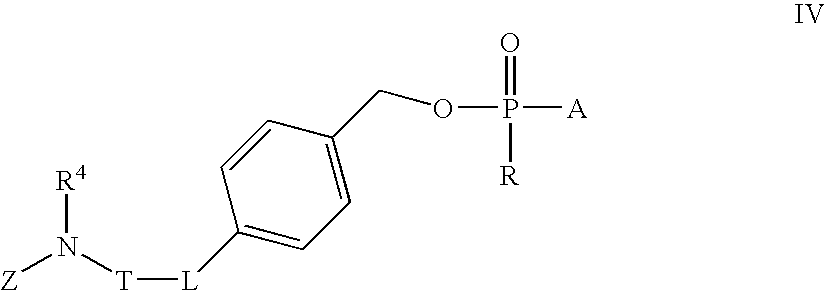
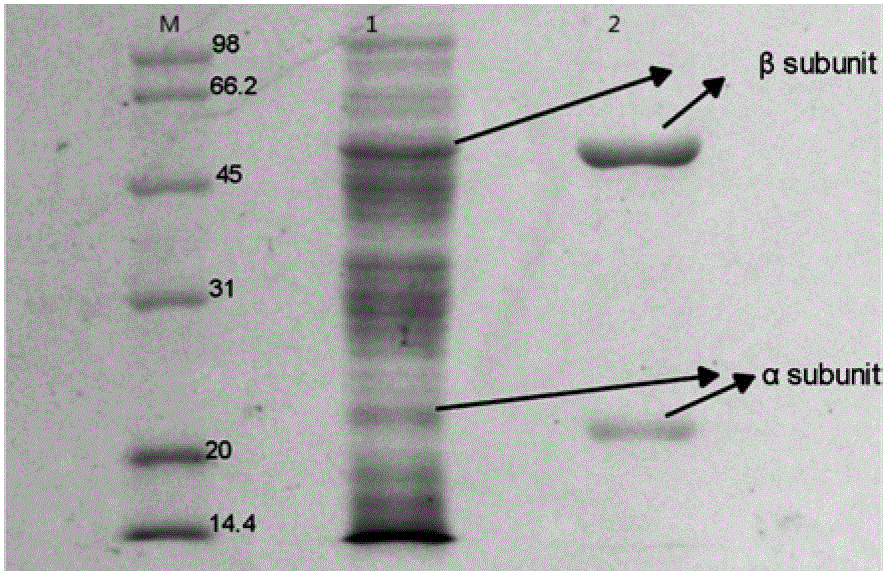
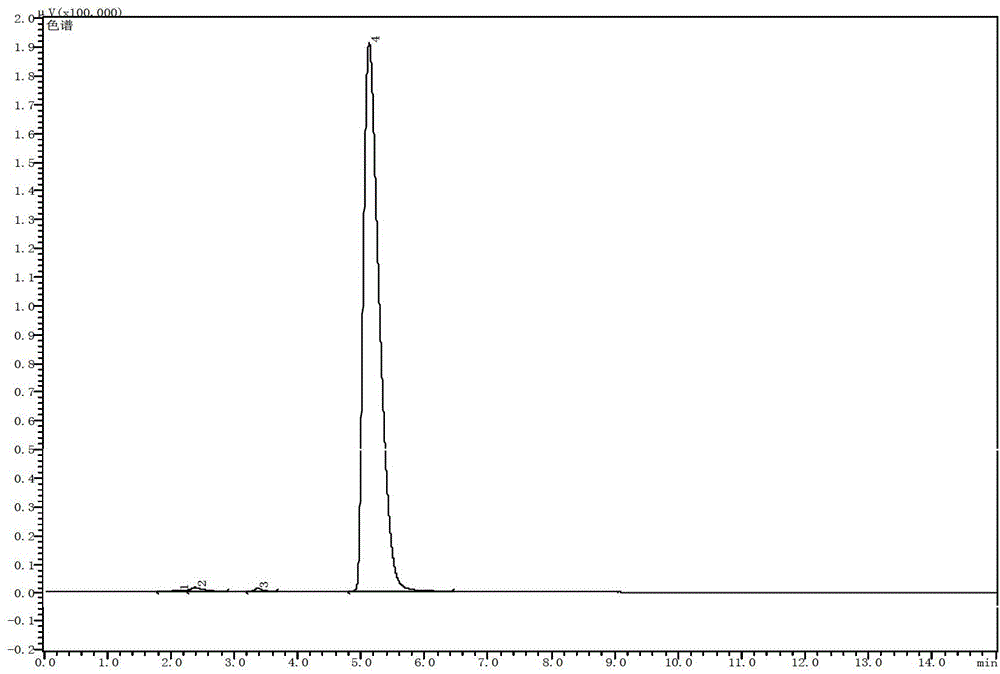
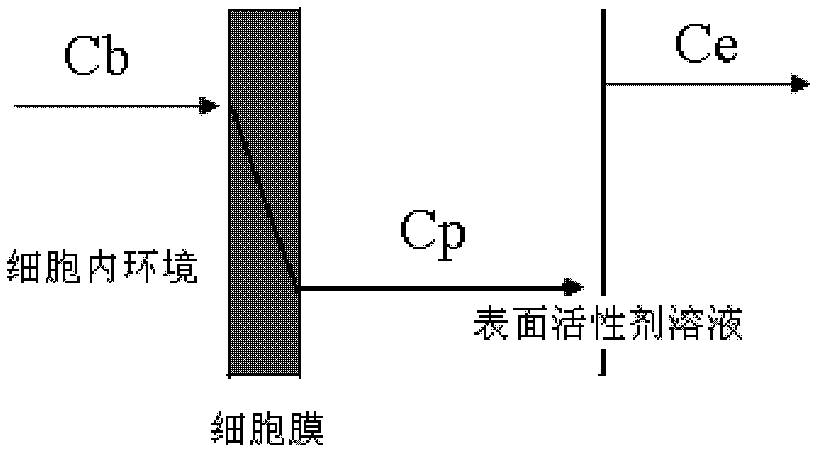
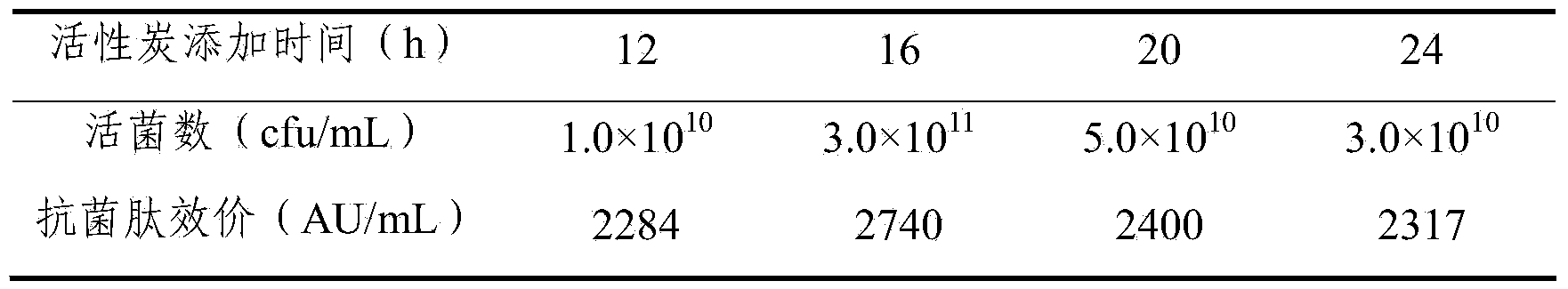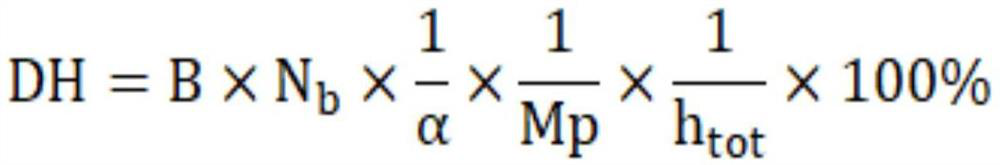Patents
Literature
122 results about "Product inhibition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Product inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the product of an enzyme reaction binds to the enzyme and inhibits its activity. This can be important in the regulation of metabolism as a form of negative feedback controlling metabolic pathways. Product inhibition is also an important topic in biotechnology, as overcoming this effect can increase the yield of a product, such as an antibiotic.
Biomass supercritical and subcritical combined continuous type pretreatment and hydrolysis equipment and method
InactiveCN101613377AAchieving processing powerAchieve hydrolysis conversionSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationFiberElectronic temperature
The invention relates to biomass supercritical and subcritical combined continuous type pretreatment and hydrolysis equipment and a method. The equipment comprises a water storage tank, a material storage tank with a stirring device, a preheating system, a supercritical reaction system, a primary cooling system, a subcritical reaction system, a final cooling system, a product collection system and an electronic temperature controlling system. The method comprises the following processing steps: water reaching preheat temperature and biomass material paste are rapidly mixed and then injected into the supercritical reaction system to be pretreated under supercritical condition; the reaction product is cooled through the primary cooling system and depressurized through a pressure reducing valve and then enters into the subcritical reaction system to be hydrolyzed sequentially, therefore fermentable sugars are continuously generated and collected. The invention utilizes the advantages of the supercritical method that the reaction is rapid, activator is not required and product inhibition does not exit, realizes that the continuous hydrolysis conversion of wood fiber biomass can generate fermentable sugars, is the foundation of subsequent resource recovery technologies, such as ethanol production by fermentation and the like, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for continuously producing biological butanol by fermentation, separation and coupling of static bed
InactiveCN101979615AReduce pollutionExtended operating timeMicroorganism based processesFermentationContinuous fermentationContinuous use
The invention discloses a method for continuously producing biological butanol by fermentation, separation and coupling of a static bed. The method comprises the following steps of: filling a modified immobilized medium into the static bed, and circularly connecting in series with a bioreactor; incubating a butanol producing strain into the bioreactor, culturing the butanol producing strain in a fermentation medium, circulating fermentation liquor between the static bed and the bioreactor, and gradually absorbing free thallus cells into the static bed; pumping the fermentation liquor into a pervaporation membrane module for separation when the concentration of the butanol in the bioreactor is between 3 and 7g / L, collecting penetrating fluid, and returning liquid intercepted by a membrane to the bioreactor for continuous use; meanwhile, adding the fermentation medium into the midstream of the bioreactor, and continuously fermenting to produce the butanol. The method obviously weakens the pollution of the pervaporation membrane existing in the process of in situ separation and coupling, prolongs the operation time and service life of the membrane, eliminates butanol product inhibition in a fermentation process, and realizes the high-efficient and continuous production of the biological butanol.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing glutathione based on enzymic method in vitro
The invention relates to a method for producing glutathione based on enzymic method in vitro. Through expression and catalysis of glutathione compound difunctional enzymes and polyphosphoric acid kinases, tetraphosphate and hexametaphosphate serve as phosphoric acid donors to regenerate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), and the glutathione is generated under the catalytic action of the glutathione compound difunctional enzymes by taking glutamic acid, glycine and cysteine as substrates. Compared with existing glutathione production methods, the method has the advantages that inhibition effect of the glutathione compound difunctional enzymes is low, and the content of the glutathione obtained from a reaction system is high; sodium and kali salt of phosphoric acid donors, such as the tetraphosphate and the hexametaphosphate, used in the reaction process is low in cost and easy to get; the phosphoric acid donors serve as substrates of the polyphosphoric acid to generate the ATP, and accordingly, production cost is reduced greatly; the amino acid ratio of Gly:Gys:Gly is lowered to 2:1:2, the content of amino acid in the system is low, and later product separation is facilitated.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Biological sterol transforming process with cyclodextrin and its application
InactiveCN101020919AImprove solubilityPromote biotransformationMicroorganism based processesFermentationSolubilityMicroorganism
The present invention belongs to the field of biological sterol transforming technology, and is especially biological sterol transforming process with cyclodextrin and its derivative and its preparation. In a transforming system, cyclodextrin or its derivative in certain amount is added, or substrate and cyclodextrin or its derivative in certain ratio are made to form inclusion compound, so as to facilitate transformation. The process of the present invention is especially suitable for microbial transformation of hydrophobic compound, and can raise the solubility of reaction substrate in water solution, raise the substrate utilizing rate and reaction rate, release substrate and product inhibition and raise product converting rate. When the substrate concentration is 3-20g / L, the present invention has conversion period shorted to 3-4 days, conversion rate of 50-95 % and high industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Universal linker compositions for the release or transfer of chemical agents from a polynucleotide
InactiveUS20060199192A1Simple and inexpensive to prepareMonoazo dyesNanotechLeaving groupReaction rate
A universal linker structure is provided, in which a functional group and activating leaving group are placed on a tether, allowing the placement of an electrophile at the end of any nucleic acid sequence. The electrophile on the tether can react with a second nucleic acid carrying a nucleophile when the two nucleic acids are hybridized near one another, resulting in release of the leaving group, and creation of a functional change. The linker can be designed to destabilize the ligation product without slowing the rate of reaction. This lowers product inhibition, and the target DNA or RNA can become a catalyst for isothermally generating multiple signals for detection. This enhanced signal is demonstrated in solution experiments and in solid supported assays. The universal linkers of the present invention are simple and inexpensive to prepare, and can be appended to any polynucleotide in automated steps on a standard DNA synthesizer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for producing butanol
InactiveCN101418320AImprove in situ separation efficiencyRaise the ratioMicroorganism based processesFermentationAlcoholUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a method for producing butyl alcohol. The method comprises the step of obtaining the butyl alcohol by utilizing butyl alcohol producing strain fermented on a fermentation medium, wherein in the method, a step of extracting the butyl alcohol from the fermentation product is also included. In the method, by liquid-liquid extraction and gas stripping, the butyl alcohol and the like is separated from the fermentation product in time, thereby lowering the inhibition action of the fermentation product on the fermentation reaction, on the basis of not adding equipment, the method improves in situ separation efficiency of the butyl alcohol, lowers the product inhibition of the butyl alcohol and improves the fermentation efficiency. Therefore, the method solves the problems of product inhibition, lower production strength and production efficiency of the butyl alcohol and higher recovery cost presently existing in the acetone butylalcohol fermentation, and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Natural product inhibitors of 3dg
InactiveUS20130266638A1Prevent skinAvoid conversionBiocideCosmetic preparationsDiseaseNatural product
Compositions are disclosed which have as a component thereof an inhibitor of the enzymatic production of 3-deoxyglucosone (3DG) from fructoselysine and / or an inactivator of 3DG, and which are useful for the treatment or prophylaxis of a condition or disease state that is alleviated by inhibiting such 3DG production. Methods of using such compositions, e.g., for improving the appearance, texture and / or elasticity of aging skin, are also disclosed.
Owner:TOBIA ANNETTE +3
Trichoderma viride W2 capable of producing thermophilic ethanol-resistant beta-glucosidase and application thereof
InactiveCN102080050AImprove toleranceFeedback inhibition is evidentFungiMicroorganism based processesReaction temperatureCellobiose
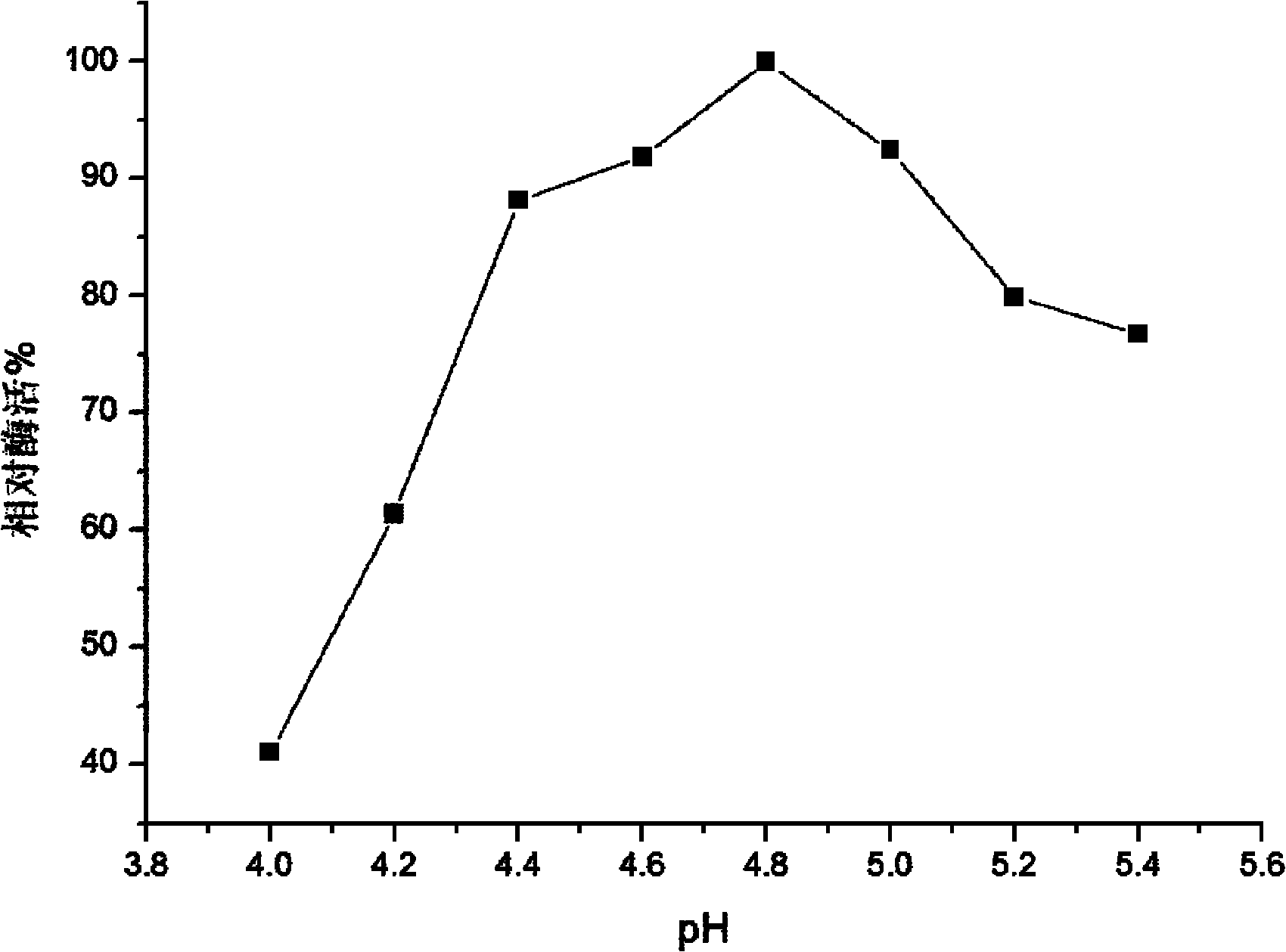
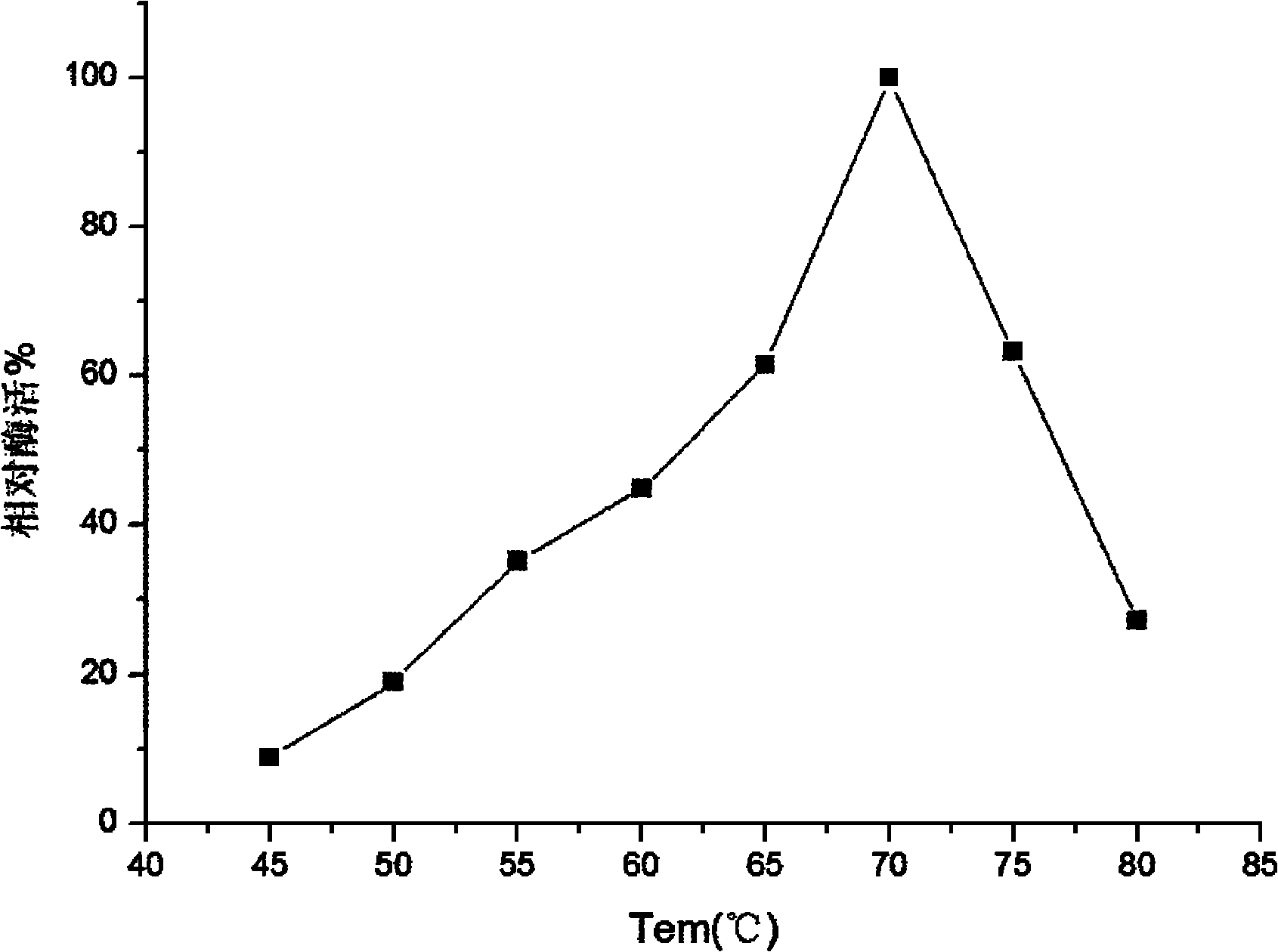
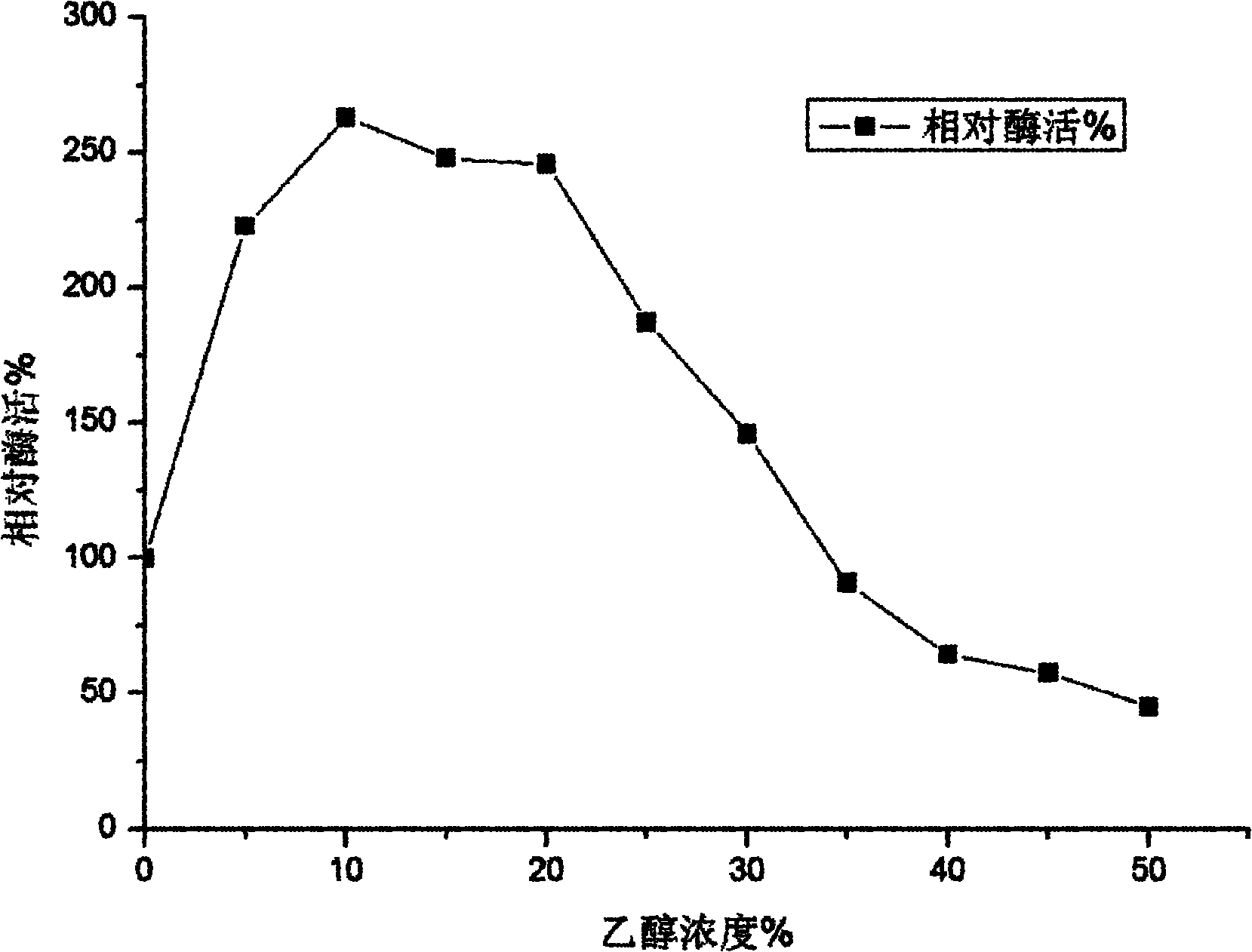
The invention discloses a trichoderma viride W2 capable of producing a thermophilic ethanol-resistant beta-glucosidase and an application thereof. The trichoderma viride W2 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on August 23, 2010, and the preservation number of the trichoderma viride W2 is CGMCC No.4098. The trichoderma viride W2 can produce a new beta-glucosidase, the enzymatic activity of the new beta-glucosidase reaches 346.7U / mL, the optimal reaction pH value is 4.8, the optimal reaction temperature is 70 DEG C, and the new beta-glucosidase is suitable for pyrohydrolysis and has an obvious glucose feedback inhibition effect. The ethanol the concentration of which is 10% has a maximal effect on promoting the enzymatic activity and improves the enzymatic activity of the beta-glucosidase by 1.6 times, and the resistant ability of the ethanol reaches 30%, so that the cellobiose inhibition can be effectively eliminated, the yield of the ethanol is improved by nearly 3 times, and the terminal product inhibition is effectively eliminated. Thus, the beta-glucosidase can be used for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of lignocellulose raw materials, has a rare promoting effect in China, effectively increases the yield of the cellulosic ethanol, lowers the production cost, and accelerates the industrialized progress of the cellulosic ethanol.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant escherichia coli for preparing (S)-4-chlorine-3-hydroxyl ethyl butyrate by adopting asymmetric transformation and application of recombinant escherichia coli
InactiveCN104651292AImprove conversion rateHigh optical purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHydroxybutyric acid
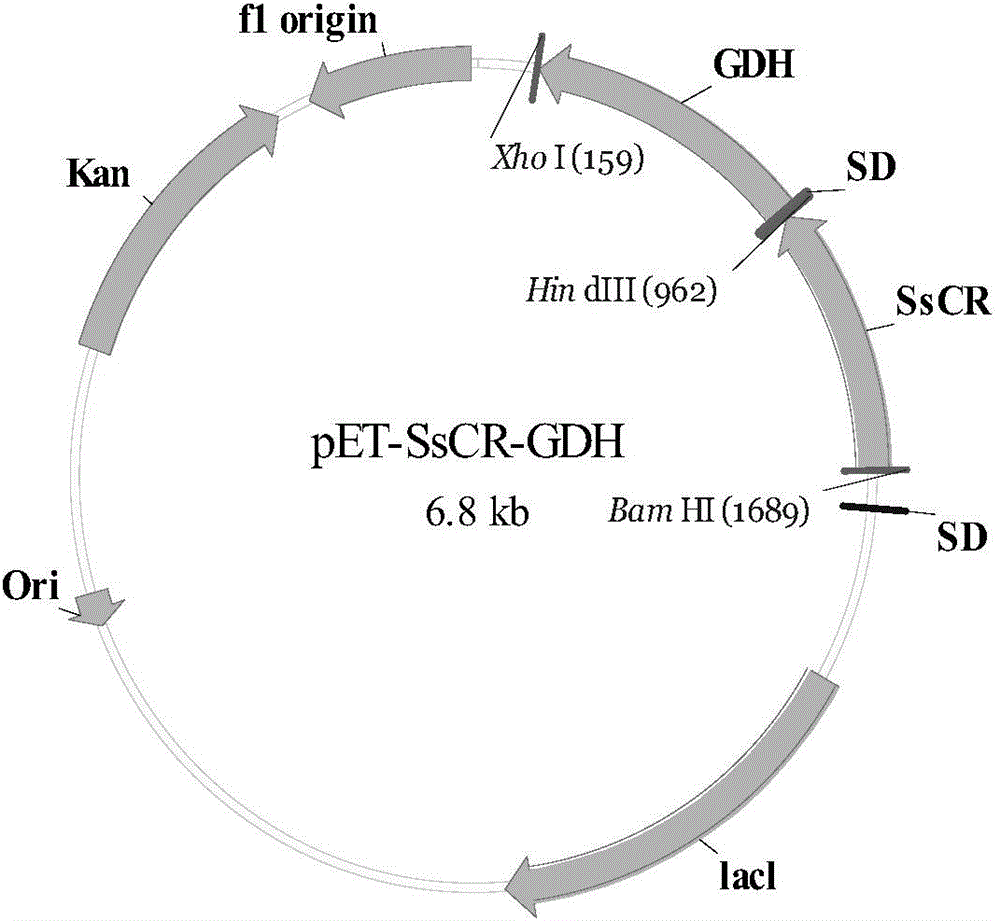
The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli for preparing (S)-4-chlorine-3-hydroxyl ethyl butyrate by adopting asymmetric transformation and an application of the recombinant escherichia coli. The recombinant escherichia coli simultaneously comprises a carbonyl reductase gene and a glucose dehydrogenase gene; the sequences of the carbonyl reductase gene and the glucose dehydrogenase gene are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.3. The recombinant escherichia coli provided by the invention can be applied to high-activity and high-selectivity catalysis of COBE to generate (S)-CHBE; the enzyme activity can be up to 33.1U / mg, and reaches the highest level reported in the literature; substrate and product inhibition are removed in situ by virtue of macroreticular resin, so that the accumulation of the final product (S)-CHBE can reach 3,000mM; the transformation rate of the final substrate can be up to 100%; the optical purity e.e% of the product cam reach 99.4%; and compared with the prior art, the optical purity is significantly improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing antimicrobial peptide through fermentation of brevibacillus laterosporu
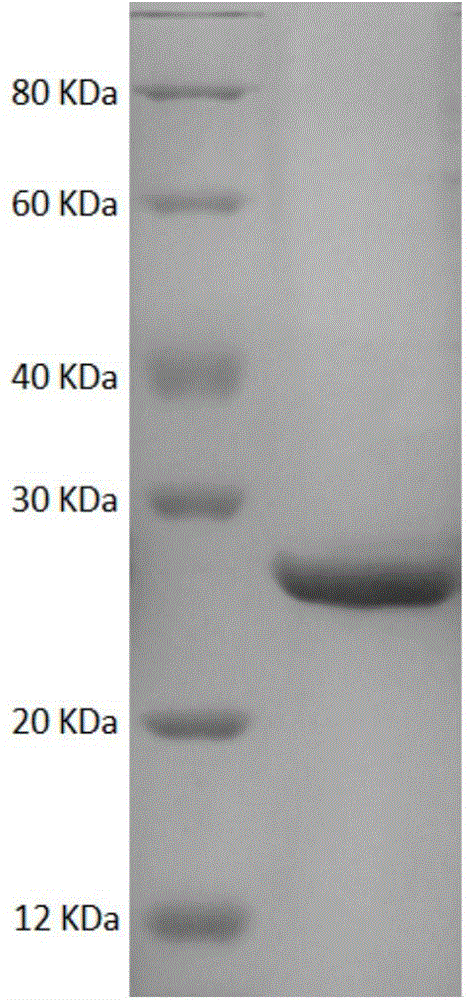
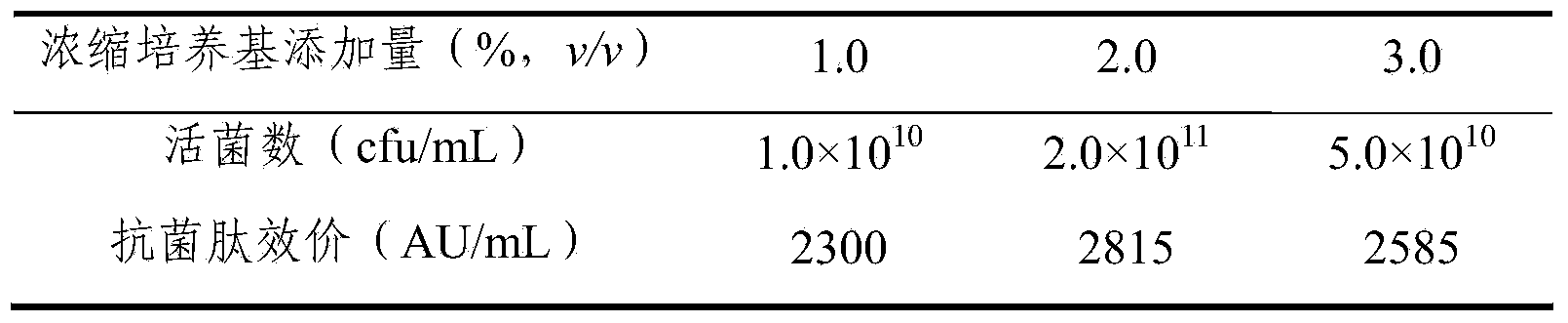
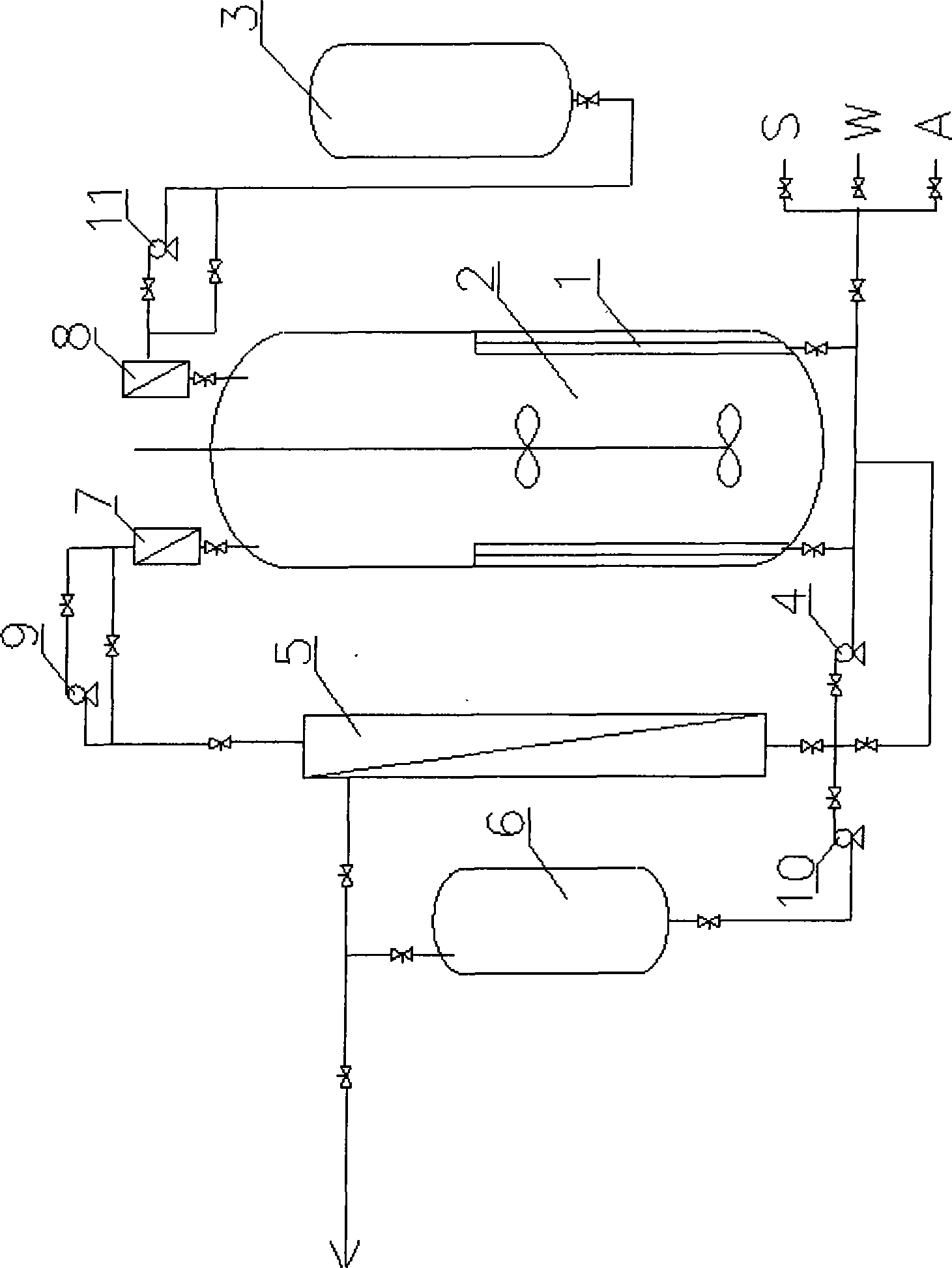
ActiveCN104004803AImprove securityRealize multiple reuseMicroorganism based processesFermentationActivated carbonDesorption
The invention provides a method for producing antimicrobial peptide through fermentation of brevibacillus laterosporu. In fermentation of the brevibacillus laterosporu, when the yield of the antimicrobial peptide is no longer increased, active carbon is directly added into the fermentation liquor; as the active carbon adsorbs the fermentation product, the inhibiting effect of the product is relieved, and the density of the thallus and the yield of the antimicrobial peptide are greatly improved. According to the method, the active carbon is taken as an adsorption stripping coupling agent, has low cost, is environmentally friendly, and can be directly added in the fermentation process without being activated in advance; the antimicrobial peptide can be adsorbed without regulating the pH value of the fermentation liquor; and the method is simple and easy to promote, and the active carbon can be regenerated through desorption after fermentation, thus being recycled repeatedly, and lowering the production cost.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
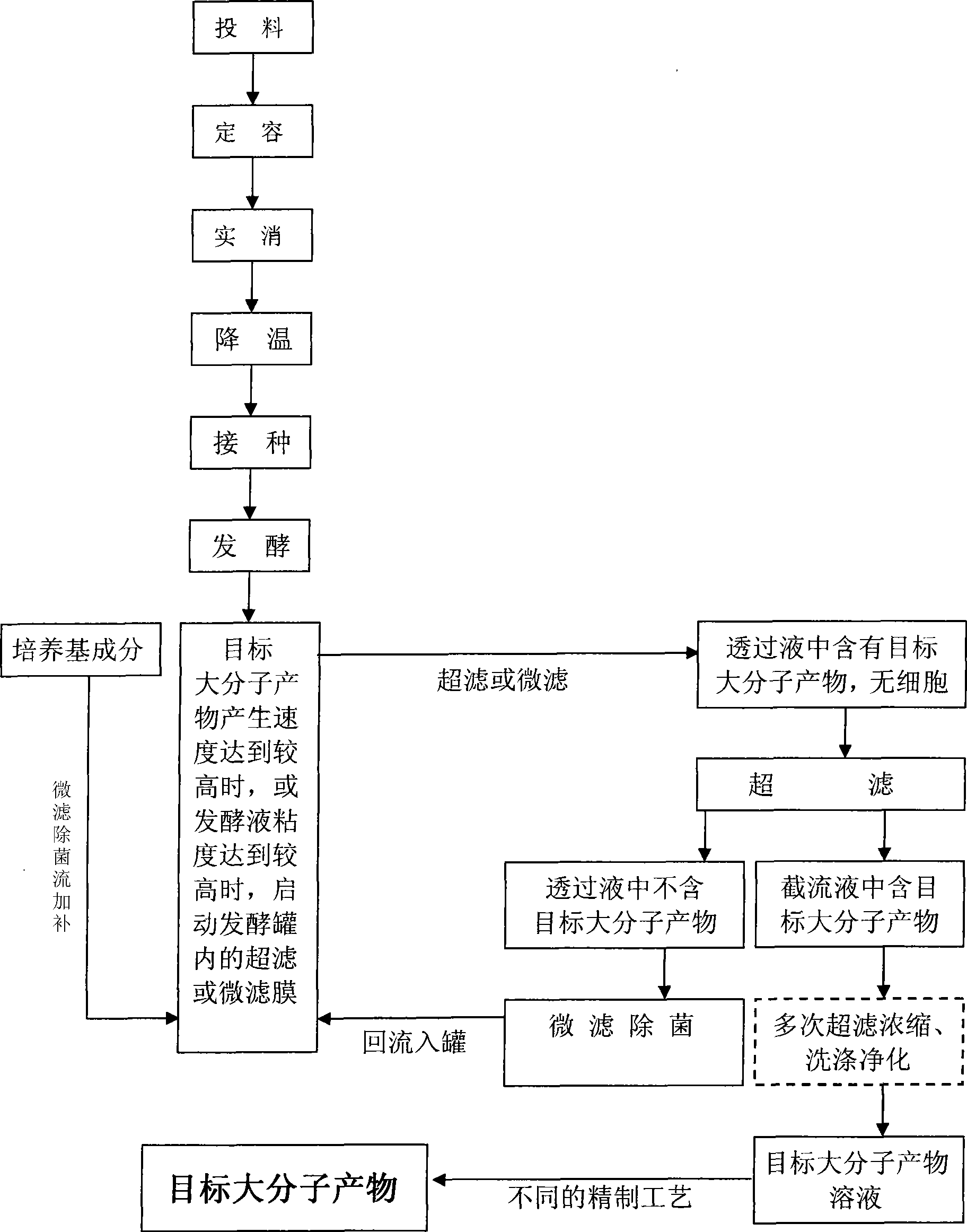
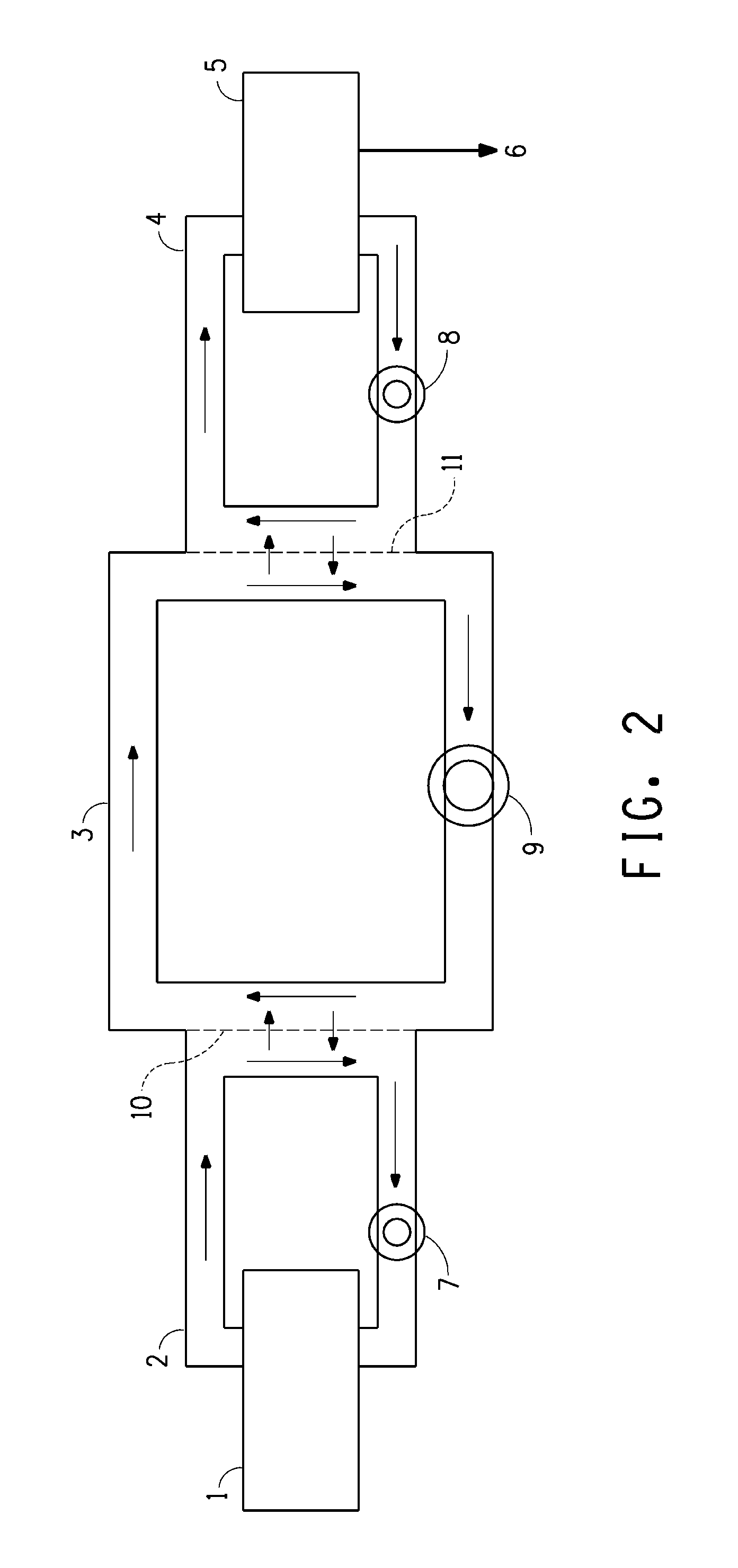
Method and device for continuous fermentation and separation coupling of biomacromolecule product
InactiveCN101503707AGuaranteed permeabilityReduce viscosityApparatus sterilizationFermentationBiological macromoleculePollution
The invention discloses a method and a device for the continuous fermentation and separate coupling of biomacromolecule products. By utilizing membrane in a fermentor and a membrane separation device outside the fermentor, while target biomacromolecules are fermented and produced, target products are continuously separated out from the fermentor through a membrane system so as to remove the product inhibition of fermentation and reduce the viscosity of fermentation broth. Continuous or semi-continuous fermentation and separate coupling are realized through one set or a plurality of sets of fed-batch devices so as to improve equipment utilization rate and raw-material conversion rate, reduce production cost and raise the continuous and automation level of a process. As fermentation and product extraction are hermetically carried out in a container and a pipeline, external pollution and interference are reduced. In addition, for certain extrazellular synthetic biomacromolecules, due to the separation control of the membrane on molecular weight, the molecular weight of macromolecules can be simultaneously controlled during fermentation so as to obtain products uniform in molecular weight.
Owner:姜泓芳
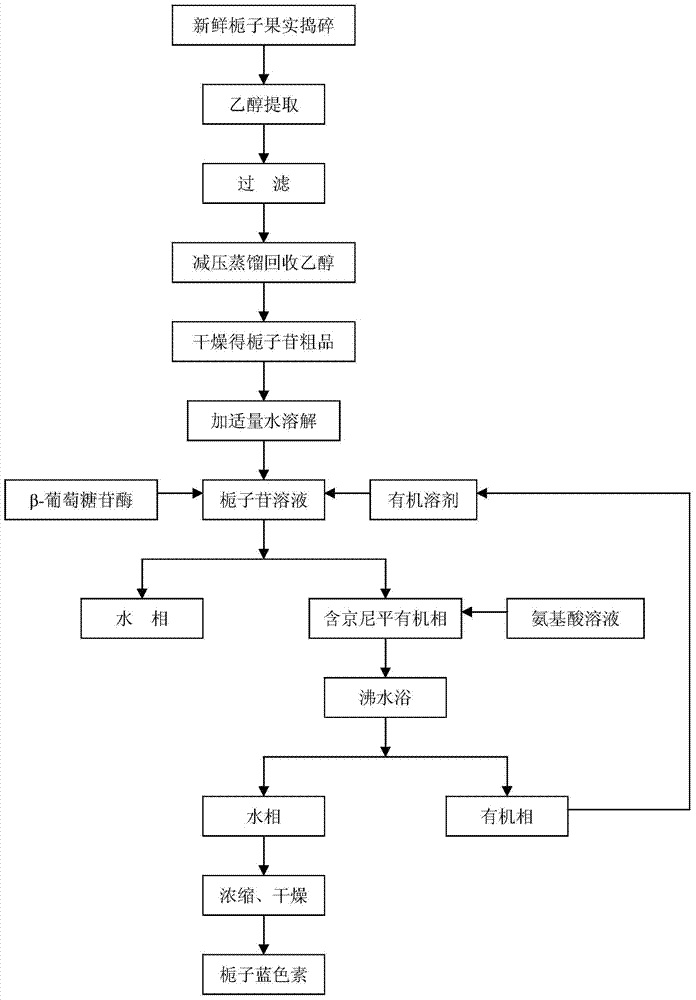
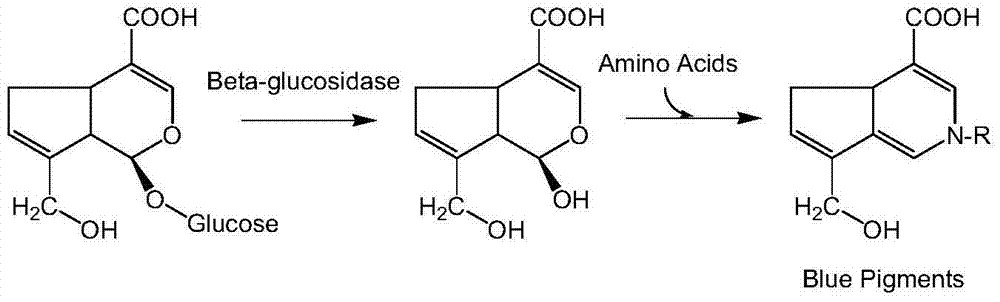
Method for preparing gardenia blue by utilizing phase-transfer catalysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing gardenia blue by utilizing phase-transfer catalysis. The method comprises the following steps: peeling off gardenia jasminoides fruits, crushing into fruit powder, adding ethanol water for supersonic extraction, filtering, performing vacuum concentration on the filtrate, recycling ethanol, drying the solid obtained through concentration, and dissolving the solid into water so as to obtain a crude geniposide product solution; mixing the crude geniposide product solution with beta-glucosidase to be used as a water phase, performing catalytic hydrolysis reaction under the condition of oscillation or stirring so as to obtain an intermediate product genipin by using an organic solvent as an organic phase; adding a solution of hydrophilic amino acid into the organic phase, subsequently reacting under the condition of oscillation or stirring so as to prepare the gardenia blue; concentrating and drying the water phase in vacuum so as to obtain gardenia blue powder. According to the method, a reaction-extraction technique is utilized, product inhibition and side product degradation reaction when the genipin is prepared by using an ordinary method are effectively prevented, and the conversion rate of geniposide is high, and meanwhile high-purity gardenia blue can be obtained through reverse extraction by using an amino acid solution, and an organic solvent can be recycled.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
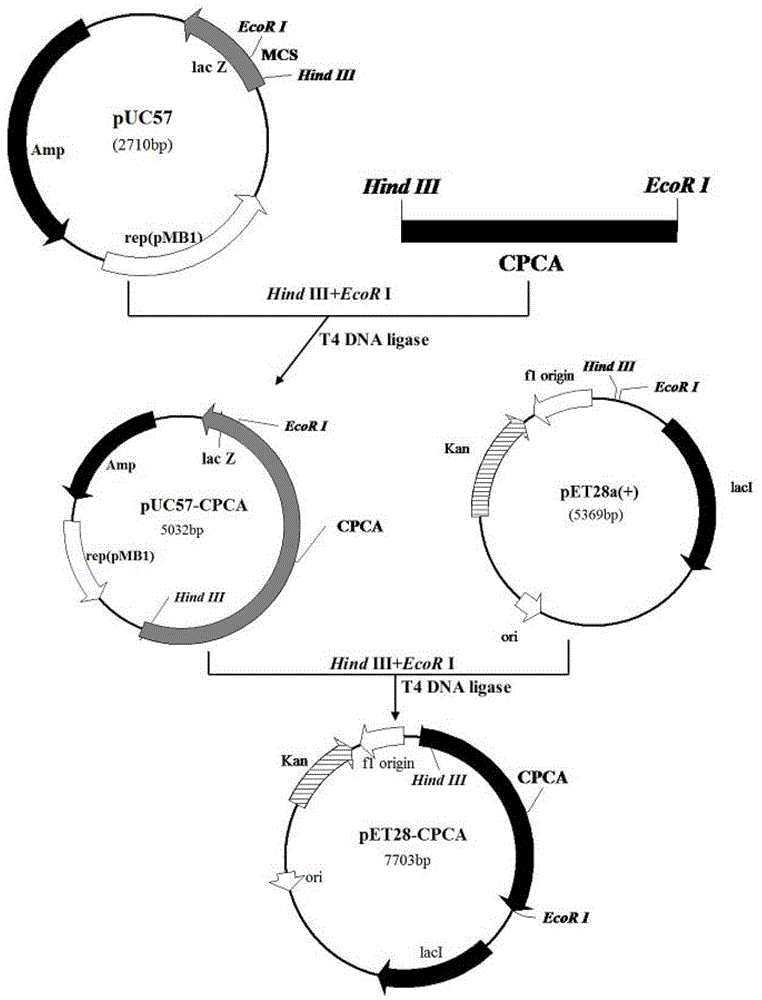
Mutant cephalosporin C acylase, method for preparing same and method for converting 7-aminocephalosporin acid (ACA)
ActiveCN102978192AImprove stabilitySmall steric hindranceHydrolasesFermentationAmino acid substitutionMutant
The invention provides a mutant cephalosporin C acylase. One or a plurality of amino acid locus replacement is carried out on an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table to obtain a mutant amino acid sequence; and one or more of 288-locus valine, 296-locus histidine and 417-locus histidine is or are adopted as amino acid locus(es). The technical problems that the mutant cephalosporin C acylase of the prior art has small catalytic activity, seriously influenced enzymatic activity by the outside and product inhibition are solved.
Owner:HUNAN FLAG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Microbial zymogene prepn and feed and alcohol producing process with zymogene prepn
The present invention has the technology scheme of adopting microbial zymogene preparation containing neurospora and saccharomycete. The fermentation process with the microbial zymogene preparation of the present invention to produce feed or alcohol is to add the microbial zymogene preparation components simultaneously or gradually and to process the obtained material for producing feed or alcohol. The present invention has the beneficial effect that the coupled and synergistic fermentation with the microbial zymogene preparation can eliminate the feedback suppression and saccharide or ethanol product suppression in the fermentation, raise the protein content, soften material, generate spirit fragrance, improve the taste of feed and raise production efficiency and product quality.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for perstraction of fermented microbial intracellular product with non-ionic surfactant
ActiveCN102443605AChange in permeabilityDisinhibitionMicroorganism based processesEnzymesMicrobial enzymesSecondary metabolite
The invention discloses a method for perstraction of a fermented microbial intracellular product with a non-ionic surfactant. Specifically, during fermentation of a microbial intracellular product, a non-ionic surfactant micellar solution formed by addition of the non-ionic surfactant concentration or a cloud point system formed thereby is adopted as a microbial fermentation medium, by which the intracellular product can be penetrated to an extracellular environment so as to improve the product level of microbial fermentation. Simultaneously, perstraction and fermentation of the microbial intracellular product can be realized. The method of the invention is especially suitable for the fermentation process of an intracellular product, such as production of intracellular microbial enzymes, production of intracellular organic small molecule substances as well as production of intracellular oil compounds, etc. The method provided in the invention effectively eliminates intracellular product inhibition, enhances the concentration of a microbial fermentation product, and adjusts the composition of a microbial fermentation secondary metabolite, thus improving the volume yield of microbial fermentation as well as the efficiency of intracellular product fermentation, product release and other processes.
Owner:JECHO BIOPHARM CO LTD
Biological transformation method by utilizing hydrophobic compound of cyclodextrin
InactiveCN101168765AImprove conversion rateIncrease the rate of conversion reactionsMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismReaction rate
The invention discloses a bioconversion method by using cyclodextrin and the hydrophobic compound of the derivative thereof, belongs to the bioconversion technical field, in particular relates to the bioconversion method by using the cyclodextrin and the hydrophobic compound of the derivative thereof, and provides the bioconversion method by using the cyclodextrin and the hydrophobic compound of the derivative thereof. The method of the invention is particularly suitable for the microbial conversion of hydrophobic compounds, can effectively improve the dissolubility of reaction substrate in aqueous solution, improve the utilization rate and the reaction rate of the substrate, release the inhibition of the substrate and the product to a certain extent, and improve the conversion rate of the product. The invention adopts a conversion system including the cyclodextrin, the special structure of the cyclodextrin ensures the cyclodextrin to have a certain solubilizing power, and strengthens the bioavailability of the substrate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Compositions and methods for enhancing amino acid levels in plants
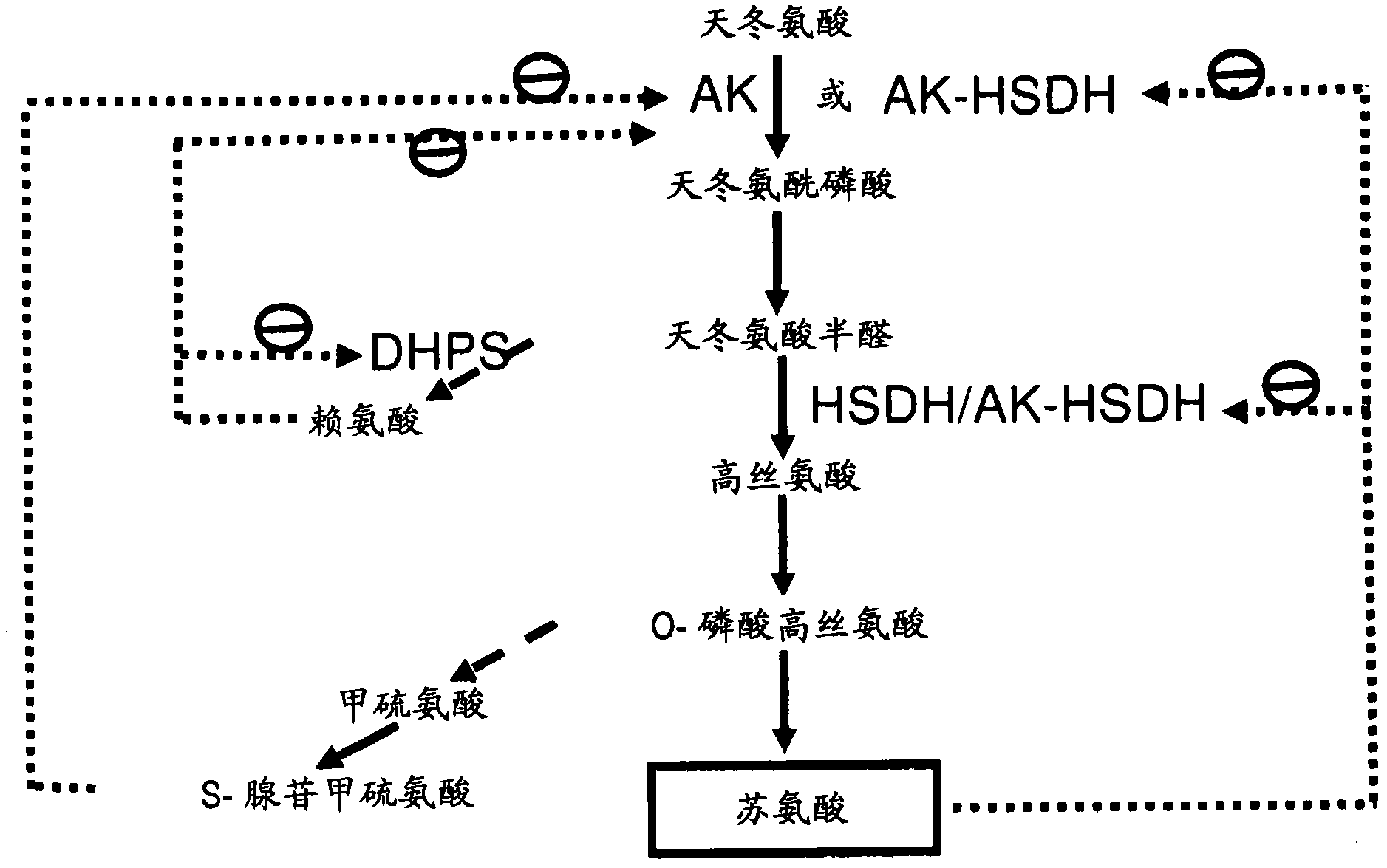
Threonine is an essential amino acid for humans and in the animal feed industry where its levels in feed rations can significantly impact the cost of production of important meat sources, such as swine and poultry. Threonine as well as essential amino acids lysine and methionine are all synthesized via the aspartate family pathway. Aspartate kinase (AK) is the first enzyme in the pathway, and catalyzes the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of aspartate to form ss-aspartyl phosphate. AK constitutes the main regulatory step controlling the metabolic flux through the pathway, and is subject to end product inhibition by Lys and / or Thr. The current invention provides a method to produce a transgenic high free threonine soybean via the overexpression of feedback-resistant AK enzymes in developing soybean plants and seeds. These modifications provide a method to enhance both plant nitrogen metabolism and crop growth performance.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
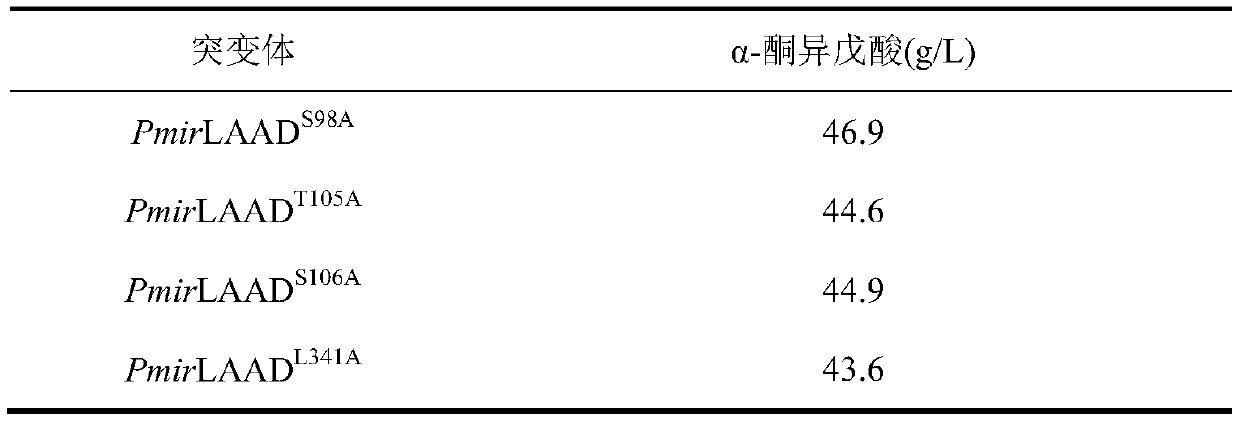
Preparation and application of L-amino acid deaminase mutant
ActiveCN111269900AHigh catalytic activityIncrease productivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBinding siteGene engineering
The invention discloses preparation and an application of an L-amino acid deaminase mutant, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. According to a modification method disclosed by theinvention, through protein modification of pmirLAAD, by analyzing a flexible Loop ring structure around a binding site of a pmirLAAD product and designing an optimal mutant, a defect that catalytic efficiency of a previous wild type enzyme is reduced due to product inhibition is overcome, and experimental verification is performed. And the optimal mutant pmirLAADM4 is obtained, and the catalytic efficiency (1.61 mM<-1>. Min<-1>) and a product inhibition constant (5.4 mM) are improved by 5.2 times and 5.7 times respectively compared with those of a contrast group. A yield of alpha-ketoisovaleric acid can reach 96.5 g / L, and a conversion rate is greater than 97%. By using the method provided by the invention, cost can be greatly reduced, and an industrial process of producing the alpha-ketoisovaleric acid by an enzymatic conversion method is accelerated.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
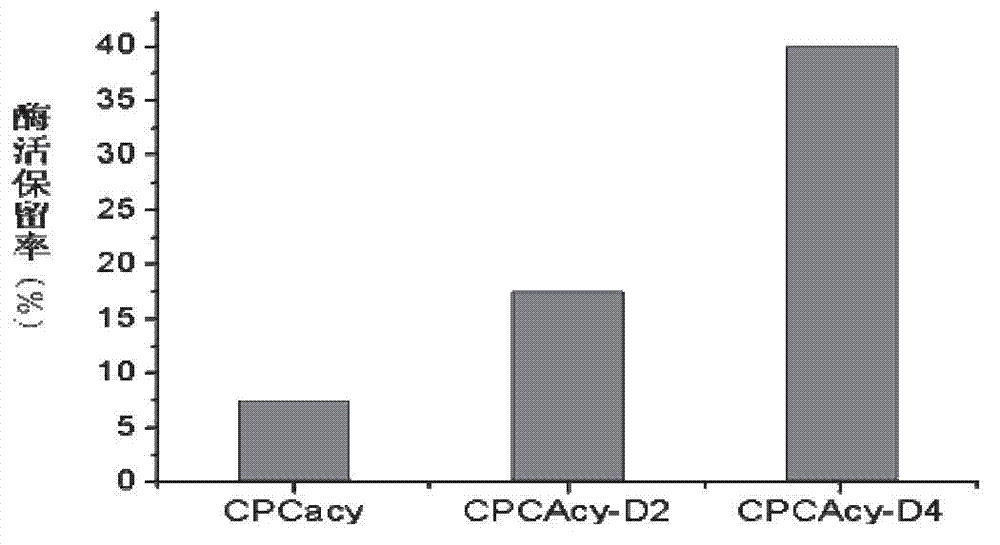
Mutated cephalosporin C acylase
The invention discloses a product-resistant inhibitory mutated cephalosporin C acylase, a gene carrier and a transformant of the enzyme, and application of the enzyme in one-step enzymatic production of 7-aminocephalosporanic acid, belonging to the technical field of enzyme engineering and biotechnology industry. The amino acid sequence of the enzyme is obtained by conducting deletion mutation on the amino acid sequence of cephalosporin C acylase coded by the gene sequence SEQ ID NO:1 to obtain enzyme CPCAcy-D2 and CPCAcy-D4. The amino acid sequences are shown as SEQ ID NO:2 and SEQ ID NO:3, respectively. The invention also discloses the gene carrier, the transformant, and the application of the enzyme. The enzyme has high expressing activity, and also the tolerance of the product is improved significantly, so that CPC is catalyzed efficiently to produce 7-ACA.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Compartmentalized simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of biomass
ActiveUS20110212495A1Facilitated releaseImprove production yieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFermentationStereochemistry
Methods and apparatus' are disclosed for the simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of biomass providing for the compartmentalization of the saccharification process and the fermentation process resulting in decreased enzymatic end-product inhibition.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP
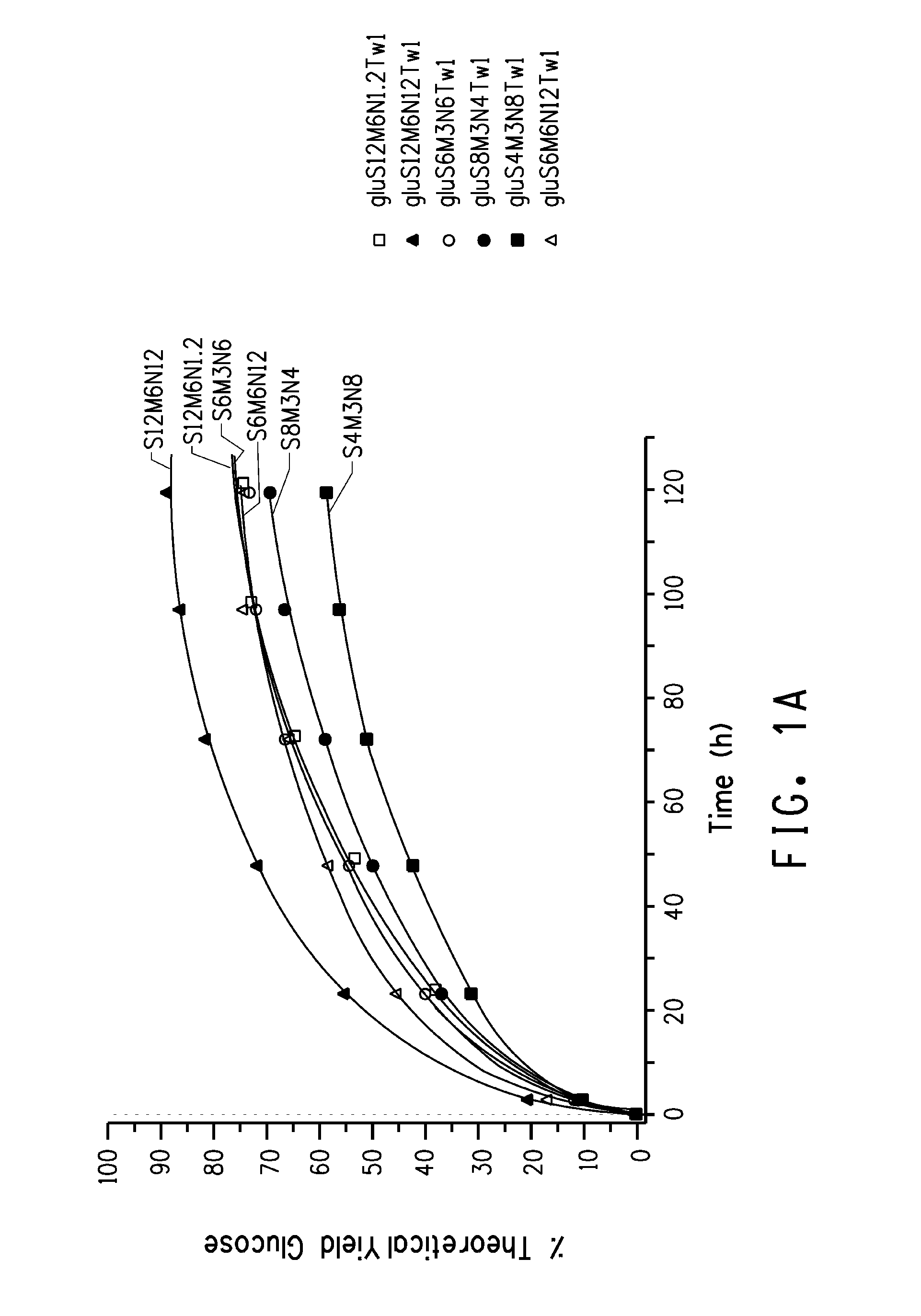
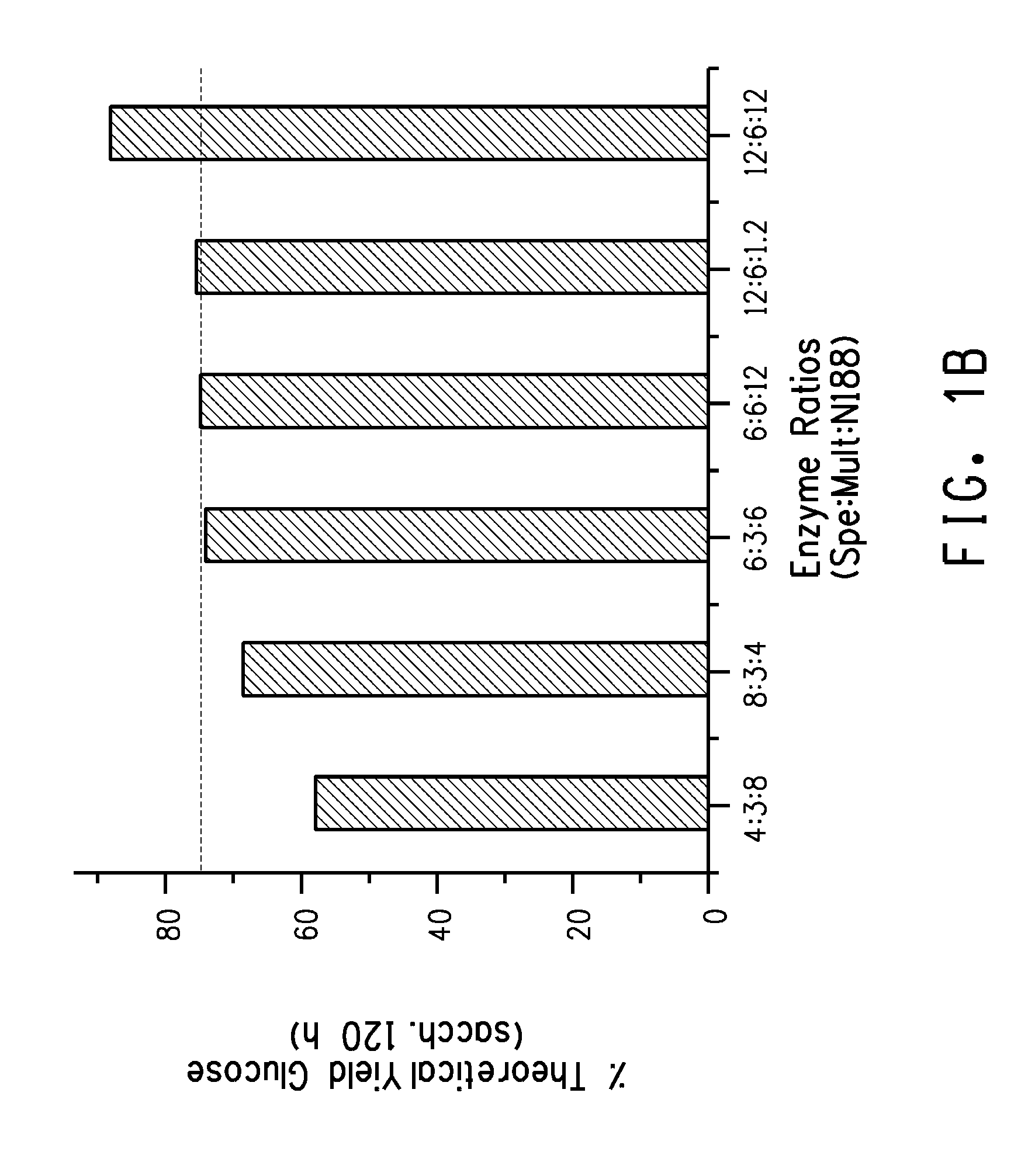
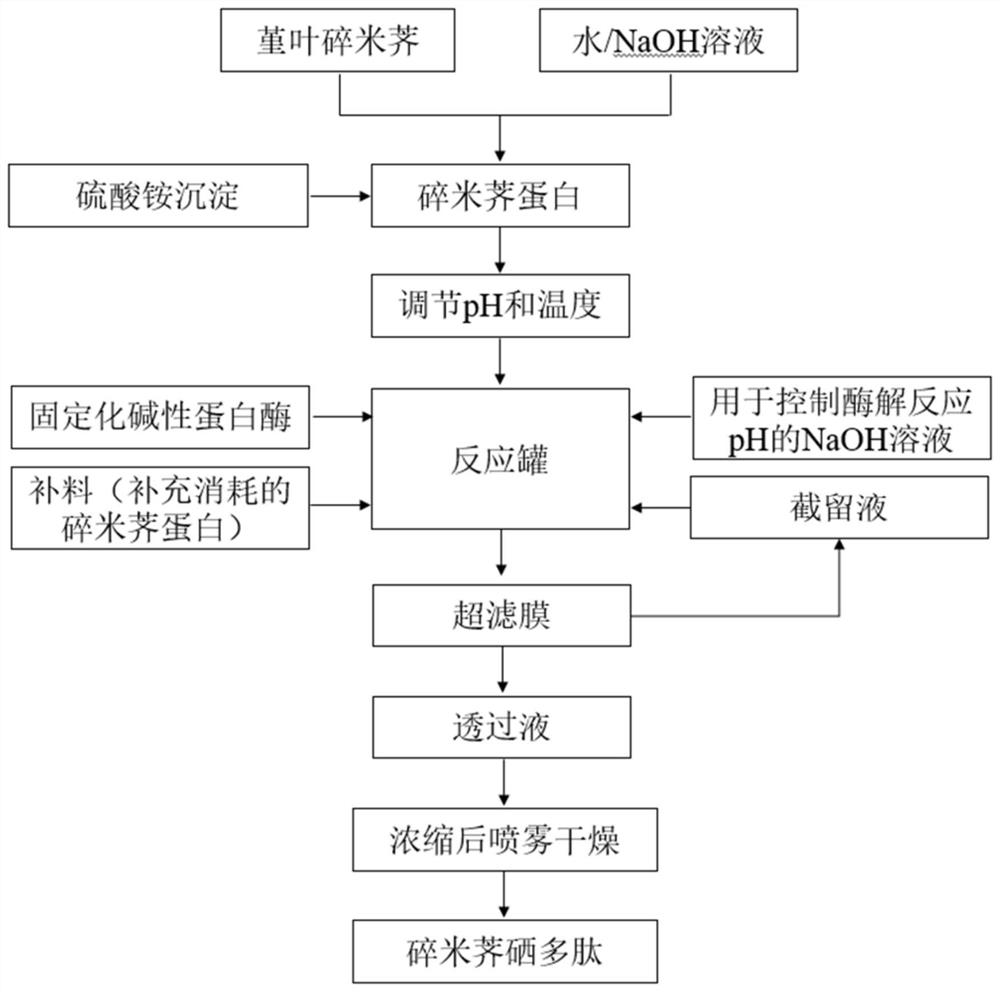
Method for preparing cardamine selenium polypeptide through continuous enzymolysis and cardamine selenium polypeptide
PendingCN112458140AImprove stabilityEasy to useHydrolasesPeptide preparation methodsHydrolysateEnzyme membrane
The invention belongs to the field of peptide preparation, and particularly relates to a method for preparing cardamine selenium polypeptide through continuous enzymolysis and the cardamine selenium polypeptide. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing cardamine protein powder; constructing immobilized enzyme; performing pre-enzymolysis; performing ultrafiltration and material supplementation; concentrating and drying. The method integrates reaction, product separation and enzyme recycling, and can realize continuous operation. According to the method, substrate protein is subjected to continuous enzymolysis through an immobilized enzyme membrane reactor, so that a reaction product can be selectively removed, the product inhibition phenomenon is reduced, and the reaction rateand the substrate conversion rate are increased; through the selectivity of a membrane, the molecular weight of a hydrolysate can be controlled; the molecular weight of the cardamine selenium polypeptide obtained by the method is intensively distributed at 300-3,000Da, and the DH (degree of hydrolysis) can reach about 27 percent and is increased by 8.4 percent compared with the DH value of the conventional intermittent enzymolysis.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Dilute chemical reaction process
InactiveUS20150050706A1Lower the volumeReduce in quantityMembranesOrganic compound preparationChemical reactionFiltration membrane
Disclosed is a process for carrying out a cyclisation reaction, a polymerization reaction, an enzymatic reaction showing substrate inhibition, an enzymatic reaction showing product inhibition, a reaction showing precipitation of the substrate or of a reactant, the process comprising the steps ofa) diluting a fresh substrate with solvent to form a diluted substrate-solvent mixture, and supplying this mixture to a reactor,b) causing the reaction medium in the reactor to react,c) discharging reaction mixture comprising reaction product, solvent, and substrate that has not reacted, to a first filtration membrane which is permeable to the solvent and impermeable to the substrate and to the catalyst or at least one of the reactants,d) returning solvent from the permeate side of the first membrane to dilute the fresh substrate, ande) returning retentate comprising substrate which has not reacted, from the first filtration membrane to the reactor.
Owner:VLAAMSE INSTELLING VOOR TECHNOLOGISCH ONDERZOEK NV VITO
Efficient preparation method of intermediate of heterocyclic drugs
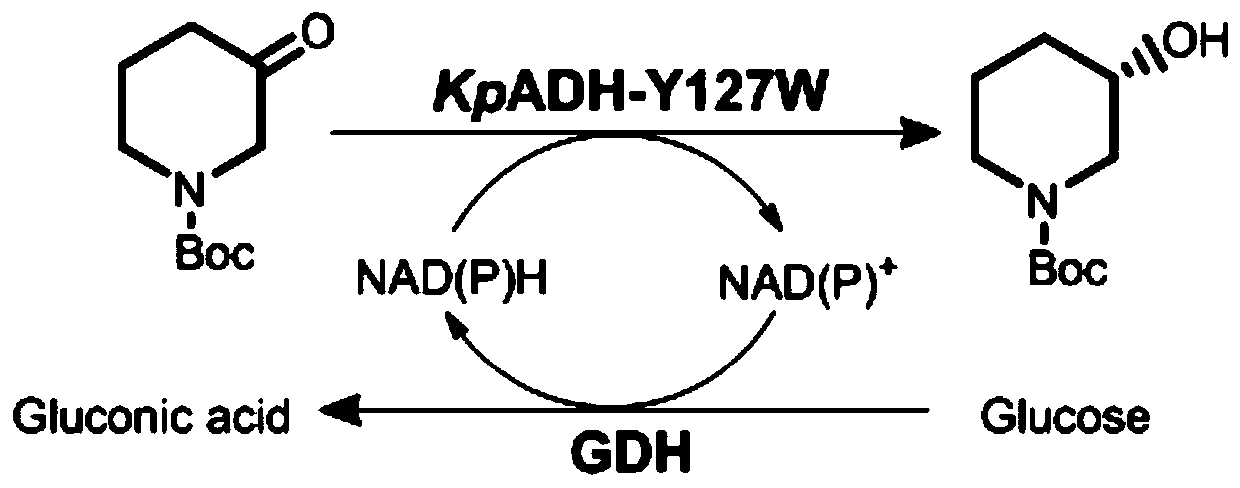
ActiveCN110777125AHigh catalytic efficiencyHigh stereoselectivityOxidoreductasesFermentationTyrosineTryptophan
The invention discloses an efficient preparation method of an intermediate of heterocyclic drugs. According to the efficient preparation method of the intermediate of the heterocyclic drugs, the intermediate of the heterocyclic drugs are produced by catalyzing a heterocyclic substrate by coupling an alcohol dehydrogenase mutant and glucose dehydrogenase; and the alcohol dehydrogenase mutant is prepared by mutating tyrosine at position 127 of a alcohol dehydrogenase female-parent with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 2 into tryptophan. The alcohol dehydrogenase mutant, namely mutant Y127W, utilized in the efficient preparation method of the intermediate of the heterocyclic drugs is capable of reducing product inhibition effects in a single aqueous system without addition of any co-solvent, thereby achieving a conversion rate higher than 99% within 12 hours. Being coupled with the glucose dehydrogenase (BmGDH), the mutant Y127W is capable of realizing gram-level preparation ata scale of 50 ml in a single aqueous system without addition of any exogenous coenzyme or organic co-solvent when substrate concentration is up to 600g x L<-1>; and the catalyst loading capacity is 3.3%. As for a final product, namely (S)-NBHP, the e.e. value is up to 99.4%; the space-time yield is about 1400g x L<-1> x d<-1>; and the product purity is 99.58%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Dark fermentation-light fermentation coupled biological hydrogen preparing process
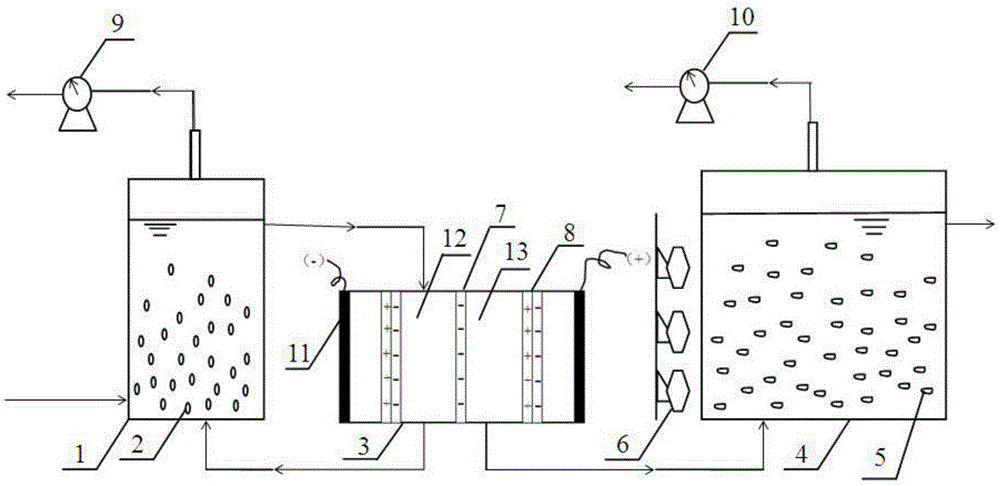
InactiveCN106520842AIncrease profitImprove coupling hydrogen production efficiencyMicroorganism based processesChemical recyclingAcetic acidPh regulation
The invention discloses a dark fermentation-light fermentation coupled biological hydrogen preparing process. According to the dark fermentation-light fermentation coupled biological hydrogen preparing process, a bipolar membrane electrodialysis unit is added behind a dark fermentation reactor, the components of the outgoing water obtained after dark fermentation are separated, thus the concentrated acetic acid is obtained, after pH regulation, the concentrated acetic acid is taken as incoming water of a light fermentation reactor, and meanwhile, the not utilized substrate is recycled and returns to the dark fermentation reactor to be reutilized. The product inhibition at the dark fermentation hydrogen production stage can be relieved, the pH of a fermentation system is controlled to be within the optimal range, the substrate is effectively recycled and reutilized, the total utilization ratio of the substrate is improved, the optimal substrate, namely, acetic acid is provided for the light fermentation hydrogen production stage, NH<4+> in the outgoing water obtained by dark fermentation is removed, then the inhibiting for the dinitrogenase of light fermentation bacteria is relieved, meanwhile, the interception and separation for the dark fermentation bacteria are completed, and the steps including centrifugalization, filtering and sterilization of the original process are replaced; the optimal hydrogen production conditions are provided for the dark fermentation and light fermentation stages, and the two-step coupled hydrogen production efficiency adopting the dark fermentation bacteria and the light fermentation bacteria is improved.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Mycobacterium applied for fuel oil thiirane desulfuration and uses thereof
InactiveCN101134944ARemove inhibitionEliminate poisonBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFuel oilBacterial strain
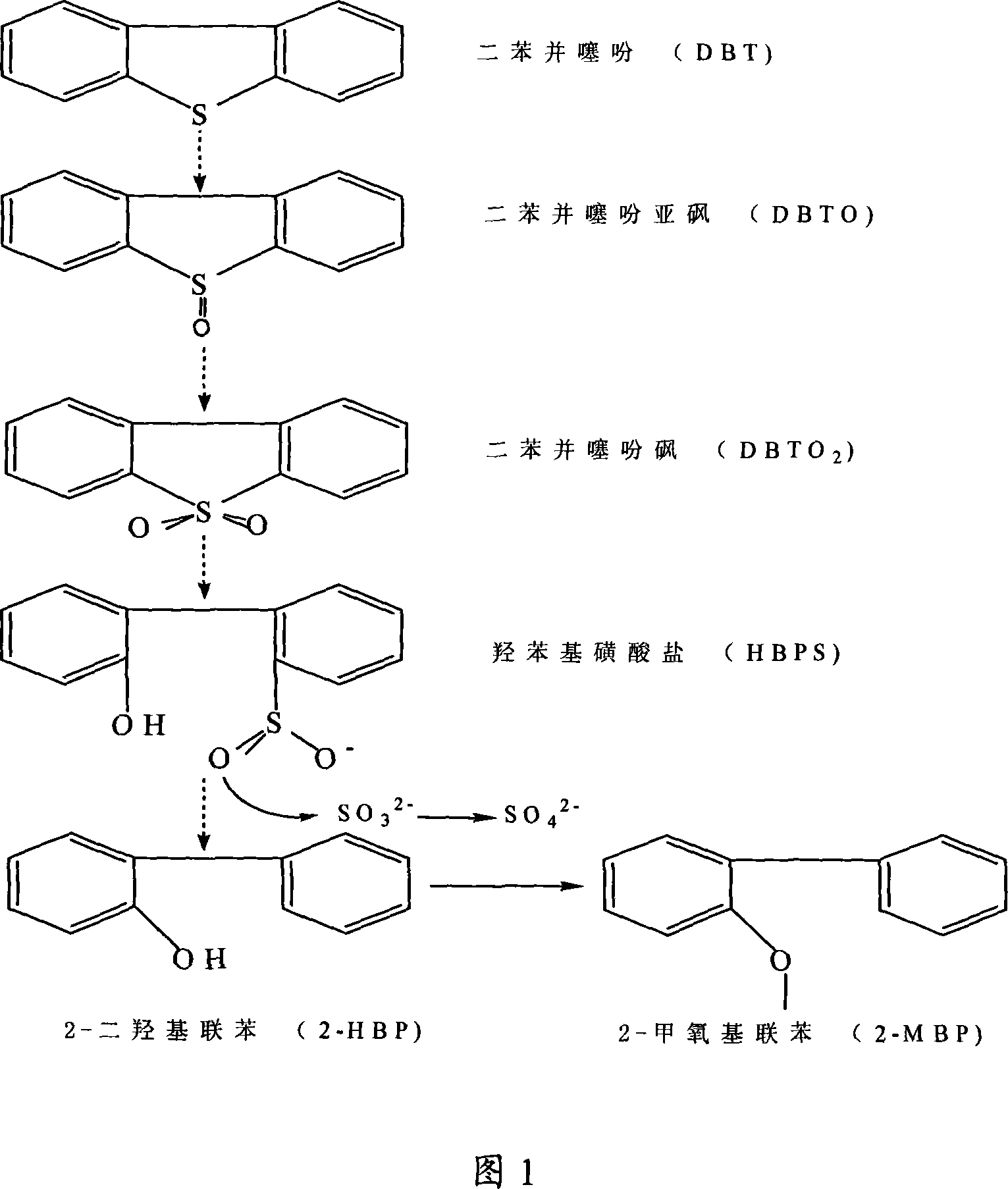
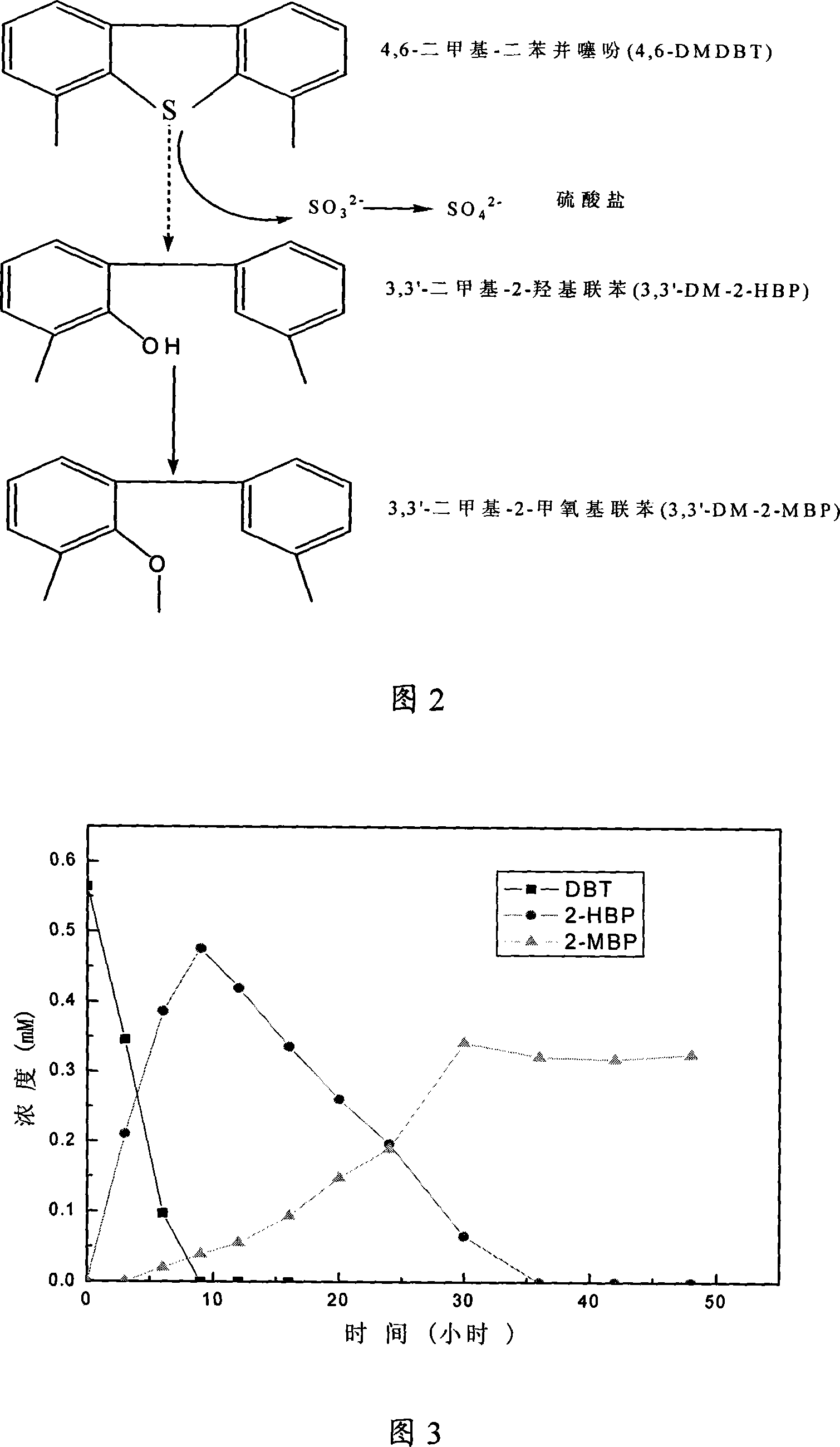
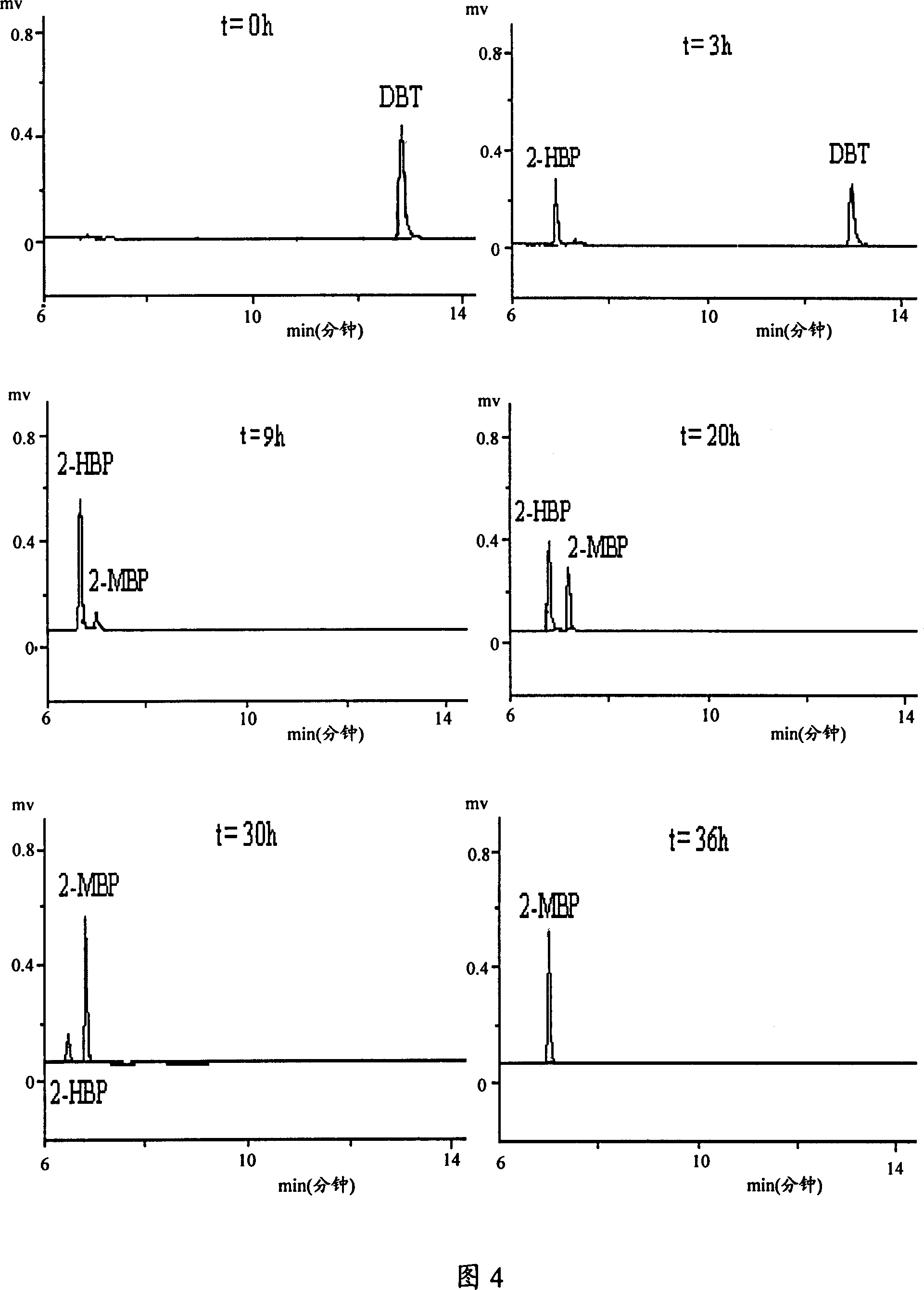
The present invention discloses one kind of bacterial strain for desulfurizing sulfur-containing heterocyclic ring compound in fuel oil. The bacterial strain is named as Mycobacterium ZD-19, and has the preservation number of CGMCC No. 1817. The present invention also discloses the specific desulfurizing use of eliminating sulfur-containing heterocyclic ring compound in fuel oil. By means of biological desulfurizing technology with the strain as the catalyst, sulfur-containing heterocyclic ring compound in fuel oil is degraded. The process of degrading dibenzothiophene and its derivative 4, 6-dimethyl dibenzothiophene follows one unique 'expanded 4S path', and the traditional 'expanded 4S path' products 2-hydroxy biphenyl and 3, 3'-dimethyl-2-hydroxy biphenyl are further methylated to produce final products 2-methoxyl biphenyl and 3, 3'-dimethyl-2- methoxyl biphenyl in effectively reduced product inhibition.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
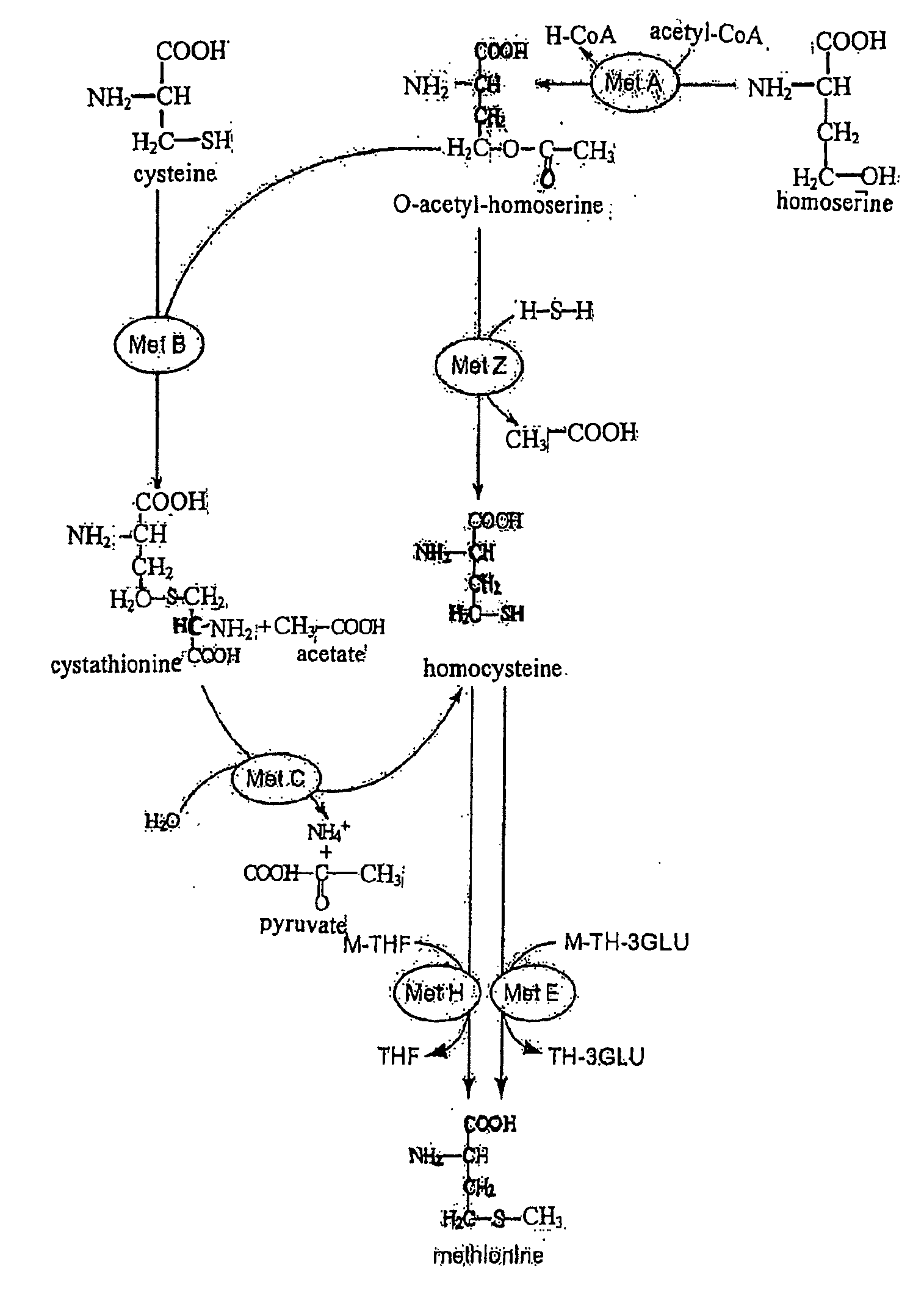
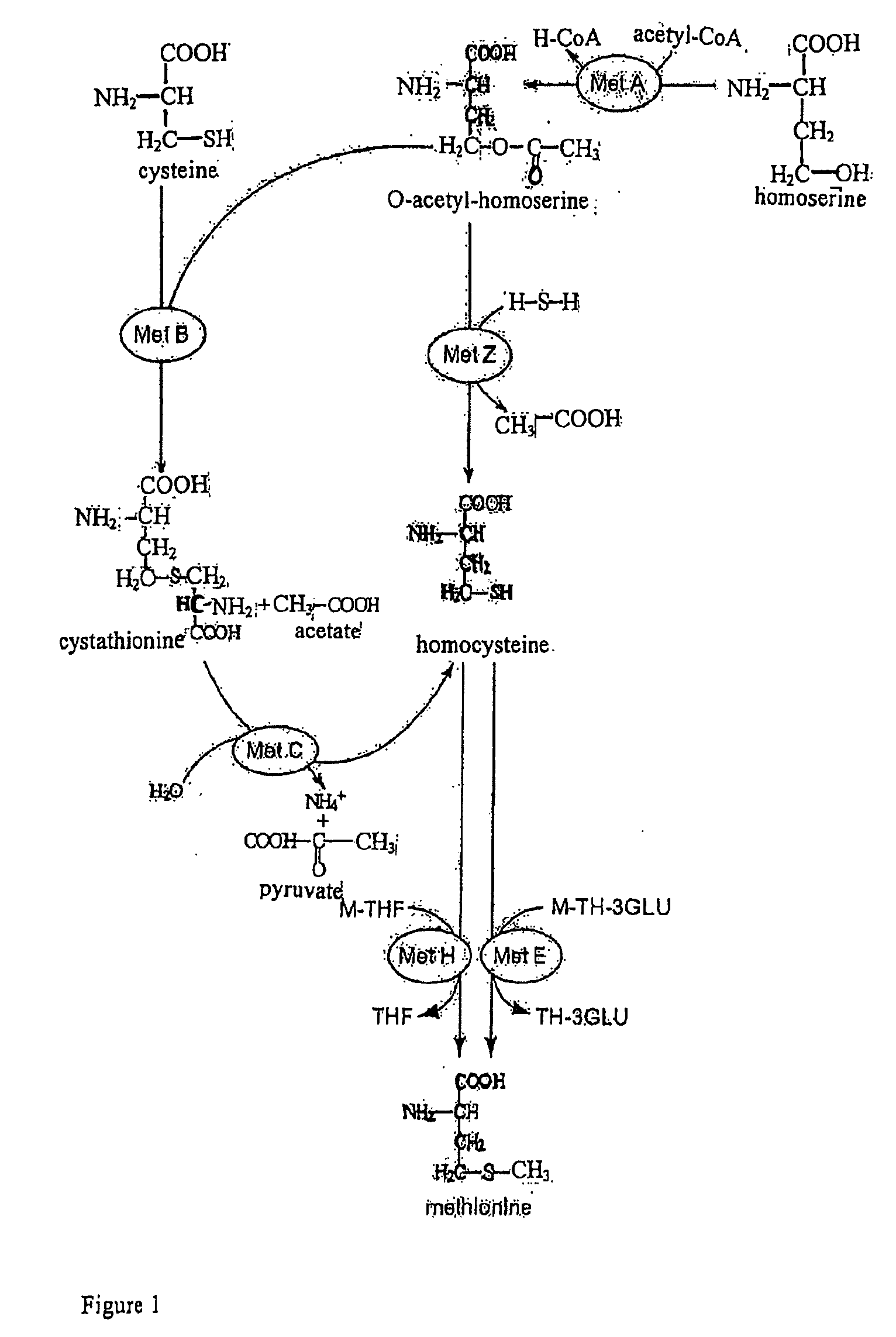
Methionine Synthases with Reduced Product Inhibition
The present invention relates to nulceotide sequences encoding enzymatically active cobalamin-methionine synthase and functional fragments thereof being modified in comparison to the respective wild-type enzyme such that said enzymes show reduced product inhibition by methionine. The present invention also relates to polypeptides being encoded by such nucleotide sequences and host cells comprising such nucleotide sequences. Furthermore, the present invention relates to methods for producing methionine in host organisms by making use of such nucleotide sequences.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Method of improving concentration of butanol in process of acetone butanol fermentation
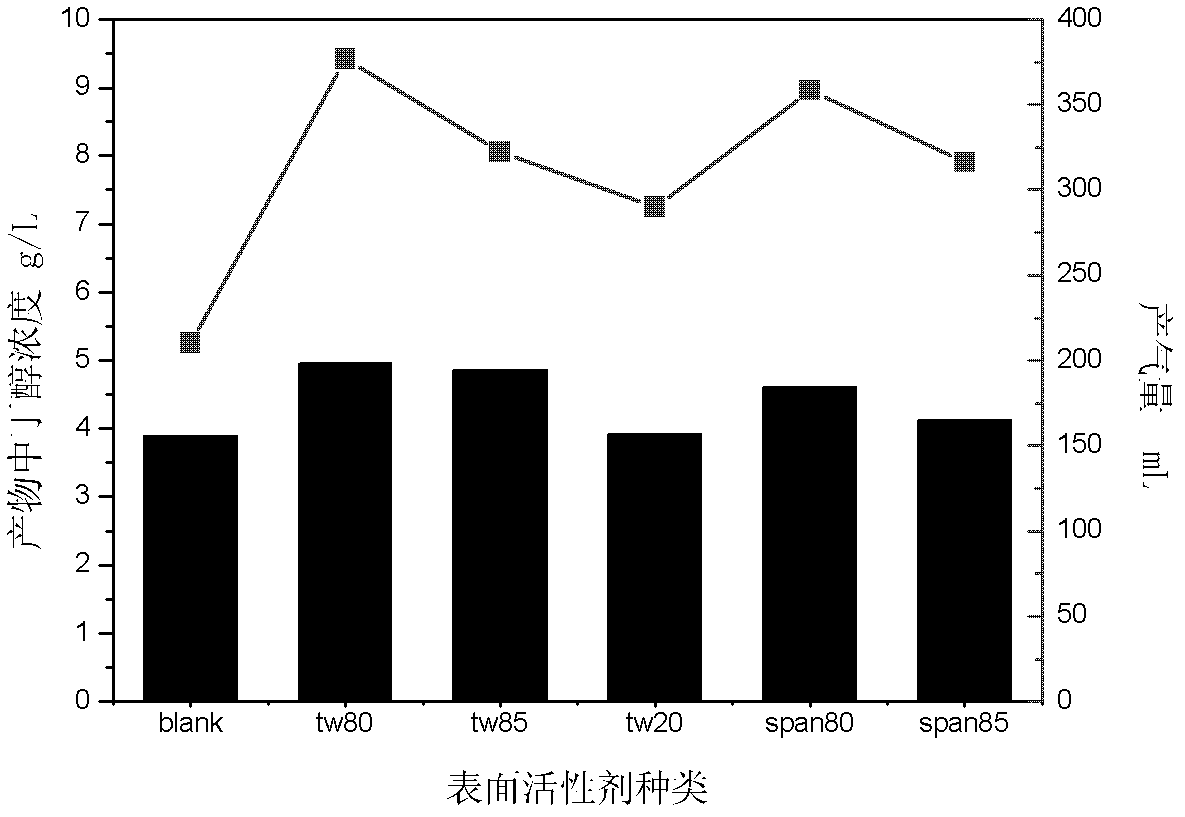
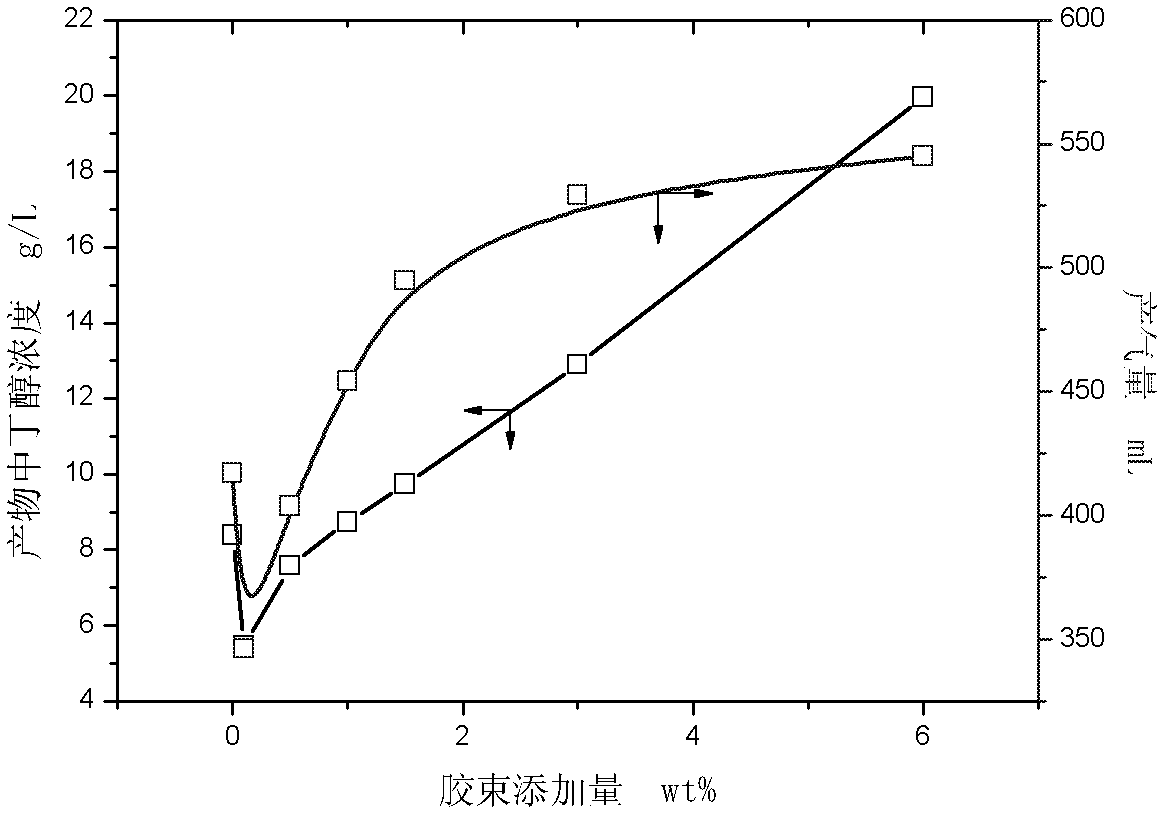
ActiveCN103131732AReduce dosageNon-toxicMicroorganism based processesFermentationN-ButanolSurface-active agents
The invention belongs to the field of the biochemical industry and particularly relates to a method of improving the concentration of butanol in the process of acetone butanol fermentation. The method of improving the concentration of the butanol in process of the acetone butanol fermentation includes the following steps of adding a surface active agent to a culture medium in the process of the acetone butanol fermentation and extracting and improving the concentration of the butanol by means of micelle formed by the surface active agent. The method of improving the concentration of butanol in the process of the acetone butanol fermentation is directed against the product inhibition effect existing in the process of the acetone butanol fermentation and extracts the butanol by means of the micelle formed by the surface active agent serving as an extraction agent, relieving the inhibition effect in the process of the acetone butanol fermentation, increases the final concentration of the butanol in fermentation liquor, and therefore energy consumption of rectification in a later period is reduced.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Industrial fermentation production process for improving yield of biosurfactin
PendingCN112608831AConducive to survivalFlip to achieveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyIndustrial fermentation
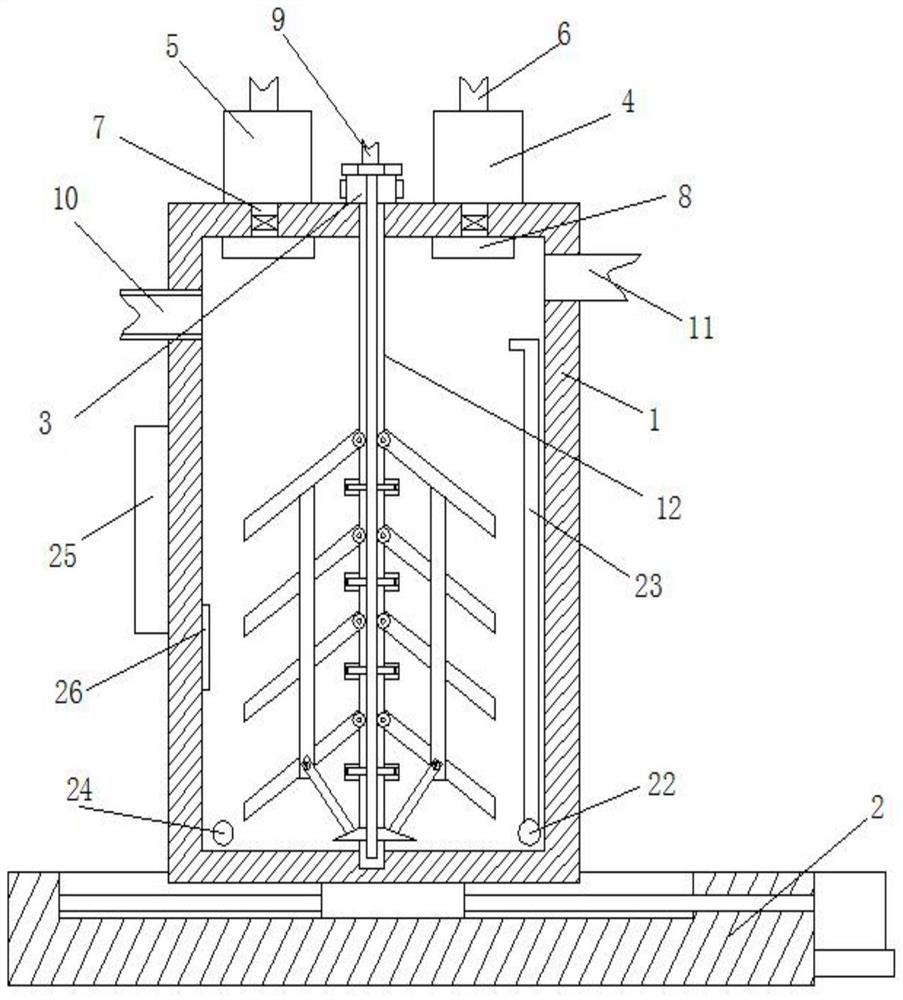
The invention discloses an industrial fermentation tank for improving the yield of biosurfactin, which comprises a tank body and a fixing base, wherein the tank body is slidably connected with the top of the fixing base, a culture solution inlet is formed in the top of the left side wall of the tank body, an air outlet is formed in the top of the right side wall of the tank body, an acid storage box is arranged on the left side of the top of the tank body, an alkaline storage box is arranged on the right side of the top of the tank body, feeding ports are formed in the tops of the alkaline storage box and the acid storage box, guide pipes are communicated with the bottoms of the alkaline storage box and the acid storage box, spray heads are communicated with the ends, extending into an inner cavity of the tank body, of the guide pipes, a driving mechanism is arranged on the tank body between the alkaline storage box and the acid storage box, an air inlet pipe is communicated to the top part of the driving mechanism, and one end, extending to the inner cavity of the tank body, of the driving mechanism is connected with a rotating shaft. The design is reasonable, and the pH staged regulation and the overflow separation surfactant removal product inhibition are organically combined so as to obtain the maximum yield and the maximum yield of the fermentation production of the biological surfactant.
Owner:湖南普菲克生物科技有限公司
Whole-plant hybrid paper mulberry biological feed leavening agent
PendingCN110973355AFully degradedAddress Feedback InhibitionAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a whole-plant hybrid paper mulberry biological feed leavening agent. The biological feed leavening agent is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 30 to50 percent of compound enzyme, 30 to 45 percent of beneficial bacteria and 10 to 20 percent of fermentation promoter; according to the invention, the compound enzyme, the compound beneficial bacteriaand the fermentation promoter have an organic synergistic effect in the fermentation process; the product inhibition effect in the hybrid paper mulberry fermentation degradation process is obviously reduced; cellulose is degraded into glucose, organic acid and small molecular polysaccharide, lignin is degraded into small molecular aromatic compounds, paper mulberry protein is degraded into small molecular oligopeptide or amino acid, so the overall biotransformation utilization rate reaches 80% or above, and the small molecular polysaccharide can be further converted into monosaccharide to be absorbed by animals by ingesting animal endogenous enzymes.
Owner:安徽宝楮生态农业科技有限公司
Technology for realizing high-yield polyoxins by continuous fermentation coupled with separation
InactiveCN105821100AHigh potencyShort cycleMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsContinuous fermentationNitrogen source
The invention discloses a technology for realizing high-yield polyoxins by continuous fermentation coupled with separation. The technology includes inoculating the polyoxins producing strain seed liquid into a fermentation cylinder to perform fermental cultivation, starting a membrane filter in the fermentation cylinder when the fermentation is at later stage of the logarithmic phase, making the fermentation broth containing polyoxins go through the membrane filter and enter a separating device out of the fermentation cylinder, collecting the broth to obtain a fermentation broth A, intercepting the bacterial cell in the fermentation cylinder to perform fermentation, feeding nitrogen source medium into the fermentation cylinder while starting the membrane filter in the fermentation cylinder to maintain steady fermentation system in the fermentation cylinder, performing continuous fermentation to the end, collecting the broth to obtain a fermentation broth B, and performing refining and purifying processing of the fermentation broth A and fermentation broth B to obtain polyoxins. The technology releases the product inhibition in the fermentation, reduces the viscosity of the fermentation broth, shortens the fermentation period, and improves the product titer. Moreover, the technology couples continuous fermentation with separation with feeding device and separating device, improves the utilization rate of the device, and reduces the production cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com