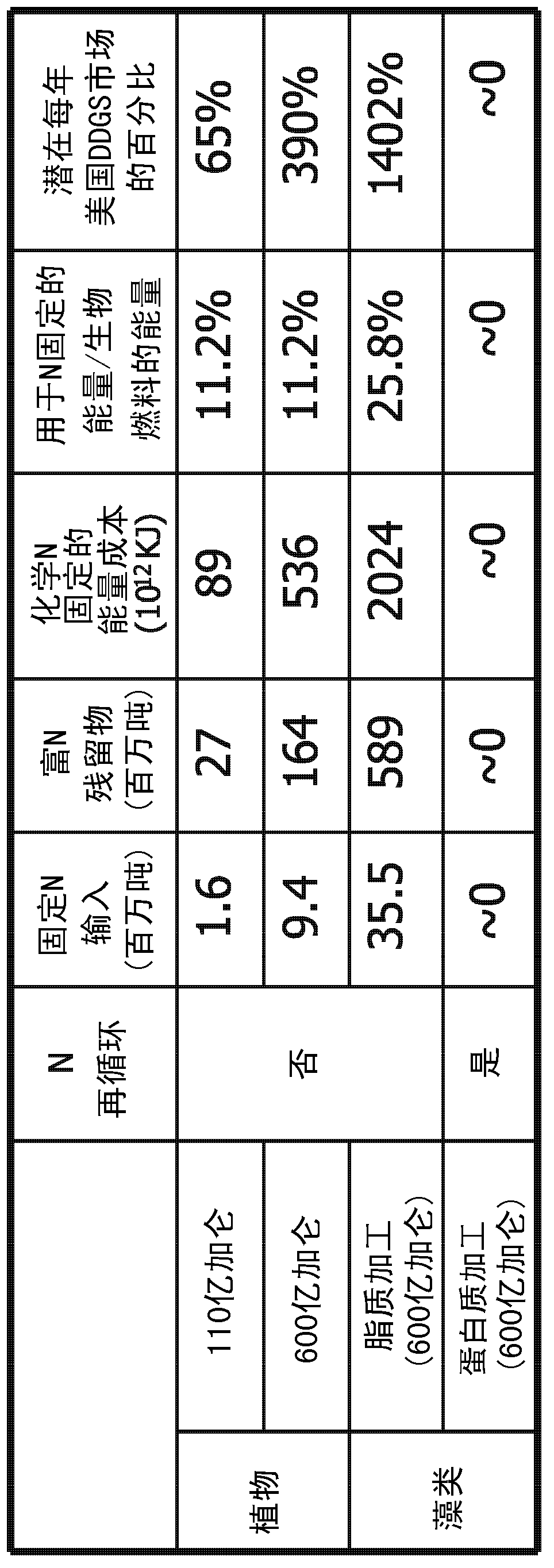
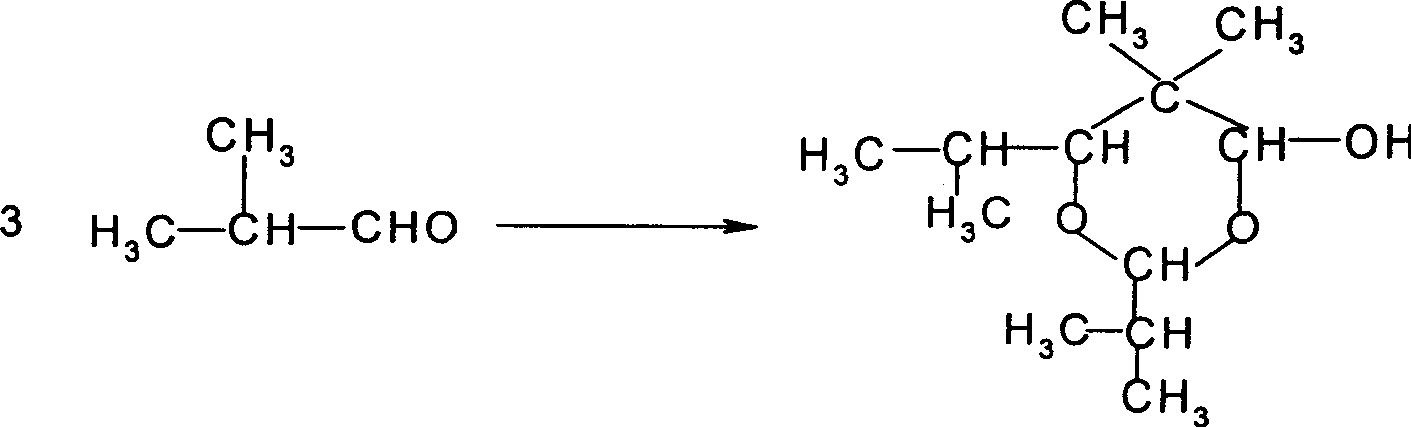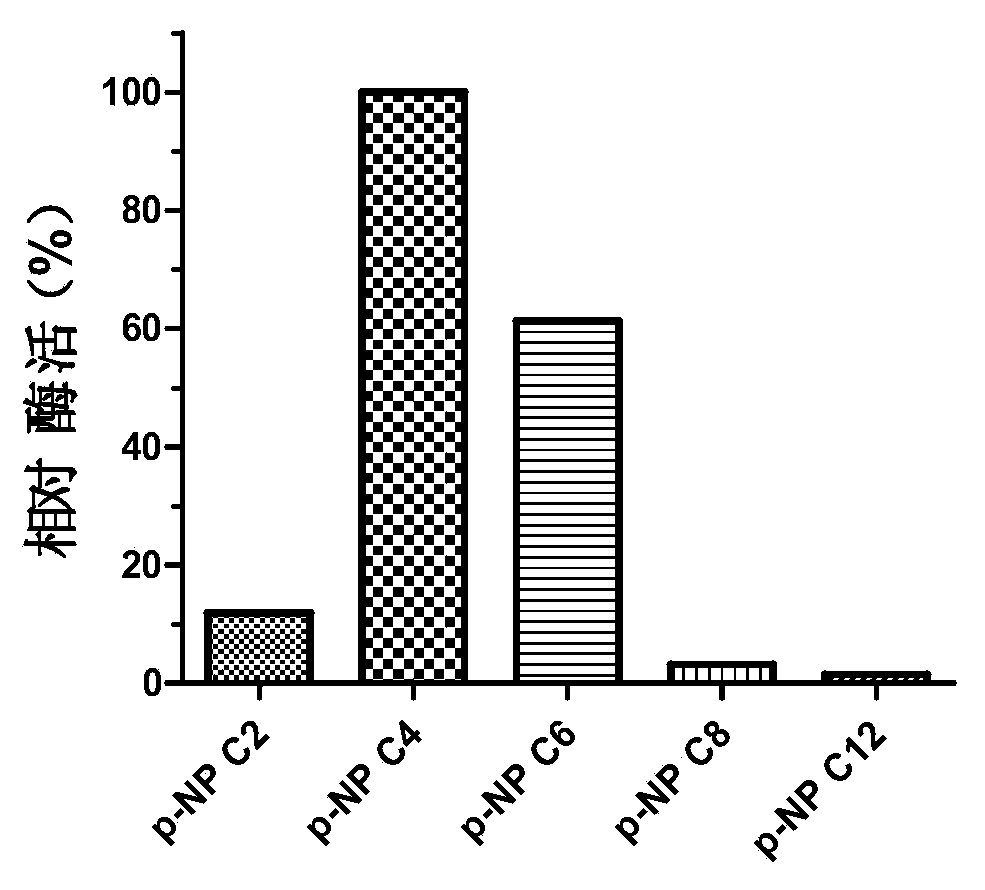Patents
Literature
433 results about "Isobutyric acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Isobutyric acid, also known as 2-methylpropanoic acid, is a carboxylic acid with structural formula (CH₃)₂CHCOOH. It is a colorless liquid with a somewhat unpleasant odor. It is soluble in water and organic solvents. Isobutyric acid is an isomer of n-butyric acid. Deprotonation or esterification of isobutyric acid gives derivatives called isobutyrates. Isobutyric acid is found in the free state in carobs (Ceratonia siliqua), in vanilla, and in the root of Arnica dulcis, and as an ethyl ester in croton oil.
Gene products of bacillus licheniformis which form odorous substances and improved biotechnological production methods based thereon
InactiveUS20070190605A1Reduce formationImprove filtering effectBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisPropanoic acid
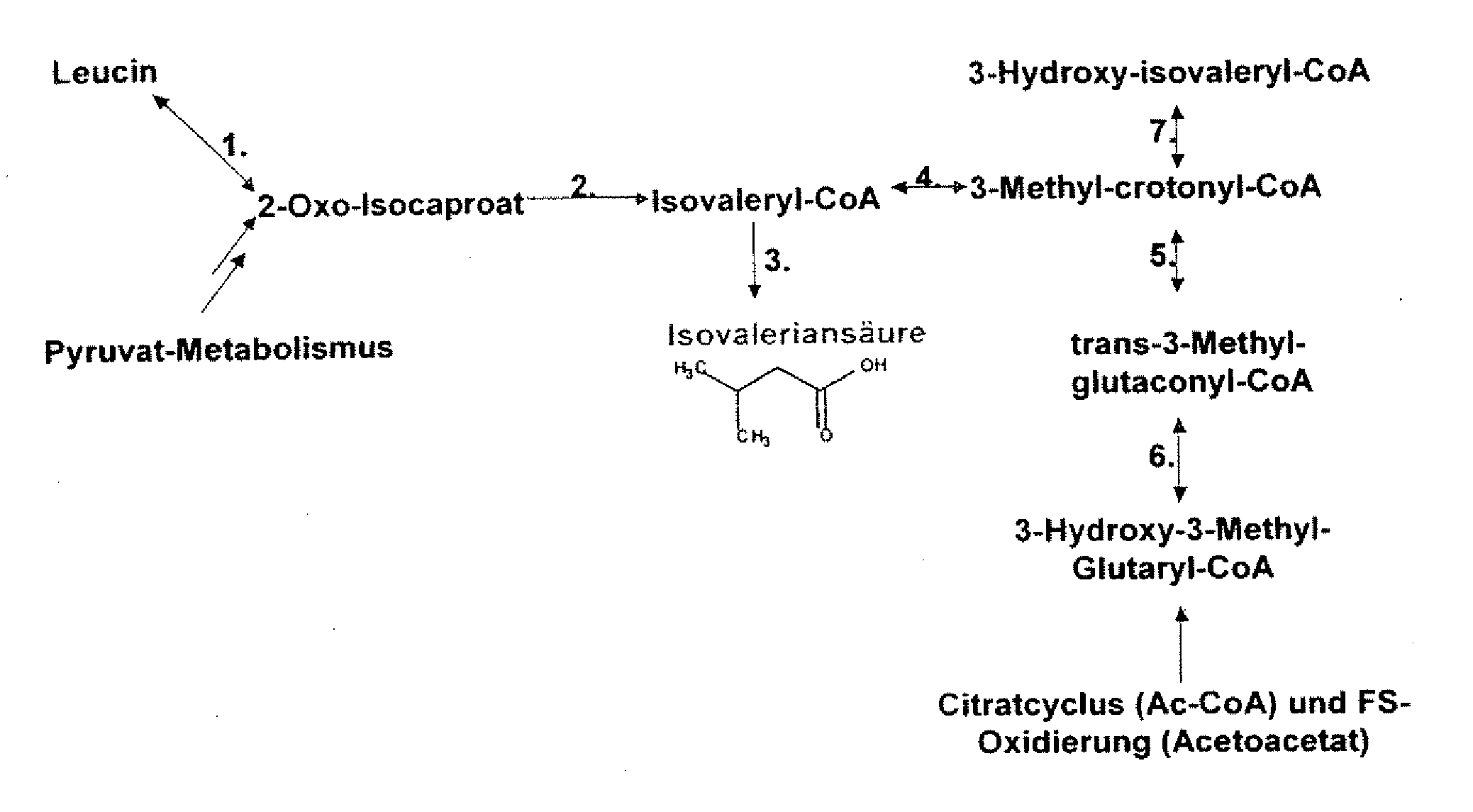
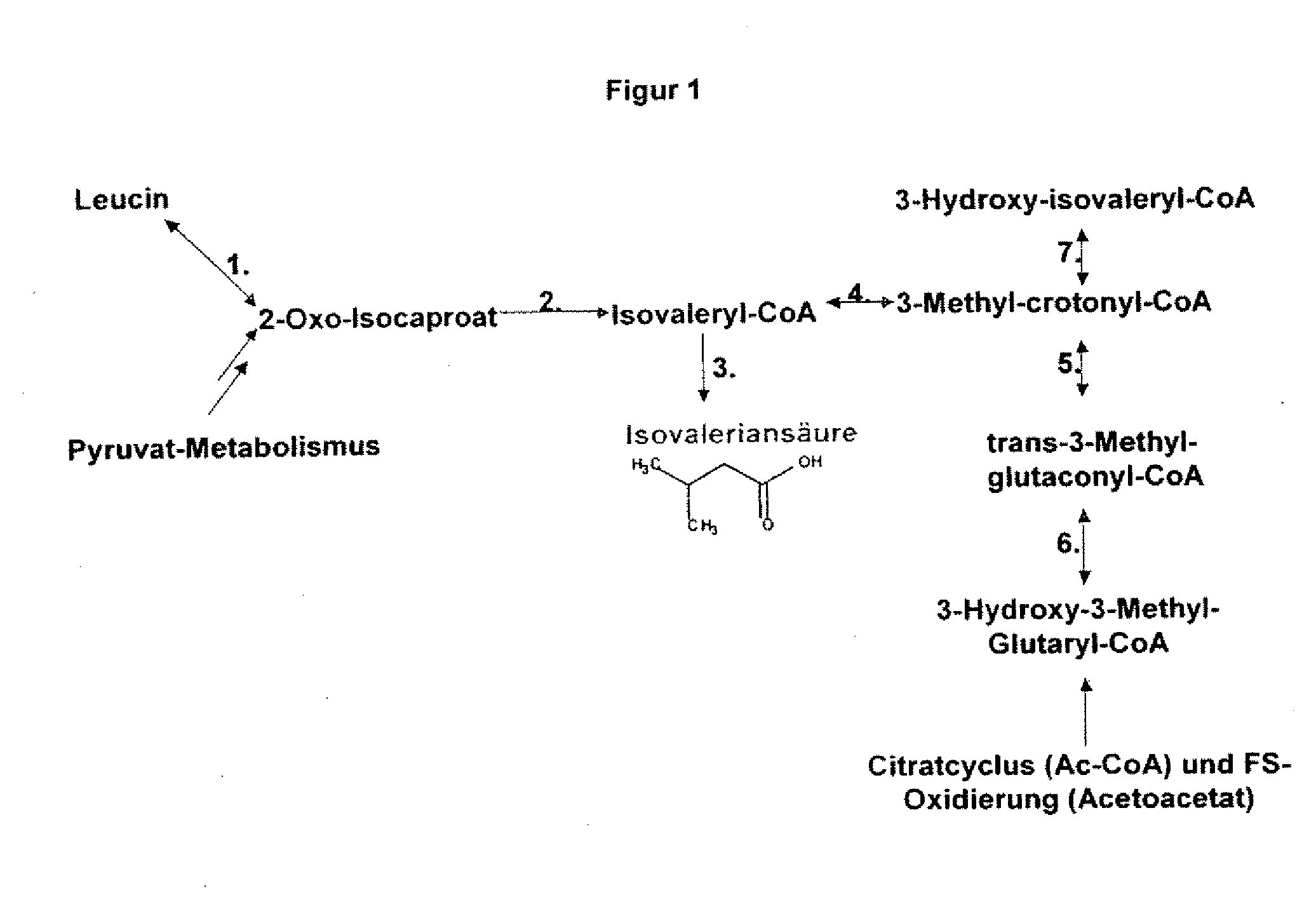
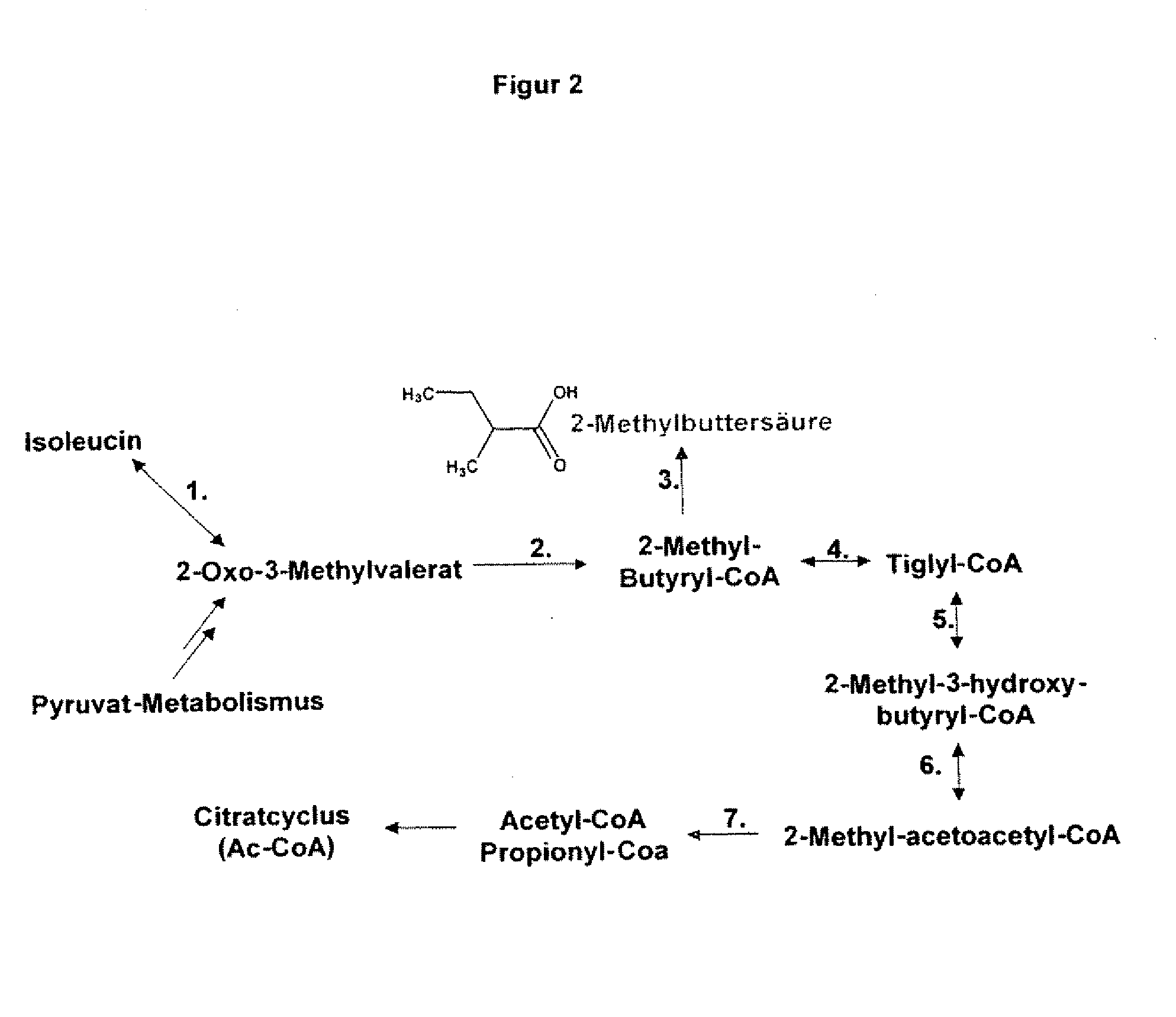
The present invention relates to 25 hitherto undescribed genes of B. licheniformis and gene products derived therefrom and all sufficiently homologous nucleic acids and proteins thereof. They occur in five different metabolic pathways for the formation of odorous substances. The metabolic pathways in question are for the synthesis of: 1) isovalerian acid (as part of the catabolism of leucine), 2) 2-methylbutyric acid and / or isobutyric acid (as part of the catabolism of valine and / or isoleucine), 3) butanol and / or butyric acid (as part of the metabolism of butyric acid), 4) propyl acid (as part of the metabolism of propionate) and / or 5) cadaverine and / or putrescine (as parts of the catabolism of lysine and / or arginine). The identification of these genes allows biotechnological production methods to be developed that are improved to the extent that, to assist these nucleic acids, the formation of the odorous substances synthesized via these metabolic pathways can be reduced by deactivating the corresponding genes in the micro-organism used for the biotechnological production. In addition, these gene products are thus available for preparing reactions or for methods according to their respective biochemical properties.
Owner:BASF AG
Pharmaceutical composition and process
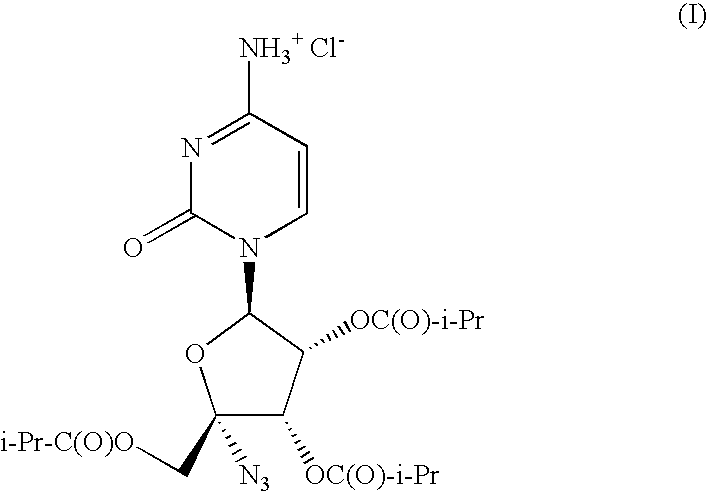
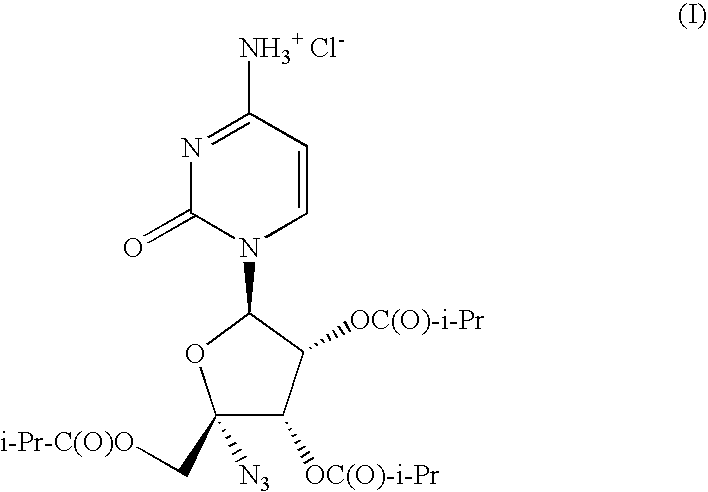
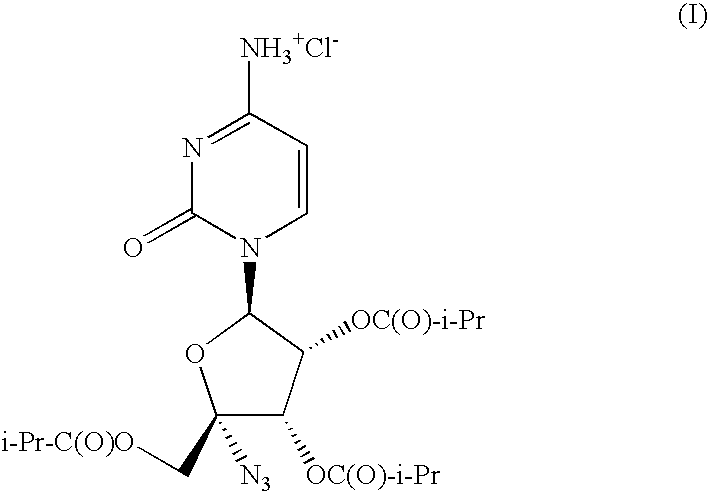
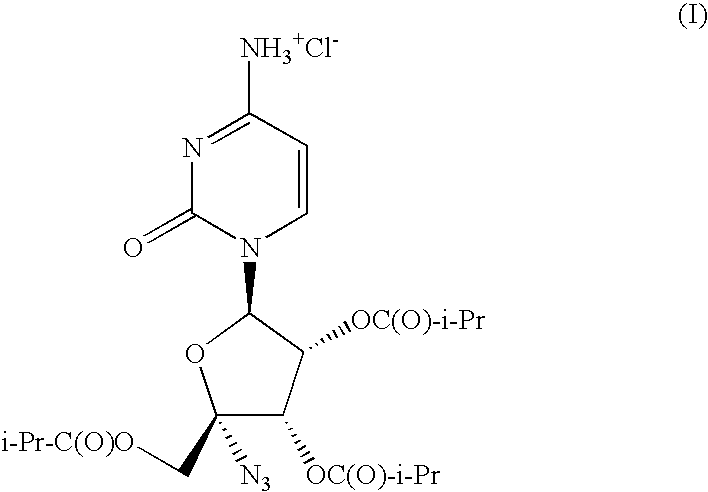
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a solid suspension prepared by hot melt extrusion of isobutyric acid (2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-2H-pyrimidin-1-yl)-2-azido-3,4-bis-iso-butyryloxy-tetrahydro-furan-2-ylmethyl ester; hydrochloride salt (I) and a polyethylene glycol (PEG) / polypropylene glycol (PPG) block copolymer.
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
Synergistic fungicidal compositions containing a 5-fluoropyrimidine derivative for fungal control in cereals
InactiveUS20110053966A1Good curative effectOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBiotechnologyChlorothalonil
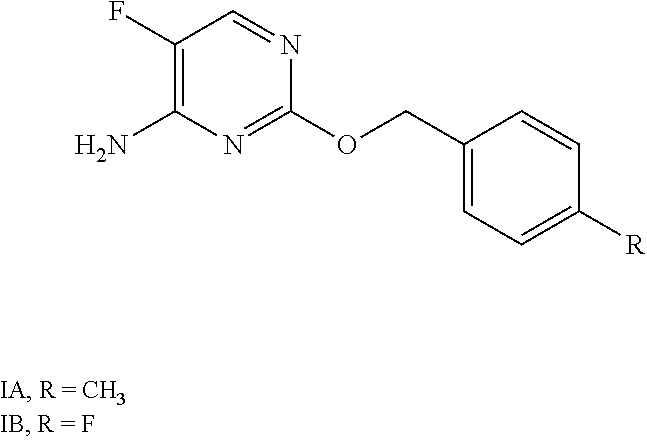
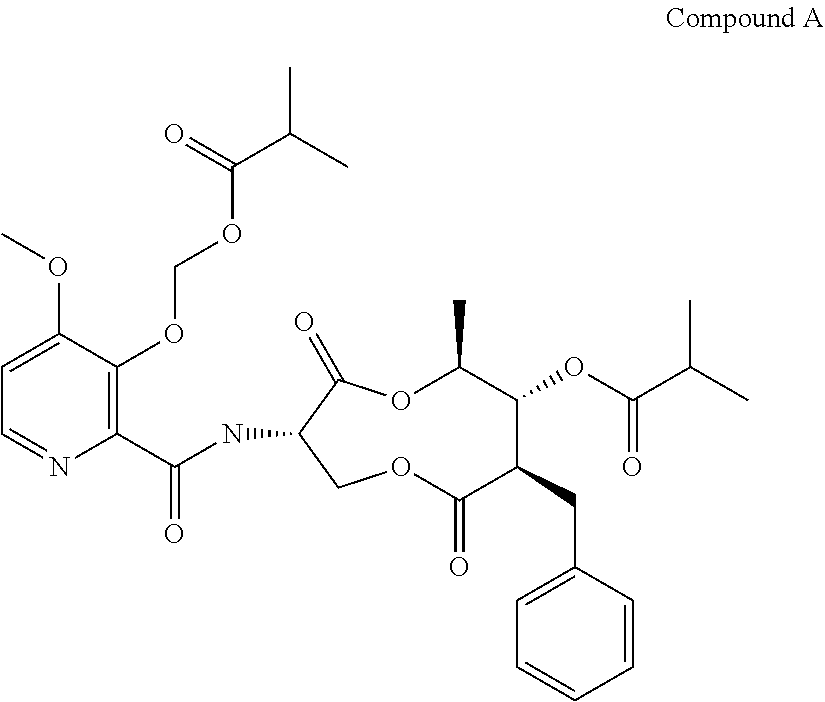
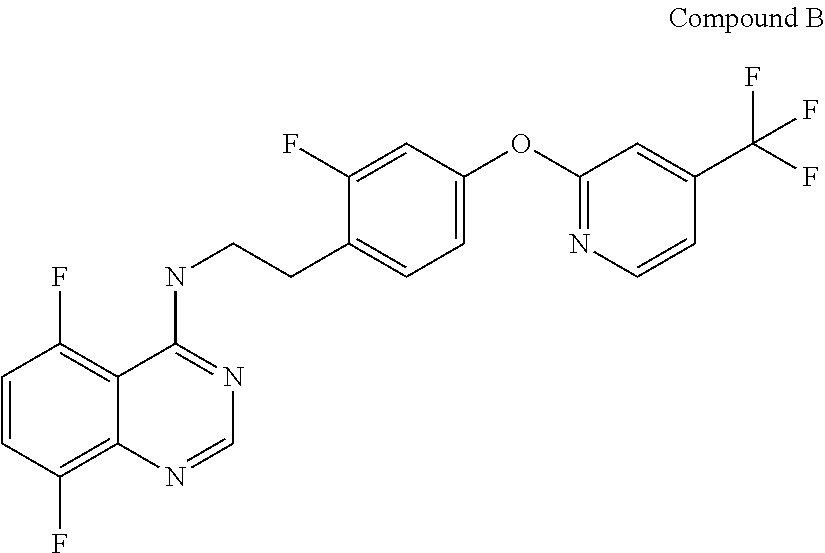
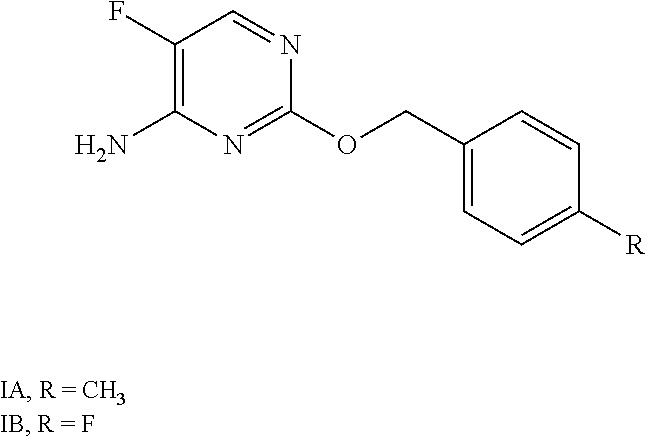
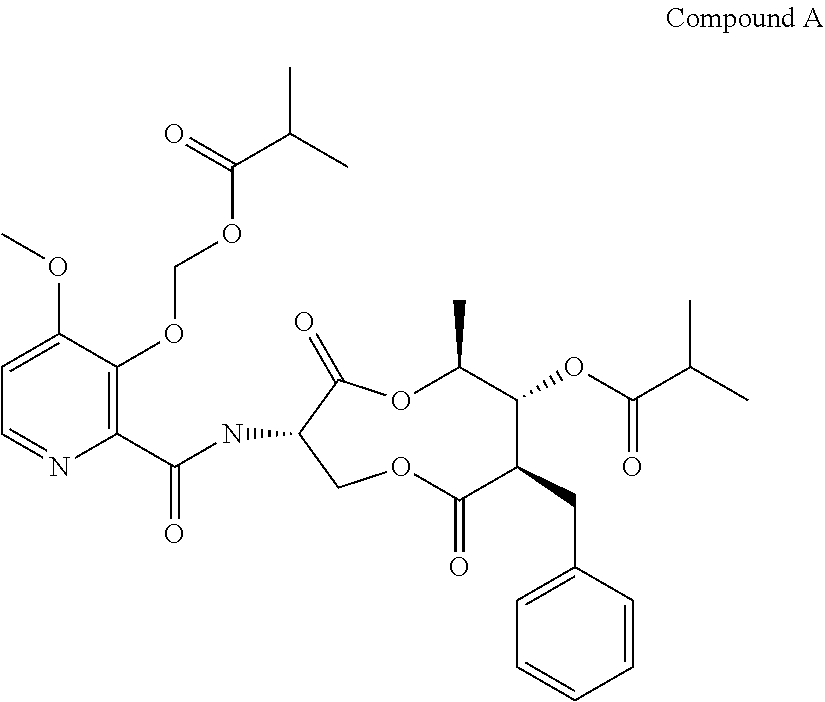
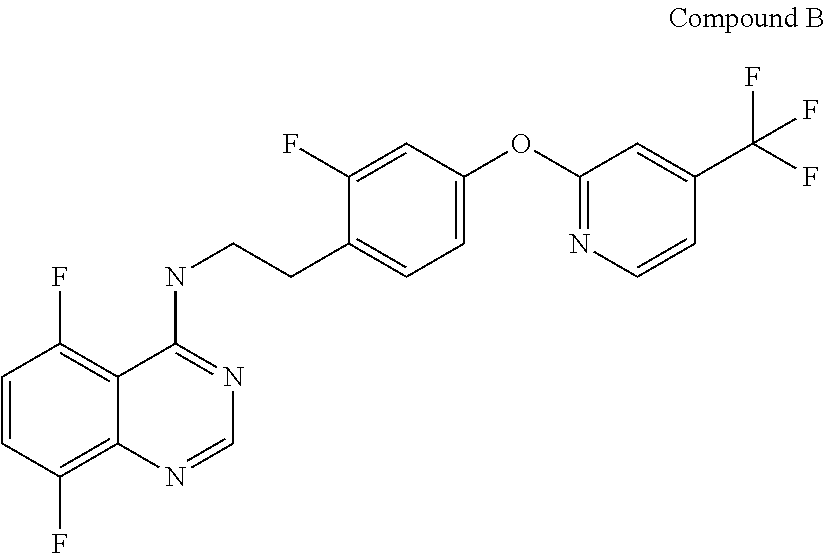
A fungicidal composition containing a fungicidally effective amount of a) a compound of Formula IA and / or IB and (b) at least one fungicide selected from the group consisting of epoxiconazole, prothioconazole, azoxystrobin, pyraclostrobin, penthiopyrad, isopyrazam, bixafen, boscalid, prochloraz, chlorothalanil, isobutyric acid (3S,6S,7R,8R)-8-benzyl-3-[(3-isobutyryloxymethoxy-4-methoxypyridine-2-carbonyl)-amino]-6-methyl-4,9-dioxo-[1,5]dioxonan-7-yl ester, and (5,8-difluoroquinazolin-4-yl)-{2-[2-fluoro-4-(4-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yloxy)-phenyl]-ethyl}-amine provides synergistic control of selected fungi.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Process for preparing a catalyst for use in production of methacrylic acid and process of preparing methacrylic acid
InactiveUS6498270B1Lower performance requirementsHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsGas phaseDehydrogenation
The present invention provides a process for preparing a catalyst and the same for use in production of methacrylic acid, which is characterized by molding a raw material including a powder containing phosphorus and molybdenum at the specific pressure. The invention also provides a process for preparing methacrylic acid by gas phase oxidation and / or oxidative dehydrogenation of at least one compound selected from the group consisting of methacrolein, isobutyraldehyde and isobutyric acid in the presence of the catalyst.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Synergistic fungicidal compositions containing a 5-fluoropyrimidine derivative for fungal control in cereals
A fungicidal composition containing a fungicidally effective amount of a) a compound of Formula IA and / or IB and (b) at least one fungicide selected from the group consisting of epoxiconazole, prothioconazole, azoxystrobin, pyraclostrobin, penthiopyrad, isopyrazam, bixafen, boscalid, prochloraz, chlorothalanil, isobutyric acid (3S,6S,7R,8R)-8-benzyl-3-[(3-isobutyryloxymethoxy-4-methoxypyridine-2-carbonyl)-amino]-6-methyl-4,9-dioxo-[1,5]dioxonan-7-yl ester, and (5,8-difluoroquinazolin-4-yl)-{2-[2-fluoro-4-(4-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yloxy)-phenyl]-ethyl}-amine provides synergistic control of selected fungi.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Process for producing catalyst for methacrylic acid production
InactiveUS20070010394A1High yieldHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsGas phaseWater insoluble
The object of the present invention is to provide a method for preparing a catalyst for producing methacrylic acid by subjecting methacrolein, isobutyl aldehyde or isobutyric acid to gas phase catalytic oxidation with high yield and high selectivity. A method for preparing a catalyst for producing methacrylic acid by subjecting methacrolein, isobutyl aldehyde or isobutyric acid to gas phase catalytic oxidation, the method comprising: (a) a step of blending compounds each containing any one of Mo, V, P, Cu, Cs or NH4 with water to prepare an aqueous solution or dispersion of the compounds (hereinafter referred to, both included, as a slurry); (b) a step of drying the slurry obtained in the step (a) to obtain a dried slurry; (c) a step of calcining the dried slurry obtained in..the step (b) to obtain a calcined body; (d) a step of filtering a mixture obtained by blending the calcined body obtained in the step (c) with water to separate an aqueous solution and water-insoluble matter; and (e) a step of drying the water-insoluble matter obtained in the step (d) to obtain a dried water-insoluble body.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Total sesquiterpene lactone extract of centipeda minima, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101732383AInhibition of proliferative abilityInhibition of tumor proliferationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistrySilica gelTumor cells
The invention provides a total sesquiterpene lactone extract of centipeda minima, a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: crushing dried total centipeda minima, and extracting centipeda minima volatile oil by a supercritical carbon dioxide extracting method; and enriching the centipeda minima volatile oil through macroporous adsorption resin column chromatography or silica gel column chromatography to obtain the total sesquiterpene lactone extract of the centipeda minima. According to the method, the total sesquiterpene lactone with effect of inhibiting tumor proliferation is extracted from Chinese medicament centipeda minima and is enriched for the first time; the extract is rich in short-leaf geraniin; the extract contains at least nine sesquiterpene lactone compounds, wherein the angelic acid centipeda minima and the isobutyric acid centipeda minima are new active sesquiterpene lactone compounds; by the preparation method, the yield is high; the method is suitable for industrialized production; and the extract has the effect of inhibiting tumor cell proliferation, and can be used for preparing various medicaments or health-care products with anti-tumor effect.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Biofuel and chemical production by recombinant microorganisms via fermentation of proteinacious biomass
Provided herein are metabolically modified microorganisms characterized by having an increased keto-acid flux when compared with the wild-type organism and comprising at least one polynucleotide encoding an enzyme, and causing the production of a greater quantity of a chemical product when compared with the wild-type organism. The recombinant microorganisms are useful for producing a large number of chemical compositions from various nitrogen containing biomass compositions and other carbon sources. More specifically, provided herein are methods of producing alcohols, acetaldehyde, acetate, isobutyraldehyde, isobutyric acid, n- butyraldehyde, n-butyric acid, 2-methyl-l-butyraldehyde, 2-methyl-l -butyric acid, 3- methyl-l-butyraldehyde, 3 -methyl- 1 -butyric acid, ammonia, ammonium, amino acids, 2,3-butanediol, 1,4-butanediol, 2-methyl-l, 4-butanediol, 2-methyl- 1,4-butanediamine, isobutene, itaconate, acetoin, acetone, isobutene, 1,5-diaminopentane, L-lactic acid, D- lactic acid, shikimic acid, mevalonate, polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), isoprenoids, fatty acids, homoalanine, 4-aminobutyric acid (GABA), succinic acid, malic acid, citric acid, adipic acid, p-hydroxy-cinnamic acid, tetrahydrofuran, 3-methyl-tetrahydrofuran, gamma-butyrolactone, pyrrolidinone, n-methylpyrrolidone, aspartic acid, lysine, cadeverine, 2-ketoadipic acid, and / or S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM), from a suitable nitrogen rich biomass.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Pharmaceutical composition and process
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a solid suspension prepared by hot melt extrusion of isobutyric acid (2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-2H-pyrimidin-1-yl)-2-azido-3,4-bis-iso-butyryloxy-tetrahydro-furan-2-ylmethyl ester; hydrochloride salt (I) and a polyethylene glycol (PEG) / polypropylene glycol (PPG) block copolymer.
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
Concentrated feed for simultaneous reduction of nitrogen, phosphorus and methane emission of cow
InactiveCN106212911AIncrease milk productionIncrease profitFood processingAnimal feeding stuffSodium bicarbonateSpanish oregano
The present invention relates to a concentrated feed for simultaneous reduction of nitrogen, phosphorus and methane emission of cow. The concentrated feed includes: 46%-50% of corn, 5%-8% of a concentrated molasses fermentation liquid, 18%-24% of wheat bran, 6%-10% of cottonseed meal, 6%-10% of soybean meal, 0.7%-1.2% of salt, 1%-2% of sodium bicarbonate, 0.5%-1% of magnesium oxide, 1.0%-2.0% of stone flour, 0.15%-0.25% of isobutyric acid, and 0.08%-0.12% of 1% oregano oil powder. The invention uses the concentrated feed to regulate rumen fermentation of cow, improve intestinal amino acid balance and reduce dietary phosphorus levels in order to improve the utilization of nitrogen, phosphorus and energy, and the rate of milk production, as well as to reduce emissions of nitrogen, phosphorus and methane in dairy. The invention has economic benefits of reduce feeding cost and improving the utilization of nitrogen, energy and phosphorus of the cow, and milk yield, and has ecological benefits of reducing the emissions of nitrogen, phosphorus and methane in dairy to reduce environmental pollution, and integrates production increase, energy saving and emission reduction in one.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Synthesis method of photoinitiator 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propyl ketone
ActiveCN103613492AReduce consumptionQuick responseOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by condensationKetone synthesisCatalytic effect
The invention relates to a synthesis method of a photoinitiator 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propyl ketone, which comprises the following steps: reacting high-purity gas phosgene with isobutyric acid to synthesize isobutyryl chloride; and carrying out chlorine substitution reaction by a cascade technique: exhaust of a first reaction kettle after chlorine introduction is connected into a second reaction kettle in cascade, and hydrogen chloride and chlorine in the exhaust released by the first reaction enter the second reaction kettle to catalyze the absorption and utilization. The method can well enhance the purity of isobutyryl chloride and further enhance the purity and yield of the product 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propyl ketone; and the catalytic action of hydrogen chloride in the exhaust is utilized to increase the reaction speed, lower the chlorine consumption and enhance the product content. The generated exhaust is recycled after innocent treatment, thereby solving the problem of environmental pollution of the exhaust.
Owner:岳阳市国发植物用药工程技术研究中心有限公司
Conductive slurry
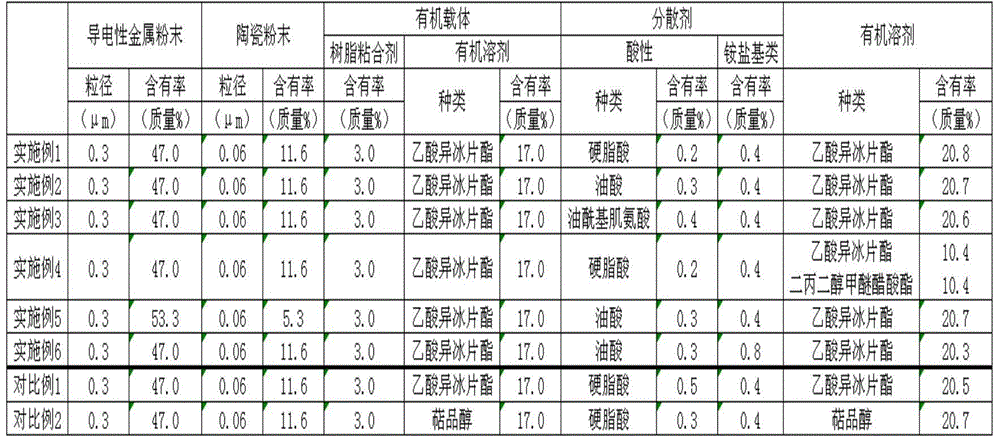
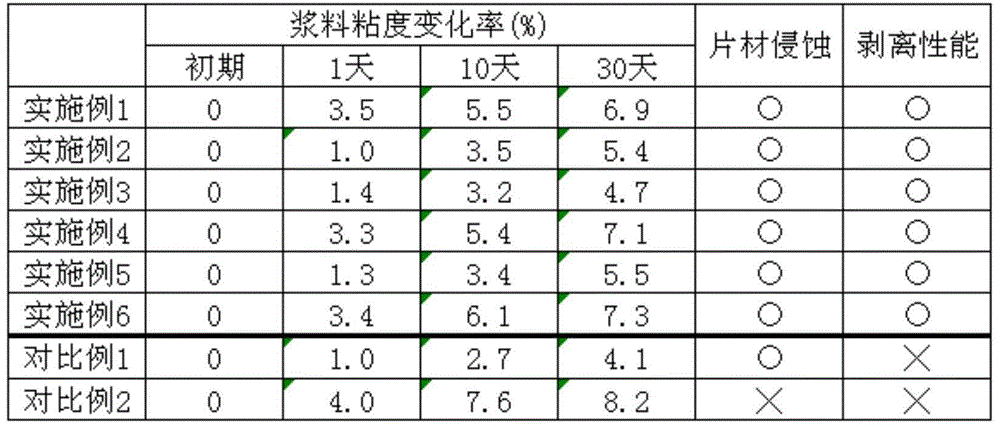
ActiveCN105321711AAvoid erosionSuppresses problems such as poor peelingFixed capacitor electrodesStacked capacitorsSlurryIsobornyl thiocyanoacetate
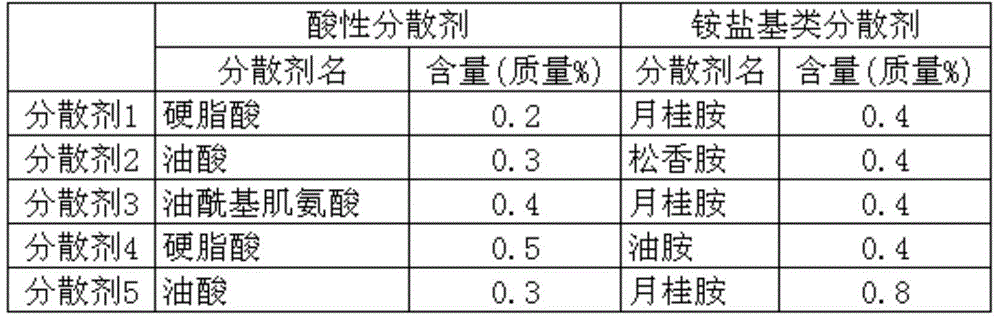
The invention provides a conductive slurry which is used in the stacking ceramic electronic member for forming an internal electrode; the conductive slurry is a compound that does not produce sheet erosion and has viscosity that decreases along with the time change. The conductive slurry used for the stacking ceramic device contains conductive metal powder, ceramic powder, resin binder, dispersant and organic solvent. The organic solvent is formed by at least one of dihydroabietic alcohol acetate, isobornyl acetate, isobonyl propionate, butyrate isobornyl thiocyanoacetate and isobutyric acid isobornyl thiocyanoacetate. The above dispersant contains the acid dispersant with the weight being over the 0.4% of the total conductive slurry.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
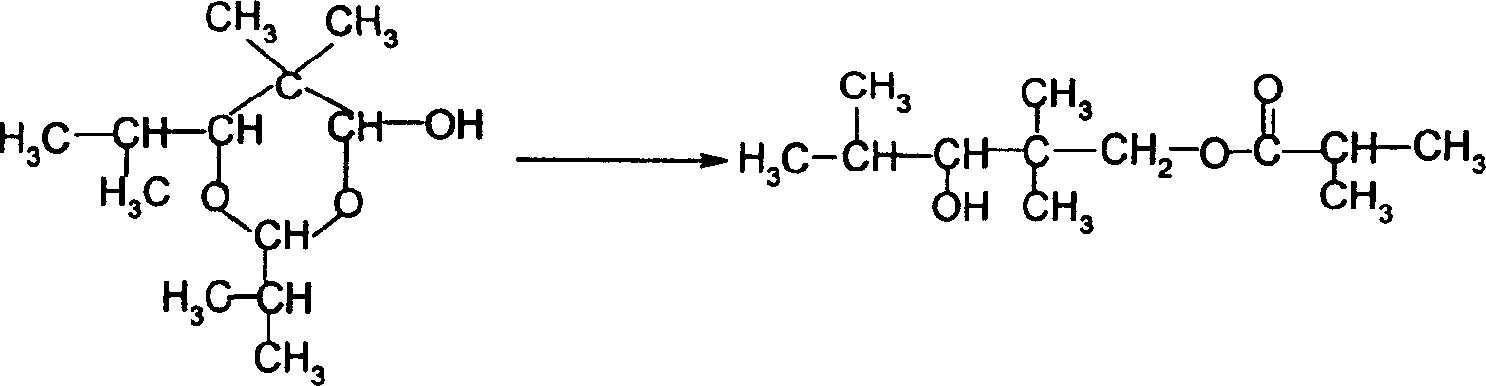
A method for preparing 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate
InactiveCN102267896AEmission reductionExtended service lifeOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationFixed bedSolid acid
A process for preparing 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate by esterification, using 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoisobutyrate Butyrate and isobutyric acid are used as raw materials, and a solid acid catalyst is used for a fixed-bed continuous esterification reaction. The esterification temperature is 70-150 ° C. The generated water is removed by azeotropic distillation; the esterification reaction product is rectified and removed. And recover unreacted 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoisobutyrate and isobutyric acid to obtain 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol Diisobutyrate. The method of the invention realizes the continuous production of 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate, has a simple operation mode, significantly improves production efficiency, reduces its production cost, and can reduce solid Pollutants and wastewater discharge, with excellent large-scale industrial application value.
Owner:江苏天音化工有限公司 +1
Natural banana essence
InactiveCN101513250AOvercoming the defect of not being pure and cleanPure natural feelingFood preparationPropionateISOAMYL BUTYRATE
The invention discloses natural banana essence. The natural banana essence is characterized by comprising the following components in weight percentages: 12-15% of isoamyl acetate, 6-9% of isoamyl butyrate, 0.10-0.15% of benzyl propionate, 0.01-0.02% of methyl heptine carbonate, 0.035-0.05% of gamma-decalactone, 0.05-0.08% of isobutyric acid cinnamyl ester, 0.1-0.15% of hexenyl acetate, 0.03-0.05% of isoamyl hexanoate, 0.5-1% of banana concentrate, 0.01-0.03% of acetal and 80.385-73.19% of propylene glycol. The natural banana essence overcomes a shortcoming of unnatural and impure flavor of the traditional banana essence formulation, and the banana essence also has more natural flavor by adding raw materials such as the banana concentrate, the gamma-decalactone, the methyl heptine carbonate and the like.
Owner:广州市凯虹香精香料有限公司
Oil soluble hydrogen sulfide scavenger
ActiveUS20150025258A1Fatty acid chemical modificationFatty acids production/refiningParticulatesScavenger
The concentration of hydrogen sulfide in a hydrocarbon can be mitigated by intruding therein a zinc carboxylate oxo complex composition prepared by reacting particulate zinc oxide with a mixture of two or more carboxylic acids wherein the zinc carboxylate oxo complex composition is soluble in hydrocarbons. Useful acids useful include acetic acid, oleic acid, isobutyric acid, lineoleic acid, cekanoic acid, and neodecanoic acid.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Production of 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,-3-pentadiol mono-isobutyric acid
InactiveCN1817850AImprove one-way yieldMild reaction conditionsPreparation by aldehyde oxidation-reductionHydrotalciteHomogeneous catalysis
Production of 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoester isobutyrate is carried out by condensation pre-treating isobutyl aldehyde, and Knigcharlo reacting in molecule under the action of hydrotalcite-like solid catalyst to obtain the final product. It has high single-pass recovery rate, gentle reactive condition and no corrosion.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Method for preparing waterborne plastic toy paint
The invention provides a method for preparing a waterborne plastic toy paint. The paint comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 50 to 70 percent of copolymer emulsion A of butyl acrylate, styrene and acrylonitrile, 10 to 15 percent of copolymer emulsion B of methyl methacrylate, styrene and N-methylol acrylamide, 2 to 5 percent of propylene glycol butyl ether film forming auxiliary agent, 5 to 7 percent of mono-isobutyric acid trimethyl pentanediol ester film forming auxiliary agent, 0.1 to 0.4 percent of polysiloxane and polyester copolymer leveling agent, 0.1 to 0.4 percent of polysiloxane mixture defoaming agent, 0.1 to 0.4 percent of associative type polyurethane thickener, 0.1 to 0.4 percent of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol organic amine neutralizer, 2 to 6 percent of hard polyethylene wax emulsion, 0 to 15 percent of deionized water and 0 to 25 percent of color paste; and the preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding all the acrylic acid emulsion, deionized water, organic amine neutralizer, leveling agent, defoaming agent, film forming auxiliary agents and wax emulsion to a paint mixing kettle with stirring at a rotary speed of 60 to 120rpm, stirring the mixture at a rotary speed of 200 to 300rpm for 10 to 20min, adding the color paste to the mixture at a rotary speed of 60 to 120rpm, stirring the mixture at a rotary speed of 200 to 300rpm for 10 to 20min, adding the thickener until the viscosity of the mixture meets the index of 70 to 110s(paint-1 cup) and the adhesive force of the spraying plate paint film reaches the first grade(by the cut test on an ABS plate), and filtering and packaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI FINE CHEM CO LTD
Preparation method of microzyme magnetic blotting composite microsphere adsorbent
InactiveCN103920471AImprove adsorption capacityImprove mechanical propertiesOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesFunctional monomerAdsorption equilibrium
The invention relates to a preparation method of a microzyme magnetic blotting composite microsphere adsorbent, and belongs to the technical field of environmentally-friendly functional material preparation. The method comprises the following steps: preparing ferriferrous oxide nanoparticles through a coprecipitation process, carrying out hydrophobic modification on the surface of the nanoparticles, preparing a stable Pickering emulsion with an oleic acid modified microzyme aqueous solution as a water phase, cyhalothrin as a template molecule, methacrylic acid and 4-vinylpyridine as functional monomers, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as a cross-linking agent, dimethyl 2,2'-azobis(2-methylpropionate) as an initiator and hydrophobic Fe3O4 as an oil phase, and carrying out thermal-initiated polymerization to prepare the microzyme magnetic blotting composite microsphere adsorbent. Blotting microspheres obtained in the invention have a good magnetic stability, and the adsorption balance, the dynamics and the selection identification performance of the adsorbent are researched through static state adsorption experiments. Results show that the blotting adsorbent prepared in the invention has a good adsorption capacity, fast adsorption kinetics, and has a selection identification performance on LC.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method of dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride-modified porous diatomaceous earth
InactiveCN105727903AGood physical and chemical stabilityHigh mechanical strengthFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesOther chemical processesSorbentAllyl chloride
The invention discloses a preparation method of dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride-modified porous diatomaceous earth.The preparation method is characterized by comprising the steps that diatomaceous earth is pretreated; the diatomaceous earth is prepared into porous diatomaceous earth; the surface of the diatomaceous earth is organized; 24%-34% by mass of deionized water and 42%-52% by mass of dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride are added in a reactor and stirred to be dissolved, then 18%-28% by mass of organized porous diatomaceous earth is added, uniform mixing is performed, 2%-5% by mass of dimethyl 2,2'-azobis(2-methylpropionate) is added, and the sum of all the components is 100%; a reflux reaction under stirring is performed for 6-8 h at the constant temperature of 65+ / -2 DEG C, solid-liquid separation is performed after cooling is performed, separated solids are washed with the deionized water until filtrate is neutral, filtering and drying are performed, and then the dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride-modified porous diatomaceous earth is obtained.The adsorbent has the very high adsorption capacity on grease and the good physical, chemical and mechanical properties and is high in regeneration capacity, more in repeated using time, low in cost, green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
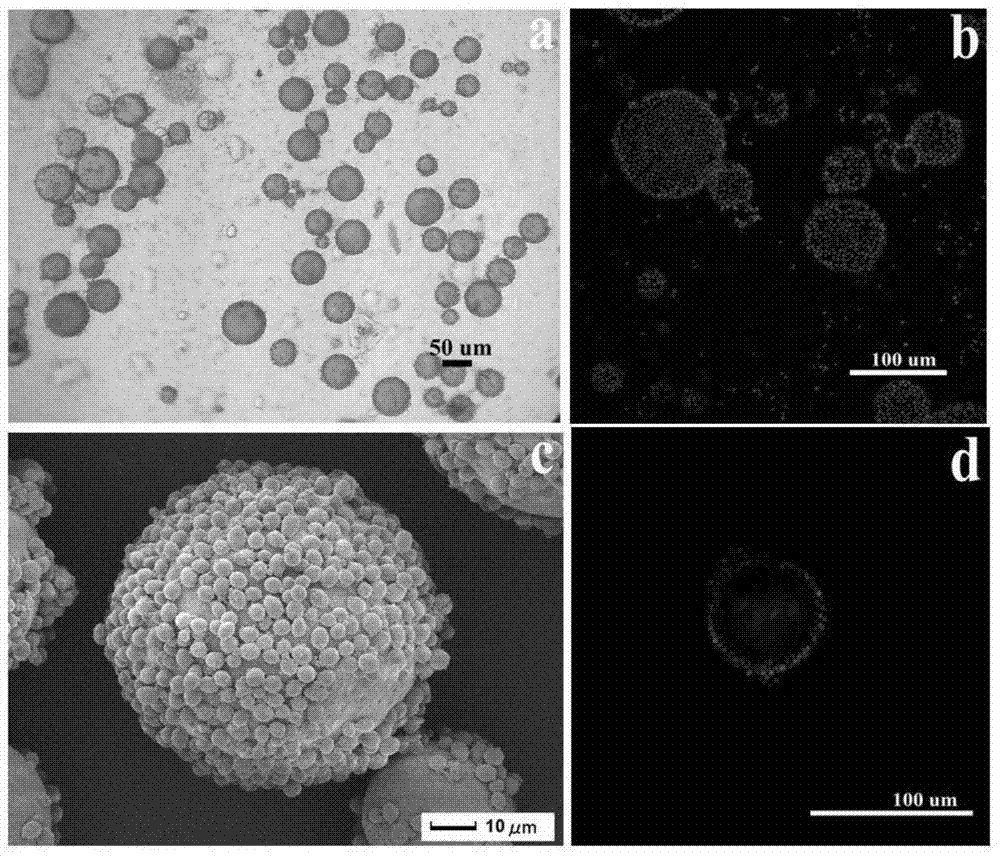
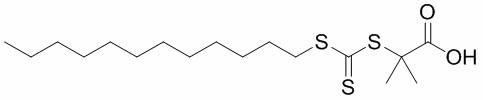
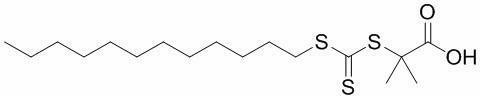
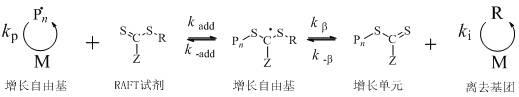
Preparation method for efficient chain transfer agent trithiocarbonate used for RAFT (reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer) polymerization
InactiveCN102690217AThe synthesis method is simpleHigh purityOrganic chemistryDistillationDissolution
The invention belongs to the field of polymer nano biological medicinal materials, particularly relates to a preparation method for efficient chain transfer agent trithiocarbonate used for RAFT polymerization. The method is characterized in that the chemical formula of the trithiocarbonate is C17H32O2S3, and comprises the following steps: adding potassium phosphate, a solvent and carbon bisulfide into a round-bottom flask for reaction 1-3 hours; adding do-decyl mercaptans to conduct addition reaction for 1-3 hours; and finally adding 2-bromine isobutyric acid to conduct esterification reaction for 13-24 hours. The brilliant orange trithiocarbonate can be obtained from the reacted solvent subjected to procedures of reduced pressure distillation for removal, dissolution, extraction, and washing, wherein the mass ratio of the potassium phosphate to the carbon bisulfide is 1:(1-3), as well as the mass ratio of the do-decyl mercaptans to the carbon bisulfide, and the mass ratio of the 2-bromine isobutyric acid to the carbon bisulfide are also 1: (1-3). According to the method provided by the invention, the synthesizing is simple, the purification is convenient, and the stability of the product is good. Moreover, the RAFT polymerization has an efficient chain transfer effect. Therefore, the method is favorable for advancing the RAFT large-scale industrial production, and has an extensive application prospect.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Novel esterase as well as coding gene and application of esterase
InactiveCN104140959AImprove qualityMild reaction conditionsHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesPropanoic acidNucleotide
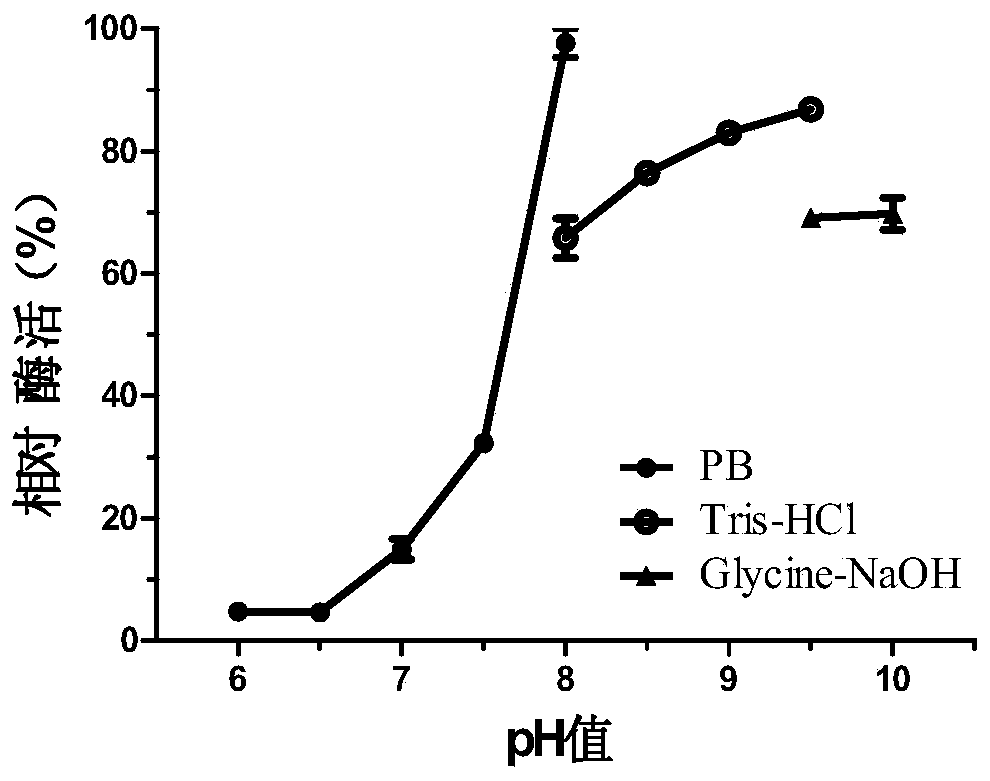
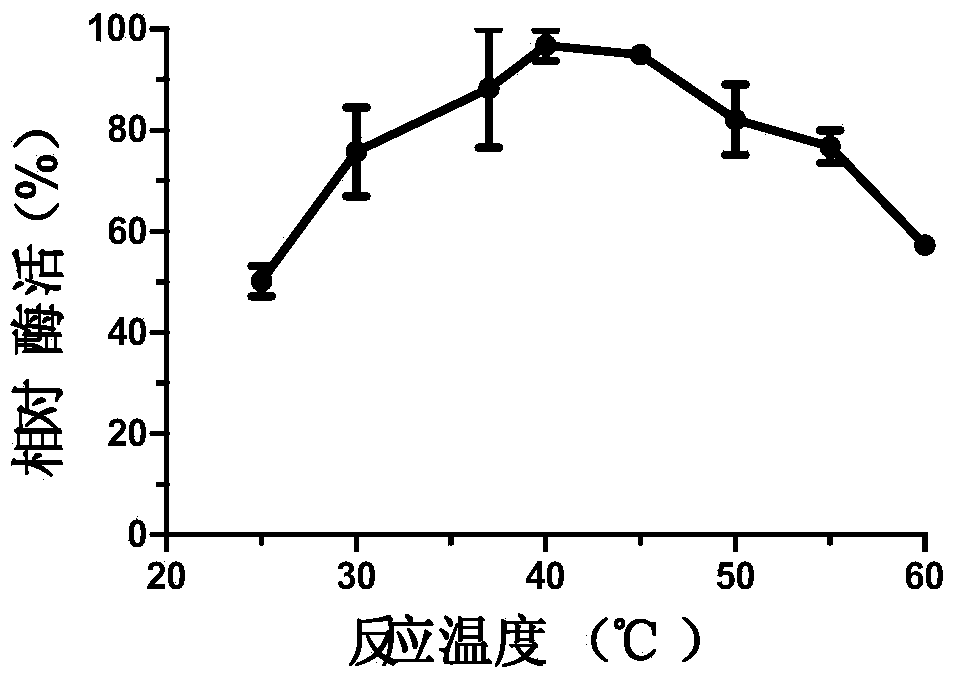
The invention discloses a novel esterase as well as a coding gene and an application of esterase. The esterase EST04211 has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The amino acid sequence of the gene of the esterase EST04211 is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The novel esterase disclosed by the invention is obtained by cloning Bacillus SCSIO15121 derived from deep sea of the Indian Ocean. The esterase has the largest characteristic that the esterification rate is 97% in catalytic synthesis of ethyl isobutyrate, and under similar conditions, the esterase can also catalyze propionic acid, butyric acid, valeric acid, caproic acid and ethanol, propanol, butanol, pentanol and hexanol to synthesize corresponding short-chain aromatic ester flavors, such as ethyl propionate, propyl propionate and butyl propionate, the esterification rate mostly reaches 85%-95%. The esterase can be applied in the industrial bio-manufacturing of the short-chain aromatic flavors, such as ethyl isobutyrate and the ester flavors are high in quality, belongs to natural products and can be applied in production industries, such as foods, cigarettes and daily chemical products.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for producing catalyst for methacrylic acid production
InactiveCN1795047AOrganic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalytic oxidationMethacrolein
The object of the present invention is to provide a method for preparing a catalyst for preparing methacrylic acid by gas-phase catalytic oxidation of methacrolein, isobutyraldehyde or isobutyric acid with high yield and high selectivity. The method comprises: (a) mixing compounds each containing any one of Mo, V, P, Cu, Cs or NH4 with water to prepare aqueous solutions or dispersions of these compounds (hereinafter, these two are referred to as slurries; ); (b) drying the slurry formed in step (a) to obtain a dry slurry; (c) calcining the dry slurry obtained in step (b) to obtain a calcined body; (d) filtering through mixing A step of separating the obtained mixture of the calcined body obtained in step (c) and water into an aqueous solution and a water-insoluble substance; (e) drying the water-insoluble substance obtained in step (d) to obtain a dry insoluble substance Water substance steps.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Culex attractant
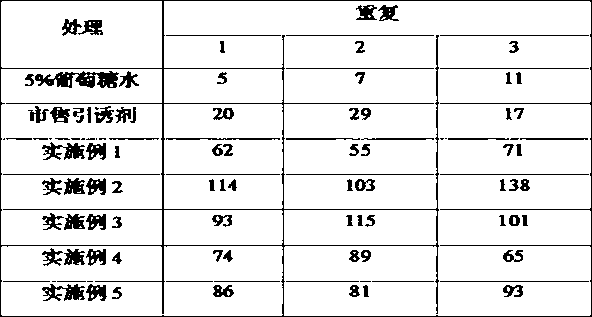
The invention belongs to the technical field of attractant tools and particularly relates to a Culex attractant. The Culex attractant disclosed by the invention consists of the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 0.0001-1% of 1-matsutake alcohol, 0.0001-1% of lactic acid, 0.0001-1% of L-lactic acid, 0.0001-1% of n-heptanoic acid, 0.0001-1% of hexanoic acid, 0.0001-1% of acetone, 0.0001-1% of benzaldehyde, 0.0001-1% of isobutyric acid, 0.0001-1% of phenylalanine, 0.0001-1% of ethyl acetate, 1-70% of glucose, 1-50% of ethanol and the balance of water. The Culex attractant disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the attractive force to Culex is strong, the environment pollution and the odor are avoided, and the use is simple and convenient; and the Culex attractant is nontoxic to human and livestock and is a safe, environment-friendly, efficient, simple and convenient Culex prevention and treatment product.
Owner:德清科中杰生物科技有限公司
Biomarker of depression, method for measuring biomarker of depression, computer program, and recording medium
Provided is a method for using low molecular weight compounds found in the body as a biomarker for diagnosing depression. Specifically, more than one compound selected from a group comprising the following are used: ADP-ribose, ATP, ADP, AMP, serotonin, tryptophan, kynurenine, SDMA (symmetrical dimethylarginine), threonine, glyceric acid, serine, N-acetylaspartic acid, glutamic acid, trigonelline, creatine, 2-methylserine, sphingosine, homovanillic acid, piperidine, sulfoxidized methionine, pipecolic acid, sphinganine, gamma-butyrobetaine, guanidinoacetic acid, isobutyric acid, creatinine, sarcosine, 3-methylbutyric acid, nicotinamide, betaine, ornithine, carnitine, ethanolamine, phosphoethanolamine, taurine, hypotaurine, aspartic acid, methionine, and tyrosine.
Owner:HUMAN METABOLOME TECH
Process for synthesizing 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propyl ketone
InactiveCN102304033AReduce pollutionThe synthesis process is reasonableOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationKetoneAlkaline hydrolysis
The invention relates to a process for synthesizing 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propyl ketone, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: obtaining a crude product of 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propyl ketone by using isobutyric acid as raw material via acylation, Friedel-Crafts and alkaline hydrolysis reaction; then finely steaming to obtain a finished product of the 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propyl ketone. The synthesis process provided by the invention is more reasonable, no sulfur dioxide gas is released in the production process, the generated sodium chloride has less environment pollution, and the product yield is high.
Owner:LIANYUNGANG SHENGNAN CHEM
Method for preparing 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate
InactiveCN104341304AAvoid the needEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationEsterification reactionChemistry
The present invention discloses a method for preparing 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate. According to the method, green oxane(2,4-diisopropyl-5,5-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane) and isobutyric acid are subjected to the catalysis cracking and esterification reaction under the catalyst effect to synthesize the 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate, wherein the isobutyric acid is added in a dropwise manner, and a molar ratio of the (2,4-diisopropyl-5,5-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane) to the isobutyric acid is 1:2-1:5. The method has characteristics of simple process, clean process and high yield.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of coumarin molecularly-imprinted electrochemical sensor
InactiveCN105353007AHigh selectivityHigh affinityMaterial electrochemical variablesN dimethylformamideDeoxygenation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a coumarin molecularly-imprinted electrochemical sensor. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the steps of firstly, modifying a glassy carbon electrode with a silane coupling agent and nano-gold, adding, by mass, 12-22% of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, 2.5-10% of methyl methacrylate, 63-83% of N, N-dimethylformamide, 1.0-2.0% of dimethyl 2,2'-azobis(2-methylpropionate) and 1.0-4.0% of coumarin into a reactor, stirring and dissolving the ingredients, introducing nitrogen for conducting deoxygenation for 10 minutes, conducting stirring and a reaction for 10-12 hours at the temperature of 75-80 DEG C under the nitrogen atmosphere, removing template molecules with a mixed solution of ethyl alcohol and hydrochloric acid, conducting drying, obtaining coumarin molecularly-imprinted polymer, then applying the polymer to a modified electrode, obtaining the coumarin molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor, and connecting the sensor with an electrochemical workstation for forming a sensor capable of conducting specific template molecular recognition. The sensor prepared through the preparation method is low in cost, high in sensitivity, good in specificity, high in detection speed and capable of being used repeatedly.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Conductive paste, lamination ceramics electronic assembly and method for manufacturing the electronic assembly
InactiveCN101154478AGood peeling effectSuppress wrinklesFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricPropanoic acidAliphatic hydrocarbon
The invention provides conductive paste for forming the inner electrode of the laminated ceramic electronic parts, which is characterized in that the conductive paste includes conductive power and organic carrier. An organic adhesion agent in the organic carrier has the ethyl cellulose resin and / or the alkide resin as the main components. The solvent in the organic carrier comprises one or more components selected from propionic acid isoborneol ester, butyrate isoborneol ester and isobutyric acid isoborneol ester and the aliphatic hydrocarbon with the carbon atoms of 5-40. The conductive paste may effectively prevent the sheet material from corrading even under the solvent drying temperature of 40-90 DEG C when the ceramic crude sheet is thinner.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Resourceful treatmentmethod for isobutyrate waste water
ActiveCN107176739AHigh salt concentrationA decrease in the amount of free waterCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesAlkali metal sulfite/sulfate purificationChemical oxygen demandDistillation
The invention discloses a resourceful treatment method for isobutyrate waste water, and relates to the technical field of comprehensive utilization of industrial waste. The method includes the steps: enabling isobutyrate to transform into water solution of isobutyric acid and sulfate by the aid of concentrated sulfuric acid; enabling the content of isobutyric acid in sulfate water solution to reduce to 0.5-1wt% at the salting-out temperature ranges from 32 DEG C to 75 DEG C under the salting-out action of sodium sulfate; performing simple distillation, and enabling COD (chemical oxygen demand) in a water phase to reduce to 2000mgO2 / L or less. The mass fraction of organic matters in obtained sodium sulfate or calcium sulfate is lower than 0.2wt%, the organic matters can serve as product to be sold, the obtained isobutyric acid can be circularly used for production of sixteen alcohol ester after be refined, and the isobutyrate waste water is recycled.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
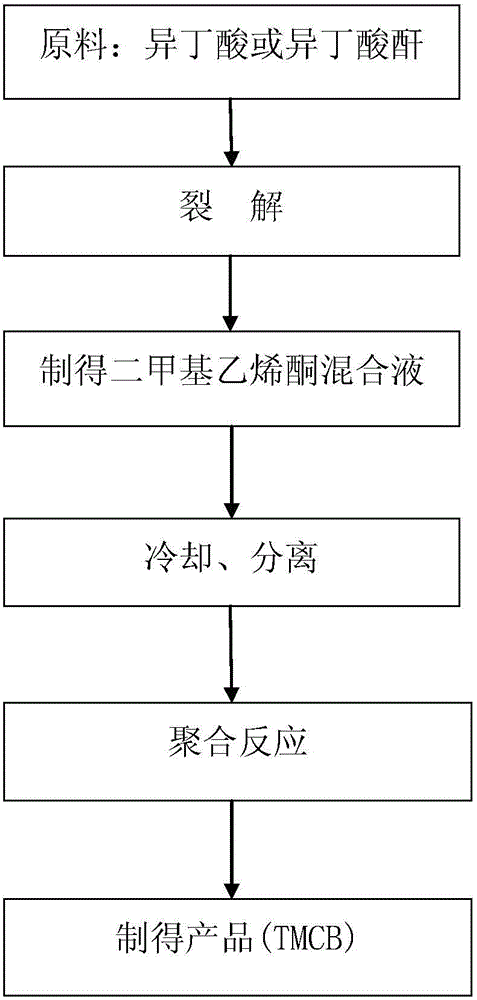
Method for synthesis of 2, 2, 4, 4-tetramethyl-1, 3-cyclobutanedione
InactiveCN105732354AAvoid heavy consumptionReduce investmentOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationSimple Organic CompoundsFixed bed
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic compound preparation, and is a preparation method for 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanedione, which comprises isobutyric acid or isobutyric anhydride and Under the condition that the volume ratio of the inert gas is 1 / 10 to 1 / 5, the cracking reaction is carried out through a fixed bed cracking reactor to obtain dimethyl ketene; Direct polymerization in solution to obtain 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanedione. Advantages of the present invention: the preparation process of 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanedione is optimized, that is, the product after cracking is directly polymerized, equipment investment is reduced, and washing tower or absorption The tower avoids a large amount of absorption liquid consumption and energy loss; the above-mentioned features make the inventive technology more flexible than the methods currently used in industrial production, and compared with other competitive processes.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com