Patents
Literature
699 results about "Arabidopsis thaliana" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arabidopsis thaliana, the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small flowering plant native to Eurasia and Africa. A. thaliana is considered a weed; it is found by roadsides and in disturbed land.
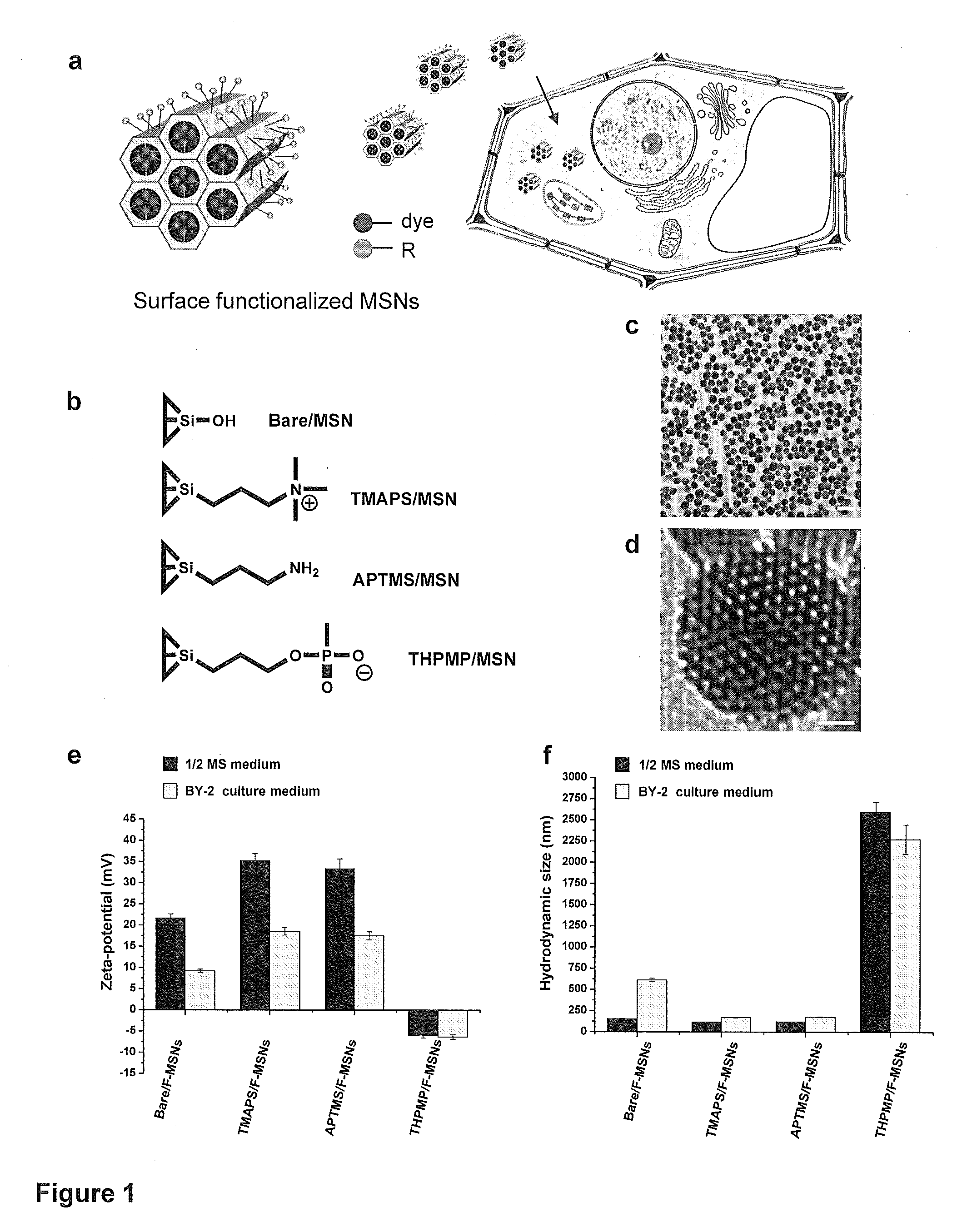
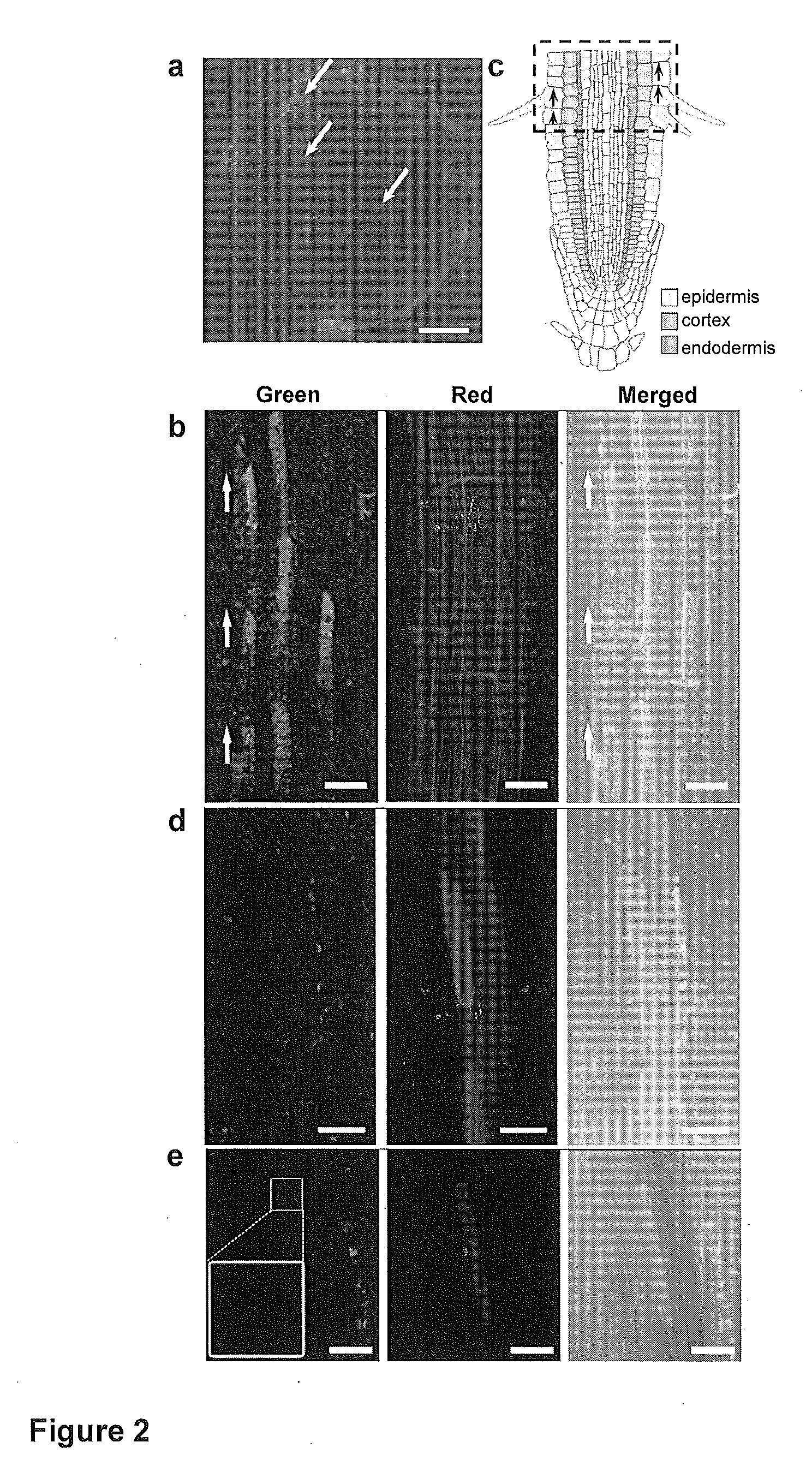
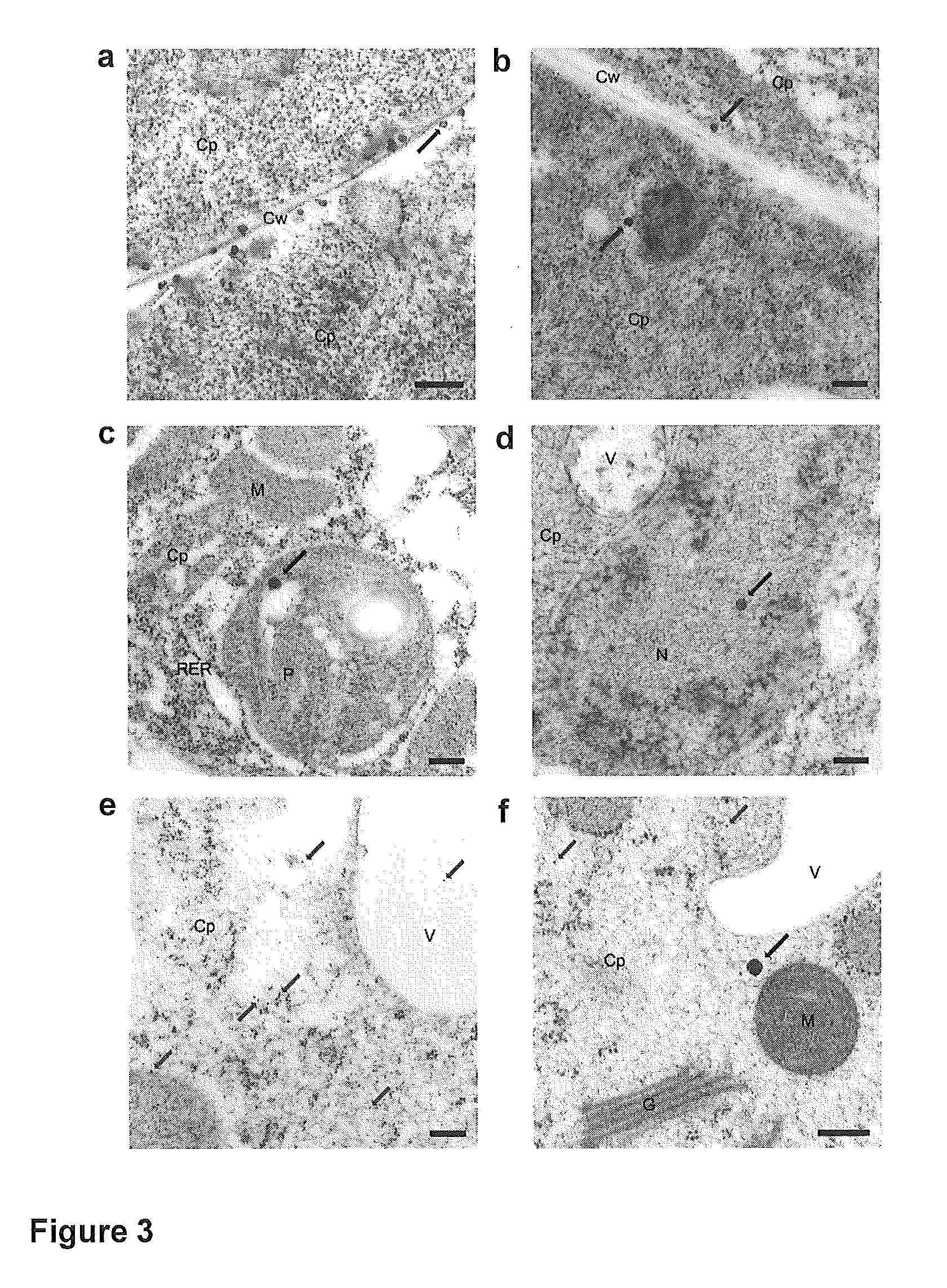
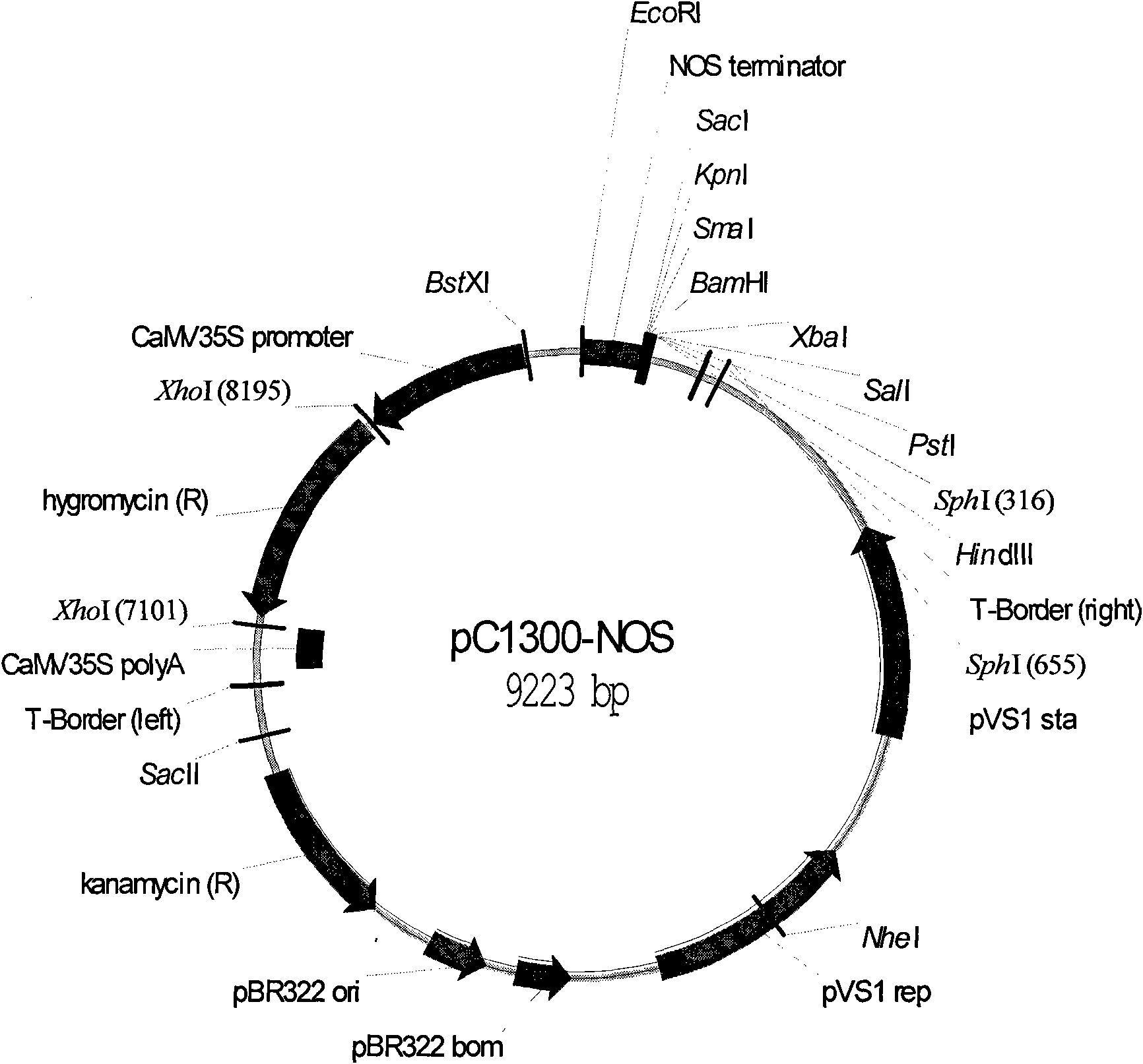
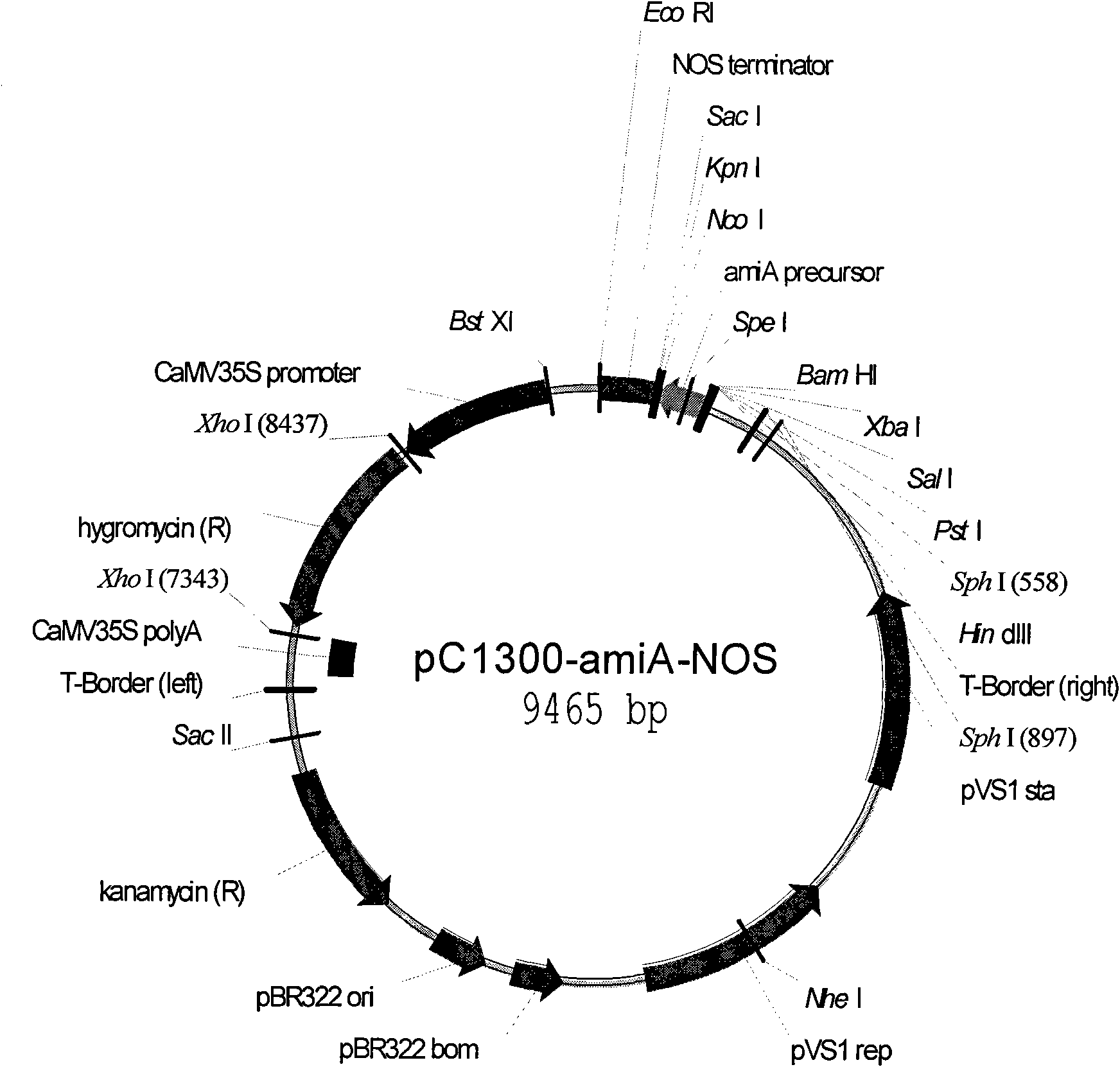
Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-mediated delivery of DNA into arabidopsis root
InactiveUS20130185823A1MicroorganismsOther foreign material introduction processesGerm layerGene delivery
Transient gene expression is a powerful tool for plant genomics studies. Recently, the use of nanomaterials has drawn great interest. Delivery with mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) has many advantages. We used surface-functionalized MSNs to deliver and express foreign DNA in Arabidopsis thaliana root cells without the aid of particle bombardment. Gene expression was detected in the epidermis layer and in the more inner cortex and endodermis root tissues. This method is superior to the conventional gene-gun method to deliver DNA, which delivers the gene to the epidermis layer only. Less DNA is needed for the MSN method. Our system is the first use of nanoparticles to deliver DNA to plants with good efficiency and without external aids. MSNs, with multifunctionality and the capability of cargo delivery to plant cells as we demonstrated, provide a versatile system for biomolecule delivery, organelle targeting, and even agriculture, such as improved nutrient uptake.
Owner:ACAD SINIC +1
Environmental stress-tolerant plants
InactiveUS6670528B1Improve toleranceFree from dwarfingSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesA-DNATransgene
According to the present invention, there is provided a transgenic plant transformed with a DNA coding for the Arabidopsis thaliana DREB1A transcription factor of SEQ ID NO: 2, that binds to a stress responsive element, and regulates the transcription of genes located downstream of the element, the transgenic plant having improved tolerance to environmental stresses such as dehydration, low temperature and salt, and being free from dwarfing.
Owner:INC AMINISTATIVE AGENCY NAT +1
Ω-3 fatty acid desaturase
InactiveUS6884921B2Great proportionTissue cultureOther foreign material introduction processesFatty acidArabidopsis thaliana
Recombinant expression of fat-1 gene of Caenorhabditis elegans in a wide variety of cells, including cells of Arabidopsis thaliana and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, produces a polypeptide having ω-3 desaturase activity.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
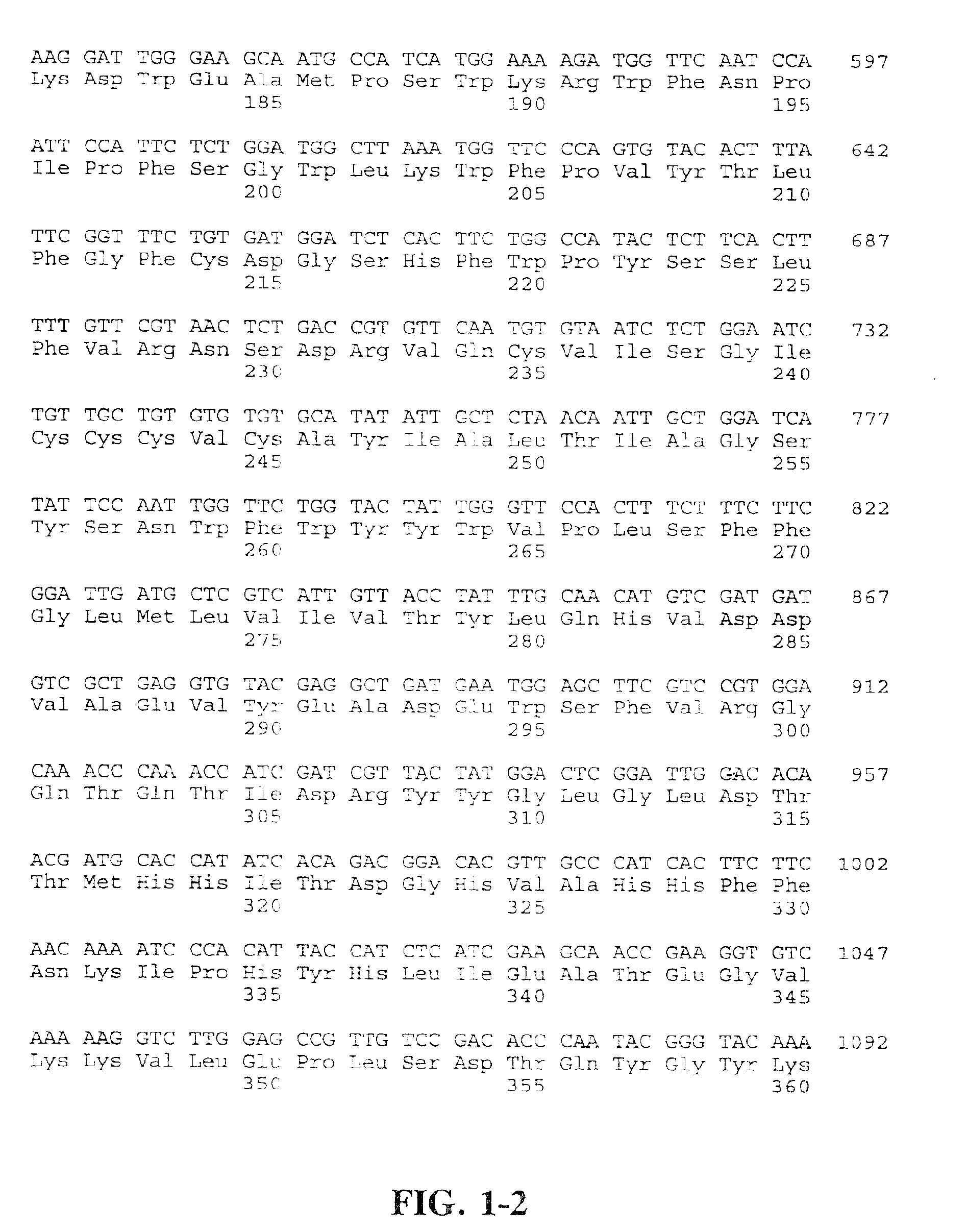
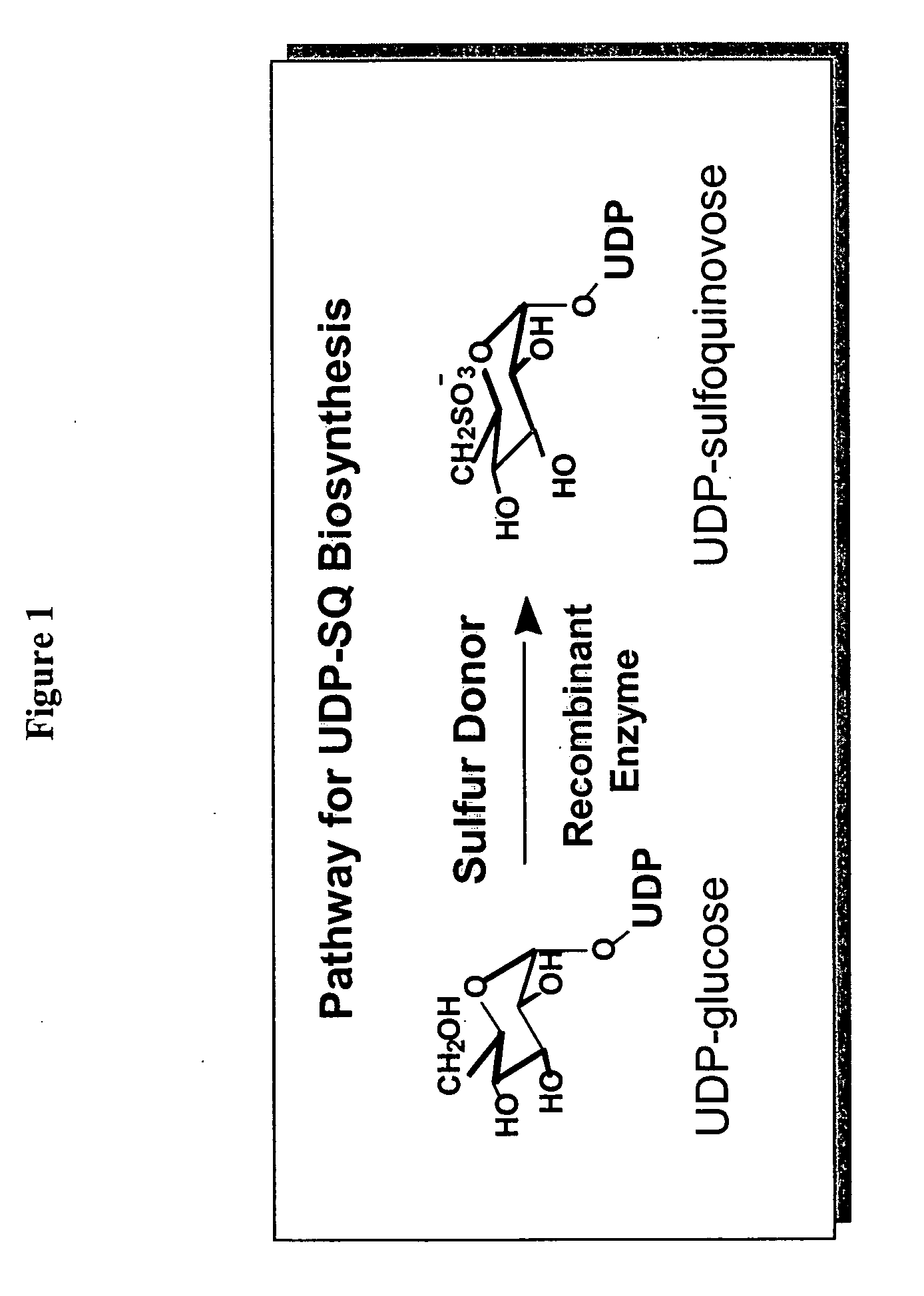
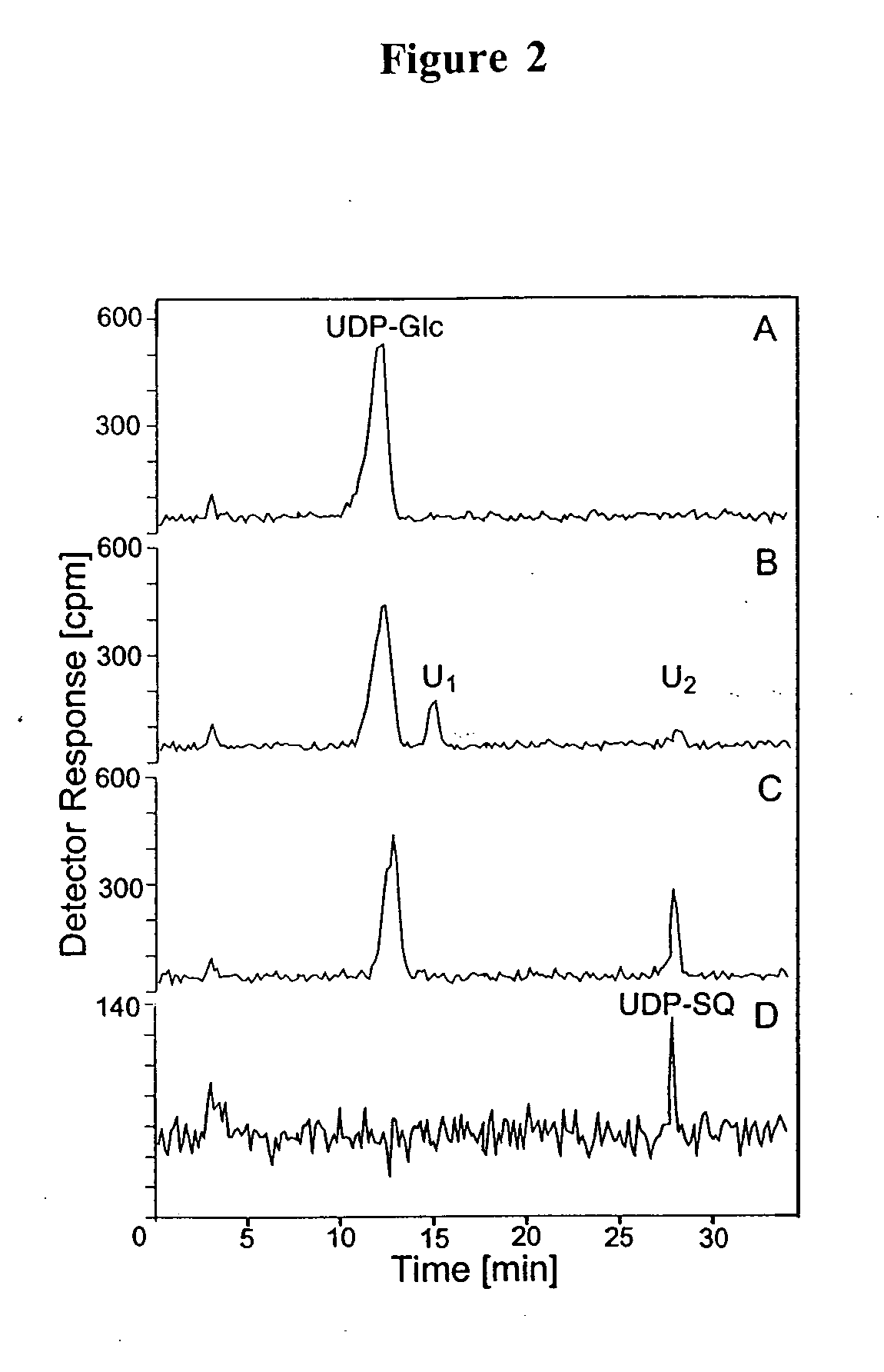
Compositions and methods for the synthesis and subsequent modification of uridine-5'-diphosphosulfoquinovose (UDP-SQ)
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods related to the synthesis and modification of uridine-5′-diphospho-sulfoquinovose (UDP-SQ). In particular, the methods of the present invention comprise the utilization of recombinant enzymes from Arabidopsis thaliana, UDP-glucose, and a sulfur donor to synthesize UDP-SQ, and the subsequent modification of UDP-SQ to form compounds including, but not limited to, 6-sulfo-α-D-quinovosyl diaclyglycerol (SQDG) and alkyl sulfoquinovoside. The compositions and methods of the invention provide a more simple, rapid means of synthesizing UDP-SQ, and the subsequent modification of UDP-SQ to compounds including, but not limited to, SQDG.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Method for producing steviol synthetase gene and steviol
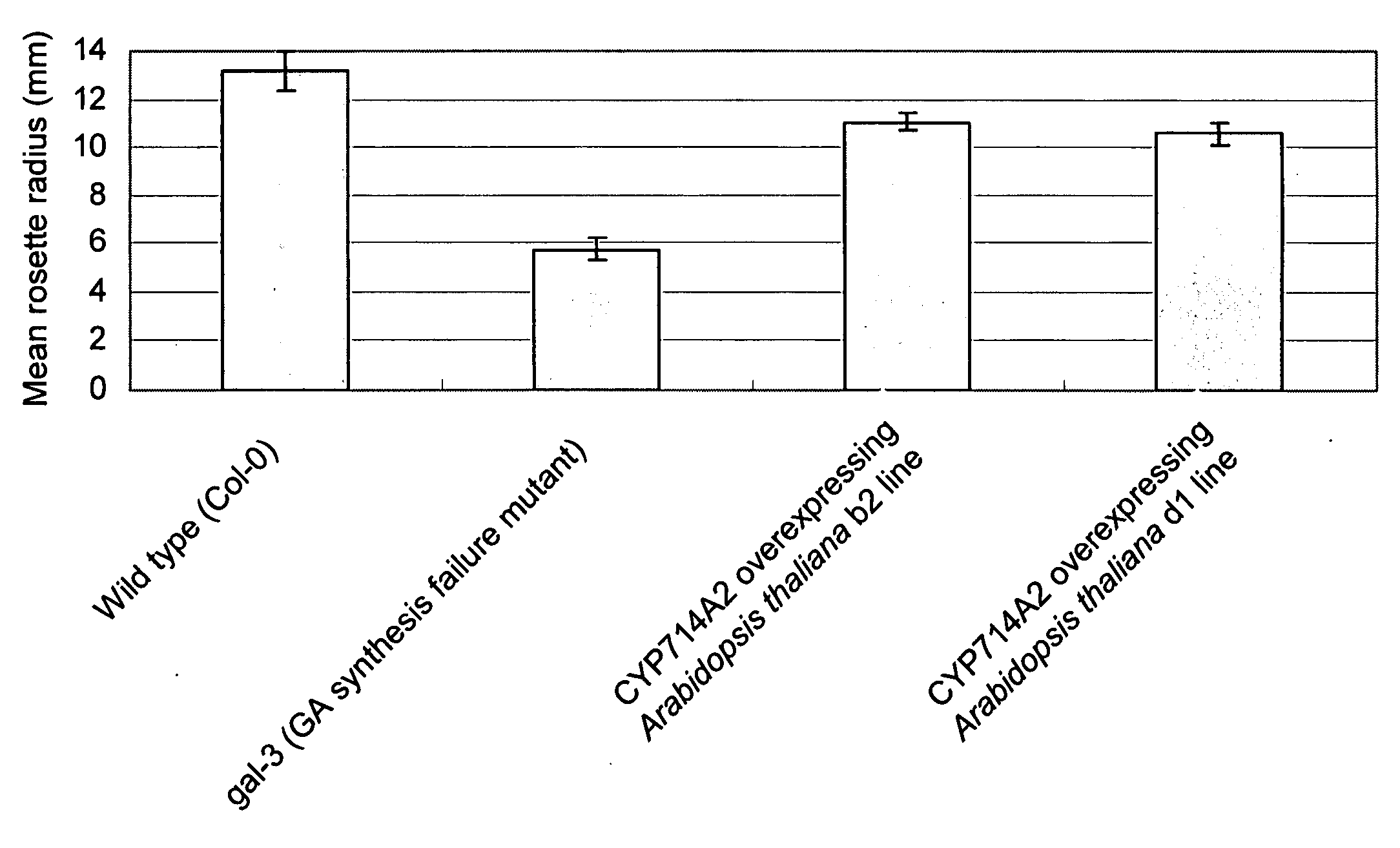
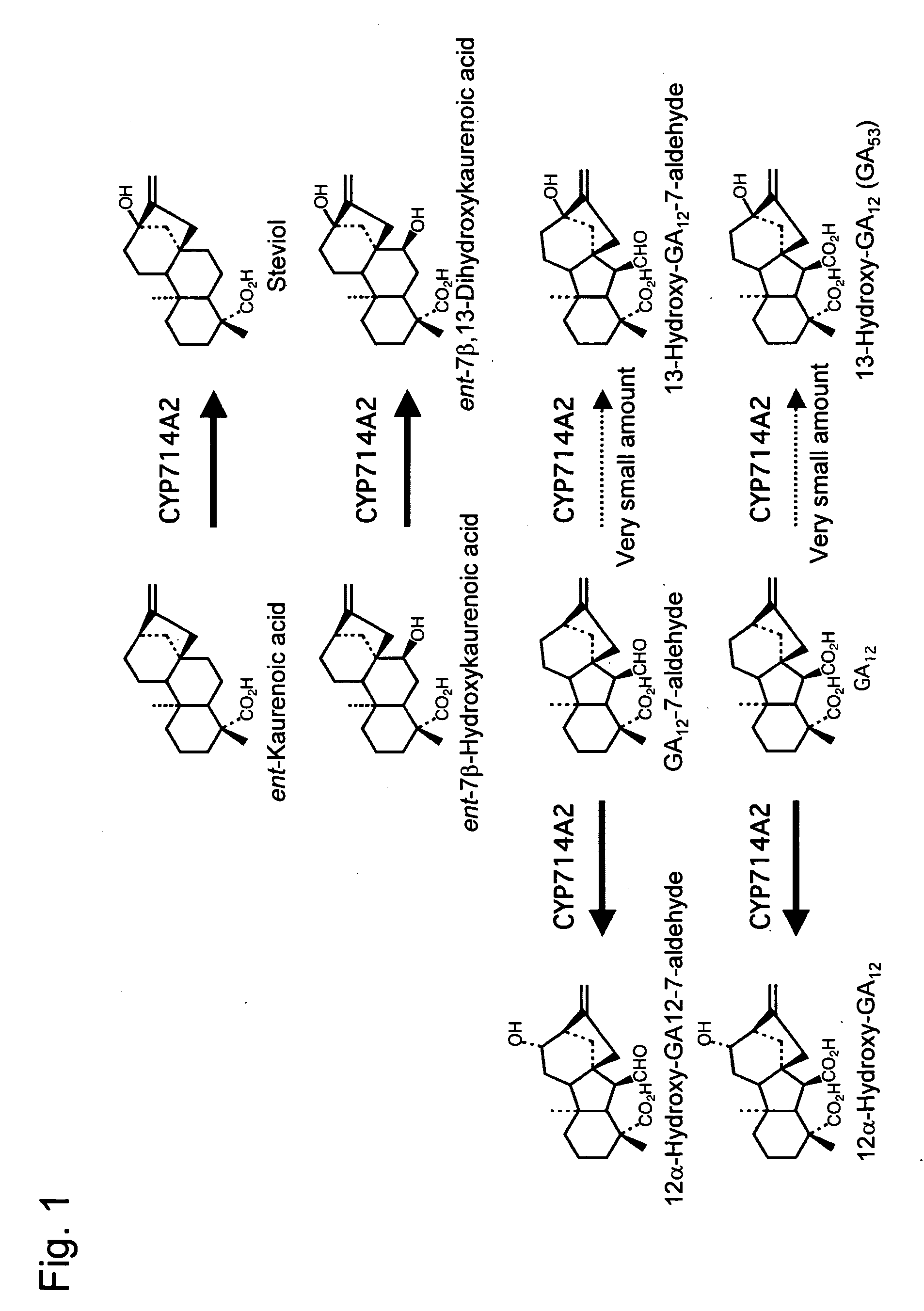
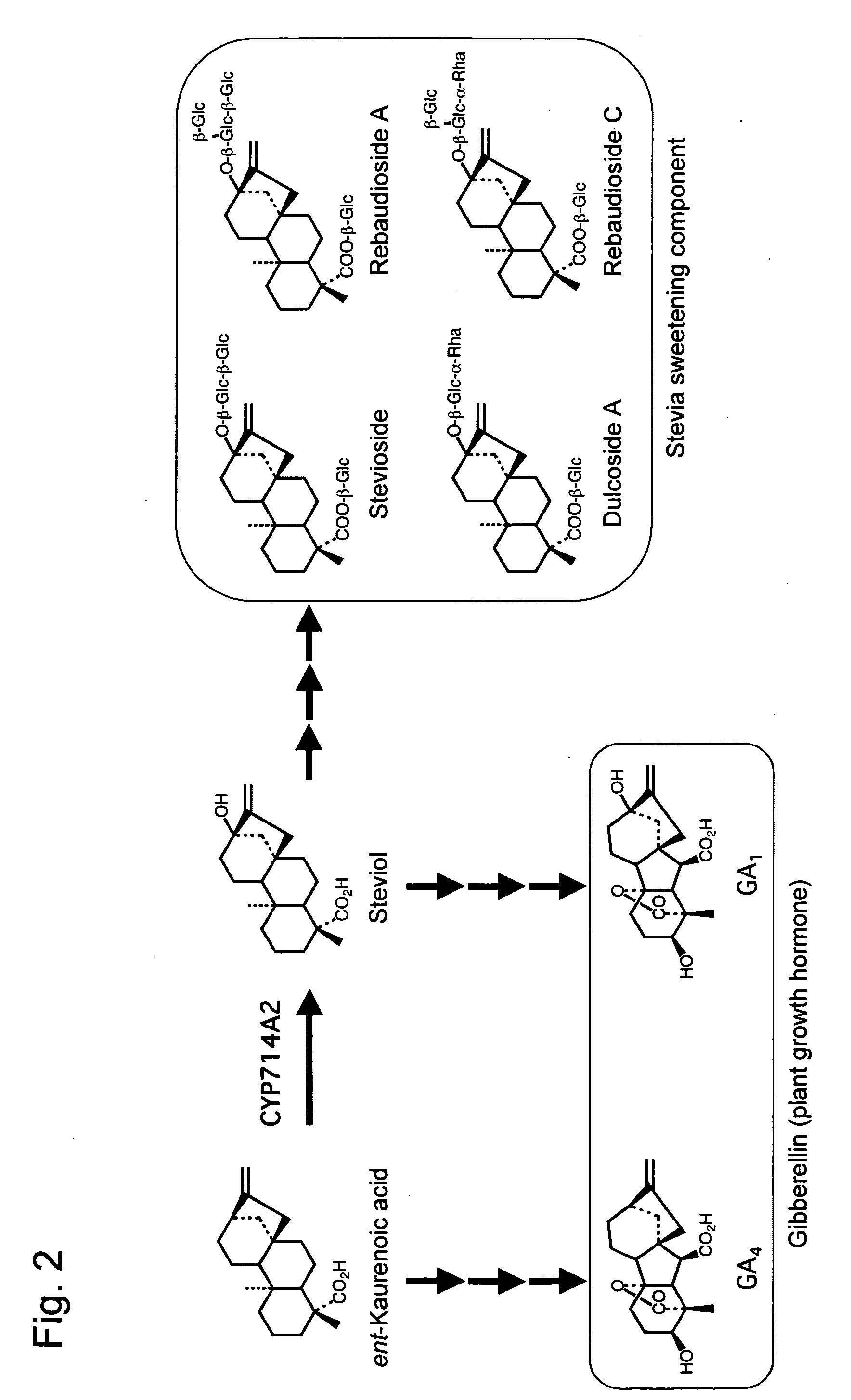
InactiveUS20080271205A1Recovery ratioChange ratioSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPolynucleotideArabidopsis thaliana
Owner:RIKEN
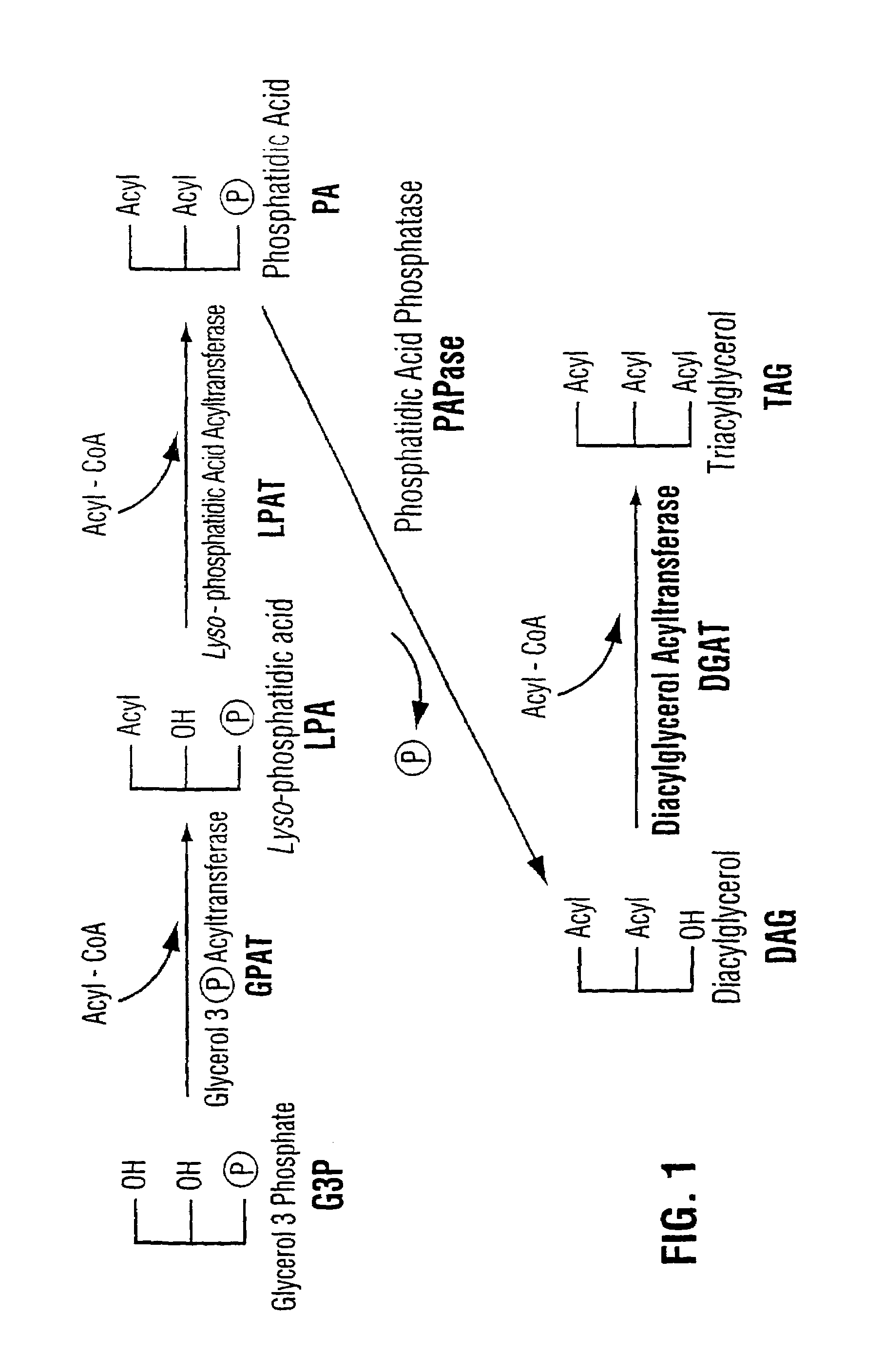
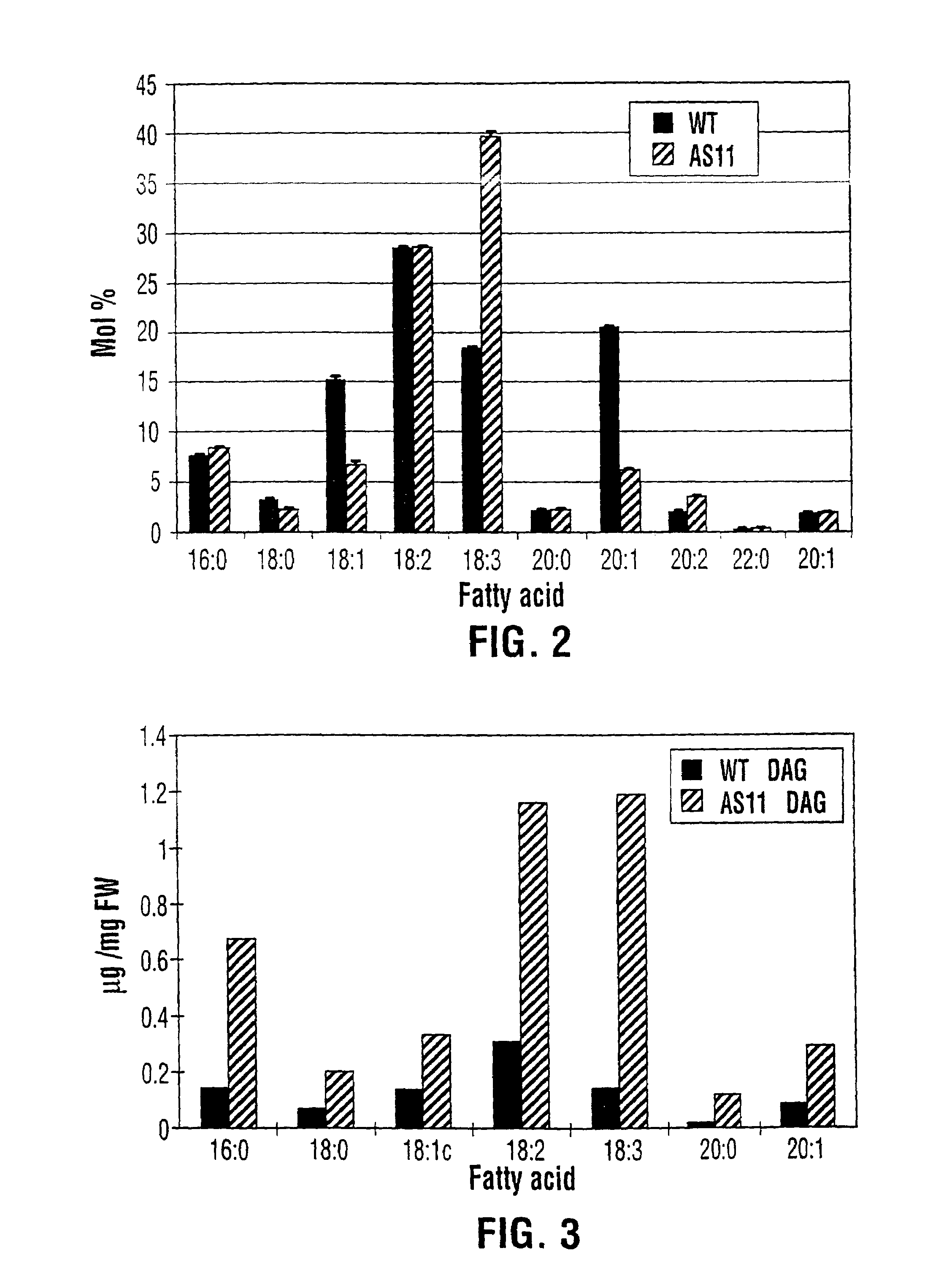
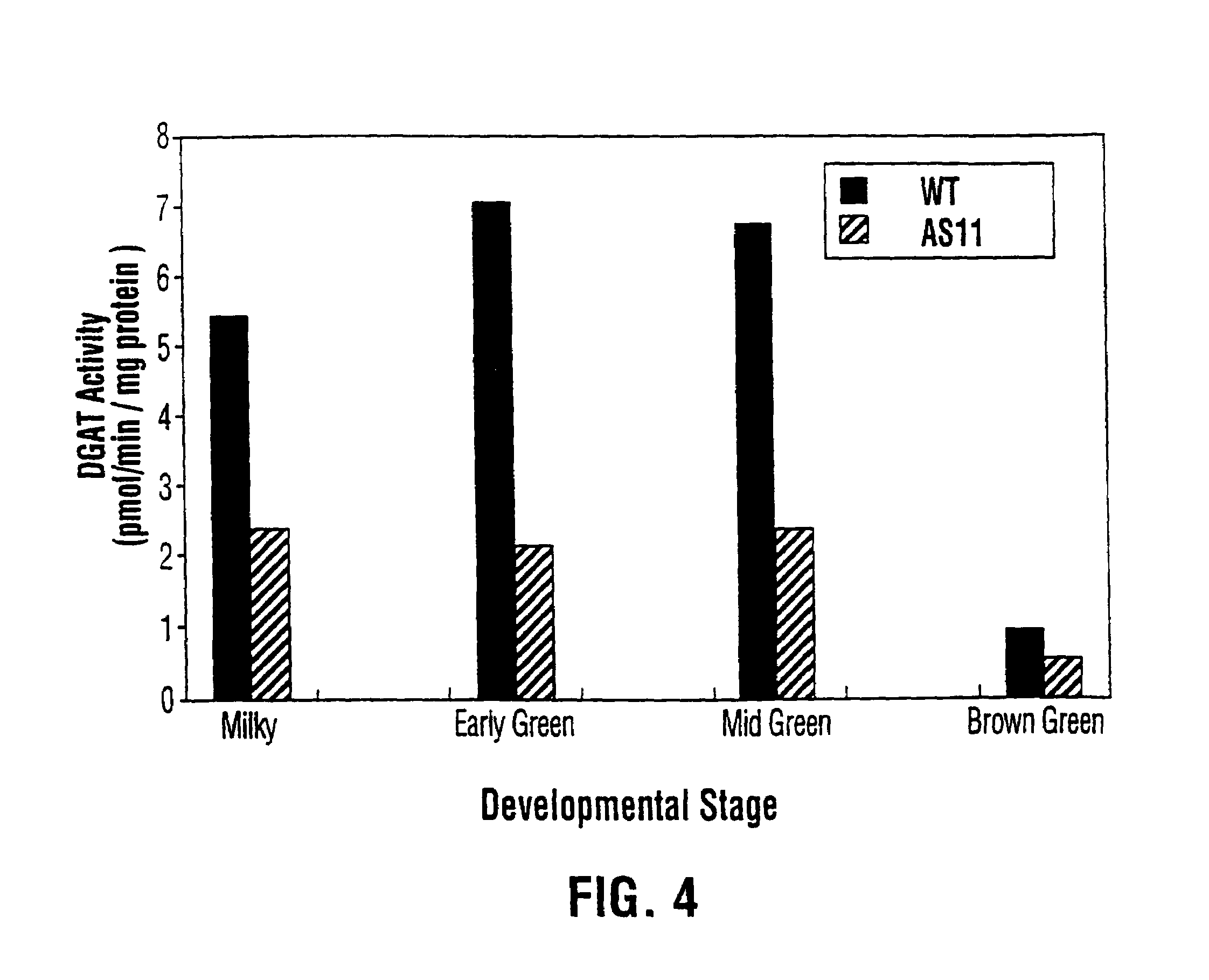
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase gene from plants
InactiveUS7015373B1Reduced DGAT activityReduce rateSugar derivativesTransferasesBrassicaceaePlanting seed
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Plant Genome Sequence and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080113342A1Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsGenomic DNAPlant cell
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid sequences from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana plants. The invention encompasses nucleic acid molecules present in non-coding regions as well as nucleic acid molecules that encode proteins and fragments of proteins. In addition, the invention also encompasses proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding these proteins or fragments. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
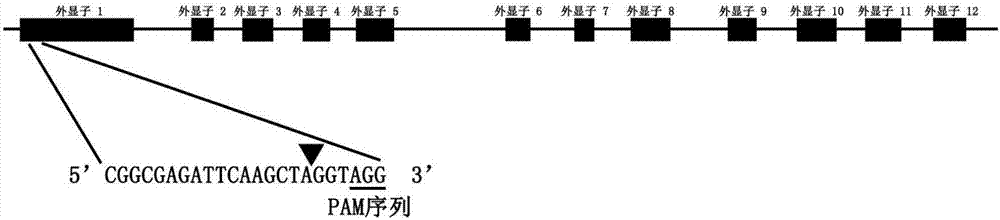
sgRNA sequence for specifically targeting arabidopsis ILK2 gene and application of sgRNA sequence
InactiveCN107236737AKnockout EfficientKnockout fastHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide sequencingArabidopsis thaliana
The invention discloses a sgRNA sequence for specifically targeting an arabidopsis ILK2 gene and application of the sgRNA sequence. The nucleotide sequence of the sgRNA sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. Two single-chain oligo DNA sequences are designed and synthesized according to a sgRNA guide sequence, a double chain is formed through annealing and is linked with a Cas9 carrier, a sgRNA coding sequence and a CRISPR system are introduced into Arabidopsis by using an agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation technique, a target sequence is shorn by a Cas9 protein under the guidance of sgRNA, and therefore, the knockout of an ILK2 gene is realized. According to the sgRNA sequence provided by the invention, the ILK2 gene can be knocked out or edited by virtue of a CRISPR-Cas9 system, so as to analyze the functions of the arabidopsis ILK2 gene.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for improving rice resistance to bacterial leaf blight by using leaf specific expression artificial microRNA
InactiveCN101979548AReduce other adverse outcomesVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetically modified riceDisease
The invention relates to the technical field of plant gene engineering, in particular to design, verification and application of a rice disease resistance related DNA molecule of 21nt. An artificial microRNA sequence of the 21nt is artificially designed, and an artificial microRNA precursor is constructed by using a natural microRNAosa-mi528 precursor as a skeleton. In transgenic rice, the artificial microRNA precursor is specifically expressed by using a leaf specific promoter of a rice or arabidopsis thaliana source so that the resistance of the transgenic rice to bacterial leaf blight can be enhanced and important agronomic traits of the transgenic rice such as fertility and the like is not affected at the same time.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Water-planting method for arabidopsis thaliana
InactiveCN101142893AReduce manufacturing costReduce the rate of contaminationAgriculture gas emission reductionCultivating equipmentsNutrient solutionMoisture
The invention discloses a water-culture method for the mouseearcress and comprises the procedures that 1) sprouting of the seed-the seed of the mouseearcress after the yarovization is cultivated in a cultivation room to be a young seedling; 2) a cultivation tool is made; 3) transplanting the seedling-the seedling obtained in the procedure 1) is transplanted to a cultivation pipe obtained in the procedure 2) in the cultivation room and the root of the young seedling contacts the moisture vermiculite; after the young seedling is cultivated for eight to nine days to be a small seedling; 4) culture of seedling-the vermiculite inside the cultivation pipe is primarily removed; Hoagland nutrition solution with one fourth concentration is arranged inside a water tank that is used as the water-culture device; then the cultivation pipe is vertically arranged inside the water tank arranged inside the cultivation room, thereby the root of the small seedling is immersed in the Hoagland nutrition solution. Adopting the method of the invention to cultivate the mouseearcress can effectively improve the survival rate and is convenient and simple to operate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Device for directly seeding and culturing arabidopsis thaliana in water and application thereof
InactiveCN101731135AImprove survival rateEasy to makeAgriculture gas emission reductionCultivating equipmentsEngineeringNutrient solution
The invention discloses a device for seeding directly and culturing arabidopsis thaliana in water and the application thereof. The device comprises an open container; a supporting flat plate is arranged in the open container; one or more small holes are disposed on the supporting flat plate; a hollow pipe is inserted in each small hole; solid culture medium is filled in each hollow pipe; water or nutrient solution is filled in the open container; the supporting flat plate is arranged above the level of the water or the nutrient solution; the upper end of each hollow pipe is arranged above the supporting flat plate; and the lower end of each hollow pipe is inserted in the water or the nutrient solution. The device is used for seeding directly and culturing the arabidopsis thaliana in water. The method and the device are simple, are easy to obtain the raw materials and can obtain a large number of plant organs such as roots, stems and leaves used for the biochemical and physiological research.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
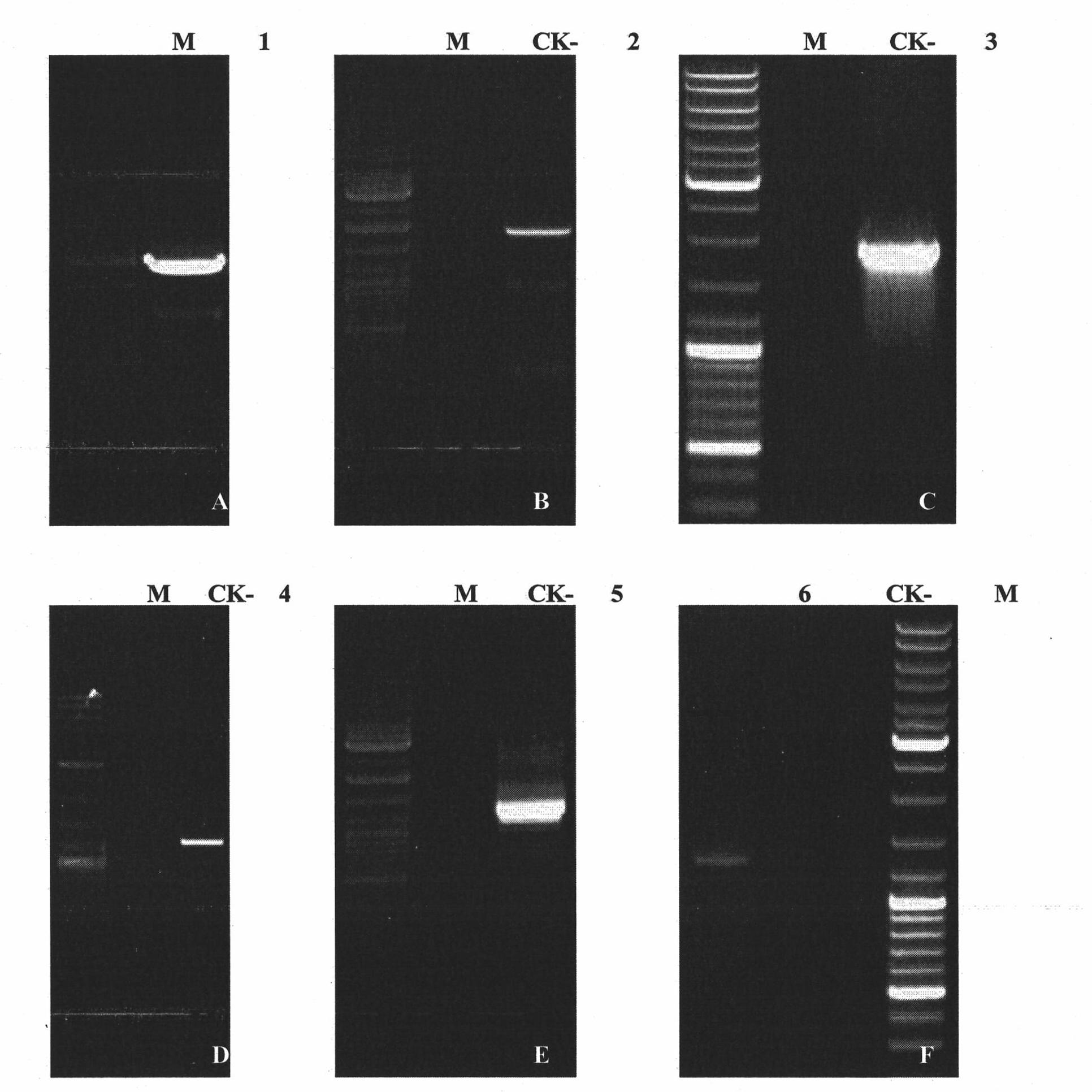
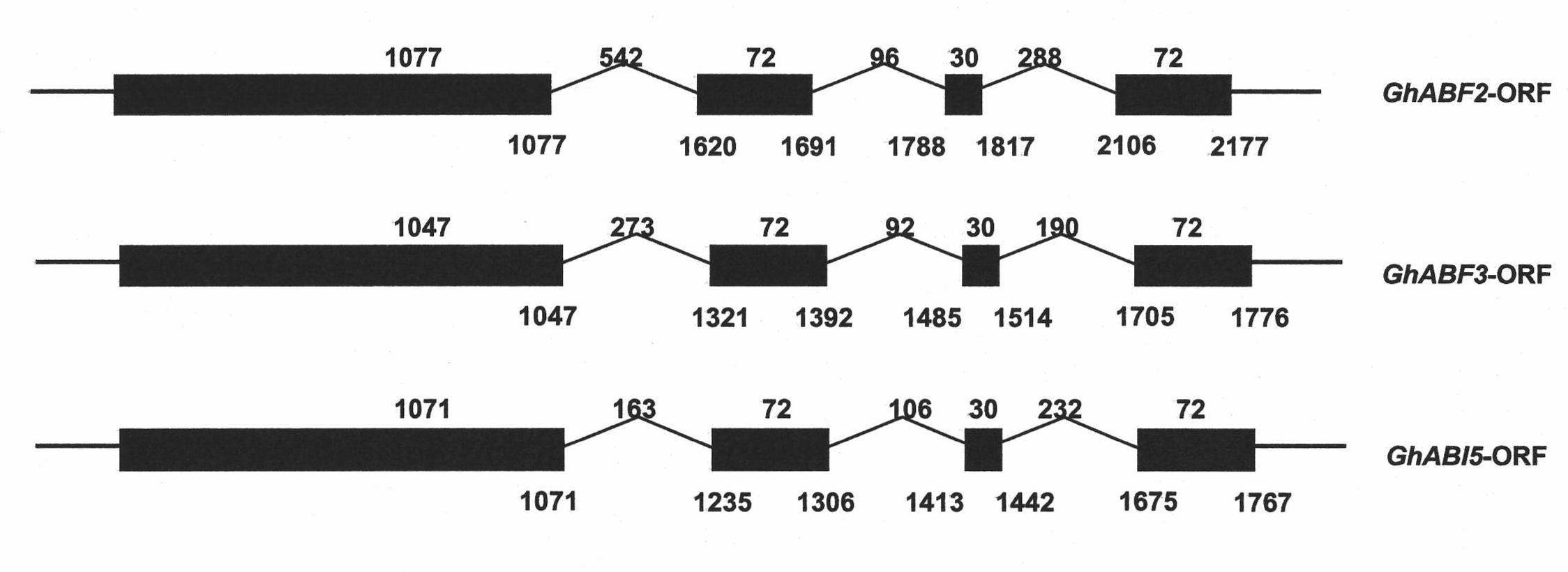
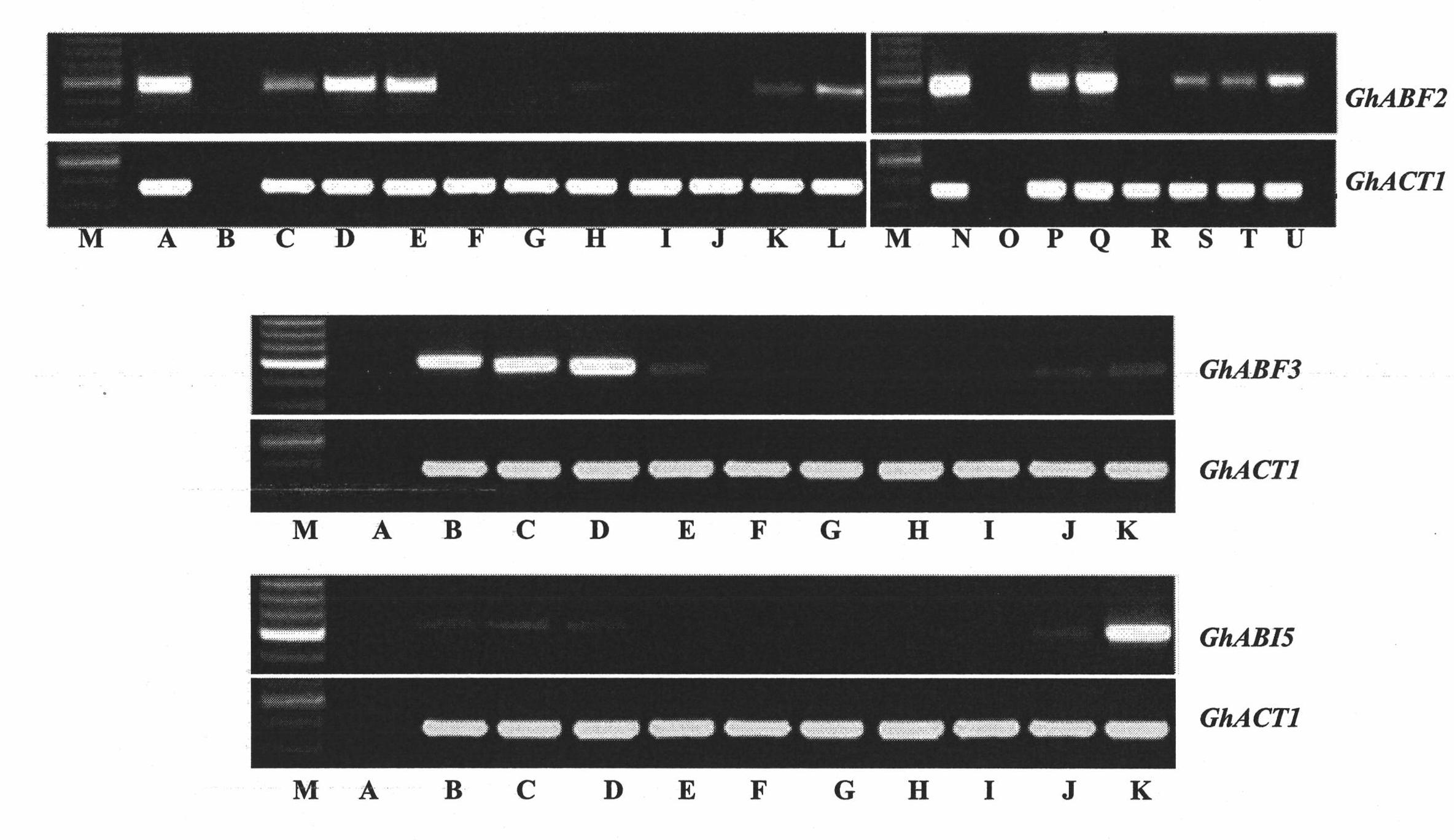
Three cotton ABF/AREB/ABI5/DPBF type transcription factors and coding genes and application thereof
InactiveCN102060919AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses three novel cotton ABF / AREB / ABI5 / DPBF type transcription factors GhABF2, GhABF3 and GhABI5, and coding genes and application thereof. Amino acid sequences of the GhABF2, GhABF3 and GhABI5 are shown as SEQ ID NO: 2, 5 and 8 respectively. Nucleotide sequences of the coding genes GhABF2, GhABF3 and GhABI5 are shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, 4 and 7 respectively. The invention also discloses the structural characteristics on genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and a ribonucleic acid (RNA) editing law of reading frame regions of the coding genes GhABF2, GhABF3 and GhABI5. The invention also discloses the cotton expression characteristics and yeast expression characteristics of the three genes and the characteristic that the three genes can improve the drought resistance of arabidopsis thaliana. The genes provide gene resources for culturing a plant variety resistant to abiotic stress, and have great significance for improving the abiotic stress resistance of plants.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Application of berberine as herbicide
ActiveCN102349520AWide variety of sourcesRaw materials are easy to getBiocideAnimal repellantsMikania micranthaRoot growth
The invention discloses an application of berberine as an herbicide. It is found through researches that berberine has an obvious weeding effect of clearing various weeds. In particular, berberine mixed with other herbicides such as glyphosate or acetochlor has a better weeding effect, wherein the mass ratio of berberine to other herbicide is preferably 1-2: 1. Berberine can be used to observablyinhibit the root growth or plant growth of weeds such as water lettuce, water hyacinth, duckweed, Arabidopsis thaliana, Bidens pilosa, Celosia argentea, Conyza bonariensis, Mikania micrantha and the like, and has a good weeding effect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
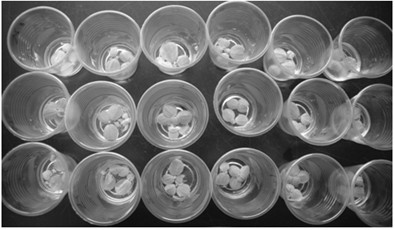
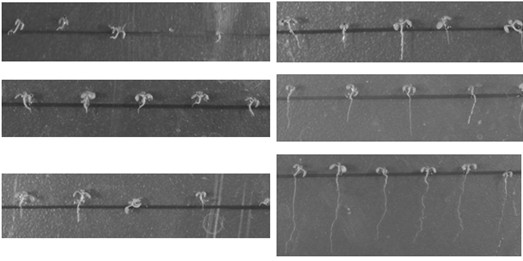
Bacillus pumilus NMCN1 and application thereof
InactiveCN101928681APromote longGood antibacterial effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsArabidopsis thalianaMicrobiological culture
The invention relates to bacillus pumilus NMCN1, which is collected at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Centre (CGMCC) on November 2, 2009 with a collection number of CGMCC No. 3377. The bacillus pumilus NMCN1CGMCC No. 3377 is biocontrol bacillus which is separated from lakeside soil of Tibet Namsto Lake; and the biocontrol bacillus can grow at the temperature of 10 DEG C, is favorable for playing a role in growth promotion and biological control, can suppress pathogenic bacteria and yeast of tomato gray mold, promote the growth of arabidopsis thaliana and tomato, particularly has a prevention and control effect of 75 percent on the tomato gray mold and can also increase the output of the tomato by 12 percent.
Owner:NANJING HOUJI BIO TECH
Broad-spectrum high-efficiency plant RNA extracting kit
The invention discloses a broad-spectrum and high-efficiency method for extracting RNA from various plant tissues and belongs to the technical field of biochemistry. In the invention, boric acid buffer solution is used as a buffer system, the plant tissue RNA is effectively separated and enriched first, the mixture of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (tris), hydrochloric acid (HCl), ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt (EDTA-Na2) and sodium chloride (NaCl) is used as extraction buffer solution, hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) is used as a detergent, 1 mol / L guanidinium isothiocyanate is used as a strong denaturant for inhibiting the activity of RNase, and thus high-quality RNA is extracted. The method can extract RNA from tissues such as ovules, anthers, blades and fibers of cotton and can extract high-quality RNA from recalcitrant plants such as arabidopsis thaliana, rice, draba matangensis, banana (peel and meat), masson pine and deodar. When the method is used for extracting RNA, the yield is high, the purity is high, and salt pollutant is avoided.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Topical composition for anti-aging skin treatment using dual DNA repair mechanism and method of use
InactiveUS8911774B2Reduction of degreeReduce pigmentationBiocideCosmetic preparationsSkin colorMethylsulfonylmethane
A topical composition for anti-aging treatment of the skin includes water soluble extract of Uncaria species, Arabidopsis thaliana extract, lipoic acid, dimethylethanolamine, tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate, dimethyl sulfoxide, Glycyrrhiza Glabra(Licorice) root extract, methylsulfonylmethane, phytosterols, D-ribose, tocotrienol, tocopherol, glucosamine hydrochloride, Pisum sativum extract; Bambusa vulgaris extract, and a dermatologically acceptable liposomal delivery medium. Further disclosed is a method using the topical composition for anti-aging skin treatment utilizing DNA repair in both the nucleus and the mitochondria. The topical composition can be applied on the skin of a person daily, and can also be applied in a dermal infusion treatment, with or without micro-dermal abrasion or skin suction. Topical application of the composition achieves effective reduction of pigmentation spots and degree of winkles, and improvement of skin color tone.
Owner:LIFE SCI INT
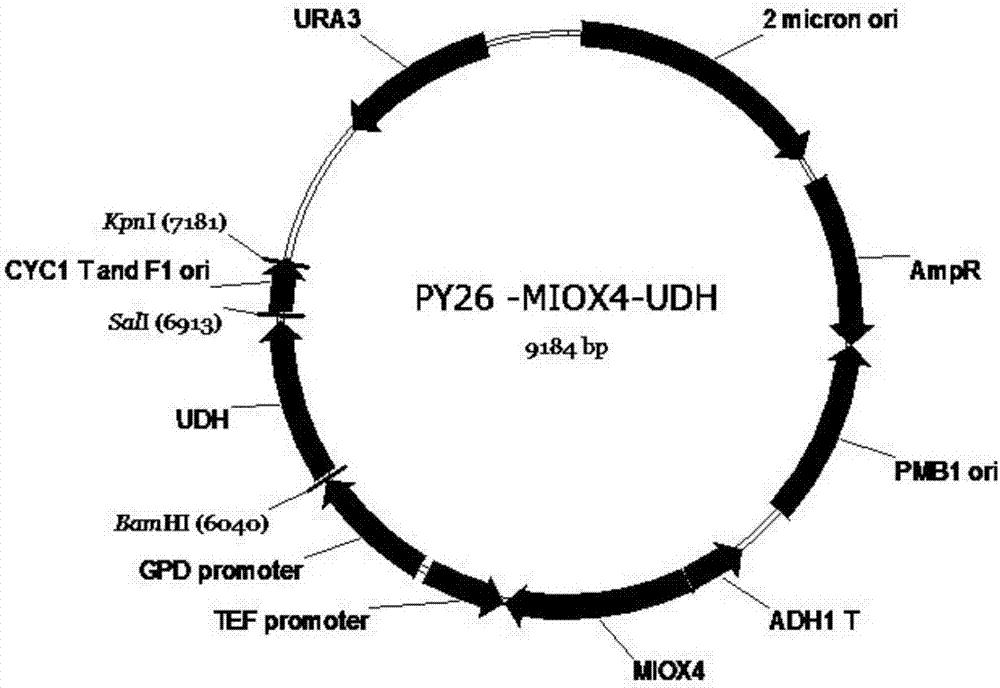
Method for producing glucaric acid by constructing recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae and fermenting
ActiveCN107164255AAvoid non-selectiveImprove energy performanceFungiHydrolasesHigh energyInositol monophosphatase
The invention discloses a method for producing glucaric acid by constructing recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae and fermenting and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: knocking out an OPI gene of saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741; introducing myo inositol-1-phosphate synthase and inositol monophosphatase from the saccharomyces cerevisiae, inositol from arabidopsis thaliana and uronic acid dehydrogenase from pseudomonas syringae into the saccharomyces cerevisiae through constitutive plasmid pY26-GPD-TEF, and realizing approach construction of the saccharomyces cerevisiae from glucose to the glucaric acid. According to the method disclosed by the invention, by use of a constructed metabolic pathway, non-selectivity, high energy consumption property and high cost performance of a chemical oxidation method are avoided; the low-priced glucose is directly transformed into D-glucaric acid with high added value by fermentation culture of engineering bacteria; the method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, high transformation rate and fewer byproducts; production cost can be greatly reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Small regulatory RNAs and methods of use
InactiveUS20070111227A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingRegulatory rnaArabidopsis thaliana
The present invention relates to unique small ribonucleic acid molecules, for example siRNAs and miRNAs, identified and isolated using MPSS. Specifically, the invention is directed to the identification of a library of unique small RNA sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana. In another aspect, the small RNA sequences themselves are useful for performing biological functions, such as for example, RNA interference.
Owner:GREEN PAMELA +4
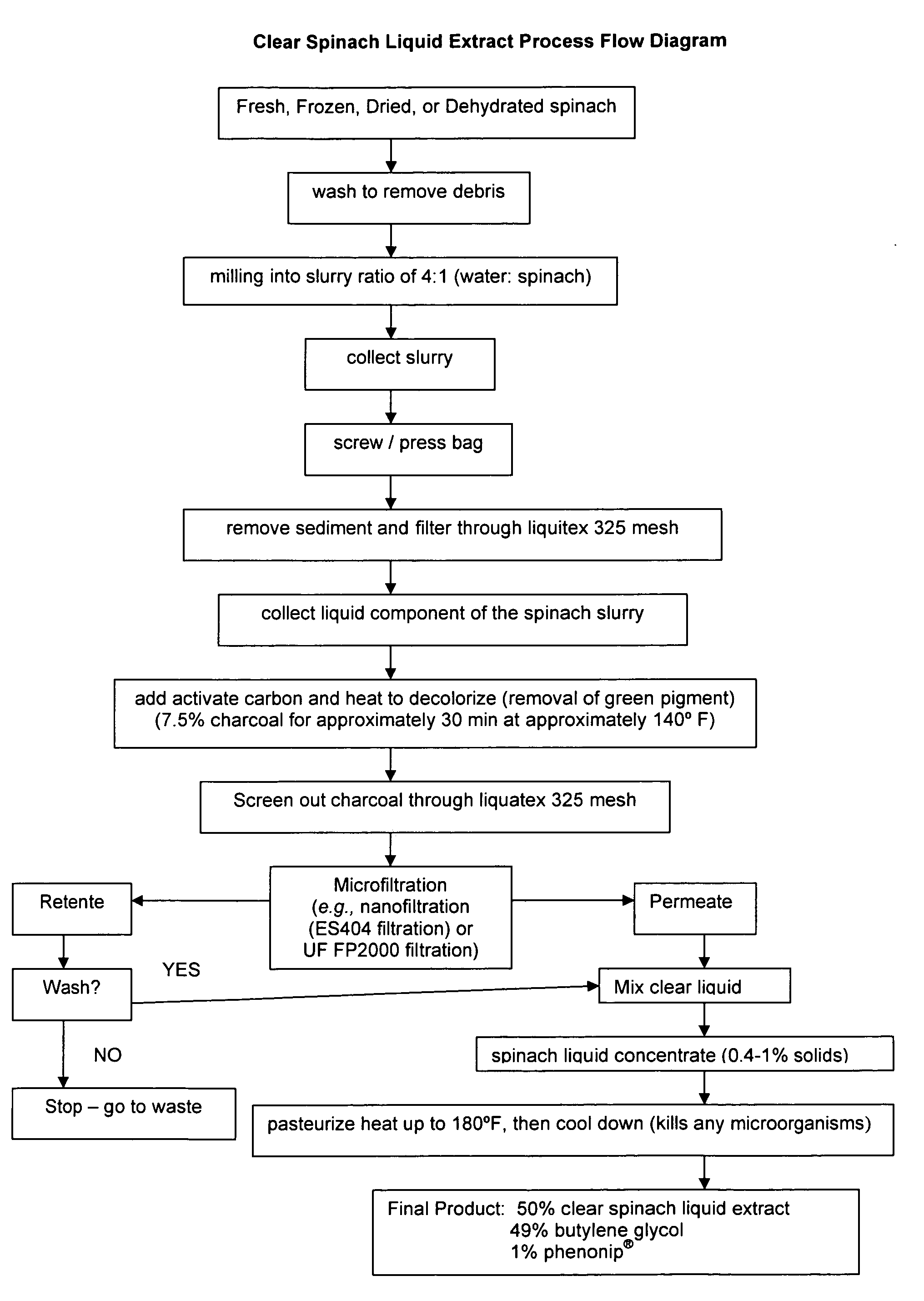
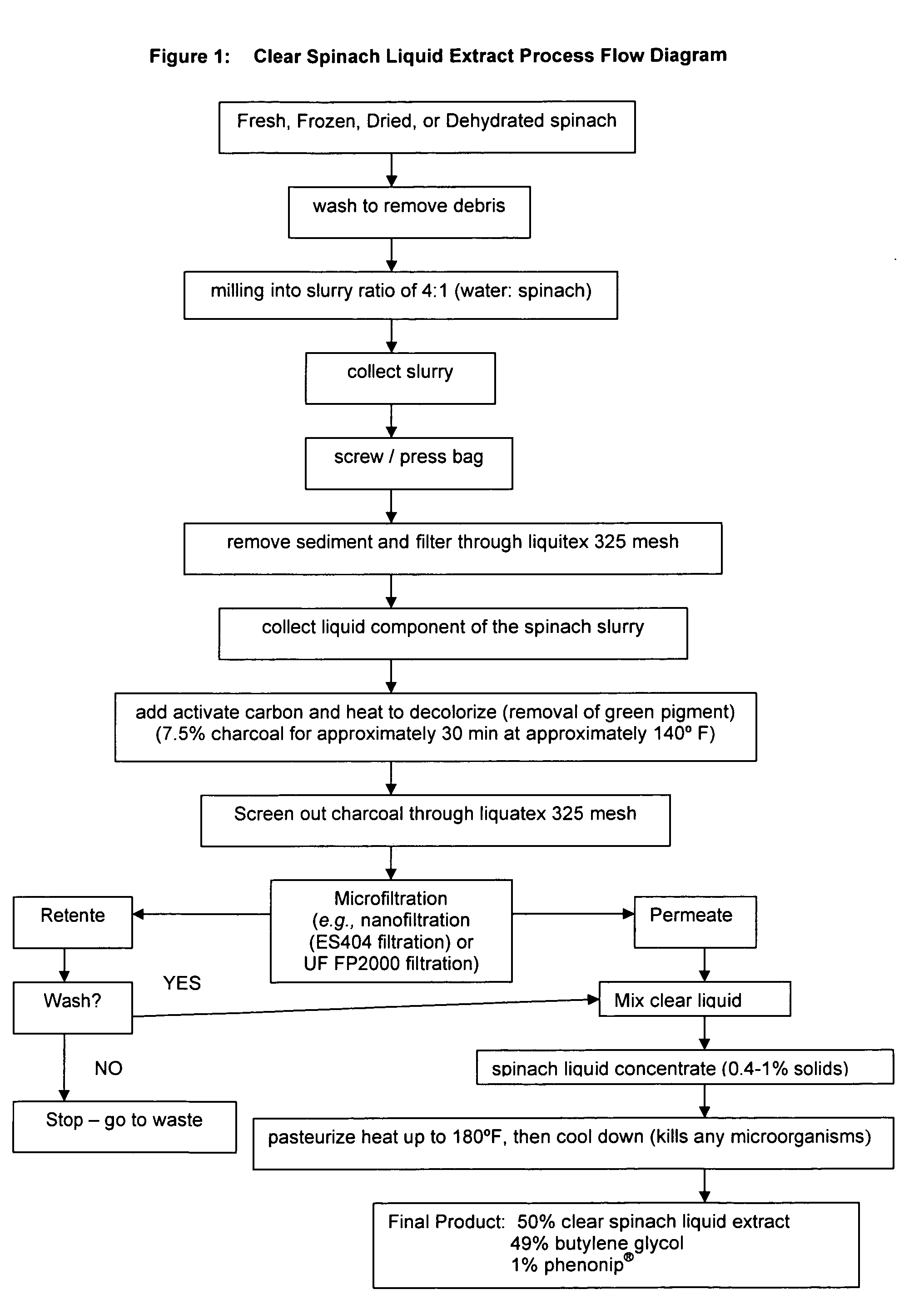
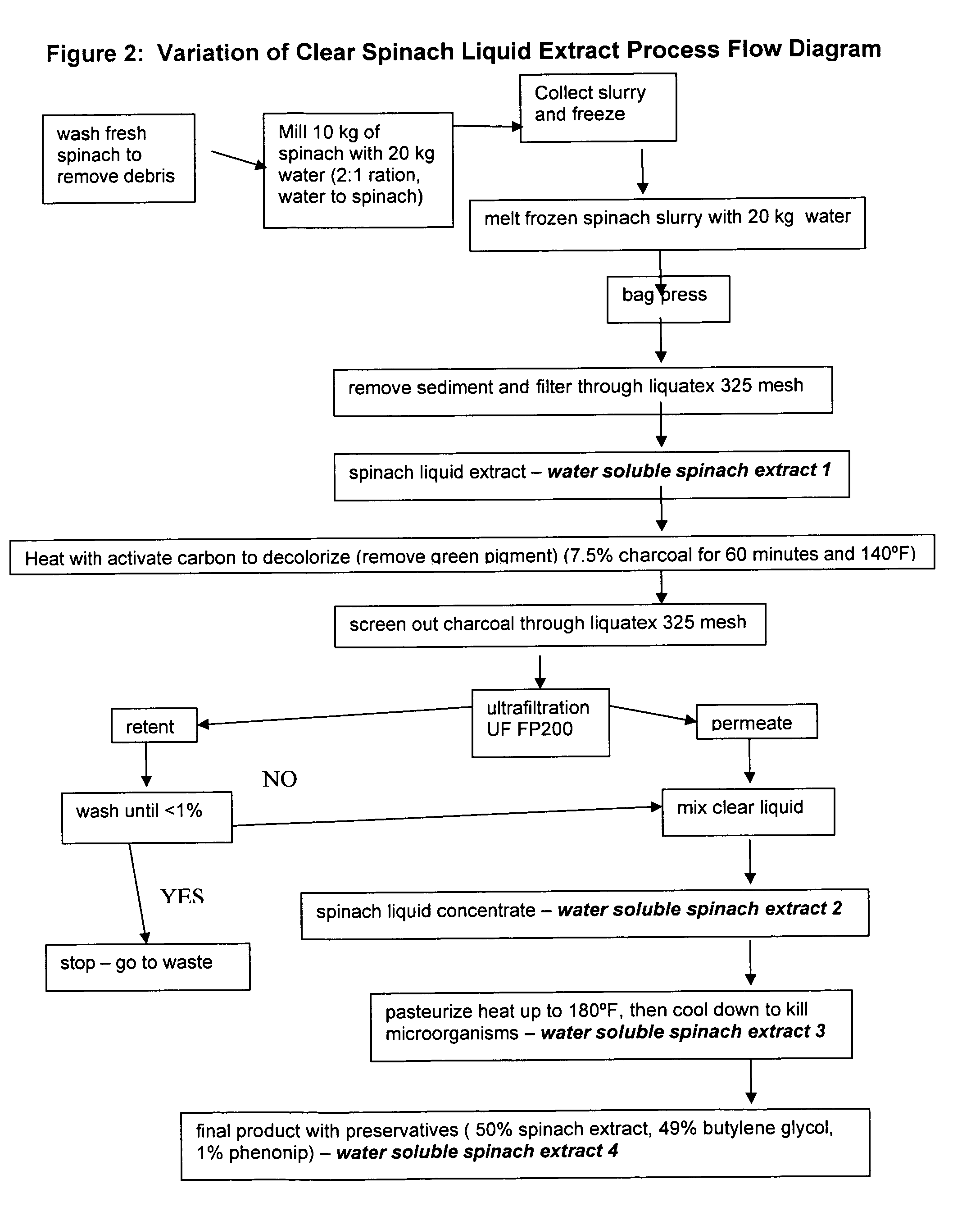
Water soluble extract of spinach for prevention and repair of DNA damage
InactiveUS20080138393A1Prevents and decrease damagePromotes and increases productionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAdjuvantAntioxidant
Compositions comprising a water soluble spinach extract, compositions comprising a water soluble spinach extract, a liposome, a cardiolipin, and at least one antioxidant, compositions comprising a water soluble spinach extract, an extract of Arabidopsis thaliana or of the mustard (Brassica) plant, a liposome, a cardiolipin, and at least one antioxidant, processes for obtaining such compositions, and methods of using such compositions to repair damage to nuclear DNA, mitochondrial DNA, or both, prevent or decrease damage to such DNA from, for example, reactive oxygen species or 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine and / or to repair or prevent mitochondrial damage and loss of membrane fluidity are disclosed. Compositions of the present invention may be topically administered, orally administered or parenterally, such as administration by injection. When topically administered, additives such as penetration enhancers, fragrances, preservatives, moisturizers and cosmetic adjuvants may be included in compositions of the present invention.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
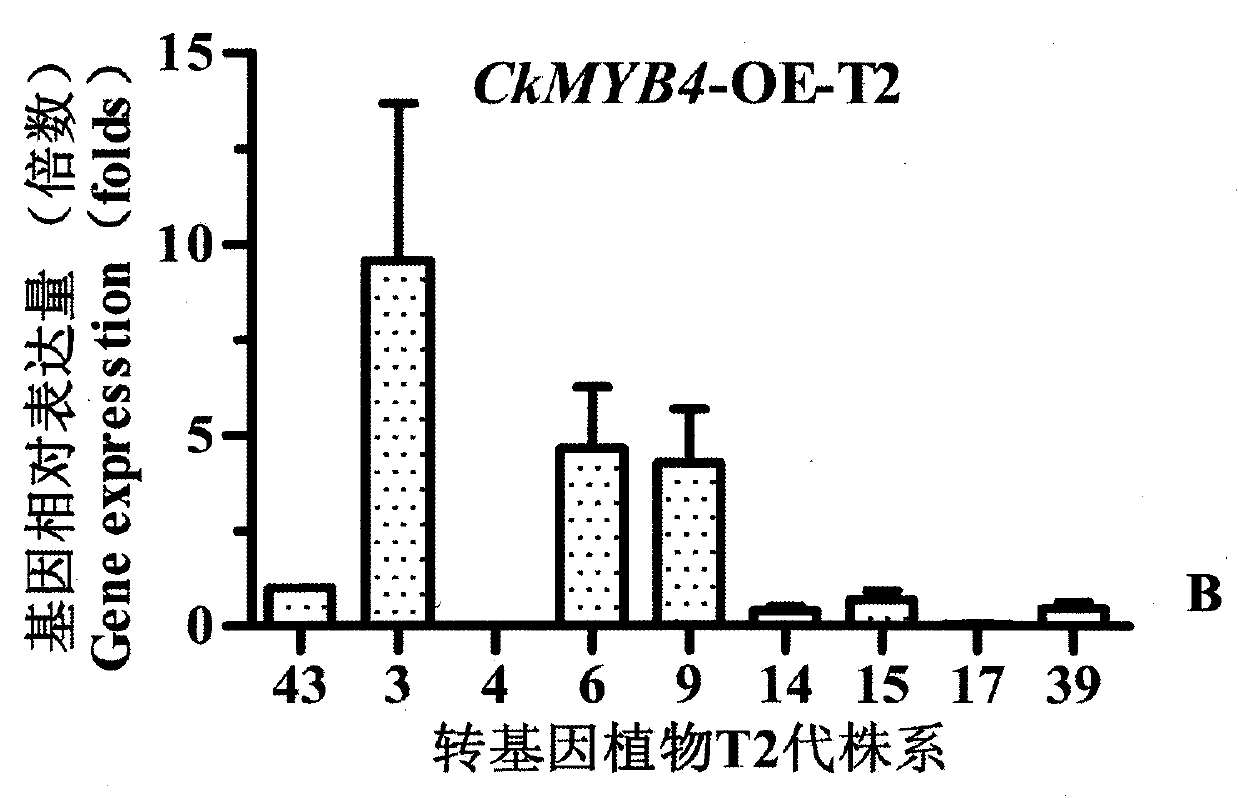
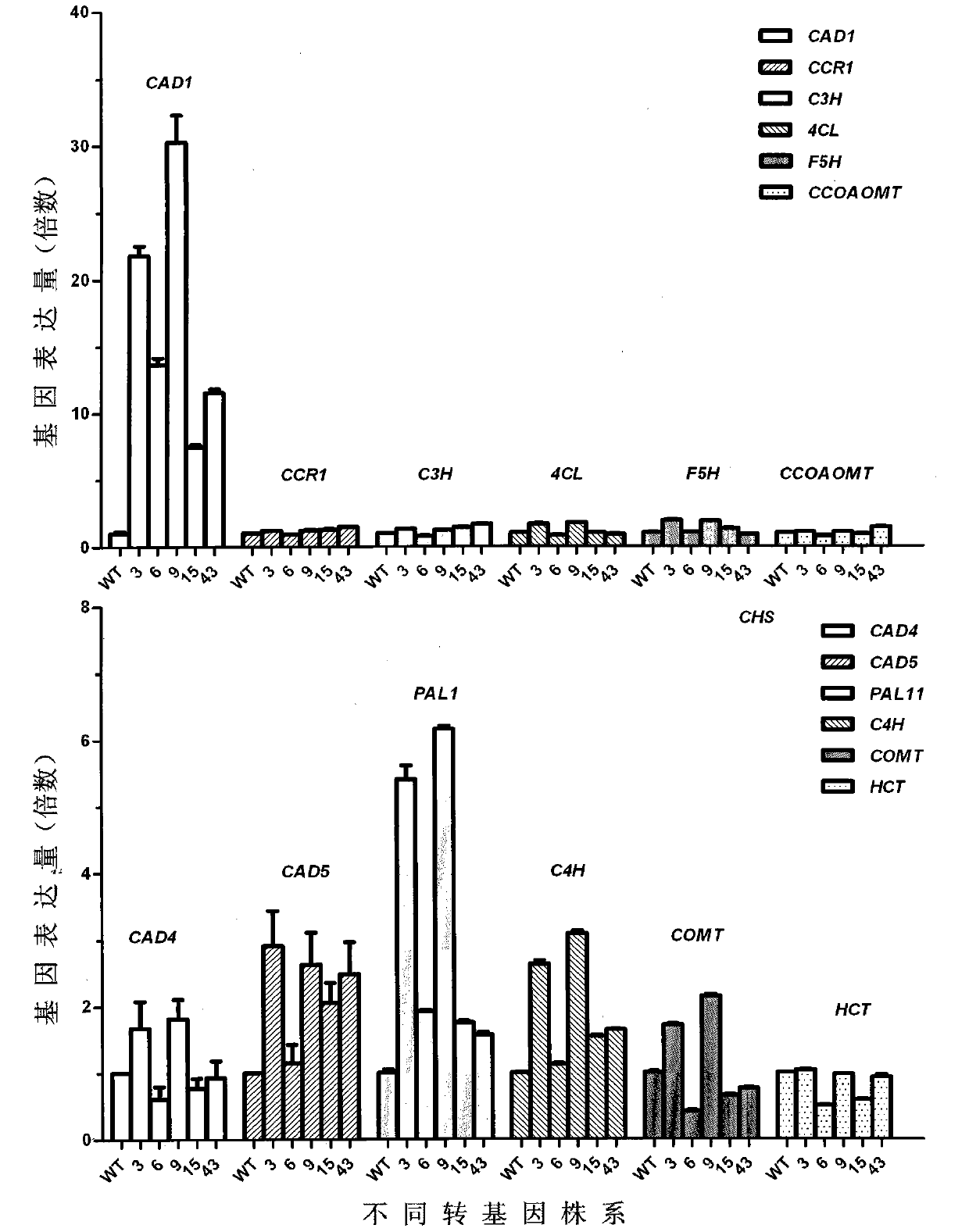
Caragana korshinskii Kom. transcription factor CkMYB4 and its gene
The invention provides a new CkMYB4 transcription factor and its gene. The gene originates from Leguminosae Caragana shrubs Caragana korshinskii Kom., and codes R2R3 MYB transcription factors. The full length cDNA sequence of the gene comprises 1106bps, comprises a 798bp open reading frame, and codes 266 amino acids. The cDNA sequence obtained after cloning is used for constructing a plant expression vector, and the vector is transformed into wild Arabidopis thaliana to obtain a transgenic plant. Transgenic Arabidopis thaliana lignin synthetase gene and lignin content detection results show that the gene provided by the invention can change the expression of the plant lignin synthesis gene and the lignin content.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Soybean holy bean 9# NAC transcription factor gene GmST1 and application thereof
ActiveCN102660554AImprove salt/drought toleranceImproves salt/drought toleranceFermentationGenetic engineeringTransgeneGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a soybean holy bean 9# NAC transcription factor gene GmST1 and a plant expression vector of the gene GmST1 and further discloses application of the gene GmST1 in improving salt / drought resistance of arabidopsis thaliana and soybean plants. An experiment proves that compared with a non-transgenic plant, the salt / drought resistance of a transgenic plant is greatly improved. Therefore, the theory basis and the practice foundation are provided for improving the salt / drought resistance of plants through genetic engineering means. The soybean holy bean 9# NAC transcription factor gene GmST1 can be widely used for cultivating salt / drought resistant plant varieties.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
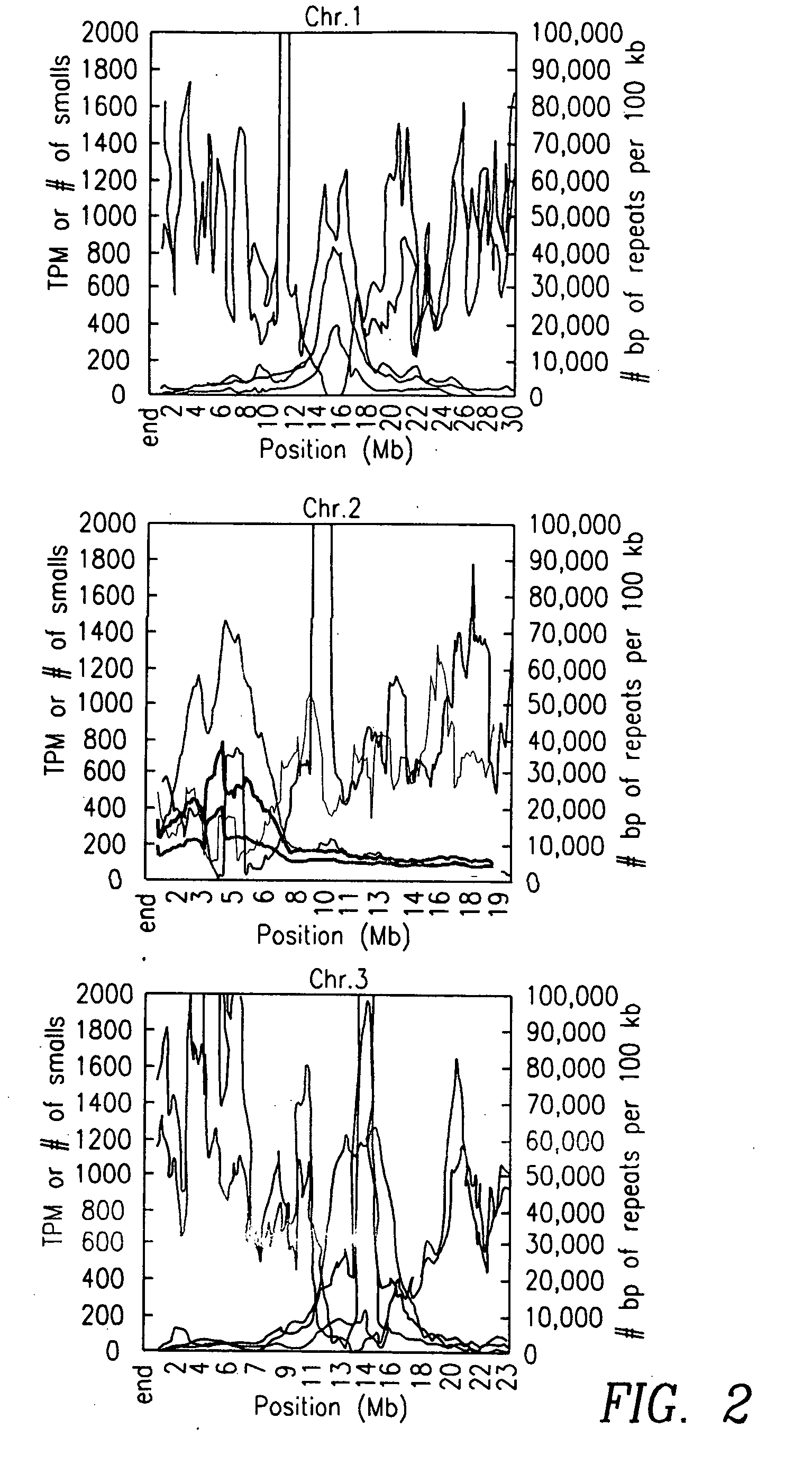
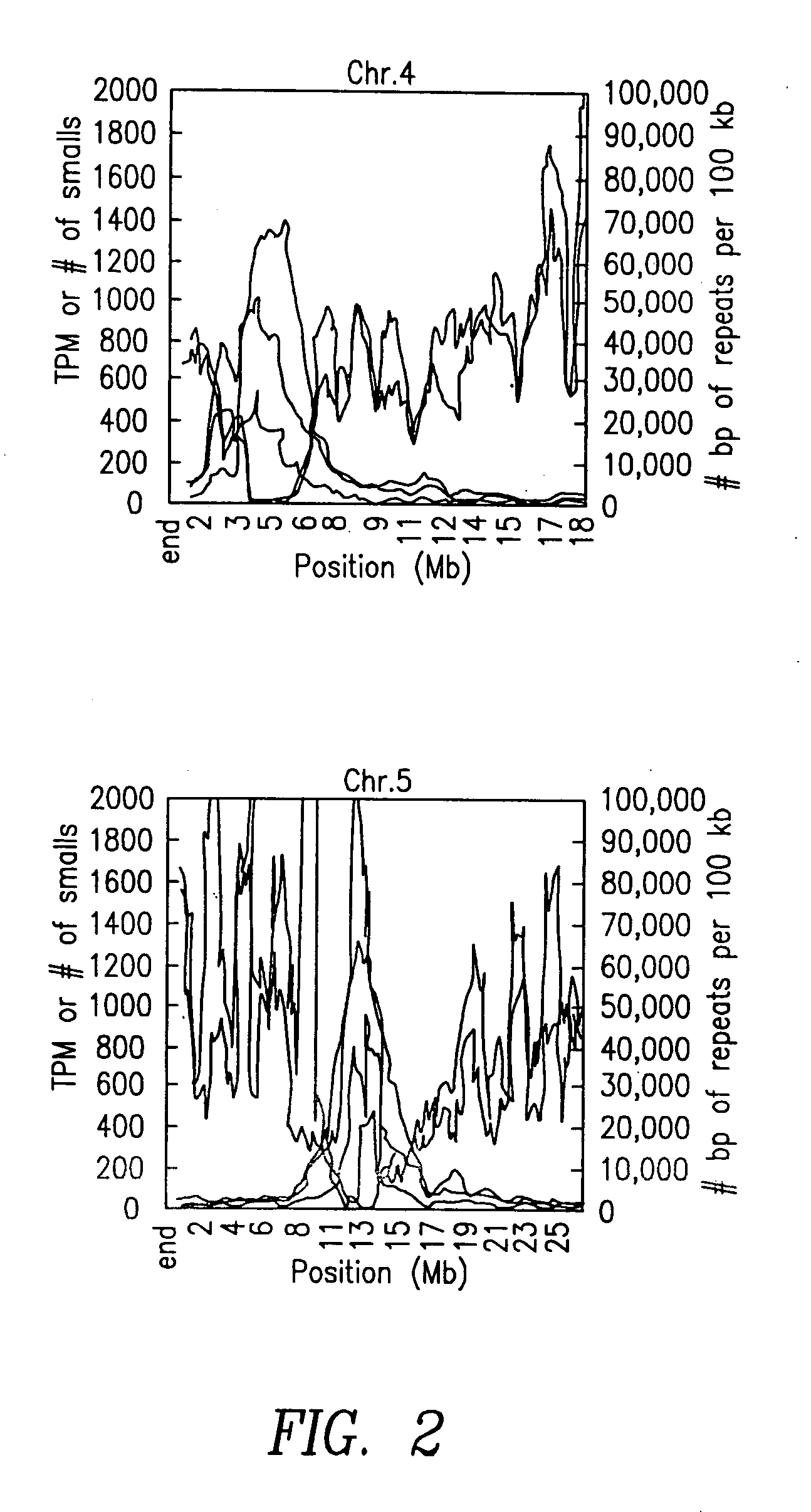
Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]
The invention is isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding Na+ / H+ exchanger polypeptides with 95% identity to a Na+ / H+ exchanger polypeptide from Arabidopsis thaliana for extrusion of monovalent cations from the cytosol of cells to provide the cell with increased salt tolerance. Crop species transformed with the nucleic acid molecule are capable of surviving in soil with high salt levels that would normally inhibit growth of the crop species.
Owner:BLUMWALD EDUARDO +1
Nematode-feeding structure specific gene and its application to produce nematode resistant plants
The invention provides a regulatory DNA sequence obtainable from Arabidopsis thaliana that is capable of promoting root knot and cyst nematode-inducible transcription of an associated DNA sequence when re-introduced into a plant, a gene sequence which is specifically expressed in the nematode feeding structure and the use of the regulatory DNA sequence.
Owner:PUZIO PIOTR S +1
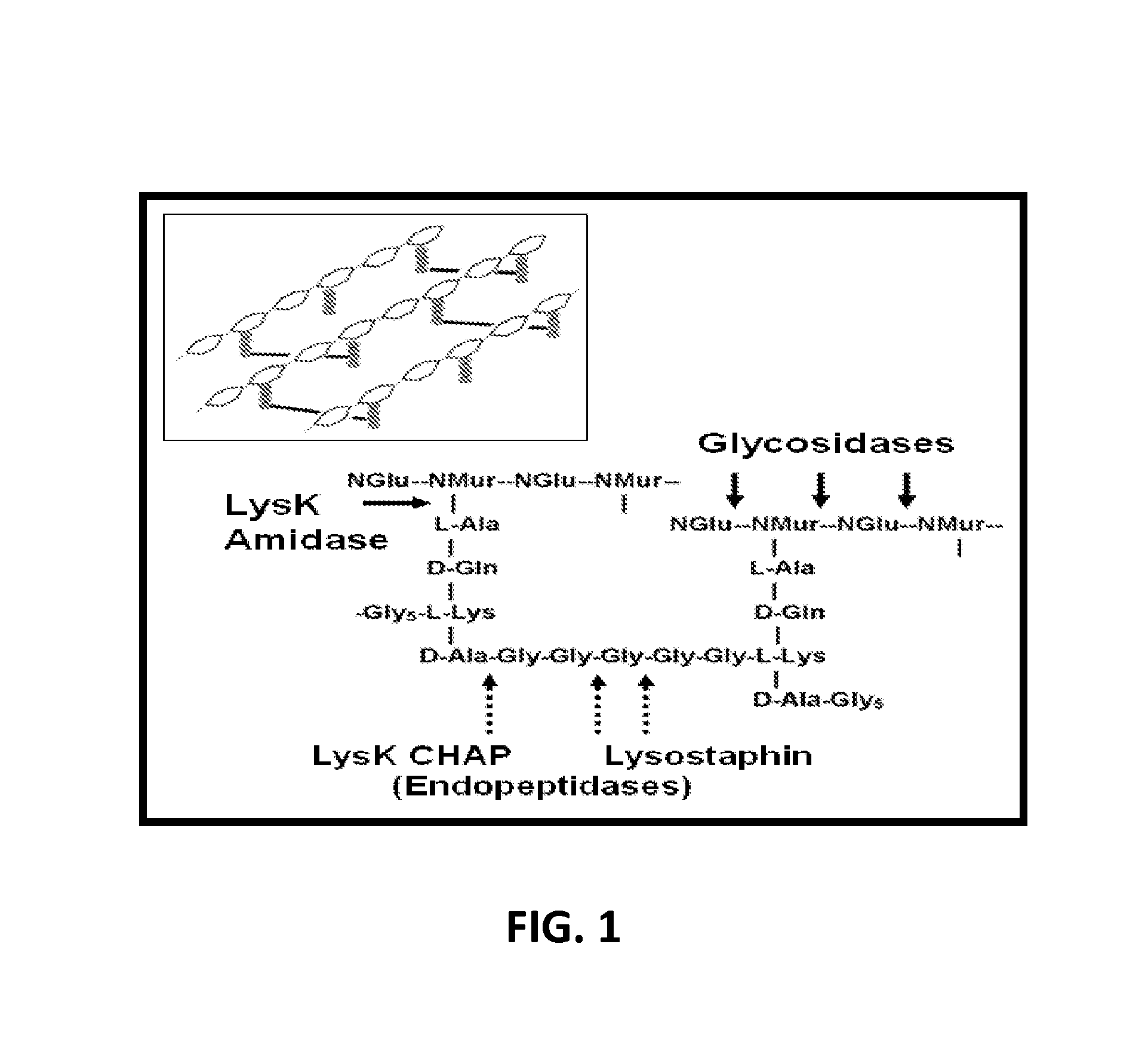
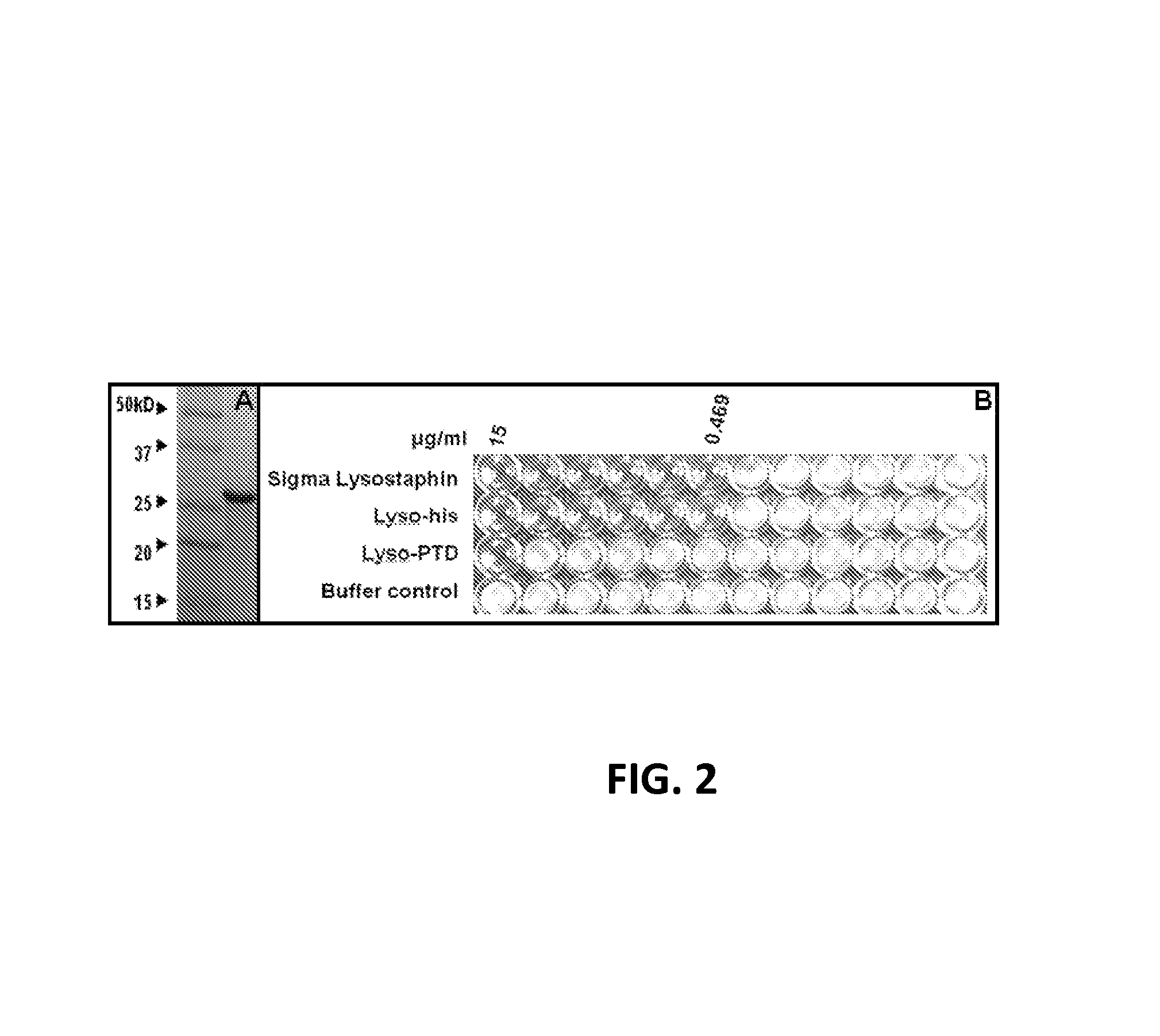
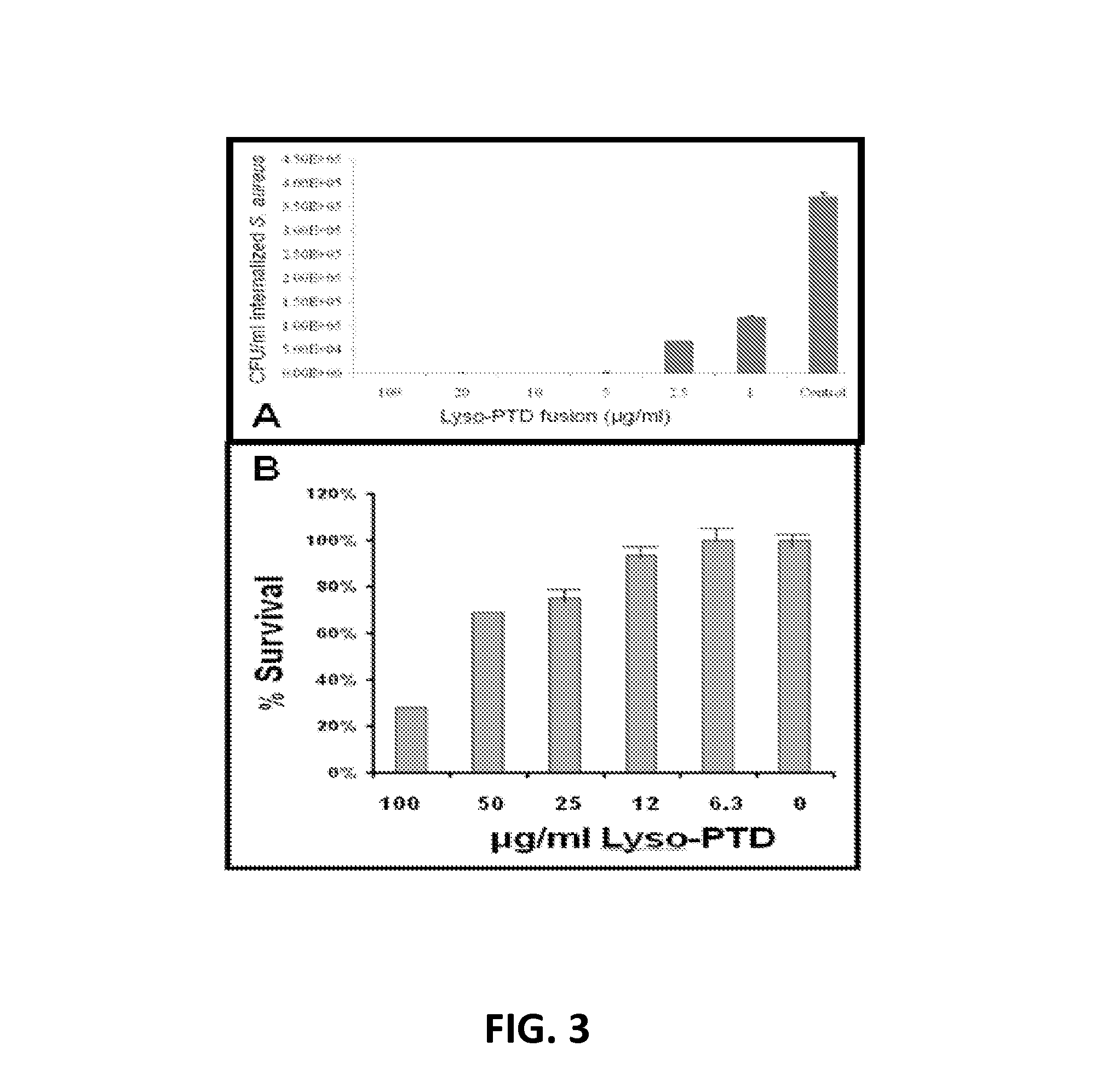
Fusion of peptidoglycan hydrolase enzymes to a protein transduction domain allows eradication of both extracellular and intracellular gram positive pathogens
InactiveUS8383102B2Facilitate its translocationEffective treatmentPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibacterial agentsPeptidoglycan HydrolaseGram
Lysostaphin is a bacteriocin secreted by S. simulans to kill S. aureus, and has been shown to also be a potent antimicrobial for many antibiotic-resistant strains of S. aureus. By adding a ˜13 amino acid protein transduction domain (PTD) from the HIV-TAT protein to lysostaphin to form lysostaphin-PTD, both extracellular and intracellular forms of S. aureus and MRSA are killed in all (multiple) cell types examined.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
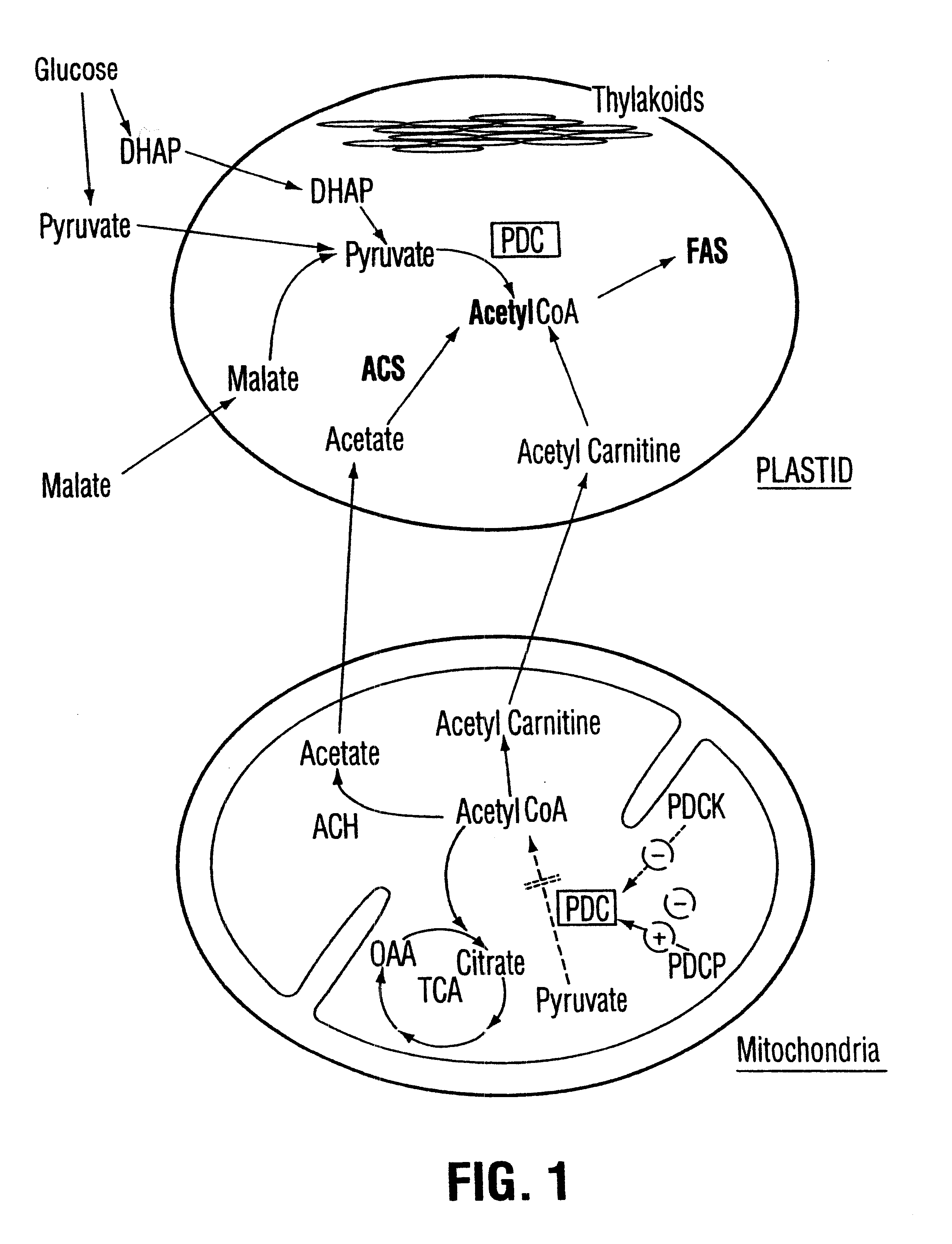
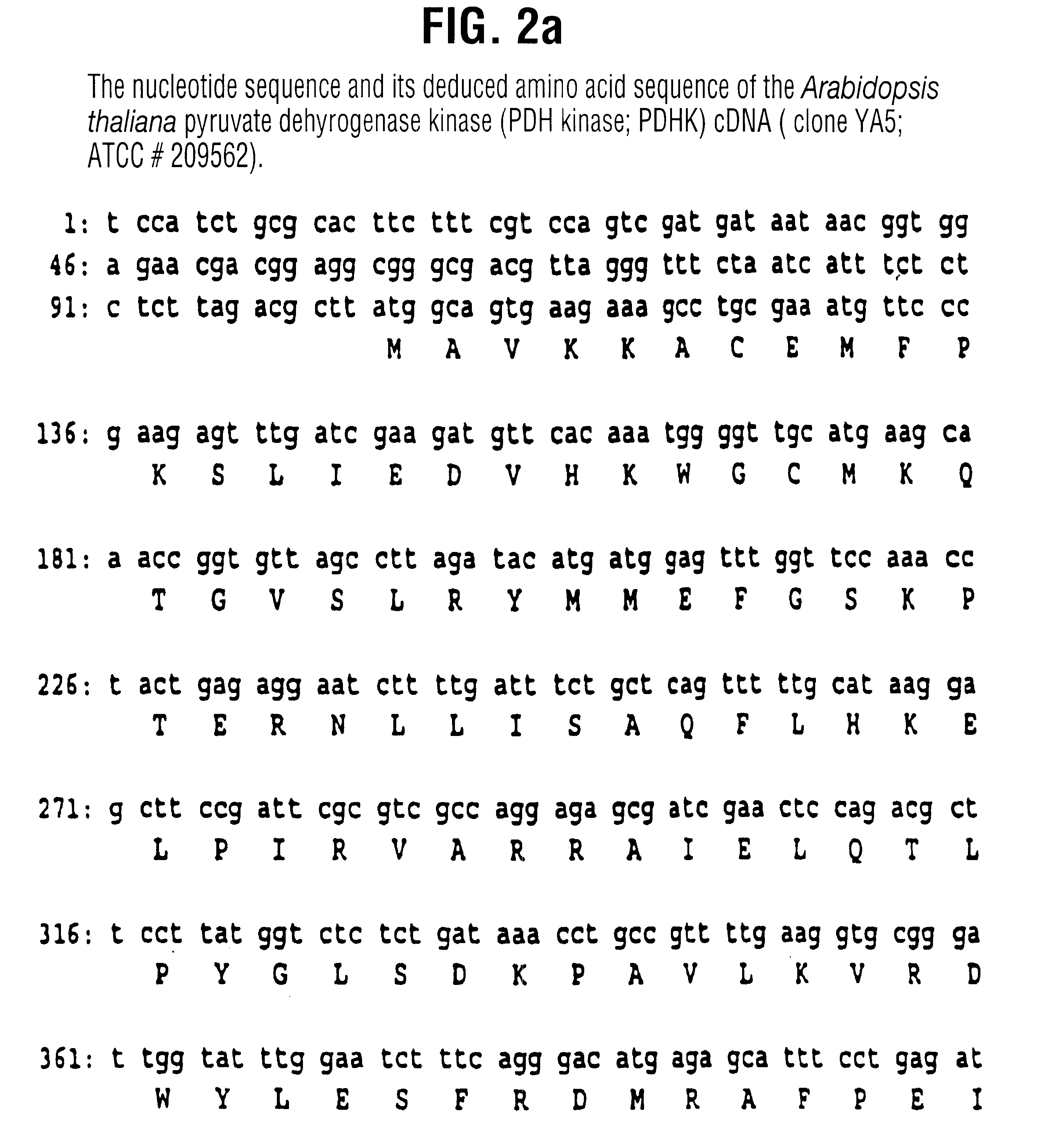
Plant pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase gene
InactiveUS6500670B1High activityImprove availabilitySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationBrassicaceaePlanting seed
The present invention relates to the isolation, purification, characterization and use of a mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDHK) gene [SEQ ID NO:1](pYA5; ATCC No 209562) from the Brassicaceae (specifically Arabidopsis thaliana). The invention includes isolated and purified DNA of the stated sequence and relates to methods of regulating fatty acid synthesis, seed oil content, seed size / weight, flowering time, vegetative growth, respiration rate and generation time using the gene and to tissues and plants transformed with the gene. The invention also relates to transgenic plants, plant tissues and plant seeds having a genome containing an introduced DNA sequence of SEQ ID NO:1; or a part of SEQ ID NO:1 characterized in that said sequence has been introduced into an antisense or sense orientation, and a method of producing such plants and plant seeds. The invention also relates to substantially homologous DNA sequences from plants encoding proteins with deduced amino acid sequences of 25% or greater identity, and 50% or greater similarity, isolated and / or characterized by known methods using the sequence information of SEQ ID NO:1, and to parts of reduced length that are still able to function as inhibitors of gene expression by use in an anti-sense, co-suppression or other gene silencing technologies.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Herpes virus type I PCR (polymerase chain reaction) fluorescence quantitative rapid test kit and method
ActiveCN102337355AGuaranteed credibilityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesReference productFluorescence
The invention aims at providing a herpes virus type I PCR (polymerase chain reaction) fluorescence quantitative rapid test kit which can detect the specific nucleic acid sequence of pure herpes virus type I in a clinical sample and further achieve the purpose of rapidly judging the existence of the pure herpes virus type I. In order to realize the purpose, the technical scheme of the invention isas follows: the herpes virus type I PCR fluorescence quantitative rapid test kit provided by the invention comprises a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) extraction solution, a PCR reaction solution, a DNA polymerase, a positive quality control product, a weak positive quality control product, a negative quality control product and a quantitative reference product, wherein the PCR reaction solution comprises primers and a fluorescent probe, and the primers are divided into an upstream primer and a downstream primer. The herpes virus type I PCR fluorescence quantitative rapid test kit has the beneficial effect of filling in the blank of a fluorescence PCR kit for clinically detecting the pure herpes virus type I (HSV I) in China. Furthermore, a Taqman core technology platform and an arabidopsis thaliana internal control system are utilized for detecting the pure herpes virus type I (HSV I), so that the herpes virus type I PCR fluorescence quantitative rapid test kit has the advantages of highsensitivity, high specificity, stability, timeliness, convenience in operation and the like.
Owner:泰普生物科学(中国)有限公司
Arabidopsis thaliana floral organ specificity promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN103589726AImplement directional operationsVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyOrgan Specificity
The invention relates to a newly discovered DNA sequence which can be used as a promoter for regulating and controlling a target gene to be specifically expressed in a floral organ of arabidopsis thaliana. An AtcpSecY1 gene promoter sequence is cloned from a model plant arabidopsis thaliana; subsequently in a transgenic arabidopsis thaliana, the promoter is confirmed to be capable of driving a GUS reporter gene to be specifically expressed in the floral organ of arabidopsis thaliana. With the application of the promoter, a 'floral organ specificity promoter-target gene to be expressed' fusion gene is obtained by construction, arabidopsis thaliana is transformed, and the transgenic plant having the target gene specifically expressed in the floral organ can be obtained. The promoter not only provides important molecular elements for in-depth research of plant floral organ differentiation, formation, growth and development molecular mechanisms and other theory researches, but also provides important molecular regulating and controlling elements for plant genetic engineering seed breeding, especially the gene engineering seed breeding for regulating and controlling flower shapes, flower colors, flower aromas, ornamental life and the like of famous and valuable flowers, and has wide application value.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
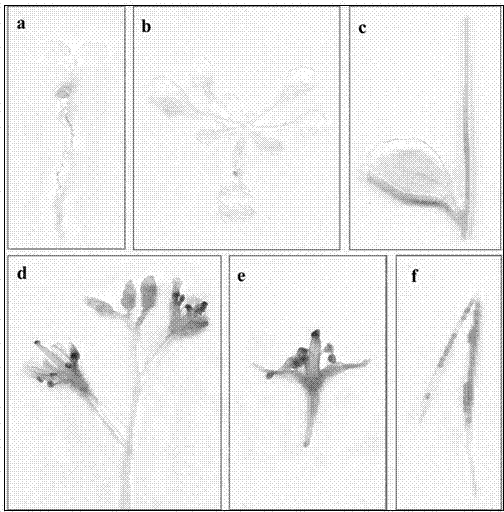
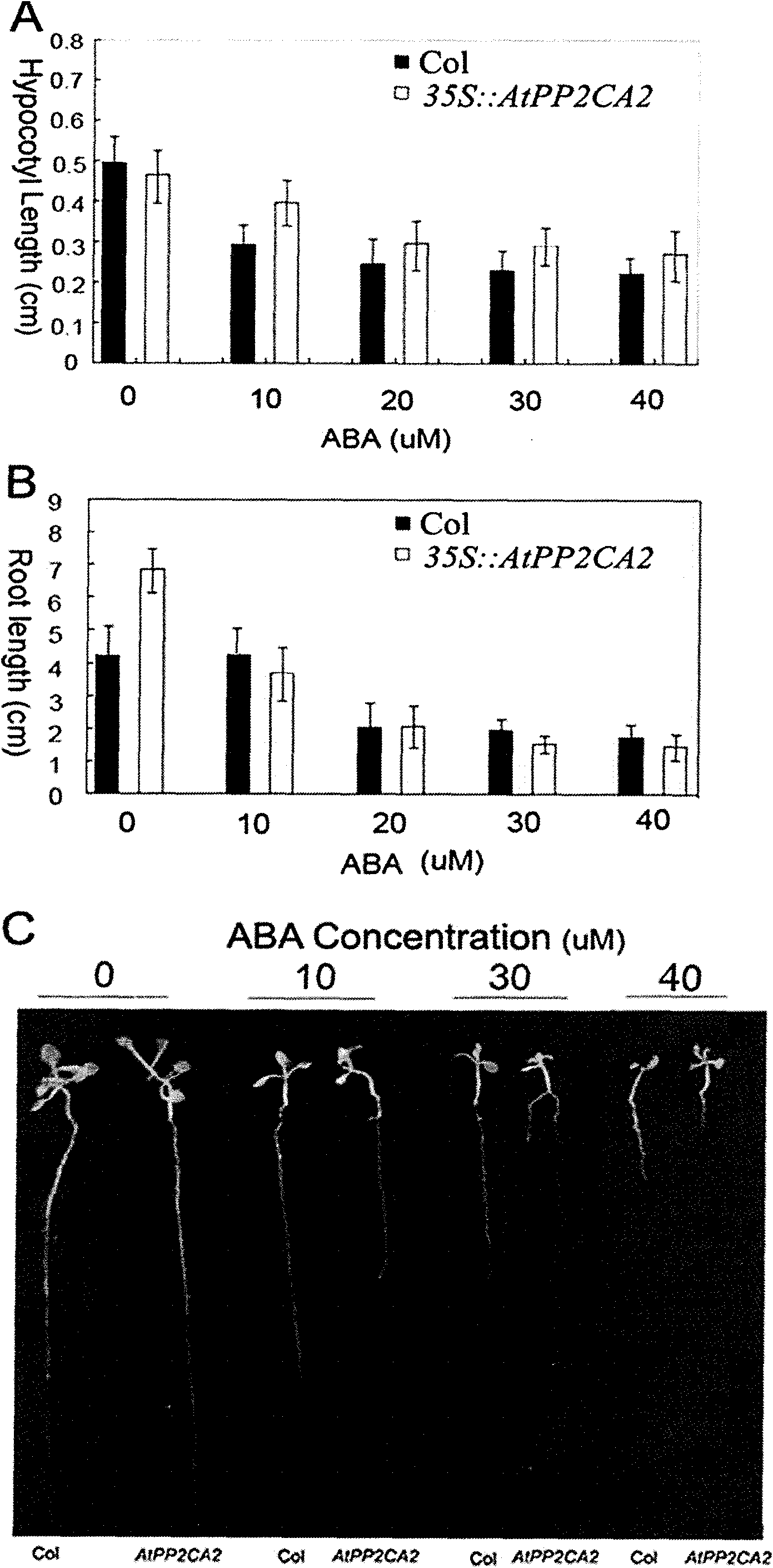
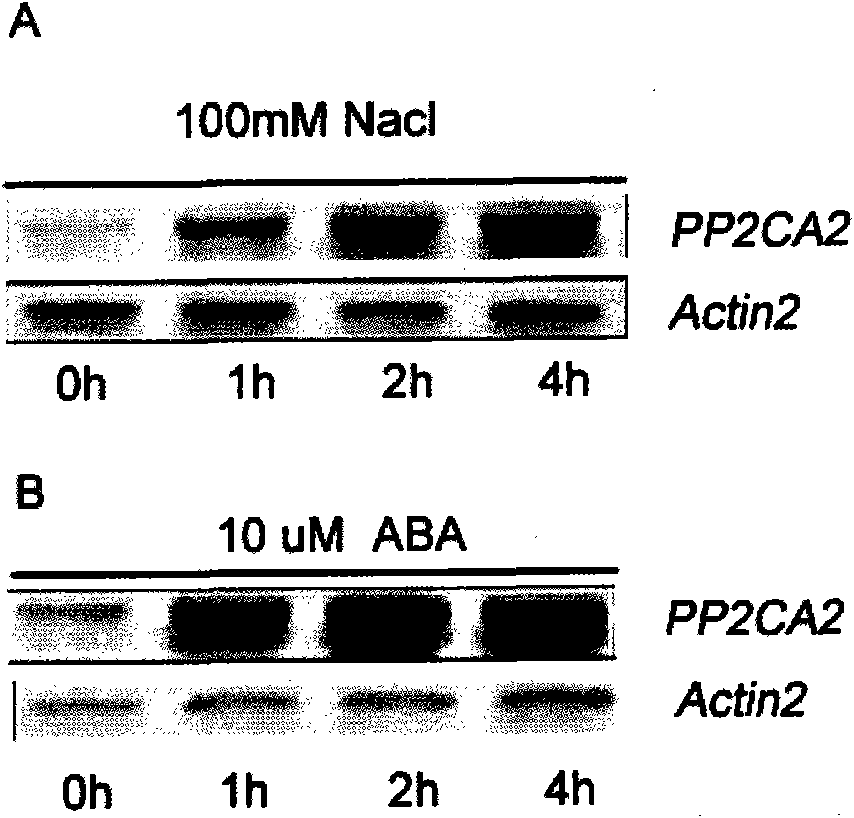
Arabidopsis thaliana AtPP2CA2 gene and application thereof
The invention discloses protein phosphatases 2C of arabidopsis thaliana and encoding gene and application thereof. The invention aims at providing the protein phosphatases 2C of the arabidopsis thaliana, the encoding gene thereof, and application thereof to controlling growth and development and stress resistance of plants. The AtPP2CA2 gene disclosed by the invention is found through screening from a cDNA database of arabidopsis thaliana processed by ABA (Abscisic Acid), salt and drought induction by using a gene chip method, the number of the AtPP2CA2 gene in GenBank is At5g59220, the length of cDNA of the gene is 1242bp, and the gene encodes 413 aa proteins. The gene disclosed by the invention and the encoding protein thereof have great theoretic and practical significance in research of inverse resistance mechanism of plants and improvement of inverse resistance such as drought endurance, salt tolerance and the like and relevant properties, and play an important role in the improvement of inverse-resistance gene engineering of plants, and have broad application prospect.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Topical Composition For Anti-Aging Skin Treatment Using Dual DNA Repair Mechanism and Method of Use
InactiveUS20100291190A1Reduction of pigmentation spotImprove skin toneBiocideCosmetic preparationsSkin colorSativum
A topical composition for anti-aging treatment of the skin includes water soluble extract of Uncaria species, Arabidopsis thaliana extract, lipoic acid, dimethylethanolamine, tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate, dimethyl sulfoxide, Glycyrrhiza Glabra(Licorice) root extract, methylsulfonylmethane, phytosterols, D-ribose, tocotrienol, tocopherol, glucosamine hydrochloride, Pisum sativum extract; Bambusa vulgaris extract, and a dermatologically acceptable liposomal delivery medium. Further disclosed is a method using the topical composition for anti-aging skin treatment utilizing DNA repair in both the nucleus and the mitochondria. The topical composition can be applied on the skin of a person daily, and can also be applied in a dermal infusion treatment, with or without micro-dermal abrasion or skin suction. Topical application of the composition achieves effective reduction of pigmentation spots and degree of winkles, and improvement of skin color tone.
Owner:LIFE SCI INT
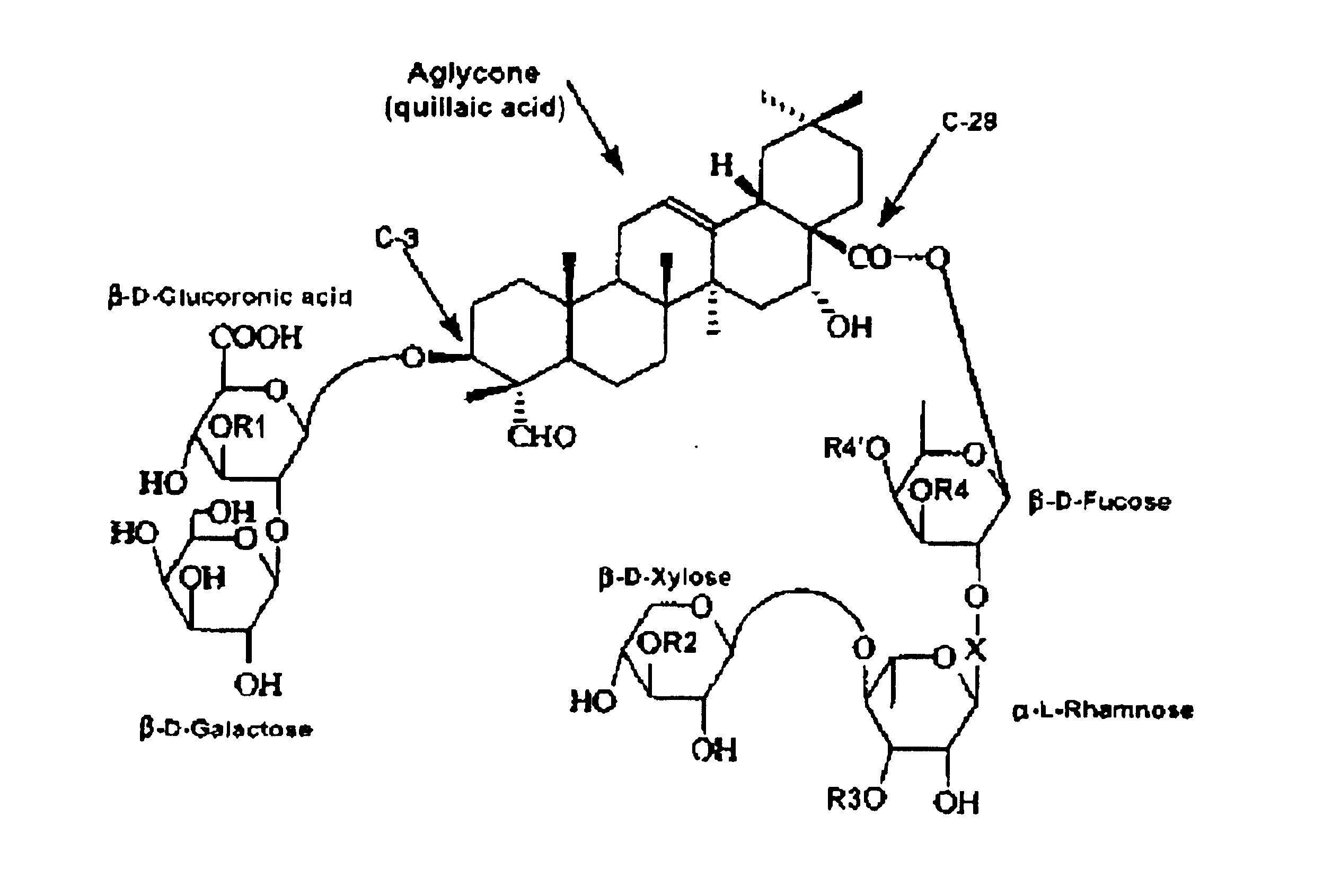
Compositions and methods based on exracts of quillaja saponaria molina for controlling nematodes
A method for the control of plant parasitic nematodes, comprising applying an extract of Quillaja saponin Molina, a product for the control of plant parasitic nematodes present in agricultural crops, comprising an aqueous extract from Quillaja saponaria Molina, said extract comprising a saponin fraction with 2 to 14% by weight of said fraction of saponin, and a non saponin fraction with at least 5% of said fraction of polyphenols.
Owner:SAN MARTIN RICARDO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
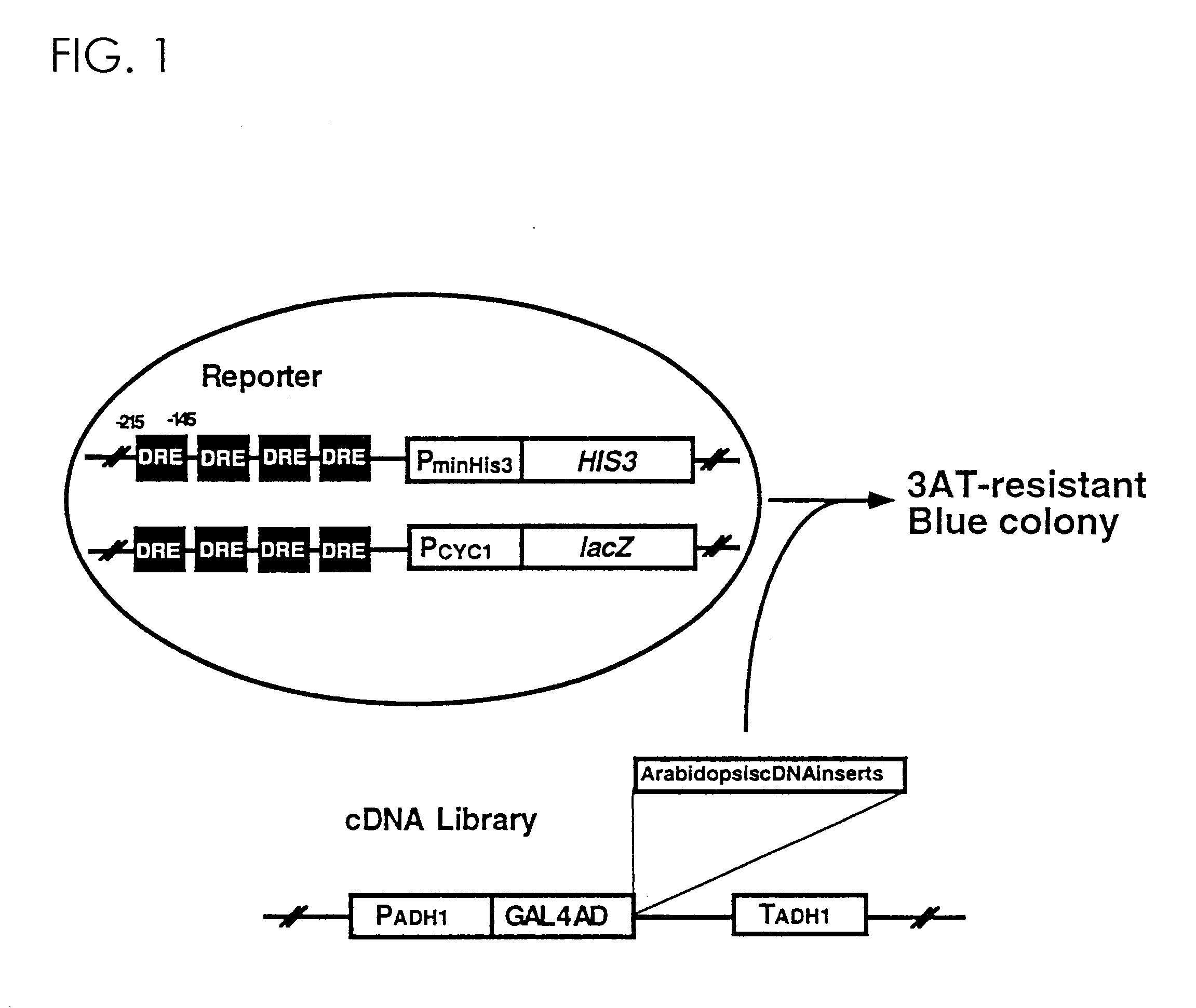
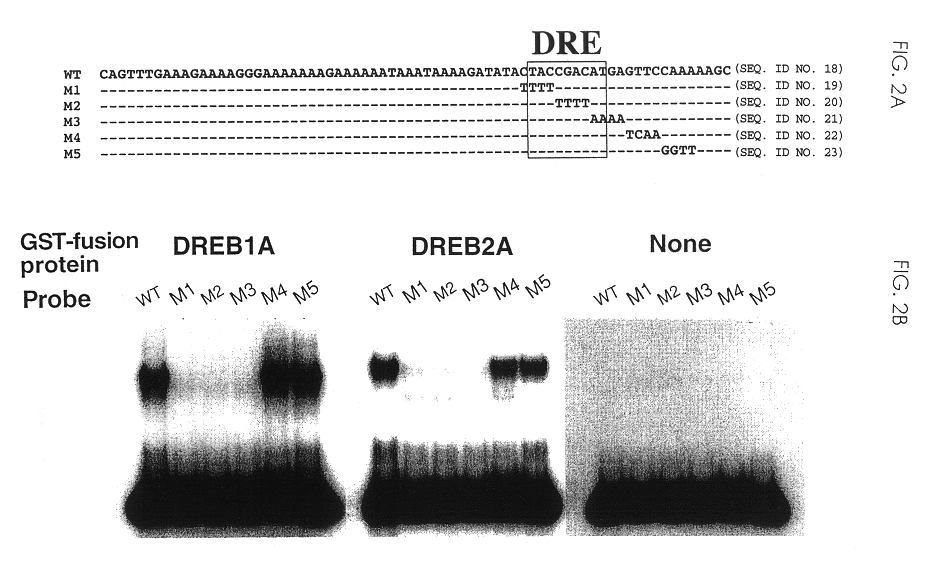
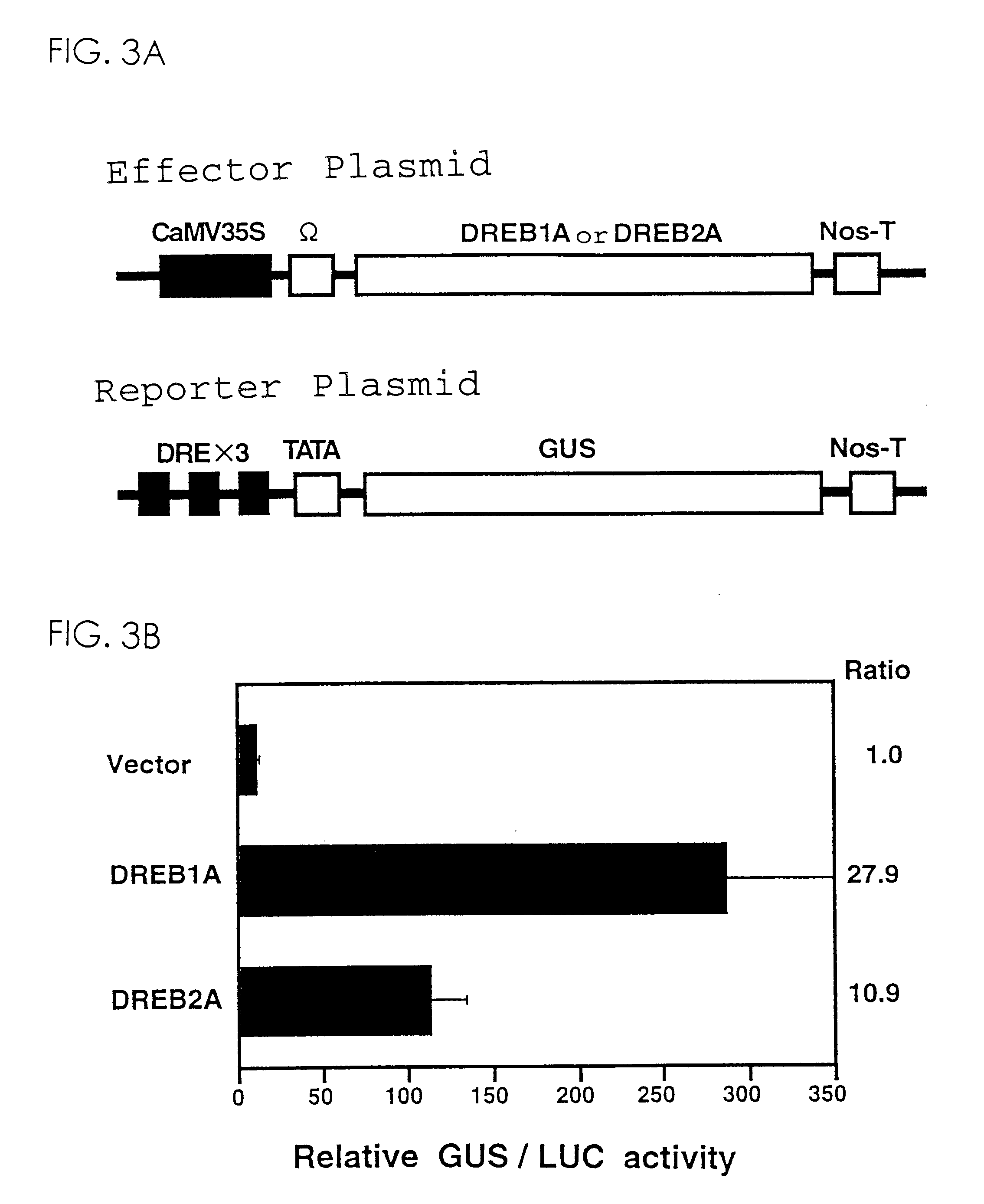
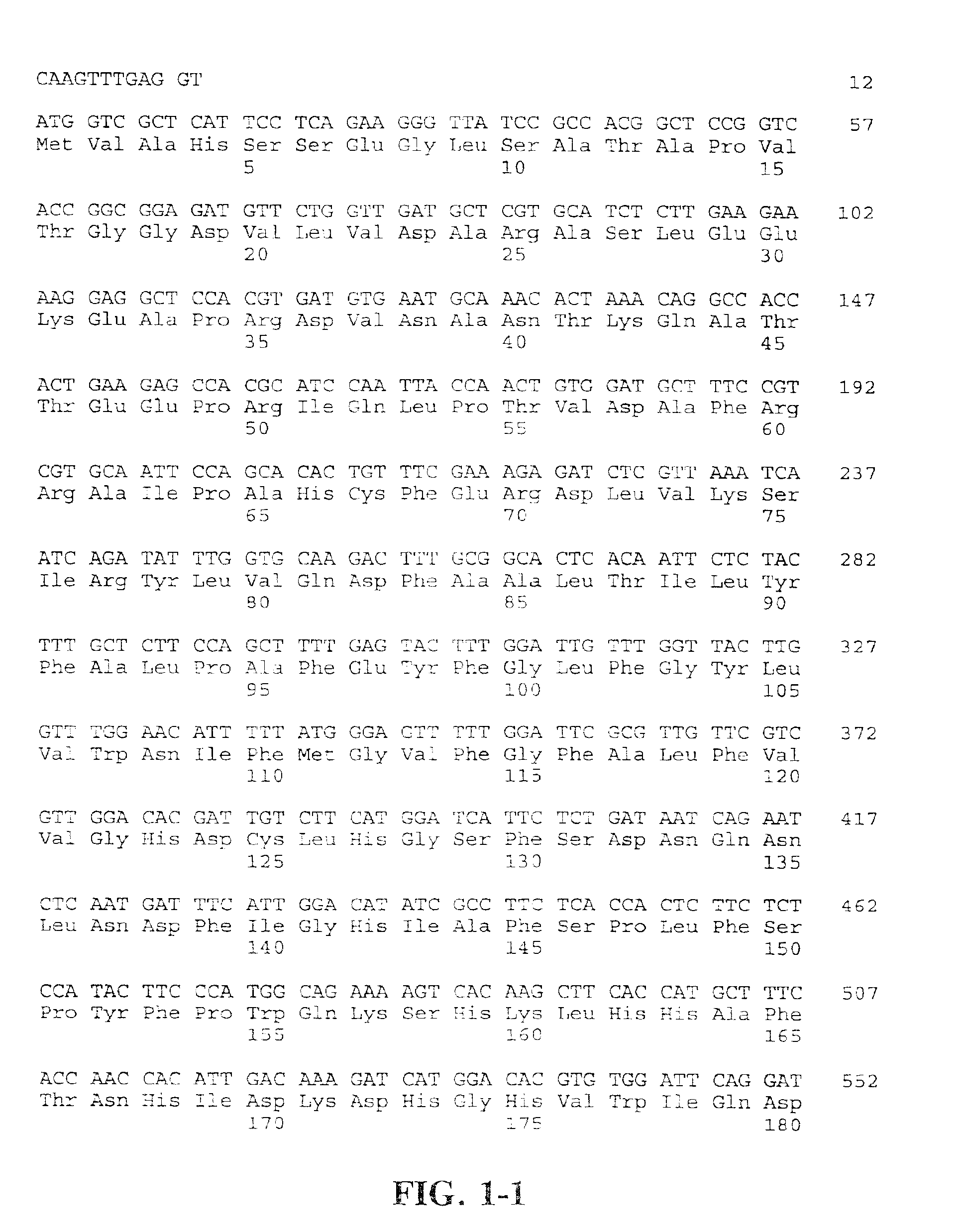



![Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s] Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d91cdd0d-3efd-4cb2-8c59-845405780aee/US06936750-20050830-D00001.png)
![Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s] Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d91cdd0d-3efd-4cb2-8c59-845405780aee/US06936750-20050830-D00002.png)
![Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s] Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d91cdd0d-3efd-4cb2-8c59-845405780aee/US06936750-20050830-D00003.png)