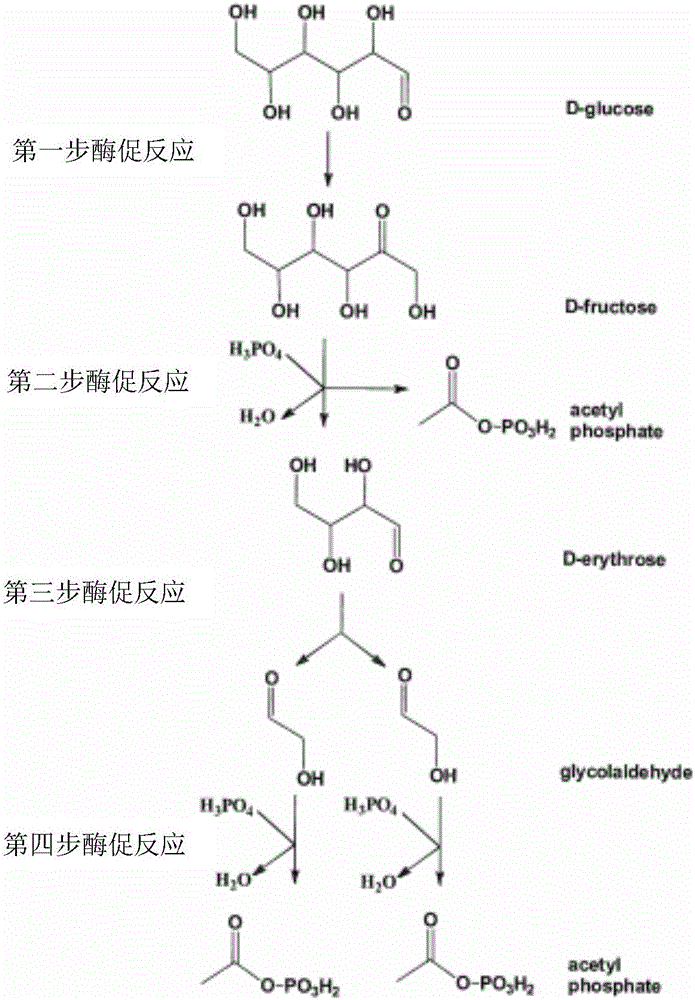
New way for synthesizing acetyl coenzyme A and derivative product thereof using glycolic aldehyde
An acetyl coenzyme and glycolaldehyde technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of low reaction rate, low efficiency, and difficulty in accumulating high concentrations of glycolaldehyde, and achieve high catalytic activity, high reaction efficiency, and good stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
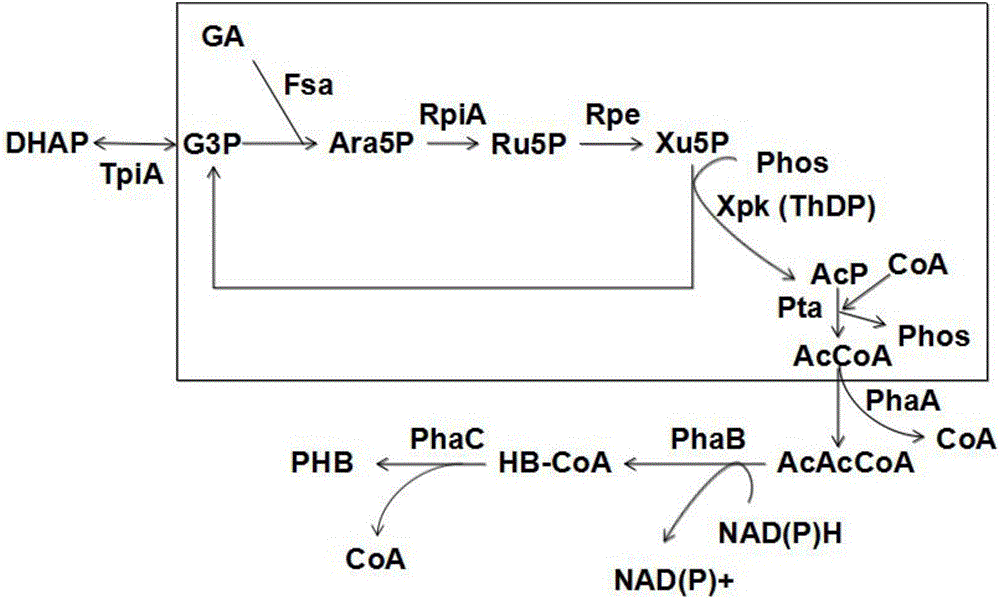
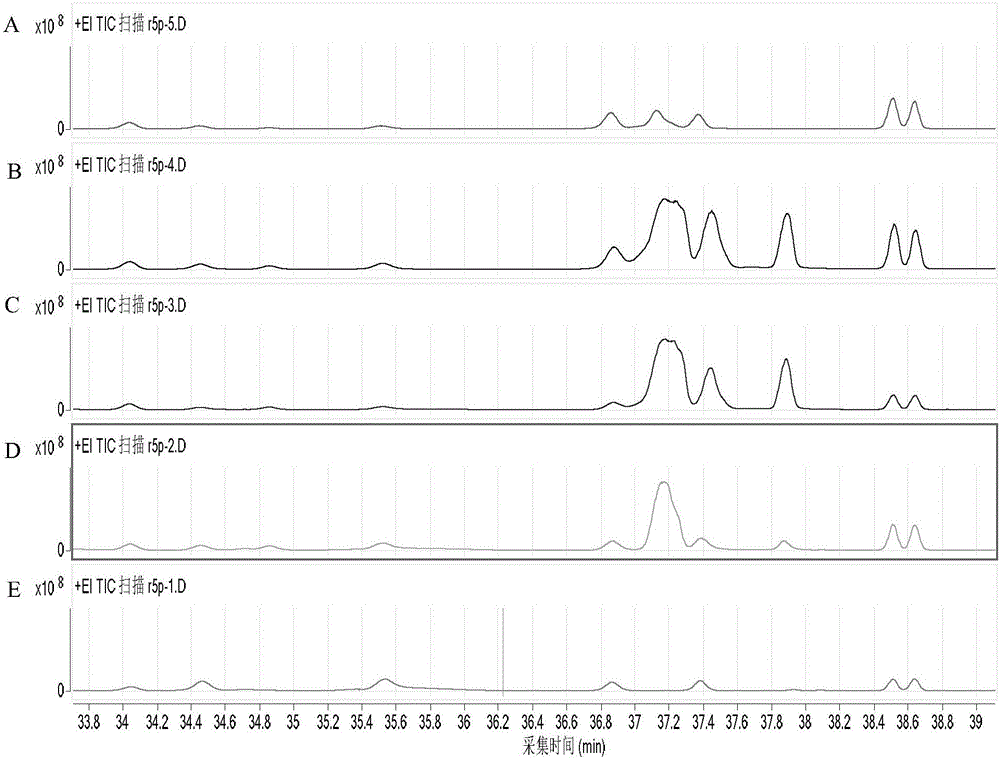
[0078] At an initial concentration of glycolaldehyde of 15 mM, the mutant enzyme Tal B of Transaldolase Tal B derived from Escherichia coli F178Y (On the basis of the original enzyme, the 178th amino acid residue is mutated from F to Y), add 5mM G3P, and carry out the preparation reaction of Ara5. After 1 hour of reaction, the reaction solution is lyophilized and derivatized, and quantitatively detected by GC-MS The obtained Ara5P content was 2.5mM, and the average synthesis rate of Ara5P was 52.1μmol(Ara5P) / min / mg(enzyme protein).
Embodiment 2
[0080] Glycolaldehyde at an initial concentration of 15mM, ThDP concentration was 1mM, PO 4 3+ The concentration was 2mM, and Fpk (EC 4.1.2.22) derived from Bifidobacterium adolescentis, aldolase (Fsa, EC 4.1.2.13) derived from Escherichia coli, 2mM G3P and trace amounts of Rpi A and Rpe were added to prepare AcP. After testing, the conversion rate of glycolaldehyde was 16.3 μmol (glycolaldehyde) / min / mg (enzyme protein).
[0081] The above data is the average rate of the reaction system for 3 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0083] Glycolaldehyde at an initial concentration of 15mM, ThDP concentration was 1mM, PO 4 3+ The concentration is 2mM, add the mutant enzyme Tal B of Xpk (EC 4.1.2.9) derived from Pseudomonas stutzeri A1501 and Transaldolase (Tal B, EC 2.2.1.2) derived from Escherichia coli F178Y , 2mM G3P and trace amounts of Rpi A and Rpe to prepare AcP. After testing, the conversion rate of glycolaldehyde was 19.7 μmol (glycol aldehyde) / min / mg (enzyme protein).
[0084] The above data is the average rate of the reaction system for 3 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com