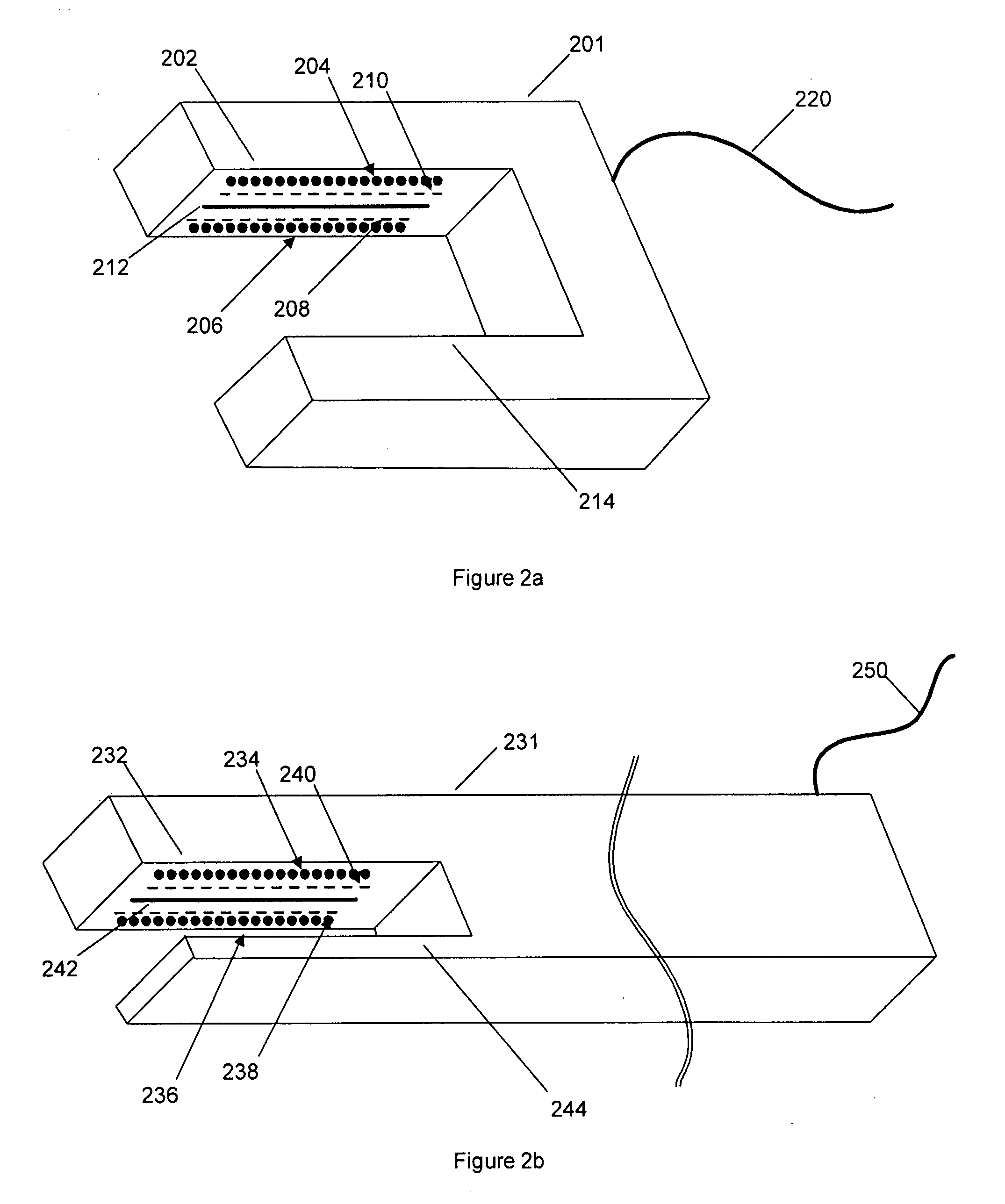
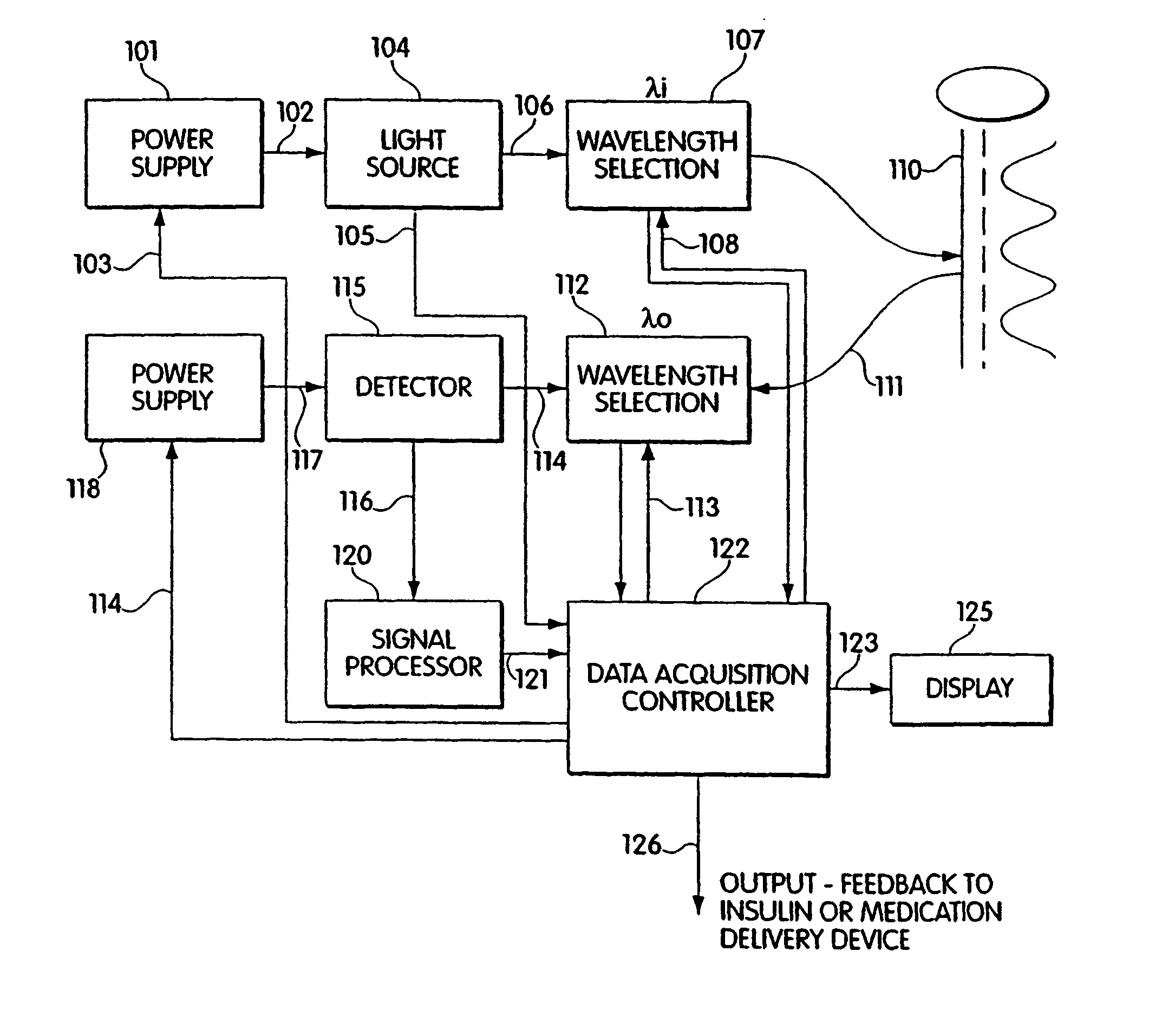
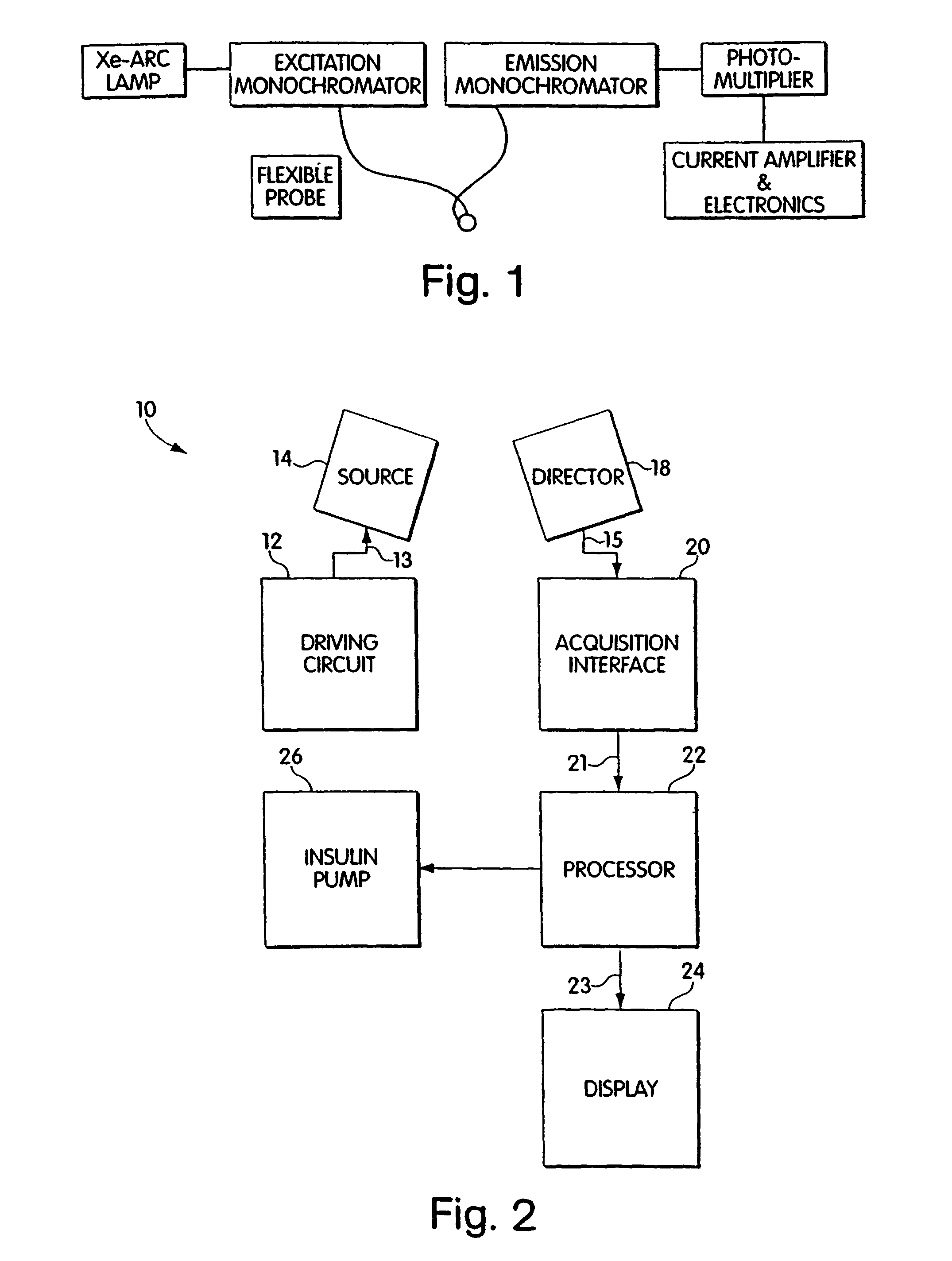
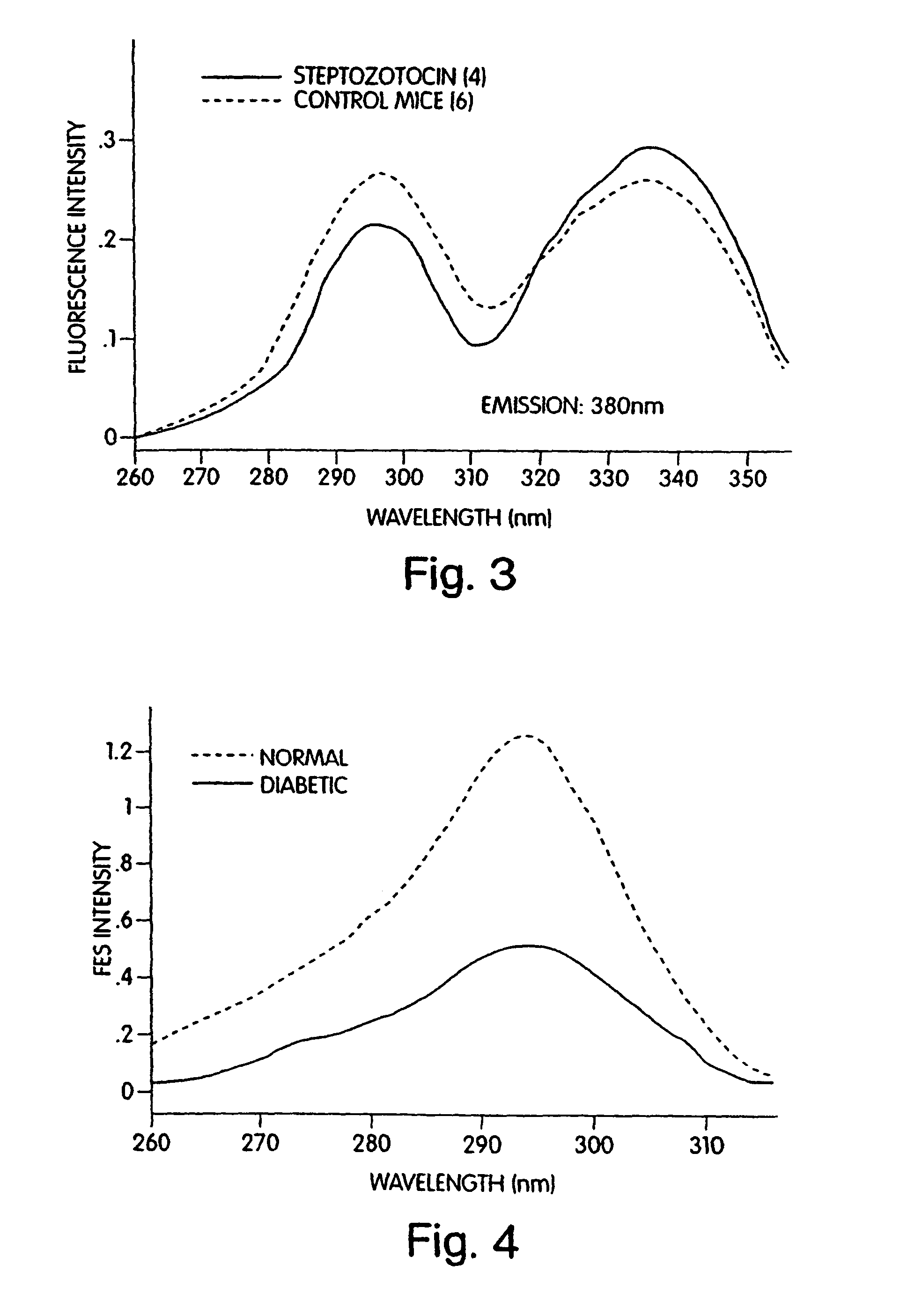
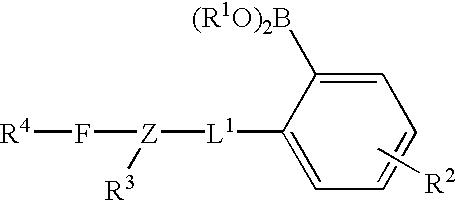
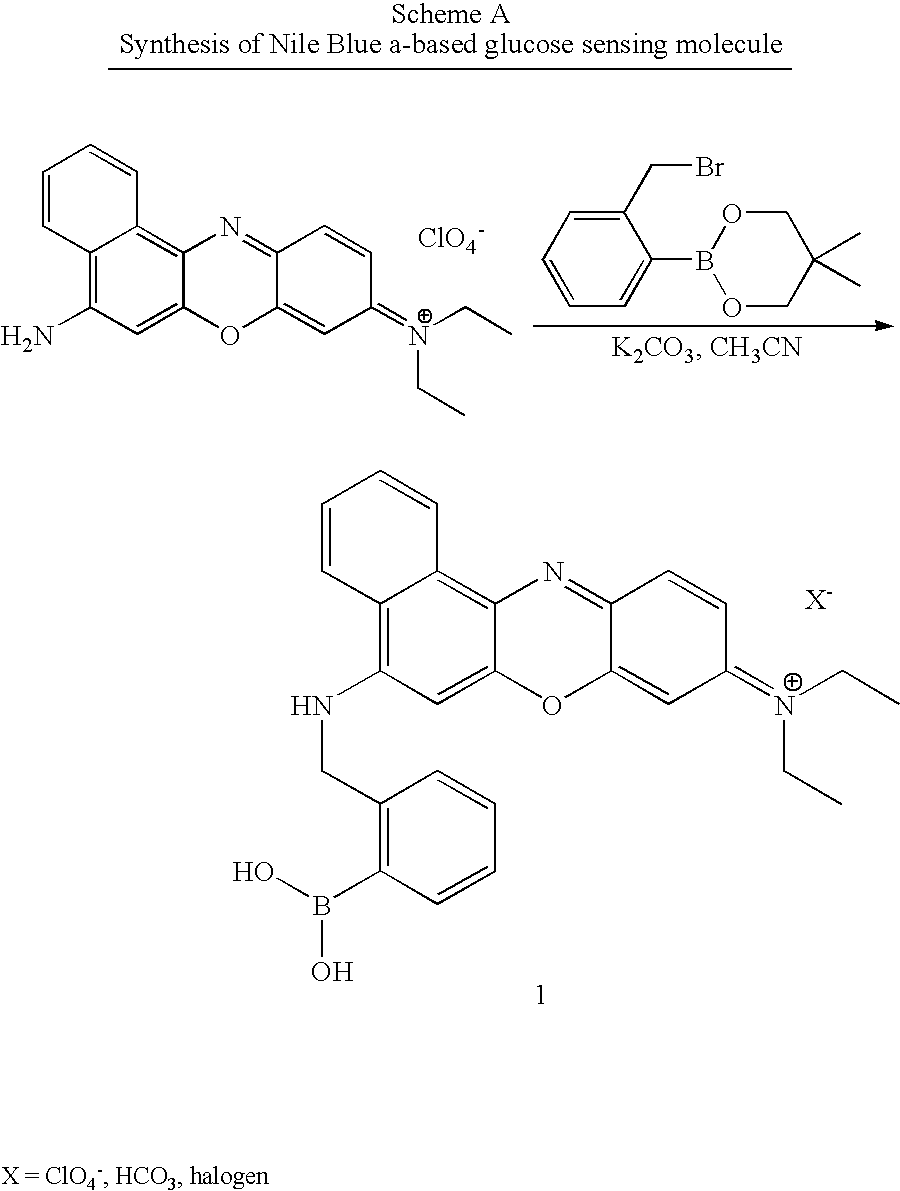
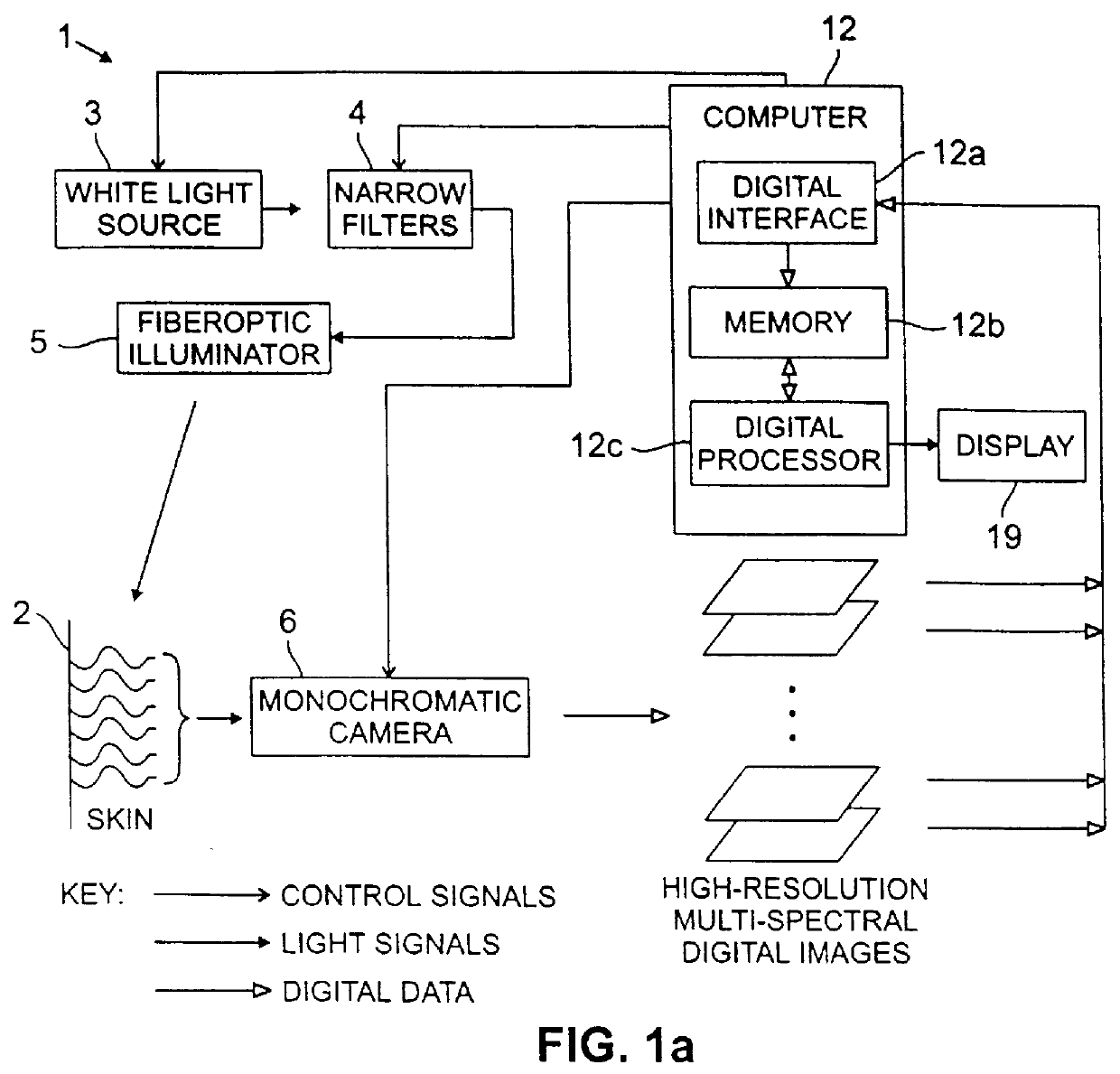
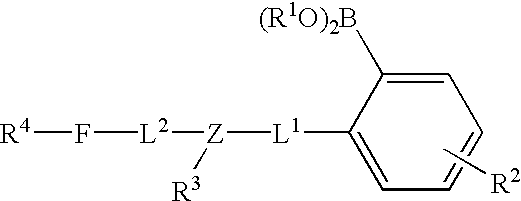Patents
Literature
2513results about "Diagnostics using fluorescence emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
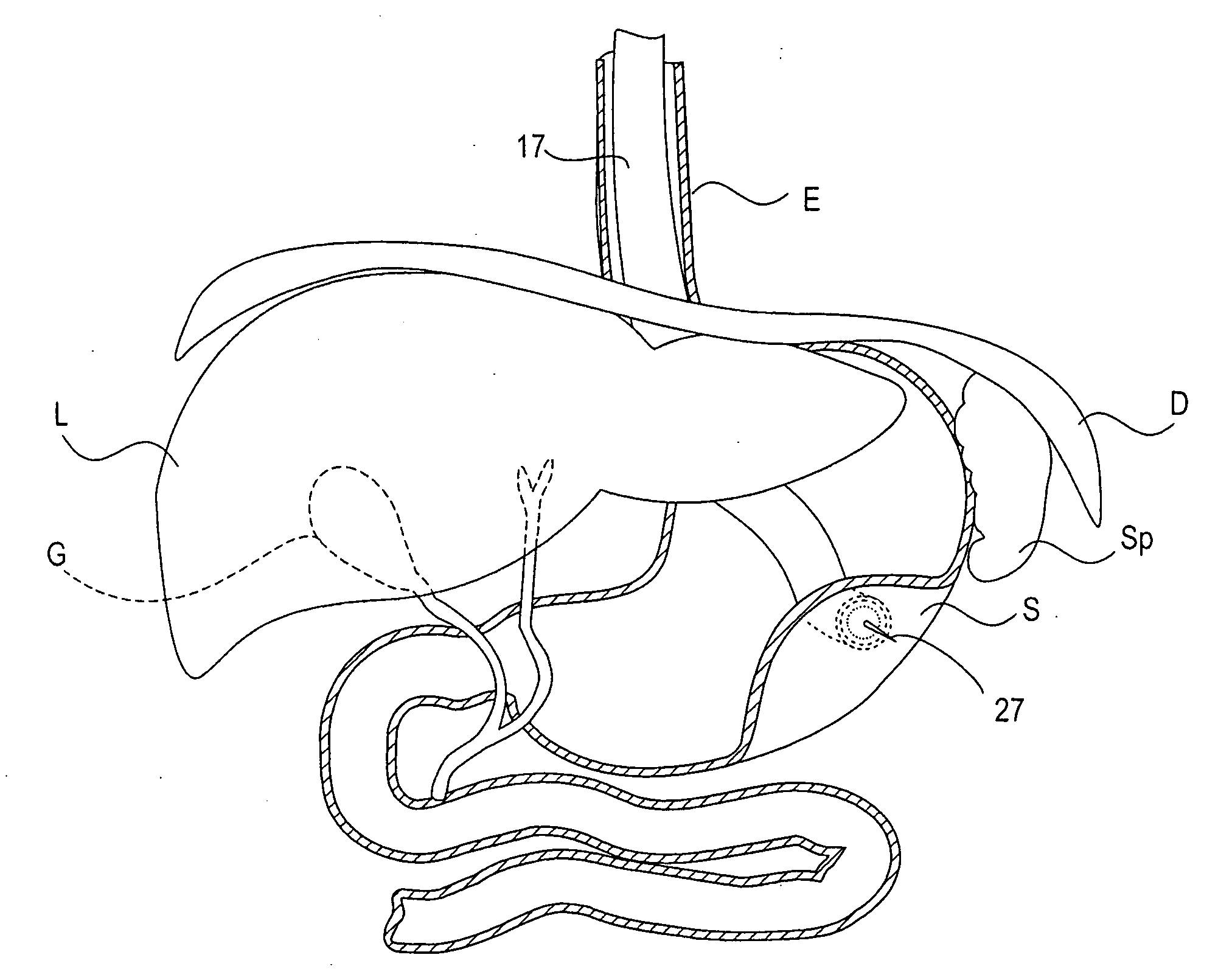
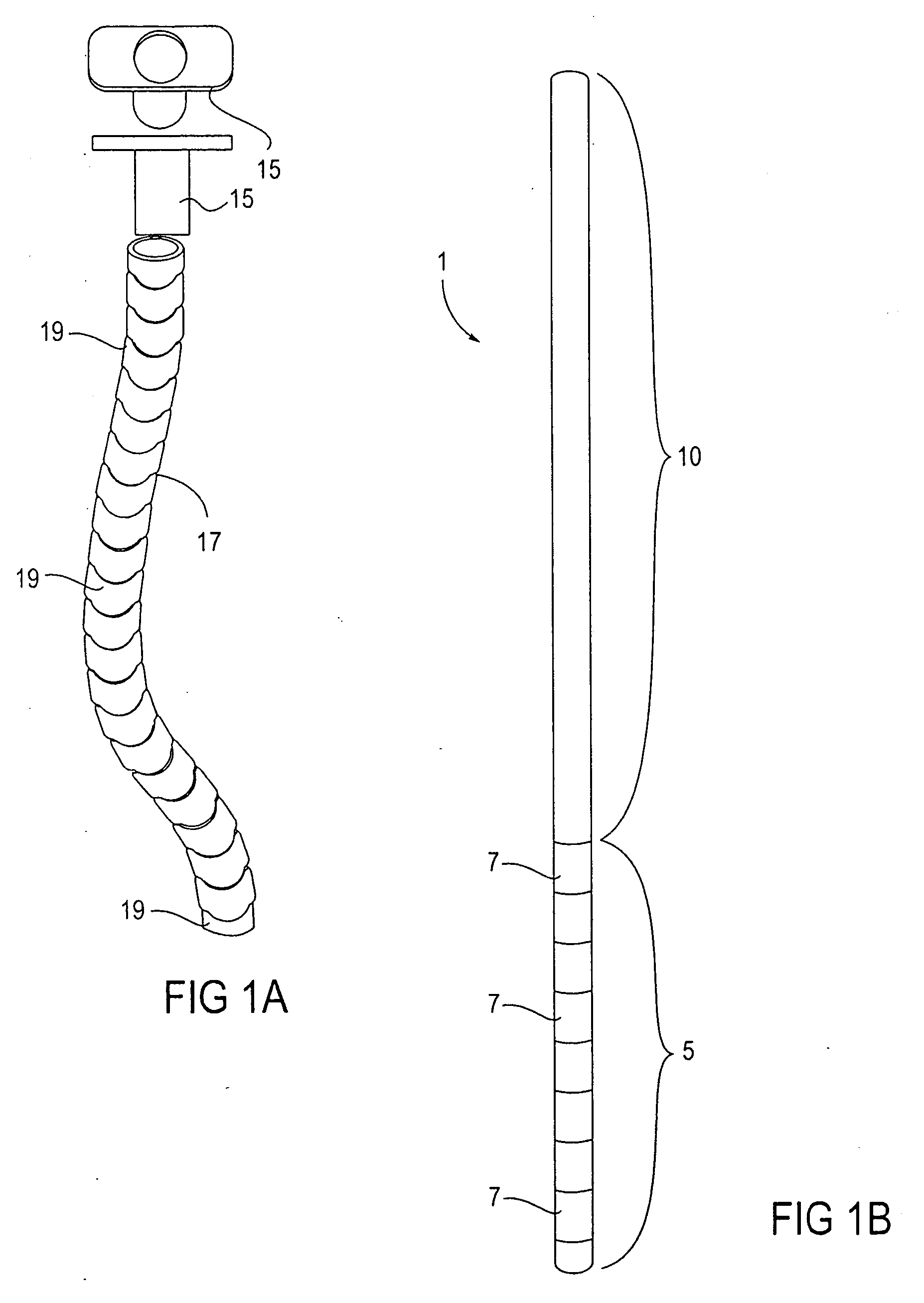
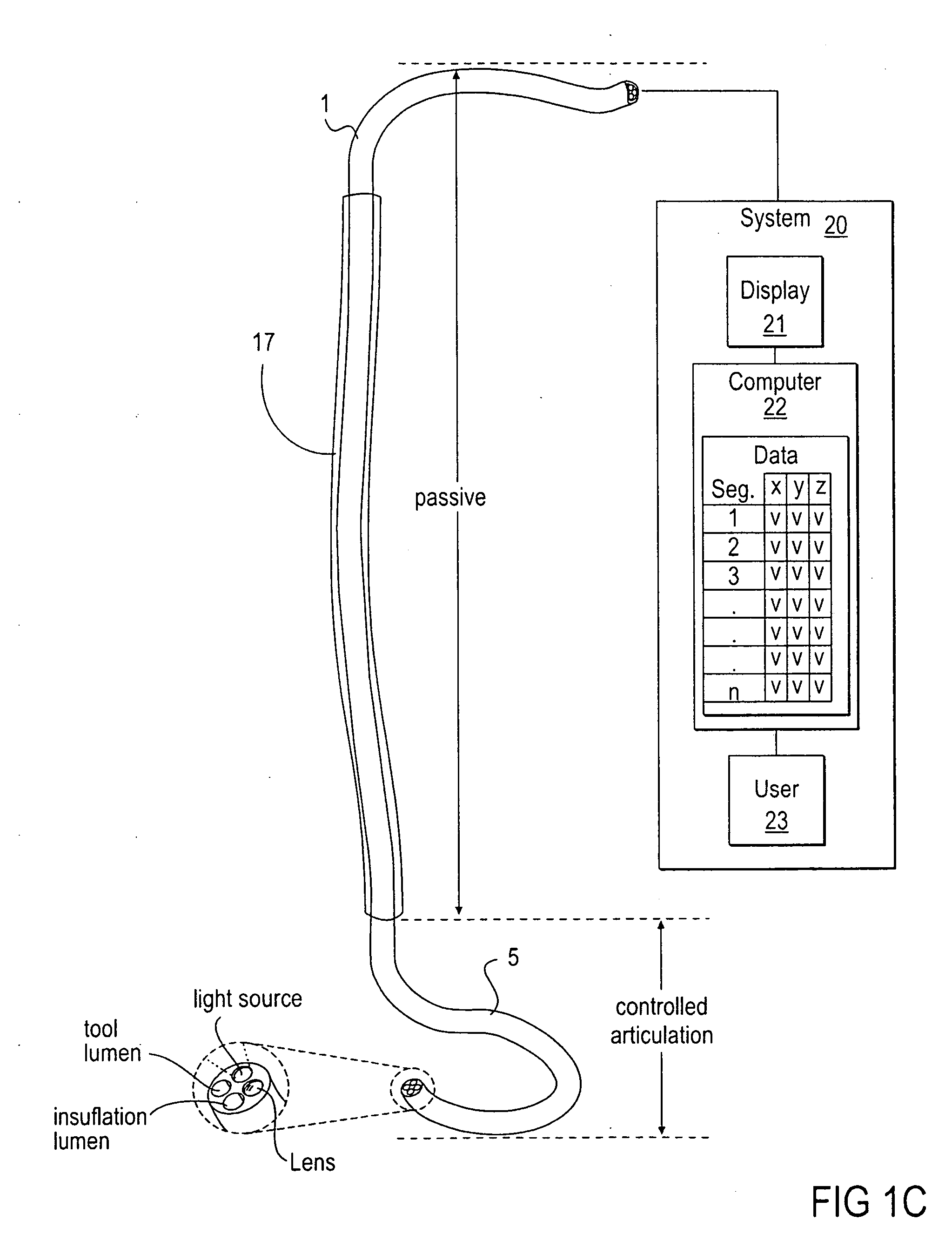
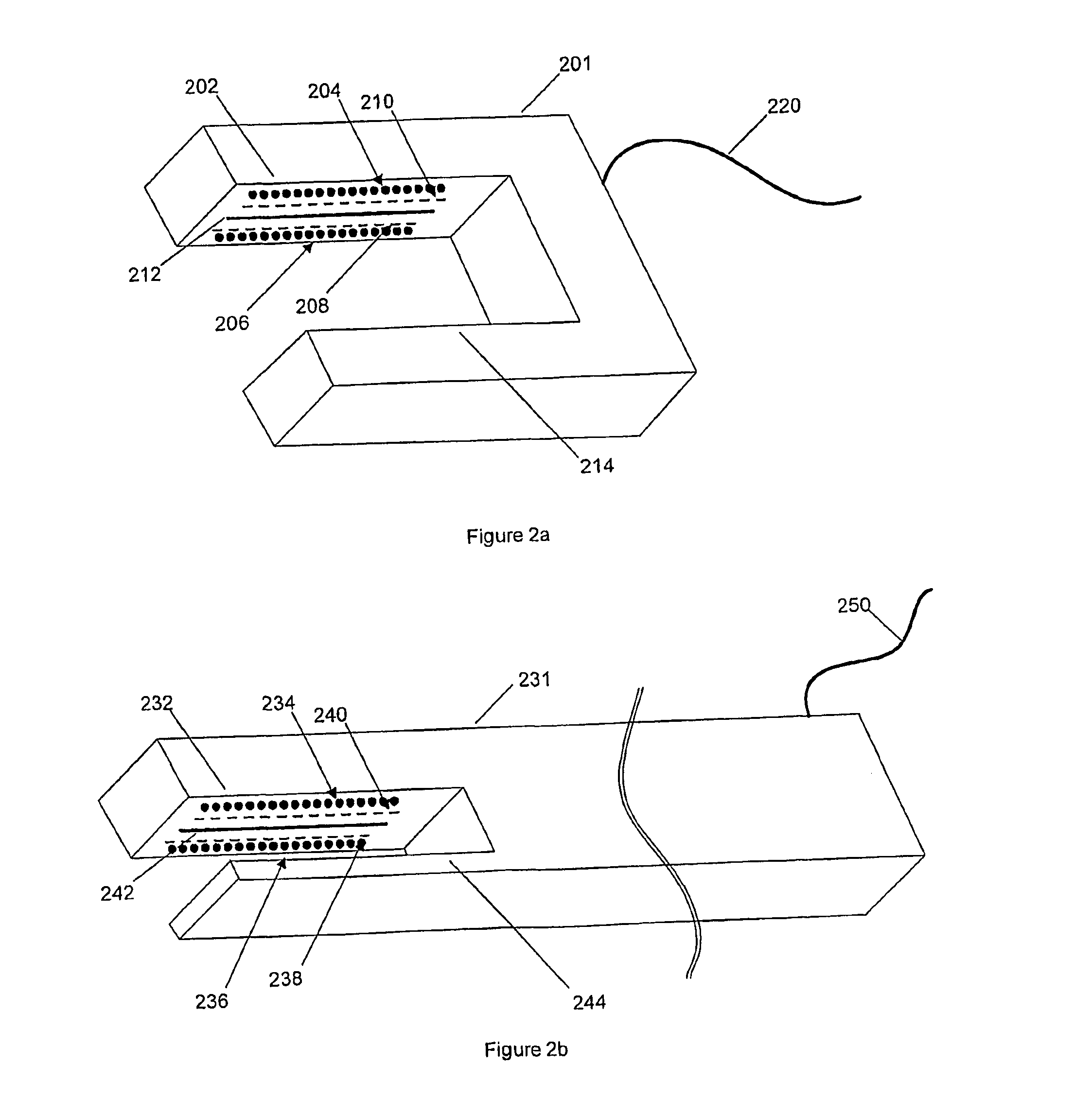
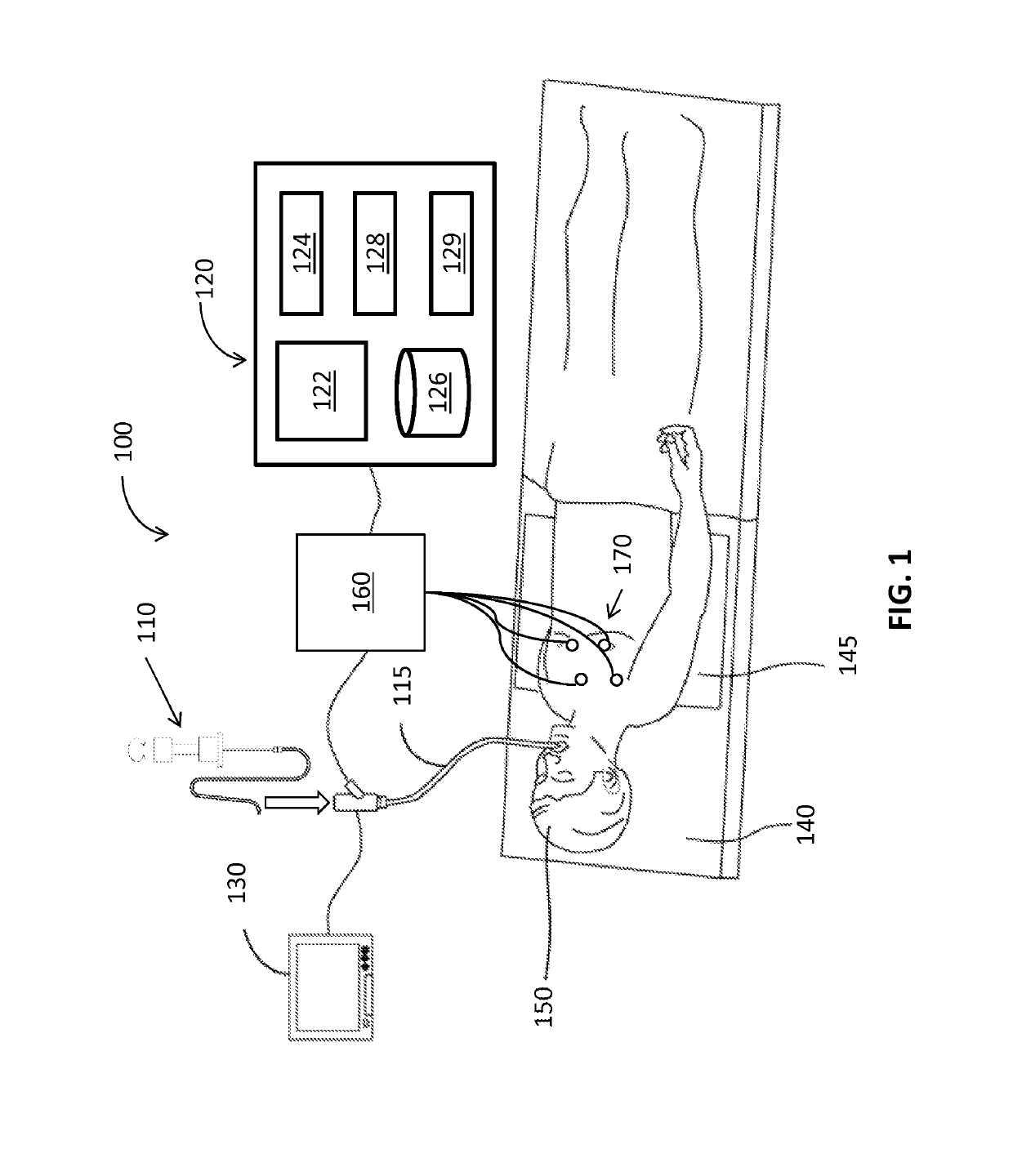
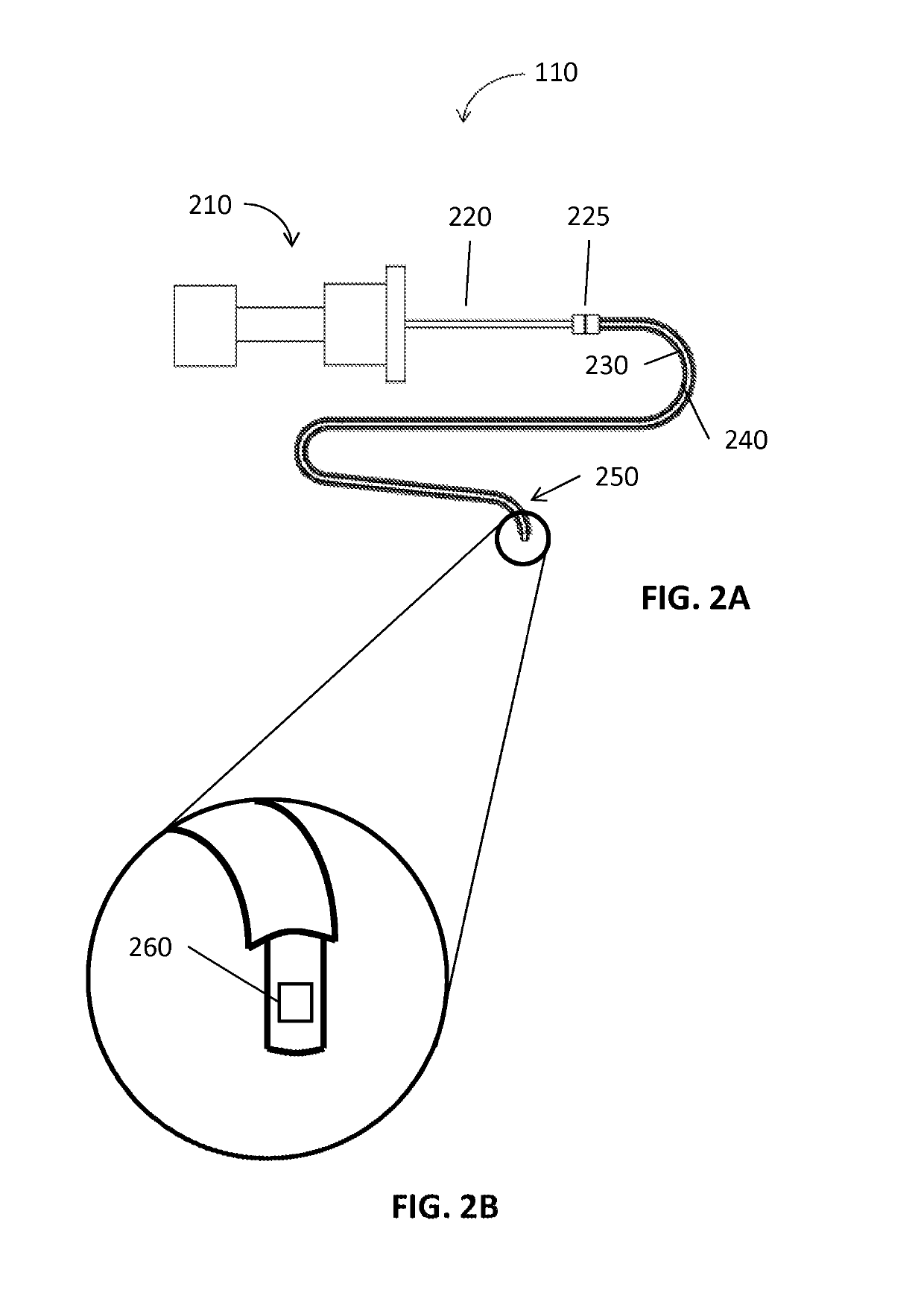
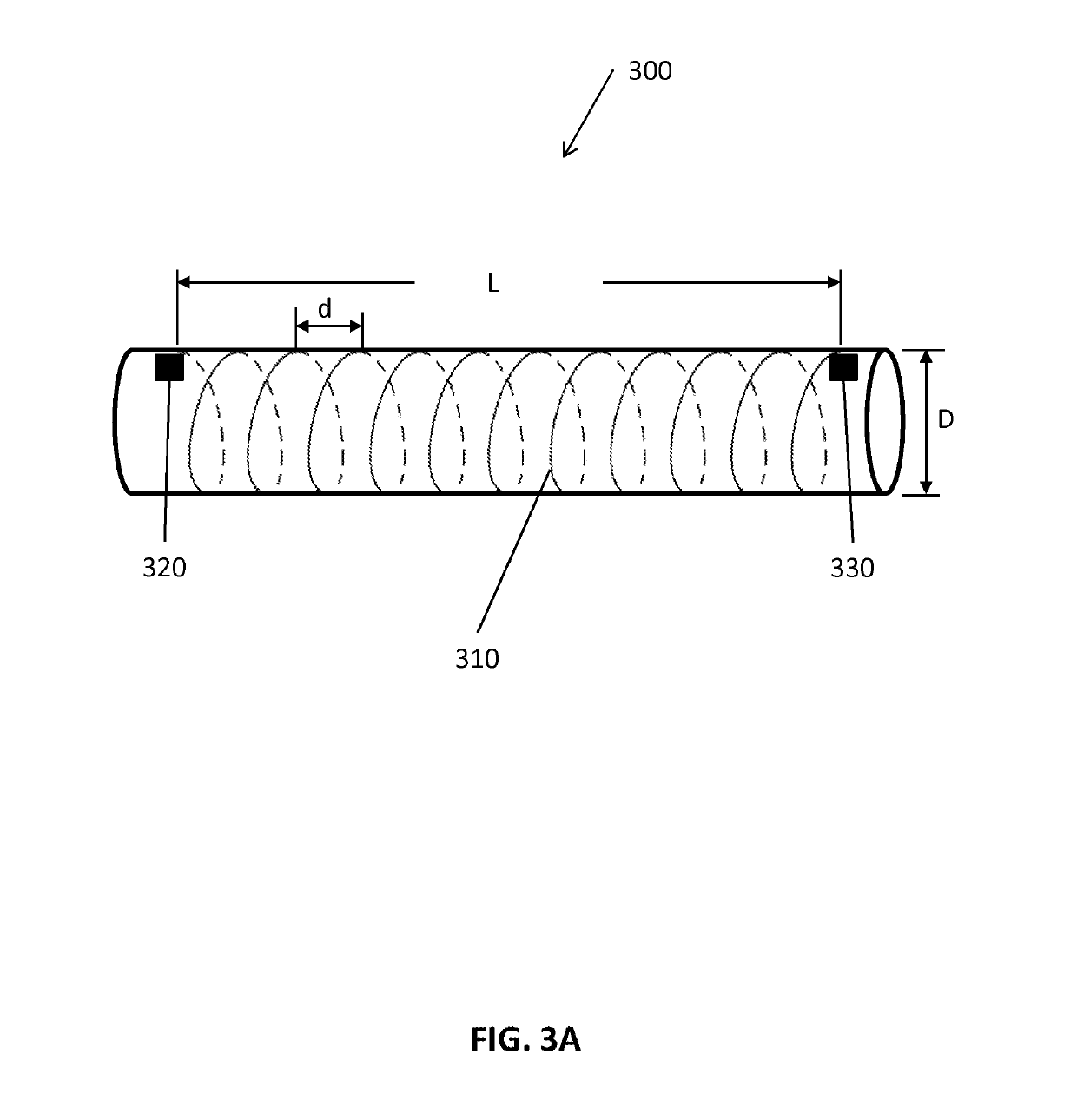
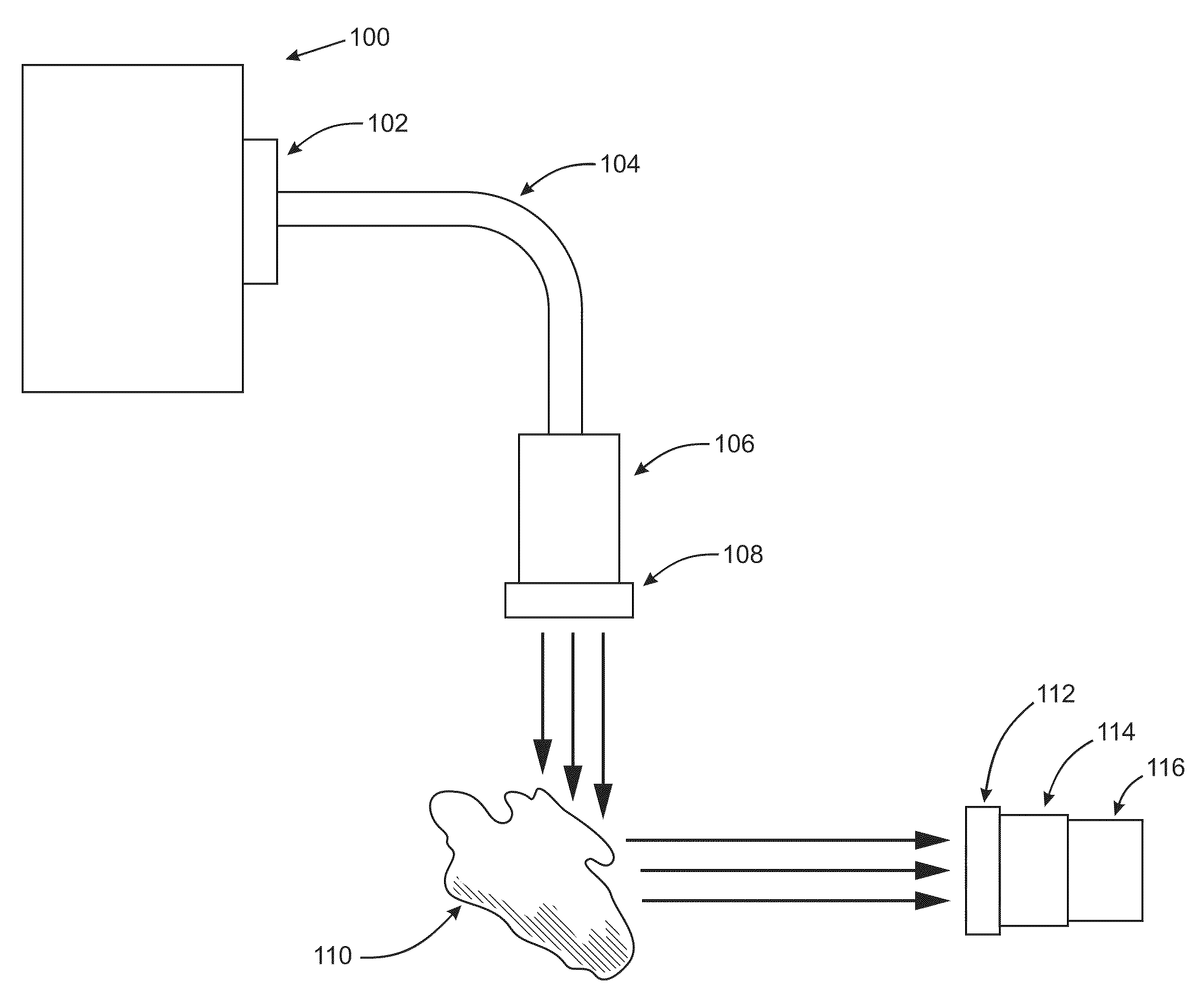
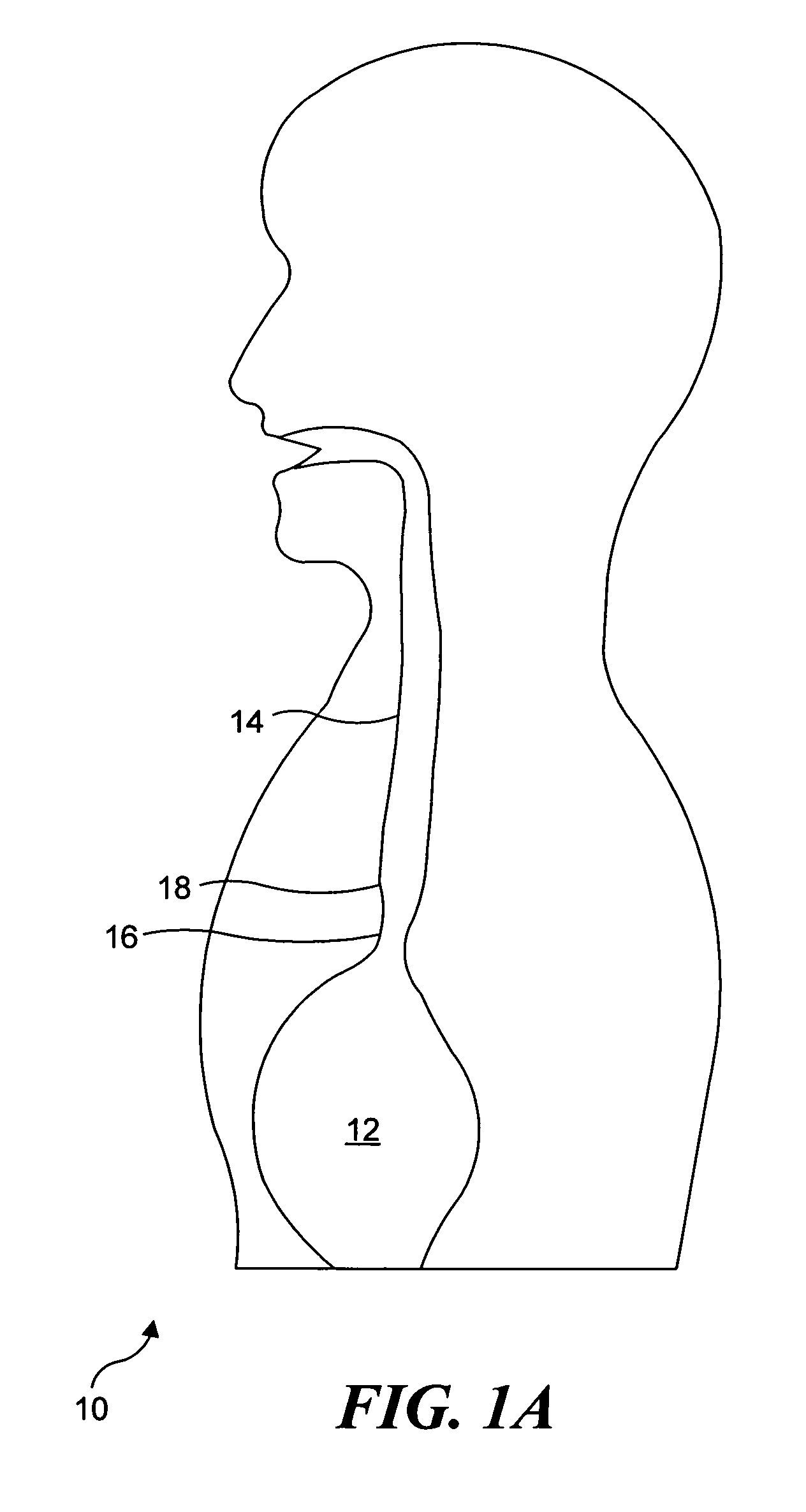
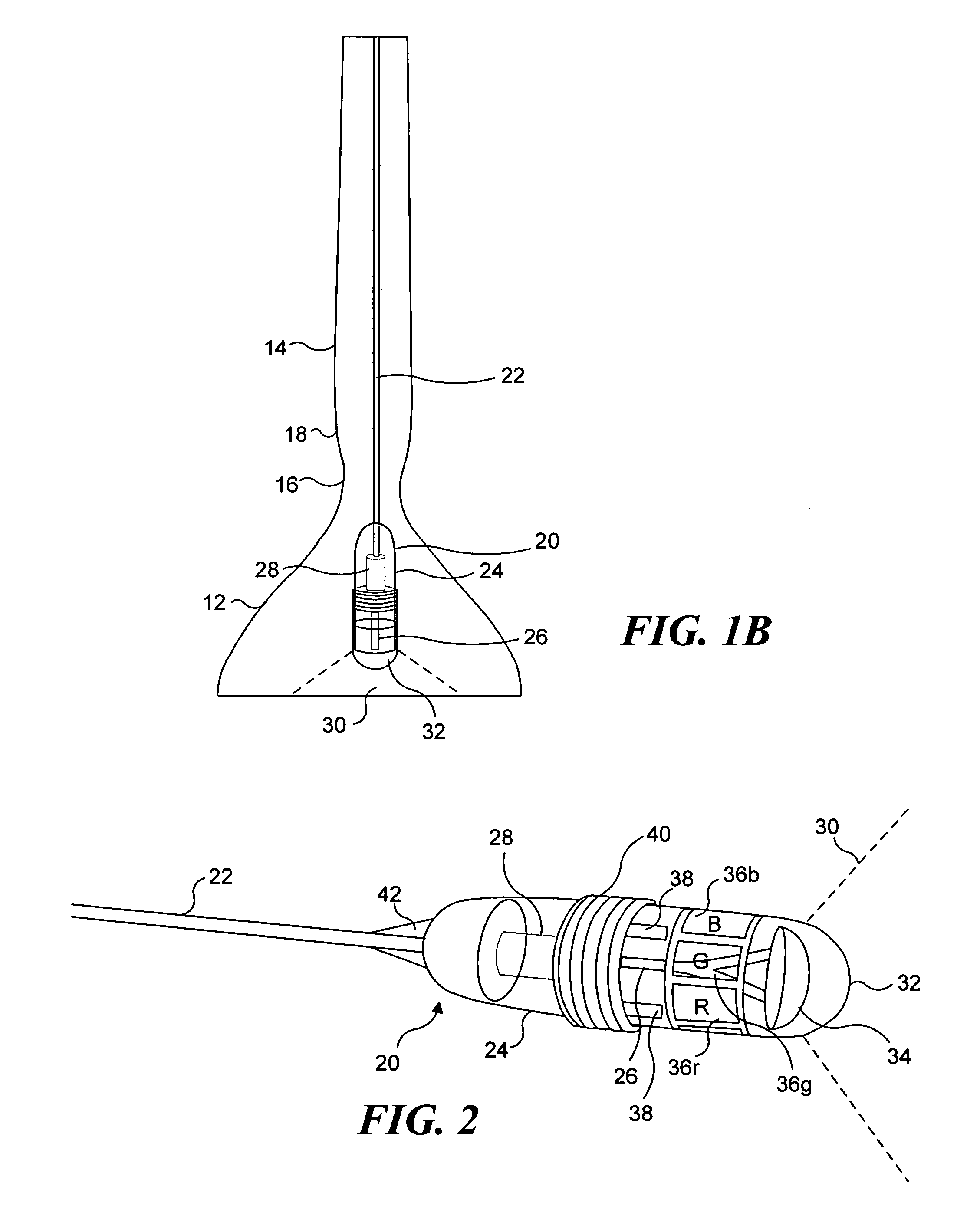
Methods and apparatus for performing transluminal and other procedures
InactiveUS20070135803A1Prevent overflowPrevent leakageSuture equipmentsEar treatmentSurgeryInstrumentation
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
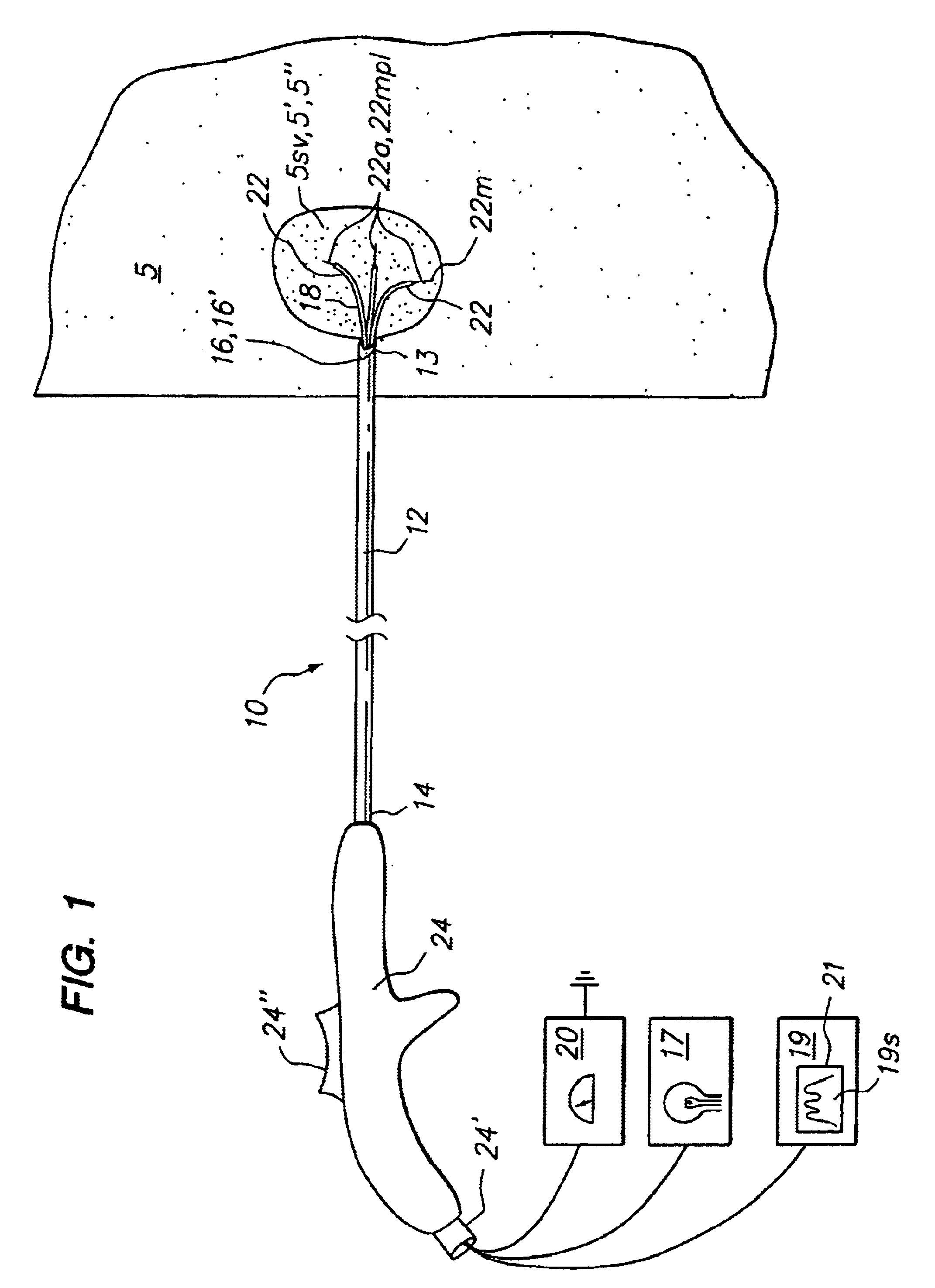
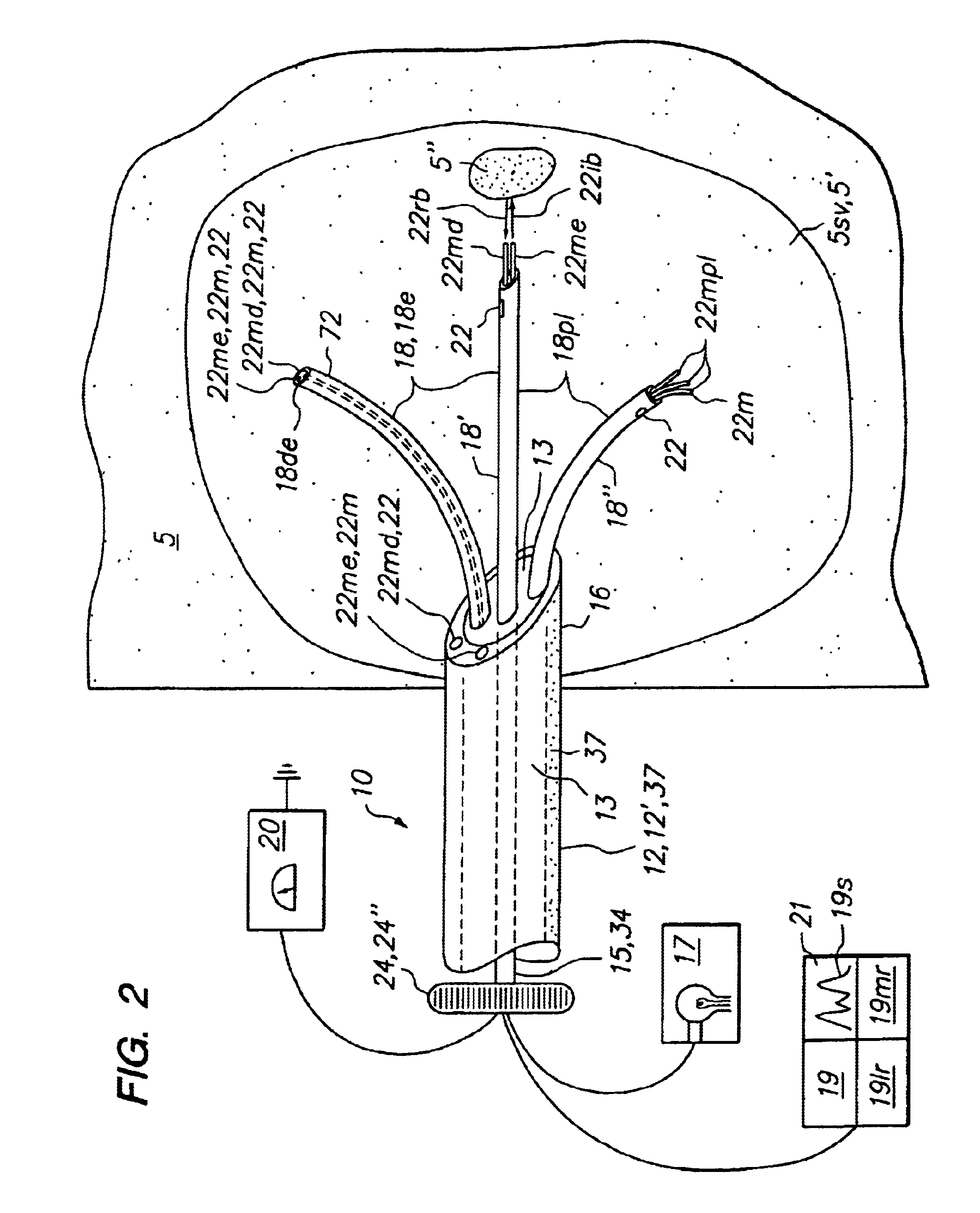
Tissue biopsy and treatment apparatus and method
InactiveUS6869430B2Improve clinical outcomesPrecise positioningSurgical needlesControlling energy of instrumentSensor arrayTissue biopsy
An embodiment of the invention provides a tissue biopsy and treatment apparatus that comprises an elongated delivery device that is positionable in tissue and includes a lumen. A sensor array having a plurality of resilient members is deployable from the elongated delivery device. At least one of the plurality of resilient members is positionable in the elongated delivery device in a compacted state and deployable with curvature into tissue from the elongated delivery device in a deployed state. At least one of the plurality of resilient members includes at least one of a sensor, a tissue piercing distal end or a lumen. The sensor array has a geometric configuration adapted to volumetrically sample tissue at a tissue site to differentiate or identify tissue at the target tissue site. At least one energy delivery device is coupled to one of the sensor array, at least one of the plurality of resilient members or the elongated delivery device.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
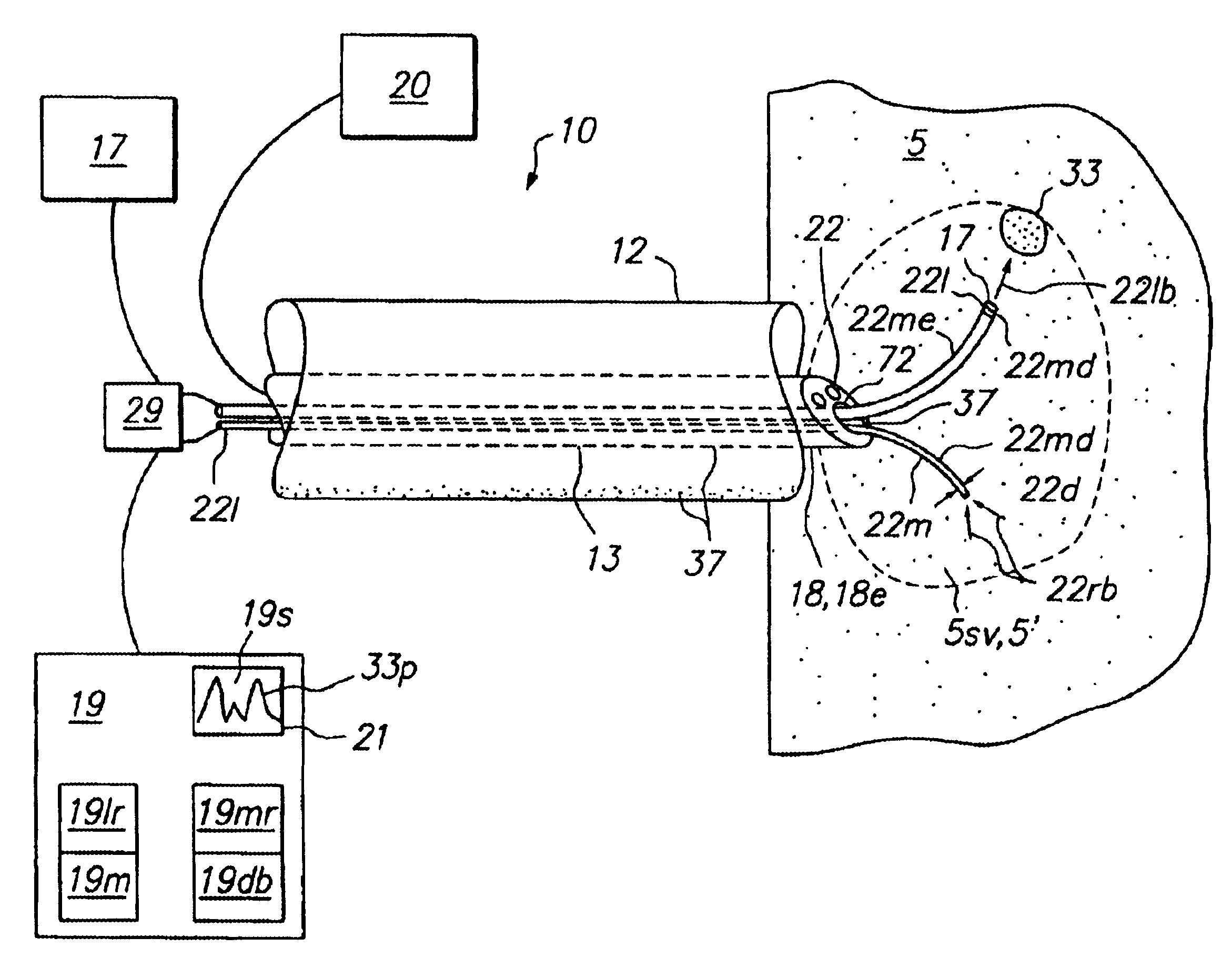
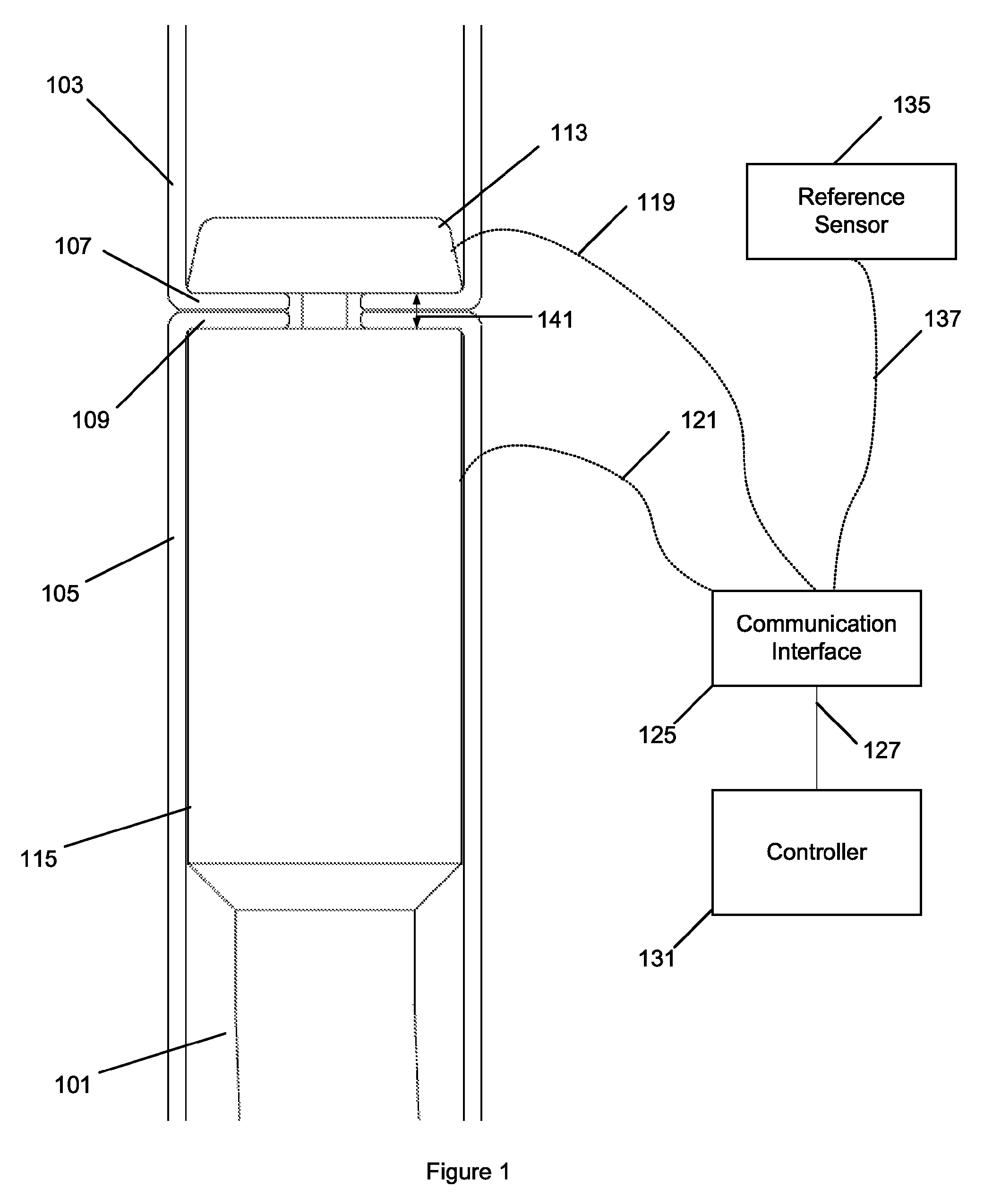
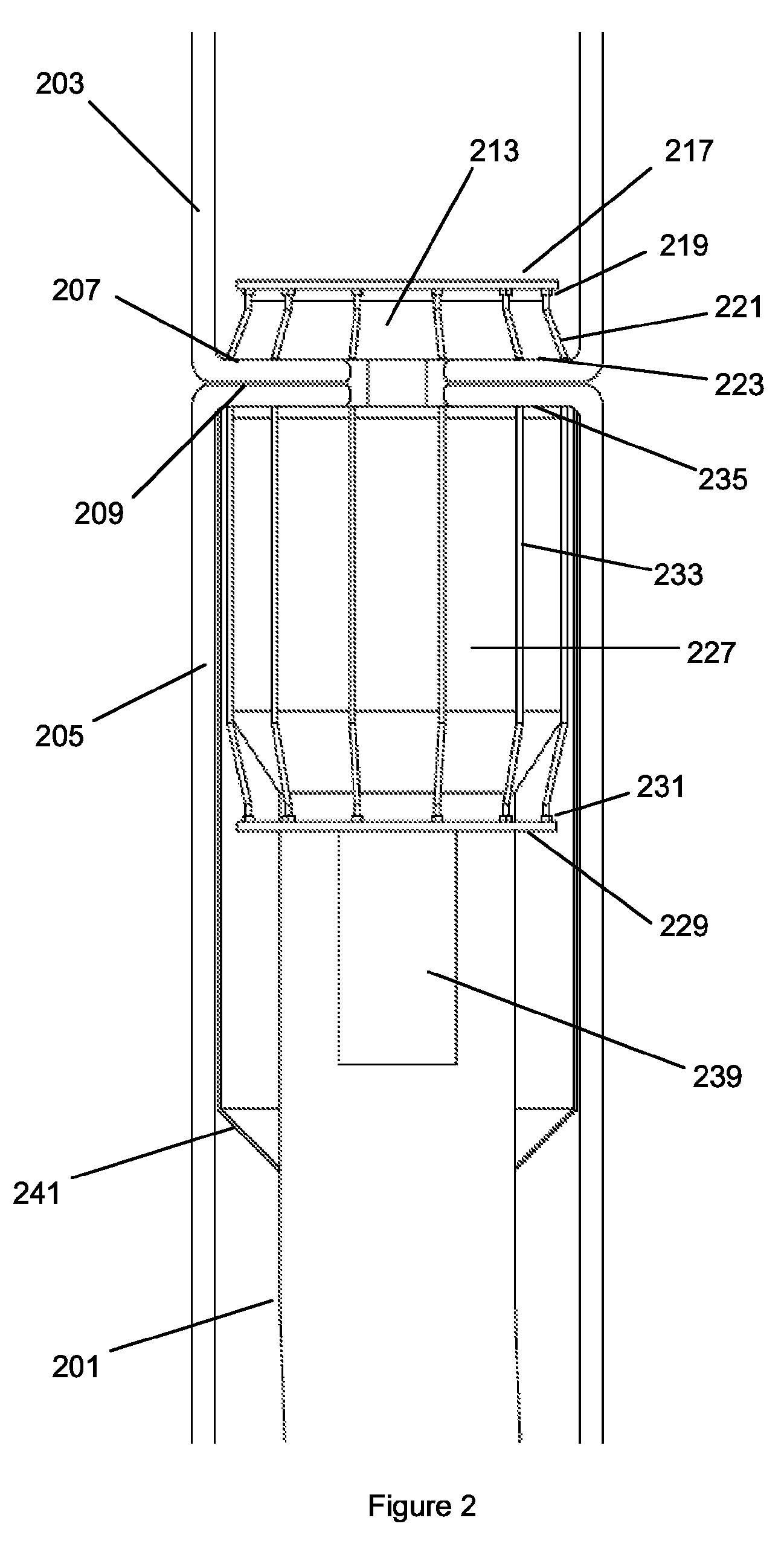
Surgical instruments with sensors for detecting tissue properties, and system using such instruments
ActiveUS9204830B2Avoiding and detecting failurePredict successDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterData setPatient state
A system is provided that furnishes expert procedural guidance based upon patient-specific data gained from surgical instruments incorporating sensors on the instrument's working surface, one or more reference sensors placed about the patient, sensors implanted before, during or after the procedure, the patient's personal medical history, and patient status monitoring equipment. Embodiments include a system having a surgical instrument with a sensor for generating a signal indicative of a property of a subject tissue of the patient, which signal is converted into a current dataset and stored. A processor compares the current dataset with other previously stored datasets, and uses the comparison to assess a physical condition of the subject tissue and / or to guide a procedure being performed on the tissue.
Owner:SURGISENSE CORP
Sensing adjunct for surgical staplers
ActiveUS8118206B2Avoiding and detecting failureSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringSurgical Staplers
A device and method in accordance with the invention for generating a signal indicative of a property of a subject tissue in contact with the working surface of a surgical instrument. The invention describes a sensing adjunct to surgical staplers. The adjunct can take the form of an optionally coupled accessory to a surgical stapler, or a stand-alone substitutive component acting to serve as a replacement for a component of the surgical stapler such as an anvil, housing or cartridge. Embodiments include a sensing anvil serving to act in place of a non-sensing surgical stapler anvil to monitor tissue properties of an anastomosis for the purpose of avoiding anastomotic failure.
Owner:SURGISENSE CORP
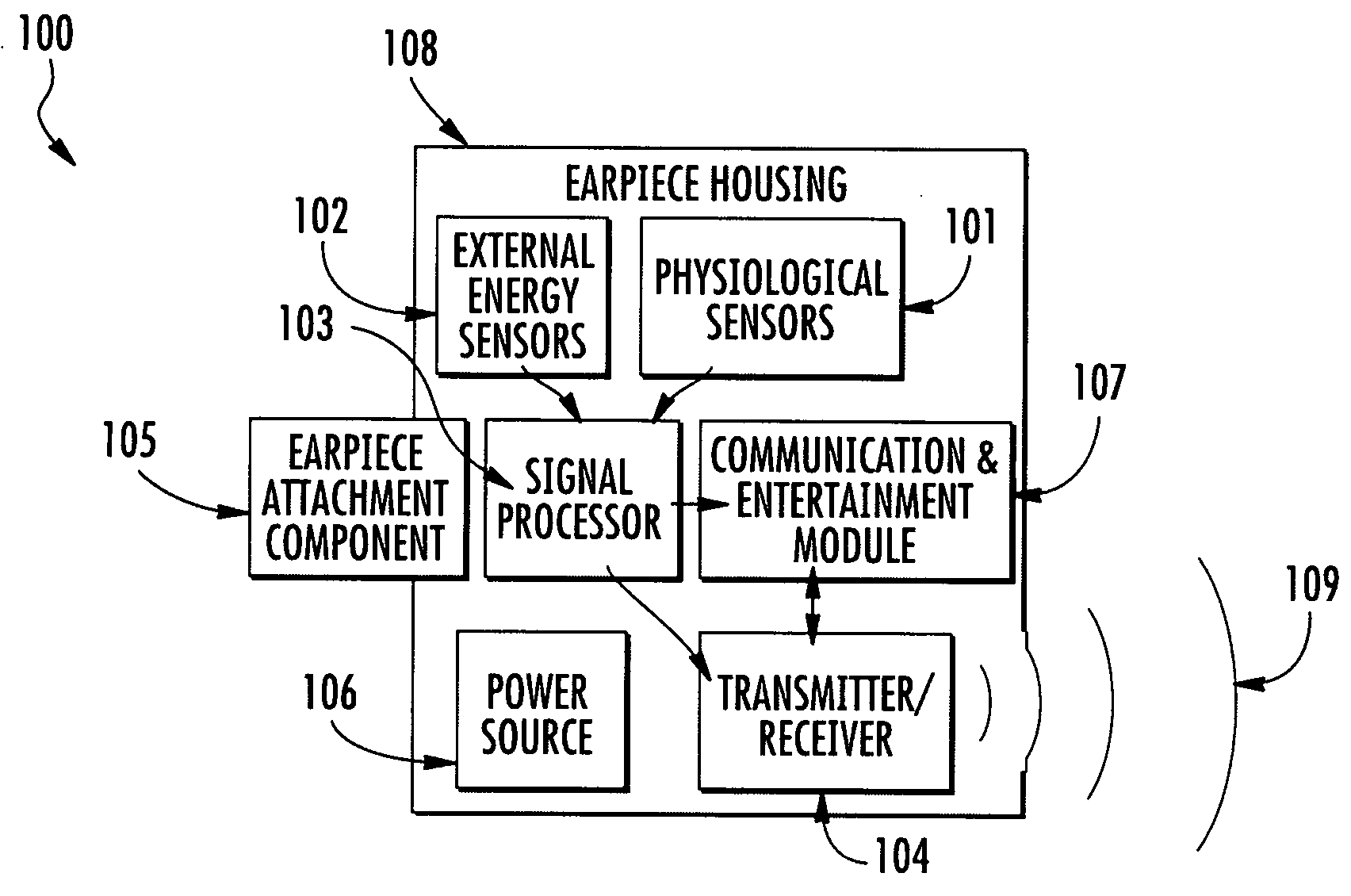
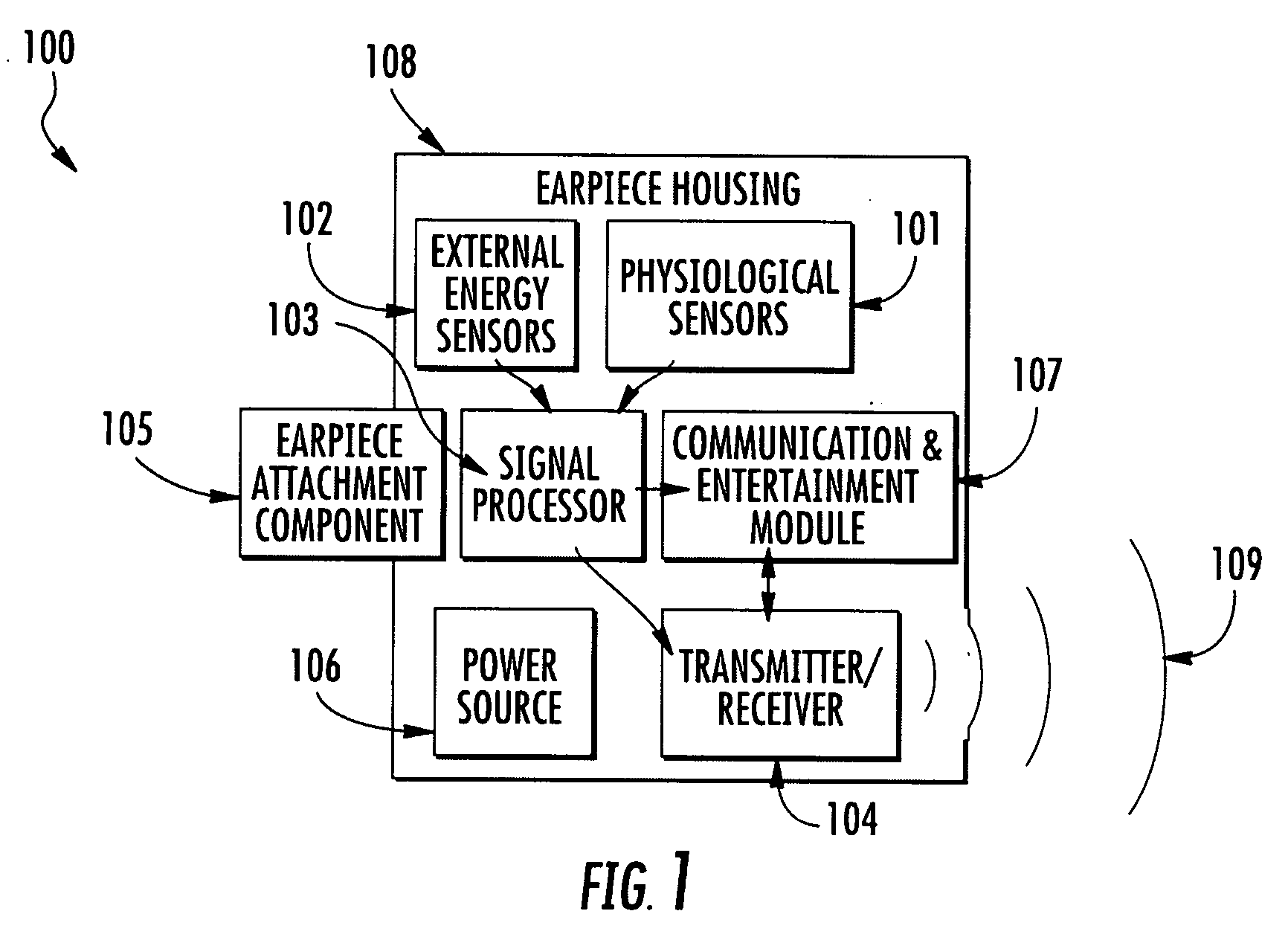
Telemetric apparatus for health and environmental monitoring
Wearable apparatus for monitoring various physiological and environmental factors are provided. Real-time, noninvasive health and environmental monitors include a plurality of compact sensors integrated within small, low-profile devices, such as earpiece modules. Physiological and environmental data is collected and wirelessly transmitted into a wireless network, where the data is stored and / or processed.
Owner:YUKKA MAGIC LLC
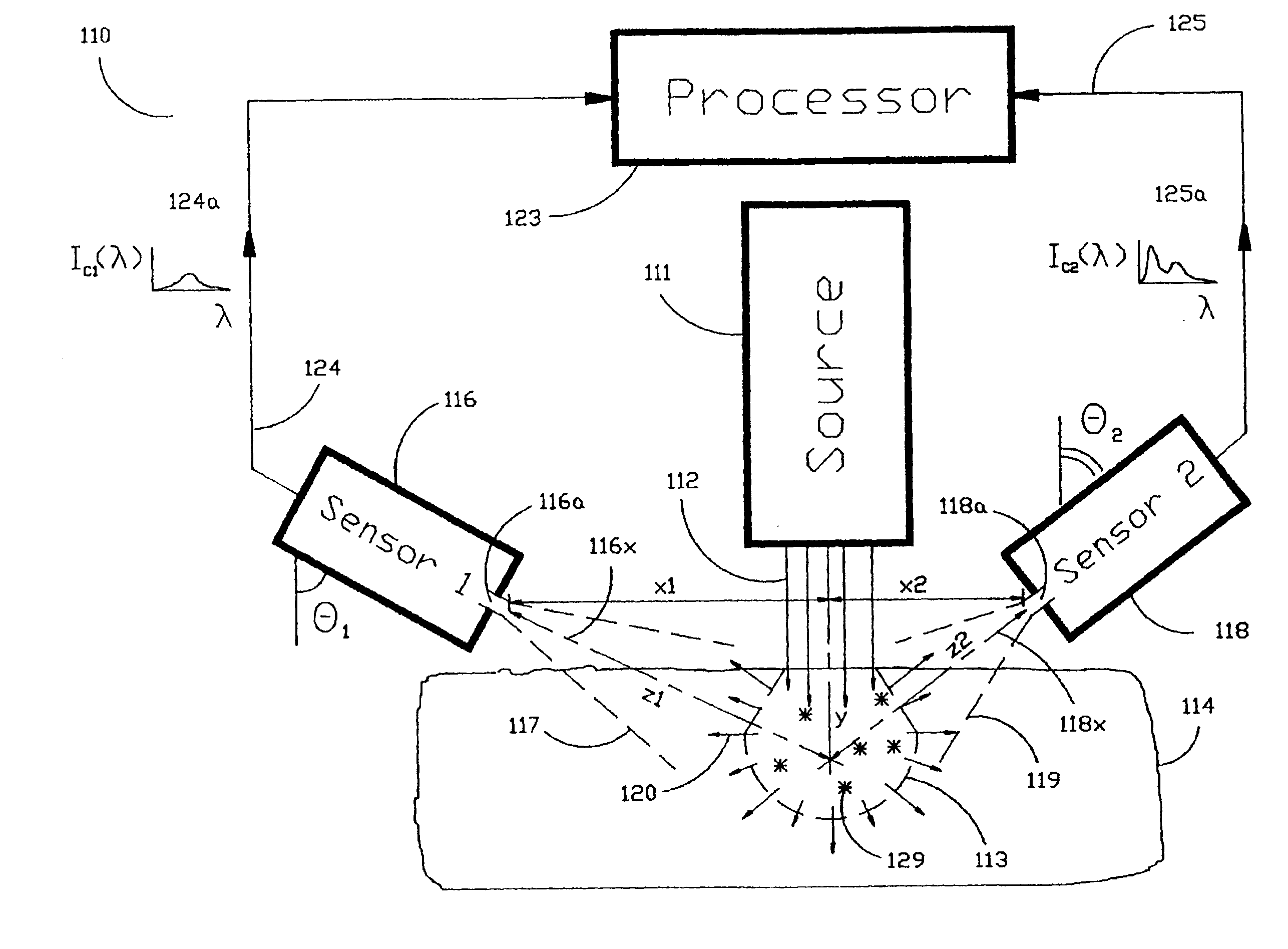
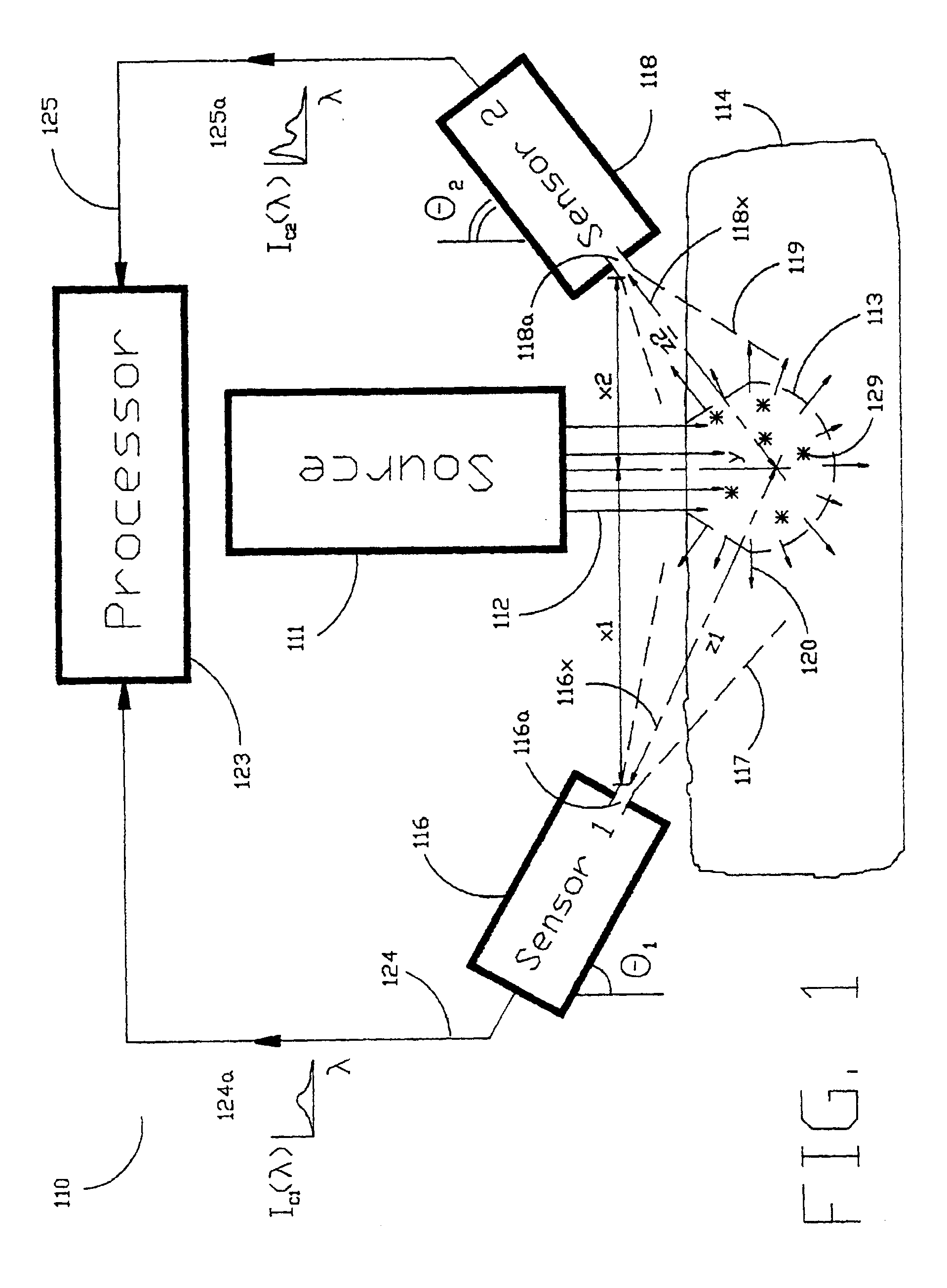
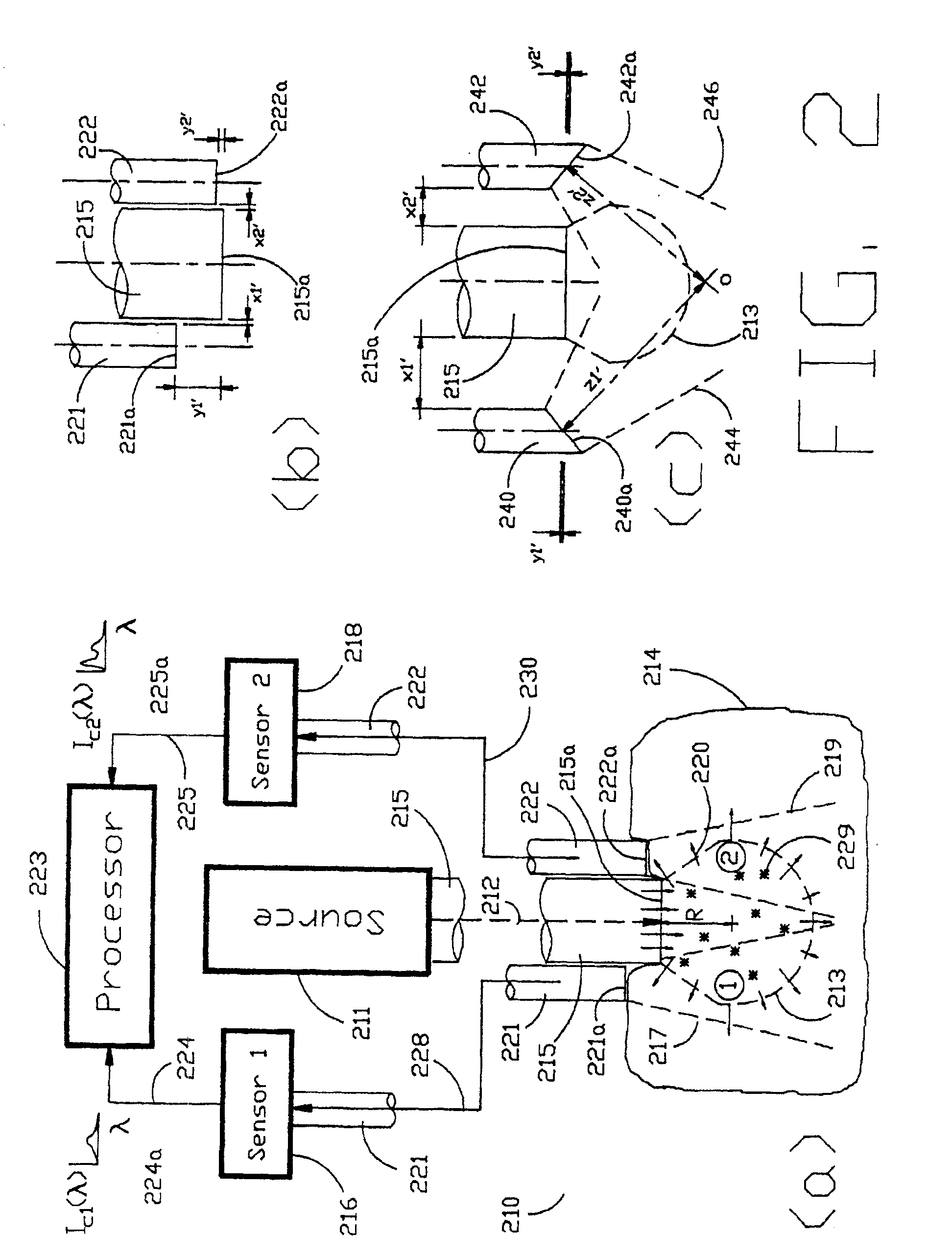
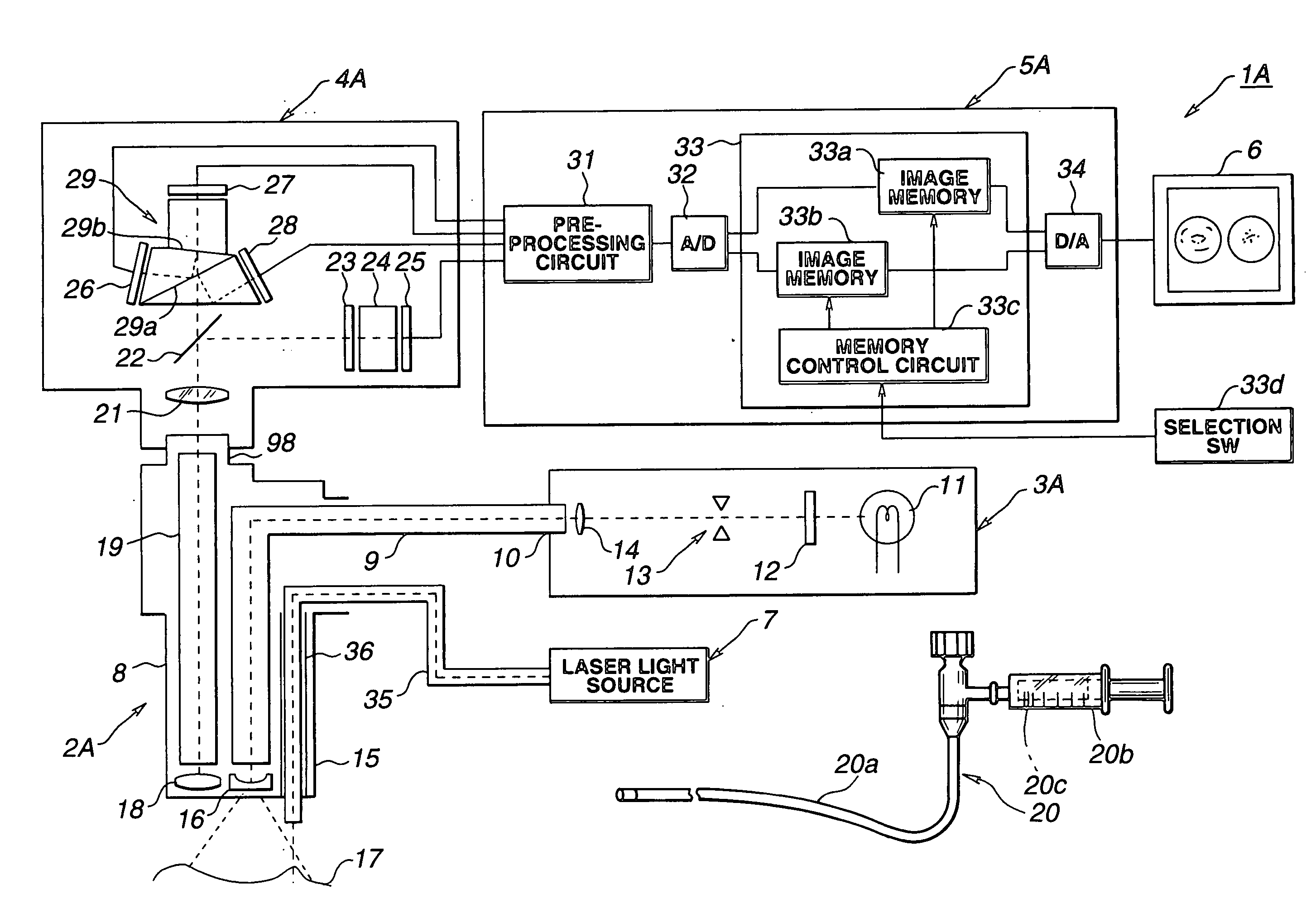
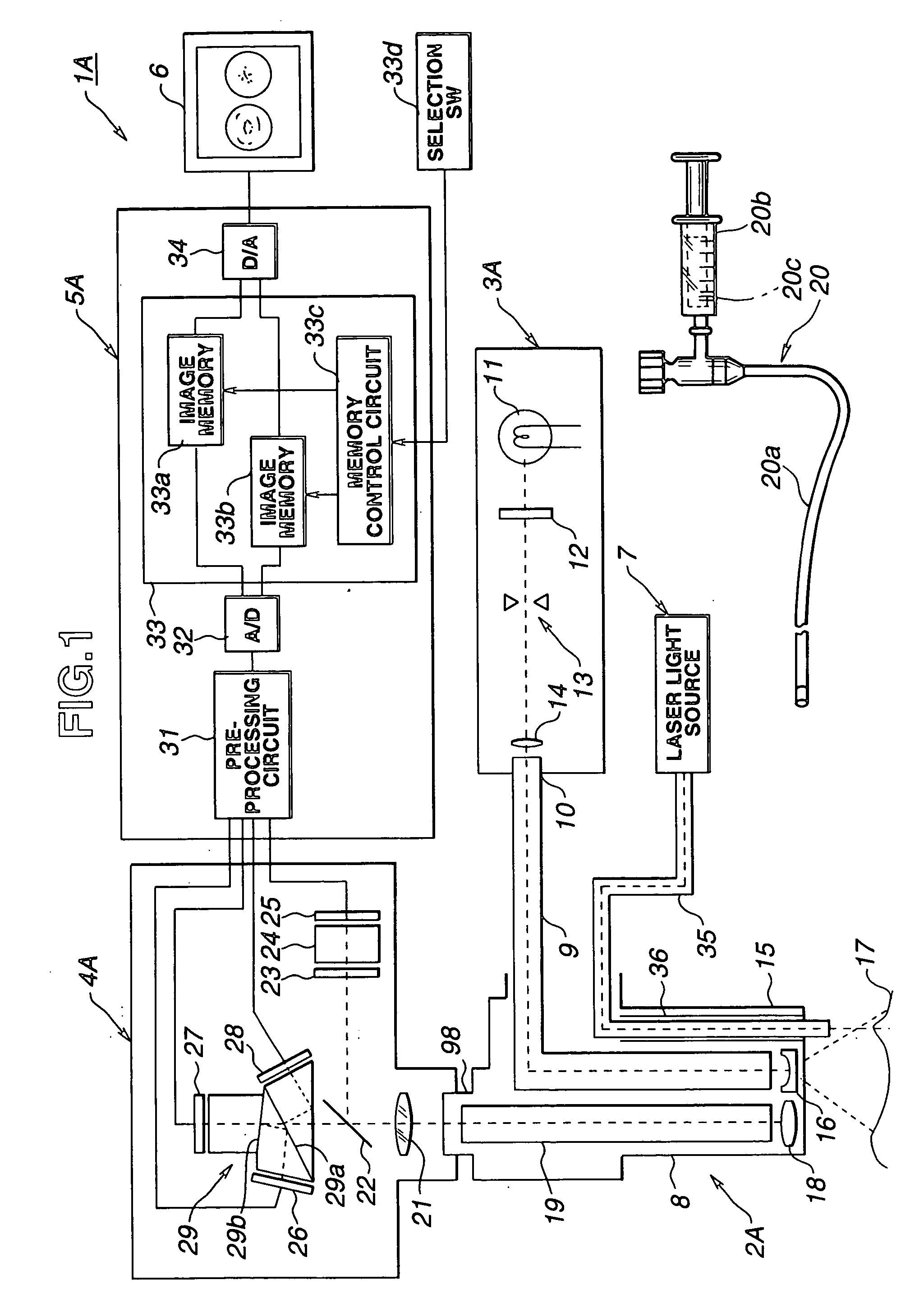
Method and devices for laser induced fluorescence attenuation spectroscopy
InactiveUSRE39672E1Large signal to noise ratioSurgeryScattering properties measurementsUltrasound attenuationSpectroscopy
The Laser Induced Fluorescence Attenuation Spectroscopy (LIFAS) method and apparatus preferably include a source adapted to emit radiation that is directed at a sample volume in a sample to produce return light from the sample, such return light including modulated return light resulting from modulation by the sample, a first sensor, displaced by a first distance from the sample volume for monitoring the return light and generating a first signal indicative of the intensity of return light, a second sensor, displaced by a second distance from the sample volume, for monitoring the return light and generating a second signal indicative of the intensity of return light, and a processor associated with the first sensor and the second sensor and adapted to process the first and second signals so as to determine the modulation of the sample. The methods and devices of the inventions are particularly well-suited for determining the wavelength-dependent attenuation of a sample and using the attenuation to restore the intrinsic laser induced fluorescence of the sample. In turn, the attenuation and intrinsic laser induced fluorescence can be used to determined a characteristic of interest, such as the ischemic or hypoxic condition of biological tissue.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Surgical instruments with sensors for detecting tissue properties, and system using such instruments
ActiveUS20090054908A1Avoiding and detecting failurePredict successDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterData setPatient status
A system is provided that furnishes expert procedural guidance based upon patient-specific data gained from surgical instruments incorporating sensors on the instrument's working surface, one or more reference sensors placed about the patient, sensors implanted before, during or after the procedure, the patient's personal medical history, and patient status monitoring equipment. Embodiments include a system having a surgical instrument with a sensor for generating a signal indicative of a property of a subject tissue of the patient, which signal is converted into a current dataset and stored. A processor compares the current dataset with other previously stored datasets, and uses the comparison to assess a physical condition of the subject tissue and / or to guide a procedure being performed on the tissue.
Owner:SURGISENSE CORP
Non-invasive tissue glucose level monitoring
Instruments and methods are described for performing non-invasive measurements of analyte levels and for monitoring, analyzing and regulating tissue status, such as tissue glucose levels.
Owner:MASIMO LAB INC
Long wave fluorophore sensor compounds and other fluorescent sensor compounds in polymers
InactiveUS6766183B2Improve sensor sensitivityReduction in the tissue autofluorescence backgroundMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceConcentrations glucoseFluorophore
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC +1
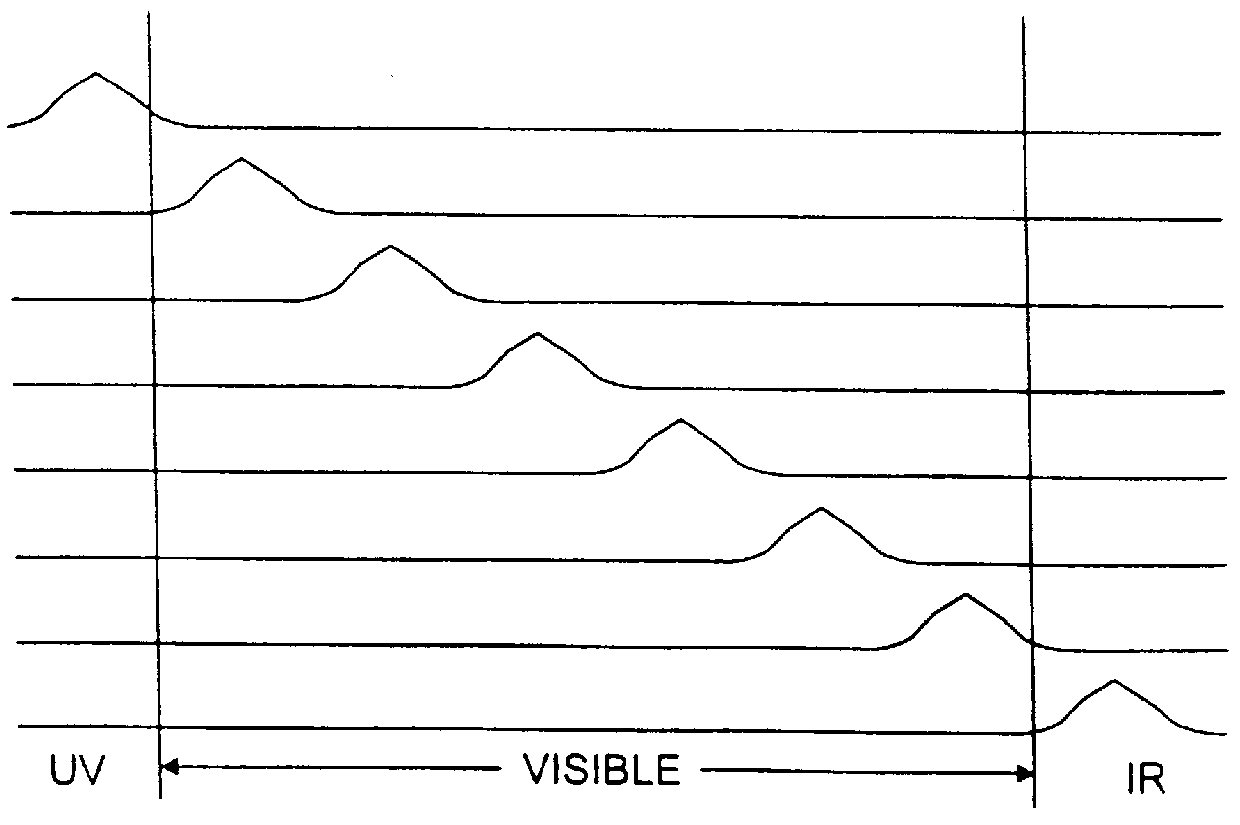
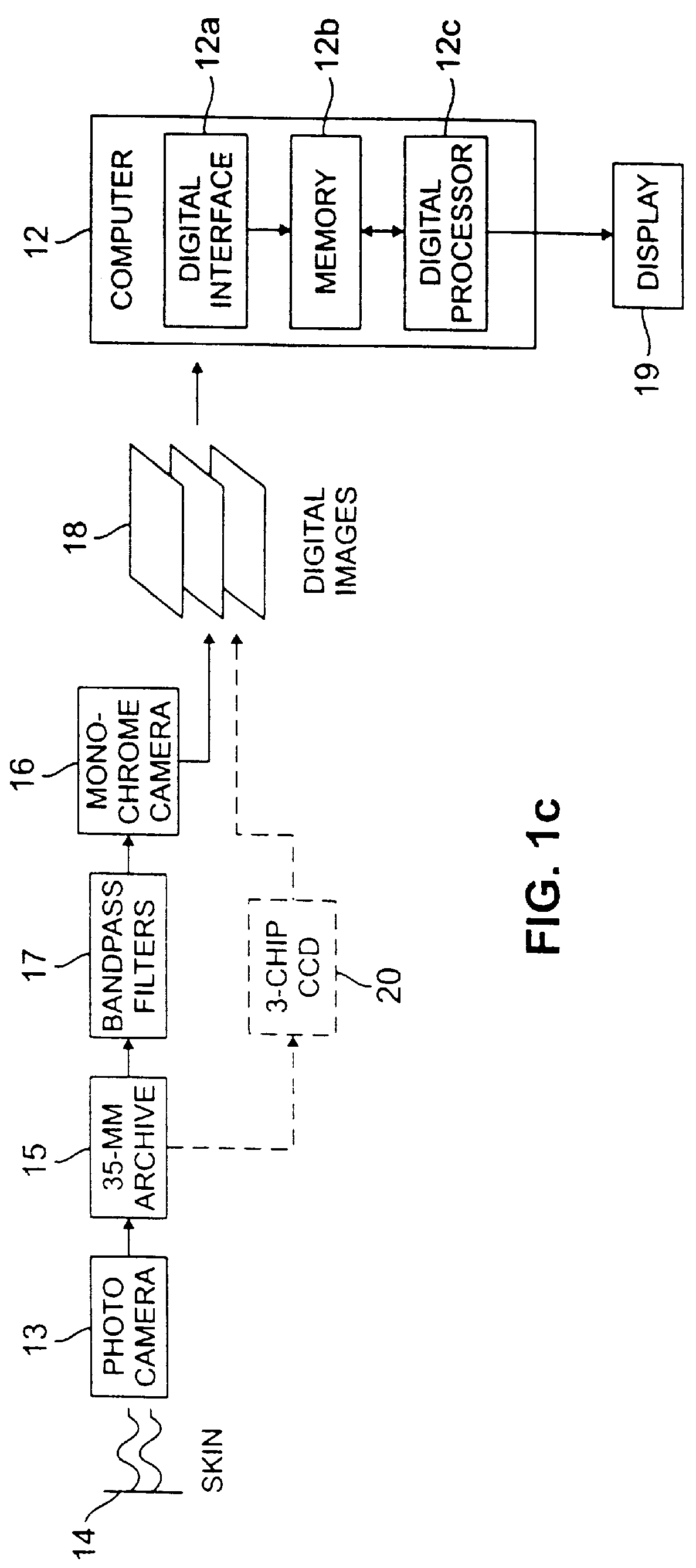
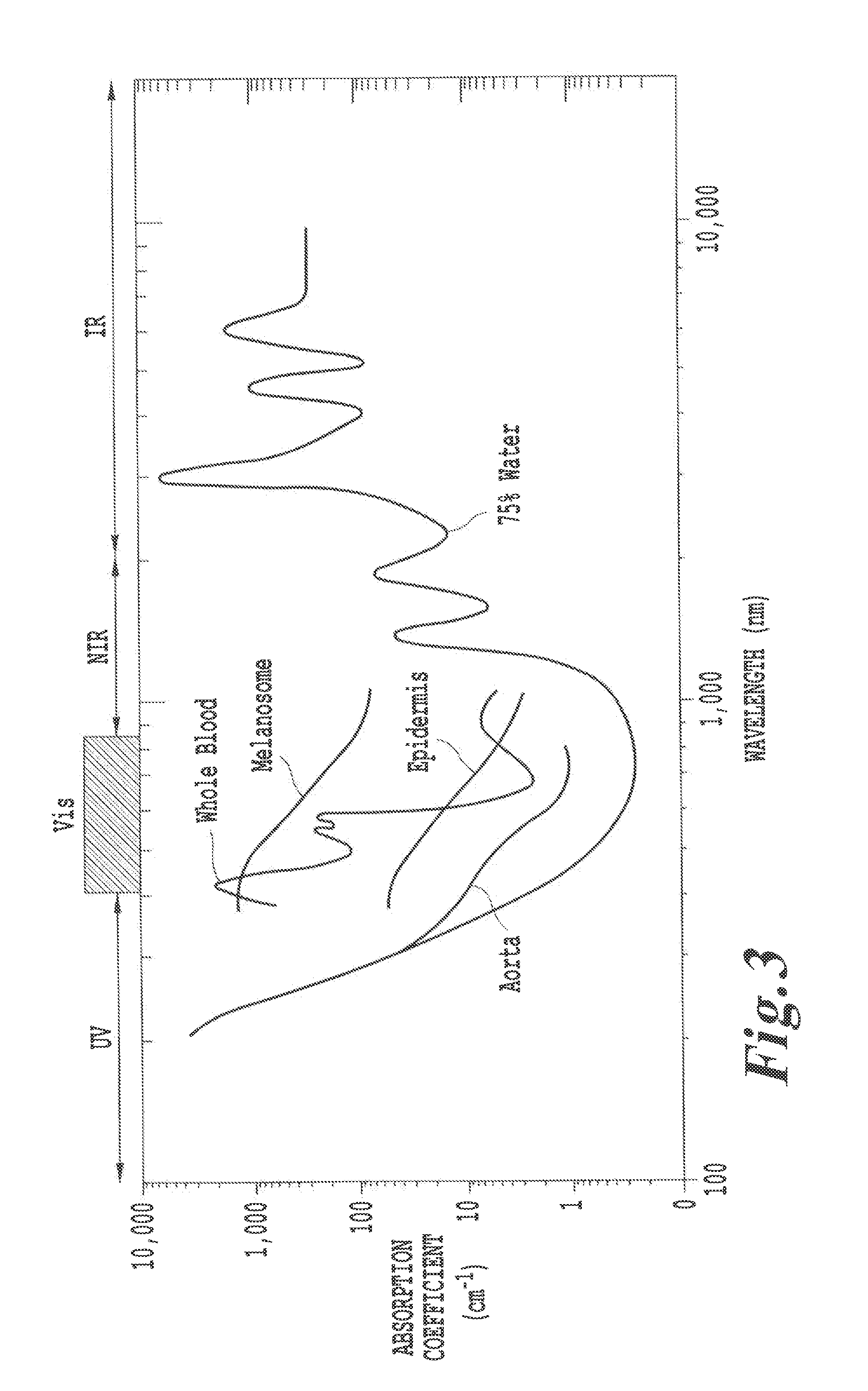
Systems and methods for the multispectral imaging and characterization of skin tissue
InactiveUS6081612AReduce background noiseImage enhancementImage analysisRegion of interestDigital processor
Systems and methods for the multispectral imaging of skin tissue enables automatic characterization of the condition of a region of interest of the skin, based on direct digital imaging of the region of interest or the digitization of color photographic slides of the region of interest, illuminated by appropriately filtered light. Preferably, a digital image at a low spectral band is automatically segmented and that segmented mask is used to segment the other images by a digital processor. Parameters are estimated through wavelet maxima representations. Parameters related to the texture, asymmetry, blotchiness and border irregularities are also automatically estimated. The region of interest is automatically characterized by the digital processor, based on those parameters. The region of interest may include a skin lesion, in which case the present invention enables the characterization of the lesion as malignant or benign. The region of interest may also include wounds or burns.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
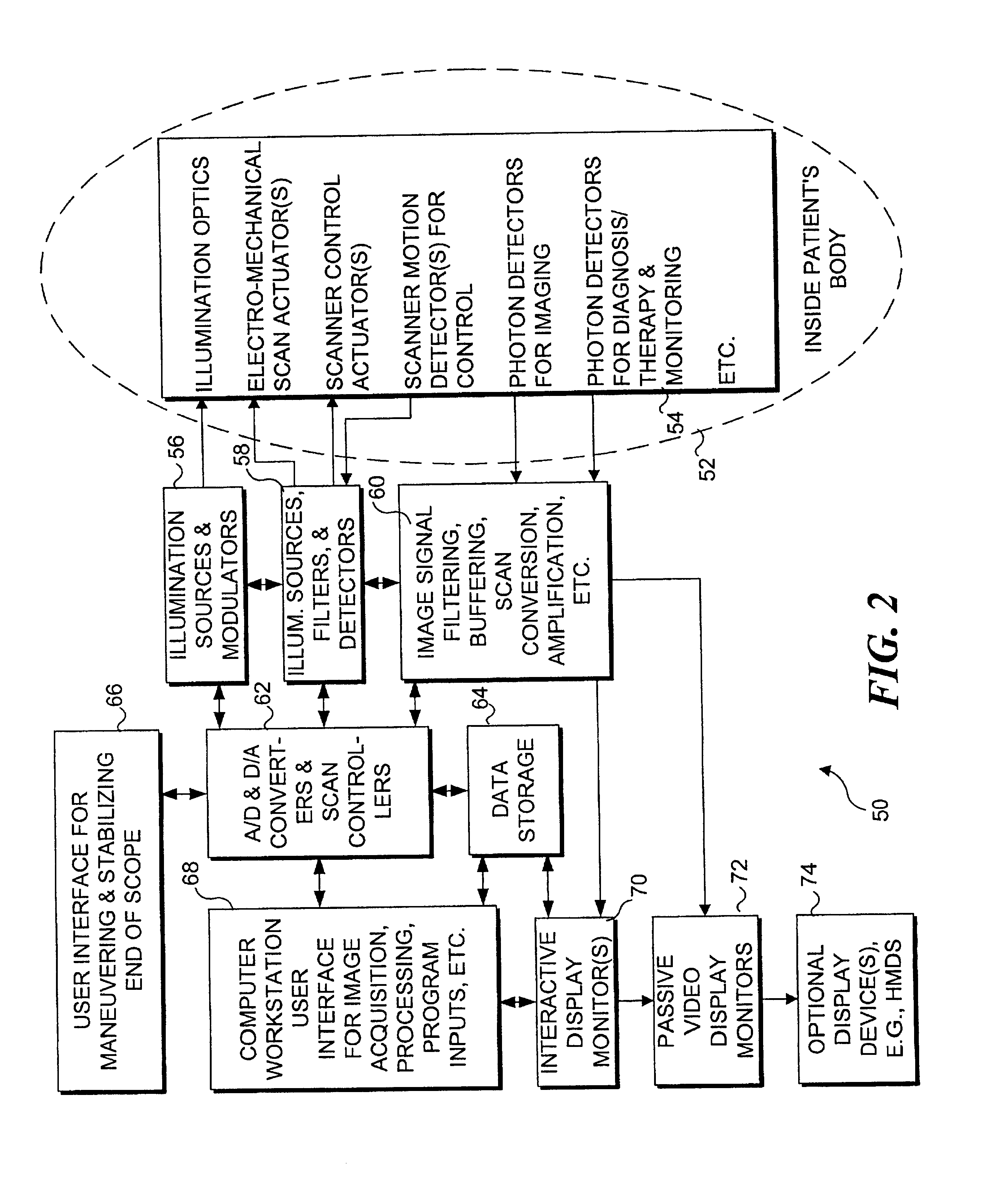
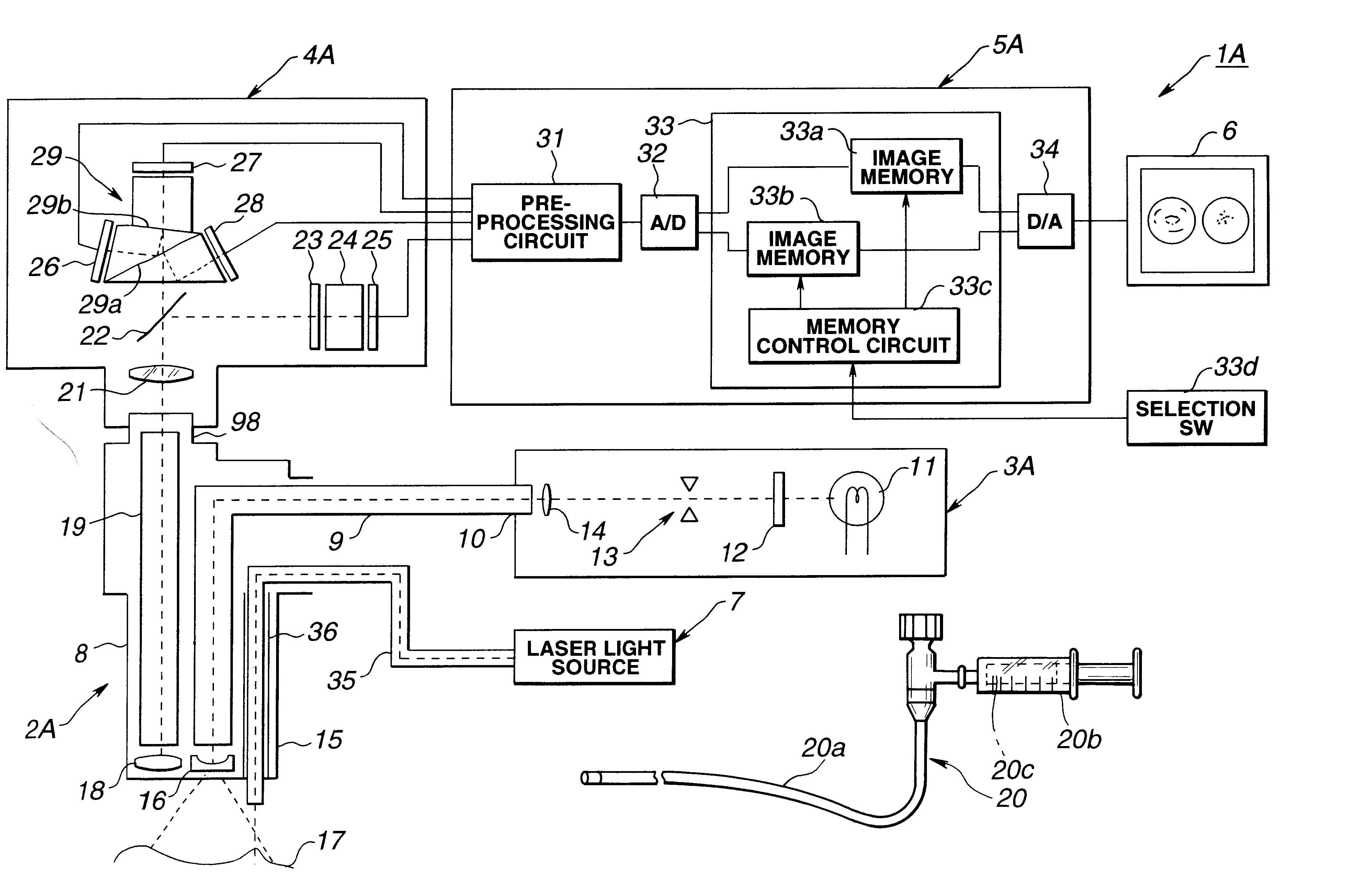
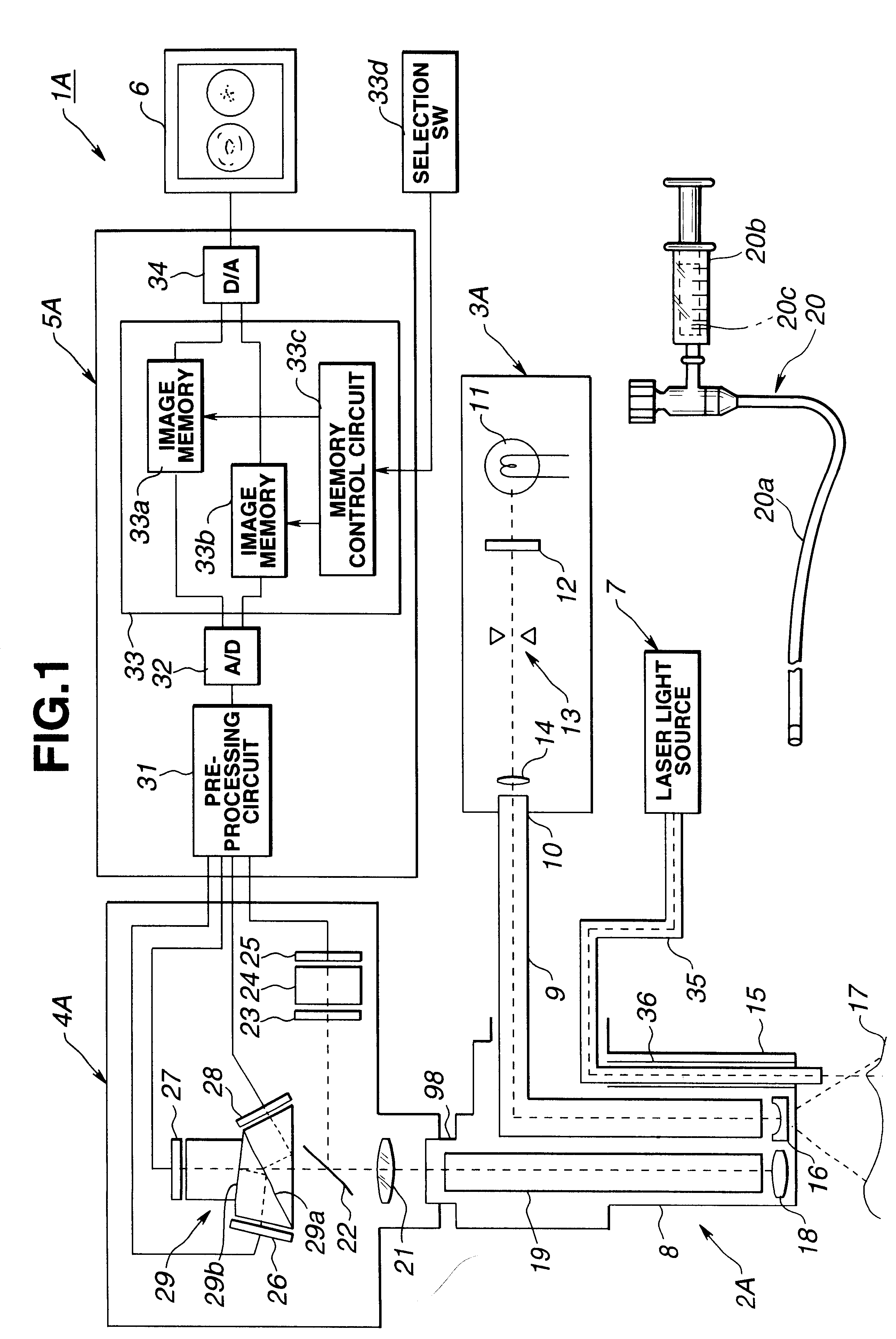
Medical imaging, diagnosis, and therapy using a scanning single optical fiber system
InactiveUS6975898B2High resolutionEasy to viewEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsFlexible endoscopyHigh resolution imaging
An integrated endoscopic image acquisition and therapeutic delivery system for use in minimally invasive medical procedures (MIMPs). The system uses directed and scanned optical illumination provided by a scanning optical fiber or light waveguide that is driven by a piezoelectric or other electromechanical actuator included at a distal end of an integrated imaging and diagnostic / therapeutic instrument. The directed illumination provides high resolution imaging, at a wide field of view (FOV), and in full color that matches or excels the images produced by conventional flexible endoscopes. When using scanned optical illumination, the size and number of the photon detectors do not limit the resolution and number of pixels of the resulting image. Additional features include enhancement of topographical features, stereoscopic viewing, and accurate measurement of feature sizes of a region of interest in a patient's body that facilitate providing diagnosis, monitoring, and / or therapy with the instrument.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
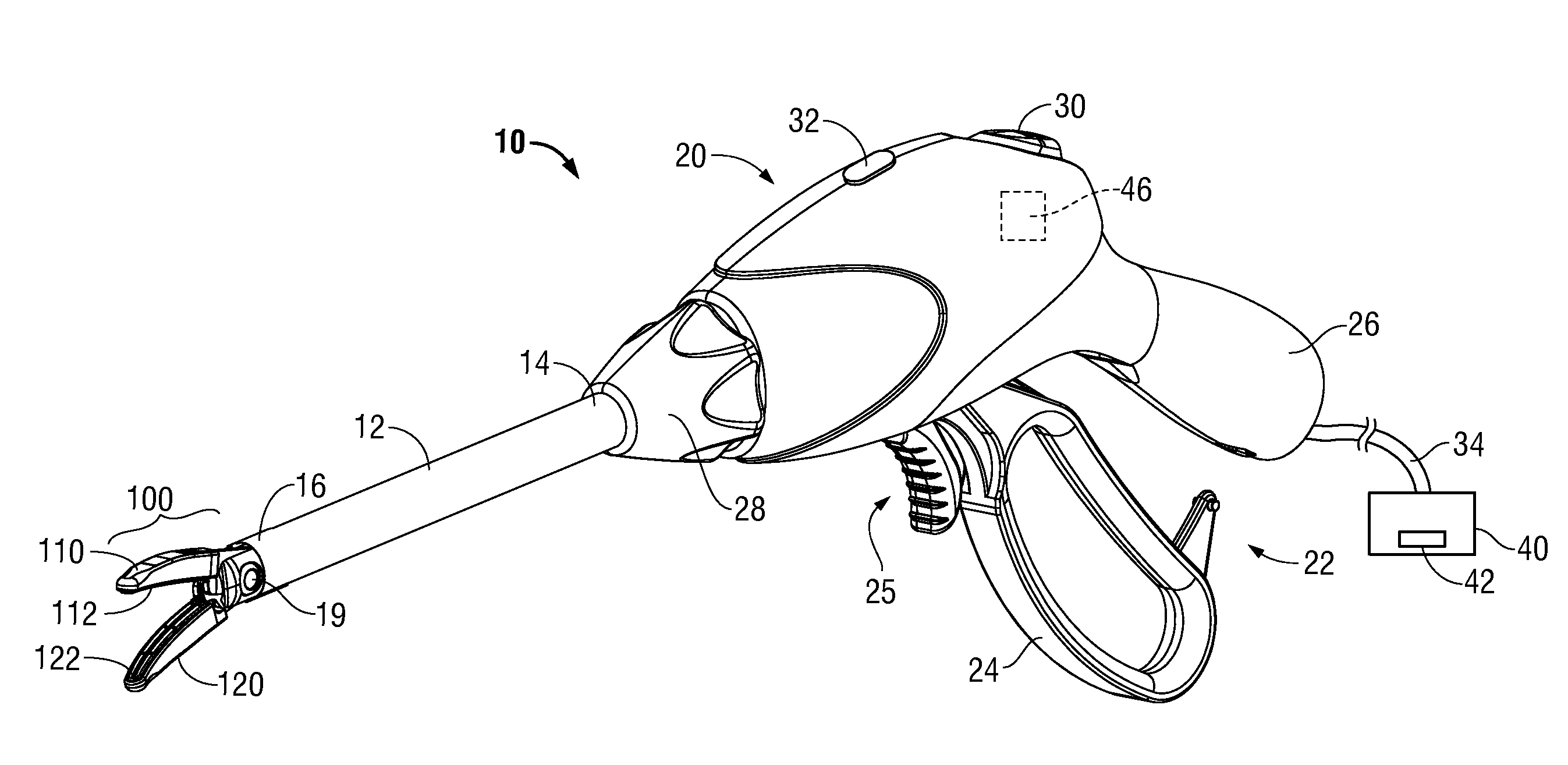
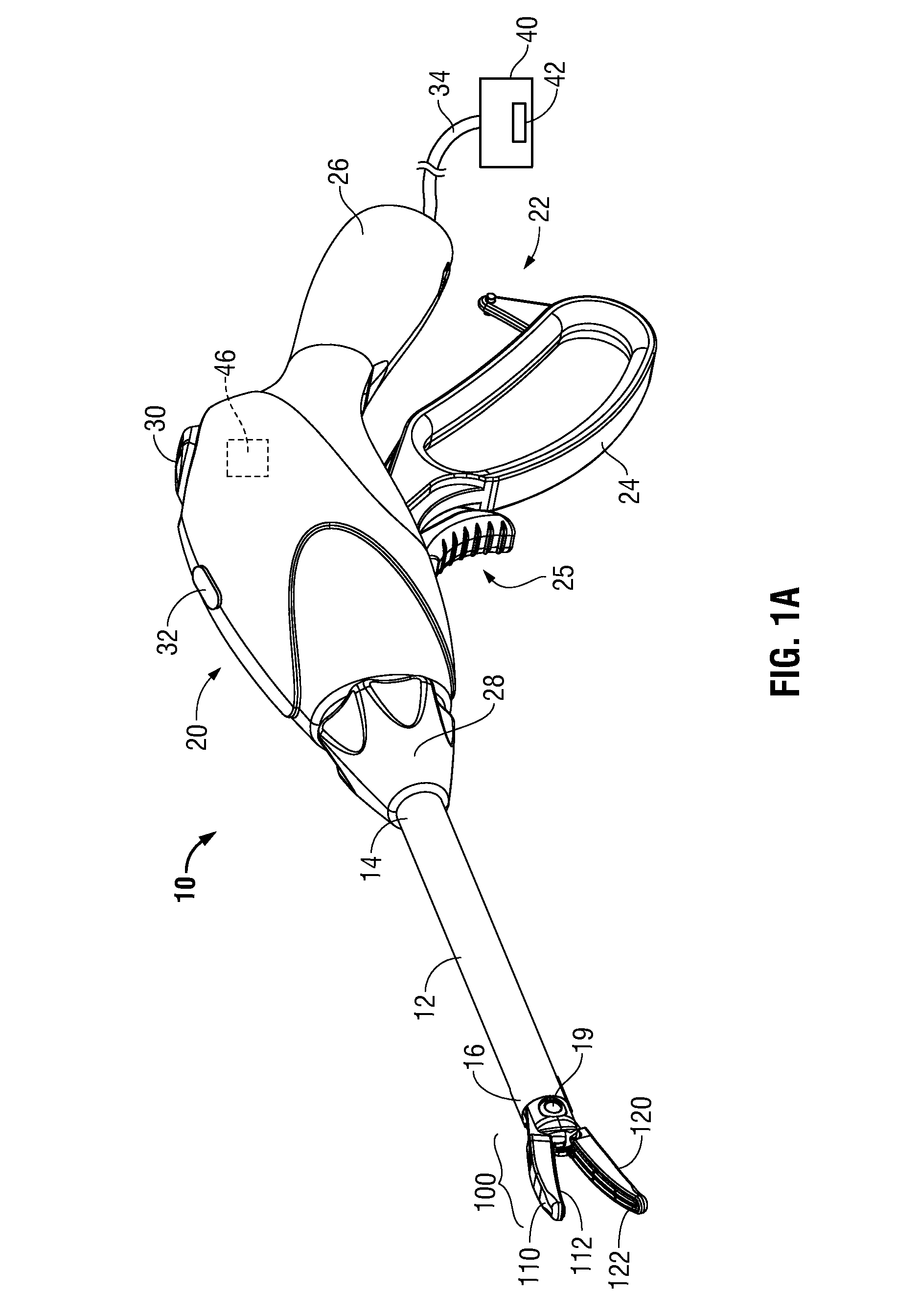
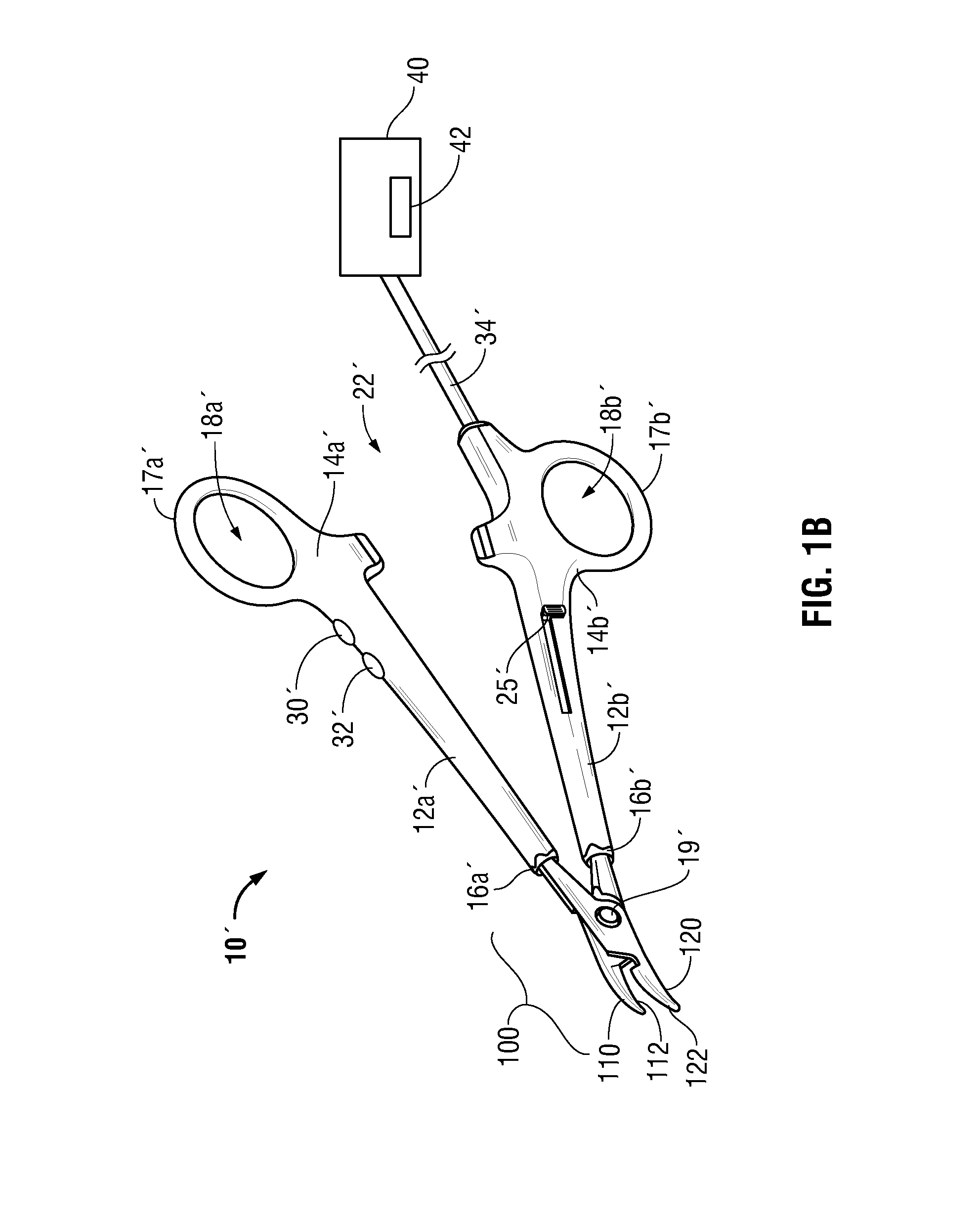
Surgical device with an end-effector assembly and system for monitoring of tissue during a surgical procedure
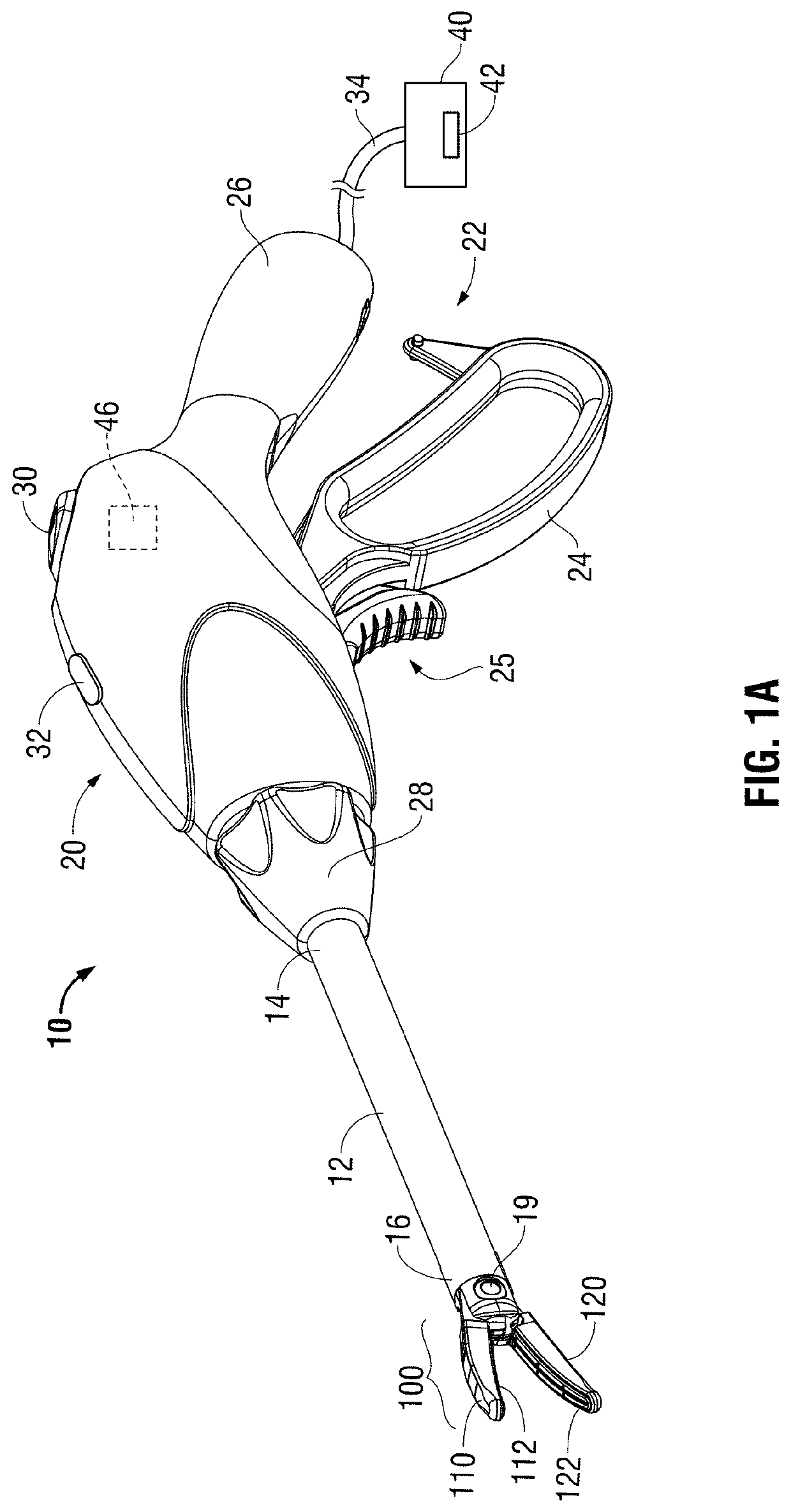
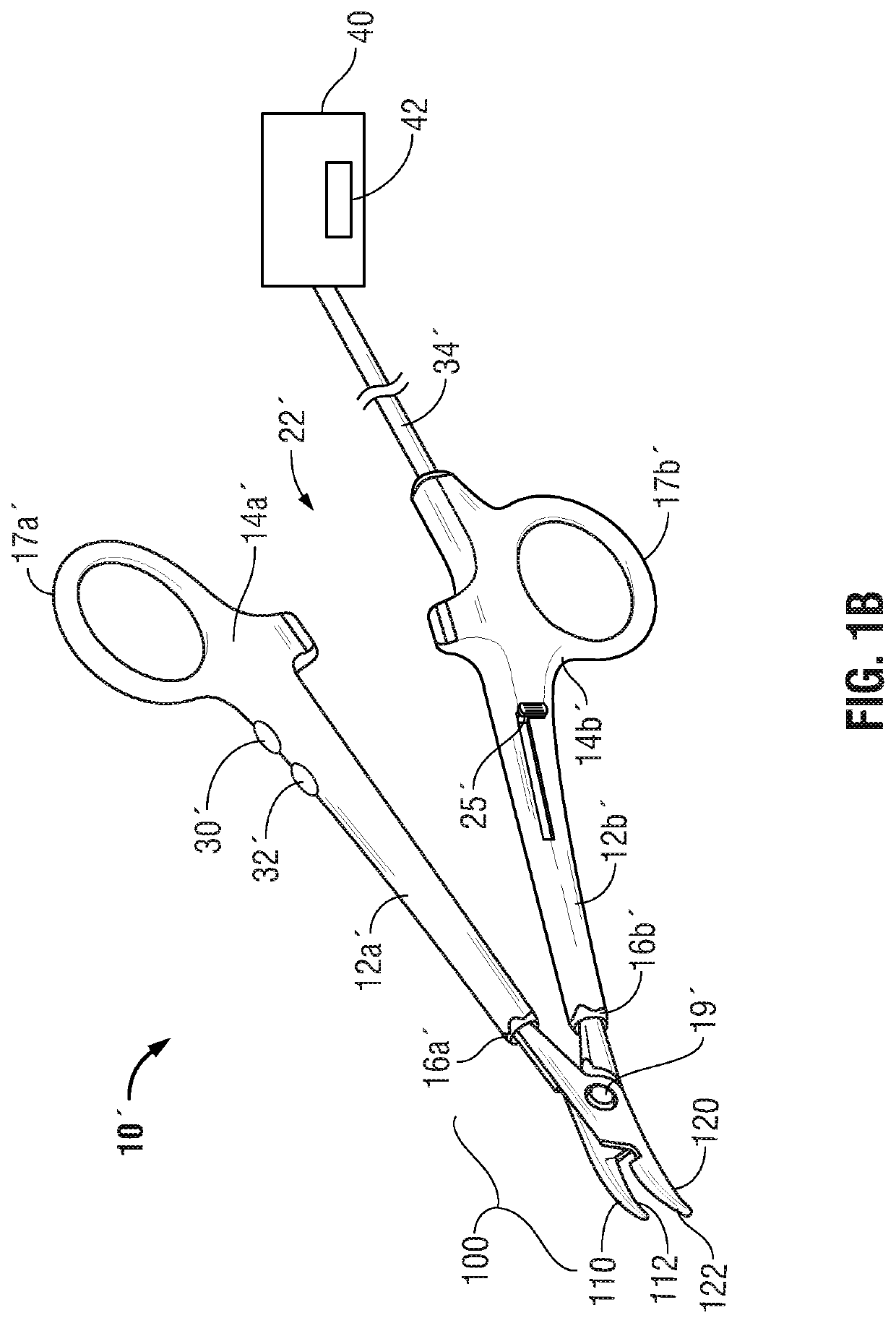
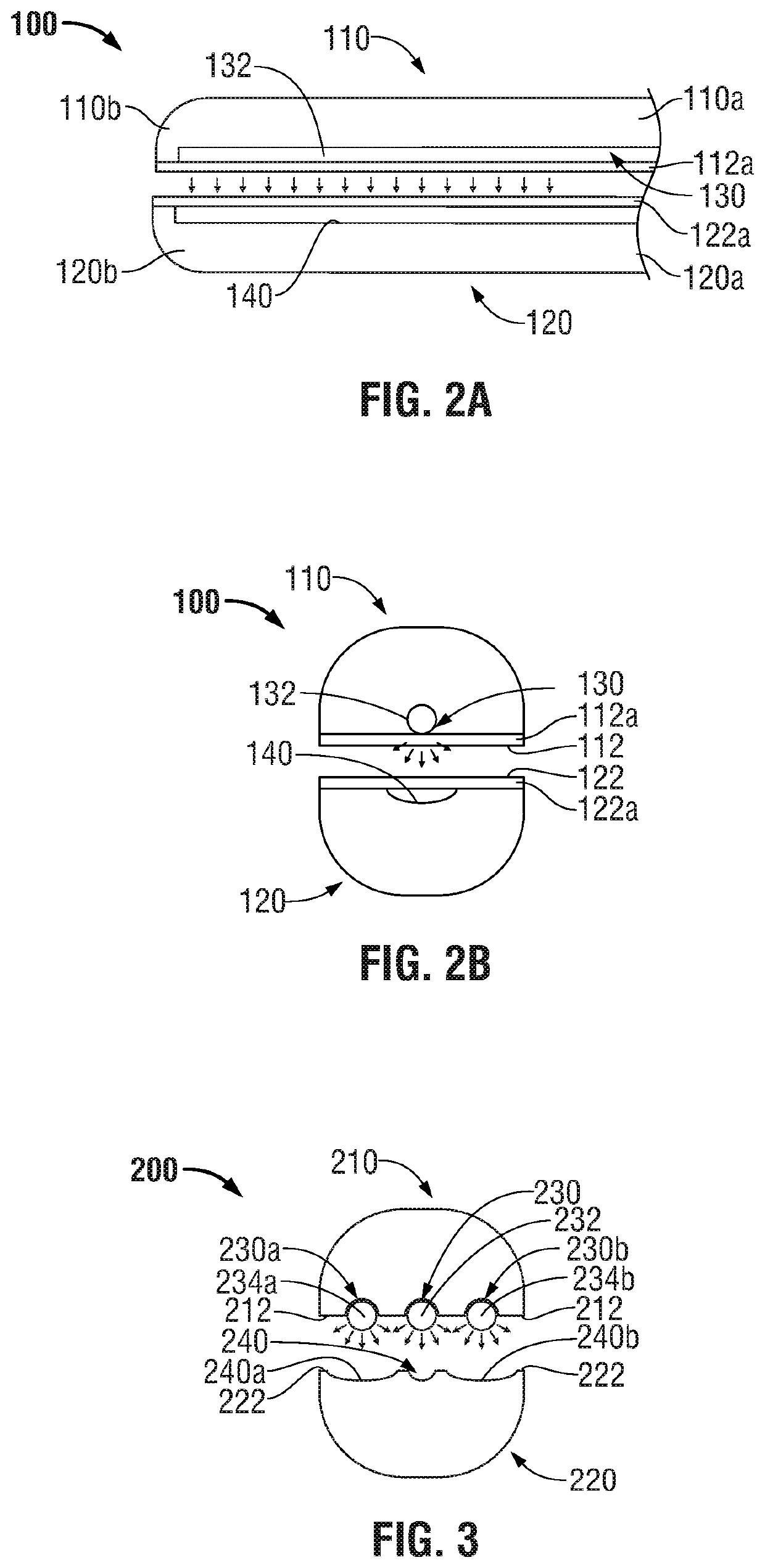
ActiveUS20160089198A1Good indicationExcessive damageDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionLight energyEngineering
A medical instrument is provided and includes a housing and a shaft coupled to the housing. The shaft has a proximal end and a distal end. An end-effector assembly is disposed at the distal end of the shaft. The end-effector assembly includes first and second jaw members. At least one of the first and second jaw members is movable from a first position wherein the first and second jaw members are disposed in spaced relation relative to one another to at least a second position closer to one another wherein the first and second jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue therebetween. The medical instrument also includes one or more light-emitting elements and one or more light-detecting elements configured to generate one or more signals indicative of tissue florescence. The one or more light-emitting elements are adapted to deliver light energy to tissue grasped between the first and second jaw members.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Surgical device with an end-effector assembly and system for monitoring of tissue during a surgical procedure
ActiveUS10722292B2Good indicationExcessive damageDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionLight energyTissue fluorescence
A medical instrument is provided and includes a housing and a shaft coupled to the housing. The shaft has a proximal end and a distal end. An end-effector assembly is disposed at the distal end of the shaft. The end-effector assembly includes first and second jaw members. At least one of the first and second jaw members is movable from a first position wherein the first and second jaw members are disposed in spaced relation relative to one another to at least a second position closer to one another wherein the first and second jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue therebetween. The medical instrument also includes one or more light-emitting elements and one or more light-detecting elements configured to generate one or more signals indicative of tissue florescence. The one or more light-emitting elements are adapted to deliver light energy to tissue grasped between the first and second jaw members.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
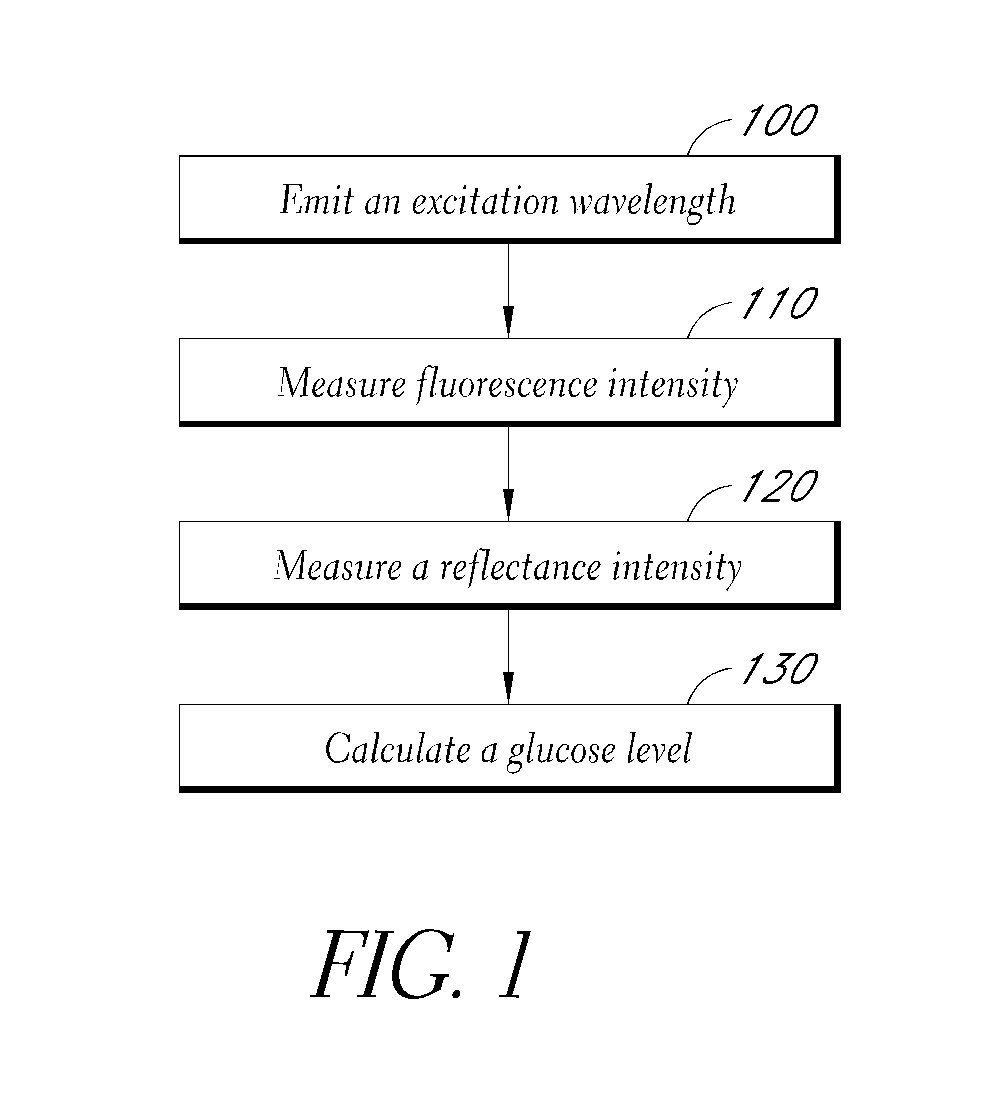
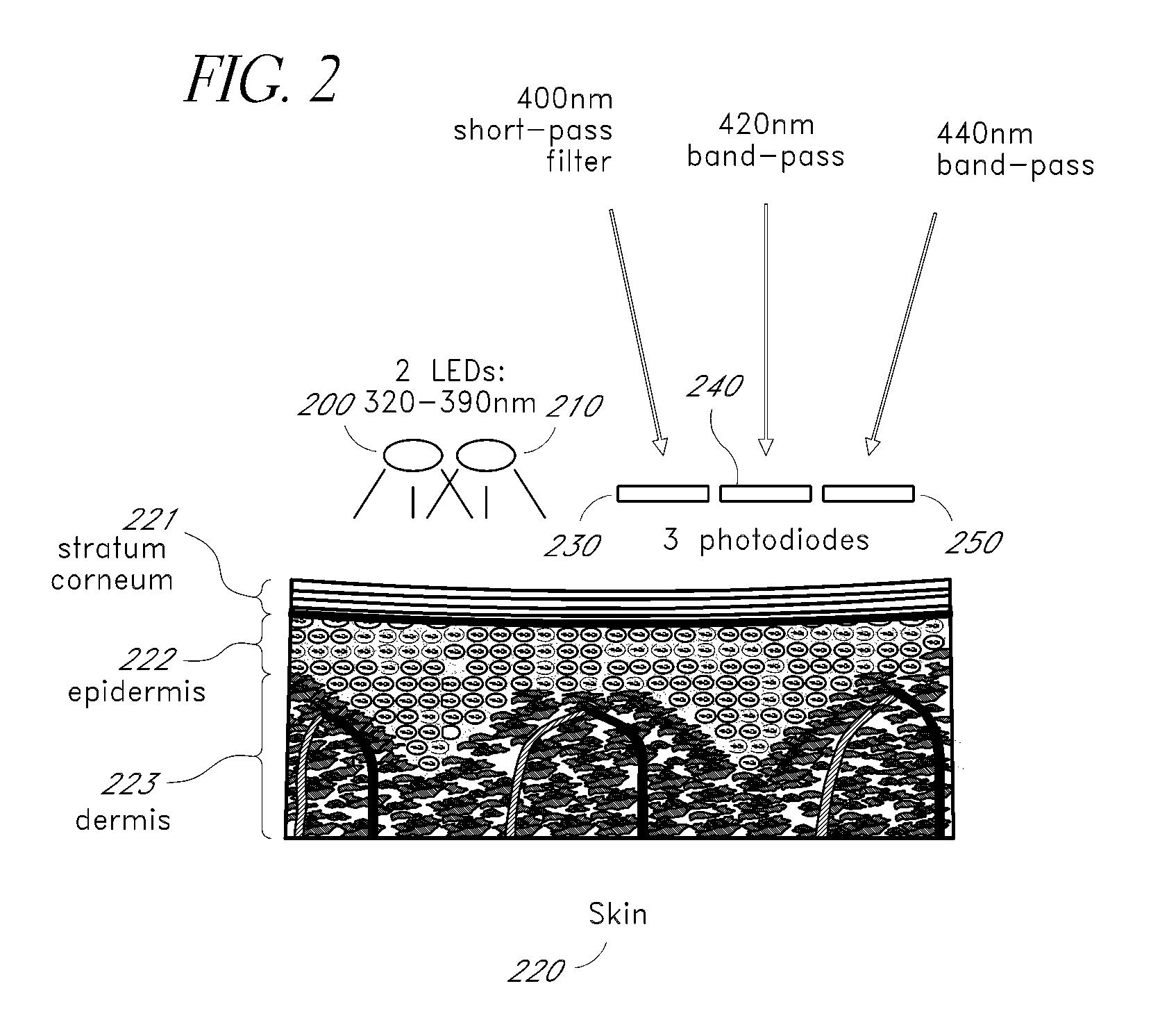
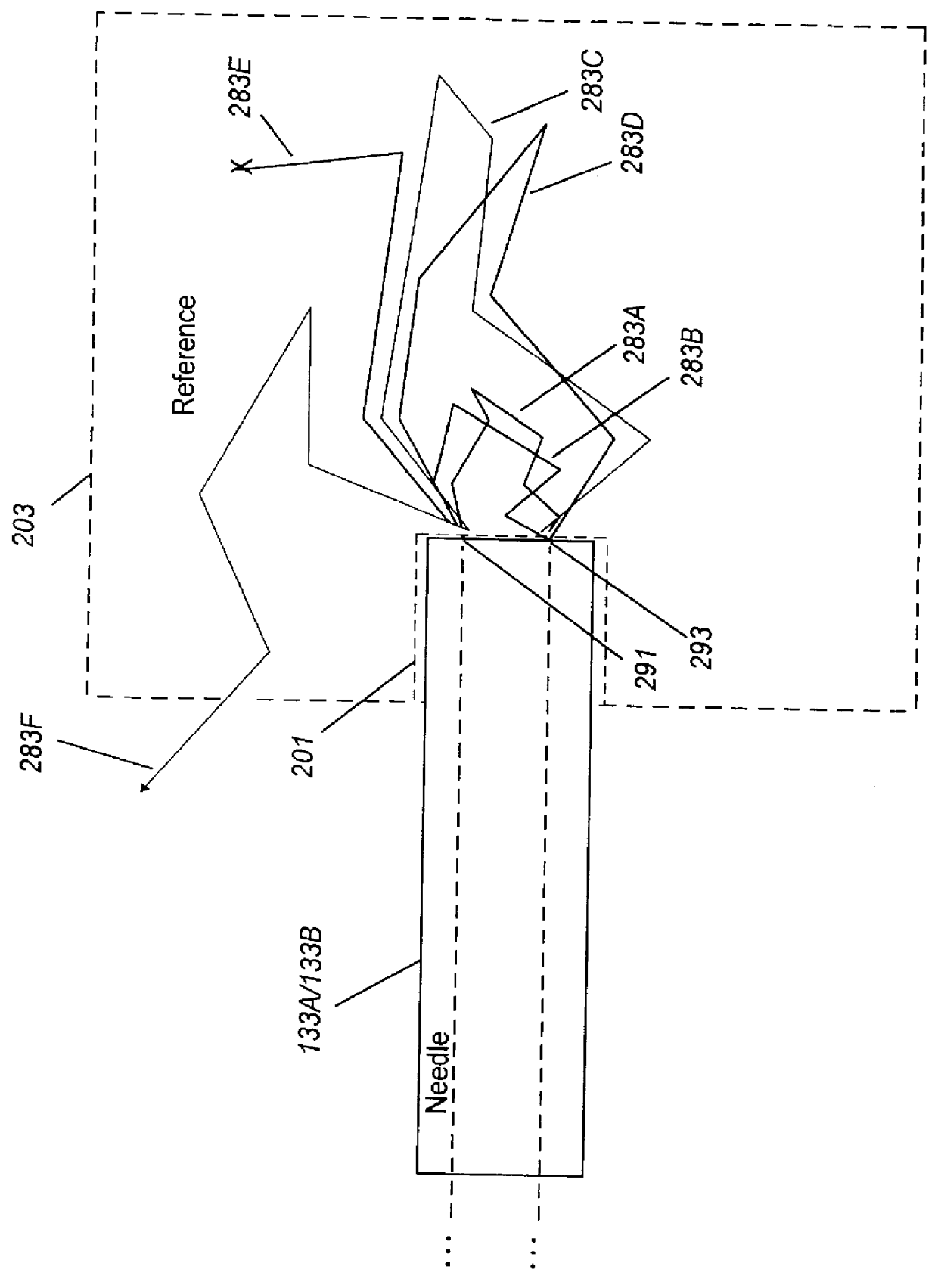
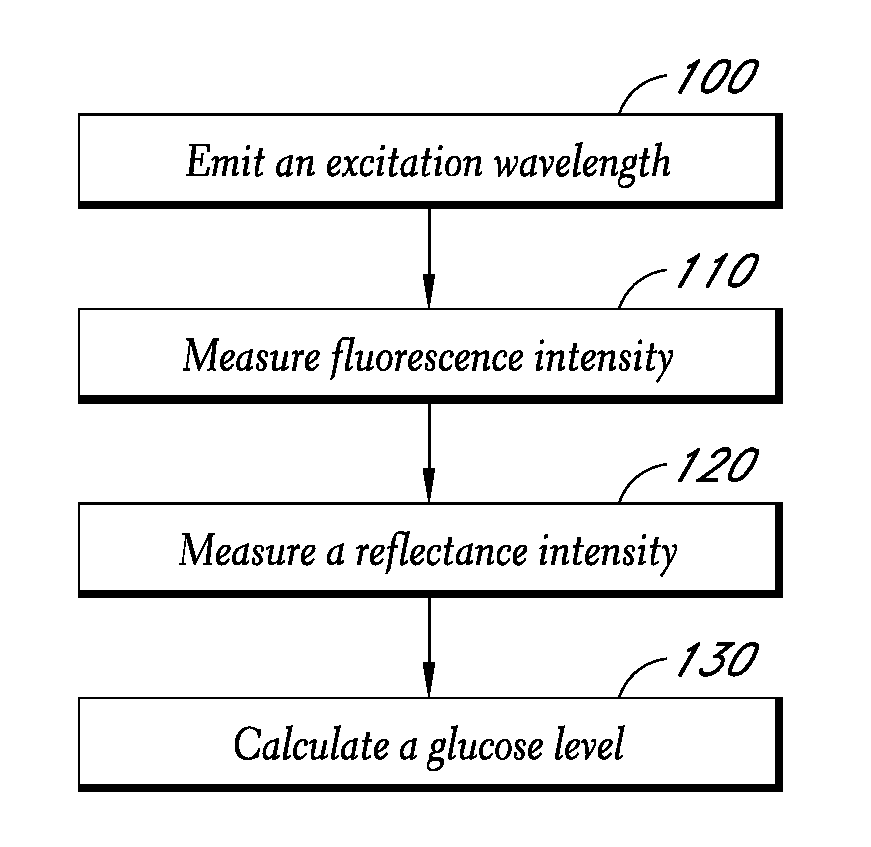
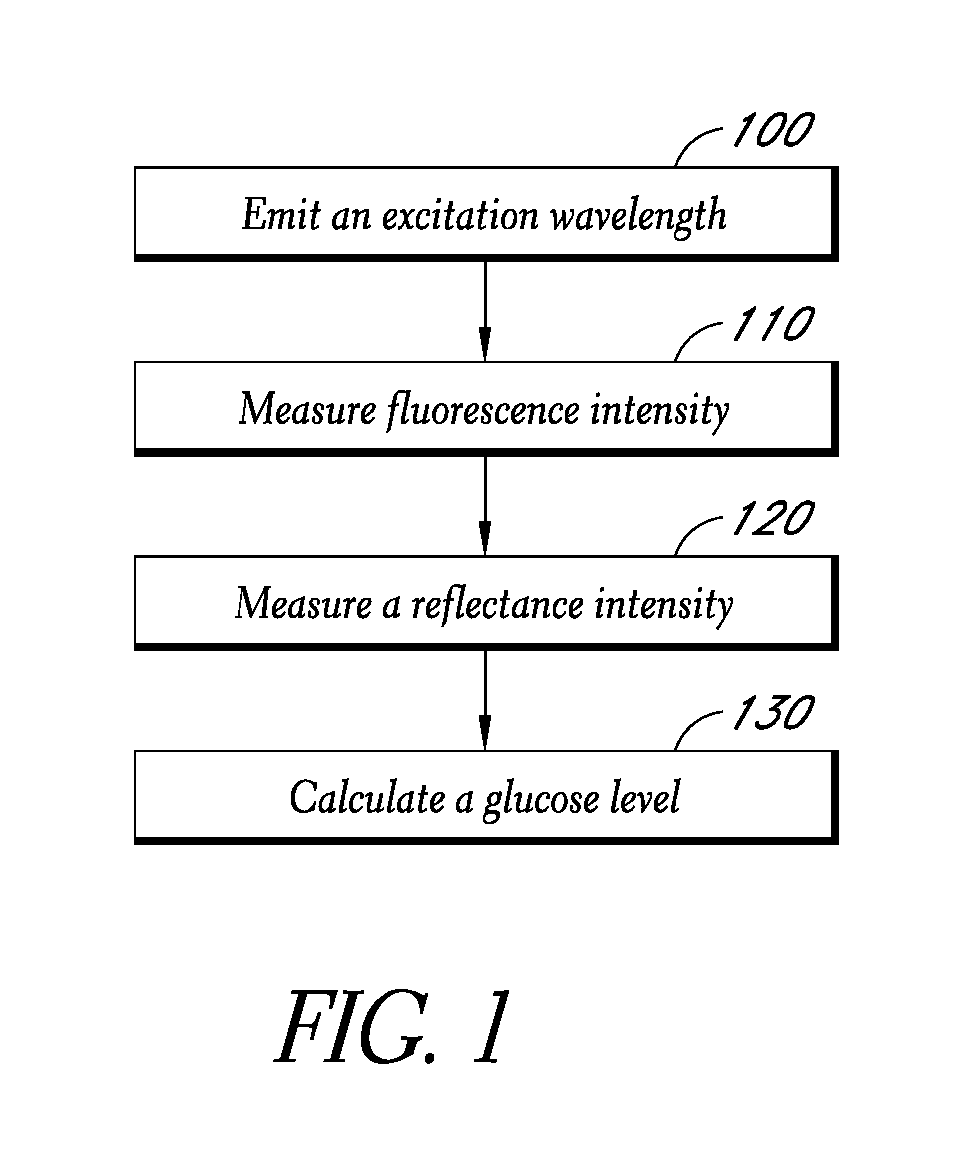
Reflectance calibration of fluorescence-based glucose measurements
InactiveUS20140330098A1Easy to detectDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionMetaboliteMedicine
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
Fluorescent endoscope system enabling simultaneous normal light observation and fluorescence observation in infrared spectrum
InactiveUS6293911B1Inhibition of lesionsHigh light transmittanceSurgeryEndoscopesLength waveFluorescence endoscopy
Excitation light for normal light observation with wavelengths in the visible spectrum, which is output from a lamp, and excitation light with wavelengths in the infrared spectrum for exciting a fluorescent substance characteristic of being accumulated readily in a lesion are irradiated simultaneously to a living tissue, to which the fluorescent substance has been administered, through an endoscope. Fluorescence components are separated from light stemming from the living tissue by means of a separator such as a dichroic mirror, introduced to a first imaging device, and then imaged. Light components with wavelengths in the visible spectrum are introduced to a second imaging device and then imaged. Signals representing the images are subjected to signal processing, whereby a video signal is produced. For better diagnosis, two images are displayed while, for example, one of the images is superimposed on the other.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
Optical systems and methods for ratiometric measurement of blood glucose concentration
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Medical instrument with sensor for use in a system and method for electromagnetic navigation
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Laser ablation process and apparatus
InactiveUS20020045811A1Reduce Fresnel reflectionMaximize transmitted lightControlling energy of instrumentDiagnostics using spectroscopyFiberLaser light
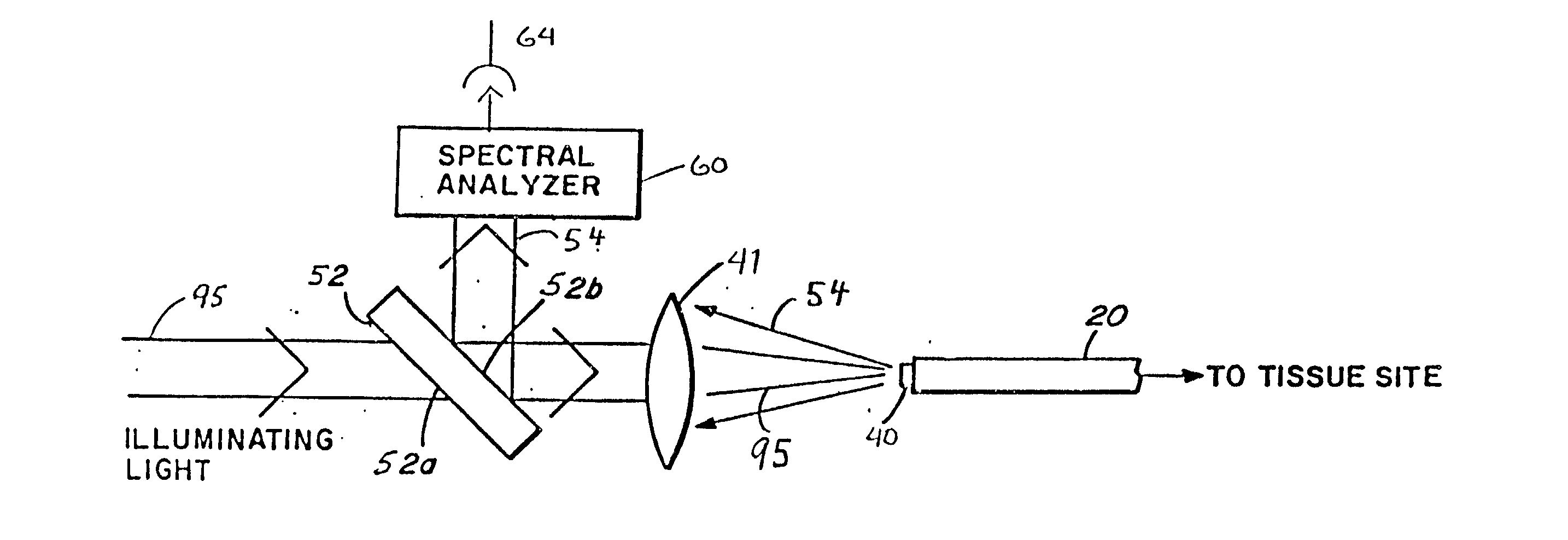
A laser catheter is disclosed wherein optical fibers carrying laser light are mounted in a catheter for insertion into an artery to provide controlled delivery of a laser beam for percutaneous intravascular laser treatment of atherosclerotic disease. A transparent protective shield is provided at the distal end of the catheter for mechanically diplacing intravascular blood and protecting the fibers from the intravascular contents, as well as protecting the patient in the event of failure of the fiber optics. Multiple optical fibers allow the selection of tissue that is to be removed. A computer controlled system automatically aligns fibers with the laser and controls exposure time. Spectroscopic diagnostics determine what tissue is to be removed.
Owner:KITTRELL CARTER +2
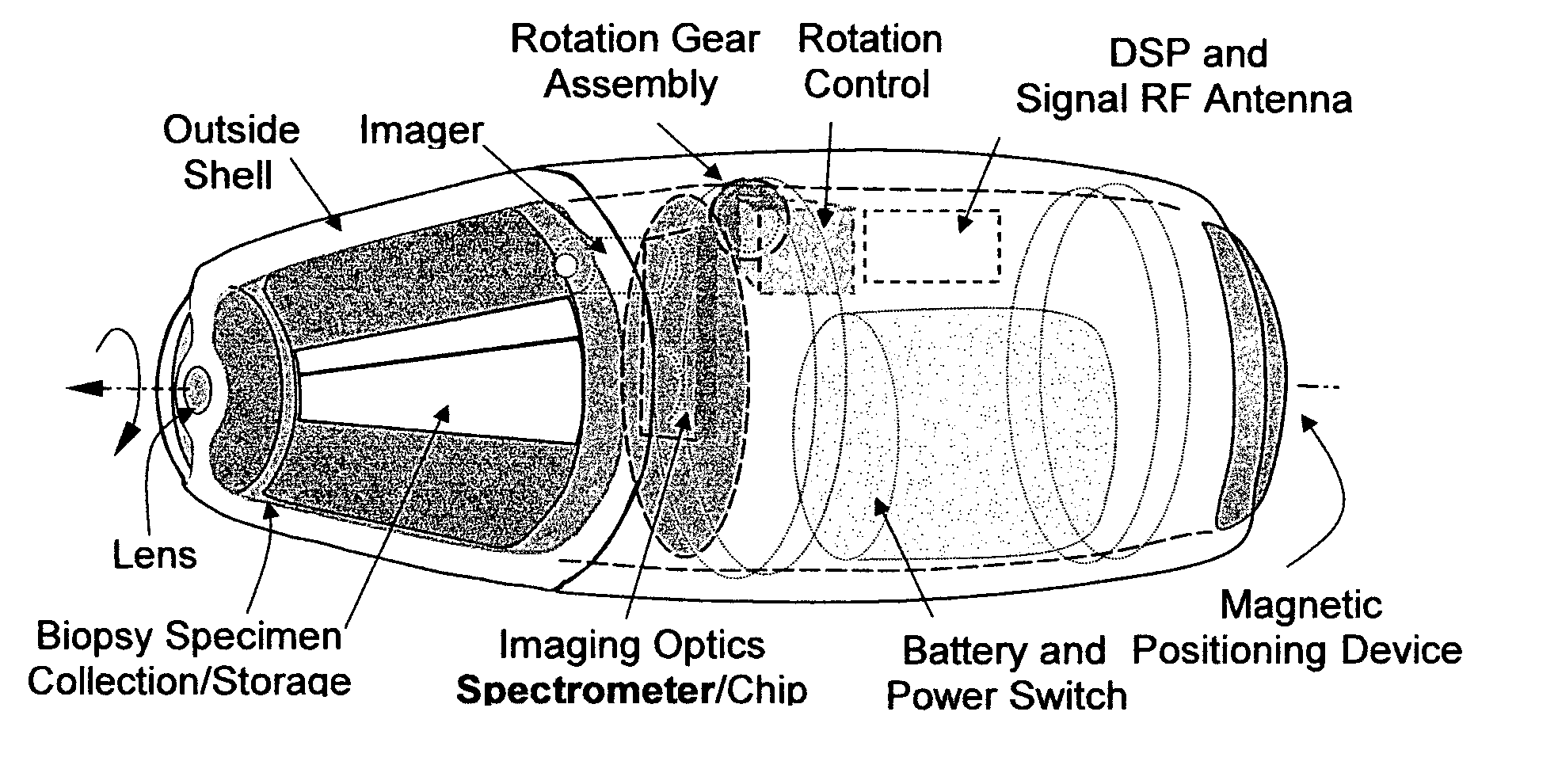
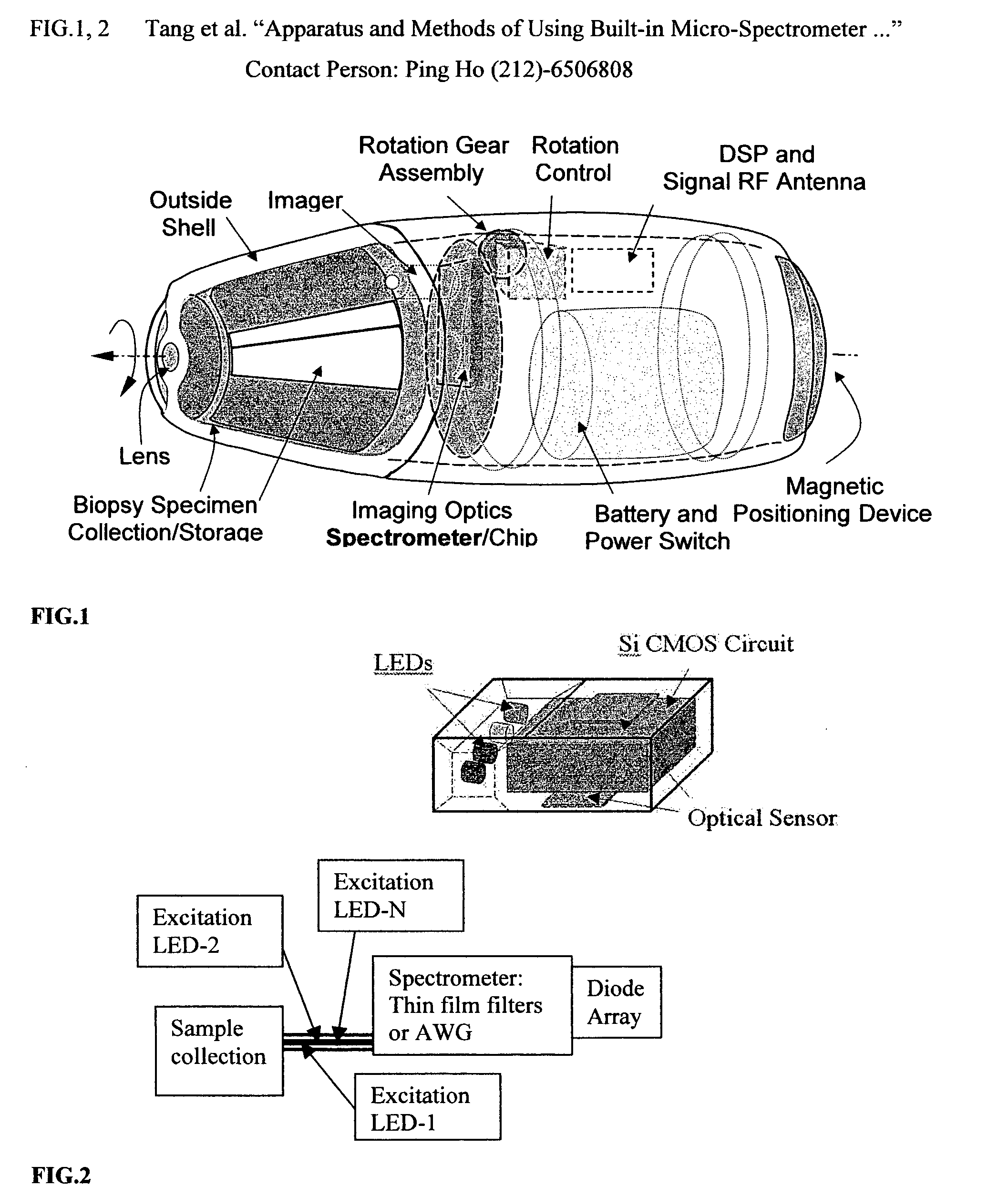
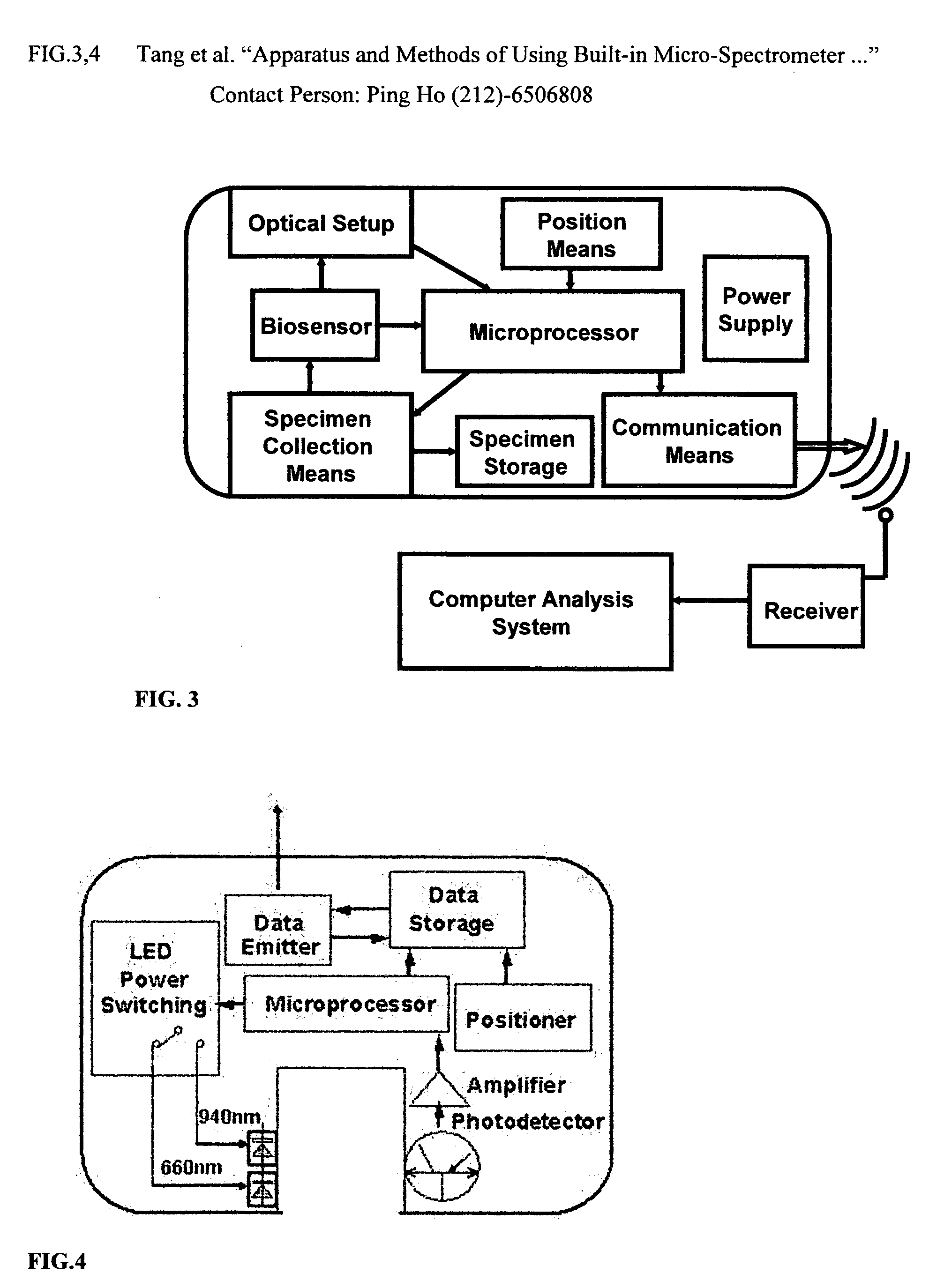
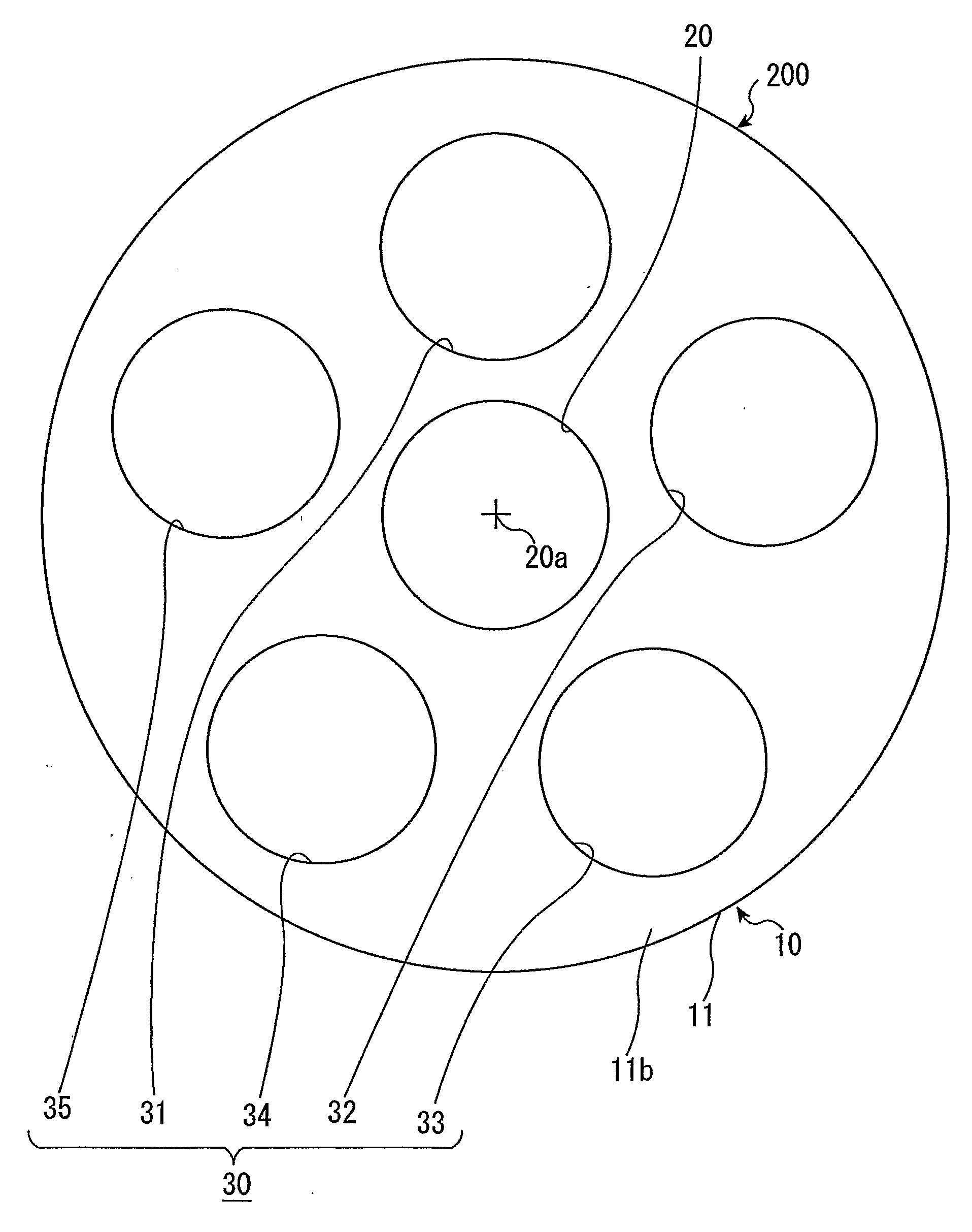
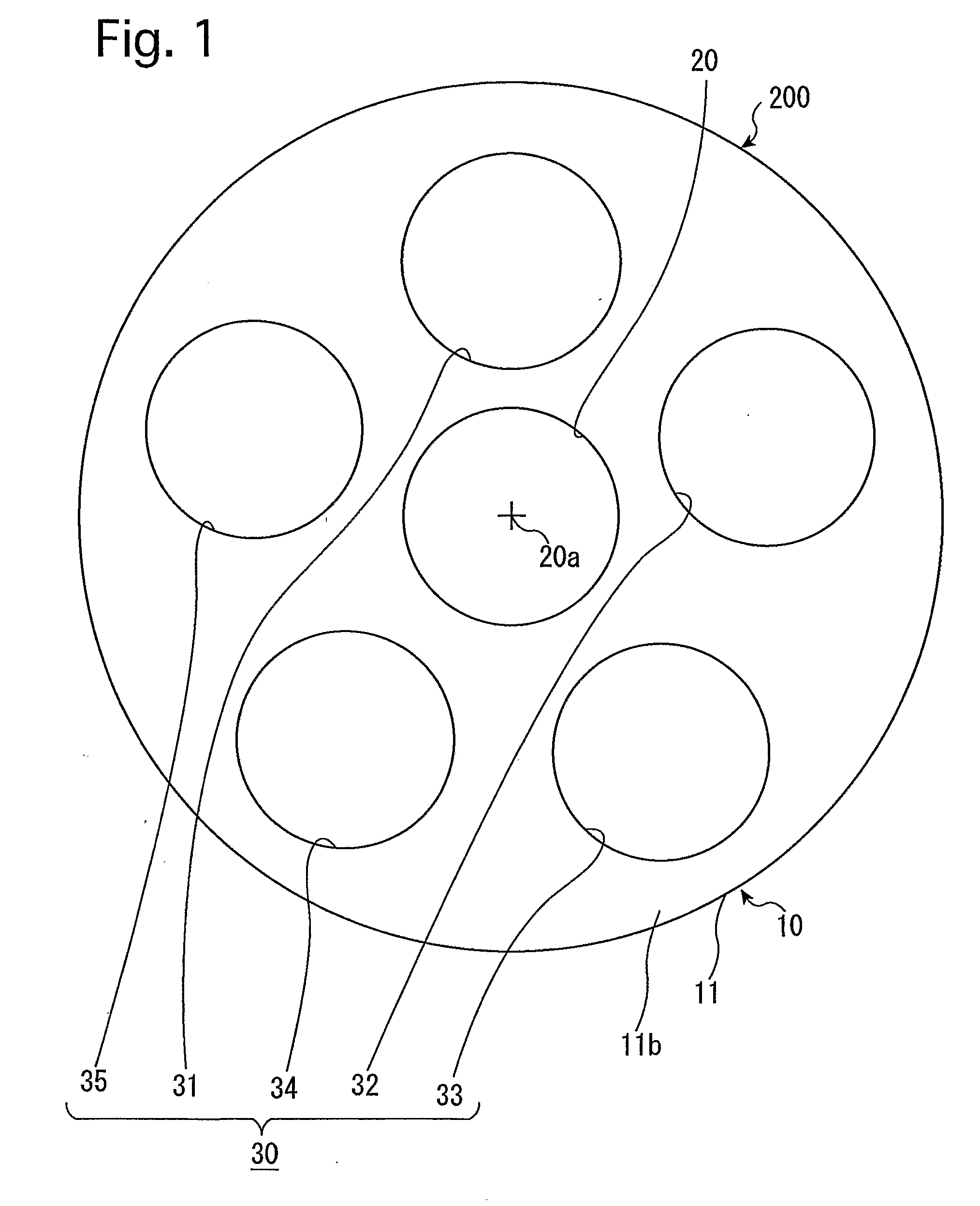
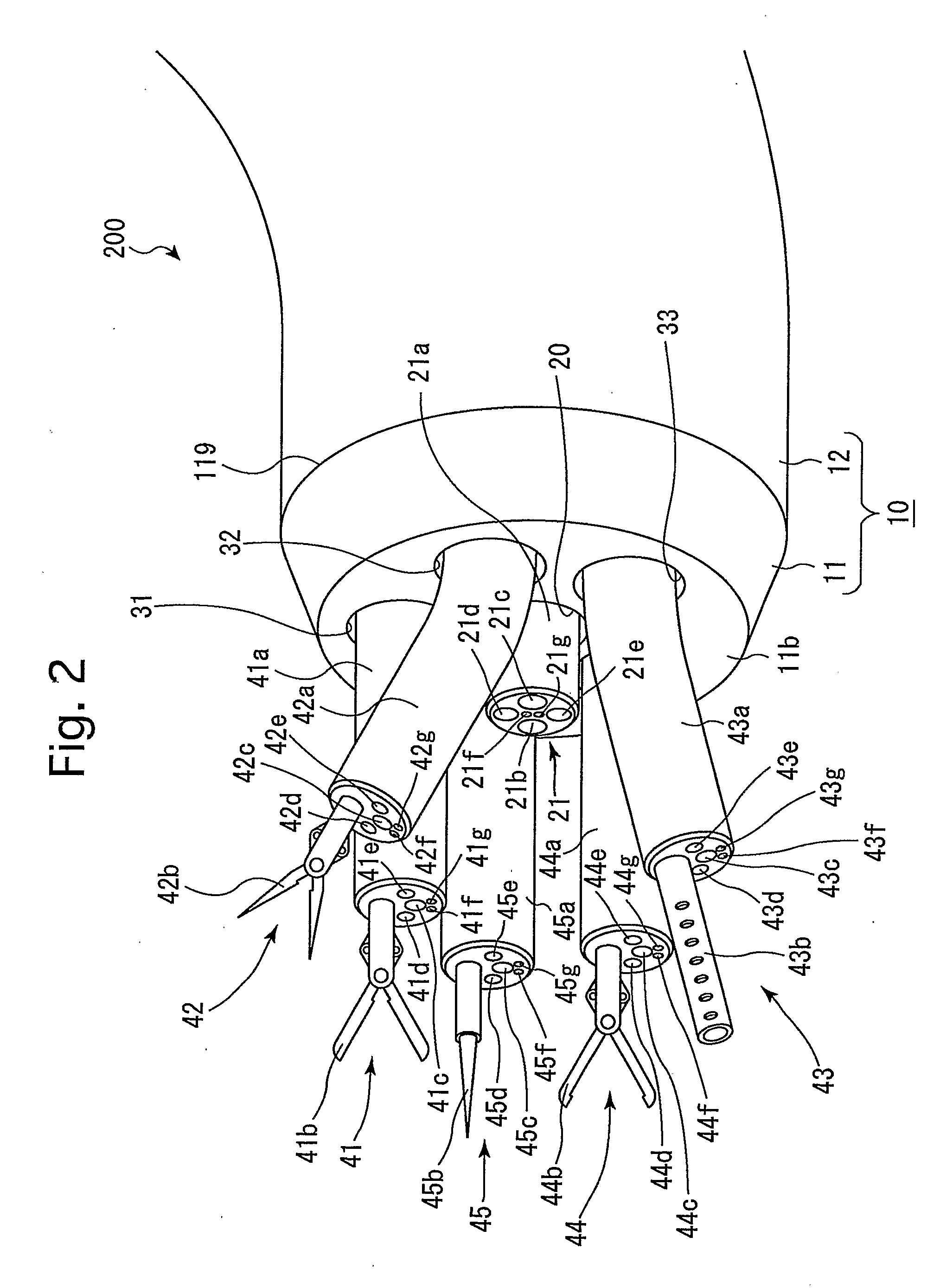
Apparatus and methods of using built-in micro-spectroscopy micro-biosensors and specimen collection system for a wireless capsule in a biological body in vivo
A wireless capsule as a disease diagnosis tool in vivo can be introduced into a biological body by a native and / or artificial open, or endoscope, or an injection. The information obtained from a micro-spectrometer, and / or an imaging system, or a micro-biosensor, all of which are built-in a wireless capsule, can be transmitted to the outside of the biological body for medical diagnoses. In addition, a real-time specimen collection device is integrated with the diagnostic system for the in-depth in vitro analysis
Owner:TANG JING +4
Internal Treatment Apparatus for a Patient and an Internal Treatment System for a Patient
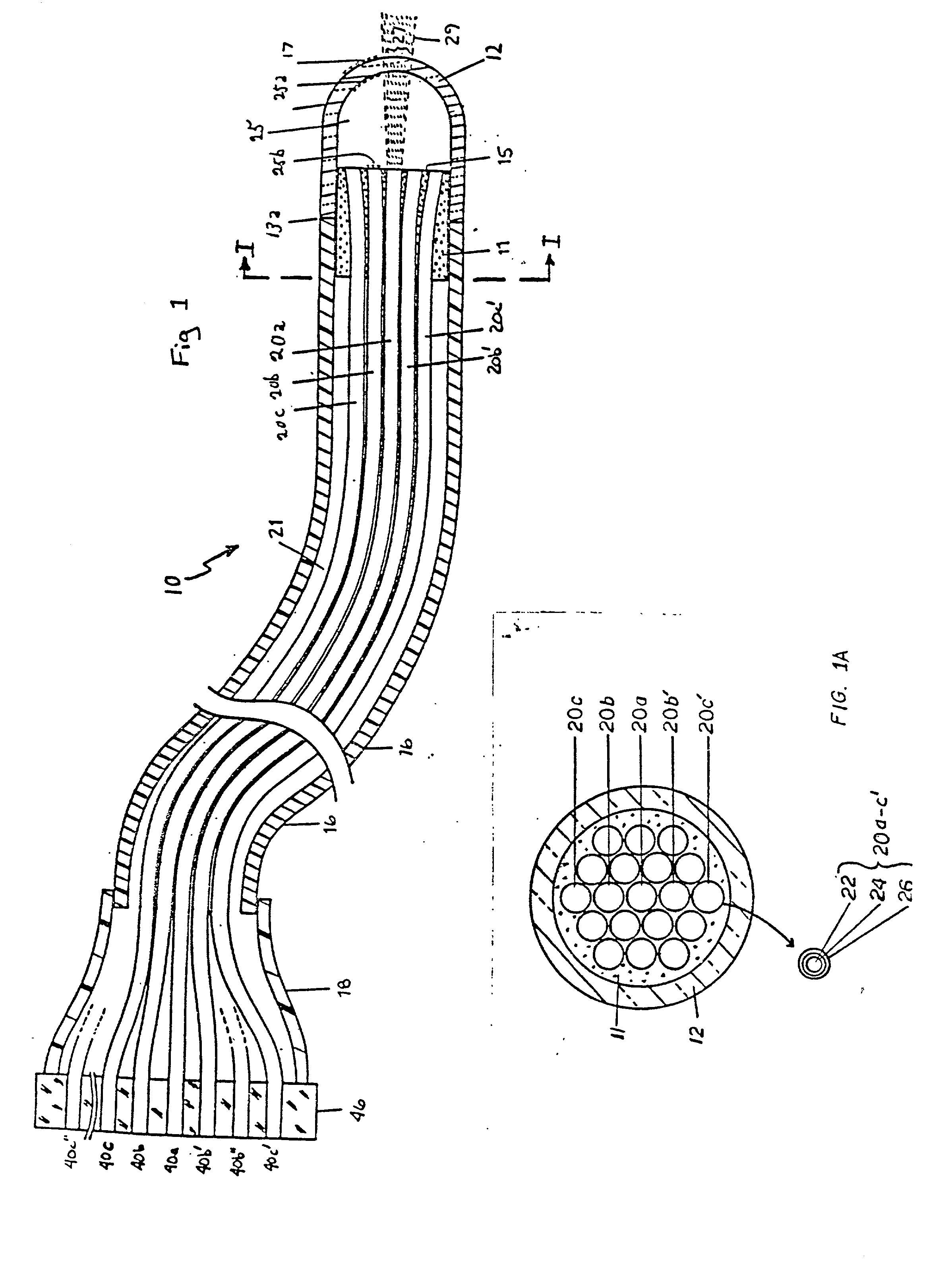
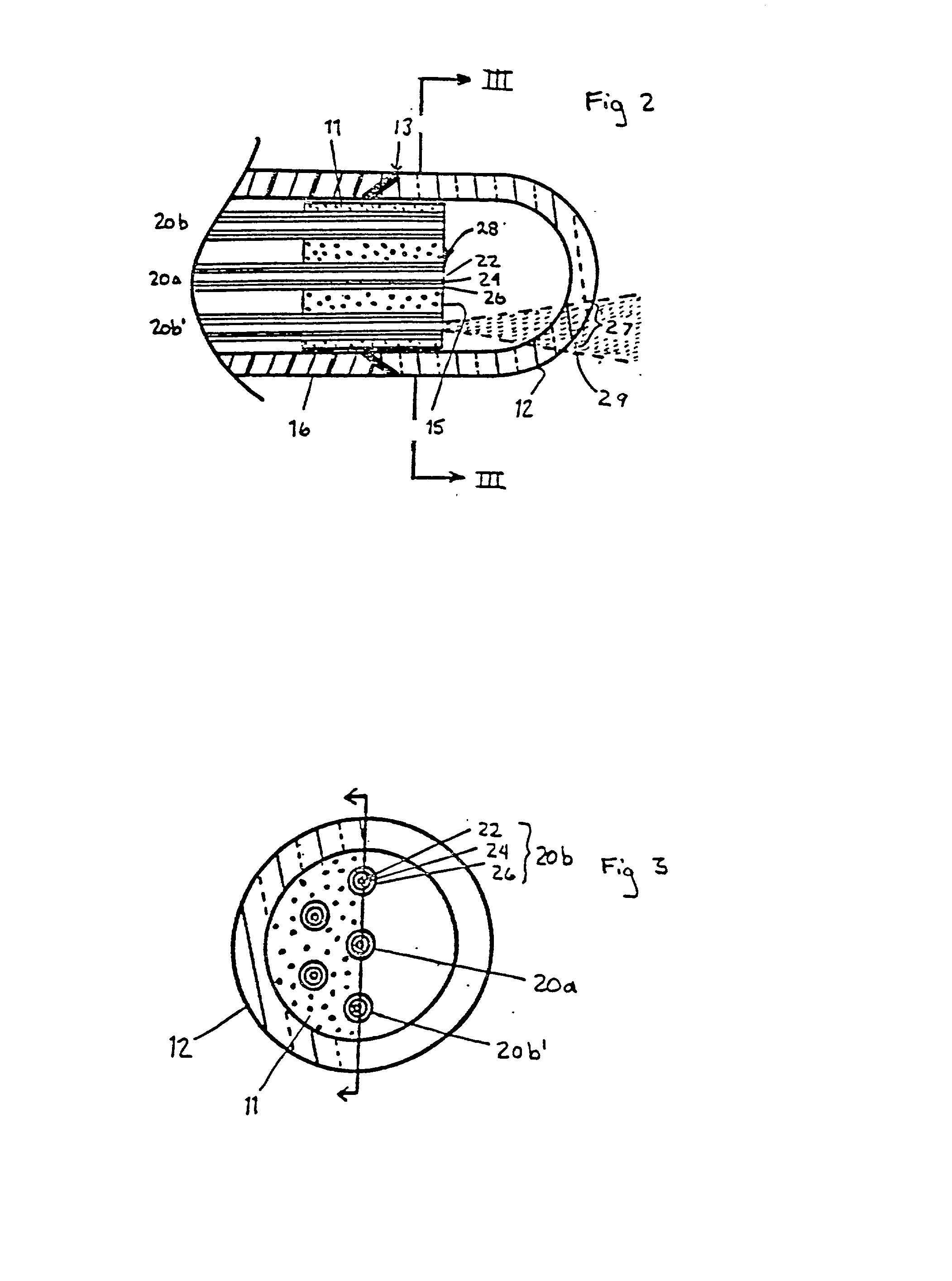
An internal treatment apparatus for a patient having a flexible tubular body to be introduced into a patient includes a center opening for inserting therethrough an endoscope for observing a target site, the center opening being circular in cross section and disposed at a center of an end face of the flexible tubular body; and a plurality of circumferential apertures through which surgical instruments are inserted for performing a surgical procedure on the target site, the plurality of circumferential apertures being provided in the flexible tubular body at equi-angular intervals around the center opening.
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT +1
Digital light processing hyperspectral imaging apparatus
A hyperspectral imaging system having an optical path. The system including an illumination source adapted to output a light beam, the light beam illuminating a target, a dispersing element arranged in the optical path and adapted to separate the light beam into a plurality of wavelengths, a digital micromirror array adapted to tune the plurality of wavelengths into a spectrum, an optical device having a detector and adapted to collect the spectrum reflected from the target and arranged in the optical path and a processor operatively connected to and adapted to control at least one of: the illumination source; the dispersing element; the digital micromirror array; the optical device; and, the detector, the processor further adapted to output a hyperspectral image of the target. The dispersing element is arranged between the illumination source and the digital micromirror array, the digital micromirror array is arranged to transmit the spectrum to the target and the optical device is arranged in the optical path after the target.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Tethered capsule endoscope for Barrett's Esophagus screening
ActiveUS7530948B2Effective movementPromote peristalsisOesophagoscopesSurgeryPink colorTethered Capsule Endoscope
A capsule is coupled to a tether that is manipulated to position the capsule and a scanner included within the capsule at a desired location within a lumen in a patient's body. Images produced by the scanner can be used to detect Barrett's Esophagus (BE) and early (asymptomatic) esophageal cancer after the capsule is swallowed and positioned with the tether to enable the scanner in the capsule to scan a region of the esophagus above the stomach to detect a characteristic dark pink color indicative of BE. The scanner moves in a desired pattern to illuminate a portion of the inner surface. Light from the inner surface is then received by detectors in the capsule, or conveyed externally through a waveguide to external detectors. Electrical signals are applied to energize an actuator that moves the scanner. The capsule can also be used for diagnostic and / or therapeutic purposes in other lumens.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Fluorescent endoscope system enabling simultaneous achievement of normal light observation based on reflected light and fluorescence observation based on light with wavelengths in infrared spectrum
InactiveUS20040186351A1Inhibition of lesionsHigh light transmittanceSurgeryEndoscopesLength waveEndoscope
Excitation light for normal light observation with wavelengths in the visible spectrum, which is output from a lamp, and excitation light with wavelengths in the infrared spectrum for exciting a fluorescent substance characteristic of being accumulated readily in a lesion are irradiated simultaneously to a living tissue, to which the fluorescent substance has been administered, through an endoscope. Fluorescence components are separated from light stemming from the living tissue by means of a separator such as a dichroic mirror, introduced to a first imaging device, and then imaged. Light components with wavelengths in the visible spectrum are introduced to a second imaging device and then imaged. Signals representing the images are subjected to signal processing, whereby a video signal is produced. For better diagnosis, two images are displayed while, for example, one of the images is superimposed on the other.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Digital light processing hyperspectral imaging apparatus
A hyperspectral imaging system having an optical path. The system including an illumination source adapted to output a light beam, the light beam illuminating a target, a dispersing element arranged in the optical path and adapted to separate the light beam into a plurality of wavelengths, a digital micromirror array adapted to tune the plurality of wavelengths into a spectrum, an optical device having a detector and adapted to collect the spectrum reflected from the target and arranged in the optical path and a processor operatively connected to and adapted to control at least one of: the illumination source; the dispersing element; the digital micromirror array; the optical device; and, the detector, the processor further adapted to output a hyperspectral image of the target. The dispersing element is arranged between the illumination source and the digital micromirror array, the digital micromirror array is arranged to transmit the spectrum to the target and the optical device is arranged in the optical path after the target.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
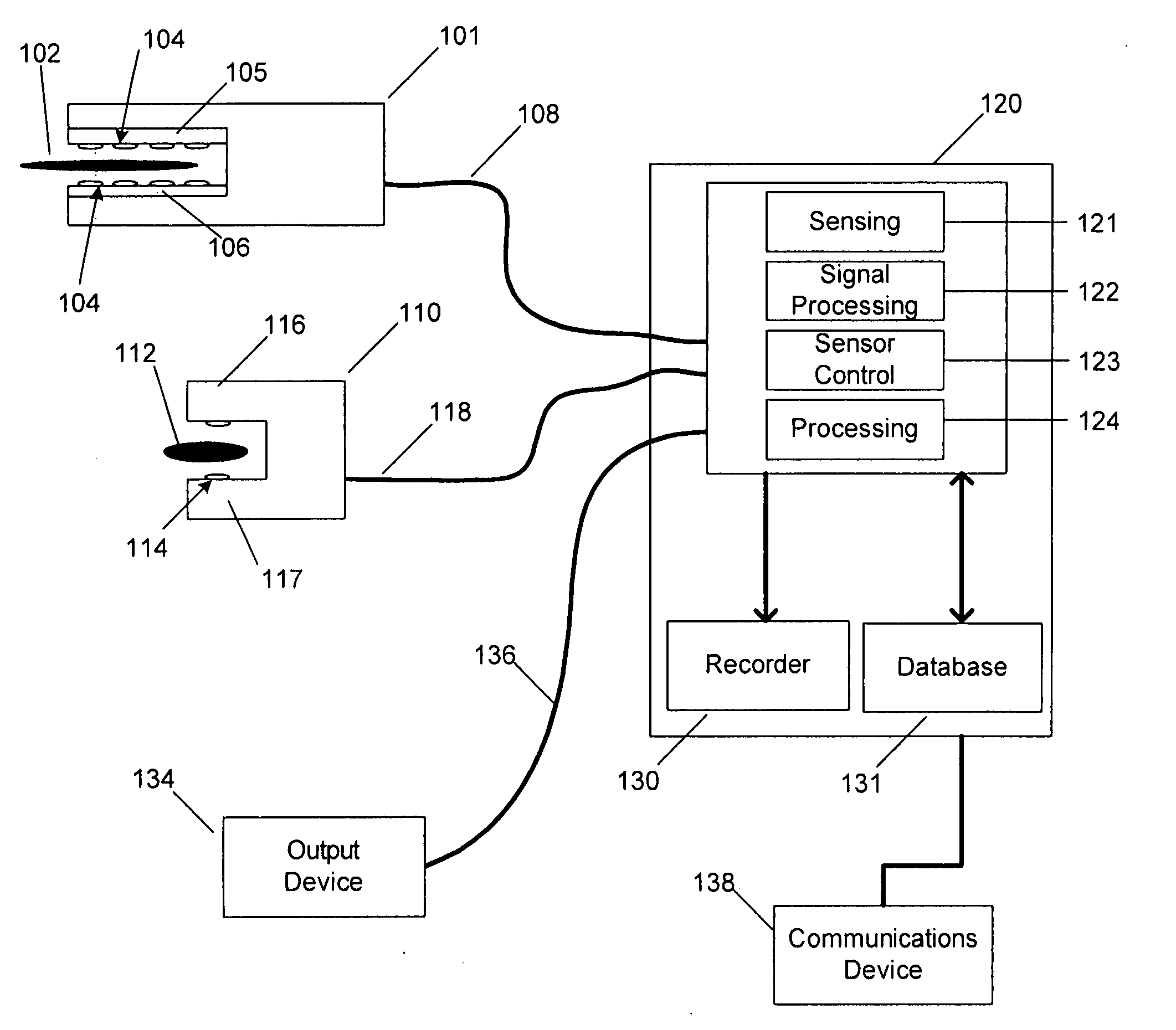
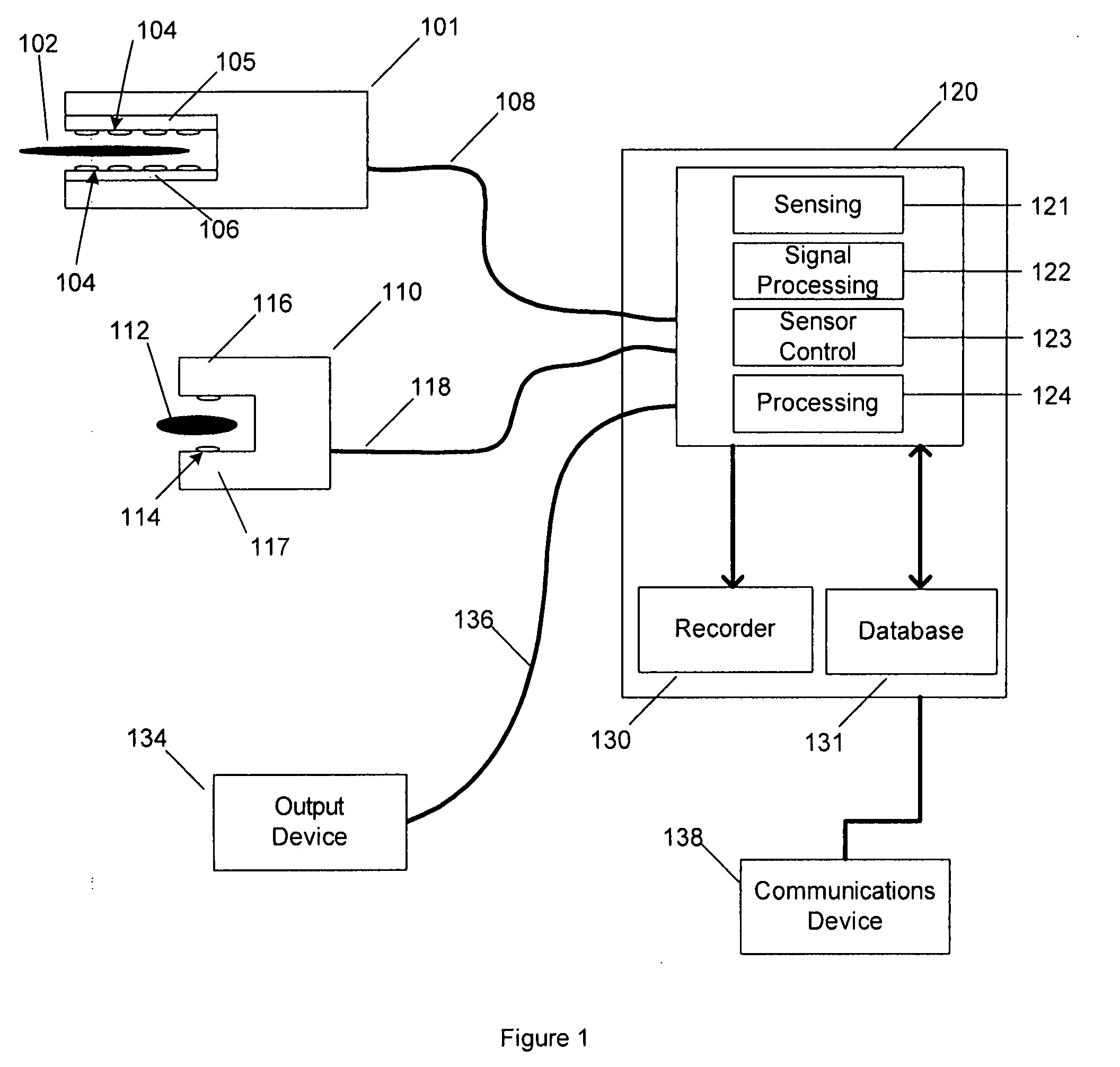
Detecting, localizing, and targeting internal sites in vivo using optical contrast agents
InactiveUS6246901B1Rapid imaging and localization and positioning and targetingNanoinformaticsDiagnostics using spectroscopyIn vivoOptical contrast
Owner:J FITNESS LLC
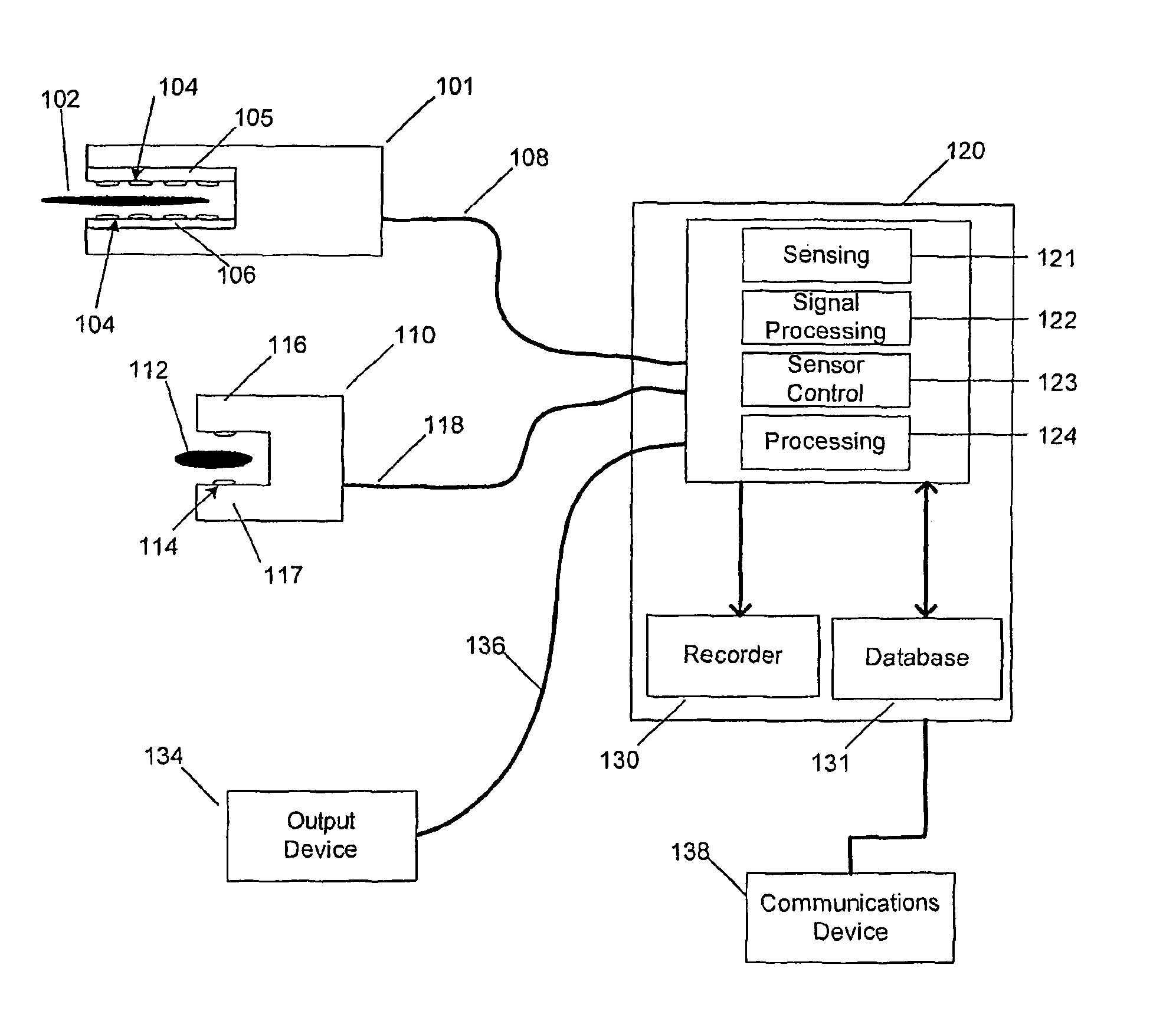
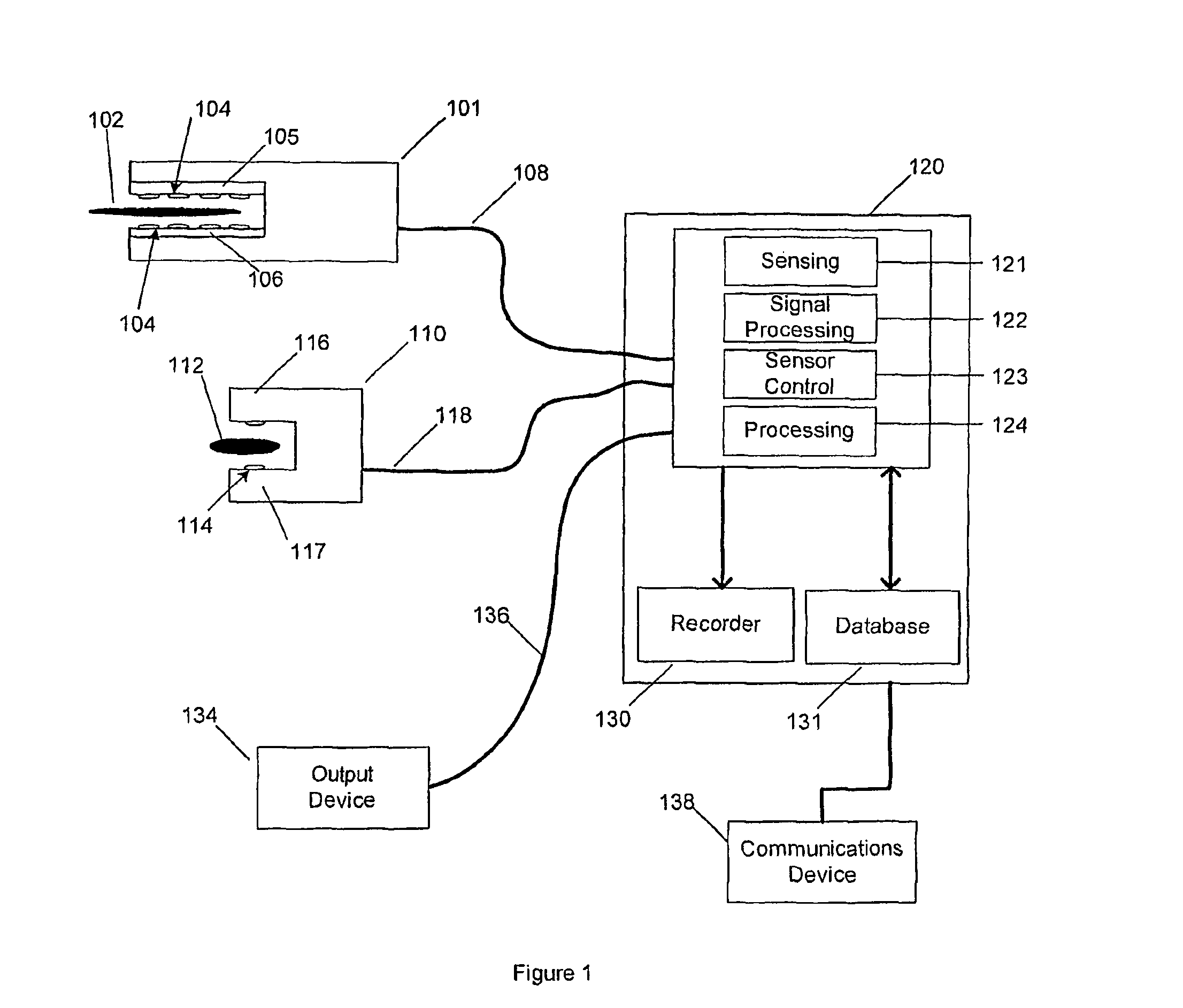
Detecting, localizing, and targeting internal sites in vivo using optical contrast agents
InactiveUS6167297ARapid localizationRapid imaging and localization and positioning and targetingNanoinformaticsDiagnostics using spectroscopyInstrumentationMedical procedure
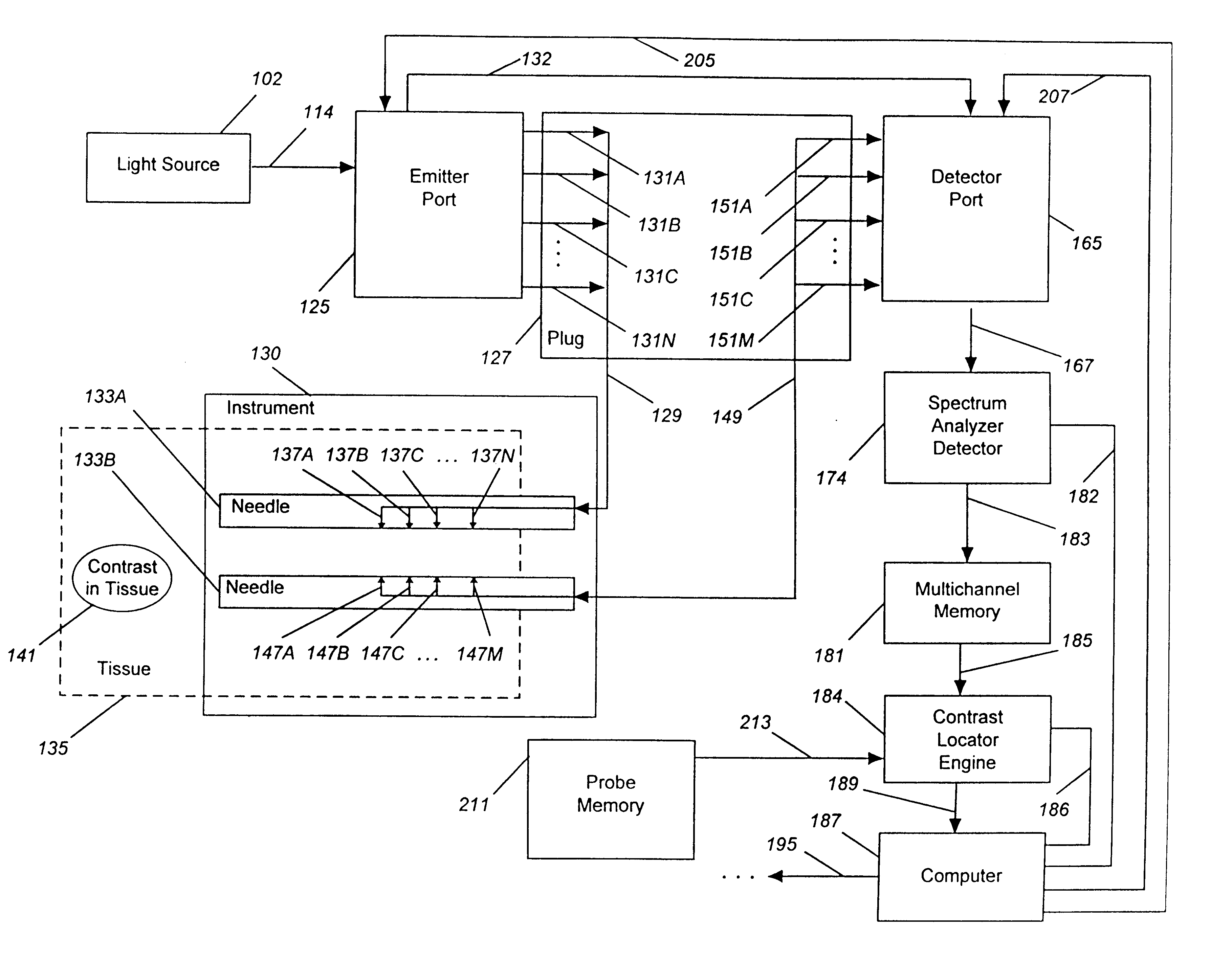
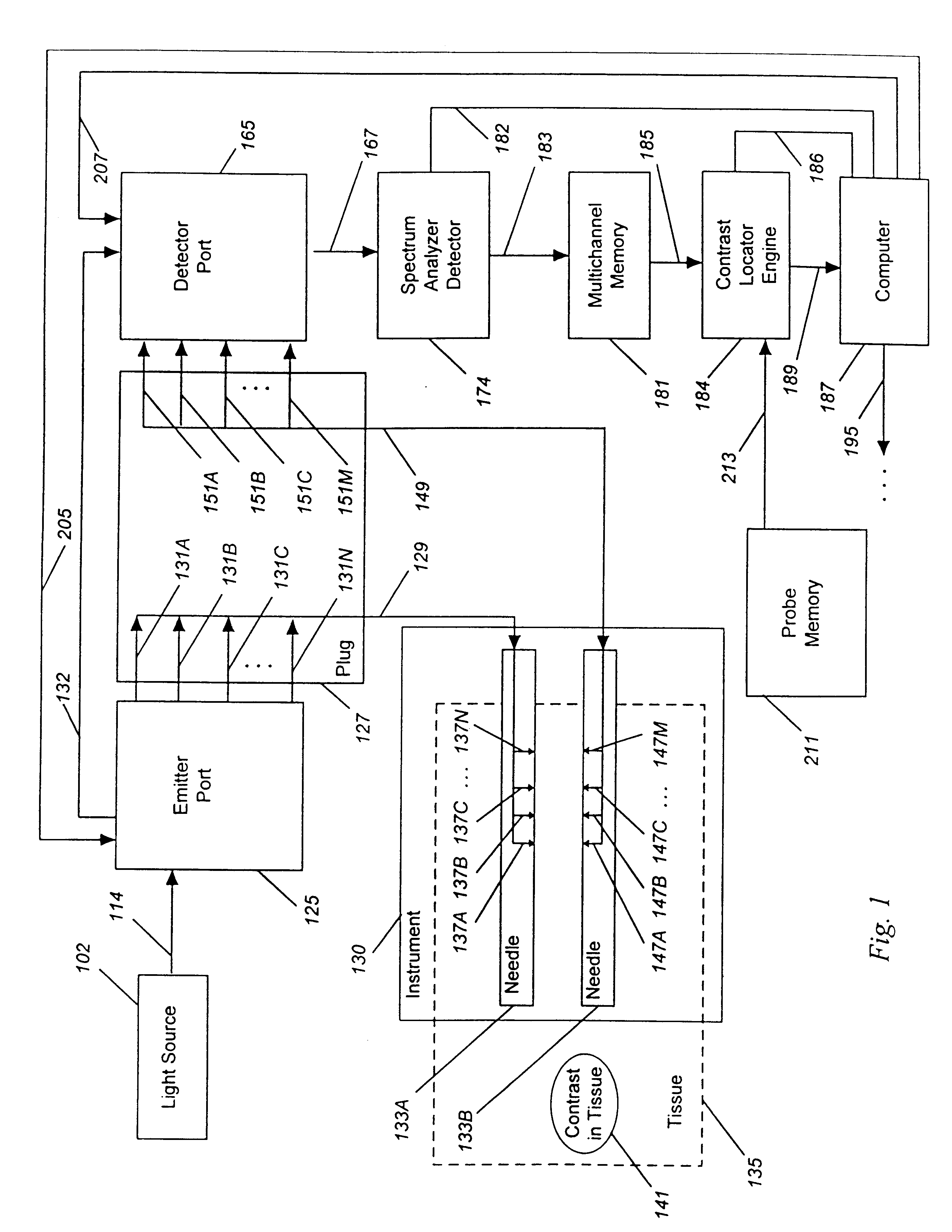
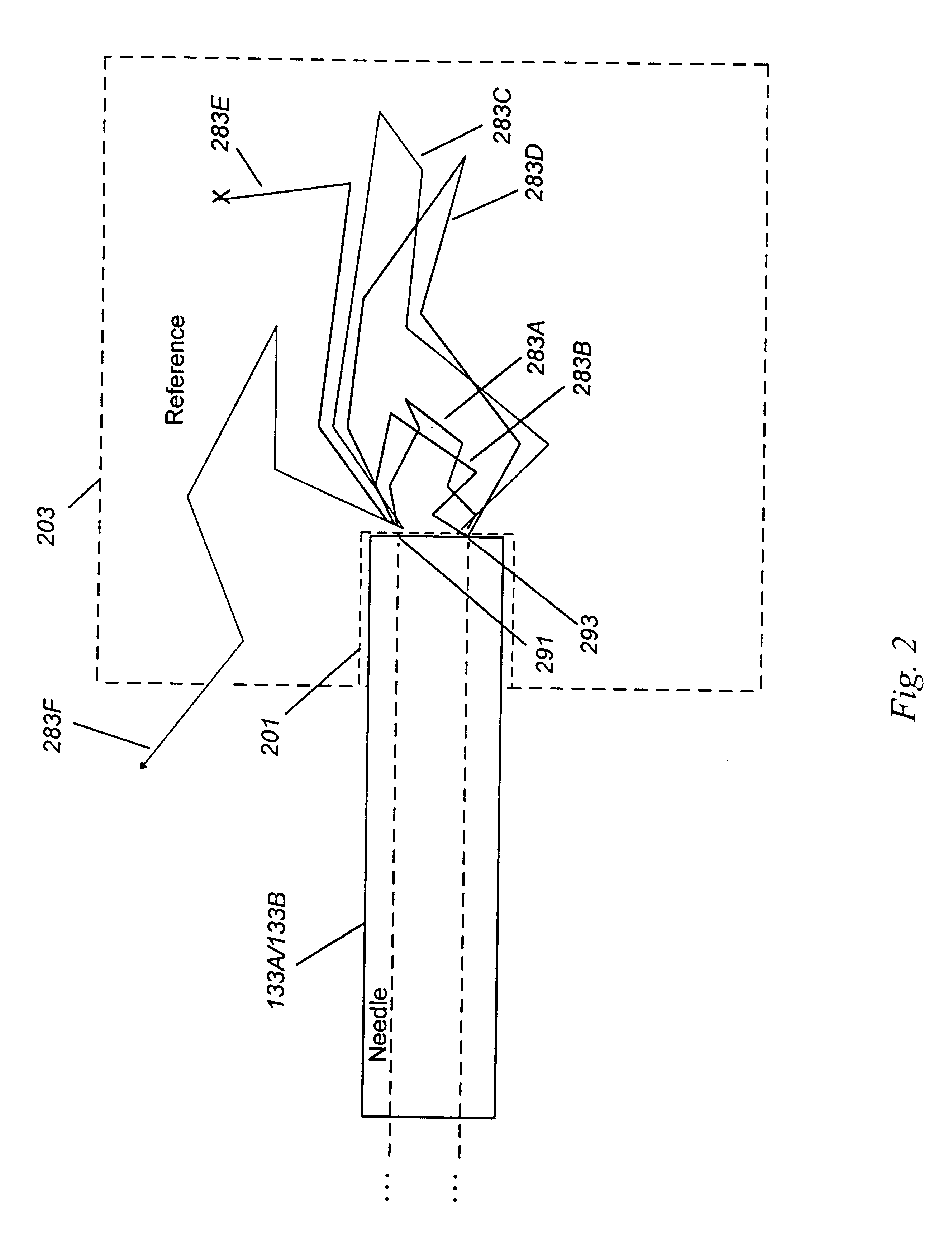
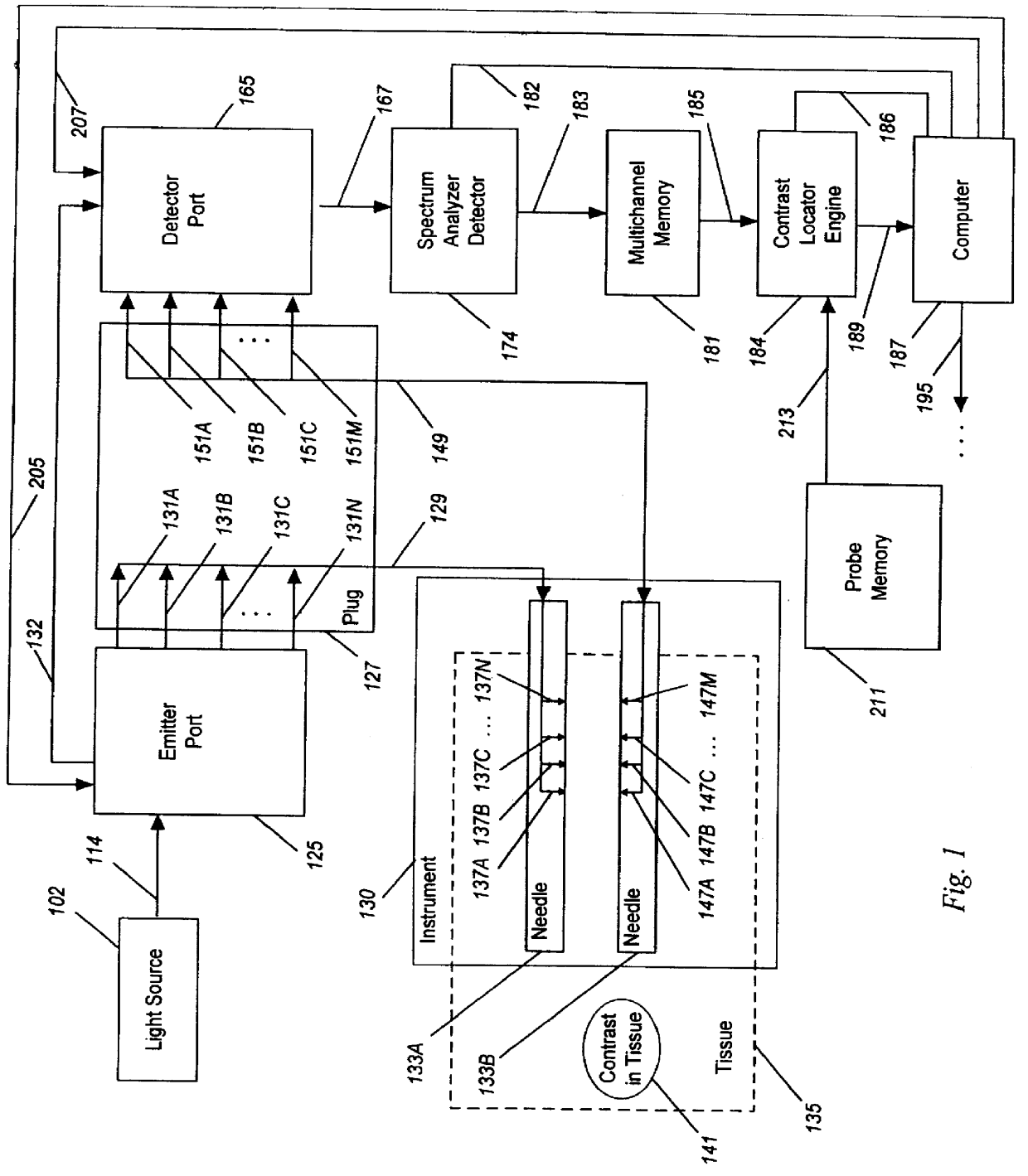
A system for detecting, localizing and targeting a medical instrument toward a target tissue within the body using an optical contrast agent in which a light source (102) is optically coupled to the tissue to be diagnosed (135), a light detector (174) is optically coupled to the tissue to detect a portion of the light which passes through the tissue, and either one or both of the light source and light detector are coupled to a medical instrument (130) used in a medical procedure. A contrast locator engine (184) receives a signal from the detector and provides an target tissue output signal (195) based upon the localization and distribution of the contrast agent, allowing the target tissue to be detected, located, or imaged, and for the medical instrument to positioned or targeted relative to the target tissue, and for allowing the accuracy of placement or the progress of a procedure to be assessed in real time. A method for the system is also described.
Owner:J FITNESS LLC
Reflectance calibration of fluorescence-based glucose measurements
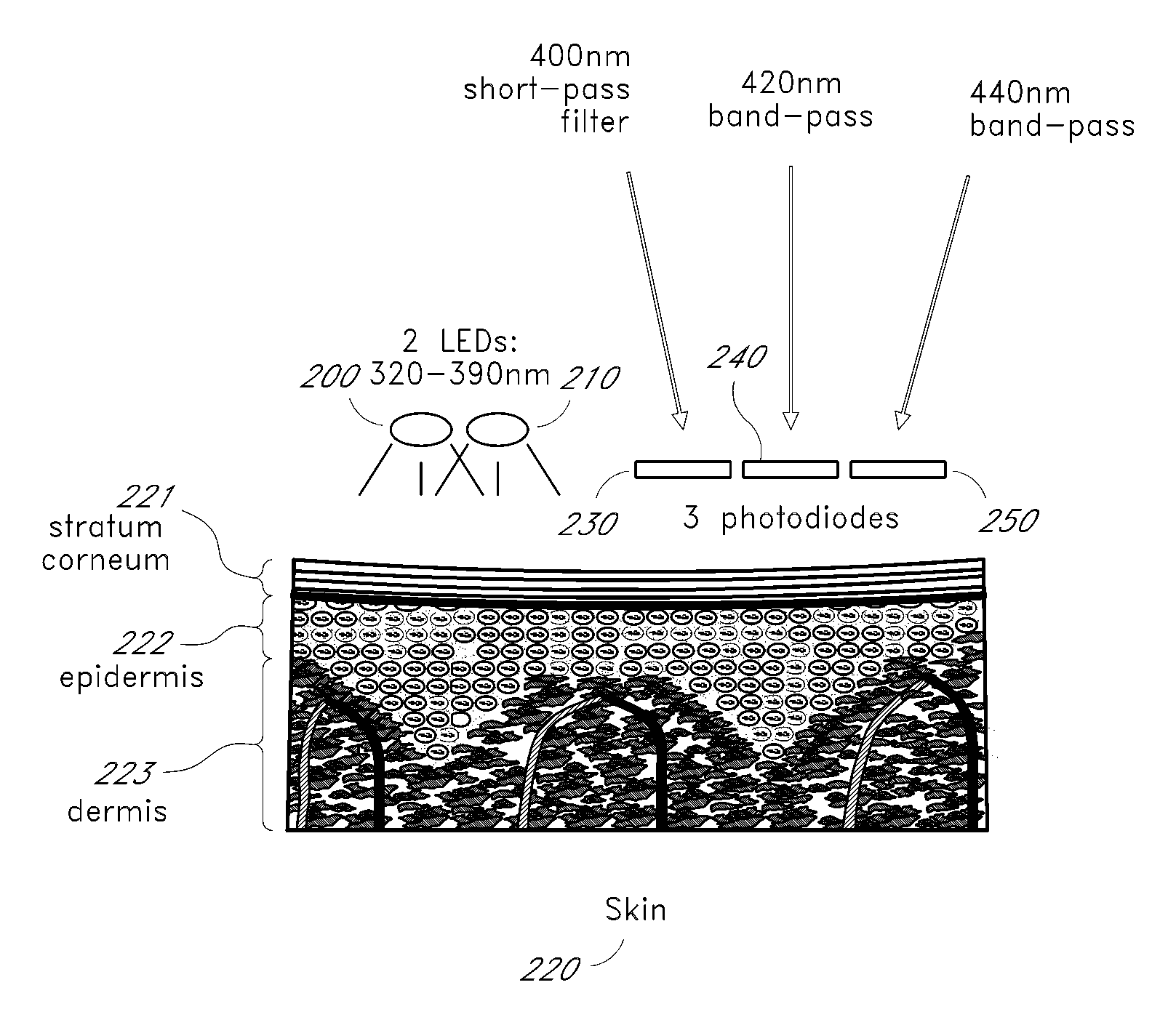
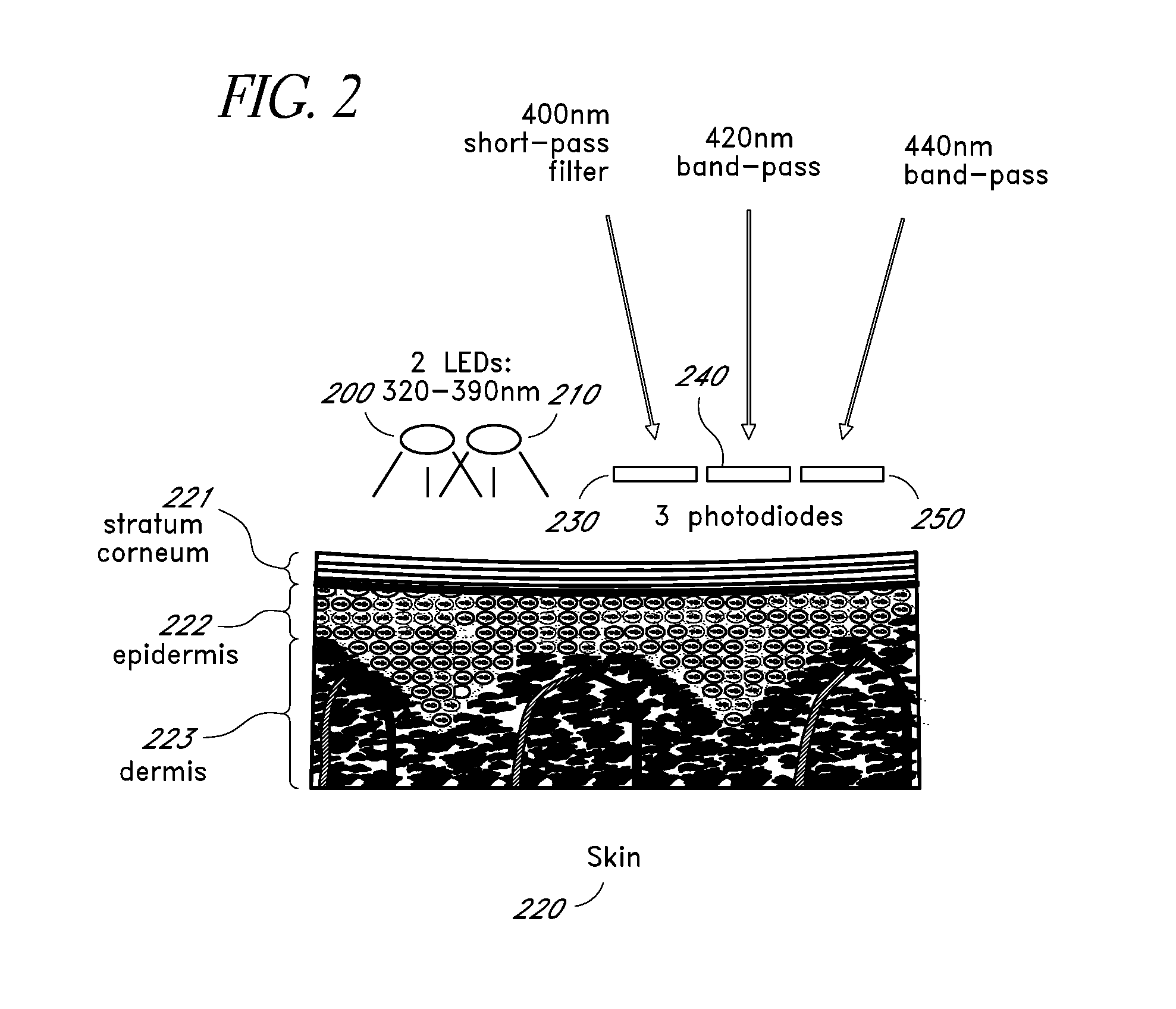
InactiveUS20110028806A1Easily detected fluorescenceEasy to detectDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionMetaboliteLight energy
A noninvasive or minimally invasive procedure and system for measuring blood glucose levels is disclosed. A set of photodiodes detects the fluorescence and reflectance of light energy emitted from one or more emitters, such as LEDs, into a patient's skin. In an embodiment, small molecule metabolite reporters (SMMRs) that bind to glucose are introduced to the measurement area to provide more easily detected fluorescence.
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
Multivariate analysis of green to ultraviolet spectra of cell and tissue samples
InactiveUS20010034477A1Diagnostics using lightSpectrum investigationMultivariate classificationTissue sample
This invention relates to methods for processing in vivo skin auto-fluorescence spectra for determining blood glucose levels. The invention also relates to methods of classifying cells or tissue samples or quantifying a component of a cell or tissue using a multivariate classification or quantification model.
Owner:ARGOSE
Tissue biopsy and treatment apparatus and method
InactiveUS7025765B2Improve clinical outcomesPrecise positioningElectrotherapySurgical needlesSensor arrayTissue biopsy
A method of treating a tumor includes providing a tissue biopsy and treatment apparatus that includes an elongated delivery device that has a lumen and is maneuverable in tissue. A sensor array having a plurality of resilient members is deployable from the elongated delivery device. At least one of the plurality of resilient members is positionable in the elongated delivery device in a compacted state and deployable with curvature into tissue from the elongated delivery device in a deployed state. At least one of the plurality of resilient members includes at least one of a sensor, a tissue piercing distal end or a lumen. The sensor array has a geometric configuration adapted to volumetrically sample tissue at a tissue site to differentiate or identify tissue at the tissue site. At least one energy delivery device is coupled to one of the sensor array, at least one of the plurality of resilient members or the elongated delivery device. The apparatus is then introduced into a target tissue site. The sensor array is then utilized to distinguish a tissue type. The tissue type information derived from the sensor array is utilized to position the energy delivery device to ablate a tumor volume. Energy is then delivered from the energy delivery device to ablate or necrose at least a portion of the tumor volume. The sensor array is then utilized to determine an amount of tumor volume ablation.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
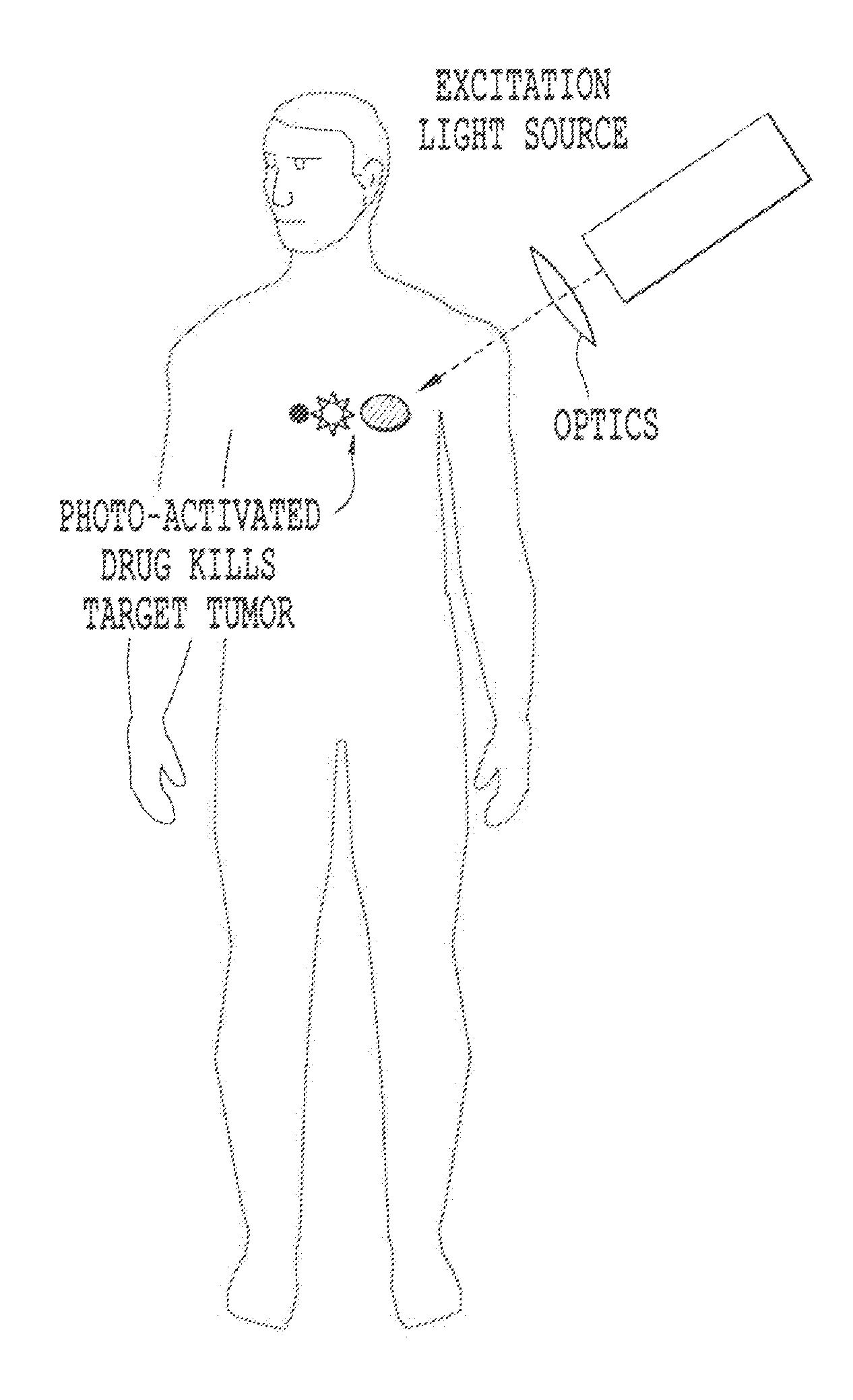
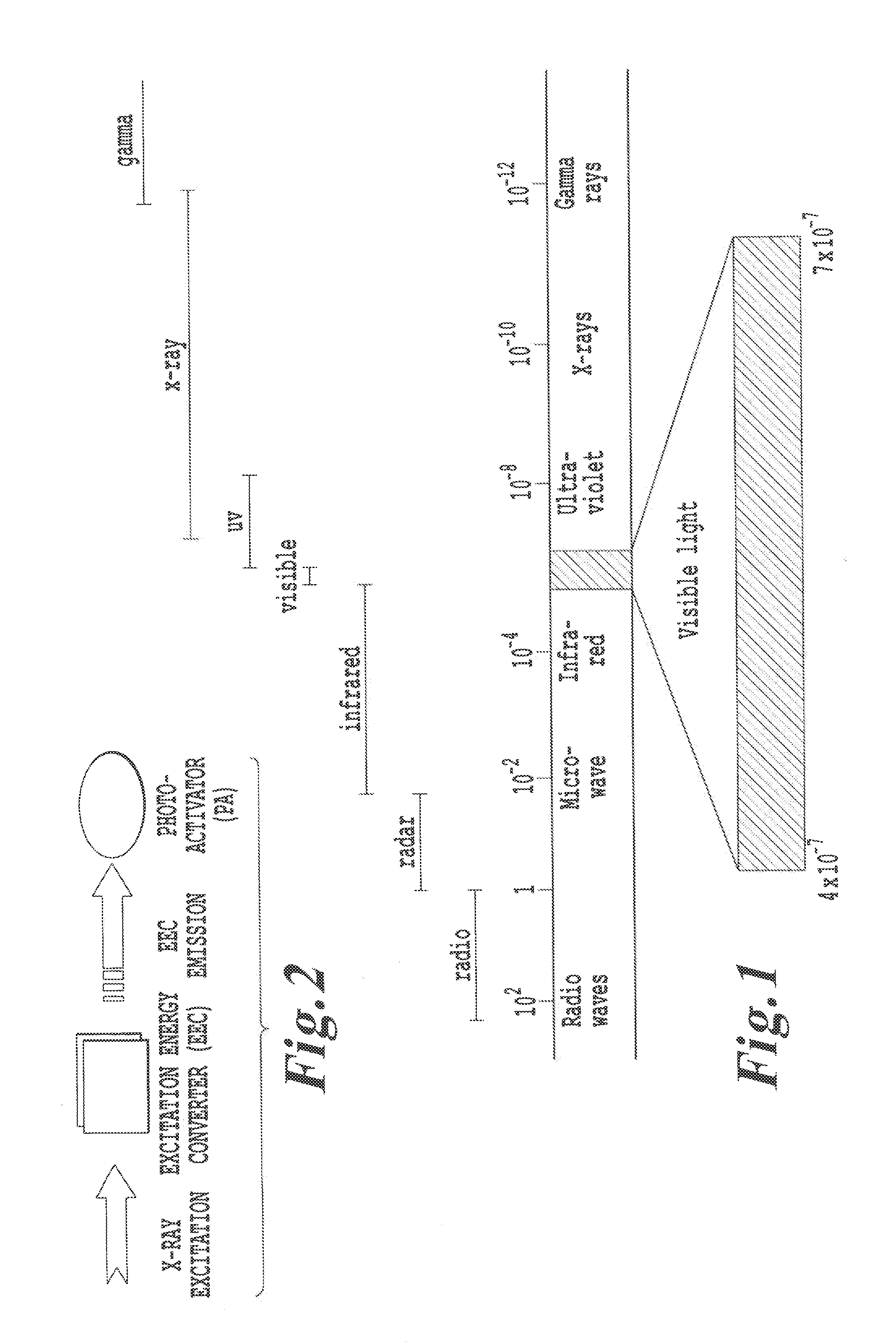
Non-invasive energy upconversion methods and systems for in-situ photobiomodulation
ActiveUS20110021970A1High selectivityAvoid the needAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseaseHigh energy
Products, compositions, systems, and methods for modifying a target structure which mediates or is associated with a biological activity, including treatment of conditions, disorders, or diseases mediated by or associated with a target structure, such as a virus, cell, subcellular structure or extracellular structure. The methods may be performed in situ in a non-invasive manner by placing a nanoparticle having a metallic shell on at least a fraction of a surface in a vicinity of a target structure in a subject and applying an initiation energy to a subject thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure directly or via a modulation agent. The nanoparticle is configured, upon exposure to a first wavelength λ1, to generate a second wavelength λ2 of radiation having a higher energy than the first wavelength λ1. The methods may further be performed by application of an initiation energy to a subject in situ to activate a pharmaceutical agent directly or via an energy modulation agent, optionally in the presence of one or more plasmonics active agents, thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure. Kits containing products or compositions formulated or configured and systems for use in practicing these methods.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com