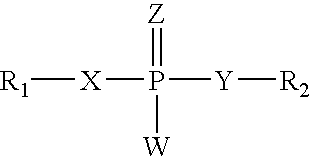Patents
Literature
114 results about "MYB" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Myb genes are part of a large gene family of transcription factors found in animals and plants. In humans, it includes Myb proto-oncogene like 1 and Myb-related protein B in addition to MYB proper. Members of the extended SANT/Myb family also include the SANT domain and other similar all-helical homeobox-like domains.
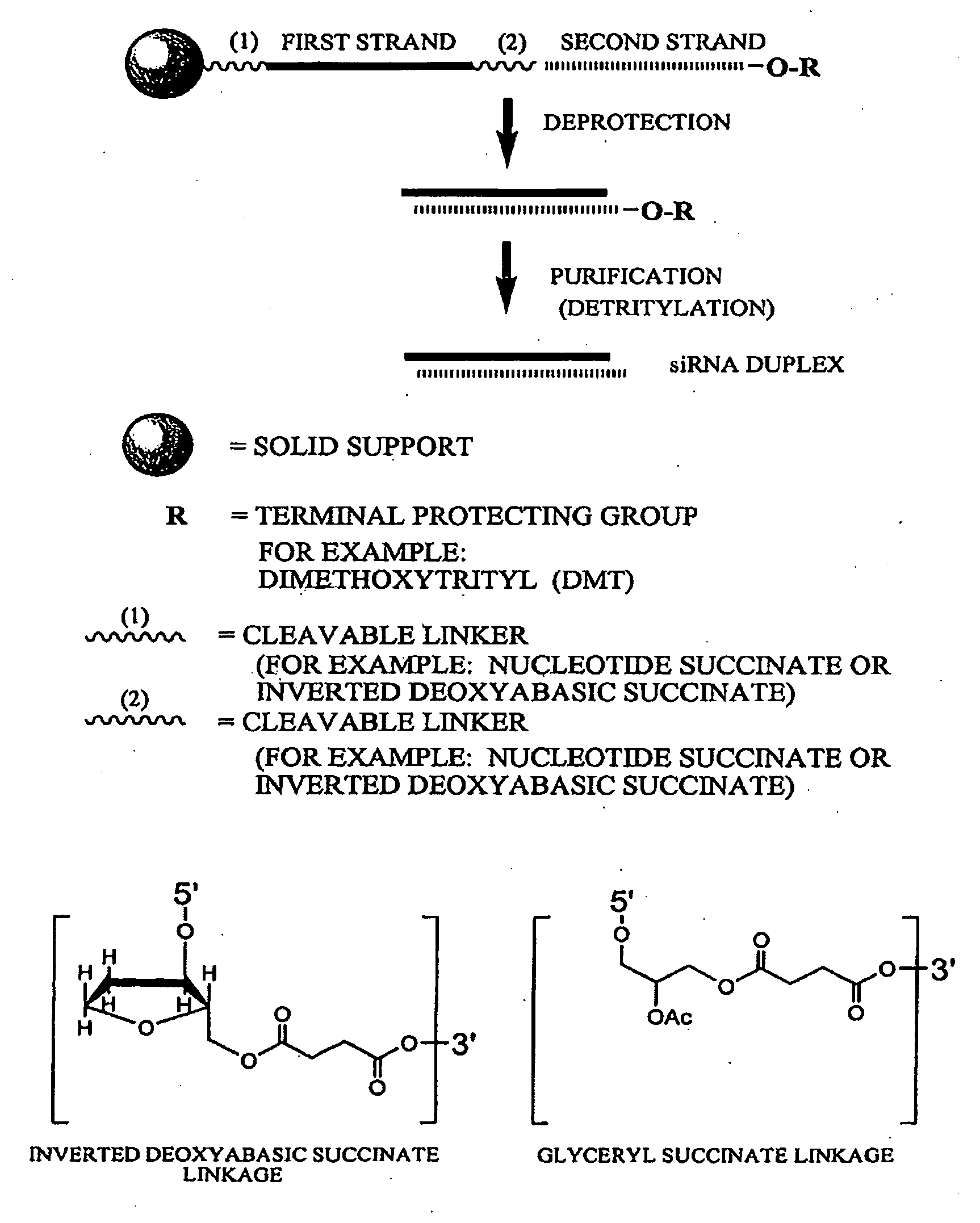
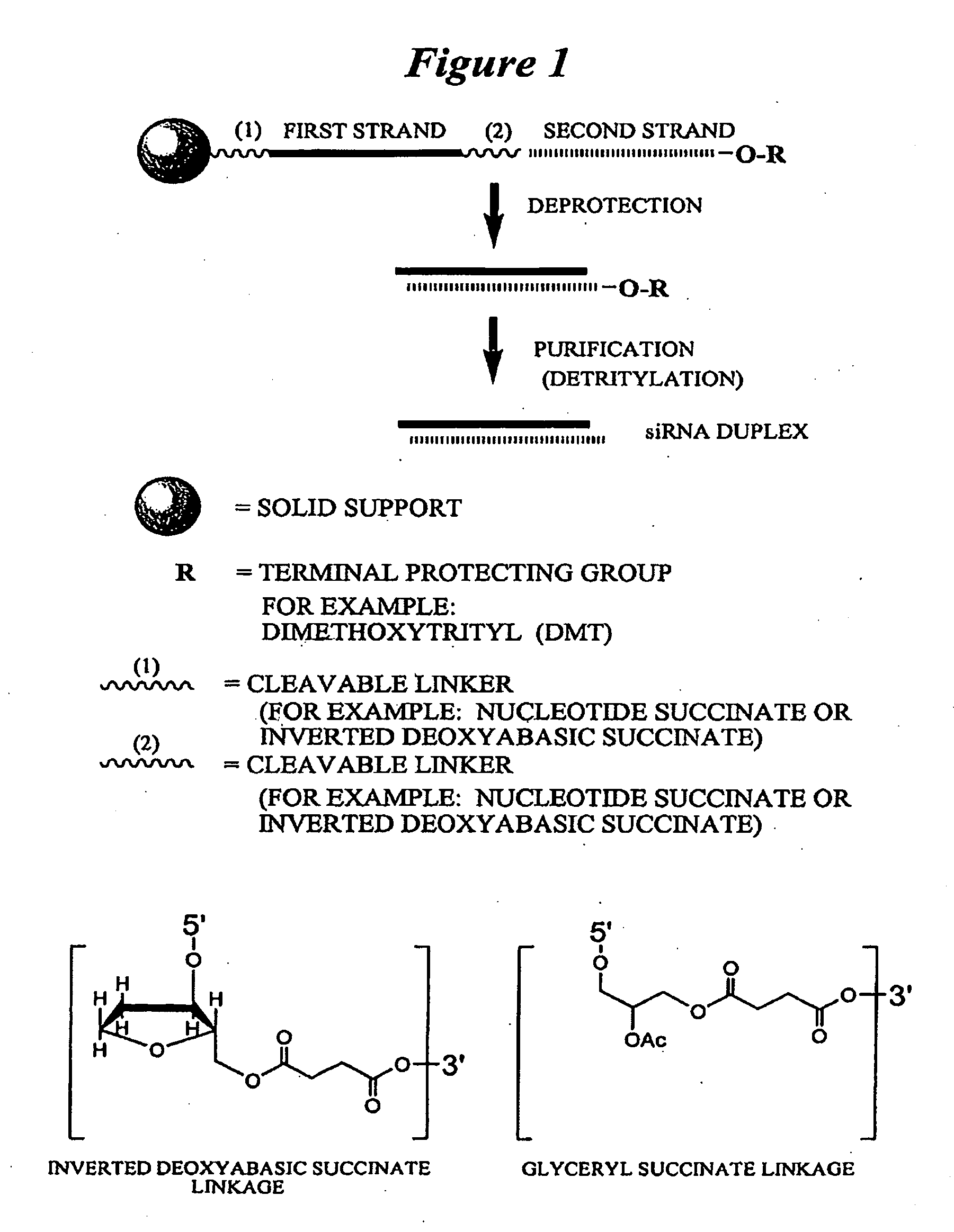
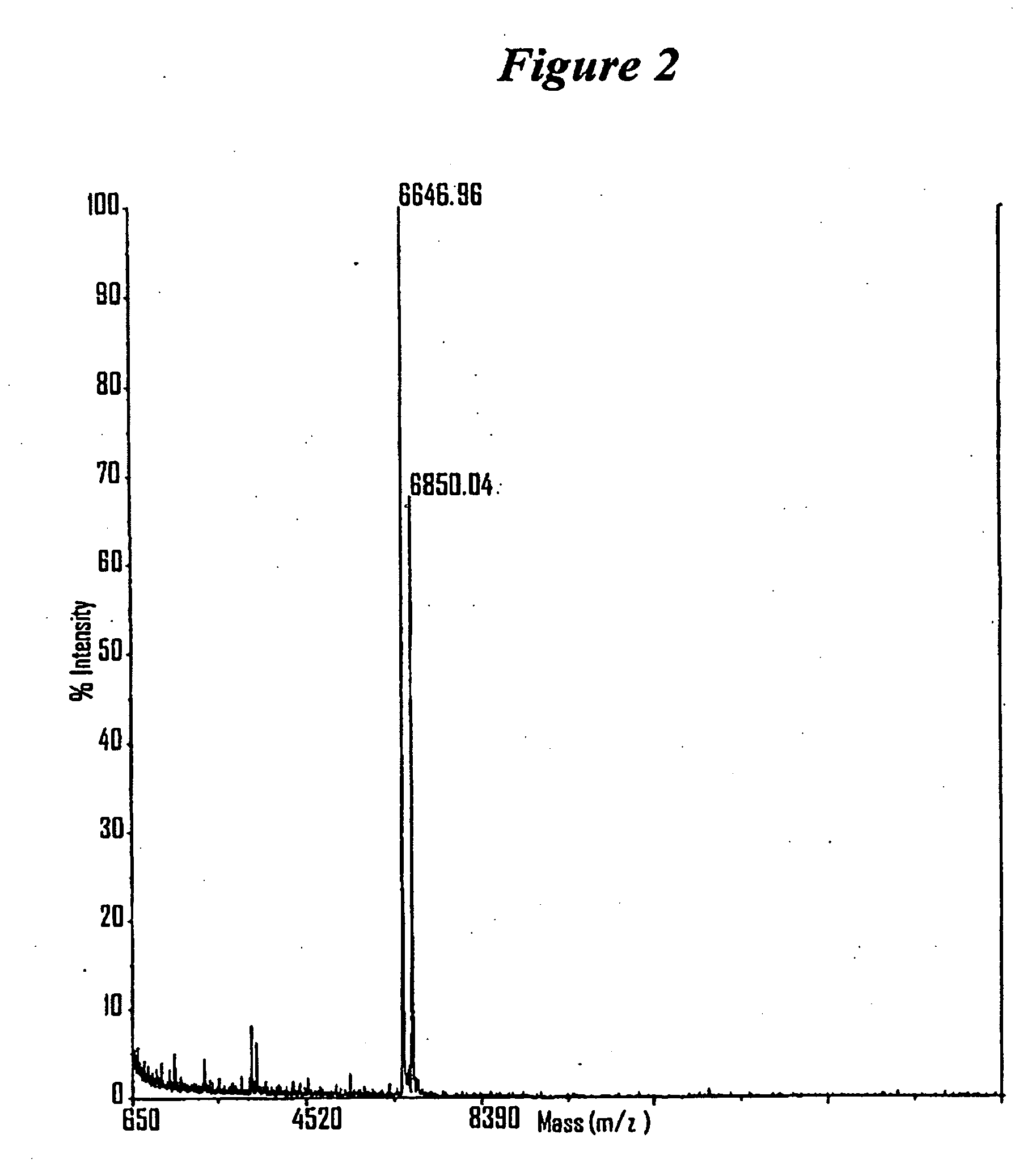
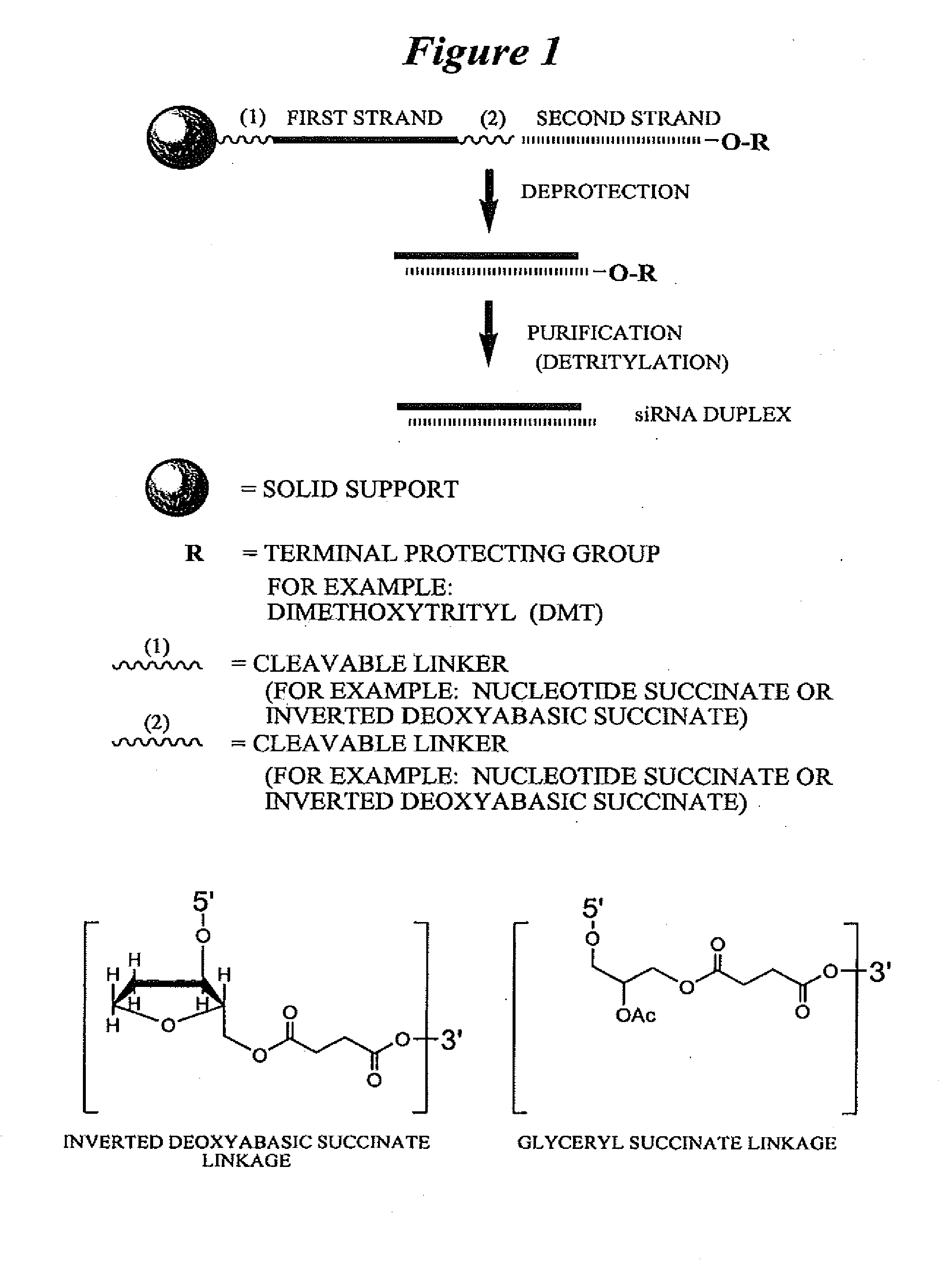
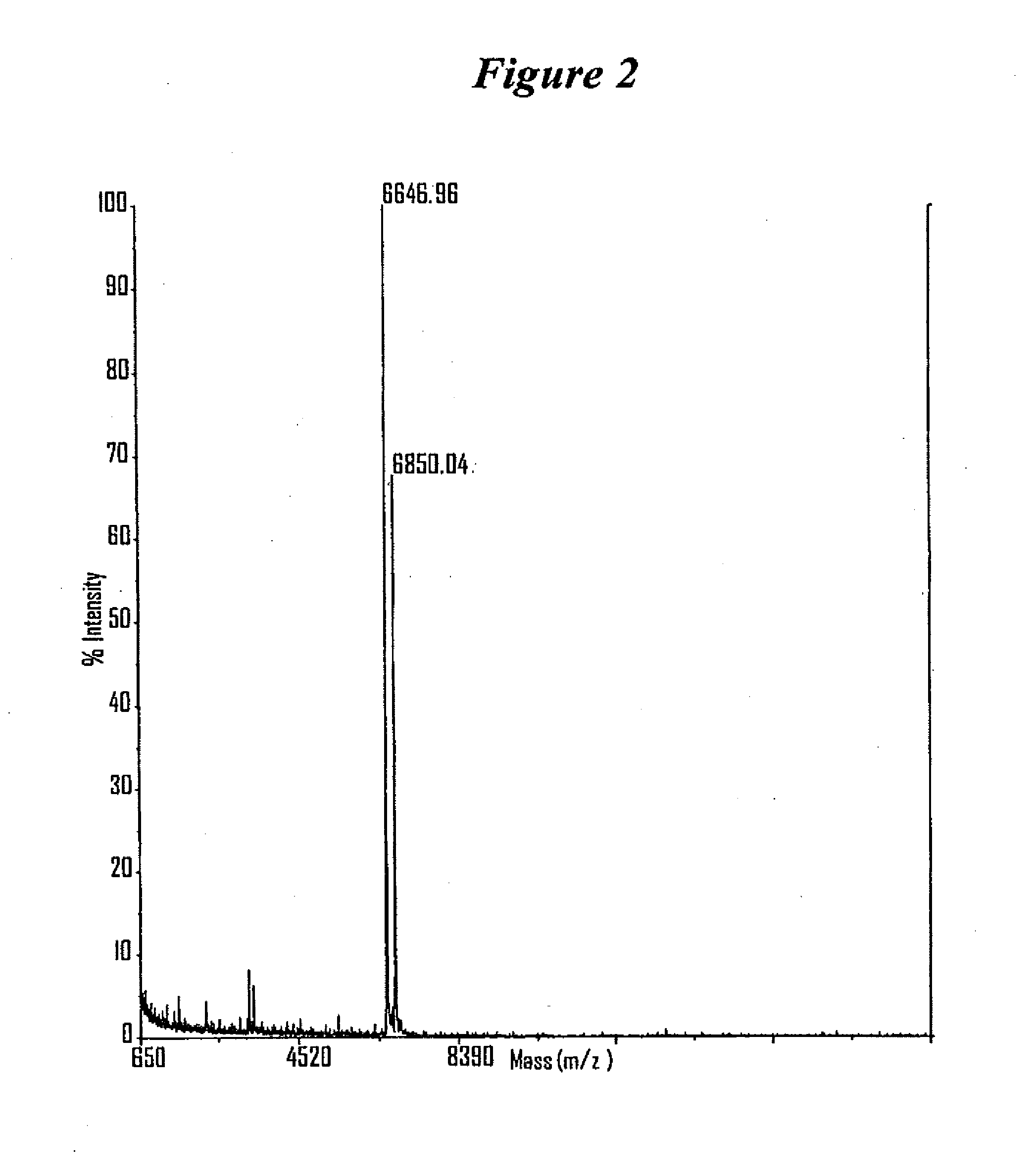
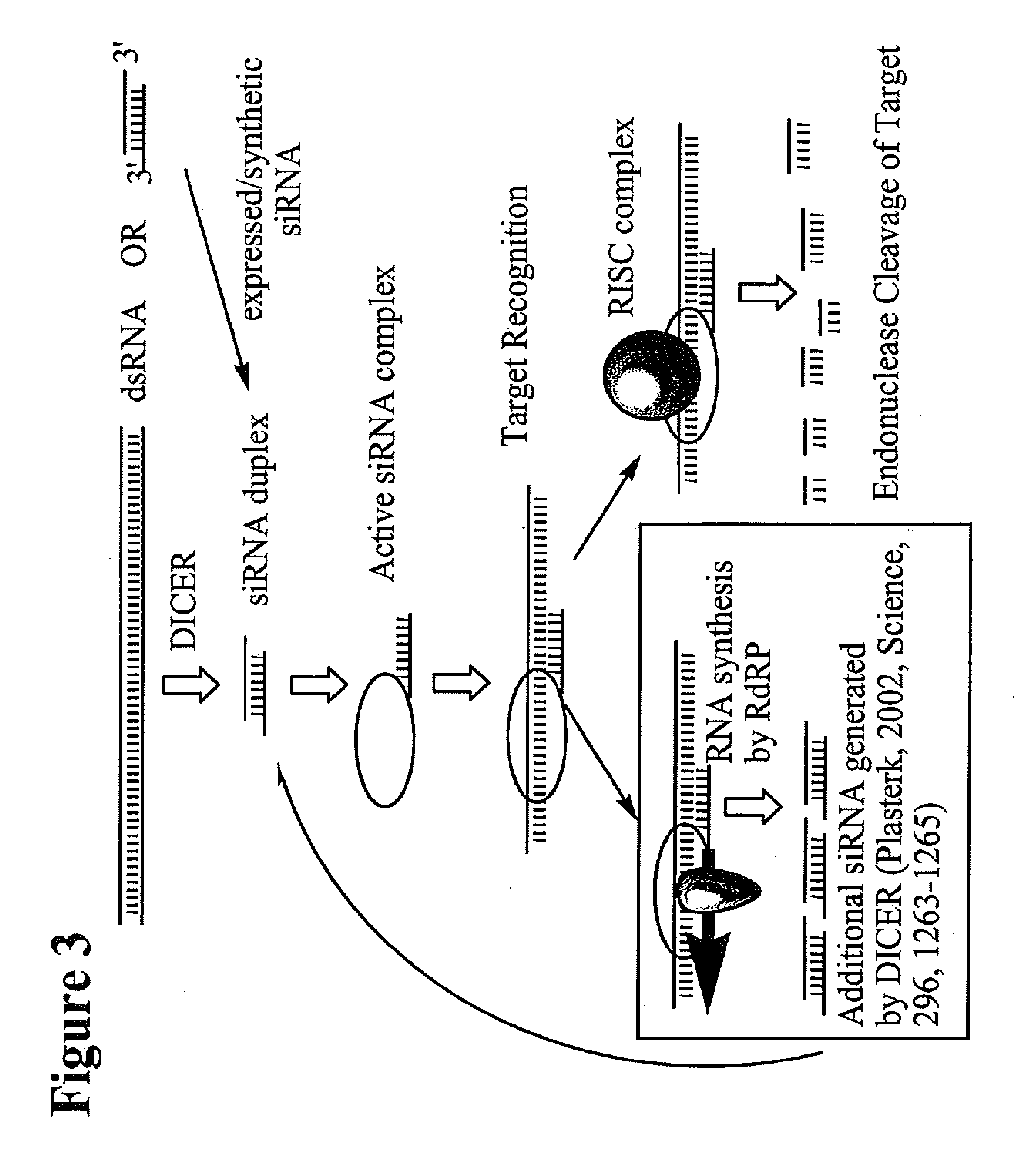
RNA interference mediated inhibition of Myc and/or Myb gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050159378A1Improve bioavailabilityMinimize the possibilityCompounds screening/testingSpecial deliveryDiseaseN-Myc
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating Myc and / or Myb gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of Myc and / or Myb gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of Myc and / or Myb (e.g., c-Myc, N-Myc, L-Myc, c-Myb, a-Myb, b-Myb, and v-Myb) genes. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of cancer and other diseases and disorders.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
RNA INTERFERENCE MEDIATED INHIBITION OF MYC AND/OR MYB GENE EXPRESSION USING SHORT INTERFERING NUCLEIC ACID (siNA)
InactiveUS20090099115A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseN-Myc
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating Myc and / or Myb gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of Myc and / or Myb gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of Myc and / or Myb (e.g., c-Myc, N-Myc, L-Myc, c-Myb, a-Myb, b-Myb, and v-Myb) genes. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of cancer and other diseases and disorders.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
RNA INTERFERENCE MEDIATED INHIBITION OF MYC AND/OR MYB GENE EXPRESSION USING SHORT INTERFERING NUCLEIC ACID (siNA)
InactiveUS20100093835A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseN-Myc
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating Myc and / or Myb gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of Myc and / or Myb gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of Myc and / or Myb (e.g., c-Myc, N-Myc, L-Myc, c-Myb, a-Myb, b-Myb, and v-Myb) genes. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of cancer and other diseases and disorders.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Transcriptional factor relevant to resistant adversity from Arabidopsis thaliana, coded gene, and application
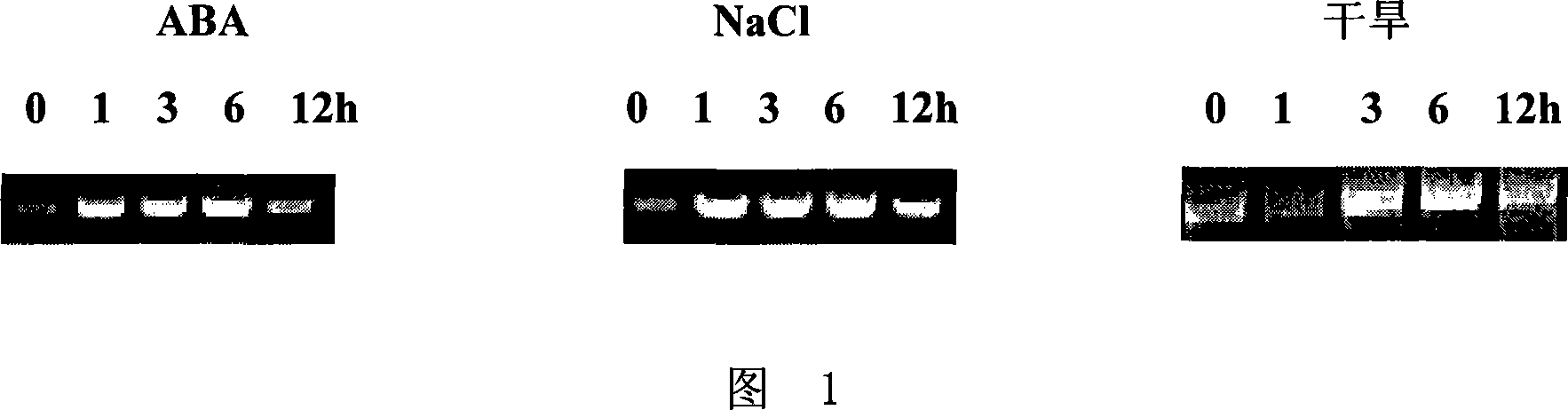
This invention discloses stress-tolerant R2R3 MYB transcription factor, its coding gene and application. The stress-tolerant R2R3 MYB transcription factor is derived from Arabidoesis thaliana, and can be applied in culturing stress-tolerant plants that can resist abscisic acid, high salt and draught. The transcription factor is one of the following amino acid residue sequences: (1) SEQ ID NO.1; (2) protein by substituting, deleting or adding 1-10 amino acid residues of SEQ ID NO.1, which can regulate the stress tolerance of plants. The protein and its coding gene have important meaning to research on plant stress-tolerant mechanism, and method for improving draught, salt and stress tolerance of plants. The protein and its coding gene have potential application in stress-tolerant genetic engineering of plants.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Plant flavonoid synthesis regulation gene and its application
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Disease-resistant correlated wheat MYB albumen, coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses wheat MYB protein correlated to plant disease resistance, encoding gene and application thereof. The protein is protein (a) and protein (b): protein (a) is composed of amino acid sequence of sequence 2 in a sequence table; and protein (b) is made by performing substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on amino acid residue sequence of the sequence 2 in the sequence table, is correlated to flowering time, and is derived from protein (a). The wheat MYB protein correlated to plant disease resistance is transferred into plants to improve disease resistance of the plants. The method for culturing transgenic plant having improved disease resistance has important theoretical and practical significance and exerts important effect on genetic improvement of the plants.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
MYB transcription factor implicated in anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation
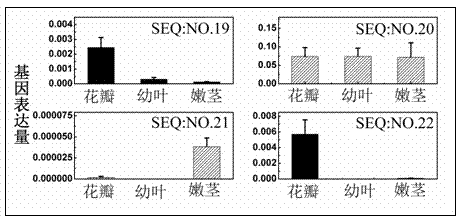
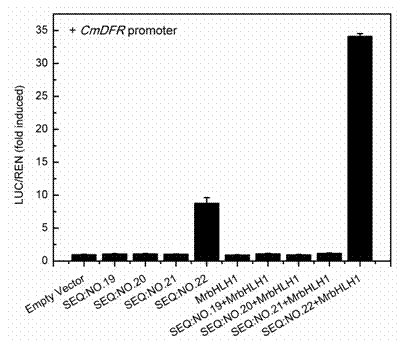
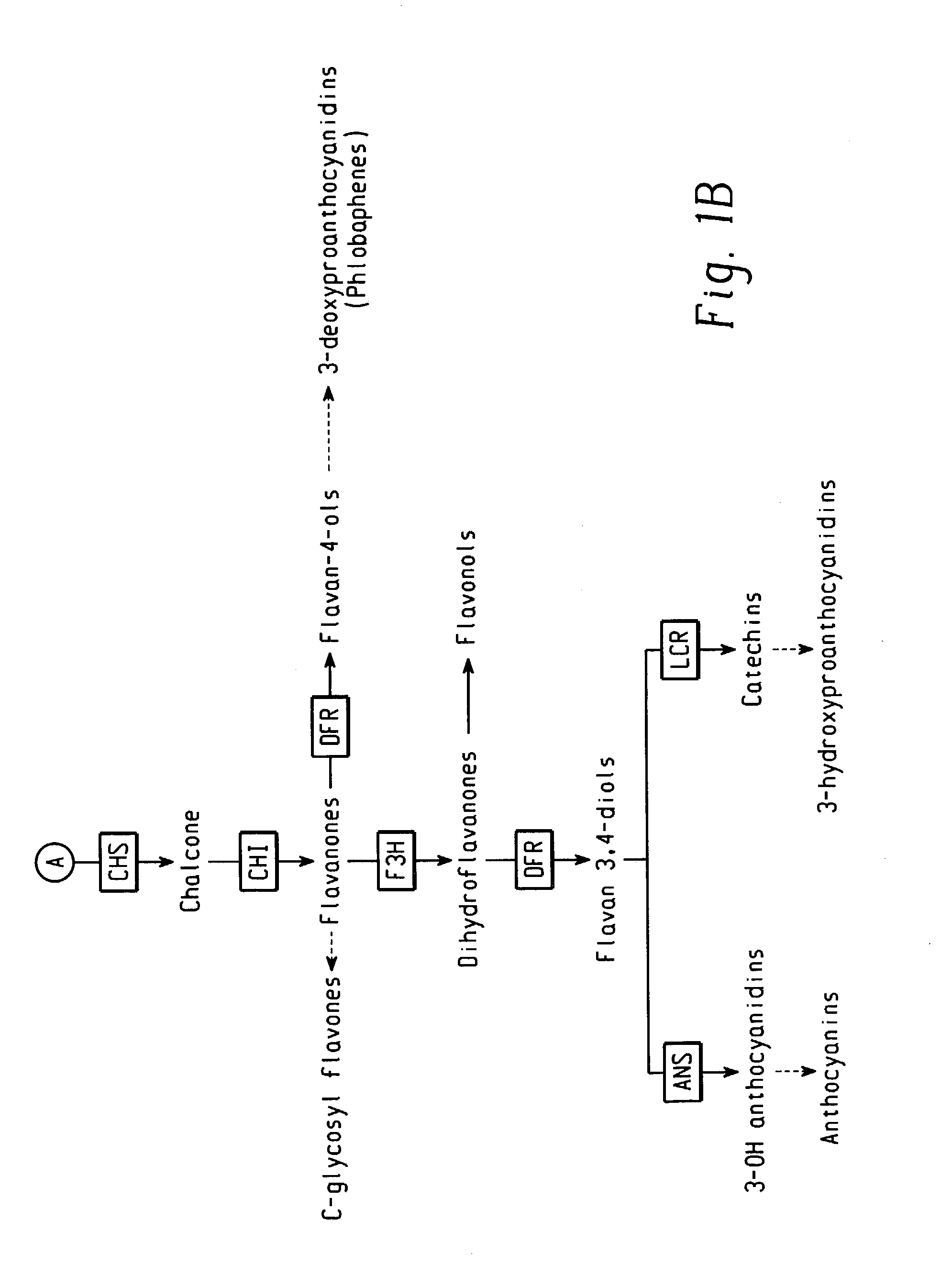
The invention provides an MYB transcription factor CmMYB6 implicated in chrysanthemum petal anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation. The coding region sequence of the MYB transcription factor CmMYB6 contains 765 nucleotides. A CmMYB6 amino acid sequence contains a conserved R2R3 MYB domain, a [D / E]Lx2[R / K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif and an ANDV motif exist in the R3 domain, the [D / E]Lx2[R / K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif can interact with bHLH, and the ANDV motif is the characteristic motif of the MYB transcription factor implicated in anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation. The gene expression of CmMYB6 rises in the petal growth process and is significantly and positively correlated with anthocyanin synthesis the CmMYB6 can induce the activity of synthesis of a key gene CmDFR promoter from anthocyanin, and the CmMYB6 has substantially enhanced induction usefulness and can strongly induce accumulation of tobacco leaf anthocyanin during cooperative expression of the CmMYB6 and MrbHLH1. The MYB transcription factor can be used in transcription regulation of plant anthocyanin biosynthesis and plant color modification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cloning and function expression method of adversity stress AhMYBL6 gene in peanut
ActiveCN103060340AIncreased transcript levelsImprove stress resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOpen reading frameComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
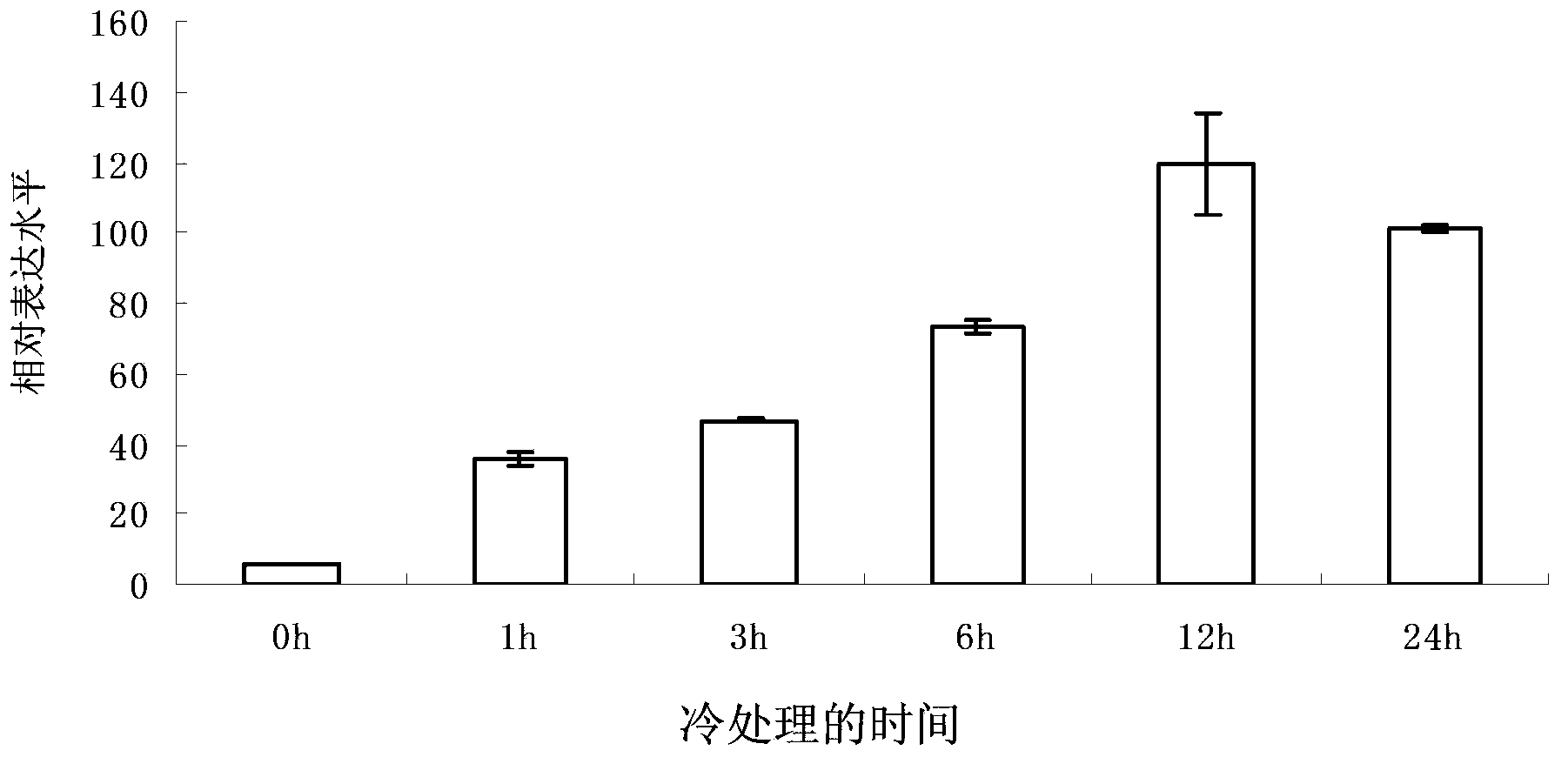
The invention relates to a cloning and function expression method of an adversity stress AhMYBL6 gene in peanut. The adversity stress AhMYBL6 gene is synthesized by RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) cloning by the steps of preparation and treatment of materials, extraction of RNA (ribonucleic acid) and synthesis of cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid). The open reading frame of the gene is 861bp, and 287 amino acids are coded totally. The homology of the amino acid sequence of the gene with the MYb family proteins GmMYB4, GmMYB29 and GmMYB29A2 of the soybean is higher than 60%. The fluorescent quantitative PCR verifies the expression patterns of the AhMYBL6 under low temperature, salt stress and drought stress; the result indicates that the expression levels of the AhMYBL6 are obviously enhanced after various stress treatment for 1 hour, and kept at high levels all the time thereafter; and the expression level of the AhMYBL6 in the leaf subjected to low-temperature treatment is maximally enhanced by 20 times. After the gene is transferred into peanut by transgenic means, compared with the control, the transgenic plant has obvious characteristics of cold tolerance, salt tolerance and drought tolerance. The AhMYBL6 gene can obviously enhance the stress tolerance of the peanut.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
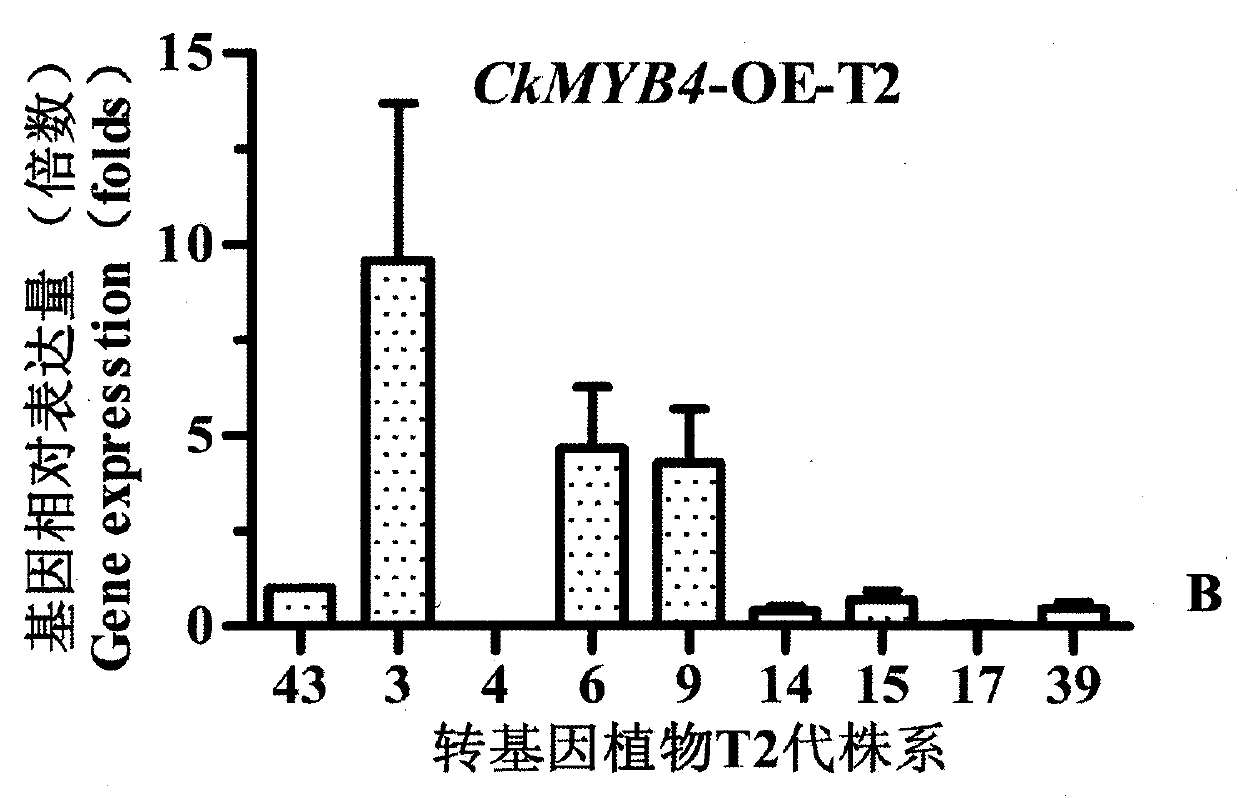
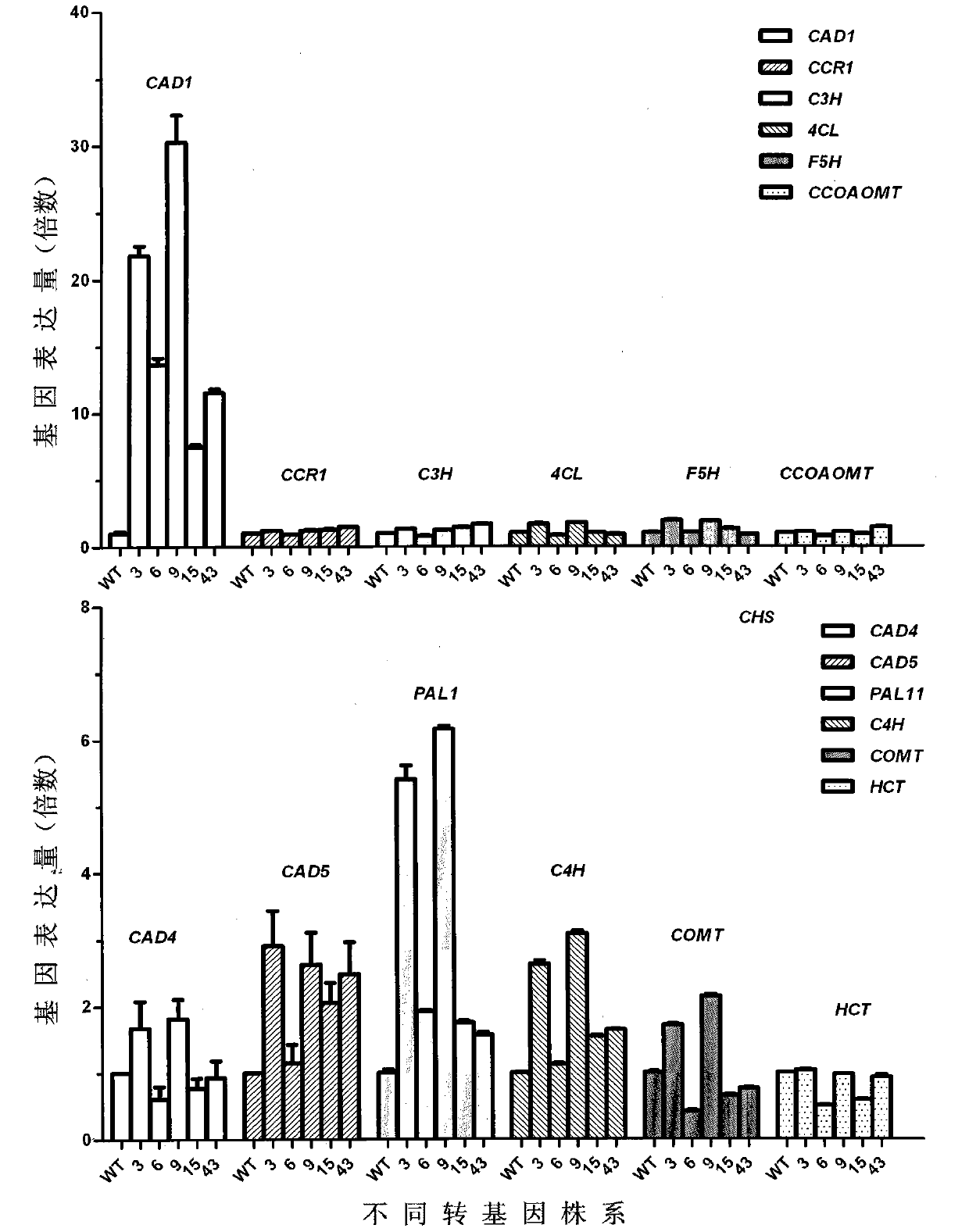
Caragana korshinskii Kom. transcription factor CkMYB4 and its gene
The invention provides a new CkMYB4 transcription factor and its gene. The gene originates from Leguminosae Caragana shrubs Caragana korshinskii Kom., and codes R2R3 MYB transcription factors. The full length cDNA sequence of the gene comprises 1106bps, comprises a 798bp open reading frame, and codes 266 amino acids. The cDNA sequence obtained after cloning is used for constructing a plant expression vector, and the vector is transformed into wild Arabidopis thaliana to obtain a transgenic plant. Transgenic Arabidopis thaliana lignin synthetase gene and lignin content detection results show that the gene provided by the invention can change the expression of the plant lignin synthesis gene and the lignin content.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for obtaining plant hairy roots with high anthocyanin content
ActiveCN103695460AHigh in anthocyaninsVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsPlant tissueBhlh genes
The invention discloses a method for obtaining plant hairy roots with high anthocyanin content, and relates to the technical field of plants. The method comprises the following steps of respectively constructing an MYB gene and a bHLH gene AmDEL for regulating anthocyanin anabolism into a carrier PJAM 1502 and a carrier pK7WG2D to obtain PJAM1502::AmROS1 and pK7WG2D::AmDEL; converting PJAM1502::AmROS1 and pK7WG2D::AmDEL into agrobacterium rhizogenes to obtain the agrobacterium rhizogenes containing plasmids PJAM1502::AmROS1 and pK7WG2D::AmDEL; and inducing out hairy roots with high anthocyanin content after utilizing the converted agrobacterium rhizogenes to infect plant tissue organs for co-culturing and screening-culturing. The method disclosed by the invention simultaneously expresses transcription factor MYB gene and bHLH gene for regulating anthocyanin anabolism to obtain the special plant hairy roots with high anthocyanin content.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
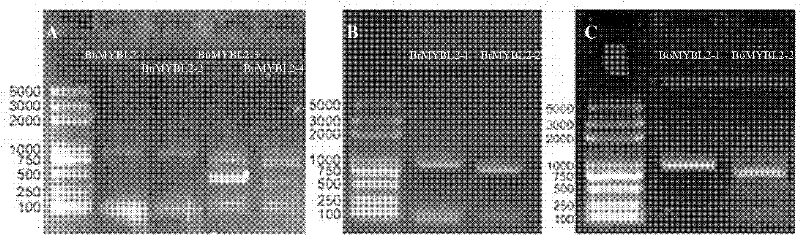
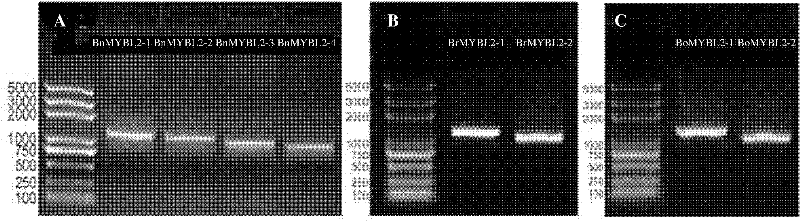
Brassica napus, parent species Chinese cabbage, cabbage MYBL2 (v-myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog-like 2) gene family and application thereof
InactiveCN102226193AReduced seed coat pigmentSeed coat thinningFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBrassicaHigh homology
The invention discloses a Brassica napus, parent species Chinese cabbage, cabbage MYBL2 (v-myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog-like 2) gene family. The Chinese cabbage MYBL2 gene family comprises a BrMYBL2-1 gene and a BrMYBL2-2 gene. The cabbage MYBL2 gene family comprises a BoMYBL2-1 gene and a BoMYBL2-2 gene. The Brassica napus MYBL2 gene family comprises a BnMYBL2-1 gene, a BnMYBL2-2 gene, a BnMYBL2-3 gene, a BnMYBL2-4 gene. Eight MYBL2 genes have higher homology. The invention also discloses the application of the above gene families in molecular breeding with characters, such as plant seed coat color, seed coat thickness and the like. After a just overexpression plant carrier is built and double 10 number in the black Brassica napus variety, the Brassica napus is compared with the contrast of the explant of a non-transgenosis, transgenosis plants normally grow and develop, pigments such as Proanthocyanidins in the seed coat are reduced, and meanwhile the seed coat becomes thin to form the transgenosis yellow seed character.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Transgenic plants with altered levels of phenolic compounds
InactiveUS20080235829A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPhenylpropanoidPresent method
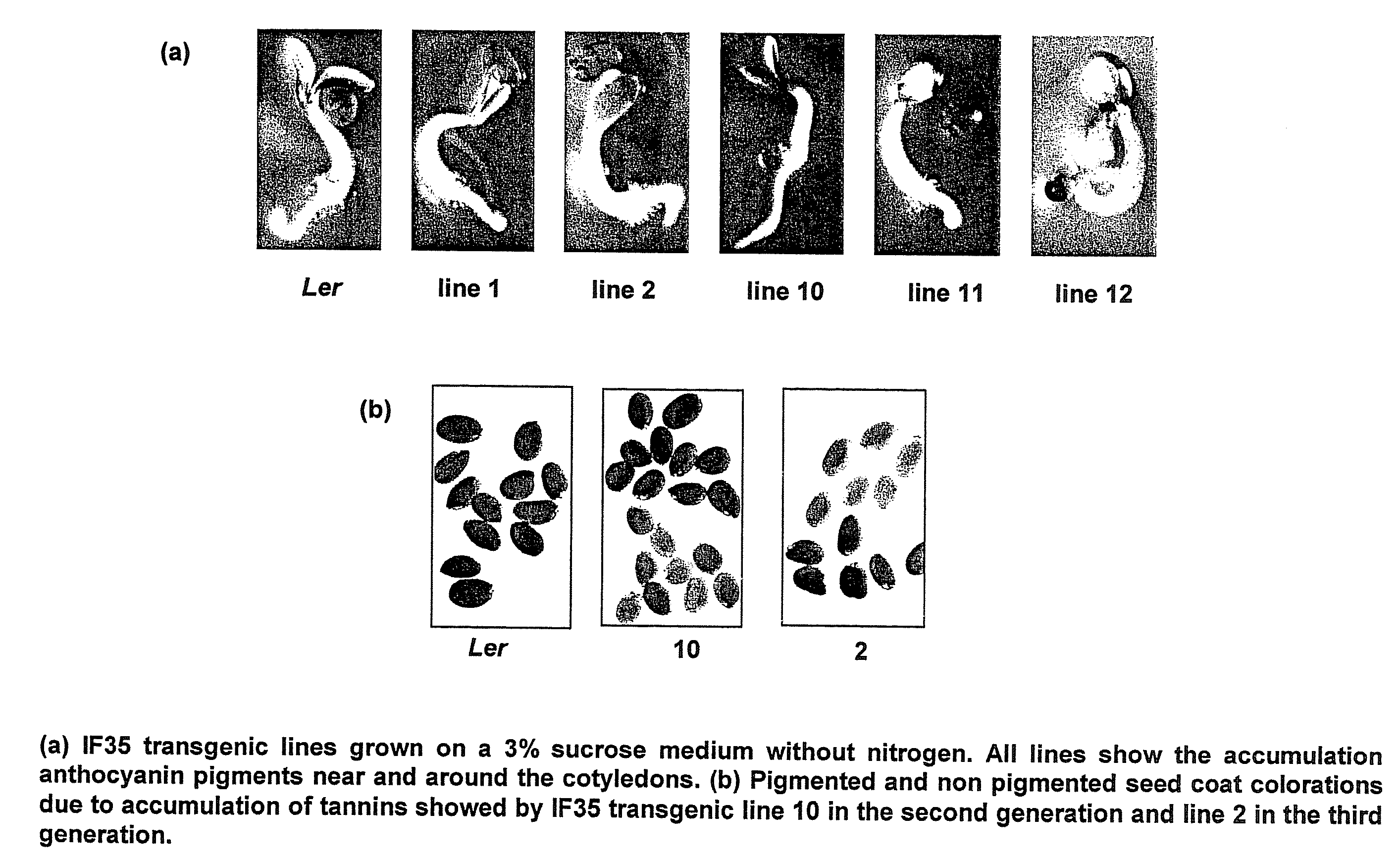
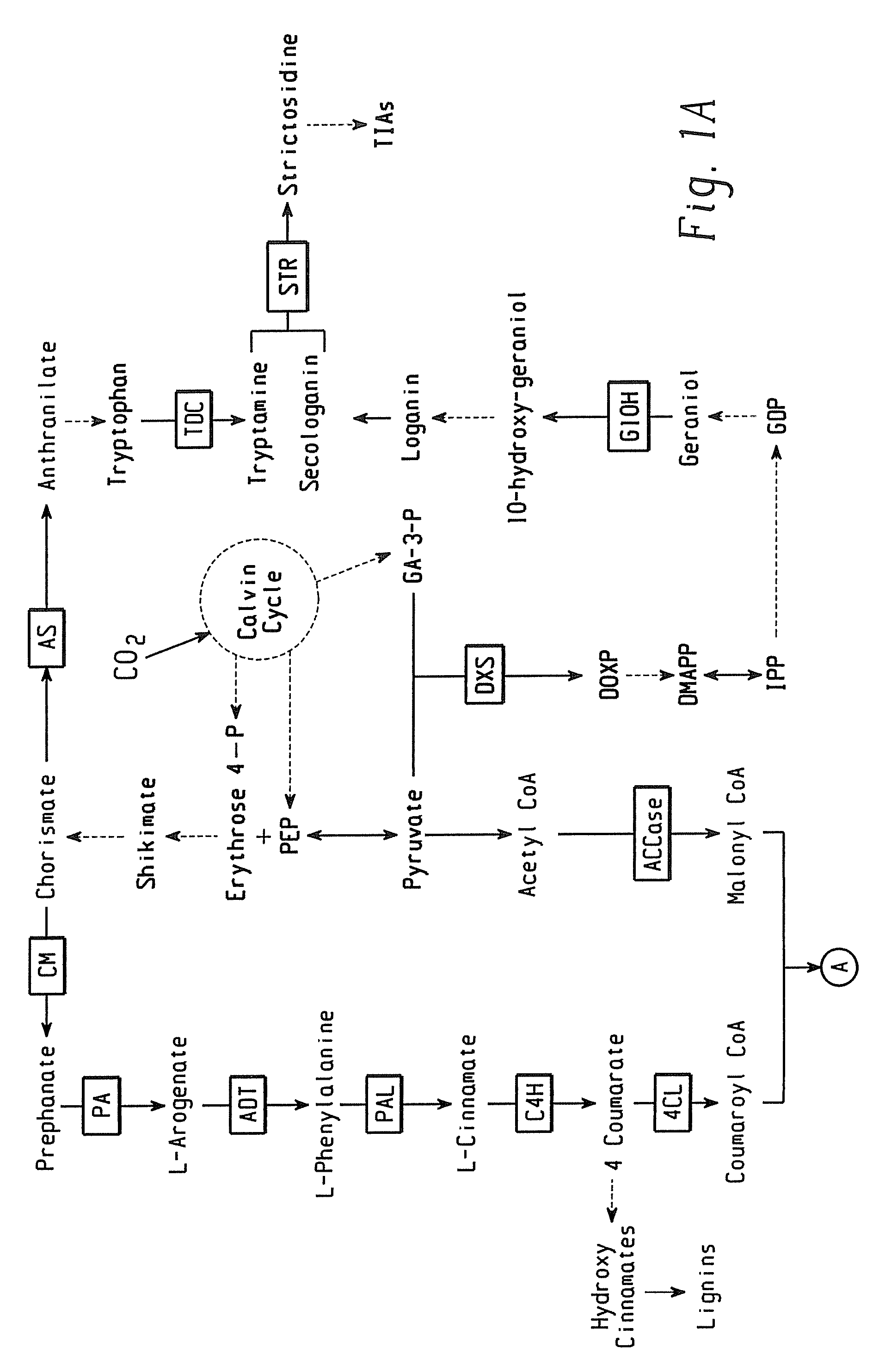
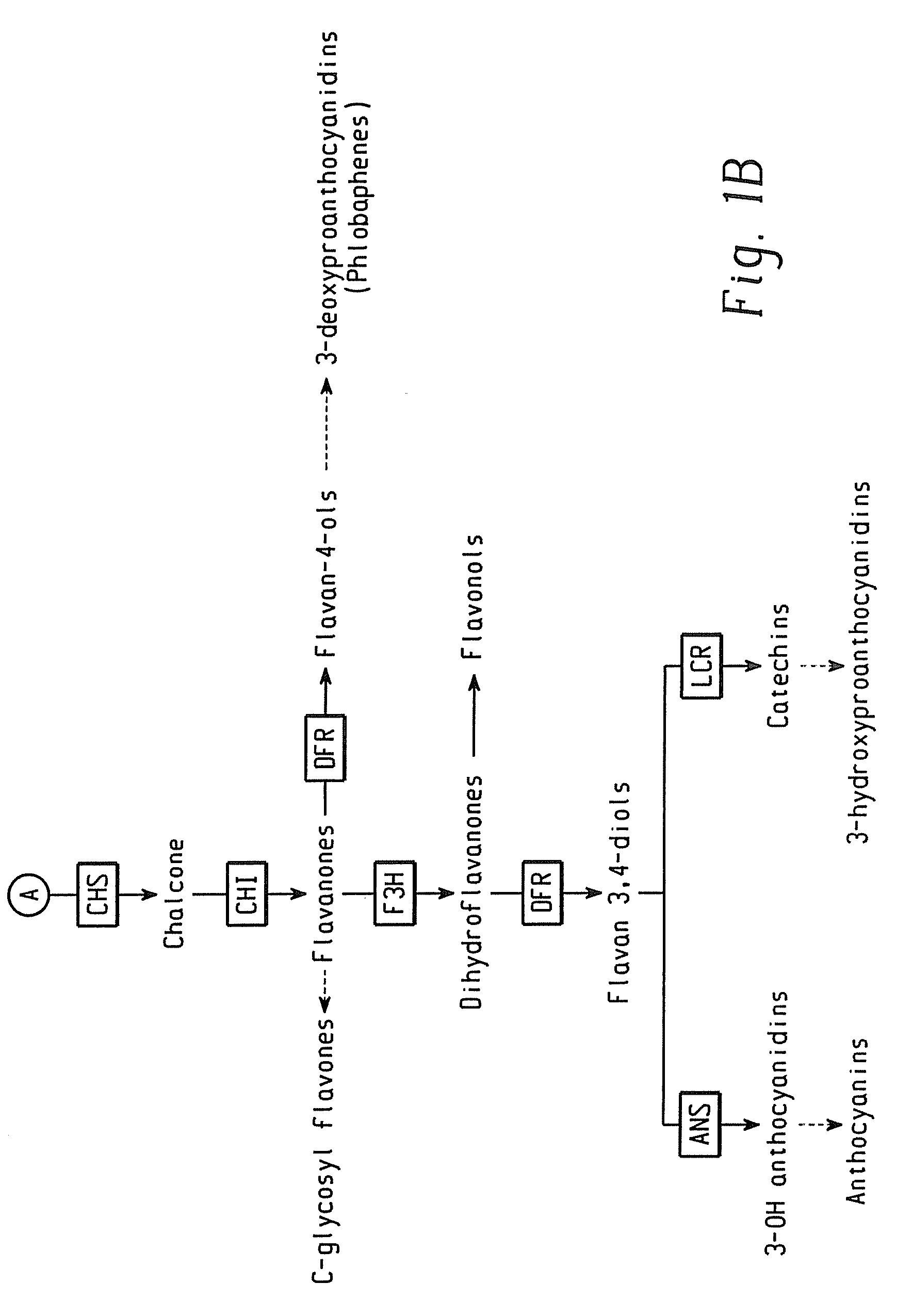
Methods for altering levels in plants of one or more phenolic compounds that are intermediates or final products of the plant phenylpropanoid pathway are provided. One method comprises transforming a plant cell with an expression construct comprising a nucleic acid which encodes a transactivator protein comprising the myb domain of the maize “ZmMyb-IF35” protein and an activation domain. Another method comprises transforming a plant cell with an expression construct comprising a transgene which encodes an antisense ZmMyb-IF35 RNA. The present invention also relates to expression constructs and vectors used in the present methods, transformed plant cells and transgenic plants prepared according to the present methods, and the seeds of such transgenic plants.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
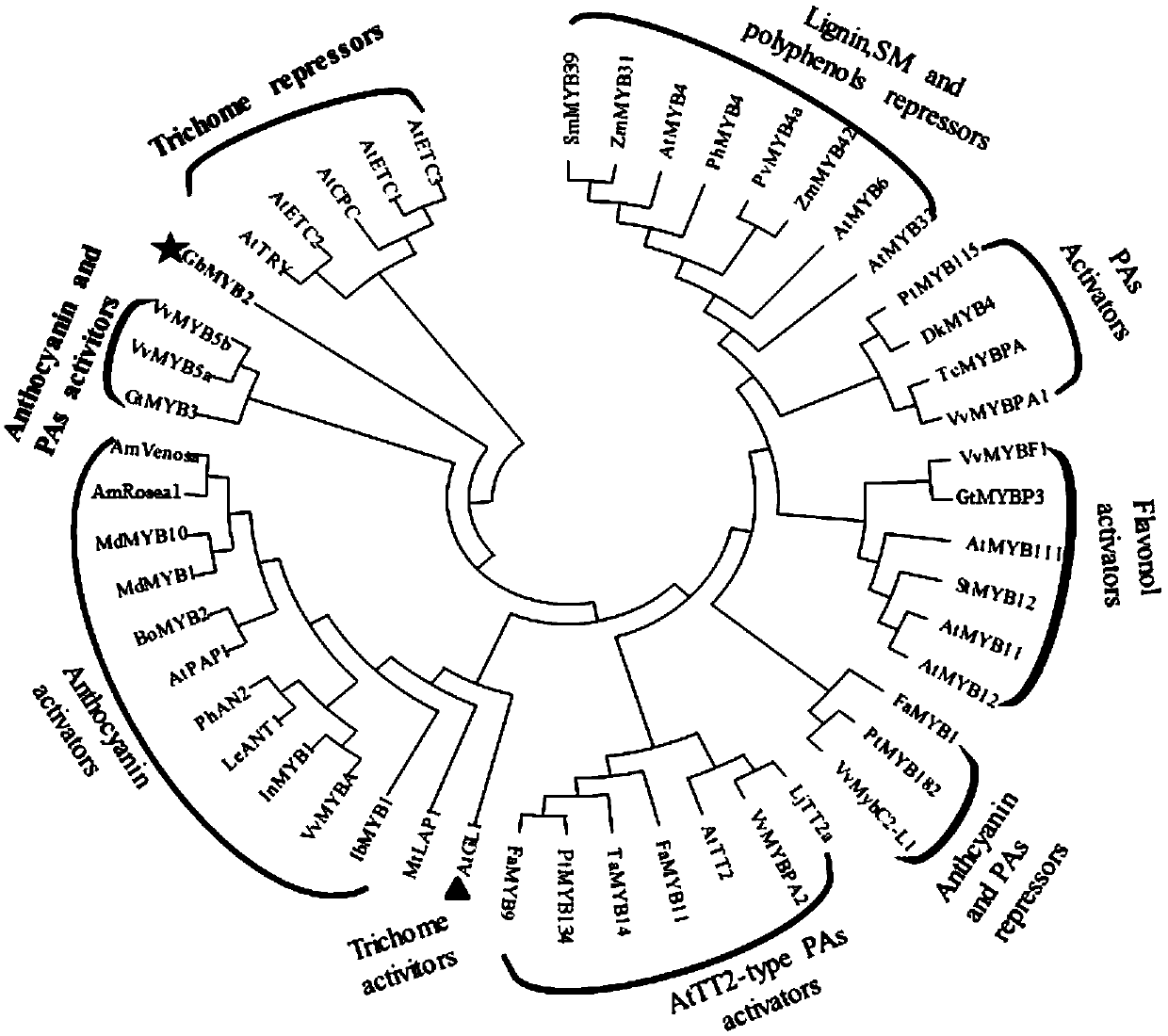
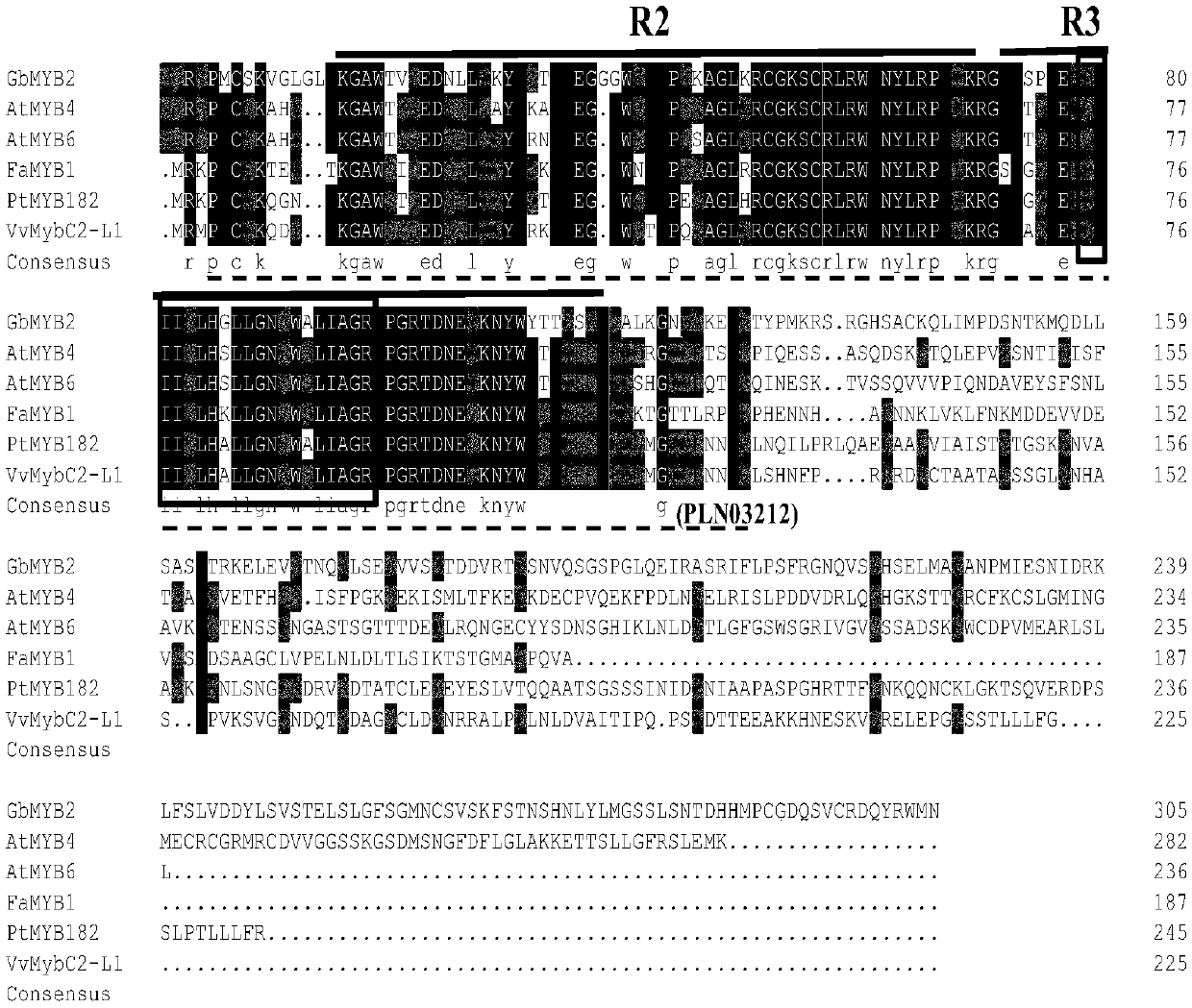
Multifunctional MYB transcription factor gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a multifunctional MYB transcription factor participating in multiple approaches. The MYB type transcription factor gene is GbMYB2 identified from a 'living fossil' plant gingko, wherein the gene sequence of the MYB type transcription factor gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the coded protein sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. In addition, the invention discloses application of the gene. According to the application of the gene, coded protein can regulate and control plant flavonoid, lignin and plant growth and development. The MYB transcription factor gene and theapplication thereof have the advantages that an MYB2 transcription factor gene is cloned from the ginkgo, and system identification is carried out on the functions of the MYB2 transcription factor gene, and therefore it is discovered that the gene participates in a plurality of metabolic pathways and is a multifunctional transcription factor.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI CAAS
Plant salt tolerance related miRNA (microribonucleic acid) and application thereof
The invention discloses plant salt tolerance related miRNA (microribonucleic acid) which is derived from thellungiella halophila and named tsa-miRn646. The tsa-miRn646 has an RNA sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table; and a precursor of the tsa-miRn646 has an RNA sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:2 in the sequence table. The tsa-miRn646 disclosed by the invention can promote the mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) degradation of transcription factor MYB, bZIP and bHLH genes and inhibit the expression of the transcription factor MYB, bZIP and bHLH genes. By overexpressing the miRNA shown as SEQ ID NO:1 or the miRNA precursor shown as SEQ ID NO:2 or inhibiting the expression of the miRNA shown as SEQ ID NO:1 or the miRNA precursor shown as SEQ ID NO:2 in crops such as wheat, rice, corn and cotton, transgenic crops having high salt tolerance can be cultivated. The tsa-miRn646 disclosed by the invention has important meanings and potential application values in the cultivation of salt-tolerant crops.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Plant disease-resistant protein BjMYB9 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN106146634AIncrease resistanceImprove disease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyPromoter activity
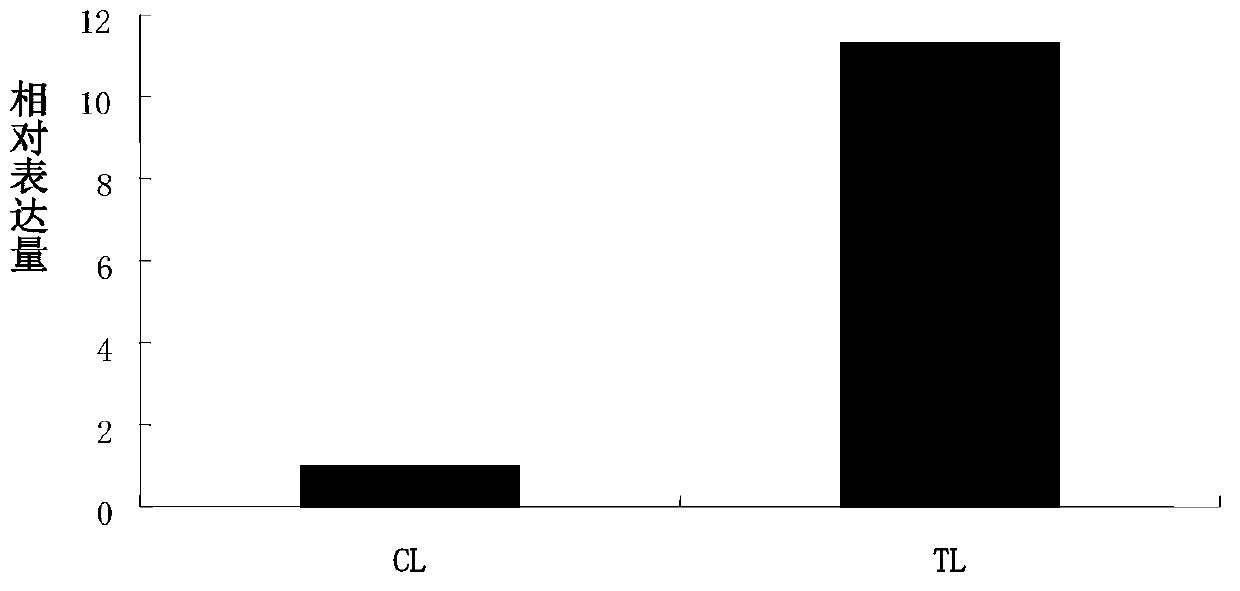
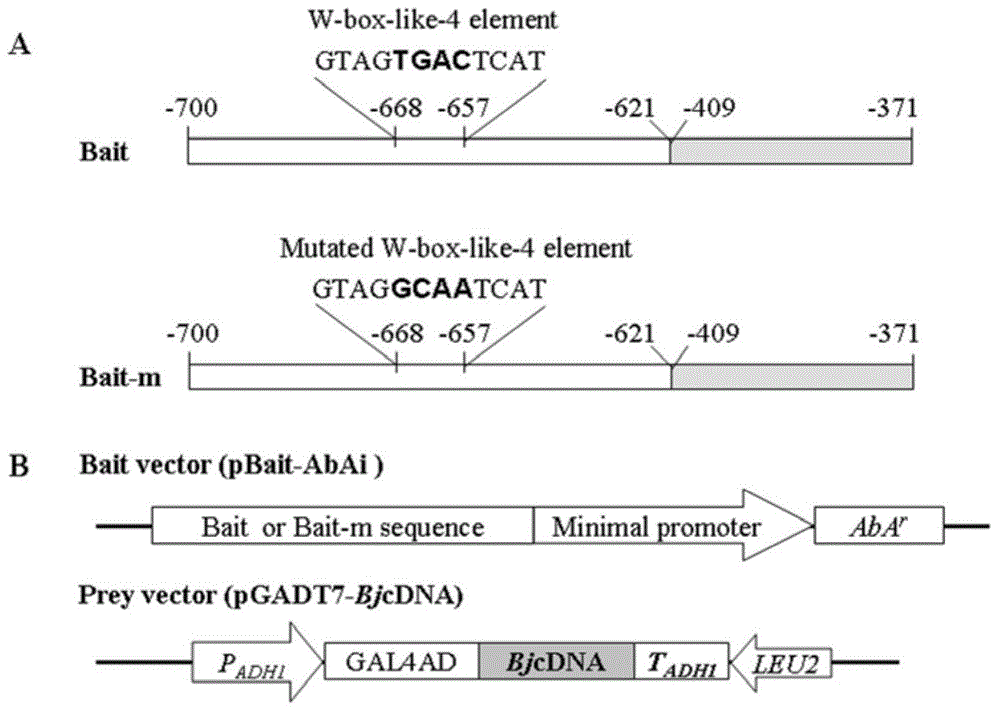
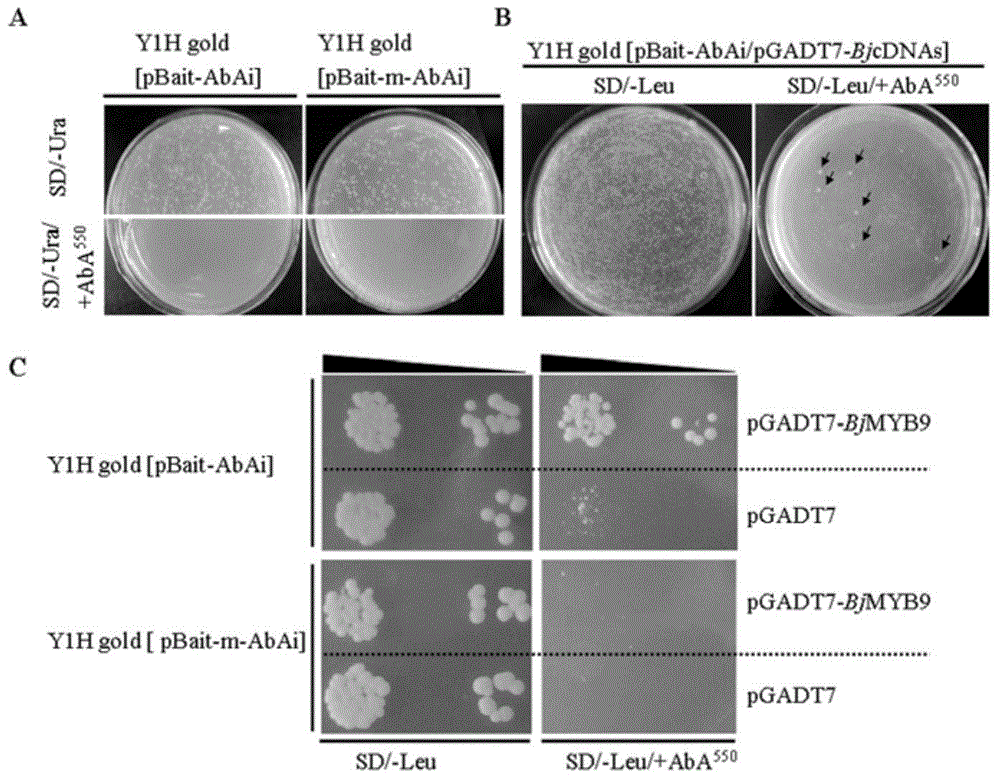
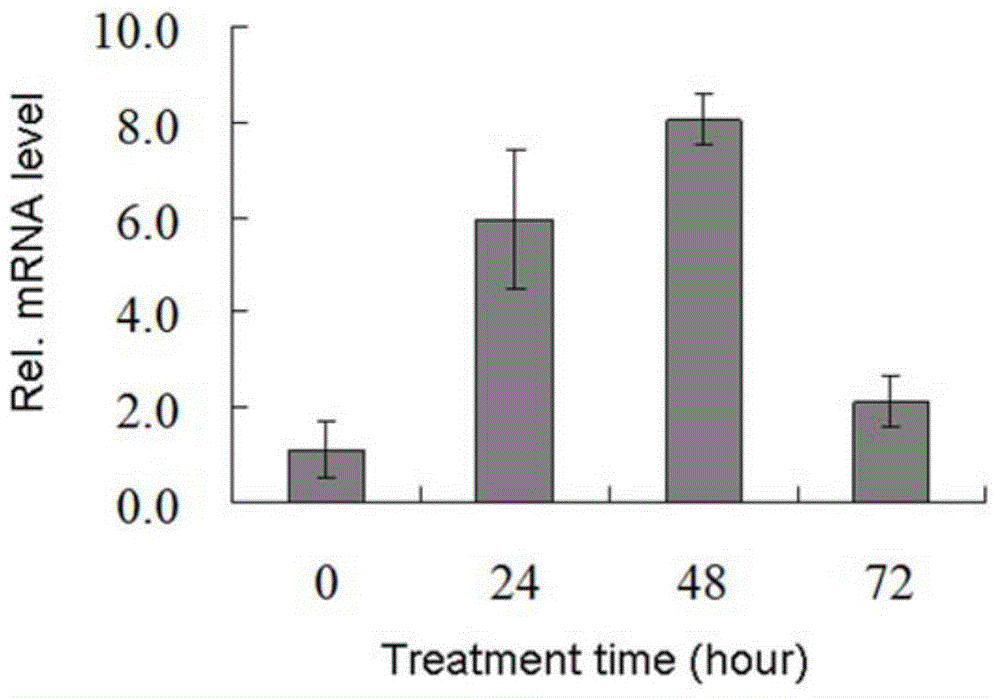
The invention discloses Brassica juncea disease-resistant protein BjMYB9 as well as an encoding gene sequence and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the disease-resistant protein BjMYB9 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene of the disease-resistant protein BjMYB9 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. A R2R3-MYB type transcription factor capable of being specifically bound with a fungus inducing core element W-box-like-4 in a promoter BjC-P of a Brassica juncea disease-resistant gene BjCHI1 is screened with a yeast one-hybrid technology and is named as BjMYB9. A gel retardation experiment and a tobacco transient expression experiment prove that BjMYB9 can be specifically bound with W-box-like-4 and activates the promoter. Expression of the BjMYB9 gene in Brassica juncea RNA is obviously induced by fungi, the gene can significantly enhance the resistance of arabidopsis thaliana to Botrytis cinerea after overexpression in a model plant arabidopsis thaliana, thereby providing an experimental basis and genetic resource for revealing of the plant disease-resistant mechanism and cultivation of disease-resistant varieties.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cold induced promoter p-LTT1 for rice and application thereof
The invention discloses a cold induced promoter p-LTT1 for rice and application thereof. The invention provides a DNA fragment having the function of the promoter, the DNA fragment is derived from oryzae rufipogon (O.rufipogon Griff.), and is a DNA molecule of the following 1), 2) or 3): 1) a DNA molecule expressed by sequence 1 of a sequence table; 2) a DNA molecule capable of hybridizing with the DNA sequence limited by the 1) under strict conditions and having the function of the promoter; and 3) a DNA molecule having over 90 percent of homology with the DNA sequence limited by the 1) and having the function of the promoter. The DNA fragment has the function of the promoter, comprises ABRE and MYB and other stress response elements, is specifically expressed in rice bud, stigma and anther, and has the characteristics of low temperature induced expression. The cold induced promoter p-LTT1 has important theoretical and practical significance for researches on a cold-resistant molecular mechanism of the rice and cold-resistant molecule breeding of the rice. The promoter has broad application and market prospect in the field of agriculture.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Gene for regulating polar wood yield and application thereof
InactiveCN105755010AGreat research valueGreat application potentialPlant peptidesFermentationMYBGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and particularly discloses a gene for regulating polar wood yield and application thereof.A base sequence of an R2R3-MYB gene PagMYB199 is shown as in SEW ID No.1.The application refers to application of the PagMYB199 gene serving as a regulating gene for increasing polar wood yield so as to shorten breeding circle of polar.The PagMYB199 gene is obtained by cloning in hybrid polar (Populus albaXP.glandulosa cv''84k') and has wide application prospect and great economic value.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Soybean specific response low-phosphorous transcription factor GmPHRLP and application
InactiveCN108728451APromote absorptionIncrease biomassPlant peptidesFermentationBinding sitePhosphate Transporters
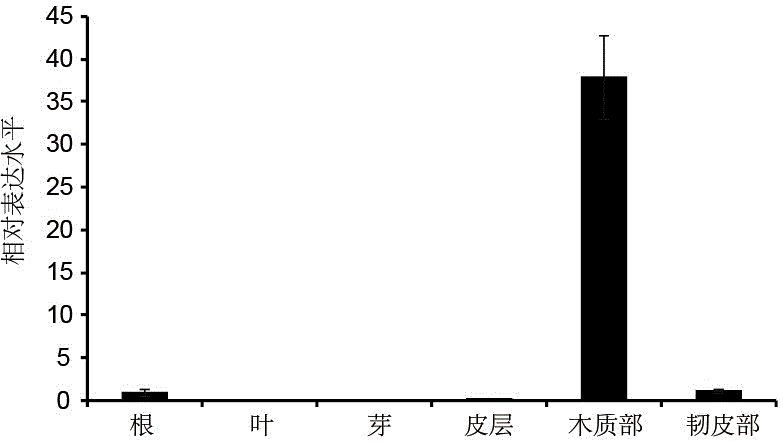
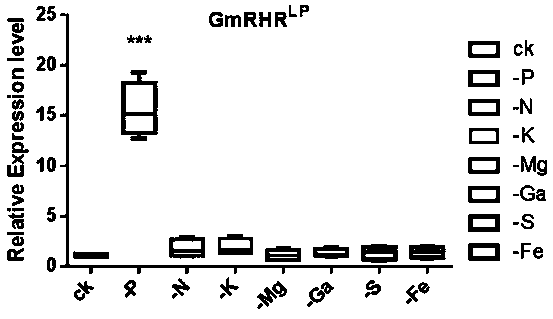
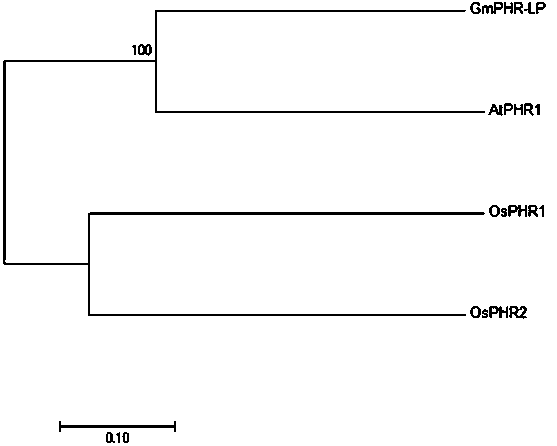
The invention provides a soybean specific response low-phosphorous transcription factor GmPHRLP and an application. A soybean variety 'BX10' serves as a material, a transcription factor is discoveredby RNA-seq, the expression level of the transcription factor is remarkably improved under the condition of phosphorus deficiency, a specific primer of a gene is designed by a sequencing joint sequence, cloned and subjected to homologous analysis, a result discovers that the transcription factor belongs to an MYB-CC family, the transcription factor and a phosphorous signal center regulating factorof model plant Arabidopsis and rice have high protein homology, P1BS (PHR1 Binding Sites) can be combined, expression of the transcription level of the transcription factor is affected by low-phosphorus specific induction, expression of a phosphate transporter protein can be induced, and absorption and transport of phosphorus are increased under low phosphorus. The gene is over-expressed in soybean hair roots, so that phosphorus absorption of soybeans can be improved, and biomass of the soybeans is remarkably improved under low-phosphorus culture conditions.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
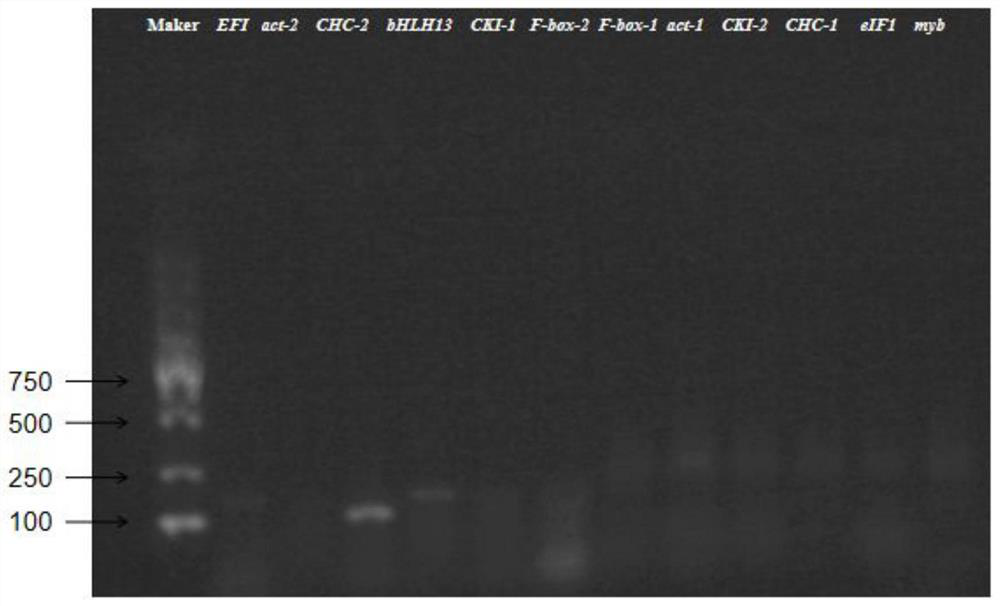
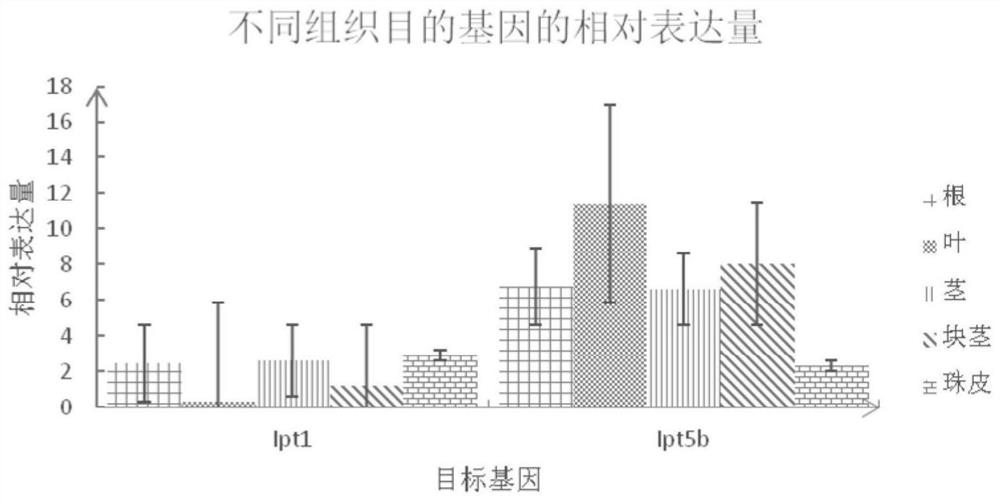
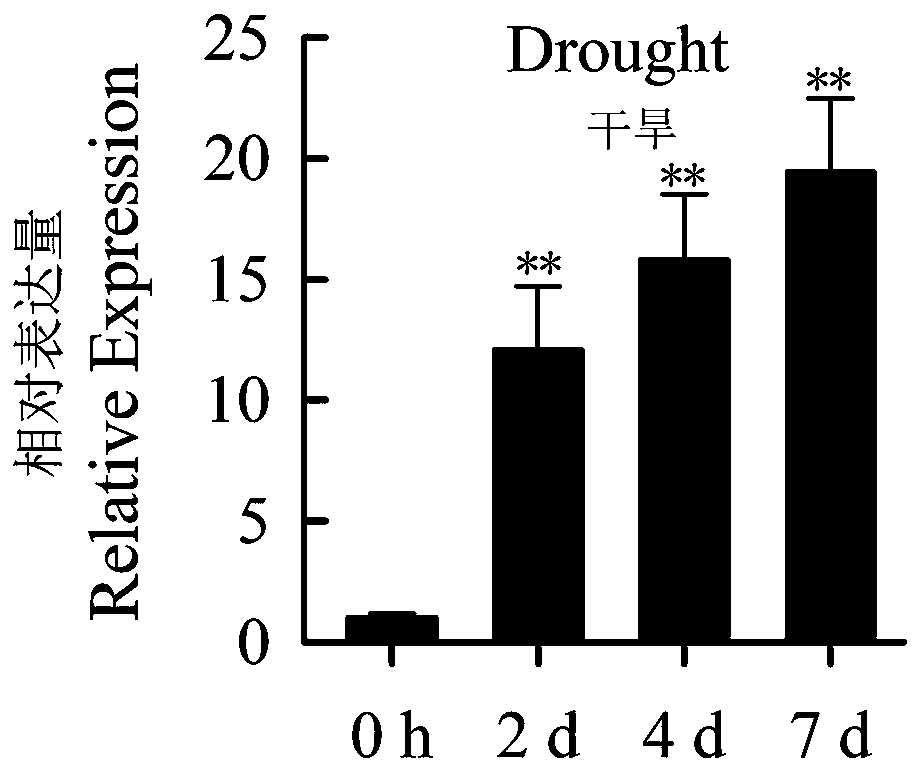
Reference gene for fluorescence quantification of different tissues of Chinese yam and primers and application thereof
ActiveCN112575010AMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesCandidate Gene Association StudyTissue fluorescence
The invention relates to a reference gene for fluorescence quantification of different tissues of Chinese yam and primers and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology of Chinese yam. The nucleotide sequence of the reference gene CKI-2 is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The nucleotide sequence of a PCR amplification primer of the reference gene CKI-2 is as follows: anupstream primer is shown as SEQ ID NO.2; and the downstream primer is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3. Protein kinase I, myb, F-box, actin gene, EF1, bHLH13, eIF1, grid heavy chain protein and other genes are selected as candidate genes of different tissues. The stability of candidate genes is evaluated through qRT-PCR in combination with RefFind, reference genes stably expressed in different tissues ofthe Chinese yams are selected out through screening, and a reference basis is provided for later development of research work such as gene function verification of growth and development and metabolicmechanisms of the Chinese yams.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
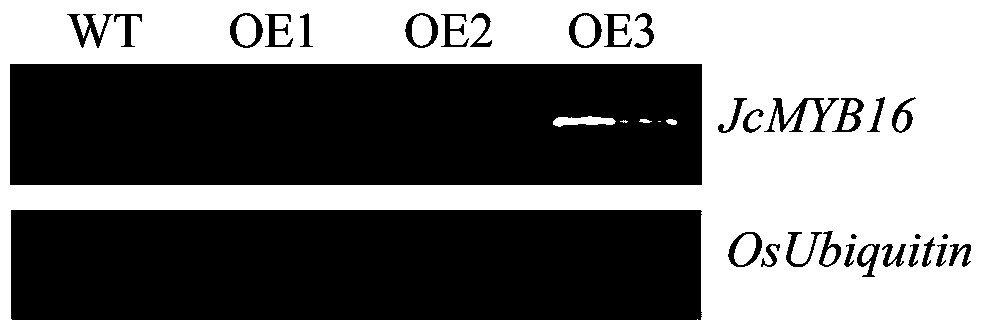
Jatropha curcas L MYB class transcription factor JcMYB16 gene and application in improving plant drought resistance
ActiveCN110643618AImprove drought resistanceImprove drought stress resistanceBacteriaPlant peptidesOpen reading frameNucleotide
The invention provides a Jatropha curcas L MYB class transcription factor JcMYB16 gene. A gene nucleotide sequence of the Jatropha curcas L MYB class transcription factor JcMYB16 gene is SEQ ID NO.1,a nucleotide sequence of a gene open reading frame of the Jatropha curcas L MYB class transcription factor JcMYB16 gene is SEQ ID NO.2, overexpression of JcMYB16 gene does not affect plant growth anddevelopment, and drought stress resistancecan be significantly improved. The gene can be used in the cultivation of drought resistance varieties of cereal crops, such as Jatropha curcas L, rice and wheat, and can further be used in the cultivation of drought resistance varieties of crops, such as barley, sorghum, corn, arabidopsis, tomatoes, tobacco, soybeans and potatoes.
Owner:ZHOUKOU NORMAL UNIV
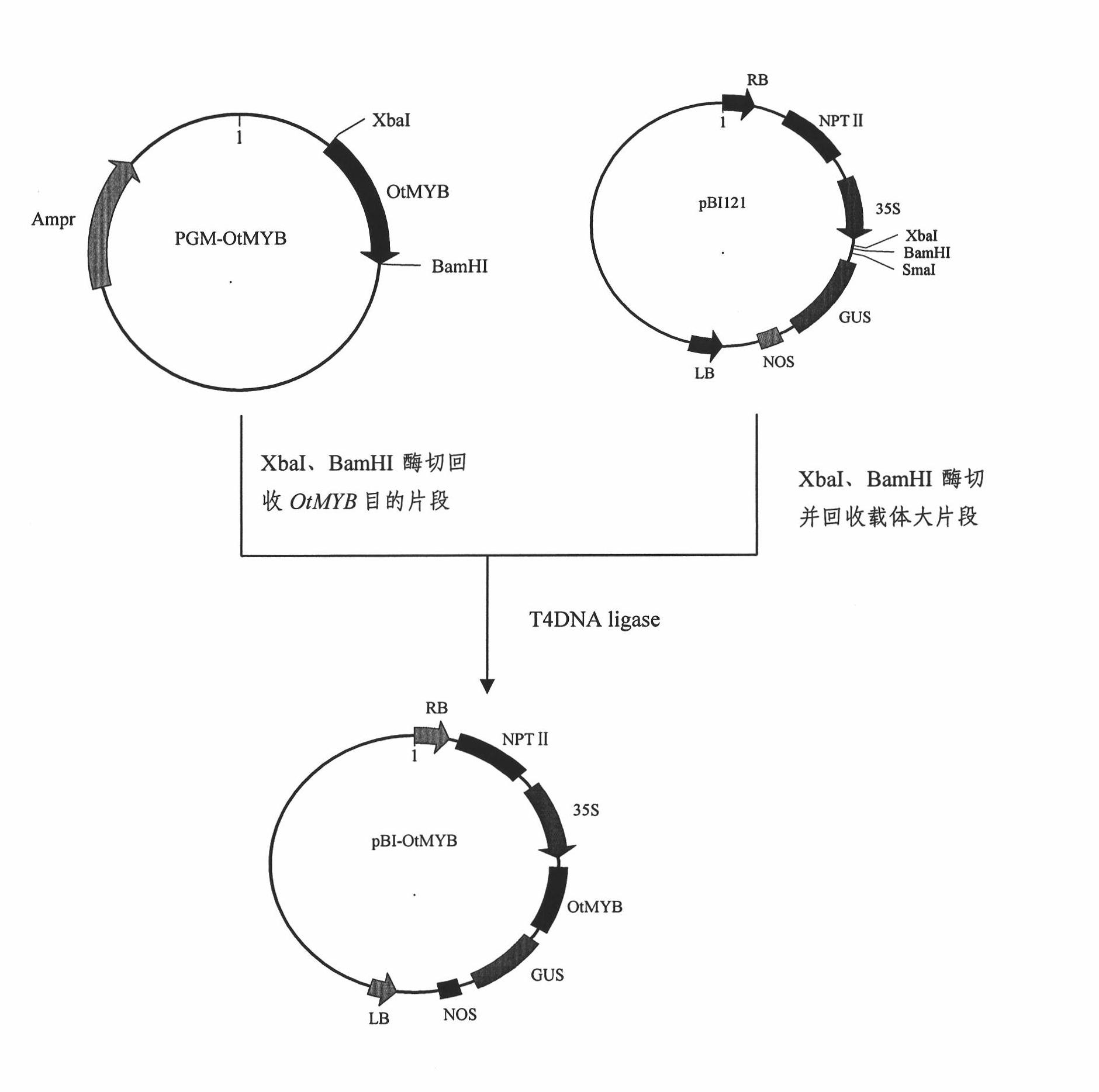
Chrysanthemum drought-tolerant gene and application thereof
ActiveCN101928337AIncrease resistanceImprove stress resistanceFungiBacteriaDrought toleranceDrought resistance
The invention relates a chrysanthemum drought-tolerant related gene OtMYB, and simultaneously relates to application of the OtMYB gene in improving chrysanthemum drought-tolerant capability. The chrysanthemum drought-tolerant gene has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1. The gene has a DNA bond zone of two typical MYB transcription factors, belonging to a typical R2R3-MYB transcription factor. The OtMYB is related to the chrysanthemum drought tolerance, and the gene is transcribed to a common chrysanthemum variety through genetic transformation, so that the resistance of the chrysanthemum variety on drought stress can be effectively improved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Prognostic and treatment response predictive method
PendingUS20200239968A1Avoiding unwanted side effectAggressive treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDPYDPredictive methods
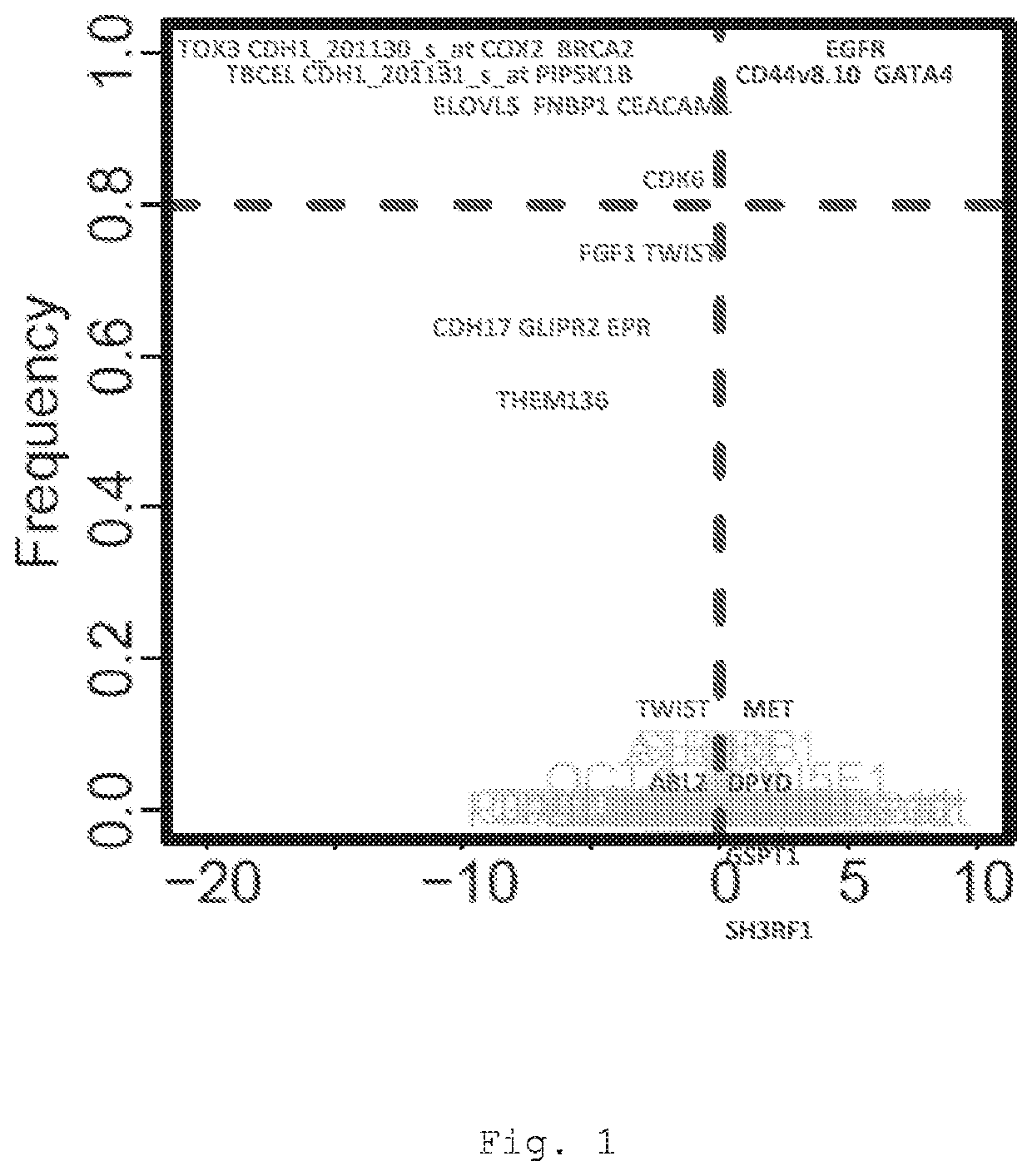
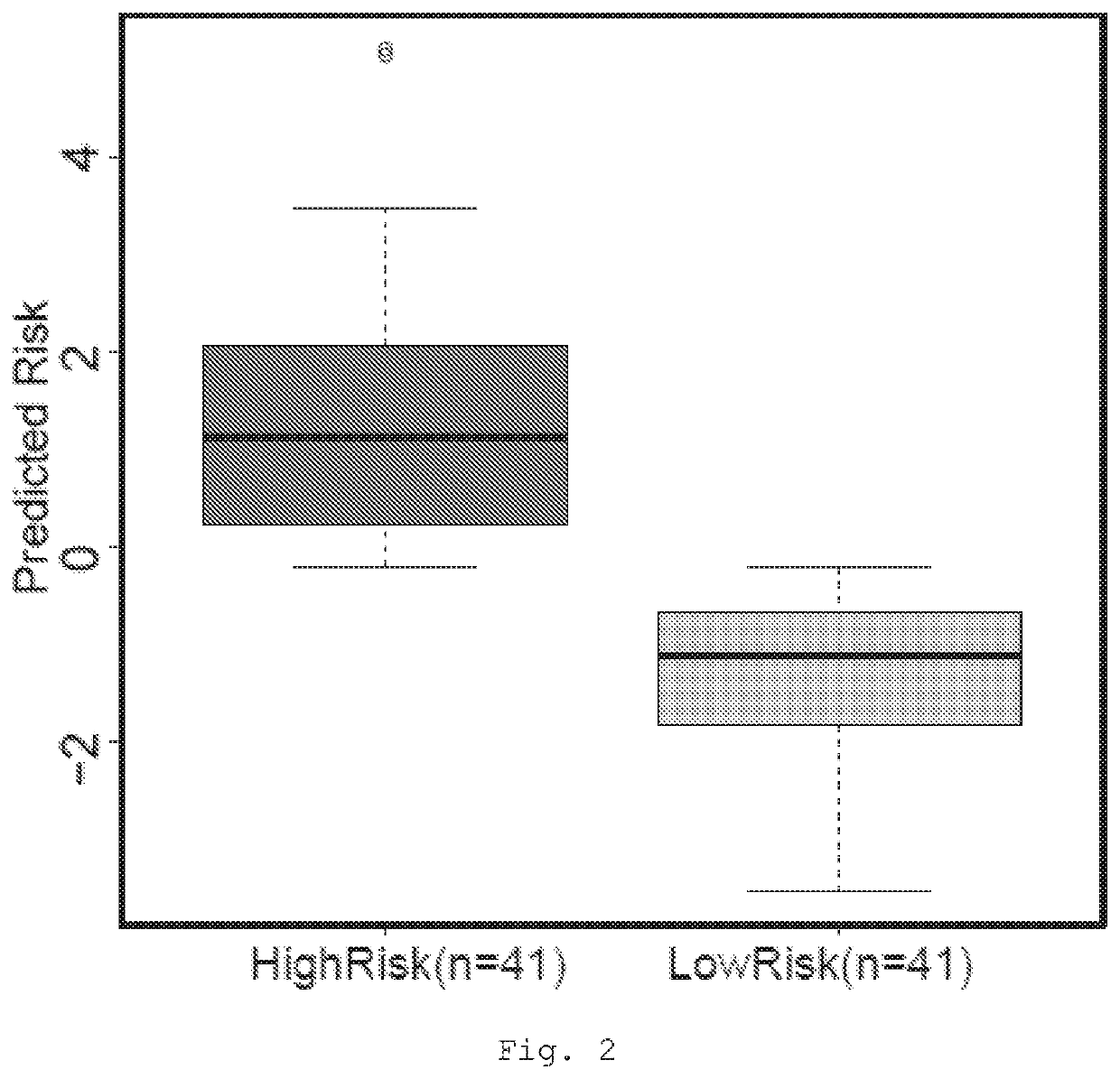
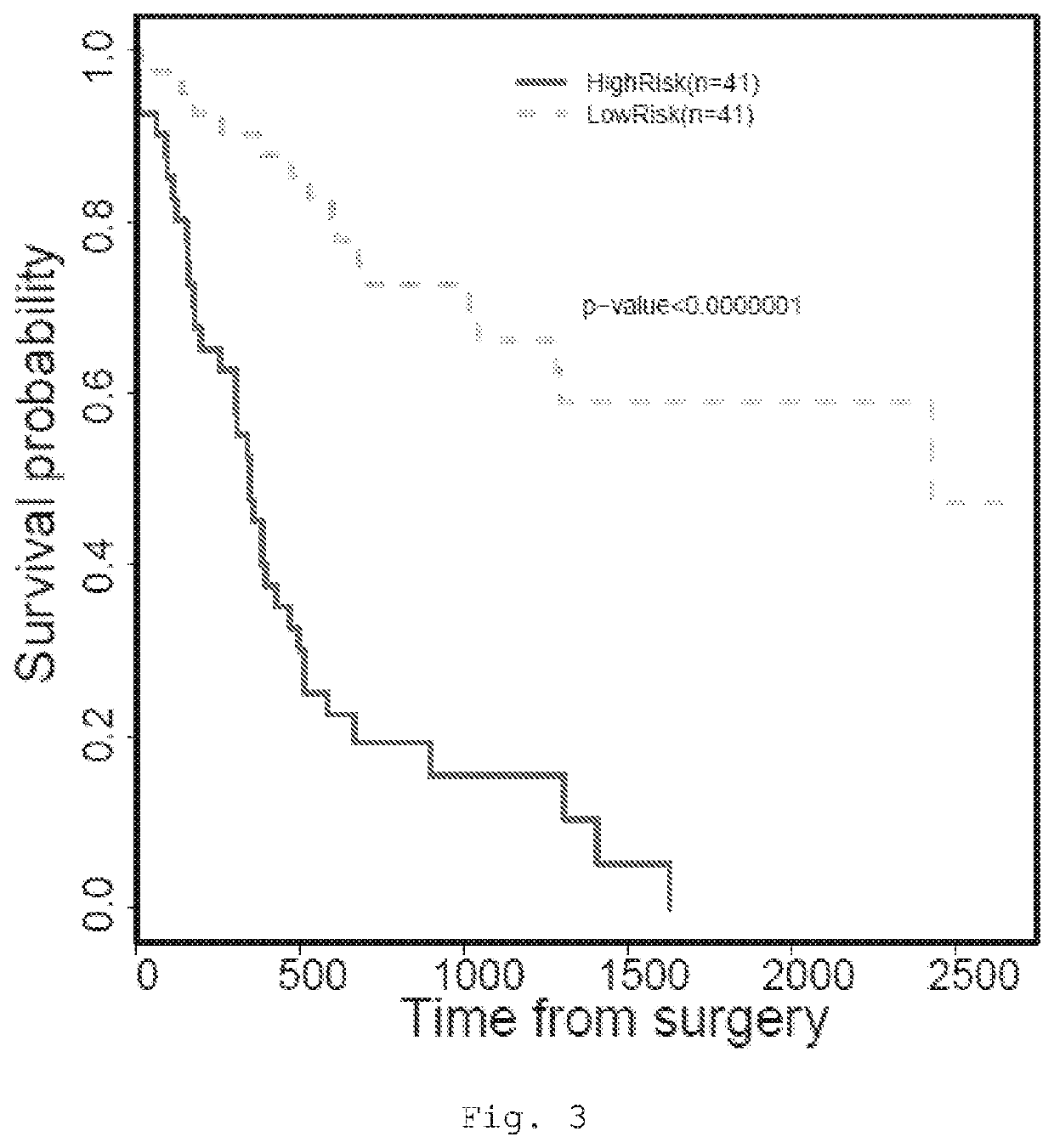
The present invention provides a method for predicting the treatment response of a human gastroesophageal cancer patient, the method comprising: a) measuring the gene expression of at least 3 of the following genes: CDH1, CDK6, COX2, ELOVL5, GATA4, EGFR, TBCEL, FGF7, CDH17, FNBP1, PIP5K1B, TWIST, CD44, MET, CEACAM1, TOX3, GLIPR2, GSTP1, RON, TMEM136, MYB, BRCA2, FGF1, POU5F1, EPR, DPYD, ABL2 and SH3RF1 in a sample obtained from the gastroesophageal tumour of the patient to obtain a sample gene expression profile of at least said genes; and b) making a prediction of the treatment response and / or prognosis of the patient based on the sample gene expression profile. Also provided are related computer-implemented methods and methods of treatment of gastroesophageal cancer.
Owner:THE INST OF CANCER RES ROYAL CANCER HOSPITAL +2
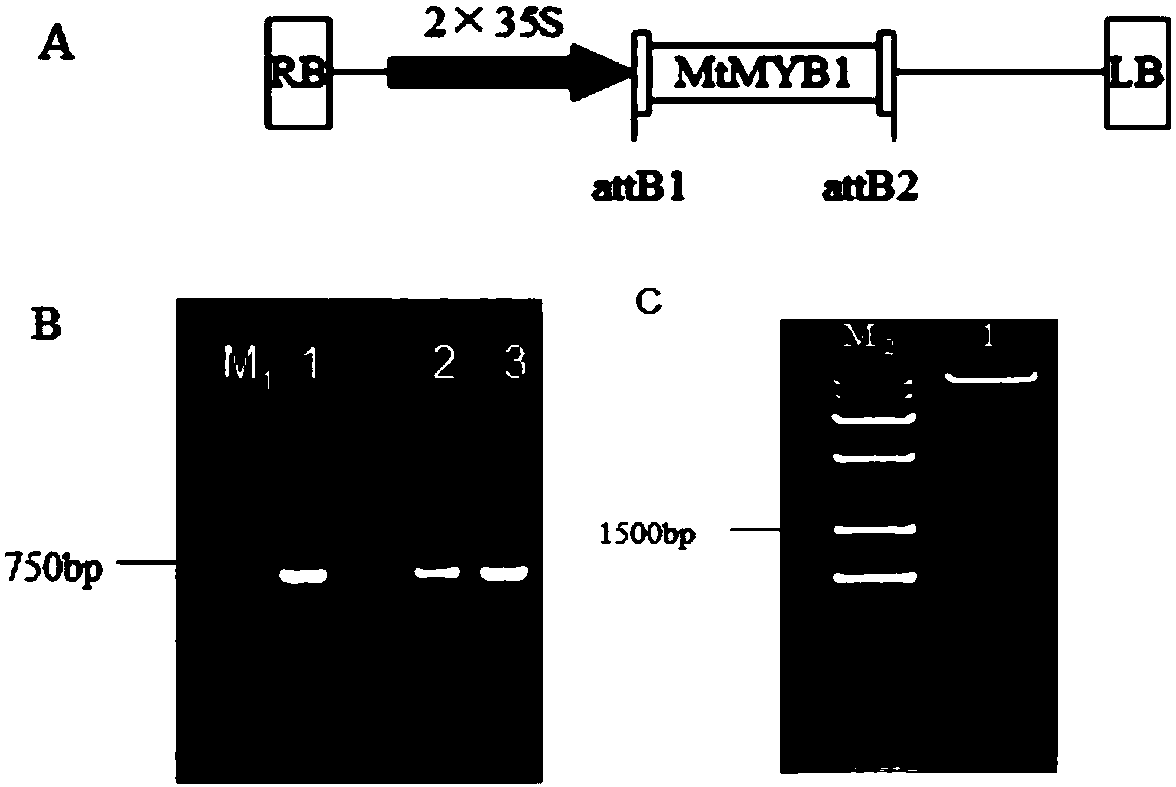
Application of medicago truncatula MYB transcription factor MtMYB1
ActiveCN107937413AImprove the efficiency of seed production servicesIncrease productionPlant peptidesFermentationType transformationArabidopsis
The invention discloses application of a medicago truncatula MYB transcription factor MtMYB1. According to the invention, a gene MtMYB1 for regulating and controlling development, flowering phase andgrowth period of floral organs and changing a plant type is colonized from medicago truncatula flower, and the sequence of the gene MtMYB1 is SEQ ID NO.1. The analysis of mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid) expression of the gene shows that the MtMYB1 is expressed in flower tissues with strong advantages; phenotypic change of arabidopsis thaliana for further over-expression of the MtMYB1 shows thatthe MtMYB1 has an important regulation and control effect on the development, the flowering phase and the growth period of the floral organs and the plant type. The invention discloses the applicationof the gene in genetic engineering of morphology, the flowering phase and the growth period of the floral organs as well as plant type transformation.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
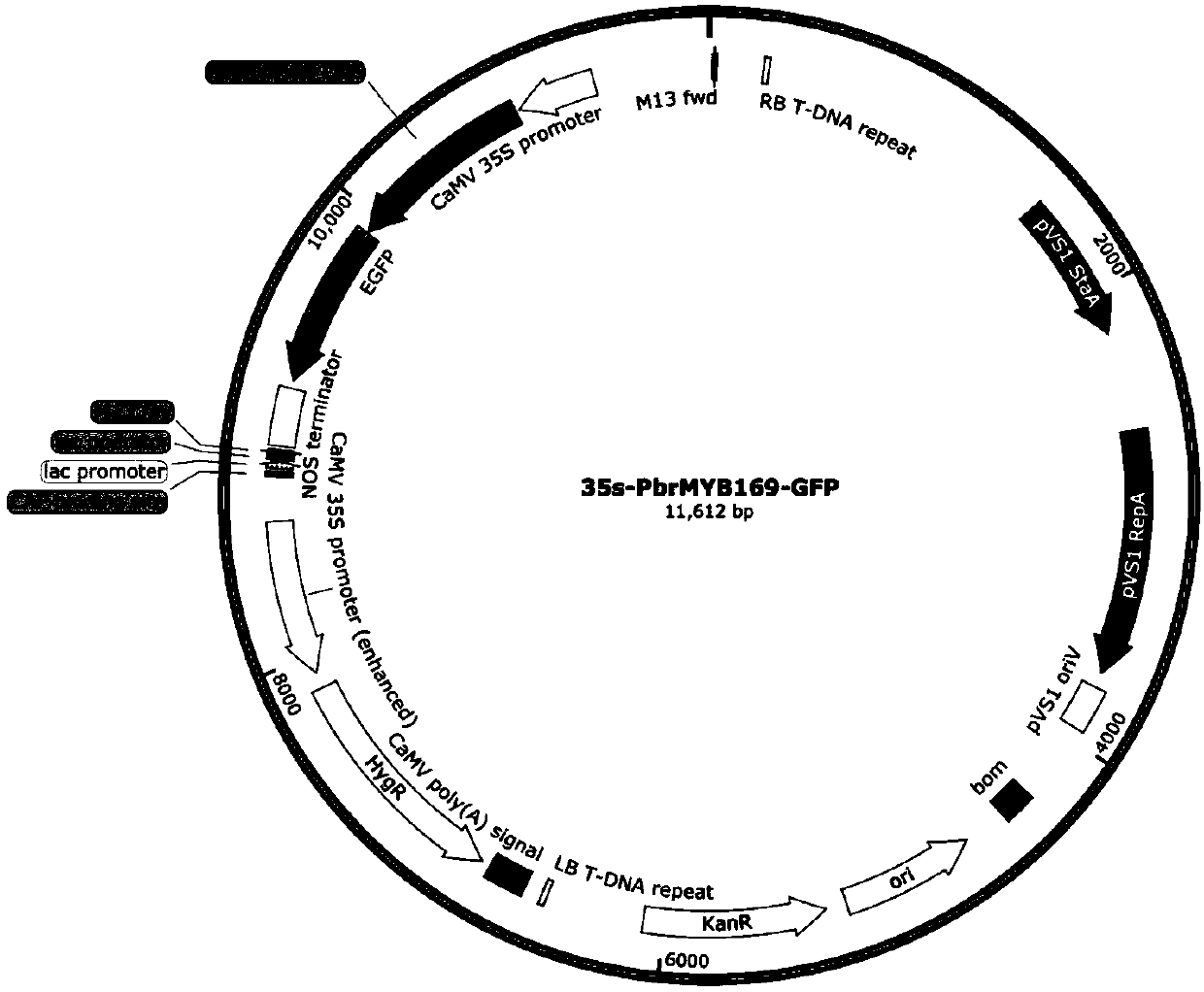
Pear transcription factor PbrMYB169 and application thereof
ActiveCN109609514AAchieve friendlyReduce the cost of farmingBacteriaPlant peptidesAgricultural scienceSclereid
The invention discloses a pear transcription factor PbrMYB169 and an application thereof. The pear transcription factor PbrMYB169 is separated from Dangshan crisp pears, and has MYB family member PbrMYB169 genes capable of adjusting and controlling development of sclereid of pear fruits, the nucleotide sequence of the pear transcription factor PbrMYB169 is as shown in SEQID No.1, and the coding amino acid sequence of the pear transcription factor PbrMYB169 is as shown in a sequence table SEQID No.2. Through an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated heredity conversion method, PbrMYB169 transcription factors are converted into arabidopsis thaliana, and transgenic plants are obtained; biological function verification indicates that the PbrMYB169 gene cloned through the pear transcription factorPbrMYB169 has the function of promoting synthesis of arabidopsis thaliana inflorescence stem lignin, besides, the PbrMYB169 transcription factor has the advantage of being capable of adjusting and controlling a plurality of genes, and an efficient way is provided for molecular breeding. New genetic resources are provided for reduction of molecular breeding of synthesis of organism lignin, new heredity resources are provided for implementing green agriculture, and reduction of the agriculture cost and realization of an environmental-friendly purpose can be facilitated through development and utilization of the heredity resources.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Safflower MYB (v-myb myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (avian)) gene and application thereof
InactiveCN104845978AIncrease contentFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyViral Oncogene
The invention discloses a safflower MYB (v-myb myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog (avian)) gene. The safflower MYB gene has the advantages that the expression characteristic of a transcriptional modulatory gene is realized; by utilizing the transcription to modulate the expression of the related flavone metabolism gene, the content of total flavone in the safflower is improved, and a firm foundation is laid for culturing new products with high flavone contents.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
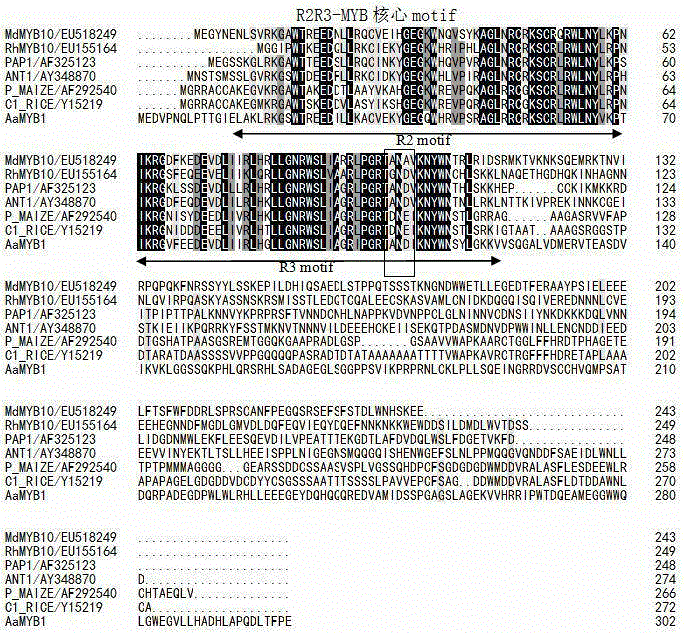
Anthurium myb transcription factor AaMYB1 and carrier, engineering bacterium and application thereof
The invention discloses an anthurium myb transcription factor AaMYB1 and a carrier, engineering bacterium and application thereof. The complete prediction amino acid sequence of the transcription factor AaMYB1 is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, and encoding genes are shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. The transcription factor synthesized by MYB regulating anthocyanin is cloned from anthurium for the first time, and the ability of a target plant to synthesize the anthocyanin is improved by means of over-expression.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XIAOSHAN COTTON & FLAX RES INST
Transgenic plants with altered levels of phenolic compounds
InactiveUS7154023B2Change levelSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPresent methodPlant cell
Methods for altering levels in plants of one or more phenolic compounds that are intermediates or final products of the plant phenylpropanoid pathway are provided. One method comprises transforming a plant cell with an expression construct comprising a nucleic acid which encodes a transactivator protein comprising the myb domain of the maize “ZmMyb-IF35” protein and an activation domain. Another method comprises transforming a plant cell with an expression construct comprising a transgene which encodes an antisense ZmMyb-IF35 RNA. The present invention also relates to expression constructs and vectors used in the present methods. transformed plant cells and transgenic plants prepared according to the present methods, and the seeds of such transgenic plants.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
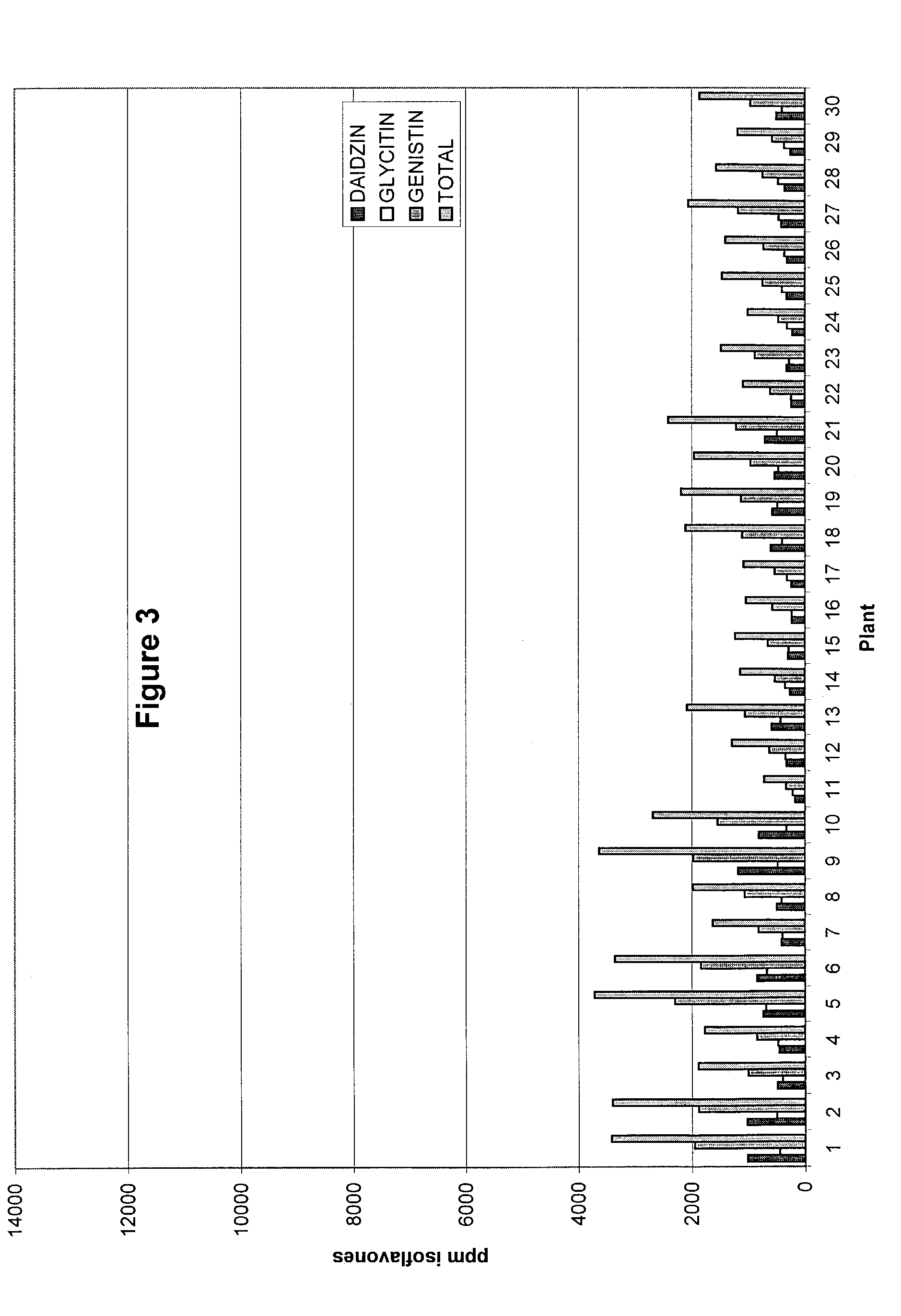
Methods to increase the isoflavonoid levels in plants and plants producing increased levels of isoflavonoids
InactiveUS7189895B2Easy to synthesizeImprove the level ofSugar derivativesHydrolasesIsoflavonoidIsoflavones
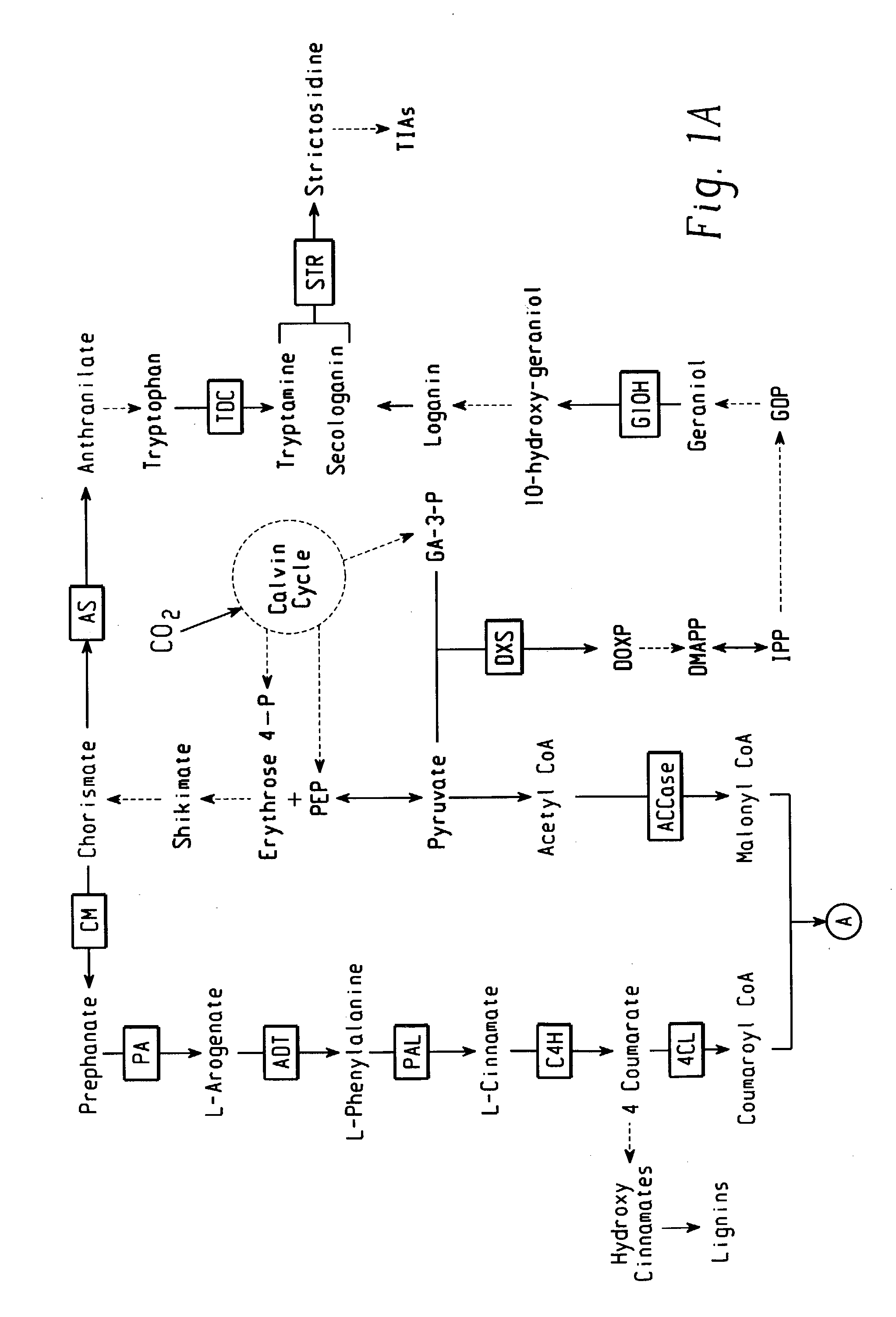
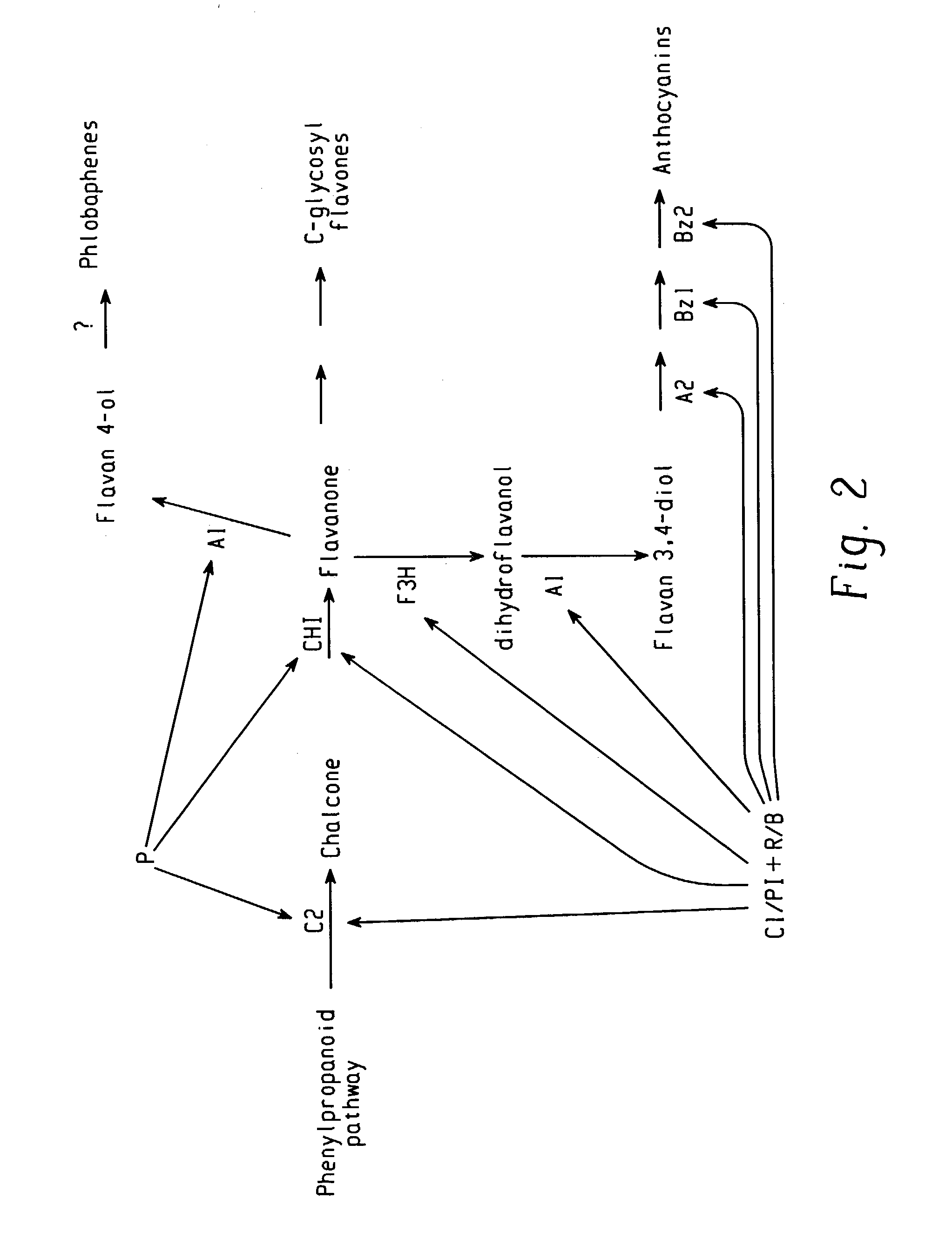
This invention pertains to methods of increasing isoflavonoid production in isoflavonoid-producing plants by transforming plants with at least one construct expressing at least a portion of a flavanone 3-hydroxylase, a C1 myb transcription factor, and an R-type myc transcription factor that regulate expression of genes in the phenylpropanoid pathway.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Methods of modulating production of phenylpropanoid compounds in plants
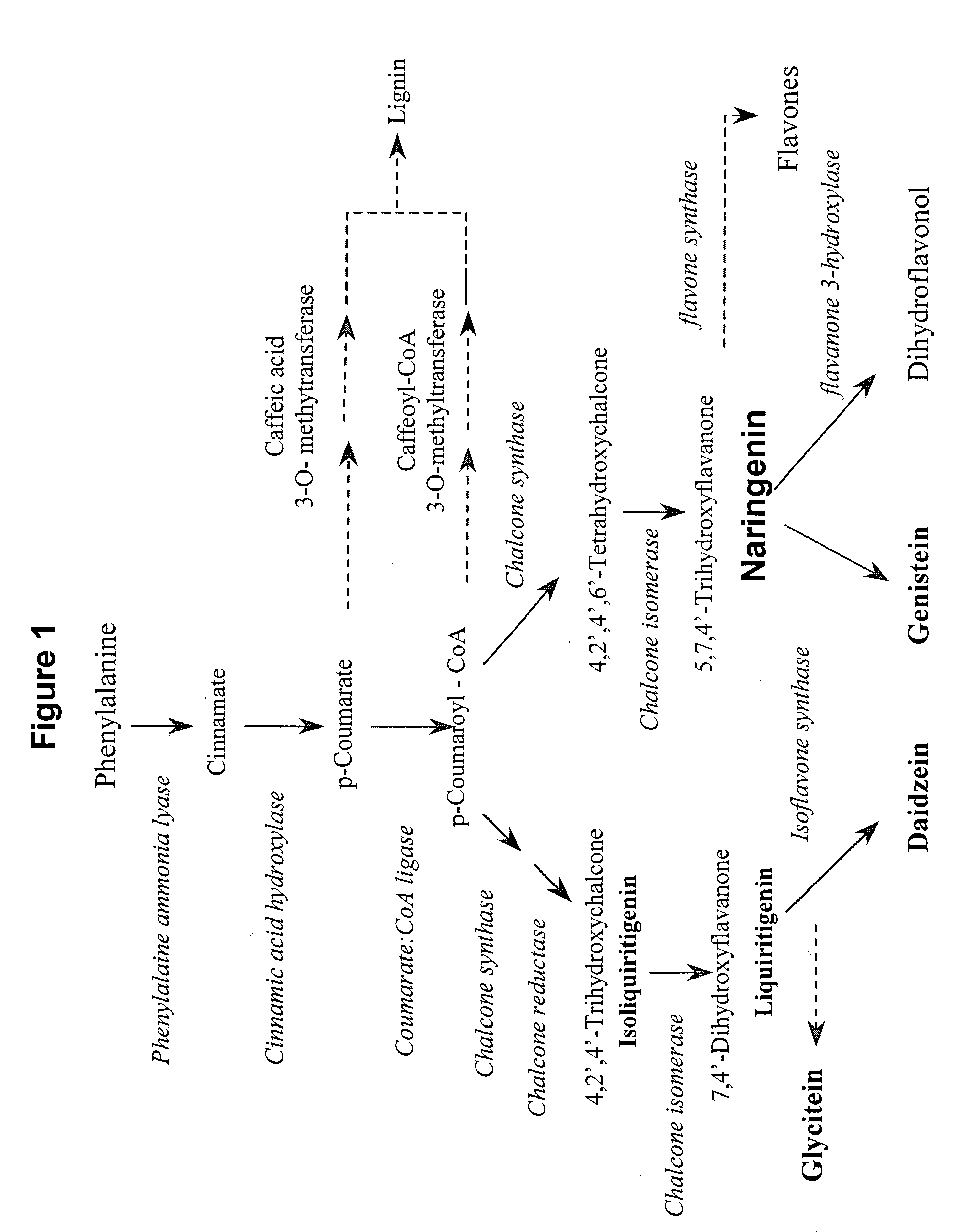
InactiveUS20100319091A1Increase productionImprove compoundSugar derivativesDepsipeptidesBenzeneBiotechnology
A method of enhancing production of a phenylpropanoid compound in a plant or plant cell is disclosed. The method comprising: (a) expressing in the plant or plant cell a heterologous polynucleotide which produces a myb gene of the phenylpropanoid pathway; and (b) contacting the plant or plant cell with at least one substrate of the phenylpropanoid pathway, the substrate being upstream to the production of the phenylpropanoid compound, thereby enhancing the production of a phenylpropanoid compound in the plant or plant cell.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
cDNA sequence of MYB transcription factors for positively regulating anthocyanin synthesis
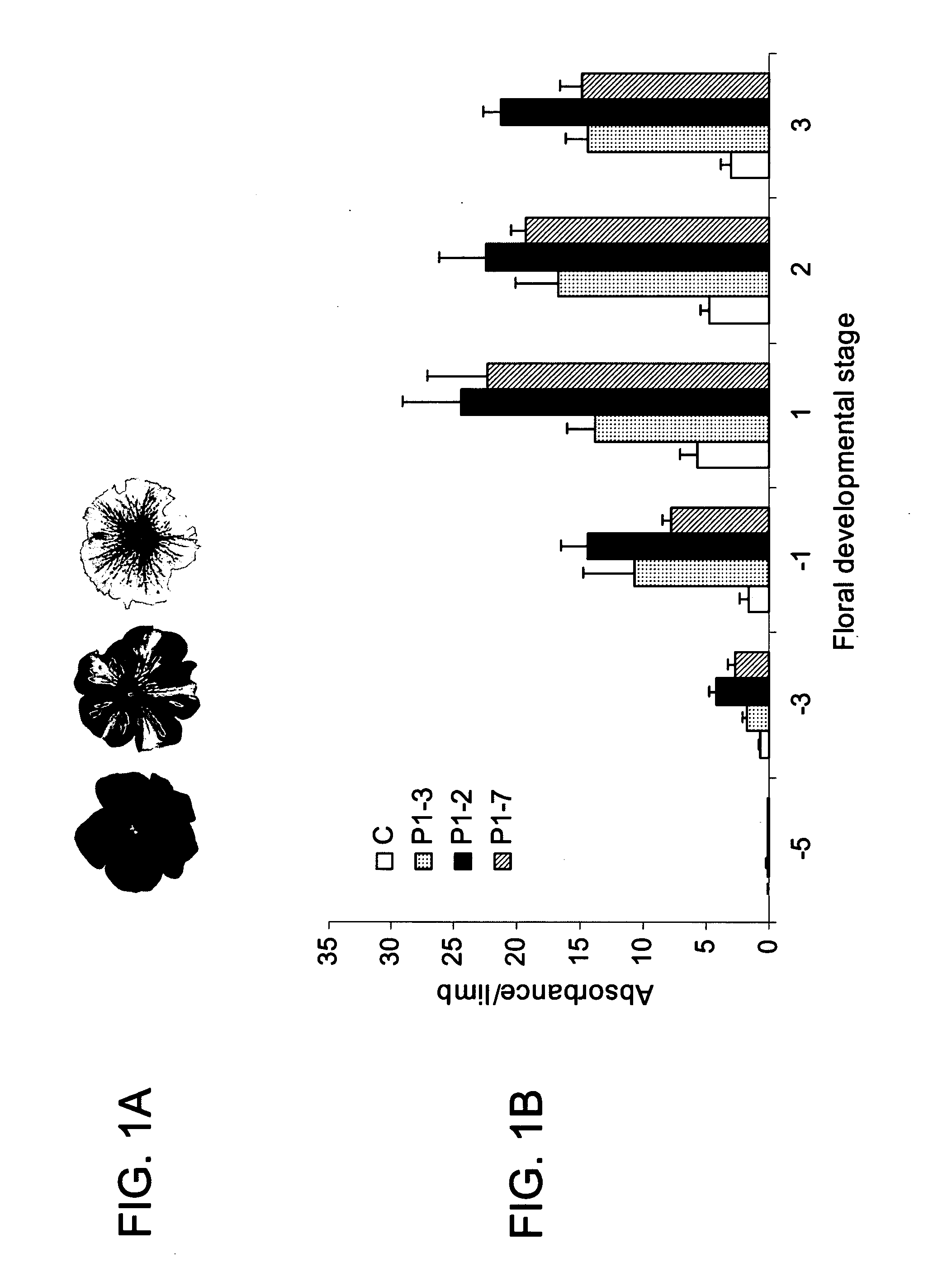
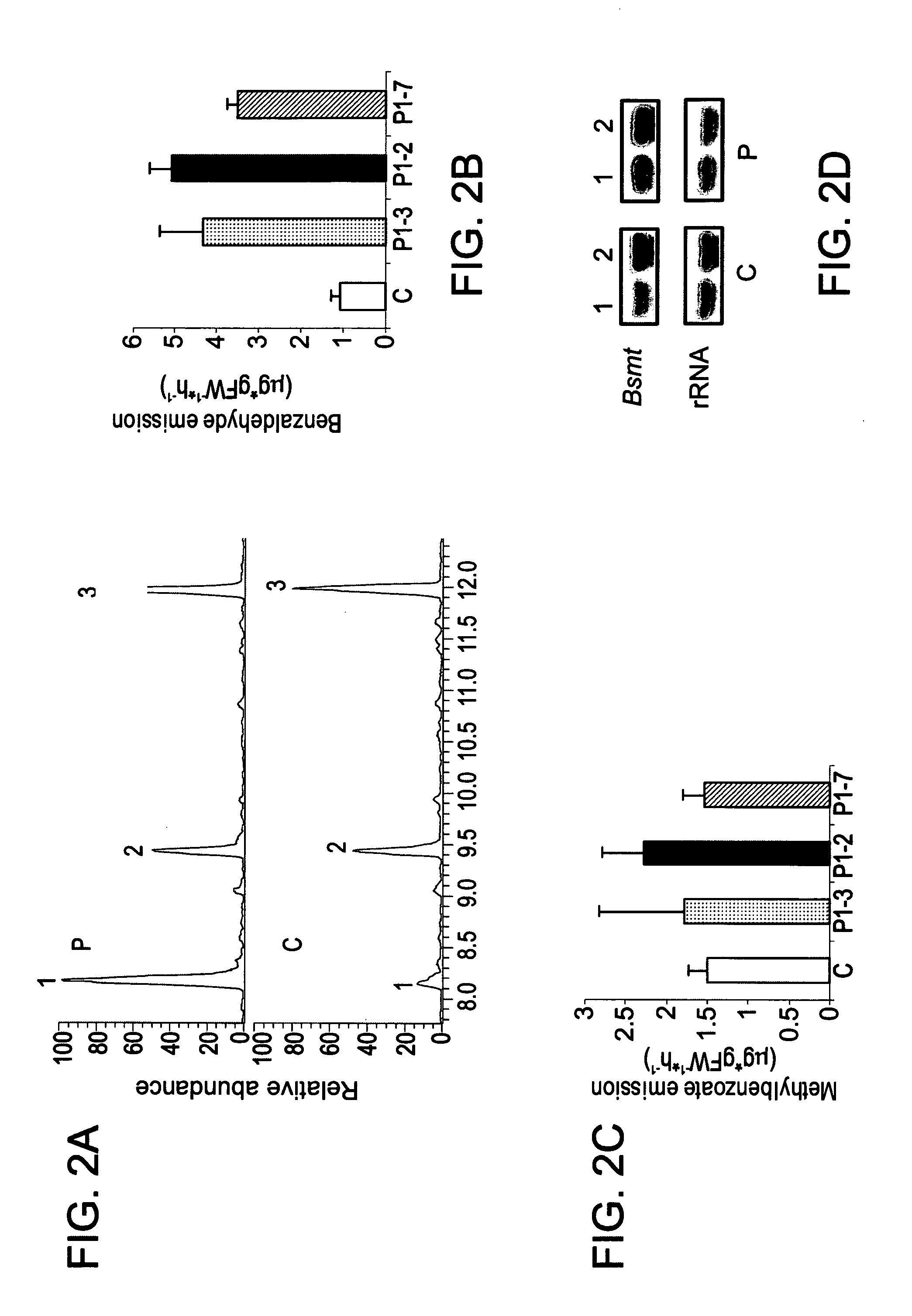
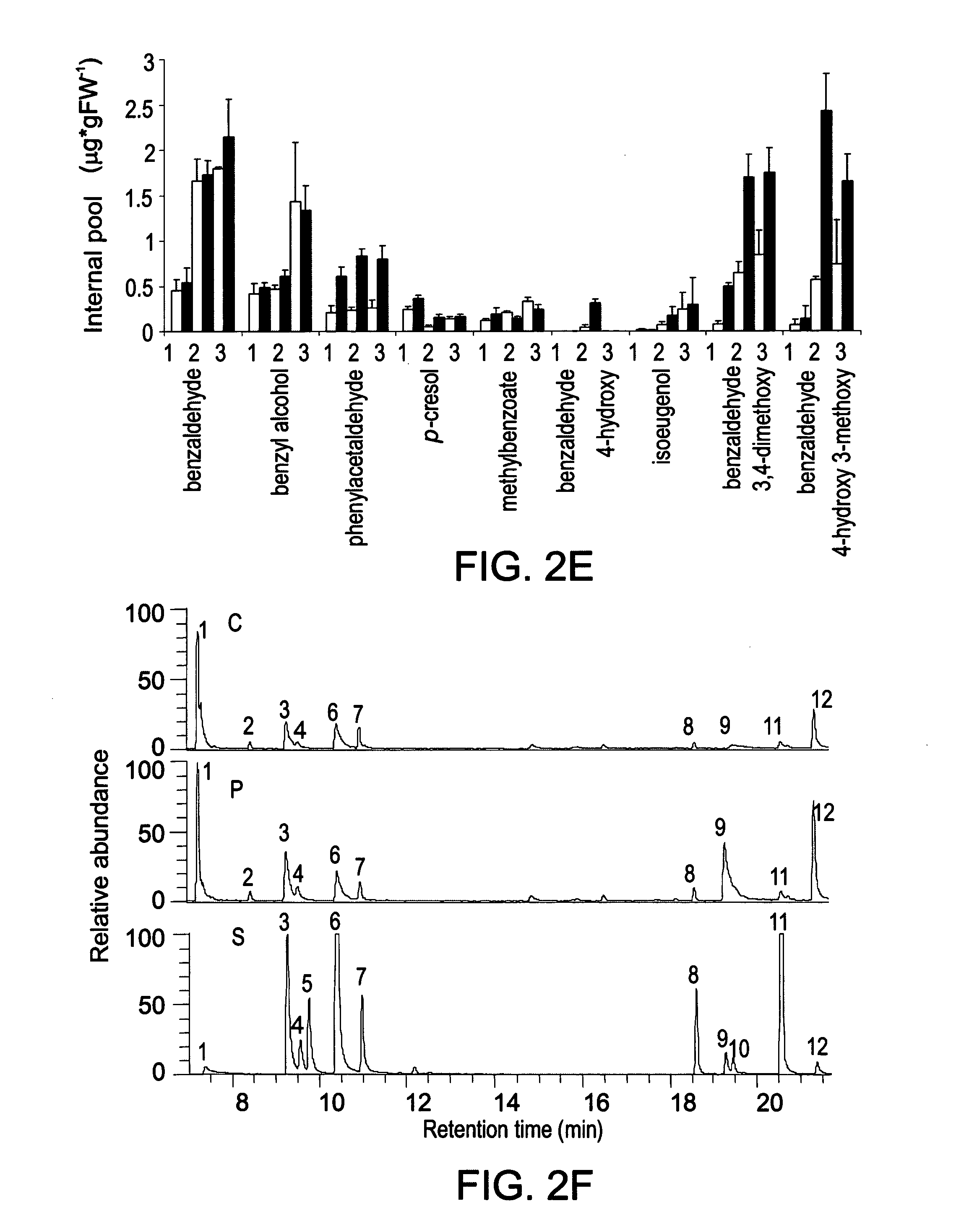
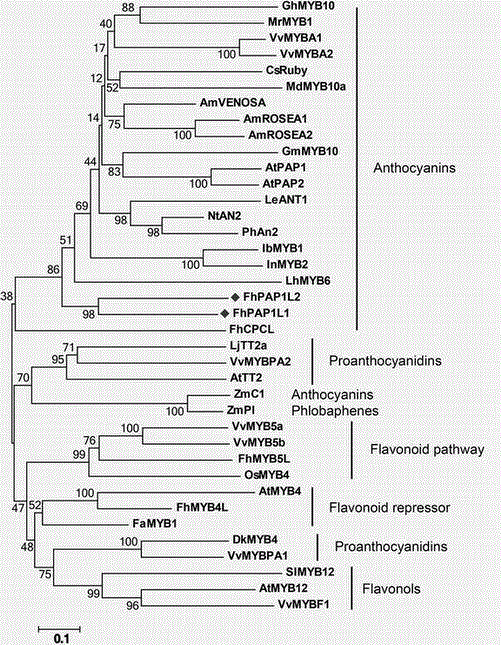
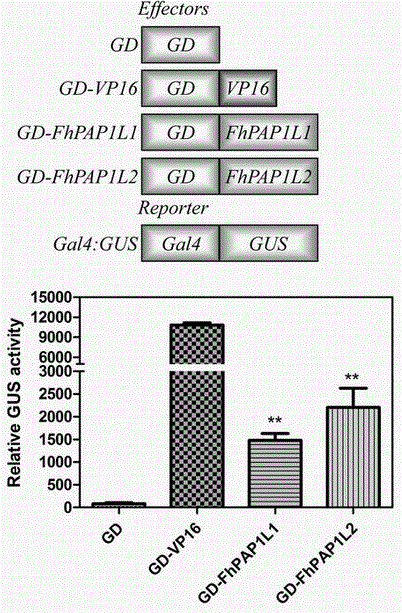
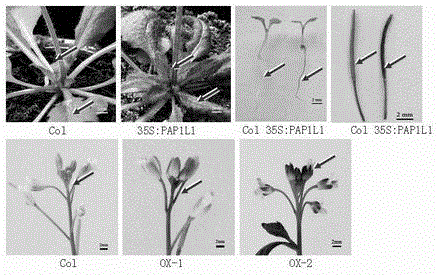
The invention discloses a cDNA sequence of two MYB transcription factors (FhPAP1L1 and FhPAP1L2) which are cloned from petals of freesia refracta for the first time and are used for positively regulating anthocyanin synthesis, and a coded amino sequence is obtained through conjecture. Through over-expression of FhPAP1L1 and FhPAP1L2 in arabidopsis thaliana and tobacco, coloring of plant tissues can be significantly enhanced, so that the function of the FhPAP1L1 and FhPAP1L2 of participating in the positive regulation for plant anthocyanin synthesis is determined.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com