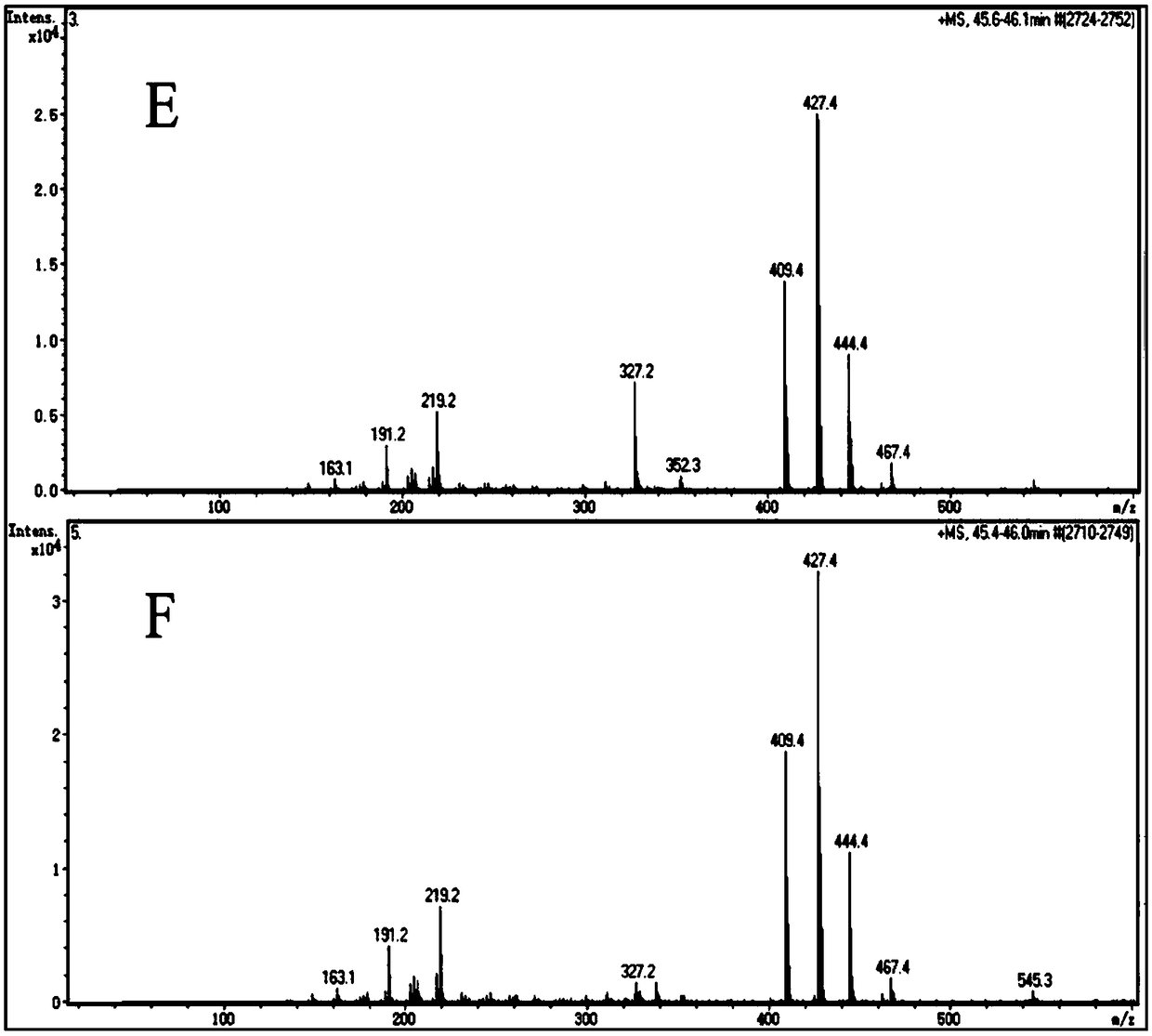
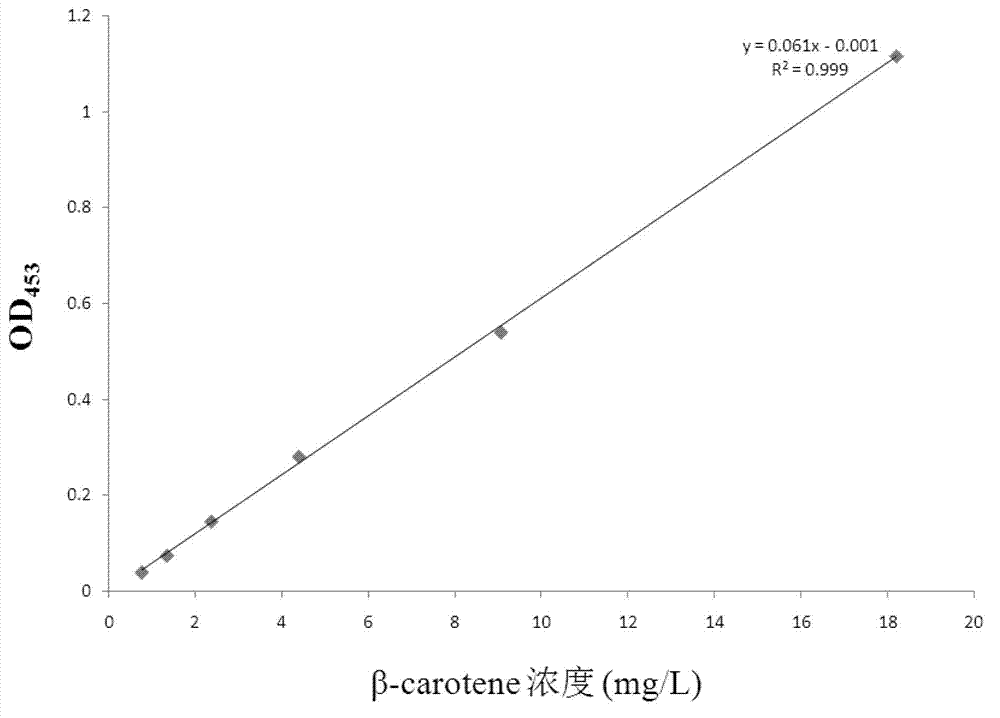
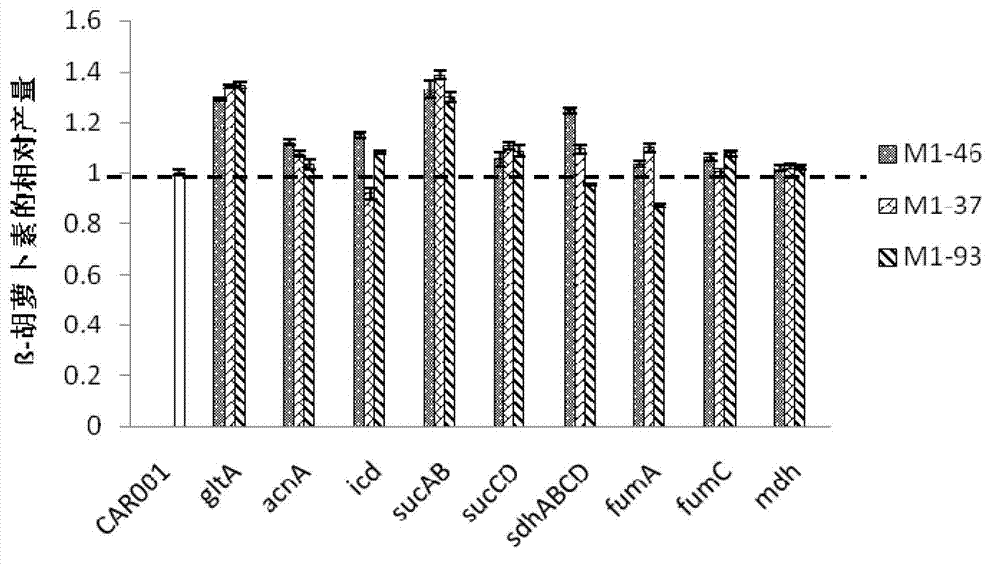
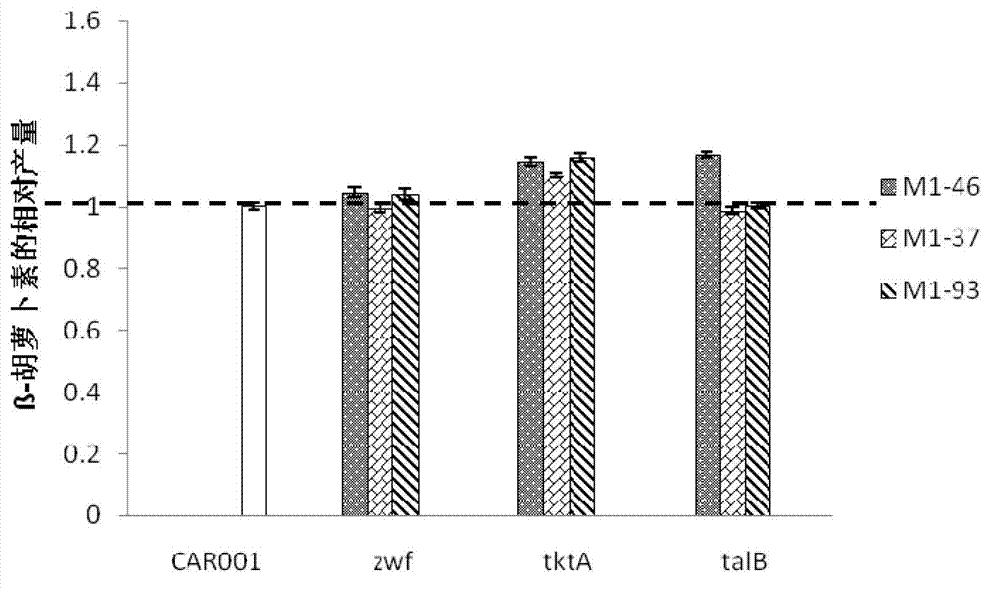
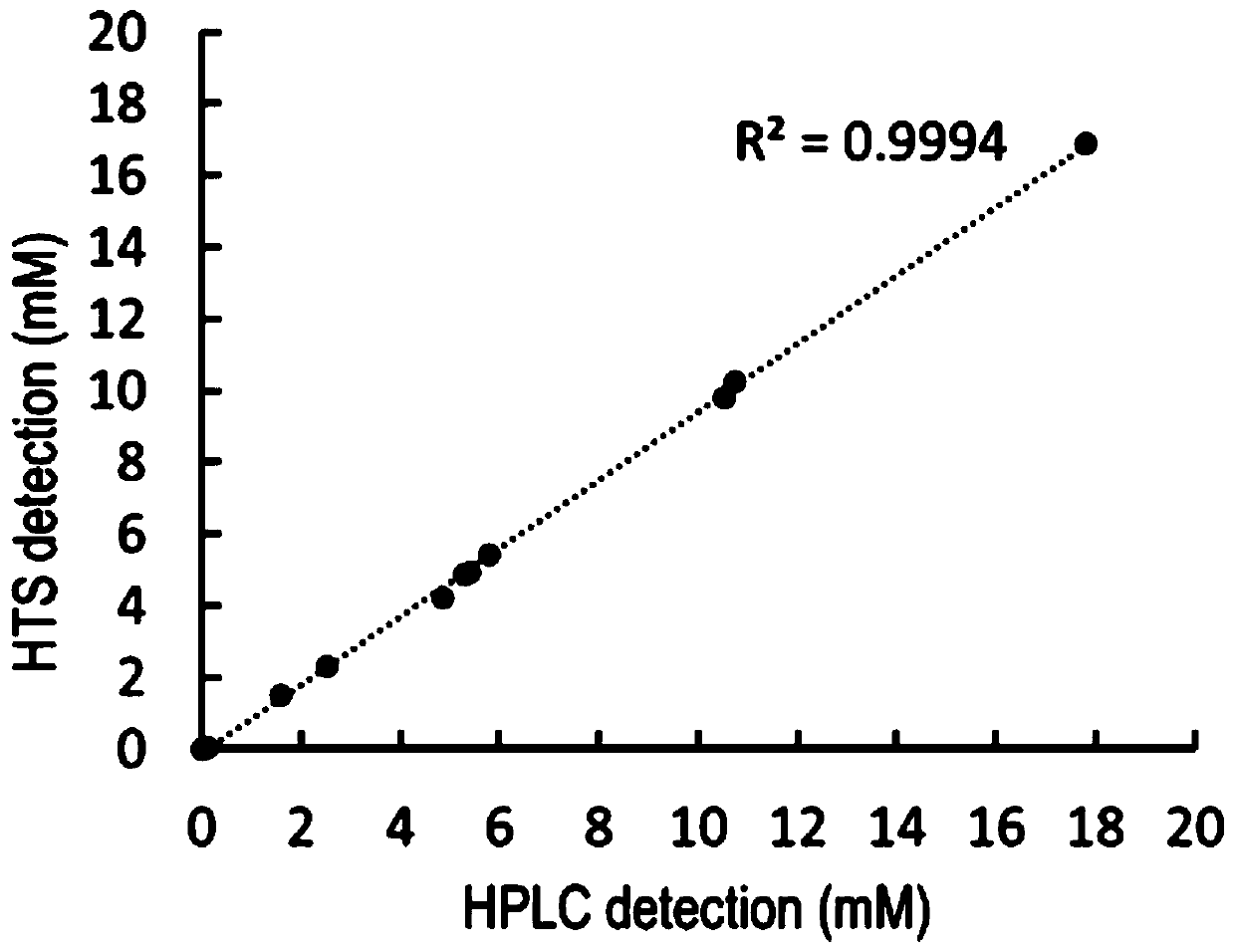
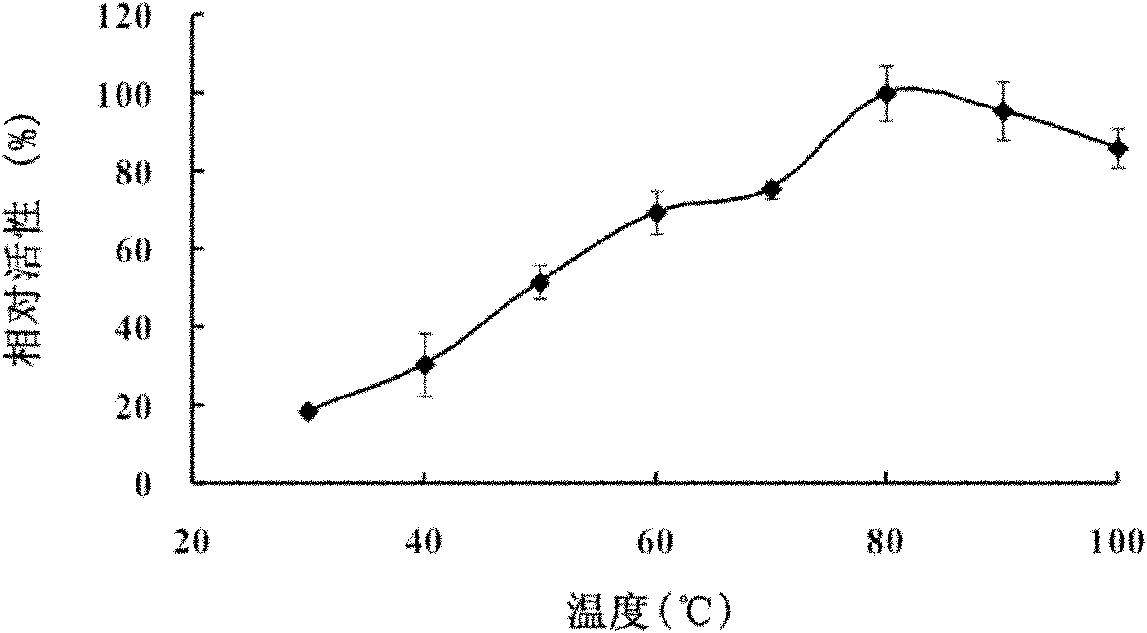
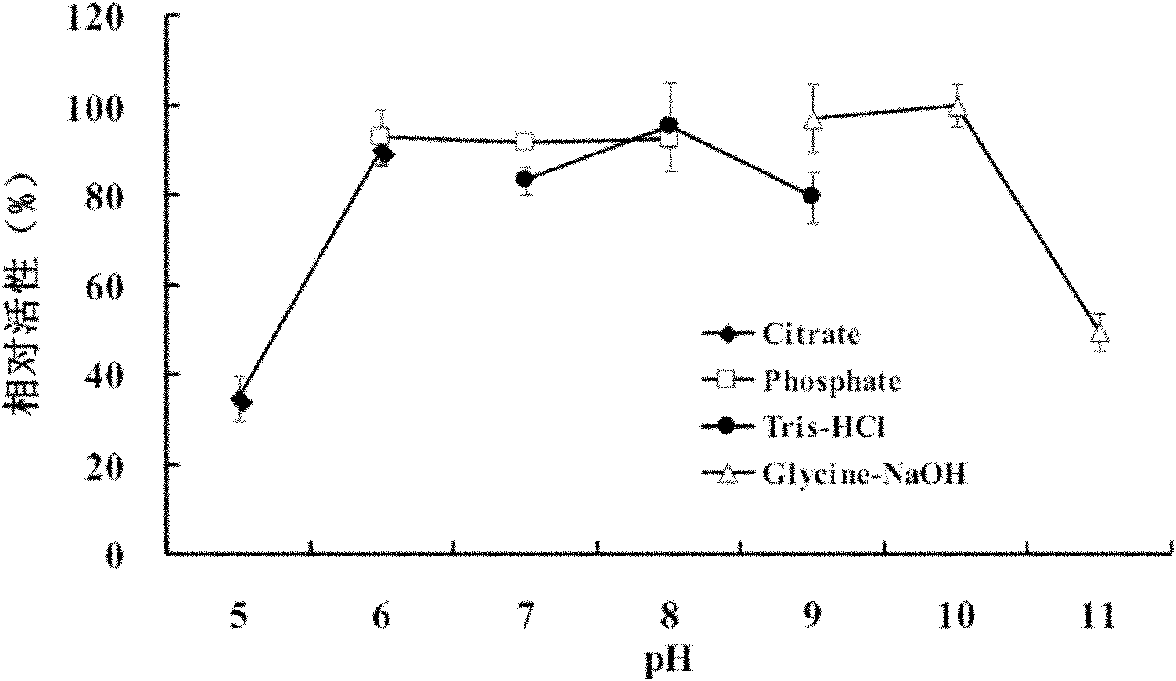
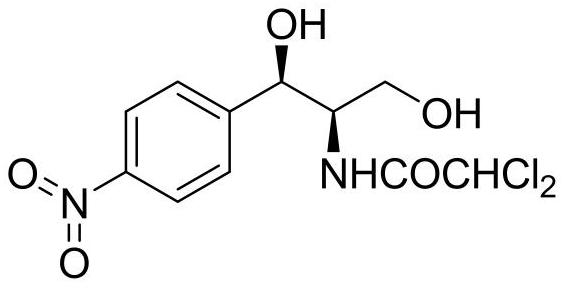
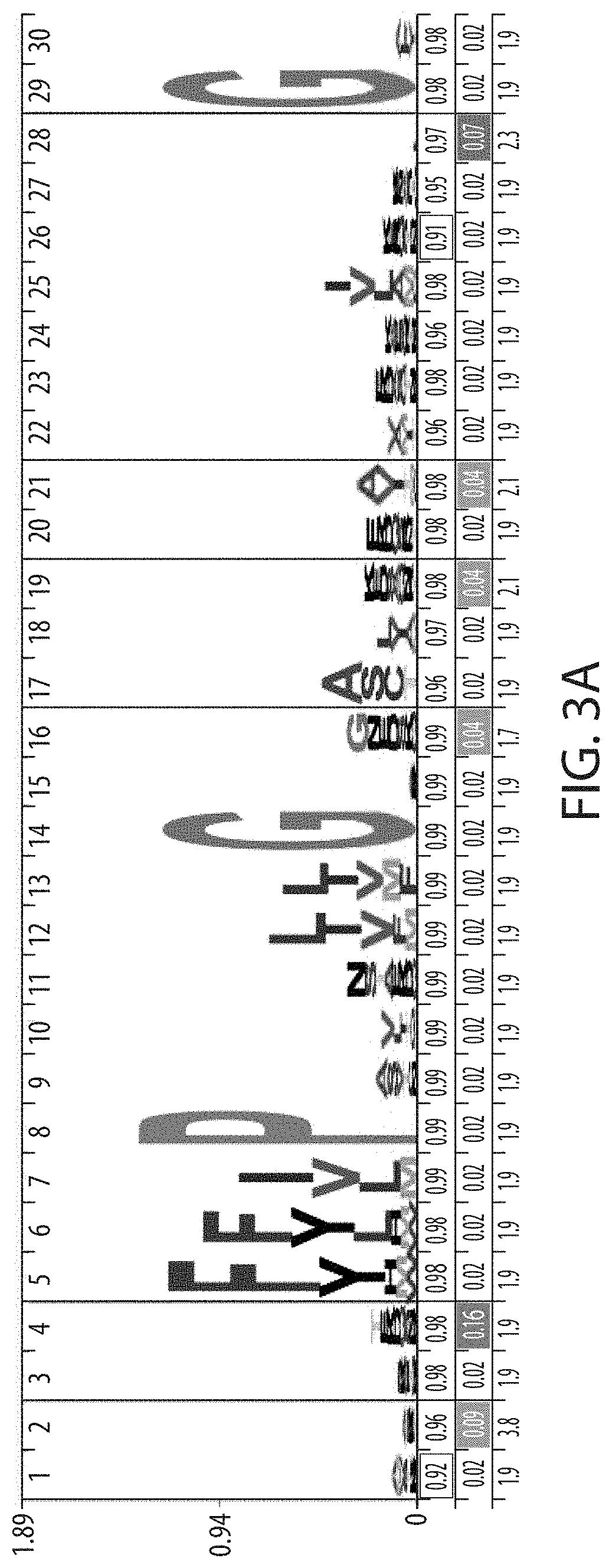
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Transaldolase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
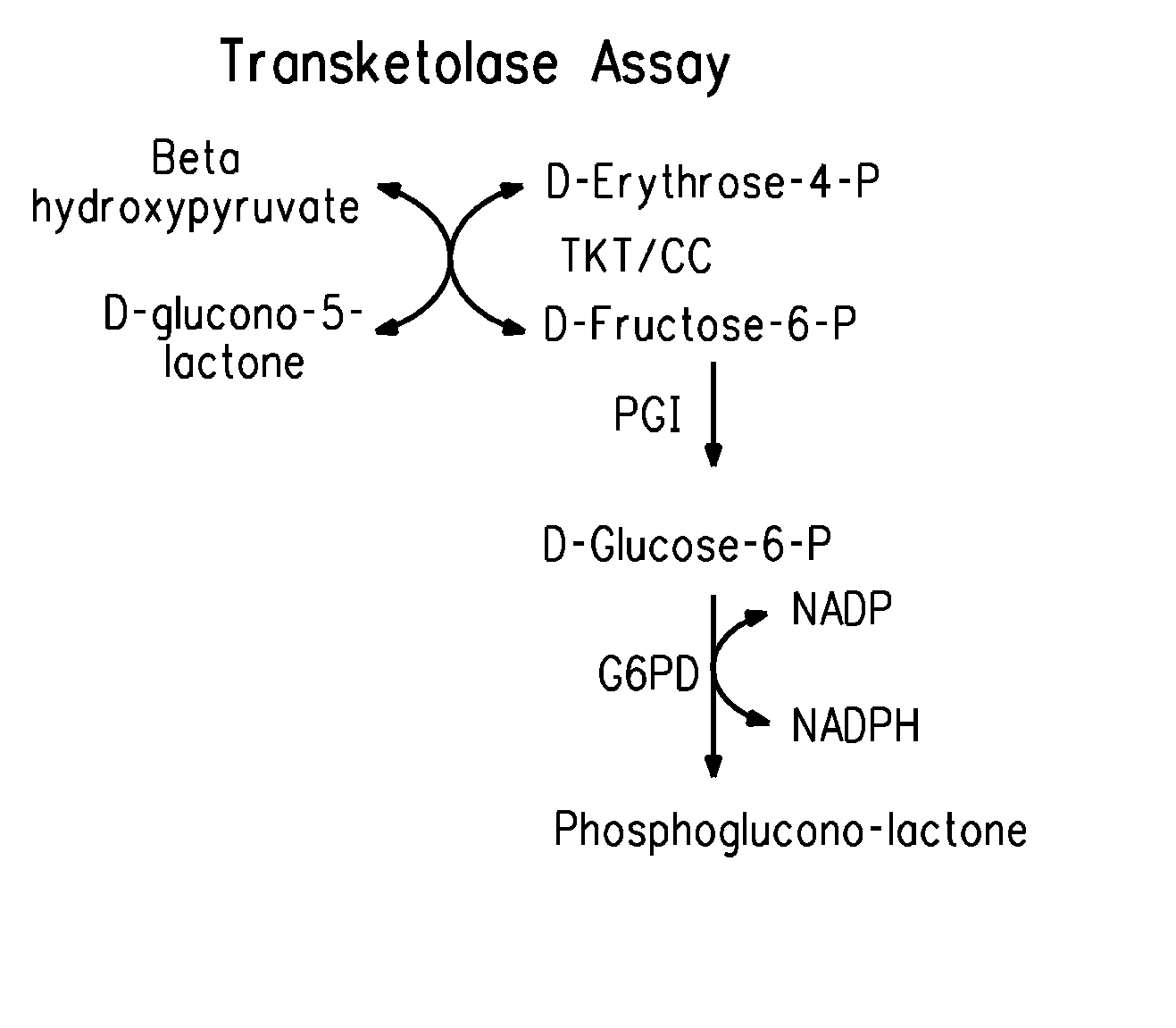
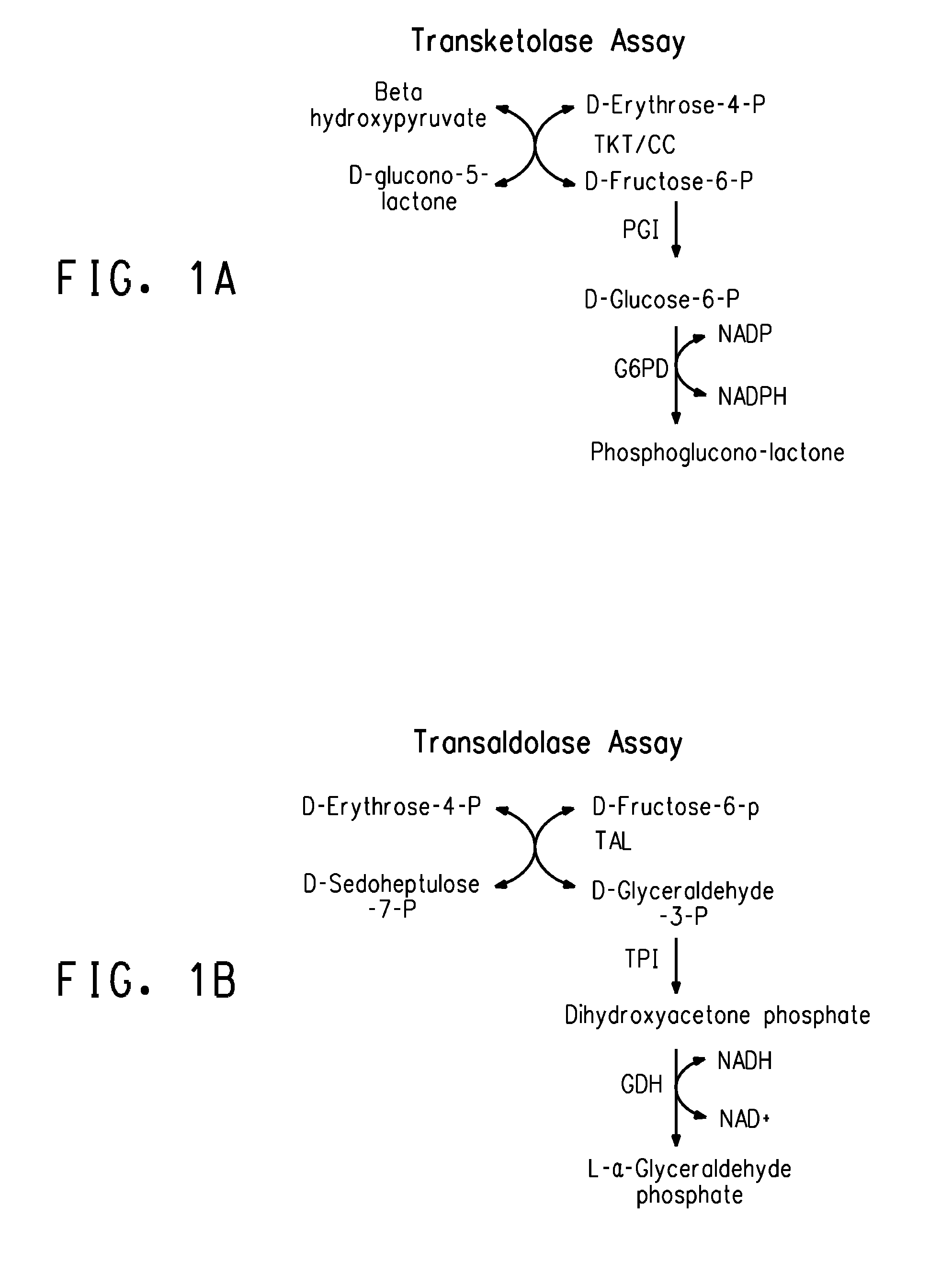
Transaldolase is an enzyme (EC 2.2.1.2) of the non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway. In humans, transaldolase is encoded by the TALDO1 gene. The following chemical reaction is catalyzed by transaldolase: sedoheptulose 7-phosphate + glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate ⇌ erythrose 4-phosphate + fructose 6-phosphate
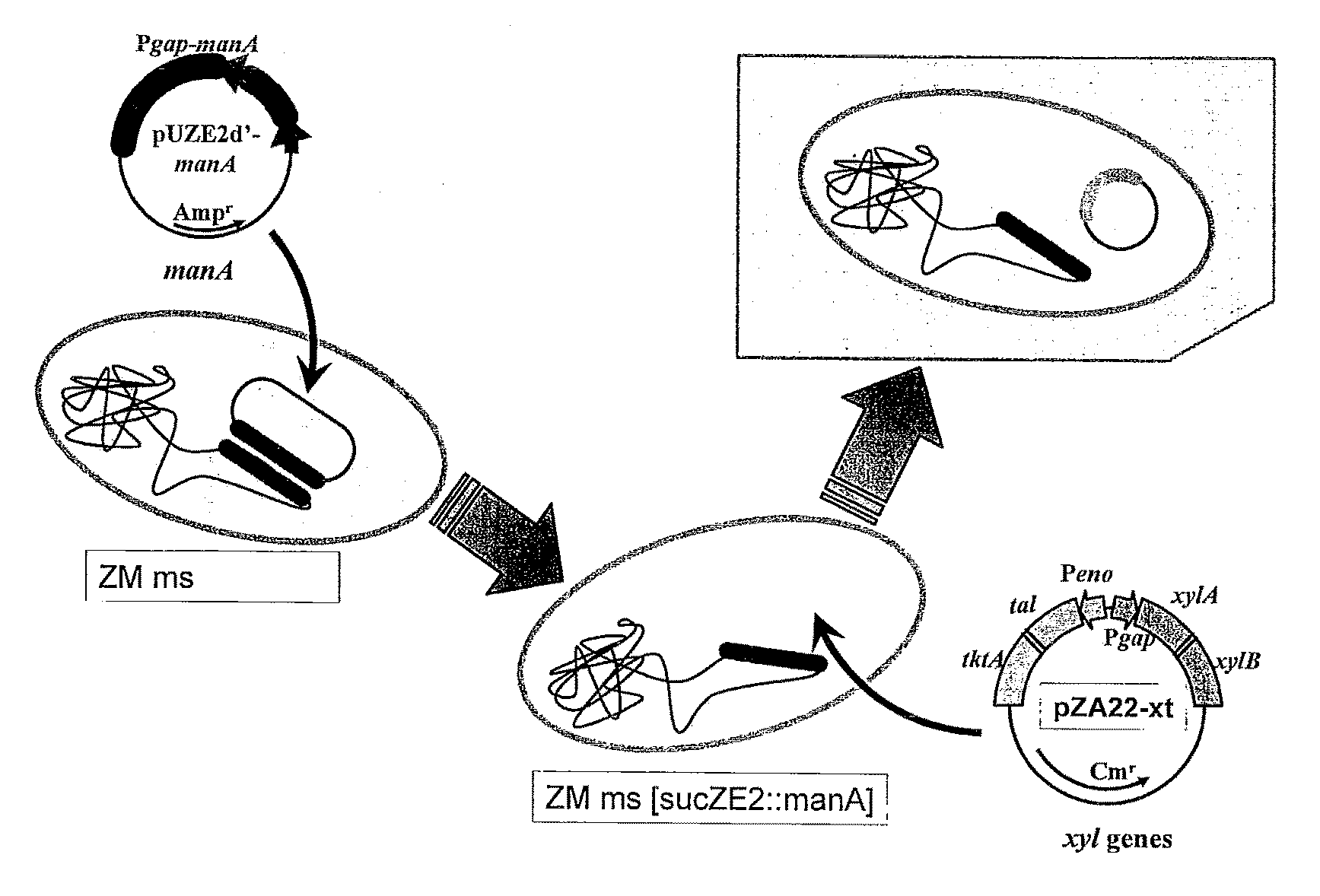
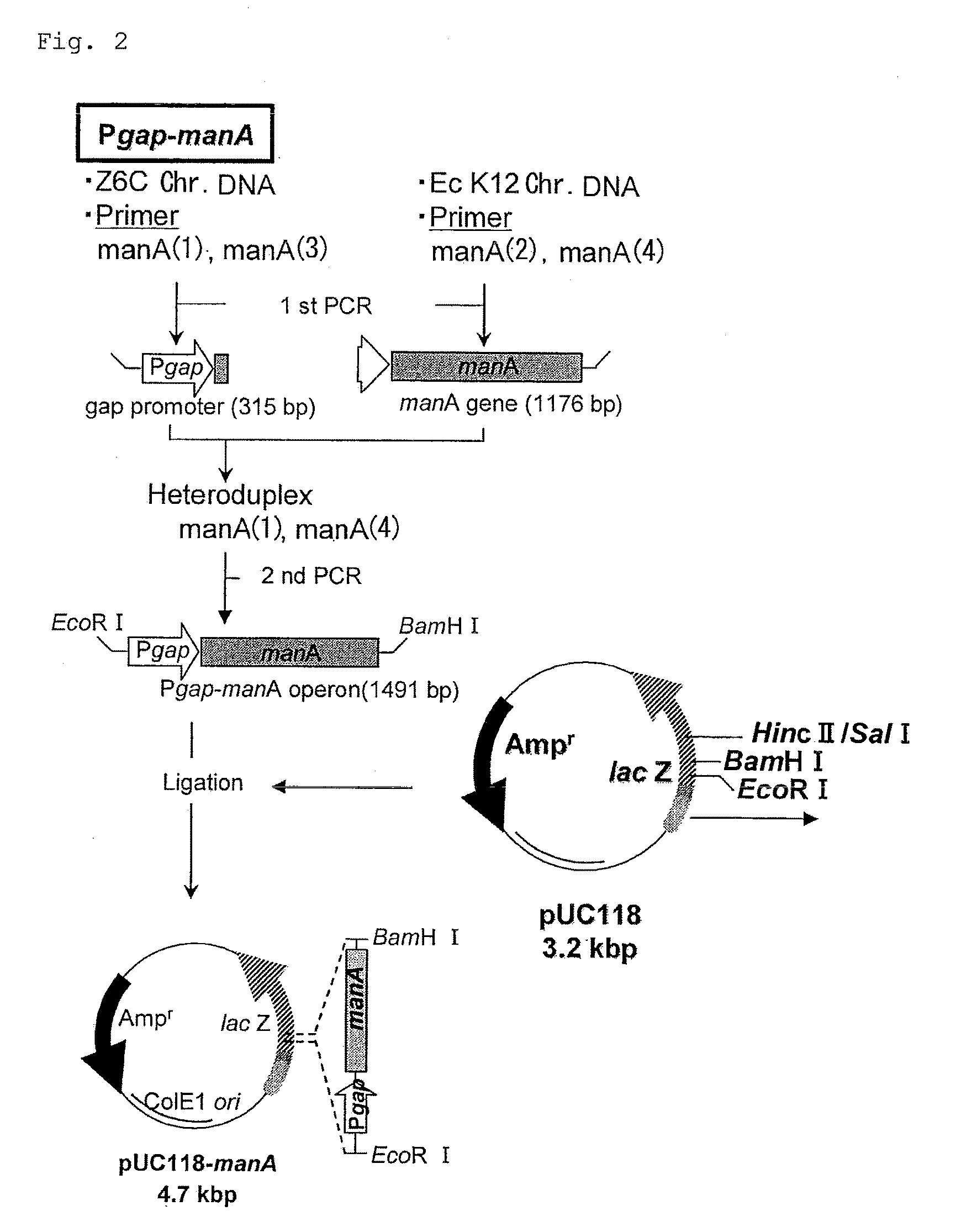
Zymomonas with improved xylose utilization
ActiveUS20090246846A1High expressionImproved xylose utilizationSugar derivativesBacteriaTransketolaseGlyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Gene
Strains of Zymomonas were engineered by introducing a chimeric xylose isomerase gene that contains a mutant promoter of the Z. mobilis glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. The promoter directs increased expression of xylose isomerase, and when the strain is in addition engineered for expression of xylulokinase, transaldolase and transketolase, improved utilization of xylose is obtained.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
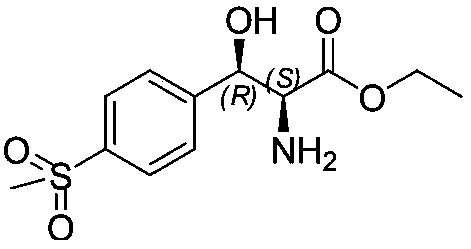
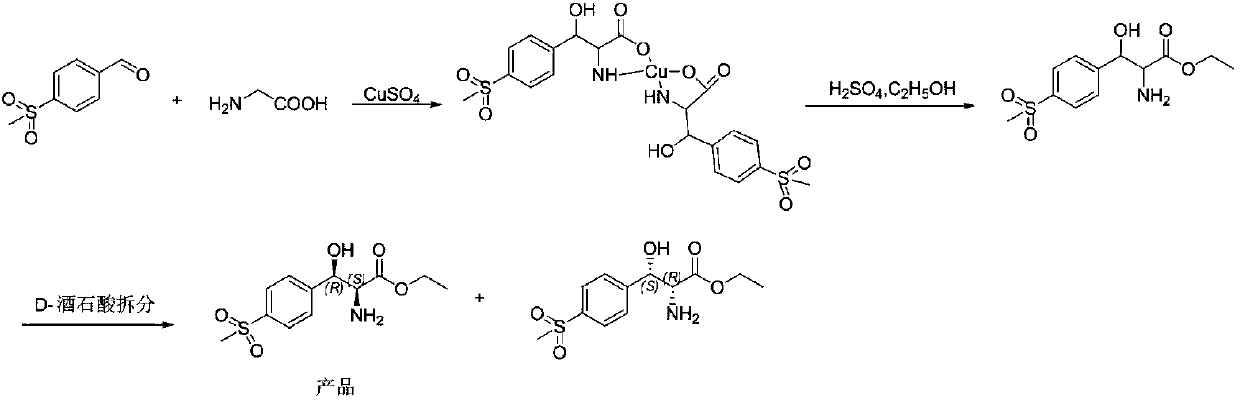
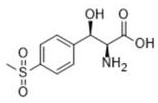
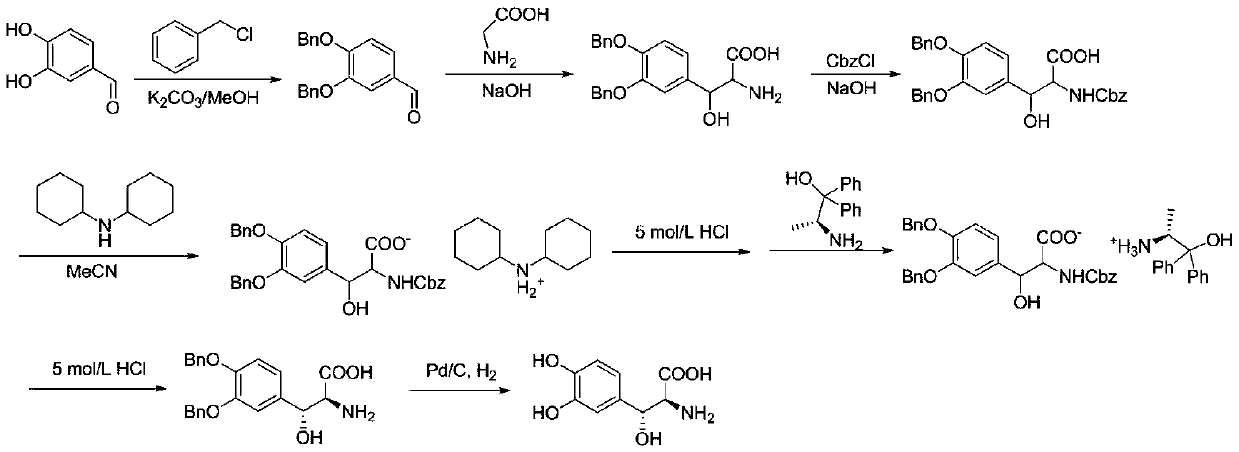
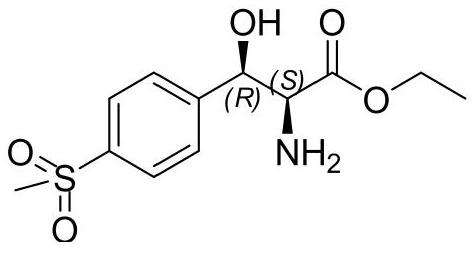
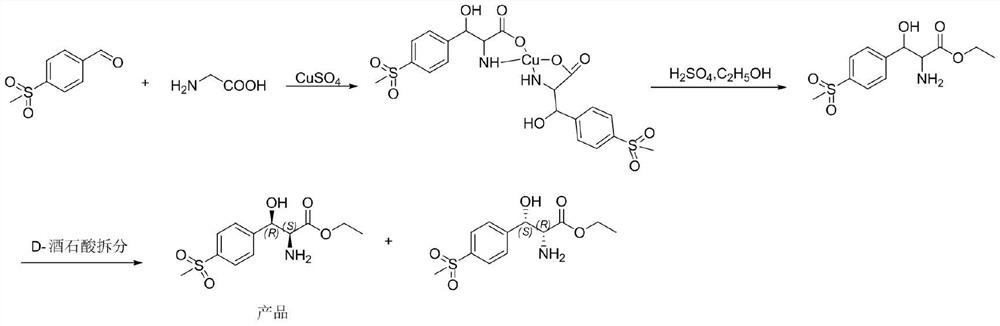
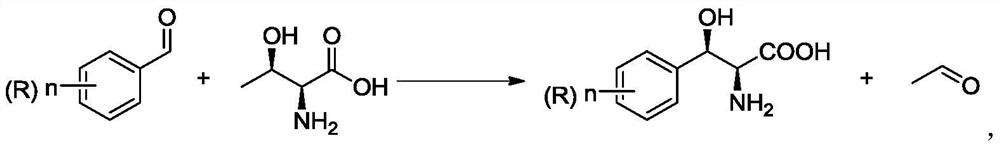
Method for preparing chiral (2S,3R)-p-methyl sulfone phenyl ethyl serinate
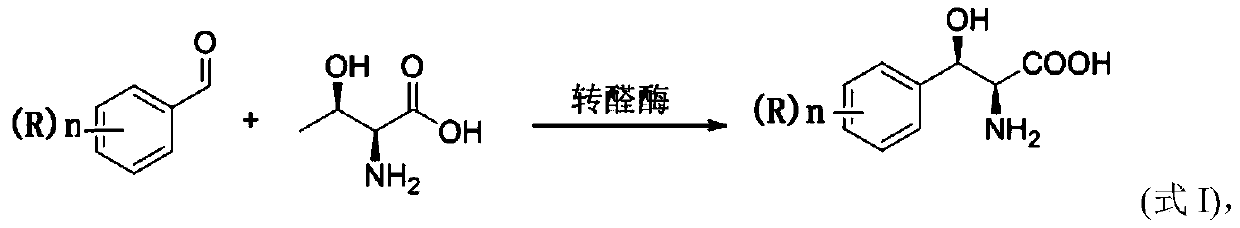
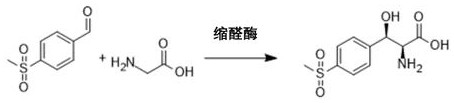
ActiveCN109836362AEasy to operateMild conditionsOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationL-threonineBenzaldehyde
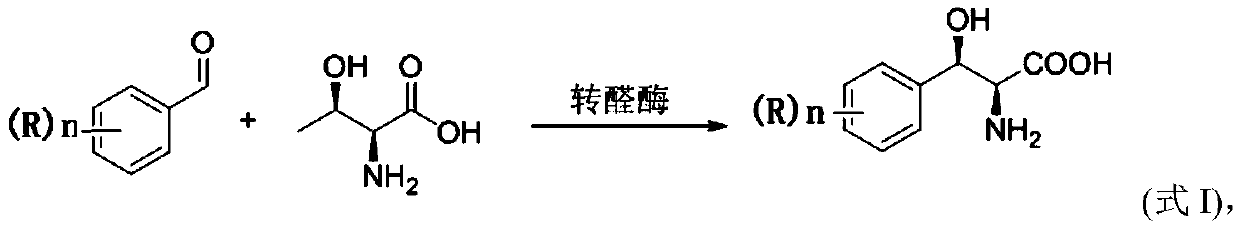
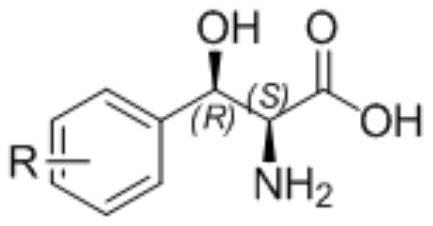
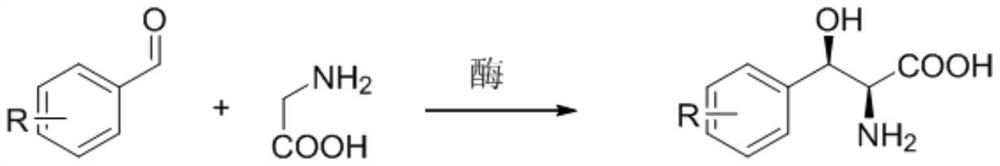
The invention provides a method for preparing (2S, 3R)-p-methyl sulfone phenyl ethyl serinate from the cheap and easily available methylsulfonyl benzaldehyde and L-threonine under the action of transaldolase. The amino acid intermediate then undergoes ethyl esterification to obtain a target product (2S, 3R)-p-methyl sulfone phenyl ethyl serinate.
Owner:SUZHOU LEAD BIOTECH CO LTD
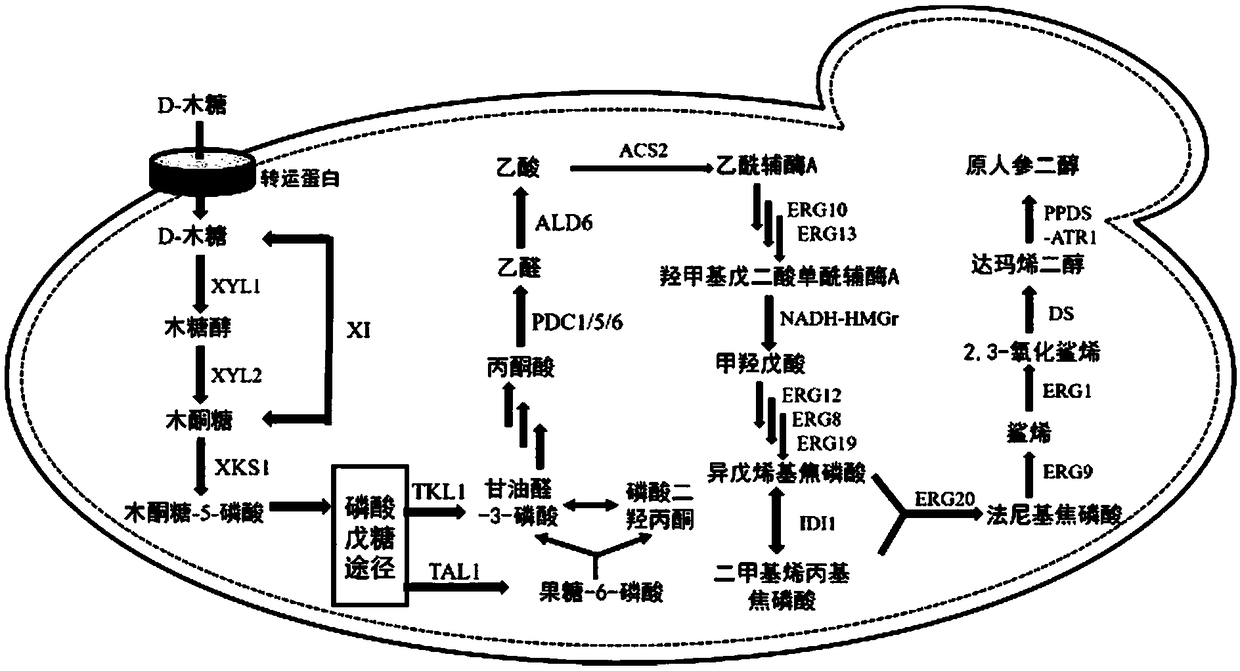
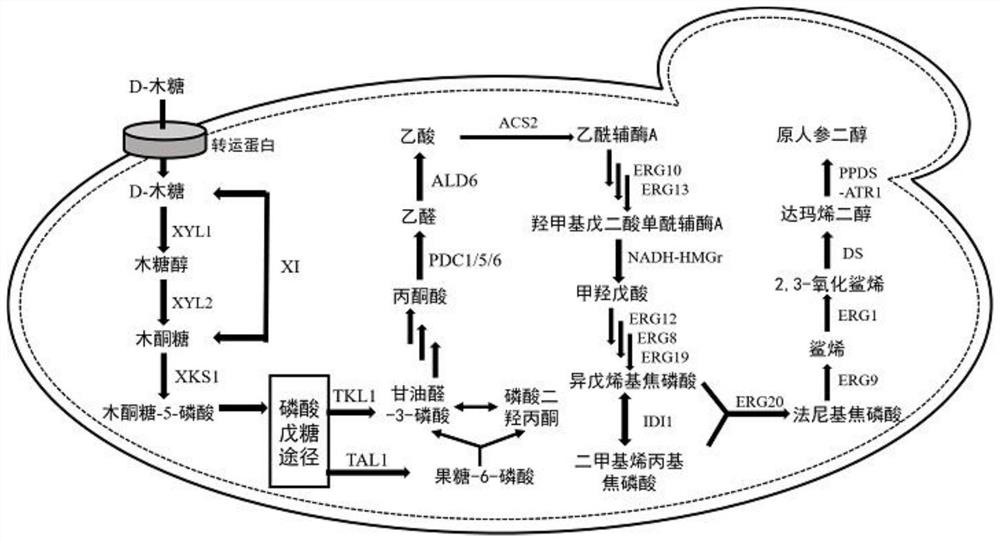
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and construction method
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and a construction method. The construction method comprises the steps of replacing a promoter of a saccharomyces cerevisiae xylulokinase gene XKS1 with a promoter PFBA1 by virtue of a homologous recombination method, introducing xylose reductase XYL1 and a xylitol dehydrogenase XYL2 expression cassette, increasing the activities of transketolase TKL1 and transaldolase TAL1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 1, introducing a farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase gene ERG9, a squalene monooxygenase gene ERG1 and a dammarenediol synthase gene DS into the recombinant bacteria 1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 2, and introducing a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene NADH-HMGr, farnesyl diphosphatesynthase ERG20 and a protopanoxadiol synthase-cytochrome P450 reductase fusion protein gene PPDS-ATR1 into the recombinant bacteria 2, so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 3. According to the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae, dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol can be artificially synthesized by virtue of xylose.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Modified yeast consuming L-arabinose
The present invention relates to a method for producing a L-arabinose utilizing yeast strain for the production of ethanol, whereby a yeast strain is modified by introducing and expressing araA gene (L-arabinose isomerase), araB gene (L-ribulokinase D121-N) and araD gene (L-ribulose-5-P 4-epimerase) and carrying additional mutations in its genome or overexpressing a TAL1 (transaldolase) gene, enabling it to consume L-arabinose, to use it as the only carbon source, and to produce ethanol, as well as a method for producing ethanol using such a modified strain.
Owner:FORSKARPATENT I SYD AB
Recombinant microorganism for generating terpenoid and construction method thereof
ActiveCN103087972AIncrease production capacityHigh strengthBacteriaOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Transformant containing transaldolase gene
InactiveUS20050266517A1Efficient productionSuitable lengthBacteriaTransferasesTransaldolaseRiboflavin
The present invention relates to a novel transaldolase gene, and to a polypeptide encoded by the gene, a recombinant DNA obtained by ligating the gene, a transformant carrying the recombinant DNA, and a process for producing the polypeptide, aromatic amino acids, aromatic vitamins, L-histidine, riboflavin, nucleic acids, nucleic acid-associated substances, novel saccharides and others by utilizing the transformant.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KOGYO CO LTD
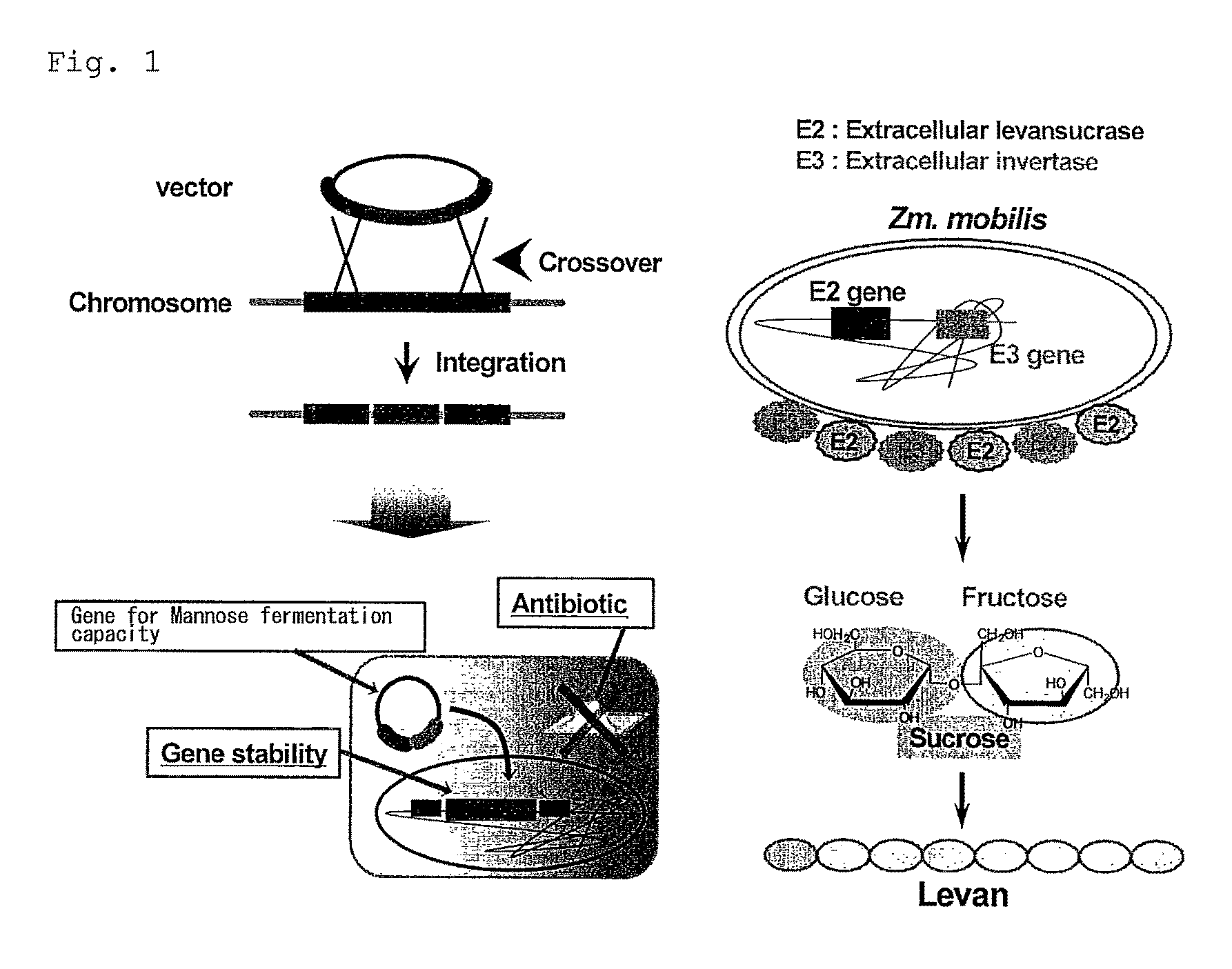
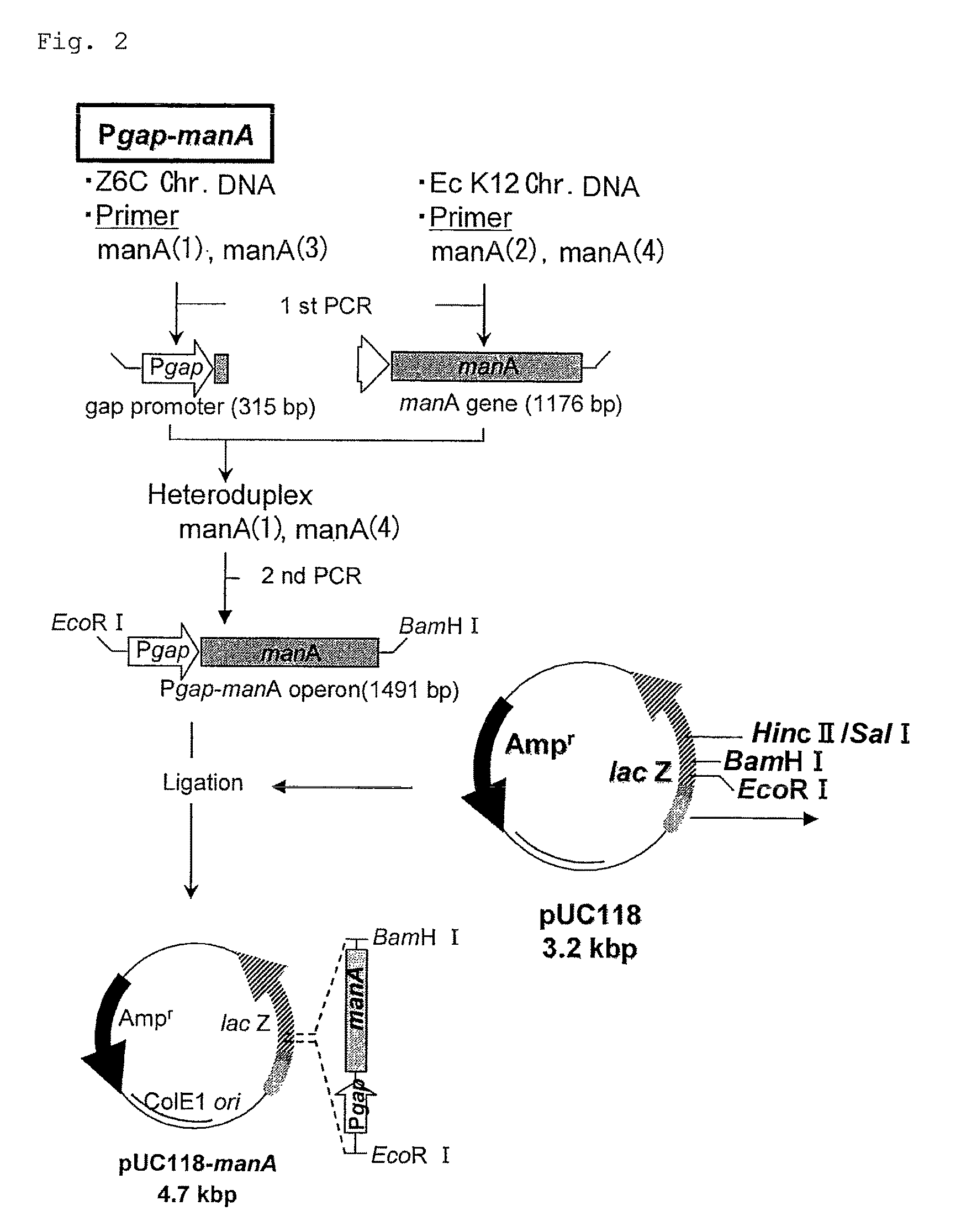
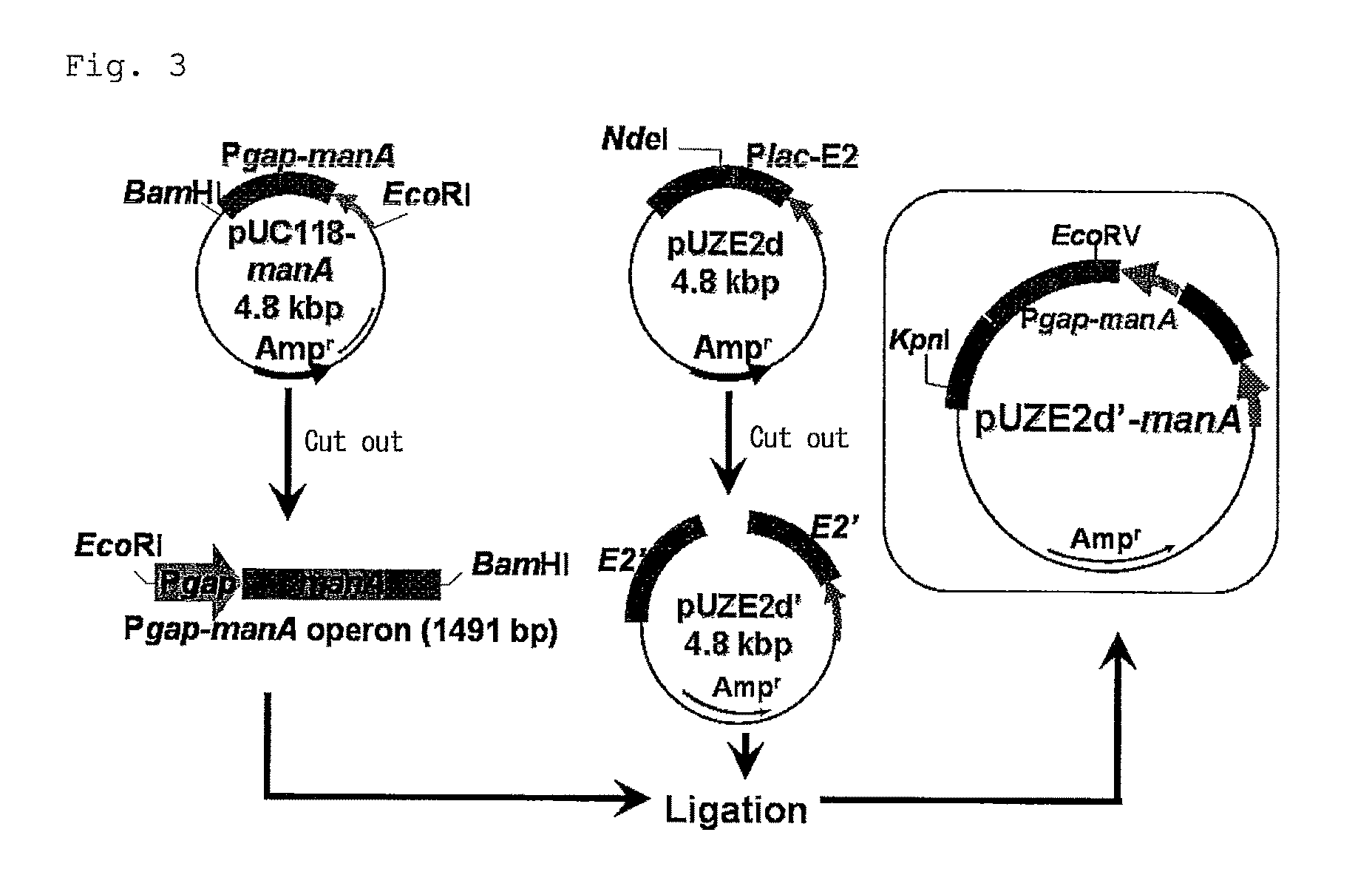
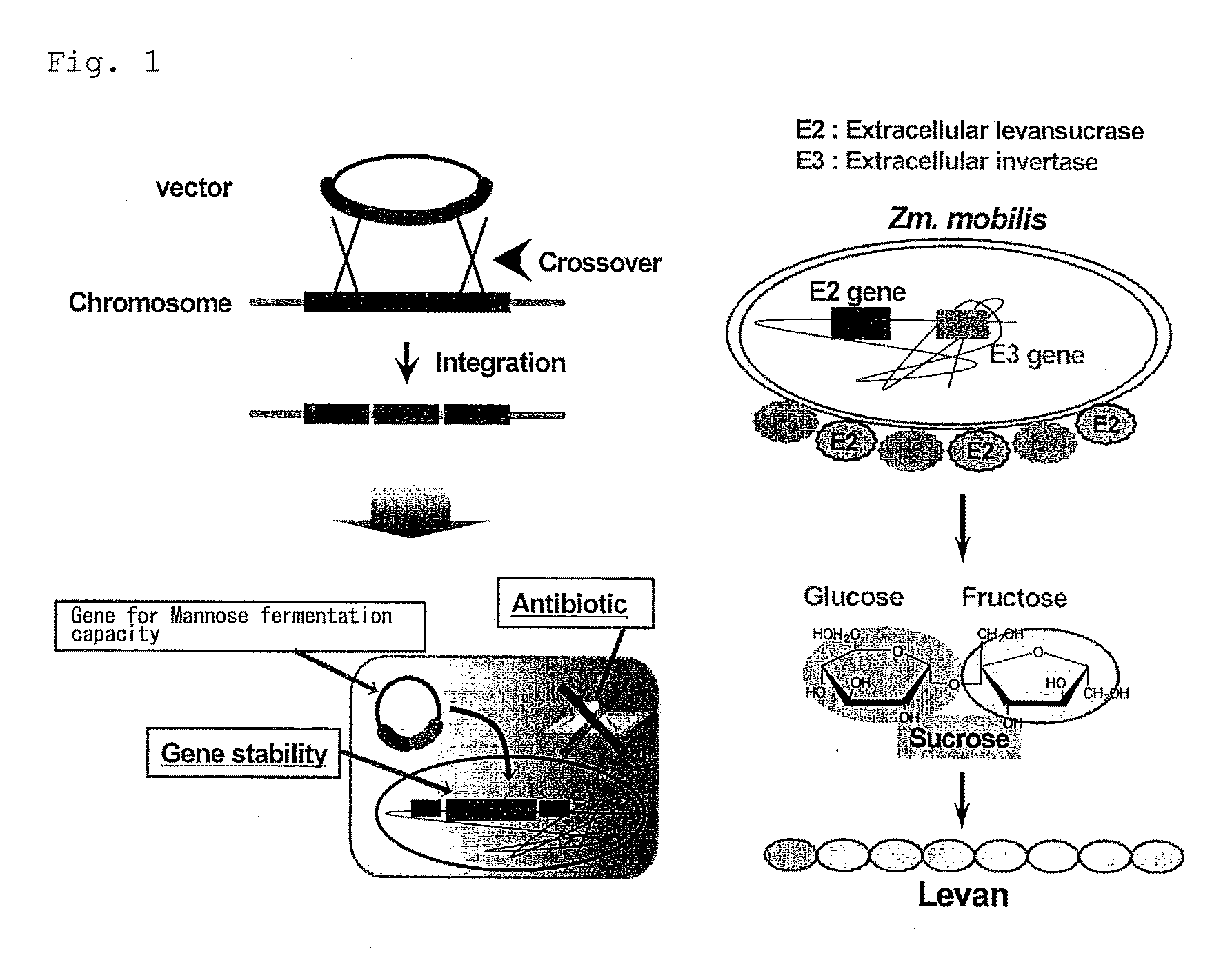
Bacterium capable of fermenting glucose, mannose and xylose simultaneously, and method for production of bioethanol using the bacterium
InactiveUS8383377B2Strong glucose fermentation capacityImprove fermentation performanceBacteriaBiofuelsTransketolaseEscherichia coli
The object is to develop a bacterium capable of fermenting glucose, mannose and xylose simultaneously, which can ferment a saccharified solution of a cellulose-type or lignocellulose-type biomass resource to produce ethanol, and to construct an energy-saving high-efficiency bioethanol conversion process. Thus, disclosed is Zymomonas mobilis bacterium which is prepared by integrating a gene encoding a phosphomannose isomerase derived from Escharichia coli into a levansucrase gene located on the chromosome by the double cross-over by means of a homologous recombsination method, and then introducing recombinant DNA prepared by binding a DNA fragment containing genes encoding a xylose isomerase, a xylulokinase, a transaldolase and a transketolase, respectively, all derived from Escherichia coli to a vector. Also disclosed is a method for producing ethanol by continuously fermenting a saccharified solution of a cellulose-type biomass resource in a system on which the Zymomonas mobilis bacterium is immobilized.
Owner:TOTTORI UNIVERSITY
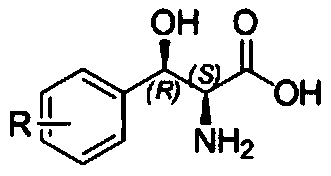
Method for preparing 3-phenyl-L-serine or derivative thereof and ethyl ester of 3-phenyl-L-serine
ActiveCN111377839ALow costSolve the problem of enzyme inactivationOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsThreonineAcyl group
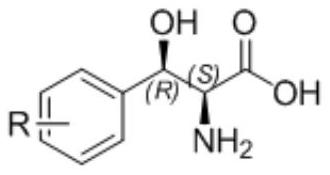
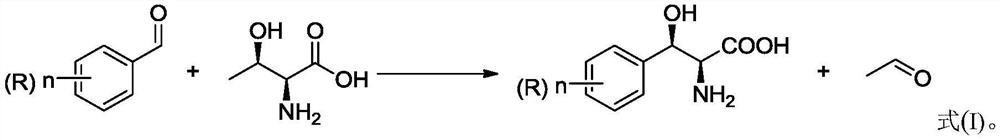
The invention relates to a method for preparing 3-phenyl-L-serine or a derivative thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: a, obtaining 3-phenyl-L-serine or a derivative thereof according to a reaction general formula as shown in a formula I, in which R is selected from a hydrogen group, an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, an alkyl sulfonyl group, an alkyl sulfinyl group, analkyl sulfenyl group, a sulfonic group, a sulfinyl group, a sulfydryl group, a nitro group and halogen; n is 0, 1, 2 or 3; wherein the transaldolase is L-threonine transaldolase,; and acetaldehyde reductase is added in the step a.
Owner:SUZHOU LEAD BIOTECH CO LTD
Process for the production of beta-lysine
InactiveCN101400799AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTransketolase
Process for the production of -lysine by constructing a recombinant microorganism which has a deregulated lysine 2,3-aminomutase gene and at least one deregulated gene selected from the group (i) which consists of aspartokinase, aspartatesemialdehyde dehydrogenase, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydrodipicolinate reductase, tetrahydrodipicolinate succinylase, succinyl-amino-ketopimelate transaminase, succinyl-diamino-pimelate desuccinylase, diaminopimelate epimerase, diaminopimelate dehydrogenase, arginyl-tRNA synthetase, diaminopimelate decarboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, transketolase, transaldolase, 6-phosphogluconolactonase, fructose 1,6-biphosphatase, homoserine dehydrogenase, phophoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, succinyl-CoA synthetase, methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, provided that if aspartokinase is deregulated as gene (i) at least a second gene (i) other than aspartokinase has to be deregulated, and cultivating said microorganism.
Owner:BASF SE
Process for the production of beta-lysine
InactiveUS20090029425A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTransketolase
Process for the production of -lysine by constructing a recombinant microorganism which has a deregulated lysine 2,3-aminomutase gene and at least one deregulated gene selected from the group (i) which consists of aspartokinase, aspartatesemialdehyde dehydrogenase, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydrodipicolinate reductase, tetrahydrodipicolinate succinylase, succinyl-amino-ketopimelate transaminase, succinyl-diamino-pimelate desuccinylase, diaminopimelate epimerase, diamino-pimelate dehydrogenase, arginyl-tRNA synthetase, diaminopimelate decarboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, transketolase, transaldolase, 6-phosphogluconolactonase, fructose 1,6-biphosphatase, homoserine dehydrogenase, phophoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, succinyl-CoA synthetase, methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, provided that if aspartokinase is deregulated as gene (i) at least a second gene (i) other than aspartokinase has to be deregulated, and cultivating said microorganism.
Owner:BASF AG
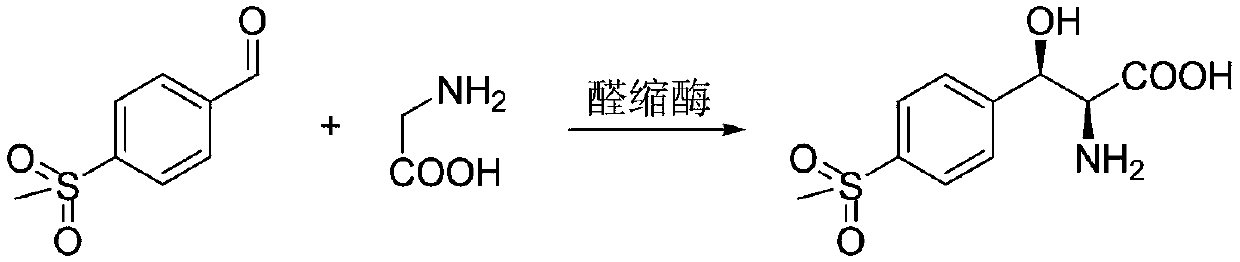
Method for synthesizing 2S,3R-p-methylsulfonephenylserine
InactiveCN112725390AMild reaction conditionsReduce manufacturing costFermentationThreonineOxidative enzyme
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing 2S,3R-p-methylsulfonephenylserine, wherein cheap p-methylsulfonebenzaldehyde and threonine are used as substrates, transaldolase is applied to drive a reaction, and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase and NAD oxidase are simultaneously added to eliminate the generation of by-product acetaldehyde. According to the invention, the method has mild reaction conditions, can greatly reduce the production cost, and can perform large-scale reactions.
Owner:天津工微生物科技有限公司
Building method of pediococcus acidilactici ZP26 for producing D-lactic acid by co-fermenting glucose and xylose
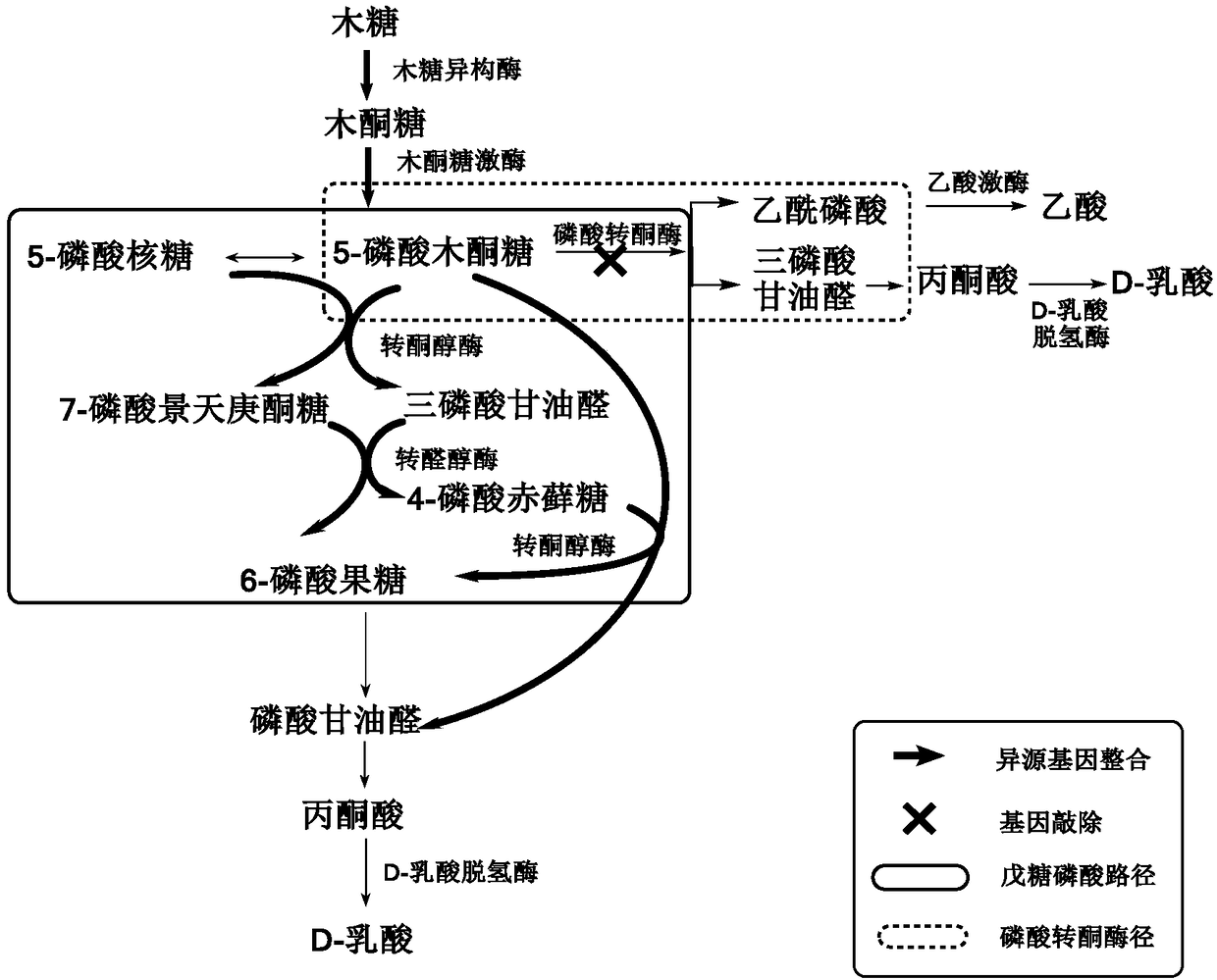
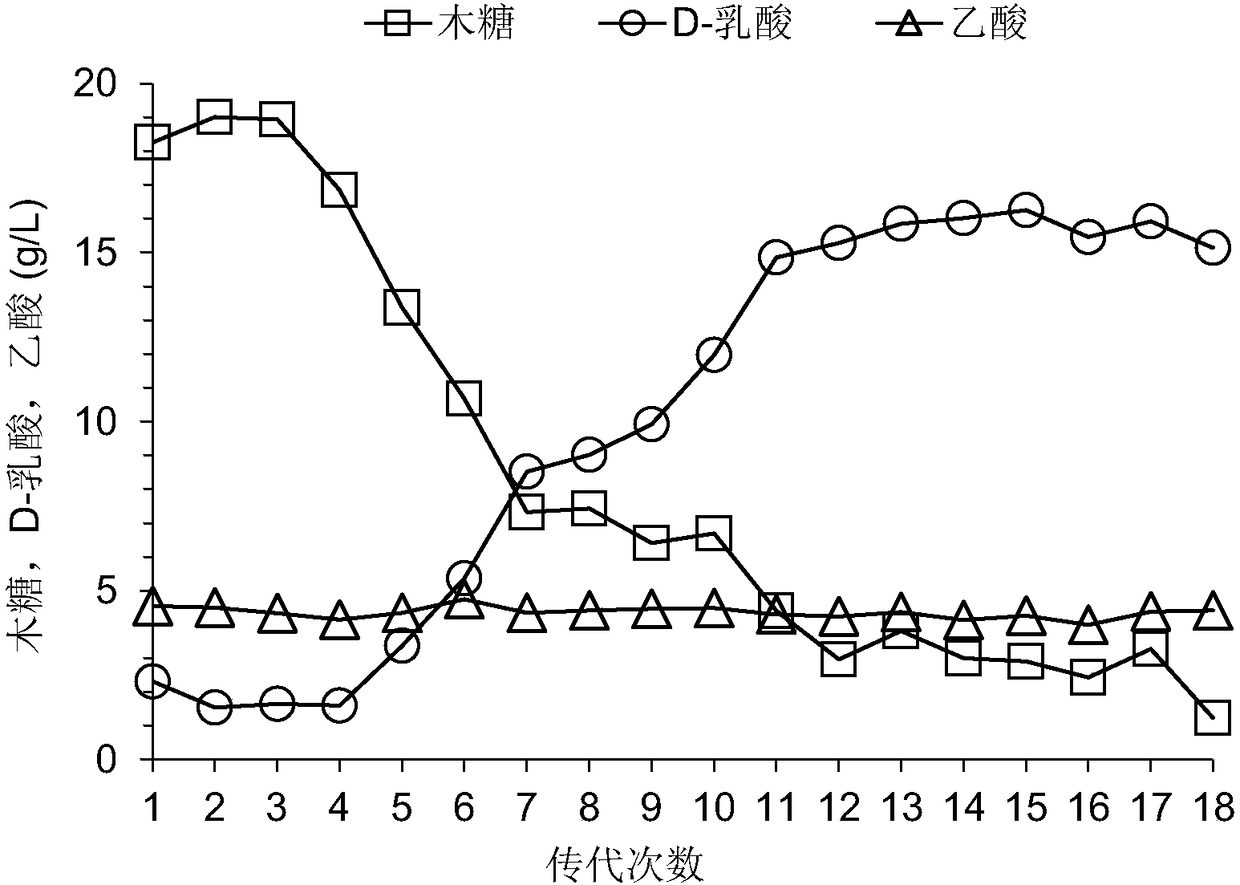
The invention discloses a building method of pediococcus acidilactici ZP26 for producing D-lactic acid by co-fermenting glucose and xylose, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following building steps of integrating heterogenous xylose isomerase, xylulokinase, transketolase and transaldolase encoding genes onto pediococcus acidilactici ZP26 (with the preservationnumber being CGMCC NO.8665) genomes by using a thermosensitive knock-out system; knocking out phosphotransferase encoding genes so as to block the generation of byproducts of acetic acids; the capability of the engineering strain for co-fermenting glucose and xylose is obviously improved through an adaptive domestication strategy. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the building of the xylose metabolism path is successfully realized for the first time; the engineering strain for producing optical pure D-lactic acid by co-fermenting glucose and xylose at high efficiency is obtained, is named as P.acidilactici ZY15, and has the preservation number of CGMCC NO.13612.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
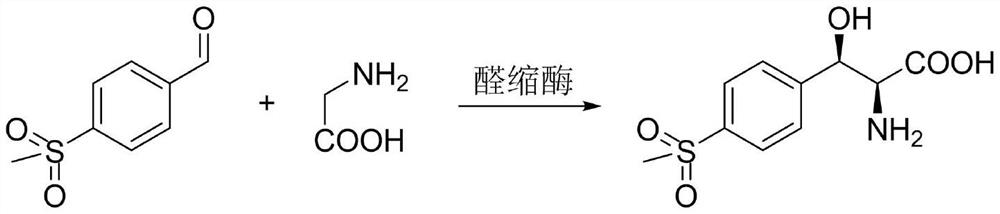
Application of L-threonine transaldolase to synthesis of florfenicol chiral intermediates
ActiveCN110540977AIncrease added valueSave separation and purificationTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliBenzaldehyde
The invention provides application of L-threonine transaldolase to synthesis of florfenicol chiral intermediates. The L-threonine transaldolase is selected from any one of the following groups that (1) polypeptide contains an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1; (2) polypeptide contains an amino acid sequence greater than or equal to 90% homology shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and the polypeptide hascatalytic activity; and (3) derived polypeptide is formed by substitution, deletion or addition of 1-5 amino acid residues to the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and with the retention of catalytic activity. According to the application, new L-threonine transaldolase genes are screened through gene mining, the L-threonine transaldolase derived from recombinant escherichia coli is expressed by adopting a genetic engineering method, methylsulfonyl benzaldehyde and the L-threonine transaldolase are used as raw materials, (2S,3R)-methylsulfonyl phenylserine is synthesized through a wholecell catalyzed reaction, fluorfenicol key chiral synthesis blocks can be obtained by a one-step reaction under the room temperature and pressure, environmental protection is achieved, and the application is an environment-friendly biosynthetic pathway.
Owner:福建昌生生物科技发展有限公司
Broad host range plasmid carrying xylose metabolism related gene and construction method thereof
InactiveCN101475955AEfficient productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTransketolase
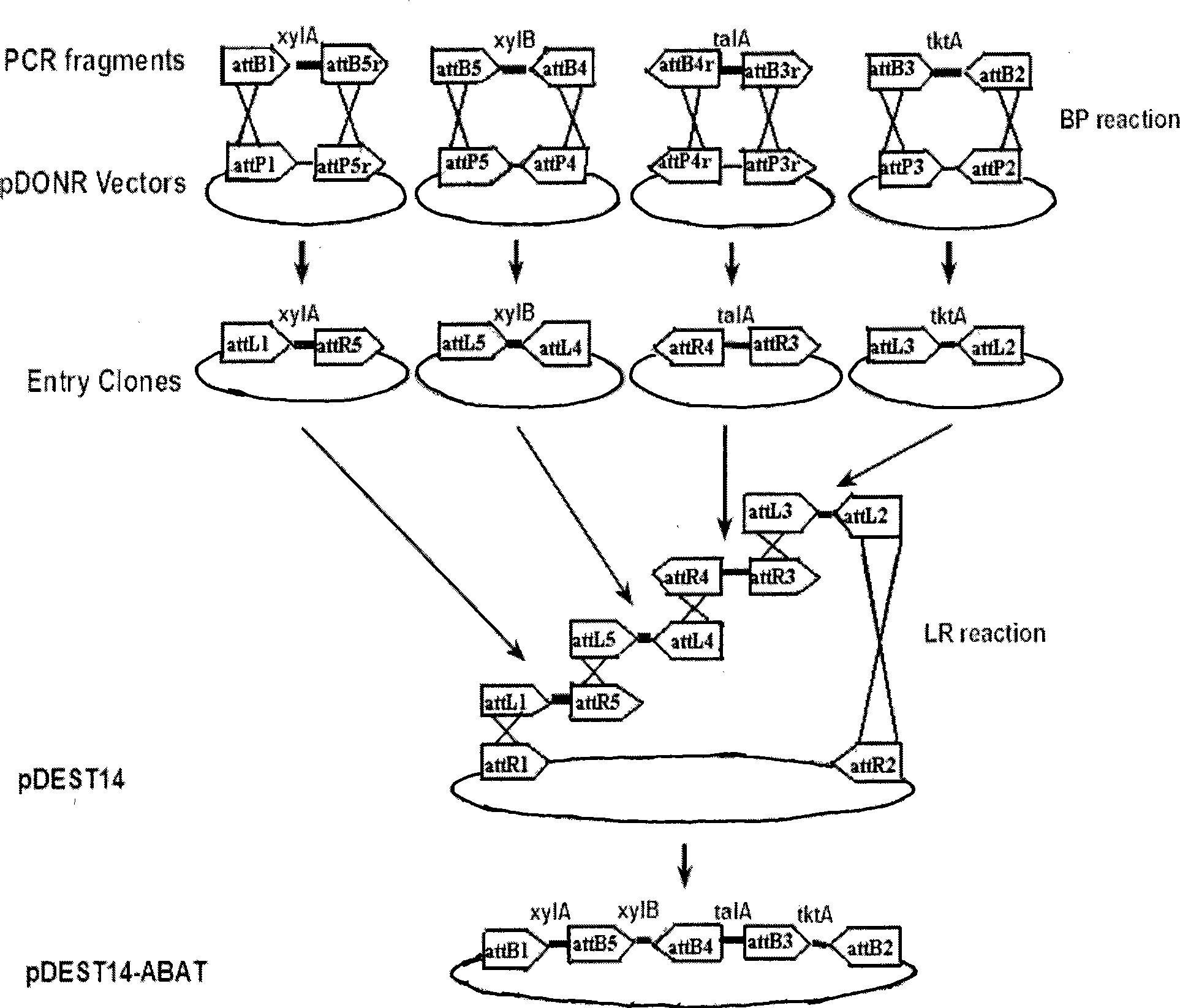
The invention discloses a wide host plasmid carrying xylose metabolism related genes and construction method thereof, belonging to the field of molecular biology techniques. The plasmid contains four xylose metabolism related enzyme genes, xylose isomerase (xylA), xylulokinase (xylB), transaldolase (talA) and transketolase (tktA), which are derived from E.coli DH5alpaha strain. The plasmid construction method uses the Gateway technology, to respectively design specific primers of four target genes xylA, xylB, talA and tktA, takes the E.coli DH5alpaha strain as the origin stain of the target genes to amplify the corresponding gene through the PCR; the PCR product performs BP recombination with the corresponding pDONR vector, and then the obtained Entry clones perform LR recombination with the pDEST14, to obtain the pDEST14-ABAT plasmid; the pDEST14-ABAT plasmid is connected to the Xha I single zyme cutting vector pBBR1MCS2 through the Xba I and Nhe I double zyme cutting product to obtained the recombinant plasmid pBBR1MCS2-ABAT. The superior strain shifted in the plasmid can greatly reduce production costs of cellulosic ethanol.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Recombinant microorganism for preparing terpenoid and method for constructing recombinant microorganism
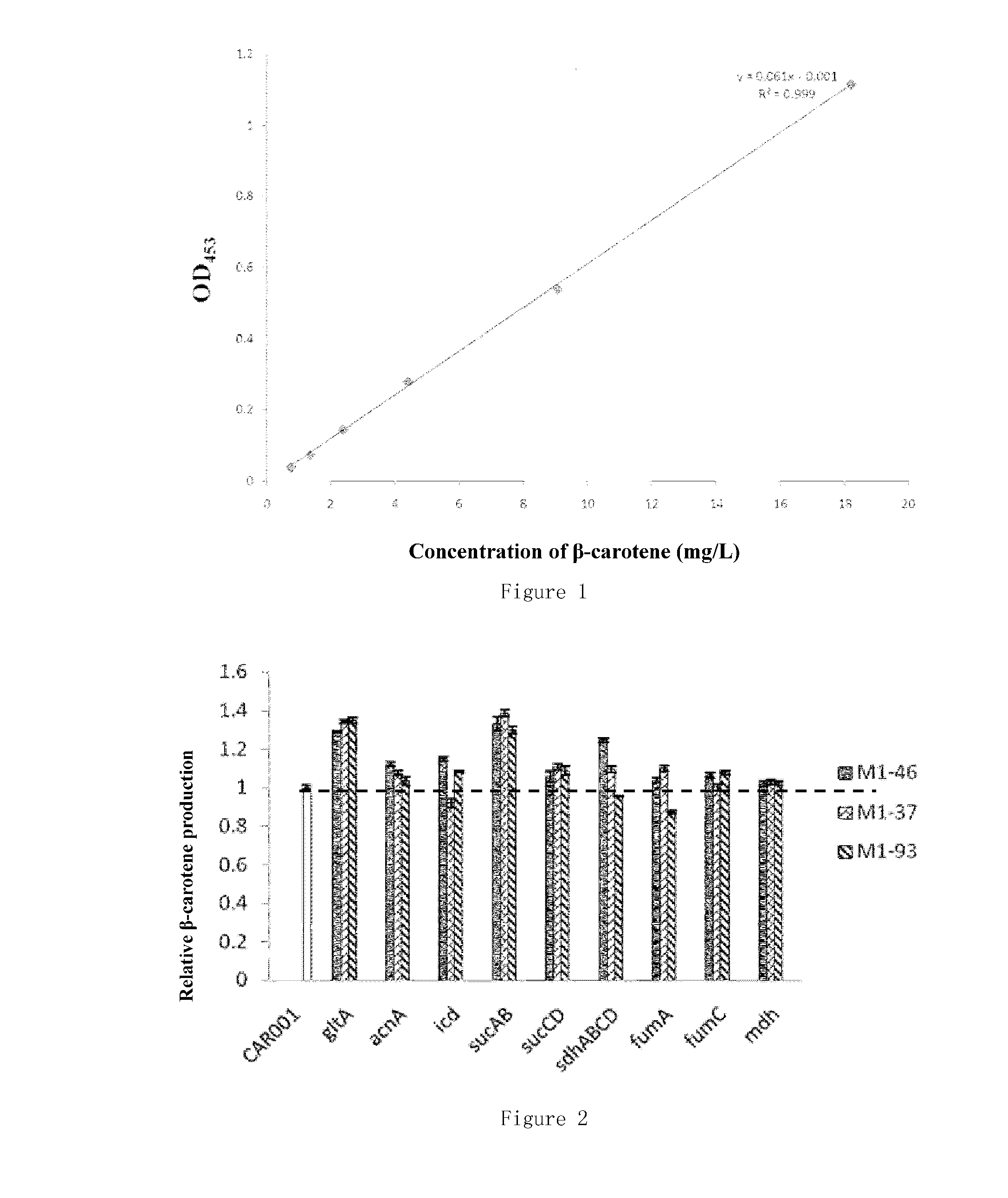
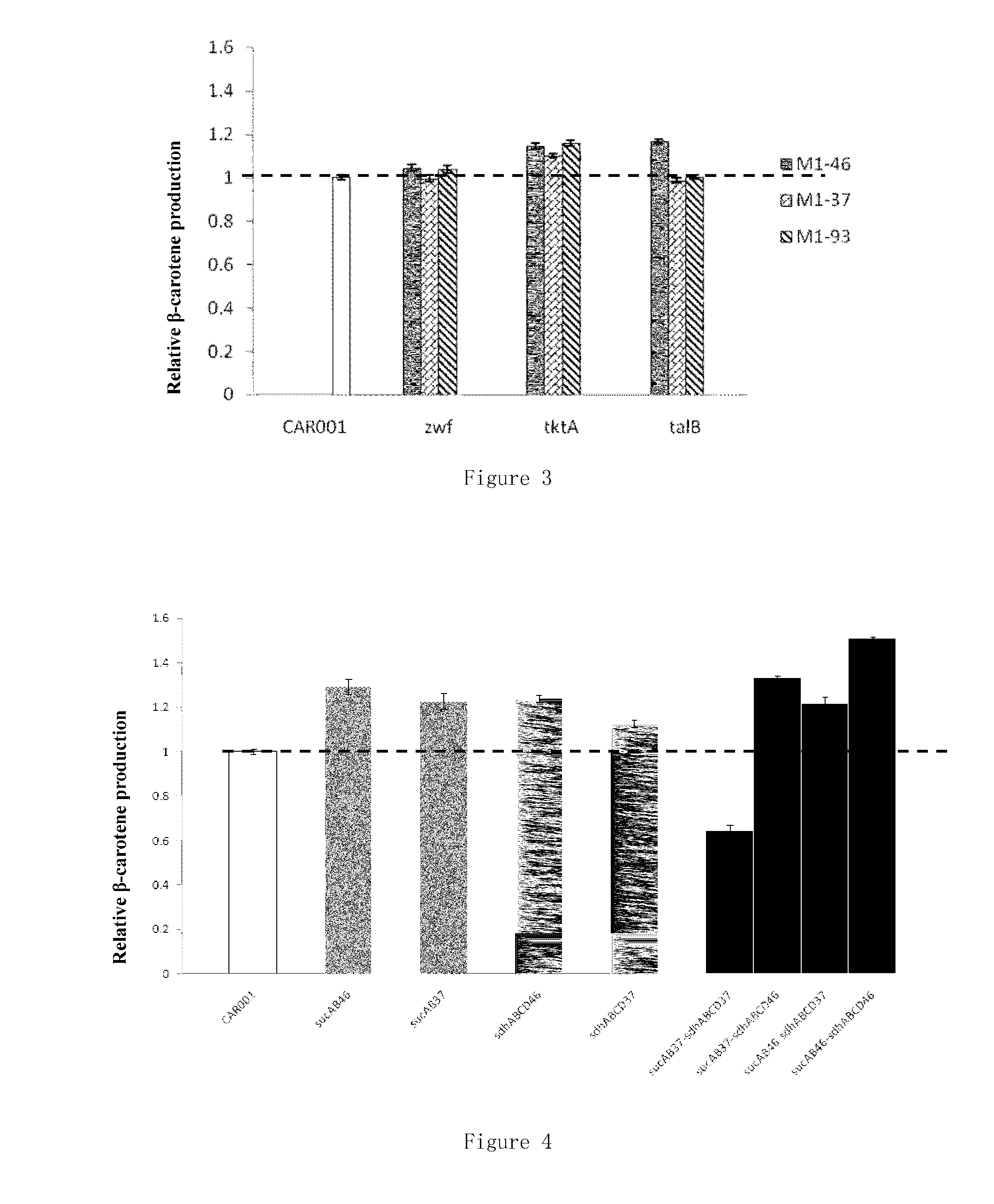
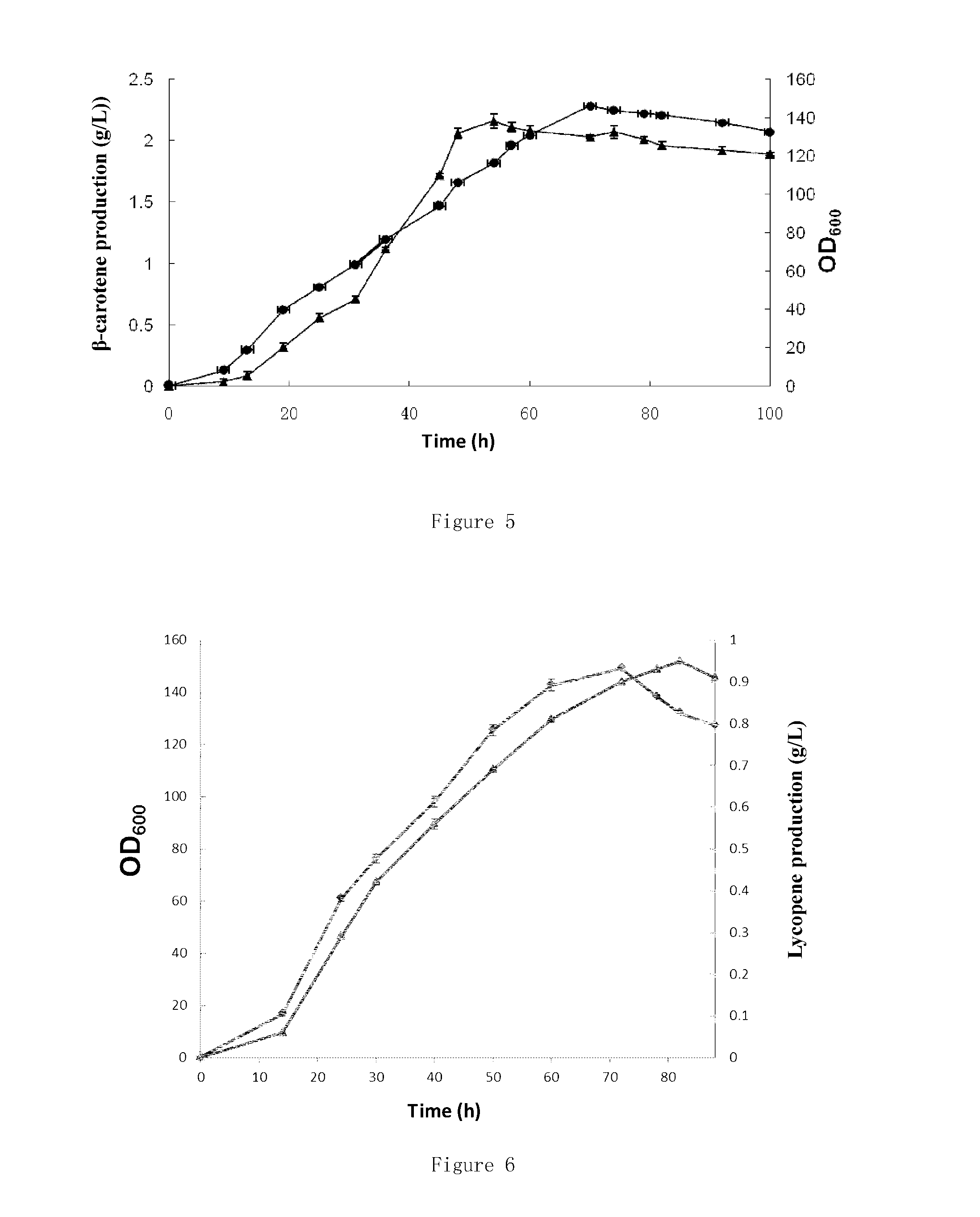
Provided are a recombinant strain for preparing a terpenoid, and method for constructing the recombinant strain. Also provided is a recombinant bacterium 1, the recombinant bacterium 1 being a recombinant bacterium obtained in order to improve the enzymatic activity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in escherichia coli or the mutant thereof. The method for improving the enzymatic activity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in escherichia coli or the mutant thereof is replacing the original regulating element of the ketoglutarate dehydrogenase gene (sucAB) in escherichia coli or the mutant thereof with any of the following regulating elements: artificial regulating element M1-46, M1-37, and M1-93. Also provided are a plurality of recombinant bacteria. By improving the enzymatic activity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, succinic acid dehydrogenase and transaldolase therein and improving the ability of a cell to synthesize NADPH and ATP, the efficiency of the MEP pathway and the production capacity of terpenoid are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
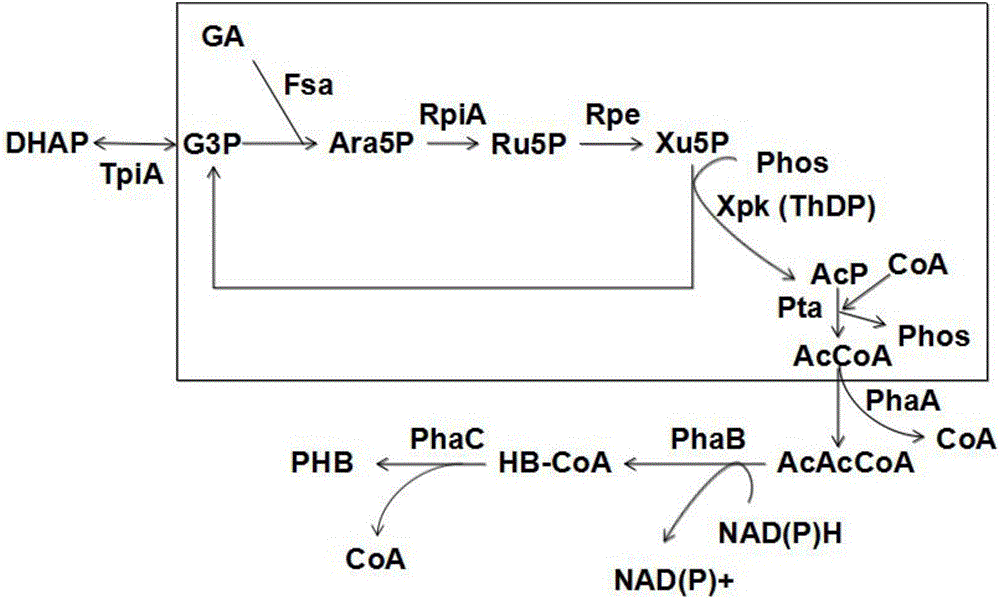
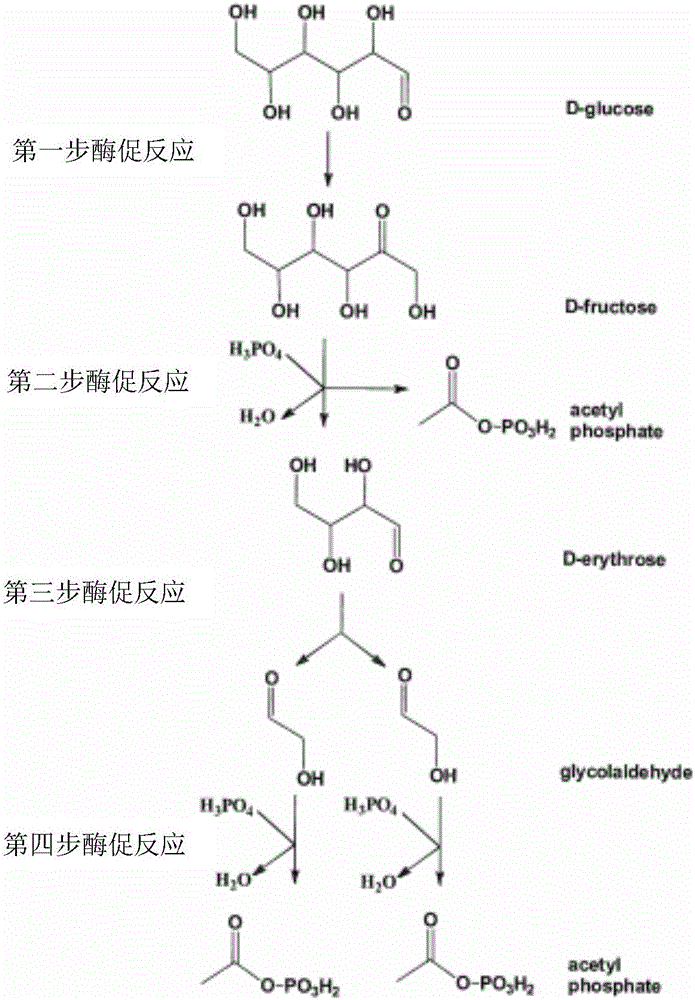
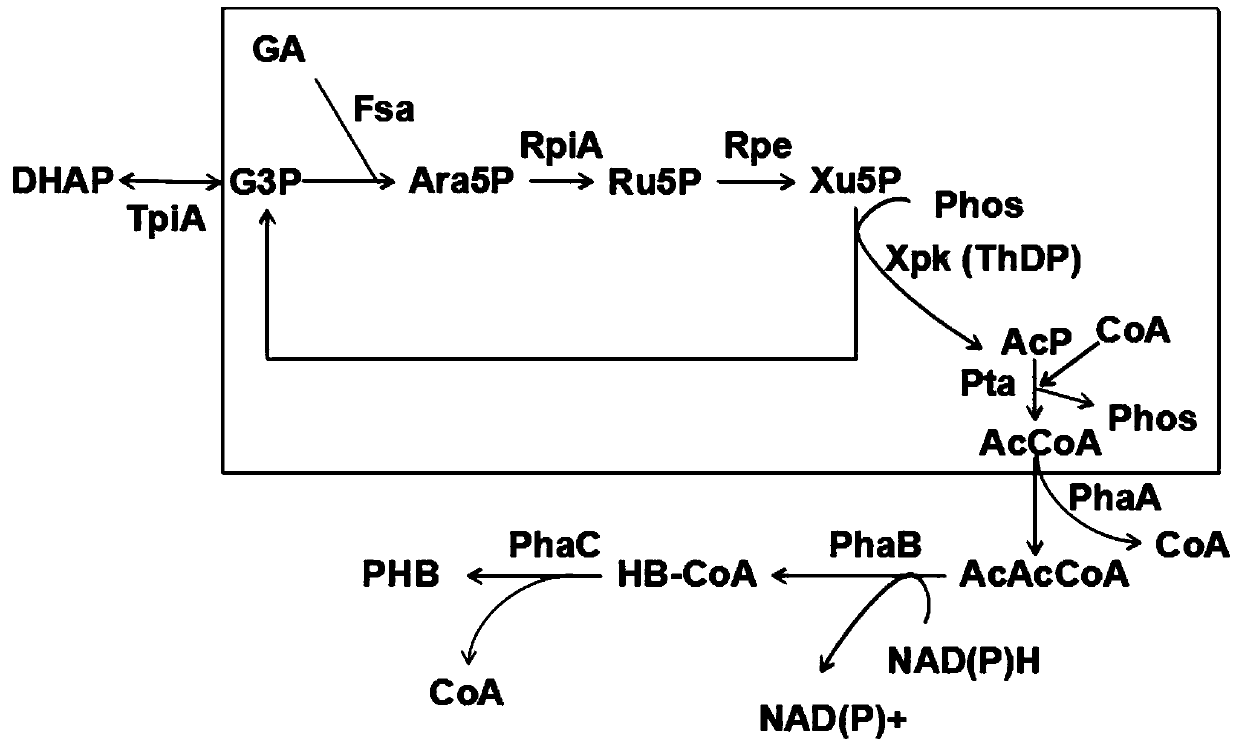
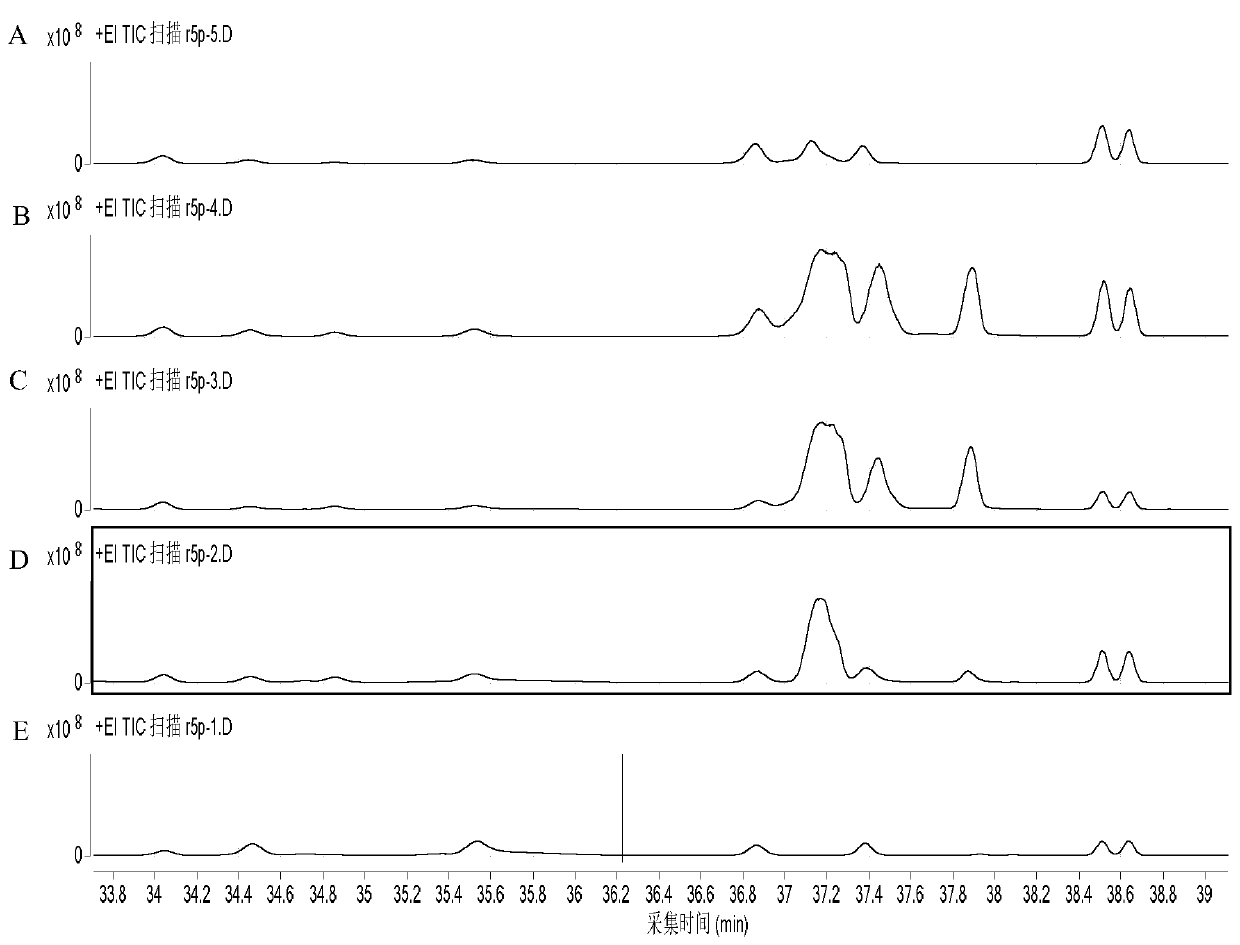
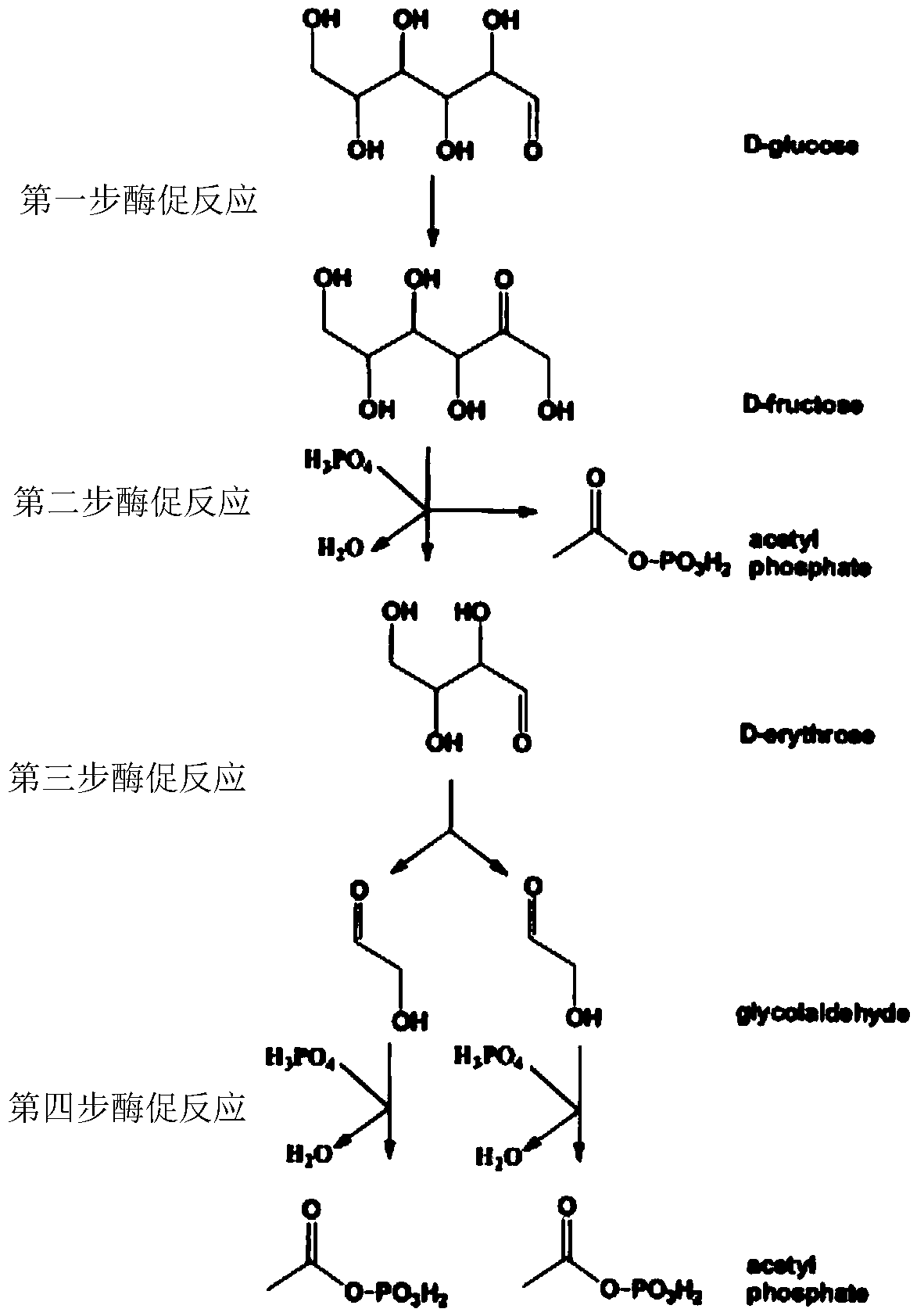
New way for synthesizing acetyl coenzyme A and derivative product thereof using glycolic aldehyde
ActiveCN106755172AHigh affinityIncrease enzyme activityFermentationPhosphoric acidBatch fermentation
The invention discloses a new way for synthesizing acetyl coenzyme A and a derivative product thereof using glycolic aldehyde. The method comprises reaction that glycolic aldehyde reacts with 3-glyceraldehyde phosphate under enzyme catalysis to generate 5-phosphoric acid arabinose, wherein the enzyme is selected from aldolase, transaldolase and isozyme thereof and mutate enzyme. The method is relatively high in catalytic rate; the theoretical yield of carbon of a reaction route is 100%; the carbon loss avoided; G3P, an enzyme and a coenzyme all can be recycled; the reaction efficiency is relatively high; and the cost is reduced. In addition, the coenzymes RpiA and Rpe from a pentose phosphate pathway are high in affinity with a substrate and high in catalytic activity. According to the method, more obvious advantages are developed in the production processes, of in vitro continuous polyenzyme catalysis, fed-batch fermentation and continuous fermentation, capable of controlling the substrate level.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
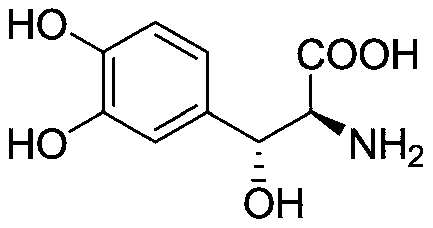
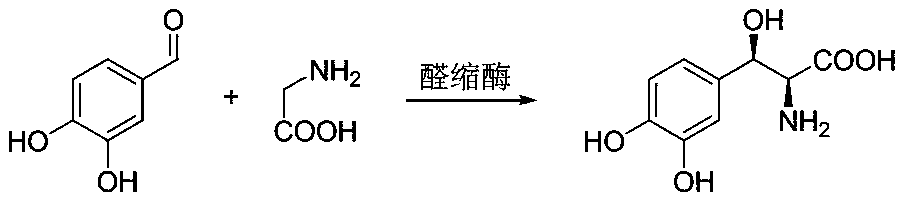
Method for preparing droxidopa
The invention discloses a method for preparing droxidopa. The method is characterized in that 3,3-dihydroxy benzaldehyde and L-threonine are used as raw materials to synthesize the droxidopa under theexistence of transaldolase.
Owner:湖南引航生物科技有限公司
Modified yeast consuming L-arabinose
The present invention relates to a method for producing a L-arabinose utilizing yeast strain for the production of ethanol, whereby a yeast strain is modified by introducing and expressing araA gene (L-arabinose isomerase), araB gene (L-ribulokinase D121-N) and araD gene (L-ribulose-5-P 4-epimerase) and carrying additional mutations in its genome or overexpressing a TALl (transaldolase) gene, enabling it to consume L-arabinose, to use it as the only carbon source, and to produce ethanol, as well as a method for producing ethanol using such a modified strain.
Owner:SCANDINAVIAN TECH GRP AB
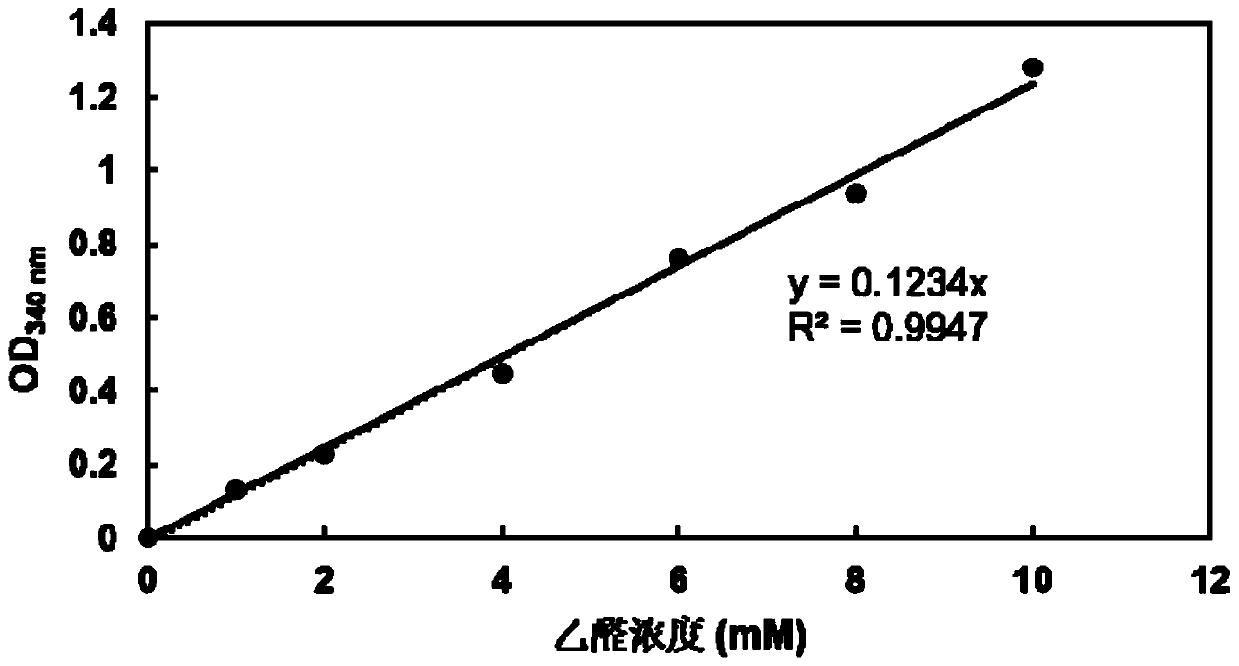
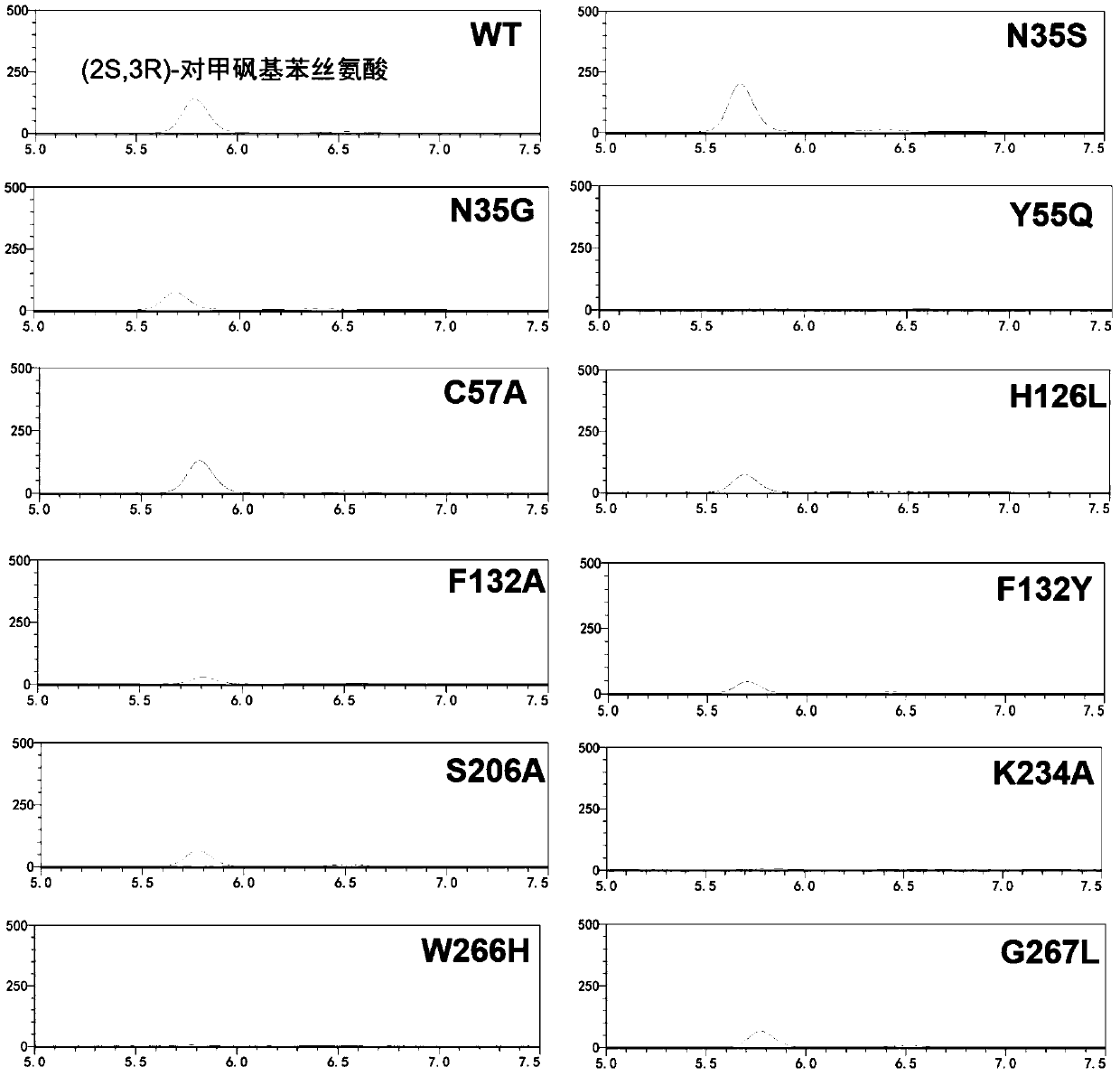
High-throughput rapid screening method for L-threonine transaldolase mutant
PendingCN110904188AUndisturbedQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEthanol dehydrogenaseCentrifugation
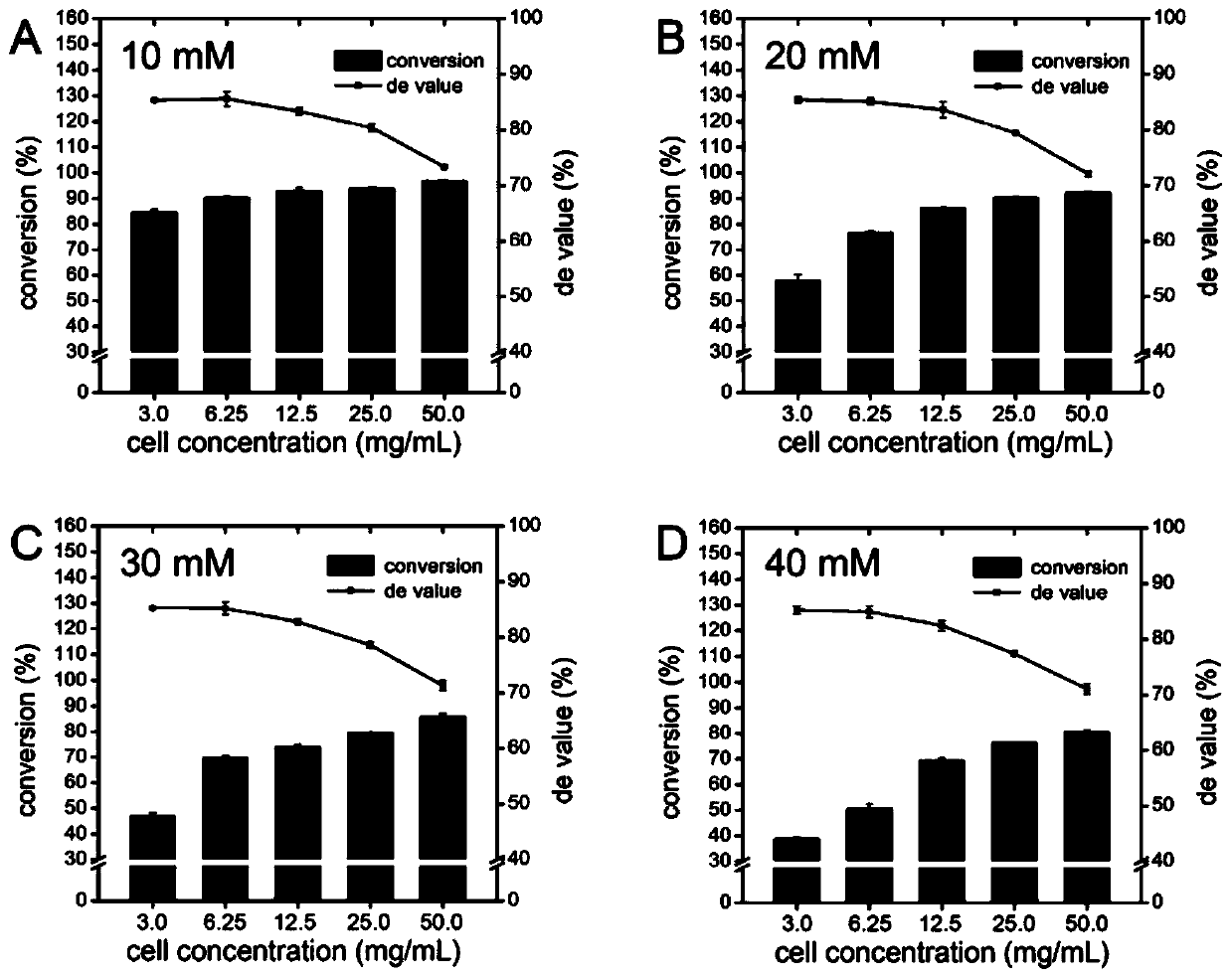
The invention discloses a high-throughput rapid screening method for L-threonine transaldolase mutant, and belongs to the fields of biochemistry and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, acetaldehyde and ethanol dehydrogenase reaction solutions are taken and then placed in a microplate reader to detect the change of OD340nm with time, and the average reaction rate VOD340nm of OD340nm decline is calculated. Taking acetaldehyde concentration as the independent variable x and VOD340nm as the dependent variable y, the regression equation y=ax and the acetaldehyde standard curve are obtained. After fully mixing and reaction of a transaldehyde reaction solution and an L-threonine transaldolase mutant whole cell reaction solution, the cell precipitate is removed by centrifugation, the supernatant and ethanol dehydrogenase reaction solution are taken and then placed into a microplate reader, the change of OD340nm with time is detected, and the average rate of OD340nm decline VOD340nmis calculated. The concentration of acetaldehyde in the reaction solution is calculated by VOD340nm, and the L-threonine transaldolase mutant is screened by the concentration of acetaldehyde. The method is not interfered by impurities in the reaction liquid, has high sensitivity and accuracy and good repeatability, is simple to operate, and is convenient for promotion and application.
Owner:福建昌生生物科技发展有限公司
High-temperature-resistant transaldolase and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to high-temperature-resistant transaldolase and a preparation method thereof in the technical field of biological genetic engineering. A nucleotide sequence of zymoprotein of the high-temperature-resistant transaldolase is shown in SEQ ID No.1. An amino acid sequence of the high-temperature-resistant transaldolase is shown in SEQ ID No.2. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: amplifying the transaldolase by taking a whole genome sequence of thermotoga maritima as a template according to forward and reverse primers to obtain a deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) fragment; carrying out double digestion by using NedI and SalI endonuclease after the fragment is recovered; connecting the fragment subjected to endonuclease digestion to an expression plasmid vector pET28a which is also subjected to endonuclease digestion by using endonuclease; transforming Escherichia coli E.coliDH5alpha; screening recombinant plasmids and transforming E.coliBL21; cultivating the transformed E.coliBL21 until the outer diameter (OD) is between 0.5 and 0.8; adding isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside and continuously cultivating to obtain thalli; then adding tri(hydroxymethyl) aminomethane hydrochloride (Tris-HCl) buffer solution and sufficiently and uniformly stirring; carrying out ultrasonication treatment; centrifuging disintegrated solution; and carrying out nickel column affinity chromatography on supernate containing a soluble transaldolase protein which contains induction expression to obtain the purified transaldolase protein.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for preparing chloramphenicol
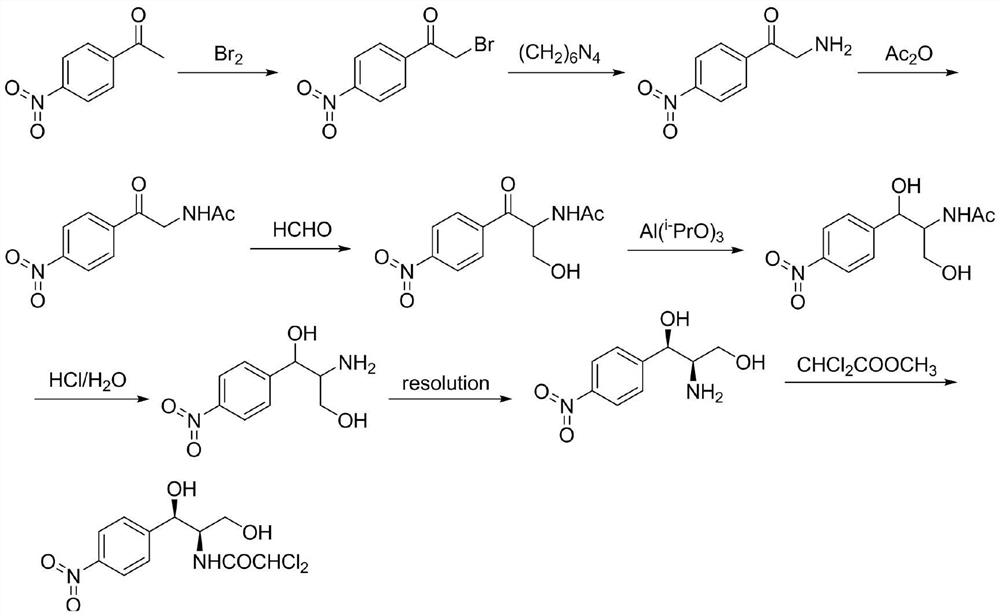
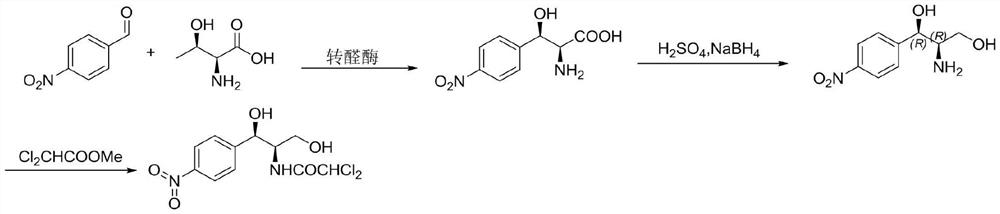
The invention provides a method for preparing chloramphenicol. (2S,3R)-p-nitrophenyl serine is prepared from p-nitrobenzaldehyde and L-threonine which are low in price and are easy to obtain under action of transaldolase, and a target product chloramphenicol is obtained through reduction and dichloroacetylation of the amino acid intermediate.
Owner:湖南引航生物科技有限公司
Bacterium capable of fermenting glucose, mannose and xylose simultaneously, and method for production of bioethanol using the bacterium
InactiveUS20100311140A1Strong glucose fermentation capacityStable mannose fermentation capacityBacteriaBiofuelsTransketolaseEscherichia coli
The object is to develop a bacterium capable of fermenting glucose, mannose and xylose simultaneously, which can ferment a saccharified solution of a cellulose-type or lignocellulose-type biomass resource to produce ethanol, and to construct an energy-saving high-efficiency bioethanol conversion process. Thus, disclosed is Zymomonas mobilis bacterium which is prepared by integrating a gene encoding a phosphomannose isomerase derived from Escharichia coli into a levansucrase gene located on the chromosome by the double cross-over by means of a homologous recombsination method, and then introducing recombinant DNA prepared by binding a DNA fragment containing genes encoding a xylose isomerase, a xylulokinase, a transaldolase and a transketolase, respectively, all derived from Escherichia coli to a vector. Also disclosed is a method for producing ethanol by continuously fermenting a saccharified solution of a cellulose-type biomass resource in a system on which the Zymomonas mobilis bacterium is immobilized.
Owner:TOTTORI UNIVERSITY
A method for preparing chiral (2s, 3r)-p-thymphenylphenylserine ethyl ester
ActiveCN109836362BEasy to operateMild conditionsOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationBenzaldehydeThreonine
The invention provides a method for preparing (2S, 3R)-p-methyl sulfone phenyl ethyl serinate from the cheap and easily available methylsulfonyl benzaldehyde and L-threonine under the action of transaldolase. The amino acid intermediate then undergoes ethyl esterification to obtain a target product (2S, 3R)-p-methyl sulfone phenyl ethyl serinate.
Owner:SUZHOU LEAD BIOTECH CO LTD
Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae and construction method for producing dammarenediol and protopanaxadiol using xylose
The invention discloses a recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and a construction method for producing dammarenediol and protopanaxadiol by using xylose. Through homologous recombination, the promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae xylulokinase gene XKS1 is replaced with a promoter Sub P FBA1 , and then introduce xylose reductase XYL1, xylitol dehydrogenase XYL2 expression cassettes, and then increase the activity of transketolase TKL1 and transaldolase TAL1 to obtain recombinant bacterium 1, and then introduce farnesyl diphosphate into recombinant bacterium 1 Farnesyltransferase gene ERG9, squalene monooxygenase gene ERG1 and dammarene diol synthase gene DS were obtained to obtain recombinant bacteria 2, and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-hydroxymethyl was introduced into recombinant bacteria 2 Glutaryl-CoA reductase gene NADH-HMGr, farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase ERG20, protopanaxadiol synthase-cytochrome P450 reductase fusion protein gene PPDS-ATR1 were obtained to obtain recombinant bacteria 3, the recombinant brewing wine of the present invention Yeast uses xylose to synthesize dammarenediol and protopanaxadiol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Immobilized modified threonine transaldolase and application thereof
The invention provides immobilized modified threonine transaldolase and application of the immobilized modified threonine transaldolase in catalytic synthesis of 3-phenyl-L-serine and derivatives thereof. Compared with a free enzyme, the immobilized enzyme has the advantages that the purity of the product is improved, and the use cost of the enzyme and the purification cost of subsequent reaction are reduced.
Owner:湖南引航生物科技有限公司
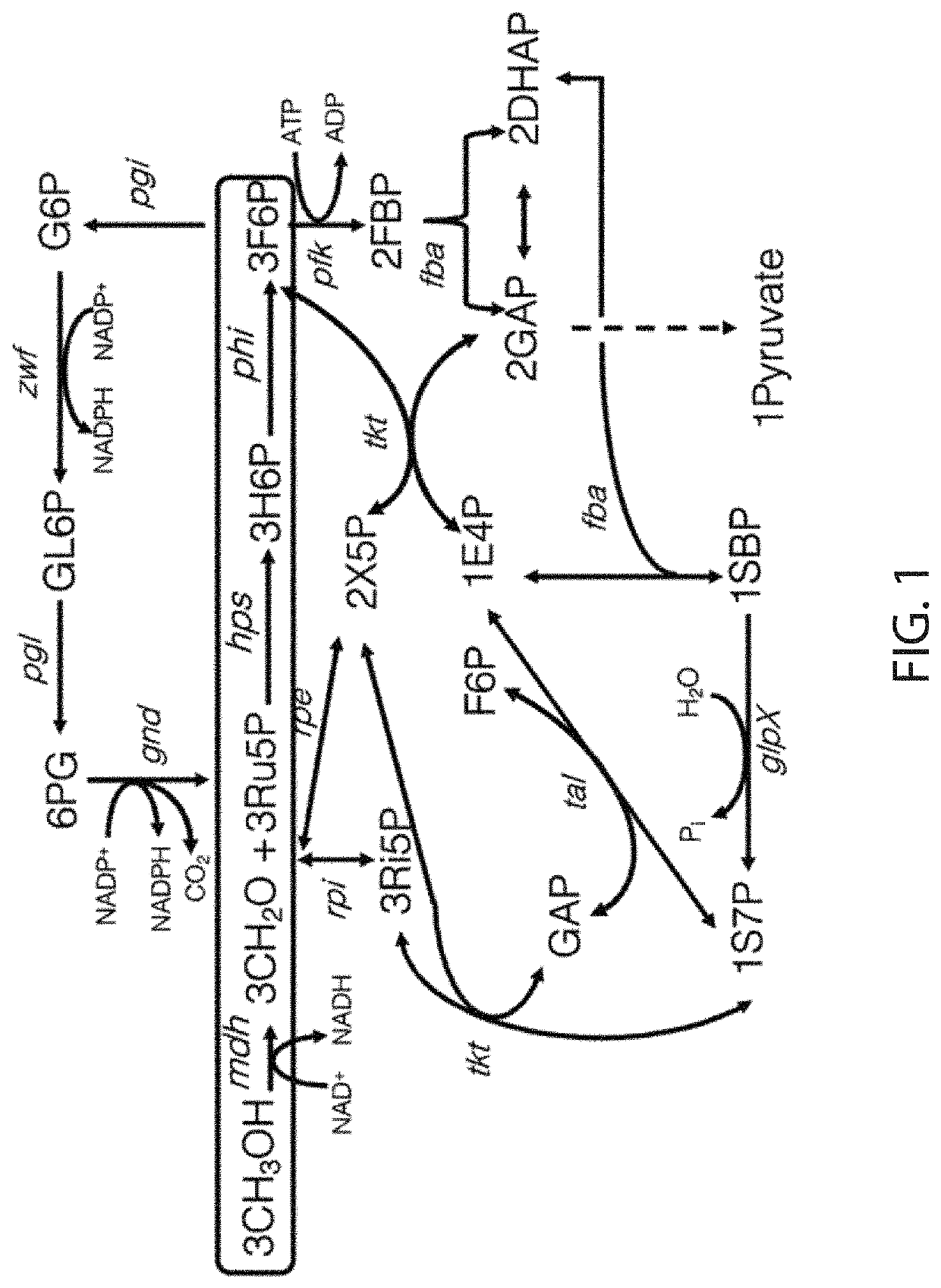
Methanol utilization
Described herein are enzymes, such as for example, methanol dehydrogenase (MDH), 3-hexulose-6-phosphate isomerase (PHI), 3-hexulose-6-phosphate synthase (HPS), ribose-5-phosphate isomerase (RPI), ribulose 5-phosphate 3-epimerase (RPE), transketolase (TKT), transaldolase (TAL) enzymes, phosphofructokinase (PFK), Sedoheptulose 1,7-Bisphosphatase (GLPX), fructose-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA), 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (GND), and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (ZWF); recombinant host cells expressing the enzymes; methods of producing methylotrophic cells; and methods of producing amino acids (e.g., lysine).
Owner:GINKGO BIOWORKS INC
A new pathway for the synthesis of acetyl-CoA and its derivatives from glycolaldehyde
Disclosed is a new approach for synthesizing an acetyl coenzyme A and a derivative product thereof (5-phosphoarabinose, acetyl phosphoric acid, acetyl phosphate, and an acetyl coenzyme A derivative compound) using glycolaldehyde. The approach comprises a reaction of glycolaldehyde and 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde under the catalysis of an enzyme to generate 5-phosphoarabinose, wherein the enzyme is selected from an aldolase, a transaldolase, an isoenzyme and a mutant enzyme thereof.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Modified threonine transaldolase and application thereof
The present invention relates to a modified L-threonine transaldolase (LTTA). In particular, the modified LTTAs of the present invention have improved activity of catalyzing the reaction of contacting benzaldehyde or a derivative thereof with L-threonine compared to its beginning. The invention also relates to polynucleotides encoding the modified LTTAs of the invention, vectors and host cells expressing the modified LTTAs of the invention, and methods of producing 3-phenyl-L-serine and derivatives thereof using the modified LTTAs and host cells of the invention.
Owner:SUZHOU LEAD BIOTECH CO LTD
Application of a l-threonine transaldolase in the synthesis of florfenicol chiral intermediates
ActiveCN110540977BIncrease added valueSave separation and purificationTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliBenzaldehyde
Owner:福建昌生生物科技发展有限公司
A kind of method for preparing drsidopa
Owner:湖南引航生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com