Transcriptional factor relevant to resistant adversity from Arabidopsis thaliana, coded gene, and application
A transcription factor and stress tolerance technology, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problem of no ABRE consensus sequence, etc., achieve the effect of improving tolerance and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1. Screening of Arabidopsis thaliana R2R3 MYB-type transcription factor coding gene DRM related to stress tolerance and acquisition of its cDNA
[0047] After the seeds of Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia (Col-0) were vernalized at 4°C for 3-5 days, they were treated with 70% alcohol for 2-3 minutes on an ultra-clean bench, and then washed once with sterile water (1-2 minutes). ), then the seeds were treated with 15% sodium hypochlorite for 15 minutes, washed 5-6 times with sterile water, fully oscillated and mixed each time, and finally the seeds were suspended in 0.1% agar, and evenly spread on the culture medium containing MS medium Seal the Petri dish with a parafilm, place it at 23°C, and grow in the culture room with 24h continuous light.
[0048] After two weeks of growth with the above-mentioned Arabidopsis materials, the seedlings were taken, ground with liquid nitrogen, and the total RNA of the leaves was extracted with an RNA extraction kit (QIAGEN) accor...
Embodiment 2
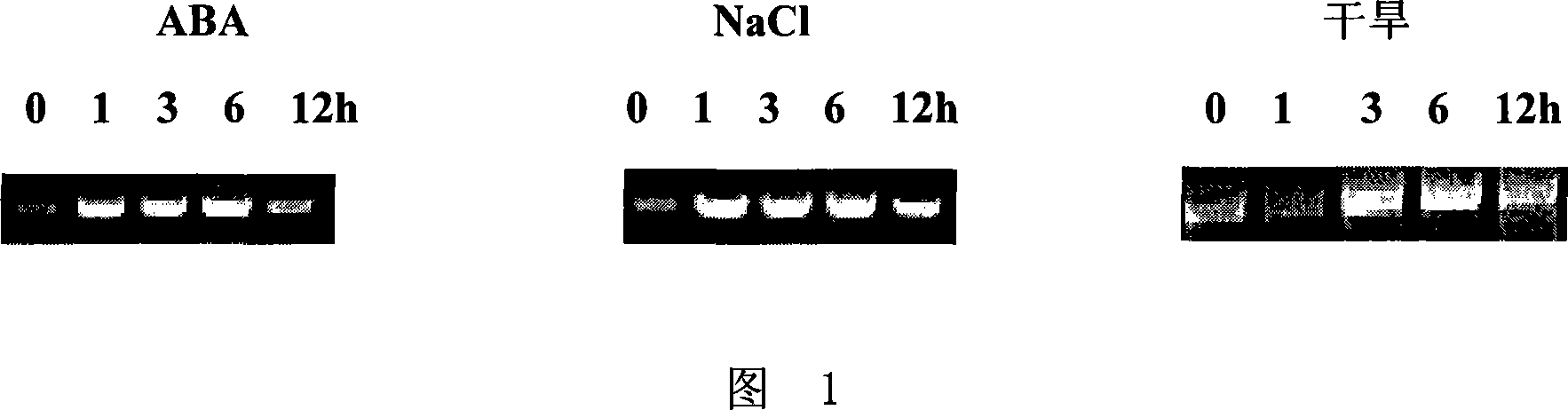
[0049] Example 2, the expression characteristics of the R2R3 MYB transcription factor encoding gene DRM related to stress tolerance in Arabidopsis under abiotic stress
[0050] 1. Detection of the expression characteristics of the R2R3 MYB-type transcription factor coding gene DRM in Arabidopsis thaliana under abiotic stress
[0051] The Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia was subjected to drought, NaCl, and ABA treatments respectively to analyze the expression of the Arabidopsis DRM obtained in Example 1 under abiotic stress. The specific method was: plant the seeds of Arabidopsis Columbia in pots After growing for 2 weeks, the seedlings were subjected to the following stress treatments:
[0052] Drought treatment: Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings were taken out from the soil to absorb the water on the roots, placed on dry filter paper, and then cultured under light conditions for 0 hour (control), 1 hour, 3 hours, 6 hours and 12 hours respectively. sampling.
[0053] Salt treatment...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3, Functional identification of DRM-encoded protein
[0066] Detect the impact of overexpressing DRM on plants with the following transgenic test, and the specific process includes the following steps:
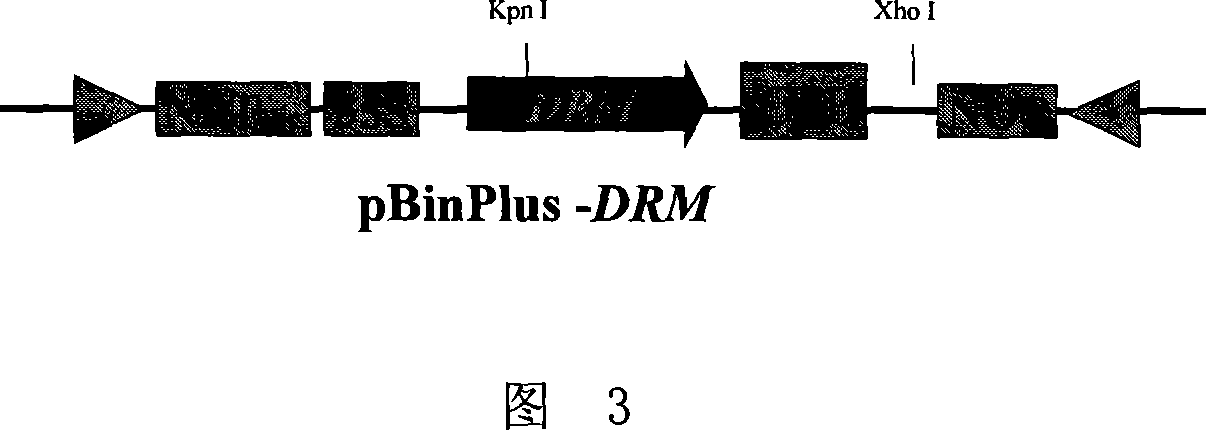
[0067] 1. Construction of DRM gene overexpression vector using 35S strong promoter
[0068] The recombinant vector pGEM-T-DRM carrying the DRM gene obtained in step 1 was double-digested with restriction endonucleases BamH I and Sma I, and the 858bp DRM gene fragment was recovered and purified. The cut vector pJIT163 (http: / / www.pgreen.ac.uk) was ligated to obtain a recombinant vector containing DRM and GFP coding regions, and then the recombinant vector was double-digested with restriction endonucleases Kpn I and Xho I , and then combined with the plant expression vector pBinPlus (Van Engelen, F.A., Molthoff, J.W., Conner, A.J., Nap, J.P., Pereira, A. and Stiekema, W.J.1995. based on pBIN19.Transgenic Res.4, 288-290) ligation, the ligation product was transfo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com