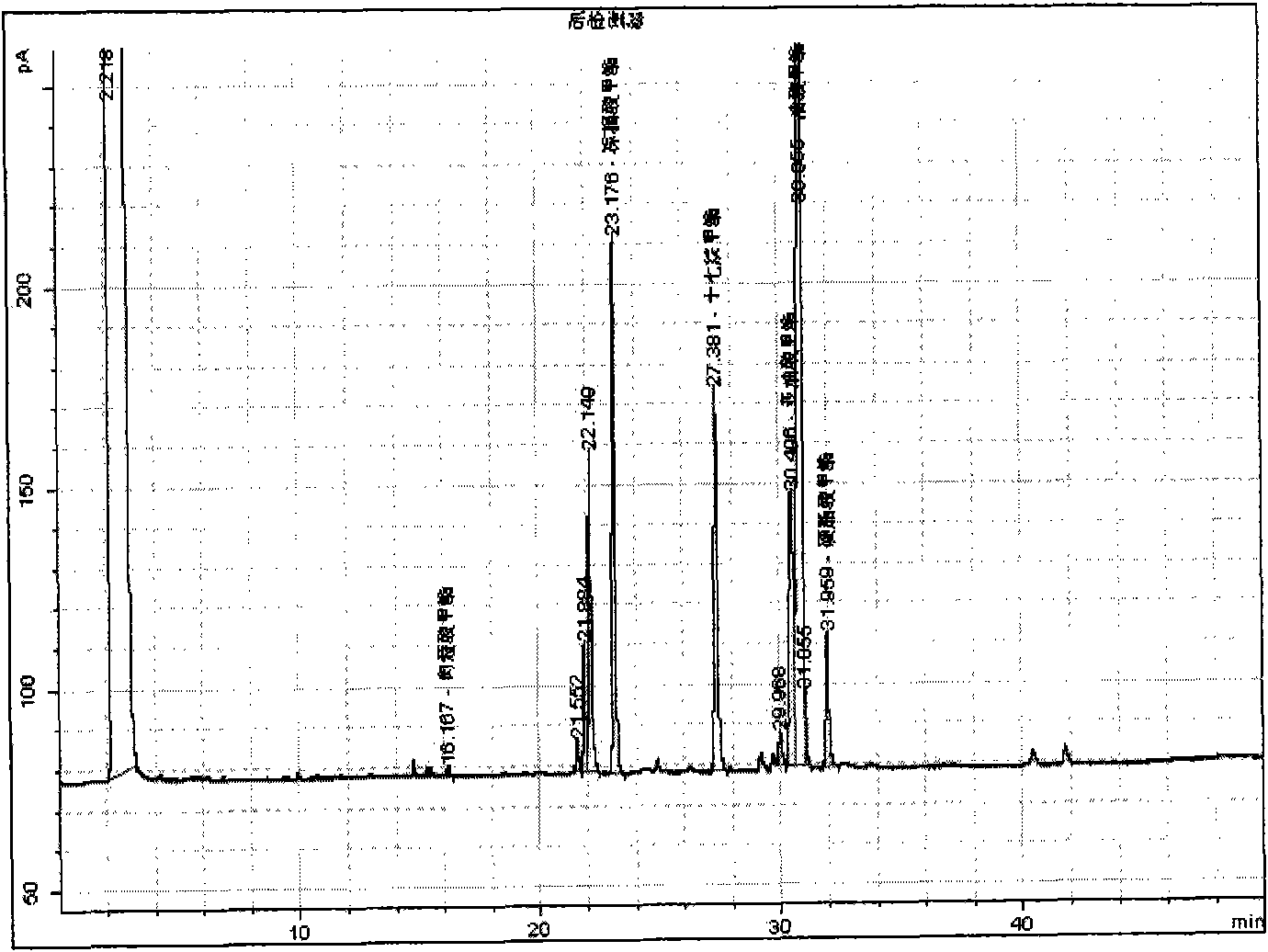
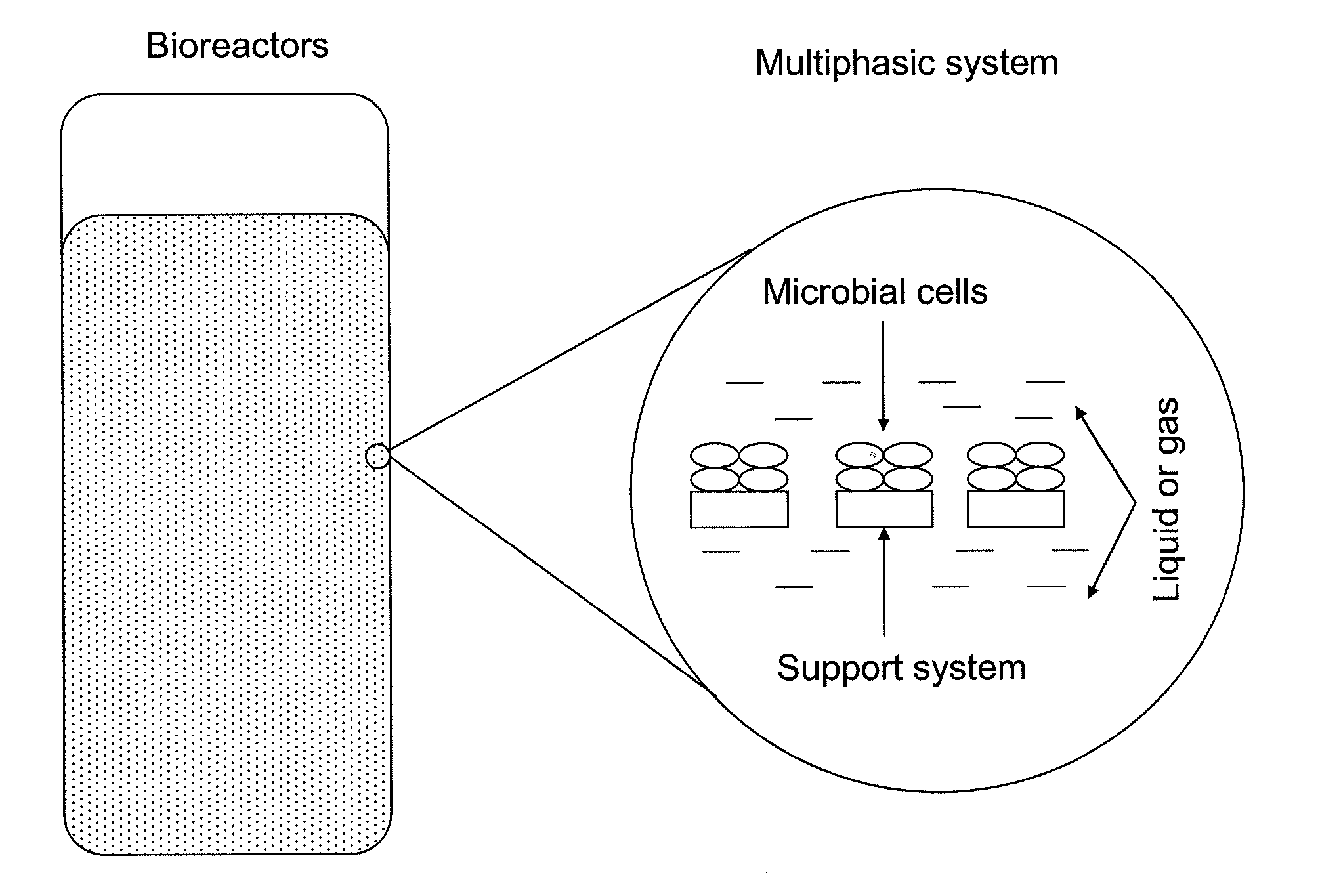
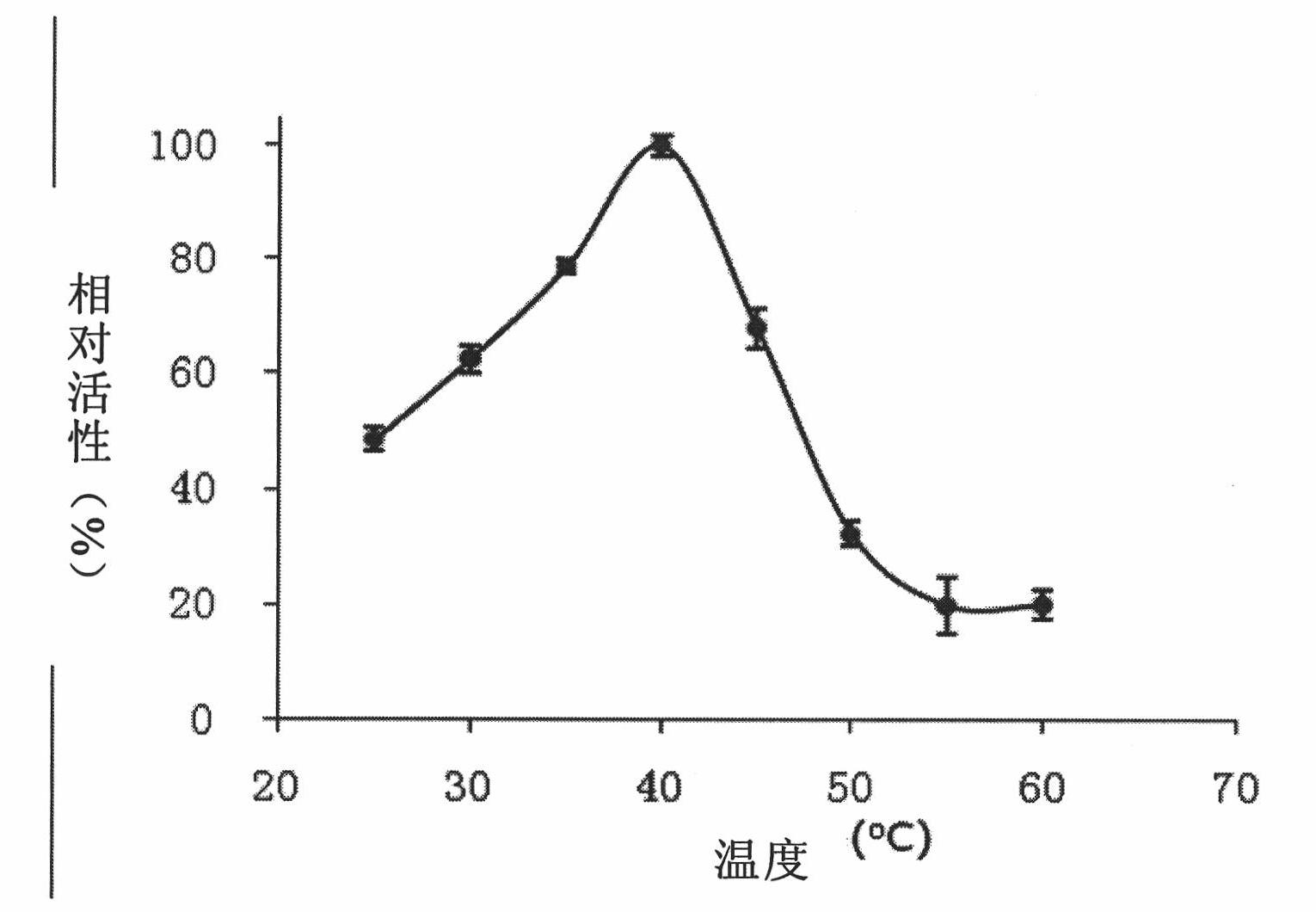
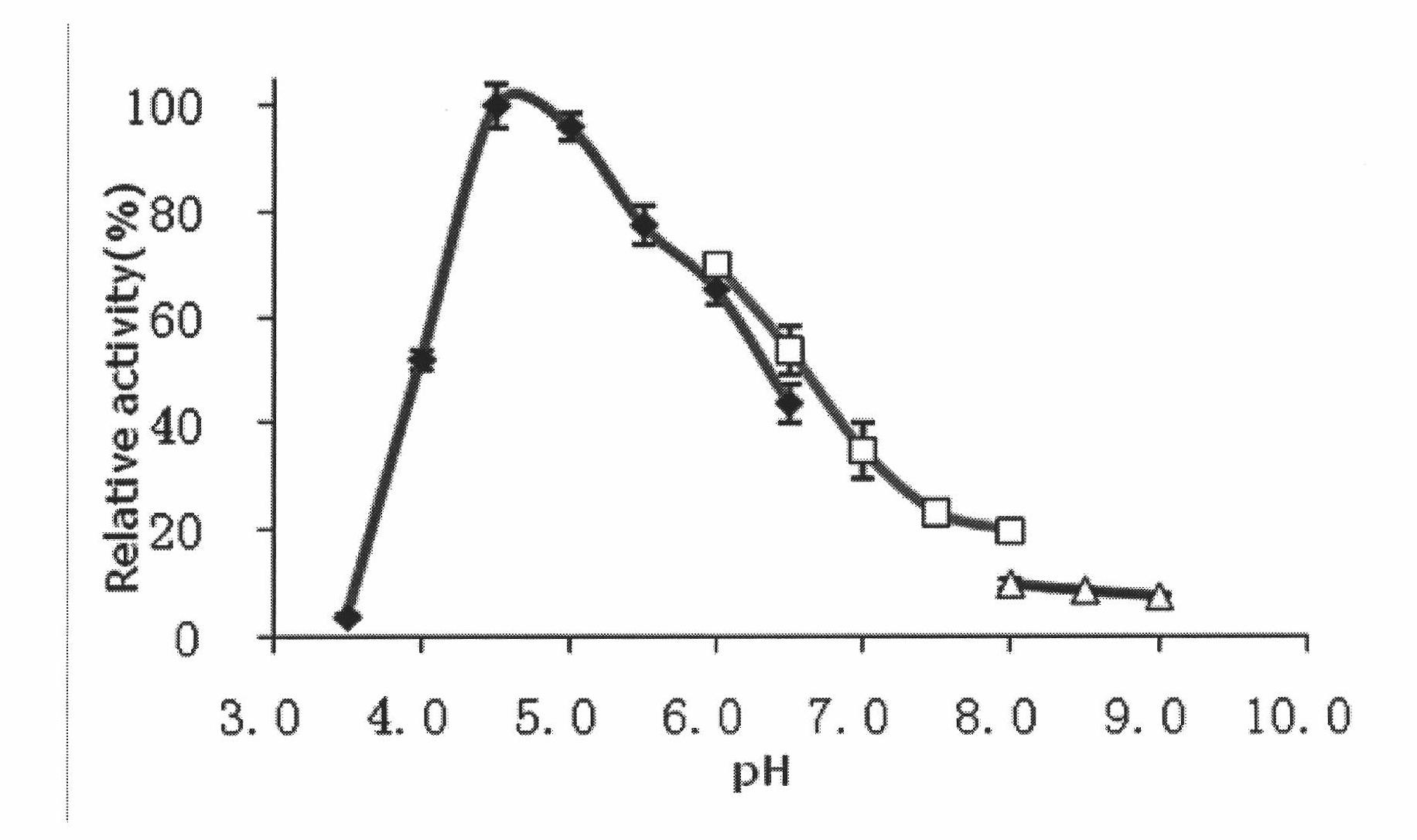
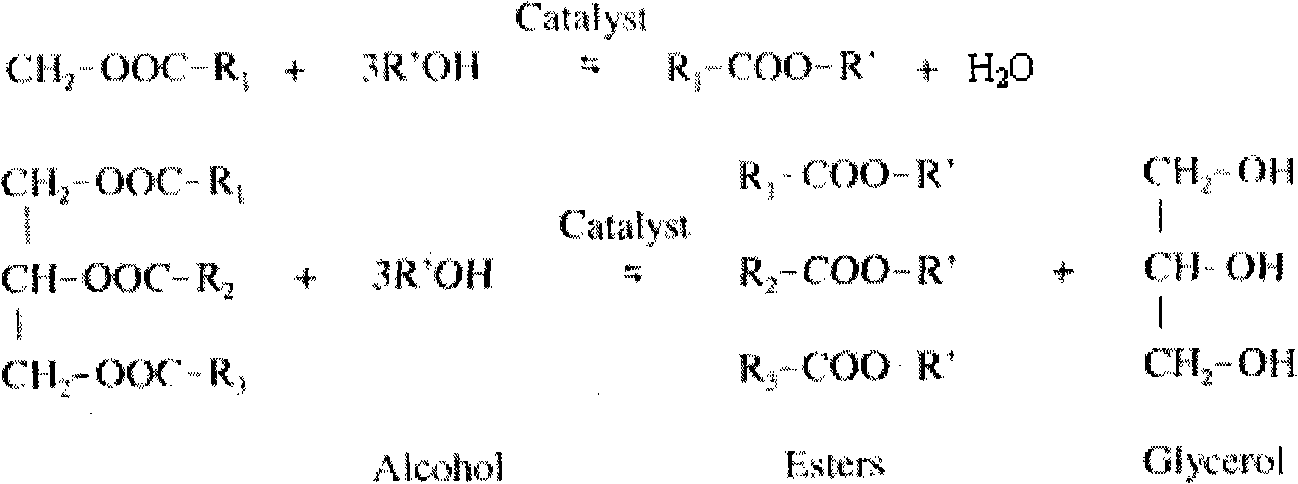Patents
Literature
438 results about "Bioenergy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioenergy is renewable energy made available from materials derived from biological sources. Biomass is any organic material which has stored sunlight in the form of chemical energy. As a fuel it may include wood, wood waste, straw, and other crop residues, manure, sugarcane, and many other by-products from a variety of agricultural processes. By 2010, there was 35 GW (47,000,000 hp) of globally installed bioenergy capacity for electricity generation, of which 7 GW (9,400,000 hp) was in the United States.
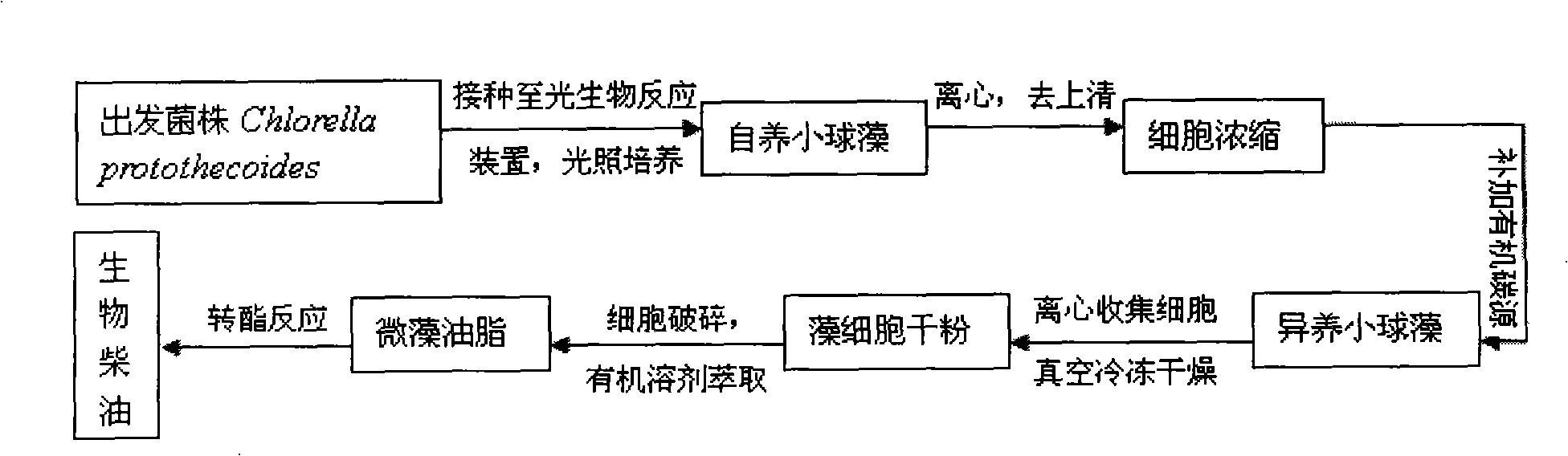
Method for producing biodiesel by autotrophic culture and heterotrophic culture of chlorella
InactiveCN101280328AReduce consumptionReduce releaseFatty acid esterificationUnicellular algaeBiodiesel feedstockOil and grease
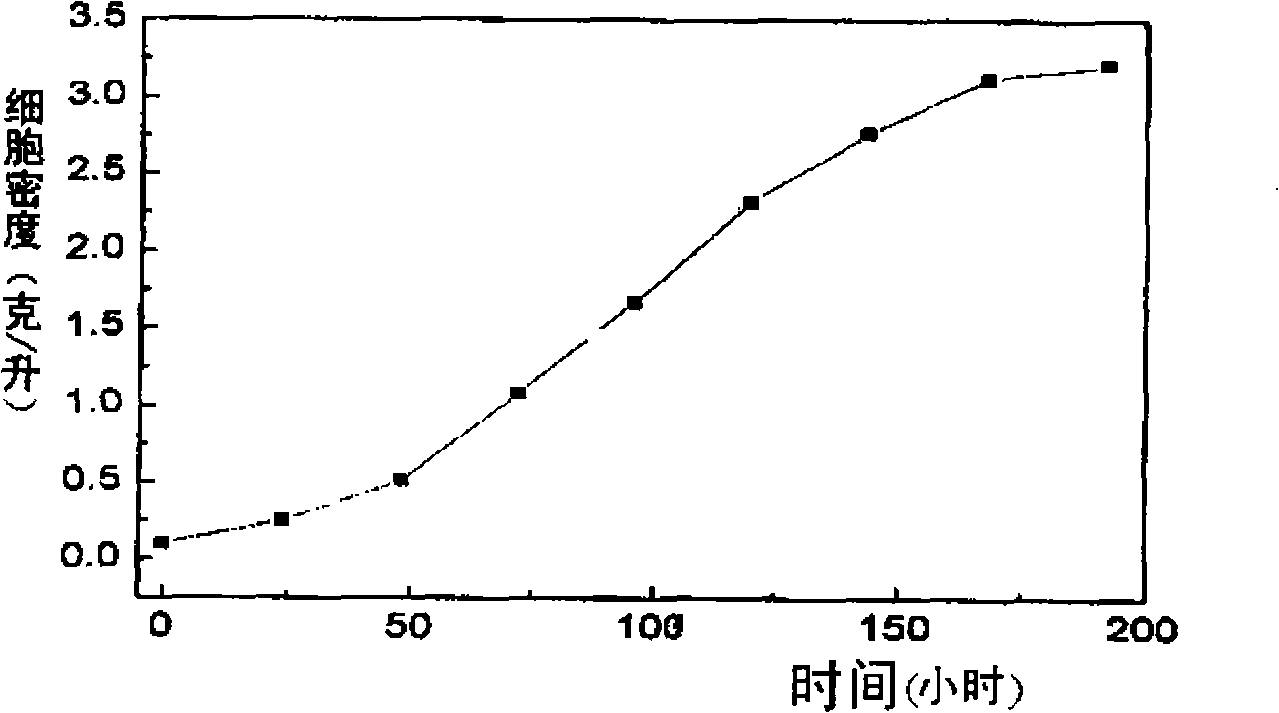
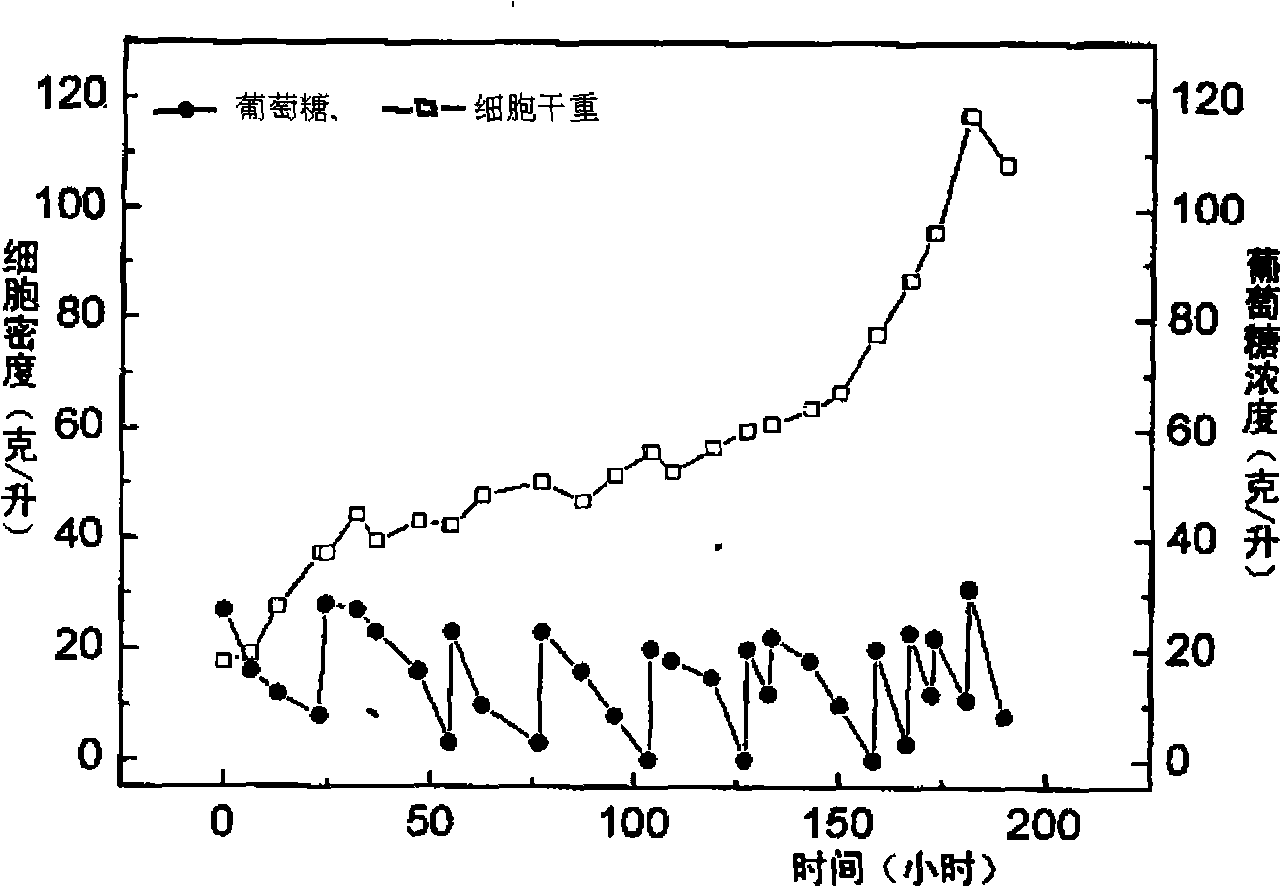
The invention discloses a method for producing biological diesel oil by two steps of culture of chlorellas, namely, autotrophy and heterotrophy, which belongs to the renewable biological energy field. Concentrated autotrophic algae is put into a fermentation tank to perform heterotrophic growth from the processes of autotrophic culture, cell concentration and fermentation pollution controlling of the chlorellas, to ensure the chlorellas to be synthesized into neutral fat. Effective feeding strategy is established to ensure the fat to be synthesized into optimal after the optimization of the fermentation conditions and the process control. The biomass can reach 108g.L-1, and the grease content can reach 52 percent of cell dry weight. After the culturing is finished, biological diesel oil can be prepared after extracting algal oil and transesterification reaction. The cell concentration technology adopted by the invention can effectively avoid the problem of light restriction during the high density culture process Not only is the carbon dioxide emission reduced, but also the organic carbon source consumption is reduced, thus the preparation cost of the biological diesel oil material is saved. The whole technical line is environmental friendly, high efficient, and can meet the industrial application requirements of the microalgae biological diesel oil.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Biomass energy prepared by one-step method of microalgae
ActiveCN101580857AWon't happenRelieve pressurePreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionBiofuelsDownstream processingBiodiesel
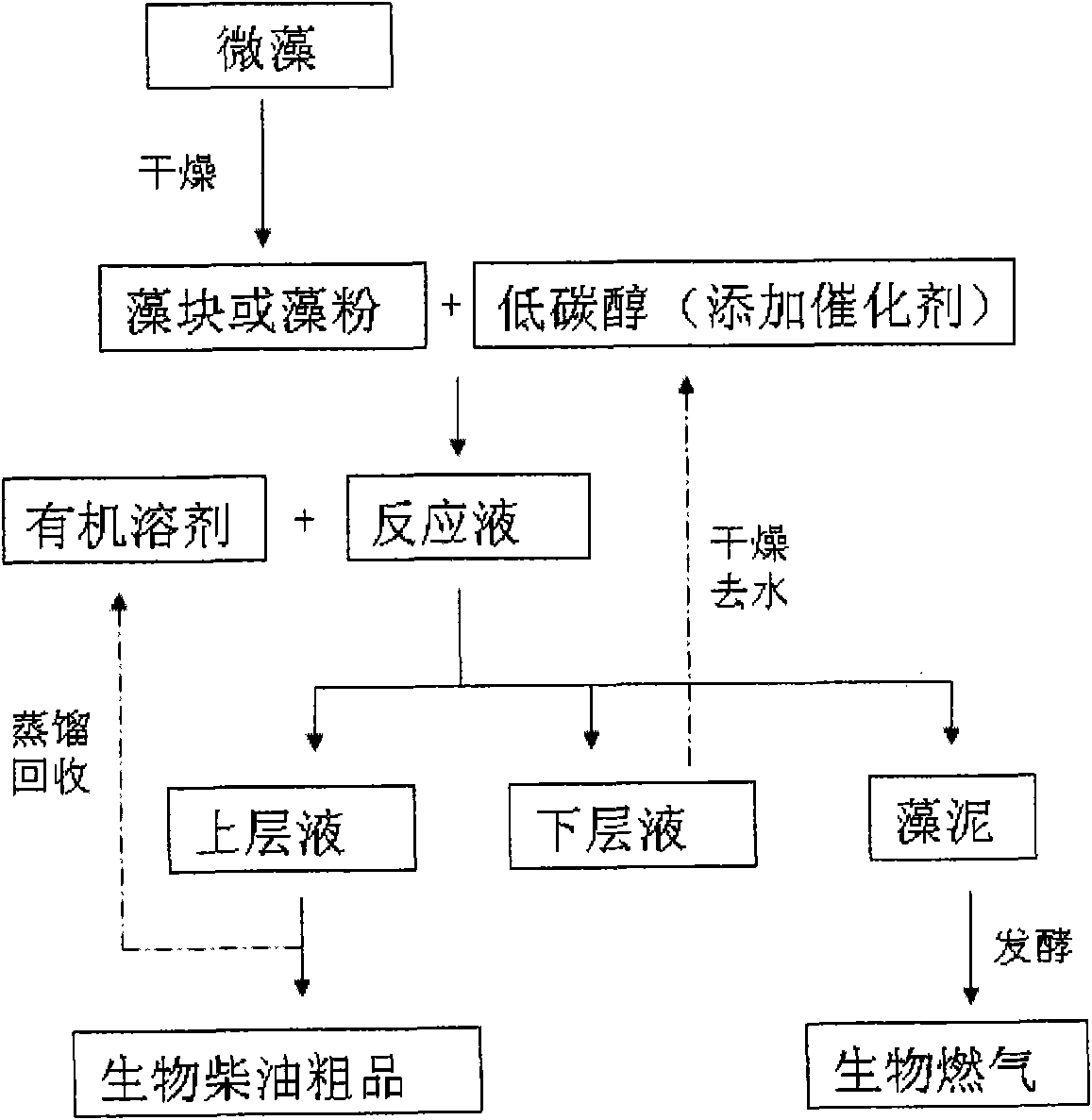
The invention provides a method for preparing biodiesel from microalgae. The method comprises the following steps of: a. changing collected microalgae from the wet algae into algae block or algae powder; b. mixing a catalyst into low-carbon alcohol, directly adding the algae block or the algae powder obtained by the step a, and carrying out ester exchange reaction to prepare the biodiesel; c. after the reaction is stopped, adding an organic solvent for extracting reaction solution which is divided into organic solvent phase used for extraction, low-carbon alcohol water-adding phase and algae mud; and d. after the extraction is completed, collecting the organic solvent phase used for extraction, removing the organic solvent by distillation, and obtaining oily liquid, namely crude products of the biodiesel. After preparing the biodiesel, the steps that the low-carbon alcohol water-adding phase is used circularly after dewatered by a solid drying agent, and the produced algae mud is used for producing biogas by biological fermentation are added. The invention completes the oil extraction of microalgae and biodiesel production by one step, simplifies the technique steps and equipment, saves cost; the sulphuric acid and low-carbon alcohol used for production can be recovered, then dewatered by drying, then utilized repeatedly, the cost is reduced, the final product is neutral, does not need washing and reduces the downstream processing pressure; and simultaneously, chlorophyll is mainly concentrated in the low-carbon alcohol, reduces the interference of the chlorophyll to the color of the product and does not need the step of decoloring.
Owner:ENN SCI & TECH DEV
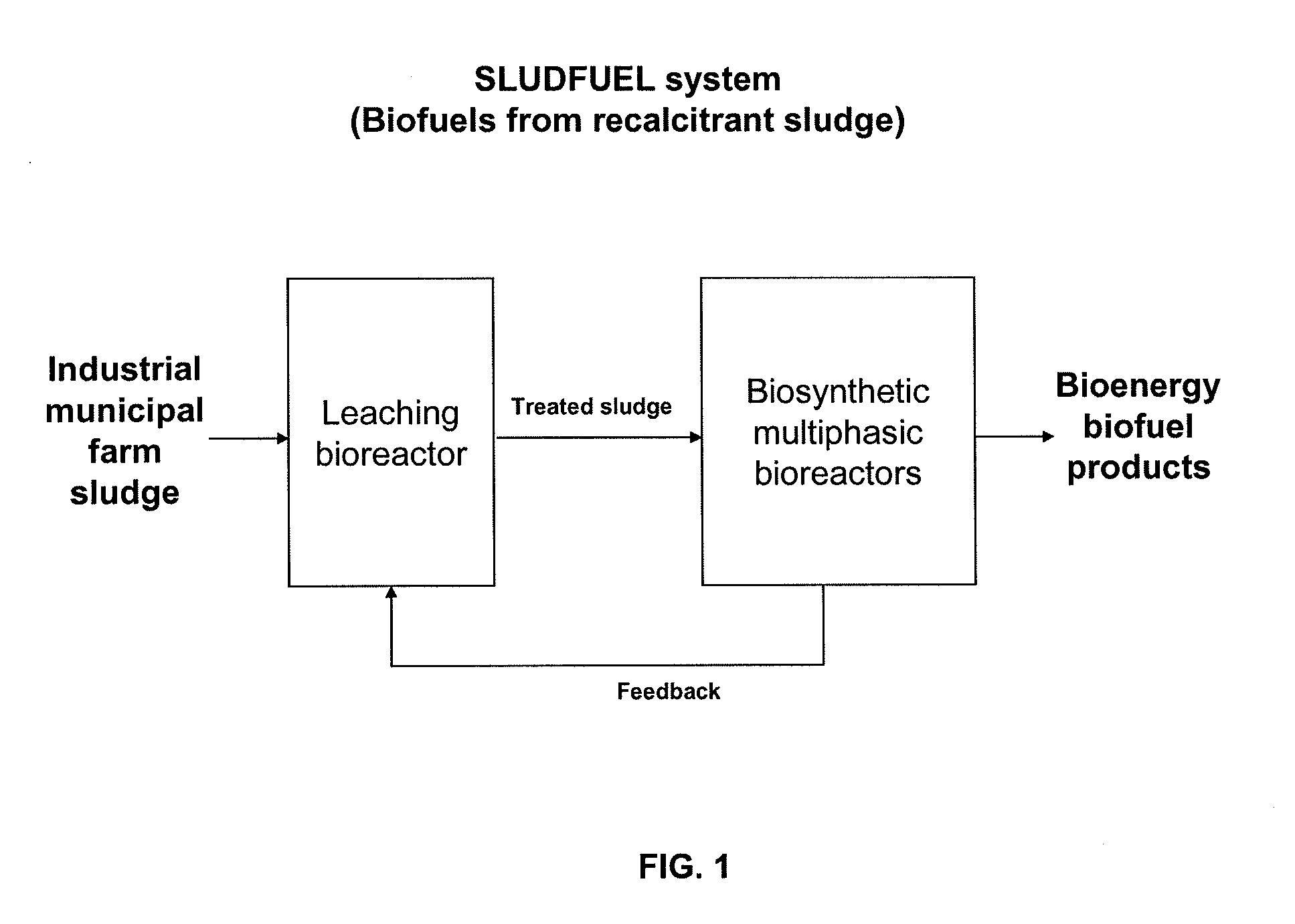
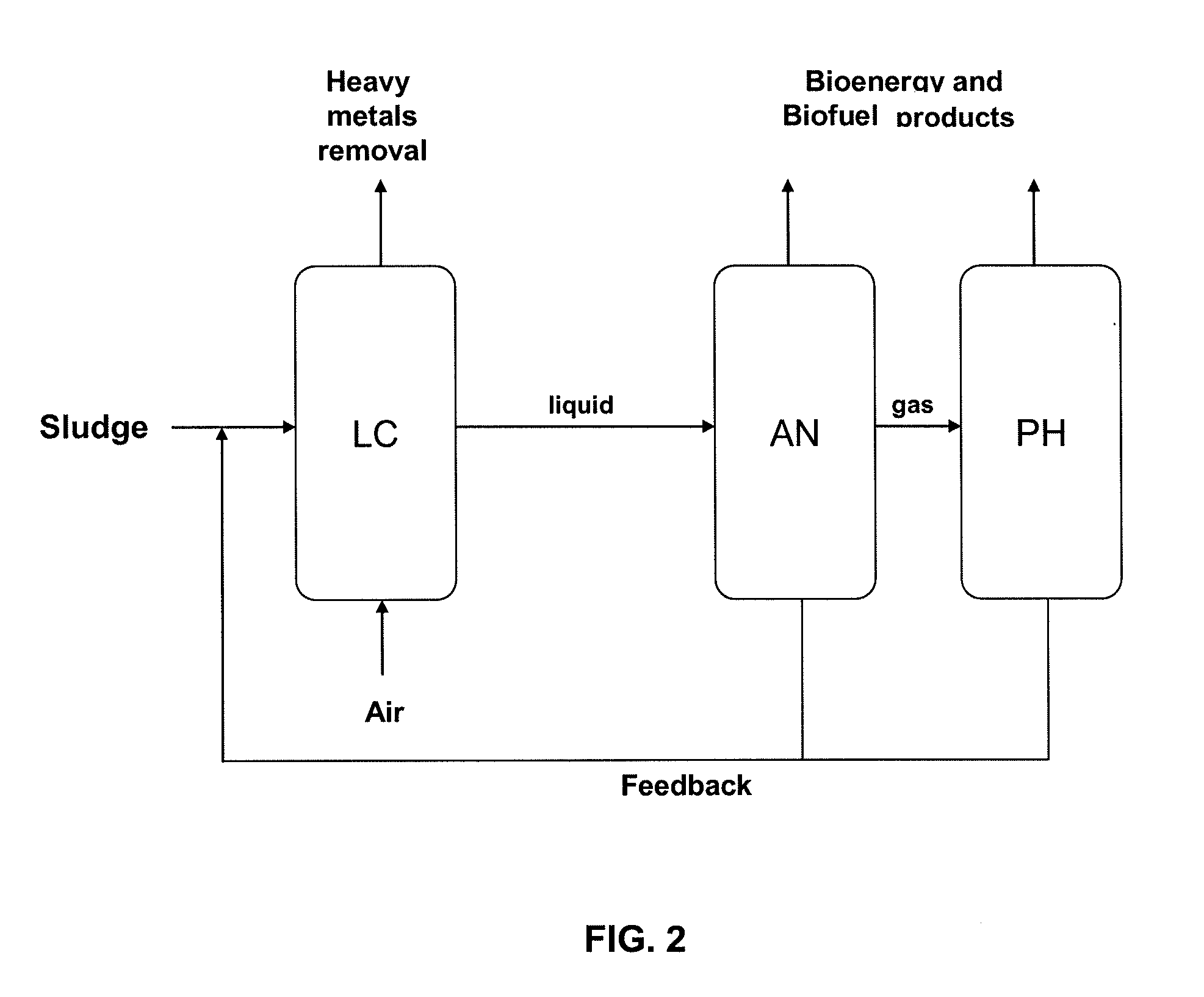
Methods and systems for production of biofuels and bioenergy products from sewage sludge, including recalcitrant sludge
InactiveUS20090325253A1Improper useReduce and eliminate pathogenBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh concentrationMicroorganism
The present invention provides methods and systems (SLUDFUEL system) for producing biofuel and bioenergy products using, as starting raw material, municipal, industrial, and / or farm sewage sludge, including recalcitrant sludge containing high concentrations of heavy metals, and produced after waste treatment. In accordance with the invention, municipal, industrial, and farm sewage sludge, including recalcitrant sludge, can serve as a carbon source to support the metabolism of synthetic microorganisms to produce biofuels and bioenergy products.
Owner:ASCON MIGUEL +1
Microorganism fermentation grease and method for preparing organism diesel oil from the same
InactiveCN1923960AAbundant raw materialsLow costBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionOil and greaseYeast
The invention discloses a biological diesel preparing method of fat fermented by microbe in the biological energy and biological catalytic technological domain, which comprises the following steps: grafting yeast microbe in the fat-producing bacterial culture medium; centrifuging; separating; extracting to obtain the fat; esterifying under catalyst to obtain biological diesel and glycerine as by-product.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Microalga photosynthetic aerobic high-density fermentation culture method utilizing inorganic nitrogen source and application
ActiveCN103805514APromote rapid proliferationThe cultivation process is stable and controllableUnicellular algaeDispersed particle separationCulture mediumsNutrient
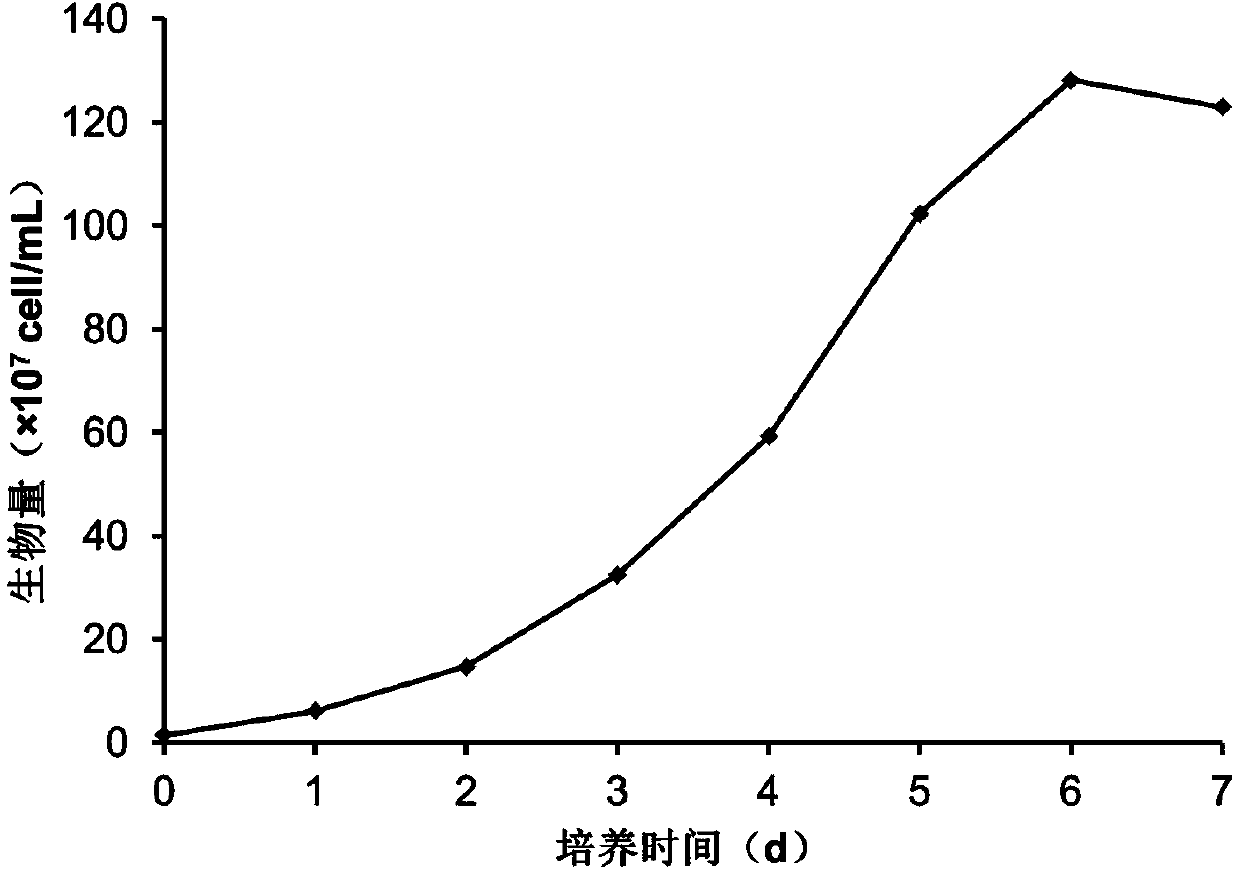
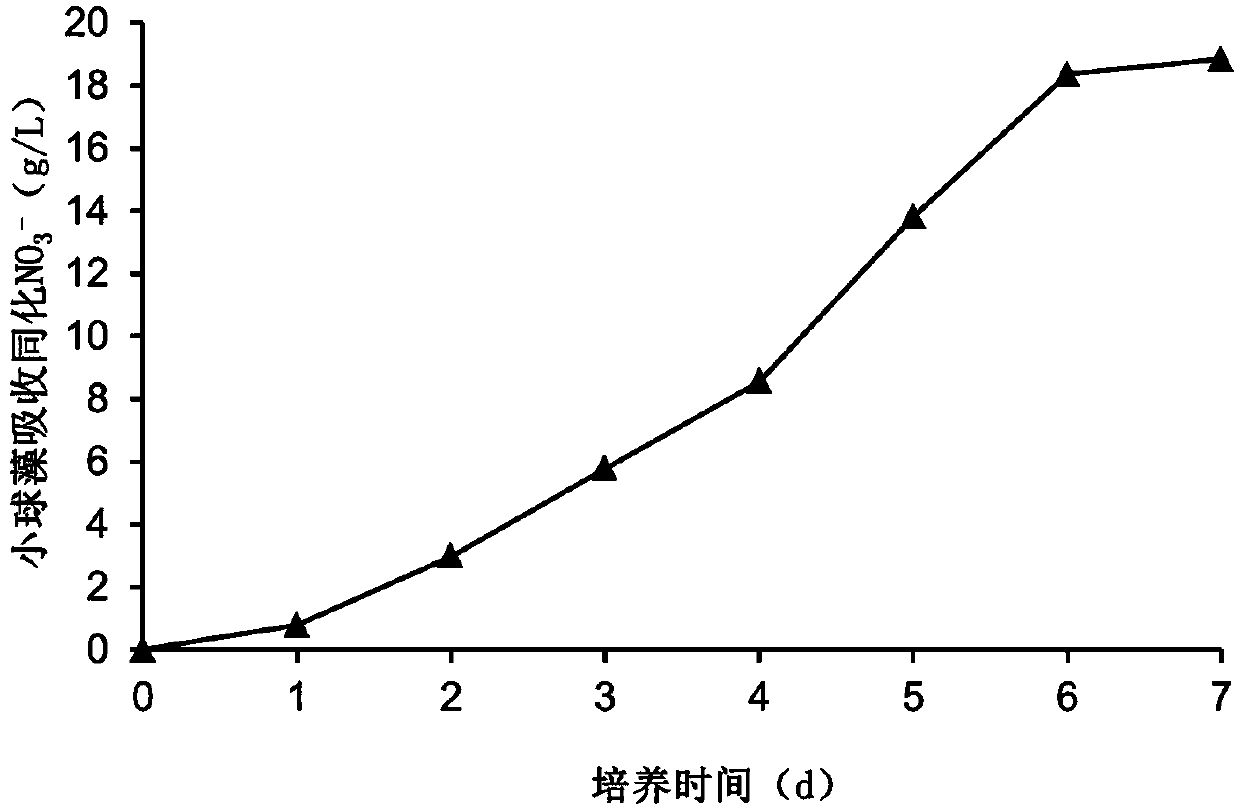
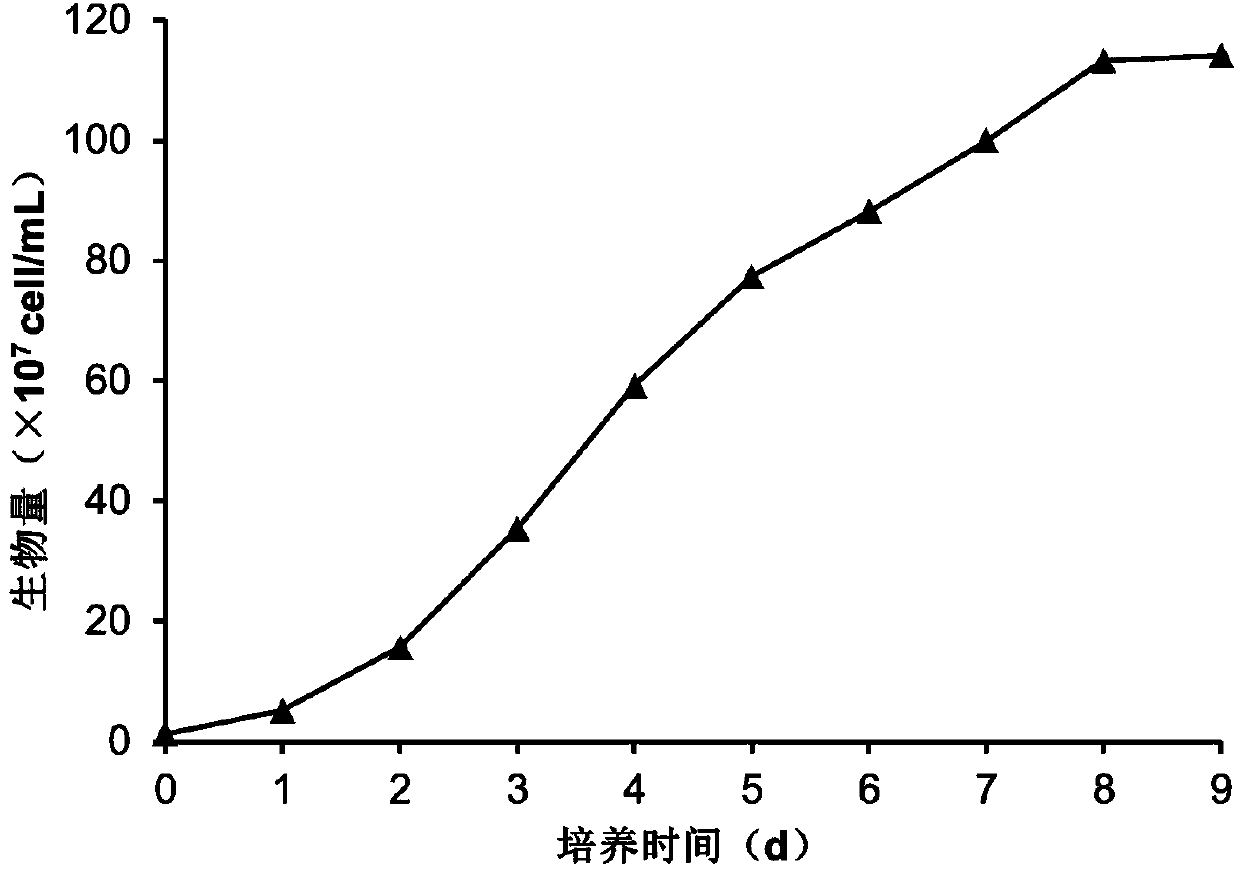
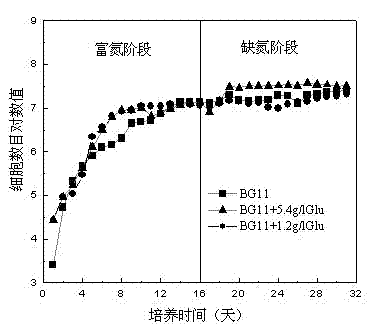
The invention discloses a microalga photosynthetic aerobic high-density fermentation culture method utilizing an inorganic nitrogen source and an application. The invention relates to a microalga high-density fermentation culture method utilizing the inorganic nitrogen source, wherein photosynthetic aerobic culture is performed in a culture medium in which inorganic nitrogen salt is taken as the inorganic nitrogen source and glucose is taken as an organic carbon source; glucose, inorganic nitrogen salt and other nutrient salts are segmentally replenished according to consumption of the nitrogen source and carbon source of the culture medium and the biomass growth condition; the concentration of the nutrient salts, pH value, ventilatory capacity, light intensity and alga liquid stirring speed are reasonably regulated, so that microalgae can be rapidly proliferated in a short time, the culture time is shortened, high-density growth of the microalgae is guaranteed, rapid growth of the biomass of microalga cells is realized, and high-efficiency absorption and assimilation of inorganic nitrogen are realized. The method disclosed by the invention is suitable for high-density photosynthetic aerobic fermentation production of the microalgae by utilizing the inorganic nitrogen salt as a nitrogen source, and the method lays the foundation of an economic feasibility research on environmental and ecological applications and bioenergy production of the microalgae.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
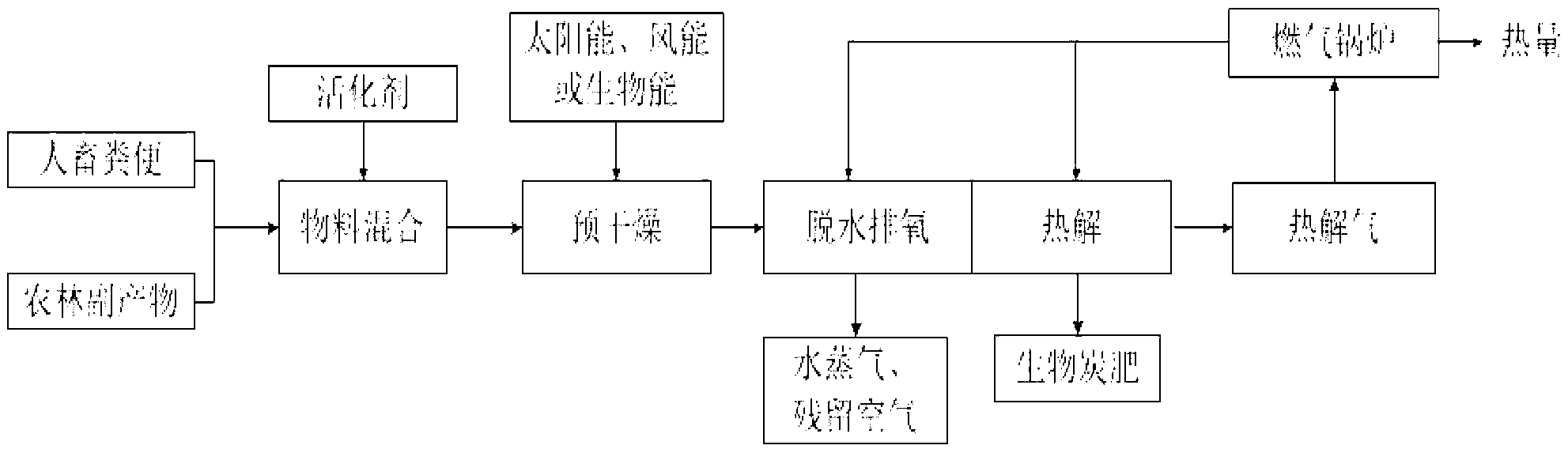
Method for producing charcoal fertilizer
InactiveCN103274778ASolve the problem of insufficient fertilizer efficiencyAbundant microporous structureEnergy inputResource utilizationAgricultural residue
The invention belongs to the field of resource utilization of biomass, particularly relates to a method for producing a charcoal fertilizer by using an activating agent on the basis of human and animal excreta and forestry and agricultural residues, and aims to enhance the cellular performance and fertilizer efficiency of the charcoal fertilizer through the activating agent and overcome the defects that the human and animal excreta is difficult to process and conventional charcoal has insufficient fertilizer efficiency. The method comprises the steps as follows: the human and animal excreta, ground forestry and agricultural by-products and the activating agent are mixed uniformly according to a certain proportion; moisture content of a material is reduced to 30% below by using solar energy, wind energy or bioenergy; a mixture is placed in a pyrolysis material bin and then heated to the temperature of 150-200 DEG C, so that further dehydration is performed, and residual air in the material bin is removed; the material is carbonized at the temperature of 450-550 DEG C; and cooling is performed, so that a charcoal fertilizer product can be obtained. According to the method, compared with a charcoal fertilizer which is prepared without addition of the activating agent, cellular structures are increased by more than 25%, and the total amount of phosphorus and potassium which can be used by plants is increased by more than 20%.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
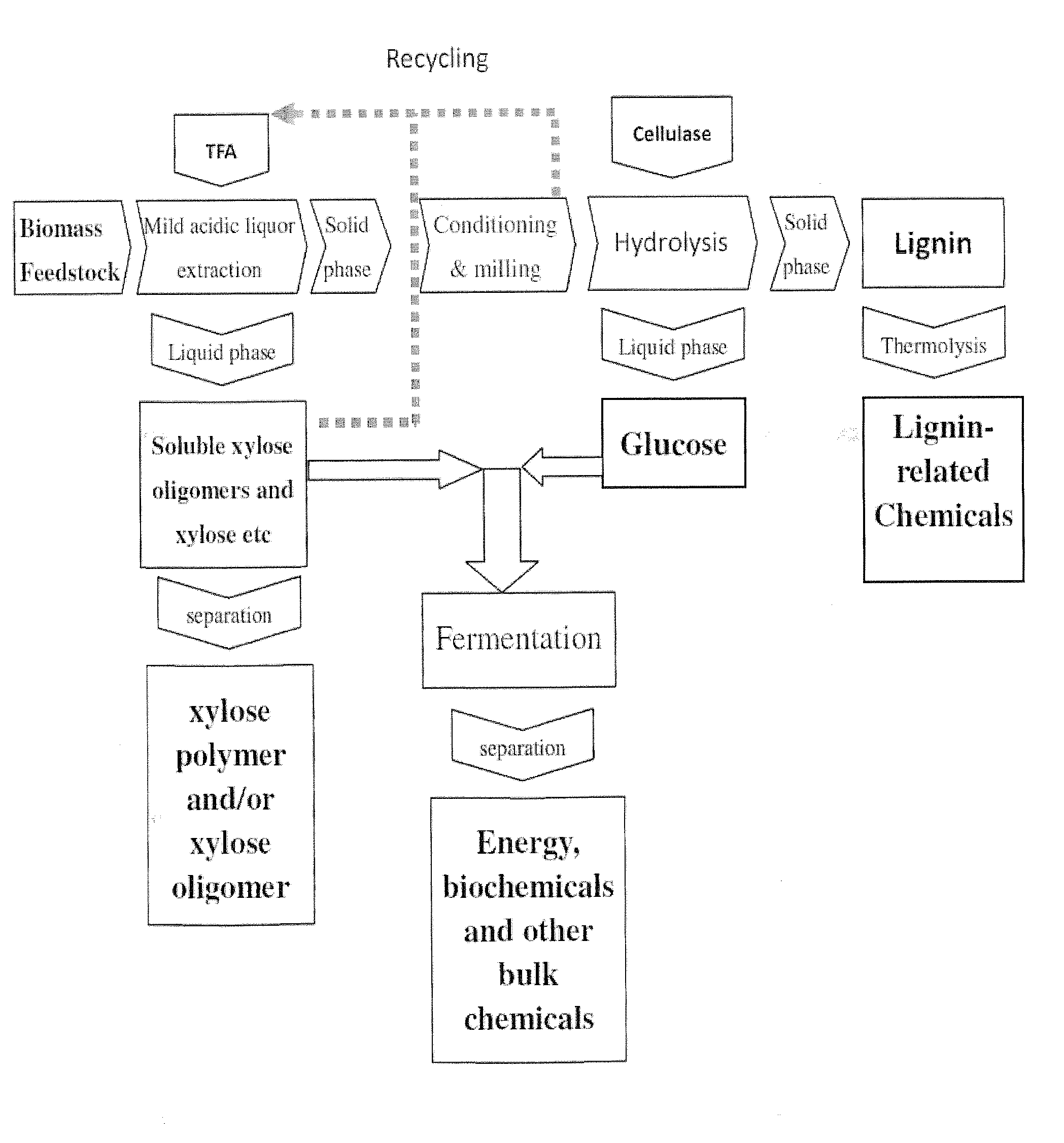
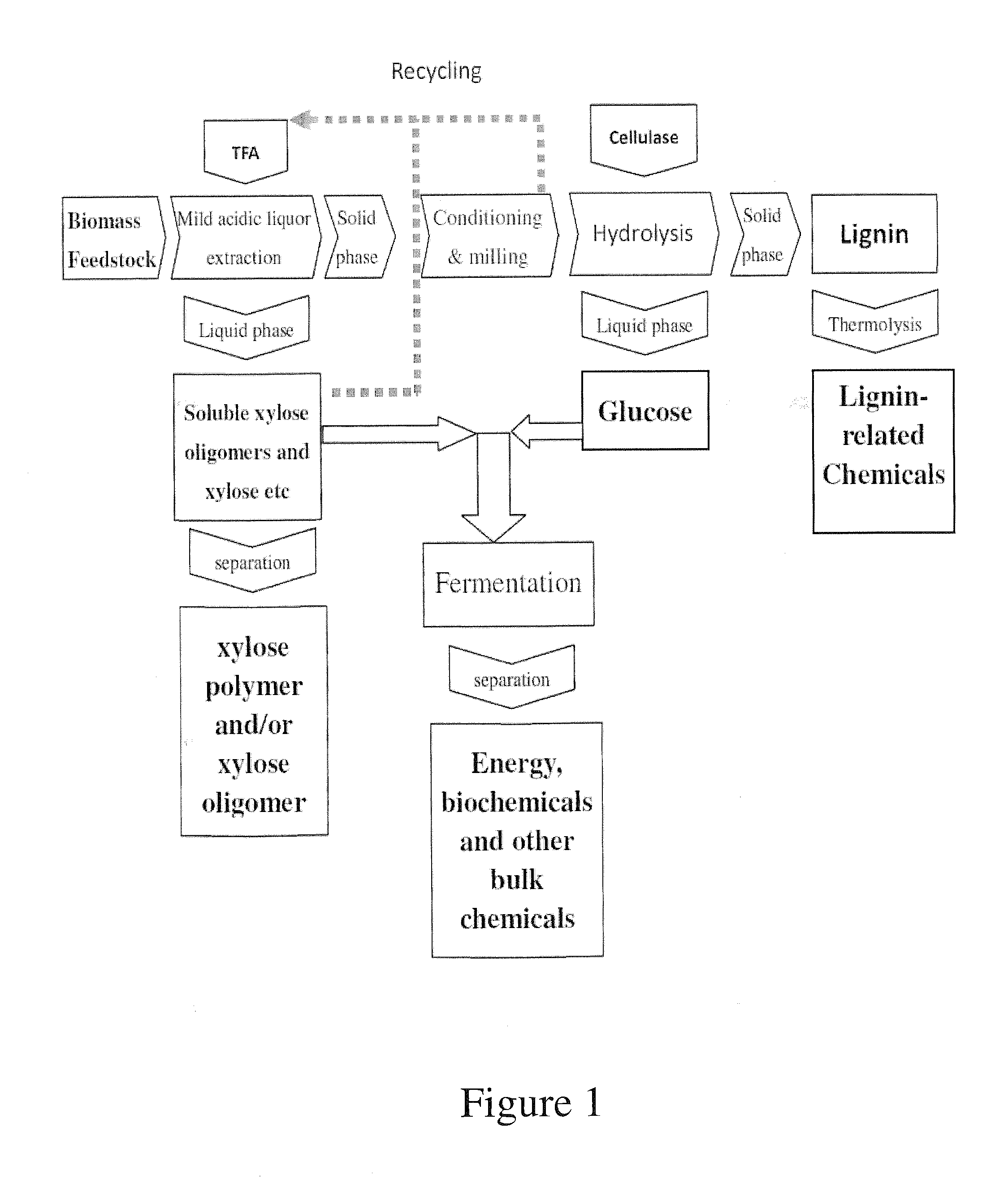
Process for biomass conversion
InactiveUS20100297704A1Easy to GrindIncrease ratingsSugar productsPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsPolymer scienceEnergy products
The present invention relates to a clean process of preparing high grade biomass products, and their use in the production of health care products, bio-energy products, biochemicals, bio-originated chemicals and biodegradable plastics.
Owner:LI RONGXIU
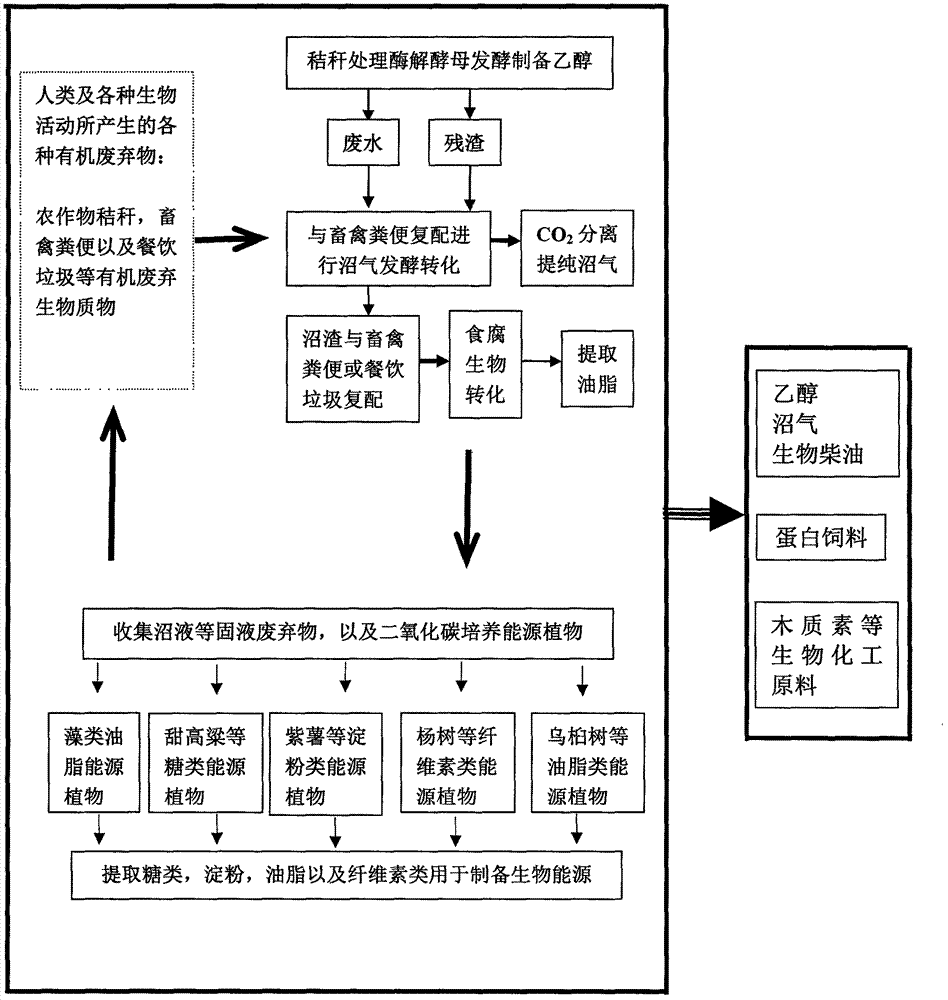
Co-production method for preparing ethanol, biogas and biodiesel by using organic waste
ActiveCN103923948AHigh yieldAbundant raw materialsBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationCelluloseBiodiesel
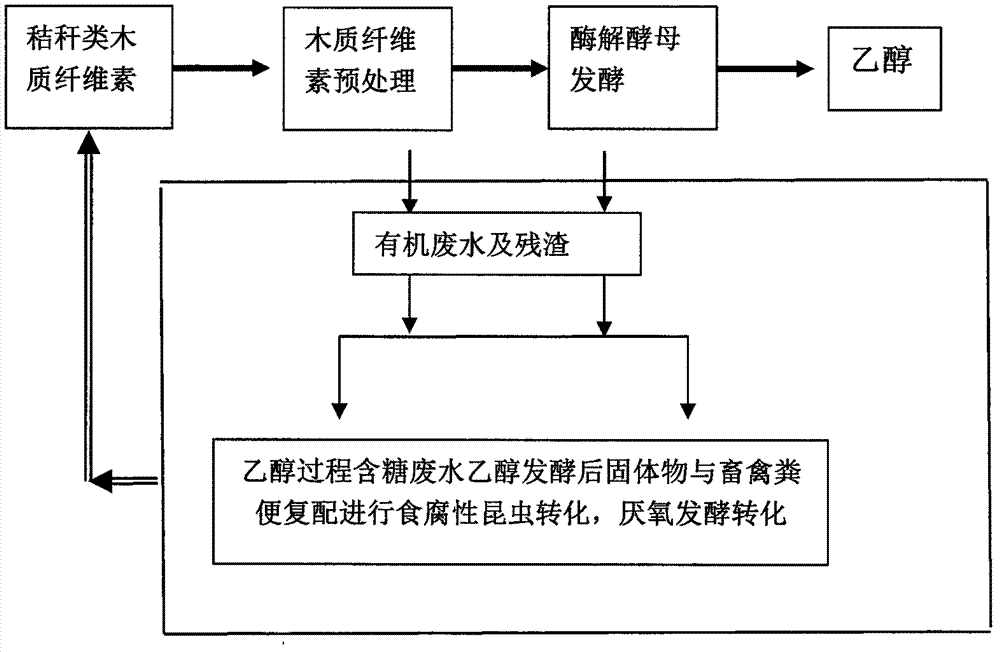
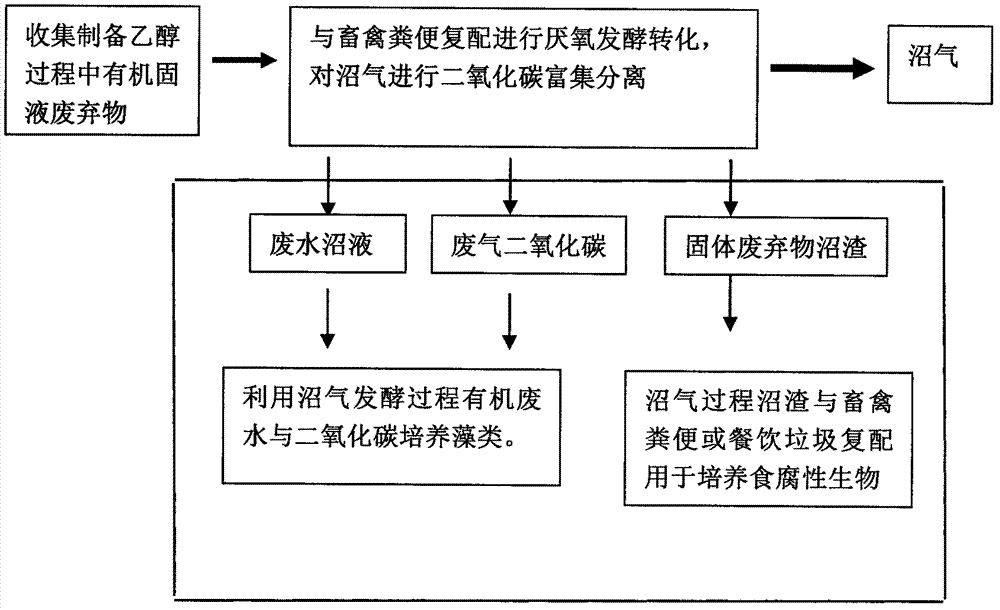
The present invention provides a method for co-producing ethanol, biodiesel, biogas and other biological energy sources by using organic waste as a raw material. The method comprises that: a lignocellulose raw material is pretreated, enzymolysis sugar production and ethanol fermentation are performed, livestock and poultry manure is added to the enzymolysis residue, anaerobic fermentation is performed to produce biogas, the biogas residue is converted through saprophagous insects, organic wastewater is adopted to culture microalgae, and the insects and the microalgae are adopted to prepare the biodiesel; and an energy source plant conversion and utilization system is adopted to collect the process wastewater, the biogas liquid, the waste gas, the biogas residue and other solids and separate and enrich the biogas process carbon dioxide so as to be used for culture of sweet sorghum, sugar cane and other sugar-containing energy source plants, purple sweet potato and other starch-containing energy source plants, aspen and other cellulose-containing energy source plants, and sapium sebiferum and other grease-containing energy source plants, and the biomass produced by the energy source plants can further be used for extracting sugar sources, starch, fat and cellulose for biological energy source production.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
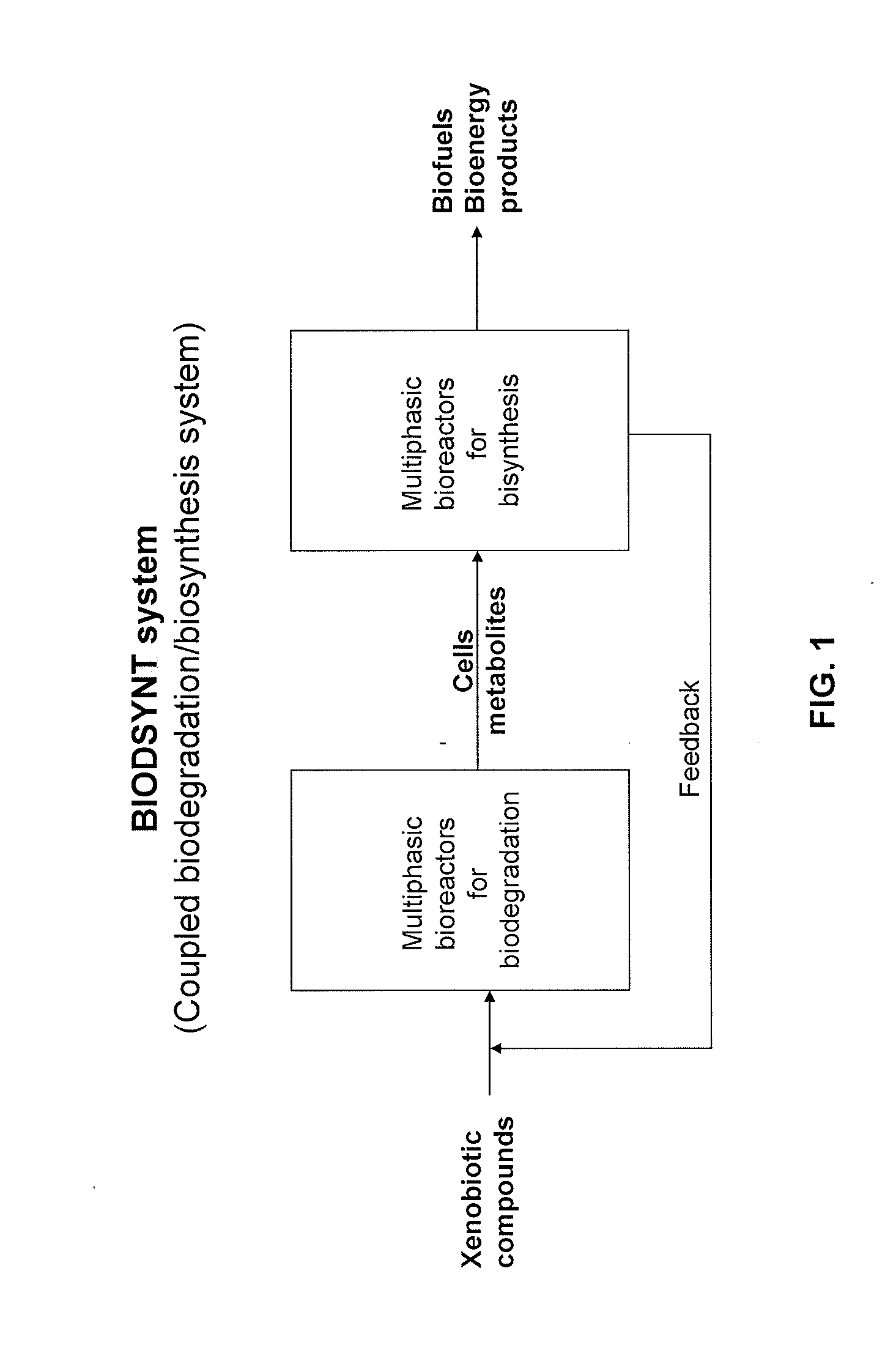
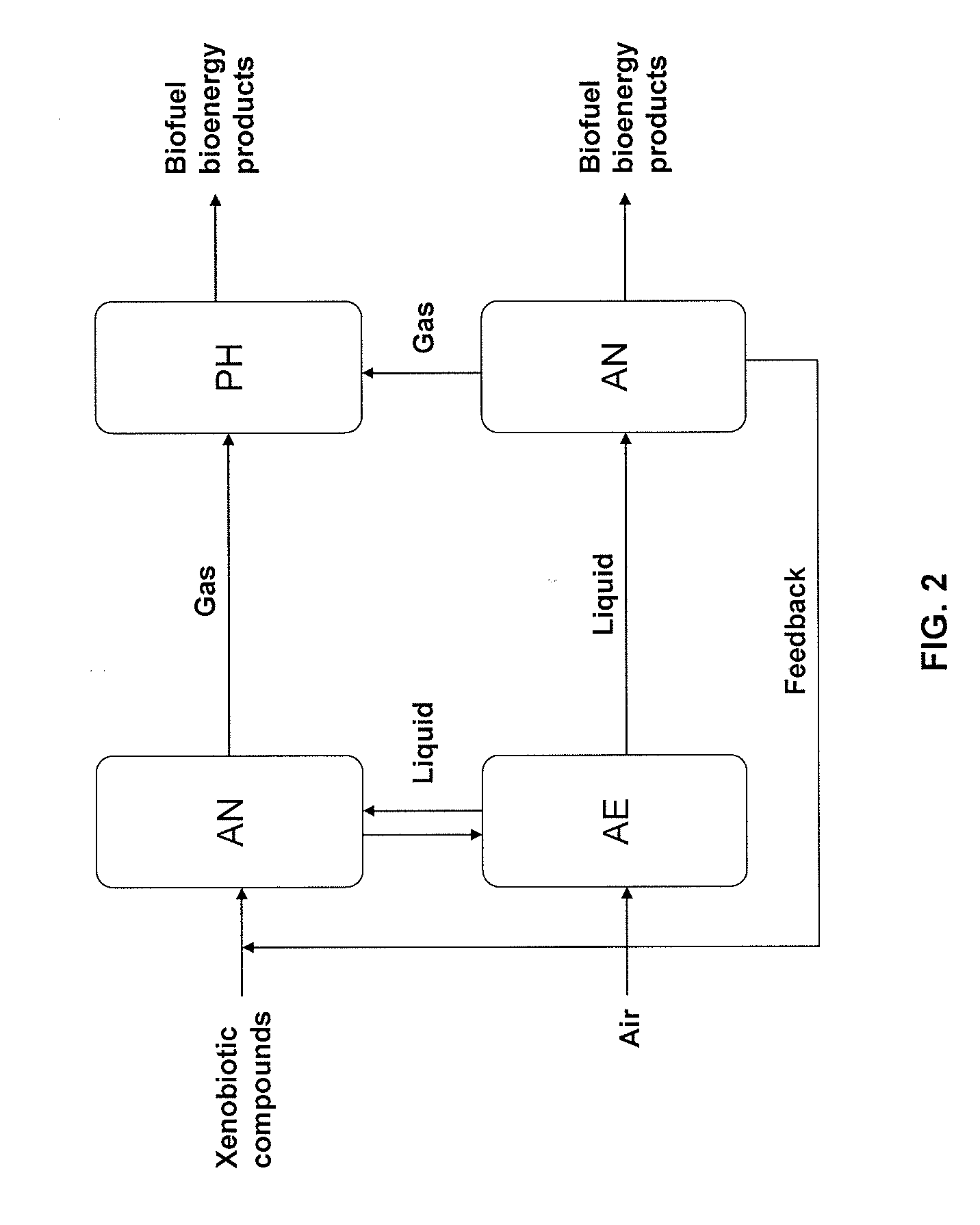
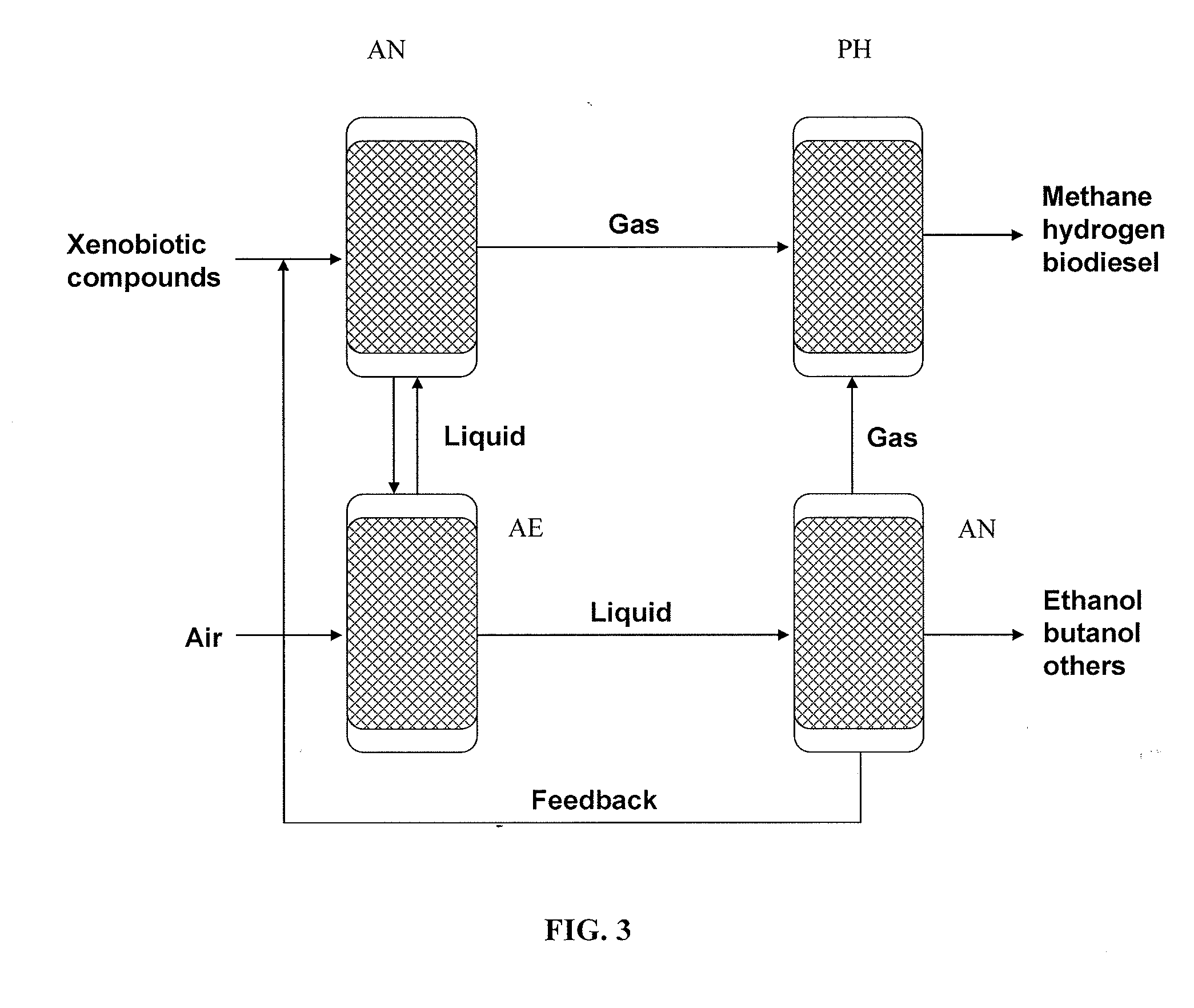
Methods and systems for producing biofuels and bioenergy products from xenobiotic compounds
InactiveUS20100159539A1Reduce contaminationReduce pollutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiodieselDecomposition
The present invention provides methods and systems for producing biofuel and bioenergy products using, as starting raw material, xenobiotic materials or compounds. The xenobiotic materials or compounds may originate from industrial or chemical plants, municipal waste, pharmaceutical products, cosmetic and personal care products, or other sources, and may include aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated organic solvents and other halogenated hydrocarbons, as well as heteroaromatic compounds. In accordance with the invention, these materials act as a carbon source to support the metabolism of xenobiotic-degrading microorganisms, thereby producing biomass and / or biogas that may be converted to bioenergy products by microbial synthesis. For example, the biomass may be converted to products such as ethanol, methanol, butanol, and methane, among others. The biogas may be converted to hydrogen gas and biodiesel, among others. Thus, the present invention couples the microbial breakdown (decomposition) of xenobiotic materials with the microbial synthesis of biofuel, thereby supplying needed (inexpensive) energy products, while reducing environmental pollution and contamination, and reducing the costs associated with disposal of hazardous waste.
Owner:ASCON MIGUEL +1
Ligno-cellulose material pre-treatment method capable of obtaining conversable substrates
InactiveCN101392268AReduce manufacturing costHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelCellulosePretreatment method
The invention provides a pretreatment method for obtaining ligno-cellulose materials of a transformable substrate required in the production of bio-refinery, bio-energy, biological medicine, food processing, light chemical products, biological feedstuff and fertilizers, which adopts baisdiomycete strains or flora that can selectively destroy the structure of ligno-cellulose to carry out continuous pretreatment of solid fermentation to various ligno-cellulose materials in an open condition. The transformable substrate can be obtained directly and simply by extraction after the pretreatment or obtained by combining the treatment of the physical and chemical biomass white-rot fungus degradation system with the complex enzymatic method. The method of the invention puts biological degradation, modification and biomass transformation in leading position, partially combines with the physical and chemical enzymatic treatment process technology and has the advantages of strong operability, wide application scope, and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
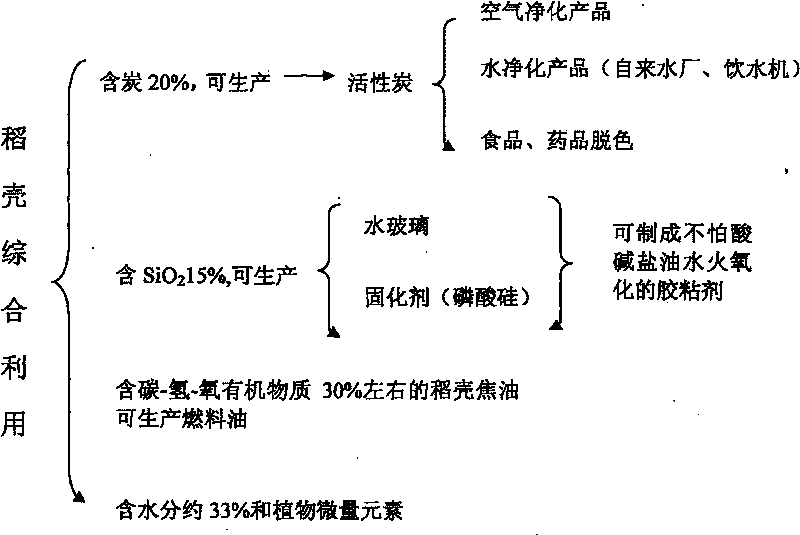
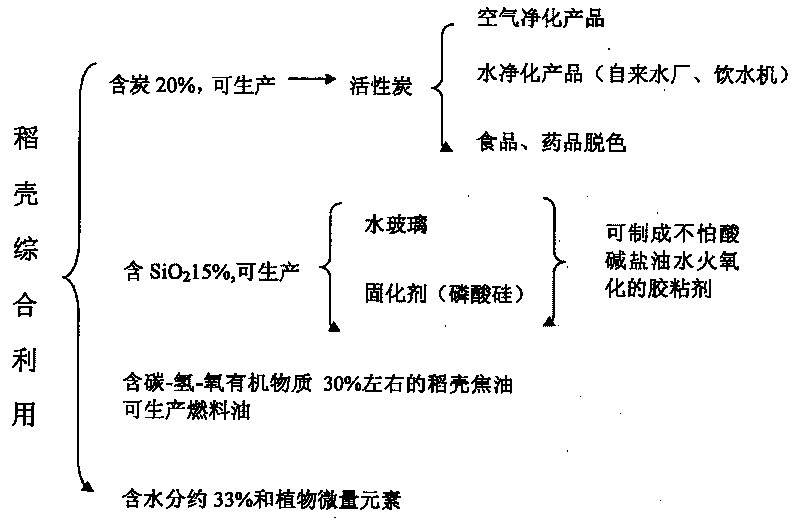
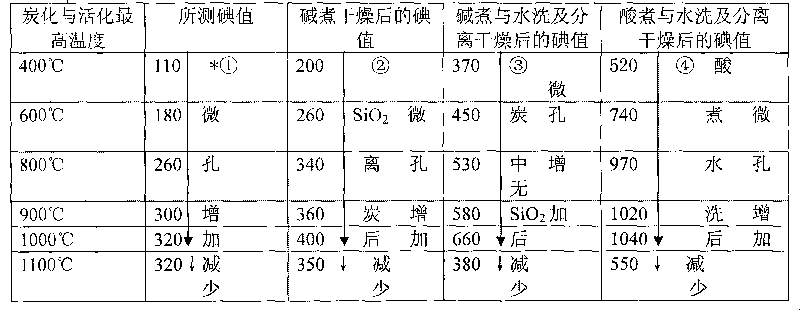
Method for preparing active carbon and rice hull tar by comprehensively utilizing rice hulls and co-producing water glass or silicon phosphate
InactiveCN101700883AIncrease profitSimple processCarbon compoundsBiofuelsHazardous substanceAdhesive
The invention provides a method for preparing active carbon with strong adsorptivity and rice hull tar by comprehensively utilizing rice hulls and co-producing water glass or silicon phosphate, comprising the following steps of: slowly sifting the rice hulls into an activated carbonization furnace; carbonizing and depositing in the activated carbonization furnace to form a carbon shell and generate a gas; condensing the gas to obtain the rice hull tar; and processing the carbon shell by sodium hydroxide or a phosphoric acid to obtain the active carbon and the water glass or a silicon phosphate curing agent. The method has simple process, and the produced products have good quality, high output, low cost and no pollution, thereby large-scale industrialized production can be realized. The obtained rice hull active carbon contains no heavy metal ion, i.e. lead, cadmium, arsenic, mercury, and the like which are toxic to human bodies and other toxic and harmful substances and is a purifying agent, a decolorizing agent and a catalyst which are urgently needed in the fields of foods, medicines and environmental protection; the rice hull curing water glass is a non-toxic harmless aqueous inorganic adhesive and has wide application range; in addition, the rice hull tar is renewable biological energy. The method has good social benefit and economic value.
Owner:成如山
Planting method of sweet sorghum in coastal server saline-alkali soil
The invention discloses a planting method of sweet sorghum in coastal server saline-alkali soil. The method comprises the following steps: A, preparing soil, and constructing a strip or platform field; B, irritating with salt water in winter, and icing; C, covering with a plastic film; D, sowing; E, managing in a growing phase; and F, harvesting when the sweet sorghum is ripe. According to the method, by means of a series of measures, such as soil preparation, salt water irrigation and icing in winter, salt water ice melting and showering in spring, plastic film covering to inhibit salt and preserve soil moisture and the like, the salt content of the soil at the root layer of the sweet sorghum is reduced, and the sweet sorghum grows normally. The method is operated simply, has low cost, is applicable to coastal saline-alkali areas to promote development of sugar making and biological energy industries in China, and has remarkable economic, social and ecological benefits.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
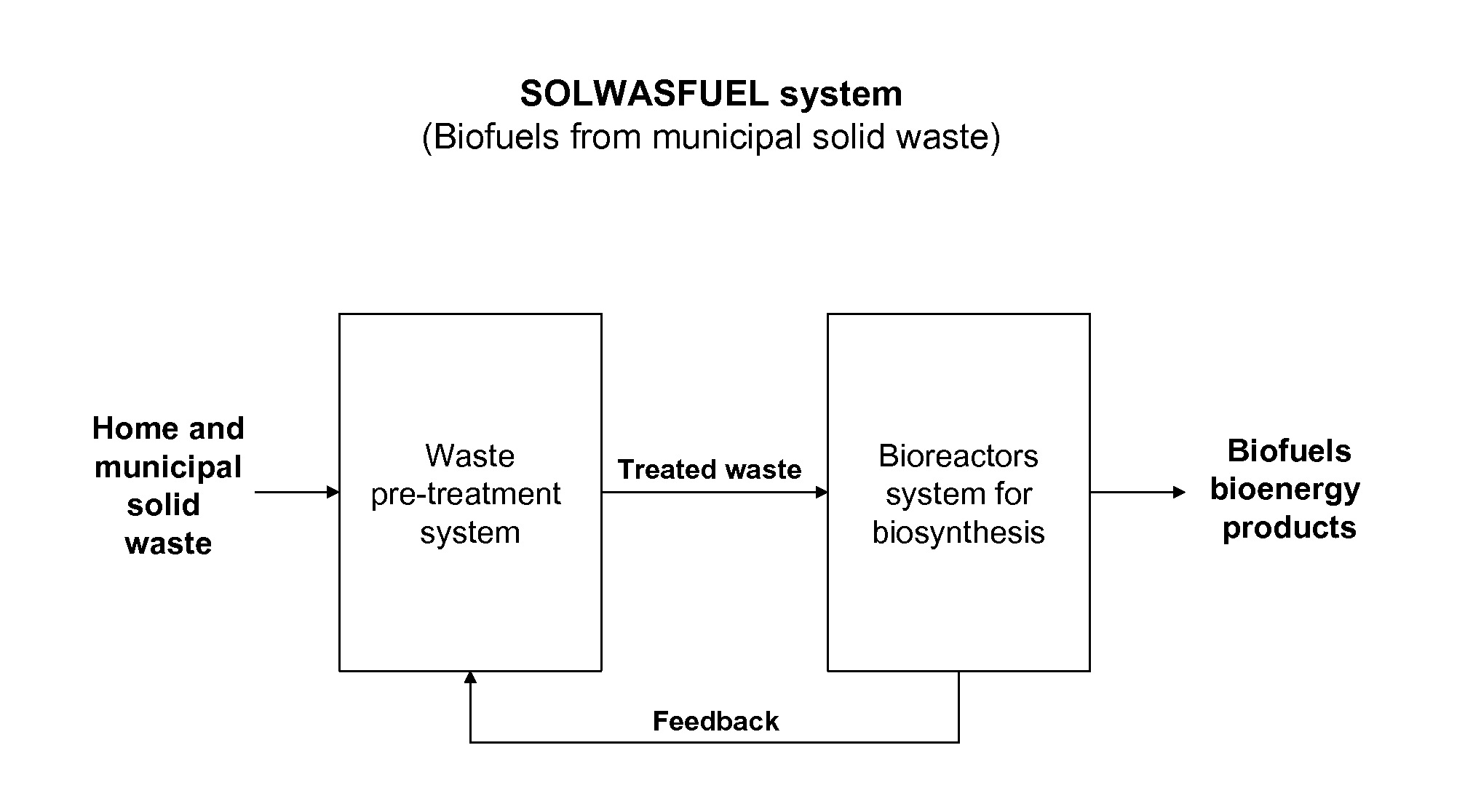
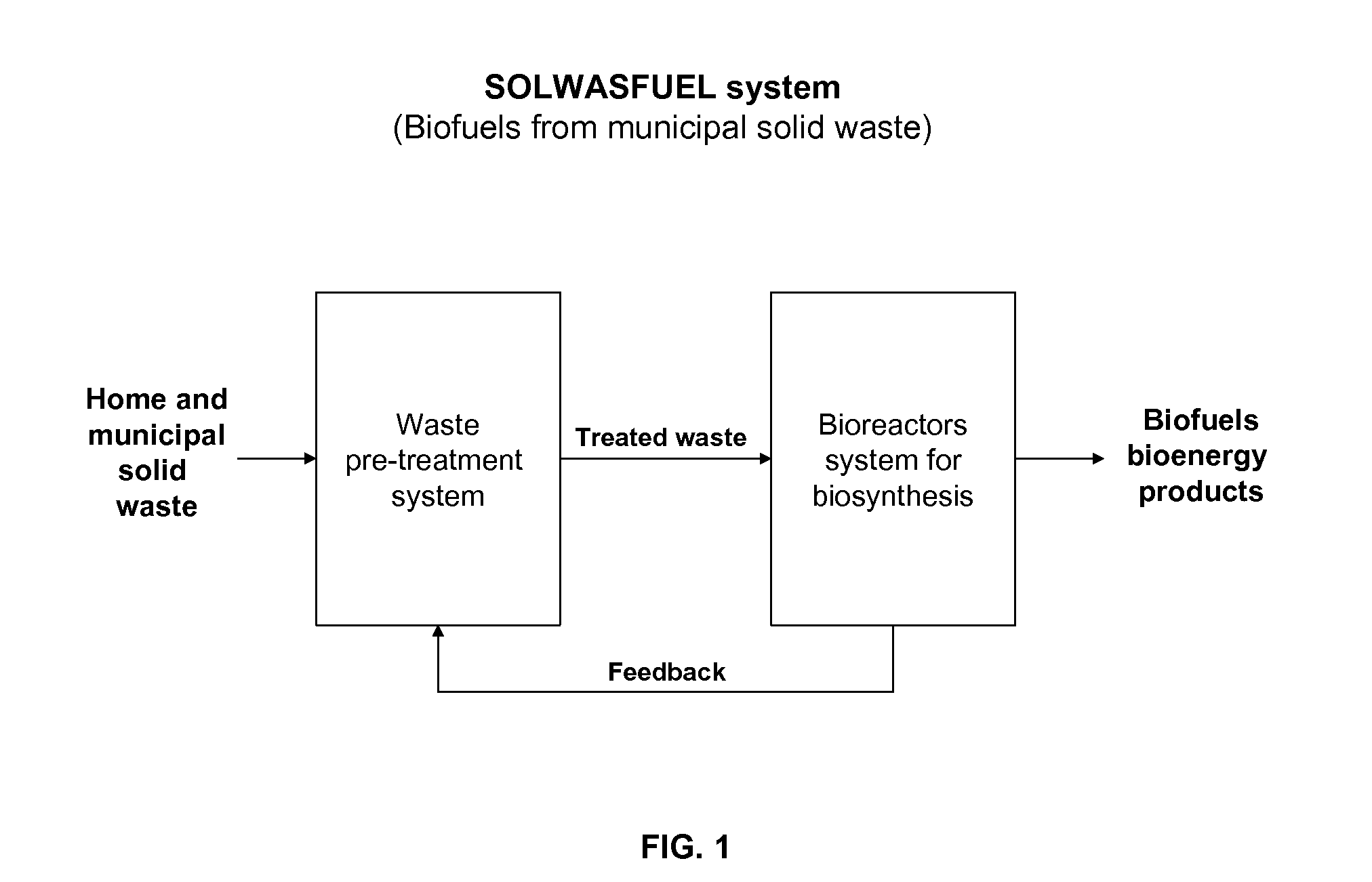
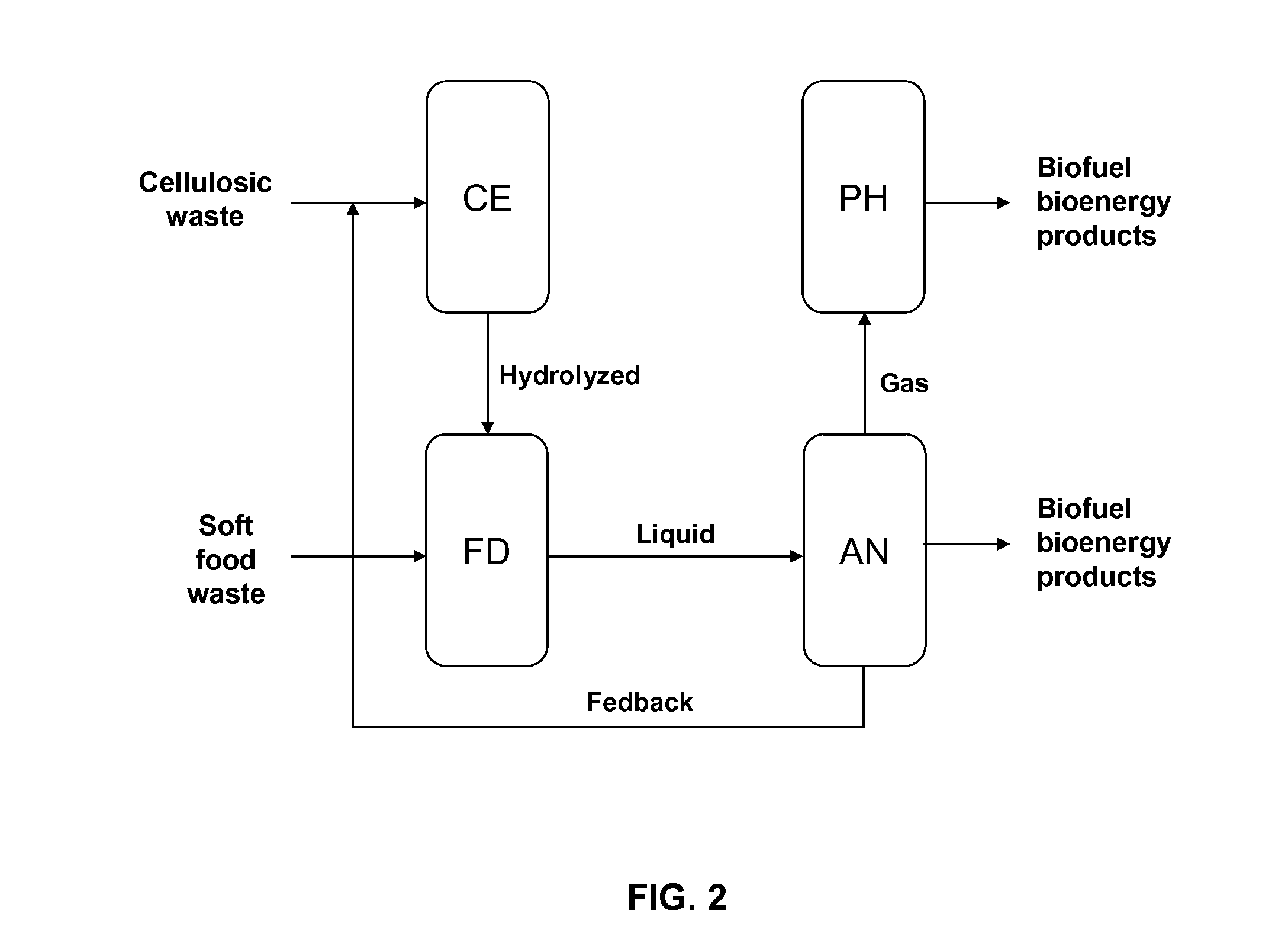
Refinery process to produce biofuels and bioenergy products from home and municipal solid waste
InactiveUS20110165639A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCardboardCellulose
The present invention provides methods of a process (SOLWASFUEL system) for producing biofuel and bioenergy products using, as starting raw material, home and municipal organic solid waste, including recalcitrant lignocellulosic materials of paper, cardboards, organic plastics, cellulose plants, and food waste. In accordance with the invention, home and municipal solid waste, can serve as a carbon source to support the metabolism of synthetic microorganisms to produce biofuels and bioenergy products.
Owner:BRIJEN BIOTECH
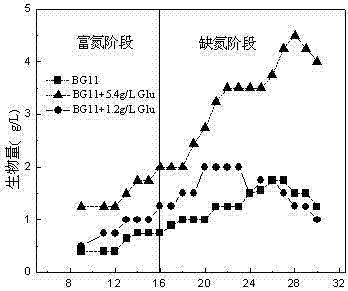
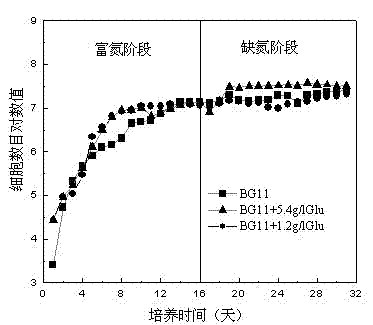
A method for improving the biomass and oil accumulation of oleaginous microalgae using a two-stage culture strategy of admixture and nitrogen-enrichment-nitrogen deficiency
InactiveCN102268377APromote accumulationUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesOil and greaseConcentrations glucose
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
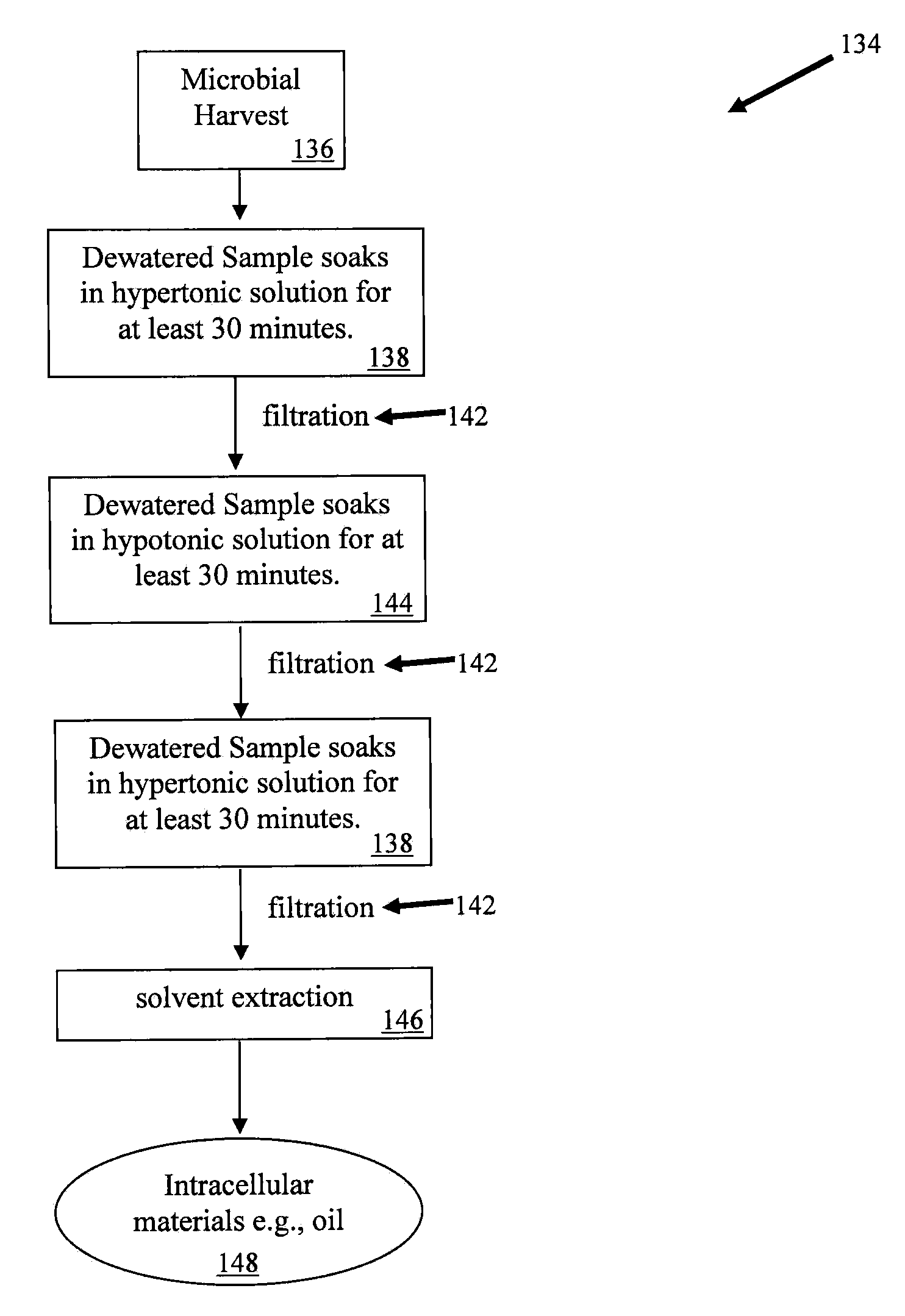
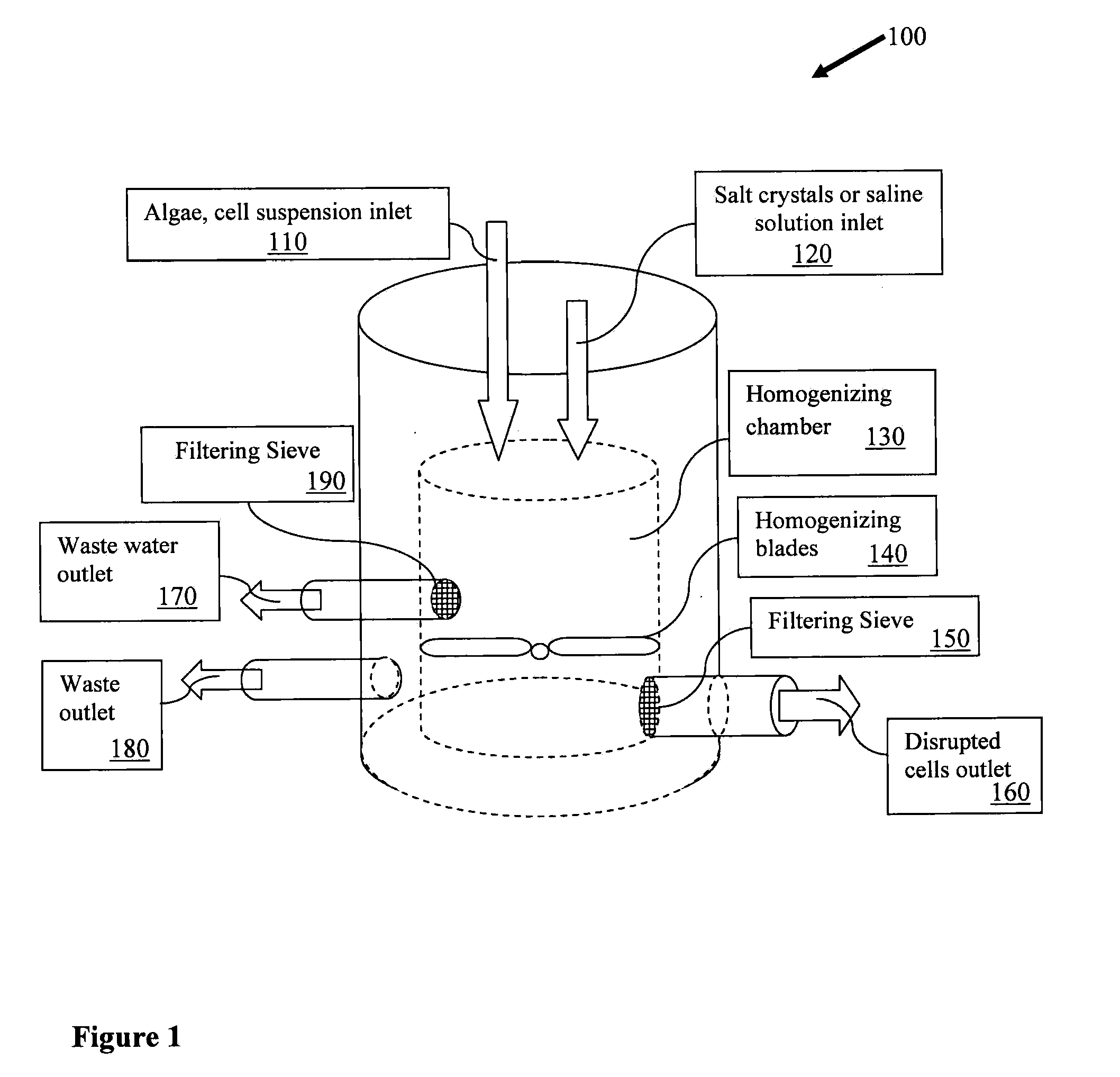
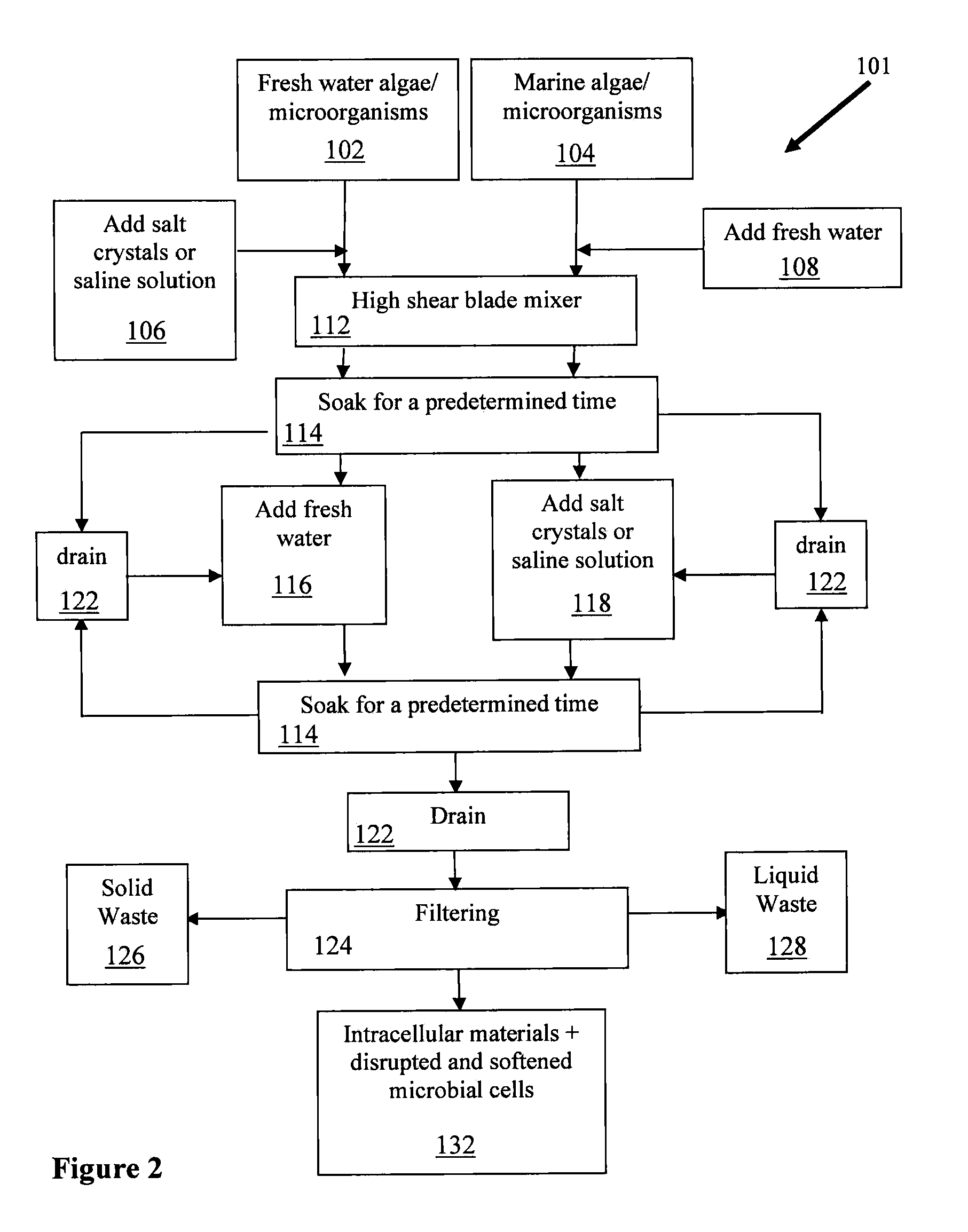
Apparatus and method for enhanced disruption and extraction of intracellular materials from microbial cells
Provided are surprisingly beneficial osmotic stress shock methods for facilitating disruption and / or extraction of microorganisms, comprising a synergistic combination of at least one hypotonic shock and at least two hypertonic shocks, wherein the last shock is a hypertonic shock. Preferred aspects of the invention relate to facilitating disruption of a broad spectrum of microorganisms (e.g., algae, bacteria, yeast, fungus, etc.). In particular aspects the microbial cells are subjected to: a hypertonic / hypotonic / hypertonic tertiary shock; a hypotonic / hypertonic / hypertonic tertiary shock; or a hypotonic / hypertonic / hypotonic / hypertonic quaternary shock. Particular aspects further comprise disrupting and / or extracting of the shocked microbial cells, and isolating a cellular constituent or bioproduct (e.g., biofuel, biocrude, bioenergy, biogas, biodiesel, bioethanol, biogasoline, pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, food, vitamins, feedstock, dyes, colorants, sulfur, fertilizer, bioplastic) therefrom. In particular preferred aspects, facilitation of algae disruption and / or extraction is provided and in certain embodiments, isolation of at least one of lipid, oil, and triacylglycerol is enhanced.
Owner:DHAMWICHUKORN SRISUDA
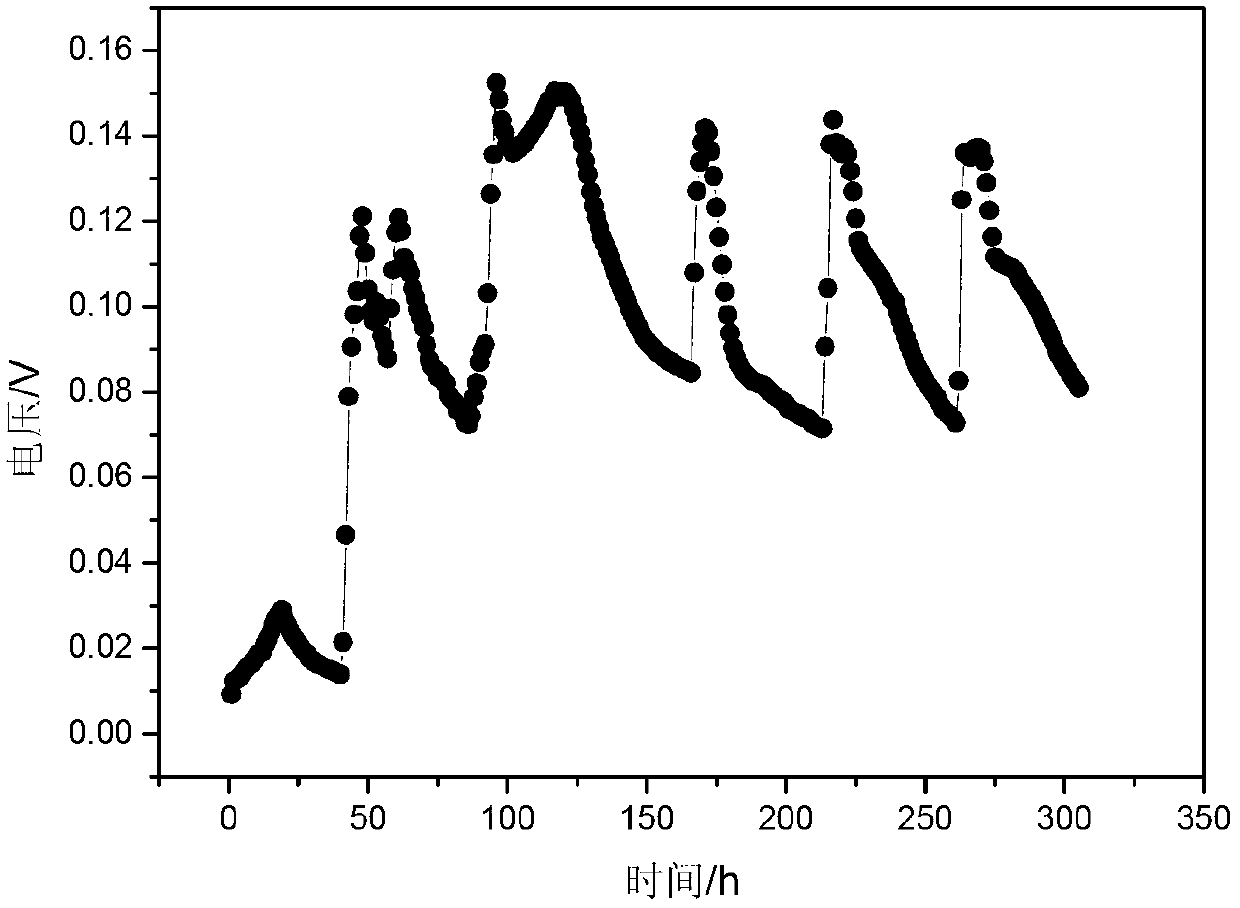
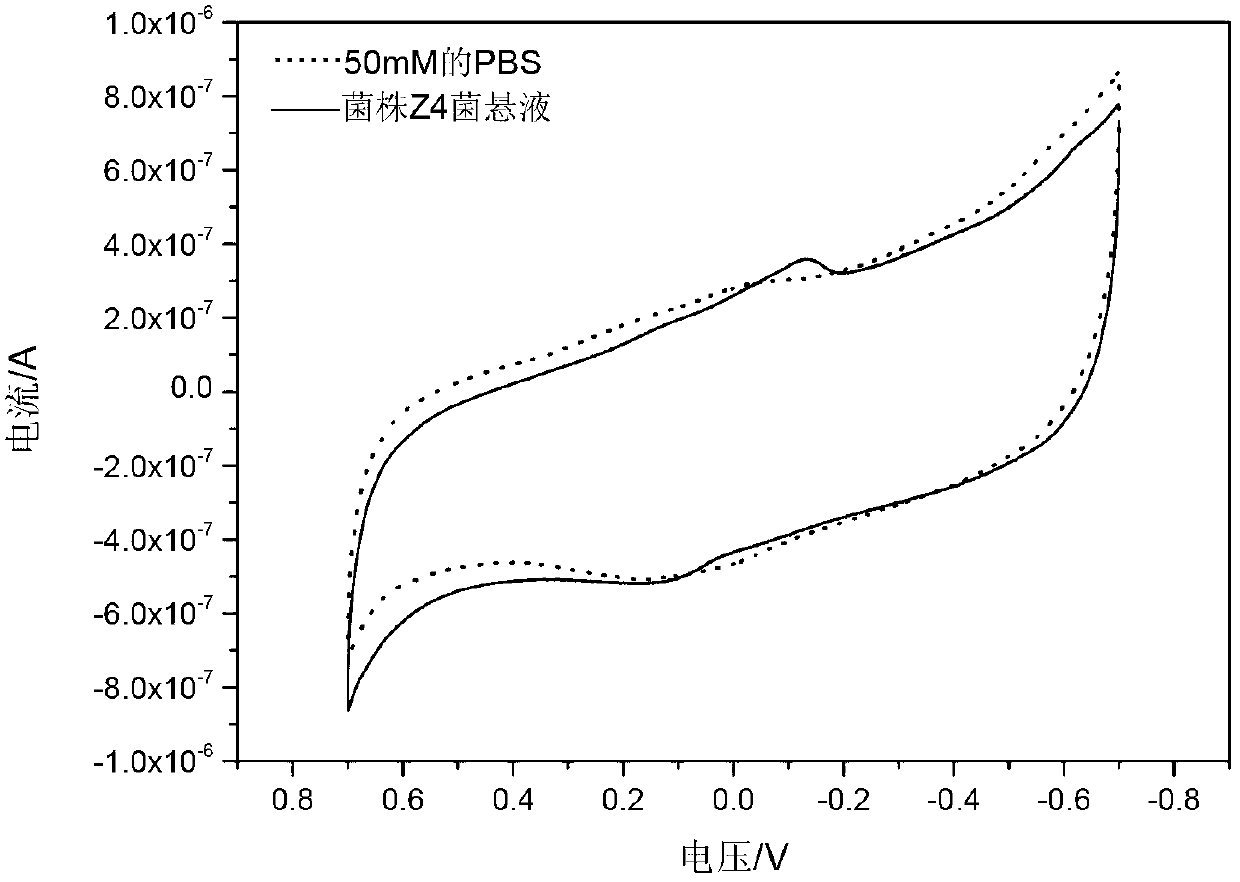
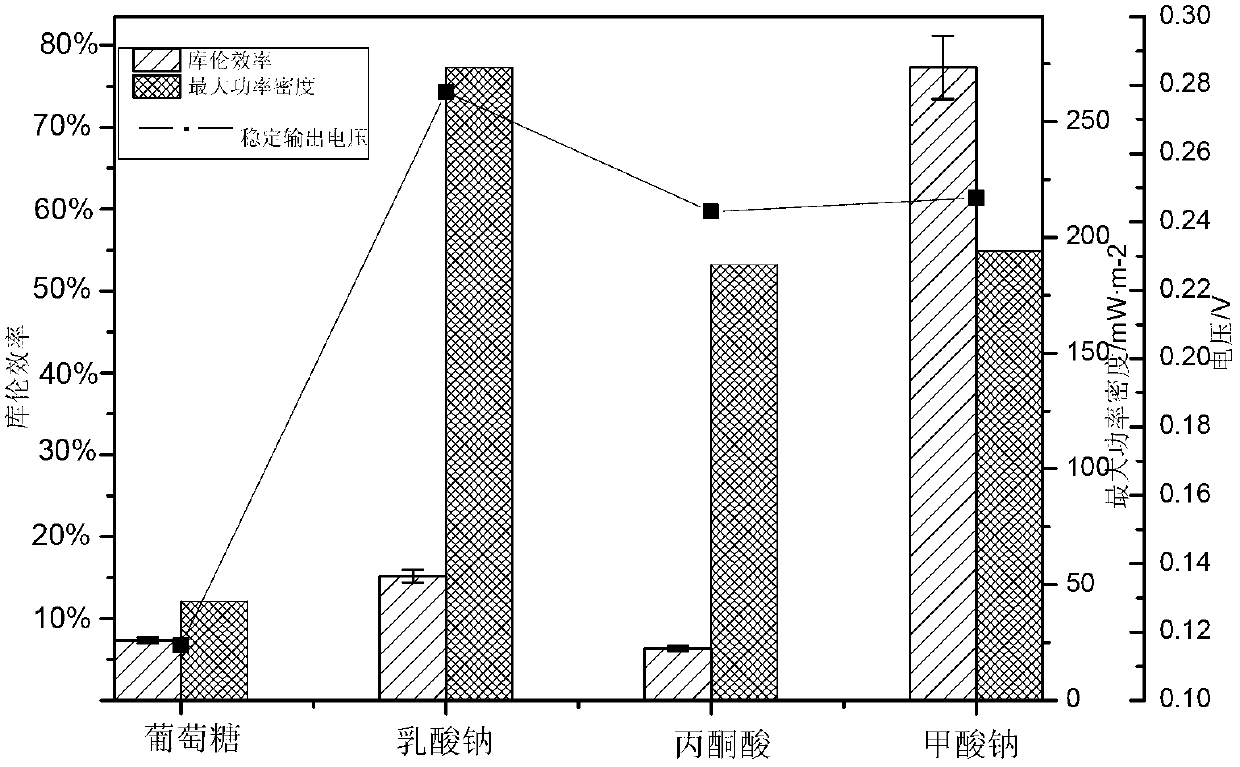
Shewanella haliotis strain and its application in bioelectricity generation
ActiveCN103275887ALower requirementImprove electrochemical activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnergy recoveryShewanella putrefaciens
The invention discloses a Shewanella haliotis strain and its application in bioelectricity generation. The Shewanella haliotis strain is Shewanella haliotis Z4, is preserved by China Center for Type Culture Collection called CCTCC for short, has a preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2012444, and is preserved on Nov., 6, 2012. The strain can transmit electrons to an extracellular electron acceptor under an anaerobic condition, and can degrade organic matters and generate electric energy when the strain is inoculated to a microbial fuel cell. The Shewanella haliotis Z4 has a very strong electrochemical activity, and can generate electricity by utilizing a plurality of types of organic matters as a sole carbon source. The Shewanella haliotis Z4 has a very good application prospect in polluted environment restoration and biological energy recovery based on the above characteristics.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Process and system for producing ethanol through solid-state continuous fermentation and distillation of sorgo straws
ActiveCN101724661AUniform and complete fermentationHigh yieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDifferential pressureDistillation
The invention relates to a process and a system for producing ethanol through solid-state continuous fermentation and distillation of sorgo straws, wherein the process comprises a raw material pulverizing and preprocessing step, a strain adding step, a solid-state fermentation step and a solid-state distillation step; the solid-state fermentation step is continuously finished in a multilayer multisection solid-state continuous fermentation device, and the solid-state distillation step is continuously finished in a multilayer differential pressure type solid-state continuous distillation device, thereby radically overcoming the abuse that the past solid-state fermentation and distillation processes can not continuously produce, realizing continuous, mass and automated production and processing, greatly improving the production efficiency of preparing the fuel ethanol from the sorgo straws, and achieving the purposes for lowering the production cost, improving the yield and improving the economic benefit; an adopted continuous production system device is particularly suitable for industrialized large-scale production, thereby promoting the generalization and the application of a biological energy source technology.
Owner:天津实发中科百奥工业生物技术有限公司 +1
Method for planting beet in coastal heavy saline-alkali soil
ActiveCN102301905AGuaranteed normal growthGuaranteed activityHorticultureSoil-working methodsAlkali soilSalt content
The invention discloses a method for planting beet in coastal heavy saline-alkali soil. The method comprises the following steps: A. arranging land, and building an elongated farmland or a raised field; B. irrigating and icing by salt water in winter; C. covering by a mulching film; D. culturing seedlings and transplanting; E. managing in a growth period; and F. harvesting when the beet is mature. According to a series of measures of arranging land, icing and irrigating by salt water in winter, melting and spraying by salt water in spring, covering by the mulching film, inhibiting salt, preserving soil moisture and the like, the salt content in soil of a beet root layer is lowered, and the beet can be guaranteed to normally grow. The method is simple to operate, has the advantages of low cost and obvious economic, social and ecological benefits, and is suitable to be applied in coastal saline-alkali zones; and by the method, the development of sugar manufacture and biological energy industry in China can be promoted.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
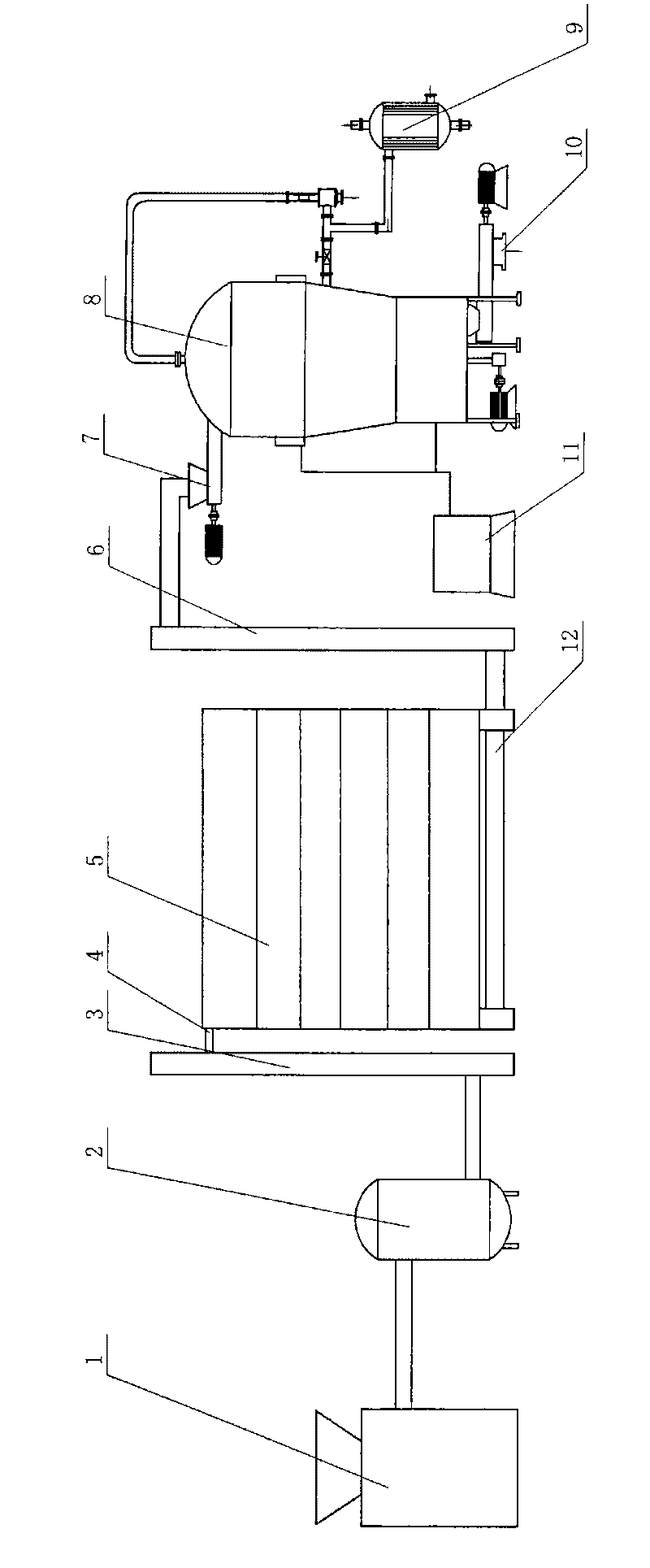
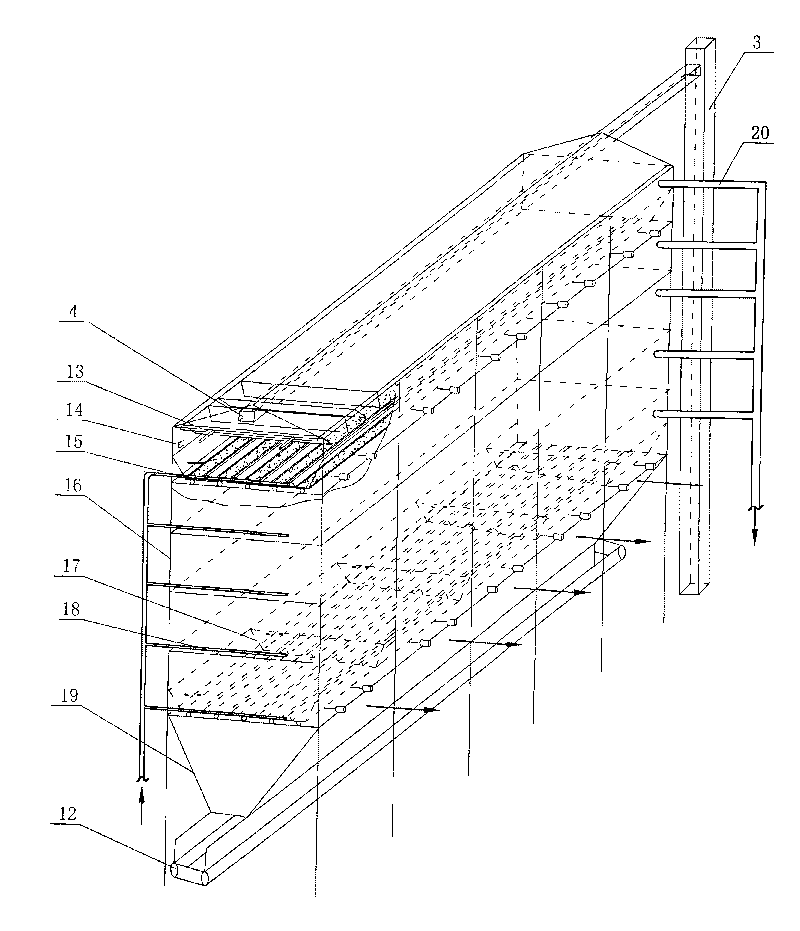
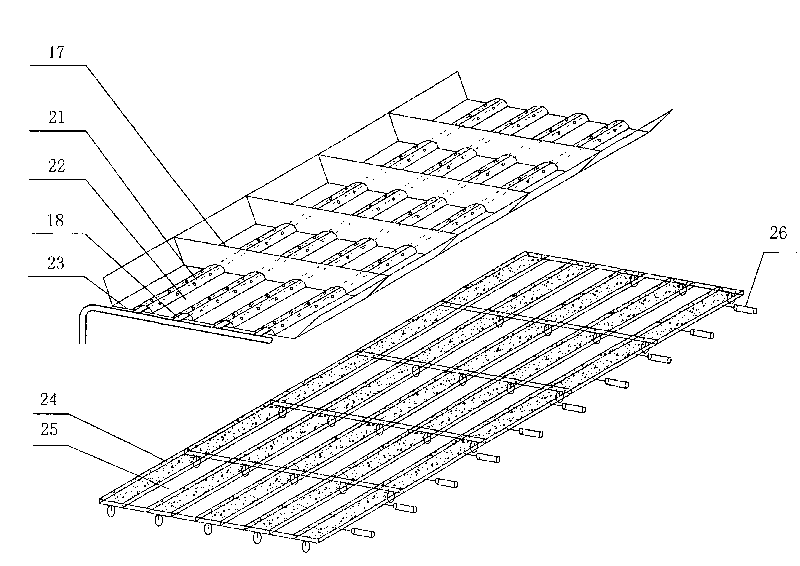
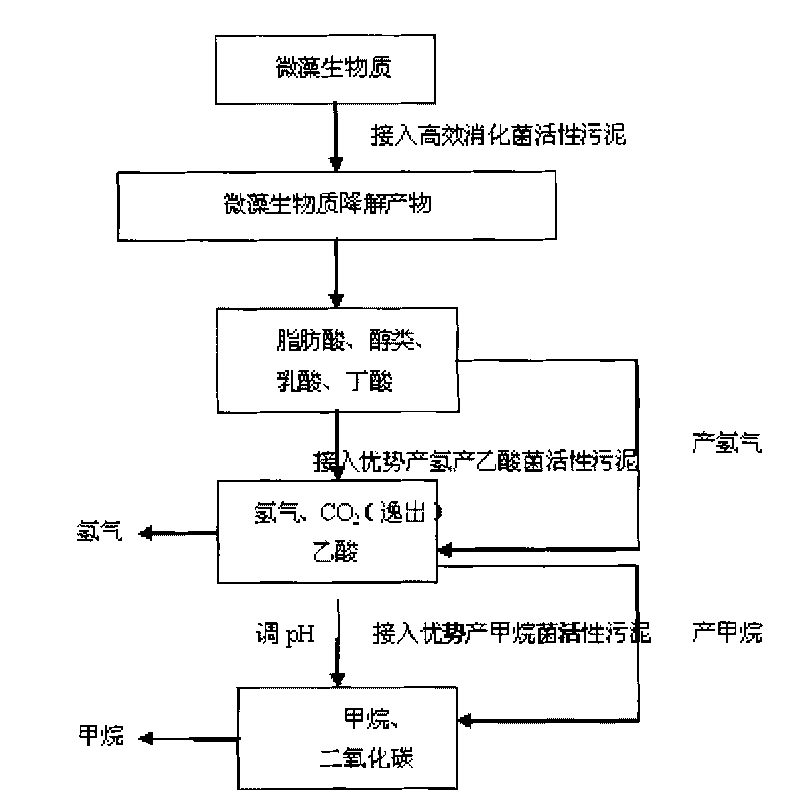
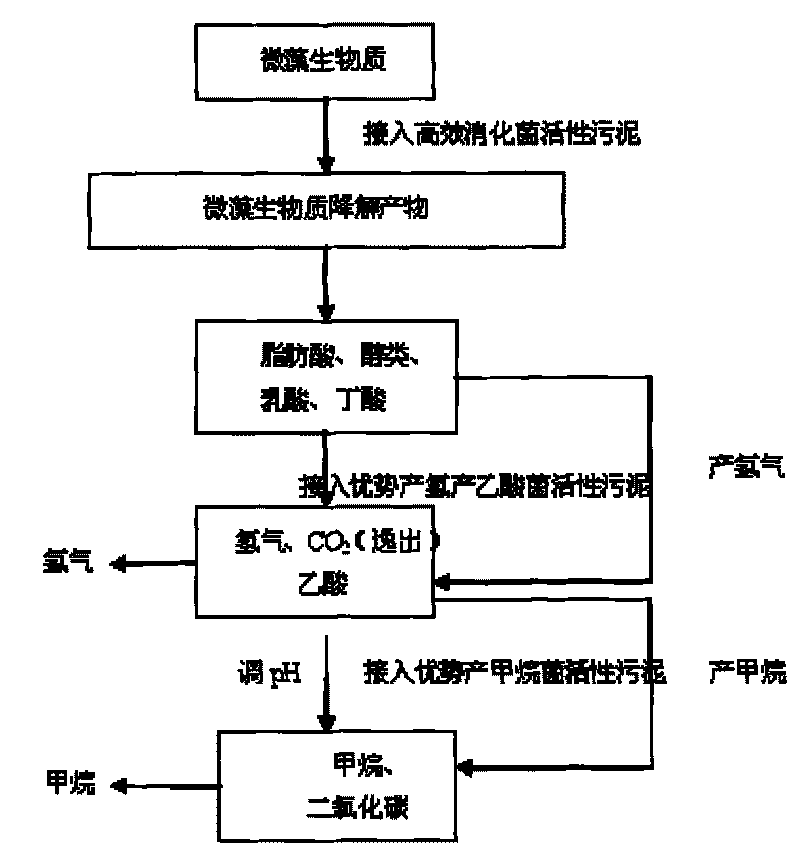
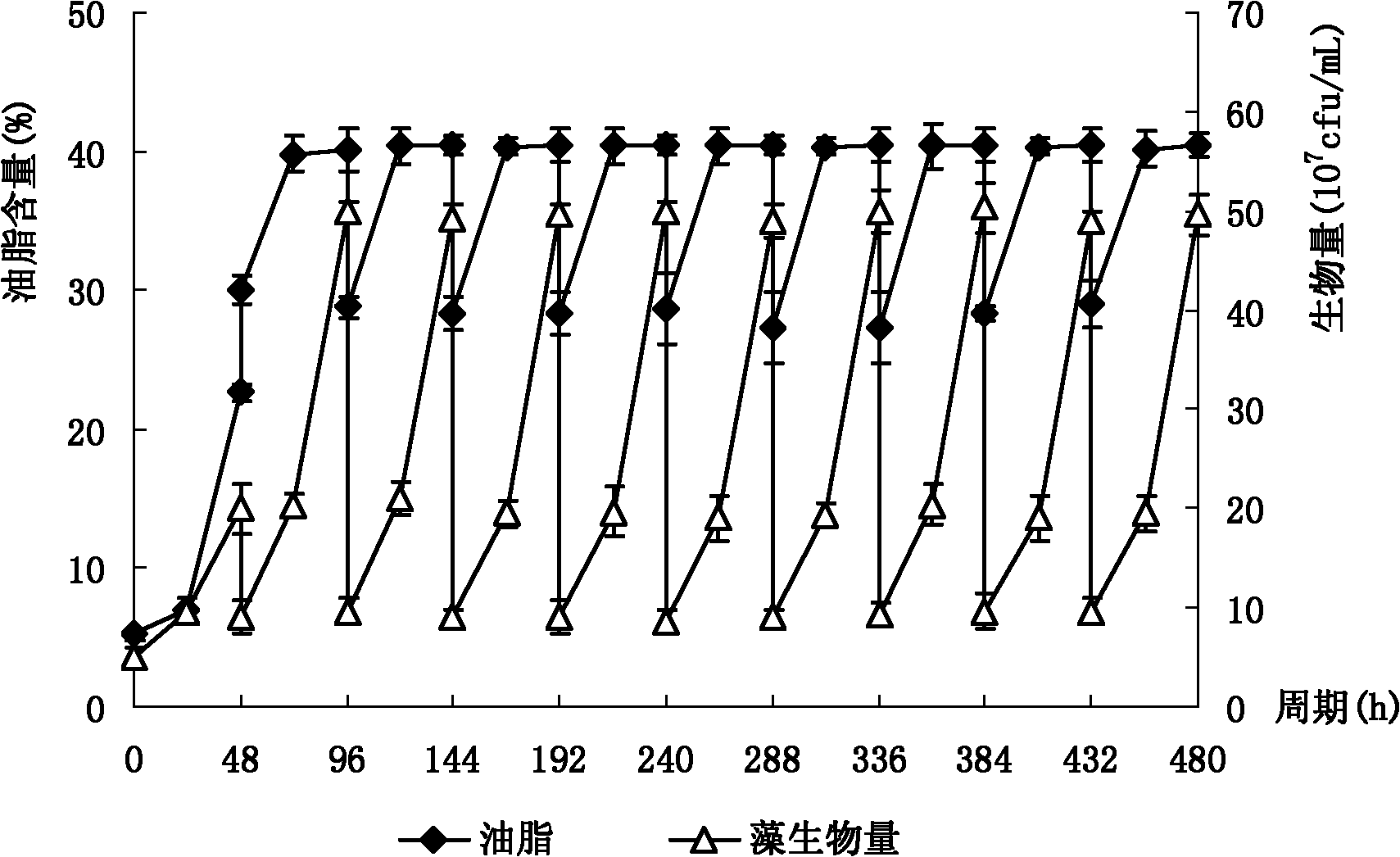
Method for producing bioenergy through microalgae two-step method
ActiveCN101760432AFast growth rateShort doubling timeBio-organic fraction processingInternal combustion piston enginesHydrogenNew energy
The invention relates to a method for producing bioenergy through microalgae two-step method, which belongs to the technical field of environmental protection and new energies and uses microalgae organisms to prepare bioenergy (hydrogen and methane). The method for producing bioenergy through microalgae two-step method mainly includes the steps of culturing microalgae, collecting microalgae biomass and processing, then preparing hydrogen and methane through organisms, and comprehensively using products and residues. As the method uses the microalgae to produce bioenergy through a two-step method, the method not only can obtain two stable bioenergies (hydrogen and methane), but also can absorb CO2, and ease the greenhouse effect; the generated clean energy substances can effectively ease energy crisis, and reach the goals of improving the environment and increasing new energies.
Owner:ENN SCI & TECH DEV
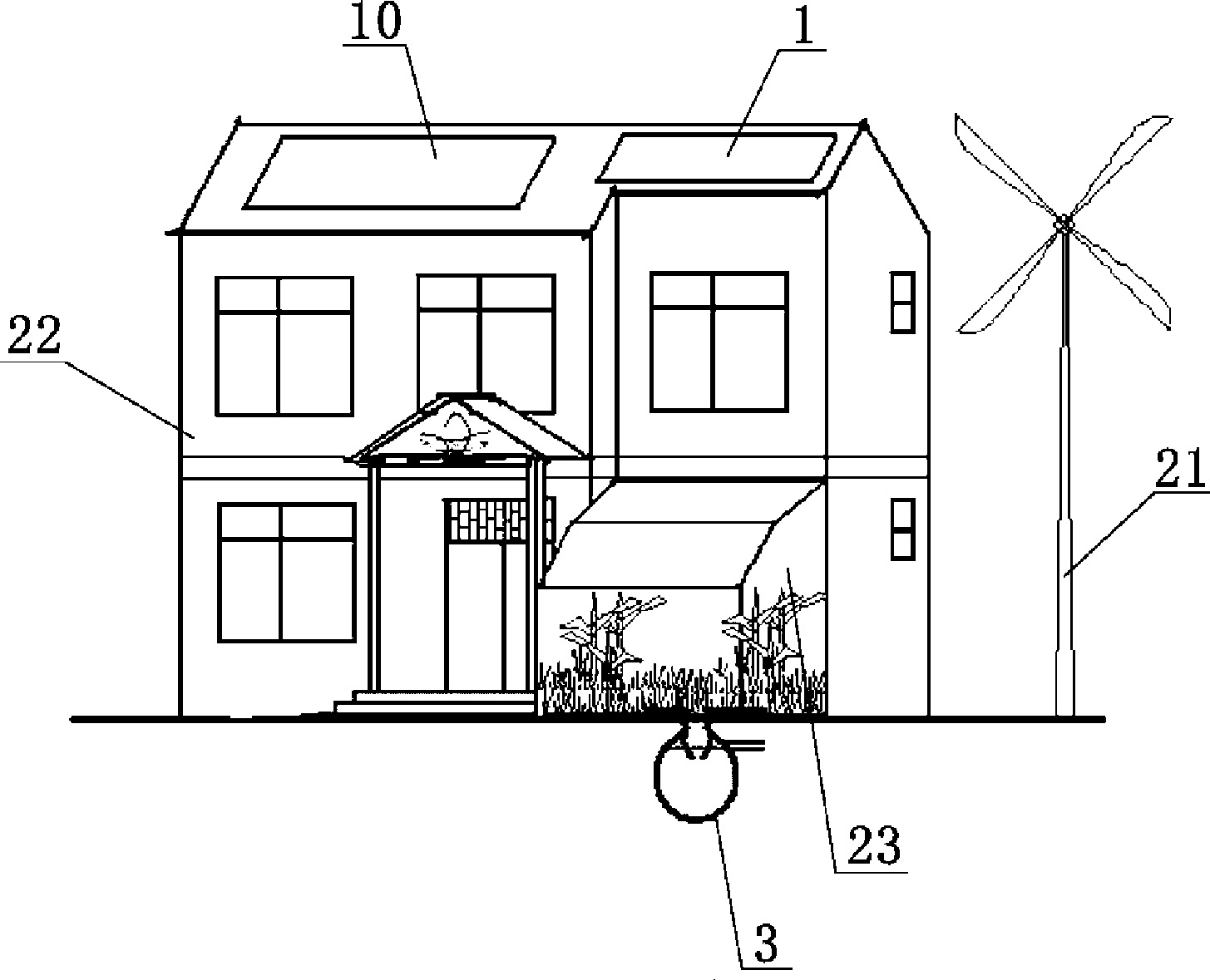
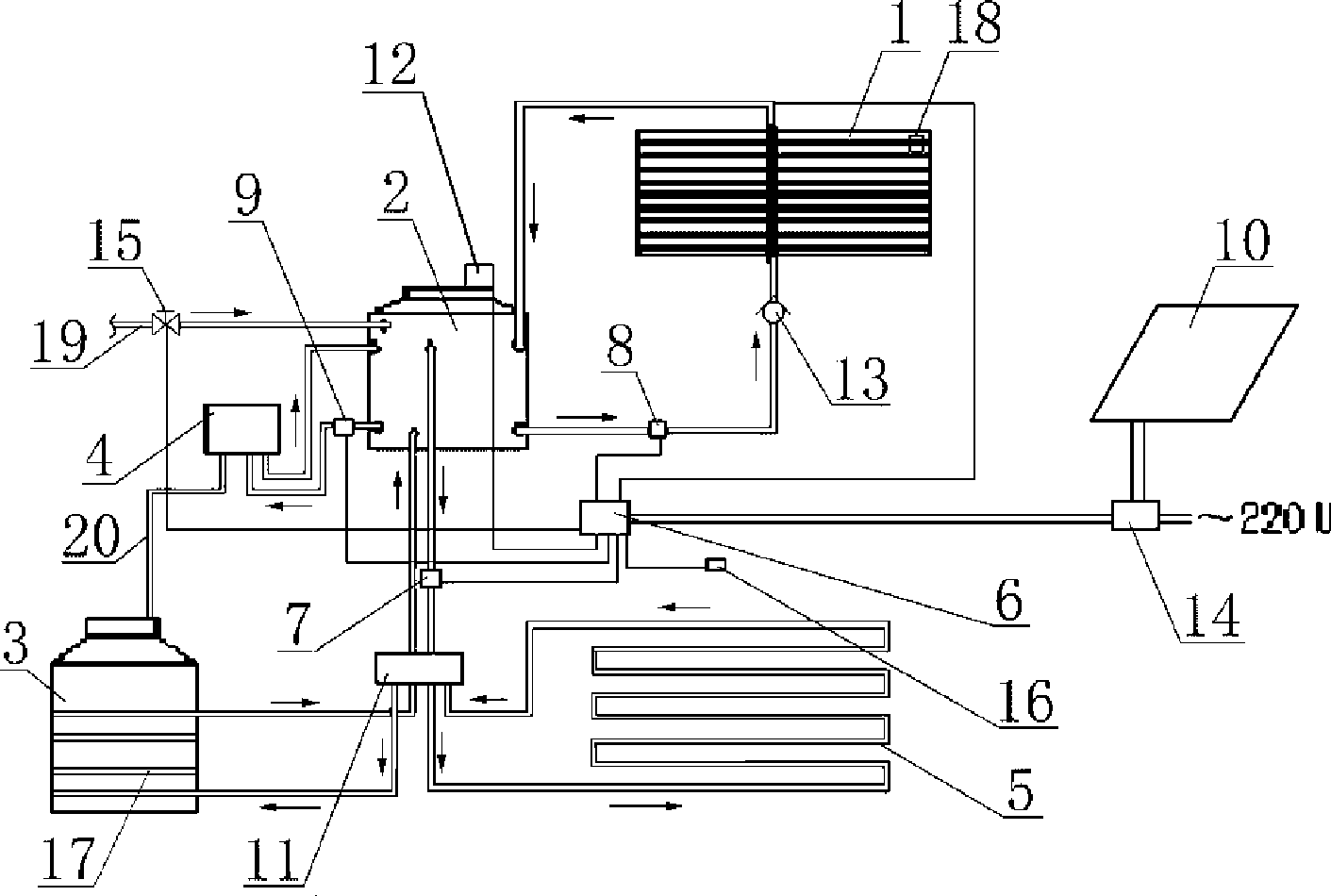
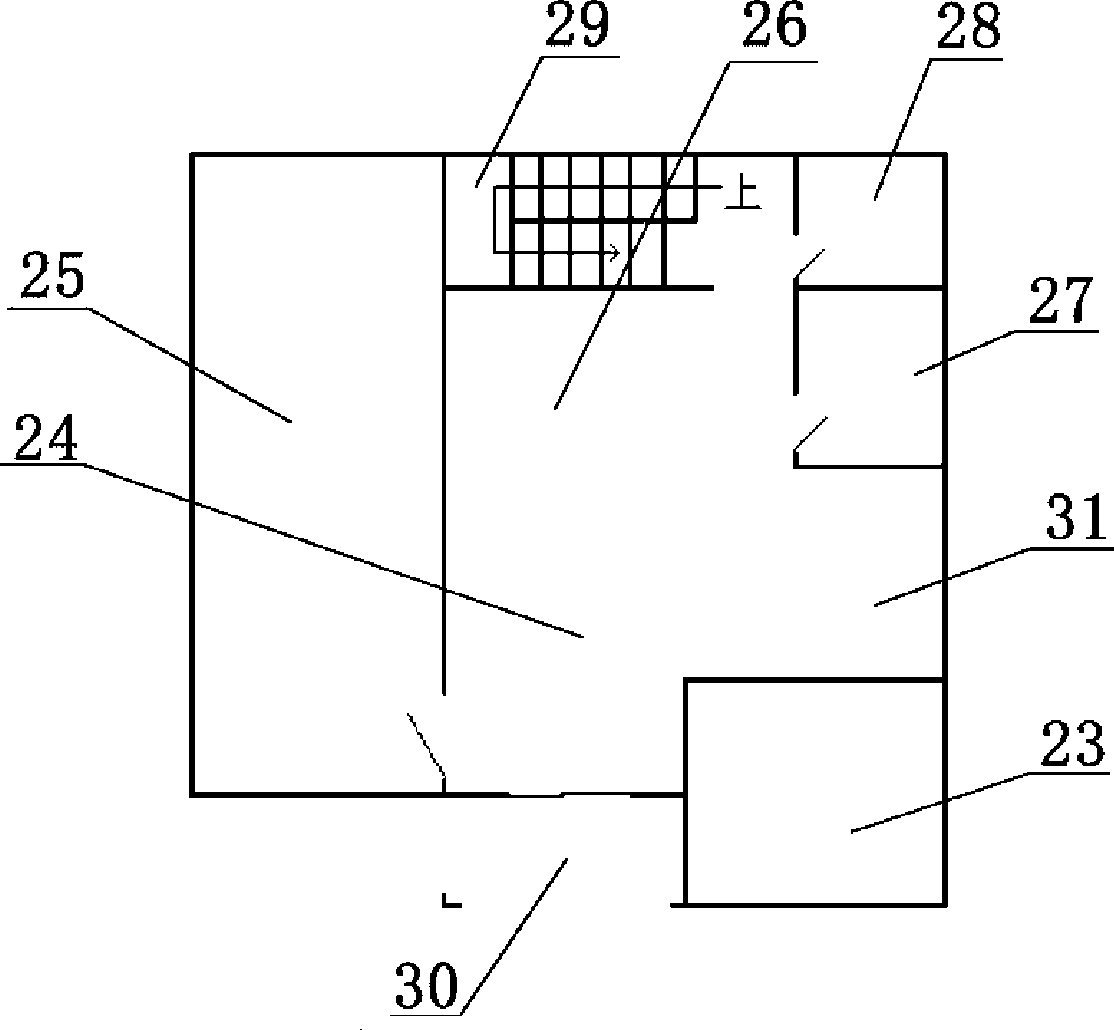
Green ecological zero energy consumption integration house
InactiveCN101457594AIncrease heatIncrease gas productionWallsSolar heat devicesLiving roomCollector device
The invention relates to a green ecological zero energy integrated building, a first floor of the building is provided with a living room, a bedroom, a dinning room, a kitchen, a toilet; a second floor of the building is provided with a bedroom and a toilet; a heat supply system is arranged inside the room, the building is connected with a heliogreenhouse on the ground and is connected with a methane tank under the ground. A solar thermal collector arranged at the top of the building is communicated with a temperature-holder box arranged inside the rooms of the building by a circulating pipe of the first line, the temperature-holder box is communicated with a water heating pipe of a gas-fuel heater by the circulating pipe, a gas line of the gas-fuel heater is communicated with the methane tank by a methane pipe. A hot water outlet of the temperature-holder box is respectively communicated with a PE-RT pipe and a heating pipe of the methane tank which is buried near the methane tank. A water tank temperature sensor, a room temperature sensor and a collector temperature sensor are connected with an intelligent controller. With the solar energy, bioenergy and wind energy complementing each other, the building has the characteristics of comfort, environmental protection, energy saving and zero-pollution.
Owner:赵民忠
Application of black soldier fly larvae as oil-crop insect
InactiveCN101880593ARelieve stressHigh nutritional valueBiofuelsFatty-oils/fats productionChemical industryBiodiesel
The invention belongs to the fields of foods or bioenergy and develops a new oil source, i.e. black soldier fly larvae as an oil-crop insect. Oil can be obtained by using a compression method (larvae is fed into a screw-type press while hot to press oil out) after black soldier fly adult and larvae are dried by hot wind or microwave. The oil can be used as raw oil for eating, chemical industry and biodiesel. The oil content of the black soldier fly larvae is 30-35 percent, through analyzing the nutritious components of the oil, and oil extracted from the black soldier fly larvae contains various unsaturated fatty acids needed by human bodies, thereby being high-quality health oil. The black soldier fly larvae has short growth period which is only 20-30 days and very small floor area, can be cultured under the condition of high density, reaches the oil production per mu of 4t / mu.year, can be carried out in an industrial factory building without occupying land area, contains no toxin, is safe and reliable, and has simple extraction process.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
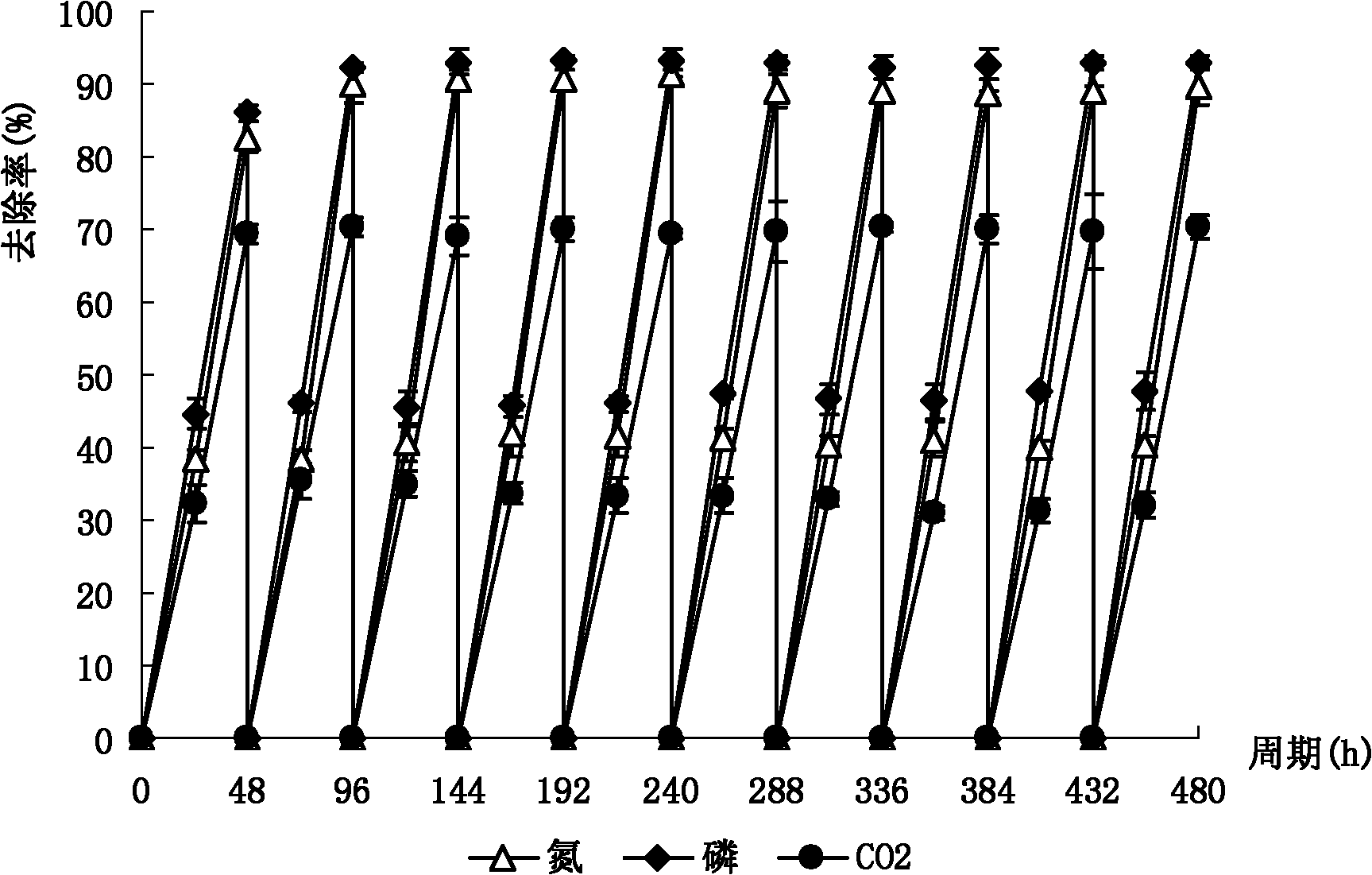
Method for treating high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater through nutrition conversion of mixotroph
ActiveCN105712490ALow costMeet processingBacteriaUnicellular algaeHigh concentrationMetabolism pathway
The invention discloses a method for treating high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater through nutrition conversion of mixotroph. The method for treating the high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater through nutrition conversion of the mixotroph comprises the following steps: 1, conducting transferring and culture on the mixotroph; 2, conducting high density culture in a culture medium rich in organic carbon or wastewater rich in organic carbon; 3, harvesting heterotrophic cells of the mixotroph; 4, transferring the heterotrophic cells into the high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater for autotrophic culture, absorbing high-concentration nitrogen and ammonia, and purifying the wastewater. According to the method, the method for changing the nutrition metabolism pathway of the mixotroph is introduced for treating the high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater, the treated wastewater can be recycled, the requirement of industrialized wastewater treatment conducted through microalgae is met, and the method is a new approach for conducting sewage treatment through produced microalgae economically and efficiently. The harvested microalgae cells can be further treated and used for preparing biological energy source, animal feed and the like.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Glucosidase/xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102041251AHigh activityReduce complexityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesChemical industryCellulose
The invention relates to a novel beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The coding sequence of amino acid of the RuGBGX2 contains 18-755th sites of an SEQ ID NO 2 sequence. The RuGBGX2 is sourced from the rumen microorganism of yak from China, a novel coding gene of the beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 is obtained by function screening and sequencing analysis on a rumen metagenome cosmid library and a subclone library. The beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme provided by the invention can be widely applied to the degradation of cellulose and the fields such as cellulose biotransformation, chemical industry, spinning, foods, bioenergy, feed additives, medical industry and the like. By utilizing the difunctional enzyme RuGBGX2 to degrade wood fiber, the varieties of added enzymes can be reduced, and an enzymolysis process can be simplified.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Double heat energy heating biogas system
InactiveCN102533535AAvoid lossGood warming effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh concentrationThermal energy
The invention discloses a double heat energy heating biogas system, which comprises a fermentation tank, a feeding device, a biogas purification device and a biogas residue treatment device. A stirrer device and a heating device are arranged in the fermentation tank; the heating device comprises a solar energy heating device and an auxiliary heat energy heating device; the auxiliary heat energy heating device is a bioenergy heating house or a fully enclosed boiler directly-heated type heating house; the feeding device comprises a blending tank and a sedimentation tank; the biogas residue treatment device comprises a biogas slurry afterheat conducting tank and a solid-liquid separator connected with a biological fertilizer making equipment; the side faces of the blending tank are provided with the sedimentation tank, the biogas slurry afterheat conducting tank and a grit chamber; the biogas purification device comprises a multifunctional automatic regulator and a purifier; and the multifunctional automatic regulator comprises a gas-water separator and a positive and negative pressure protector. The system has the advantages of high concentration, high temperature, high stirring rate, high gas production rate, high energy conservation, high cost performance, low tank body, low investment, low danger and low operating cost.
Owner:方朝阳
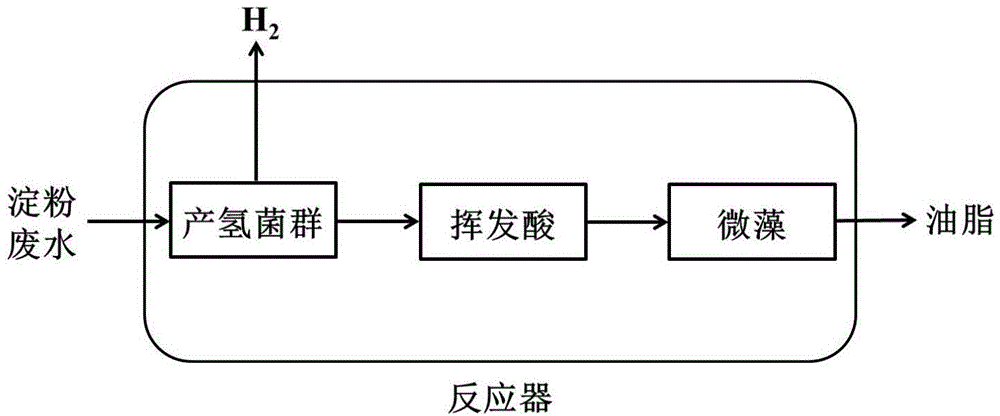
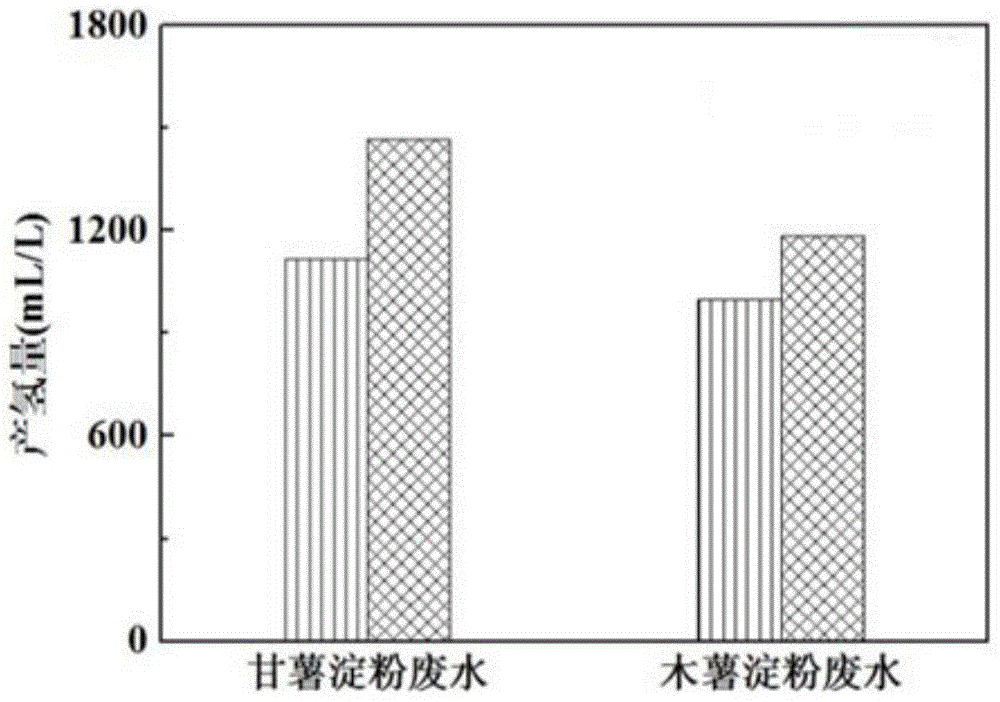
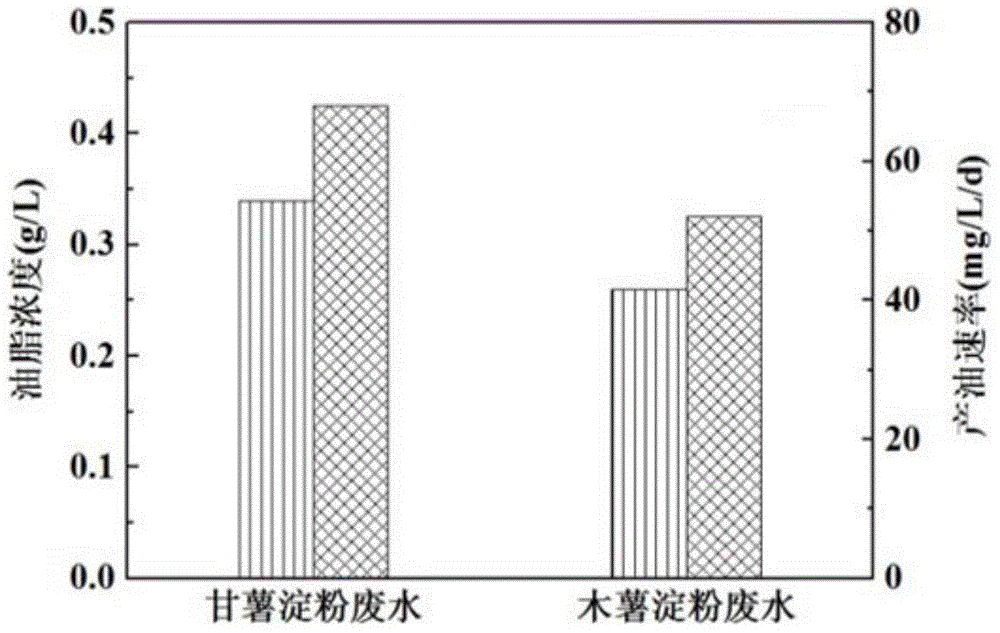
Method for treatment of starch wastewater and synchronous energy production by coculture of bacteria and microalgaes
InactiveCN104789602AImprove processing efficiencyAvoid spendingWaste water treatment from food industryFermentationOrganic acidWastewater
The invention relates to a method for treatment of starch wastewater and synchronous energy production by coculture of bacteria and microalgaes and relates to the method for treatment of the starch wastewater and synchronous energy production by coculture of the bacteria and the microalgaes. The invention aims at solving the problem that the hydrogen production is reduced because a large amount of volatile organic acids are produced in the existing dark fermentation hydrogen production process and the method comprises the following steps: 1) taking the starch wastewater, regulating the pH and putting the wastewater into a closed reactor; 2) performing pretreatment on a hydrogen production inoculation matter to obtain a mixture containing hydrogen production bacteria; and 3) mixing the mixture containing the hydrogen production bacteria with the microalgaes, inoculating into the starch wastewater, further putting into a shaking table and performing shaking culture to complete the process. According to the method provided by the invention, the wastewater is used for fermentation and energy production, so that the wastewater is effectively treated, the environmental pollution is reduced, and a method for synchronous preparation of clean energy is provided. According to the method provided by the invention, the energy production is improved by more than 95%, and the sewage treatment efficiency is improved by more than 170%. The method provided by the invention is applied to the field of bio-energy and sewage treatment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
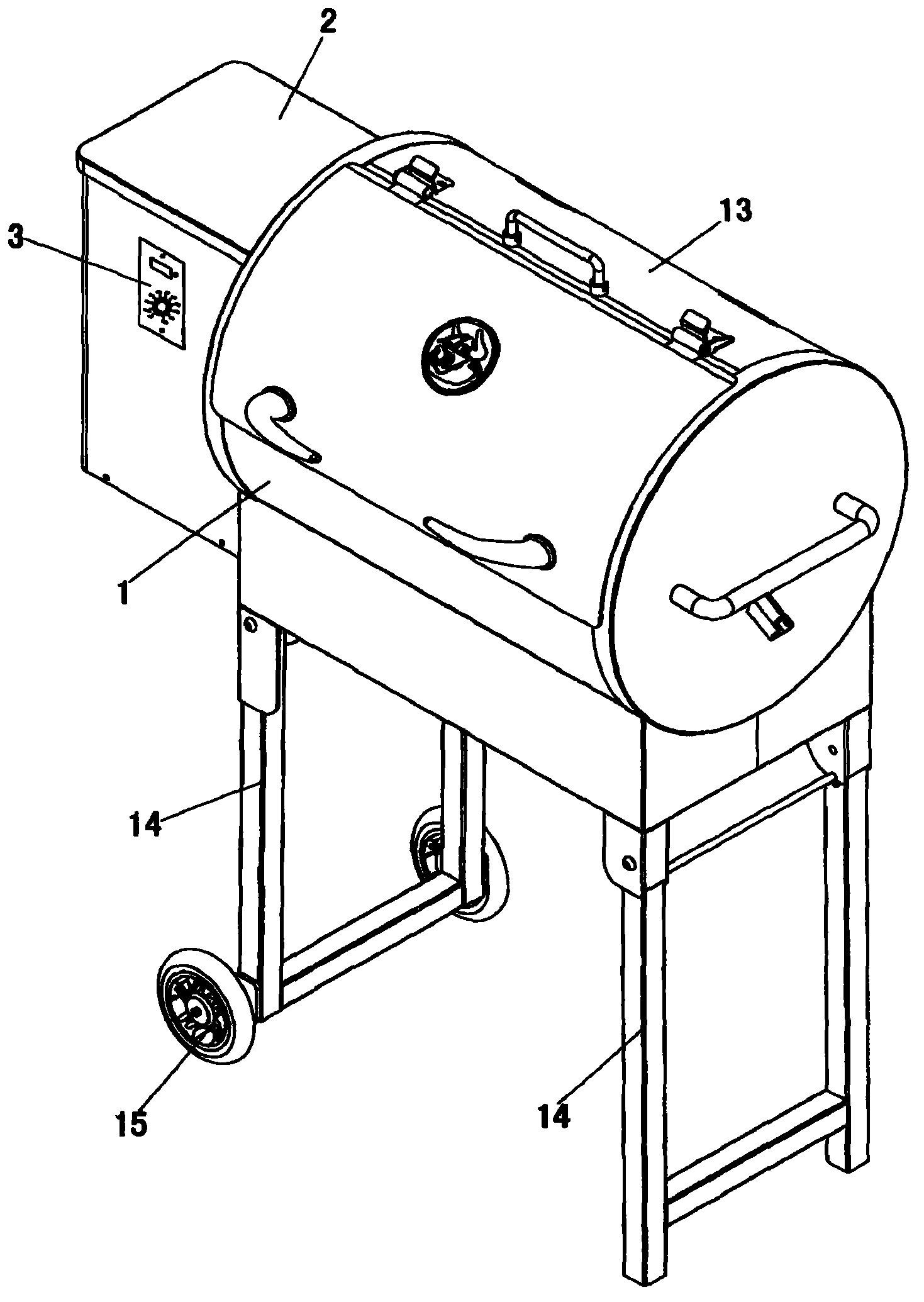
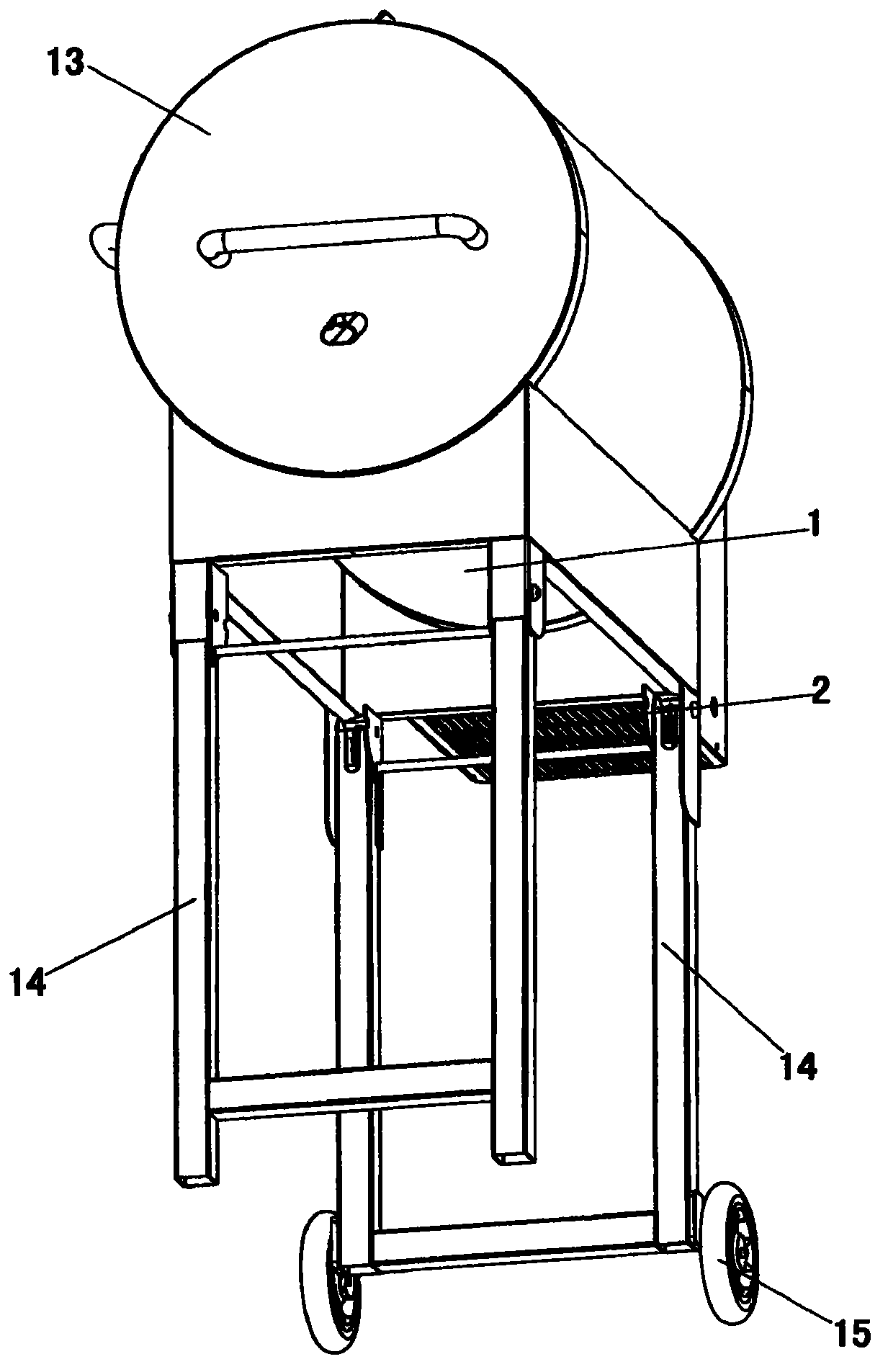
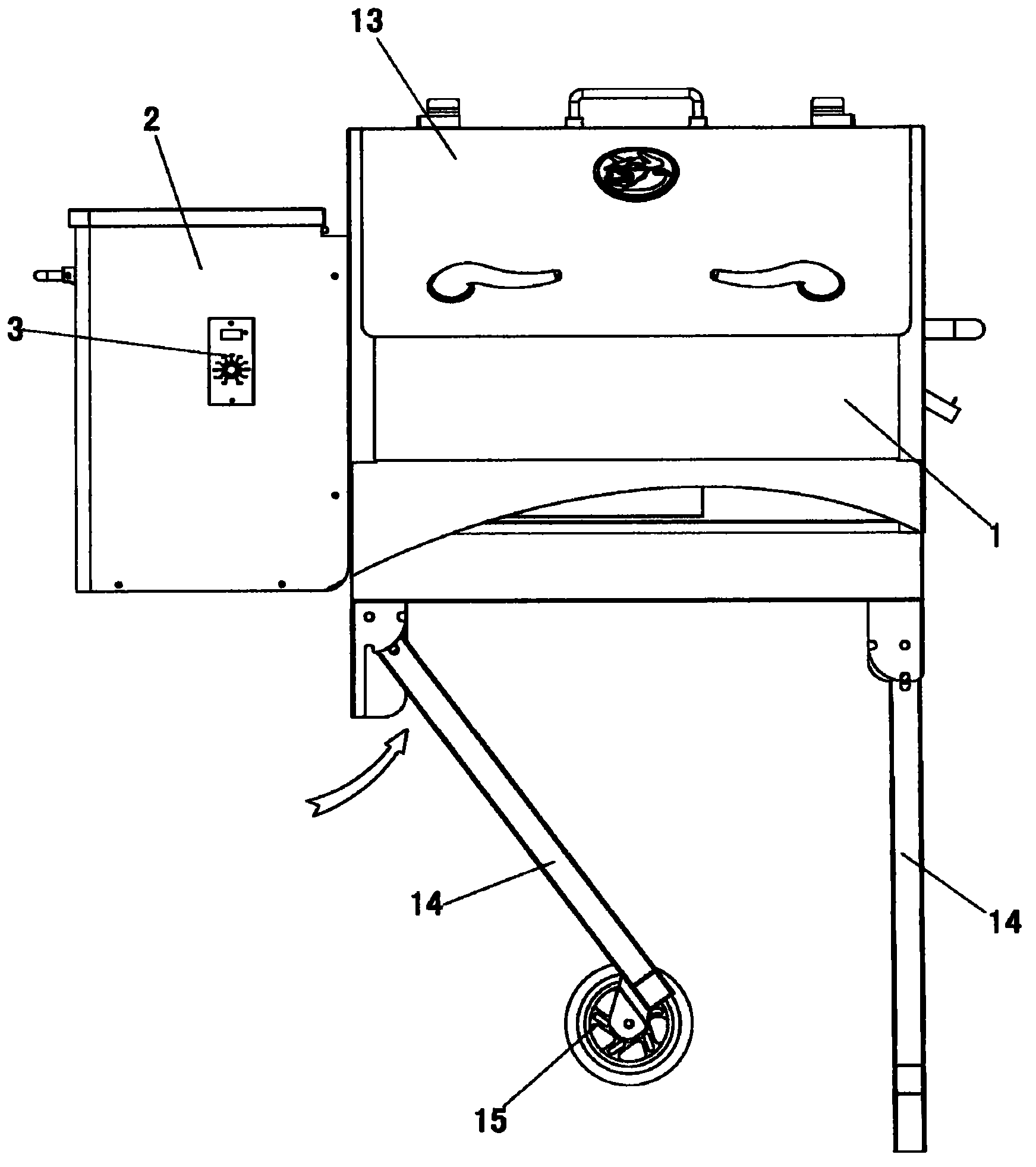
Bioenergy barbecue oven
The invention discloses a bioenergy barbecue oven. The oven comprises an oven body and a hopper which is arranged on one side of the oven body, wherein the oven body and a lumen of the hopper are communicated; a material loading motor is arranged in the lumen of the hopper, an output shaft of the material loading motor is connected with one end of a material loading auger, and the other end of the material loading auger extends into the lumen of the oven body; a fire rod is arranged below the lumen of the oven body which is positioned at the other end of the material loading auger, both the other end of the material loading auger and the fire rod extend into a combustion box which is fixed in the lumen of the oven body, a barbecue dish which is positioned above the combustion box is arranged in the lumen of the oven body, a fan is arranged at the bottom of the barbecue dish, a temperature sensor and a computer control board are arranged in the oven body, and all electrical components of the barbecue oven are controlled by programs of the computer control board to orderly work. The bioenergy barbecue oven disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the structure is simple, the operation is convenient, the supplied energy resources are clean and inexpensive, and the environmental hazards can be reduced.
Owner:JINHUA XINAN ELECTRICAL CO LTD
Common chlorella as well as culturing method and application thereof
ActiveCN102586116ALow costStrong toleranceUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesSpecial designOil production
The invention provides a common chlorella, which is chlorella C9-JN2010 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2010373; and the invention further provides a culturing method of the common chlorella. The culturing method comprises the following steps: using secondary outlet water, which is obtained by treating municipal sewage and / or industrial sewage in a sewage treatment plant, as a culture medium; and culturing the chlorella after the chlorella is inoculated, wherein the initial inoculating density is 1.0 multiplied by 107 cfu / ml-6.0 multiplied by 107 cfu / ml, and the culturing conditionis that the light cycle is 10h:14h-16h:8h, the light intensity is 5000-15000 lux, the culturing temperature is 20-30 DEG C, the pH value is 6.5-8.5, the CO2 gas throughput is 0.01-0.2 VVm, and the CO2 concentration is 15.0%-30.0% (v / v). The invention further provides an application of the common chlorella in sewage treatment and oil production. The common chlorella provided by the invention has the advantages of strong CO2 tolerance and high production strength; through the adoption of the culturing method provided by the invention, the sewage treatment and the production of the biological energy are combined with other side products (such as proteins, cosmetic raw materials, and animal feeds), so that the production cost is reduced, the waste resources are comprehensively utilized as well as the energy-saving and emission reducing green production is realized; and the culturing method provided by the invention has the advantages of skillful and special design as well as suitability for being popularized and applied on a large scale.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
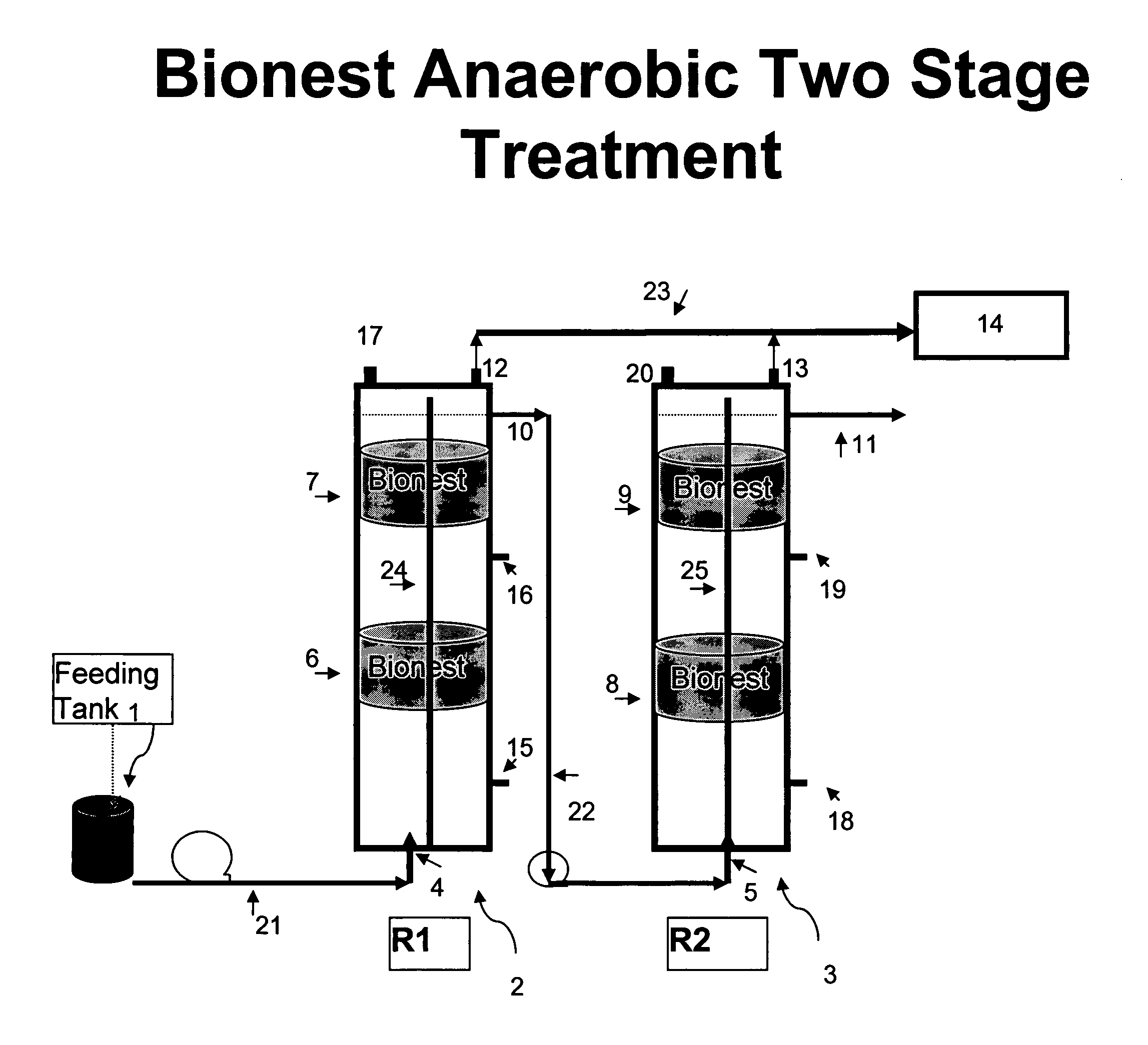
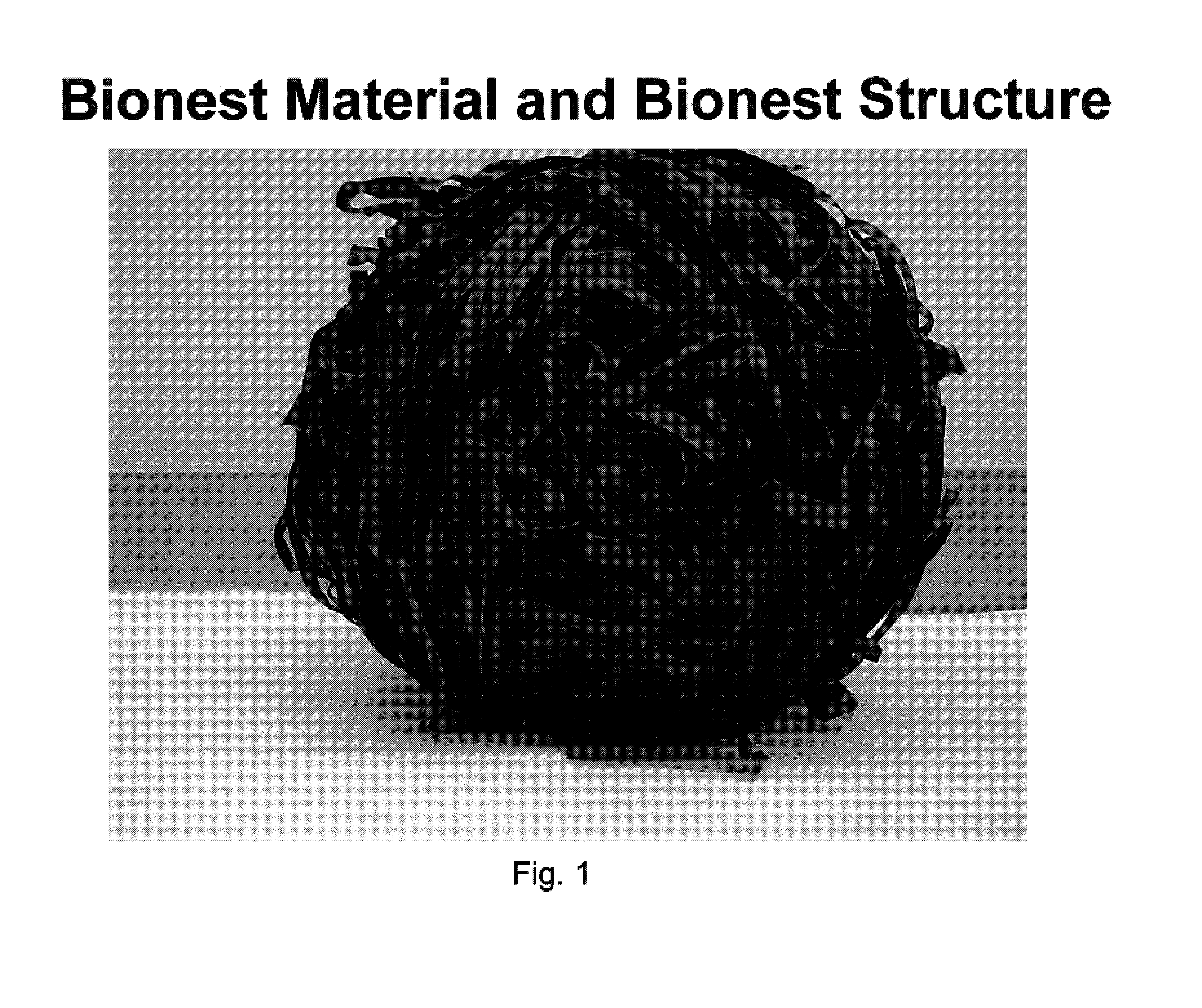
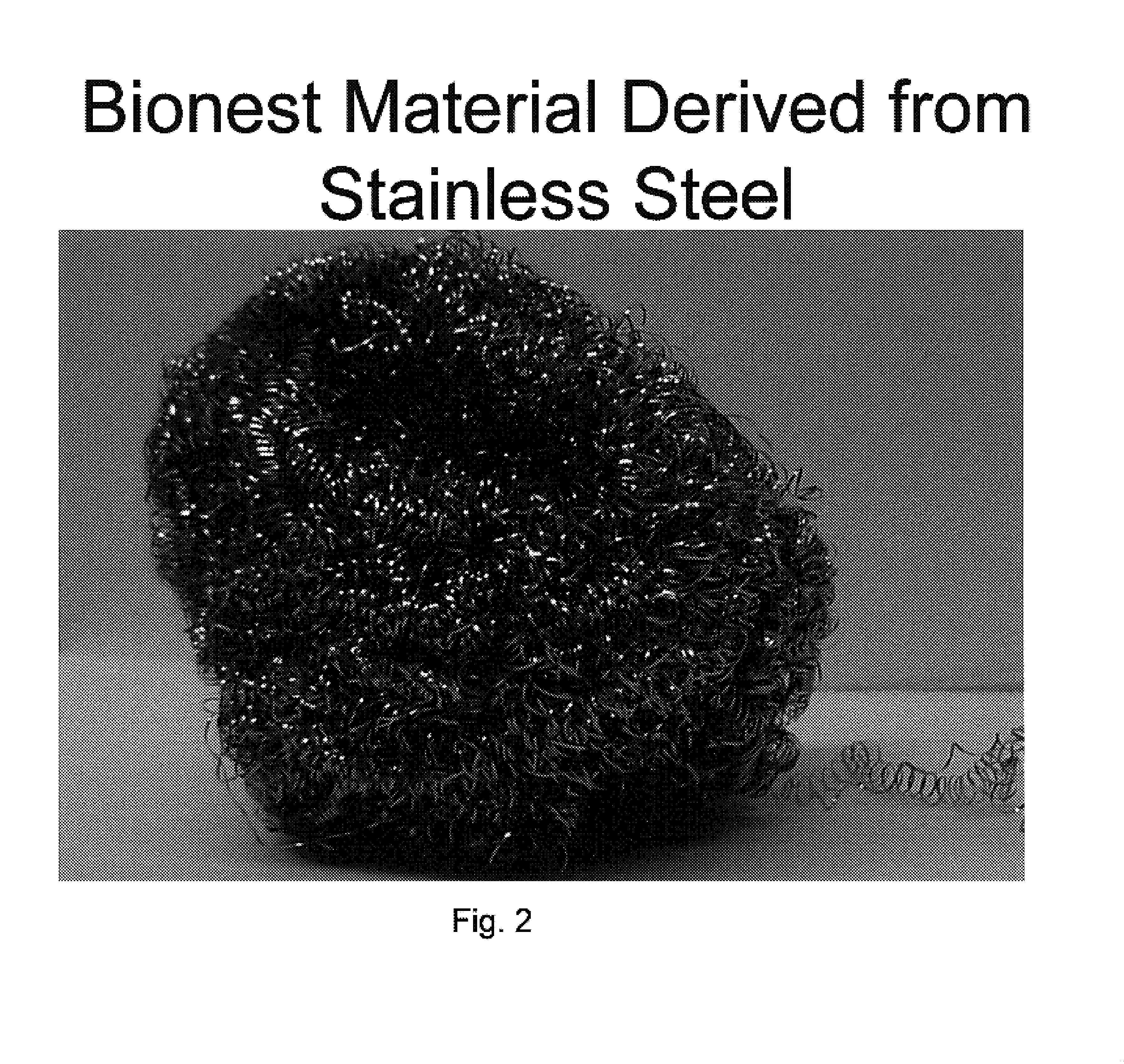
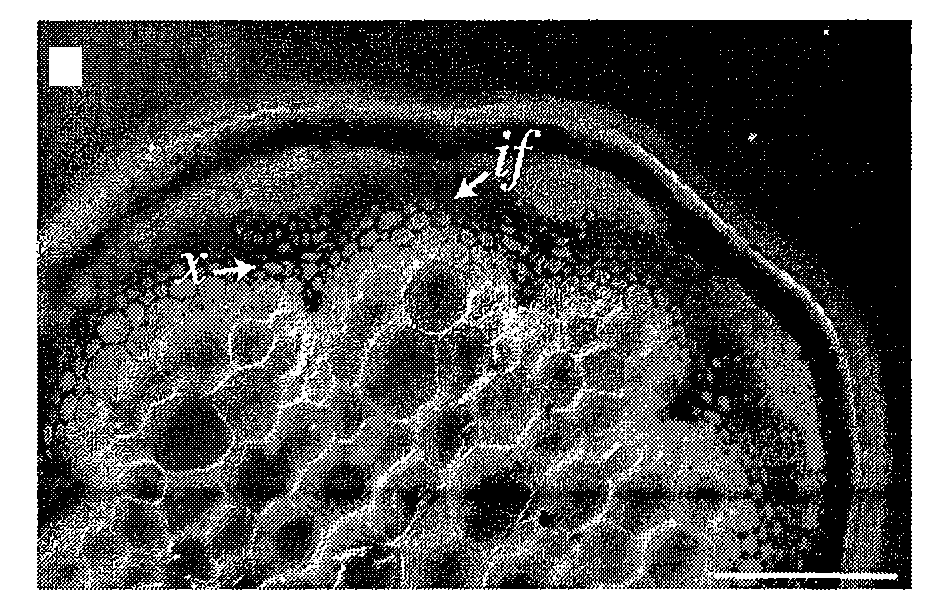
Bionest reactor for the application of anaerobic wastewater treatment and bioenergy recovery
InactiveUS7226539B2Uniform hydraulic retention timeLiquid degasificationWaste based fuelDigestionBioreactor
A method of treating wastewater using an anaerobic bioreactor which contains a “bio-nest” structure to retain the microbial content and improve digestion efficiency is disclosed. The bionest system results in a longer SRT, good sludge mixing, and reduced wash-out of sludge. The system is particularly useful for treatment of lipid rich wastewater such as dairy wastewater.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
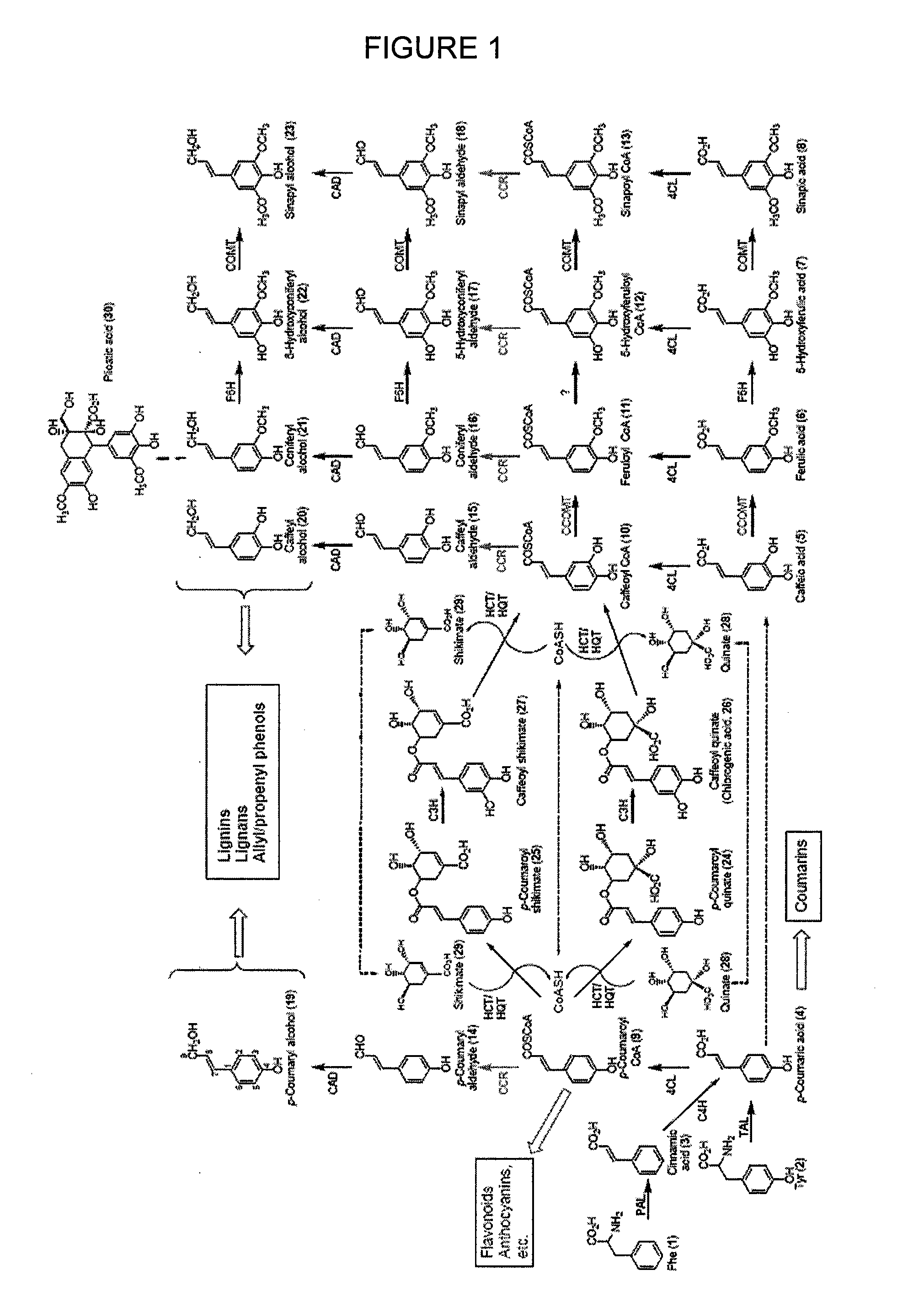
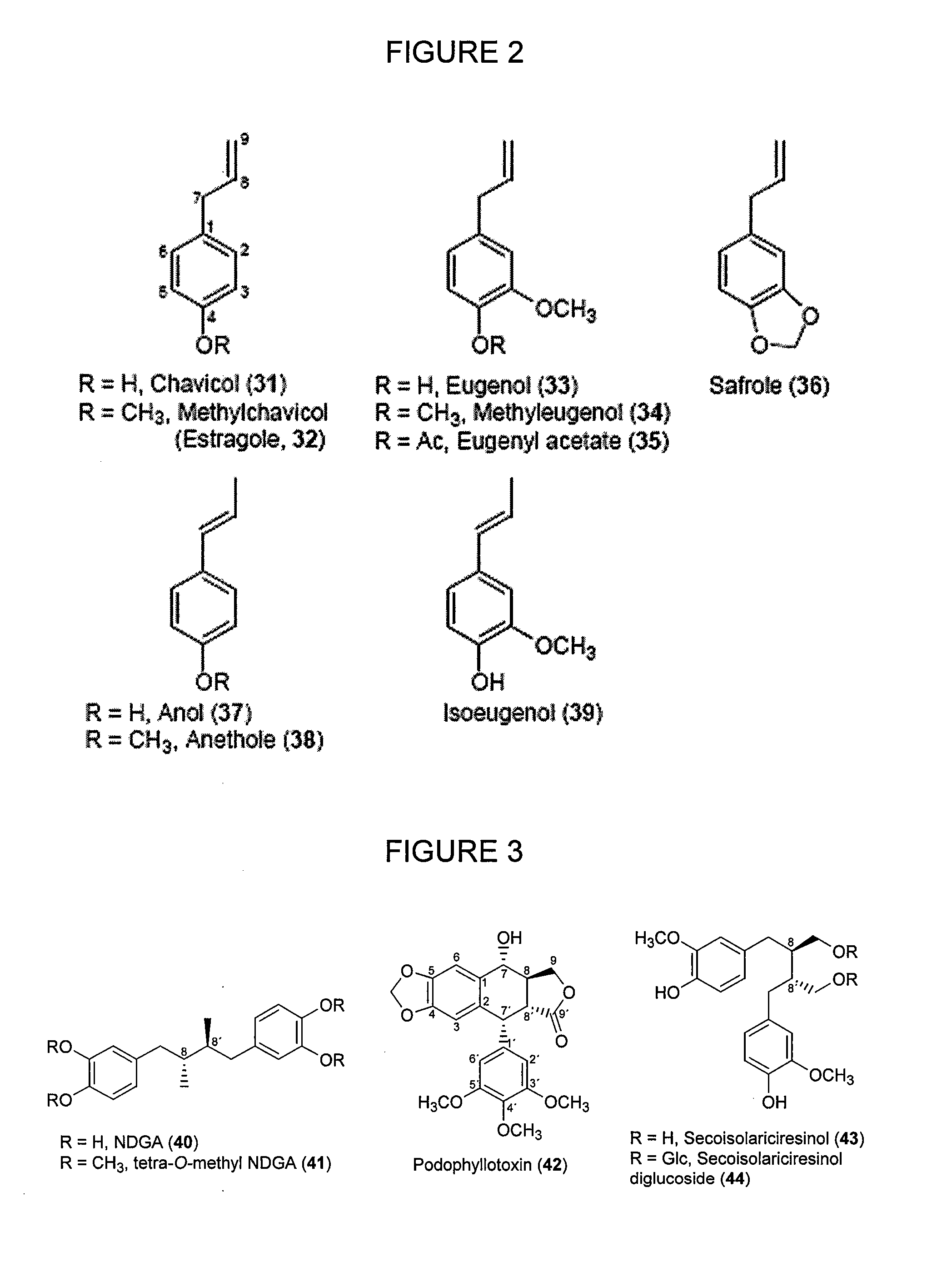
Genes encoding chavicol/eugenol synthase from the creosote bush larrea tridentata
Particular aspects provide novel methods for redirecting carbon allocation in plants or cell culture from lignification to inherently more useful and tractable materials, and to facilitate the generation of, e.g., biofuels from the remaining plant roculture biomass. Particular aspects provided novel methods for converting monolignols into allyl / propenyl phenols, and for chavicol / eugenol formation or production. Additional aspects relate to the discovery of novel chavicol / eugenol synthases that convert p-coumaryl / coniferyl alcohol esters into chavicol / eugenol, and to novel compositions (e.g., novel proteins and nucleic acids encoding same), and novel methods using same for producing or forming chavicol / eugenol and other derivatives in cell culture and / or genetically modified plants, and for re-engineering the composition of plant biomass. Particular aspects provide novel methods for generation in culture or in planta of liquid / combustible allyl / propenyl phenols, and these phenolic products are utilized for (non-ethanol) biofuel / bioenergy purposes, while the remaining plant biomass facilitates the generation of other biofuels.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
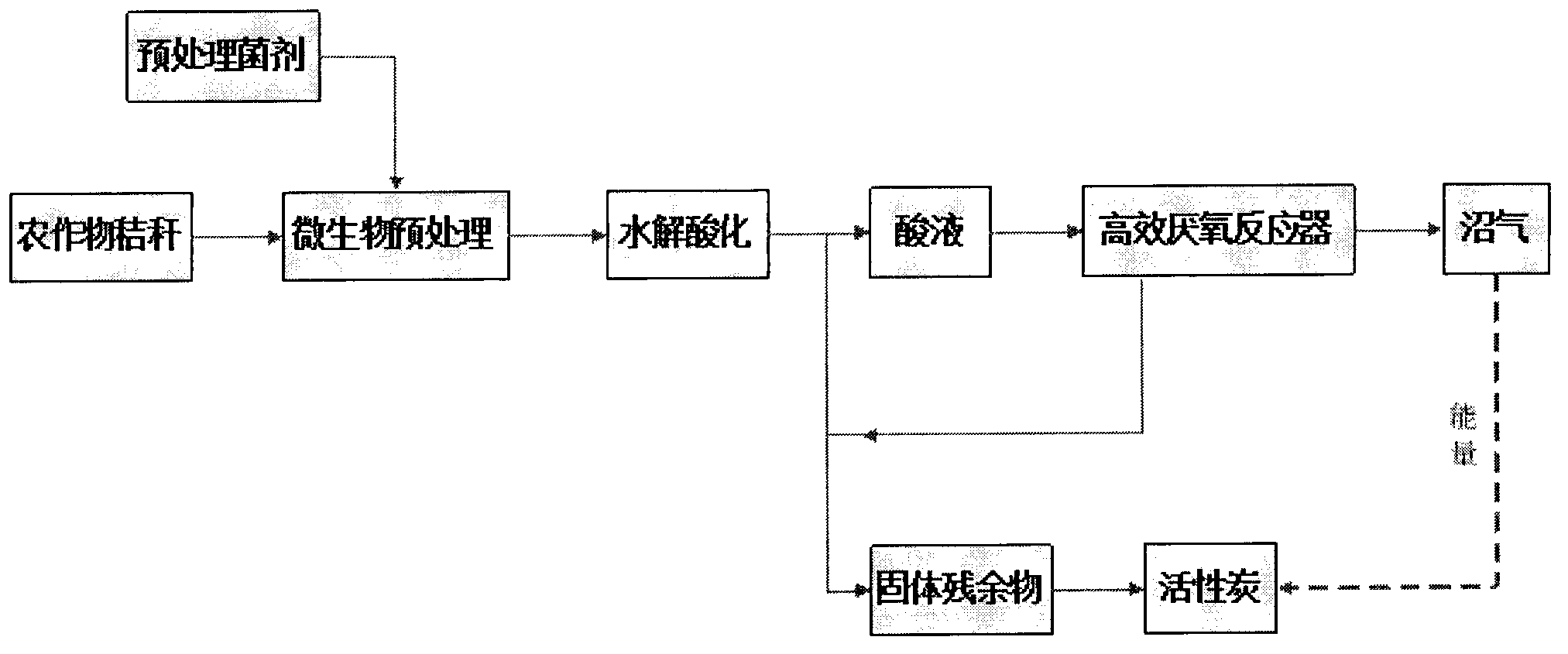
Method for comprehensively utilizing crop straw
InactiveCN103255178AImprove use valueSolve the use problemCarbon compoundsWaste based fuelActivated carbonCombustion
Crop straw is one of the richest biomass energy resources. At present, most straws are consumed in modes of combustion, padding and the like. If the straw is combusted, a great amount of biomass resources are lost, environmental pollution is caused, the traffic security is affected and fire risk is caused. The invention provides a method for realizing resource treatment and comprehensive utilization of the crop straw. According to the method, a part of methane generated through anaerobic fermentation of the crop straw is used as energy and the methane residue is used as the raw material to prepare activated carbon, so that the comprehensive utilization of the crop straw as energy / resource is realized, biomass energy, namely methane and activated carbon, can be obtained, and the utilization value of the crop straw is increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com