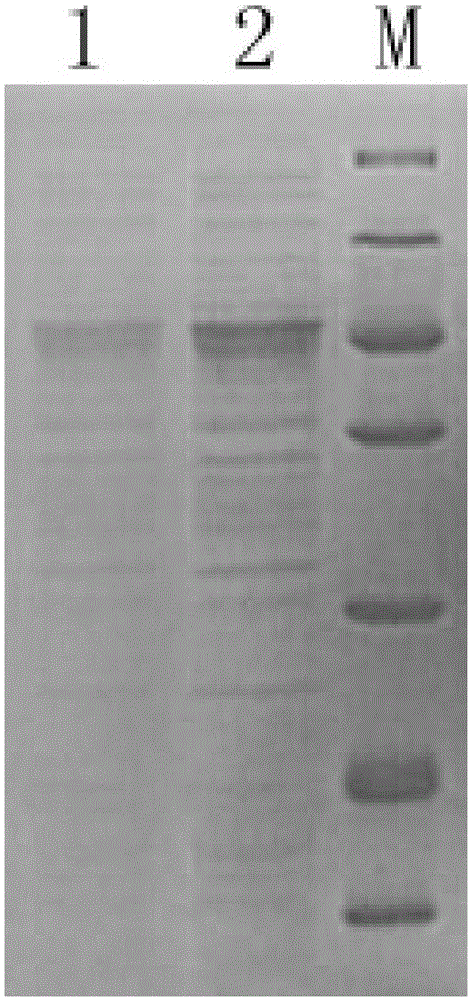
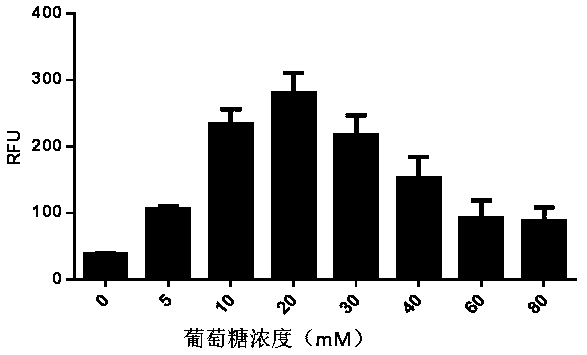
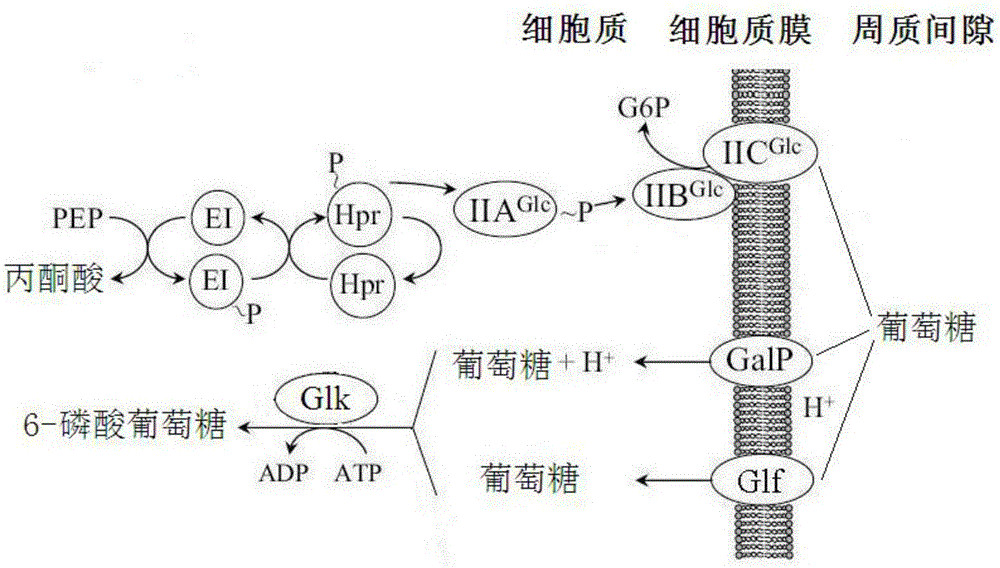
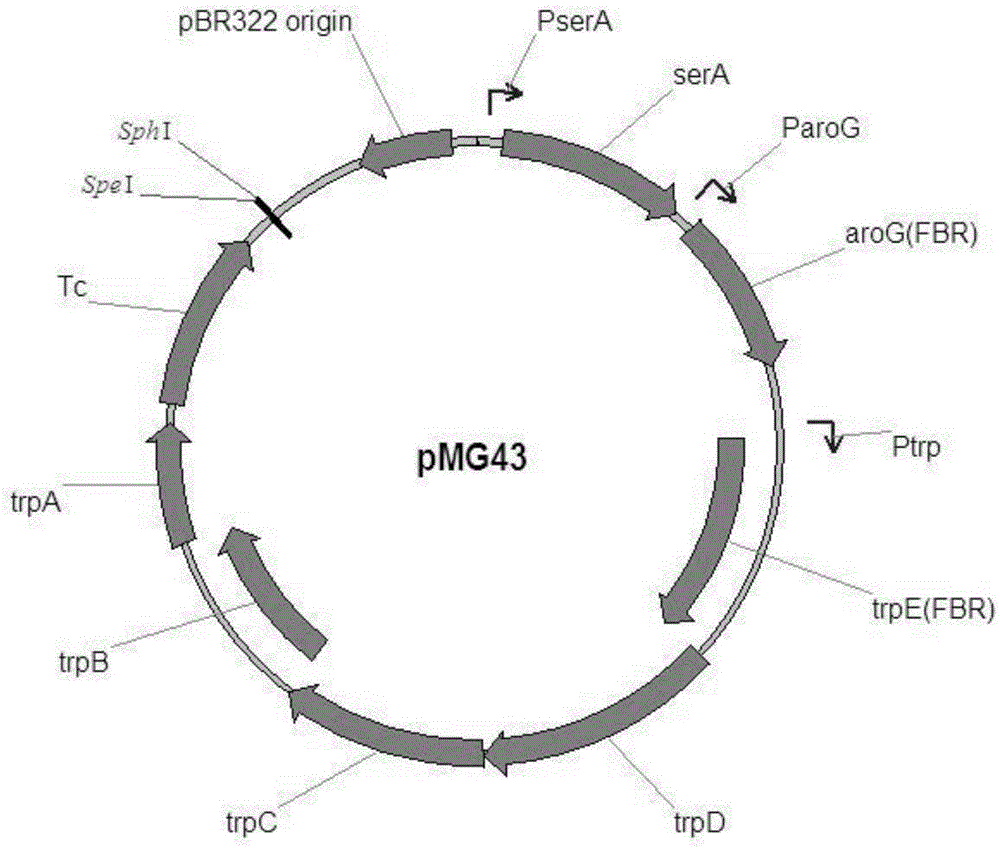
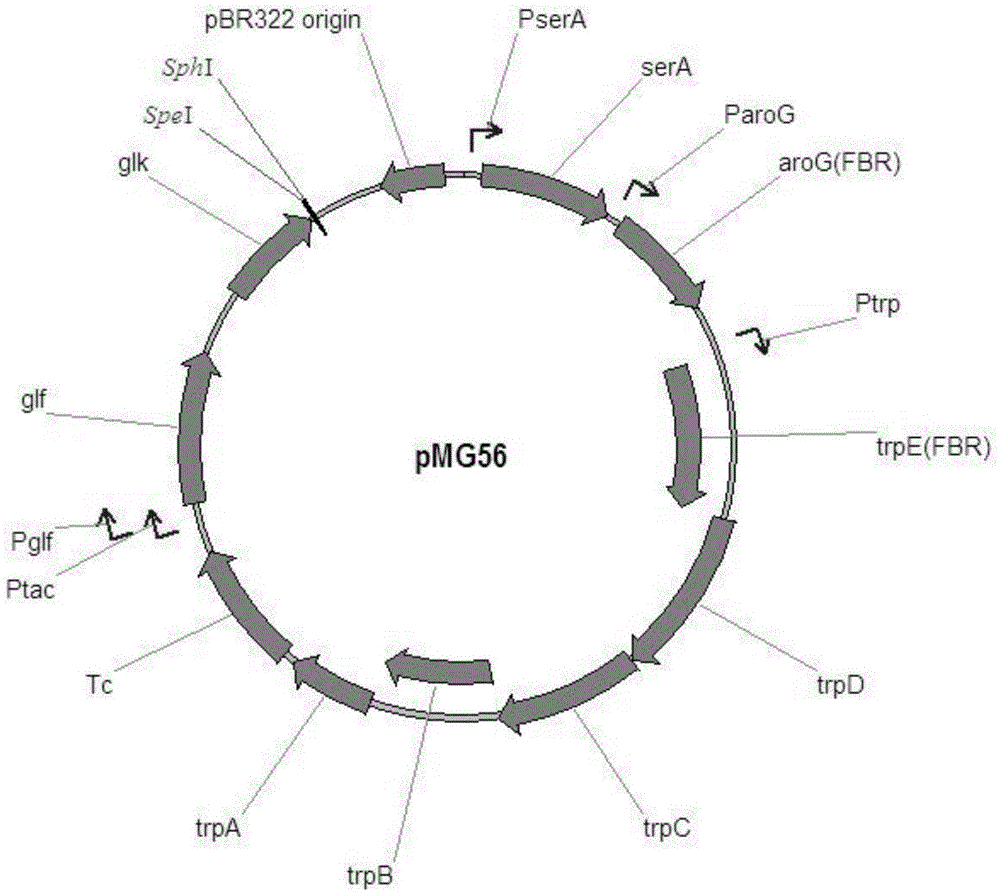
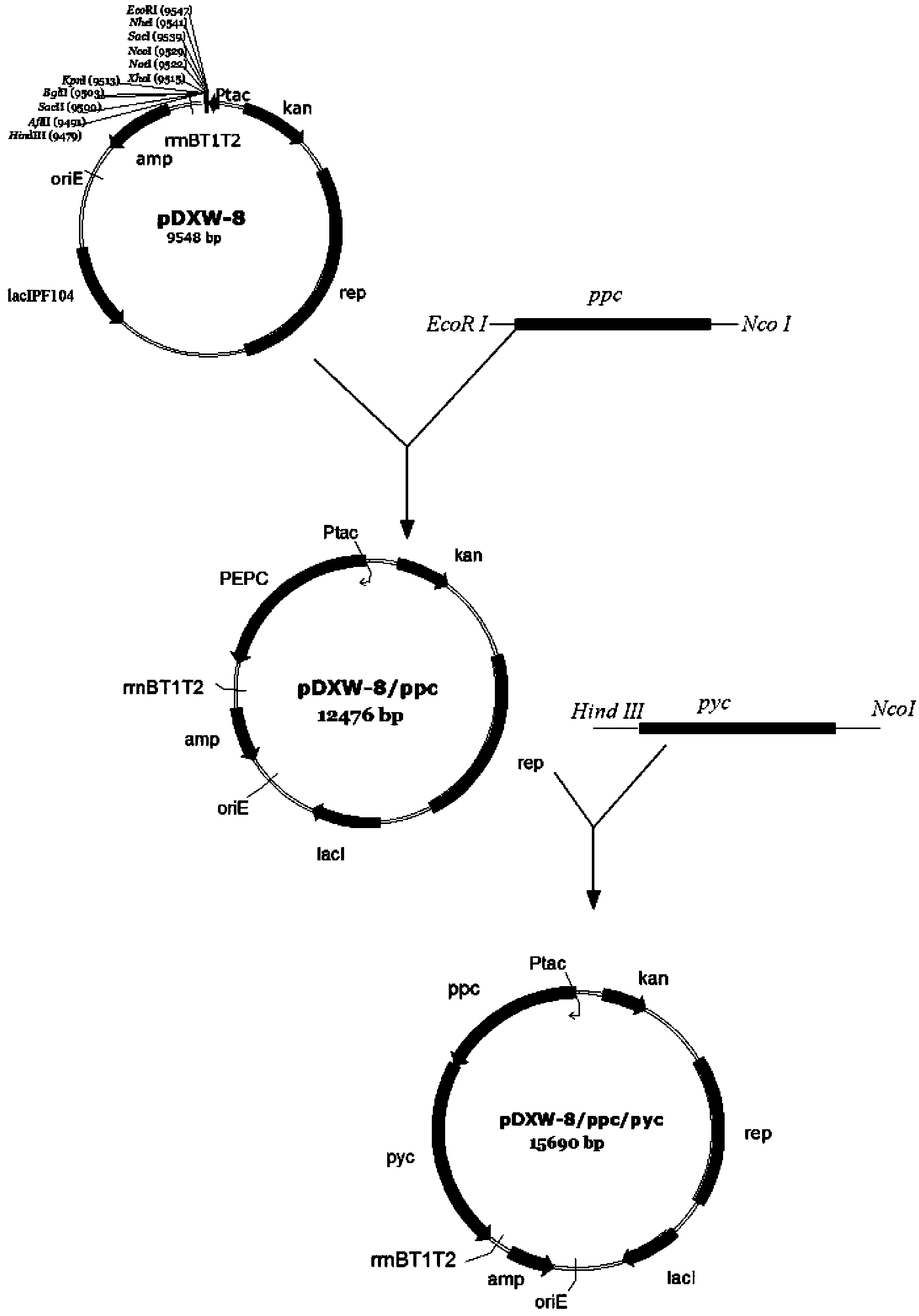
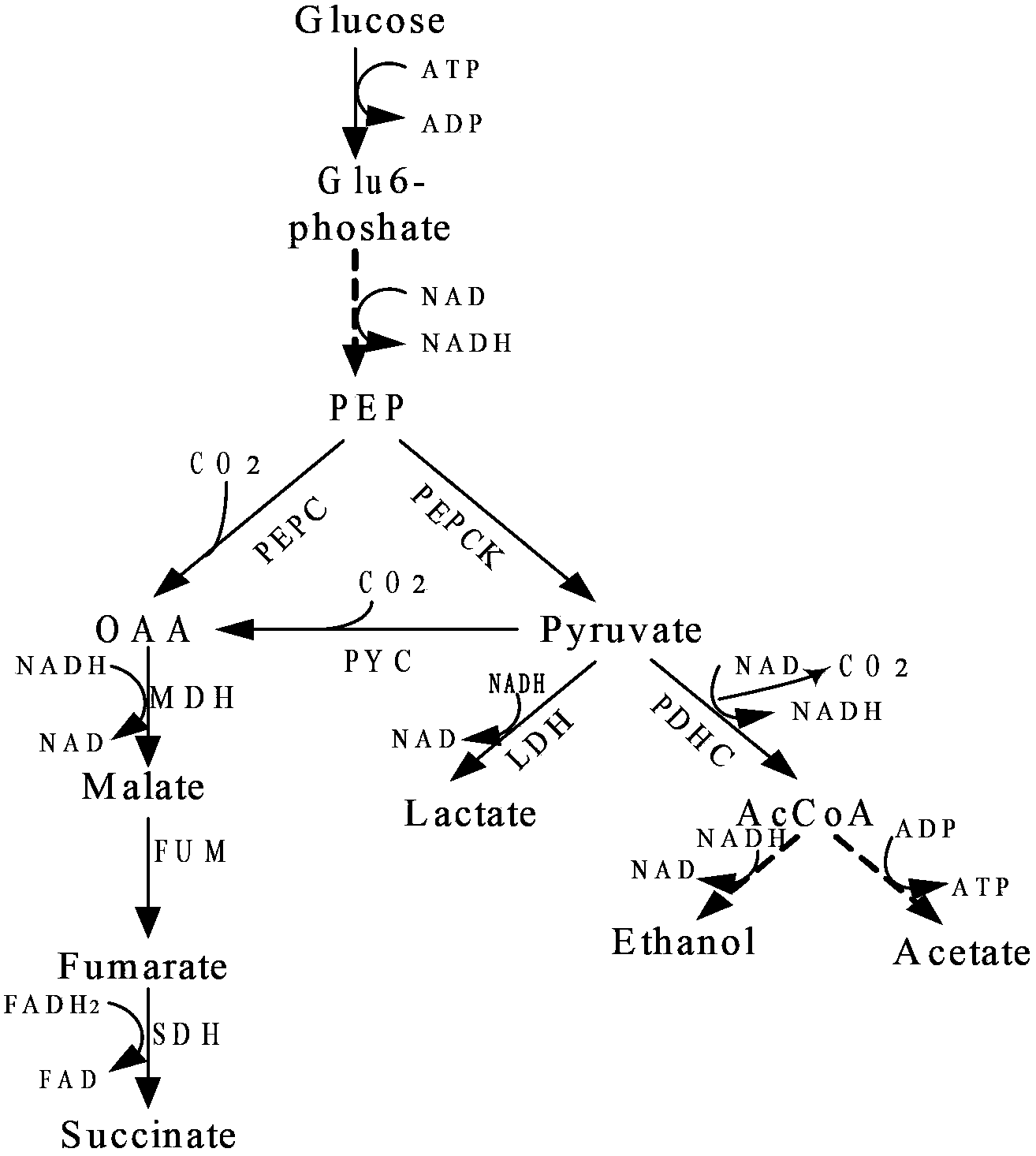
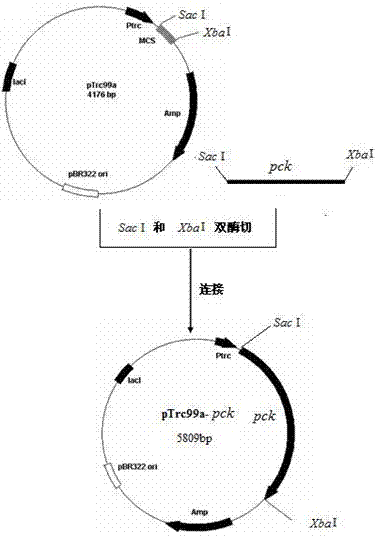
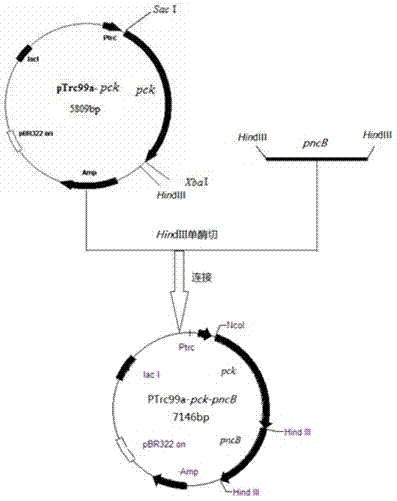
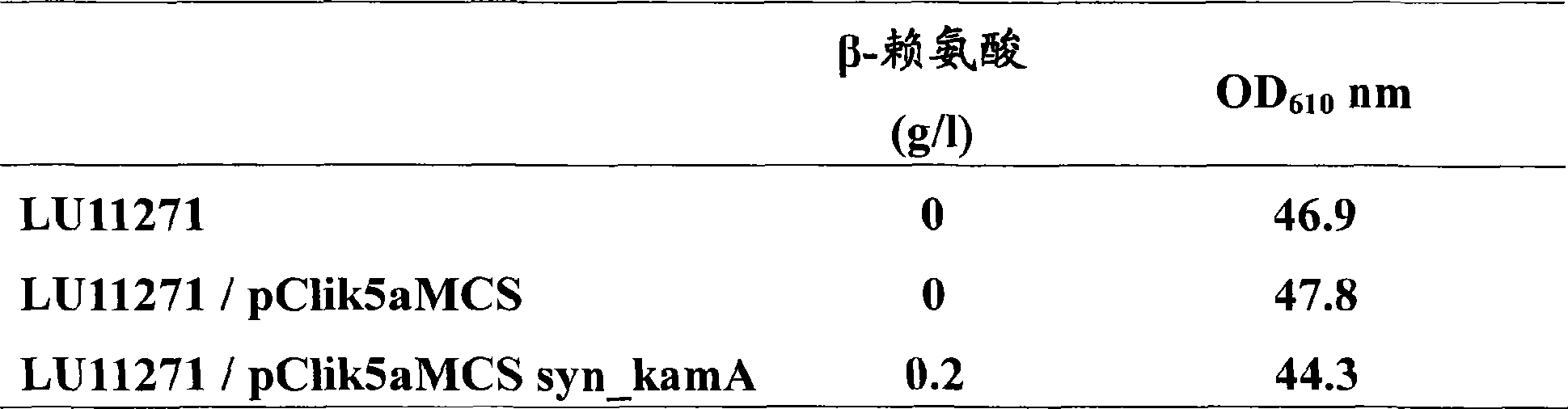
Patents
Literature
217 results about "Phosphoenolpyruvic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
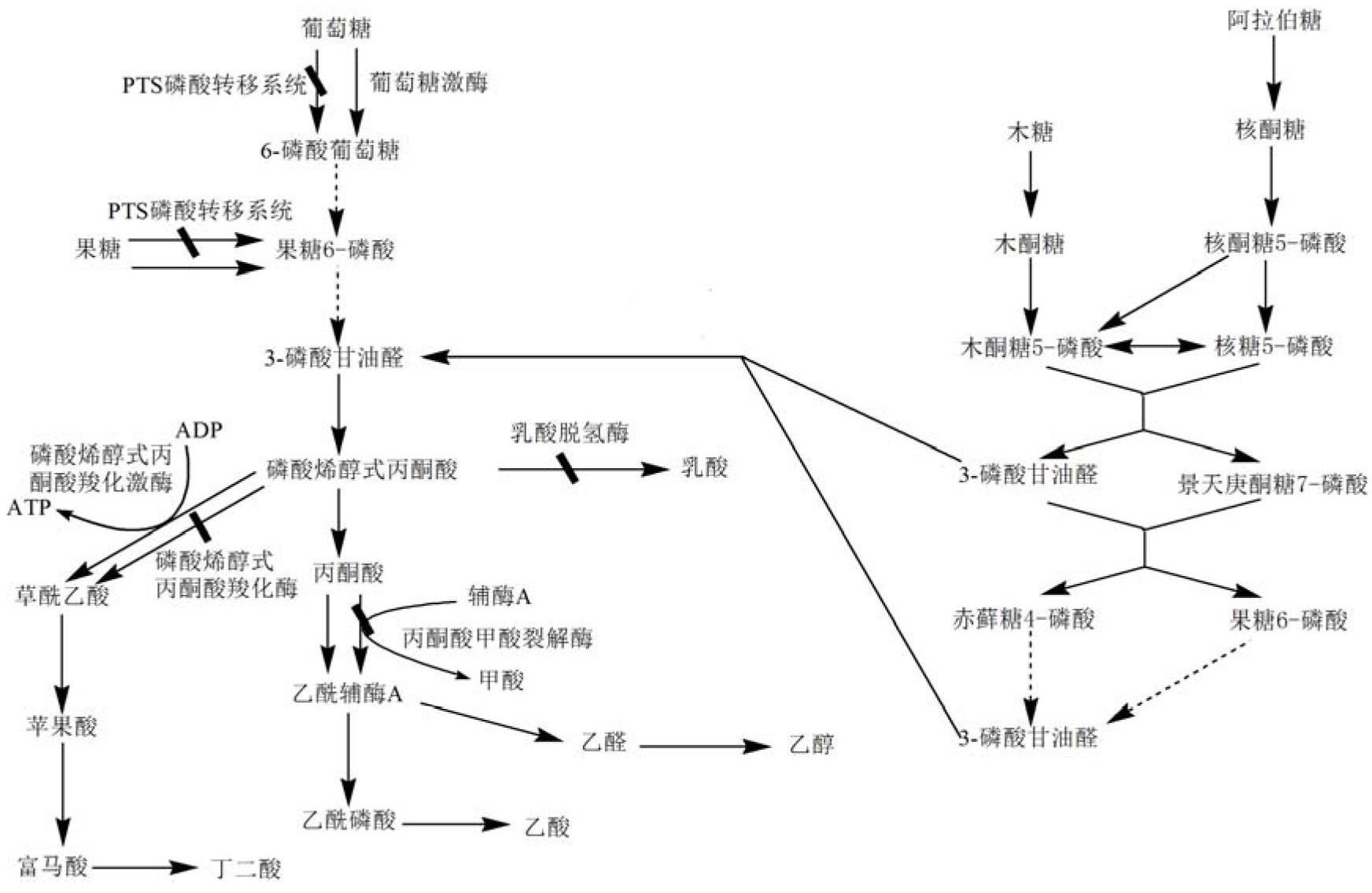
Phosphoenolpyruvate (2-phosphoenolpyruvate, PEP) is the ester derived from the enol of pyruvate and phosphate. It exists as an anion. PEP is an important intermediate in biochemistry. It has the highest-energy phosphate bond found (−61.9 kJ/mol) in organisms, and is involved in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. In plants, it is also involved in the biosynthesis of various aromatic compounds, and in carbon fixation; in bacteria, it is also used as the source of energy for the phosphotransferase system.
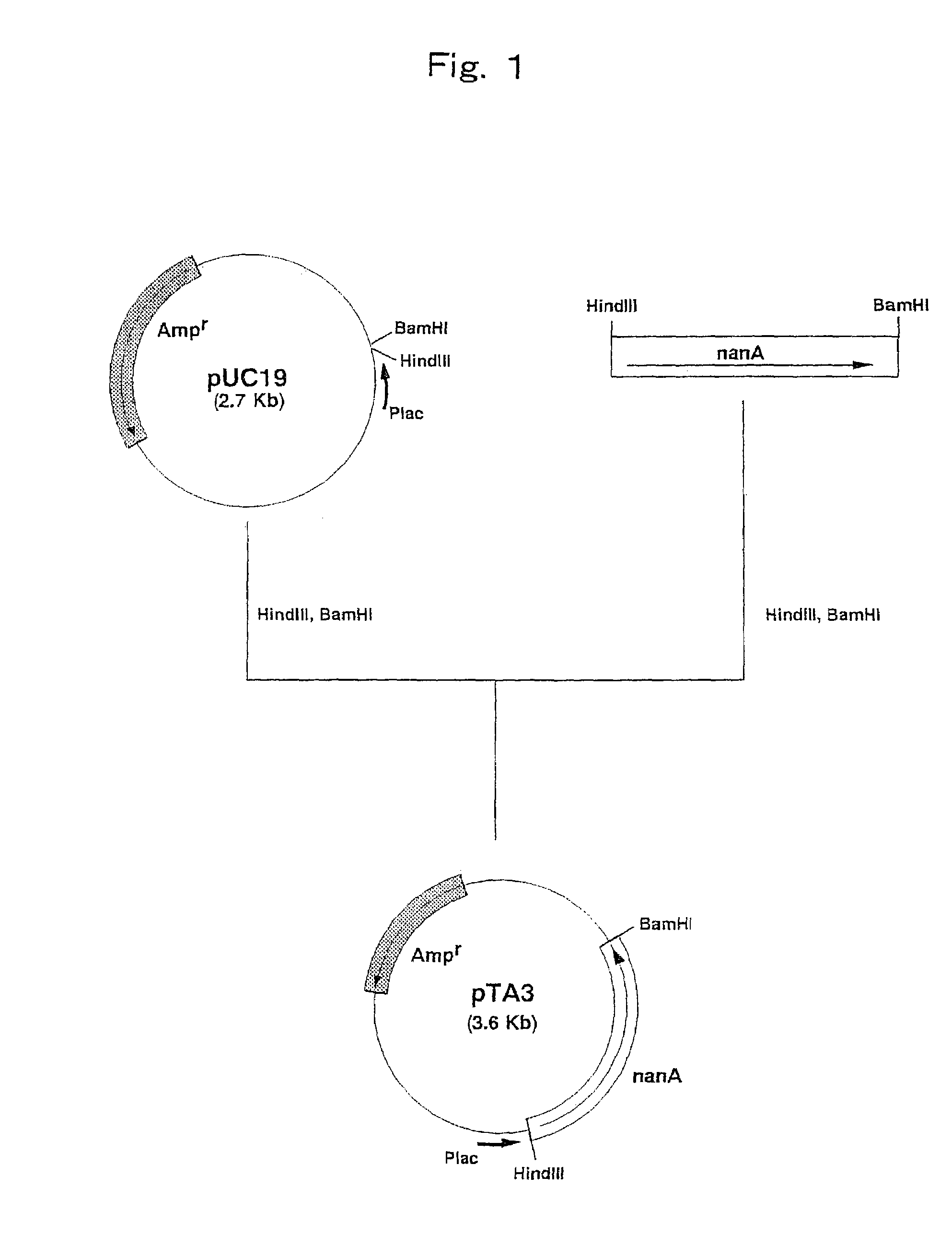
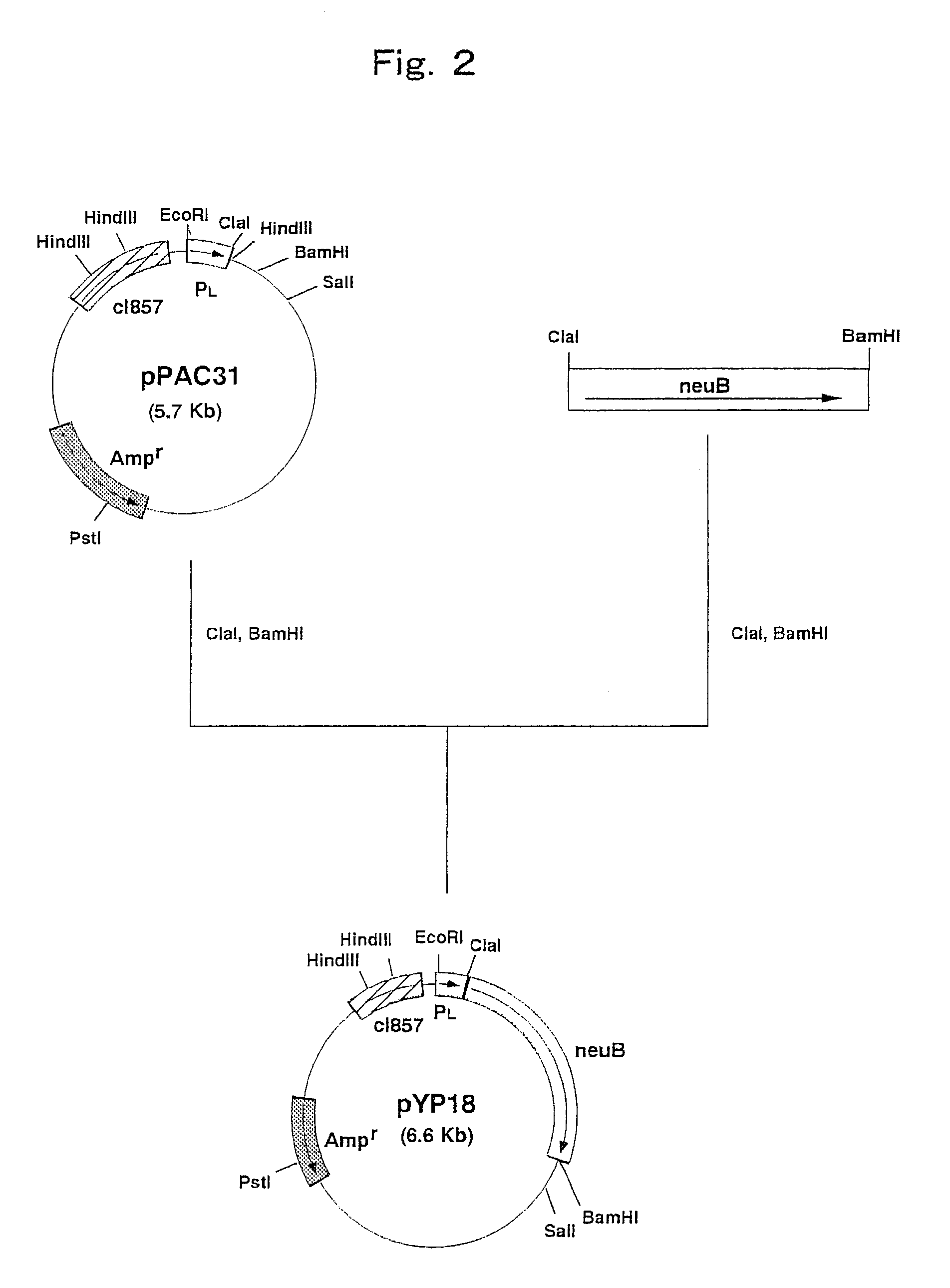
Recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of increasing yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of increasing the yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Supply of phosphoenolpyruvic acid in the synthesis pathway of N-acetylneuraminic acid is increased by taking bacillus subtilis (bacillus subtilis 168 delta nagP delta nagP delta gamP delta gamA delta nagA delta nagB delta 1dh delta pta::lox72; delta ctc::p43-Gna1, pP43NMK-AGE-NeuB) as an expression host and knocking out ptsG of a glucose specific enzyme EIICBA component of a phosphotransferase system, and therefore the synthesis passway is enhanced; compared with an original strain, the recombinant bacillus subtilis has the advantages that the yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid is increased to 660 mg / L from 190 mg / L, and a foundation is laid for improving N-acetylneuraminic acid production from bacillus subtilis in metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Blood ammonia content determination method and blood ammonia diagnosis kit
InactiveCN1769481AStrong specificityLess susceptible to interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementLactate dehydrogenaseMedical testing
The invention relates to a method for determining the content of blood ammonia, and also the reagent kit for blood ammonia diagnosis. The reagent kit comprises cushioning solution, adenosine triphosphate, phosphoenolpyruvate phosphatase, deacidized type coenzyme, ammonia kinase, pyruvate kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, and stabilizer. By mixing sample and reagent of a predetermiend volumetric ratio, generating coupling reaction between them, subjecting the final reactant to biochemiscal analyser, the main wavelength absorbancy variance ratio (speed) can be detected, and the blood ammonia content can thus be measured. The method of the invention can be used to obtain the needed measurement result purely through biochemical analytic instruments, and advantages of the method include higher sensibility, better accuracy, less susceptibility to contamination of internal or external materials, and easy application.
Owner:王尔中
Liquid double reagent diagnostic reagent kit for determining content of potassium ions in serum and blood plasma
ActiveCN101717814AFast measurementImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsLactate dehydrogenasePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a liquid double reagent diagnostic reagent kit for determining the content of potassium ions in serum and blood plasma. By using the reaction principle that phosphoenolpyruvic acid (PEP) can be catalyzed by K+dependency pyruvate kinase (PK) to be converted into pyruvic acid and taking lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) as indicator enzyme by means of NADH, the reagent kit detects the reduction amount of the NADH at 340 nm and obtains the result that the change of the absorbance every minute (delta / min) is directly proportional to the content of K+, thereby establishing an enzyme coupling method for continuously determining the potassium ions. In addition, enzyme and a primer system required by slowly generating reduction type nicotinoyl coenzyme are added in a system andan enzyme-primer-coenzyme slow reaction system is formed in a reagent, so that the coenzyme can be slowly and circularly supplemented and the reagent can be stabilized when the concentration reaches a certain balance. The liquid double reagent diagnostic reagent kit is convenient and concise to use, carries out rapid detection on a common ultraviolet / visible light analyzer or a semiautomatic / fully-automatic chemical analyzer, needs no special or extra instrument and has low cost.
Owner:BEIJING STRONG BIOTECH INC
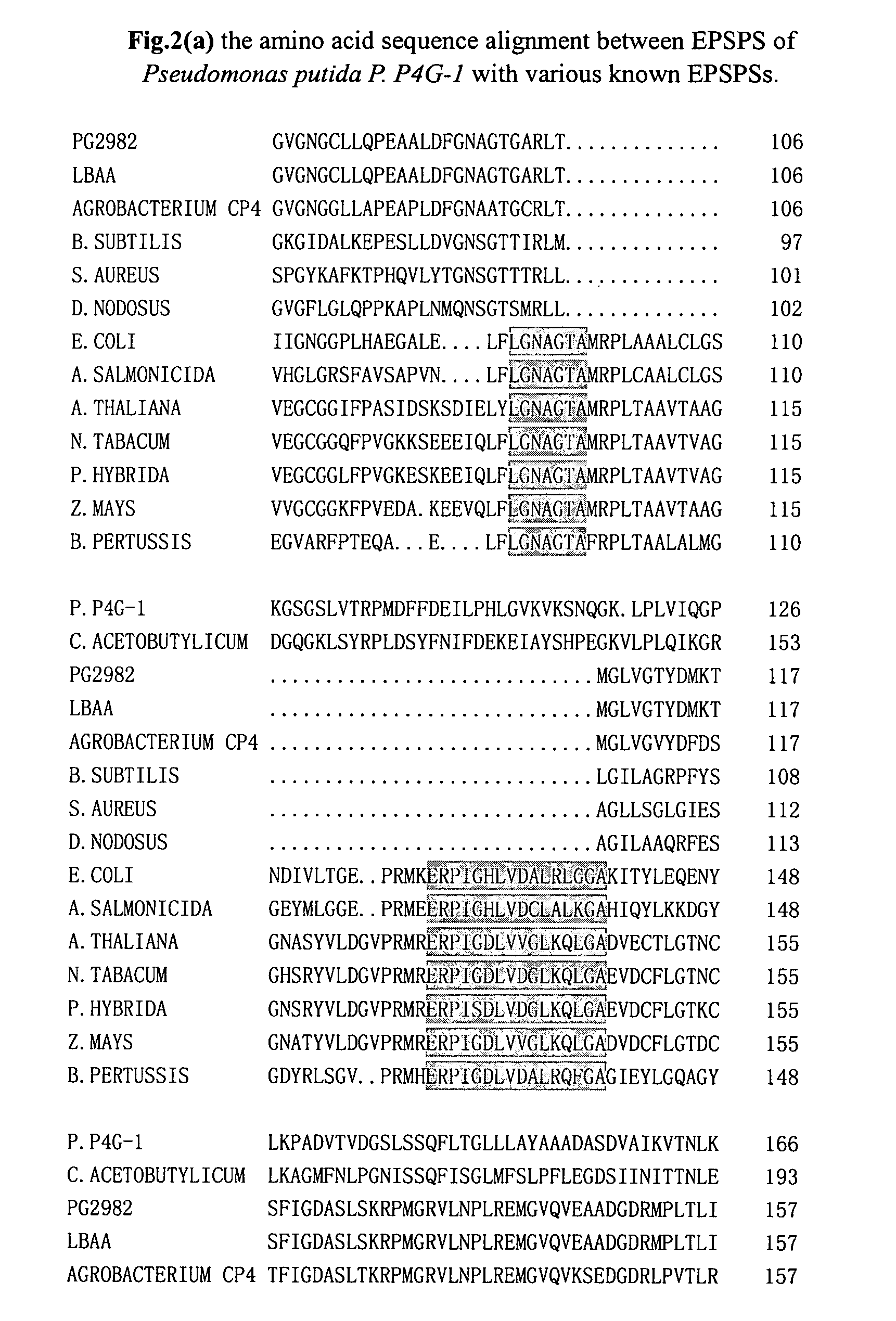
Glyphosate-tolerant 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase and the gene encoding the same
InactiveUS7214535B2Convenient ligationRaise the possibilityFungiSugar derivativesGlyphosatePhosphoric acid
The present invention relates to a novel 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). It is highly tolerant to glyphosate, the competitive inhibitor of the substrate phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). The invention also relates to a gene encoding the synthase, a construct and a vector comprising said gene, and a host cell transformed with said construct or vector.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
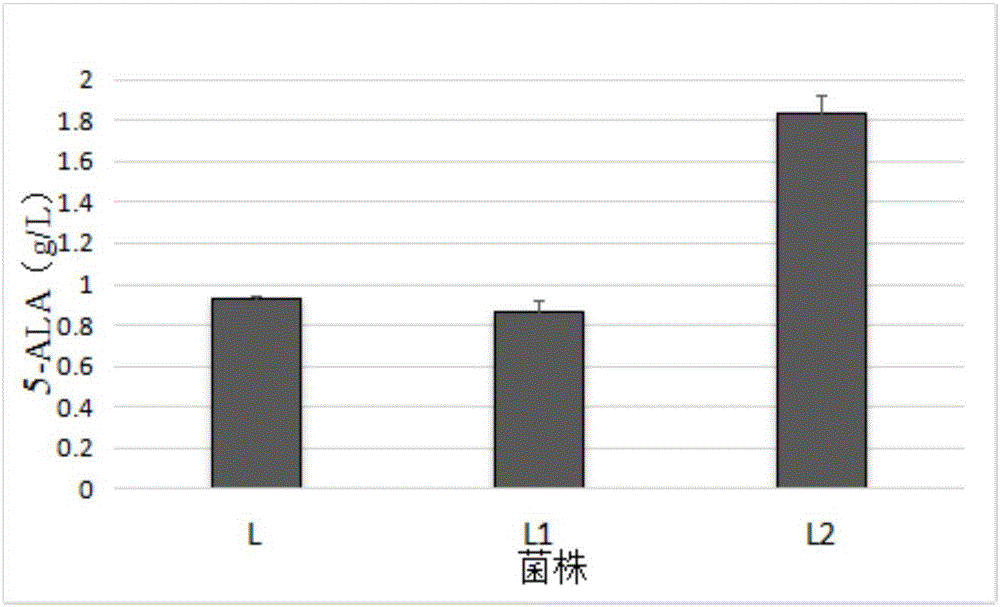
High-yield 5-aminolevulinic acid strain and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN103981203BImprove conversion rateIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphatePhosphoric acid
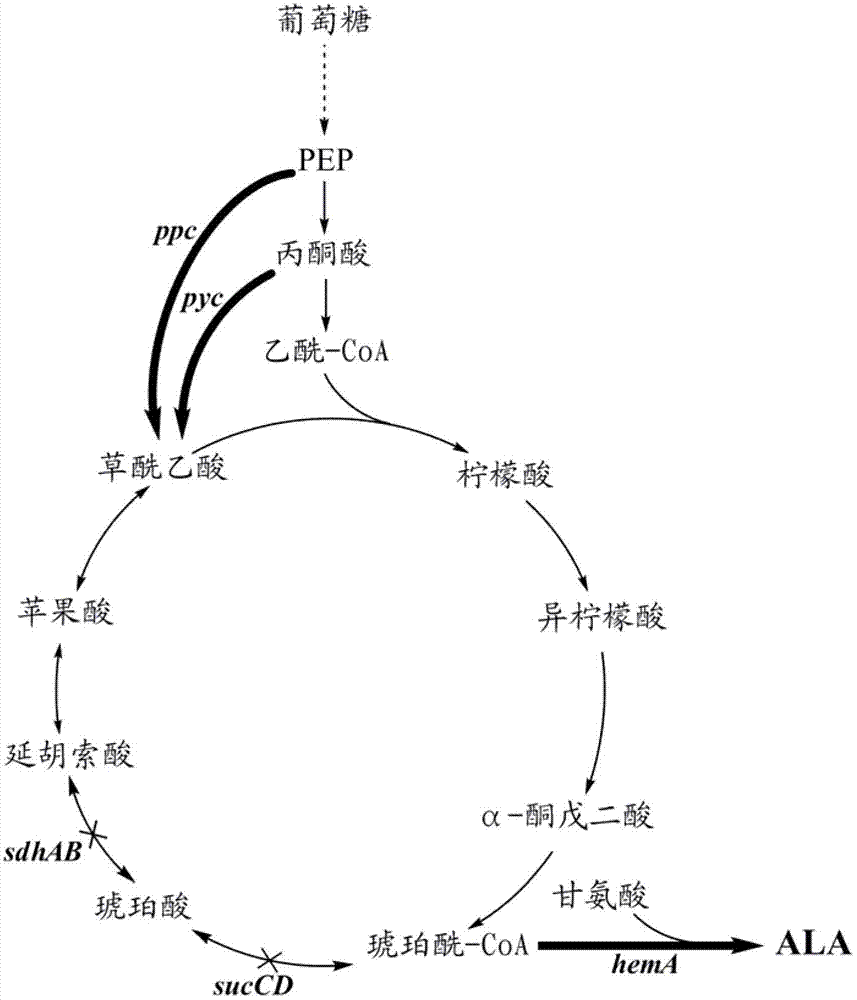
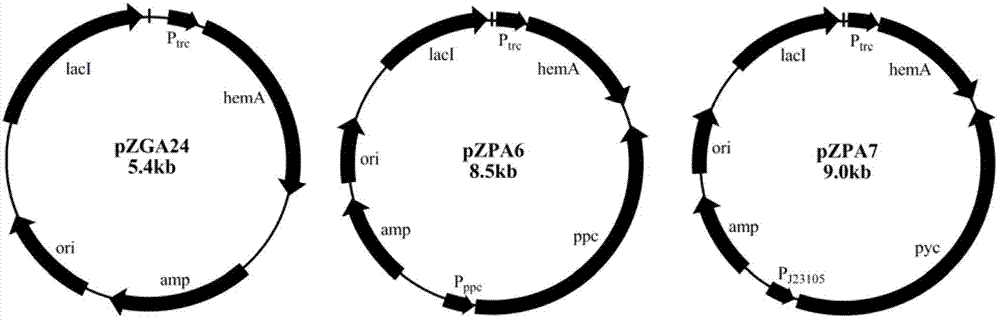
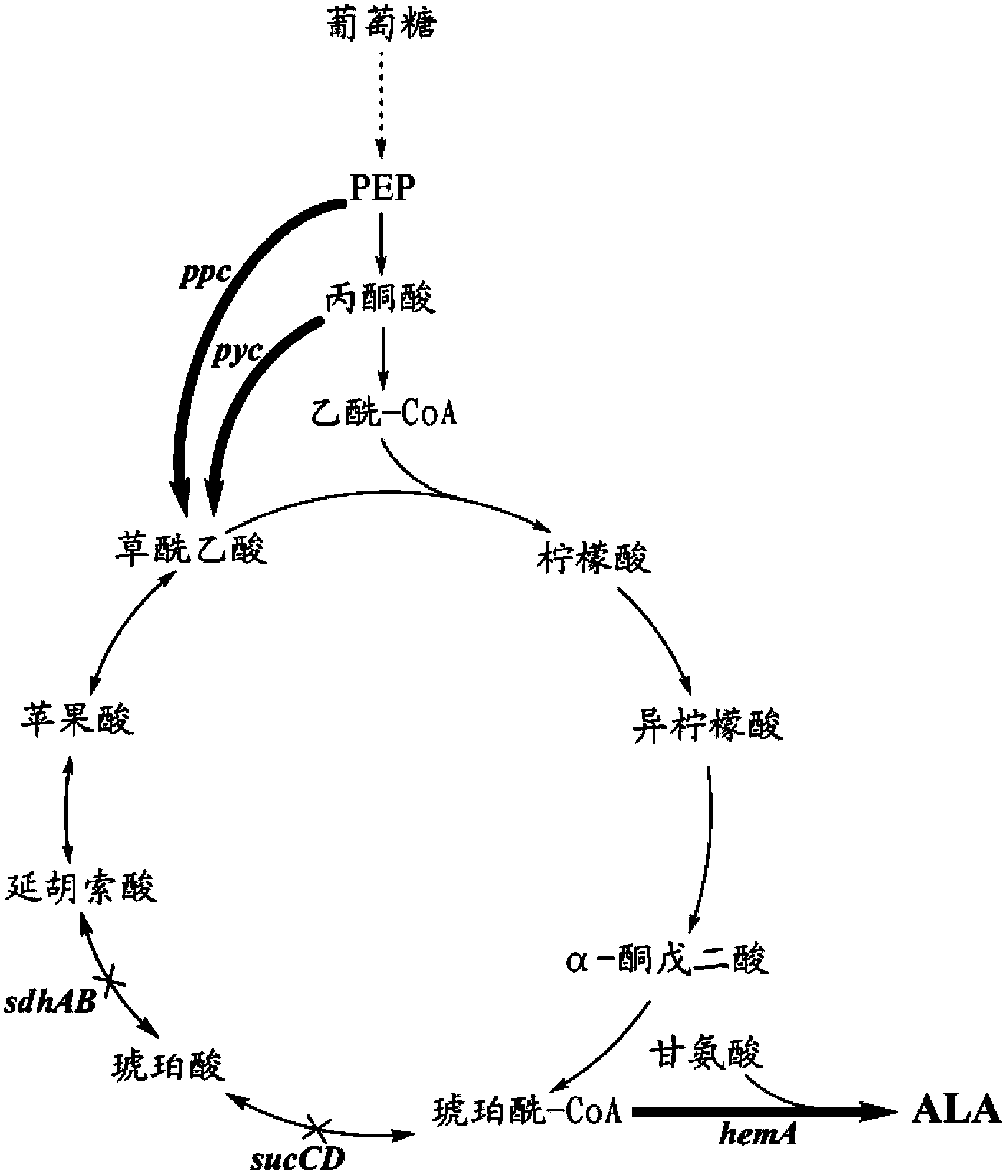
The invention discloses a method for constructing an ALA production strain, that is, enhancing the activity of related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate in the 5-aminolevulinic acid production strain or introducing exogenous related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate , such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase, and / or weaken the succinyl-CoA downstream metabolic pathway-related enzymes in the strain, such as succinyl-CoA synthetase or succinate dehydrogenase active. The invention also discloses an ALA high-yield strain constructed by the method and a method for preparing ALA by using the strain. The bacterial strain of the invention can produce ALA efficiently, at low cost and with low pollution without adding exogenous succinic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
5-amino levulinic acid (ALA) high-yield strain and preparation method and application thereof
A method for constructing an ALA production bacterial strain, the method enhances the activity of related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate and in the 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) production bacterial strain, or introducing exogenous related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate, such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase, and / or reducing the activity of related enzymes in the downstream metabolic pathway of succinyl coenzyme A in the bacterial strain, such as succinyl coenzyme A synthetase or succinate dehydrogenase, and / or reducing the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylated kinase and / or malic enzyme. An ALA high-yield bacterial strain constructed by utilizing the method, and method for utilizing the bacterial strain to prepare ALA.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
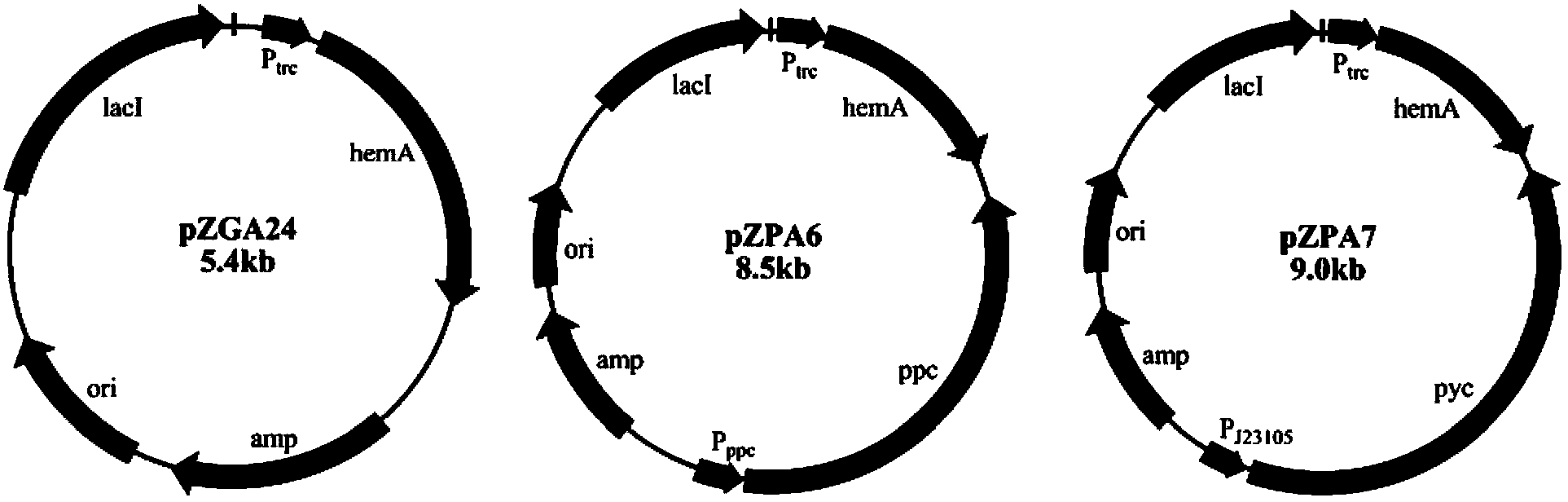
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for efficiently synthesizing acetylglucosamine
ActiveCN105255803AHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseGlucose polymers
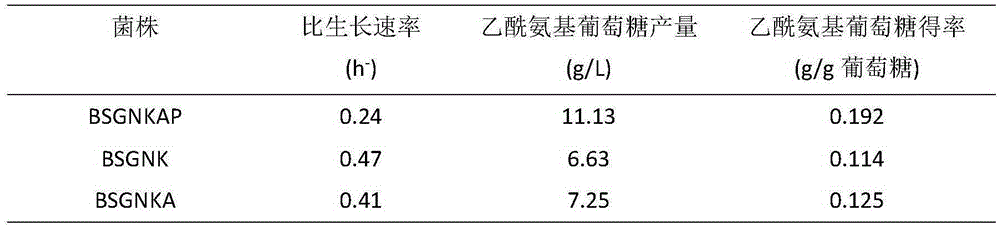
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis for efficiently synthesizing acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis, based on bacillus subtilis BSGNK, the enol phosphate type pyruvate carboxylase encoding gene pckA and pyruvate kinase encoding gene pyk (NCBI upper Gene ID: 938206) are knocked out, the BSGNK regards B.subtilis168delta nagP delta gamP delta gamA delta nag A delta nag B delta ldh delta pta::lox <72> as the host, promoters PxylA and P43 are utilized for controlling recombinant ecpression of glmS and GNAl, and accordingly the glucose kinase encoding gene glcK is knocked out. According to the recombinant bacillus, glucose can be effectively utilized for synthesizing acetylglucosamine, the shake flask fermentation yield can reach 11.13 g / L, the yield is increased by 67.8% compared with a strain before knocking out, and a basis is provided for further improvement of bacillus subtilis for producing glucosamine of metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
In-vitro cell-free protein synthesis system and application thereof
The present invention discloses an in-vitro cell-free protein synthesis system. The system comprises cell extract, carbohydrate and a phosphate compound, wherein the carbohydrate is maltodextrin, lactose, or a combination of the maltodextrin and glucose, or a combination of the lactose and the glucose, or a combination of the maltodextrin, the lactose and the glucose. ATP is provided for an in-vitro reaction by low-cost substances such as the glucose, the maltodextrin and the lactose instead of energy sources such as phosphoenolpyruvic acid, phosphocreatine and acetyl phosphate, so that whilethe cost is reduced, a mode of providing energy by slow release prolongs the reaction time and increases the yield of target protein.
L-tryptophan production genetically engineered bacterium and construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and discloses an L-tryptophan production genetically engineered bacterium and a construction method and application thereof. A common pathway of an Escherichia coli central carbon metabolic pathway is modified through a genetic engineering method, a phosphoric enol pyruvic acid-phosphotransferase system with phosphoric enol pyruvic acid as a substrate of escherichia coli is knocked out, a glucose transfer system with non-PEP as a substrate is enhanced, a glucose transfer endocytosis pathway is changed, the L-tryptophan production genetically engineered bacterium is obtained, and consumption of L-tryptophan synthesis precursor phosphoric enol pyruvic acid in the glucose transferring process is avoided, so that the intracellular PEP level is improved, and then the capability of L-tryptophan produced through strain fermentation is improved. An experiment shows that the constructed L-tryptophan production genetically engineered bacterium is an escherichia coli L-tryptophan high-producing strain, L-tryptophan can be effectively accumulated, the yield of the L-tryptophan is improved, and a foundation is laid for industrial production of the L-tryptophan.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
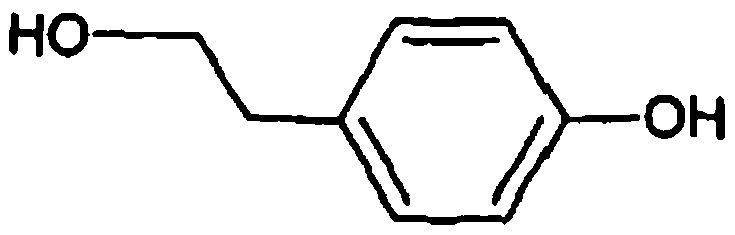
Recombinant yeast, construction method thereof and application thereof for producing tyrosol and derivative
InactiveCN109929883AAltered carbon flux distributionOptimizing Metabolic PathwaysFungiGenetically modified cellsHydroxytyrosolTyrosol
Owner:YANTAI HUAKANG BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for cell-free expression of signal protein and expression system
ActiveCN106011163ASolve the problem of low expressionHigh protein expressionNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliCreatine kinase
The invention relates to a method for cell-free expression of signal protein and an expression system. The method includes joining a target gene of the signal protein on a pIX3.0 vector to obtain expression plasmids; extracting escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3) by S30 buffer solution to obtain escherichia coli extract; preparing an energy supply system comprising PEP (phosphoenolpyruvic acid) / PK (pyruvate kinase), CP (phosphocreatine) / CK (creatine kinase) and glucose; preparing an amino acid mixture and a saline solution; preparing lecithin / cholesterol liposome; adding the expression plasmids into a cell-free protein expression system comprising the escherichia coli extract, the energy supply system, the amino acid mixture, the saline solution and the lecithin / cholesterol liposome for expression. The method is capable of solving the problem of small signal protein expression quantity.
Owner:CUSABIO TECH LLC
Escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium and method for producing L-threonine by using escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium
ActiveCN106867952AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
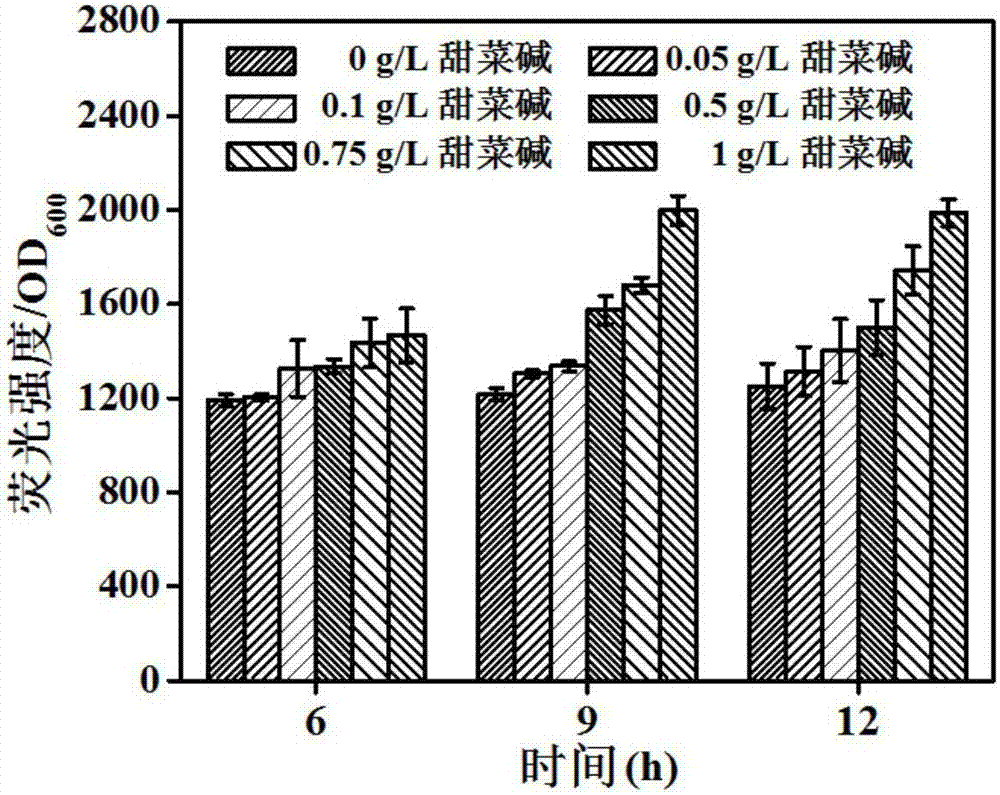
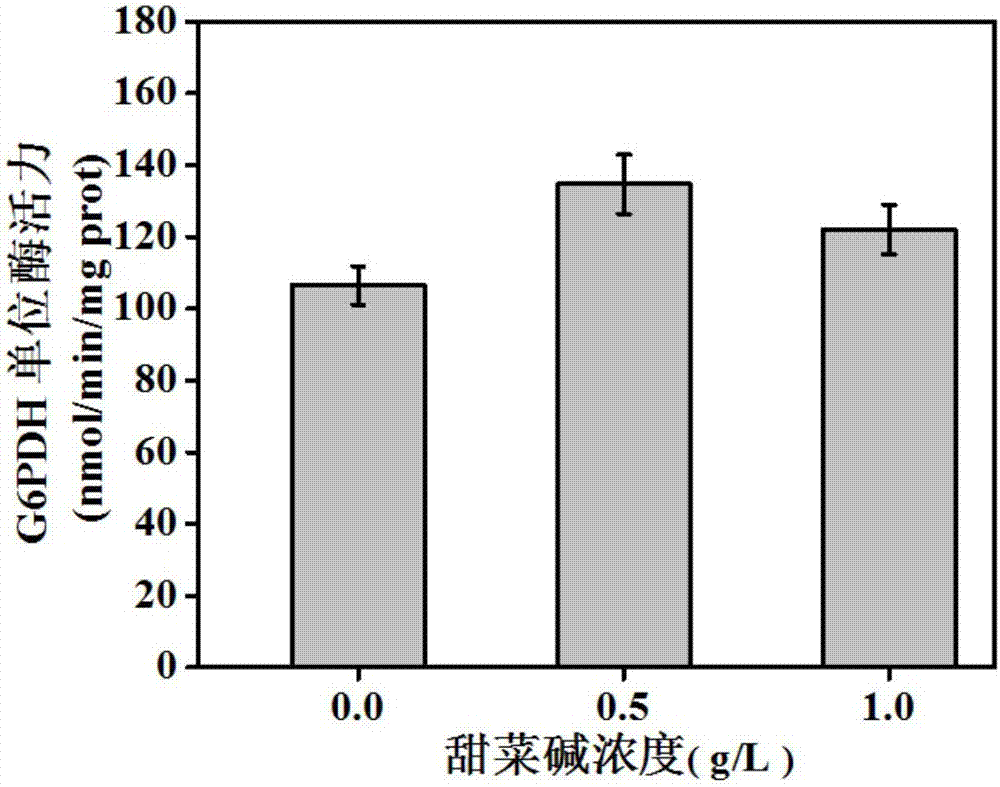
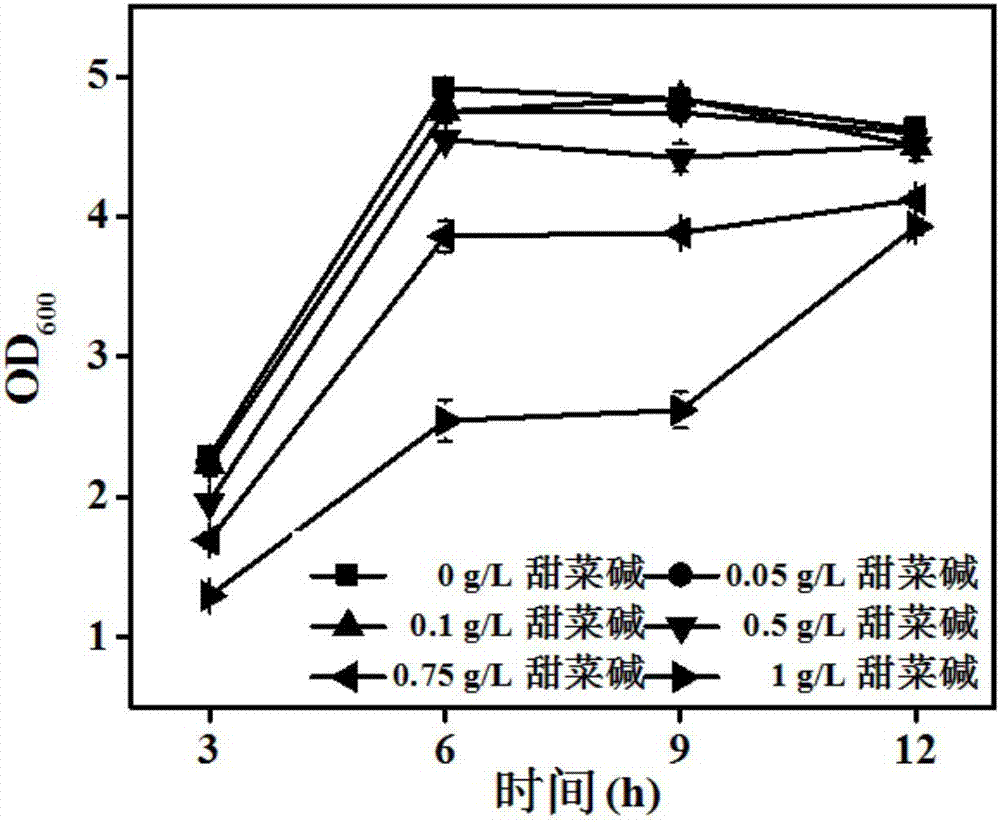
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to an escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium and a method for producing L-threonine by using the escherichia coli gene engineering bacterium. The gene engineering bacterium is characterized in that a promoter P<ppc> of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) of an initial strain is replaced into a promoter P<zwf> of 6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (zwf), so that the goal of regulating the L-threonine production capacity by glycine betaine is achieved. In the fermentation process, the glycine betaine is added, so that the L-threonine yield through shaking flask fermentation can reach 50 to 55g / L; the 5L fermentation tank yield reaches 120 to 150g / L; the saccharic acid conversion rate reaches 59 to 61 percent.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
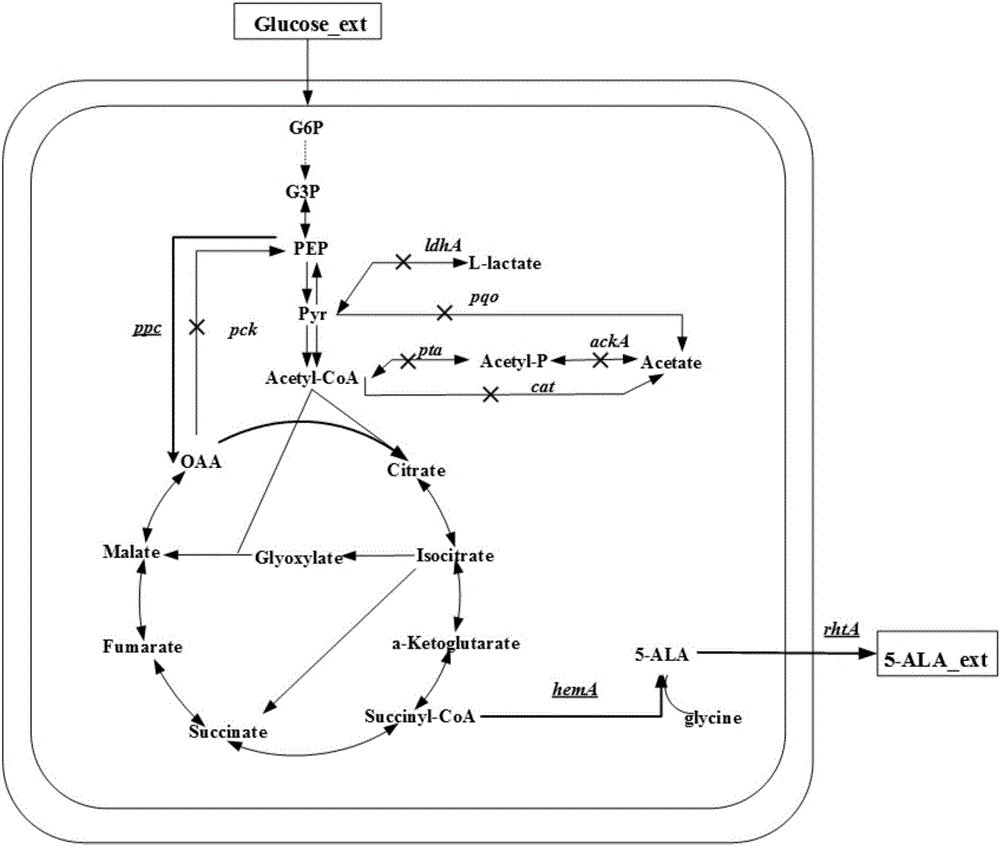
Corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain
InactiveCN106047916AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylasePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain. A construction method includes: (1) deleting a lactic dehydrogenase coding gene 1dhA and acetic acid generation genes pta-ackA, pqo and cat in corynebacterium glutamicum to obtain a strain named CB4; inserting a strong sod promoter in front of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase coding gene ppc in the strain CB4 to obtain a strain CB5; deleting a gene pck in the strain CB5 to obtain a strain CB6; (2) transferring plasmid pXA and plasmid pEP2<tuf>-rhtA into the strain CB6. The strain constructed according to the method is capable of generating 2.78g / L 5-aminolevulinic acid in a culture medium with 10g / L glucose serving as a carbon source, which lays a foundation for subsequent continuous feeding of a fermentation tank to increase yield of the 5-aminolevulinic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant bacteria for increasing yield of succinic acid and construction method thereof
ActiveCN103131663AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
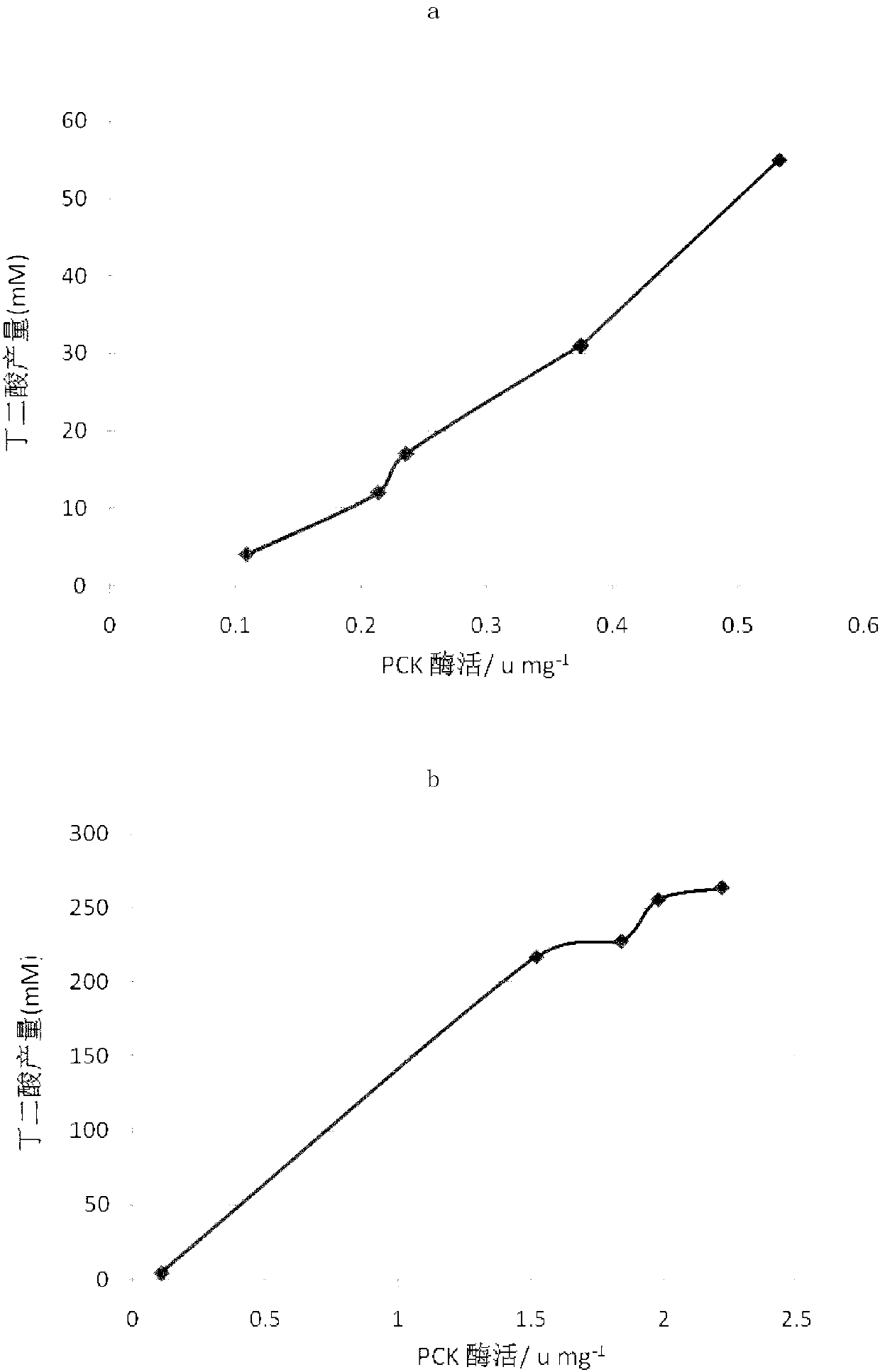
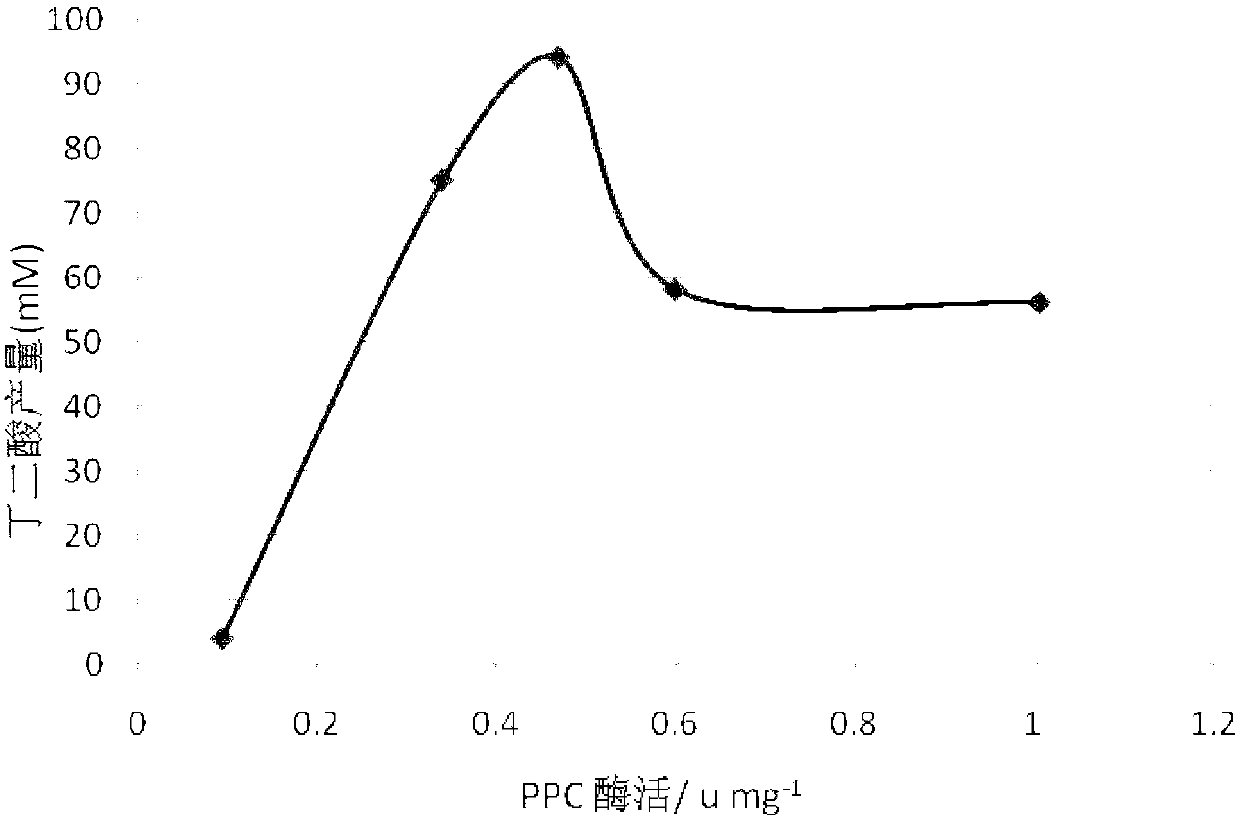
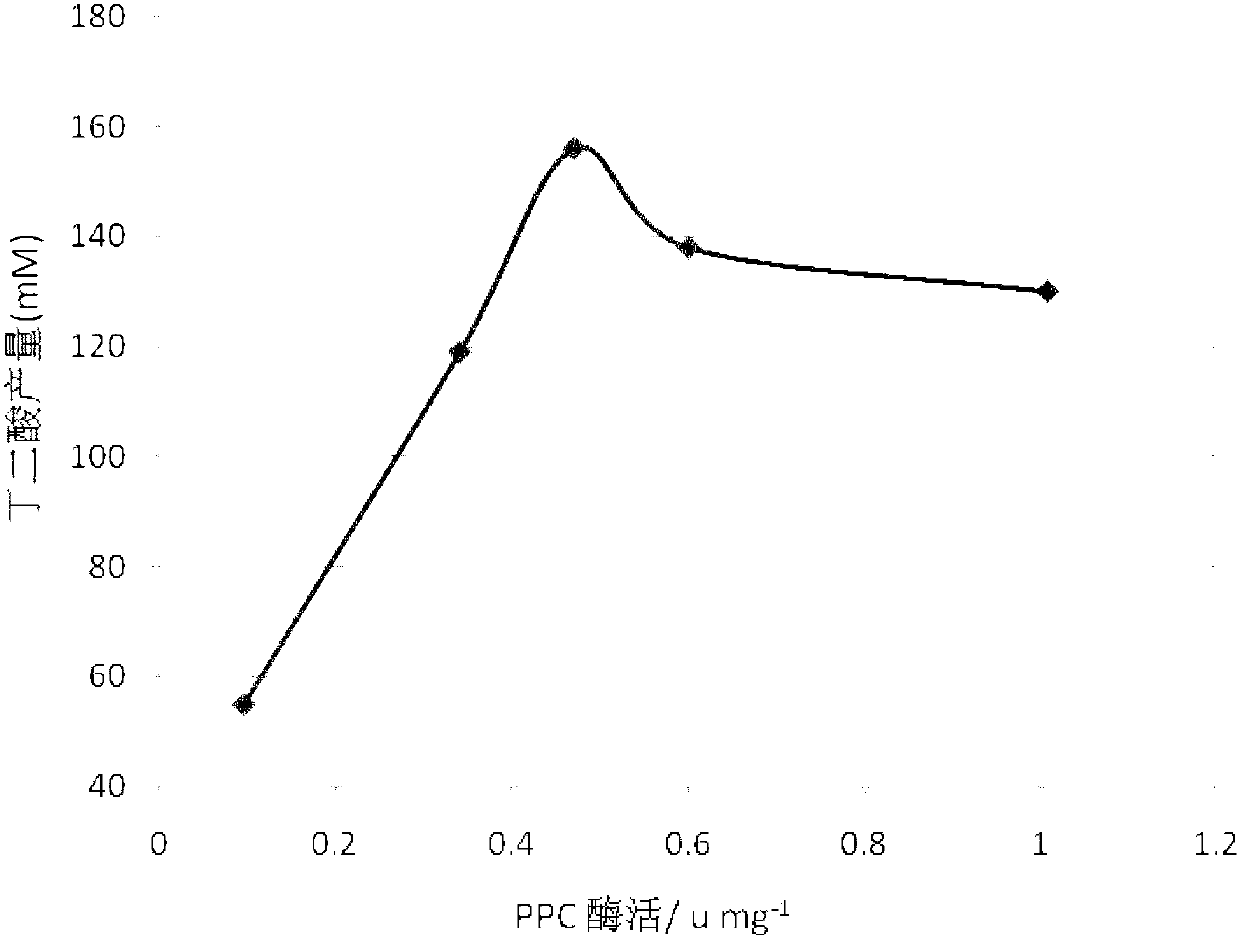
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria for increasing the yield of succinic acid and a construction method thereof. The recombinant bacteria disclosed by the invention are obtained so as to increase the enzyme activities of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PPC) and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PCK) in escherichia coli or mutant strains of the escherichia coli. Experiments prove that the expressions of ppc and pck genes of the E.coli are respectively regulated and controlled by using constitutive controlling elements with different expression intensity, and the law between the enzyme activities of the PPC and the PCK and the succinic acid production is explored; and on the basis, the PPC and PCK catalyzing enzymes are simultaneously used for giving play to respective catalyzing advantages through coordinated regulation of the ppc and pck genes of the E.coli, so that the yield and the conversion rate of the E.coli succinic acid are obviously increased.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and application thereof
InactiveCN103074292AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolaseEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and a method for producing the L-phenylalanine (Phe) by fermentation and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. According to the invention, a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering strain C.glutamicum19AF / 99TP capable of being used for highly yielding the L-Phe is obtained in a corynebacterium glutamicum type strain ATCC13032 by carrying out induction expression on the following four genes: a 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase gene, a chorismate mutase / prephenate dehydratase gene which has resistance to feedback inhibition, a transketolase gene and a phosphoenolpyruvic acid synthetase gene. A shikimic acid metabolic pathway of an L-Phe synthetic metabolic pathway is over-expressed in the C.glutamicum ATCC13032; a key enzyme gene of a chorismic acid metabolic pathway enables the yield of the L-Phe to reach 3.47g / L; two enzyme genes which combines an expression center metabolic pathway to improve a precursor enables the highest yield of the L-Phe to reach 4.86g / L; and the original strain ATCC13032 which is used as a contrast strain cannot detect accumulation of the L-Phe in the integral fermenting process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid and method for producing succinic acid by fermentation of genetic engineering bacteria
InactiveCN102399738AImprove biosynthetic abilityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
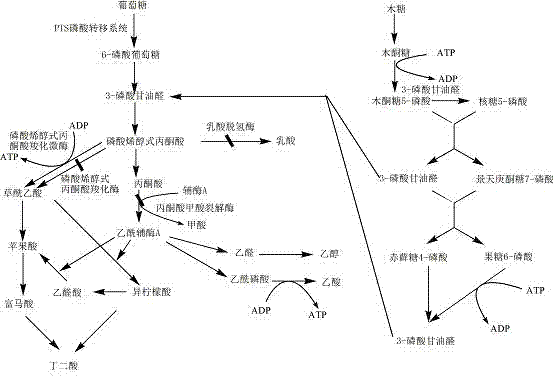
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and relates to a genetic engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid and a method for producing the succinic acid by fermentation, in particular to a recombinant strain which is grown by utilizing xylose efficiently and is used for producing the succinic acid and a method for producing the succinic acid by utilizing the fermentation of the strain. The genetic engineering strain for producing the succinic acid belongs to the class of Escherichia coli BA204, and the conservation register number is CCTCC No:M2011207. A construction process comprises the steps of: inactivating or removing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, and over-expressing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylation kinase, so that the recombinant Escherichia coli can be grown by utilizing xylose metabolism to improve the synthetic efficiency of the succinic acid is improved substantially. In the fermentation method, a two-stage fermentation mode is adopted, wherein in an aerobic stage, biomass is improved; and in an anaerobic stage, acid is produced by the fermentation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Corynebacterium glutamicum for producing high-yield succinic acid by utilizing straw hydrolysate, and construction and applicaitons
InactiveCN107012161AHigh final concentrationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolasePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum for producing high-yield succinic acid by utilizing straw hydrolysate, and a construction and applications. The method comprises the following steps: (1) knocking out side products acetic acid and lactic acid formation pathway related genes from corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032, and introducing anaplerotic pathway phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and pyruvate carboxylase and phosphopentose pathway transketoaldehydase and transketolase on a strong promoter overexpression chromosome; and introducing xylose transport gene on the chromosome; and (2) expressing pyruvate carboxylase, succinic acid export protein and citrate synthase as well as xylose isomerase and xylulokinase on the corynebacterium glutamicum obtained in the step (1). 98.6gL<-1> of succinic acid can be anaerobically produced after 22.5h by utilizing mixed glucose and xylose in straw hydrolysate, with the yield of 0.98g succinic acid / g total sugar. The final concentration, yield and productivity of succinic acid achieve higher level, and the corynebacterium glutamicum has good industrial potential.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
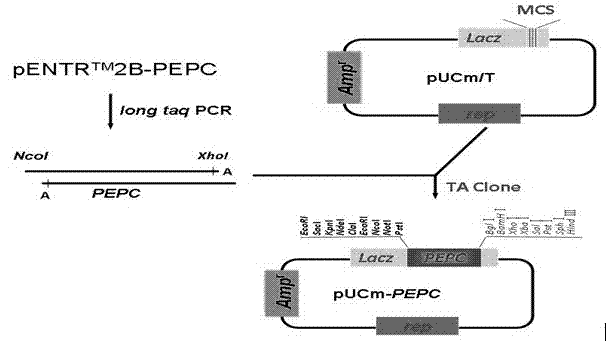
Carrier for enhancing aluminum-tolerance of plant, and method for establishing the same
InactiveCN102199620ALarge amount of synthesisPromote growthVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseNicotiana tabacum
The invention provides a carrier for enhancing aluminum-tolerance of a plant, and a method for establishing the same. The carrier is a plant expression vector having photoinduction promoters and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) genes. The method for establishing the carrier comprises the following steps: searching for the sequence of the full length gene of Synechococcus vulcanus PEPC in GenBank and designing a pair of primers with sequences as described in the specification; recovering and purifying PEPC full length gene segments and connecting the segments to a pUCm-T vector; establishing an entry vector pENTER*-PrbcS-PEPC; establishing a plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-PEPC. In the invention, the activity of citrate synthase of tabacoo with transgenic PEPC and CS genes is 2.4 to 2.6 times that of wild tobacco, and the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of such tabacco is 2.2 to 2.4 times that of wild tobacco. The special-purpose carrier provided in the invention can exert great influence on the improvement of aluminum-tolerance of a plant, and particularly, can significantly promote aluminum-tolerance of plants grown in acid red soil in southern China, thereby providing a novel approach for variety improvement of plants.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
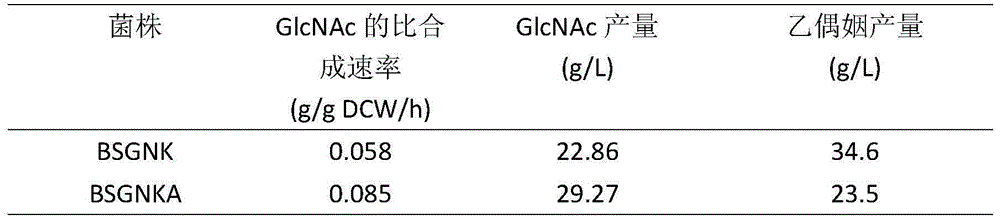
Method for knocking out pckA to promote synthesis of acetylglucosamine through bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN105238724AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTricarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a method for knocking out pckA to promote synthesis of acetylglucosamine through bacillus subtilis and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The method comprises the steps that BSGNK-PxylA-glmS-P43-GNA1 serves as original strains, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (pckA) genes are knocked out through homologous recombination, the reaction that enolphosphopyruvate is converted into oxaloacetic acid in host bacterium cells is blocked, the carbon flux flowing to a tricarboxylic acid cycle is reduced, and accumulation of acetylglucosamine is promoted. In the process that a composite culture medium is used for fermentation, the acetylglucosamine yield of recombination bacillus subtilis with pckA knocked out reaches 29.27 g / L and is increased by 28.1% compared with that of control strains. The method lays a foundation for transforming bacillus subtilis to produce acetylglucosamine in metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGSU HEVI BIOTECH CO LTD
Process for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid
The present invention provides a process for economically producing N-acetylneuraminic acid without using expensive materials such as pyruvic acid and phosphoenolpyruvic acid. The process comprises: allowing (i) a culture of a microorganism having N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase activity or N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase activity, or a treated matter of the culture, (ii) a culture of a microorganism capable of producing pyruvic acid or a treated matter of the culture, or a culture of a microorganism capable of producing phosphoenolpyruvic acid or a treated matter of the culture, (iii) N-acetylmannosamine, and (iv) an energy source which is necessary for the formation of pyruvic acid or phosphoenolpyruvic acid to be present in an aqueous medium to form and accumulate N-acetylneuraminic acid in the aqueous medium; and recovering N-acetylneuraminic acid from the aqueous medium.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO BIO CO LTD
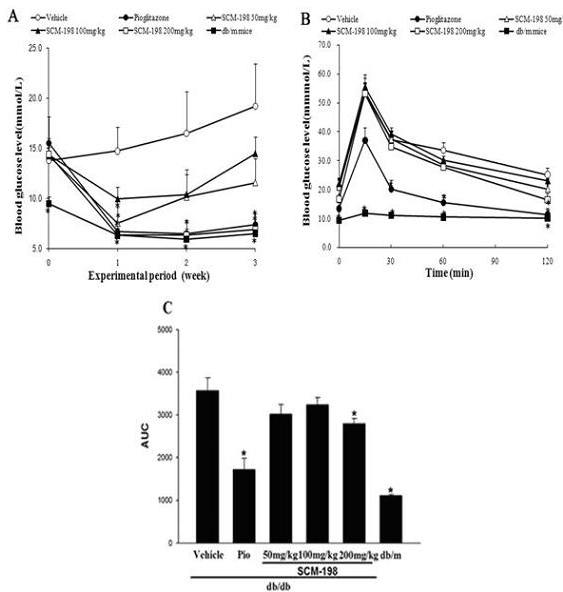
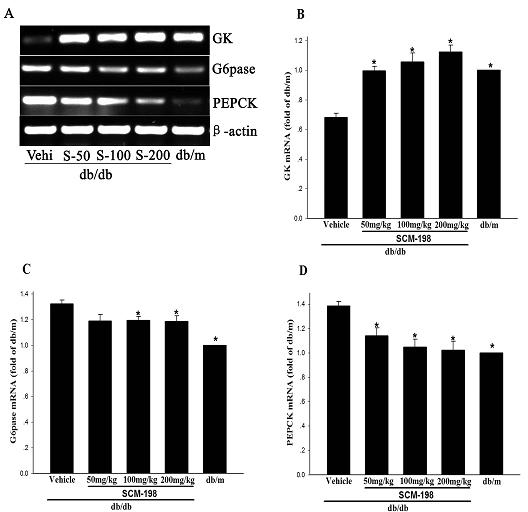
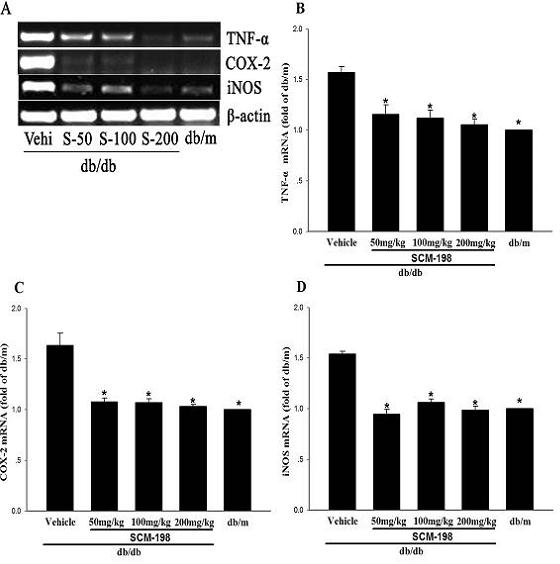
Application of leonurine to preparation of medicament for treating 2-type diabetes
The invention belongs to the field of traditional Chinese medicine manufacturing, and relates to application of leonurine to preparation of a medicament for treating 2-type diabetes. Animal experiments prove that the fasting blood glucose of a 2-type diabetes mouse, i.e., a db / db mouse, can be lowered by the leonurine, and the tolerance of oral glucose is improved; and meanwhile, fasting plasma insulin is increased, the plasma triglyceride is reduced and the content of the plasma high-density lipoprotein is increased. Experiment results also show that the expression of liver glucose metabolic enzymes such as glucokinase, glucose-6-phosphatase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxyl enzyme is adjusted by the leonurine in an Akt dependent mode; and the biological response of an inflammatory mediator, such as generation of TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor)-alpha, degradation of IkB-alpha and subsequent phosphorylation of NF-kBp65, is suppressed. Through the leonurine, the inflammatory state of the 2-type diabetes can be corrected, and the symptoms of the 2-type diabetes can be improved; and the leonurine can be used as a treatment medicament to be applied to the treatment of the 2-type diabetes.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-aspartic acid through fermentation
ActiveCN106434510AGet Rid of Reliance on Petroleum-Based Fumaric AcidCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliDry weight
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for directly producing L-aspartic acid through fermentation. The classification naming of the genetically engineered bacterium is Escherichia coli CM-AS-115, and the preservation number of the genetically engineered bacterium is CCTCC NO: M 2016457. The bacterial strain relates to inactivation of multiple genes, evolution, metabolism and domestication are simultaneously carried out on the bacterial strain which knockouts the multiple genes, and a mutant strain, namely, CM-AS-105, which has a lower respiratory quotient under the aerobic condition and of which the highest dry cell weight is 60-70% of dry weight of an original strain W1485 is obtained; meanwhile, the bacterial strain further relates to over expressions of two genes, wherein the two genes comprise an enol phosphate type pyruvate carboxylase encoding gene (ppc) and an aspartase encoding gene (aspA), and the obtained bacterial strain is CM-AS-115. The genetically engineered bacterium for directly producing L-aspartic acid through fermentation achieves a way of completely adopting renewable biomass resources such as starch and cellulose as raw materials to ferment and prepare the L-aspartic acid, and the way is green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:CHANGMAO BIOCHEMICAL ENG CO LTD
Corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for highly producing succinic acid and building method thereof
InactiveCN103509747AIncrease productionReduce generationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
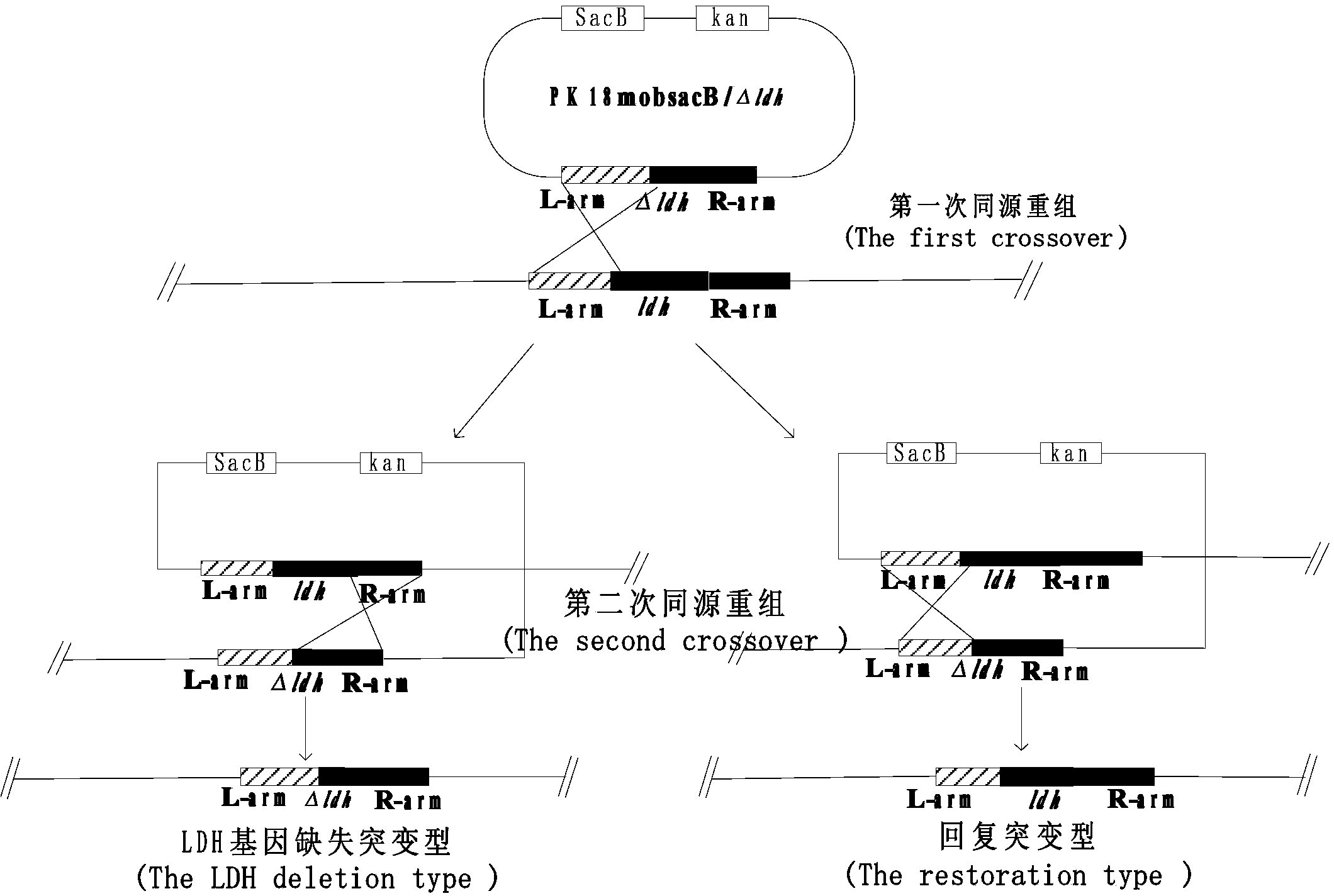
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for anaerobic conversion to produce succinic acid, and a building method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. A pyruvate carboxylase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from escherichia coli are cloned to corynebacterium glutamicum (ATCC13032); a lactate dehydrogenase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum is knocked out in a homologous recombination manner. By adopting the lactic dehydrogenase-defective corynebacterium glutamicum for coexpression of a carboxylase gene, anaerobic production of succinic acid is carried out in a cell reutilization manner, so that the yield of succinic acid can be greatly improved; the yield can be up to 75g / L; the conversion rate of saccharic acid is 75%; the corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium has a good application prospect; a fermentation model, especially a fermentation model for cell reutilization is built according to the optimum condition for biological transformation of succinic acid; the acid-production performance in repeated batch transformation process of cells can be basically kept stable.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid
InactiveCN106434513AEasy to transportIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseAminolevulinic acid synthase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid. An establishing method comprises steps as follows: (1) a lactic dehydrogenase encoding gene ldhA and acetic acid producing genes pta-ackA, pqo and cat are knocked out from corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 1303, and a strain CG4 is obtained; an sod promoter is inserted in front of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase encoding gene in the CG4, and a strain CG5 is obtained; a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase encoding gene pck is knocked out from the CG5, and a strain CG6 is obtained; (2) plasmids of an overexpressed 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase gene are transferred into the CG6, and a recombinant strain L is obtained; (3) 5-aminolevulinic acid transport protein plasmids are transferred into the L. The recombinant strain can promote 5-aminolevulinic acid to be transported outside corynebacterium glutamicum cells, and the yield of 5-aminolevulinic acid is 112.3% higher than that of a contrast strain.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant bacteria for high-yield production of N-acetylneuraminic acid by utilizing manual double carbon sources
ActiveCN108441461AEasy to synthesizeEfficient supplyBacteriaTransferasesPhosphoric acidGluconic acid
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria for high-yield production of N-acetylneuraminic acid by utilizing manual double carbon sources and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. A gluconicacid kinase gene gntK and gluconic acid permease gntP are overexpressed through a strong promoter P43, and the manual double carbon sources including glucose and sodium gluconate are used for fermenting to realize efficient supply of phosphoenolpyruvic acid in an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis way and the synthesis way is strengthened. Compared with a starting strain, recombinant bacillus subtilis has the advantage that the yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid is improved to 1.52g / L from 1.02g / L; a foundation is laid for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid by carrying out further metabolic engineering modification on the recombinant bacillus subtilis.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Gene engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid, and method for producing succinic acid by fermentation by using same
InactiveCN102643775AIncrease productionIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, and relates to a gene engineering bacterium strain for producing succinic acid, and a method for producing succinic acid by fermentation by using the same. The classification designation of the gene engineering bacterium strain for producing succinic acid is Escherichia coli BA305, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2012102. The construction process mainly comprises the following steps: inactivating or knocking out phosphoenolpyruvic acid carboxylase gene and ptsG gene in a phosphate translocation system; and overexpressing the phosphoenolpyruvic acid carboxylase so that the recombinant colibacillus can efficiently utilize glucose, xylose, arabinose, levulose and other monosaccharides and efficiently utilize mixed saccharides in various proportions and cellulose hydrolysate, thereby greatly enhancing the synthesis efficiency of the succinic acid. The fermentation method adopts a two-stage fermentation mode: the aerobic stage can enhance the biomass, and the anaerobic stage is used for fermentation to produce the acid.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
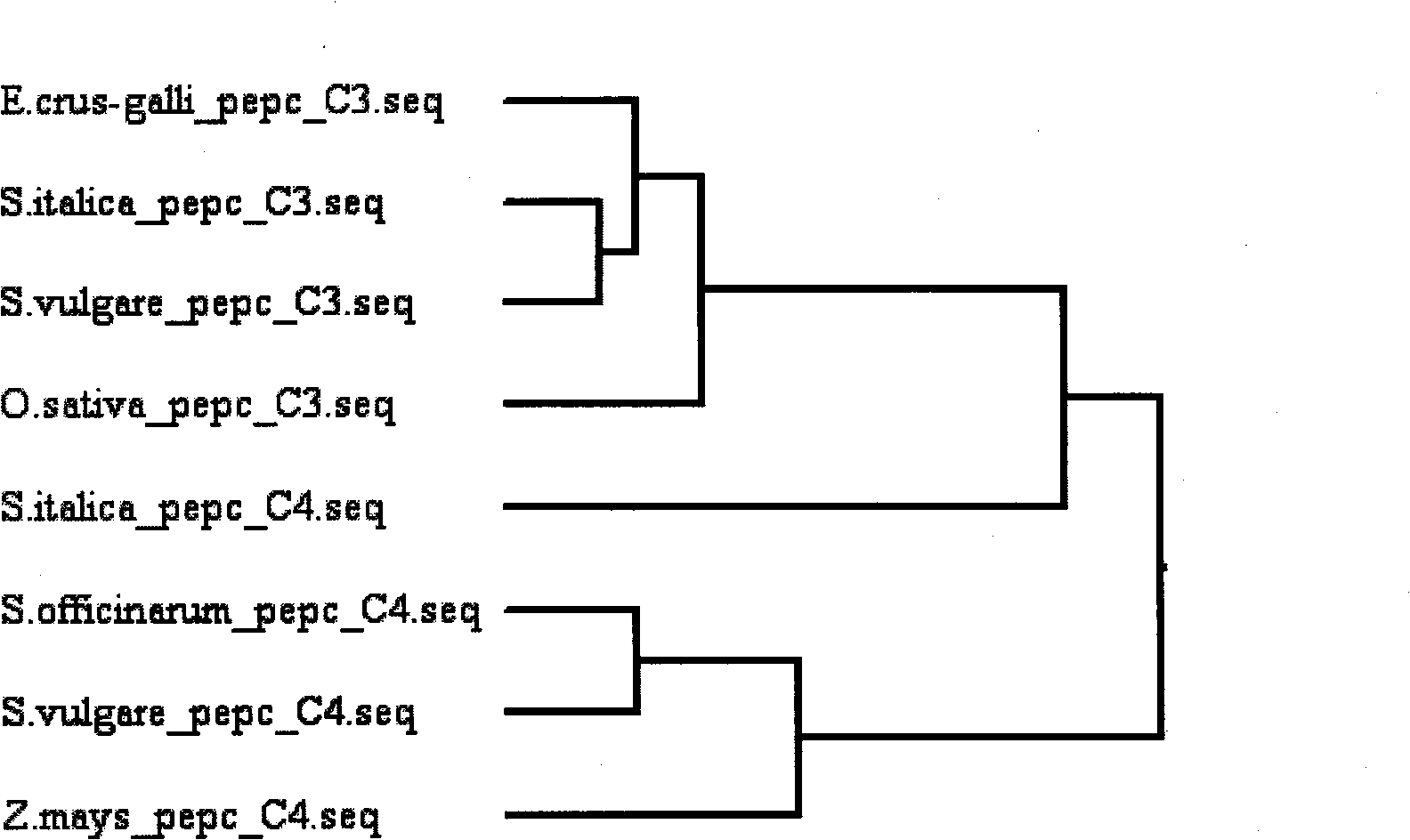
Corn C4 phosphoric acid enol pyruvic acid carboxylase gene and uses in producing wheat
InactiveCN101492689AIncrease net photosynthetic rateImprove photosynthetic efficiencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionTriticeaePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a corn C4 type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene and an application thereof in wheat production. The gene is as indicated in SEQ ID No:1 of a sequence table, a gene clone vector is pMD19-pepc, an eucaryon expression vector is p3301-pepc, host bacteria is E.coli competent cell DH5 alpha, carboxylase is has an amino acid sequence as indicated by SEQ ID No:2. In the invention, the corn C4 type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase is led into the wheat, functional analysis on transgenic plants indicates that net photosynthetic rate of the transgenic plants is greatly improved compared with the net photosynthetic rate of the plants which are not transgenic, enjoying an increase of 1.39 times. The research is so far the research in which the net photosynthetic rate of C3 crop is raised to the largest degree. The result of the functional analysis of the transgenic plants indicates that the related corn C4 type high light efficiency pepc gene can greatly improve the net photosynthetic rate of C3 crops such as wheat and the like and provides important technological and material support for high light efficiency transgenic breeding of crops such as wheat and the like.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
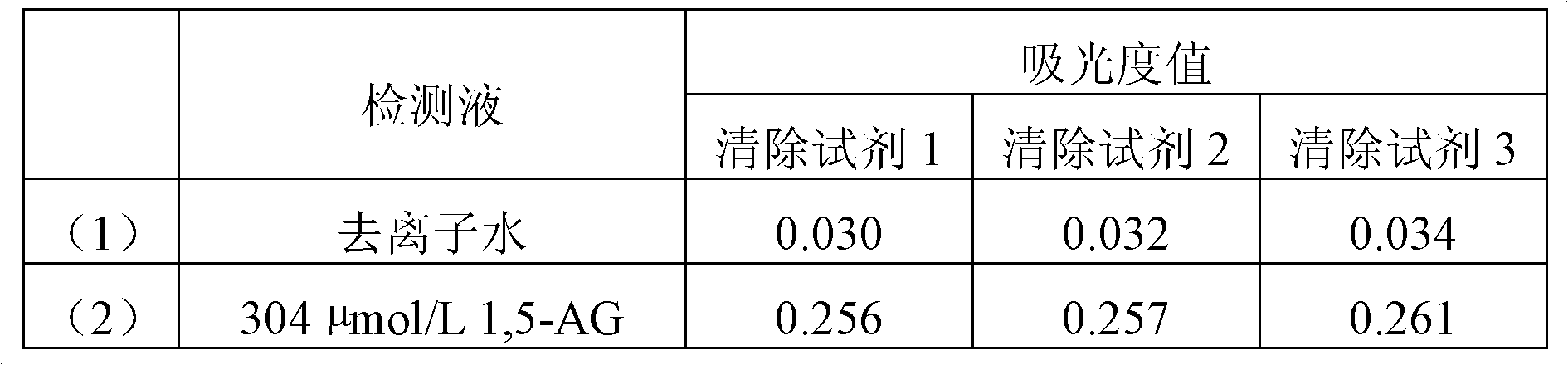
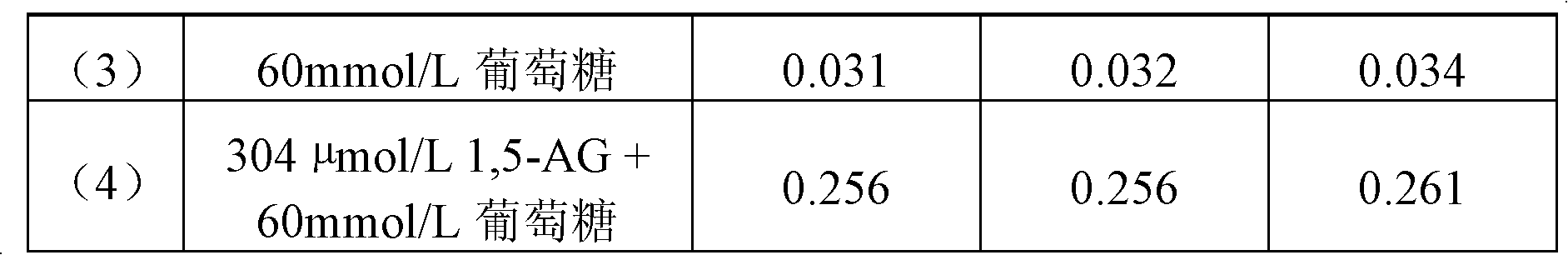
High-concentration glucose removal method and kit for determining serum 1,5 anhydro-D-glucitol based on pyranose oxidase method
The invention discloses a high-concentration glucose removal method for determining serum 1,5 anhydro-D-glucitol based on a pyranose oxidase method, which comprises the following steps: preparing a 2-morpholinoethanesulfonic acid (MES) buffer solution having a pH value of 6.0-9.0, wherein the MES buffer solution contains a certain amount of glucokinase (GK), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), pyruvate kinase (PK), phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP); and adding into a serum sample containing glucose (Glu), and reacting at 20-50 DEG C for 3-5 minutes, wherein the GK converts the Glu into glucose-6-phosphoric acid (G6P) in the presence of the ATP, and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) is generated at the same time; the G6P is further converted into glucose-6-phosphate lactone (G6PL) by the G6PD in the presence of the NADP+; and the ADP generated in the reaction is converted into ATP again under the action of thePK in the presence of the PEP. The glucose removal agent prepared by the method can be stably stored at 2-8 DEG C for 14 months, and can be used for a clinical biochemical autoanalyzer extensively used at present.
Owner:浙江夸克生物科技有限公司
Genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose and acidogenic fermentation method thereof
InactiveCN102533626AOvercomes the inability to utilize glucoseBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the field of biology engineering technology, and relates to a genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose and an acidogenic fermentation method of the genetic engineering strain. The genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose is named as Escherichia coli BA205 and the preservation number is registered as CCTCC No.M2011447. In the construction process, Escherichia coli which is short of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) gene and Pyruvate formate-lyase (PFL) gene activity is mainly used as an original strain; phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PPC) gene is removed by utilizing a homologous recombination technology; and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyl transferase are excessively co-expressed; therefore the synthesis efficiency of succinic acid is greatly increased. In the fermentation method, a two-stage fermentation manner is adopted, the biomass is improved in an aerobic stage and the acidogenic fermentation is carried out in an anaerobic stage.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Process for the production of beta-lysine
InactiveCN101400799AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTransketolase
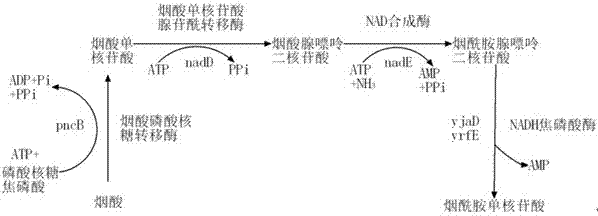
Process for the production of -lysine by constructing a recombinant microorganism which has a deregulated lysine 2,3-aminomutase gene and at least one deregulated gene selected from the group (i) which consists of aspartokinase, aspartatesemialdehyde dehydrogenase, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydrodipicolinate reductase, tetrahydrodipicolinate succinylase, succinyl-amino-ketopimelate transaminase, succinyl-diamino-pimelate desuccinylase, diaminopimelate epimerase, diaminopimelate dehydrogenase, arginyl-tRNA synthetase, diaminopimelate decarboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, transketolase, transaldolase, 6-phosphogluconolactonase, fructose 1,6-biphosphatase, homoserine dehydrogenase, phophoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, succinyl-CoA synthetase, methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, provided that if aspartokinase is deregulated as gene (i) at least a second gene (i) other than aspartokinase has to be deregulated, and cultivating said microorganism.
Owner:BASF SE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com