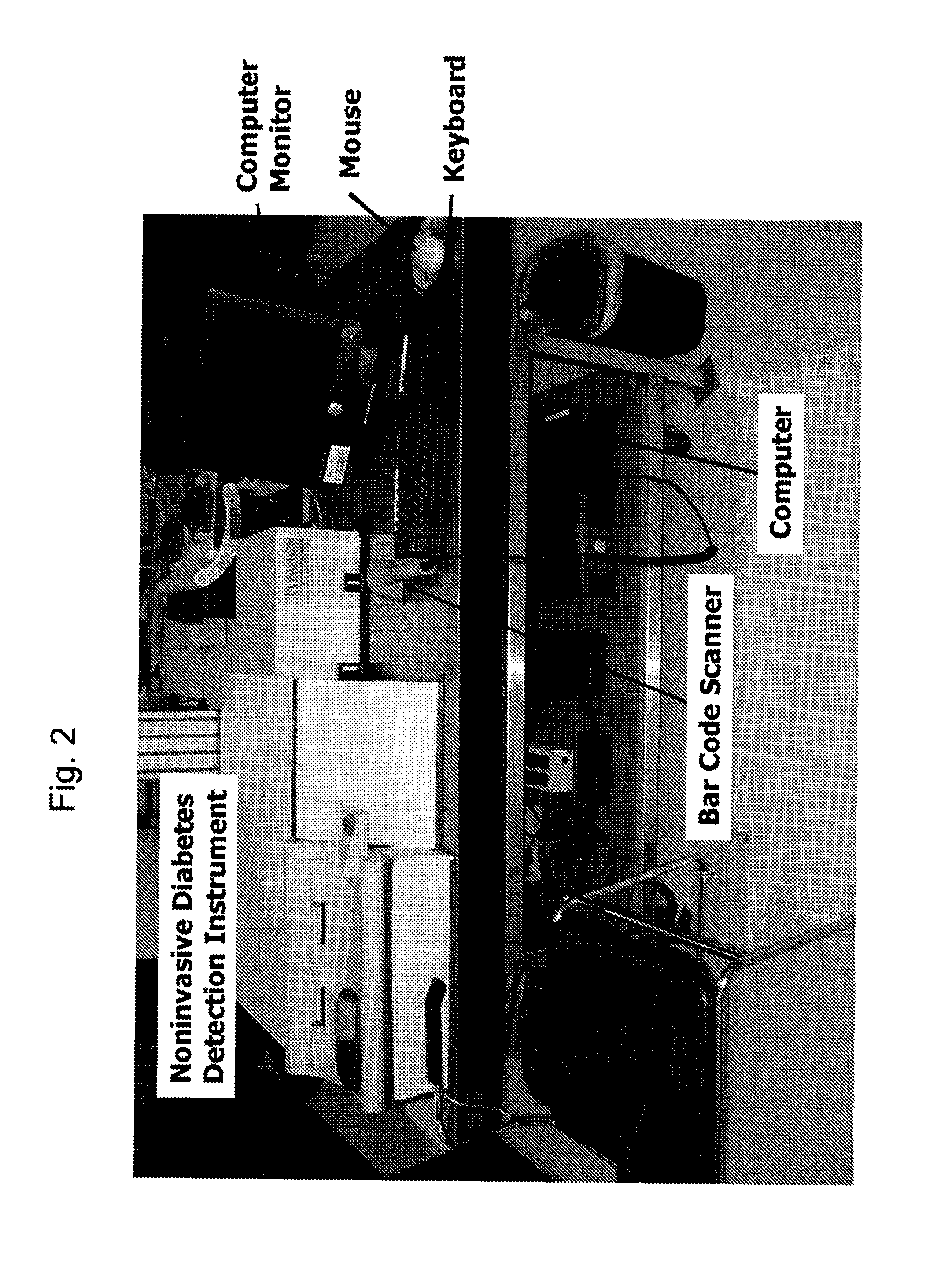
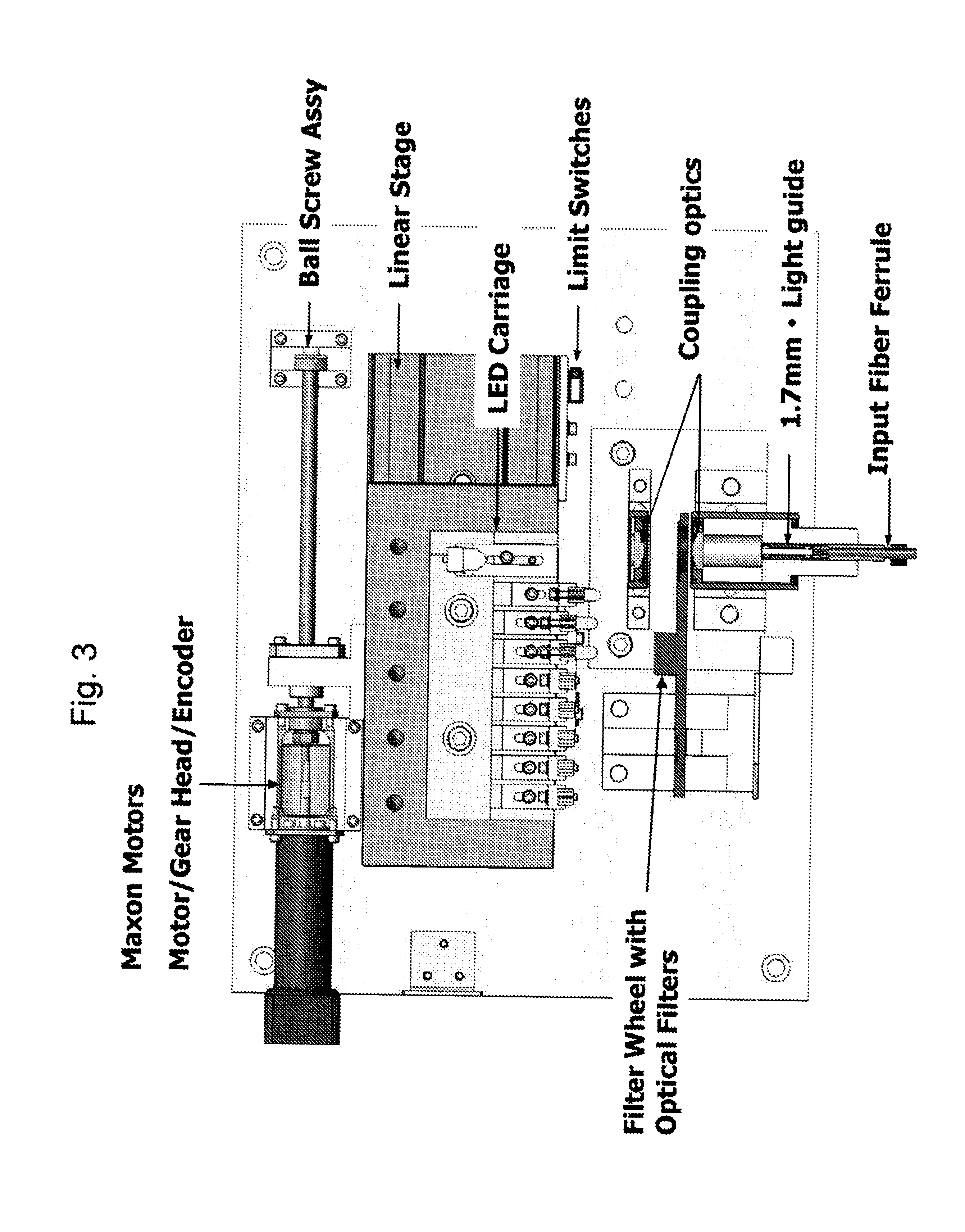
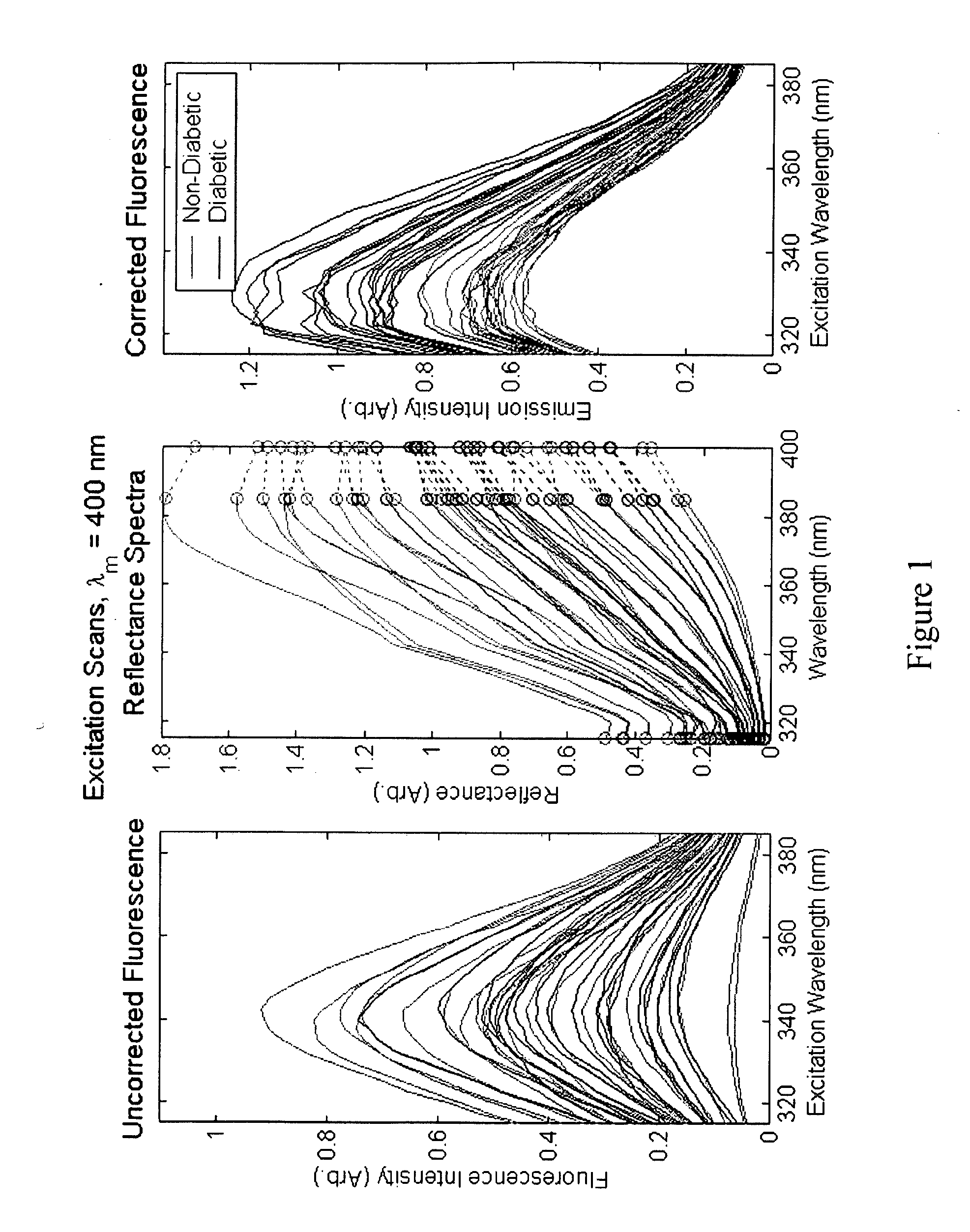
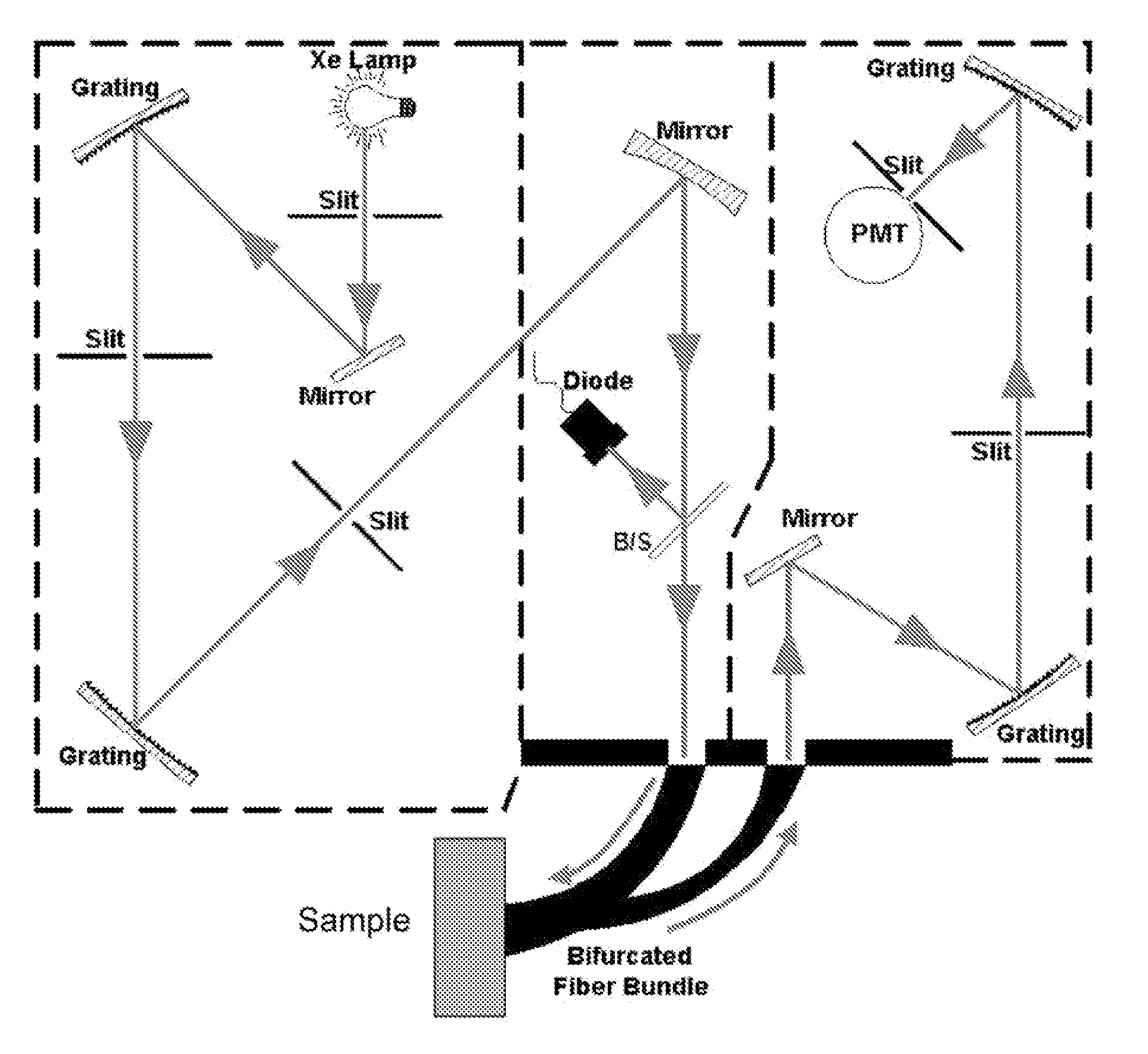
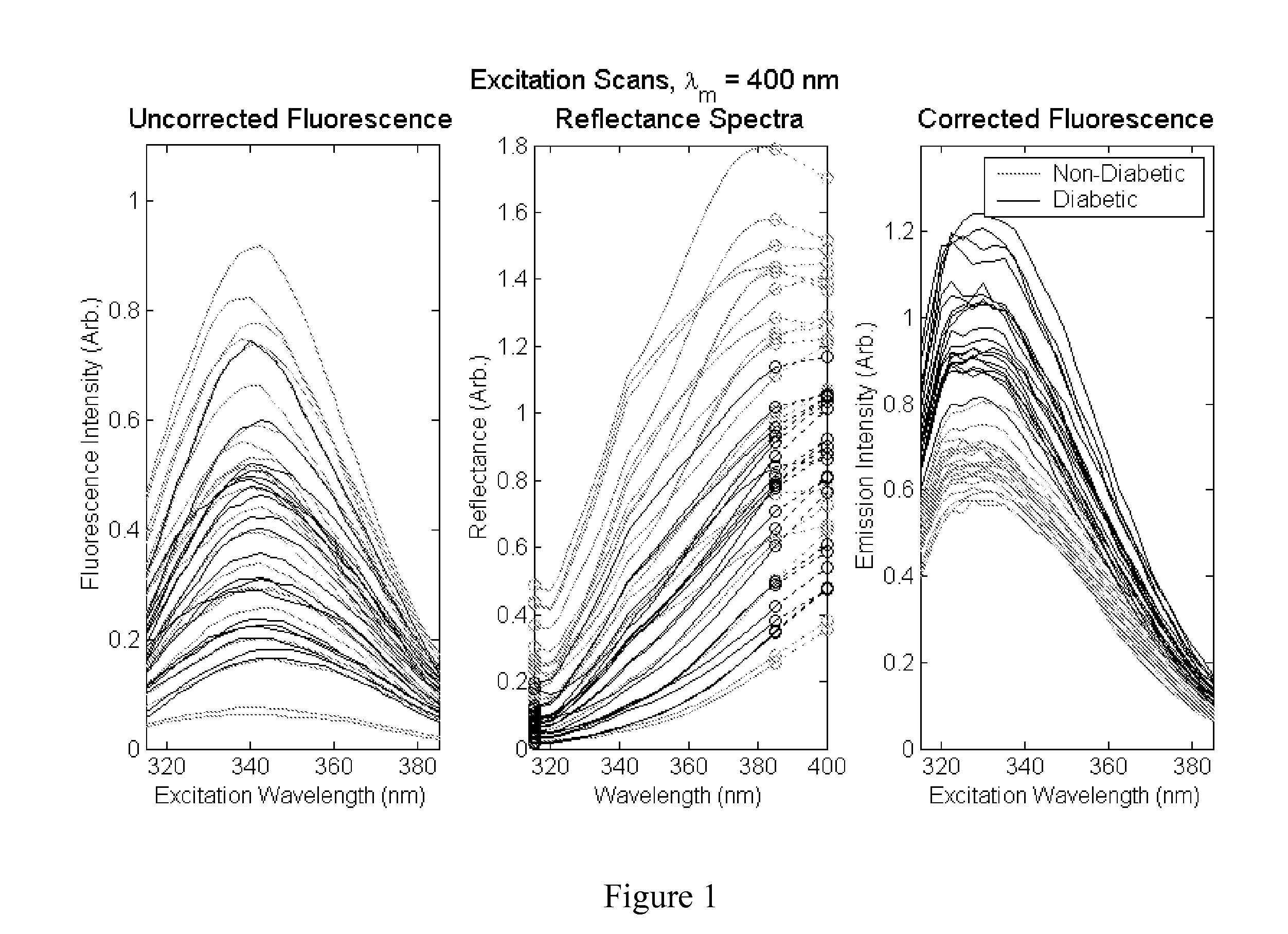
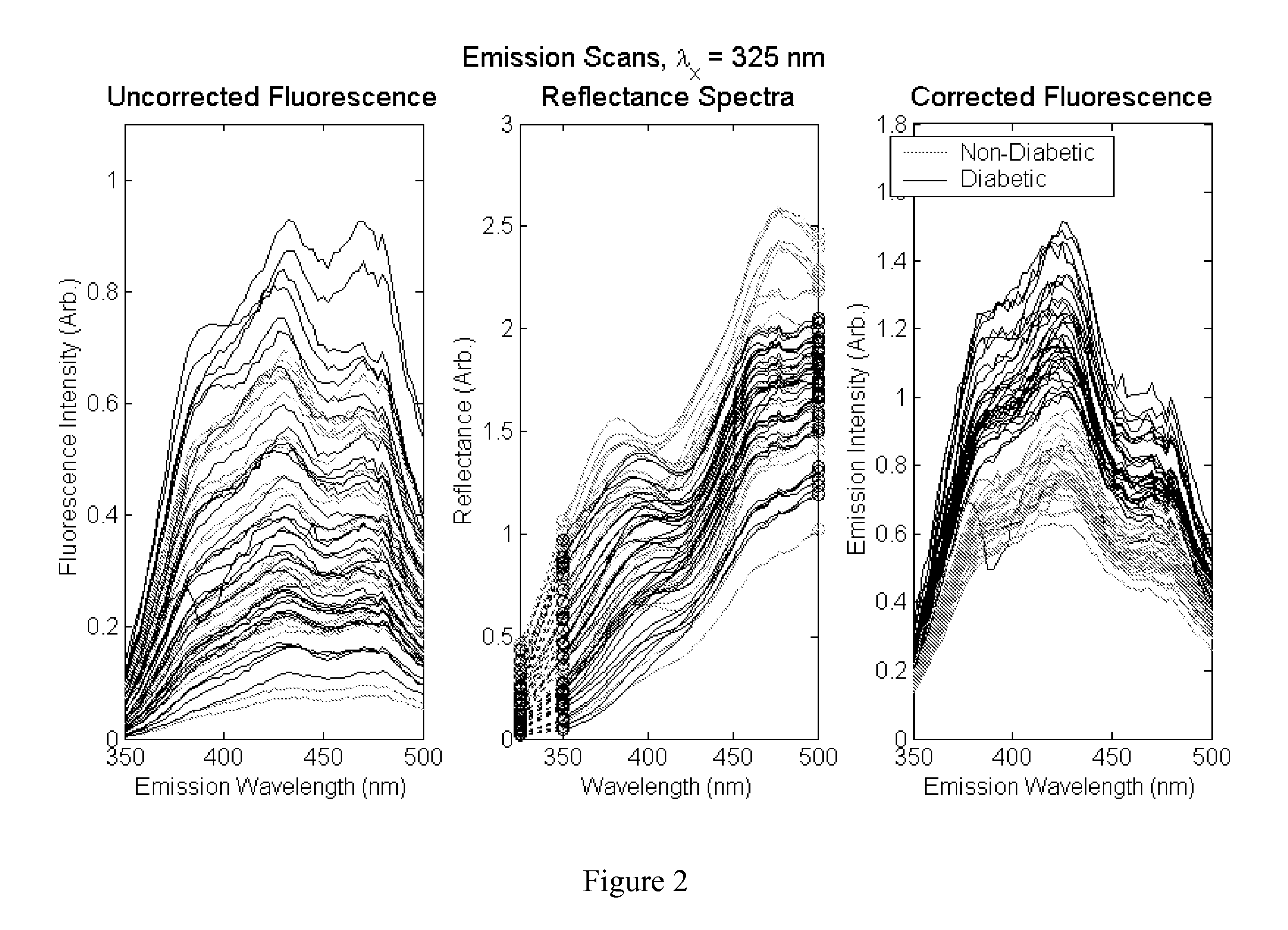
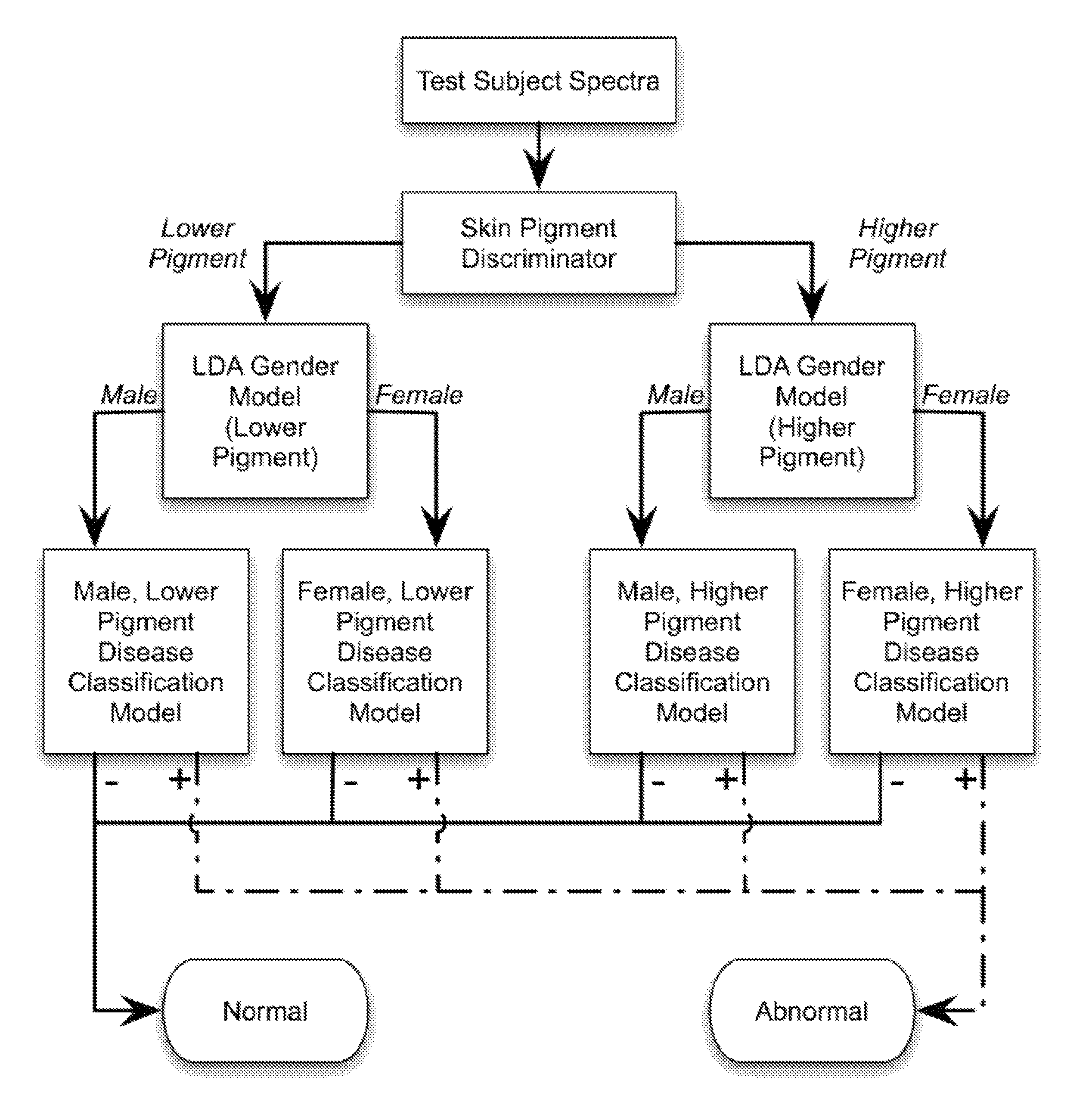
Patents
Literature
49 results about "Tissue fluorescence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
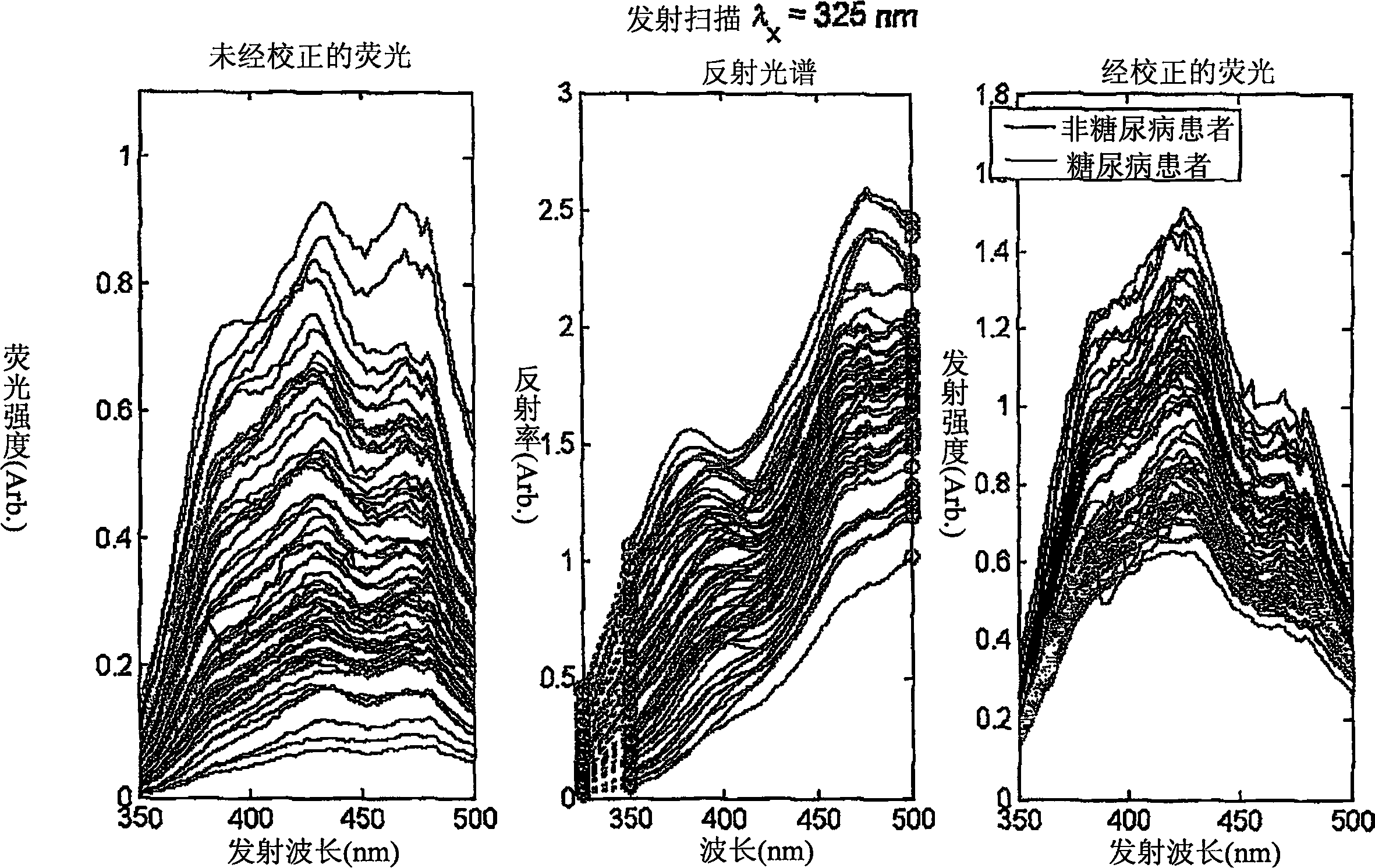
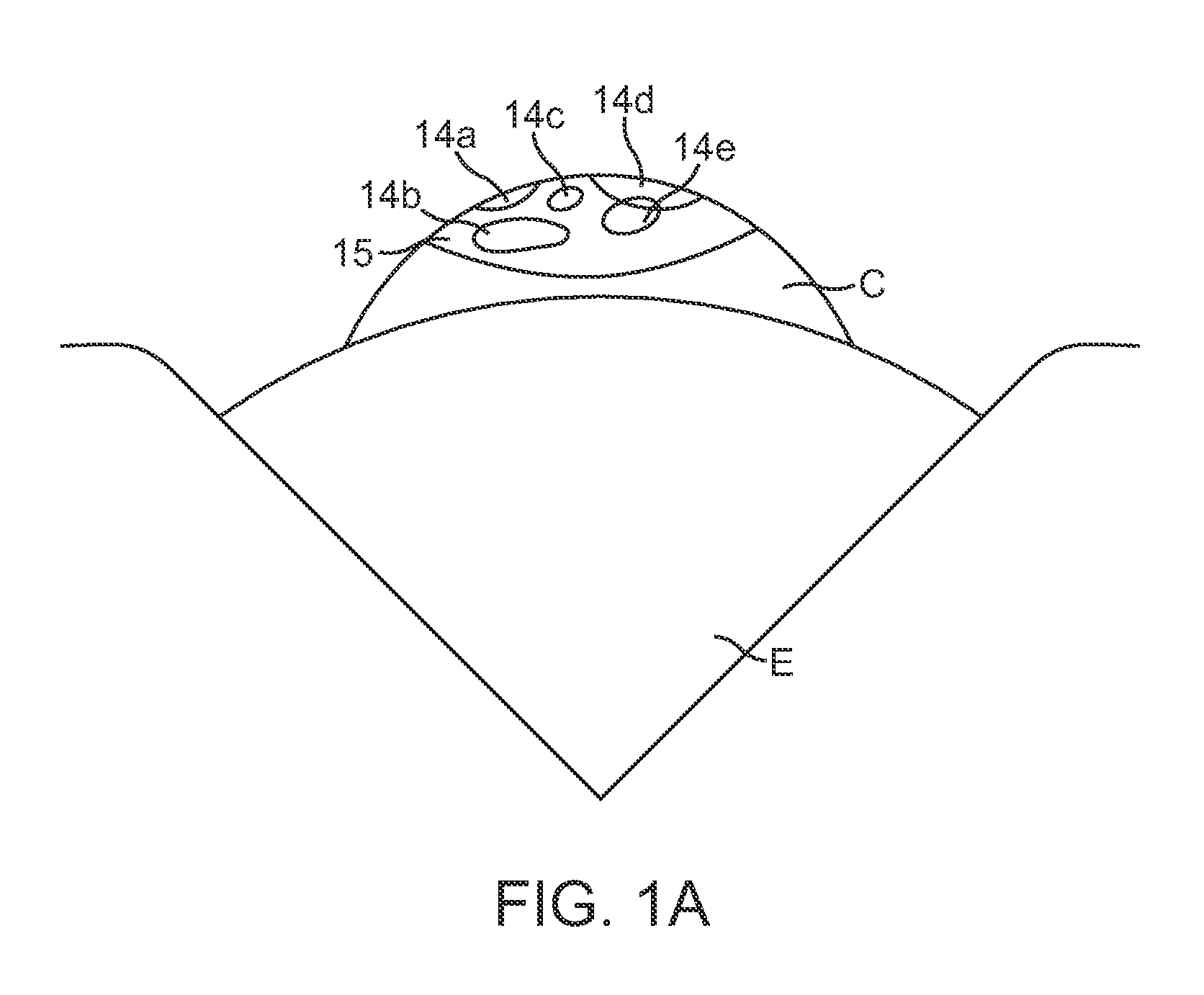
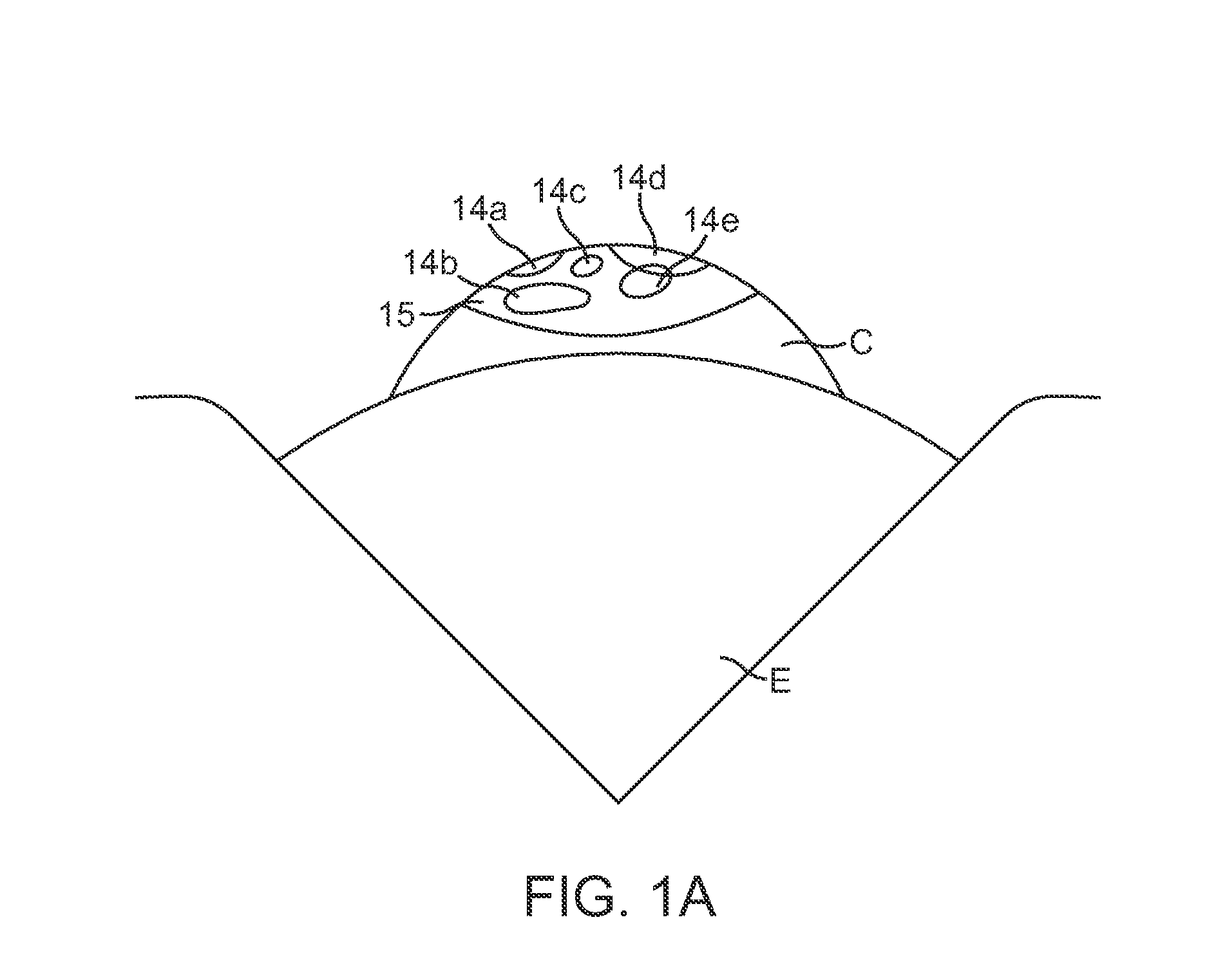
The basic premise of tissue fluorescence visualization is that it may enable clinicians to see the effects of cellular, structural, and/or metabolic activity changes in oral mucosal tissues by observing the fluorescence response of oral tissues in response to light excitation. Natural tissue fluorescence is caused by “fluorophores”.
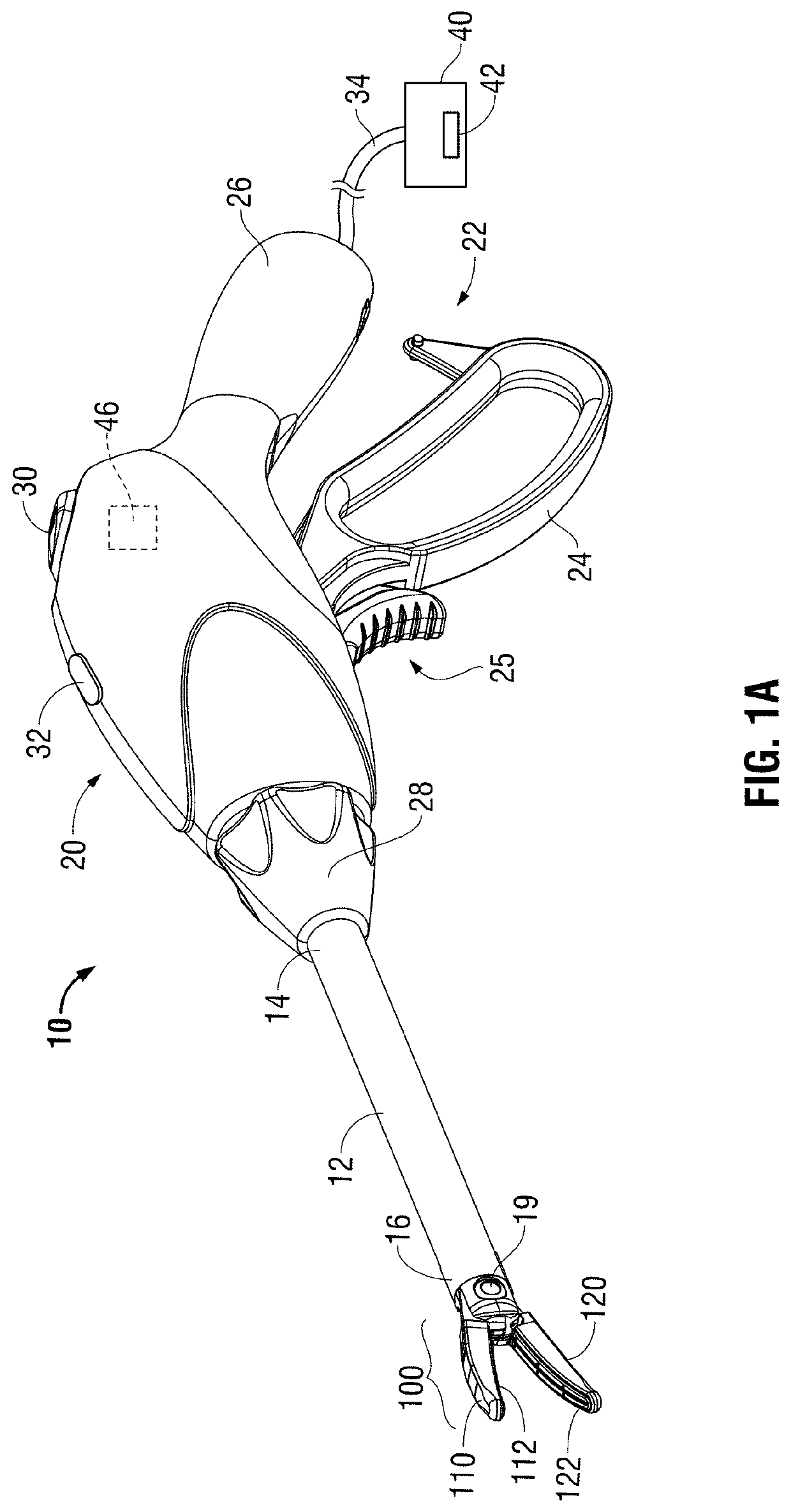
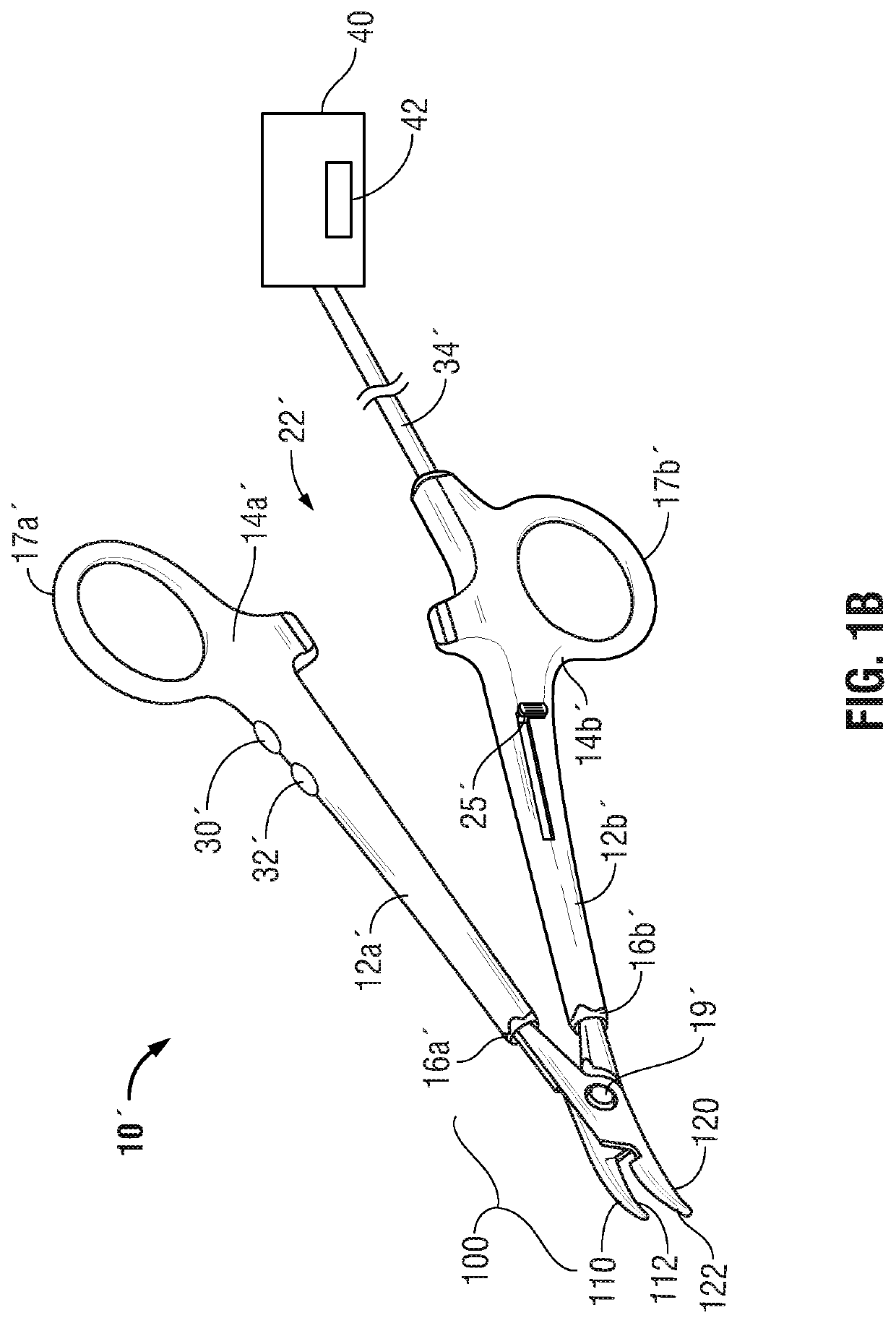
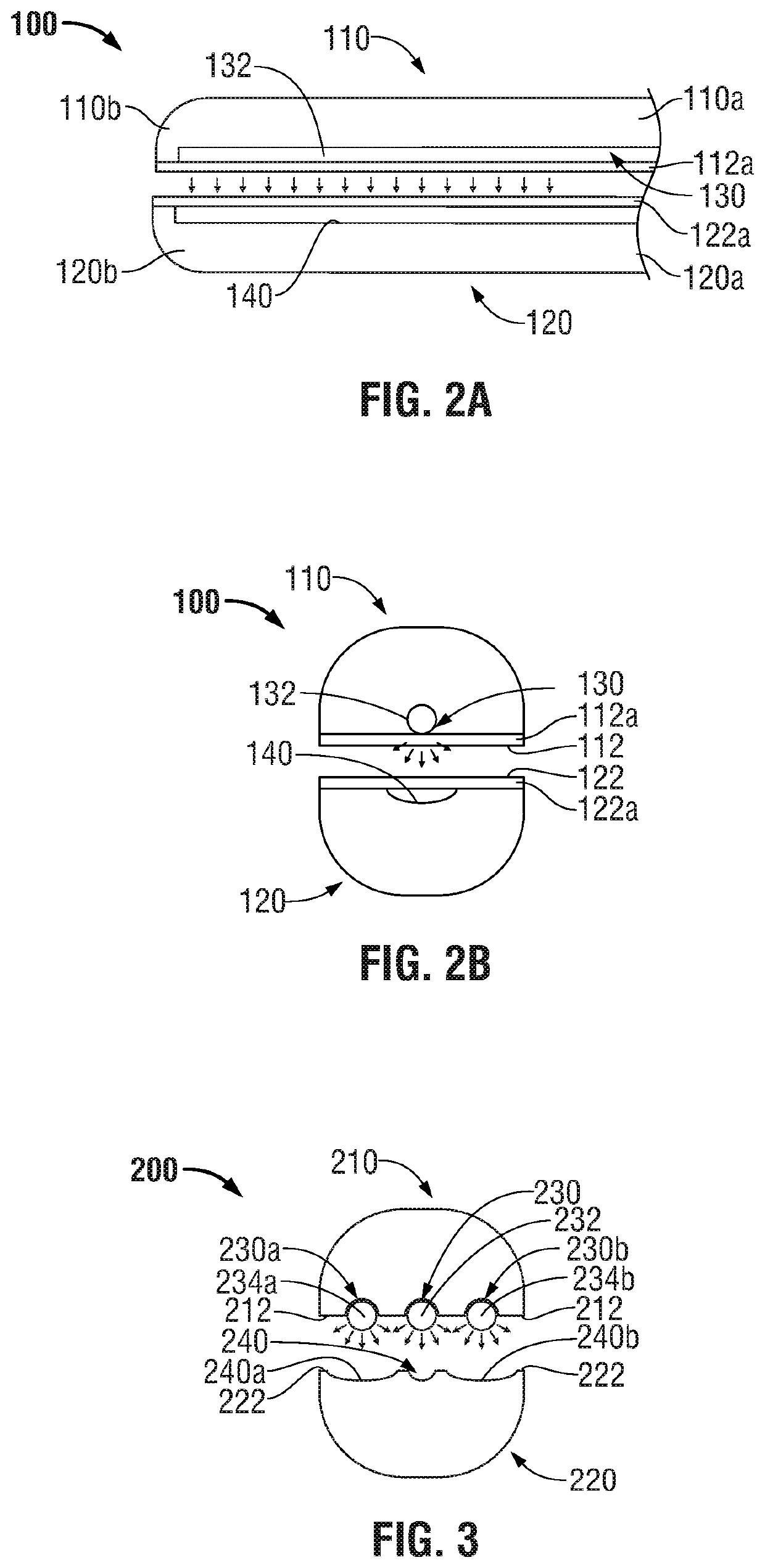
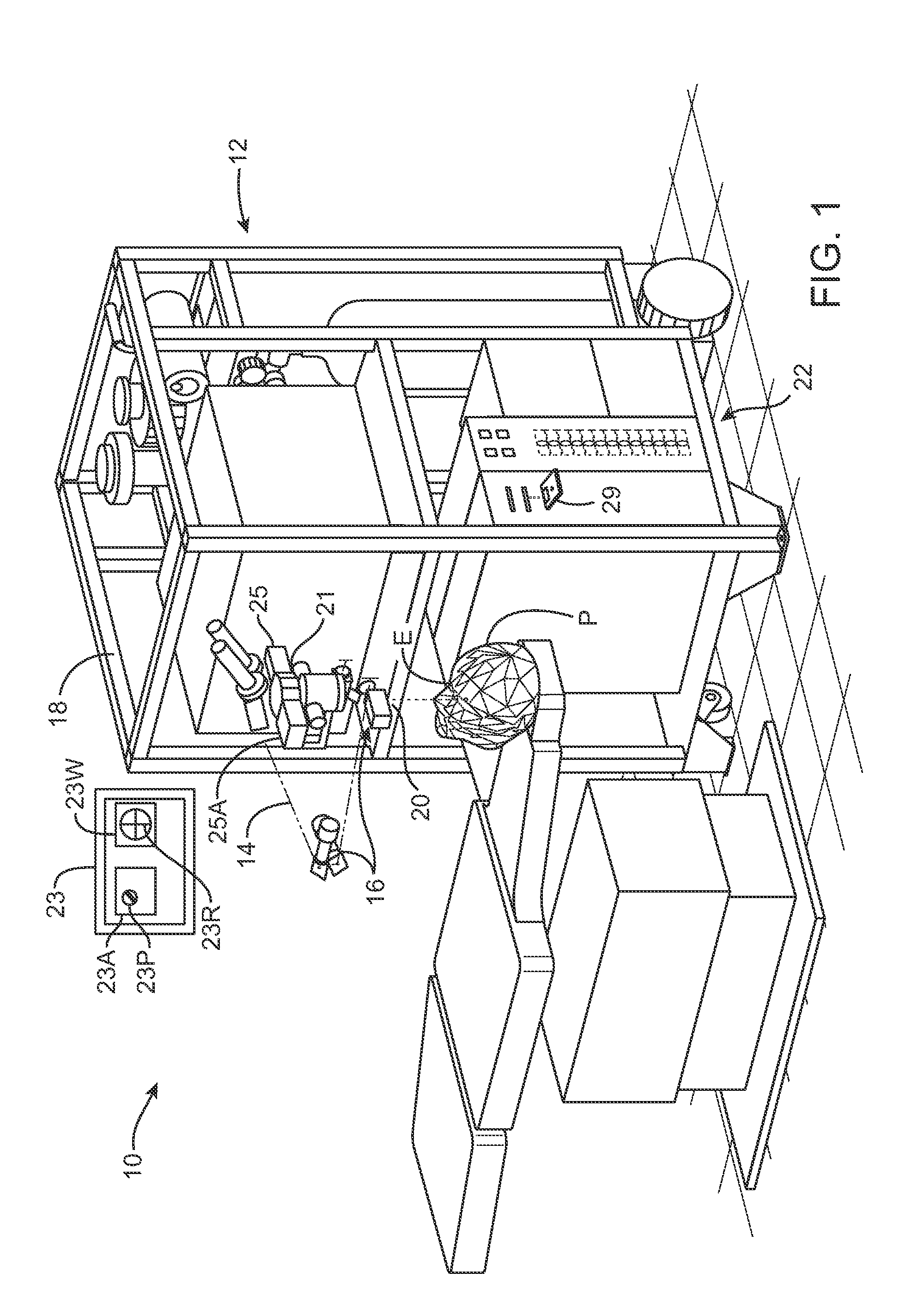
Surgical device with an end-effector assembly and system for monitoring of tissue during a surgical procedure
ActiveUS10722292B2Good indicationExcessive damageDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionLight energyTissue fluorescence
A medical instrument is provided and includes a housing and a shaft coupled to the housing. The shaft has a proximal end and a distal end. An end-effector assembly is disposed at the distal end of the shaft. The end-effector assembly includes first and second jaw members. At least one of the first and second jaw members is movable from a first position wherein the first and second jaw members are disposed in spaced relation relative to one another to at least a second position closer to one another wherein the first and second jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue therebetween. The medical instrument also includes one or more light-emitting elements and one or more light-detecting elements configured to generate one or more signals indicative of tissue florescence. The one or more light-emitting elements are adapted to deliver light energy to tissue grasped between the first and second jaw members.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
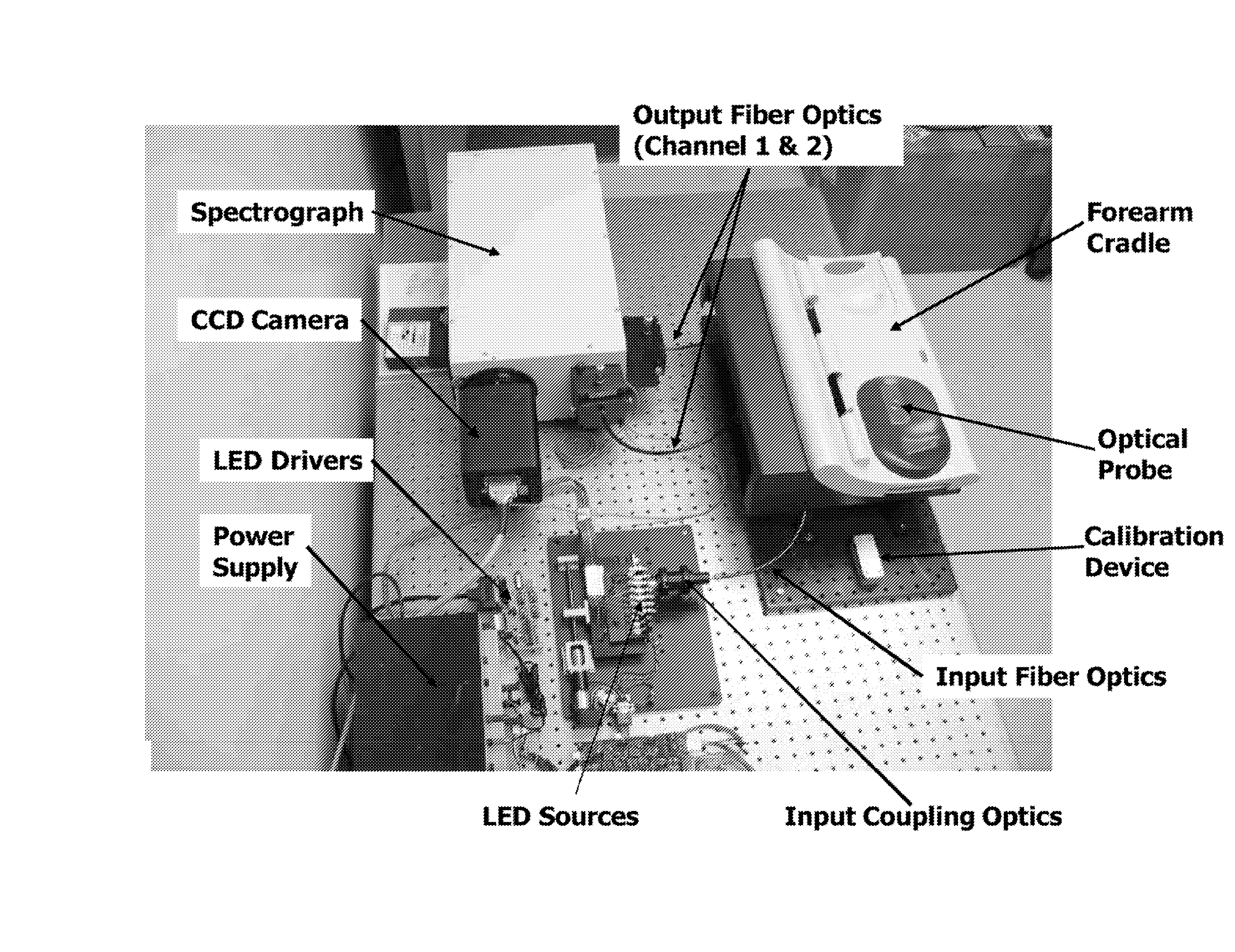
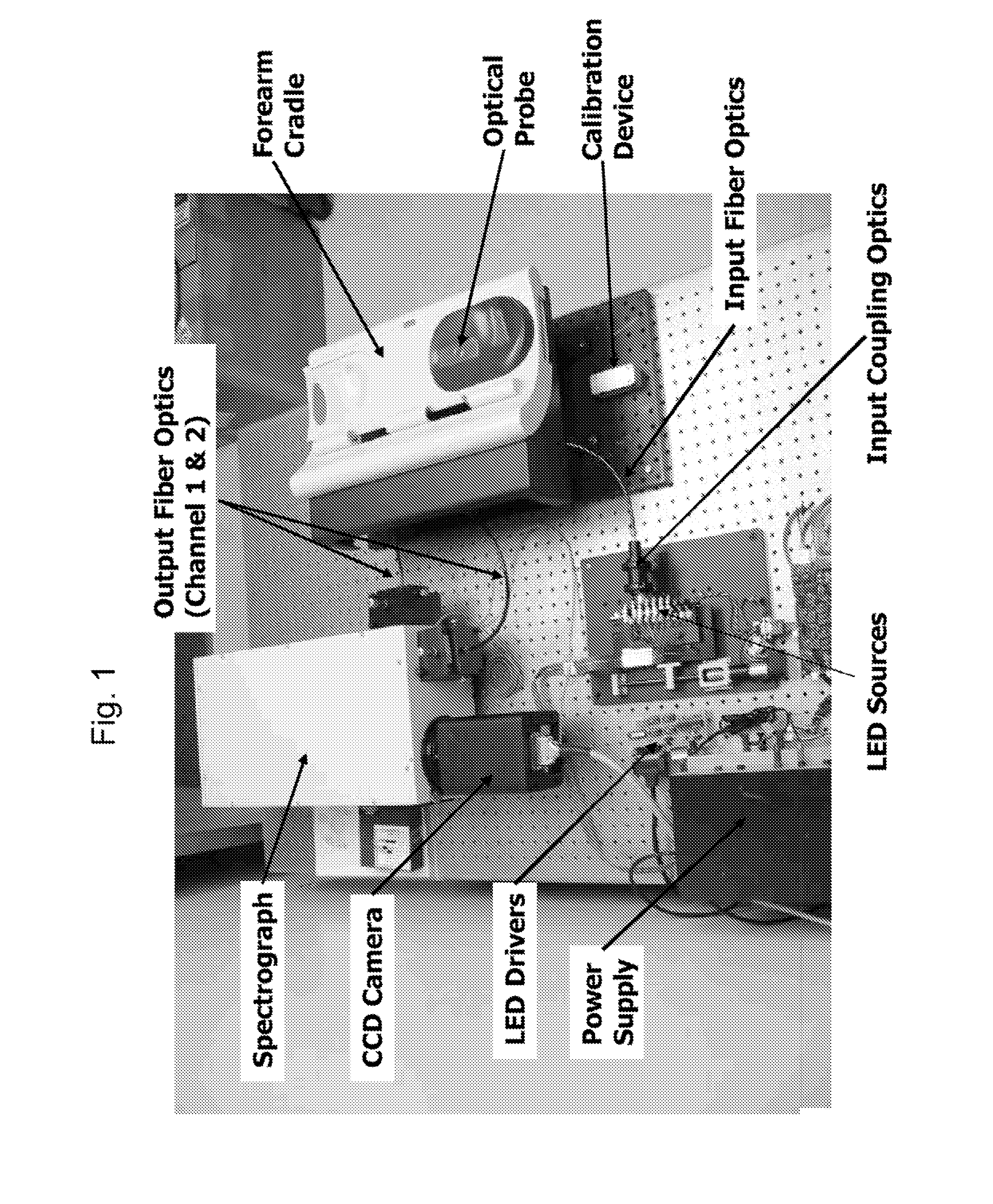
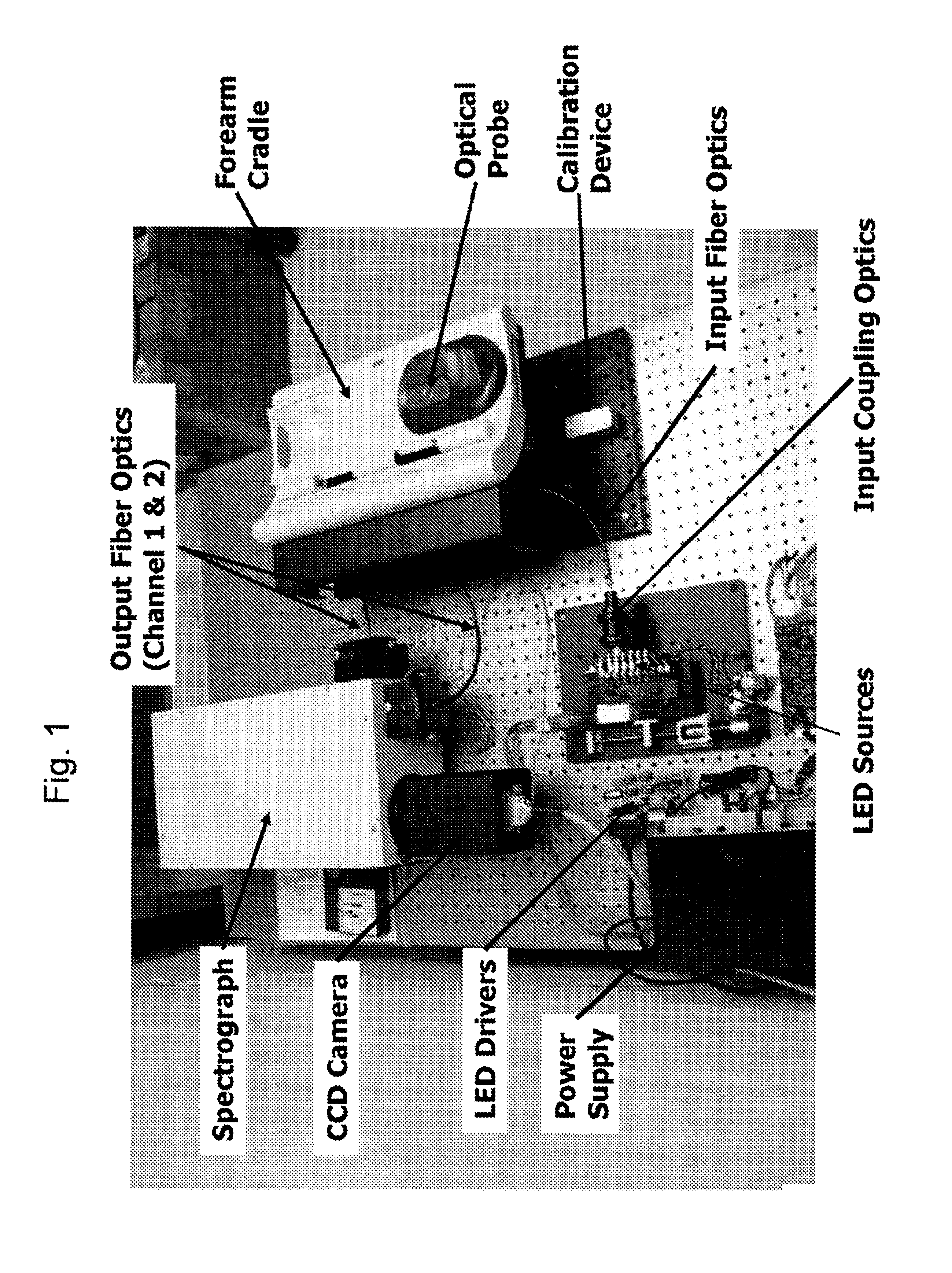
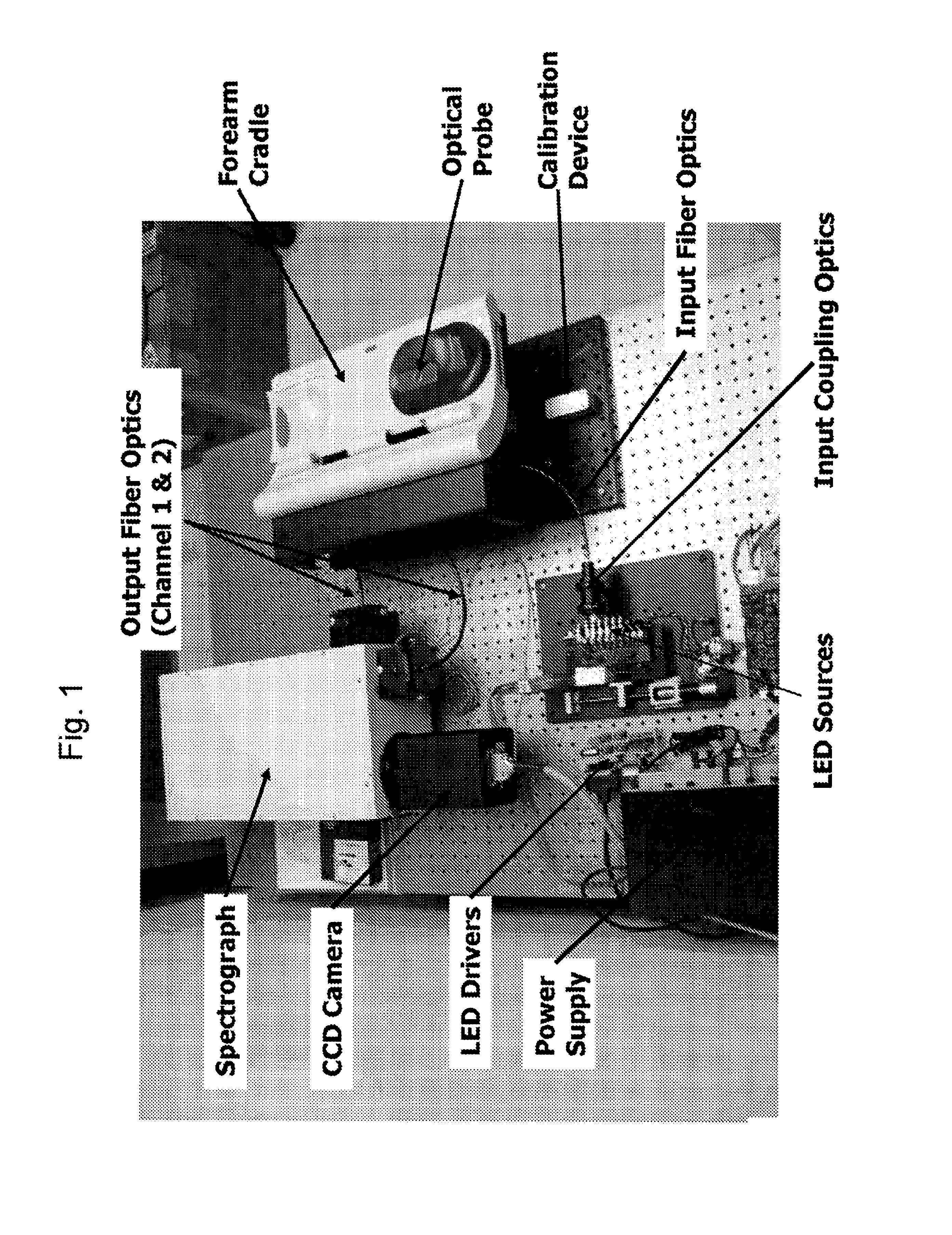
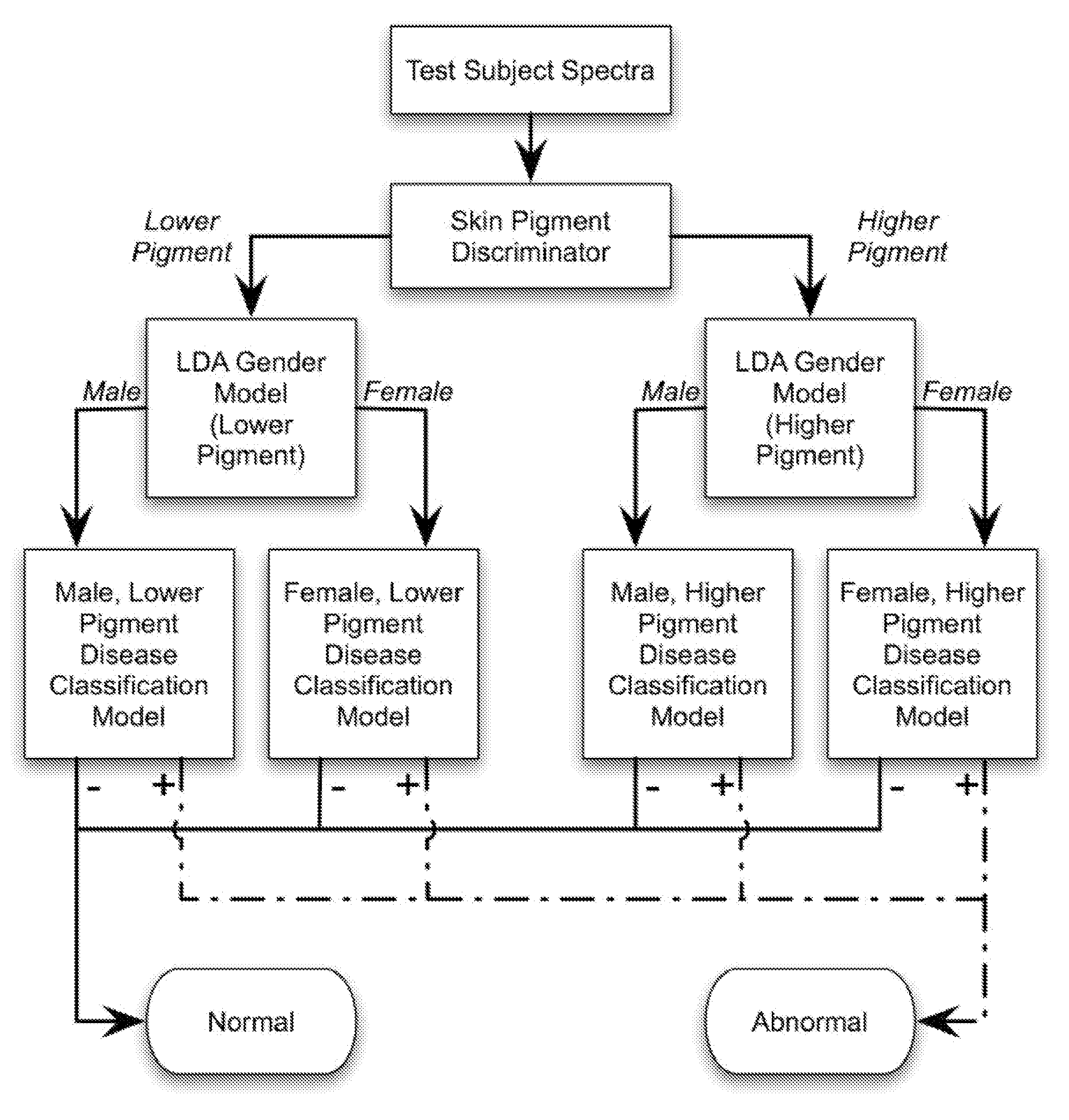
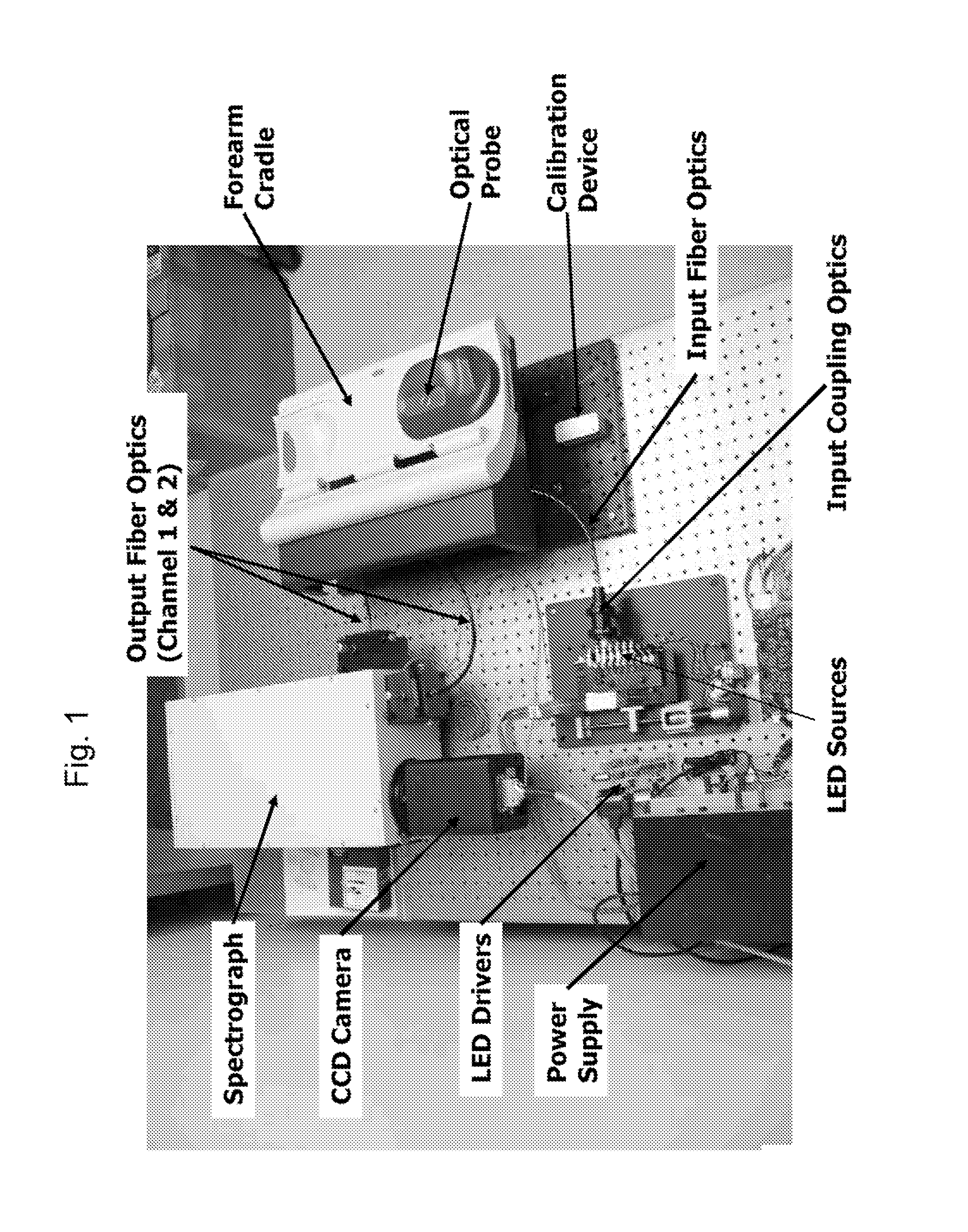
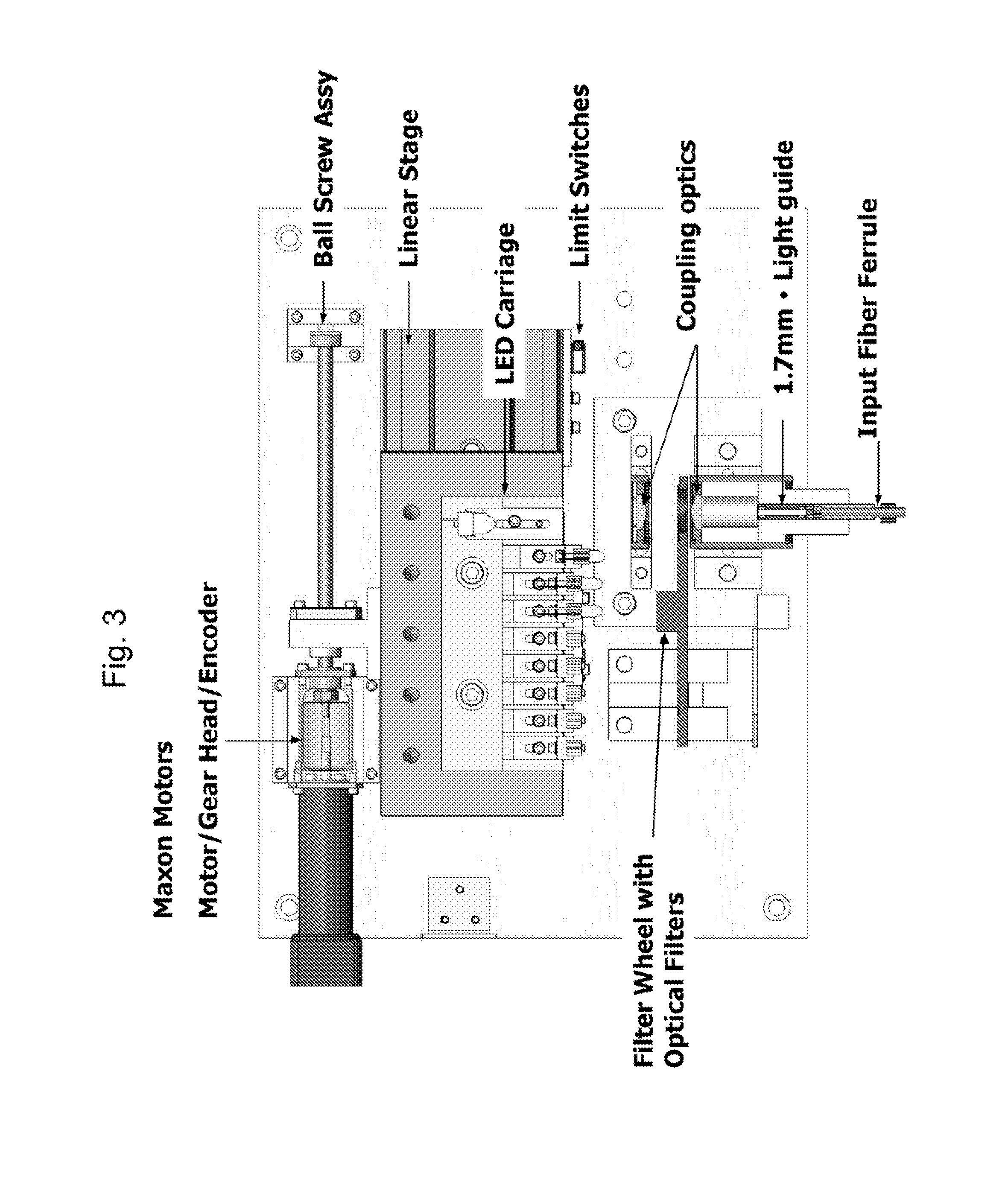
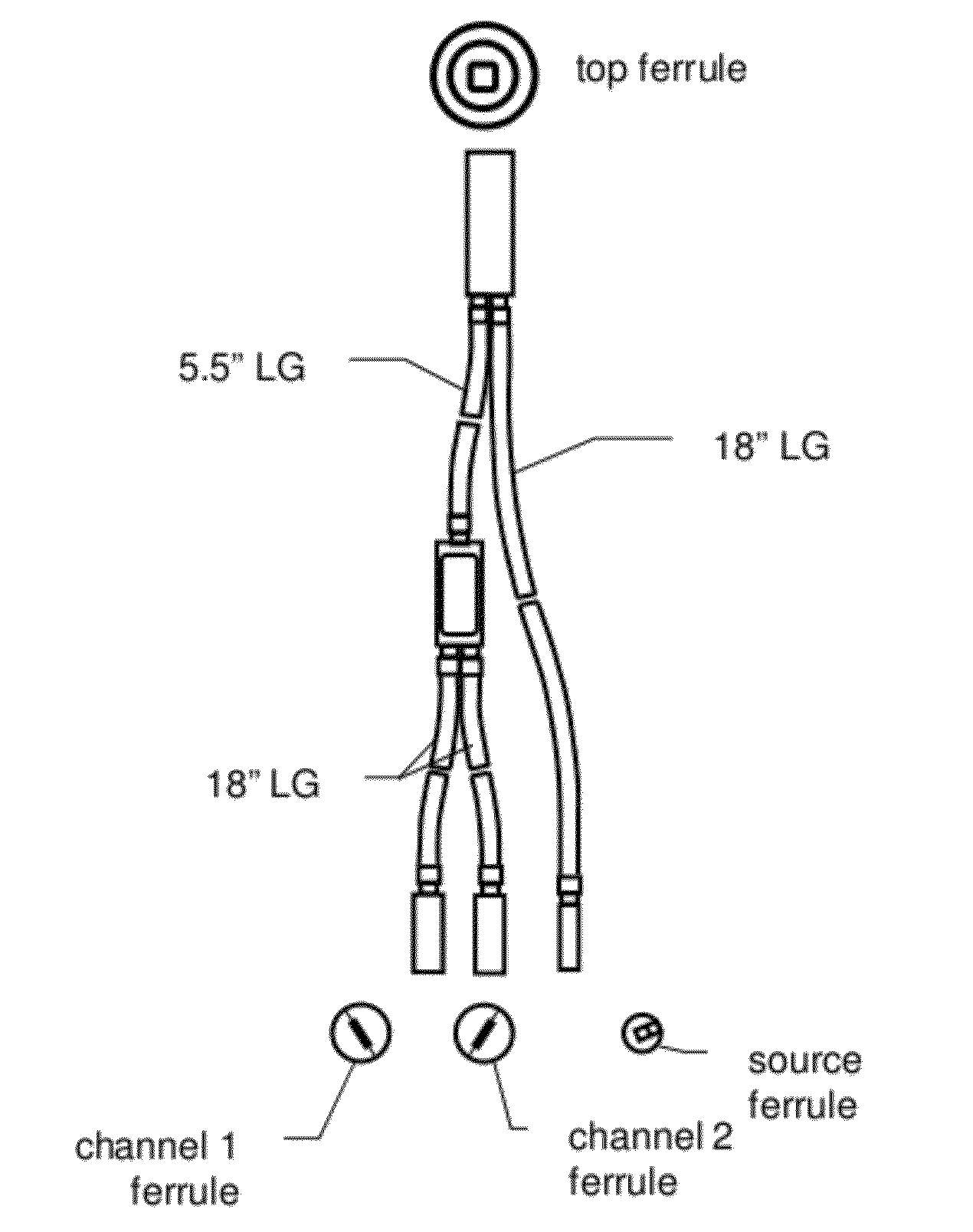
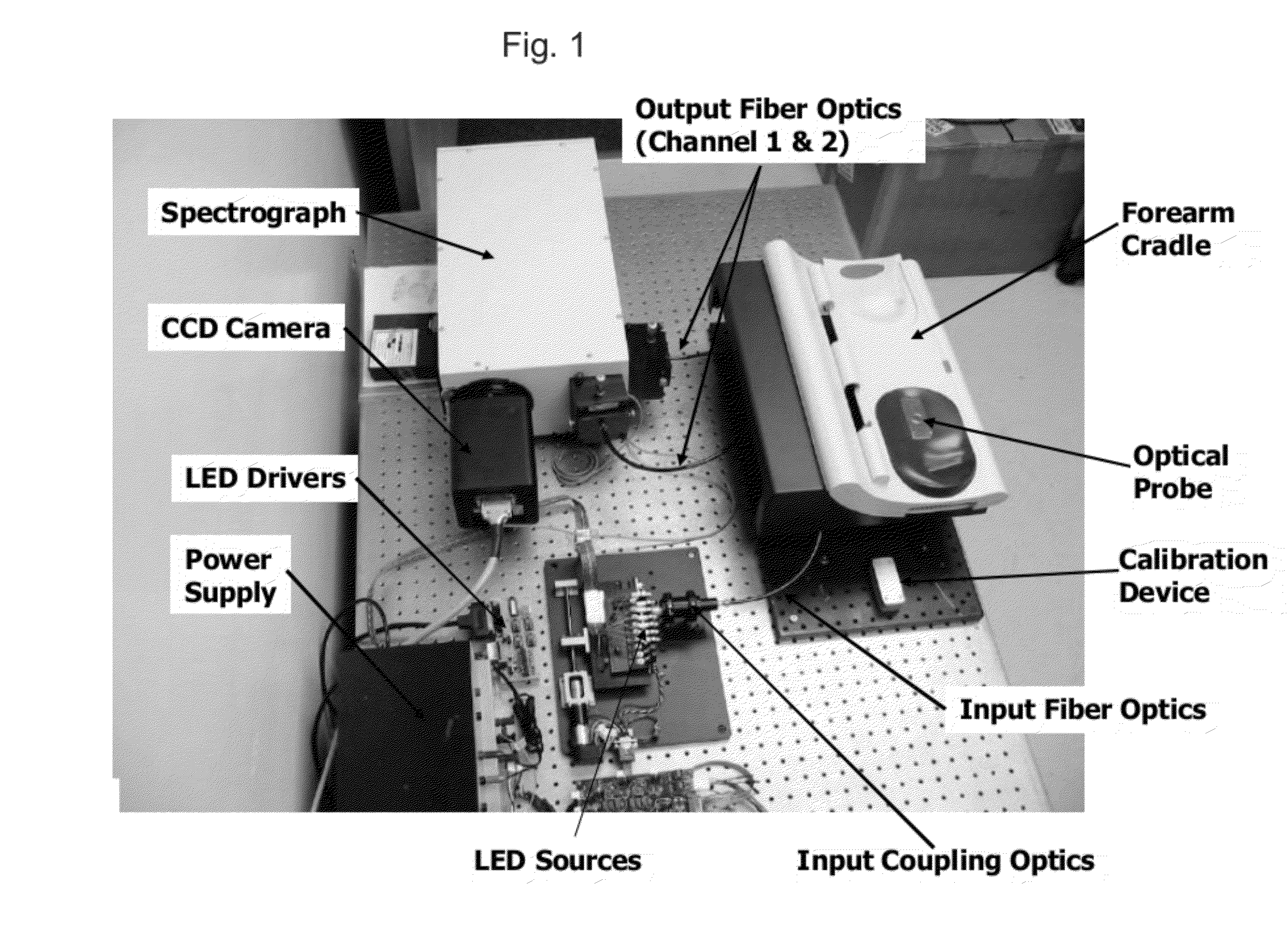
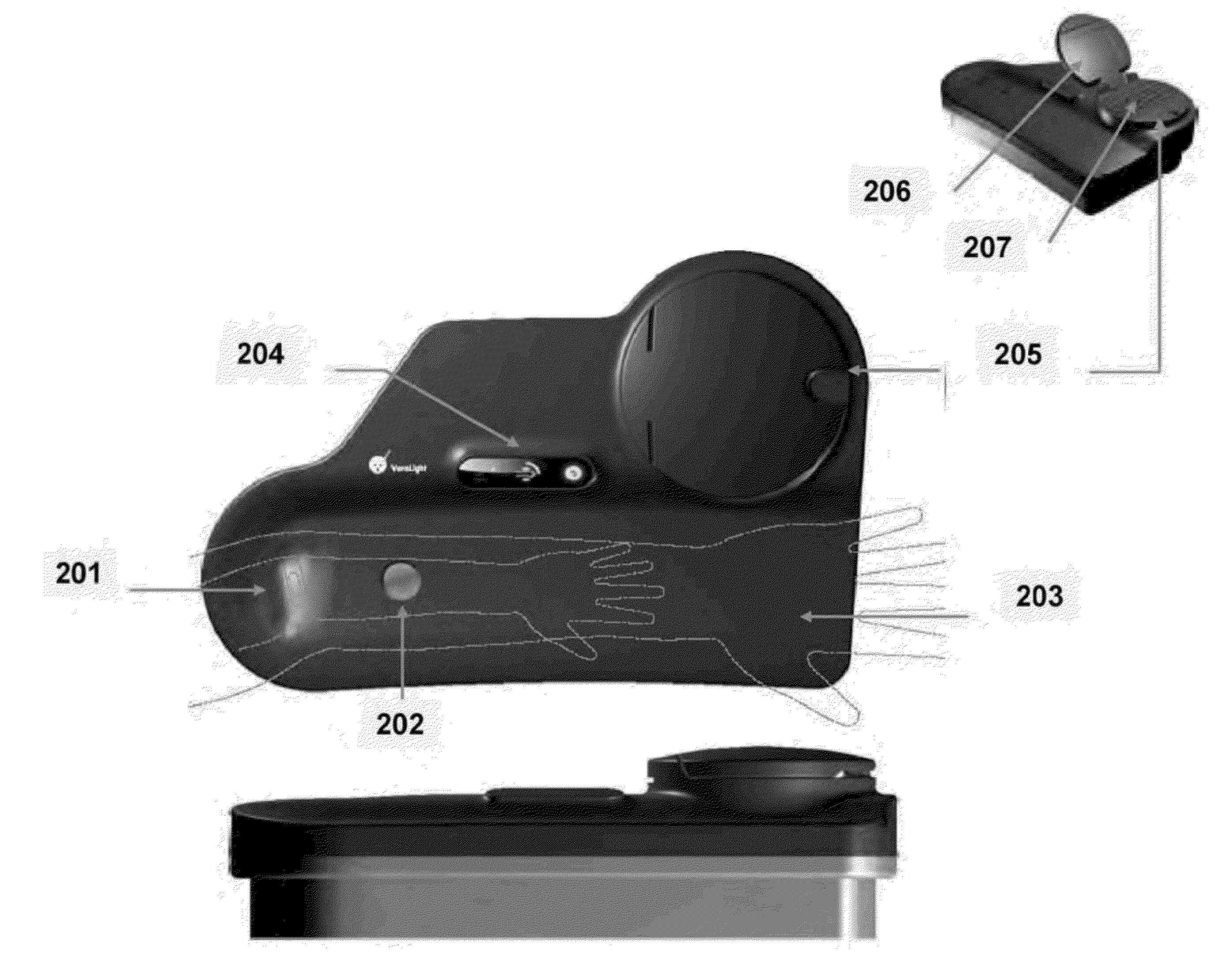
Determination of a Measure of a Glycation End-Product or Disease State Using a Flexible Probe to Determine Tissue Fluorescence of Various Sites
InactiveUS20070265532A1Improve accuracyImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostics using spectroscopyScattering properties measurementsOptical spectrometerTissue fluorescence
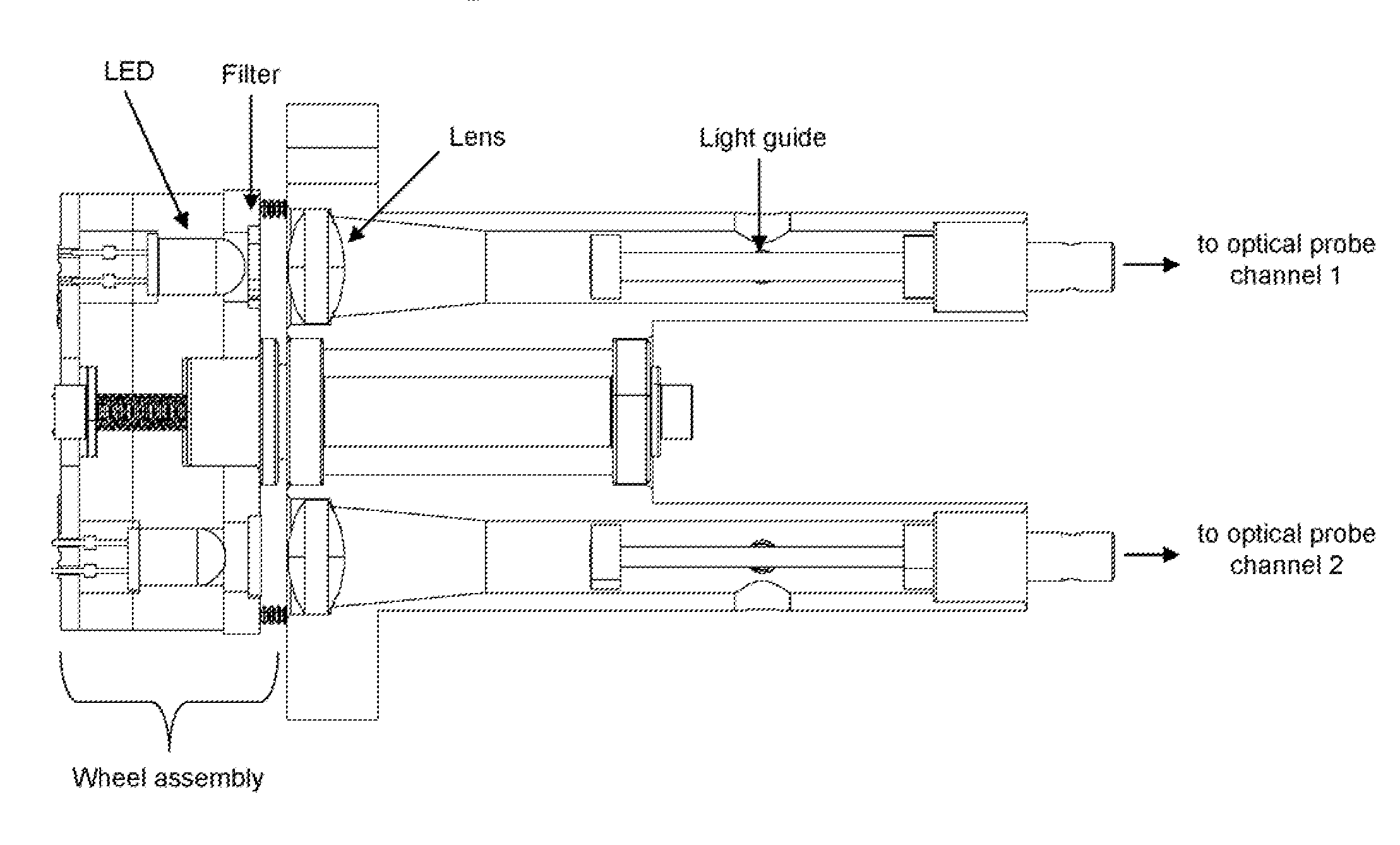
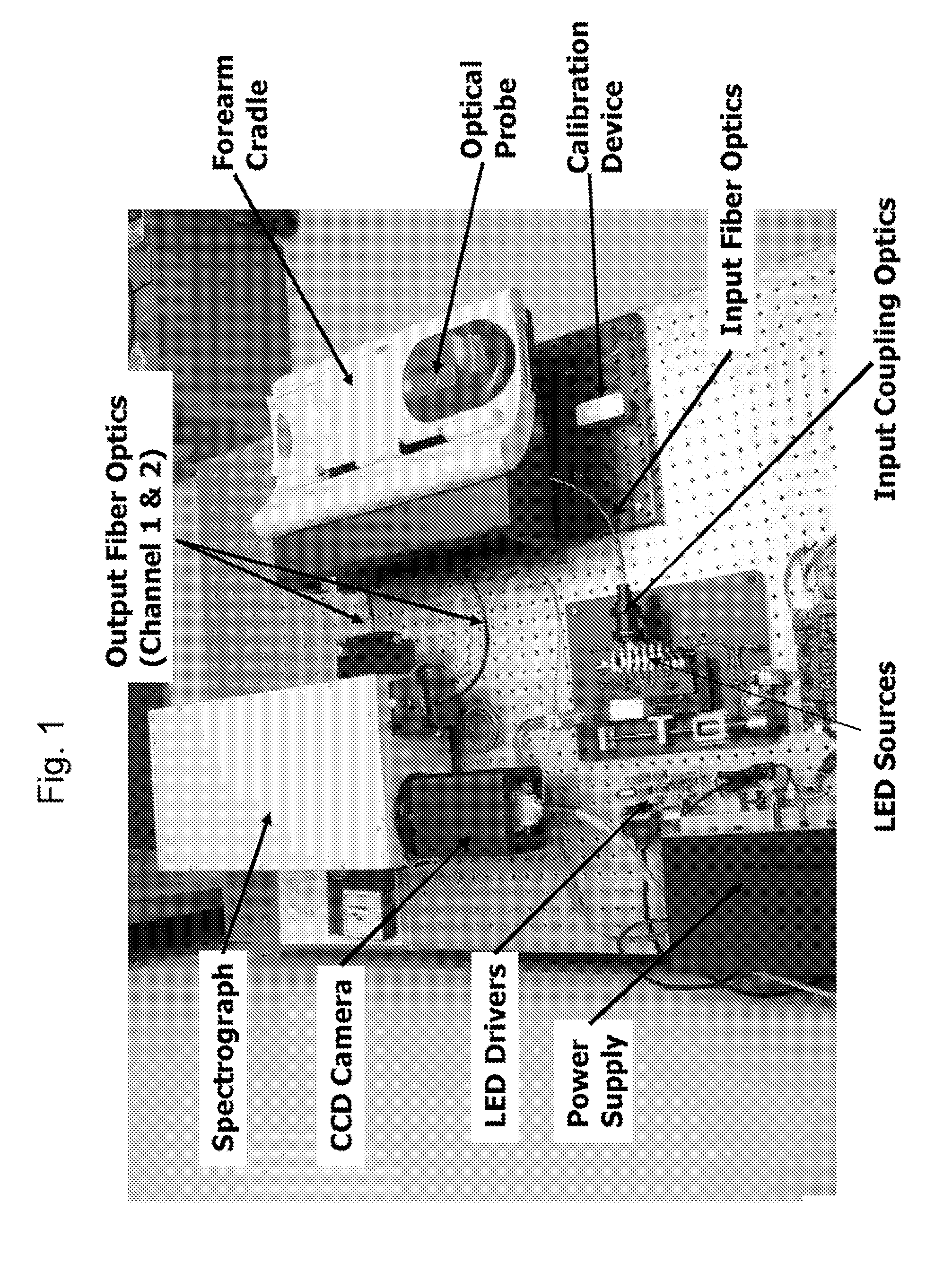
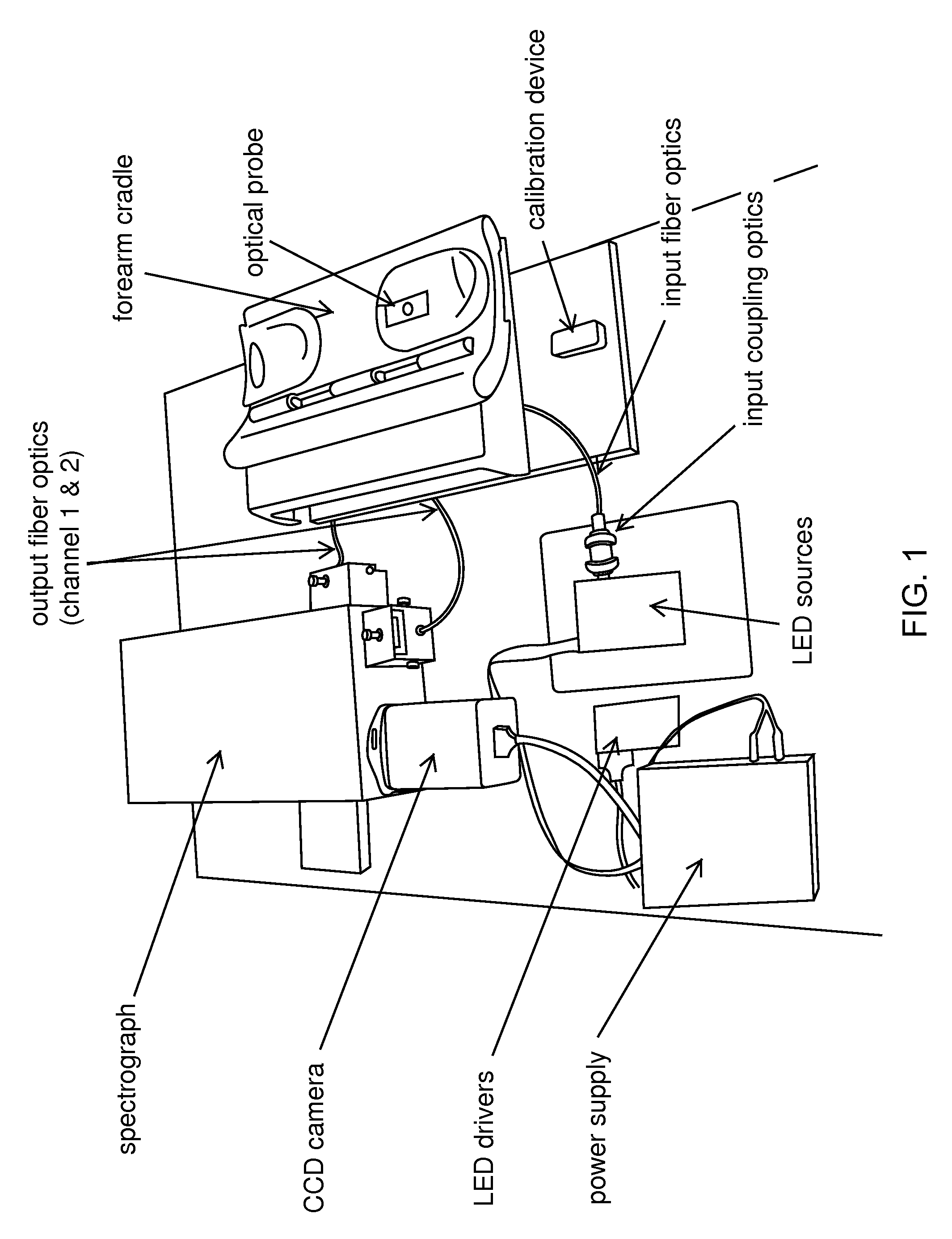
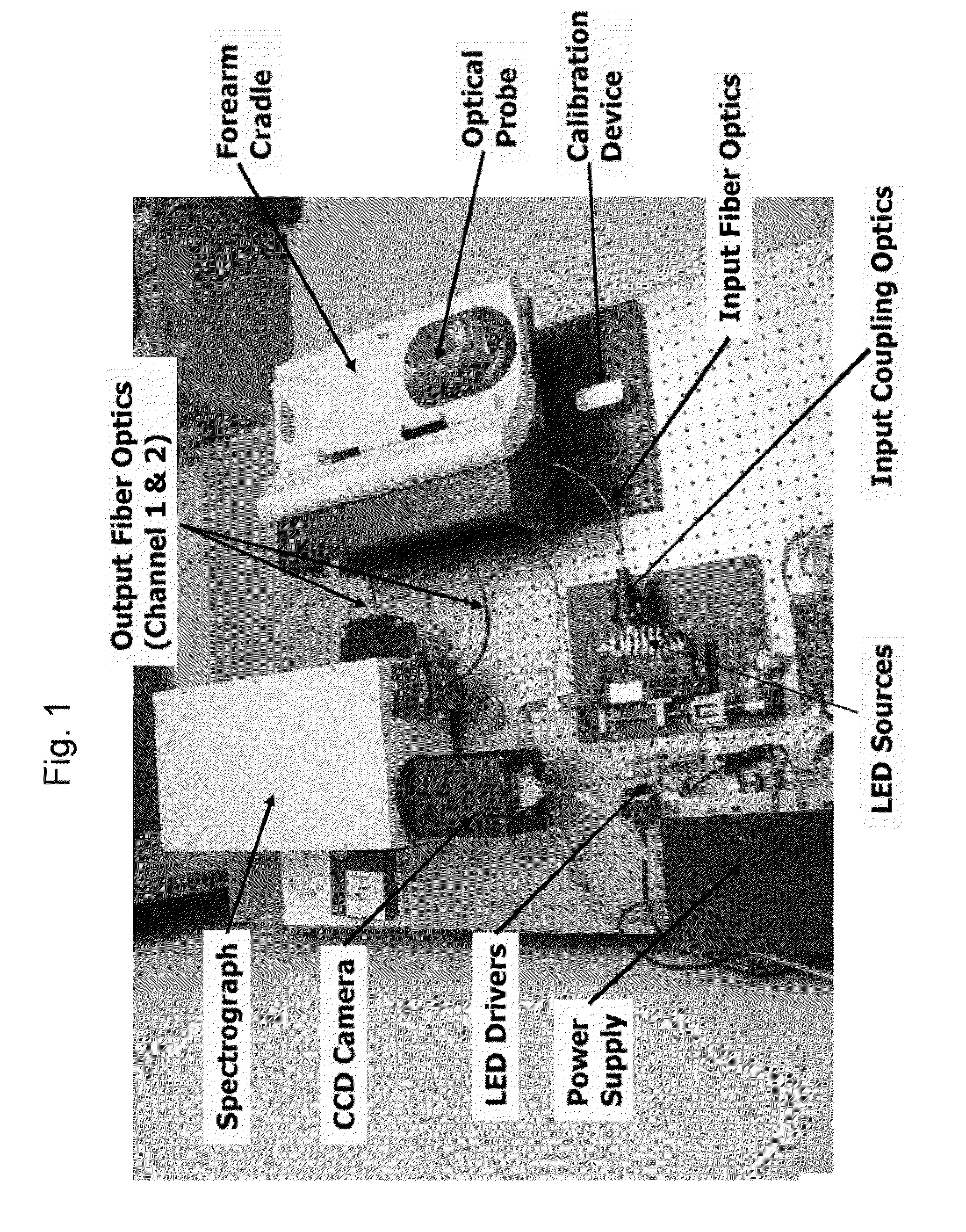
Embodiments of the present invention provide an apparatus with a flexible probe suitable for determining properties of in vivo tissue from spectral information collected from various tissue sites. An illumination system provides light at a plurality of broadband ranges, which are communicated to a flexible optical probe. Light homogenizers and mode scramblers can be employed to improve the performance in some embodiments. The optical probe in some embodiments physically contacts the tissue, and in some embodiments does not physically contact the tissue. The optical probe receives light from the illumination system and transmits it to tissue, and receives light diffusely reflected in response to the broadband light, emitted from the in vivo tissue by fluorescence thereof in response to the broadband light, or a combination thereof. The optical probe can communicate the light to a spectrograph which produces a signal representative of the spectral properties of the light. An analysis system determines a property of the in vivo tissue from the spectral properties.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Method and Apparatus for Determination of a Measure of a Glycation End-Product or Disease State Using Tissue Fluorescence
InactiveUS20080103396A1Diagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionTissue CollectionTissue fluorescence
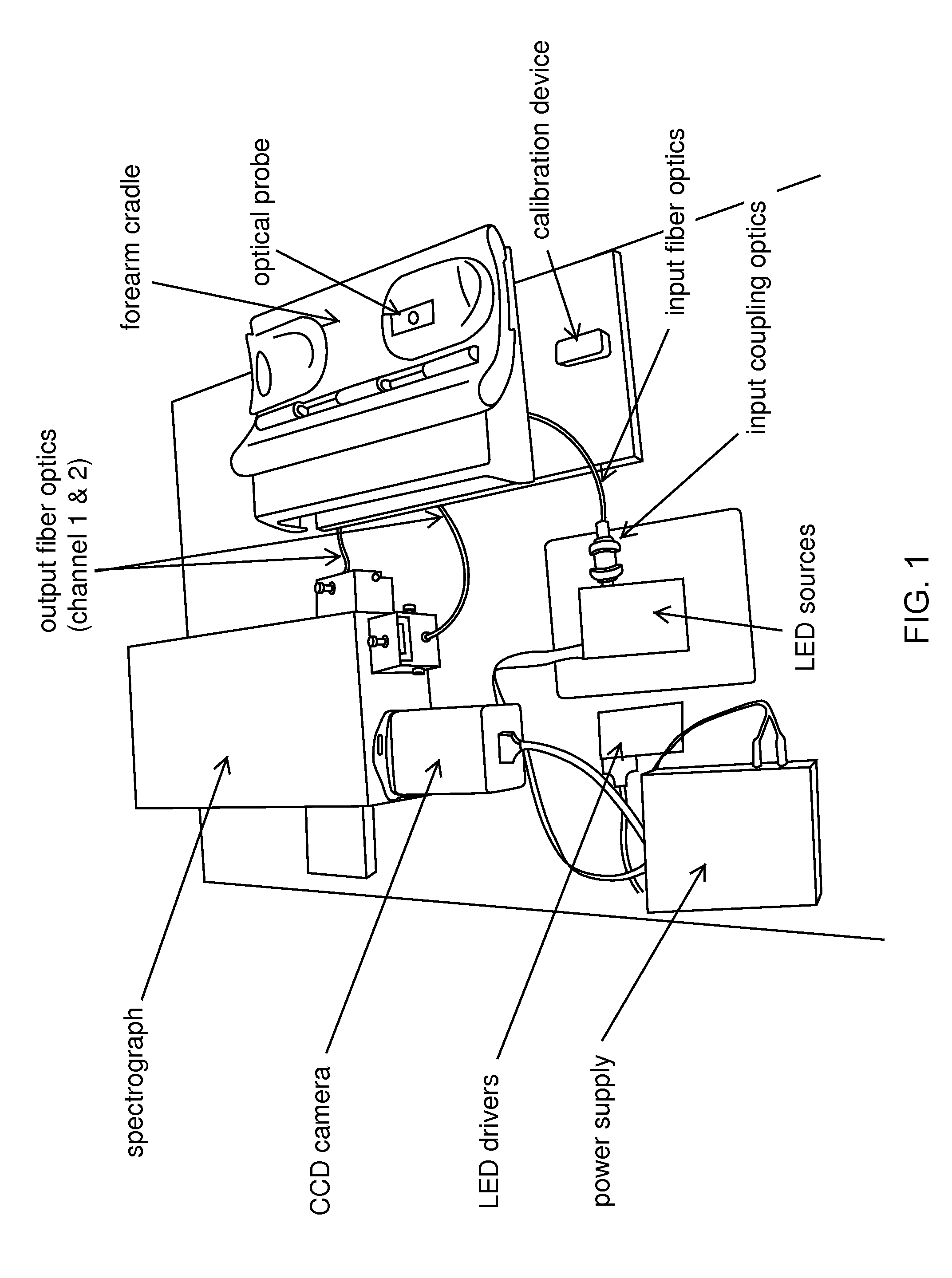
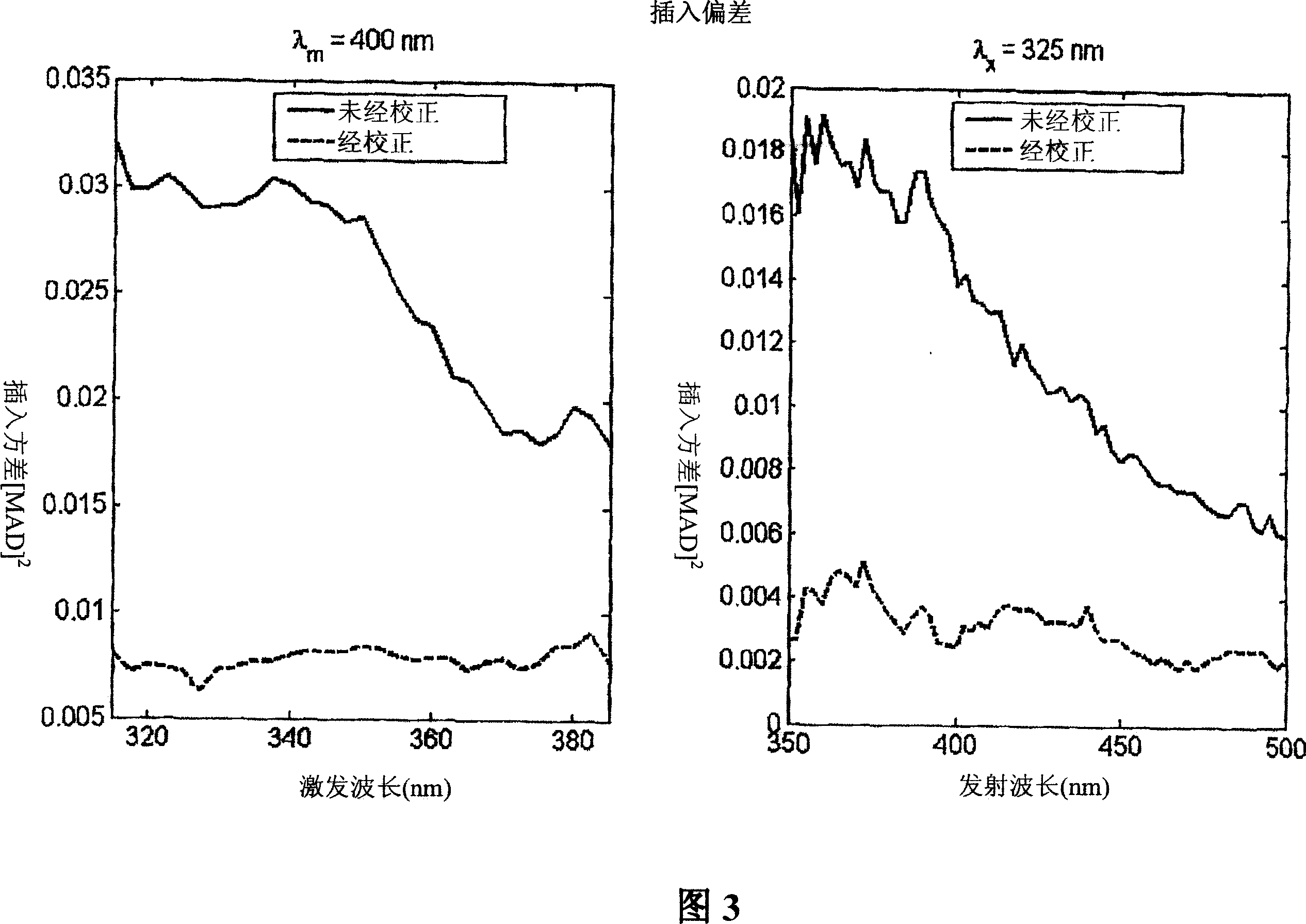
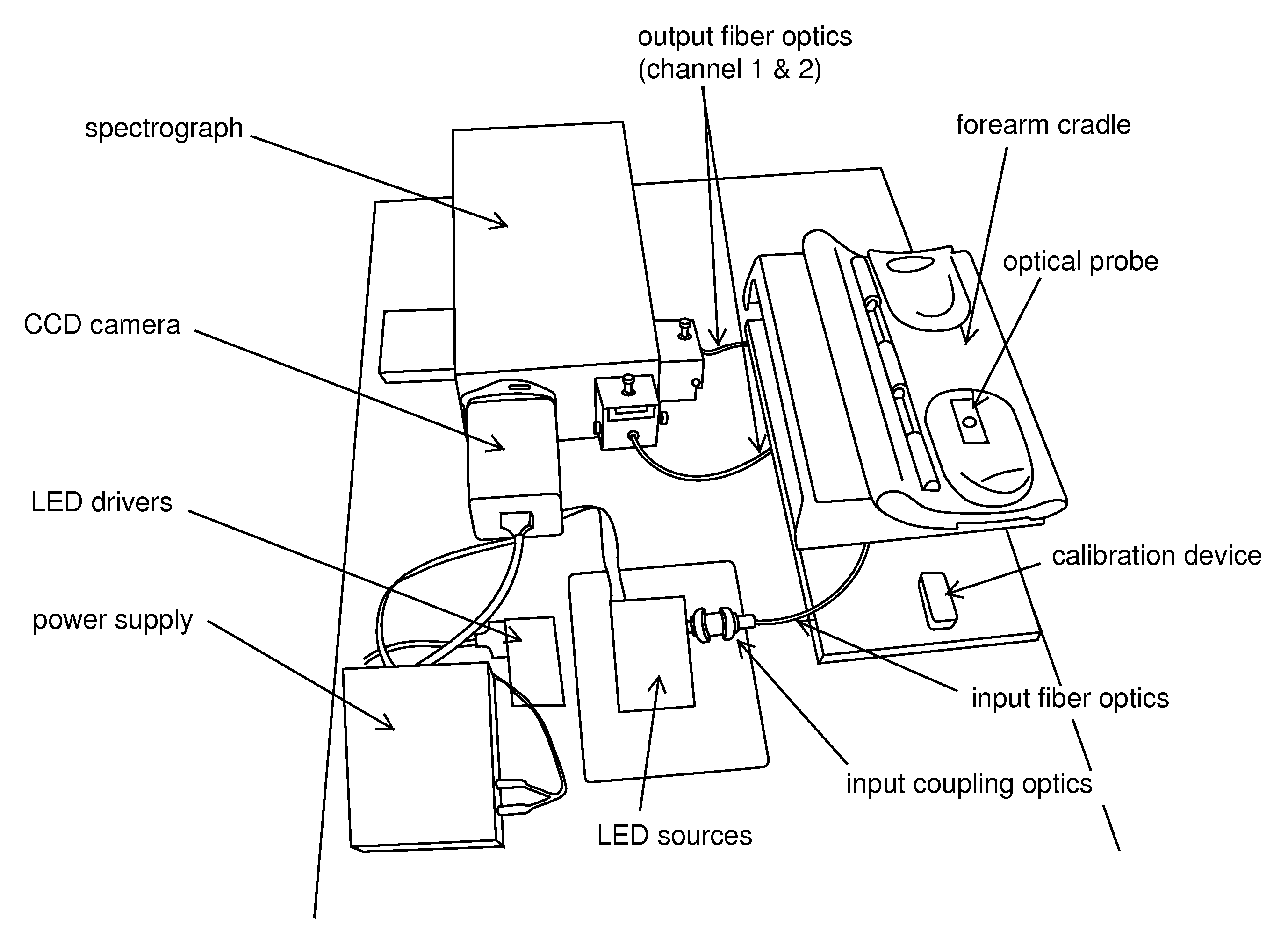
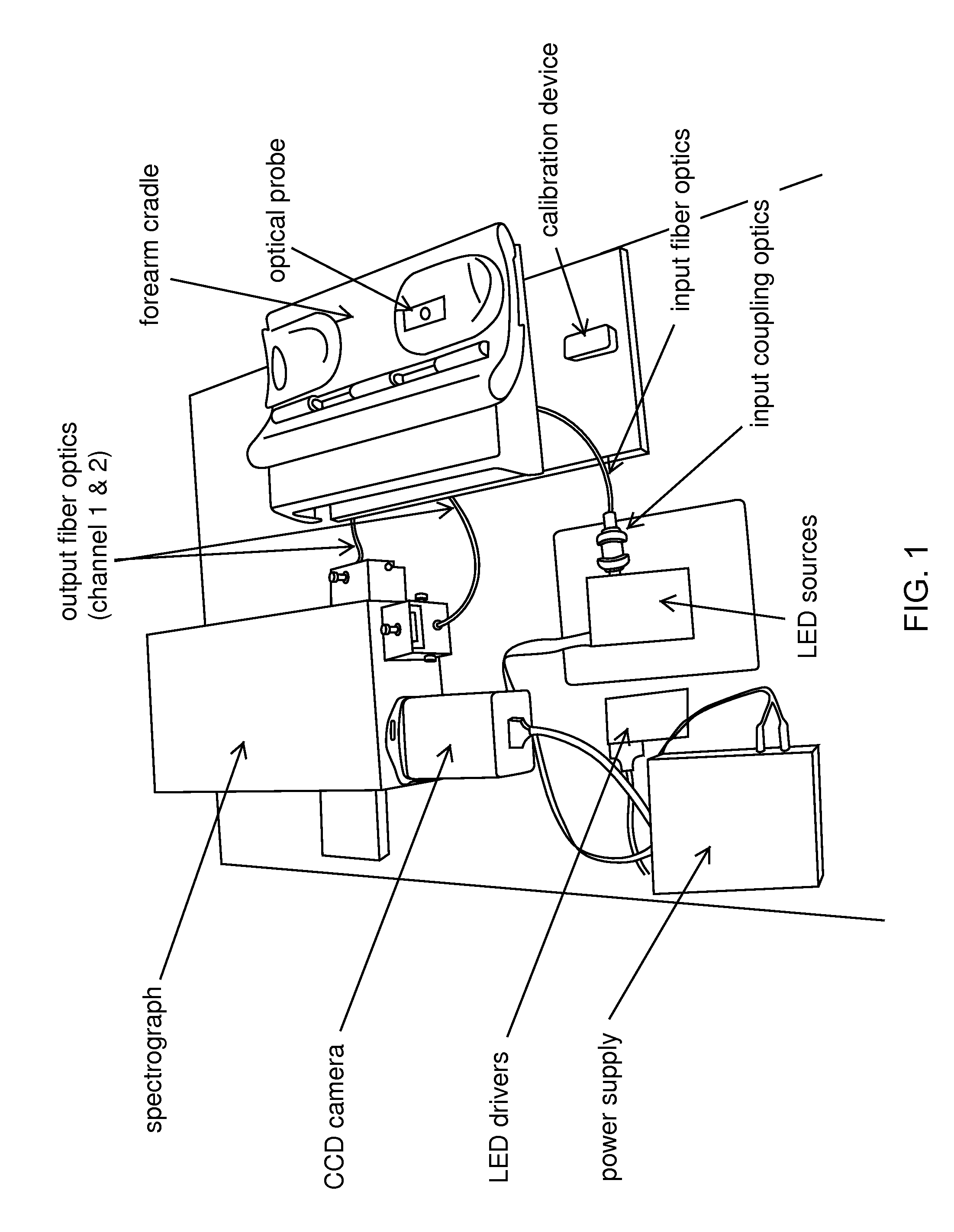
Embodiments of the present invention provide an apparatus suitable for determining properties of in vivo tissue from spectral information collected from the tissue. An illumination system provides light at a plurality of broadband ranges, which are communicated to an optical probe. The optical probe receives light from the illumination system and transmits it to in vivo tissue, and receives light diffusely reflected in response to the broadband light, emitted from the in vivo tissue by fluorescence thereof in response to the broadband light, or a combination thereof. The optical probe communicates the light to a spectrograph which produces a signal representative of the spectral properties of the light. An analysis system determines a property of the in vivo tissue from the spectral properties. A calibration device mounts such that it is periodically in optical communication with the optical probe.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Determination of a measure of a glycation end-product or disease state using tissue fluorescence
InactiveUS20050148834A1Reduce determination errorImpaired glucose toleranceDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyTissue fluorescenceMulti method
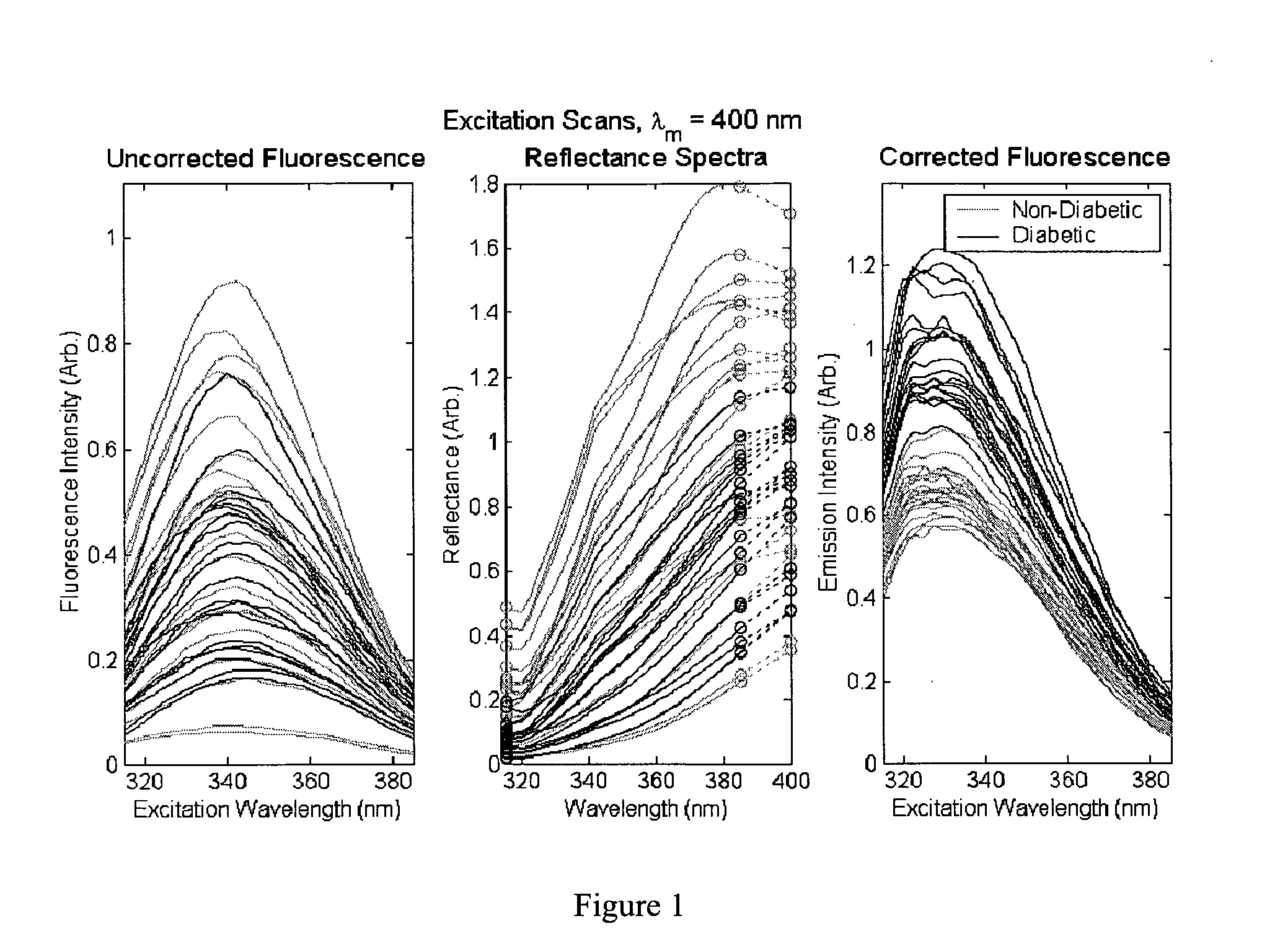
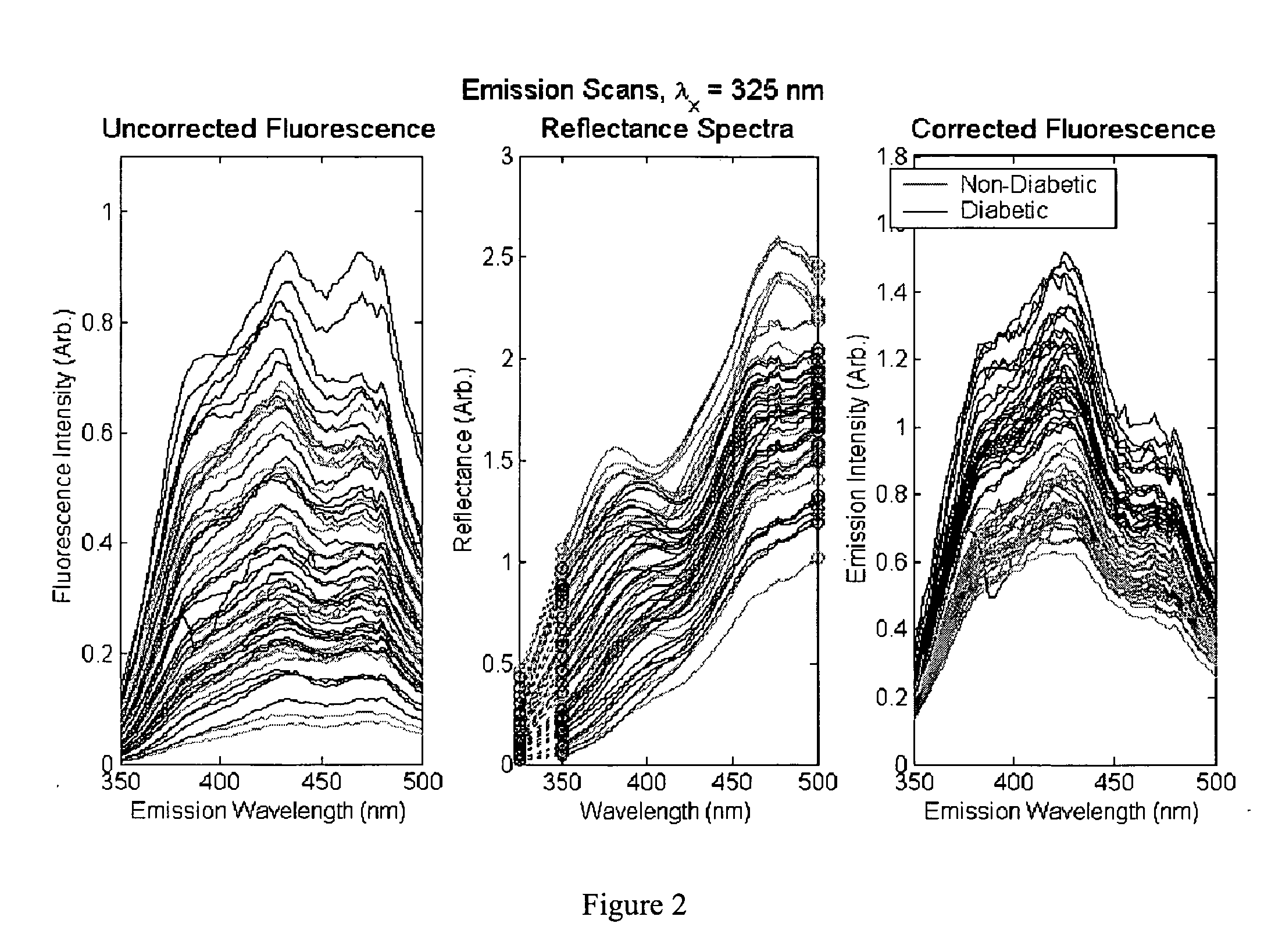
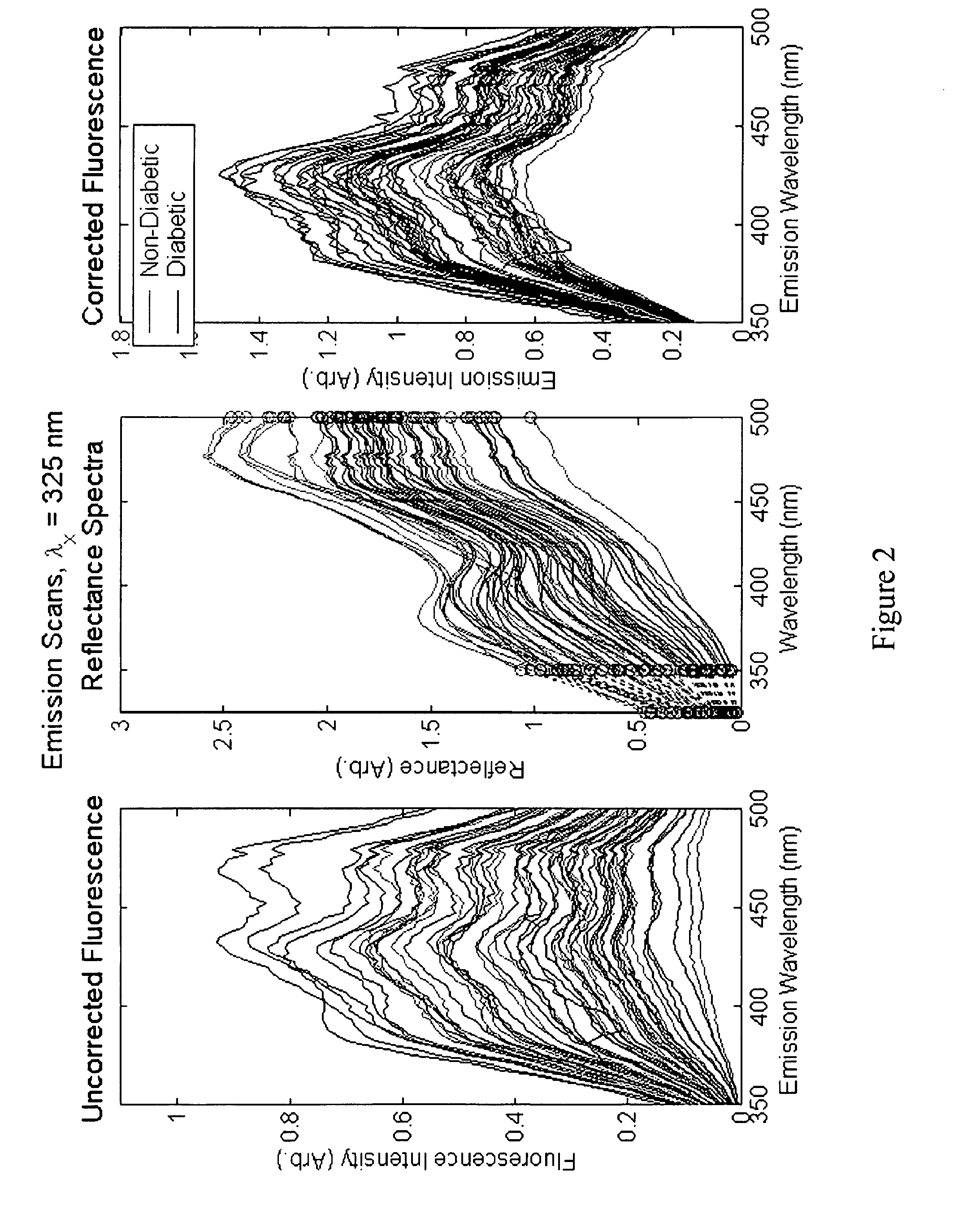
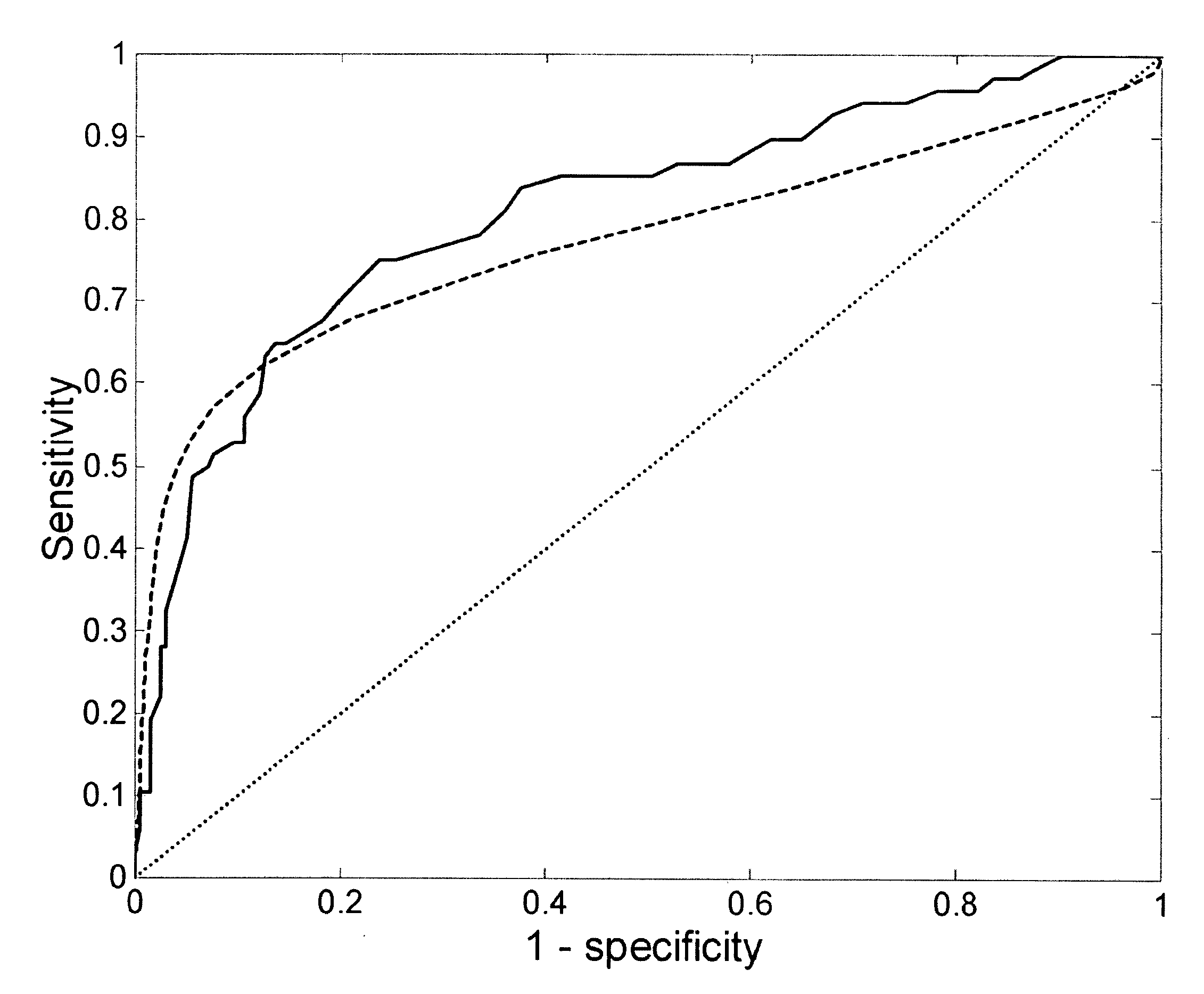
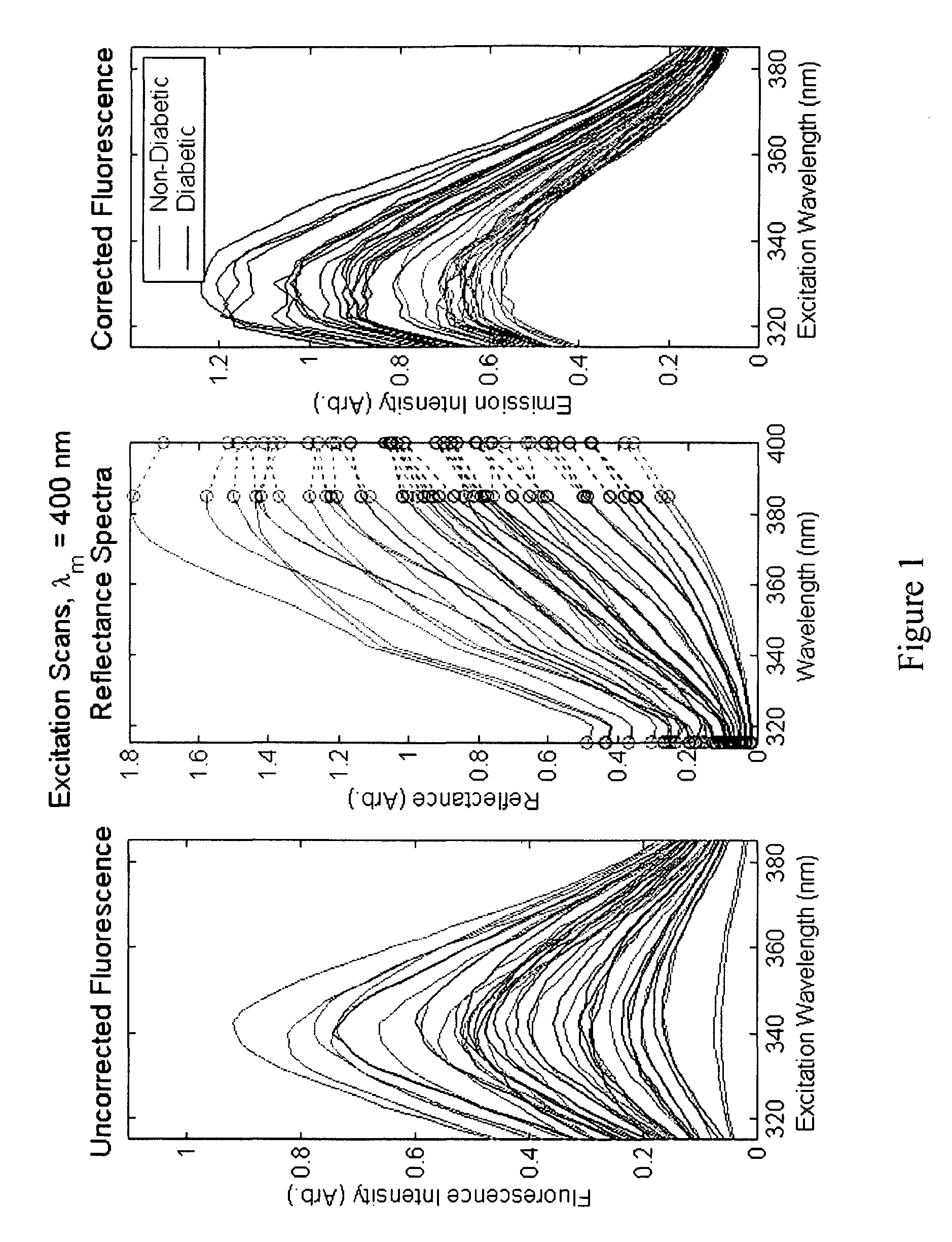
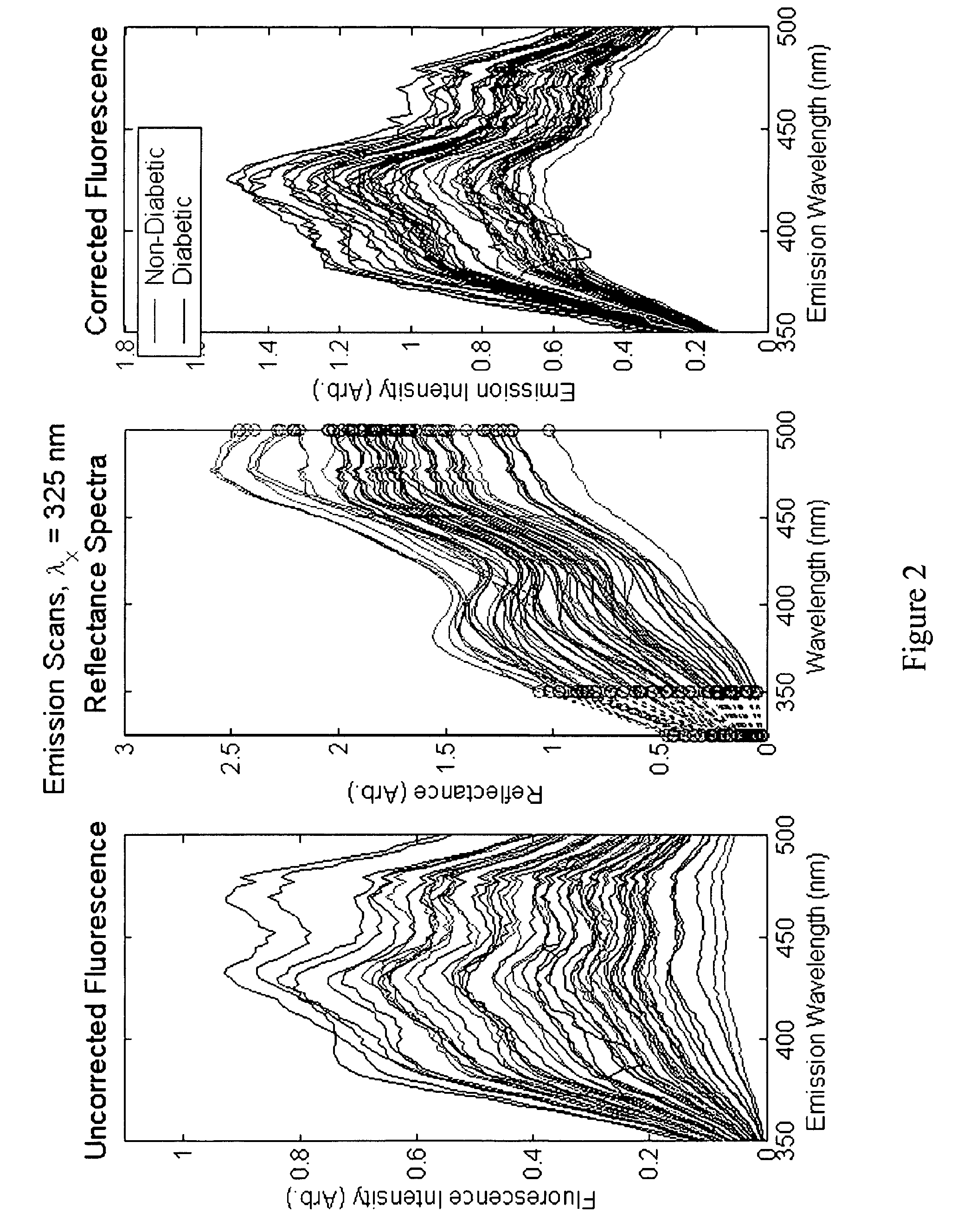
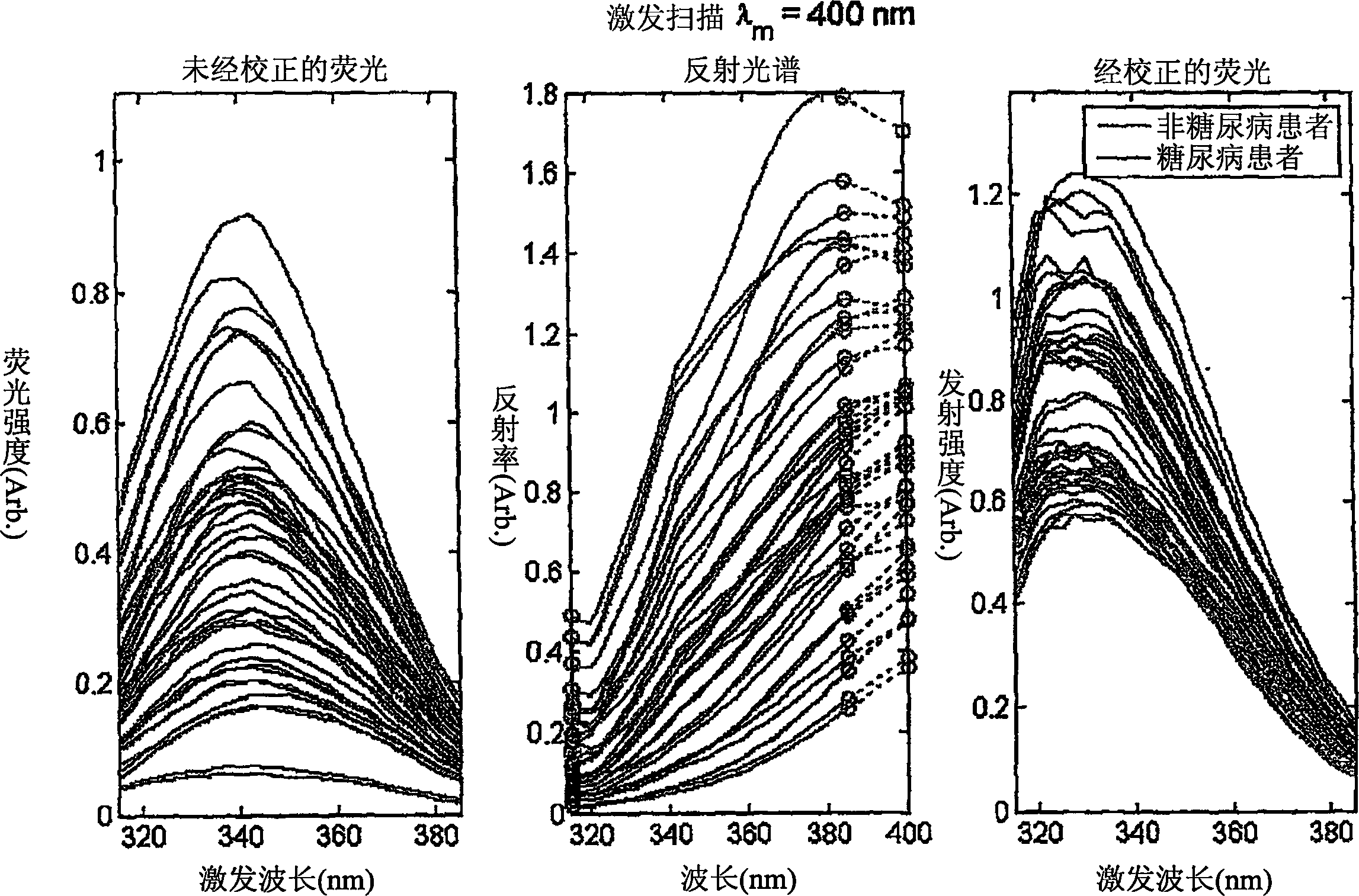
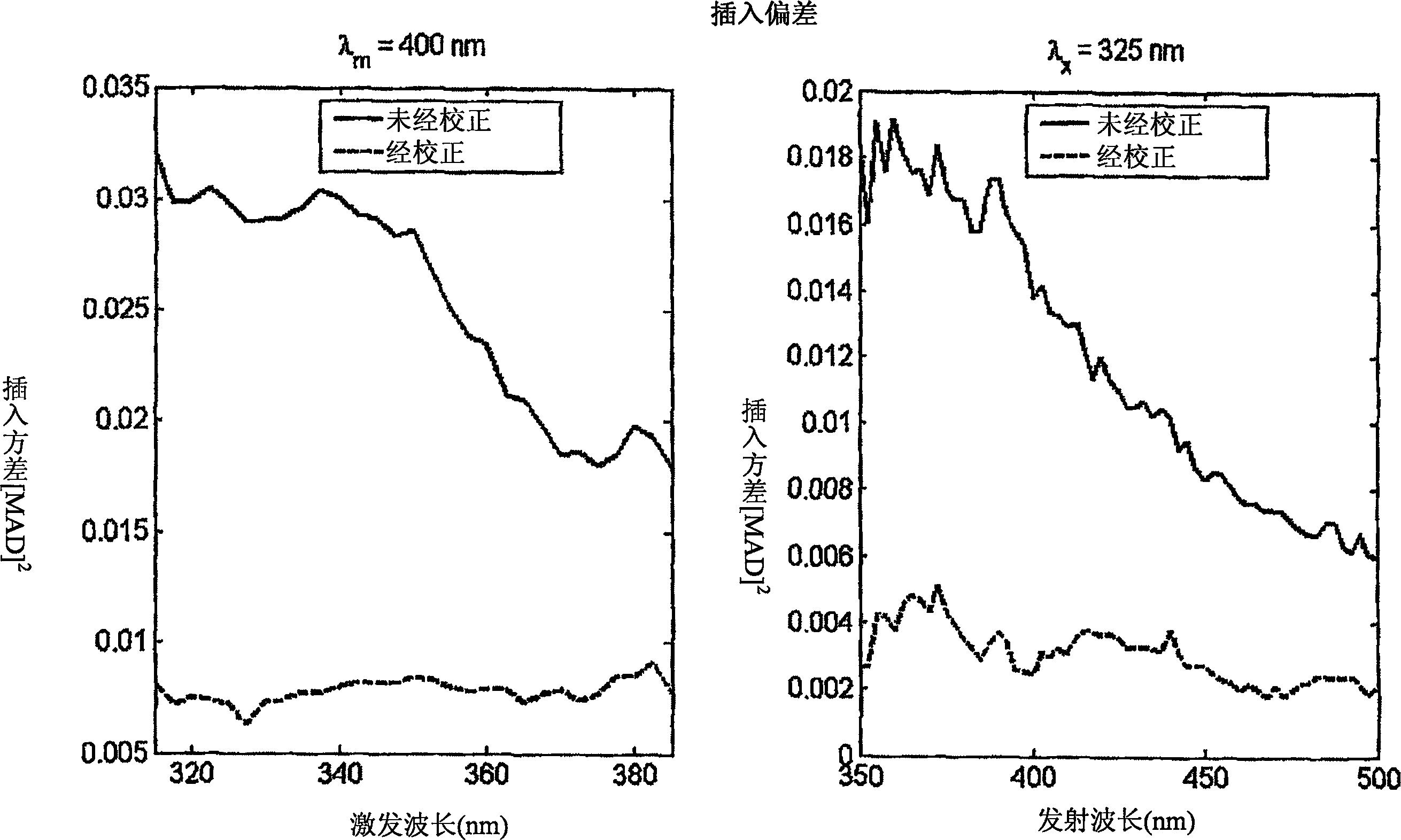
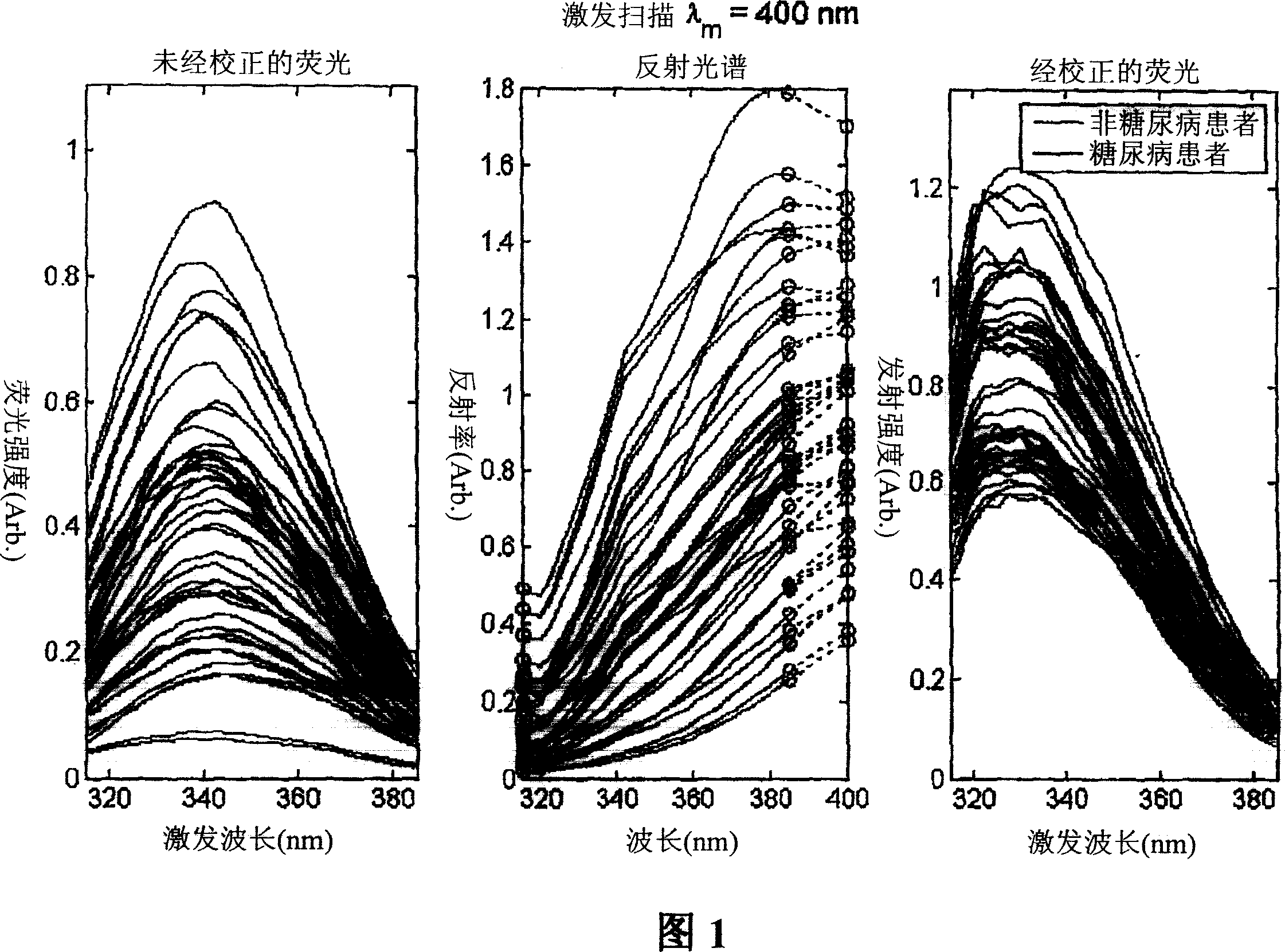
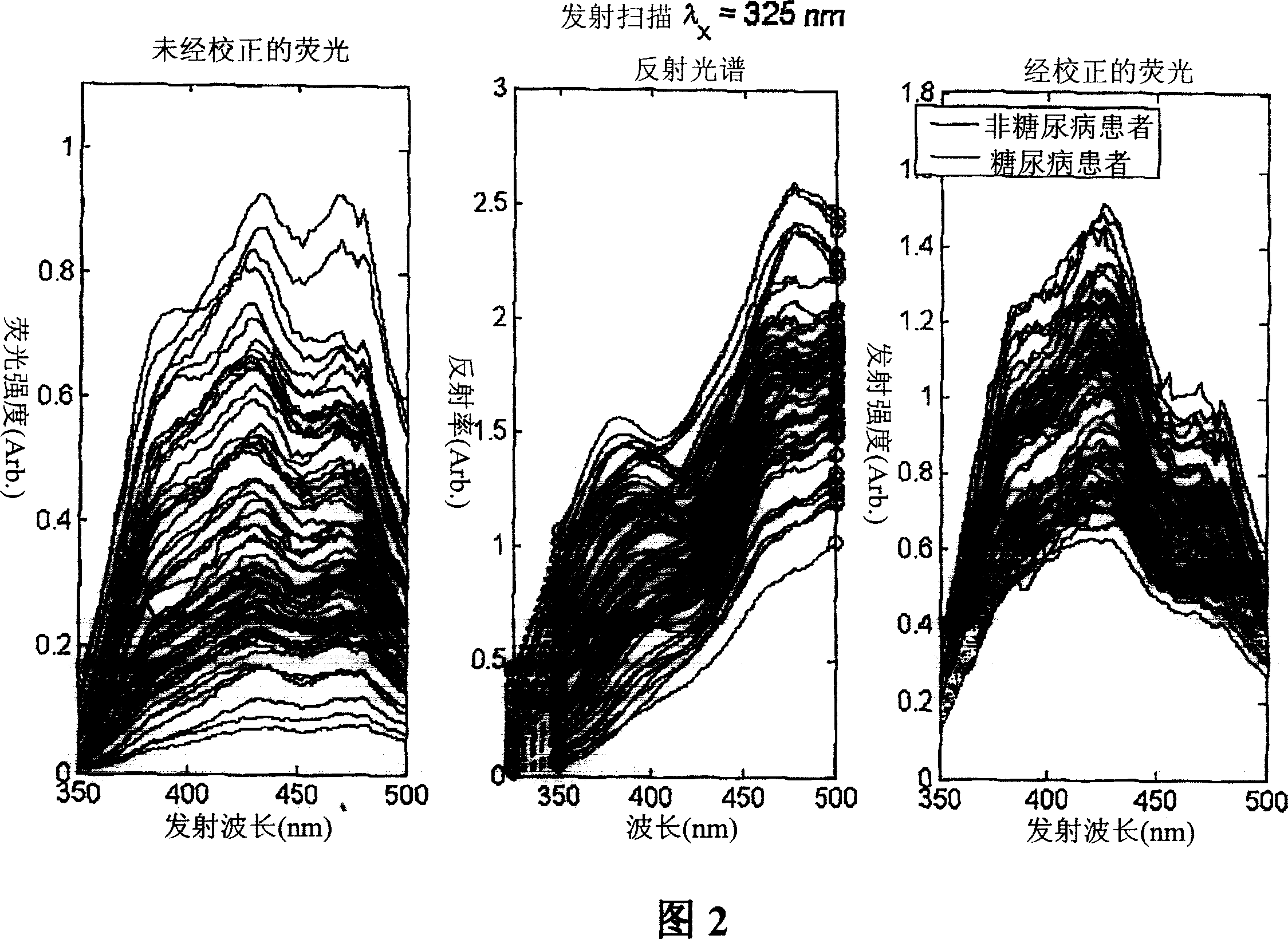
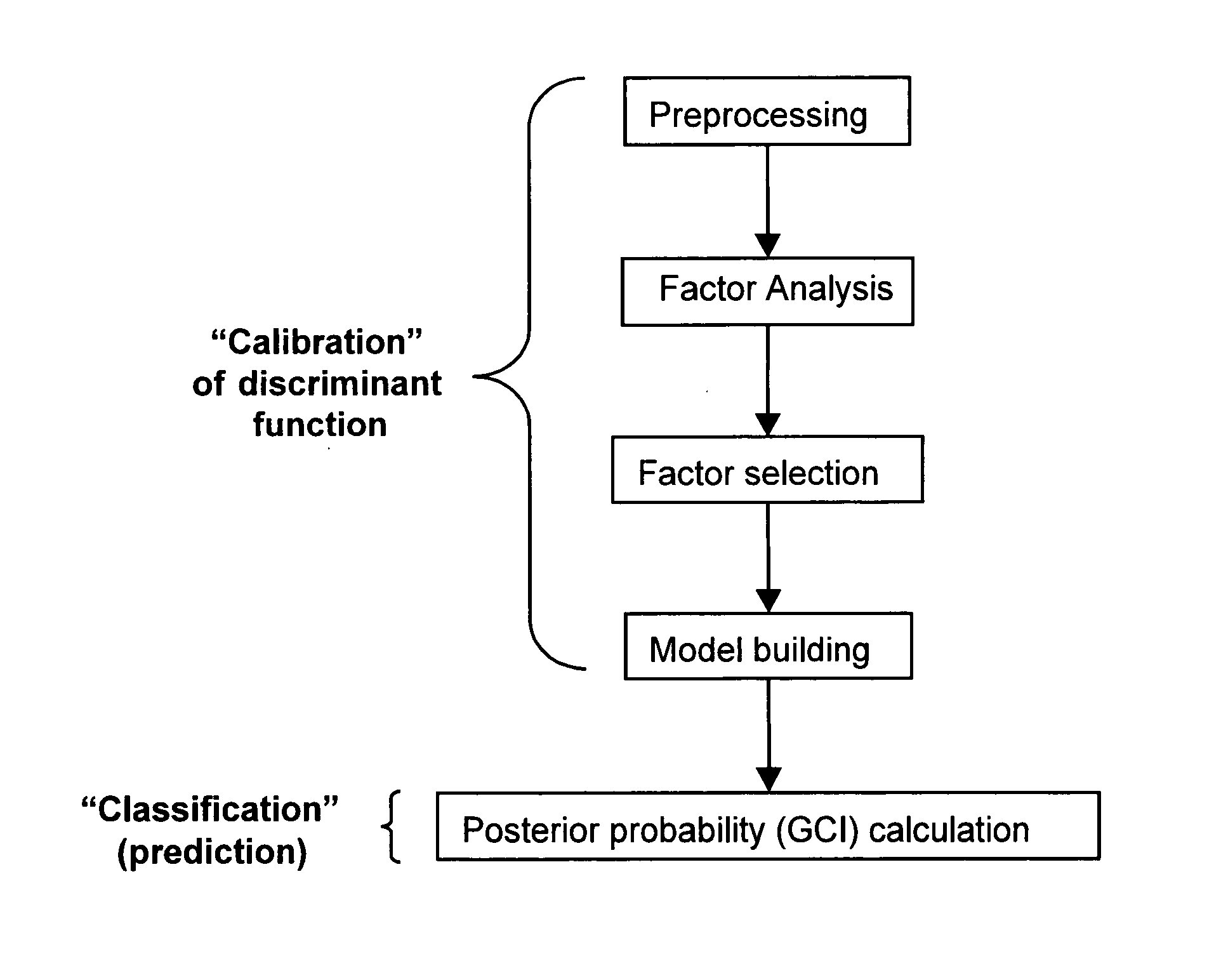
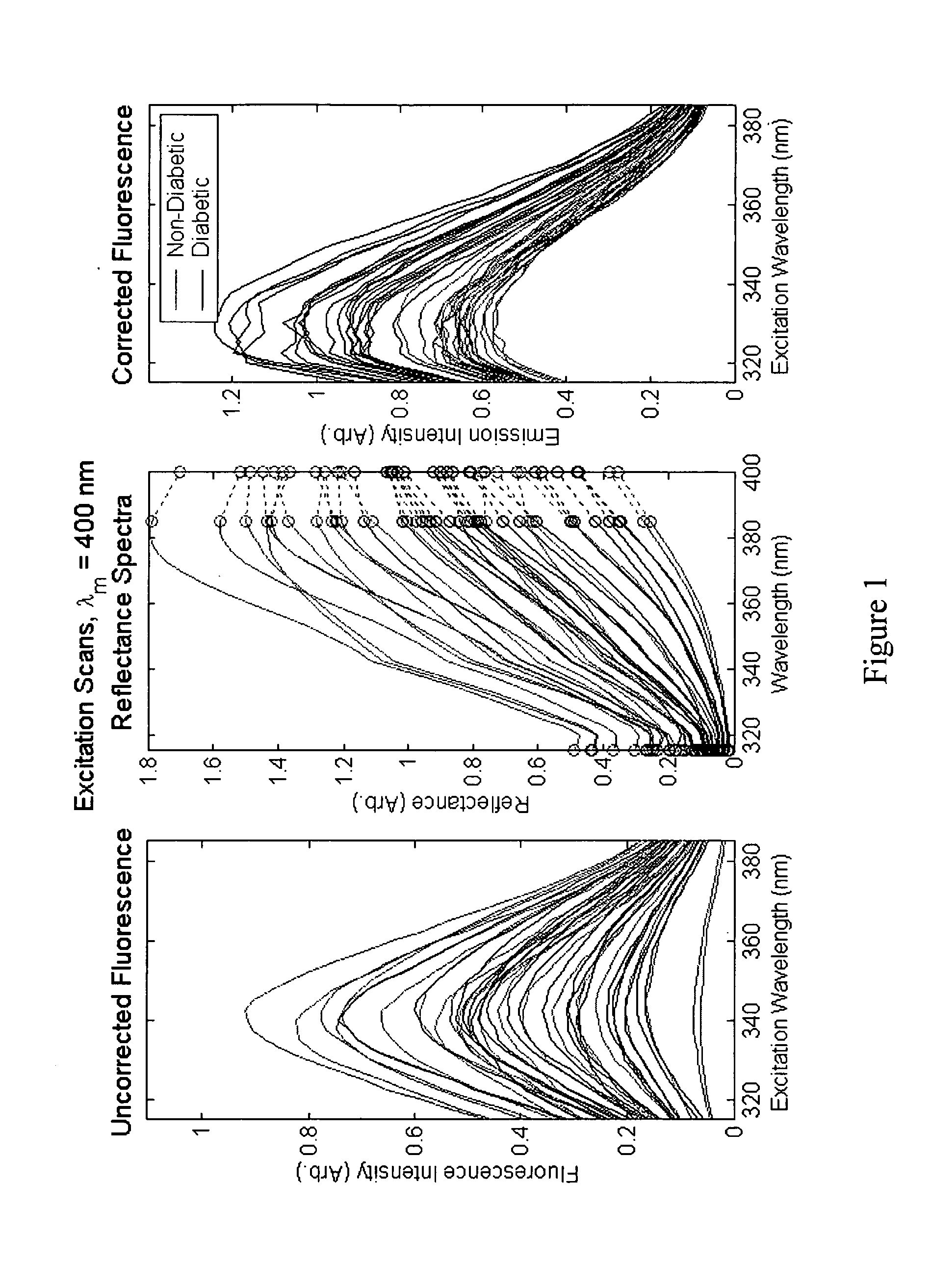
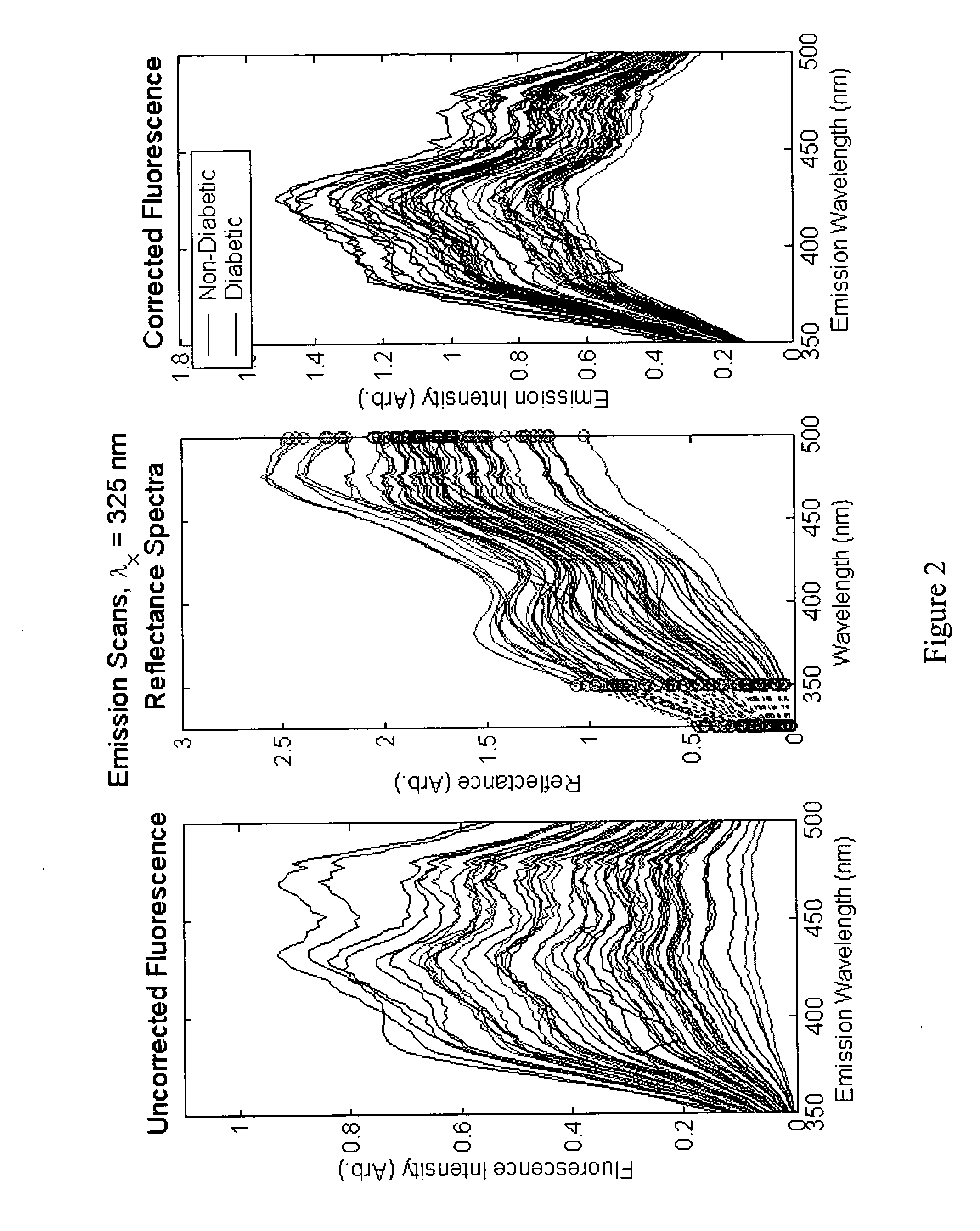
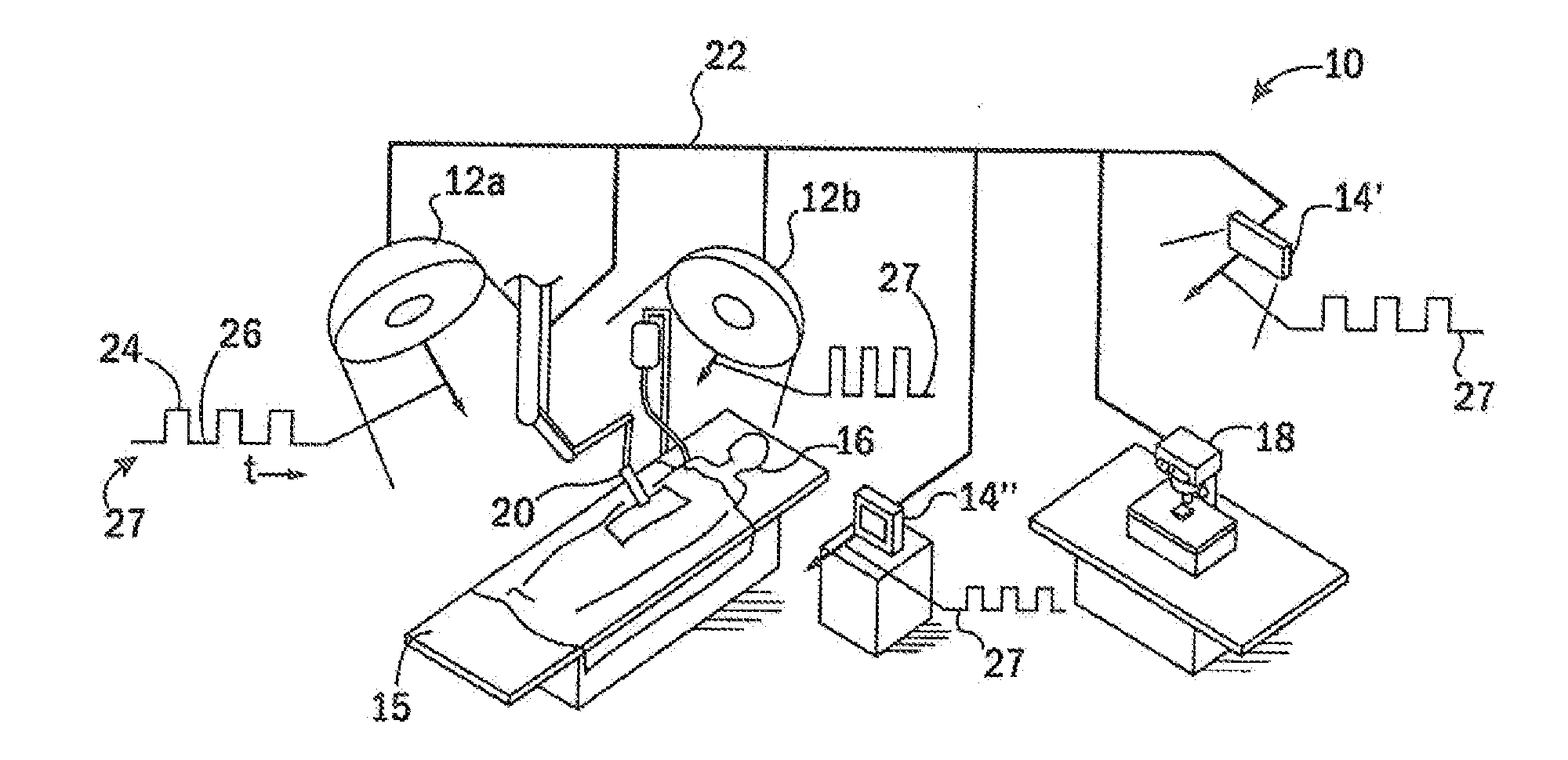
A method of determining a measure of a tissue state (e.g., glycation end-product or disease state) in an individual. A portion of the tissue of the individual is illuminated with excitation light, then light emitted by the tissue due to fluorescence of a chemical with the tissue responsive to the excitation light is detected. The detected light can be combined with a model relating fluorescence with a measure of tissue state to determine a tissue state. The invention can comprise single wavelength excitation light, scanning of excitation light (illuminating the tissue at a plurality of wavelengths), detection at a single wavelength, scanning of detection wavelengths (detecting emitted light at a plurality of wavelengths), and combinations thereof. The invention also can comprise correction techniques that reduce determination errors due to detection of light other than that from fluorescence of a chemical in the tissue. For example, the reflectance of the tissue can lead to errors if appropriate correction is not employed. The invention can also comprise a variety of models relating fluorescence to a measure of tissue state, including a variety of methods for generating such models. Other biologic information can be used in combination with the fluorescence properties to aid in the determination of a measure of tissue state. The invention also comprises apparatuses suitable for carrying out the method, including appropriate light sources, detectors, and models (for example, implemented on computers) used to relate detected fluorescence and a measure of tissue state.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
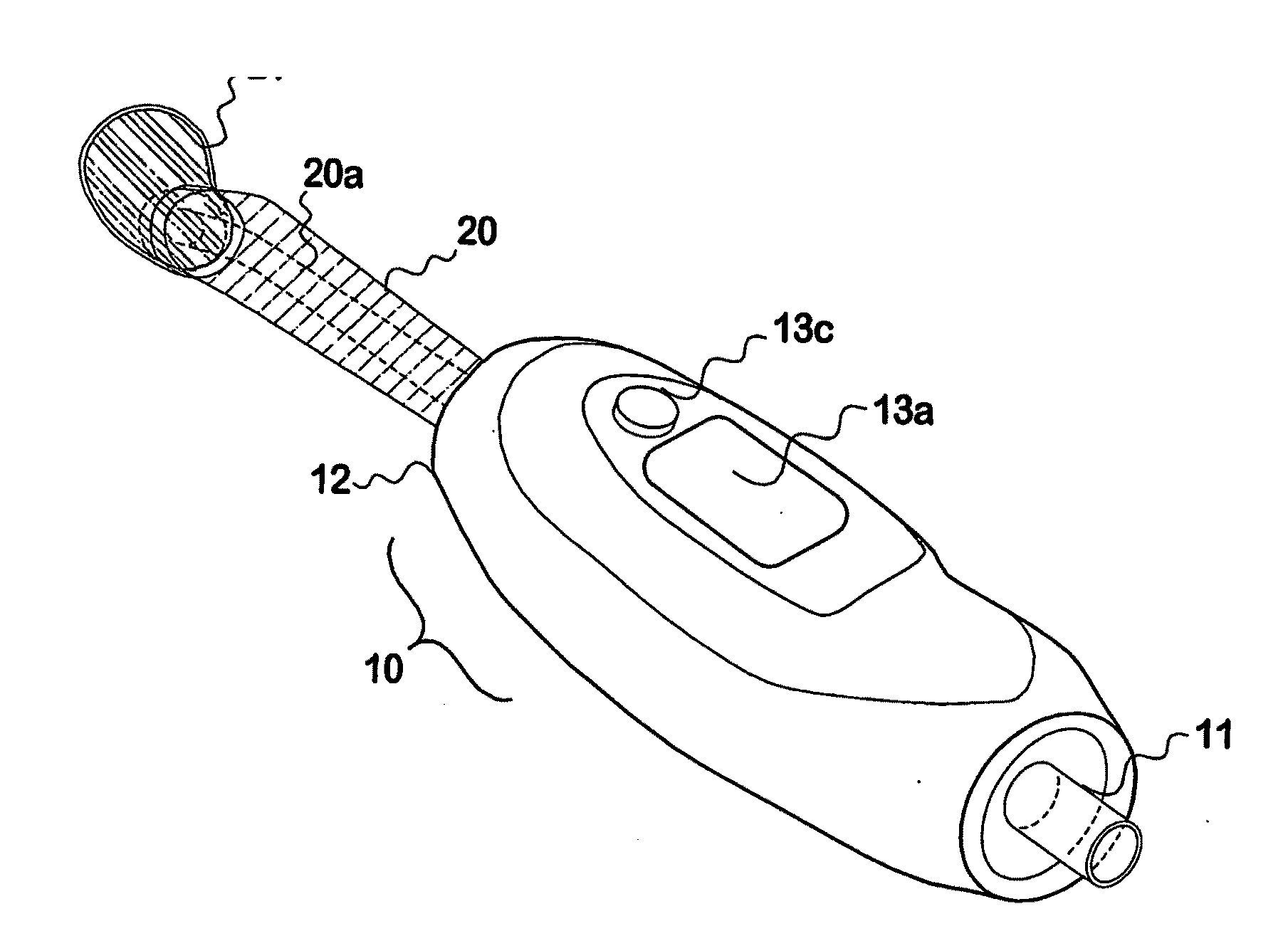
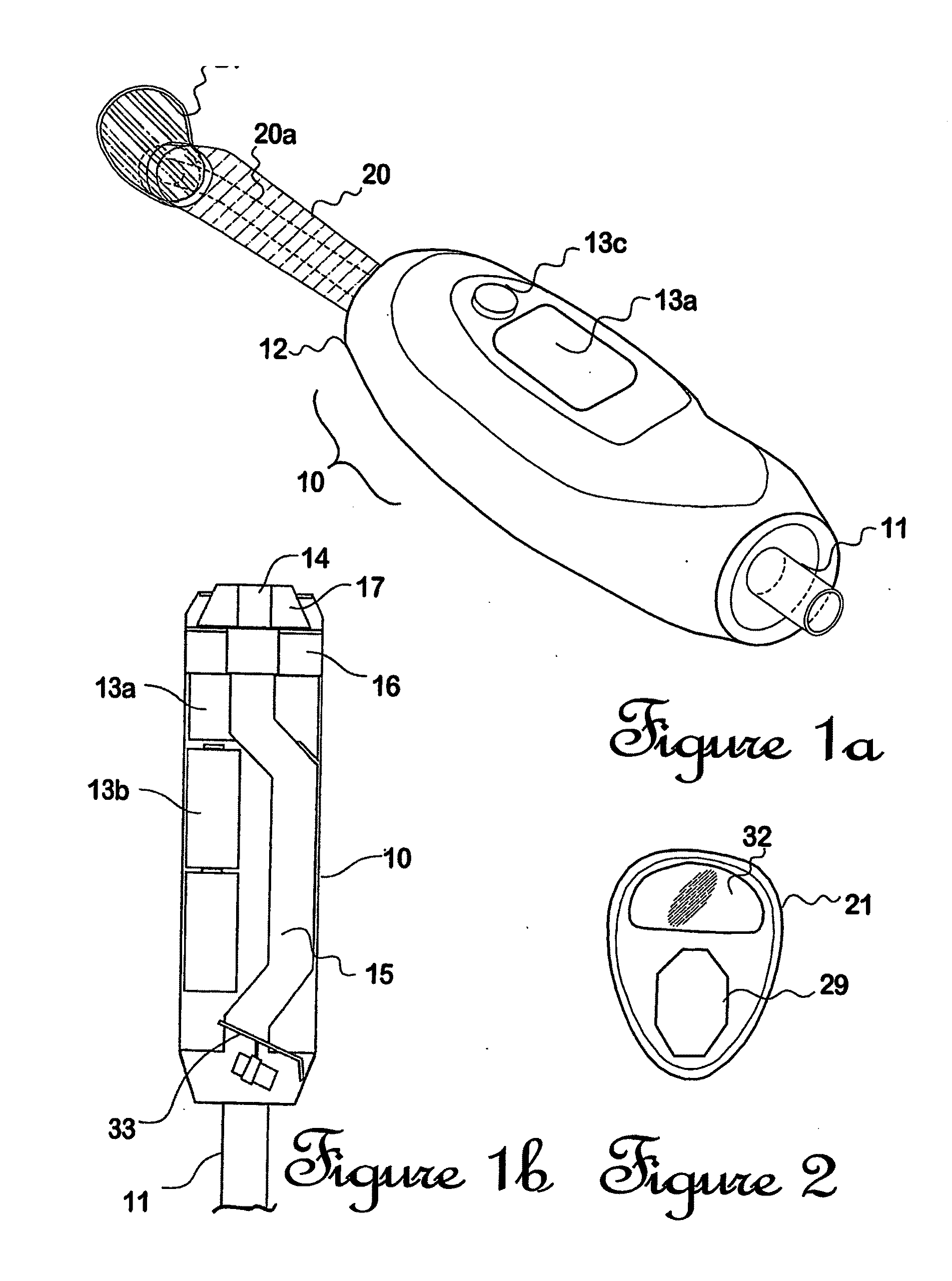
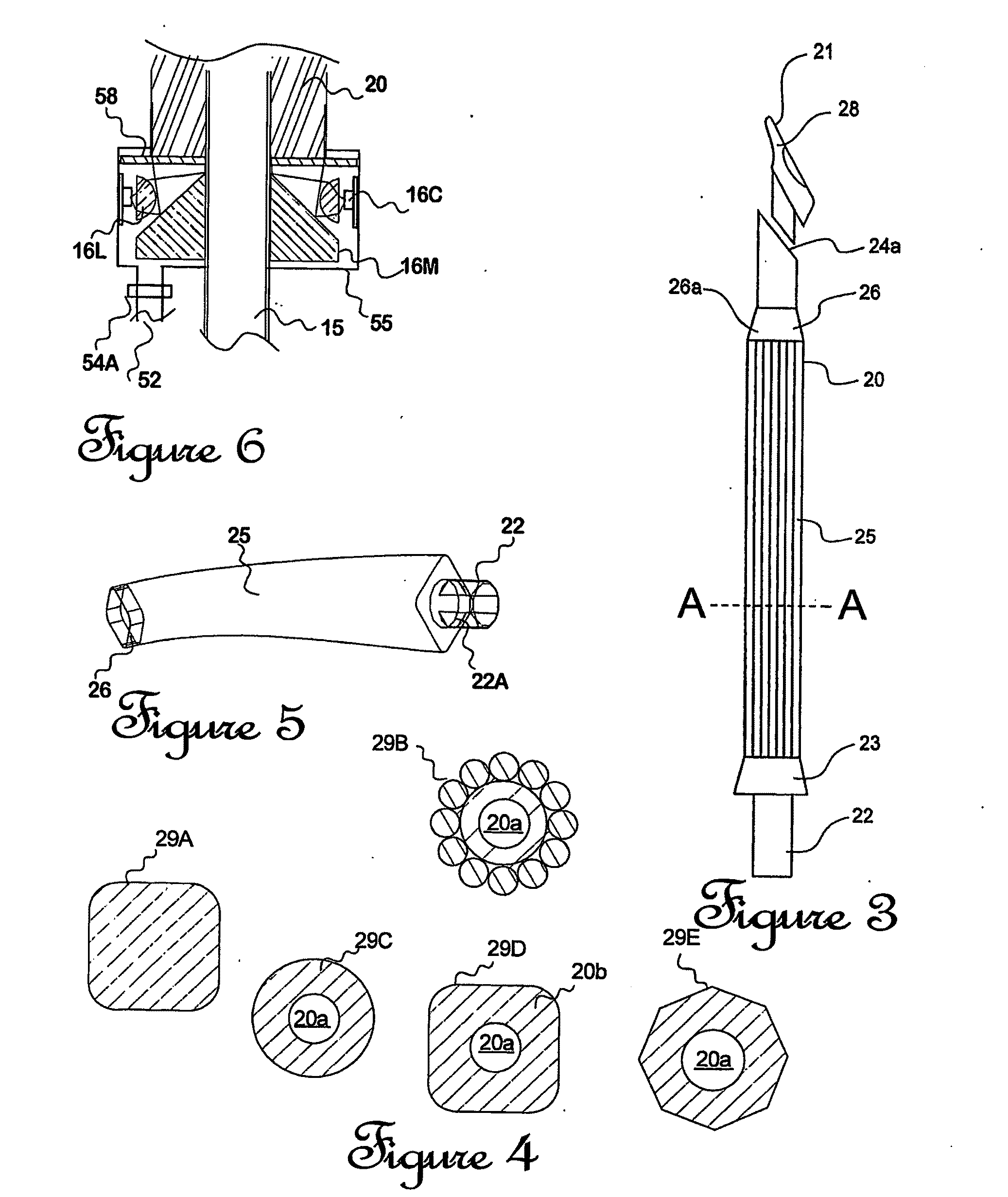
Combination dental hand tool
A hand-held self-powered combination dental tool is capable of performing multiple concurrent functions including suction, retraction, and intra-oral lighting so that dental treatment can be carried out easily under good lighting. (A suction connection is required). Another lighting mode (blue to ultraviolet) also allows inspection of the oral cavity for lesions such as hyperplasia or neoplasia using local changes in tissue fluorescence as an indicator. Internal batteries are rechargeable. Measurements of tissue fluorescence can be made and reported using internal detection and digital measurement.
Owner:PAZ MONY
Method and Apparatus to Compensate for Melanin and Hemoglobin Variation in Determination of a Measure of a Glycation End-Product or Disease State Using Tissue Fluorescence
InactiveUS20080103373A1Improve accuracyImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionCardiac cycleTissue fluorescence
A method of determining a measure of a tissue state (e.g., glycation end-product or disease state) in an individual is disclosed. A portion of the skin of the individual is illuminated with excitation light, then light emitted by the tissue due to fluorescence of a chemical with the tissue responsive to the excitation light is detected. The detected light can be combined with a model relating fluorescence with a measure of tissue state to determine a tissue state. The invention can illuminate the skin and detect responsive light over a time that spans a plurality of cardiac cycles of the individual, which can, as an example, help mitigate the effects of time-varying signals such as those due to hemoglobin. The invention can also determine the amount of light to be directed to the skin, for example by controlling the time that a light source is energized. The amount of illumination light can be determined from a skin reflectance characteristic such as pigmentation or melanin in the skin. Controlling the amount of light directed to the tissue can reduce the dynamic range required of a corresponding optical system, for example by allowing a single system to accurately measure individuals with very light skin and individuals with very dark skin.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Determination of a Measure of a Glycation End-Product or Disease State Using Tissue Fluorescence Lifetime
InactiveUS20080097174A1Diagnostics using lightMaterial analysis by optical meansTime domainTissue fluorescence
A method of determining a measure of a tissue state (e.g., glycation end-product or disease state) in an individual. A portion of the tissue of the individual is illuminated with excitation light, then light emitted by the tissue due to fluorescence of a chemical with the tissue responsive to the excitation light is detected. The detected light can be combined with a model relating fluorescence with a measure of tissue state to determine a tissue state. The invention can comprise measuring the fluorescence lifetime in either time-domain or frequency domain modes. The invention can also comprise a variety of models relating fluorescence to a measure of tissue state, including a variety of methods for generating such models. For example, multivariate models can be developed that relate lifetime trends of one or more constituents to increasing propensity to diabetes and pre-diabetes. Other biologic information can be used in combination with the fluorescence properties to aid in the determination of a measure of tissue state. The invention also comprises apparatuses suitable for carrying out the method, including appropriate light sources, detectors, and models (for example, implemented on computers) used to relate detected fluorescence and a measure of tissue state.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Determination of a measure of a glycation end-product or disease state using tissue fluorescence lifetime
InactiveUS8238993B2Diagnostics using lightMaterial analysis by optical meansTime domainTissue fluorescence
A method of determining a measure of a tissue state (e.g., glycation end-product or disease state) in an individual. A portion of the tissue of the individual is illuminated with excitation light, then light emitted by the tissue due to fluorescence of a chemical with the tissue responsive to the excitation light is detected. The detected light can be combined with a model relating fluorescence with a measure of tissue state to determine a tissue state. The invention can comprise measuring the fluorescence lifetime in either time-domain or frequency domain modes. The invention can also comprise a variety of models relating fluorescence to a measure of tissue state, including a variety of methods for generating such models. For example, multivariate models can be developed that relate lifetime trends of one or more constituents to increasing propensity to diabetes and pre-diabetes. Other biologic information can be used in combination with the fluorescence properties to aid in the determination of a measure of tissue state. The invention also comprises apparatuses suitable for carrying out the method, including appropriate light sources, detectors, and models (for example, implemented on computers) used to relate detected fluorescence and a measure of tissue state.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Determination of a measure of a glycation end-product or disease state using a flexible probe to determine tissue fluorescence of various sites
Embodiments of the present invention provide an apparatus with a flexible probe suitable for determining properties of in vivo tissue from spectral information collected from various tissue sites. An illumination system provides light at a plurality of broadband ranges, which are communicated to a flexible optical probe. Light homogenizers and mode scramblers can be employed to improve the performance in some embodiments. The optical probe in some embodiments physically contacts the tissue, and in some embodiments does not physically contact the tissue. The optical probe receives light from the illumination system and transmits it to tissue, and receives light diffusely reflected in response to the broadband light, emitted from the in vivo tissue by fluorescence thereof in response to the broadband light, or a combination thereof. The optical probe can communicate the light to a spectrograph which produces a signal representative of the spectral properties of the light. An analysis system determines a property of the in vivo tissue from the spectral properties.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Determination of a measure of a glycation end-product or disease state using tissue fluorescence
InactiveCN1882278ADiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionDiseaseMedicine
A method of determining a measure of a tissue state (e.g., glycation end-product or disease state) in an individual. A portion of the tissue of the individual is illuminated with excitation light, then light emitted by the tissue due to fluorescence of a chemical with the tissue responsive to the excitation light is detected. The detected light can be combined with a model relating fluorescence with a measure of tissue state to determine a tissue state. The invention also can comprise correction techniques that reduce determination errors due to detection of light other than that from fluorescence of a chemical in the tissue (for example, the reflectance of the tissue). Other biologic information can be used in combination with the fluorescence properties to aid in the determination of a measure of tissue state.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Determination of a Measure of a Glycation End-Product or Disease State Using Tissue Fluorescence
InactiveUS20070276199A1Improve accuracyImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionSensorsTissue CollectionMedicine
Embodiments of the present invention provide an apparatus suitable for determining properties of in vivo tissue from spectral information collected from the tissue. An illumination system provides light at a plurality of broadband ranges, which are communicated to an optical probe. The optical probe receives light from the illumination system and transmits it to in vivo tissue and receives light diffusely reflected in response to the broadband light, emitted from the in vivo tissue by fluorescence thereof in response to the broadband light, or a combination thereof. The optical probe communicates the light to a spectrograph which produces a signal representative of the spectral properties of the light. An analysis system determines a property of the in vivo tissue from the spectral properties. A calibration device mounts such that it is periodically in optical communication with the optical probe.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Operator-controlled scanning laser procedure designed for large-area epithelium removal
ActiveUS20080287928A1Improve accuracyImprove efficacyLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsEpitheliumPulse beam
Systems and methods for removing an epithelial layer disposed over a stromal layer in a cornea irradiate a region of the epithelial layer with a pulsed beam of ablative radiation. The ablative radiation is scanned to vary the location of the beam within the region in accordance with a pulse sequence. The pulse sequence is arranged to enhance optical feedback based on a tissue fluorescence of the epithelial layer. The penetration of the epithelial layer is detected in response to the optical feedback. The use of scanning with the pulse sequence arranged to enhance optical feedback allows large areas of the epithelium to be ablated such penetration of the epithelial layer can be detected.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Determination of a measure of a glycation end-product or disease state using tissue fluorescence in combination with one or more other tests
InactiveUS20120078075A1Diagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionDiseaseMedicine
The present invention provides a method of determining disease state in an individual. A portion of the tissue of the individual is illuminated with excitation light, then light emitted by the tissue due to fluorescence of a chemical in the tissue responsive to the excitation light is detected. The HbA1c or FPG measurement of the individual (or other secondary indication of disease state) can also be determined. A model combining the tissue fluorescence and one or more of the secondary indications can be used to determine the disease state of the individual. In some embodiments, the tissue fluorescence can be used as an initial screen, and the combination with secondary indications only made for those individuals for whom the fluorescence screen indicates an increased likelihood of disease.
Owner:MAYNARD JOHN D +1
Determination of a measure of a glycation end-product or disease state using tissue fluorescence of various sites
InactiveUS8131332B2Diagnostics using fluorescence emissionSurgical instrument detailsMedicineTissue fluorescence
Embodiments of the present invention provide an apparatus suitable for determining properties of in vivo tissue from spectral information collected from various tissue sites. An illumination system provides light at a plurality of broadband ranges, which are communicated to an optical probe. The optical probe can be a flexible probe in some embodiments, allowing ease of application. Light homogenizers and mode scramblers can be employed to improve the performance in some embodiments. The optical probe in some embodiments physically contacts the tissue, and in some embodiments does not physically contact the tissue. The optical probe receives light from the illumination system and transmits it to tissue, and receives light diffusely reflected in response to the broadband light, emitted from the in vivo tissue by fluorescence thereof in response to the broadband light, or a combination thereof. The optical probe can communicate the light to a spectrograph which produces a signal representative of the spectral properties of the light. An analysis system determines a property of the in vivo tissue from the spectral properties.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Determination of a measure of a glycation end-product or disease state using tissue fluorescence
InactiveCN100998499ADiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionDiseaseMedicine
A method of determining a measure of a tissue state (e.g., glycation end-product or disease state) in an individual is disclosed. A portion of the individual's tissue is illuminated with excitation light from a light source subsystem (A) and light emitted by the tissue due to fluorescence of a chemical within the tissue responsive to the excitation light is detected by a detection subsystem (C). The detected light can be combined with a model stores in the signal processor (D), which relates fluorescence with a measure of tissue state to determine a tissue state. Correction techniques can be used to reduce errors due to the detection of non-fluorescent light, such as the reflectance of the tissue. Other biologic information can also be sued in combination with the fluorescence properties to aid in the determination of a measure of tissue state.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Method and apparatus to compensate for melanin and hemoglobin variation in determination of a measure of a glycation end-product or disease state using tissue fluorescence
InactiveUS8676283B2Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionDiseaseCardiac cycle
A method of determining a measure of a tissue state (e.g., glycation end-product or disease state) in an individual is disclosed. A portion of the skin of the individual is illuminated with excitation light, then light emitted by the tissue due to fluorescence of a chemical with the tissue responsive to the excitation light is detected. The detected light can be combined with a model relating fluorescence with a measure of tissue state to determine a tissue state. The invention can illuminate the skin and detect responsive light over a time that spans a plurality of cardiac cycles of the individual, which can, as an example, help mitigate the effects of time-varying signals such as those due to hemoglobin. The invention can also determine the amount of light to be directed to the skin, for example by controlling the time that a light source is energized. The amount of illumination light can be determined from a skin reflectance characteristic such as pigmentation or melanin in the skin. Controlling the amount of light directed to the tissue can reduce the dynamic range required of a corresponding optical system, for example by allowing a single system to accurately measure individuals with very light skin and individuals with very dark skin.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Determination of a measure of a glycation end-product or disease state using tissue fluorescence preferentially from the dermis
InactiveUS20060211928A1Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyTissue fluorescenceMulti method
A method of determining a measure of a tissue state (e.g., glycation end-product or disease state) in an individual. A portion of the tissue of the individual is illuminated with excitation light, then light emitted by the tissue due to fluorescence of a chemical with the tissue responsive to the excitation light is detected. The detected light can be combined with a model relating fluorescence with a measure of tissue state to determine a tissue state. The invention can comprise single wavelength excitation light, scanning of excitation light (illuminating the tissue at a plurality of wavelengths), detection at a single wavelength, scanning of detection wavelengths (detecting emitted light at a plurality of wavelengths), and combinations thereof. The invention also can comprise correction techniques that reduce determination errors due to detection of light other than that from fluorescence of a chemical in the tissue. For example, the reflectance of the tissue can lead to errors if appropriate correction is not employed. The invention can also comprise a variety of models relating fluorescence to a measure of tissue state, including a variety of methods for generating such models. Other biologic information can be used in combination with the fluorescence properties to aid in the determination of a measure of tissue state. The invention also comprises apparatuses suitable for carrying out the method, including appropriate light sources, detectors, and models (for example, implemented on computers) used to relate detected fluorescence and a measure of tissue state.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
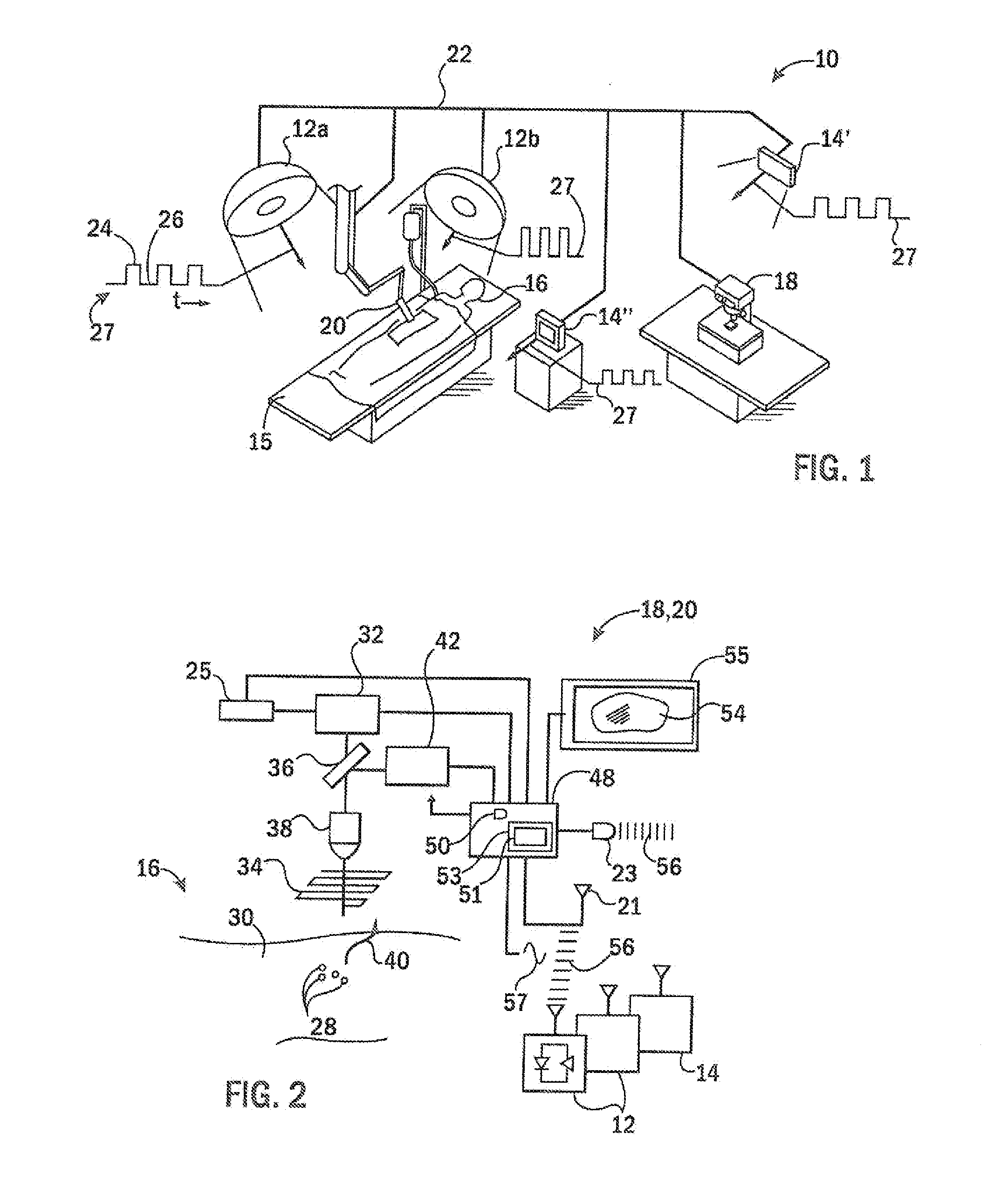
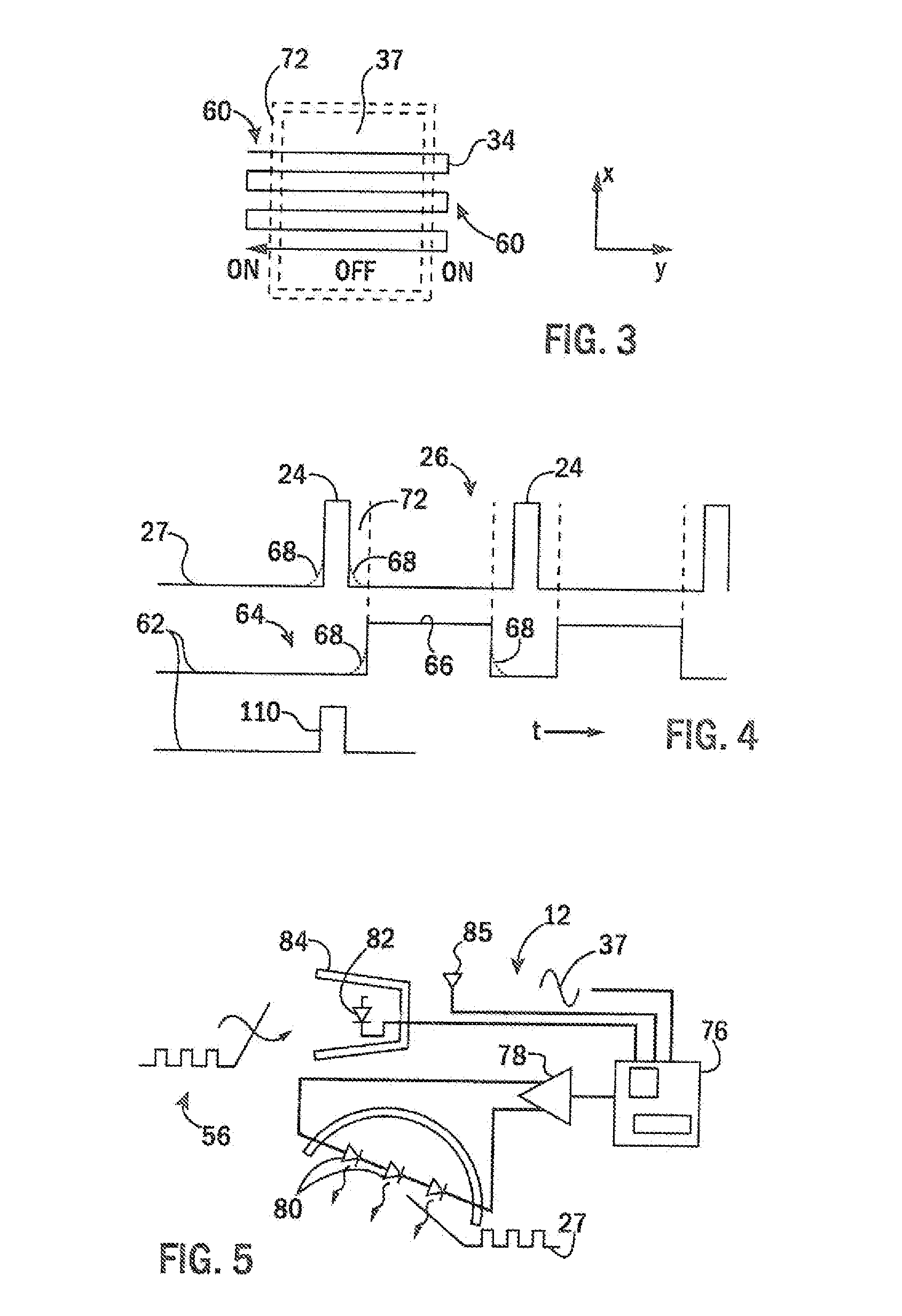
Tissue Fluorescence Monitor With Ambient Light Rejection
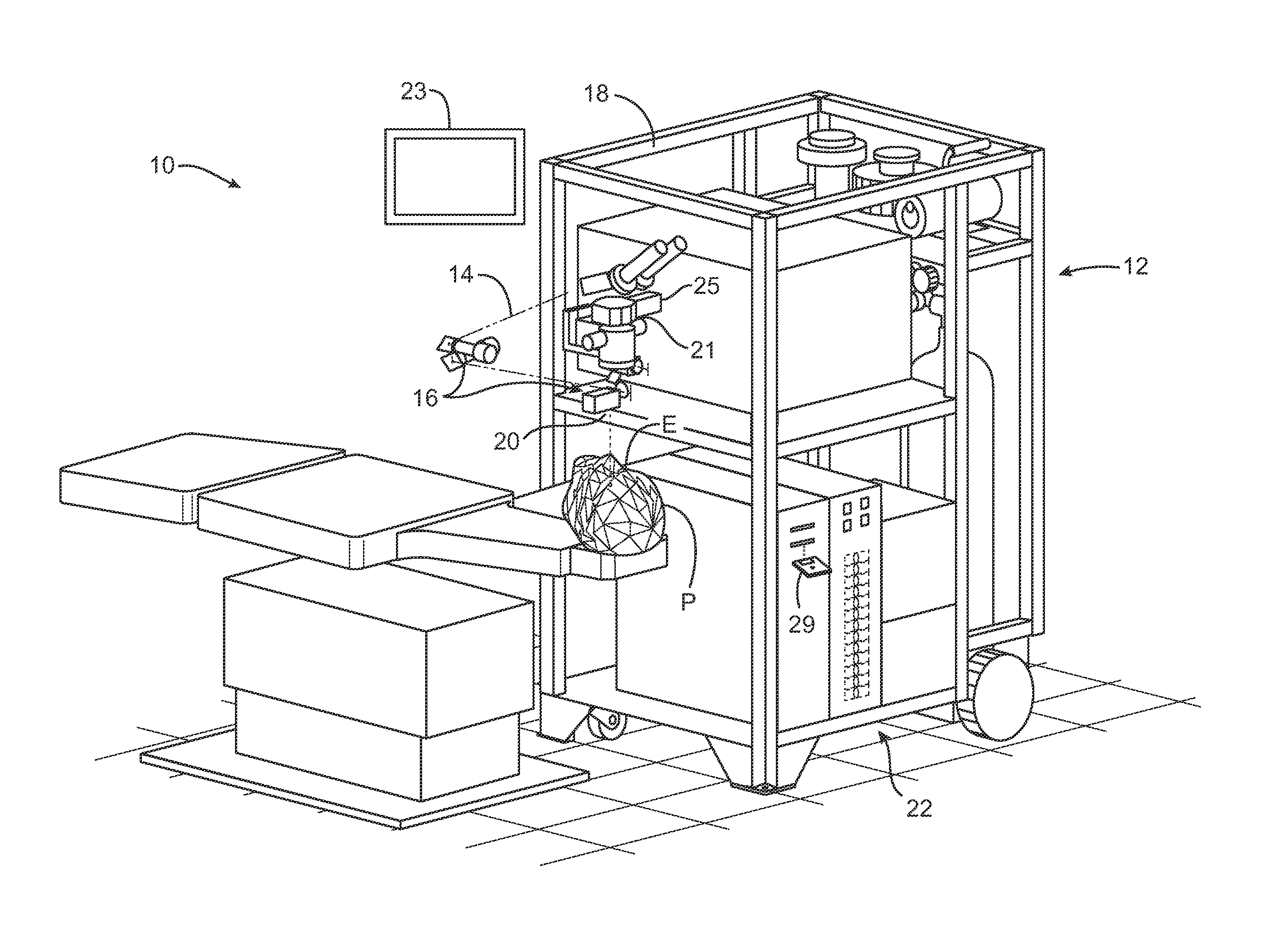
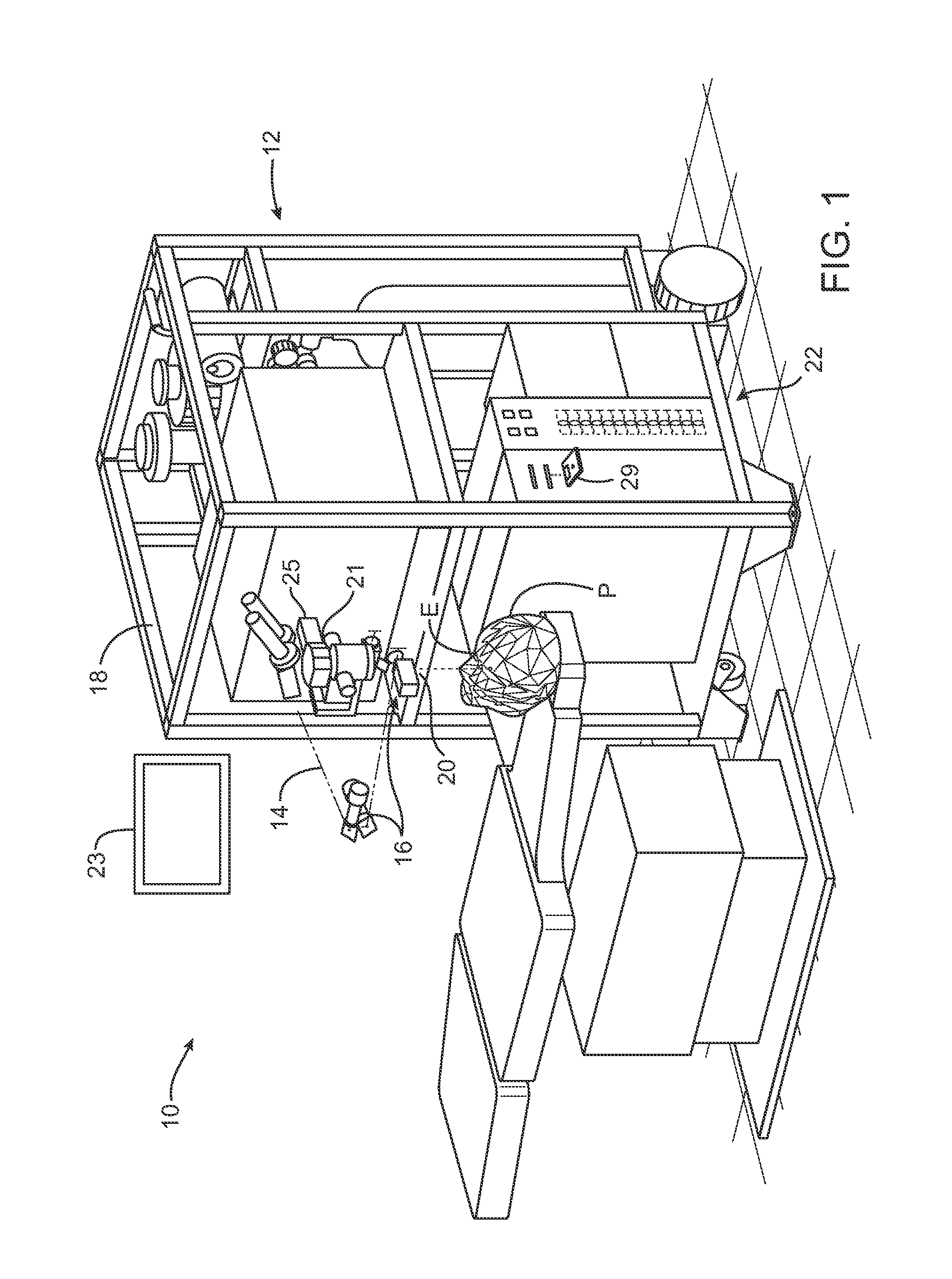
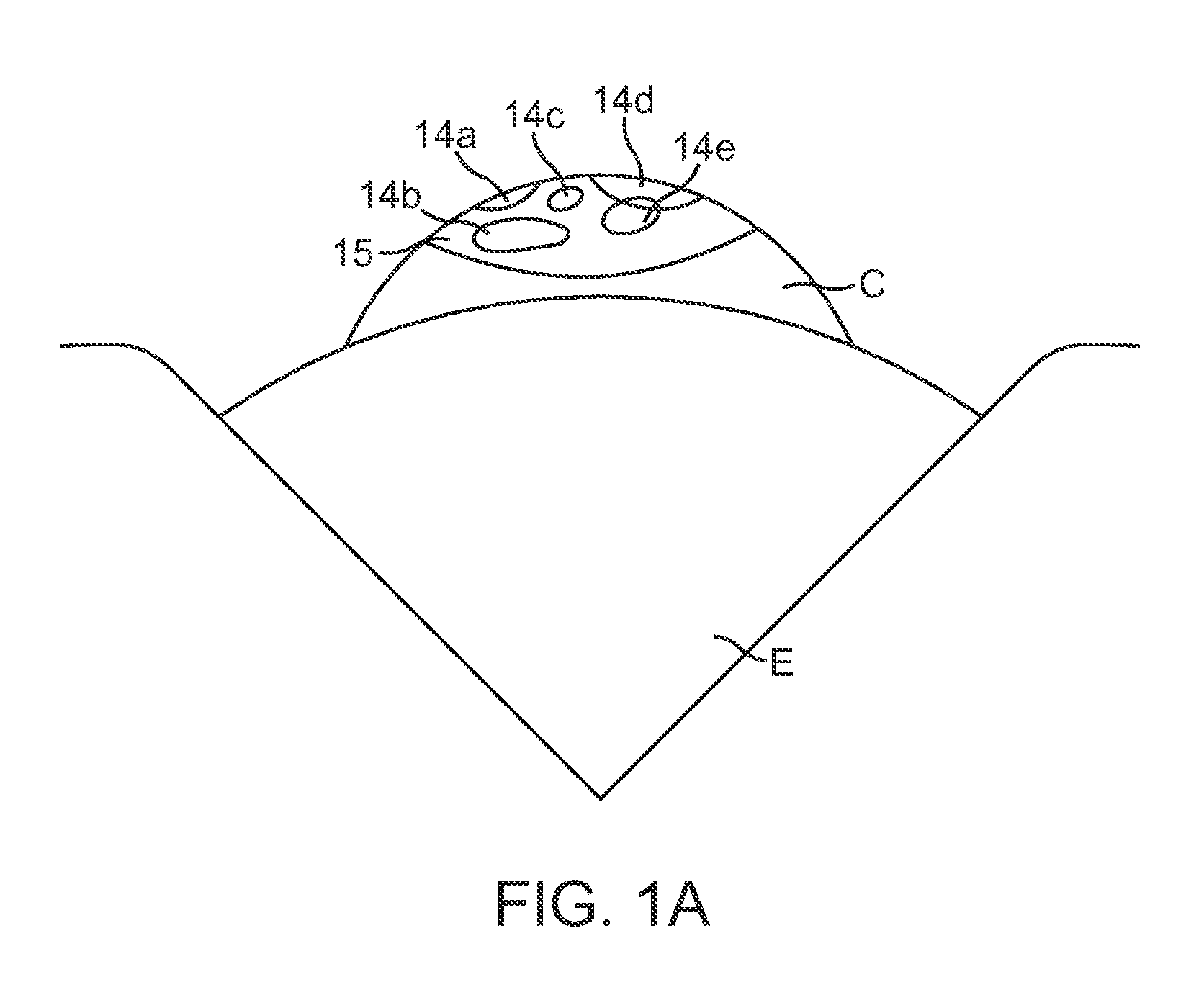
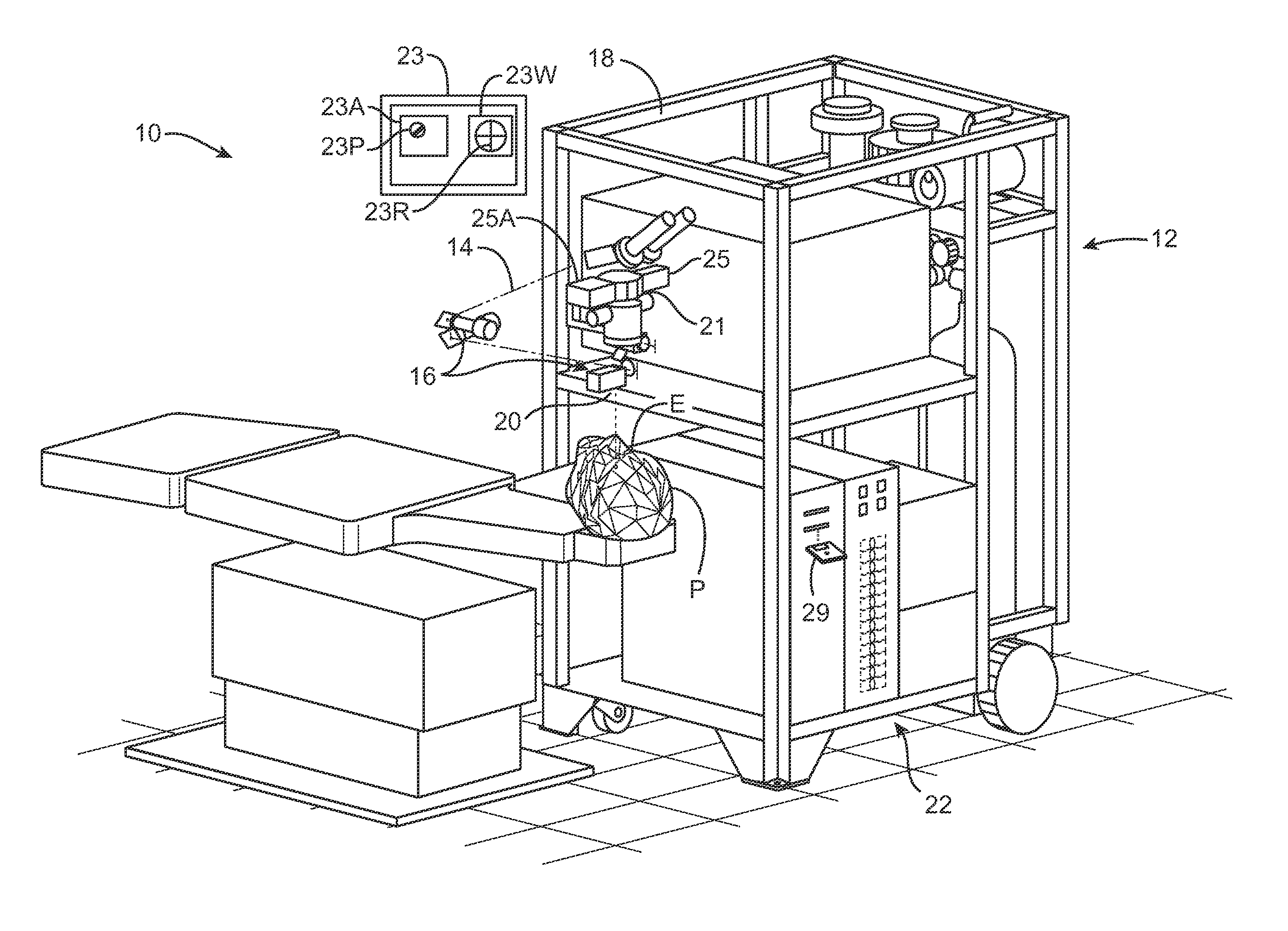
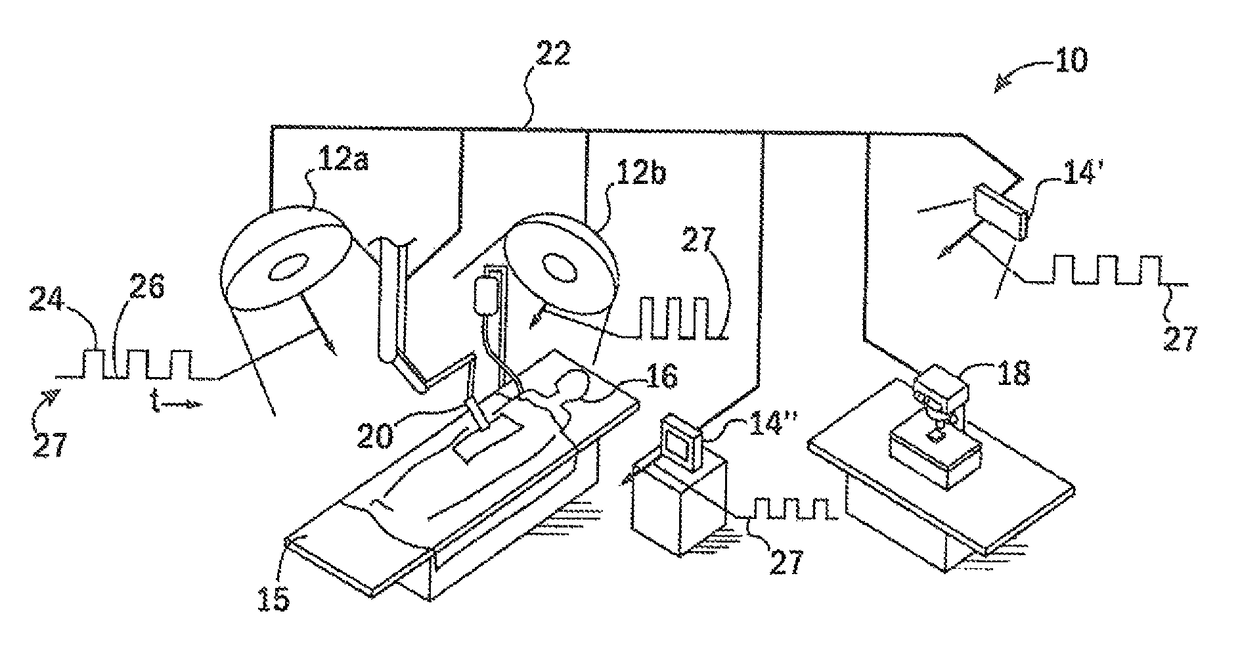
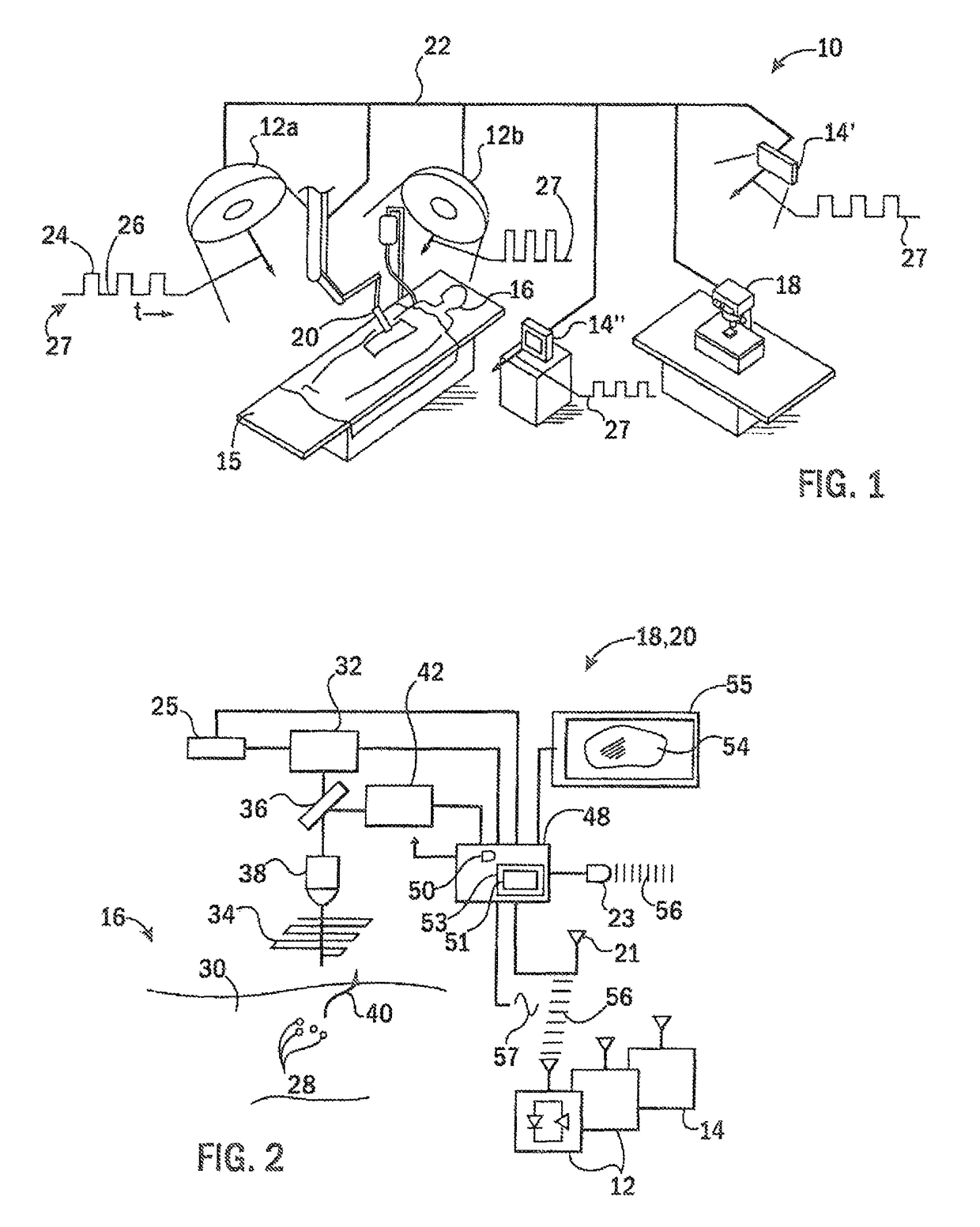
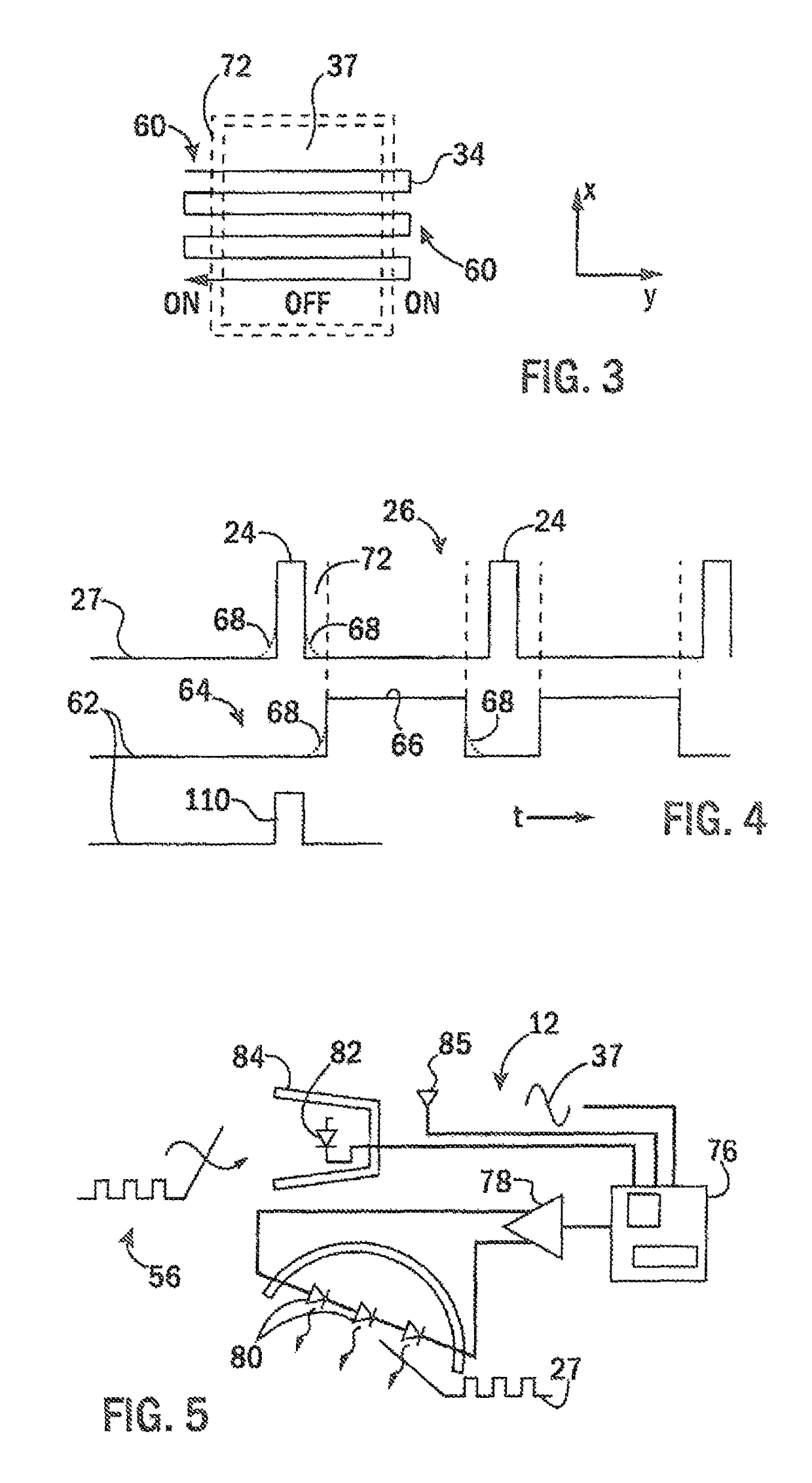
ActiveUS20150025391A1Minimal loss of capture timeRaman/scattering spectroscopySurgeryAmbient lightingTissue fluorescence
Fluorescent markers used to identify a tissue may be imaged in a bright environment by synchronizing the imaging process with rapidly switched ambient lighting so that imaging occurs in phase with a switching off of the ambient lighting. In this way, valuable fluorescent imaging may be performed in an environment that appears to be brightly illuminated, for example in the area of a surgical suite.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
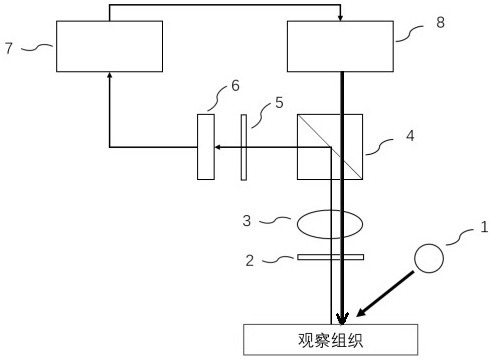
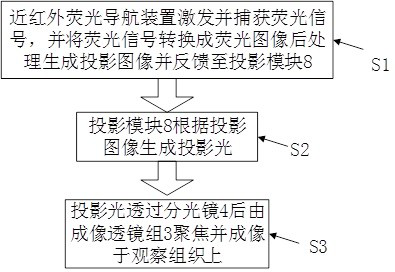
Augmented reality near-infrared fluorescence navigation system and method
PendingCN111616799ASolve the display effectResolve locationSurgical navigation systemsPicture reproducers using projection devicesBeam splitterTissue fluorescence
The invention discloses an augmented reality near-infrared fluorescence navigation system and method. The system comprises a near-infrared fluorescence navigation device, which is used for exciting and capturing a fluorescence signal, converting the fluorescence signal into a fluorescence image, and processing the fluorescence image and then generating a projection image, and comprises an excitation light source, an optical filter group, an imaging lens group and a spectroscope; and a projection module, used for receiving the generated projection image and generating projection light accordingto the projection image, wherein the generated projection light passes through the spectroscope, and is imaged on an observation tissue after being focused by the imaging lens group. Through the projection technology, invisible near-infrared fluorescence is visualized, the reality enhancement effect is achieved, and the problem that traditional intraoperative navigation equipment needs to repeatedly observe a display image and check the position of an actual biological tissue fluorescence signal is solved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPTO MEDIC TECH CO LTD
Method and Apparatus for Determination of a Measure of a Glycation End-Product or Disease State Using Tissue Fluorescence
InactiveUS20110313296A9Diagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionTissue CollectionMedicine
Embodiments of the present invention provide an apparatus suitable for determining properties of in vivo tissue from spectral information collected from the tissue. An illumination system provides light at a plurality of broadband ranges, which are communicated to an optical probe. The optical probe receives light from the illumination system and transmits it to in vivo tissue, and receives light diffusely reflected in response to the broadband light, emitted from the in vivo tissue by fluorescence thereof in response to the broadband light, or a combination thereof. The optical probe communicates the light to a spectrograph which produces a signal representative of the spectral properties of the light. An analysis system determines a property of the in vivo tissue from the spectral properties. A calibration device mounts such that it is periodically in optical communication with the optical probe.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
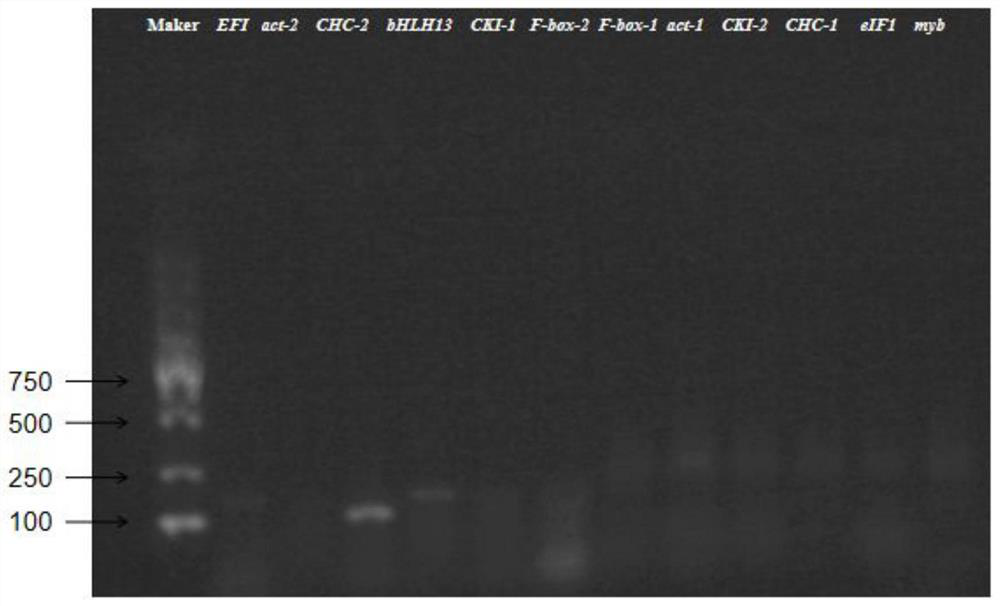
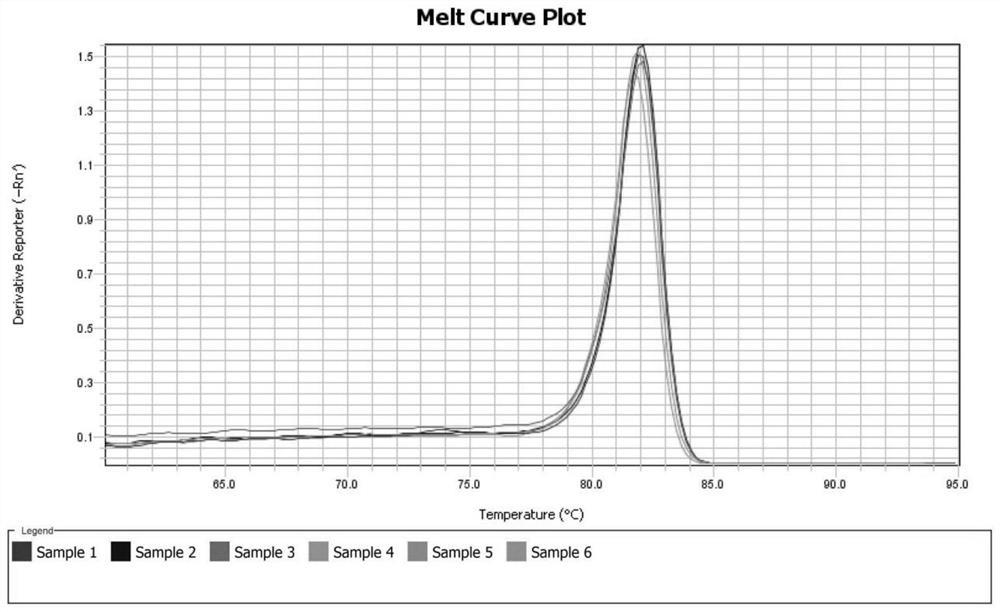
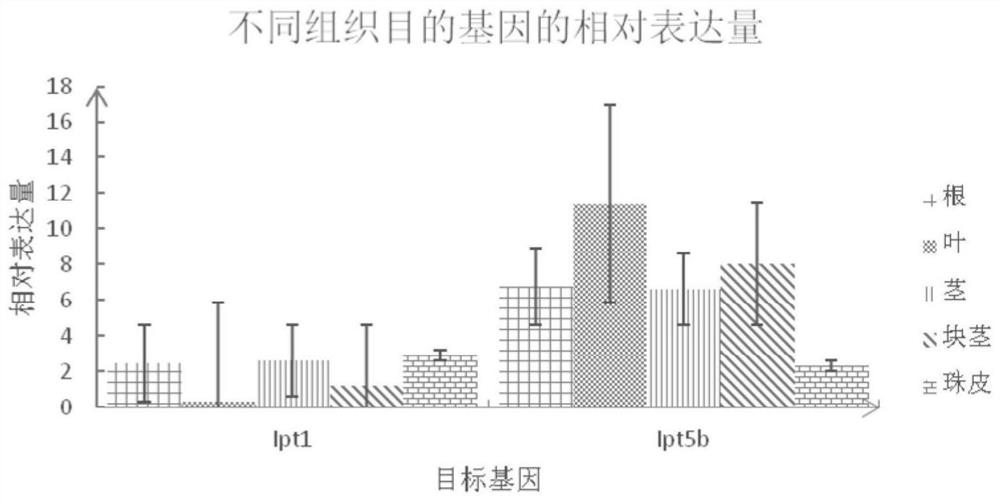
Reference gene for fluorescence quantification of different tissues of Chinese yam and primers and application thereof
ActiveCN112575010AMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesCandidate Gene Association StudyTissue fluorescence
The invention relates to a reference gene for fluorescence quantification of different tissues of Chinese yam and primers and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology of Chinese yam. The nucleotide sequence of the reference gene CKI-2 is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The nucleotide sequence of a PCR amplification primer of the reference gene CKI-2 is as follows: anupstream primer is shown as SEQ ID NO.2; and the downstream primer is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3. Protein kinase I, myb, F-box, actin gene, EF1, bHLH13, eIF1, grid heavy chain protein and other genes are selected as candidate genes of different tissues. The stability of candidate genes is evaluated through qRT-PCR in combination with RefFind, reference genes stably expressed in different tissues ofthe Chinese yams are selected out through screening, and a reference basis is provided for later development of research work such as gene function verification of growth and development and metabolicmechanisms of the Chinese yams.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Operator-Controlled Scanning Laser Procedure Designed for Large-Area Epithelium Removal
Systems and methods for removing an epithelial layer disposed over a stromal layer in a cornea irradiate a region of the epithelial layer with a pulsed beam of ablative radiation. The ablative radiation is scanned to vary the location of the beam within the region in accordance with a pulse sequence. The pulse sequence is arranged to enhance optical feedback based on a tissue fluorescence of the epithelial layer. The penetration of the epithelial layer is detected in response to the optical feedback. The use of scanning with the pulse sequence arranged to enhance optical feedback allows large areas of the epithelium to be ablated such that an operator can detect penetration of the epithelial layer.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Determination of a Measure of a Glycation End-Product or Disease State Using Tissue Fluorescence of Various Sites
InactiveUS20120179010A1Diagnostics using fluorescence emissionSensorsTissue fluorescenceSpectrograph
Embodiments of the present invention provide an apparatus suitable for determining properties of in vivo tissue. An illumination system communicates light at a plurality of broadband ranges to an optical probe, which can comprise a flexible probe. Light homogenizers and mode scramblers can be employed in some embodiments. The optical probe can physically contact the tissue, or can be maintained separate from the tissue. The optical probe receives light from the illumination system and transmits it to tissue, and receives light diffusely reflected in response to the broadband light, emitted from the in vivo tissue by fluorescence thereof in response to the broadband light, or a combination thereof. The optical probe can communicate the light to a spectrograph which produces a signal representative of the spectral properties of the light. An analysis system determines a property of the in vivo tissue from the spectral properties.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Fluorescent microscope method for observing growing situation of plant pollen tube in pistil with high efficiency and high definition
ActiveCN109490268AWeakening of luminescenceReduce distractionsPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh concentrationTissue fluorescence
The invention discloses a fluorescent microscope method for observing the growing situation of a plant pollen tube in a pistil with high efficiency and high definition. The method can be used for greatly weakening the phenomenon of pistil tissue fluorescence and reducing disturbance of the pistil in pollen tube observation when the pistil is amplified by a relatively large factor, so that a high-definition image of growth in a pollen tube at high amplified factor can be easily obtained, and details are ideally represented. According to the fluorescence microscope method, the softening transparent time is greatly shortened to several hours, the dyeing time is shortened from several hours in the prior art to several minutes, an observation experiment can be completed in one day, and the experiment efficiency is greatly improved; and application of a high-concentration NaOH solution is prevented, the material size can be kept in the original state in the softening transparent process, thephenomenon of water-loss shrinkage cannot happen, and re-watering treatment is not required.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
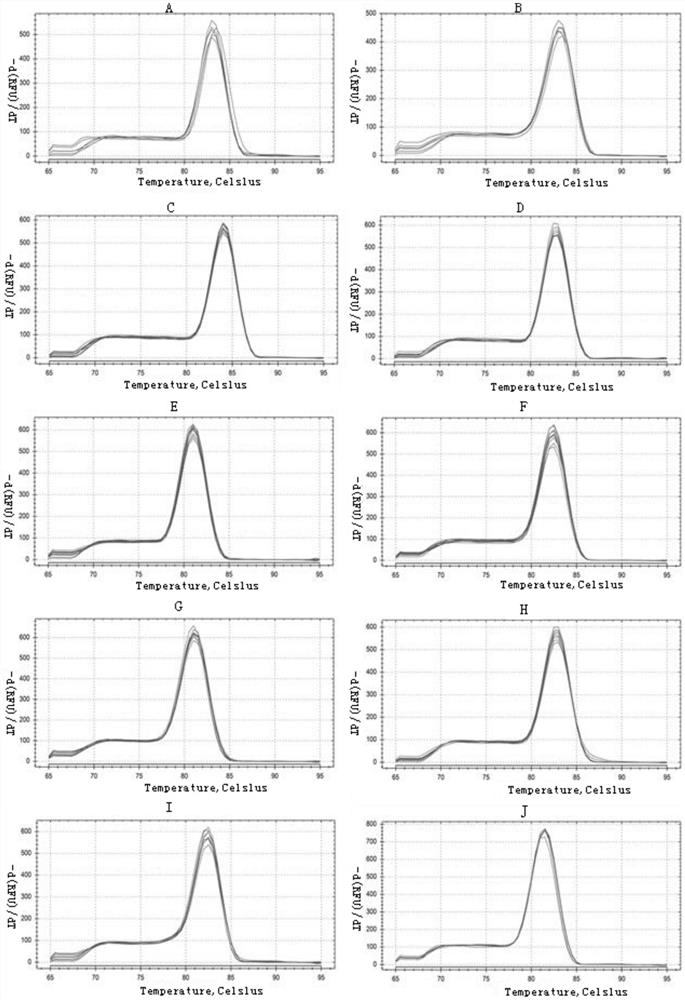
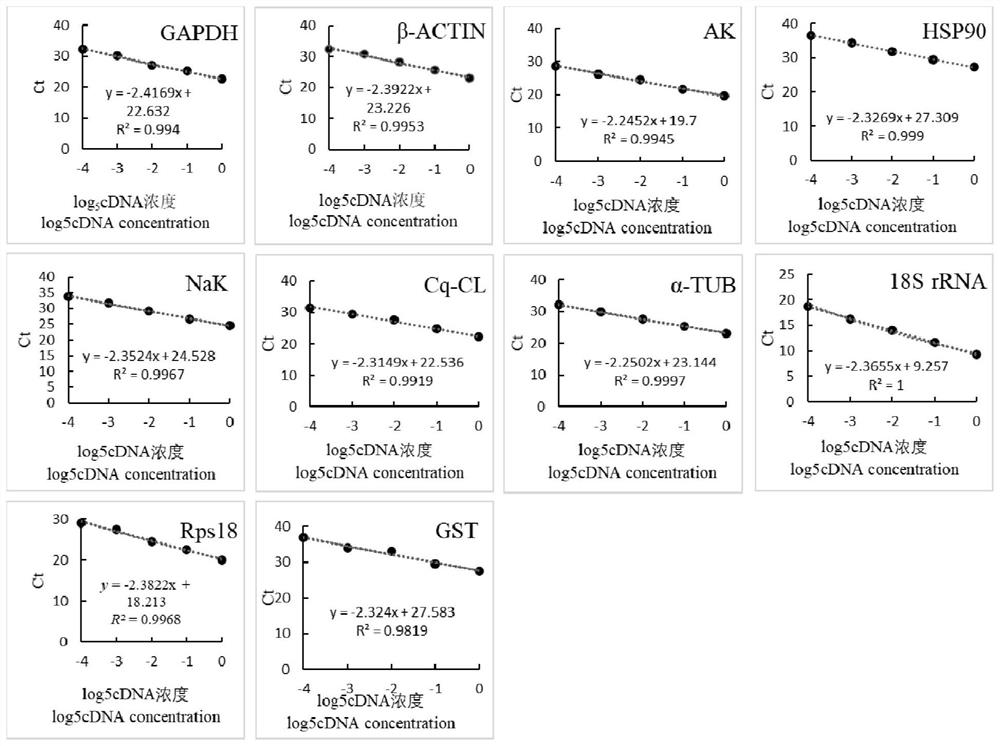
Reference genes for fluorescence quantitative detection of seven tissues of cherax quadricarinatus, screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN112342300AAccurate analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerReference genes
The invention discloses reference genes for fluorescence quantitative detection of seven tissues of cherax quadricarinatus, screening method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical fieldof molecular biology. The invention comprises reference genes GAPDH and GST, which are used for fluorescence quantitative detection of seven tissues of cherax quadricarinatus; special primers for amplifying the reference genes, nucleotide sequence (shown as SEQ ID NO.1) of a forward primer F1 and nucleotide sequence (shown as SEQ ID NO.2) of a reverse primer R1 for amplifying the GAPDH gene, nucleotide sequence (shown as SEQ ID NO.3) of a forward primer F2 and nucleotide sequence (shown as SEQ ID NO.4) of a reverse primer R2 for amplifying the GST gene. According to the invention, appropriateand stable reference genes are screened out for research on gene expression of different tissues of the cherax quadricarinatus, which is conducive to accurately analyze the gene expression rule of the cherax quadricarinatus in experiments with different purposes, and provides a necessary molecular basis for subsequent research on the molecular mechanism of the cherax quadricarinatus.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Operator-controlled scanning laser procedure designed for large-area epithelium removal
Systems and methods for removing an epithelial layer disposed over a stromal layer in a cornea irradiate a region of the epithelial layer with a pulsed beam of ablative radiation. The ablative radiation is scanned to vary the location of the beam within the region in accordance with a pulse sequence. The pulse sequence is arranged to enhance optical feedback based on a tissue fluorescence of the epithelial layer. The penetration of the epithelial layer is detected in response to the optical feedback. The use of scanning with the pulse sequence arranged to enhance optical feedback allows large areas of the epithelium to be ablated such that an operator can detect penetration of the epithelial layer.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Operator-controlled scanning laser procedure designed for large-area epithelium removal
ActiveUS8926600B2Improve accuracyImprove efficacyLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPulse beamEpithelium
Systems and methods for removing an epithelial layer disposed over a stromal layer in a cornea irradiate a region of the epithelial layer with a pulsed beam of ablative radiation. The ablative radiation is scanned to vary the location of the beam within the region in accordance with a pulse sequence. The pulse sequence is arranged to enhance optical feedback based on a tissue fluorescence of the epithelial layer. The penetration of the epithelial layer is detected in response to the optical feedback. The use of scanning with the pulse sequence arranged to enhance optical feedback allows large areas of the epithelium to be ablated such penetration of the epithelial layer can be detected.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
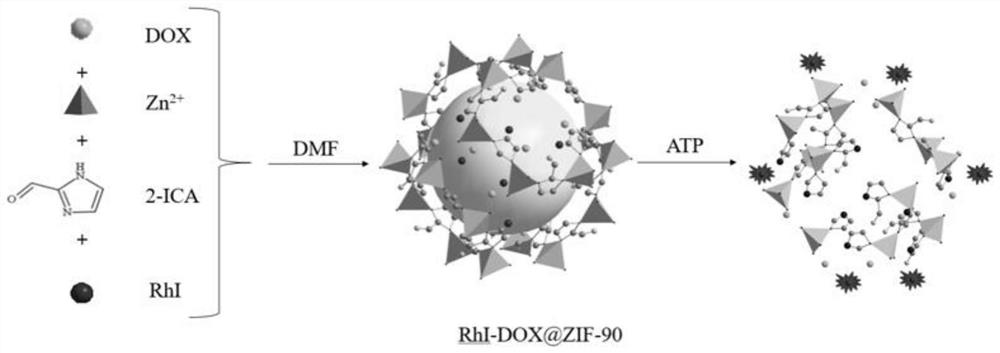
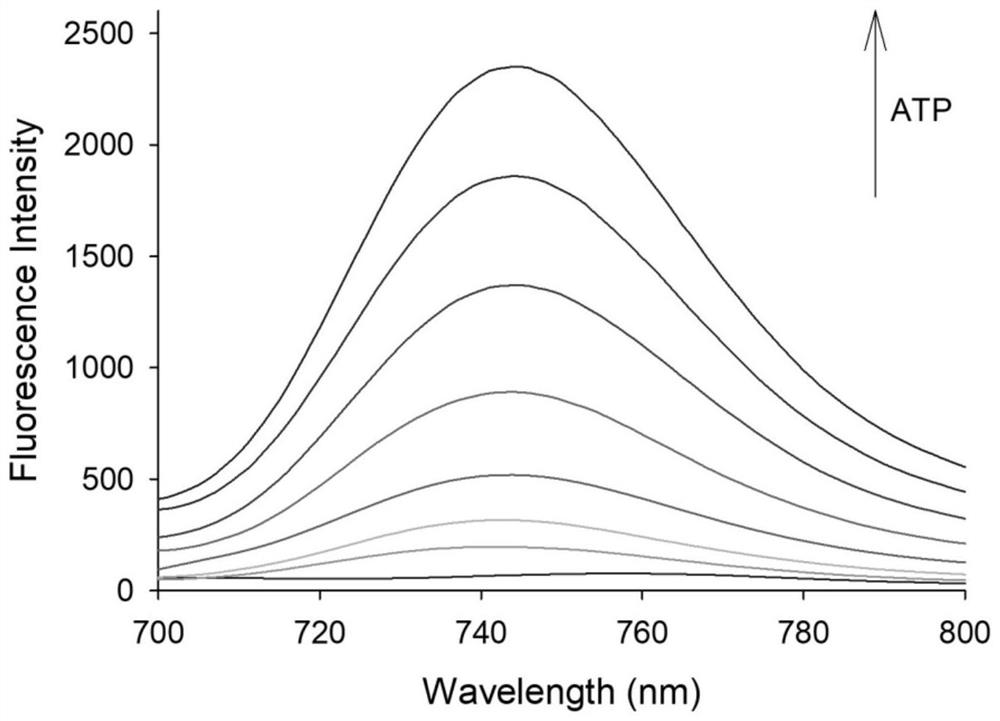
Preparation and application of near-infrared fluorescent probe based on MOF material
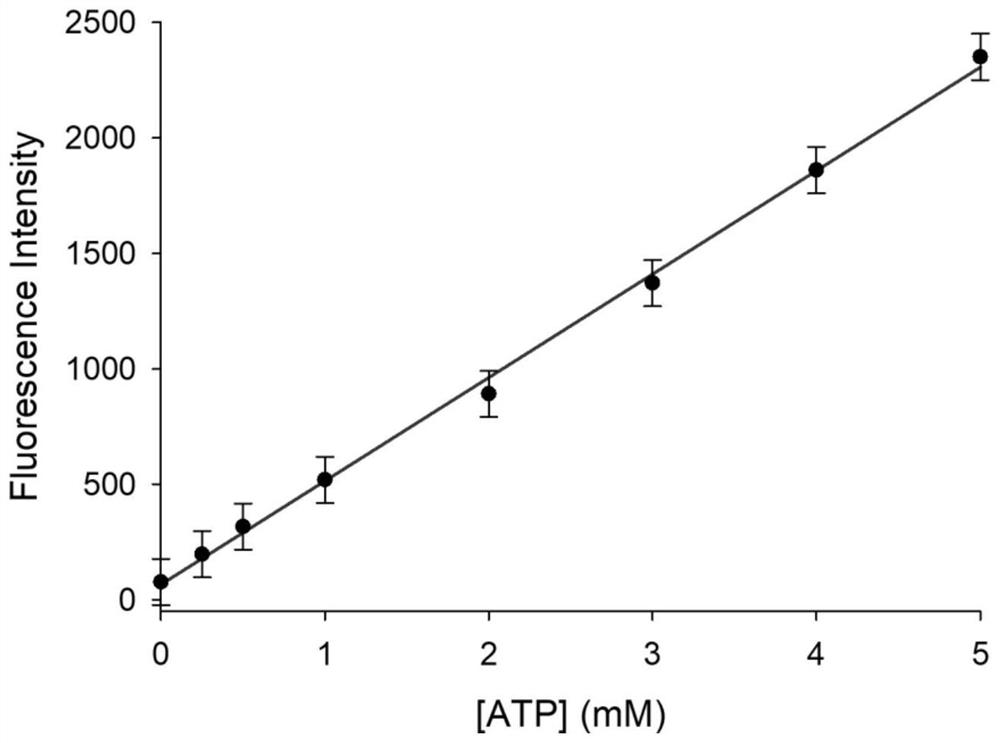
PendingCN111849463AGood spectral response performanceChange in fluorescencePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsBenzoic acidFluoProbes
The invention relates to preparation and application of a near-infrared fluorescent probe based on an MOF material. The invention provides a preparation method for synthesizing the fluorescent probe by taking adriamycin, 2-(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxybenzoyl) benzoic acid, Fisher aldehyde, zinc acetate dehydrate, imidazole-2-formaldehyde and the like as raw materials. The fluorescent probe is the near-infrared fluorescent probe based on the MOF material. Firstly, the fluorescent probe is simple in synthesis method, and a near-infrared fluorescence monitoring controllable drug release system whichresponds to a tumor microenvironment is synthesized by adopting a ZIF-90 nano material and a near-infrared dye; secondarily, the fluorescent probe can quickly react with ATP, and the response time iswithin 200 seconds; and thirdly, as the ATP concentration in cancer cells is higher than that of surrounding normal tissues, the fluorescent probe has relatively ideal selectivity on the ATP, the probe can be well enriched in the cancer cells, and the premise of improving the cancer treatment effect is achieved; and finally, the probe has excellent drug loading characteristics, so that the cancertreatment effect is greatly improved.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Tissue fluorescence monitor with ambient light rejection
ActiveUS10045696B2Minimal loss of capture timeRaman/scattering spectroscopySurgeryAmbient lightingTissue fluorescence
Fluorescent markers used to identify a tissue may be imaged in a bright environment by synchronizing the imaging process with rapidly switched ambient lighting so that imaging occurs in phase with a switching off of the ambient lighting. In this way, valuable fluorescent imaging may be performed in an environment that appears to be brightly illuminated, for example in the area of a surgical suite.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method and Apparatus for Determination of a Measure of a Glycation End-Product or Disease State Using Tissue Fluorescence
InactiveUS20140235972A1Improve accuracyImprove signal-to-noise ratioOptical sensorsBlood characterising devicesDiseaseTissue Collection
Embodiments of the present invention provide an apparatus suitable for determining properties of in vivo tissue from spectral information collected from the tissue. An illumination system provides light at a plurality of broadband ranges, which are communicated to an optical probe. The optical probe receives light from the illumination system and transmits it to in vivo tissue, and receives light diffusely reflected in response to the broadband light, emitted from the in vivo tissue by fluorescence thereof in response to the broadband light, or a combination thereof. The optical probe communicates the light to a spectrograph which produces a signal representative of the spectral properties of the light. An analysis system determines a property of the in vivo tissue from the spectral properties. A calibration device mounts such that it is periodically in optical communication with the optical probe.
Owner:VERALIGHT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com