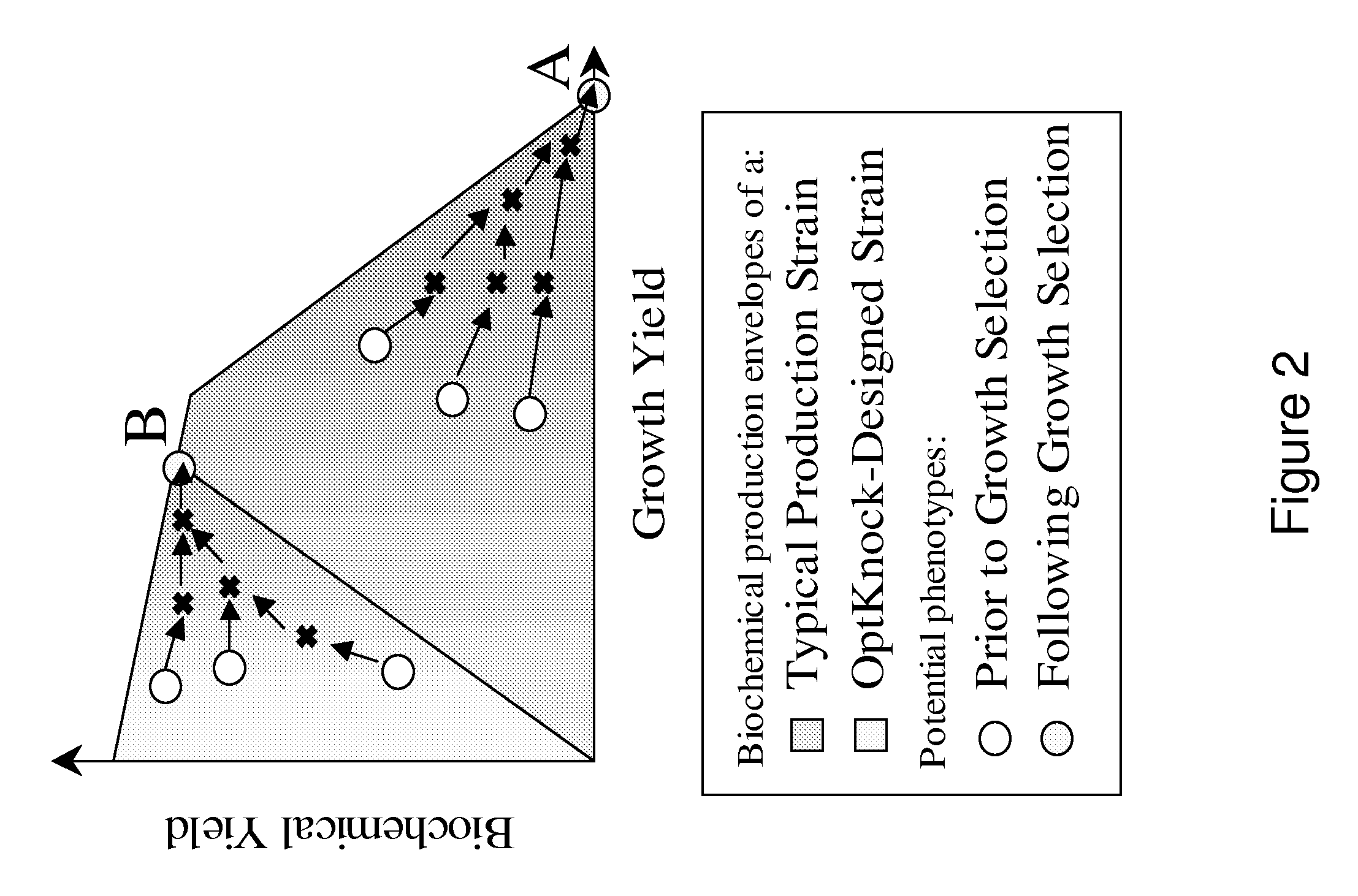
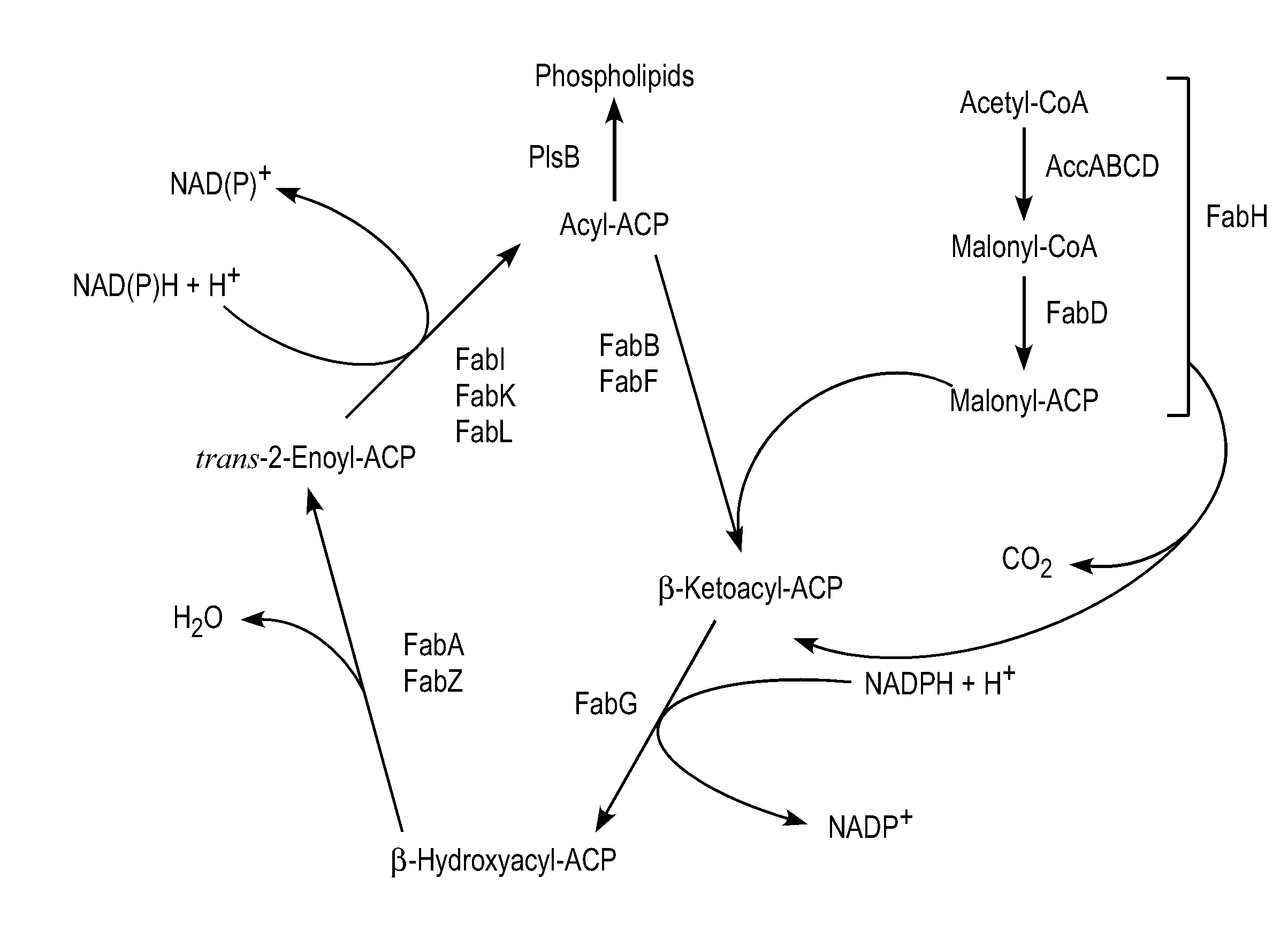
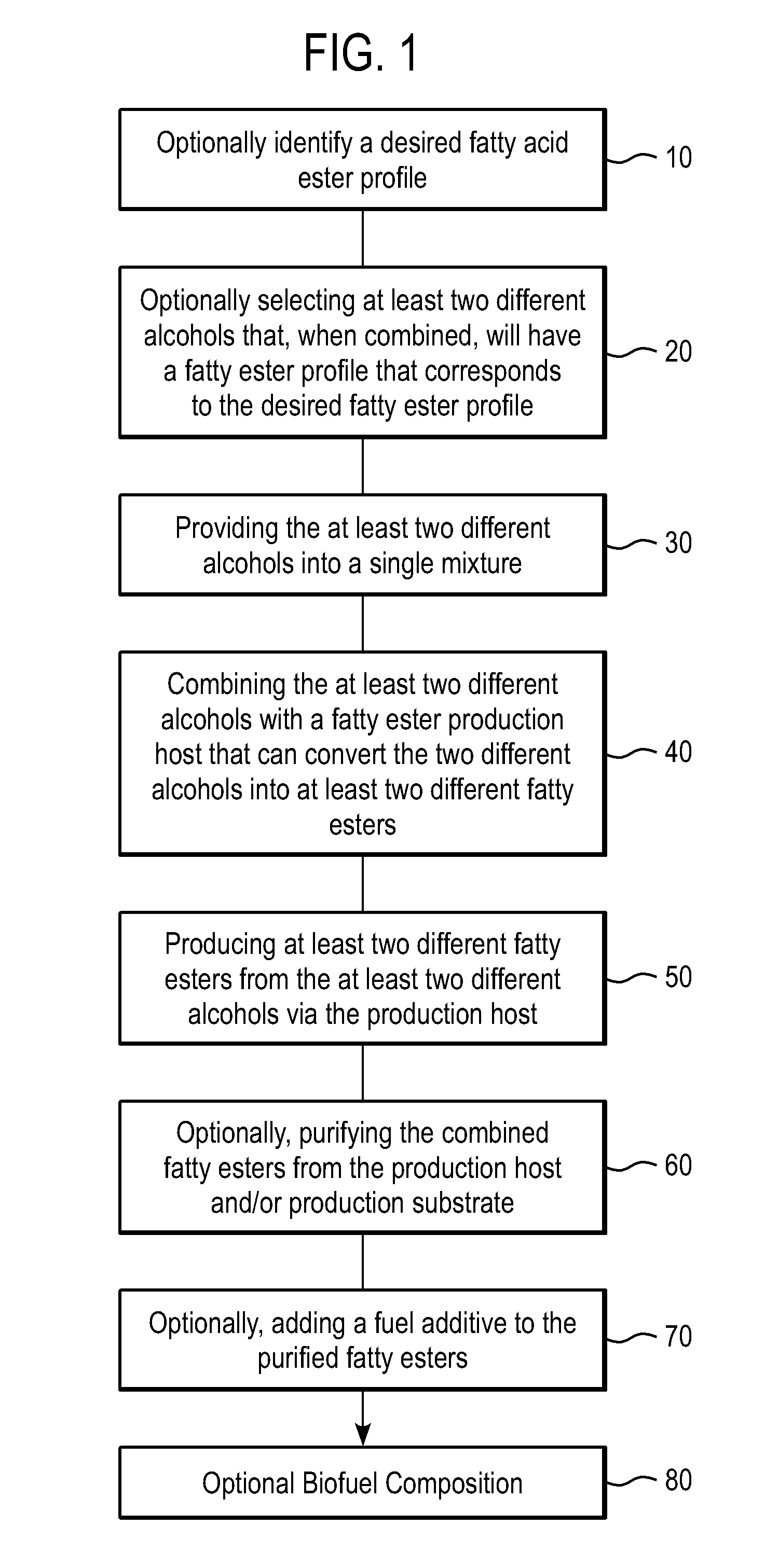
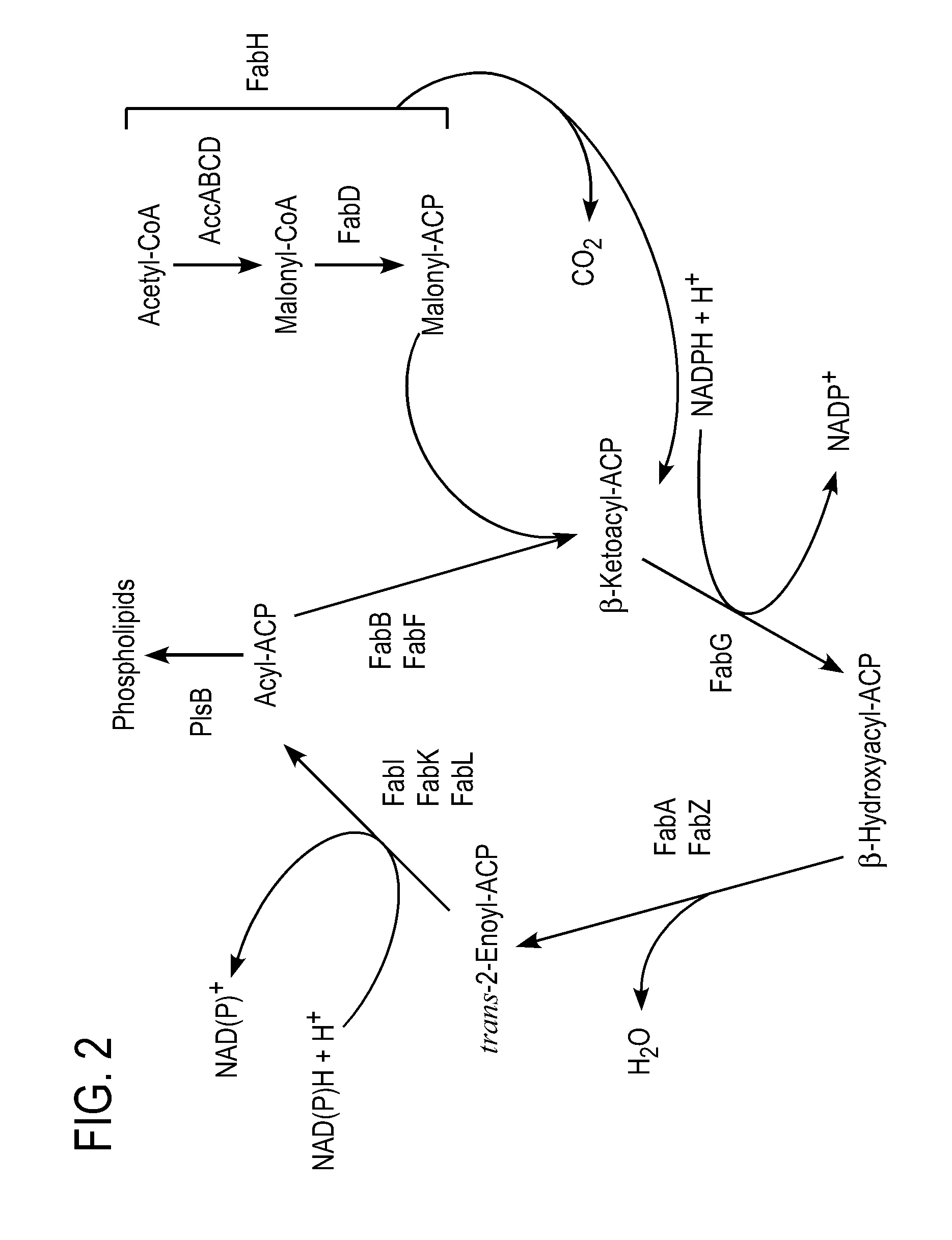
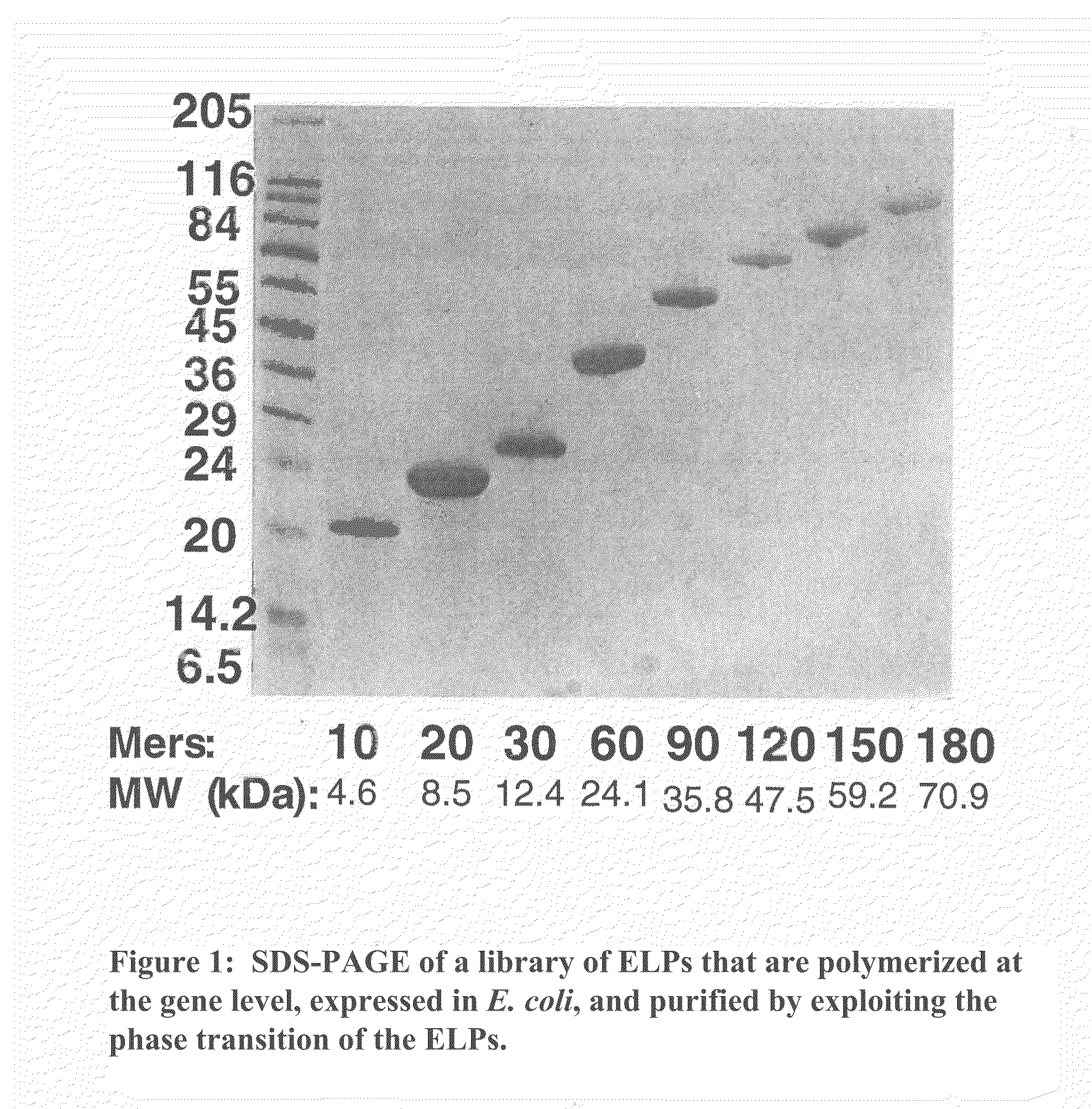
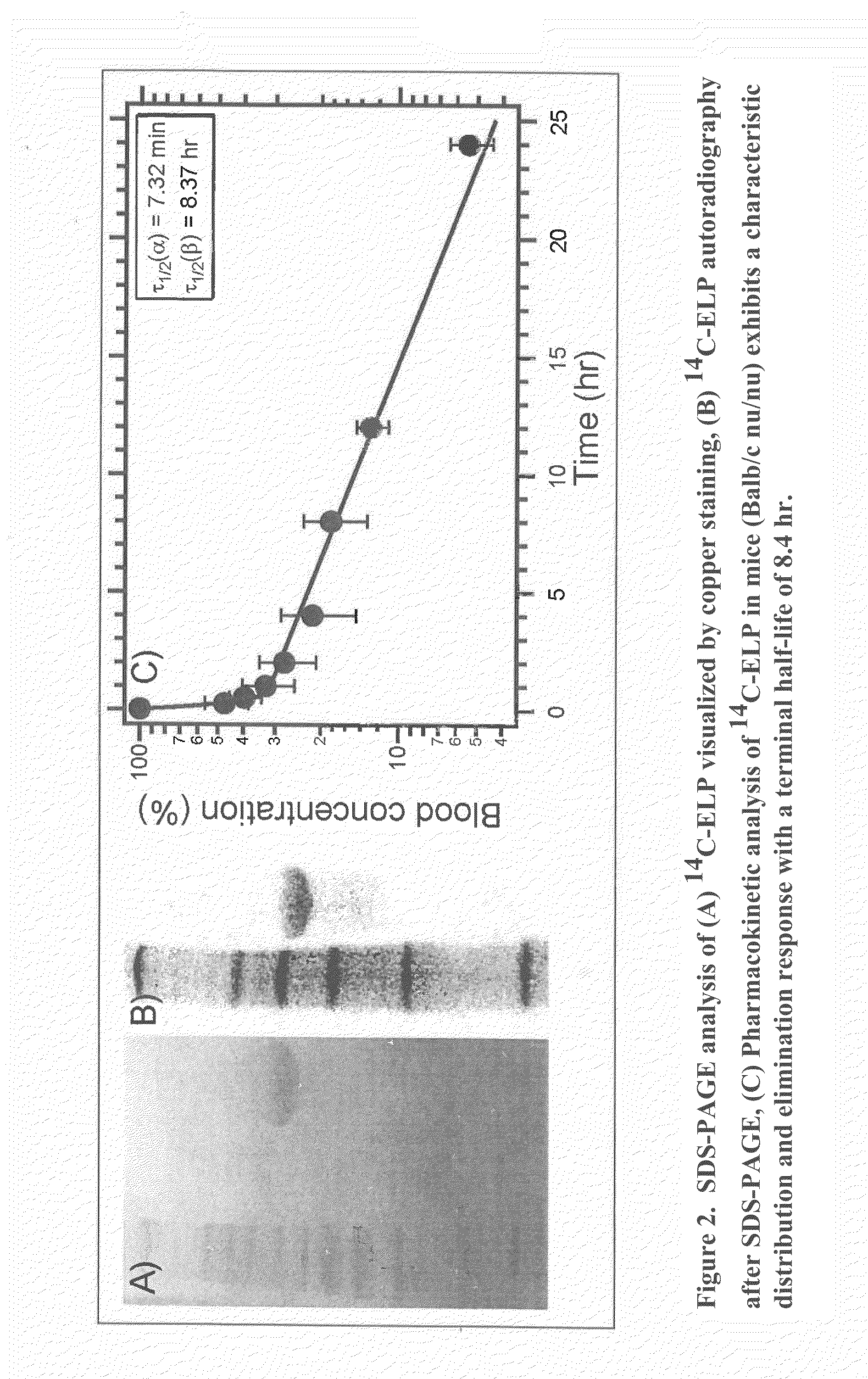
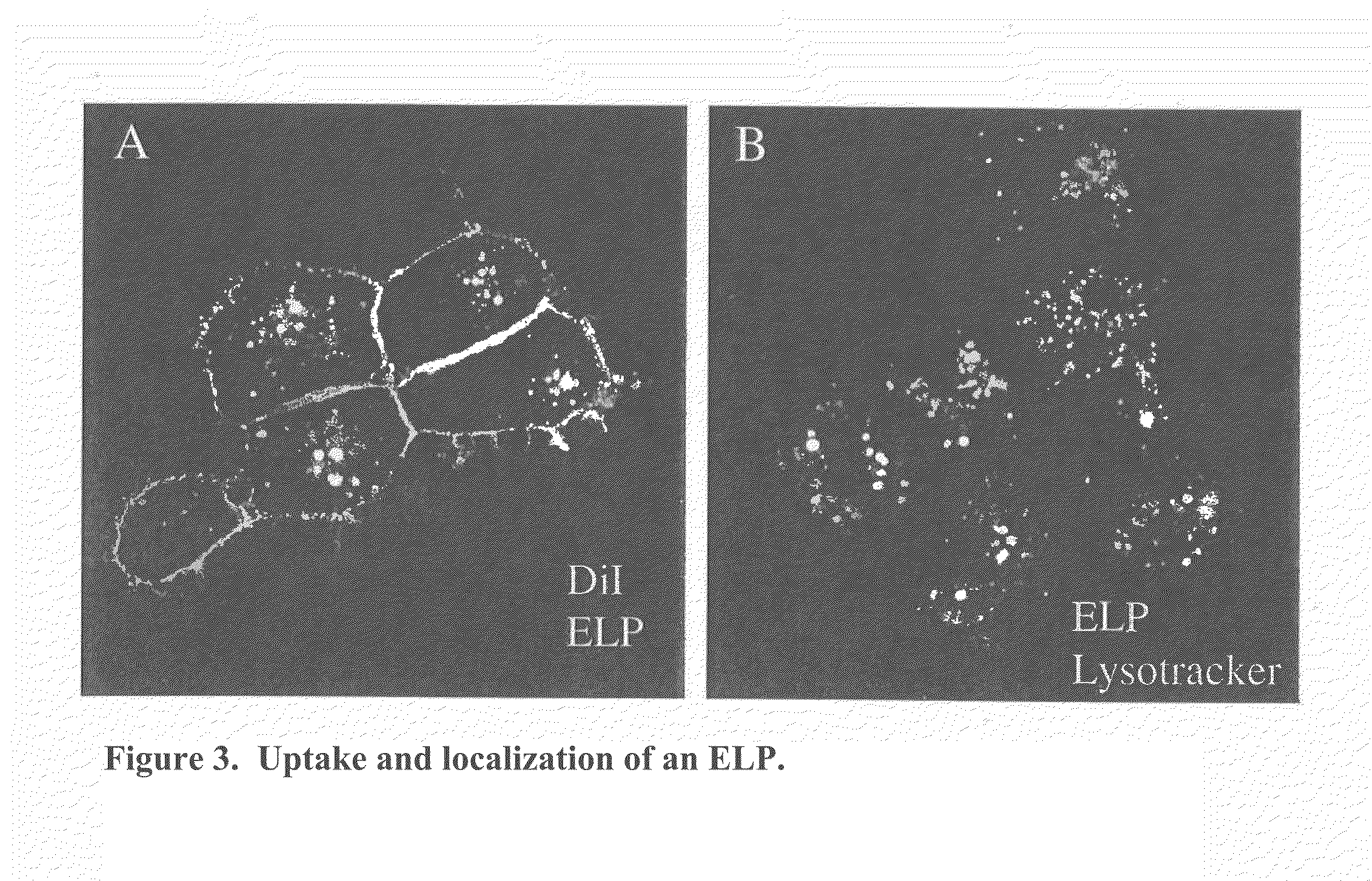
Patents
Literature
1697results about "Acyltransferases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fermentive production of four carbon alcohols
Owner:GEVO INC
Gene products of bacillus licheniformis which form odorous substances and improved biotechnological production methods based thereon
InactiveUS20070190605A1Reduce formationImprove filtering effectBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisPropanoic acid
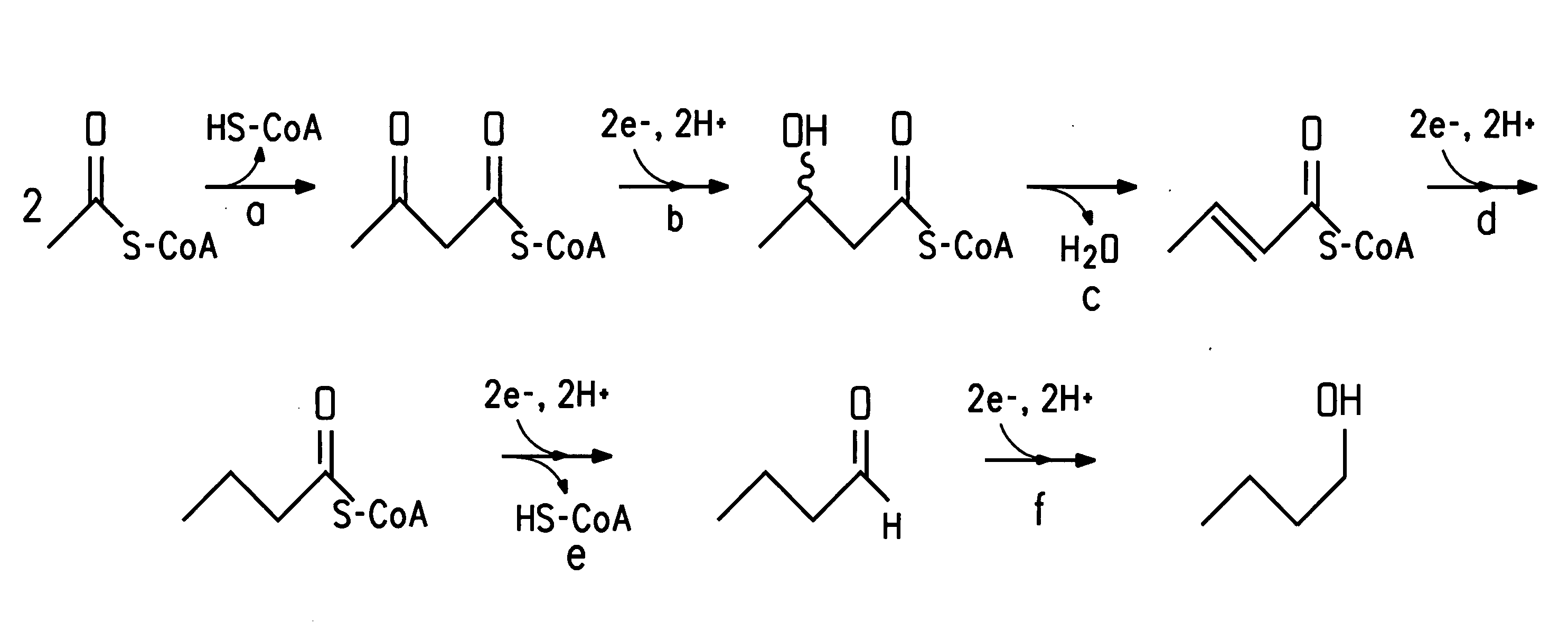
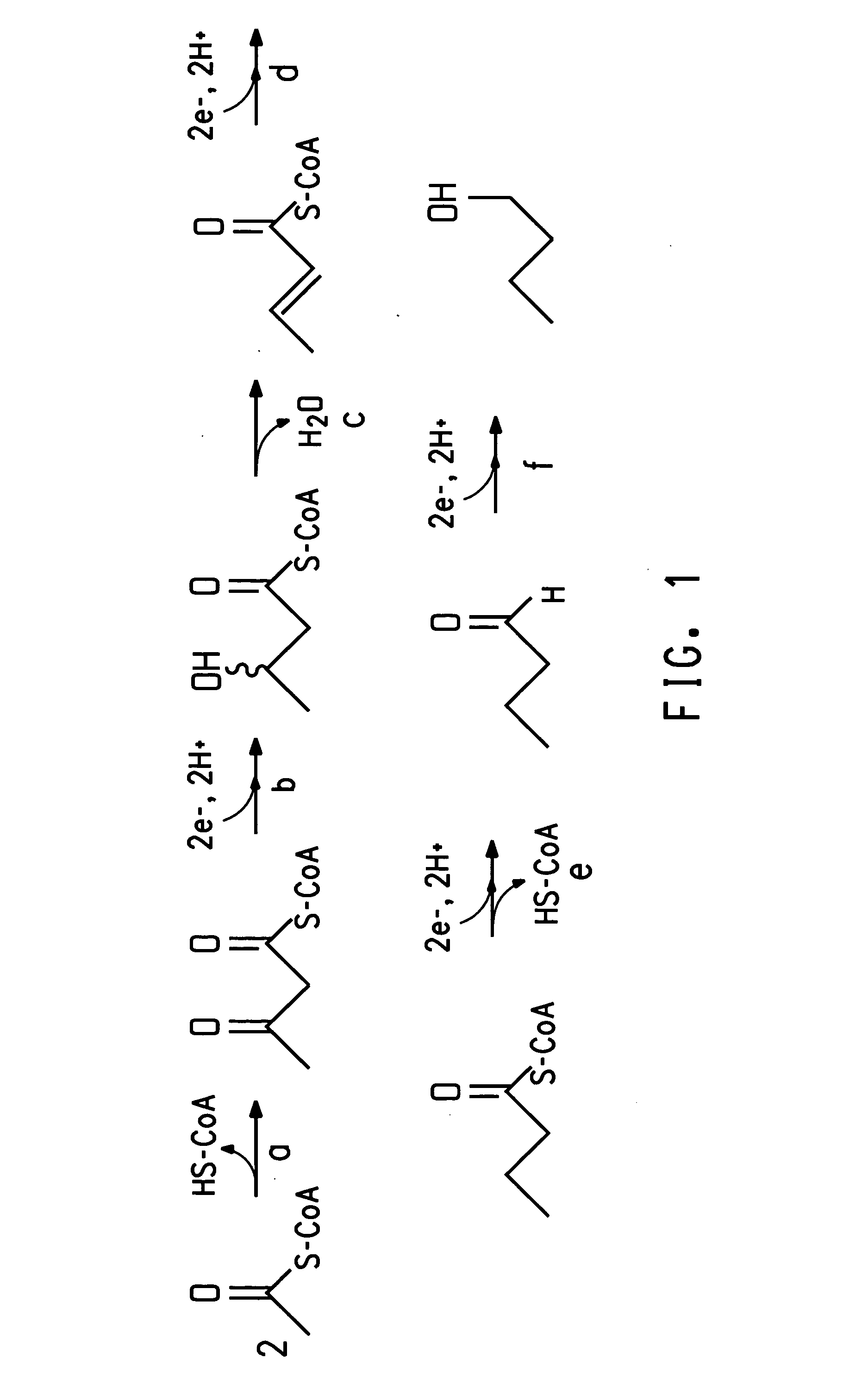
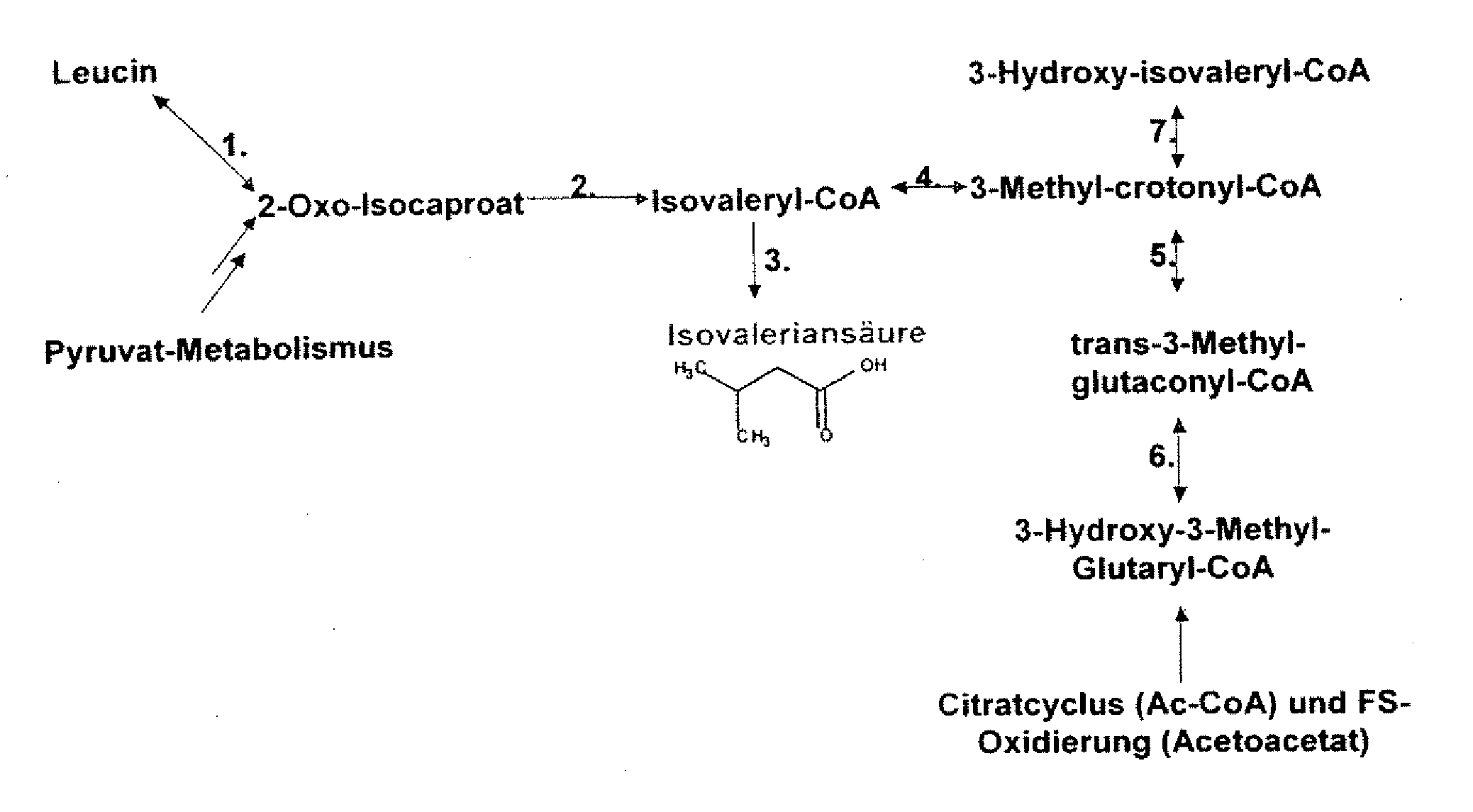
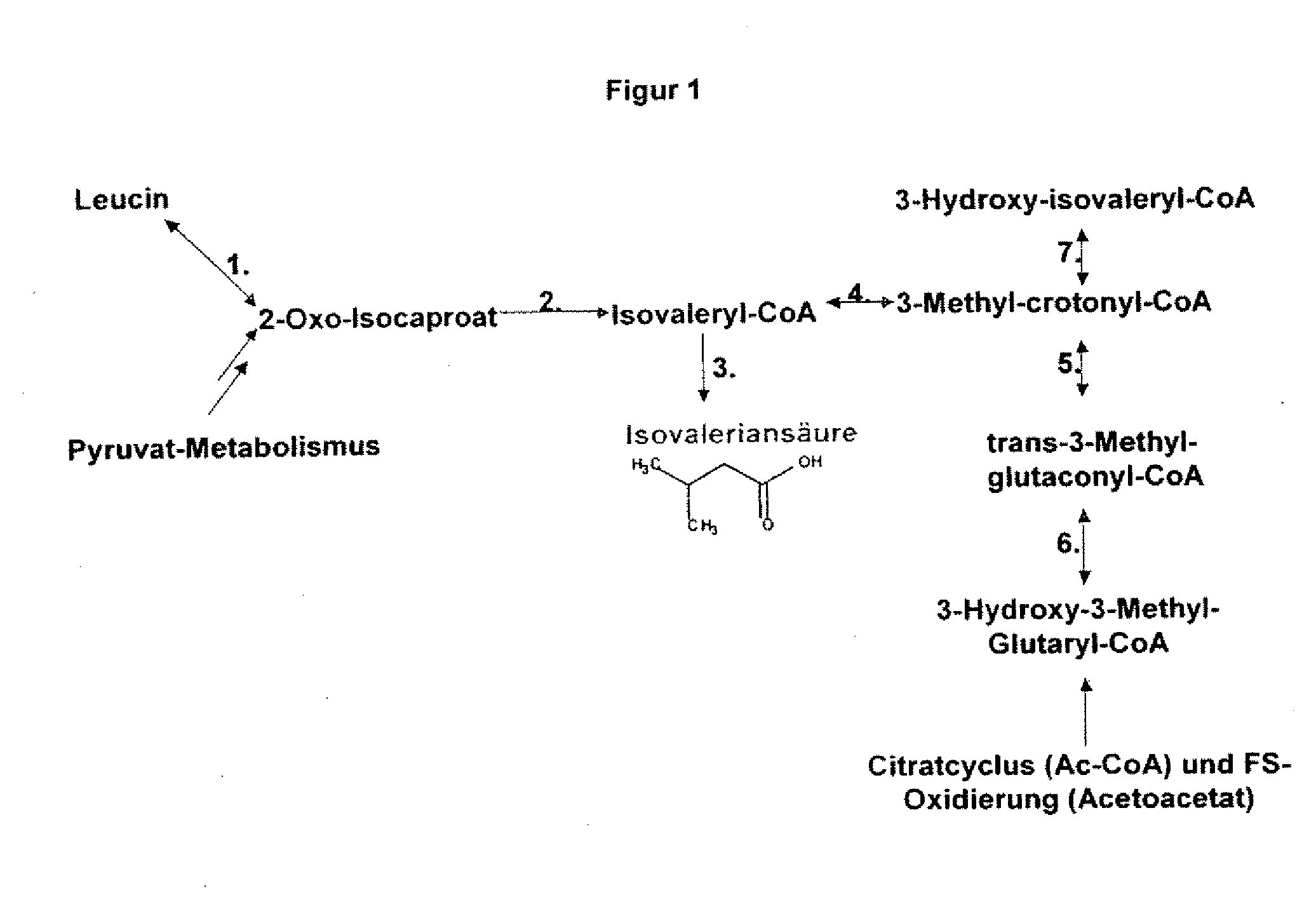
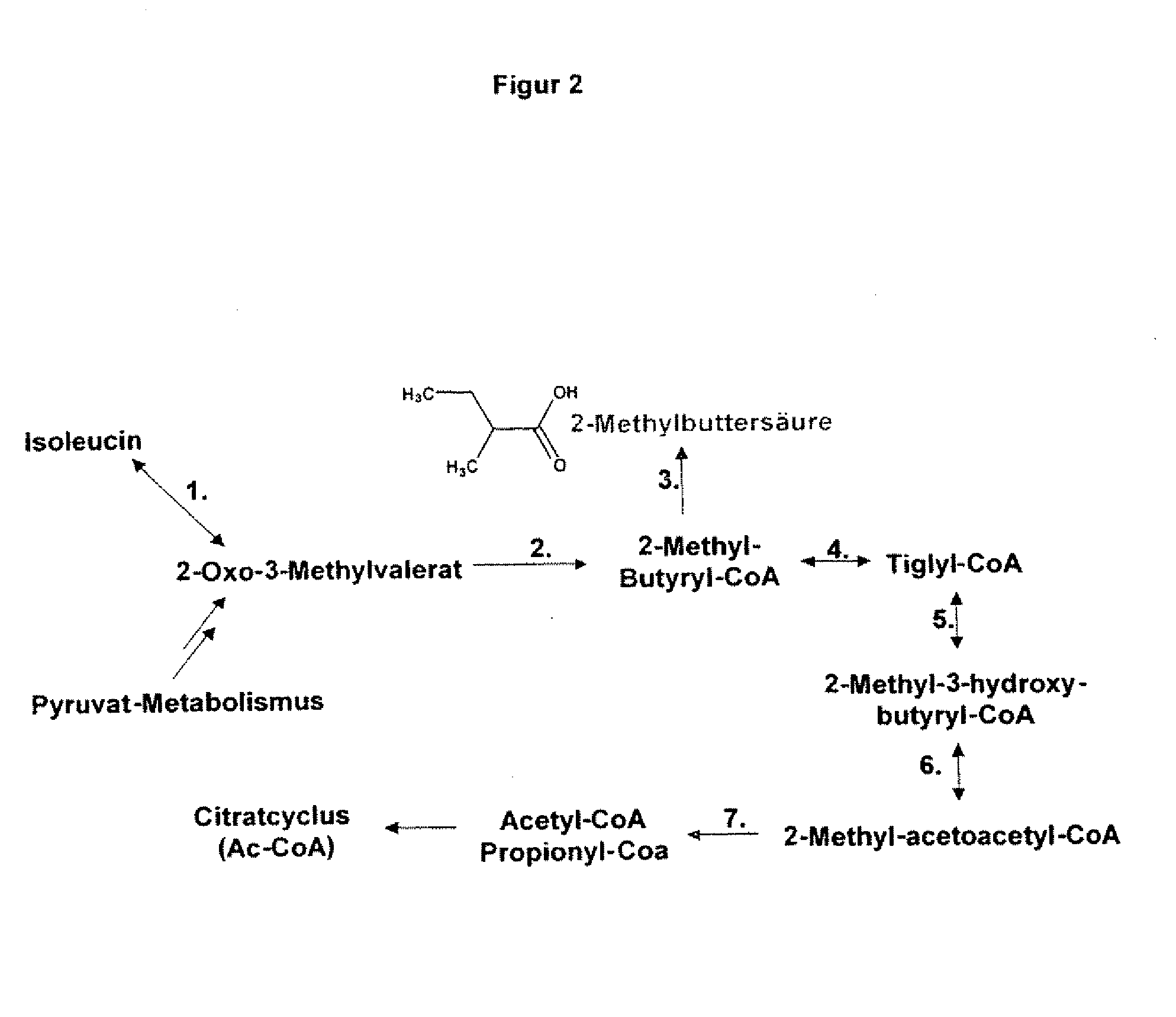
The present invention relates to 25 hitherto undescribed genes of B. licheniformis and gene products derived therefrom and all sufficiently homologous nucleic acids and proteins thereof. They occur in five different metabolic pathways for the formation of odorous substances. The metabolic pathways in question are for the synthesis of: 1) isovalerian acid (as part of the catabolism of leucine), 2) 2-methylbutyric acid and / or isobutyric acid (as part of the catabolism of valine and / or isoleucine), 3) butanol and / or butyric acid (as part of the metabolism of butyric acid), 4) propyl acid (as part of the metabolism of propionate) and / or 5) cadaverine and / or putrescine (as parts of the catabolism of lysine and / or arginine). The identification of these genes allows biotechnological production methods to be developed that are improved to the extent that, to assist these nucleic acids, the formation of the odorous substances synthesized via these metabolic pathways can be reduced by deactivating the corresponding genes in the micro-organism used for the biotechnological production. In addition, these gene products are thus available for preparing reactions or for methods according to their respective biochemical properties.
Owner:BASF AG
Methods for the improvement of product yield and production in a microorganism through the addition of alternate electron acceptors
ActiveUS8956851B2Reduce formationSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationBiotechnologyHeterologous
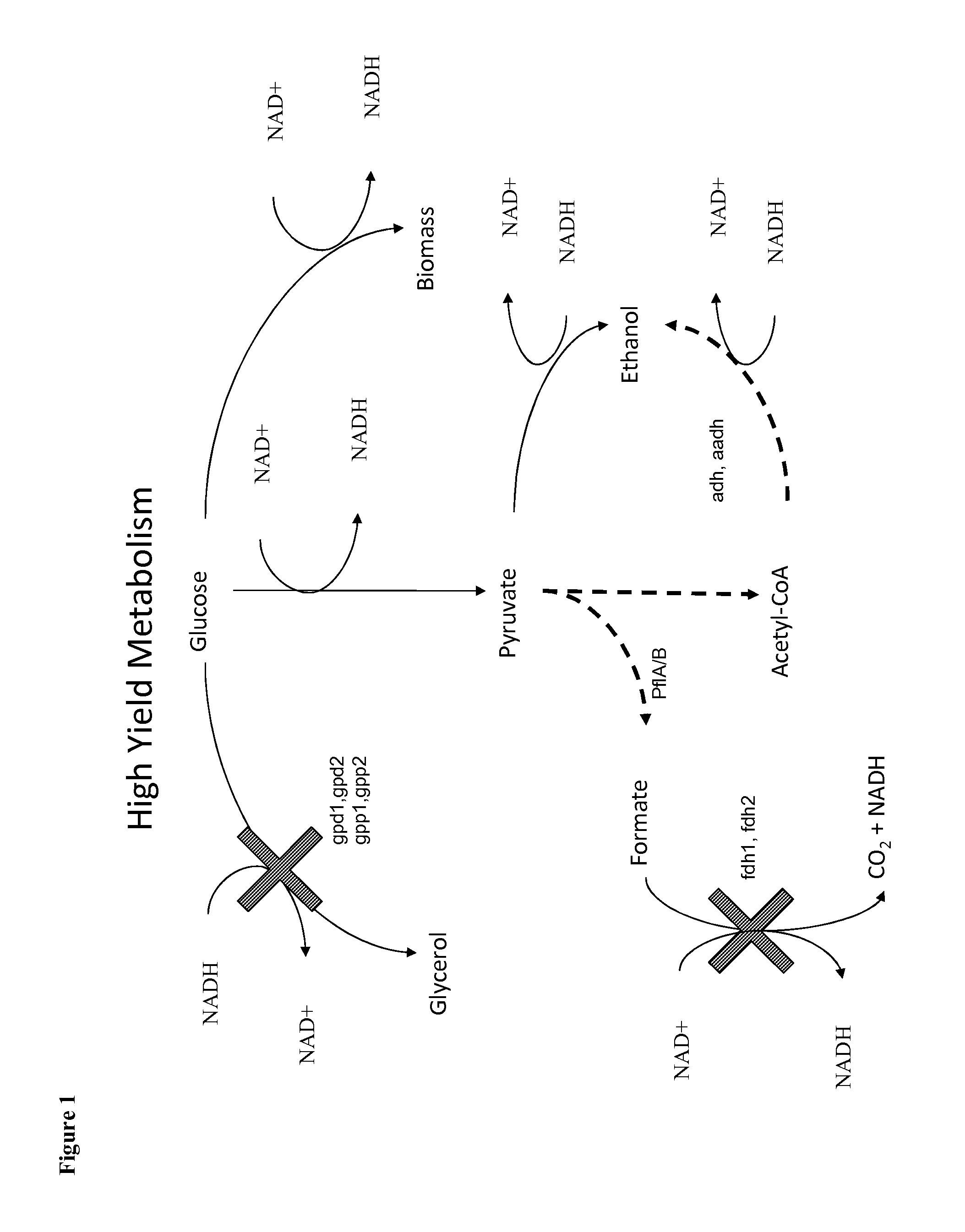
The present invention provides for novel metabolic pathways to reduce or eliminate glycerol production and increase product formation. More specifically, the invention provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising a deletion of one or more native enzymes that function to produce glycerol and / or regulate glycerol synthesis and one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more engineered metabolic pathways to convert a carbohydrate source, such as lignocellulose, to a product, such as ethanol, wherein the one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated, or downregulated. The invention also provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising one or more heterologous enzymes that function to regulate glycerol synthesis and one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more engineered metabolic pathways to convert a carbohydrate source to ethanol, wherein said one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated or downregulated.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
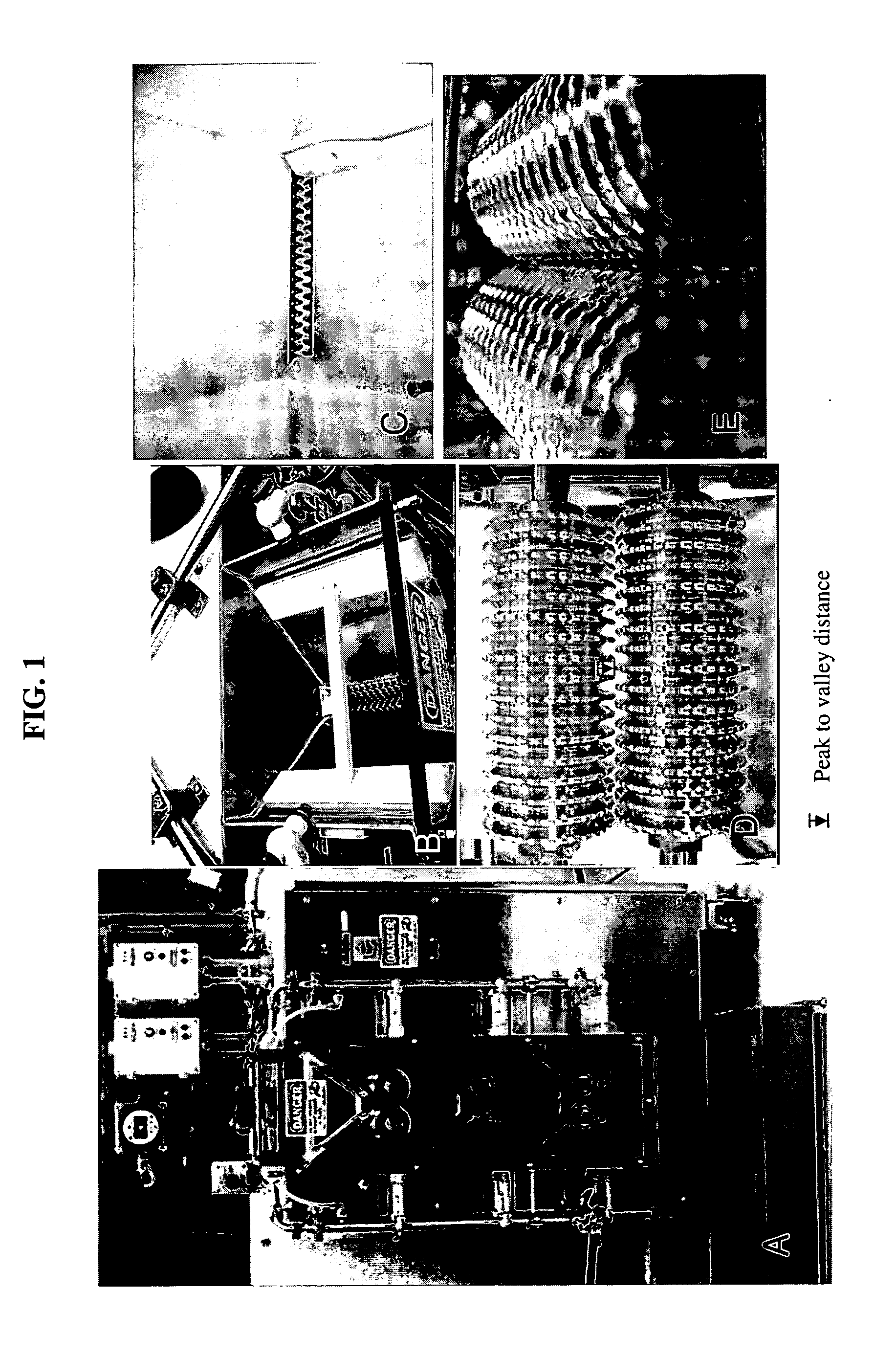
Preparation and use of plant embryo explants for transformation
ActiveUS20080280361A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEmbryoBiology
The present invention relates to excision of explant material comprising meristematic tissue from seeds, and storage of such material prior to subsequent use in plant tissue culture and genetic transformation. Methods for tissue preparation, storage, and transformation are disclosed, as is transformable meristem tissue produced by such methods, and apparati for tissue preparation.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
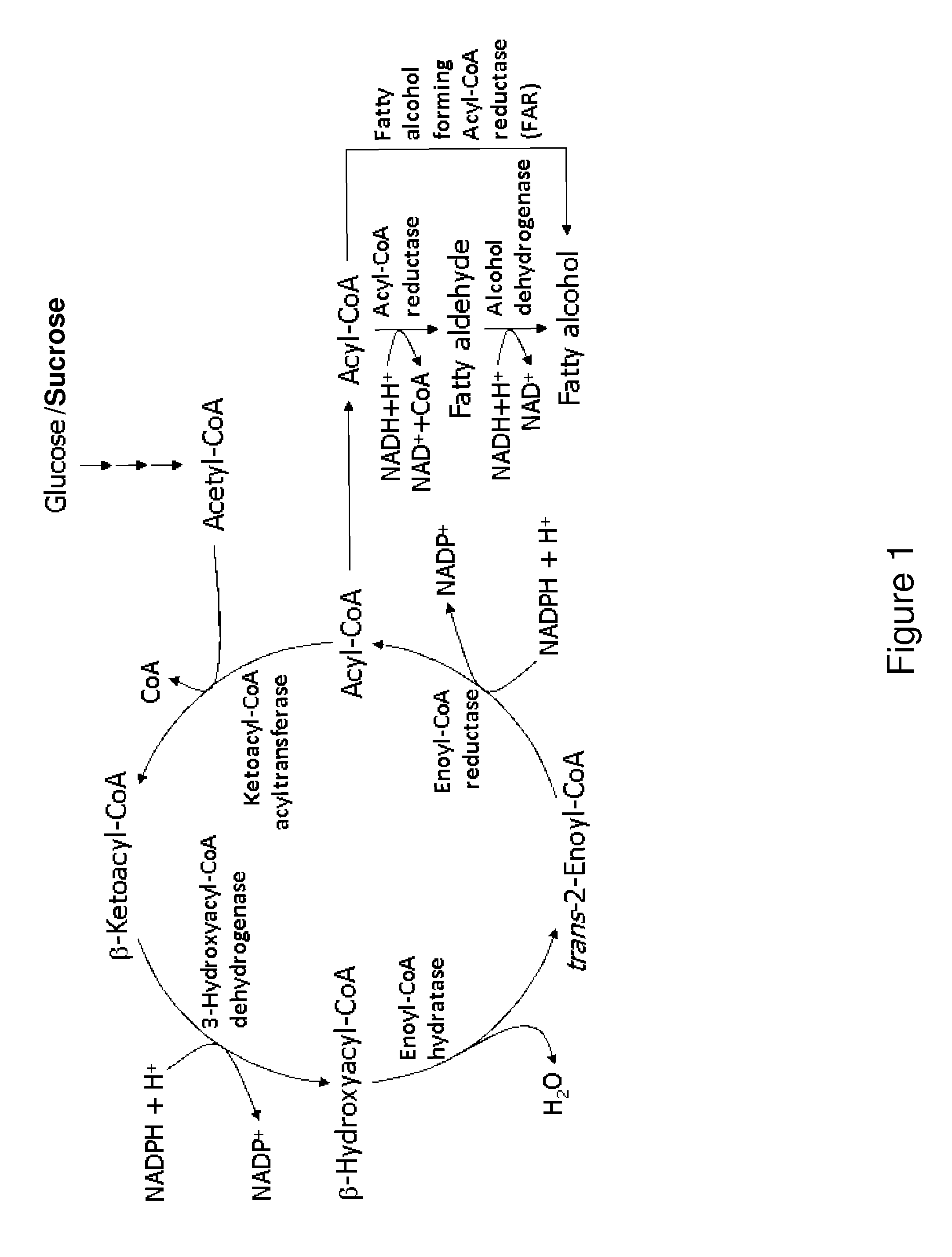
Primary alcohol producing organisms
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having a microbial organism having at least one exogenous gene insertion and / or one or more gene disruptions that confer production of primary alcohols. A method for producing long chain alcohols includes culturing these non-naturally occurring microbial organisms.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Systems and methods for production of mixed fatty esters
InactiveUS20100071259A1Reduce the amount requiredBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlcoholChemistry
Disclosed herein are various embodiments regarding the production of mixed fatty esters. Disclosed herein are various embodiments regarding the use of mixed alcohol compositions for the production of fatty esters.
Owner:LS9 INC +1
Methods and compositions for delivering active agents with enhanced pharmacological properties
InactiveUS20130172274A1Good curative effectImprove efficacyOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsActive agentIn vivo
Provided herein are methods of enhancing in vivo efficacy of an active agent, comprising: administering to a subject an active agent that is coupled to a bioelastic polymer or elastin-like peptide, wherein the in vivo efficacy of the active agent is enhanced as compared to the same active agent when administered to the subject not coupled to (or not associated with) a bioelastic polymer or ELP.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Production of fatty acid derivatives
InactiveUS20110162259A1Low amountClean emission profilesOrganic chemistryBacteriaFatty acid derivatives
Methods and compositions for producing fatty acid derivatives, for example, fatty esters, and commercial fuel compositions comprising fatty acid derivatives are described.
Owner:LS9 INC +1
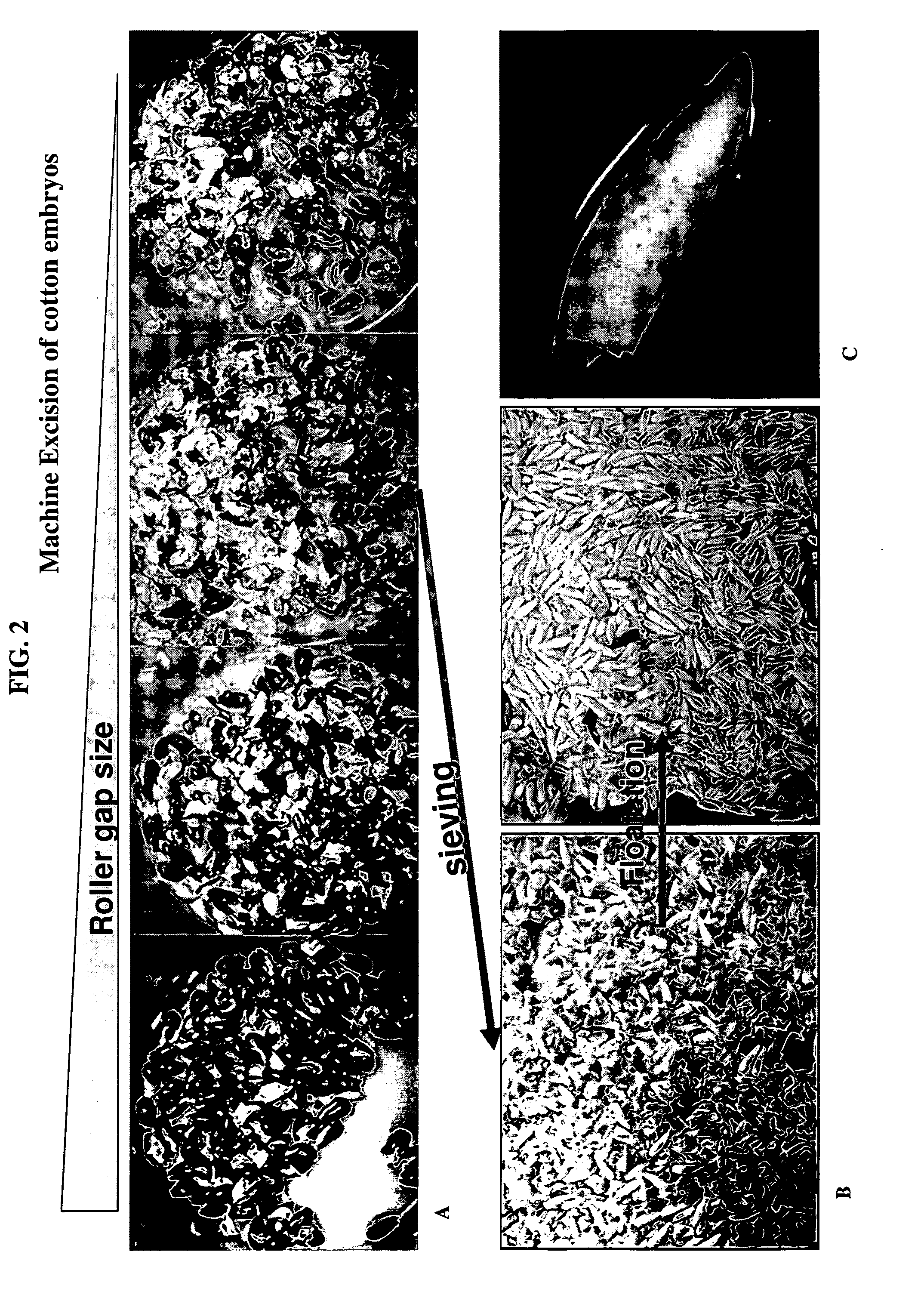
Method of meristem excision and transformation
ActiveUS20080256667A1Enrich the fraction of explants amenable to transformationMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesBiologyTissue Preparation
The present invention relates to excision of explant material comprising meristematic tissue from cotton seeds. Methods for tissue preparation, storage, transformation, and selection or identification of transformed plants are disclosed, as are transformable meristem tissues and plants produced by such methods, and apparati for tissue preparation.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods and compositions for consumables
ActiveUS9011949B2Increase aromaAdd flavorMilk preparationAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyConsumables
Owner:IMPOSSIBLE FOODS
Thermophilic Organisms For Conversion Of Lignocellulosic Biomass To Ethanol
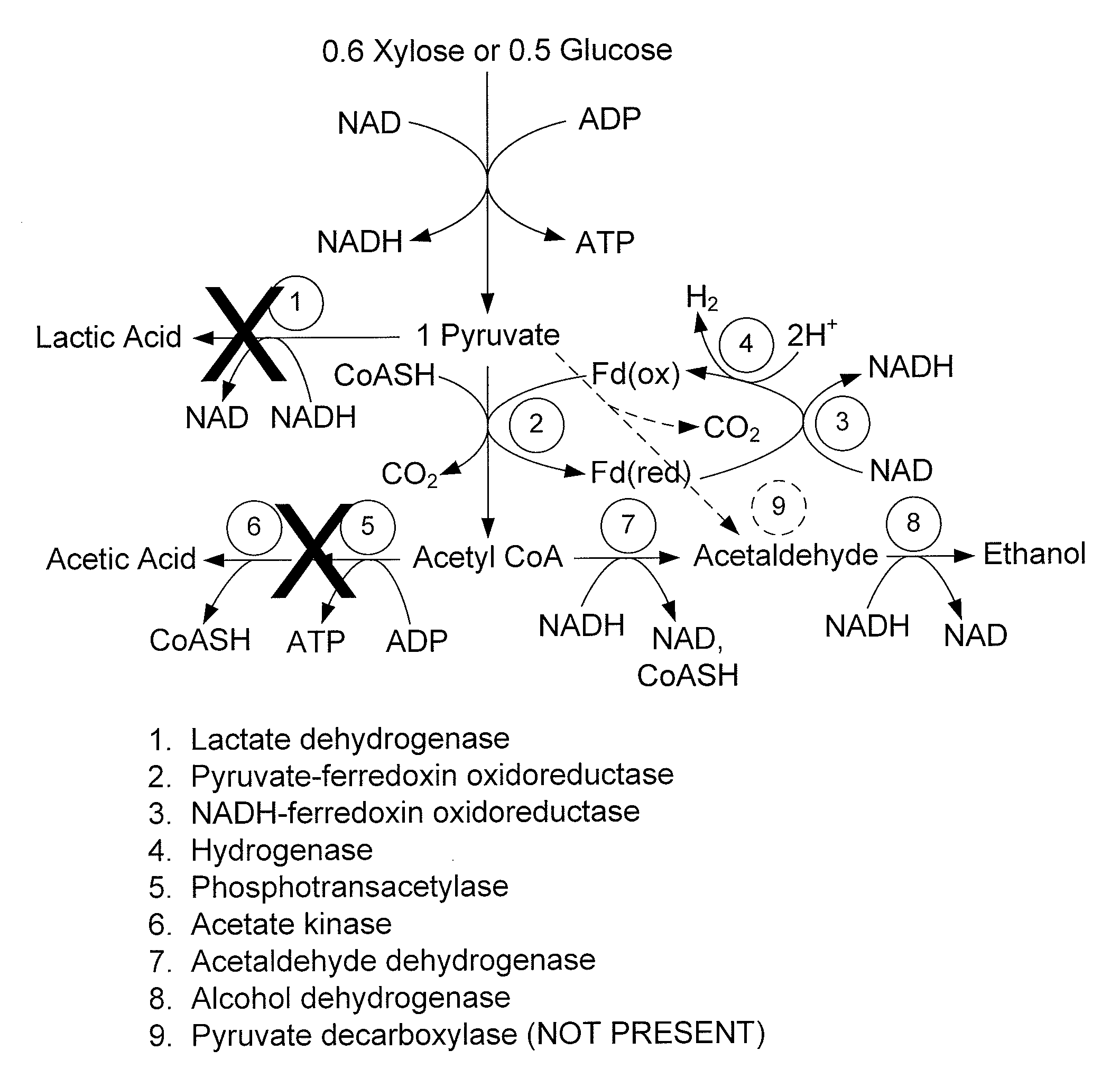
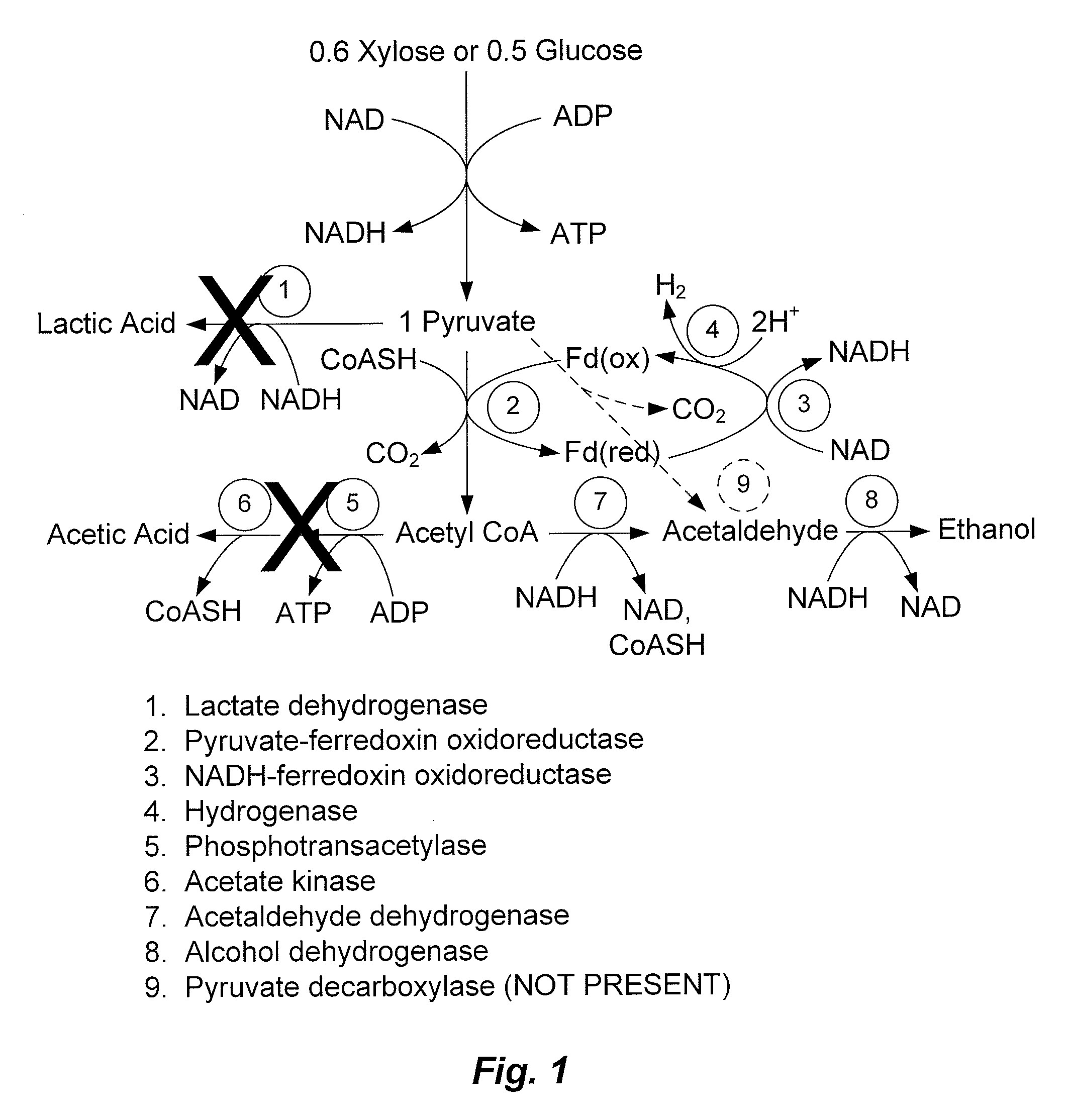
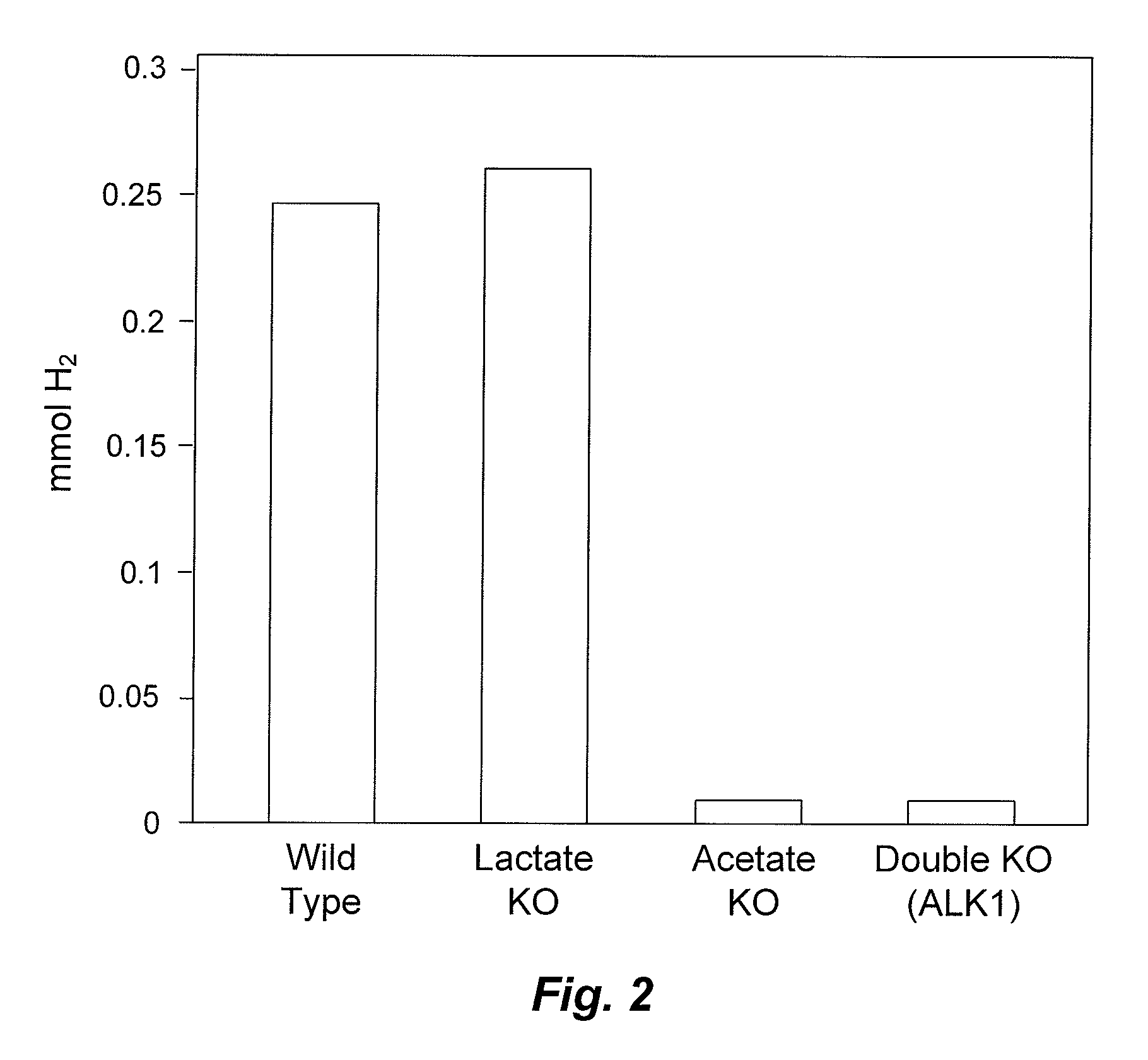
Mutant thermophilic organisms that consume a variety of biomass derived substrates are disclosed herein. Strains of Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum with acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase expression eliminated are disclosed herein. Further, strain ALK1 has been engineered by site directed homologous recombination to knockout both acetic acid and lactic acid production. Continuous culture involving a substrate concentration challenge lead to evolution of ALK1, and formation of a more robust strain designated ALK2. The organisms may be utilized for example in thermophilic SSF and SSCF reactions performed at temperatures that are optimal for cellulase activity to produce near theoretical ethanol yields without expressing pyruvate decarboxylase.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Novel Selectable Marker Genes
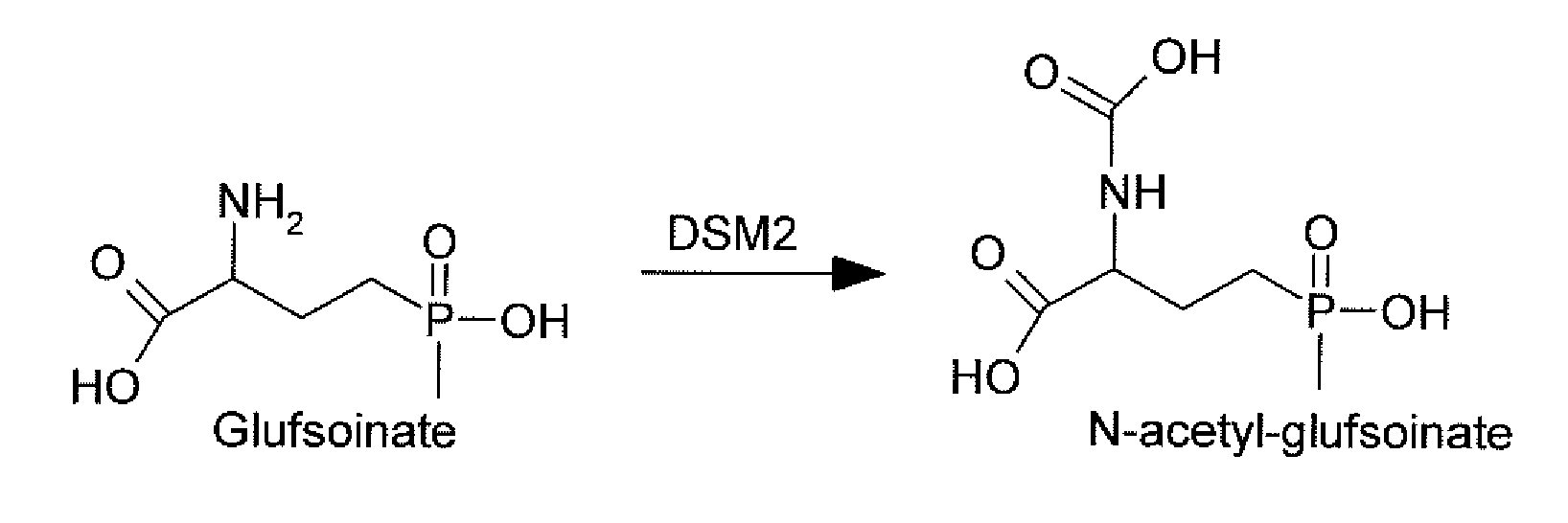
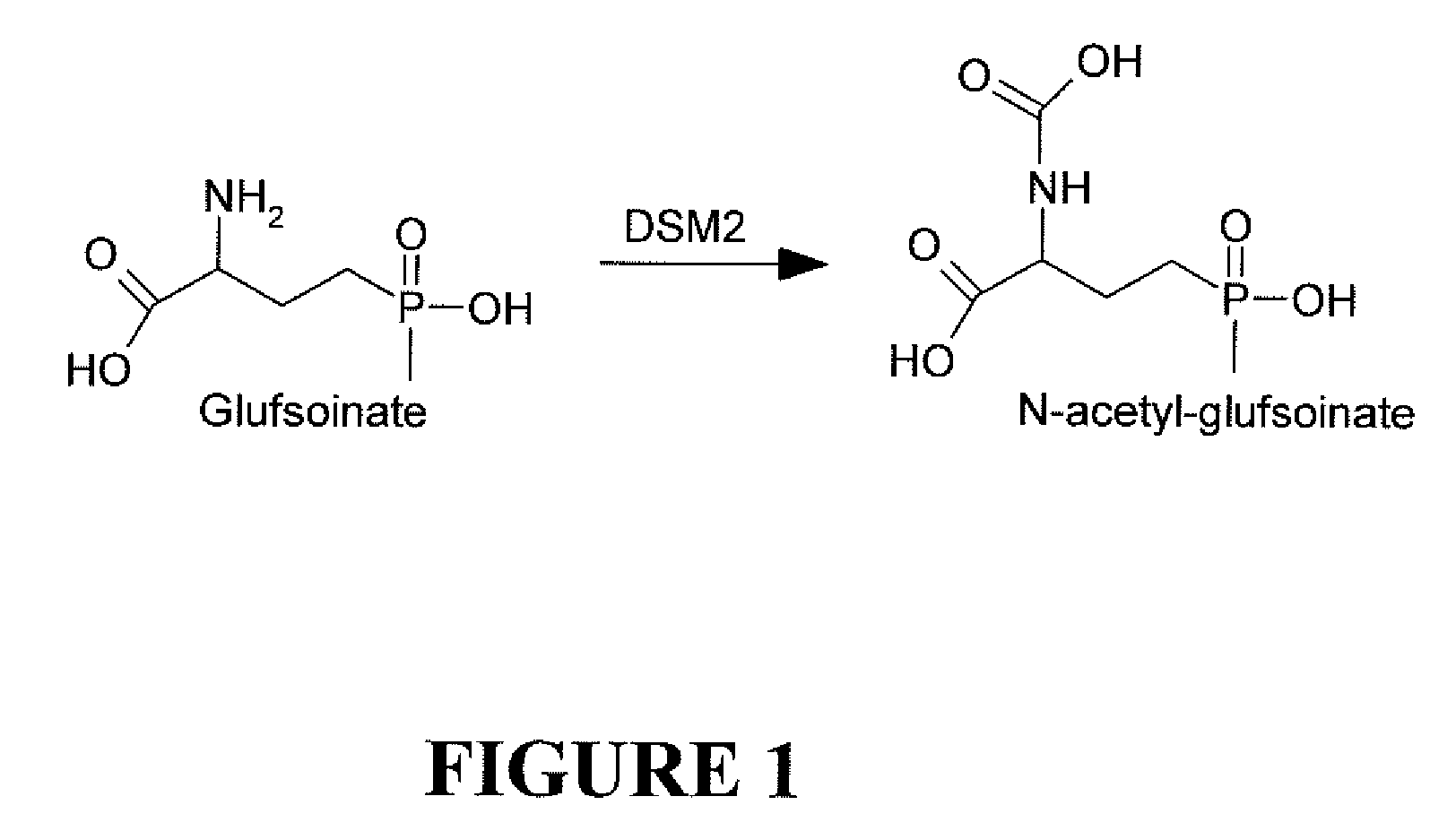
The subject invention relates to a novel gene referred to herein as DSM-2. This gene was identified in Sterptomyces coelicolor A3. The DSM-2 protein is distantly related to PAT and BAR. The subject invention also provides plant-optimized genes encoding DSM-2 proteins, DSM-2 can be used as a transgenic trait to impart tolerance in plants and plant cells to the herbicides glufosinate and bialaphos. One preferred use of the subject genes are as selectable markers. The use of this gene as a selectable marker in a bacterial system can increase efficiency for plant transformations. Use of DSM-2 as the sole selection marker eliminates the need for an additional medicinal antibiotic marker (such as ampicillin resistance) during cloning. Various other uses are also possible according to the subject invention.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
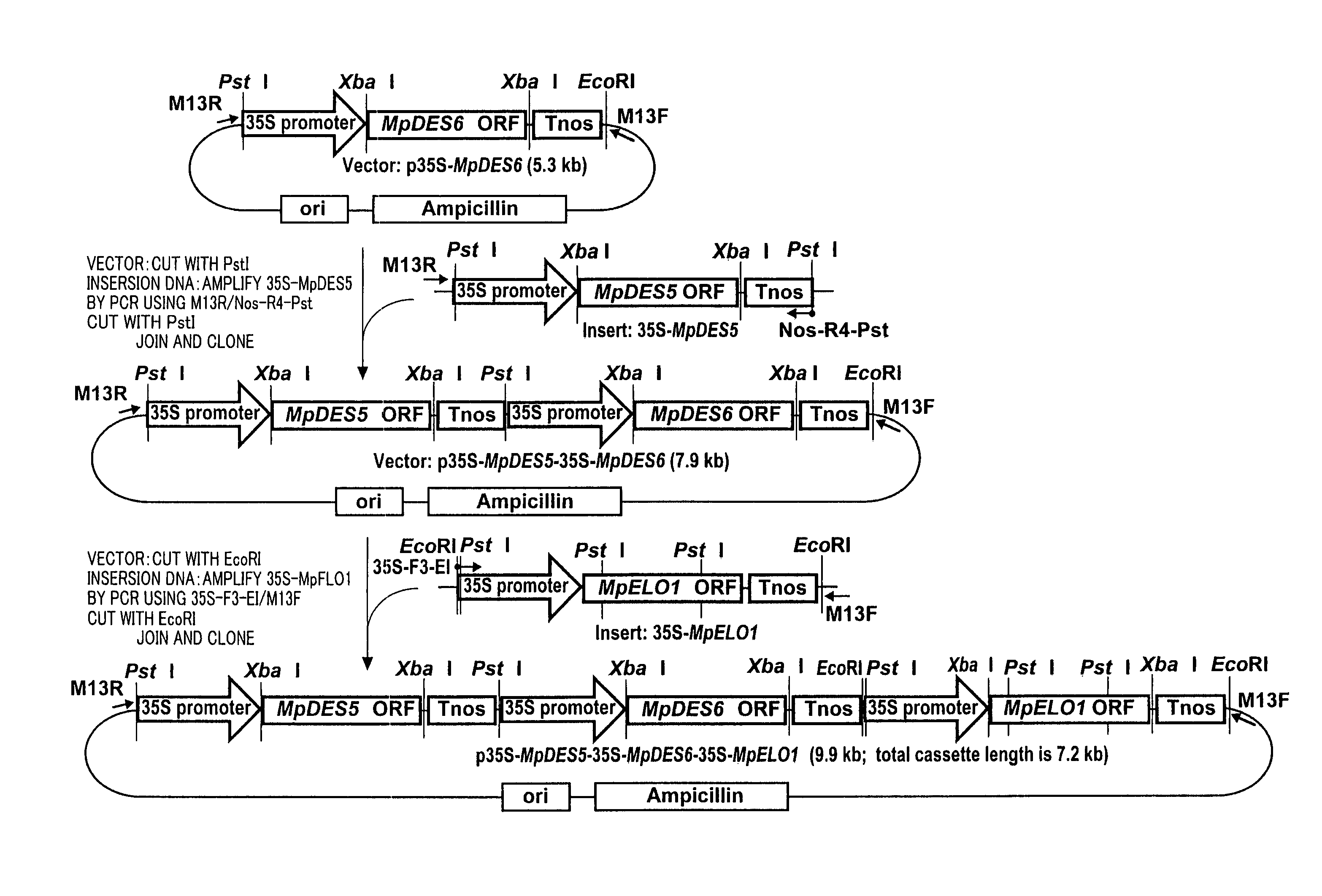
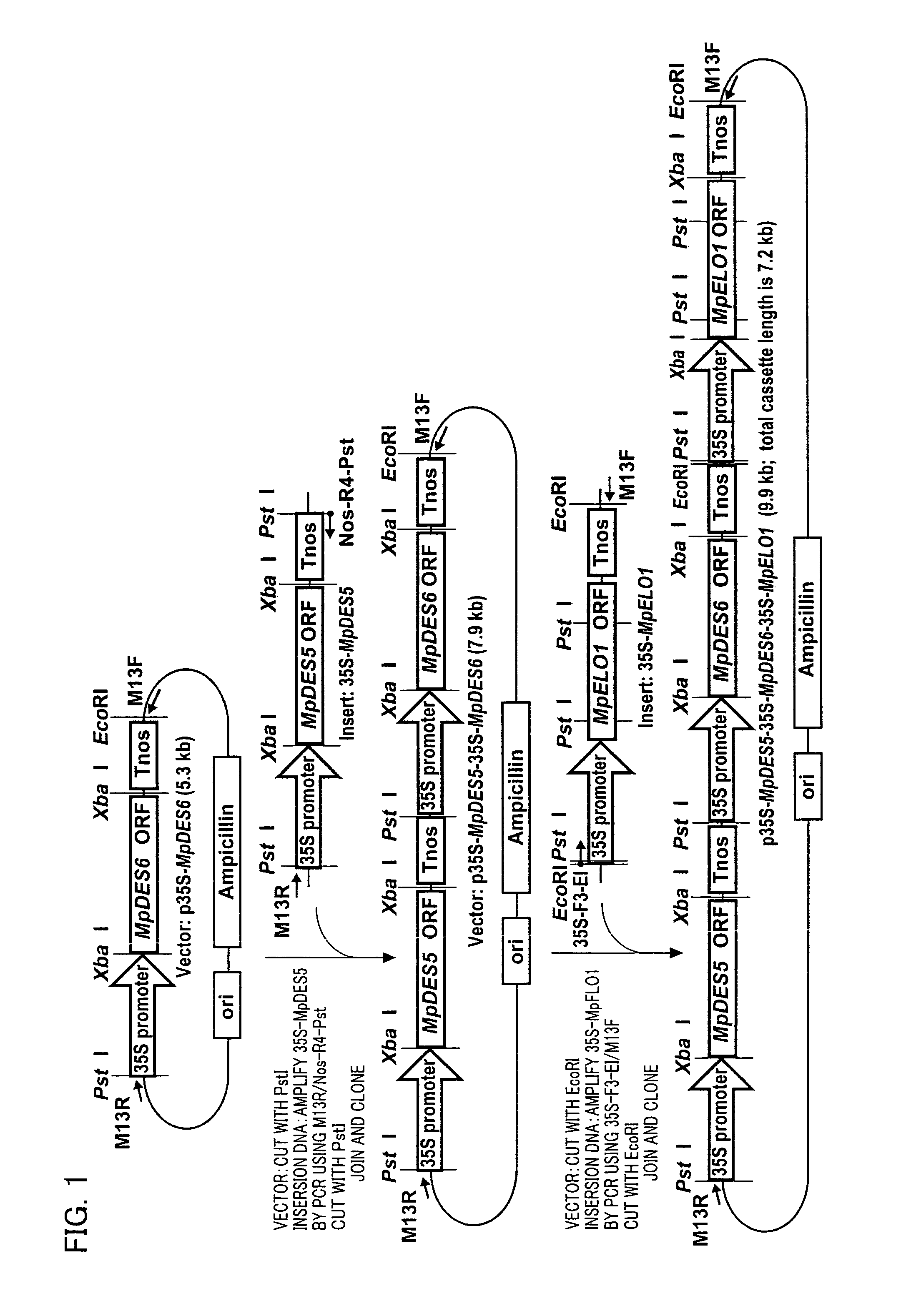
Marchantiales-Derived Unsaturated Fatty Acid Synthetase Genes And Use Of The Same
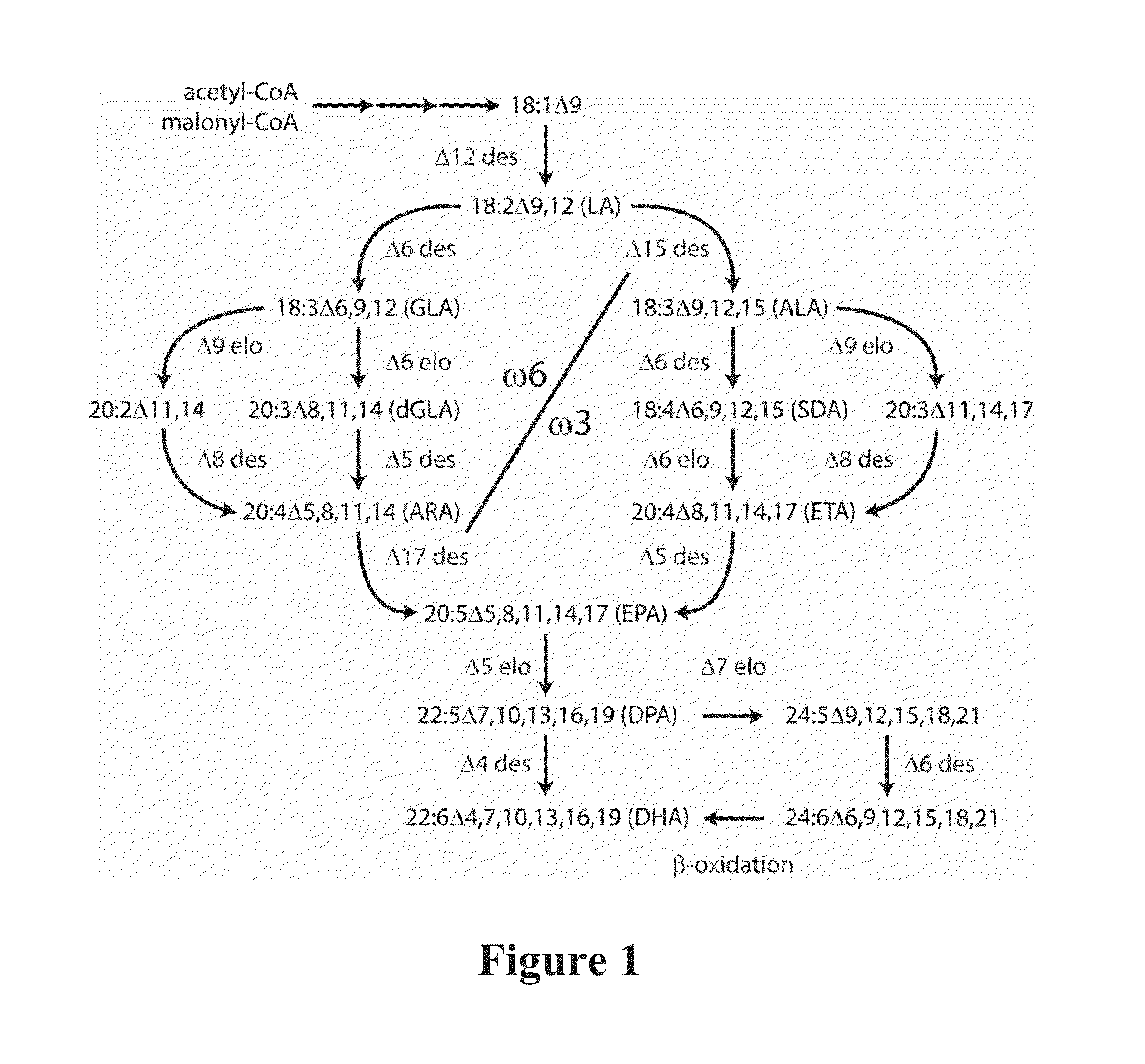
InactiveUS20080057495A1ImmunoglobulinsOxidoreductasesUnsaturated fatty acid synthesisEicosapentaenoic acid
A Δ5 fatty acid desaturase gene, a Δ6 fatty acid desaturase gene, and a Δ6 fatty-acid-chain elongase gene are isolated from a single species of Marchantiales. By introducing these genes into higher plants, transformed plants which can produce arachidonic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) are obtained.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Primary alcohol producing organisms
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having at least one exogenous gene insertion and / or one or more gene disruptions that confer production of primary alcohols. A method for producing long chain alcohols includes culturing these non-naturally occurring microbial organisms.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
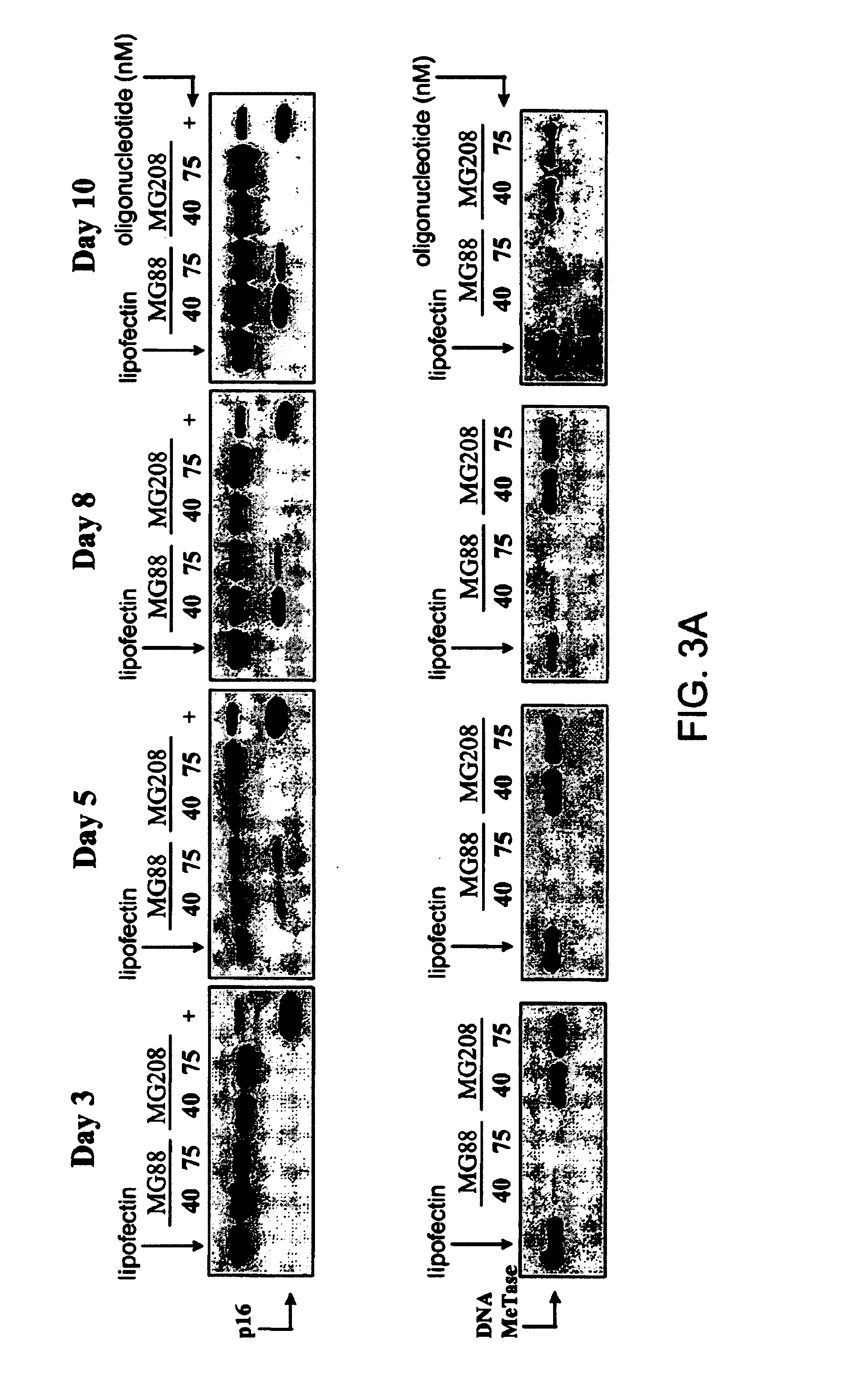
Modulation of gene expression by combination therapy
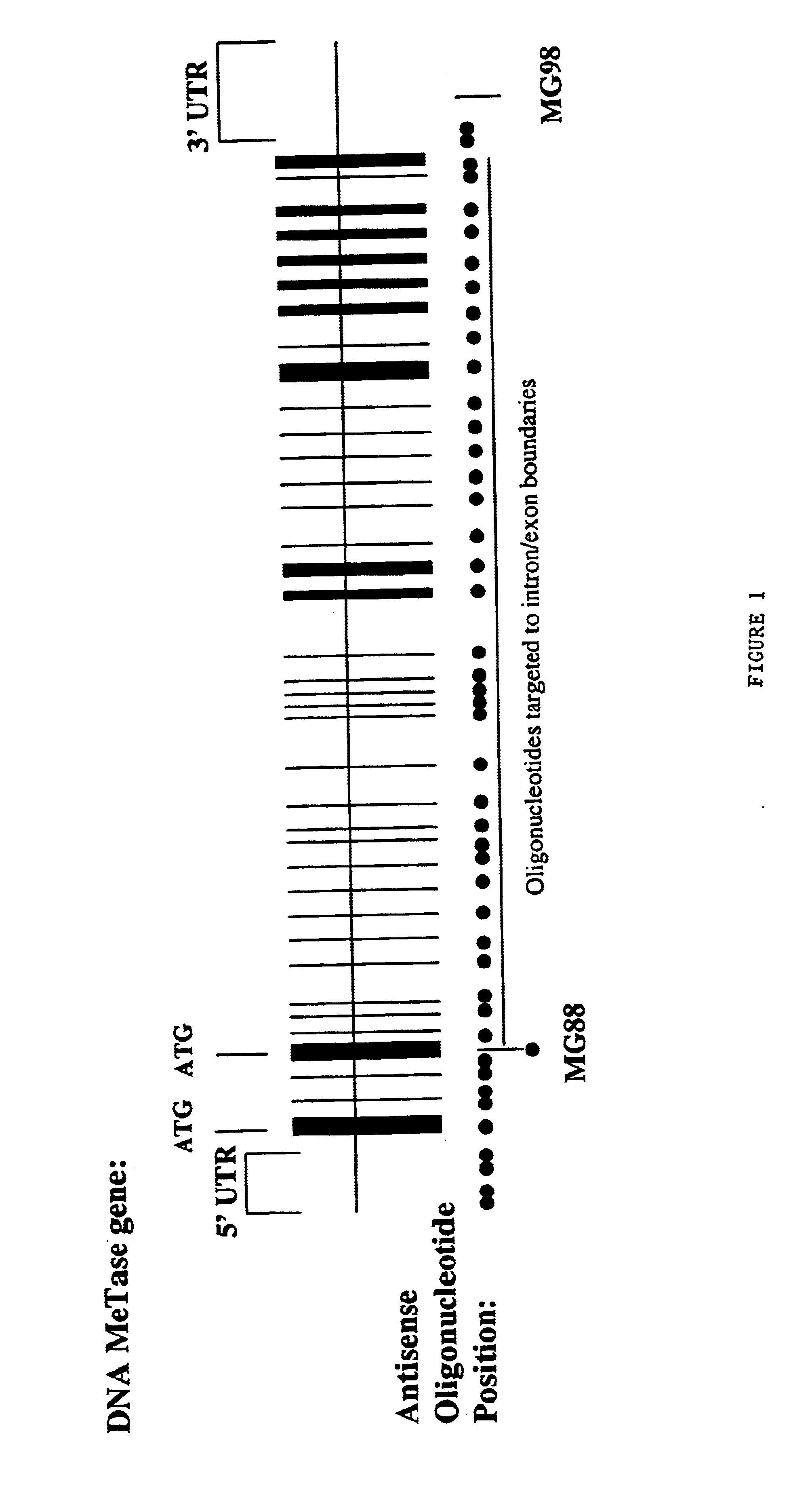
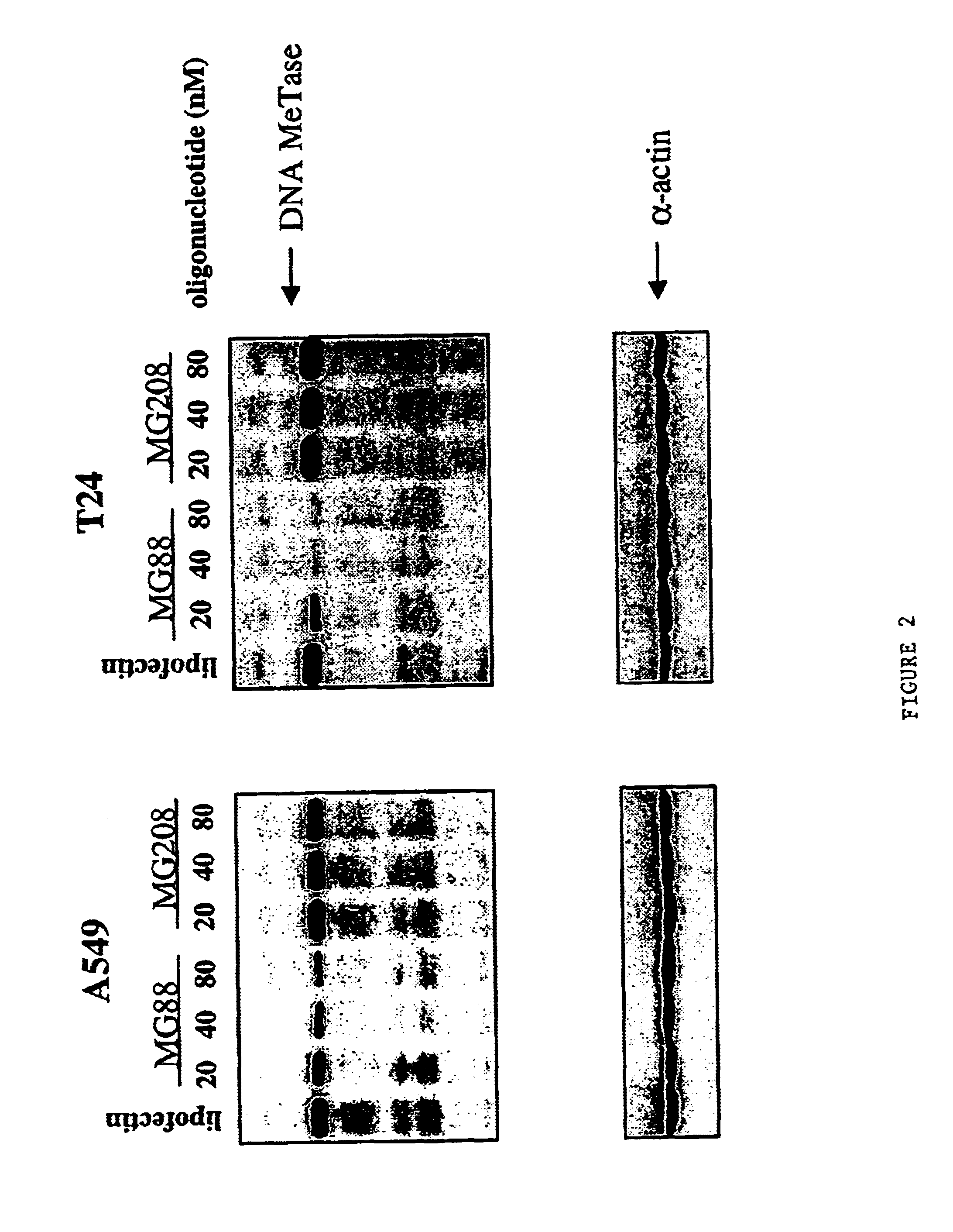
InactiveUS6953783B1Suppress gene expressionModulate methylation levelBiocideSugar derivativesCombined Modality TherapyGene product
The invention relates to the modulation of gene expression. In particular, the invention relates to compositions comprising antisense oligonucleotides which inhibit expression of a gene in operable association with protein effectors of a product of that gene, and methods of using the same.In addition, the invention relates to the modulation of mammalian gene expression regulated by methylation.
Owner:METHYLGENE
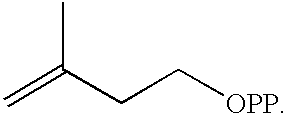
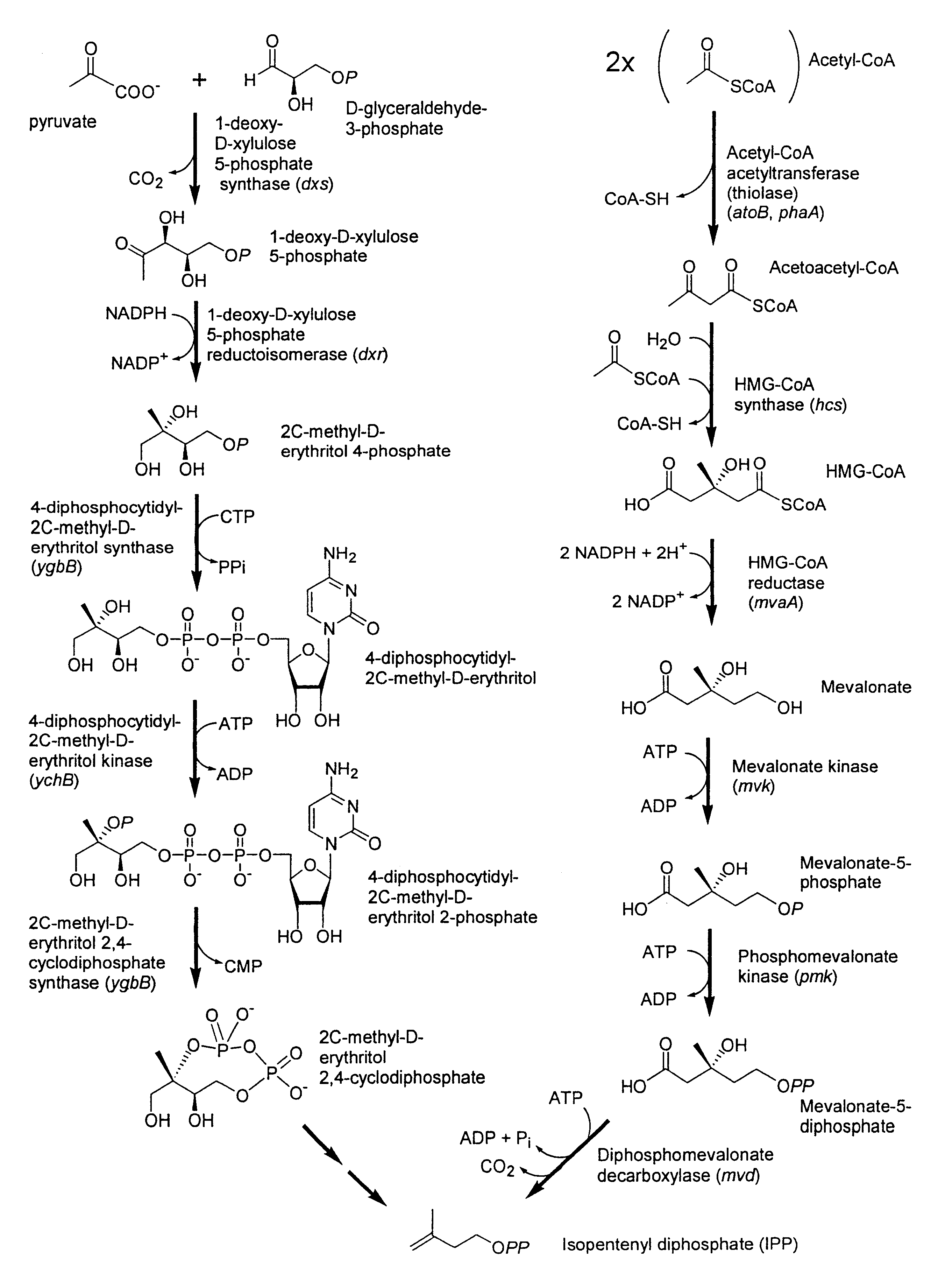
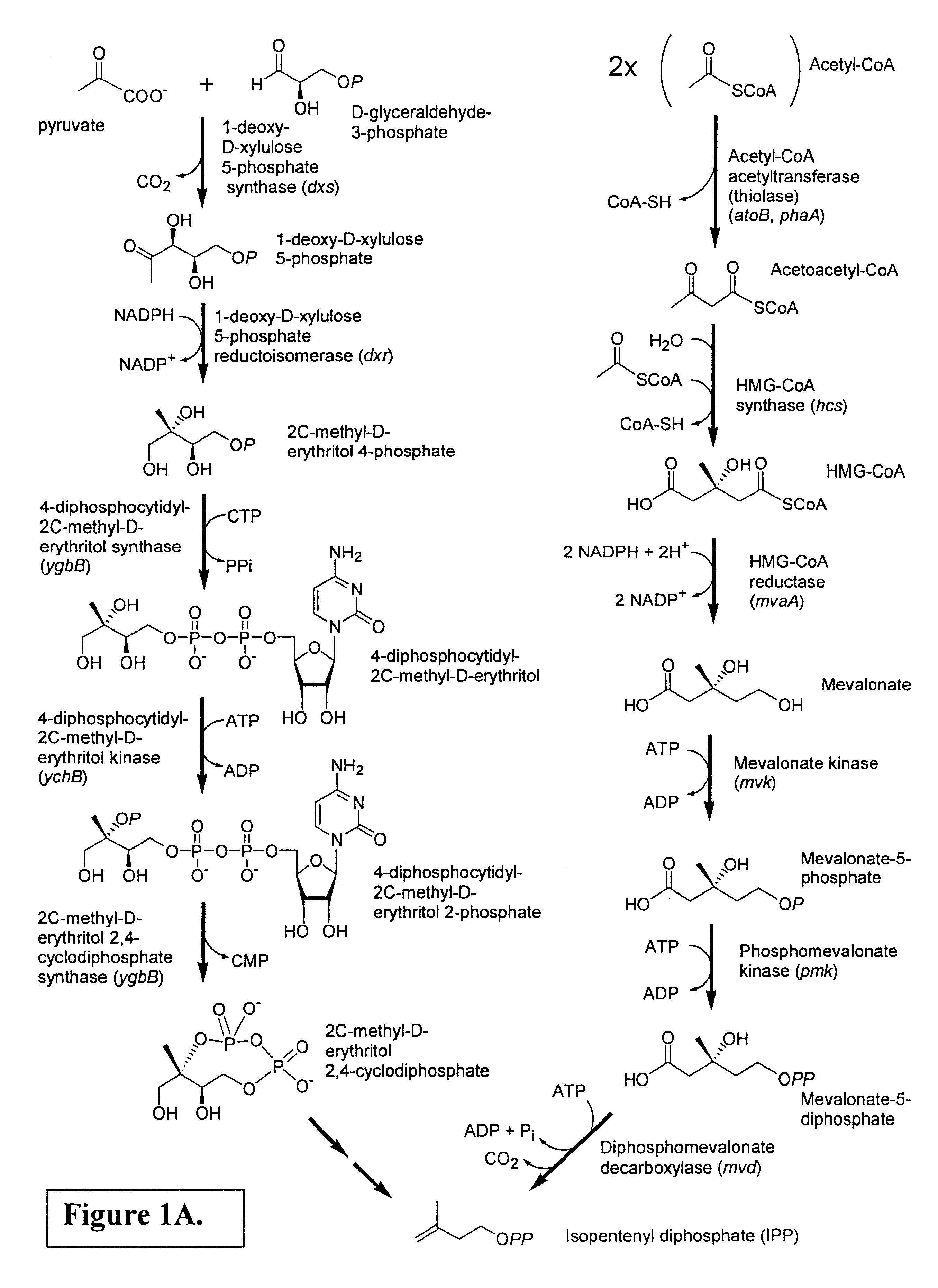
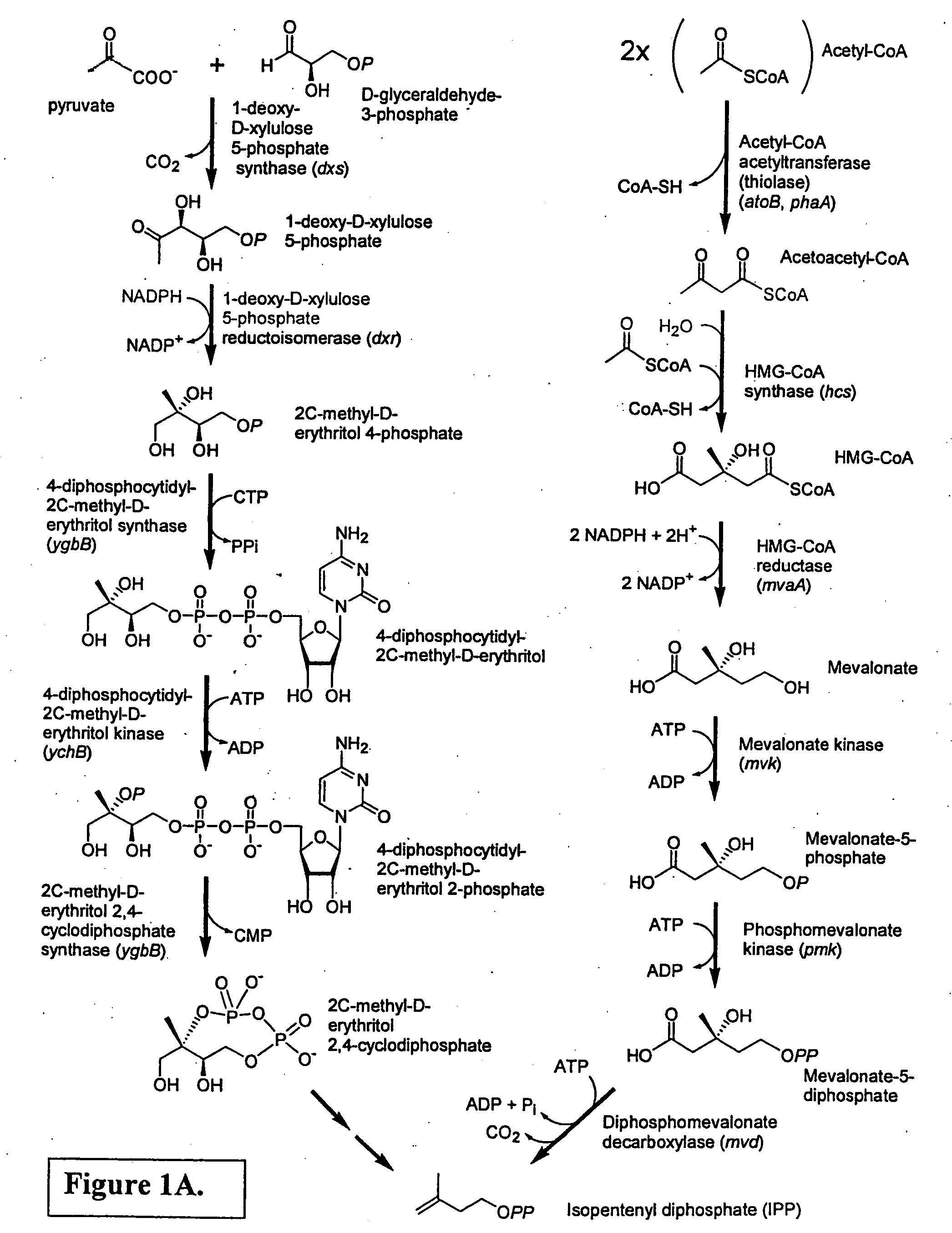
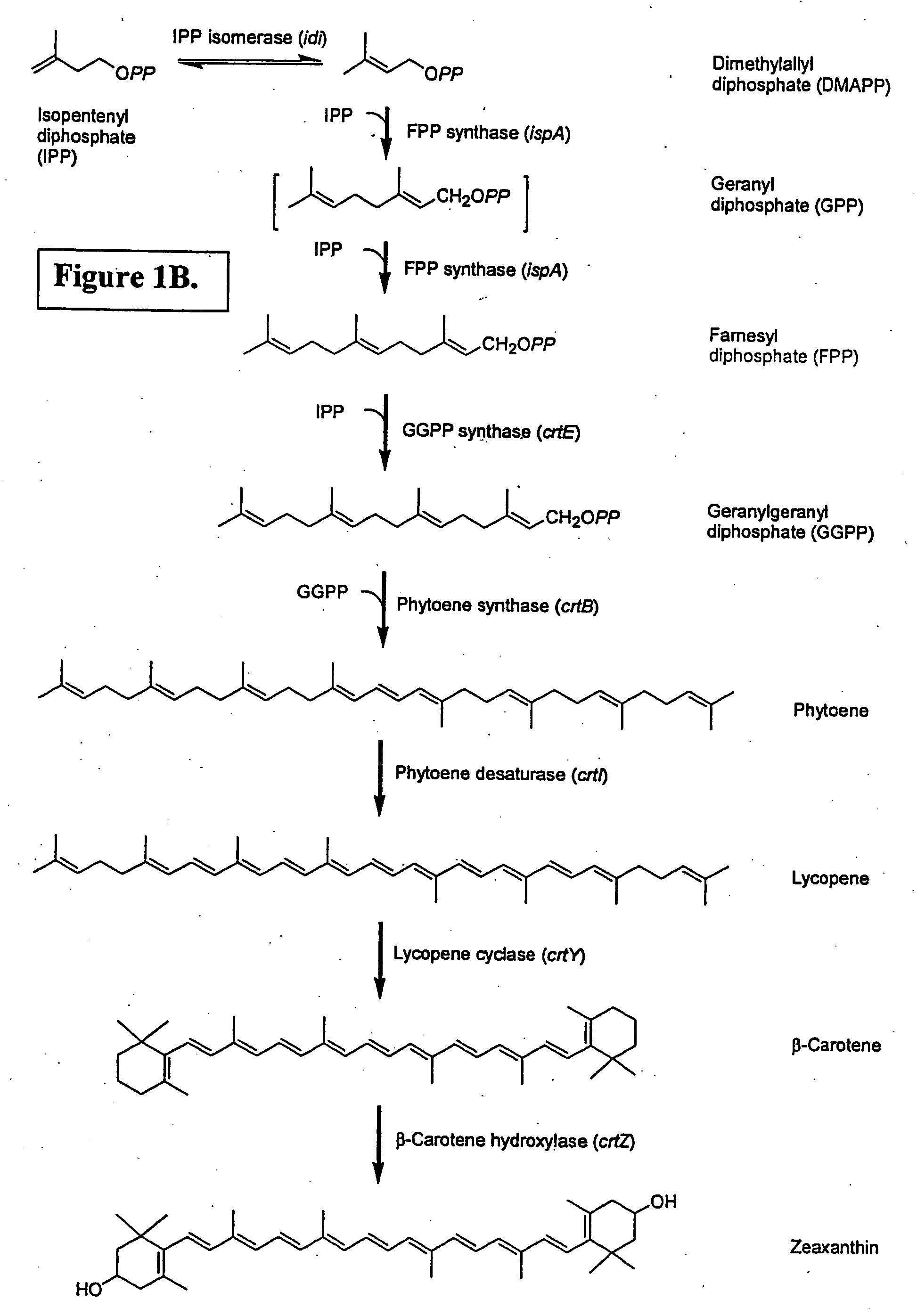
Isoprenoid production
Owner:DSM NUTRITIONAL PROD +1
Compositions and methods for producing isoprene
The invention features methods for producing isoprene from cultured cells. The invention also provides compositions that include these cultured cells.
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
Lipid comprising long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids
ActiveUS20150166928A1Efficient production of LC-PUFABiocideOrganic chemistryIodo fatty acidBiotechnology
The present invention relates to extracted plant lipid or microbial lipid comprising docosahexaenoic acid, and / or docosapentaenoic acid, and processes for producing the extracted lipid.
Owner:NUSEED PTY LTD +2
Methods for producing potato products
The present invention relates to methods for producing consumable products from potatoes, comprising: (a) treating a potato substance with an effective amount of one or more exogenous enzymes selected from the group consisting of an amyloglucosidase, glucose oxidase, laccase, lipase, maltogenic amylase, pectinase, pentosanase, protease, and transglutaminase, and (b) processing the enzyme-treated potato substance to produce a potato product. The invention also relates to consumable products obtained from potatoes by the methods of the present invention.
Owner:NOVO NORDISKBIOTECH INC
Isoprenoid production
Isolated polynucleotides encoding polypeptides having the activity of enzymes in the mevalonate pathway are provided. These sequences are useful for recombinantly producing isoprenoid compounds, such as carotenoids, in particular zeaxanthin. Expression vectors, cultured cells, and methods of making isoprenoid compounds are also provided.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
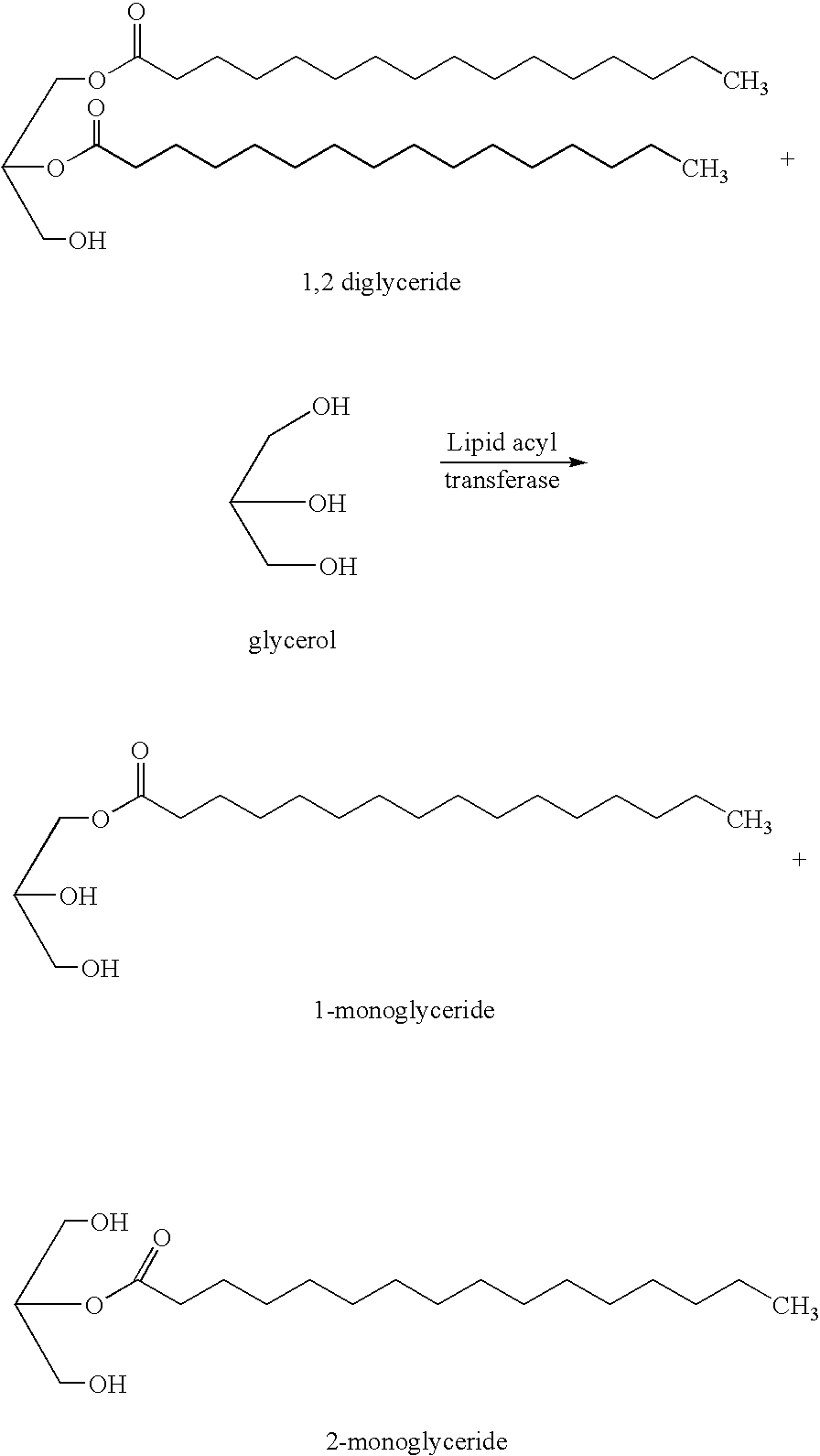
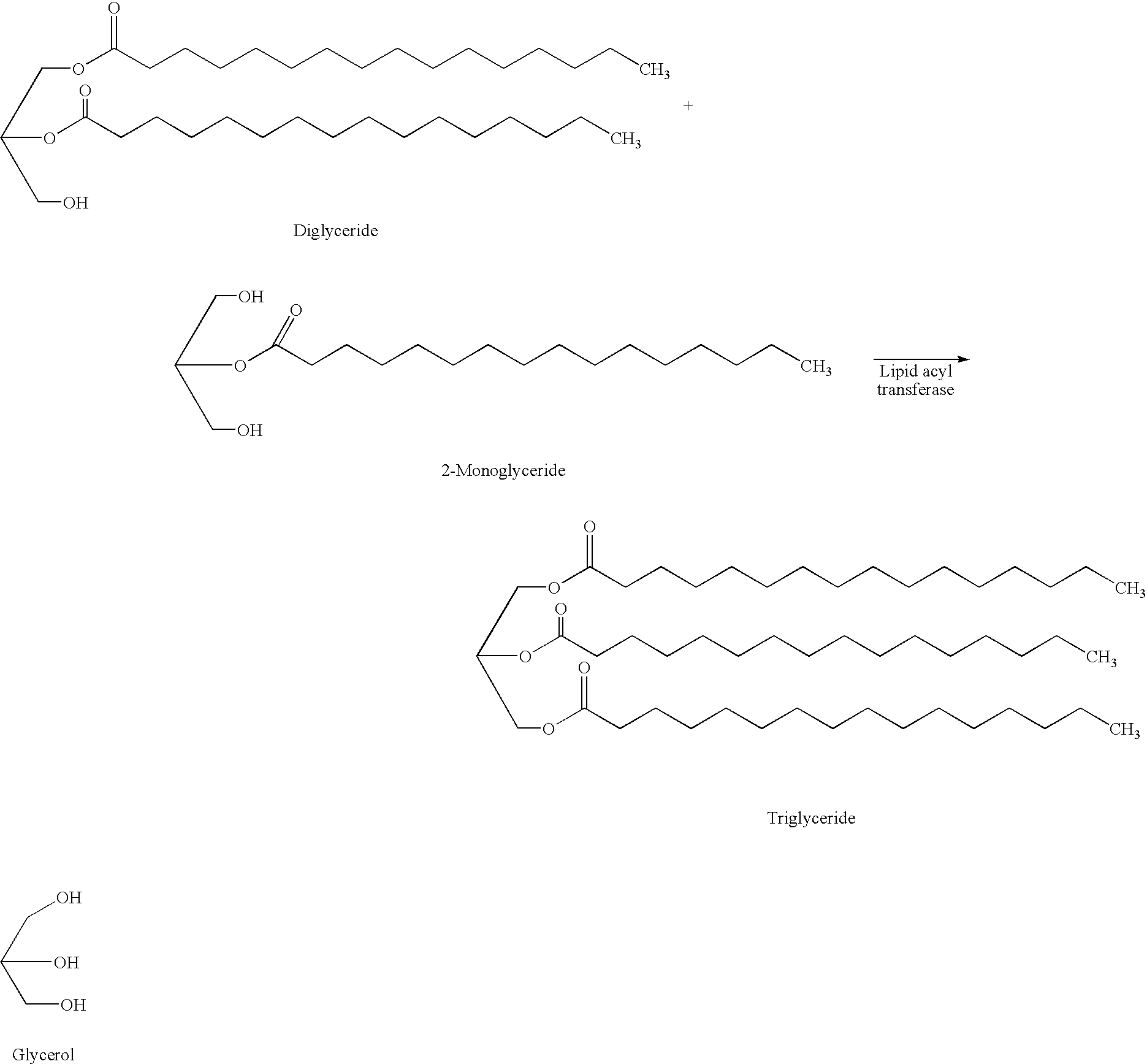
Method
The present invention relates to a method of reducing and / or removing diglyceride from an edible oil, comprising a) admixing an edible oil with an acyl acceptor substrate and a diglyceride:glycerol acyltransferase, wherein the diglyceride:glycerol acyltransferase is characterized as an enzyme which in an edible oil is capable of transferring an acyl group from a diglyceride to glycerol. Preferably, the diglyceride:glycerol acyltransferase comprises the amino acid sequence motif GDSX, wherein X is one or more of the following amino acid residues L, A, V, I, F, Y, H, Q, T, N, M or S. Furthermore the present invention relates to the use of a diglyceride:glycerol acyltransferase characterized as an enzyme which in an edible oil is capable of transferring an acyl group from a diglyceride to glycerol, in the manufacture of an edible oil, for reducing and / or removing (preferably selectively reducing and / or removing) diglyceride from said edible oil and to the use of said enzyme in the manufacture of a foodstuff comprising an edible oil for improving the crystallization properties of said foodstuff.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
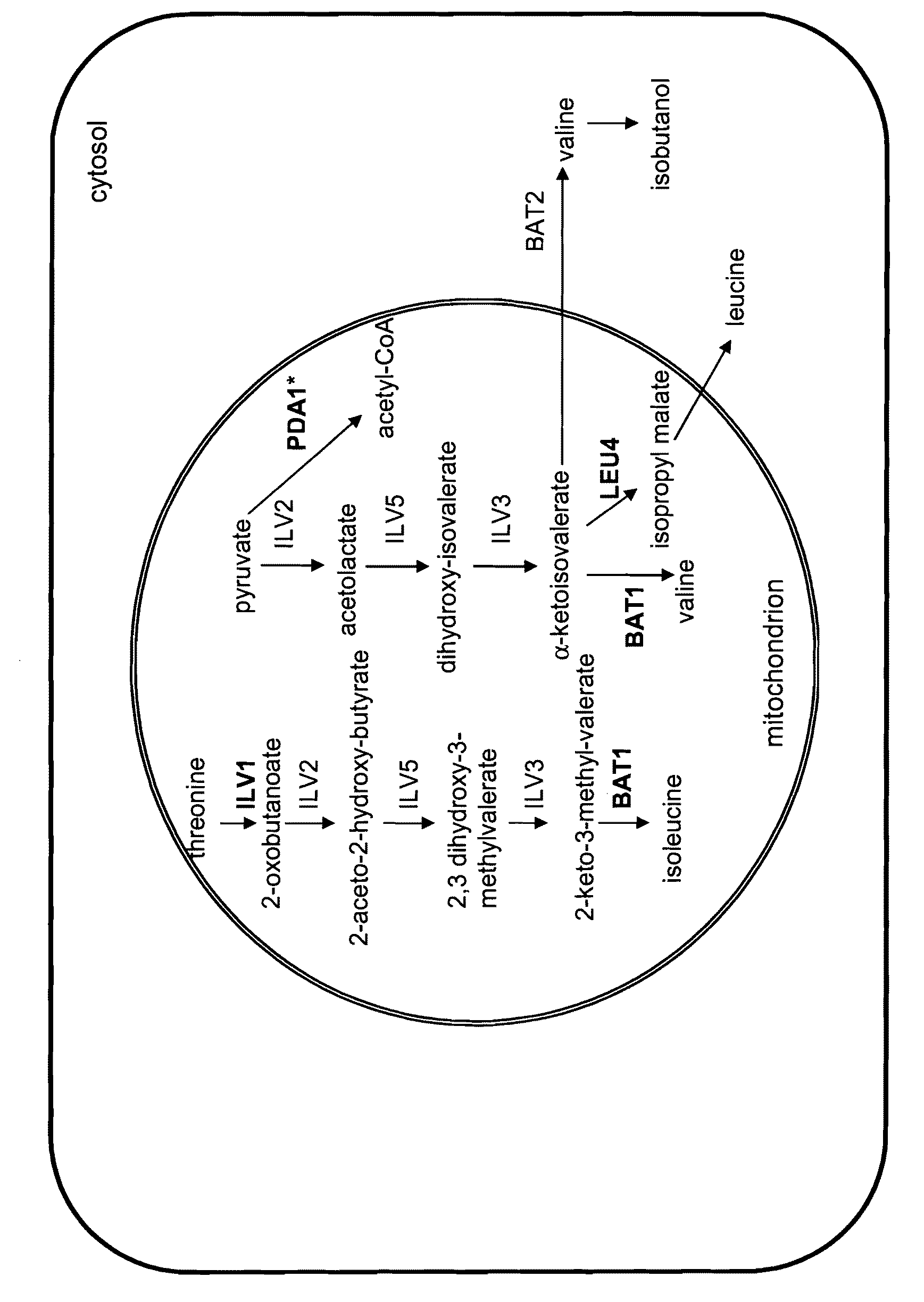
Increased production of isobutanol in yeast with reduced mitochondrial amino acid biosynthesis
ActiveUS8465964B2Reduced activityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesMicroorganismsIsobutanolBranched-chain-amino-acid transaminase
Owner:GEVO INC
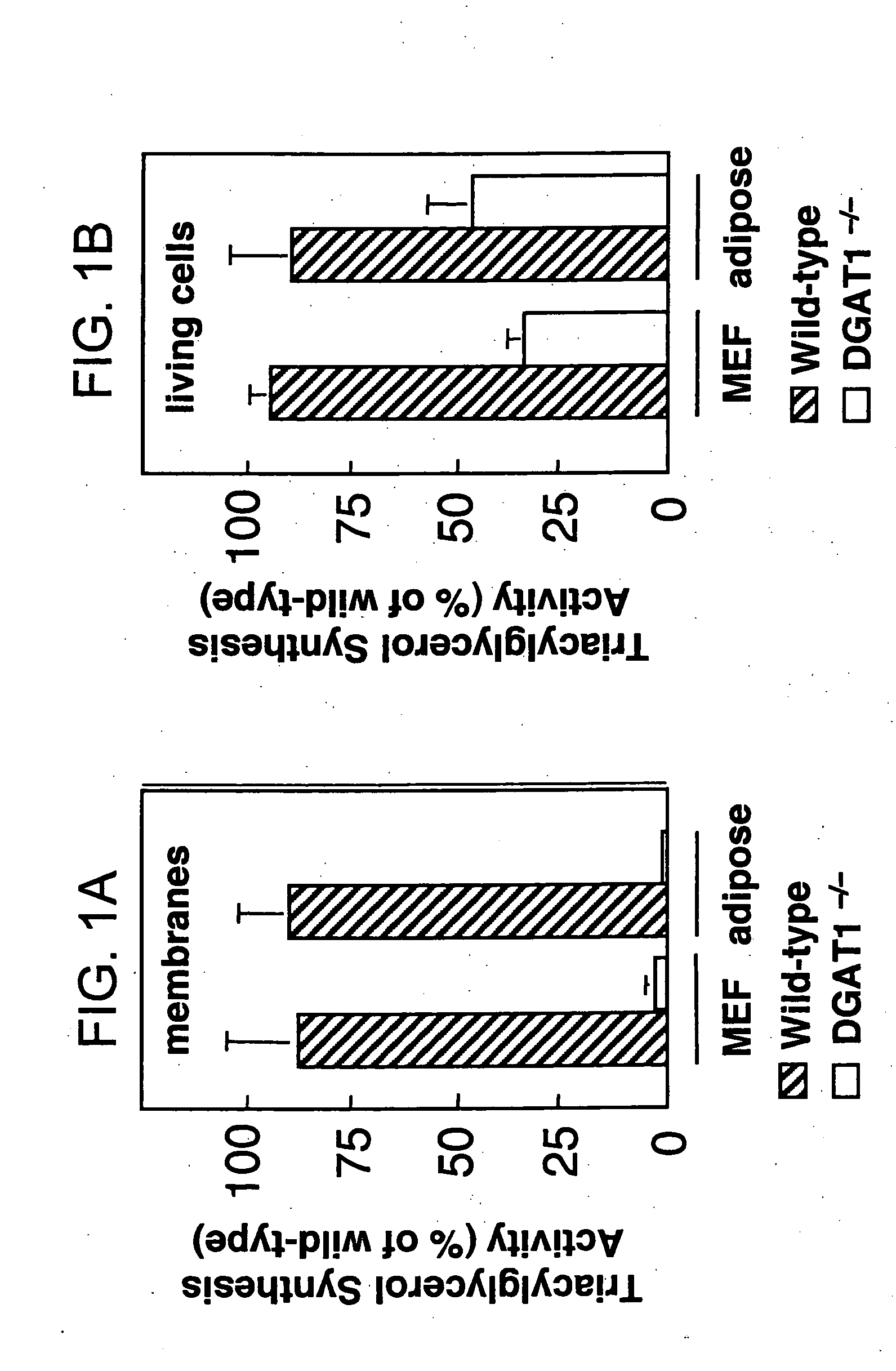
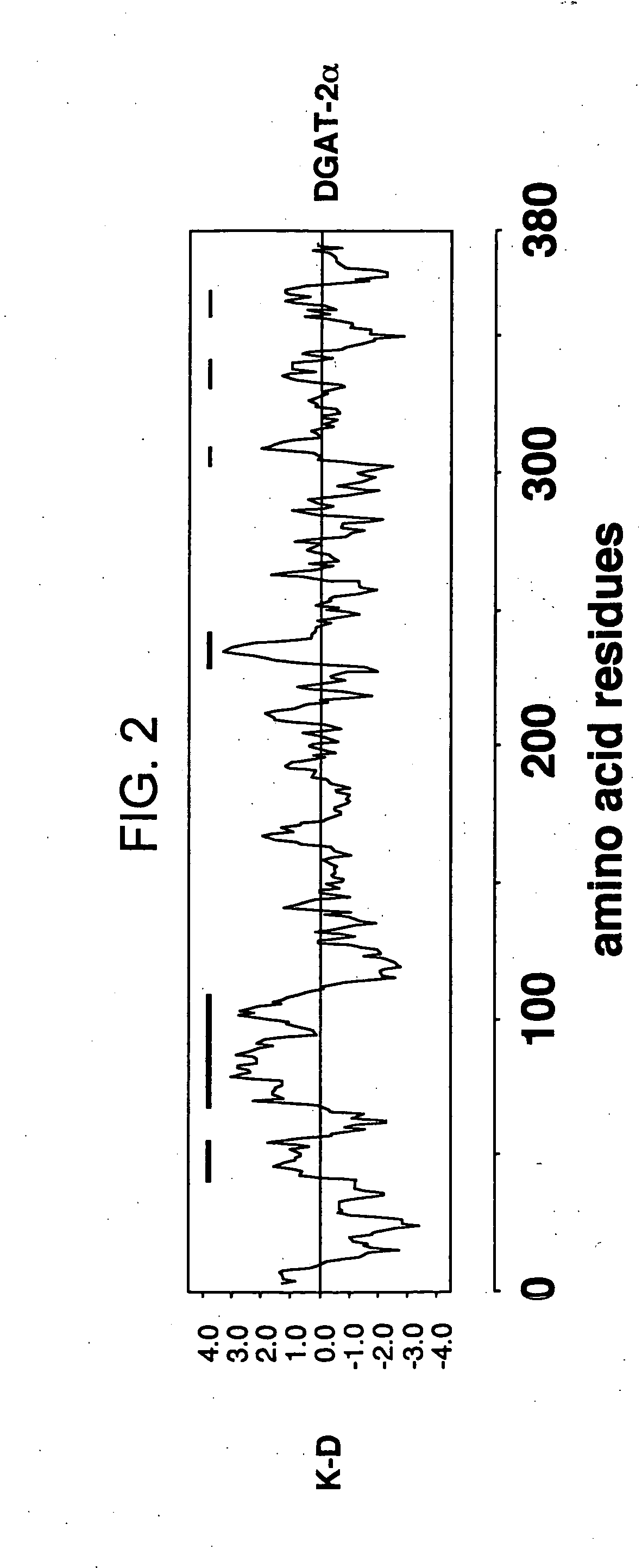
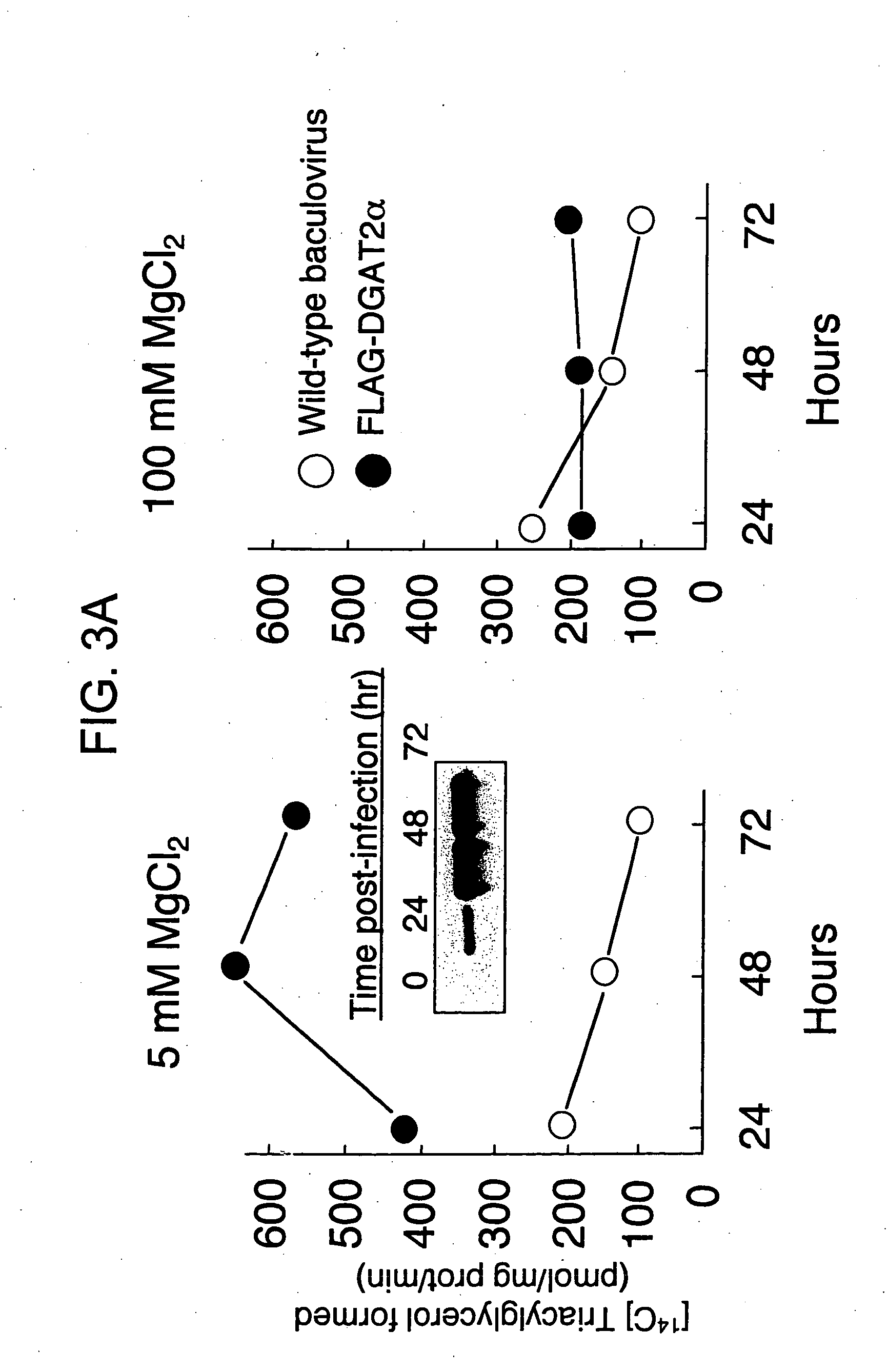
Mono-and diacylglycerol acyltransferases and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20050106697A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsMonoacylglycerol acyltransferaseDiglyceride acyltransferase
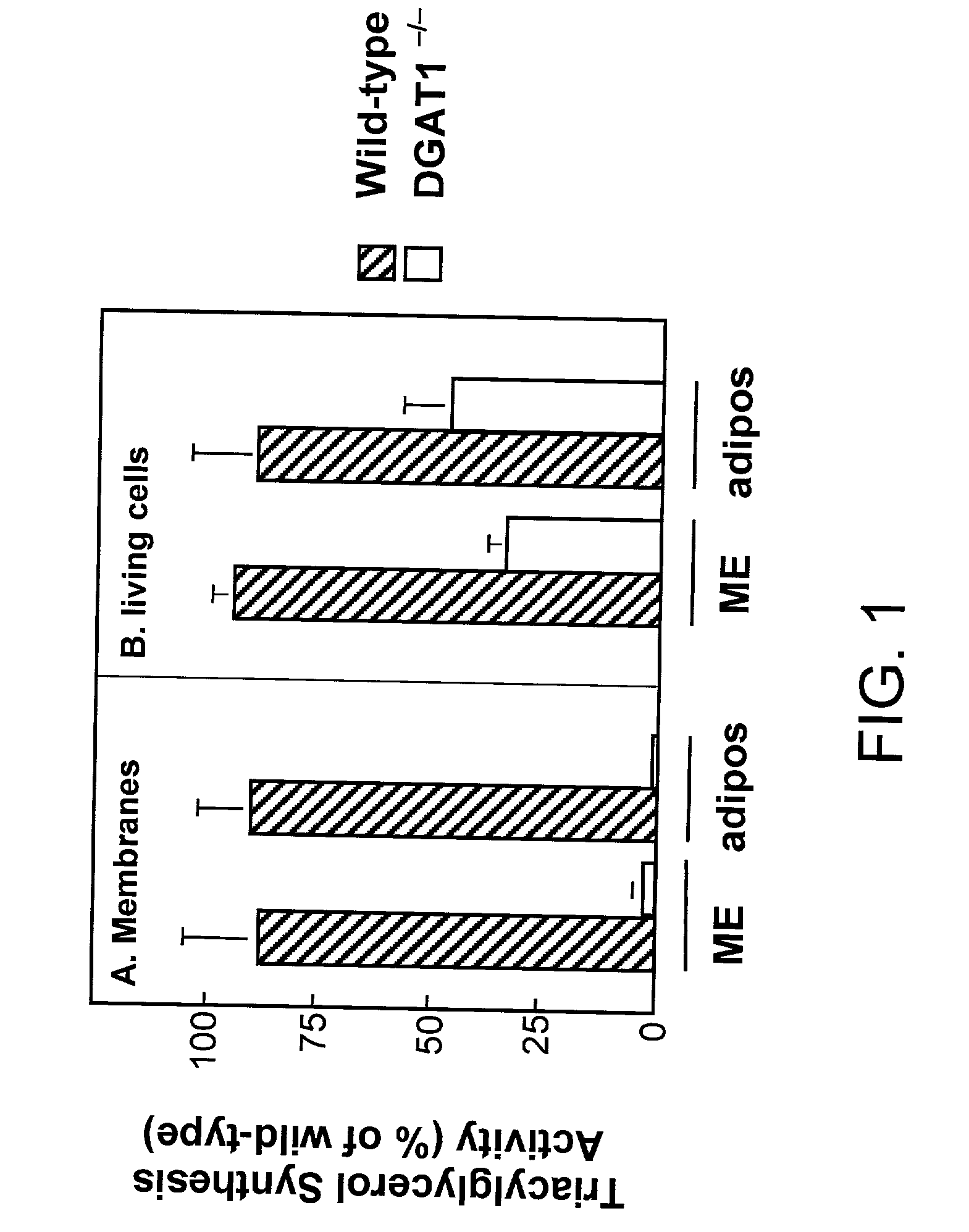
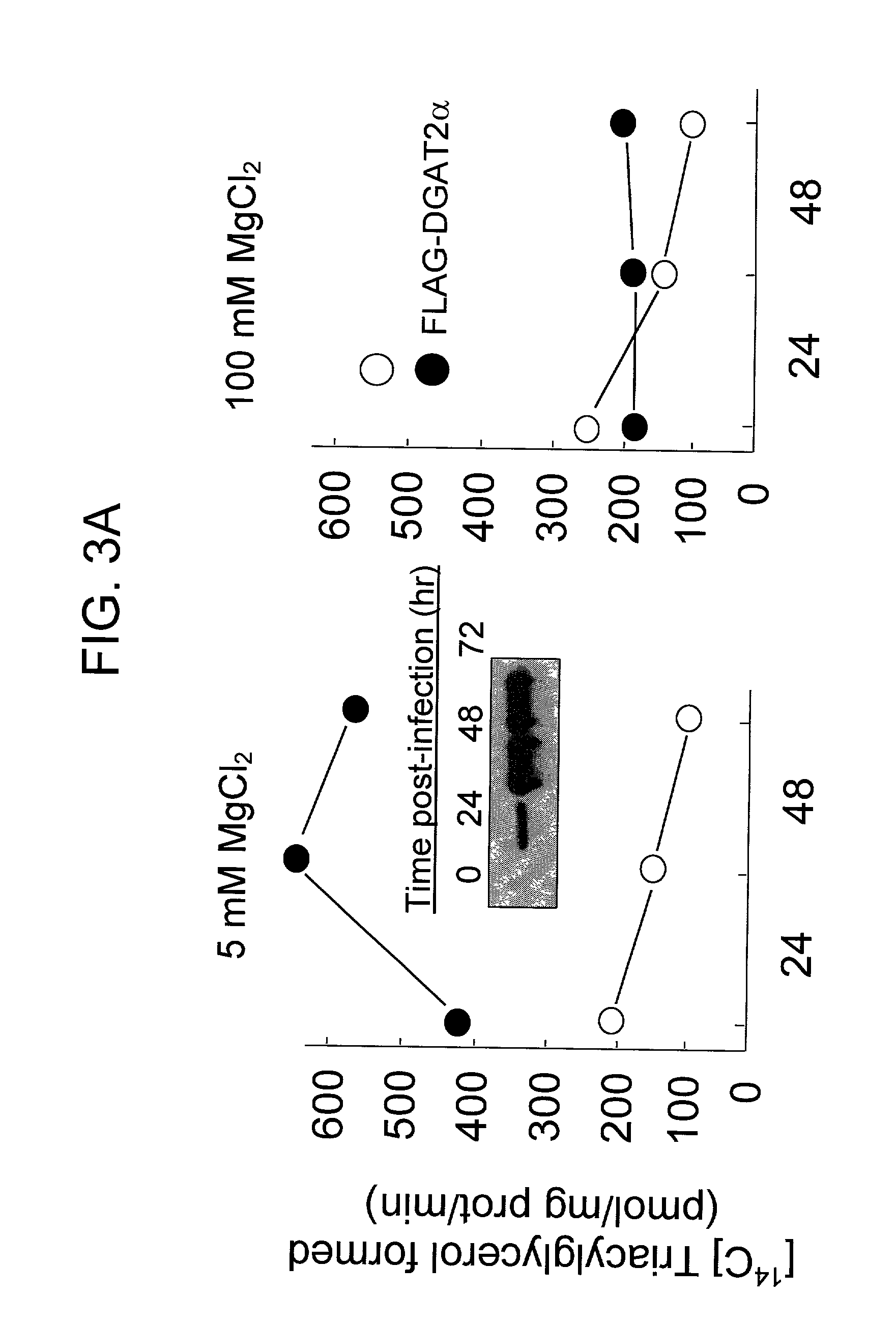
Nucleic acid compositions encoding polypeptide products with diglyceride acyltransferase and / or monoacylglycerol acyltransferase activity, as well as the polypeptide products encoded thereby, i.e., mammalian DGAT2α, MGAT1, or MGAT2 polypeptide products, and methods for producing the same, are provided. Also provided are: methods and compositions for modulating DGAT2α, MGAT1, or MGAT2 activity; DGAT2α, MGAT1, or MGAT2 transgenic cells, animals and plants, as well as methods for their preparation; and methods for making diglyceride, diglyceride compositions, triglycerides and triglyceride compositions, as well as the compositions produced by these methods. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of different applications, including research, medicine, agriculture and industry applications.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Methods of making nylon intermediates from glycerol
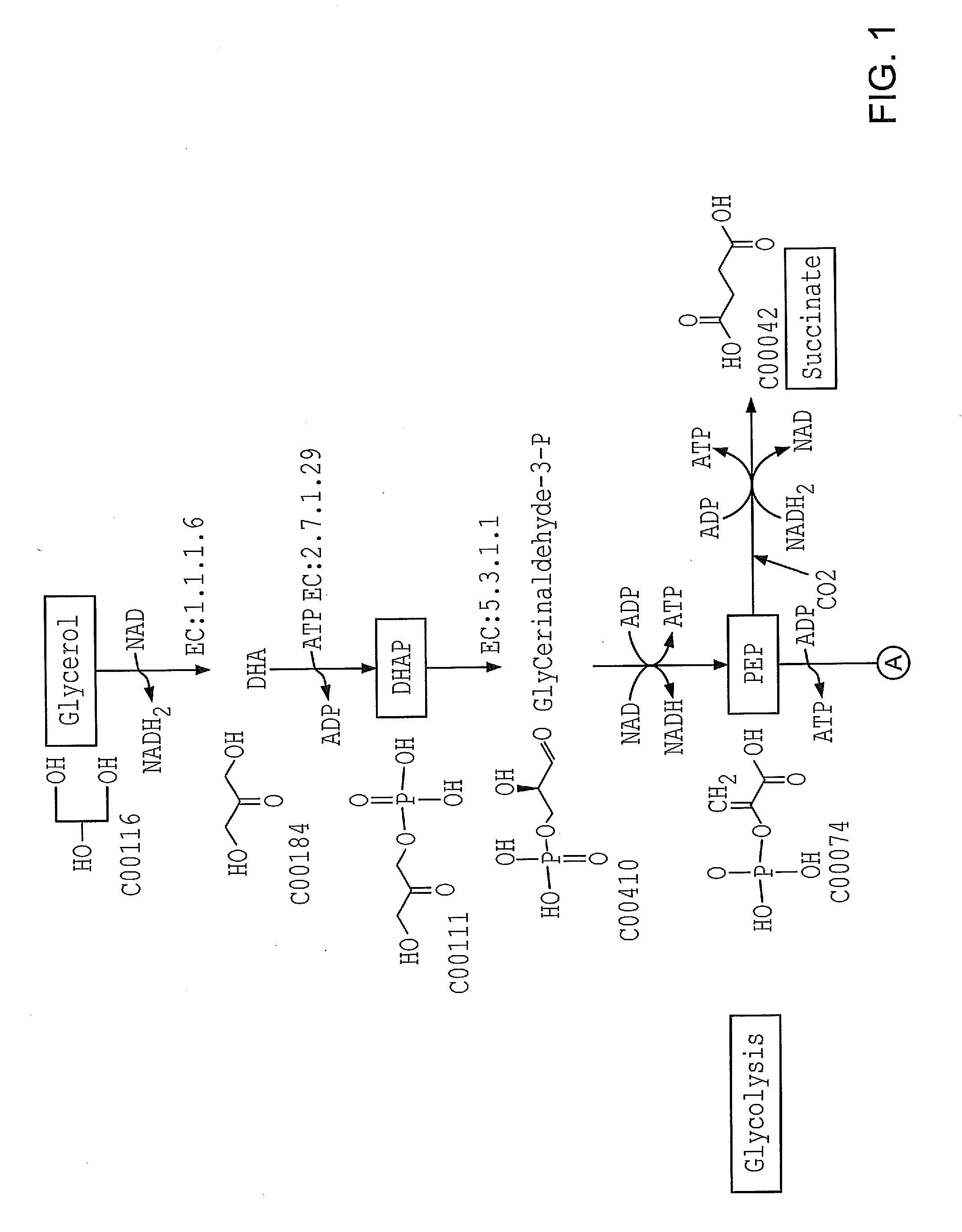
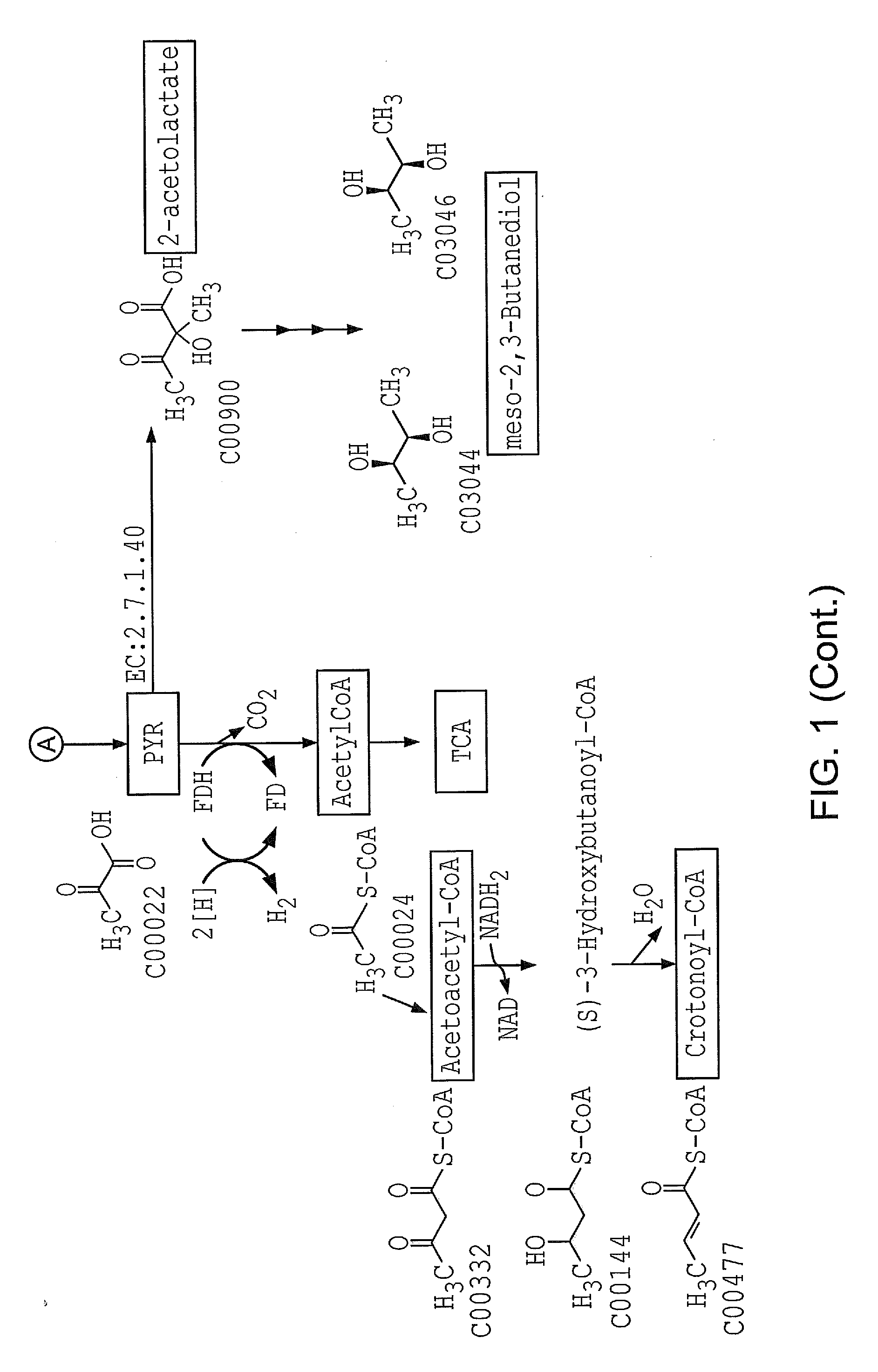
ActiveUS20130210090A1Reduce usageRate minimisedBacteriaHydrolases3-Hydroxypropionic acid2,3-Butanediol
Embodiments of the invention relate to the enzymatic conversion of bioderived feedstocks to commercially valuable chemicals. The enzymatic conversions of the embodiments of the invention offer the potential for lower cost routes to these value-added chemicals. Some of the chemicals that are useful include nylon intermediates such as caprolactam, adipic acid, 1,6-hexamethylene diamine; butanediols such as 1,4-butanediol, 1,3-butanediol, and 2,3-butanediol; butanols such as 1-butanol, and 2-butanol; succinic acid, butadiene, isoprene, and 3-hydroxypropanoic acid.
Owner:INV NYLON CHEM AMERICAS LLC
Patellar prosthetic arrangement and associated surgical method
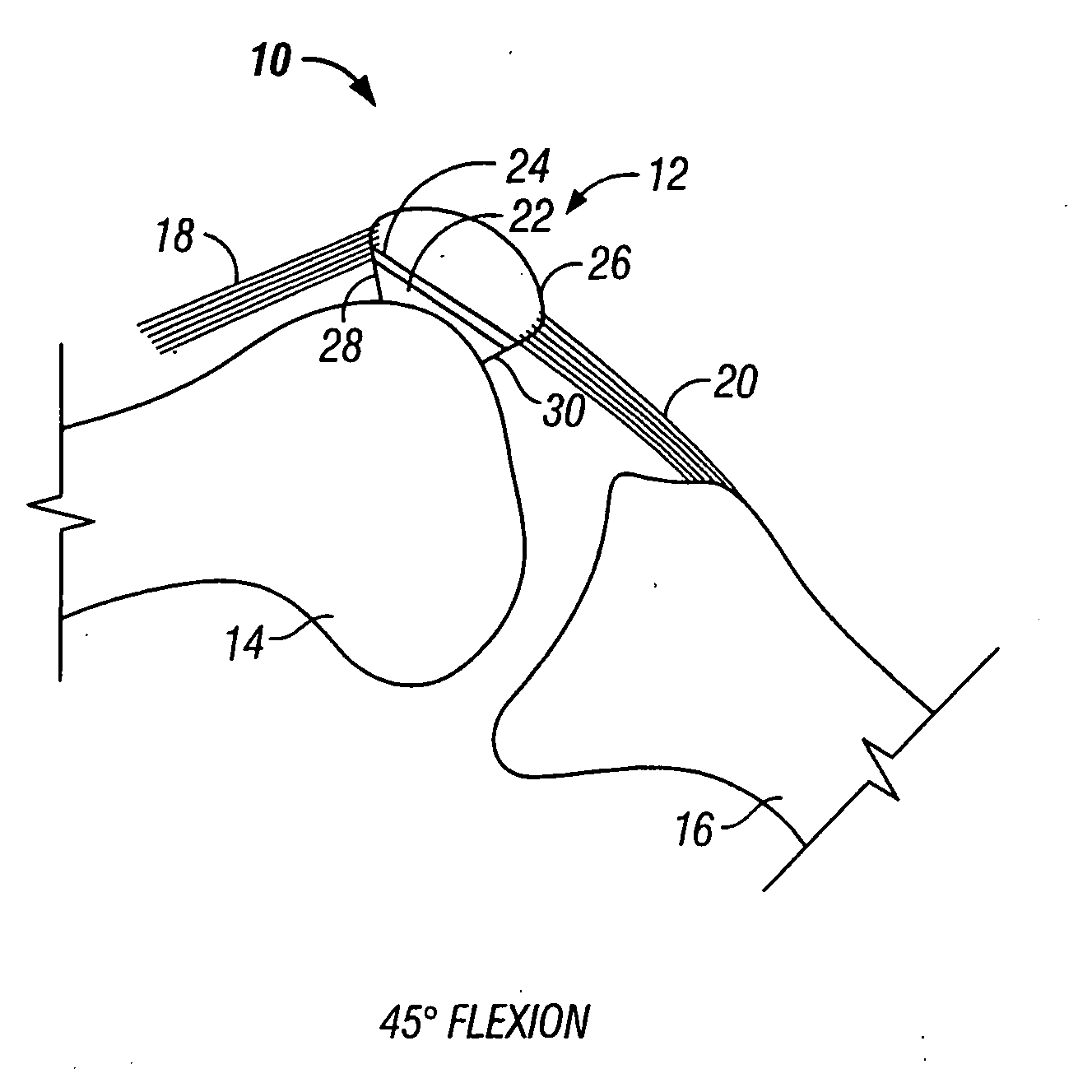
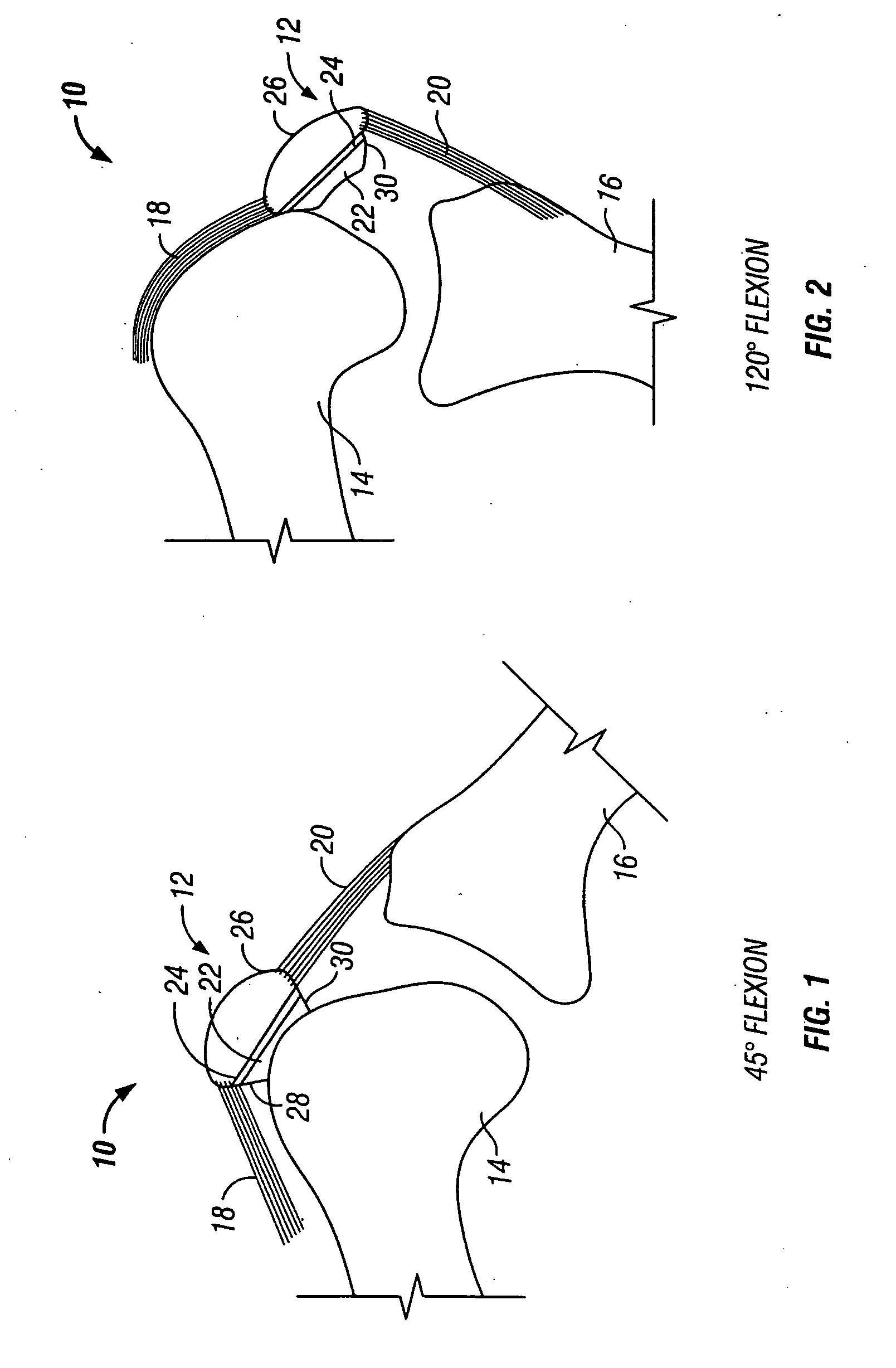
InactiveUS20050143830A1Reduce the possibilityEasy to trackJoint implantsAcyltransferasesEdge surfaceProximate
A prosthetic patellar component includes a base and a bearing element that includes first and second femoral engaging surfaces disposed between first and second (superior / inferior) edge surfaces. The edge surfaces are curved to provide a gradual transition from a posterior facing portion to a nearly vertical superior or inferior facing portion. Moreover, the inferior-superior dimension of the component is at least approximately 90% of the medial-lateral dimension. The relative height and gradually transitioning edges significantly reduce the likelihood of sudden posterior rotation during deep flexion movement. The edge surfaces extend from a substantially posterior facing portion proximate to the first and second femoral engaging surfaces and a substantially vertical facing portion proximate the base. The curved edge surfaces can include a plurality of adjacent medial-laterally extending surface portions having angular displacement relative to an adjacent surface portion of less than 30 degrees in the anterior-posterior direction.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Diacylglycerol o-acyltransferase 2alpha (DGAT2alpha)
InactiveUS20020119138A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsSubject matterDiglyceride acyltransferase activity
Nucleic acid compositions encoding mammalian DGAT2alpha polypeptide products with diglyceride acyltransferase activity, as well as the mammalian DGAT2alpha polypeptide products encoded thereby and methods for producing the same, are provided. The subject DGAT2alpha polypeptide and nucleic acid compositions find use in a variety of applications, including research, diagnostic, and therapeutic agent screening applications, as well as in treatment therapies and in the production of triacylglycerols.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Primary alcohol producing organisms
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having a microbial organism having at least one exogenous gene insertion and / or one or more gene disruptions that confer production of primary alcohols. A method for producing long chain alcohols includes culturing these non-naturally occurring microbial organisms.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Biological Conversion of Multi-Carbon Compounds from Methane
Multi-carbon compounds such as ethanol, n-butanol, sec-butanol, isobutanol, tert-butanol, fatty (or aliphatic long chain) alcohols, fatty acid methyl esters, 2,3-butanediol and the like, are important industrial commodity chemicals with a variety of applications. The present invention provides metabolically engineered host microorganisms which metabolize methane (CH4) as their sole carbon source to produce multi-carbon compounds for use in fuels (e.g., bio-fuel, bio-diesel) and bio-based chemicals. Furthermore, use of the metabolically engineered host microorganisms of the invention (which utilize methane as the sole carbon source) mitigate current industry practices and methods of producing multi-carbon compounds from petroleum or petroleum-derived feedstocks, and ameliorate much of the ongoing depletion of arable food source “farmland” currently being diverted to grow bio-fuel feedstocks, and as such, improve the environmental footprint of future bio-fuel, bio-diesel and bio-based chemical compositions.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Biorefinery system, methods and compositions thereof
ActiveUS20140013658A1Efficiently and cost-effectively producingTaxing environmentFungiBacteriaBiofuelEngineering
The present disclosure relates to bioengineering approaches for producing biofuel and, in particular, to the use of a C1 metabolizing microorganism reactor system for converting C1 substrates, such as methane or methanol, into biomass and subsequently into biofuels, bioplastics, or the like.
Owner:CALYSTA
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol as well as building and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
PendingCN105385615AReduce outputOvercome flavor incongruityFungiHydrolasesEster hydrolaseBio engineering
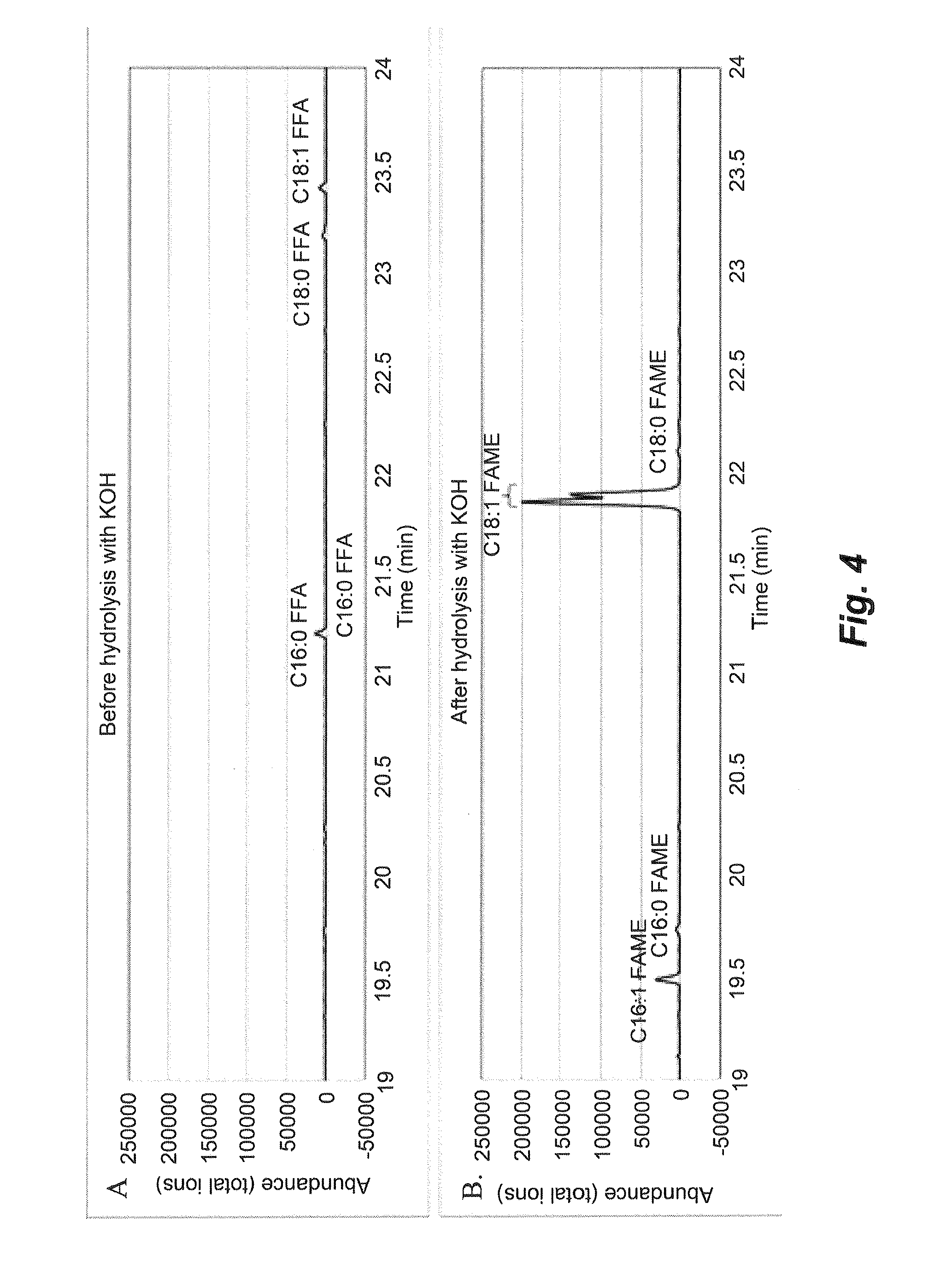
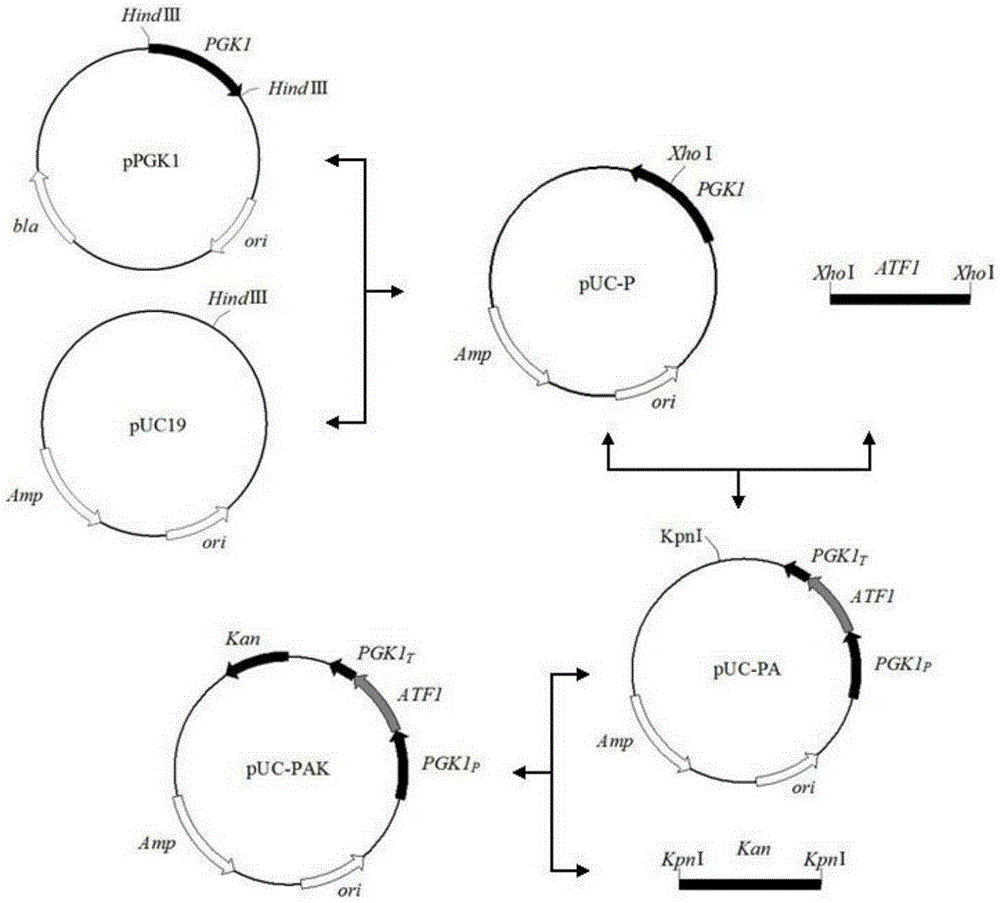
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol as well as a building method of the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the building method provided by the invention, through completely knocking out an amino acid transaminase gene BAT2 and an ester hydrolase gene IAH1 in an original strain, and selecting a strong promoter PGK1 over-expression alcohol acetyltransferase I gene ATF1 at the same time, the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol is obtained. Compared with a parent strain, other fermentation performances of built recombinant bacteria are not affected, the total quantity of acetic acid ester is obviously increased and reaches 1303.6mg / L, wherein the content of ethyl acetate is 52 times that of the original strain, isoamyl acetate is increased to 73.7mg / L, the content of main higher alcohol is 151.8mg / L and is reduced by 61.4 percent in comparison with that of the original strain. By using the saccharomyces cerevisiae, ester yield is significantly increased while the higher alcohol yield is reduced, the higher requirements of white spirit related fields on yeast are met and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com