Patents
Literature
4838 results about "Promoter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
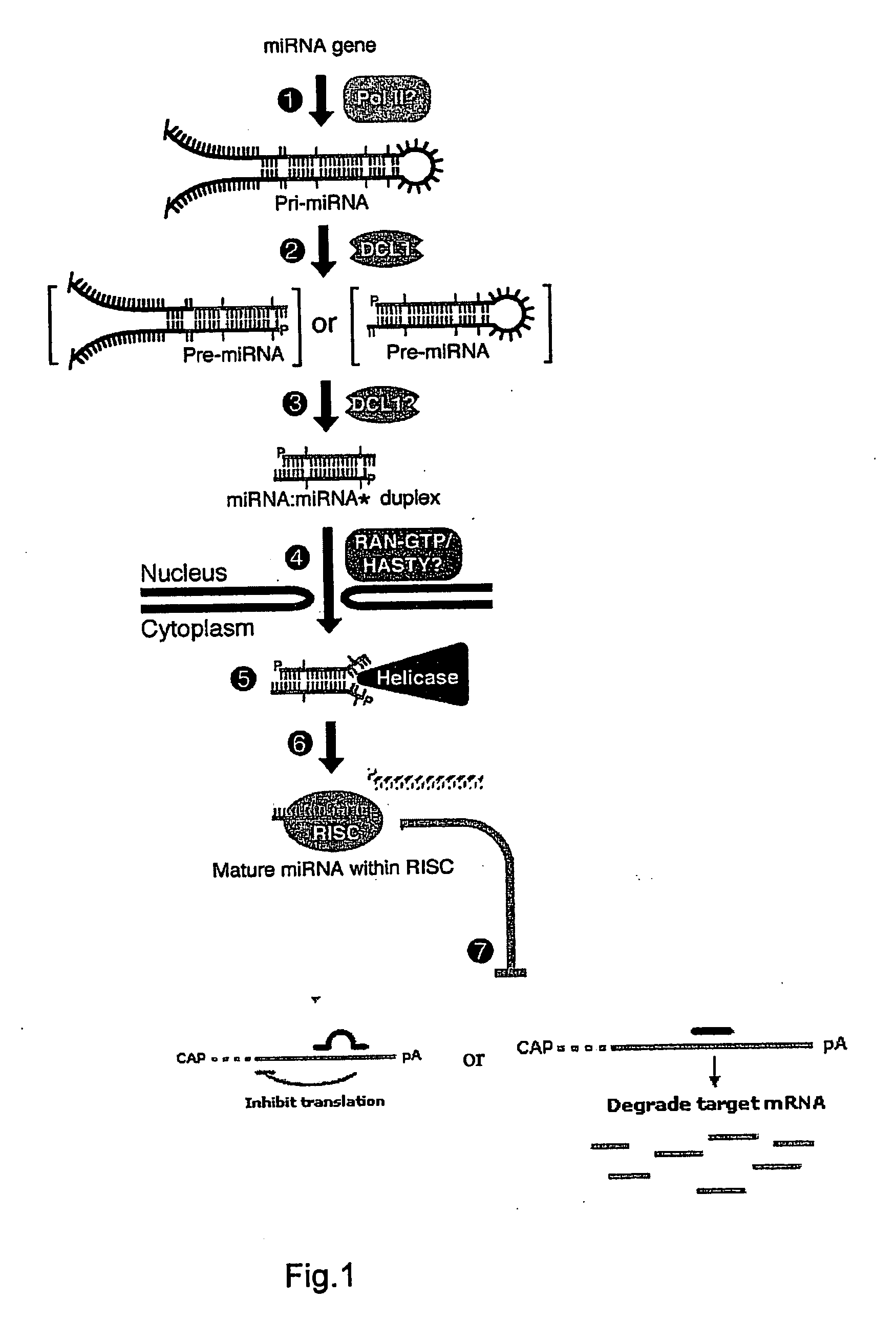
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that leads to initiation of transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand). Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.
Seed specificity highly effective promoter and its application
InactiveCN101063139AReduce adverse effectsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousNucleotide
The invention discloses a special promoter separated from millet, expressing carrier with nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1 host with the expressing carrier and appliance of the promoter, which is characterized by the following: utilizing Tail-PCR (colored body step moving method); getting the special promoter from gene group DNA; possessing nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1; ;linking downstream of the promoter to non-homologous or homologous gene; constructing plant expressing carrier; transferring host plant; driving the downstream gene to high effective and special express goal protein in the seed; realizing genetic modification of plant; or using as effective tool for studying plant and biological reactor.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for linear mRNA amplification
InactiveUS6132997ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntisense RNAReverse transcriptase
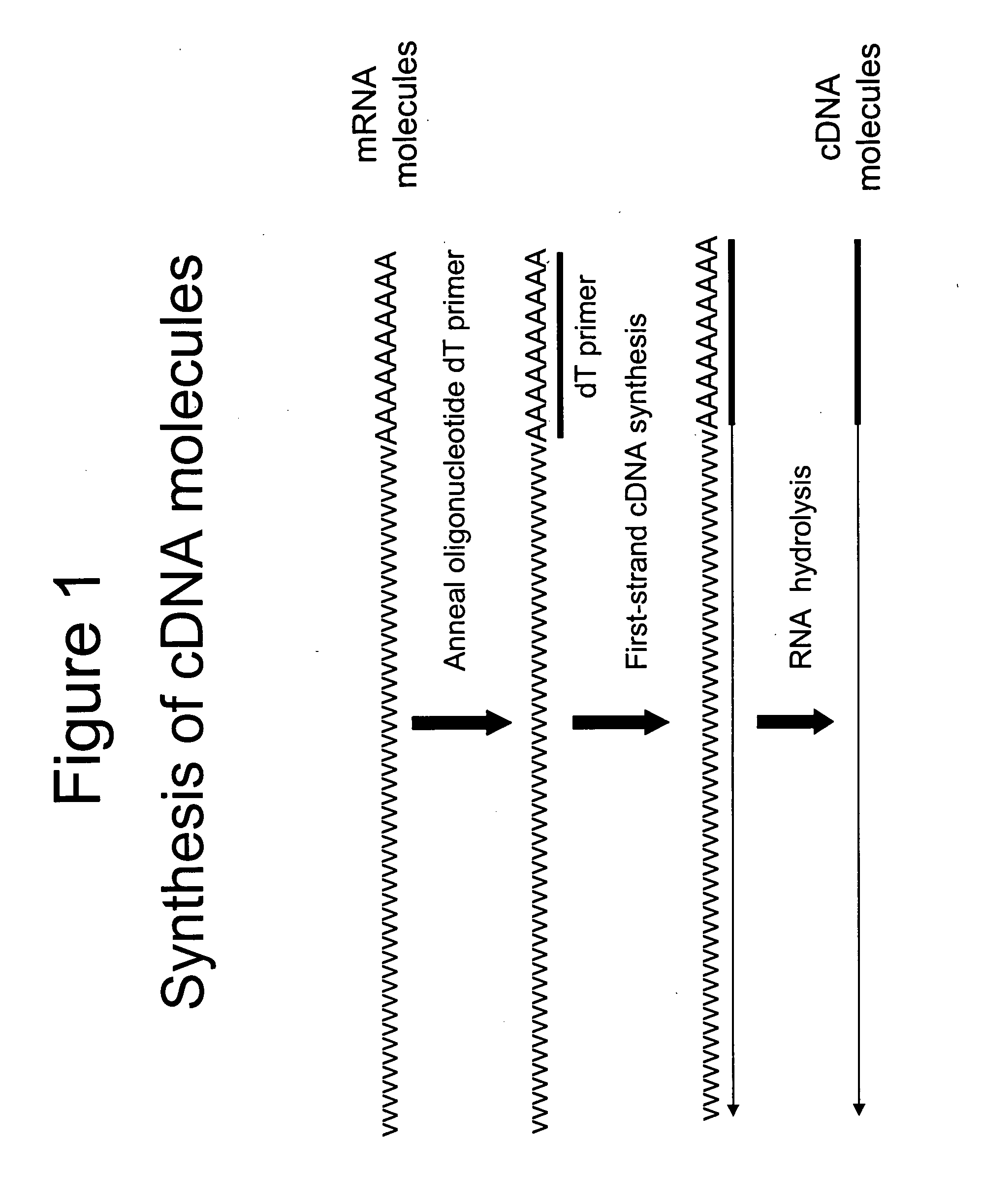
Methods for linearly amplifying mRNA to produce antisense RNA are provided. In the subject methods, mRNA is converted to double-stranded cDNA using a promoter-primer having a poly-dT primer site linked to a promoter sequence so that the resulting double-stranded cDNA is recognized by an RNA polymerase. The resultant double-stranded cDNA is then transcribed into antisense RNA in the presence of a reverse transcriptase that is rendered incapable of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity during this transcription step. The subject methods find use a variety of different applications in which the preparation of linearly amplified amounts of antisense RNA is desired. Also provided are kits for practicing the subject methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Single-primer nucleic acid amplification methods
ActiveUS7374885B2Reduce appearanceHigh levelMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
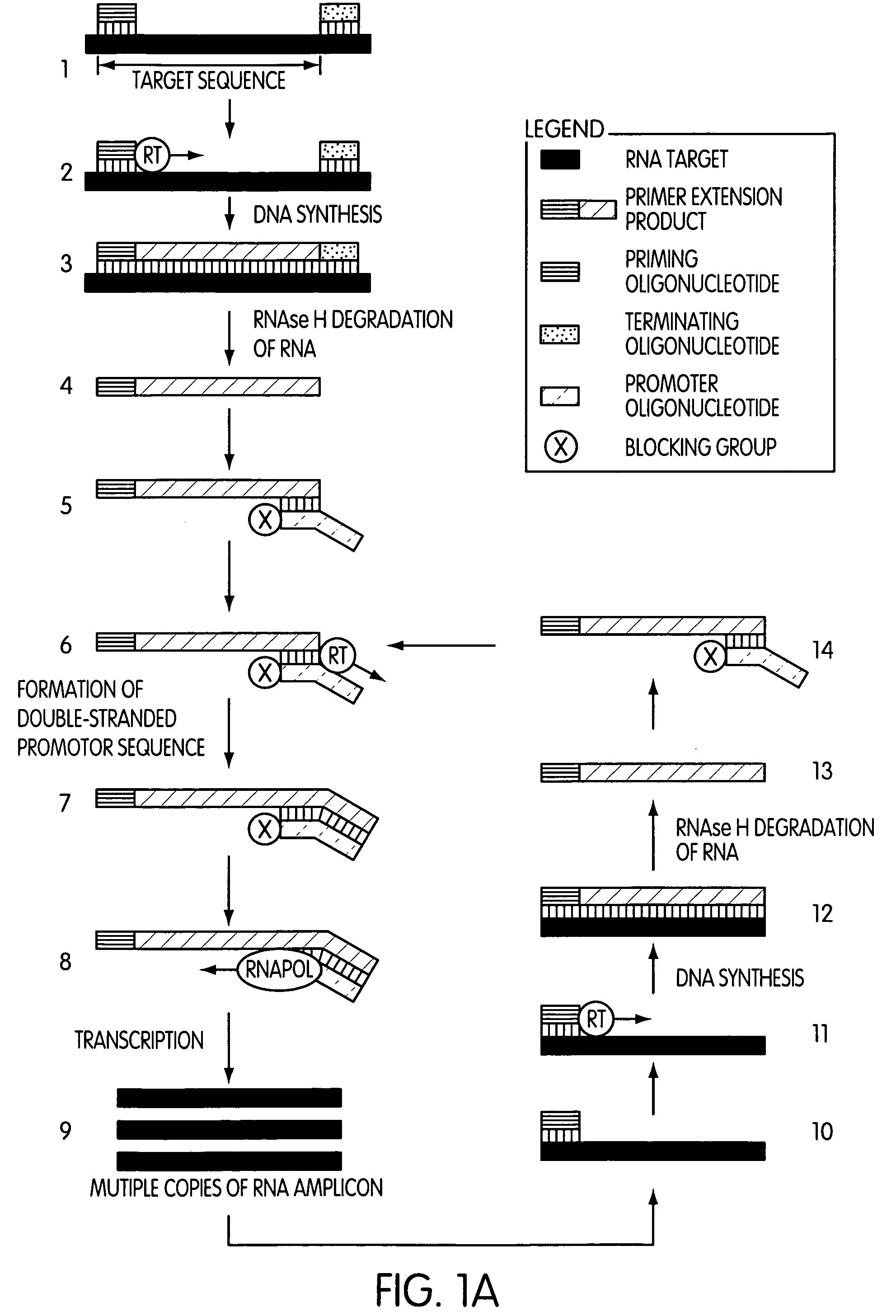
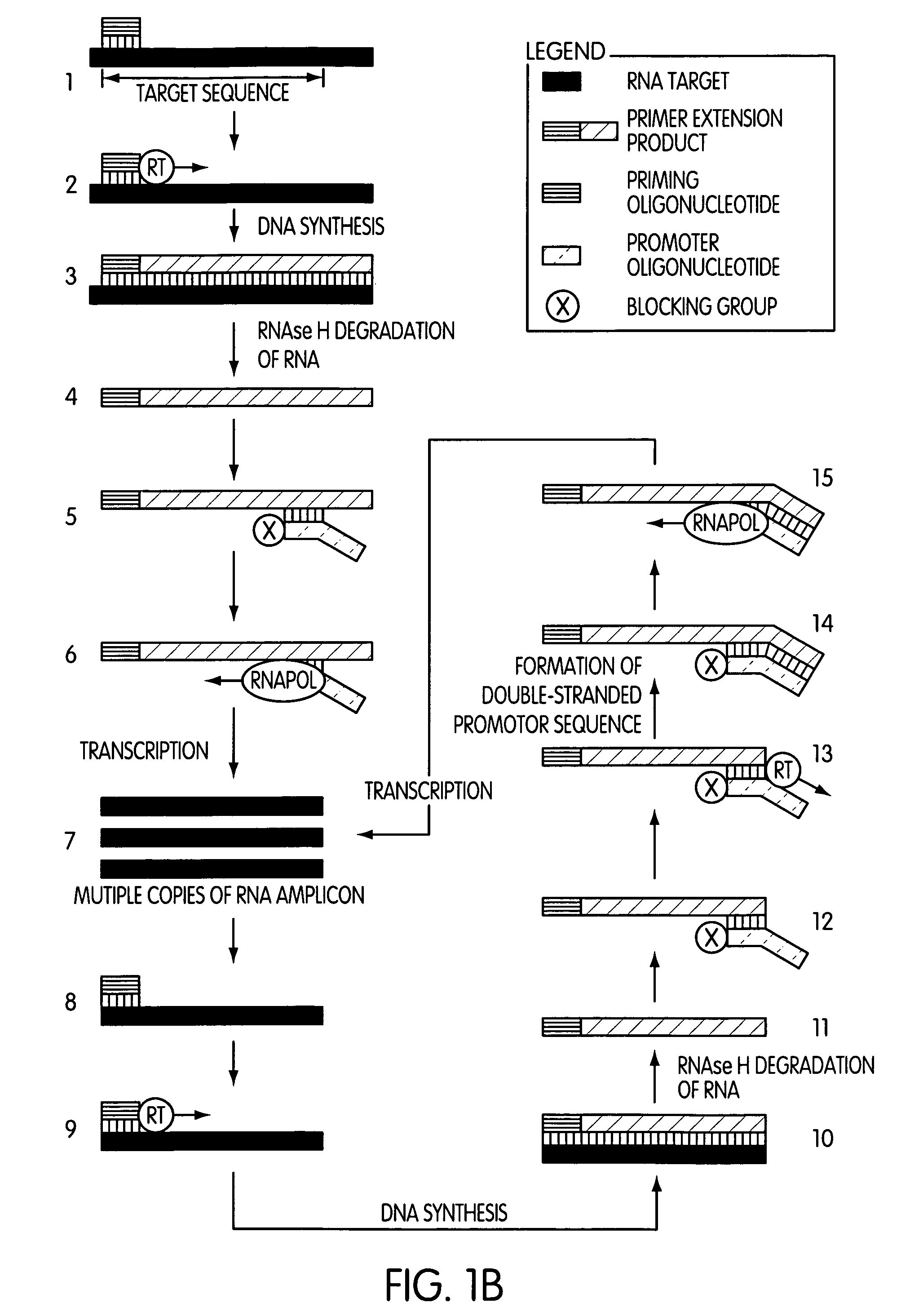
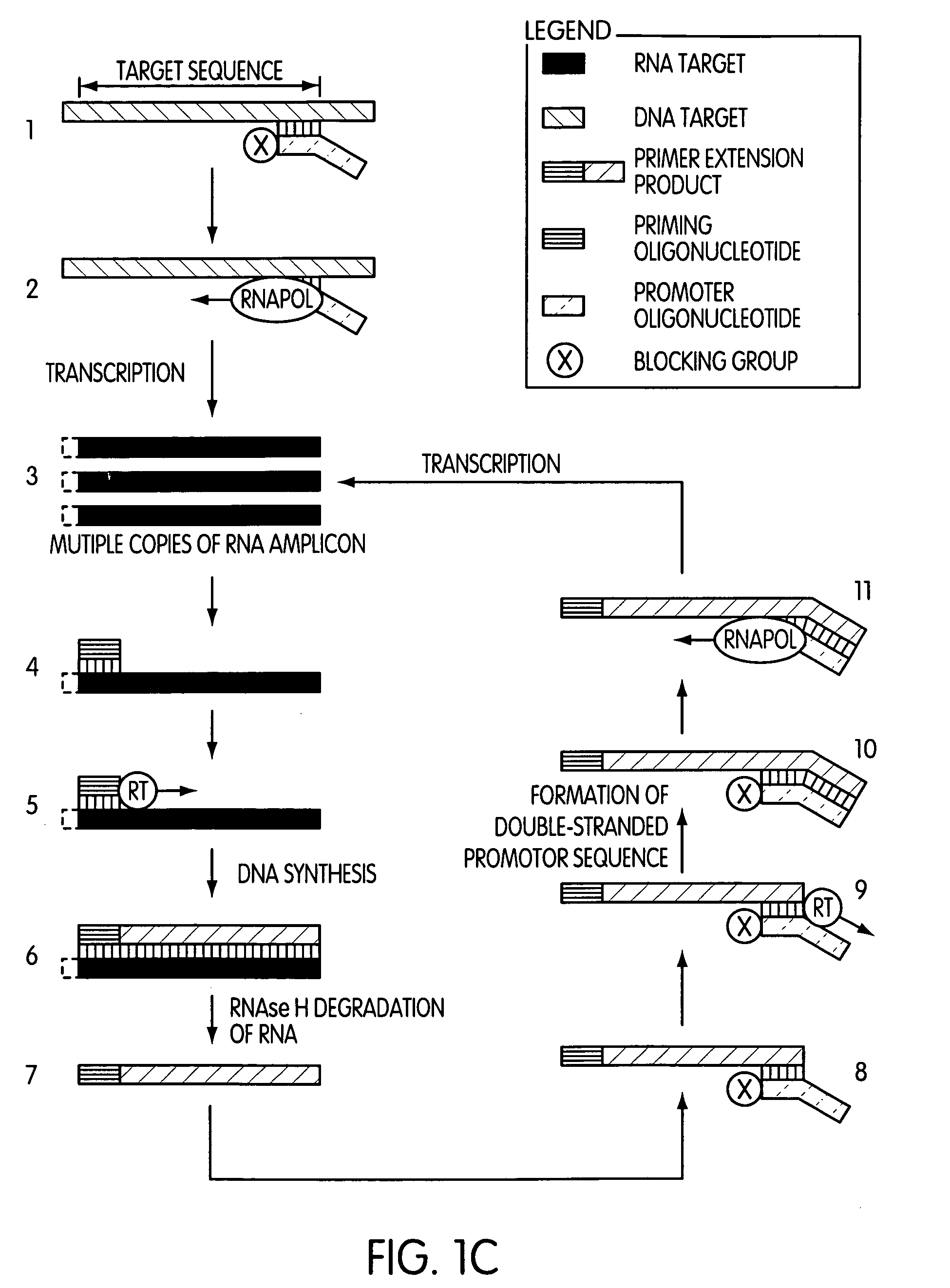
The present invention is directed to novel methods of synthesizing multiple copies of a target nucleic acid sequence which are autocatalytic (i.e., able to cycle automatically without the need to modify reaction conditions such as temperature, pH, or ionic strength and using the product of one cycle in the next one). In particular, the present invention discloses a method of nucleic acid amplification which is robust and efficient, while reducing the appearance of side-products. The method uses only one primer, the “priming oligonucleotide,” a promoter oligonucleotide modified to prevent polymerase extension from its 3′-terminus and, optionally, a means for terminating a primer extension reaction, to amplify RNA or DNA molecules in vitro, while reducing or substantially eliminating the formation of side-products. The method of the present invention minimizes or substantially eliminates the emergence of side-products, thus providing a high level of specificity. Furthermore, the appearance of side-products can complicate the analysis of the amplification reaction by various molecular detection techniques. The present invention minimizes or substantially eliminates this problem, thus providing an enhanced level of sensitivity.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Promoter and uses thereof
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Oligonucleotides for genotyping thymidylate synthase gene
ActiveUS20070031829A1Sensitive and convenient detectionEasy to aimSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGenomic DNA
Oligonucleotides for genotyping the thymidylate synthase gene are provided. The number of tandem repeats in the promoter region of the thymidylate synthase gene can be identified based on the hybridization of an oligonucleotide of the invention to the genomic DNA of a subject. Therefore, the genotype of the thymidylate synthase gene can be identified based on the number of tandem repeats. The genotype relates to the responsiveness of a subject towards an antitumor agent.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
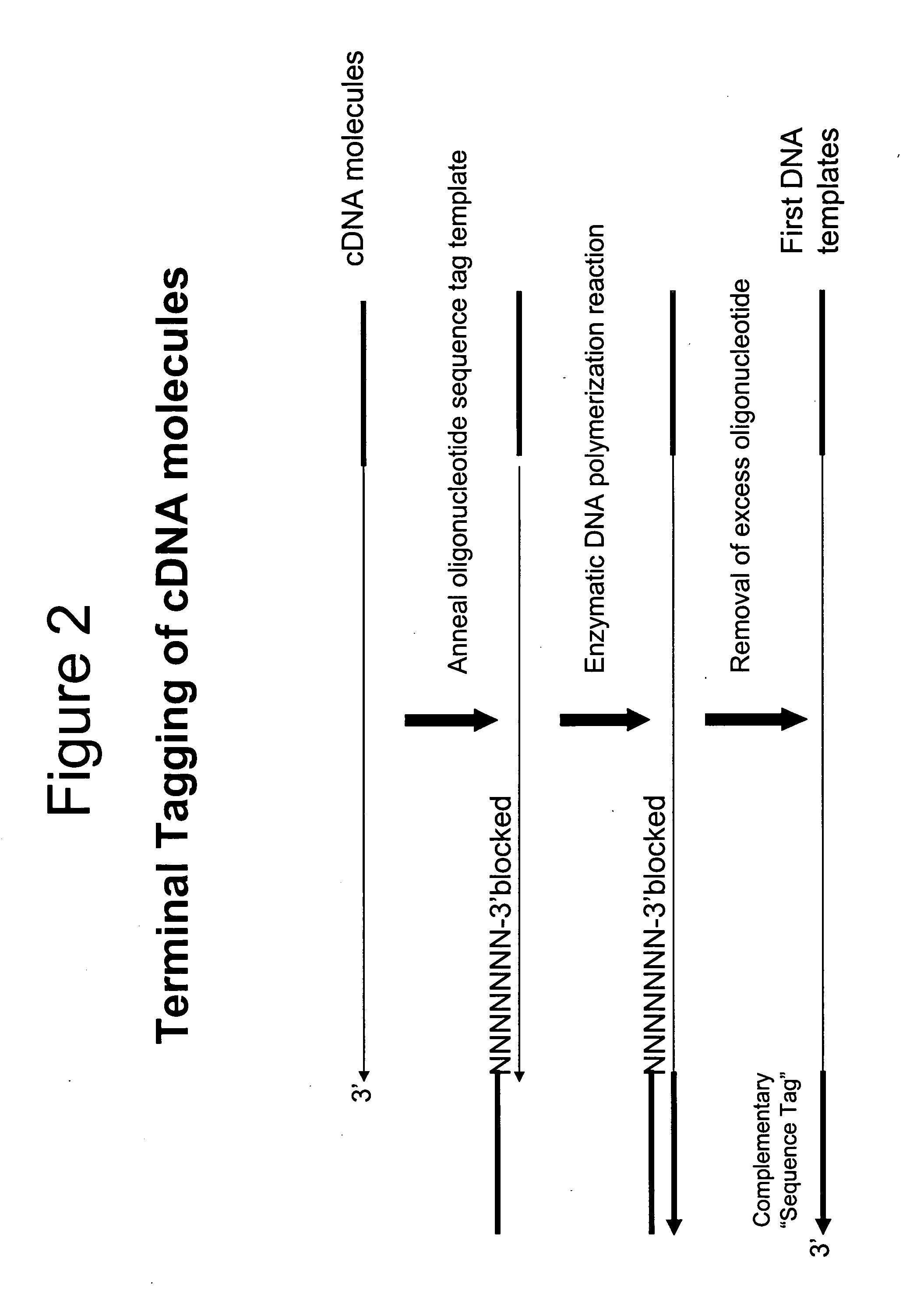
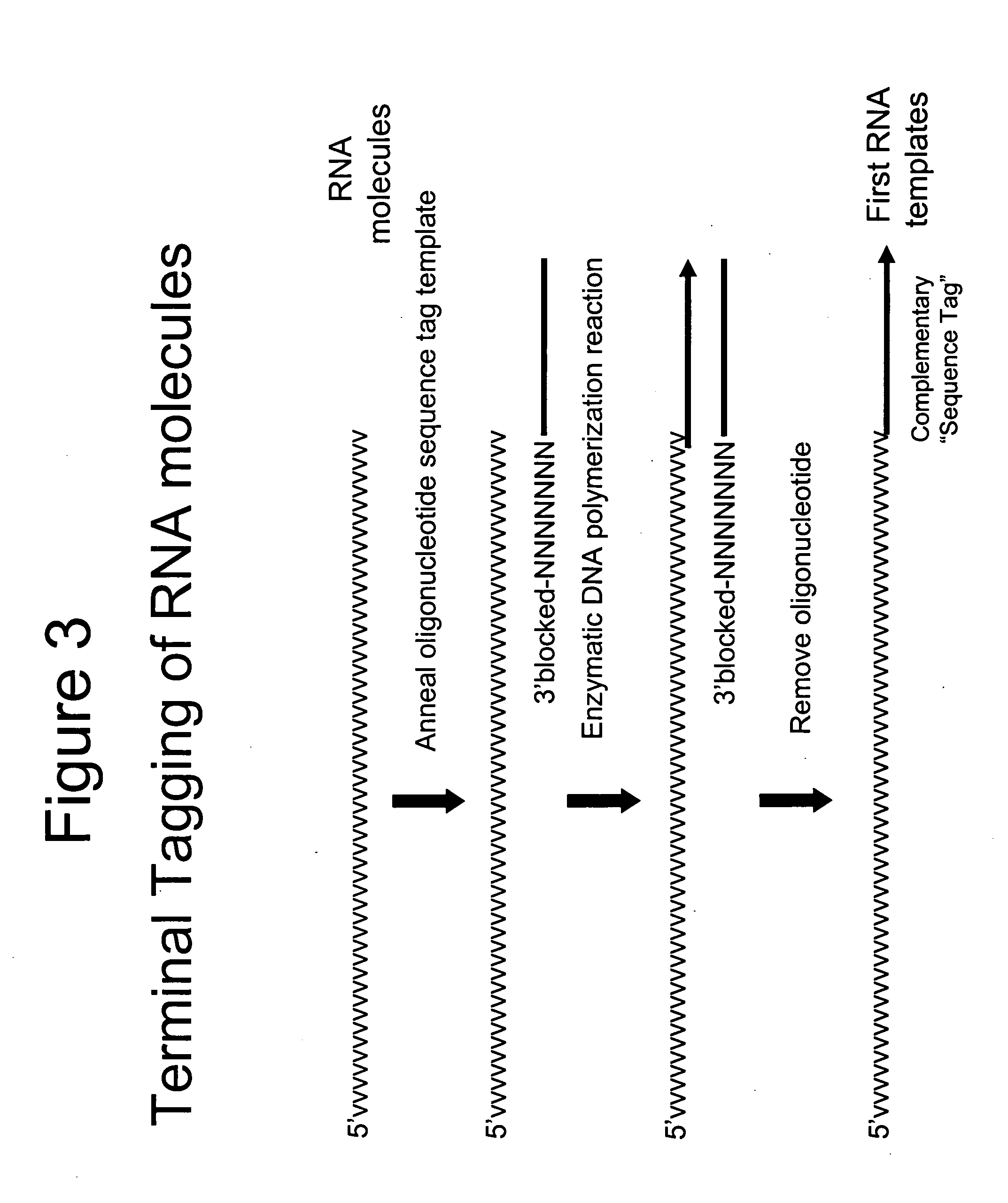
Selective terminal tagging of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20050153333A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationDna amplificationDouble stranded
A method is provided for adding a terminal sequence tag to nucleic acid molecules for use in RNA or DNA amplification. The method involves contacting with a mixture of oligonucleotides, each having a sequence tag template, a random sequence and a blocked 3′ terminus, under conditions such that, the random sequence anneals with the nucleic acid molecules and the nucleic acid molecules are extended using the sequence tag template as template. For synthesis of RNA from DNA molecules having terminal sequence tags, the method includes forming DNA templates having a double stranded promoter sequence and synthesizing RNA from the DNA templates. For amplification of sequences from DNA molecules having terminal sequence tags, the method includes forming DNA templates by extension of one primer having a sequence that is complementary to the terminal sequence tag and another primer having a sequence that is derived form one of the DNA molecules.
Owner:EPICENT BIOTECH
Genomic plant sequences and uses thereof
The present invention discloses rice genomic promoter sequences. The promoters are particularly suited for use in rice and other cereal crops. Methods of modifying, producing, and using the promoters are also disclosed. The invention further discloses compositions, transformed host cells, transgenic plants, and seeds containing the rice genomic promoter sequences, and methods for preparing and using the same.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Chimeric gene for the transformation of plants
InactiveUSRE37287E1Most efficientPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesPolyadenylationIncreased tolerance
Chimeric gene for conferring to plants an increased tolerance to a herbicide having as its target EPSPS comprises, in the direction of transcription, a promoter region, a transit peptide region, a coding sequence for glyphosate tolerance and a polyandenylation signal region, wherein the transit peptide region comprises, in the direction of translation, at least one transit peptide of a plant gene encoding a plastid-localized enzyme and then a second transit peptide of a plant gene encoding, a plastid-localized enzyme. Production of glyphosate-tolerant plants is disclosed.
Owner:BAYER SAS
Modulation of gene expression by oligomers targeted to chromosomal DNA
Synthesis of a target transcript of a gene is selectively increased in a mammalian cell by contacting the cell with a polynucleotide oligomer of 12-28 bases complementary to a region within a target promoter of the gene under conditions whereby the oligomer selectively increases synthesis of the target transcript.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
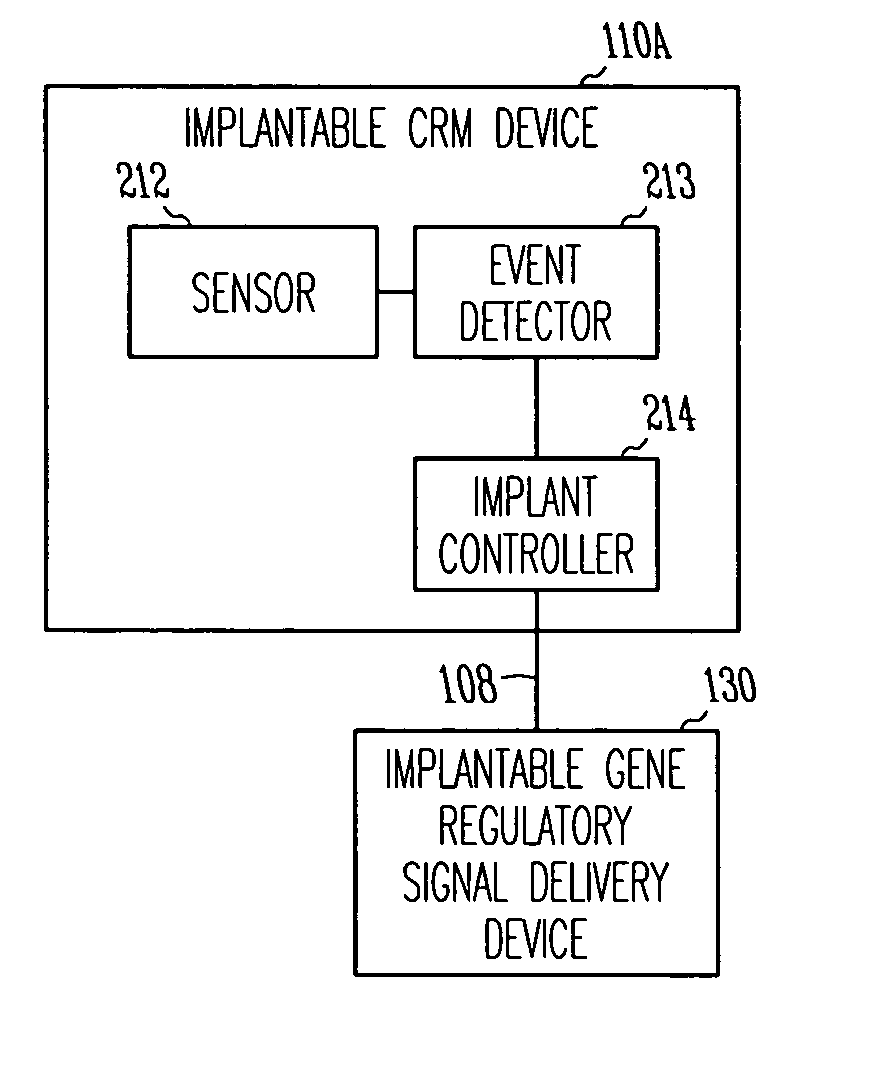
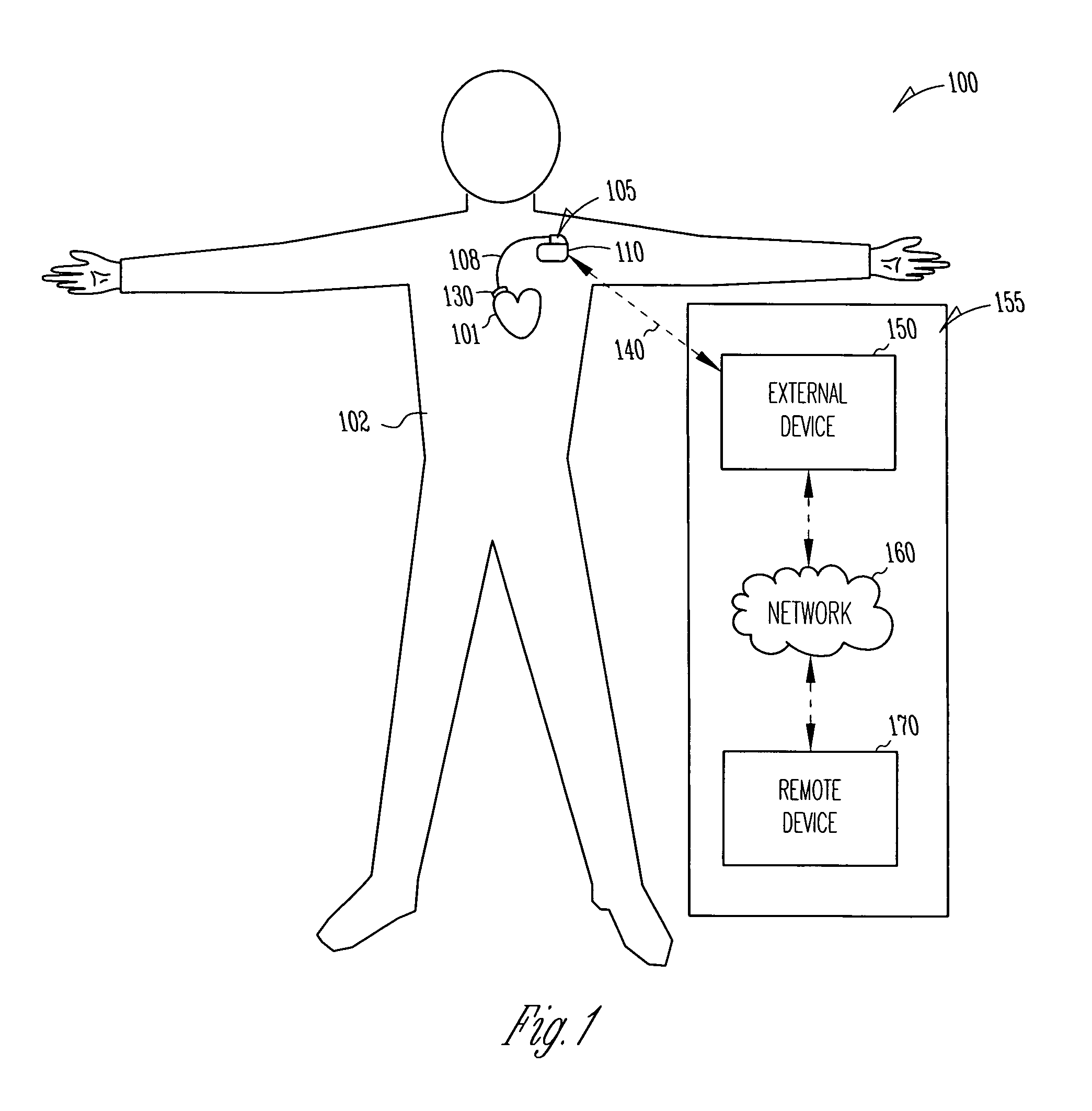
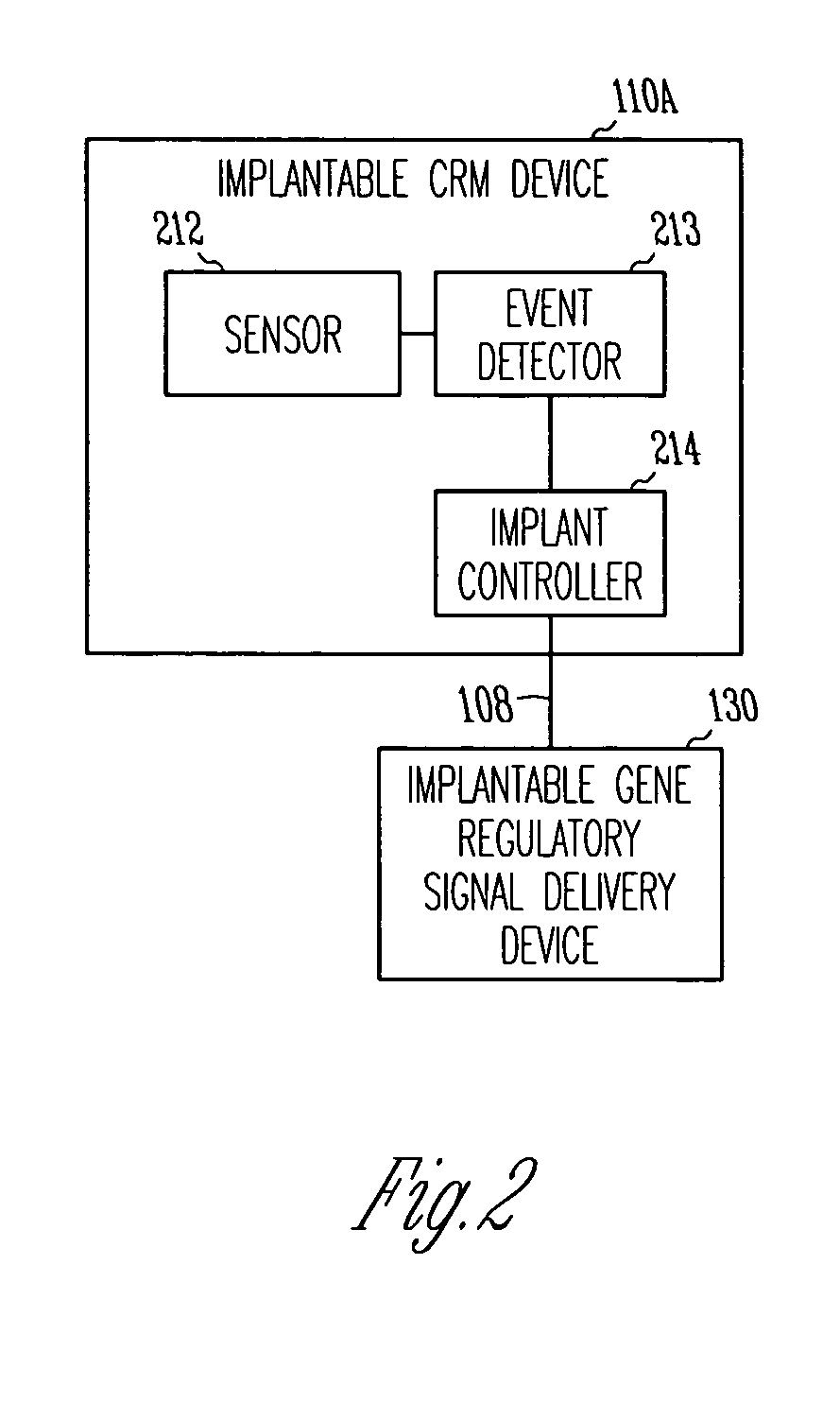
Method and apparatus for device controlled gene expression
InactiveUS20050192637A1Readily be titratedPreventing and inhibiting and cardiac conditionGenetic material ingredientsHeart defibrillatorsForms of energyRegulator gene
A gene regulatory system controls gene therapy by emitting one or more forms of energy that regulate gene expression by triggering promoters. The system includes a sensor to sense a signal indicative of a need for the gene therapy as well as responses to the gene therapy. The regulation of the gene expression is controlled based on the sensed signal and / or a user command. In one embodiment, the system delivers one or more electrical therapies in conjunction with the gene therapy.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
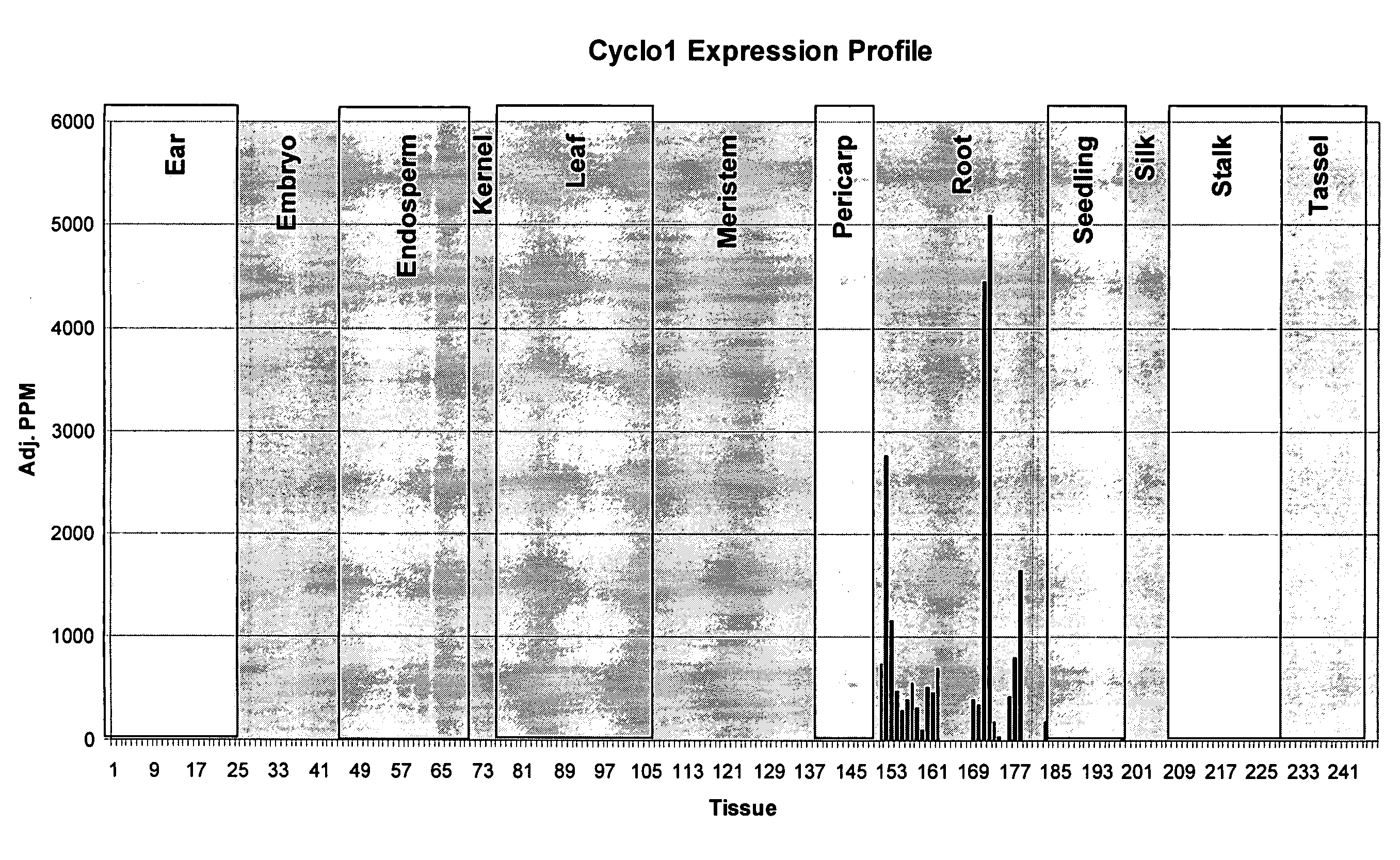
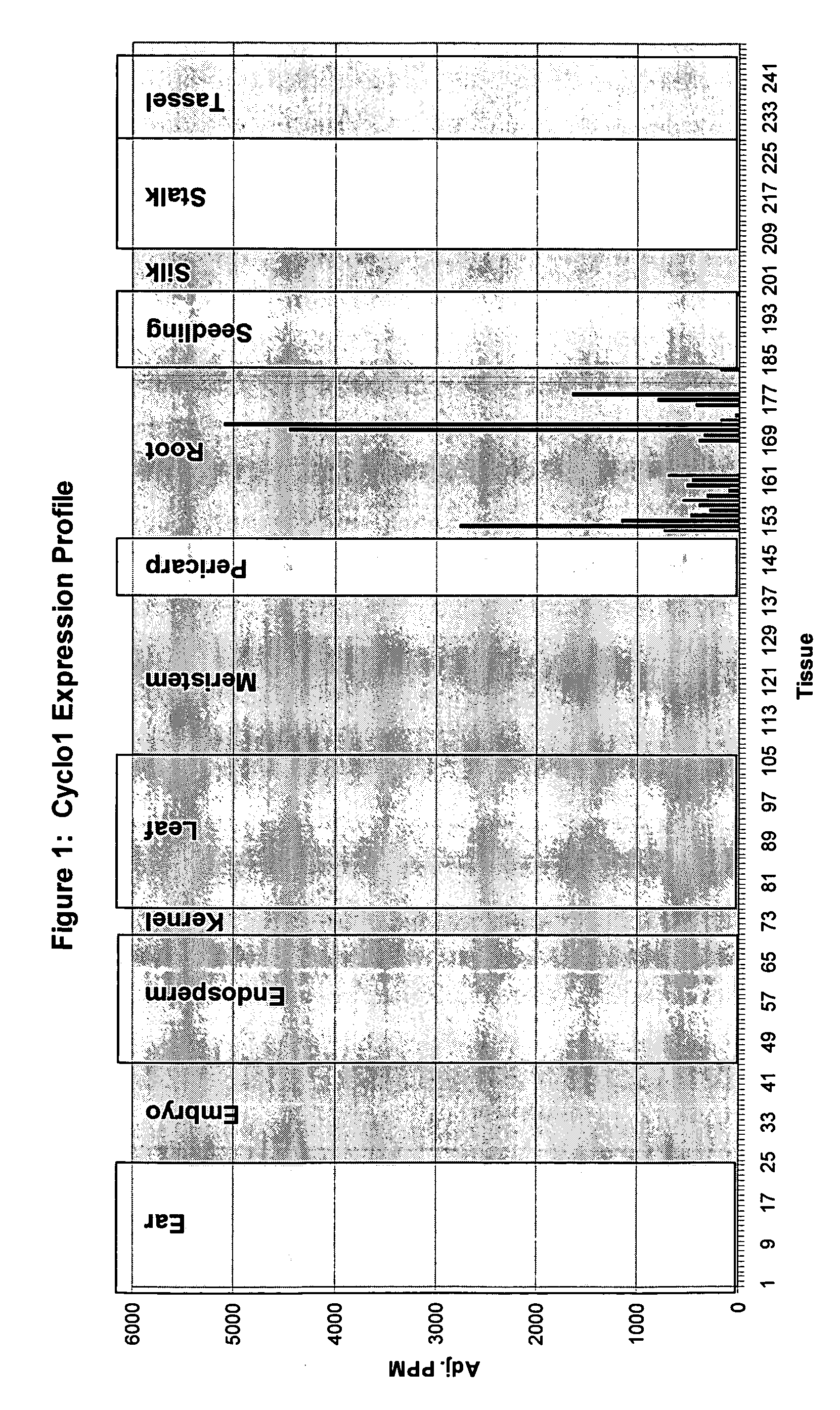
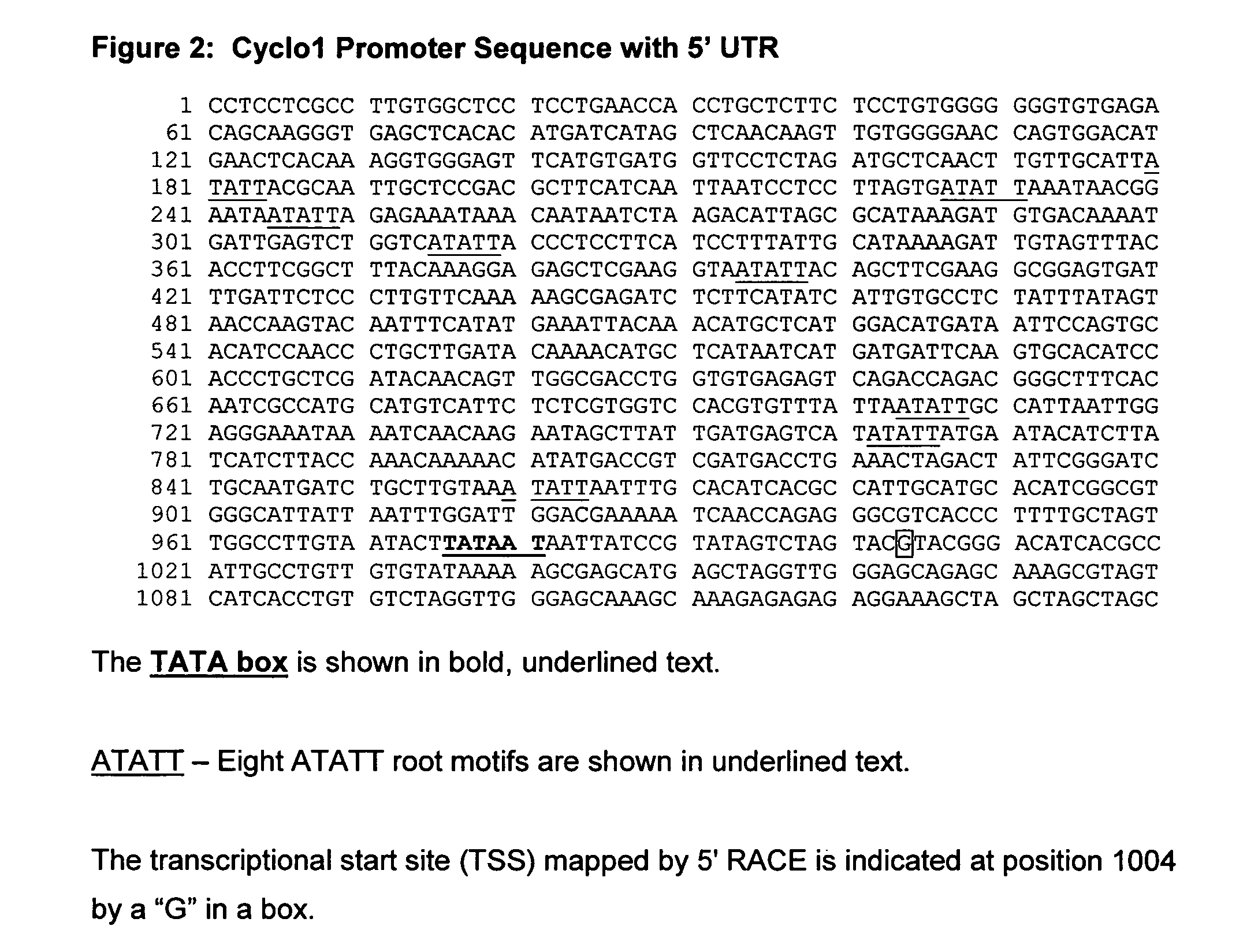
Maize Cyclo1 gene and promoter
ActiveUS20060156439A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The present invention provides compositions and methods for regulating expression of heterologous nucleotide sequences in a plant. Compositions include a novel nucleotide sequence for a root-preferred promoter for the gene encoding Cyclo1. A method for expressing a heterologous nucleotide sequence in a plant using the promoter sequences disclosed herein is provided. The method comprises stabling incorporating into the genome of a plant cell a nucleotide sequence operably linked to the root-preferred promoter of the present invention and regenerating a stably transformed plant that expresses the nucleotide sequence. The present invention also relates to isolated nucleic acids encoding plant cyclotides. The invention relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the plant cyclotides, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in the production of altered levels of plant cyclotides in a transformed host cell.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Improved Methods Controlling Gene Expression
The present invention is in the field of genetics, especially plant genetics, and provides agents capable of controlling gene expression. The present invention specifically provides sequences of naturally occurring, tissue-specifically expressed microRNAs. The invention further provides for transgenic expression constructs comprising sequences encoding said microRNAs. By incorporation of the microRNA encoding sequence the expression from said expression construct is specifically silenced in the tissue where the naturally occurring microRNA is naturally expressed. Thereby the expression profile resulting from the promoter is modulated and leakiness is reduced. The invention further provides for a method for modulating transgenic expression by incorporating sequences encoding said microRNAs into transgenic expression constructs. The compositions and methods of the invention can be used to enhance performance of agricultural relevant crops and for therapy, prophylaxis, research and diagnostics in diseases and disorders, which afflict mammalian species.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Compositions and methods for administering Borrelia DNA
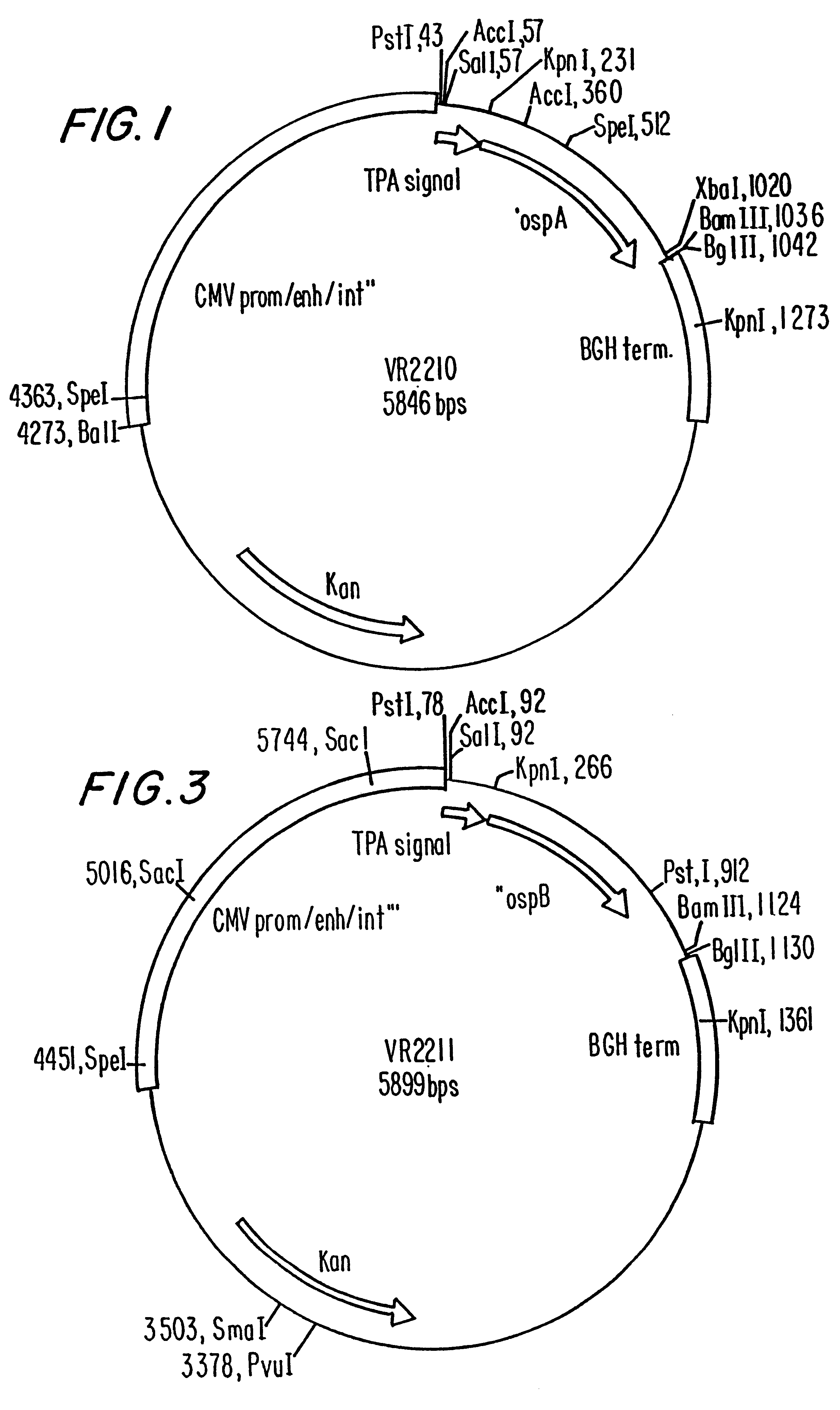
Disclosed is a vaccine against Lyme Disease or its causative agent Borrelia burgdorferi (sensu stricto or sensu lato) containing a plasmid a DNA encoding a promoter for driving expression in a mammalian cell, DNA encoding a leader peptide for facilitating secretion / release of a prokaryotic protein sequence from a mammalian cell, a DNA encoding Borrelia OspA or OspB, and a DNA encoding a terminator. Disclosed too is an immunogenic composition against Lyme Disease or its causative agent Borrelia burgdorferi (sensu stricto or sensu lato) containing a plasmid comprising a DNA encoding a promoter for driving expression in a mammalian cell, DNA encoding a leader peptide for facilitating secretion / release of a prokaryotic protein sequence from a mammalian cell, a DNA encoding a Borrelia OspC, and a DNA encoding a terminator. And, methods for making and using such vaccines and the immunogenic composition are also disclosed.
Owner:PASTEUR MERIEUX SERUMS & VACCINS SA
Plant genes involved in defense against pathogens
InactiveUS20070016976A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesCancer researchPlant genes
Methods to identify genes, the expression of which are altered in response to pathogen infection, are provided, as well as the genes identified thereby and their corresponding promoters.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Plant promoters for use in early seed development
The present invention relates to DNA molecules that encode transcription regulatory regions. Furthermore, this present invention relates to nucleotide sequences encoding transcription regulatory regions that promote early seed enhanced or seed coat enhanced transcription of contiguous nucleotide sequences.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
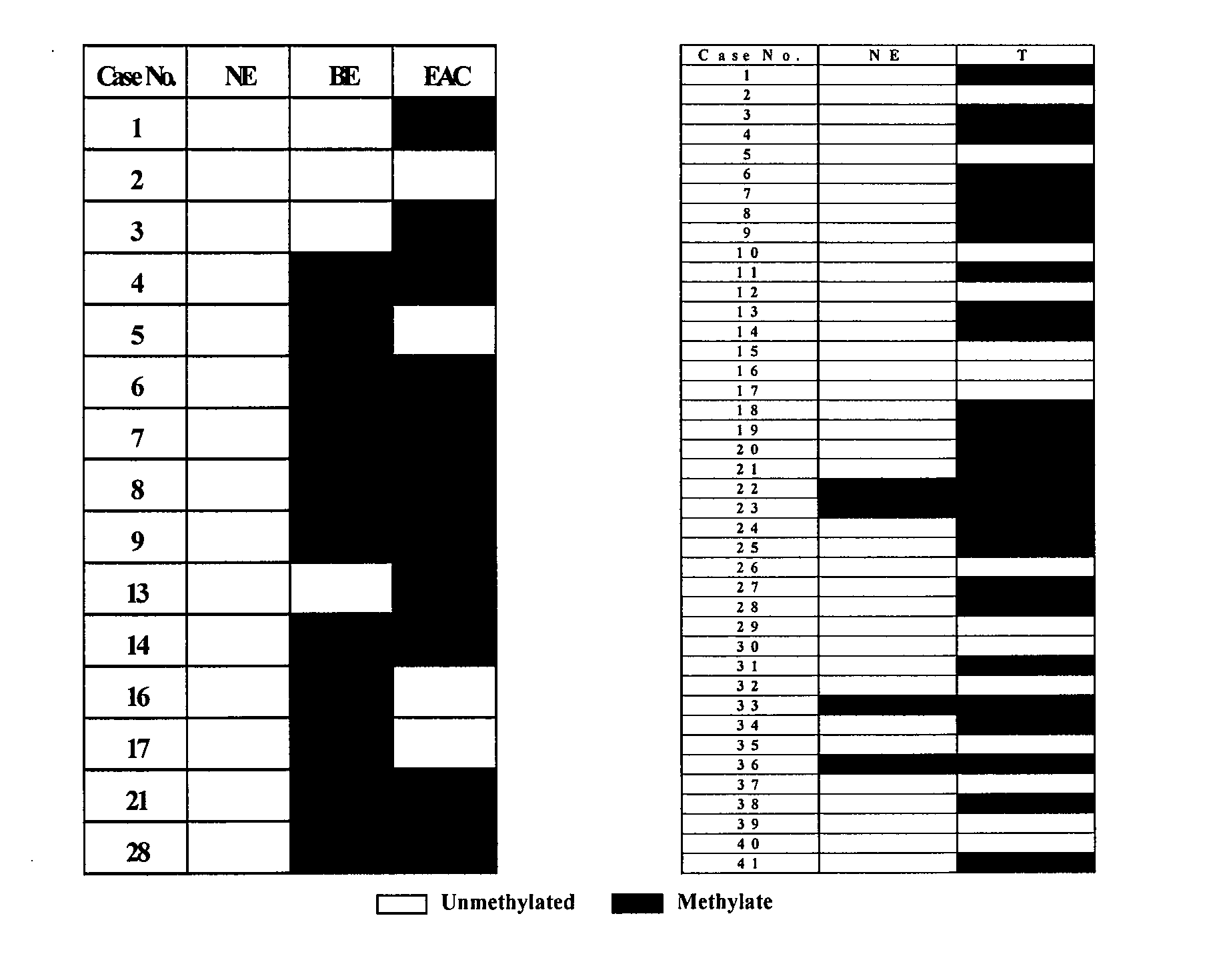
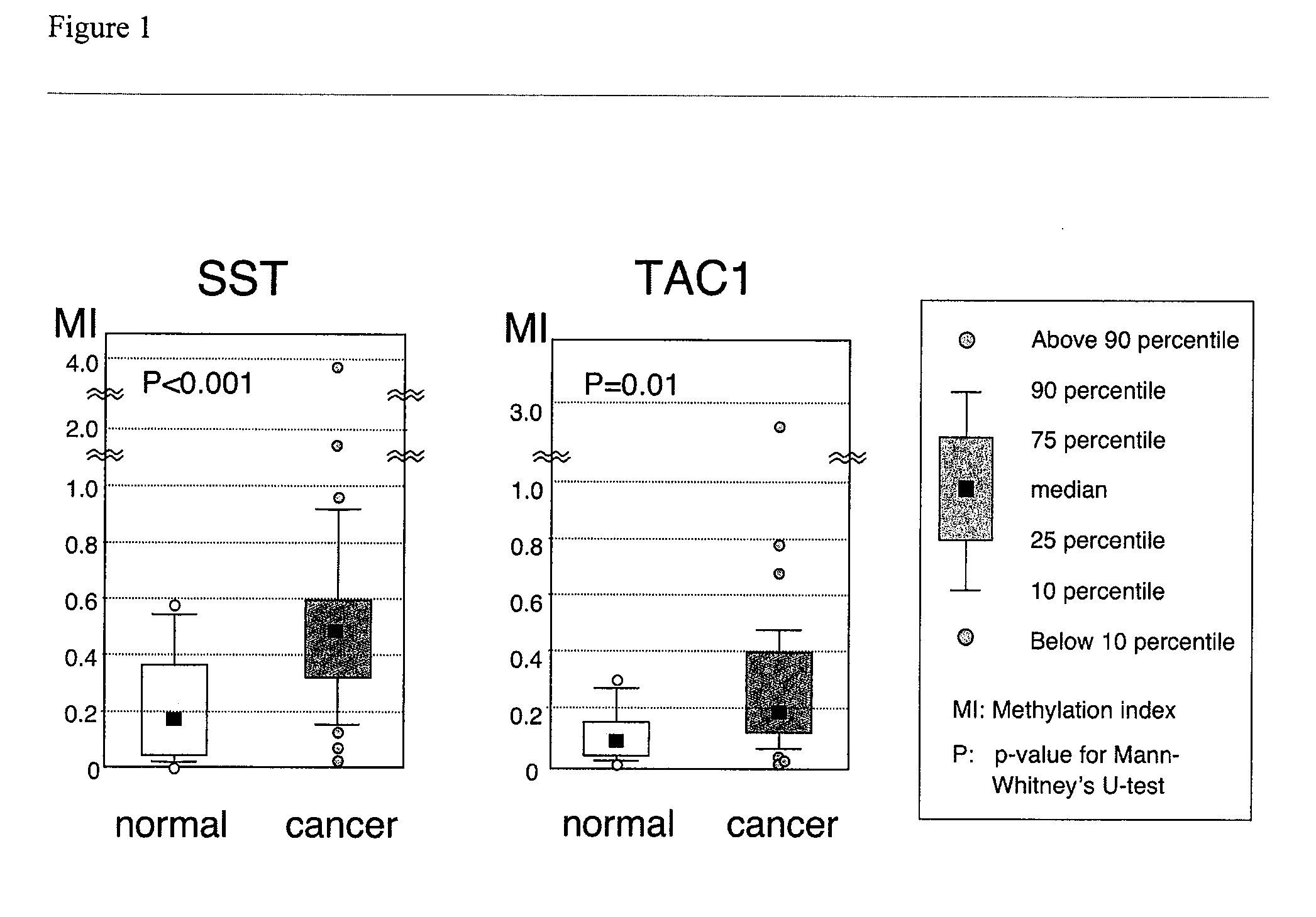
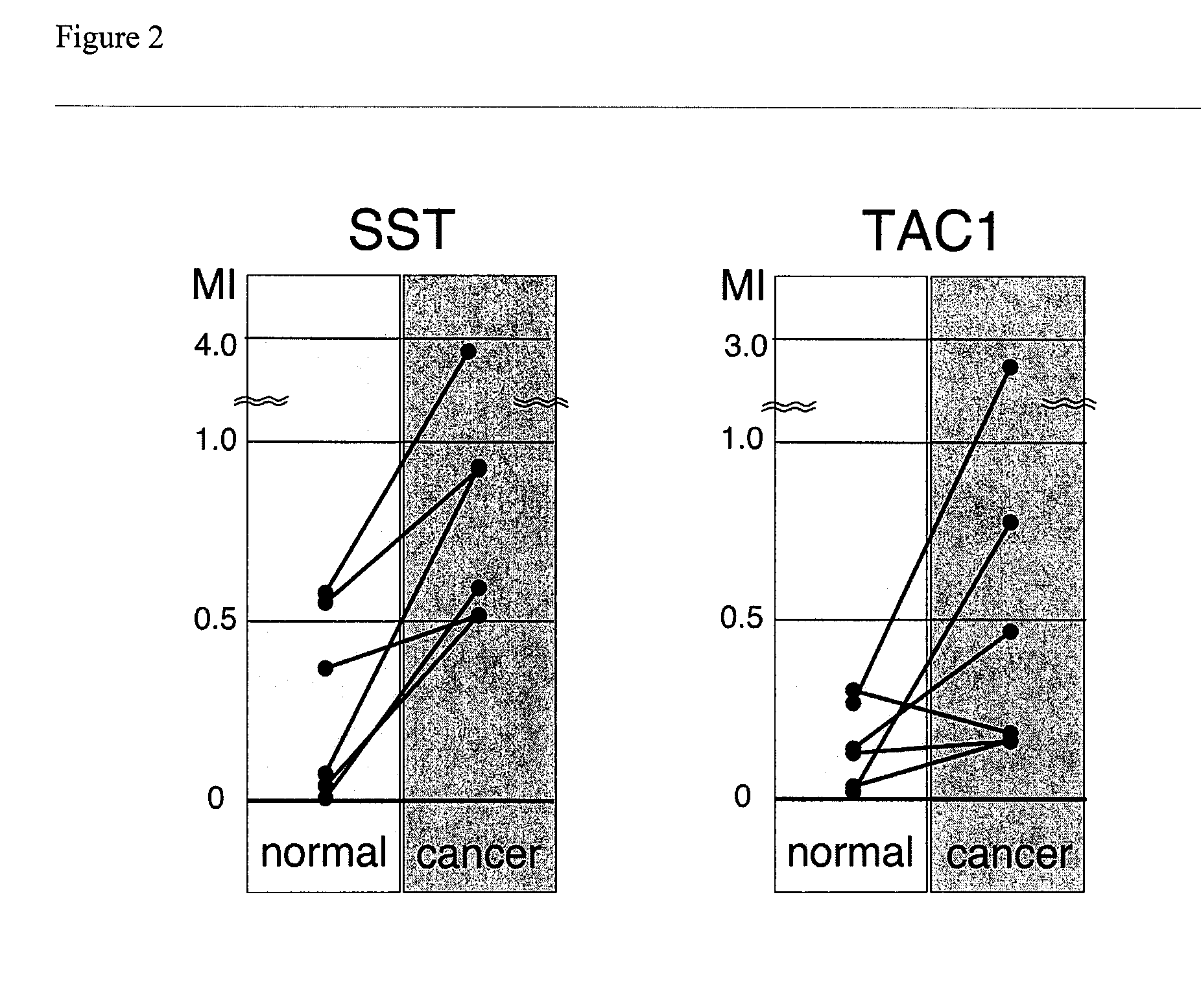
Methylated promoters as biomarkers of colon cancer
The present invention provides methods for identifying or assessing probabilities for having or developing an abnormal condition in subject and for the recurrence of the abnormal condition in the subject after receiving treatment. The method comprises determining the methylation status of at least the tachykinin-1 (TAC1) gene in the subject and comparing this methylation status to normal methylation status. Differences between the methylation status of the TAC1 gene is indicative of the subject developing an abnormal condition or for the development or recurrence of the abnormal conditions after receiving treatment.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Antifungal polypeptides
Compositions and methods for protecting a plant from a pathogen, particularly a fungal pathogen, are provided. Compositions include novel amino acid sequences, and variants and fragments thereof, for antipathogenic polypeptides that were isolated from microbial fermentation broths. Nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences that encode the antipathogenic polypeptides of the invention are also provided. A method for inducing pathogen resistance in a plant using the nucleotide sequences disclosed herein is further provided. The method comprises introducing into a plant an expression cassette comprising a promoter operably linked to a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the invention. Compositions comprising an antipathogenic polypeptide or a transformed microorganism comprising a nucleic acid of the invention in combination with a carrier and methods of using these compositions to protect a plant from a pathogen are further provided. Transformed plants, plant cells, seeds, and microorganisms comprising a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the invention, or variant or fragment thereof, are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
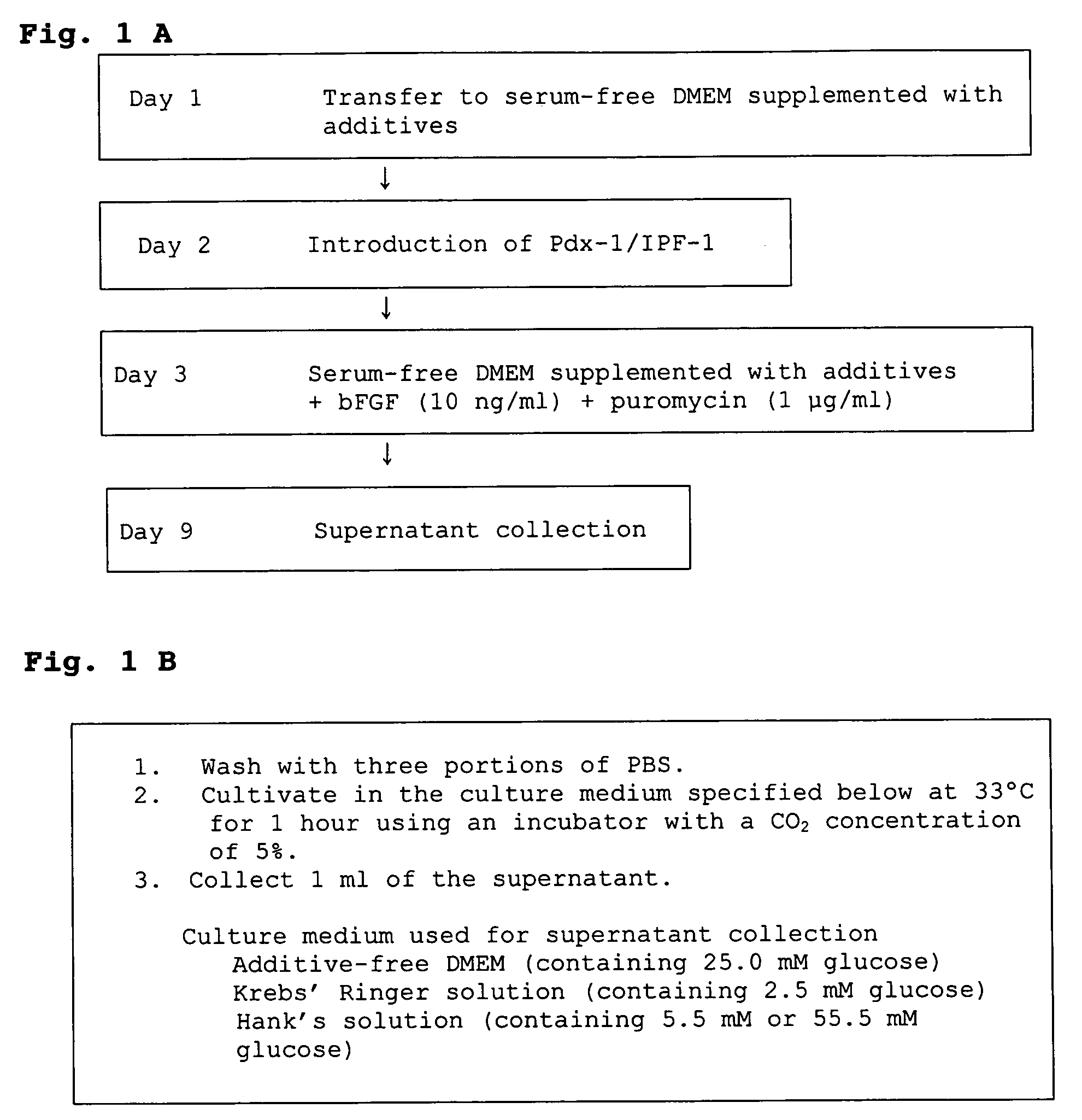
Method of forming pancreatic beta cells from mesenchymal cells
InactiveUS20050208029A1Easy to separateBiocidePancreatic cellsScreening methodBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
It is intended to provide a method of forming pancreatic β cells from mesenchymal cells characterized by comprising using mammal-origin mesenchymal cells as starting cells, culturing these cells in the presence of, for example, a pancreatic β cell-forming agent, and selecting and separating the thus obtained pancreatic βcells with the use of a gene expressed specifically in such cells as a selection marker; a remedy for glucose intolerance which comprises pancreatic β cells obtained by the above method as the active ingredient; a pancreatic β cell-forming agent such as a cytokine to be used in the above method; a method of screening a candidate compound promoting the formation of pancreatic β cells from mesenchymal cells; and a pancreatic β cell formation promoter obtained by this screening method.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
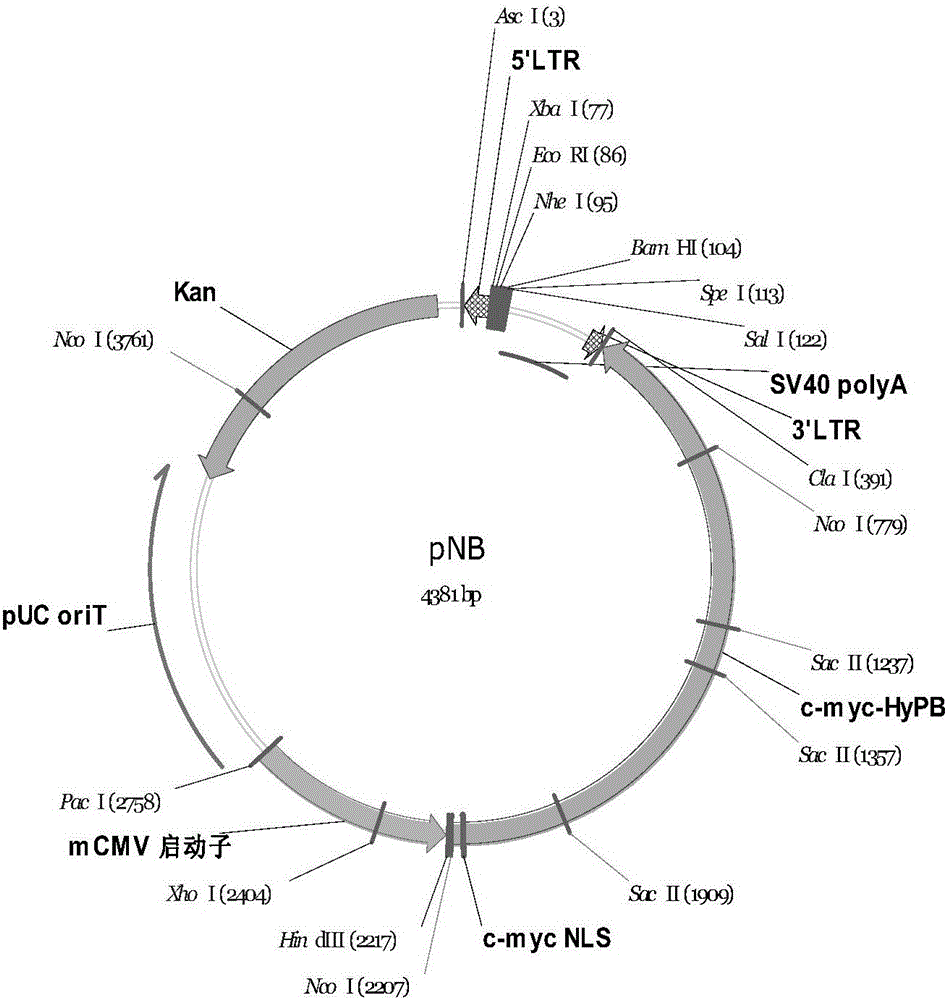
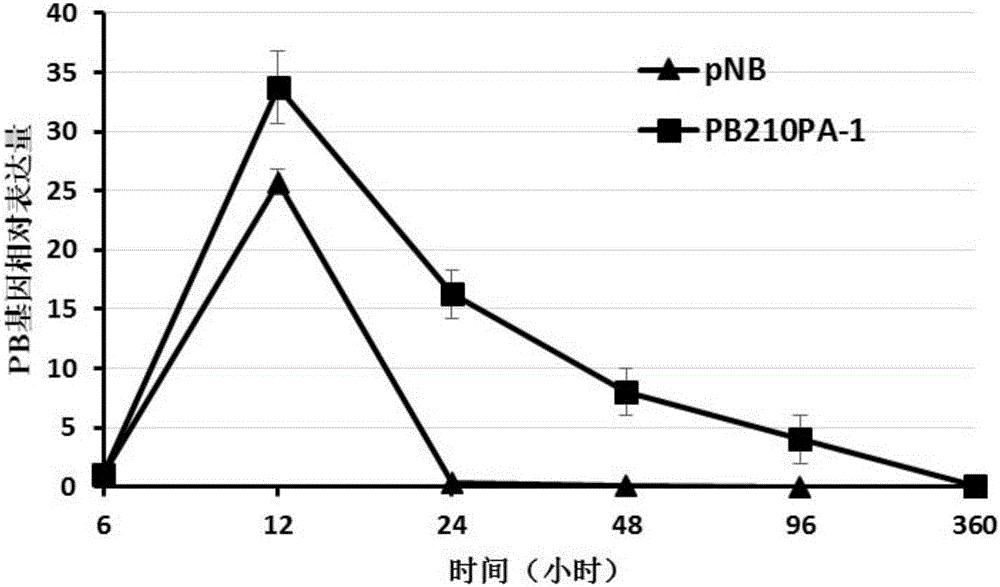
Efficient and safe transposable element integration system and application thereof
ActiveCN105154473AAvoid risks caused by random insertionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyTransposon integrationInsertion site
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, relates to an efficient and safe transposable element integration system and application thereof and further relates to a nucleic acid construction body and application thereof. The nucleic acid construction body concretely and sequentially comprises the following elements of a transposable element 5' terminal repetition sequence, a polyclone insertion site, a poly A tailing signal sequence, a transposable element 3' terminal repetition sequence, a transposase coding sequence and a promoter controlling the expression of transposase. The polyclone insertion site is used for inserting an exogenous gene coding sequence and a selective promoter for controlling the expression of exogenous genes in an operability mode. The poly A tailing signal sequence has a poly A tailing signal function in the forward and reverse directions, and the direction of an expression cassette of transposase is reverse to that of an exogenous gene expression cassette. The nucleic acid construction body can be used for efficiently and safely expressing mediated exogenous genes in host cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELL THERAPY RES INST +1
Construction and application of mammal cell high-efficiency expression vector
ActiveCN103525868AReduced transcript levelsShorten the development cycleVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsCloning SiteDeletion mutation
The invention relates to a mammal cell high-efficiency expression vector pSNEO. The vector is constructed on the basis of neomycin resistance screening gene NEO by combined strategy of weakening screening gene expression and reinforcing target gene expression. The screening gene weakening comprises the following two sides: introducing deletion mutant into the promoter to implement transcription weakening of the screening gene, and introducing a hairpin structure sequence before the translation initial site of the screening gene to implement the translation weakening of the screening gene. The expression reinforcement of the target gene is implemented by adding a transcription control element WPRE sequence between polyclone site and polyA tail of the target gene expression frame. The pSNEO vector can conveniently and quickly complete the construction of the stable high-expression cell strain of the target gene, and provides a new tool for preparing the high-polymer recombinant protein.
Owner:BIOTECH PHARMA CO LTD
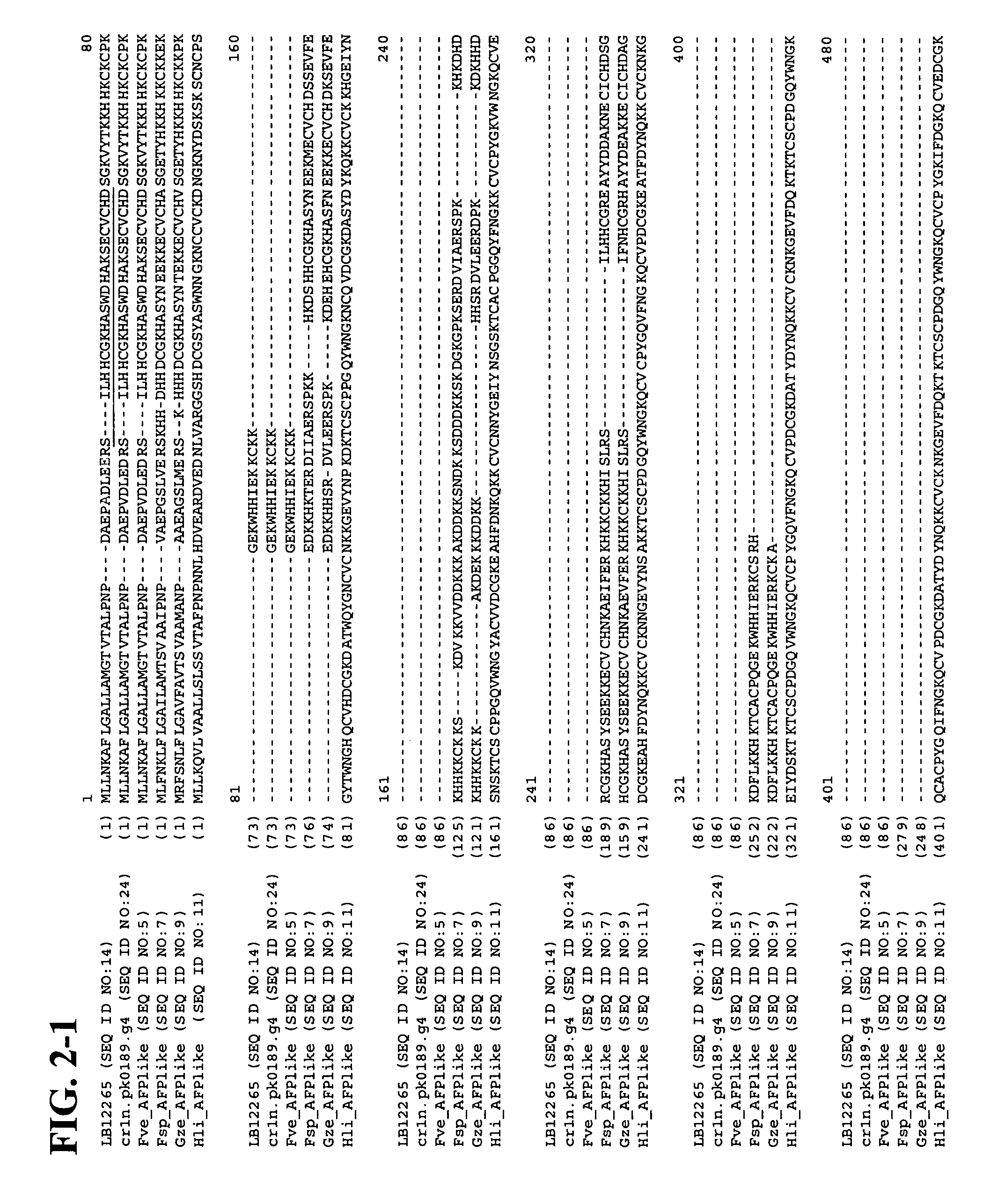
Promoter, promoter control elements, and combinations, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120084885A1Enhancing and reducing regionImmunoglobulinsFermentationGene productSynthetic DNA
The present invention provides DNA molecules that constitute fragments of the genome of a plant, and polypeptides encoded thereby. The DNA molecules are useful for specifying a gene product in cells, either as a promoter or as a protein coding sequence or as an UTR or as a 3′ termination sequence, and are also useful in controlling the behavior of a gene in the chromosome, in controlling the expression of a gene or as tools for genetic mapping, recognizing or isolating identical or related DNA fragments, or identification of a particular individual organism, or for clustering of a group of organisms with a common trait. One of ordinary skill in the art, having this data, can obtain cloned DNA fragments, synthetic DNA fragments or polypeptides constituting desired sequences by recombinant methodology known in the art or described herein
Owner:CERES INC
Novel root specific promoter driving the expression of a novel lrr receptor-like kinase
The present invention relates to the field of plant molecular biology, more particularly to the root-specific gene expression in plants. The invention provides nucleic acids for a novel transcriptional regulatory root-specific promoter and nucleic acid and protein sequences coding for a new LRR receptor-kinase protein, further specified as a root clavata 1 homolog (RCH1). Further provided are compositions comprising nucleic acids, polypeptides, antibodies and vectors. The invention further provides for methods for modifying cell fate and / or plant development and / or plant morphology and / or plant biochemistry and / or plant physiology comprising the modification of expression in particular cells, tissues or organs of a plant of the novel LRR receptor-like kinase or comprising the expressing of a gene of interest under the control of the novel transcriptional regulatory root-specific promoter. Further are provided compounds interacting with the new polypeptides for use as herbicides or growth regulators.
Owner:SCHERES BEN +1
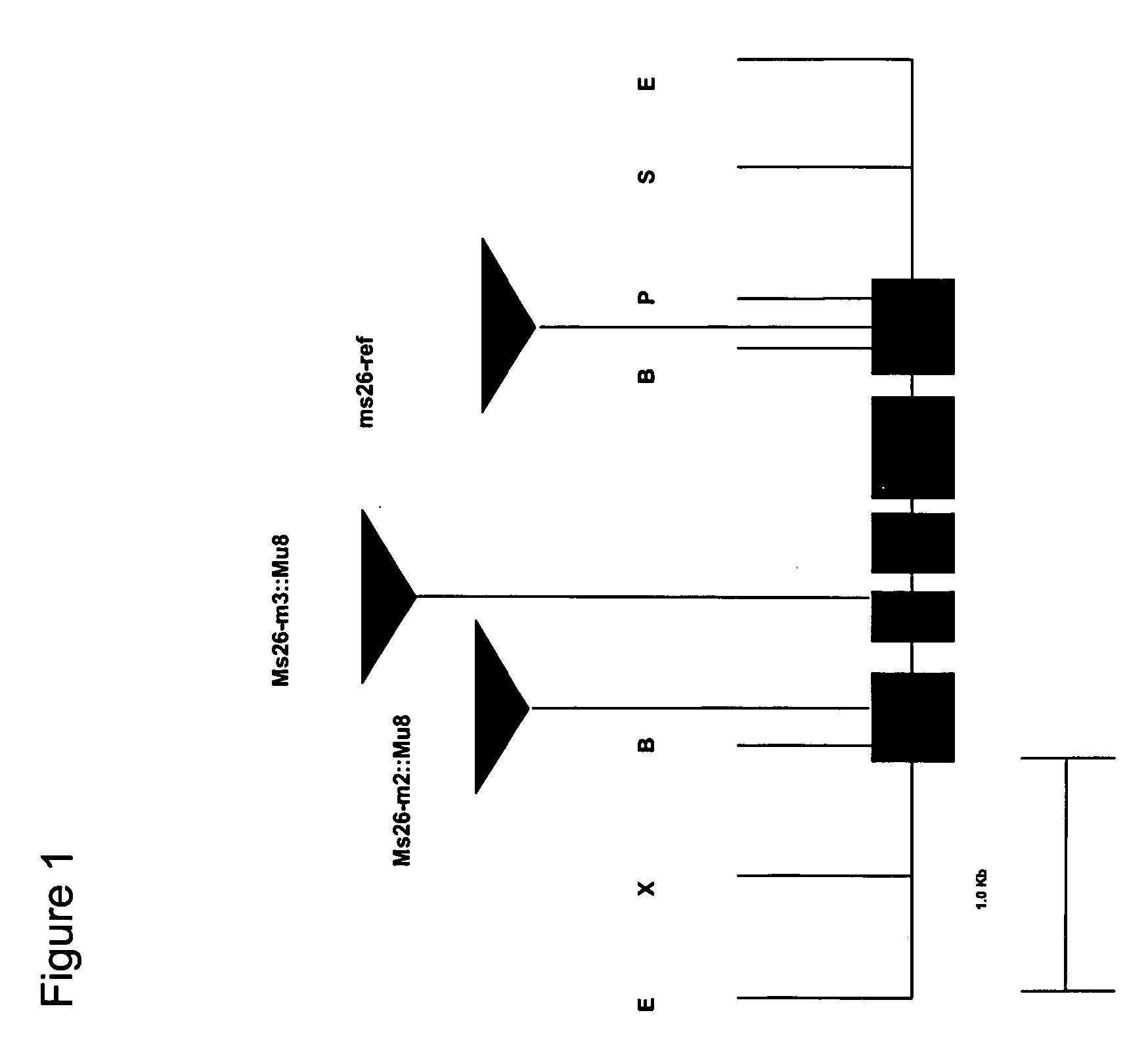
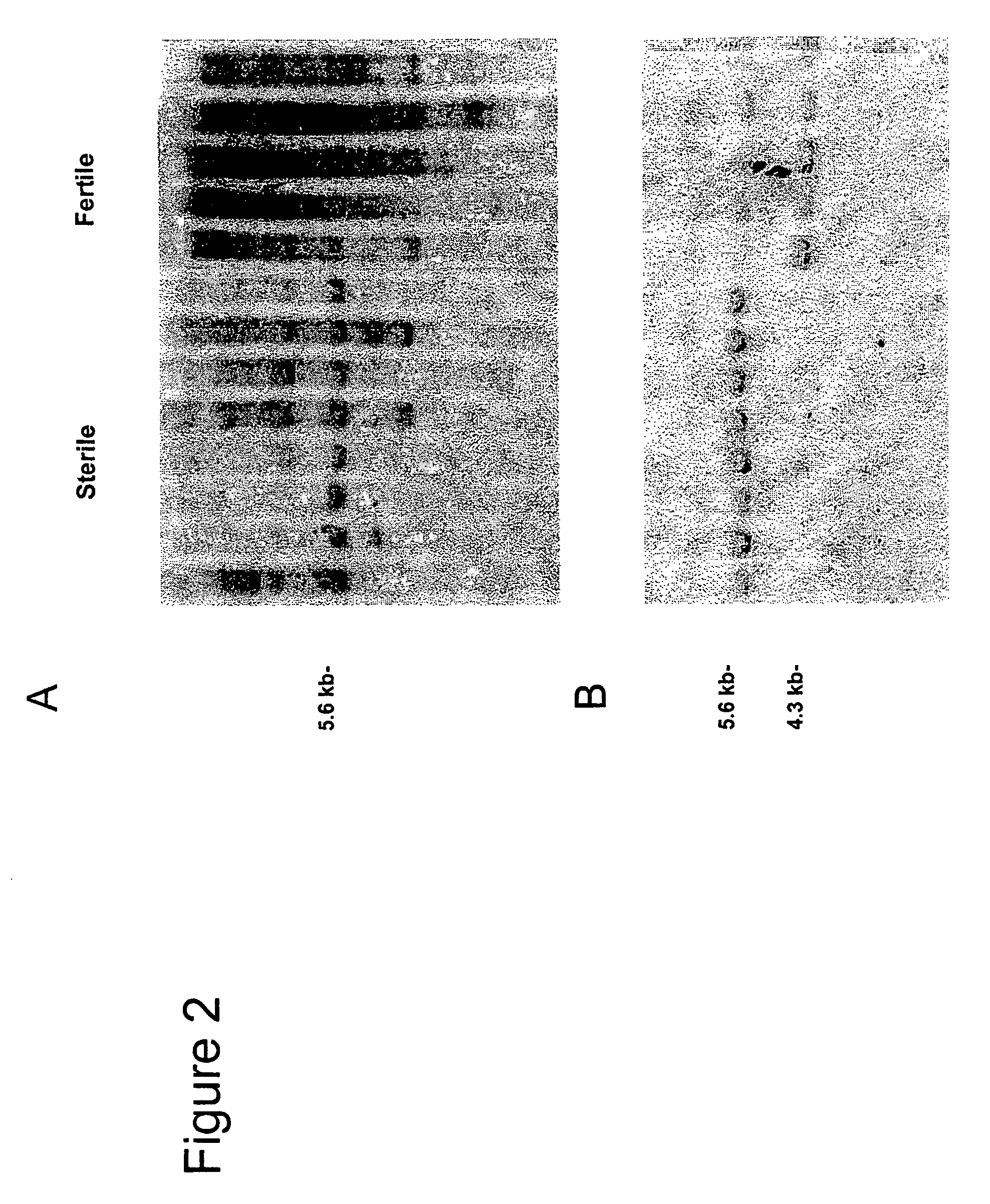
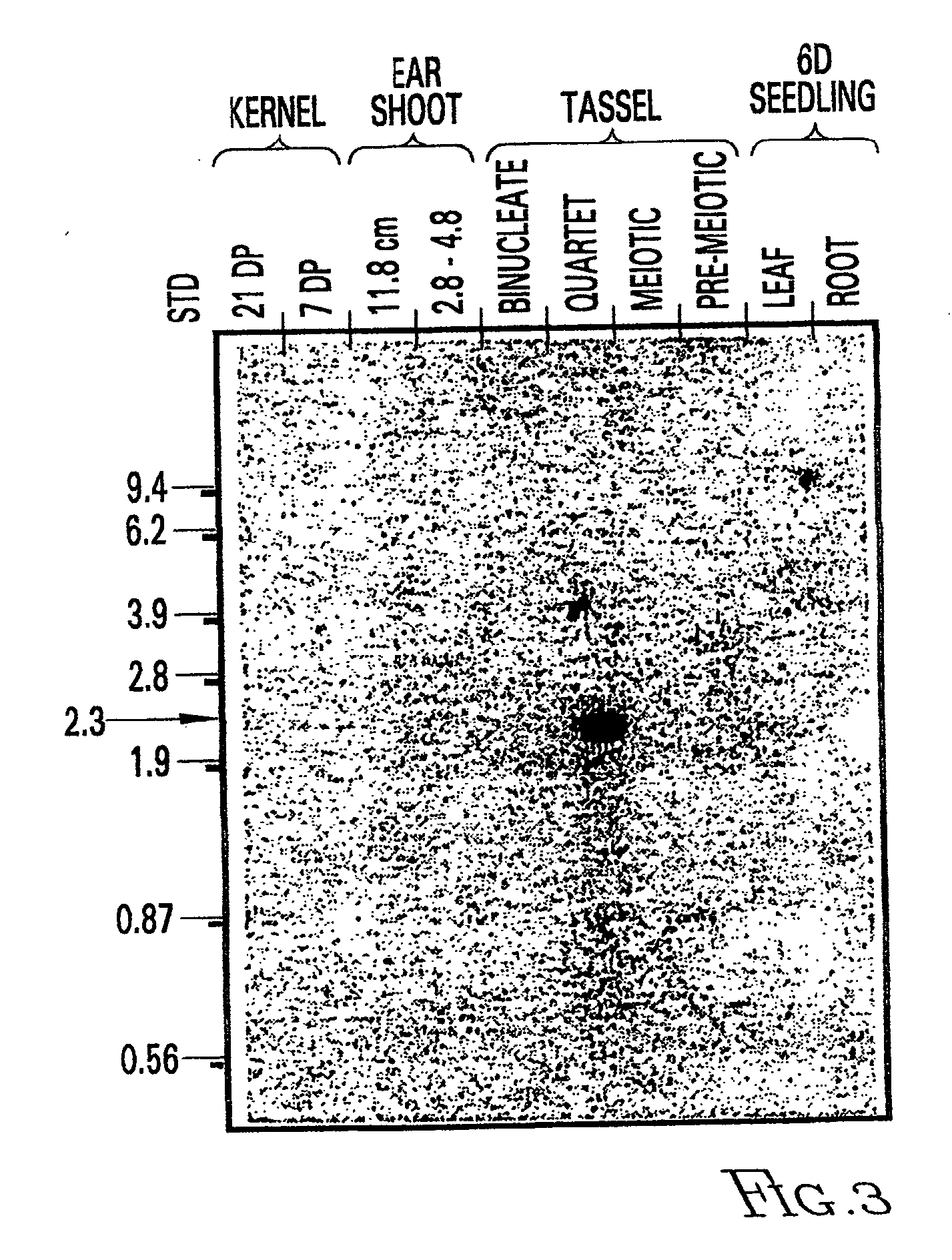
Nucleotide sequences mediating male fertility and method of using same
InactiveUS20060288440A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesAdemetionineGamete
Nucleotide sequences mediating male fertility in plants are described, with DNA molecule and amino acid sequences set forth. Promoter sequences and their essential regions are also identified. The nucleotide sequences are useful in mediating male fertility in plants. In one such method, the homozygous recessive condition of male sterility causing alleles is maintained after crossing with a second plant, where the second plant contains a restoring transgene construct having a nucleotide sequence which reverses the homozygous condition. The restoring sequence is linked with a hemizygous sequence encoding a product inhibiting formation or function of male gametes. The maintainer plant produces only viable male gametes which do not contain the restoring transgene construct. Increase of the maintainer plant is also provided by self-fertilization, and selection for seed or plants which contain the construct.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
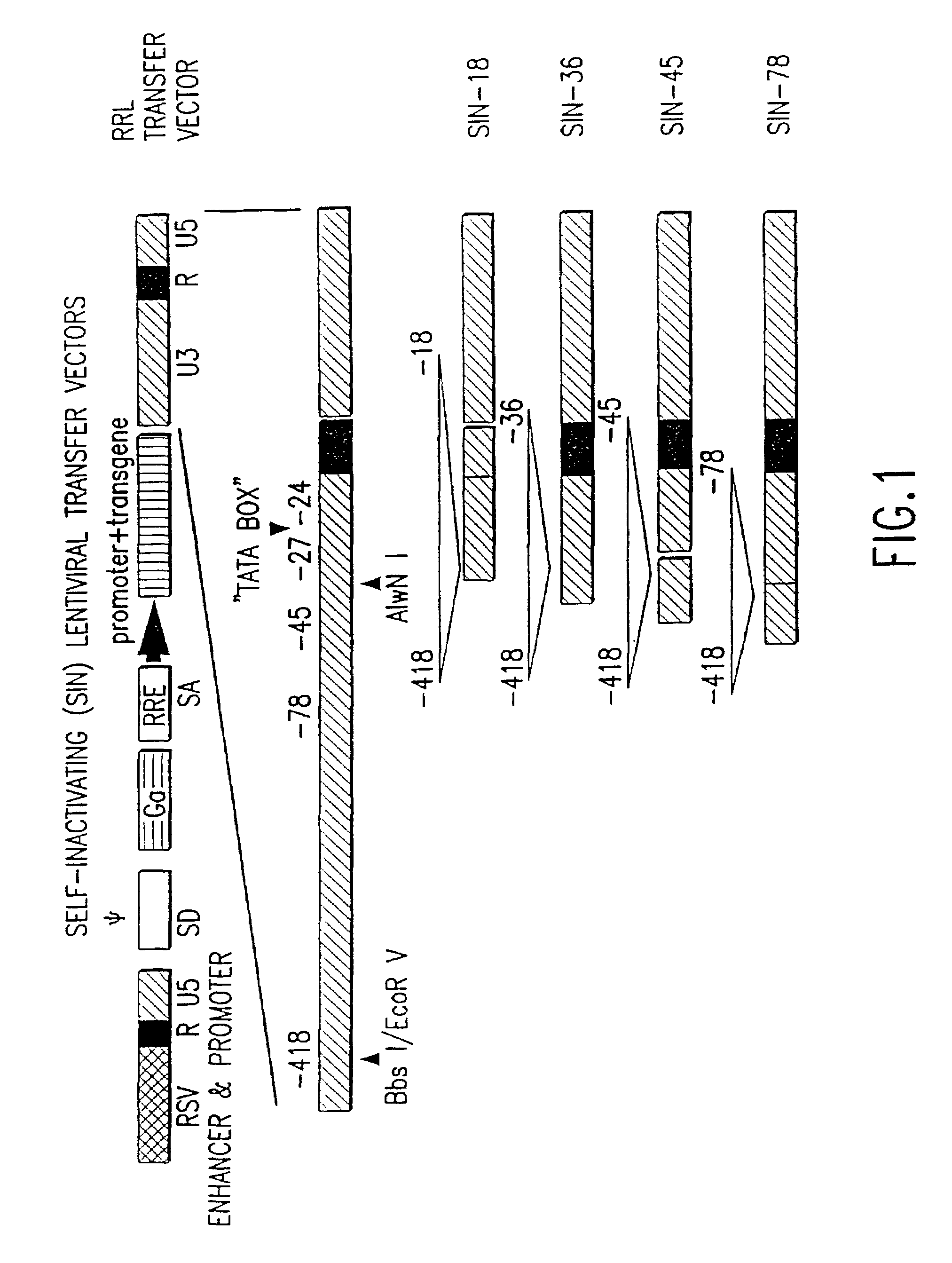
Method and means for producing high titer, safe, recombinant lentivirus vectors
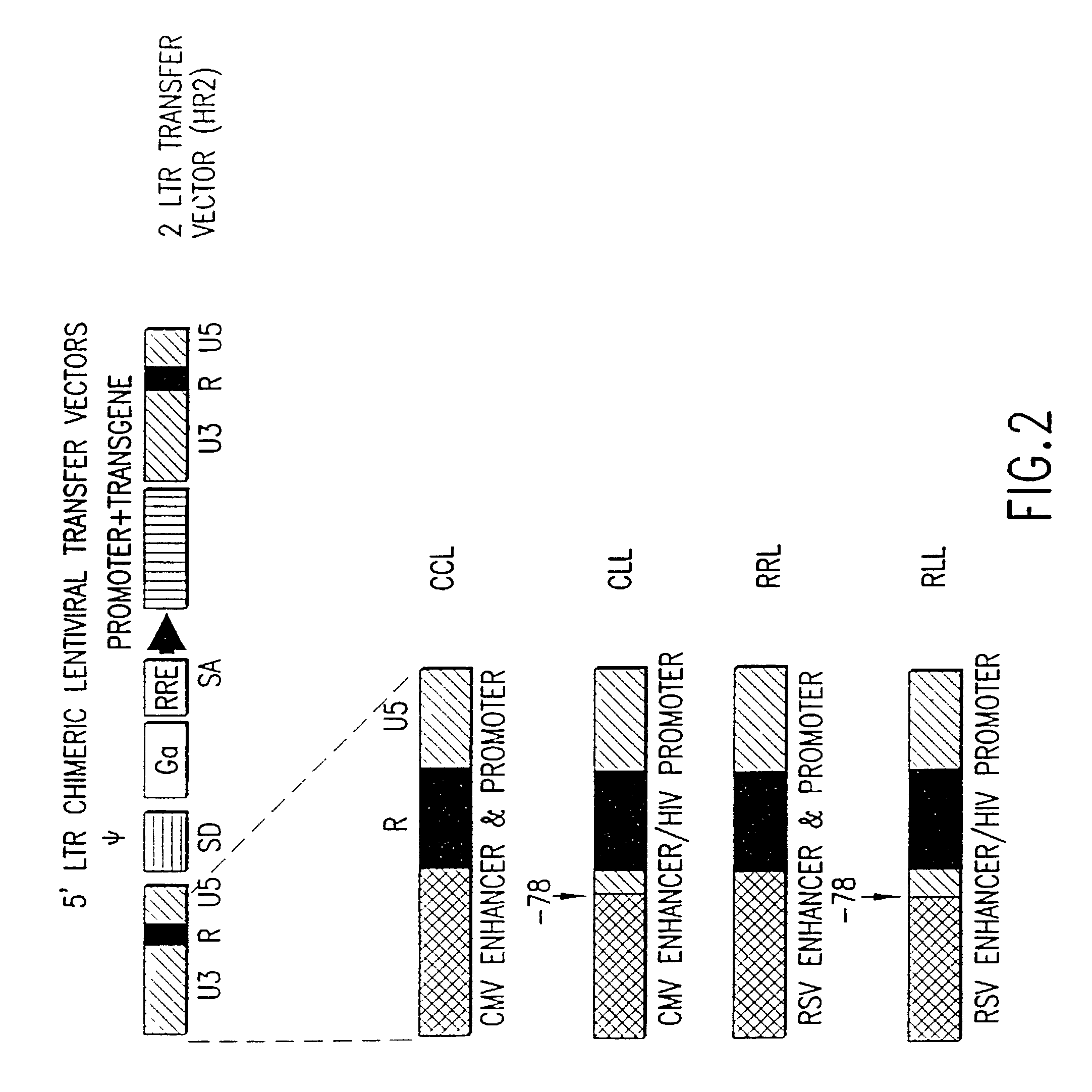
Lentiviral vectors modified at the 5′ LTR or both the 5′ and 3′ LTR are useful in the production of recombinant lentivirus vectors (See the Figure). Such vectors can be produced in the absence of a functional tat gene. Multiple transformation of the host cell with the vector carrying the transgene enhances virus production. The vectors can contain inducible or conditional promoters.
Owner:MILTENYI BIOTEC B V & CO KG
Expression in insect cells of genes with overlapping open reading frames, methods and compositions therefor
ActiveUS20090203071A1Reduce riskEfficient infectionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesOpen reading framePromoter
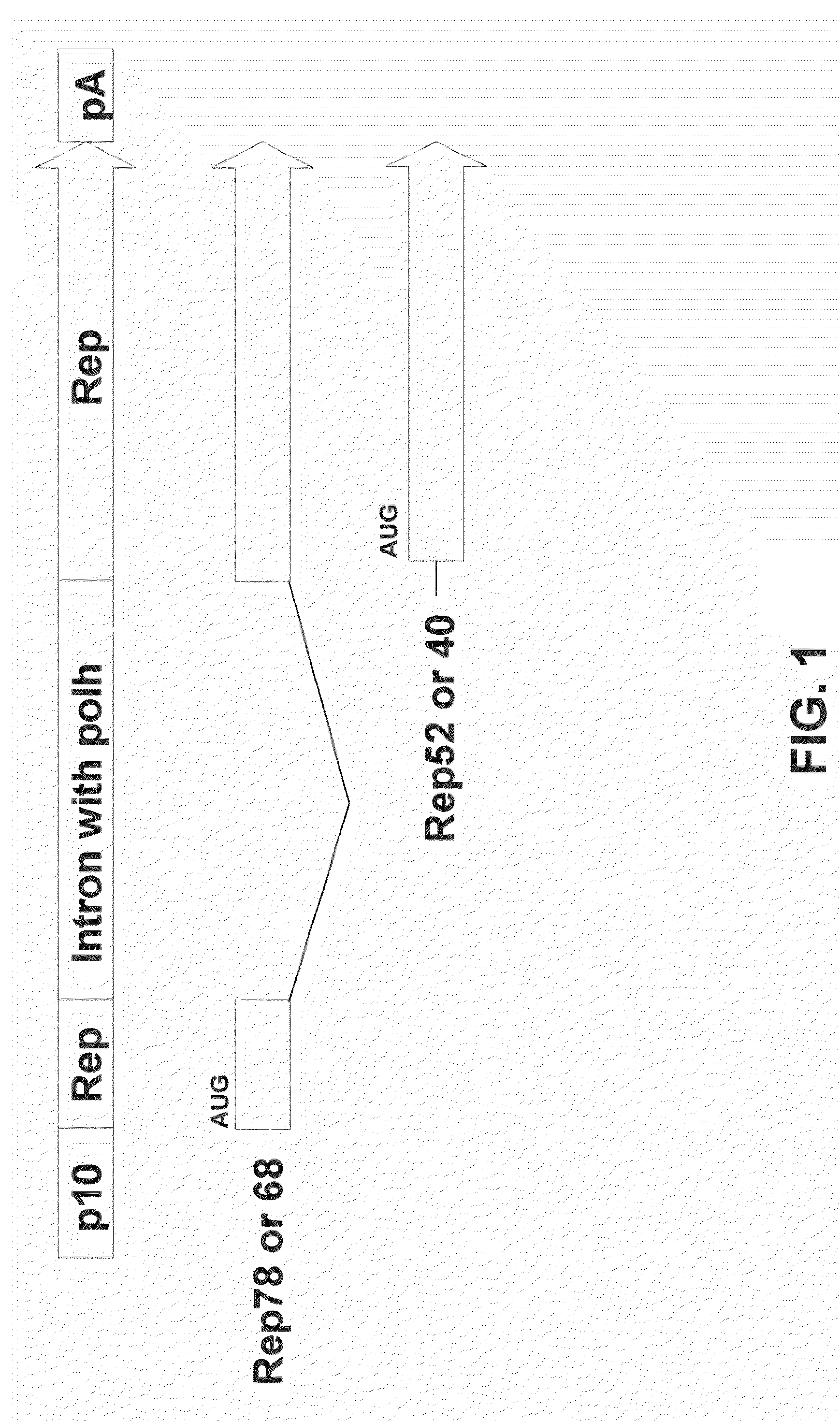
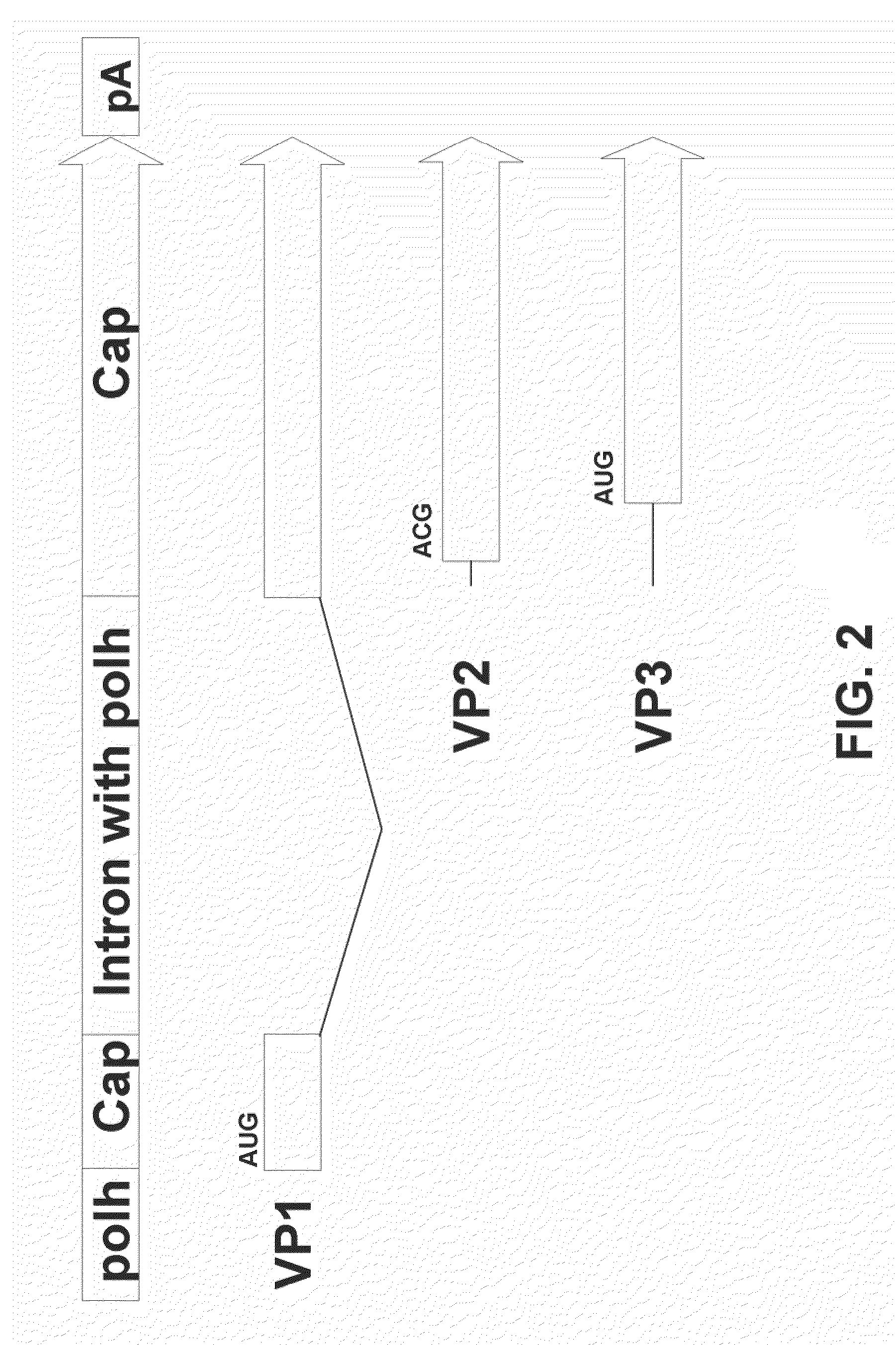
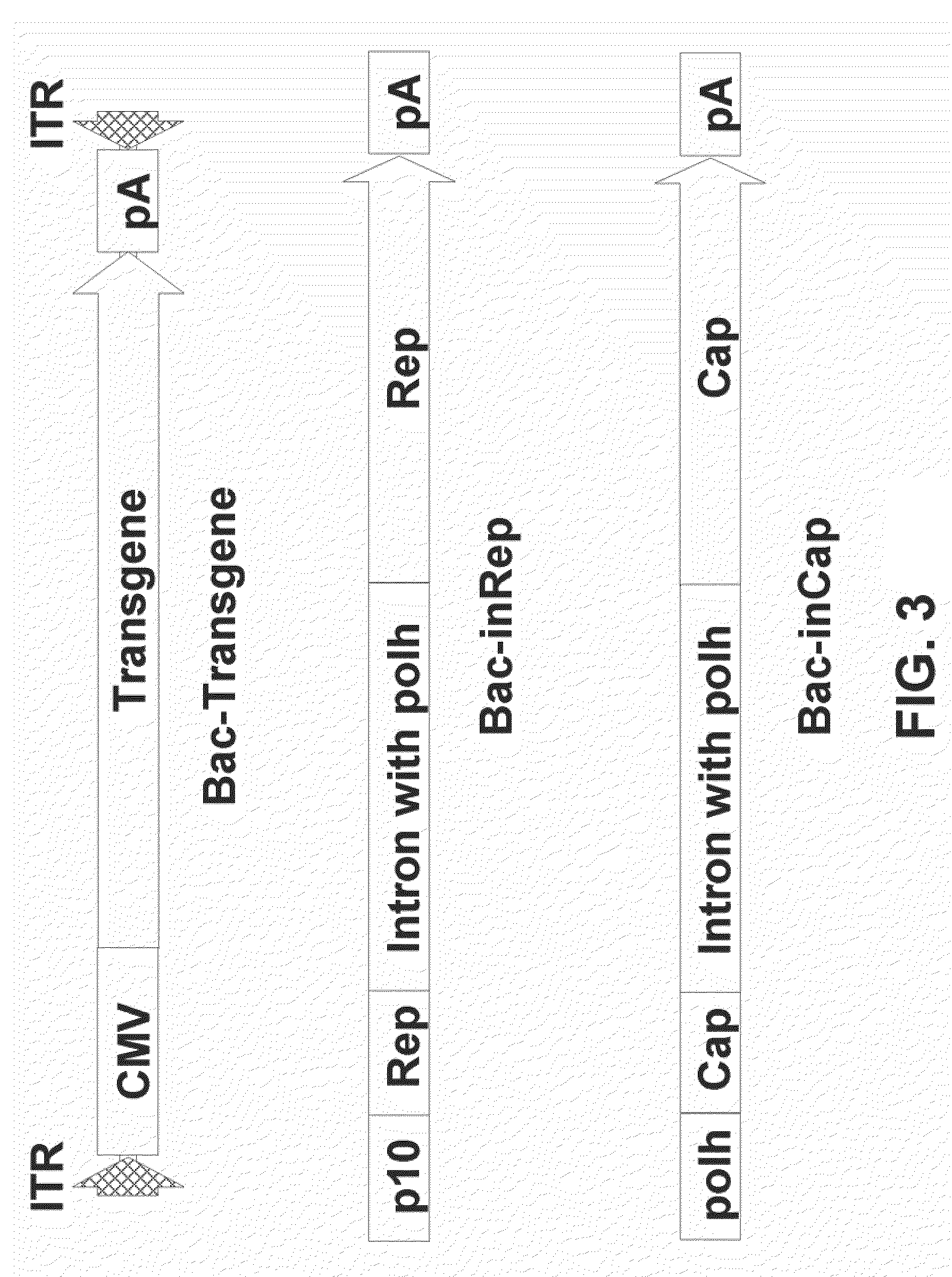
The present teachings disclose nucleic acid cassettes for expressing in an insect cell a plurality of polypeptides encoded by a gene comprising overlapping open reading frames (ORFs). A cassette comprises, in 5′ to 3′ order, a) a first insect cell-operable promoter, b) a 5′ portion of a gene comprising a first ORF of the gene, c) an intron comprising a second insect cell-operable promoter, and d) a 3′ portion of the gene comprising at least one additional ORF. Vectors and insect cells comprising the cassettes are also disclosed, as well as methods for production of recombinant adeno-associated virus in insect cells using the cassettes.
Owner:VIROVEK
Recombinant influenza vectors with a PolII promoter and ribozymes for vaccines and gene therapy
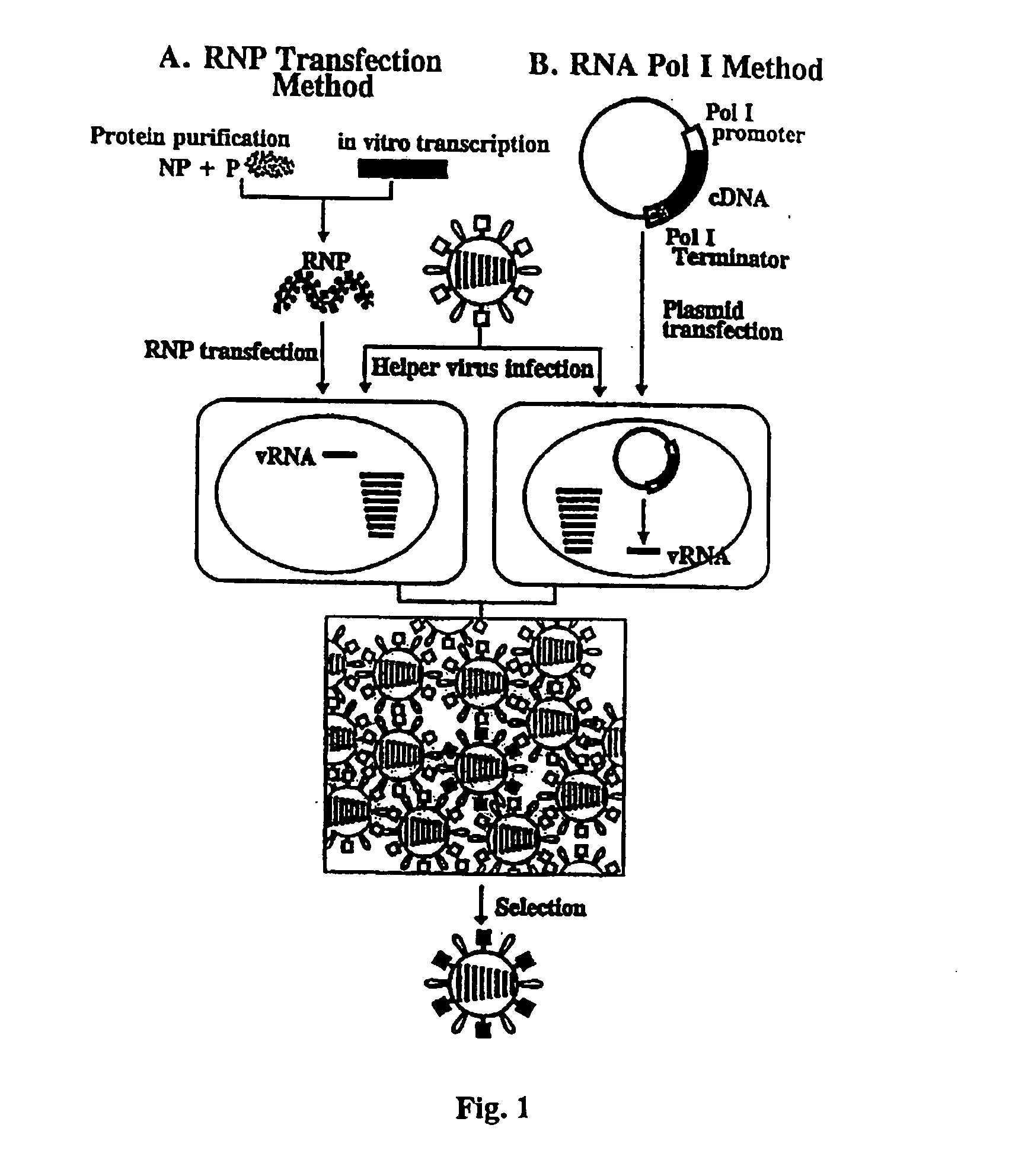
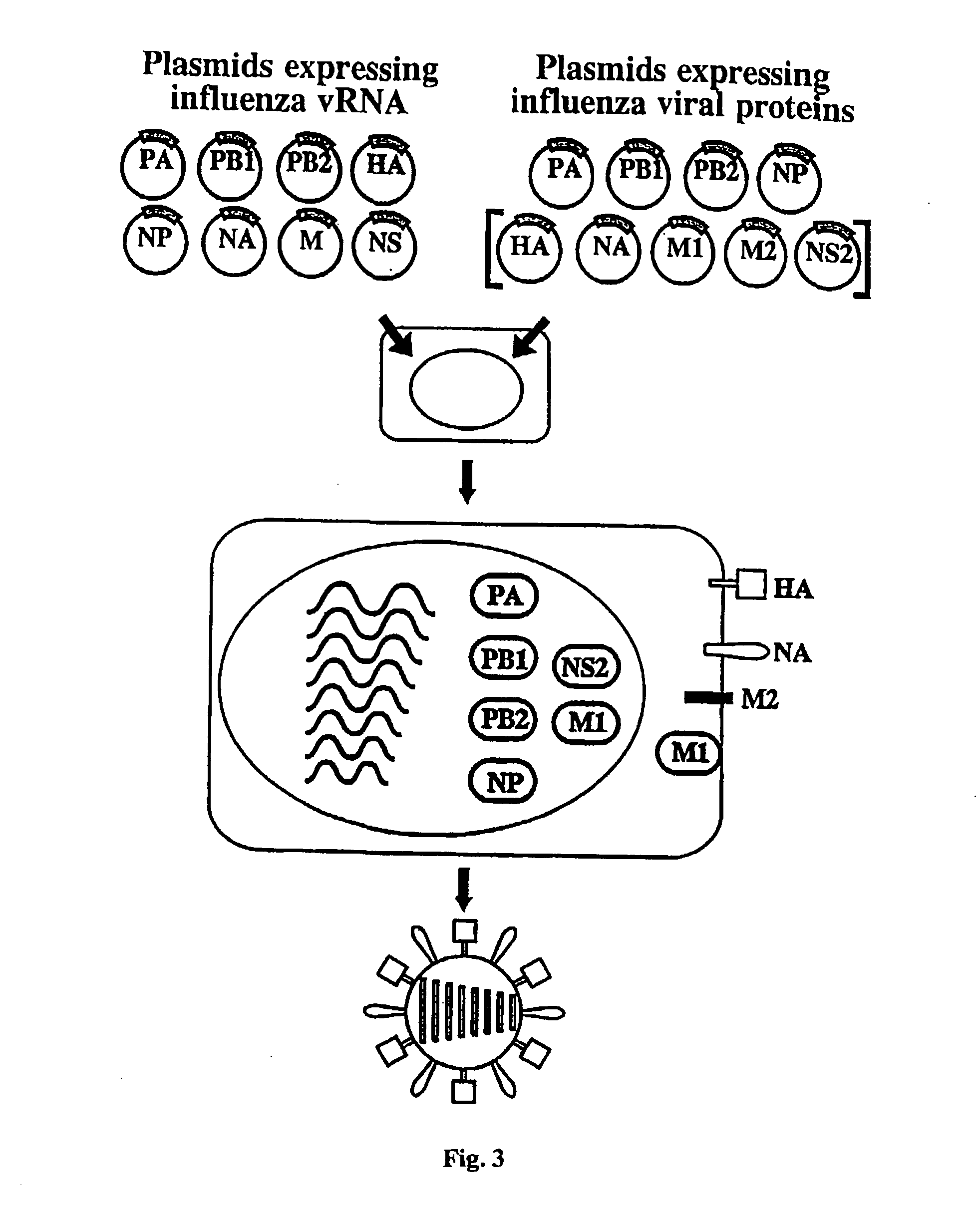
InactiveUS20050037487A1Easy to operateEnhances these viruses as vaccine vectorsSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesHelper virusViral vector
The invention provides a composition useful to prepare influenza viruses, e.g., in the absence of helper virus, using vectors which include Po1II promoters and multiple ribozyme sequences.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Methods and compositions for the introduction and regulated expression of genes in plants
InactiveUS20110167516A1Minimize premature excisionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyRegulator gene
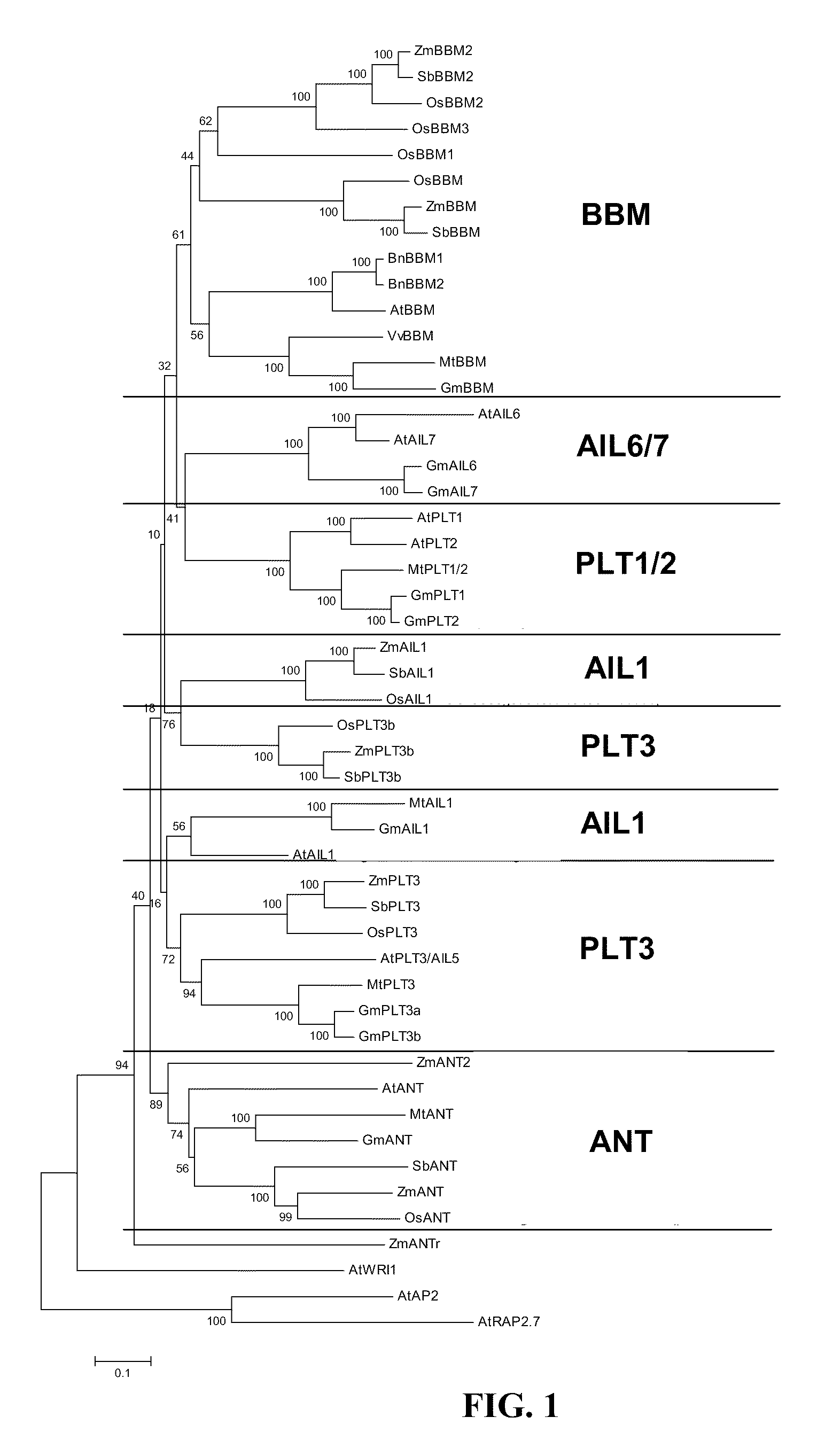
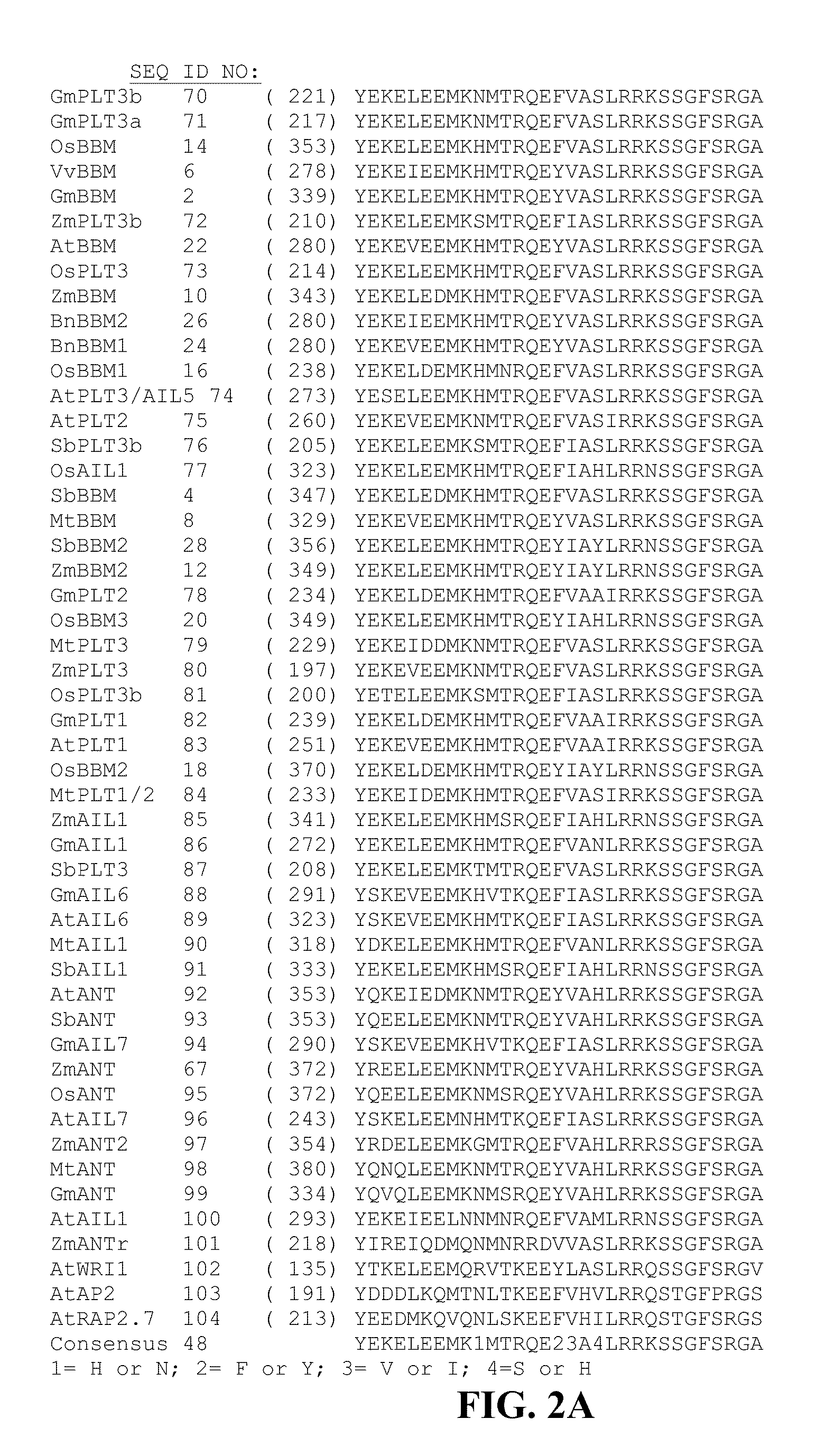
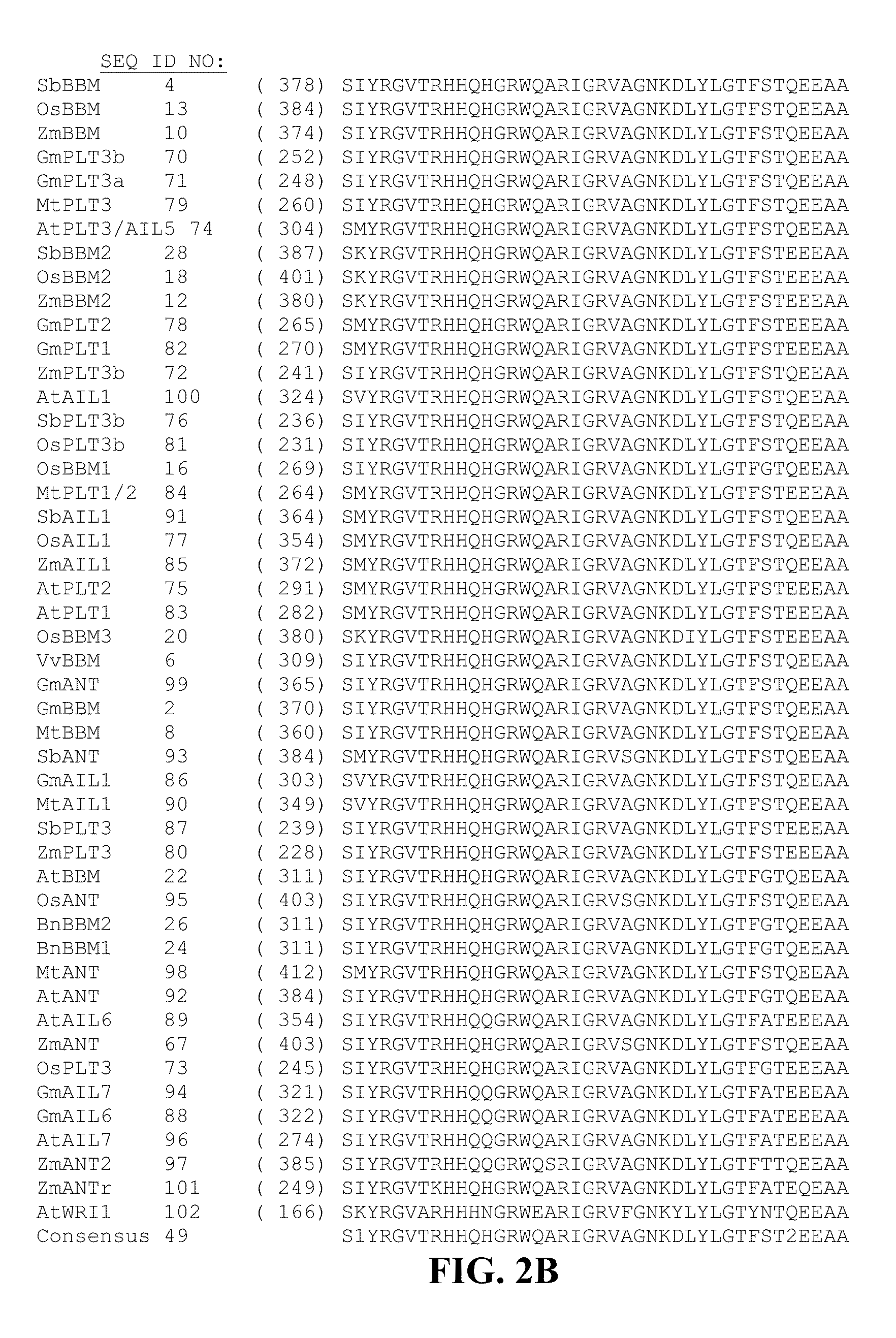
Compositions and methods are provided for the introduction and the regulated expression of genes in plants. Compositions include promoter constructs that provide a level of activity useful for the regulated expression of site-specific recombinases, while avoiding premature excision. Further provided are isolated polynucleotides encoding novel babyboom polypeptides, expression cassettes, and plants comprising the same. Methods for the introduction of genes into plants are provided, including methods for plastid transformation and methods for the transformation of tissues from mature seeds and leaves.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Antifungal polypeptides
Compositions and methods for protecting a plant from a pathogen, particularly a fungal pathogen, are provided. Compositions include an amino acid sequence, and variants and fragments thereof, for an antipathogenic polypeptide that was isolated from a fungal fermentation broth. Nucleic acid molecules that encode the antipathogenic polypeptides of the invention, and antipathogenic domains thereof, are also provided. A method for inducing pathogen resistance in a plant using the nucleotide sequences disclosed herein is further provided. The method comprises introducing into a plant an expression cassette comprising a promoter operably linked to a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the invention. Compositions comprising an antipathogenic polypeptide or a transformed microorganism comprising a nucleic acid of the invention in combination with a carrier and methods of using these compositions to protect a plant from a pathogen are further provided. Transformed plants, plant cells, seeds, and microorganisms comprising a nucleotide sequence that encodes an antipathogenic polypeptide of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +2
Continuous directed evolution
ActiveUS9394537B2Accelerating evolutionVirus peptidesDirected macromolecular evolutionViral vectorVirus
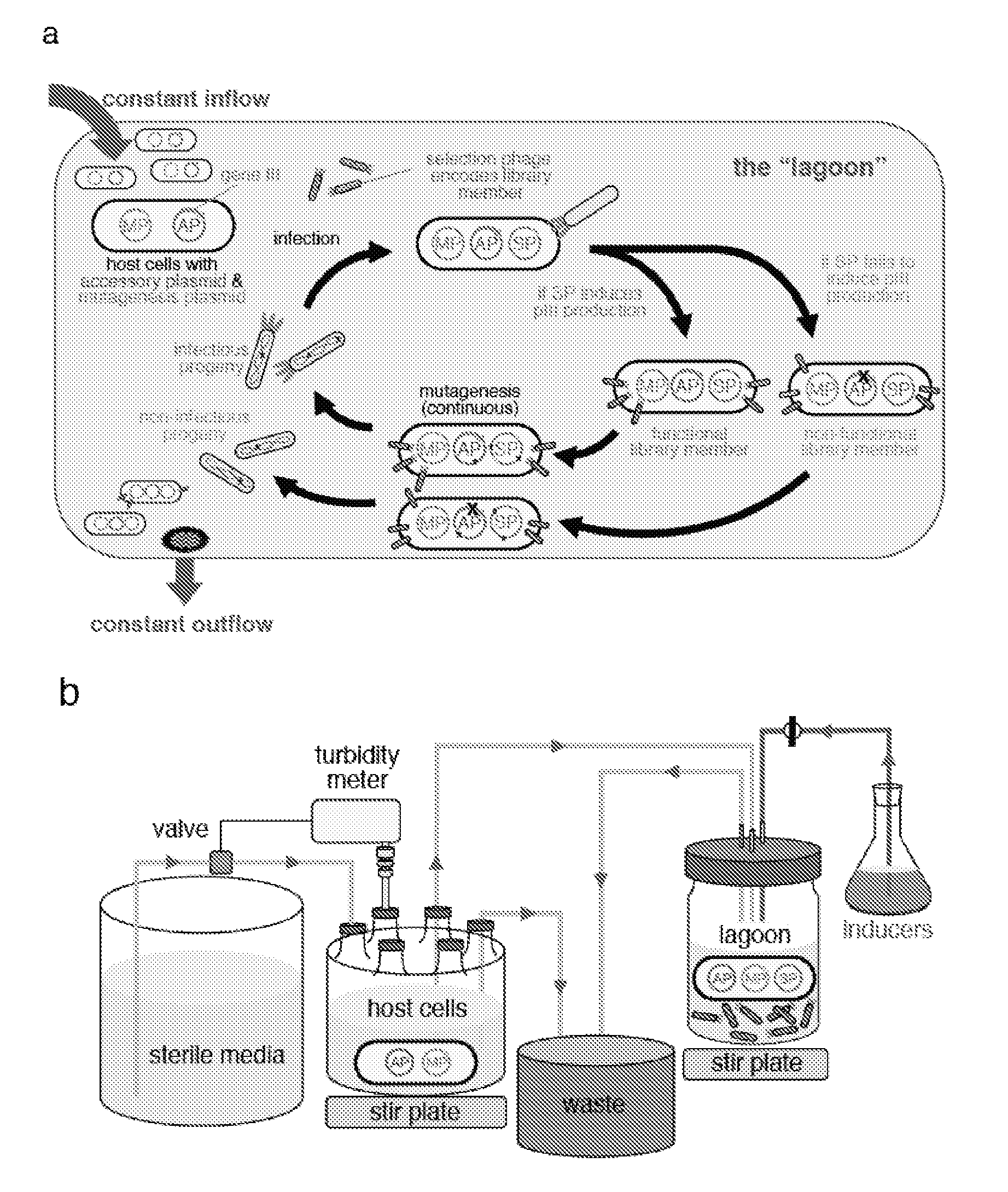
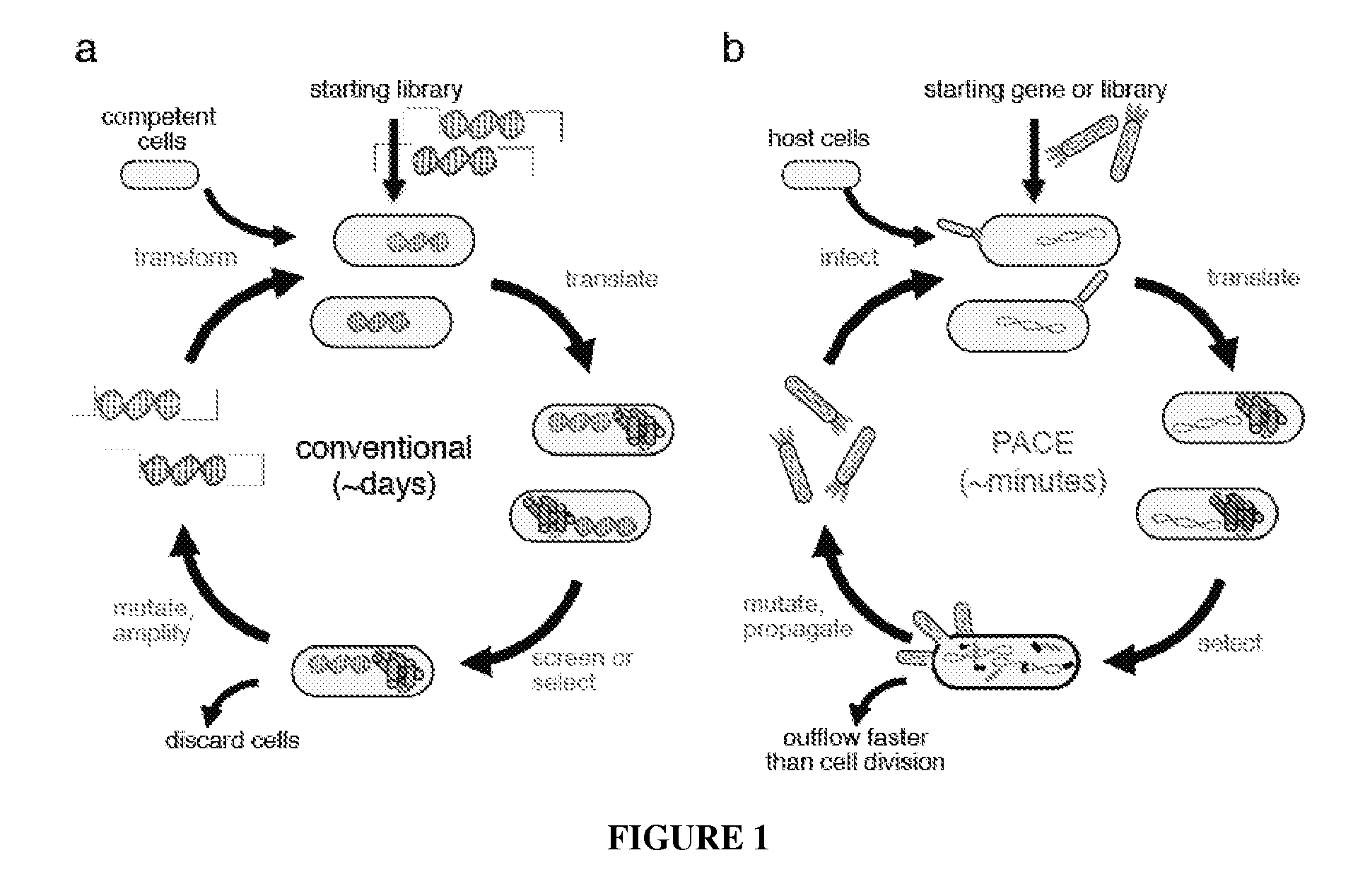
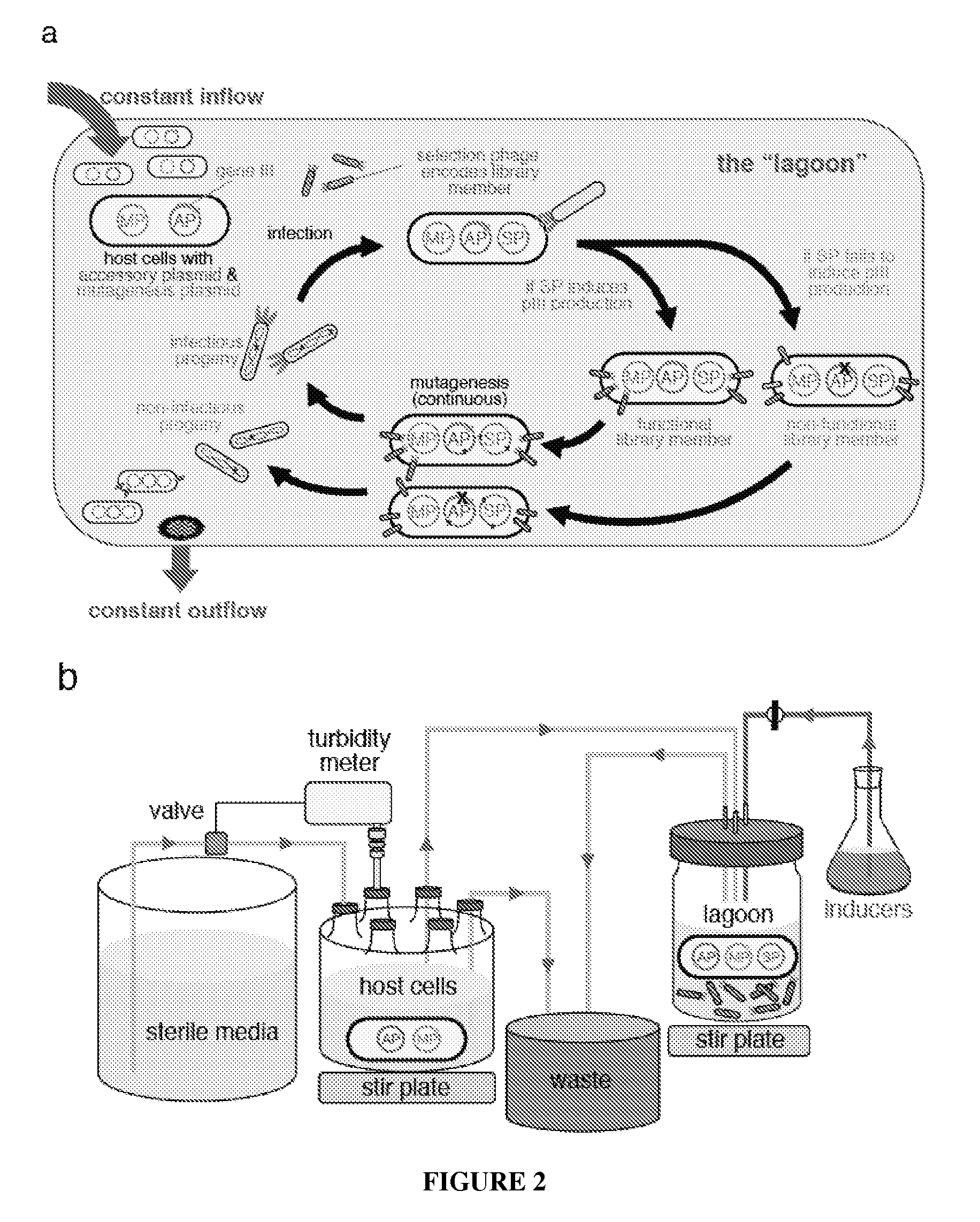
The invention provides systems, methods, reagents, apparatuses, vectors, and host cells for the continuous evolution of nucleic acids. For example, a lagoon is provided in which a population of viral vectors comprising a gene of interest replicates in a stream of host cells, wherein the viral vectors lack a gene encoding a protein required for the generation of infectious viral particles, and wherein that gene is expressed in the host cells under the control of a conditional promoter, the activity of which depends on a function of the gene of interest to be evolved. Some aspects of this invention provide evolved products obtained from continuous evolution procedures described herein. Kits containing materials for continuous evolution are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
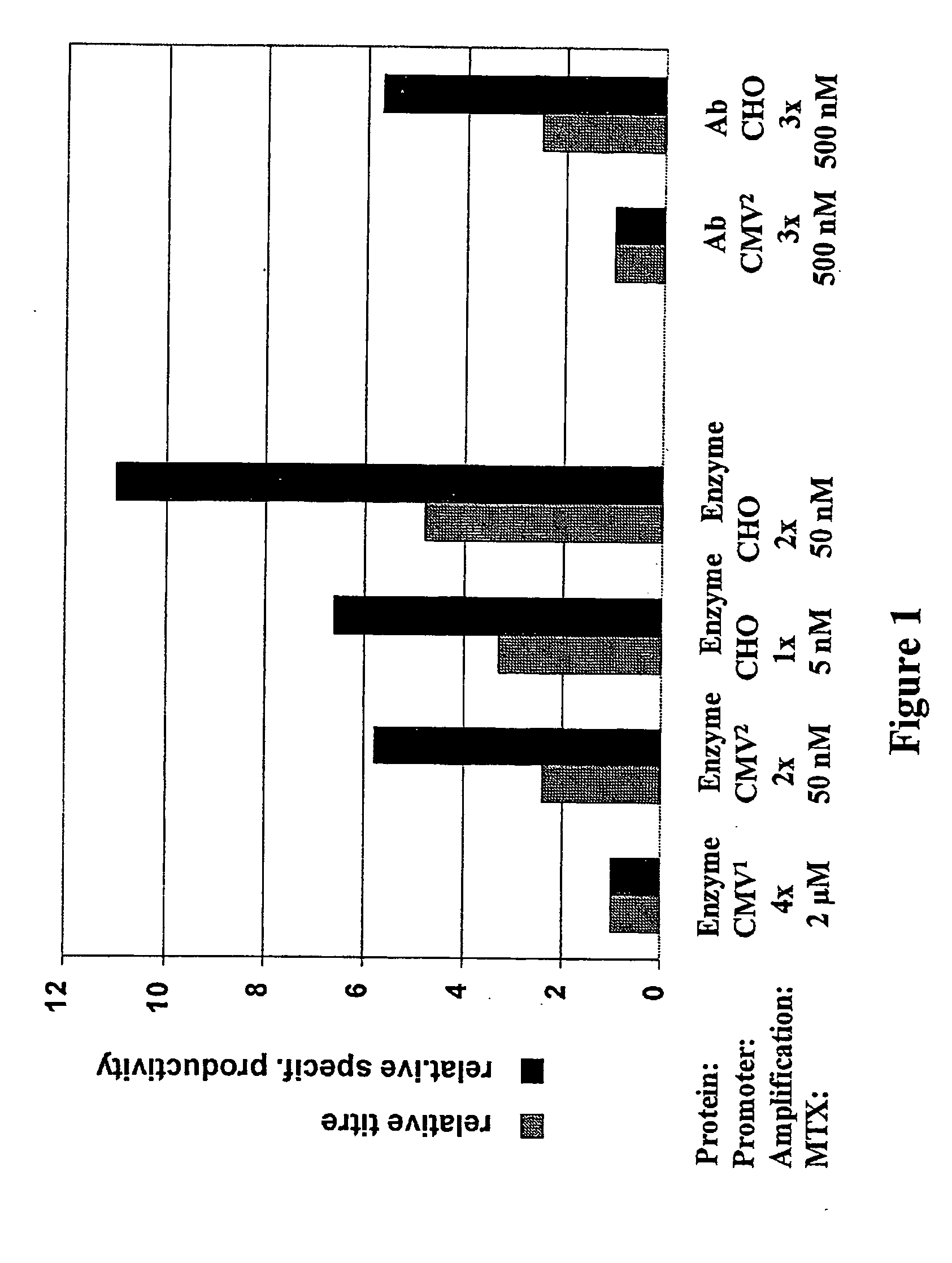
Expression vector, methods for the production of heterologous gene products and for the selection of recombinant cells producing high levels of such products
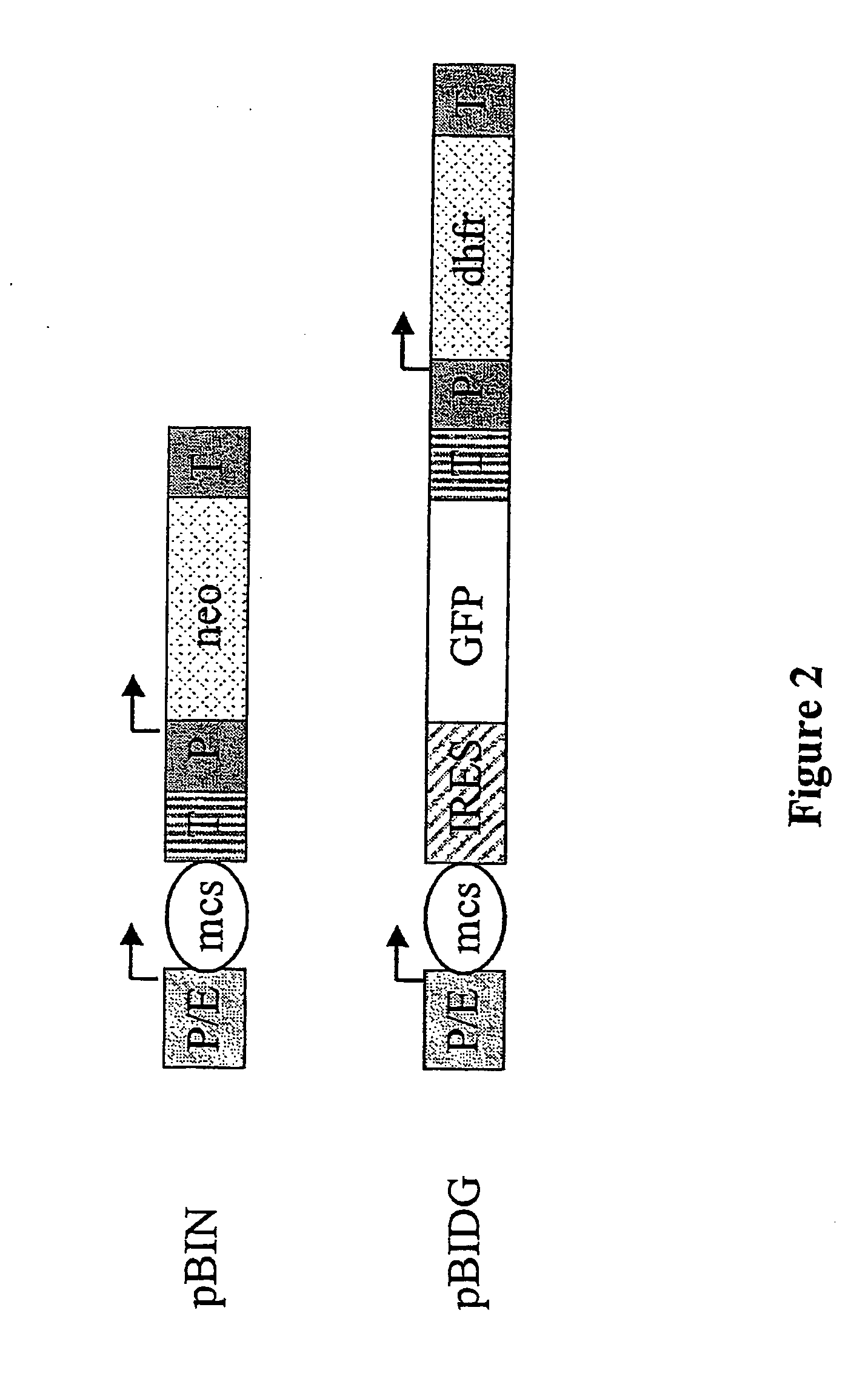
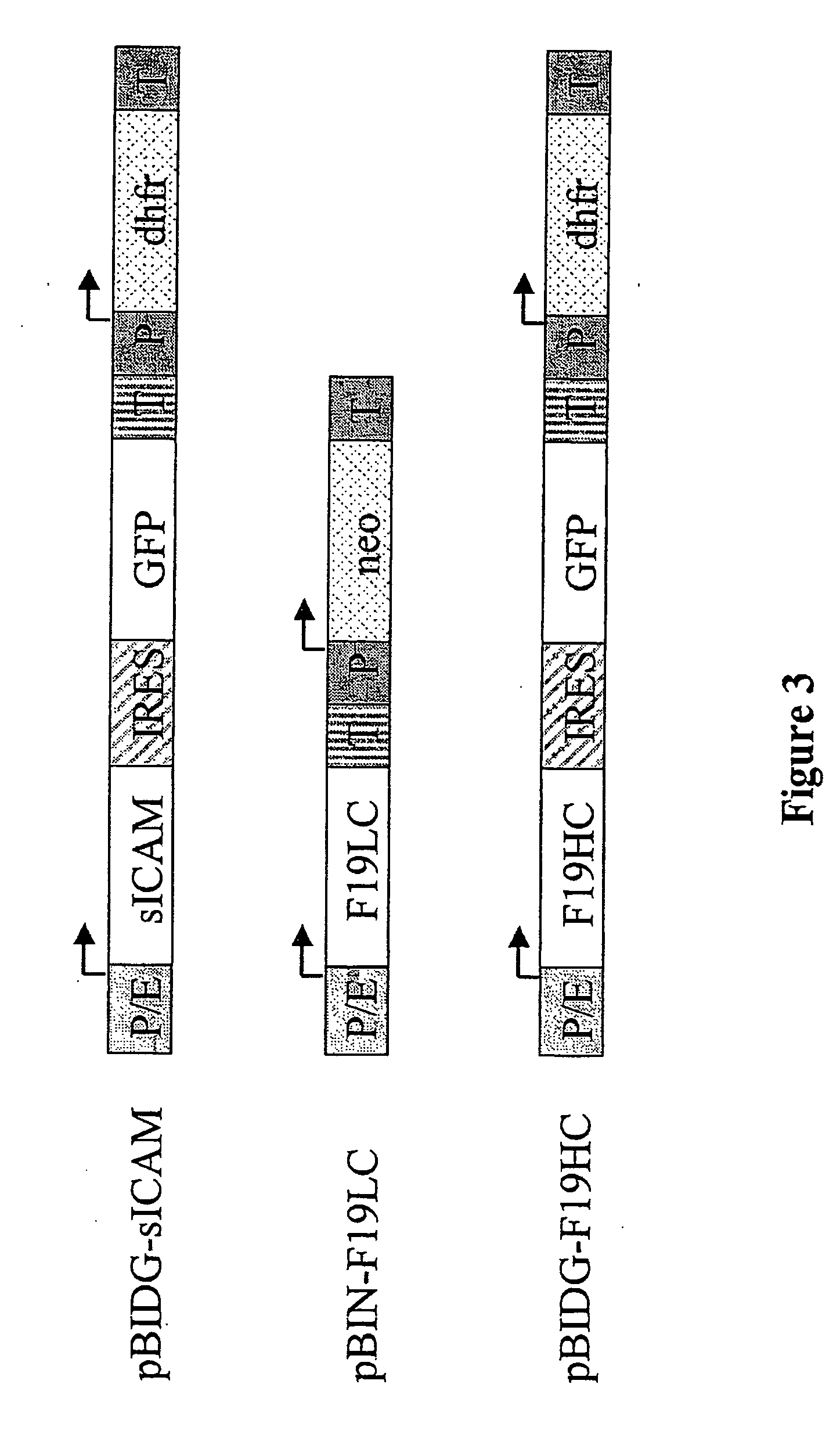
ActiveUS20040148647A1Shorten the timeReduce development costsAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousHamster
An expression vector for eukaryotic cells comprising a gene which codes for a protein of interest, functionally linked to a hamster-ubiquitin / S27a-promoter and a gene which codes for a fluorescent protein. Preferably the expression vector also contains an amplifiable selectable marker gene. The invention also describes host cells, preferably mammalian cells, which have been transfected with the expression vector, processes for producing heterologous gene products and a method of selecting high-producing cells.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARM KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com