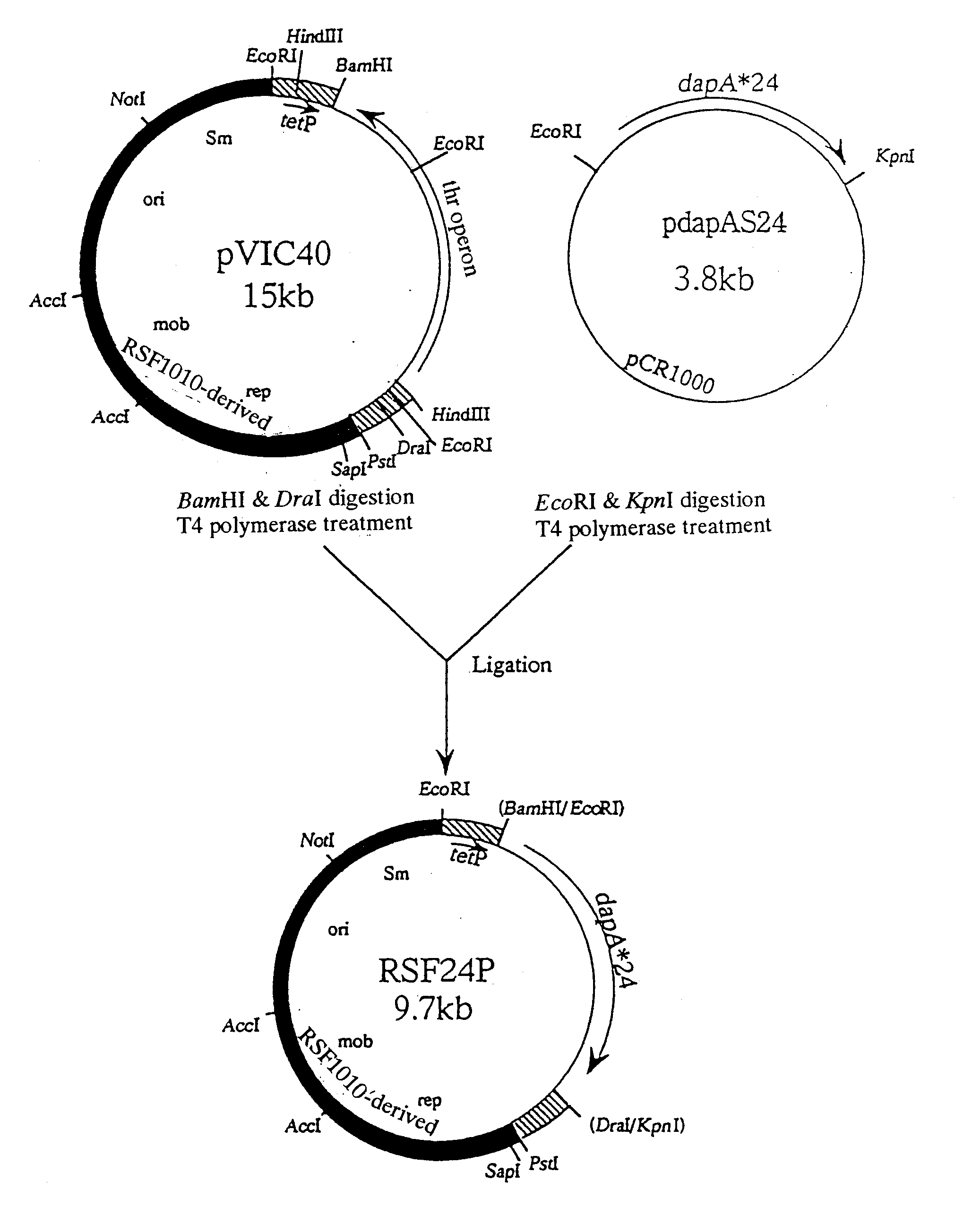
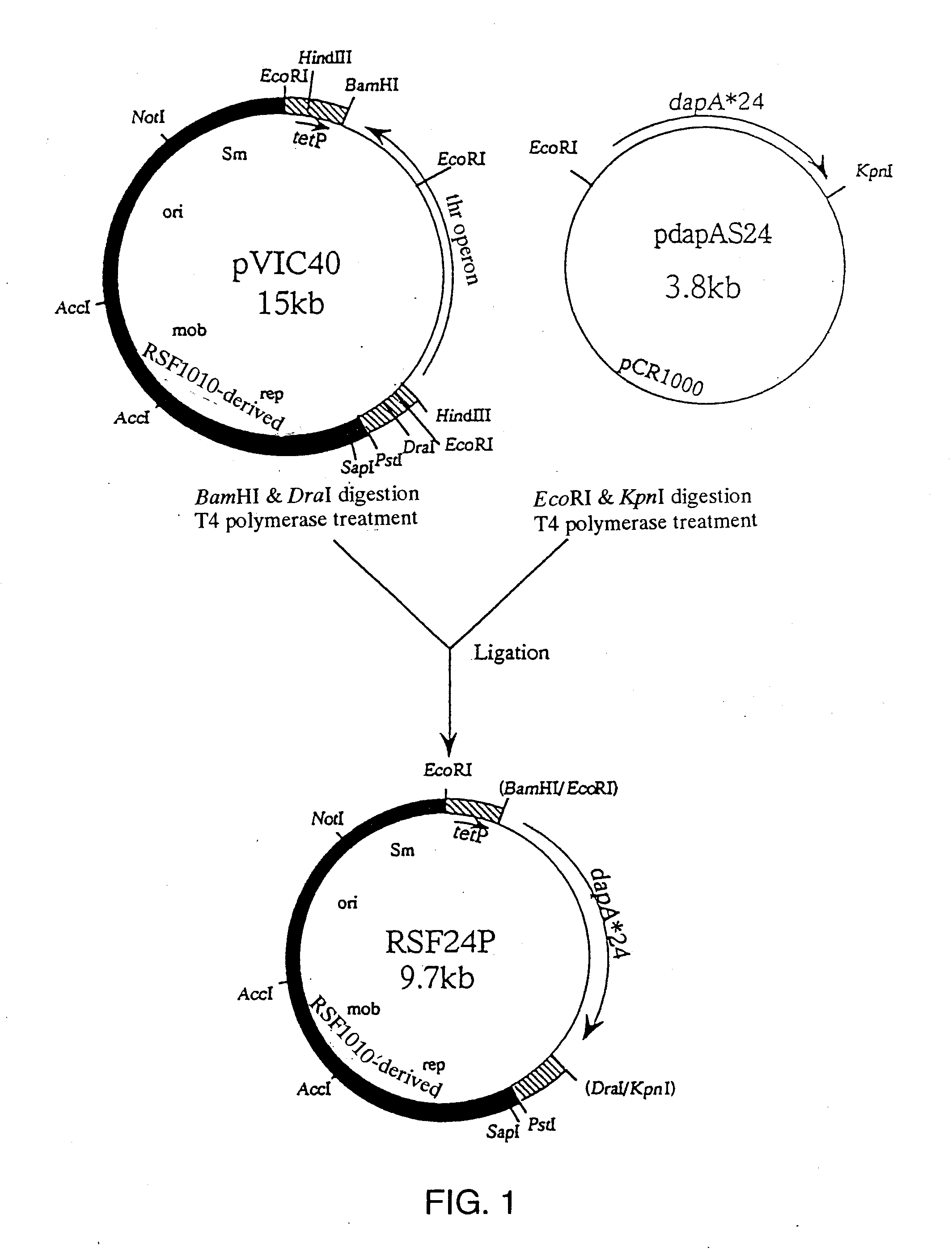
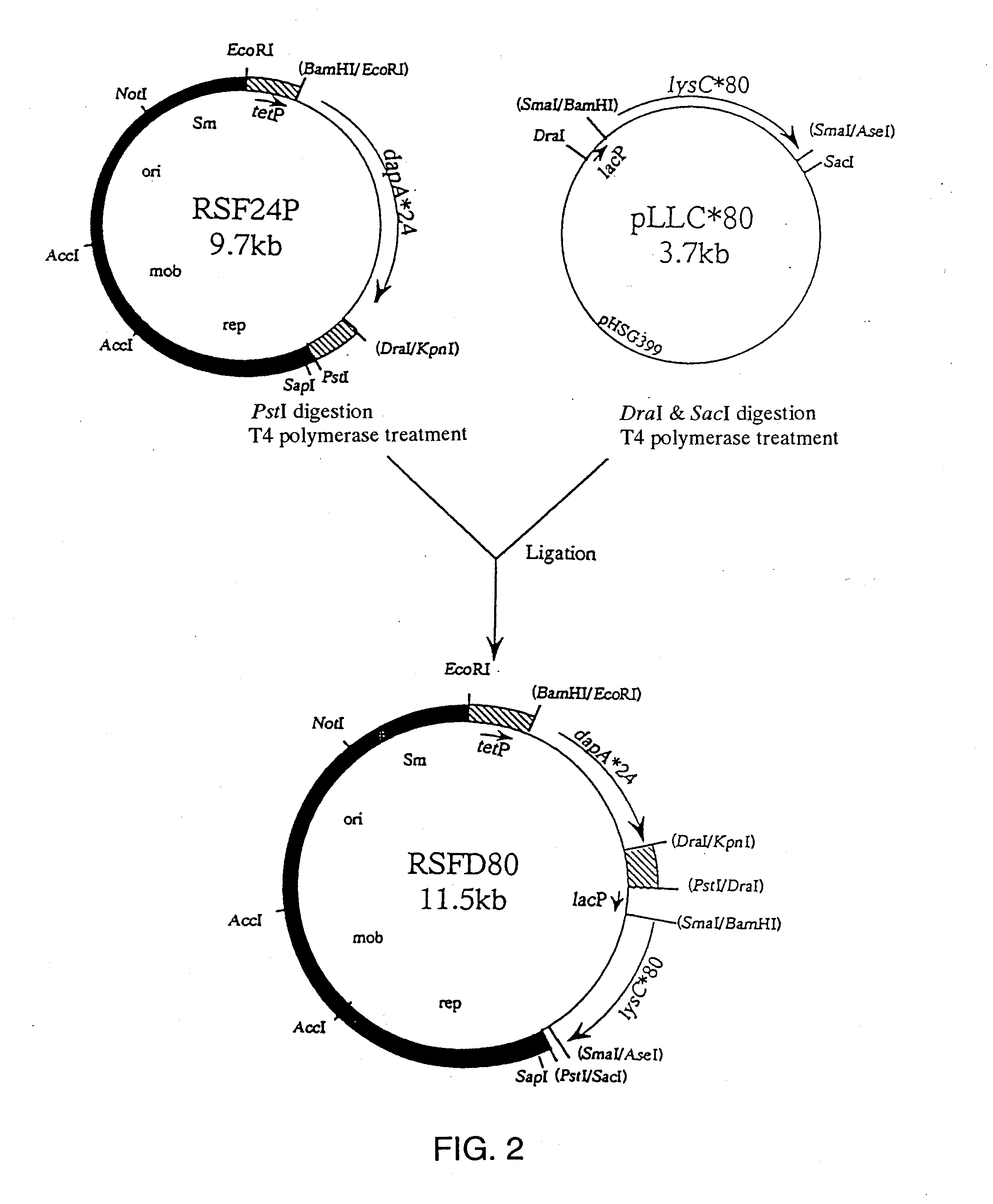
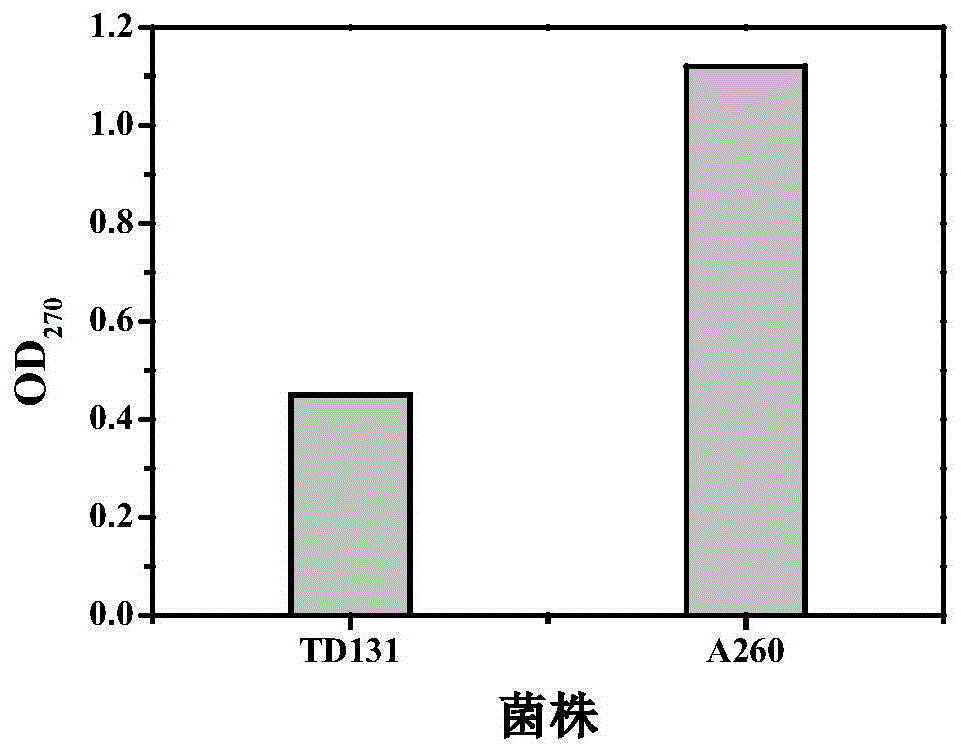
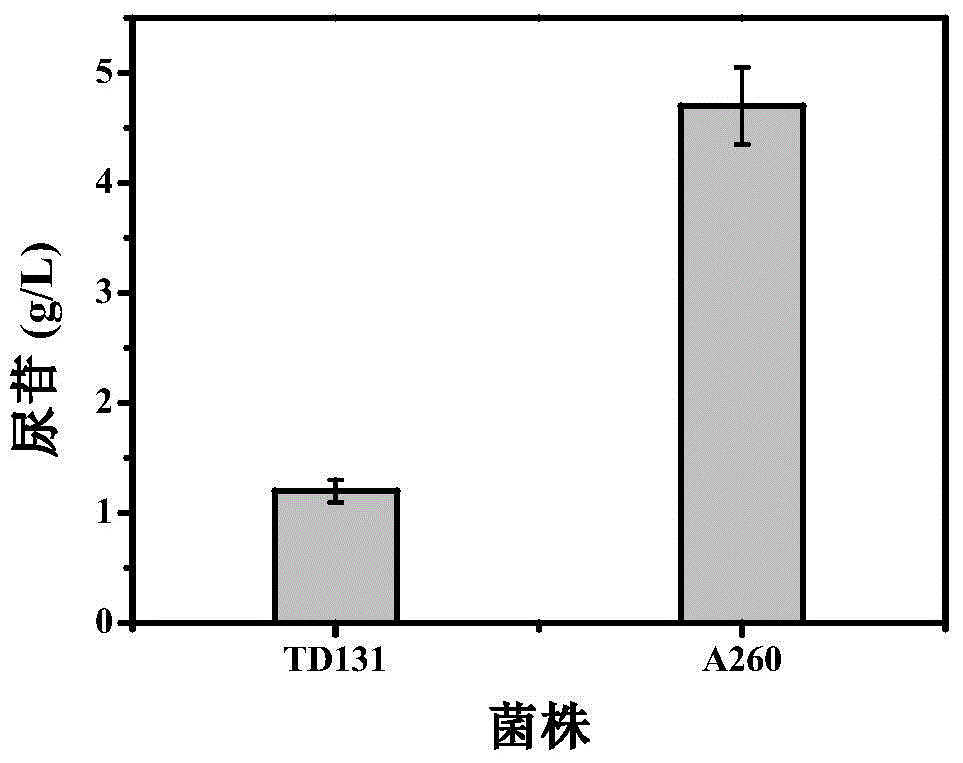
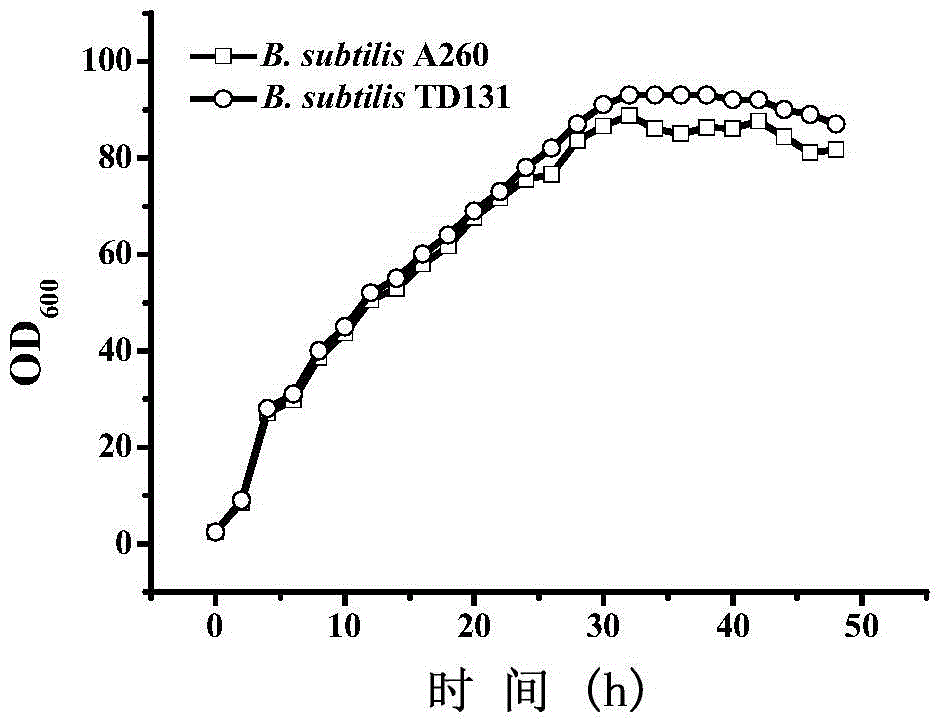
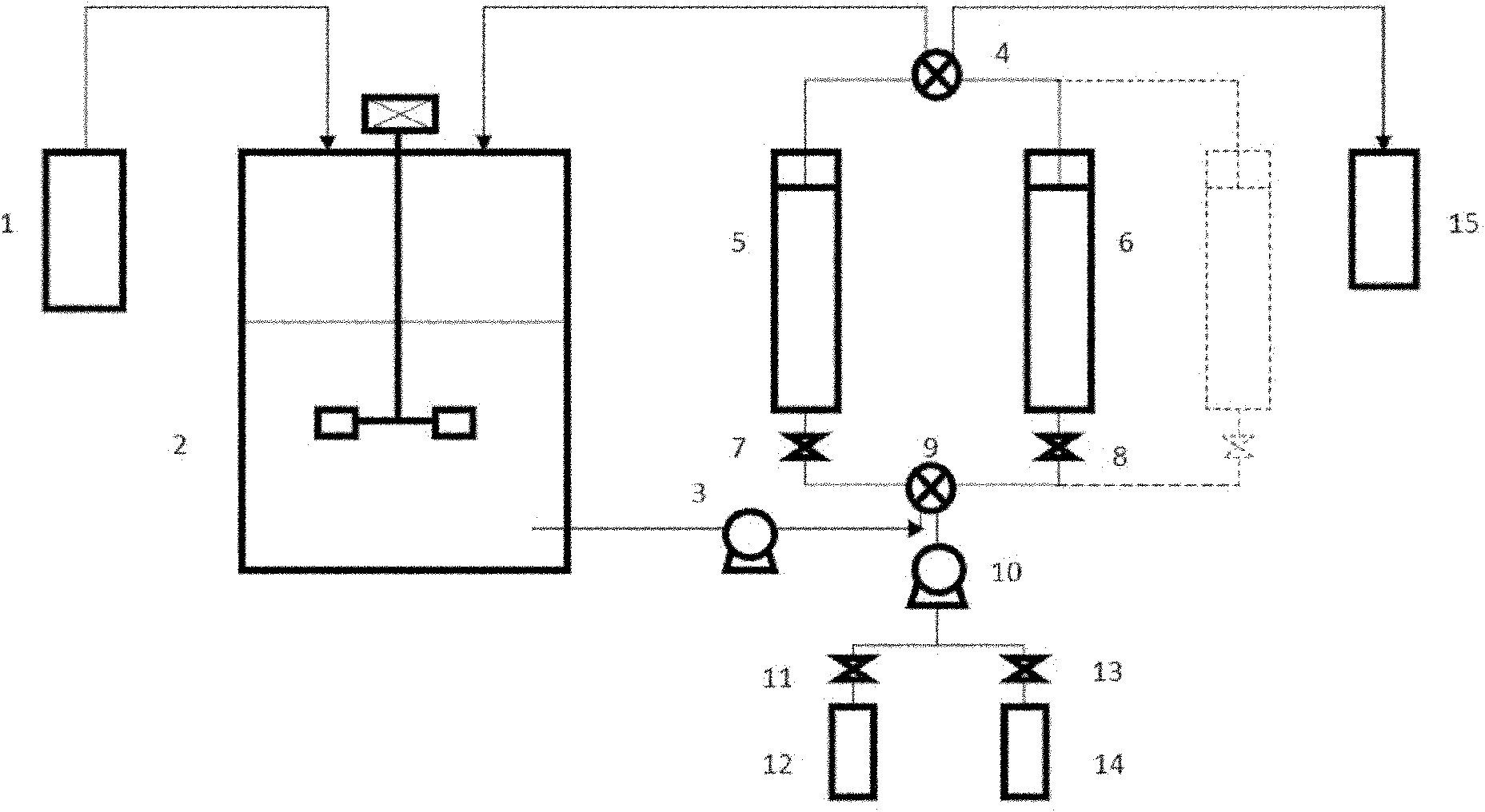
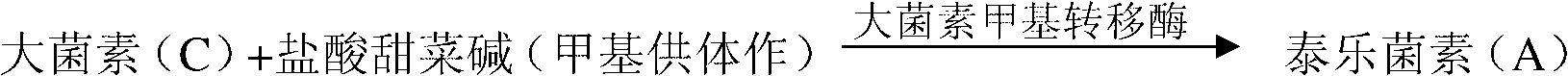Patents
Literature
202 results about "Feedback inhibition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mutant serine acetyltransferase
O-acetylserine, L-cysteine and sulphurous compounds derived therefrom may be produced using a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia which harbors a mutant feedback-resistant serine acetyltransferases in which the amino acid sequence corresponding to positions from 89 to 96 in a wild-type serine acetyltransferase is replaced with any one of the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NOS: 4 to 9, and feedback inhibition by L-cysteine in the bacterium is desensitized.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
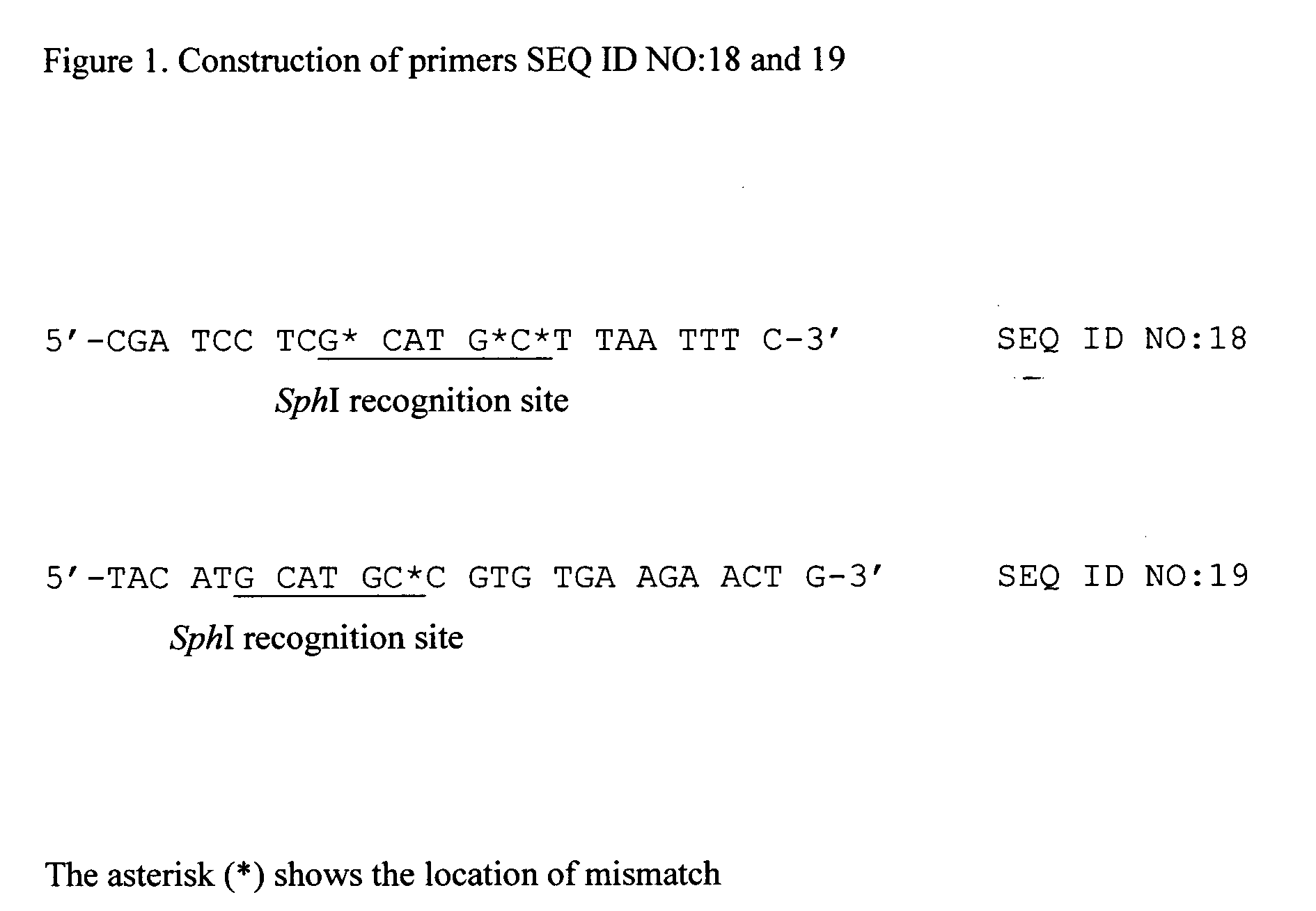
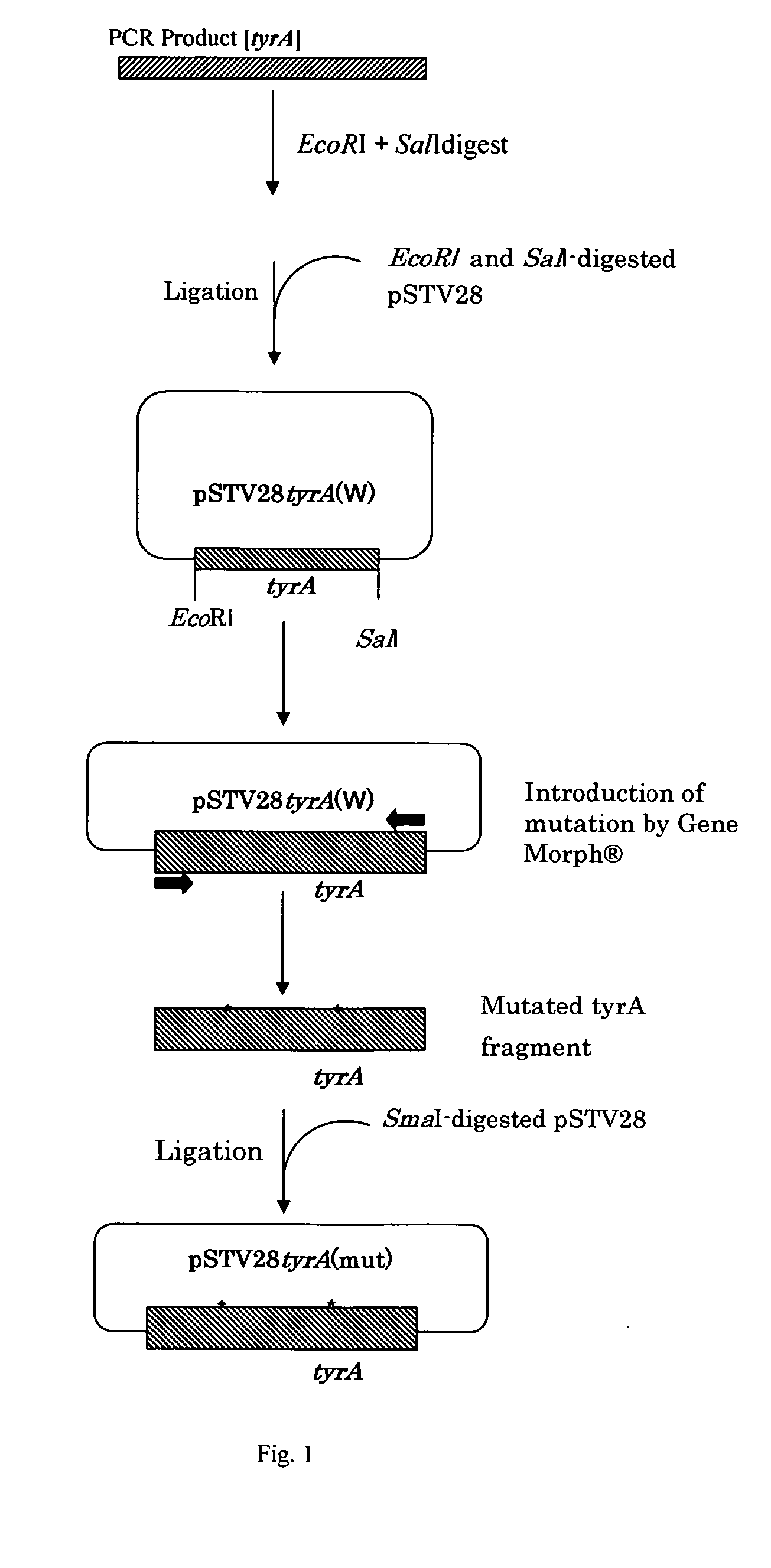
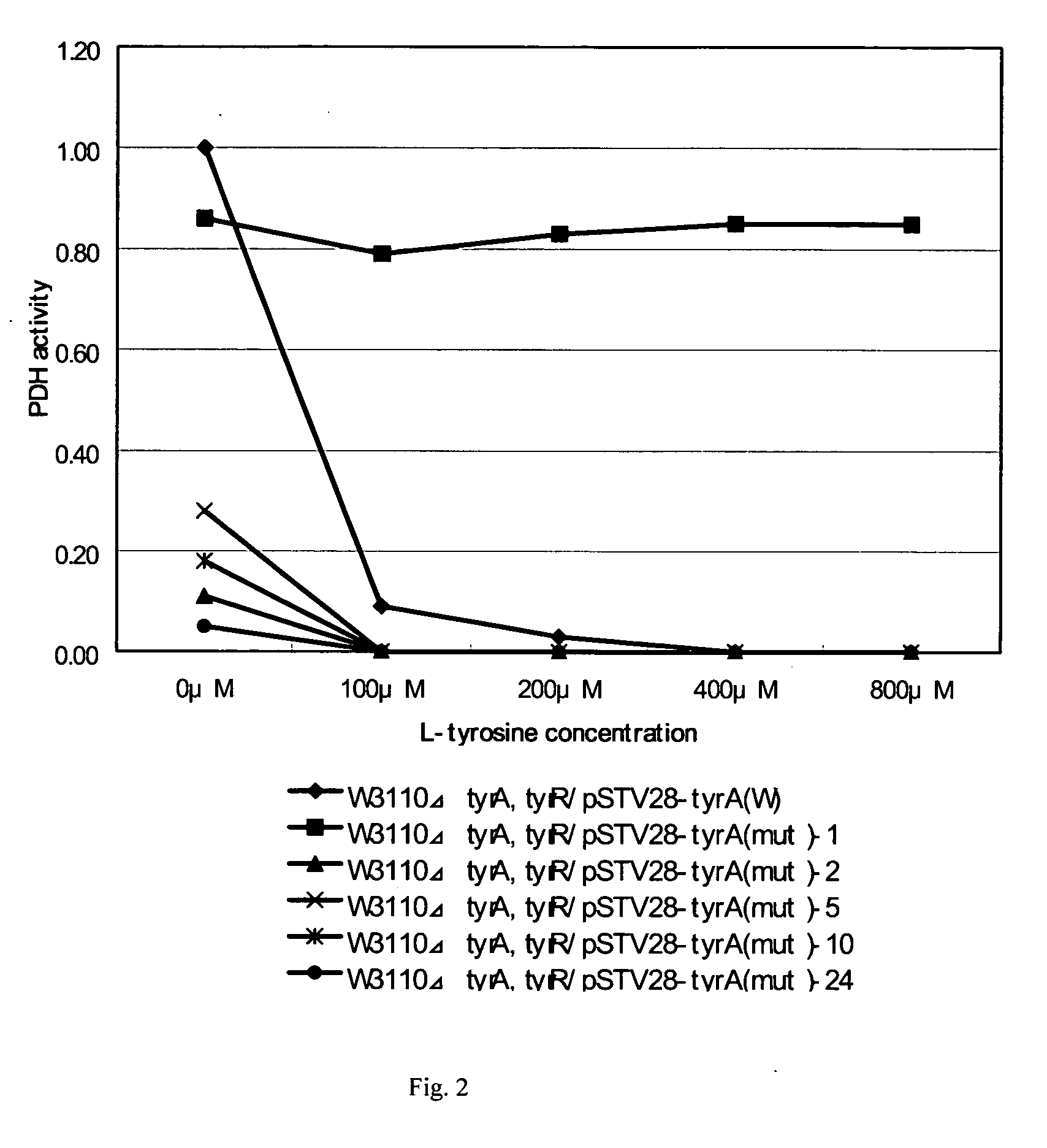
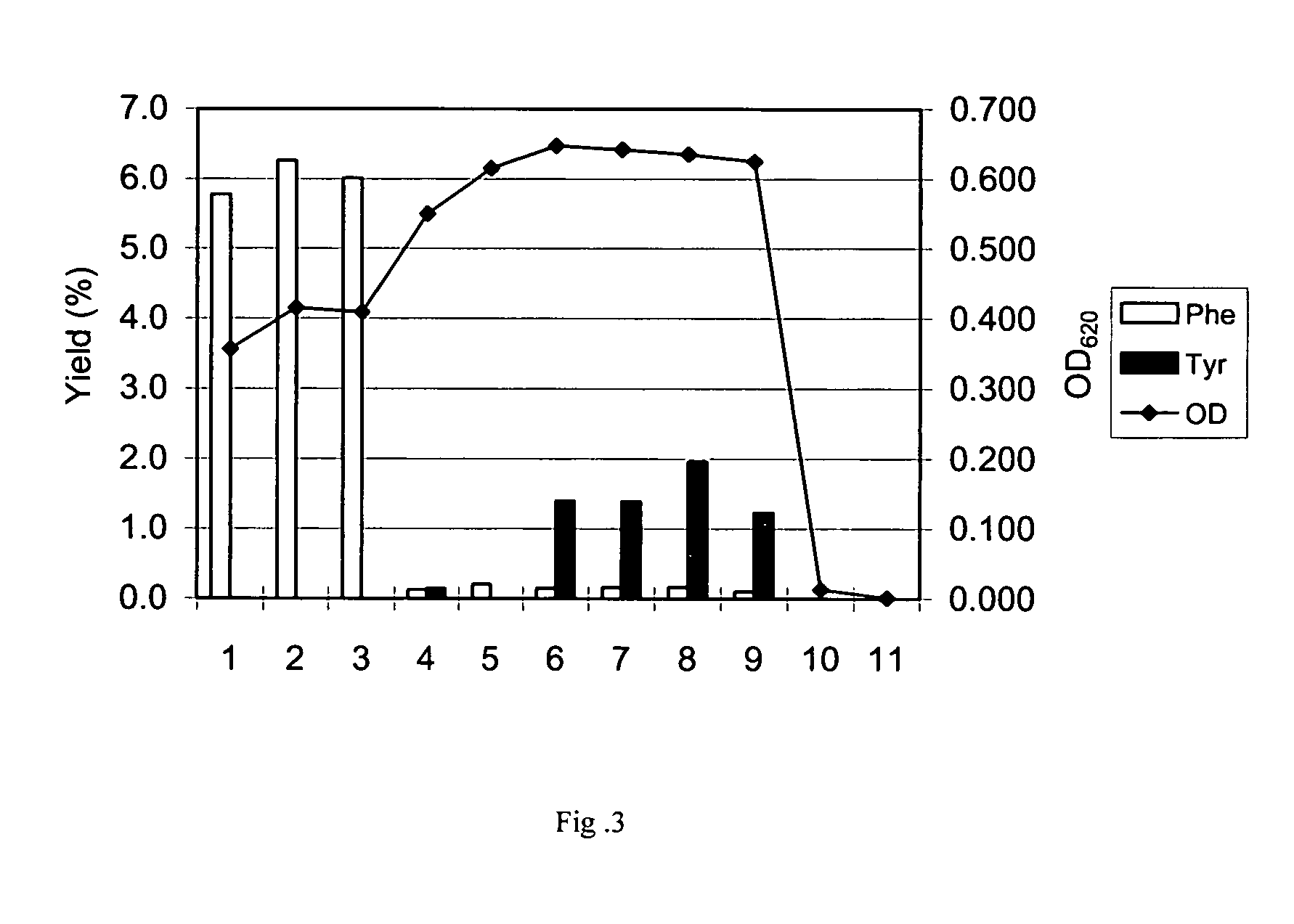
L-tyrosine-producing bacterium and a method for producing L-tyrosine
ActiveUS20050277179A1Reduced gene expressionEfficient productionBacteriaOxidoreductasesTyrosineMicrobiology
The present invention describes the production of L-tyrosine by culturing in a medium an Escherichia bacterium which has L-tyrosine-producing ability and which carries a mutant prephenate dehydrogenase which is desensitized to feedback inhibition by L-tyrosine, producing and accumulating L-tyrosine in the medium or in the bacterial cells, and collecting L-tyrosine from the medium or the bacterial cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
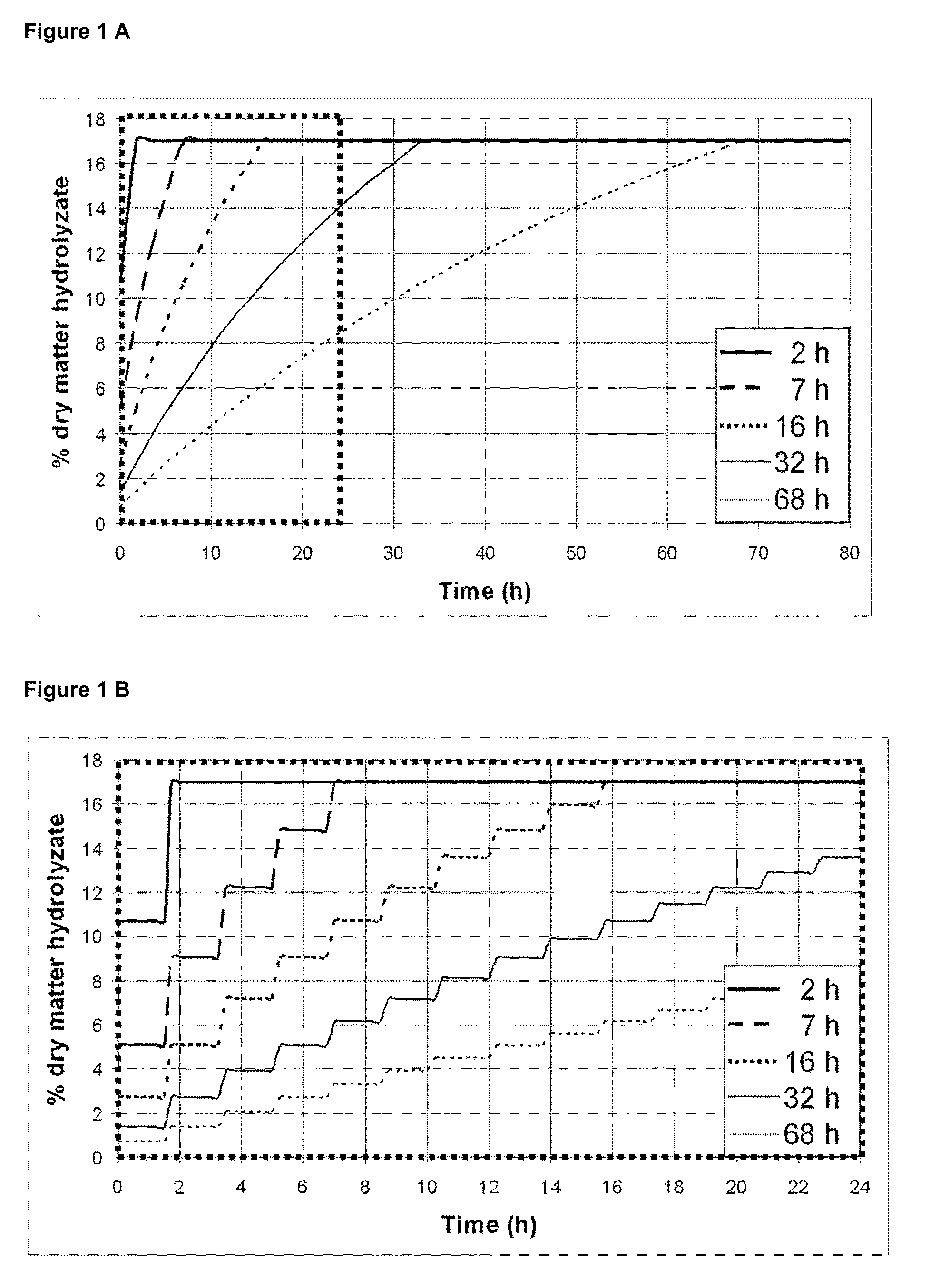
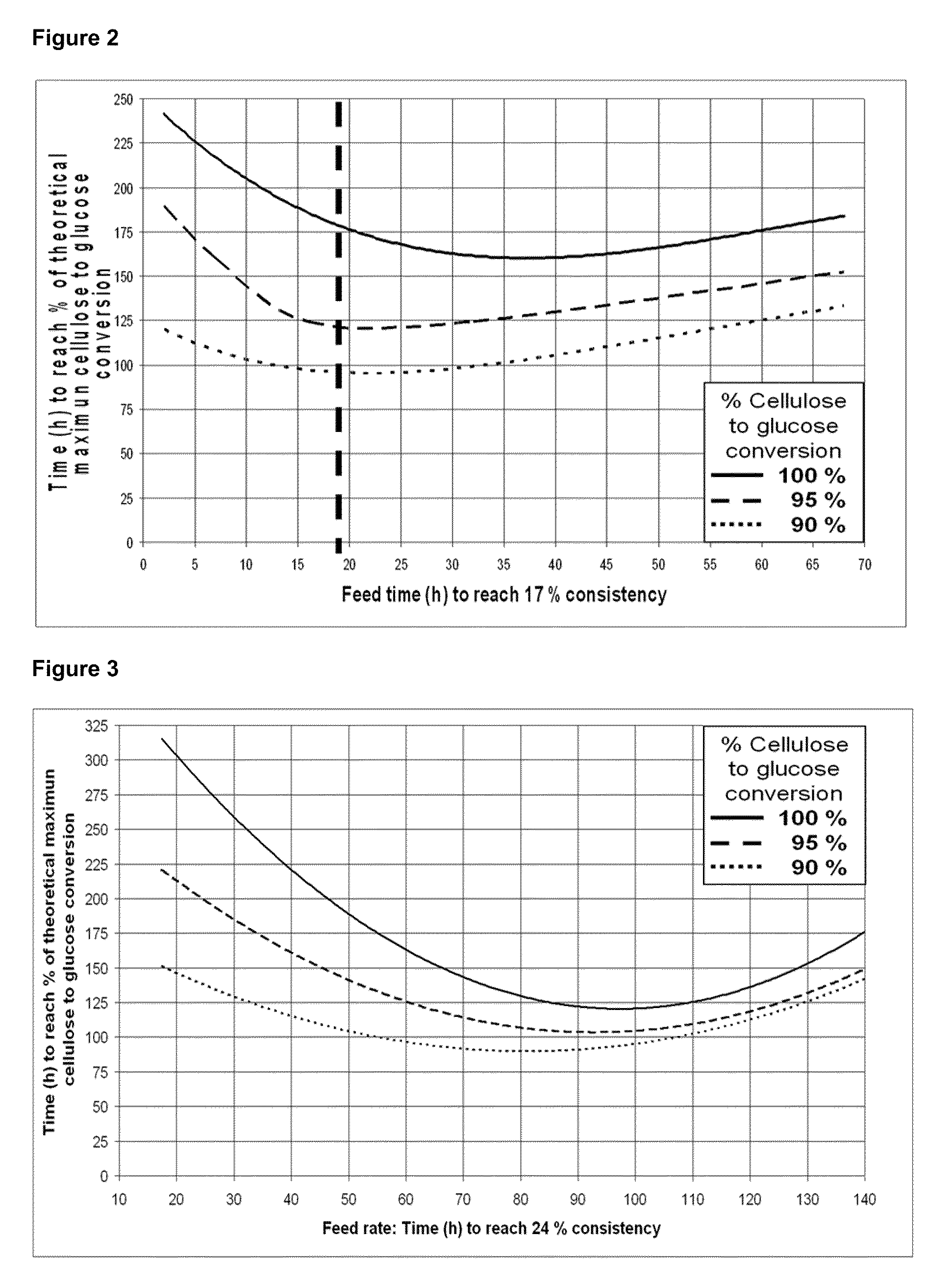
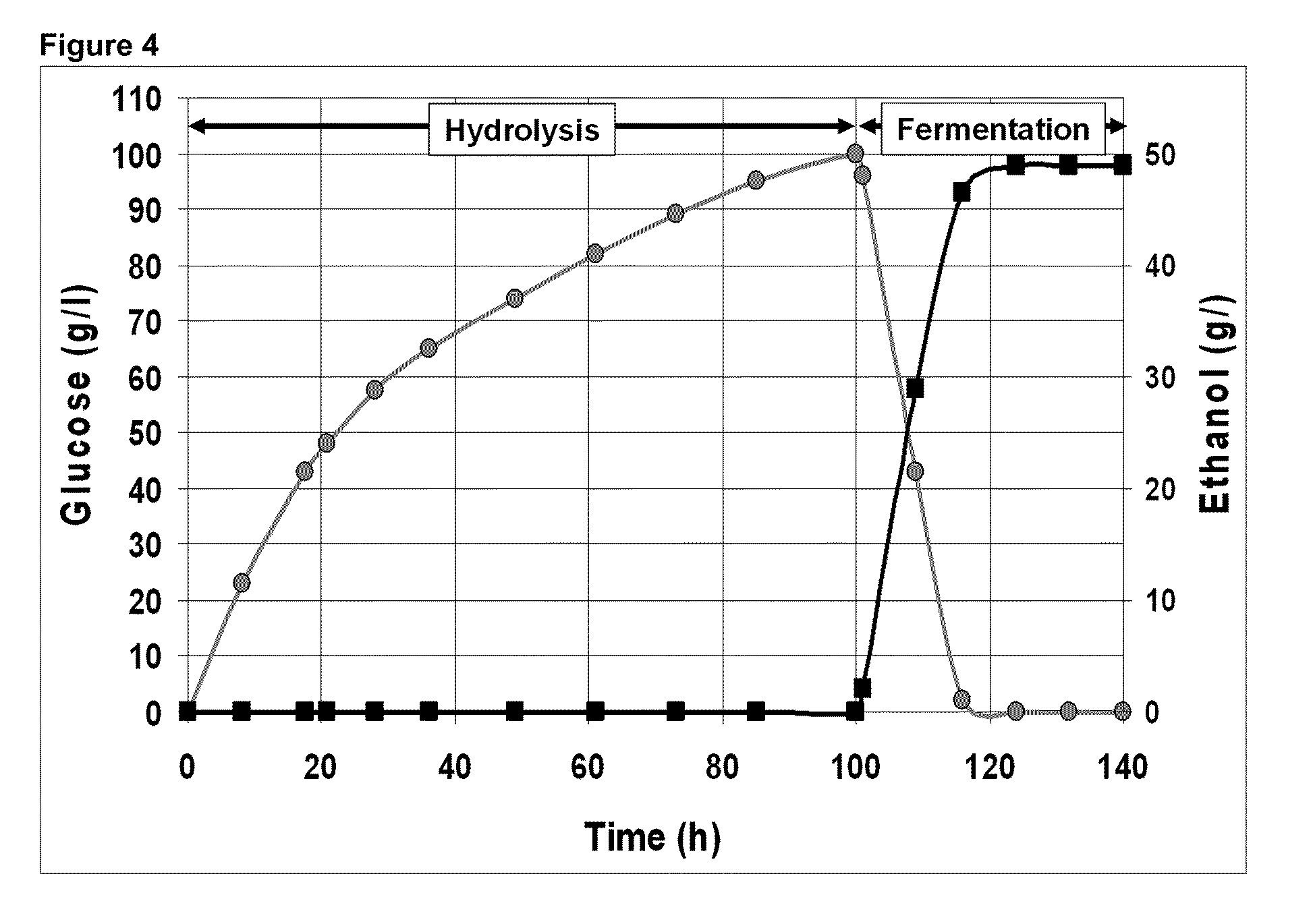
Fed batch process for biochemical conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to ethanol
InactiveUS20100255554A1Extension of timeReduce impactBiofuelsFermentationEnzymatic hydrolysisLignocellulosic biomass
A method for optimization of a fed batch hydrolysis process wherein the hydrolysis time is minimized by controlling the feed addition volume and / or batch addition frequency of the prehydrolysate and optionally also the enzyme feed. The increase over time in hydrolysate consistency and volume and / or concentration of sugars released in the reactor, so that the enzymatic hydrolysis is controlled, significantly reduces the impact of cellulase feedback inhibition, especially for enzyme contents lower than 0.5%. The overall time to reach conversion of the total prehydrolysate feed is reduced significantly where the batch addition frequency is equal to one batch each time 70% to 90%, preferably 80%, conversion of the previous batch is reached in the reaction mixture. At an enzyme load of 0.3% in the reaction mixture, the optimum frequency each time 80% conversion was reached was found to be one batch every 105 minutes.
Owner:GREENFIELD SPECIALTY ALCOHOLS
Mutant serine acetyltransferase
O-acetylserine, L-cysteine and sulphurous compounds derived therefrom may be produced using a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia which harbors a mutant feedback-resistant serine acetyltransferases in which the amino acid sequence corresponding to positions from 89 to 96 in a wild-type serine acetyltransferase is replaced with any one of the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NOS: 4 to 9, and feedback inhibition by L-cysteine in the bacterium is desensitized.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
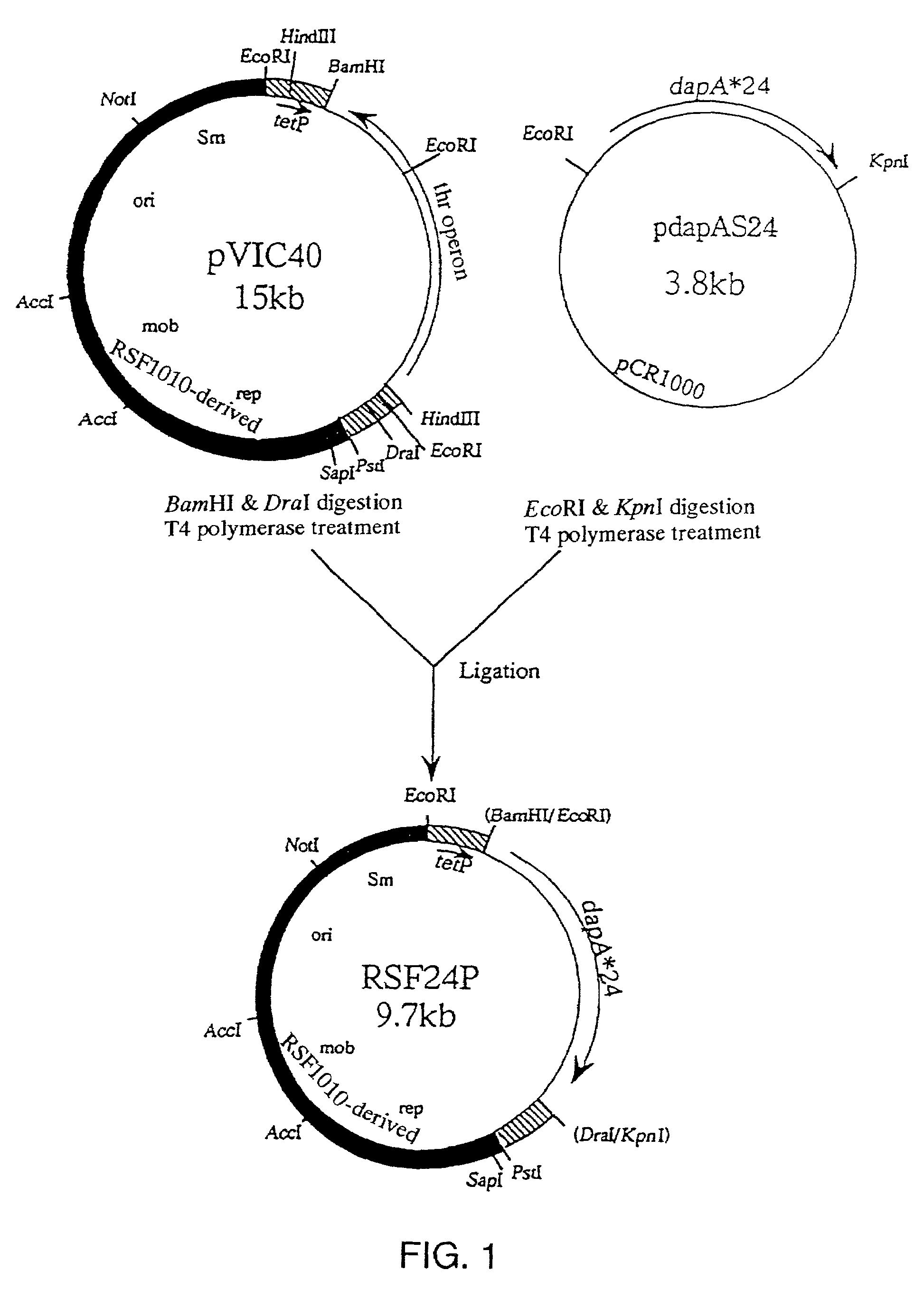
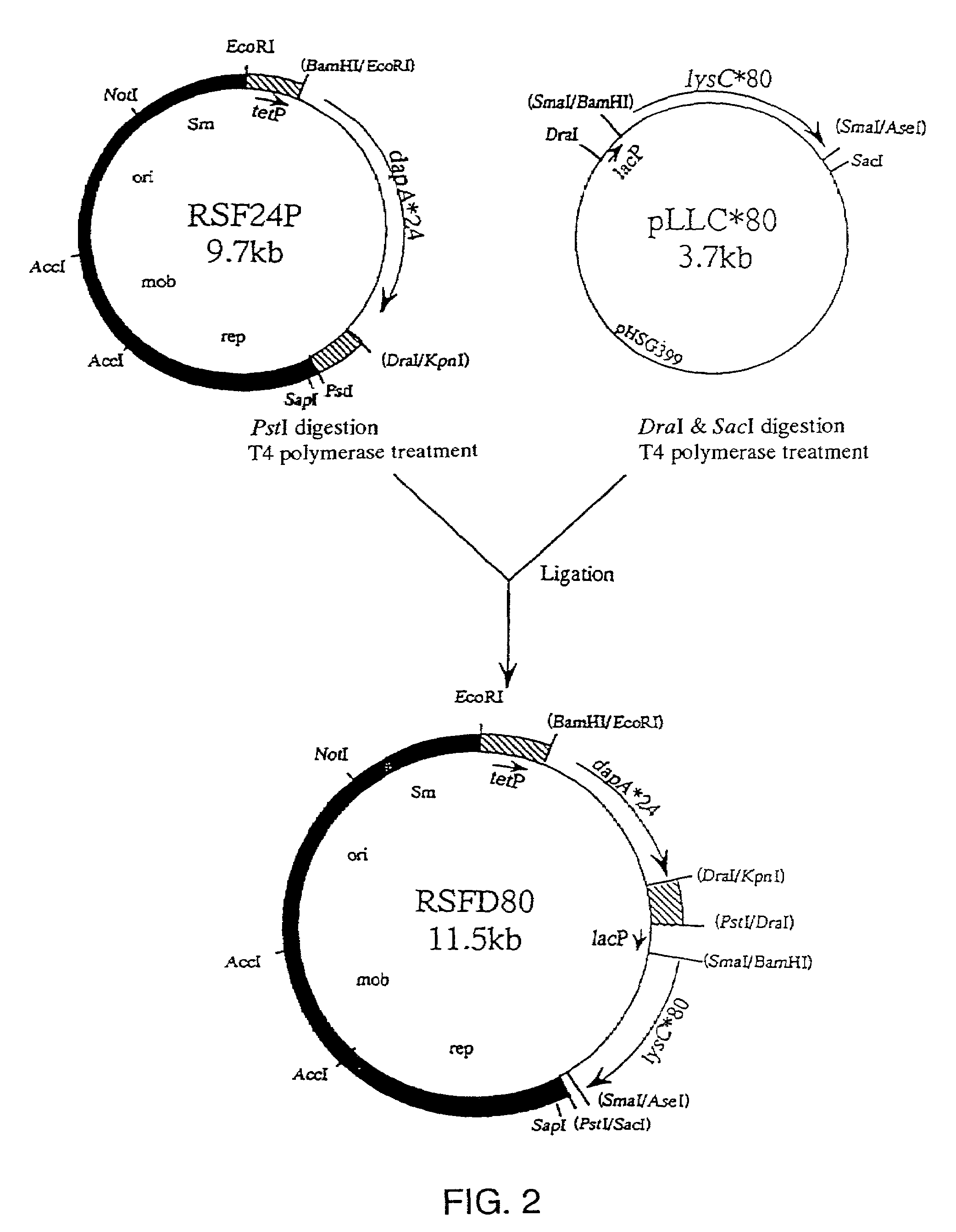
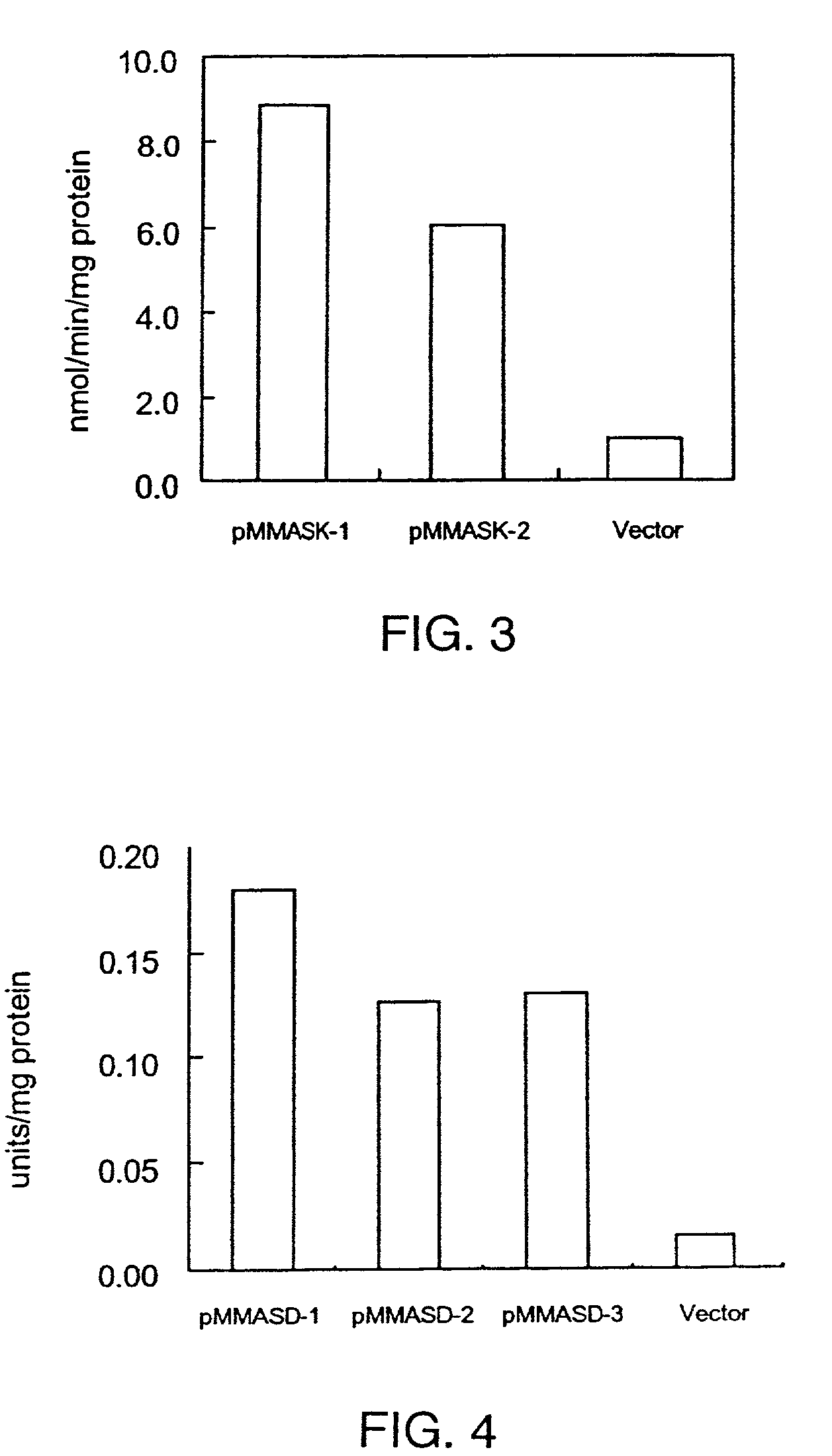
Methylophilus methylotrophus having enhanced dihydrodipicolinate synthase and/or aspartokinase activity for L-amino acid production
InactiveUS7223572B1Increase enzyme activityHigh activitySugar derivativesBacteriaGenus MethylophilusMethyl palmoxirate
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing a Methylophilus bacterium which can grow by using methanol as a main carbon source and has L-amino acid-producing ability, for example, a Methylophilus bacterium in which dihydrodipicolinate synthase activity and aspartokinase activity are enhanced by transformation through introduction into cells, of a DNA coding for dihydrodipicolinate synthase that does not suffer feedback inhibition by L-lysine and a DNA coding for aspartokinase that does not suffer feedback inhibition by L-lysine, or a Methylophilus bacterium made to be casamino acid auxotrophic, in a medium containing methanol as a main carbon source, to produce and accumulate an L-amino acid in culture, and collecting the L-amino acid from the culture.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Production of alcohol from mixed bacterial population degradable fermented bastose substance
InactiveCN1896254AReduce degradationShorten the fermentation cycleBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesAlcohol productionCellulose degradation
Production of alcohol from mixed microbial pool degradable and fermented lignocellulose substance is carried out by crushing lignocellulose substance, soaking with H2SO4, bursting by steam, solid-liquid separating, adding nutritive liquid into solid-phase substance, sterilizing, adding distiller's yeast and cellulose degrading microbe into saccharifying fermentative substrate, degradation saccharifying-fermenting synchronously, distilling and rectifying to obtain final product. It is simple, has short saccharifying and fermenting period, higher raw material utilization rate and more alcohol yield and no feedback inhibition function.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Recombinant microorganism for producing cytidine and method for producing cytidine
ActiveCN106754602ARealize large-scale industrial productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaTransferasesRibonucleosideGenetic engineering
The invention provides a recombinant microorganism for producing cytidine and a method for producing the cytidine from the recombinant microorganism. A degradation and use gene of the cytidine is knocked off, and the gene encodes cytidine ammonialyase, ribonucleotide hydrolase, cytidine / uridine kinase and nucleoside transporter. Meanwhile key enzymes in biological synthesis process of the cytidine are over-expressed, including degrading cytidine triphosphoric acid to cytidine triphosphoric acid pyrophosphorylase of the cytidine monohosphoric acid, and catalyzing the cytidine monohosphoric acid to cytidine monohosphoric acid phosphorylase of the cytidine. In addition, pyrimidine nucleoside process is subjected to genetic engineering reform, and feedback inhibition of the synthesis process is relieved. By using a biological fermentation method, the cytidine yield greater than 20g / L can be achieved for a recombinant strain in a fermentation tank of 5L, industrial on-scale production can be achieved, and meanwhile the recombinant microorganism is low in cytidine production cost, small in pollution, green and environmental-friendly and relatively high in popularization and application value.
Owner:BIOSYNTHETICA INC
Method for improving yield of arginine by mutation of Corynebacterium crenatum N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase
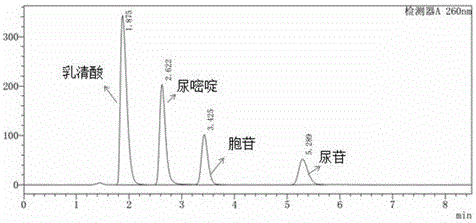
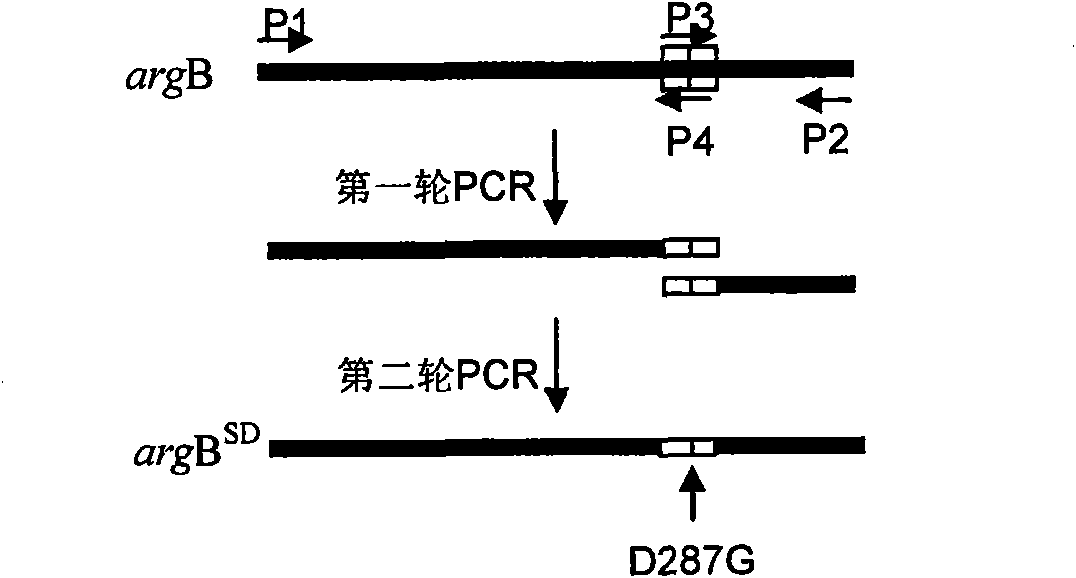
The invention relates to a method for improving the yield of arginine by the mutation of Corynebacterium crenatum N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase. L-arginine is one of semi-essential basic amino acids for a human body, and has various particular physiology and pharmacology functions. High-yield arginine mutant strain C. crenatum SYPA5-5 is compounded into the arginine through a circulating way, and N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase (NAGK) is a key enzyme in the compounding way and is subject to the feedback inhibition of the product arginine. By using an overlapping PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique, a GAT (glycerol phosphate acyl transferase) codon used for coding aspartic acid is used for substituting a GGA (General Gonadotropic activity) codon used for coding glycine at the site 287 in the coding NAGK albumen, and the NAGK which has high activity and arginine with obviously reduced by the feedback inhibition can be obtained after the mutation. An argBSD gene is brought into the Corynebacterium crenatum of the high-yield arginine through pJCl-tac, and the expression volume of the key enzyme is further improved. The final acid yield is increased to 36.3g / L from original 28g / L, and the yield of the L-arginine is increased by 29.7 percent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
L-Amino Acid-Producing Bacterium and Method for Producing L-Amino Acid
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing a Methylophilus bacterium which can grow by using methanol as the main carbon source and has L-amino acid-producing ability, for example, a Methylophilus bacterium in which dihydrodipicolinate synthase activity and aspartokinase activity are enhanced by transformation of cells with a DNA coding for dihydrodipicolinate synthase that is desensitized to feedback inhibition by L-lysine and a DNA coding for aspartokinase that is desensitized to feedback inhibition by L-lysine, or a Methylophilus bacterium which is casamino acid auxotrophic, in a medium containing methanol as a main carbon source, to produce and accumulate an L-amino acid in culture, and collecting the L-amino acid from the culture.
Owner:GUNJI YOSHIYA +6
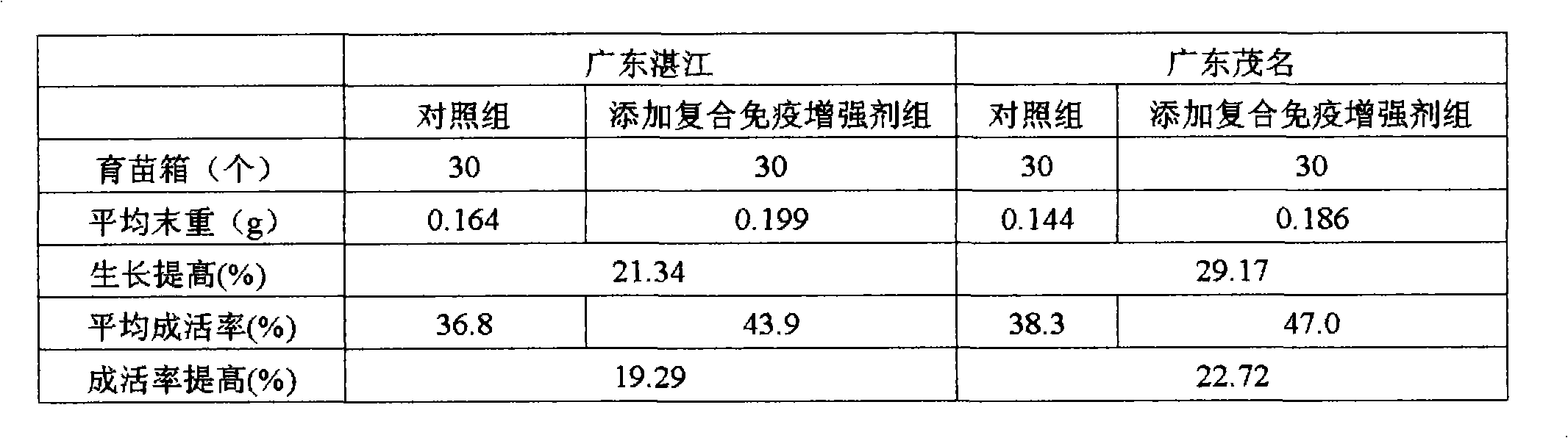
Compound immunopotentiator for post larvae of litopenaeus vannamei
InactiveCN101828640AOvercoming Feedback Inhibition ProblemsHigh activityAnimal feeding stuffPhospholipidFeed additive
The invention relates to a compound immunopotentiator for post larvae of litopenaeus vannamei, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 20-30 percent of beta-glucan, 20-30 percent of chitosan, 5-10 percent of ginsenoside, 10-20 percent of astragalus polysaccharides, 5-10 percent of phospholipid, 40-60 percent of vitamin C-2-polyphosphate ester, 10-15 percent of vitamin E, 5-10 percent of vitamin A, 10-20 percent of bacillus subtilis and 1-5 percent of clamworm powder. The invention has the following advantages that: (1) the problem of feedback inhibition of the post larvae of litopenaeus vannamei is overcome effectively; (2) the immunity of the post larvae of litopenaeus vannamei is enhanced obviously, and the survival rate is increased; (3) the activity and the growth speed of the post larvae of litopenaeus vannamei are increased obviously; (4) the compound immunopotentiator has the addition amount of only 0.2-0.3% when used as a feed additive for a particle feed of the post larvae of litopenaeus vannamei; (5) no adverse effect on the palatability of the feed exists; and (6) the source of the raw materials is stable, the cost is low, and the production process is simple.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
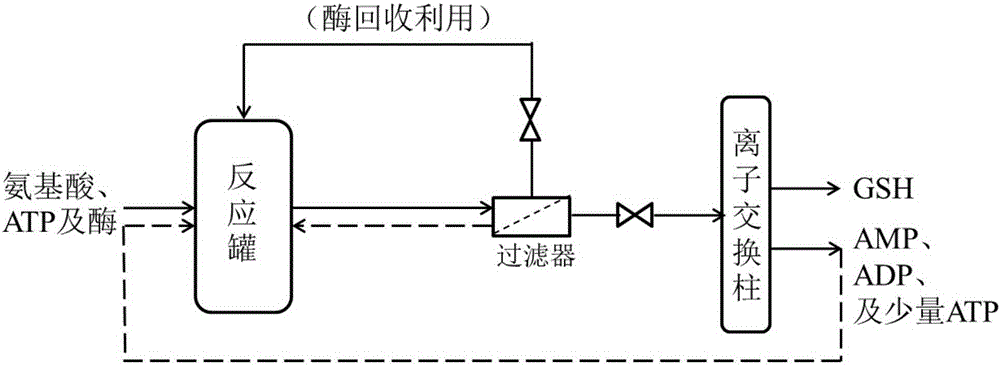
Method for preparing glutathione by means of enzymic method
The invention discloses a method for preparing glutathione by means of an enzymic method. The method comprises the following steps that 1, Gsh F is utilized for generating glutathione in a reaction kettle; 2, regenerating enzyme is added into the reaction kettle, and ADP and / or AMP generated through a reaction is regenerated to be ATP; 3, the Gsh F and the regenerating enzyme which are fixed are separated in the reaction kettle or a filter device is used for separating dissociative Gsh F and the regenerating enzyme; 4, the product GSH and ATP, ADP and AMP in a reaction solution are separated. According to the preparation method, Gsh F enzyme is used for replacing Gsh I enzyme and Gsh II enzyme, a two-step reaction is changed into the one-step reaction, time is saved, and the feedback inhibition of the GSH for the two-step reaction is lowered; an ATP regenerating system for GSH production is established, the ATP consumption is lowered, and the cost is lowered; impurities such as pigment introduced by ATP regenerated by the yeast are avoided, and purification is easy; the enzyme recycling system is built, and large-scale production can be achieved.
Owner:ANHUI GSH BIO TECH CO LTD
High-density fermentation method of engineering bacteria containing nitrilase
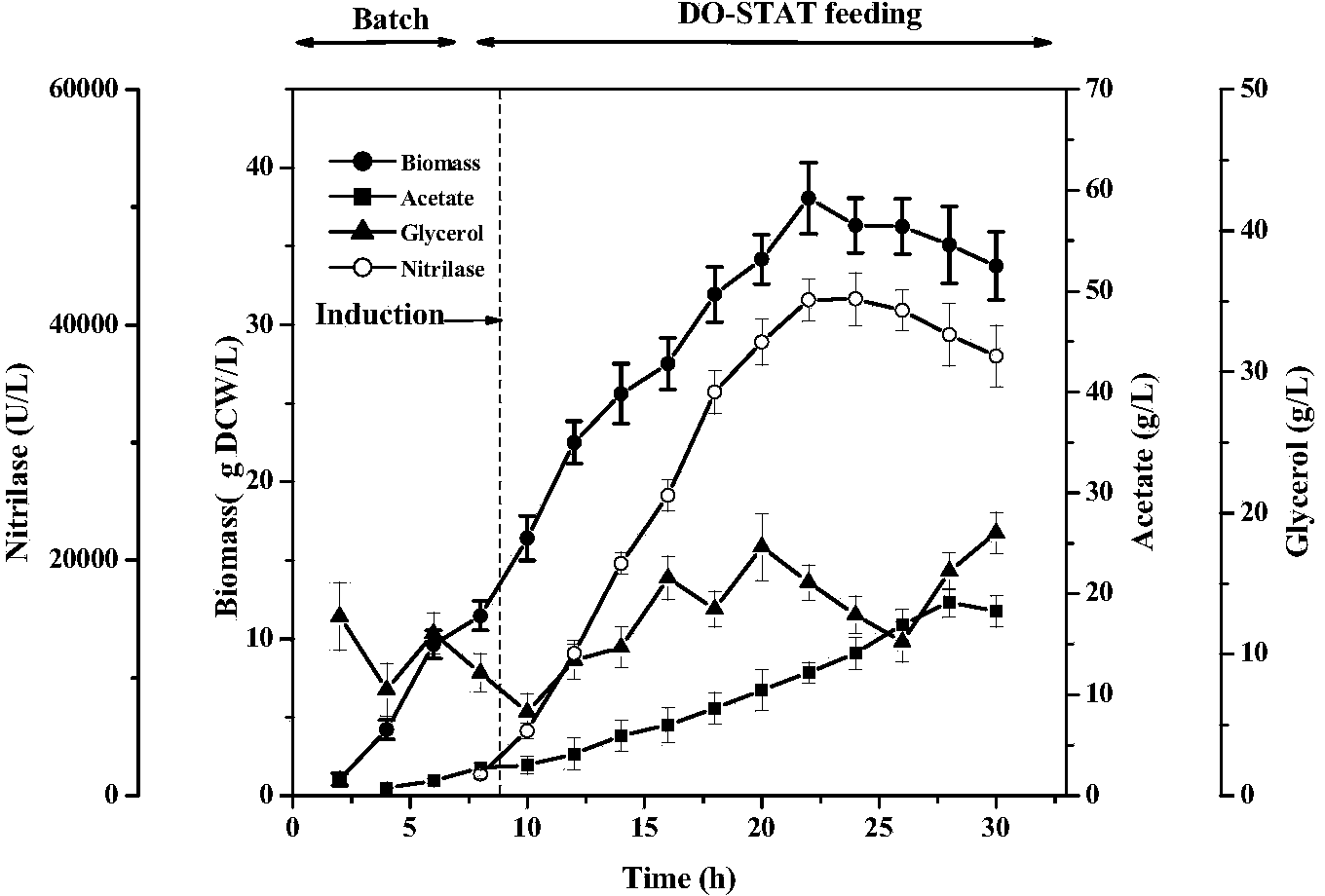
InactiveCN104212785APrevention of waste and other disadvantagesControl growth rateHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHigh concentration
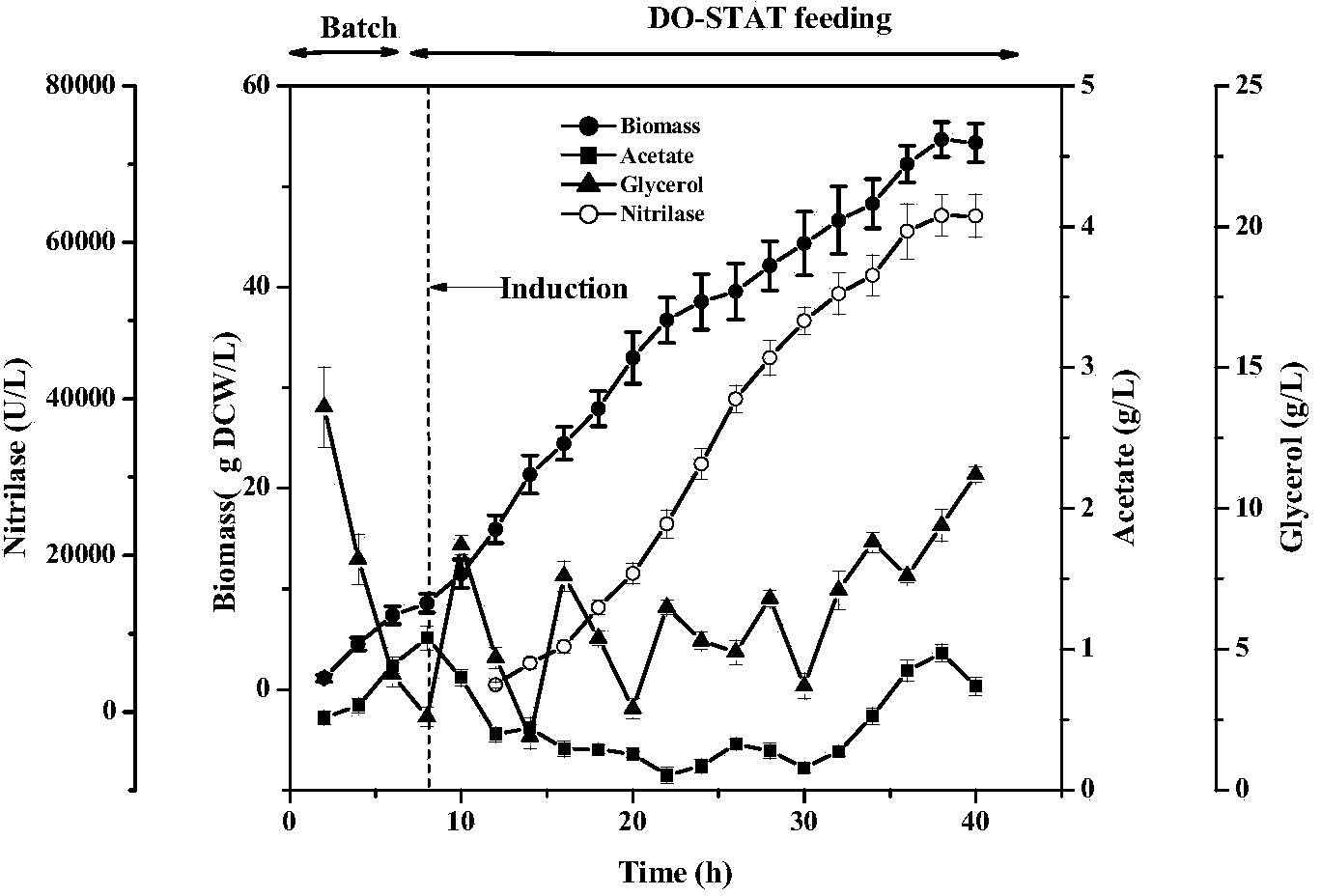
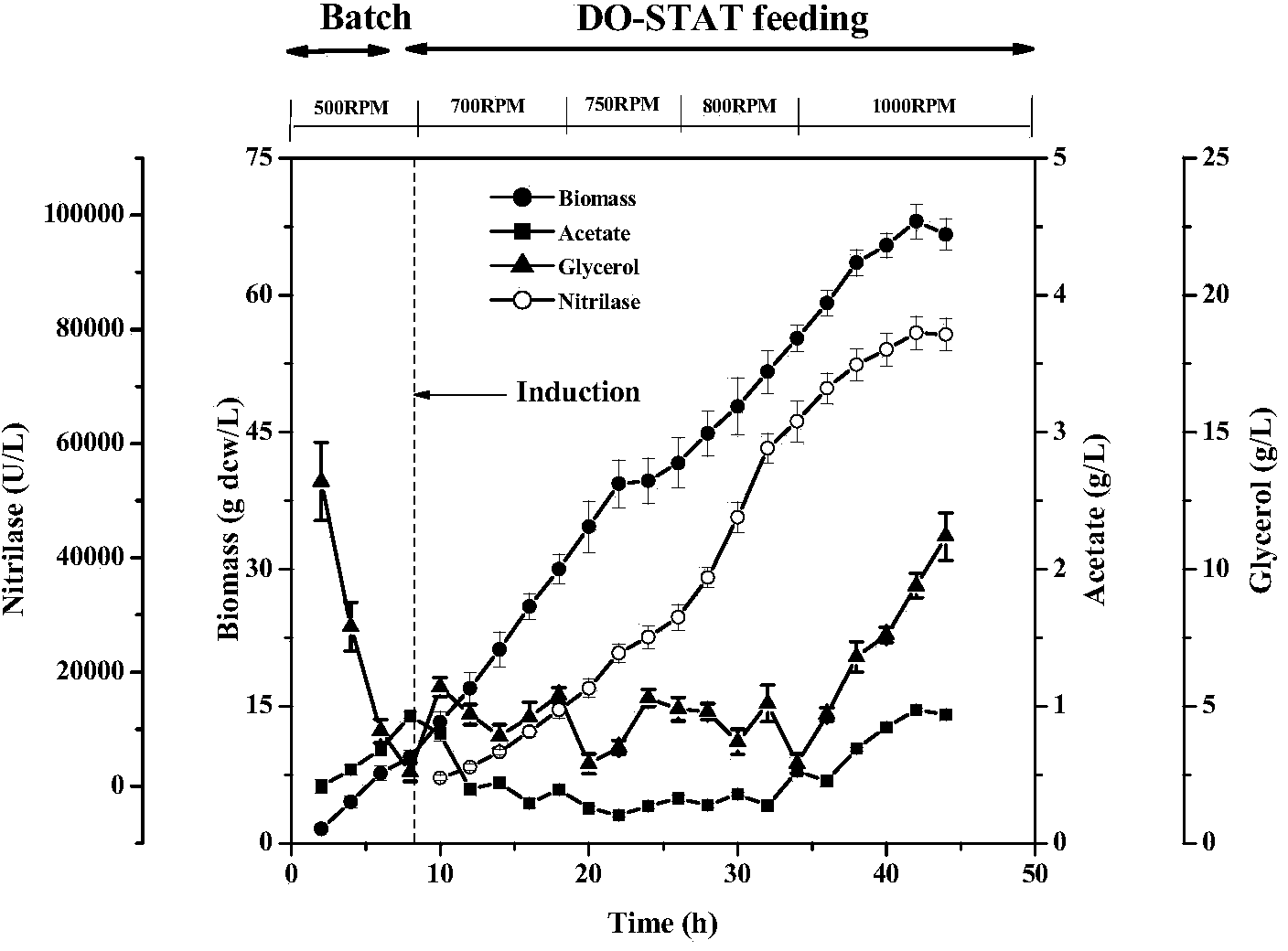
The invention discloses a high-density fermentation method of engineering bacteria containing nitrilase. The method adopts a novel recombinant Escherichia coli fermentation and supplementary material culture medium formula, and uses a method of DO-STAT coupling step-by-step induction and gradual increase of the speed stage by stage. The method not only meets the need for mixing power in the culture process with biomass increase, effectively controls the growth rate of thalli, and prevents disadvantages of produced acid accumulation caused by fast growth of thalli, feedback inhibition and culture medium waste. In addition, the induced mode of batch-by-batch lactose supplement addition avoids the high viscosity of the fermentation broth caused by high concentration of lactose, resulting in resistance of oxygen transfer and mass transfer, but also improves the induction strength. The high-density fermentation technology of the invention increase the biomass of recombinant Escherichia coli from 10.35g DCW / L to 70g DCW / L, volume enzyme activity from 18205U / L to 103530U / L, and the fermentation level by 4.7 times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant dna, bacterial strain and method for fermentative production of l-valine
InactiveCN102286505AHigh activityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAcetohydroxy Acid Synthetase
The invention relates to a recombinant DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), strain and method for producing L-valine by fermentation. The recombinant DNA comprises DNA sequence for coding acetohydroxy acid synthetase free of feedback inhibition of three branched-chain amino acids to acetohydroxy acid synthetase, DNA sequence for coding dihydroxy reduction isomerase, and DNA sequence for coding branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase. The strain is corynebacterium or brevibacterium transformed by introducing the recombinant DNA. The method is implemented by culturing the strain to produce the L-valine. In the invention, the expression L-valine is used for producing the bacterium L-valine biosynthetic gene, so the yield of the L-valine can be greatly increased; and the fermentation model, especially the high-temperature short-time fermentation model, is constructed according to the optimum temperature of the L-valine biosynthetic enzyme, so that the metabolism intensity of the strain is enhanced, the activity of the L-valine biosynthetic enzyme is enhanced, and the yield of the L-valine and the conversion rate of the sugar acid can be further increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
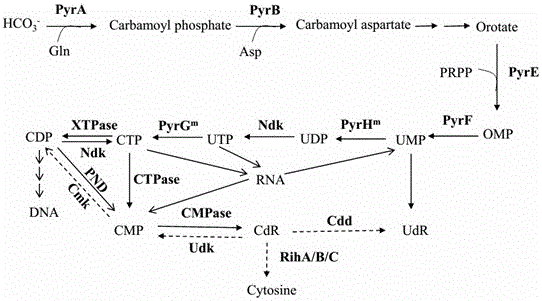
Pyrimidine nucleoside high-yielding strain and carbamyl phosphate synthetase adjusting site thereof
ActiveCN105671007AImprove toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCarbamyl PhosphateStructural analog
The invention belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering, and concretely relates to a pyrimidine nucleoside high-yielding strain and a carbamyl phosphate synthetase adjusting site thereof. The invention provides a pyrimidine nucleoside production Bacillus subtilis mutant strain and a carbamyl phosphate synthetase encoding gene. A key regulation site related to carbamyl phosphate synthetase end product feedback inhibition is defined, and provides reference for breeding of later pyrimidine nucleoside high-yielding strains. The Bacillus subtilis mutant strain allows the output of fermentation process produced nucleoside pyrimidine uridine to reach 14-16g / L, and has substantially improved tolerance to different pyrimidine nucleoside structure analogs.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
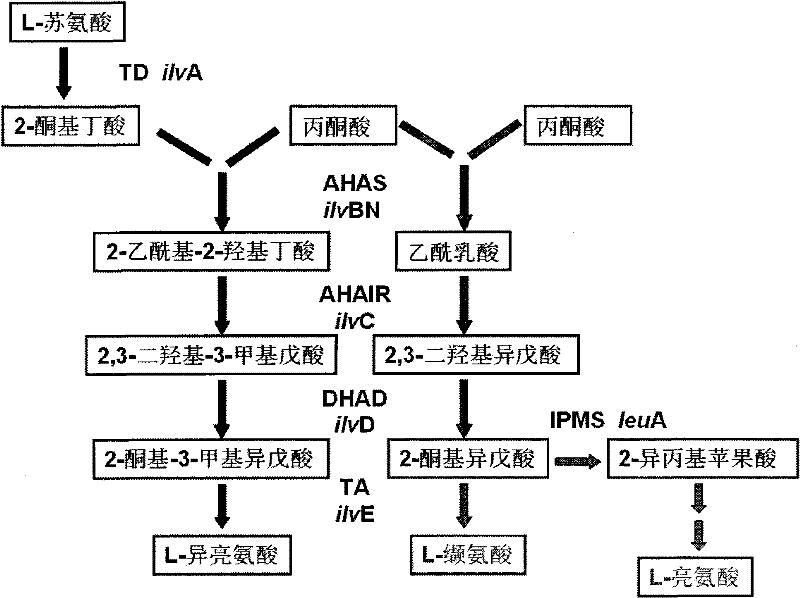
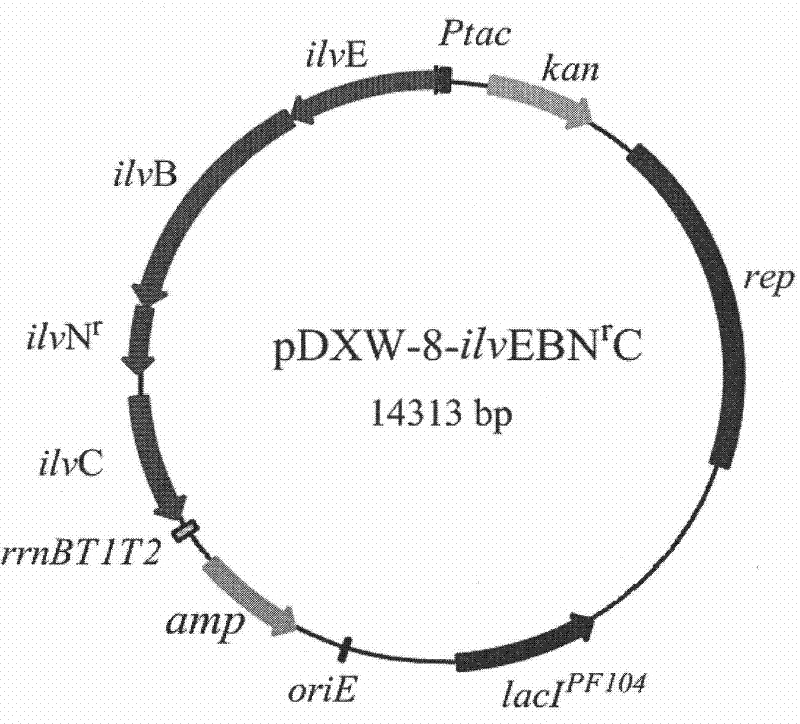
Strain for producing L-leucine and method for producing L-leucine
The invention relates to the technical field of biological engineering, in particular to a strain for producing L-leucine and a method for producing the L-leucine. According to the method, corynebacterium glutamicum is induced by using ultraviolet rays and nitrosoguanidine, then key mutants leuAG561D and ilvBG235S which are beneficial to generation of the L-leucine can be generated, research shows that under mutation conditions of leuAG561D and / or ilvBG235S, feedback inhibition of synthesis routes of the L-leucine can be released, the yield of the L-leucine can be greatly increased, a strain which can generate a great deal of the L-leucine can be obtained, the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC NO.13408, the strain is capable of achieving efficient accumulation of the L-leucine in the fermentation process, and the L-leucine can be up to 4.7g / L.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Lactic acid production process with fermentation and expanded bed for in-situ adsorption coupling
InactiveCN101914433AAvoid cloggingNo cloggingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCouplingFixed bed
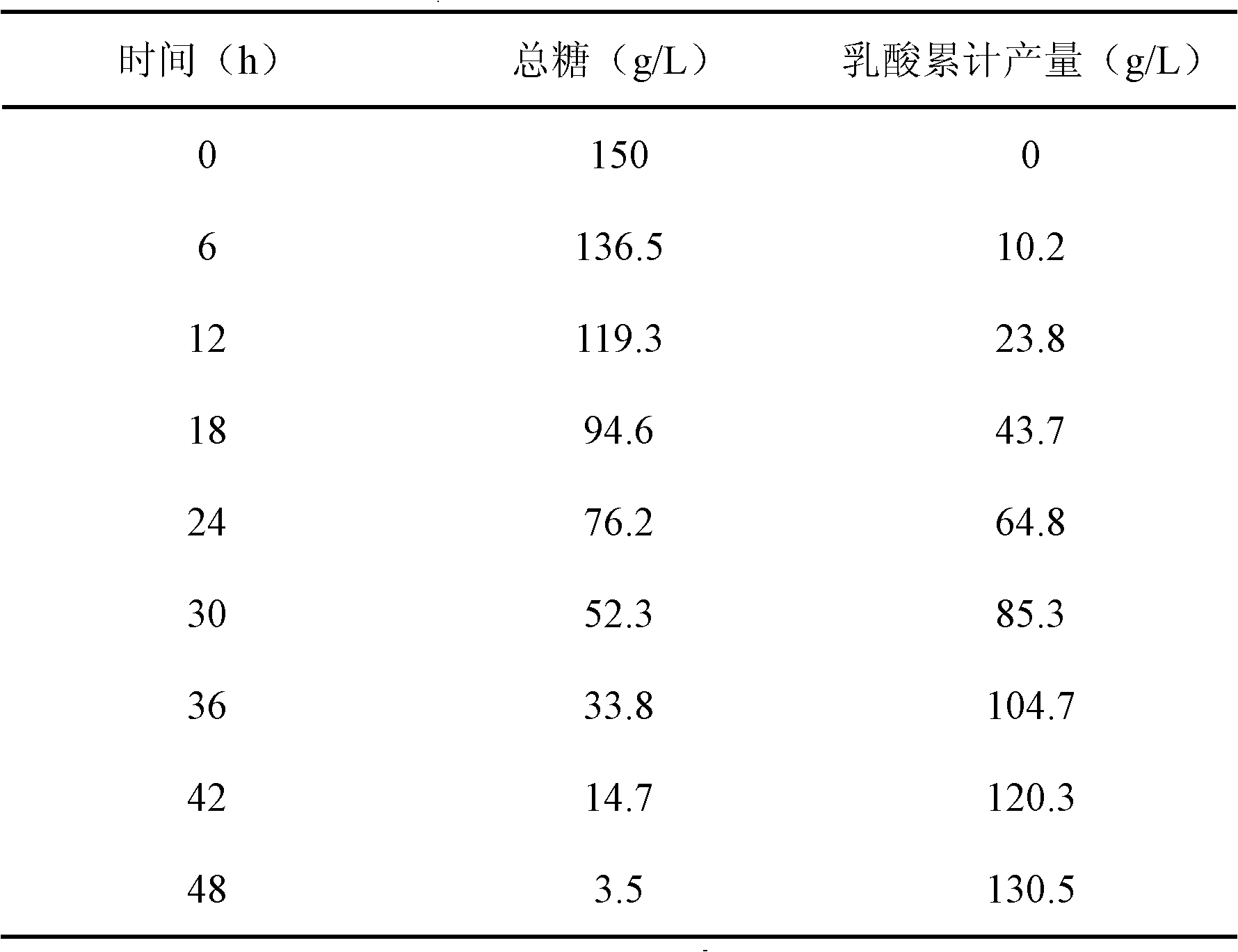
The invention discloses a lactic acid production device for fermentation and separation coupling and a lactic acid fermentation process using expanded bed in-situ adsorption to realize online separation. In the invention, an expanded bed and a fermentation tank are coupled, the online separation of lactic acid fermentation is realized by using the expanded bed method, so that the feedback inhibition of lactic acid is relieved, the yield and the conversion rate of the lactic acid fermentation are increased, and meanwhile, the problem of bed blockage by thalli when a fixed bed is used for absorbing the lactic acid in the prior art. Untreated fermentation liquor is permitted to directly enter a chromatographic column. Because the synchronization of fermentation and separation is realized, the cost of downstream extraction and separation in the prior art is greatly reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for producing glutathione by fermentation of recombinant Escherichia coli
ActiveCN102586369AIncrease productionHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationGamma-Glutamylcysteine synthetaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for producing glutathione by fermentation of recombinant Escherichia coli. The method comprises the following stages of: (1) carrying out batch culture or fed-batch culture to obtain a great deal of recombinant Escherichia coli cells expressing exogenous bifunctional glutathione synthetase, wherein the bifunctional glutathione synthetase is protein which simultaneously has activities of gamma-glutamyl cysteine synthetase and glutathione synthetase; (2) carrying out over-expression on the bifunctional glutathione synthetase obtained in the stage (1); and (3) adding L-glutamic acid, L-cysteine and glycine precursor amino acids to realize high-efficiency production of glutathione by fermentation. According to the invention, the recombinant Escherichia coli strain expressing the exogenous bifunctional glutathione synthetase is used for producing glutathione by fermentation, so that the method not only has high GSH (Glutathione) synthesizing capability, but also is free from GSH feedback inhibition, and has the advantages of rapid reaction, high glutathione yield and short production period.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Trichoderma viride W2 capable of producing thermophilic ethanol-resistant beta-glucosidase and application thereof
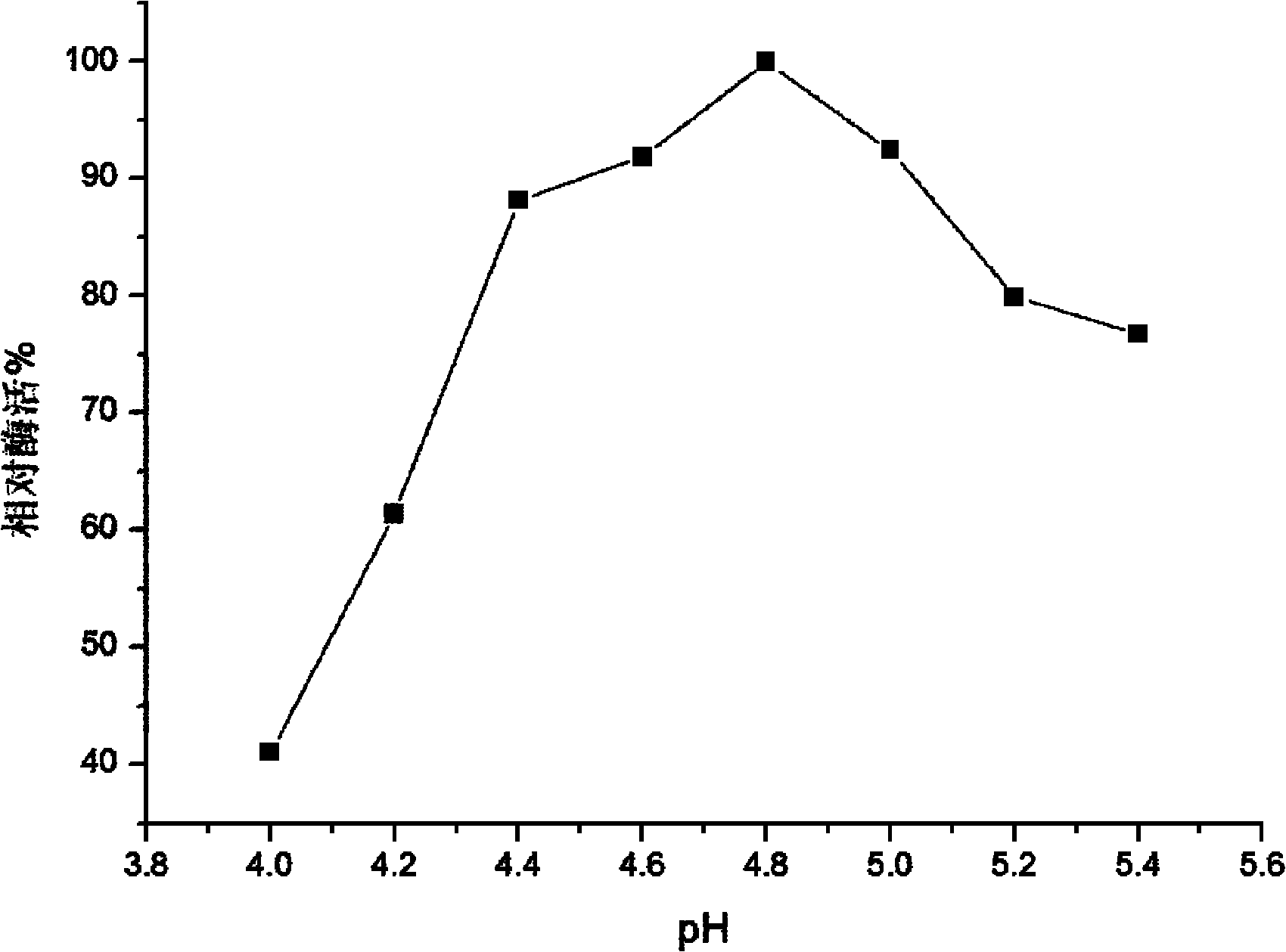
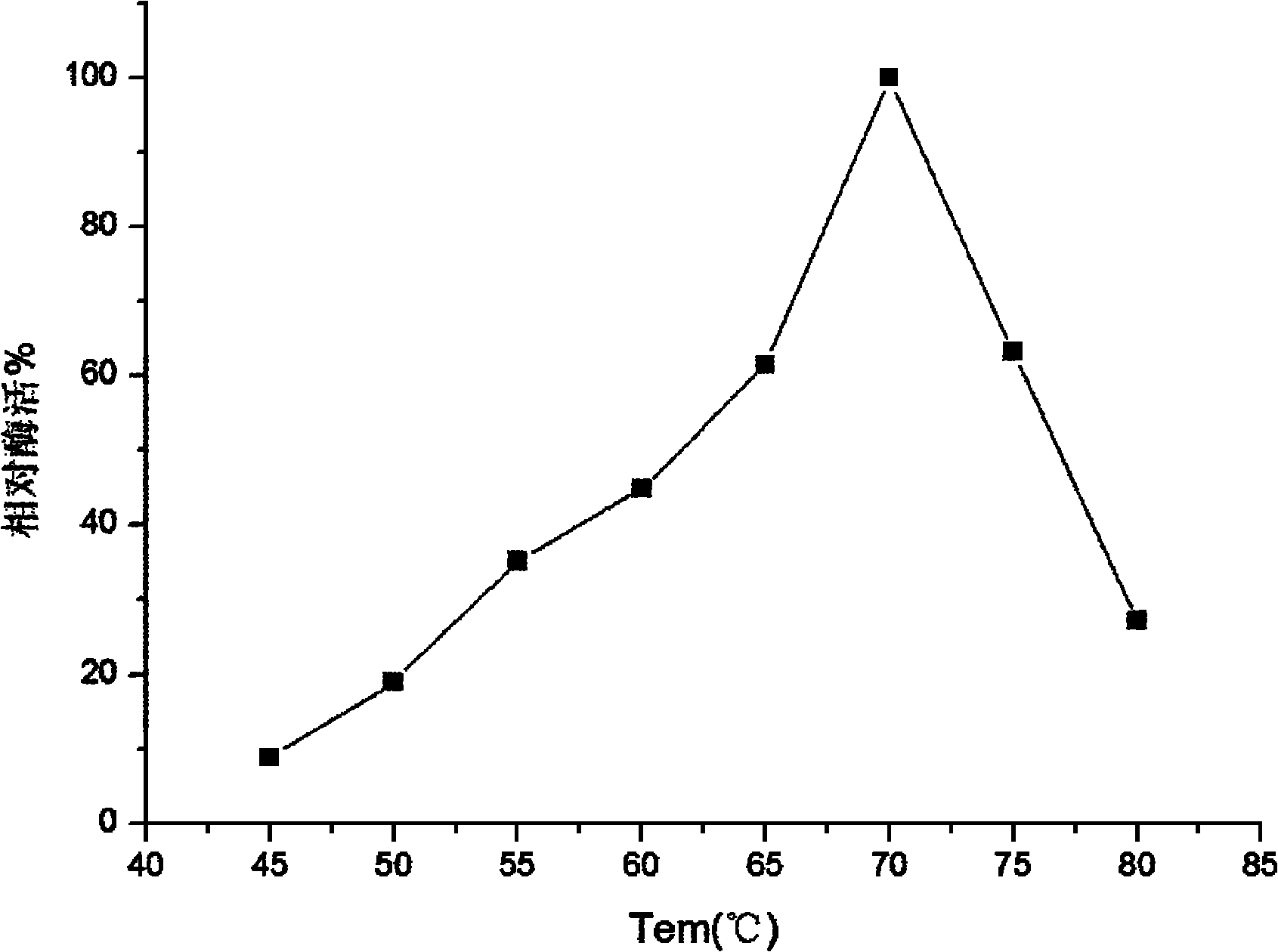
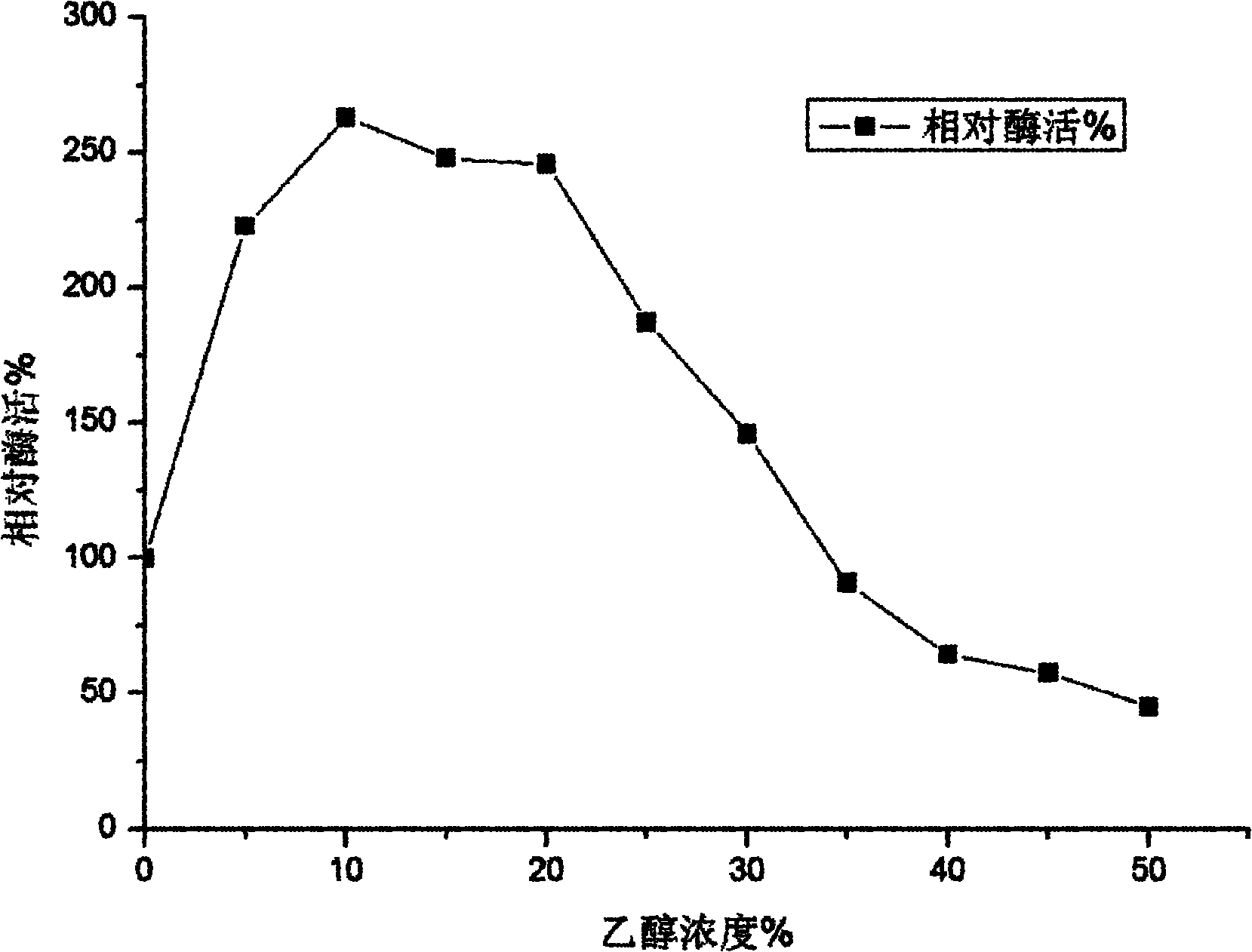
InactiveCN102080050AImprove toleranceFeedback inhibition is evidentFungiMicroorganism based processesReaction temperatureCellobiose
The invention discloses a trichoderma viride W2 capable of producing a thermophilic ethanol-resistant beta-glucosidase and an application thereof. The trichoderma viride W2 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on August 23, 2010, and the preservation number of the trichoderma viride W2 is CGMCC No.4098. The trichoderma viride W2 can produce a new beta-glucosidase, the enzymatic activity of the new beta-glucosidase reaches 346.7U / mL, the optimal reaction pH value is 4.8, the optimal reaction temperature is 70 DEG C, and the new beta-glucosidase is suitable for pyrohydrolysis and has an obvious glucose feedback inhibition effect. The ethanol the concentration of which is 10% has a maximal effect on promoting the enzymatic activity and improves the enzymatic activity of the beta-glucosidase by 1.6 times, and the resistant ability of the ethanol reaches 30%, so that the cellobiose inhibition can be effectively eliminated, the yield of the ethanol is improved by nearly 3 times, and the terminal product inhibition is effectively eliminated. Thus, the beta-glucosidase can be used for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of lignocellulose raw materials, has a rare promoting effect in China, effectively increases the yield of the cellulosic ethanol, lowers the production cost, and accelerates the industrialized progress of the cellulosic ethanol.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing bio-ethanol by taking seaweed processing waste as raw material
InactiveCN101701225AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyOpportunity for facilitationMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiberCellulose compounds
The invention relates to a method for preparing bio-ethanol by taking seaweed processing waste as raw material, which is characterized by comprising the steps: selecting the seaweed processing waste, and pretreating the raw material by sulfuric acid or hydrogen peroxide; then, adding cellulase or cellobiase for cellulose compound enzymolysis, and filtering enzymolysis liquid to remove insoluble components; and finally, supplementing inorganic salt, inoculating saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, and carrying out alcoholic fermentation under the anaerobic condition. The original structure of algae cellulose is changed by the pretreatment process, and the action probability between the cellulose and degrading enzyme can be promoted, so that the enzymolysis efficiency of the cellulose is improved; furthermore, after the cellulose is treated by the compound enzymolysis of the cellulase and the cellobiase, the feedback inhibition of the cellobiose for the cellulose can be effectively eliminated, the content of glycolysis sugar of yeast can be improved, and the yield of alcoholic fermentation is further improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for producing ethanol by simultaneous high-efficiency saccharification half enzymolysis and fermentation of straw lignocellulose
ActiveCN101899478AImprove conversion alcohol yieldAddressing Feedback InhibitionBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesCelluloseAlcohol
The invention provides a method for producing ethanol by simultaneous high-efficiency saccharification half enzymolysis and fermentation of straw lignocellulose. A pretreated straw lignocellulose raw material is subjected to pre-enzymolysis, and then is added with saccharomyces cerevisiae for simultaneous enzymolysis and fermentation. In the method, the pretreated straw lignocellulose raw material is subjected to the pre-enzymolysis process, most of the cellulose in the raw material (about 80 percent of the total cellulose) is transformed into micromolecular sugar during the process, the raw material is added with a certain amount of yeast for simultaneous enzymolysis and fermentation, the rest cellulose raw material is continuously subjected to the enzymolysis, and glucose in the enzymolysis process is timely transformed into the alcohol simultaneously, so that the feedback inhibition in the enzymolysis process is removed, and the yield of the cellulose-transformed alcohol is improved.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
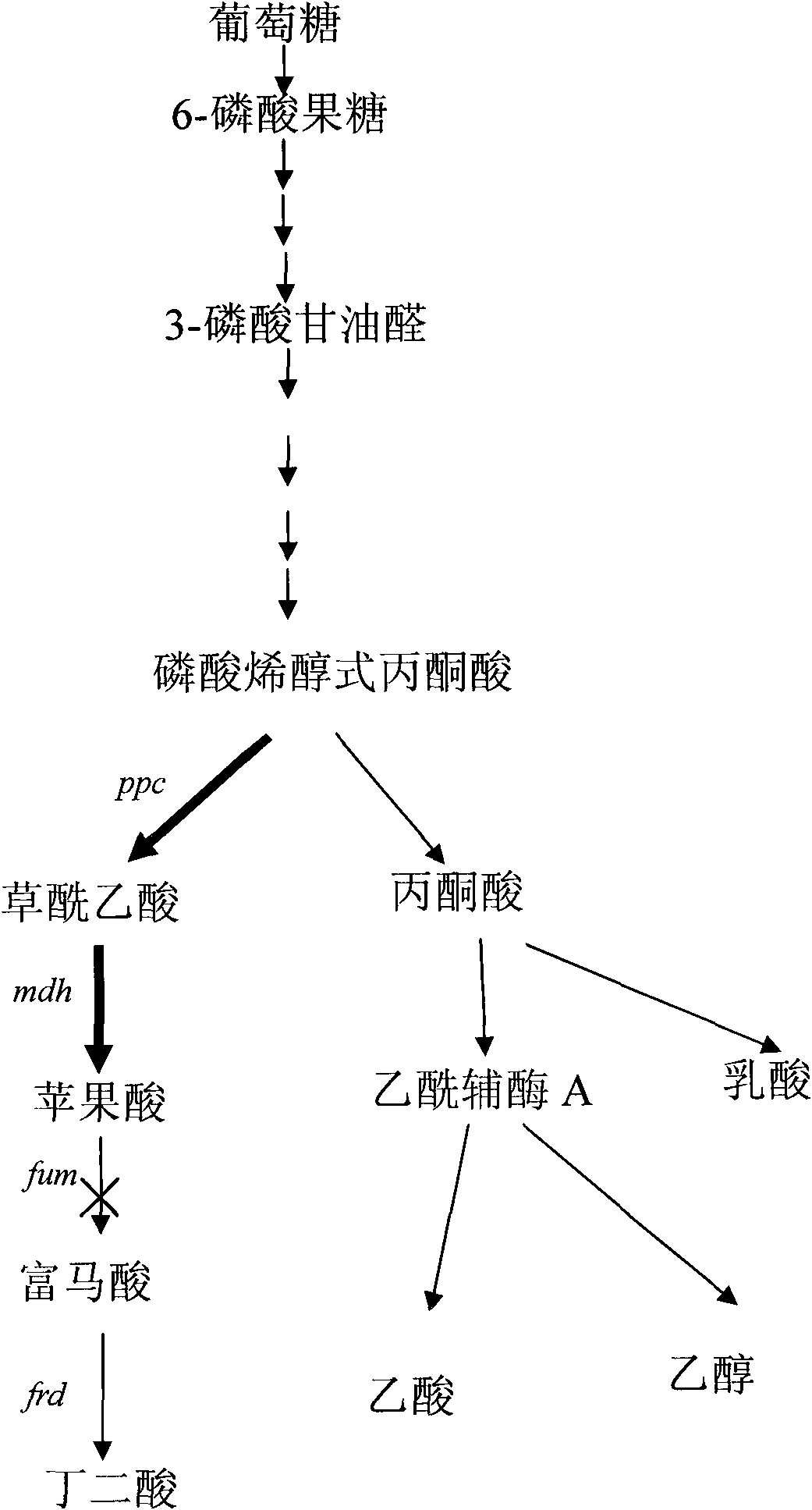
Gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid and construction method and application thereof
The invention provides a gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid as well as a construction method and application thereof. In the invention, key phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase(PEPCK) related to the L-malic acid, malate dehydrogenase (MDH) and fumarase (FumC) are transformed to obtain the gene engineering bacterial strain; a deactivation mutation is carried out on the fumCto cause the interruption of a metabolic flux at the converting position from the malic acid to the fumaric acid so as to accumulate the target product L-malic acid; before the mdh, the promoter of aninner source pepck gene is added to generate the metabolic flux biased towards the malic acid; in addition, through the inducement of monofluorine sodium acetate, the activity of the PEPCK is improved, and the product feedback inhibition is greatly reduced. The bacterial strain applied to the fermentative production of the L-malic acid so as to obviously improve the yield of L-malic acid. The invention has advantages of simple technology, obvious effect and low cost and can satisfy the demand of markets.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Method of producing tetrahydropyrimidine by fermenting recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum
ActiveCN107142234ALow costAddressing Biosecurity IssuesCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaBacterosiraFermentation
The invention provides a method of producing tetrahydropyrimidine by fermenting recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum. The recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is obtained by the steps of performing overexpression in corynebacterium glutamicum to relieve an aspartokinase gene lysC of feedback inhibition; then replacing a promoter of a dihydropyrimidine dicarboxylic acid synthetase in the recombinant bacteria to weaken the activity of the dihydropyrimidine dicarboxylic acid synthetase; and then transferring tetrahydropyrimidine synthetic path related gene ectABC into the recombinant bacteria to obtain the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum. The recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum provided by the invention can use different cheap raw materials to produce tetrahydropyrimidine by fermentation under a low salt condition, and cheap corn slurry can be also used as a nutritional component which replaces expensive yeast powder, so that the cost of the raw materials is further lowered. Meanwhile, the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum provided by the invention solves the problem of biosafety, simplifies the post-extraction process and has a good market application prospect.
Owner:北京绿色康成生物技术有限公司
Variable step size normalized sub-band adaptive filter method applied to acoustic feedback inhibition
InactiveCN107291663AGood removal effectFast convergenceComplex mathematical operationsAdaptive filtering algorithmAdaptive filter
The invention discloses a variable step size normalized sub-band adaptive filter method applied to acoustic feedback inhibition. According to a hearing-aid feedback control system based on a normalized sub-band adaptive filter algorithm, on the basis of a system noise cancellation principle, estimation is carried out through adoption of an iterative shrinkage method, thereby obtaining noiseless sub-band prior error power; and each sub-band step size is updated, thereby achieving the purpose of eliminating an acoustic feedback signal. According to the method, through adoption of the variable step size adaptive filter method, a coefficient of a sub-band filter is updated; through application of the method in the hearing-aid feedback control system with a long echo path and a short echo path, the acoustic feedback signal can be eliminated well; moreover, relatively high convergence rate and relatively low maladjustment can be obtained; and the contradiction between the steady state maladjustment and the convergence rate in the adaptive filter method is solved.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
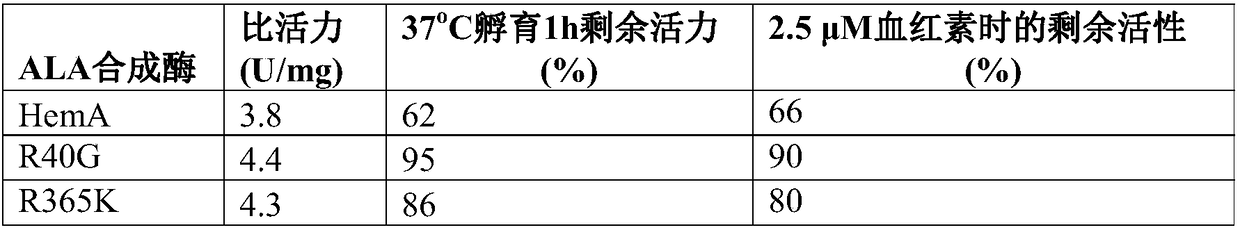
5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) synthetase mutant and host cells and application thereof
The invention provides a 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) synthetase. The amino acid sequence of the ALA synthetase has mutation at the amino acid residues of the 40th site, the 365th site, the 75th site,the 29th site and the 44th site corresponding to the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The ALA synthetase provided by the invention obviously improves the activity and also partially relieves the feedback inhibition of hemachrome. Furthermore, the invention also provides methods for preparing and modifying the ALA synthetase, an expression vector containing the ALA synthetase, host cells containing the ALA synthetase, and application of the ALA synthetase in ALA production.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
High-yield s-linalool genetic engineering strain and building method thereof
InactiveCN102071155AReduce feedback inhibitionEasy to buildFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousLinalool
The invention discloses a high-yield s-linalool genetic engineering strain and a building method, which belong to the field of genetic engineering. Through the metabolic engineering reformation, linalool synthetase from actinidiaarguta is expressed in saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK2-1 in a heterologous way, the terpene synthesis path-mevalonic acid (MVA) path carbon metabolizing flow is increased, and the high-yield s-linalool genetic engineering strain CEN. PK2 linalool is obtained. Compared with an initial strain CEN. PK2-1C, the modified genetic engineering strain CEN. PK2 linalool can metabolize and produce s-linalool, in addition, the feedback inhibition of the s-linalool is obviously reduced, the yield of the s-linalool can reach 12 mg / L, and the genetic engineering strain has good application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and method for producing L-threonine
ActiveCN113322218AThe effect of acid production is remarkableBacteriaTransferasesThreonineBacterosira
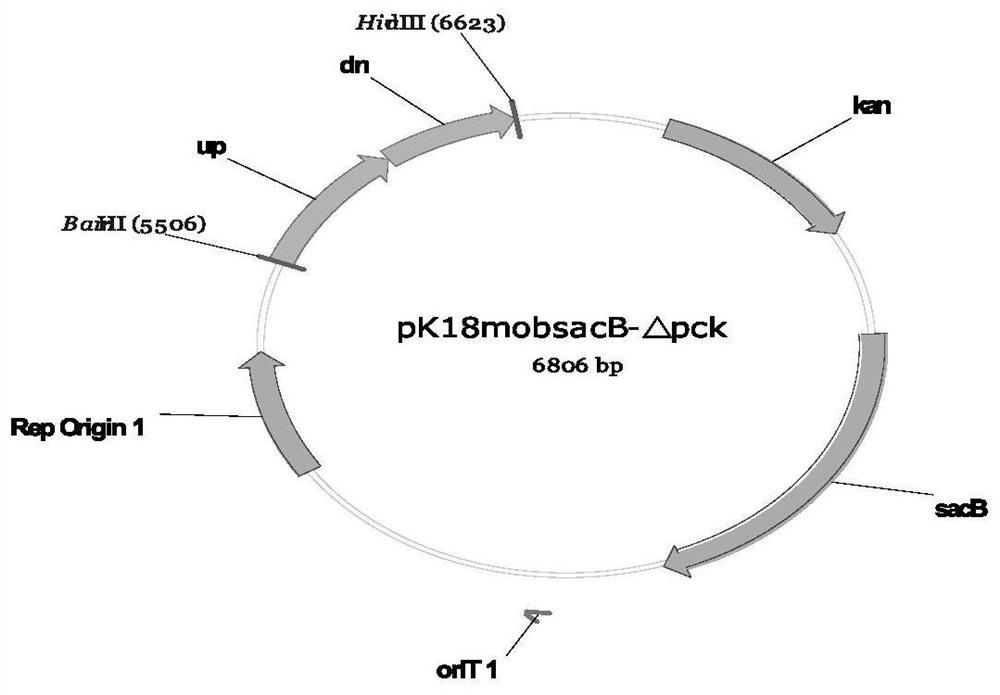
The invention relates to the technical field of bioengineering, in particular to recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and a method for producing L-threonine. The corynebacterium glutamicum for producing threonine is constructed by combining and transforming (or enhancing) a hom gene, a lysC gene, a thrC gene and the like which are resistant to feedback inhibition, and (or) a weakening (or knockout) pck gene and (or) a weakening (or knockout) pyk gene, and the acid production effect is very remarkable and far exceeds the highest level which is reported at present and reaches 20g / l.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Method for improving percent conversion of tylosin component A
ActiveCN102703549AImprove permeabilityFacilitated releaseMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicrobiologyMethyltransferase
The invention relates to a method for improving the percent conversion of a tylosin component A. With the method, streptomyces fradiae is used as a producing strain and is fermented to produce the tylosin by first-level seed tank fermentation culture, second-level seed tank fermentation culture and fermentation tank fermentation culture. The method is characterized in that nonionic surfactant of which the mass concentration is 0.5-2.5% is added into a fermentation culture medium after the fermentation tank fermentation culture enters a stable period after a logarithmic growth phase is finished. The nonionic surfactant is added into the culture medium during a fermentation culture period to the stable period so as to enhance the permeability of a mycelium cell, so that a metabolin in a cell is accelerated to quickly release out of the cell to relieve the feedback inhibition of macrosin methyltransferase and improve the enzyme activity, and finally, a tylosin component C is accelerated to quickly covert into the tylosin component A. The tylosin component A in the current industrial production generally accounts for 80-85%, and the content of the tylosin component A can finally achieve 90-94% according to the method disclosed by the invention.
Owner:宁夏泰瑞制药股份有限公司
High density fermentation medium for feeding lactobacillus, and corresponding fermentation method
ActiveCN102226156AReduce concentrationRelease feedback inhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLactobacillus salivariusVolumetric Mass Density
The invention belongs to the technical field of lactobacillus cultivation, and relates to a high density fermentation medium for feeding lactobacillus, and a corresponding fermentation method. According to the present invention, a strategy of employing pH feedback to control glucose feeding is adopted, and the density of lactic acid in fermentation broth is reduced, such that feedback inhibition effect of lactic acid is released. With the fermentation medium and the fermentation method provided by the present invention, thalline density of cultivated saliva lactobacillus is substantially improved comparing to that obtained with common fermentation method, live bacteria content is no less than 10<10>cfu / ml, which is increased by 50 times or more than the content of live bacteria cultivatedwith a common MRS medium, such that high density fermentation of saliva lactobacillus is realized. Therefore, separating cost of biomass can be reduced, production period can be shortened, productioncost can be reduced, and production efficiency can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG TECH GRP CO LTD +1
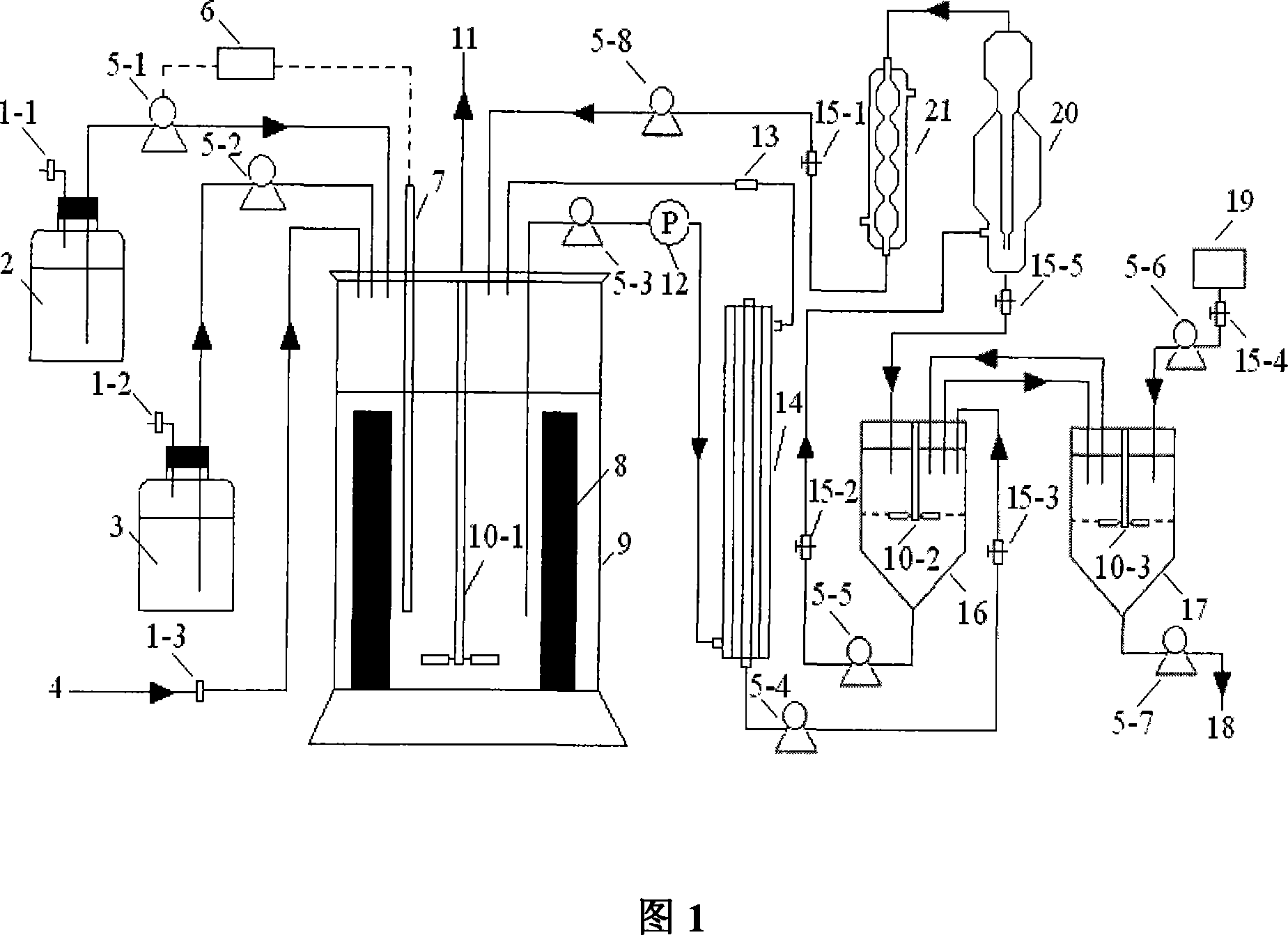
Device and technique for producing propanoic acid by coupling of fibrous bed bioreactor with extraction separation
InactiveCN101182455AEfficient fermentationImprove adsorption capacityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh densityPropanoic acid
The invention discloses a fibrous bed reactor and the equipment and process for extracting separation and coupling production of propionic acid. The invention utilizes an immobilized fibrous bed reactor unit, a membrane separation unit, an extraction and anti-extraction unit and an elution and condensation unit to realize the efficient production of propionic acid. The device has strong feasibility, simple operation, easy realization of automation, immobilized materials, long using life of the membrane and the matching equipment, convenient maintenance and good application prospect. Through extracting separation and coupling production technology, the separation of propionic acid is realized. The invention radically eliminates the feedback inhibition of propionic acid, implements the high density fermentation of propionibacterium and greatly improves the production efficiency of propionic acid through the fermentation method. The extracted water phase is returned to the reactor for recycle after elution and condensation by an elution device, which eliminates the harm of extractant for propionibacterium from the root.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
In-vitro directed coevolution method for modifying L-phenylalanine gene engineering strains
InactiveCN101698853ASpeed up evolutionHigh catalytic activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhenylalanineMetabolic balance
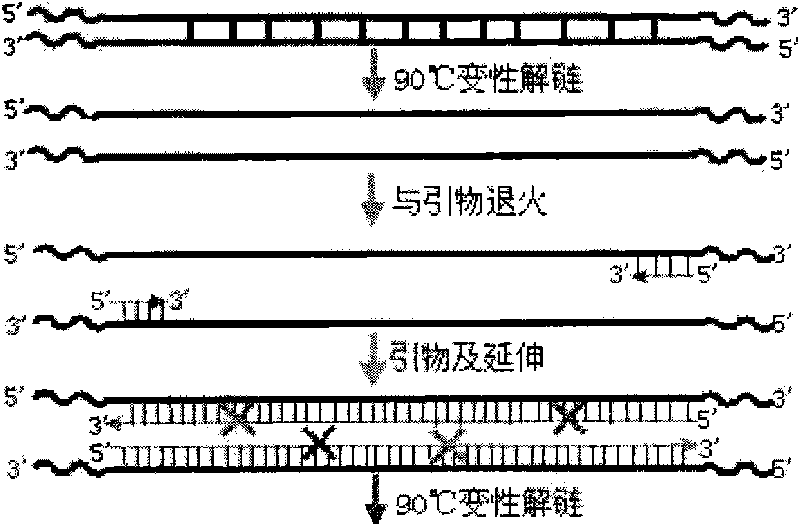
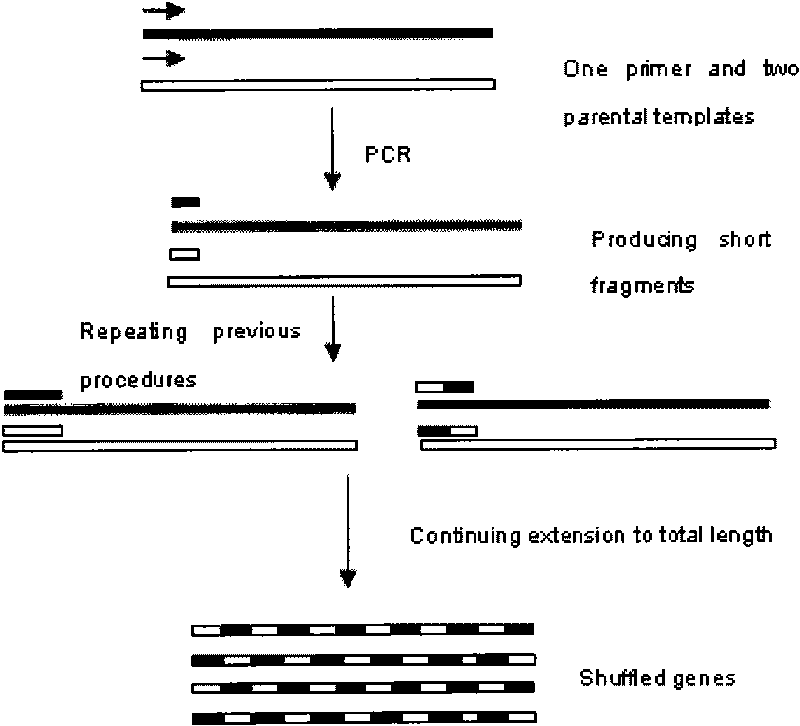
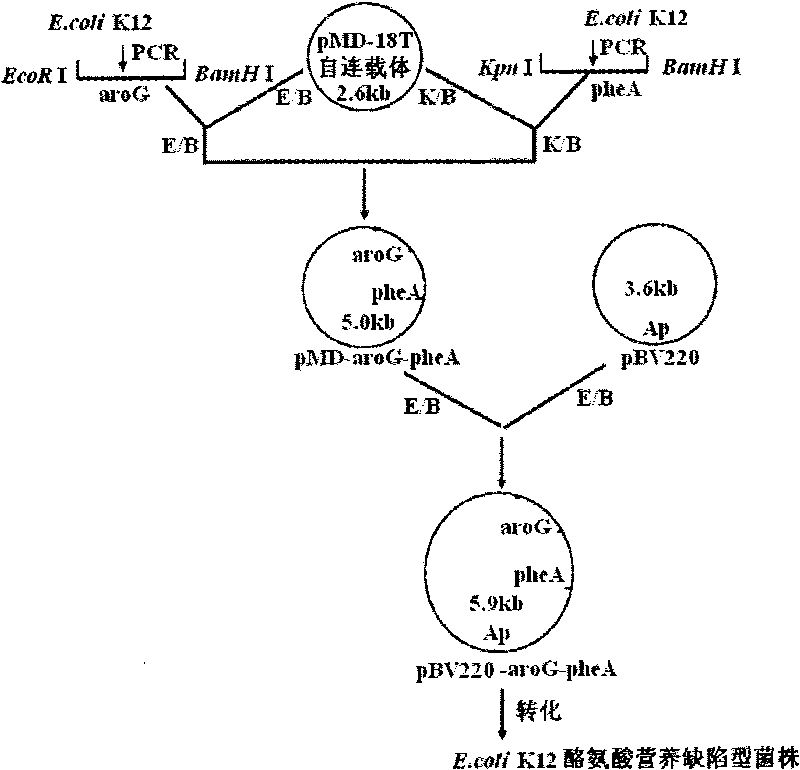
The invention relates to an in-vitro directed coevolution method for modifying L-phenylalanine gene engineering strains, which is realized in a way that: using genes aroG and pheA on an L-phenylalanine gene engineering strain constructed in the room as a whole; carrying out the in-vitro directed coevolution modification by using an error-prone PCR technology and a recombinant DNA technology; and screening to obtain a mutant strain, of which the yield of L-phenylalanine is increased by 114%. In the invention, by modifying the gene formed by coupling and connecting aroG and pheA in series, the key genes aroG and pheA in the metaboly process of the L-phenylalanine are used as a whole to carry out the directed modification, thereby obtaining a new metabolic balance, so that the expressed enzyme has high-efficiency catalytic activity and can resist the feedback inhibition of the L-phenylalanine, thereby obtaining the new modified high-yield L-phenylalanine gene engineering strain by screening. The method can provide an example for modifying the acid production rate of any amino acid gene engineering strain.
Owner:MAIDAN BIOLOGICAL GROUP FUJIAN
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com