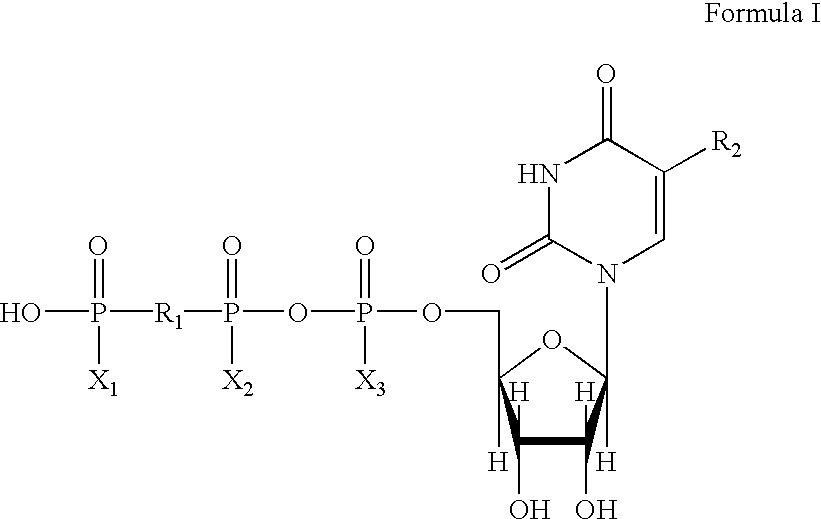
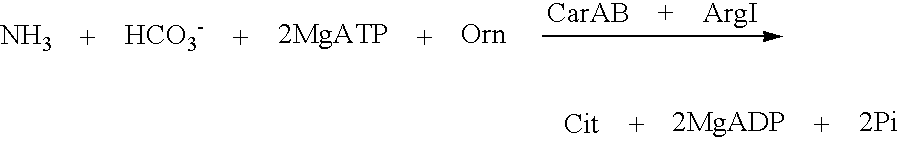Patents
Literature
193 results about "Uridine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Uridine is a glycosylated pyrimidine-analog containing uracil attached to a ribose ring (or more specifically, a ribofuranose) via a β-N₁-glycosidic bond. It is one of the five standard nucleosides which make up nucleic acids, the others being adenosine, thymidine, cytidine and guanosine. The five nucleosides are commonly abbreviated to their one-letter codes U, A, T, C and G respectively. However, thymidine is more commonly written as 'dT' ('d' represents 'deoxy') as it contains a 2'-deoxyribofuranose moiety rather than the ribofuranose ring found in uridine. This is because thymidine is found in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and not ribonucleic acid (RNA). Conversely, uridine is found in RNA and not DNA. The remaining three nucleosides may be found in both RNA and DNA. In RNA, they would be represented as A, C and G whereas in DNA they would be represented as dA, dC and dG.
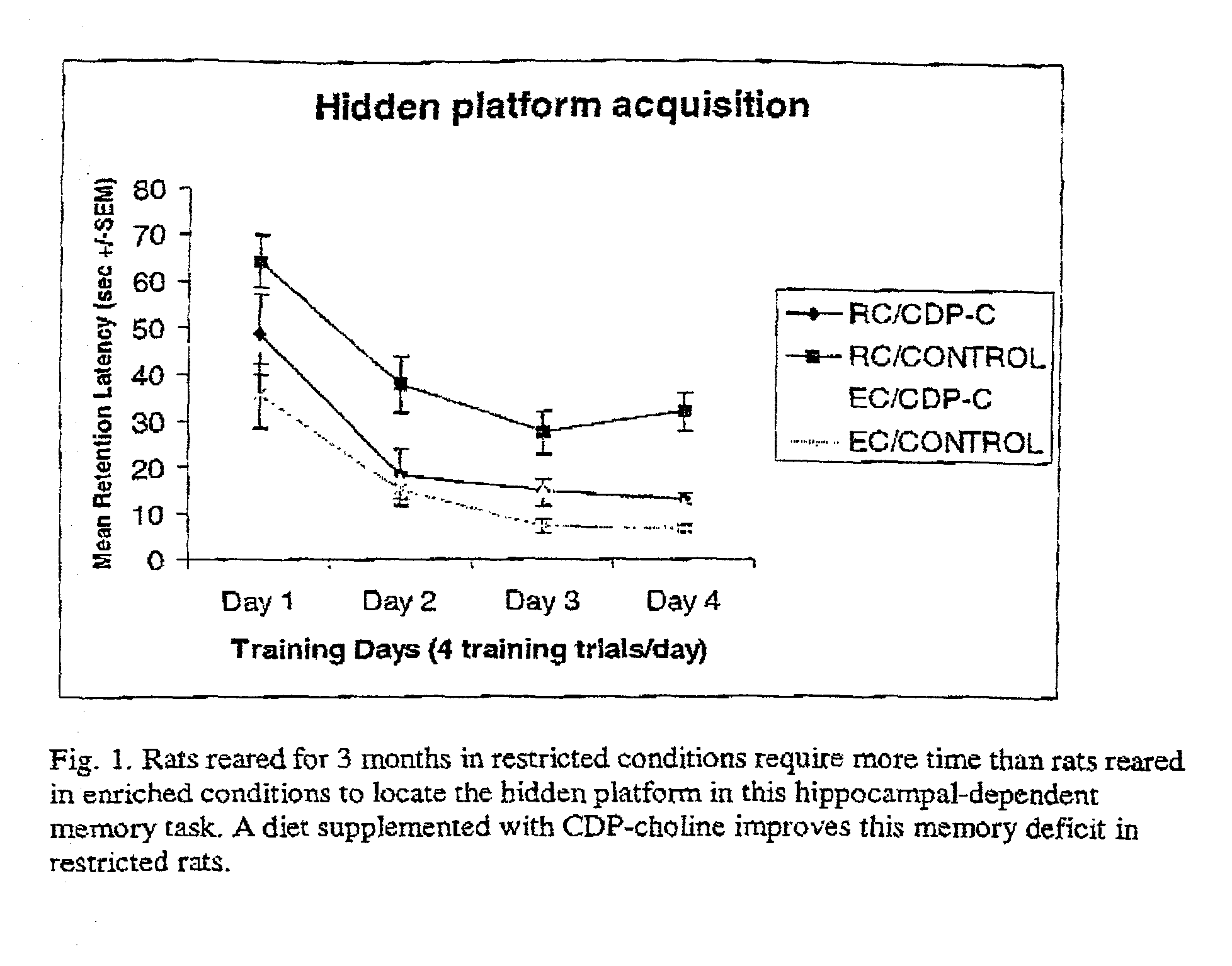
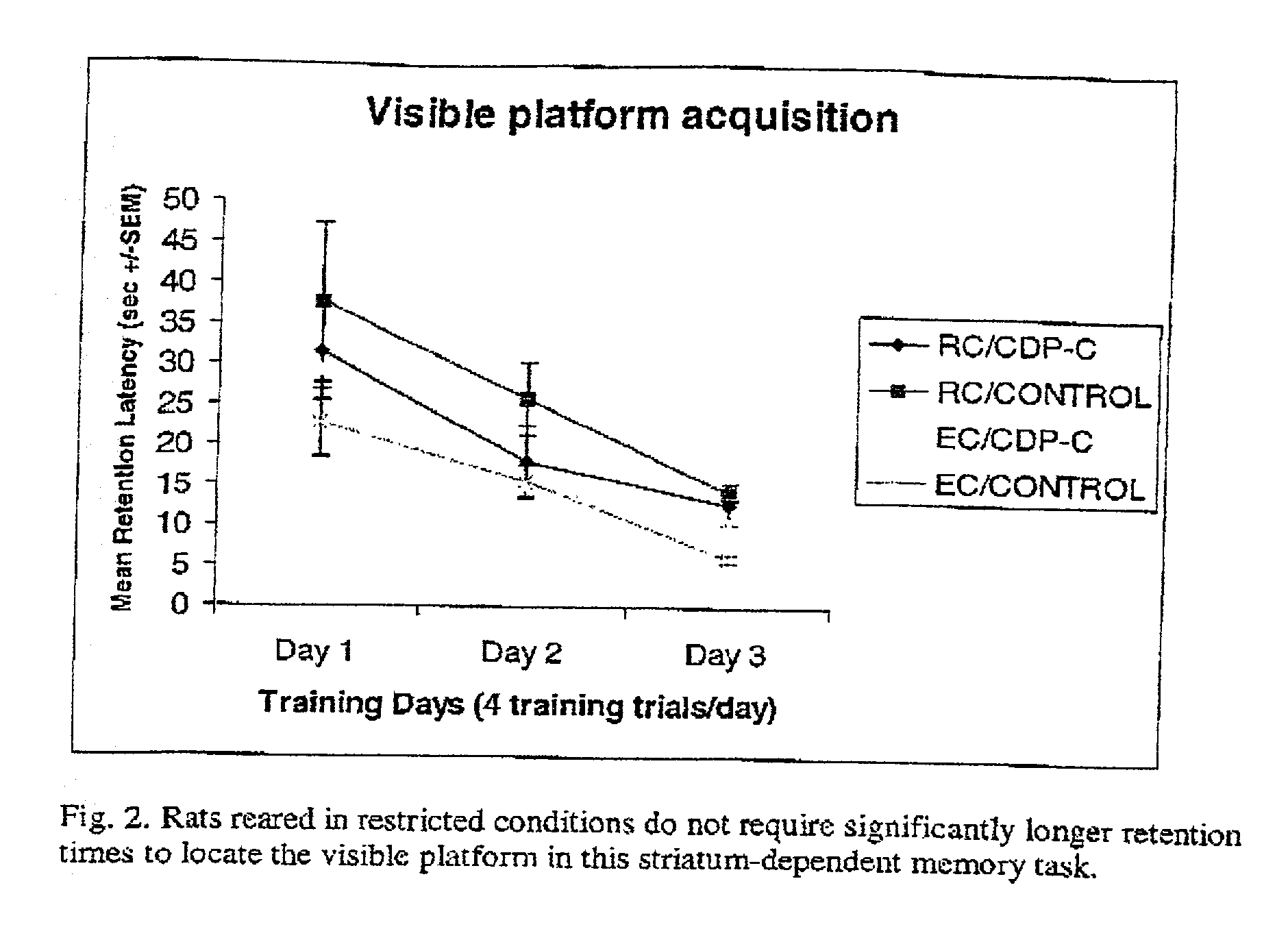
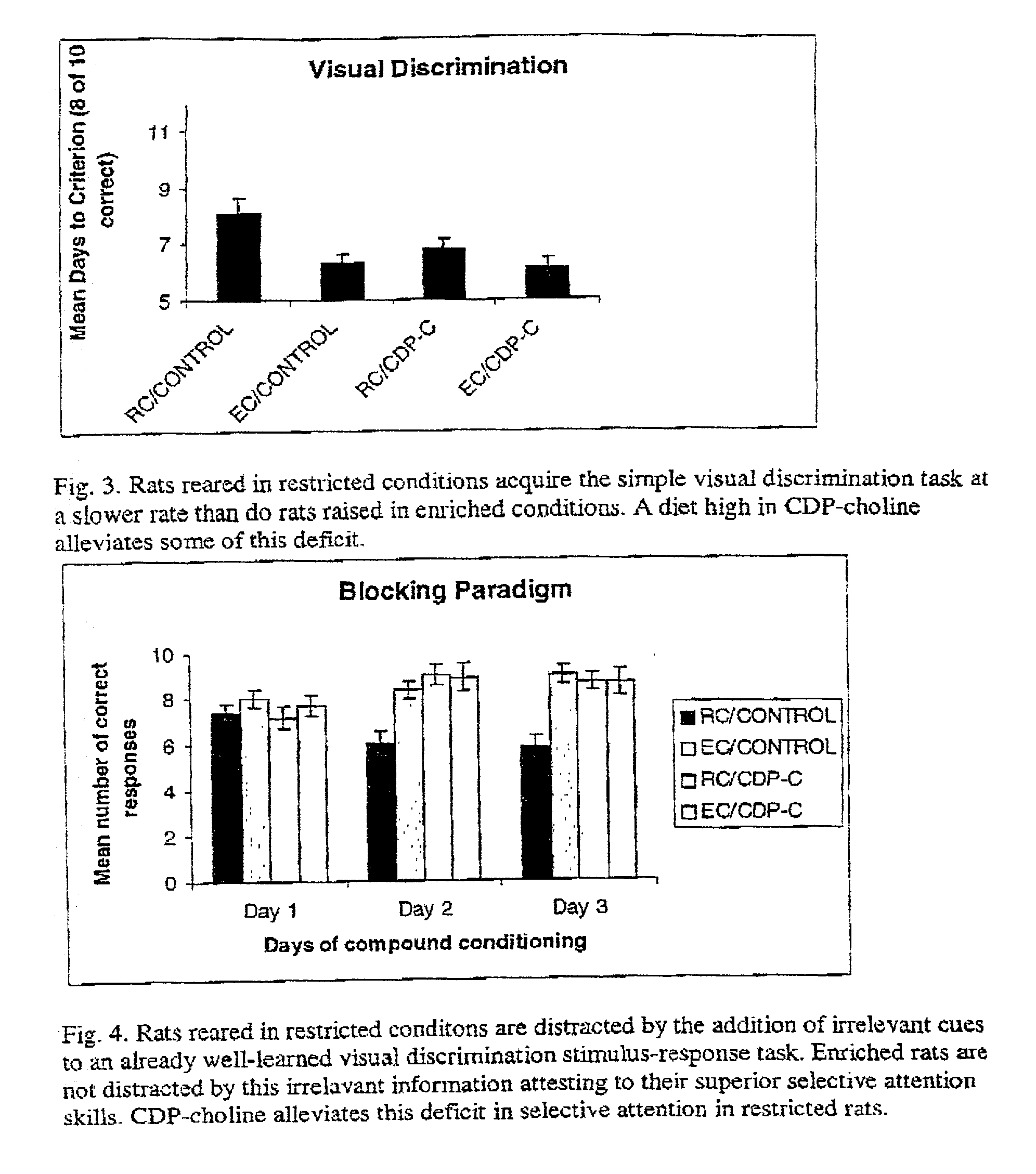
Compositions and methods for treating and preventing memory impairment using citicoline
InactiveUS20030114415A1Low toxicityAvoid damageBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsMemory disorderCiticoline
This invention relates to compositions and methods for preventing and treating cognitive dysfunction or memory impairment. The compositions include an effective amount of citicoline, or pharmaceutically-acceptable salts thereof, and one or more of the compounds selected from the group consisting of linoleic acid and linolenic acid. Other compositions of this invention include an effective amount of citicoline, or pharmaceutically-acceptable salt thereof, wherein said citicoline is metabolized to form at least one of cytidine, uridine, and choline. Still other compositions of this invention include effective amounts of choline, cytidine, and / or uridine, or their pharmaceutically-acceptable salts. This invention also encompasses methods for preparing these compositions.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
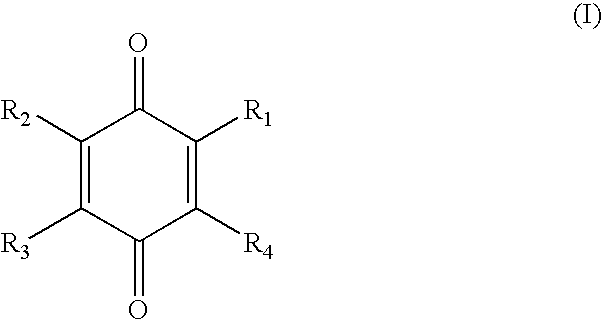
Treatment of statin side effects
The present invention relates generally to treatment of muscle pain and / or fatigue and to methods for treatment of side effects of statin therapy. In particular, the invention relates to the use of certain substituted benzoquinones, e.g. Coenzymes Q, particularly Coenzyme Q10 (Q10), in therapy. The invention also relates to the use of Q10 in combinative therapy with other agents such as uridine, its biological precursors or salts, esters, tautomers or analogues thereof ("uridine related compounds"). The invention is also directed to compositions, uses and combination packs or kits related to the treatment methods. In a preferred aspect the invention relates to a method of treatment of one or more side effects of statin therapy comprising administering to a subject in need of such treatment an effective amount of uridine, one of its biological precursors or a salt, ester, tautomer or analogue thereof either simultaneously, sequentially or separately to administration of an effective amount of at least one compound of Formula (I).
Owner:MAGRAL
Nutritional compositions containing a neurologic component and uses thereof
InactiveUS20140199265A1Promoting neurologicalPromote brainBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsDeveloping nervous systemCytidine diphosphate
The present disclosure relates to nutritional compositions comprising a neurologic component, wherein, the neurologic component may promote brain and nervous system development and further provide neurological protection and repair. The neurologic component may include phosphatidylethanolamine, sphingomyelin, cytidine diphosphate-choline, ceramide, uridine, at least one ganglioside, and mixtures thereof. The disclosure further relates to methods of promoting brain and nervous system health by providing said nutritional compositions to target subjects, which includes pediatric subjects.
Owner:MEAD JOHNSON NUTRITION
Methods and compositions for improving cognitive performance
PendingUS20100041621A1Improve performanceRaise attentionBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsPsychiatryCognitive skill
Owner:THE MCLEAN HOSPITAL CORP
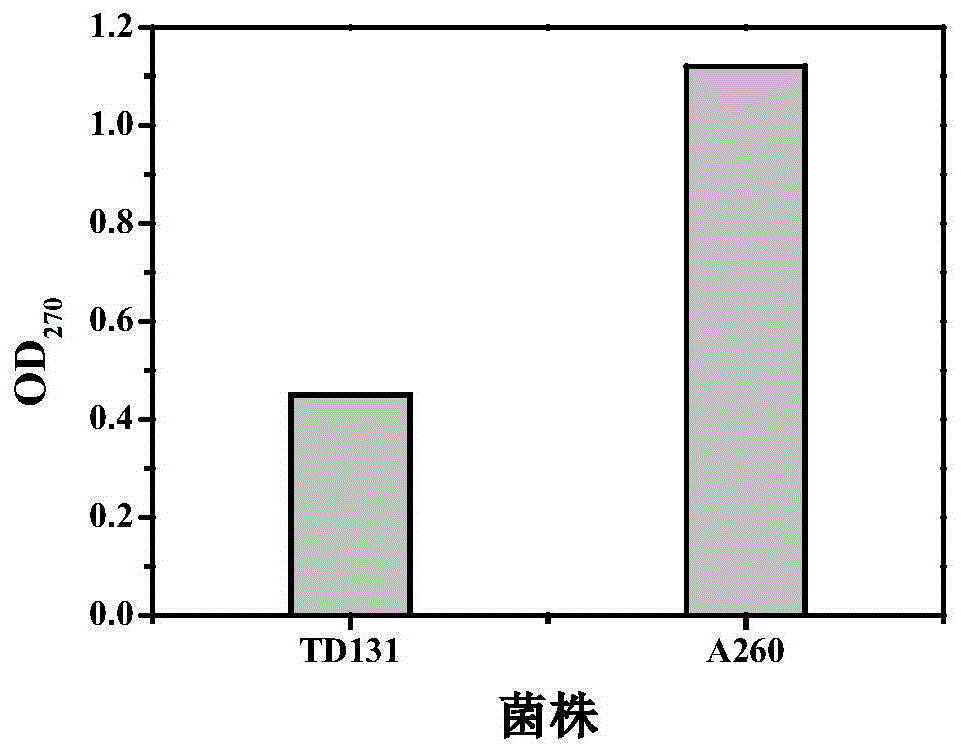
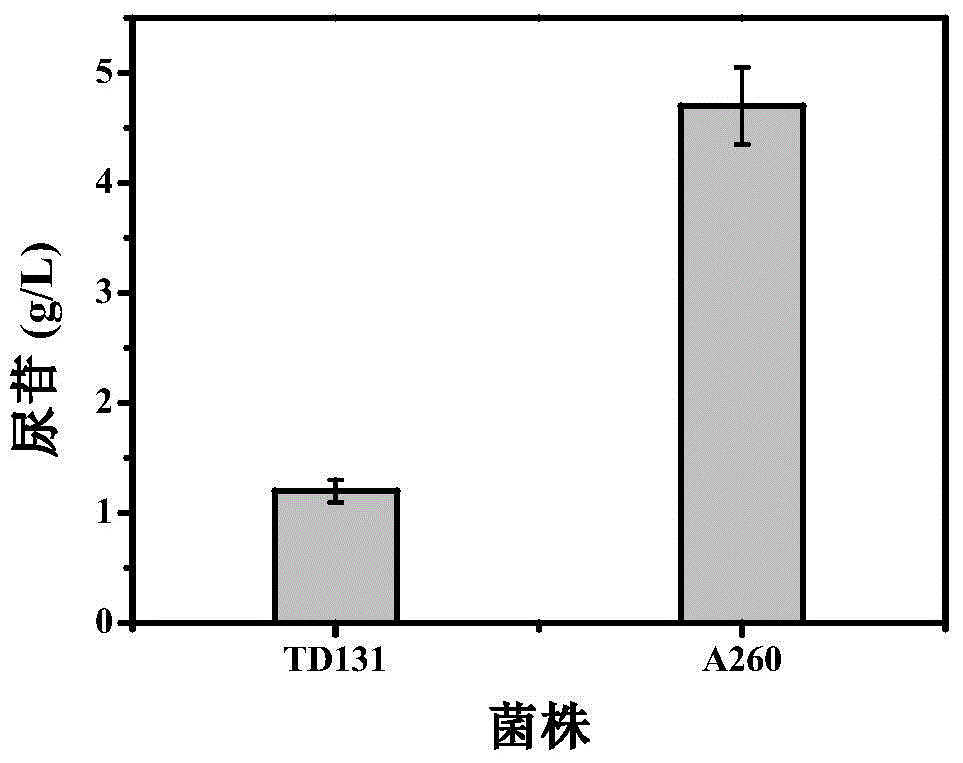
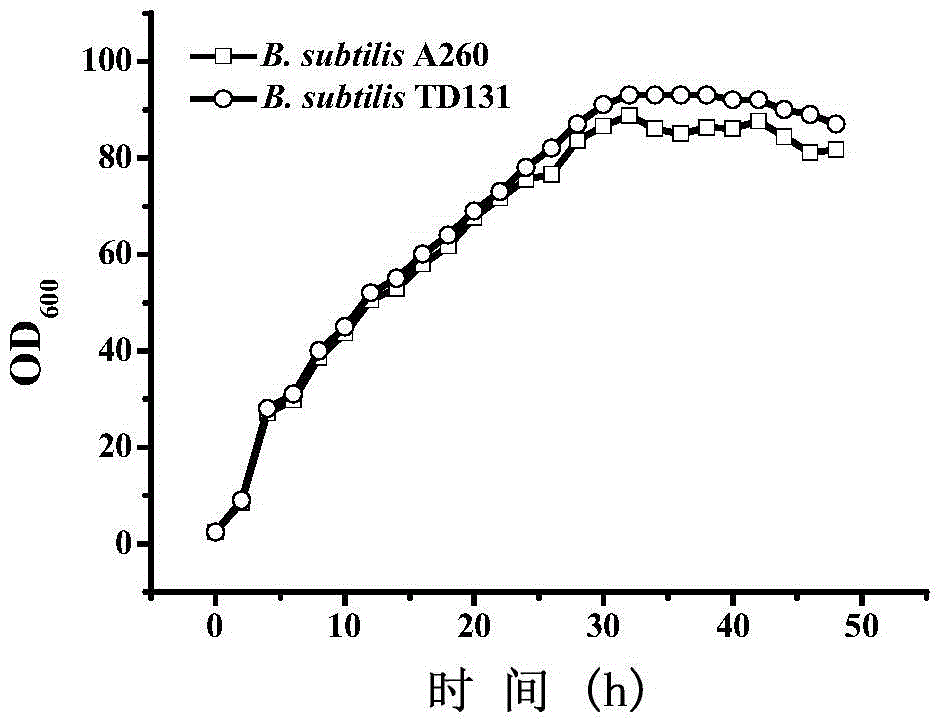
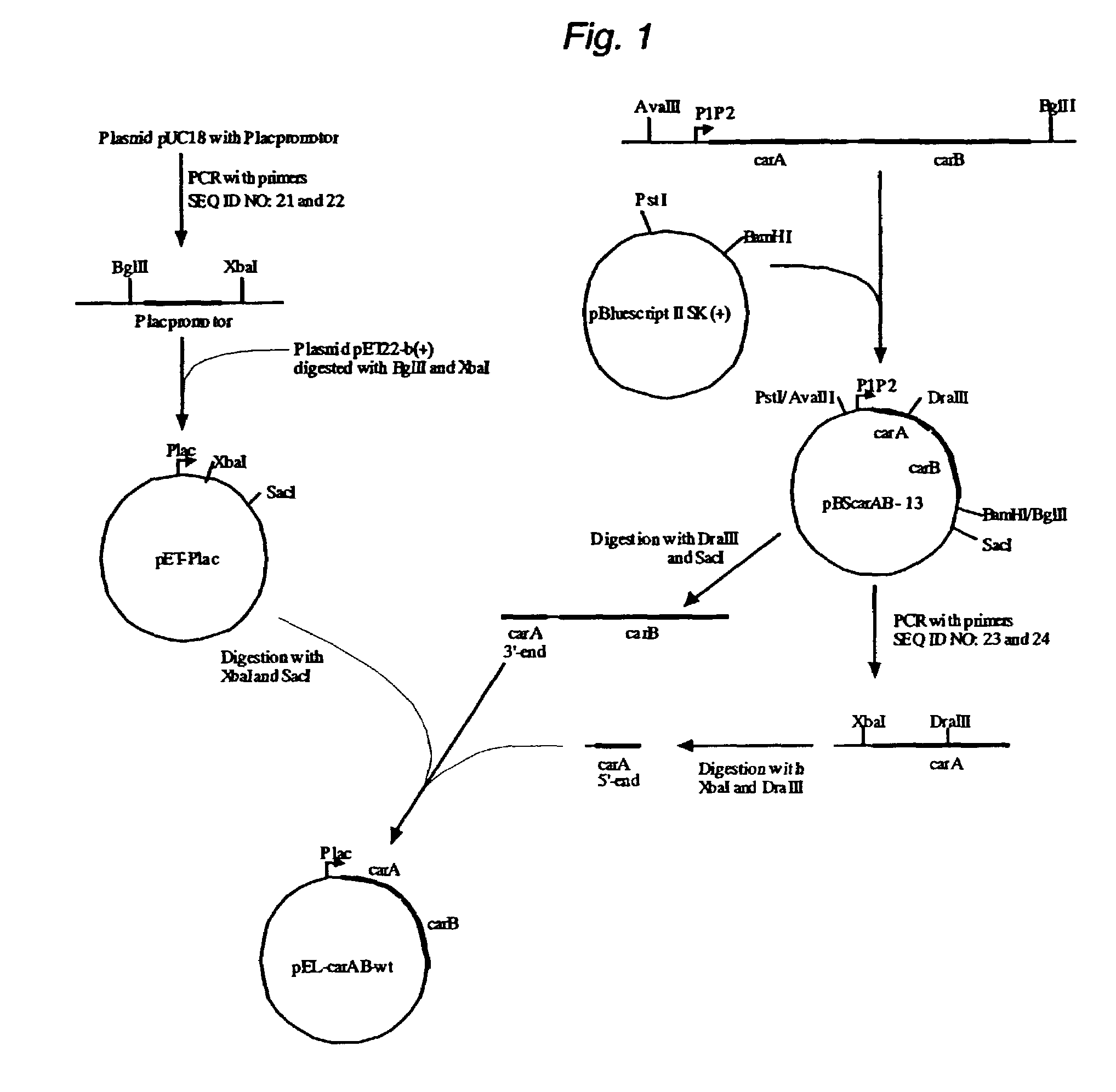
Pyrimidine nucleoside high-yielding strain and carbamyl phosphate synthetase adjusting site thereof
ActiveCN105671007AImprove toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCarbamyl PhosphateStructural analog
The invention belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering, and concretely relates to a pyrimidine nucleoside high-yielding strain and a carbamyl phosphate synthetase adjusting site thereof. The invention provides a pyrimidine nucleoside production Bacillus subtilis mutant strain and a carbamyl phosphate synthetase encoding gene. A key regulation site related to carbamyl phosphate synthetase end product feedback inhibition is defined, and provides reference for breeding of later pyrimidine nucleoside high-yielding strains. The Bacillus subtilis mutant strain allows the output of fermentation process produced nucleoside pyrimidine uridine to reach 14-16g / L, and has substantially improved tolerance to different pyrimidine nucleoside structure analogs.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Nucleic acid compounds for inhibiting erbb gene expression and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080287383A1Thermal stability is maximizedOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSilent geneRNA - Ribonucleic acid
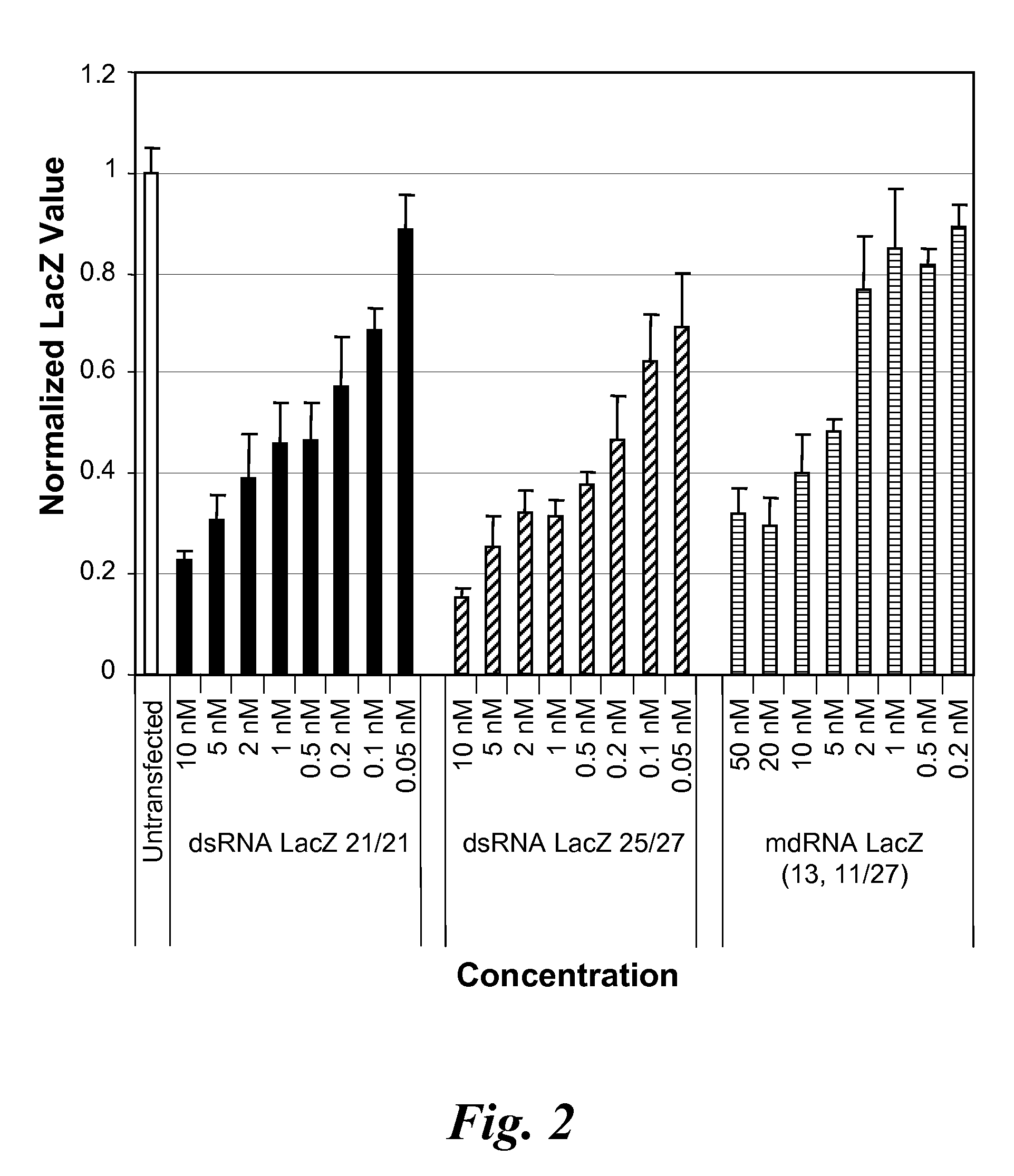
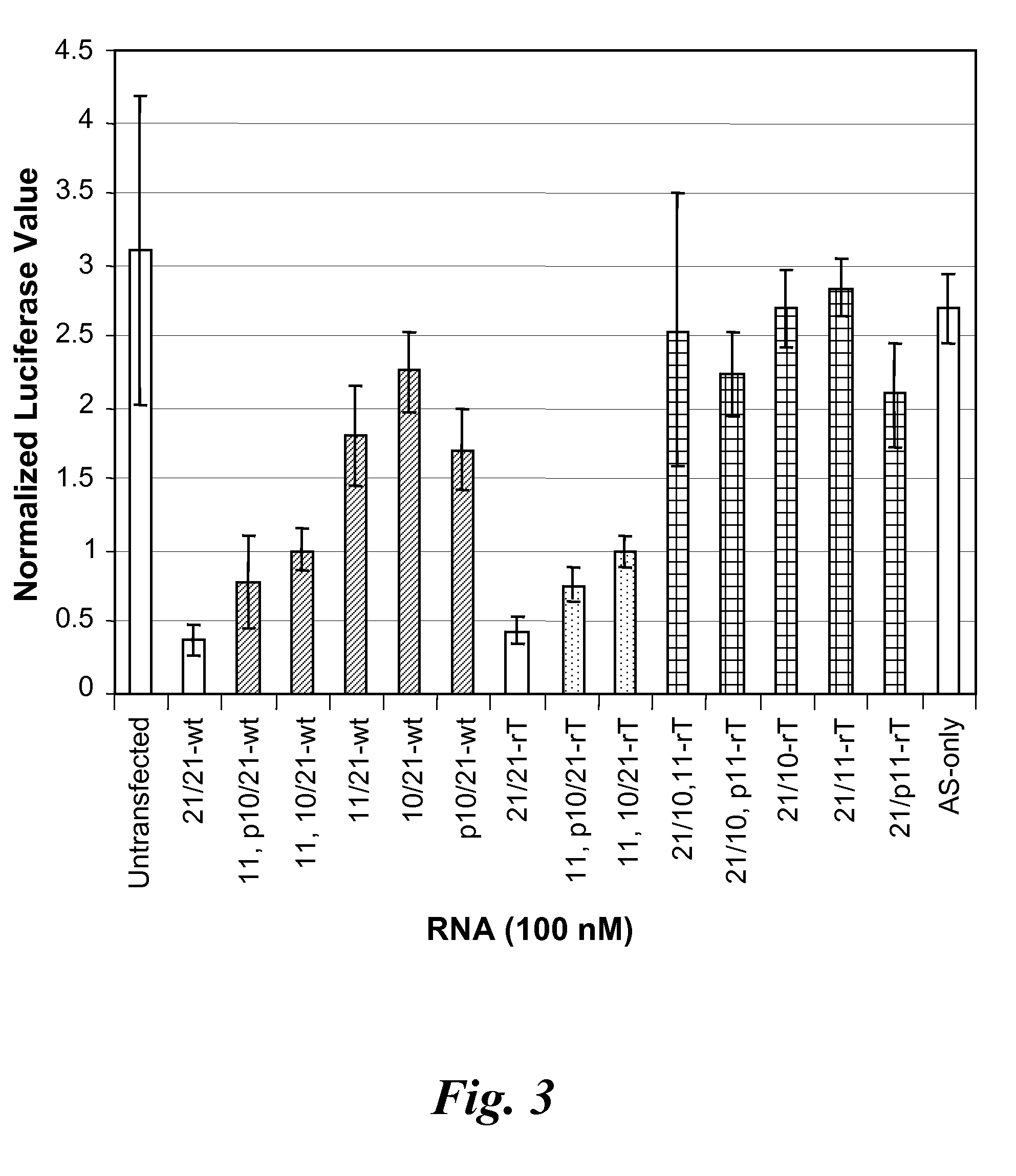
The present disclosure provides meroduplex ribonucleic acid molecules (mdRNA) capable of decreasing or silencing ERBB gene expression. An mdRNA of this disclosure comprises at least three strands that combine to form at least two non-overlapping double-stranded regions separated by a nick or gap wherein one strand is complementary to an ERBB mRNA. In addition, the meroduplex may have at least one uridine substituted with a 5-methyluridine, a nucleoside replaced with a locked nucleic acid, or optionally other modifications, and any combination thereof. Also provided are methods of decreasing expression of an ERBB gene in a cell or in a subject to treat an ERBB-related disease.
Owner:MARINA BIOTECH INC
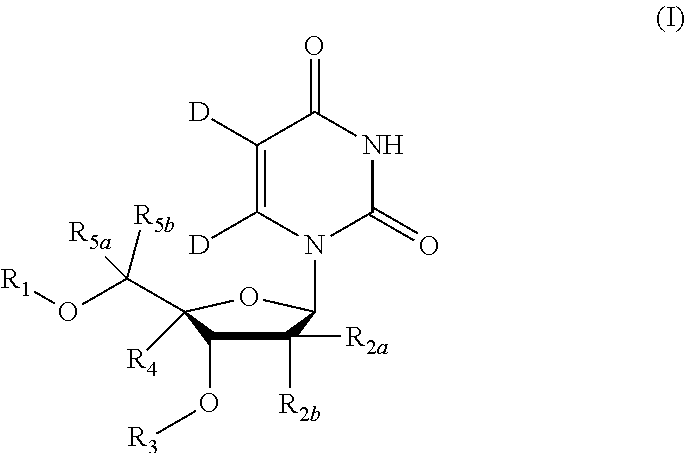
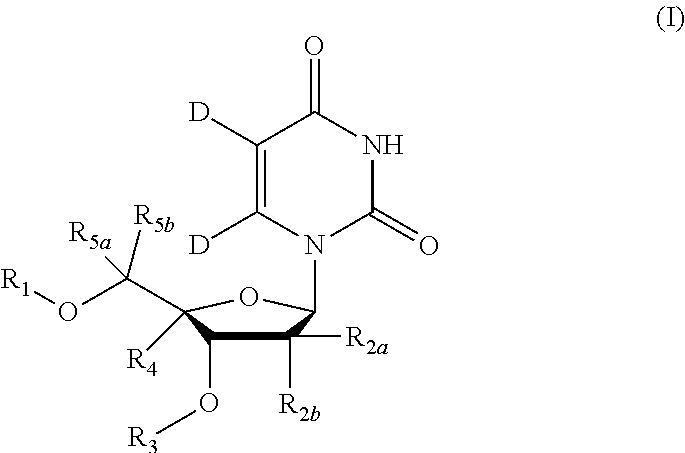
5, 6-D2 uridine nucleoside/tide derivatives
ActiveUS10034893B2Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical medicinePerylene derivatives
Owner:ENANTA PHARM INC
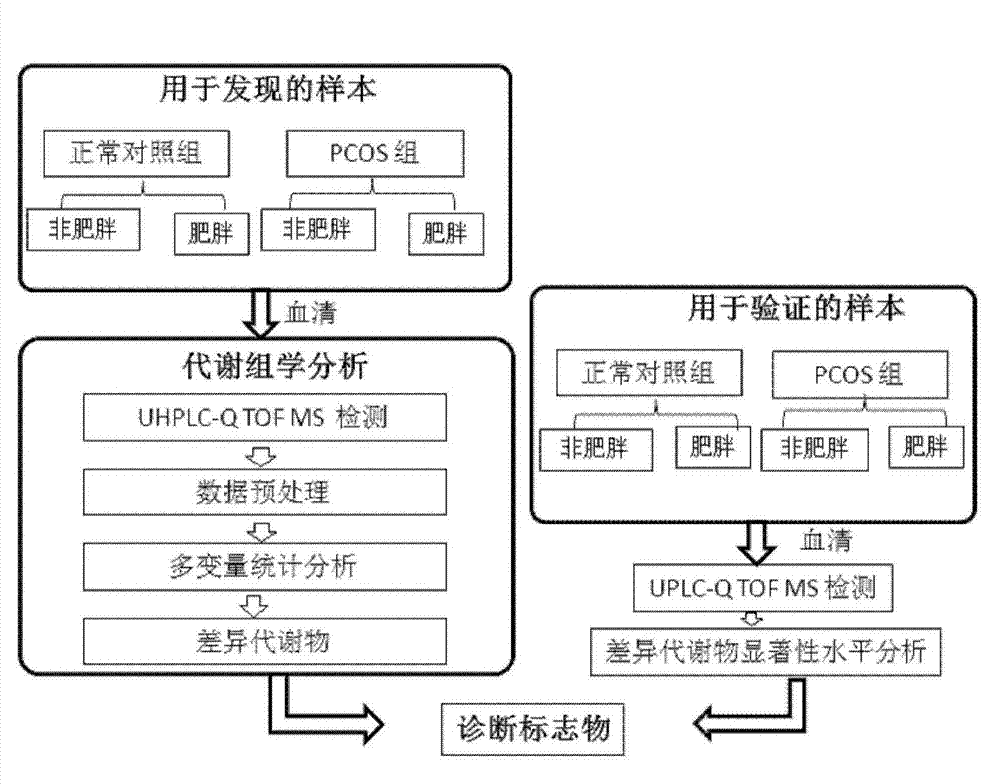
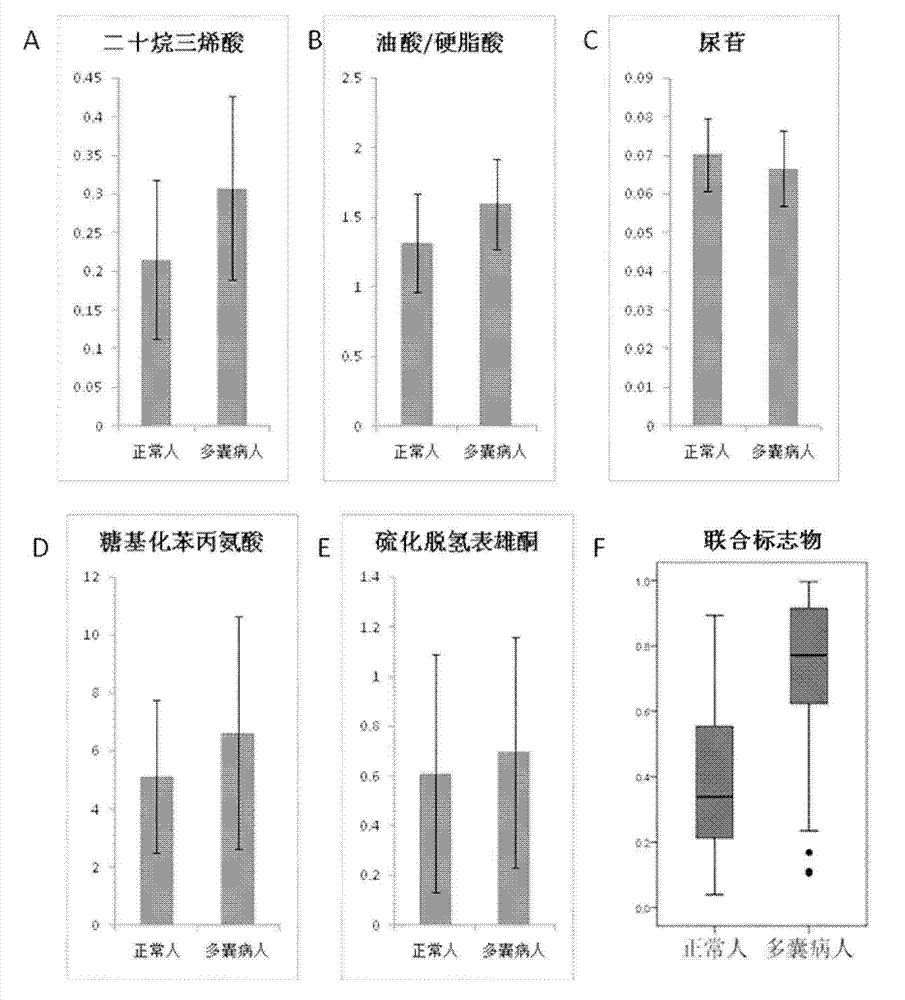
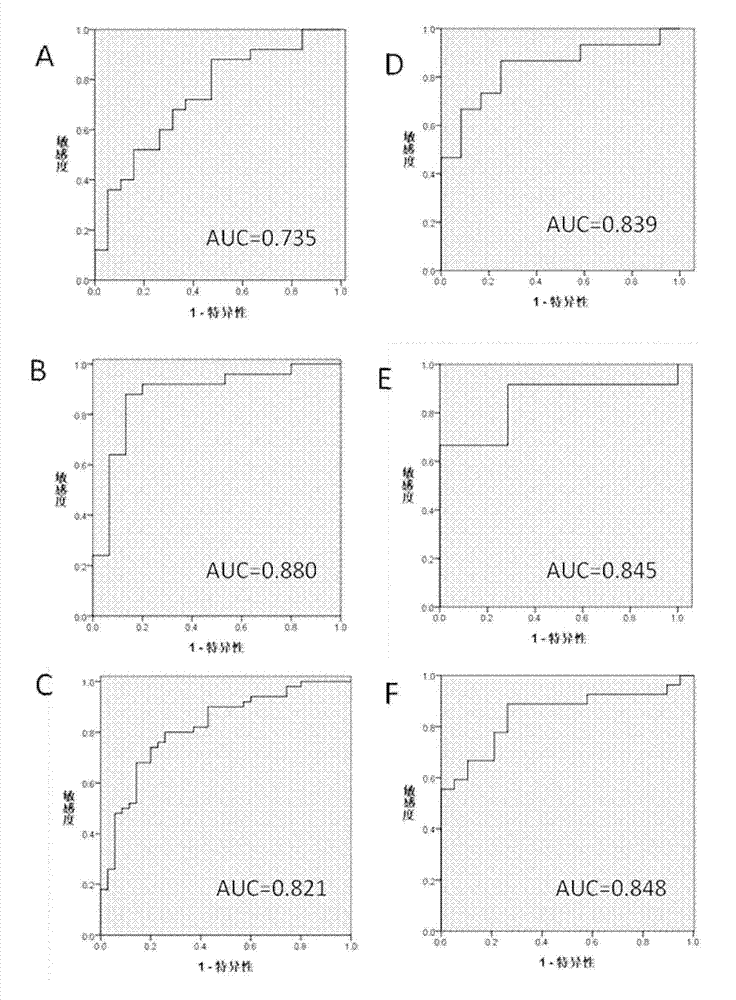
Combined markers, kit and system for diagnosis of polycystic ovarian syndrome
InactiveCN104777242AGlobal metabolic abnormalitiesEasy to identifyComponent separationMetabolitePhysiology
The invention relates to a novel use of serum sample micromolecule metabolites such as oleic acid, stearic acid, eicosatrienoic acid, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, glycosylated phenylalanine and uridine as combined markers in preparation of a kit for diagnosis of polycystic ovarian syndrome of subjects. The invention also relates to a kit of diagnosis of polycystic ovarian syndrome of subjects. The kit is used for detecting respective concentrations of the combined markers in a serum sample of a female subject, calculating combined marker variable based on a binary logistic regression equation, and determining if the subject suffers from polycystic ovarian syndrome based on the determined intercept point value. The kit can realizes high sensitivity and high efficiency detection of the micromolecular metabolites and has the characteristics of low detection cost and good repeatability. Through combined use of the micromolecular metabolites, the kit can be used in auxiliary diagnosis of different symptoms of polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Palatable nutritional composition comprising a nucleotide and/or a nucleoside and a taste masking agent
The present invention relates to the use of a taste masking agent selected from the group of cellulose; starch; xanthan gum; gellan gum; alginate; galactomannans such as fenugreek, guar gum, tara gum, locust bean gum, and cassia gum; gum karaya; gum tragacanth; carrageenan; and mixture thereof, for improving one or more of mouth feel, taste, aftertaste and smell of a liquid aqueous nutritional composition comprising a nucleotide and / or a nucleoside. It also relates to a nutritional composition comprising an unsavoury nucleotide and / or a nucleoside component, having improved sensory characteristics such as improved mouth feel, taste, aftertaste and smell. In particular, it relates to a composition comprising said un-savoury nucleotide and / or a nucleoside component, in particular comprising an uridine-containing nucleotide and / or a nucleoside in combination with an unsavoury edible oil, such as a fish oil.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
Food composition for prodromal dementia patients
ActiveUS20100323982A1High probability to developReduce developmentBiocideNervous disorderMedicinePhospho tau
A composition comprising (a) one or more ω-3 fatty acids selected from DHA, DPA and EPA, (b) uridine or its equivalent, and (c) a methyl donor, useful in the treatment of a person having characteristics of a prodromal dementia patient. The characteristics include e.g. a level of more than 350 ng Total-tau per litre cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and a weight ratio of abeta-42 / Phospho-tau-181 of less than 6.5 in CSF.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
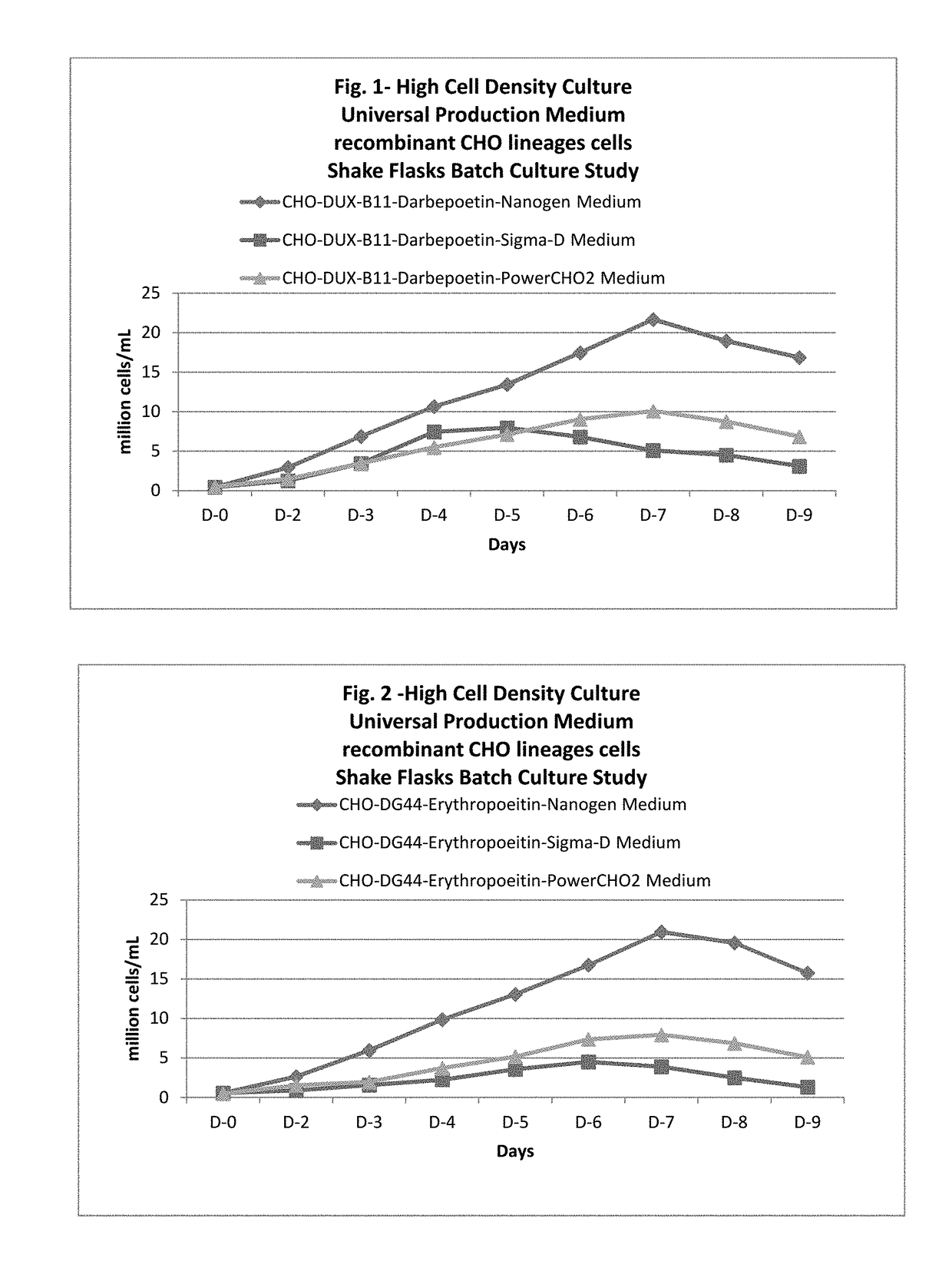
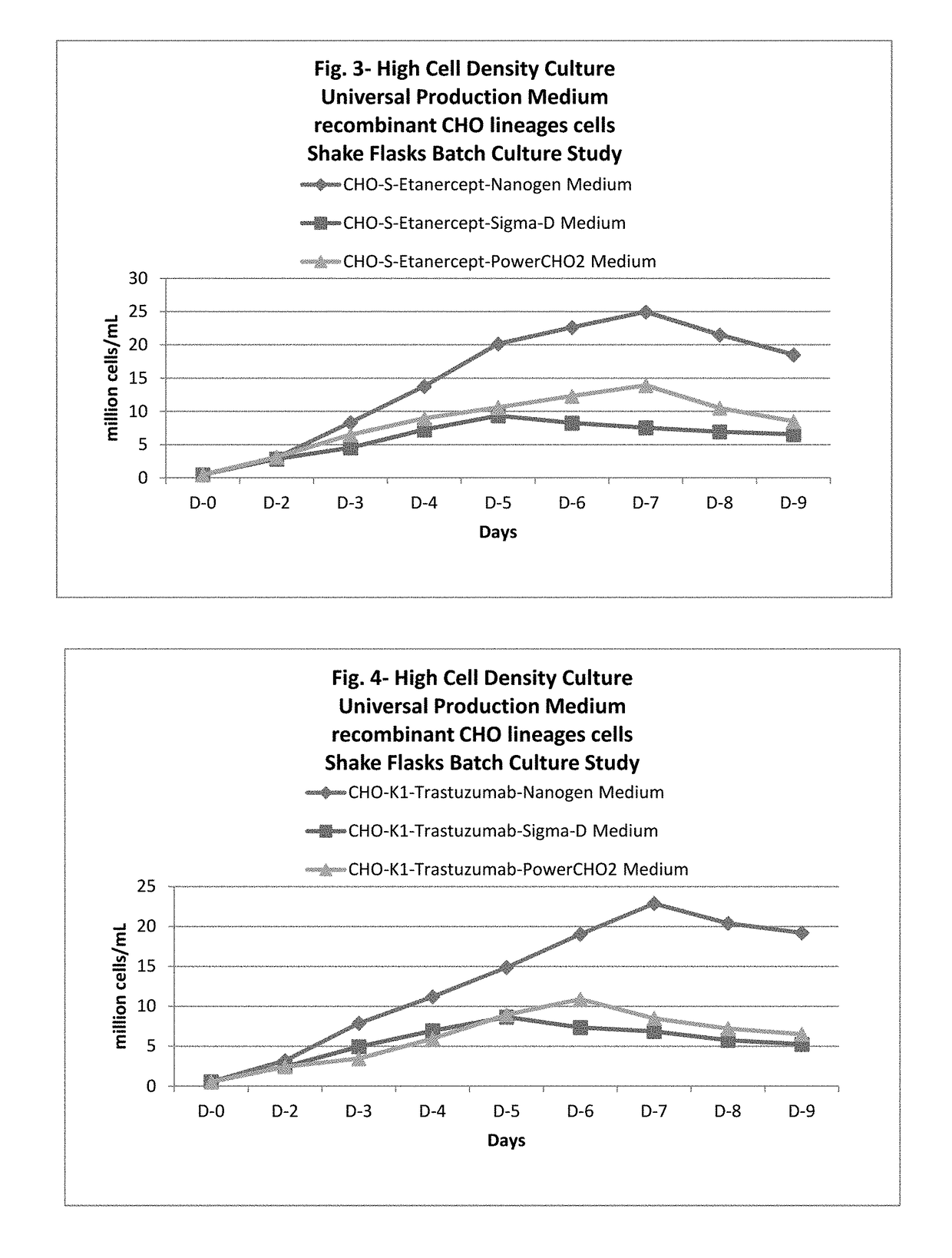
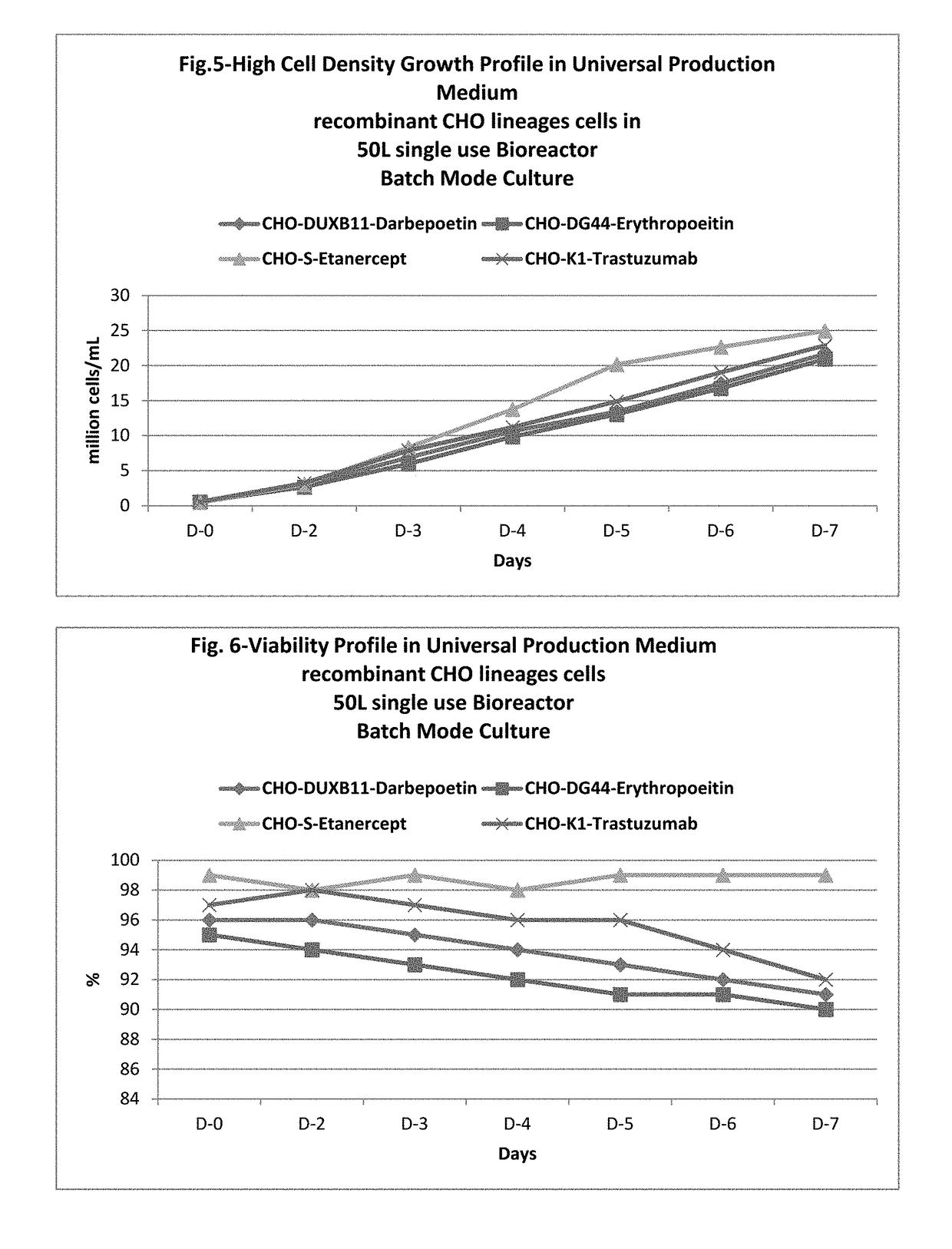
Universal, glycosylation enhancer, completely chemically defined medium formulation
ActiveUS20170218328A1Therapy is also rapidCulture processCell culture mediaSodium bicarbonateHydrolysate
In one embodiment, the present application discloses a cell culture medium for culturing cell lines suitable for producing a therapeutic protein, comprising an amino acid selected from a group consisting of L-arginine, L-asparagine, L-proline, L leucine and L hydroxyproline and a mixture thereof; a vitamin selected from a group consisting of ascorbic acid Mg2+ salt, biotin, pyridoxine HCL, folic acid, riboflavin and D-calcium pantothenate, and a mixture thereof; an element selected from a group consisting of ammonium meta vanadate, sodium meta vanadate, germanium dioxide, barium acetate, aluminum chloride, rubidium chloride, cadmium chloride, ammonium molybedate, stannous chloride, cobalt chloride, chromium sulfate, silver nitrate, sodium metasilicate, zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate H2O, manganous chloride, ferric nitrate 9H2O, ferrous sulfate 7H2O, ferric ammonium citrate, magnesium chloride anhydrous, and magnesium sulfate anhydrous, and a mixture thereof; a nucleoside selected from a group consisting of uridine and cystidine; a sugar selected from a group consisting of galactose, mannose and N-Acetyl-D-Mannosamine; and a triple buffering system comprising sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate and HEPES; wherein the cell culture medium is animal component-free, plant component-free, serum-free, growth factors-free, recombinant protein-free, lipid-free, steroid-free, and free of plant or animal hydrolysates and / or extracts.
Owner:NANOGEN PHARMA BIOTECH CO LTD
Uridine diphosphate xylose isomerase, coding gene thereof and use thereof
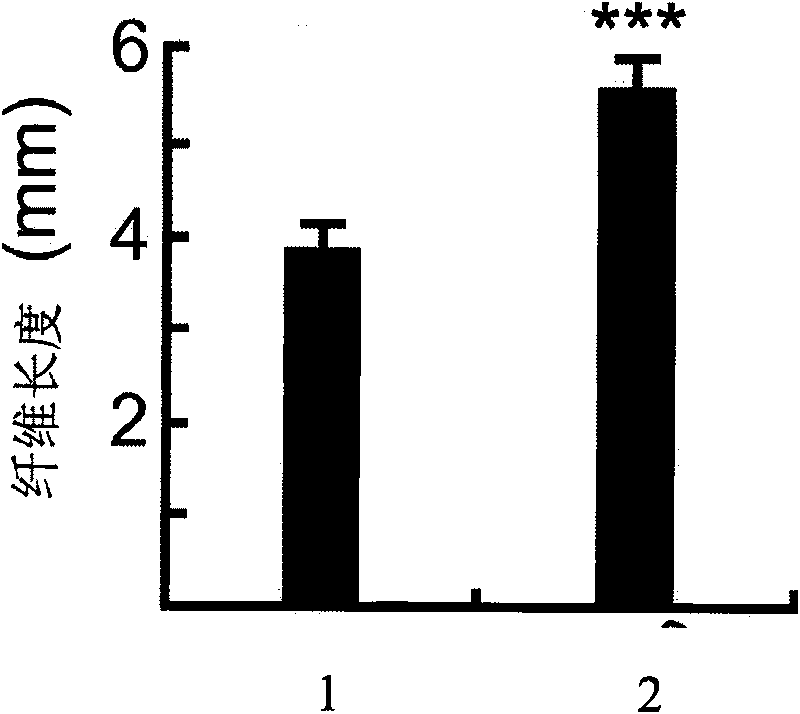
InactiveCN101698839AIncrease the lengthImprove qualityMicroorganismsIsomerasesIsomeraseUridine diphosphate
The invention discloses a uridine diphosphate xylose isomerase, a coding gene thereof and use thereof. The uridine diphosphate xylose isomerase is a protein a or a protein b, wherein the protein a has an amino acid sequence represented by the No.2 sequence in a sequence table; and the protein b is derived from the protein a by substituting and / or losing and or adding one or several amino acids in the amino acid sequence represented by the No.2 sequence in the sequence table and is related to the synthesis of the uridine diphosphate arabinose. The invention also discloses a coding gene for coding the protein. The coding gene of the uridine diphosphate xylose isomerase can be introduced into cotton to lengthen cotton fibers and improve the quality and yield of cotton fibers. The uridine diphosphate xylose isomerase and the coding gene thereof have great economic values and application prospects.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Nonsense suppression and genetic codon alteration by targeted modification
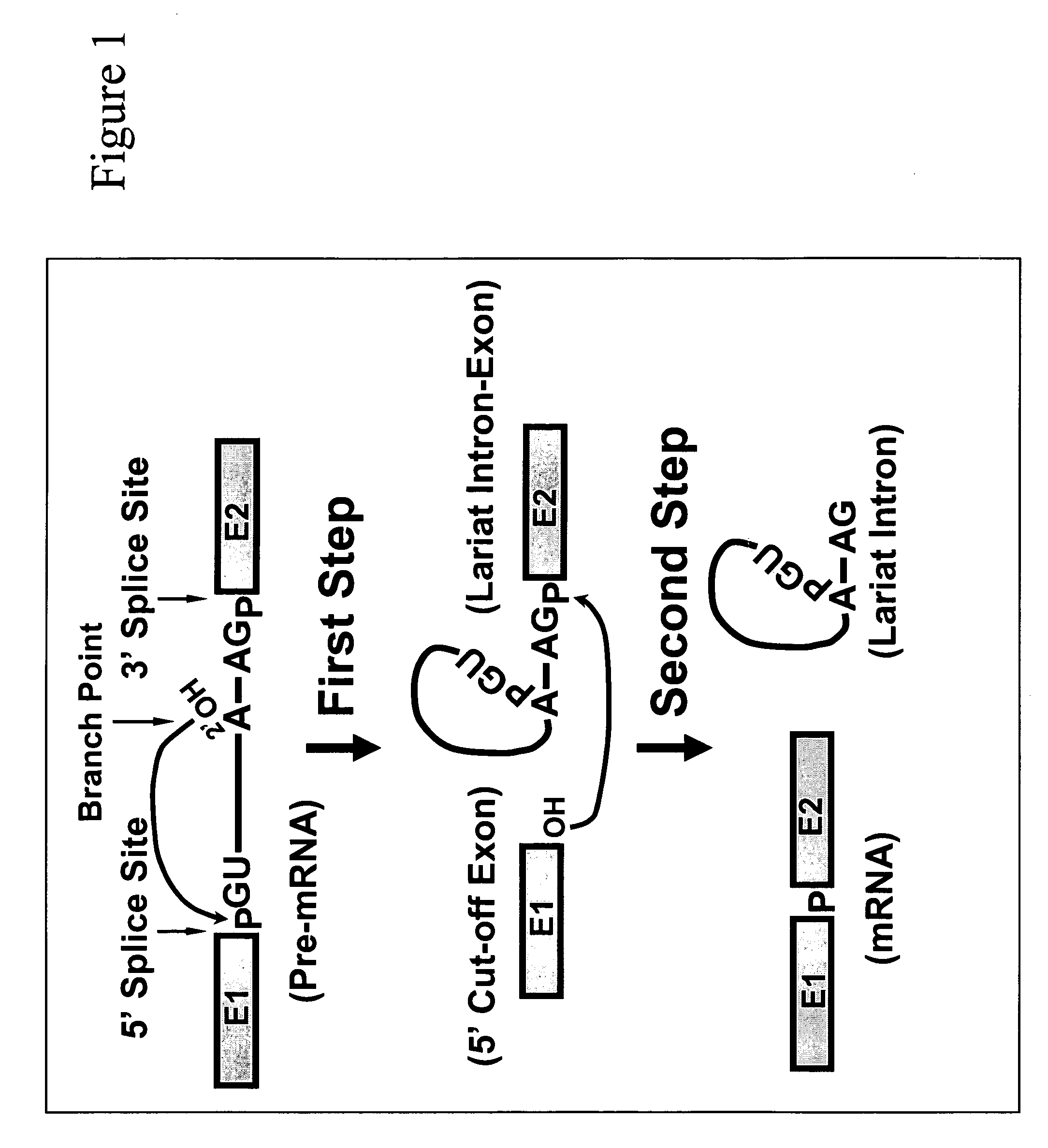
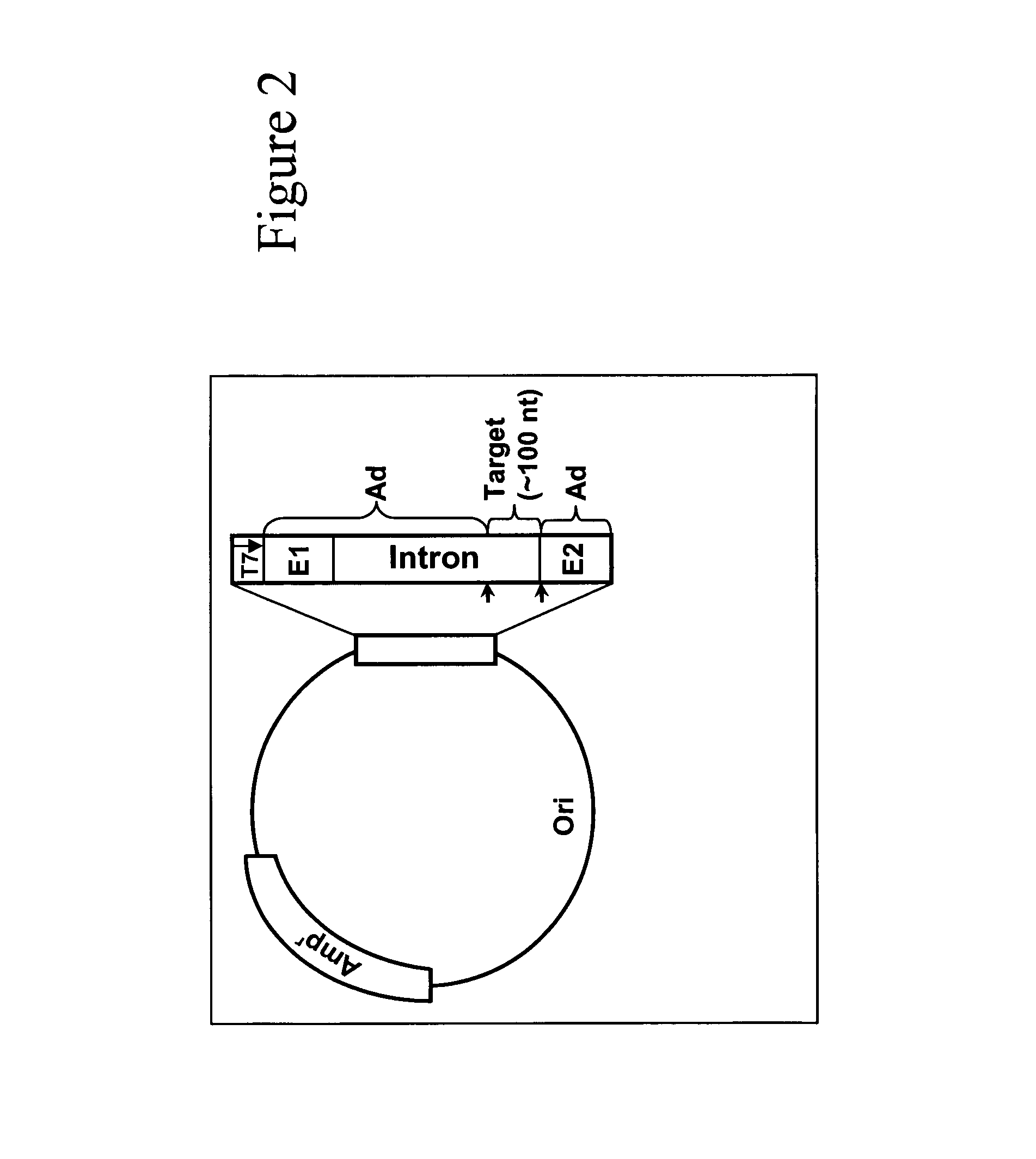
ActiveUS8603457B2Easy to identifyLarge productionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAdenosineGenetics
Methods for affecting mRNA expression or translation through the modification of pre-mRNA or mRNA transcripts are described. In one embodiment of the methods of the present invention, the branch point adenosine of a pre-mRNA transcript is 2′-O-methylated to block splicing and subsequent expression of the protein encoded by the transcript. In another embodiment, a uridine residue in a nonsense stop codon may be modified to pseudouridine, causing the translation machinery to read through the nonsense stop codon and translate a full length protein.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
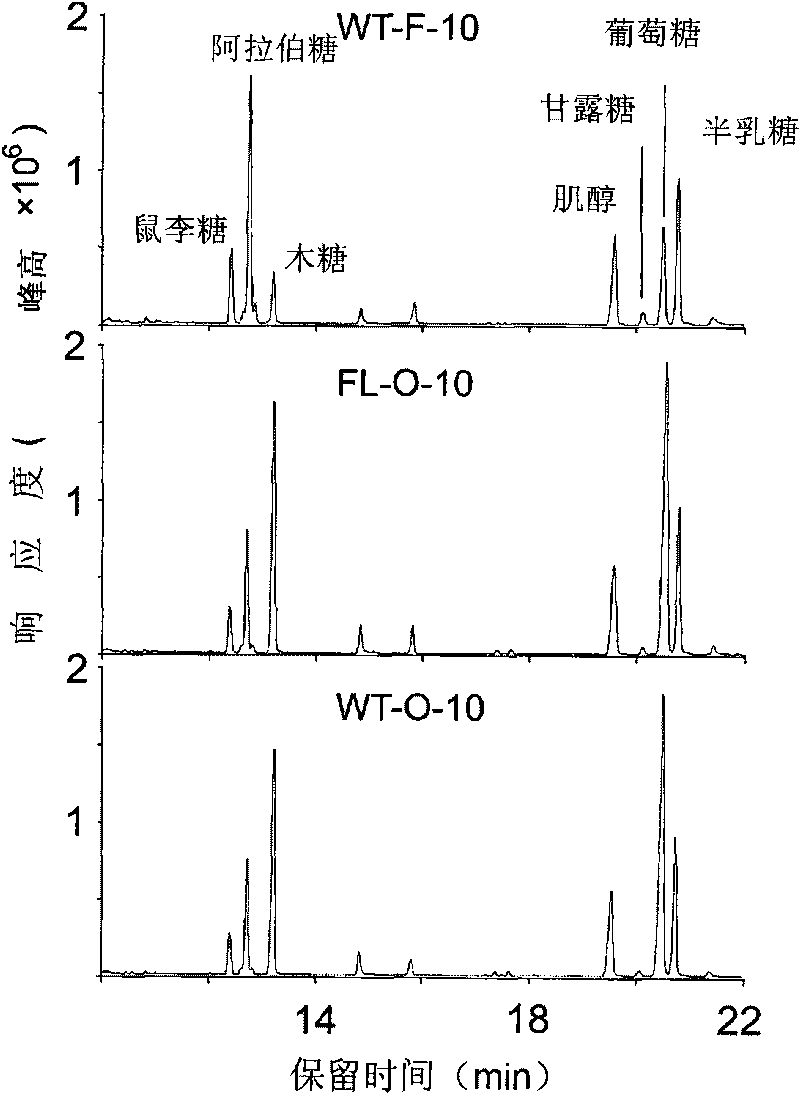
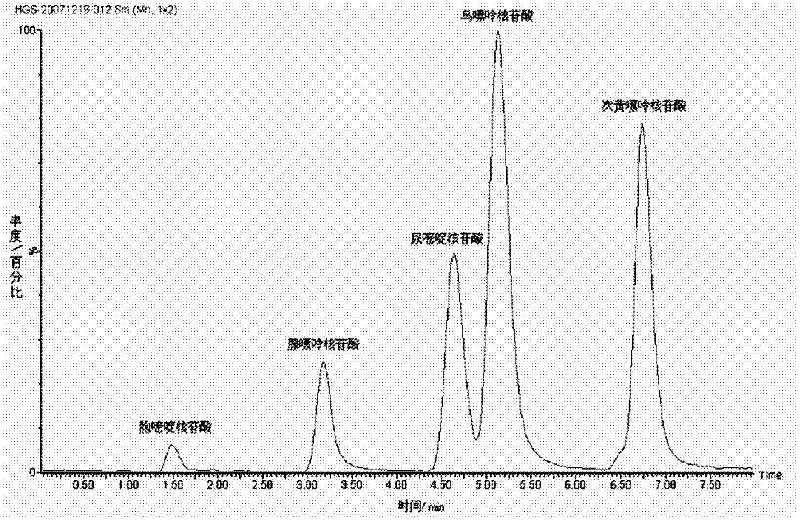
Ultra performance liquid chromatography method for simultaneously determining contents of uridine, guanosine and adenosine in rhizoma pinelliae extract
The invention belongs to the field of traditional Chinese medicine composition analytic determination technology, and discloses a method for determining the contents of uridine, guanosine and adenosine in a rhizoma pinelliae medicinal material and decoction piece extract by a UPLC method. A chromatographic column is ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 (1.7 [mu]m, 2.1*50 mm), a mobile phase is a water-methanol mixture with different-ratio gradient elution, a column temperature is 30 DEG C, the flow rate is 0.5 mL.min<-1>, and the detection wavelength is 254 nm. Uridine, guanosine and adenosine have good linear relationship in an applicable concentration range. The method is accurate, fast and reliable, and can effectively simultaneously determine the contents of uridine, guanosine and adenosine in the rhizoma pinelliae extract.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
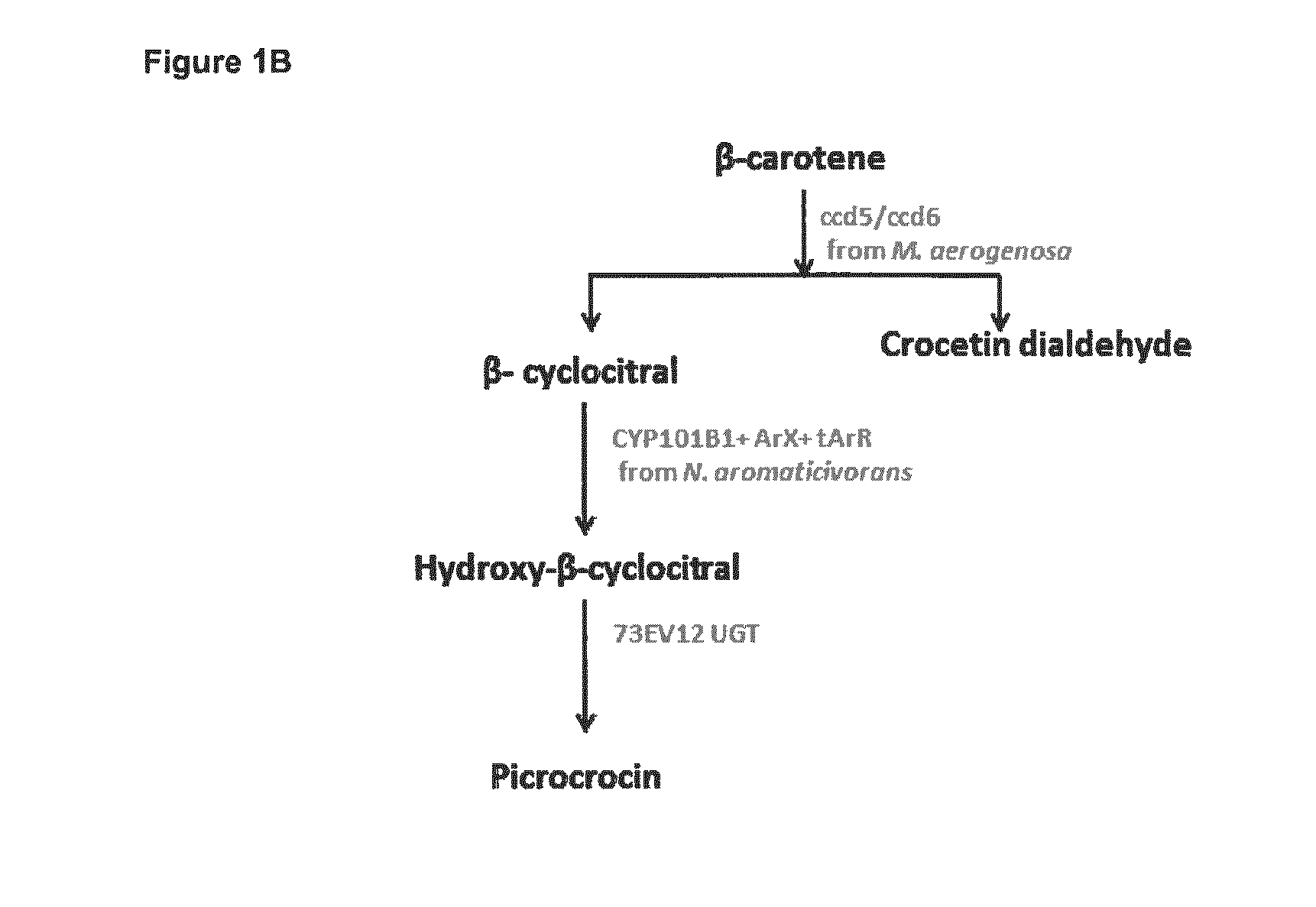
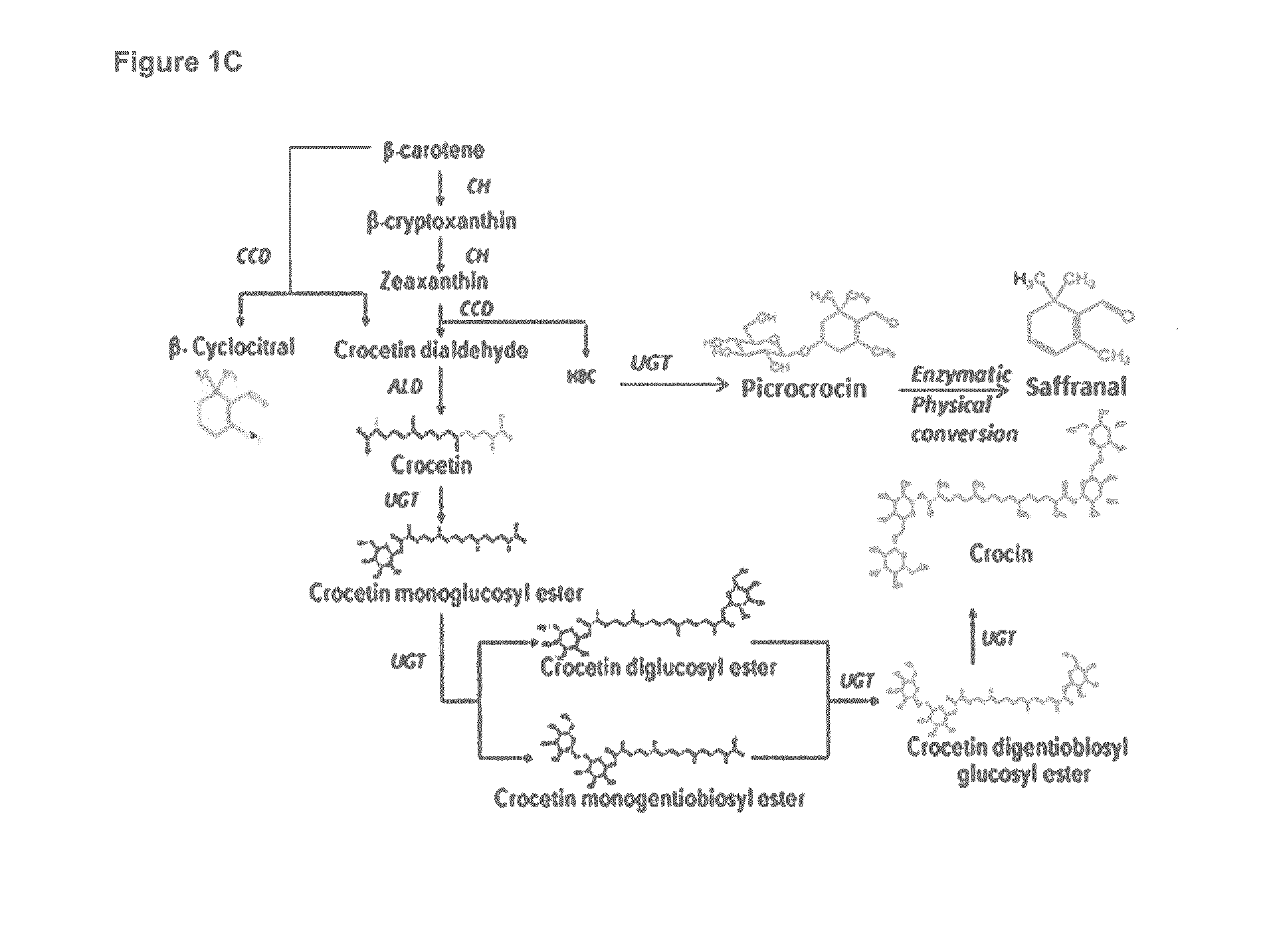
Methods for Recombinant Production of Saffron Compounds
Recombinant microorganisms and methods for producing saffron compounds including hydroxy-β-cylcocitral and picrocrocin are disclosed herein. Methods involve expression of a gene encoding a cytochrome p450 polypeptide, and optionally a gene encoding a (2Fe-2S) ferredoxin polypeptide, a gene encoding a flavin-dependent ferredoxin reductase, and a gene encoding a uridine 5′-diphospho glycosyltransferase (UGT) polypeptide.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
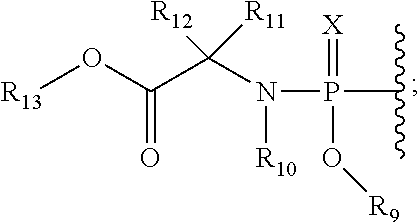
Preparation method for (2'R)-2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-methyluridine
InactiveCN104710491AReduce one step reactionReduce energy consumptionSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationUracilCombinatorial chemistry
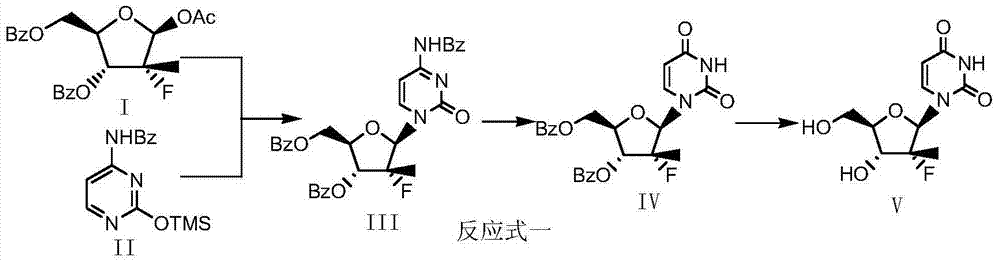
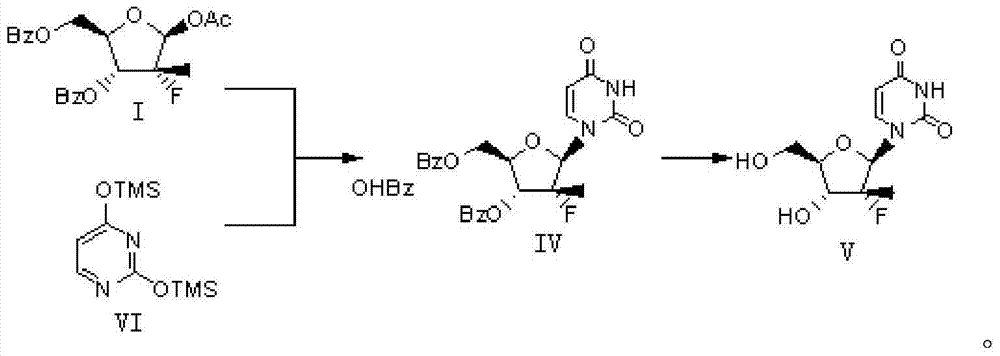
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic chemistry, and relates to a preparation method for (2'R)-2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-methyluridine. The preparation method for (2'R)-2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-methyluridine comprises the steps: with a protective fluororibose (represented by the formula I) as a starting material, carrying out a condensation reaction with a raw material ditrimethylsiyl protective uracil (represented by the formula VI) to obtain dibenzoyl uridine (represented by the formula IV), de-protecting dibenzoyl uridine to obtain the target product uridine (represented by the formula V), wherein a reaction equation is described in the specification. Compared with the prior art, the method reduces one reaction step in synthesis steps firstly, improves the production efficiency in the large-scale production, reduces the workload, reduces energy consumption and three-waste emission load, and improves the total yield of preparing the compound represented by the formula V from the compound represented by the formula I.
Owner:NINGBO CHEMGOO PHAMA TECH +1
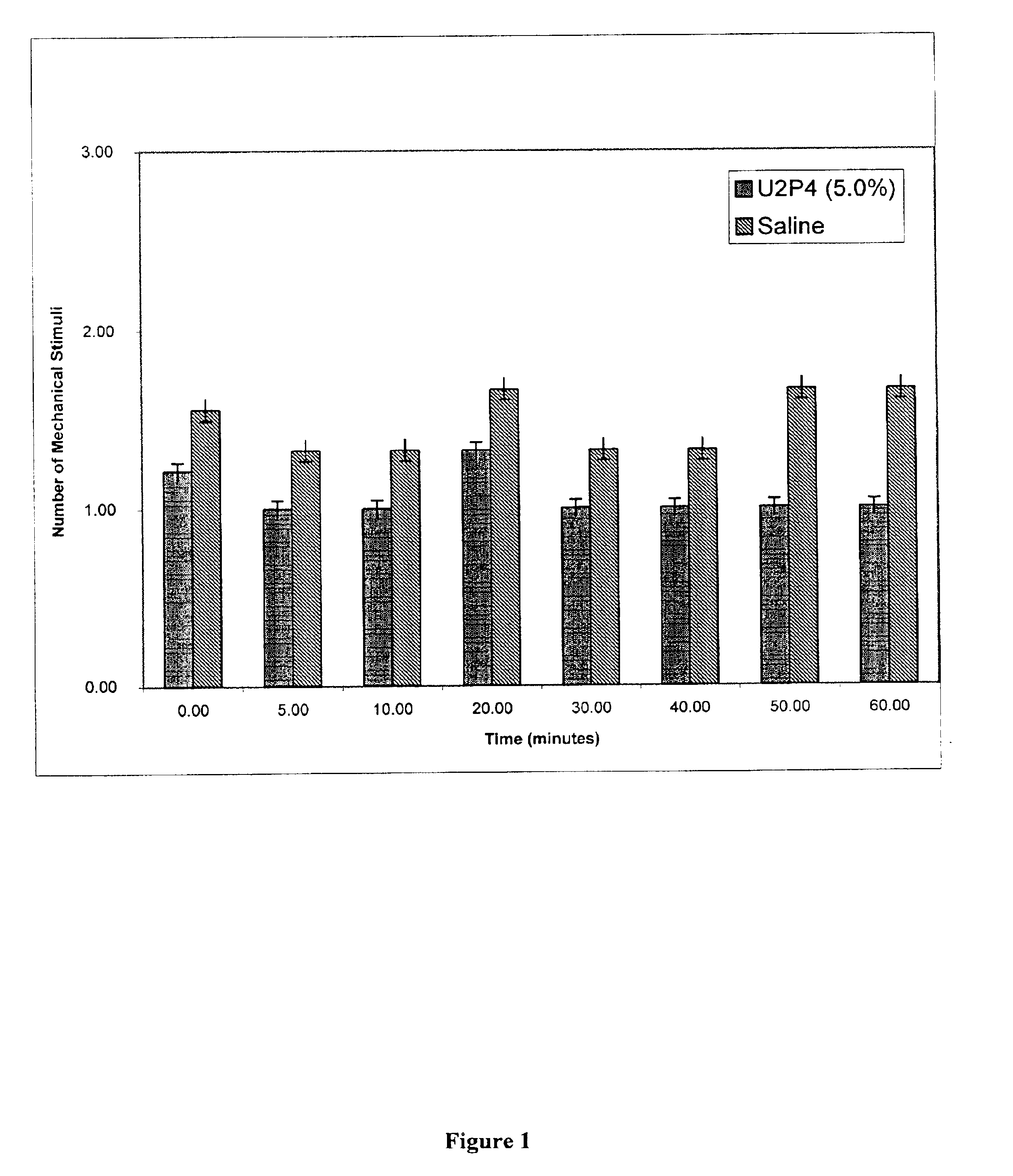
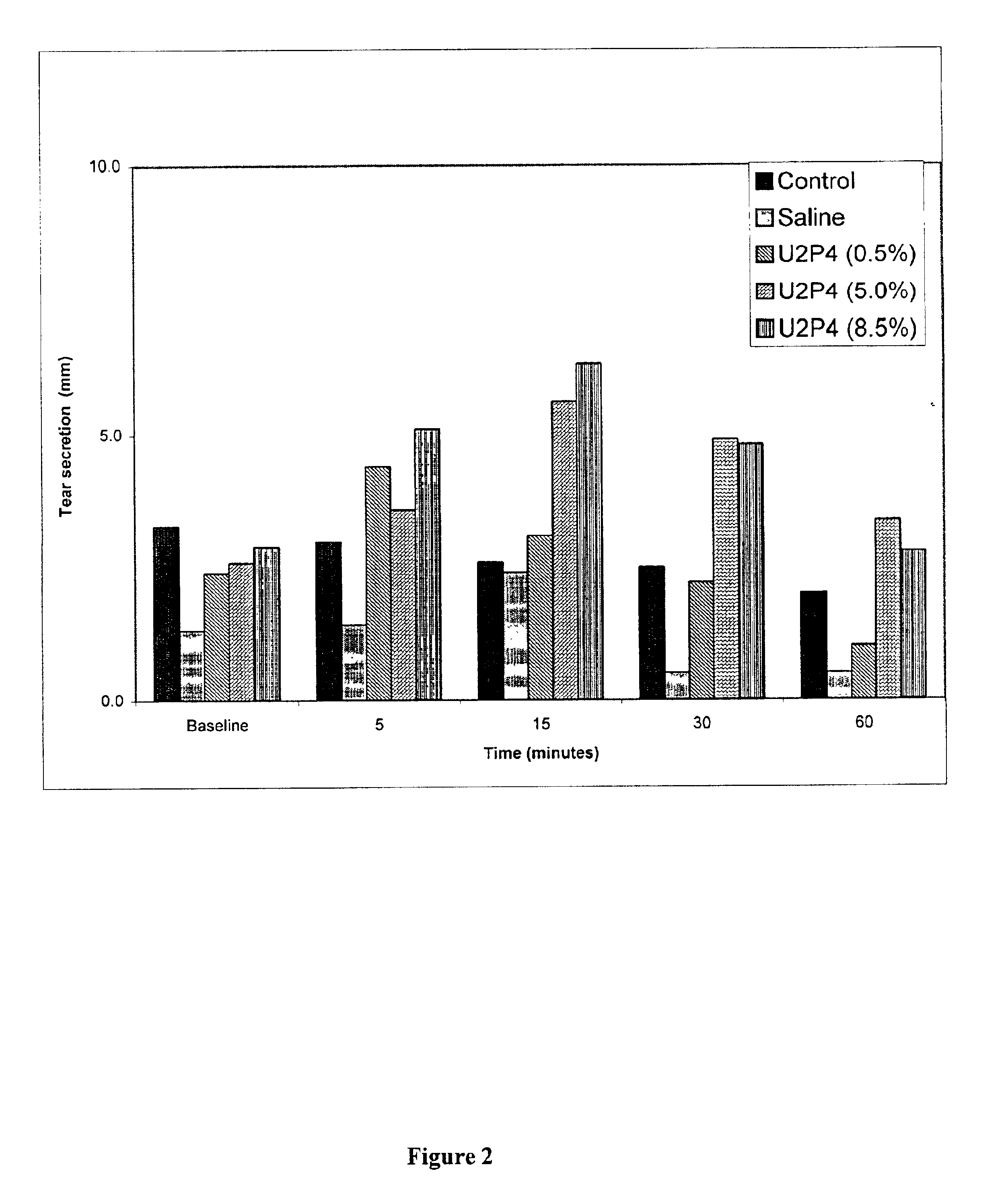
Method of treating dry eye disease with purinergic receptor agonists
A method and preparation for the stimulation of tear secretion in a subject in need of such treatment is disclosed. The method comprises administering to the ocular surfaces of the subject a purinergic receptor agonist such as uridine 5′-triphosphate (UTP), dinucleotides, cytidine 5′-triphosphate (CTP), adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP), or their therapeutically useful analogs and derivatives, in an amount effective to stimulate tear fluid secretion and enhance drainage of the lacrimal system. Pharmaceutical formulations and methods of making the same are also disclosed. Methods of administering the same would include: topical administration via a liquid, gel, cream, or as part of a contact lens or selective release membrane; or systemic administration via nasal drops or spray, inhalation by nebulizer or other device, oral form (liquid or pill), injectable, intra-operative instillation or suppository form.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
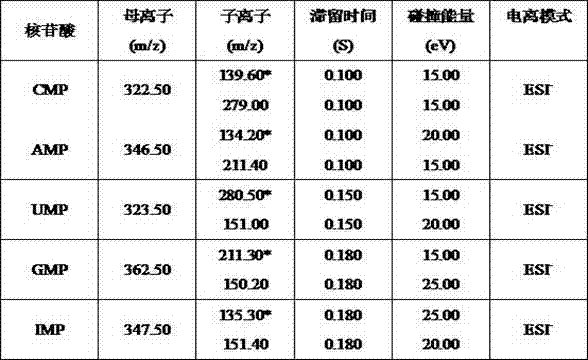
Novel method for measuring nucleotide content in infant formula milk powder
InactiveCN102331472AImprove qualitative skillsImprove detection limitComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNucleotideProtein
The invention discloses a novel method for measuring the nucleotide content in infant formula milk powder. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving an infant formula milk powder sample in water; adjusting the pH to 4.6 with a formic acid solution; precipitating proteins in the sample; ultrasonically extracting, centrifuging and filtering; separating five types of nucleotides, i.e. CMP (Cytidine), AMP (Adenosine), UMP (Uridine), GMP (Guanosine) and IMP (Inosine) in a filtrate with a reversed phase chromatographic column; performing tandem mass spectrum; scanning in a multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) scanning mode; and quantifying with a substrate by using an external reference method. In the invention, five types of nucleotides in the infant formula milk powder are measured with an LC-MS / MS (Liquid Chromatogram-Mass Spectrometry / Mass Spectrometry) method, so that the using quantity of the sample is extremely small in an ESI (Electrospray Ionization) mode, an ion source is prevented from being polluted easily, and high sensitivity and low detection limit are realized. In particular, the MRM method is adopted, interference of non-nucleotide molecular ions can be well eliminated; and meanwhile, the method has the advantages of simple sample pretreatment and wide application range.
Owner:WISSUN INT NUTRITION GRP
Hollow molecularly imprinted polymers and solid phase extraction column and preparation method and application thereof
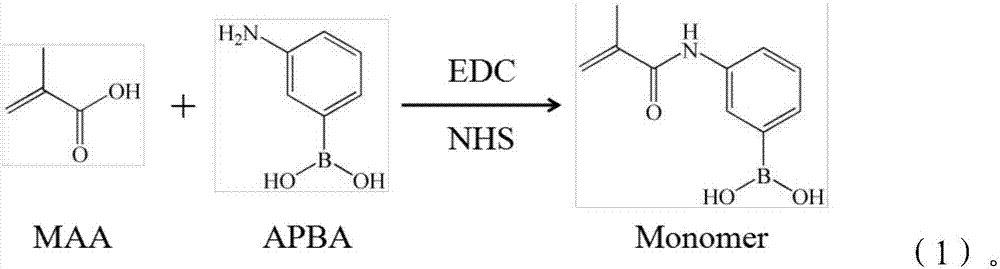
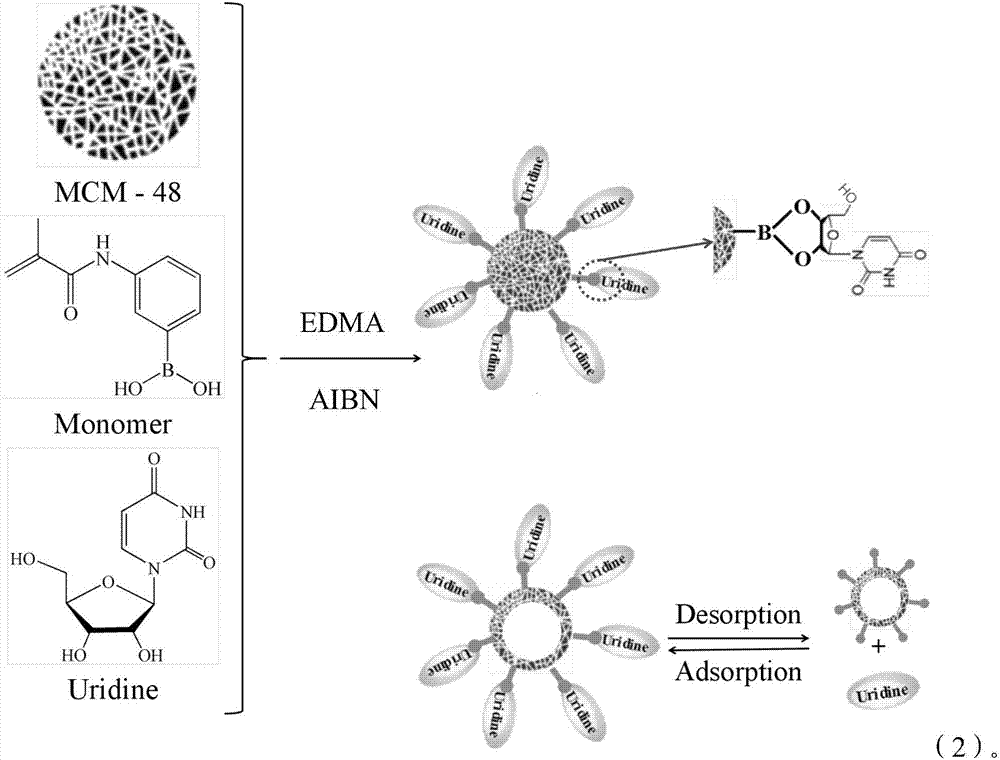
InactiveCN107189011AGood enrichment effectReversible adsorptionComponent separationSolid sorbent liquid separationFunctional monomerSynthesis methods
The invention provides hollow molecularly imprinted polymers which are modified by phenylboronic acid and an extraction column which is made by adopting the polymers. According to the synthetic method of the polymers, 3-aminophenylboronic acid is used as a modifying agent to conduct chemical modification on methacrylic acid monomers, uridine is used as a template, the modified methacrylic acid is used as functional monomers, matrixes, crosslinking agents and initiating agents are added to prepare molecularly imprinted materials, the prepared molecularly imprinted materials are subjected to template elution, the matrixes are corroded by adopting hydrofluoric acid, and the hollow molecularly imprinted polymers are obtained. The provided boron affinity hollow molecularly imprinted solid phase column has obvious enrichment effects on nucleoside type materials mainly due to the fact that molecular imprints conduct preferential adsorption on template molecules and structural analogues, and most binding sites of the hollow molecular imprints are distributed on surfaces of carrier matrix materials and in the hollow cavities and thus the adsorption efficiency is improved; furthermore, boric acid groups can carry out reversible adsorption and dissociation on the nucleoside type materials of a cis-diol structure, and therefore the boron affinity hollow molecularly imprinted solid phase column has obvious enrichment effects on the nucleoside type materials.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Immunomodulating polynucleotides, antibody conjugates thereof, and methods of their use
ActiveUS20180312536A1Good effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAntiendomysial antibodiesAntibody conjugate
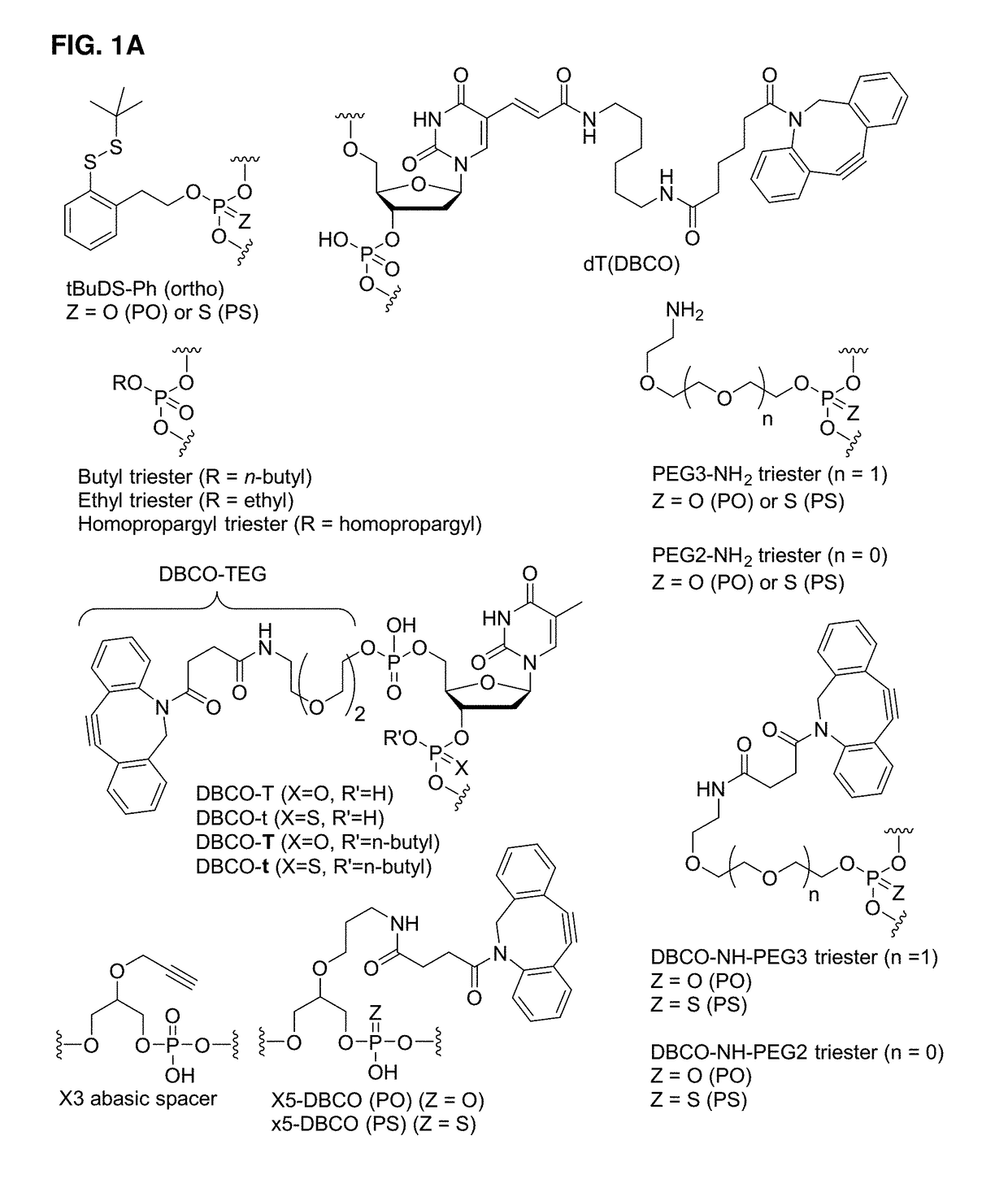
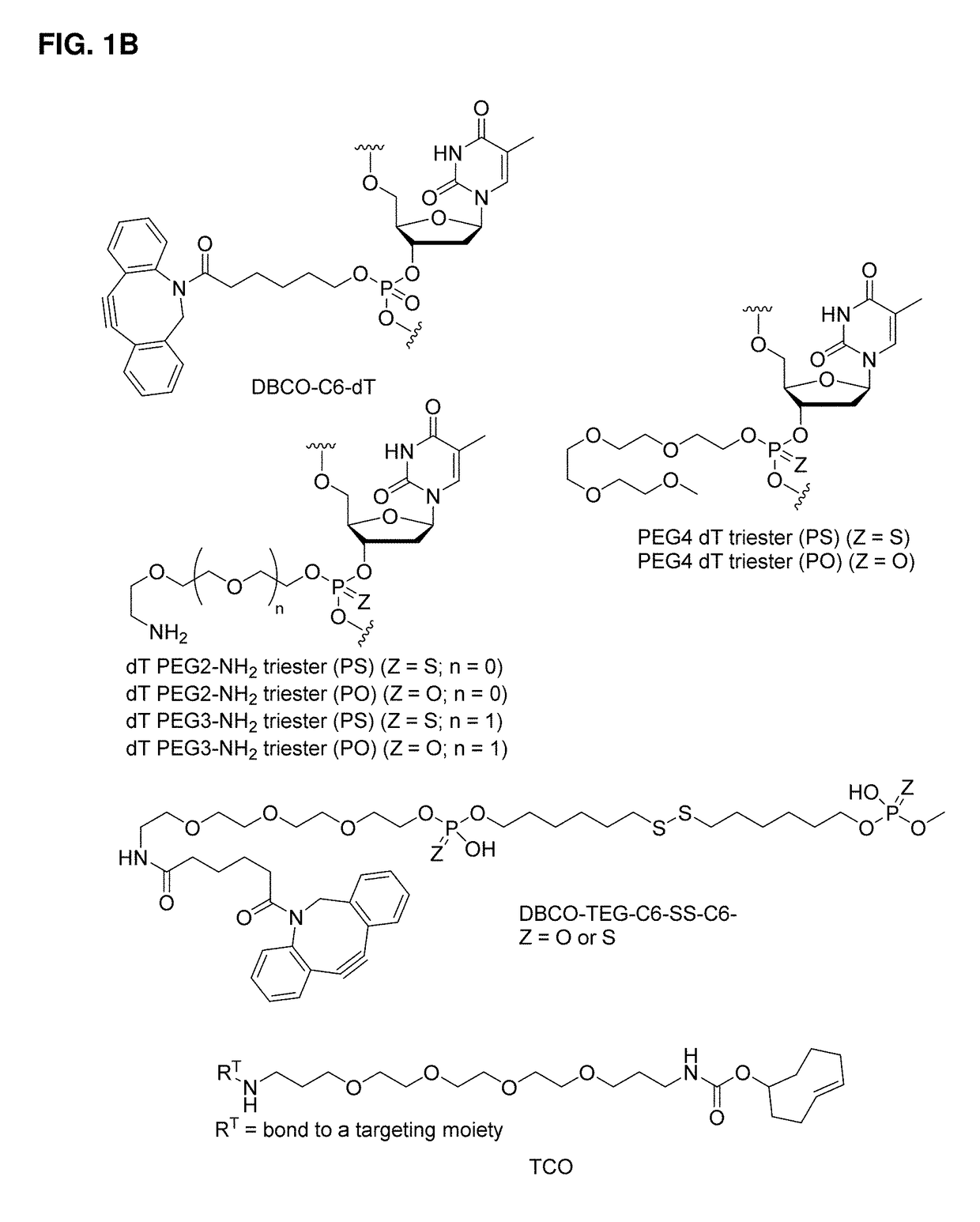
Immunomodulating polynucleotides are disclosed. The immunomodulating polynucleotides may contain 5-modified uridine, 5-modified cytidine, a total of from 6 to 16 nucleotides, and / or one or more abasic spacers and / or internucleoside phosphotriesters. Also disclosed are conjugates containing a targeting moiety and one or more immunomodulating polynucleotides. The immunomodulating polynucleotides and conjugates may further contain one or more auxiliary moieties. Also disclosed are compositions containing the immunomodulating polynucleotides or the conjugates containing one or more stereochemically enriched internucleoside phosphorothioates. Further disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions containing the immunomodulating polynucleotides or the conjugates and methods of their use.
Owner:TALLAC THERAPEUTICS INC
Uridine phosphatase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111748537AIncrease enzyme activityEffective Catalytic SynthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesO-Phosphoric AcidNicotinamide riboside
The invention discloses a uridine phosphatase mutant and a preparation method thereof. The amino acid sequence of the mutant is SEQ ID NO: 3, ribose-1-phosphoric acid can be effectively catalyzed to react with nicotinamide to generate nicotinamide ribose; the nicotinamide ribose can form a three-enzyme system together with purine nucleoside phosphorylase and nicotinamide ribose kinase to jointly catalyze a reaction of raw materials guanosine, phosphate, nicotinamide and ATP to synthesize the beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide by a one-pot method, and the product has good industrial development and application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUARUI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
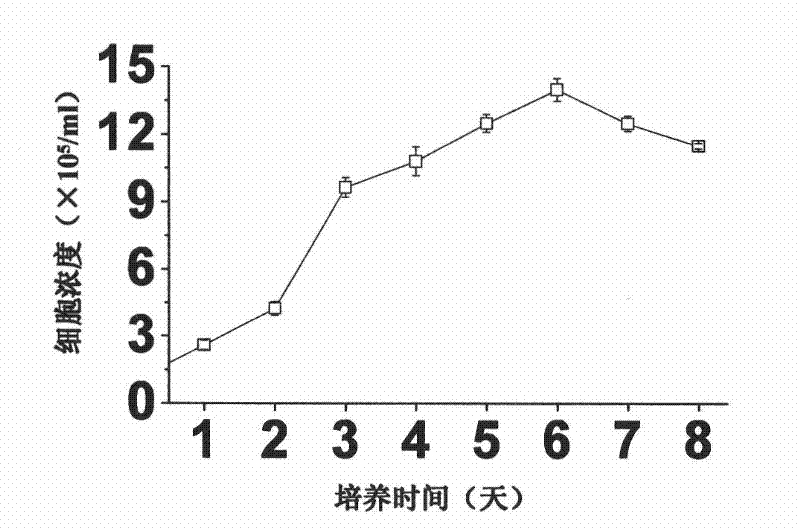
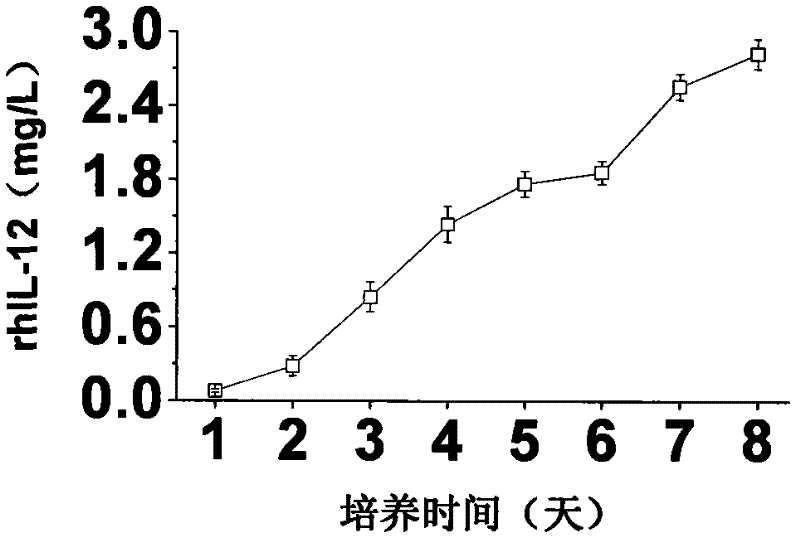
A large-scale serum-free culture method of rhil-12 engineered cells
The invention relates to a large-scale serum-free culture method for rhIL-12 engineering cells, which comprises the following step of: inoculating rhIL-12 engineering cells in a logarithmic phase into a serum-free and protein-free medium for culture, wherein the medium is a CD CHO liquid medium comprising sodium pyruvate at the final concentration of 0.8 to 1.2mM, hypoxanthine at the final concentration of 0.075 to 0.125mM, thymidine at the final concentration of 0.012 to 0.020mM, adenosine at the final concentration of 0.5 to 0.9mg / L, guanosine at the final concentration of 0.5 to 0.9mg / L, cytidine at the final concentration of 0.5 to 0.9mg / L, uridine at the final concentration of 0.5 to 0.9mg / L, L-glutamine at the final concentration of 0.4 to 0.8mg / L, L-asparagine at the final concentration of 0.4 to 0.8mg / L, L-proline at the final concentration of 1.5 to 2.0mg / L and non-essential amino acid at the final concentration of 0.08 to 0.125mM. The invention also provides a medium used in the method. By the medium and the culture method, a high-yield and high-activity recombinant human interleukin-12 can be obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
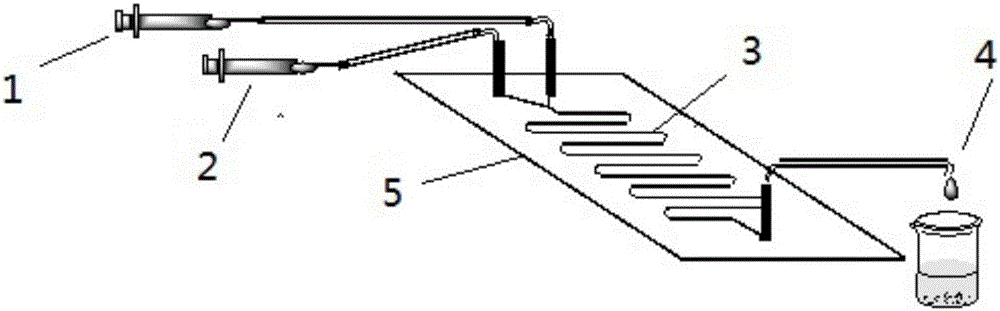
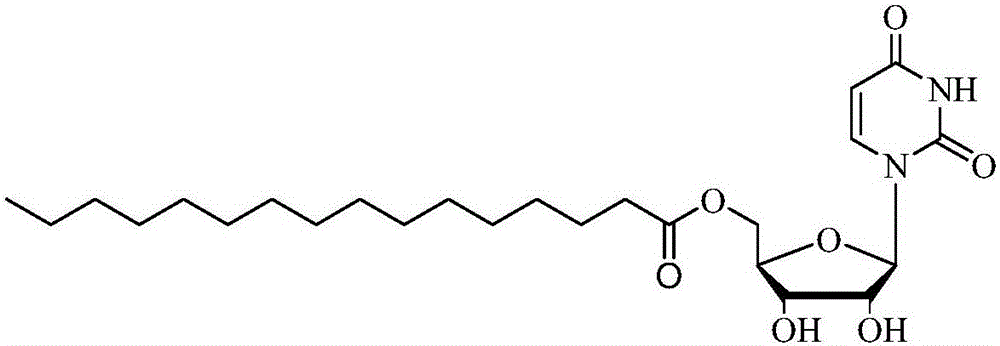
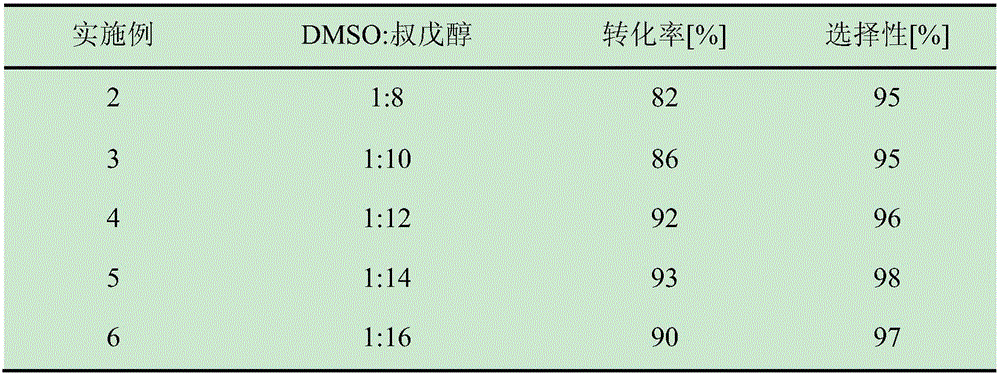
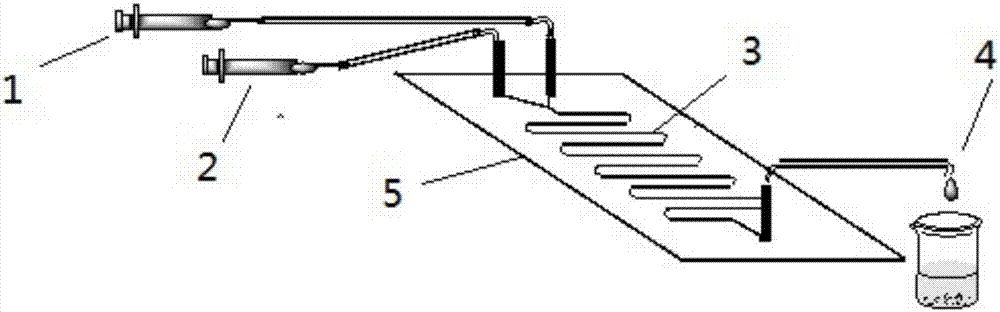
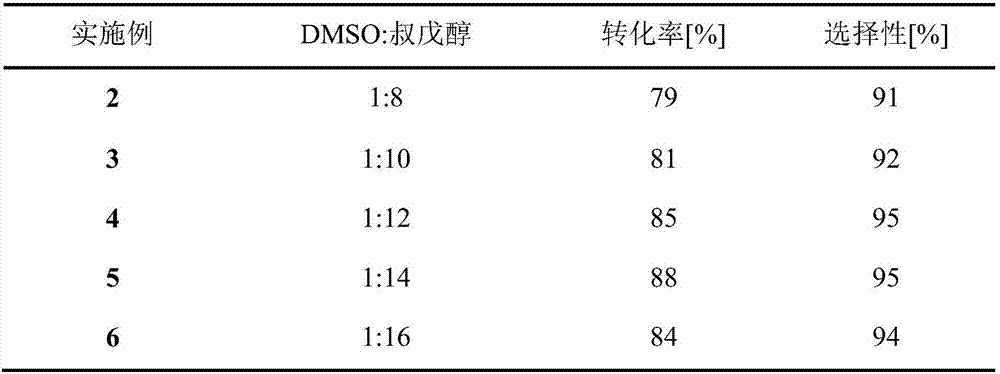
Method for online synthesizing 5'-O-palmitoyl uridine in lipozyme catalysis mode
ActiveCN105838600AShort reaction timeImprove conversion rateEnzyme production/based bioreactorsFermentationSolventPalmitic acid
The invention discloses a method for online synthesizing 5'-O-palmitoyl uridine in a lipozyme catalysis mode .The method includes the steps that dimethyl sulfoxide and tert-amyl alcohol with the volume ratio of 1:(8-16) serve as a reaction solvent, uridine and palmitic acid vinyl ester with the molar ratio of 1:(5-13) serve as raw materials, 0.5 g to 1.0 g of lipozyme TLIM serves as a catalyst, the raw materials and the reaction solvent are placed into an injector, a reaction channel of a microfluidics channel reactor is evenly filled with the lipozyme TLIM, and the raw materials and the reaction solvents are continuously led into a reaction channel device under pushing of an injection pump for an acylation reaction, wherein the inner diameter of the reaction channel of the microfluidics channel reactor is 0.8 mm to 2.4 mm, the length of the reaction channel is 0.5 m to 1.0 m, the temperature of the acylation reaction is controlled to be 15 DEG C to 50 DEG C, the concentration of the uridine in the reaction system is 0.03 mmol / mL to 0.07 mmol / mL, and the time of the acylation reaction is 20 min to 35 min; reacted liquid is online collected through a product collector and subjected to conventional aftertreatment, and the 5'-O-palmitoyl uridine is obtained .The method has the advantages of being short in reaction time and high in selectivity and yield.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
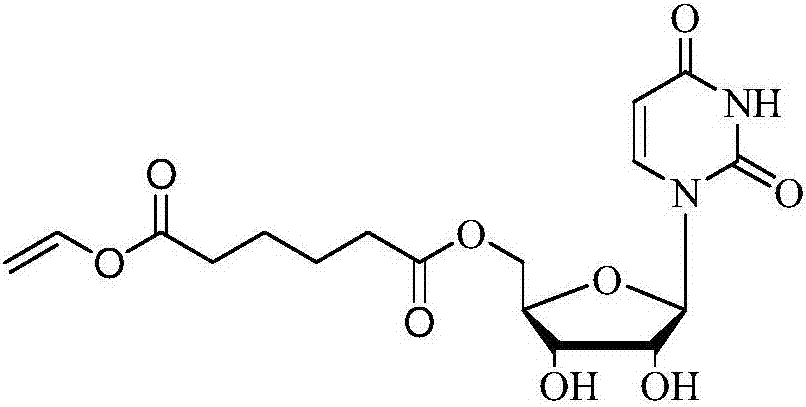
Method for 5'-O-ethylene adipyl uridine online synthesis through lipase catalysis
ActiveCN107384991AShort reaction timeImprove conversion rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReaction temperatureAdipic acid
The invention discloses a method for 5'-O-ethylene adipyl uridine online synthesis through lipase catalysis. The method comprises the steps that dimethyl sulfoxide and tert-amyl alcohol serve as reactive solvents, uridine and adipic acid divinyl ester serve as raw materials, and 0.5-1.0 g of a lipase, namely Lipozyme TLIM, serves as a catalyst, wherein the volume ratio of the dimethyl sulfoxide to the tert-amyl alcohol is 1:(8-16), and the molar ratio of the uridine to the adipic acid divinyl ester is 1:(5-13). The raw materials and the reactive solvents are placed into an injector, and a reaction passage of a microfluidic passage reactor is uniformly filled with the lipase, namely the Lipozyme TLIM. Under pushing of an injection pump, the raw materials and the reactive solvents are continuously pumped into the reaction passage for acylation reaction. The inner diameter of the reaction passage of the microfluidic passage reactor is 0.8-2.4 mm, the length of the reaction passage is 0.5-1.0 m, the acylation reaction temperature is controlled to be 15-50 DEG C, and the acylation reaction time is 20-35 min. Through a product collector, reactive solution online collection is conducted, and after a reactive solution is subjected to conventional after-treatment, 5'-O-ethylene adipyl uridine is obtained. The method for 5'-O-ethylene adipyl uridine online synthesis through lipase catalysis has the advantages that the reaction time is short, the selectivity is high, and the productive rate is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
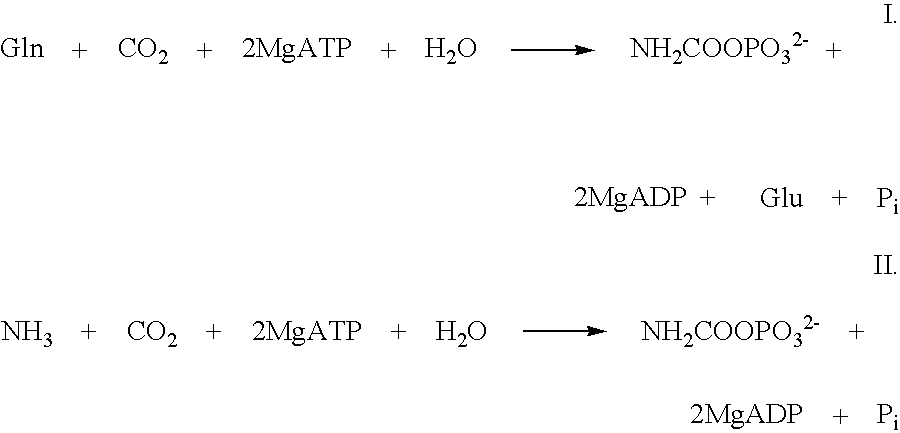
Mutant carbamoylphosphate synthetase and method for producing compounds derived from carbamoylphosphate
L-arginine, citrulline and pyrimidine derivatives including orotic acid, uridine, uridine 5'-monophosphate (UMP), cytidine and cytidine 5'-monophosphate (CMP) are produced using a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia harboring a mutant carbamoylphosphate synthetase in which the amino acid sequence corresponding to positions from 947 to 951 in a wild type carbamoylphosphate synthetase is replaced with any one of amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 1 to 9, and feedback inhibition by uridine 5'-monophosphate in the bacterium is desensitized.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Finger print allas used for controlling isatidis root, its preparation quality and medicine effect and its making method
ActiveCN1591007AEasy to operateSuitable for useTesting foodTesting medicinal preparationsMedicineReactive site
The present invention relates to a fingerprint for controlling quality of Chinese medicinal material isatis root and its medicinal preparation and its making method. Said invented fingerprint is one of antiviral active site in Chinese medicinal material isatis root, and said active site uses nucleosides as main composition portion, in which the known nucleoside components have adenosine, uridine and guanosine. Said invention utilizes the creation of fingerprint of active site of isatis root and combines it with quantitative analysis result of index components so as to comprehensively evaluate the quality and medicinal effect of isatis root and its medicinal preparation, and can make the quality of isatis root and its medicinal preparation have true controllable standard.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAIYUSN HUTCHISON WHAMPOA CHINESE MEDICINE
Mutant carbamoylphosphate synthetase and method for producing compounds derived from carbamoylphosphate
L-arginine, citrulline and pyrimidine derivatives including orotic acid, uridine, uridine 5′-monophosphate (UMP), cytidine and cytidine 5′-monophosphate (CMP) are produced using a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia harboring a mutant carbamoylphosphate synthetase in which the amino acid sequence corresponding to positions from 947 to 951 in a wild type carbamoylphosphate synthetase is replaced with any one of amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NOS: 1 to 9, and feedback inhibition by uridine 5′-monophosphate in the bacterium is desensitized.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Methods for detecting plasticizers
InactiveUS20130172214A1Material nanotechnologyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsNanoparticlePlasticizer
Nanoparticles having one or more attached sensing moieties including uridine 5′-triphosphate (UTP) and deoxythymidine 5′-triphosphate (dTTP), are disclosed herein. These nanoparticles can, for example, be used for detection of plasticizers, such as phthalates, in the sample. Methods, kits and apparatuses using these nanoparticles for detecting plasticizers in a sample are also disclosed herein.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for improving yield of L-arginine synthesized by corynebacterium crenatum
InactiveCN109943548AIntegrative mutationReduce vitalityBacteriaTransferasesArginineBatch fermentation
The invention discloses a method for improving the yield of L-arginine synthesized by corynebacterium crenatum, specifically discloses a method for improving the yield of L-arginine through integratedmutation modification of bi-functional uridyl transfer / removal enzyme GlnD, modification of pII signal transduction protein GlnK and uridine acylation of GlnK, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method successfully achieves the integrative mutation modification of the bifunctional uridyl transfer / removal enzyme GlnD, the pII signal transduction protein GlnK is overexpressedon this base, and the uridine acylation of GlnK is enhanced. A 5-L fermentation tank is used for batch fermentation, the fermentation conditions are optimized, finally the final recombinant corynebacterium crenatum Cc-HDAA / pXMJ19-glnK is fermented for 96 h, the yield of L-arginine of the recombinant bacteria reaches 52.2 g / L, the production intensity reaches 0.544 g / L h, and the high yield of L-arginine is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
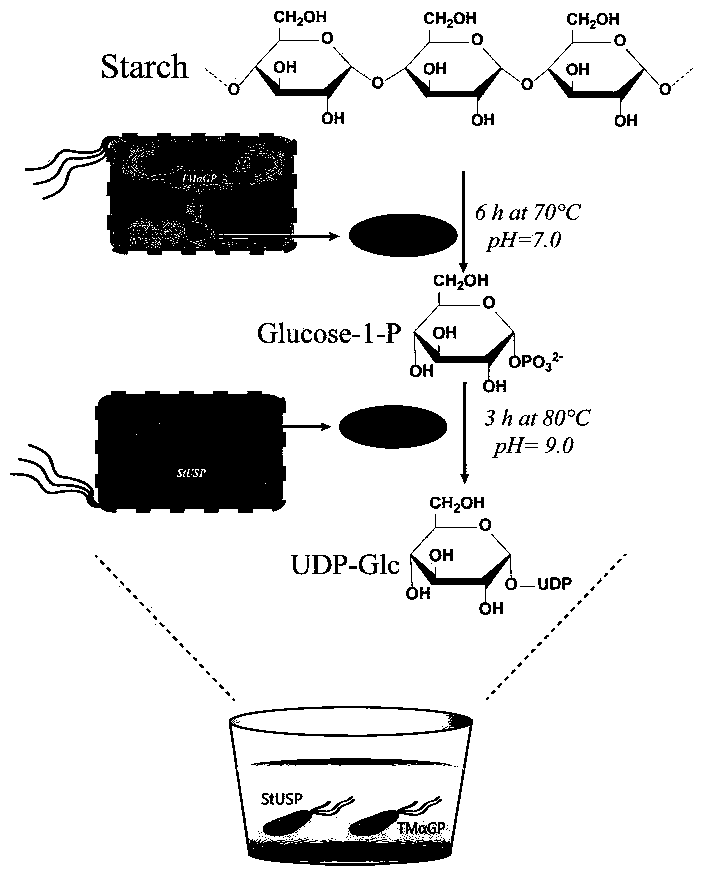
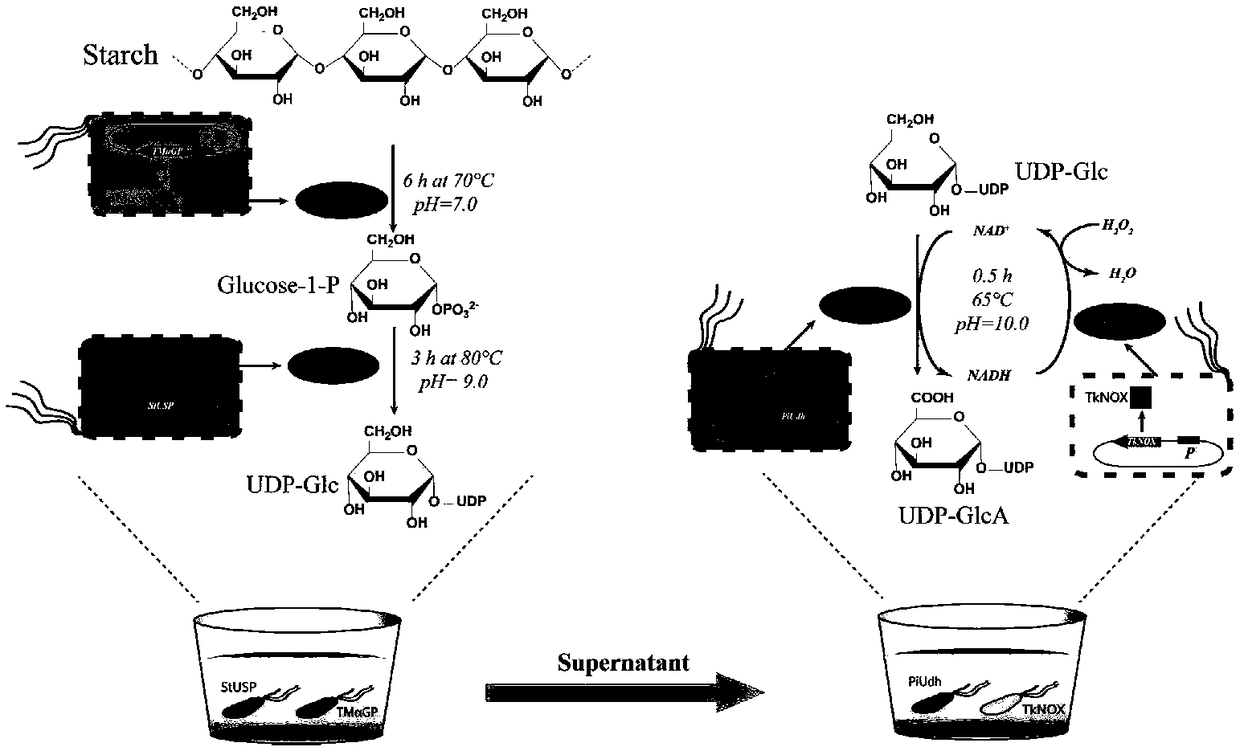
Biosynthesis method of uridine diphosphate glucose and uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid
ActiveCN109371079AEasy to transformSynthetic interferenceMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliUridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine
The invention discloses a biosynthesis method of uridine diphosphate glucose and uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid. The method includes adopting soluble starch as a main initial raw material, conducting recombinant expression on high-temperature alpha-glucan phosphorylase and high-temperature sugar-1-nucloside phosphorylase in escherichia coli respectively, and utilizing high-temperature whole cell catalysis of expressed bacteria to synthesize uridine diphosphate glucose; on this basis, conducting recombinant expression on high temperature uridine diphosphate glucose dehydrogenase in the escherichia coli, coupling a synthesis system of the uridine diphosphate glucose to conduct high temperature whole cell catalysis to synthesize the uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid, and introducing awhole cell catalysis system of high temperature NADH oxidase into the synthesis system of the uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid to form a high temperature NAD+ / NADH circulating system to reduce theuse of coenzyme NAD+. The high temperature whole cell catalysis method is utilized to successfully avoid the interference of various metabolic pathways of the bacteria in the synthesis process and reduce the purification difficulty.
Owner:安徽禾庚生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com