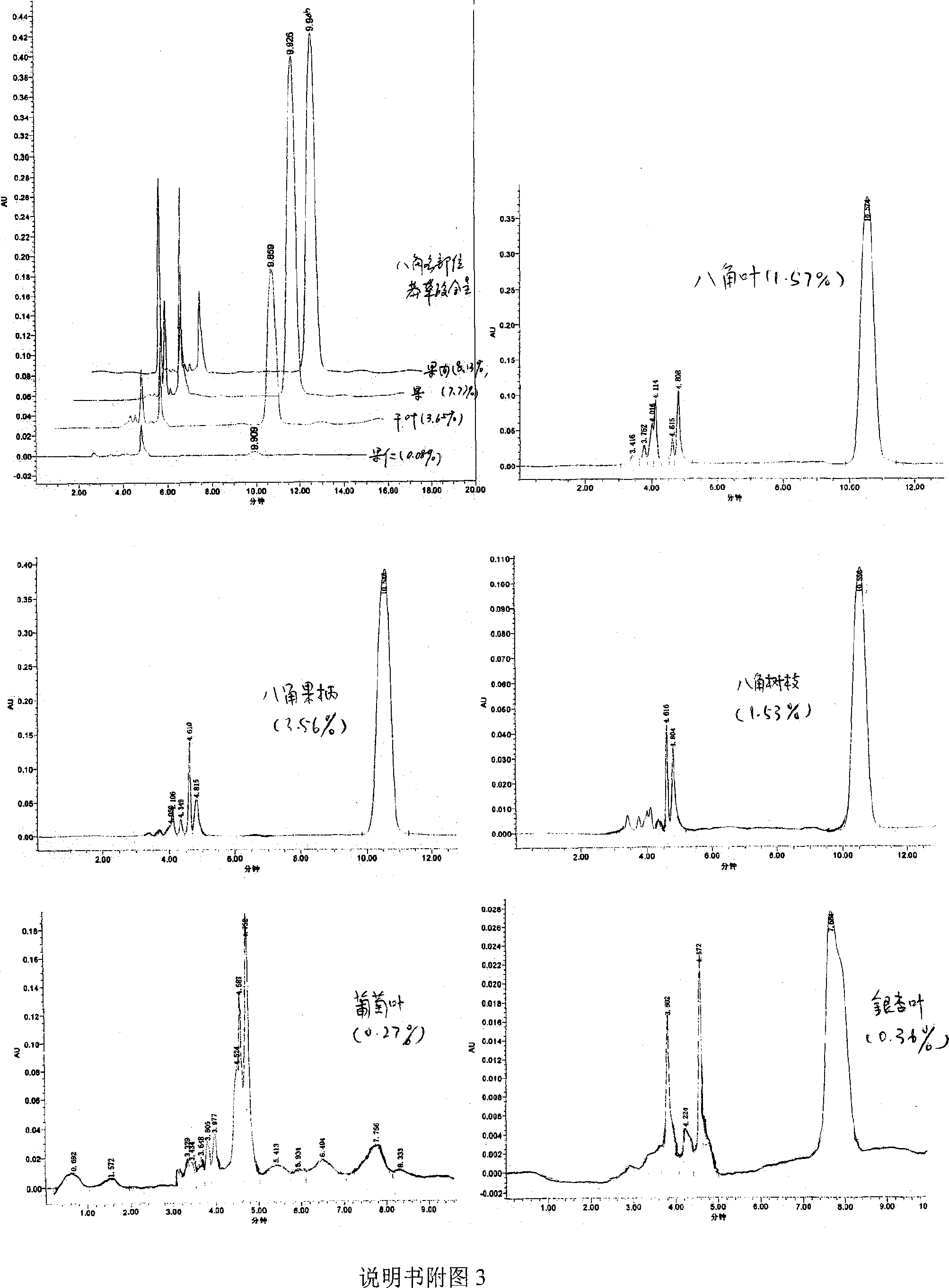
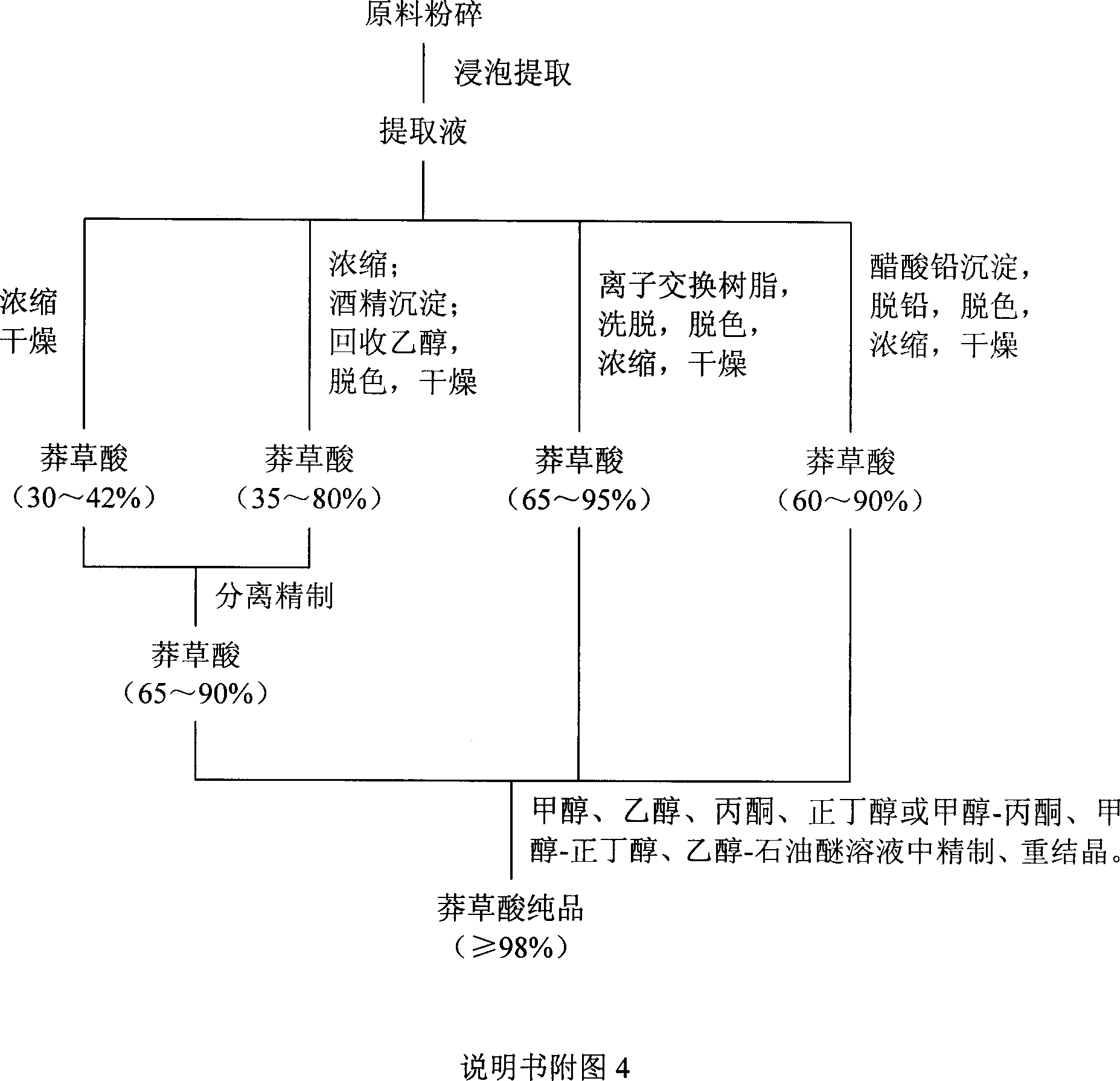
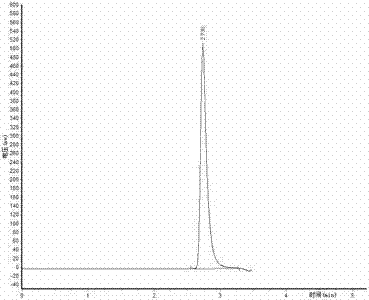
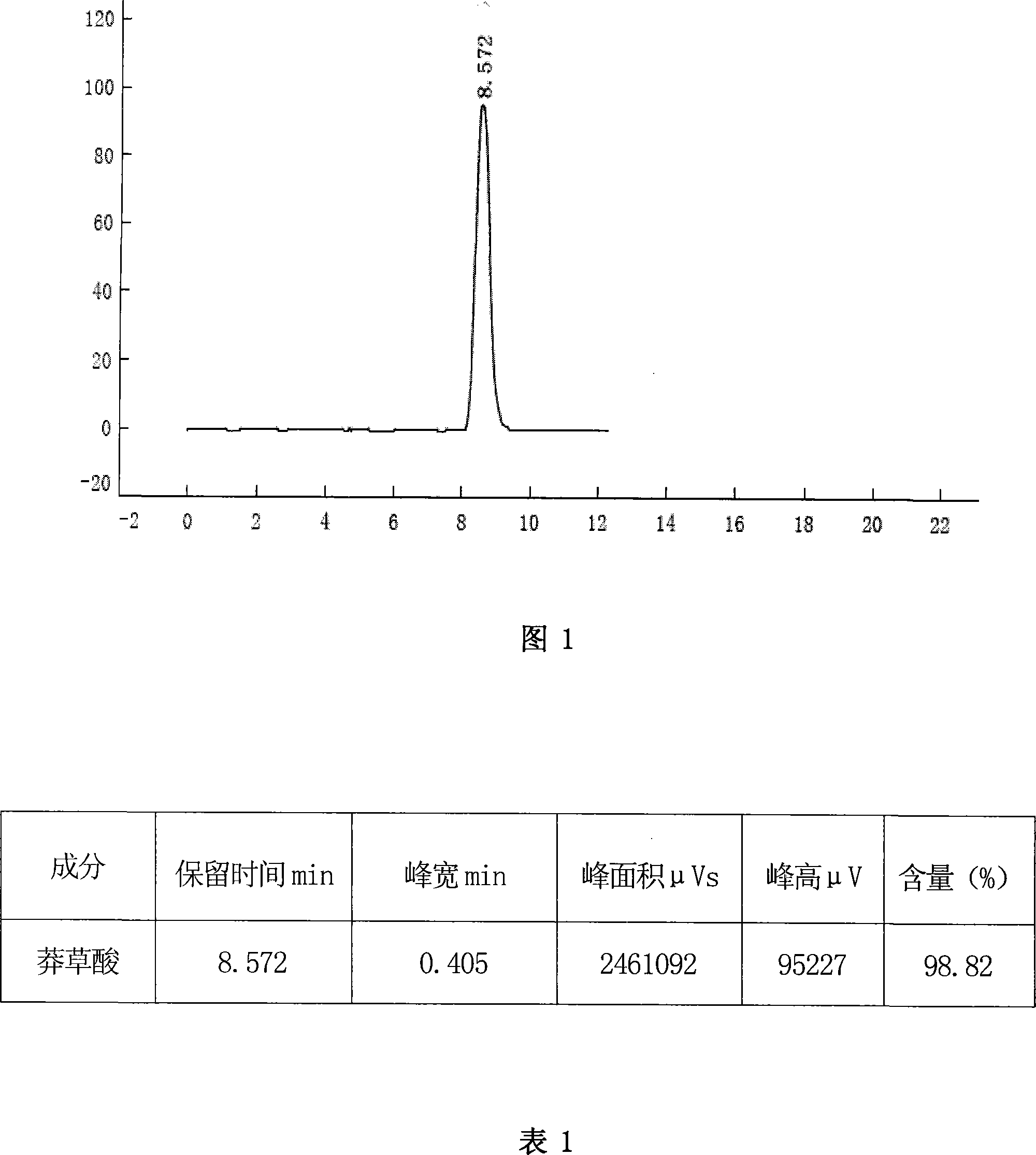
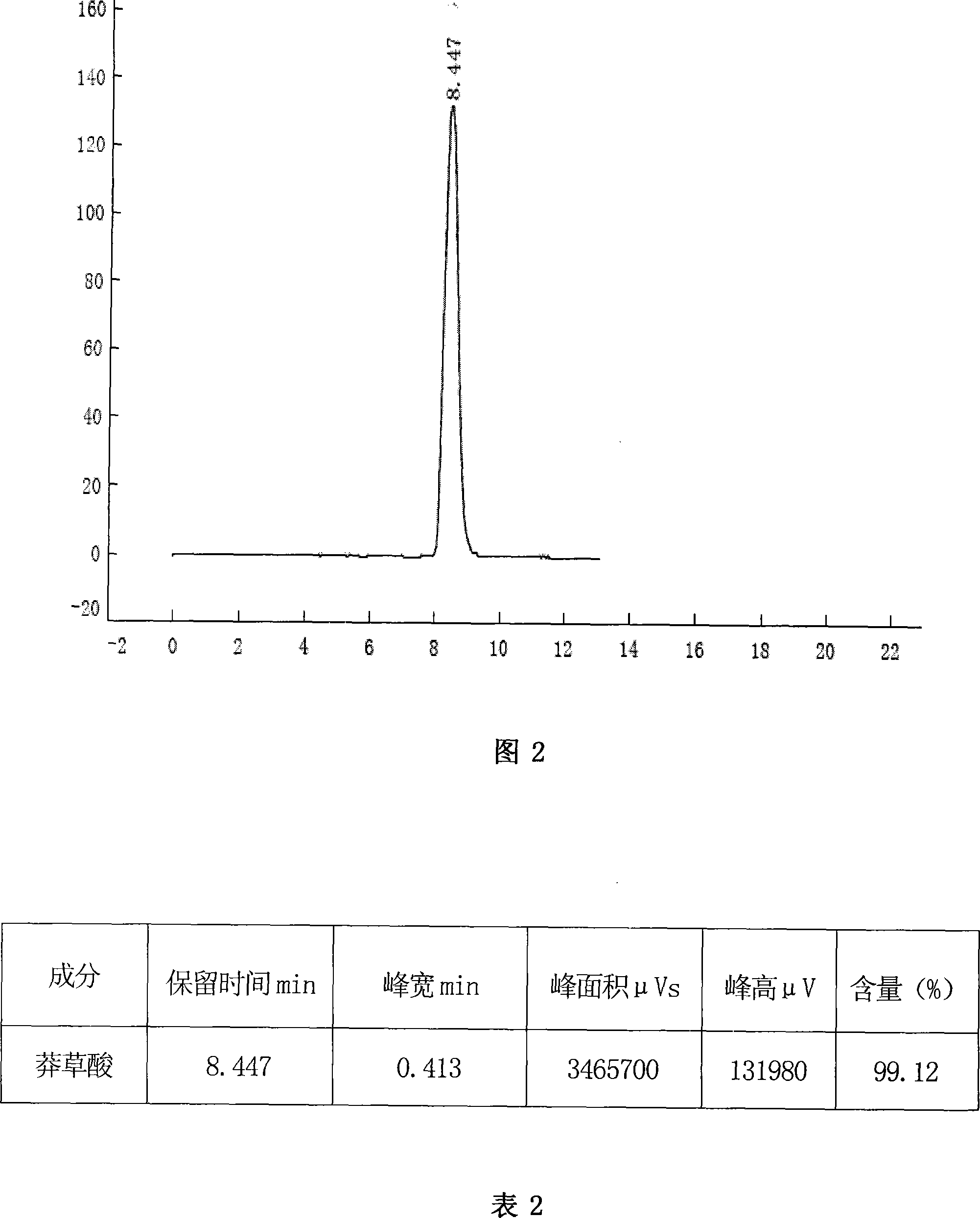
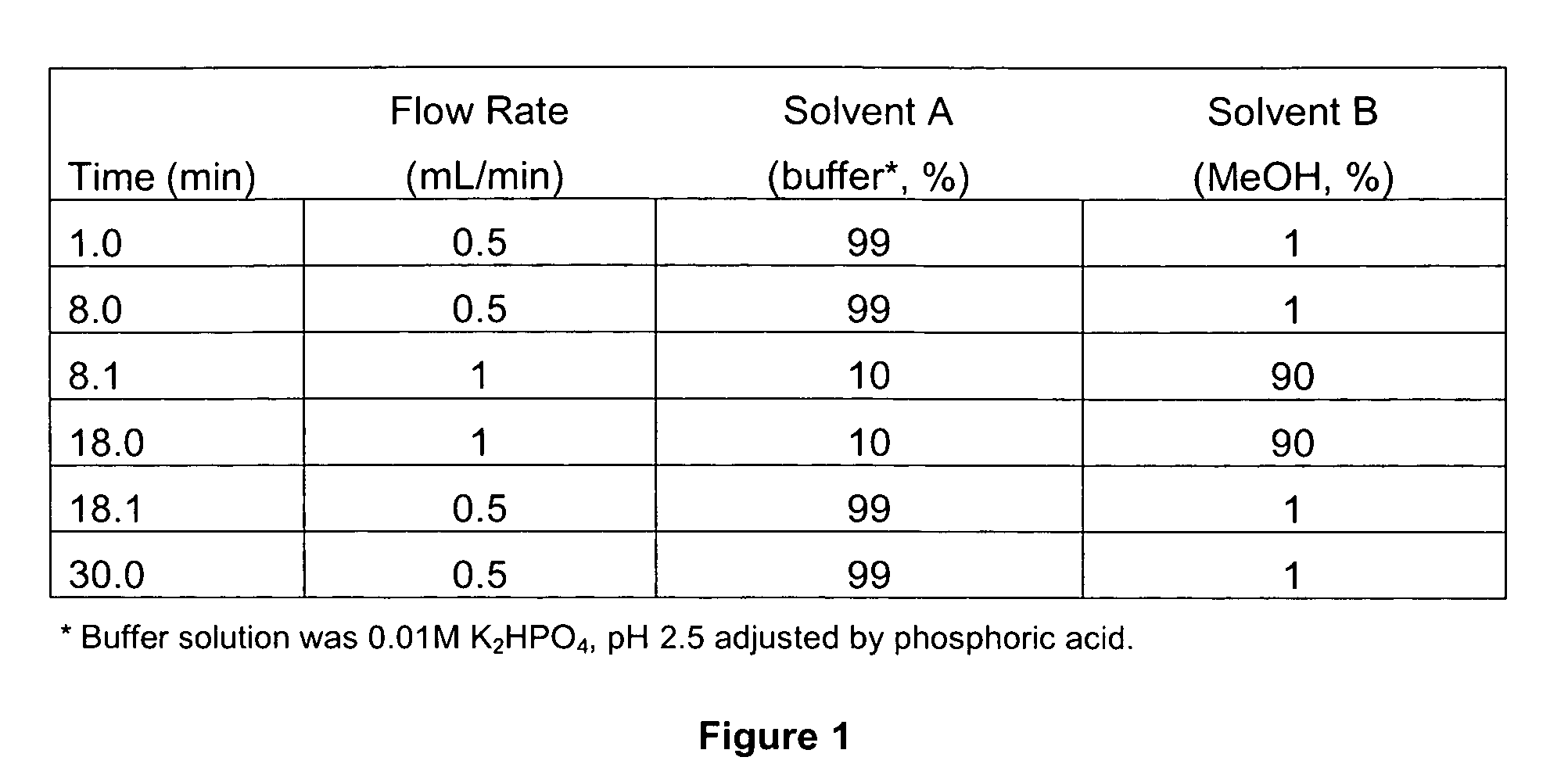
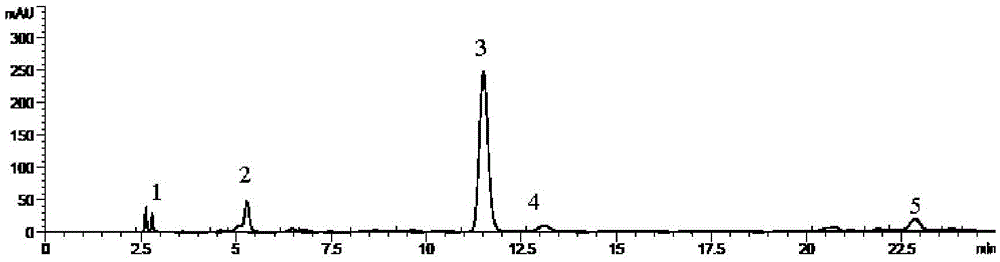
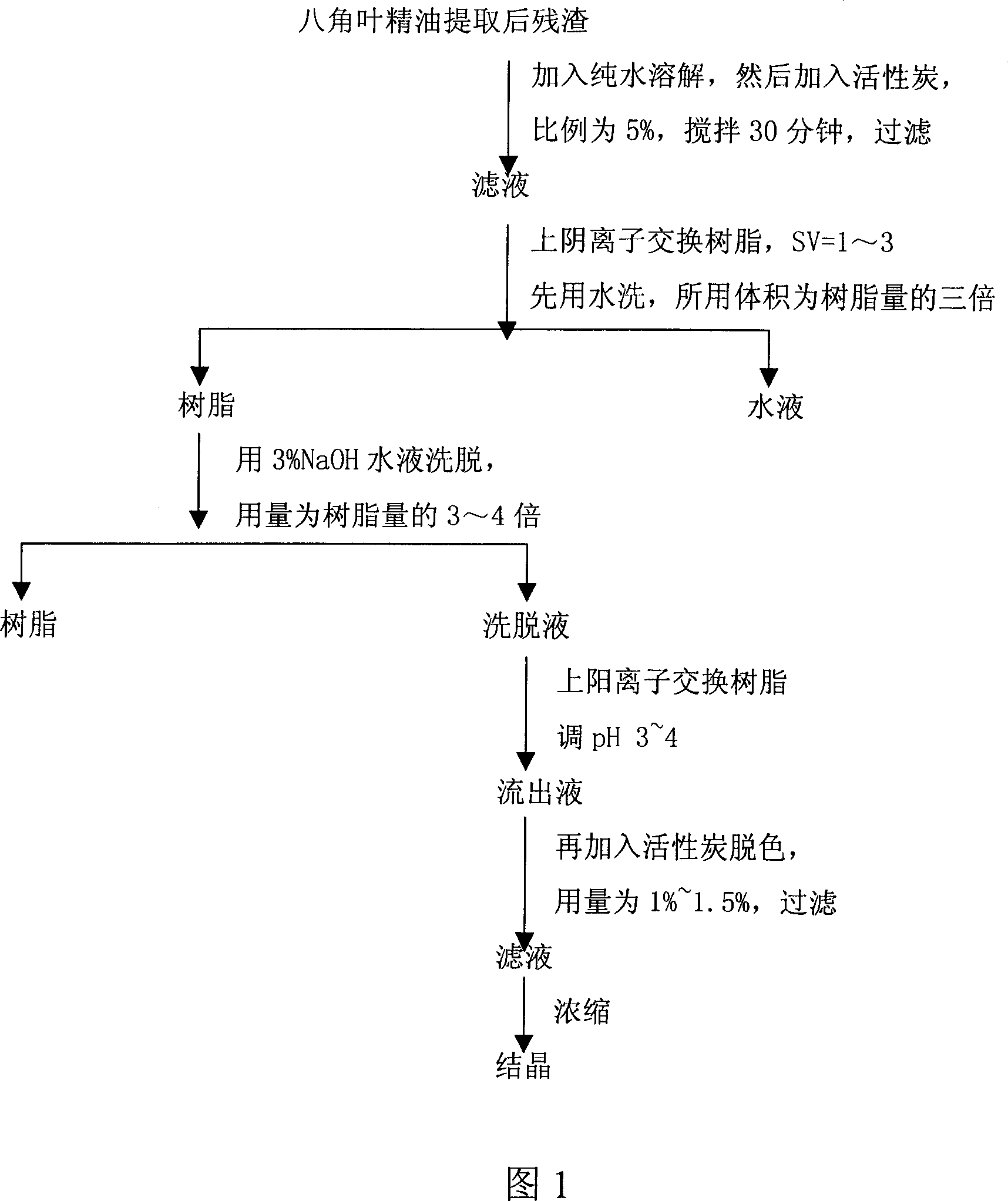
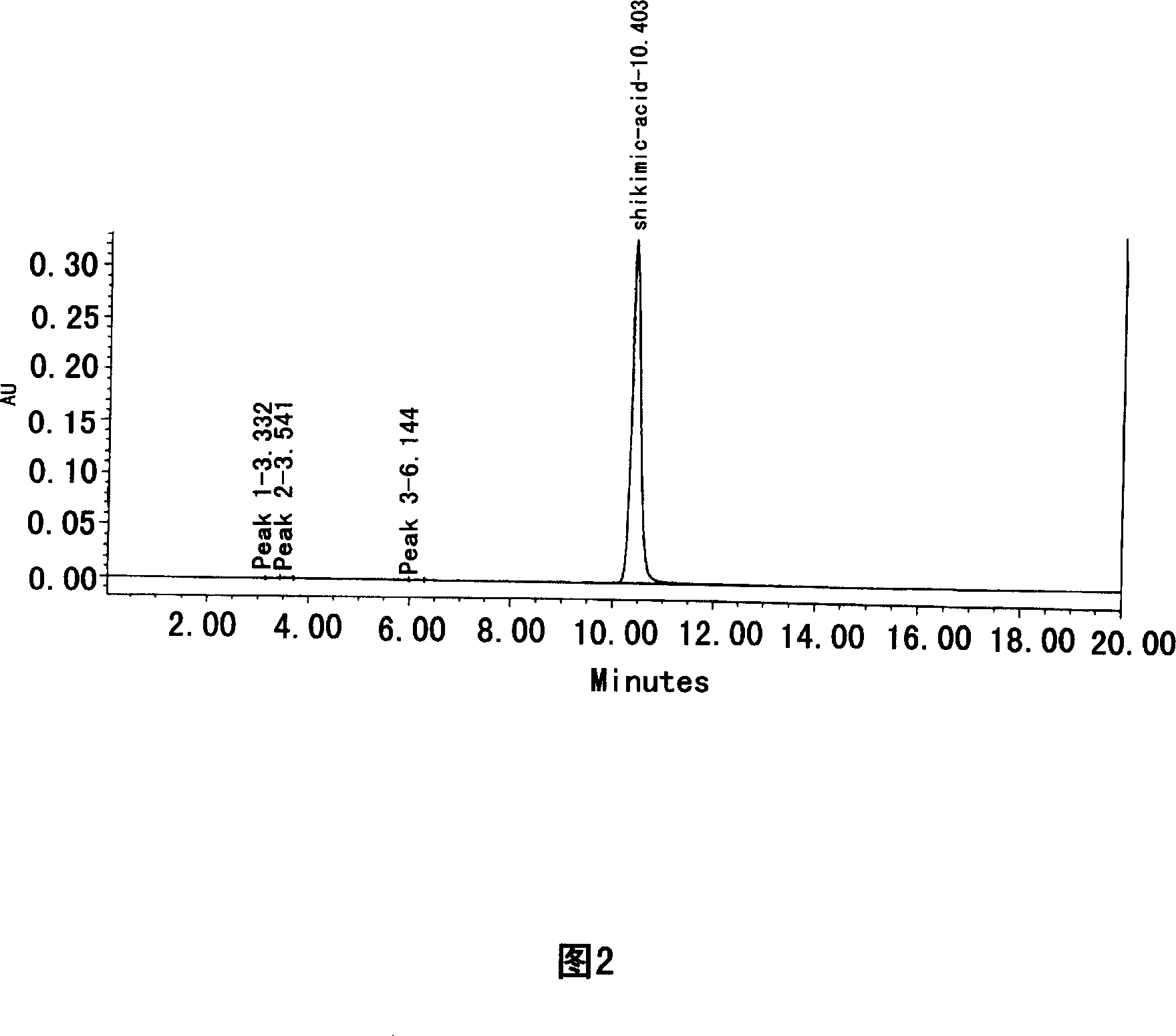
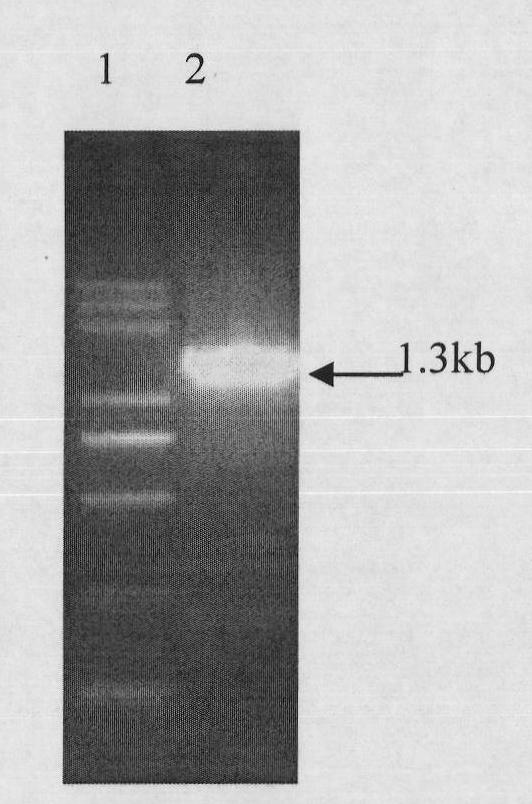
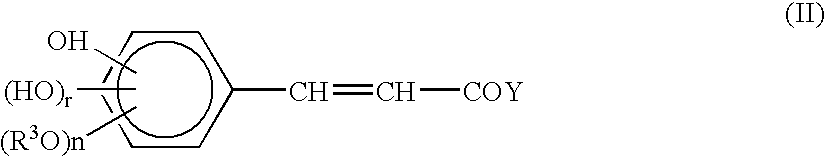Patents
Literature
341 results about "Shikimic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
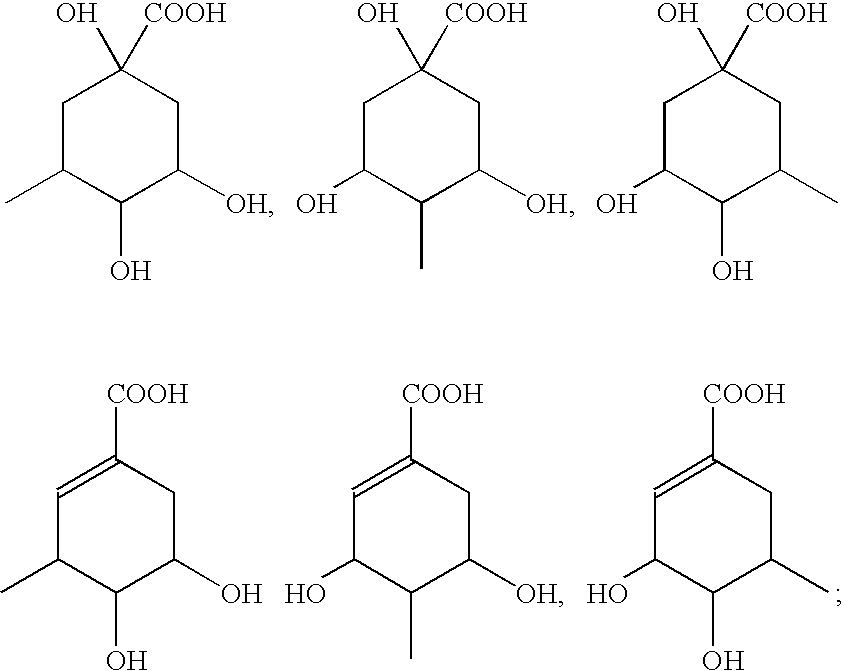
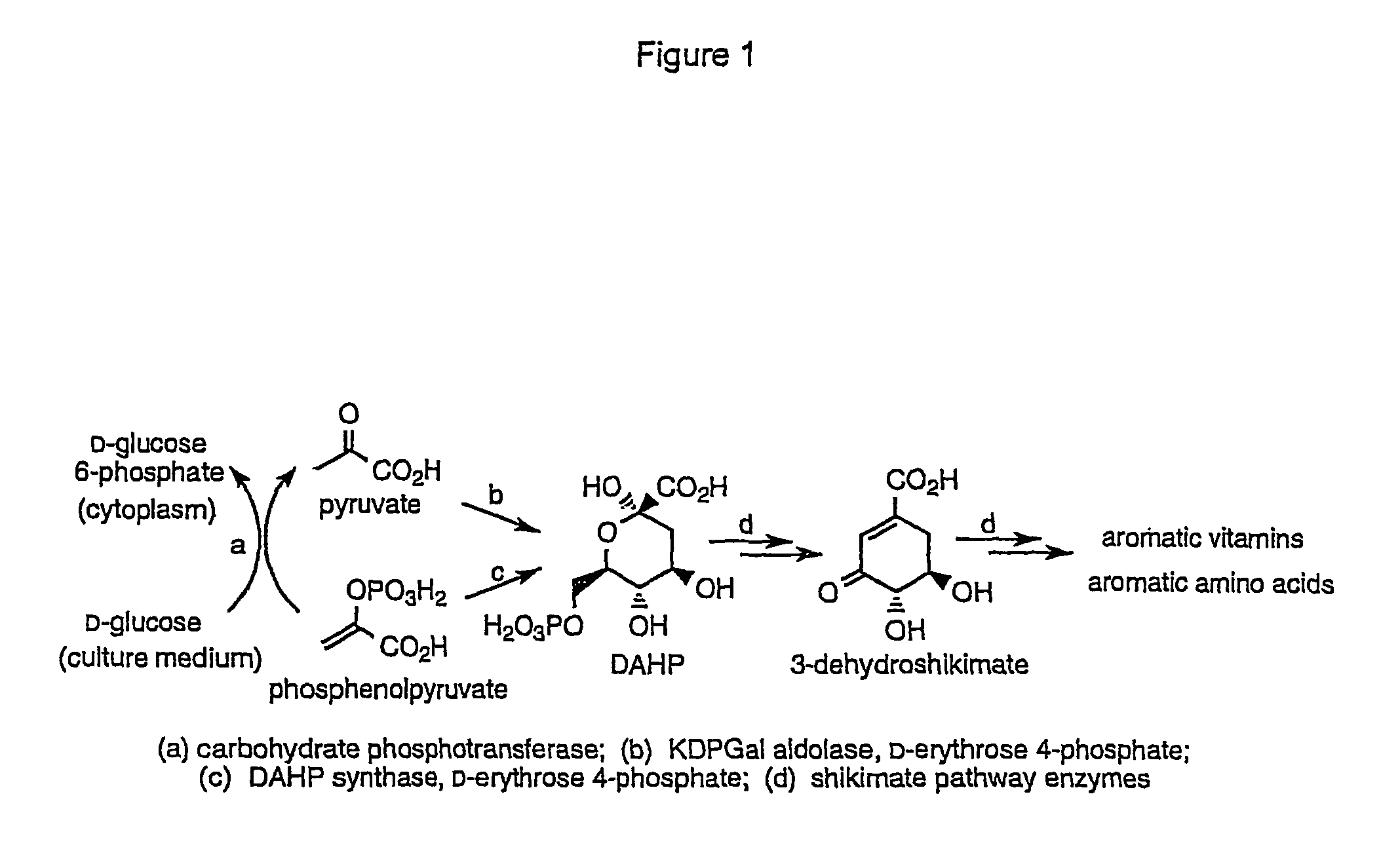
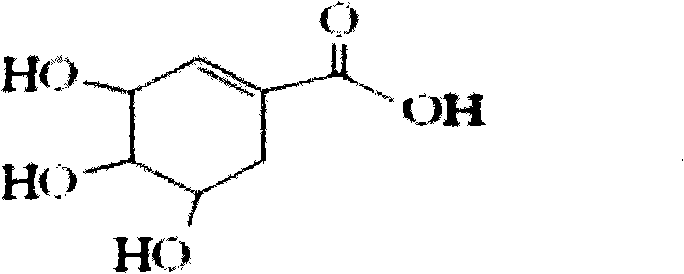
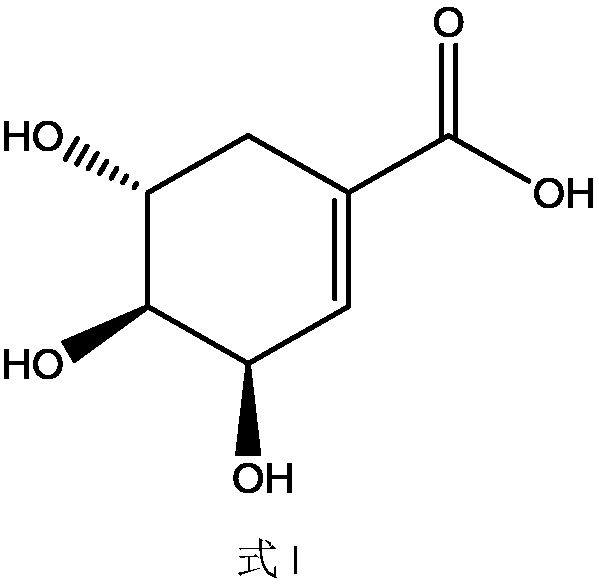
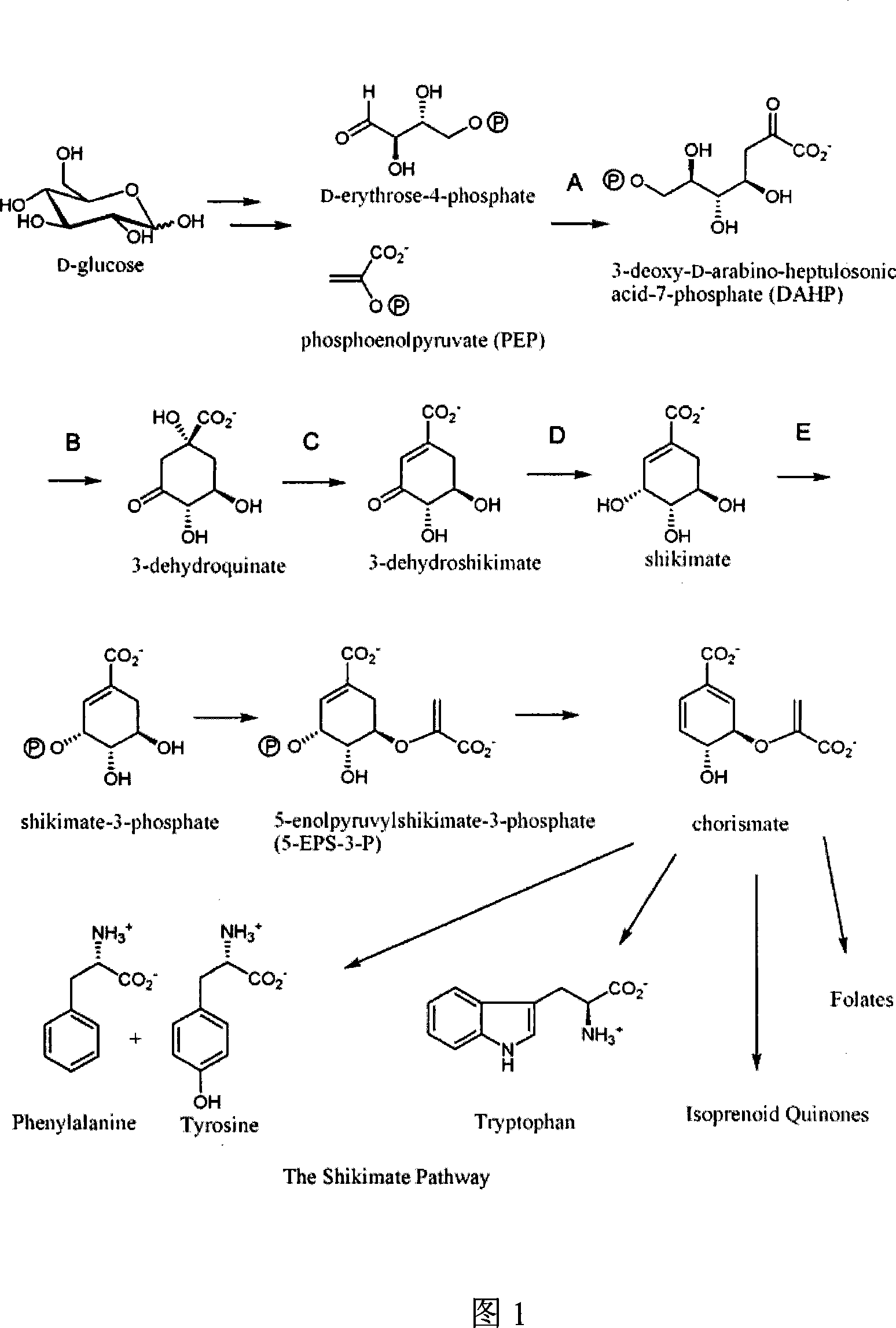
Shikimic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form shikimate, is a cyclohexene, a cyclitol and a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. It is an important biochemical metabolite in plants and microorganisms. Its name comes from the Japanese flower shikimi (シキミ, the Japanese star anise, Illicium anisatum), from which it was first isolated in 1885 by Johan Fredrik Eykman. The elucidation of its structure was made nearly 50 years later.
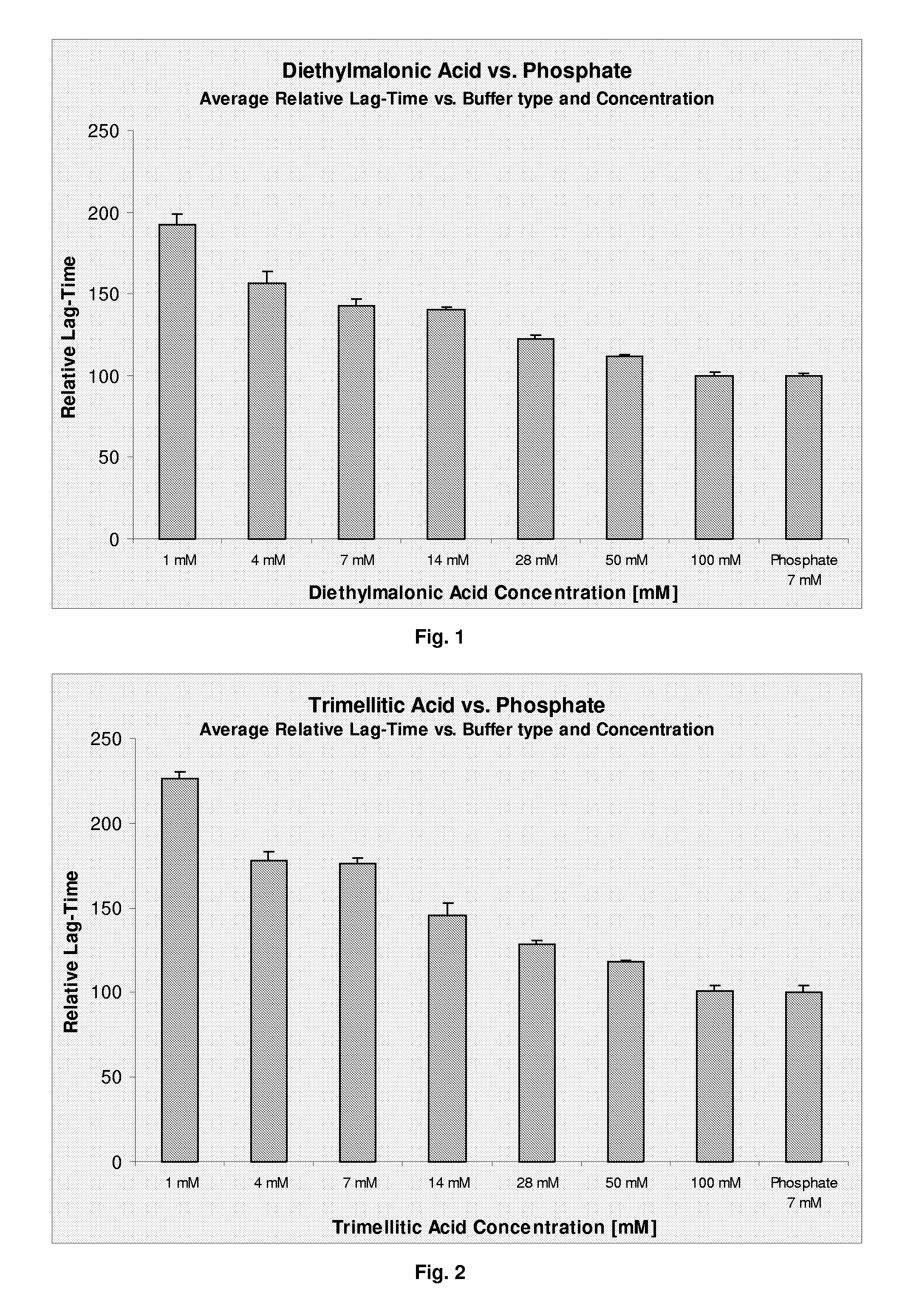
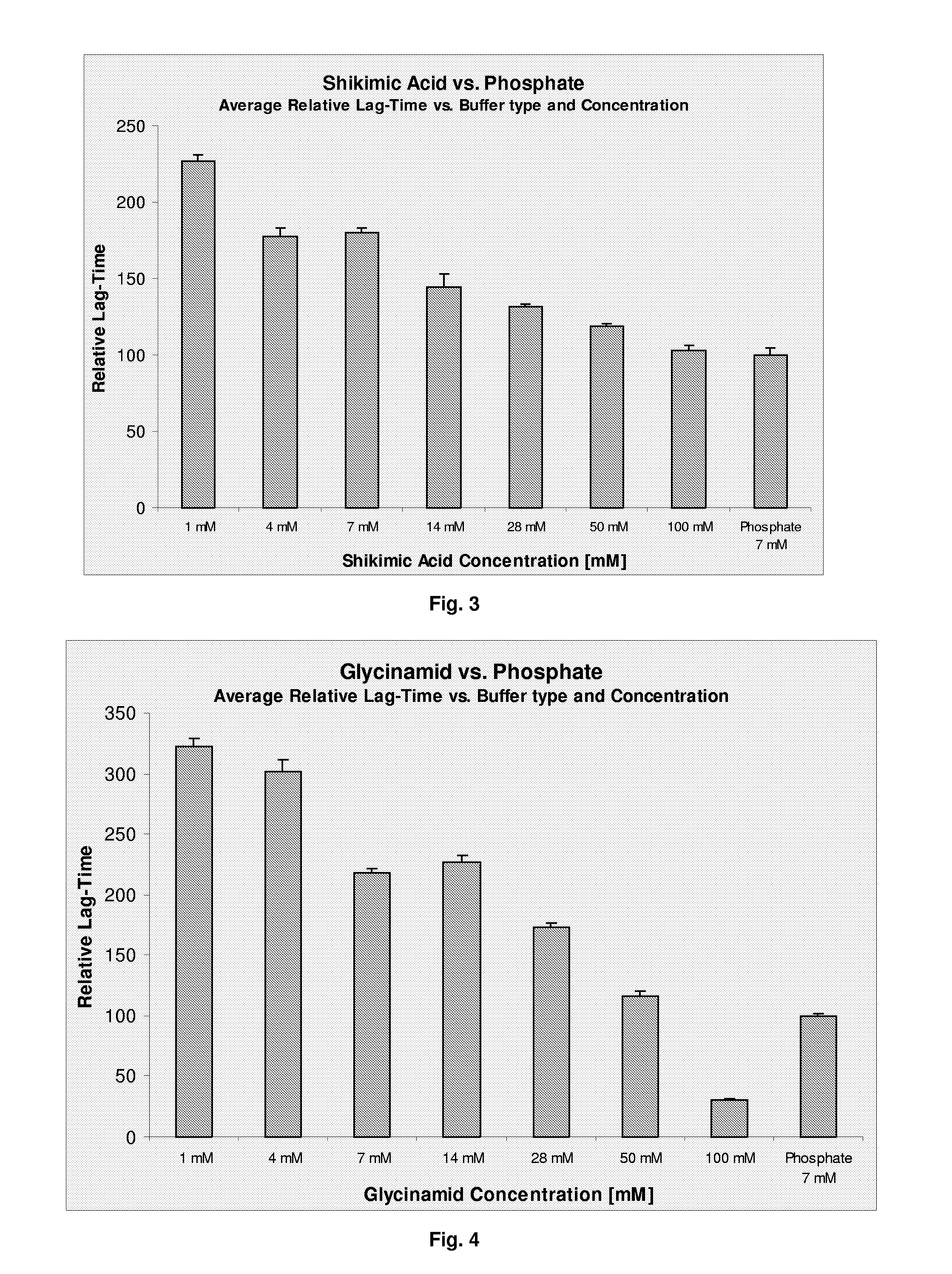
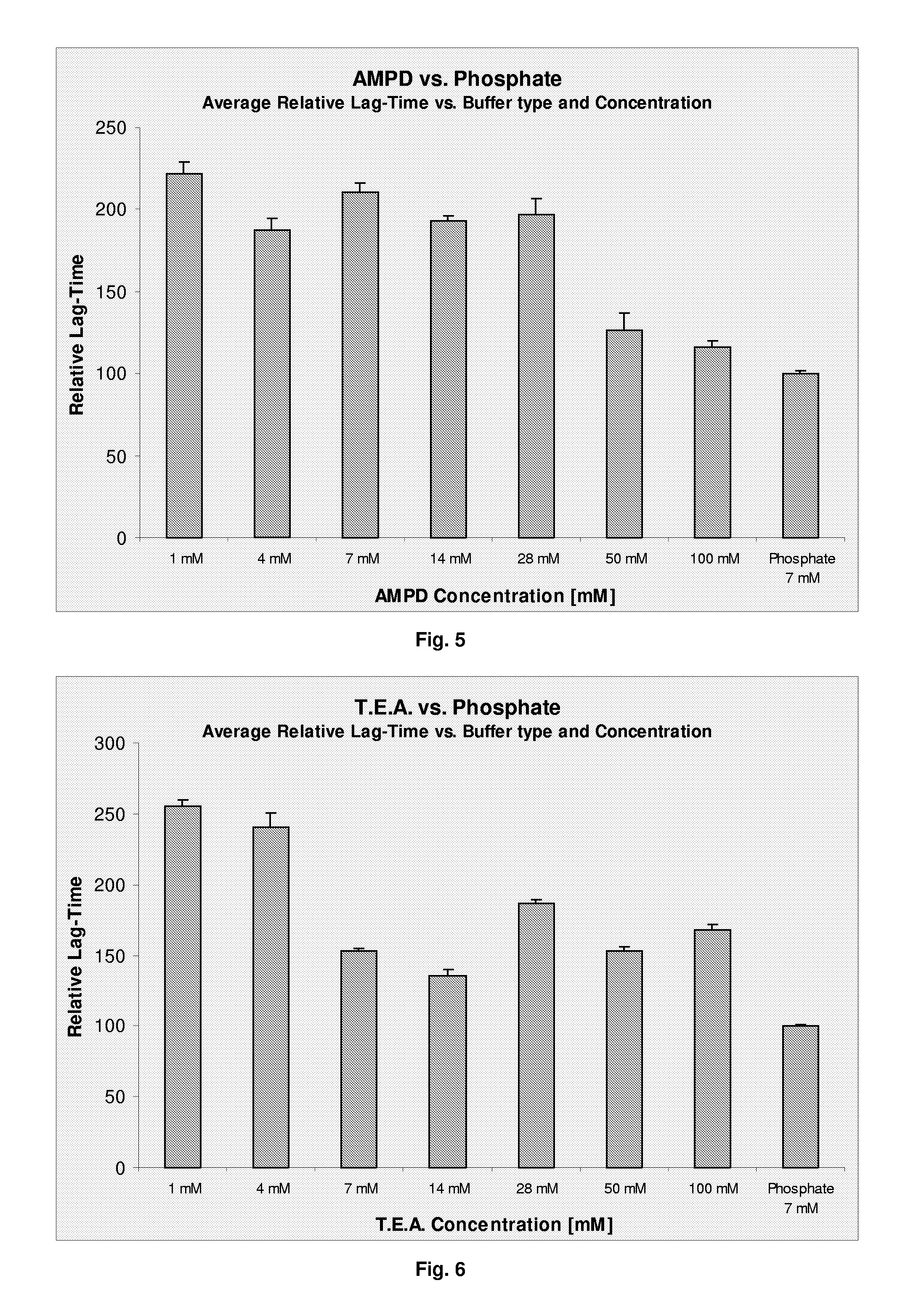
Stabilized Polypeptide Formulations
InactiveUS20090060861A1Improve physical stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderEthylmalonic acidShikimic acid
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical formulation comprising a polypeptide and a buffer selected from the group consisting of diethylmalonic acid, trimellitic acid, shikimic acid, glycinamid, 2-amino-2-methyl-1,3-propanediol (AMPD) and tetraethylammonium (T.E.A.) or salts thereof. Further more the invention relates to a method for improving stability of a polypeptide in a purification process comprising the step of applying a buffer selected from the group consisting of diethylmalonic acid, trimellitic acid, shikimic acid, glycinamid, AMPD and T.E.A. or salts thereof to said purification process.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Photoprotector and/or photoimmunoprotector compositions of the skin and their uses
InactiveUS20070025933A1Prevent and minimise damaging effectPrevent and minimise reactionCosmetic preparationsBiocideBenzoic acidPhototherapy unit
The composition comprises of a component A selected from a hydroxylated derivative of benzoic acid or of cinamic acid, their esters, amides or salts, a glycoside of a hexose, and their mixtures; and a component B selected from quinic acid, shikimic acid, their alkaline metal or alkaline earth salts, their methyl esters, and mixtures of the same. This composition is suitable for protecting the skin against ultraviolet radiation coming from the sun or artificial sources, such as those used in phototherapy units and in sun tanning rooms. For application in the field of dermatology and nutrition, and, in particular, in the photoprotection of the skin and mucosa, photo-ageing and photocarcinogenesis, including protection of the immune system associated with the skin.
Owner:IND FARM CANTABRIA
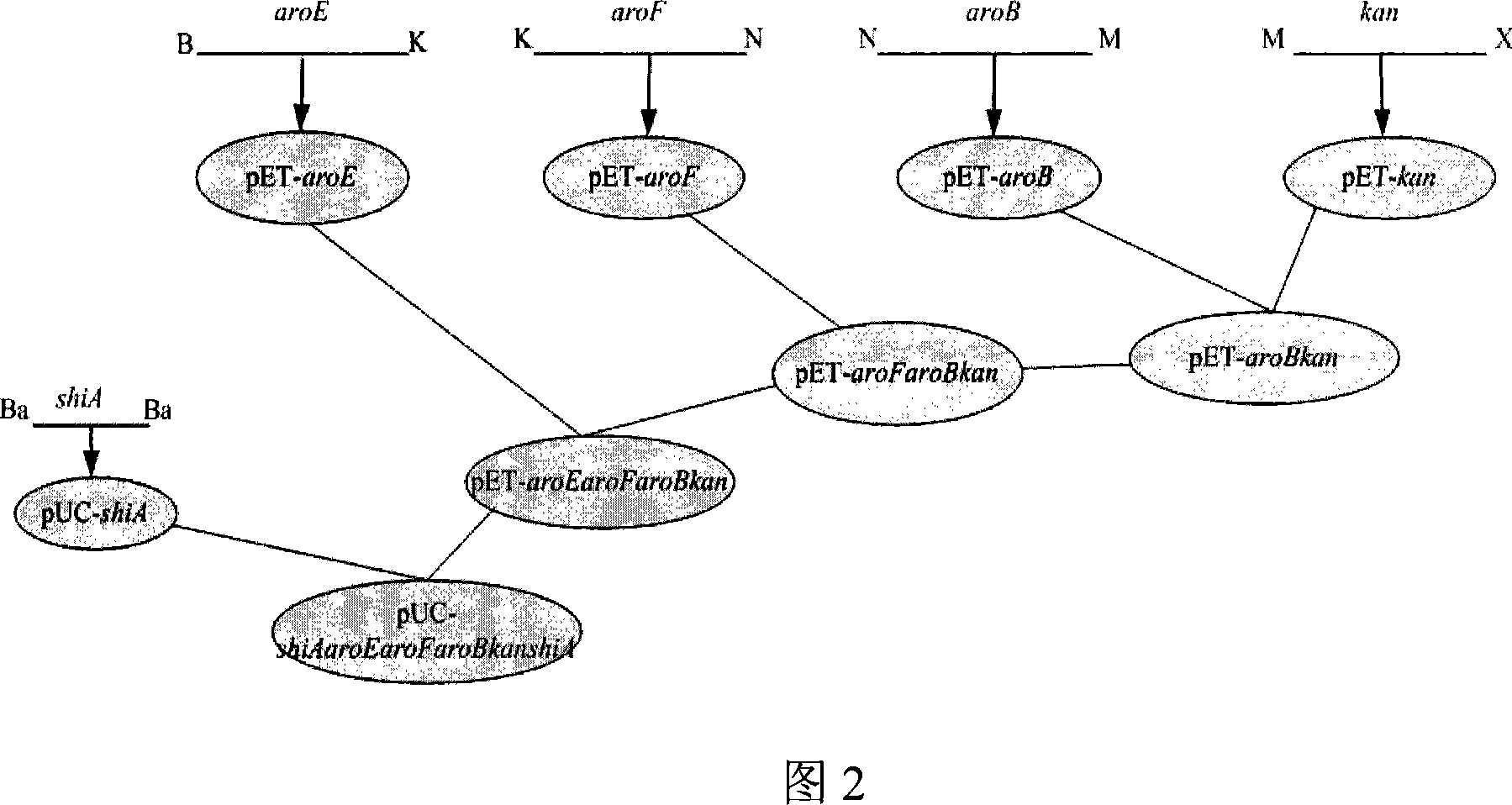
Escherichia coli recombinant strain producing shikimic acid, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102994439AEfficient accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliShikimate kinase
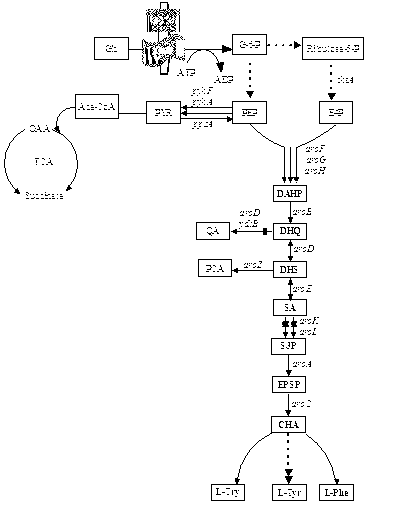
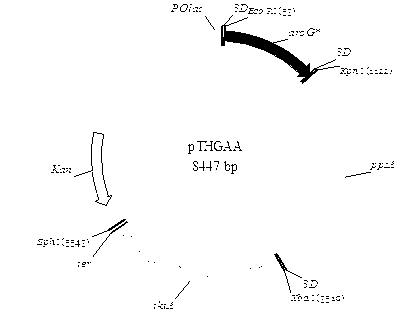
An Escherichia coli recombinant strain producing shikimic acid, and a construction method and application thereof belong to the technical field of microbial gene engineering. The invention firstly utilizes a molecular biology technique to delete shikimic acid kinase I gene (aroK) and shikimic acid kinase II gene (aroL) of Escherichia coli CICIMB0013, and a gene (ptsG) of a key protein EIIBC<Glc> and a quinin acid / shikimic acid dehydrogenase gene (ydiB) of a glucose phosphotransferase system to obtain an Escherichia coli mutant strain CICIMB0013.SA4 (delta aroK, delta aroL, delta ptsG, delta ydiB). The invention also constructs a recombinant expression plasmid pTHGAA containing key genes comprising aroG*,ppsA and tktA in a metabolic pathway of shikimic acid; and the recombinant expression plasmid pTHGAA is transferred into the recombinant strain CICIMB0013.SA4 to obtain a recombinant Escherichia coli B0013 (SA4 / pTHGAA) capable of producing shikimic acid efficiently. The Escherichia coli recombinant strain provided by the invention can realize efficient accumulation of shikimic acid in a fermentation process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A high-content natural shikimic acid extract product and a preparing method thereof
ActiveCN107353201AAlleviate resource shortagesLower requirementCarboxylic compound separation/purificationWastewaterShikimic acid
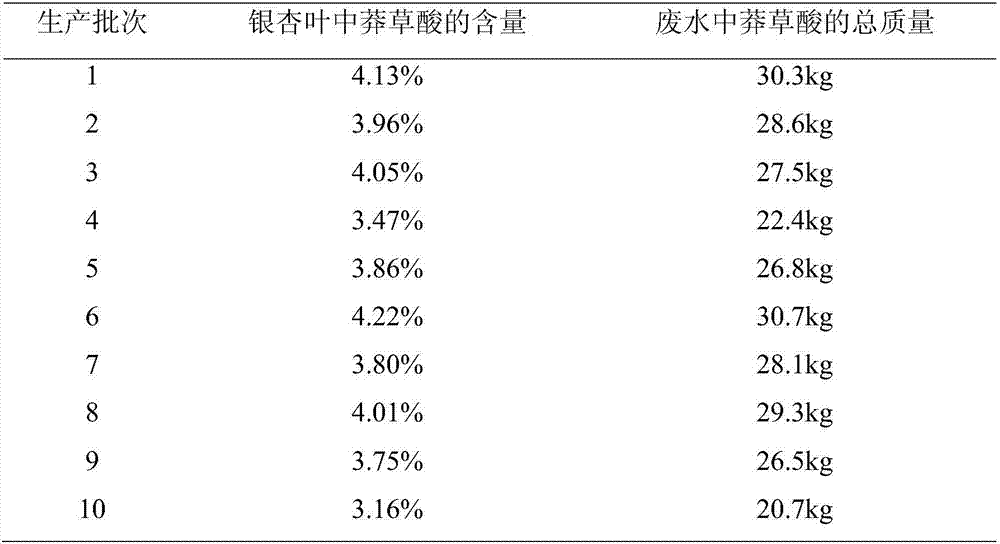
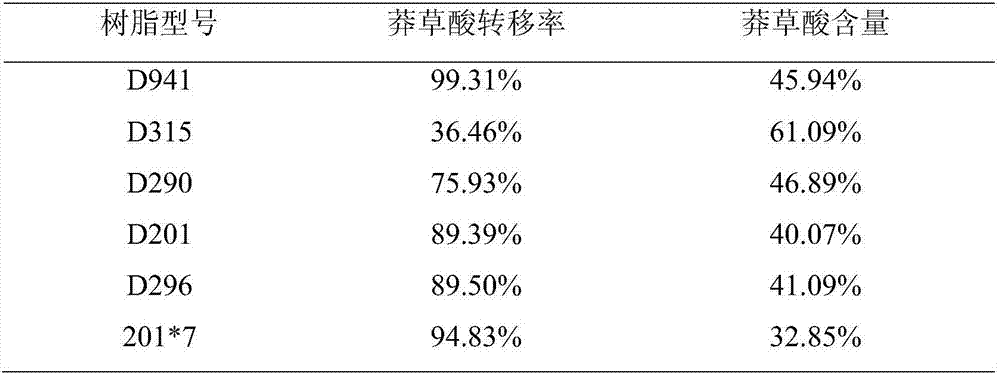
The invention discloses a high-content natural shikimic acid extract product separated and prepared from waste water generated in a ginkgo leaf extract product production process and a preparing method thereof. The content of shikimic acid is higher than 98%. The waste water generated in the ginkgo leaf extract product production process is adopted as a raw material of the method, and the method includes directly subjecting the waste water to adsorption separation with anion exchange resin, allowing the eluate obtained to pass through cation exchange resin to remove sodium, subjecting a solution after sodium removal to three combined steps of adding a shikimic acid high-purity product, performing high-temperature treatment, and allowing the mixture to stand at a low temperature in order to precipitate a shikimic acid precipitate, and recrystallizing the shikimic acid precipitate to obtain the shikimic acid extract product the shikimic acid content of which is 98% or above.
Owner:YUNNAN HIKON BIOTECH CO LTD +2
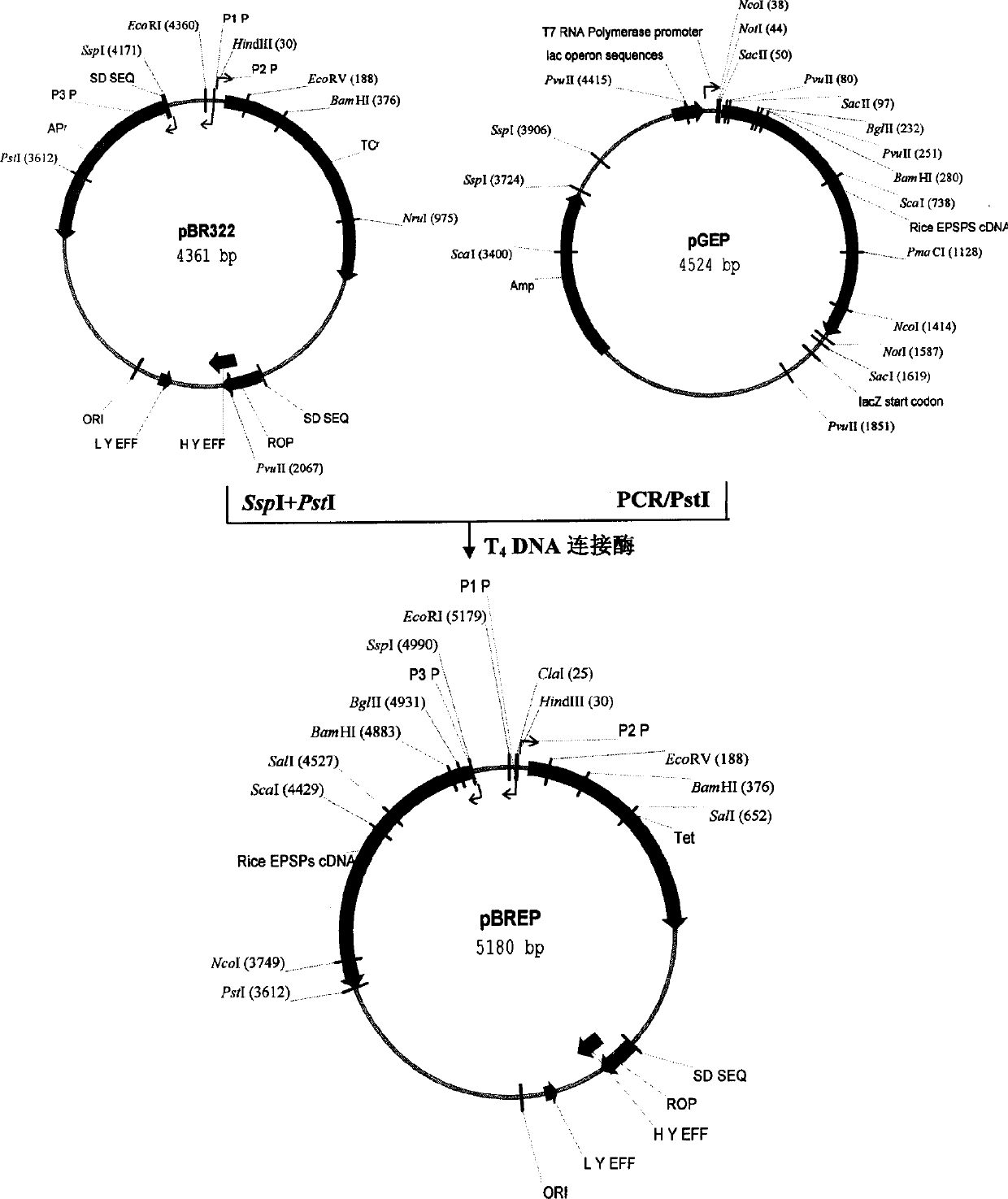
Rice EPSP synthase mutant and its coding gene, obtaining method and application
InactiveCN1810962AHigh glyphosate resistanceHigh activitySugar derivativesEnzymesAgricultural scienceShikimic acid
The present invention discloses one kind of 5-enolpyruvoyl shikimic acid-3-phosphosynthase mutant and its coding gene, obtaining method and application in culturing glyphosate resisting plant. The 5-enolpyruvoyl shikimic acid-3-phosphosynthase has the residue sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, and will take important role in the culture of glyphosate resisting plant.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and materials for the production of shikimic acid
InactiveUS7790431B2BacteriaSugar derivatives3-dehydroquinate synthase3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Method for the extraction and purification of shikimic acid
InactiveUS20070149805A1SupplyLimited supplyCarboxylic compound separation/purificationPurification methodsPlant tissue
Improved methods for producing shikimic acid and the use of sweetgum plant tissues in the production of shikimic acid.
Owner:STEPHEN F AUSTIN STATE UNIV
Construction method of genetic engineering strain for producing shikimic acid
InactiveCN102304539AReduce the content of intermediate productsIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme GeneTryptophan
The invention discloses a construction method of a genetic engineering strain for producing shikimic acid. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, constructing an escherichia coli strain of which the aroA gene is knocked out; 2, constructing a recombinant expression plasmid pAR63 containing key enzyme genes aroGFBR, aroE, aroB, aroD, tktA and ppsA in the metabolic pathway of the shikimic acid, so that the genes are subjected to transcriptional control of a tryptophan promoter Ptrp; and 3, transferring the recombinant expression plasmid pAR63 into the escherichia coli strain of which the aroA gene is knocked out to obtain a production strain for expressing the shikimic acid. In the method, the aim of interrupting the metabolism of the shikimic acid is fulfilled by the knock-out of the single gene aroA, a small number of genes are knocked out, the operating difficulty is low, and the expression of the genes is in the state of starting and stopping automatically and is started automatically in the middle and late period without the induction of inducers, so the possibility of adding toxic substances into a culture medium is reduced, and the shikimic acid has high yield.
Owner:河南孟成生物药业股份有限公司
Preparation of shikimic acid
InactiveCN1982279ALow costEasy to operateCarboxylic compound separation/purificationAlcoholShikimic acid
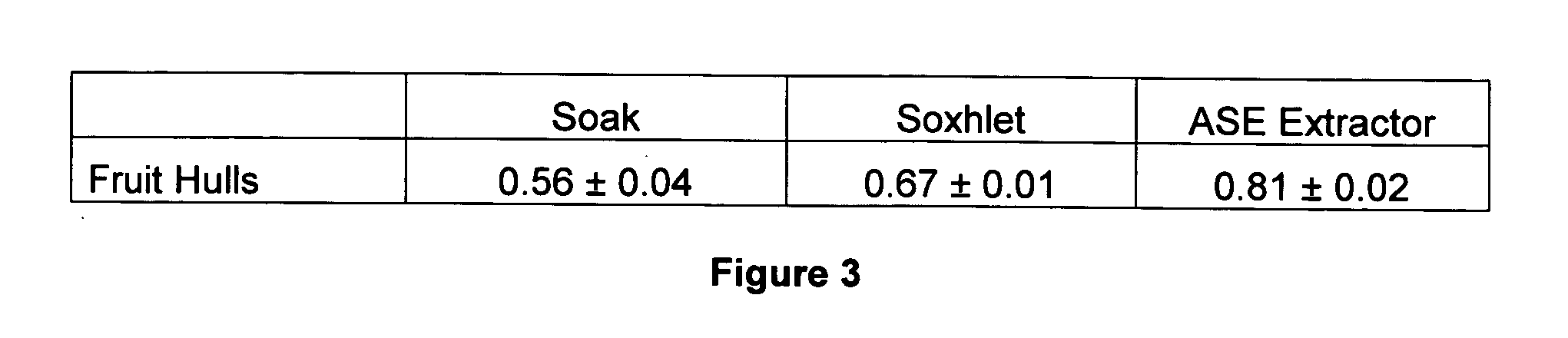
Production of shikimic acid and use of Chinese Star Anise oil residual waste are disclosed. The process is carried out by taking Chinese Star Anise or Chinese Star Anise leaf as raw materials, crushing, decoction extracting by water or agitating to fast extract, depositing by alcohol, removing impurities, de-coloring by active carbon or porous resin, treating by lead acetate or enriching resin while anion-exchanging, crystallizing and re-crystallizing to obtain various-purity shikimic acid. It's cheap and convenient and has colorful raw materials.
Owner:邓薏
Extraction process for shikimic acid in fermentation liquor
InactiveCN102584571AFacilitate the ultrafiltration processReduce workloadCarboxylic compound separation/purificationBiochemical engineeringShikimic acid
The invention relates to an extraction process for shikimic acid in fermentation liquor. The extraction process specially comprises the steps of conducting microfiltration on the fermentation liquor through a ceramic film to obtain filtrate, conducting exchange adsorption on the filtrate through anion exchange resin, then eluting the filtrate through acetic acid solution to obtain eluent, concentrating, destaining, crystallizing, crystal washing and drying the eluent to obtain finished shikimic acid. The process is simple and environment-friendly, and the finished shikimic acid extracted by the process is stable in quality, the purity of the finished shikimic acid is more than 98.5%, and the yield of the finished shikimic acid is more than 75%.
Owner:河南孟成生物药业股份有限公司
Method for extracting and separating shikimic acid from star anise
ActiveCN101168503AReduce consumptionLess quantityCarboxylic compound separation/purificationFood additiveActivated carbon
The invention relates to a process for extracting and separating shikimic acid from star anise, which comprises degreasing broken star anise, thermally refluxing and extracting the degreased material for 2-3 times by using 5-6 times amount organic solvent, filtering and concentrating to obtain quintessence with specific density of 1.20-1.30, adding water at 2-5 times amount of water, and using active carbon to decolorize until the liquid is stramineus, depressurizes and concentrates at vacuum until relative density is 1.20-1.22, then centrifugaling, filtering and drying to obtain shikimic acid extractive. The invention can resolve the technical problems in background technique as high production cost and low yield, while the invention has simple production art, short period, little environment pollution, and high product purity of more than 98%, while the degreased start anise fat can be used as food additive.
Owner:SHAANXI JIAHE PHYTOCHEM
Processes for the extraction and purification of shikimic acid and the products of such processes
InactiveUS20070161818A1Easy to produceHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationPurification methodsPlant tissue
Processes for producing shikimic acid through extraction from sweetgum, pine and cedar plant tissues and the shikimic acid produced by such processes.
Owner:LI SHIYOU +5
Escherichia coli for producing adipic acid precursor namely cis,cis-muconic acid and application of escherichia coli
Cis,cis-muconic acid is an important chemical organic acid, has a wide range of application and can be used as a precursor of adipic acid. The cis,cis-muconic acid can be used for producing polymers including nylon 66 and the like after being converted into adipic acid through hydrogenation. The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli TIB-LEc340 CGMCC No 6435 for producing cis,cis-muconic acid, wherein the recombinant escherichia coli is established by the steps of combining 3-dehydrogenated shikimic acid dehydrase which comes from different microbes and is optimized by codons, protocatechuic acid decarboxylase, catechol 1,2-dioxidase and artificially designed constitutive promoters and terminators into a heterologous expression module, and then introducing the heterologous expression module into shikimic acid dehydrogenase mutated escherichia coli. The escherichia coli TIB-LEc340 CGMCC No 6435 is fermented for 16-120 hours at 30-40 DEG C to obtain fermentation liquor, and the maximum content of cis,cis-muconic acid in the fermentation liquor can reach 52g / L, so that the escherichia coli has a wide application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Process of extracting and separating shikimic acid from aniseed
InactiveCN1931823AReduce pollutionReduce energy consumptionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationShikimic acidSodium hydroxide
The present invention is process of extracting and separating shikimic acid from aniseed. The process includes the steps of water extraction to obtain extracted solution, exchanging and adsorbing shikimic acid from the extracted solution with anionic resin column, eluting with 1-8 % sodium hydroxide solution to obtain eluted solution, desalting the eluted solution in cationic resin column, concentrating the desalted solution and crystallizing in acetone to obtain shikimic acid crystal. Compared with traditional technology, the present invention has the advantages of low power consumption, low production cost and less environmental pollution.
Owner:GUANGXI WANSHAN SPICE +1
Method for determining content of organic acid in ginkgo leaf extract
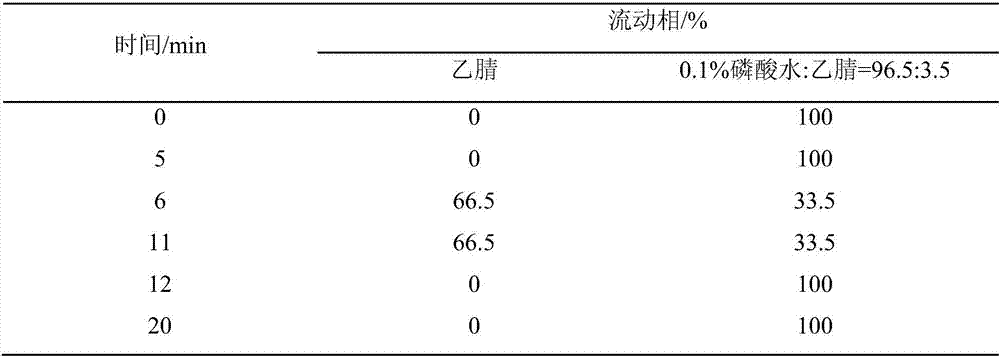
The invention discloses a method for determining the content of organic acid in a ginkgo leaf extract. The method comprises the following steps: pretreatment of a ginkgo leaf extract sample; preparation of a test article solution, high performance liquid chromatograph analysis and the like. The method is characterized in that ultrasonic extraction is carried out by using an aqueous solution containing bovine serum albumin in a pretreatment process of the ginkgo leaf extract sample, so that the interference of procyanidine is removed; a sample is prepared by using an aqueous solution containing 0.1 percent of phosphoric acid in a preparation process of the testing article solution, so that the interference of part of impure peaks is removed, and the chromatographic behavior and the separation effect are greatly improved. After the method is adopted for analyzing, an organic acid pattern of the ginkgo leaf extract can be obtained, and the contents of five organic acid components such as shikimic acid, gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, 6-hydroxykynurenic acid and p-hydroxybenzonic acid can be simultaneously quantitated.
Owner:云南康恩贝植物研究院有限公司
Method for separating and purifying shikimic acid
InactiveCN1978422AHigh purityHigh recovery rateCarboxylic compound separation/purificationOrganic solventShikimic acid
The invention discloses a method for reusing the residue after extracting the anise leaves essential oil. The residues which is left after extracting the anise leaves essential oil with shikimic acid is dissolved in water, then the eluate that is processed by the strong base anion exchange resin and strong acid cation pay exchange resin is concentrated and crystallized in low temperature to get the shikimic acid with high purity. The process of this invention is simple without the need of special equipment, can produce the shikimic acid with high purity of 98% more and recovery rate of 80% more. So it greatly reduces the cost and energy, shortens the production cycle, lessens the solvent consumption, nearly does not use the organic solvent, which is suitable for the general pharmaceutical factory.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for preparing shikimic acid from folium ginkgo extraction waste liquor
ActiveCN109593034AReasonable process designHigh purityCarboxylic compound separation/purificationOrganic solventHydrolysate
The invention relates to the field of extraction and purification of plant effective components, in particular to a method for preparing shikimic acid from folium ginkgo extraction waste liquor. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out enzymolysis on the folium ginkgo extraction waste liquor; and collecting an enzymatic hydrolysate, filtering by an organic membrane, carrying out adsorption elution by an anion exchange resin column, concentrating, crystallizing and drying. The method is simple to operate, economical and practical and proper to popularize, and does not need an organic solvent. Moreover, the obtained shikimic acid is high in purity and good in appearance condition, and the mass content is greater than 99%.
Owner:GUILIN NATURAL INGREDIENTS CORP
Gene for encoding 5-enolpyrul-shikimate-3-phosphate synthase and application thereof
The invention discloses a gene for encoding 5-enolpyrul-shikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The EPSPS has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2, the gene has the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the gene is obtained by cloning from the strain of an ochrobactrum anthropi obtained by separating a soil sample collected at the periphery of a Nalati grassland in Xinjiang by a homologous cloning method. Through an experiment of glyphosate resistance, the gene is found to have good glyphosate resistance and is an excellent gene in the genes of the same kind. The invention also provides a cloning vector and an expression vector thereof which are used for biotransformation and used for transforming crops, thereby the purpose of resisting a herbicide by plants is achieved.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for improving shikimic acid volume of production with zymotechnics
InactiveCN101245357AIncrease productionWay to increaseMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhosphateMonopotassium phosphate
A method for improving the yield of a fermentation method for producing shikimic acid pertains to the biochemical field. The invention comprises the steps that: 1) Seed culture: a lactose fermentation bacillus brevis is inoculated in a seed culture medium of pH7.0 to pH7.4, the culture is carried out in a 120 to 180rpm shake bed for 12 to 18 hours at 30 DEG C; the seed culture medium (g / L) includes: 25 to 35 parts of glucose, 15 to 25 parts of ammonium sulfate, 1.0 to 2.0 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.1 to 1.0 part of magnesium sulfate, 0.5 to 2.0 parts of urea, 20 to 30 parts of corn pulp and the rest of water, the pH is regulated to pH 7.0 to pH 7.4, and the sterilization is carried out for 30 minutes at 115 DEG C. 2) Fermentation culture: the seed is inoculated in a fermentation culture medium at pH7.0 to pH7.4, the inoculation amount is 5 percent, the culture is carried out in the 120 to 180rpm shake bed for 48 to 60 hours at 30 DEG C; a glyphosate inhibitor is added till the fermentation is going on for 16 to 30 hours; the fermentation culture medium (g / L) includes: 100 to 160 parts of glucose, 30 to 50 parts of ammonium sulfate, 0.5 to 2.0 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.1 to 1.0 part of magnesium sulfate, 20 to 30 parts of corn pulp, 30 to 50 parts of calcium carbonate and the rest of water, the pH is regulated to pH7.0 to pH7.4, and the sterilization is carried out for 30 minutes at 115 DEG C. The yield of the shikimic acid can achieve 1.667 to 2.887 times of the yield before the adding of the glyphosate, and the production is stable and reliable.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for preparing shikimic acid extract from chromatographic waste liquor of ginkgo biloba extract
InactiveCN109369373AReduce dosageReduce volumeOther chemical processesSilicon compoundsBenzeneAfter treatment
The invention discloses a method for preparing shikimic acid extract from chromatographic waste liquor of a ginkgo biloba extract. The method specifically comprises the following steps: taking waste liquor produced during preparation of the ginkgo biloba extract by macroporous resin column chromatography, and concentrating the waste liquor to the volume of 1 / 5 of the original volume so as to obtain pretreatment waste liquor; extracting the pretreatment waste liquor with chloroform so as to obtain an aqueous phase I; extracting the aqueous phase I with benzene to obtain an aqueous phase II; extracting the aqueous phase II with petroleum ether to obtain an aqueous phase III; diluting the aqueous phase III with water, adding a modified vermiculite adsorbent, stirring, standing, filtering andcollecting filter residues; adding water equivalent to an amount of 50 times that of the weight of the filter residues into the filter residues, performing ultrasonic treatment at a temperature of 60-80 DEG C, filtering after treatment completion, and collecting the filtrate; and performing vacuum concentration on the filtrate, and re-crystallizing, thereby obtaining the shikimic acid extract. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the shikimic acid in the waste liquor produced during preparation of the ginkgo biloba extract by the macroporous resin column chromatography can be well extracted, and the obtained product is high in quality and high in content and has wide application prospects.
Owner:YANGTZE NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and application thereof
InactiveCN103074292AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolaseEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and a method for producing the L-phenylalanine (Phe) by fermentation and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. According to the invention, a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering strain C.glutamicum19AF / 99TP capable of being used for highly yielding the L-Phe is obtained in a corynebacterium glutamicum type strain ATCC13032 by carrying out induction expression on the following four genes: a 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase gene, a chorismate mutase / prephenate dehydratase gene which has resistance to feedback inhibition, a transketolase gene and a phosphoenolpyruvic acid synthetase gene. A shikimic acid metabolic pathway of an L-Phe synthetic metabolic pathway is over-expressed in the C.glutamicum ATCC13032; a key enzyme gene of a chorismic acid metabolic pathway enables the yield of the L-Phe to reach 3.47g / L; two enzyme genes which combines an expression center metabolic pathway to improve a precursor enables the highest yield of the L-Phe to reach 4.86g / L; and the original strain ATCC13032 which is used as a contrast strain cannot detect accumulation of the L-Phe in the integral fermenting process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of shikimic acid
InactiveCN101759557AReduce dissolutionImprove adsorption capacityCarboxylic compound separation/purificationOxalateShikimic acid
The invention relates to a method for purifying shikimic acid by water extraction, membrane separation, ion exchange resin absorption enrichment, graphite concentrator concentration and recrystallization. The method solves the problems of excessive sorts and difficult recycling of organic reagent, small resin exchange capacity, low concentration capacity of glass concentrators and easy erosion of stainless steel concentrators. The method has the advantages of short cycle, high yield and low cost when used in shikimic acid production, and easily realizes industrialization.
Owner:NANJING ZELANG MEDICAL TECH
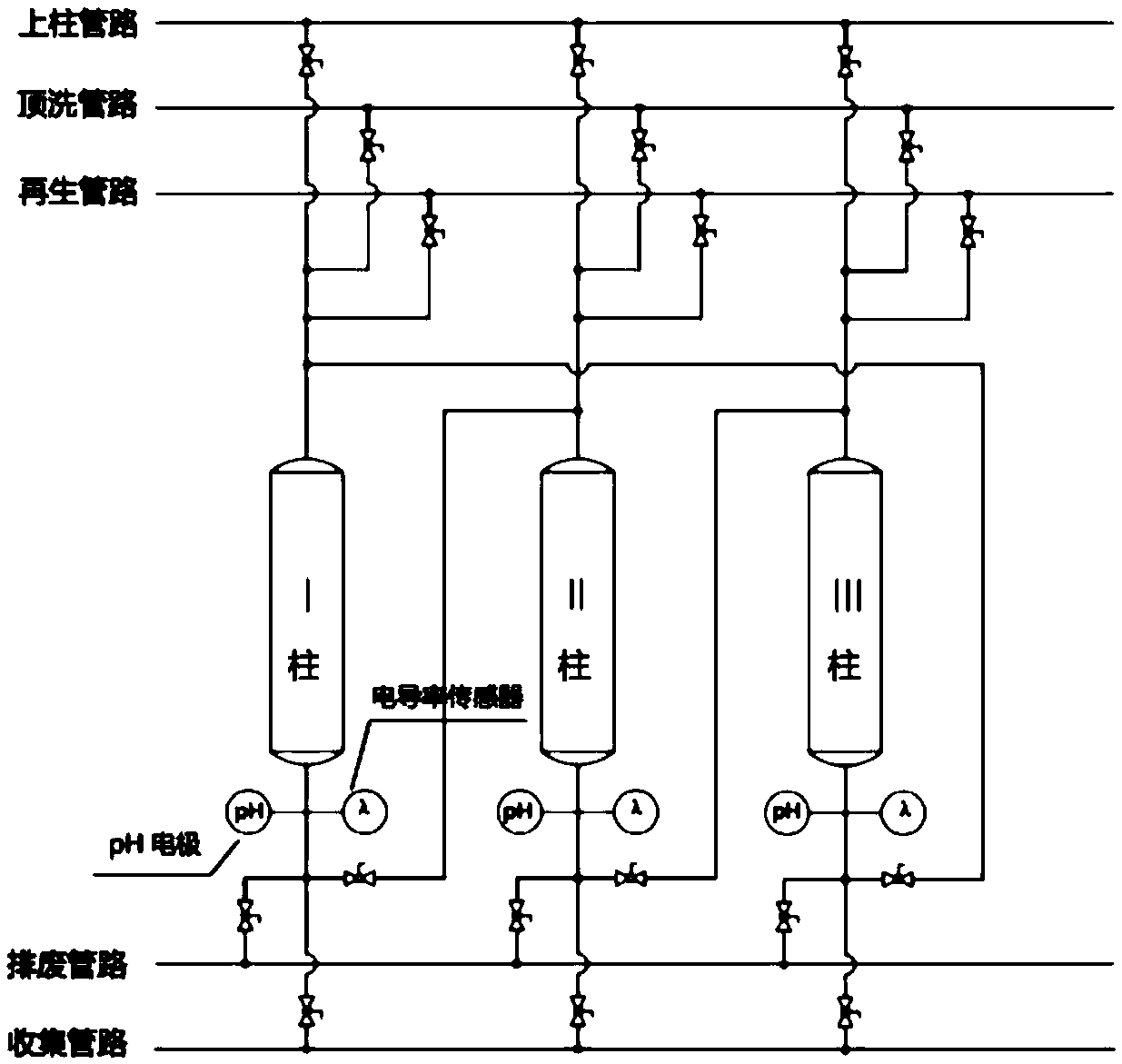
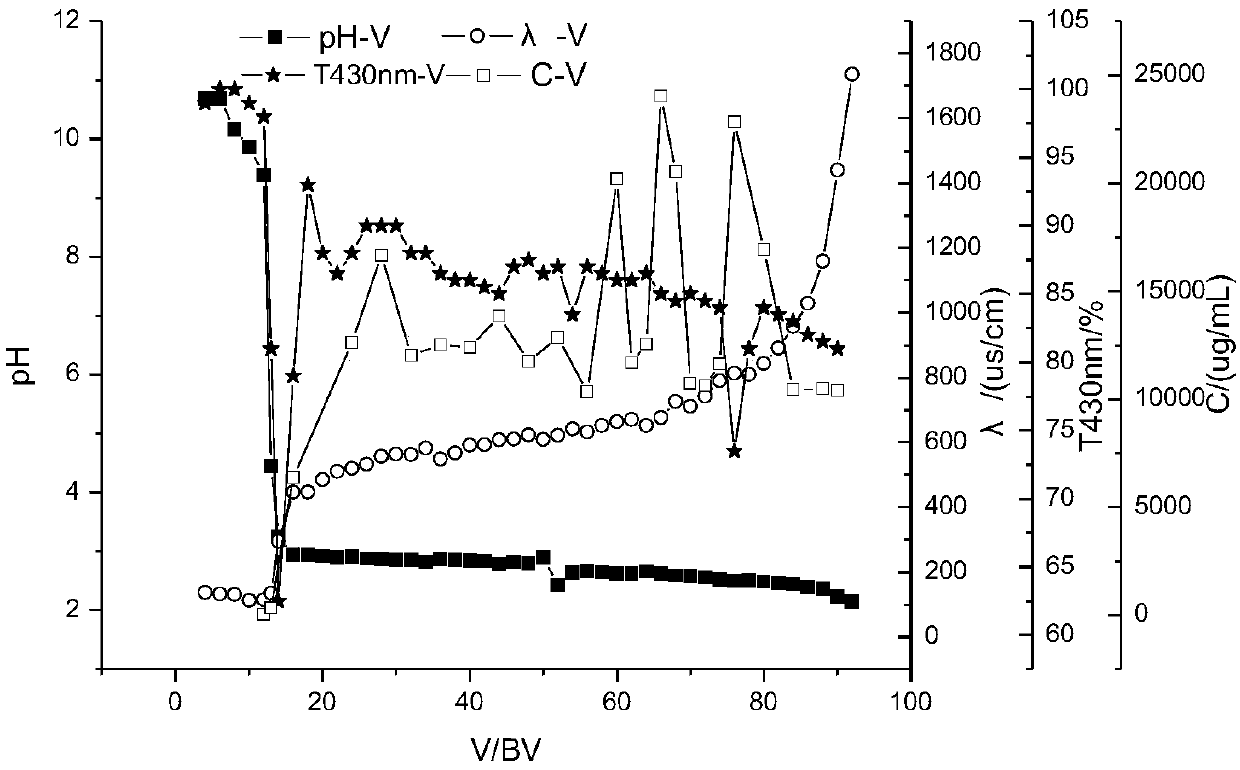
Process for efficiently purifying shikimic acid by utilizing continuous ion exchange technology
ActiveCN109721487AIncrease profitReduce usageCarboxylic compound separation/purificationShikimic acidIon exchange
The invention discloses a process for efficiently purifying shikimic acid by utilizing a continuous ion exchange technology, and the process comprises: carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain afermentation filtrate, and carrying out pre-purification on the fermentation filtrate by virtue of cation exchange resin to obtain a pre-purified liquid a; and pre-purifying the pre-purified liquid athrough a continuous ion exchange system to obtain a pre-purified liquid b; and finally, carrying out fine purification and spray drying on the pre-purified liquid b to obtain the shikimic acid. Theprocess has the advantages that the process is simple and stable, continuous and automatic production can be realized, the chromatographic purity and the content of the prepared shikimic acid finishedproduct are both higher than 99%, the utilization rate of the resin is greatly improved, the total usage amount of the resin is reduced by about 80%, an eluent is not used in the pre-purification process, wastewater is greatly reduced, the production cost is greatly reduced, the market competitiveness of the product is enhanced, and the process is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
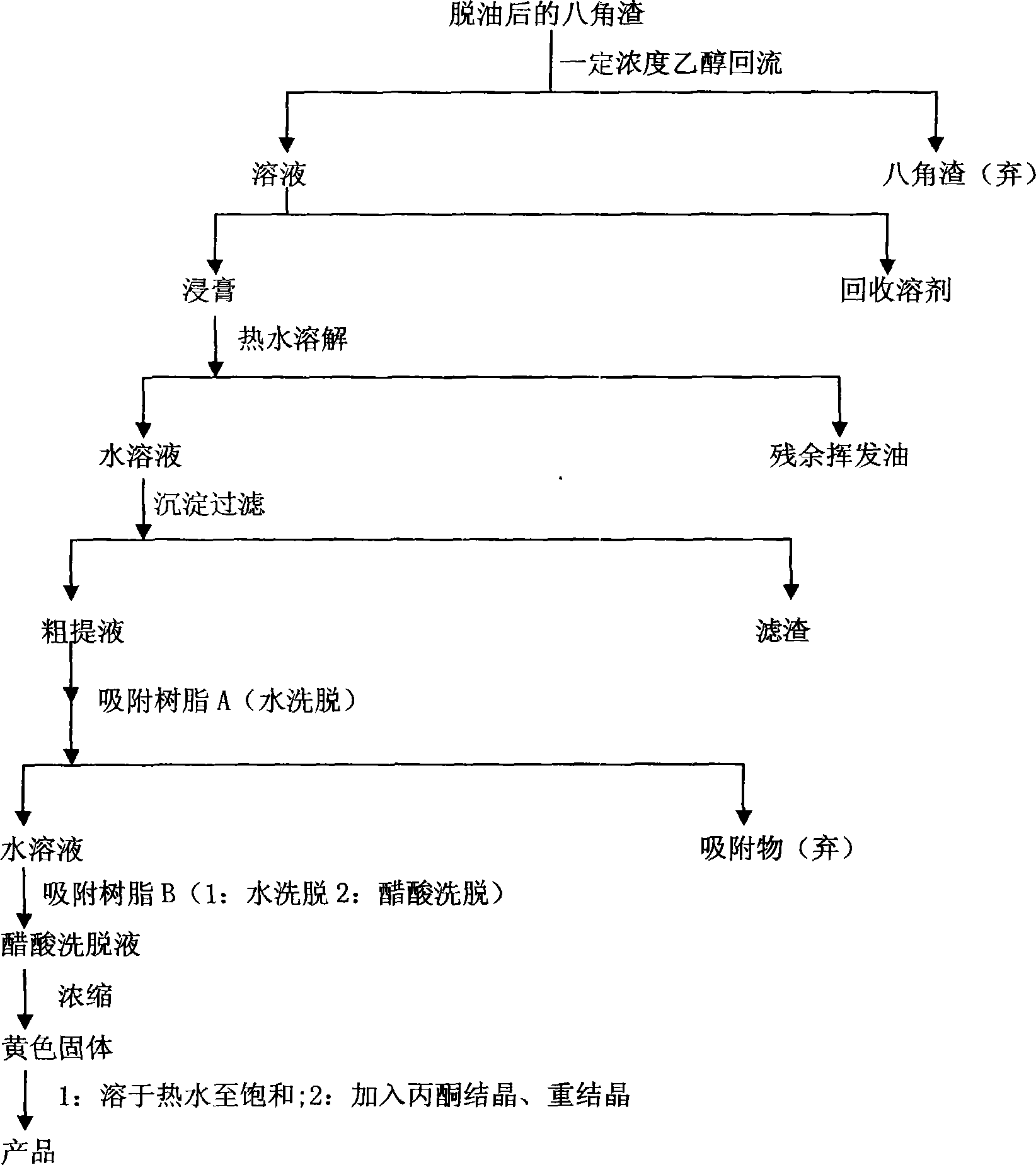
Method for extracting high-pure shikimic acid from scarlet octagonal fruit
InactiveCN101250104AImprove adsorption capacityChromatography is fastCarboxylic compound separation/purificationPlant ingredientsSlagUltrafiltration
A method for extracting high-purity shikimic acid from red illicium comprises breaking dry illicium via general technique, deoiling and drying, refluxing via industrial alcohol to extract the deoiled illicium slag, combining and concentrating extract liquors into extractive, dissolving via hot water, bathing in hot water, absorbing oil and filtering, concentrating and removing impurity via neutral macroporous adsorption resin, purifying via alkali anion exchange resin, volatilizing the solvent in crude shikimic acid, dissolving in hot water, adding acetone, freezing and crystallizing, and recrystallizing to obtain fine shikimic acid product. The invention uses alcohol for extraction and uses different resins to absorbe impurity and shikimic acid, thereby reducing the effect of soluble impurity, and the extract liquor can be filtered easily to avoid ultrafiltration device, and the resins have high adsorption capacity and high chromatography speed, thereby saving organic solvent, reducing production cost and improving product quality.
Owner:GUANGXI TEACHERS EDUCATION UNIV
Method for extracting shikimic acid from aniseed
InactiveCN101560150AEasy to proposeSimple processReverse osmosisBulk chemical productionRoom temperatureShikimic acid
The invention discloses a method for extracting shikimic acid from aniseed. The steps are as follows: firstly, supercritical CO2 fluid is used for extracting anise oil from the aniseed; secondly, room temperature water is used for steeping the deoiled aniseed; thirdly, a reverse osmosis membrane device is used for concentrating shikimic acid extract; and the shikimic acid can be obtained after the operations of decolourization and crystallization are carried out. The method has the advantages that the process is simple and stable and is easy to control, and the extraction percentage of the shikimic acid can be more than 9 percent; by adopting the reverse osmosis membrane device for concentration, the method reduces the consumption of energy and time.
Owner:中科检测技术服务(广州)股份有限公司
Shikimic acid prepared bacterial strain and constructing method
InactiveCN101139566AEfficient accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesShikimic acidMicrobiology
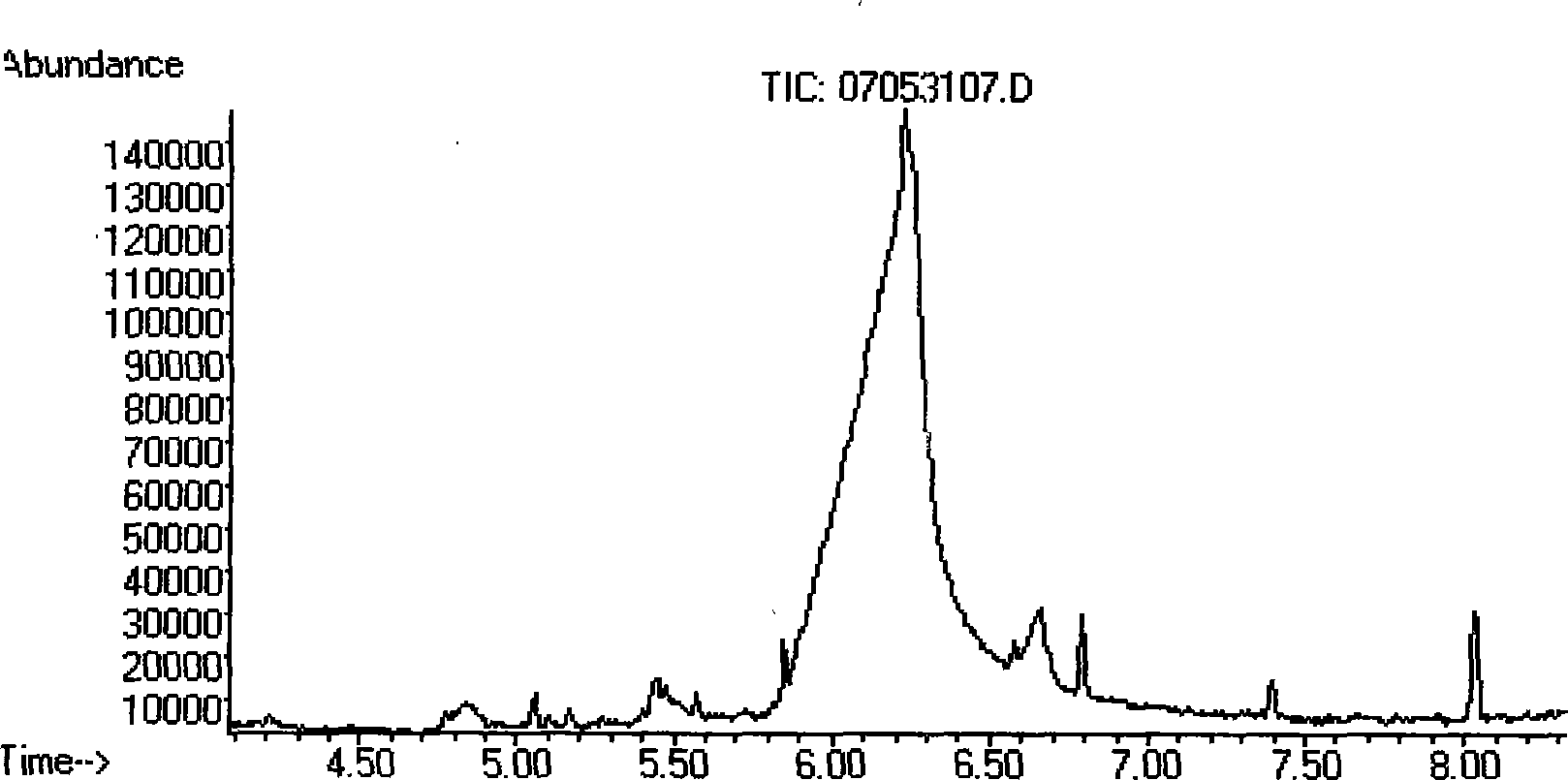
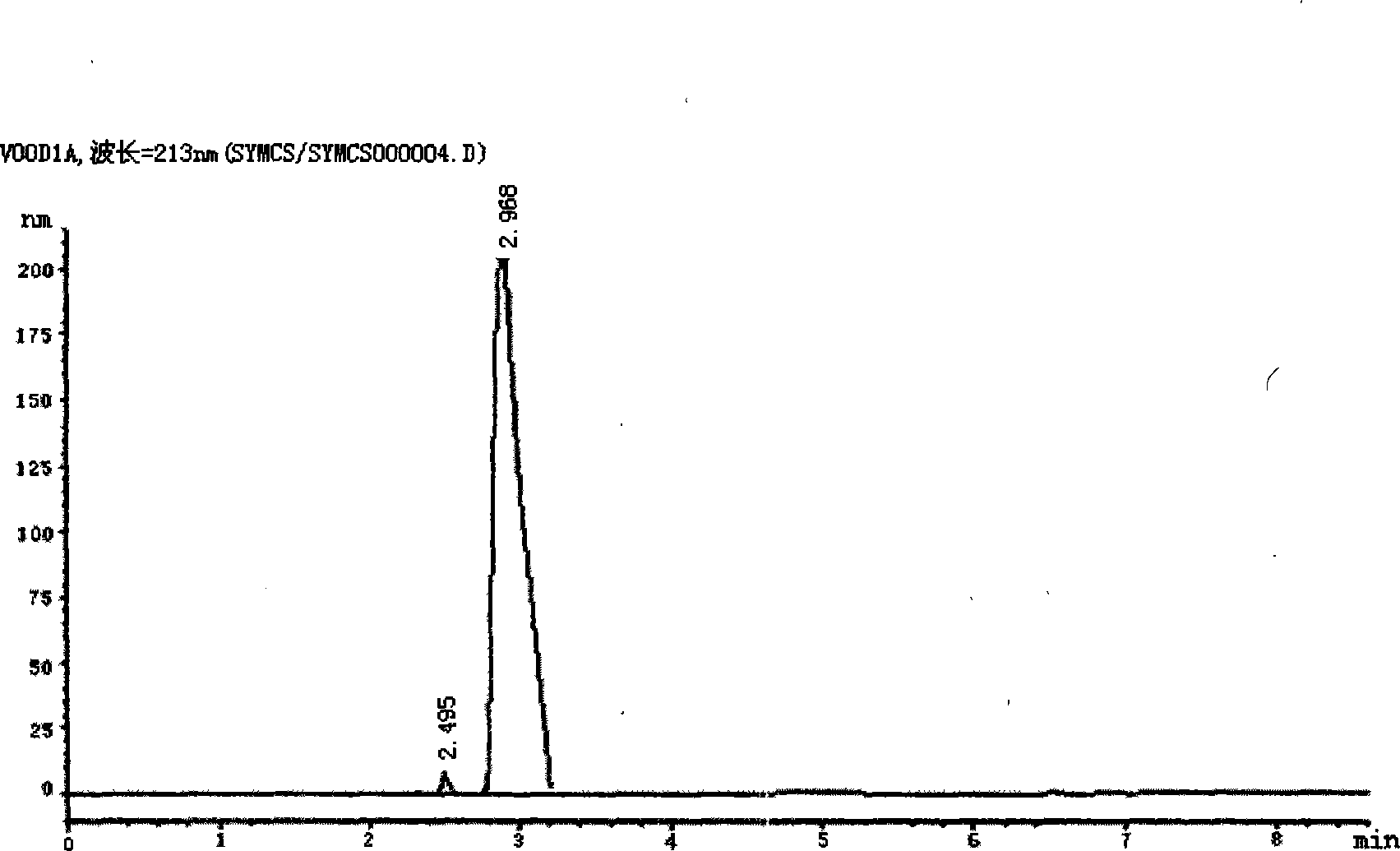
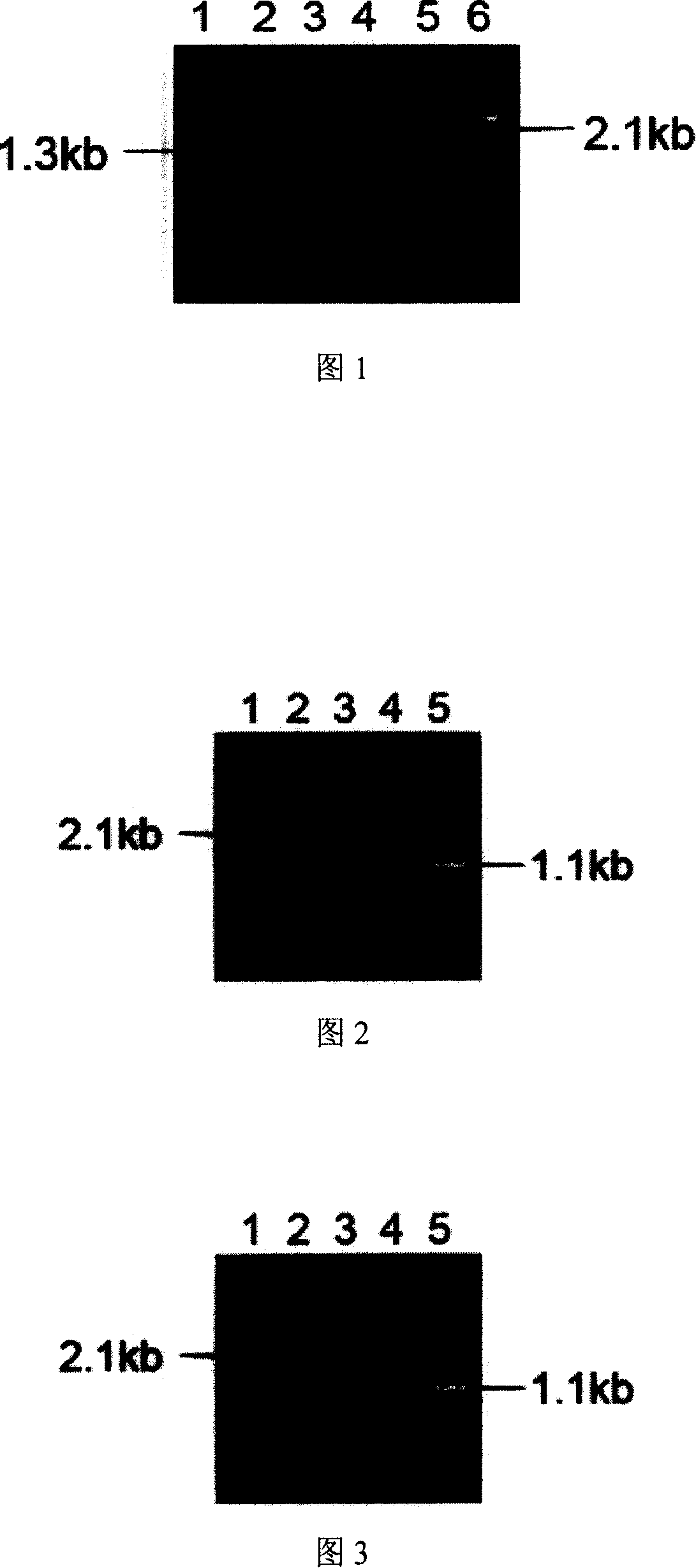
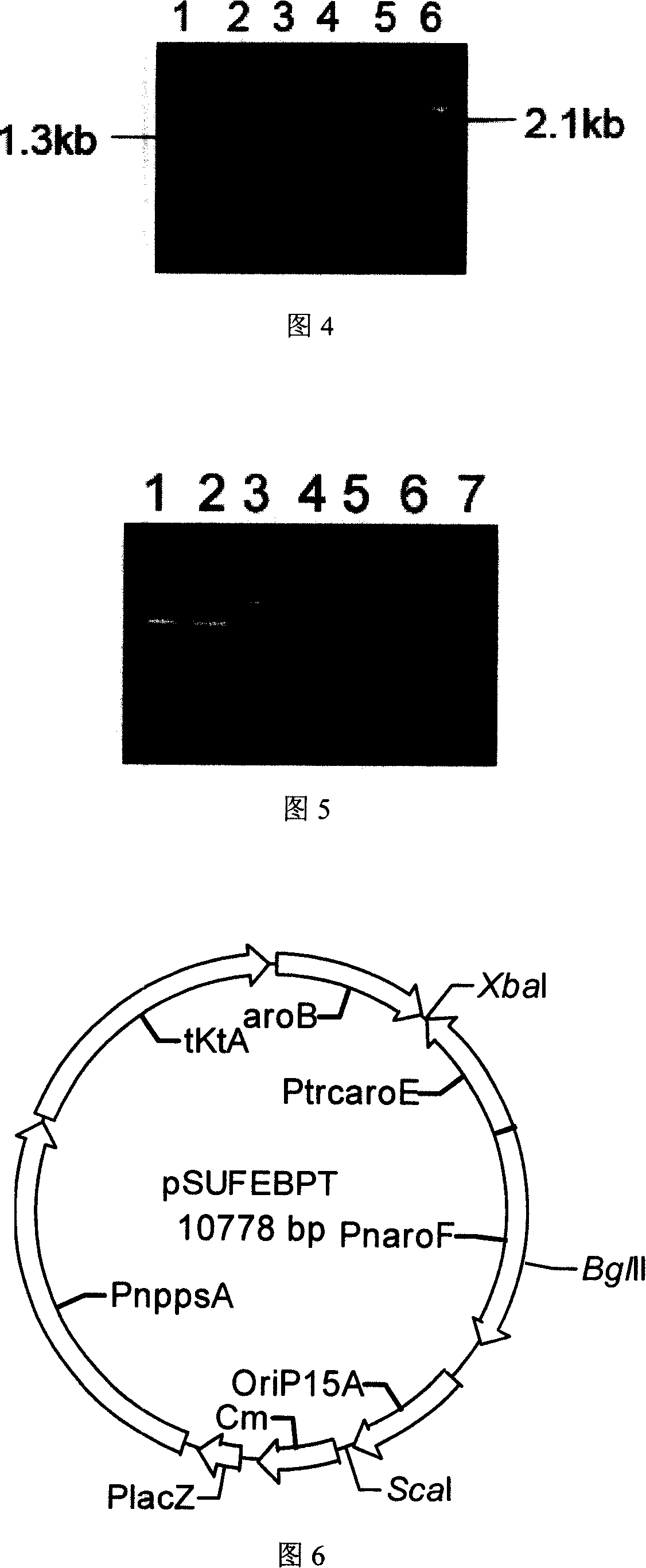
The invention discloses a shikimic-acid-producing bacterial strain and a constructing method for the bacterial strain. First, bacterial strain W3110 (delta aroL delta aroK) with gene aroL and aroK knocked out is constructed, and a recombination expression plasmid pSUFEBPT containing key gene aroF, aroE, aroB, ppsa and tktA in the metabolism of shikimic acid is constructured, then the recombination expression plasmid is transferred into the bacterial strain W3110 (delta aroL delta aroK) with gene aroL and aroK knocked out, so as to get the shikimic-acid-producing bacterial strain. The shikimic-acid-producing bacterial strain in the invention can achieve the effective accumulation of shikimic acid in fermentation, and lay a foundation for the industrialization of shikimic-acid production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for producing shikimic acid
InactiveCN101024609AReduce labor intensityReduce usageCarboxylic compound separation/purificationPlant ingredientsAcetic acidOrganic solvent
The invention supplies a shikimic acid producing method that includes the following steps: adding water into raw material chinese anise, taking recycling for 6-8 hours at 50-80 degree centigrade, concentrating to skikimic acid extractive raw material; mixing and whisking raw material and silica gel according to 1:1, leaching by ethyl acetate, testing and collecting eluate, concentrating and filtering to gain shikimic primary crystallization, taking recrystallization by using the same method. The invention sharply simplifies distilling process, improves working efficiency, decreases producing cost, and could shikimic acid of 90-95% purity.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for separation and purification of shikimic acid from ginkgo biloba leaves
ActiveCN106316830ARelieve demand pressureIncrease production costCarboxylic compound separation/purificationSilica gelEthyl acetate
The invention discloses a method for separation and purification of shikimic acid from ginkgo biloba leaves, which comprises the following steps: 1, drying and smashing the ginkgo biloba leaves and refluxing and extracting through ethyl alcohol with the mass percentage being 70%, and then concentrating the mixture into a concrete shape; 2, using ultrasound to dissolve the concentrate obtained in step one in deionized water and then using petroleum ether, ethyl acetate and n-butyl alcohol to extract sequentially, and obtaining aqueous phase concrete after the aqueous phase is fully concentrated; 3, dissolving the aqueous phase concrete obtained from step two into methyl alcohol, blending with 100-200 parts of target silica gel and then drying the mixture; 4, packing the dry substance obtained in step three, eluting the substance through the mixture of ethyl acetate and methyl alcohol, gathering elution fluid, concentrating the elution fluid until the fluid is fully dry, and obtaining rough shikimic acid; 5, producing shikimic acid crystal through the recrystallization of the methyl alcohol. The method for separation and purification of shikimic acid from ginkgo biloba leaves uses ginkgo biloba leaves as the raw materials, and realizes the cyclic utilization of waste resources, having the advantages of simple extraction process and low cost; meanwhile, the shikimic acid has high production rate and purity.
Owner:贵州北极兴药业有限公司
Method for preparing shikimic acid extract from folium ginkgo extract chromatography waste liquid
InactiveCN108191639ATake advantage ofHigh purityCarboxylic compound separation/purificationGinkgo bilobaShikimic acid
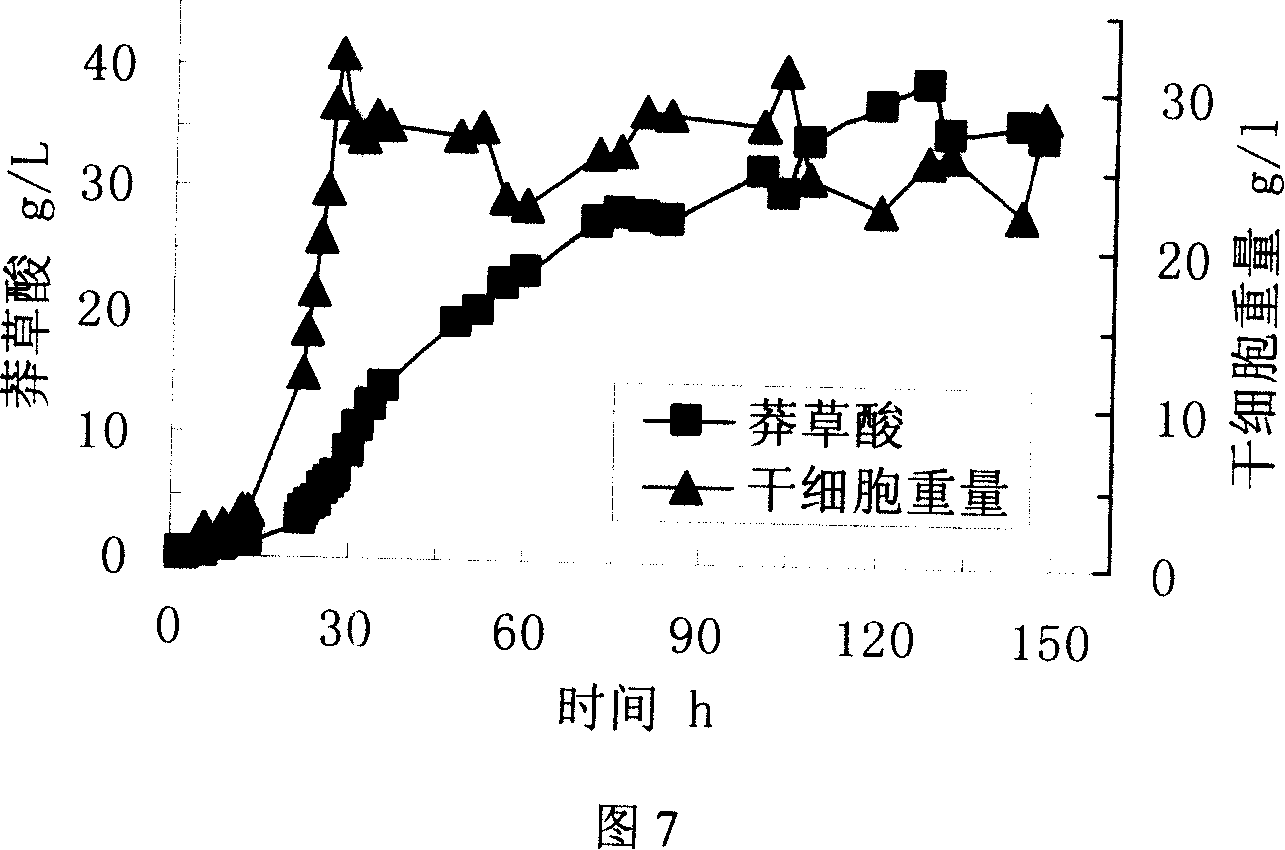
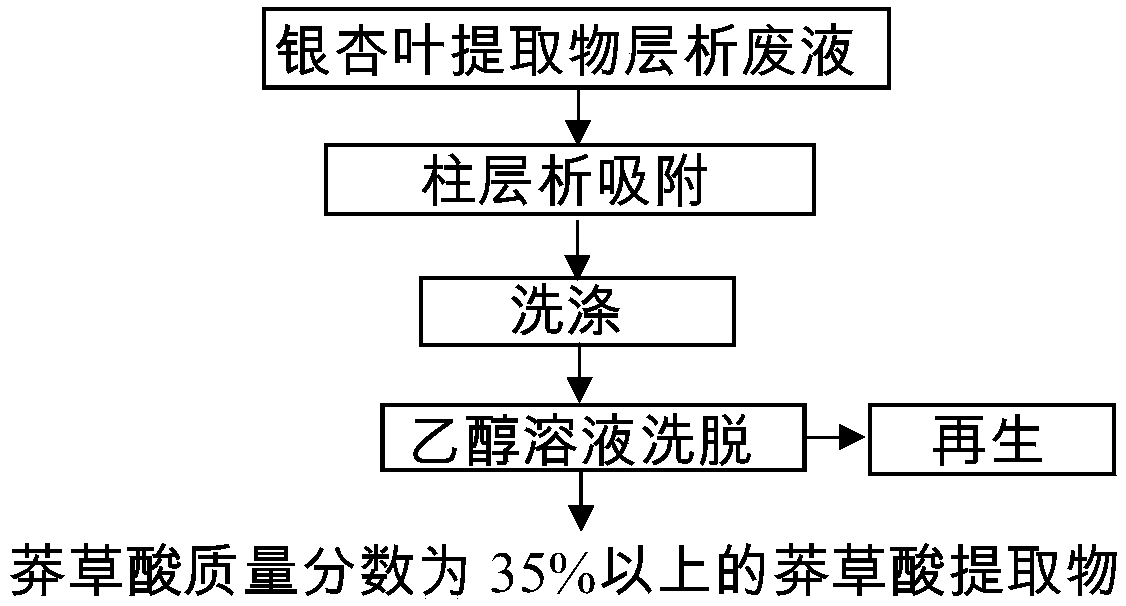
The invention relates to a method for preparing shikimic acid extract from folium ginkgo extract chromatography waste liquid. The method specifically comprises the following steps: 1) the shikimic acid extract is prepared from the waste liquid, generated during preparation of folium ginkgo extract with the chromatography technology, as a raw material, wherein the waste liquid comprises chromatography flow-through liquid or washing liquid in the chromatography process; 2) the folium ginkgo extract chromatography waste liquid is enriched and purified by a chromatography column, a washing liquidis added for impurity removal, shikimic acid is eluted with an eluent, an eluate is collected and concentrated, and the shikimic acid extract with shikimic acid mass fraction of 35% or higher is obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANBANG PHARMA
Method for preparing shikimic acid using biosynthesis technology and engineered bacteria
InactiveCN101085998AThe operation method is simple and preciseEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for preparing shikimic acid by using biological synthesis technique, and the employed recombined bacillus coli. The method comprises following steps: constructing carrier for speed- limit enzyme polygene box containing shikimic acid metabolic pathway; repalcing shiA gene with polygene box; removing shikimic acid kinase- mb in bacteria by using Red recombinant system; fermenting recombinant engineering bacteria and getting shikimic acid and purifying shikimic acid. The invention can increase expression amount for shikimic acid, reduces production cost and provides raw material for preparing medicine Duffy that can prevent influenza.
Owner:汪莉
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com