Patents
Literature
639 results about "Protein detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
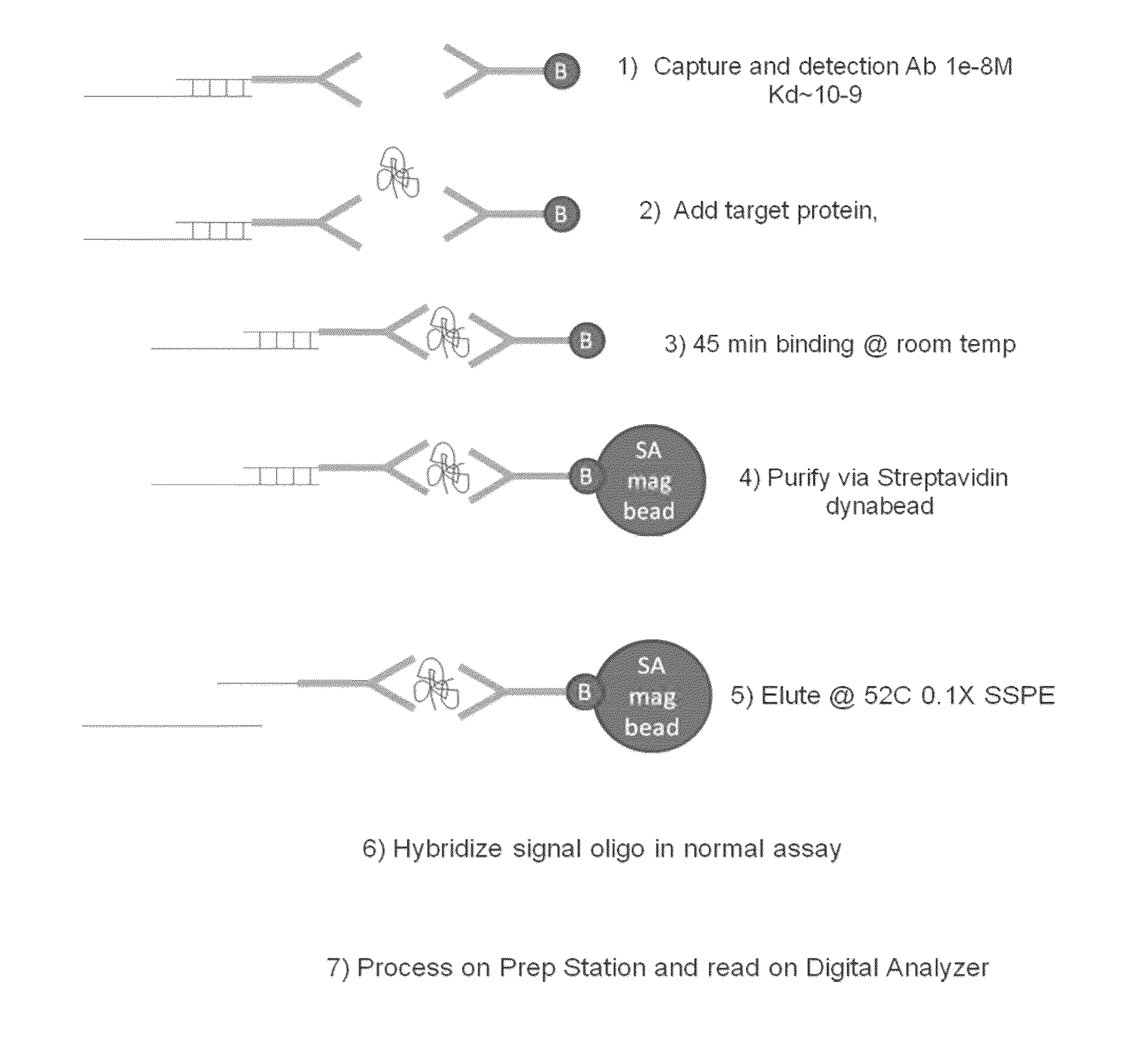
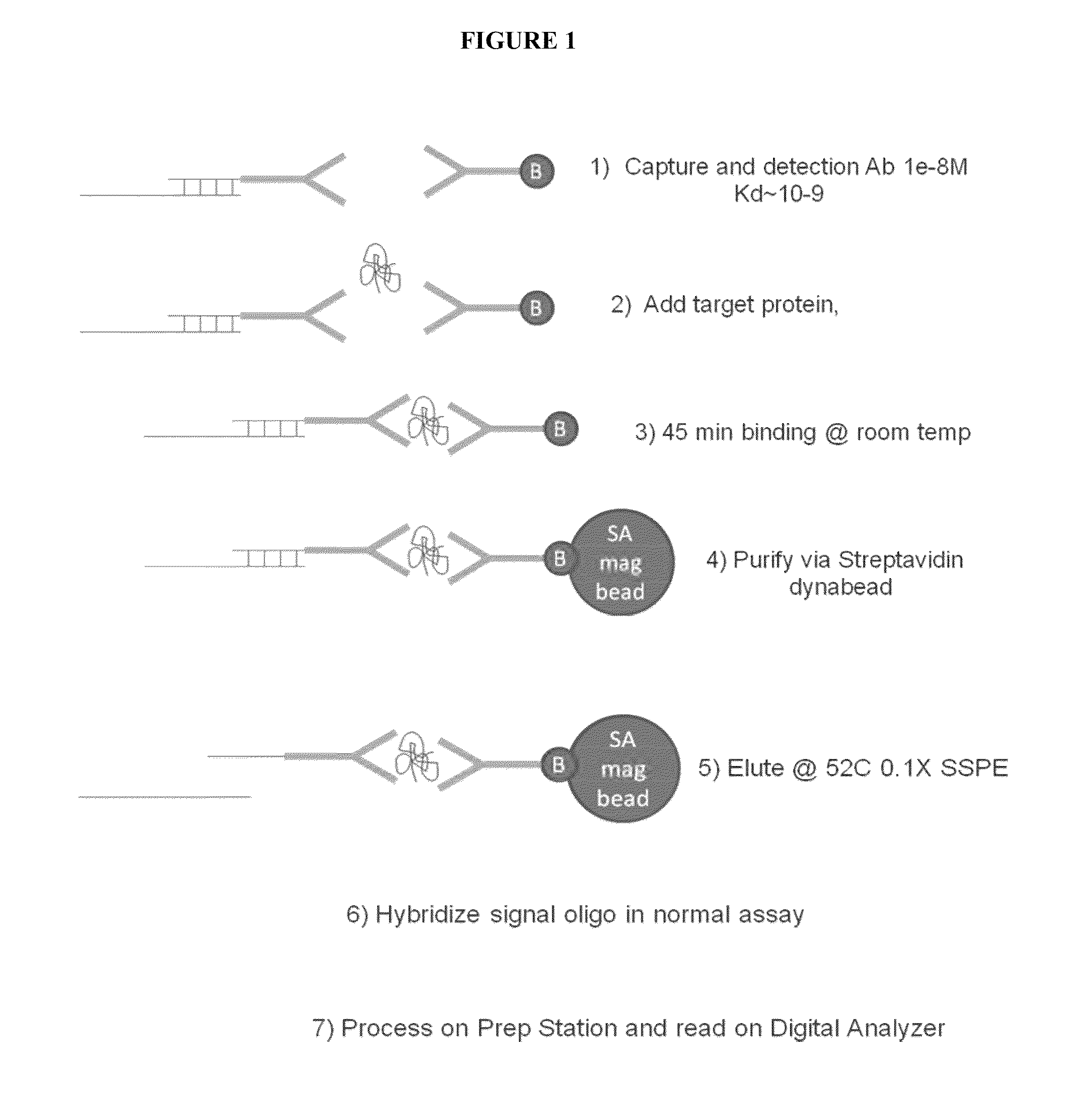
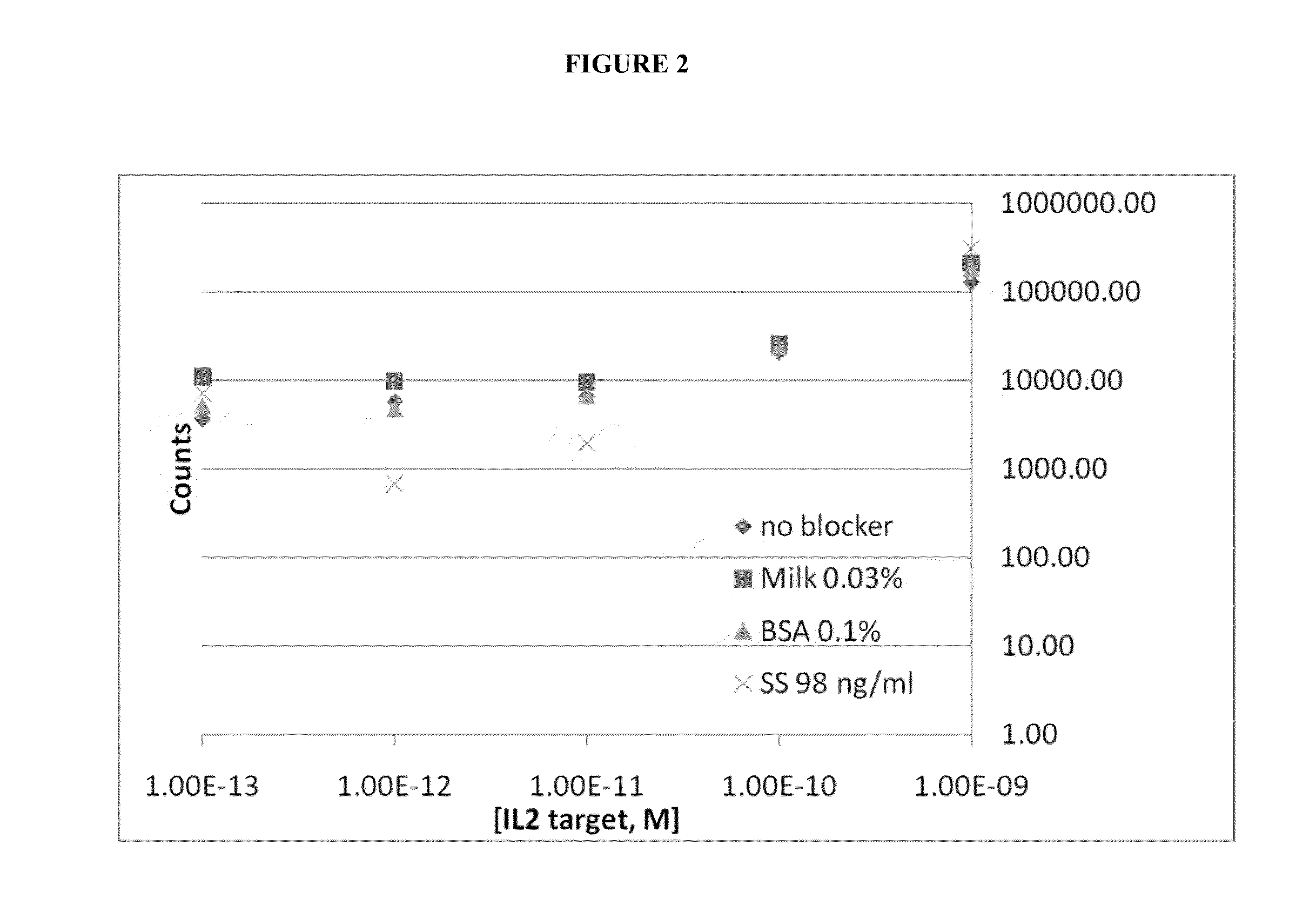
Protein Detection Via Nanoreporters
ActiveUS20110086774A1Peptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein detectionBiochemistry
The invention provides methods, compositions, kits and devices for the detection of proteins. In some embodiments, the invention allows for multiplexed protein detection.
Owner:NANOSTRING TECH INC
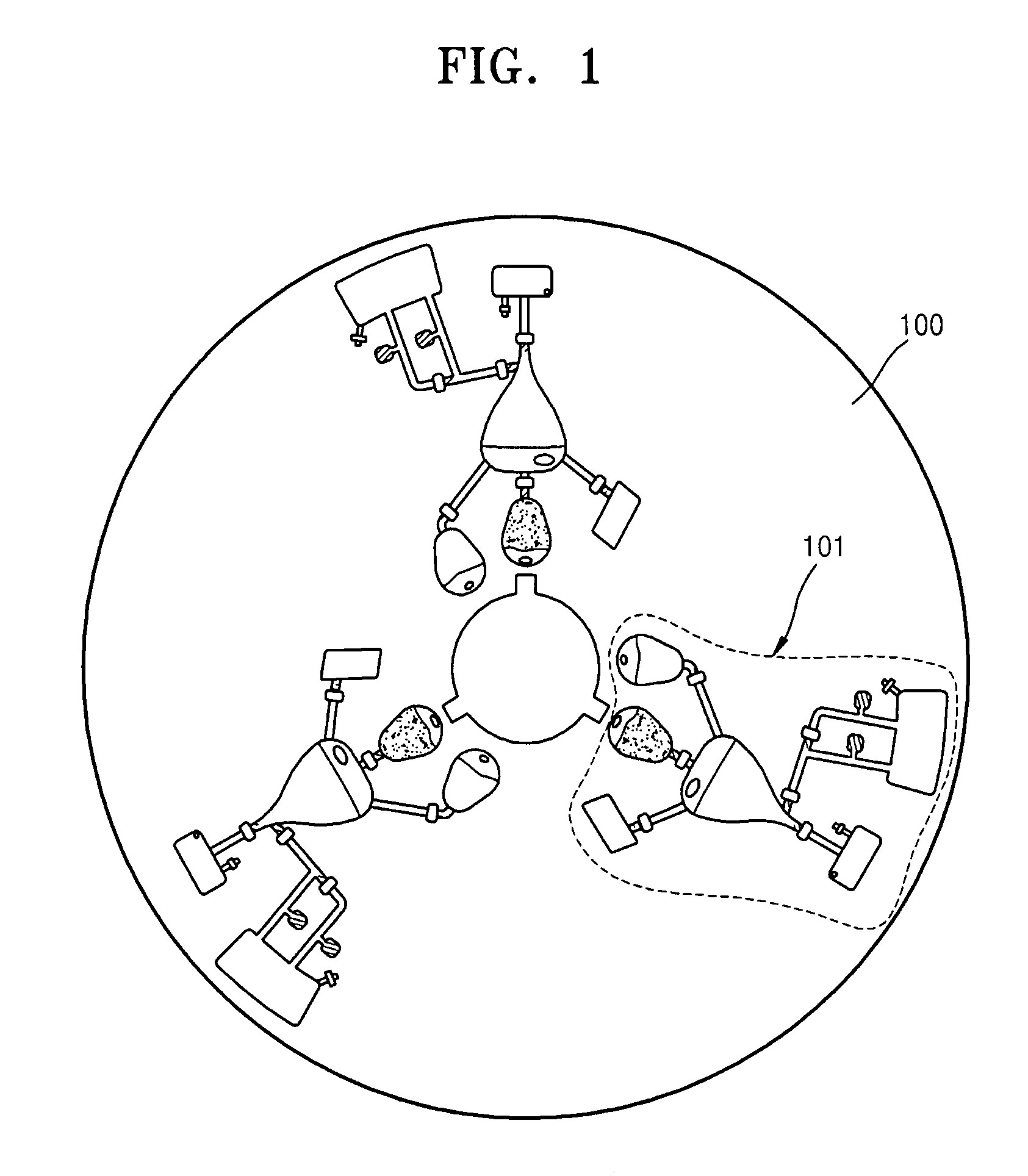
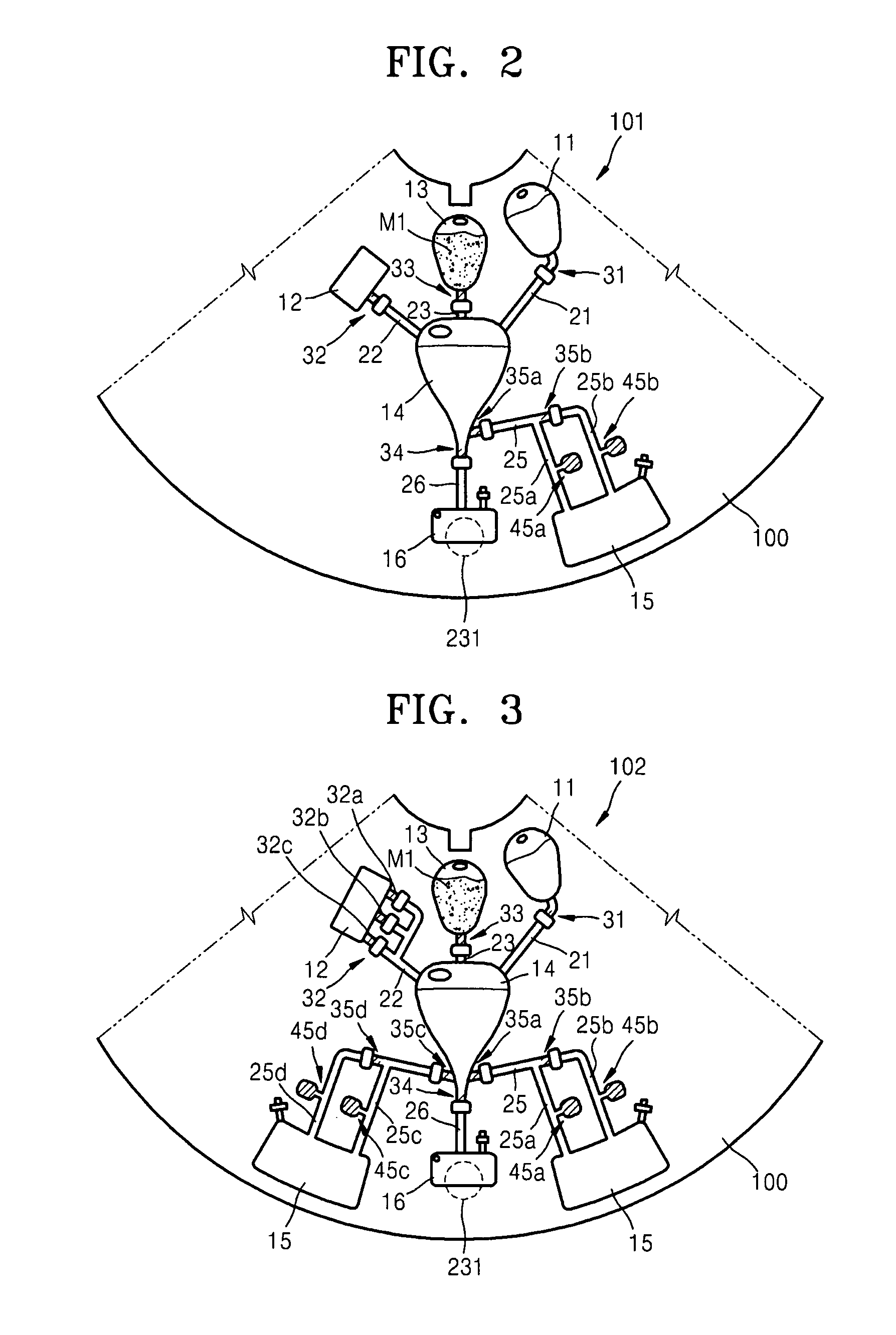
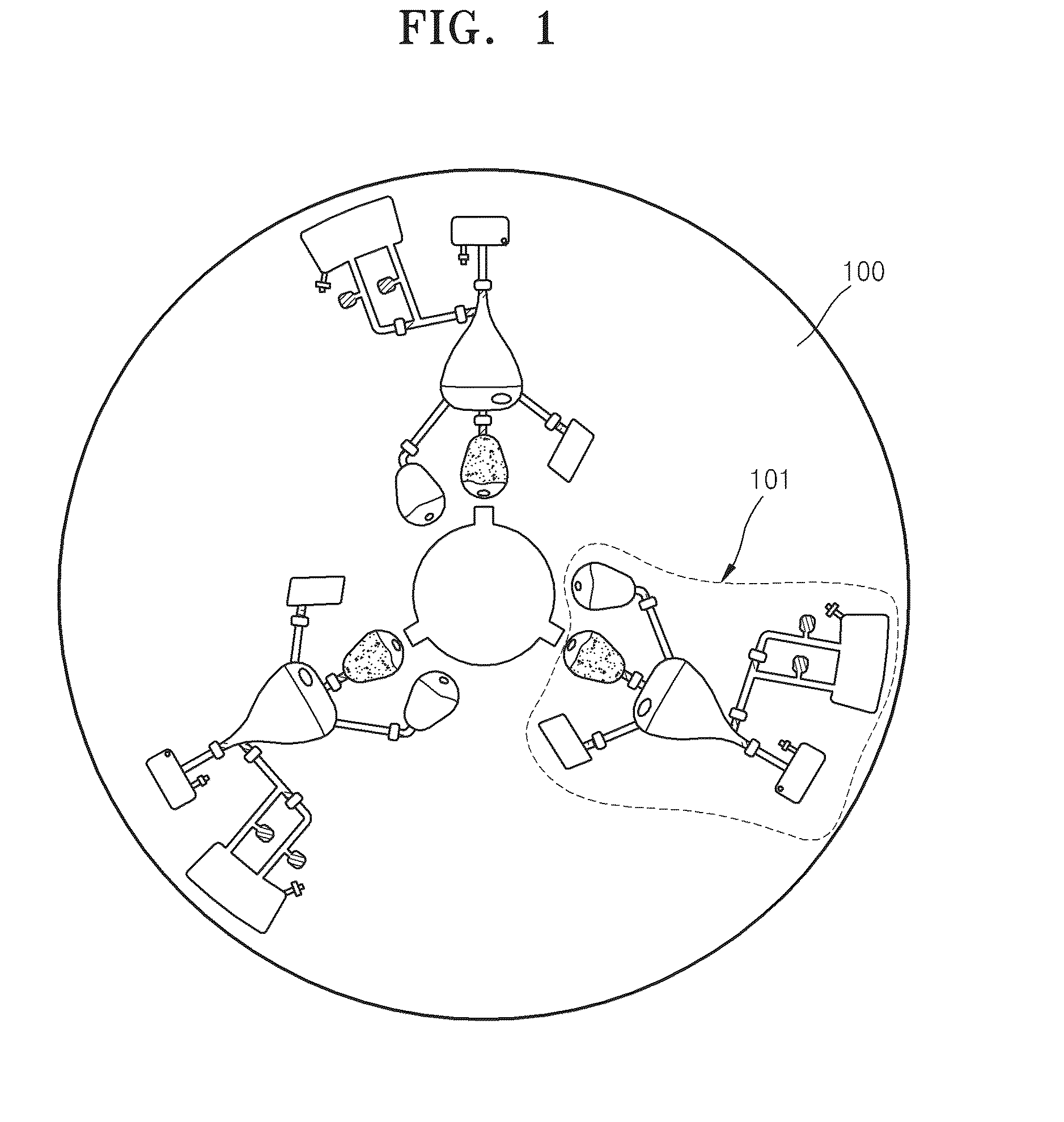
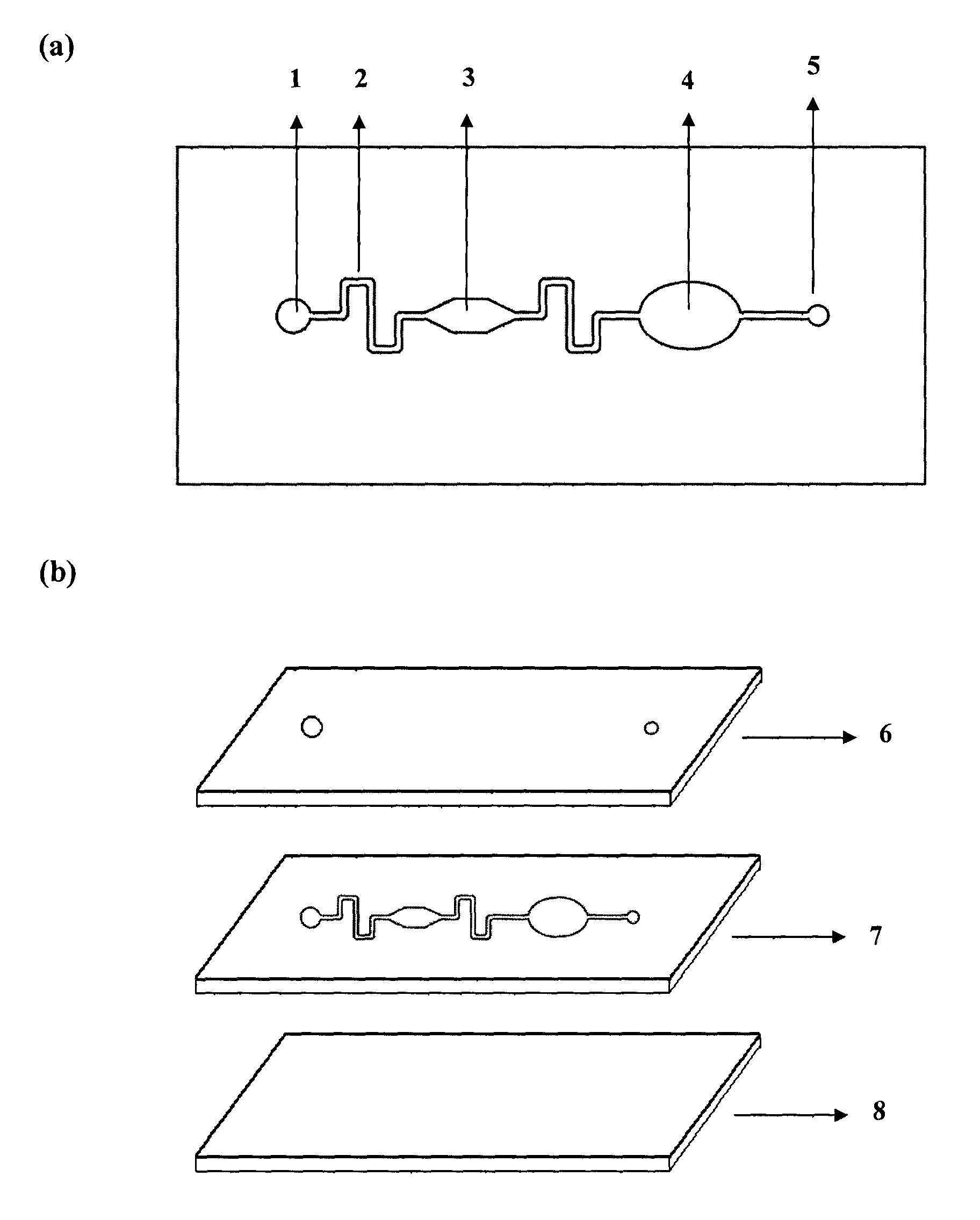
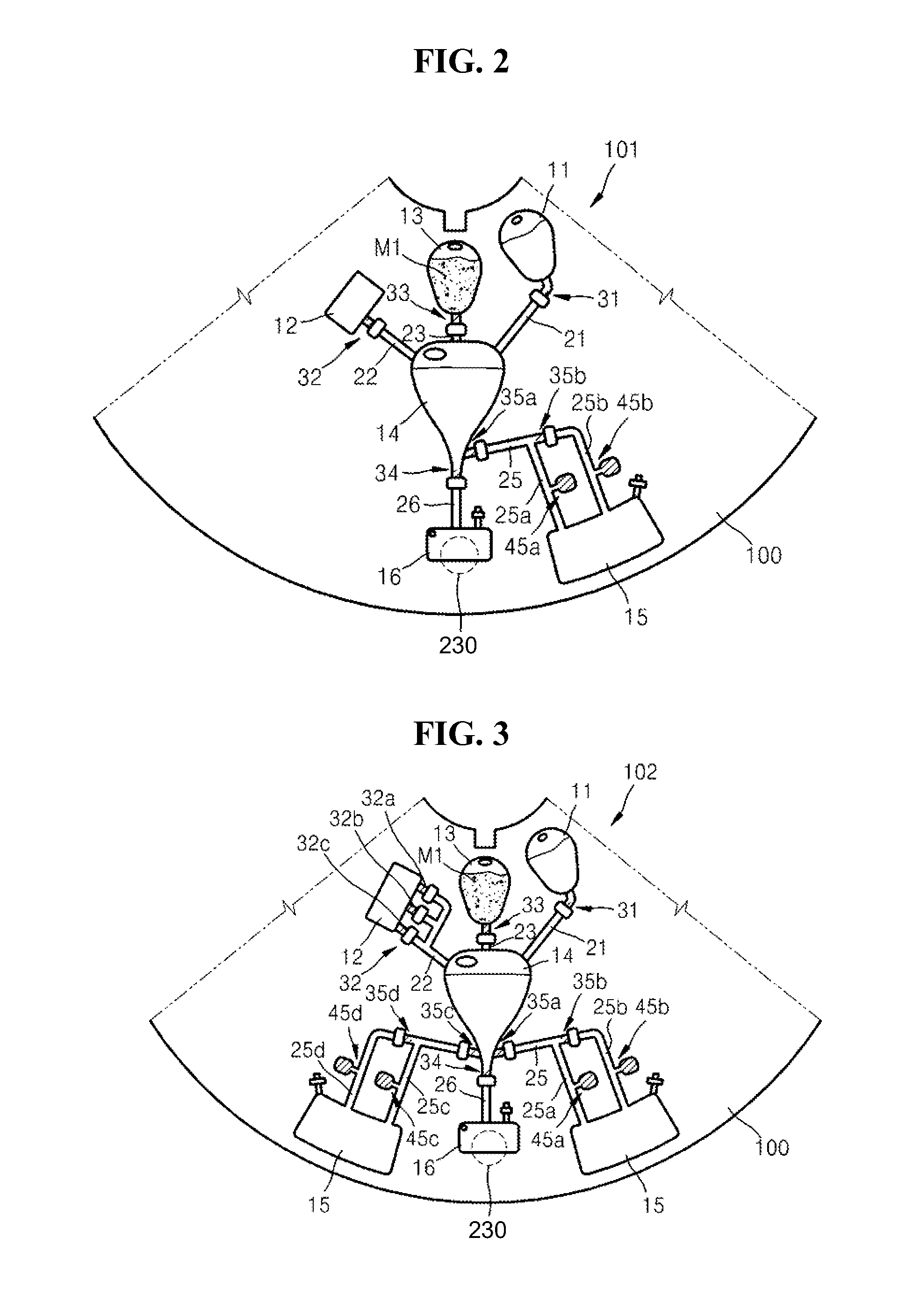
Centrifugal force-based microfluidic device for protein detection and microfluidic system including the same
ActiveUS20080056949A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein detectionProtein target
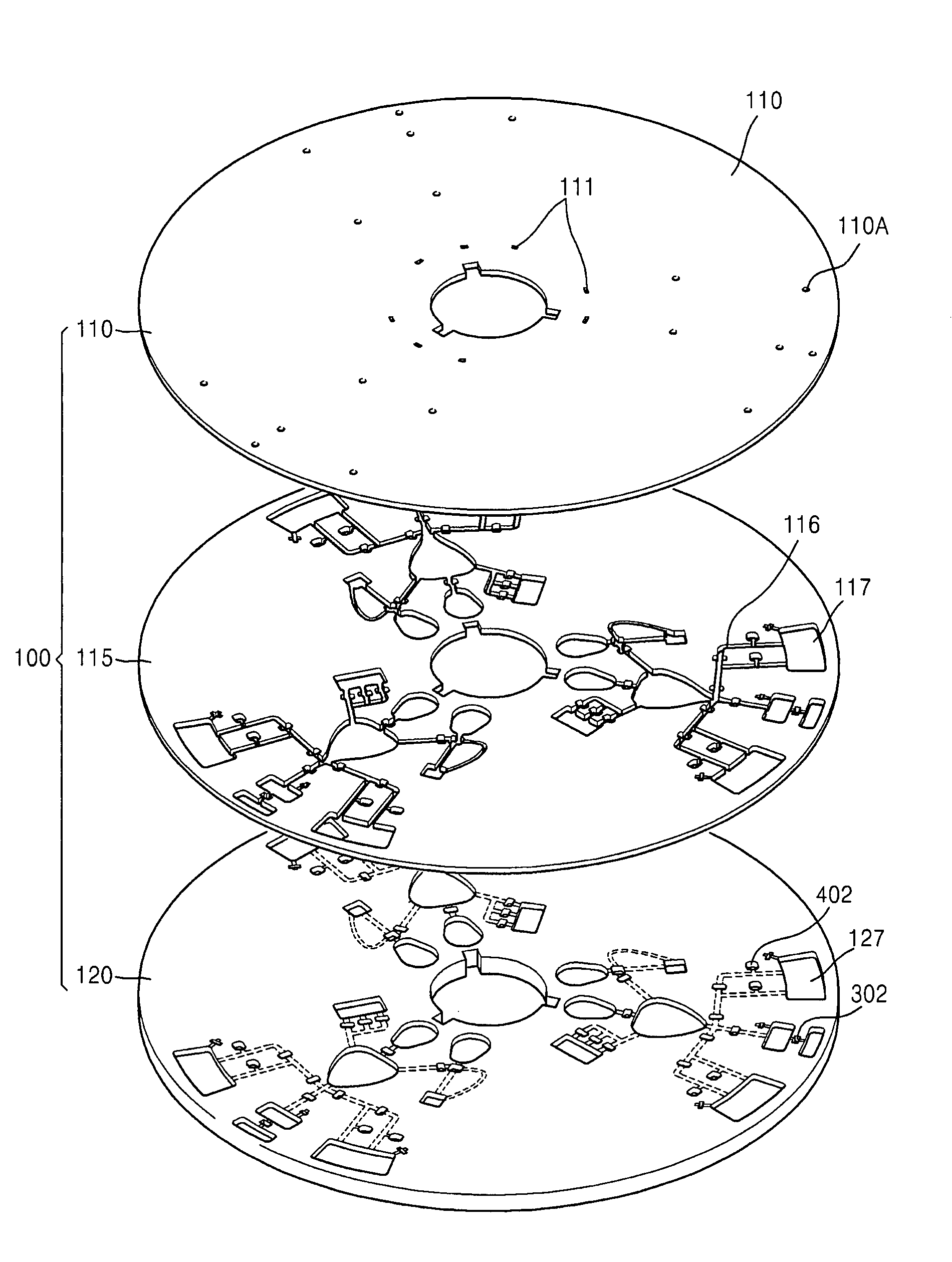
A centrifugal force-based microfluidic device for the detection of a target biomolecule and a microfluidic system including the same are provided. The device includes a body of revolution; a microfluidic structure disposed in the body of revolution including chambers, channels connecting the chambers, and valves disposed in the channels to control fluid flow, the microfluidic structures transmitting fluid using centrifugal force due to rotation of the body of revolution; and beads disposed in the microfluidic structures, the beads having capture probes on the surfaces thereof which are selectively bonded with target protein; and a detection probe disposed in the microfluidic structures and selectively bonded to the target protein, and which includes a material required to express an optical signal, wherein the microfluidic structure mixes the beads, biological samples, and the detection probe to react and washes and separates the beads after the reaction.
Owner:PRECISIONBIOSENSOR INC
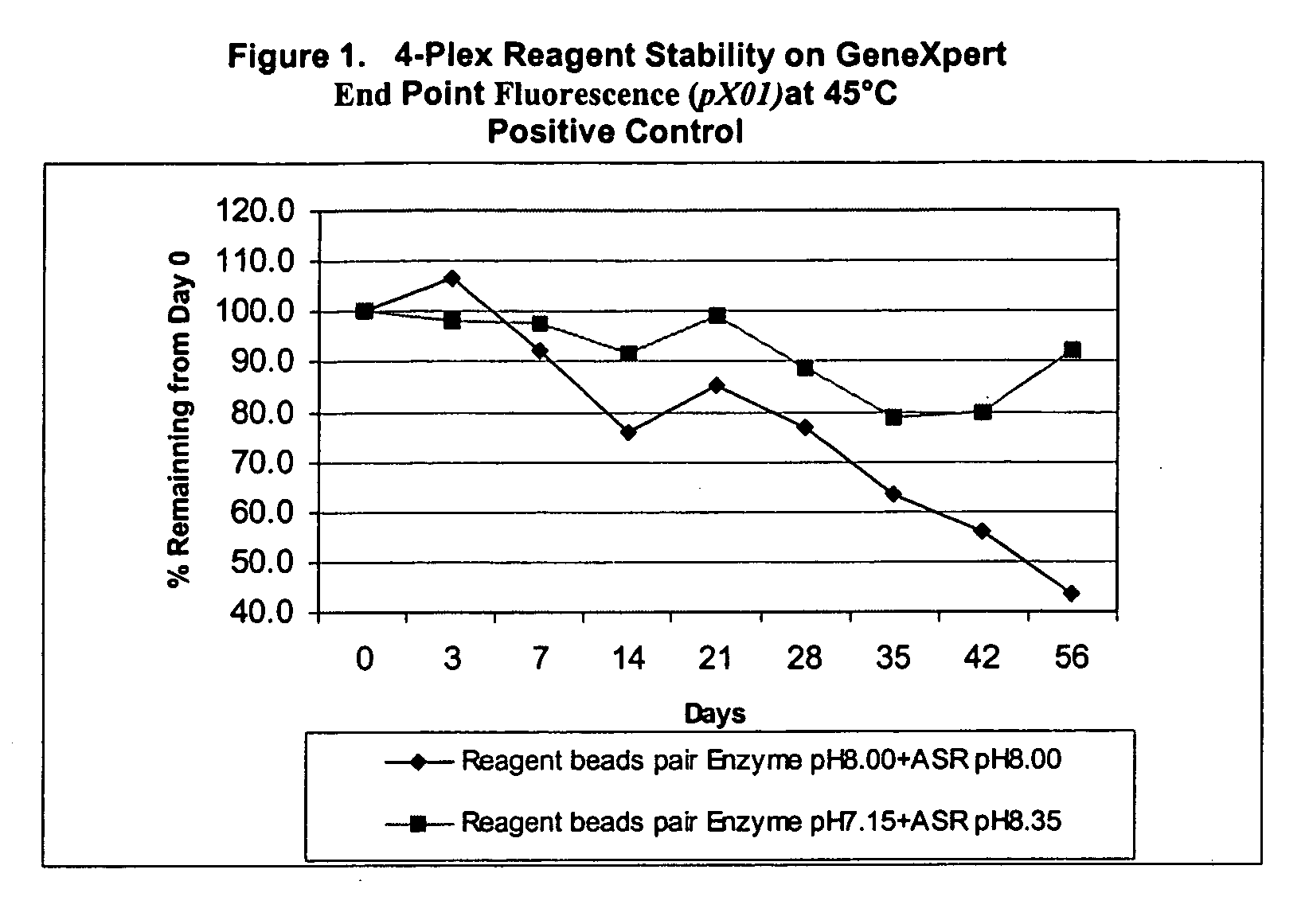
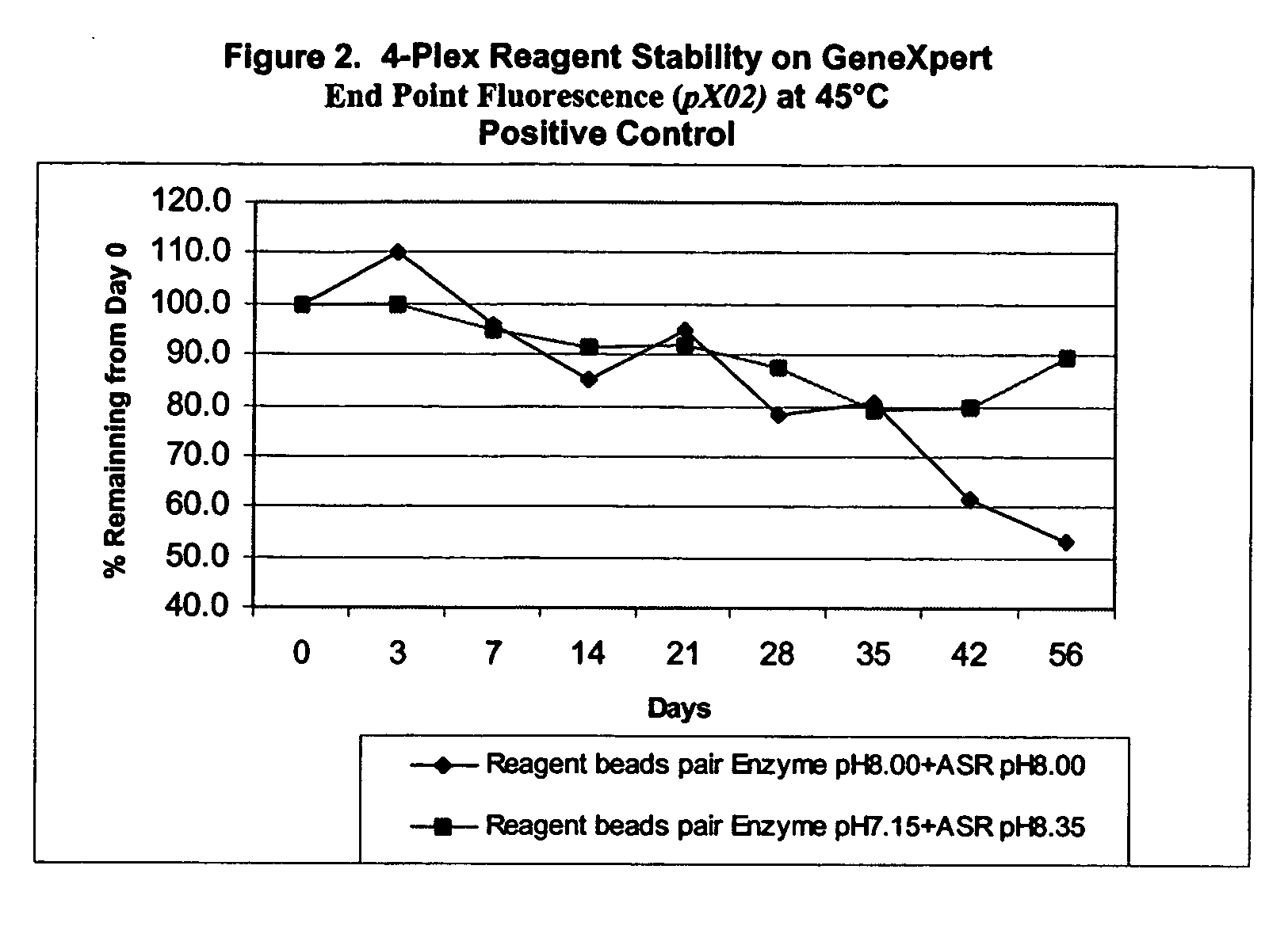
Multiple bead reagent system for protein based assays with optimized matrices
InactiveUS20060068399A1High activityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein stabilizationActivity level
The invention provides a multi-bead assay system for a protein based assay comprising at least two different beads. The first bead comprises protein and a protein stabilization matrix. The first bead forms a first solution when dissolved in liquid, and the first solution permits a first activity level for the assay. The second bead comprises a potentiation bead matrix that when dissolved in the first solution forms a second solution that potentiates the protein based assay to achieve a second activity level that is higher than the first activity level.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering and Multiplexed Diagnostic Assays
Multiplexed lateral flow assays, related methods, and devices are disclosed which are capable of simultaneously detecting multiple analytes. The assays are preferably immunoassays and can be multiplexed spatially, spectrally, and both spatially and spectrally. Multiplexed assays are disclosed employing quantum dots for applications including the detection of human proteins and the monitoring of microorganisms relevant to water contamination. The multiplexed assays can employ one or more species of Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering nanoparticles, with one or more species having a unique Raman shift spectrum. The invention is widely adaptable to a variety of analytes such as biowarfare agents, human clinical markers, and other substances.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Protein detecting device
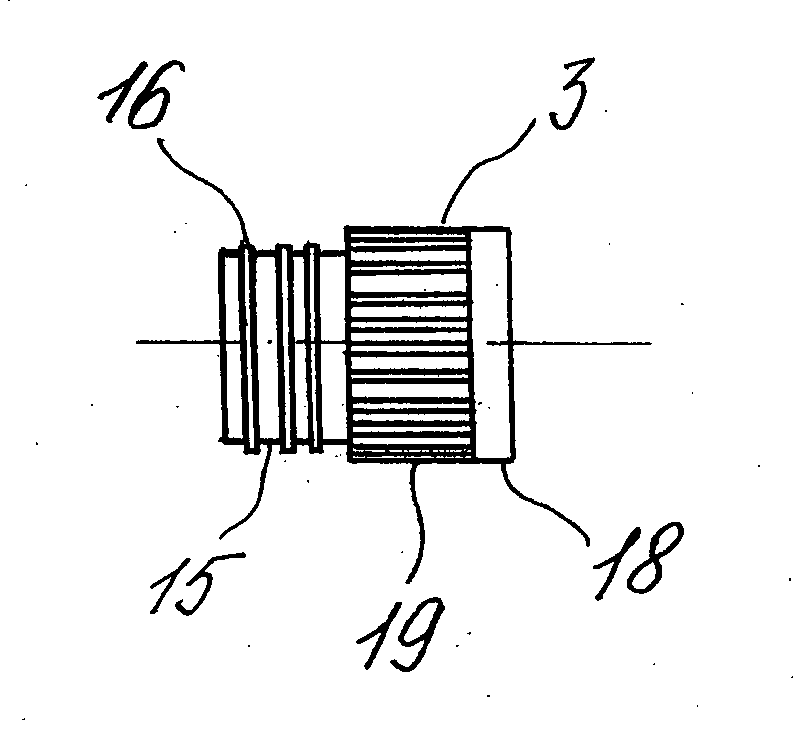
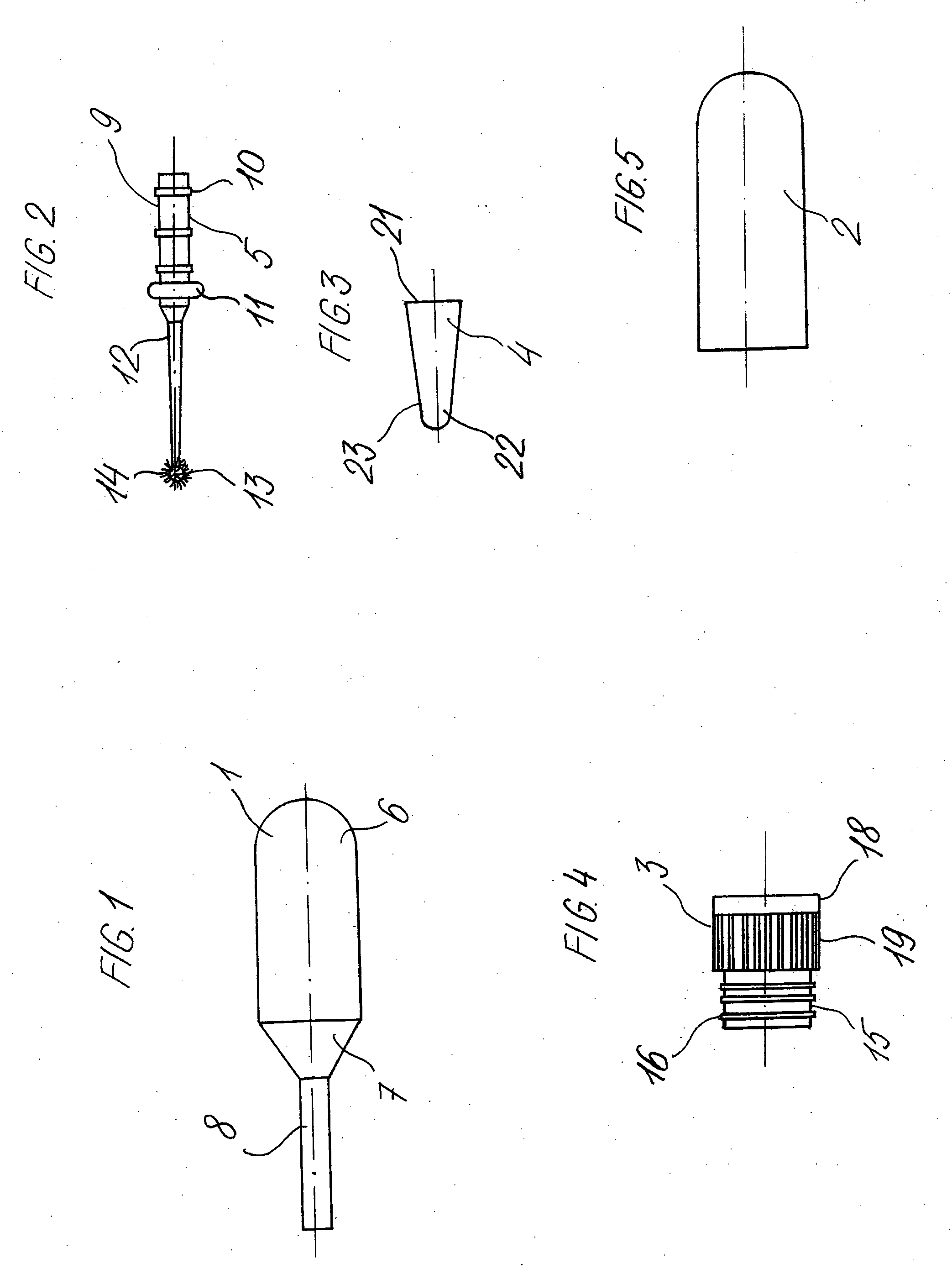
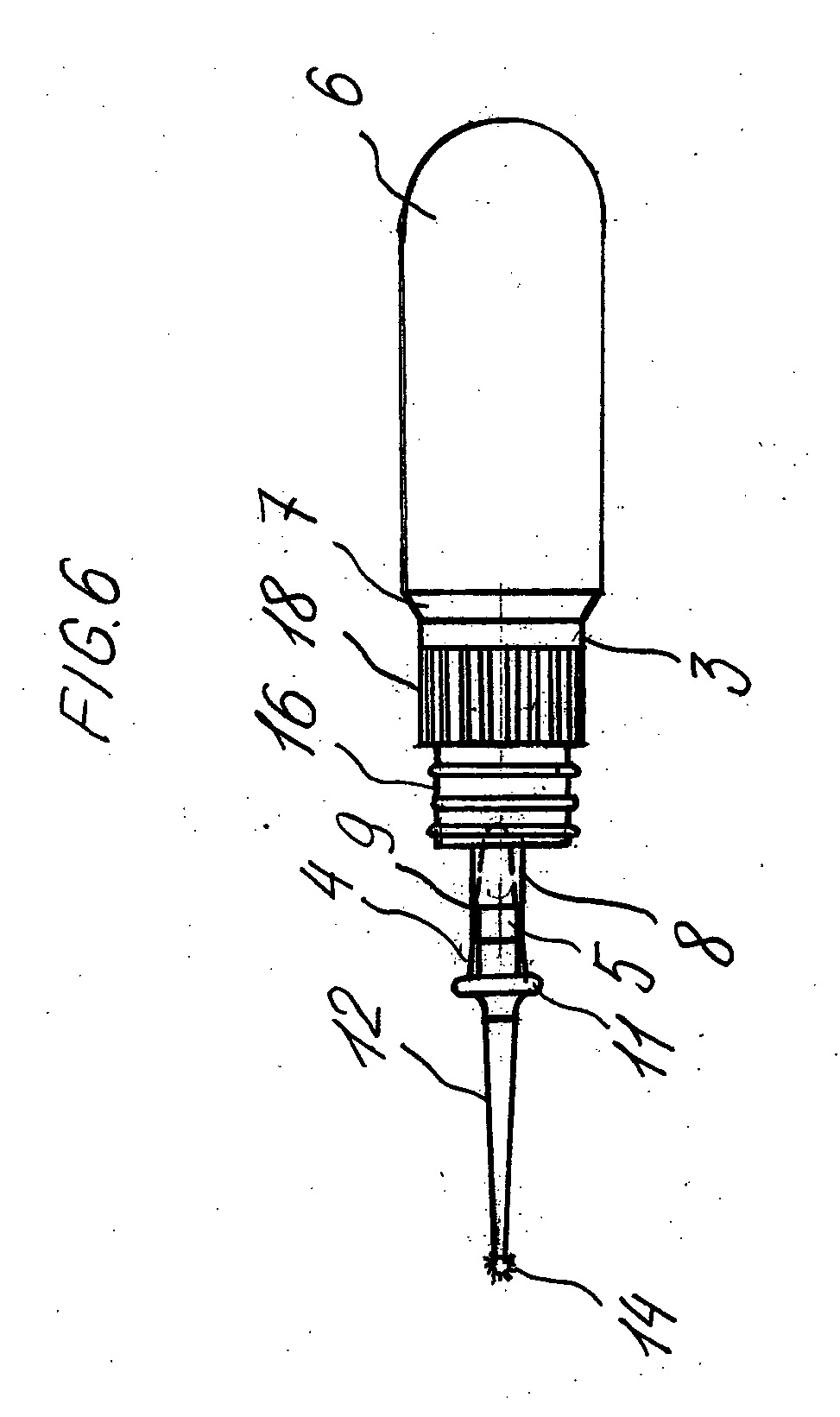
InactiveUS20060110286A1Easy to transportEasy accessAnalysis using chemical indicatorsLaboratory glasswaresProtein detectionBiomedical engineering
A protein detecting device is disclosed. The device includes a reagent reservoir that is squeezable. The reagent reservoir has an end portion with a with a tubular member extending therefrom. This tubular member is hollow and in communication with the reservoir. The tubular member has an open end opposite the reservoir and has a cone shaped gasket in its open end. The cone shaped gasket has its base connected to an elongated member extending from the open end of the tubular member. The elongated member has a micro-brush at its end.
Owner:BOUKAS ALEX
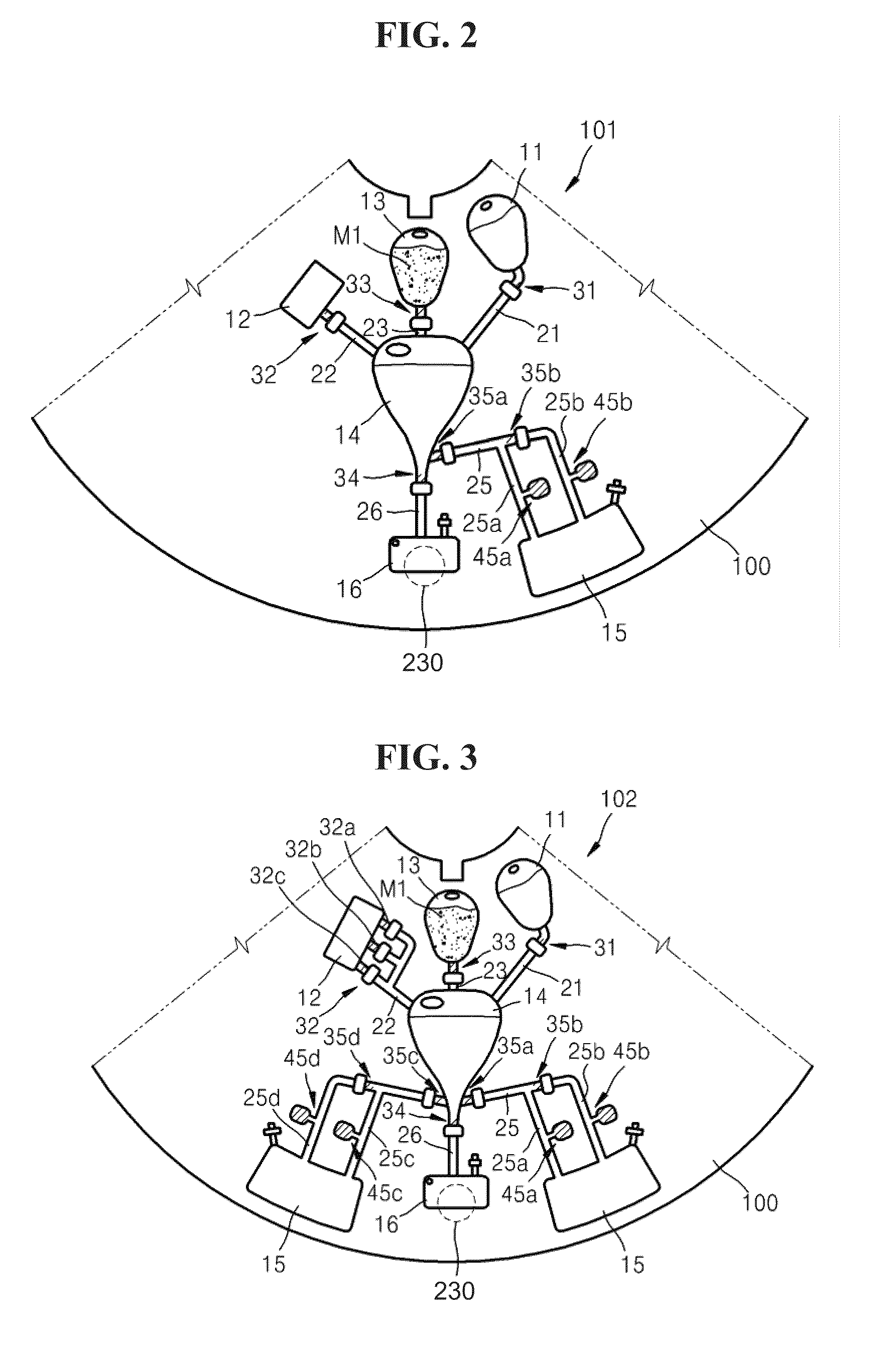
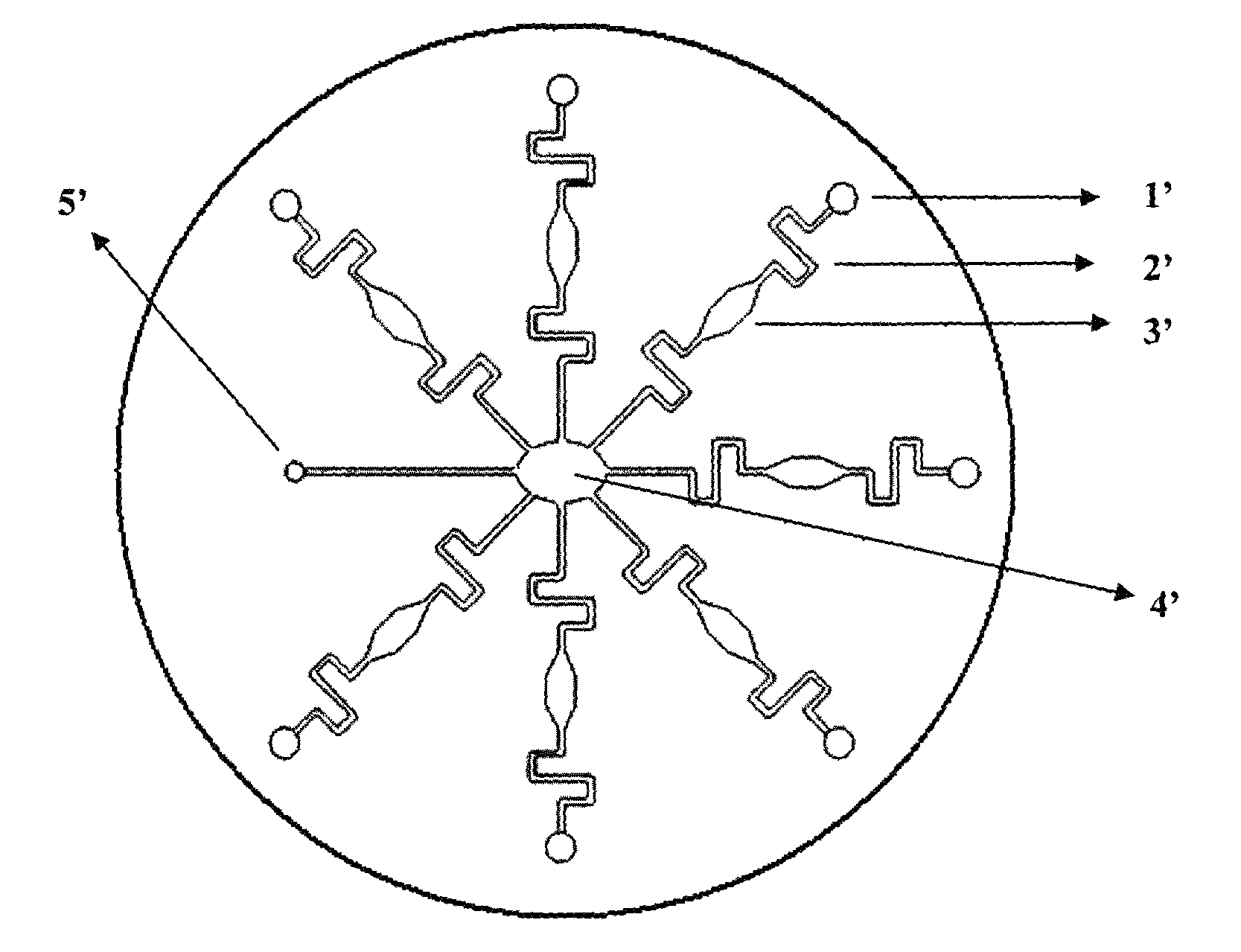
Centrifugal force-based microfluidic device for protein detection and microfluidic system including the same
ActiveUS20110020194A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein detectionProtein target
A centrifugal force-based microfluidic device for the detection of a target biomolecule and a microfluidic system including the same are provided. The device includes a body of revolution; a microfluidic structure disposed in the body of revolution including chambers, channels connecting the chambers, and valves disposed in the channels to control fluid flow, the microfluidic structures transmitting fluid using centrifugal force due to rotation of the body of revolution; and beads disposed in the microfluidic structures, the beads having capture probes on the surfaces thereof which are selectively bonded with target protein; and a detection probe disposed in the microfluidic structures and selectively bonded to the target protein, and which includes a material required to express an optical signal, wherein the microfluidic structure mixes the beads, biological samples, and the detection probe to react and washes and separates the beads after the reaction.
Owner:PRECISIONBIOSENSOR INC
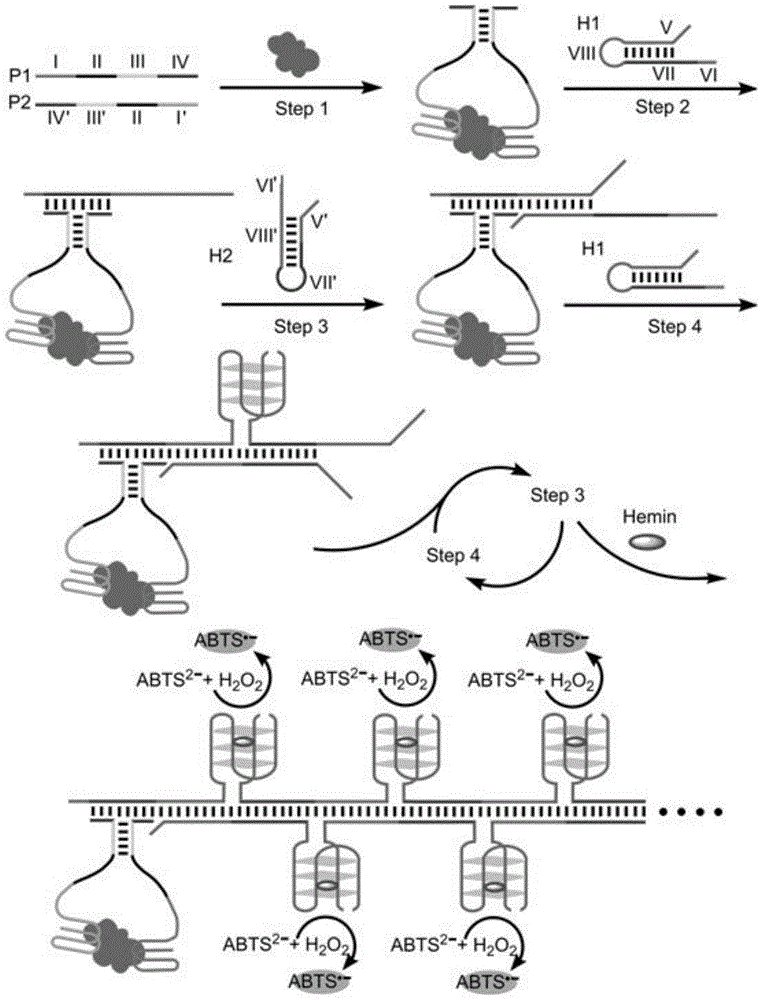
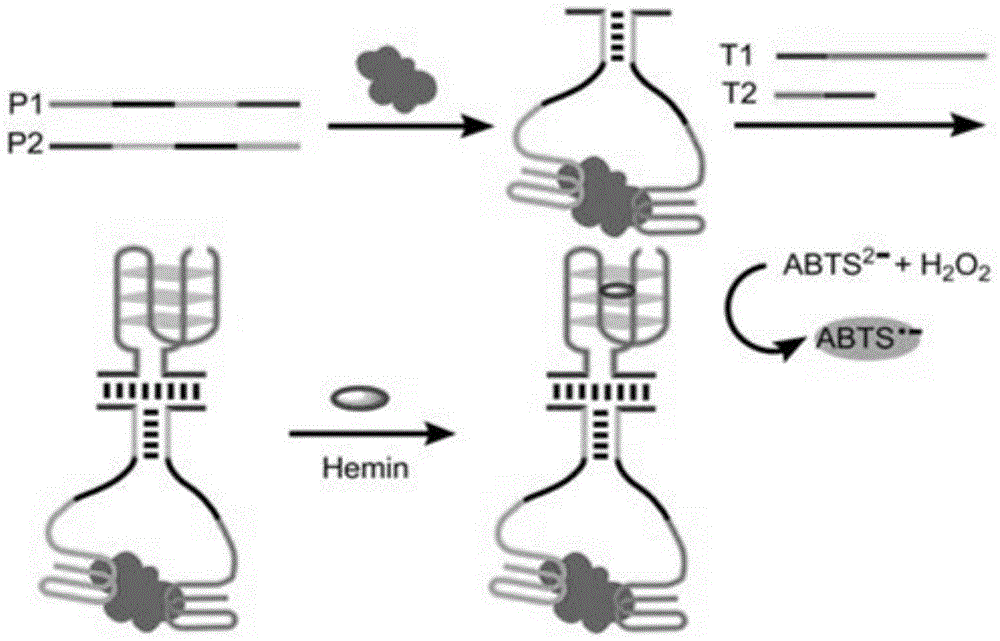
Probe based on G-quadruplex-chlorine heme DNA enzyme and application of probe
InactiveCN105018474AAchieving magnified detectionExcellent long-term storage stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationProtein detectionHeme
The invention provides a probe based on a G-quadruplex-chlorine heme DNA enzyme and a method for detecting protein. The method for detecting the protein facilitates detecting operation and is low in cost and free of marking. The probe has the advantages of being high in sensitivity and low in background noise. When the protein is detected, the detecting operation is easy, consumed time is short, cost is low, and the problems that a method for detecting the protein in the prior art is long in consumed time, high in cost and complex in detecting probe manufacturing are solved.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE
Environmental sensitive fluorogenic compounds and their application for singlet oxygen and protein detection
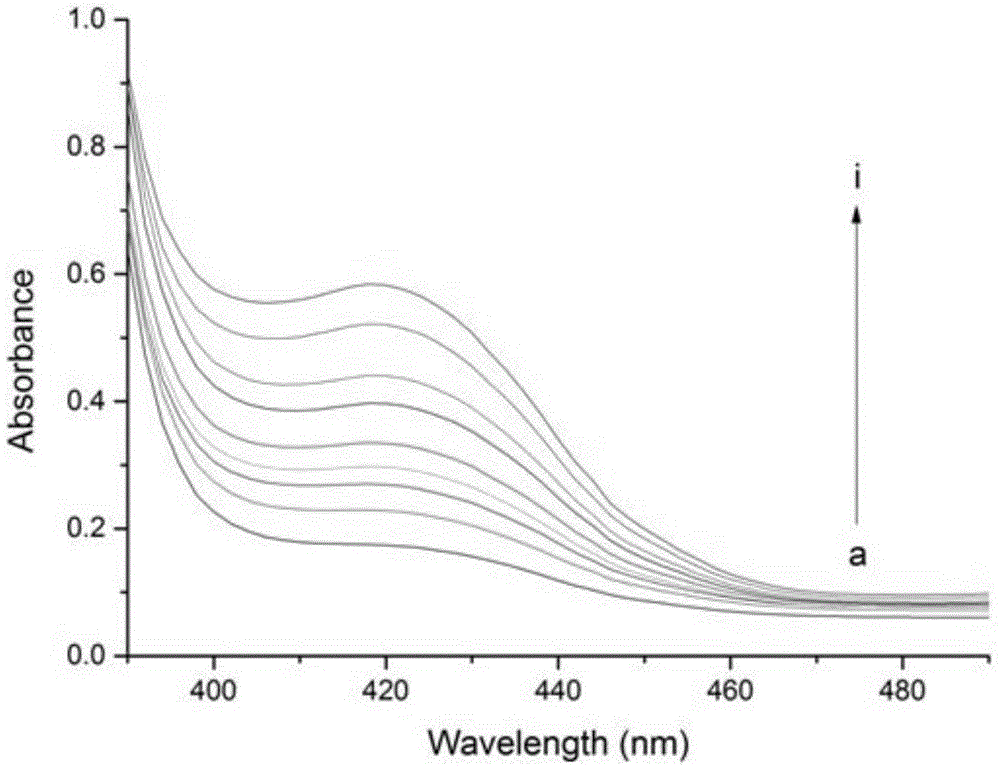
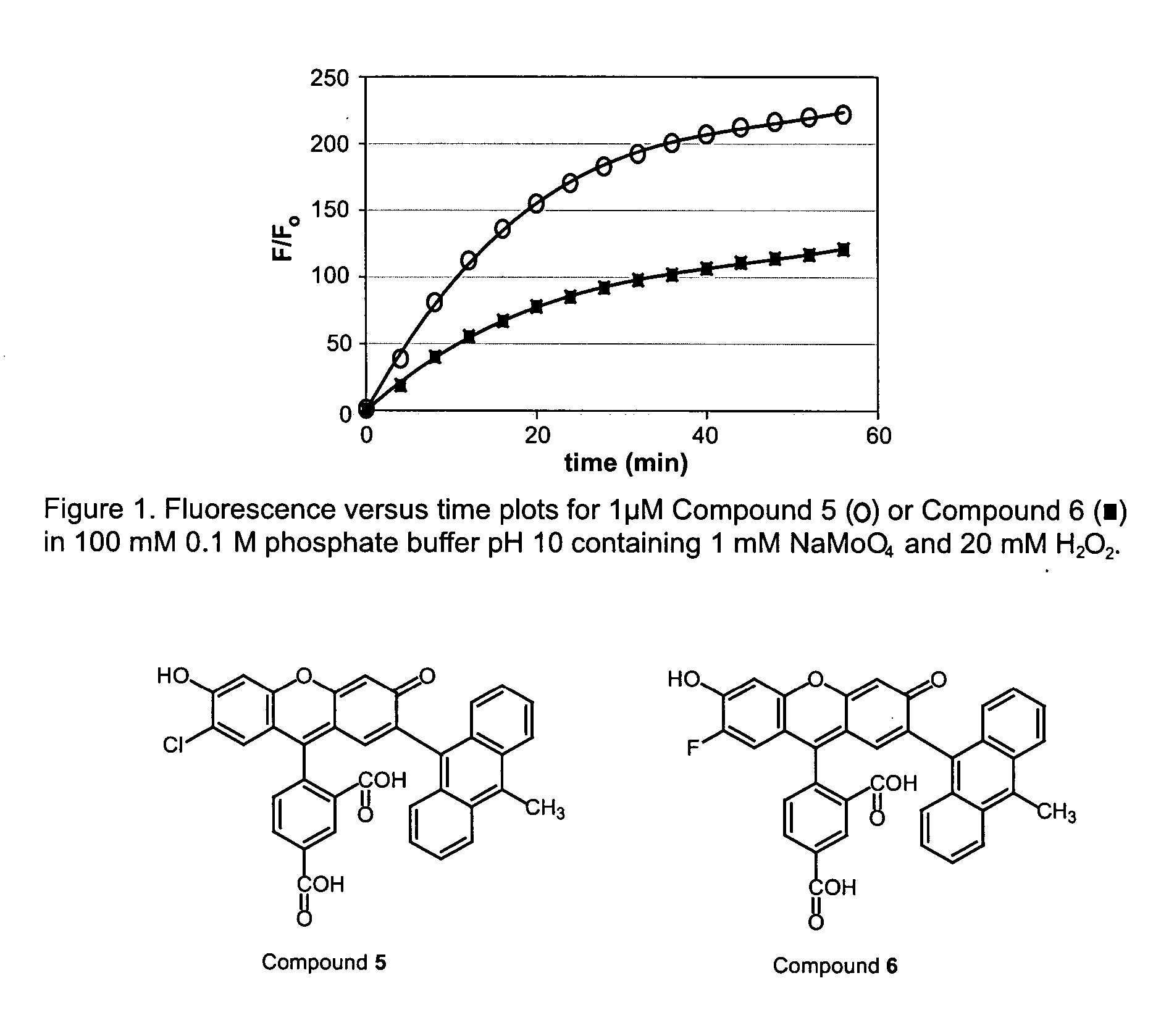
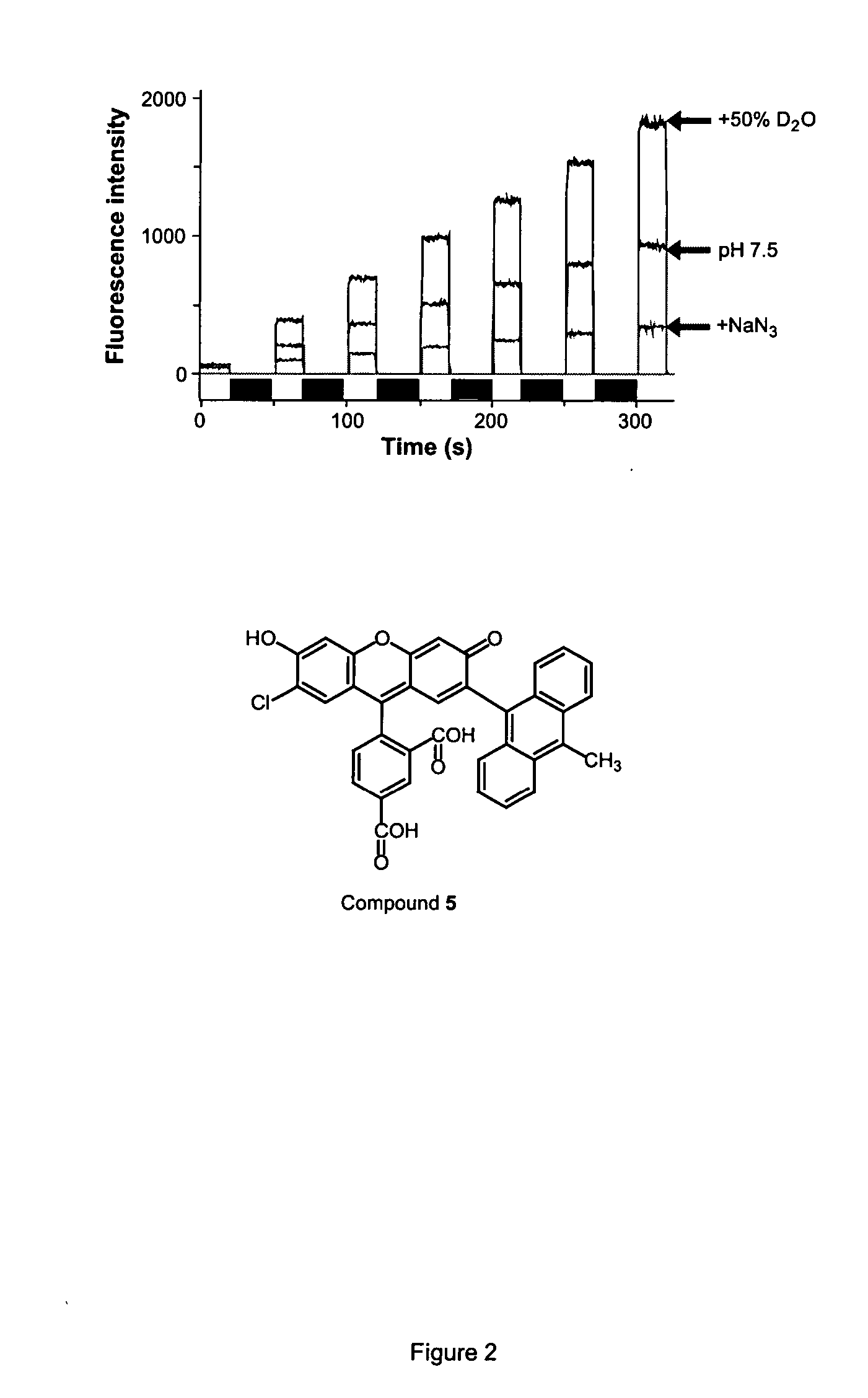
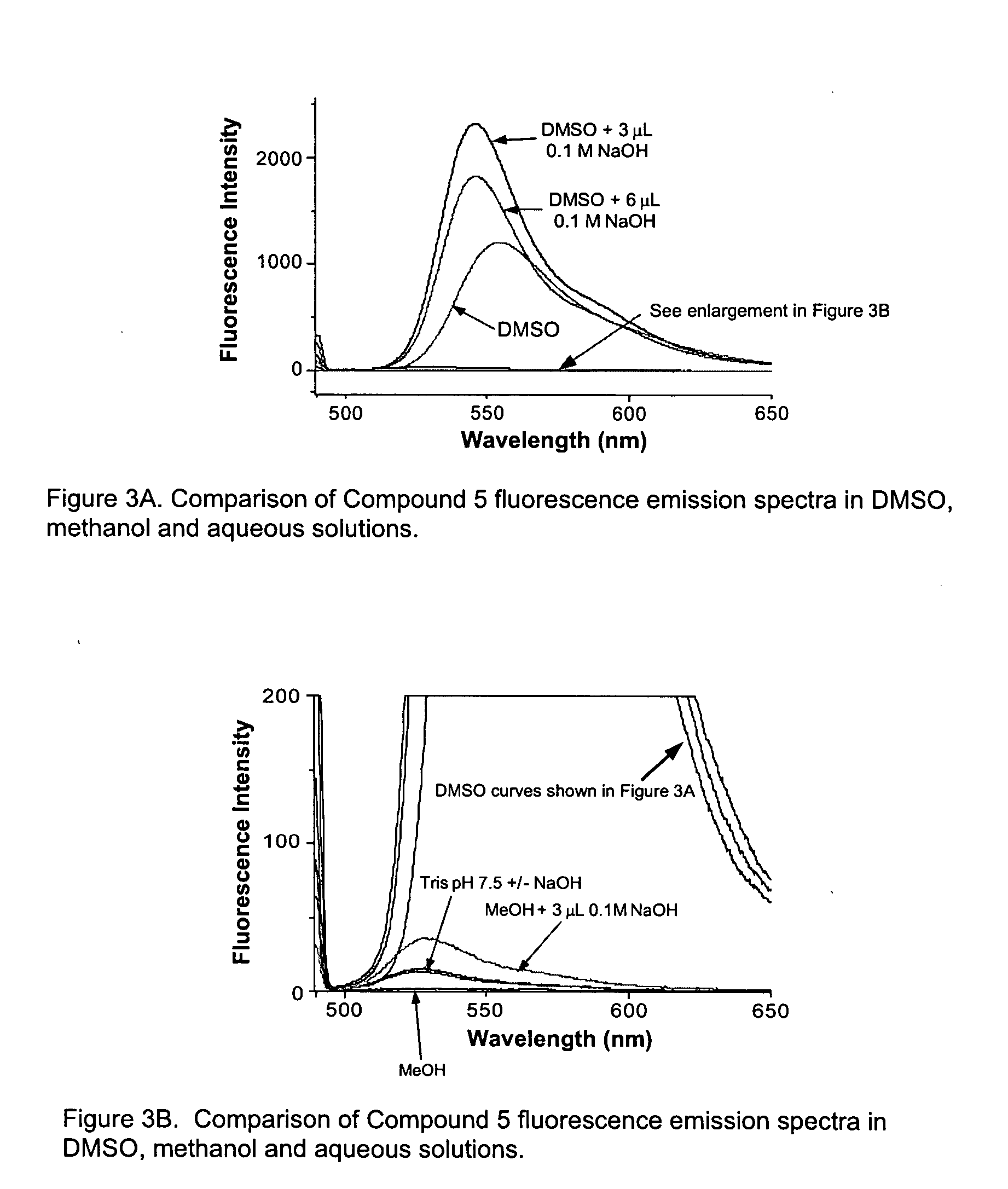
InactiveUS20050214807A1More sensitiveSensitive measurementOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein detectionFluorescence
Owner:JOHNSON IAIN +3
Micro-fluidic chip for glycosylated hemoglobin immunodetection
The invention provides a micro-fluidic chip for glycosylated hemoglobin immunodetection in serum, comprising a sample introduction pool, a micro-fluid channel, a reaction tank, a detection tank, a waste liquor tank and a pump valve interface, wherein the sample introduction pool, the micro-fluid channel, the water liquor tank and the pump valve interface are serially connected by the micro-liquid channel; antigens or antibodies necessary for protein detection are fixed in the reaction and detection tanks in advance, a serum sample solution to be detected successively flows in the reaction tank by virtue of the sample introduction pool and the micro-fluid channel by an externally connected pump valve system, completes antigen or antibody specific reaction in the reaction tank and agglomerates, and the reaction product is subjected to absorbancy analysis to obtain the immune agglutination reaction and detection of the sample to be detected. The chip is convenient for sample introduction, less in sample consumption, high in reaction efficiency and short in detection time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG PUSHKANG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
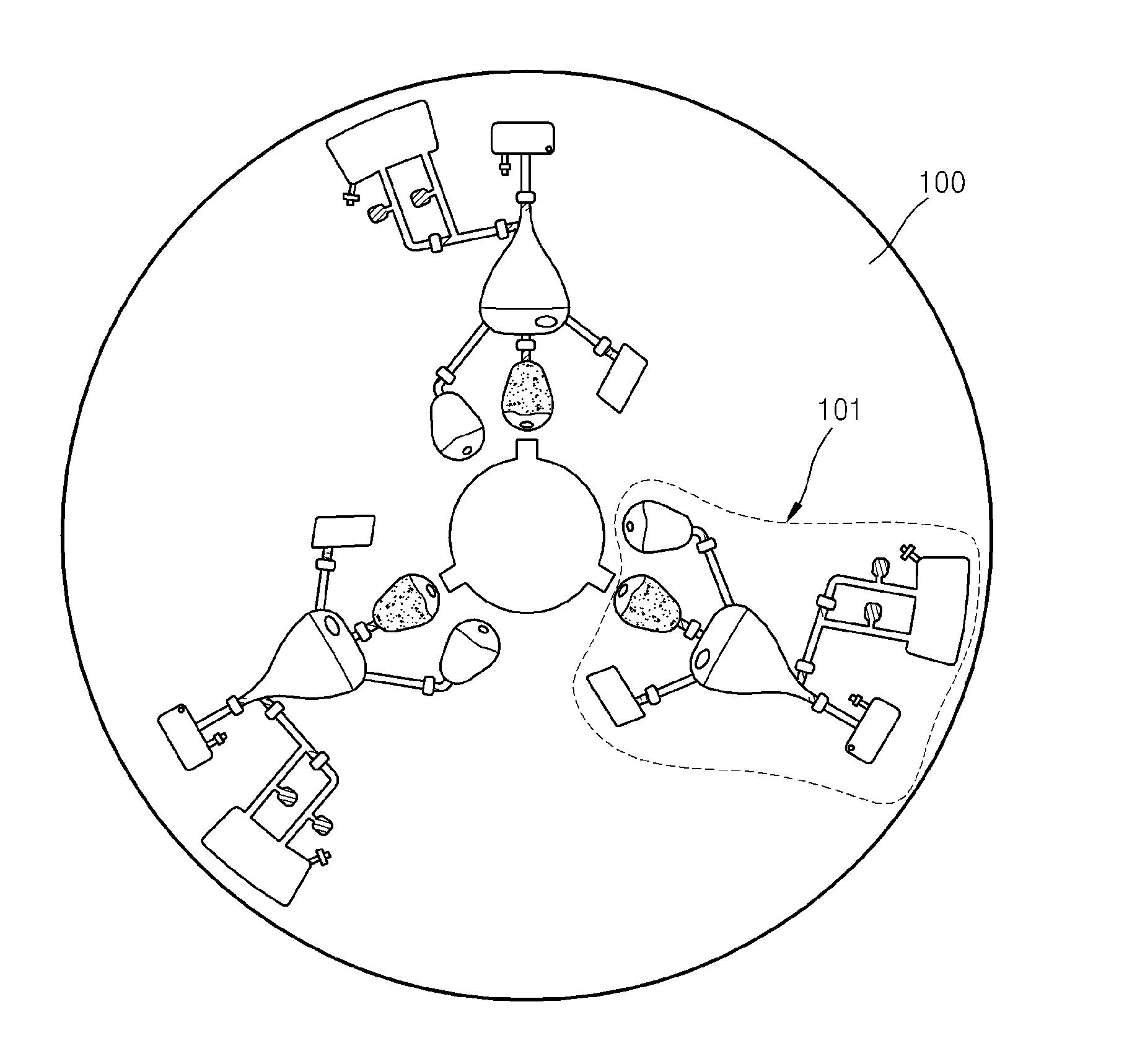
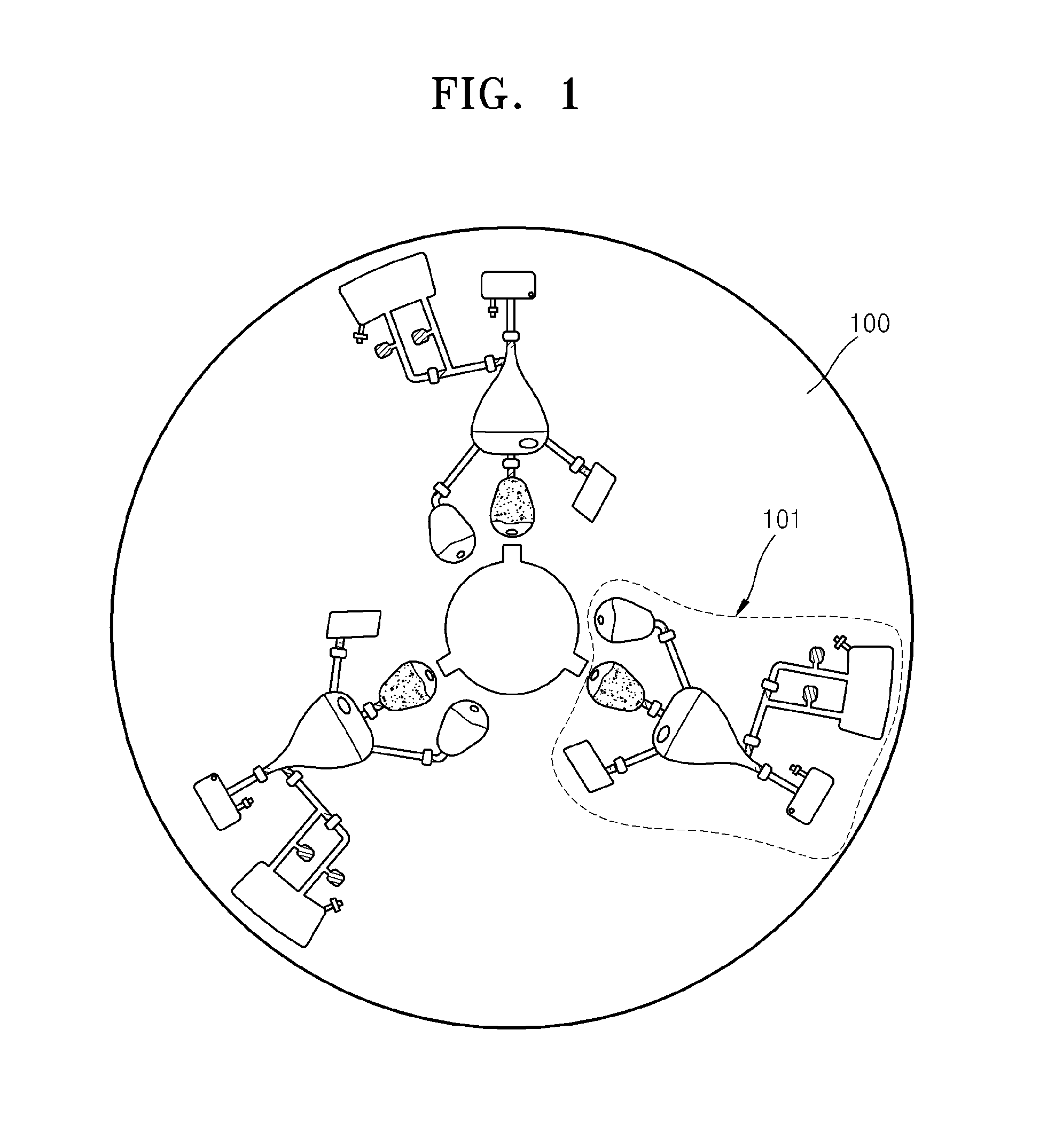
Centrifugal force-based microfluidic device for protein detection and microfluidic system including the same
InactiveUS20110201101A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein detectionCentrifugal force
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
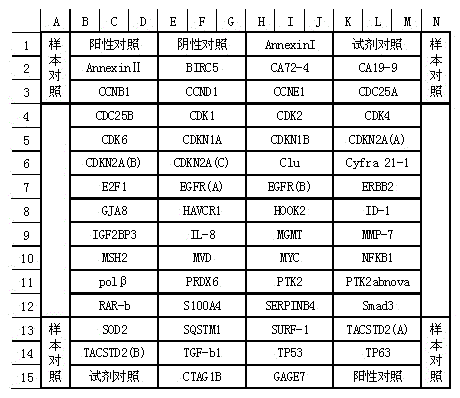
Protein chip for detecting esophageal squamous carcinoma marker and kit box of protein chip
The invention discloses a high-throughput multi-index protein chip for screening esophageal squamous carcinoma specific protein markers, and discloses a kit supporting the use. 55 types of esophageal squamous carcinoma differential proteins in the serum or blood plasma are selected and used as the esophageal squamous carcinoma protein markers and protein contrast prepare the protein chip; and the protein chip comprises a substrate, protein detection indicators and a contrast detection indicator coating, wherein the protein detection indicators are distributed as arrays on the substrate. Detection liquid of a supplementary experiment reagent is filled in the kit. By adopting the protein chip, the protein profiles of three types of people, namely, normal people, people subjected to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma precancerous lesions, and people subjected to the esophageal squamous carcinoma, can be determined; and means are provided for screening the esophageal squamous carcinoma in the early stage, diagnosing in mid stage and late stage, as well as monitoring the state of illness.
Owner:JIANGSU YUANHUA BIO TECH
Protein detecting device
InactiveUS6861224B2Precise detection/determinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein detectionPhysical chemistry
A protein detecting device, which comprises: (1) a detecting unit having a bonding section, which has properties for specifically bonding to a protein to be detected, a detecting section for detecting the bonding of the protein to be detected to the bonding section, the detecting section being made up of a polynucleotide double strand and a charge separating group, and an electrode section detecting the change in electrical conductivity of, or amount of transferred charge in, the polynucleotide double strand modified by the bond of the protein, (2) a standard electrode, (3) a reference electrode, (4) a container for housing the detecting unit, the standard electrode and the reference electrode, and containing a sample solutions comprising the protein to be detected, and (5) a measuring unit for measuring the protein based on a signal detected in the detecting unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Nanotechnology-based trace protein detection method
InactiveCN101943703AWide linear rangeLow detection limitColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingAntigenBiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention relates to a nanotechnology-based trace protein detection method, which combines enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology, tyramine signal amplification technology and the aggregation phenomenon of gold nanoparticles modified by different biological molecules, so an experimental method used for detecting trace proteins such as prostate specific antigen (PSA) and the like is established. The method comprises the following steps of: fixing an antibody aiming at the protein to be detected (such as the PSA) on the surface of a substrate; incubating another antibody with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) activity of the protein to be detected (such as the PSA) after capturing the protein to be detected in a sample, wherein the HRP catalyzes biotin-tyramide to generate biotin deposition under certain conditions; further amplifying a signal by using the aggregation phenomenon of the gold nanoparticles modified by biotin-labeled DNA and the gold nanoparticles modified by streptavidin; performing silver staining; and performing data analysis on an experimental result by using software. The method has the advantages of extremely low detection limit, wider detection range, capacity of detecting the antigen in a rabbit serum with complex compositions, and important application prospect.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Protein detection system
InactiveUS7527977B1Rapid and high sensitivity analysisEliminates beam divergenceAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWithdrawing sample devicesFiberProtein detection
The present embodiment describes a miniature, microfluidic, absorption-based sensor to detect proteins at sensitivities comparable to LIF but without the need for tagging. This instrument utilizes fiber-based evanescent-field cavity-ringdown spectroscopy, in combination with faceted prism microchannels. The combination of these techniques will increase the effective absorption path length by a factor of 103 to 104 (to ˜1-m), thereby providing unprecedented sensitivity using direct absorption. The coupling of high-sensitivity absorption with high-performance microfluidic separation will enable real-time sensing of biological agents in aqueous samples (including aerosol collector fluids) and will provide a general method with spectral fingerprint capability for detecting specific bio-agents.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Approximate quick clustering and index method for mass data
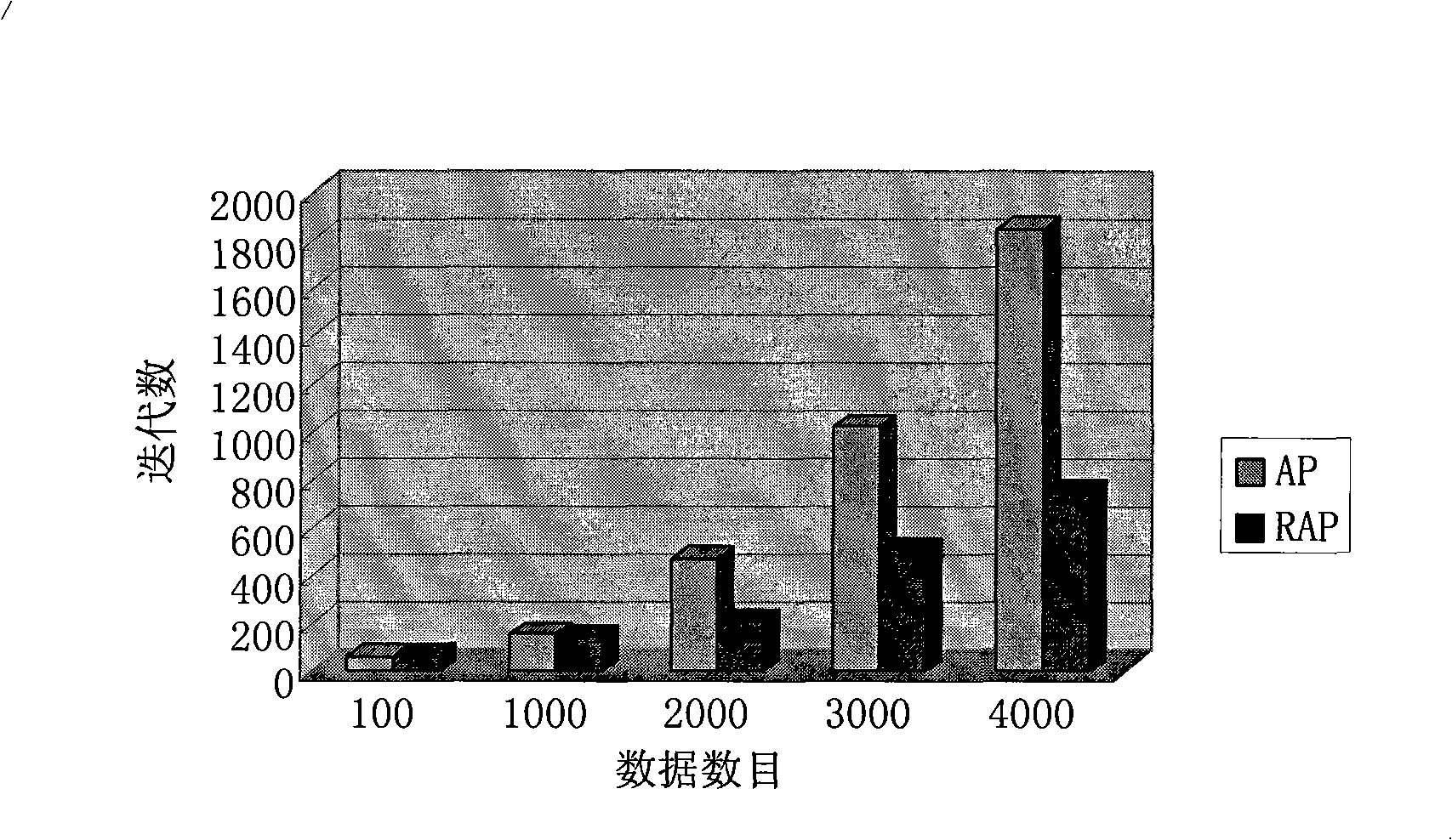
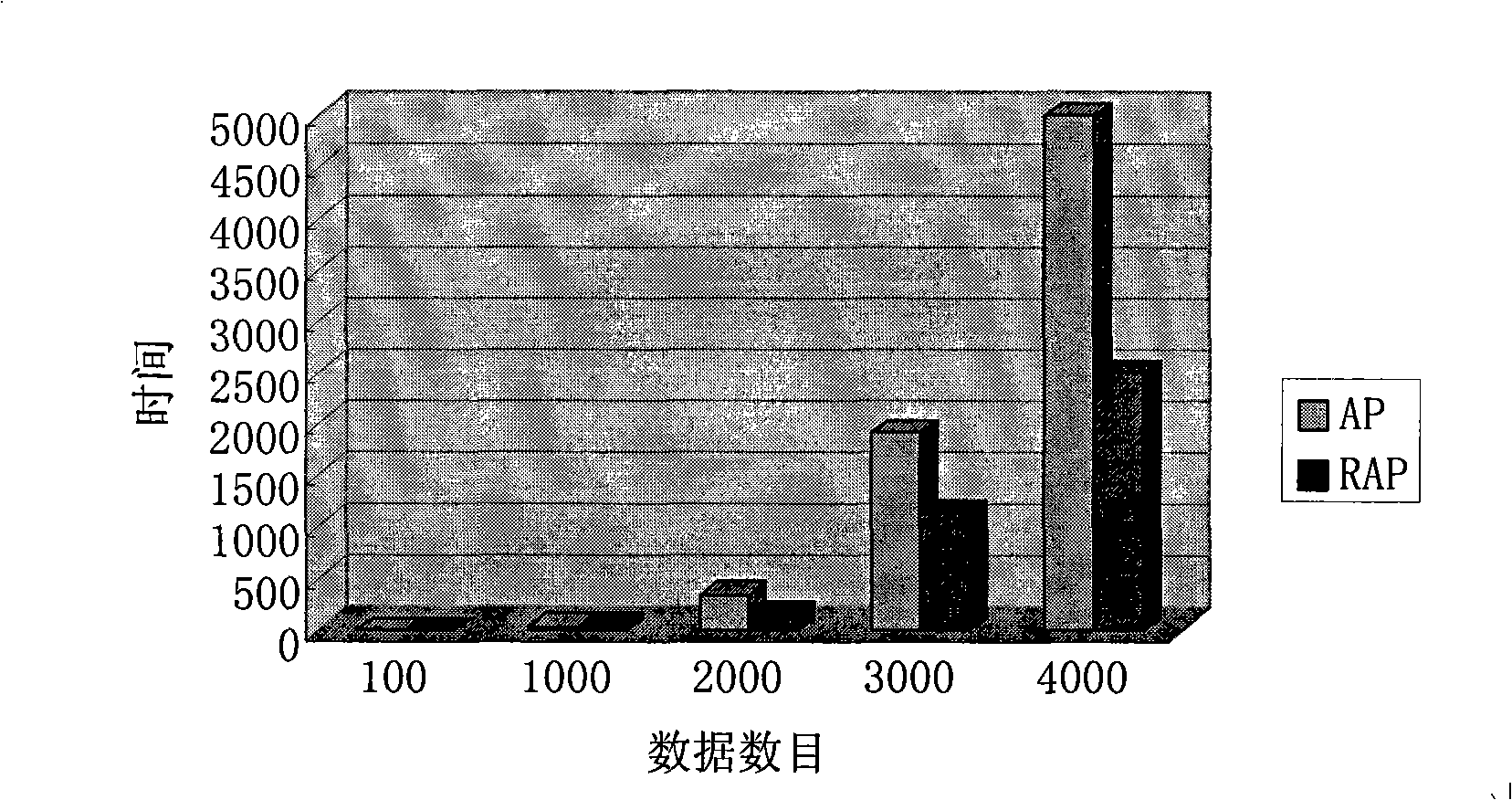
InactiveCN101339553AReduce the number of iterationsHigh speedSpecial data processing applicationsProtein detectionThe Internet
The invention discloses a massive data-oriented recursive blocking information transfer clustering and indexing method. By using the method, the accurate and fast clustering of various massive data can be realized, and the method is suitable for an index structure of the query and the updating. Users can deal with massive and unordered data and can carry out fast clustering and indexing, thus being beneficial to the later query, search, maintenance and updating. The invention can be applied to the fast clustering and indexing of massive internet-oriented texts, images, videos, frequency, and the like, and can also be applied to similarity comparison of massive biological gene sequence and homologous protein detection. The invention also discloses a proximate and fast clustering method of massive data. The clustering method of the invention can ensure that the speed of the clustering can be increased exponentially under the circumstance of little loss of clustering effect and can be better beneficial to the clustering, inserting and updating of data outside a training set, therefore, the method can generally applied to the fast clustering and indexing of various complex massive data.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
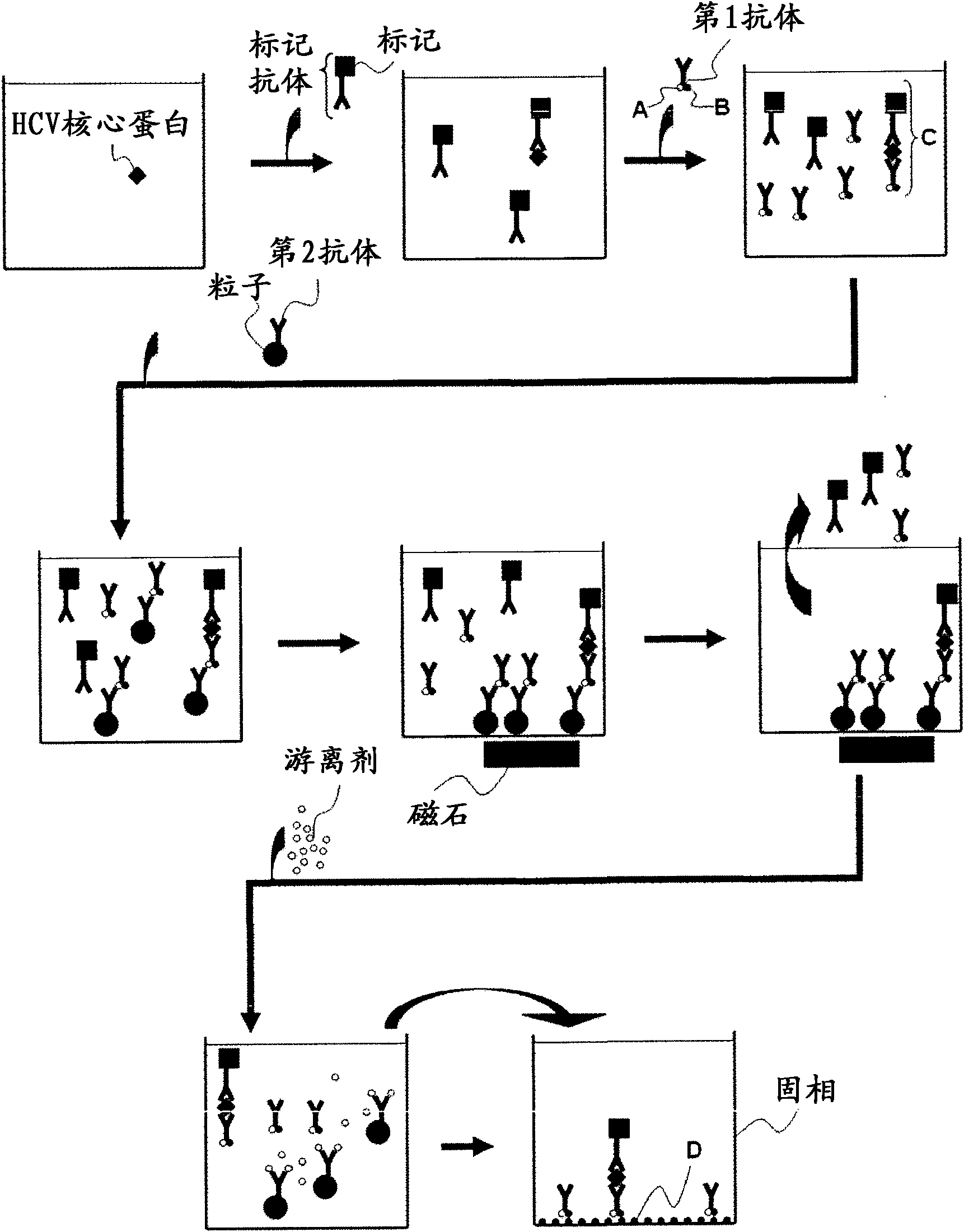
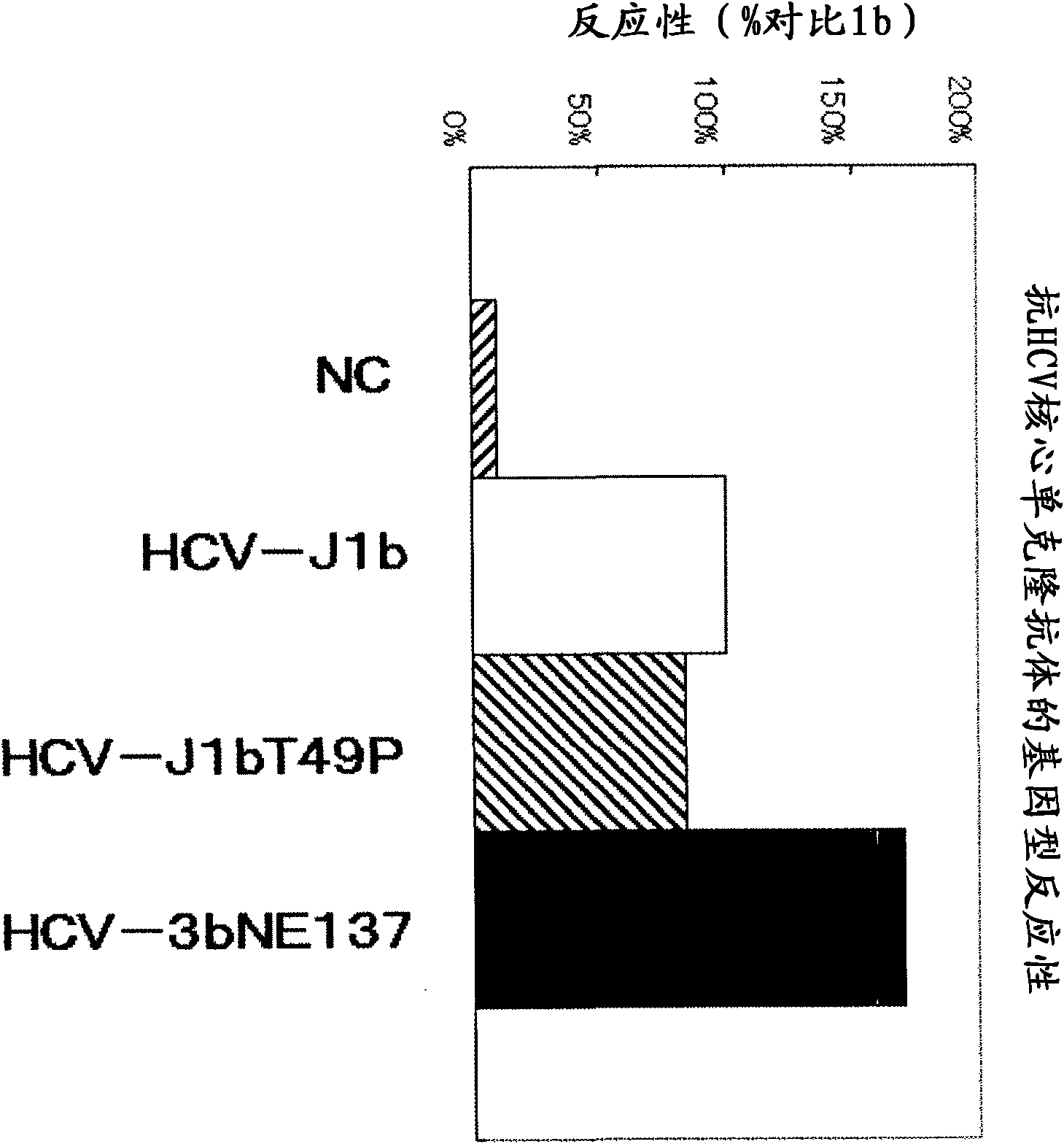
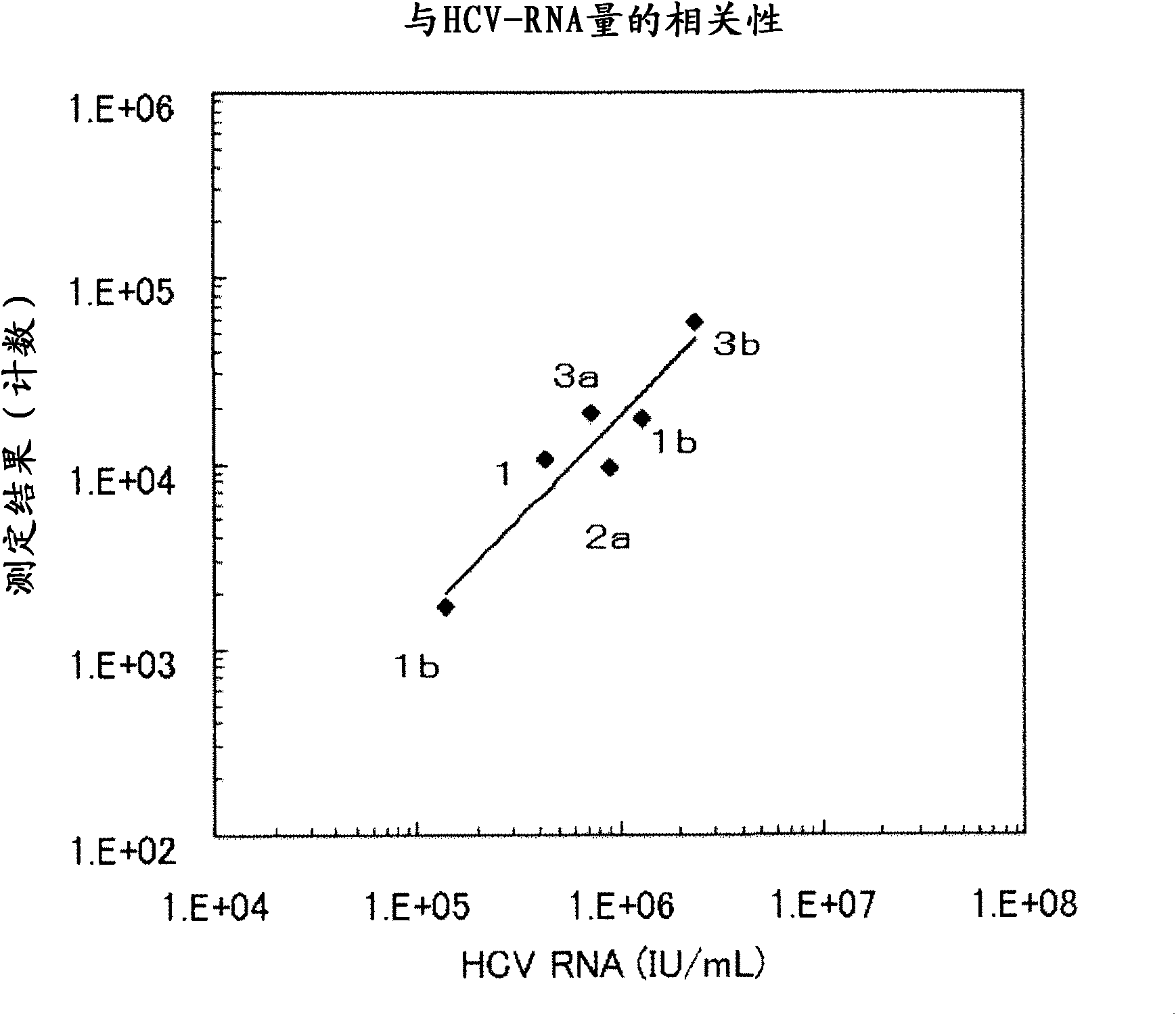
Method for pretreating sample and method for immunoassay of hcv
InactiveCN102081018APrevent agglutinationAgglutination does not occurPreparing sample for investigationTissue cultureProtein detectionVirus
There are provided: a method for pretreating a sample for HCV core protein detection by an immunoassay using particles, which includes treating a sample suspected of containing hepatitis C virus (HCV) with an alkaline material-containing reagent and neutralizing the sample with an acid material-containing reagent, wherein at least one of the reagents contains a reducing agent; a reagent kit for HCV core protein detection; a method for determining the presence or absence of hepatitis C virus in a sample; and a method for immunoassay of HCV.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Target detecting device and target capturer, device and method for molecular adsorption or desorption, and device and method for protein detection
InactiveUS20060003437A1Shorten speedExposed surface is smallBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein detectionDesorption
The present invention provides, for example, a target detecting device comprising a target capturer, means for releasing the target capturer, light irradiating means and light detecting means, the target capturer at least partially containing a region interactive with an electrically conductive member, being capable of capturing a target, and being capable of emitting light upon irradiation with light in the case of not interacting with the electrically conductive member, the means for releasing the target capturer serving to release the target capturer from the electrically conductive member by ceasing the interaction between the target capturer and the electrically conductive member, the light irradiating means serving to apply light to the electrically conductive member, and the light detecting means serving to detect light emitted by the target capturer upon irradiation of light applied by the light irradiating means. It also provides a target capturer comprising an interacting section, a capturing section and a light emitting section, the interacting section at least partially containing a region interactive with an electrically conductive member, the capturing section capable of capturing a target, and the light emitting section capable of emitting light upon irradiation with light when the region in the interacting section does not interact with the electrically conductive member.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
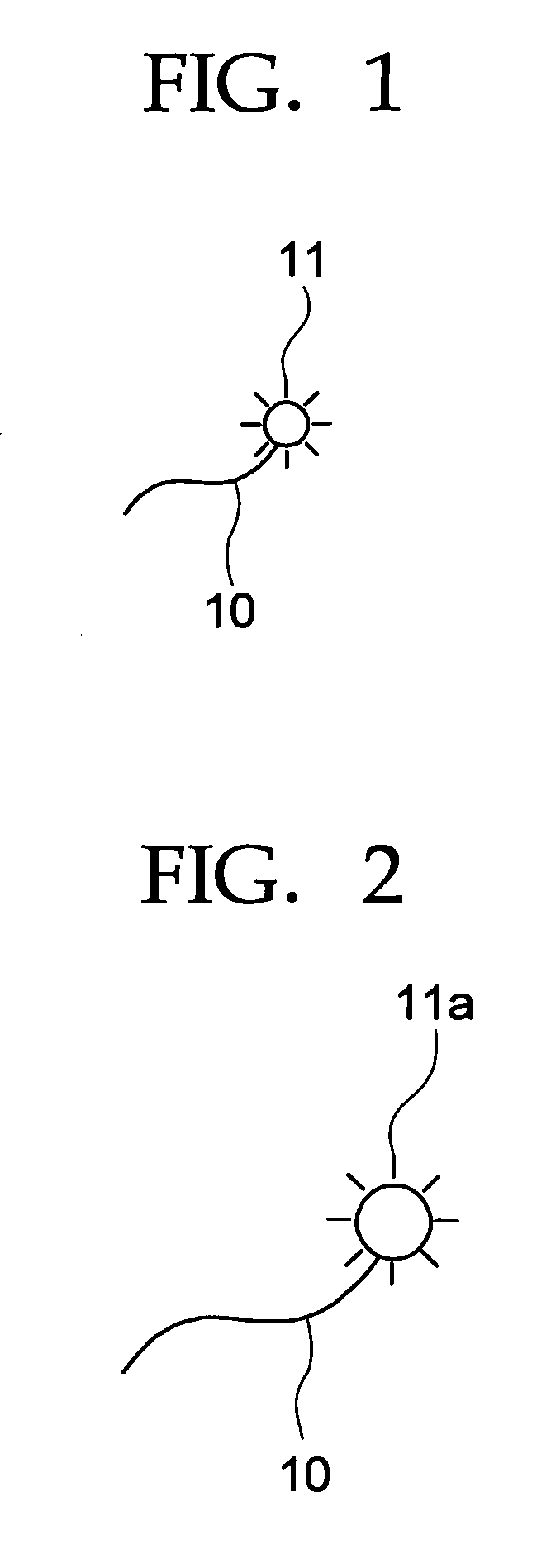
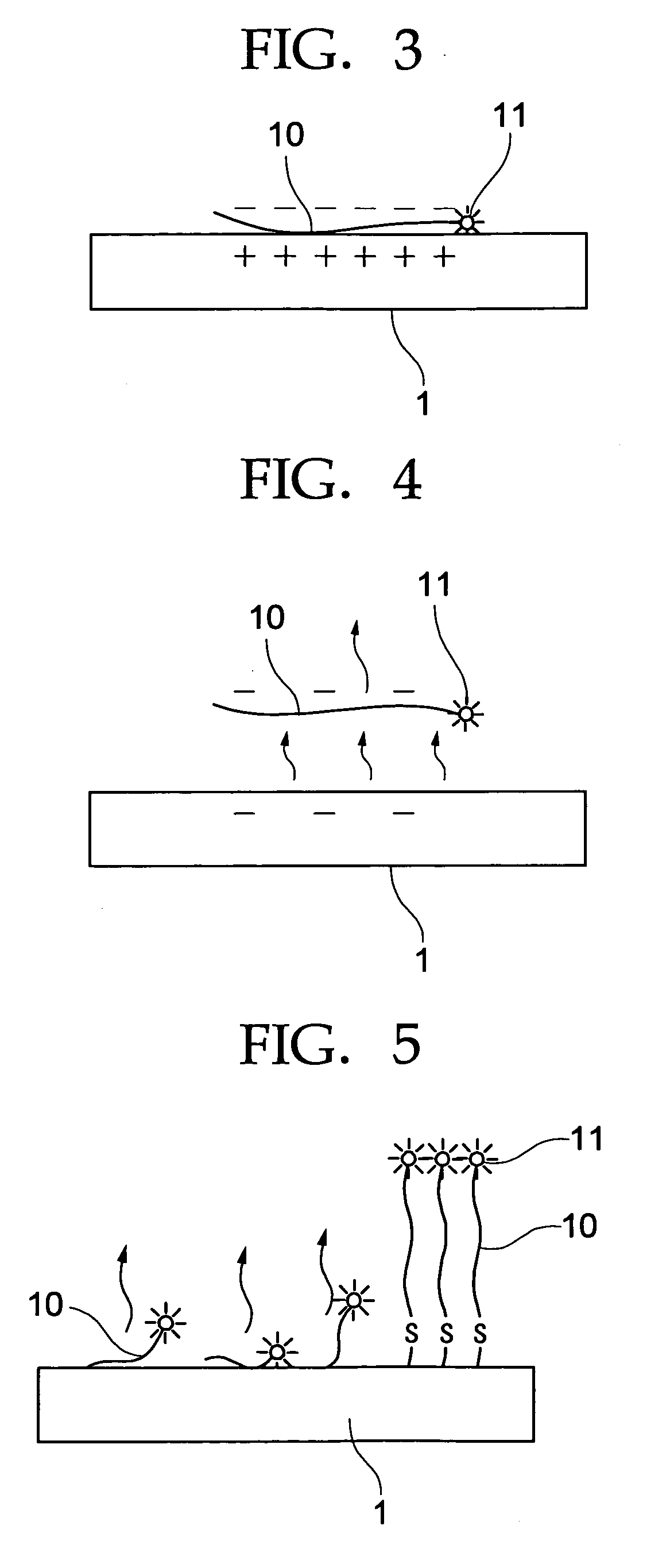
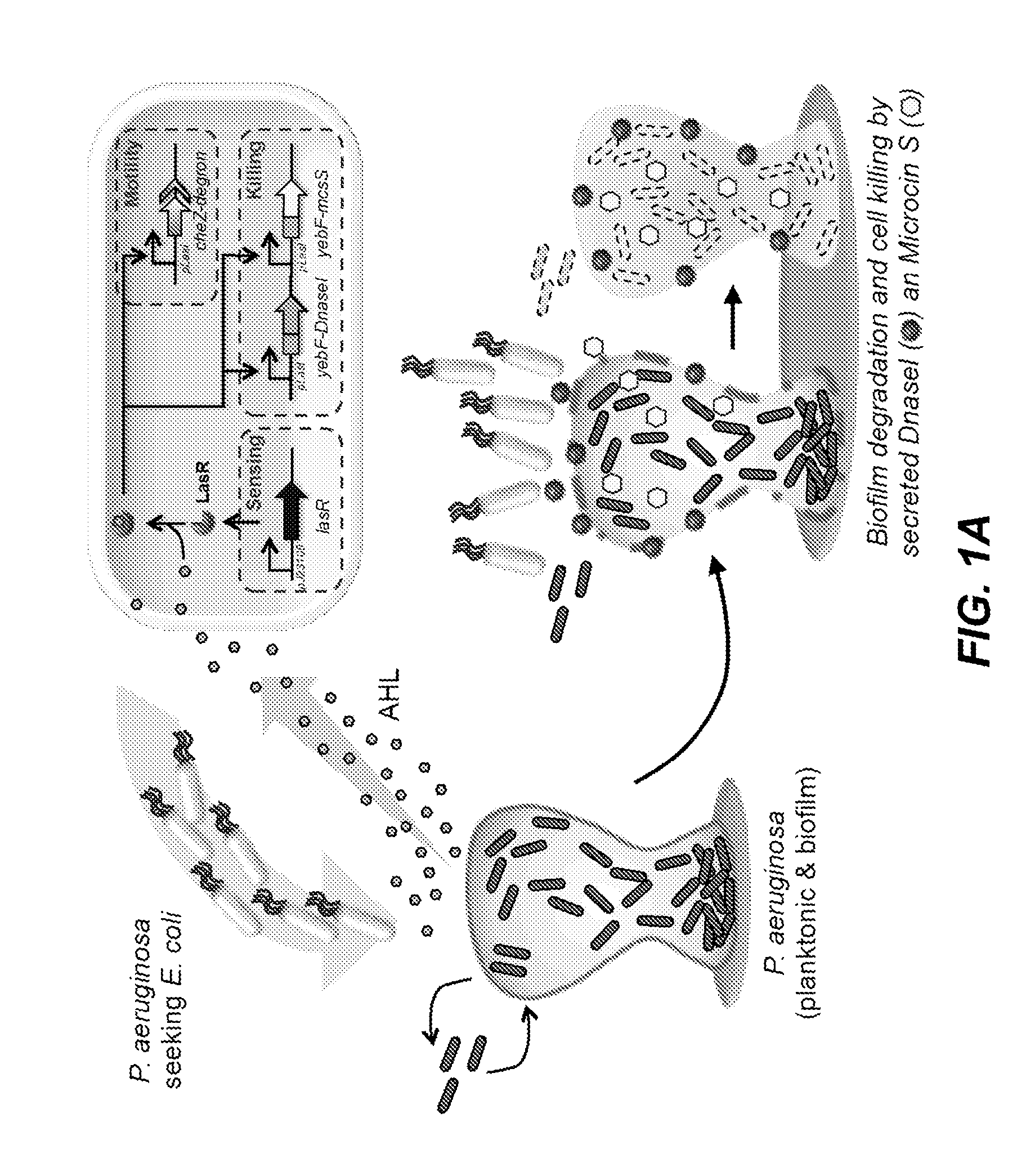
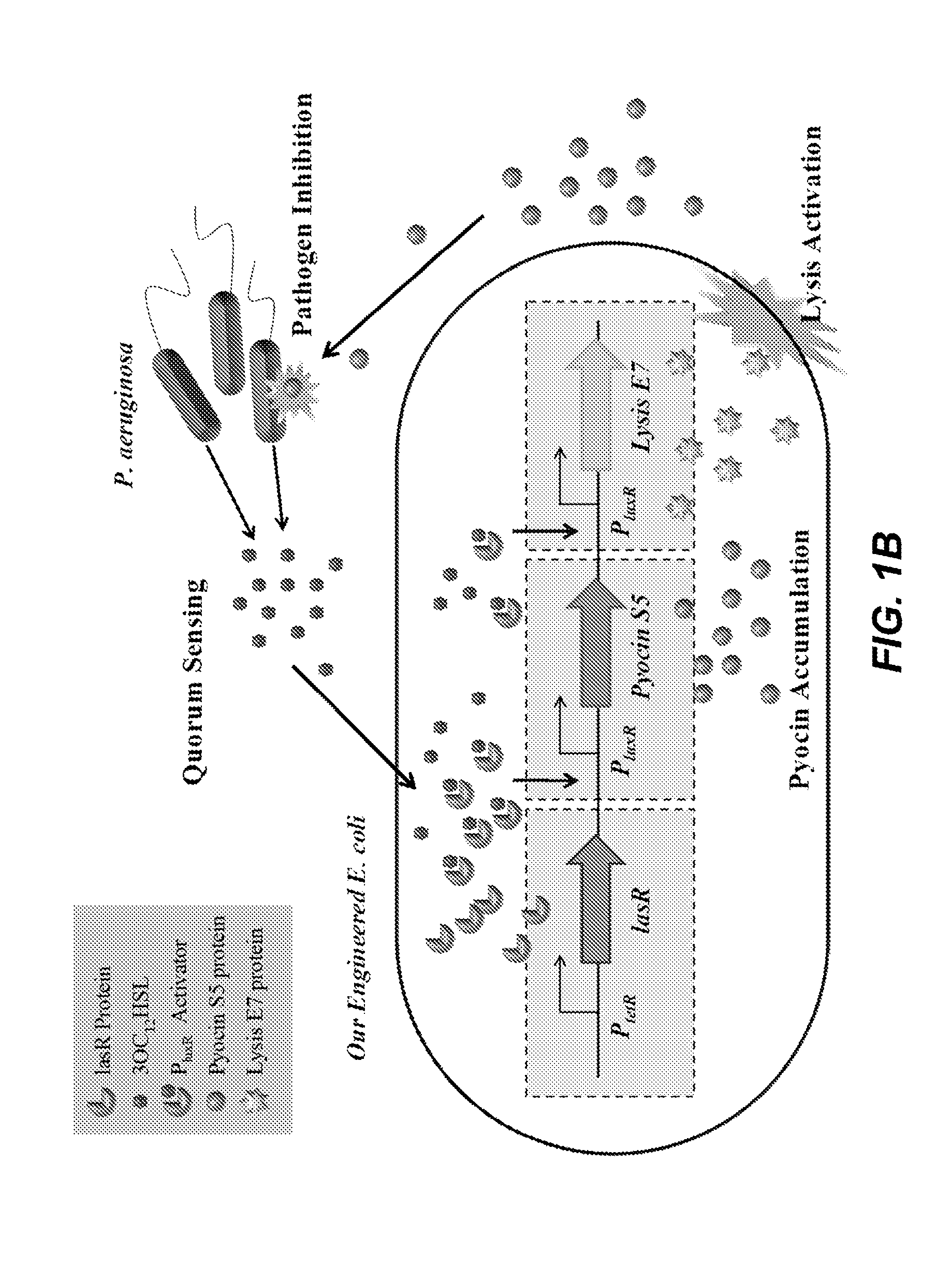
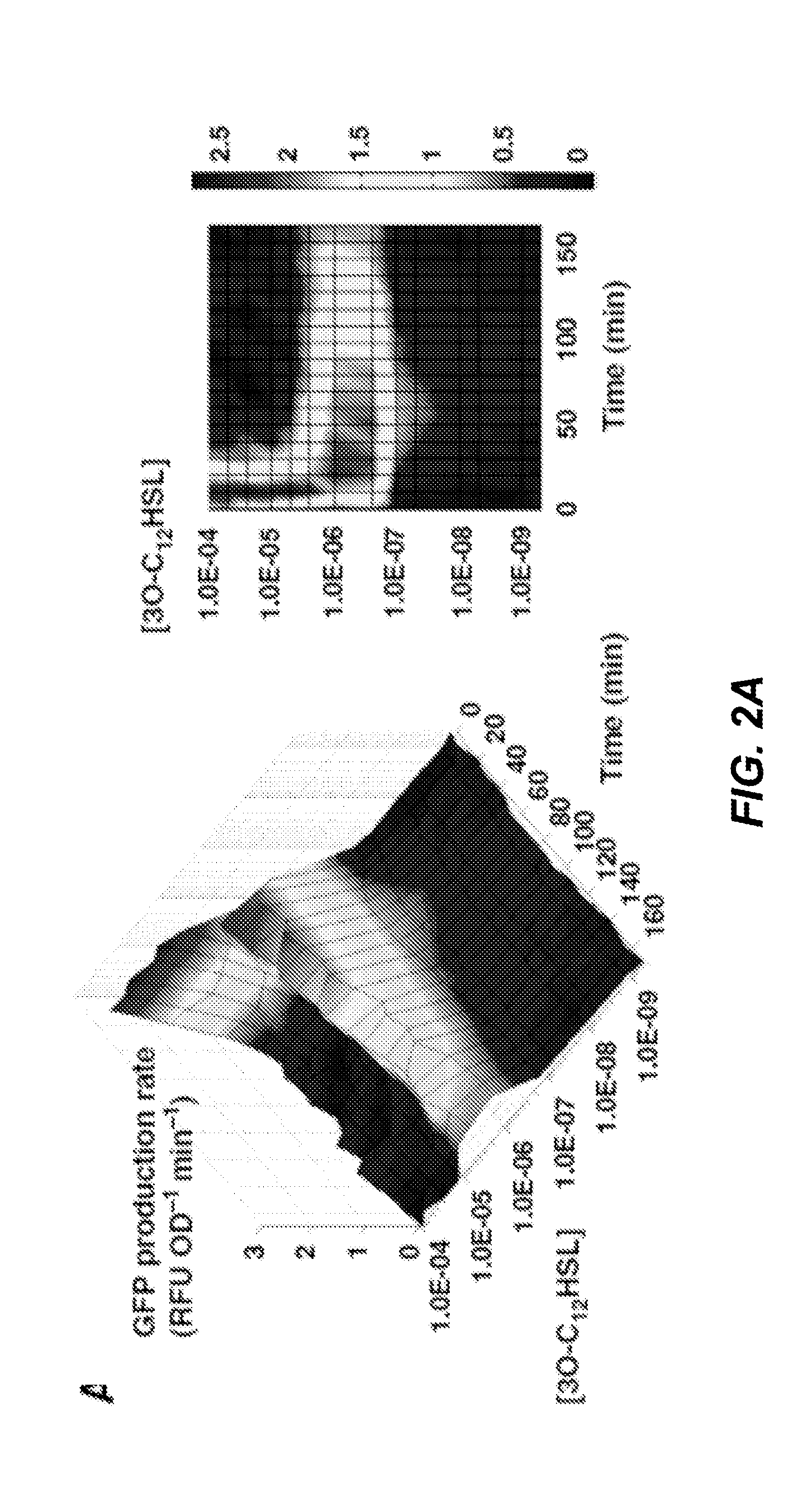
Isolated nucleotide molecule and method of sensing and killing of pathogenic microorganism
The present invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid molecule comprising (a) a first nucleotide sequence encoding a protein that detects the presence, amount or both of a pathogenic microorganism by forming a complex with a quorum sensing molecule produced by said pathogenic microorganism, (b) one or more second nucleotide sequence said one or more second nucleotide sequence being under control of a promoter that is induced by the complex of the protein encoded by the first nucleotide sequence and the quorum sensing molecule produced by said pathogenic microorganism and encoding (i) an antimicrobial peptide, wherein the antimicrobial peptide is effective against the pathogenic microorganism detected by the protein encoded by the first nucleotide sequence; and / or an antibiofilm enzyme wherein the antibiofilm enzyme is effective against the pathogenic microorganism detected by the protein encoded by the first nucleotide sequence; and (c) optionally a third nucleotide sequence encoding a protein that controls the motility of the host organism, wherein the protein that controls the motility of the host organism directs the motility of the host organism towards said pathogenic microorganism. A recombinant microorganism comprising the isolated nucleic acid molecule and a method of sensing and killing pathogenic microorganisms is also described.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Seneca valley virus based compositions and methods for treating disease
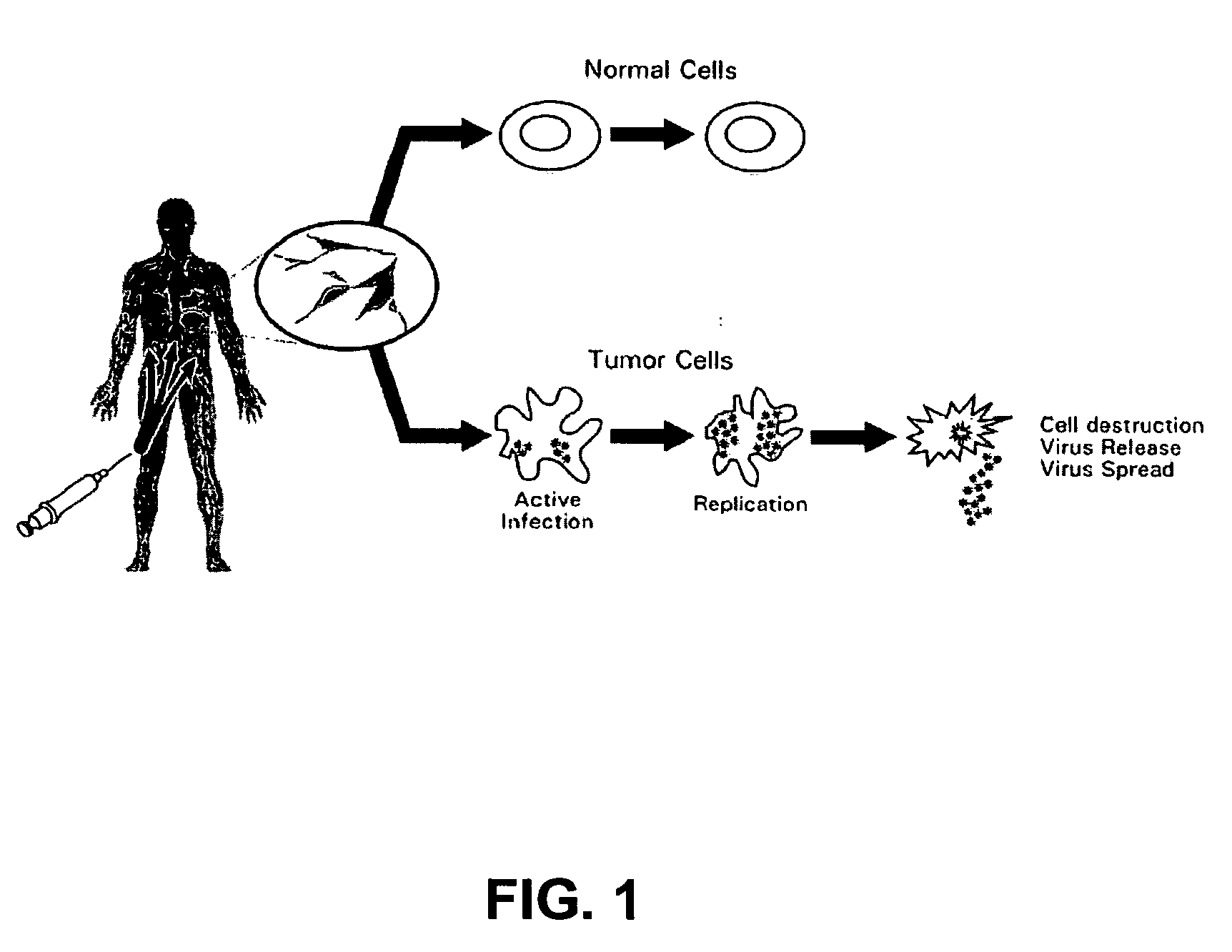
ActiveUS20060159659A1High therapeutic indexSafe and effective and new lineBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseAbnormal tissue growthProtein detection
The present invention relates to a novel RNA picornavirus that is called Seneca Valley virus (“SVV”). The invention provides isolated SVV nucleic acids and proteins encoded by these nucleic acids. Further, the invention provides antibodies that are raised against the SVV proteins. Because SVV has the ability to selectively kill some types of tumors, the invention provides methods of using SVV and SVV polypeptides to treat cancer. Because SVV specifically targets certain tumors, the invention provides methods of using SVV nucleic acids and proteins to detect cancer. Additionally, due to the information provided by the tumor-specific mechanisms of SVV, the invention provides methods of making new oncolytic virus derivatives and of altering viruses to have tumor-specific tropisms.
Owner:PERCEIVER PHARMA +1
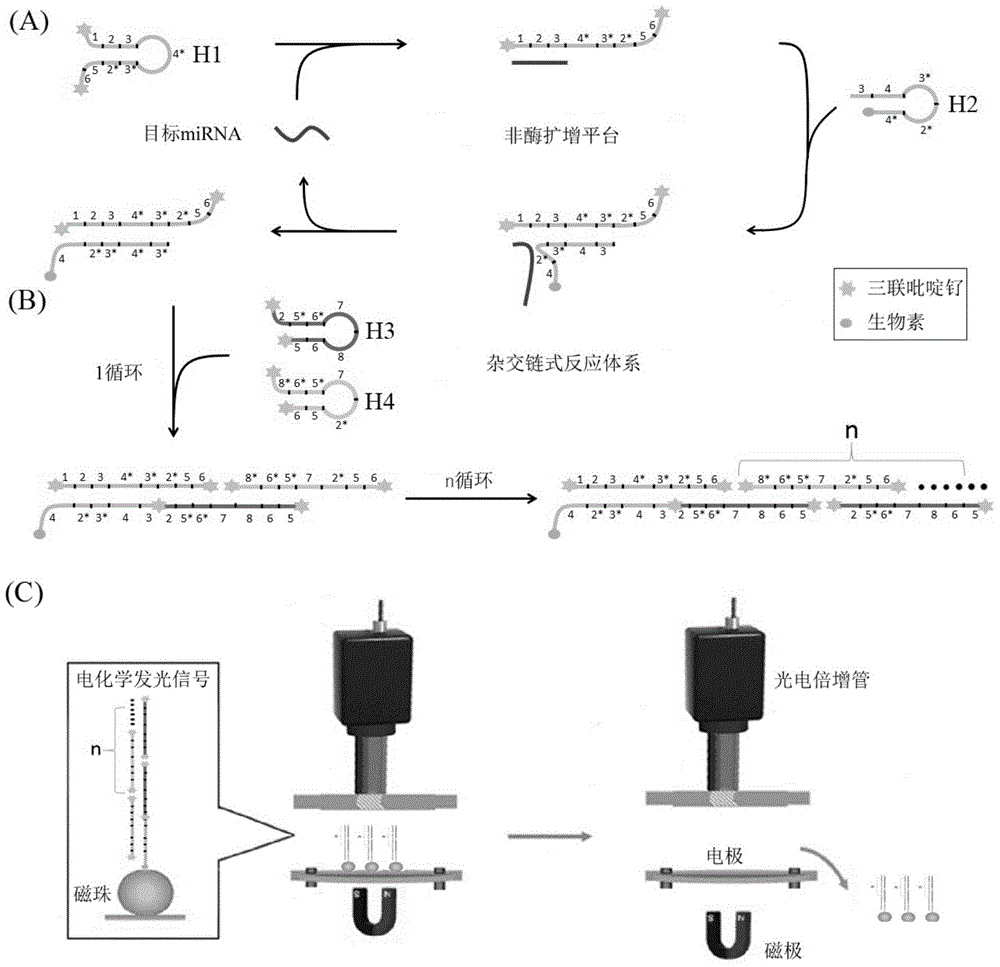
MicroRNA trace detection method based on exponential order non-enzymatic amplification and electrochemical luminescence principle
InactiveCN104450920AThe principle is simpleReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiotin-streptavidin complexProtein detection
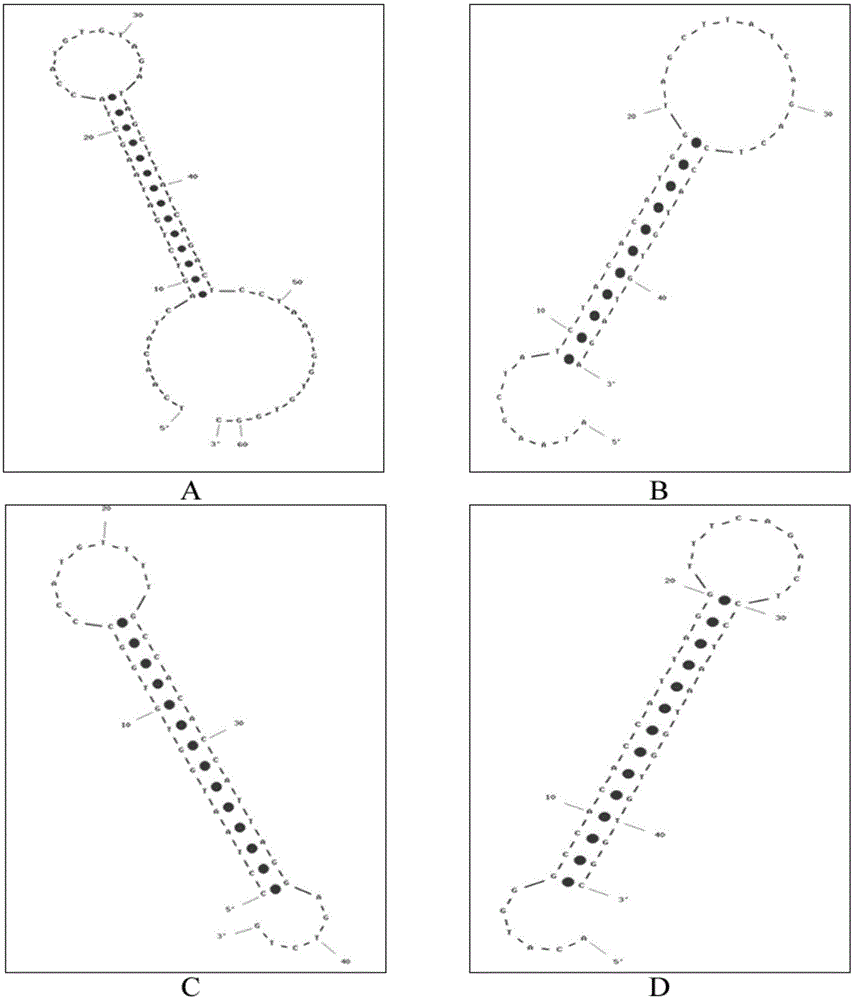
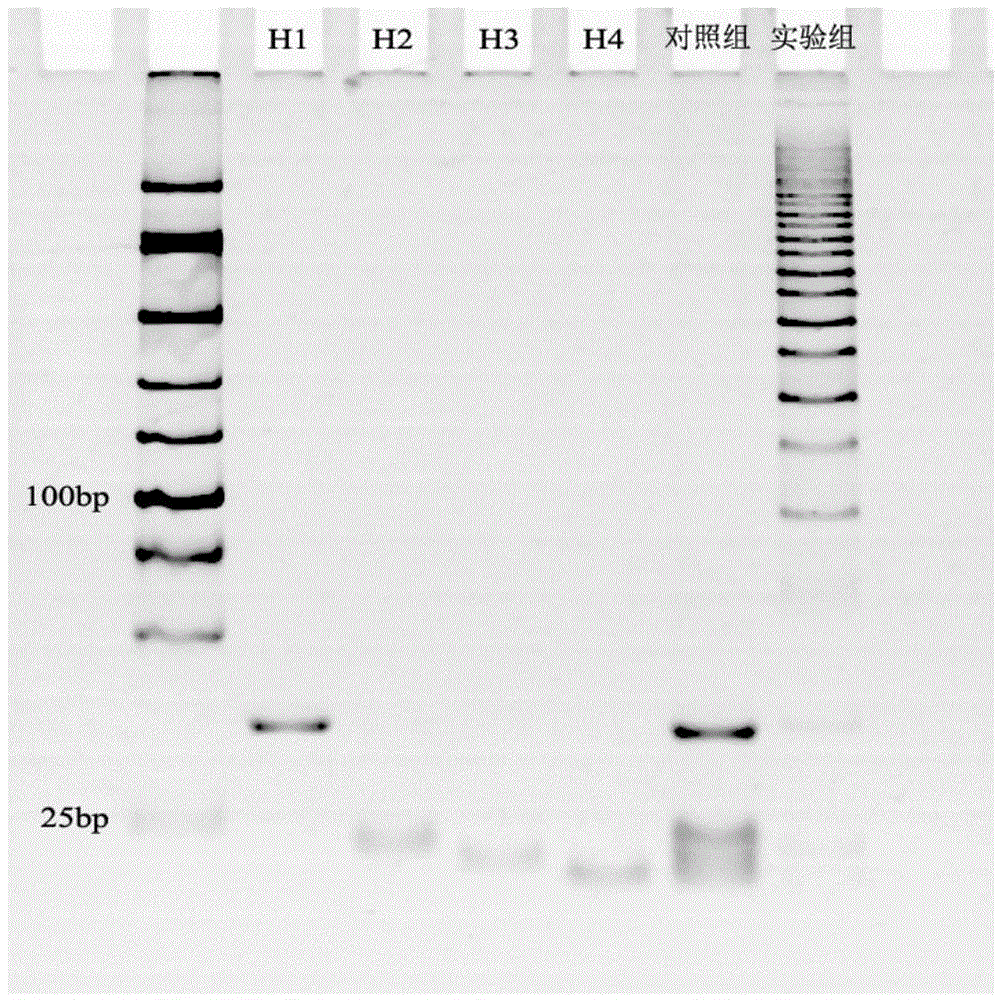
The invention discloses a microRNA trace detection method based on an exponential order non-enzymatic amplification and electrochemical luminescence principle. A non-enzymatic amplification and hybrid chain type reaction system is adopted, and the specific sequences of DNA hairpin probes H1, H2, H3 and H4 are designed based on a detection target microRNA sequence; when an amplification system contains to-be-detected microRNA, the subsequent hybrid chain type reaction process is triggered by virtue of an H1+H2 double-chain composite structure, and is finished by H3 and H4 together; and moreover, an amplification product is captured by virtue of streptavidin magnetic bead capture, and an electrochemical luminescence signal is generated and detected by virtue of an electrochemical detection system. According to the method, an enzyme is not involved in the whole process, the principle is simple, and the detection cost is low; and the method has the advantages of constant temperature amplification, high sensitivity, simple operation, simplicity in popularization and the like. The method is applied to nucleic acid detection and can be combined with a protein aptamer related technology to be used for protein detection.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing electrochemical immunosensor for pcsk9 protein detection
InactiveCN107389949AImprove conductivityHigh sensitivityBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesProtein detectionStaphylococcus aureus
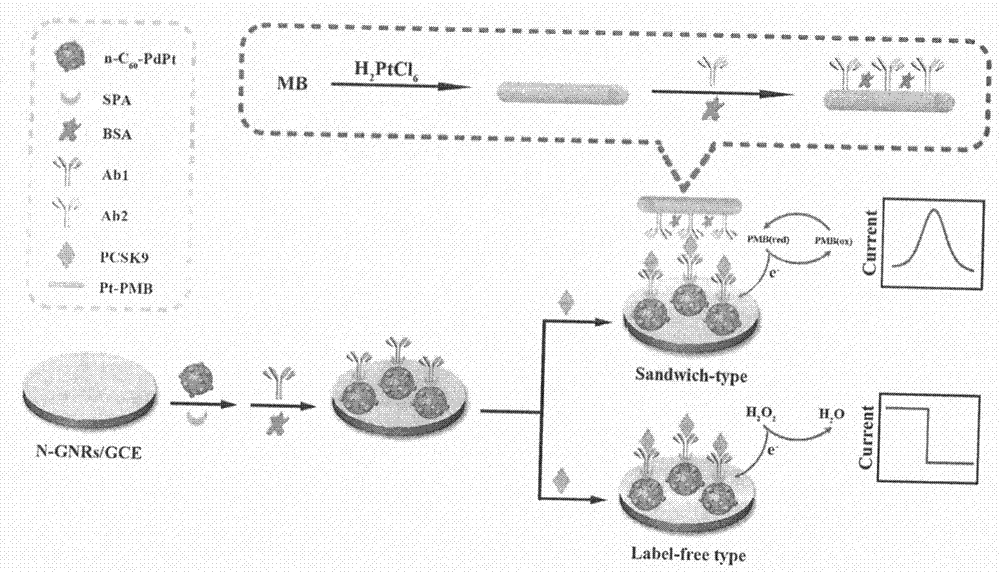
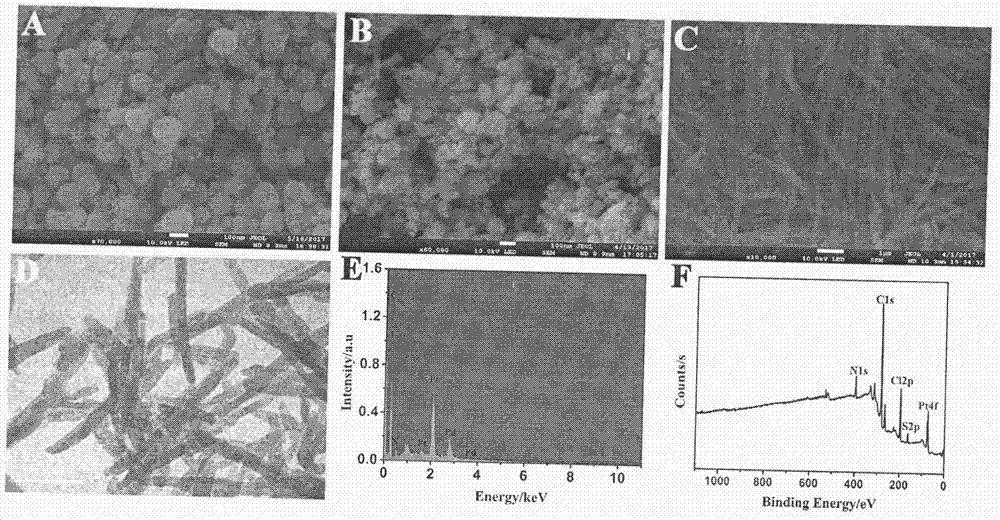
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of an electrochemical immunosensor for a biomarker, namely a recombinant proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (pcsk9) protein for predicting and diagnosing cardiovascular diseases, and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical detection. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, performing nitrogen doping on a graphene nanobelt (n-gnrs), performing amination on a fullerene-palladium-platinum nanoparticle (n-C60 / pdpt) composite material and a staphylococcus aureus a protein (spa), and performing layer-by-layer self-assembling so as to immobilize a pcsk9 antibody (ab1); mixing the synthesized nanoparticle-poly-methylene blue (pt-pmb) with the pcsk9 antibody (ab2), and preparing a nano beacon, thereby obtaining the electrochemical immunosensor for pcsk9 protein detection. The electrochemical immunosensor has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, good in specificity and rapid and convenient in detection. A novel method for pcsk9 protein detection is provided, and useful information is provided for clinical prediction and diagnosis on cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Di-pyrene modified perylene bisimide derivative fluorescent probe and synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN106632326ABroad wavelength absorption rangeHigh fluorescence quantum yieldOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein detectionSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a di-pyrene modified perylene bisimide derivative fluorescent probe and a synthesis method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of protein detection. The preparation of the fluorescent probe comprises the following steps that in a protective atmosphere, 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone solution of a pyrene sulfonyl derivative is added into a 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone solution of perylene; then, anhydrous zinc acetate is added to obtain a mixed solution; next, the mixed solution is stirred; heating reflux is performed for 10 to 15h at 150 to 200 DEG C; after the reaction liquid obtained after the reflux is cooled to the room temperature, filtering is performed to obtain filter liquid; the filter liquid is subjected to acid washing; precipitates occur; suction filtration is performed; filter cake is obtained; the filter cake is washed and dried to obtain the di-pyrene modified perylene bisimide derivative fluorescent probe. The fluorescent probe provided by the invention has the advantages that the chemical stability is high; the response speed is high; the sensitivity is high; the discrimination performance is good; the sample consumption quantity is small; the data collection is simple, and the like. The instant and on-line detection of the protein can be realized. The fluorescent probe provided by the invention can be used for respectively realizing the distinguished detection of various proteins.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Methods and compositions for determination of glycated proteins
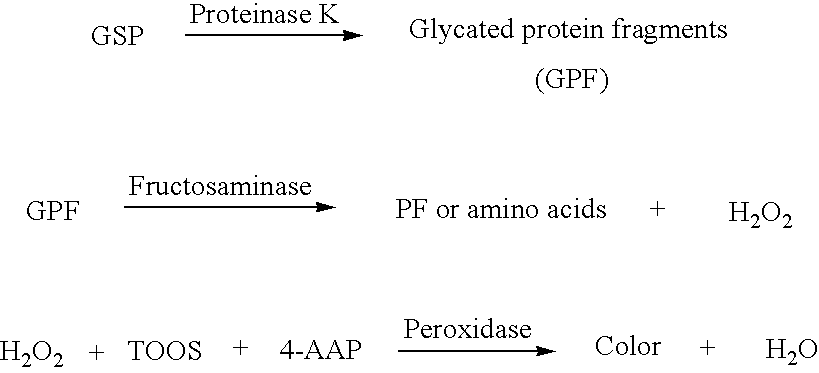
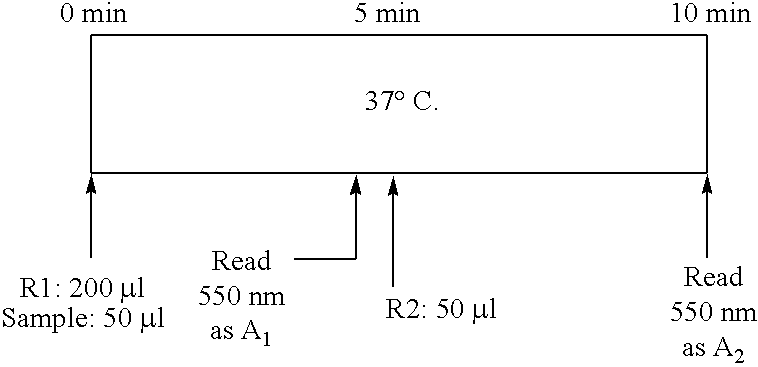
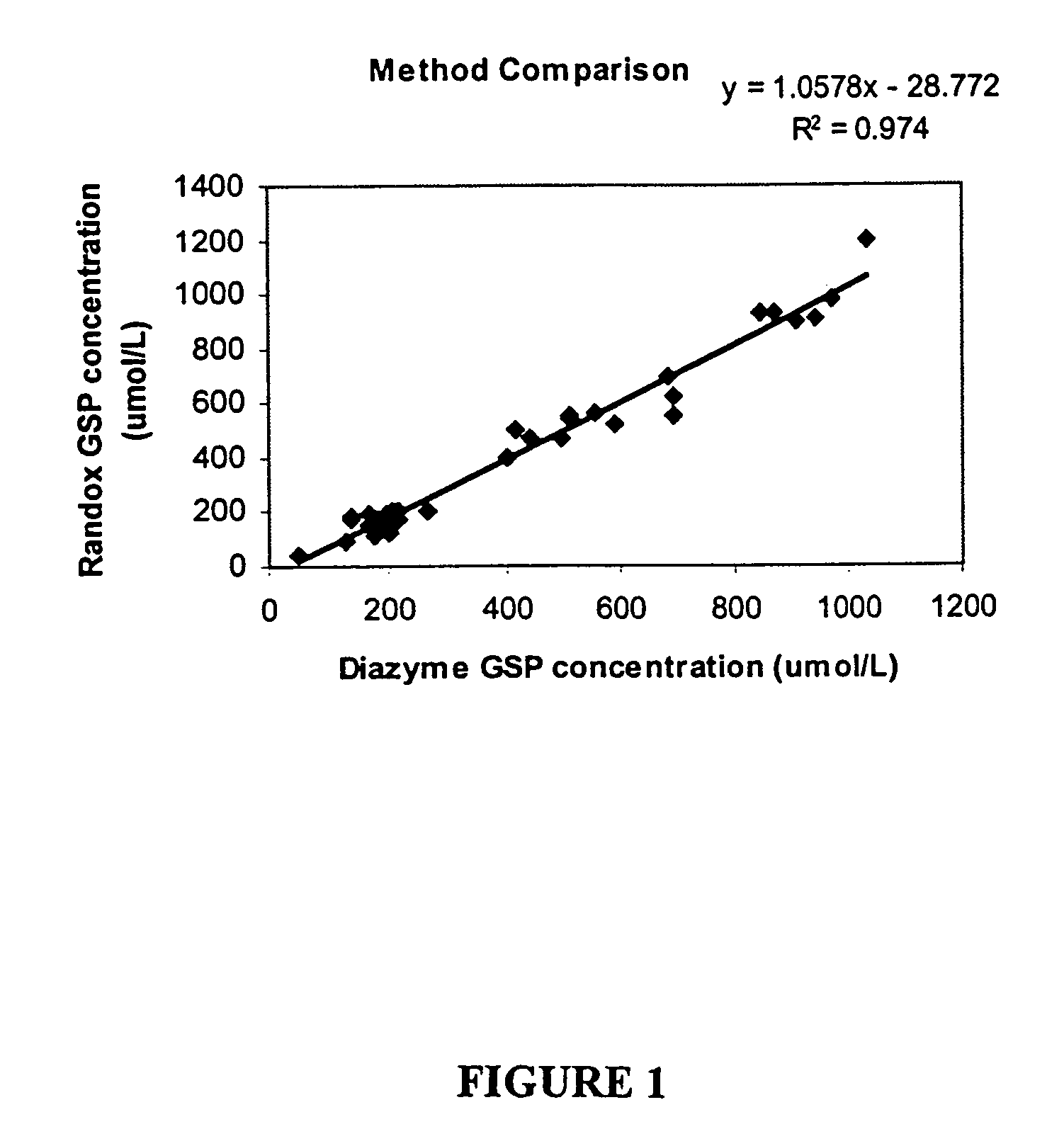
This invention relates generally to the field of glycated protein detection. In particular, the invention provides chimeric proteins, nucleic acids encoding the chimeric proteins, methods and kits for assaying for a glycated protein in a sample, using inter alia, an amadoriase.
Owner:DIAZYME LAB INC
Identification of etiology of autism
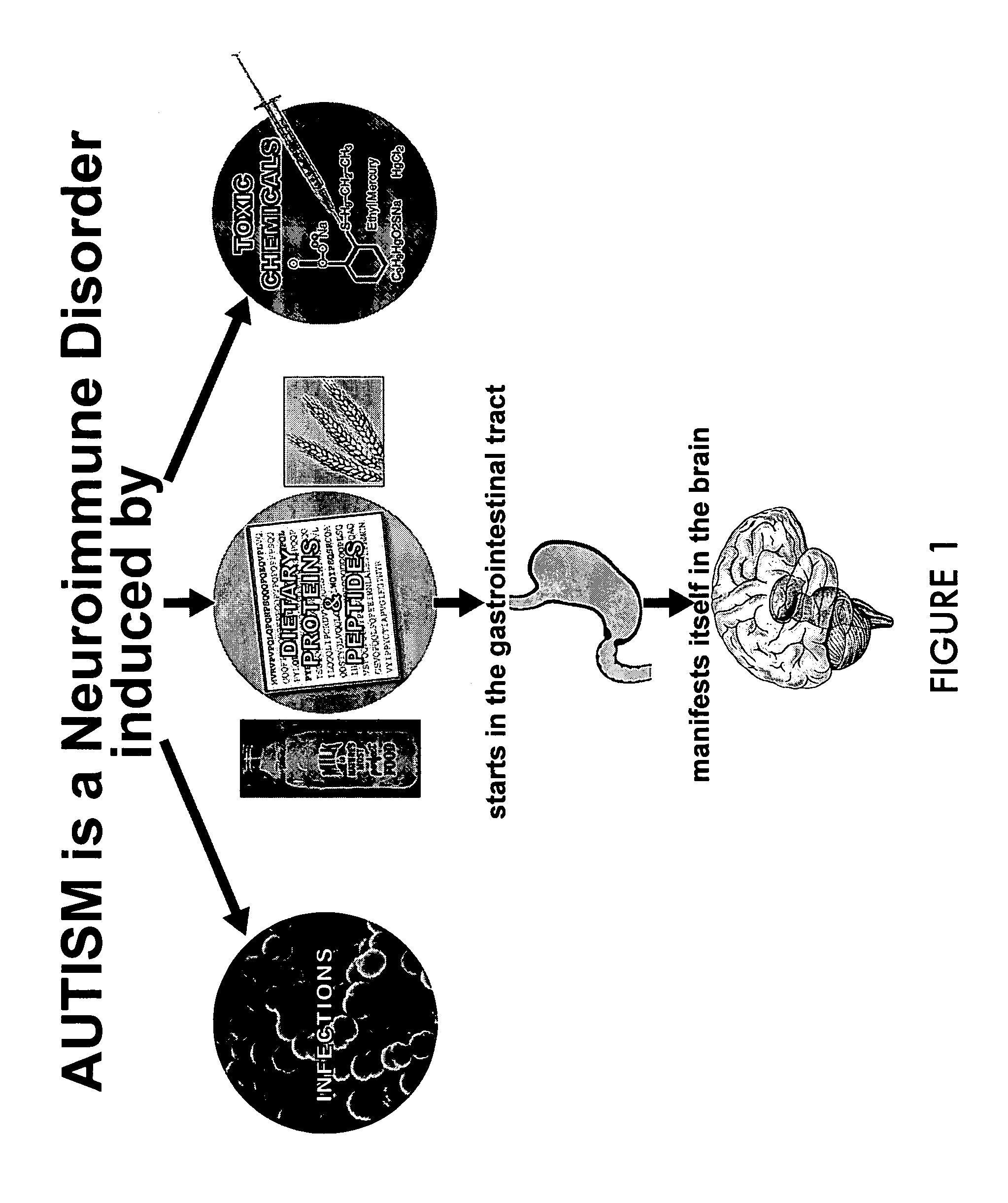
InactiveUS7252957B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenEtiology
Disclosed herein is a method for following up a prognosis of children with autism before and after treatment with different modalities administered by their clinicians, confirming the involvement of infectious agents, dietary proteins, and toxic chemicals in development of autism. The method utilizes detection of increased amounts of antibodies against an antigen based on infectious agent, toxic chemicals, or dietary proteins. Another method utilizes detection of antibodies to a self-tissue or peptide.
Owner:IMMUNOSCI LAB
Insecticidal crystal protein CrylAc enzyme linked immunosorbent detection kit
InactiveCN102095855AReduce testing costsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiotechnologyProtein detection
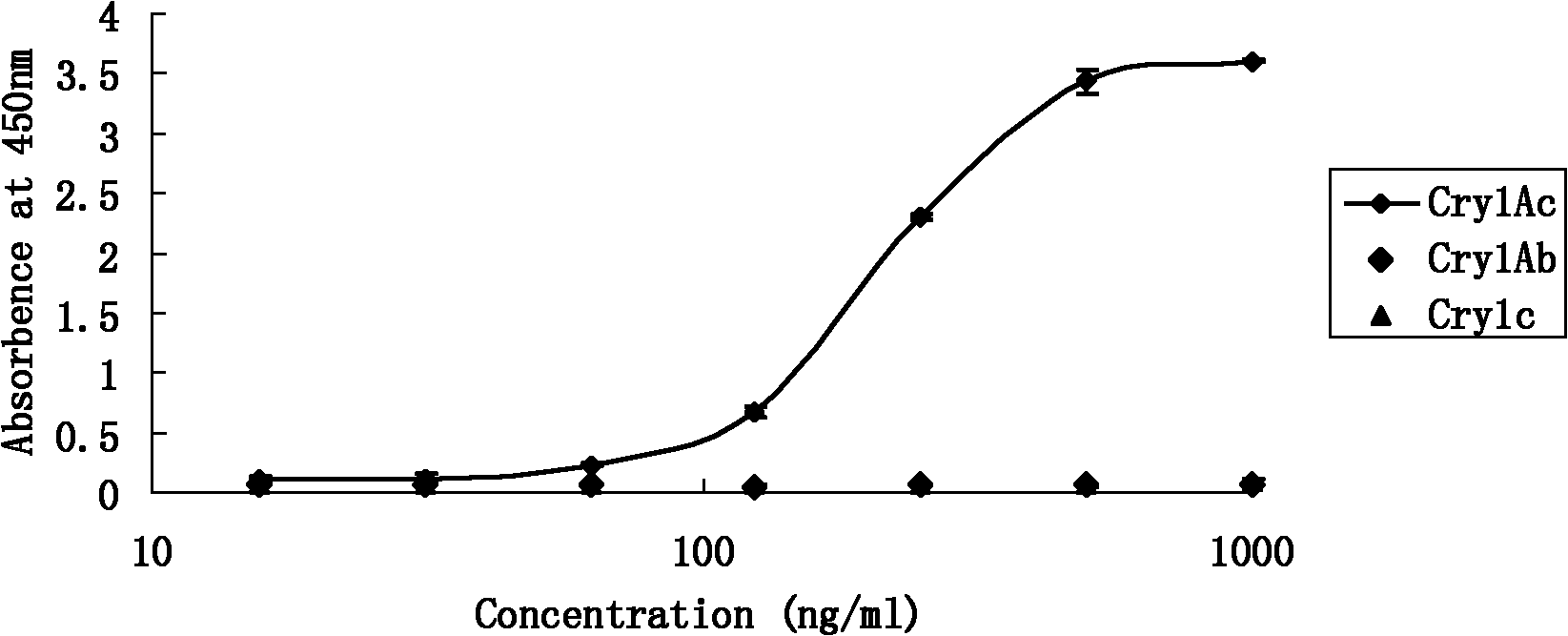
The invention discloses an insecticidal crystal protein CrylAc enzyme linked immunosorbent detection kit. In the CrylAc protein detection of the kit, the lowest detection limit is 7.81ng / mL, the linear detection range is 62.5-500ng / mL, the linear interval fitted equation y is equal to 1.1136Ln(x)-4.164, and R2 is equal to 0.9991. No cross reaction occurs among the kit and CrylAb and Crylc proteins. The kit is suitable for qualitative detection of the CrylAc protein in transgenic plant leaves, fruits and derivatives. The kit can detect large batch of samples simultaneously, is convenient and fast, has very important realistic significance in analyzing related transgenic articles, simultaneously ensures the detection cost to be greatly reduced and has potential economic value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Construction and application of impedance type electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer with magnetic surface
InactiveCN104181217AGood biocompatibilityImprove adhesionMaterial electrochemical variablesProtein detectionElectrochemistry
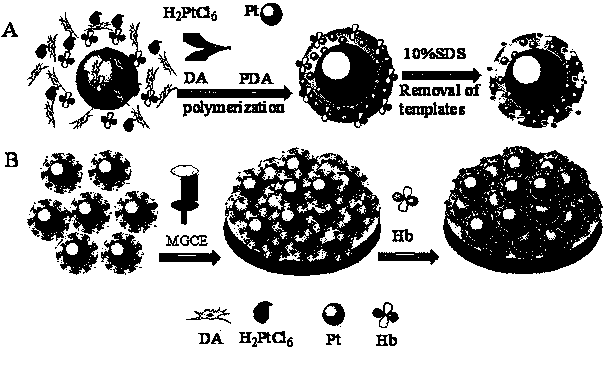
The invention discloses a construction method of an impedance type electrochemical sensor based on a molecularly imprinted polymer with a magnetic surface and an application of the sensor in protein detection, and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical sensing. The construction method comprises the following steps: synthesizing the molecularly imprinted polymer on the surface of a magnetic nano particle by taking hemoglobin as a template molecule and dopamine as a monomer and by using the self polymerization performance and the good adhesive capacity of the dopamine; eluting the hemoglobin, so as to prepare the molecularly imprinted polymer with the magnetic surface, wherein the molecularly imprinted polymer with the magnetic surface has the good identification effect on the hemoglobin; and fixing the polymer on the surface of a magnetic glassy carbon electrode under the action of a magnetic field, so as to construct a hemoglobin sensing interface based on the molecularly imprinted polymer with the magnetic surface, wherein the hemoglobin sensing interface based on the molecularly imprinted polymer with the magnetic surface is used for hemoglobin detection. The constructed electrochemical sensor based on the molecularly imprinted polymer with the magnetic surface is simple in method, high in hemoglobin detection sensitivity and good in selectivity.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 S protein detection method
PendingCN111273006ASolve the problem of inability to effectively detect the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2S proteinFast preparationImmunoassaysAngiotensin-converting enzymeProtein detection
The invention discloses a novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 S protein detection method. SARS-CoV-2 virus depends on spike protein on the surface to be combined with angiotensin converting enzyme 2 on the surface of a cell so as to enter the cell; according to the method, raw materials commonly used in chemiluminescence immunoassay and ACE2 are easy to purchase from the market, the biotin labeling and the alkaline phosphatase labeling are rapid, the reagent for SARS-CoV-2 S protein detection can be rapidly prepared, and the positive coincidence rate, the negative coincidence rate and the total coincidence rate are high compared with the SARS-CoV-2 fluorescence quantitative PCR result.
Owner:SICHUAN ORIENTER BIOLOGICAL TECH
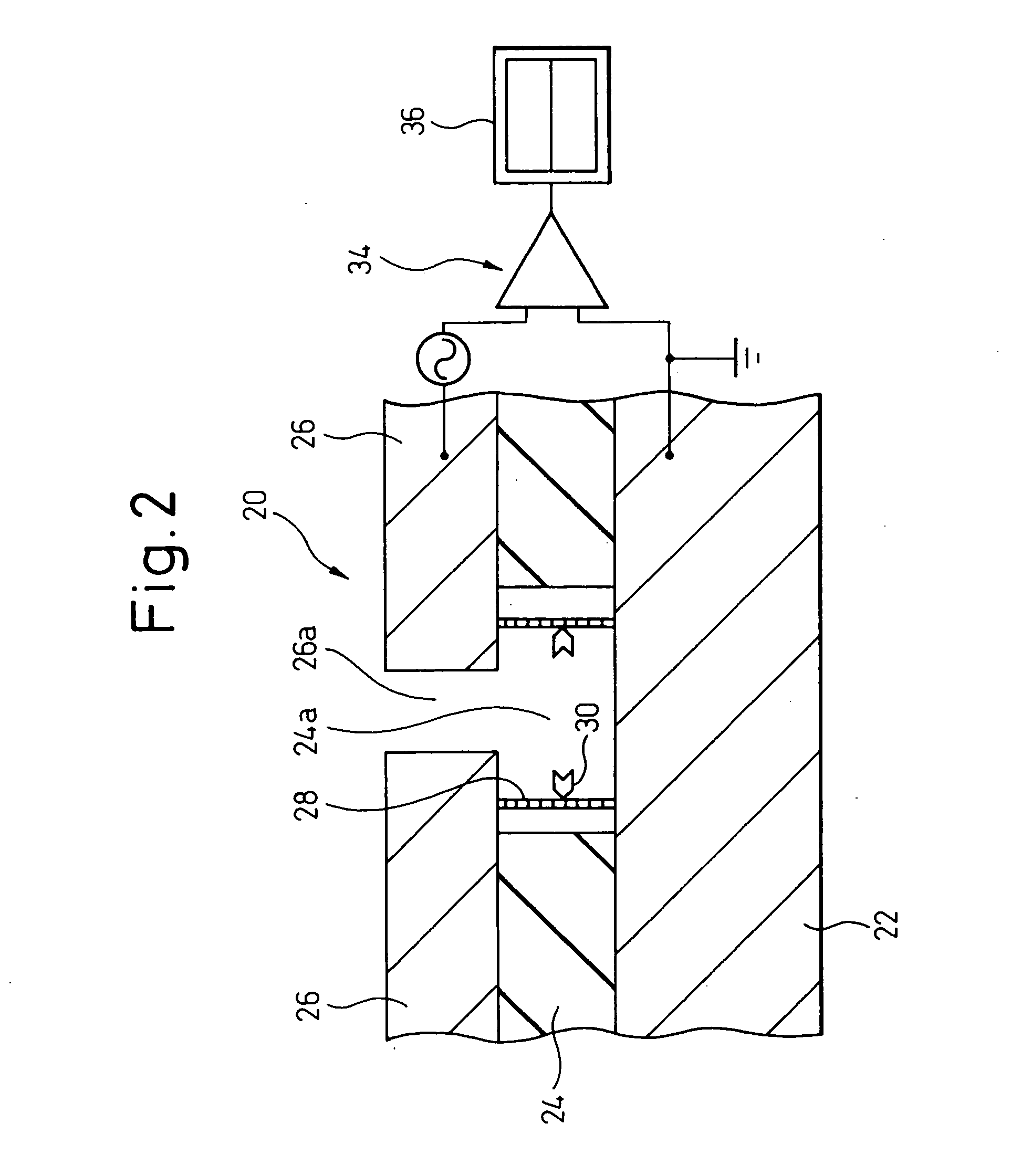
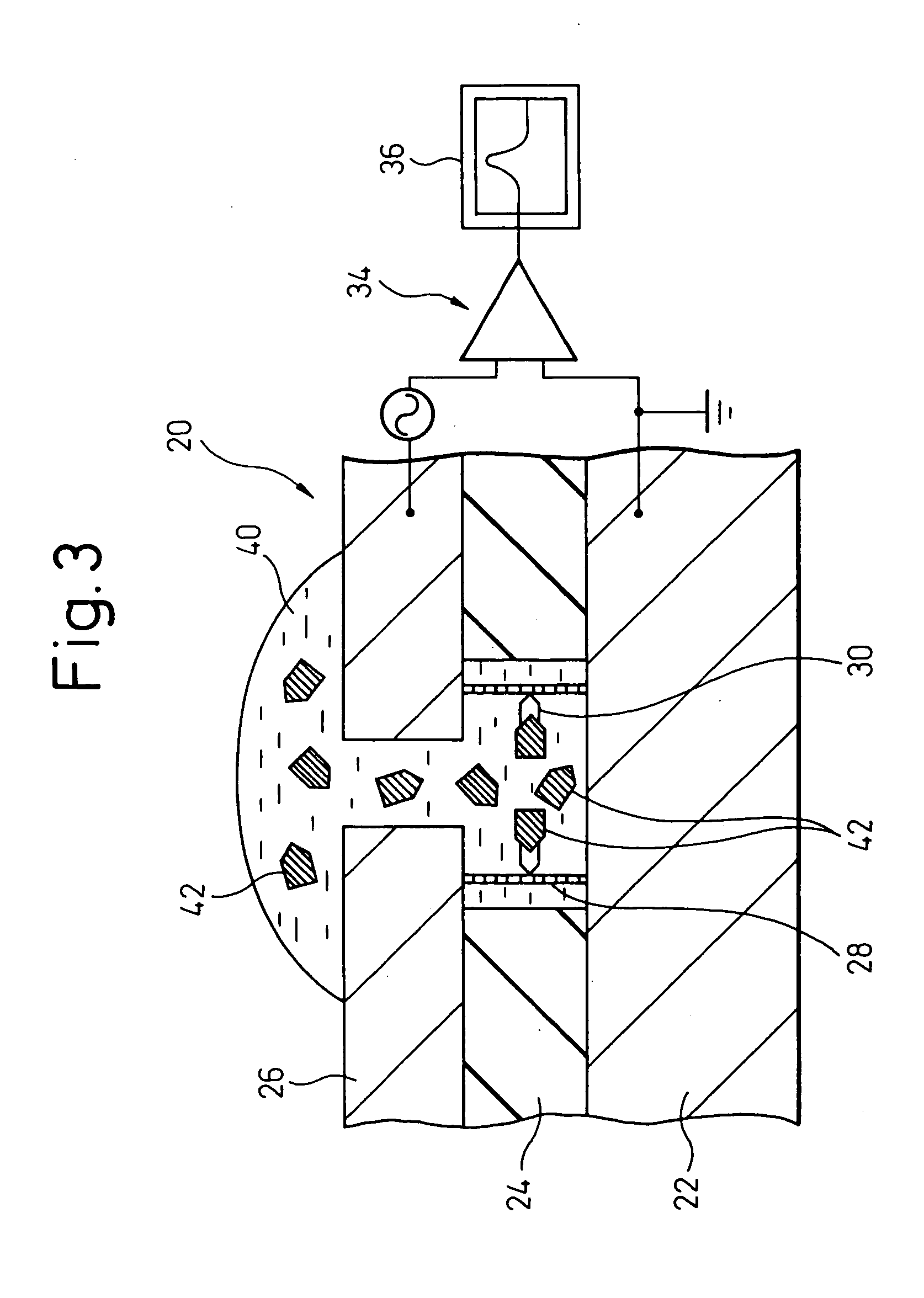
Cavity electrode structure, and sensor and protein detection device using the same
InactiveUS20050164371A1Suitable for handlingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein detectionProtein target
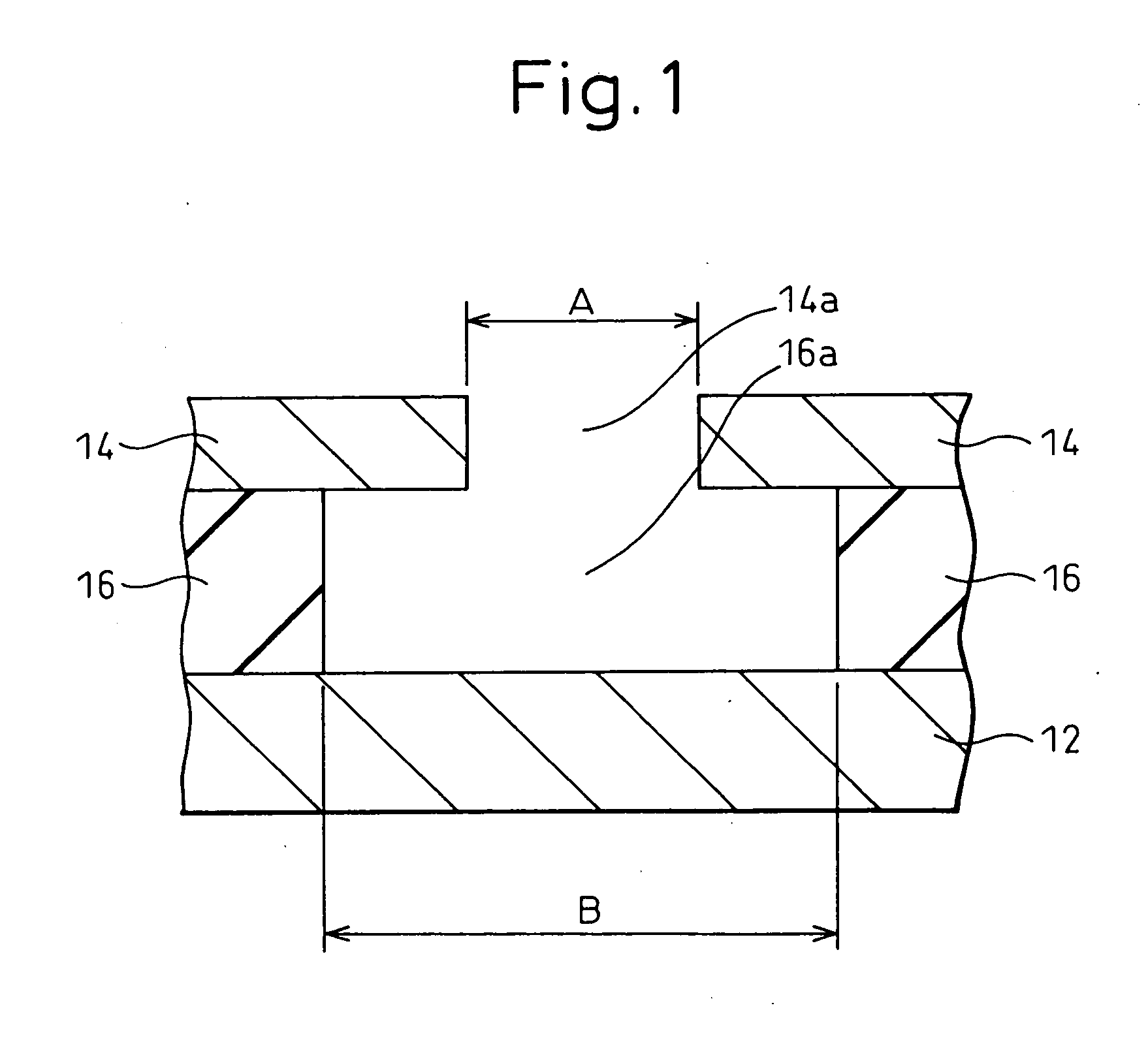
A cavity electrode structure, which is provided with a pair of opposing electrodes having a precisely formed narrow gap, and a sensor and a protein detection device, in which the cavity electrode structure is used, are provided. The cavity electrode structure comprises a first electrode, an insulating layer located on this first electrode and having a through hole that partially exposes the first electrode, and a second electrode opposed to the exposed surface of the first electrode by protruding towards the inside of the through hole of the insulating layer and provided with an opening that leads to the through hole of the insulating layer, the structure having a cavity that is formed by the exposed surface of the first electrode, the inner walls of the through hole of the insulating layer, and the surface of the second electrode that opposes the first electrode. The sensor comprises an electrically conductive bridging member of which one end is fixed to the exposed surface of the first electrode of the aforementioned cavity electrode structure, while the other end is fixed to the opposing surface of the second electrode, and which has a site that specifically binds to a target protein to be detected. The protein detection device uses a bridging member provided with a site that specifically binds to a target protein to be detected.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
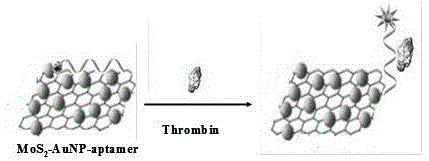
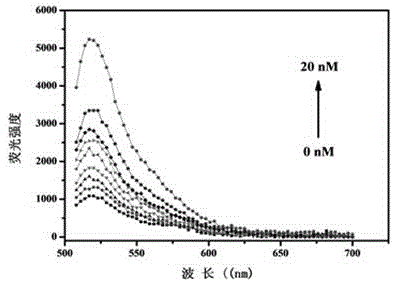
Molybdenum disulfide based sensor as well as preparation method and application thereof
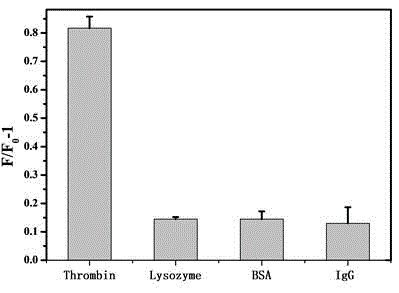
The invention relates to a molybdenum disulfide based sensor as well as a preparation method and an application thereof and belongs to a protein detection method in the biomedical field. According to the technical scheme, the method mainly comprises steps as follows: firstly, an MoS2-AuNP compound is prepared; a nucleotide aptamer of thrombin is synthesized; the synthesized nucleotide aptamer is added to an aqueous solution of MoS2-AuNP, Tween 80 is added, a mixed solution is obtained, reacts for 30 min at the room temperature, then is heated for 2.5 h in a water bath with the temperature of 70 DEG C and is centrifuged at the speed of 10,000 r for 15 min, and then, precipitates are dispersed in a 0.1 M PBS (phosphate buffer solution); and the sensor is prepared. The characteristic that MoS2-AuNP can quench fluorescence is sufficiently utilized, an FAM (carboxyfluorescein)-marked nucleotide aptamer sequence is combined with thrombin specificity, trace detection of thrombin can be realized in a high-sensitivity, rapid and low-cost manner through quenching and recovery of FAM fluorescence, and the actual LOD (limit of detection) of the MoS2-AuNP-nucleotide aptamer sensor to thrombin is increased to 0.4 pM due to addition of Tween 80.
Owner:镇江永晨科技有限公司
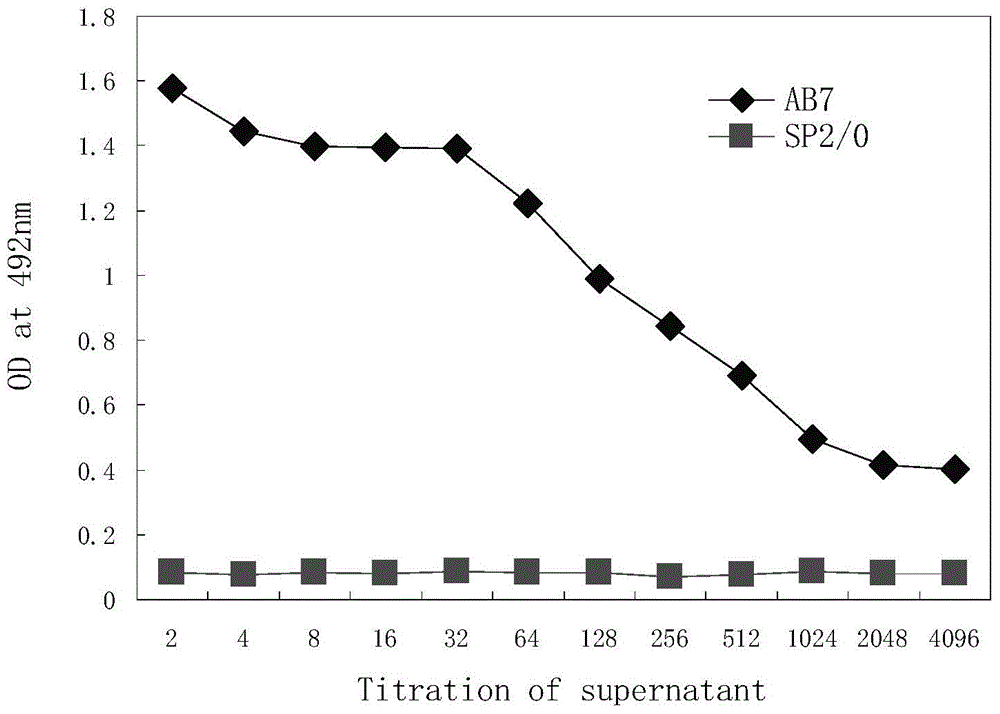
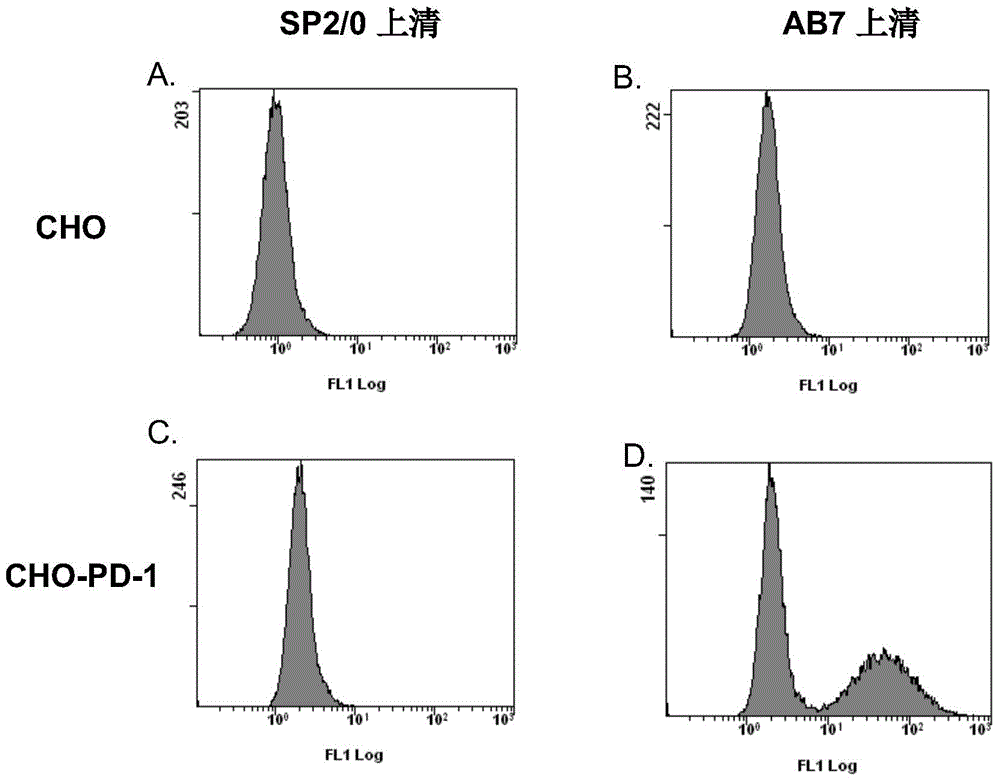
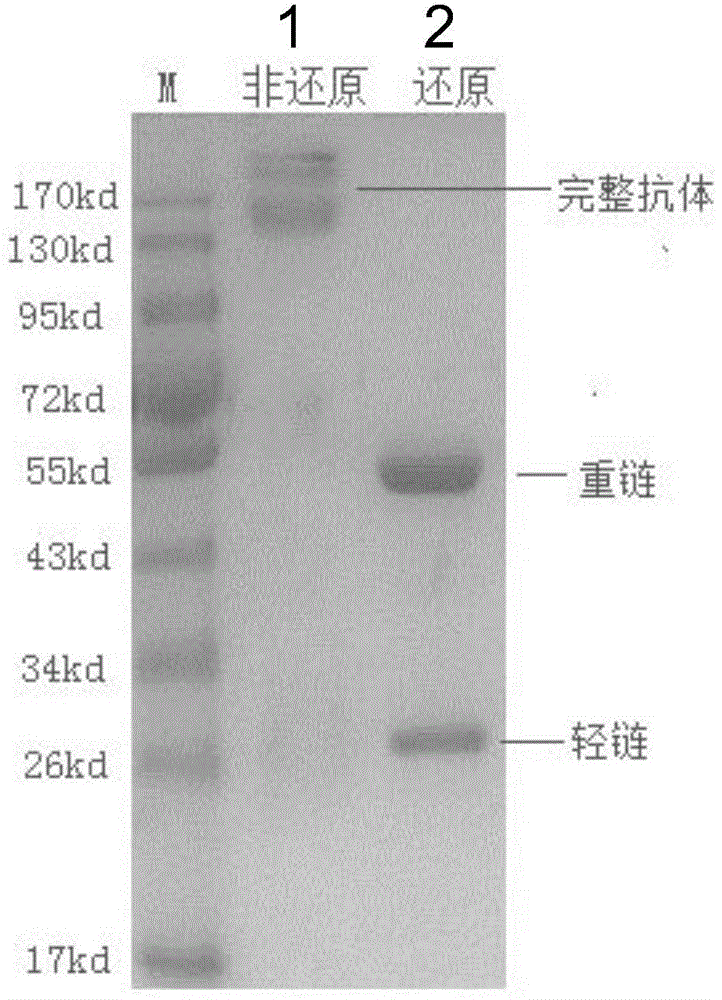
Monoclonal antibody capable of antagonizing and inhibiting bonding of programmed death-1 receptor (PD-1) and ligand thereof as well as encoding sequence and use of monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN104558177AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsProtein detectionHeavy chain
Disclosed in the present invention are a mouse monoclonal antibody for antagonizing and inhibiting the binding of a programmed death-1 (PD-1) to the ligand thereof, and the heavy chain variable region and light chain variable region amino acid sequences thereof. Also disclosed in the present invention is a DNA molecule nucleotide sequence encoding the heavy chain variable region and light chain variable region of the antibody. Also disclosed in the present invention are a method for preparing a human-mouse chimeric antibody of the antibody and derivatives thereof, and the use thereof in PD-1 protein detection.
Owner:ACROIMMUNE BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com