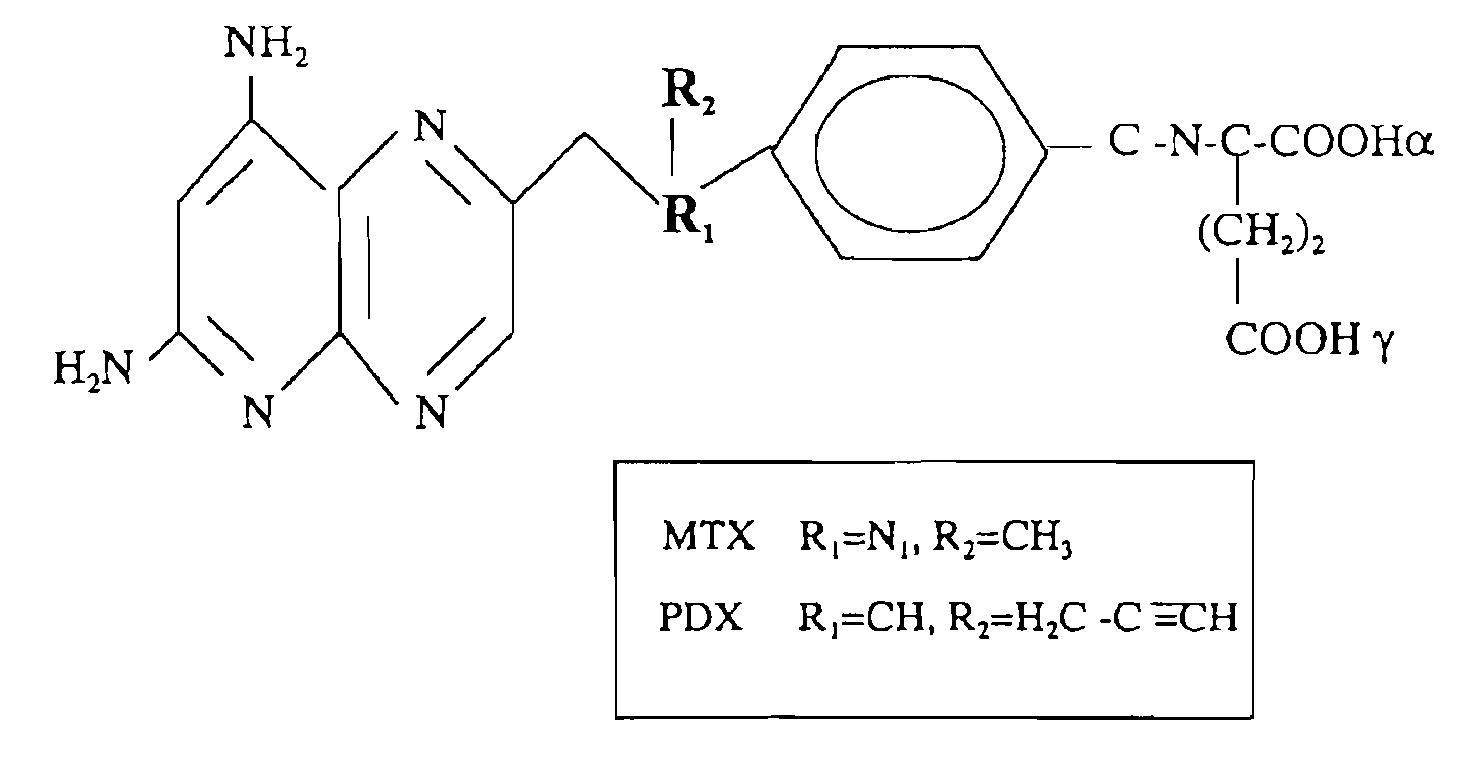Patents
Literature
53 results about "Thymidylate synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
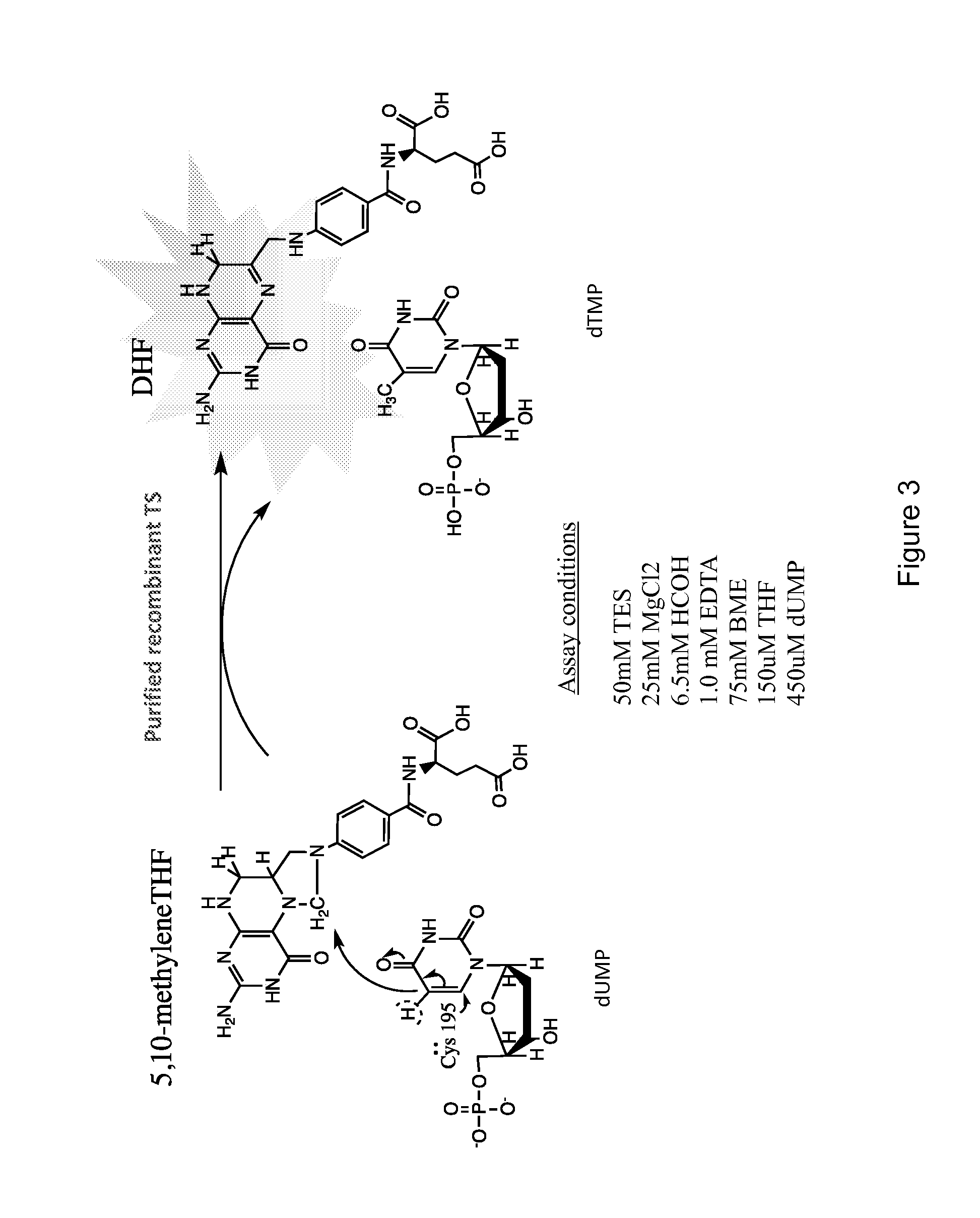
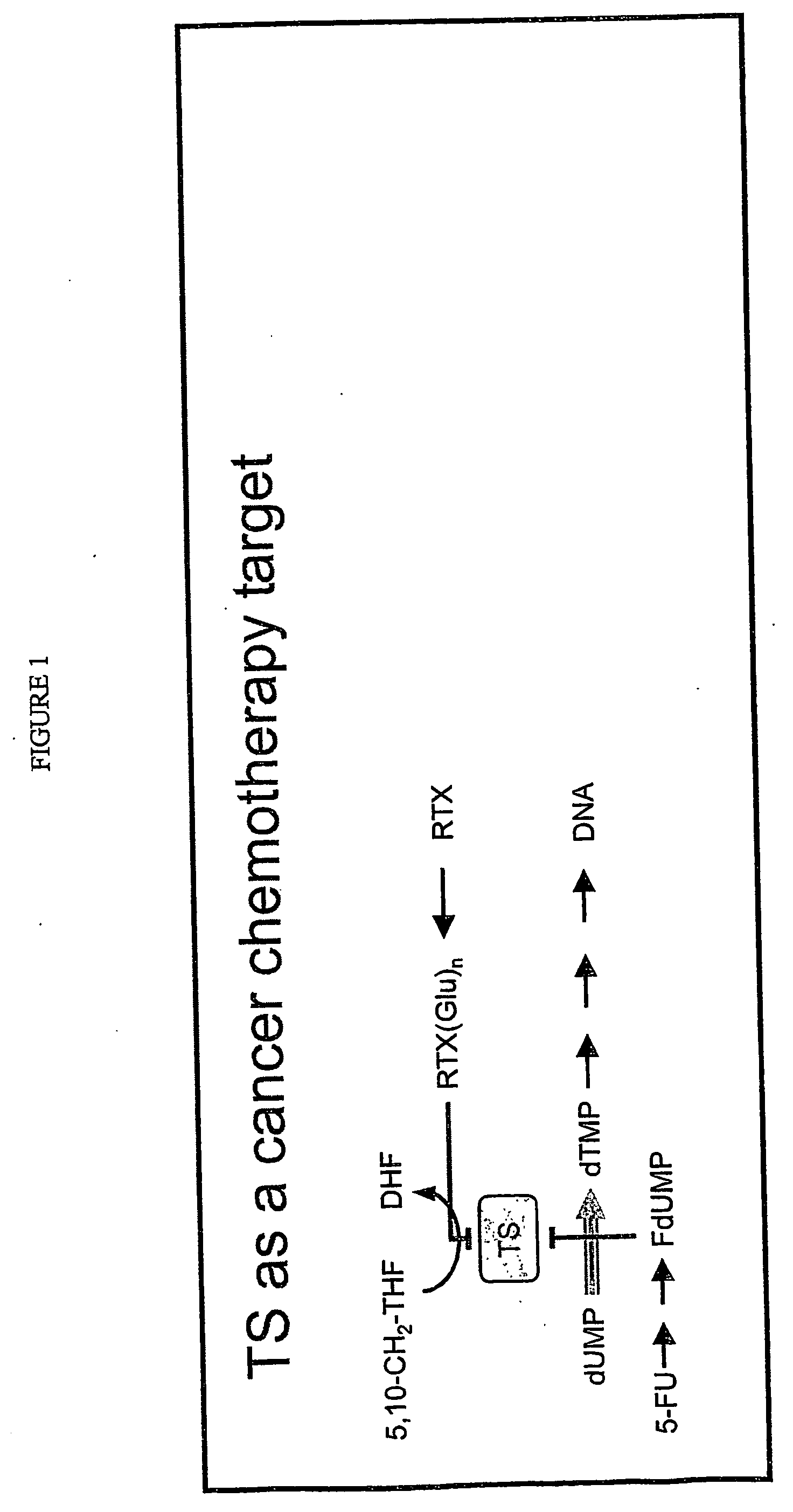
Thymidylate synthase (TS) (EC 2.1.1.45) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). Thymidine is one of the nucleotides in DNA. With inhibition of TS, an imbalance of deoxynucleotides and increased levels of dUMP arise. Both cause DNA damage.
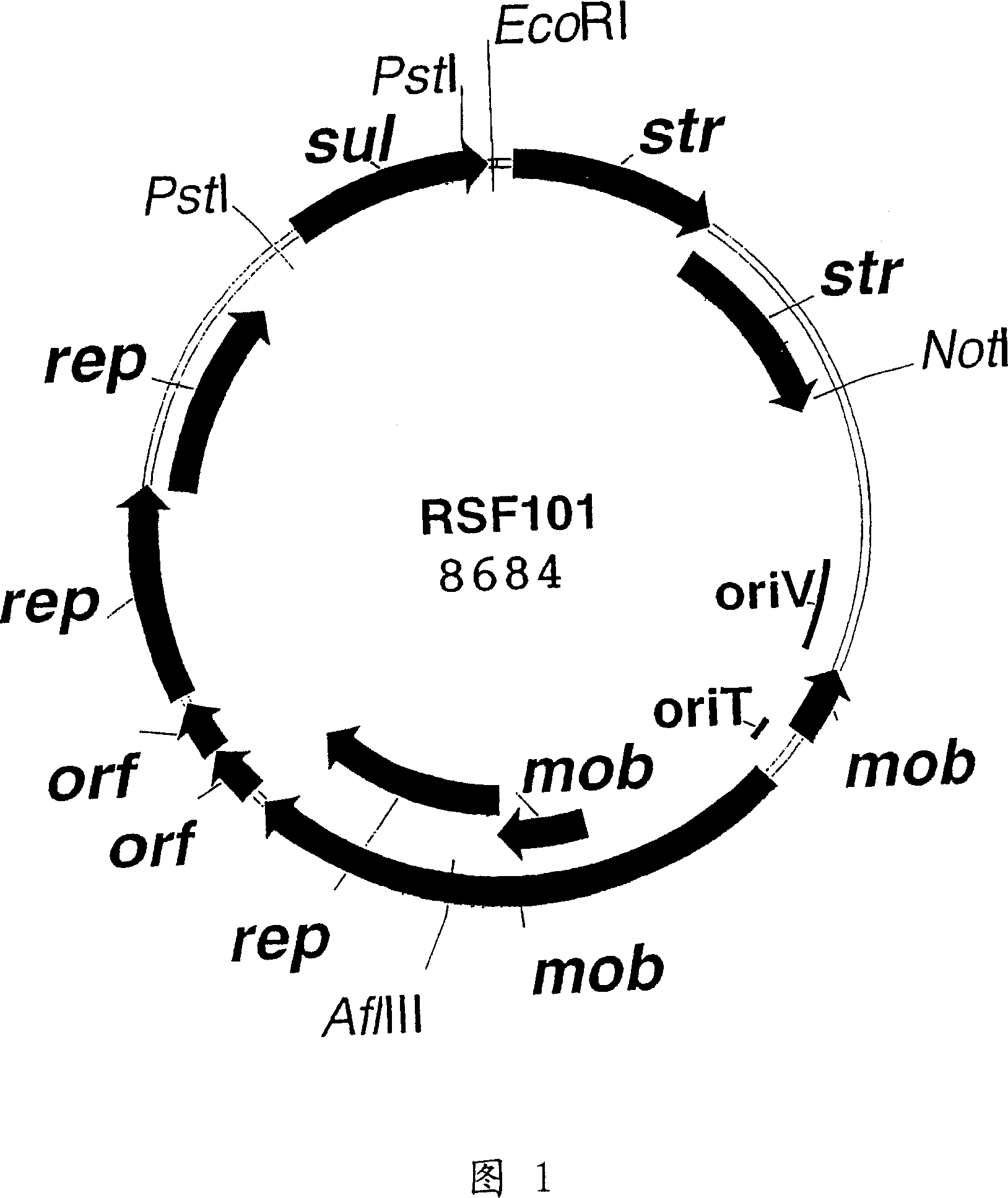
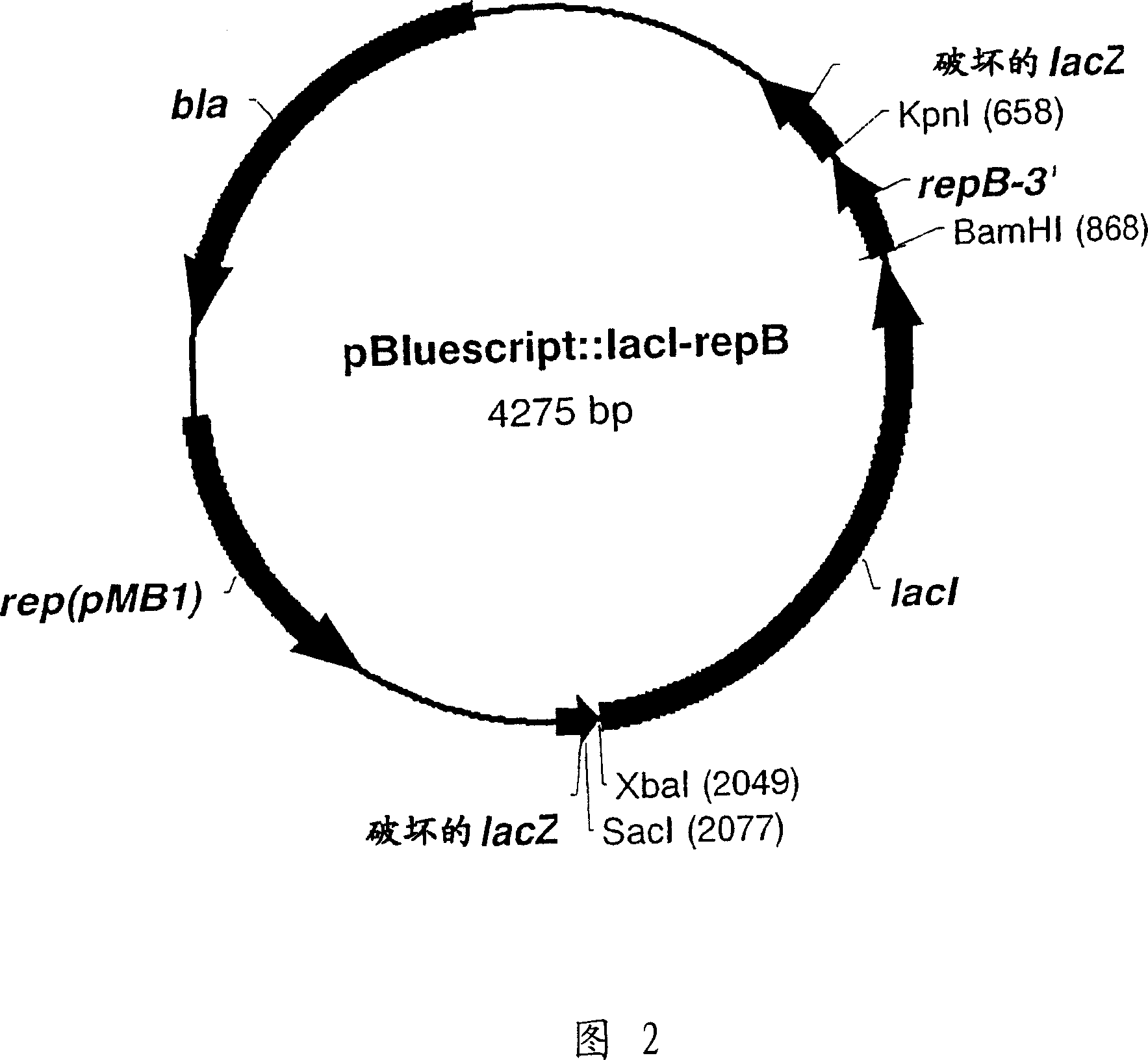
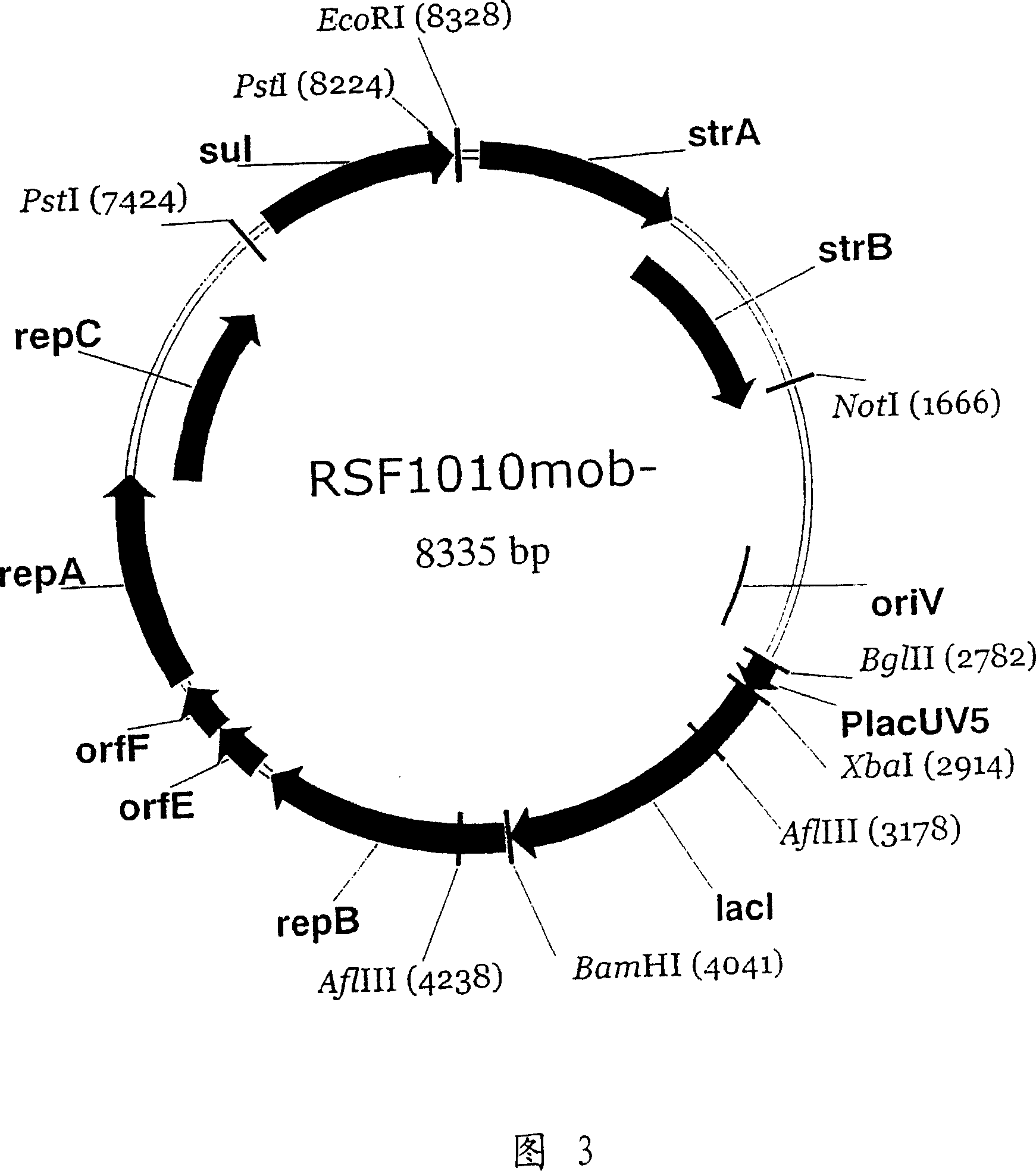
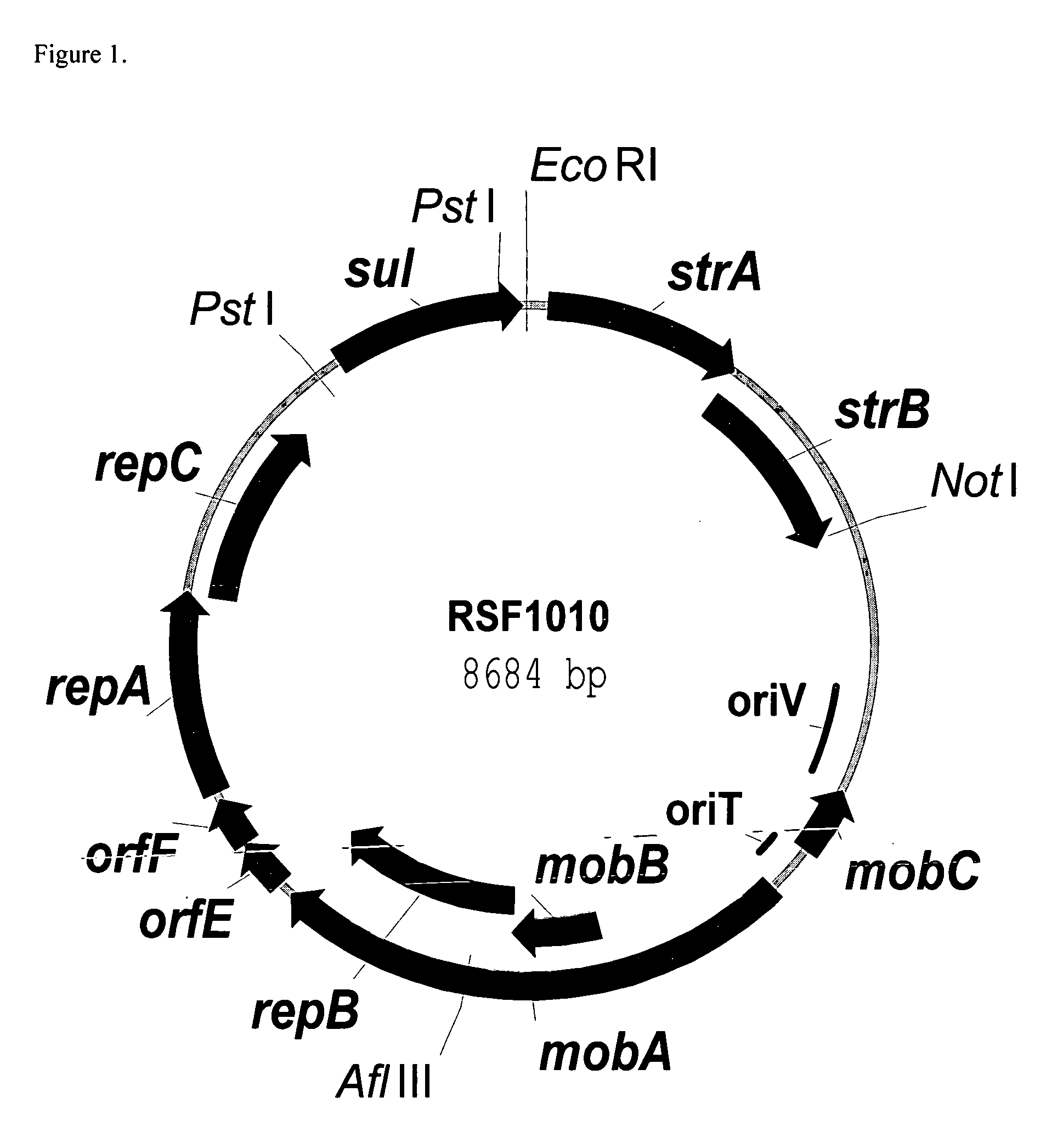
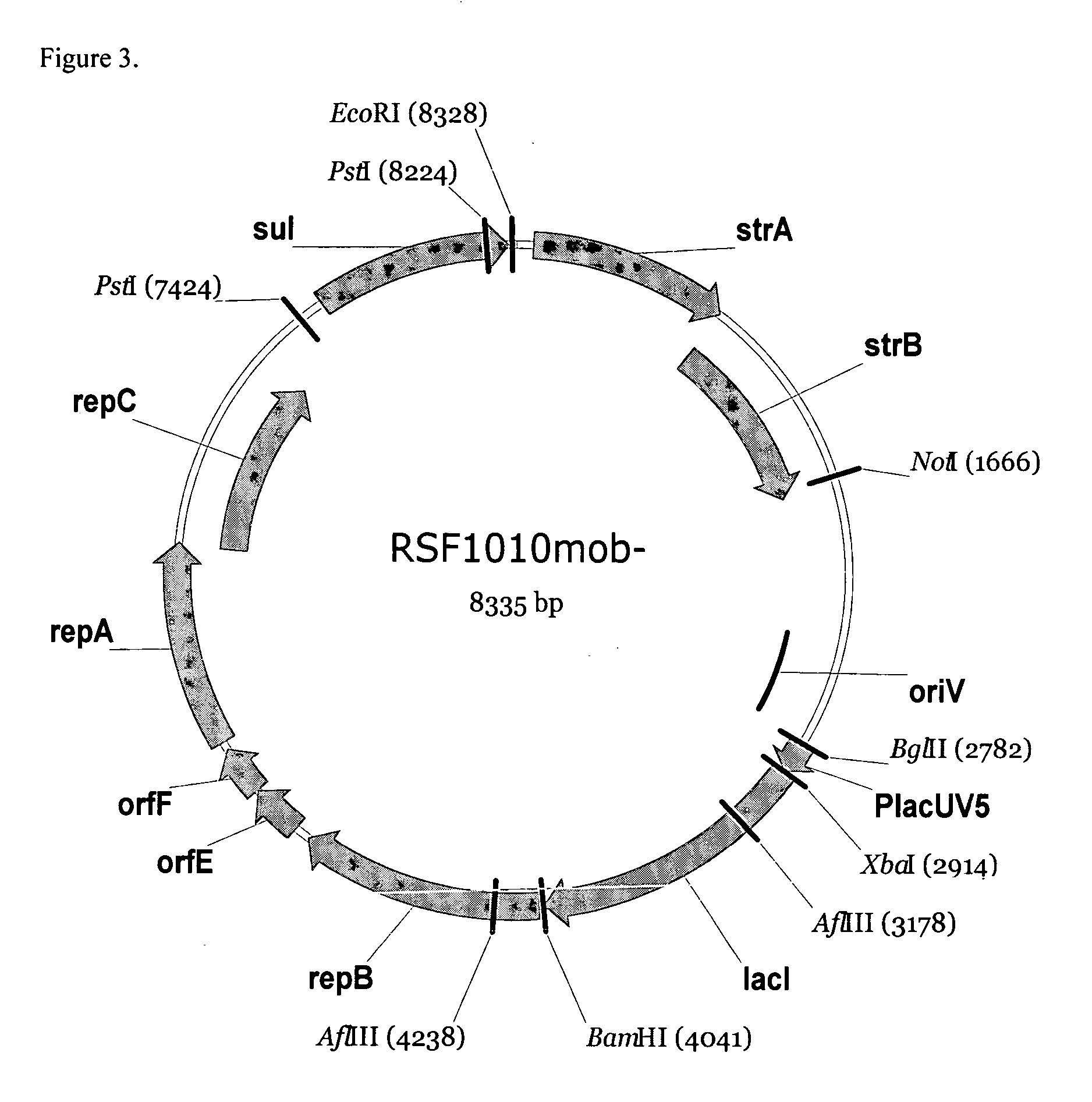
RSF1010 derivative Mob' plasmid containing no antibiotic resistance gene, bacterium comprising the plasmid and method for producing useful metabolites
A Mob− plasmid having a RSF1010 replicon, comprising a gene coding for Rep protein and said plasmid has been modified to inactivate gene related to mobilization ability. The present invention also describes a bacterium having an ability to produce useful metabolites, comprising the plasmid and said bacterium lack active thymidylate synthase coded by thyA gene and thymidine kinase coded by tdk gene, and a method for producing useful metabolites, such as native or recombinant proteins, enzymes, L-amino acids, nucleosides and nucleotides, vitamins, using the bacterium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
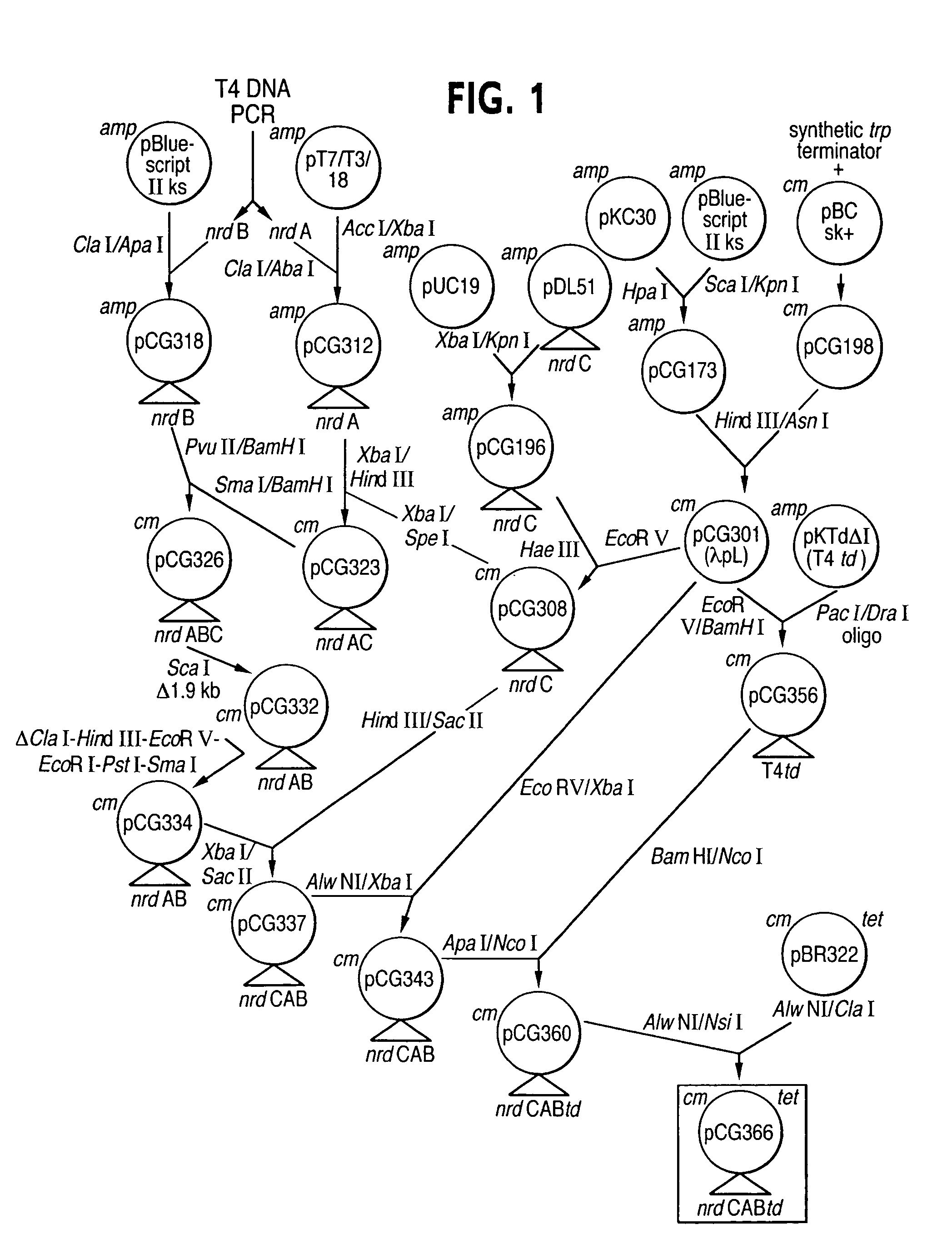
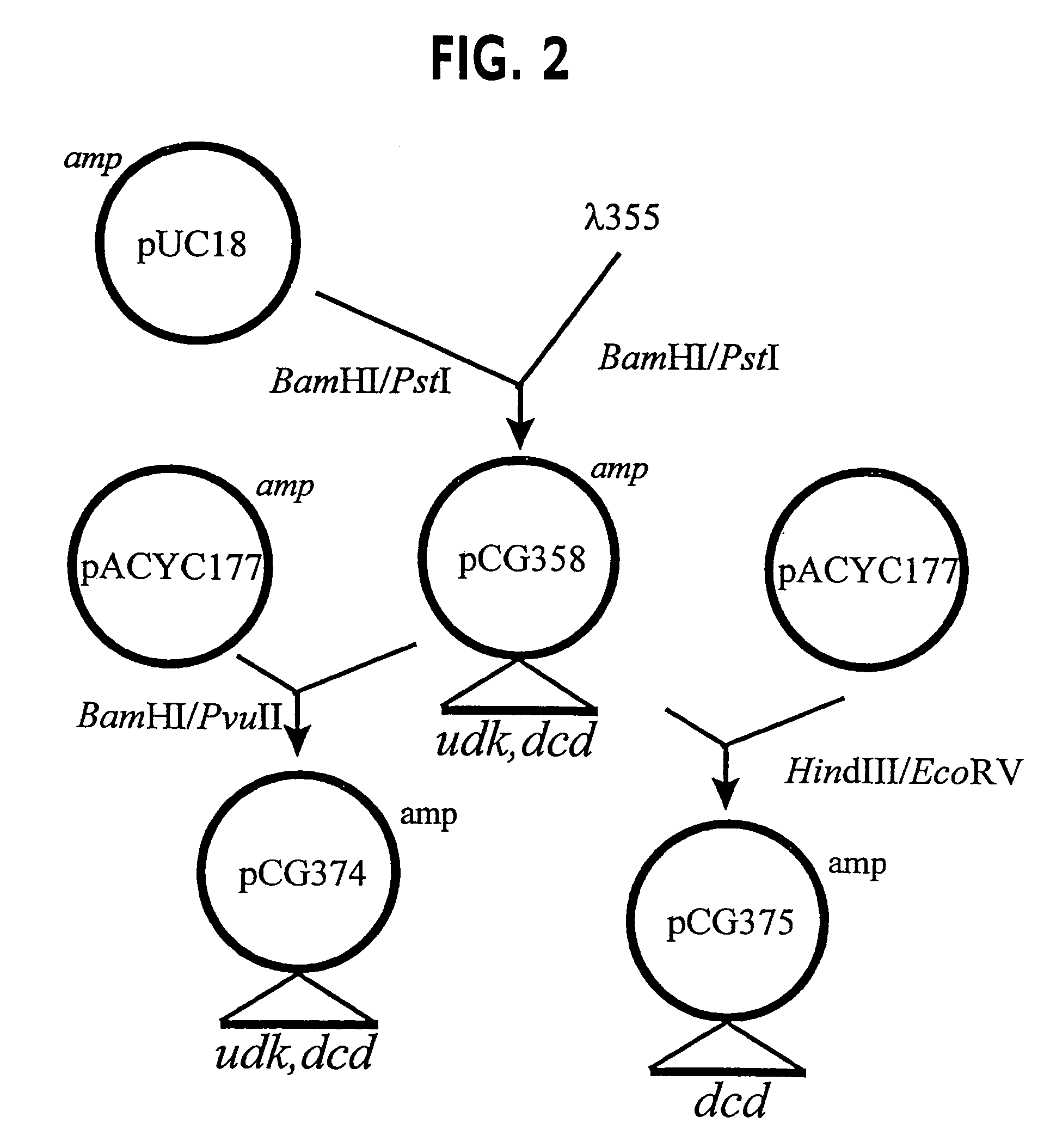
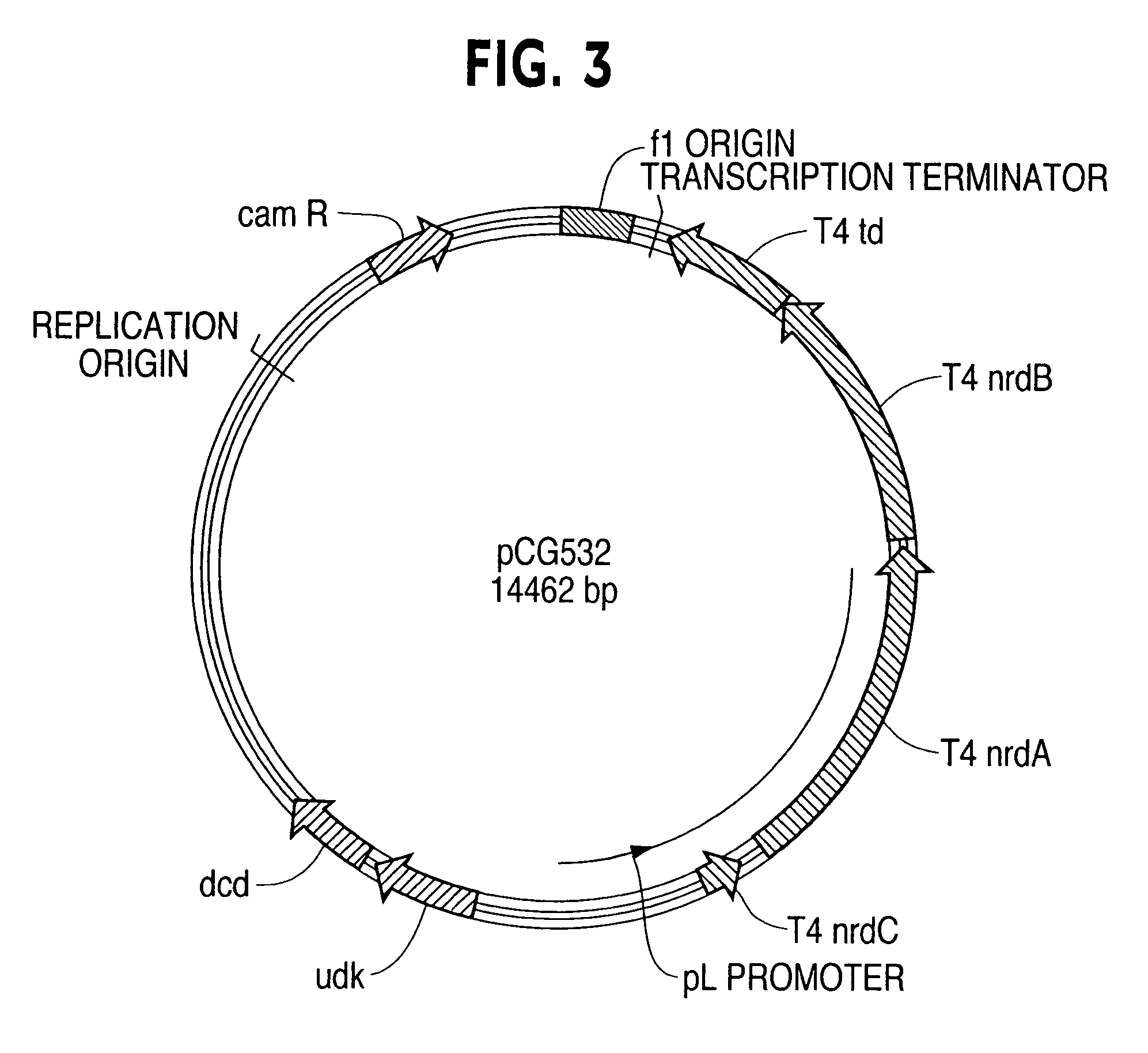
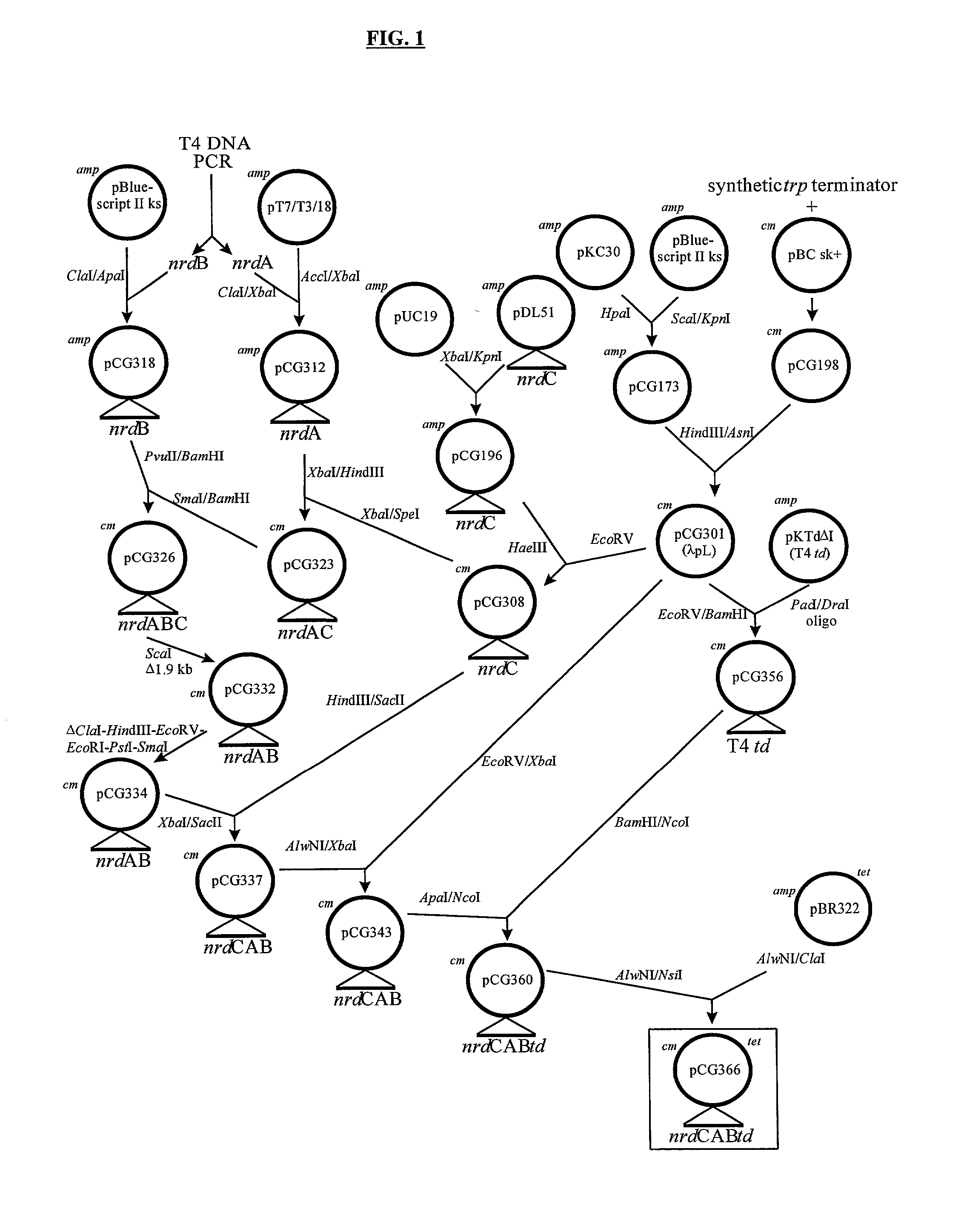
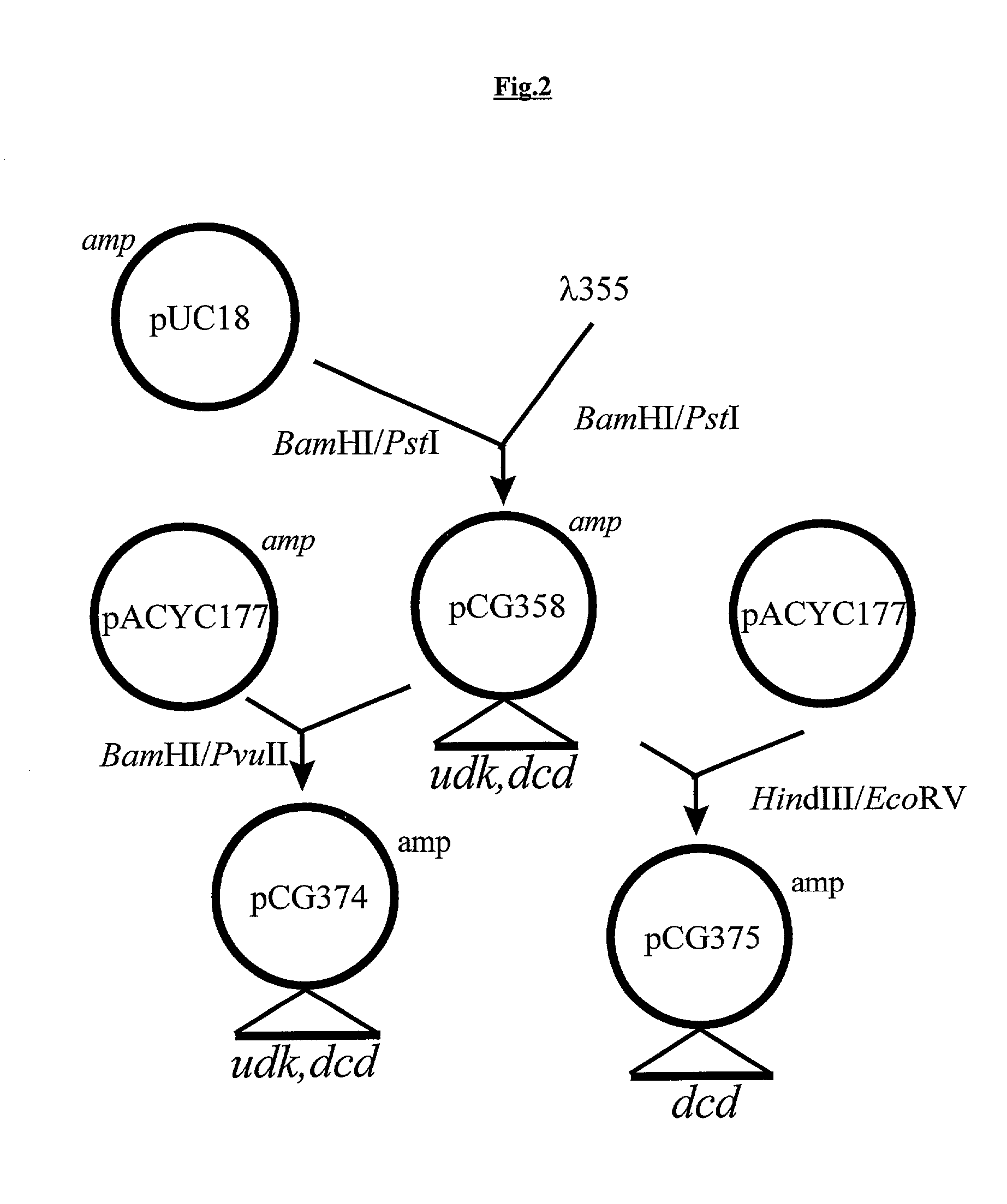
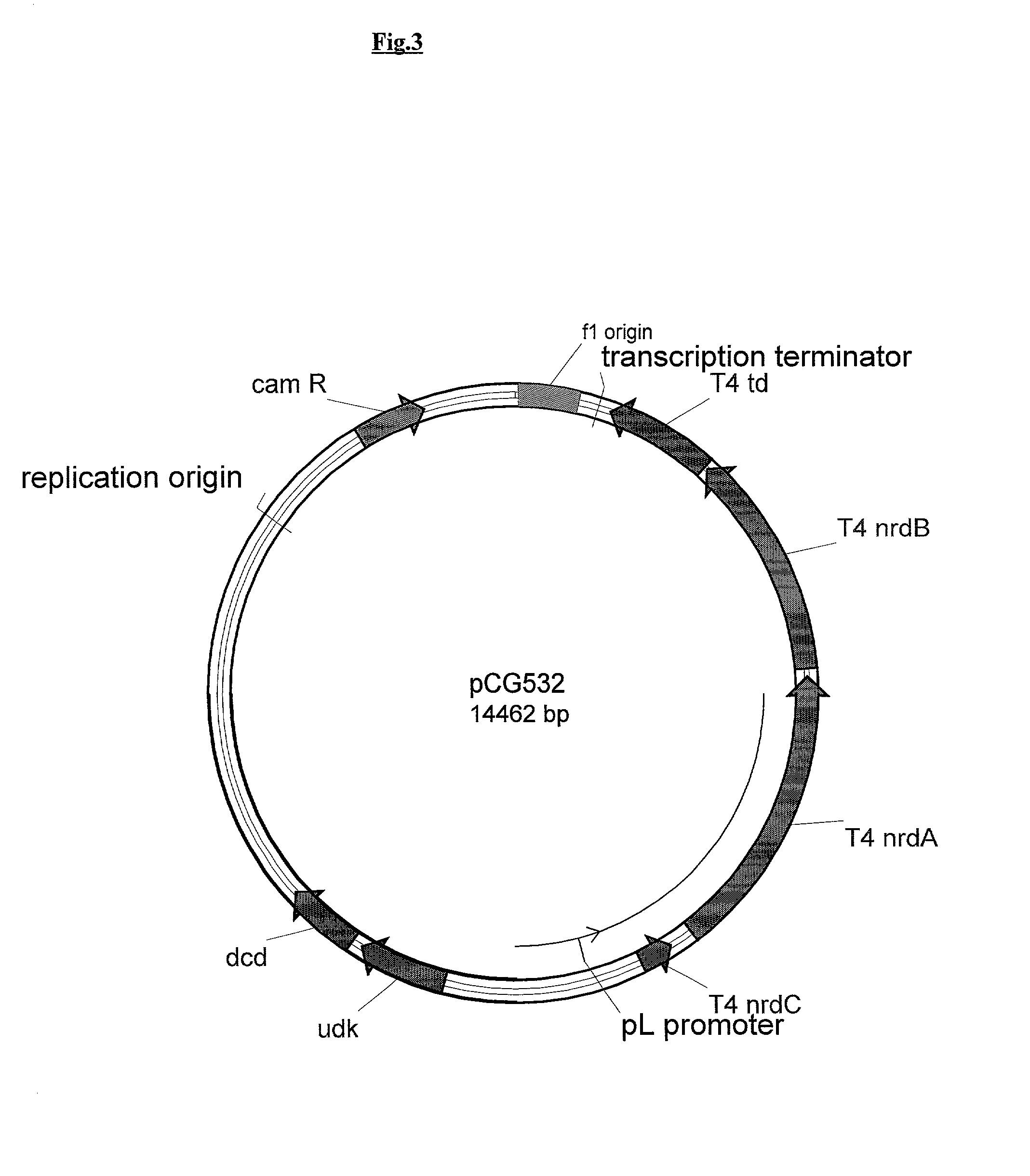
Vectors, cells and processes for pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides production
Novel DNA constructs and host cells comprising the same are disclosed. DNA constructs comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin. In preferred embodiments, constructs further comprise DNA sequences encoding for thymidylate synthase and / or transcription units comprising sequences encoding for uridine kinase preferably together with dCTP deaminase. In particularly preferred embodiments, host cells comprising constructs having all of the above characteristics wherein the host cell displays repressed or no uracil DNA glycosylase activity. This may be achieved by removal of the host cell ung gene. Use of host cells in the manufacture of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides e.g. thymidine is also disclosed.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
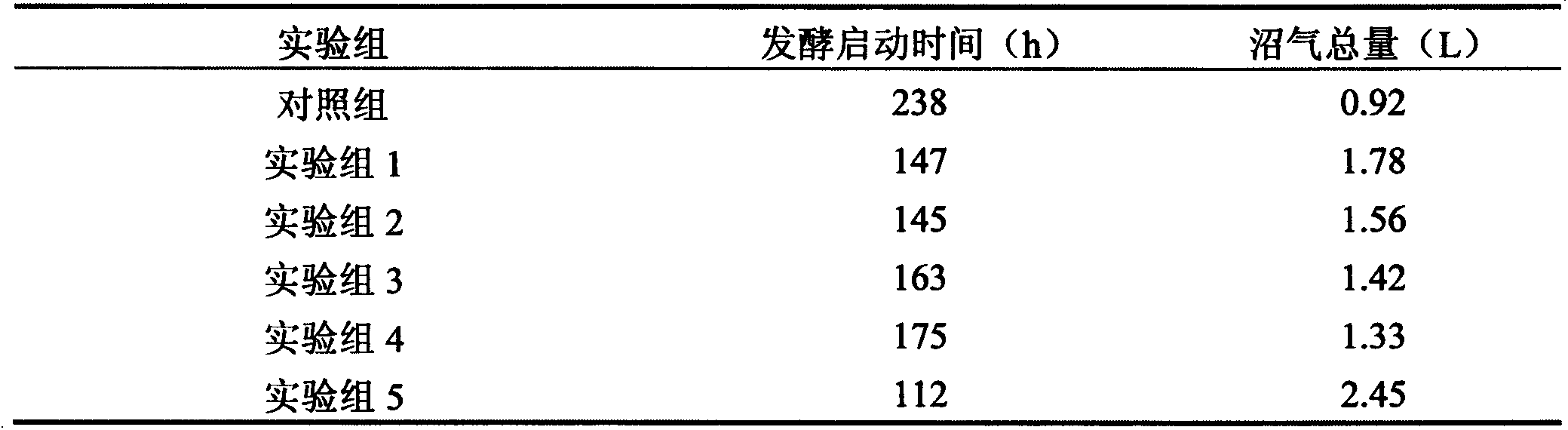
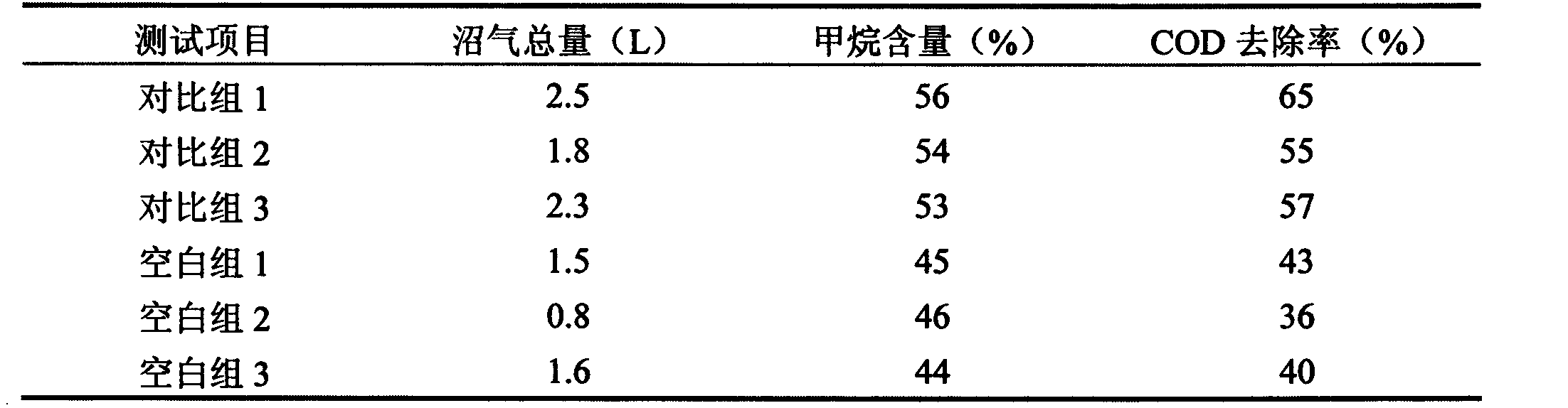
Biogas fermentation accelerant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103255179AThe promotion effect is obviousWaste based fuelFermentationChemical oxygen demandTrace metal
The invention discloses a preparation method of a biogas fermentation accelerant. The fermentation accelerant comprises trace metal elements such as Fe, Co, Ni and Zn. The preparation method comprise the following steps of preparing a thick salt solution in a chloride form; adding quantified thick salt solution into a fermenting methane pool every day, then stirring for well mixing the metal elements in fermentation liquor. The accelerant has good effect for biogas fermentation taking cow dung, pig manure and sheep manure as raw materials, and has good immediate effect on methanogens in biogas fermentation; if the accelerant is added in biogas fermentation, the methane yield can be improved and the methane content of the methane can be improved, the removal rate of COD (chemical oxygen demand), TS (thymidylate synthase) and VS can be obviously improved, and the accelerant has good prospect for promotion and application of the biogas fermentation.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Tricyclic compounds having cytostatic and/or cytotoxic activity and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20090062318A1Reduce resistanceOvercome costsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsThymidylate synthaseDihydrofolate reductase
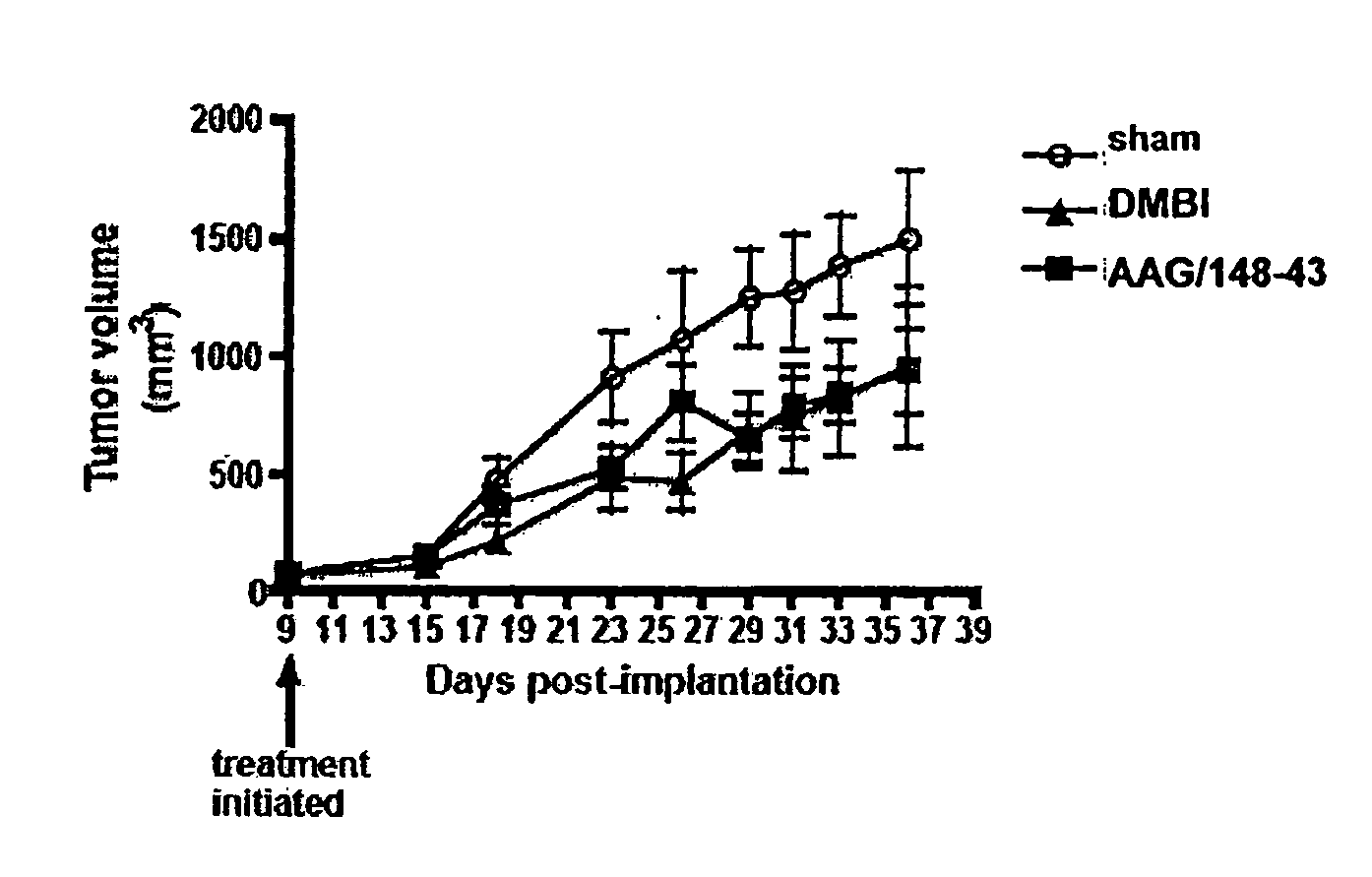
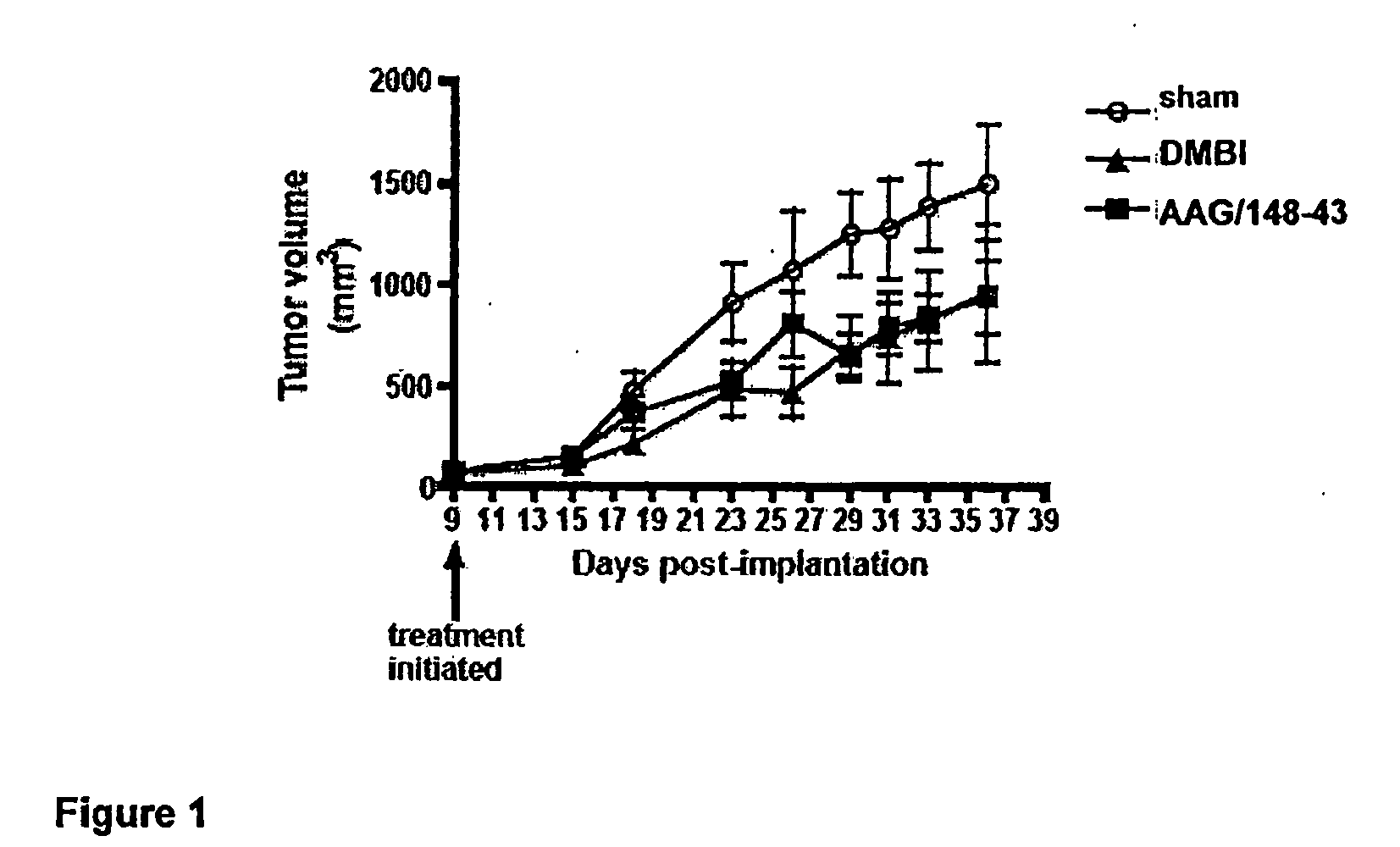
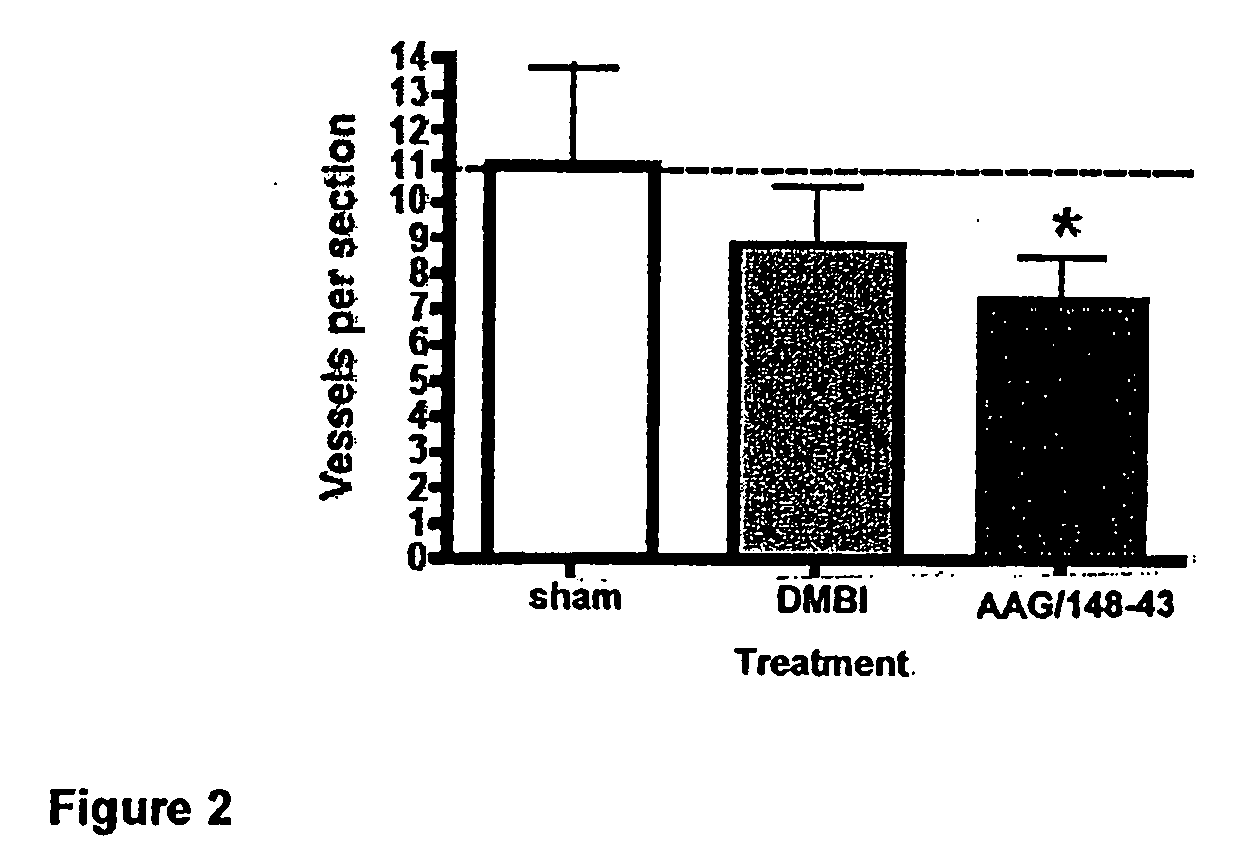
The present invention provides tricyclic compounds having cytostatic and cytotoxic activity in a single molecule having receptor tyrosine kinase(s), dihydrofolate reductase, thymidylate synthase and / or dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitory activity, which are useful as anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor agents. Also provided are methods of utilizing these inhibitors to treat tumor cells and other proliferative diseases and disorders.
Owner:DUQUESNE UNIVERSITY
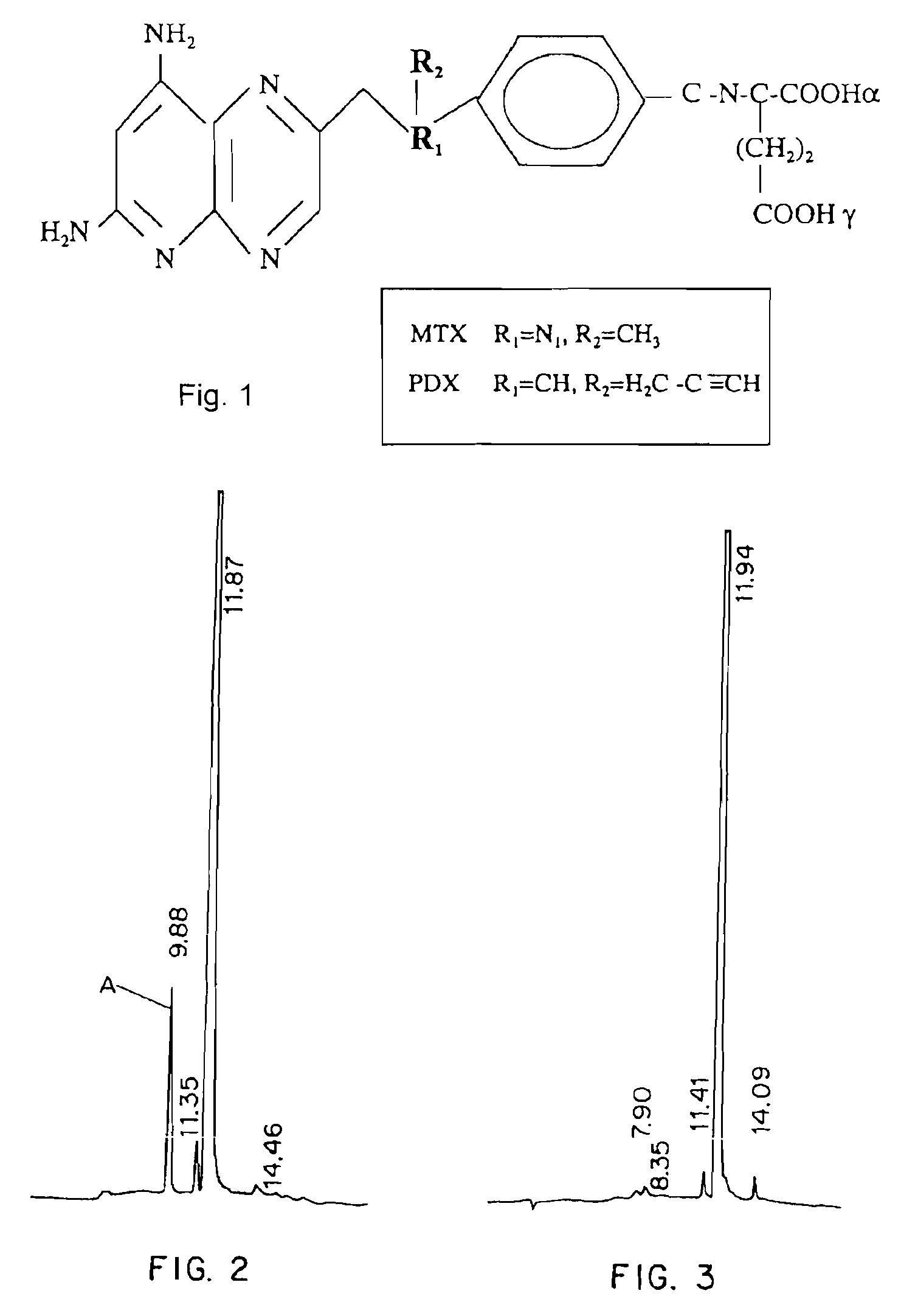
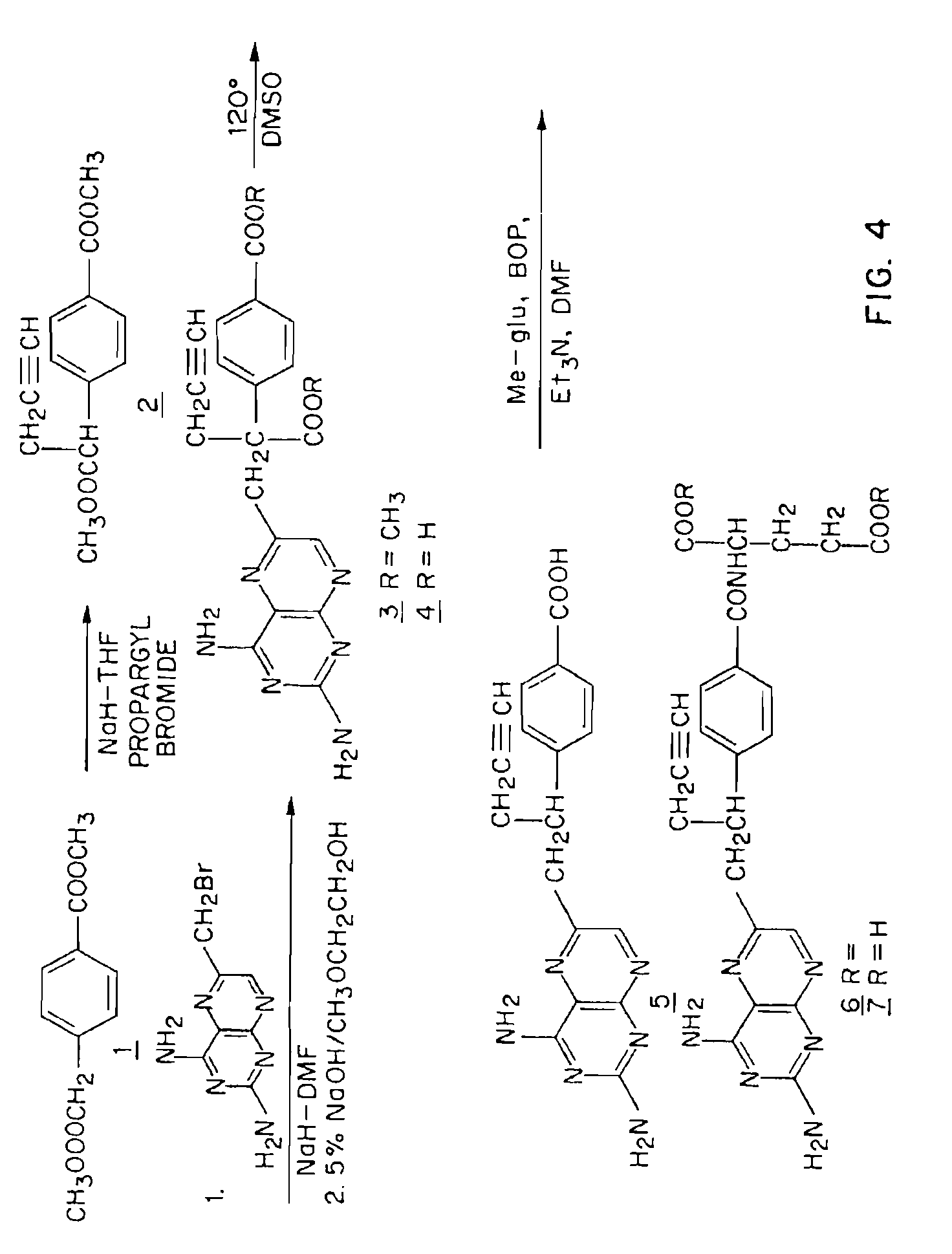
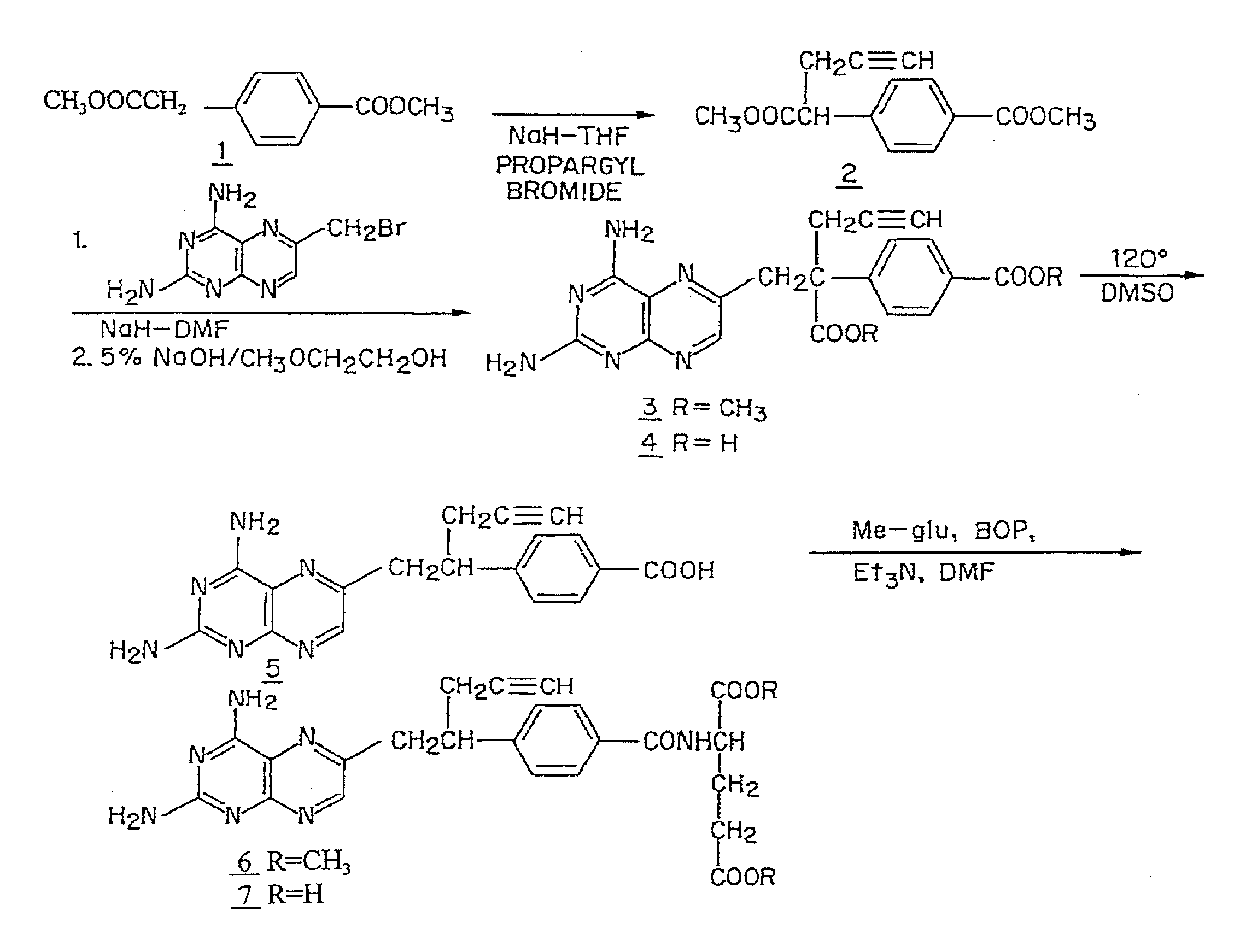
Methods for assessing cancer for increased sensitivity to 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin
ActiveUS20110111436A1Disease diagnosisGlycinamide Ribonucleotide FormyltransferaseThymidylate synthase
Sensitivity of a patient's cancer to treatment with 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin is assessed and patients are selected for treatment of cancer with 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin, by determining the amount of a selected polypeptide expressed by the cancer and comparing the amount with the amount of the selected polypeptide expressed by a reference cancer. The polypeptide includes a member of a folate pathway polypeptide within a cell and may include at least one of reduced folate carrier-1 enzyme (RFC-1), dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), folylpoly-gamma-glutamate synthetase (FPGS), thymidylate synthase (TS), γ-glutamyl hydrolase (GGH), and glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase (GARFT).
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
Tricyclic compounds having cytostatic and/or cytotoxic activity and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7960400B2Reduce resistanceOvercome costsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDihydrofolate reductaseThymidylate synthase
The present invention provides tricyclic compounds having cytostatic and cytotoxic activity in a single molecule having receptor tyrosine kinase(s), dihydrofolate reductase, thymidylate synthase and / or dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitory activity, which are useful as anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor agents. Also provided are methods of utilizing these inhibitors to treat tumor cells and other proliferative diseases and disorders.
Owner:DUQUESNE UNIVERSITY
Method of Treating Cancer by Inhibition of DNA Repair Proteins
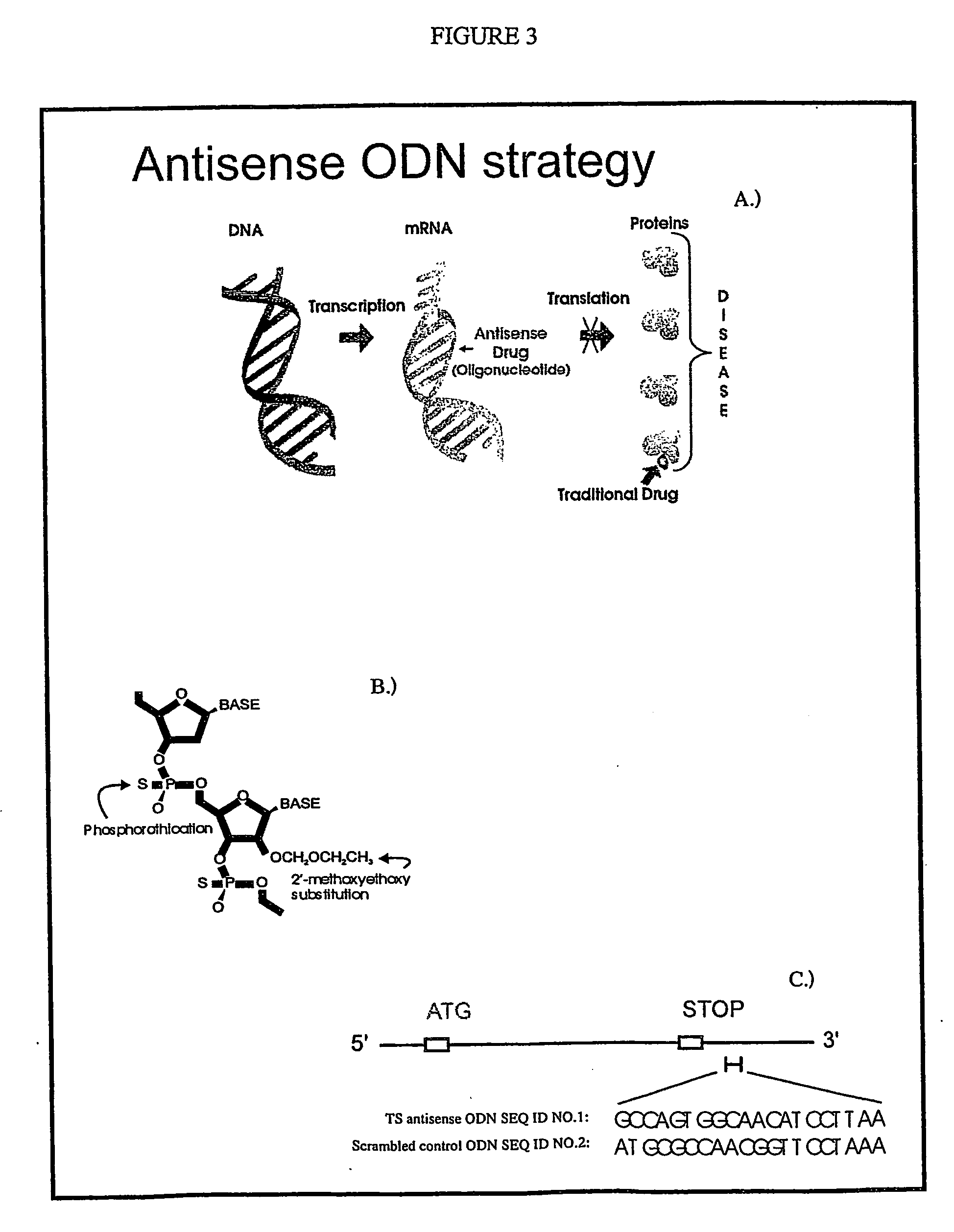
Methods of treating cancer using antisense oligonucleotides directed against DNA double-strand break repair proteins such as BRCA2 or RAD51 are provided. The antisense oligonucleotides can be used alone, in tandem or in combination with other cancer therapies, in particular with therapies that lead to DNA damage, inhibition of DNA repair or inhibition of DNA synthesis, such as radiation, platinum drugs, alkylating agents, PARP inhibitors, or inhibitors of thymidylate synthase.
Owner:SARISSA
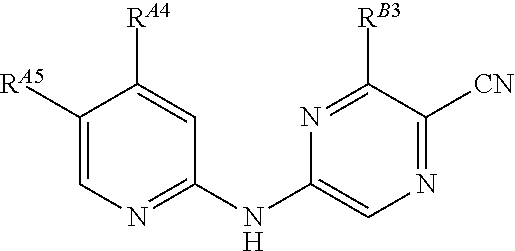
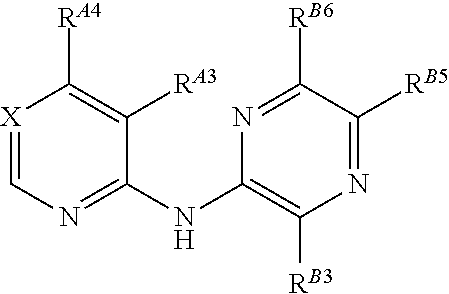
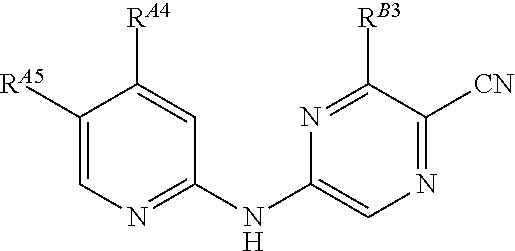
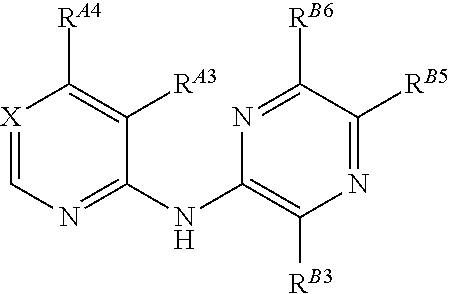
5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof
The present invention pertains generally to the field of therapeutic compounds. More specifically the present invention pertains to 5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile compounds (referred to herein as “TFM compounds”) which, inter alia, inhibit Checkpoint Kinase 1 (CHK1) kinase function. The present invention also pertains to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, and the use of such compounds and compositions, both in vitro and in vivo, to inhibit CHK1 kinase function, and in the treatment of diseases and conditions that are mediated by CHK1, that are ameliorated by the inhibition of CHK1 kinase function, etc., including proliferative conditions such as cancer, etc., optionally in combination with another agent, for example, (a) a DNA topoisomerase I or II inhibitor; (b) a DNA damaging agent; (c) an antimetabolite or a thymidylate synthase (TS) inhibitor; (d) a microtubule targeted agent; (e) ionizing radiation; (f) an inhibitor of a mitosis regulator or a mitotic checkpoint regulator; (g) an inhibitor of a DNA damage signal transducer; or (h) an inhibitor of a DNA damage repair enzyme.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
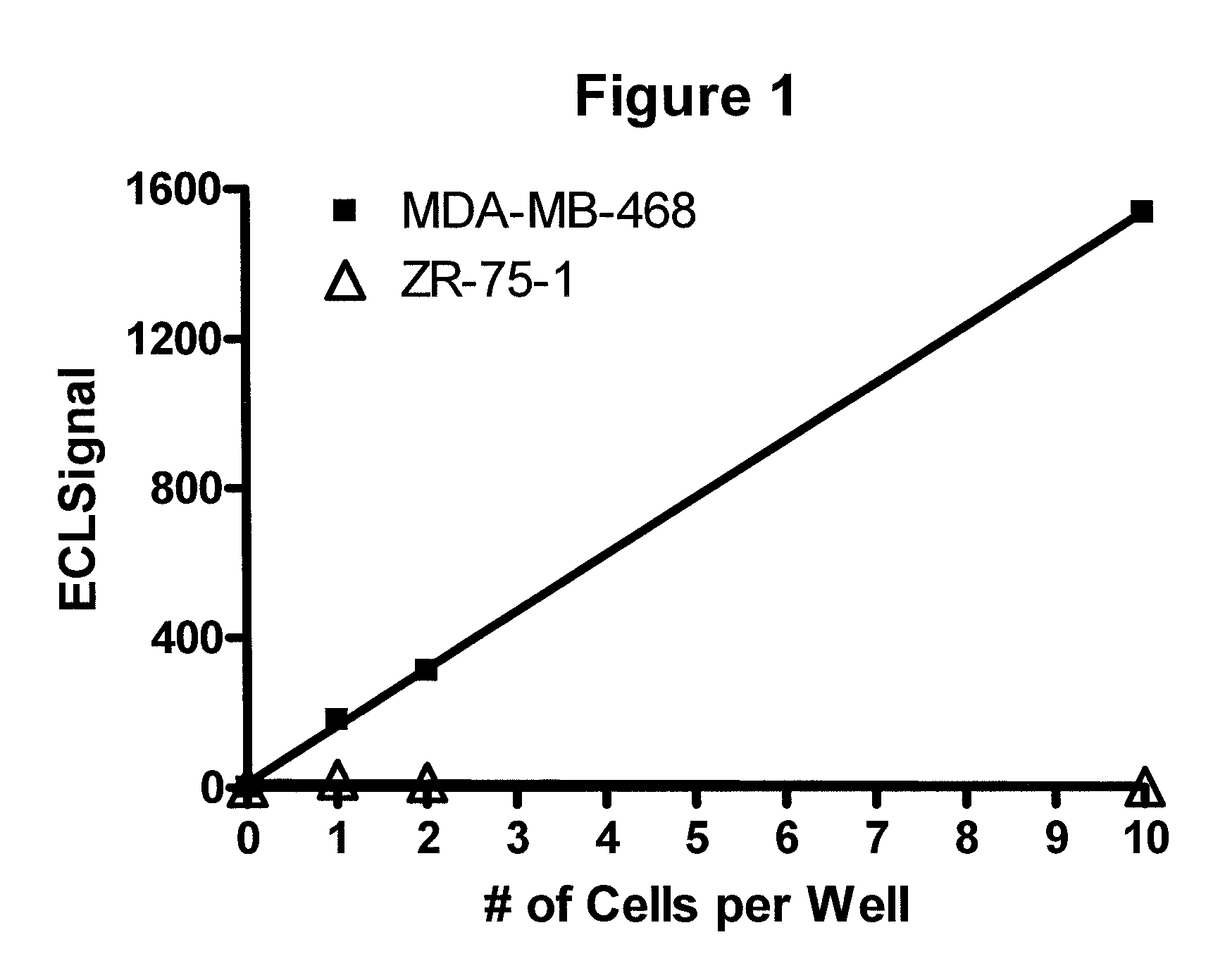
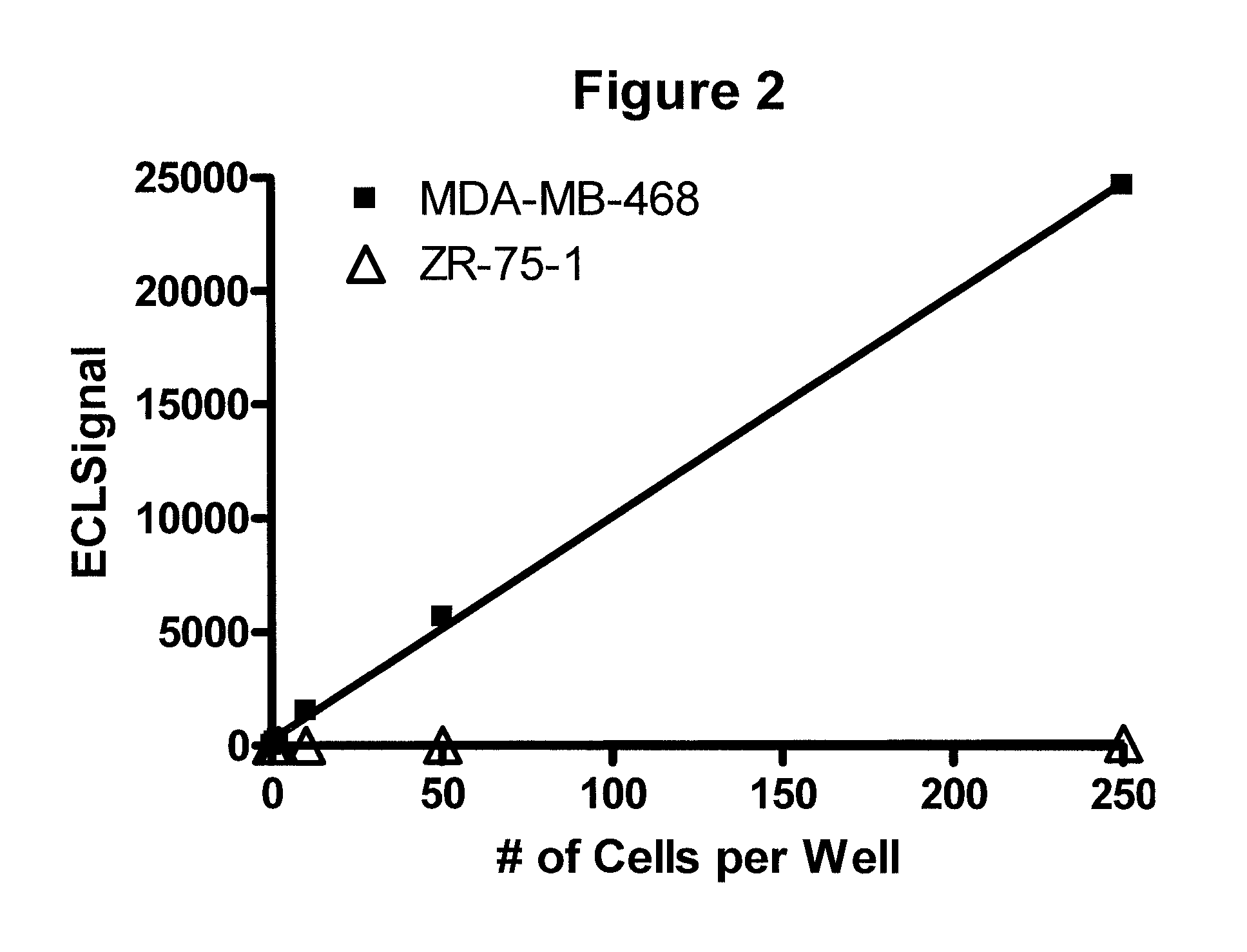
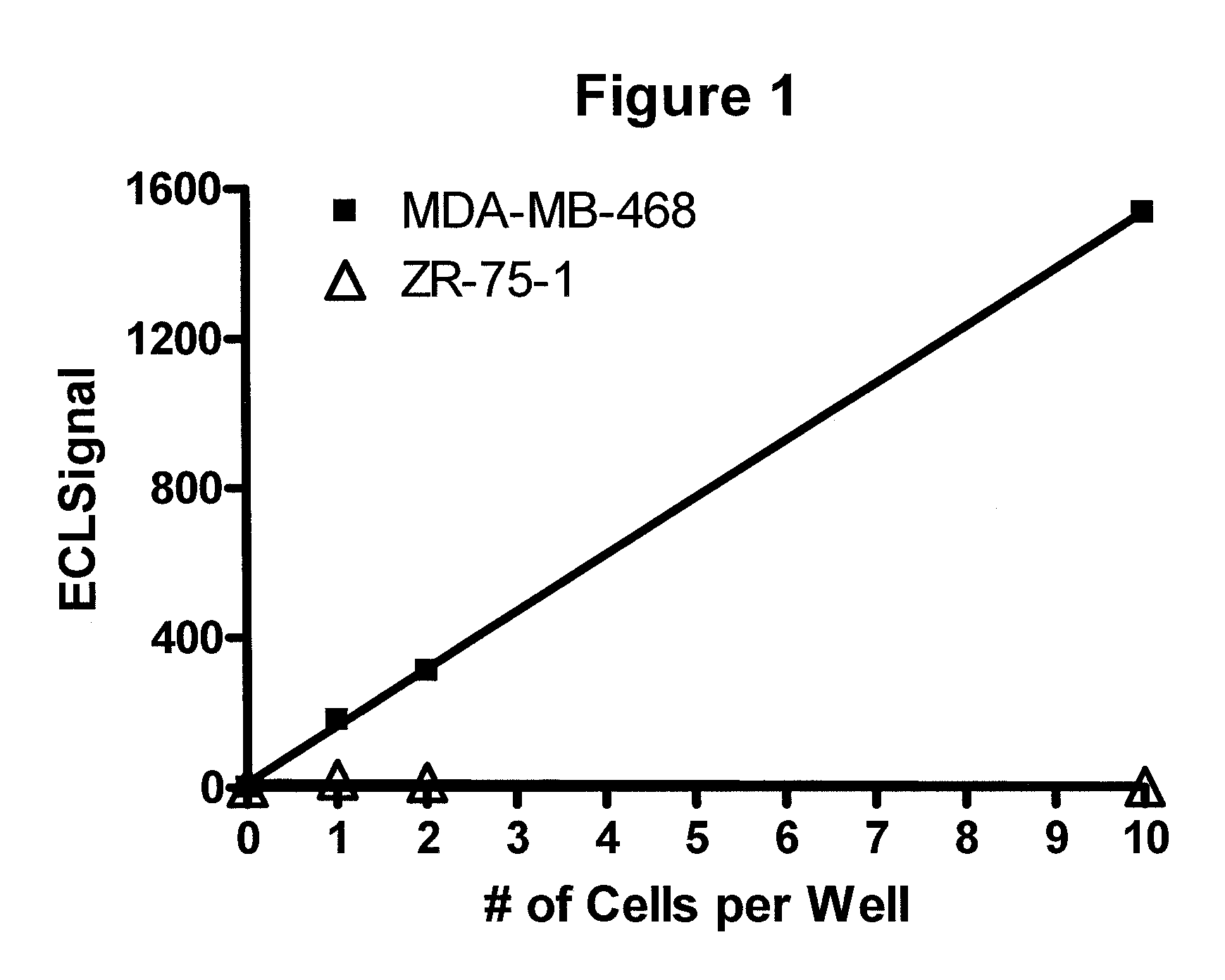
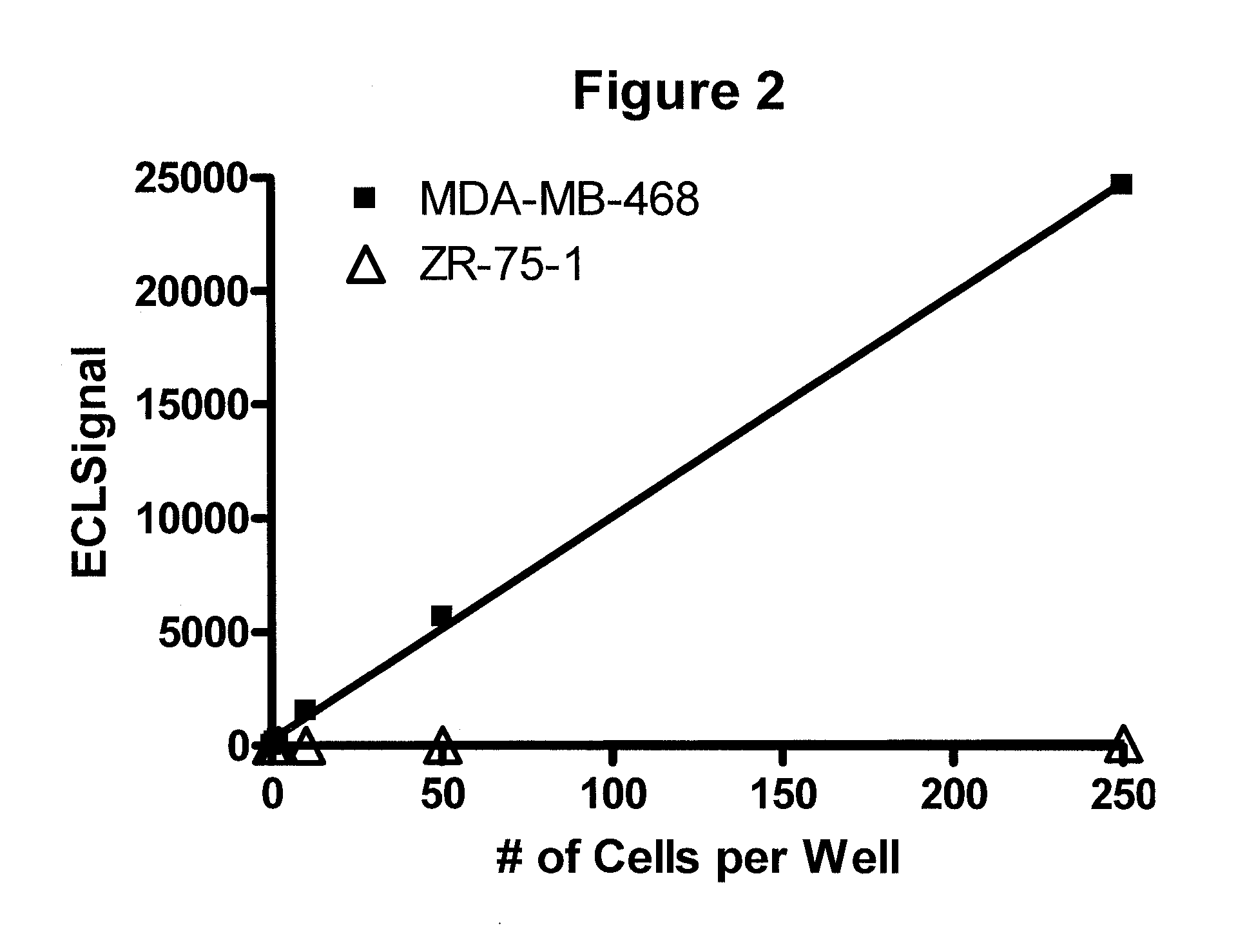
Detection of proteins from circulating neoplastic cells
InactiveUS20090098138A1The process is convenient and fastPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsErlotinibCancer cell
The protein EGFR, ERCC1, RRM1, thymidylate synthase, or beta-tubulin from cancer cells is detected in a blood sample by enriching the cancer cells from the blood sample followed by performing on the enriched cancer cells an immunoassay capable of detecting the proteins mentioned above. Cancer patients overexpressing EGFR are treated with an anti-EGFR agent, for example cetuximab, panitumumab, erlotinib or gefitinib.
Owner:WELLSTAT BIOLOGICS CORP
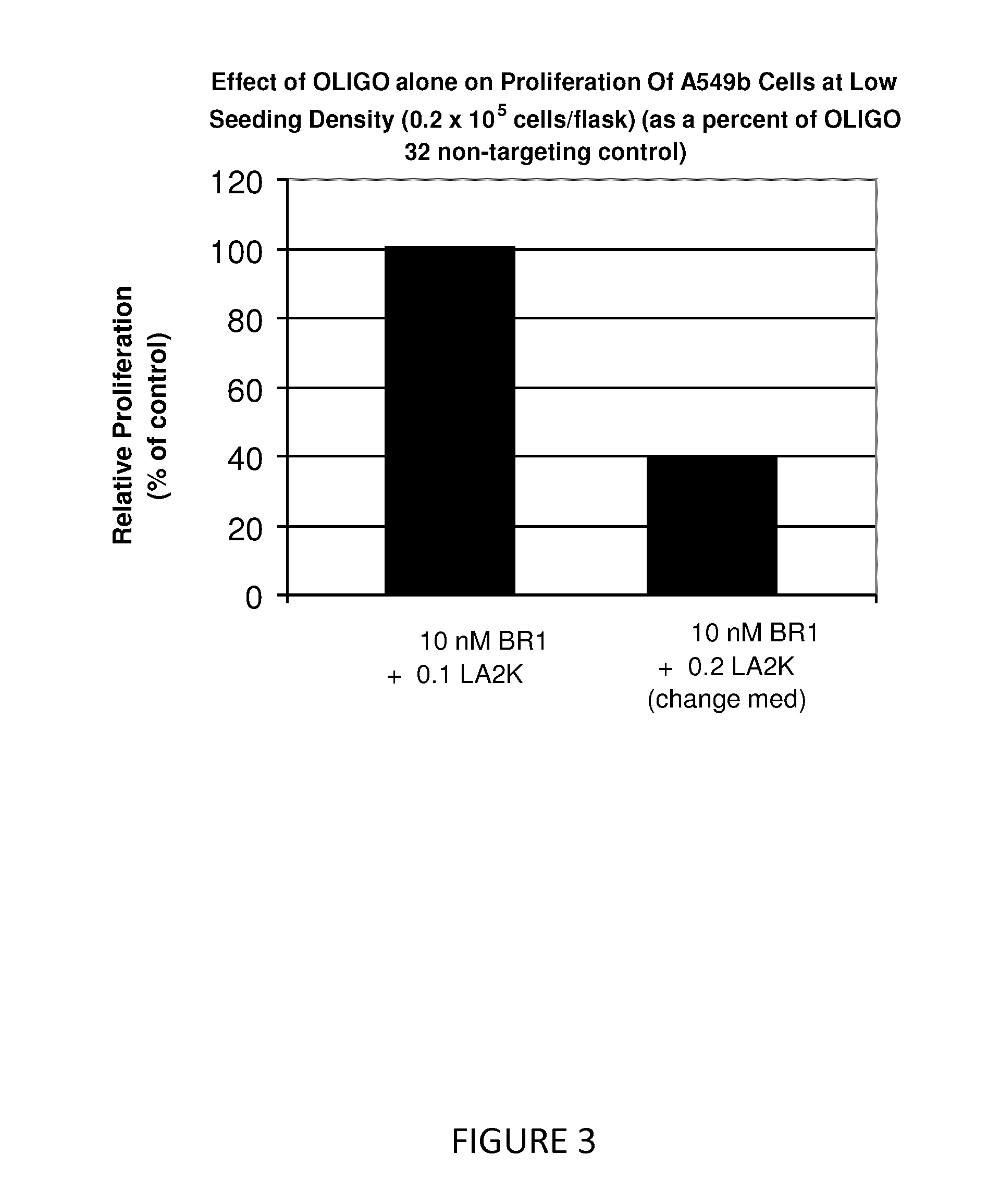
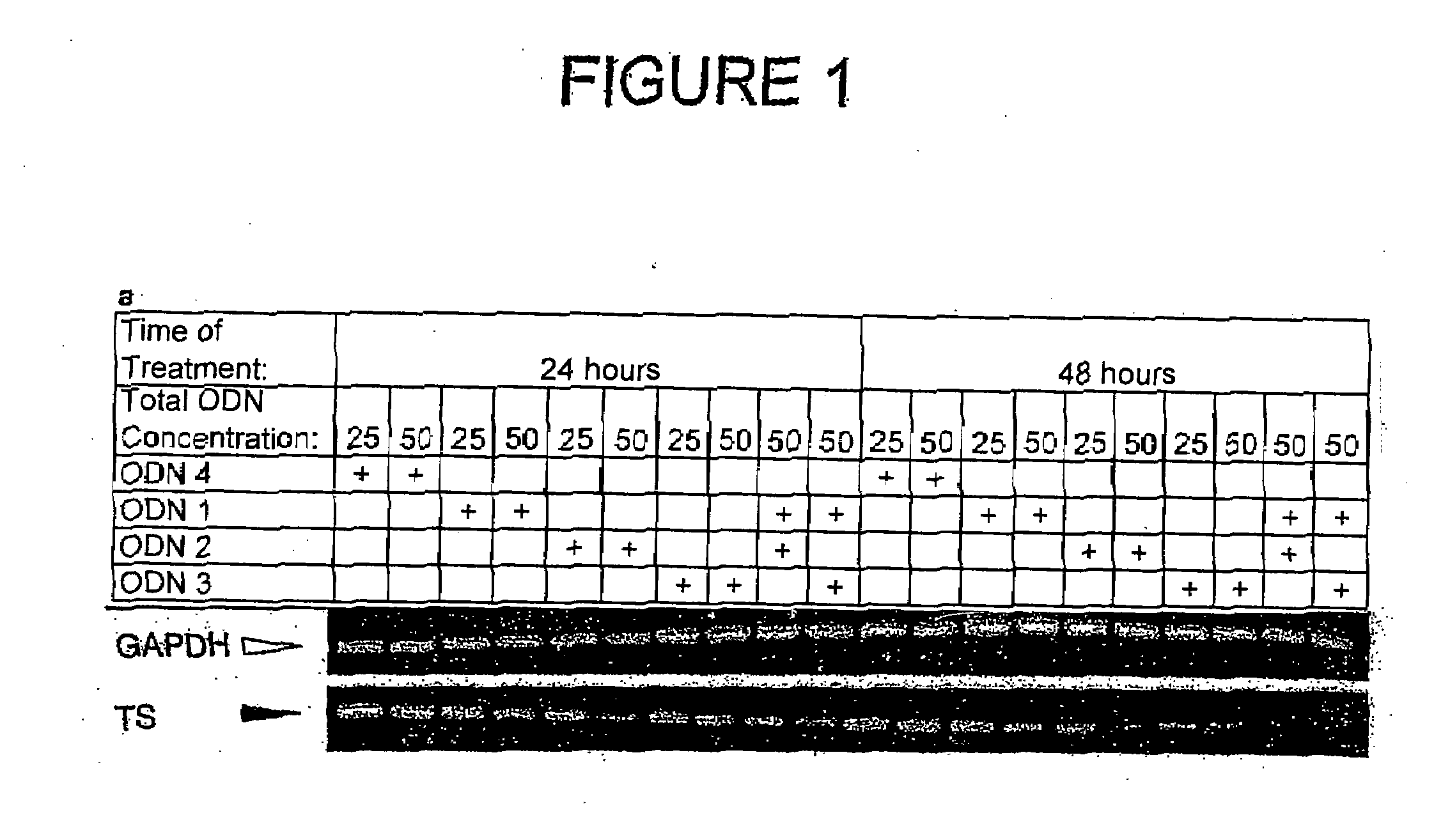
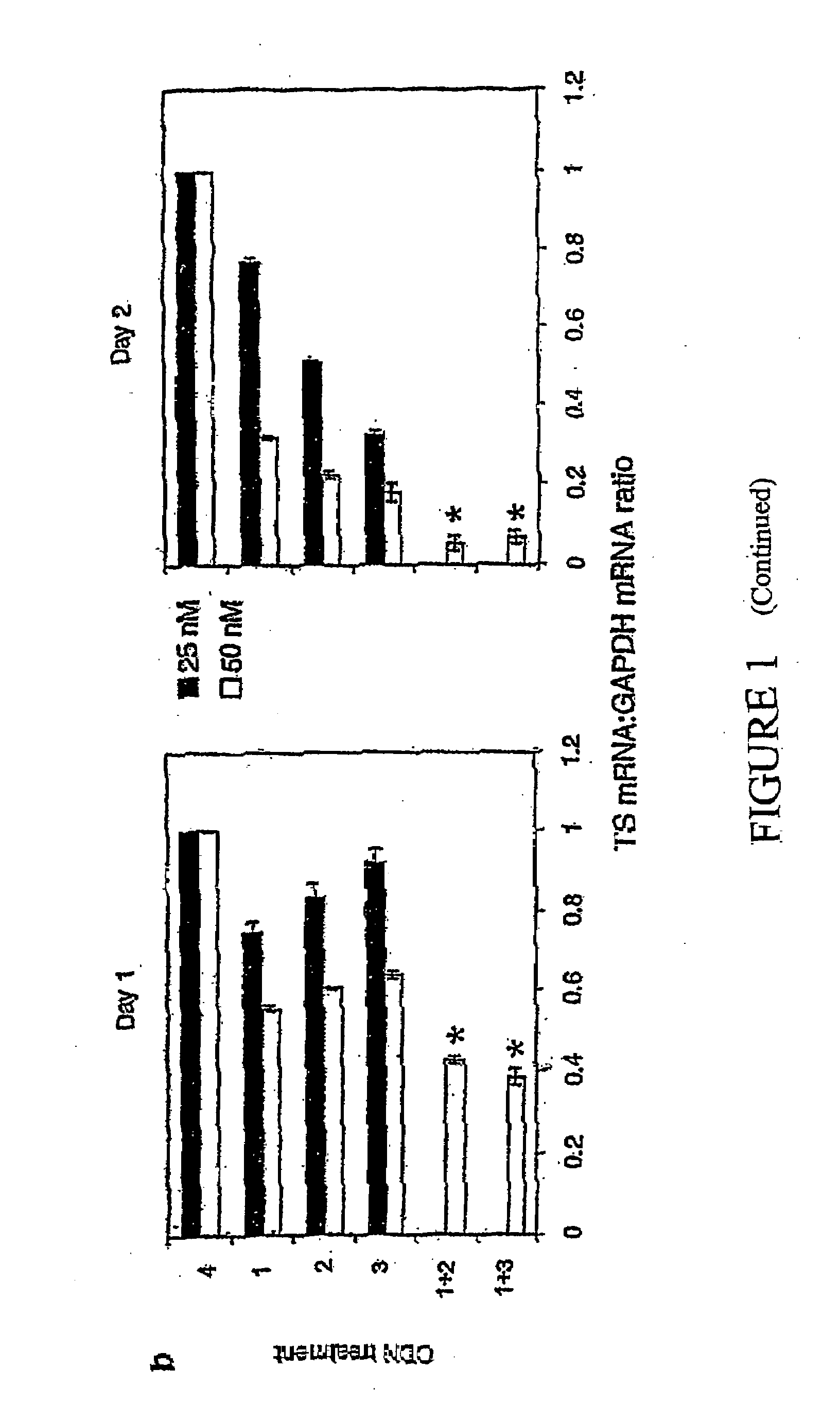
Antisense oligonucleotide strategies for the enhancement of cancer therapies
InactiveUS20080255066A1Good effectReduce the amount requiredOrganic active ingredientsFermentationAgent CombinationCancer therapy
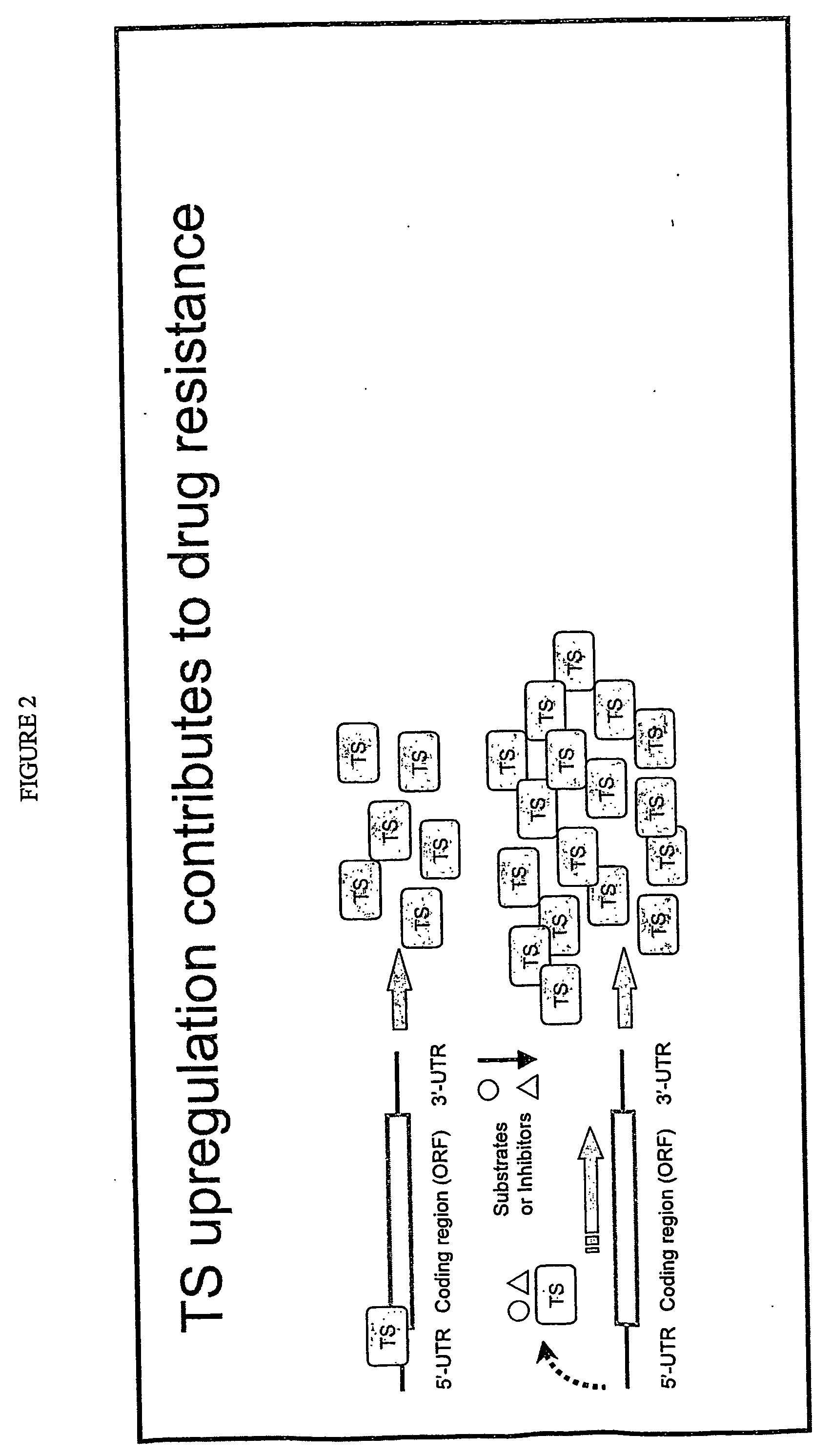
Effective combinations of antisense agents directed against thymidylate synthase mRNA are provided for use in cancer therapies. Combinations of antisense agents have enhanced activity compared to the activity of the individual antisense agents when used alone. The combinations may be used in conjunction with one or more chemotherapeutic agents to enhance the effects of the chemotherapeutic(s). Such antisense agent combinations constitute improved antisense therapies with application to a variety of cancers or proliferative disorders, including drug resistant cancers.
Owner:SARISSA
5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof
ActiveUS20150126471A1Increased endogenous replicative stressIncreased endogenous activationBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseasePyrazine
The present invention pertains generally to the field of therapeutic compounds. More specifically the present invention pertains to 5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile compounds (referred to herein as “TFM compounds”) which, inter alia, inhibit Checkpoint Kinase 1 (CHK1) kinase function. The present invention also pertains to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, and the use of such compounds and compositions, both in vitro and in vivo, to inhibit CHK1 kinase function, and in the treatment of diseases and conditions that are mediated by CHK1, that are ameliorated by the inhibition of CHK1 kinase function, etc., including proliferative conditions such as cancer, etc., optionally in combination with another agent, for example, (a) a DNA topoisomerase I or II inhibitor; (b) a DNA damaging agent; (c) an antimetabolite or a thymidylate synthase (TS) inhibitor; (d) a microtubule targeted agent; (e) ionising radiation; (f) an inhibitor of a mitosis regulator or a mitotic checkpoint regulator; (g) an inhibitor of a DNA damage signal transducer; or (h) an inhibitor of a DNA damage repair enzyme.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
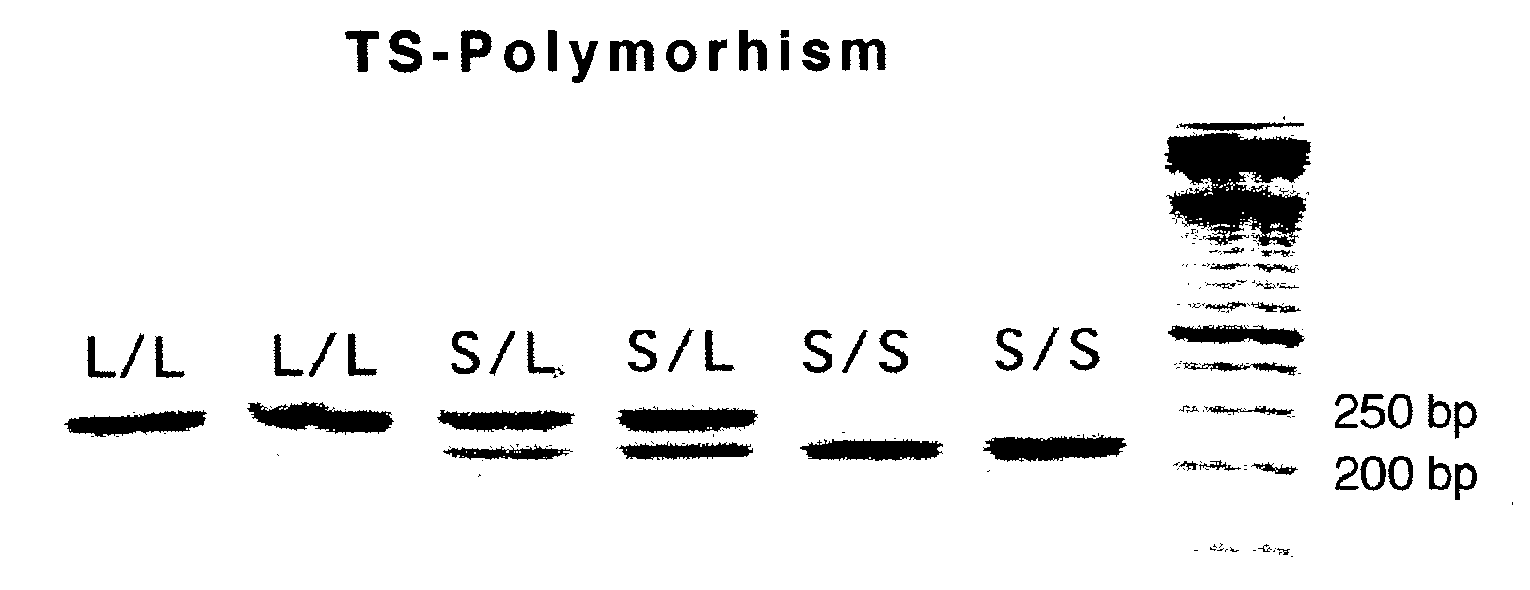
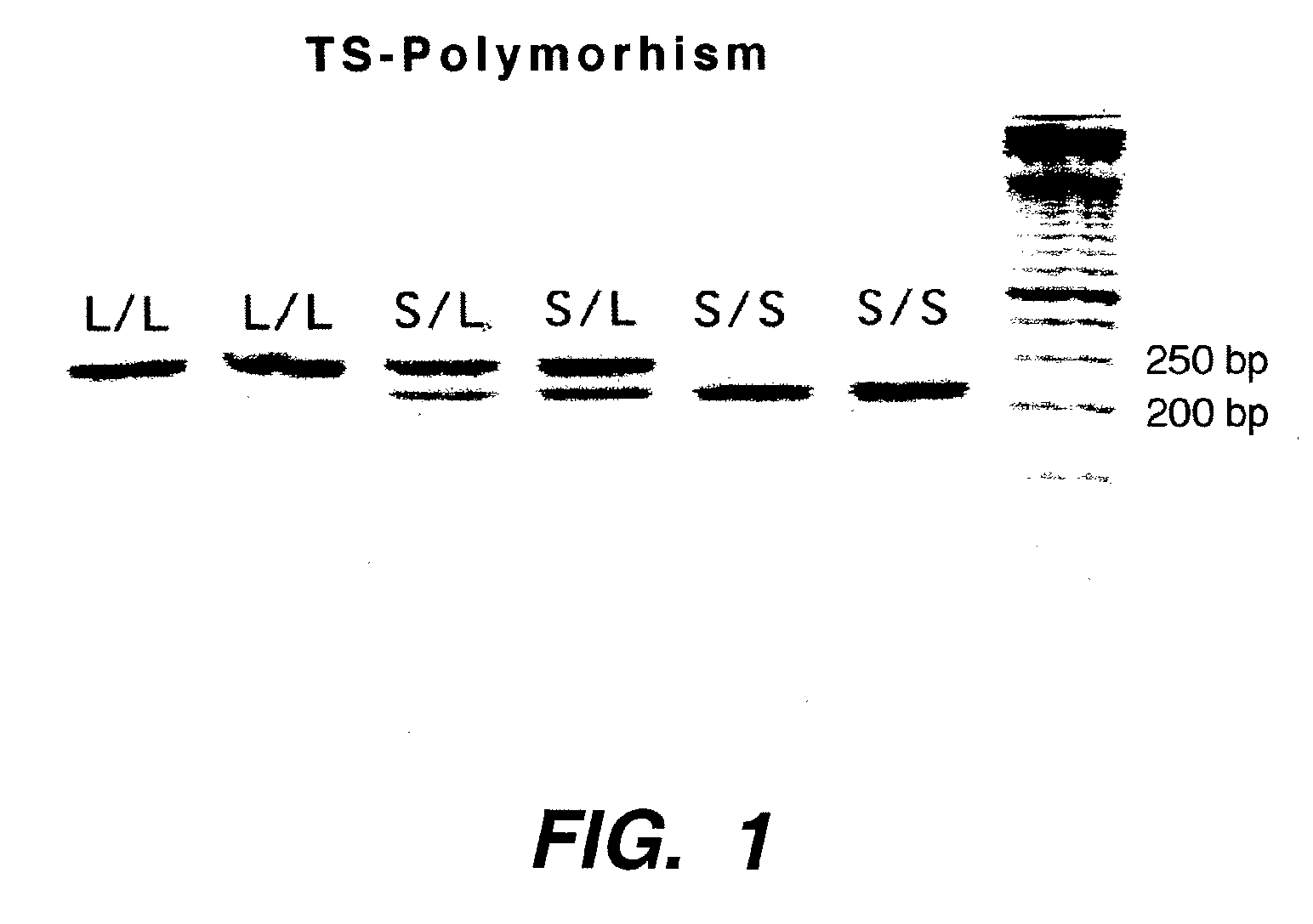
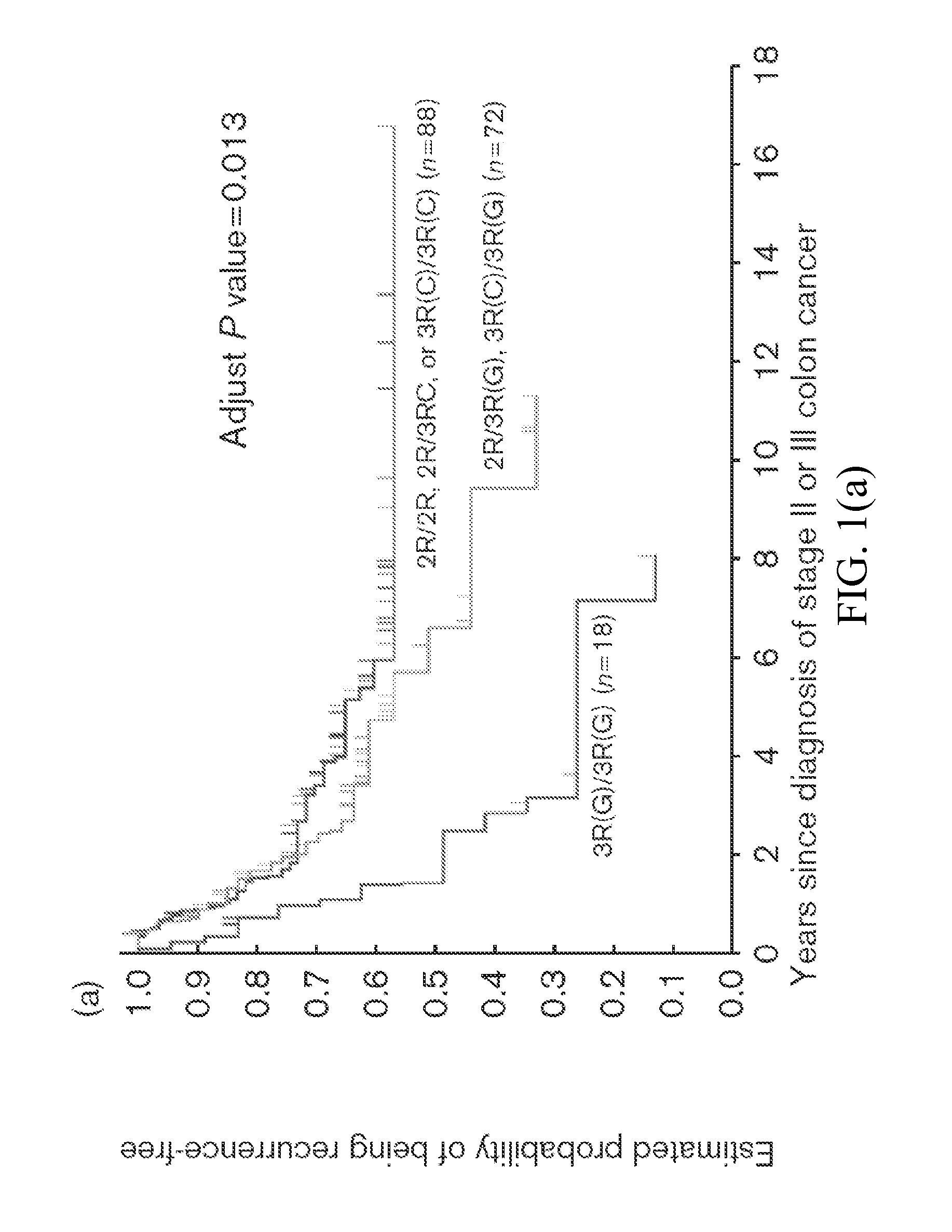
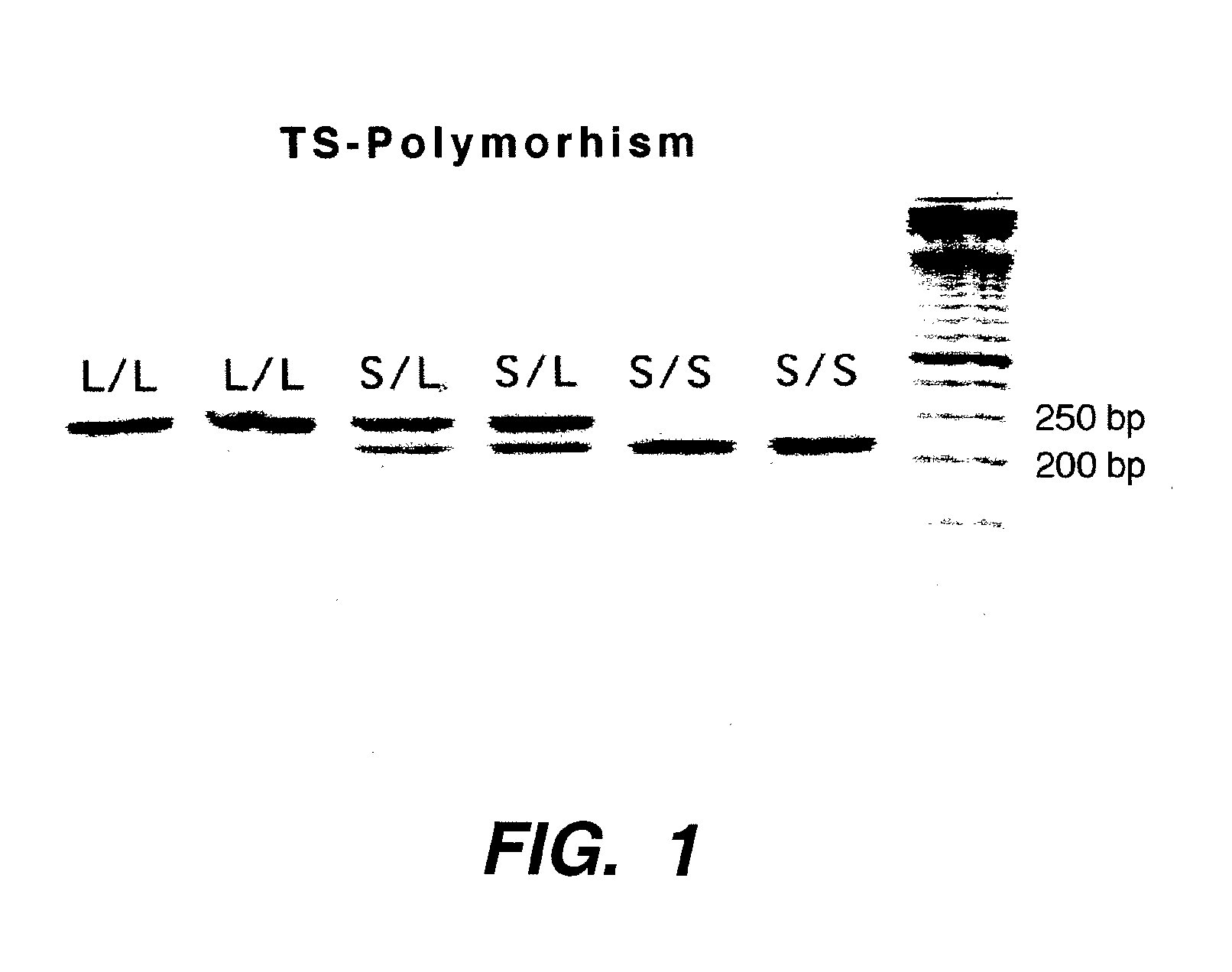
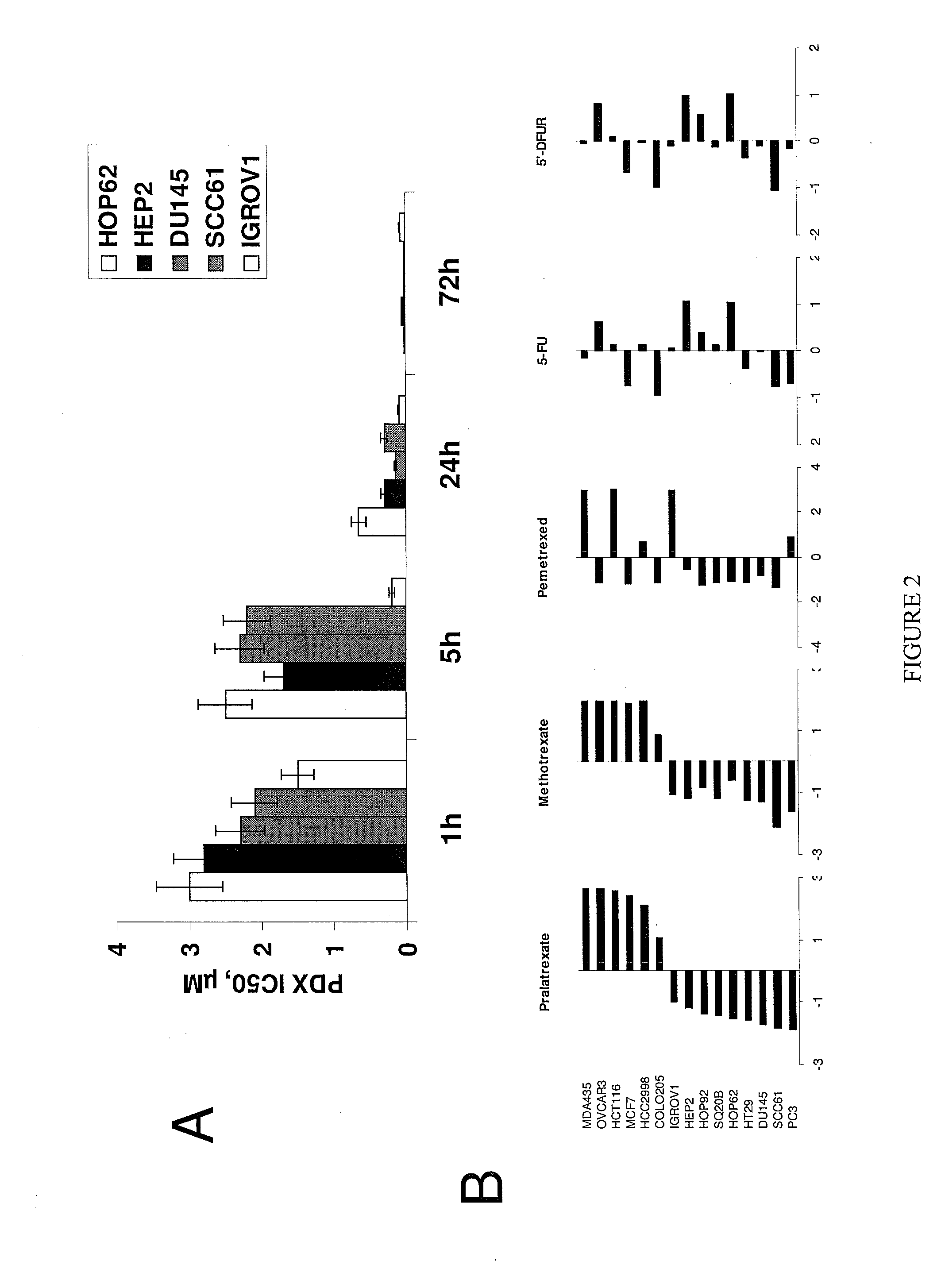
Genomic polymorphism for predicting therapeutic response
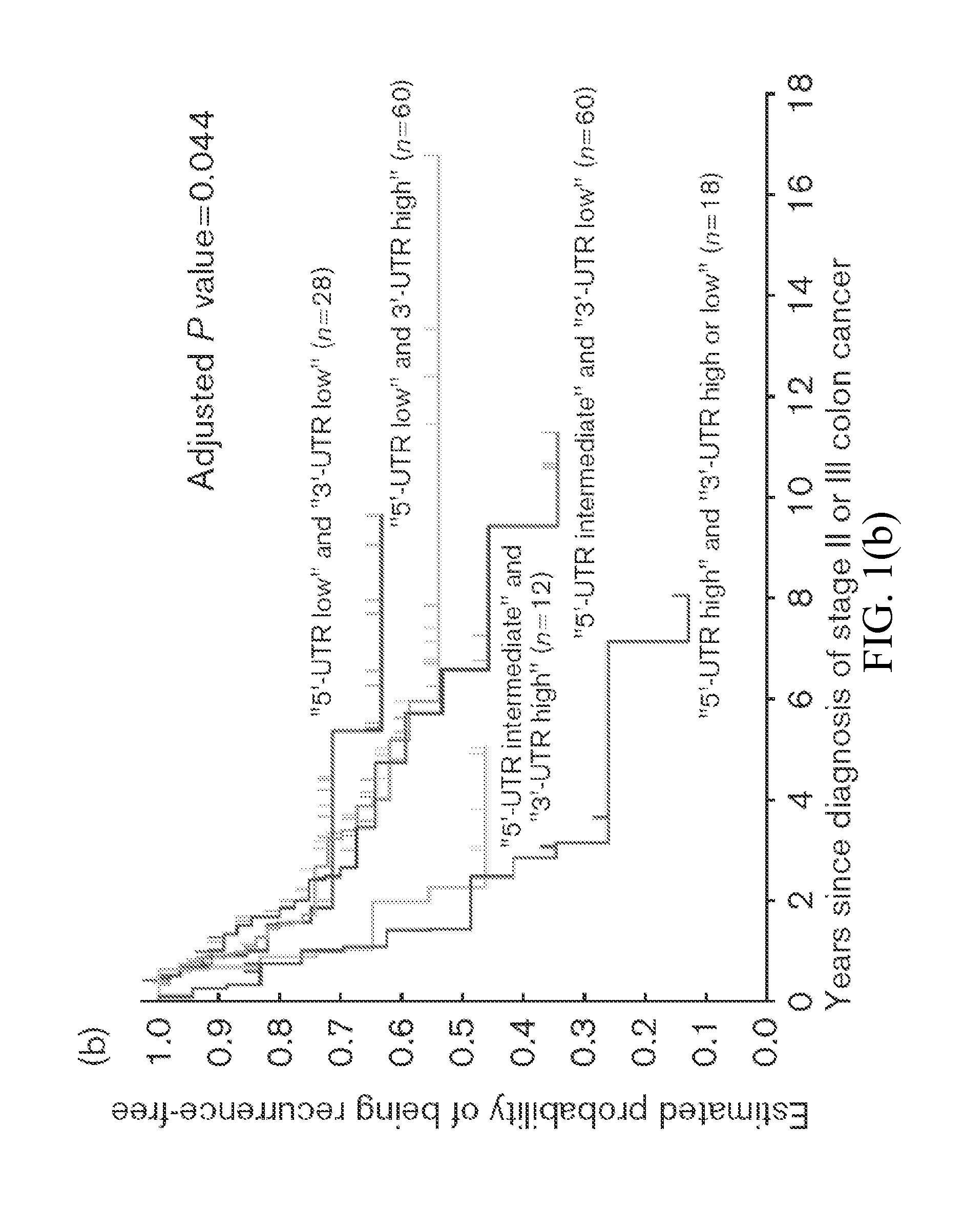
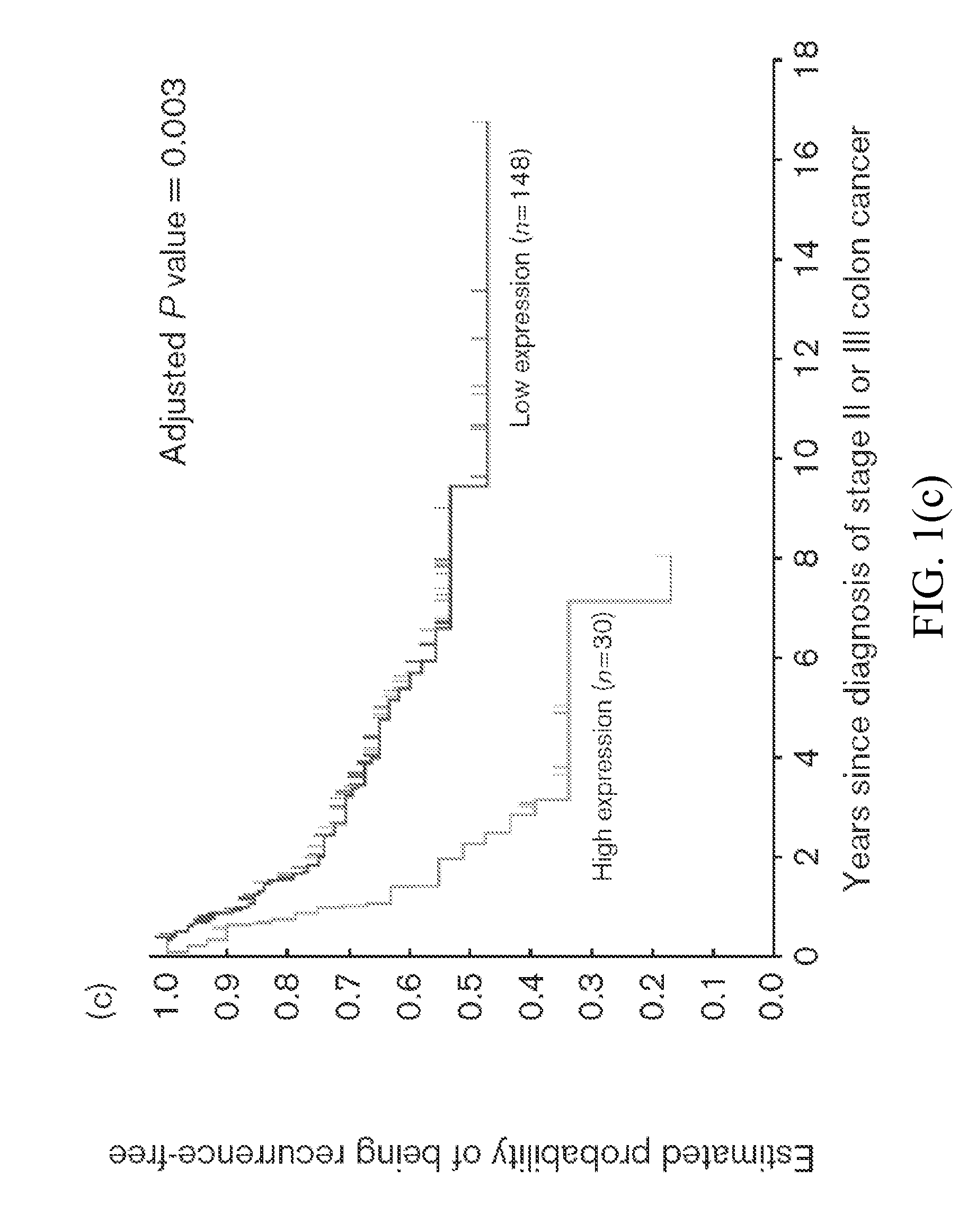
The present invention relates to the use of genomic polymorphism to provide individualized therapeutic regimens to treat patients suffering from diseases such as cancer. The invention discloses methods for determining the efficacy or choice of chemotherapeutic drugs and regimens for use in treating a diseased patient by associating genomic polymorphism with the effectiveness of the drugs or regimens, or by associating genomic polymorphism with the intratumoral expression of a gene whereby the gene expression affects effectiveness of the drugs or regimens. In particular, the present invention provides novel methods for screening therapeutic regimens, which comprise determining a patient's genotype at a tandemly repeated 28 base pair region in the thymidilate synthase (TS) gene's 5′ untranslated region (UTR). Patients homozygous for a triple repeat will be least successfully treated with a thymidylate synthase directed drug, while those heterozygous for a triple and a double repeat will be more successfully treated, and those homozygous for a double repeat will be even more successfully treated. Those patients homozygous for the double repeat will likely suffer the least side effects from thymidylate synthase directed drugs such as 5-FU.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
5-(Pyridin-2-yl-Amino)-Pyrazine-2-Carbonitrile Compounds and Their Therapeutic Use
ActiveUS20140315925A1Promote apoptosisInhibiting cell cycle progressionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseasePyrazine
The present invention pertains generally to the field of therapeutic compounds. More specifically the present invention pertains to certain pyridyl-amino-pyrazine carbonitrile compounds that, inter alia, inhibit Checkpoint Kinase 1 (CHK1) kinase function. The present invention also pertains to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, and the use of such compounds and compositions, both in vitro and in vivo, to inhibit CHK1 kinase function, and in the treatment of diseases and conditions that are mediated by CHK1, that are ameliorated by the inhibition of CHK1 kinase function, etc., including proliferative conditions such as cancer, etc., optionally in combination with another agent, for example, (a) a DNA topoisomerase I or II inhibitor; (b) a DNA damaging agent; (c) an antimetabolite or thymidylate synthase (TS) inhibitor; (d) a microtubule targeted agent; and (e) ionising radiation.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
Detection of proteins from circulating neoplastic cells
InactiveUS8012480B2The process is convenient and fastPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsErlotinibCancer cell
The protein EGFR, ERCC1, RRM1, thymidylate synthase, or beta-tubulin from cancer cells is detected in a blood sample by enriching the cancer cells from the blood sample followed by performing on the enriched cancer cells an immunoassay capable of detecting the proteins mentioned above. Cancer patients overexpressing EGFR are treated with an anti-EGFR agent, for example cetuximab, panitumumab, erlotinib or gefitinib.
Owner:PHARMA CINQ LLC
Thymidylate Synthase Haplotype is Associated with Tumor Recurrence in Stage II and Stage III Colon Cancer Patients
The invention provides compositions and methods for determining the likelihood of tumor recurrence following treatment with 5-FU based adjuvant therapy for Stage II or Stage III colon cancer patients. After determining if a patient is less likely to experience tumor recurrence once treated, the invention also provides methods for treating these patients.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
5-(pyridin-2-yl-amino)-pyrazine-2-carbonitrile compounds and their therapeutic use
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
Vectors, cells and processes for pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides production
Novel DNA constructs and host cells comprising the same are disclosed. DNA constructs comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin or a uridine kinase gene and / or a dCTP deaminase gene. In preferred embodiments the constructs comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin further comprise DNA sequences encoding for thymidylate synthase and / or transcription units comprising sequences encoding for uridine kinase preferably together with dCTP deaminase. In particularly preferred embodiments, the host cells comprise constructs having all of the above characteristics wherein the host cell displays repressed or no uracil DNA glycosylase activity. This may be achieved by removal of the host cell ung gene. Use of host cells in the manufacture of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides e.g. thymidine is also disclosed.
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
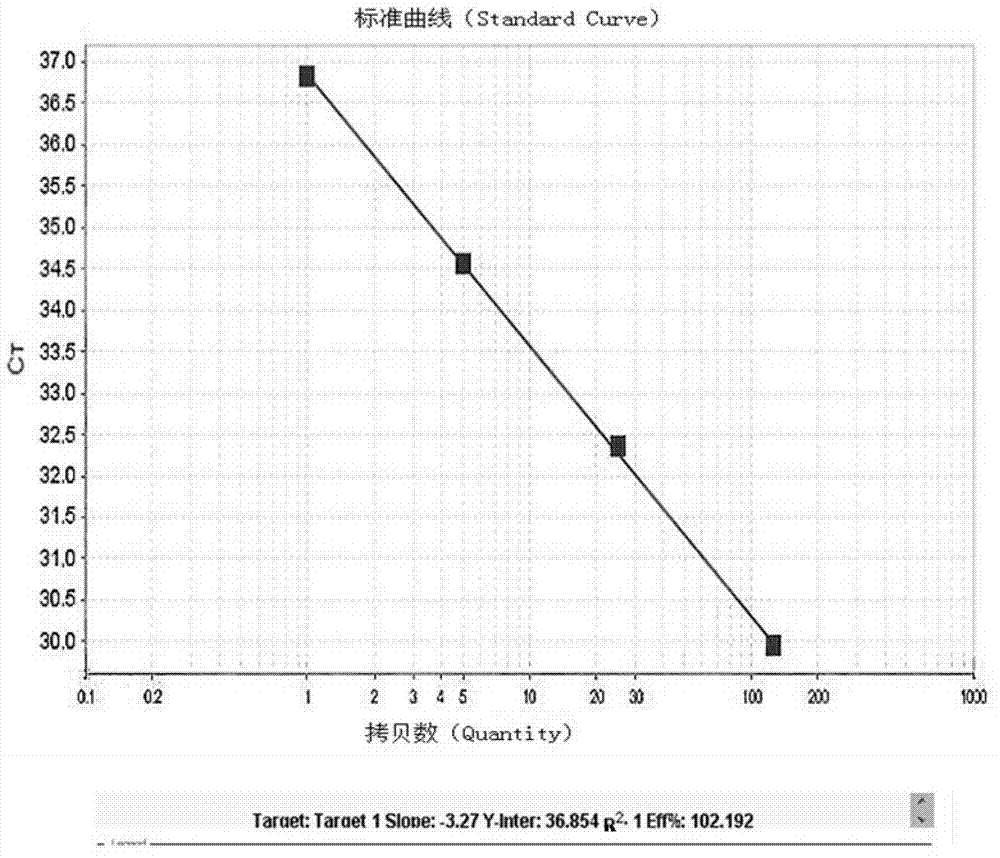
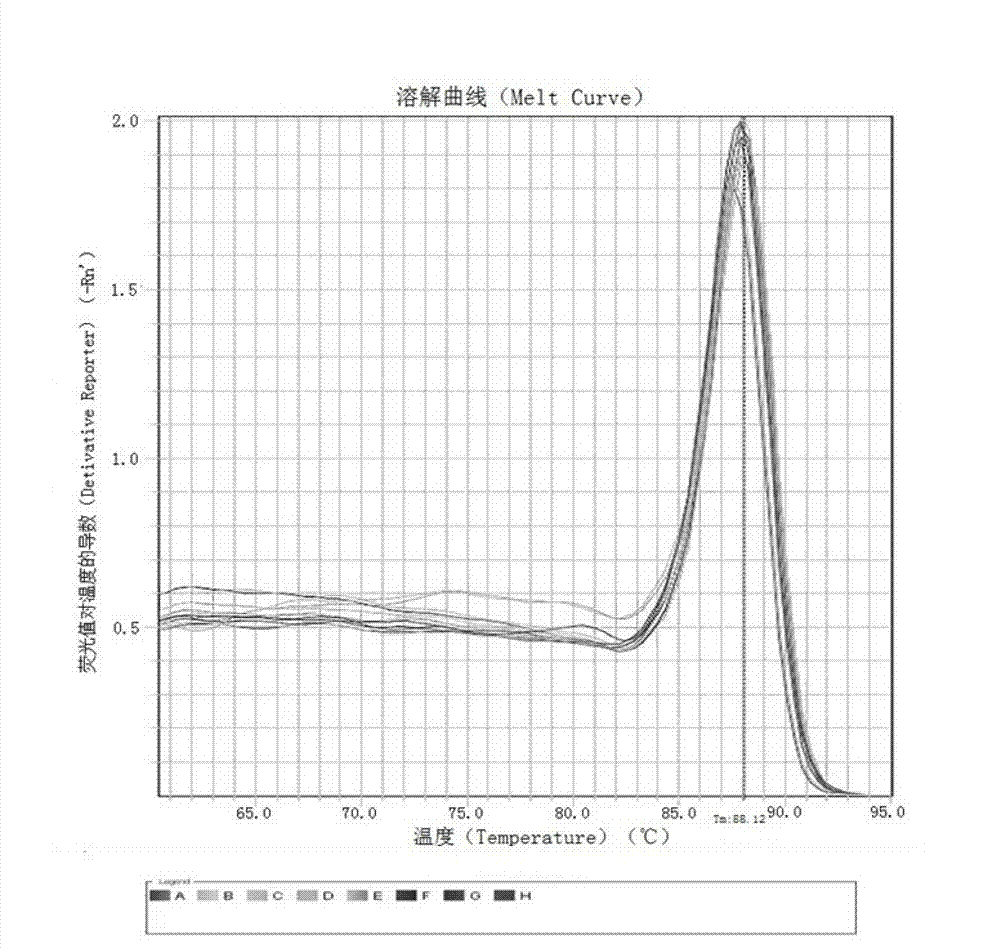
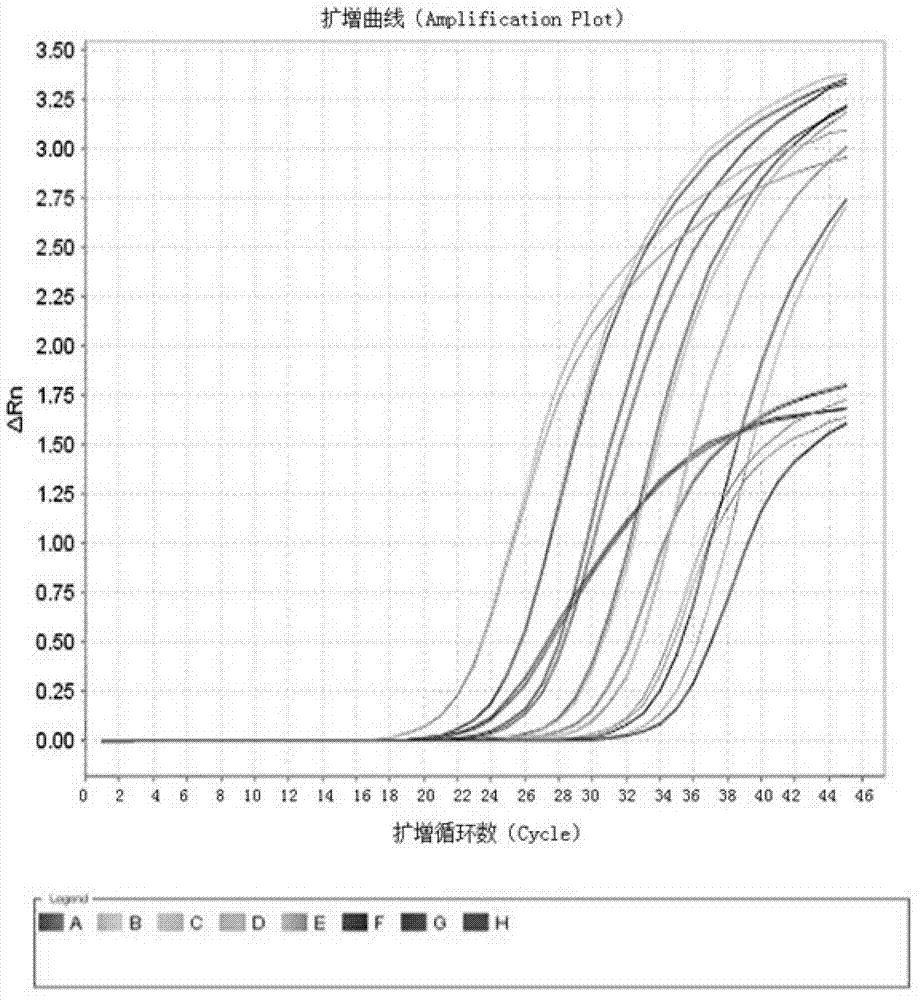
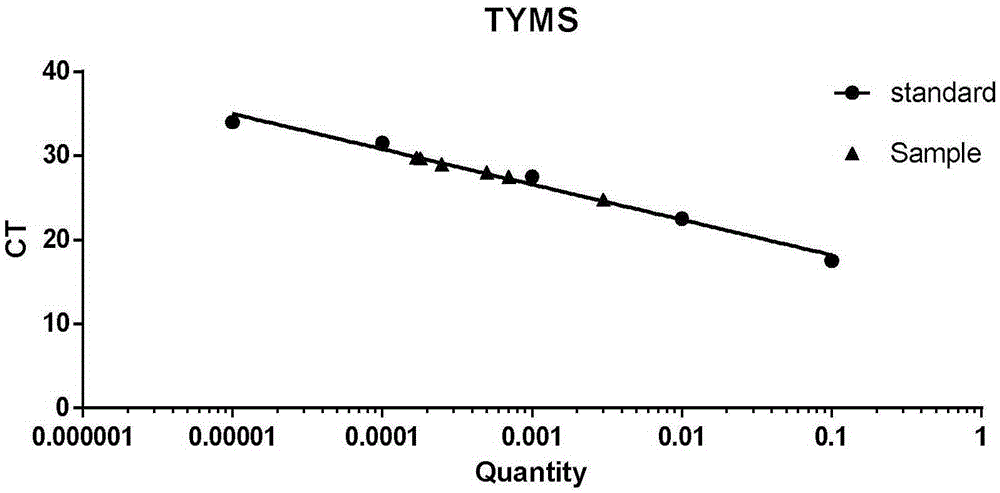
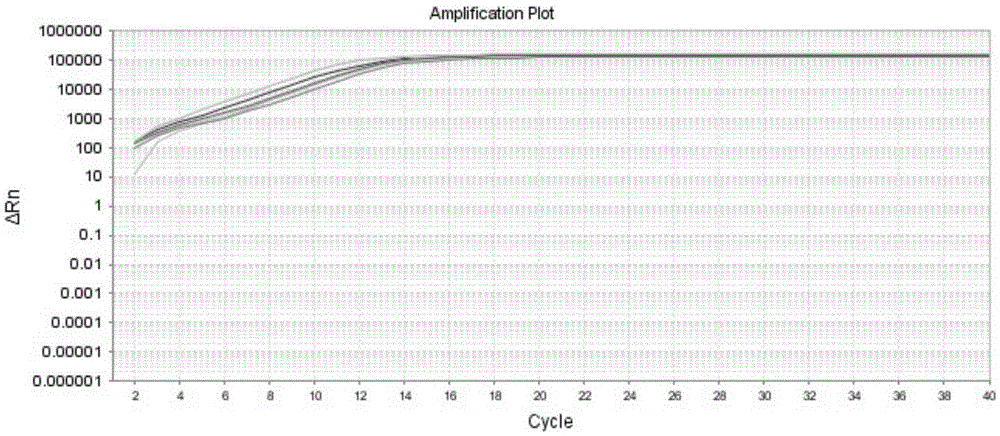
Kit and method for detecting expression level of TYMS (Thymidylate Synthetase) mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid)
InactiveCN103088122ASensitive detectionSpecific detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesThymidylate synthase
The invention discloses a kit and method for detecting the expression level of TYMS (Thymidylate Synthetase) mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid). The kit comprises a standard substance and an internal reference gene real-time quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) system, wherein the standard substance is used for making a standard curve. Through the method, the expression level of TYMS can be accurately, rapidly and quantitatively determined. If the method and the kit, disclosed by the invention, are applied in clinic, doctors can rationally select fluorine drugs for treatment.
Owner:周宏灏
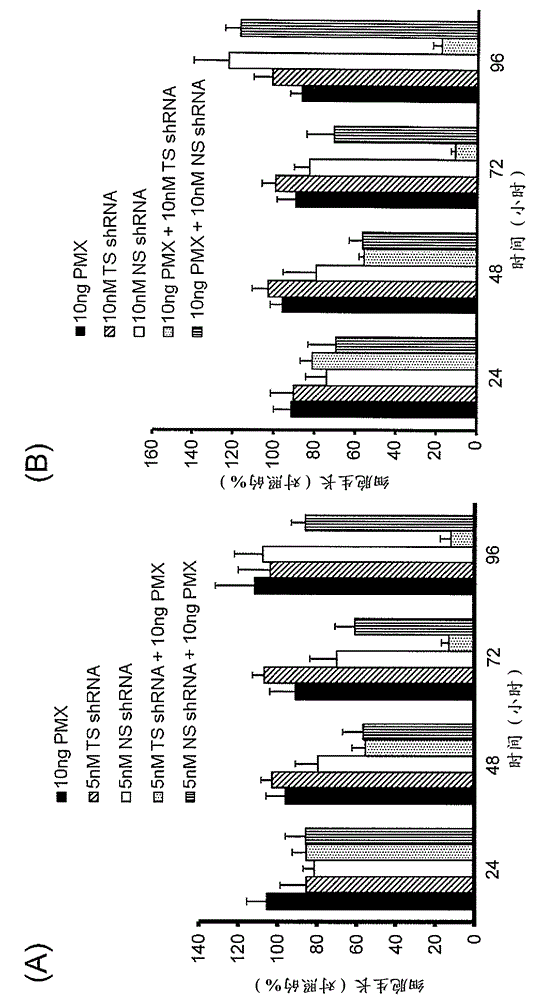
Liposome containing shRNA molecule for thymidylate synthase, and use for same
ActiveCN103561775APrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryLipofectamineThymidylate synthase
Owner:DELTA FLY PHARMA
Method of treating cancer by inhibition of DNA repair proteins
Methods of treating cancer using antisense oligonucleotides directed against DNA double-strand break repair proteins such as BRCA2 or RAD51 are provided. The antisense oligonucleotides can be used alone, in tandem or in combination with other cancer therapies, in particular with therapies that lead to DNA damage, inhibition of DNA repair or inhibition of DNA synthesis, such as radiation, platinum drugs, alkylating agents, PARP inhibitors, or inhibitors of thymidylate synthase.
Owner:SARISSA
Methods to Treat Cancer with 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin and Methods for Assessing Cancer for Increased Sensitivity to 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin
InactiveUS20080188479A1BiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycinamide Ribonucleotide FormyltransferaseThymidylate synthase
The present invention relates to a method for assessing the sensitivity of a patient's cancer to treatment with 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin and a method for selecting a patient for treatment of cancer with 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin, by determining the amount of a selected polypeptide expressed by the cancer and comparing the amount with the amount of the selected polypeptide expressed by a reference cancer, wherein the polypeptide includes a member of folate pathways within cells and may include at least one of reduced folate carrier-1 enzyme (RFC-1), dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), folylpoly-gamma-glutamate synthetase (FPGS), thymidylate synthase (TS), γ-glutamyl hydrolase (GGH), and glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase (GARFT). The present invention also relates to the use of 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin in the treatment of multiple myeloma.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
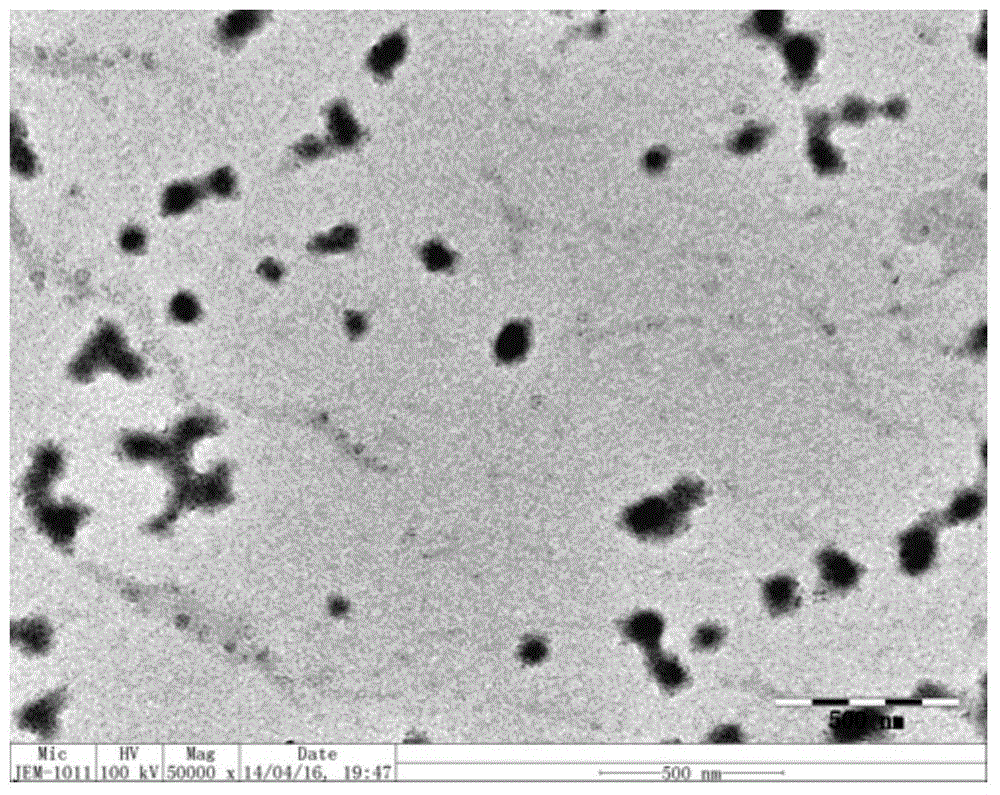
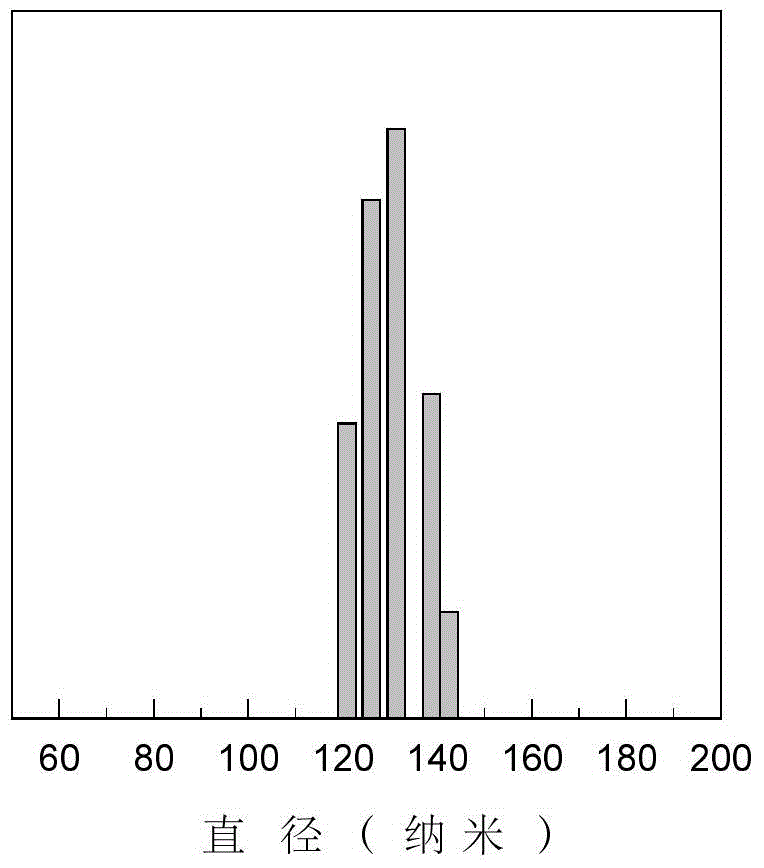
Thymidylate synthase preparation loaded albumin nano-microsphere and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104306339AUniform particle sizeGood dispersionOrganic active ingredientsGranular deliveryOrganic solventMicrosphere
The invention provides a thymidylate synthase preparation loaded albumin nano-microsphere. The nano-microsphere is prepared by the following steps: adding a solution of a thymidylate synthase preparation and an organic solvent into an albumin solution to develop and self-assemble the albumin to form a nano-microsphere; coating the thymidylate synthase preparation in the albumin nano-microsphere to form the thymidylate synthase preparation loaded albumin nano-microsphere, wherein the diameter of the albumin nano-microsphere is 40-500nm, and the thymidylate synthase preparation is 7-20 percent by mass of the albumin nano-microsphere. The nano-microsphere has the advantages of excellent biocompatibility, simple preparation process and stable physiochemical property, is capable of improving the drug stability, has a certain sustained release effect, and has potential application of clinical cancer treatment. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the thymidylate synthase preparation loaded albumin nano-microsphere.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit for TYMS (thymidylate synthase) gene expression quantity and application of kit
InactiveCN105255865AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationThymidylate synthaseGene expression
Owner:SUZHOU BEISIMAI MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
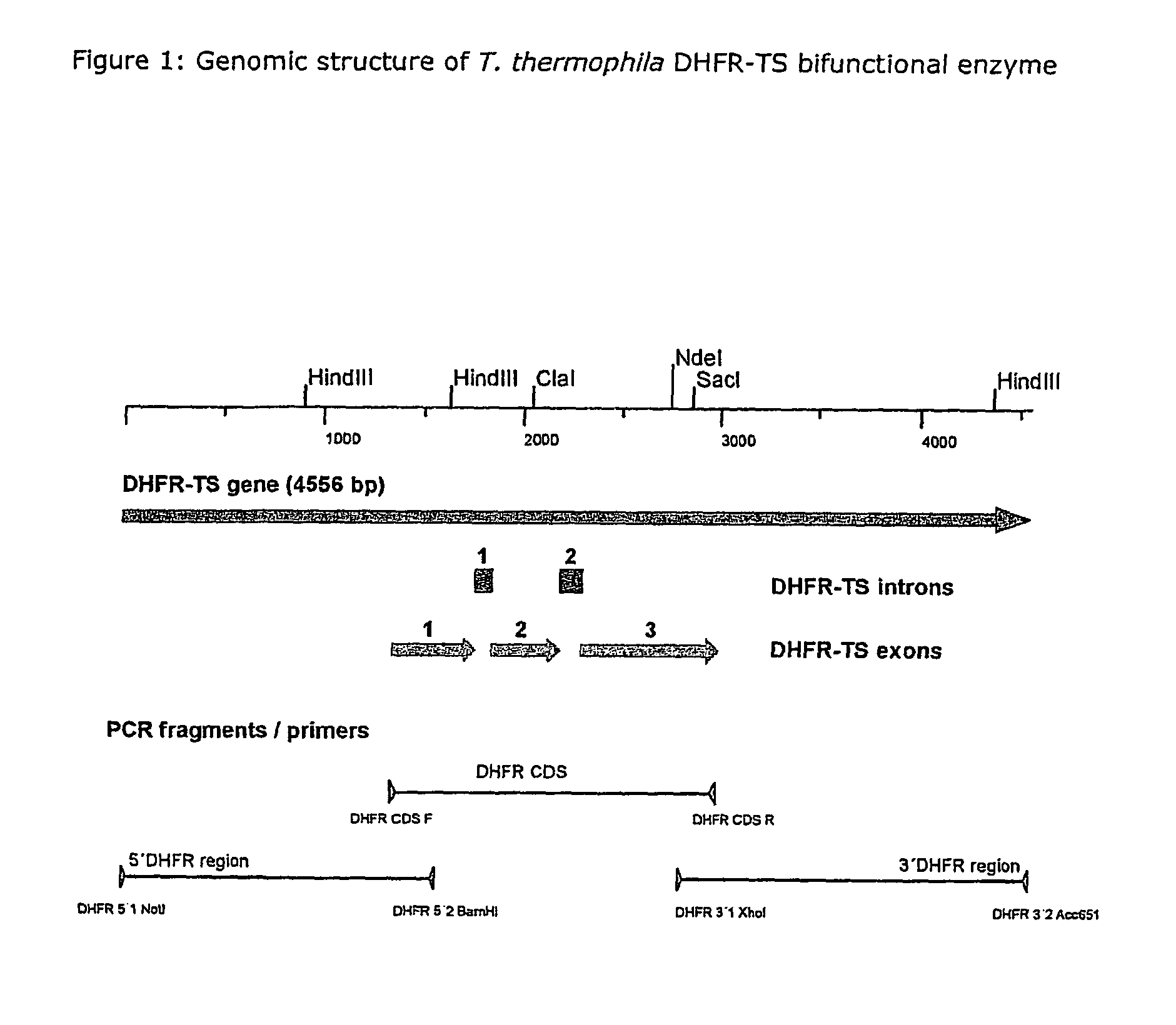
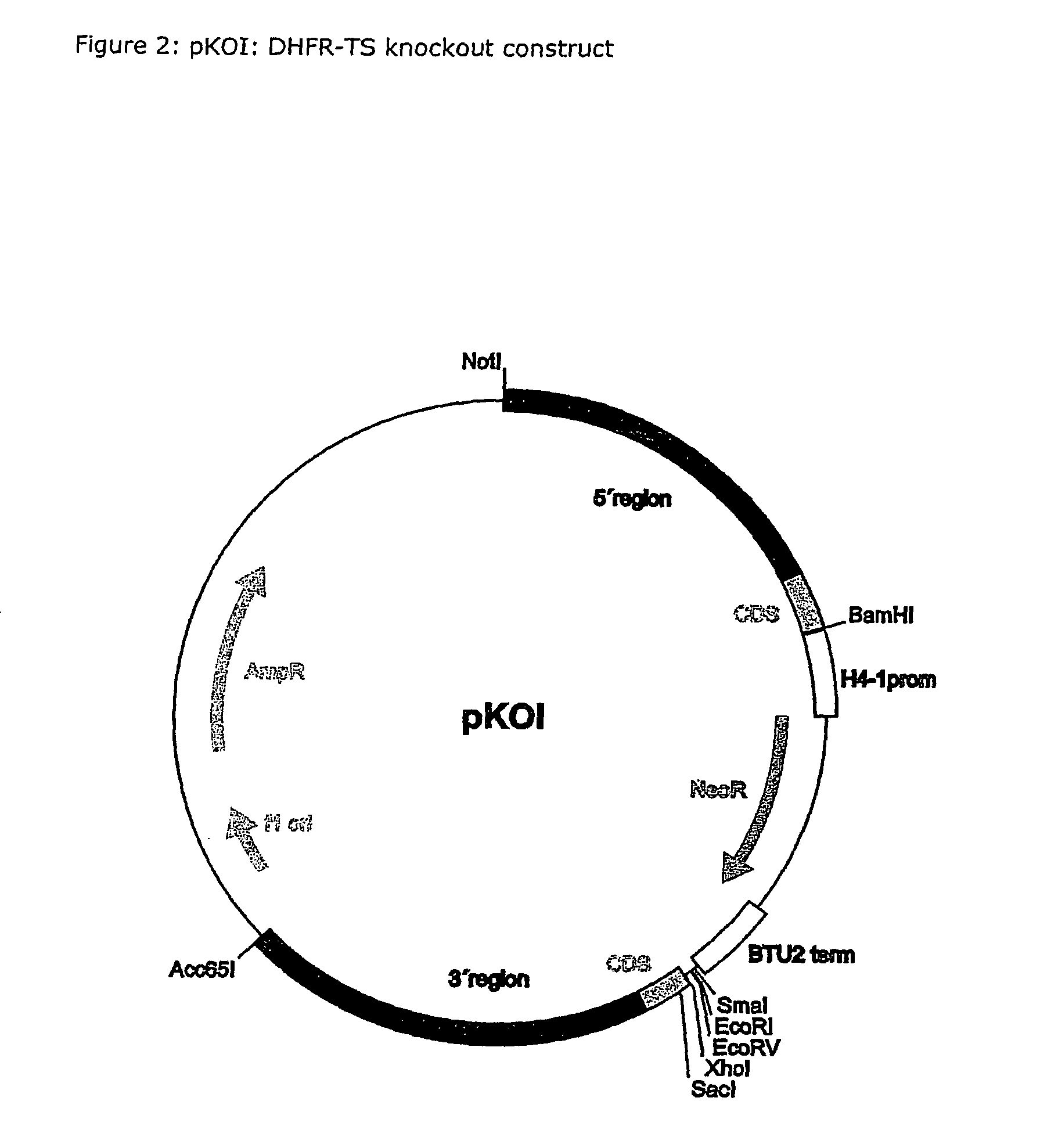
Nucleic acid and its use effecting ciliate tetrahymena bifunctional dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase deficiency
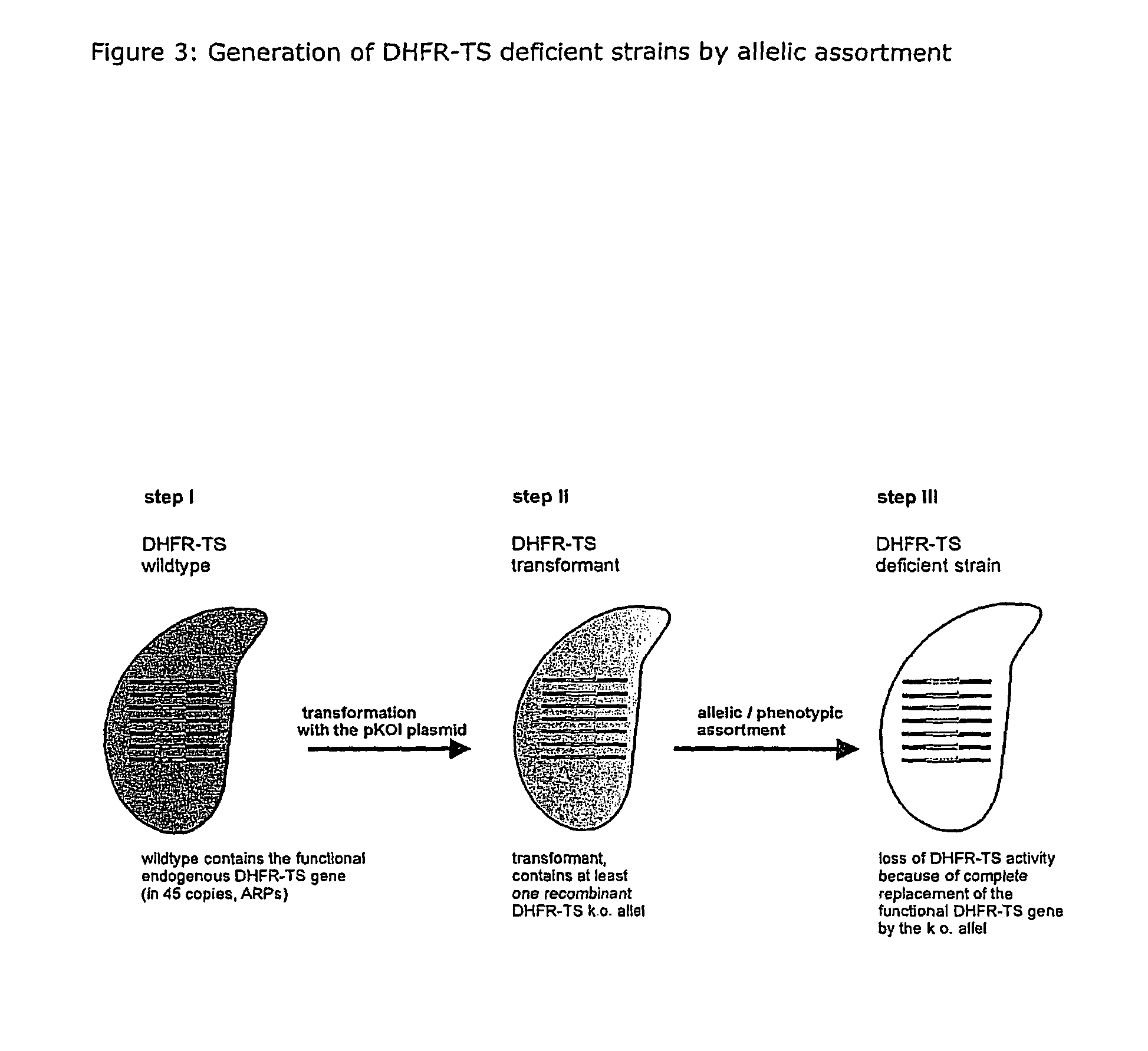
A method for producing a ciliate cell with reduced or essentially no dihydrofolate reductase (DHFS) activity or reduced or essentially no thymidylate synthase (TS) activity or both reduced or essentially no dihydrofolate reductase and thymidylate synthase (DHFR-TS) activity is claimed, comprising the steps ofa) transforming ciliate cells by inserting a construct containing an allele altering the gene encoding the endogenous DHFR-TS into at least one of the endogenous DHFR-TS genes of the ciliate macronucleus (MAC),b) inducing an allelic assortment process in the transformed ciliate cells to generate cells having the construct inserted in most or all functional DHFR-TS genes of the MAC, andc) identifying the cells generated in step b) by cultivation with or without thymidine.
Owner:CILIAN
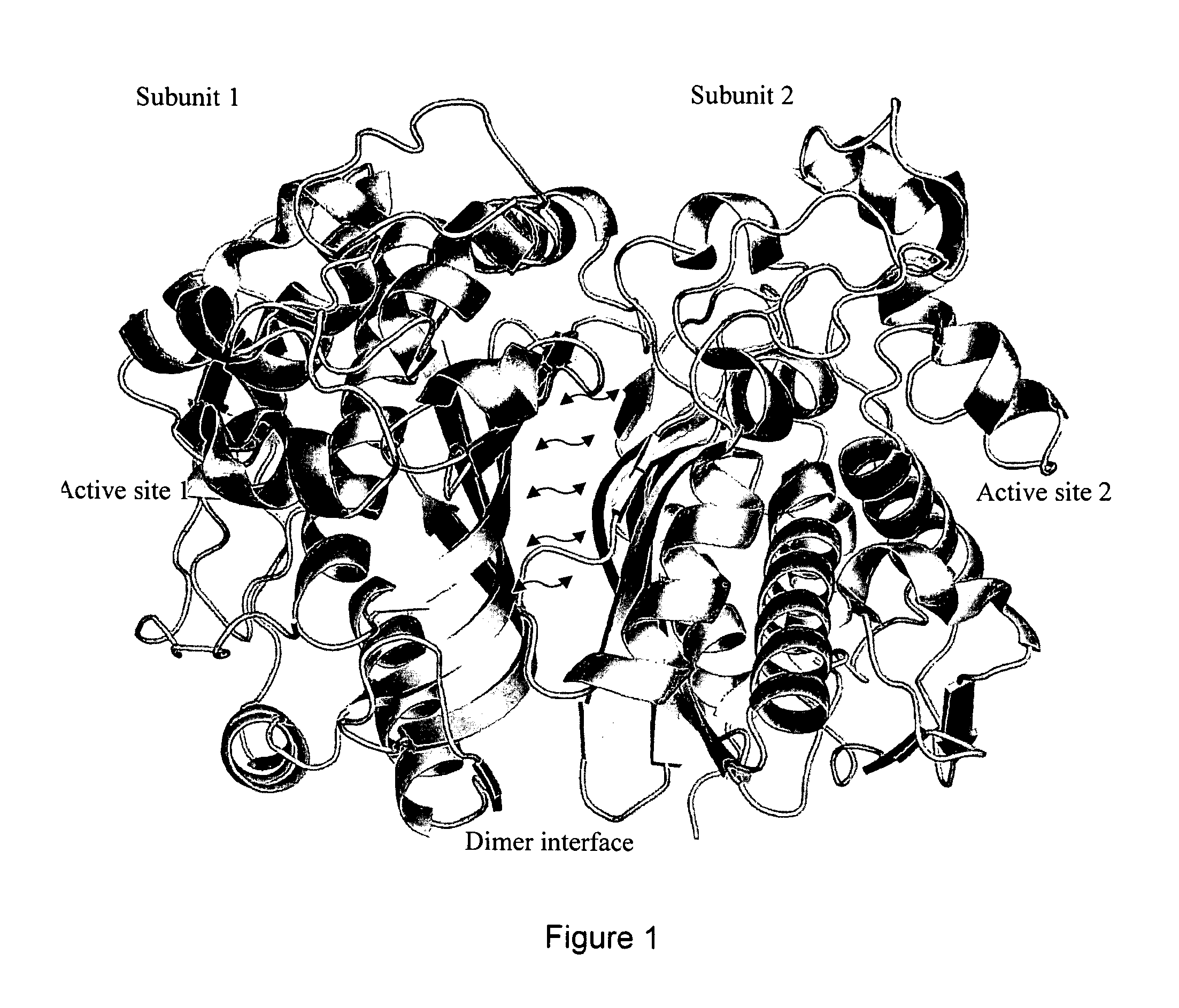
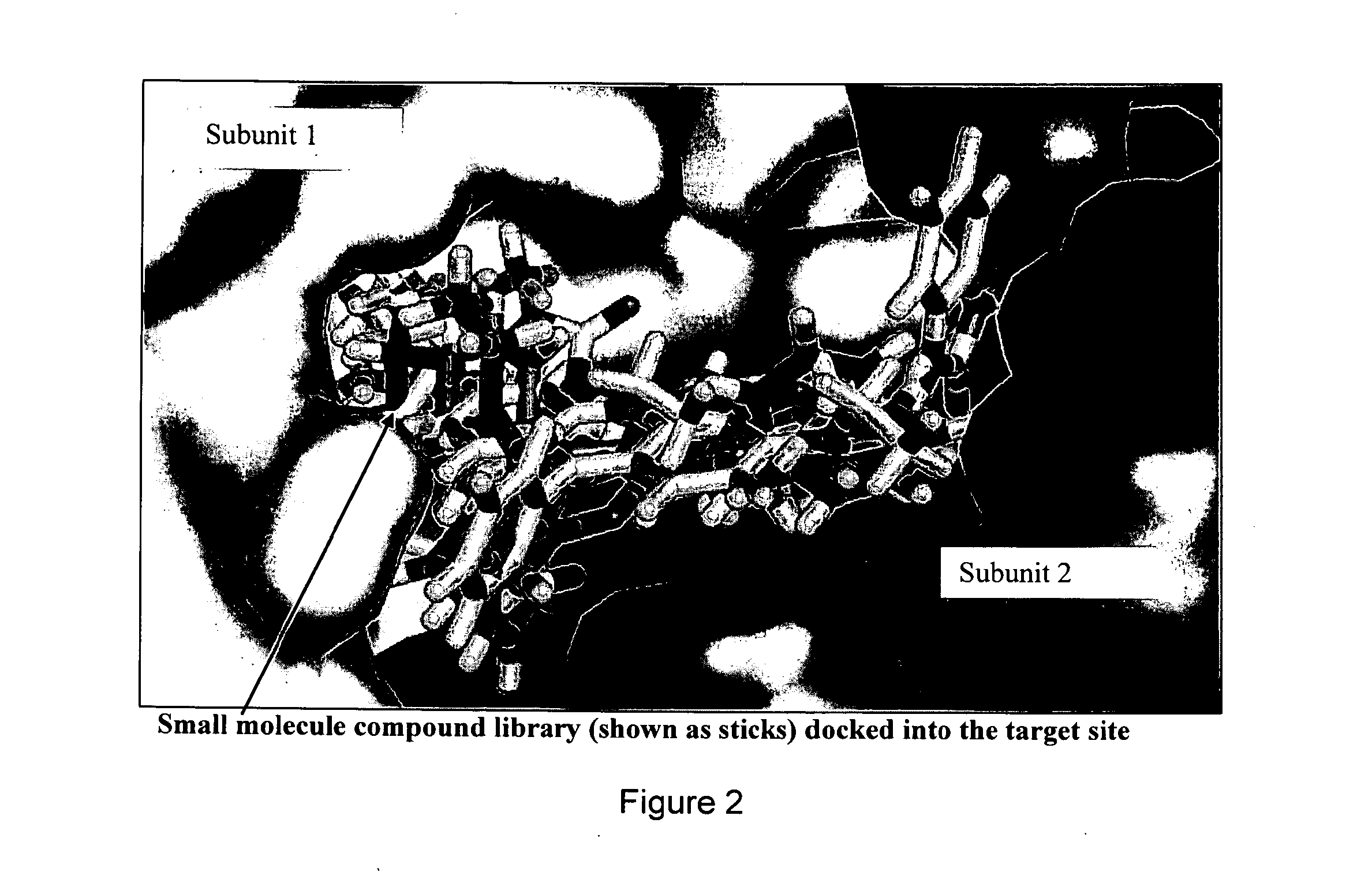
Novel allosteric inhibitors of thymidylate synthase
ActiveUS20160067240A1Strong anti-proliferative propertyLimit motionHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideMelanomaProstate cancer
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
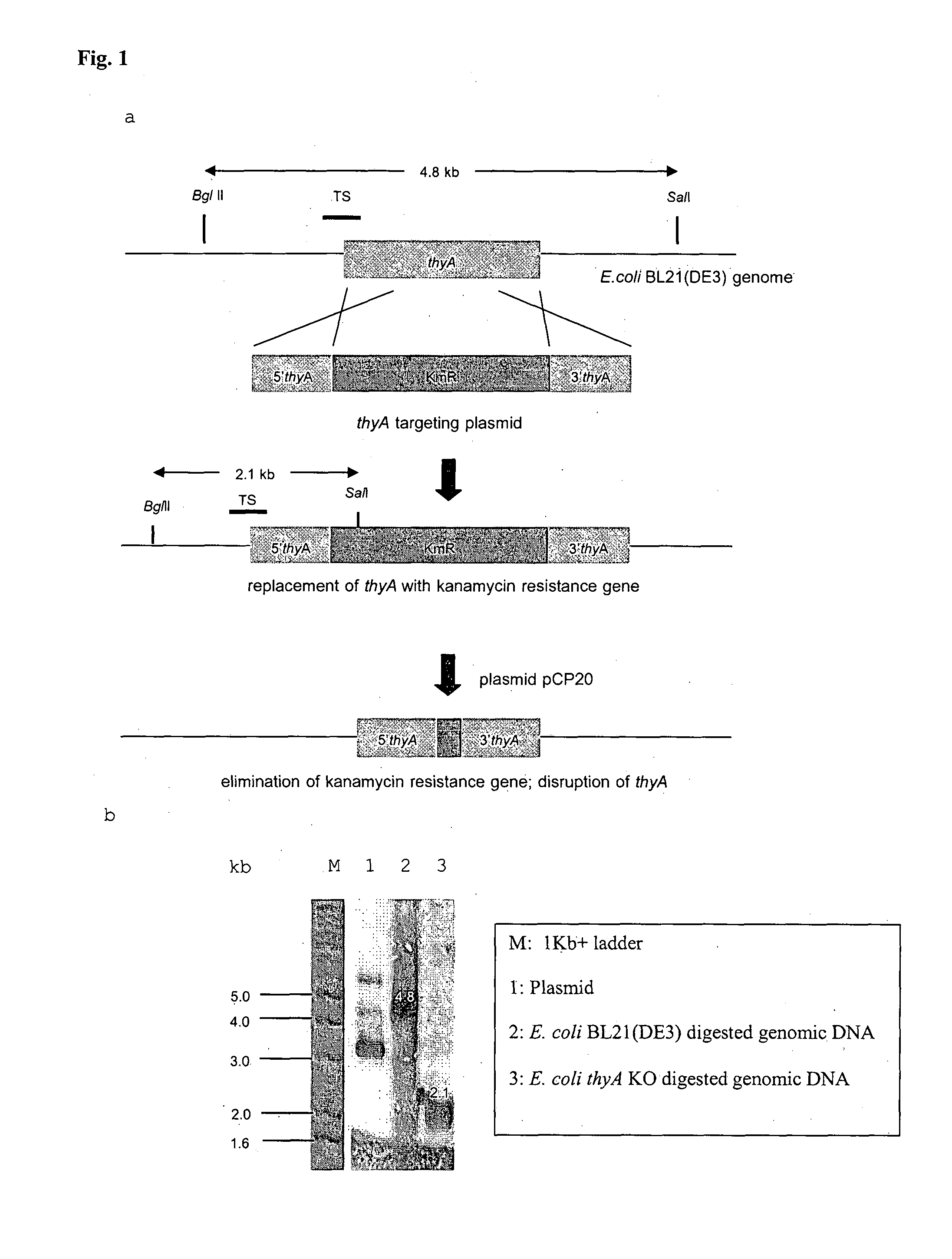
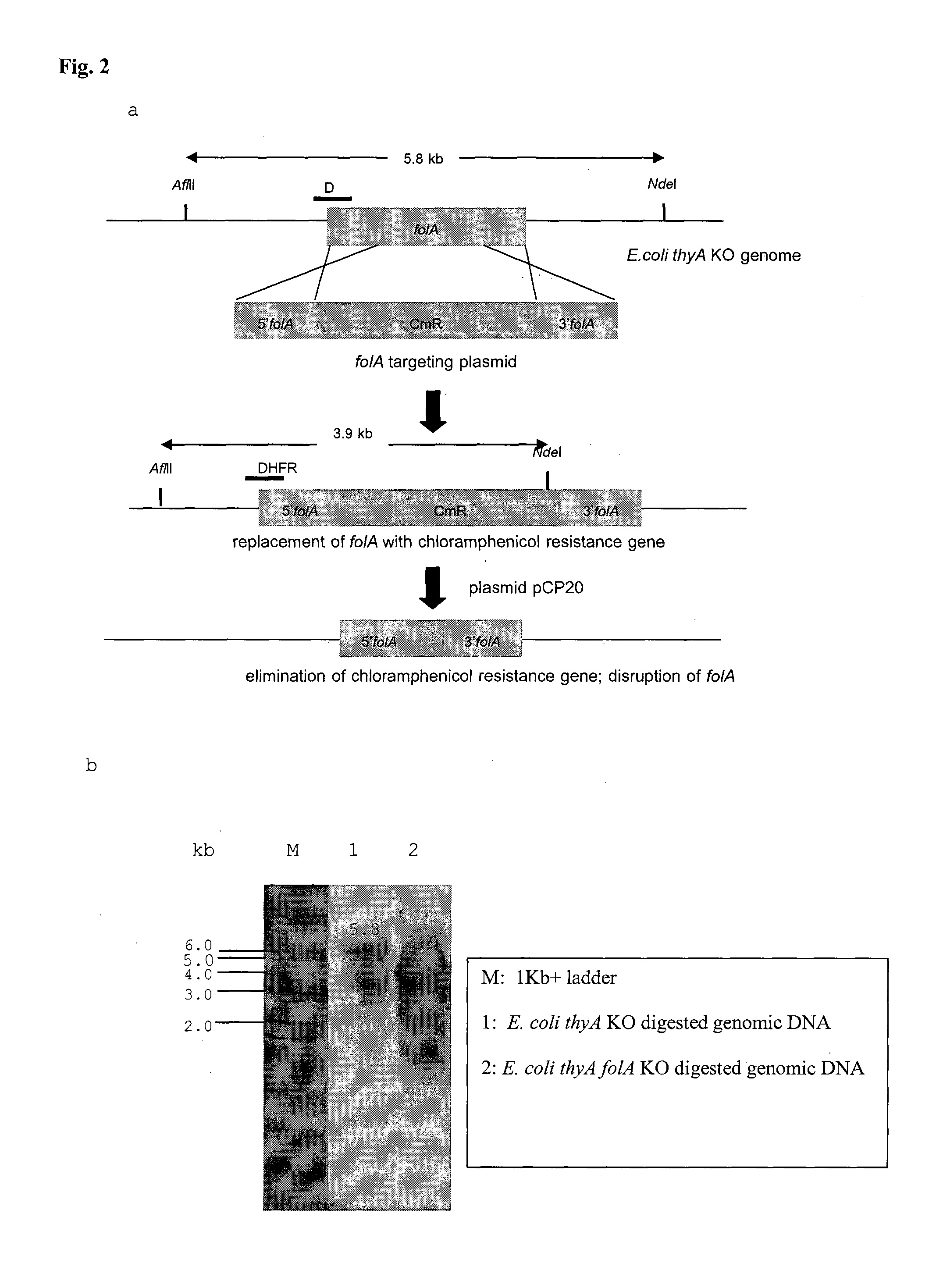
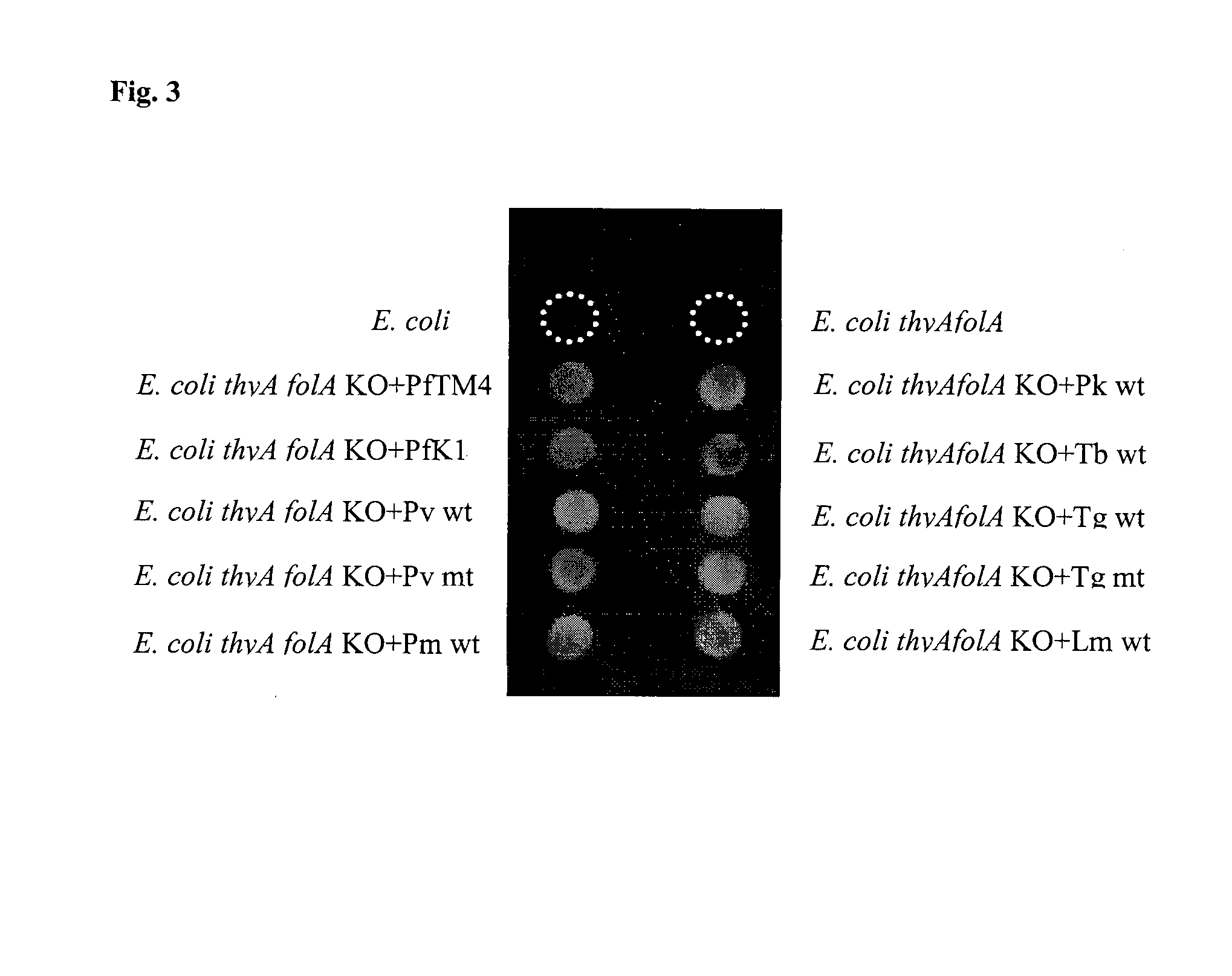
BACTERIAL SURROGATE FOR TESTING OF ANTIMALARIALS: thyA KNOCKOUT AND folA KNOCKOUT BACTERIA FOR TESTING OF INHIBITION OF MALARIAL DIHYDROFOLATE REDUCTASE-THYMIDYLATE SYNTHASE
The objective of this invention is to create a double thyA folA knockout Escherichia coli (E. coli) strain for antifolate screening against DHFR of malaria and other parasites. This strain is used together with a plasmid expressing DHFR-TS from the desired pathogenic organism, which constitutes an anti-DHFR assay against the pathogenic organism of interest. The benefit of this invention is that there is no interference from either host DHFR or trimethoprim, a bacterial DHFR inhibitor. This tool is easy to use and maintain. It provides quick and reliable results as compared with conventional anti-malarial and anti-parasitic assays. This invention should facilitate discovery of new anti-DHFR compounds against malaria and other parasitic diseases.
Owner:NAT SCI & TECH DEV AGENCY
Rsf1010 derivative mob' plasmid containing no antibiotic resistance gene, bacterium comprising the plasmid and method for producing useful metabolites
A Mob- plasmid having a RSF1010 replicon, comprising a gene coding for Rep protein and said plasmid has been modified to inactivate gene related to mobilization ability. The present invention also describes a bacterium having an ability to produce useful metabolites, comprising the plasmid and said bacterium lack active thymidylate synthase coded by thyA gene and thymidine kinase coded by tdk gene, and a method for producing useful metabolites, such as native or recombinant proteins, enzymes, L-amino acids, nucleosides and nucleotides, organic acid, vitamins, using the bacterium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
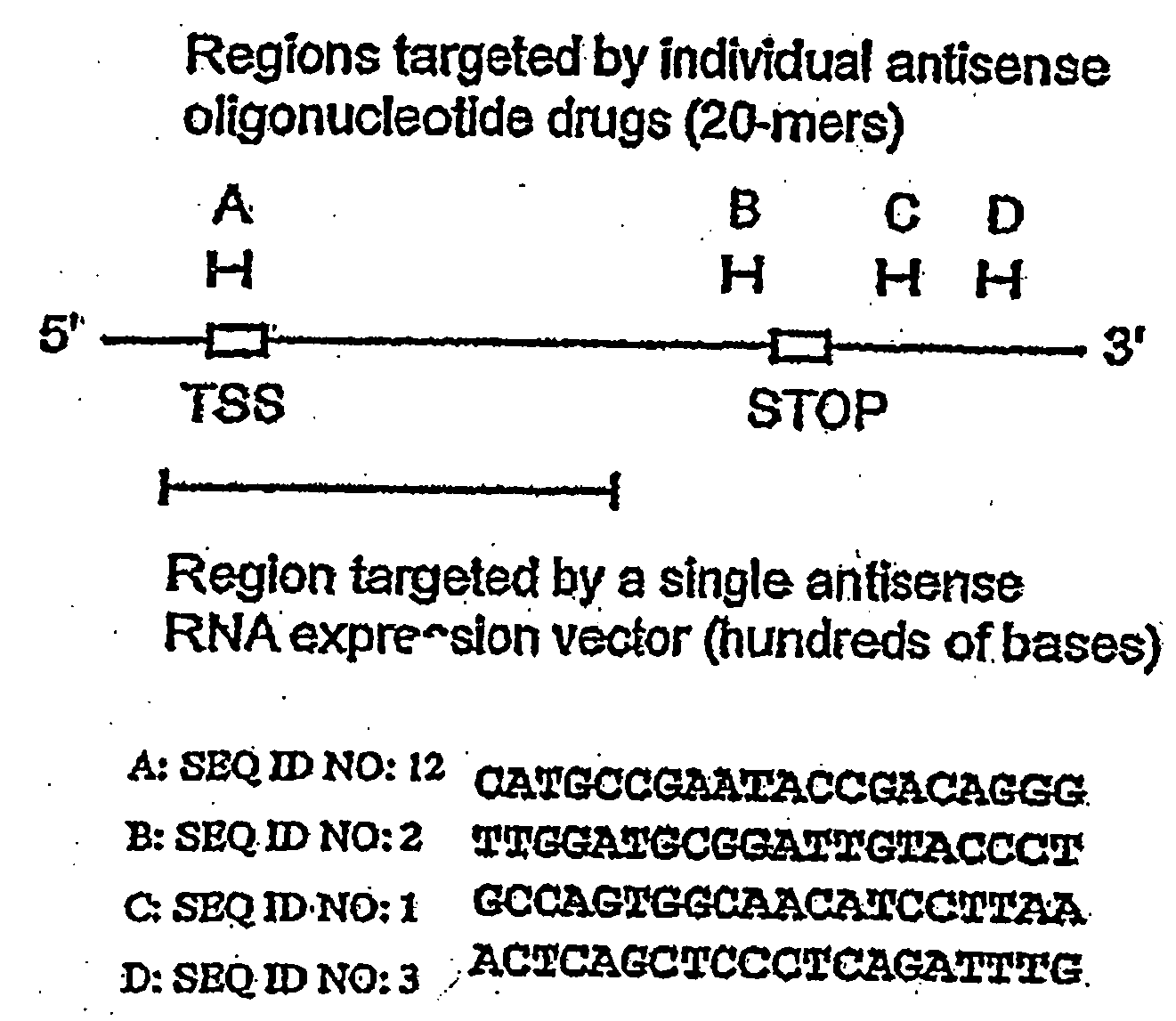
Antisense oligonucleotides for identifying drug targets and enhancing cancer therapies
InactiveUS20060089322A1Improve bioavailabilityReduce doseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCancer therapyDrug target
The present invention provides antisense oligonucleotides useful for identifying drug targets for cancer therapies and for enhancing current cancer therapies. The oligonucleotides of the invention are complementary to thymidylate synthase mRNA and affect expression of at least one other gene. For the enhancement of cancer therapies, such antisense oligonucleotides can be used in conjunction with standard chemotherapeutic agents in order to target thymidylate synthase, as well as other appropriate targets. The antisense oligonucleotides and the methods of the invention constitute improved antisense therapies with application to a variety of cancers.
Owner:VINCENT MARK +2
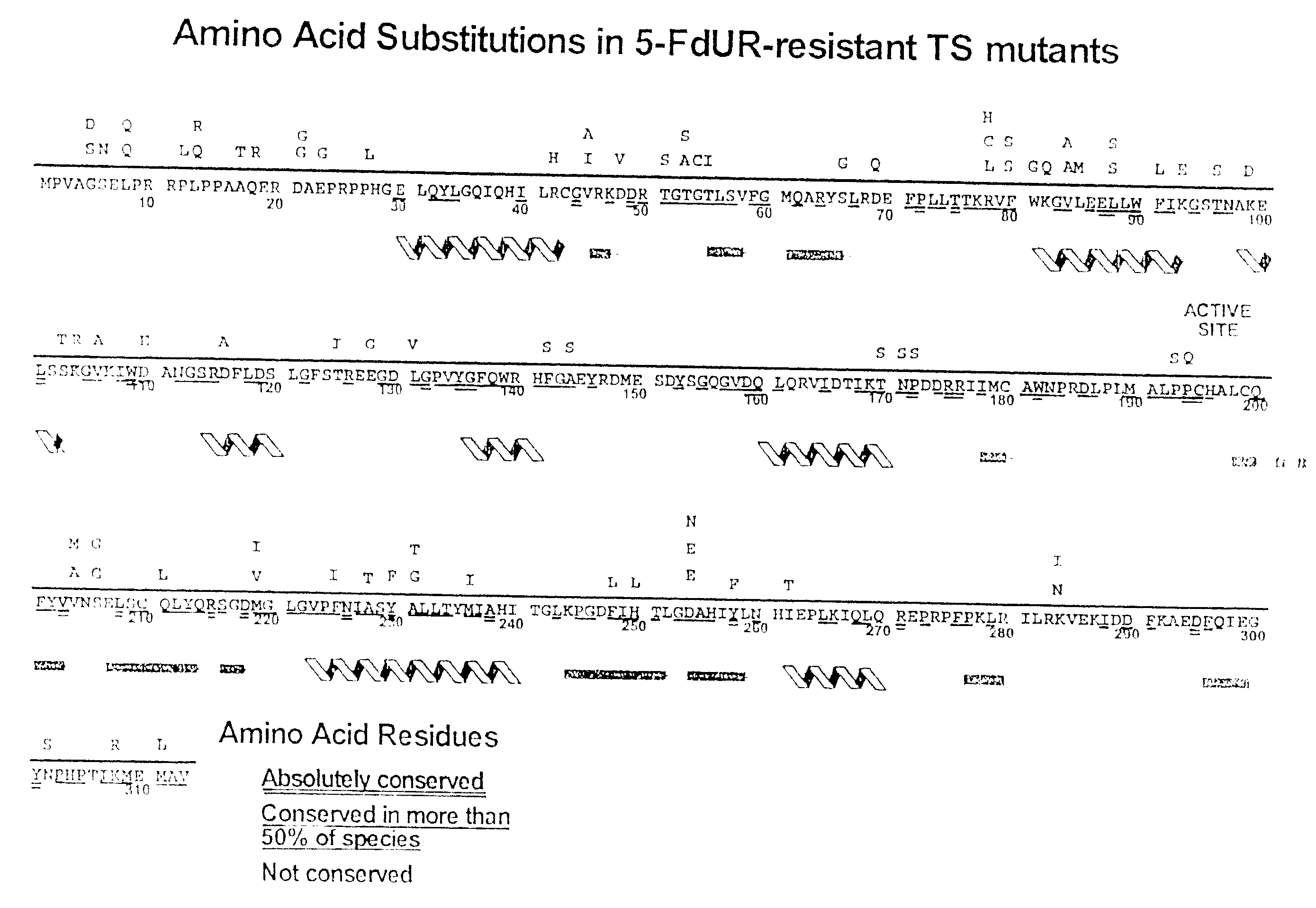
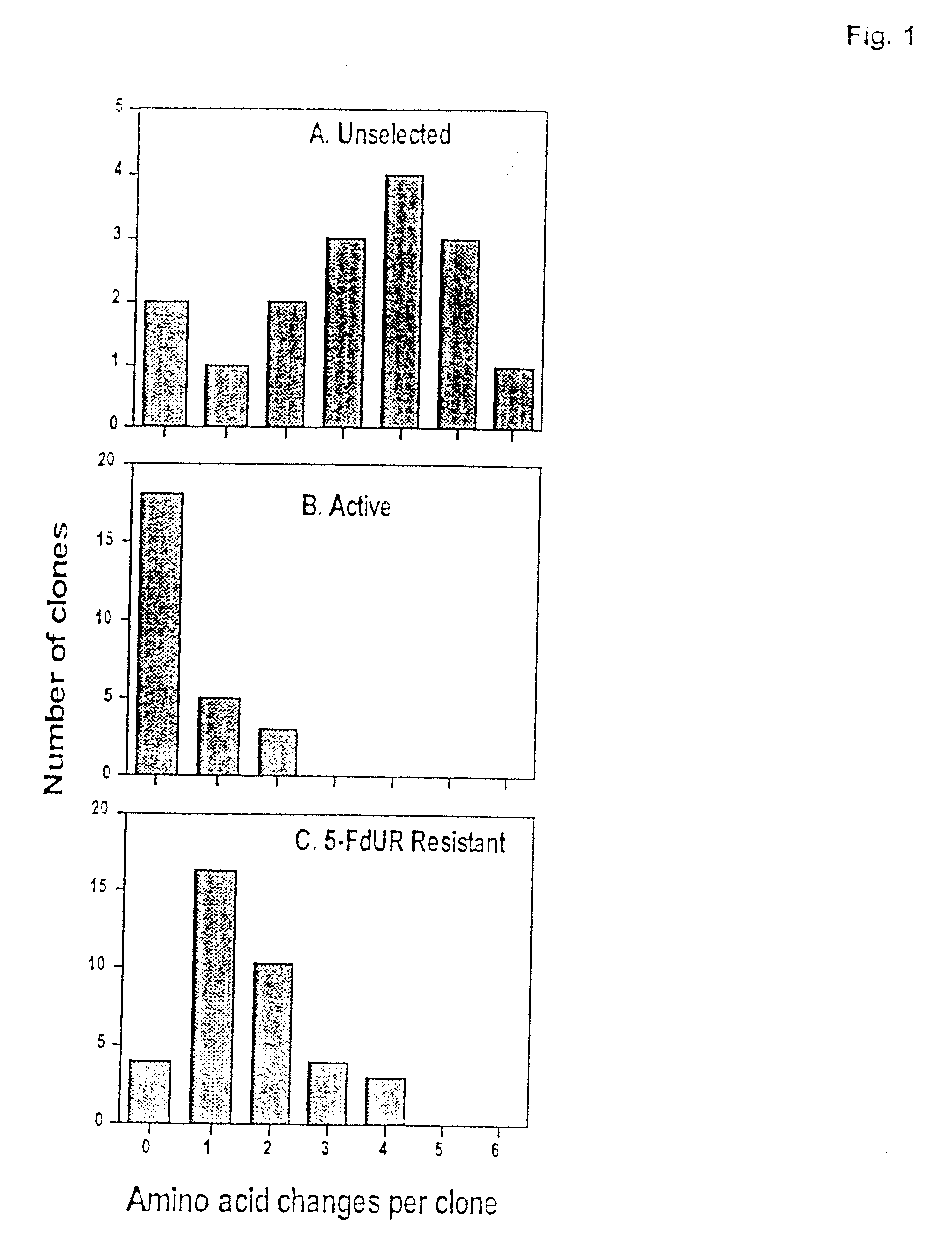
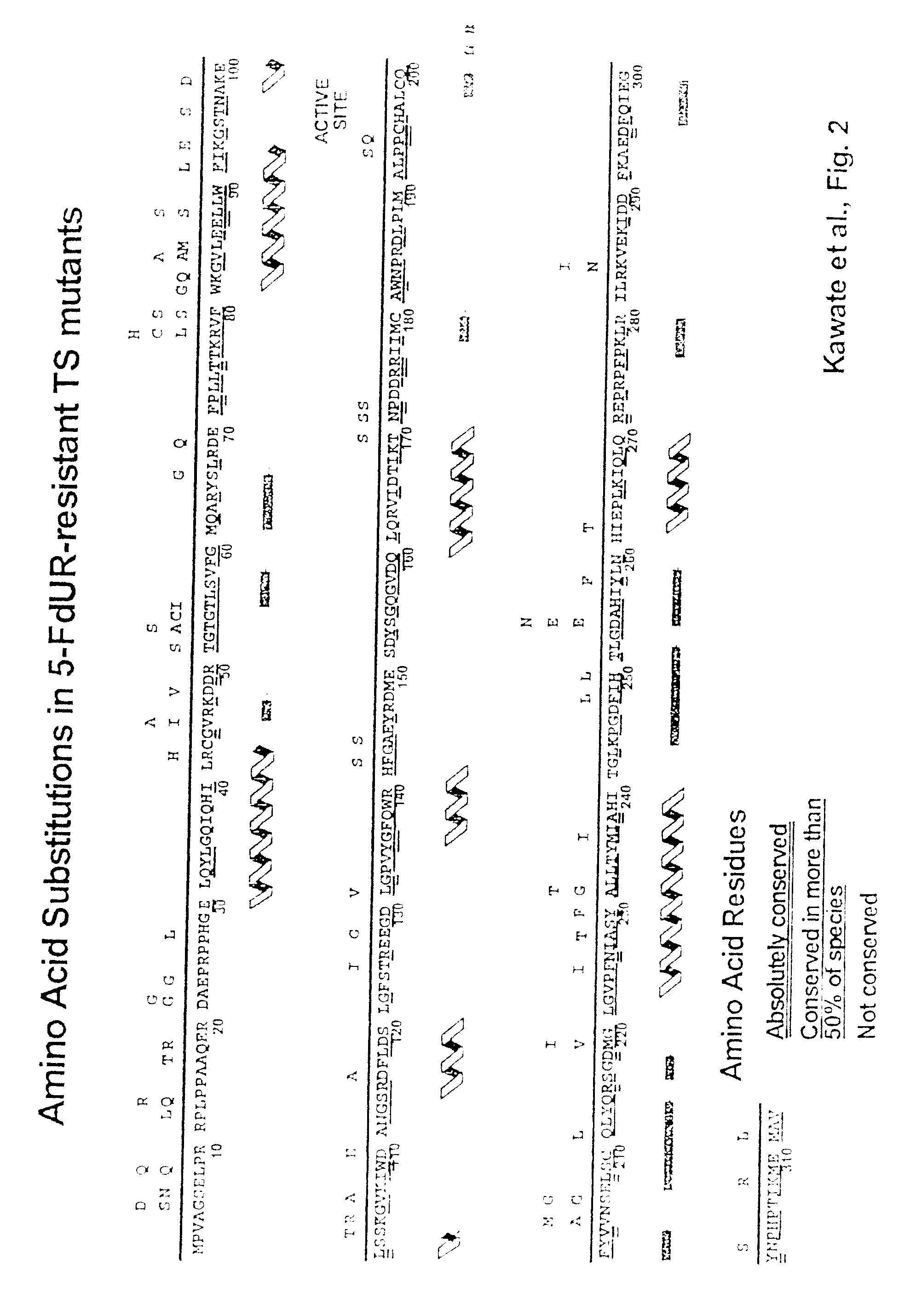
Novel thymidylate synthase mutants
InactiveUS20080045451A1Increase resistanceReduce clinically severe myelo-suppressionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGastrointestinal mucositisWild type
Novel thymidylate synthase (TS mutants) are disclosed differing from human wild type thymidylate synthase in single, double, or multiple mutations, which show intact enzyme activity and enhanced resistance to TS-inhibiting drugs like 5-fluorouracil or 5-fluoro-2-deoxyuridinemonophosphate. All these mutants can be used for the protection of normal human cell populations against the toxic manifestation of analogs that inhibited TS. Drugs for the local treatment or prevention of a mucositis in the oral cavity and the gastrointestinal tract caused by chemotherapy with TS-inhibitors are also provided.
Owner:LOEB LAWRENCE +2
Genomic polymorphism for predicting therapeutic response
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof 5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e60ea01e-2b5f-4992-b838-f479c393123c/US09663503-20170530-C00001.png)
![5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof 5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e60ea01e-2b5f-4992-b838-f479c393123c/US09663503-20170530-C00002.png)
![5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof 5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e60ea01e-2b5f-4992-b838-f479c393123c/US09663503-20170530-C00003.png)
![5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof 5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/17857fa6-d003-4440-8cbc-3466e04970e6/US20150126471A1-20150507-C00001.PNG)
![5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof 5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/17857fa6-d003-4440-8cbc-3466e04970e6/US20150126471A1-20150507-C00002.PNG)
![5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof 5-[[4-[[morpholin-2-yl]methylamino]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile and therapeutic uses thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/17857fa6-d003-4440-8cbc-3466e04970e6/US20150126471A1-20150507-C00003.PNG)