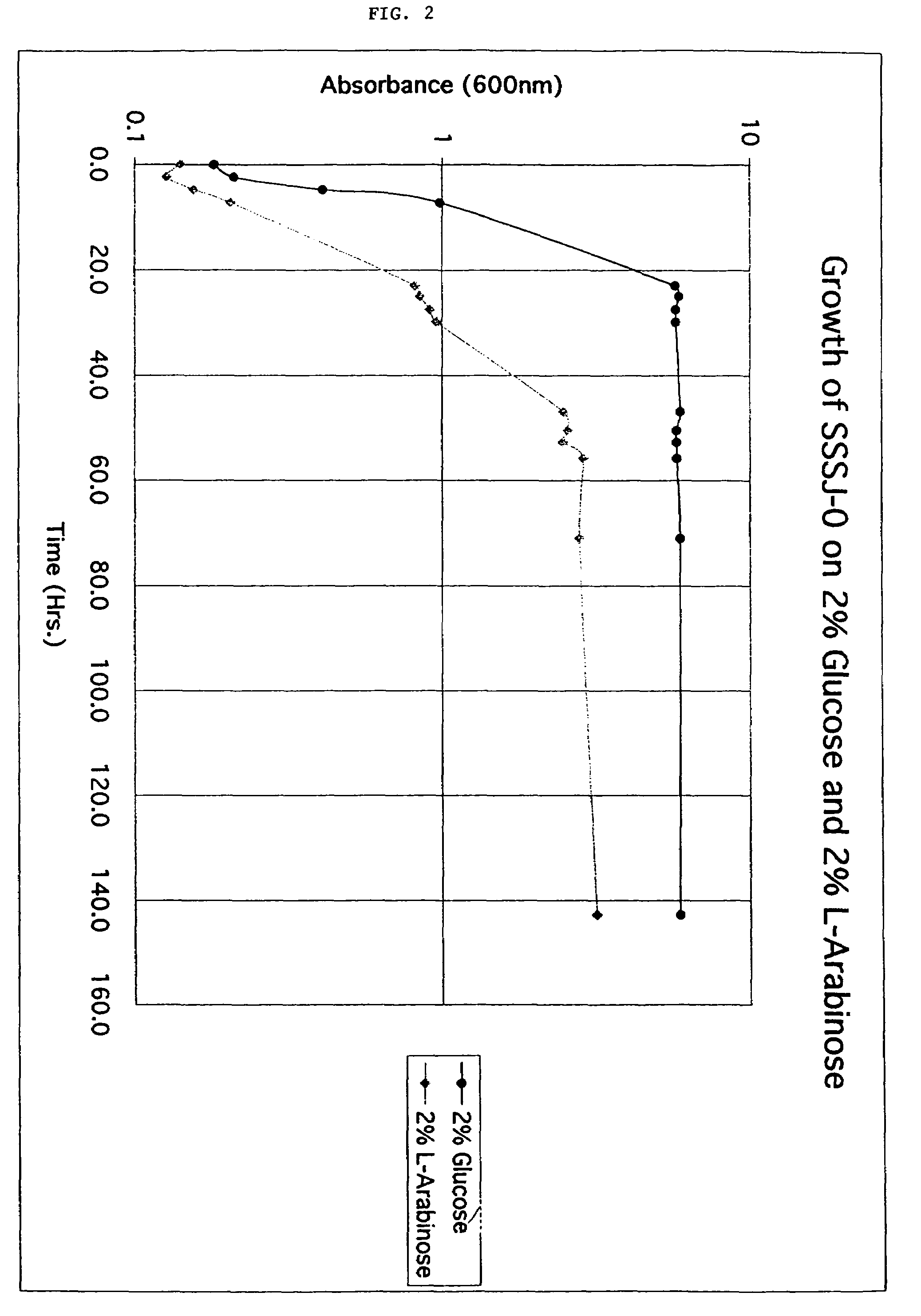
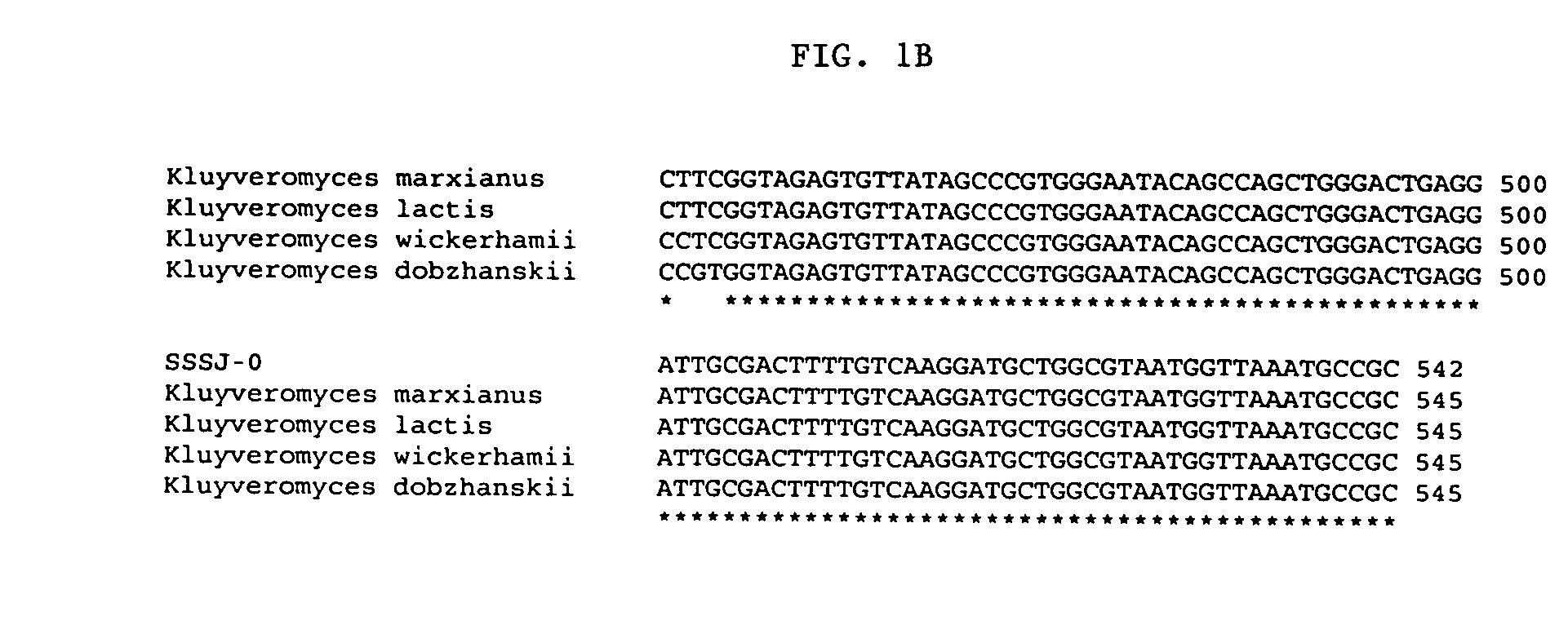
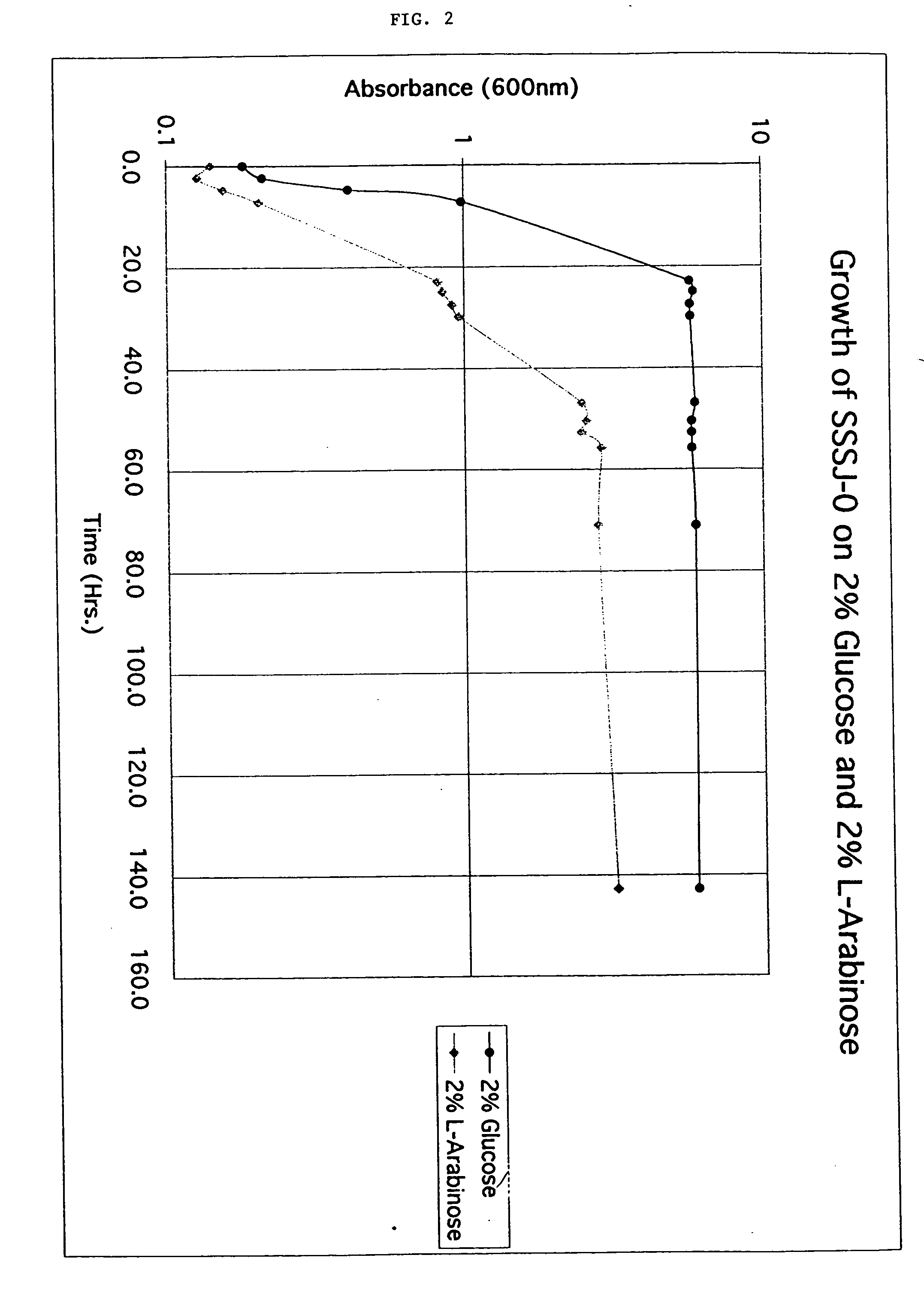
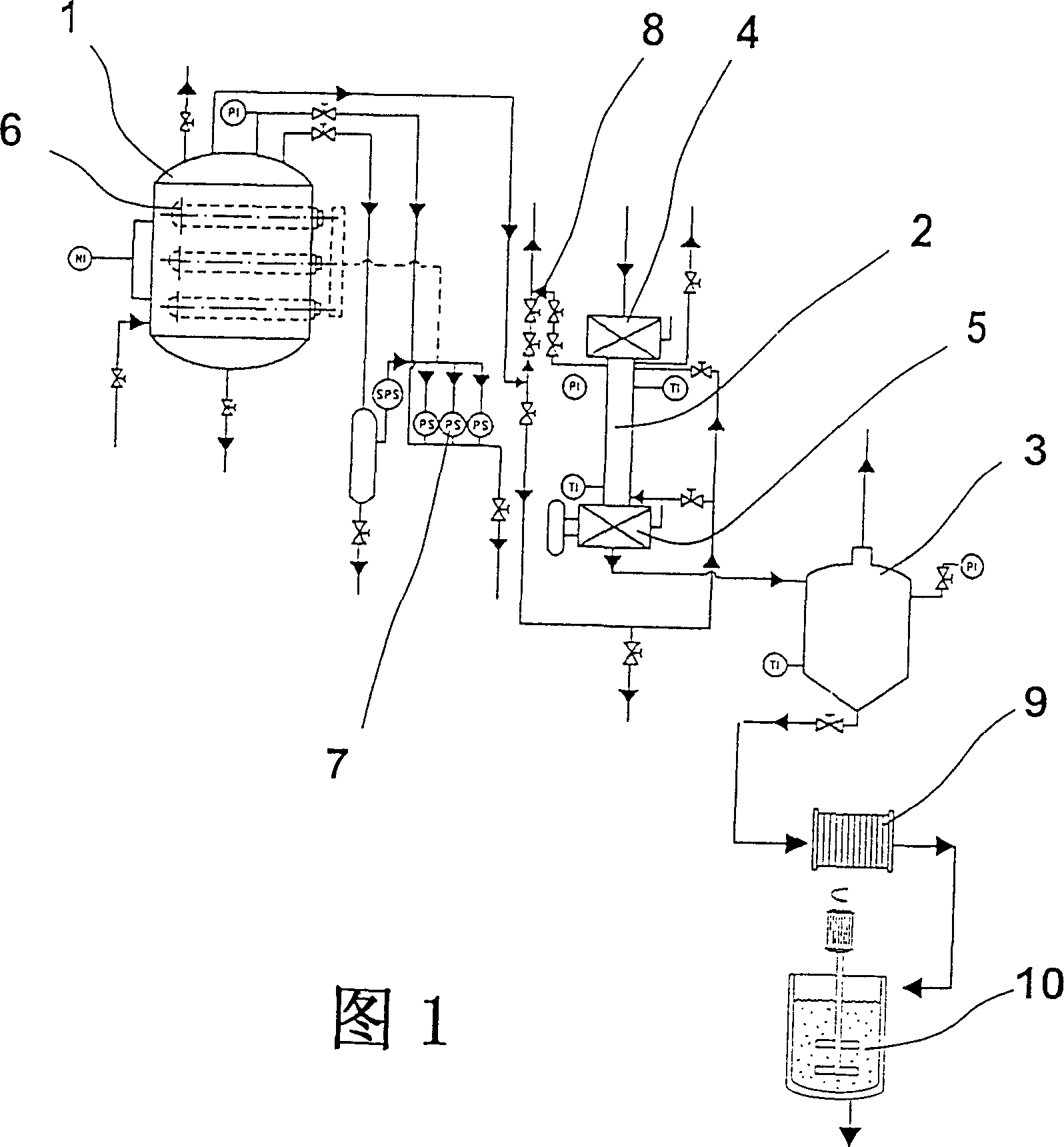
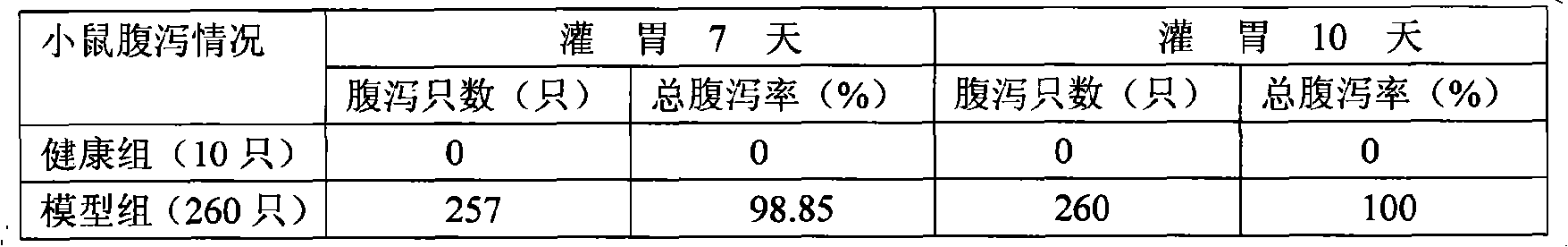
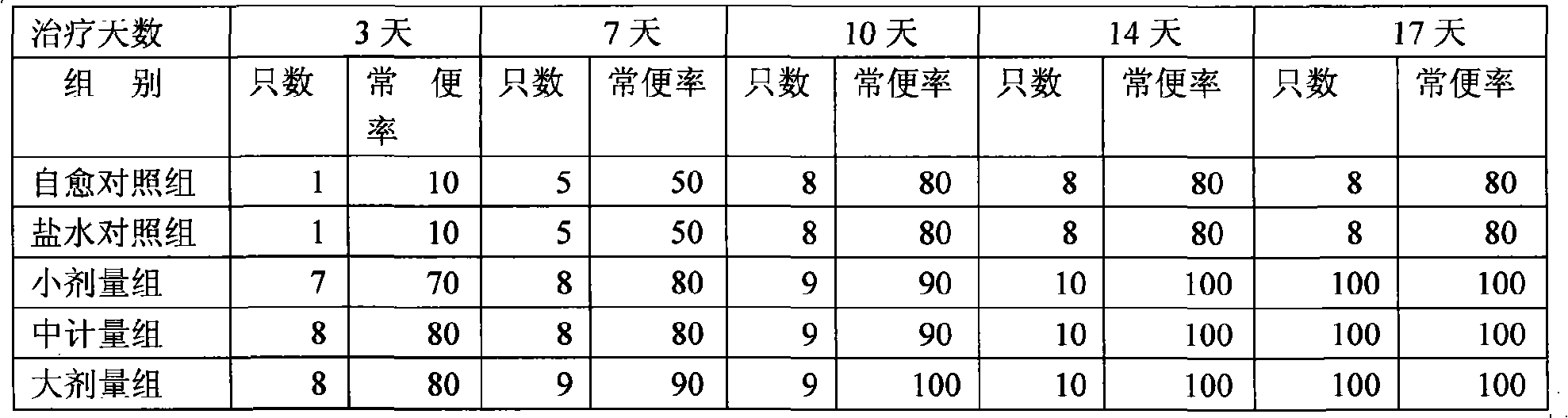
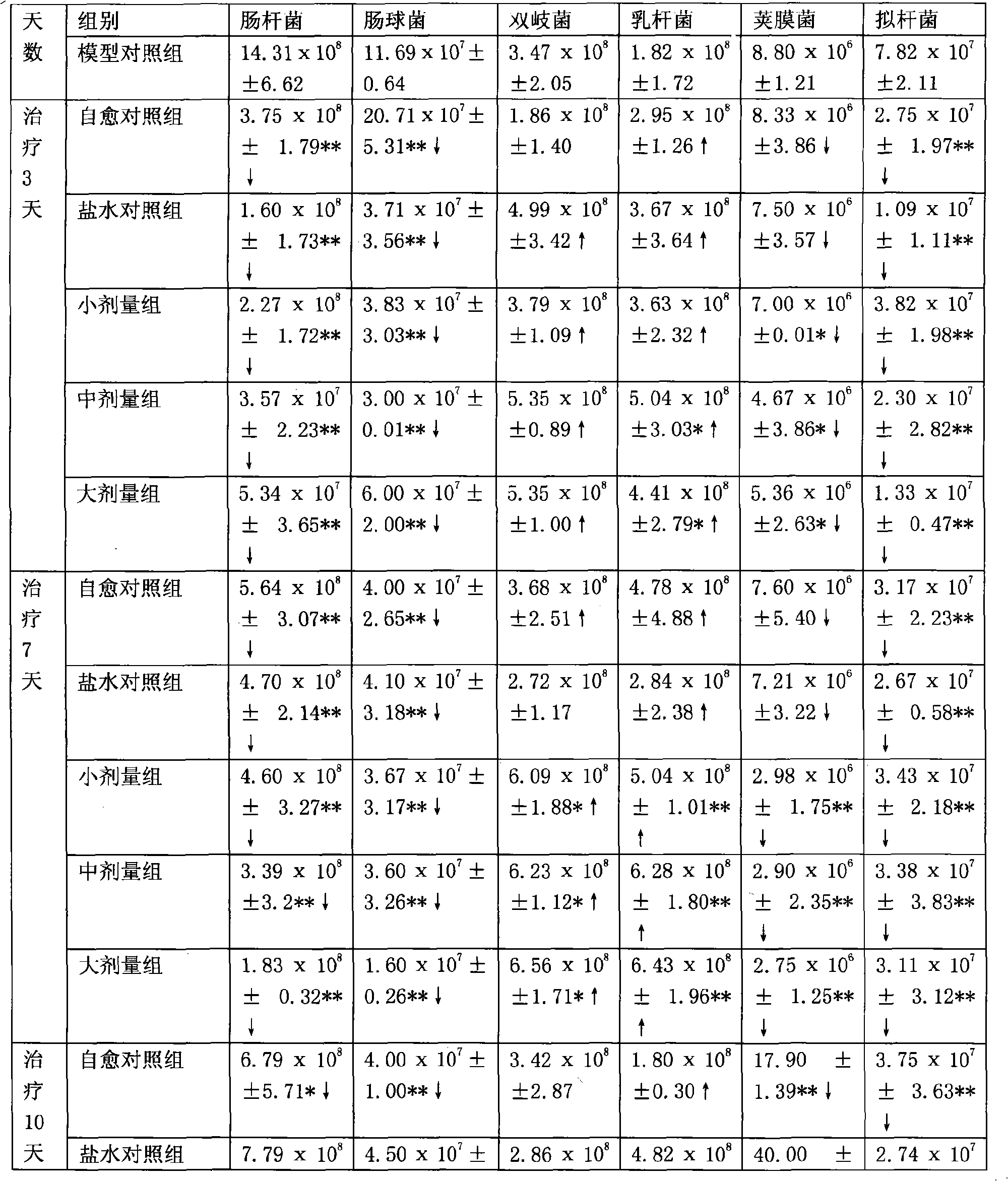
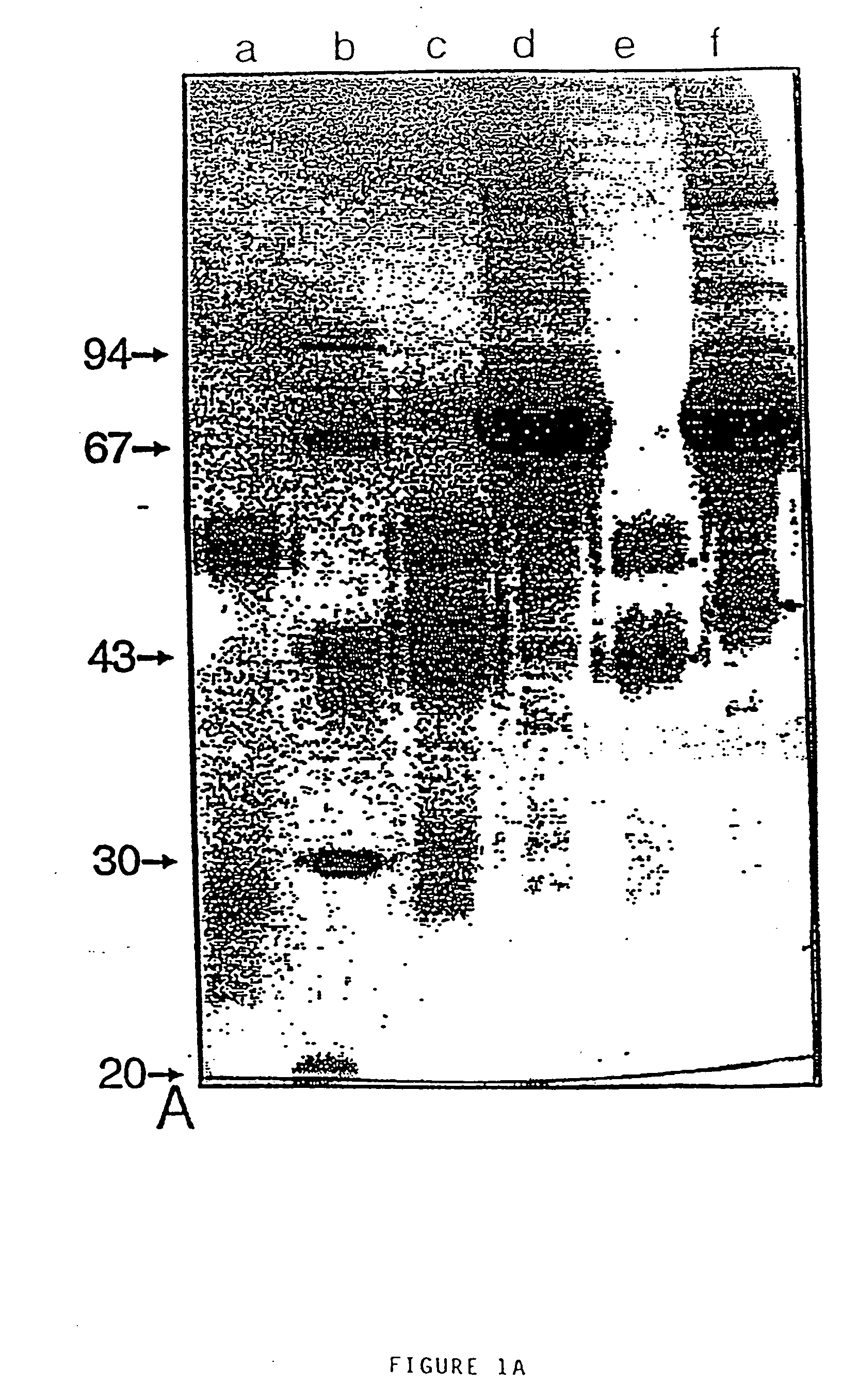
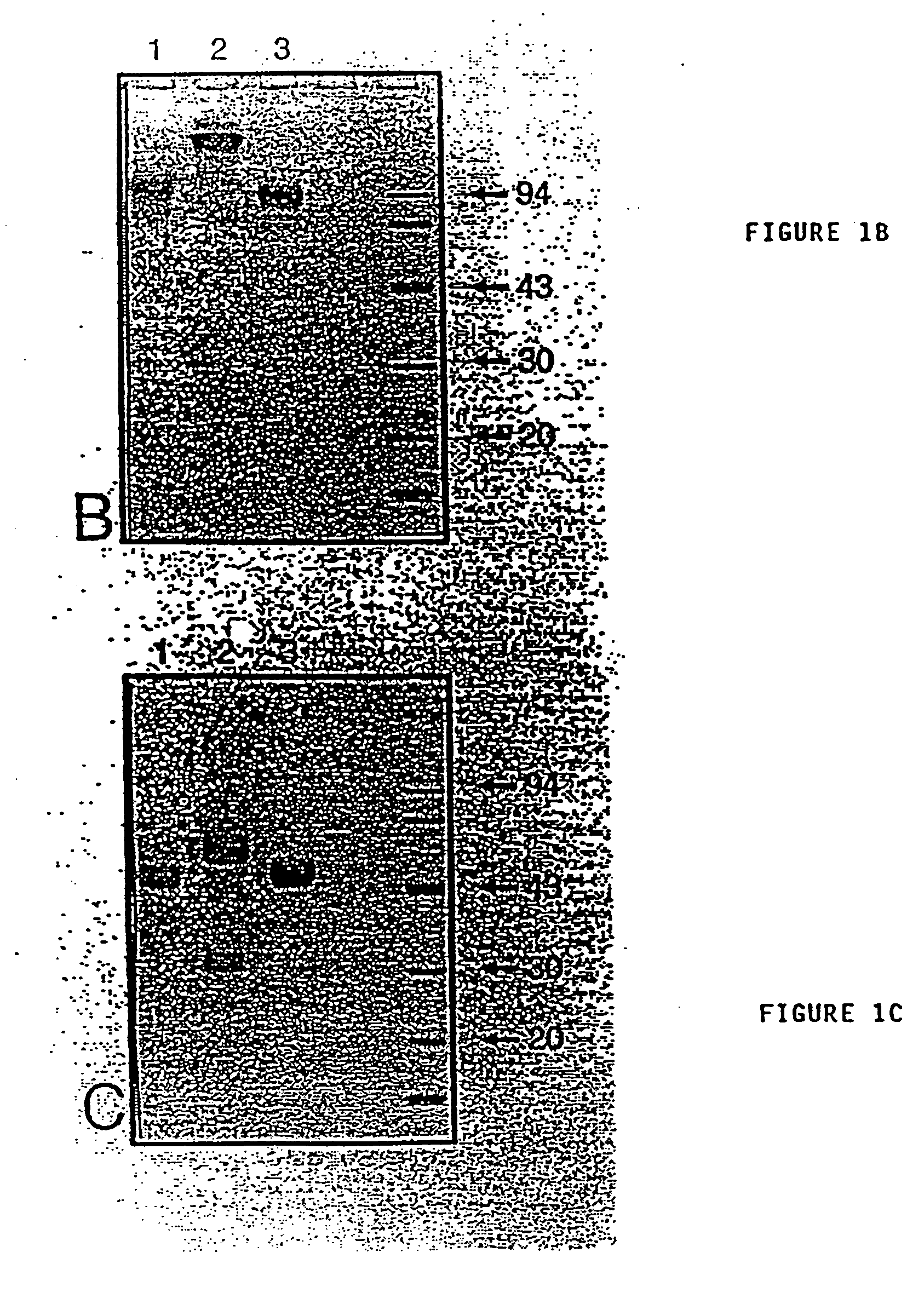
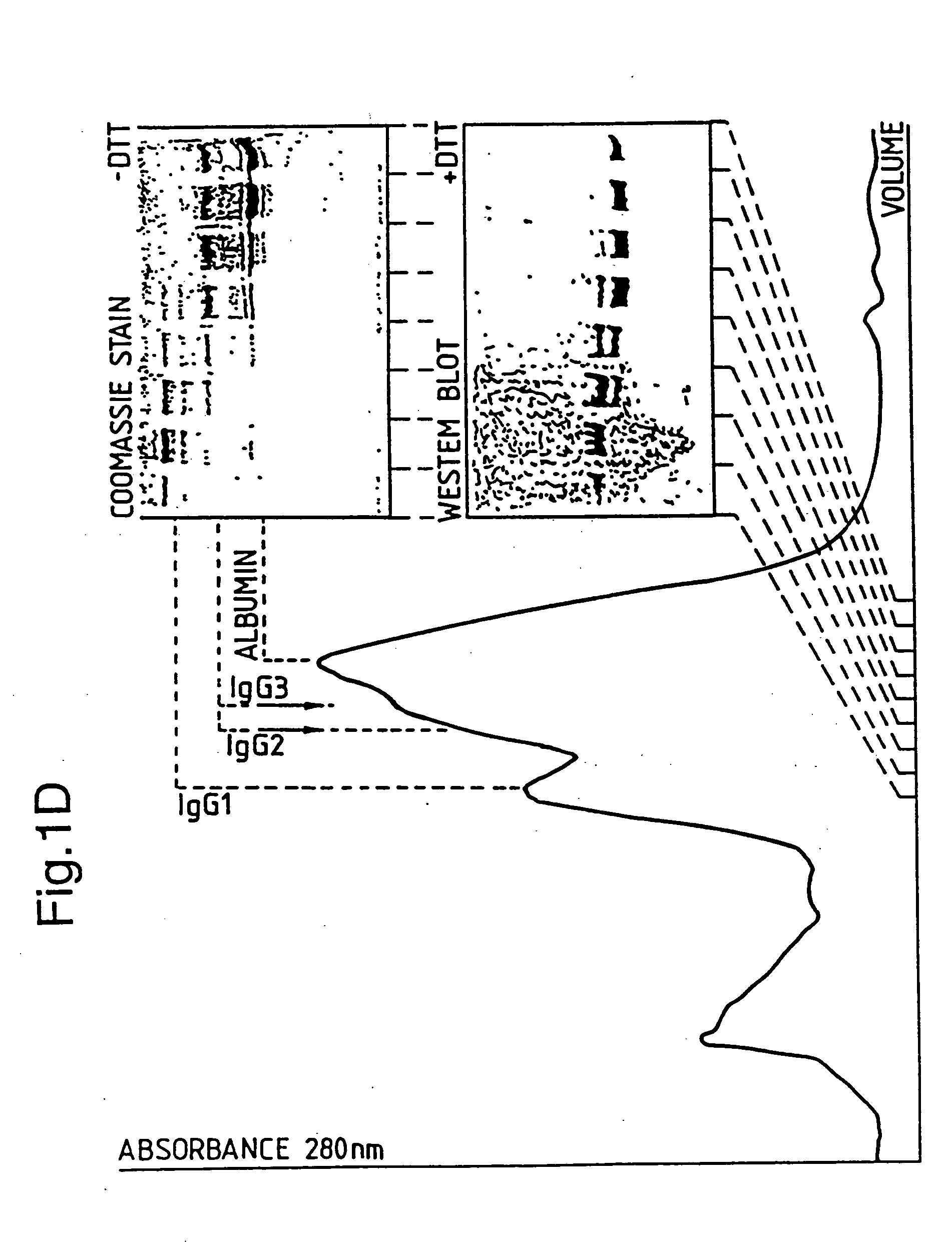
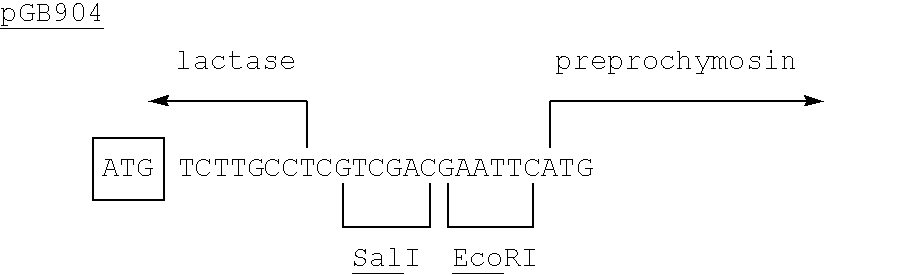
Patents
Literature
77 results about "Genus Kluyveromyces" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
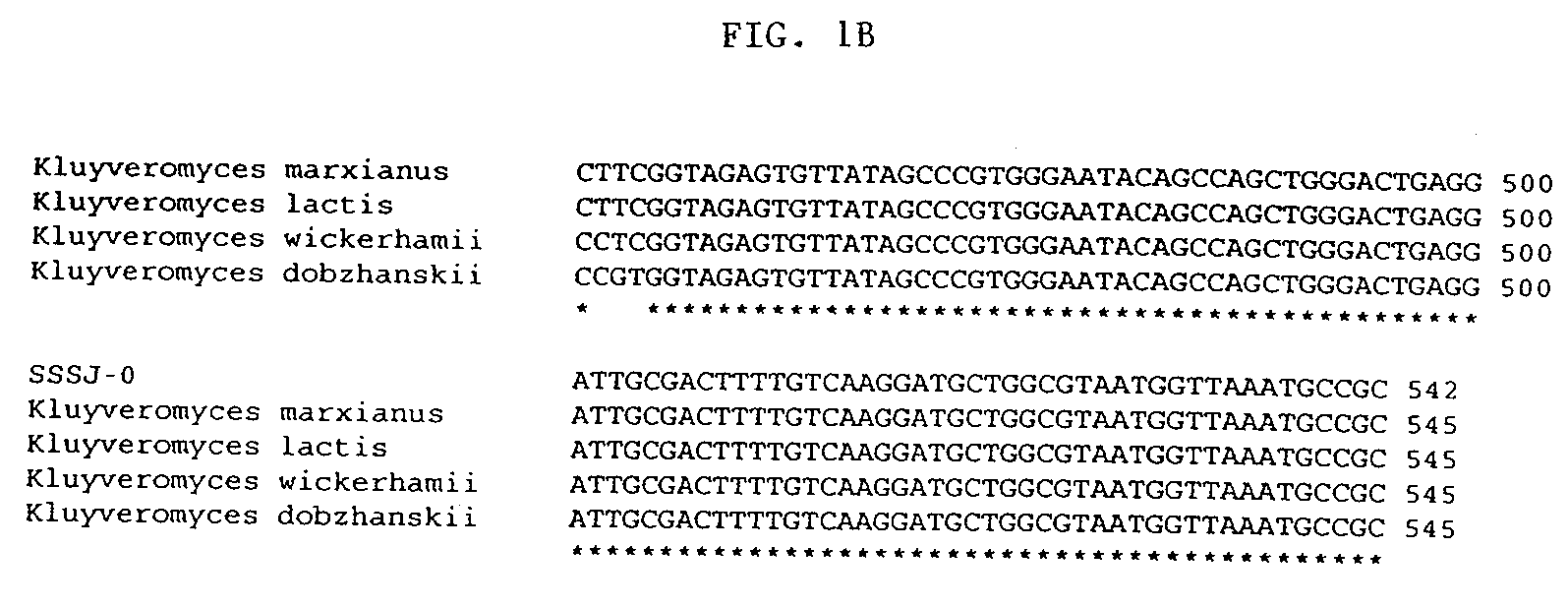
Kluyveromyces is a genus of ascomycetous yeasts in the family Saccharomycetaceae. Some of the species, such as K. marxianus, are the teleomorphs of Candida species.
Efficient CRISPR/Cas (Clustered Regulatory Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR associated) 9 gene editing system for Kluyveromyces optimization
ActiveCN107574179AStable gene editingEfficient gene editingFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTime transformation
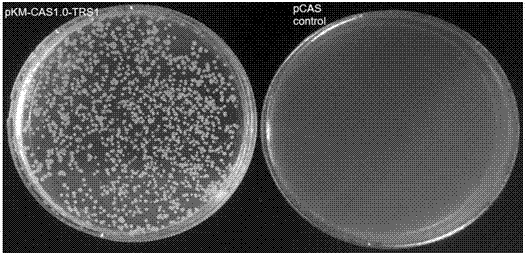
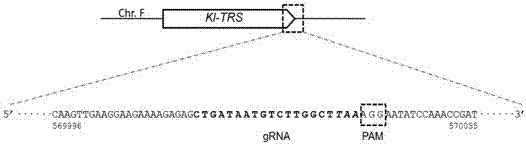
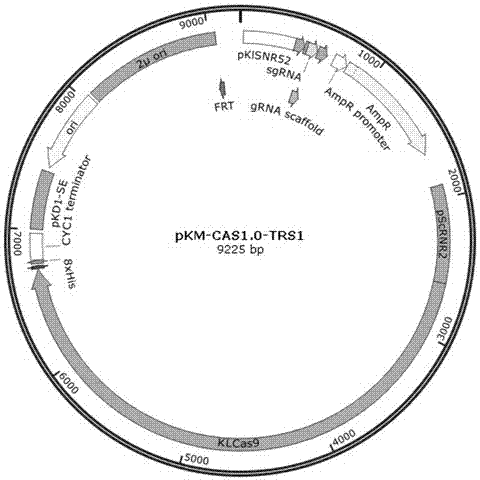
The invention relates to a special safe and efficient CRISPR / Cas (Clustered Regulatory Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats / CRISPR associated) 9 gene editing system for Kluyveromyces optimization, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. In the prior art, pCAS plasmids used in saccharomyces cerevisiae have Cas9 gene sequences and gRNA (guide RNA) elements at the same time, and efficient genomemodification in the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be realized through one-time transformation, but stable copying and expression cannot be realized in Kluyveromyces. According to the system, Cas9 / gRNAfusion plasmids are transformed in Kluyveromyces cells, the plasmids are targetedly delivered to endogenous DNA sequences of the Kluyveromyces cells, and double strand breaks are generated; and donorDNA sequences are transformed in the Kluyveromyces cells, the sequences generate homologous recombination at the double strand breaks and target sites, and Tag sequences are inserted in the target sites. Through the modification, the new safe and efficient CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system which is specially used for the Kluyveromyces and can perform stable copying and expression in the Kluyveromyces and perform gene modification is established.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
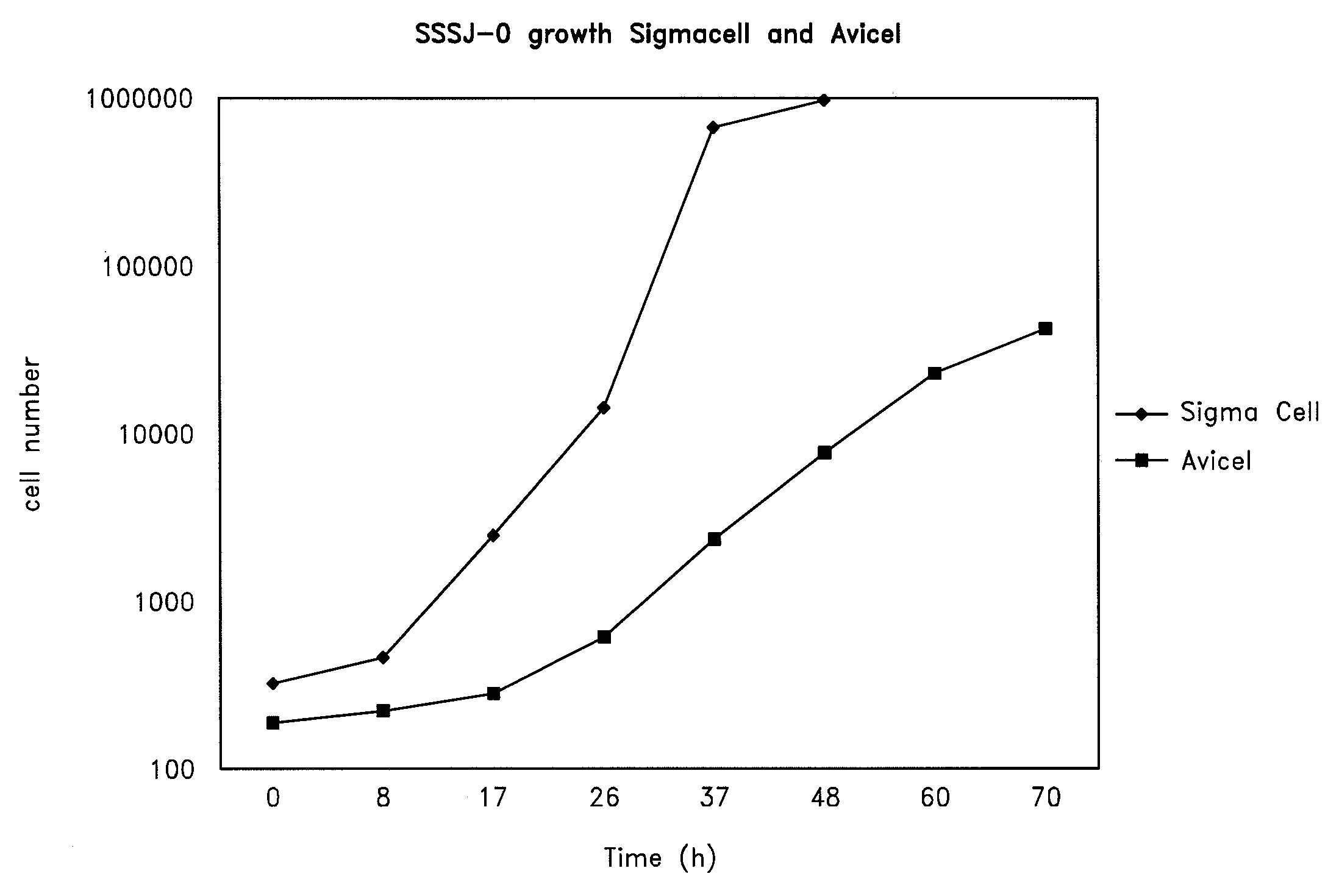
Kluyveromyces strains metabolizing cellulosic and hemicellulosic materials
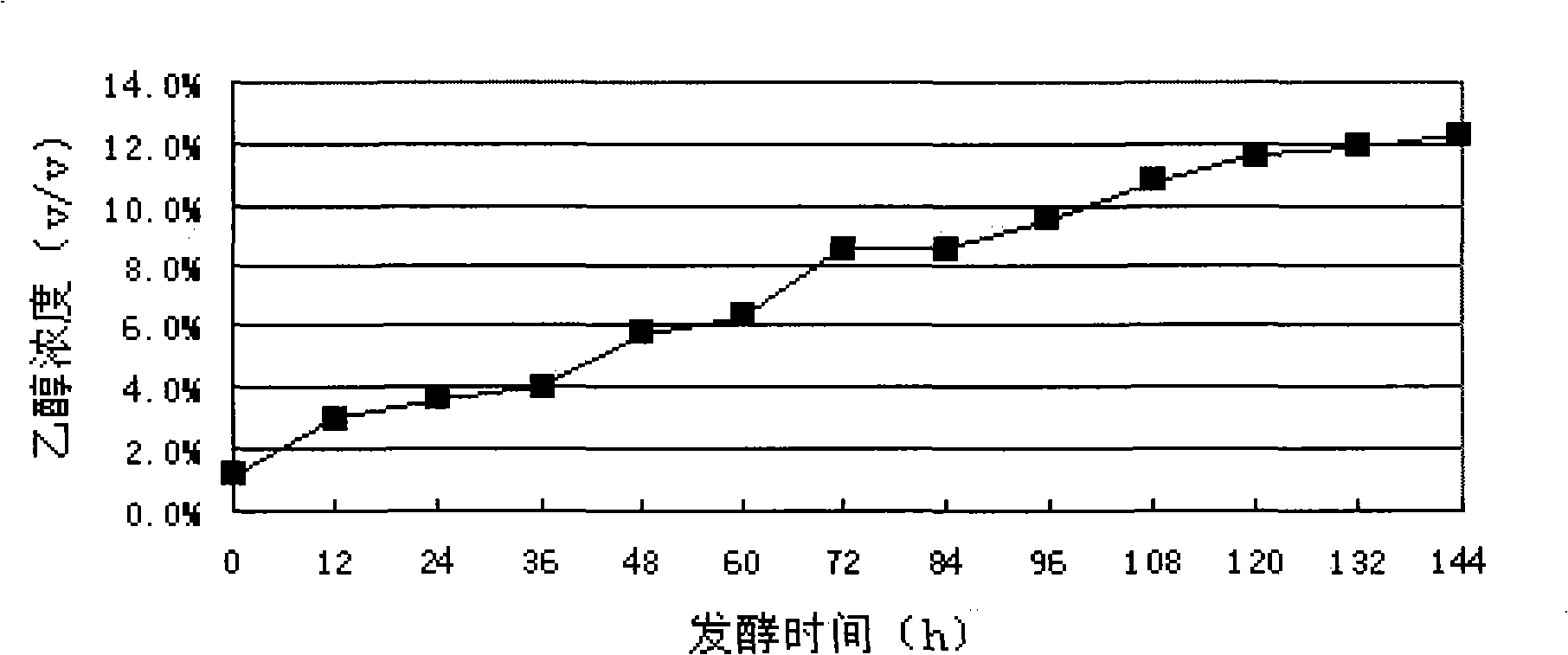
This invention relates to the use of microorganisms for the generation of ethanol from lignocellulosic waste materials. Yeast strains of the genus Kluyveromyces which have the capability to ferment cellulose, hexose sugars to ethanol are provided. Also provided are methods for converting cellulose, hexoses, or mixed hydrolysates of hexoses to ethanol by fermentation with Kluyveromyces strains. The invention also provides methods to isolate yeast strains which metabolize cellulose, pentoses, or hemicelluloses from waste materials.
Owner:NEW TECH HLDG
Kluyveromyces strains metabolizing cellulosic and hemicellulosic materials
This invention relates to the use of microorganisms for the generation of ethanol from lignocellulosic waste materials. Yeast strains of the genus Kluyveromyces which have the capability to ferment cellulose, hexose sugars to ethanol are provided. Also provided are methods for converting cellulose, hexoses, or mixed hydrolysates of hexoses to ethanol by fermentation with Kluyveromyces strains. The invention also provides methods to isolate yeast strains which metabolize cellulose, pentoses, or hemicelluloses from waste materials.
Owner:NEW TECH HLDG
Method for producing ethanol from lignocellulose biomaterial by use of neu-heat-resistant enzyme
It includes the stages of grinding the lignocellulosic biomass to a size of 15-30 mm, subjecting the product obtained to steam explosion pre-treatment at a temperature of 190-230 DEG C for between 1 and 10 minutes in a reactor (2), collecting the pre-treated material in a cyclone (3) and separating the liquid and solid fractions by filtration in a filter press (9), introducing the solid fraction in a fermentation deposit (10), adding a cellulase at a concentration of 15 UFP per gram of cellulose and 12.6 International Units of beta -glucosidase enzyme dissolved in citrate buffer pH 4.8, inoculating the fermentation deposit (10) with a culture of the heat-tolerant bacteria Kluyveromyces marxianus CECT 10875, obtained by chemical mutagenesis from strain DER-26 of Kluyveromyces marxianus and shaking the mixture for 72 hours at 42 DEG C.
Owner:RES CENT OF ENERGY SOURCE ENVIRONMENT & TECH
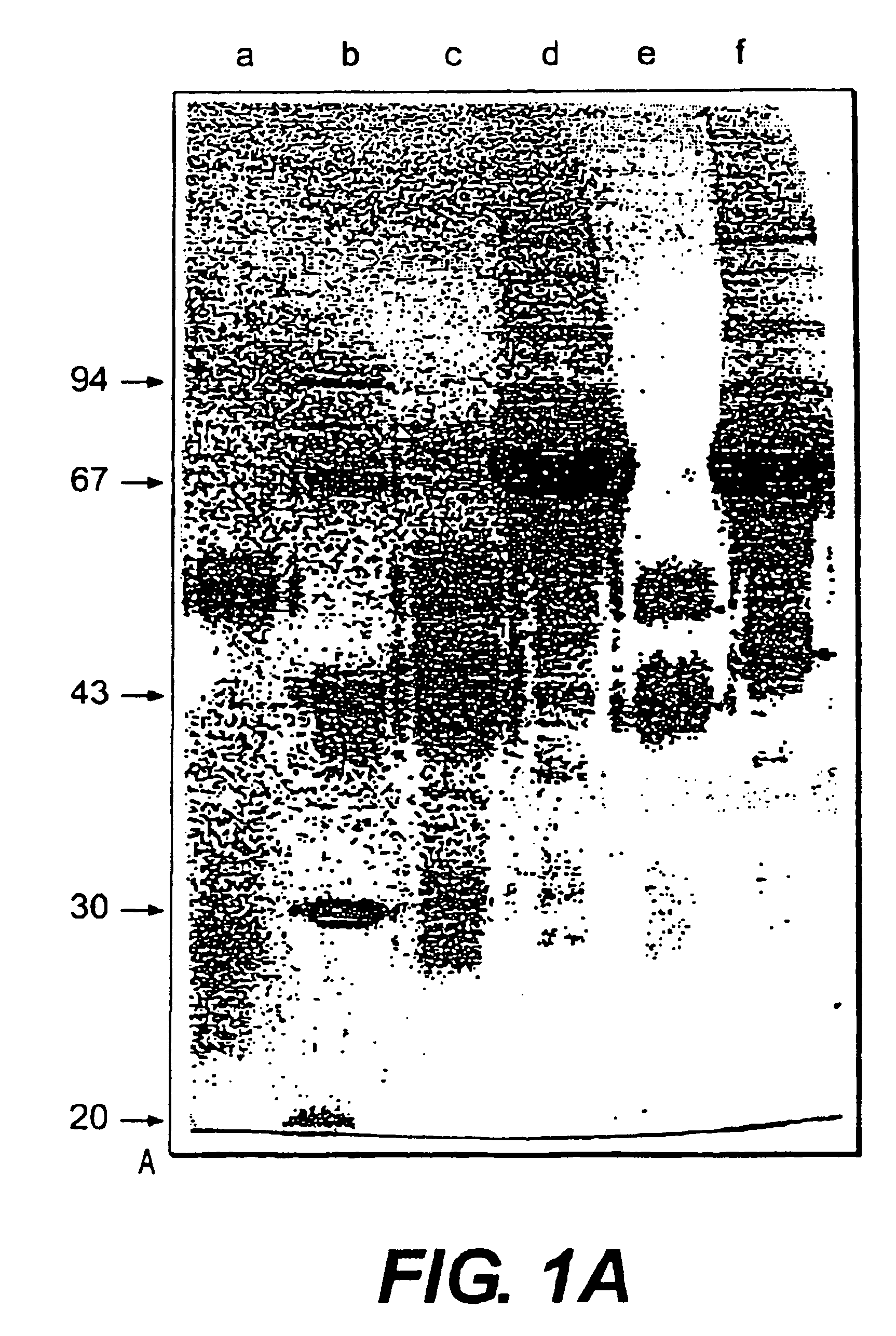
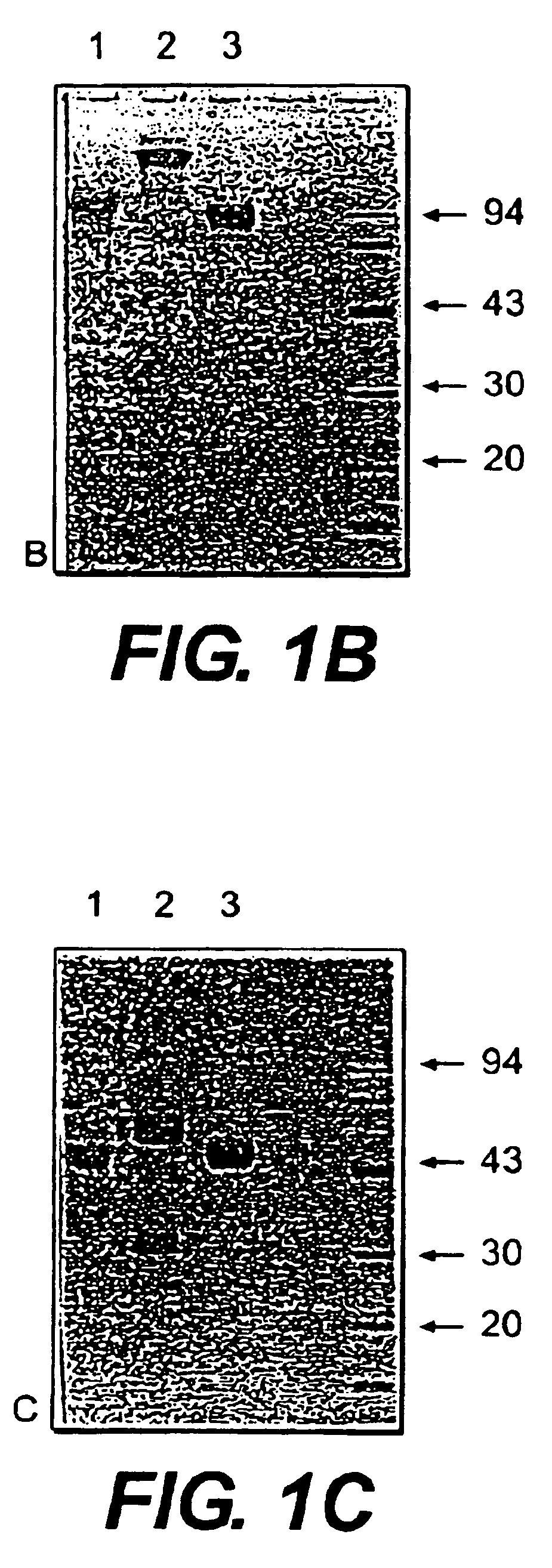
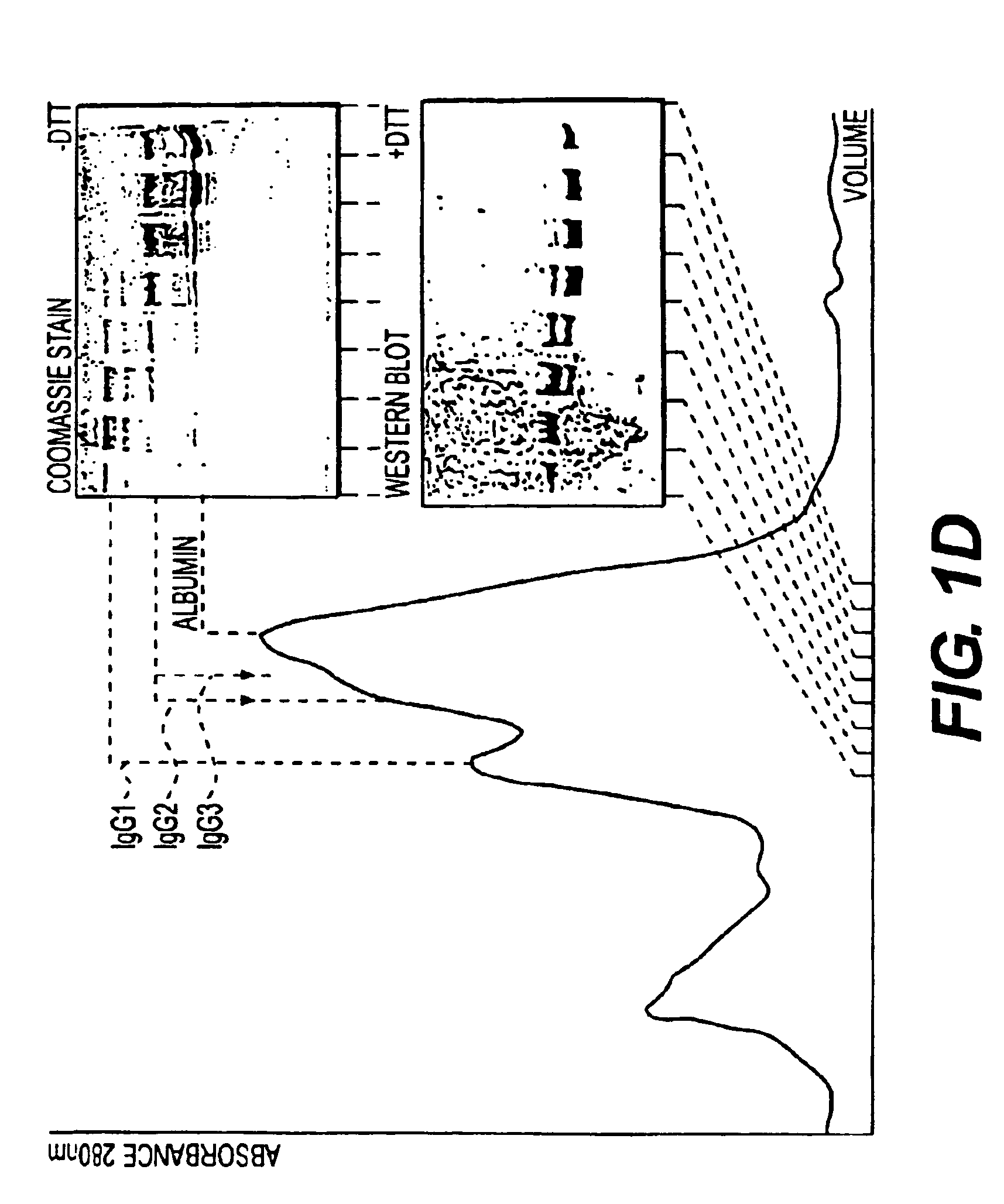
Prosuction of antibodies or (functionalized) fragments thereof derived from heavy chain immunoglobulins of camelidae
InactiveUS7794981B2High catalytic activityImprove efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNatural antibodyComplementarity determining region
A process is provided for the production of an antibody or a fragment or functionalized fragment thereof using a transformed lower eukaryotic host containing an example DNA sequence encoding the antibody or (functionalized) fragment thereof, wherein the antibody or (functionalized) fragment thereof is derived from a heavy chain immunoglobulin of Camelidae and is devoid of light chains, and wherein the lower eukaryotic host is a mould, preferably belonging to the genera Aspergillus or Trichoderma, or a yeast, preferably belonging to the yeast genera Saccharomyces, Kluyveromyces, Hansenula, or Pichia. The heavy chain fragment can contain at least the whole variable domain. A complementary determining region (CDR) different from the CDR belonging to the natural antibody ex Camelidae can be grafted on the framework of the variable domain of the heavy chain immunoglobulin. The catalytic antibodies can be raised in Camelidae against transition state molecules. The functionalized antibody or fragment thereof can comprise a fusion protein of both a heavy chain immunoglobulin from Camelidae or a fragment thereof and another polypeptide, e.g., an enzyme, preferably an oxido-reductase. Also provided are new products obtainable by a process as described, and compositions containing a product produced by a process as described, which composition may contain a new product as provided.
Owner:BAC IP
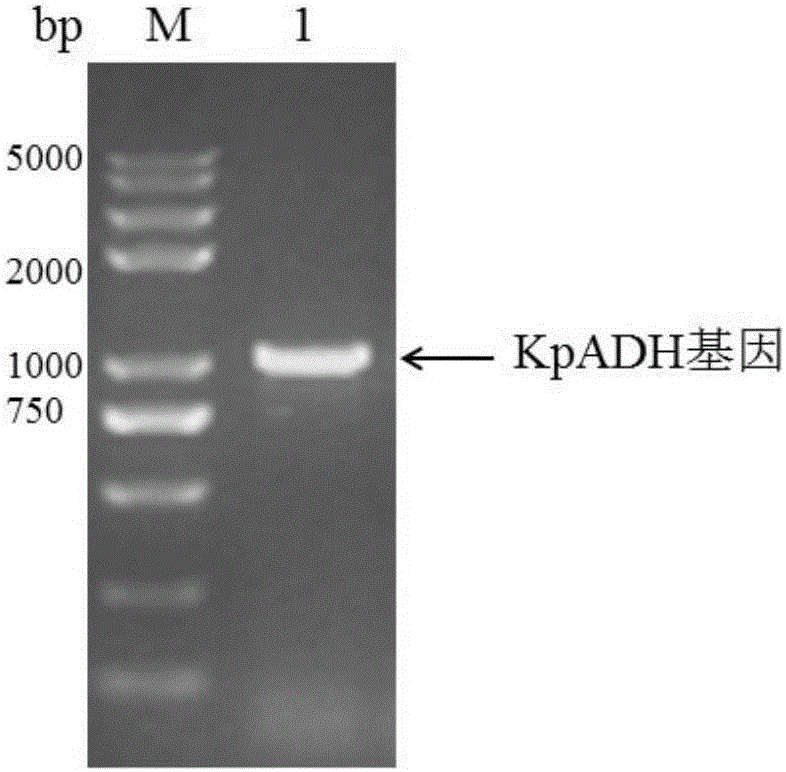
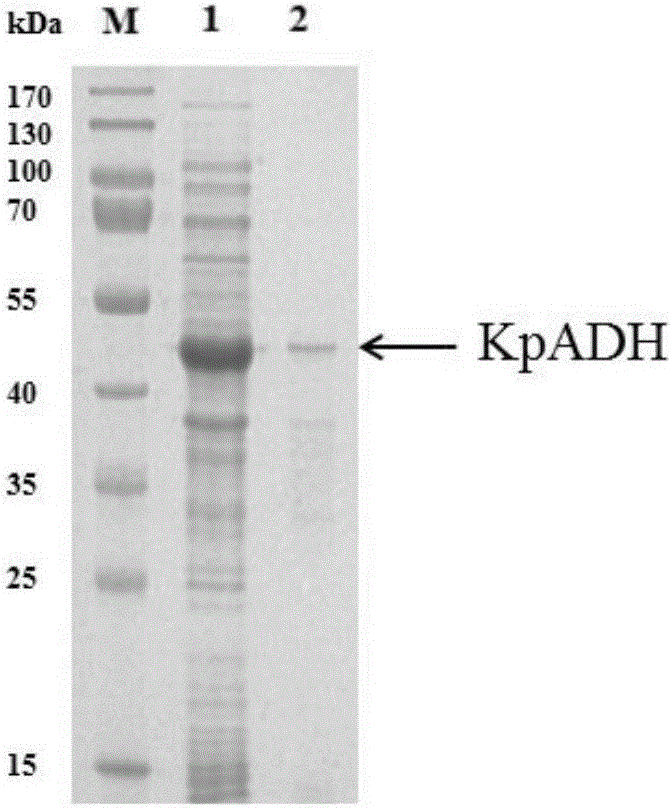
Alcohol dehydrogenase, gene and recombinase thereof, and application of alcohol dehydrogenase in synthesis of chiral diaryl secondary alcohol
InactiveCN105936909AImprove expression levelIncrease enzyme activityOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringDiaryl ketoneGenus Kluyveromyces
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase, a gene thereof, a recombinant expression vector and a recombinant expression transformant respectively containing the gene, a recombinase of the alcohol dehydrogenase, and an application of the alcohol dehydrogenase in asymmetric reduction synthesis of chiral diaryl secondary alcohol as a catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The alcohol dehydrogenase is from Kluyveromyces sp. CCTCCM2011385, has a carbonyl group reduction function, and also has a hydroxy group oxidation function. Extra addition of glucose dehydrogenase and other enzymes used for cofactor circulation is not needed when the alcohol dehydrogenase is used in the reduction of diaryl ketone into the chiral diaryl secondary alcohol as a biocatalyst, and the alcohol dehydrogenase has the advantages of high catalysis efficiency, mild reaction conditions, easy product recovery and low cost, so the alcohol dehydrogenase has very good application and exploitation prospect in the production of antihistamine medicines.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
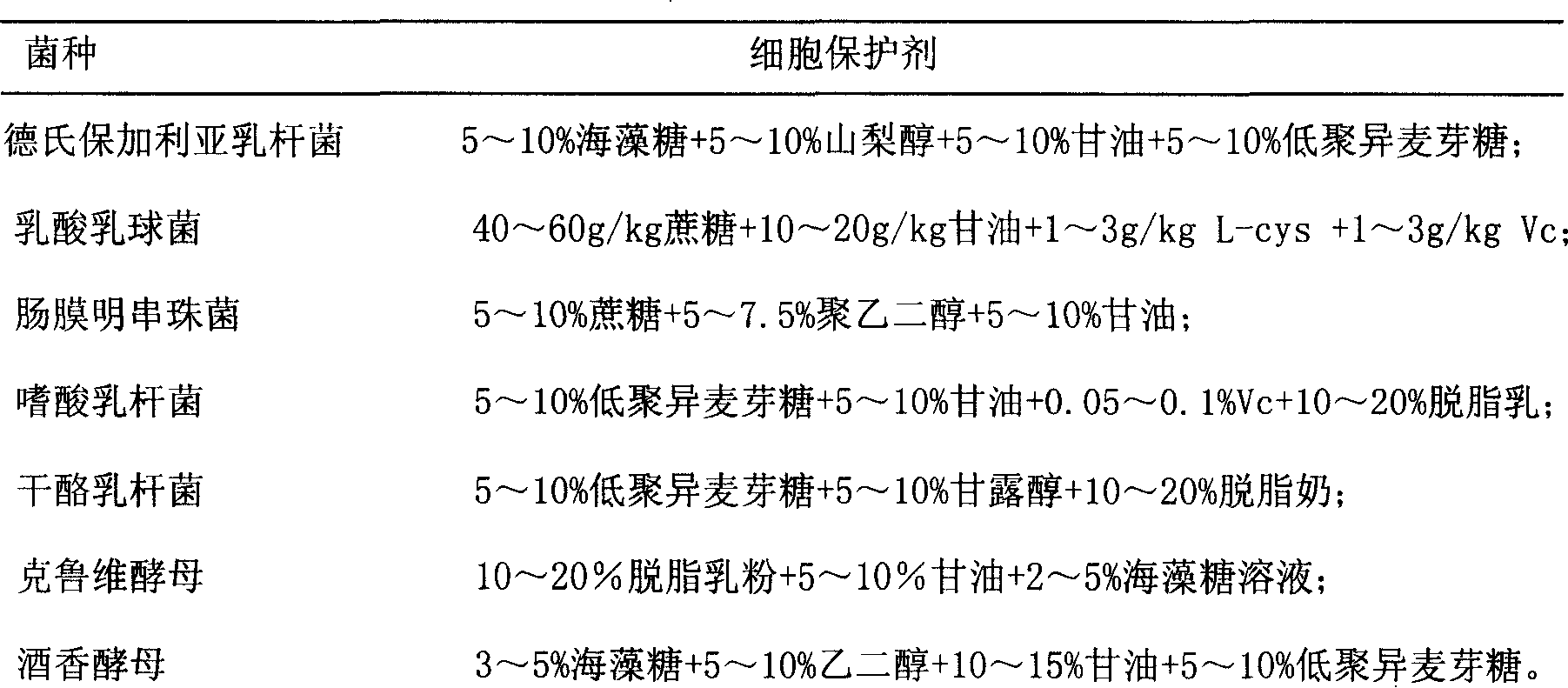
Composite bacteria leaven and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a composite strain starter and the preparation method, belonging to the microorganism fermentation field, which is mainly prepared with equivalent lactobacillus delbrueckii Bulgaria subspecies, lactococcus lactis, Leuconostoc mesenteroide, lactobacillus acidophilus, lactobacillus casei, kluyveromyces and brettanomyces. The preparation method is as follow: the strains are optimized and cultivated, and then are respectively fermented, centrifuge-treated, concentrated, added with cell protective agent, and freezed in vacuum. The invention is compounded with various functional strains; the acidophilus milk made by the omposite strain starter has the advantages of original flavor, which has the function indexes close to kefir particle fermentation acidophilus milk, and can be excellent direct distribution kefir starter; the fermented acidophilus milk has strong inhibition effect to pathogenic microorganism, and has good therapeutic effect to gastrointestinal diseases, metabolic disease, hypertension and heart disease.
Owner:马小明
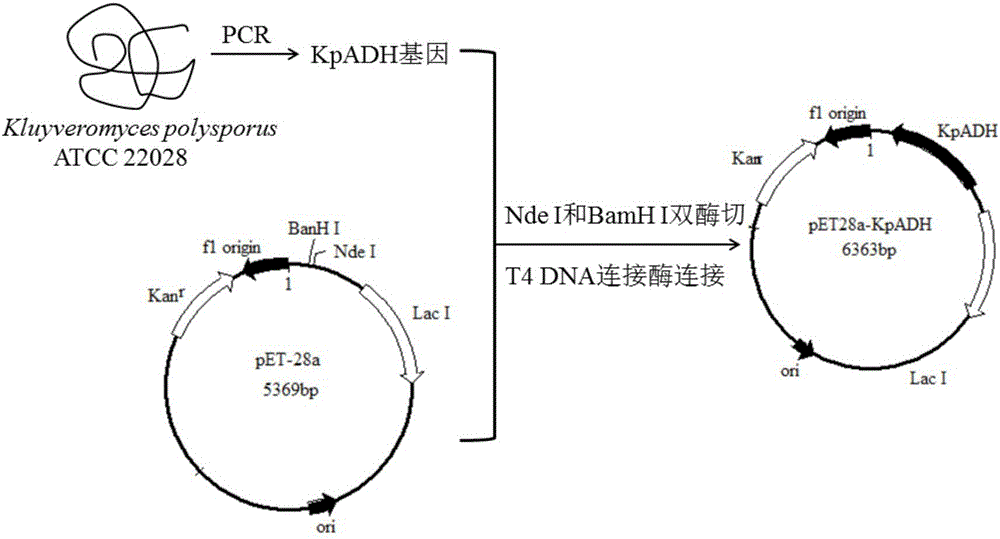
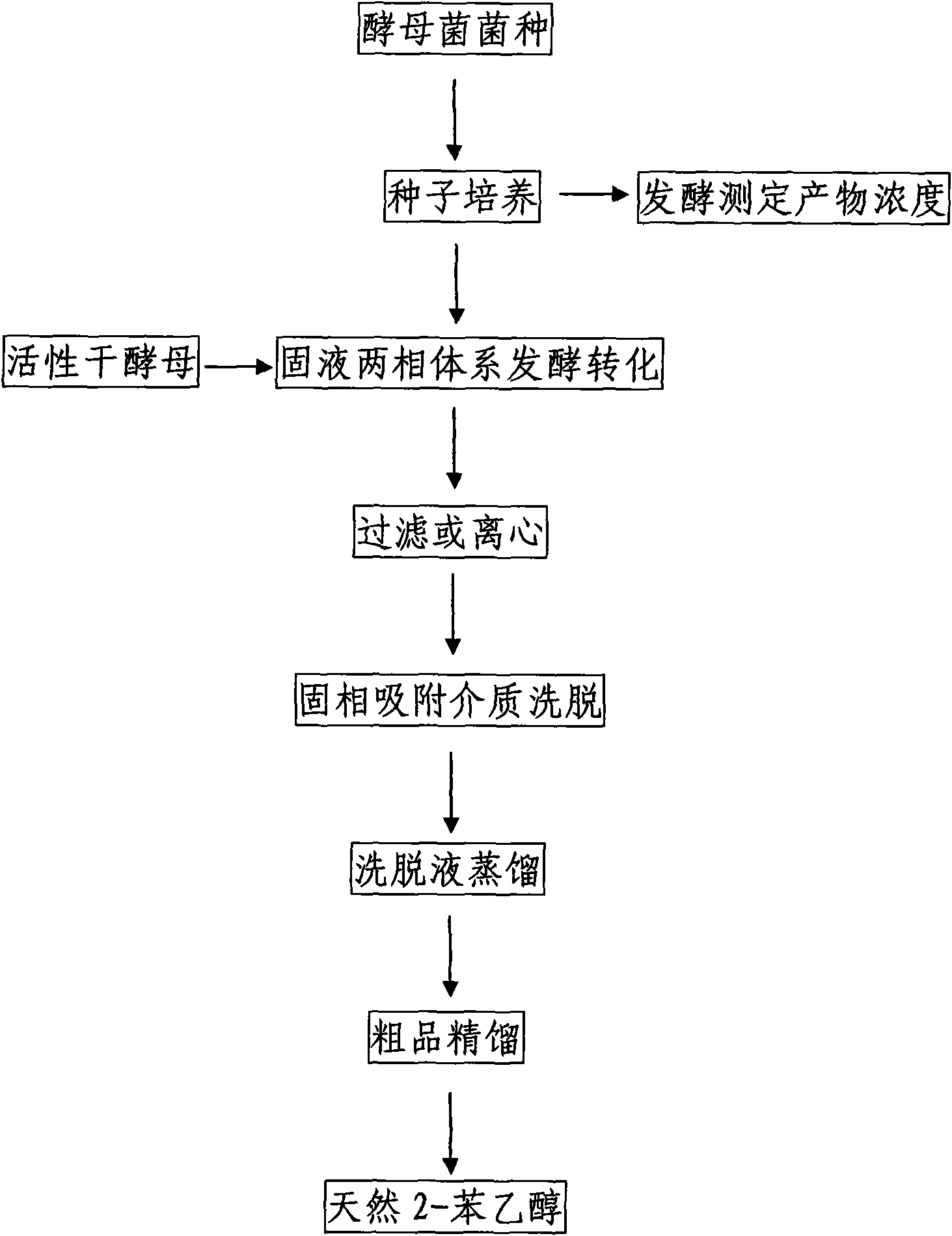
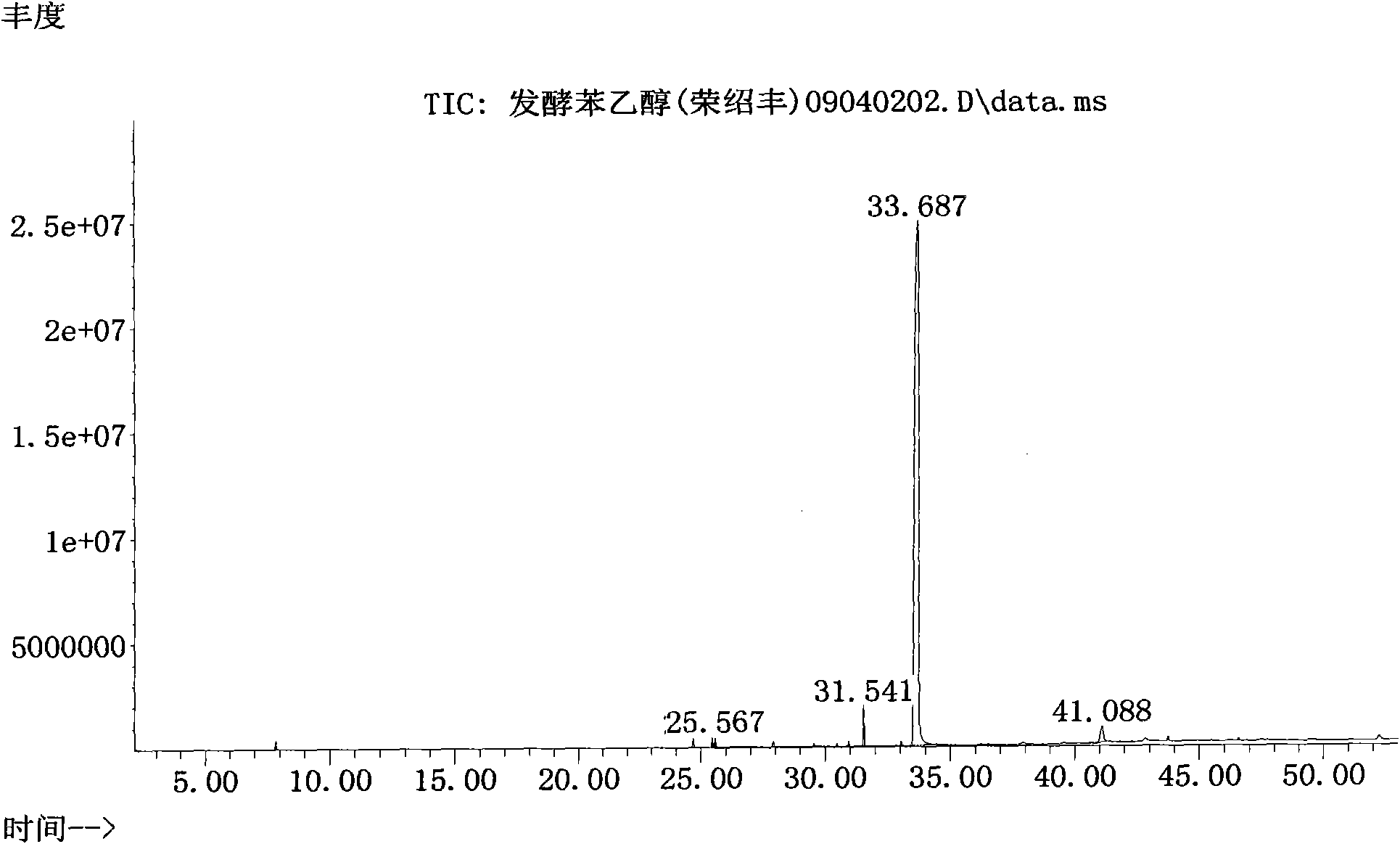
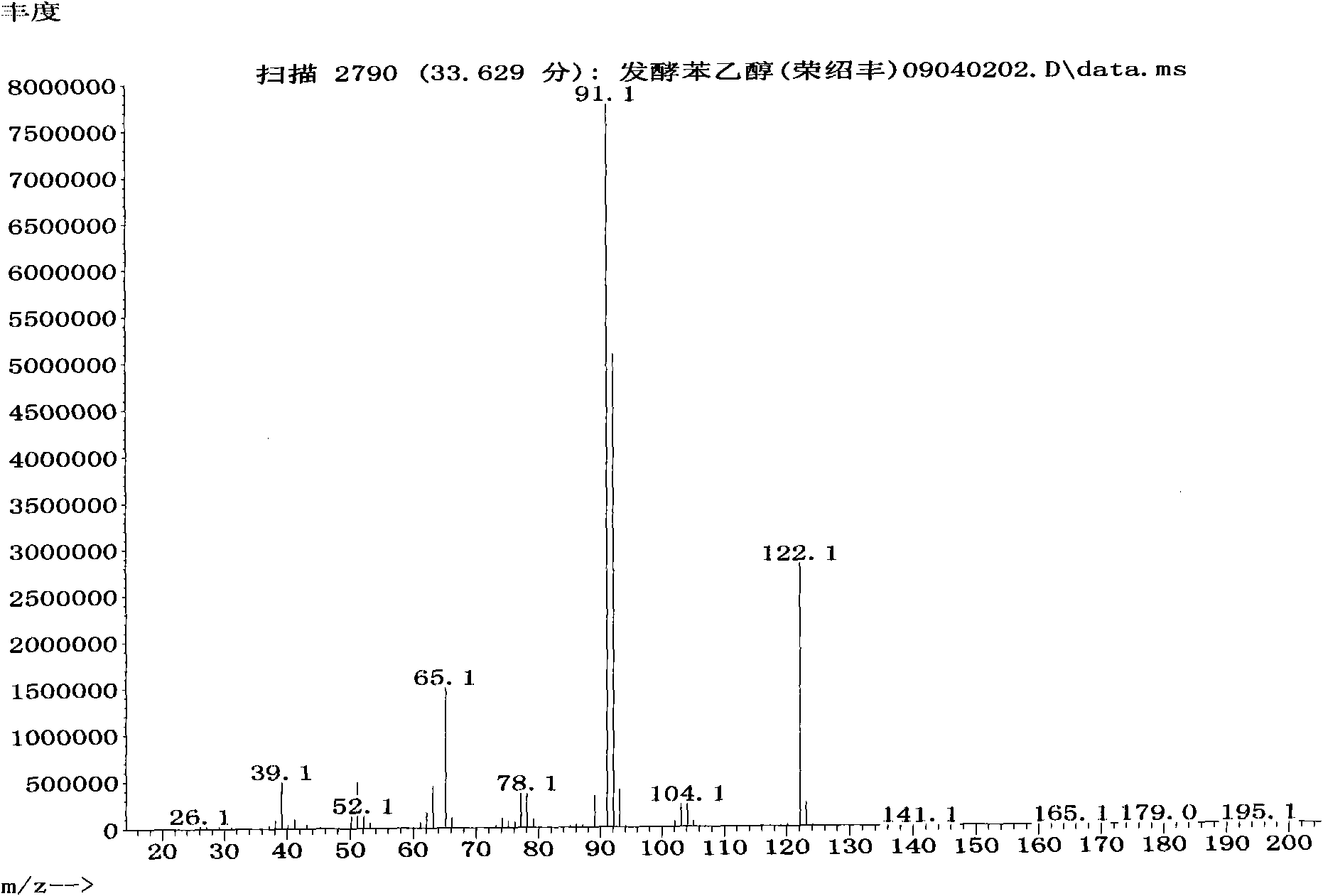
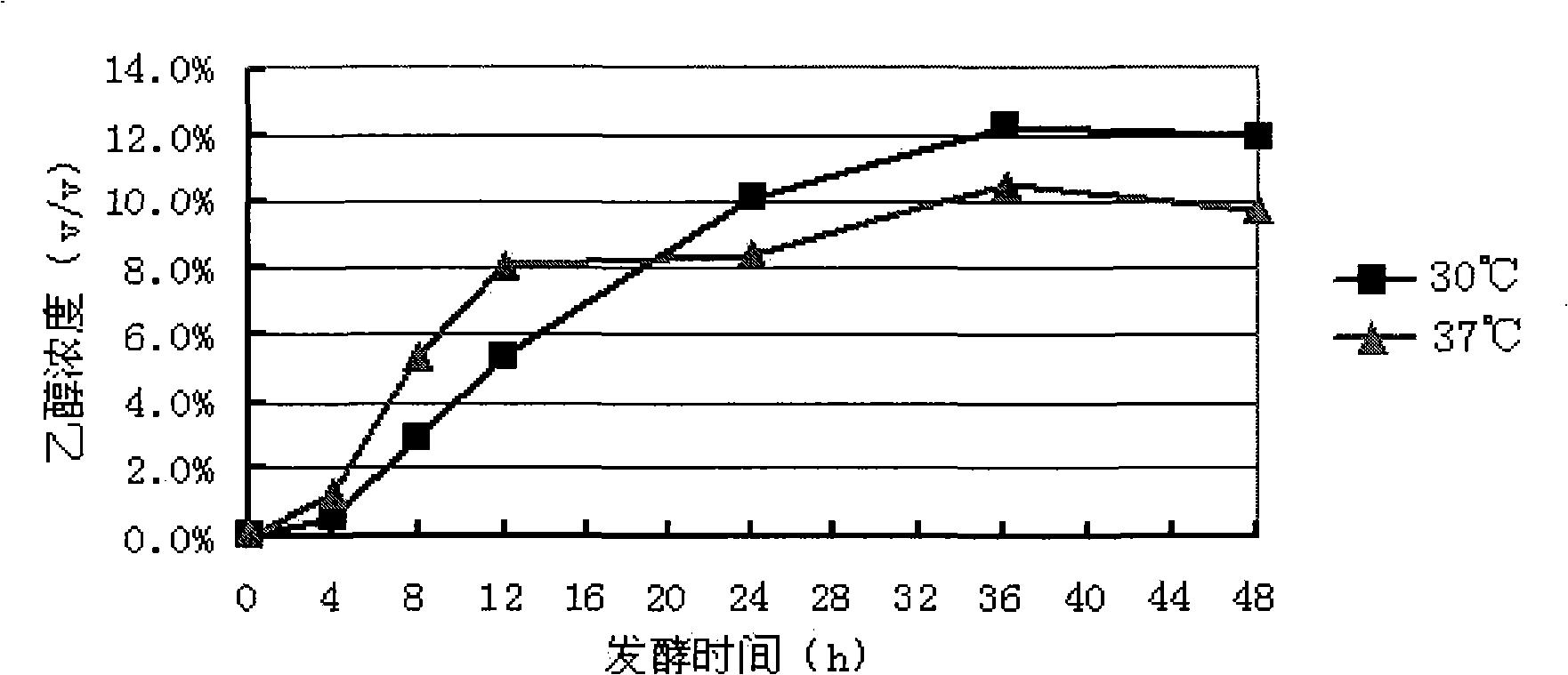
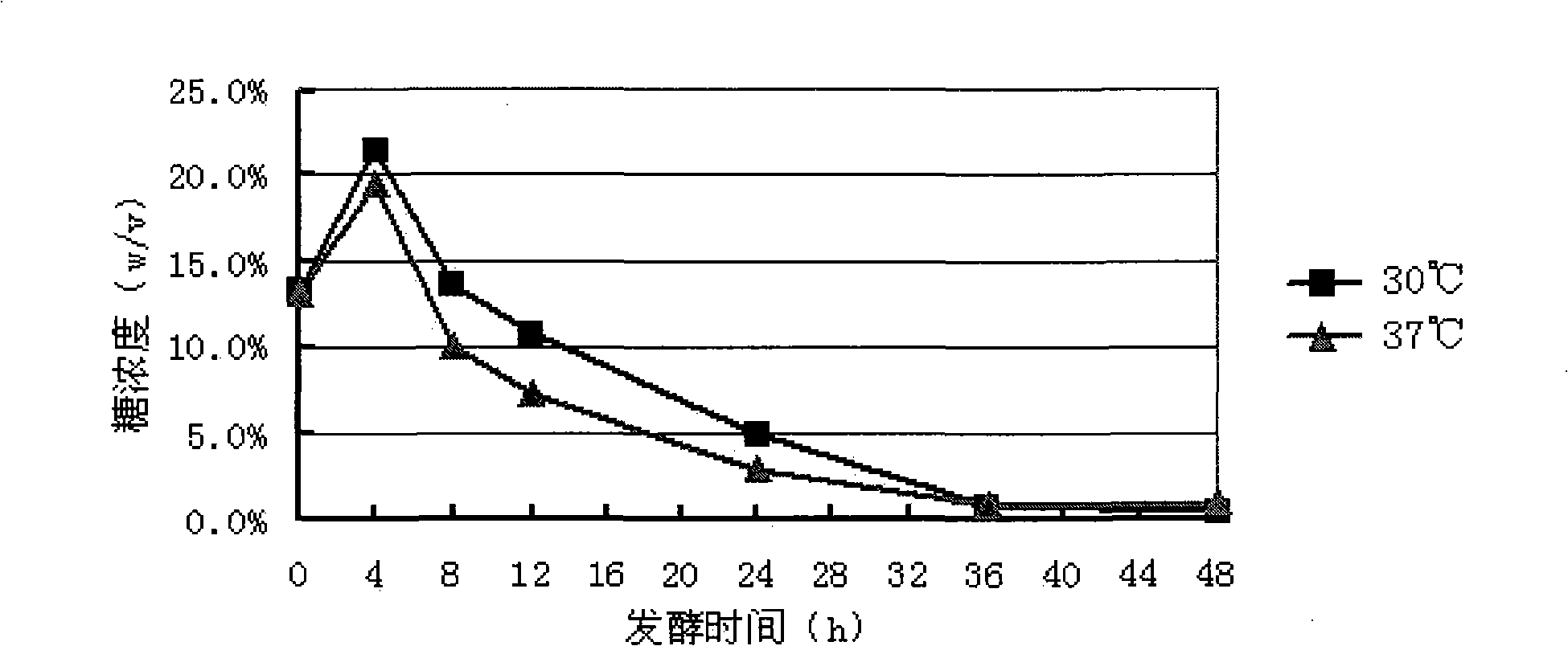
Preparation method of natural spice 2-phenethyl alcohol
InactiveCN101608190ADisinhibition effectDetoxifyMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiltrationPhenethyl alcohol
The invention discloses a preparation method of natural spice 2-phenethyl alcohol, which is implemented by selecting Candida drusei, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Kluyveromyces marxianus, inoculating cultivated seed liquid or active dried yeast powder into fermentation culture medium, taking L-PHE produced by fermentation method or enzyme method as substrate, performing liquid aerobic fermentation in a fermentation shake flask or a fermentation tank, adding solid phase absorption medium, L-PHE and glucose in the process of fermentation, obtaining the solid phase absorption medium in a filtration or centrifugation manner, then adopting an elution solvent to carry out elution on the absorption medium, further distilling the eluent to obtain the natural 2-phenethyl alcohol with purity of 97.5-99.5%. The invention combines the fermentation and absorption separation of 2-phenethyl alcohol, has low production cost and excellent aroma quality of the product.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Method for producing ethanol by synchronously saccharifying and fermenting Jerusalem artichoke raw material
InactiveCN101265485AReduce fermentation costsBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Kluyveromyces strains metabolizing cellulosic and hemicellulosic materials
Owner:NEW TECH HLDG
Processes for the bioconversion of a fermentable carbon source to 1,3-propanediol by a single microorganism
A process is provided for the bioconversion of a carbon substrate to 1,3-propanediol by a single organism utilizing microorganisms, such as, Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Clostridium, Klebsiella, Aerobacter, Lactobacillus, Aspergillus, Saccharomyces, Zygosaccharomyces, Pichia, Kluyveromyces, Candida, Hansenula, Debaryomyces, Mucor, Torulopsis, Methylobacter, Escherichia, Salmonella, Bacillus, Streptomyces and Pseudomonas, containing the genes encoding for an active glycerol or diol dehydratase enzyme by contacting these organisms with a carbon substrate under the appropriate fermentation conditions. Specifically, Citrobacter and, Klebsiella provide the source of exogenous genes for such active dehydratase enzyme.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Methods for the synthesis of lactic acid using crabtree-negative yeast transformed with the lactate dehydrogenase gene
InactiveUS7229805B2Considerable purificationSimpler and less-costlyFungiBiofuelsLactate dehydrogenaseTrichosporon
The invention provides methods and materials related to the production of lactic acid. Specifically, the invention provides methods for producing lactic acid using a crabtree-negative yeast, such as of the Kluyveromyces, Pichia, Candida, Trichosporon and Yamadazmya genera, which have been transformed with a lactate dehydrogenase gene.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Micro-ecological complex bacterial agent and method of preparing micro-ecological complex bacterial agent
InactiveCN101406489APromote digestion and absorptionTo achieve long-term effectivenessFungiBacteriaHigh concentrationBiotechnology
The invention relates to a micro-ecological composite fungus preparation and a method for preparing the same, in particular to a micro-ecological preparation and a method for preparing the same. The method solves the problems that the prior micro-ecological preparation can only temporarily increase and supplement the amount of probiotics in intestinal canal of a human body in a short period, and has poor competitiveness and viability so that the probiotics are used up after a period of time of stopping taking the micro-ecological preparation. The micro-ecological composite fungus preparation mainly comprises bacillus natto, lactic acid kluyveromyces, lactobacillus acidophilus and soybean oligosaccharides. The method comprises the following steps: culturing micro-ecological funguses; intermediately culturing the micro-ecological funguses; culturing and centrifuging the micro-ecological funguses after the micro-ecological funguses are transferred into a high concentration culture fluid; and adding auxiliary materials to the micro-ecological funguses, pre-freezing and vacuum freeze-drying the mixture, and adding the soybean oligosaccharides to the mixture to obtain the micro-ecological composite fungus preparation. The total number of viable beneficial bacteria in the micro-ecological composite fungus preparation is between 1.0 x 10<10> and 9.9 x 10<10> per gram, the micro-ecological composite fungus preparation not only has huge unit number, but also has high survival rate of the viable bacteria of more than 98 percent two years later.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
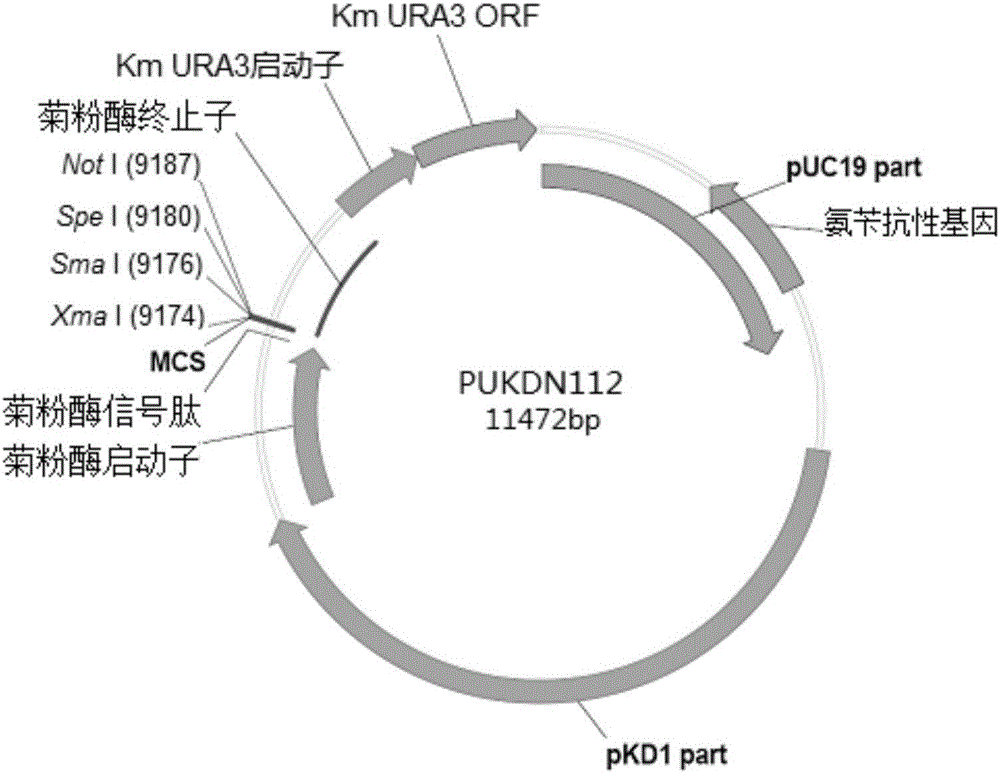
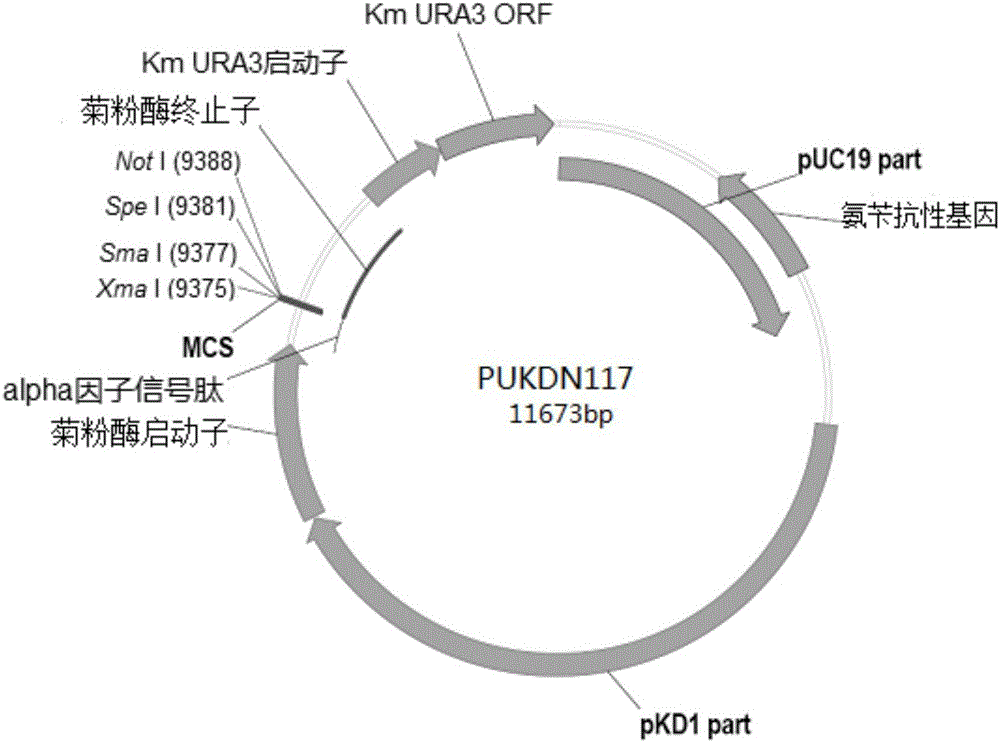
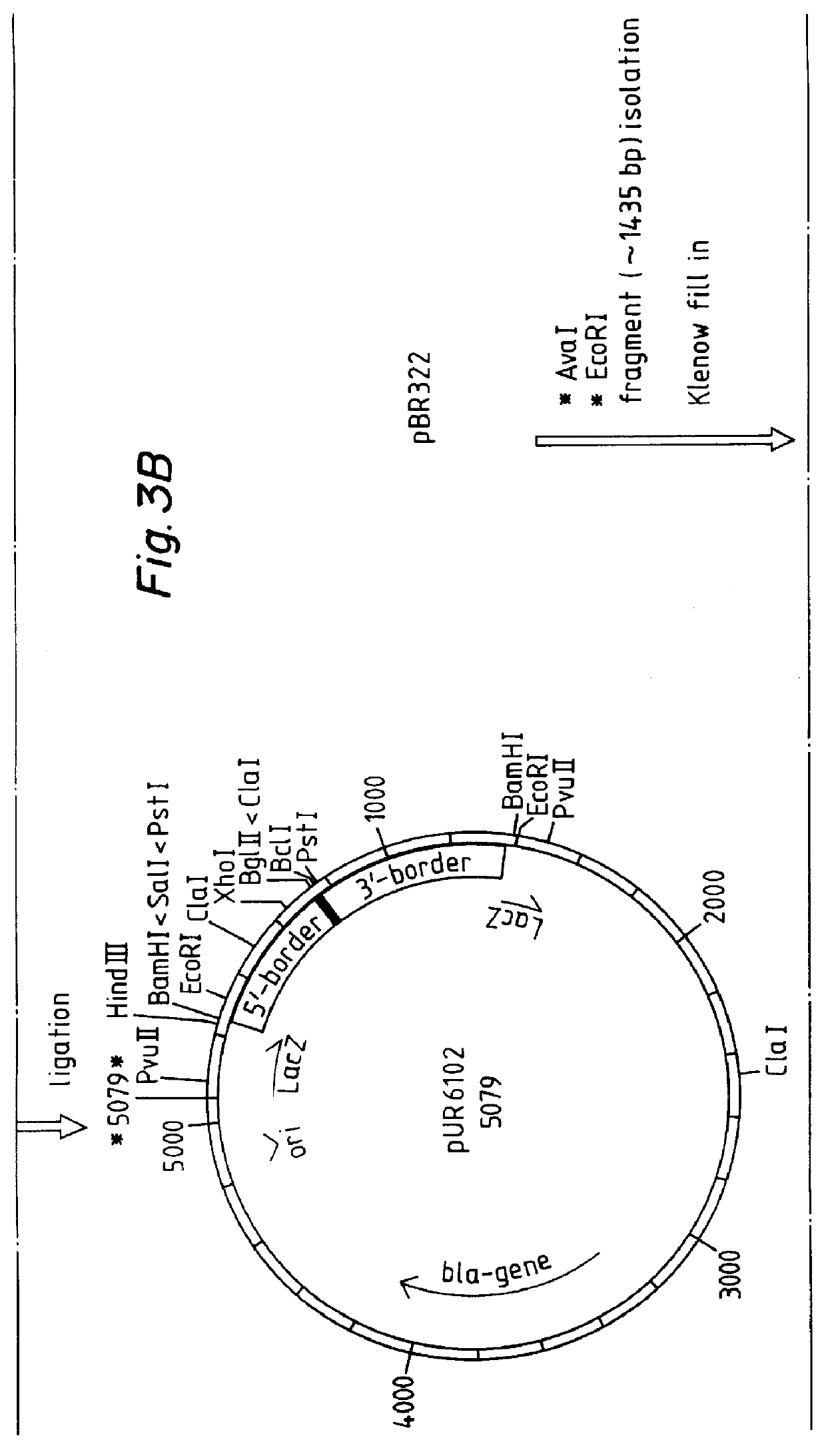
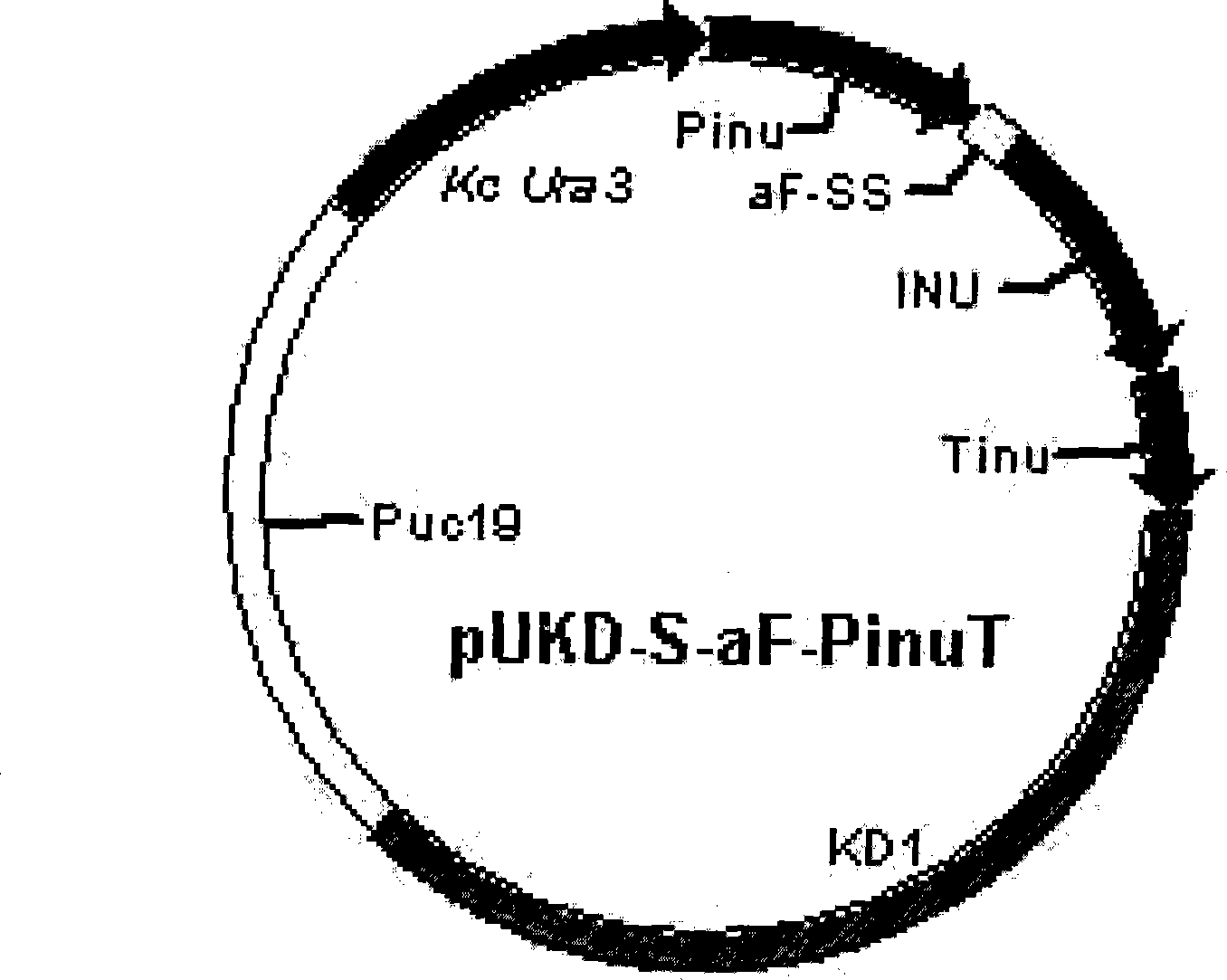
Recombinant vector used for carrying out foreign gene secretory expression in auxotrophic kluyveromyces marxianus strain
The invention provides a recombinant vector used for carrying out foreign gene secretory expression in an auxotrophic kluyveromyces marxianus strain as well as a preparation method and application of the recombinant vector. The recombinant vector comprises ampicillin resistance genes, a PKD1 vector, inulase promoters, signal peptides, multiple cloning sites, inulase terminators, nutritional gene promoters and a nutritional gene open reading flame according to the sequence. The constructed recombinant vector used for carrying out foreign gene secretory expression and the preparation method of the recombinant vector can be used for constructing a transformant to achieve secretory expression of foreign genes.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
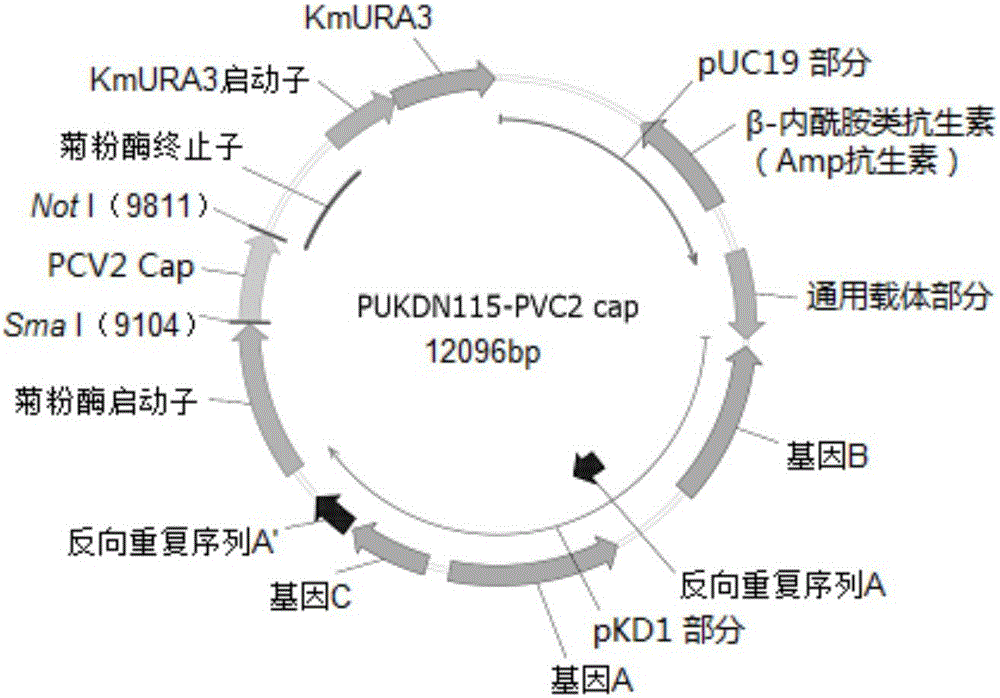
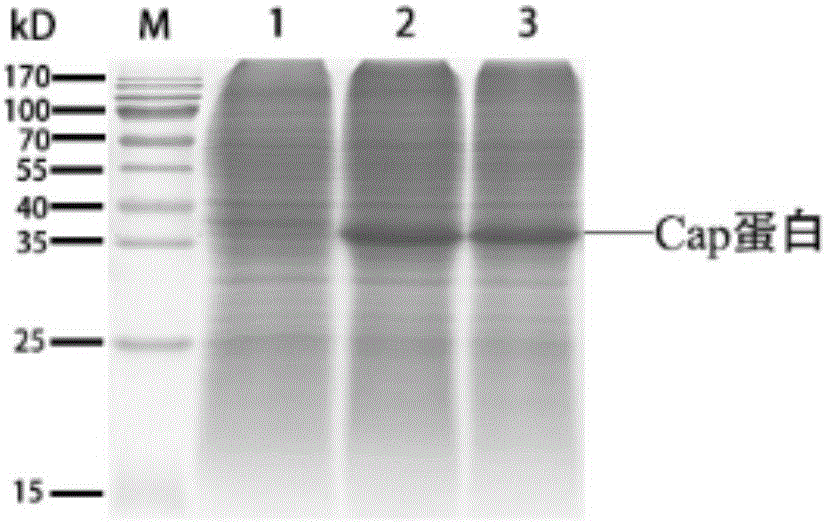
Porcine circovirus type II virus-like particle vaccine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106399350AReduce clinical symptoms associated with infection with PCV2Reduce associated clinical symptomsFungiViral antigen ingredientsHigh densityGenus Kluyveromyces
The invention provides a kluyveromyces marxianus engineering bacterium obtained from recombinant expression of porcine circovirus type II capsid protein; and porcine circovirus type II virus-like particles are obtained by cloning porcine circovirus type II capsid protein genes into an expression vector and conducting recombinant expression in kluyveromyces marxianus. The invention also provides a preparation method of a porcine circovirus type II virus-like particle vaccine, wherein the preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing the porcine circovirus type II virus-like particles through high-density fermentation of the recombinant kluyveromyces marxianus, and then conducting separation and purification so as to prepare the vaccine. The porcine circovirus type II virus-like particle vaccine provided by the invention, which can generate a high-level serum IgG antibody just by implementing injection immunization once, has the advantages of being good in immunizing effect, high in safety, simple in culture operation, high in yield, low in production cost and the like, and the porcine circovirus type II virus-like particle vaccine can achieve large-scale enlarged production; and the porcine circovirus type II virus-like particle vaccine can be used for relieving and preventing related clinical symptoms caused by the infection of porcine circovirus type II (PCV2).
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Prosuction of antibodies or (functionalized) fragments thereof derived from heavy chain immounogobulins of camelidae
InactiveUS20050130266A1Improve physical stabilityImprove efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiNatural antibodyComplementarity determining region
A process is provided for the production of an antibody or a fragment or functionalized fragment thereof using a transformed lower eukaryotic host containing an example DNA sequence encoding the antibody or (functionalized) fragment thereof, wherein the antibody or (functionalized) fragment thereof is derived from a heavy chain immunoglobulin of Camelidae and is devoid of light chains, and wherein the lower eukaryotic host is a mould, preferably belonging to the genera Aspergillus or Trichoderma, or a yeast, preferably belonging to the yeast genera Saccharomyces, Kluyveromyces, Hansenula, or Pichia. The heavy chain fragment can contain at least the whole variable domain. A complementary determining region (CDR) different from the CDR belonging to the natural antibody ex Camelidae can be grafted on the framework of the variable domain of the heavy chain immunoglobulin. The catalytic antibodies can be raised in Camelidae against transition state molecules. The functionalized antibody or fragment thereof can comprise a fusion protein of both a heavy chain immunoglobulin from Camelidae or a fragment thereof and another polypeptide, e.g., an enzyme, preferably an oxido-reductase. Also provided are new products obtainable by a process as described, and compositions containing a product produced by a process as described, which composition may contain a new product as provided.
Owner:BAC IP
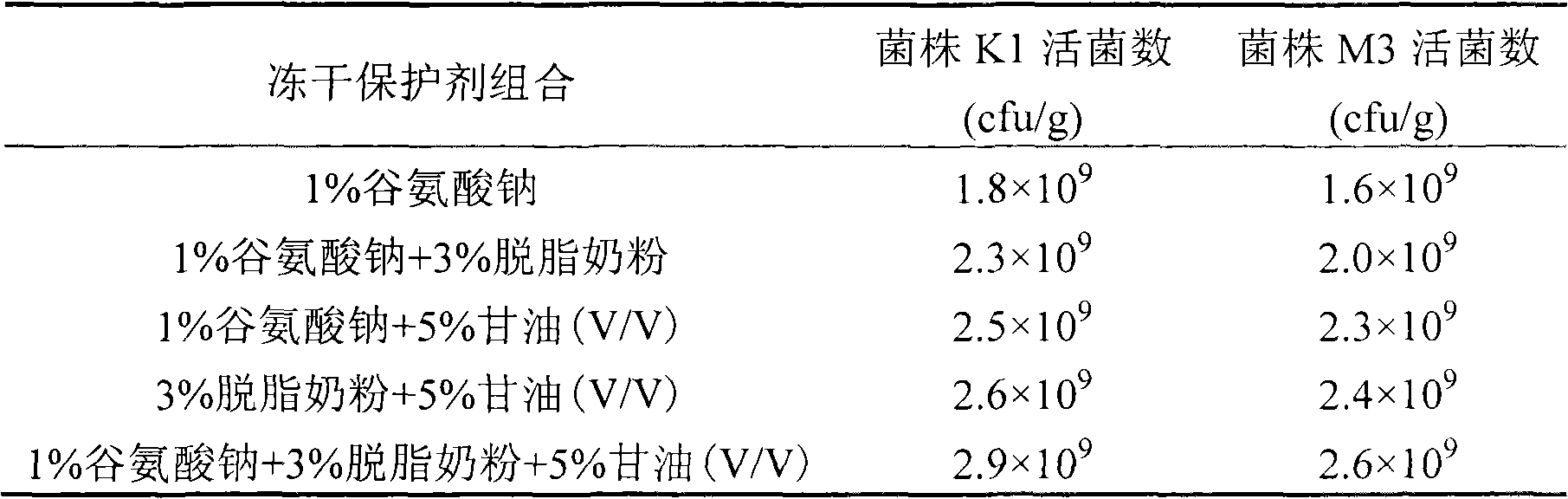
Preparation method of serum cholesterol reduction Kluyveromyces marxianus freeze-dried powder
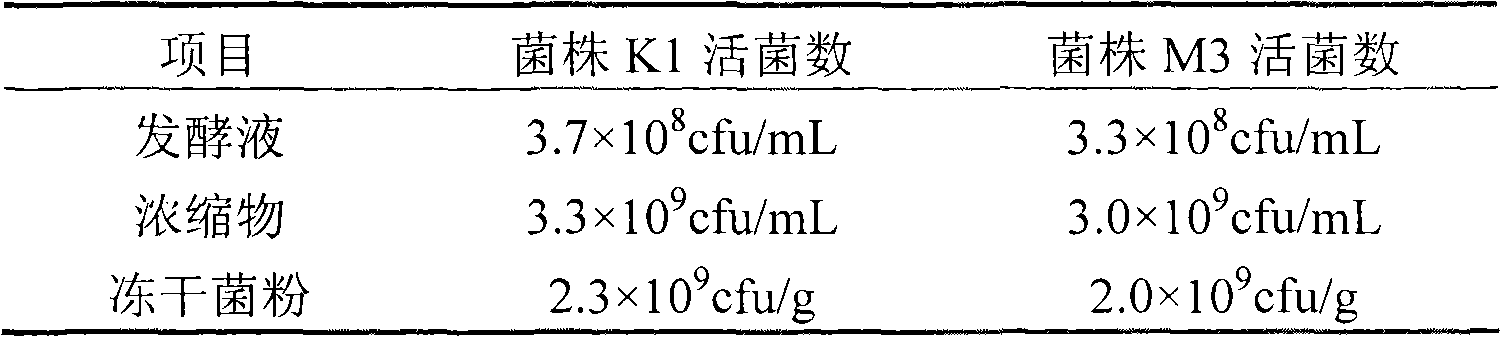
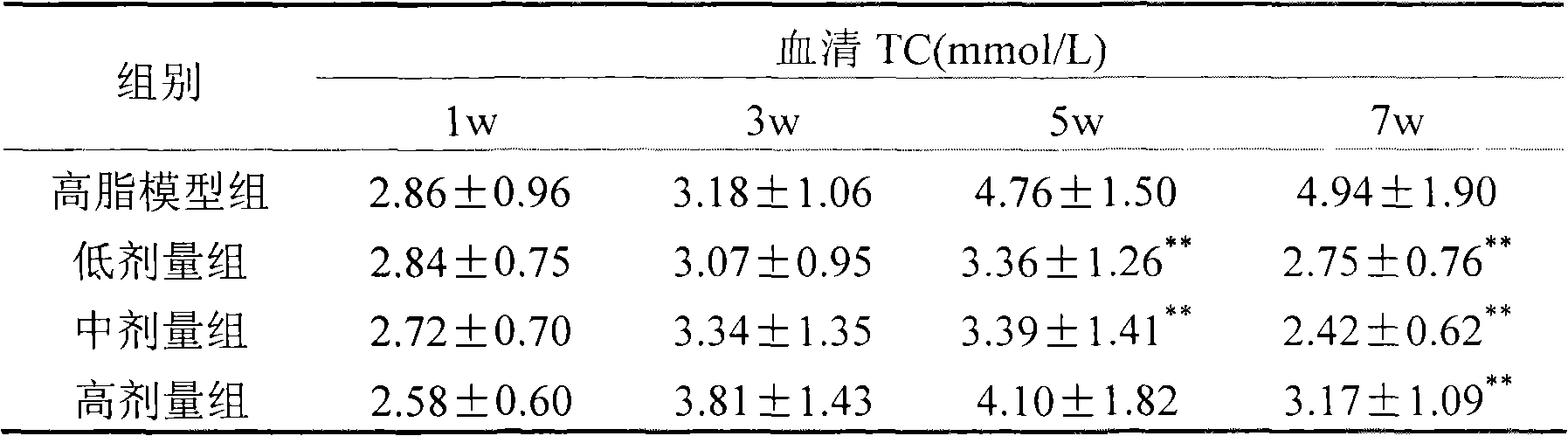
The invention relates to a preparation method of serum cholesterol reduction Kluyveromyces marxianus freeze-dried powder. The preparation method is applicable to the production of serum cholesterol reduction functional probiotic preparations and fermentation dairy products. The two serum cholesterol reduction strains of Kluyveromyces marxianus K1 and M3 screened from Tibetan kefir are utilized, and the freeze-dried powder is prepared through activation and amplification culture, fermentation, centrifugal concentration, freeze-dried protection agent addition, pre-freezing and freeze drying. A free-dried protection agent composition recipe is optimized, so the strain survival rate is higher than 65 percent, and in addition, the viable count of the free-dried powder is higher than 109cfu / g. The serum cholesterol reduction Kluyveromyces marxianus freeze-dried powder prepared by the method has various probiotic effects of reducing the serum cholesterol, improving the organism antioxidation, promoting the intestinal tract flora balance and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Process for preparing a protein by a fungus transformed by multicopy integration of an expression vector
InactiveUS6090574AImproved stability against attack by proteaseImprove stabilityFungiHydrolasesYeastAspergillus
A process is disclosed for preparing a protein by a eukaryote transformed by multicopy integration of an expression vector into the genome of a yeast, such as Saccharomyces, Hansenula, and Kluyveromyces, or of a mould such as Aspergillus, Rbizopus and Trichoderma, the expression vector containing both an "expressible gene" encoding the protein and a so-called "deficient selection marker meeded for the growth of the yeast or mould in a specific medium", such as the LEU2d, TRP1d or URA3d gene, in combination witha ribosomal DNA sequence, resulting in stable high copy integration of 100-300 copies per cell. This multicopy integration results in an increased production of the desired protein, which can be guar alpha -galactosidase, an oxidase or a hydrolytic enzyme such as a lipase.
Owner:BAC IP
Method for improving expression level of recombinant protein in kluyveromyces
InactiveCN101386868AHigh expressionReduce manufacturing costFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyProtein target
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, in particular to a technical proposal used to improve the expression level of recombinant protein. In the method, a promoter, alpha-signal peptide, target protein of an inulase gene are orderly connected with a terminal subcode sequence of the inulase gene first; then the sequence is inserted into a Kluyveromyces lactis expression vector; finally the Kluyveromyces lactis is transformed and fermented, and a fermented supernatant is taken and separated. The method can accelerate the remarkable growth of the yield of the recombinant protein expressed in the Kluyveromyces lactis. The technical proposal can be used to improve the expression amount of various proteins and provide a new method for reducing production cost and enlarging production scale.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Secretory expression method for exoinulinase from Kluyveromyces marxianus
InactiveCN101469325AFor precise cuttingHigh purityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyProtein target
The invention relates to a eukaryon expression method for exoinulinase, which mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, connecting a nucleotide sequence (as shown in SEQ ID No: 1) of the exoinulinase of Kluyveromyces marxianus with pichia expression plasmids pPICZ alpha A through a restricted enzyme site, and obtaining a recombinant expression vector; and secondly, introducing the recombinant expression vector into a thermococcus host strain X-33 or SMD1168, and expressing target proteins (the Kluyveromyces marxianus exoinulinase) through induction fermentation. The eukaryon expression method for the exoinulinase lays a foundation for developing the exoinulinase with industrial application value.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
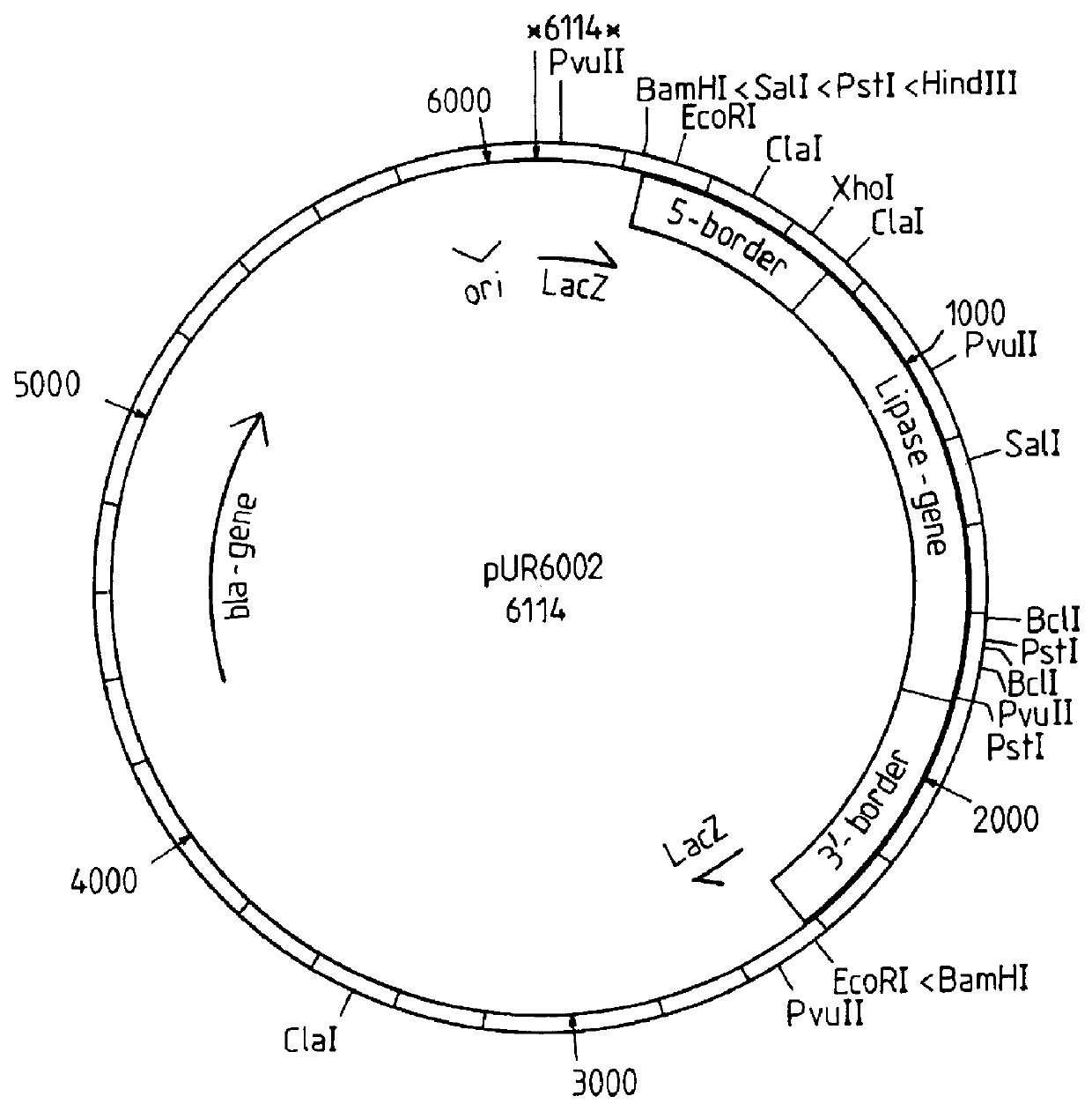
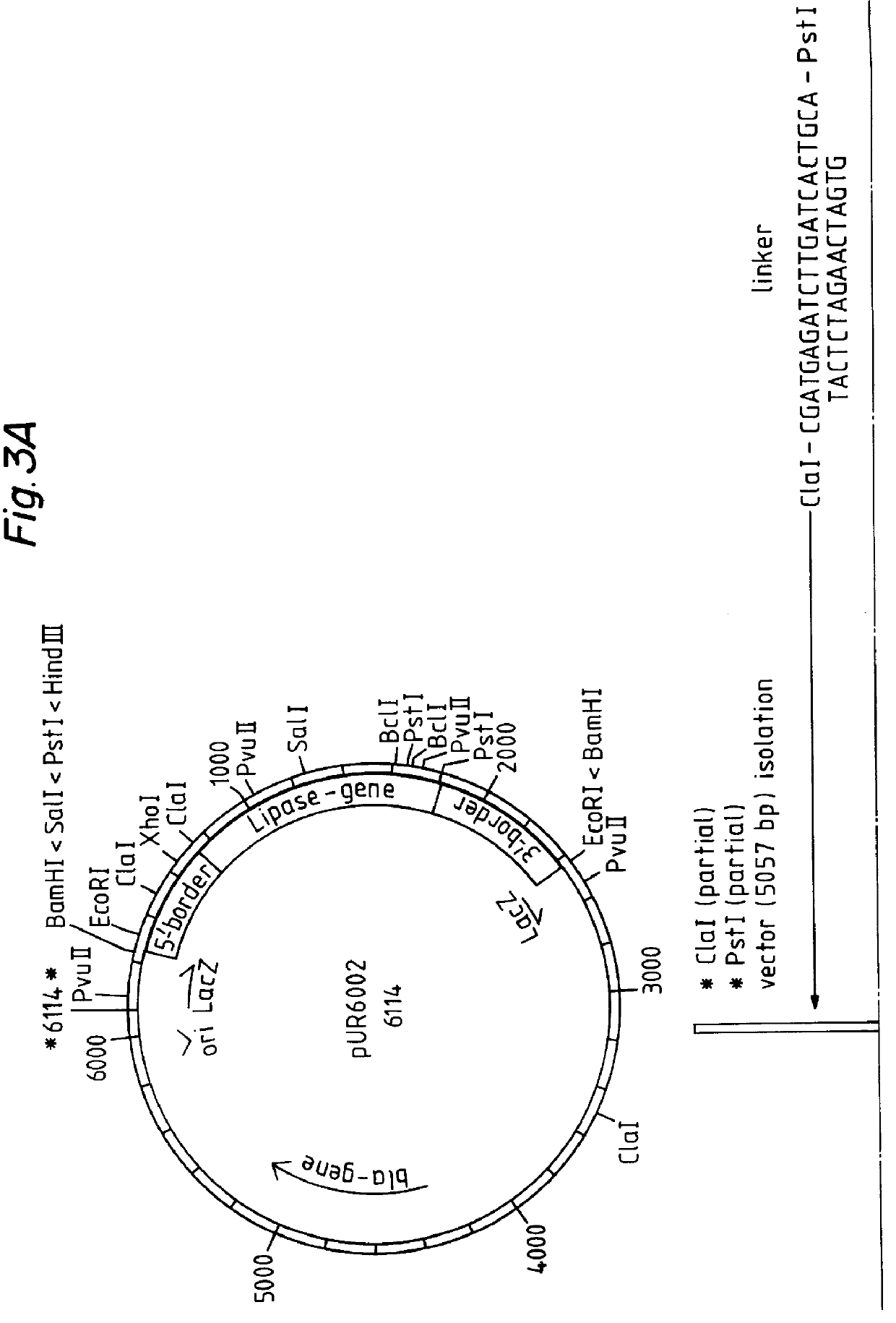
Kluyveromyces as a host strain
Kluyveromyces hosts and DNA expression cassettes for use in Kluyveromyces are provided for transcription of endogenous and / or exogenous DNA, and production of peptides, for enhancing production of an endogenous product, or producing an exogenous product. The Kluyveromyces hosts find particular use for secretion of a desired peptide product, where signal sequences may be native to the peptide or provided from endogenous or exogenous signal sequences, including synthetic sequences, functional in Kluyveromyces. A transformation procedure is provided for efficiently transforming Kluyveromyces.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Kluyveromyces marxianus yeast application
InactiveCN105707436AImprove immunityPromote digestionYeast food ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffDigestionGenus Kluyveromyces
The present invention provides an application of kluyveromyces marxianus yeast, especially the applications in feed additives and feed fermentation, and relates to a feed and a feed additive. The kluyveromyces marxianus yeast is preferably used as an animal feed additive and / or an animal feed fermentation agent, and can improve the immune system of animals, and / or improve the digestion ability of animals, and / or protect animals from free radical damage, and / or produce more nutrients. More preferably, compared to conventional yeasts, the kluyveromyces marxianus yeast can better improve animal immunity, and / or improve animal digestion, and / or protect animals from free radical damage, and / or produce more nutrients.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Feruloyl esterase gene, genetically engineered strain, and preparation method and application of feruloyl esterase
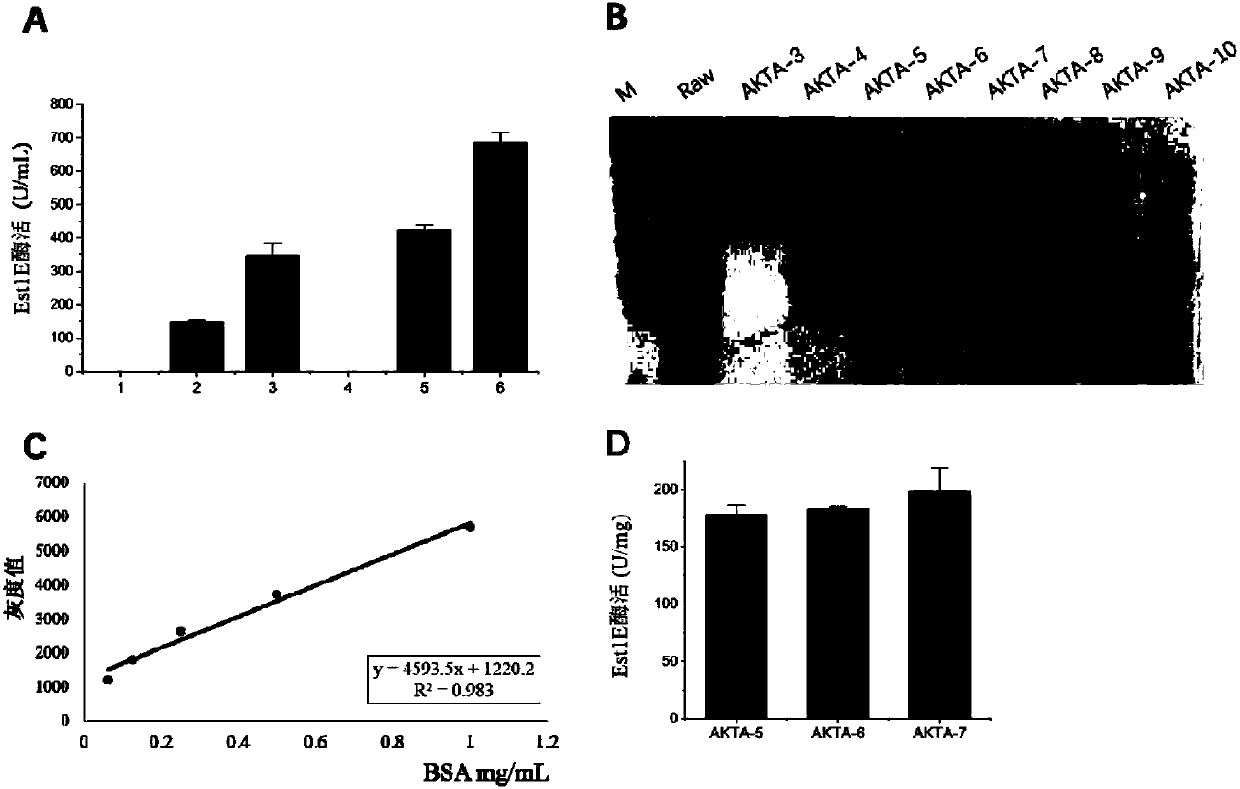
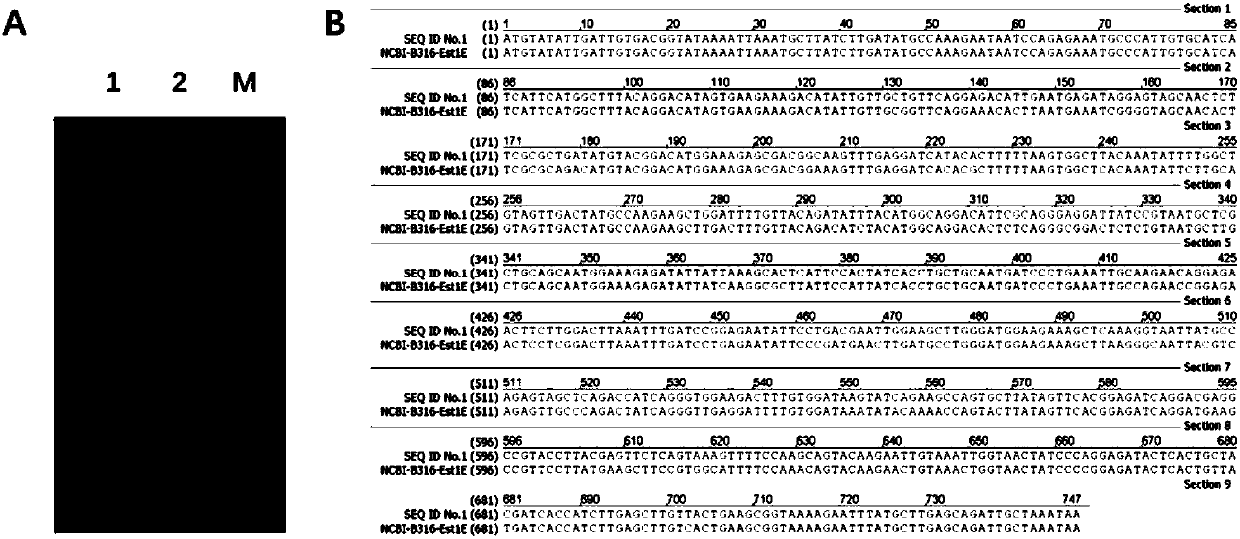
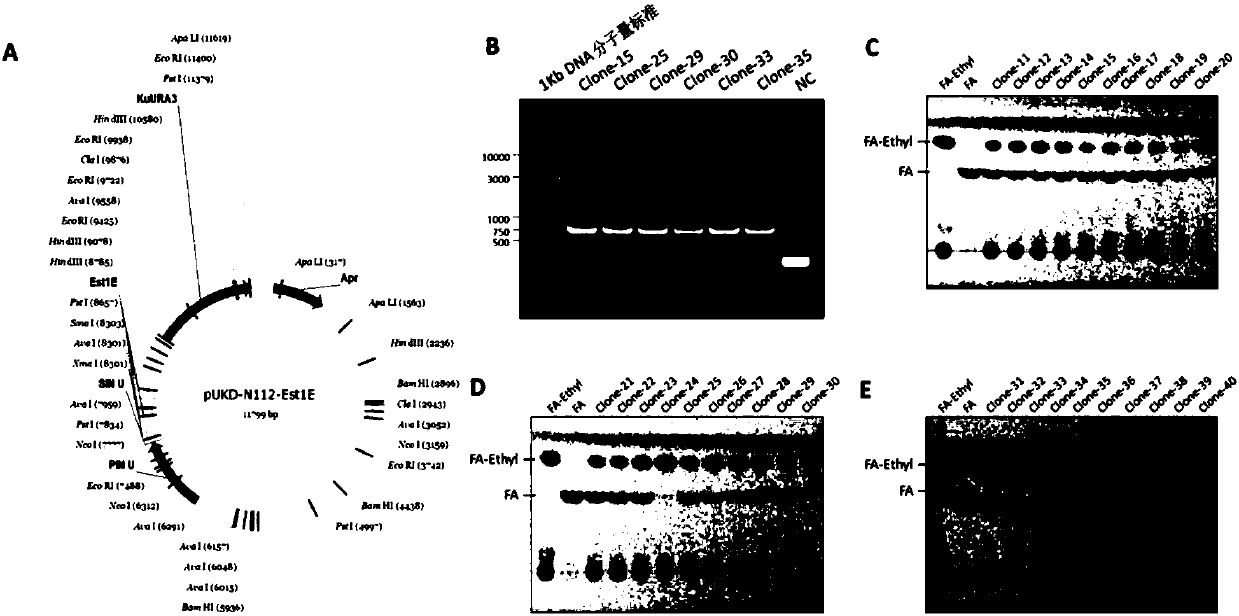
The invention provides a feruloyl esterase gene. The feruloyl esterase gene is originated from microbes in the rumen of a Chinese yak and has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, wherein the nucleotide sequence codes an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. The invention also provides a recombinant Kluyveromyces marxianus expression vector containing the gene, a genetically engineered strain, a preparation method for feruloyl esterase and application of prepared feruloyl esterase. Feruloyl esterase is subjected recombinant expression in a Kluyveromyces marxianus expression system; and after high-density fermentation for 48 h, intracellular and extracellular feruloyl esterase vitalities are 686.35 U / mL and 346.34 U / mL, respectively. Feruloyl esterase having undergone recombinant expression by Kluyveromyces marxianus can release ferulic acid in corn bran. Feruloyl esterase prepared in the invention can be applied to food processing, feed addition, biomedicine, biotransformation of cellulosic substances, bioenergy and other fields.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Composite baterial milk products and preparation proess thereof
The present invention relates to a composite bacteria milk product and its preparation method. It is characterized by that the composite bacterial culture composed of a fungus (lactic acid kluyveromyces) and a life-benefiting bacterium (lactobacillus delbruckii bulgaricus subspecies) can be inoculated in the sterilized milk so as to obtain the invented milk product with uniform gel, palatable taste and several health-care functions of regulating stomach and intestine. Said invention can do not use any food additives.
Owner:陈克铨
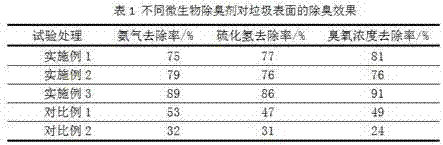
Deodorizing microbial agent and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of environmental protection and particularly discloses aa microbial deodorant for deodorization. The microbial deodorant comprises the active components: a microbial agent, molasses, amino acids and vitamins; the microbial agent is a composite bacterial agent of Kluyveromyces marxianus and Bacillus subtilis; the microbial deodorant is capable of inhibiting the growth of putrefying bacteria, improving the degrading means of organic matters and decreasing the release of ammonia and hydrogen sulfide and occurrence of ammonia matters, and is capable of deceasing methane from bacterial decomposition, thereby arriving at deodorization; the materials of the microbial deodorant are easy to obtain, the preparation method is simple, and the microbial deodorant is worthy of popularization and application.
Owner:佛山市水创科联生态科技有限公司
Bacterial strain producing beta-galactosidase and method for preparing high-purity galactooligosaccharide
The invention discloses a bacterial strain producing beta-galactosidase and a method for preparing high-purity galactooligosaccharide. The bacterial strain producing beta-galactosidase is pichia pastoris SMD1168H-pGAZaA-lac, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 8349. The invention also discloses the method for preparing high-purity galactooligosaccharide. The method includes the following steps: using pichia pastoris strain SMD1168H-pGAZaA-lac to prepare beta-galactosidase; using beta-galactosidase to catalyze lactose, so as to synthesize galactooligosaccharide; purifying galactooligosaccharide mixed liquid through Kluyveromyces marxianus; refining to obtain galactooligosaccharide with high purity. The purity of galactooligosaccharide obtained through the method is equal to or greater than 90%, and the yield is equal to or greater than 30%.
Owner:SHANDONG FREDA BIOTECH
Recombinant Kluyveromyces sp. expressing antibody or antibody analogue, and construction method and use thereof
InactiveCN101413002AExtended half-lifePromote phagocytosisFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastHeavy chain
The invention discloses a recombinant yeast Kluyveromyces for expressing antibodies or antibody analogues and application thereof. The invention provides a method for constructing the recombinant yeast Kluyveromyces for expressign antibodies or antibody analogues. The method comprises the following steps: encoding genes of the antibodies or the antibody analogues are guided into the yeast Kluyveromyces to obtain recombinant bacteria; the antibody analogues are fusion proteins formed by Fc fragments of the antibodies and proteins or protein subunits; the encoding genes of the antibodies are heavy chain and light chain encoding genes of the antibodies. The recombinant yeast Kluyveromyces for expressing antibodies or antibody analogues can be cultured to produce complete antibodies or antibody analogues. The invention uses the yeast Kluyveromyces to prepare the antibodies or antibody analogues to preliminarily overcome the difficulties of difficult antibody production, high purity and large quantity requirements for products and provide good application prospects.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Lactobacillus plantarum WZMX-2 as well as application and prepared whey pear wine thereof
ActiveCN106434473AUniform colorWith colorBacteriaAlcoholic beverage preparationGenus KluyveromycesKluyveromyces marxianus
The invention discloses Lactobacillus plantarum WZMX-2 as well as application and prepared whey pear wine thereof. Bitter-free whey pear wine is prepared by the following steps: uniformly mixing whey fermentation liquor composed of Lactobacillus plantarum WZMX-2, Kluyveromyces marxianus WWMJ-1 and saccharomyces cerevisiae at the volume ratio of 4:4:2 with whey bergamot pear juice mixed liquor; culturing at 25-37 DEG C for 24-72 hours; and fermenting when measuring that the alcohol degree reaches 7.8% vol, the total acid reaches 60.84 titration acidity, the total sugar content reaches 42.34 g / L, and the bitter peptide content reaches 0.15 g / 100 mL. The prepared whey pear wine is yellowish green, clarified and translucent, has natural color and fragrance of whey and pear, and has no bitter feeling; functional tests prove that the prepared whey pear wine can prolong weight-bearing swimming time of mice, reduces the generation of serum urea, increases the reserve of liver glycogen, has no apparent influence on weight and blood lactic acid of the mice, and has a functional effect of alleviating physical fatigue.
Owner:新疆凯瑞可食品科技有限公司
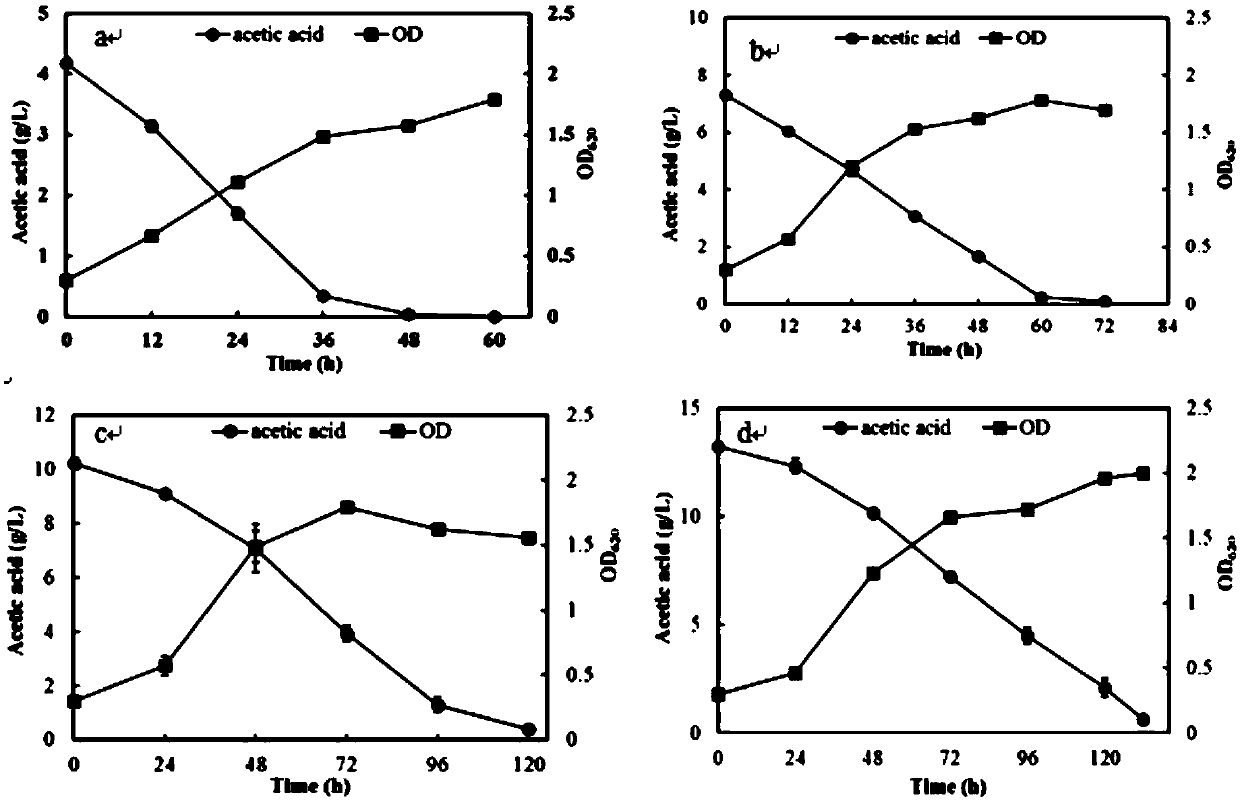
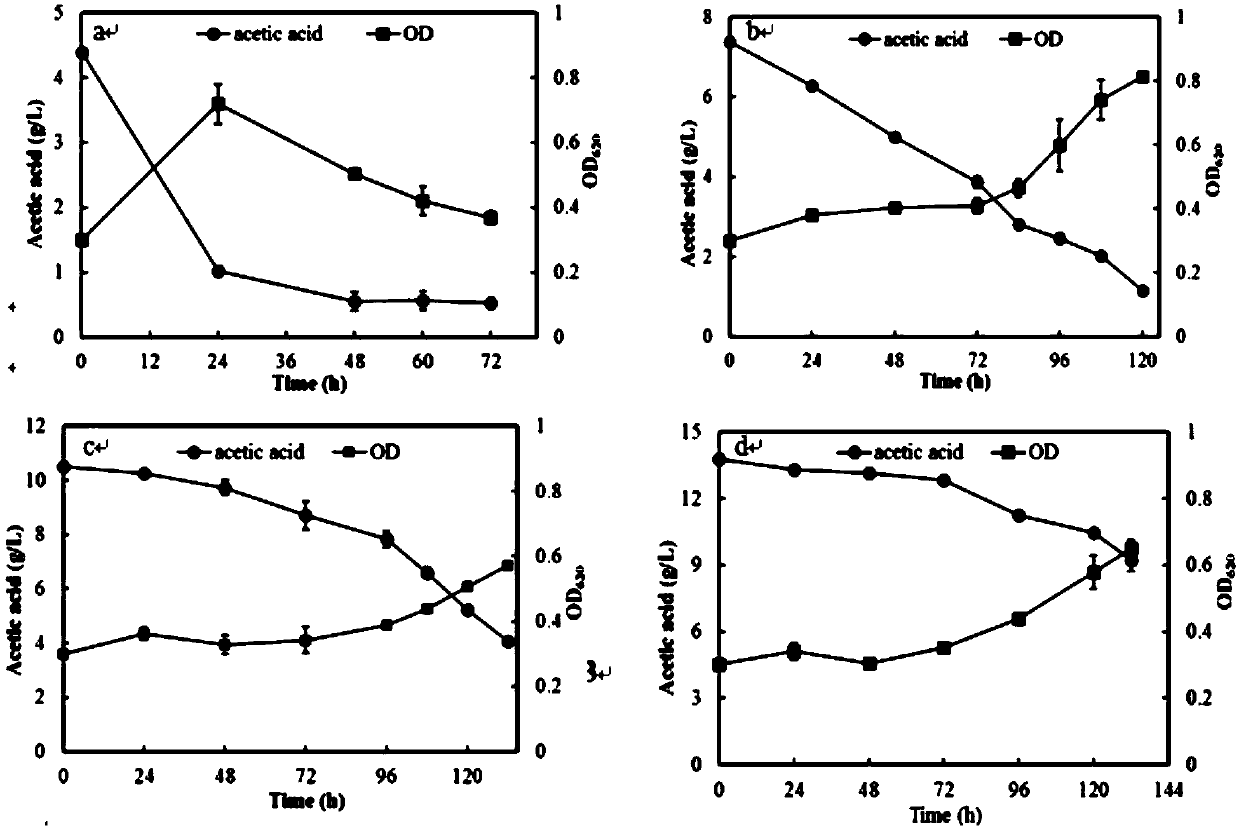
Acetic acid and xylose co-used Kluyveromyces marxianus strain and screening method
ActiveCN109593662AIncrease resistanceHigh yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesCelluloseLiquid medium
The invention discloses an acetic acid and xylose co-used Kluyveromyces marxianus strain with a biological preservation number of CGMCC No.16757. The strain is obtained by long-term orient domestication of Kluyveromyces marxianus through cellulosic hydrolysate and is prepared by the following steps: picking single yeast colonies from a YPD flat plate and carrying out 40 DEG C overnight culture; reinoculating collected cells to a fresh culture medium containing the cellulosic hydrolysate with certain concentration, enabling an optical density value of the culture medium at 620nm to be approximate to 0.3; culturing for 24 to 48 hours at 40 DEG C and 150rmp / min; when OD620 of the acetic acid and xylose co-used Kluyveromyces marxianus strain is greater than or equal to 2.0 (5 to 7 generations), collecting the cells; repeating the steps until the growth speed of the cells is obviously improved under the stress condition of an inhibitor with the concentration; improving the concentration ofthe cellulosic hydrolysate and starting new repeated culture; after continuous domestication, coating the YPD flat plate containing the cellulosic hydrolysate with the collected cells and culturing at40 DEG C for 24 to 48 hours; picking the single colonies with good growth situation and putting into a YPD liquid medium, and culturing at 40 DEG C and 150rmp / min for 24 to 48 hours; preserving dominant resistance clones in 30 percent glycerinum.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Kluyveromyces marxianus and application thereof
ActiveCN105087403AImprove secretion capacityIncrease biomassFungiHydrolasesSecretory proteinGenus Kluyveromyces
The invention provides a kluyveromyces marxianus with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 10621, and also provides the application of the kluyveromyces marxianus. Compared with existing kluyveromyces marxious such as ATCC8585 and ATCC26548, the kluyveromyces marxianus has higher protein secretion capacity and higher biomass, can be used for producing enzymic preparations, and also can be used for building a recombinant protein expression system.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com