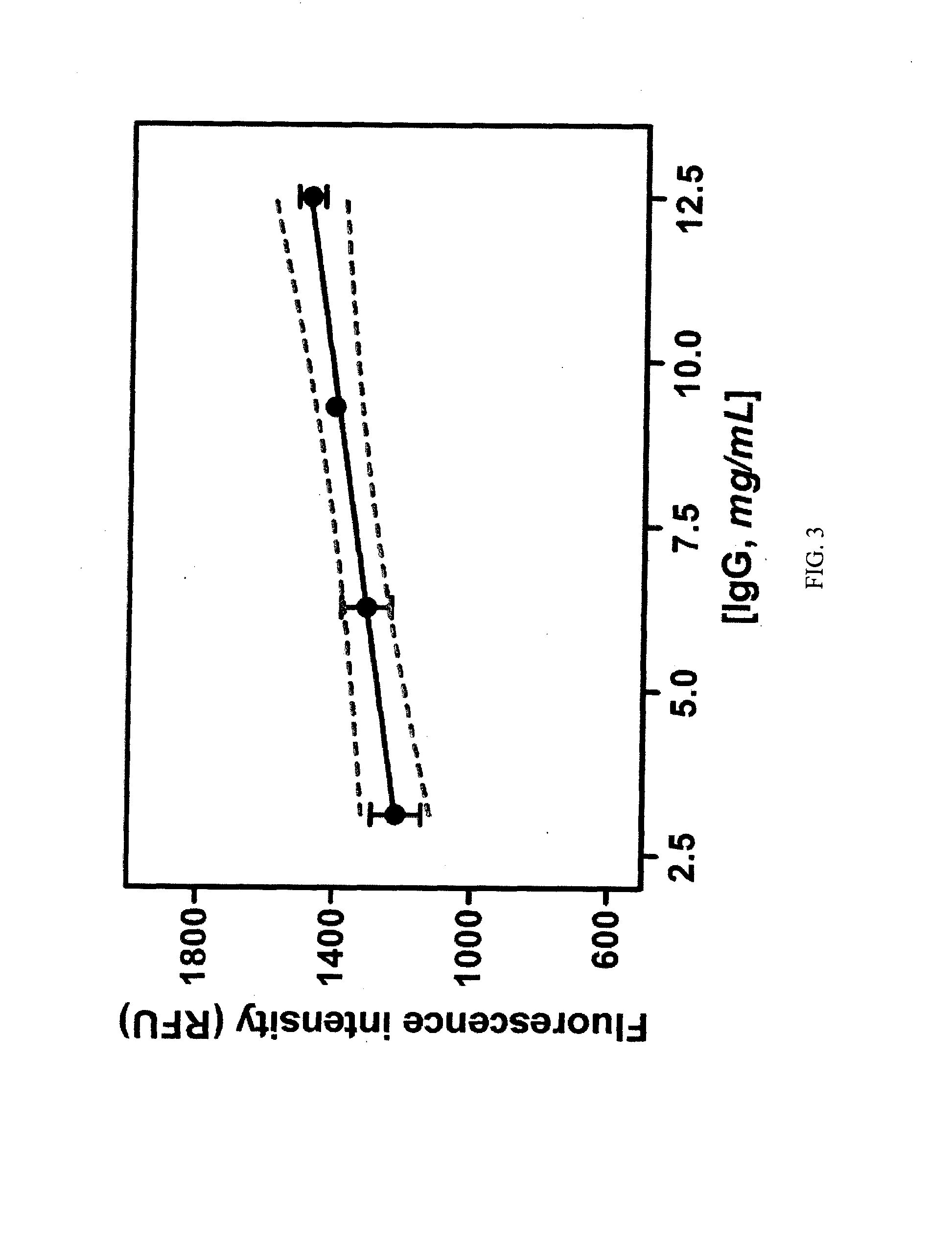
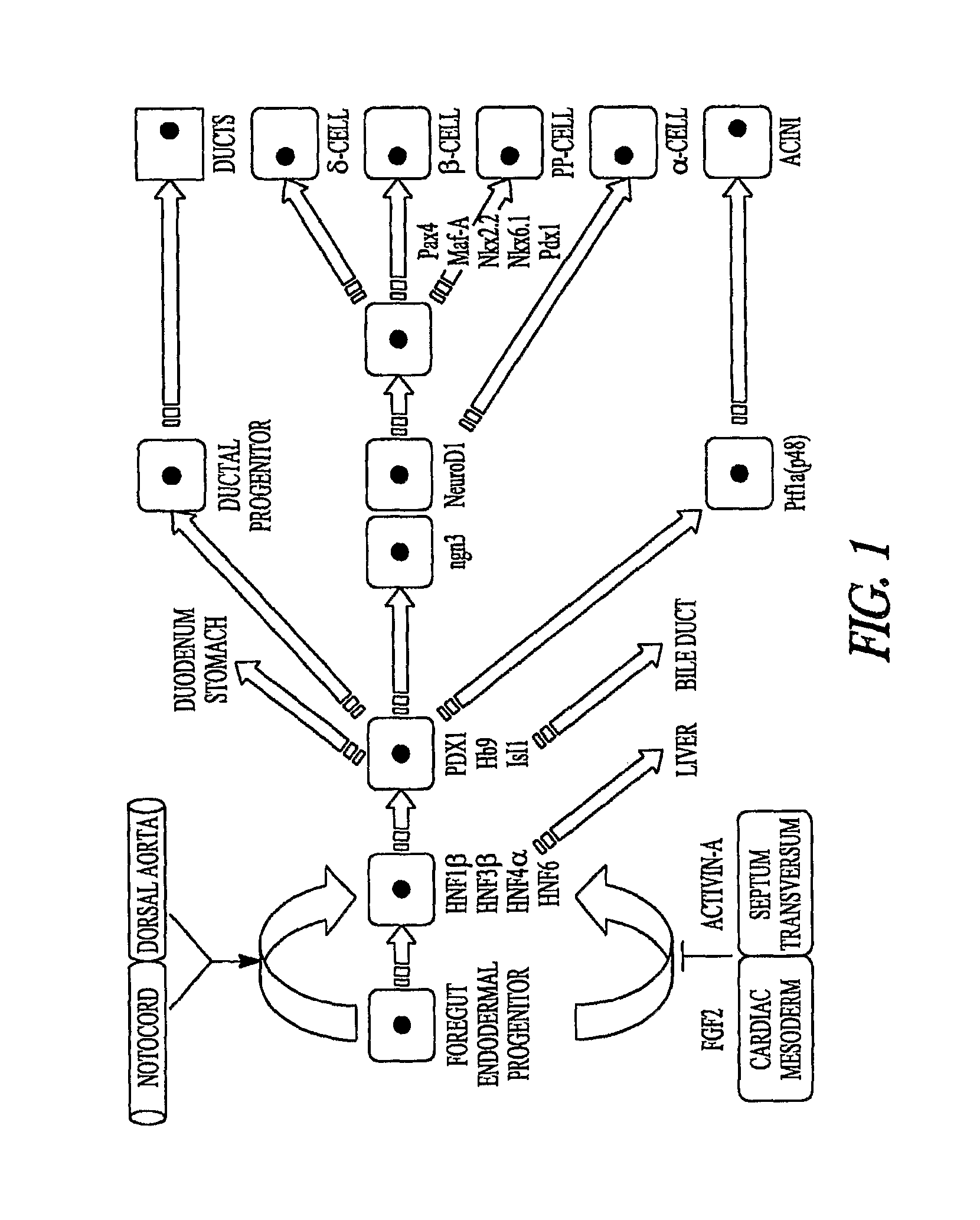
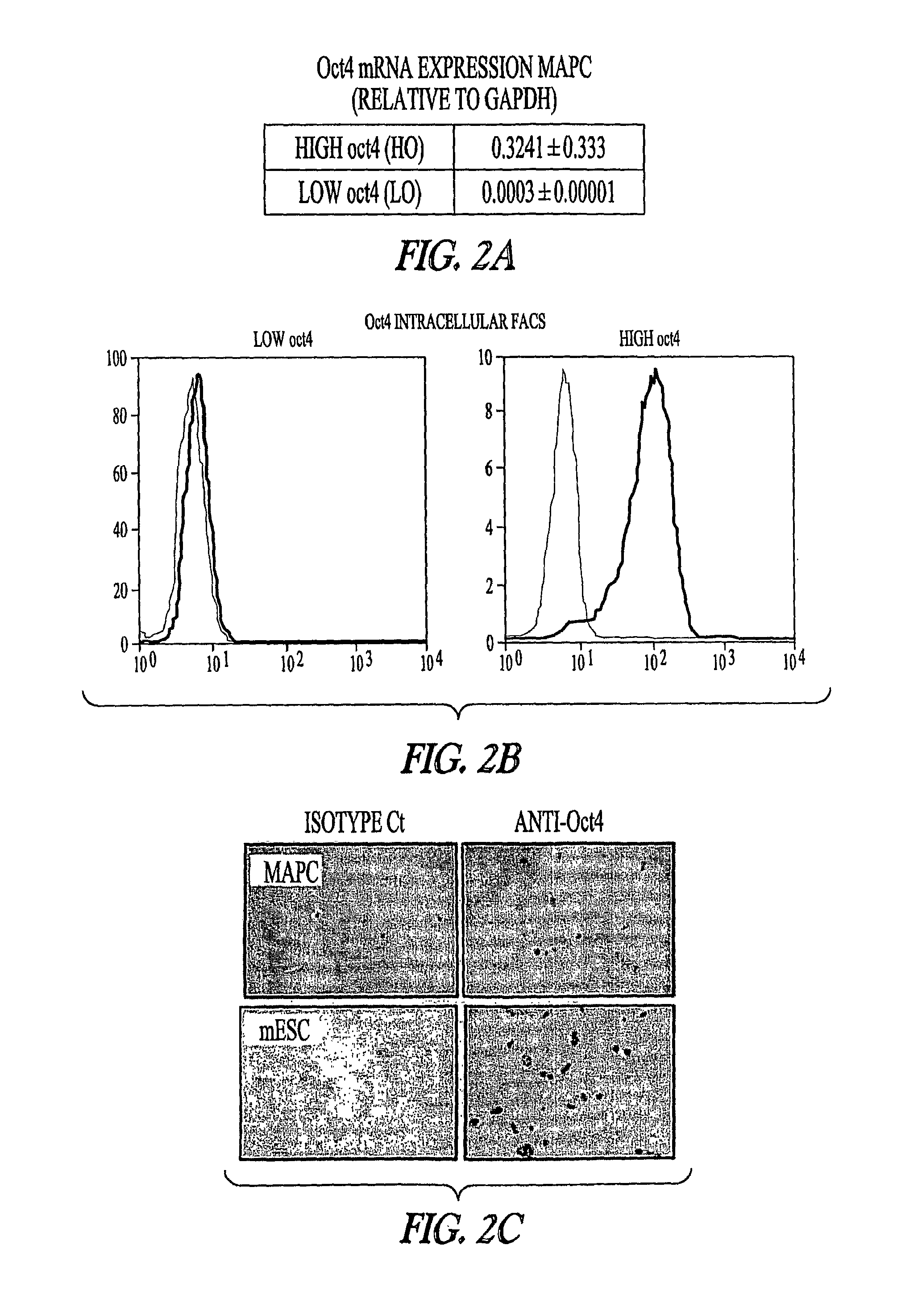
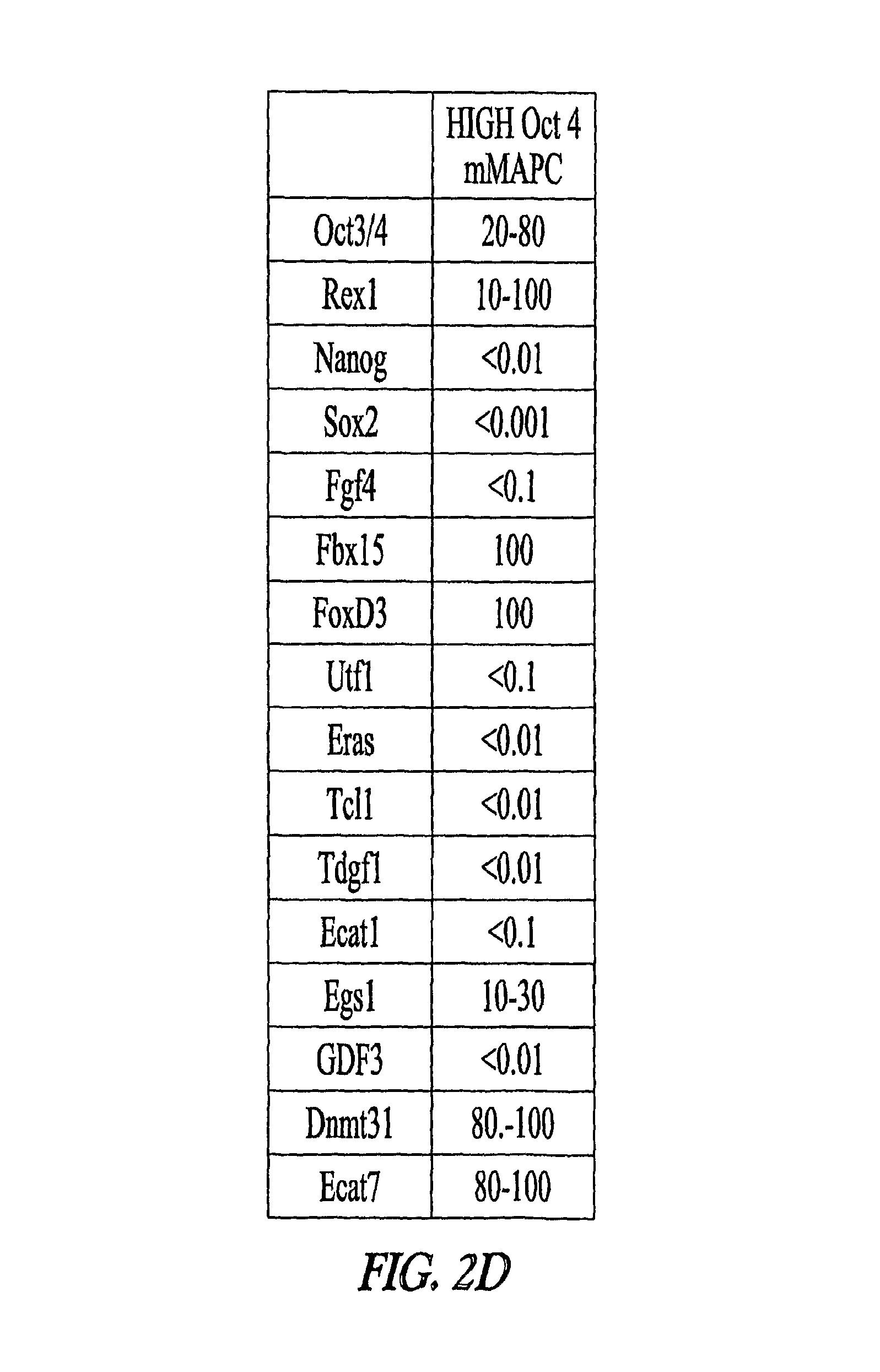
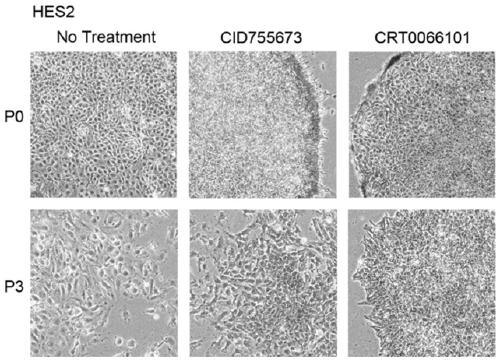
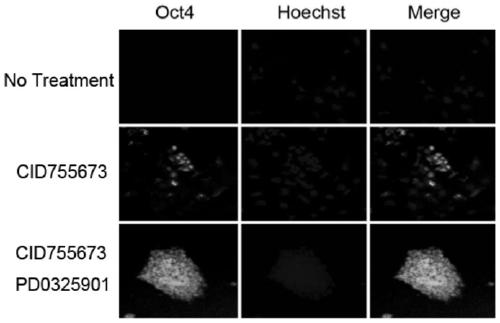
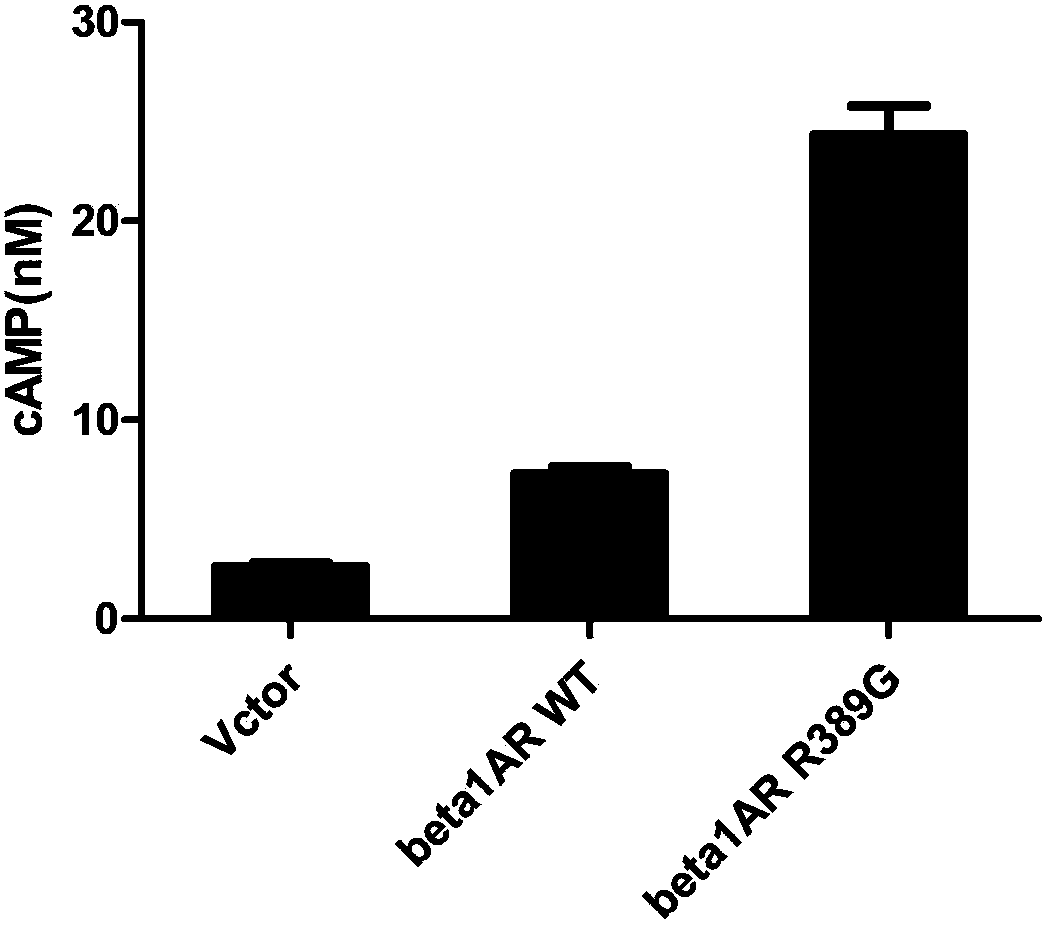
Patents
Literature
109 results about "Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) are critical tools for genetic engineering, development of stem cell based therapies, and basic research on pluripotency and early lineage commitment. However, successful derivation of germline-competent embryonic stem cell lines has, until recently, been limited to a small number of inbred mouse strains.
Multipotent amniotic fetal stem cells
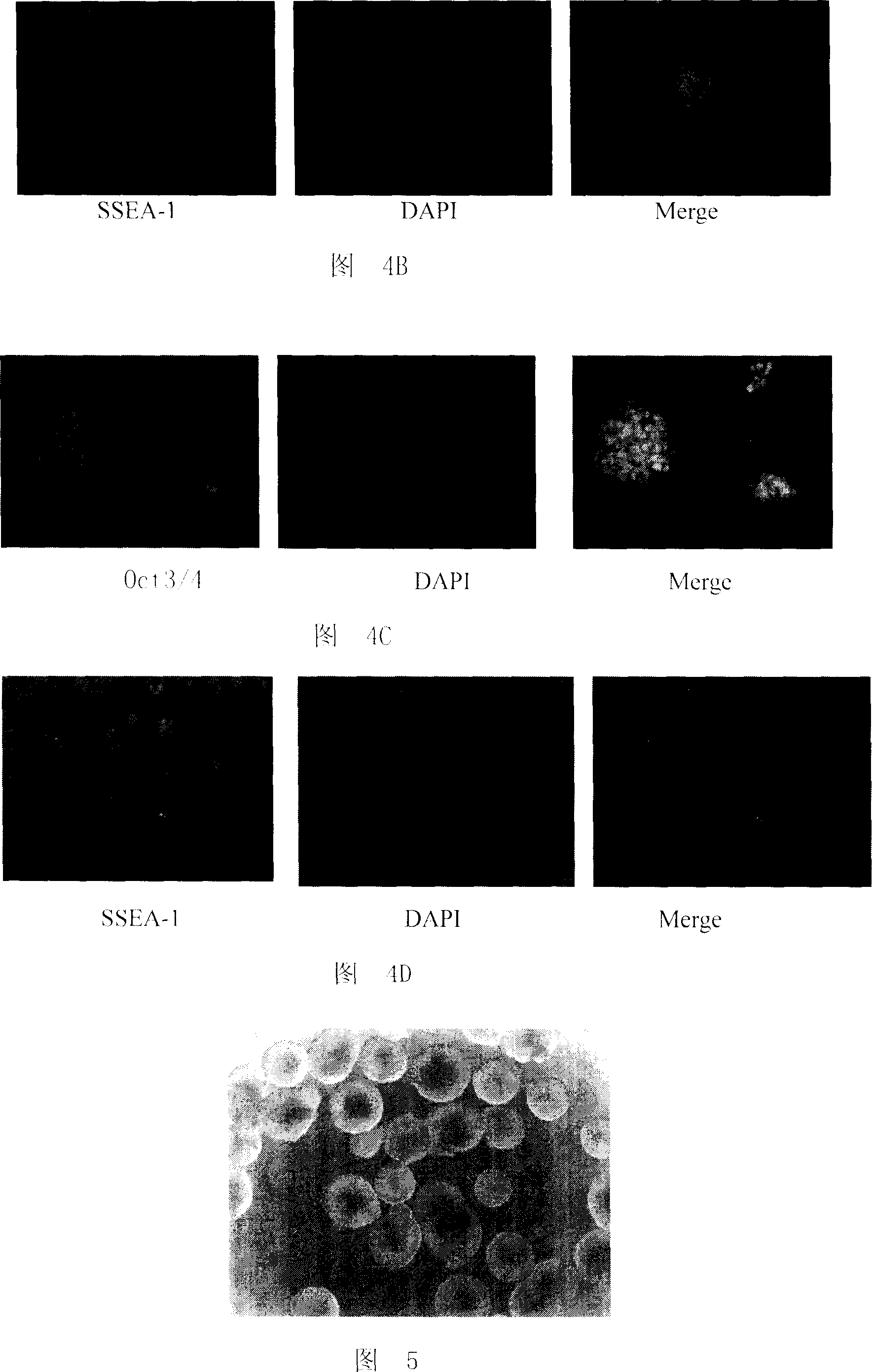
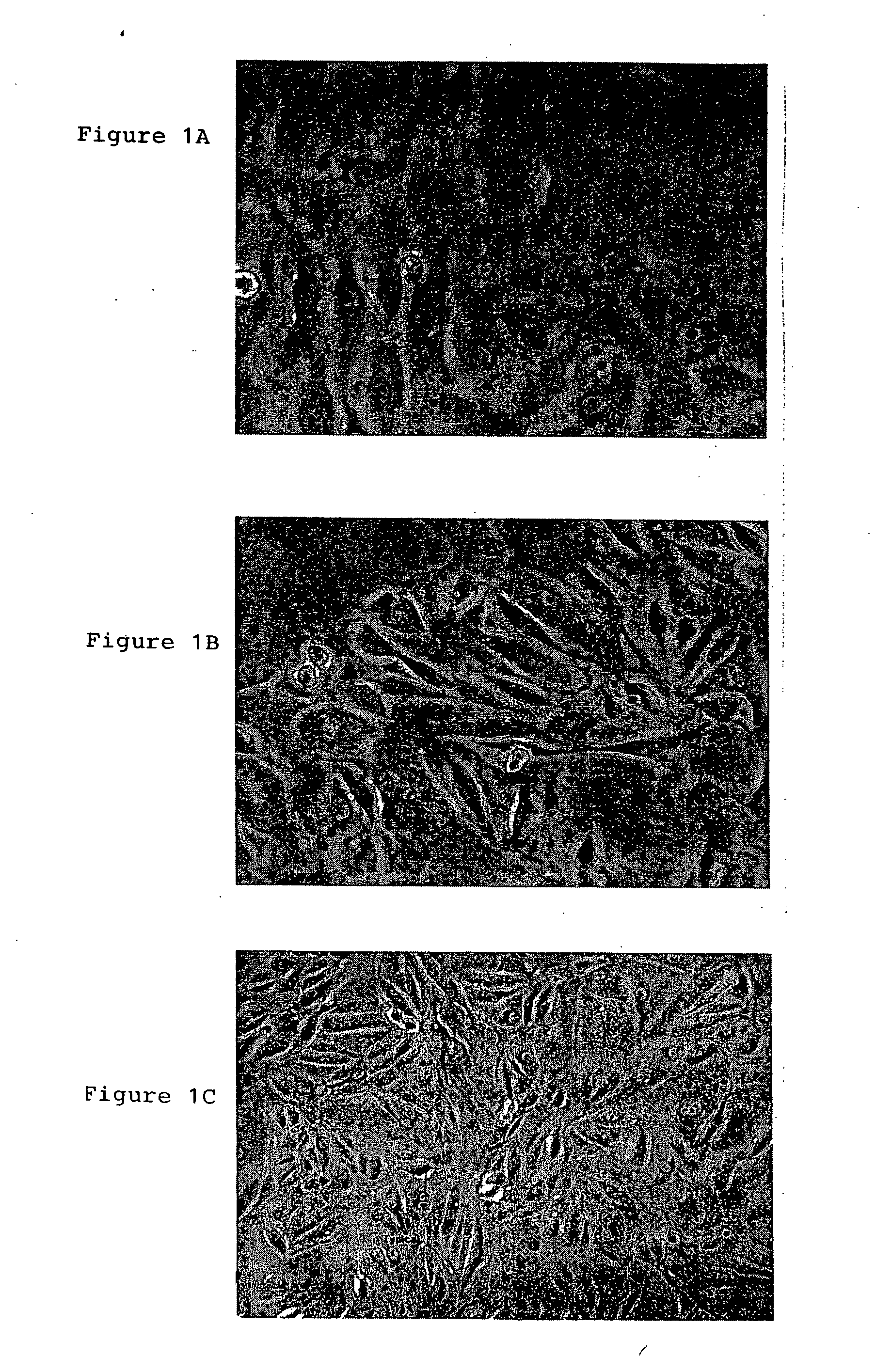
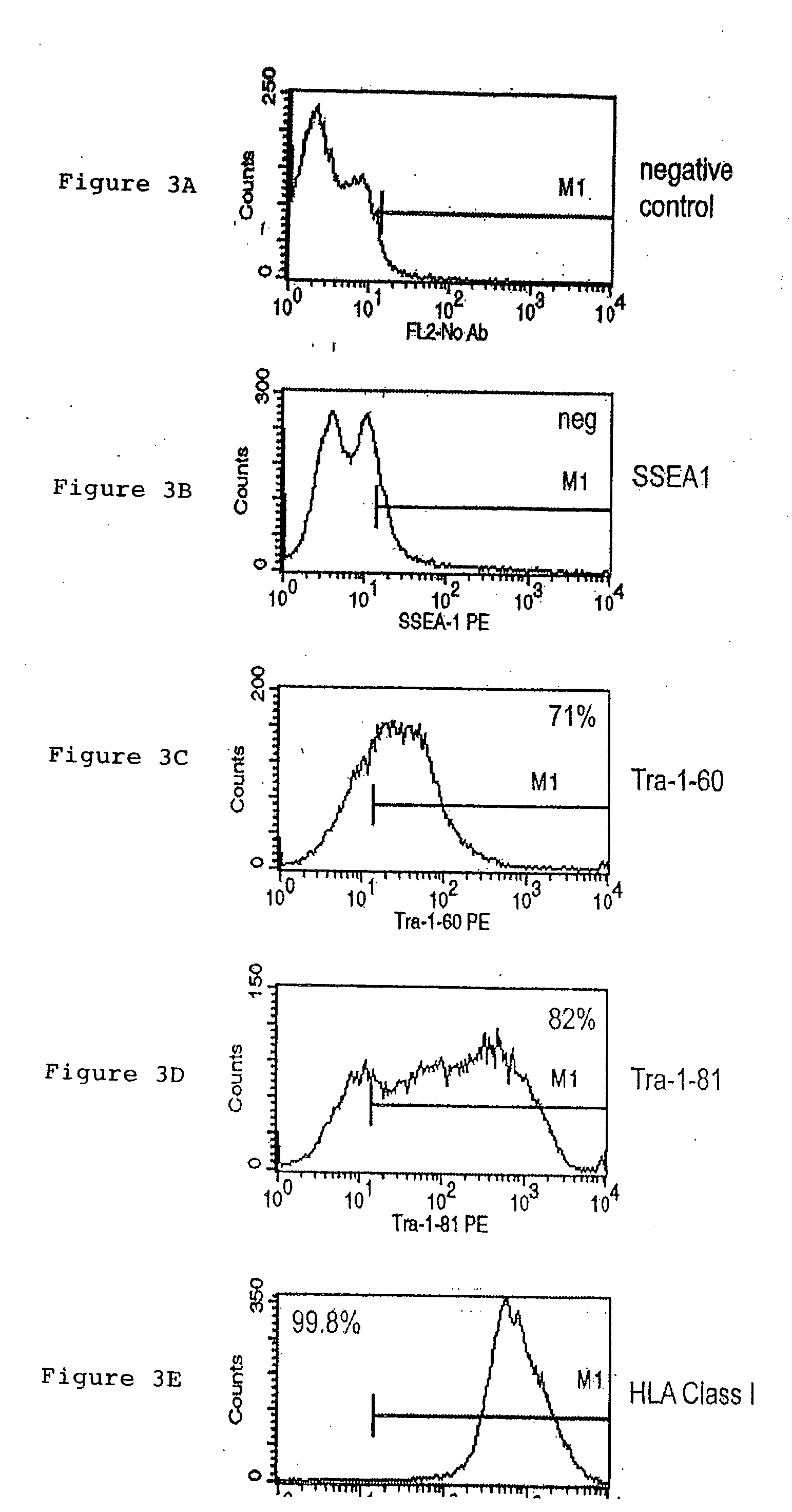
A source of multipotent amniotic fluid / fetal stem cells (MAFSCs) is disclosed. MAFSC are of fetal origin and have a normal diploid karyotype. These cells are characterized by the following cell surface markers: SSEA3, SSEA4, Tra-1-60, Tra-1-81, Tra-2-54, HLA class I, CD13, CD44, CD49b, CD105 and are distinguished by the absence of the antigen markers CD34, CD45, and HLA Class II, but are distinguished from mouse embryonic stem cells in that these cells do not express the cell surface marker SSEA1. MAFSC express the stem cell transcription factor Oct-4. MAFSC cells can be propagated for an indefinite period of time in continuous culture in an undifferentiated state. The MAFSCs have the ability to differentiate in culture in a regulated manner, into three or more subphenotypes. Cells can then be differentiated into endodermal, mesodermal and ectodermal derived tissues in vitro and in vivo. A method for isolating, identifying, expanding and differentiating MAFSCs is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Preparation method for transgenic mice capable of producing human nerve growth factor
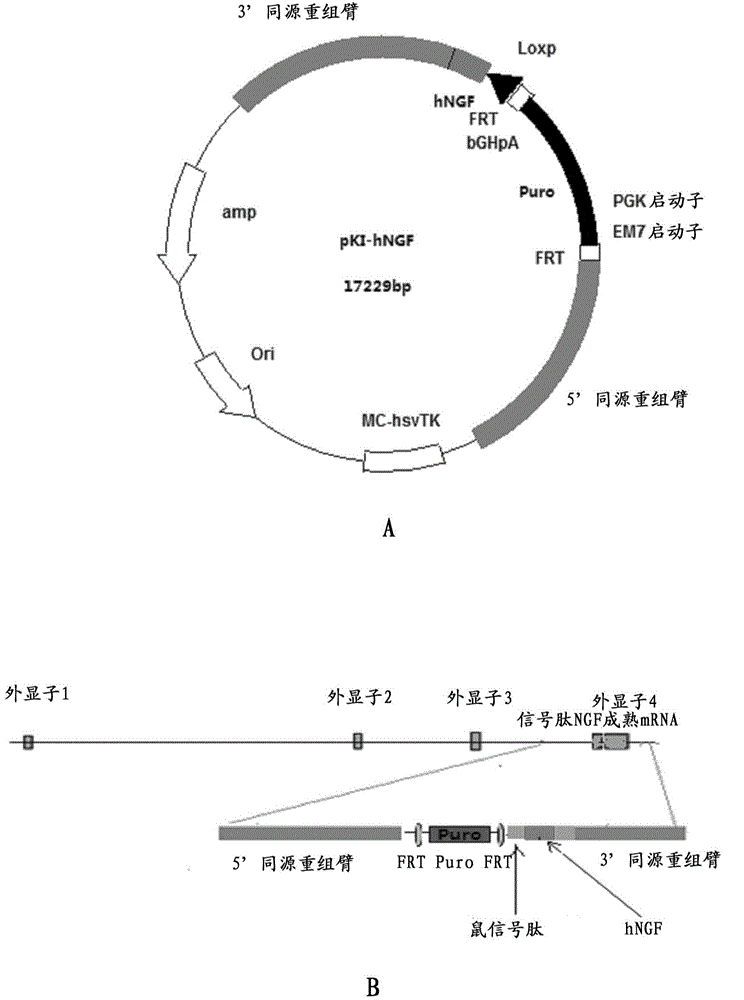
ActiveCN104561095AEasy to operateIncrease success rateAnimals/human peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionPlasmid dnaGenetically modified mouse
The invention discloses a method for producing transgenic mice through a homologous recombination technology. The method comprises the following steps: replacing mouse NGF genes on mouse chromosomes by human NGF genes through a Cas-9 / CRISPR gene knock-in technology, and obtaining the genes with homozygous human NGF genes through breeding and knocking the genes in mice, thus obtaining filial generation mice with salivary glands capable of secreting human NGF. Compared with the conventional targeting technology utilizing positive and negative double screening homologous recombination genes, the method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, capable of being realized only by transfecting mouse embryonic stem cells by three plasmid DNAs or carrying out pronucleus injection on the zygotes of mice, and high in success rate which is up to 2-5% and remarkably higher than the mouse embryonic stem cell positive rate of 0.1% of the common gene targeting technology.
Owner:深圳市国创纳米抗体技术有限公司
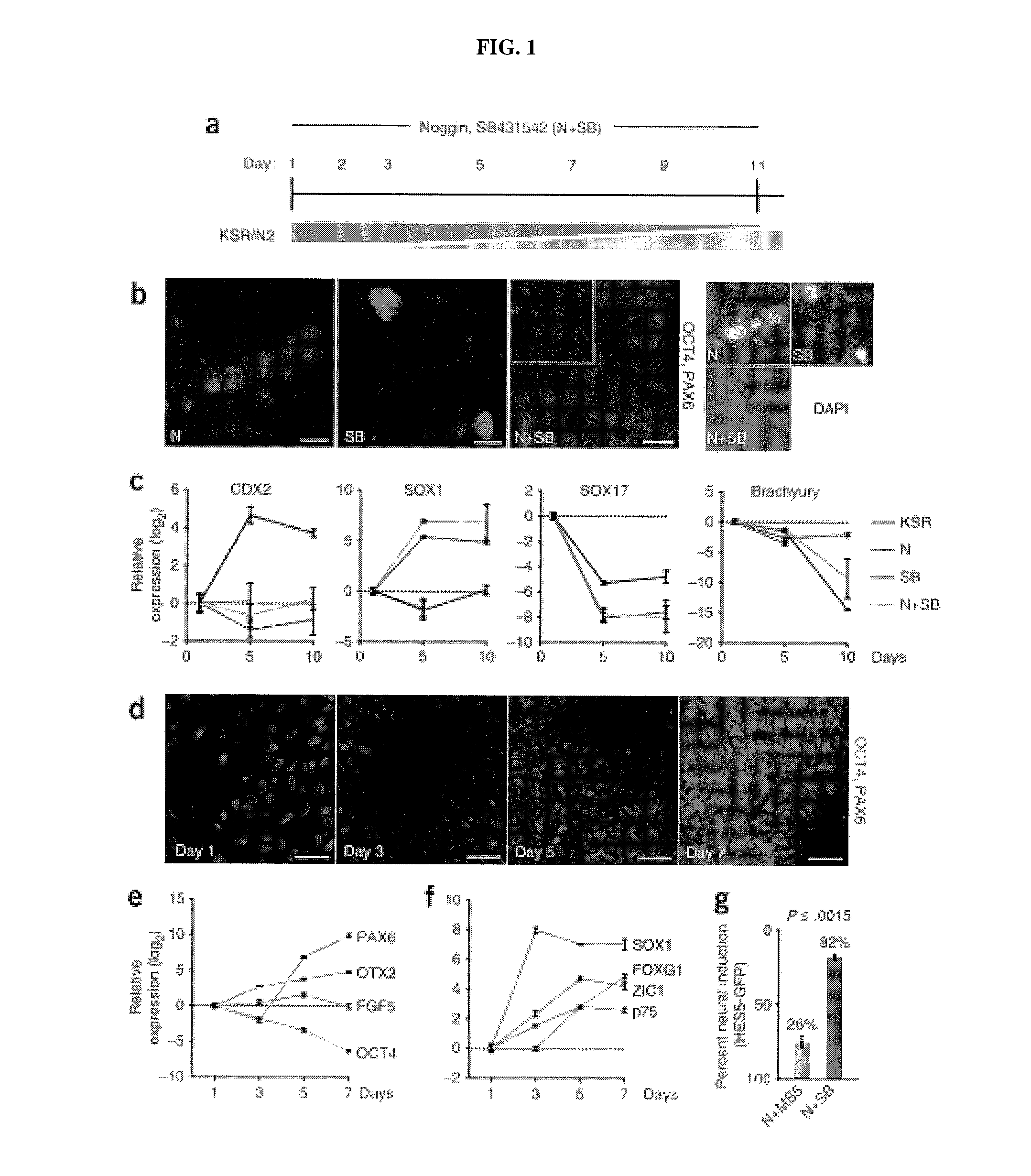
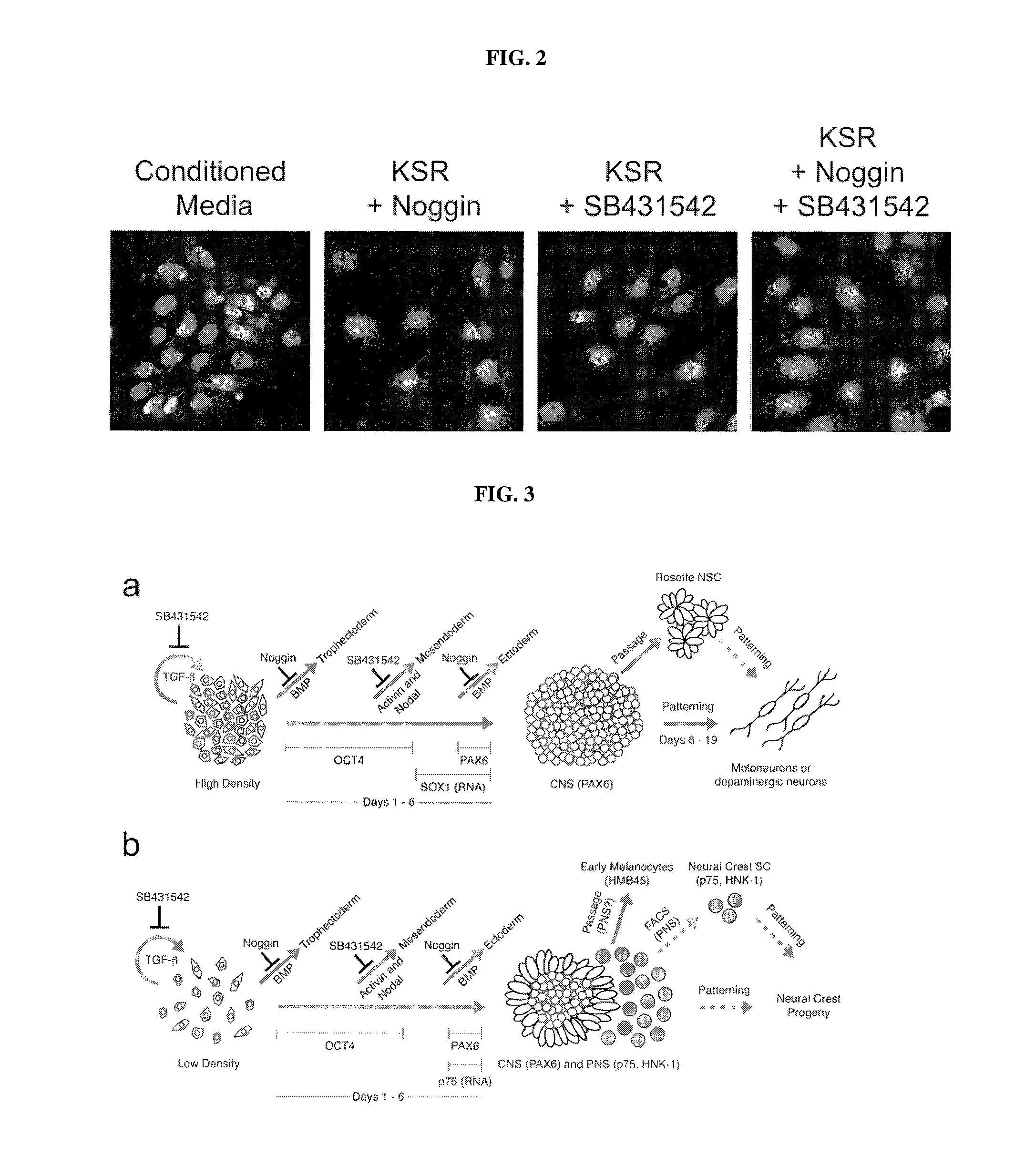
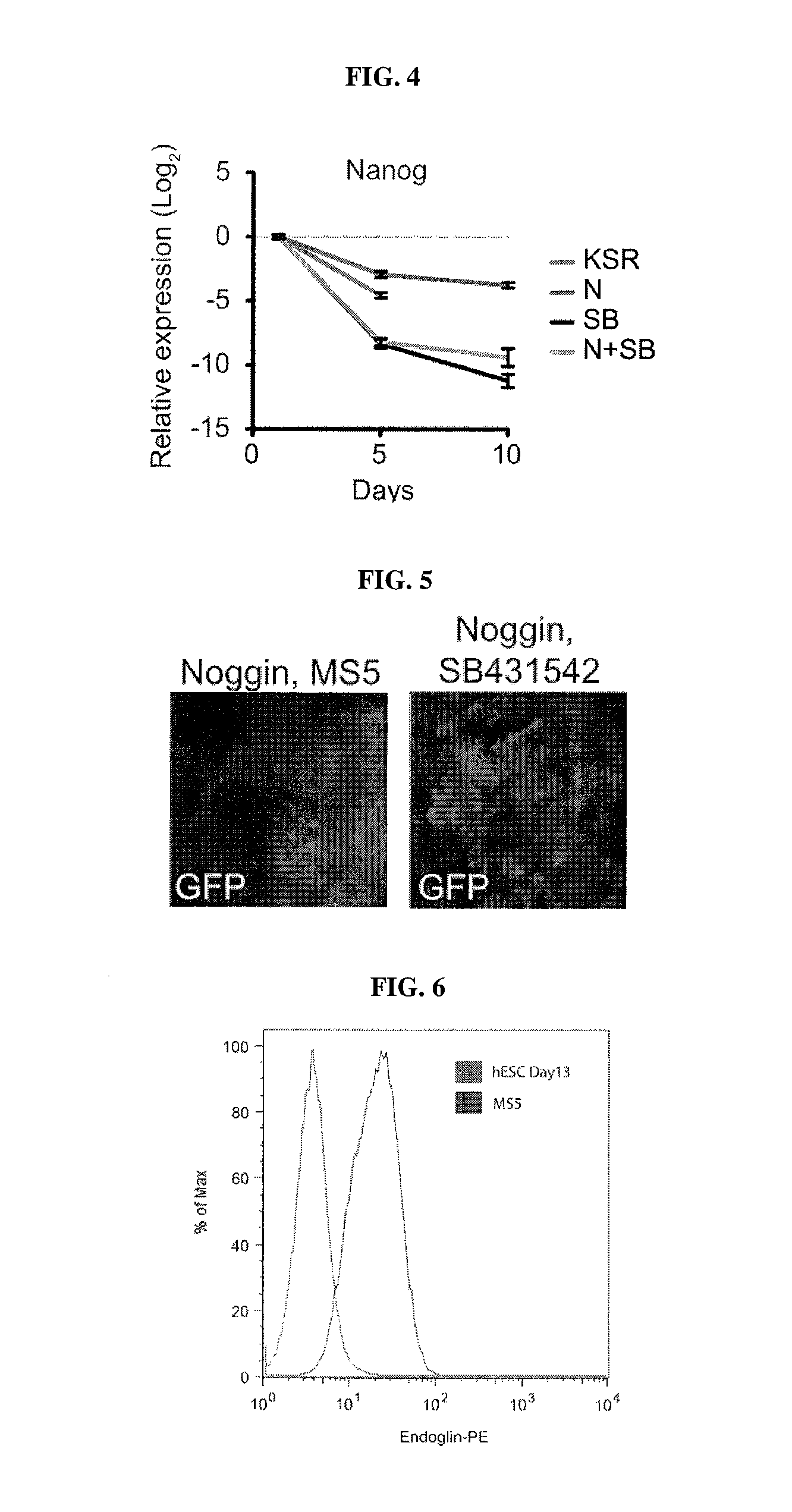
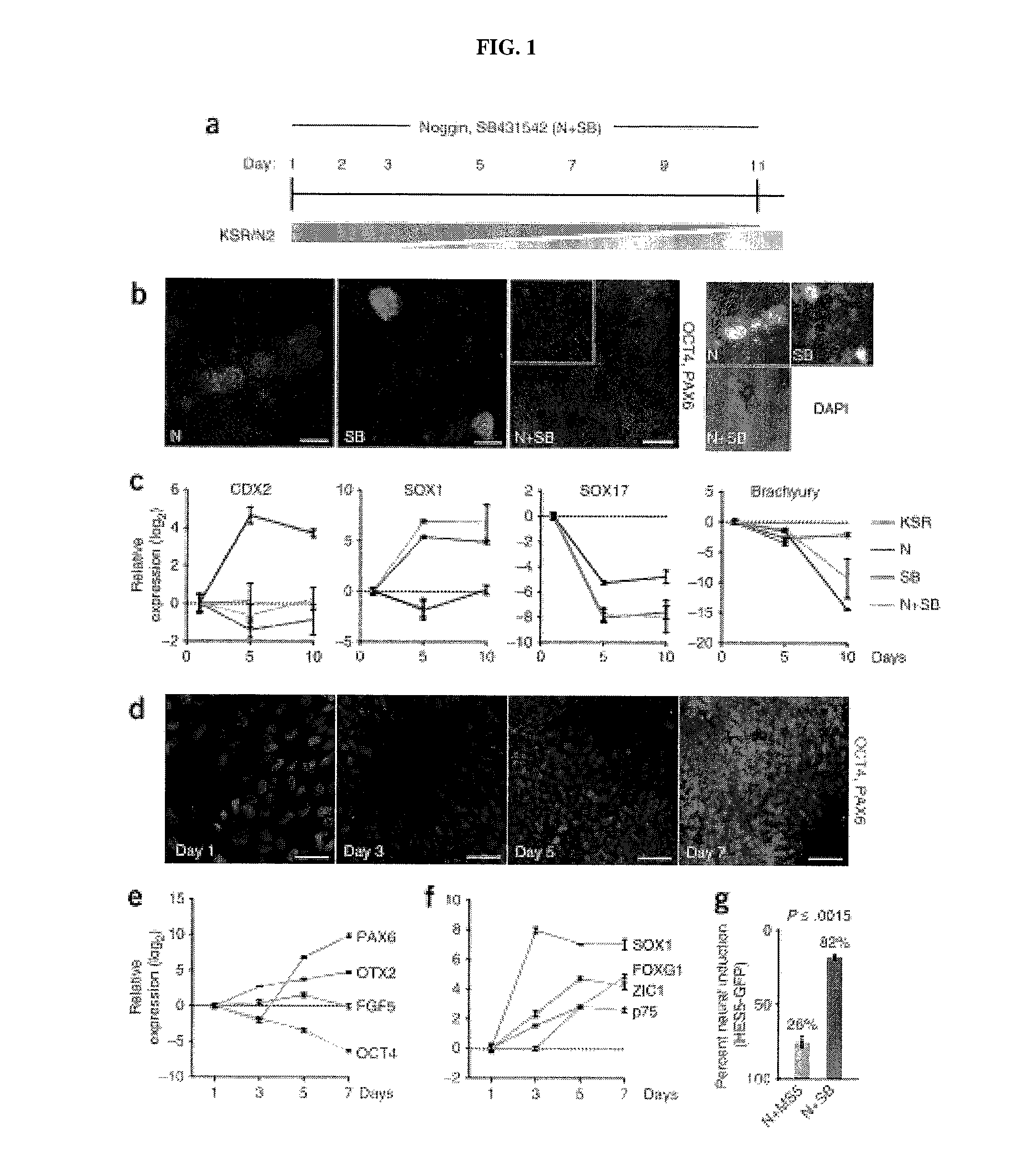
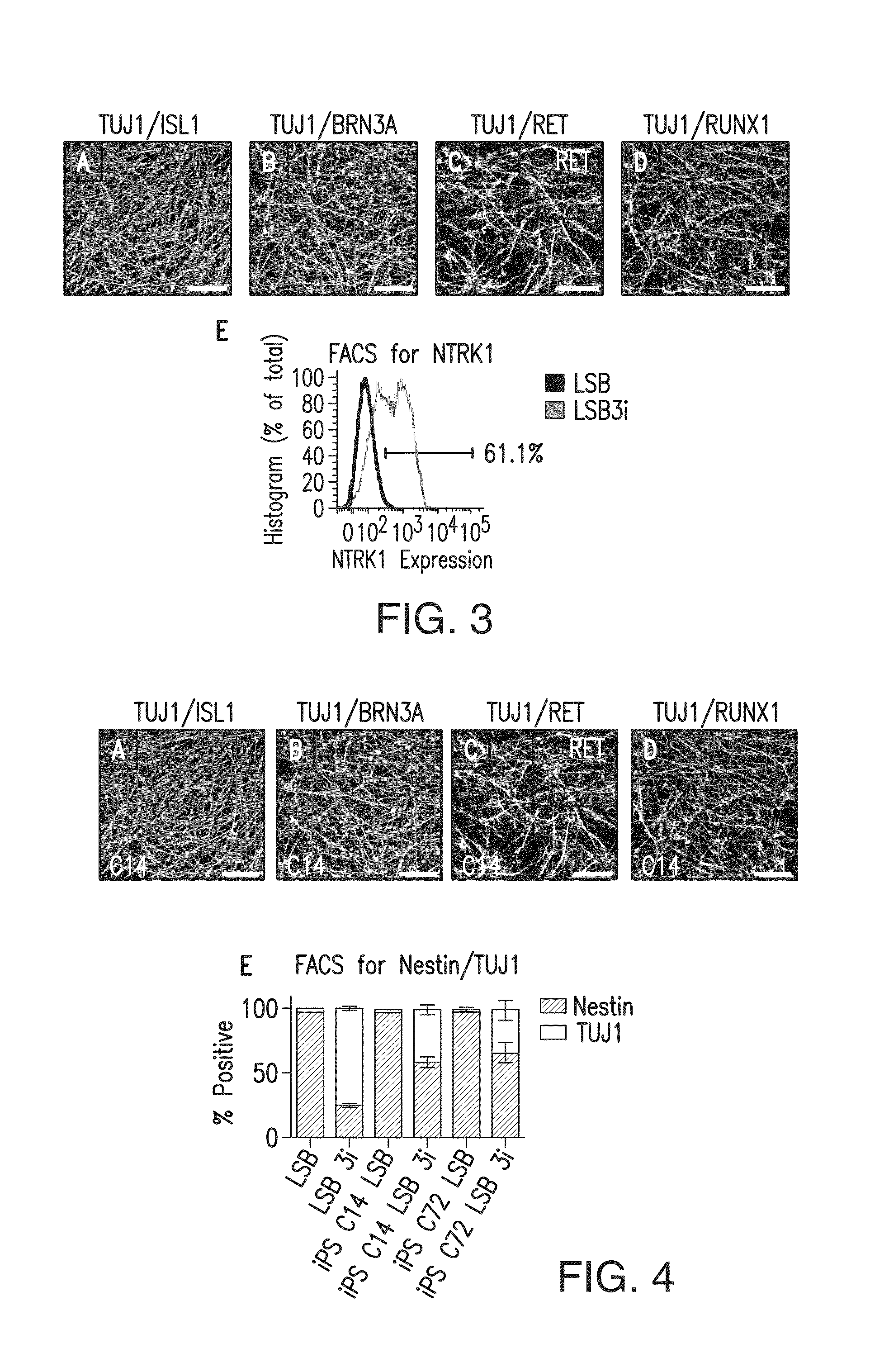
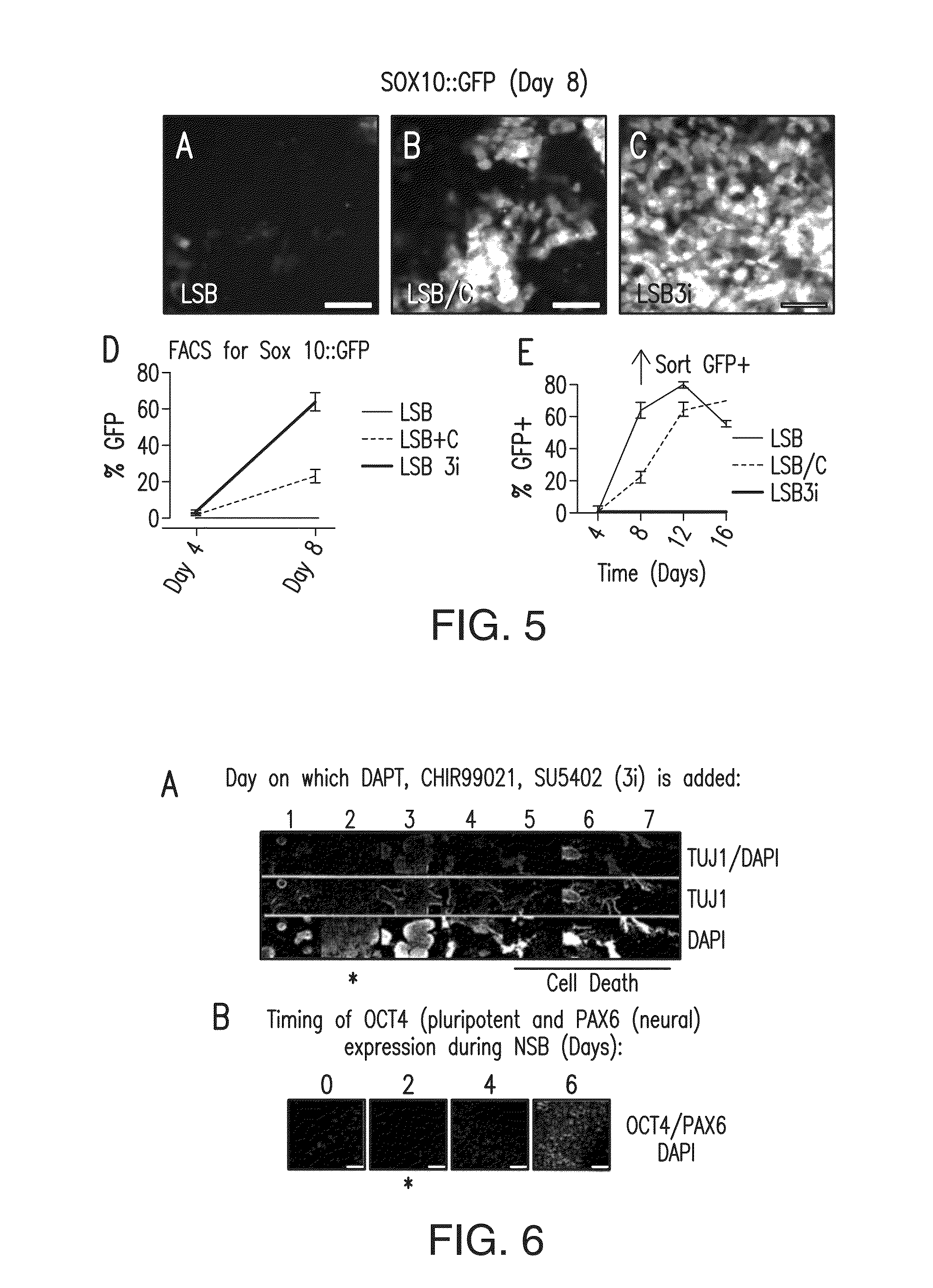
Methods of neural conversion of human embryonic stem cells
ActiveUS20120094381A1Reducing DKK- protein functionImprove featuresCulture processNervous system cellsNeural plateDirected differentiation
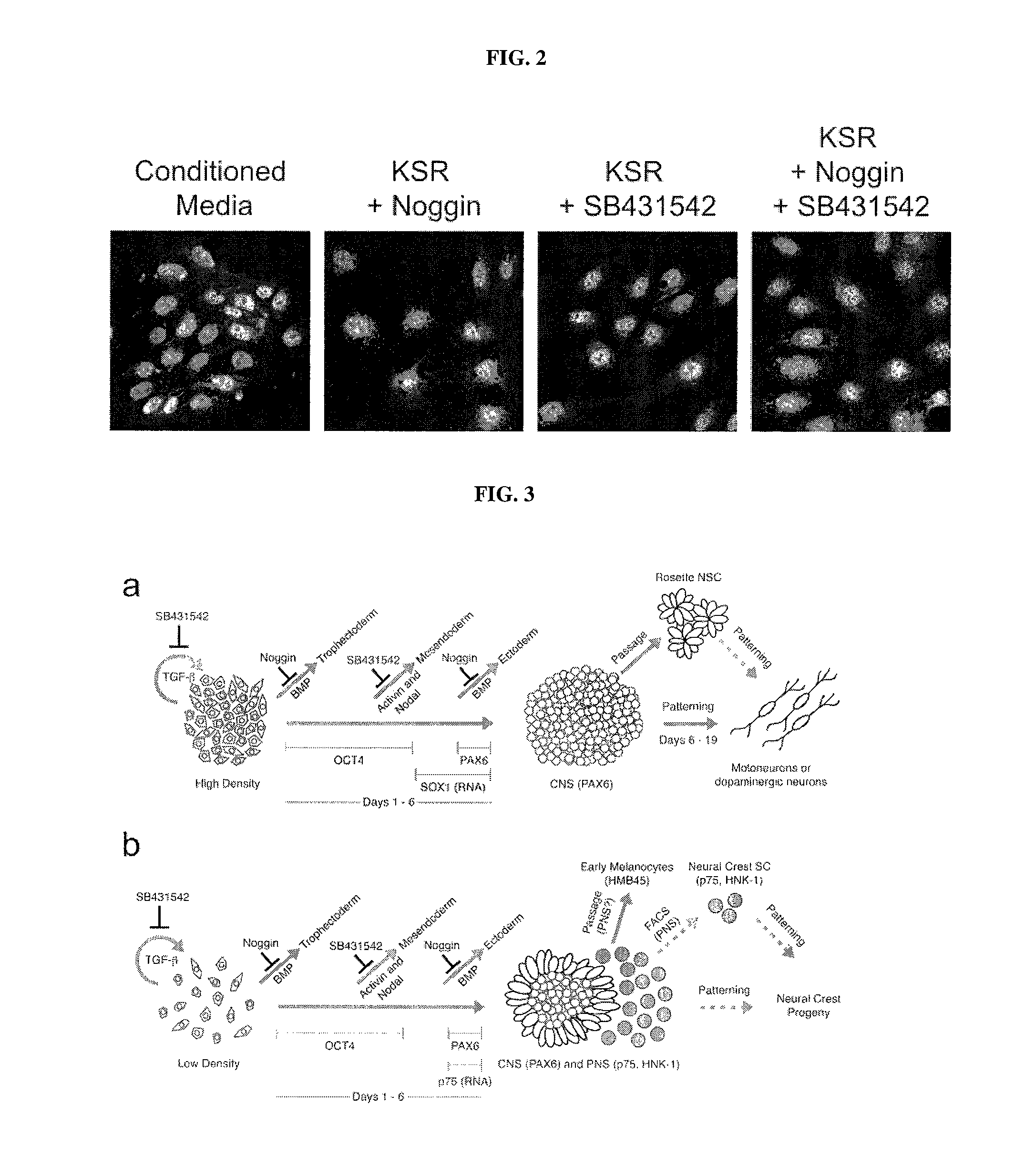
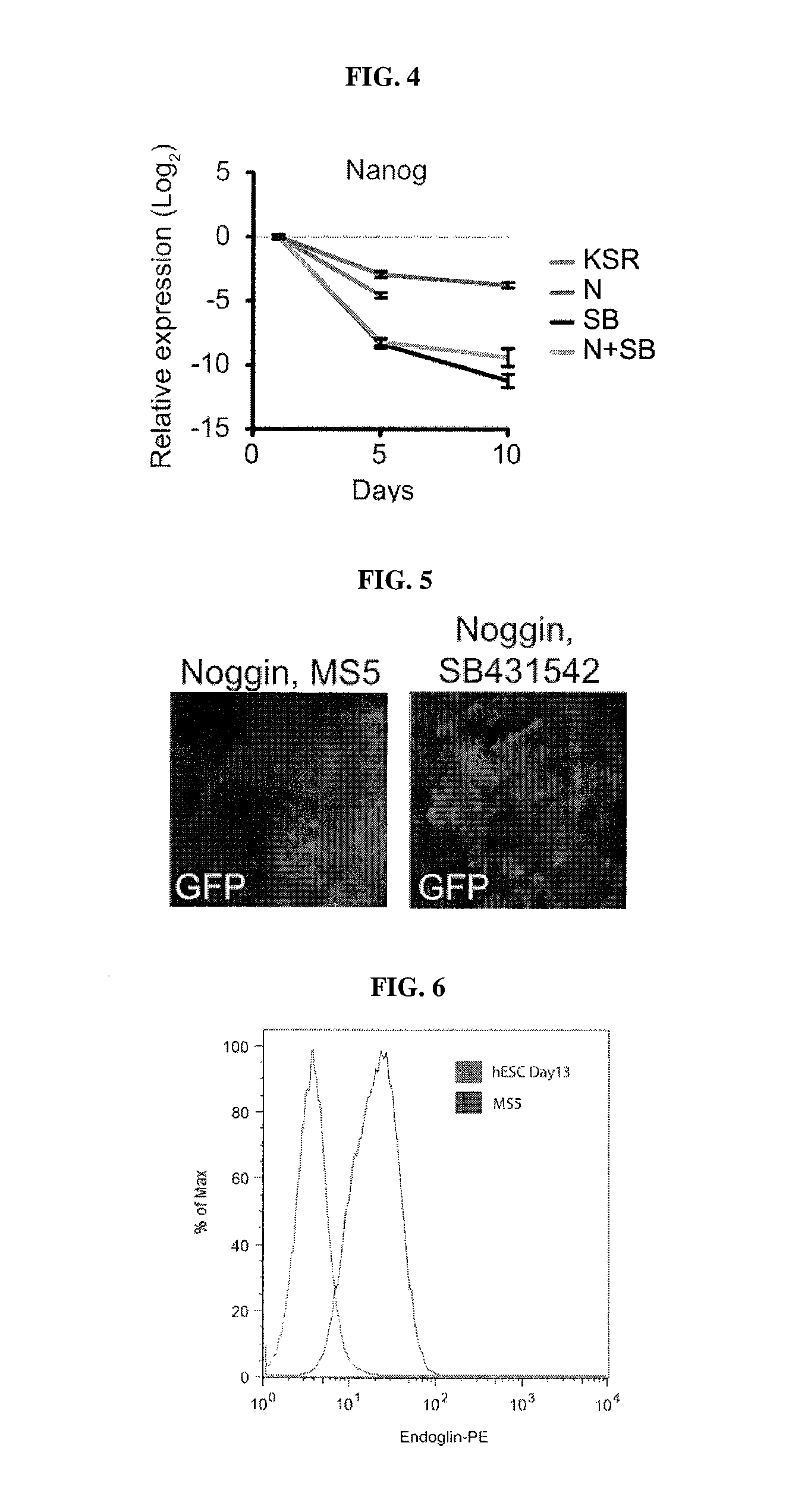
The present invention relates generally to the field of cell biology of stem cells, more specifically the directed differentiation of pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, including human embryonic stem cells (hESC), somatic stem cells, and induced human pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) using novel culture conditions. Specifically, methods are provided for obtaining neural tissue, floor plate cells, and placode including induction of neural plate development in hESCs for obtaining midbrain dopamine (DA) neurons, motorneurons, and sensory neurons. Further, neural plate tissue obtained using methods of the present inventions are contemplated for use in co-cultures with other tissues as inducers for shifting differentiation pathways, i.e. patterning.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Methods of neural conversion of human embryonic stem cells
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Application of inorganic nano-material layered double hydroxides (LDHs) in mouse embryonic stem cell culture
ActiveCN103966160AEasy to synthesizeGood function and effectEmbryonic cellsGerm cellsGerm layerMaterial synthesis
The invention relates to application of inorganic nano-material layered double hydroxides (LDHs) in mouse embryonic stem cell culture. Under the condition that LIFs are not added, the inorganic nano-material LDHs can promote expression of pluripotency genes and restrains cell differentiation, and in addition, the treated cells still have the potency of differentiating to three germ layers. The inorganic nano-material LDHs have excellent biocompatibility, low cytotoxicity, easiness in contact with cell surfaces, low cost, convenience and rapidness in material synthesis and excellent effect, and has extensive application prospect in research of embryonic stem cells.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Preparation method for hematopoietic progenitor cells and special medium for same
InactiveCN102732483AEfficient productionBlood/immune system cellsProgenitorInduced pluripotent stem cell
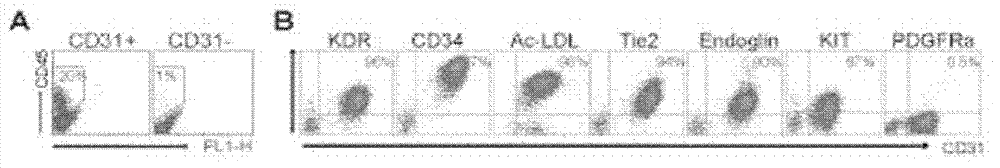
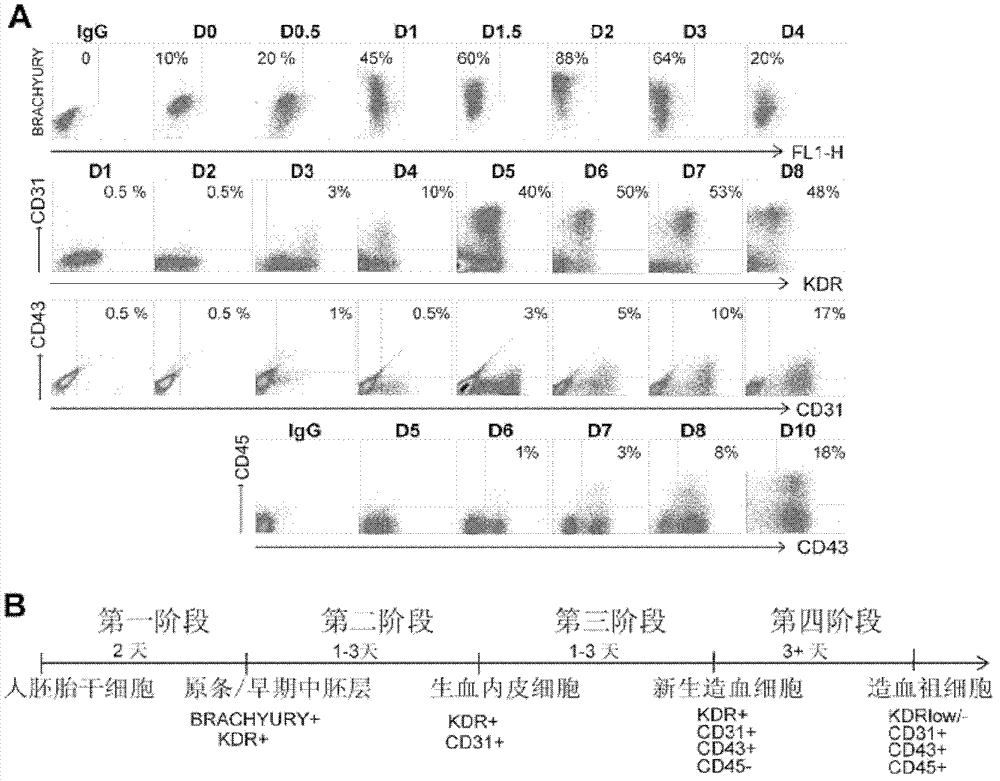
The invention discloses a preparation method for hematopoietic progenitor cells and a special medium for the same. The invention provides the medium for hematopoietic progenitor cells prepared through differentiation of human embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells, and the medium comprises cell culture fluid I, cell culture fluid II, cell culture fluid III and cell culture fluid IV. According to results of experiments in the invention, a novel system which has definite components and induces differentiation of human embryonic stem cells step by step to generate hematopoietic progenitor cells is established; the system provides a good research platform for further research of differentiation and generation of hematopoietic stem / progenitor cells and provides a differentiation method for obtaining hematopoietic progenitor cells which can be used in treatment of clinical blood diseases since the differentiation system utilizes serum-free and murine-free stromal cells and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
In Vitro Generation of Hepatocytes from Human Embryonic Stem Cells
Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells, such as human embryonic stem cells (hESC), into hepatocytes by in vitro methods is disclosed. The pluripotent stem cells are cultured in conditioned medium from the hepatocarcinoma cell line, HepG2. Specific growth factors and defined media may also be added to the medium for stage specific differentiation of the derived hepatocytes. Hepatocytes differentiated from human pluripotent stem cells may be characterized by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS), immunofluorescence analysis (IF), real time polymerase reaction (RT-PCR), and functional assays. The methods disclosed herein are able to differentiate high percentages of hepatocytes from human pluripotent stem cells using the disclosed methods. These differentiated cells may exhibit polygonal shape morphology, typical of hepatocytes, and may express hepatocyte specific genes. The differentiated cells may also be positive for definitive endoderm markers and hepatic markers.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Myocardial small molecular compound for idiosyncratically promoting proliferation of myocardial cells and application thereof
InactiveCN102382127AConservativeRescue abnormal cardiac phenotypesOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseHeart disease
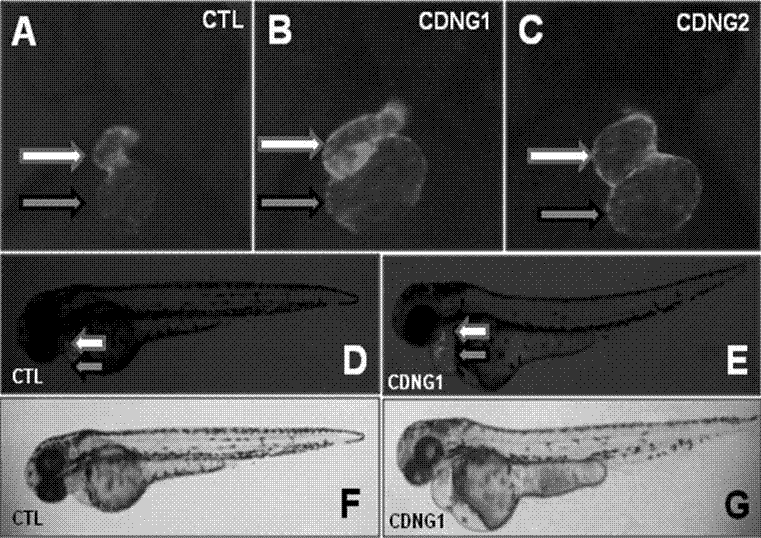
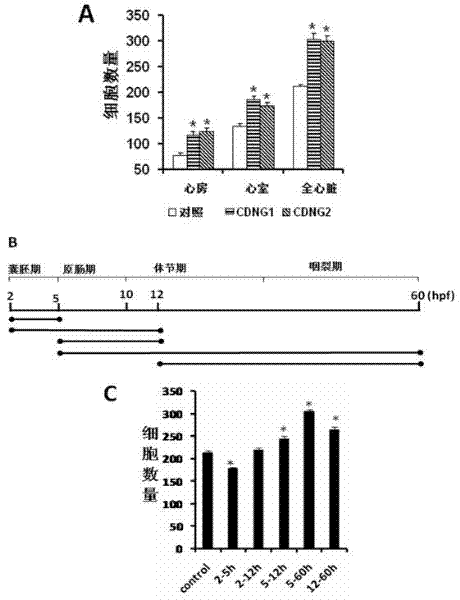
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and particularly relates to a myocardial small molecular compound for idiosyncratically promoting proliferation of myocardial cells and application thereof. The myocardial small molecular compound total comprises a type A, a type B and a type C which have a common core structure, namely (3 (1, 2, 4) triazole (3, 4-b) (1, 3, 4) bismuththiol). The myocardial small molecular compound is obtained from a small molecular compound library by means of model organism zebra fish screening, so as to be capable of idiosyncratically promoting proliferation of myocardial cells inside zebra fish bodies. Importantly, the myocardial small molecular compound is capable of inducing embryonic stem cells of a small mouse to differentiate and proliferate towards the myocardial cells. As proved, the myocardial small molecular compounds are antagonists to inhibit wnt signaling pathways. The myocardial small molecular compound can be used as pilot drugs for treating heart diseases and further is used for optimizing and evaluating candidate drug targets thereof.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
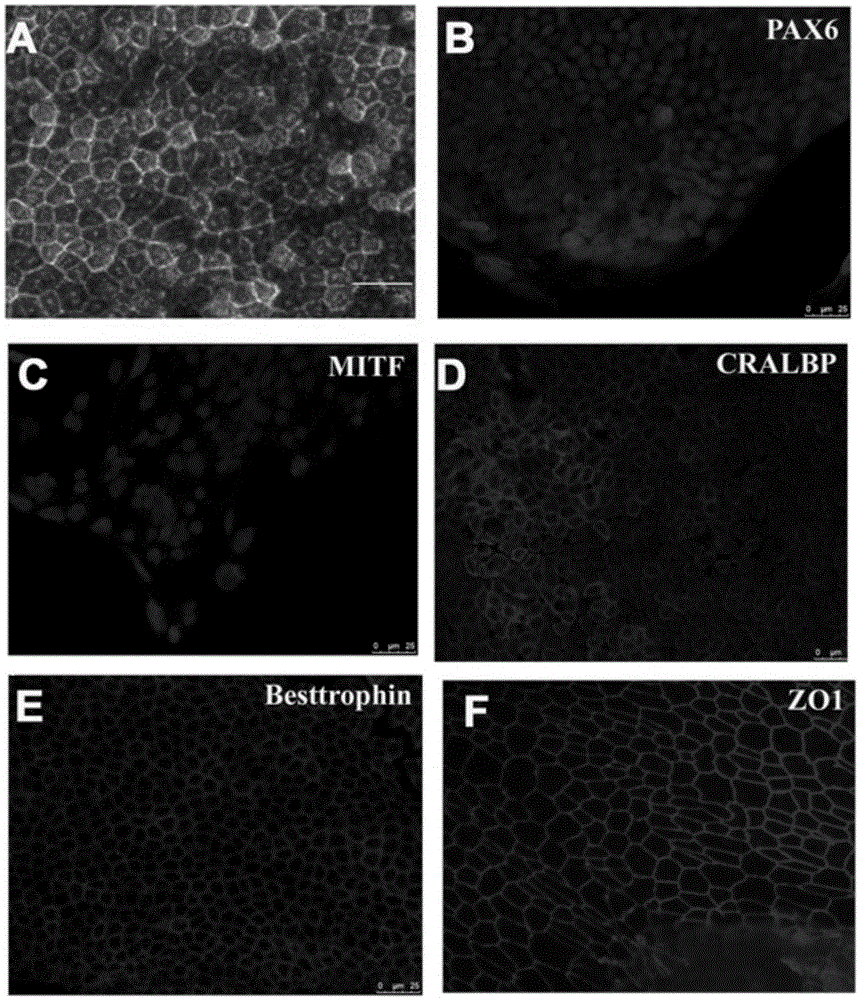
Method for inducing human embryonic stem cells to be differentiated into retinal pigment epitheliums (RPE) in vitro
ActiveCN106609256AReduce yieldShorten the differentiation timeVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsEpitheliumMouse Embryonic Stem Cell
The invention relates to a method for inducing human embryonic stem cells to be differentiated into retinal pigment epitheliums (RPE) in vitro, and belongs to the biology technical field. The pure RPEs can be obtained through one-time passage by means of induced differentiation. Compared with the prior art, the differentiation time from the human embryonic stem cells into the RPEs is shortened. By the adoption of the method, a new approach and guidance are provided for induced directional differentiation of the human embryonic stem cells into the pigment epitheliums.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
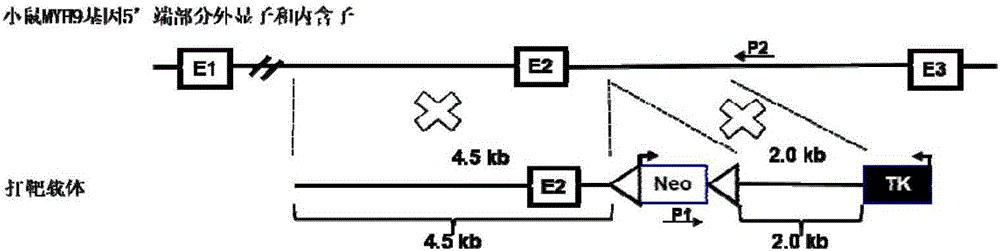
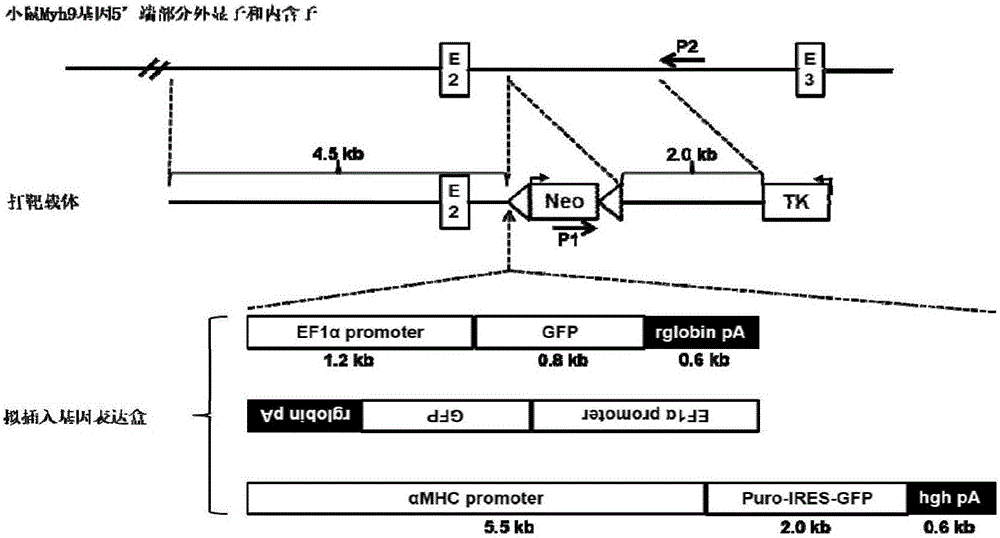
Target targeting vector, method for constructing mouse embryonic stem cell strain through targeting integration of exogenous genes to MYH9 Intron2 locus and application
ActiveCN106434750AEfficient Targeted IntegrationStable expressionNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionMouse Embryonic Stem CellGene expression
The invention discloses a target targeting vector, a method for constructing a mouse embryonic stem cell strain through targeting integration of exogenous genes to an MYH9 Intron2 locus and application. The sequence of the target targeting vector is shown as SEQ ID NO.7, and the target targeting vector is named an mpNTKV-LoxP MAI2L-MAI2R vector. A new locus sequence capable of achieving efficient, safe and targeting integration is provided. According to the targeting vector constructed based on the locus and inserted into the exogenous genes in a targeting mode, efficient targeting can be achieved, it can be guaranteed that the exogenous genes are stably expressed in mouse embryonic stem cells and endogenous gene expression is not influenced, and therefore a good platform is erected for construction of a transgenic cell line and a rat.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
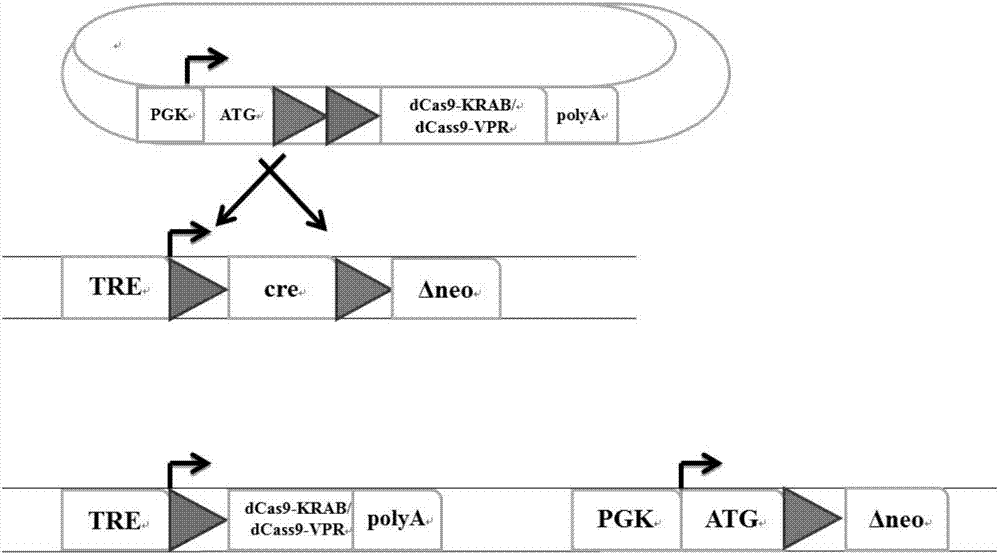
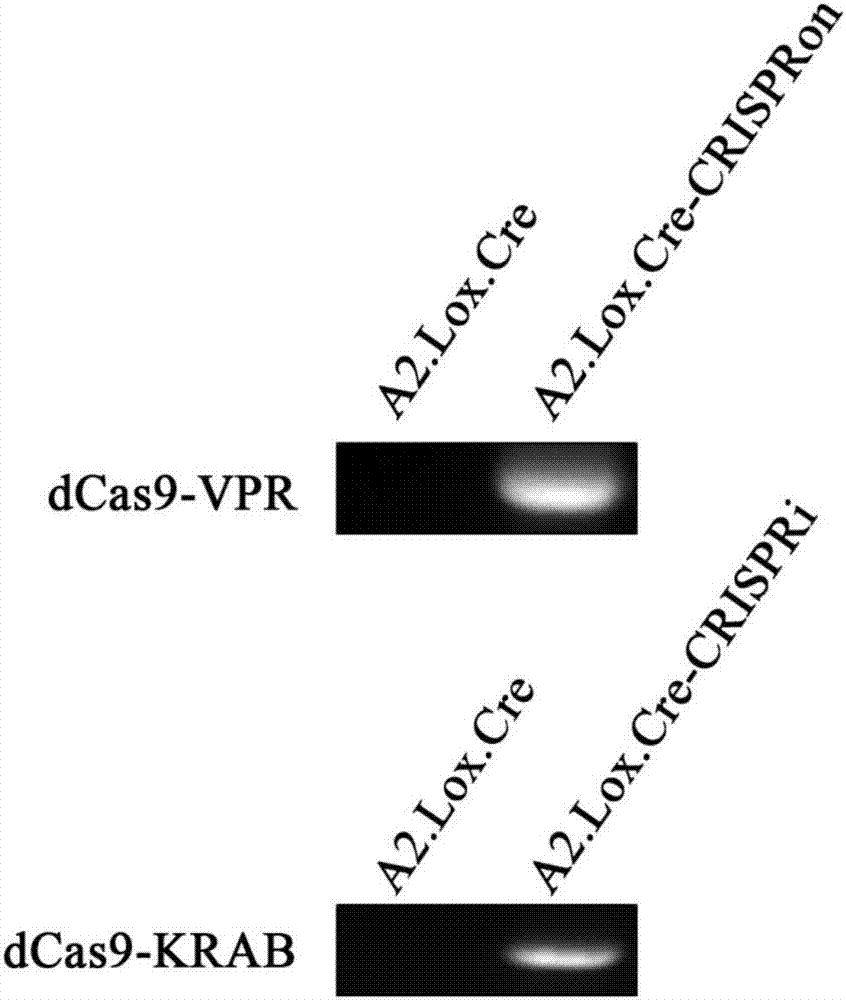
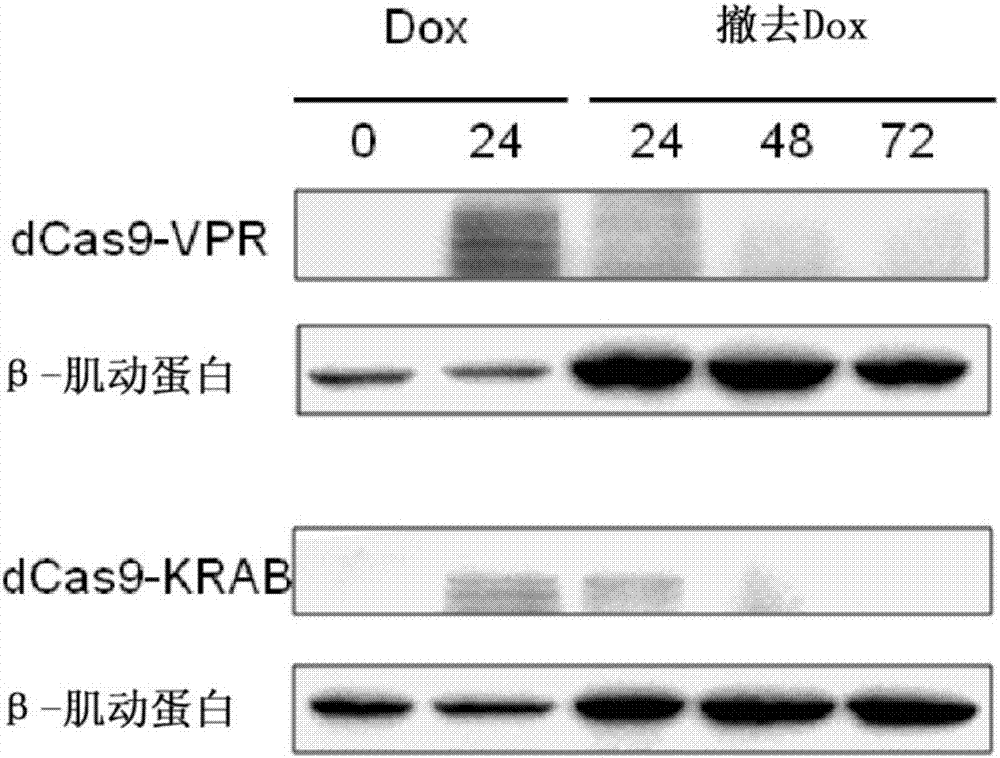
Inducible CRISPRon or CRISPRi mouse embryo stem cells and application thereof
ActiveCN107142247AHigh homologous recombination efficiencyHigh positive rate of stable clonesHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVpr ProteinEmbryo
The invention provides inducible CRISPRon or CRISPRi mouse embryo stem cells and a preparation method thereof. The mouse embryo stem cells are A2Lox.Cre cells and can reversibly express dCas9-VPR fusion protein or dCas9-KRAB fusion protein. The invention further provides a method for regulating and controlling gene expression and a kit. According to the inducible CRISPRon or CRISPRi mouse embryo stem cells provided by the invention, the construction method is simple and convenient, and the stable positive rate is up to 90 percent or higher; the genomic sequence is not edited, and gene expression is directly activated or inhibited; expression of the fusion protein has inducibility and reversibility; controllability and diversity on targeted regulation and control on the gene are achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
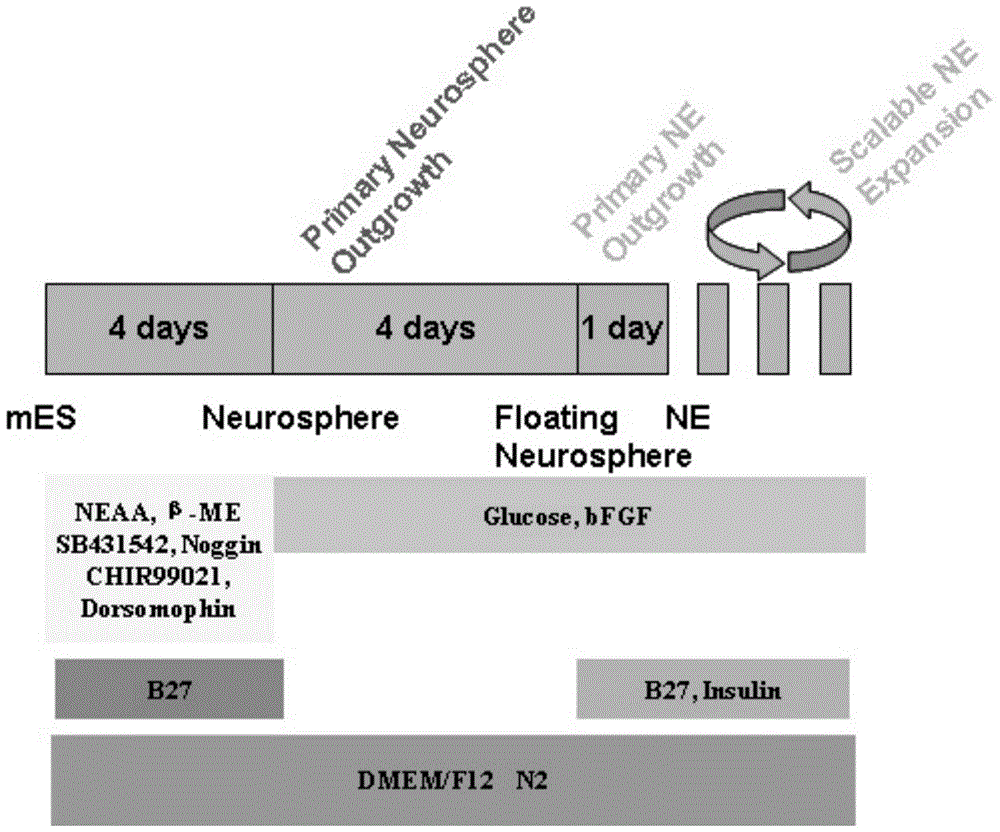
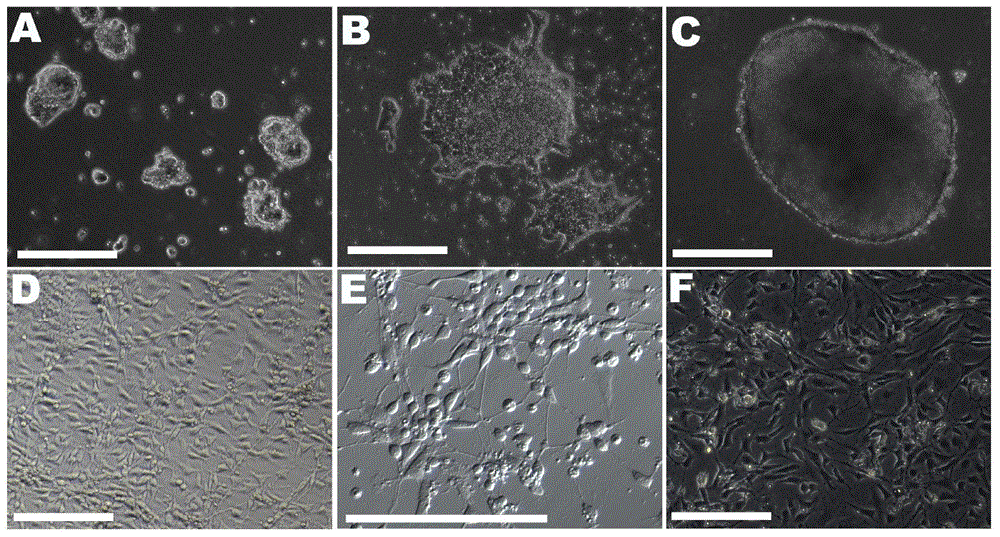
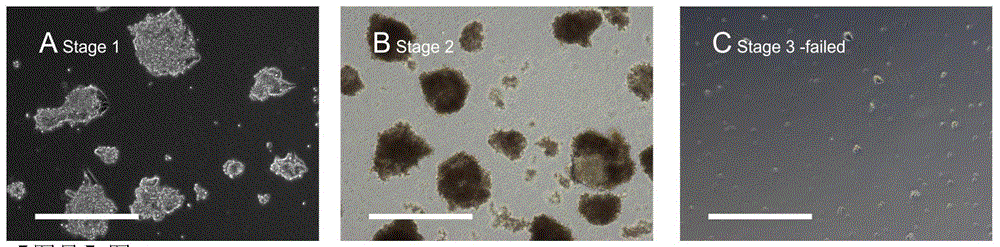
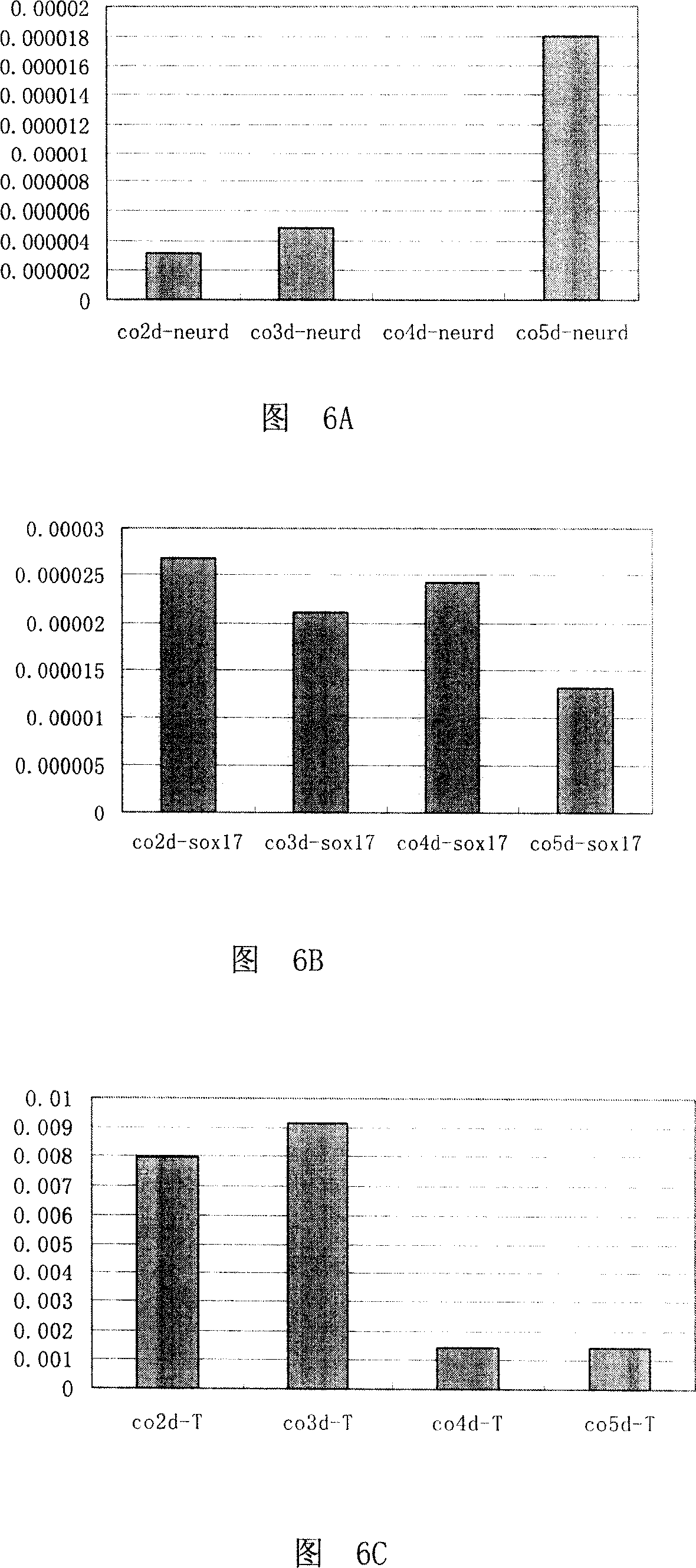
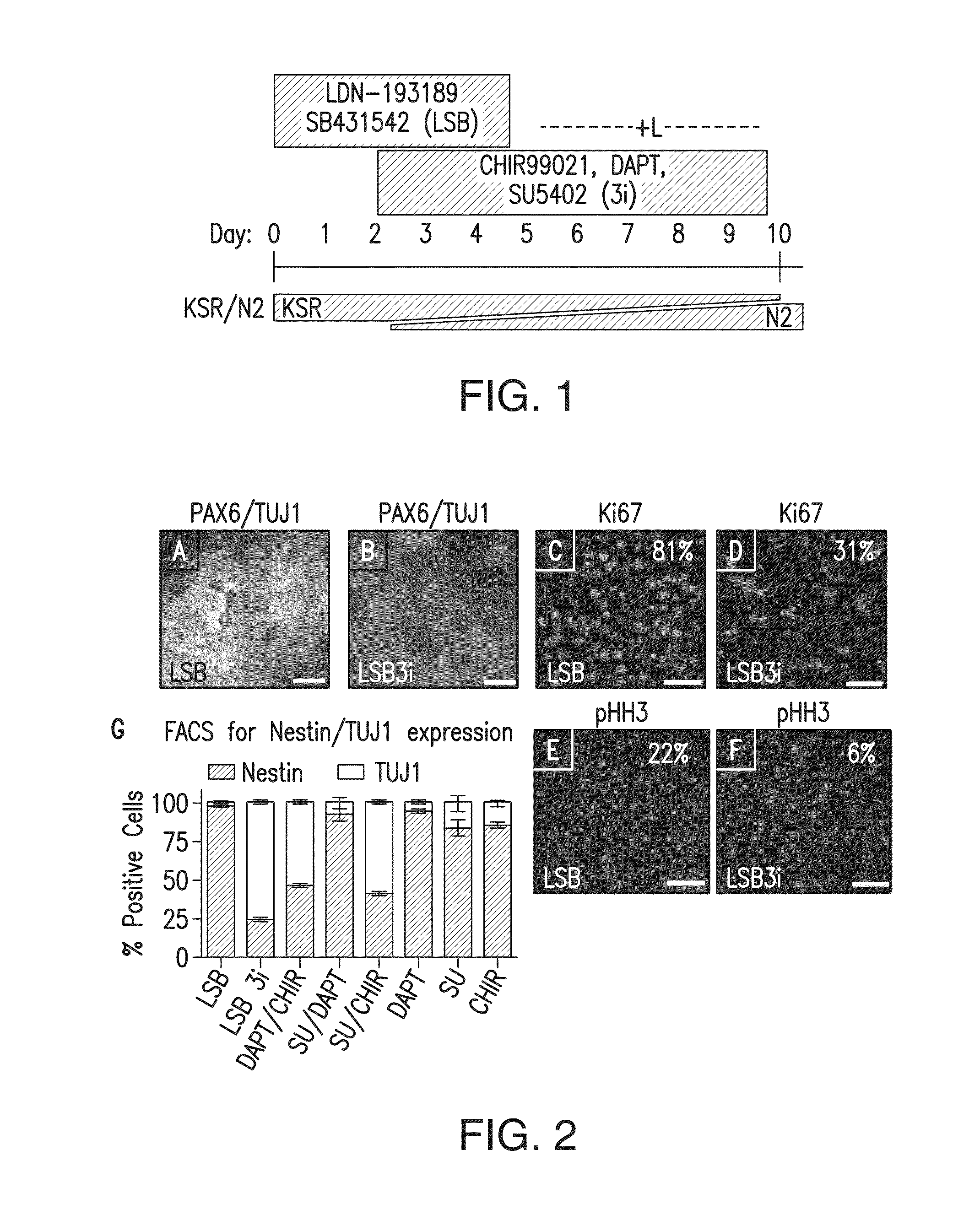
Method for quickly, directly and directionally inducing differentiation from mouse embryonic stem cells to neuroepithelial cells
ActiveCN104450618ALong-term self-replicationLong-term update capabilityNervous system cellsNeurulationNeurosphere
The invention discloses a method for quickly, directly and directionally inducing differentiation from mouse embryonic stem cells to neuroepithelial cells. The method comprises the steps of adding an induction medium containing dorsomorphin, noggin, SB431542 and CHIR99021 to a bulk clone of the mouse embryonic stem cells subjected to adherent culture, to induce the mouse embryonic stem cells to form rosette neurospheres; then adding a second stage of induction medium containing bFGF and performing suspension culture to form suspended neurospheres; and finally, digesting the neurospheres into single cells, and then performing adherent culture with a third stage of induction medium to form the neuroepithelial cells with long-term self proliferation and update. By adopting the method, the traditional EB method is abandoned, the differentiation time is shortened, and the differentiation efficiency reaches over 95%. The method can be used for quickly inducing NE cells to substitute NSC cells to treat central system injury, and has very high clinical applicability.
Owner:南通大学技术转移中心有限公司
Method for culturing mouse embryo stem cell and its dedicated culture medium
The invention discloses a mouse embryo stem cell culturing method and specific cultivating base, which cultures embryo stem cell on the trophoblast cell, wherein the trophoblast cell is epithelial cell or endothelium cell; the cultivating base consists of epithelial cell or endothelium cell and culturing liquid of embryo stem cell, which is high-sugar DMEM with 10-20% embryo cow serum or calf serum with 1. 5-3. 0*10-4mol / L Monothioglycerol, MTG.
Owner:BEIJING WEITONGDA BIOTECH
Method for inducing mouse embryonic stem cells to differentiate toward nerve cells
InactiveCN101892191ALow toxicityEasy to observe shape changesEmbryonic cellsGerm cellsFeeder LayerEmbryo
The invention relates to a method for inducing mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) to differentiate toward nerve cells. Primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (PMEF) are used as a feeder layer. The method comprises the following steps of: inoculating the mESCs to the feeder layer, inoculating the mESCs to mixed solution of stem cells and mESCs culture liquid, and culturing nerve stem cell culture solution; and gradually changing the culture into the culture of nerve cell culture solution by completely using serum-free added alkali fibroblast growth factors, wherein the optimal serum concentration of the mixed solution for primary inoculation is 12.5 percent, the optimal inoculation density of primary mESCs inoculation is 1.0*108<-1>, and the time of completely changing the serum-free culture solution is the 5th day. By induction of the method, the mouse stem cells can be differentiated into the nerve cells in vitro. The method has the advantages of short experimental period, simple and convenient experimental process and stable and efficiency inducing results, can quickly finish a cell culture period, and is favorable for subsequent experiments.
Owner:中国医科大学
Method of nociceptor differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and uses thereof
The present invention relates to the field of stem cell biology, in particular the linage specific differentiation of pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, which can include, but is not limited to, human embryonic stem cells (hESC), human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC), somatic stem cells, cancer stem cells, or any other cell capable of lineage specific differentiation. Specifically described are methods to direct the lineage specific differentiation of hESC and / or hiPSC to nociceptors (i.e. nociceptor cells) using novel culture conditions. The nociceptors made using the methods of the present invention are further contemplated for various uses including, but limited to, use in in vitro drug discovery assays, pain research, and as a therapeutic to reverse disease of, or damage to, the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Further, compositions and methods are provided for producing melanocytes from human pluripotent stem cells for use in disease modeling.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
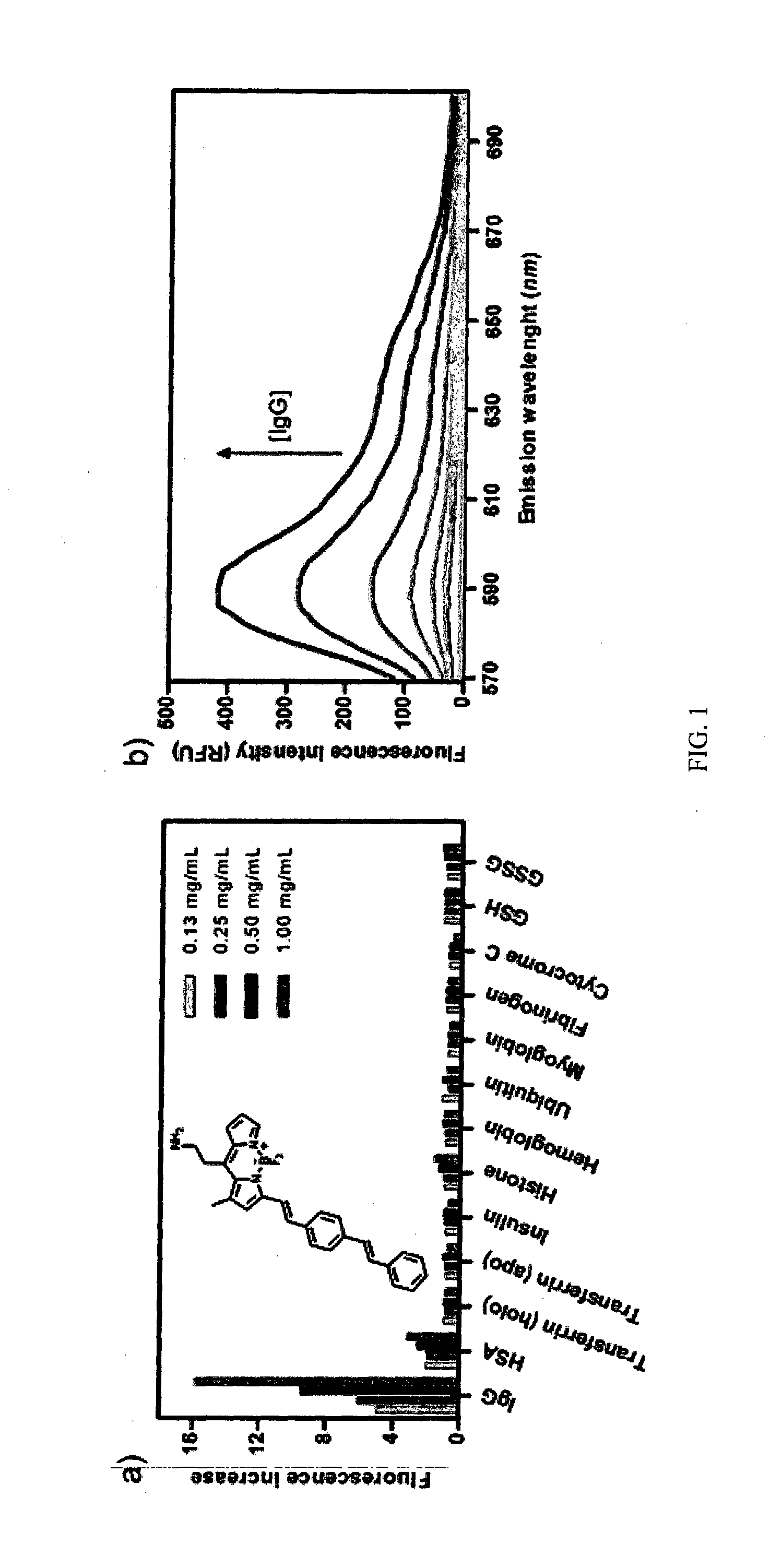
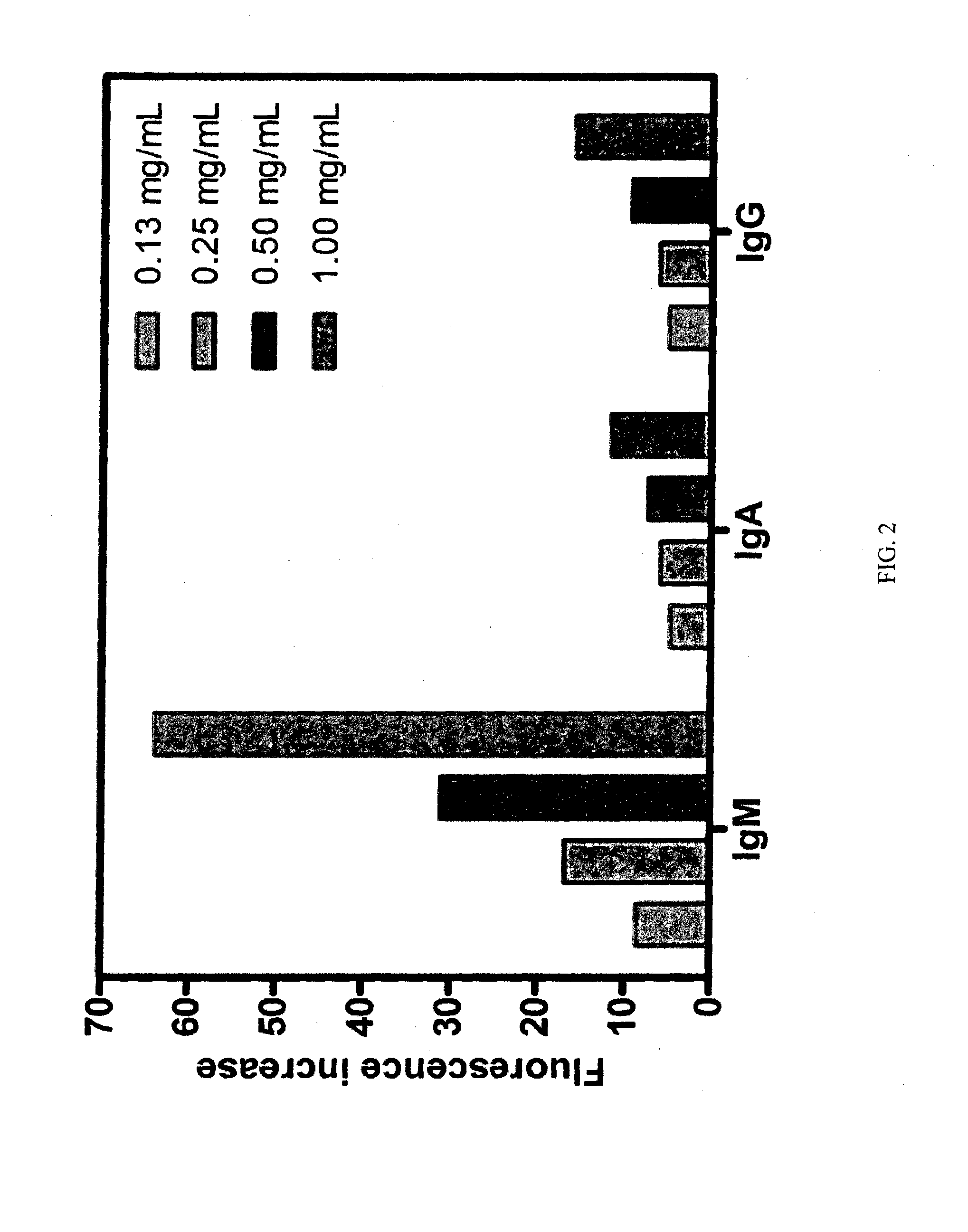
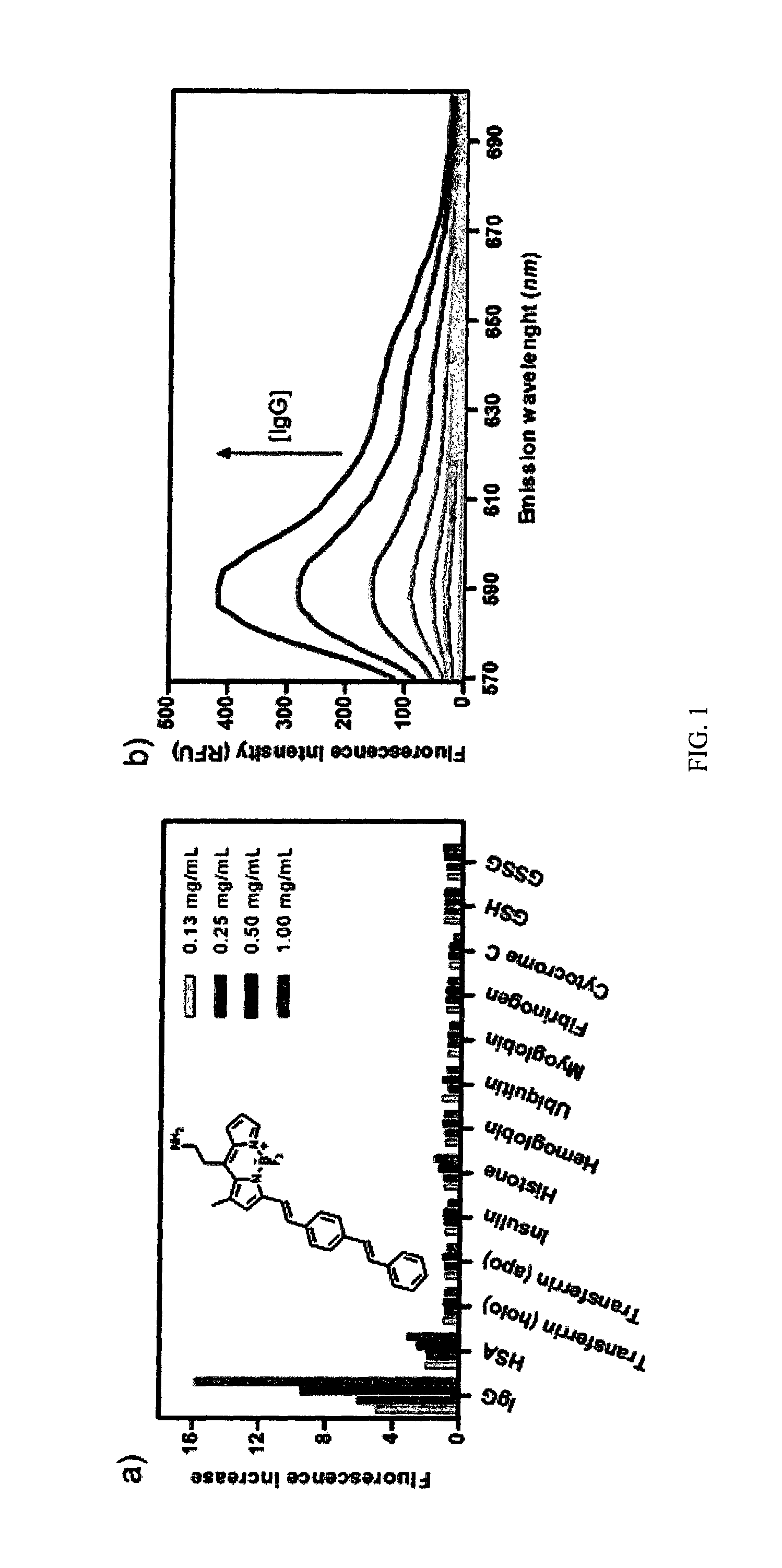
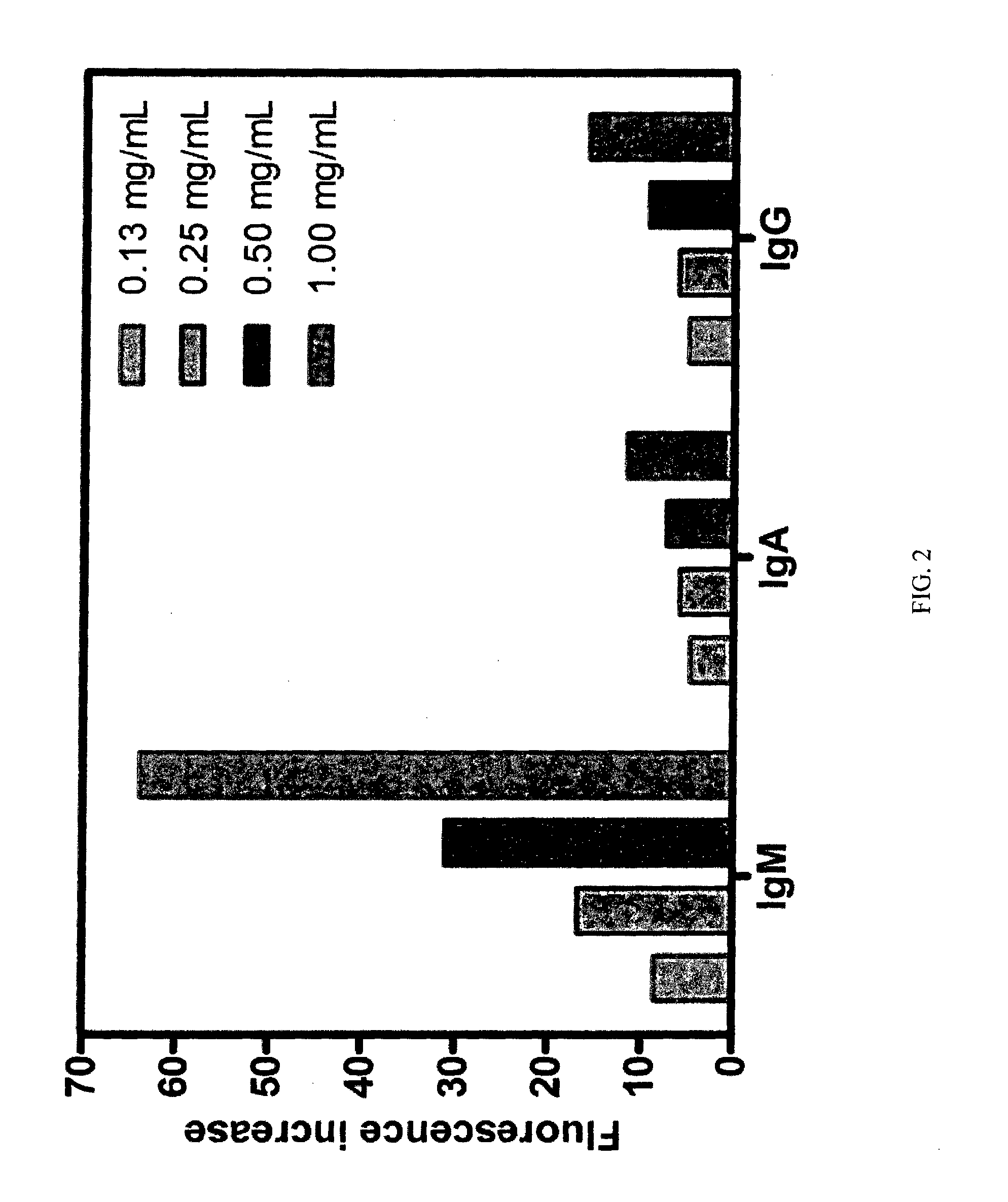
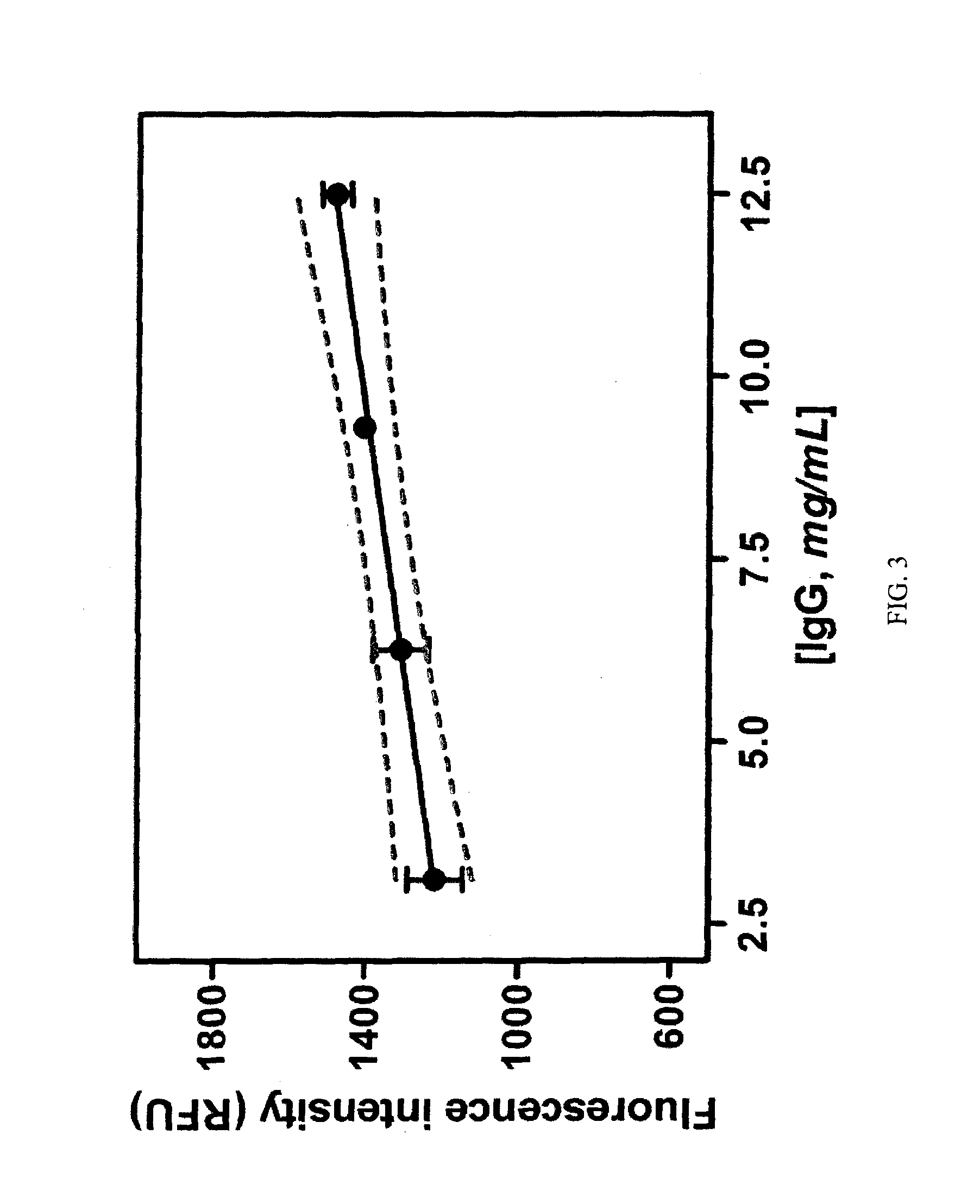
Alkylamino BODIPY Dyes As Selective Fluorescent Probes For Proteins And Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
InactiveUS20140121129A1High yieldLow material recoveryStyryl dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein detectionBODIPY
The present invention discloses a series of alkylamino BODIPY dyes, methods for preparing a library of alkyl-amino BODIPY dyes via solid-phase synthesis, and the use of the alkyl-amino BODIPY dyes as fluorescent sensors for protein detection, cell imaging and cytometry applications, and staining of certain cell line.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Differentiation of non-embryonic stem cells to cells having a pancreatic phenotype
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Method for inducing differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell to obtain inner ear hair cells
ActiveCN104403988ARaise the ratioWith electrophysiological functionVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsTrophoblastic cellNutrient solution
The invention discloses a method for inducing differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell to obtain inner ear hair cells, which comprises the following steps: using a conditioned medium and an induction nutrient solution for inducing embryonic stem cell for differentiation of precursor cells of hair cell; and then using a combination method of the induction nutrient solution and trophoblastic cells for inducing precursor cell for differentiation of mature inner ear hair cells. The method can effectively induce the differentiation of embryonic stem cell to obtain the precursor cells of inner ear hair cell and mature inner ear hair cell, the differentiation ratio is high, hair cell specific gene and protein can be expressed by cells obtained through differentiation, and the cells have certain electrophysiological function of hair cells.
Owner:HANGZHOU S EVANS BIOSCI LTD
Cell culture media to differentiate embryonic stem cells into neuronal lineages
This invention provides compositions for differentiating an isolated embryonic stem cell or an isolated embryoid body into neuronal progenitor cells and methods for using same.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Chemical embryotoxicity prediction model and establishing method thereof
InactiveCN104988116AFacilitate high-throughput screeningDistinguishing whether embryotoxicity differs between sexesMicrobiological testing/measurementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsFibroblastKaryotype
The invention provides a chemical embryotoxicity prediction model. The chemical embryotoxicity prediction model comprises a cell type. The cell type comprises myocardial cells induced and differentiated from SP3ES cells with the karyotype as XX. An establishing method of the chemical embryotoxicity prediction model comprises the steps that 1, mouse embryo fibroblasts are separated and cultured; 2, in vitro multiplication culturing of the mouse ESs is conducted; thirdly, the karyotype analysis of the mouse ESs and gender determination are conducted; fourthly, the pluripotency of the mouse ESs is maintained and evaluated; fifthly, the mouse ESs are induced and differentiated to be myocardial cells in a in-vitro mode; sixthly, chemoimmunology detection of a cardiac-specific marker protein of the myocardial cells induced and differentiated from the mouse ESs is conducted; seventhly, real-time PCR detection of the expression profile of the myocardial cells induced and differentiated from the mouse ESs is conducted; eighthly, a pattern chemical is selected; ninthly, the cytotoxicity of the pattern chemical is detected; tenthly, the restraining effect of the pattern chemical on the ES differentiative capacity is detected; eleventhly, the embryotoxicity of the pattern chemical is evaluated. The chemical embryotoxicity prediction model fills up the blank that female mouse embryonic stem cells do not exist in an EST system.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
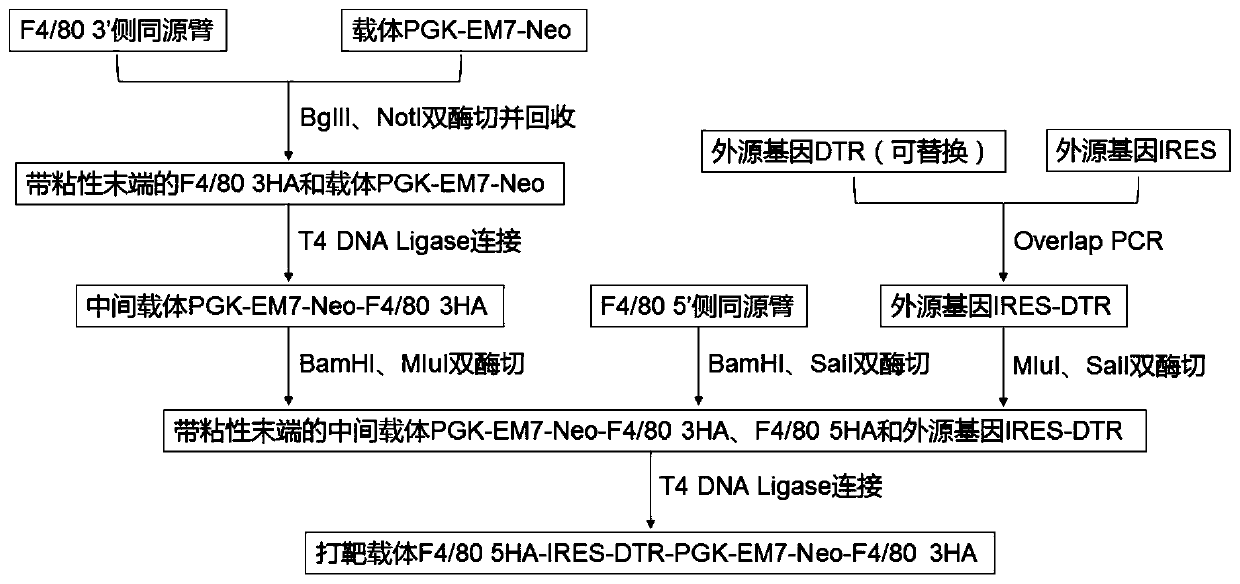
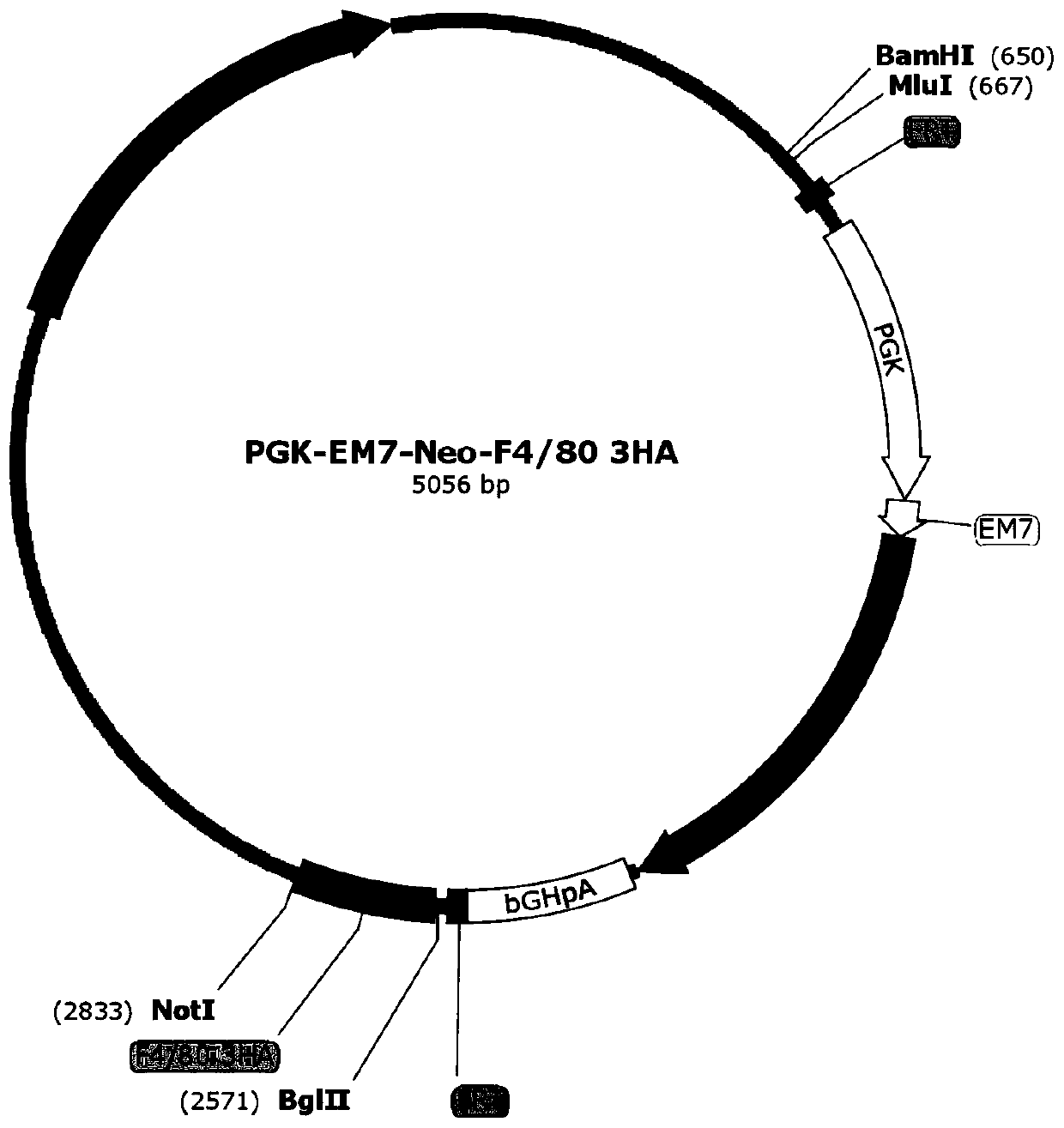
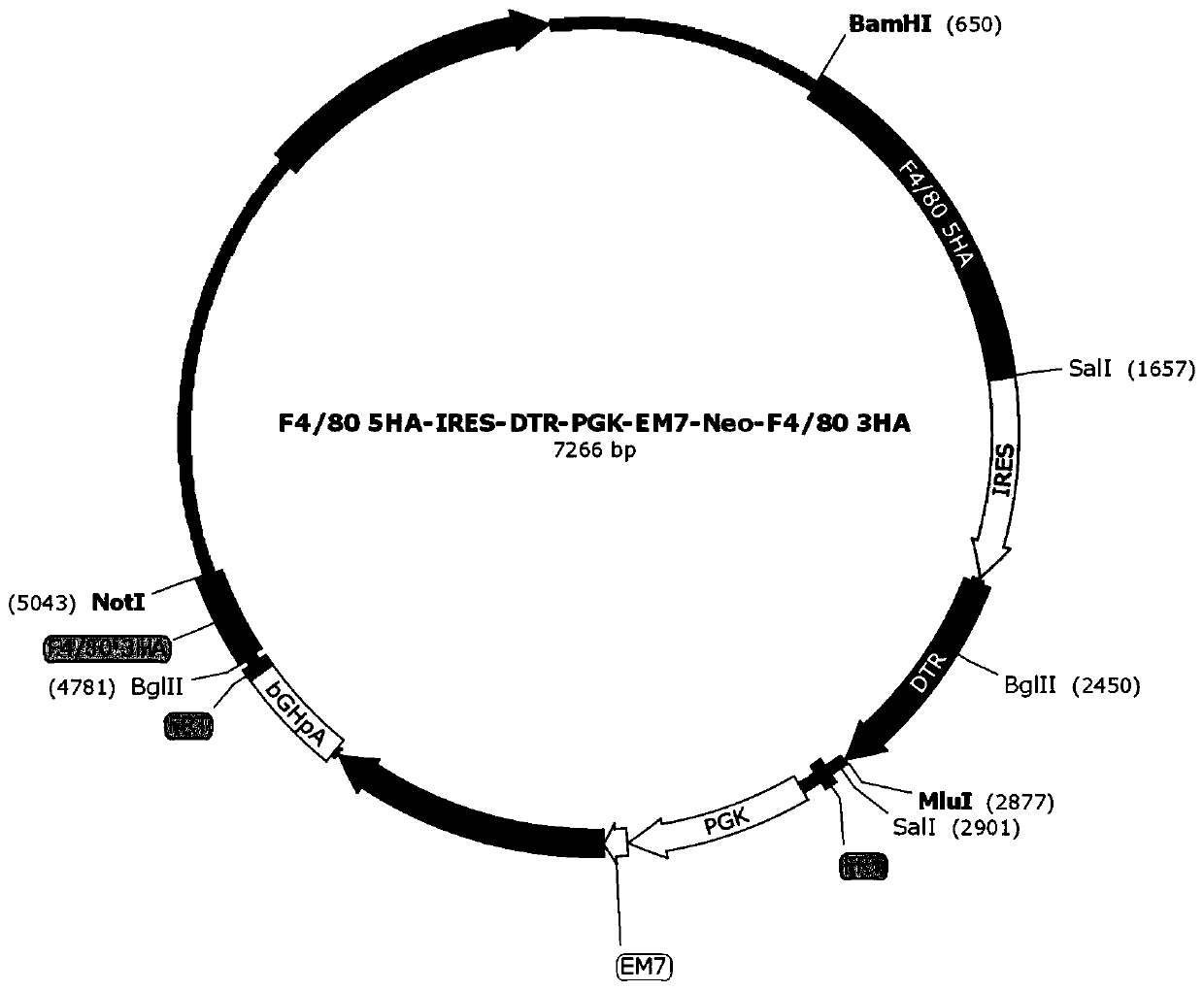
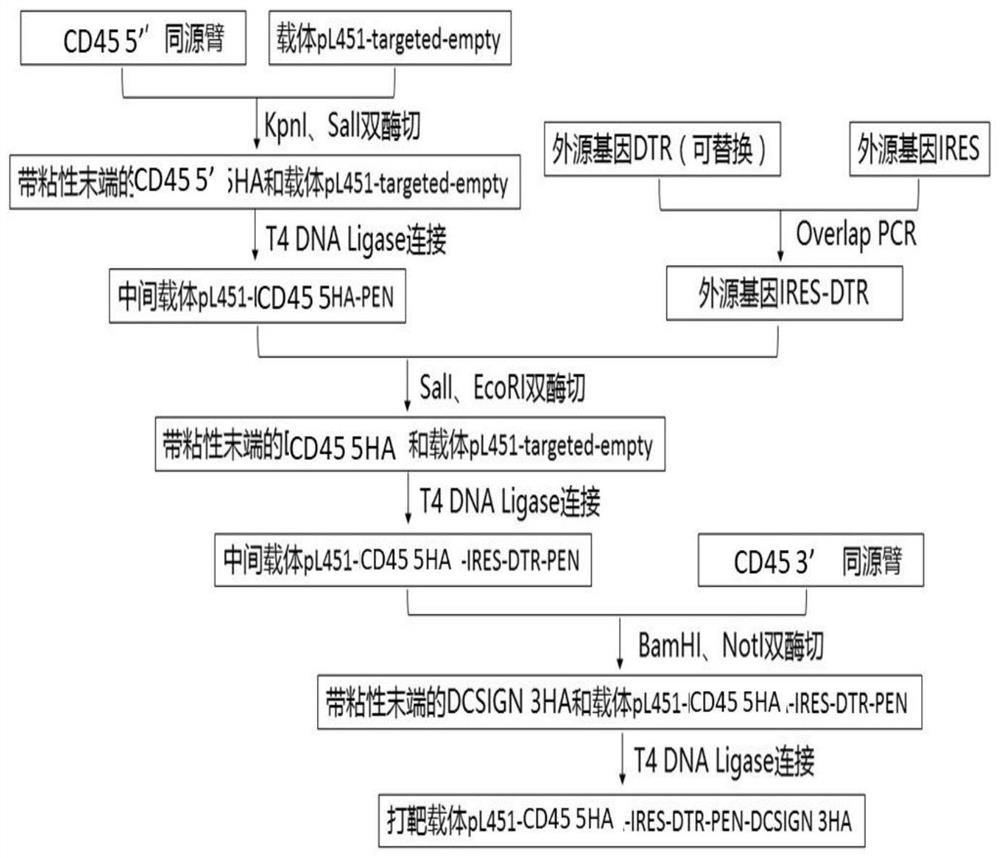
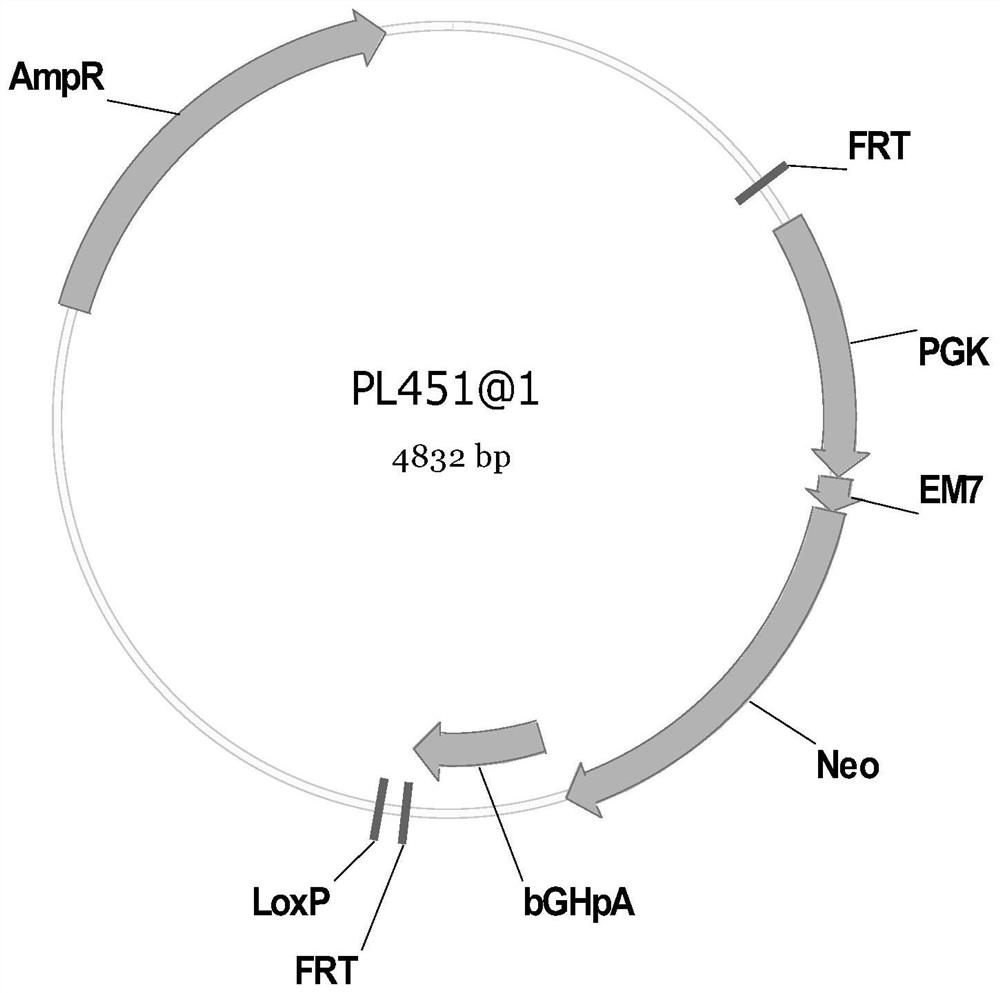
Targeted targeting vector, and method and application for targetedly integrating foreign gene to 22nd position of mouse F4/80 exon to construct BAC clone
PendingCN110938651AEfficient integrationDoes not affect functionStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorBac cloneEmbryo
The present invention belongs to the technical field of biology and discloses a targeted targeting vector, and a method and an application for targetedly integrating a foreign gene to a 22nd positionof a mouse F4 / 80 exon to construct BAC clone. A sequence of the targeted targeting vector is shown as SEQ ID NO.14 and named as a vector F4 / 80 5HA-IRES-DTR-PGK-EM7-Neo-F4 / 80 3HA. The present inventionprovides a new site sequence capable of achieving targeted integrating, the site can be used to construct the targeting vector for inserting the foreign gene, the targeting vector is verified to be capable of efficiently integrating the foreign gene into the mouse F4 / 80 BAC clone F4 / 80 exon 22th site, and the subsequently obtained targetedly inserted foreign gene F4 / 80 BAC can be used to construct mouse embryonic stem cells with the targetedly inserted foreign gene, thereby establishing a foundation for constructing a transgenic cell line and mice.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ZHEJIANG UNIV COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Method for inducing embryonic stem cell into pancreatic tissue-like cells
The invention discloses a method for inducing an embryonic stem cell into pancreatic tissue-like cells. The method comprises the following steps of: using a hanging-drop preparation method to differentiate an embryonic stem cell into three germ layer cells and using a immunomagnetic bead cell sorting method to purify finalized inner germ layer cells; further inducing the finalized inner germ layer cells so as to differentiate the cells into pancreatic precursor cells; and further differentiating the pancreatic precursor cells outside the body so as to form pancreatic tissue-like cells with high amylase secretion capability. The technical scheme of the invention adopts a plurality of induction factors for induced differentiation in different stages, which proves that the embryonic stem cell has the potentiality of being differentiated into pancreatic exocrine cells, and an effective way for inducting the embryonic stem cell into pancreatic tissue-like cells is found out, so that the pancreatic precursor cells are possible to recover injury of pancreas, and more cell sources are provided for recovering pancreas.
Owner:于涛 +1
Novel method for establishing embryonic stem cells containing exogenous chromosome
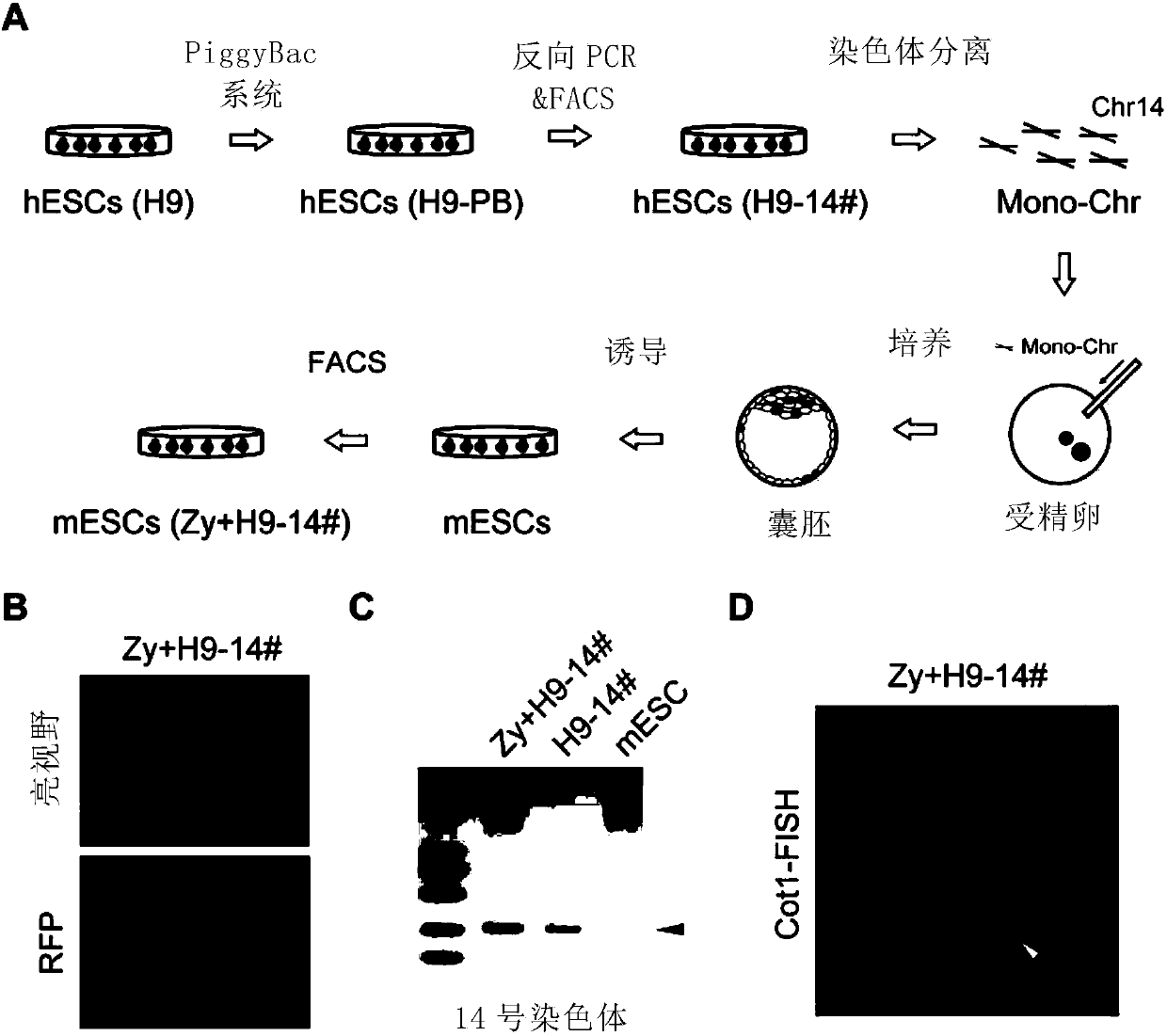
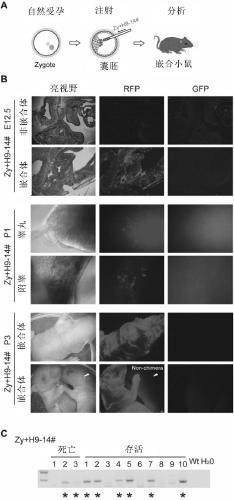
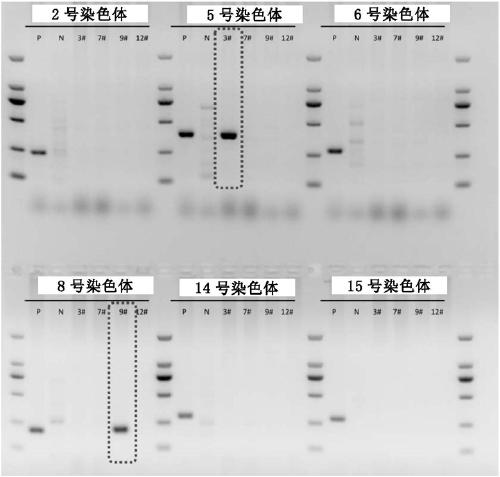
PendingCN109837307AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroinjection basedMCherry fluorescent proteinMouse Embryonic Stem Cell
The invention provides a method for establishing embryonic stem cells containing exogenous chromosome. Specifically, the method injects a single chromosome inserted into a mCherry reporter gene into mouse fertilized egg by a microinjection mode, so that the mice embryonic stem cells (ESCs) containing exogenous chromosomes is produced. The method of directly transferring modified chromosomes by single-chromosome microinjection to mediate chromosome engineering is a very effective technique, and can promote the acquisition of cells containing the exogenous chromosomes and chromosome operation.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN BRAIN SCI & INTELLIGENCE TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
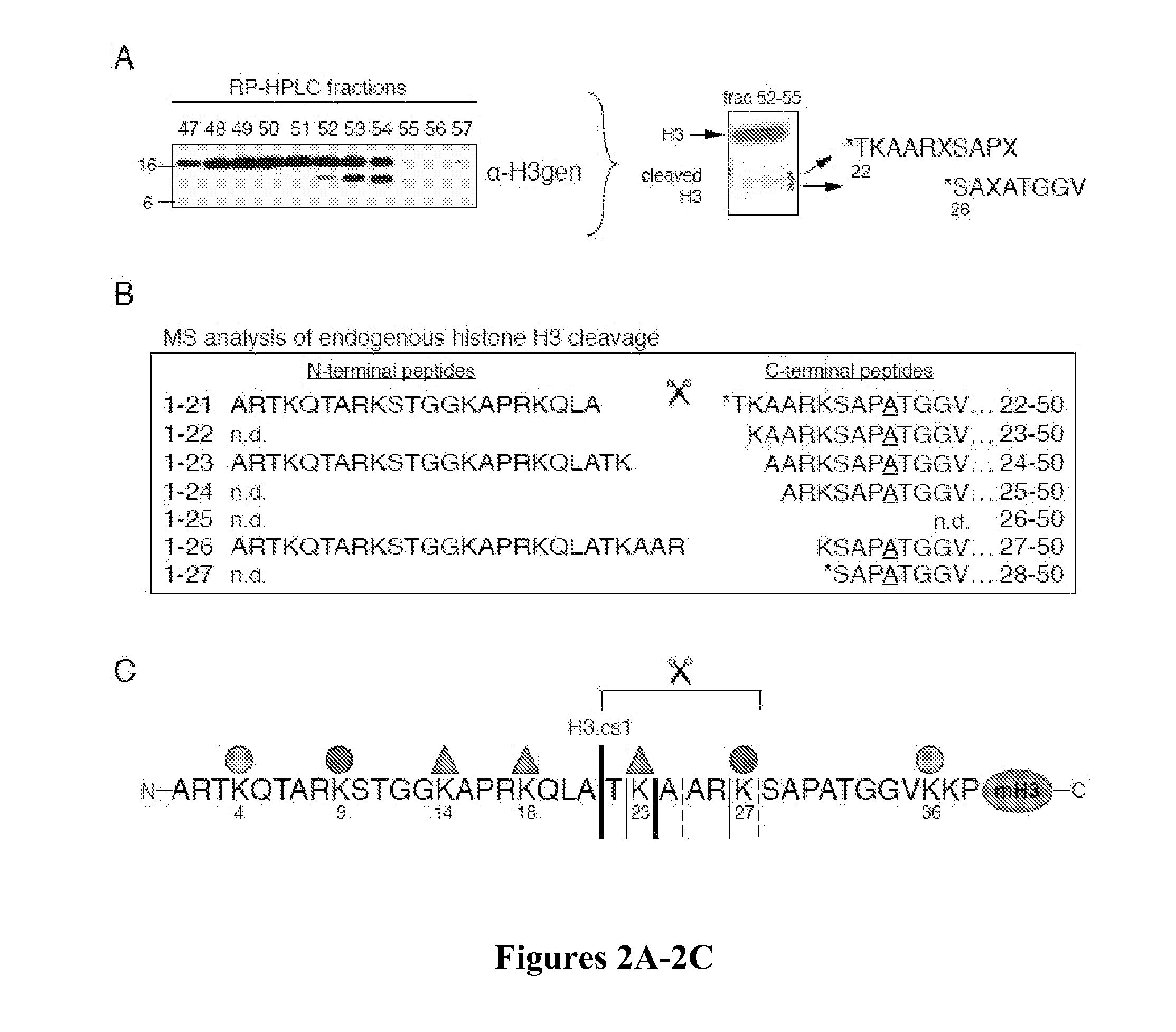
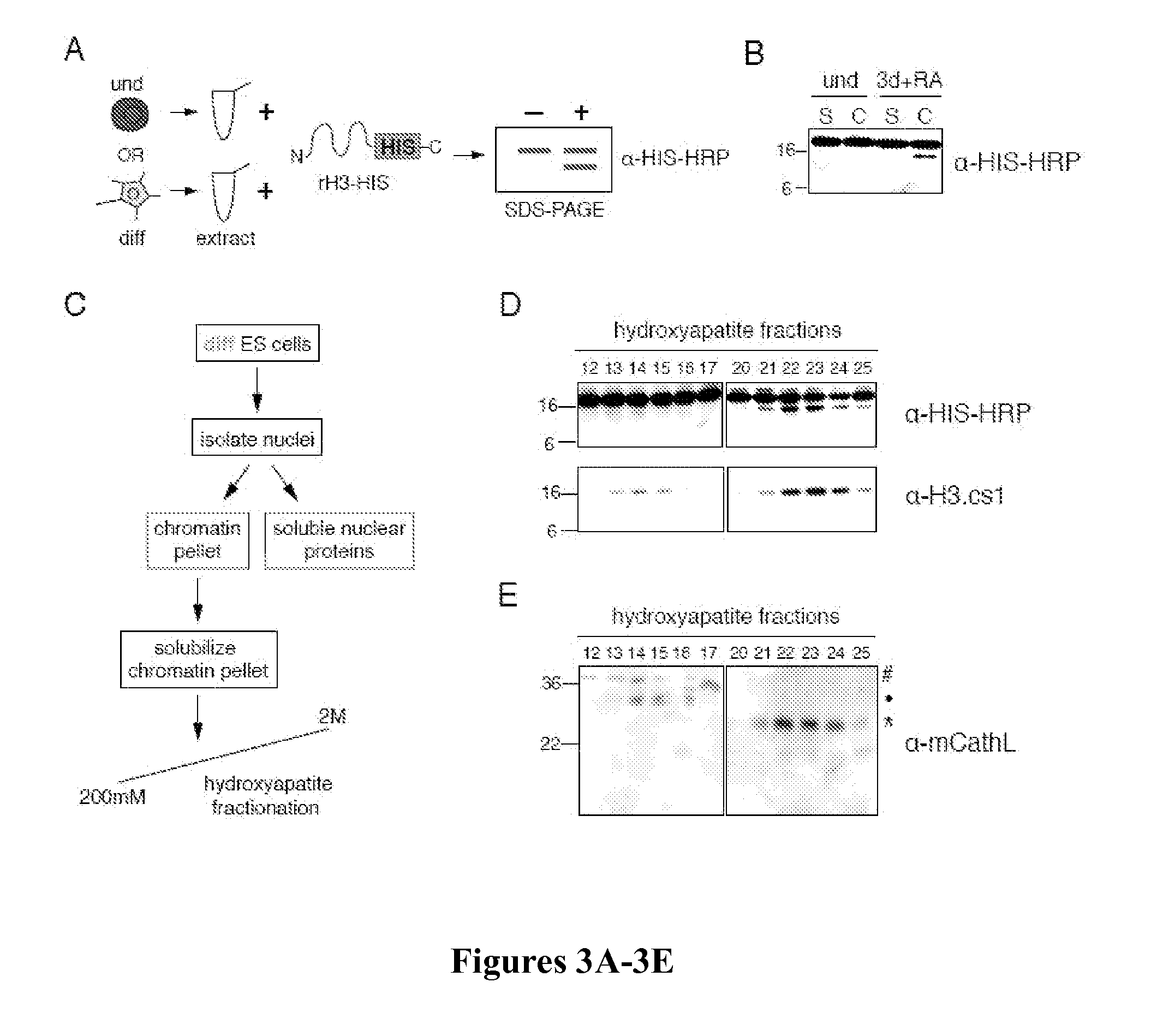
Cathepsin l proteolytically processes histone h3 during mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation
InactiveUS20110312897A1High expressionReduce expressionOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsCathepsin LAntigen Binding Fragment
Methods and agents useful for modulating histone proteolysis, stem cell differentiation, and gene transcription and for treating cancer are disclosed. Antibodies or antigen binding fragments that selectively bind to histone-3 cleavage products and are useful for diagnosing cancer and monitoring a subject's response to cancer treatment are also disclosed.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
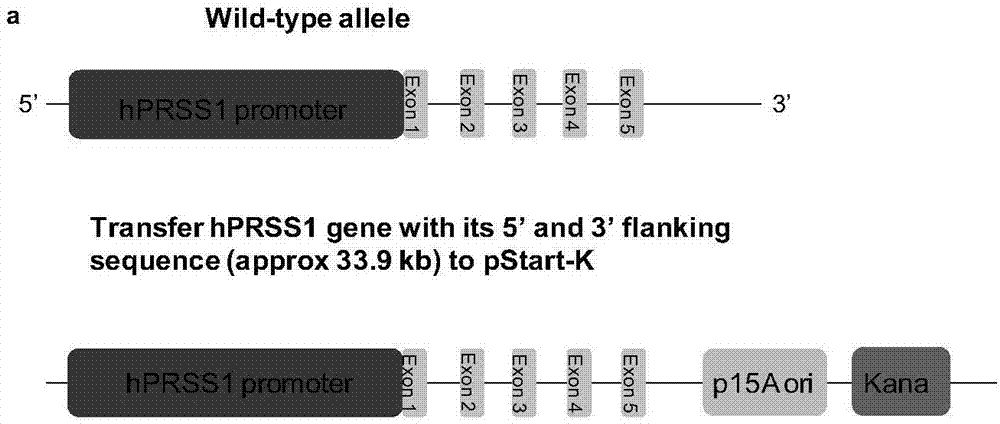
Construction method of mouse model simulating human acute pancreatitis
The invention discloses a construction method of a mouse model simulating human acute pancreatitis. Targeting vector plasmids containing PRSS1 genes are constructed and transferred to mouse embryonic stem cells electrically, and the mouse embryonic cells carrying the recombinant PRSS1 genes are obtained; the mouse embryonic cells carrying the recombinant PRSS1 genes are micro-injected into albinistic mouse blastodermal cells, the blastodermal cells receiving injection are transplanted to the uteri of pseudo-pregnant maternal mice, and chimeric mice are obtained after transplanting; male chimeric mice with the chimerism higher than 25% and wild C57BL / 6J female mice are mated, the next generation of mice are bred, and mice carrying PRSS1 genes are screened. The phenotype of the model mouse is greatly identical to the pathogenetic process of human acute pancreatitis, and the specific animal model completely simulating human acute pancreatitis from gene to phenotype is obtained and can be further widely applied to researches on pathopoiesis, pathomechanism and the like of human PRSS1 as well as screening and gene therapy tests of medicines for treating pancreatitis and the like.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
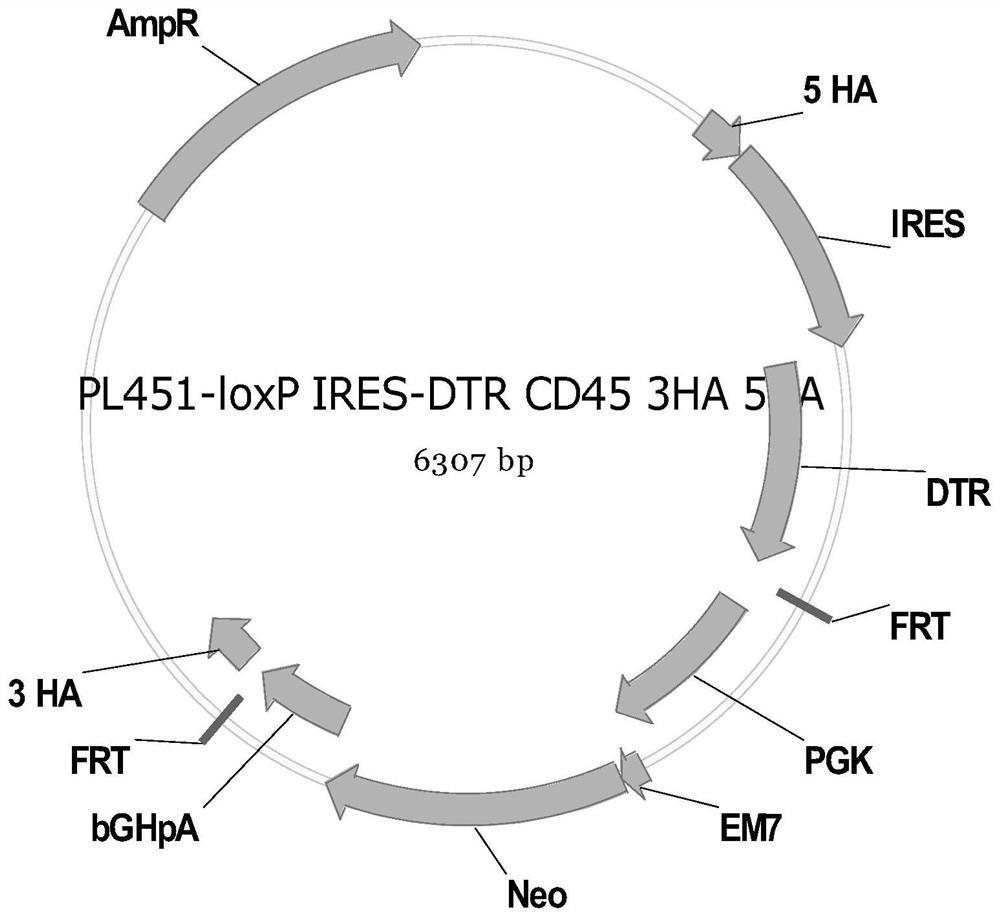
Construction method and application of CD45-DTR transgenic mouse for regulating and removing immune cells by diphtheria toxin
PendingCN111607614ANormal expressionEasy to removeStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorBALB/cEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a CD45-DTR transgenic mouse for regulating and removing immune cells by diphtheria toxin. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing enzyme digestion linearization on BAC Cone CD45-DTR; introducing BALB / C ES cells of mouse embryonic stem cells by using an electroporation method to obtain the BALB / C ES cells withIRES-DTR being inserted into the site 1 of the CD45 exon; and then, constructing a CD45-DTR transgenic mouse with the IRES-DTR being inserted into the site 1 of the CD45 exon through a blastocyst injection method by utilizing the BALB / C ES cells. The invention provides a novel construction method of a mouse model capable of inducing and selectively removing immune cells. The method can be widelyapplied to the fields of preparation of humanized mice, research of immune cell functions and the like.
Owner:乾元康安(苏州)生物科技有限公司
Method for realizing directional proliferation and differentiation of stem cell
InactiveCN1962856AMaintain biological activityPromote proliferationEmbryonic cellsGerm cellsEmbryoPolylysine
The invention discloses an oriental breeding and differentiating method of stem cell in the stem cell tissue engineering domain, which comprises the following steps: adopting sodium alginate and polylysine as raw material; preparing APA mouse microencapsulation embryo stem cell; transplanting mouse microencapsulation embryo stem cell into different anatomical positions of living body orientally; realizing oriental breeding and differentiation of stem cell. The invention simplifies the operation, which is fit for oriental transplantation, recycling and internal oriental inducing differentiation study in the stem cell body.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Alkylamino BODIPY dyes as selective fluorescent probes for proteins and mouse embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS9267949B2High yieldSimple materialStyryl dyesAzo dyesProtein detectionMouse Embryonic Stem Cell
The present invention discloses a series of alkylamino BODIPY dyes, methods for preparing a library of alkyl-amino BODIPY dyes via solid-phase synthesis, and the use of the alkyl-amino BODIPY dyes as fluorescent sensors for protein detection, cell imaging and cytometry applications, and staining of certain cell line.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Application method of small molecules capable of promoting self-status-renewal of embryonic stem cells
ActiveCN109722411AAccelerate self-renewalImprove growthEmbryonic cellsGerm cellsCell Self RenewalMouse Embryonic Stem Cell
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Method for establishing heart disease drug screening model
The invention provides a method for establishing a heart disease drug screening model, which comprises the following steps of A) establishing a virus vector comprising four transcription factors: Oct3 / 4, Sox2, c-Myc and klf4; B) transfecting the virus vector in the step A) with a virus packaging cell to obtain virus liquid; C) infecting the virus liquid in the step B) with the fibroblast of the beta adrenergic receptor wild-type gene knockout mouse; D) screening the clone similar to the mouse embryonic stem cell, and subculturing to obtain the induced pluripotent stem cells with beta adrenergic receptor wild-type gene defect; E) establishing a virus vector containing the beta adrenergic receptor mutant gene; F) transfecting the virus vector in the step E) with the virus packaging cell to obtain virus liquid; G) infecting the virus liquid in the step F) with the induced pluripotent stem cells with beta adrenergic receptor wild-type gene defect; H) selecting positive clone and performing induced differentiation into myocardial cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI BODE BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com