosed herein is a substantially pure and stable population of ECs that maintains a high degree of proliferation and phenotypic homogeneity for extended culture periods. Related pharmaceutical compositions and therapeutic methods are also disclosed. A reporter hESC line useful for tracking the development of ECs is also provided.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Multipotent stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100291042A1Easily attainable embryonic-likePromote wound healingBiocidePancreatic cellsDiseaseMHC class I
The invention provides a quiescent stem cell having the capacity to differentiate into ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, and which does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105 and CD90. The invention further provides a proliferative stem cell, which expresses genes including Oct-4, Nanog, Sox2, GDF3, P16INK4, BMI, Notch, HDAC4, TERT, Rex-1 and TWIST but does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105 and CD90. The cells of the invention can be isolated from adult mammals, have embryonic cell characteristics, and can form embryoid bodies. Methods for obtaining the stem cells, as well as methods of treating diseases and differentiated the stem cells, are also provided.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
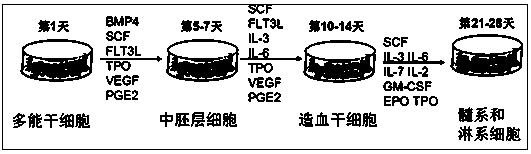
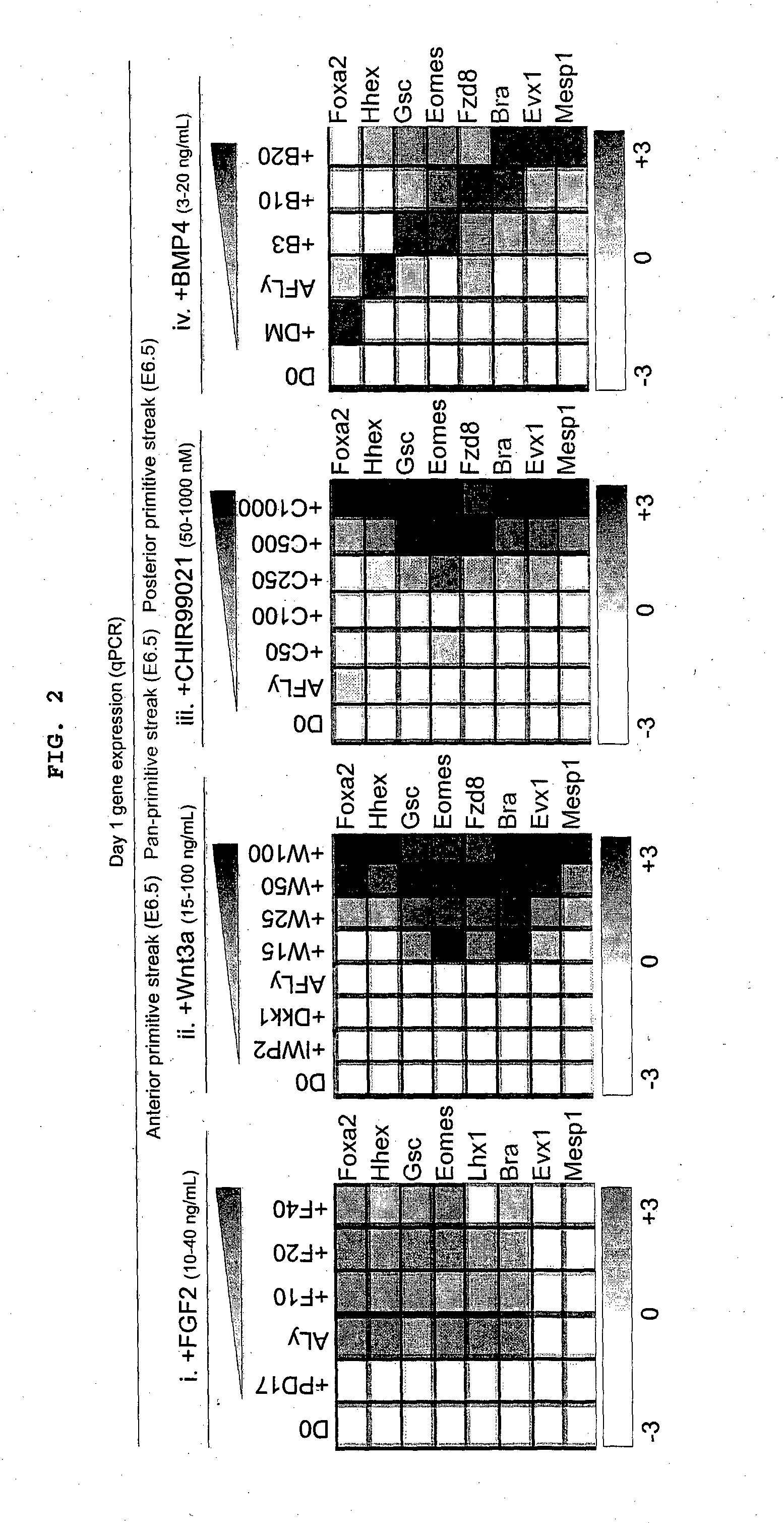
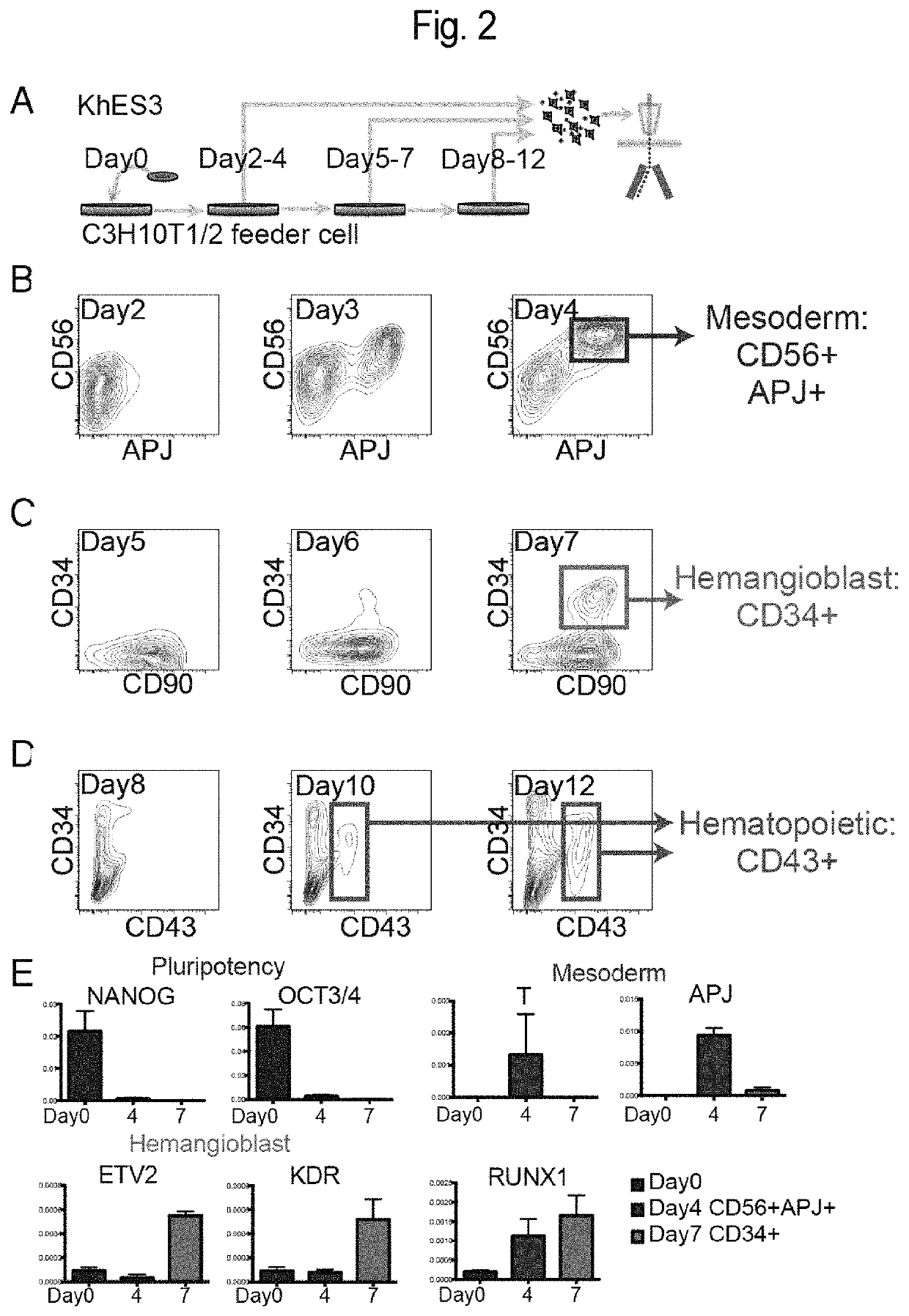
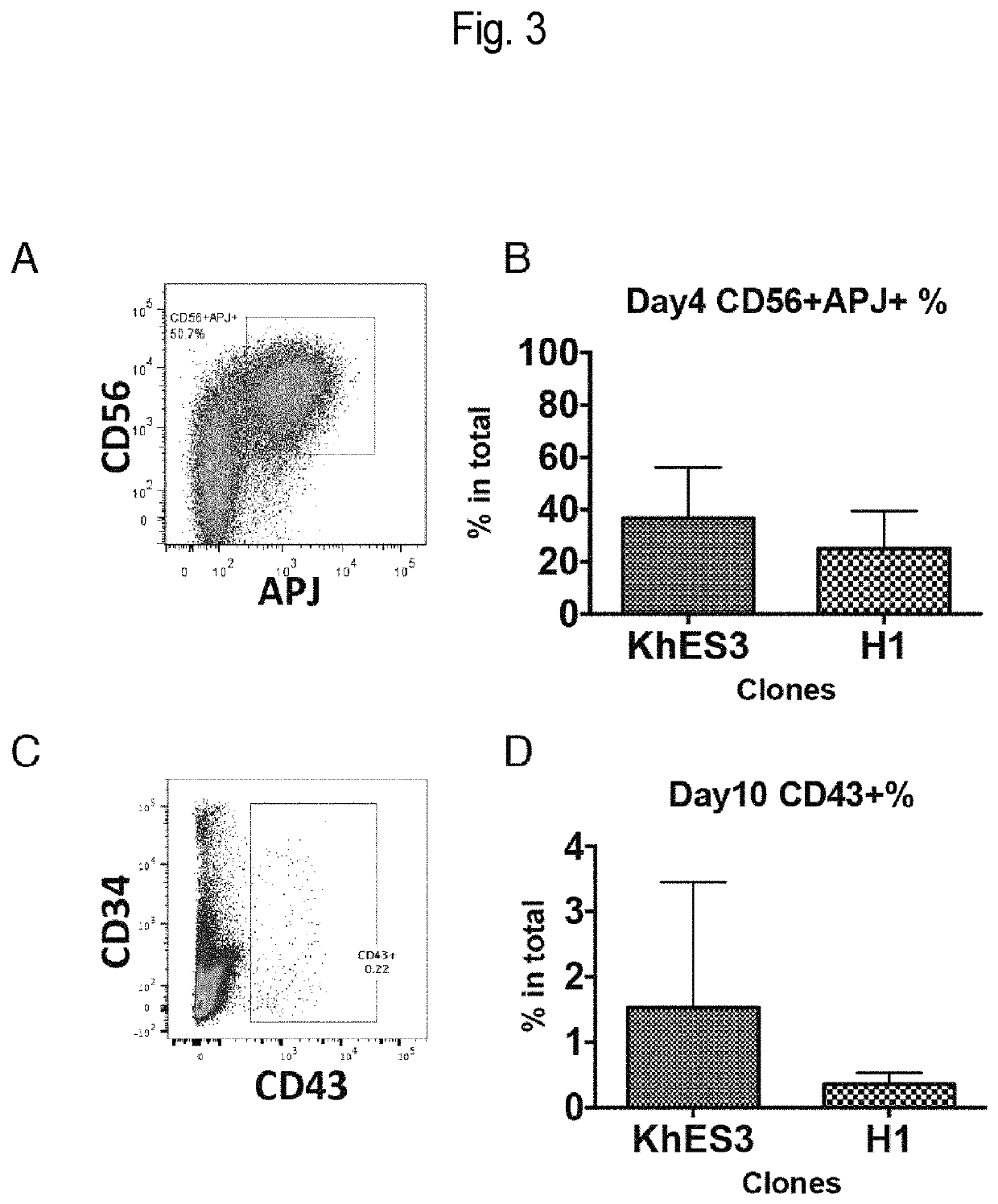
Mesoderm induction method having high blood cell differentiation capacity
ActiveUS11136547B2Efficient inductionPromote differentiationPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsPluripotential stem cellMedicine
Provided is a method for inducing mesoderm, comprising a step of bringing pluripotent stem cells into contact with bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) or CHIR for at least 3 days.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Methods of Deriving Differentiated Cells from Stem Cells
InactiveUS20100173414A1Promote productionArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsGerm layerEctoderm cell
The present invention provides a method of generating definitive endoderm, mesoderm, or ectoderm cells. The method includes culturing embryonic stem cells, parthenogenetic cells, or induced pluripotent stem cells in the presence of a demethylation agent, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, or a combination thereof, and thereafter, culturing the stem cells in the absence of the agent or combination of agents, to produce definitive endoderm cells, mesoderm, or ectoderm cells.
Owner:INT STEM CELL CORP
Induced pluripotent stem cells from human umbilical cord tissue-derived cells
InactiveUS20130157365A1Increase gene expressionArtificial cell constructsDrug compositionsGerm layerUmbilical cord tissue
We have disclosed an induced pluripotent stem cell and the method of preparing the induced pluripotent stem cell from a human umbilical cord tissue-derived cell. More particularly, we have disclosed a human umbilical cord tissue-derived iPS cell which may be differentiated into cells of ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm lineages.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Multipotential stem cell-derived mesoderm pedigree mesenchymal stem cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107937338AIncreased therapeutic functionSolve the problem of limited sourcesCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell phenotypeGerm layer
The invention discloses a multipotential stem cell-derived mesoderm pedigree mesenchymal stem cell and an induced differentiation method thereof. The multipotential stem cell-derived mesoderm pedigreemesenchymal stem cell is prepared by the following steps: performing in-vitro adherent culture on multipotential stem cells and maintaining the undifferentiation state of the multipotential stem cells; preparing unicellular or cell mass suspension from the cells, inoculating to a culture dish coated with matrix glue, and performing cultivation by using the multipotential stem cell culture liquid;after the cells adhere to the wall, adding GSK-3 pathway inhibitor combination into the culture liquid; after growing for 2 to 10 days, obtaining a mesoderm progenitor population; and after subculturing continuously for 2 to 6 times by using mesenchymal stem cell culture liquid, detecting the cell phenotype of mesenchyme. The defects that the human-derived mesenchymal stem cells and the mesenchymal stem cells derived from other non-finite induced way multipotential stem cells have heterogeneity and hybridity are overcome, and the obtained mesoderm pedigree mesenchymal stem cells have higher proliferation capability and immunoregulation capability; and the standardized induced differentiation process can guarantee that the cell populations obtained from different batches have high consistency.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Multiple mesodermal lineage differentiation potentials for adipose tissue-derived stromal cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20030166278A1Increase differentiationPromote growthMicrobiological testing/measurementMammal material medical ingredientsAdipose tissueHuman disease
The invention relates to methods and compositions for the differentiation of stromal cells from adipose tissue into hematopoietic supporting stromal cells and myocytes of both the skeletal and smooth muscle type. The cells produced by the methods are useful in providing a source of fully differentiated and functional cells for research, transplantation and development of tissue engineering products for the treatment of human diseases and traumatic tissue injury repair.
Owner:GIMBLE JEFFREY MARTIN +2
Method for differentiating human pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm
PendingCN111321110AEasy to operateSimple ingredientsCulture processArtificially induced pluripotent cellsBiotechnologyCytokine
The present invention provides a method for differentiating human pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm and belongs to the technical field of stem cell differentiation and culture. The method comprisesthe following steps: inoculating human pluripotent stem cells in a carrier after resuspending the human pluripotent stem cells in a complete culture medium and replacing a first-stage mesodermal differentiation culture medium after 24 h; and after 48 h of induction culture, realizing mesoderm differentiation of the human pluripotent stem cells. After the cell inoculation, only 2 fluid exchanges are required, only four components are contained, no expensive serum and cytokines are needed, experimental period is short, and results have good specificity.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL EAST HOSPITAL TONGJI UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Multipotent stem cells and uses thereof
ActiveUS8574567B2Easily attainable embryonic-likePromote wound healingBiocideNervous disorderMHC class ISurface marker
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Culture system and method for inducing human pluripotent stem cells into neural mesoderm progenitor cells in vitro and maintaining self-renewal and application
PendingCN112746057ADemonstrate bidirectional differentiation potentialGenetically modified cellsCulture processVitamin CPenicillin
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical engineering, and provides a culture system for inducing human pluripotent stem cells into nerve mesoderm progenitor cells in vitro and maintaining self-renewal. The culture system comprises a basic culture medium and an induced differentiation factor added in the basic culture medium, comprising 0.01 to 500 [mu] m of MTGF [beta] inhibitor, 0.01 to 500 [mu] m of MBMP inhibitor, 0.01 to 50 [mu] m of GSK3 inhibitor, 0.01 to 500 ng / mL of FGF family growth factor, and 0.01 to 500 ng / mL of LEGF family growth factor, wherein the basic culture medium comprises a liquid basic culture medium, a 0-5*B27 additive, a 0-5*N2 additive, 1% penicillin / streptomycin and 0-500 [mu] g / mL 2-phosphoric acid-vitamin C. The induction method comprises the following steps of A, culturing hPSCs until the cell density is 50-70% by adopting an hPSCs culture medium; and B, carrying out cell induction by using the culture system, changing a half amount of liquid every day, carrying out cell passage according to the ratio of 1: 6 when the cell density reaches 90%, adding Blebbistatin into the culture system during subculture, and continuously inducing for more than 10 days.
Owner:THE NAVAL MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Primate embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050158854A1High nucleus/cytoplasm ratioNervous disorderMetabolism disorderGerm layerSurface marker
A purified preparation of primate embryonic stem cells is disclosed. This preparation is characterized by the following cell surface markers: SSEA-1 (−); SSEA-4 (+); TRA-1-60 (+); TRA-1-81 (+); and alkaline phosphatase (+). In a particularly advantageous embodiment, the cells of the preparation are human embryonic stem cells, have normal karyotypes, and continue to proliferate in an undifferentiated state after continuous culture for eleven months. The embryonic stem cell lines also retain the ability, throughout the culture, to form trophoblast and to differentiate into all tissues derived from all three embryonic germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm). A method for isolating a primate embryonic stem cell line is also disclosed.
Owner:THOMSON
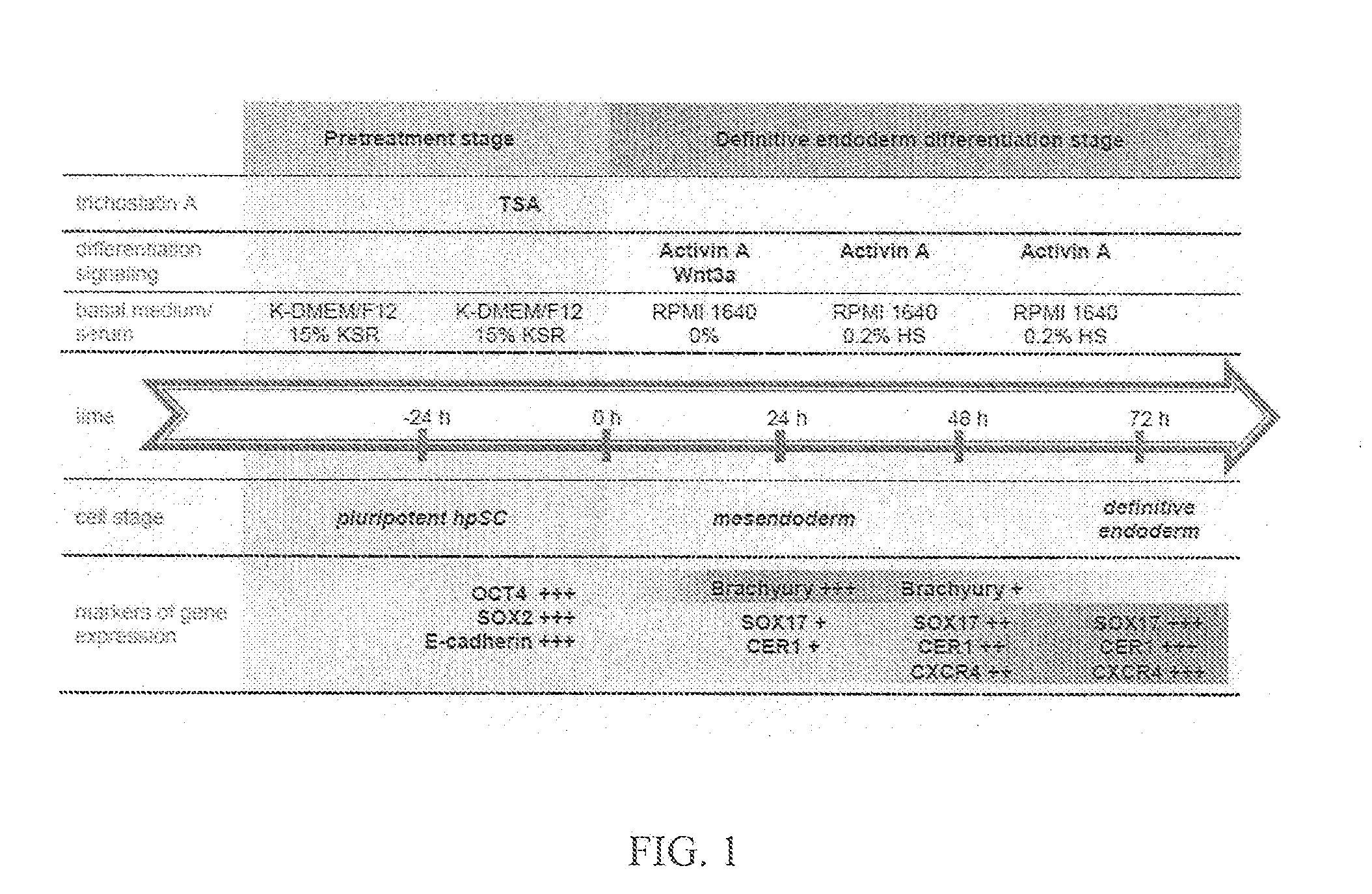
Methods of deriving definitive endoderm cells from pluripotent parthenogenetic stem cells
The present invention provides a method of generating definitive endoderm, mesoderm, or ectoderm cells. The method includes culturing embryonic stem cells, parthenogenetic cells, or induced pluripotent stem cells in the presence of a demethylation agent, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, or a combination thereof, and thereafter, culturing the stem cells in the absence of the agent or combination of agents, to produce definitive endoderm cells, mesoderm, or ectoderm cells.
Owner:INT STEM CELL CORP
Cell culture media, kits and methods of use
ActiveUS20130029414A1Efficient cultivationCulture processCell culture mediaHematopoietic cellCell culture media
Albumin-supplemented and xenogeneic product-free cell culture media, cell culture media supplements, and cell culture media kits for the support of primary culture of normal non-hematopoietic cells of mesodermal origin suitable for both research and clinical applications.
Owner:MOSCATELLO DAVID
Method for inducing differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into intermediate mesoderm cells
ActiveUS20140363888A1Reduce in quantityMethod littleArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsMultipotential stem cellIntermediate mesoderm
The present invention provides a method for inducing differentiation of a human pluripotent stem cell into an intermediate mesoderm cell without the use of a growth factor. Such method comprises performing culture in a medium containing a specific compound, so as to induce differentiation of a human pluripotent stem cell into an intermediate mesoderm cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com