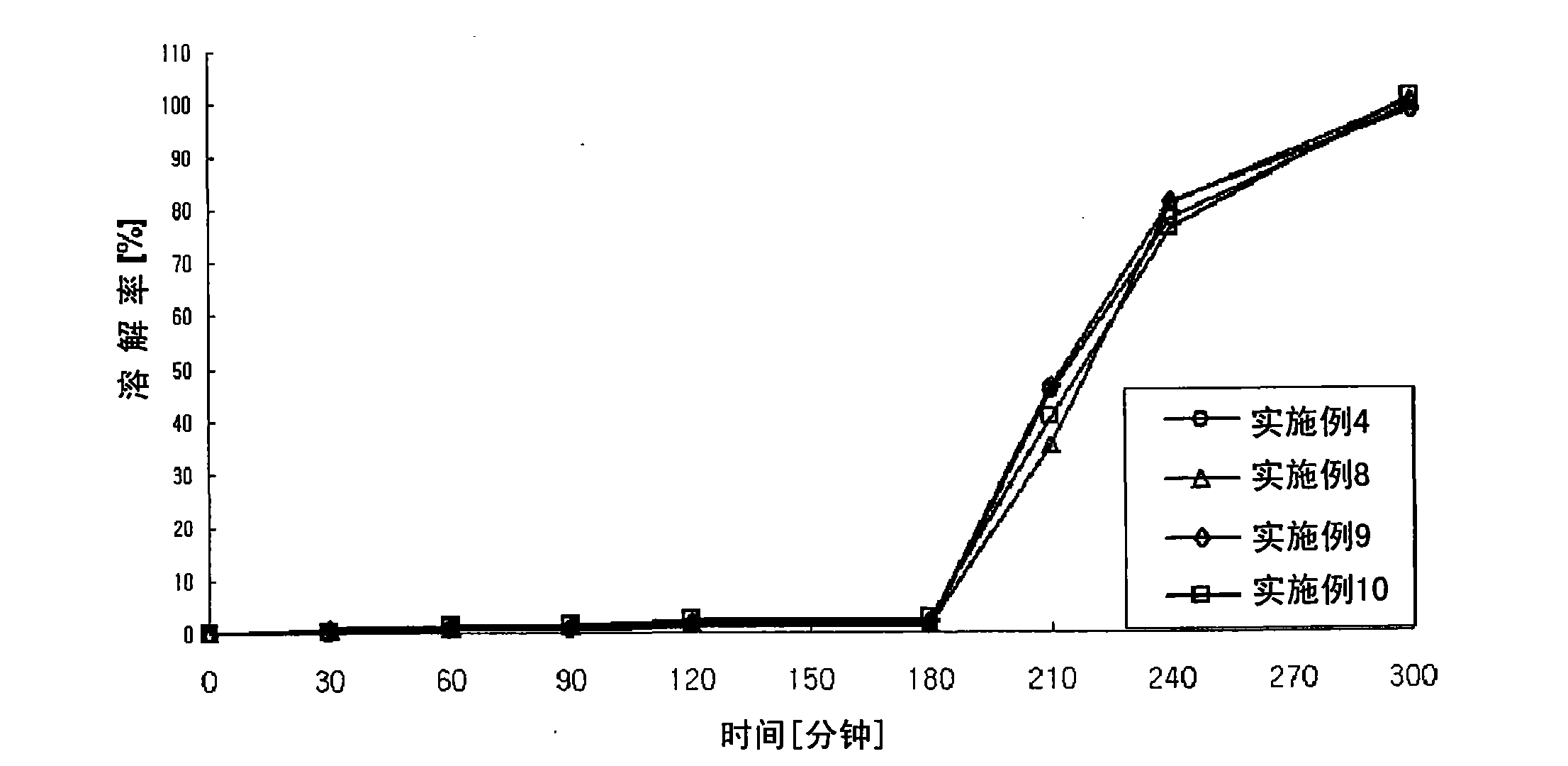
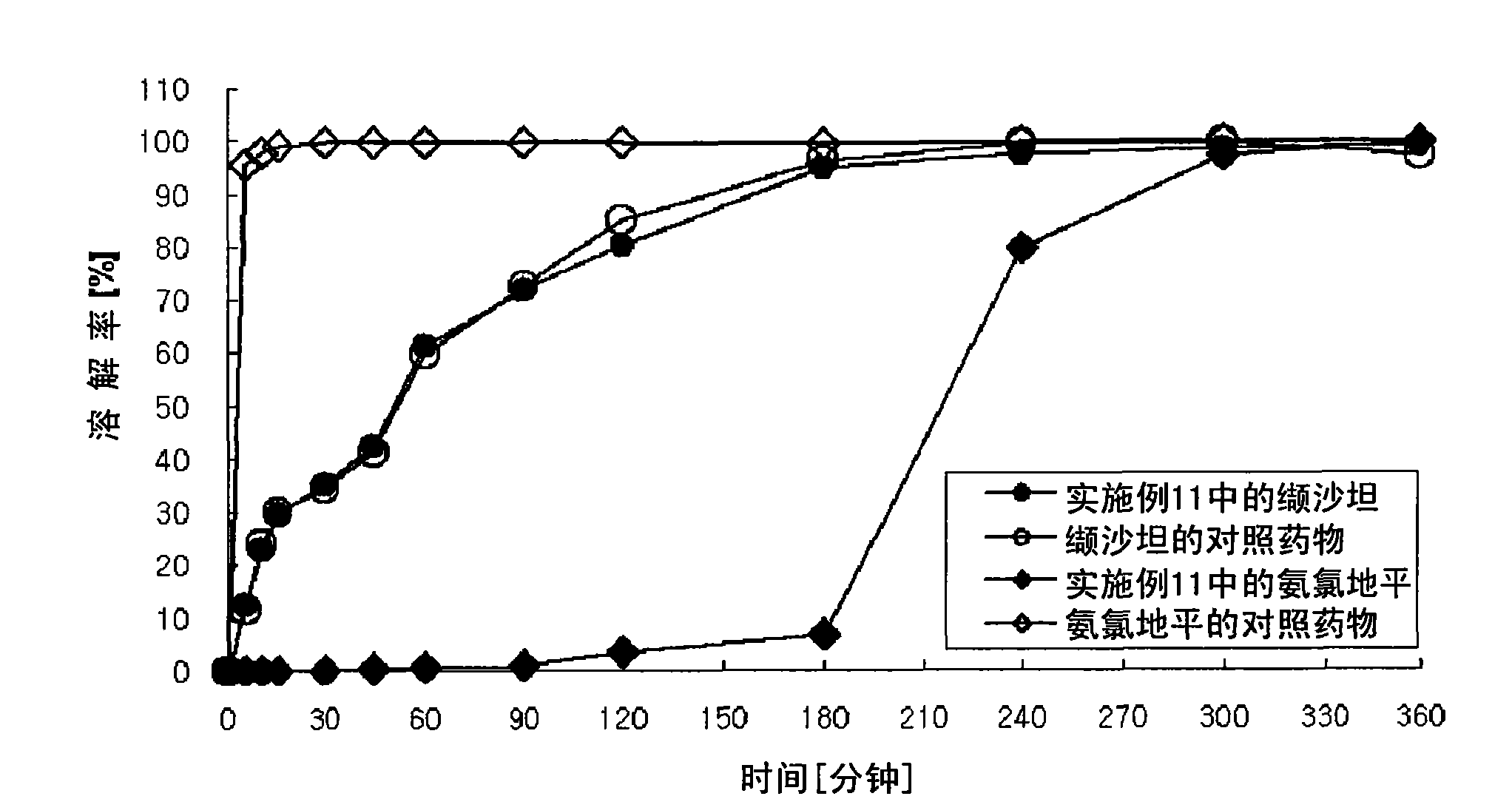
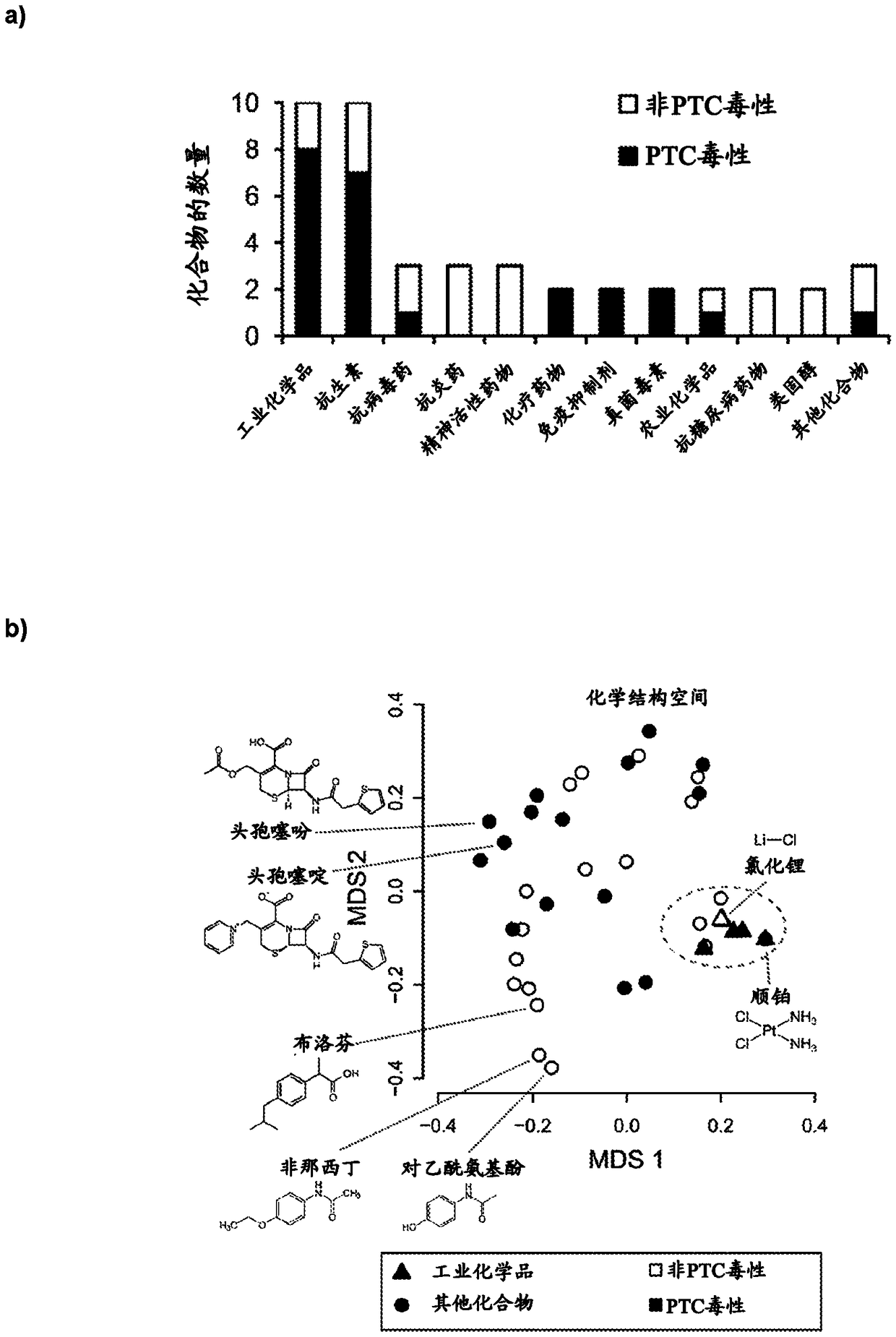
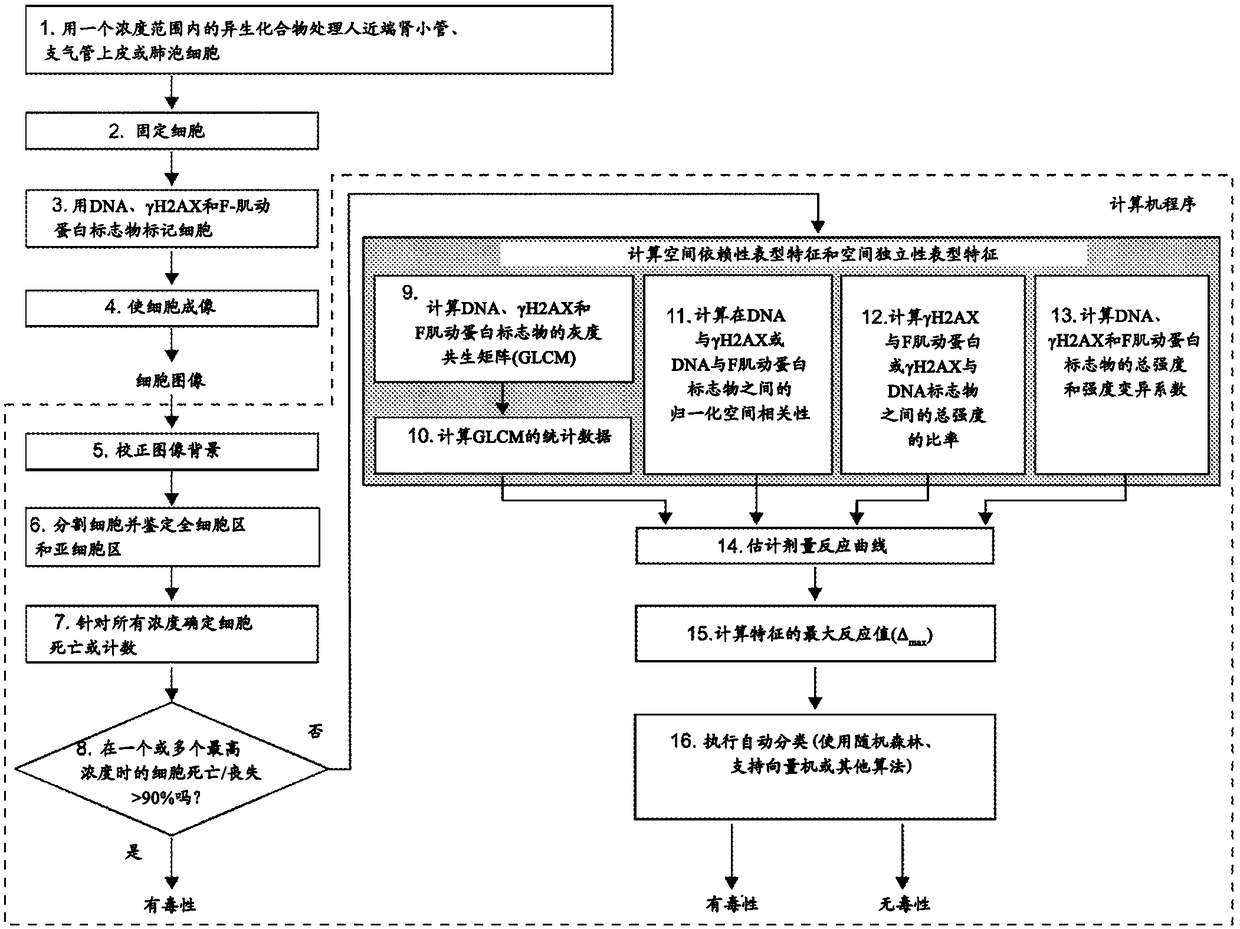
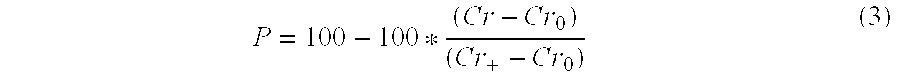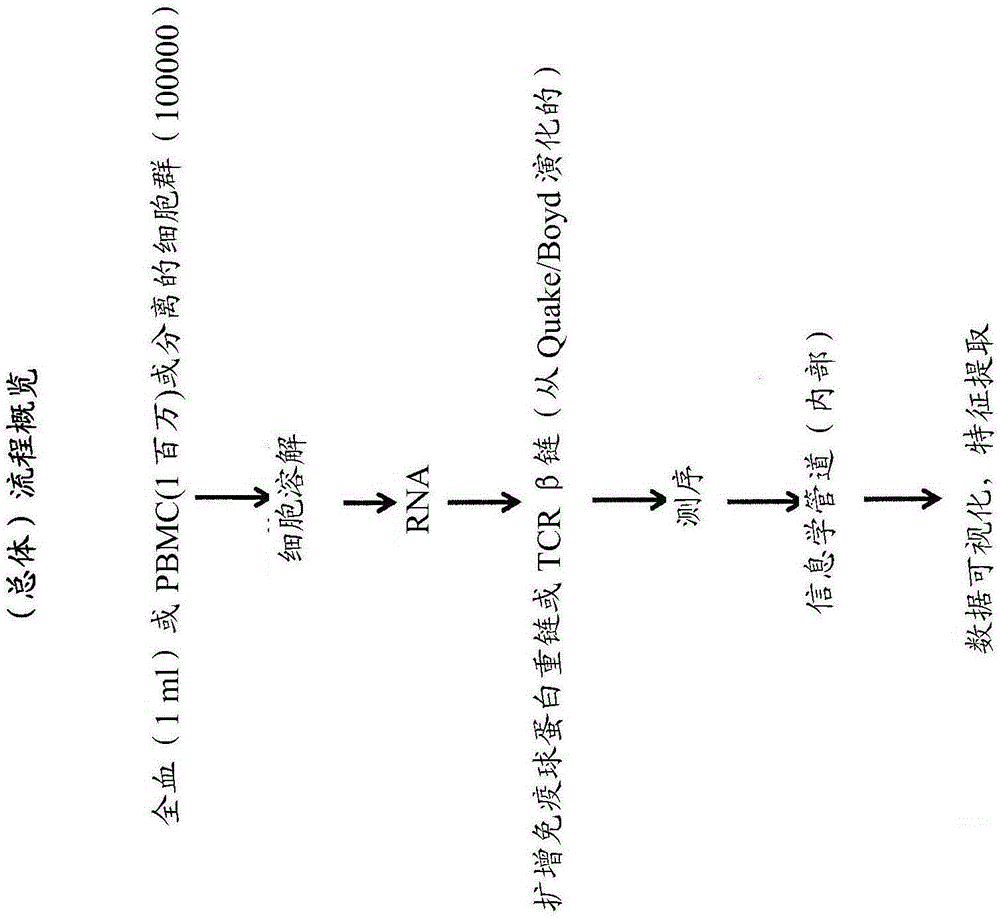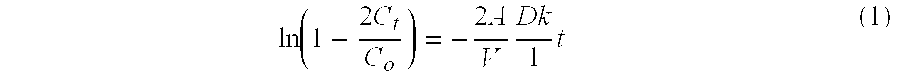Patents
Literature
56 results about "Xenobiotic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A xenobiotic is a chemical substance found within an organism that is not naturally produced or expected to be present within the organism. It can also cover substances that are present in much higher concentrations than are usual.
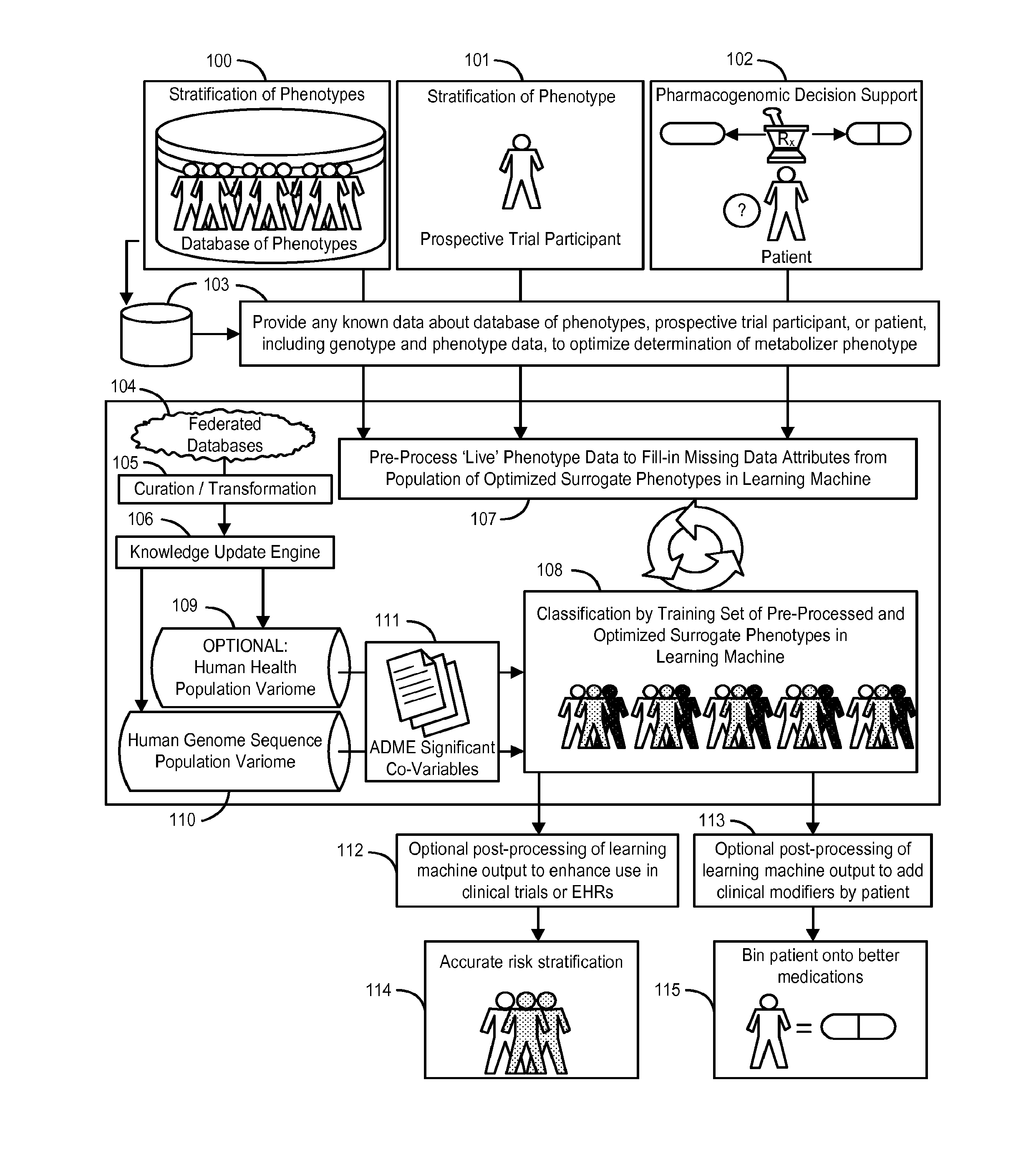
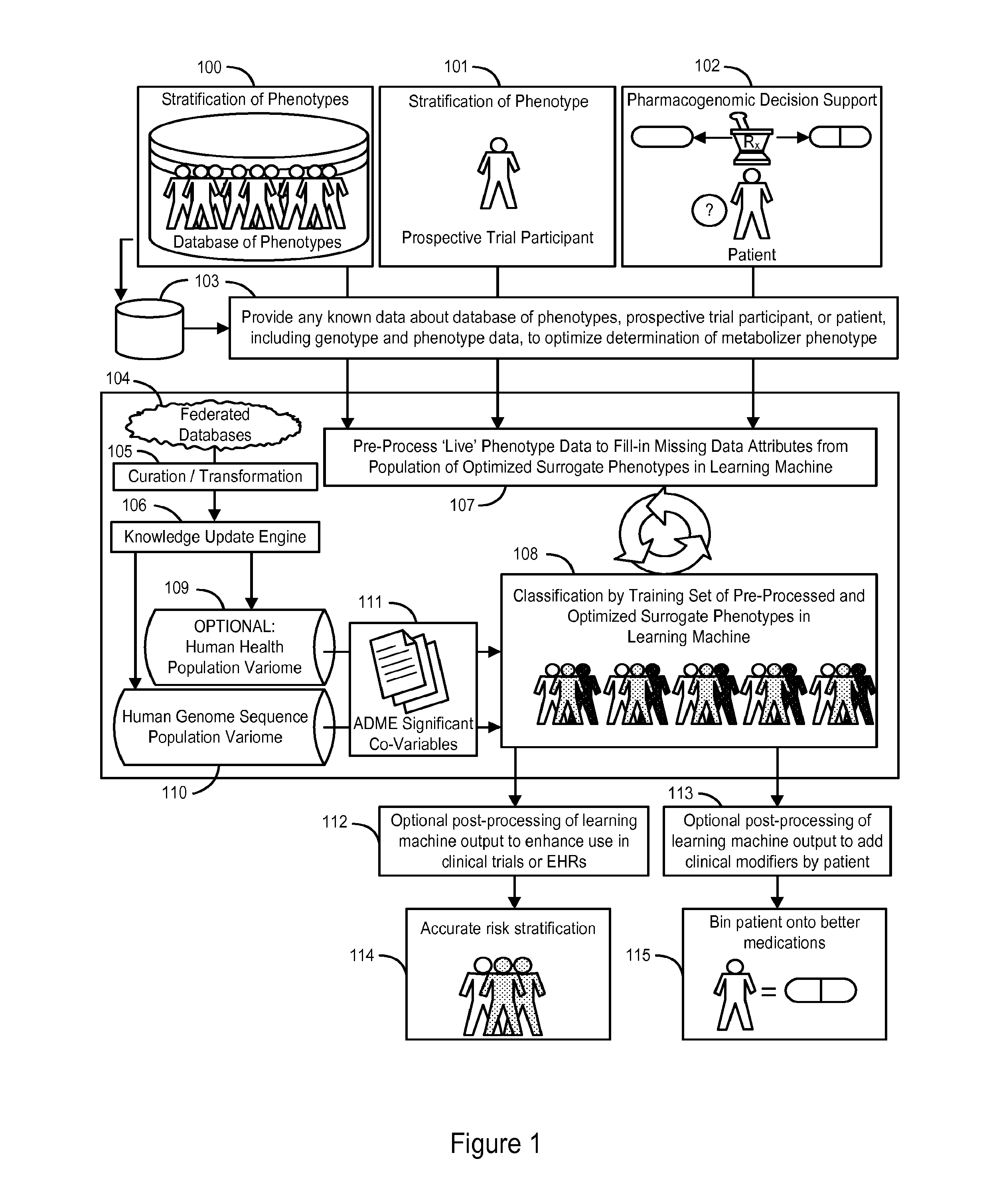
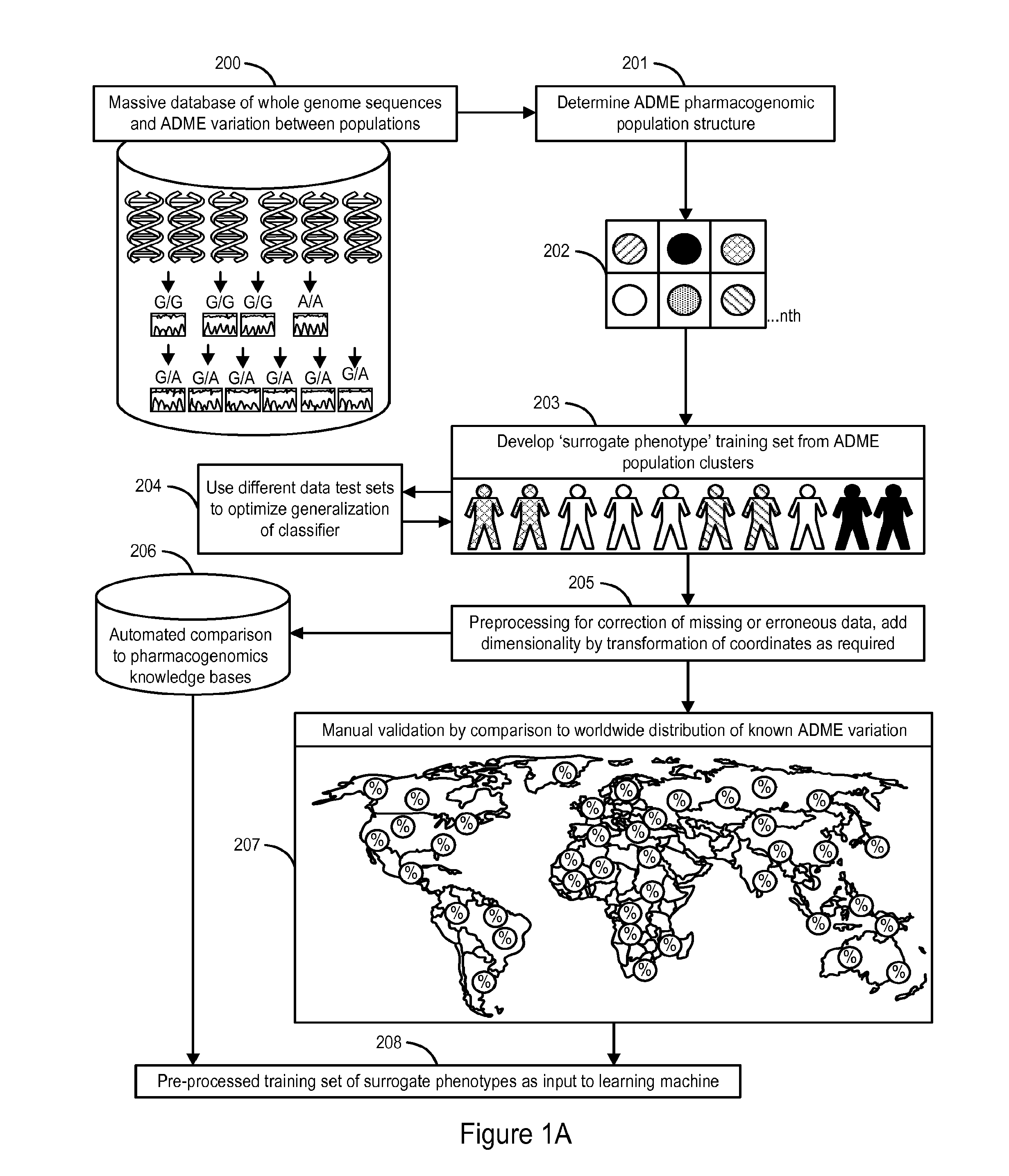
System and Methods for Pharmacogenomic Classification
InactiveUS20140222349A1Good statistical effectDataset can also become very largeBiostatisticsProteomicsGenomicsLearning machine
The invention provides a system and methods for the determination of the pharmacogenomic phenotype of any individual or group of individuals, ideally classified to a discrete, specific and defined pharmacogenomic population(s) using machine learning and population structure. Specifically, the invention provides a system that integrates several subsystems, including (1) a system to classify an individual as to pharmacogenomic cohort status using properties of underlying structural elements of the human population based on differences in the variations of specific genes that encode proteins and enzymes involved in the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) of drugs and xenobiotics, (2) the use of a pre-trained learning machine for classification of a set of electronic health records (EHRs) as to pharmacogenomic phenotype in lieu of genotype data contained in the set of EHRs, (3) a system for prediction of pharmacological risk within an inpatient setting using the system of the invention, (4) a method of drug discovery and development using pattern-matching of previous drugs based on pharmacogenomic phenotype population clusters, and (5) a method to build an optimal pharmacogenomics knowledge base through derivatives of private databases contained in pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies and academic research centers without the risk of exposing raw data contained in such databases. Embodiments include pharmacogenomic decision support for an individual patient in an inpatient setting, and optimization of clinical cohorts based on pharmacogenomic phenotype for clinical trials in drug development.
Owner:ASSUREX HEALTH INC
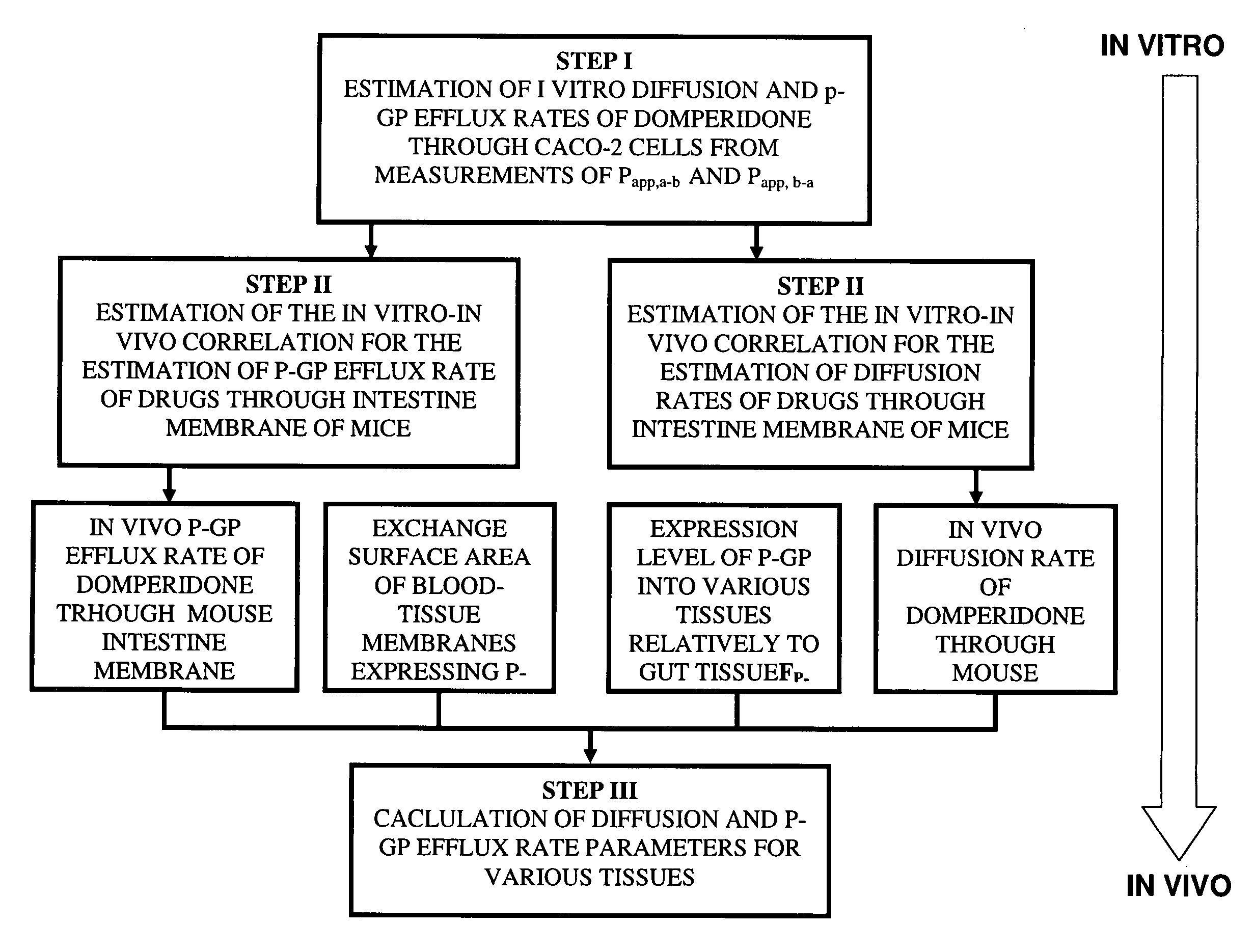
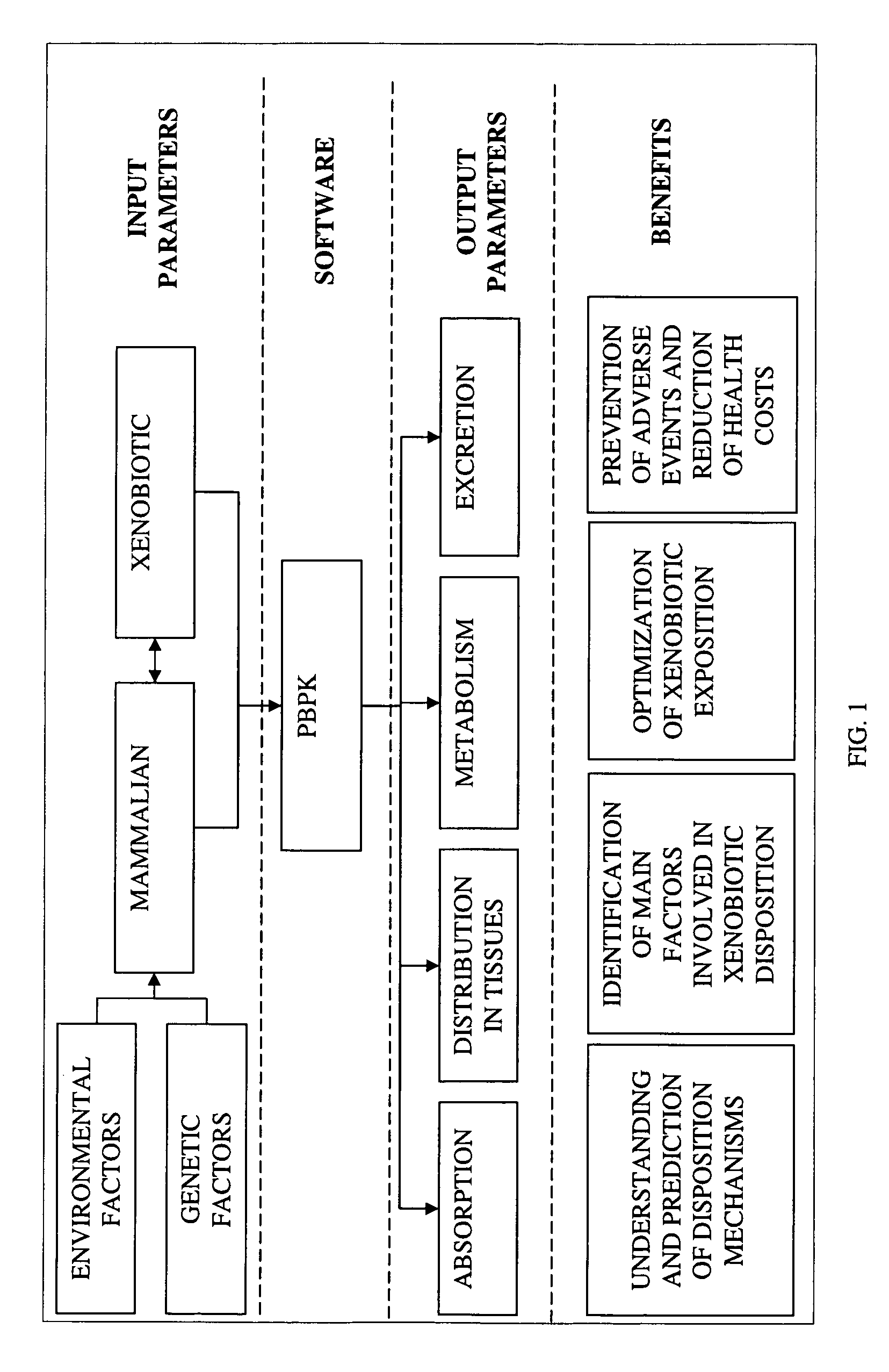
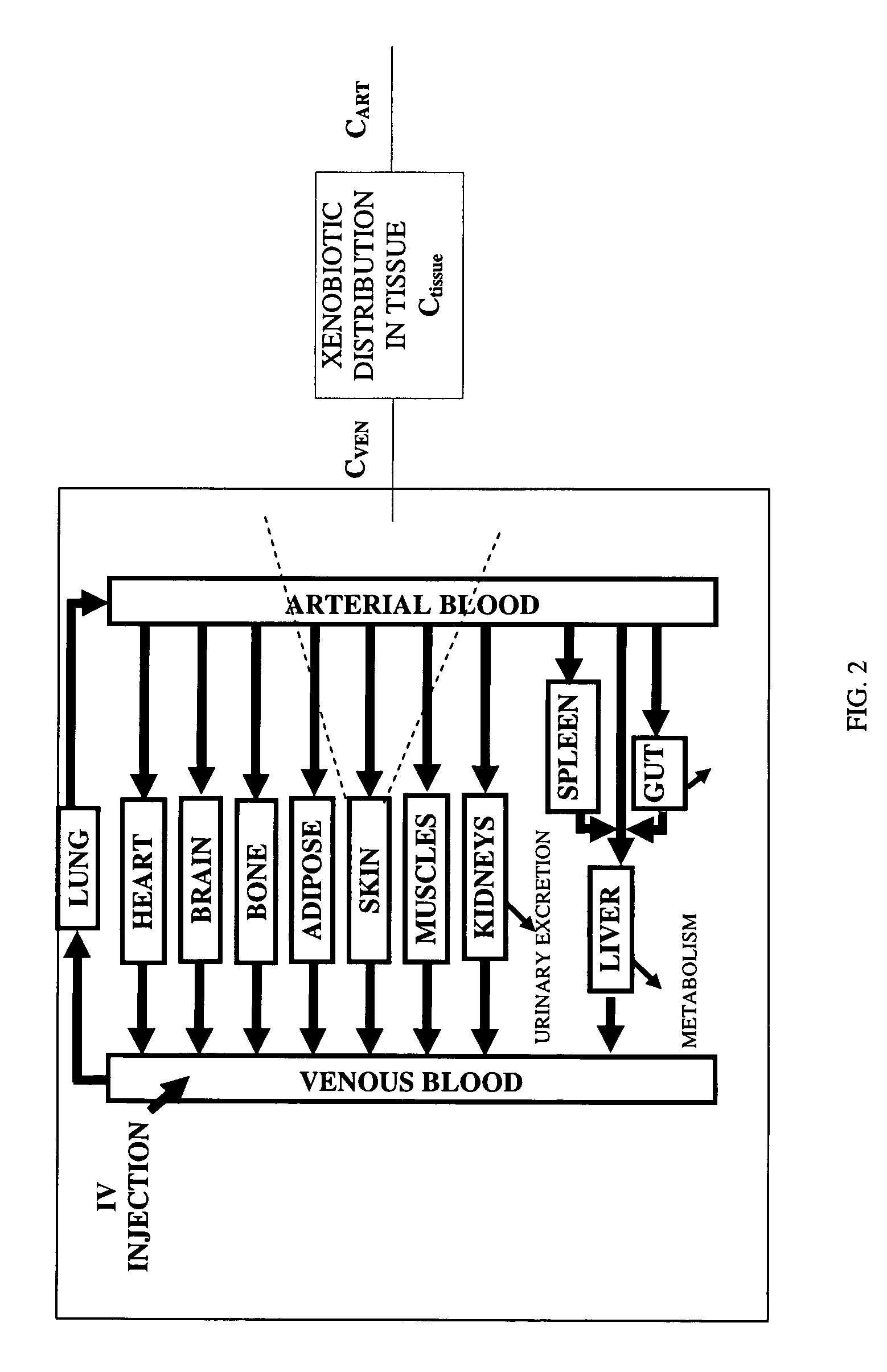
Method of developing a pharmacokinetic profile of a xenobiotic disposition in a mammalian tissue
InactiveUS20080221847A1Chemical property predictionAnalogue computers for chemical processesMammalian tissueBiology
There is provided a method of developing a pharmacokinetic profile of an xenobiotic disposition in a mammalian tissue, the method comprising inputting mammalian-specific data into a physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model, where said mammalian-specific data comprises tansporter properties related data, where said transporter properties related data reflect genetic and environmental factors associated with said mammalian; inputting xenobiotic-specific data into said PBPK model; and simulating, using said PBPK model, a pharmacokinetic profile of said xenobiotic disposition as a function of said inputted data.
Owner:FENETTEAU FREDERIQUE
Combined preparation for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases based on chronotherapy theory
InactiveUS20100047341A1Improve Medication AdherenceConstant controlBiocideAnimal repellantsCo administrationSide effect
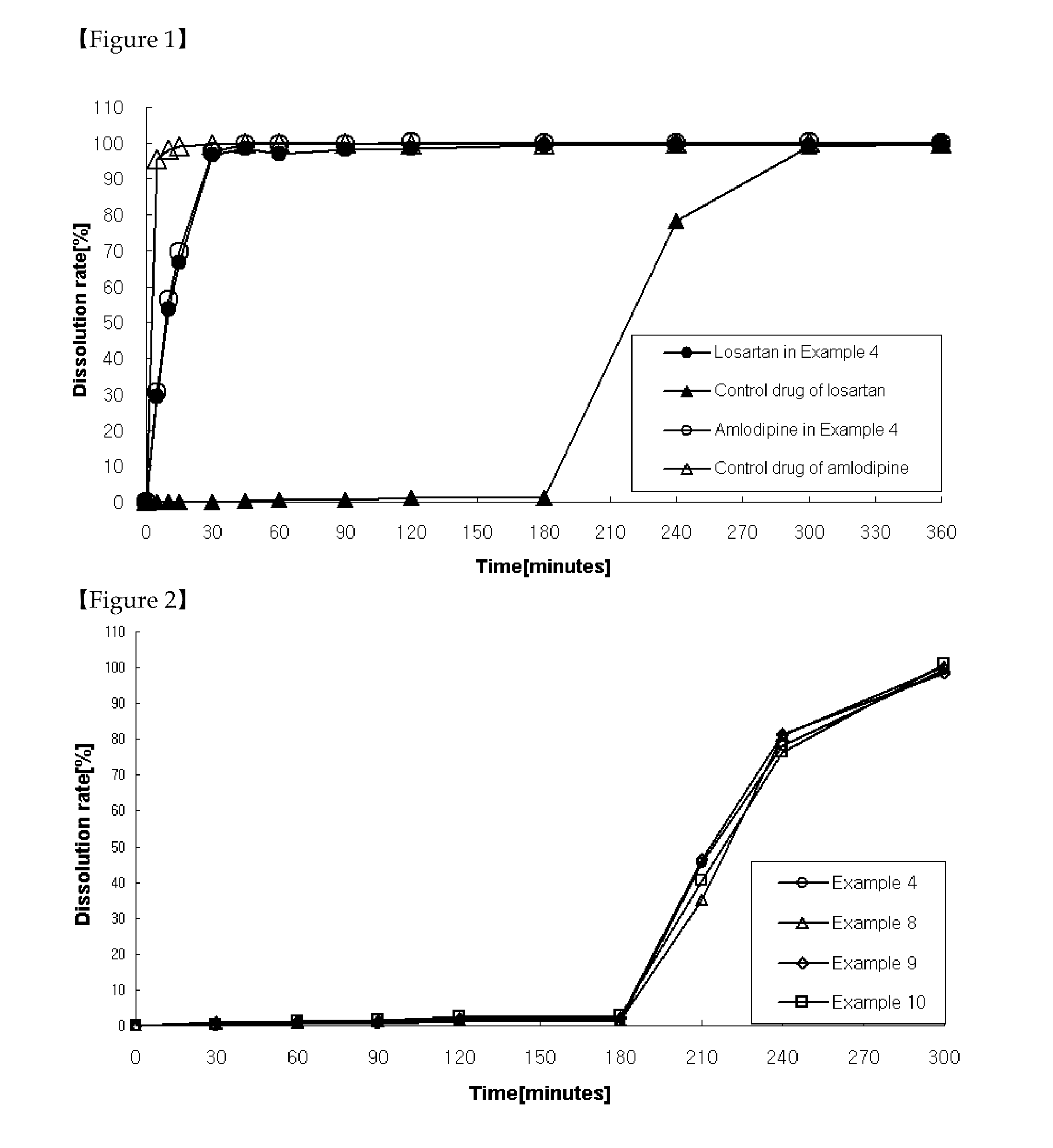
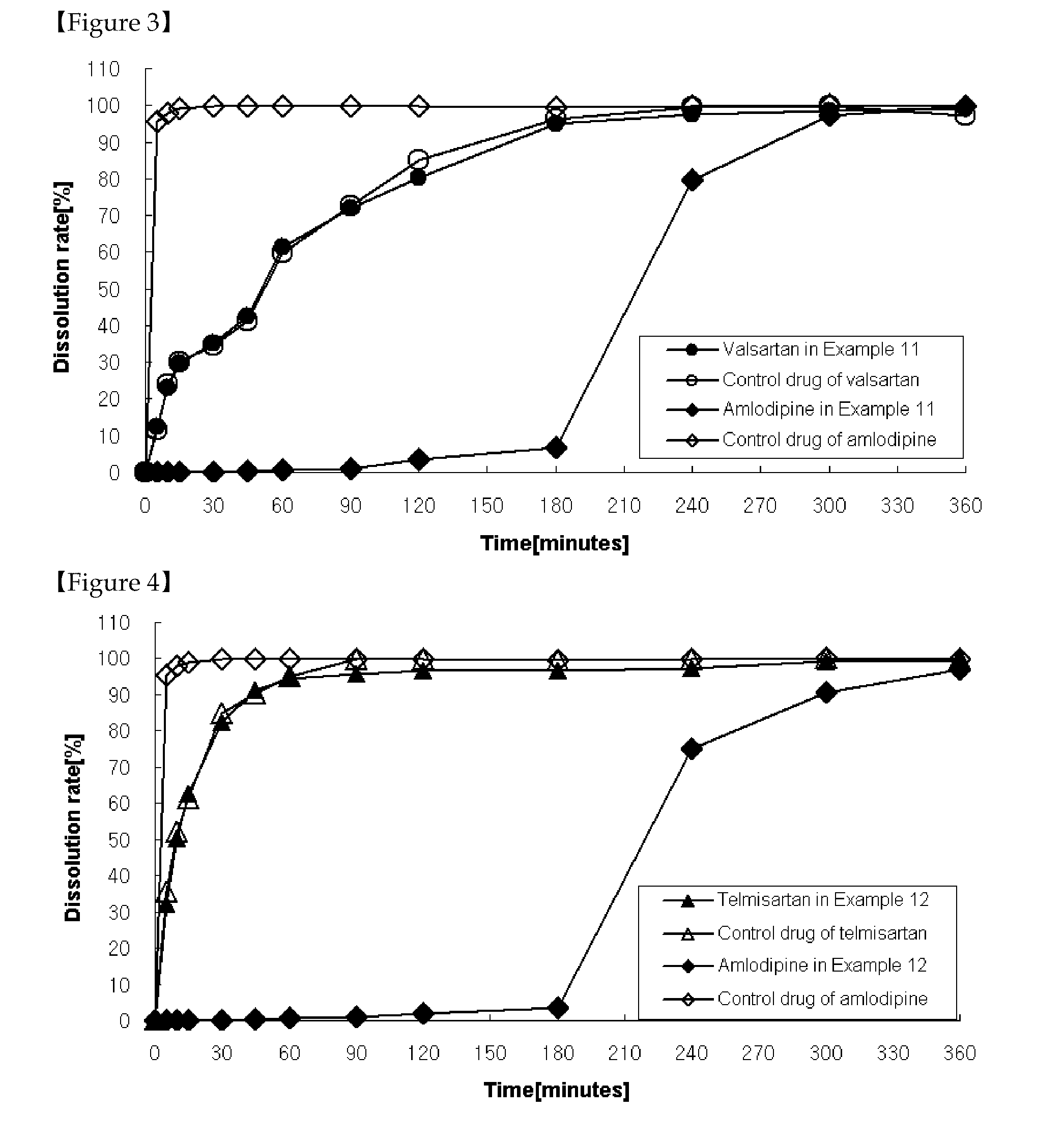
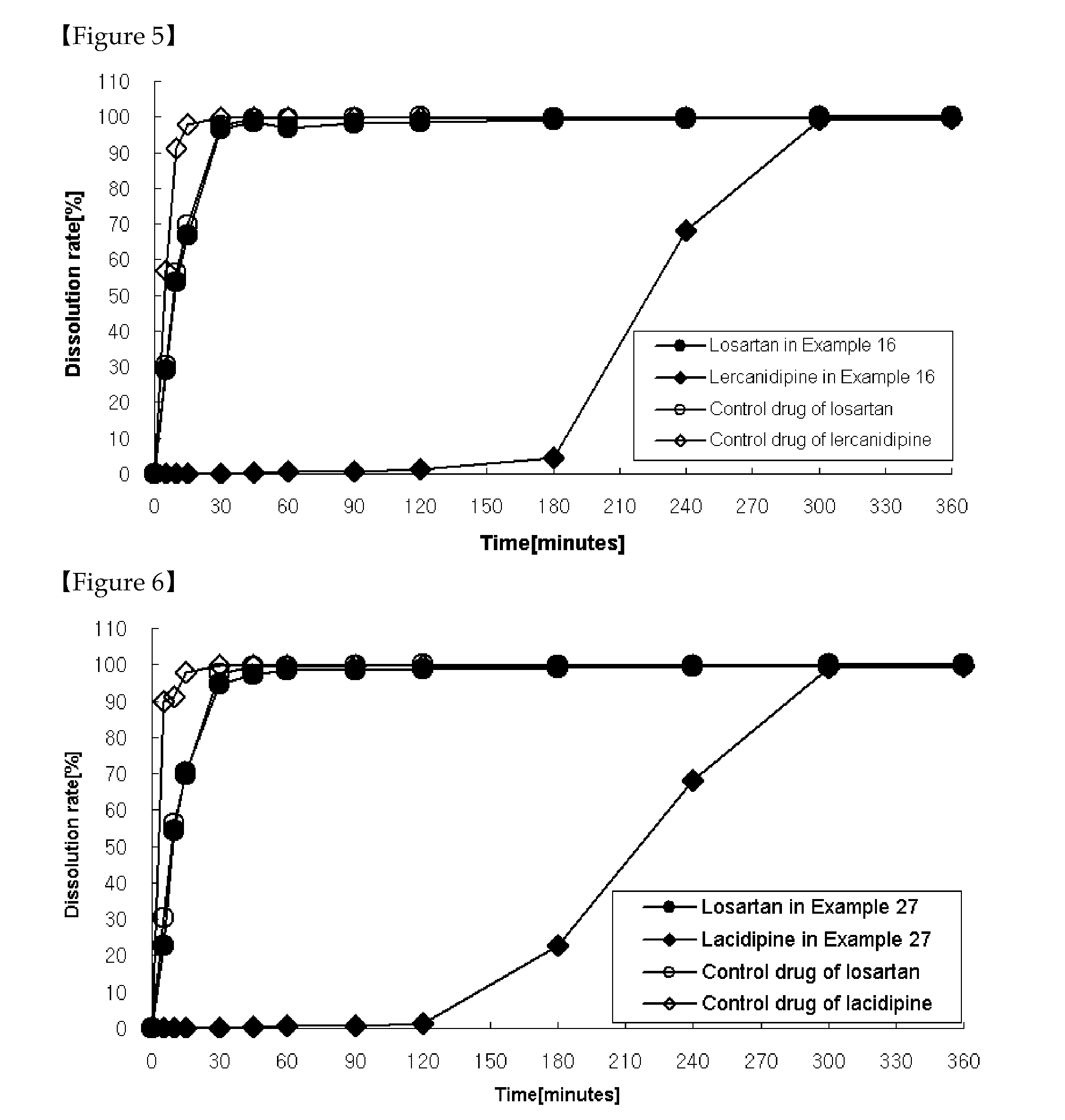
The present invention relates to a functional combination preparation comprising a dihydropyridine-based calcium channel blocker such as amlodipine and an ARB (Angiotensin-2 receptor blocker) such as losartan. In particular, the present invention relates to a chronotherapeutical combination pharmaceutical formulations with controlled-release for the prevention or treatment of cardiovascular disease, which is formulated in accordance with xenobiotics and chronotherapy for enabling the two drugs to be chronotherapeutically released, thereby improving the therapeutic activity as compared to the co-administration of each drug in the form of a single pill, while reducing side effects and maintaining the therapeutic activity as high as possible at the time of day when the risk of a complication of cardiovascular disease is highest.
Owner:HANALL PHARMA CO LTD
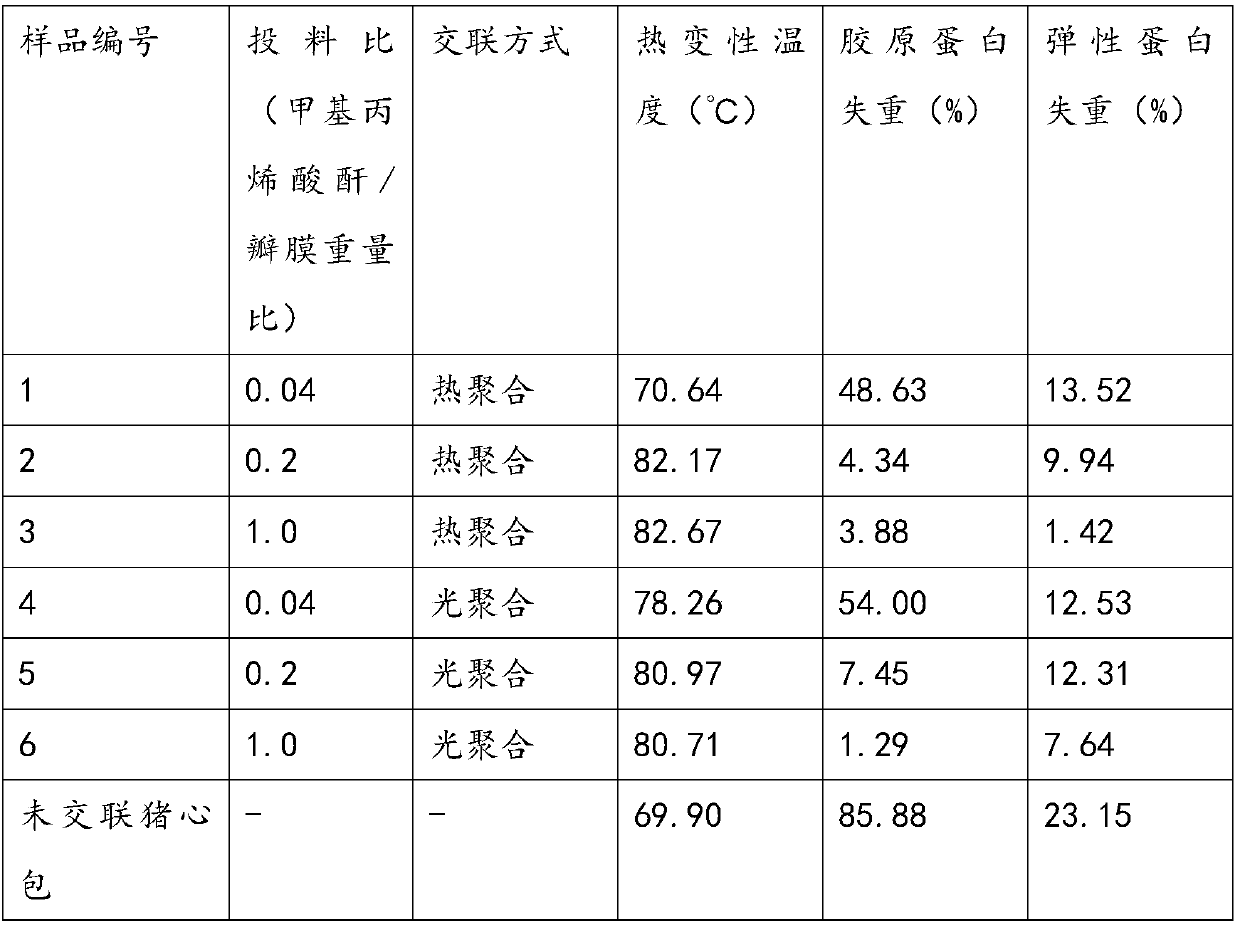
Resist calcification modified method of heterogeneity biological organization material
InactiveCN101161293AReduce degradationImprove anti-calcification propertiesProsthesisFiberTissue material
The present invention discloses a method of calcification-resisting modifying for the heterologous biology tissue material, in the method the tannic acid solution is used to immerse the tissue; the concentration of the tannic acid is between 1 and 6%, the pH value of the solution is between 4.0 and 6.0, the immersing temperature is between 18 and 32 DEG C, and the immersing time is between 24 and 96 hour. The method of the invention can simultaneously crosslink the collagen fiber, the elastic fiber and glycosaminoglycan in the cell epimatrix of the tissue material, reduce the degradation when the tissue is implanted to the body, compensate the insufficiency that the pentanedial only crosslinks the collagen fiber and remarkably increase the calcification-resisting capability of the material; has the effect of antibacterial and reducing the protein antigenicity, and helps to increase the calcification-resisting capability and bioavailability of the material. The intercrossed tissue material has the advantages of good biostability, reinforced biomechanical property and long service lifetime.
Owner:胡盛寿 +2
Antioxidant polymer nanocarriers for use in preventing oxidative injury
The present invention is a method for encapsulating active protein in a polymeric nanocarrier. The instant method employs homogenization at subzero temperatures so that enzyme activity is retained. Enzymes which can be encapsulated by the present method include, for example, antioxidant enzymes and xenobiotic detoxifying enzymes. Encapsulation of an enzyme protects it from protease degradation and increases therapeutic half-life. Advantageously, polymeric nanoparticles of the invention are permeable to enzyme substrates and therefore enzymes encapsulated by the instant method can exert their effect without release from the nanocarrier. Methods for decomposing a reactive oxygen species, protecting against vascular oxidative stress, and detoxifying a xenobiotic are also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Crosslinked bioprosthesis valve processing method
PendingCN109820625AImprove mechanical propertiesGood blood compatibilityHeart valvesCytotoxicityCalcification
The invention discloses a biovalve crosslinking method. The method includes introducing an unsaturated group to heterogeneous biological tissues such as porcine active valves, pig pericardia and bovine pericardia into through active groups on the biological tissues such as a carboxyl group, a hydroxyl group, an amino group and a sulfhydryl group reacting with an unsaturated group-containing compound to obtain an unsaturated group-modified biological tissue, and then obtaining a crosslinked biological tissue by radical polymerization. The biological tissue obtained by the crosslinking method has excellent collagen and elastin stability, blood compatibility, no cytotoxicity, good mechanical properties, anti-calcification capability and low inflammatory response.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
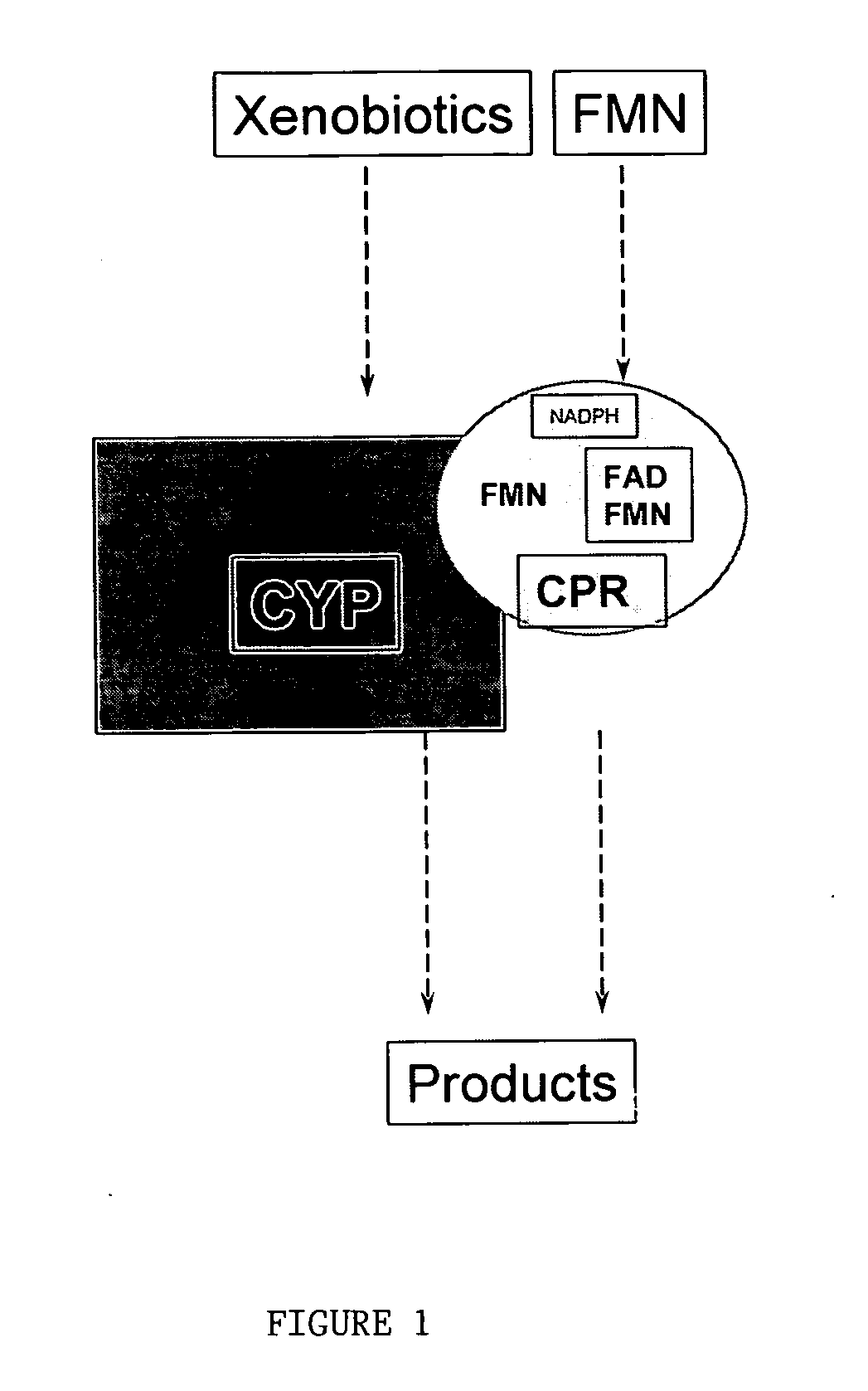
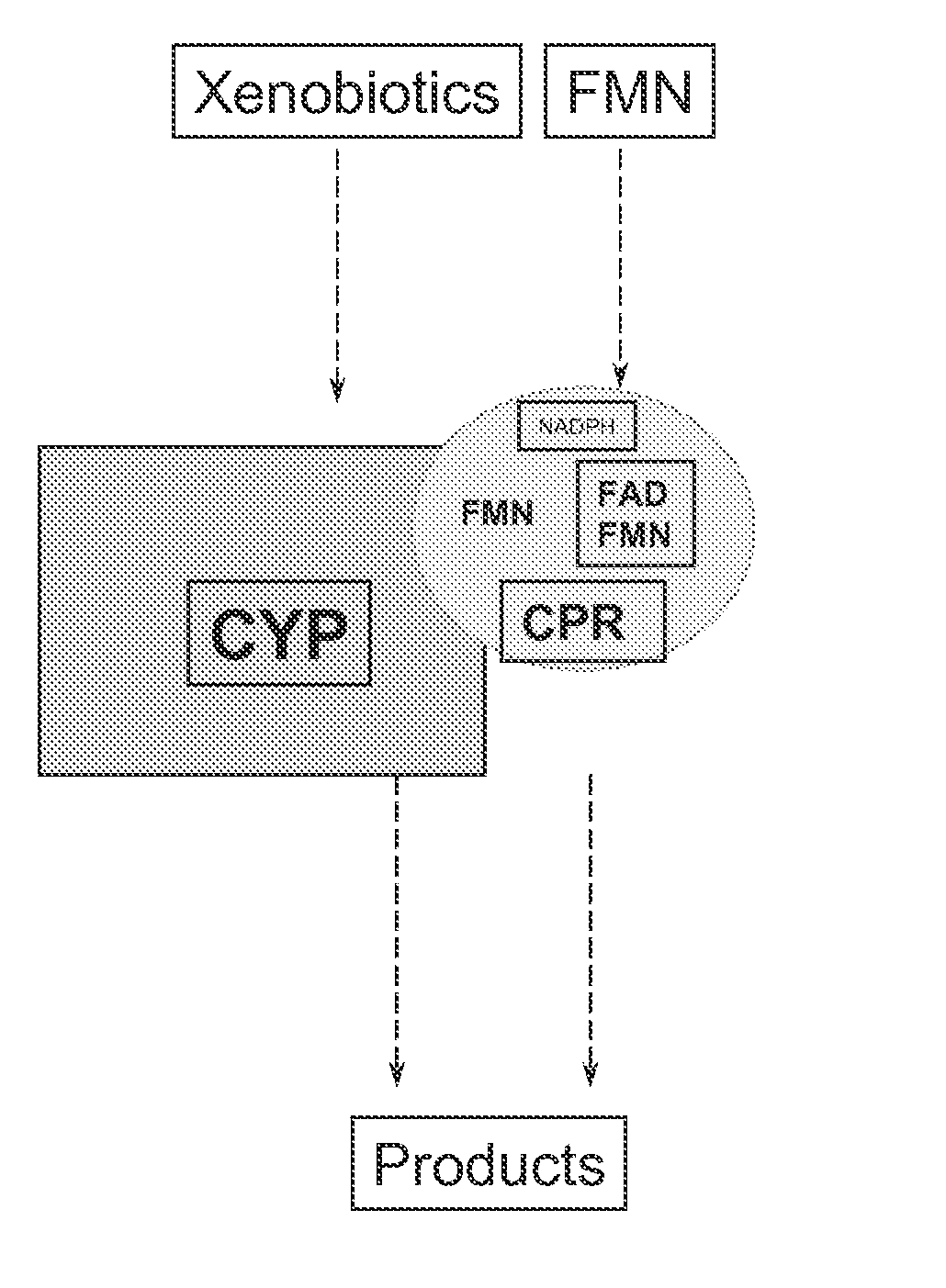
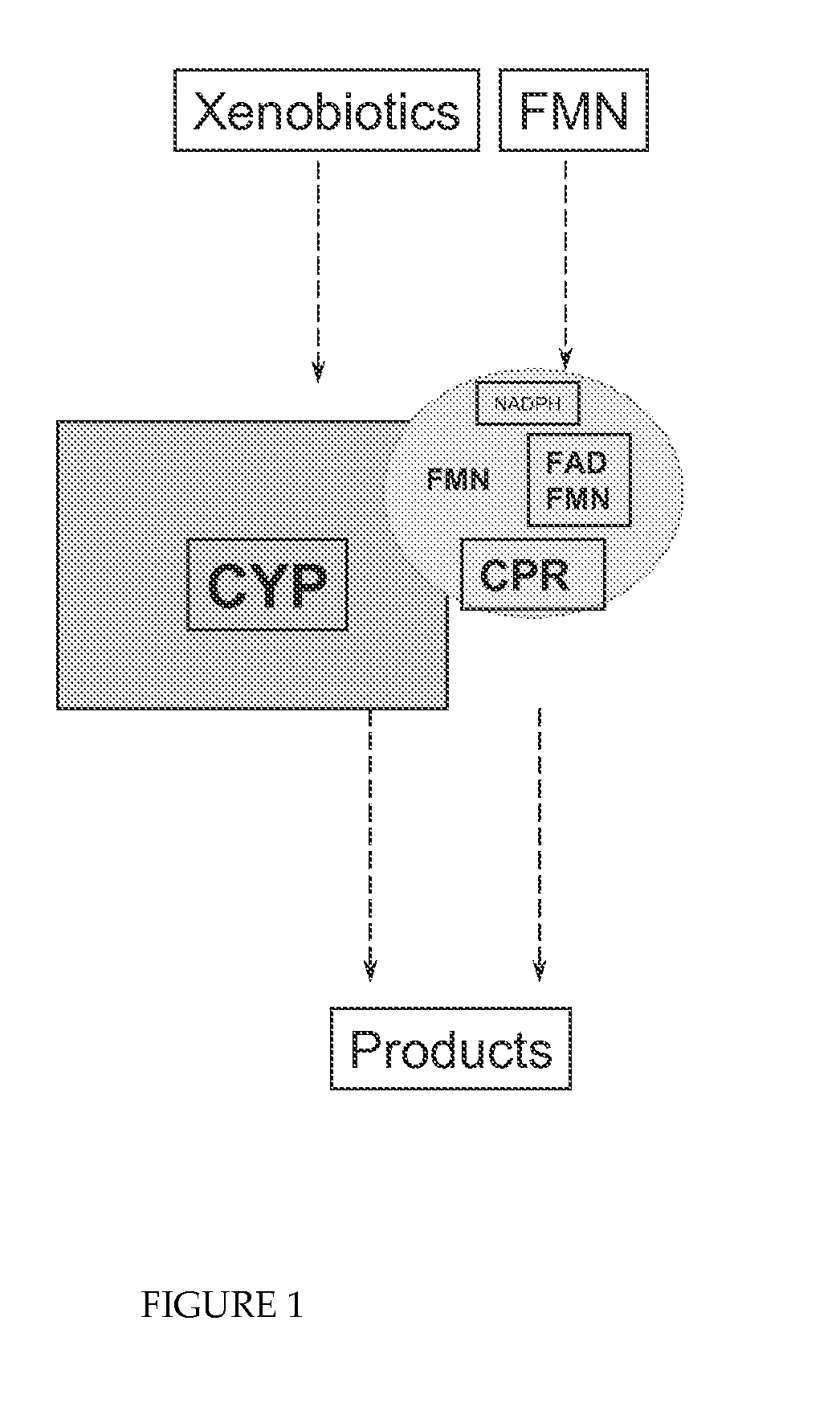
Cytochrome P450 enzyme complexes and methods of treatment using the same
InactiveUS20060140927A1Increase nutritionIncreases amount of complexOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineCytochrome p450 enzyme
The present invention provides methods and compositions for balancing electron reduction potentials of formulations in a manner that reduces susceptibility to changes from xenobiotics. The present invention also provides novel compositions of matter based on structuring from a mobile nucleotide integral to its architecture.
Owner:NONOMURA ARTHUR M
Combined preparation for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases based on chronotherapy theory
InactiveCN101528203ASignificant blood pressure lowering effectExcellent suppression of side effectsOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliverySide effectCo administration
The present invention relates to a functional combination preparation comprising a dihydropyridine-based calcium channel blocker such as amlodipine and an ARB (Angiotensin-2 receptor blocker) such as losartan. In particular, the present invention relates to a chronotherapeutical combination pharmaceutical formulations with controlled-release for the prevention or treatment of cardiovascular disease, which is formulated in accordance with xenobiotics and chronotherapy for enabling the two drugs to be chronotherapeutically released, thereby improving the therapeutic activity as compared to the co-administration of each drug in the form of a single pill, while reducing side effects and maintaining the therapeutic activity as high as possible at the time of day when the risk of a complication of cardiovascular disease is highest.
Owner:韩诺生物制约株式会社
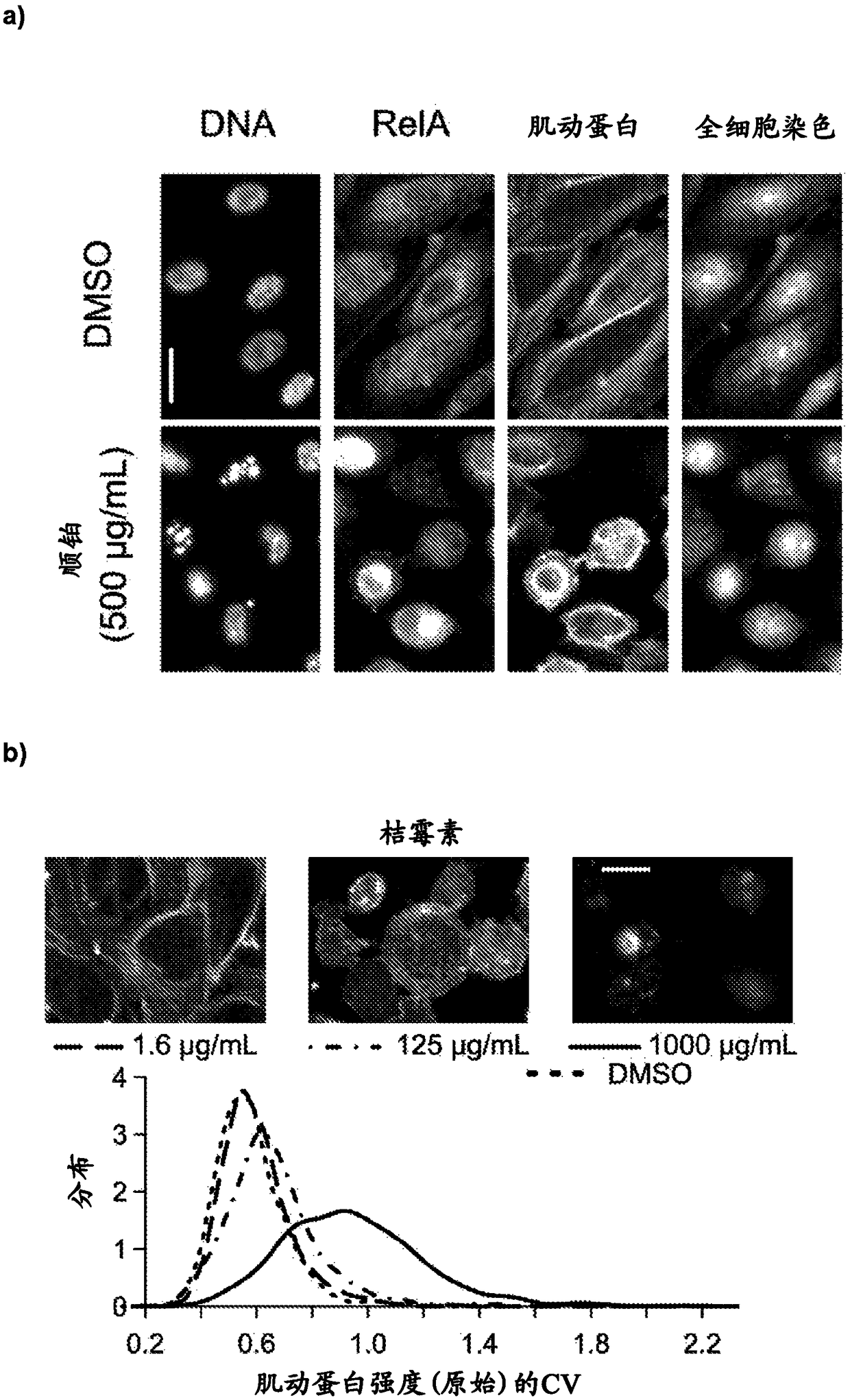
High-throughput imaging-based methods for predicting cell-type-specific toxicity of xenobiotics with diverse chemical structures
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
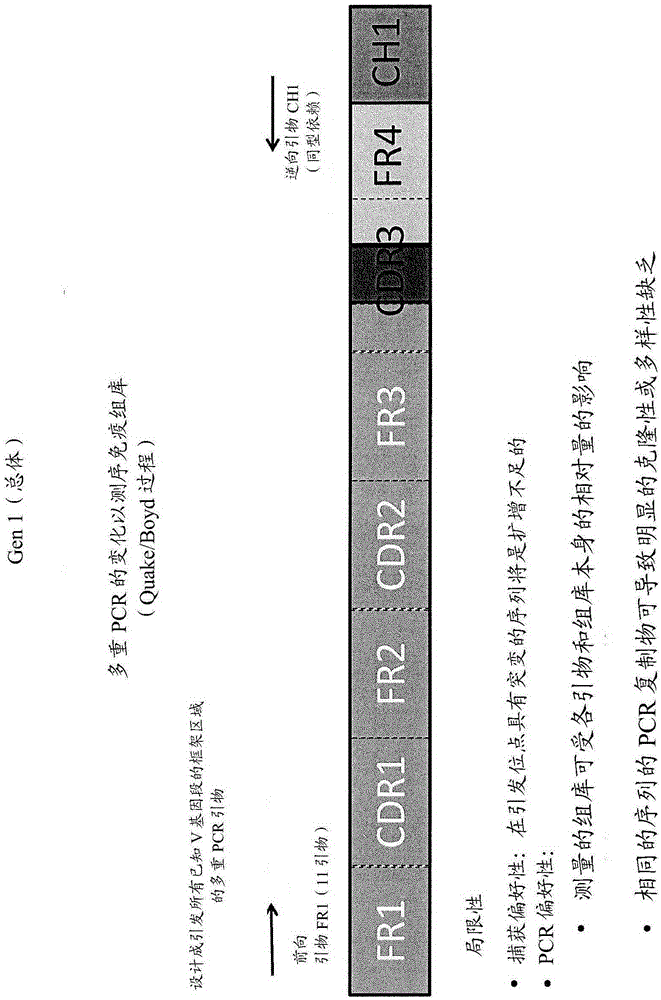
Methods of sequencing the immune repertoire
ActiveCN105189748ASequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementNon invasiveImmune repertoire
The invention provides a non-invasive technique for the detection and quantification of the immune repertoire, in a biological sample containing a plurality of distinct cell populations. Methods are conducted using sequencing technology to detect and enumerate immune repertoire within a heterogeneous biological sample.
Owner:LINEAGE BIOSCI
Methods for Detection of Promoter Polymorphism in UGT Gene Promoter
InactiveUS20070092902A1HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementPromoter polymorphismGene expression
The present invention is directed to methods for detecting the presence of genetic polymorphisms that correlate with altered gene expression. More specifically, the present invention is directed to methods for detecting the genetic polymorphisms located in the UGT1A1 promoter. The invention also provides methods for optimizing drug dosages based upon the presence of the polymorphisms. The invention further provides methods of predicting sensitivity to xenobiotics and diagnostic kits for detecting genetic polymorphisms.
Owner:DI RIENZO ANNA +2
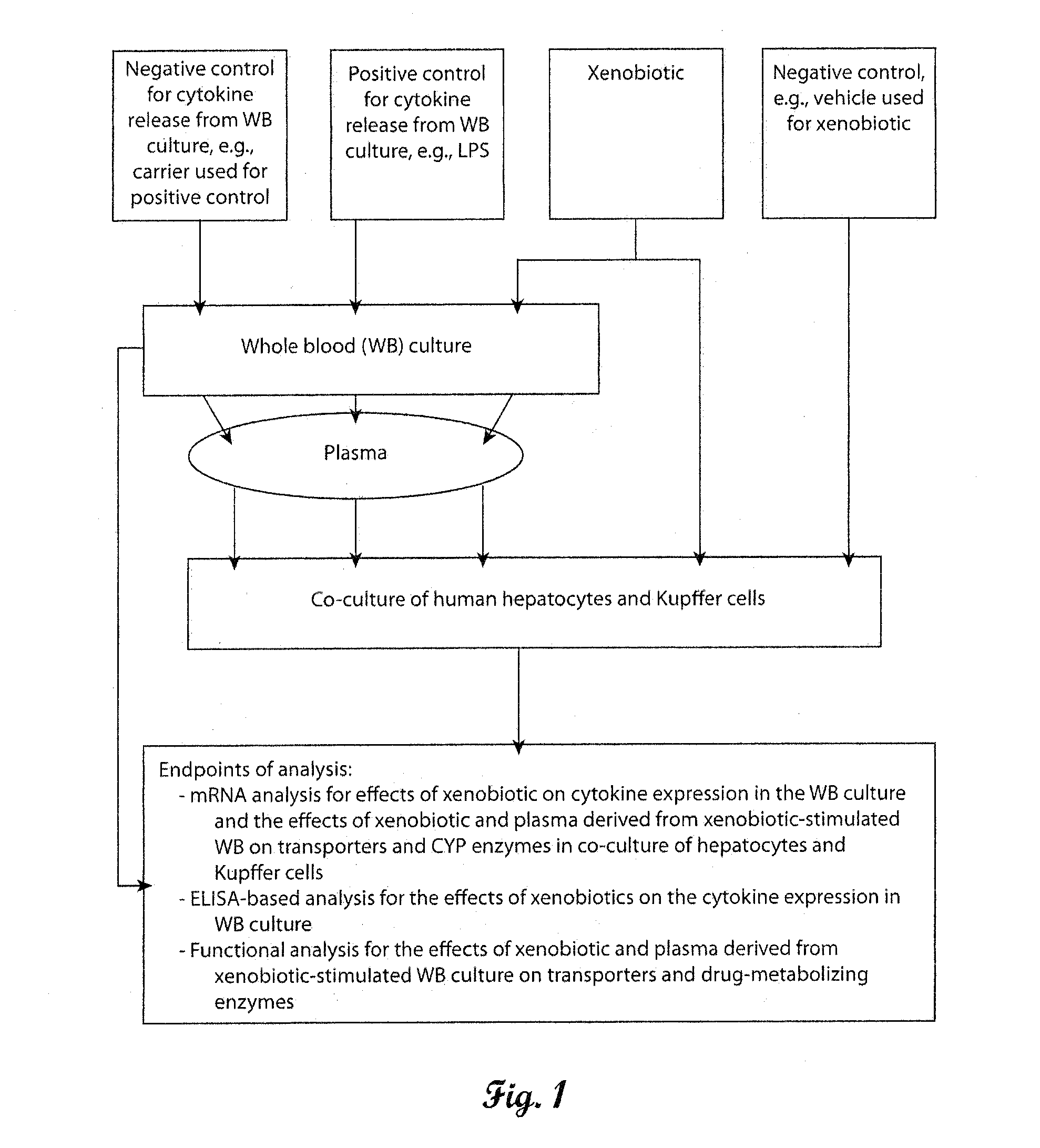
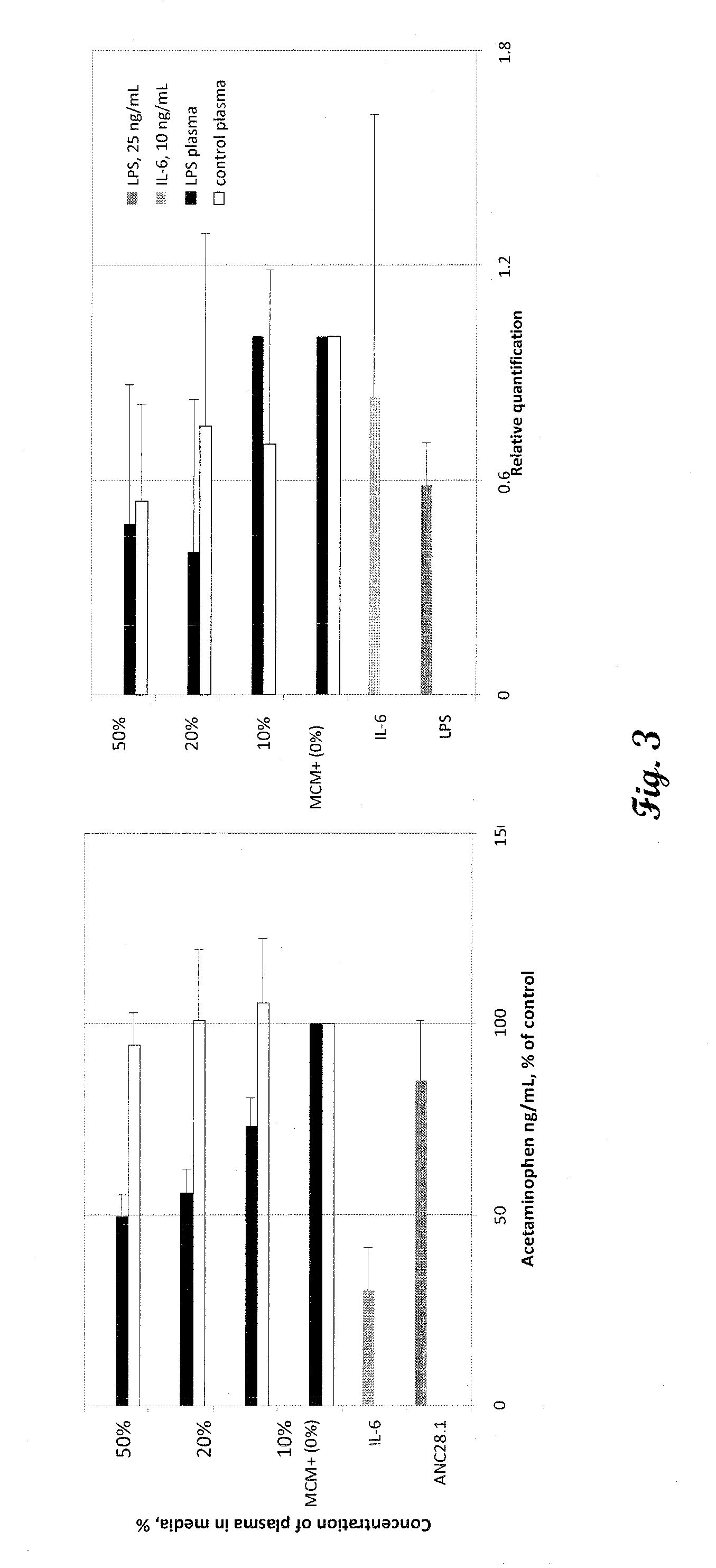
In vitro test system to evaluate xenobiotics as immune-modulators of drug transport and metabolism in human hepatocytes
A method of evaluating the effect of a xenobiotic on biomarkers, such as drug transporters and drug-metabolizing enzymes in hepatocytes is provided. The method comprises the formation of a xenobiotic-stimulated biological sample, such as whole blood, which contains a plurality of cytokines. A portion of xenobiotic-stimulated biological sample is cultured with hepatocytes. The hepatocytes are then analyzed to evaluate the activity of drug transporters and / or drug-metabolizing enzymes, or other biomarkers to determine the effect of the xenobiotic on drug metabolism in the hepatocytes.
Owner:XENOTECH CALIFORNIA
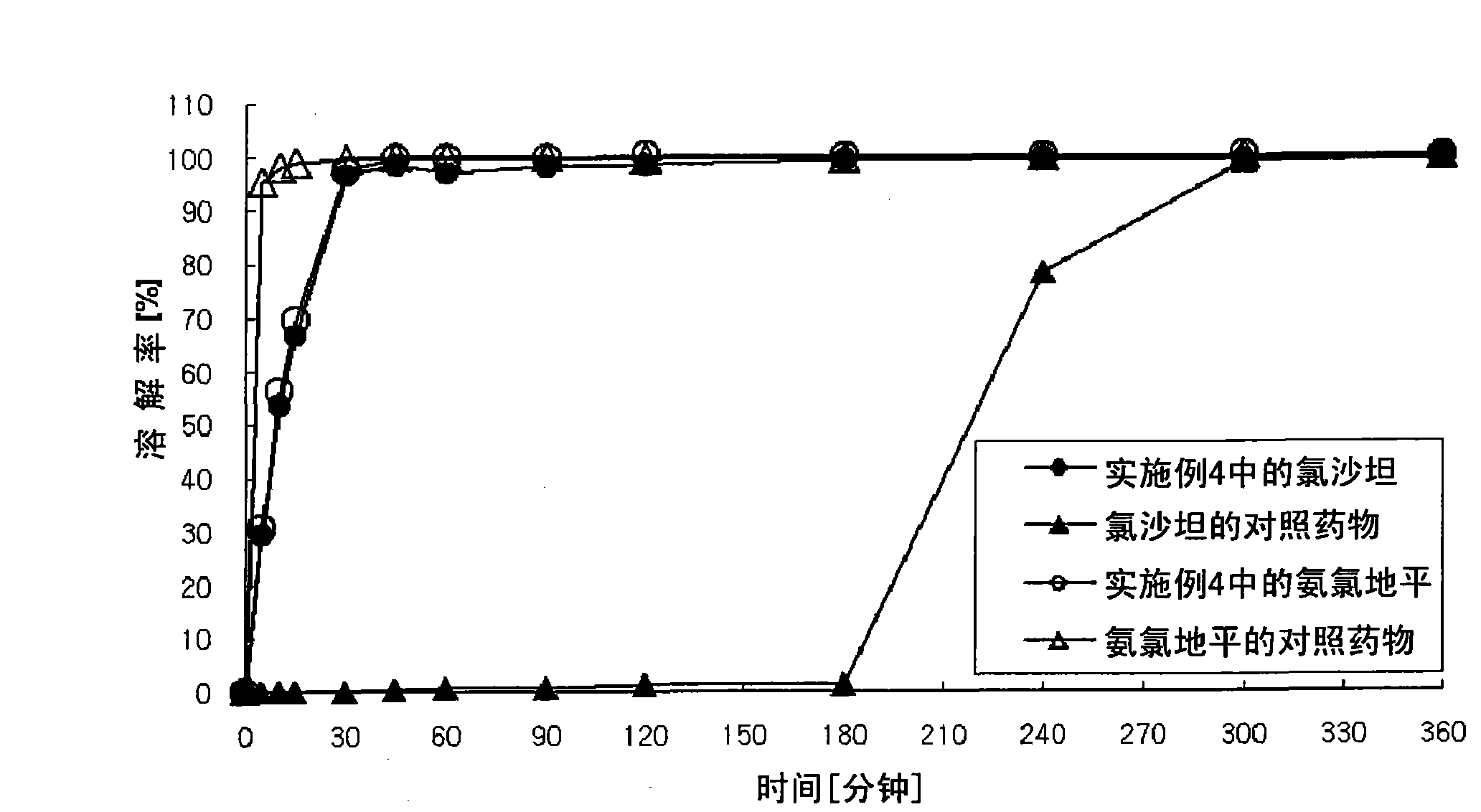
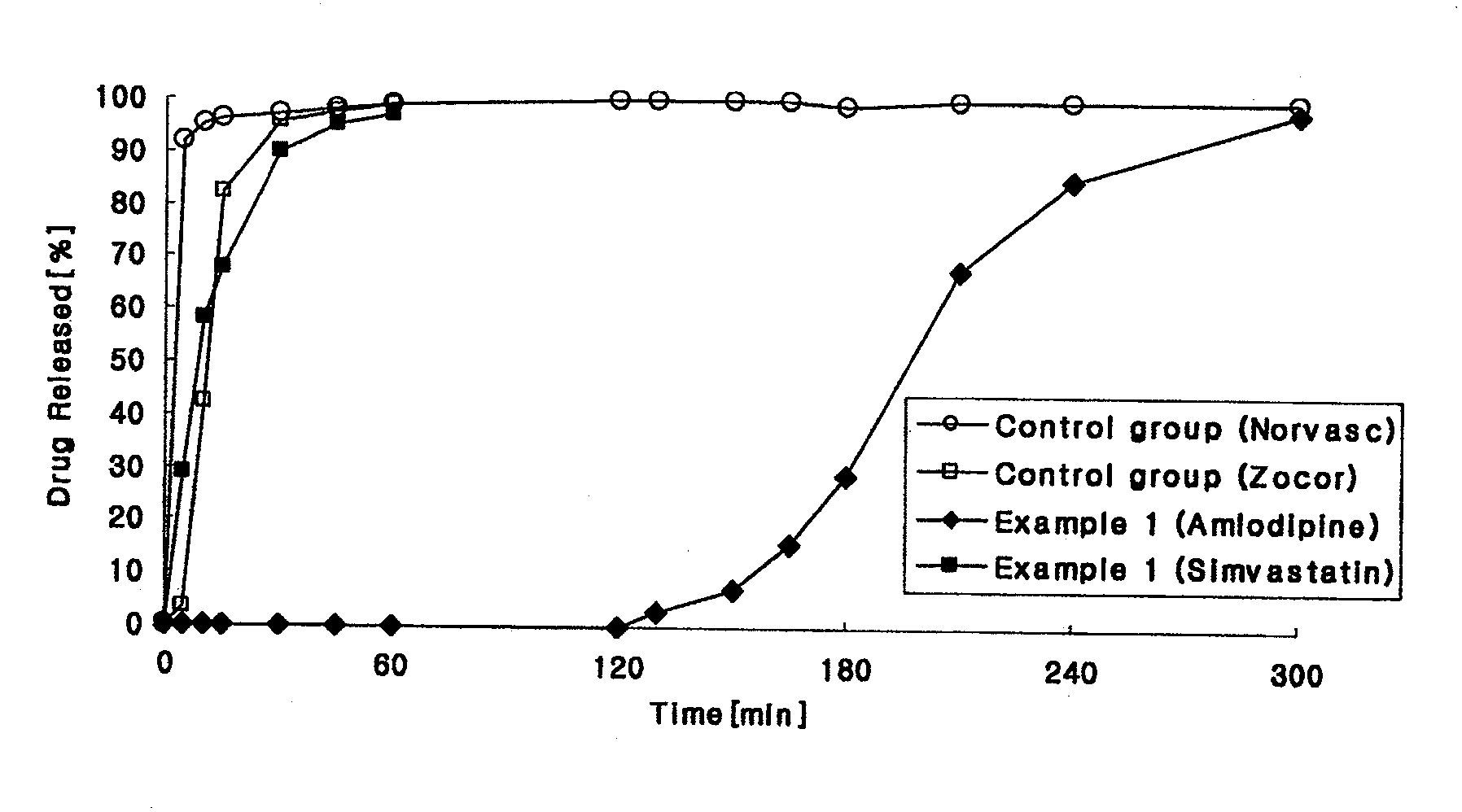
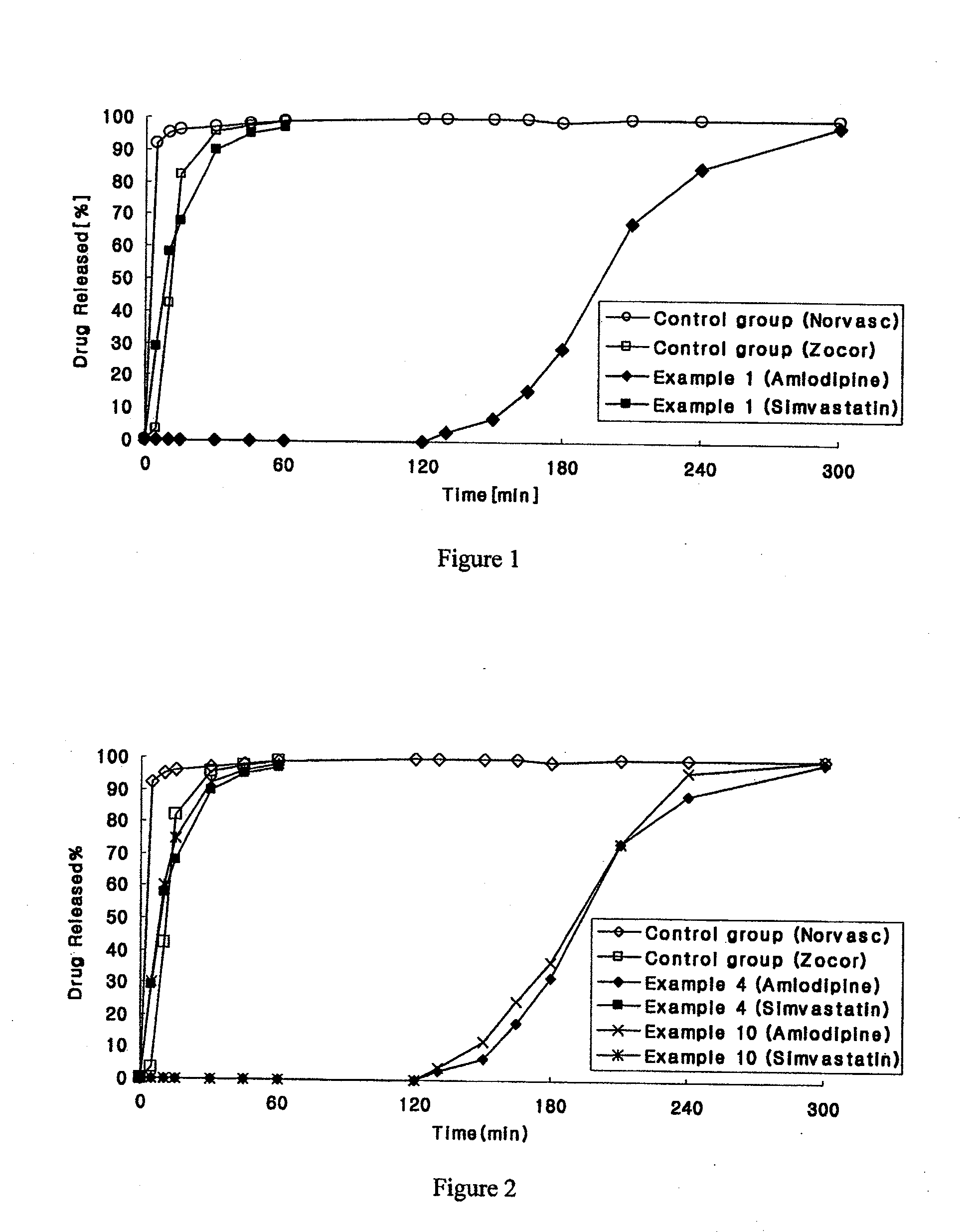
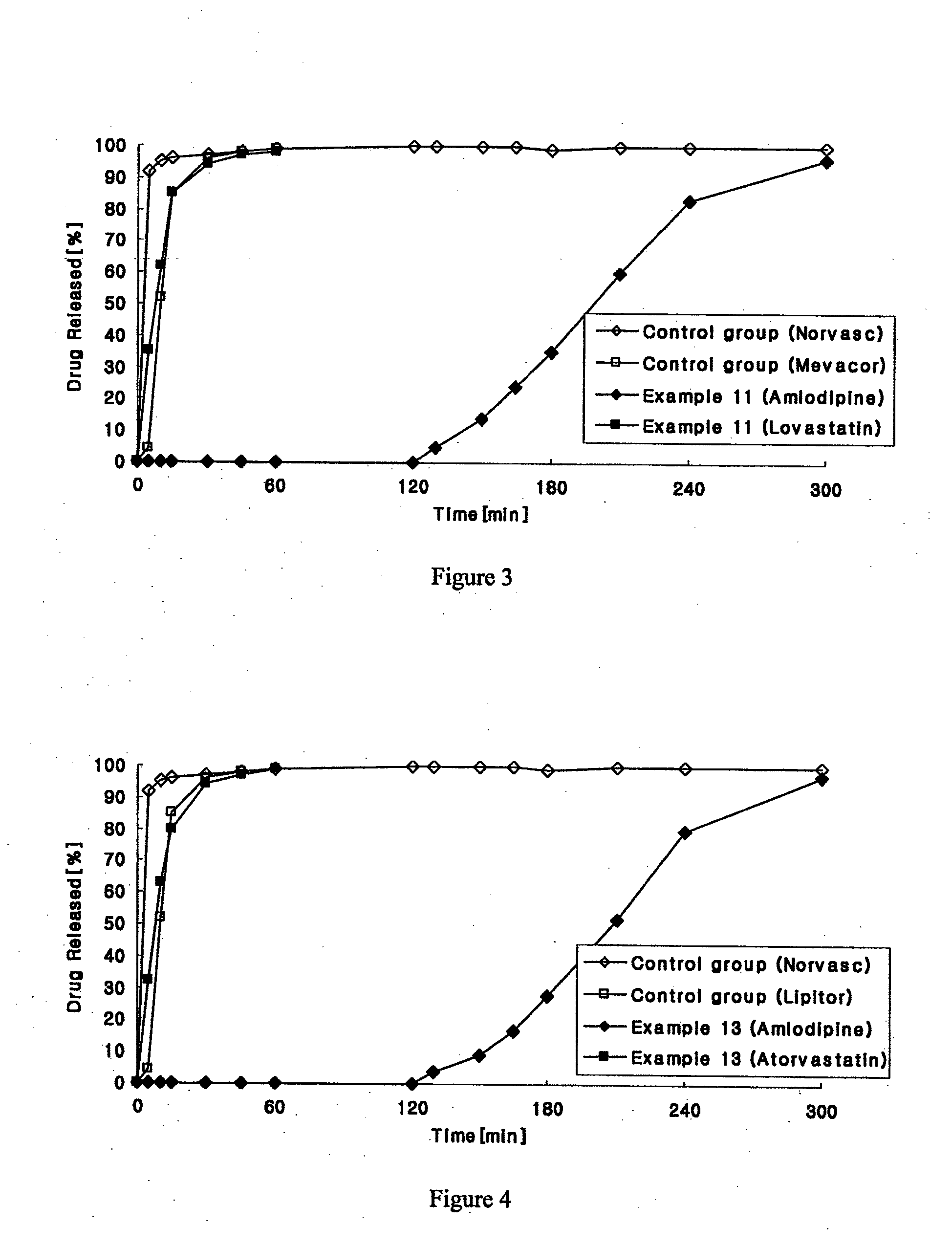
Combined pharmaceutical formulation with controlled-release comprising dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers and hmg-coa reductase inhibitors
The present invention relates to a chronotherapeutic combination pharmaceutical formulation, which is designed to control the release of each ingredient of the combined drug in a predetermined rate based on the principle of the so-called chronotherapy and xenobiotics, where drugs are administered to exhibit pharmacological activities at predetermined time intervals. The formulations of the present invention comprise a dihydropyridine, and a statin, as active ingredients. The formulations are structured and arranged such that the respective release rates of the above ingredients can be controlled, thereby reducing or preventing antagonistic effects and side effects resulting from the interaction of the above ingredients, while maintaining the synergistic effect, and providing easy medication.
Owner:HANALL PHARMA CO LTD
Antioxidant polymer nanocarriers for use in preventing oxidative injury
The present invention is a method for encapsulating active protein in a polymeric nanocarrier. The instant method employs homogenization at subzero temperatures so that enzyme activity is retained. Enzymes which can be encapsulated by the present method include, for example, antioxidant enzymes and xenobiotic detoxifying enzymes. Encapsulation of an enzyme protects it from protease degradation and increases therapeutic half-life. Advantageously, polymeric nanoparticles of the invention are permeable to enzyme substrates and therefore enzymes encapsulated by the instant method can exert their effect without release from the nanocarrier. Methods for decomposing a reactive oxygen species, protecting against vascular oxidative stress, and detoxifying a xenobiotic are also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Transgenic mice expressing a human SXR receptor polypeptide
A novel nuclear receptor, termed the steroid and xenobiotic receptor (SXR), a broad-specificity sensing receptor that is a novel branch of the nuclear receptor superfamily, has been discovered. SXR forms a heterodimer with RXR that can bind to and induce transcription from response elements present in steroid-inducible cytochrome P450 genes in response to hundreds of natural and synthetic compounds with biological activity, including therapeutic steroids as well as dietary steroids and lipids. Instead of hundreds of receptors, one for each inducing compound, the invention SXR receptors monitor aggregate levels of inducers to trigger production of metabolizing enzymes in a coordinated metabolic pathway. Agonists and antagonists of SXR are administered to subjects to achieve a variety of therapeutic goals dependent upon modulating metabolism of one or more endogenous steroids or xenobiotics to establish homeostasis. An assay is provided for identifying steroid drugs that are likely to cause drug interaction if administered to a subject in therapeutic amounts. Transgenic animals are also provided which express human SXR, thereby serving as useful models for human response to various agents which potentially impact P450-dependent metabolic processes.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Method to increase the yield of products in plant material
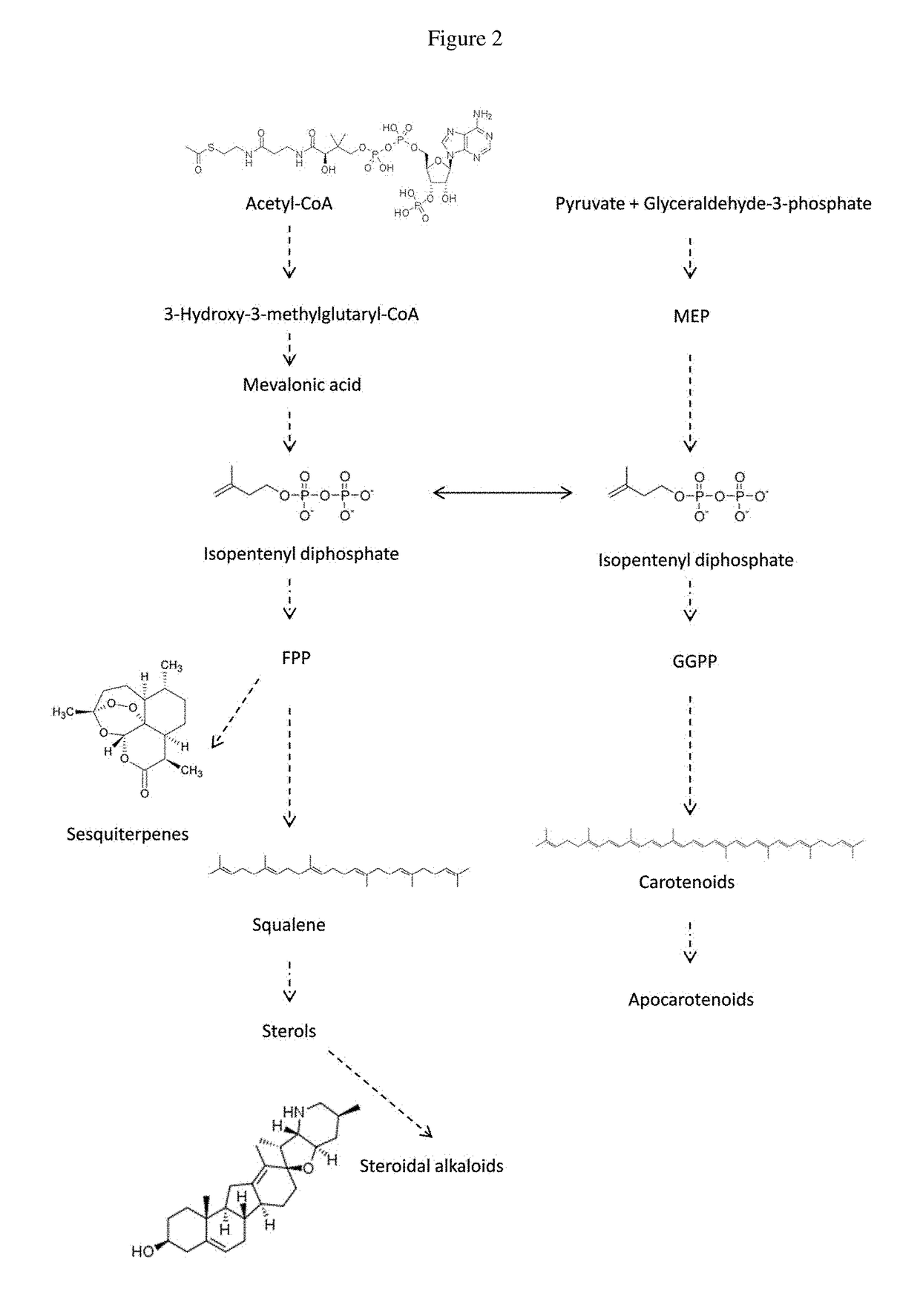
ActiveUS10144913B1Increase productionImprove efficiencyComponent separationCell culture mediaTrappingElicitor
A method or process to increase the production of products of interest in plant material including plant cultures, such as, for example, cell suspension cultures, root cultures, and hairy root cultures is provided. In one embodiment, the method is to contacting the plant material with a precursor or xenobiotic when producing a product of interest from a plant. In another embodiment the plant material is also contacted with a trapping agent. The process may also provide for contacting an elicitor of the product of interest with the plant material. An embodiment provides for contacting an elicitor, precursor and trapping agent with the plant material. The ability to produce novel compounds such as glucosides and glucuronides is provided.
Owner:ARKANSAS STATE UNIVERSITY
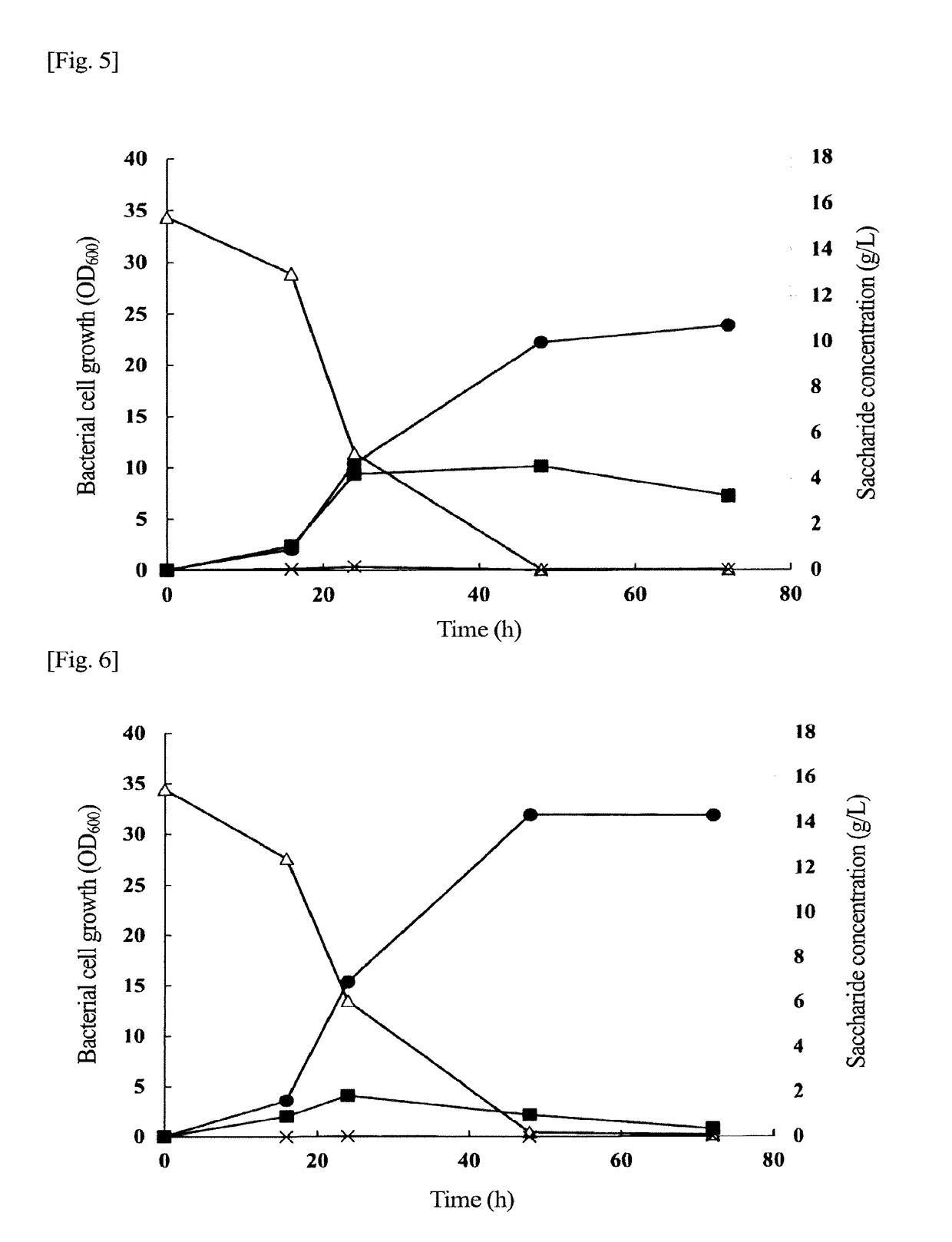
Pha-producing microorganism having sucrose assimilability, and method for producing pha using said microorganism
An object of the present invention is to provide a PHA-producing microorganism which can assimilate sucrose, and a method for producing a PHA by culturing this microorganism, using sucrose as a carbon source. A PHA-producing microorganism, comprising a PHA synthase gene, and heterogeneous-organism-derived genes in the following items (1) and (2): (1) a sucrose hydrolase gene encoding an amino acid sequence described in SEQ ID NO: 1, or a gene encoding a polypeptide which has a sequence homology of 90% or more to the amino acid sequence and which has sucrose hydrolase activity; and (2) a sucrose permease gene encoding an amino acid sequence described in SEQ ID NO: 2, or a gene encoding a polypeptide which has a sequence homology of 90% or more to the amino acid sequence and which has sucrose permease activity. The invention is also a method for producing a PHA, including the step of culturing this microorganism in a medium including sucrose as a carbon source.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Cytochrome P450 enzyme complexes and methods of treatment using the same
InactiveUS20100129890A1Enhance PImprove the quality of lifeOrganic active ingredientsEnzyme stabilisationMedicineCytochrome p450 enzyme
Owner:NONOMURA ARTHUR M
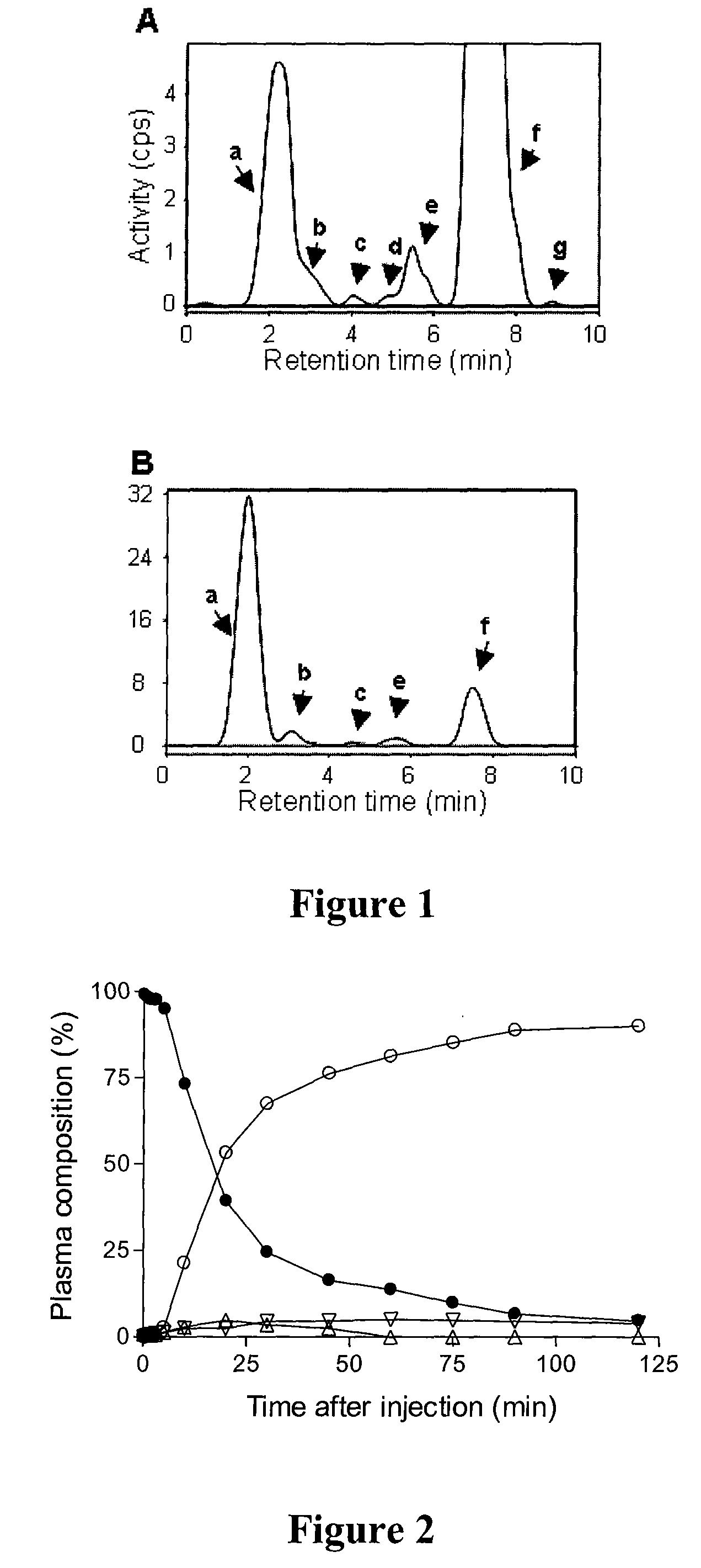
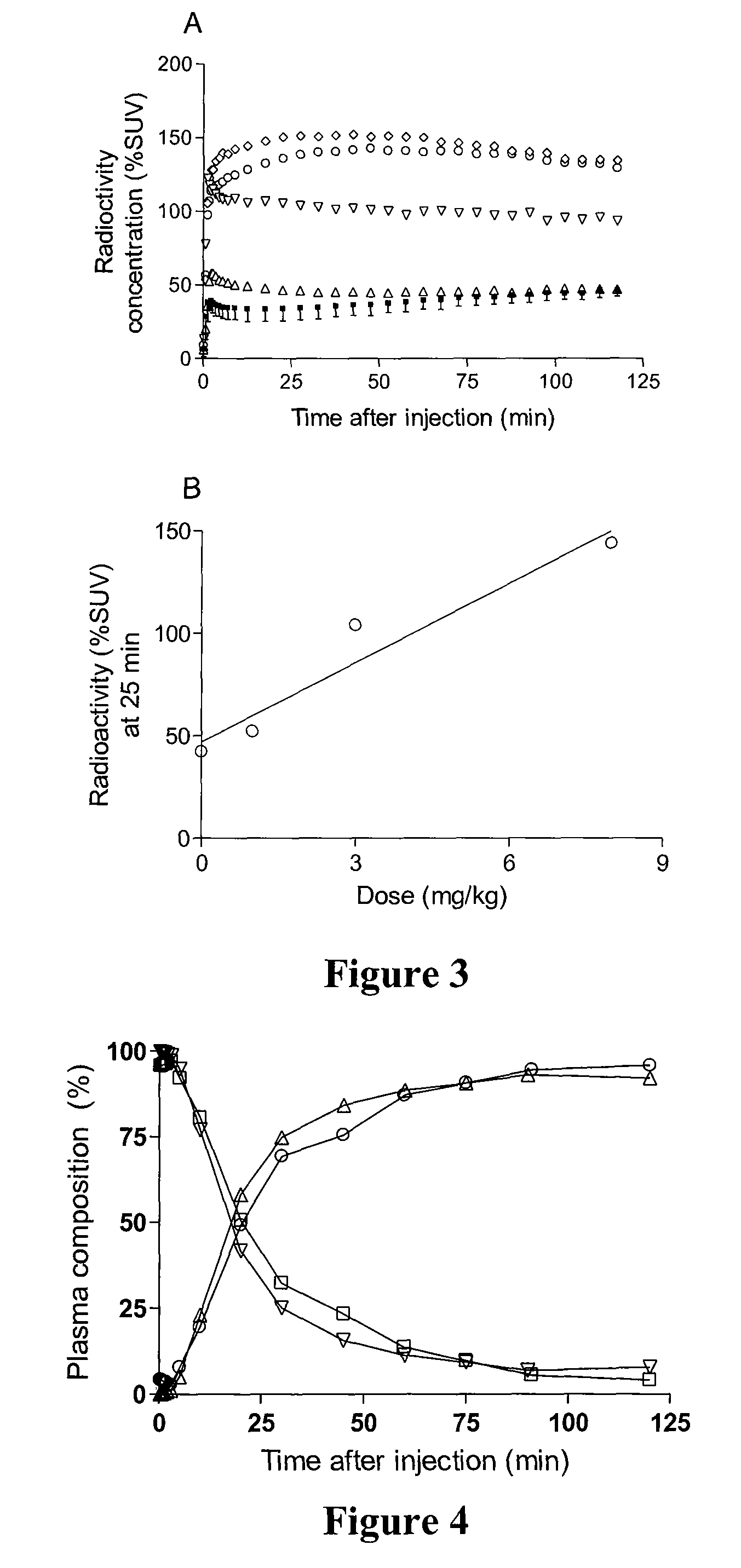
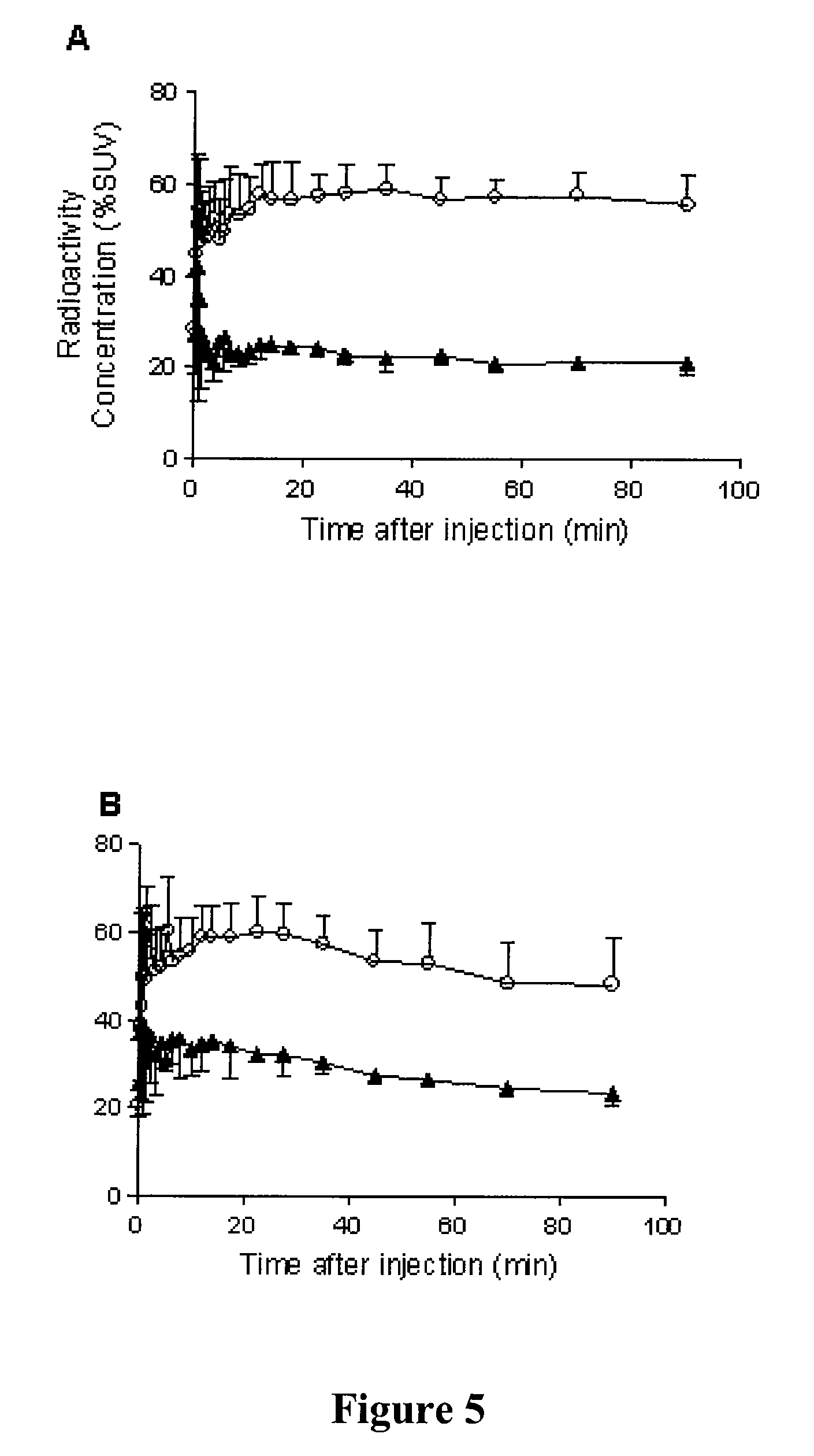
Radiotracers for imaging P-glycoprotein function
InactiveUS7989630B2BiocideIn-vivo radioactive preparationsRadioactive tracerP-Glycoprotein Transporter
P-glycoprotein transporter (P-gp) acts as a pump at the blood-brain barrier to exclude a wide range of xenobiotics (e.g., toxins, drugs, etc.) from the brain and is also expressed in a tumor in response to exposure to established or prospective chemotherapeutics (a phenomenon known as multidrug resistance). This invention concerns the preparation and use of radiotracers for imaging P-gp function in vitro and in vivo. Radiotracers of the present invention are avid substrates for P-gp and have structures based on N-Desmethyl-loperamide.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
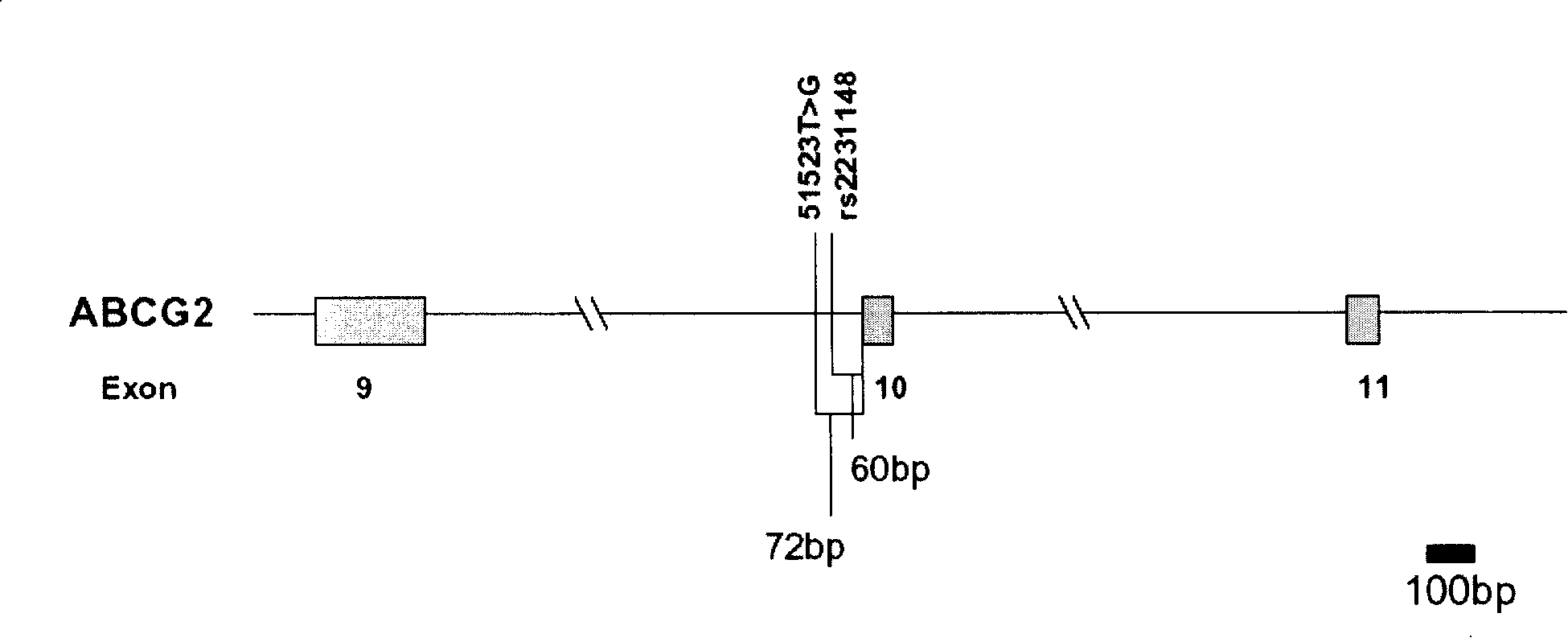
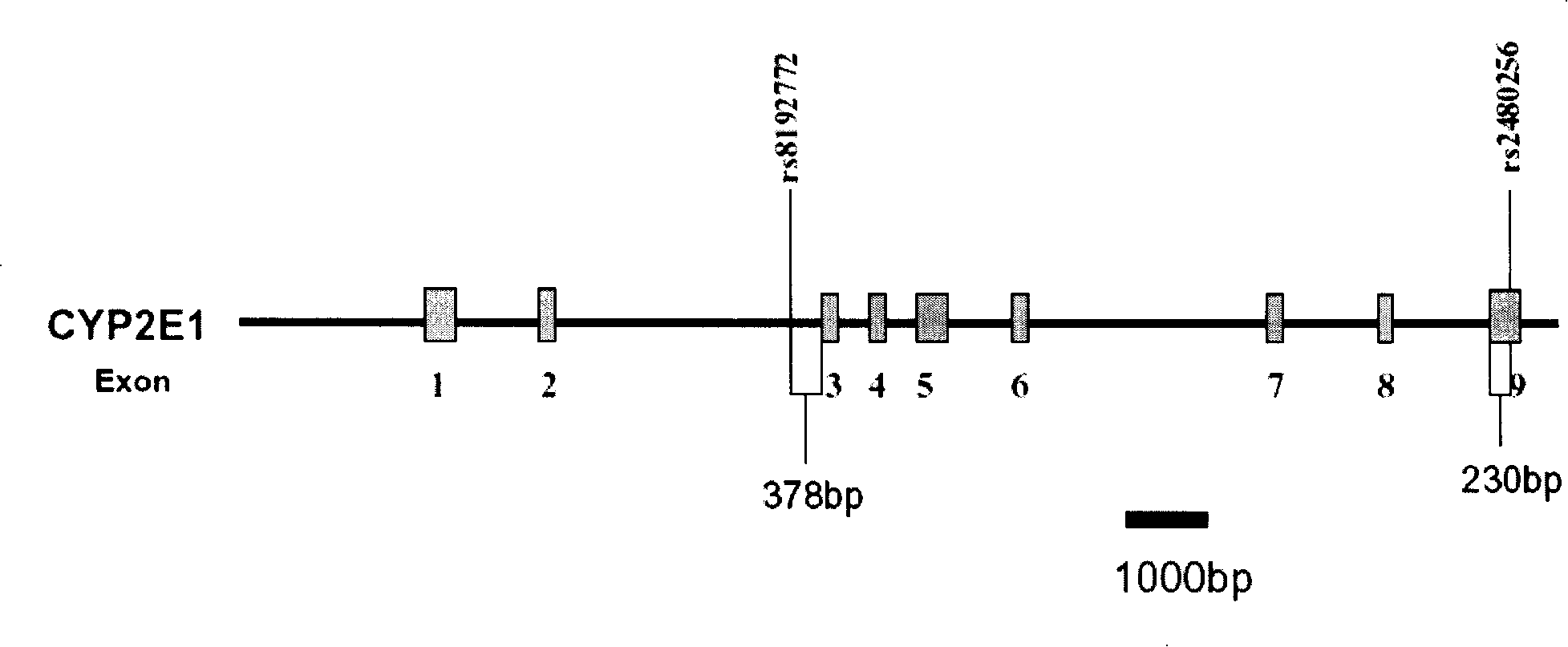
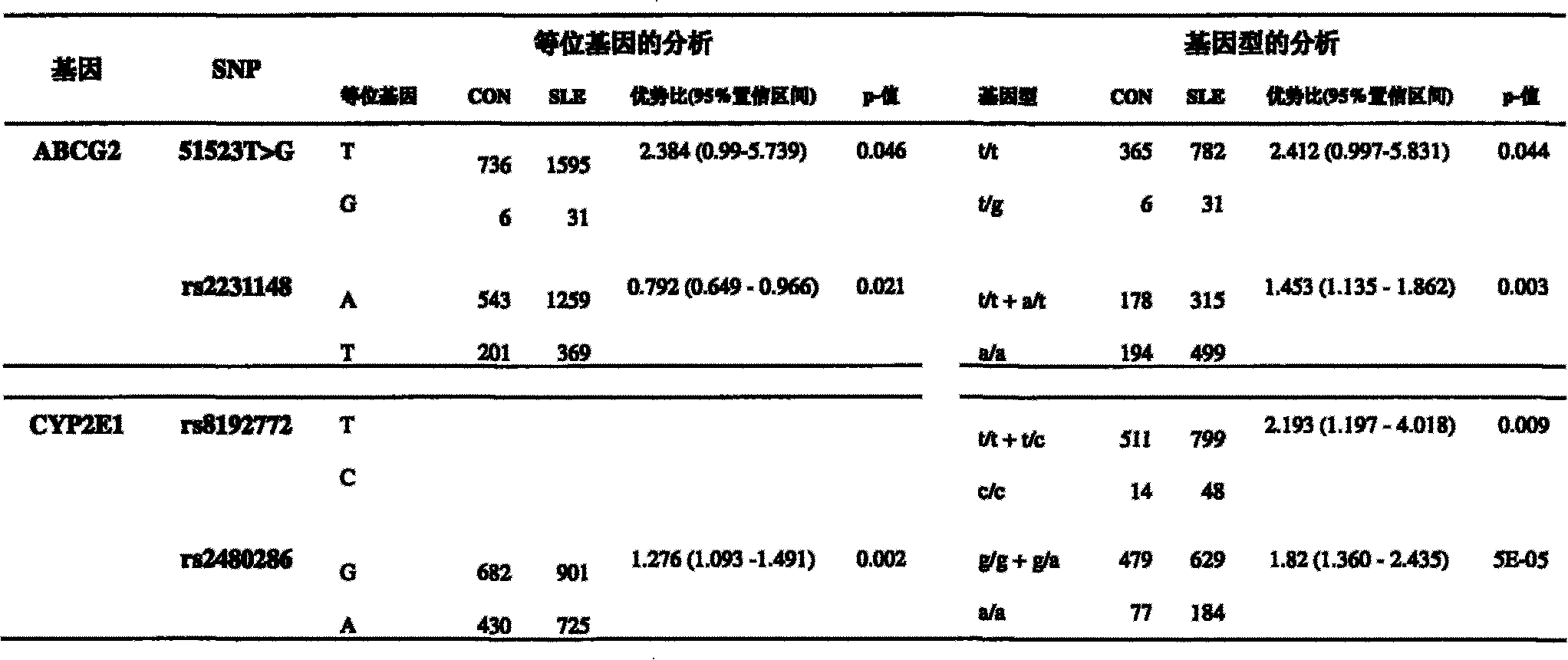
Use of human heterogeneous substance metabolic enzymes gene mononucleotide polymorphism in diagnosing and treating systemic lupus erythematosus
The invention relates to a detection of four sites of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) which are arranged on two human body xenobiotics metabolismenzyme genes including ABCG2 and CYP2E1 and which are associated with the systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The invention also can use four sites of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) to forecast the liability of systemic lupus erythematosus and to determine the drug to cure the systemic lupus erythematosus. The information provided by the invention is helpful for preventing systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and for developing effective new treatments.
Owner:廖凌虹 +2
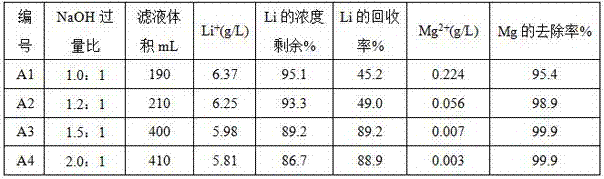
Method of simply, easily and efficiently lowering content of magnesium in salt lake brine
ActiveCN107344724AReduce shipping costsReduce lossLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesMagnesium hydroxideSalt lakeLithium carbonate
The invention discloses a method of simply, easily and efficiently lowering the content of magnesium in salt lake brine. The method comprises the following steps of adding excessive water-soluble hydroxide in the salt lake brine, and uniformly stirring, wherein the molar weight of introduced hydroxy radicals is at least 1.5 times of theoretical amount for completely precipitating Mg<2+>; standing for precipitation, and carrying out solid-liquid separation, wherein a filtrate is brine with low magnesium content. The method provided by the invention is simple in treatment technology and convenient to operate and can be implemented in the salt lake field, so that the transportation cost is greatly lowered. By adopting the method, excessive xenobiotics cannot be introduced in a salt lake region, and magnesium hydroxide as a by-product is also a resource with a great value and is environment-friendly; and the magnesium removal efficiency is high, the lithium loss is low, the filtrate after solid-liquid separation can be directly used for preparing lithium carbonate and is particularly suitable for batch magnesium-lithium separation of plateau salt lakes in a large scale.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RUISHI TIANQI ENERGY TECH
Agents for treatment of diabetic retinopathy and drusen formation in macular degeneration
InactiveUS20100204244A1Enhances availability and transportAvoid damageBiocideSenses disorderThiocarbamateQuinone
Agents that stimulate nuclear translocation of Nrf2 protein and the subsequent increases in gene products that detoxify and eliminate cytotoxic metabolites are provided in a method for treating diabetic retinopathy or drusen formation in age-related macular degeneration. The structurally diverse agents that act on the Nrf2 / ARE pathway induce the expression of enzymes and proteins that possess chemically versatile cytoprotective properties and are a defense against toxic metabolites and xenobiotics. Agents include certain electrophiles and oxidants such as a Michael Addition acceptor, diphenol, thiocarbamate, quinone, 1,2-dithiole-3-thione, butylated hydroxyanisole, flavonoid other than genistein, an isothiocyanate, 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxytoluene, ethoxyquin, a coumarin, combinations thereof, or a pharmacologically active derivative or analog thereof.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Application of GAD67 and epigenetic mark thereof which serve as early marker of fetal-original bipolar affective disorder susceptibility
ActiveCN108192967AQuick collectionQuick storageMicrobiological testing/measurementWhite blood cellEpigenetic Profile
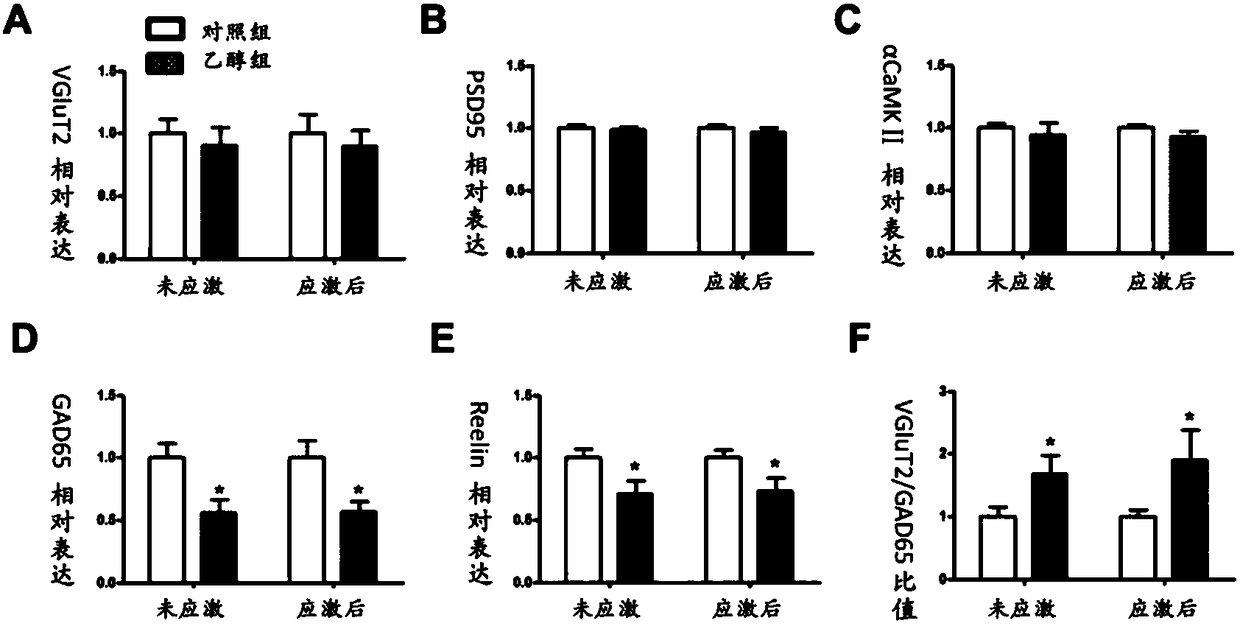
The invention discloses application of GAD67 and an epigenetic mark thereof which serve as early markers of fetal-original bipolar affective disorder susceptibility, and belongs to the field of gene functions and application. Research results show that in hippocampi and white blood cells of fetal rats in a pregnancy ethanol exposure group, compared with a normal control group, the methylation level of a GAD67 promoter region is significantly reduced, and the gene expression of the GAD67 promoter region is improved; after growing up, the rats in the xenobiotic exposure group show high hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis stress sensibility and bipolar affective disorder susceptibility under the condition of chronic unpredictable stress. Therefore, risks that offspring have bipolar affective disorder after growing up can be judged by detecting the epigenetic modification and expression levels of the GAD67 genes in the white blood cells of fetal blood / umbilical cord blood. Research bases are provided for an early warning technology of the fetal-original bipolar affective disorder, and meanwhile, possibilities are provided for effectively treating the fetal-original bipolar affective disorder in early stages.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Emulsion of perfluoroorganic compounds for medical purposes, a process for the preparation thereof and methods for treating and preventing diseases with the use thereof
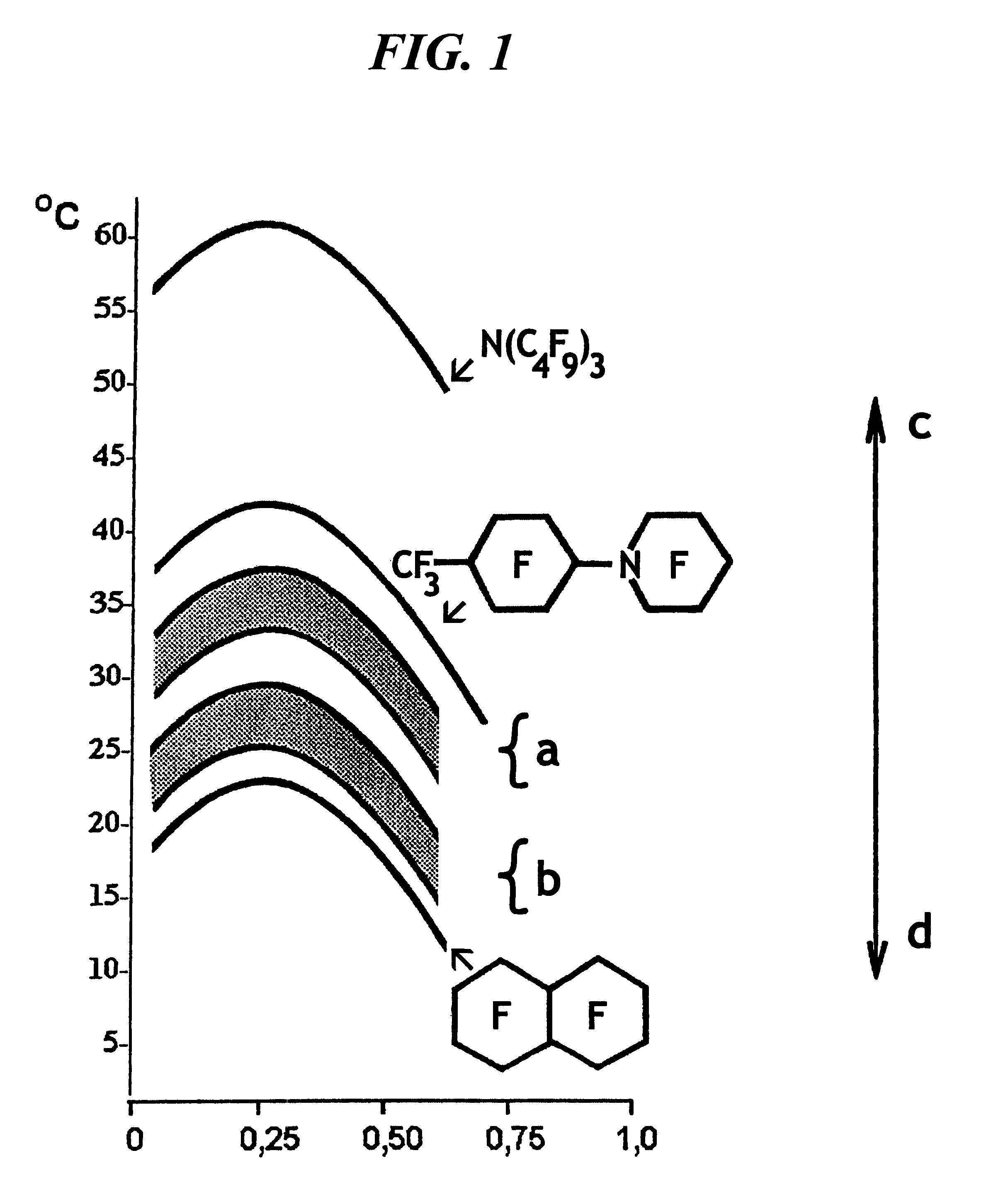
An emulsion of perfluoroorganic compounds (PFOC) comprises a rapidly eliminable perfluorocarbon (PFC) and a slowly eliminable perfluorinated cyclic tertiary amine, perfluoro-N-4-(methylcyclohexyl)-piperidine and additionally comprises not less then three rapidly eliminable and three slowly eliminable PFOC admixtures with the critical temperature of dissolution in hexane (CTDH) close to that of main PFOC. The PFOC emulsion is stabilized with a polyoxyethylene-polyoxypropylene copolymer having low viscosity to provide high dynamic oxygen capacity and enhancing oxygen delivery to tissues. To prepare the emulsion the stabilizing agent is heated up to 75° C., all components are saturated with carbon dioxide gas to minimize the reactogenicity in intravessel injection as a means of compensation for mass blood loses, perfusion of organs cut of blood flow, treating air-and fat embolism, obliterating vascular injuries of extremities and preventing toxic injuries caused by various xenobiotics.
Owner:MASLENNIKOV IGOR ALEXEEVICH
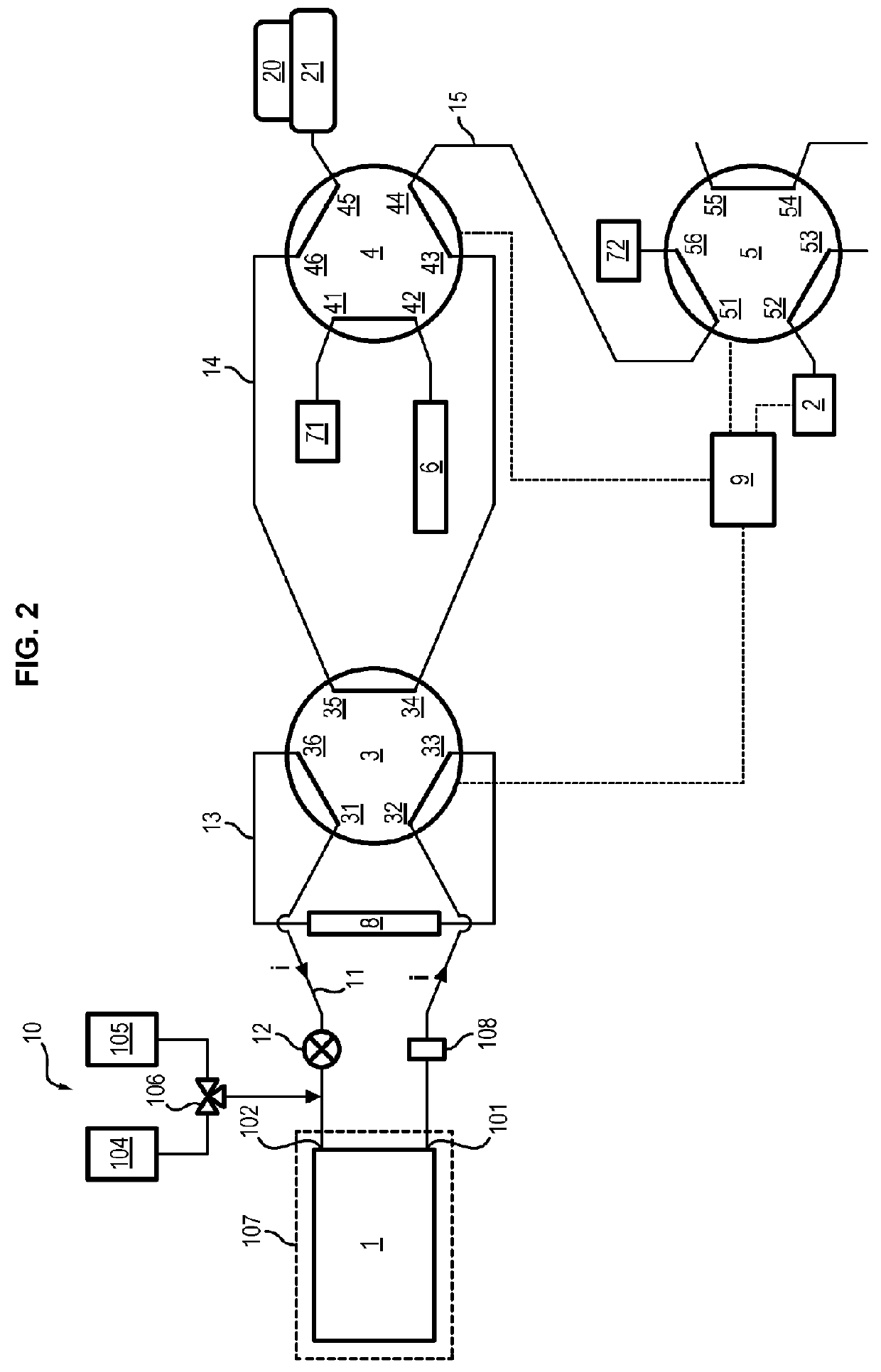
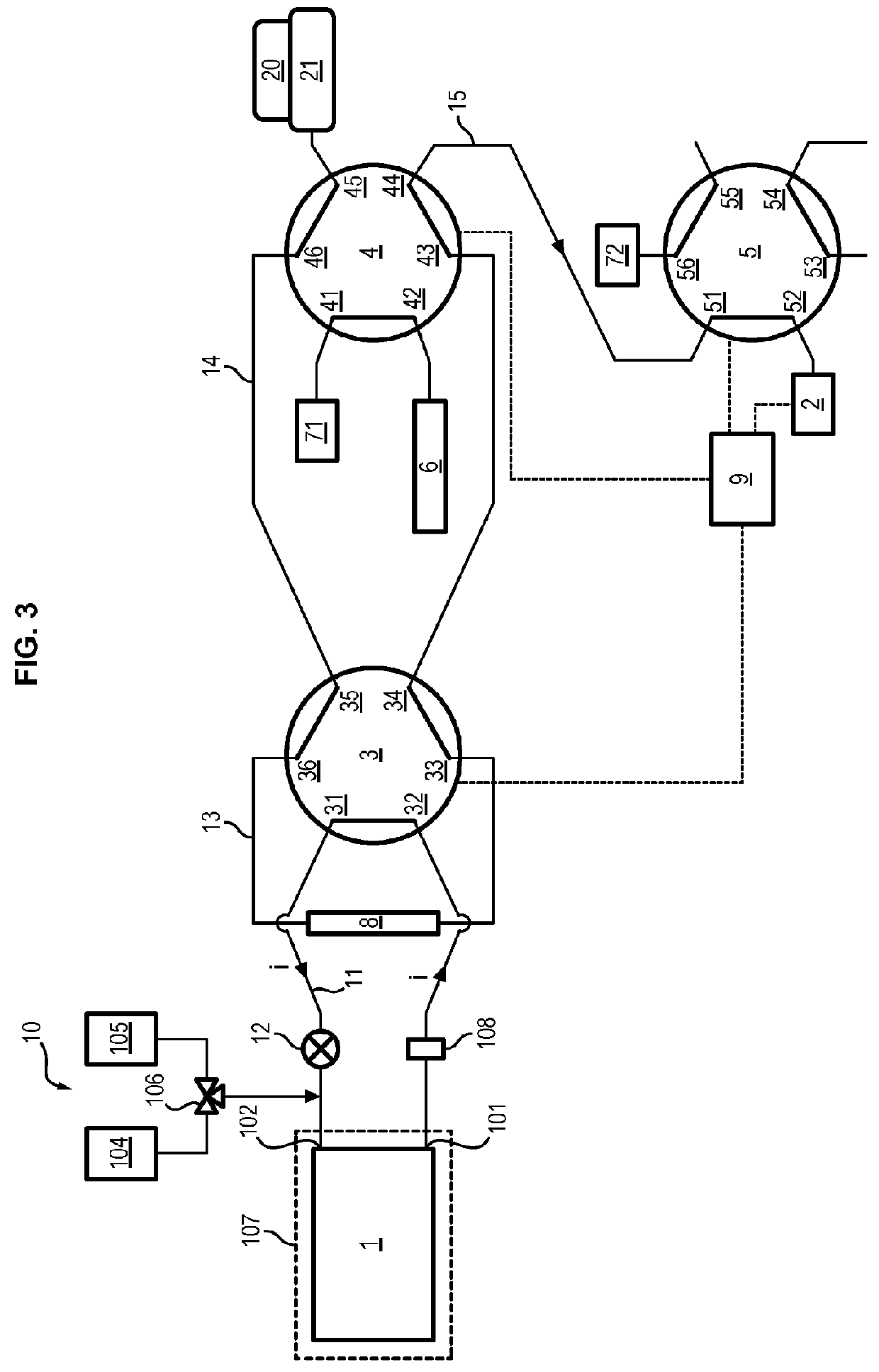
Facility for coupling a bioreactor with a device for physicochemically analysing or collecting samples
ActiveUS9963669B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringCleaning product
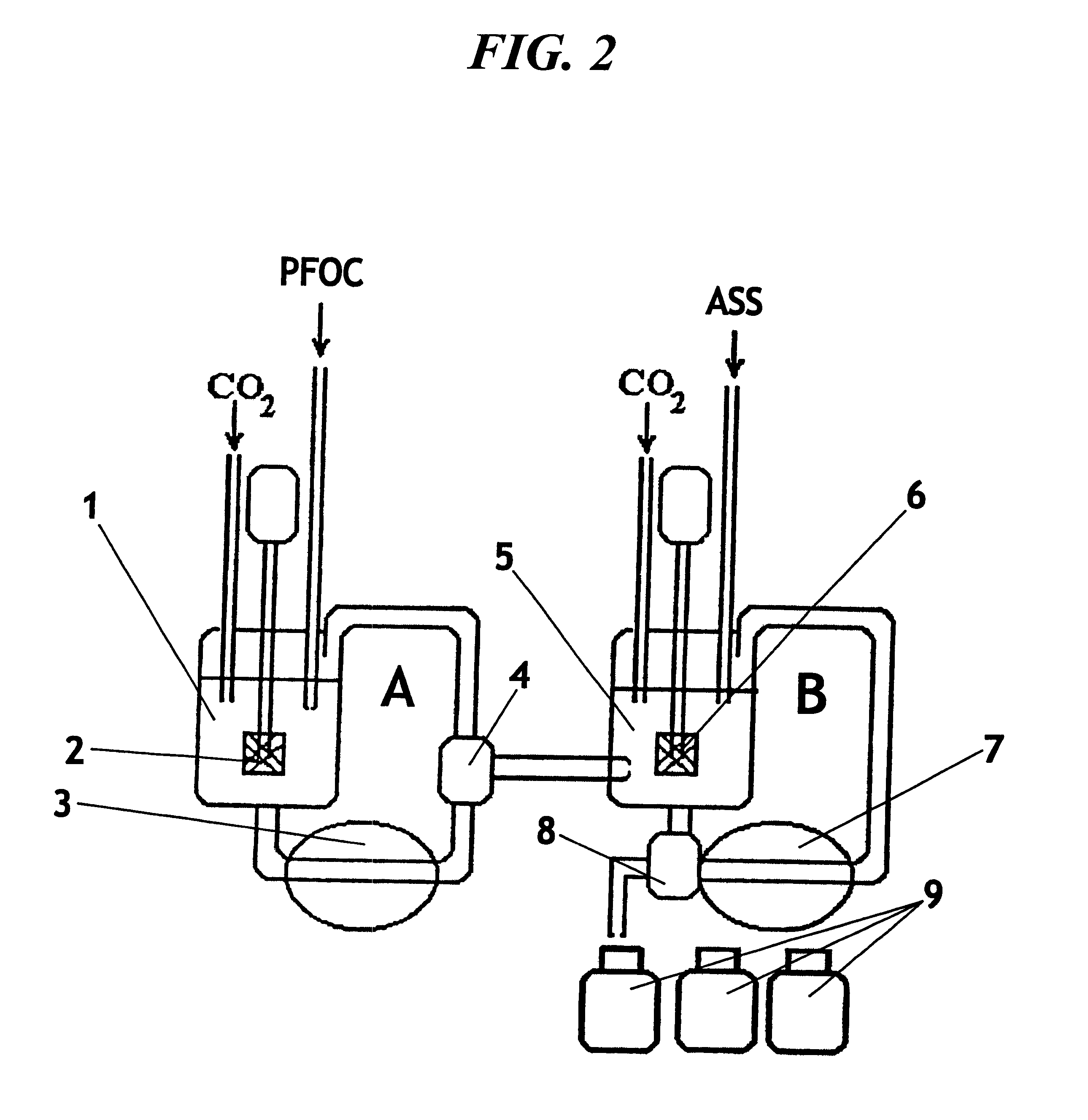
The invention concerns a facility for coupling a bioreactor for culturing bio-organisms, in dynamic mode, with at least one device for physicochemically analyzing a fluid from this bioreactor or collecting samples of this fluid, the device being equipped with a pump and an injector, the bioreactor being equipped with means for supplying culture medium and xenobiotic(s). The facility is remarkable in that the bioreactor is connected to a closed perfusion loop provided with a pump, fitted with a sampling loop and in that the facility comprises:a device for injecting a cleaning product into said sampling loop,two six-way valves, the first valve being connected to the closed perfusion loop, to the sampling loop and to a cleaning loop, the second valve being connected to the cleaning loop and an injection loop that connects the injector to at least one of the devices.
Owner:UNIV DE TECH DE COMPIEGNE UTC +1
Method for preparing heterogeneous biological amniotic membrane product
InactiveCN109939263AWide variety of sourcesAchieving Scale AcquisitionProsthesisBiotechnologySpecific function
The invention provides a method for preparing a heterogeneous biological amniotic membrane product. The method comprises the following main steps of 1, placenta acquisition and peeling; 2, cleaning sterilization and fixation; 3, irradiation inactivation; 4, packaging and program freezing. Compared with the prior art, the method has the following advantages that the product related derives from heterogeneous mammals (including pigs, cattle, sheep and the like), and raw materials are controllable and scalable; animal-derived materials are subjected to non-destructive treatment, and a natural amniotic membrane structure and active ingredients are maintained as much as possible; under the protection of preservation liquid with specific functions, the sterilization and inactivation of the product are achieved by irradiation, and the safety and effectiveness of the product are both achieved. The method brings a novel solution to the raw material source and standardization problem of the biological amniotic membrane product, and also provides a reference method and technical way for the high value reuse of the traditional animal husbandry biological waste.
Owner:广州锐澄医疗技术有限公司
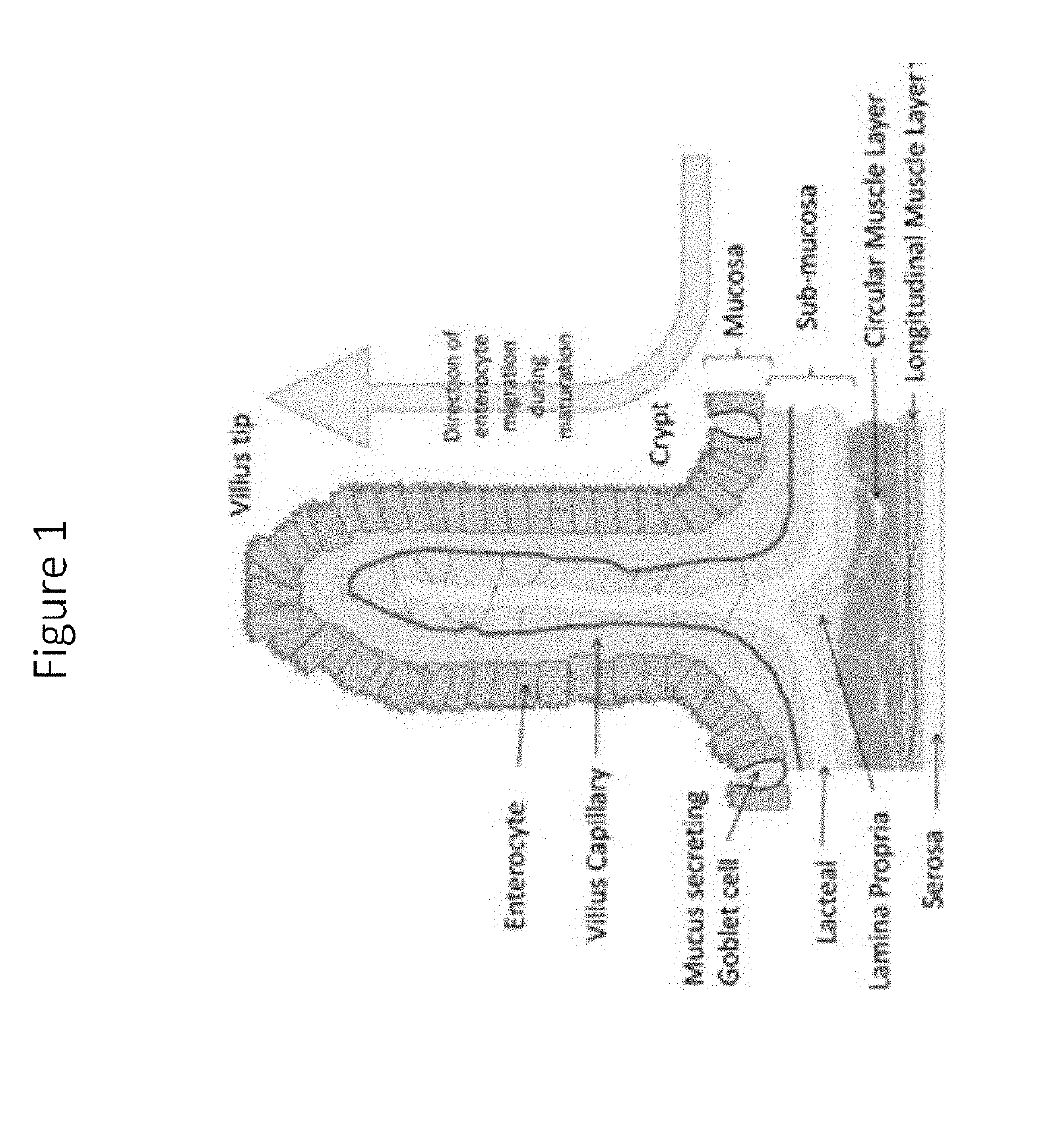
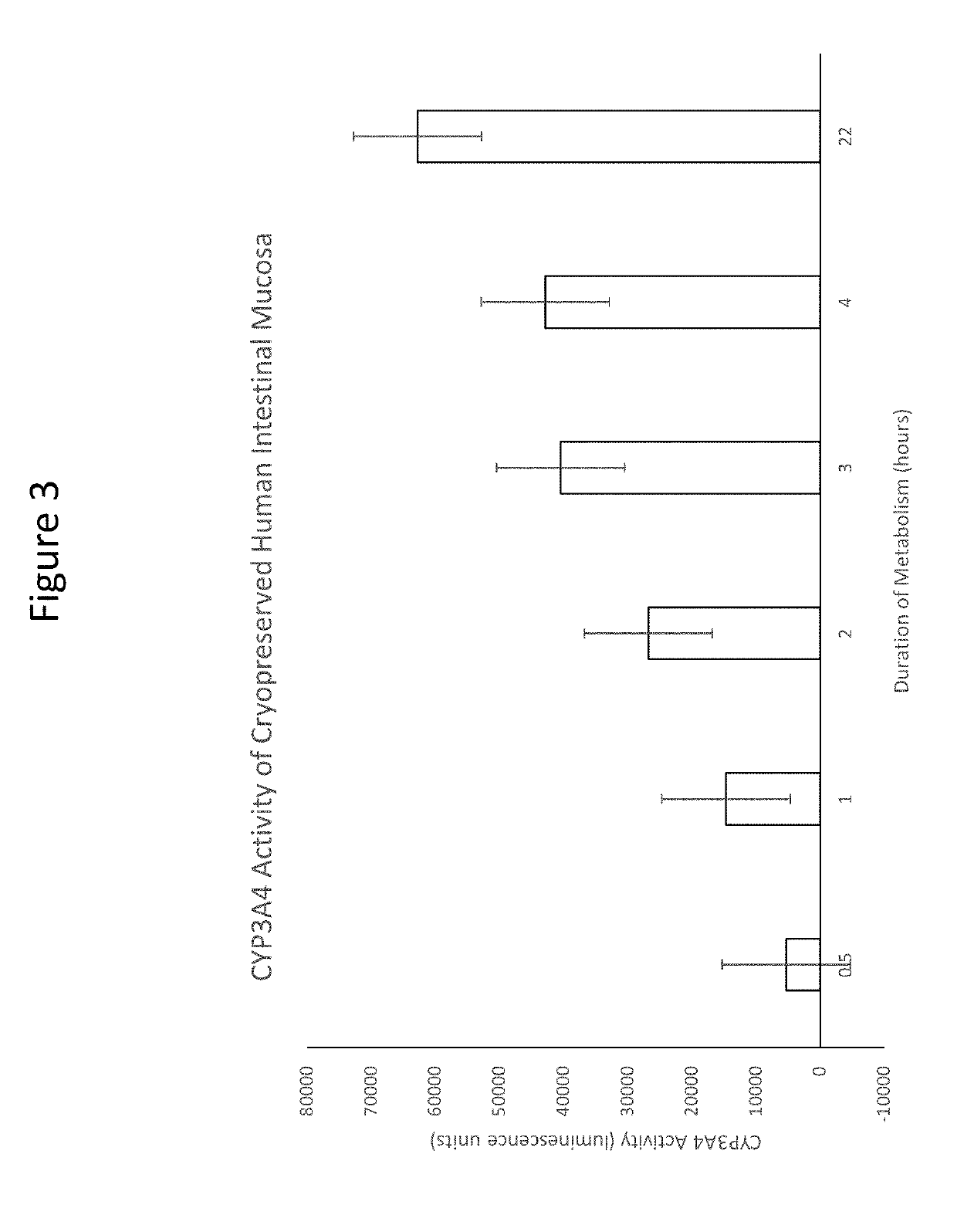
Isolated intestinal mucosa and uses thereof
The present disclosure provides an in vitro reagent for evaluating xenobiotic metabolism in a cell culture based assay. The in vitro reagent is an admixture of a cell culture medium and isolated intestinal mucosa comprising villi wherein the intestinal mucosa was eluted from a lumen of the intestine. The isolated mucosa comprises metabolically competent cells. Addition of a xenobiotic test compound to the in vitro reagent allows metabolism of the test compound by the isolated intestinal mucosa comprising villi.
Owner:DISCOVERY LIFE SCI LLC
Detection of phenols using engineered bacteria
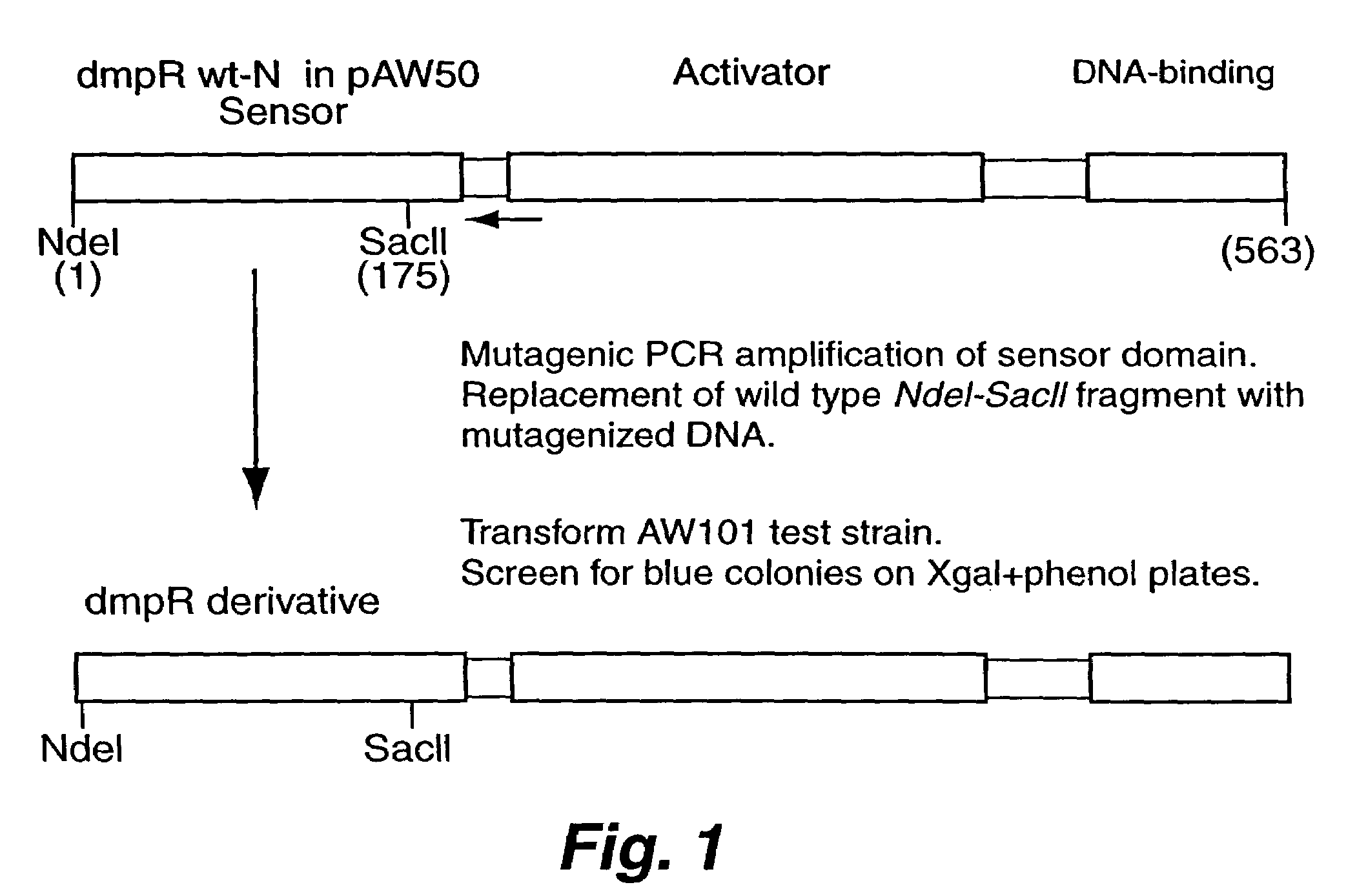
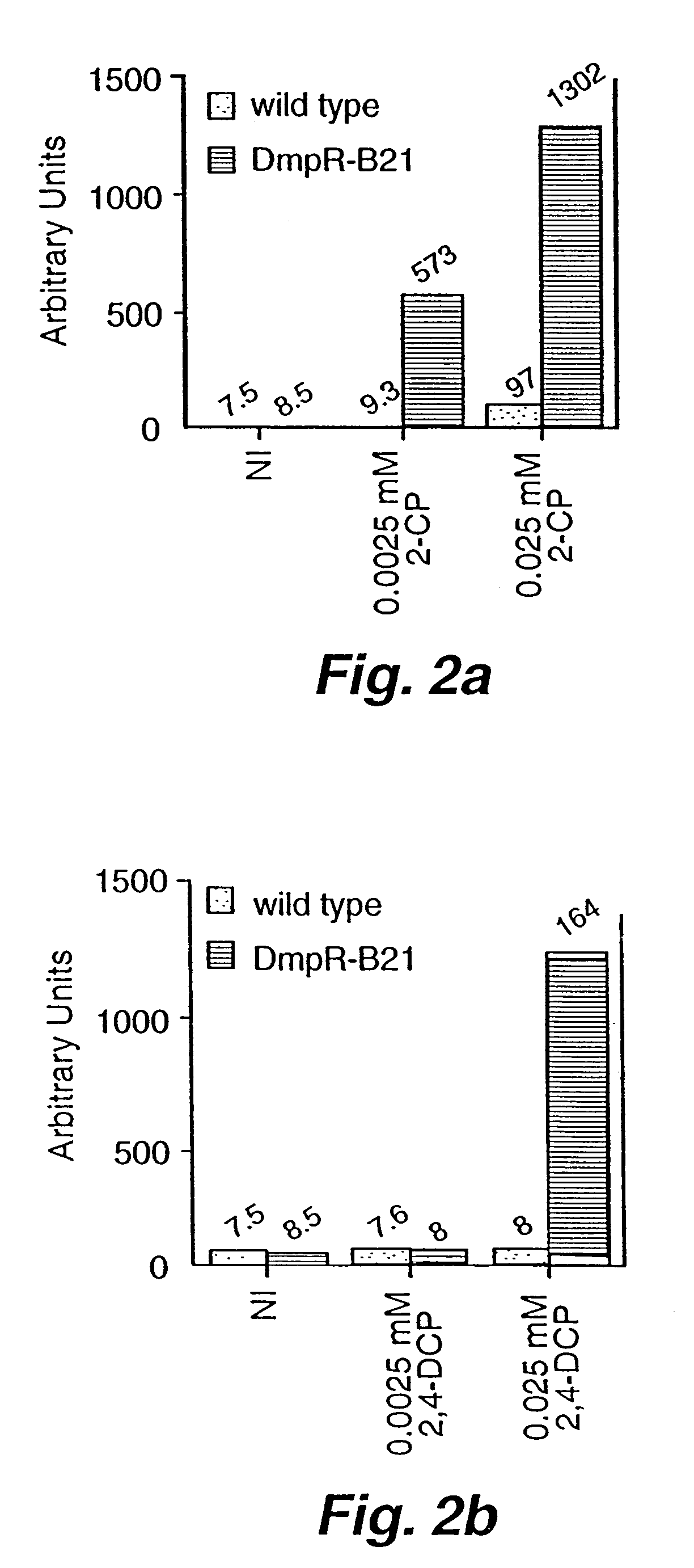
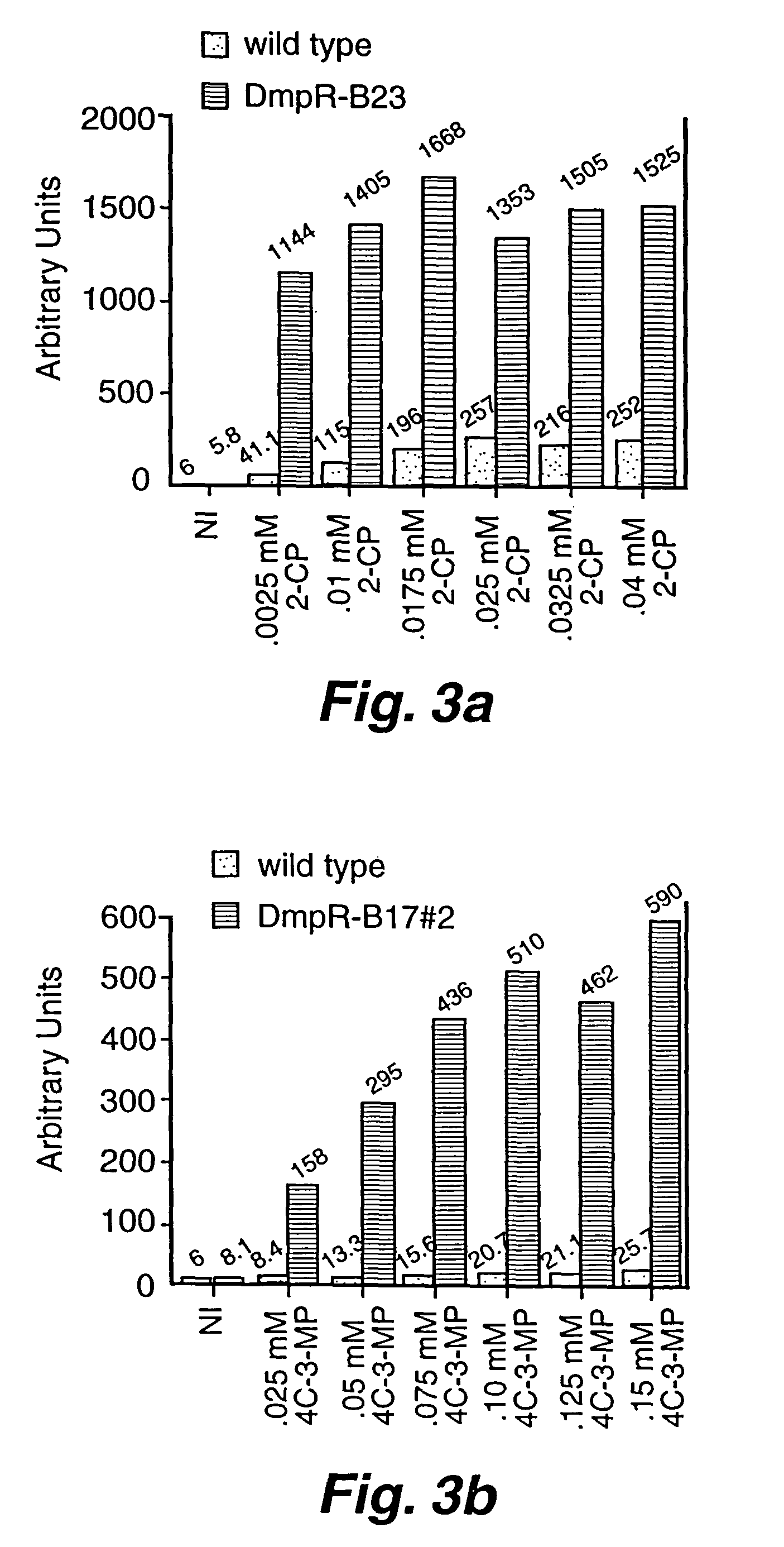
Detection of phenols using engineered bacteria. A biosensor can be created by placing a reporter gene under control of an inducible promoter. The reporter gene produces a signal when a cognate transcriptional activator senses the inducing chemical. Creation of bacterial biosensors is currently restricted by limited knowledge of the genetic systems of bacteria that catabolize xenobiotics. By using mutagenic PCR to change the chemical specificity of the Pseudomonas species CF600 DmpR protein, the potential for engineering novel biosensors for detection of phenols has been demonstrated. DmpR, a well-characterized transcriptional activator of the P. CF600's dmp operon mediates growth on simple phenols. Transcription from Po, the promoter heading the dmp operon, is activated when the sensor domain of DmpR interacts with phenol and mono-substituted phenols. By altering the sensor domain of the DmpR, a group of DmpR derivatives that activate transcription of a Po-lacZ fusion in response to eight of the EPA's eleven priority pollutant phenols has been created. The assays and the sensor domain mutations that alter the chemical specificity of DmpR is described.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
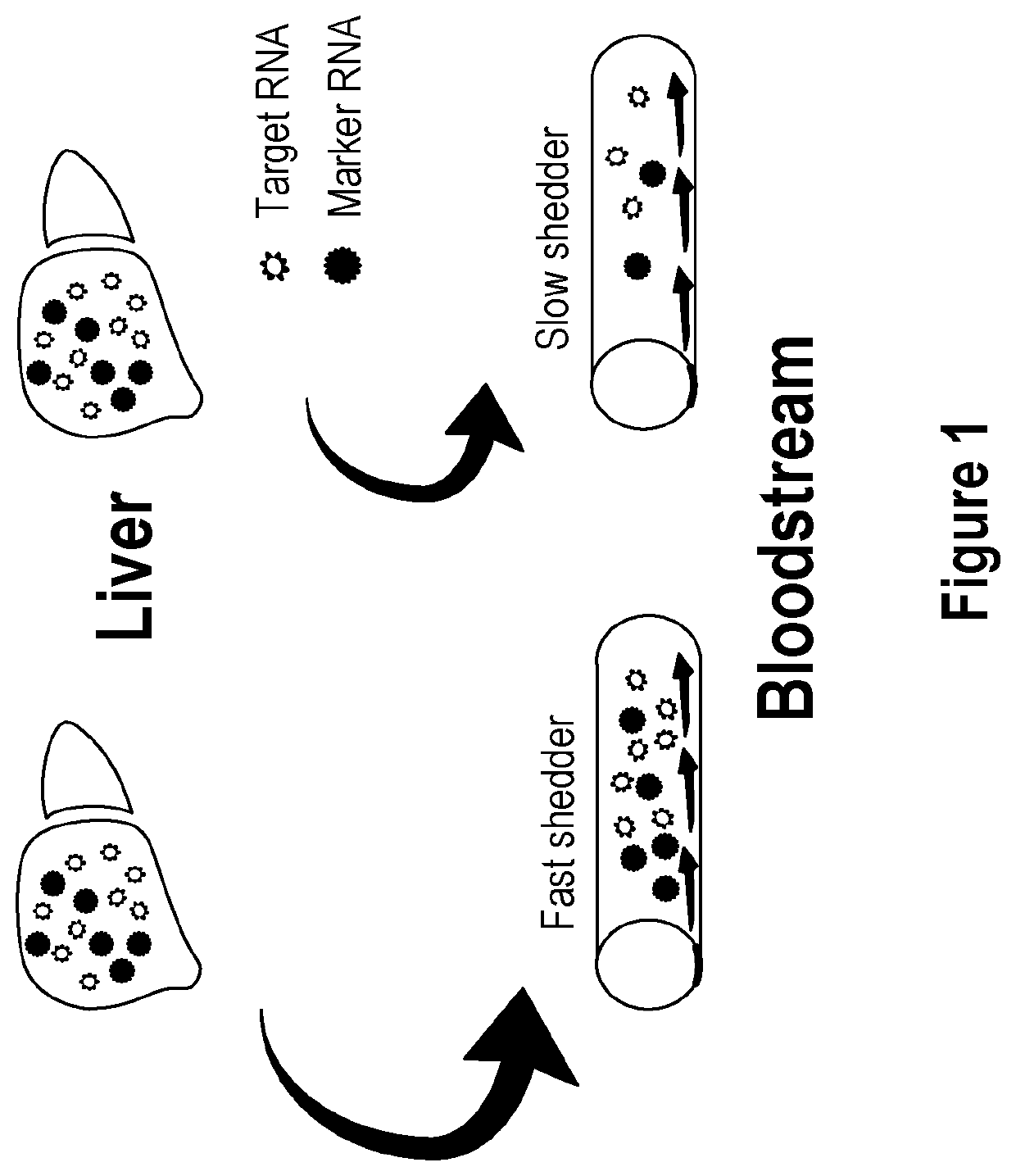
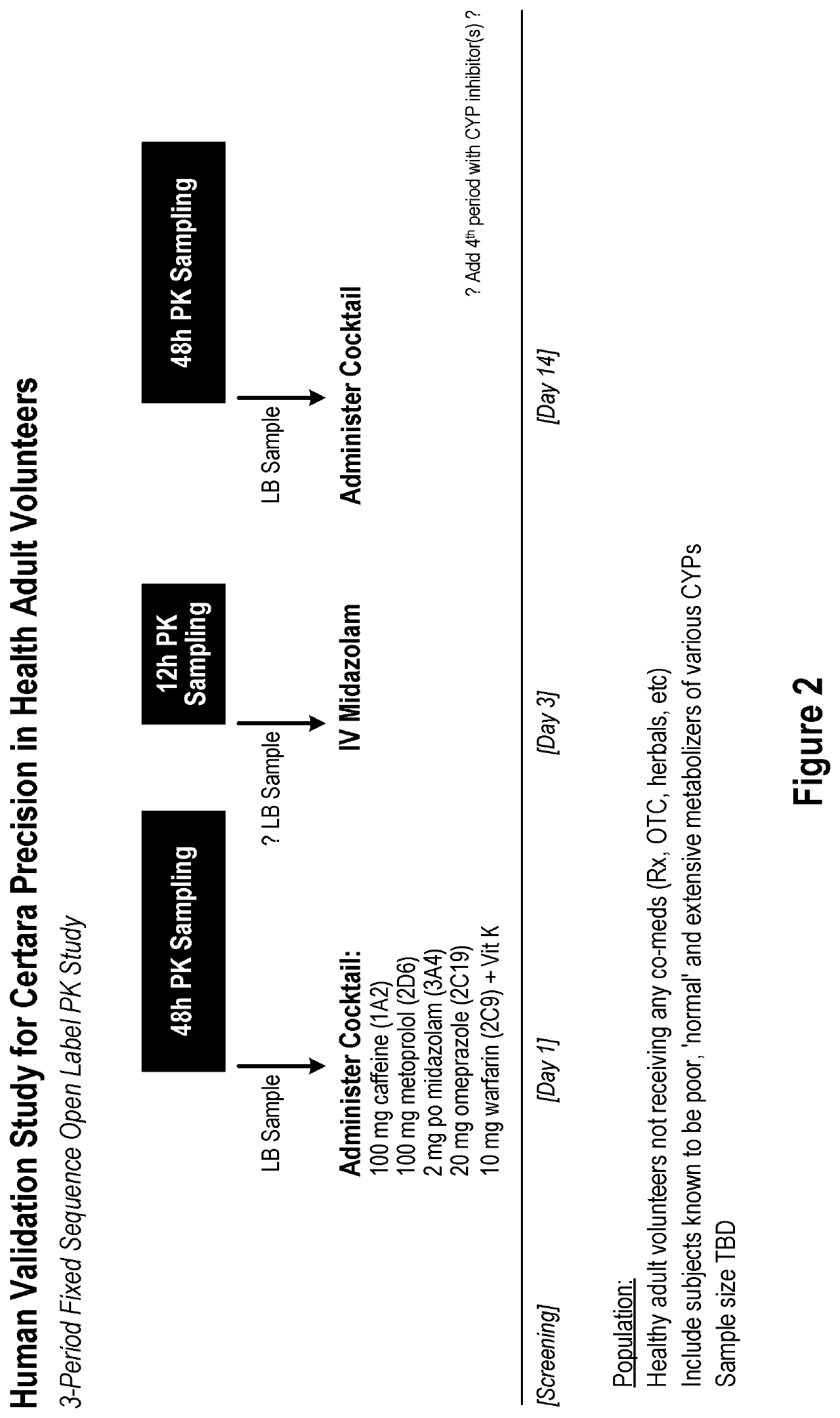
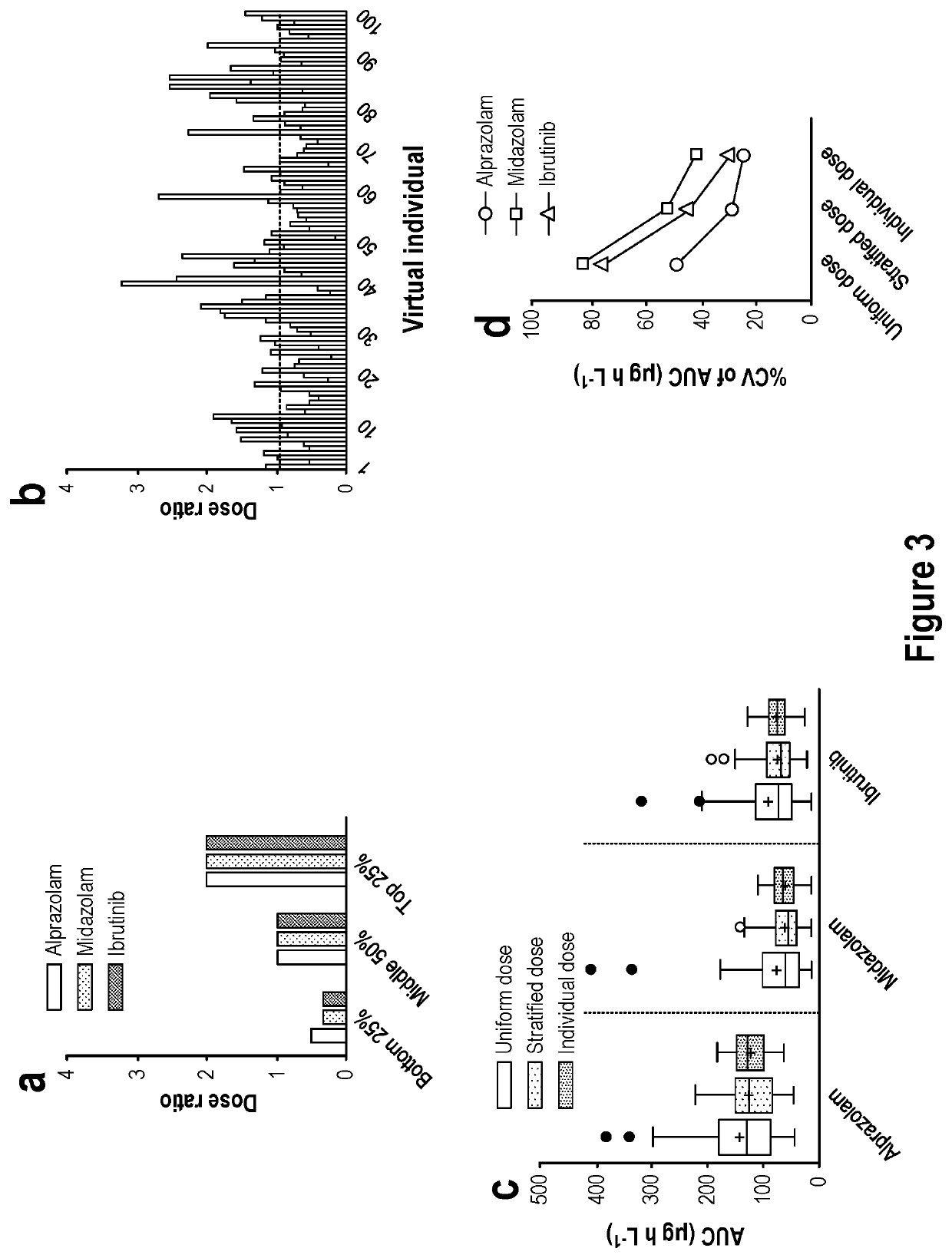
Methods and apparatus for generating a virtual model of xenobiotic exposure using transcriptomics analysis of liquid biopsy samples
PendingUS20220215898A1Improve the level ofReduce variationChemical property predictionMicrobiological testing/measurementCell freeProtein
Processes are provided for establishing a virtual physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model in a population comprised of a plurality of individual subjects that has been or may be exposed to a xenobiotic molecule. The processes are derived from the identification of an abundance of a protein that is involved in absorption; distribution; localization; biotransformation; and excretion of the xenobiotic molecule from a liquid biopsy of corresponding cell free RNA. Personalised PBPK models for precision dosing, as well as methods of treatment are also provided.
Owner:CERTARA USA INC
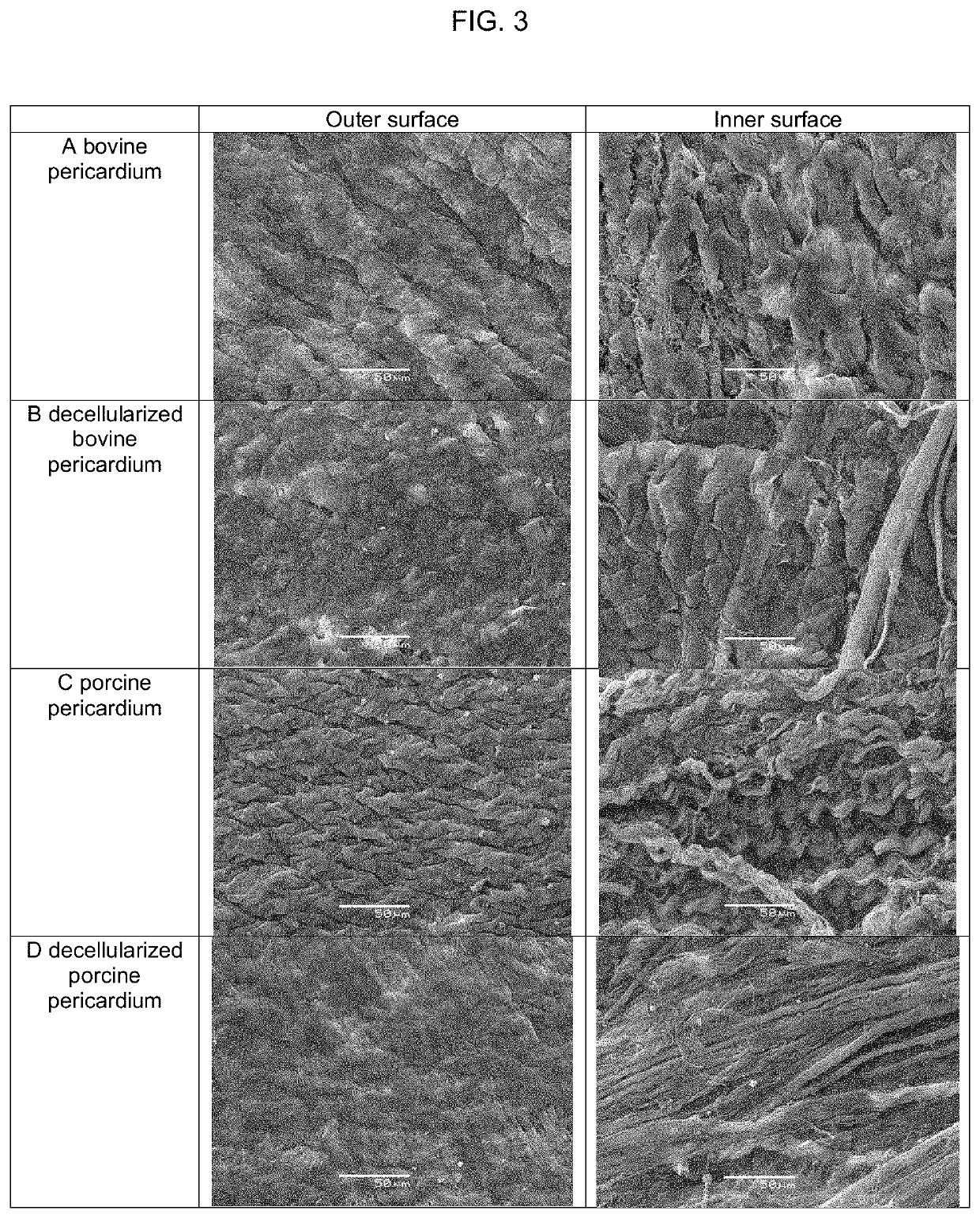
Decellularization method
PendingUS20220354991A1Decreased mineralizationLow immunogenicityCulture processMammal material medical ingredientsHuman bodyDecellularization
The purpose of the present invention is to provide: detergent-free decellularization method of xenogenic biological tissues for human body surgery, in which the pericardium, blood vessels, other membrane-like biological tissues, and the like are decellularized so as to have resistance to mechanical property loss, mineralization and immune reactivity; and decellularized tissue. Decellularized tissue, according to the present invention, when compared to untreated tissue, has greater calcification reduction in vivo, blood compatibility and biocompatibility improvement, tissue thickness reduction, and increases in tensile strength, kink resistance and the like.
Owner:S&G BIOTECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com