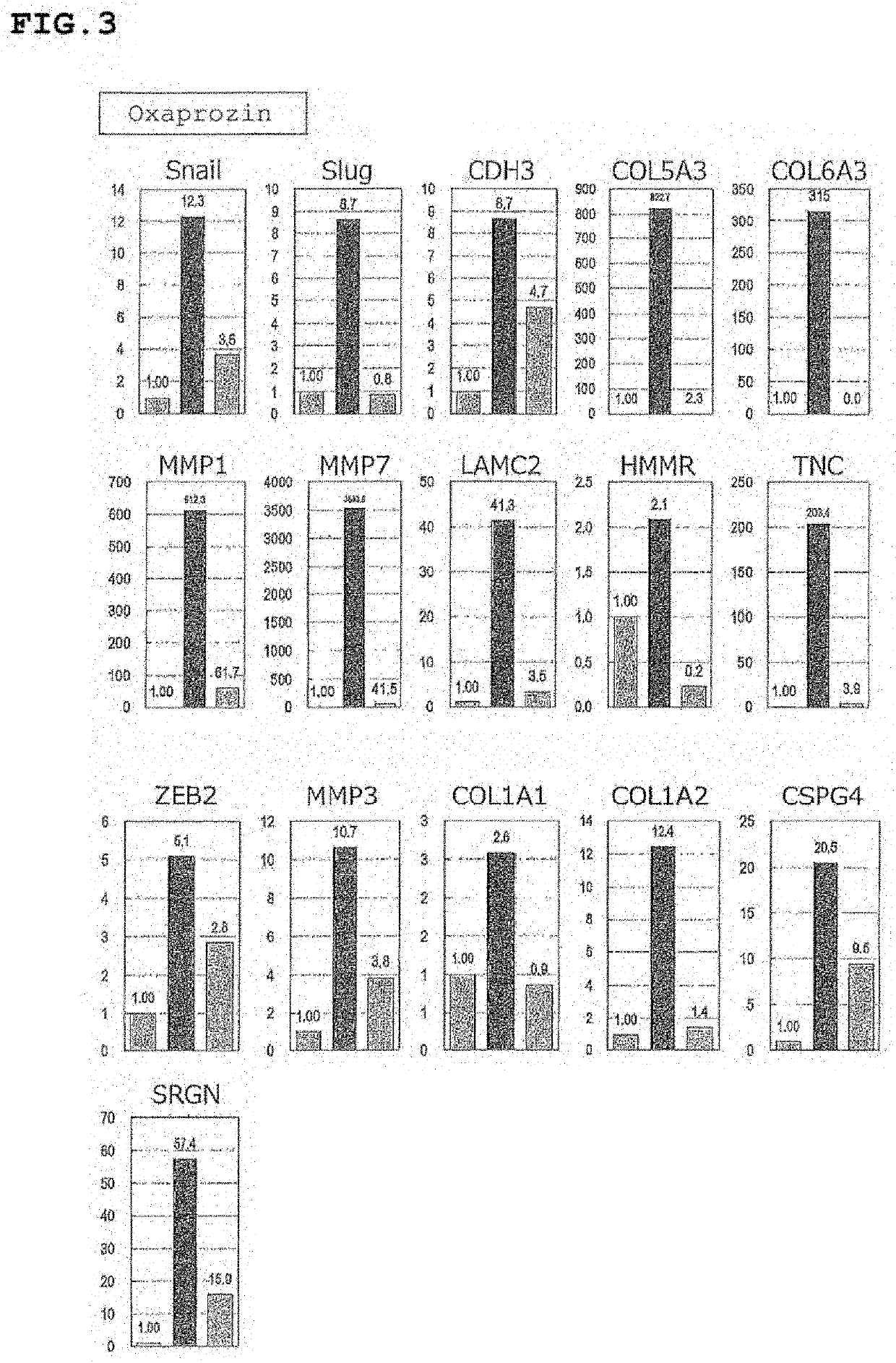
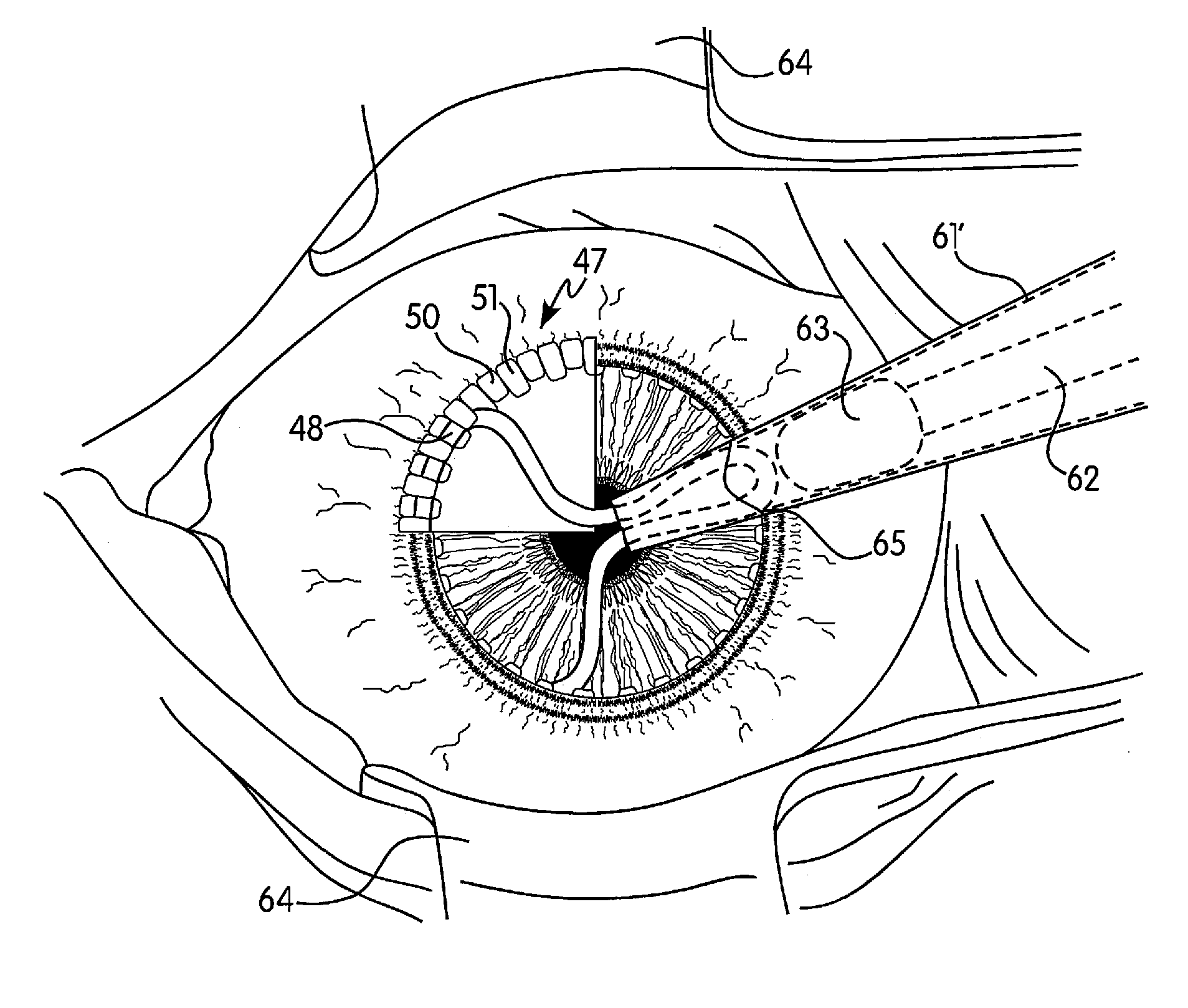
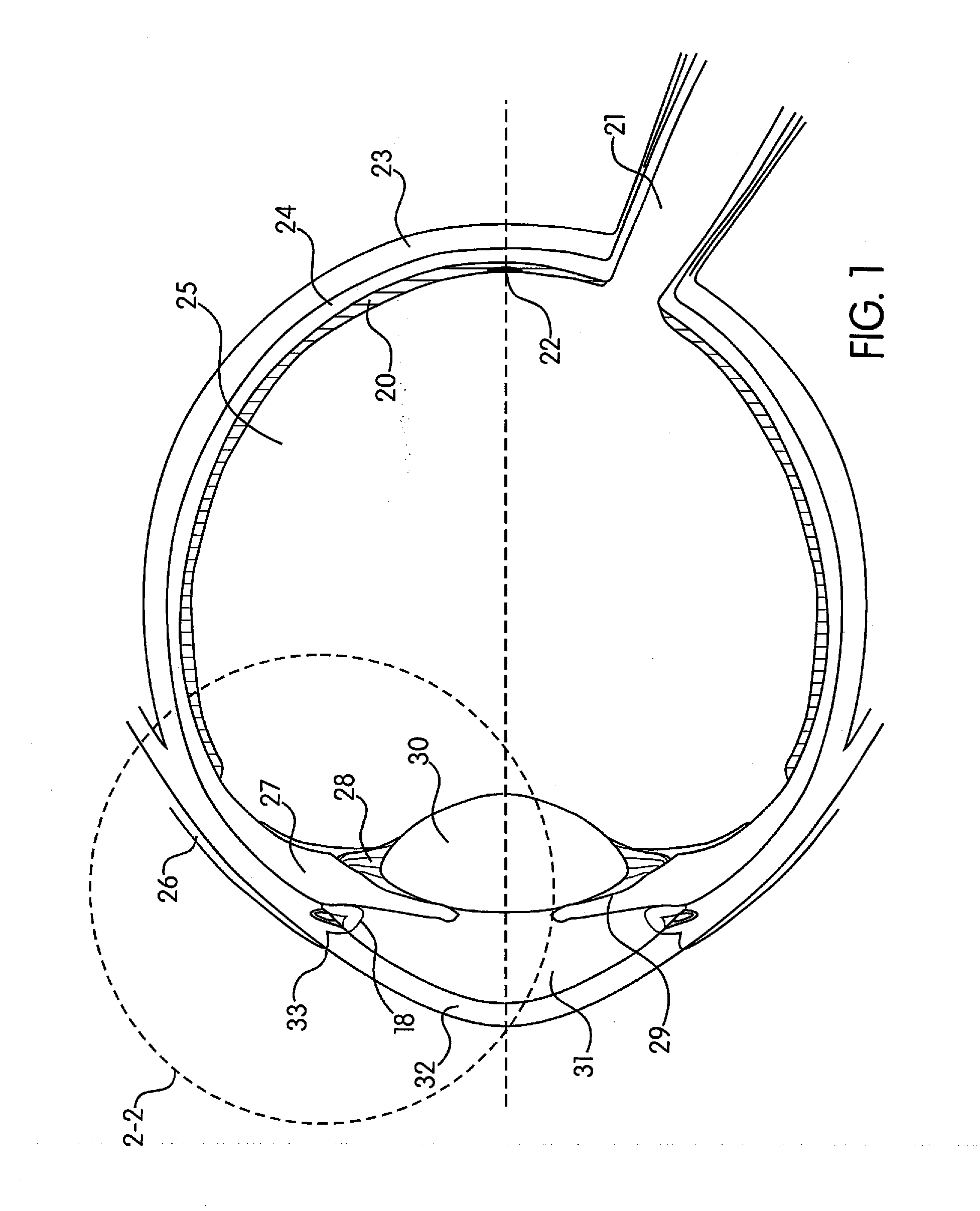
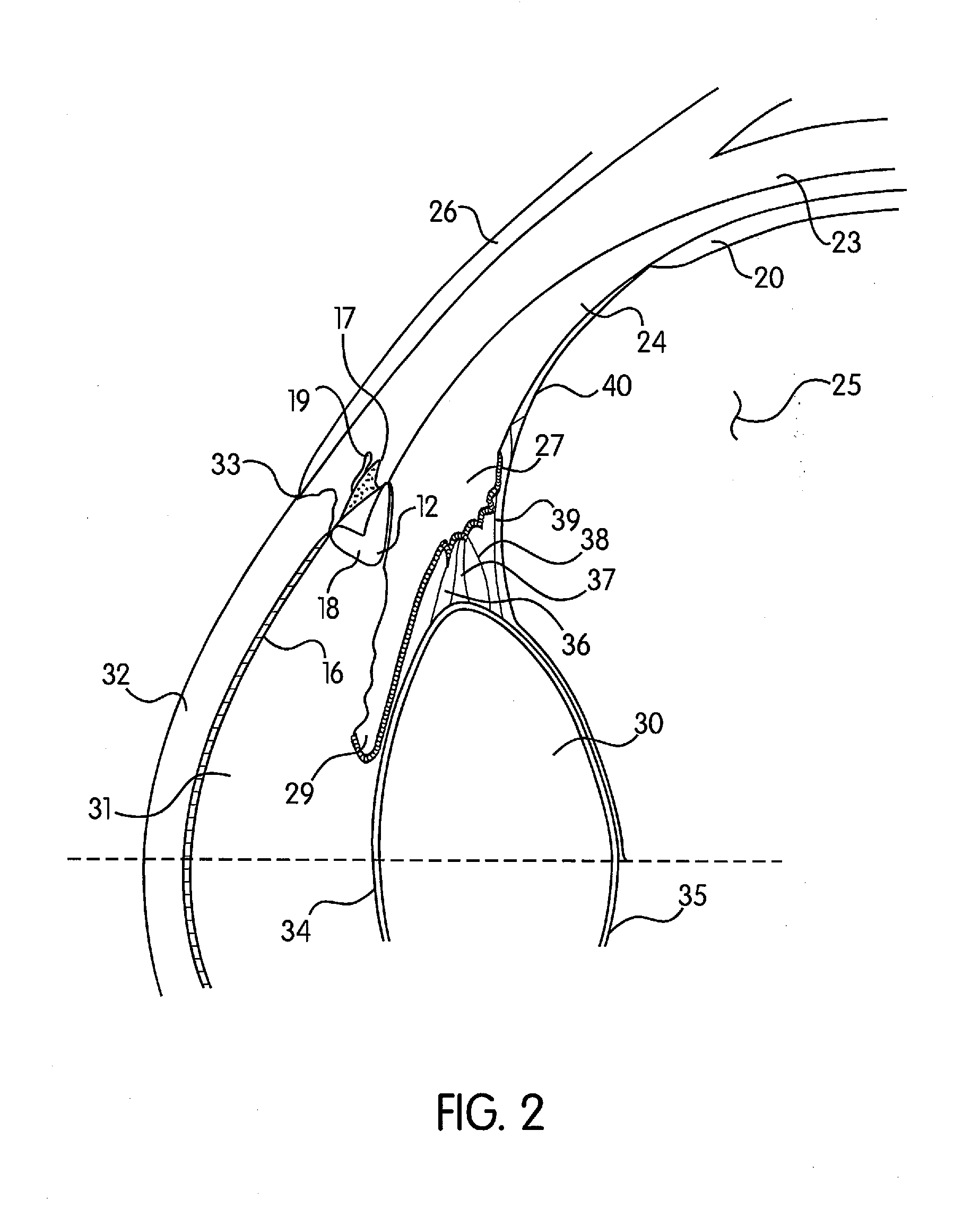
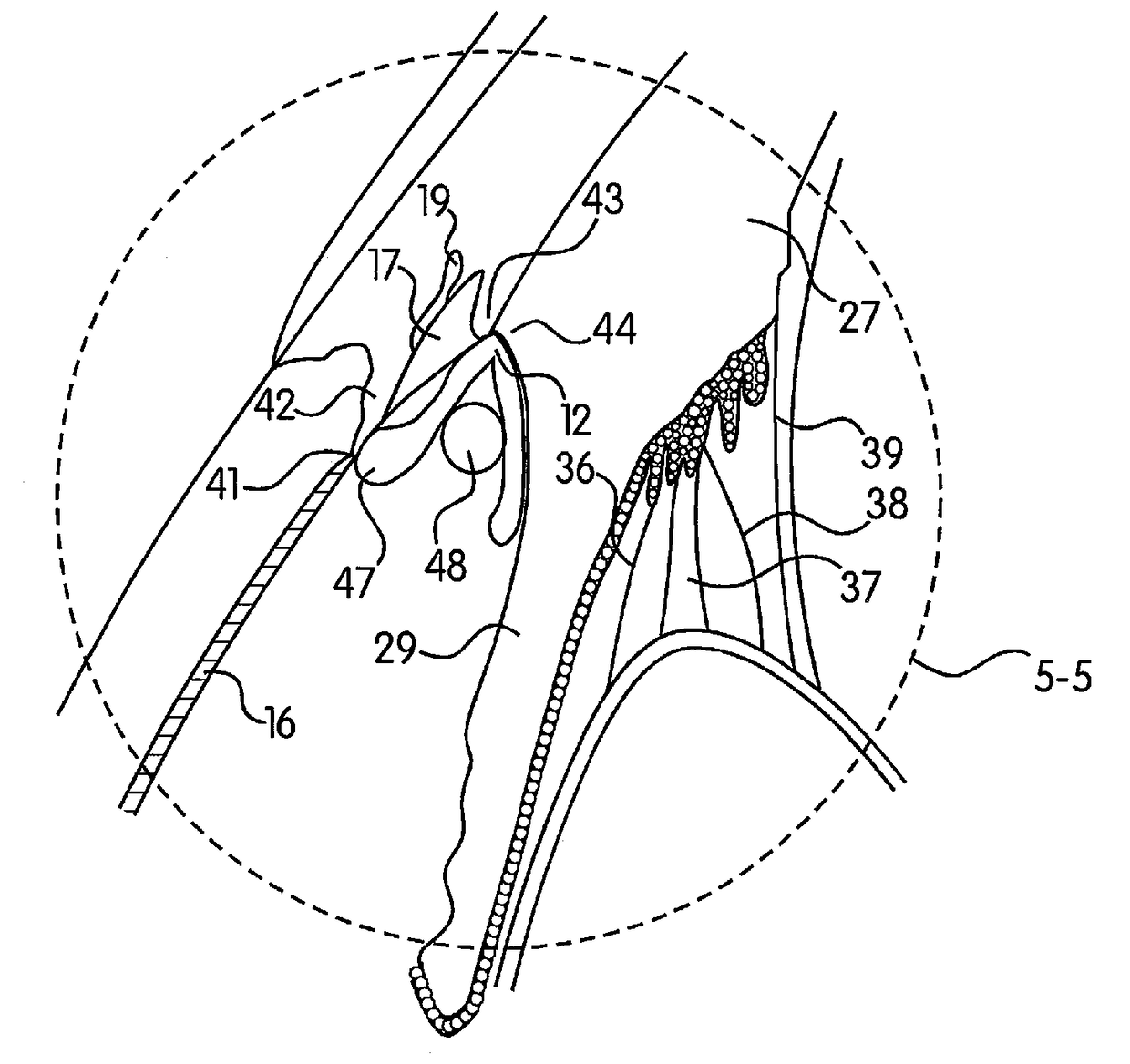
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Drusen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
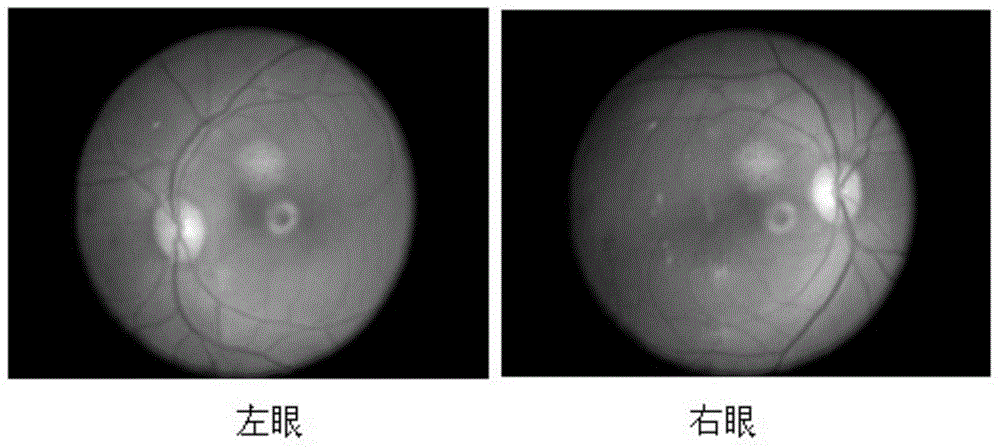
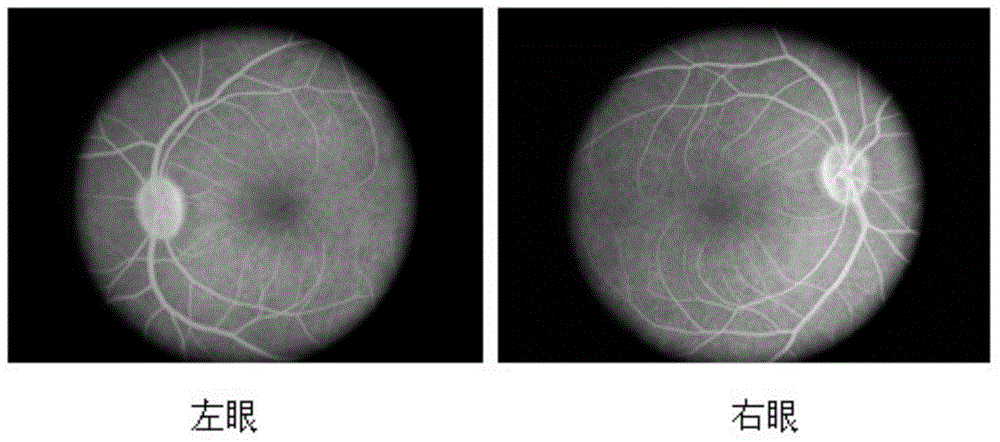
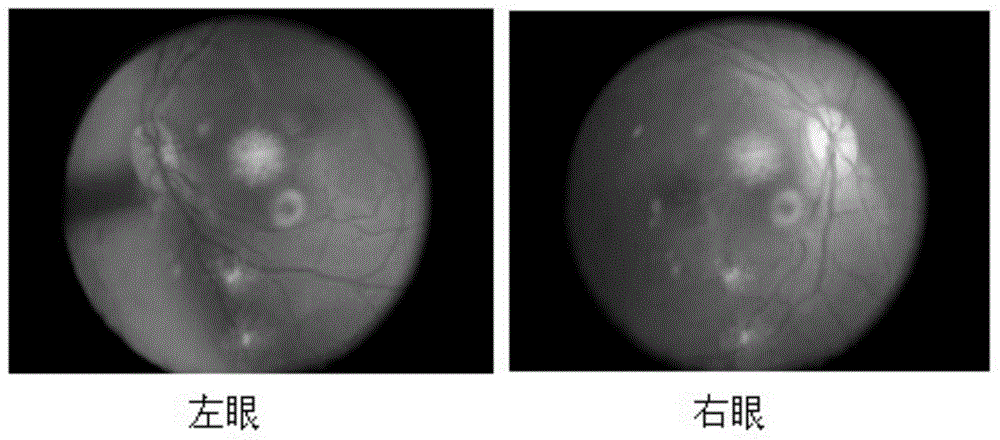
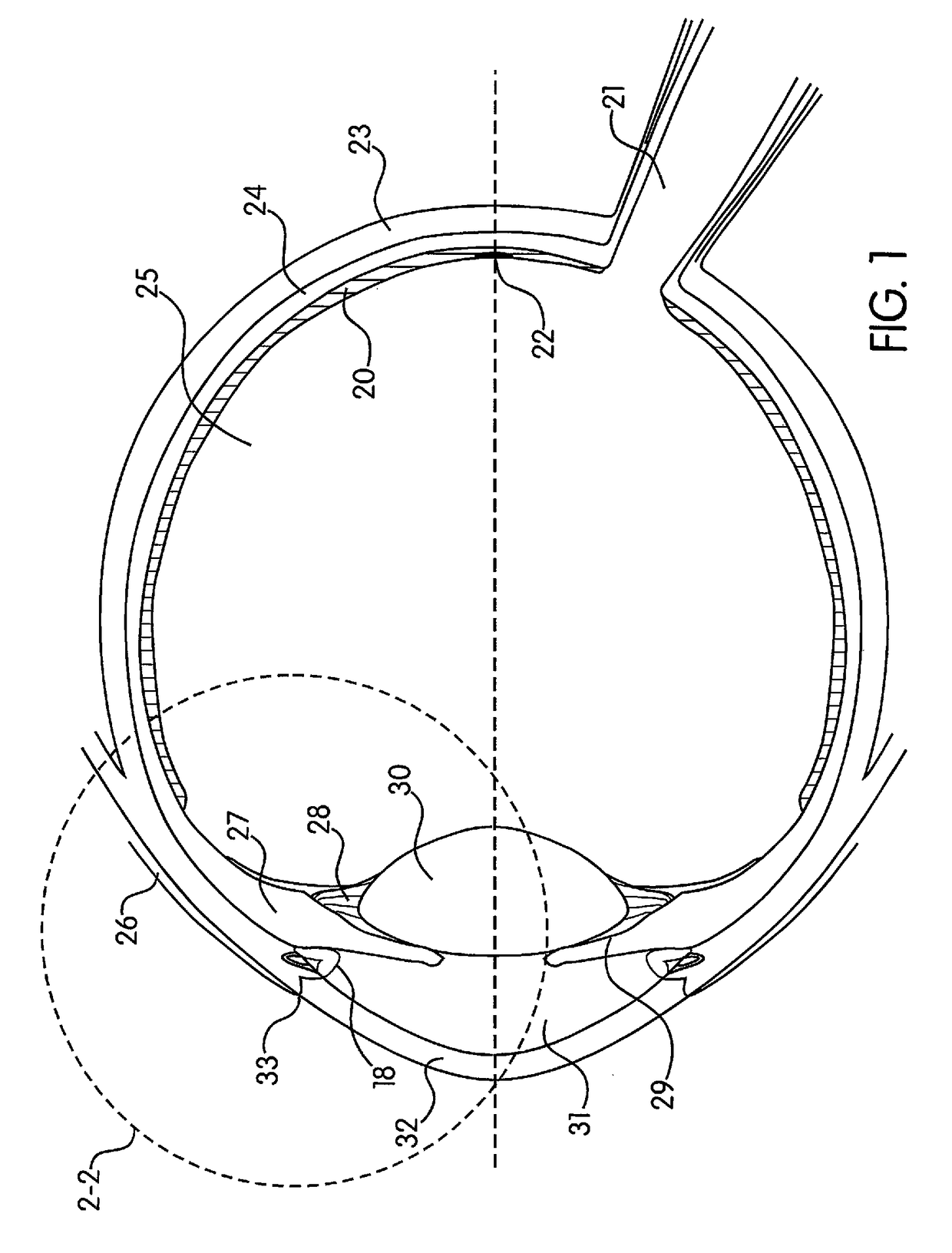
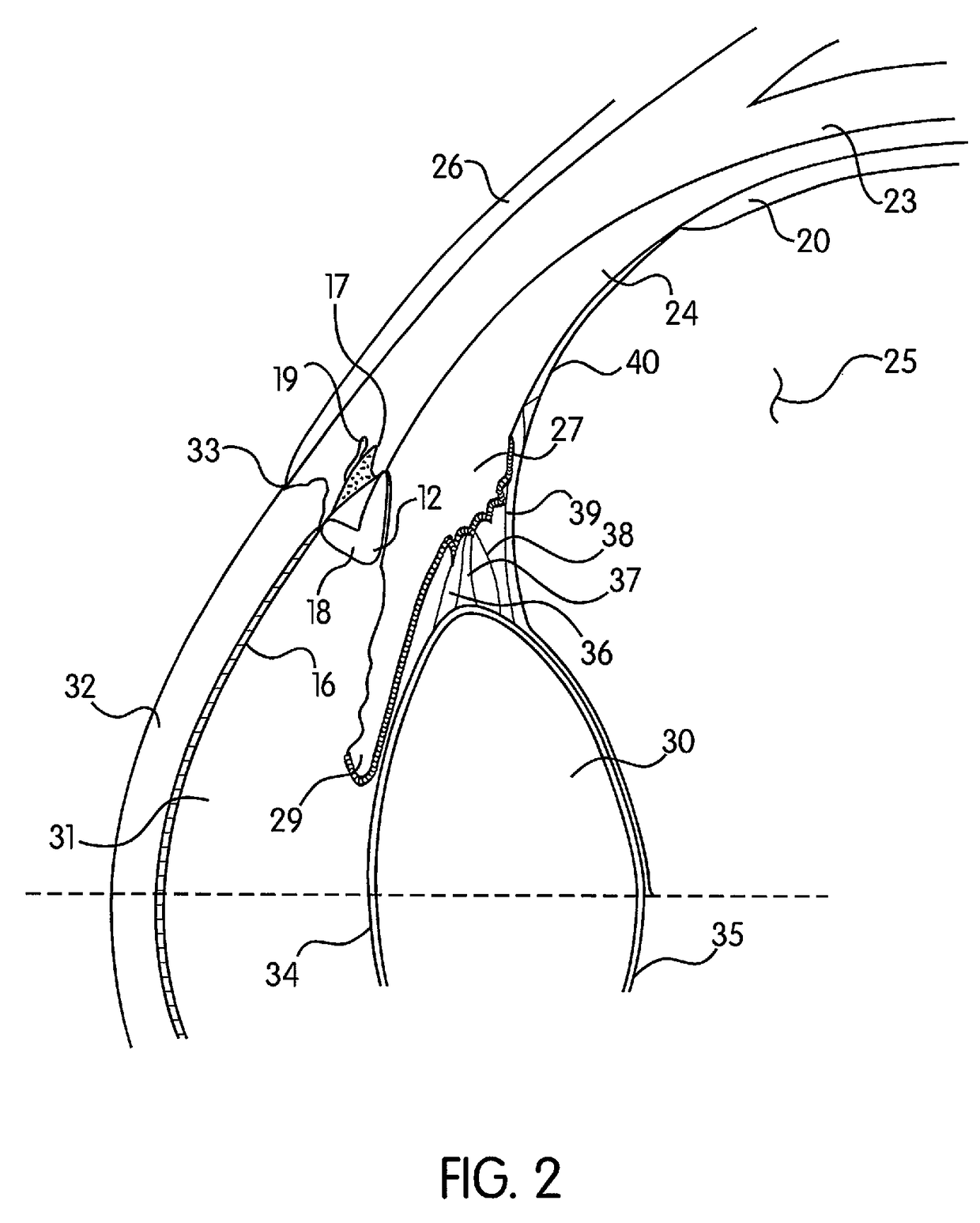
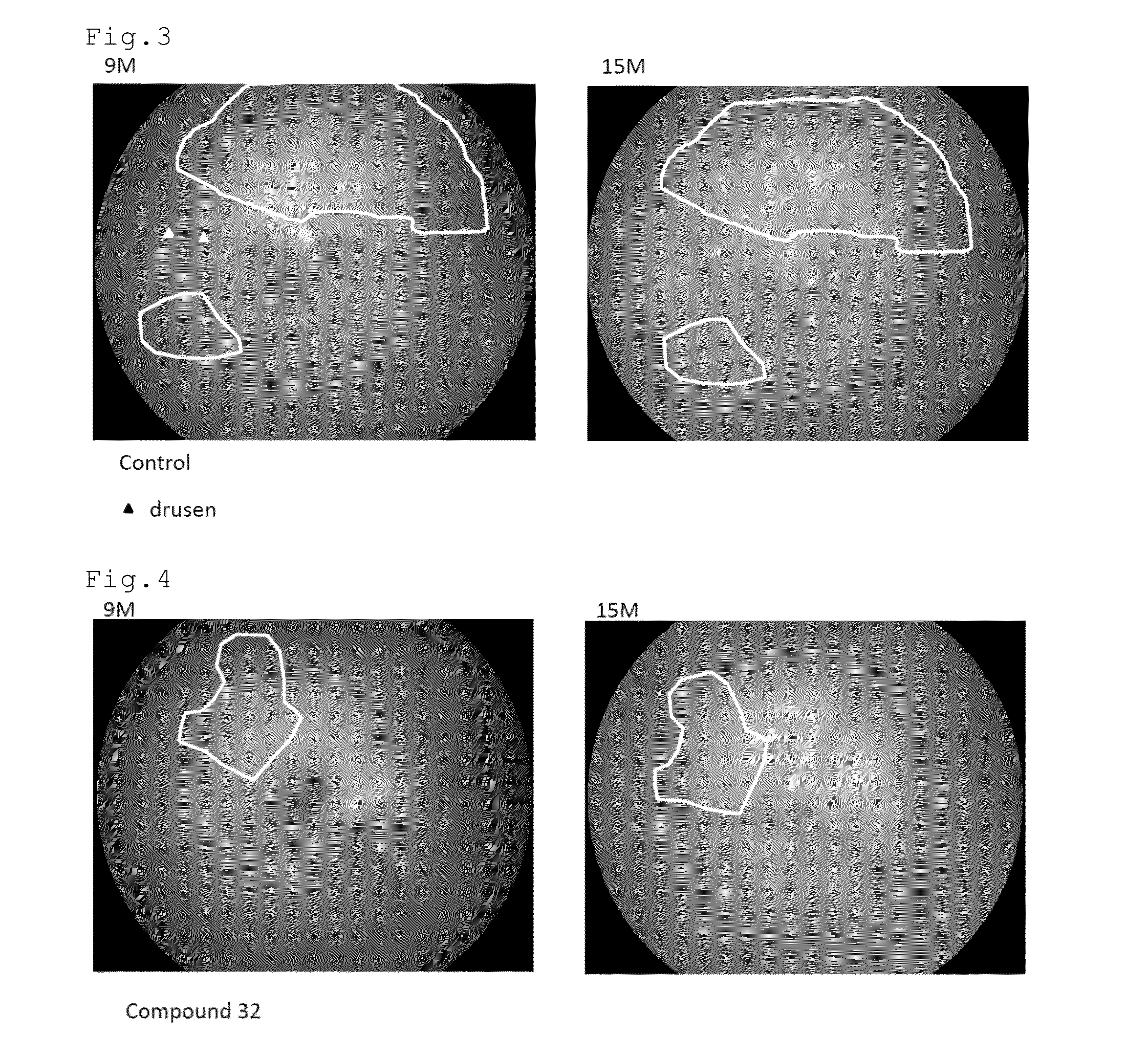
Drusen, from the German word for node or geode (singular, "Druse"), are tiny yellow or white accumulations of extracellular material that build up between Bruch's membrane and the retinal pigment epithelium of the eye. The presence of a few small ("hard") drusen is normal with advancing age, and most people over 40 have some hard drusen. However, the presence of larger and more numerous drusen in the macula is a common early sign of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
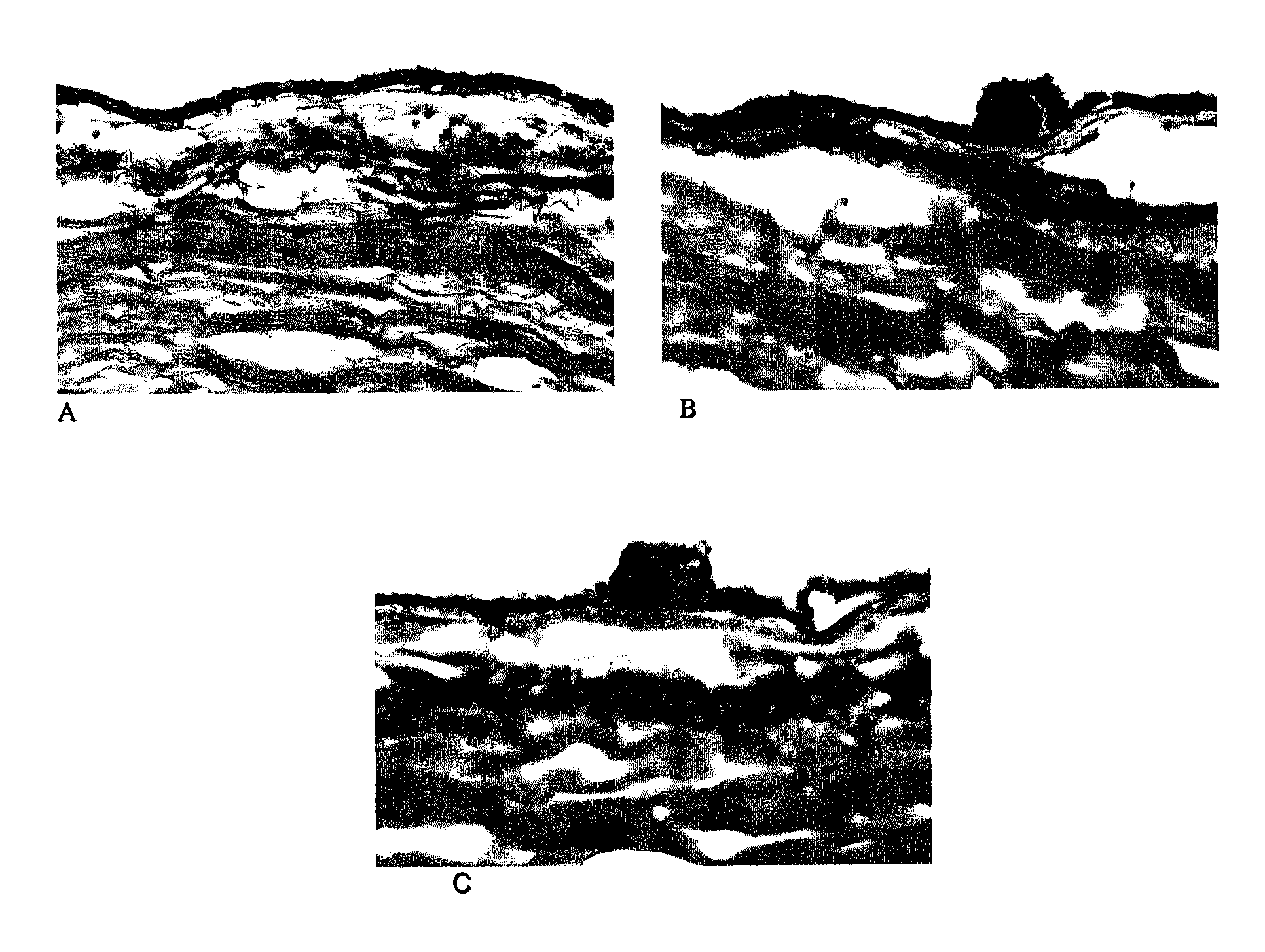
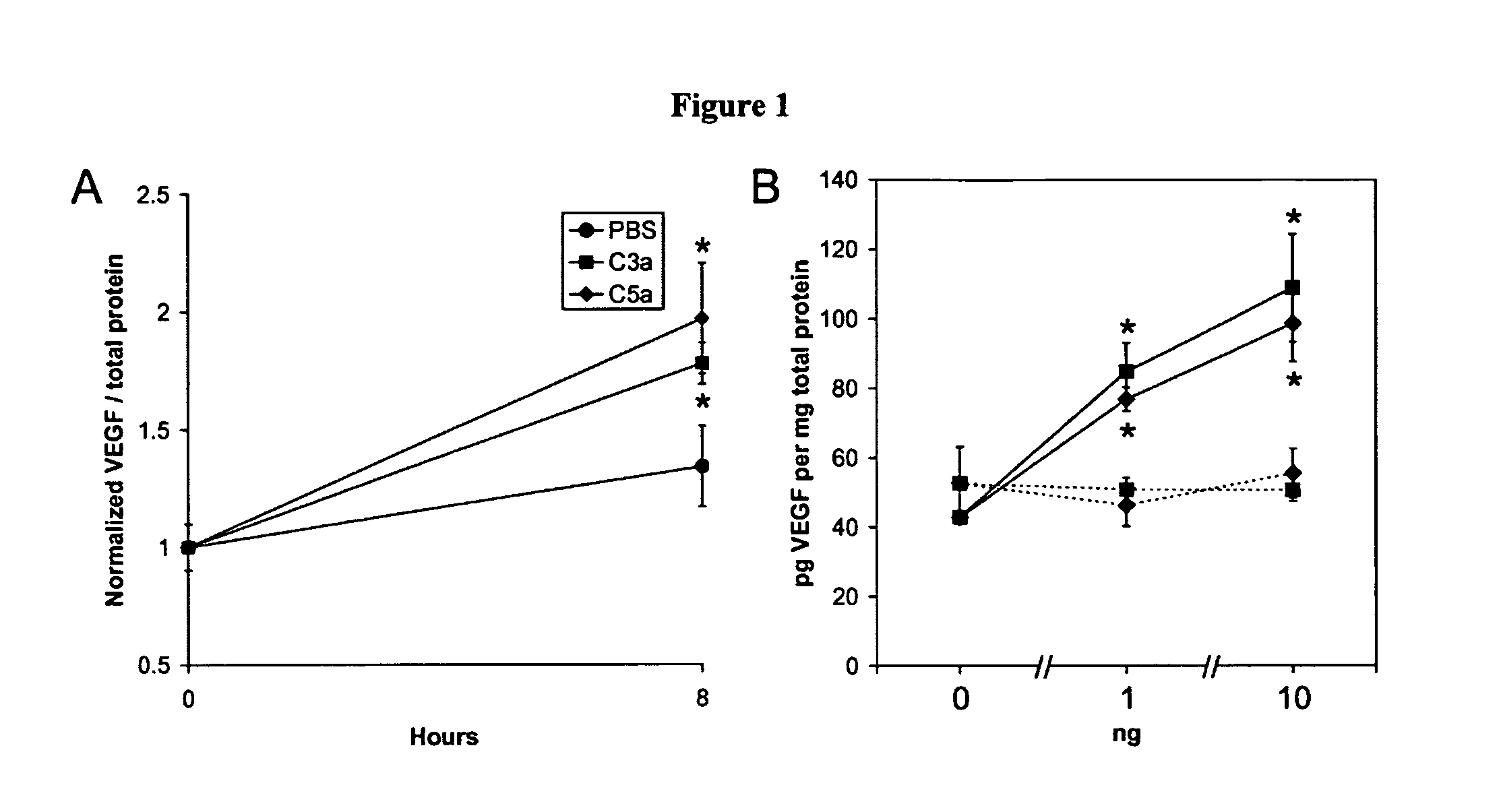
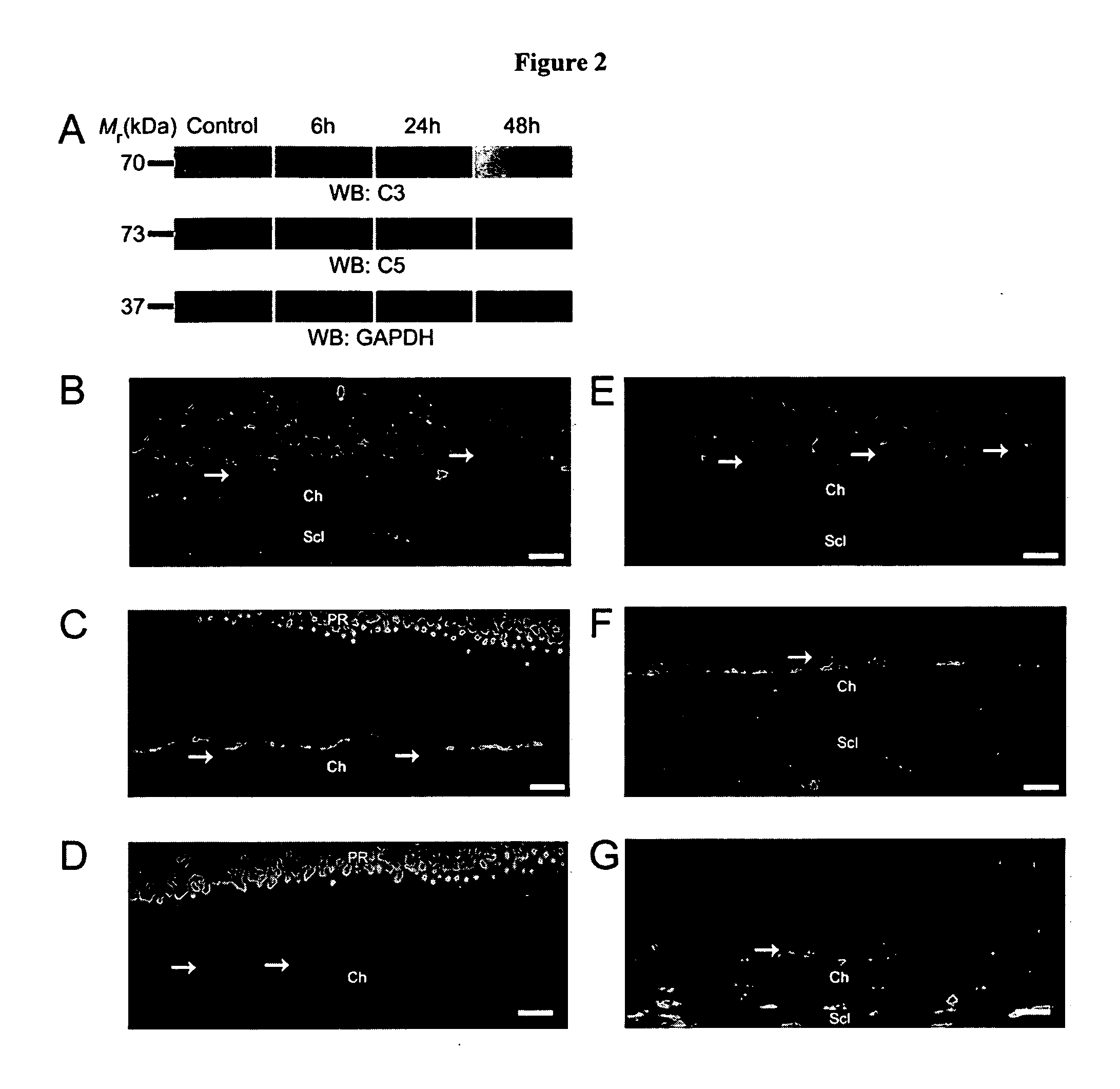
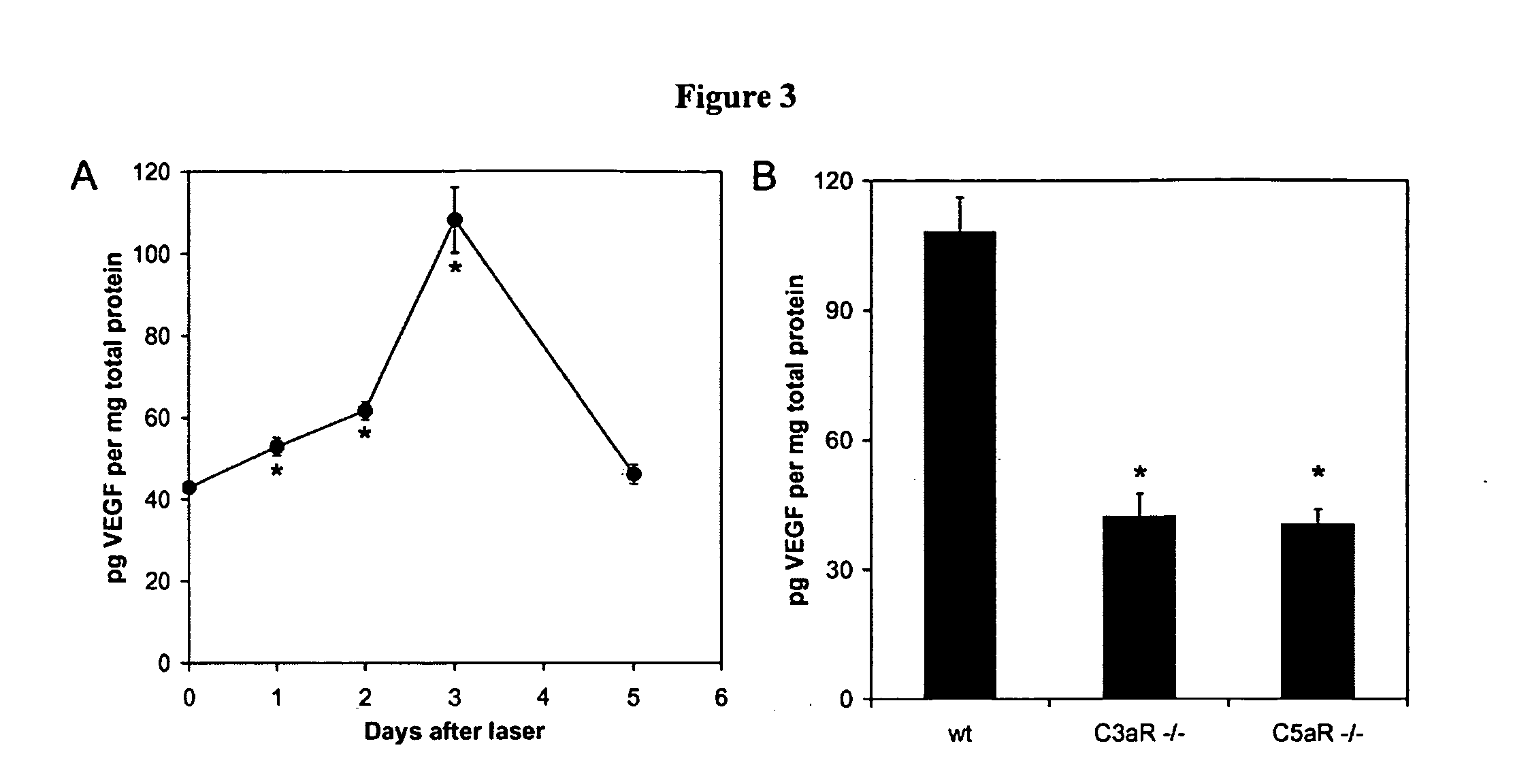
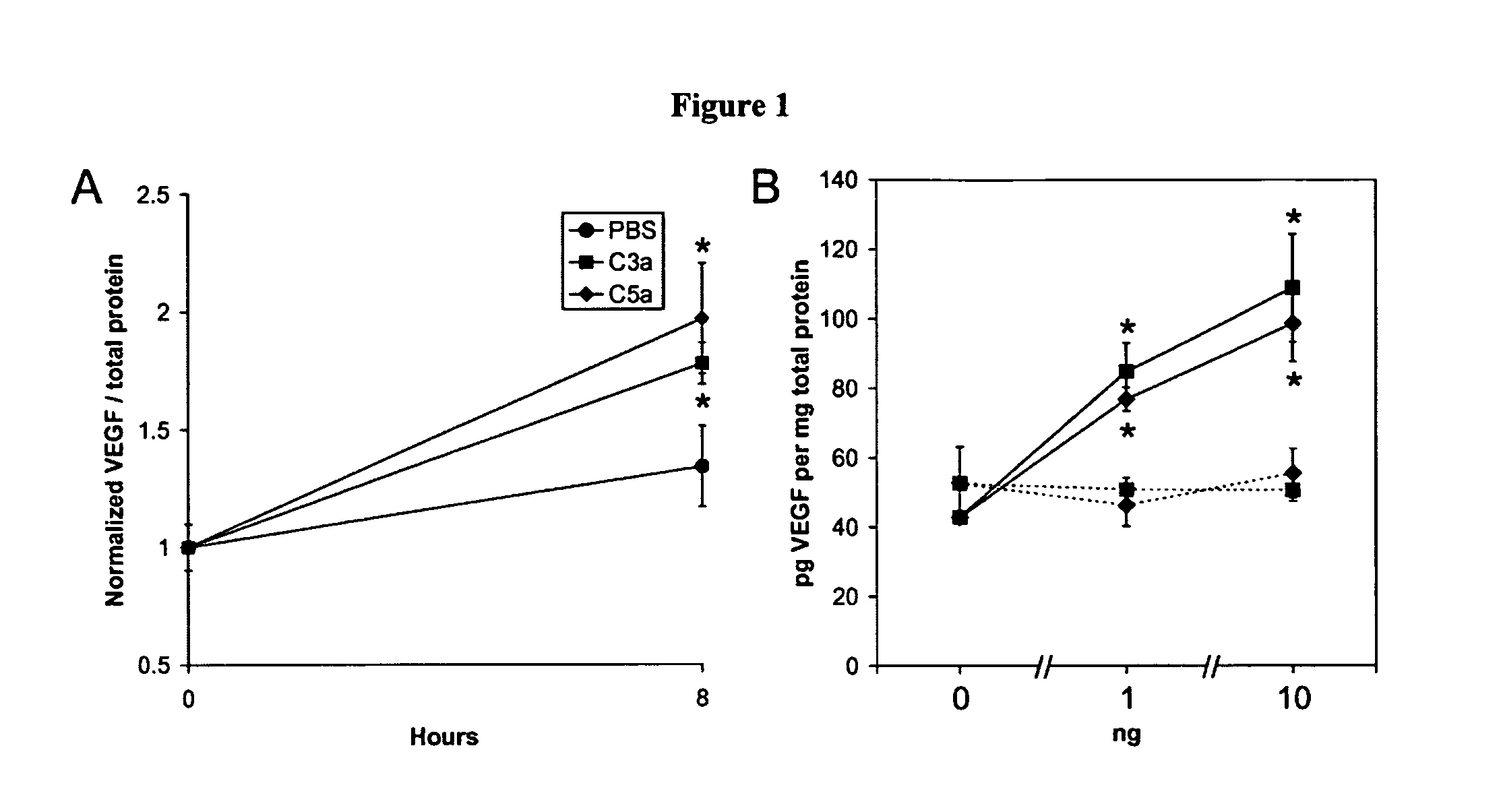
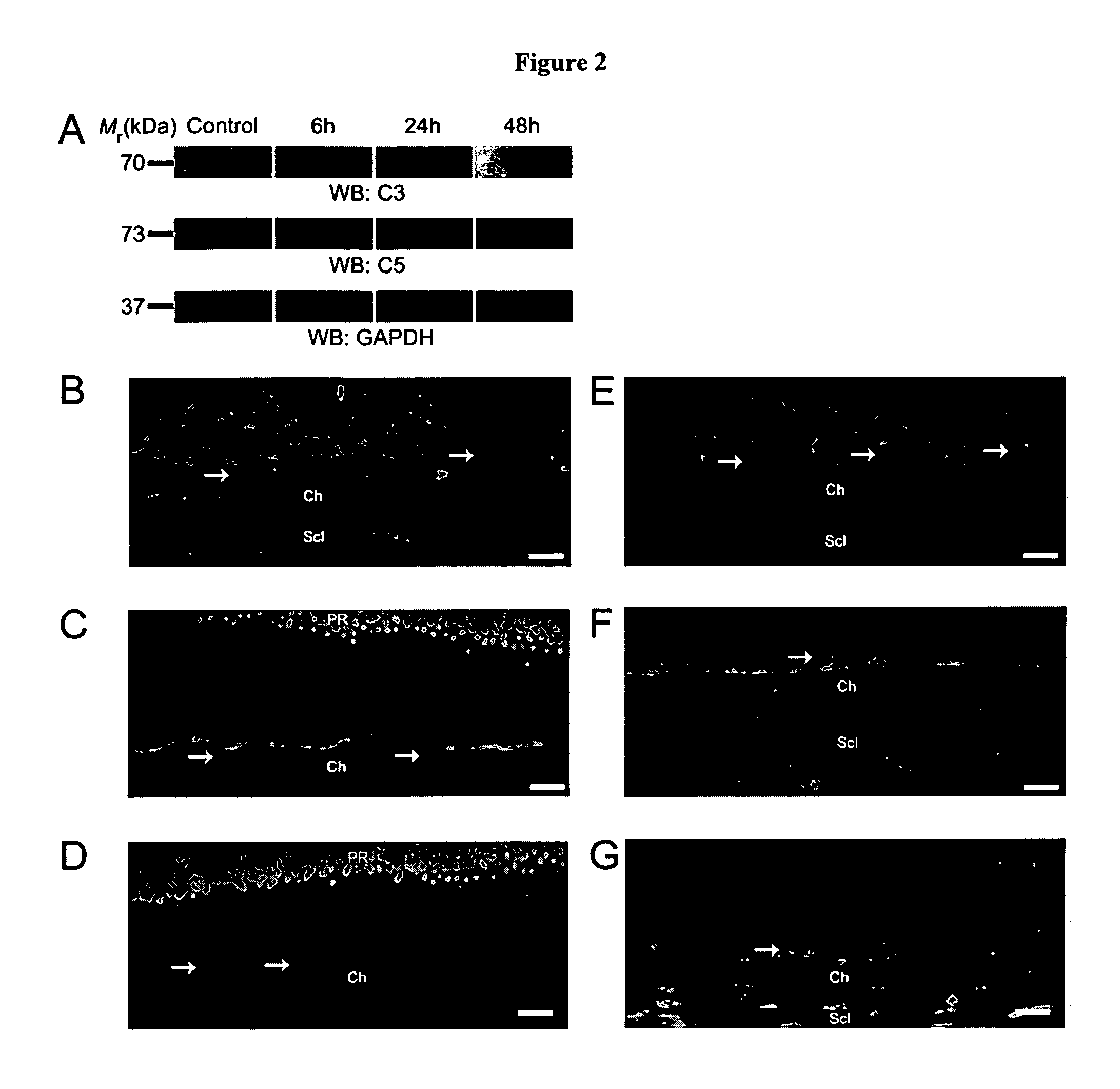
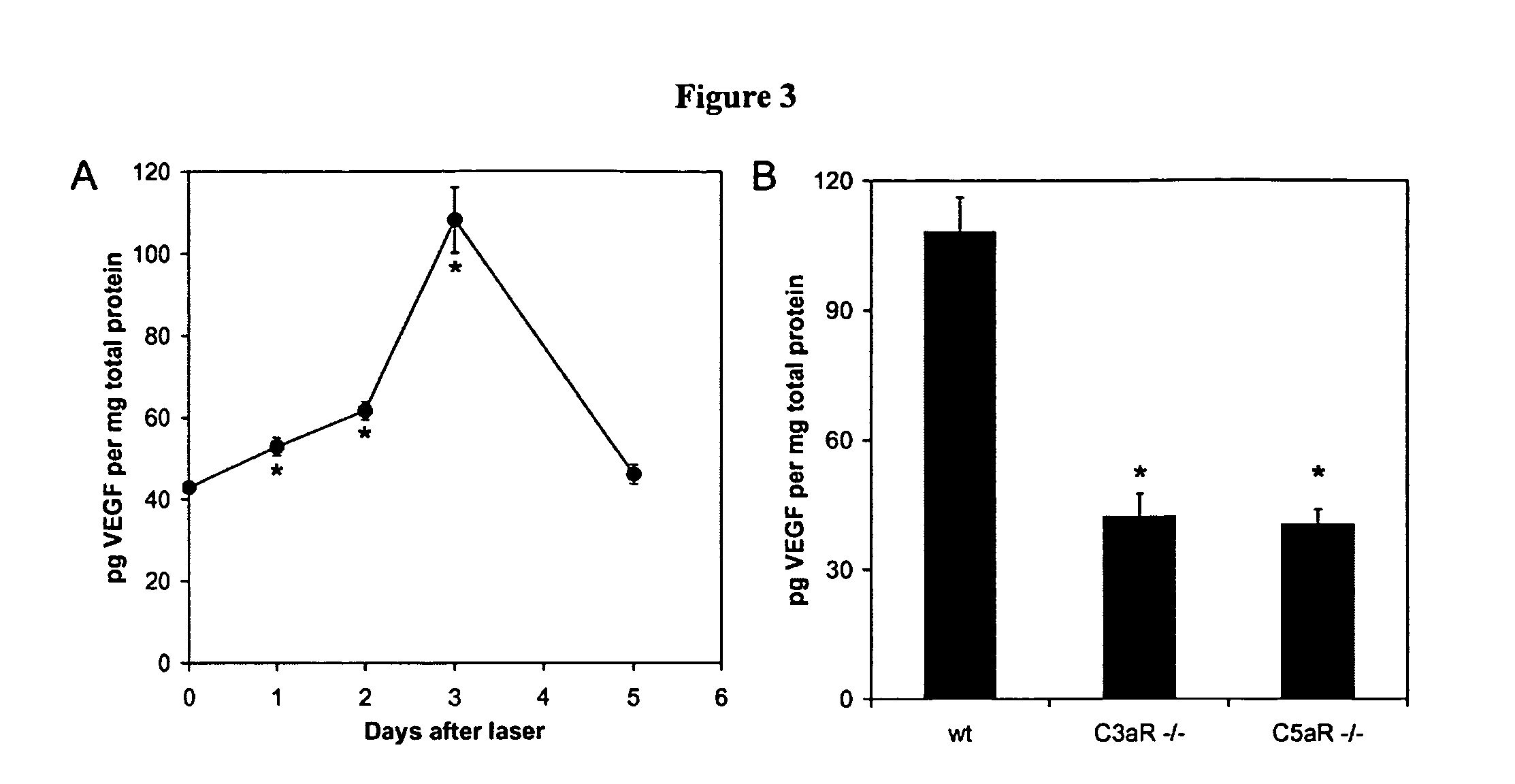
Compositions and methods for inhibiting drusen complement components C3a and C5a for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration
InactiveUS20060067935A1Reduces VEGF expressionReduce expressionGenetic material ingredientsAntibody ingredientsIn vivoBiology
Activated C3 (C3a) and its receptor (C3aR) and activated C5 (C5a) and its receptor (C5aR) have been shown to induce vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in vitro and in vivo. Compositions and methods for inhibiting C3a, C3aR, C5a and C5aR for the treatment and / or prevention of neovascular disease are provided. Also provided are Novel therapeutic targets and diagnostic markers for choroidal neovascularization.
Owner:KENTUCKY UNIVERISTY OF
Compositions and methods for inhibiting drusen complement components C3a and C5a for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration
Activated C3 (C3a) and its receptor (C3aR) and activated C5 (C5a) and its receptor (C5aR) have been shown to induce vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in vitro and in vivo. Compositions and methods for inhibiting C3a, C3aR, C5a and C5aR for the treatment and / or prevention of neovascular disease are provided. Also provided are Novel therapeutic targets and diagnostic markers for choroidal neovascularization.
Owner:KENTUCKY UNIVERISTY OF
Compositions useful to treat ocular neovascular diseases and macular degeneration
InactiveUS20060134226A1Inhibit angiogenesisPrevent visual impairmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideVitamin CLutein
The present invention provides a composition that includes: (a) xanthophylls; (b) vitamin C; (c) vitamin E; (d) zinc; and (e) copper. The present invention also provides a method of treating macular degeneration in a human, inhibiting angiogenesis in a human, preventing impairment of the vision or for improving impaired vision of a human whose eye has drusen, and / or treating a disease associated with ocular neovascularitis in a human. The methods include administering to a human in need of such treatment an effective amount of the composition of the present invention.
Owner:NU TEIN
Method and System for Evaluating Progression of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
ActiveUS20160174830A1Accurate identificationImage enhancementImage analysisVolumetric Mass DensityCvd risk
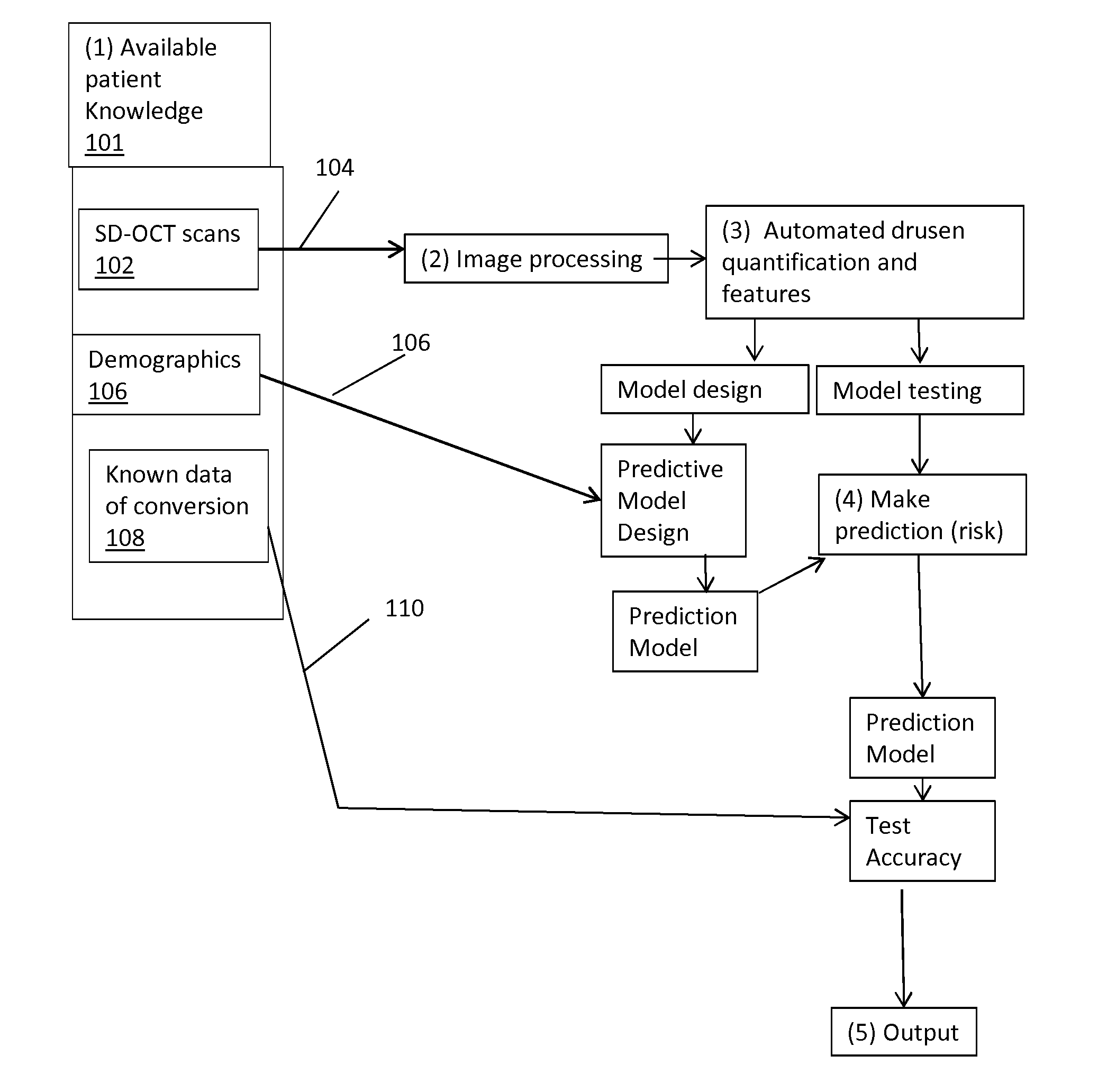
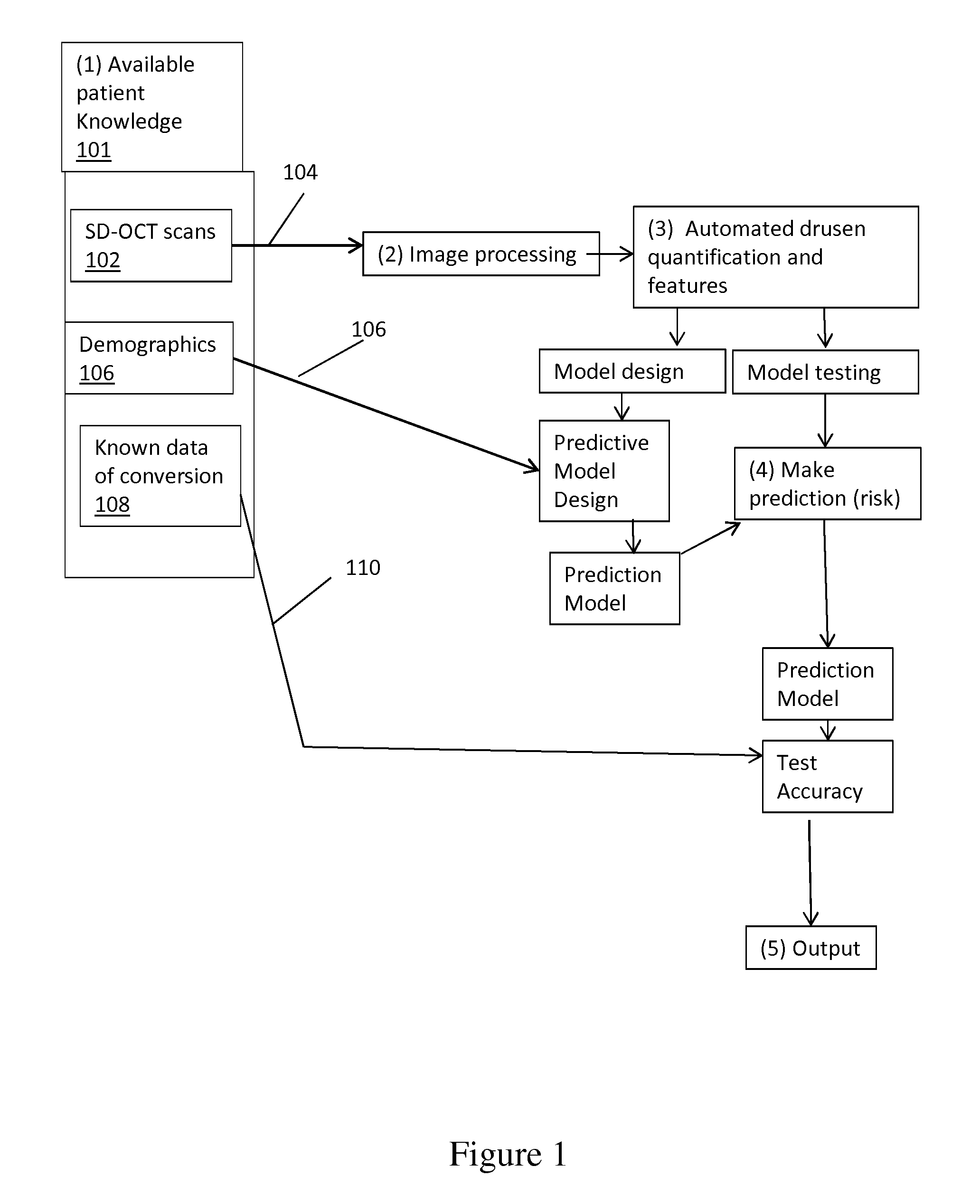
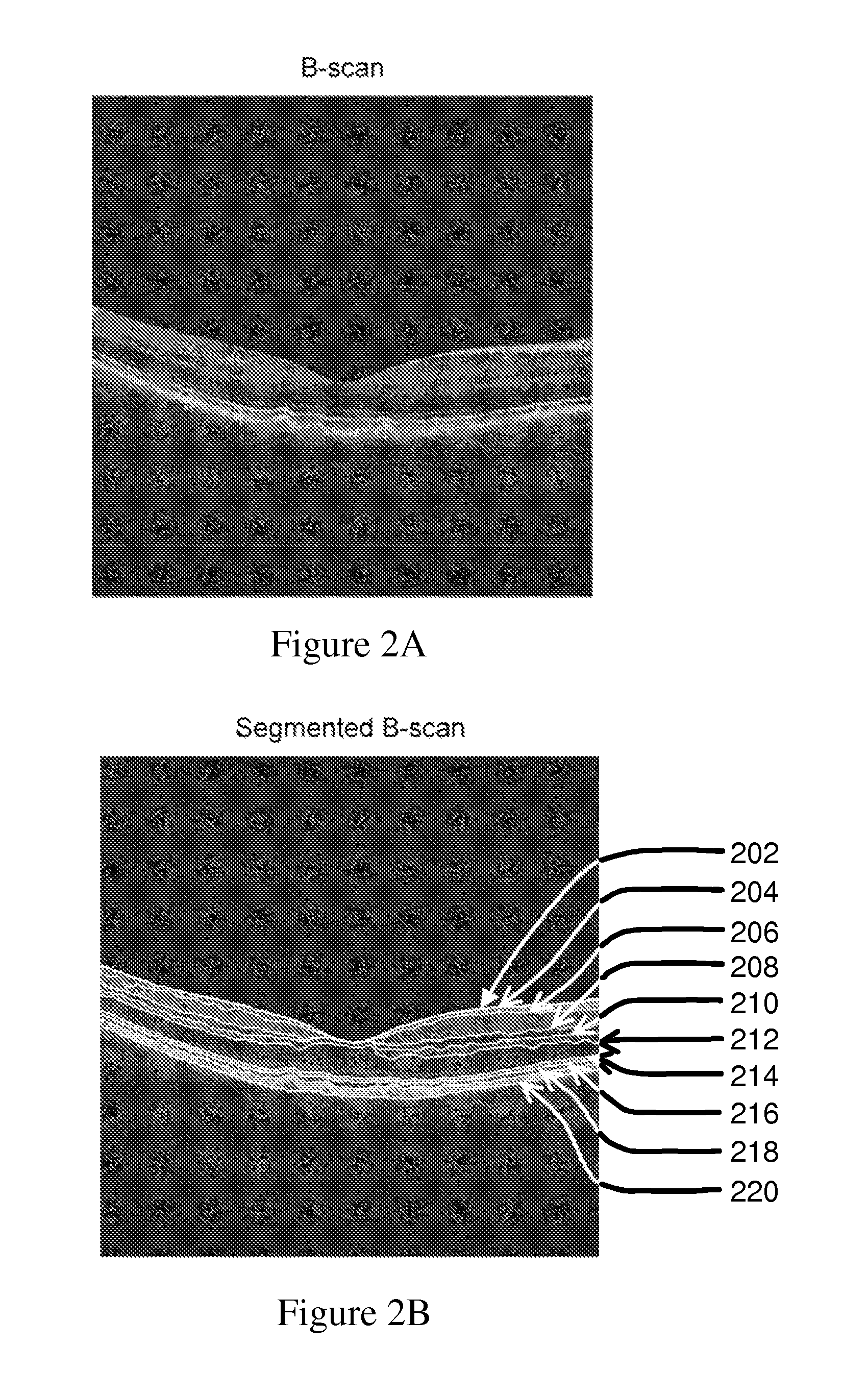
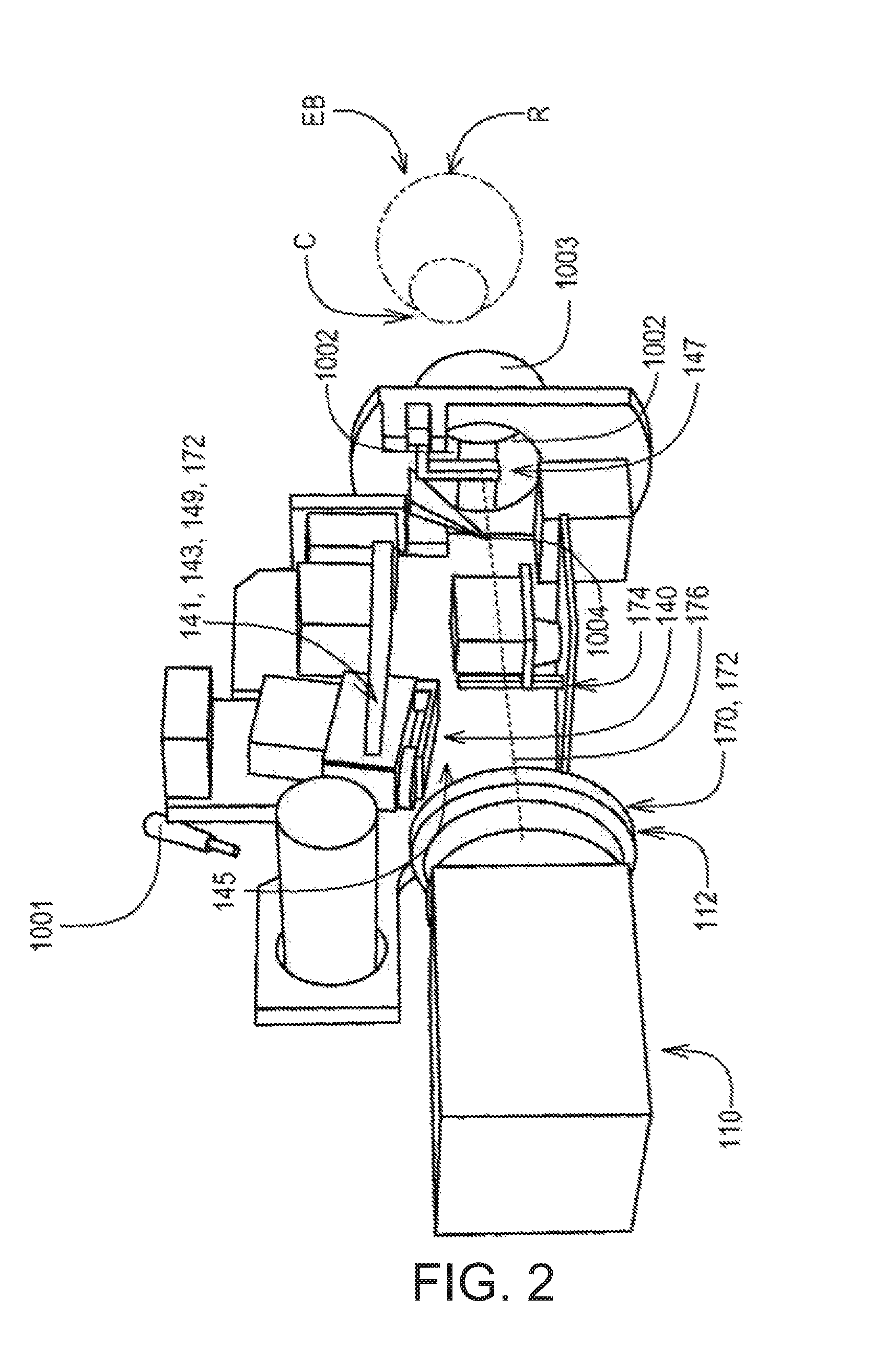
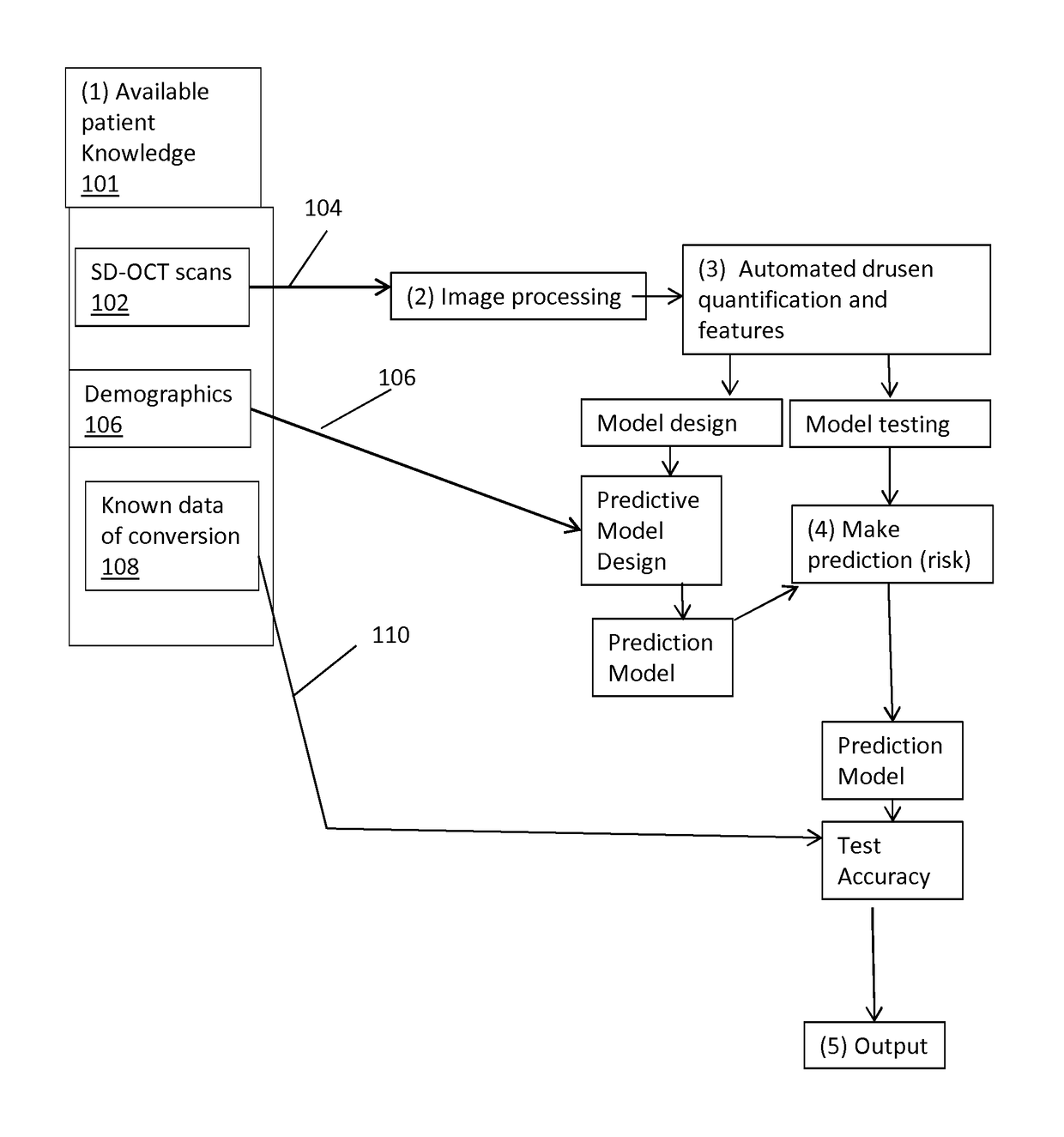
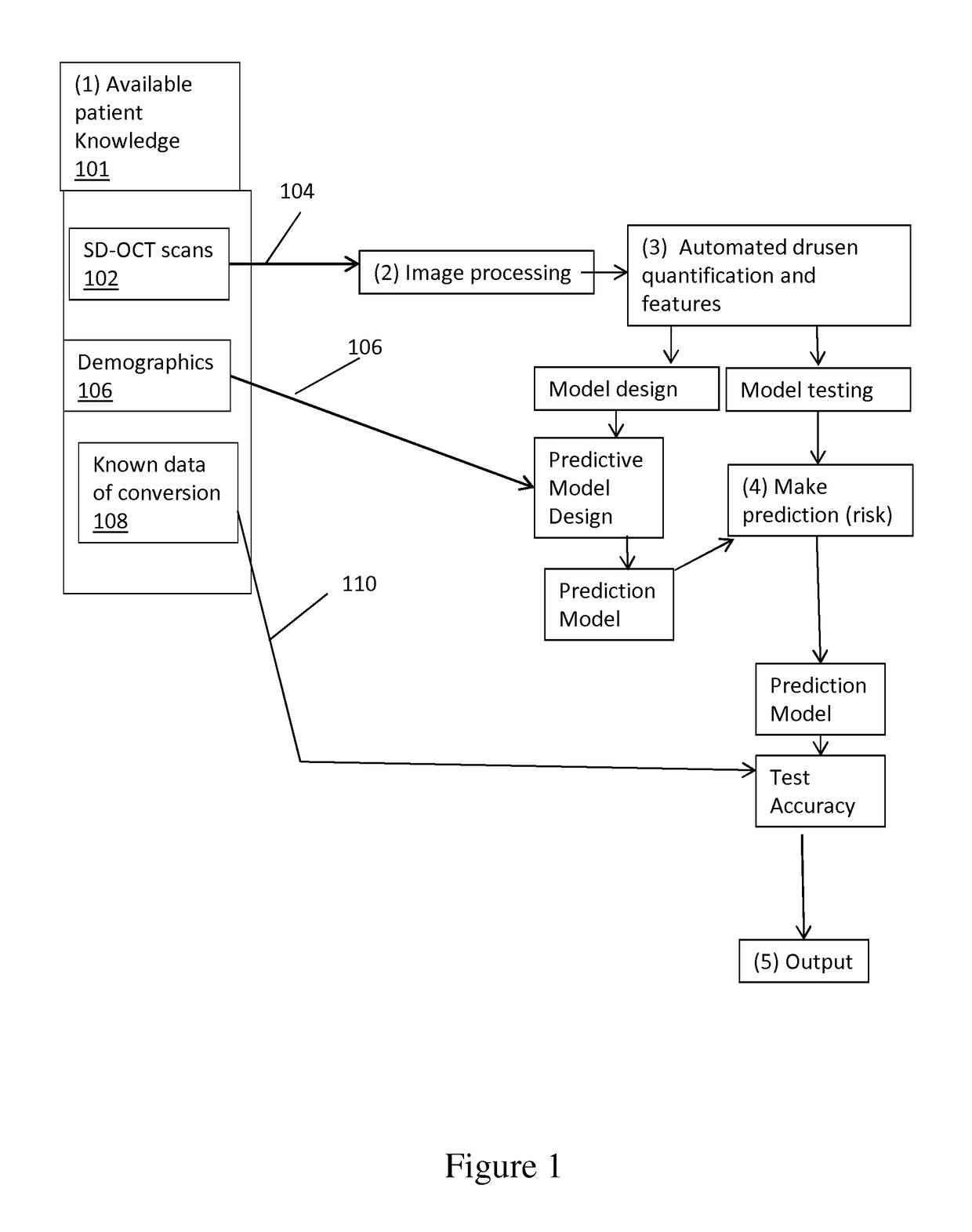
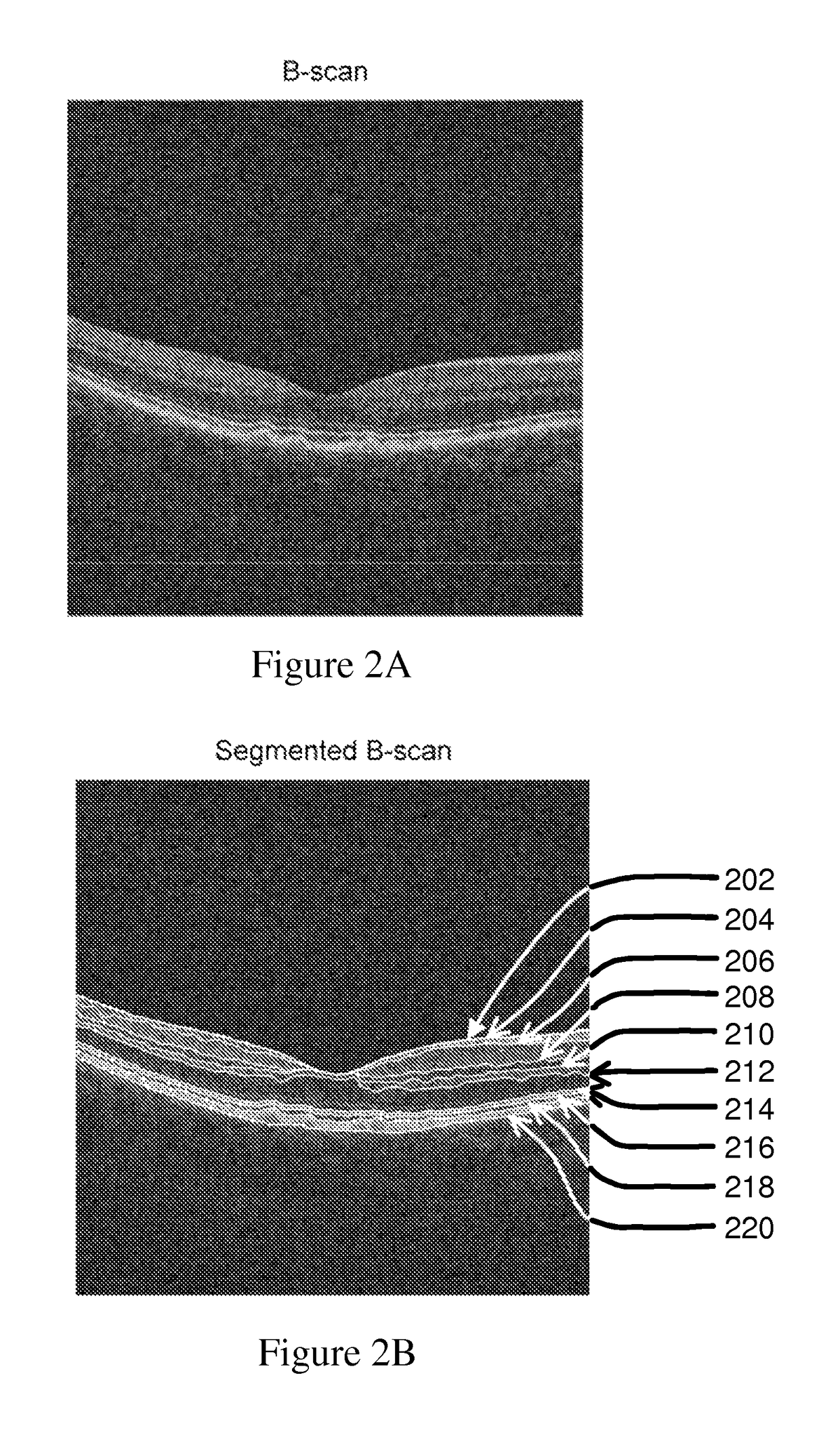
Disclosed is a method for analyzing retinal image data obtained using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT). The image data comprise a cross-section of the retina and an en face image of the retina of a subject having AMD (age-related macular degeneration). The image data are processed to obtain an accurate structure showing locations, shape, size, and other data on drusen (deposits under the retina). This structural information is processed to extract quantitative drusen features that are indicative of a risk of progression of AMD from the dry form to the wet form of the disease in a given subject and defined time period, including short time intervals (one year or less). Relevant drusen features used include number, en face area and volume of drusen detected; shape of drusen detected; density of drusen; and reflectivity of drusen. The method uses the extracted drusen features in combination with clinical data and measurement of the changes of the quantitative image features over time to derive a risk score for whether or not the subject will progress from dry AMD to wet AMD in a defined time period.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Use of cyclodextrins as an active ingredient for treating dry AMD and solubilizing drusen
The present invention is directed to the treatment of disorders involving the accumulation of drusen, such as dry age-related macular degeneration and geographic atrophy via administration of therapeutically effective amounts of at least one monomeric or polymeric cyclodextrin.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
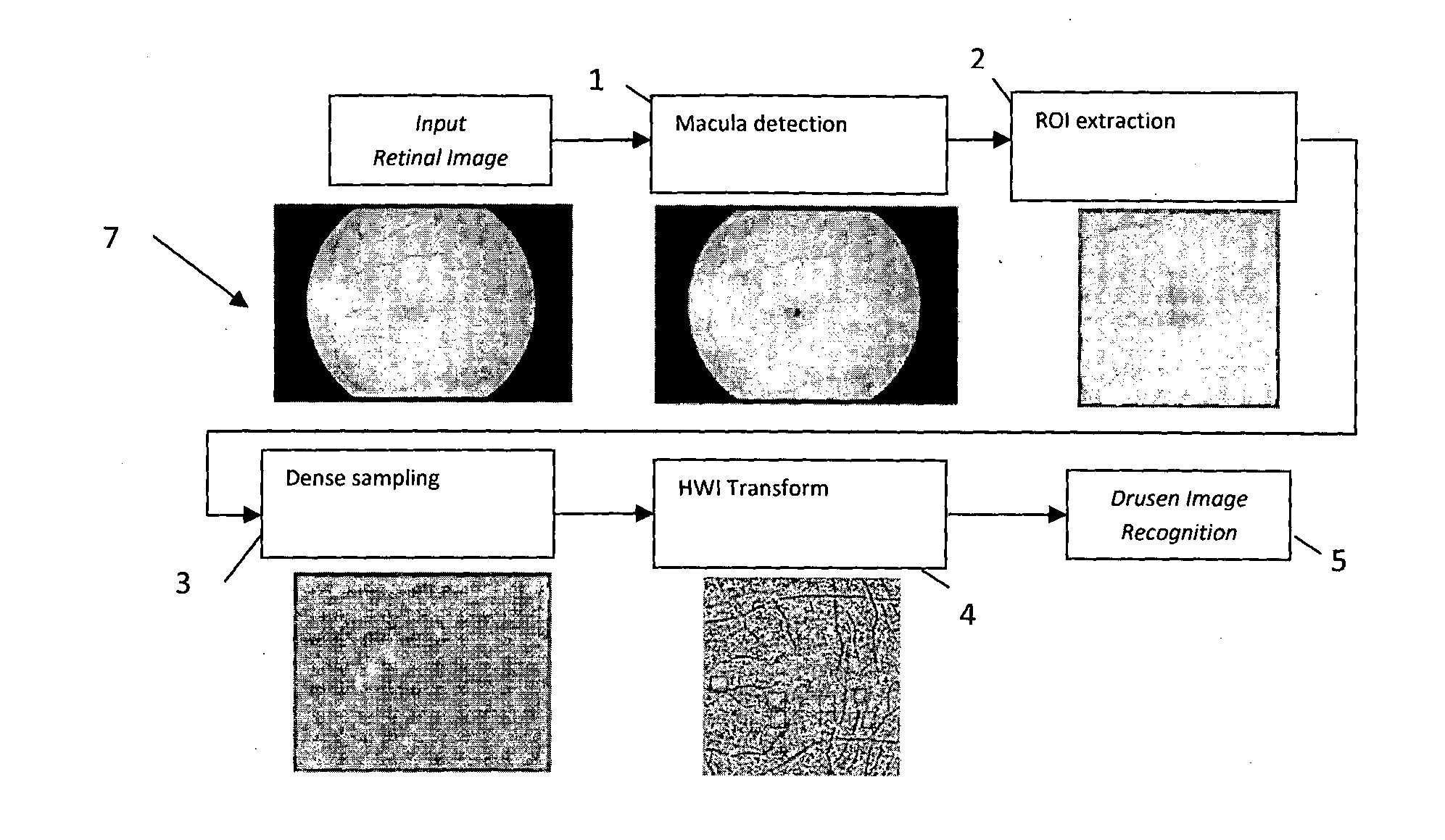
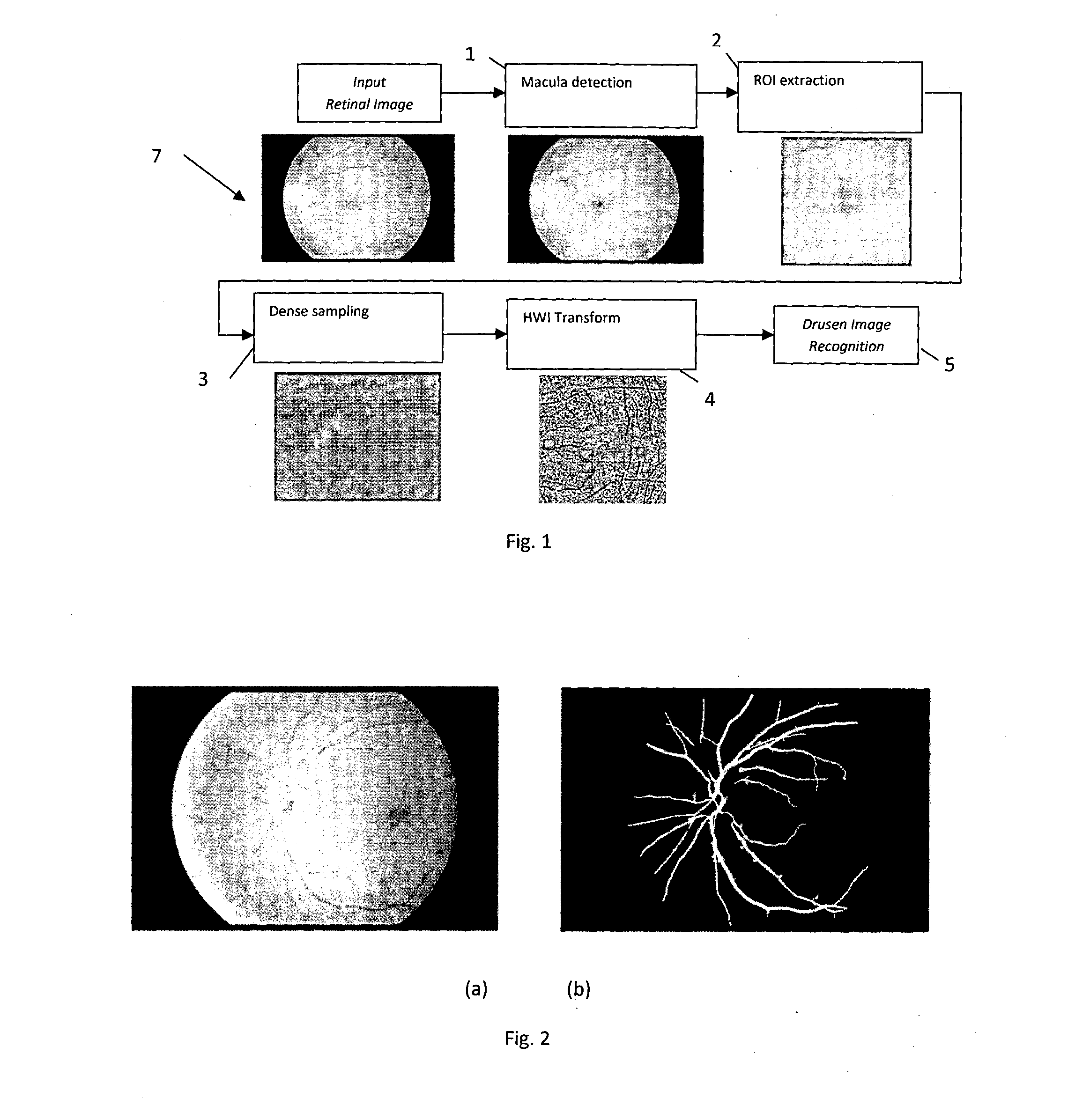
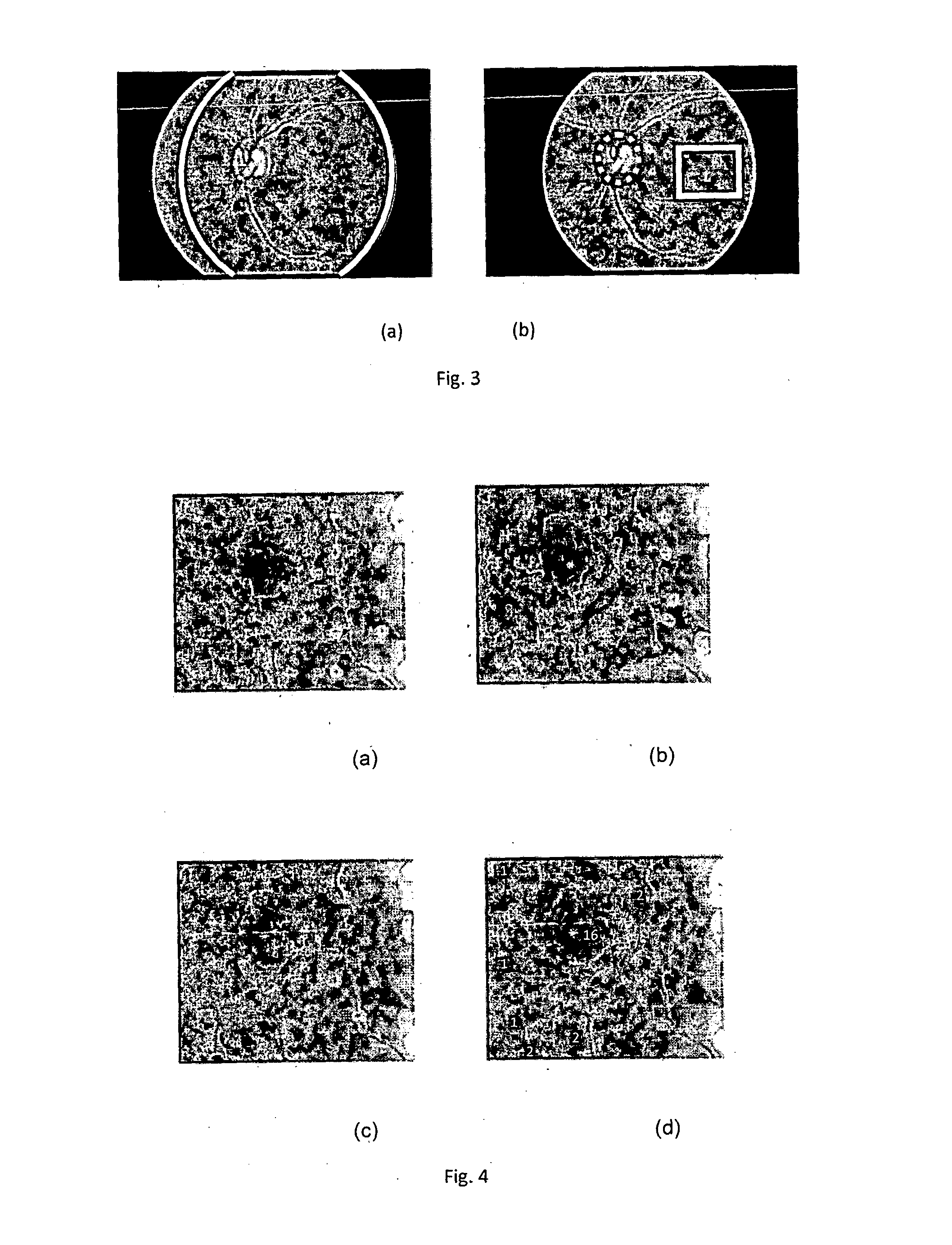
Drusen lesion image detection system
InactiveUS20150125052A1Fast and objective and less labour-intensivePromote resultsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage detection
A method is proposed for automatically analysing a retina image, to identify the presence of drusen which is indicative of age-related macular degeneration. The method proposes dividing a region of interest including the macula centre into patches, obtaining a local descriptor of each of the patches, reducing the dimensionality of the local descriptor by comparing the local descriptor to a tree-like clustering model and obtaining transformed data indicating the identity of the cluster. The transformed data is fed into an adaptive model which generates data indicative of the presence of drusen in the retinal image. Furthermore, the trans formed data can be used to obtain the location of the drusen within the image.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Use of agents that prevent the generation of amyloid-like proteins and/or drusen, and/or use of agents that promote sequestration and/or degradation of, and/or prevent the neurotoxic effects of such proteins in the treatment of macular degeneration
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating age-related macular degeneration (AMD). More specifically, the methods of the invention target amyloid proteins and drusen that tend to accumulate in the eyes of those patients suffering from AMD. AMD is treated in the methods of the invention by providing agents that sequester and / or degrade such amyloid deposits and / or drusen such that a patient's vision is improved or restored.
Owner:ALCON INC
Agents for treatment of diabetic retinopathy and drusen formation in macular degeneration
InactiveUS20050137147A1Enhances availability and transportAvoid damageBiocideSenses disorderThiocarbamateQuinone
Agents that stimulate nuclear translocation of Nrf2 protein and the subsequent increases in gene products that detoxify and eliminate cytotoxic metabolites are provided in a method for treating diabetic retinopathy or drusen formation in age-related macular degeneration. The structurally diverse agents that act on the Nrf2 / ARE pathway induce the expression of enzymes and proteins that possess chemically versatile cytoprotective properties and are a defense against toxic metabolites and xenobiotics. Agents include certain electrophiles and oxidants such as a Michael Addition acceptor, diphenol, thiocarbamate, quinone, 1,2-dithiole-3-thione, butylated hydroxyanisole, flavonoid other than genistein, an isothiocyanate, 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxytoluene, ethoxyquin, a coumarin, combinations thereof, or a pharmacologically active derivative or analog thereof.
Owner:ALCON INC
Age related macular degeneration treatment
InactiveUS20120156202A1Reduce edemaReducing blood cholesterolSenses disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBlood vesselInsulin humulin
A method for treating age related macular degeneration (AMD) using an insulin preparation applied topically to the conjunctival sac of the affected eye. Another aspect of this invention is using antiangiogenic adjuvant therapeutic agents such as bevacizumab, ranibizumab, pegaptanib, etanercept, instilled in to the afflicted eye conjunctival sac with insulin to prevent further formation of new blood vessels, and shrink the existing pathologically formed blood vessels and reduce the edema in wet AMD. This method incorporates putting the patients on low fat diet, aerobic exercise, ketamine-a NMDA blocker, reducing the blood cholesterol using adjuvant therapeutic agents selected from Statins, that are inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A, (i.e. HMG-Co A) reductase which in turn reduce drusen formation that leads to AMD, combined with insulin ophthalmic drops.
Owner:SHANTHA TOTADA R +2
Compositions and Methods for Inhibiting Drusen Formation and for Diagnosing or Treating Drusen-Related Disorders
InactiveUS20110020237A1Facilitating break-down and degradation and clearanceInhibition formationHeavy metal active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseDrusen
Compositions of matter and methods for inhibiting drusen or drusen-like deposits and / or for treating diseases related to drusen or drusen-like deposits in human or animal subjects by administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of i) a conformational epitope of an aggregate that contributes to the formation or biosynthesis of drusen or drusen-like deposits and / or ii) an antibody that binds to a conformational epitope of an aggregate that contributes to the formation or biosynthesis of drusen or the drusen-like deposit.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multi-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Derivatives and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20180009758A1Macular degeneration is suppressed and preventedWet macular degenerationOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTyrosine-kinase inhibitorDrusen
The present invention is directed to multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor compounds. The present invention is further directed to compositions comprising those compounds. Finally, the present invention is directed to methods of treating eye conditions including, but not limited to, diabetic background retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, diabetic proliferative retinopathy, diabetic macular edema with proliferative retinopathy, proliferative fibrovascular disease, diabetic macular edema with proliferative fibrovascular disease, retinopathy of prematurity, dry macular degeneration, dry macular degeneration with drusen and wet macular degeneration, using compounds and compositions of the invention.
Owner:ONTOGENESIS LLC
Hydroxylamines and derivatives for the inhibition of complement activation
Methods for the inhibition of complement activation, for the treatment of complement-mediated pathologies, and for the treatment of drusen-mediated pathologies are disclosed. The methods utilize hydroxylamine compounds and ester derivatives thereof, administered to subjects in effective amounts.
Owner:COLBY PHARMA CO
Method for inducing primate macular degeneration model by high fat
ActiveCN104982379AGood model carrierPromote formationFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAnimal sciencePrimate
The present invention discloses a method for inducing a primate macular degeneration model by high fat. The method comprises: feeding an inhuman primate suffered from drusen lesion with a high-fat feed and feeding the inhuman primate for three times every day with the feeding amount of 75-100g per time; and feeding the inhuman primate for 60-110 days to obtain a stable macular degeneration model. According to the method disclosed by the present invention, a dry or wet macular degeneration animal model close to spontaneous occurring of human beings can be obtained and the integrity of a Bruch's film can be kept; the model is stable and irreversible, and has good animal obedience; animals do not need to be subjected to surgeries or be killed to be checked; the modeling cost is very low; and an ideal animal model is provided for researching a pathogenesis of the macular degeneration model, screening treatment medicines and carrying out pharmacodynamic evaluation.
Owner:广西南宁灵康赛诺科生物科技有限公司
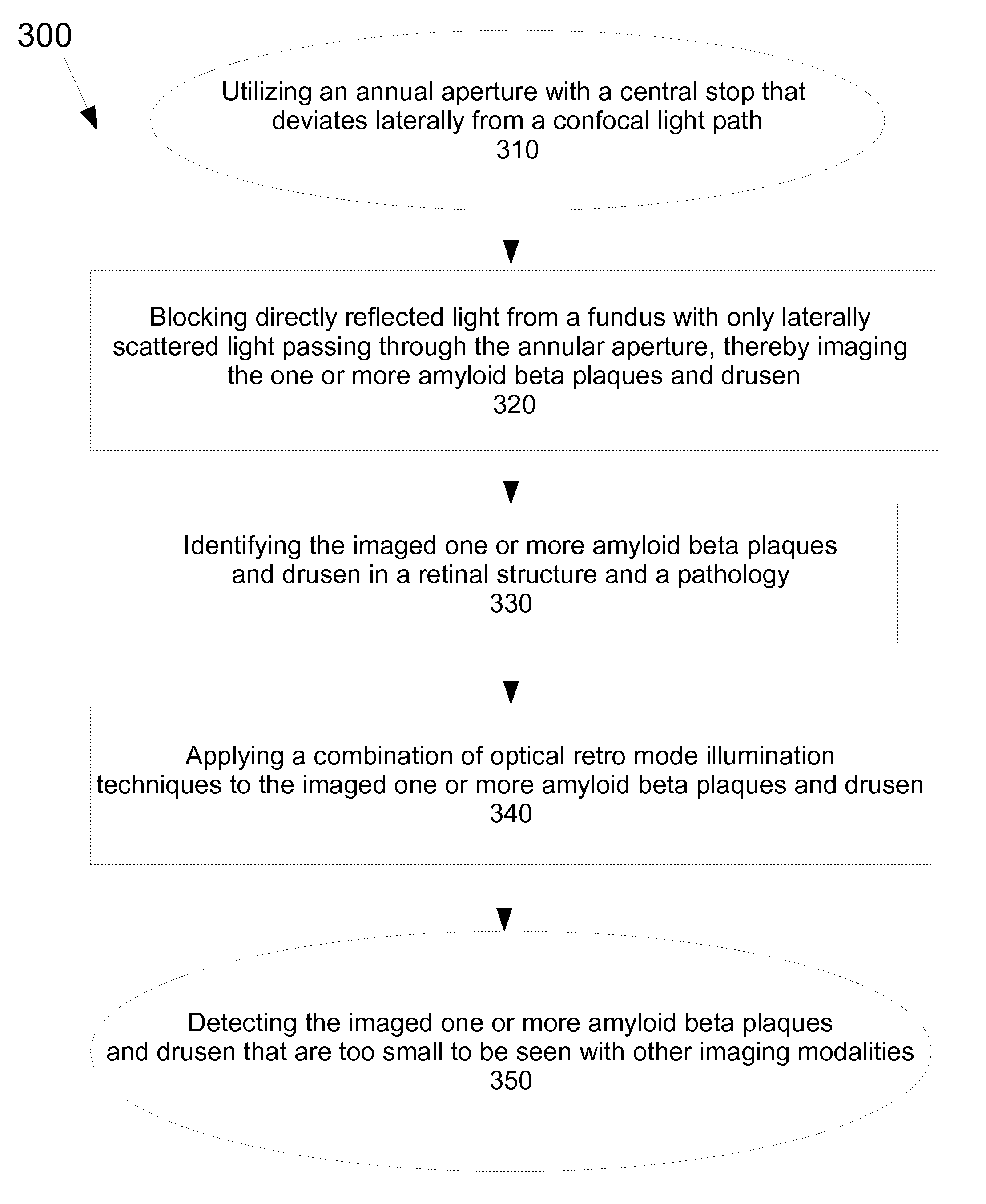
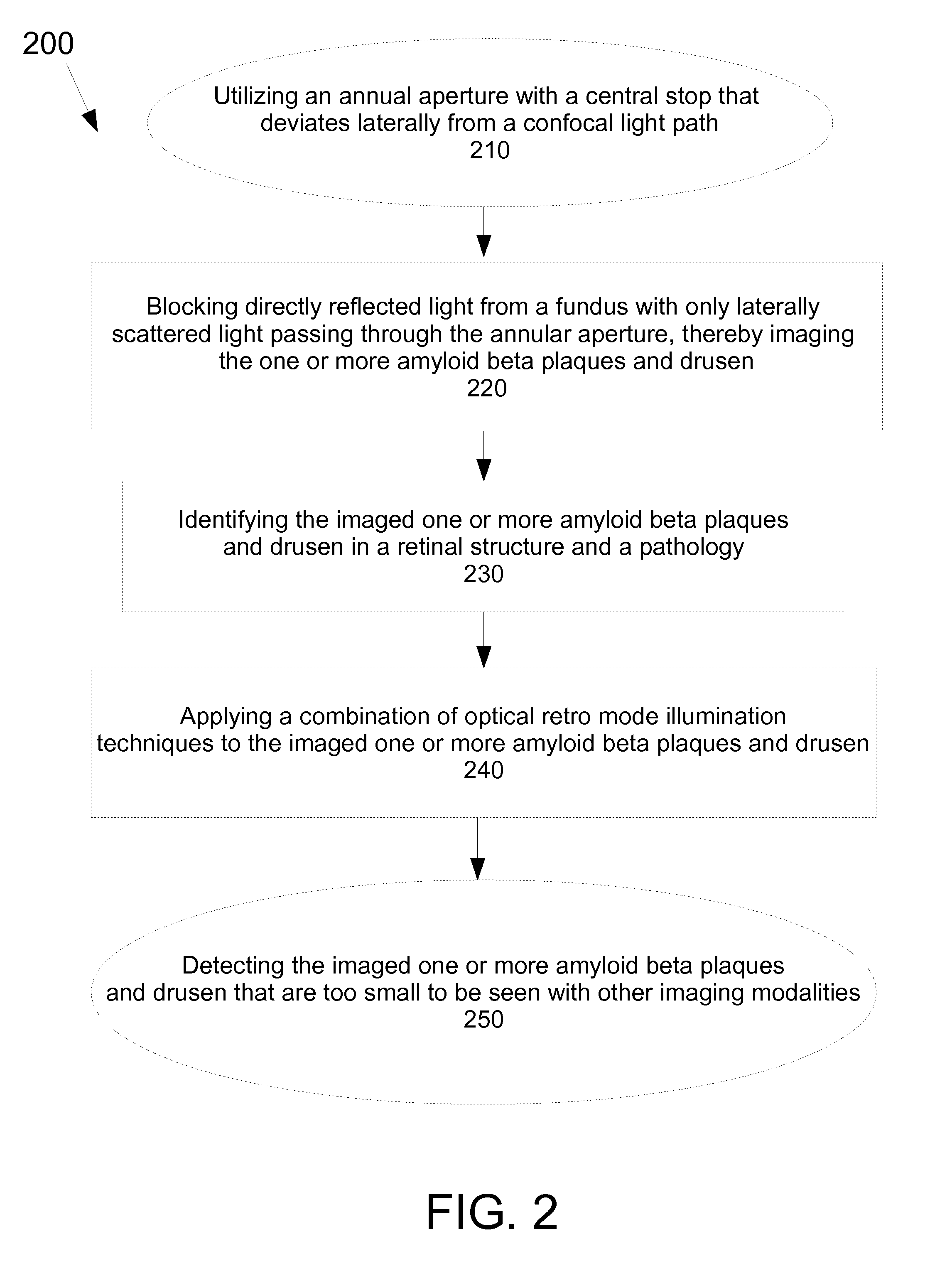
Method for detecting amyloid beta plaques and drusen
A method for detecting amyloid beta plaques and drusen is disclosed. The method for detecting amyloid beta plaques and drusen may include applying a combination of optical retro mode illumination techniques to acquire a plurality of amyloid beta plaques and drusen images that are too small to be seen with other imaging modalities. The amyloid beta plaques and drusen images may also be detected with a non-transitory computer storage media having instructions stored thereon which, when executed, execute the method for detecting amyloid beta plaques and drusen. The method may track changes in plaque, size, area and density of the amyloid beta plaques and drusen over a predetermined period of time.
Owner:NEUROVISION IMAGING INC
Method and system for evaluating progression of age-related macular degeneration
Disclosed is a method for analyzing retinal image data obtained using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT). The image data comprise a cross-section of the retina and an en face image of the retina of a subject having AMD (age-related macular degeneration). The image data are processed to obtain an accurate structure showing locations, shape, size, and other data on drusen (deposits under the retina). This structural information is processed to extract quantitative drusen features that are indicative of a risk of progression of AMD from the dry form to the wet form of the disease in a given subject and defined time period, including short time intervals (one year or less). Relevant drusen features used include number, en face area and volume of drusen detected; shape of drusen detected; density of drusen; and reflectivity of drusen. The method uses the extracted drusen features in combination with clinical data and measurement of the changes of the quantitative image features over time to derive a risk score for whether or not the subject will progress from dry AMD to wet AMD in a defined time period.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Multi-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Derivatives and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20170342033A1Macular degeneration is suppressed and preventedWet macular degenerationSenses disorderAlbumin peptidesDrusenEye disease
The present invention is directed to multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor compounds. The present invention is further directed to compositions comprising those compounds. Finally, the present invention is directed to methods of treating eye conditions including, but not limited to, diabetic background retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, diabetic proliferative retinopathy, diabetic macular edema with proliferative retinopathy, proliferative fibrovascular disease, diabetic macular edema with proliferative fibrovascular disease, retinopathy of prematurity, dry macular degeneration, dry macular degeneration with drusen and wet macular degeneration, using compounds and compositions of the invention.
Owner:ONTOGENESIS LLC
Agents for treatment of diabetic retinopathy and drusen formation in macular degeneration
InactiveUS20100204244A1Enhances availability and transportAvoid damageBiocideSenses disorderThiocarbamateQuinone
Agents that stimulate nuclear translocation of Nrf2 protein and the subsequent increases in gene products that detoxify and eliminate cytotoxic metabolites are provided in a method for treating diabetic retinopathy or drusen formation in age-related macular degeneration. The structurally diverse agents that act on the Nrf2 / ARE pathway induce the expression of enzymes and proteins that possess chemically versatile cytoprotective properties and are a defense against toxic metabolites and xenobiotics. Agents include certain electrophiles and oxidants such as a Michael Addition acceptor, diphenol, thiocarbamate, quinone, 1,2-dithiole-3-thione, butylated hydroxyanisole, flavonoid other than genistein, an isothiocyanate, 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxytoluene, ethoxyquin, a coumarin, combinations thereof, or a pharmacologically active derivative or analog thereof.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Choroidal neovascularization suppressor or drusen formation suppressor, and method for assessing or screening for same
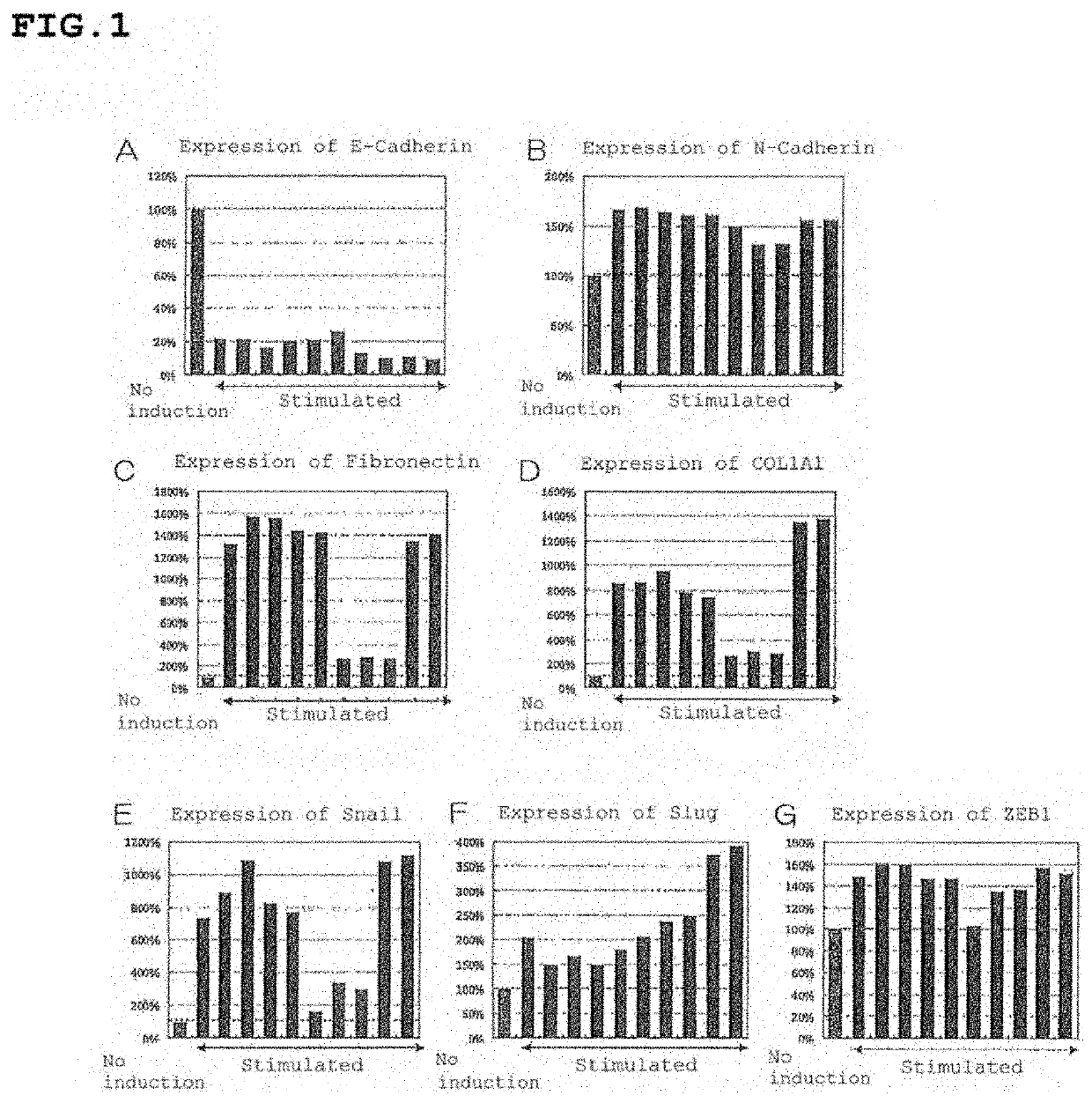
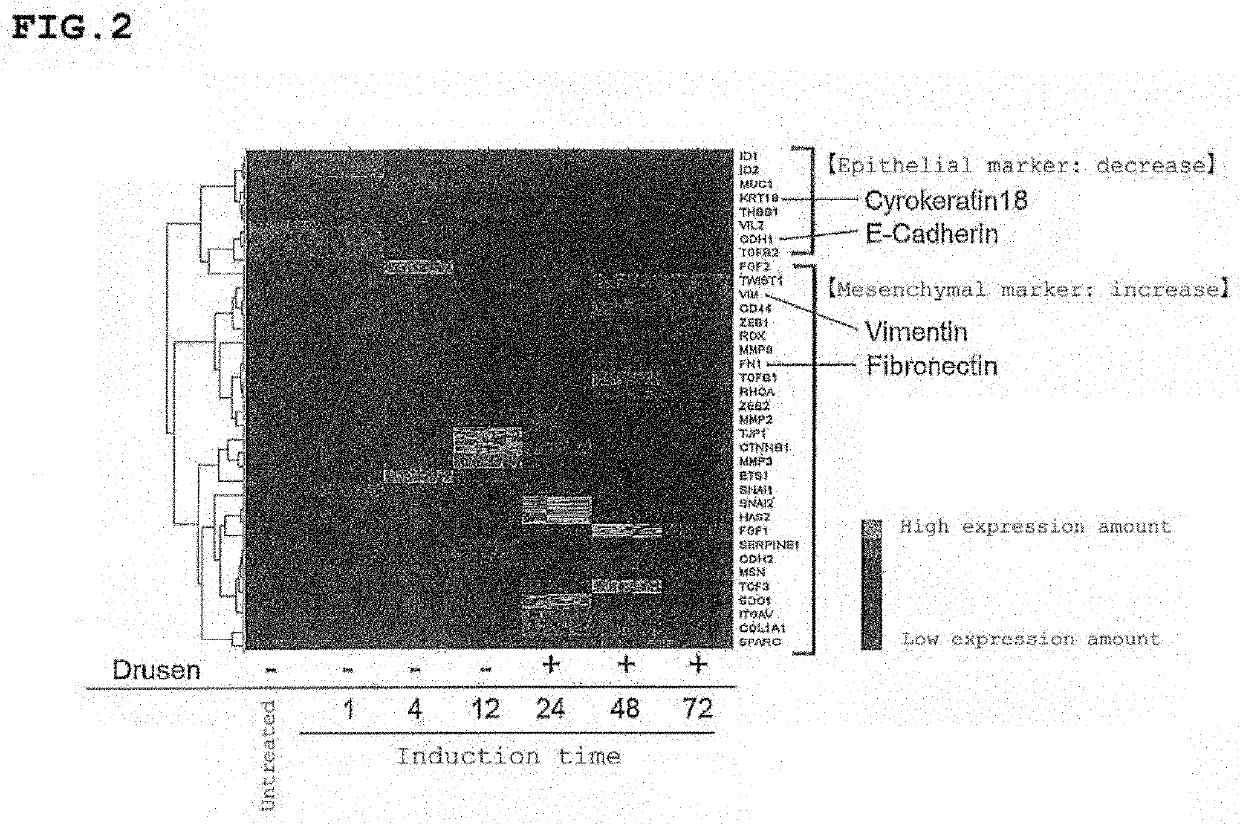
ActiveUS10761087B2Inhibit expressionSuppressing EMTSenses disorderBiological testingBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTRetinal pigment epithelial cell
The existent therapeutic drugs for CNV are merely pharmaceuticals for a symptomatic therapy, and therapeutic drugs for radical cure are strongly demanded. Also, a therapeutic drug for Dry AMD does not exist, and therapeutic drugs for radical cure are strongly demanded. The present invention provides a prophylactic and / or therapeutic agent for choroidal neovascularization, containing a compound having an activity of suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in retinal pigment epithelial cells, as an active ingredient. Also, the present invention provides a drusen suppressor comprising a compound having an activity of suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in retinal pigment epithelial cells, as an active ingredient.
Owner:LINK GENOMICS +1
Method of Reducing the Occurrence of Macular and Neuroretinal Degenerations by Alleviating Age Related Retinal Stresses as a Contributing Factor in a Mammalian Eye
InactiveUS20150164635A1Restore some accommodative abilityRestore levelStentsEye implantsCorneal endotheliumInsertion stent
A method of reducing the risk of macular degeneration is provided. The method includes inserting an intraocular collar stent into a portion of a mammalian eye, such that the stent is in contact with soft tissue of the anterior chamber. When inserted in the eye, the stent applies pressure to a surface centered on a transition zone, between an anterior limit of a trabecular meshwork and a posterior limit of a corneal endothelium of the eye, to a surface of the peripheral iris of the eye, and in circumferentially expanding direction to the irideocorneal angle. The pressure is applied continually. The method also includes creating an environment of a reduced negative pressure state within the retina as a result of the application of the pressure; and, while the reduced negative pressure state is present, permitting drusen precursors formed by extracellular material to flow through the eye for removal by vasculature of the eye.
Owner:RENKE PETER
Application of notoginsenoside extract in preparation of medicinal preparation for eyes
PendingCN110075148AHigh activityPromotes damage repairSenses disorderNervous disorderHyphemaDiabetes retinopathy
The invention discloses application of a notoginsenoside extract in preparation of drugs for treating xerophthalmia, ocular injuries, ocular vascular disease or ocular neurogenic disease; the xerophthalmia, ocular injuries, ocular vascular disease or ocular neurogenic disease include but not limited to xerophthalmia, retina retrogressive disease, retinal vein obstruction, retinal periphlebitis, hyphema, vitreous hemorrhage, corneal injury, retinal contusion, glaucomatous optic atrophy, drusen, age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy. A mode of eye local drug delivery adoptedby the invention has the advantages of being low in dose, high in safety, less in adverse reaction, and good in patient compliance; the safety risk brought by injection delivery is avoided; furthermore, after changing the drug delivery route, the metabolic pathways, action mechanisms and other aspects thereof are different from the injection, and better clinical application prospect is realized.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Method of reducing the occurrence of macular and neuroretinal degenerations by alleviating age related retinal stresses as a contributing factor in a mammalian eye
InactiveUS9974645B2Restore some accommodative abilityRestore levelStentsEye implantsExtracellular materialCvd risk
Owner:RENKE PETER
Compositions And Methods For Inhibiting Drusen
InactiveUS20150051212A1Reduce and inhibt drusen formationAmeliorate and prevent and inhibit drusen-associated disorderBiocideAntinoxious agentsDrusenCancer research
Owner:REGENERATIVE RES FOUND
N-Acylalkyl Prodrugs of Multi-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20160376239A1Proliferative retinopathy is preventedFibrovascular proliferative disease is preventedBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
The present invention is directed to N-acylalkyl prodrugs of nitrogen-containing multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitors. The present invention is further directed to compositions comprising compounds of the invention. Finally, the present invention is directed to methods of treating eye conditions including, but not limited to, diabetic background retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, diabetic proliferative retinopathy, diabetic macular edema with proliferative retinopathy, proliferative fibrovascular disease, diabetic macular edema with proliferative fibrovascular disease, retinopathy of prematurity, dry macular degeneration, dry macular degeneration with drusen and wet macular degeneration, using compounds and compositions of the invention.
Owner:ONTOGENESIS LLC
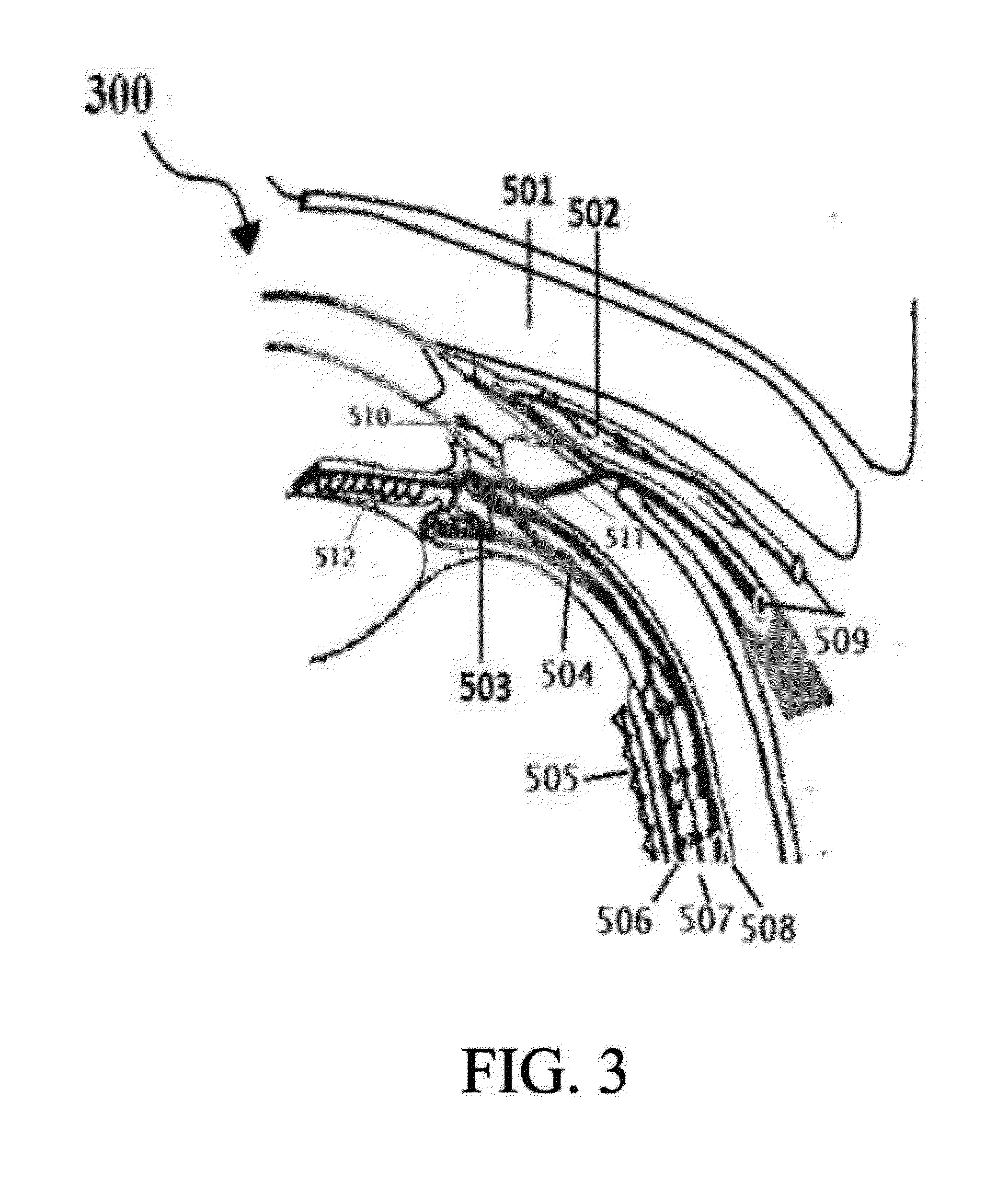
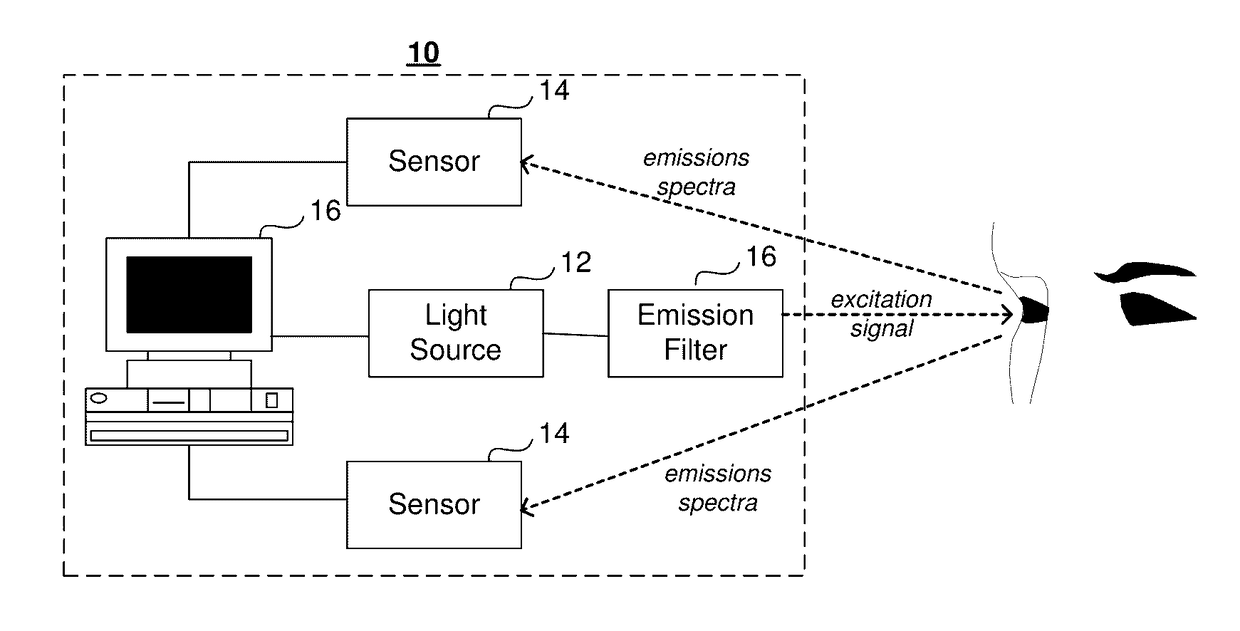
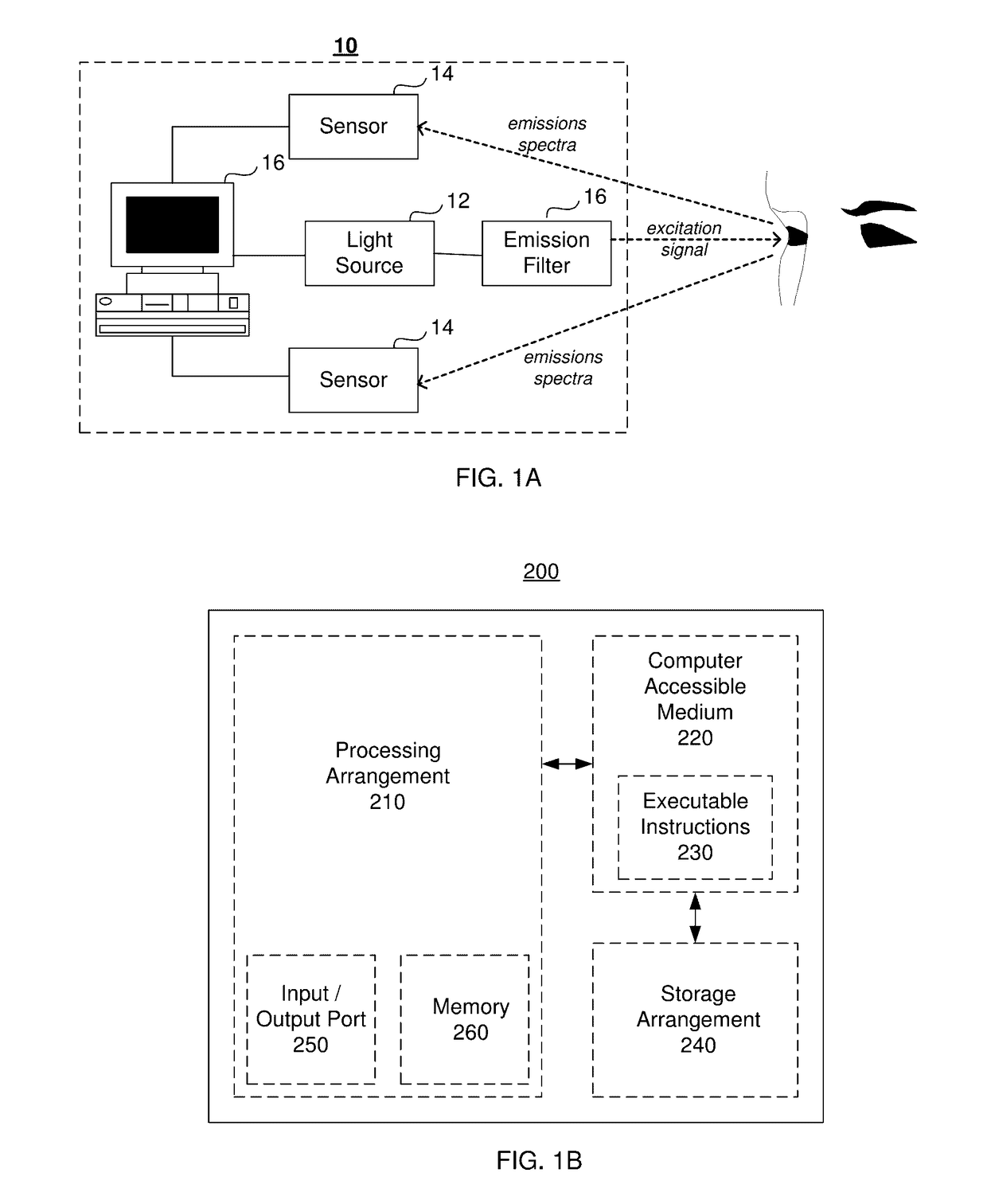
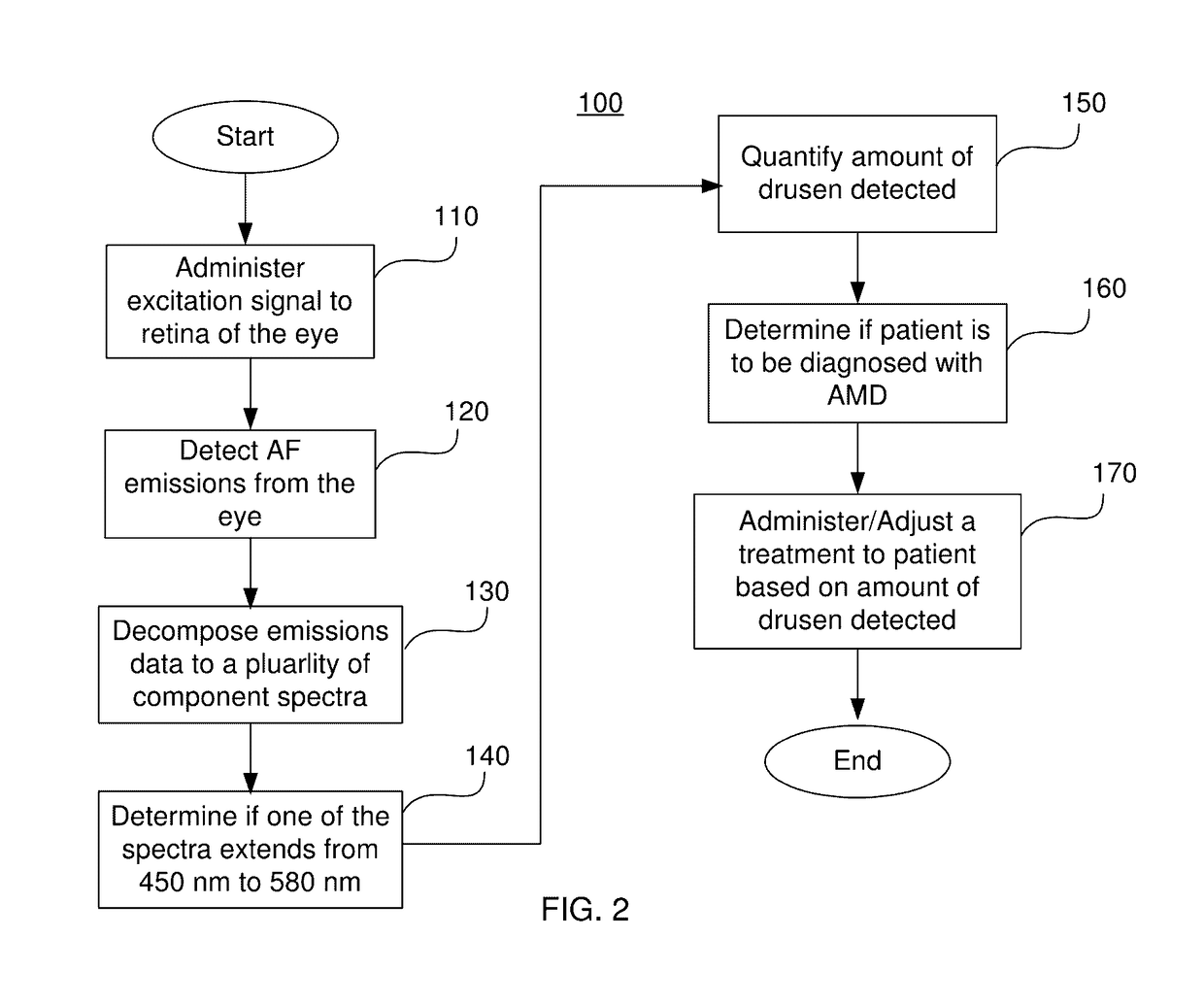
System And Method For In Vivo Detection Of Fluorescence From An Eye
A system and method for in vivo detection and quantification of drusen present in the retina via administering an excitation signal to the retina of the eye and detecting an electromagnetic emissions spectrum from the retina in response to the excitation signal. The electromagnetic emissions spectrum may be used to identify a plurality of component emissions spectra, each component emissions spectrum corresponding to fluorescence from a component of the retina, one of the component emissions spectra corresponding to a target emissions spectrum.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method For Treating Eye Diseases
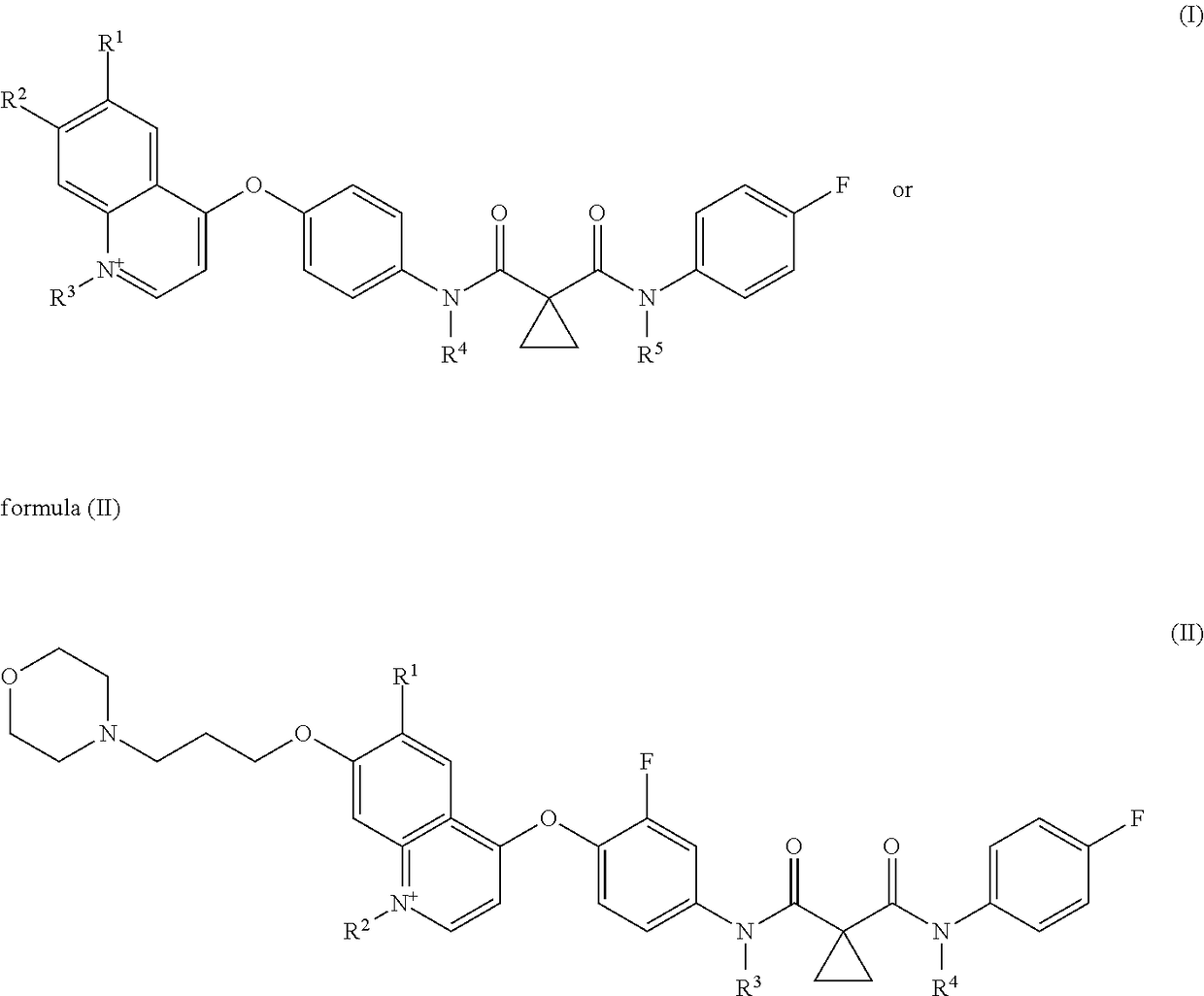
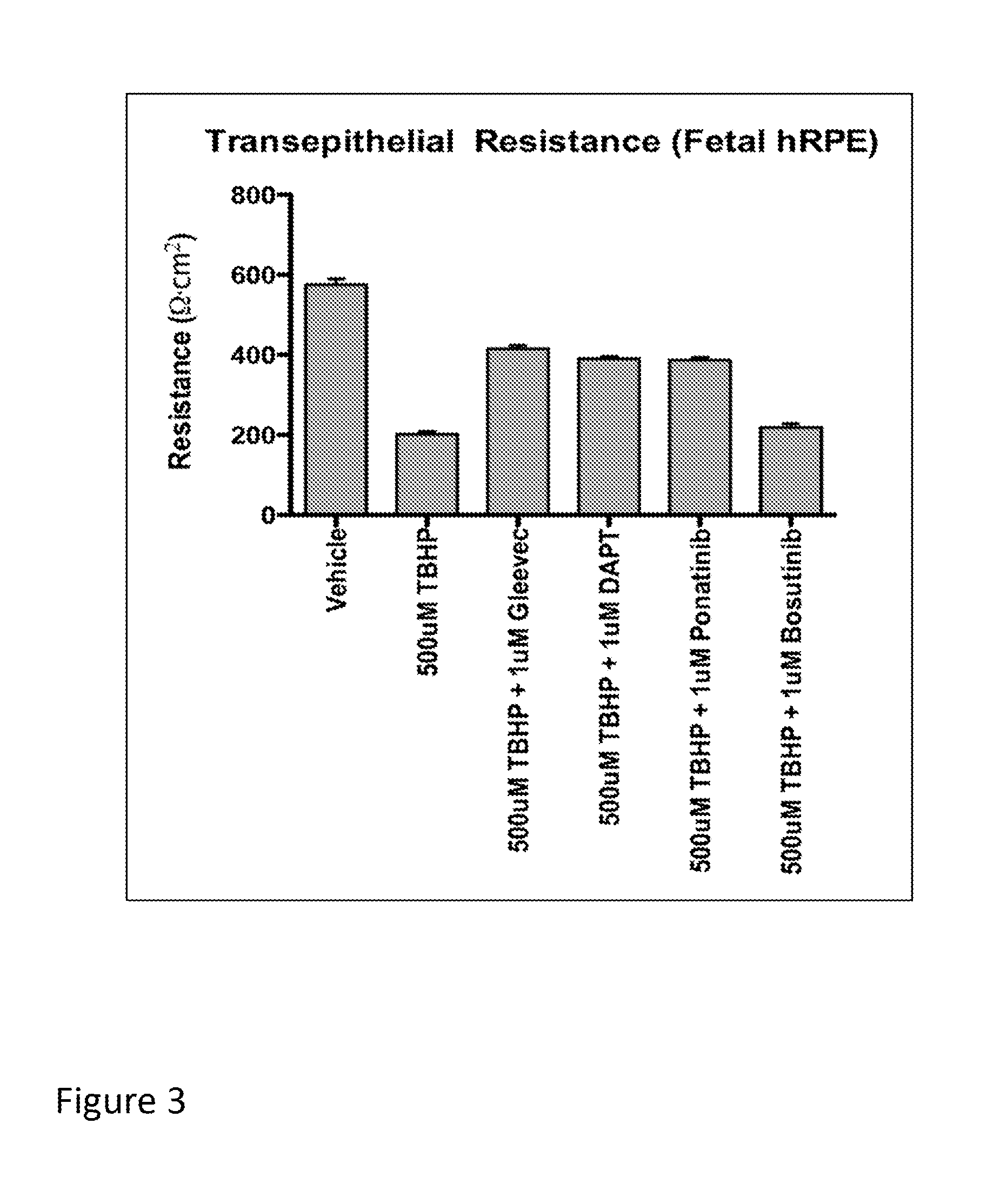
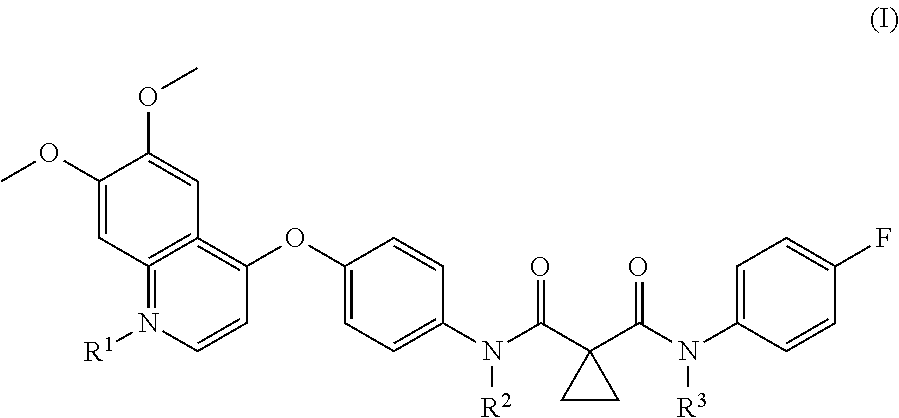
ActiveUS20160000810A1Inhibition formationPrevent macular degenerationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideArylMedicine
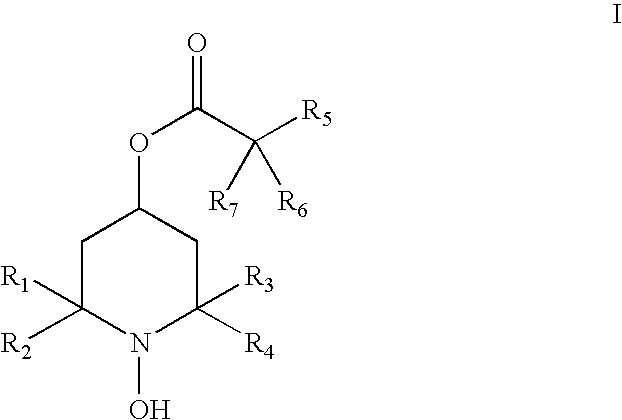
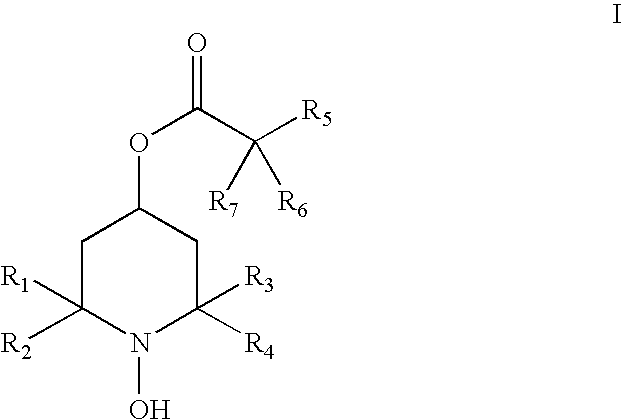
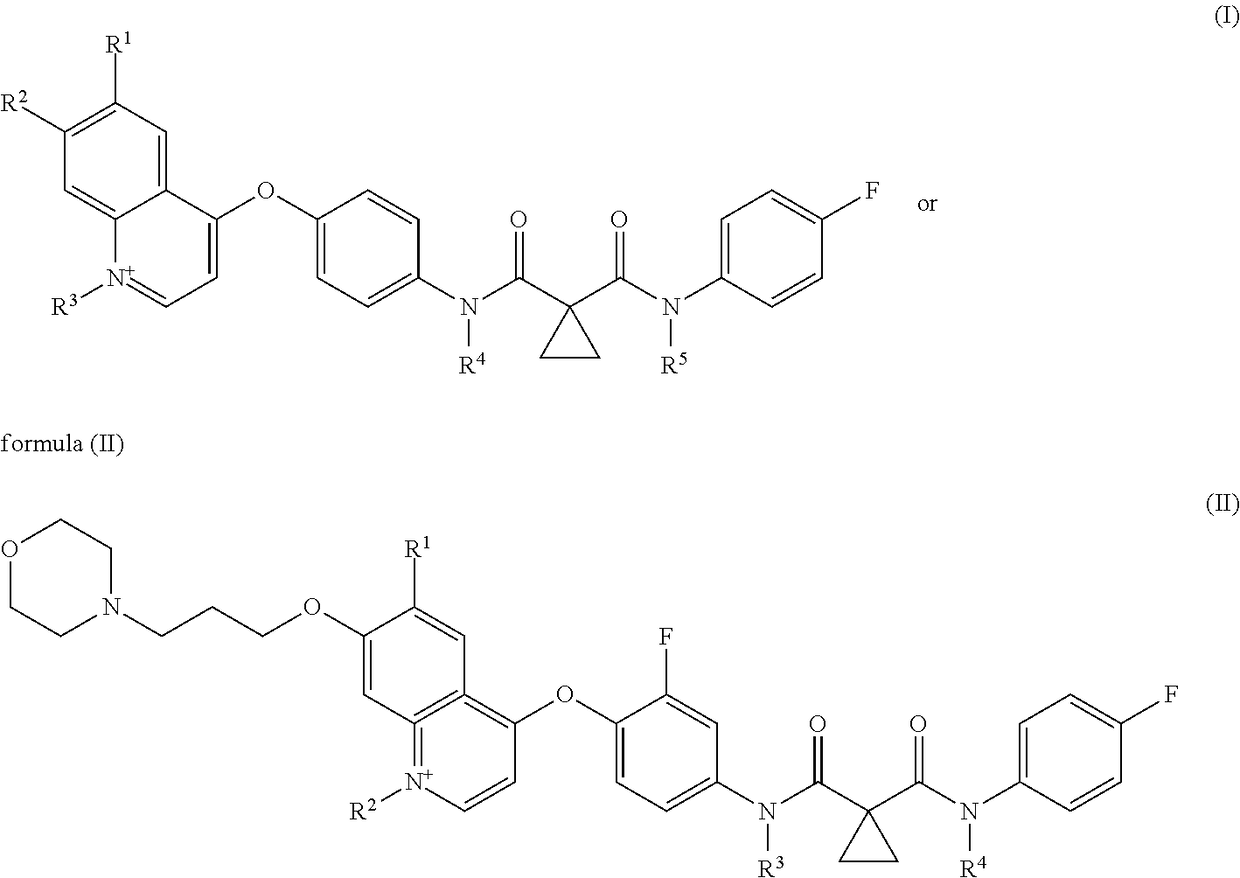
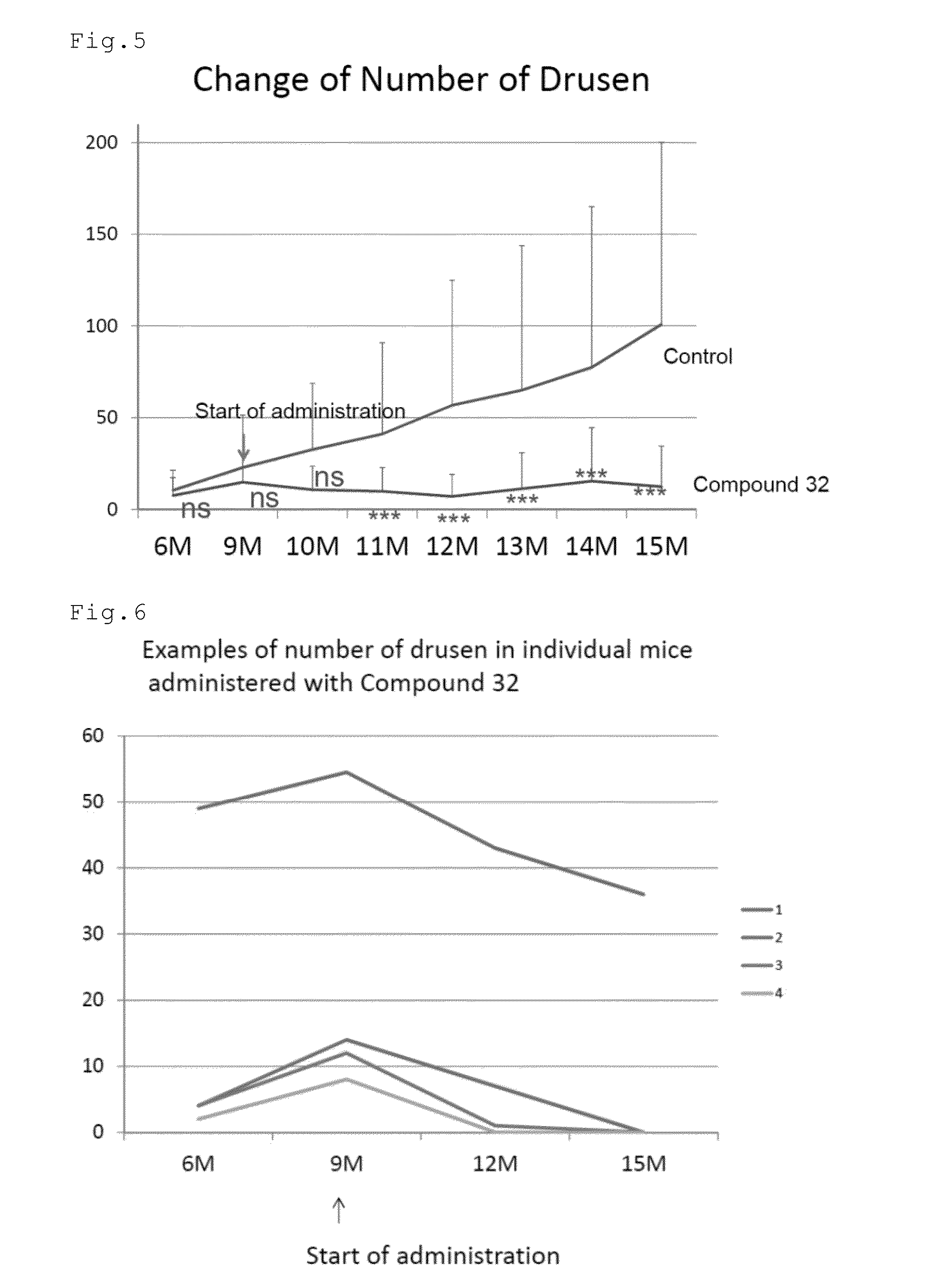
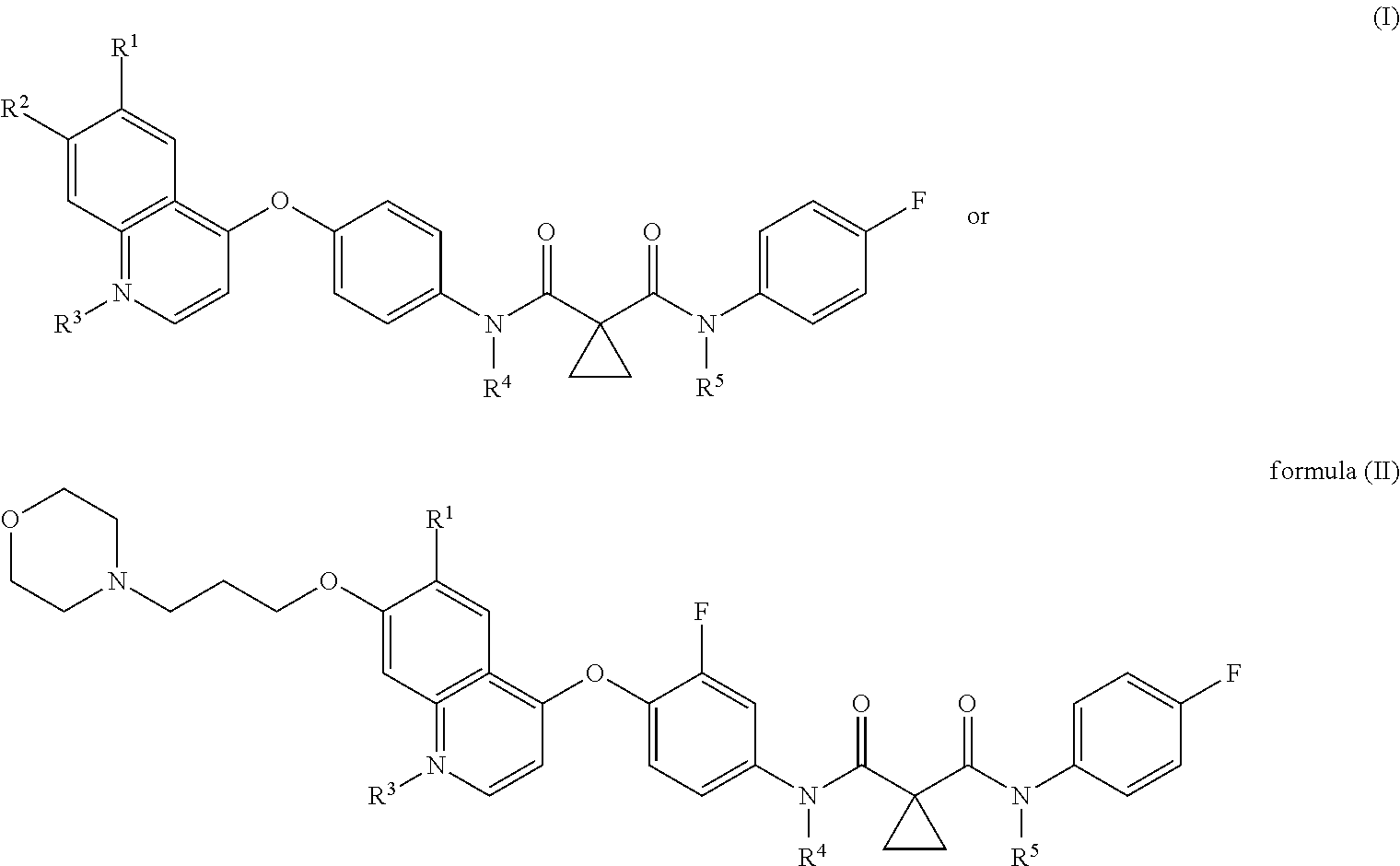
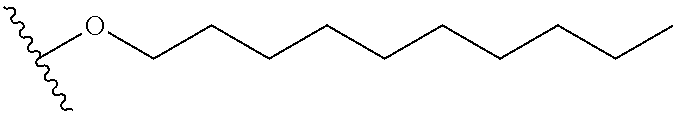
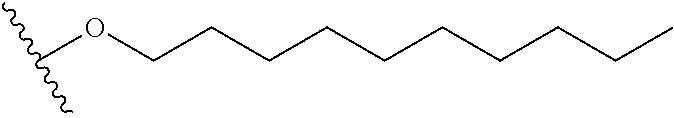
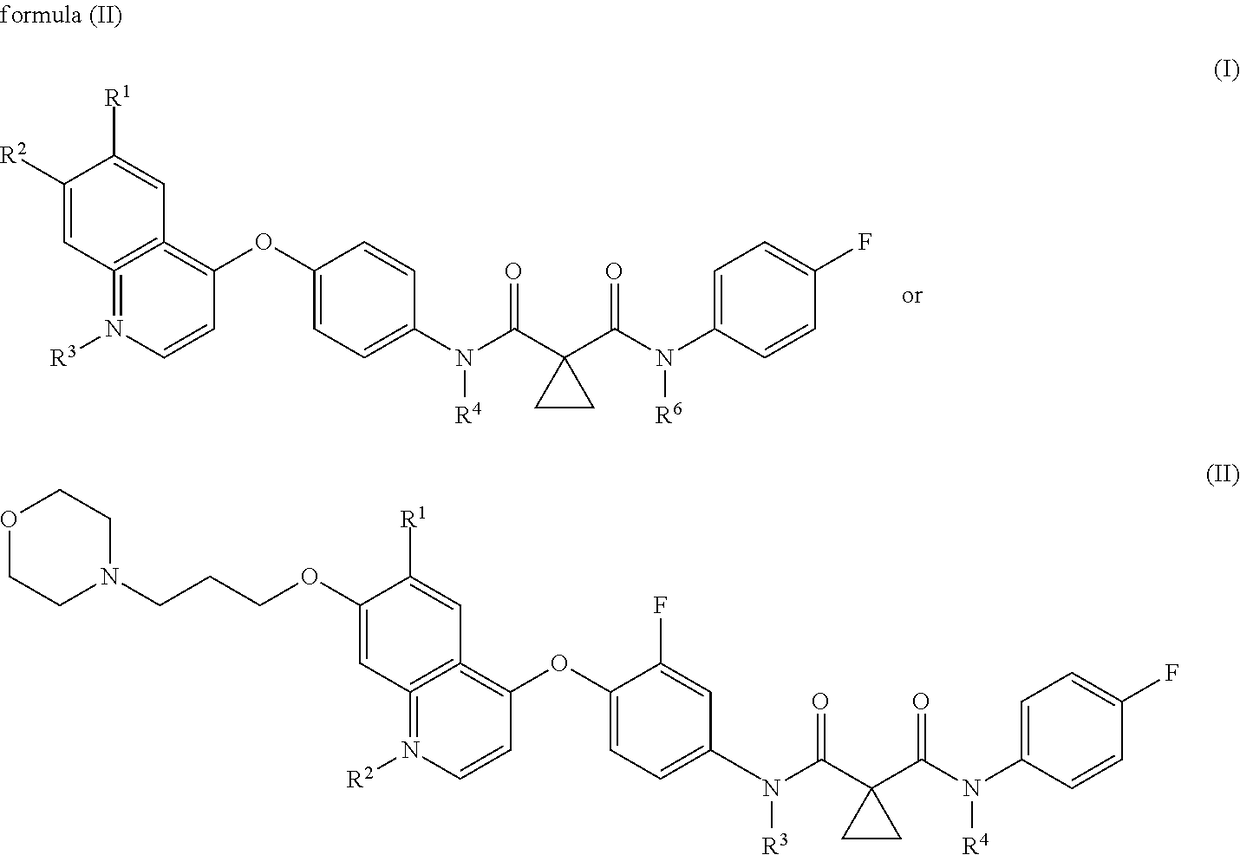
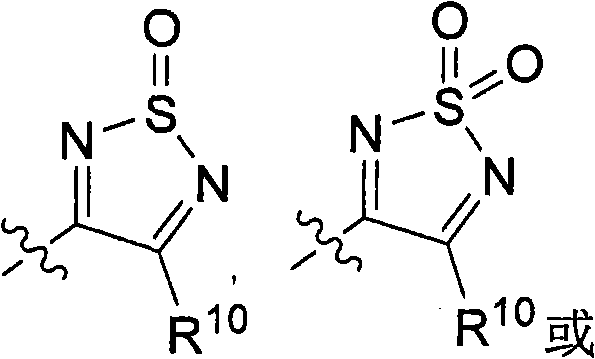
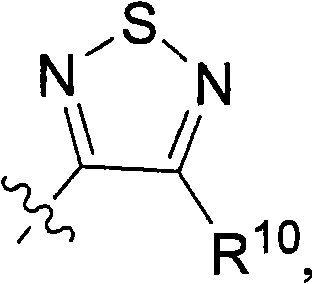
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for removing drusen, suppressing formation of drusen, and / or treating and / or preventing age-related macular degeneration comprising the compound of formula (I) wherein Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of halo, hydroxy, alkyl, halo-substituted alkyl, aryl, halo- or alkyl-substituted aryl, alkoxy, hydroxy- or carboxy-substituted alkoxy, aryloxy, halo- or alkyl-substituted aryloxy, CHO, C(O)-alkyl, C(O)-aryl, C(O)-alkyl-carboxyl, C(O)-alkylene-carboxy ester and cyano, and m is an integer selected from 0 to 4.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
N-Acylalkyl Prodrugs of Multi-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20170020856A1Proliferative retinopathy is preventedFibrovascular proliferative disease is preventedOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
The present invention is directed to multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor compounds. The present invention is further directed to compositions comprising those compounds. Finally, the present invention is directed to methods of treating eye conditions including, but not limited to, diabetic background retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, diabetic proliferative retinopathy, diabetic macular edema with proliferative retinopathy, proliferative fibrovascular disease, diabetic macular edema with proliferative fibrovascular disease, retinopathy of prematurity, dry macular degeneration, dry macular degeneration with drusen and wet macular degeneration, using compounds and compositions of the invention
Owner:ONTOGENESIS LLC
Multi-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Derivatives and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20170143688A1Proliferative retinopathy is preventedFibrovascular proliferative disease is preventedOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDiseaseTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
The present invention is directed to multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor compounds. The present invention is further directed to compositions comprising those compounds. Finally, the present invention is directed to methods of treating eye conditions including, but not limited to, diabetic background retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, diabetic proliferative retinopathy, diabetic macular edema with proliferative retinopathy, proliferative fibrovascular disease, diabetic macular edema with proliferative fibrovascular disease, retinopathy of prematurity, dry macular degeneration, dry macular degeneration with drusen and wet macular degeneration, using compounds and compositions of the invention.
Owner:ONTOGENESIS LLC
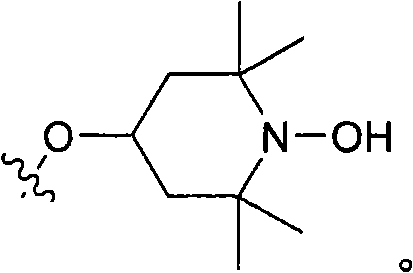
Hydroxylamine compounds and methods of their use
The present disclosure provides compounds that include hydroxylamines of formula (I) or (II), pharmaceutical compositions, and methods for their use. The methods utilize hydroxylamine compounds and / or their pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of angiogenesis, hepatitis, complement-mediated pathologies, drusen-mediated pathologies, macular degeneration and certain other ophthalmic conditions, inflammation, arthritis, and related diseases and for the inhibition of complement activation.
Owner:COLBY PHARMA CO
Use of agents that prevent the generation of amyloid-like proteins and/or drusen, and/or use of agents that promote sequestration and/or degradation of, and/or prevent the neurotoxic effects of such proteins in the treatment of macular degeneration
InactiveUS20090203614A1Avoid it happening againInhibitionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDrusenAmyloid deposition
Owner:ALCON INC
Method for detecting amyloid beta plaques and drusen
A method for detecting amyloid beta plaques and drusen is disclosed. The method for detecting amyloid beta plaques and drusen may include applying a combination of optical retro mode illumination techniques to acquire a plurality of amyloid beta plaques and drusen images that are too small to be seen with other imaging modalities. The amyloid beta plaques and drusen images may also be detected with a non-transitory computer storage media having instructions stored thereon which, when executed, execute the method for detecting amyloid beta plaques and drusen. The method may track changes in plaque, size, area and density of the amyloid beta plaques and drusen over a predetermined period of time.
Owner:NEUROVISION IMAGING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com