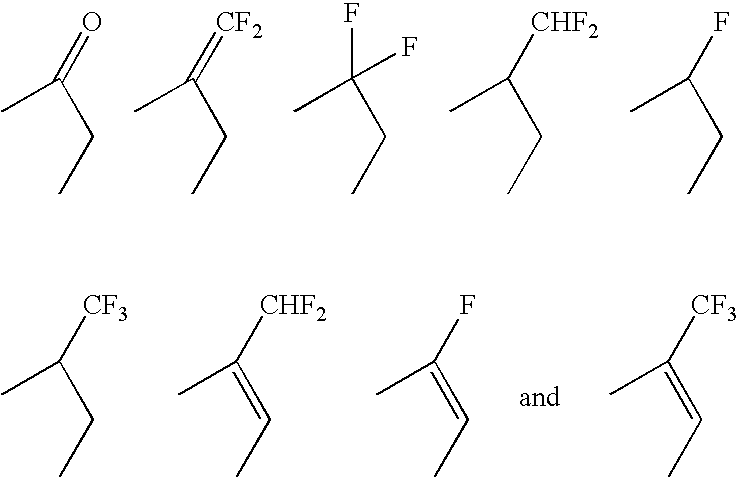
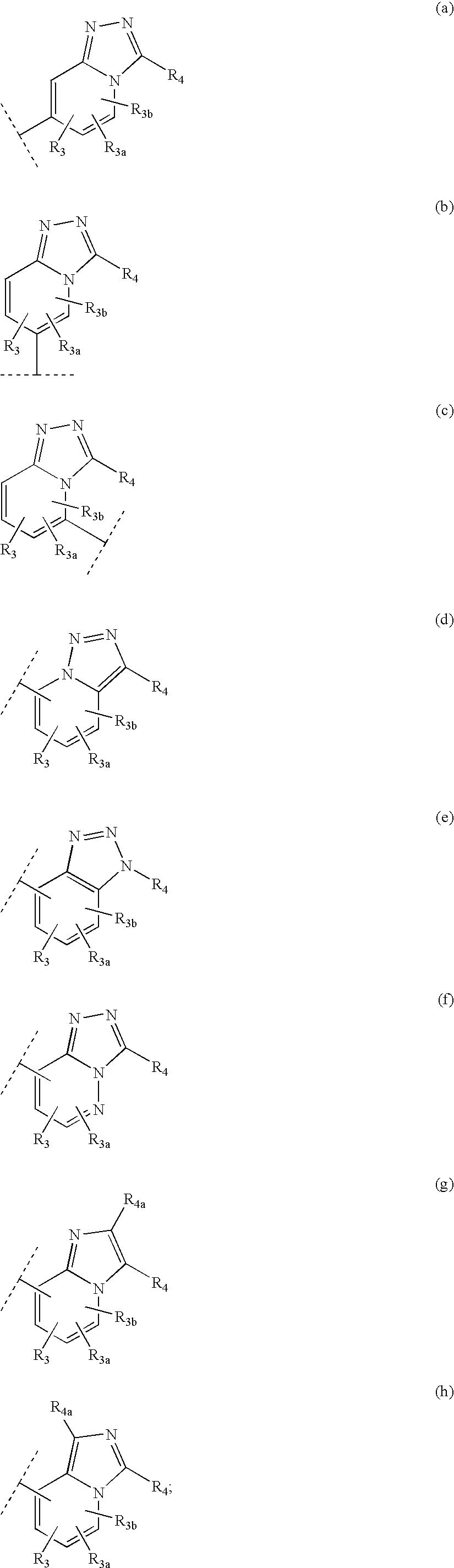
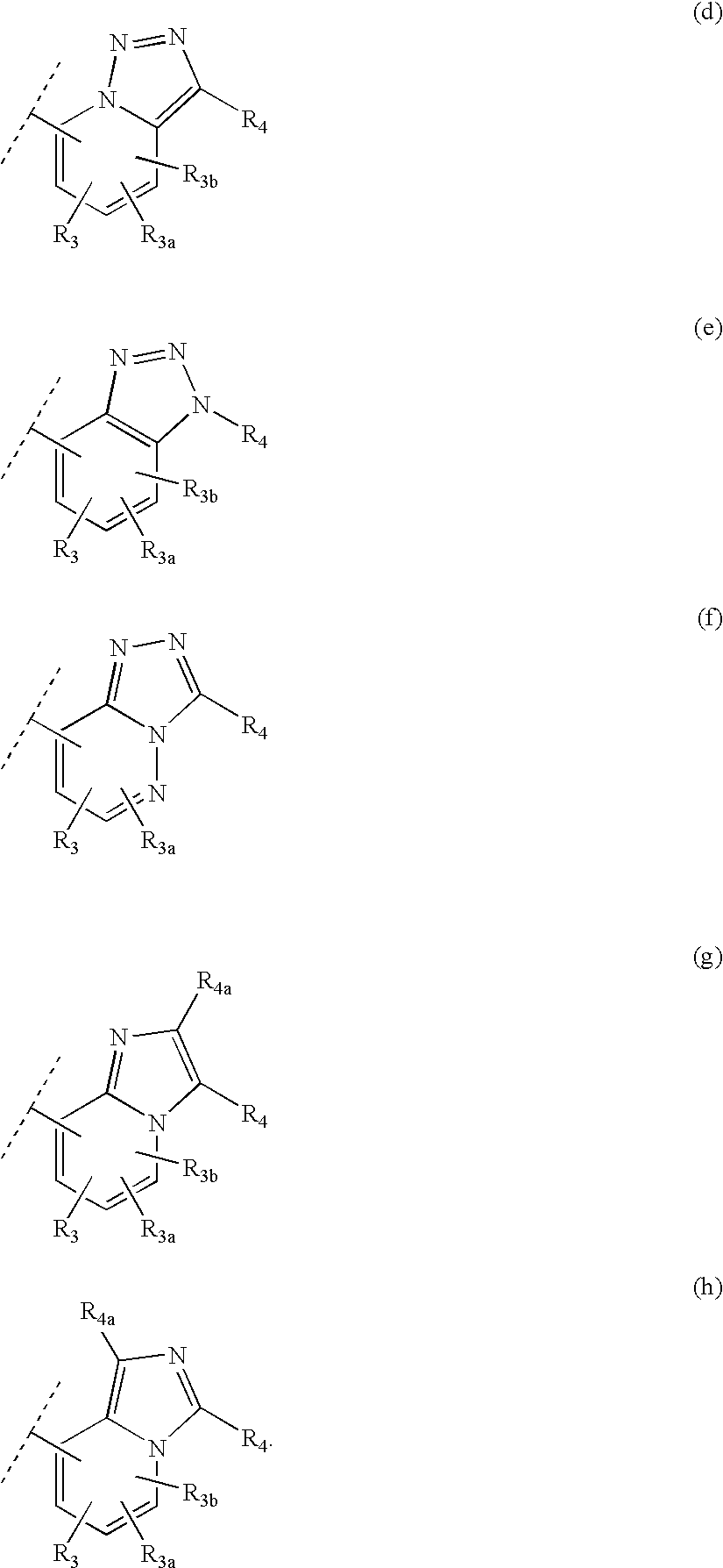
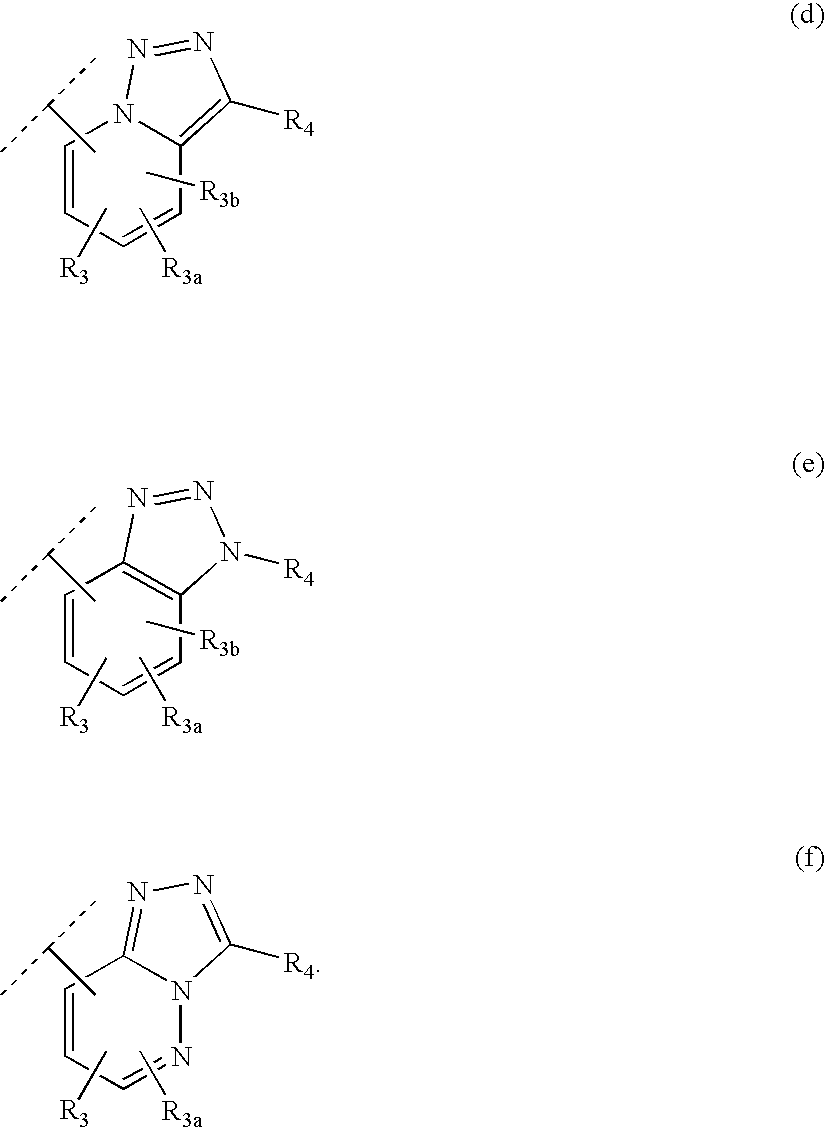
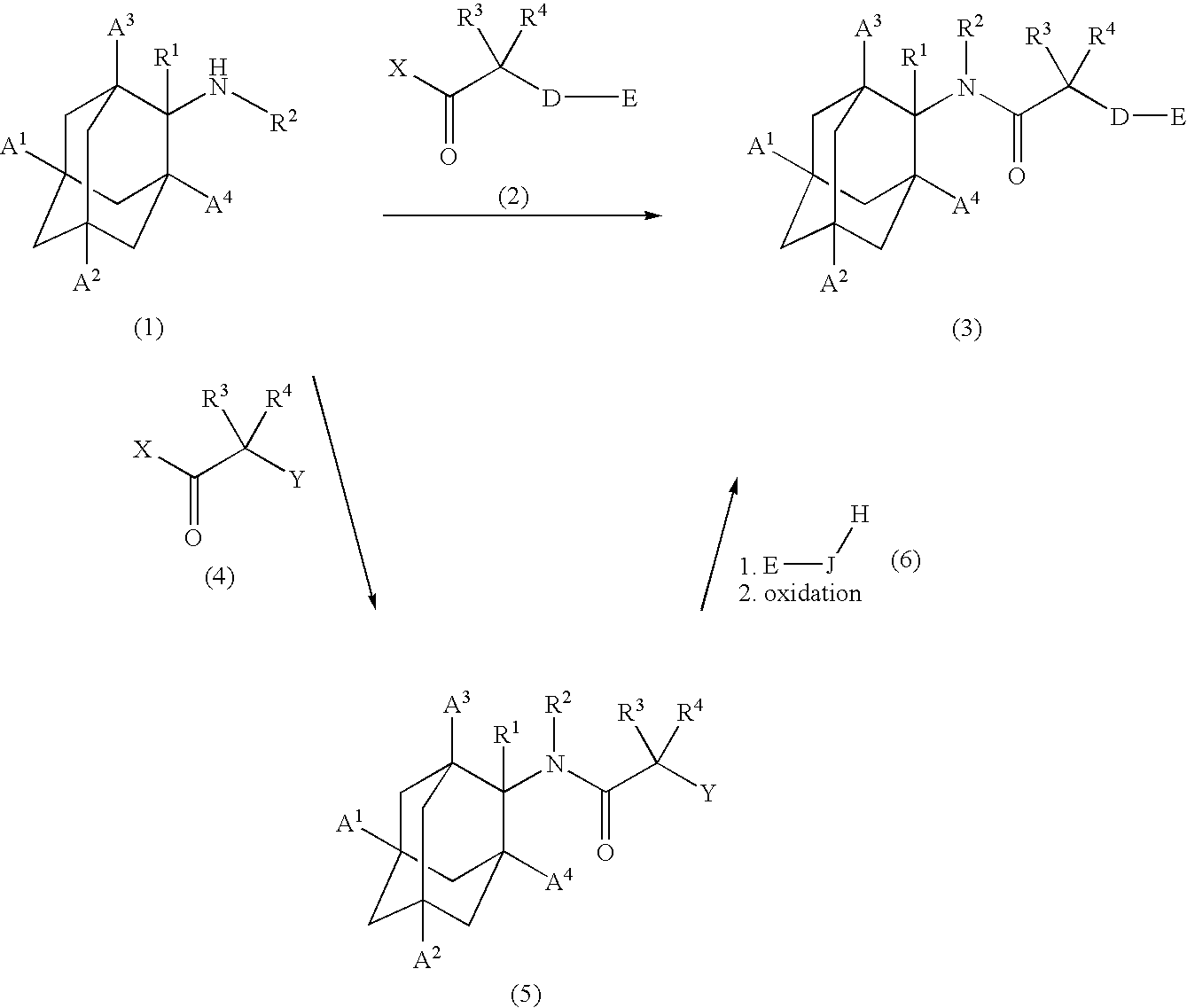
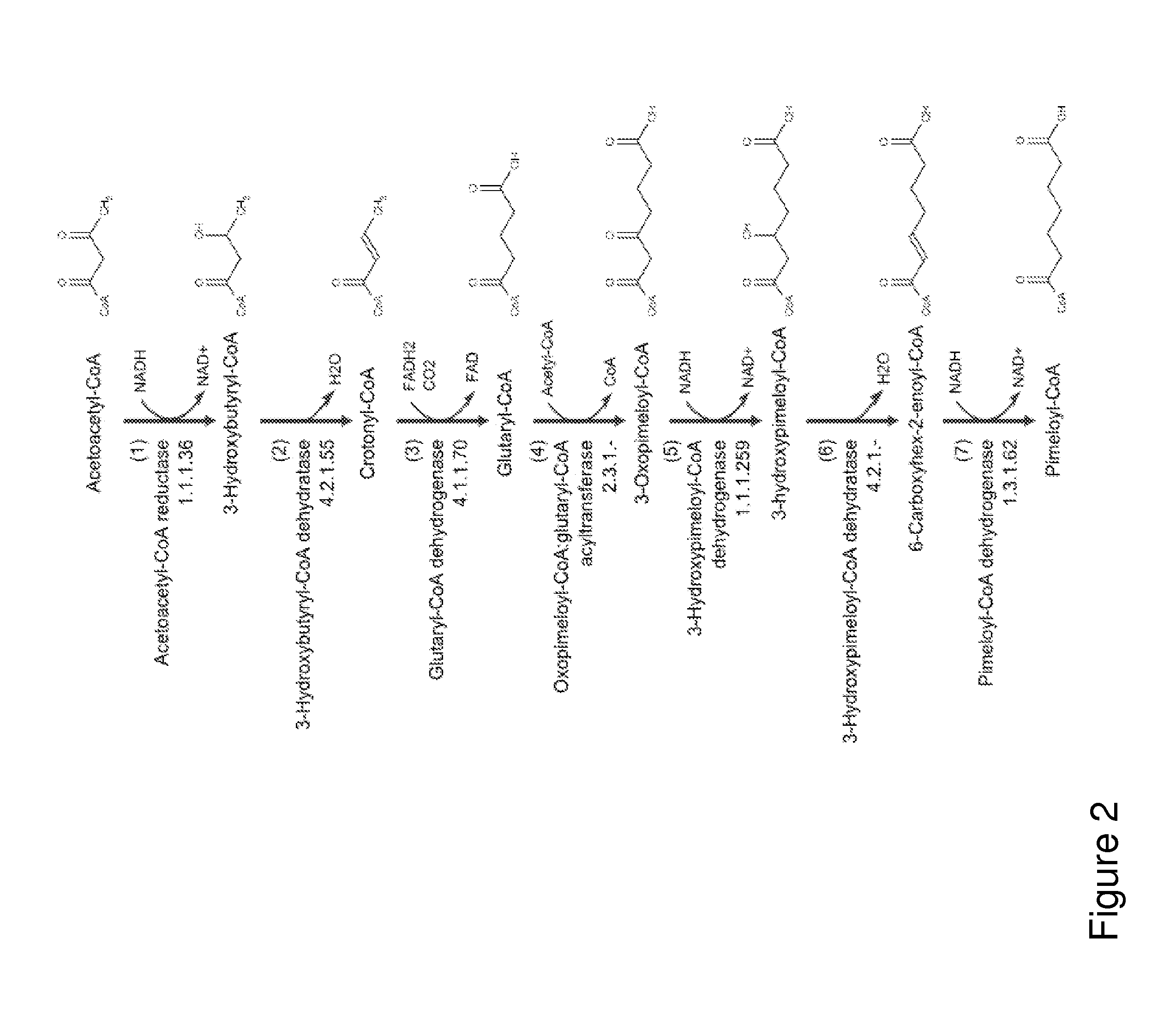
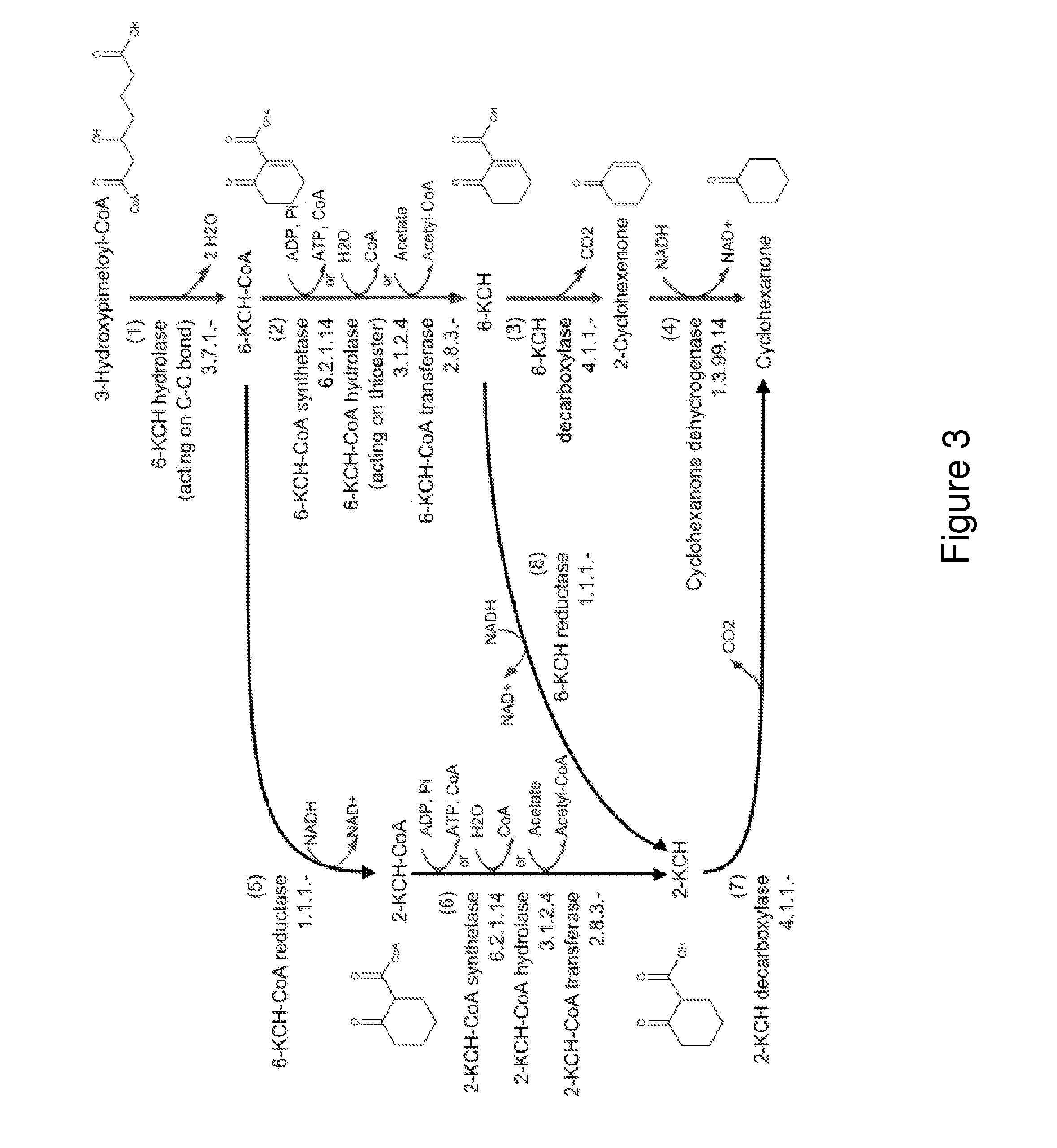
Patents
Literature
541 results about "Alcohol dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
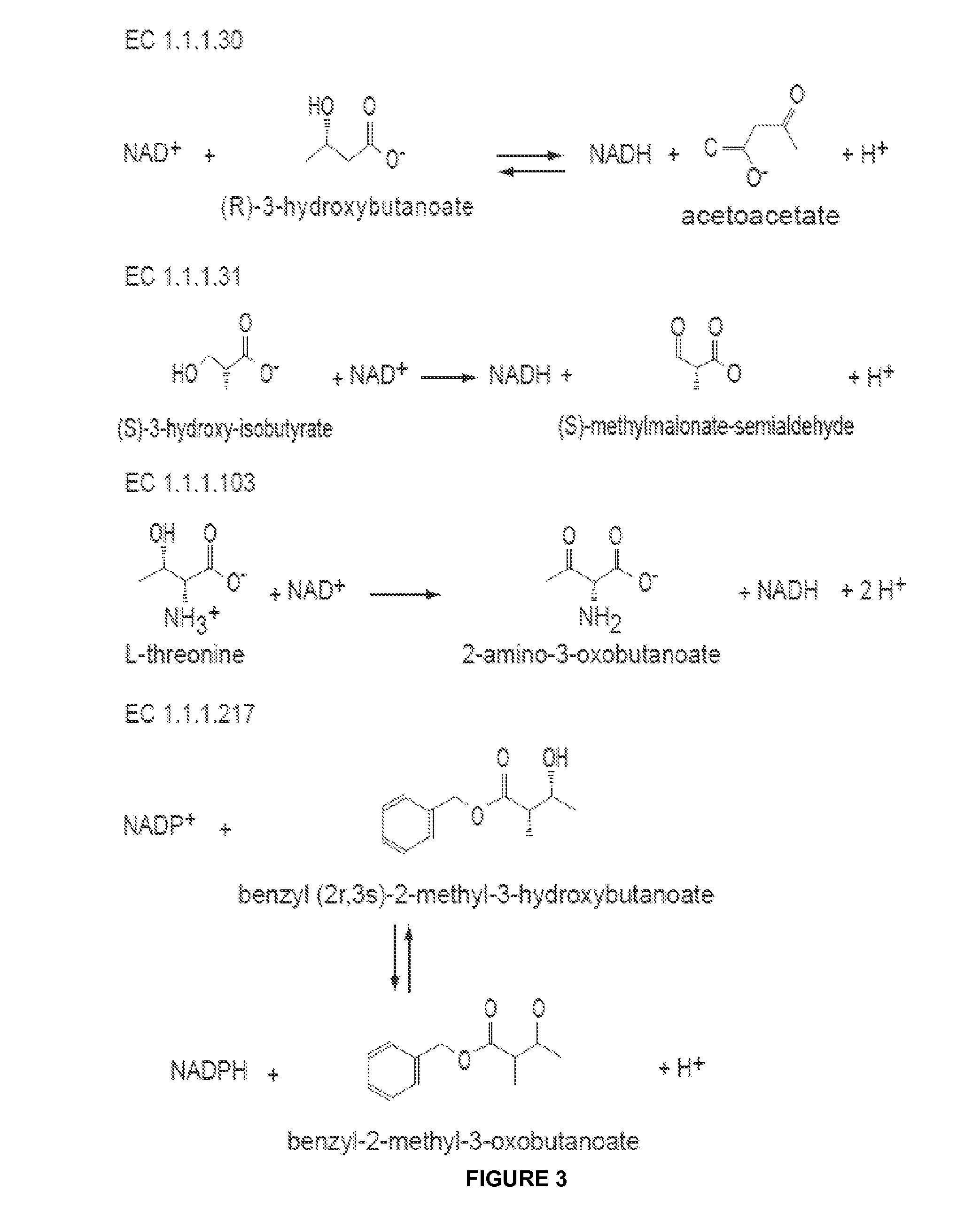
Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH) (EC 1.1.1.1) are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺) to NADH. In humans and many other animals, they serve to break down alcohols that otherwise are toxic, and they also participate in generation of useful aldehyde, ketone, or alcohol groups during biosynthesis of various metabolites. In yeast, plants, and many bacteria, some alcohol dehydrogenases catalyze the opposite reaction as part of fermentation to ensure a constant supply of NAD⁺.
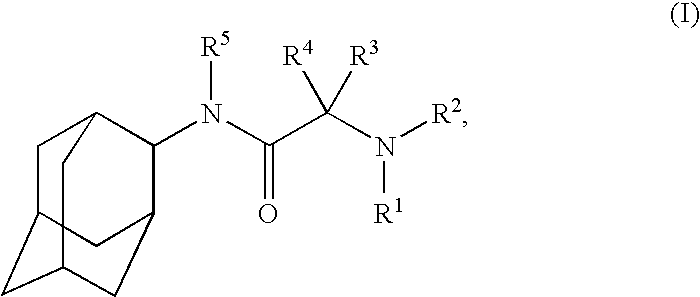
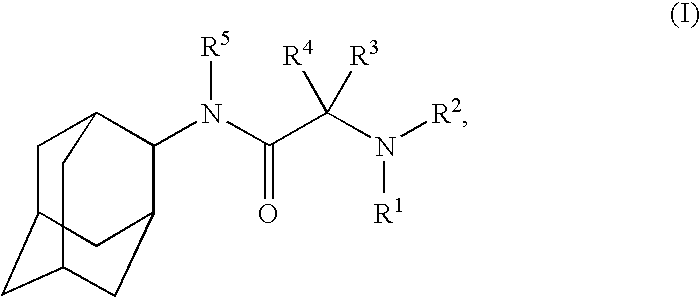
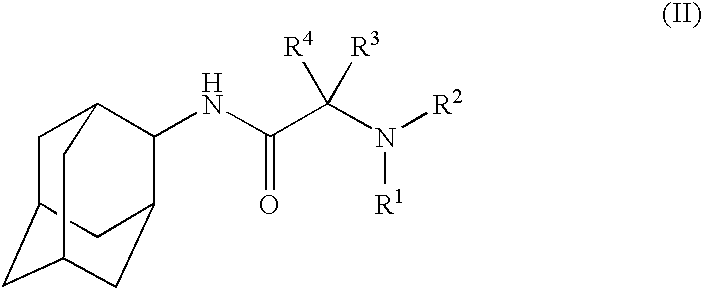
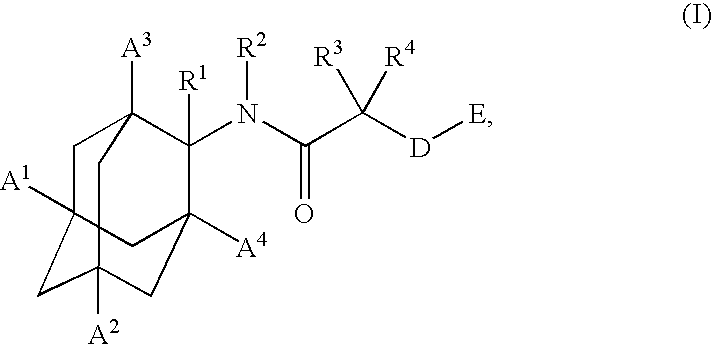
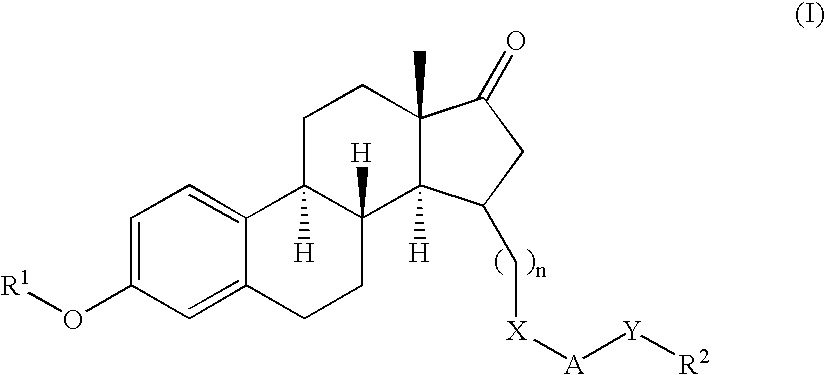
Inhibitors of the 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 enzyme
ActiveUS20060149070A1Improve throughputLimit deliveryOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryInsulin dependentEnzyme inhibitor
The present invention relates to compounds that are inhibitors of the 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase Type 1 enzyme. The present invention further relates to the use of inhibitors of 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase Type 1 enzyme for the treatment of non-insulin dependent type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, lipid disorders, metabolic syndrome and other diseases and conditions that are mediated by excessive glucocorticoid action.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
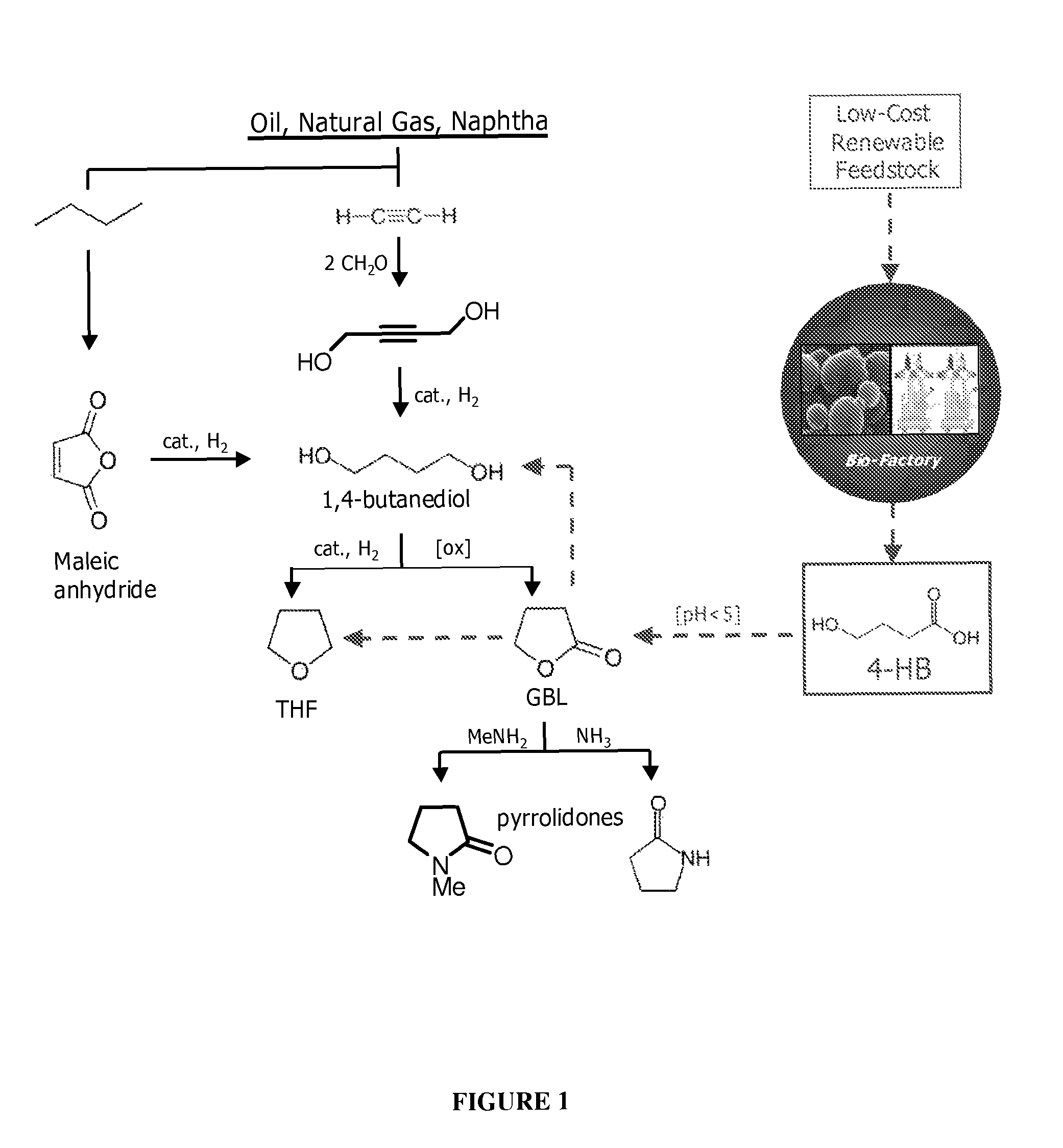
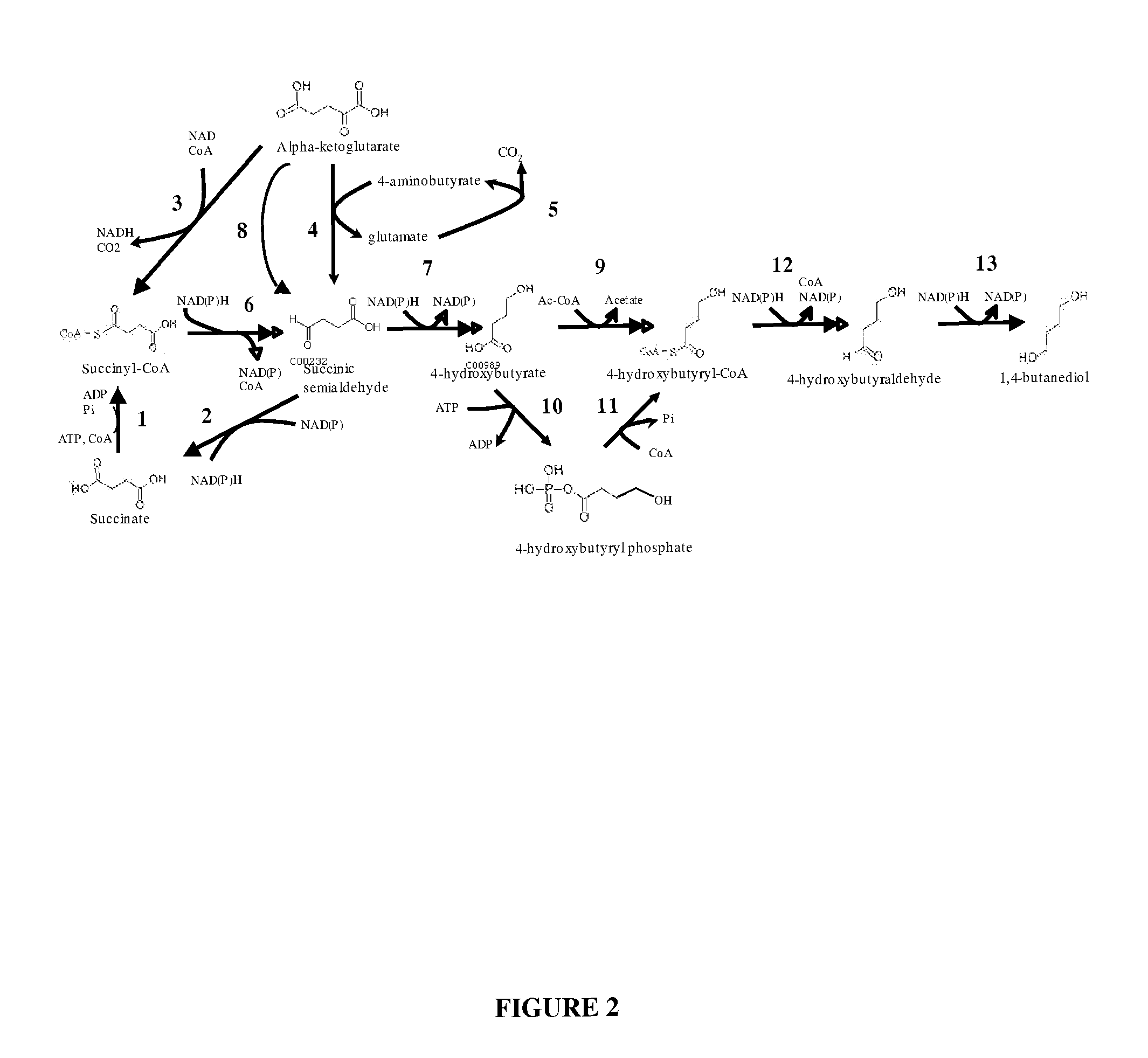
Compositions and methods for the biosynthesis of 1,4-butanediol and its precursors
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having 4-hydroxybutanoic acid (4-HB) and 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BDO) biosynthetic pathways. The pathways include exogenous nucleic acids encoding a) an α-ketoglutarate decarboxylase; b) a 4-hydroxybutanoate dehydrogenase; c) a 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA:acetyl-CoA transferase or a butyrate kinase and a phosphotransbutyrylase; d) an aldehyde dehydrogenase, and e) an alcohol dehydrogenase, wherein the exogenous nucleic acids are expressed in sufficient amounts to produce 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BDO). Also provide is a method for the production of 1,4-BDO. The method includes culturing the non-naturally occurring microbial organism having 4-HB and 1,4-BDO biosynthetic pathways substantially anaerobic conditions for a sufficient period of time to produce 1,4-BDO.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
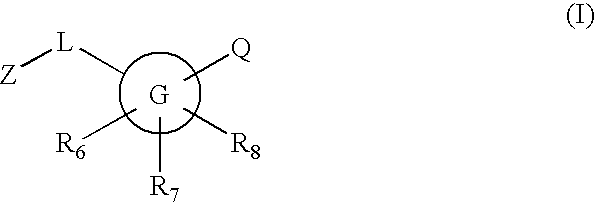
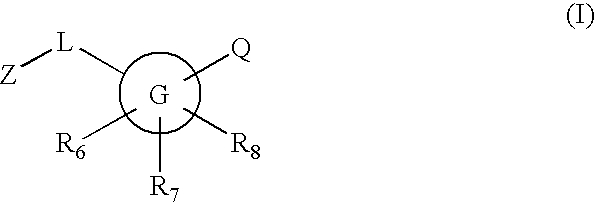
Inhibitors of 11-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I
InactiveUS20060235028A1Inhibitory activityBiocideNervous disorder11-beta-Hydroxysteroid DehydrogenasesCompound (substance)
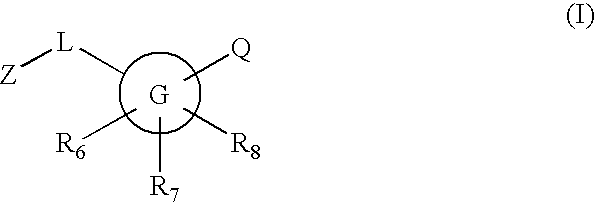
Novel compounds are provided which are 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I inhibitors. 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I inhibitors are useful in treating, preventing, or slowing the progression of diseases requiring 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I inhibitor therapy. These novel compounds have the structure: or stereoisomers or prodrugs or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein G, L, Q, Z, R6, R7, and R8 are defined herein.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Use of compositions comprising an estrogenic component for the treatment and prevention of musculoskeletal pain
InactiveUS20060276414A1Increasing cell proliferationHigh affinityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideGynecologyPresent method
The present invention relates to a method of treating or preventing musculoskeletal pain in a mammal receiving administration of an estrogen. suppressant selected from the group consisting of aromatase inhibitors, GnRH analogues, cyclo-oxy-genase 2 (COX-2) inhibitors, 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitors, progestogens, anti-estrogens and combinations thereof, said method comprising the administration of an effective amount of an estrogenic component, wherein the estrogenic component is selected from the group consisting of: substances represented by the following formula (1) in which formula R1, R2, R3, R4 independently are a hydrogen atom, a hydroxyl group or an alkoxy group with 1-5 carbon atoms; precursors capable of liberating a substance according to the aforementioned formula when used in the present method; and mixtures of one or more of the aforementioned substances and / or precursors.
Owner:COELINGH BENNINK HERMAN JAN TIJMEN +1
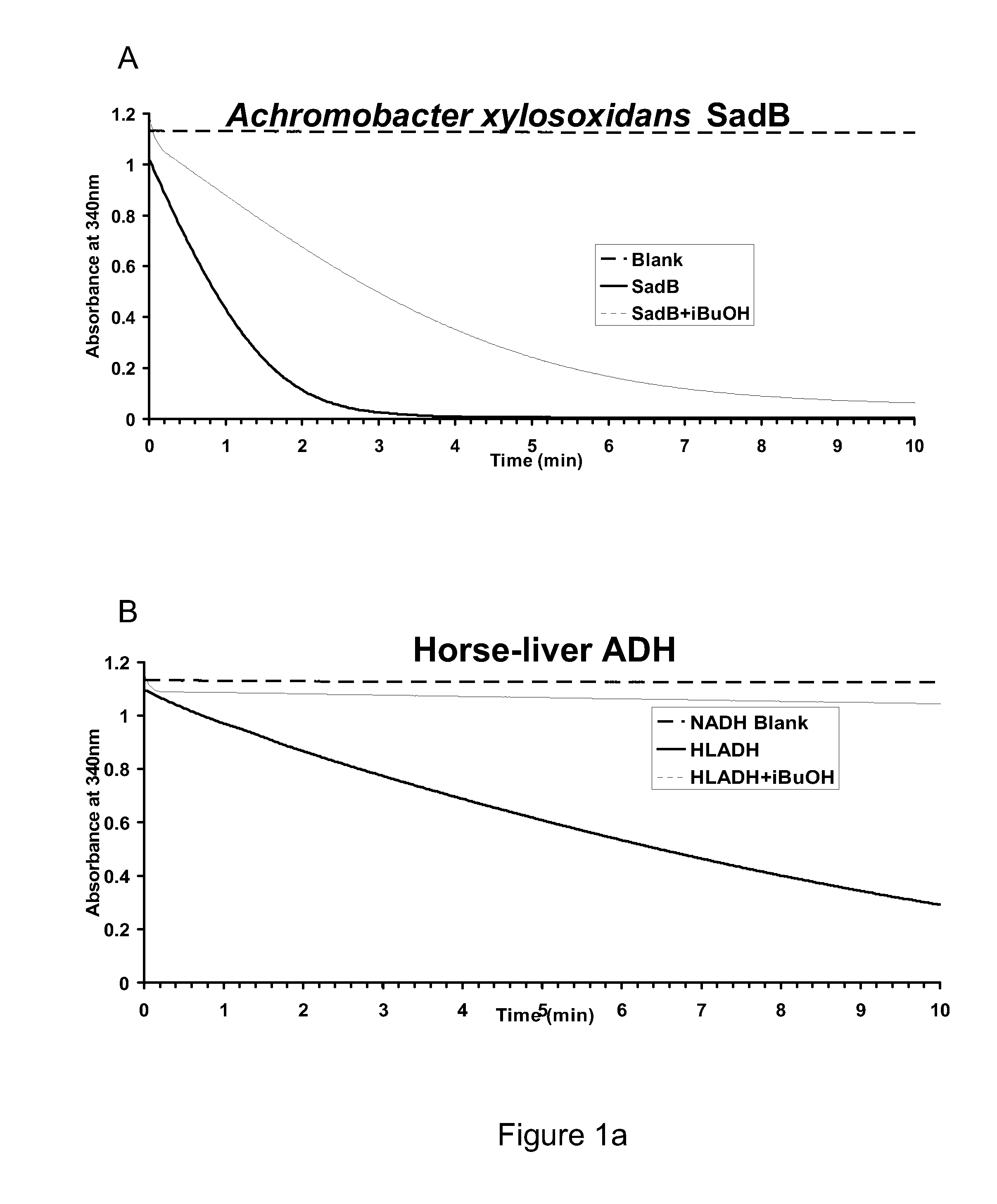
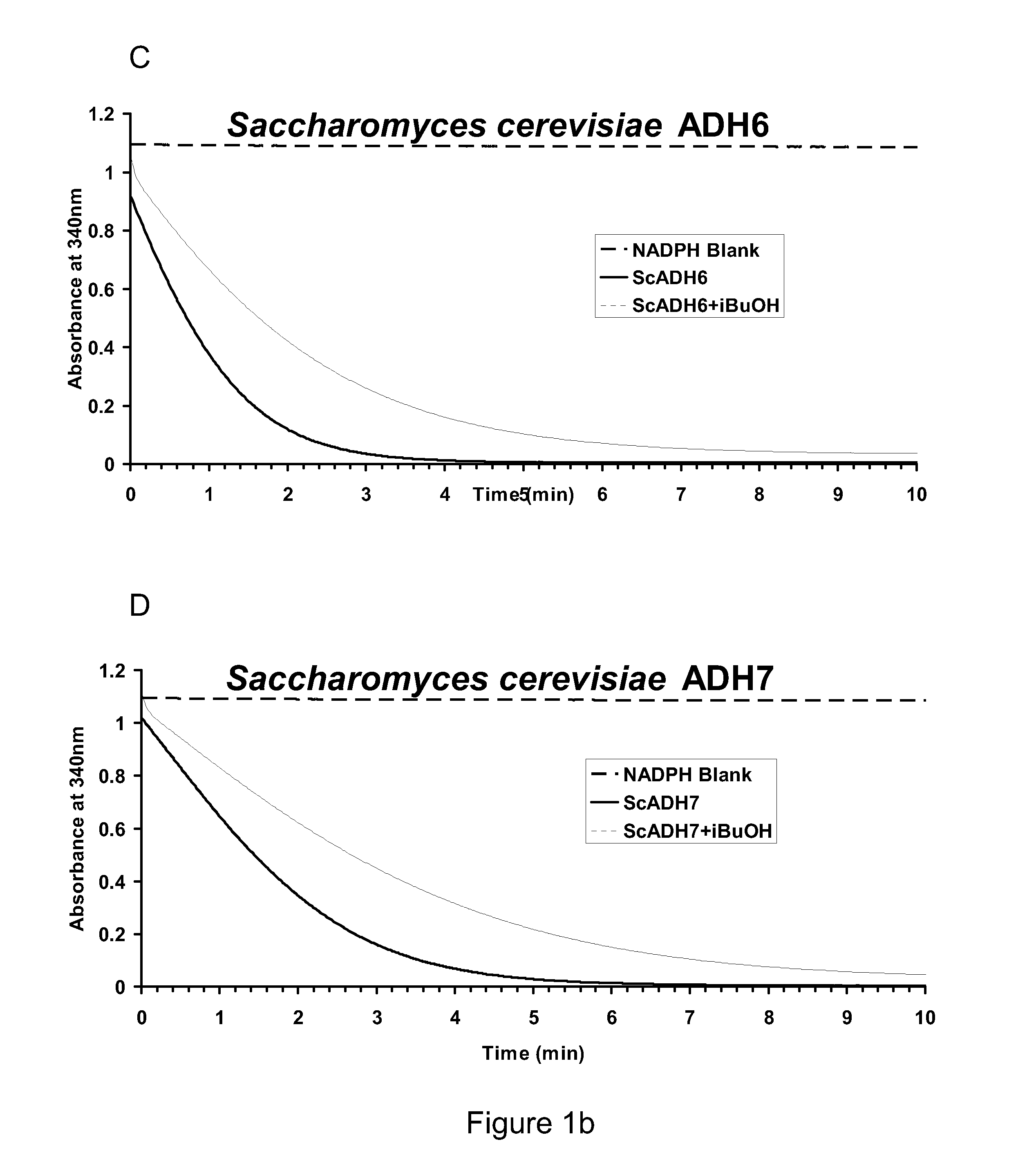
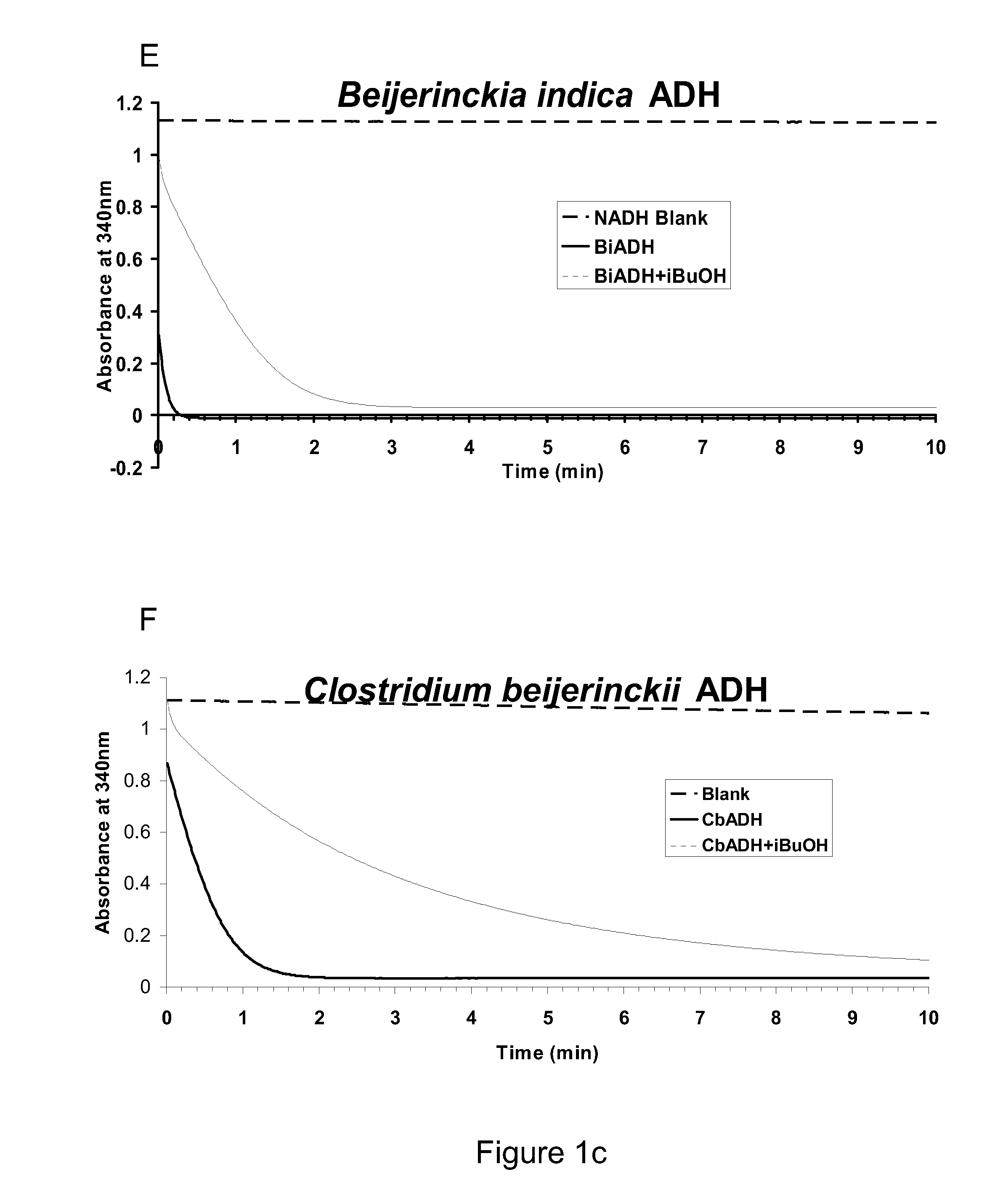
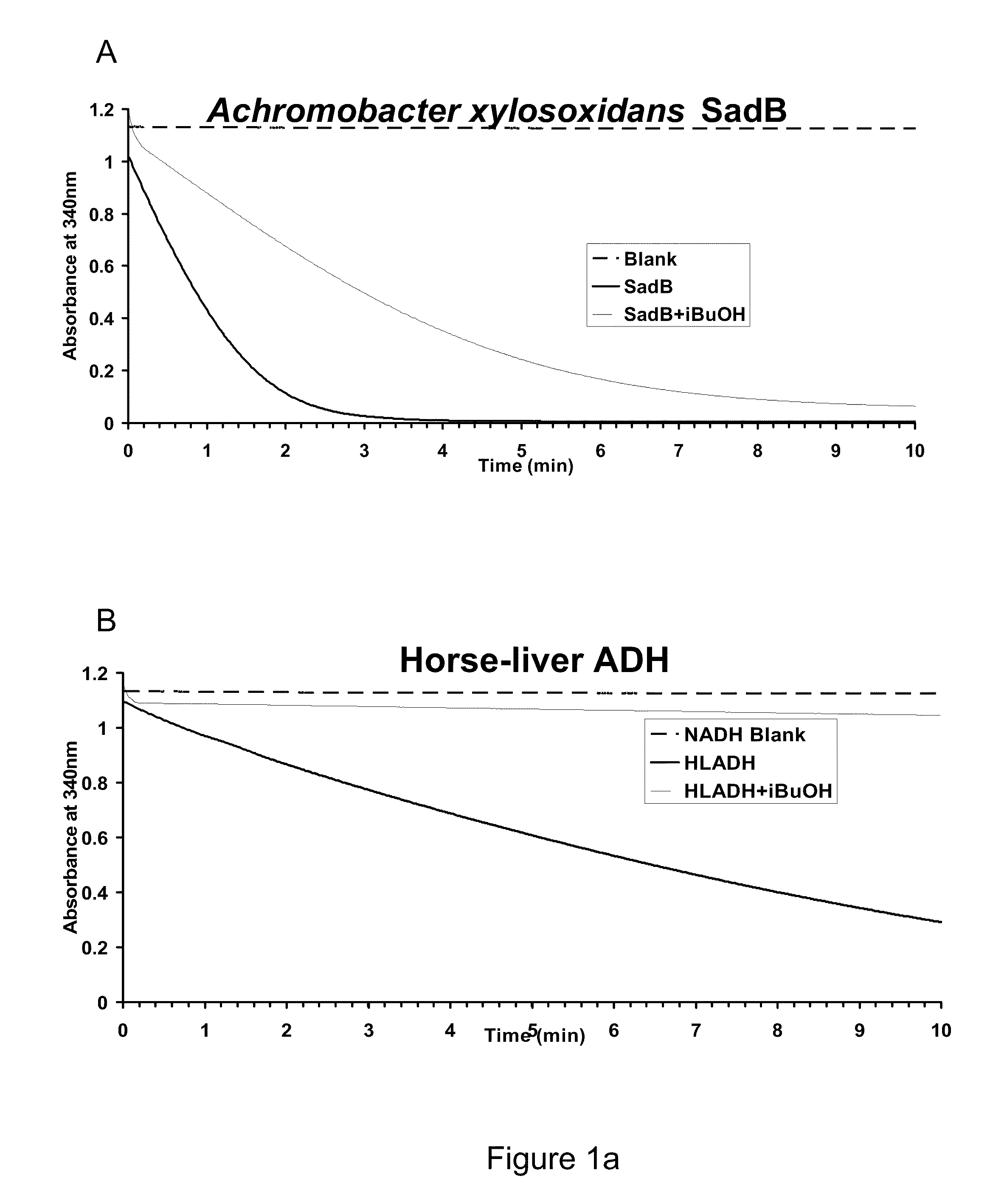
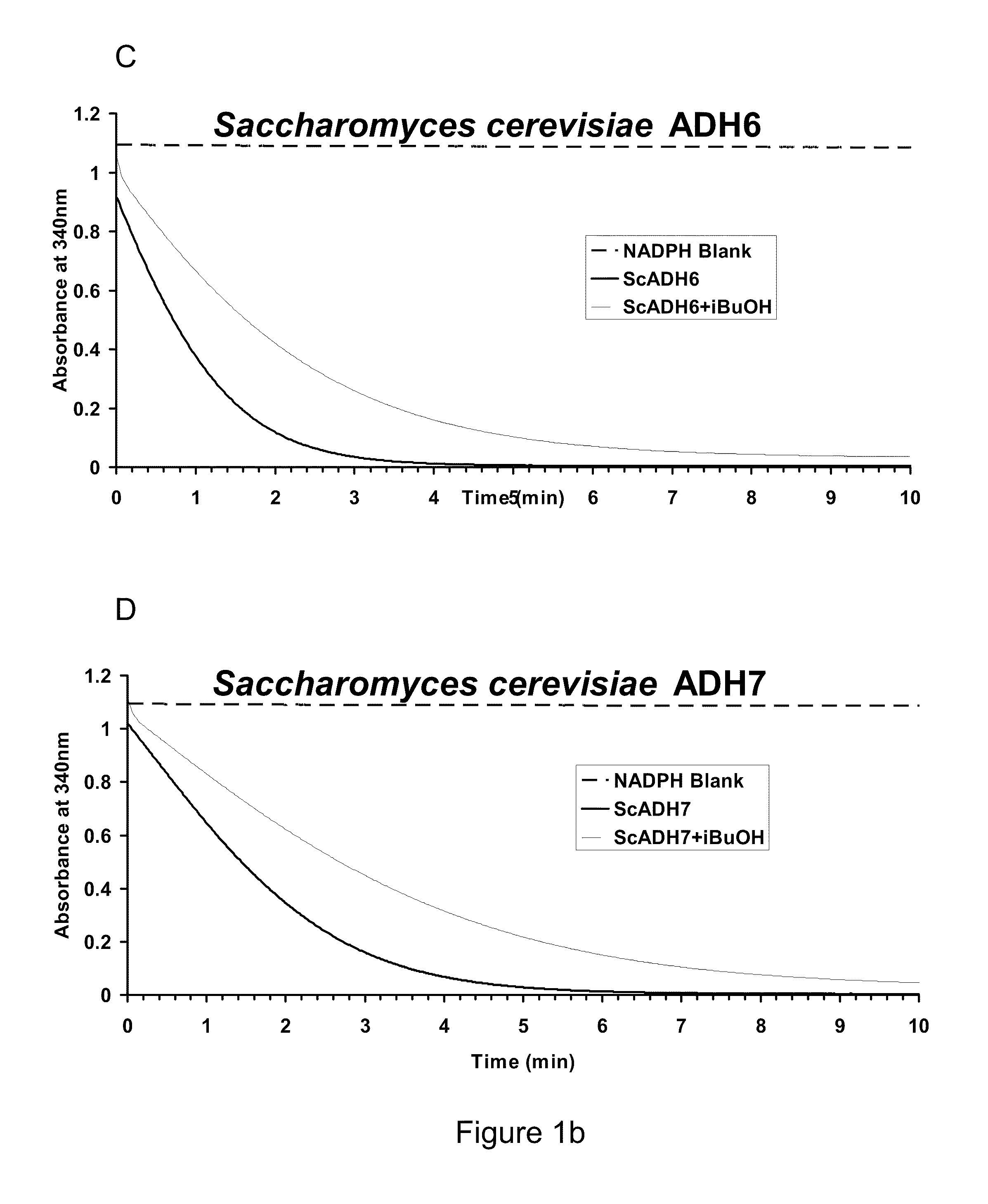
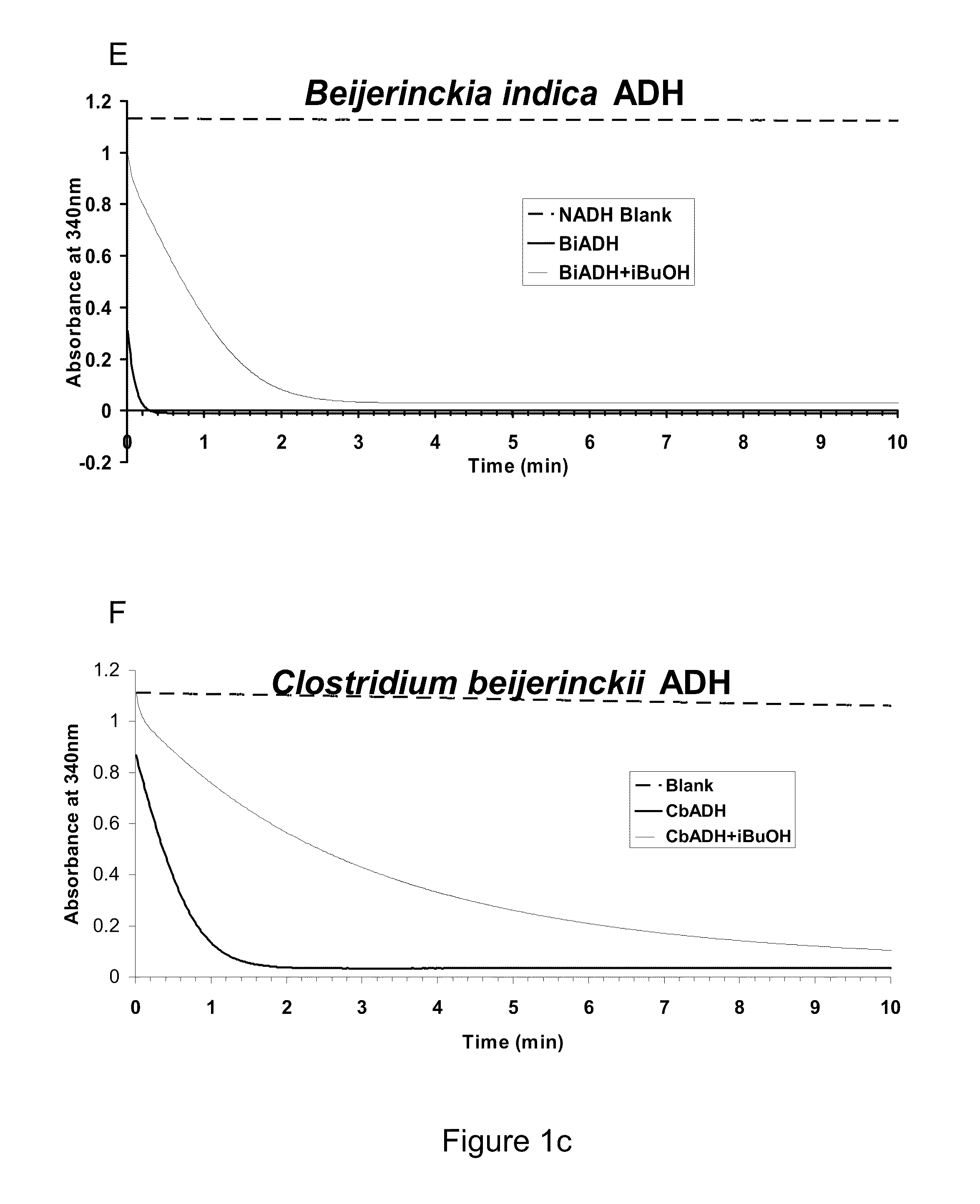
Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH) useful for fermentive production of lower alkyl alcohols
The invention relates to suitable candidate ADH enzymes for production of lower alkyl alcohols including isobutanol. The invention also relates to recombinant host cells that comprise such ADH enzymes and methods for producing lower alkyl alcohols in the same.
Owner:GEVO INC
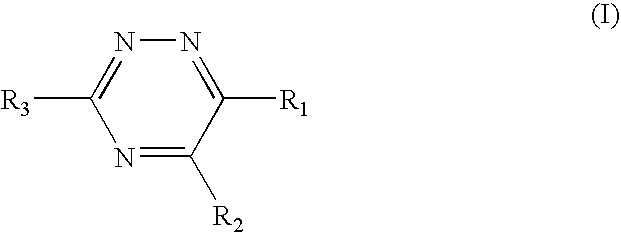
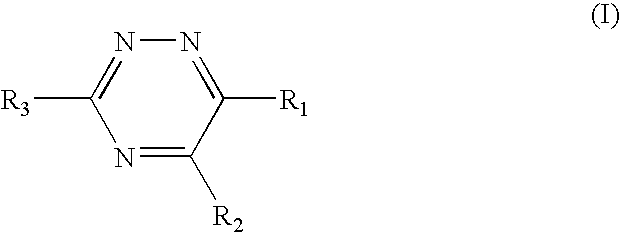
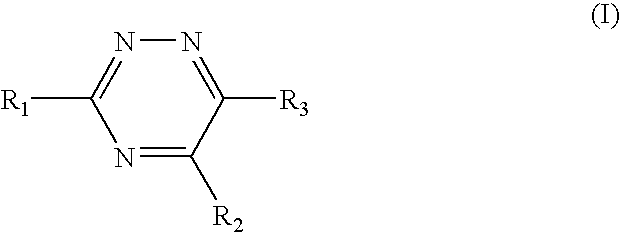
Triazine 11-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitors
Novel compounds are provided which are 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I inhibitors. 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I inhibitors are useful in treating, preventing, or slowing the progression of diseases requiring 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I inhibitor therapy. These novel compounds have the structure: or stereoisomers or prodrugs or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein R1, R2 and R3 are defined herein.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
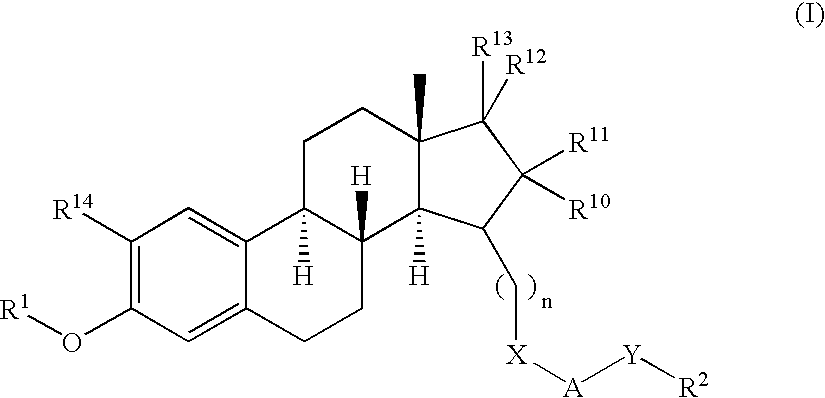
17SS-HSD1 and STS inhibitors
The present invention relates to novel substituted steroid derivatives which represent selectiv inhibitors of the 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I (17β-HSD1) and, in addition, which may represent inhibitors of the steroid sulphatase, as well as to their salts, to pharmaceutical preparations containing these compounds and to processes for the preparation of these compounds. Furthermore, the invention concerns the therapeutic use of said novel substituted steroid derivatives, particularly their use in the treatment, inhibition, prophylaxis or prevention of steroid hormone dependent diseases or disorders, such as steroid hormone dependent diseases or disorders requiring the inhibition of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I and / or steroid sulphatase enzymes and / or requiring the lowering of the endogenous 17β-estradiol concentration.
Owner:ABBVIE PHARMA GMBH
Heteroaryl 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I inhibitors
ActiveUS20060281750A1Antibacterial agentsBiocide11-beta-Hydroxysteroid DehydrogenasesStereoisomerism
Novel compounds are provided which are 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I inhibitors. 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I inhibitors are useful in treating, preventing, or slowing the progression of diseases requiring 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I inhibitor therapy. These novel compounds have the structure: W-L-Z (I) or stereoisomers or prodrugs or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein W, L and Z are defined herein.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Inhibitors of the 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenaseType 1 enzyme and their therapeutic application
The present invention relates to the use of inhibitors of the 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase Type 1 enzyme. The present invention further relates to the use of inhibitors of 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase Type 1 enzyme for the treatment or prophylactically treatment of non-insulin dependent type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, lipid disorders, metabolic syndrome, and other diseases and conditions mediated by excessive glucocorticoid action.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Inhibitors of the 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 enzyme
ActiveUS20060281773A1Improve throughputLimit deliveryBiocideNervous disorderLipid formationInsulin dependent
The present invention relates to compounds which are inhibitors of the 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase Type 1 enzyme. The present invention further relates to the use of inhibitors of 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase Type 1 enzyme for the treatment of non-insulin dependent type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, lipid disorders, metabolic syndrome and other diseases and conditions that are mediated by excessive glucocorticoid action.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Use of mixed duplex oligonucleotides to effect localized genetic changes in plants
InactiveUS7094606B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationACC oxidaseGenetic Change
Owner:CIBUS
Organisms for the production of cyclohexanone
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has cyclohexanone pathways that include at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a cyclohexanone pathway enzyme. A pathway includes a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on C—C bond), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxylate decarboxylase and an enzyme selected from a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, and a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase. A pathway includes an enzyme selected from a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on C—C bond), a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA reductase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate decarboxylase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate reductase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxylate decarboxylase, and a cyclohexanone dehydrogenase. A pathway includes an adipate semialdehyde dehydratase, a cyclohexane-1,2-diol dehydrogenase, and a cyclohexane-1,2-diol dehydratase. A pathway includes a 3-oxopimelate decarboxylase, a 4-acetylbutyrate dehydratase, a 3-hydroxycyclohexanone dehydrogenase, a 2-cyclohexenone hydratase, a cyclohexanone dehydrogenase and an enzyme selected from a 3-oxopimeloyl-CoA synthetase, a 3-oxopimeloyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), and a 3-oxopimeloyl-coA transferase. Each these pathways can include a PEP carboxykinase. A method for producing cyclohexanone includes culturing these non-naturally occurring microbial organisms.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH) useful for fermentive production of lower alkyl alcohols
The invention relates to suitable candidate alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) enzymes for production of lower alkyl alcohols including isobutanol. The invention also relates to recombinant host cells that comprise such ADH enzymes and methods for producing lower alkyl alcohols in the same.
Owner:GEVO INC
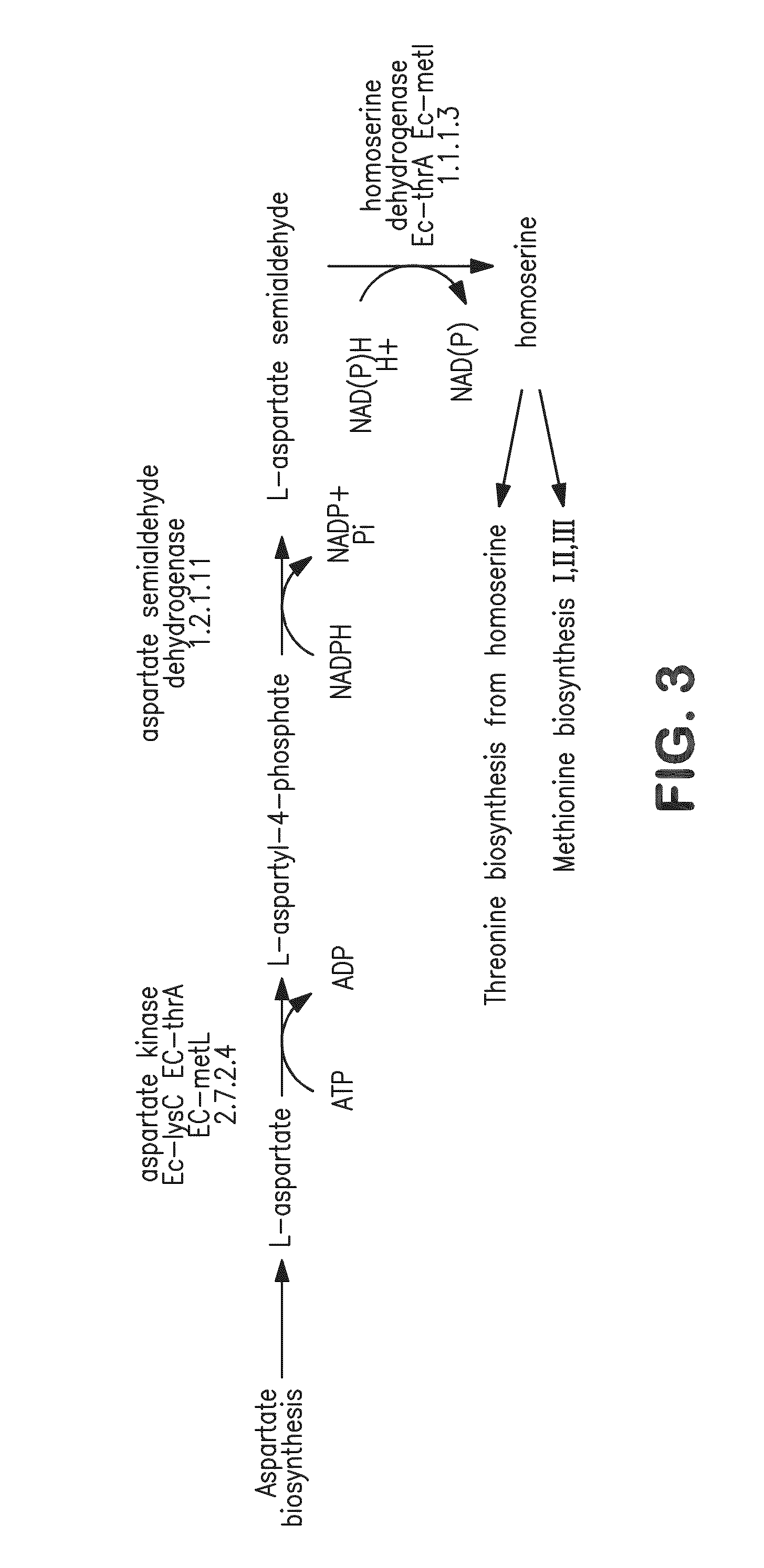
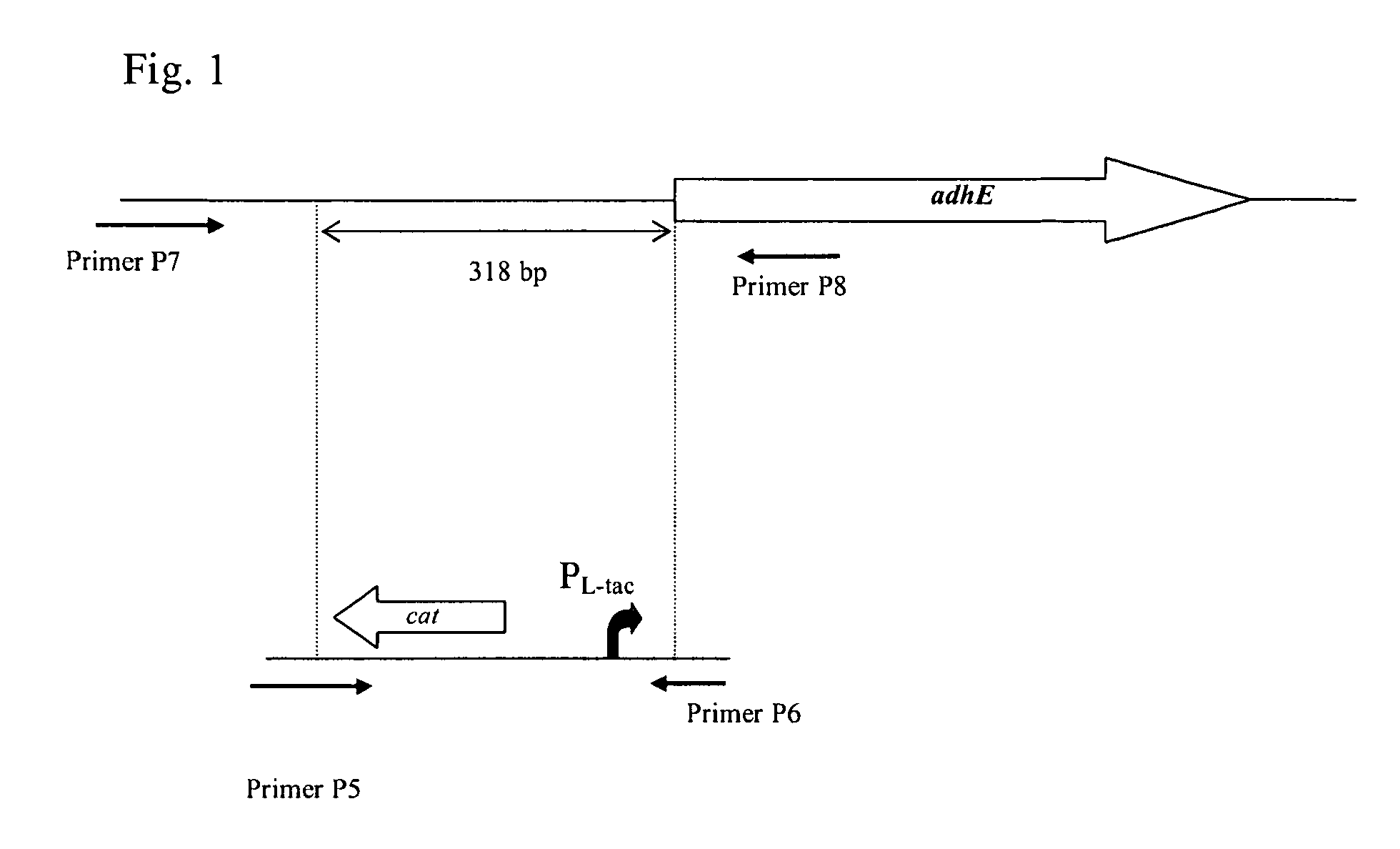
Method for producing an l-amino acid using a bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
InactiveUS20090203090A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaOxidoreductasesBacteroidesArginine
A method for producing an L-amino acid is described, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan, or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of a wild-type alcohol dehydrogenase encoded by the adhE gene or a mutant alcohol dehydrogenase which is resistant to aerobic inactivation.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
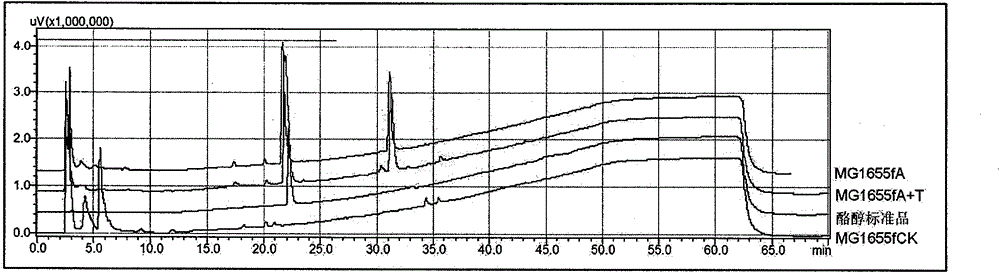
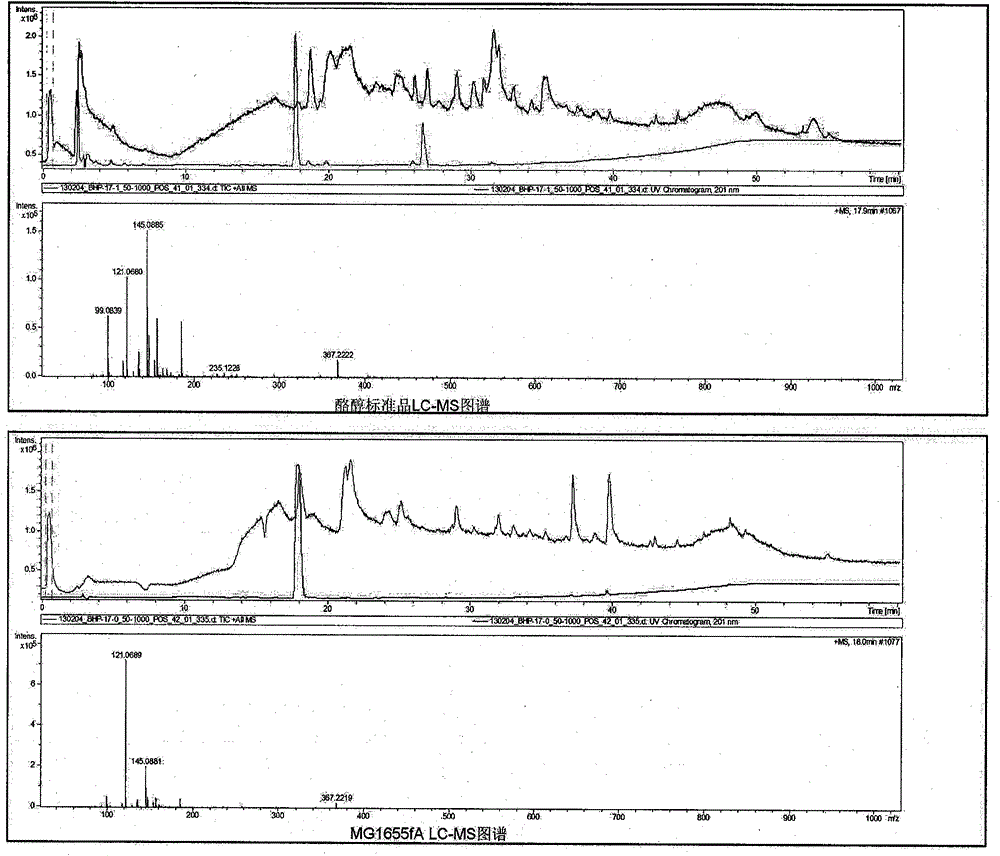
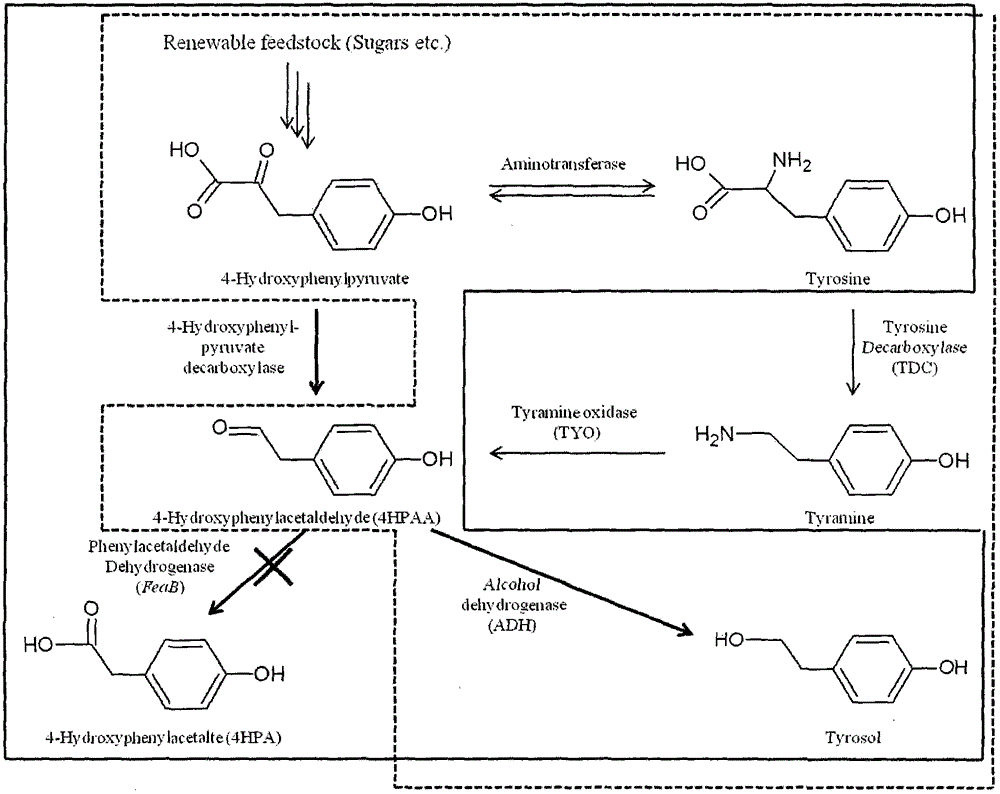
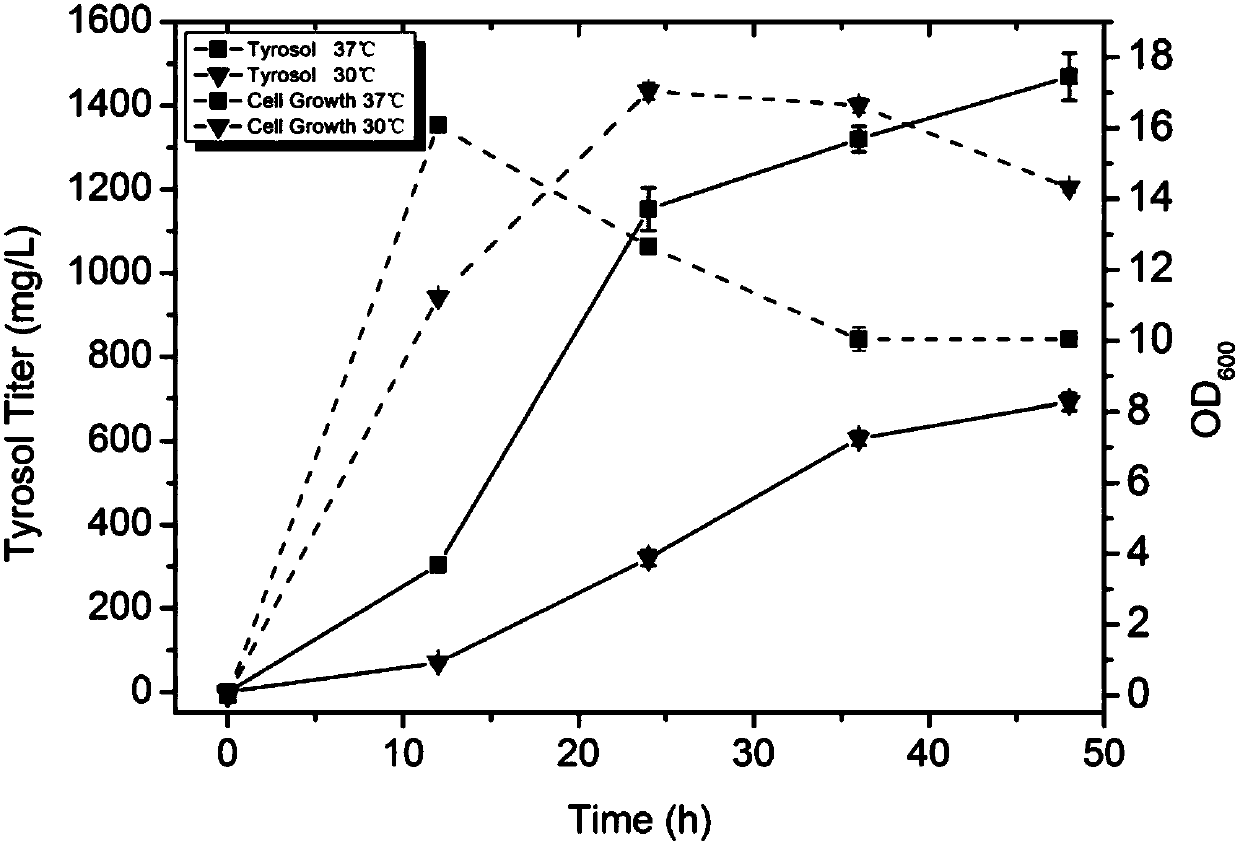
Method for biosynthesis of tyrosol in Escherichia coli and application of tyrosol
ActiveCN104099379ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPhenylacetaldehyde dehydrogenase
The invention relates to a method for biosynthesis of tyrosol in Escherichia coli and application of tyrosol, which belongs to the field of bioengineering technology. According to the method for biosynthesis of tyrosol in Escherichia coli, tyrosine or glucose is used as a substrate, (4-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvic acid is produced under the catalysis of ammonialyase coded by Escherichia coli; (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde is produced under the action of the microzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate decarboxylase; (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde is catalyzed by alcohol dehydrogenase so as to produce tyrosol; and a phenylacetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene of Escherichia coli is knocked out at the same time so as to block the transformation channel for (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde into (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid and promote accumulation of (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde and transformation of (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde into tyrosol. The invention provides a novel production approach for tyrosol; and the method lays a foundation for large-scale industrial production of tyrosol and has important economic values and social benefits.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
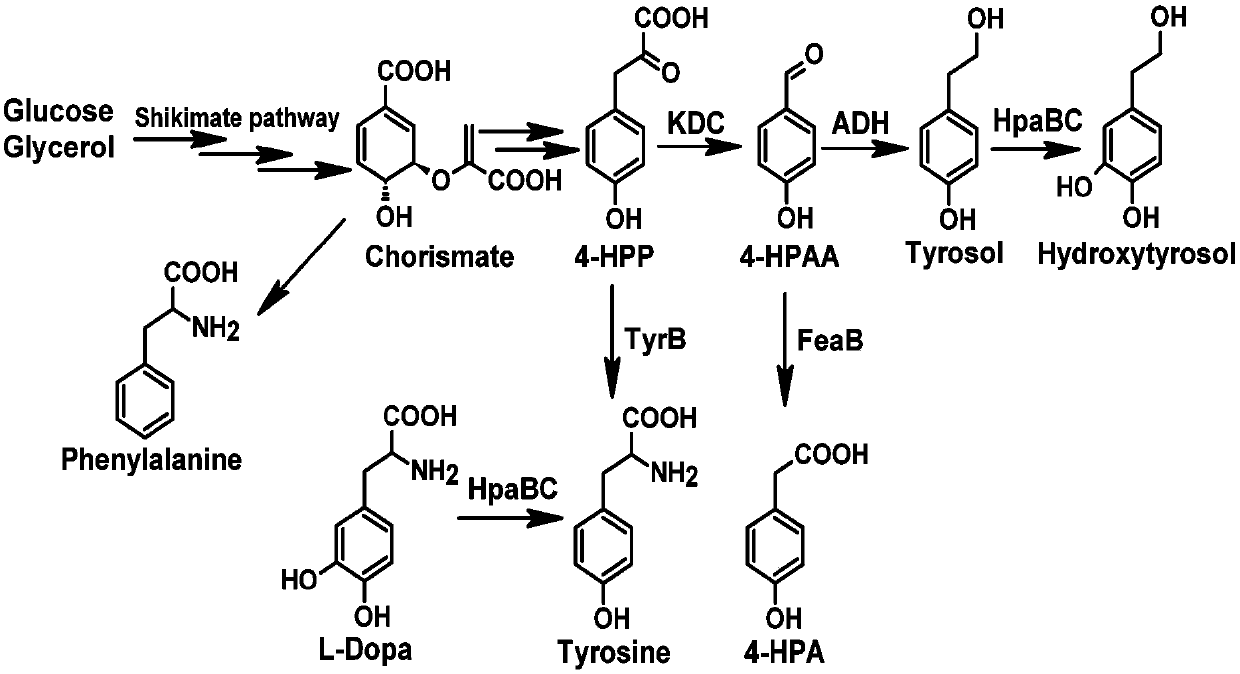
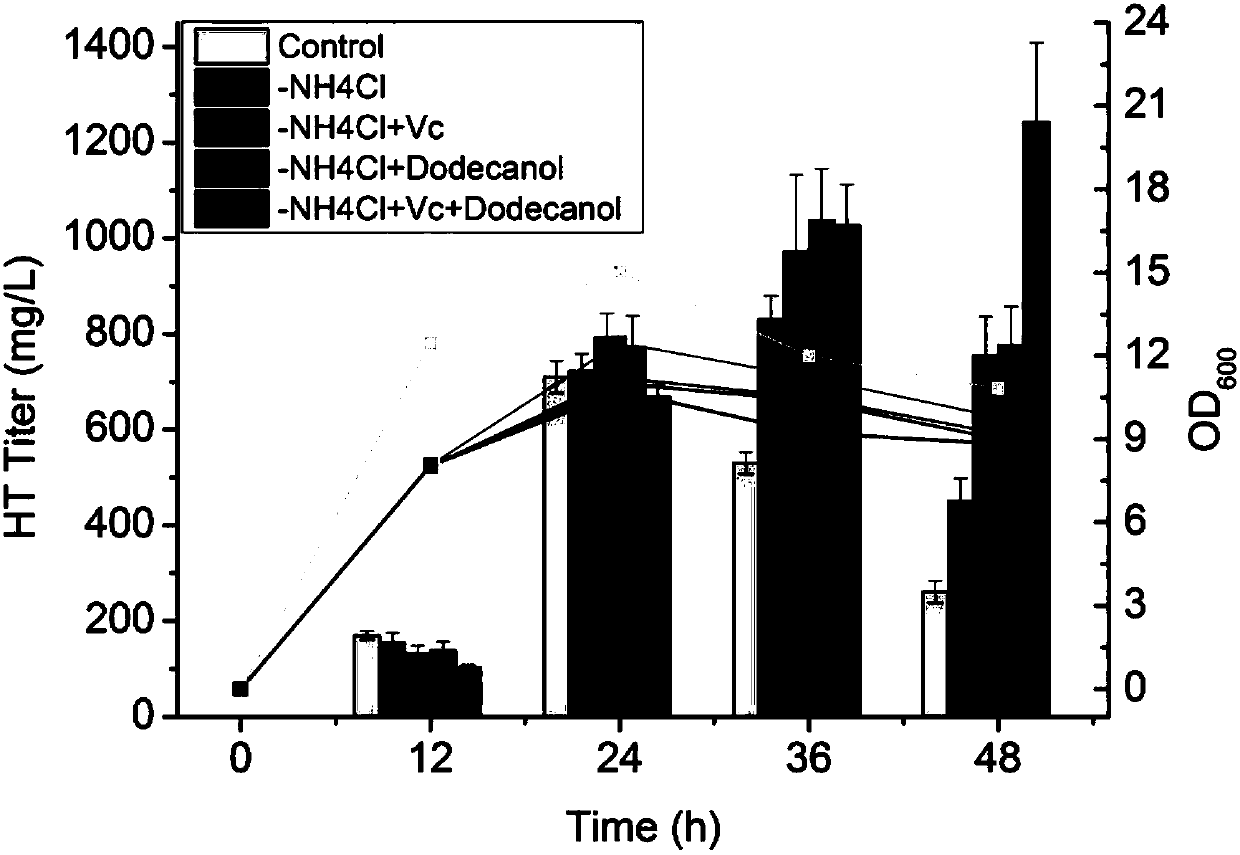
Method for producing tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol through heterologous metabolic pathways
ActiveCN107586794AEfficient extractionEfficient productionFermentationAlcohol dehydrogenaseGene code
The invention discloses a method for producing tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol through heterologous metabolic pathways, wherein metabolic pathways for producing hydroxytyrosol are introduced into hosts forproducing the hydroxytyrosol; more specifically, the method comprises the following steps: producing tyrosol by efficiently expressing aminotransferase, ketoacid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase in the hosts, then introducing 4-hydroxyphenylacetate hydroxylase to produce the hydroxytyrosol. Genes coded by the enzymes are constructed on an expression plasmid or integrated to a genome. Through the method, production hosts capable of producing the hydroxytyrosol by using glucose, glycerinum and tyrosine can be prepared by introducing the genes coded by the enzymes to the hosts; meanwhile,the invention also discloses a biphasic cultivation method, so that the production of the hydroxytyrosol is more efficient.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Production of omega-amino fatty acids
The invention provides a whole cell catalyst which expresses a recombinant α-dioxygenase or the combination of a recombinant fatty acid reductase and a phosphopantetheinyl transferase phosphopantetheinylating the fatty acid reductase, and which in addition to the α-dioxygenase and / or the combination of fatty acid reductase and phosphopantetheinyl transferase expresses a transaminase, characterized in that the phosphopantetheinyl transferase and / or transaminase is preferably recombinant; and a method for the conversion of a fatty acid, ω-hydroxy fatty acid, ω-oxo fatty acid or a monoester thereof to an amine, comprising oxidation of the fatty acid, ω-hydroxy fatty acid, ω-oxo fatty acid or the monoester thereof to an oxidation product by contacting with an alkane hydroxylase and / or alcohol dehydrogenase, contacting the oxidation product with a phosphopantetheinylated fatty acid reductase or a α-dioxygenase to give an aldehyde, and contacting the aldehyde with a transaminase.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Enzymic method for the enantioselective reduction of keto compounds
ActiveUS20090017510A1Long stable timeHigh yieldBacteriaOxidoreductasesOrganic compoundEnantio selectivity
The invention relates to an enzymatic method for the enantioselective reduction of organic keto compounds to the corresponding chiral hydroxy compounds, an alcohol dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus minor and a method for the enantioselective production of (S)-hydroxy compounds from a racemate.
Owner:SCIENCES PO
7beta-hydroxyl sterol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof to preparation of ursodeoxycholic acid
ActiveCN108546691AEasy extractionEasy to manufactureOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringSterolProtein engineering
The invention discloses a 7beta-hydroxyl sterol dehydrogenase mutant which is obtained by protein engineering and of which coenzyme preference is changed, a coding gene of the 7beta-hydroxyl sterol dehydrogenase mutant, a recombinant expression vector and a recombinant expression transformant which contain a sequence of the gene, a preparation method of a recombinant mutant enzyme preparation, andapplication of the recombinant mutant enzyme preparation to preparation of ursodeoxycholic acid. By co-enzyme regeneration of enzymic coupling, the recombinant mutant enzyme preparation disclosed bythe invention can efficiently utilize relatively cheap oxidized coenzyme I (NAD+) instead of very expensive oxidized coenzyme II (NADP+); asymmetric reduction of catalytic 7-hydroxyl lithocholic acideffectively reduces production cost; moreover, the recombinant mutant enzyme preparation has the advantages of simplicity for operation, mild reaction condition, environmental-friendliness, high yieldand the like, and has a good application prospect in preparation of ursodeoxycholic acid by epimerization of chenodesoxycholic acid.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
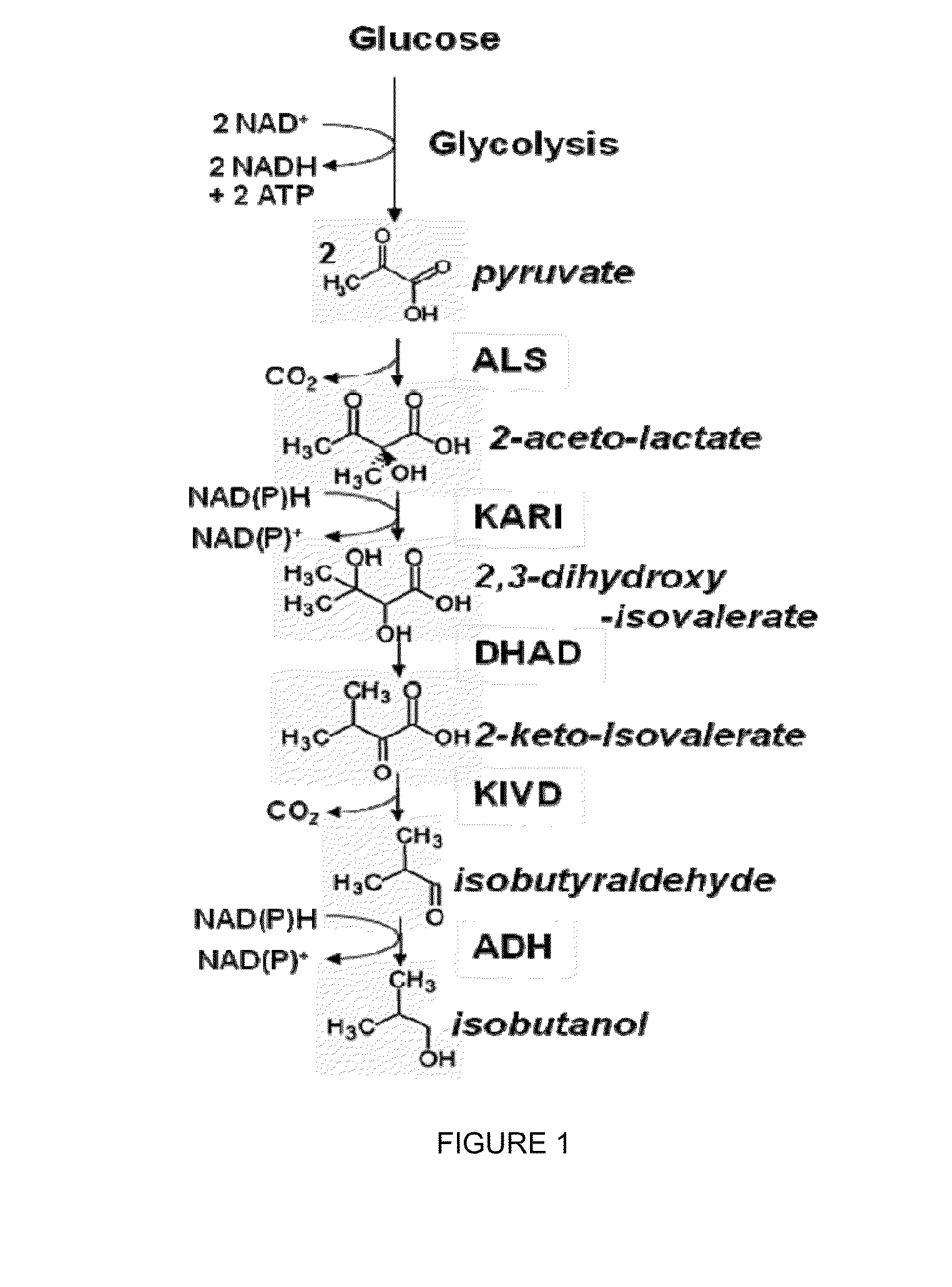
Modified alcohol dehydrogenases for the production of fuels and chemicals
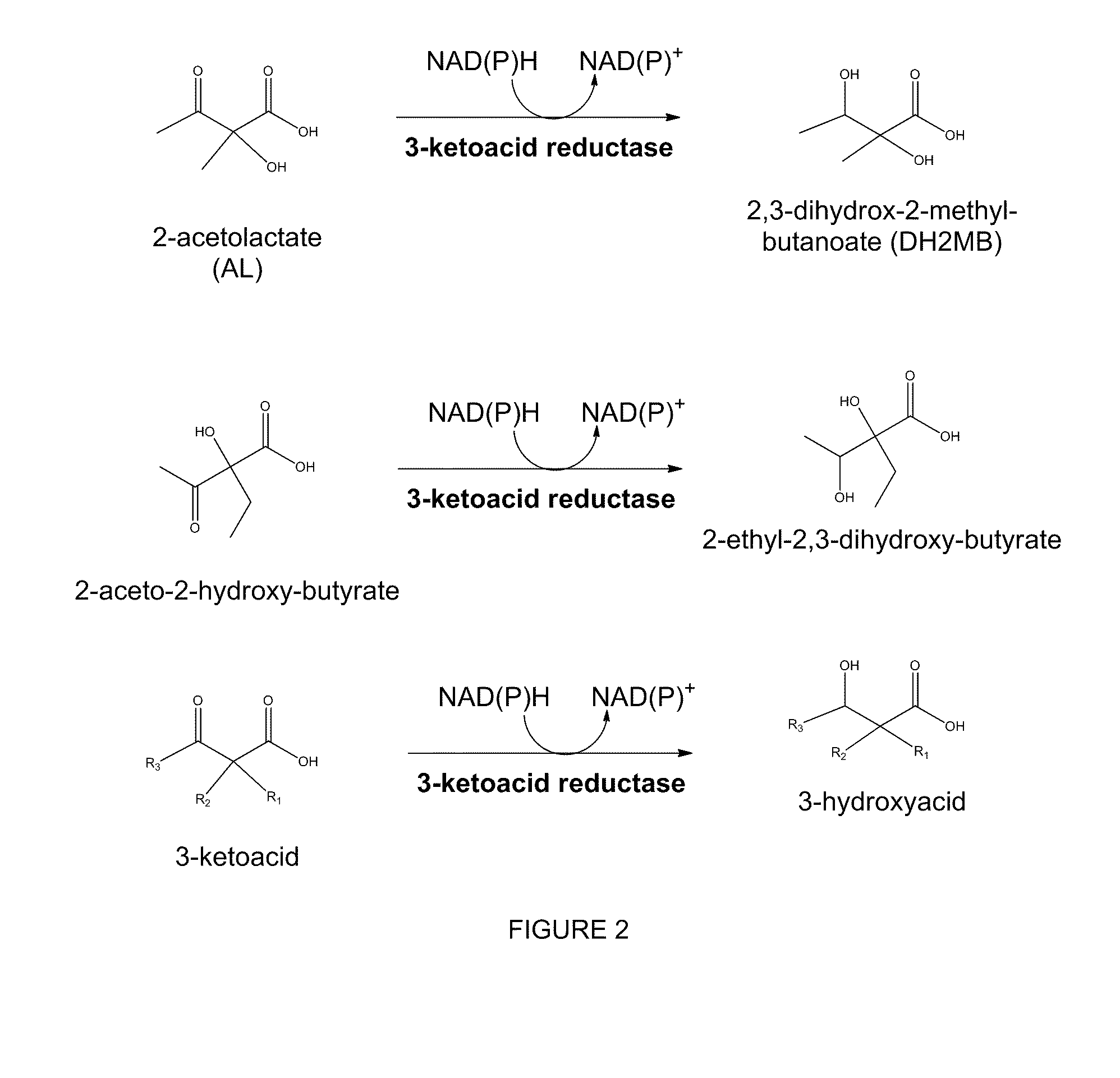
The present invention relates to recombinant microorganisms comprising biosynthetic pathways and methods of using said recombinant microorganisms to produce various beneficial metabolites. In various aspects of the invention, the recombinant microorganisms may further comprise one or more modifications resulting in the reduction or elimination of 3 keto-acid (e.g., acetolactate and 2-aceto-2-hydroxybutyrate) and / or aldehyde-derived by-products. In various embodiments described herein, the recombinant microorganisms may be microorganisms of the Saccharomyces clade, Crabtree-negative yeast microorganisms, Crabtree-positive yeast microorganisms, post-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, pre-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, and non-fermenting yeast microorganisms.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Process For The Preparation of (3R)-Hydroxybutyl (3R) -Hydroxybutyrate By Enzymatic Enantioselective Reduction Employing Lactobacillus Brevis Alcohol Dehydrogenase
ActiveUS20120064611A1Preparation from ketenes/polyketenesOxidoreductasesHydroxybutyric acidLactobacillus brevis
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD +1
Method for simultaneously detecting gene mutations of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 and alcohol dehydrogenase 2
InactiveCN102758008ASimultaneous detection of genetic polymorphismsNo risk of contaminationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescencePolymorphism Detection
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously detecting gene mutations of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 and alcohol dehydrogenase 2. Concretely, a probe effective for detection of genetic polymorphism of the ALDH2 gene rs671 and the ADH2 gene rs1229984, a method for simultaneously detecting gene mutations and a kit for the purpose are provided. Thus the invention provides a probe for polymorphism detection, namely a probe for detection of at at least one type of genetic polymorphism of the ALDH2 gene rs671 and the ADH2 gene rs1229984, characterized in that: the probe comprises at least 1 type of fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide selected from (P1) to (P3') defined in the description.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
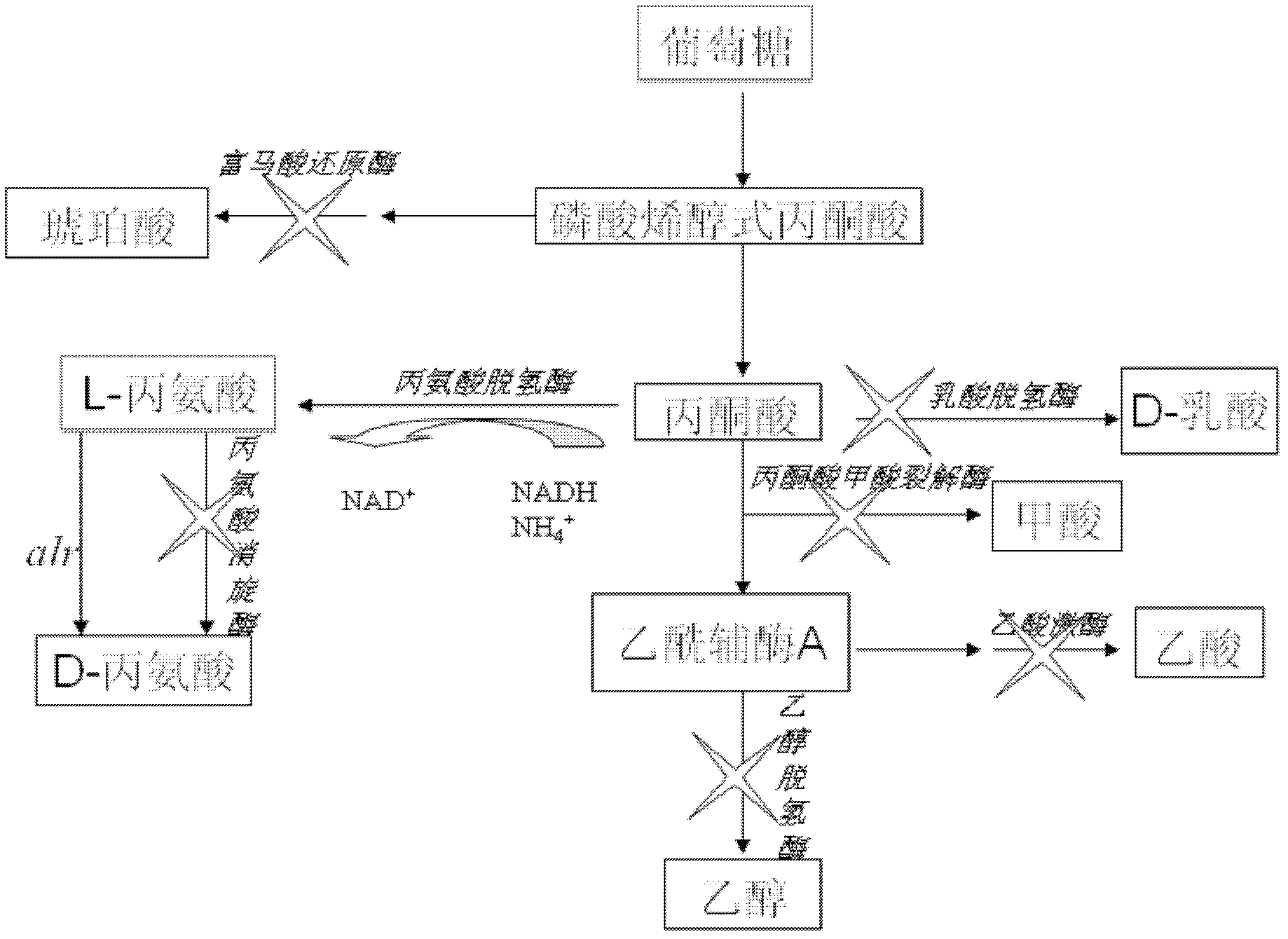
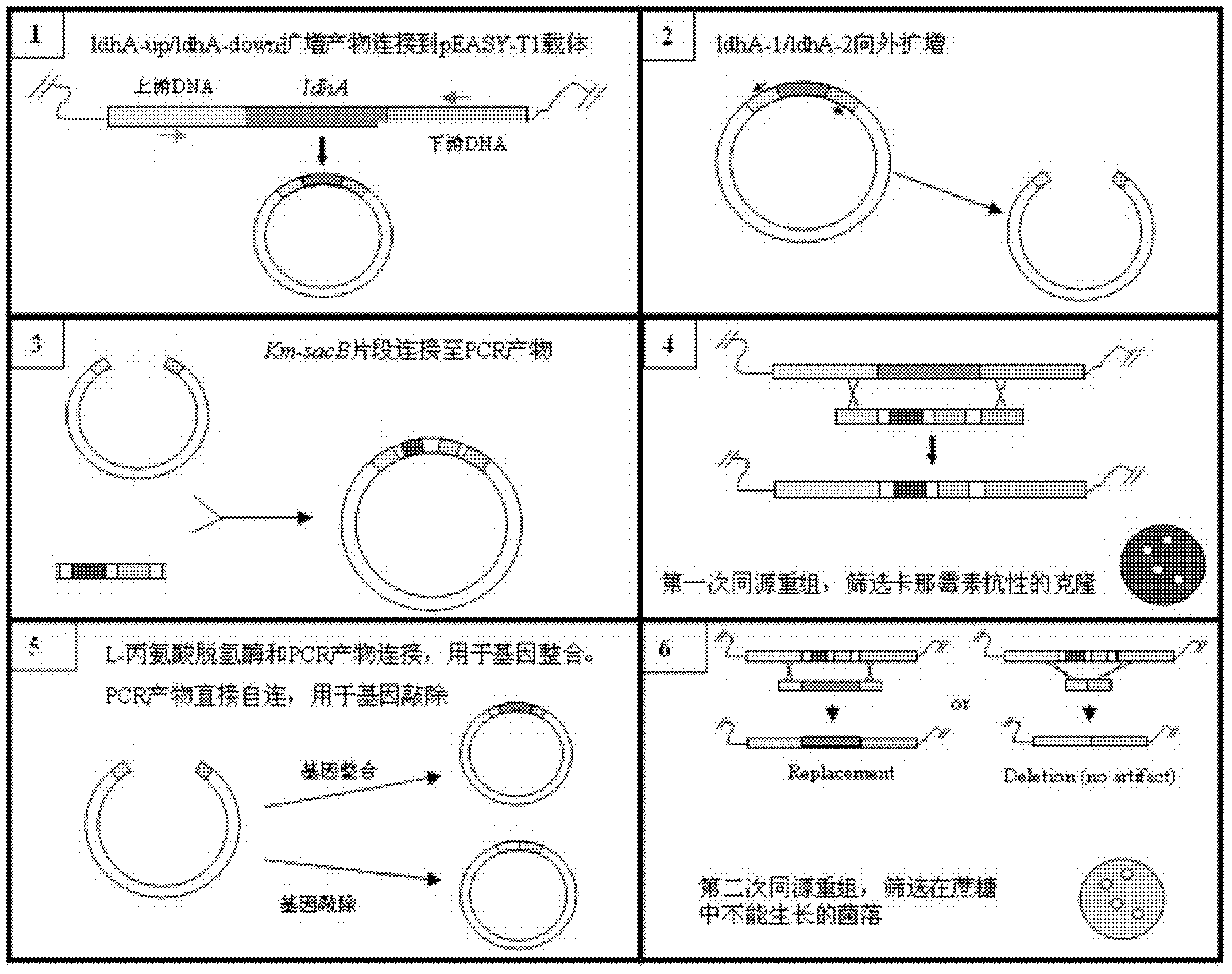
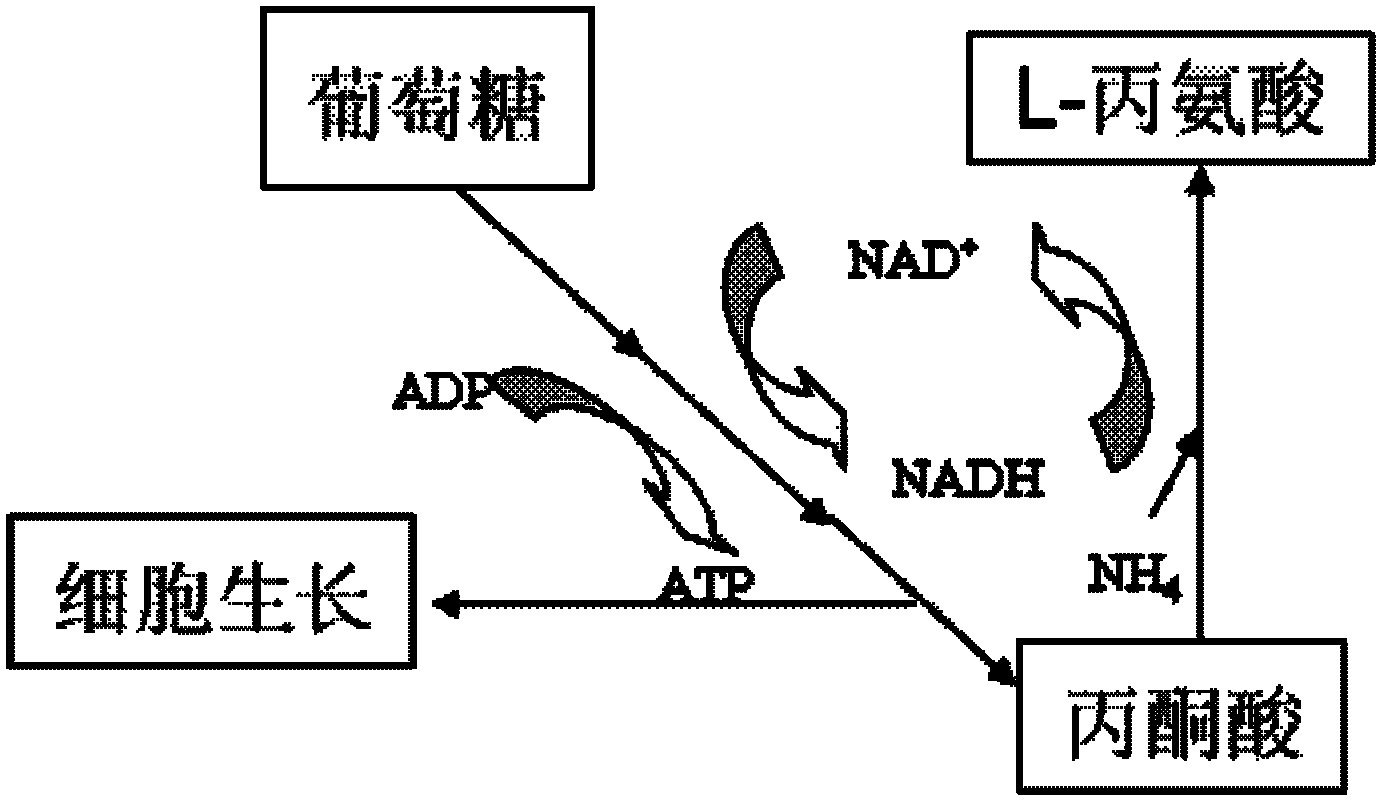
XZ-A26 bacterial strain for producing L-alanine with high yield as well as construction method and application of XZ-A26 bacterial strain
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
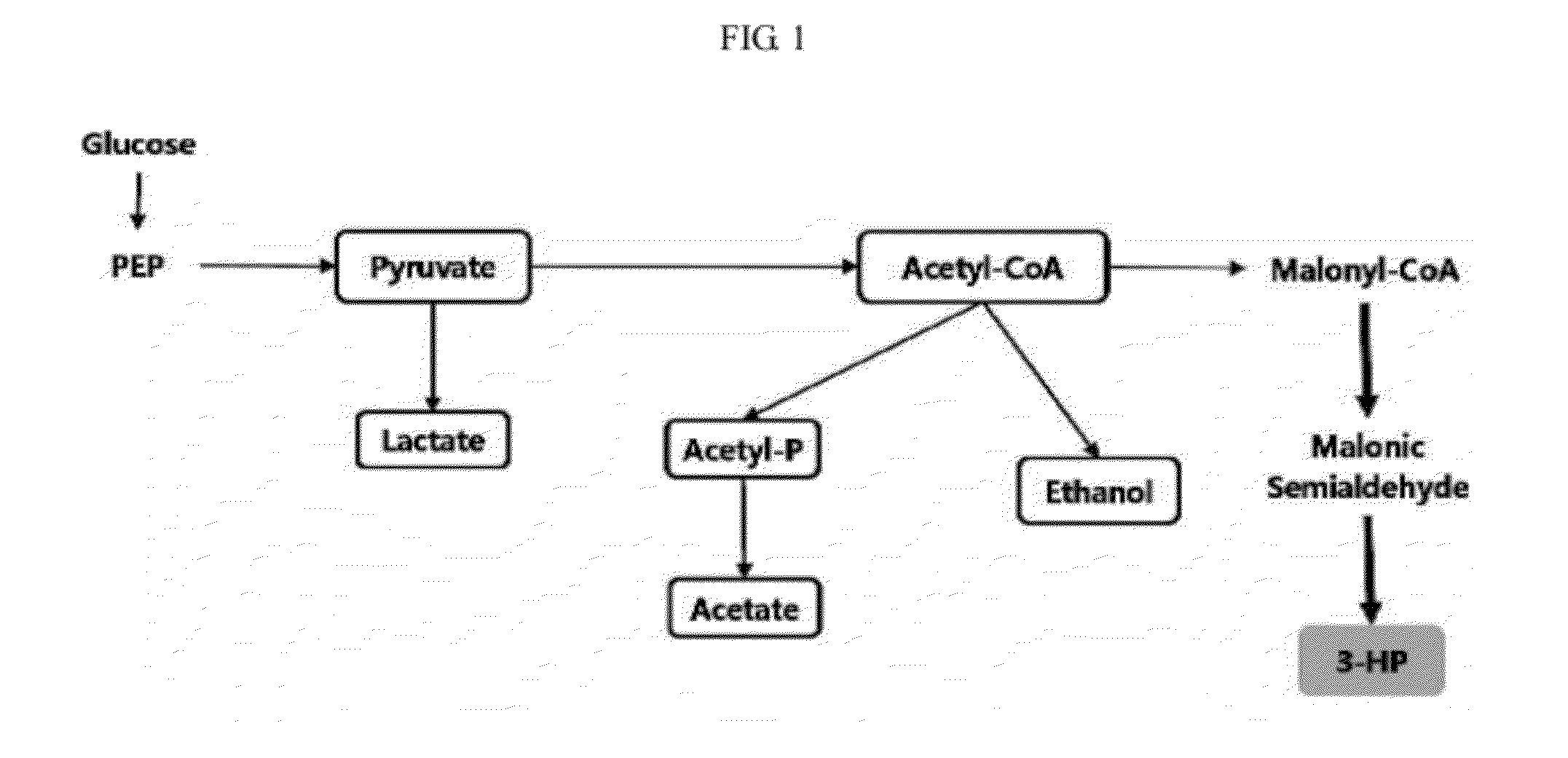
Genetic modification for production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid
InactiveUS20120329110A1Improve production yield and producibilityIncrease productivityFungiBacteriaLactate dehydrogenaseMetabolite
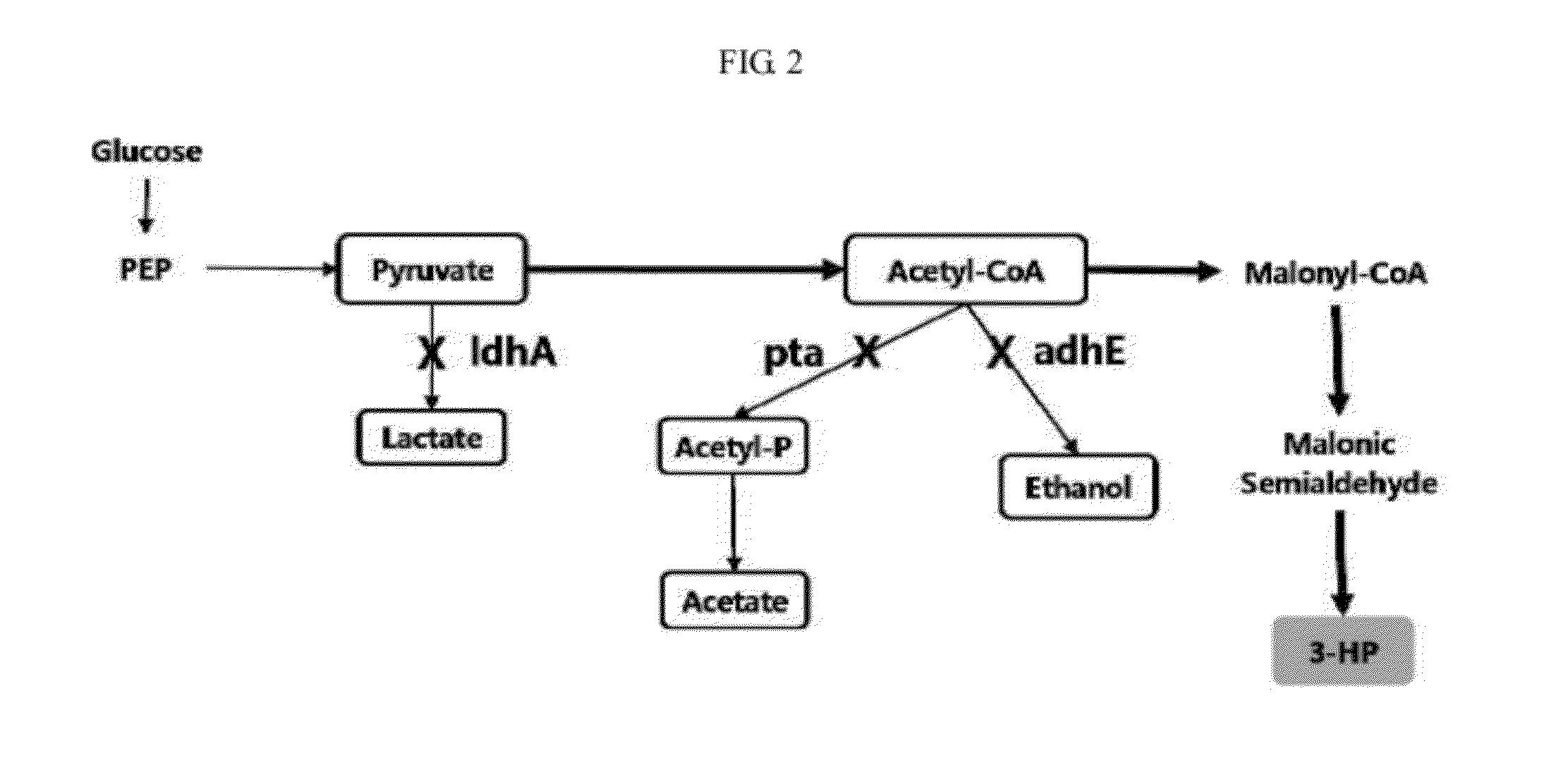
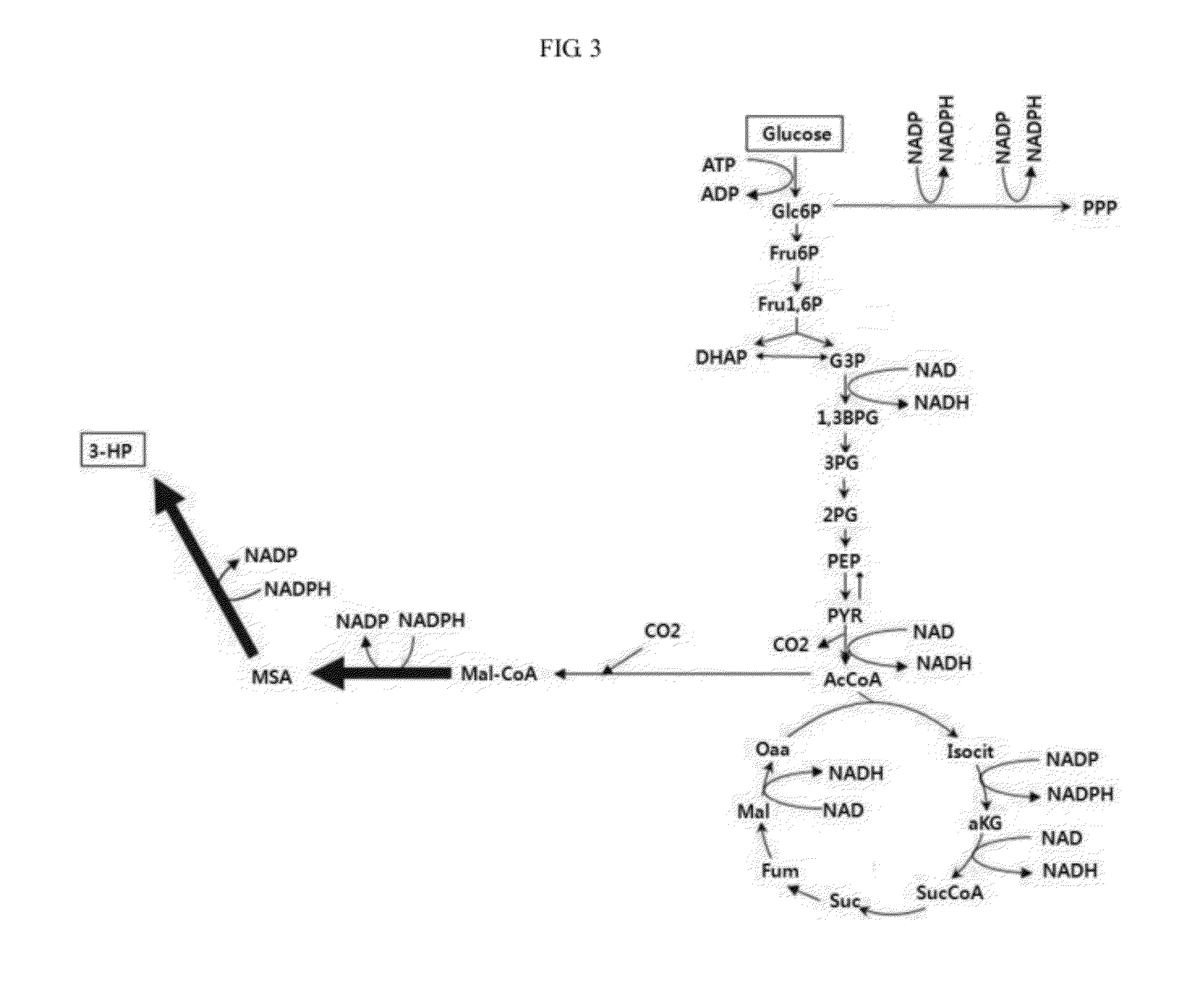
A method of increasing 3-HP production efficiency by inhibiting expression of a lactate dehydrogenase, a phosphotransacetylase, and an alcohol dehydrogenase in production of 3-HP using a malonic semialdehyde reduction pathway to prevent metabolite leak and increase a malonyl-CoA pool is disclosed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
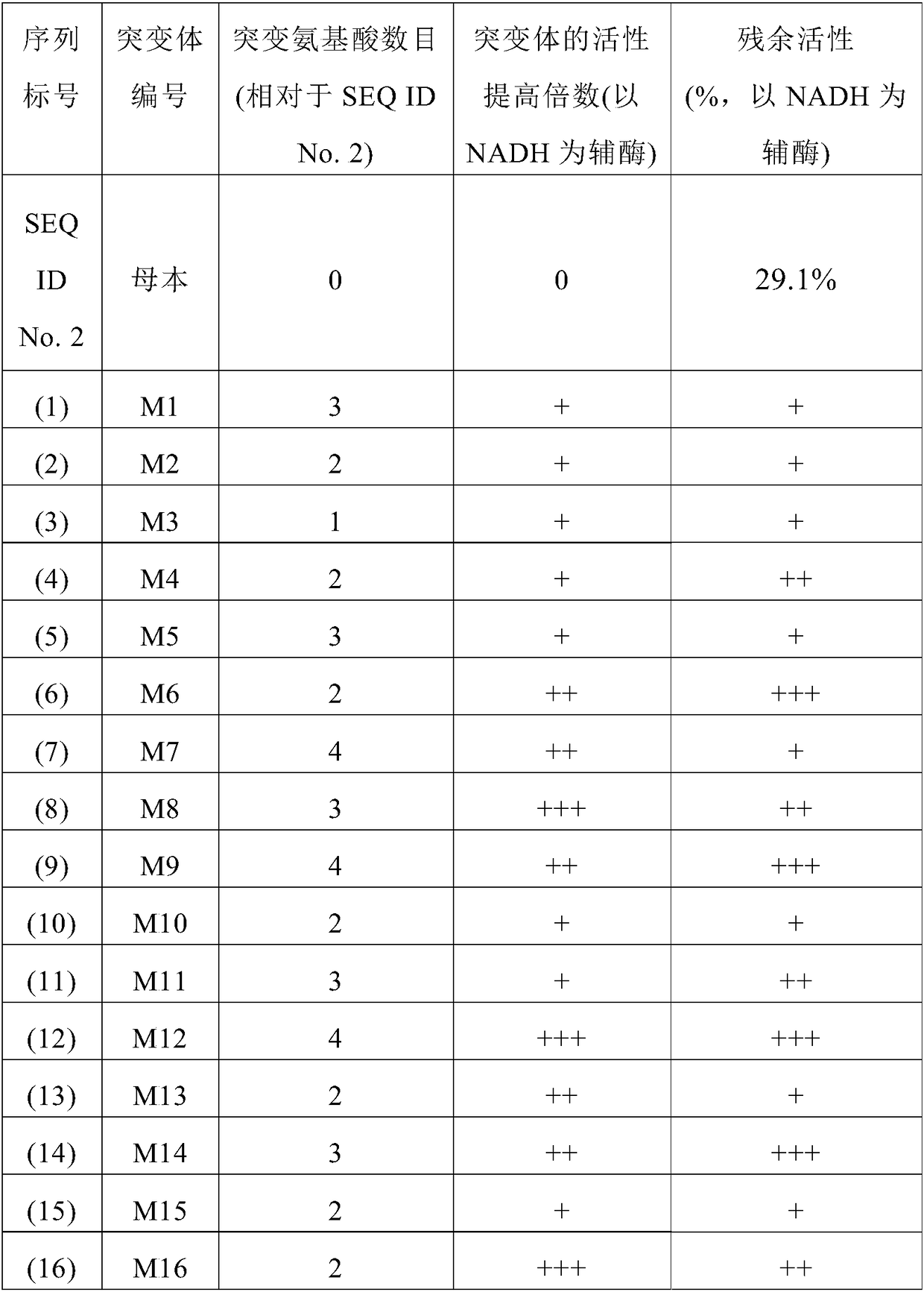
Application of alcohol dehydrogenase in catalytic generation of ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate
InactiveCN103160547AHigh yieldHigh optical activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidPtru catalyst
The invention discloses application of alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 in preparing ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate from ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate by asymmetric reduction. By using alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 as a catalyst, ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate as a substrate and NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) as a cofactor, asymmetric reduction is carried out to prepare the ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate. The invention applies the alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 in preparing ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate from ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate by asymmetric reduction for the first time, and has favorable effect. The enzyme activity is up to 5.6 U / mg, the yield of the substrate is up to 94%, and the enantiomeric excess value of the product is 100%. The yield is high, and the production cost is greatly lowered.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Novel 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I inhibitors
3,15-substituted estrone compounds which act as inhibitors of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I (17β-HSD1), salts thereof, pharmaceutical preparations containing such compounds, processes for preparing such compounds, and therapeutic uses of such compounds, particularly in the treatment or inhibition of steroid hormone dependent diseases or disorders, such as steroid hormone dependent diseases or disorders requiring the inhibition of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I enzymes and / or requiring the lowering of the endogenous 17β-estradiol concentration, as well as the general use of selective 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitors which possess in addition no or only pure antagonistic binding affinities to the estrogen receptor for the treatment or inhibition of benign gynecological disorders, particularly endometriosis.
Owner:ABBVIE PHARMA GMBH
Alcohol dehydrogenase, gene and recombinase thereof, and application of alcohol dehydrogenase in synthesis of chiral diaryl secondary alcohol
InactiveCN105936909AImprove expression levelIncrease enzyme activityOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringDiaryl ketoneGenus Kluyveromyces
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase, a gene thereof, a recombinant expression vector and a recombinant expression transformant respectively containing the gene, a recombinase of the alcohol dehydrogenase, and an application of the alcohol dehydrogenase in asymmetric reduction synthesis of chiral diaryl secondary alcohol as a catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The alcohol dehydrogenase is from Kluyveromyces sp. CCTCCM2011385, has a carbonyl group reduction function, and also has a hydroxy group oxidation function. Extra addition of glucose dehydrogenase and other enzymes used for cofactor circulation is not needed when the alcohol dehydrogenase is used in the reduction of diaryl ketone into the chiral diaryl secondary alcohol as a biocatalyst, and the alcohol dehydrogenase has the advantages of high catalysis efficiency, mild reaction conditions, easy product recovery and low cost, so the alcohol dehydrogenase has very good application and exploitation prospect in the production of antihistamine medicines.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of corn sobering-up peptide
ActiveCN102028093AClear hangover effectPromote biochemical reactionsVegetable proteins working-upEthanol dehydrogenaseUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a corn sobering-up peptide and a preparation method thereof. In the method, corn gluten meal is taken as a raw material for the product provided by the invention, alkali protease Alcalase is adopted for hydrolysis for 2 hours under optimal conditions, compound protease Protamex is further added for hydrolysis for 3 hours under the optimal conditions, and corn sobering-up peptide powder is obtained by crude separation, ultrafiltration, concentration and spray forming. The peptide section with the molecular weight of less than 1200Da in the product accounts for 73.19%, and the content of lactamic acid and the content of aminocarproic acid are greater than 6.43% and 12.42% respectively. The product can generate stable nicotinamide adenine adinucleotide (NAD<+>) by improving the concentration of the lactamic acid and aminocarproic acid in blood, enhance the activity of alcohol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, promote decomposition and metabolism of ethanol in vivo, thereby reducing the concentration of the ethanol in the blood, increasing the supply of coenzyme, playing a role in protecting liver and playing a role in preventing liver damages caused by alcohol, such as fatty liver and the like.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Glucose Dehydrogenase/Cytochrome Fusion Protein
A fusion protein of pyrroloquinoline quinone glucose dehydrogenase (PQQGDH) and a cytochrome is disclosed. PQQGDH is, for example, a water-soluble PQQGDH derived from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. The cytochrome is, for example, an electron transfer domain of quinohemoprotein ethanol dehydrogenase from Comamonas testosteroni. The fusion protein of the present invention shows intramolecular electron transfer from PQQ, a redox center, to the cytochrome, which allow construction of a direct electron transfer-type glucose sensor which requires no electron mediators.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Alcohol dehydrogenase mutant, gene thereof, and application thereof in preparation of chiral diaryl alcohol
InactiveCN105936895AHigh catalytic activityHigh enantioselectivityOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringReduction ActivityKluyveromyces sp.
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase mutant, an encoding gene thereof, and an application thereof in the preparation of chiral diaryl alcohol. The mutant is obtained through substituting serine in the 237th position of alcohol dehydrogenase from Kluyveromyces sp.CCTCC M2011385 and with the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1 with alanine. The alcohol dehydrogenase mutant has greatly higher reduction activity and stereoselectivity than wild enzymes. The mutant is especially suitable for asymmetric reduction of diaryl ketone to prepare chiral diaryl alcohol, and can be used to synthesize various antihistamine medicines. The alcohol dehydrogenase mutant has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com