Method for treatment of starch wastewater and synchronous energy production by coculture of bacteria and microalgaes
A technology for treating starch and starch wastewater, applied in chemical instruments and methods, food industry wastewater treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of reduced hydrogen production, reduce pollution, reduce costs, and improve wastewater treatment efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
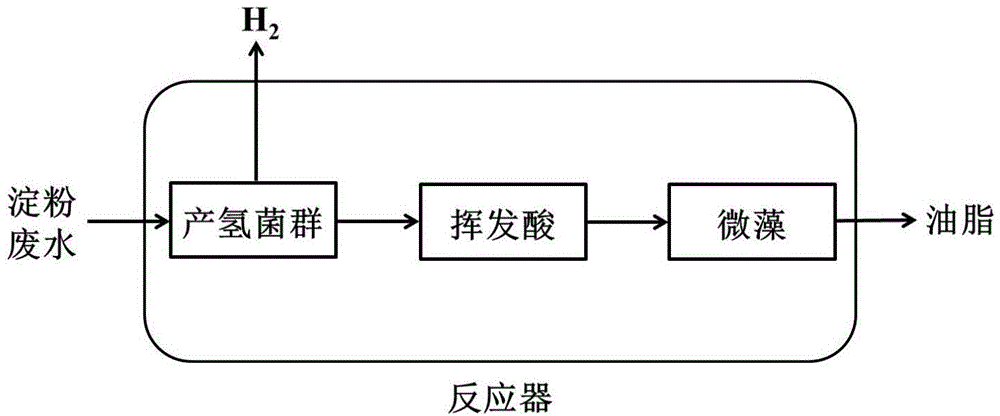
[0012] Specific Embodiment 1: In this embodiment, a method for co-cultivating bacteria and microalgae to treat starch wastewater with synchronous production capacity includes the following steps: 1. Take starch wastewater, adjust the pH, and then place it in a closed reactor; 2. Produce hydrogen The inoculum is pretreated to obtain mixture A; 3. Mix mixture A with microalgae, and then inoculate the starch wastewater in a closed reactor with an inoculation amount of 5-10% of the total volume of starch wastewater, and then react The device is placed in a shaker, and the shaking culture is completed. The mixture A contains hydrogen-producing bacterial flora, wherein the hydrogen-producing bacterial flora is mainly Clostridium flora.
[0013] The process flow diagram of this embodiment is as follows figure 1 shown.
[0014] In this embodiment, the raw material of the present invention is waste water or waste, which is beneficial to reduce the cost of production capacity and avoi...
specific Embodiment approach 2
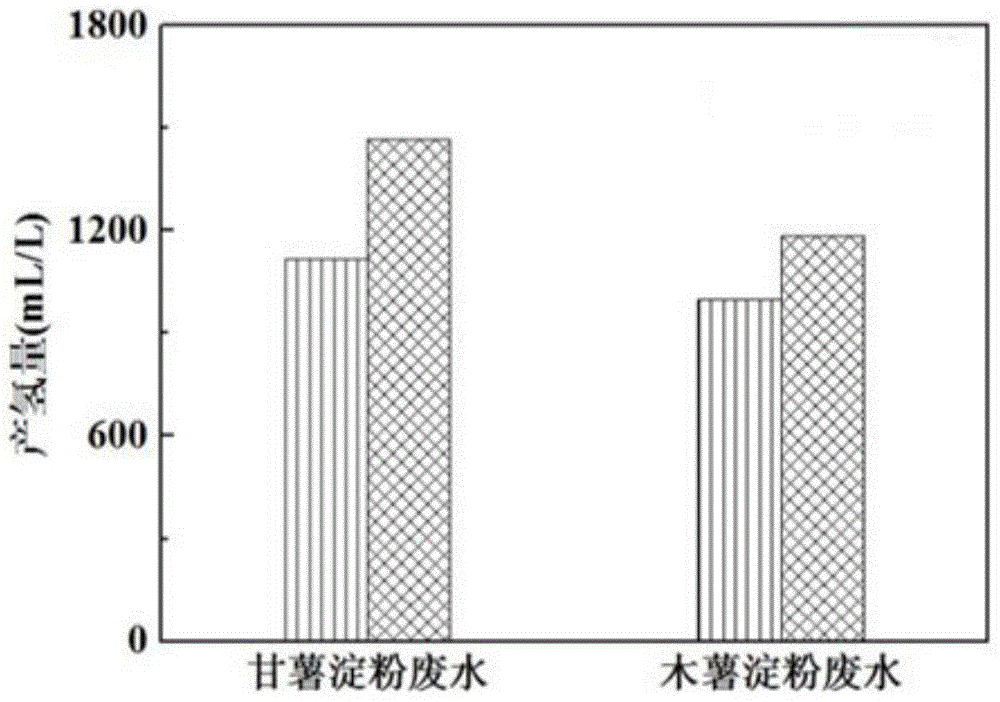
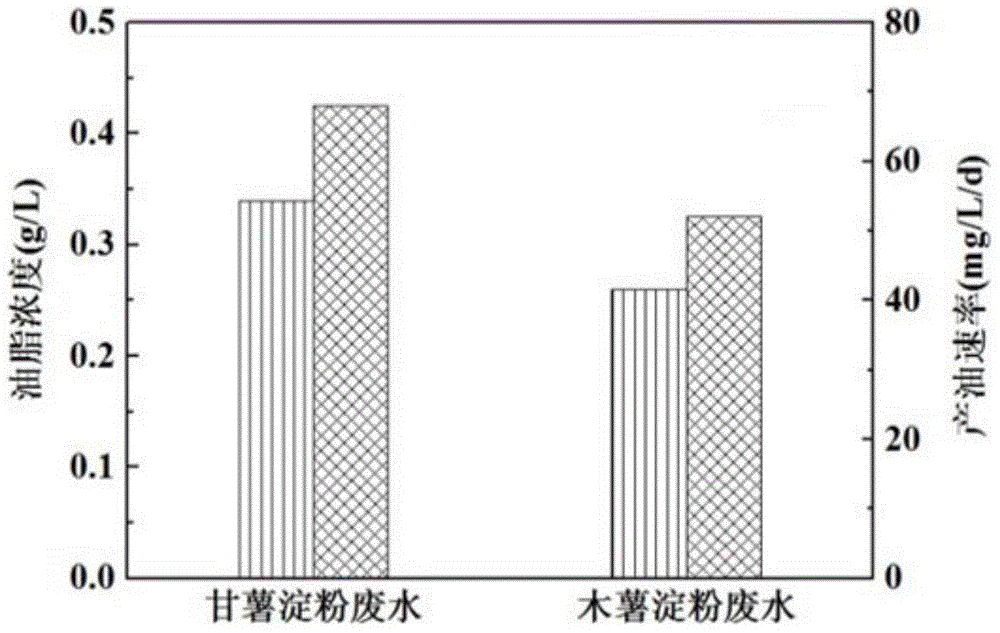
[0015] Specific embodiment two: what this embodiment is different from specific embodiment one is: the starch waste water described in step one is sweet potato starch waste water, tapioca starch waste water, mung bean starch waste water, potato starch waste water, wheat starch waste water, water chestnut starch waste water A mixture of one or more of lotus root starch wastewater and corn starch wastewater in any ratio. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0016] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the pH adjustment described in step 1 is regulated by HCl solution with a concentration of 1 mol / L or NaOH solution with a concentration of 1 mol / L. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com