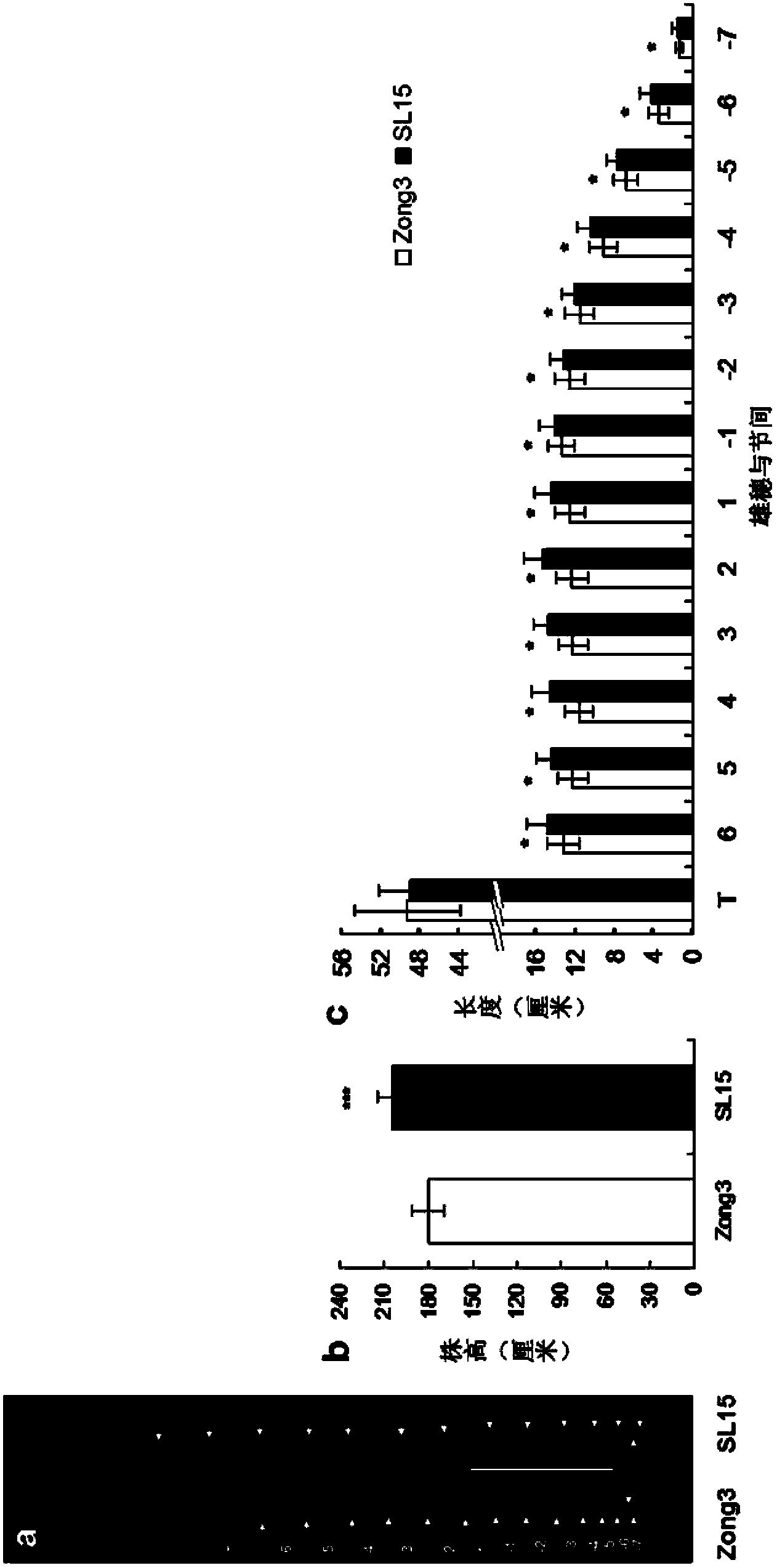
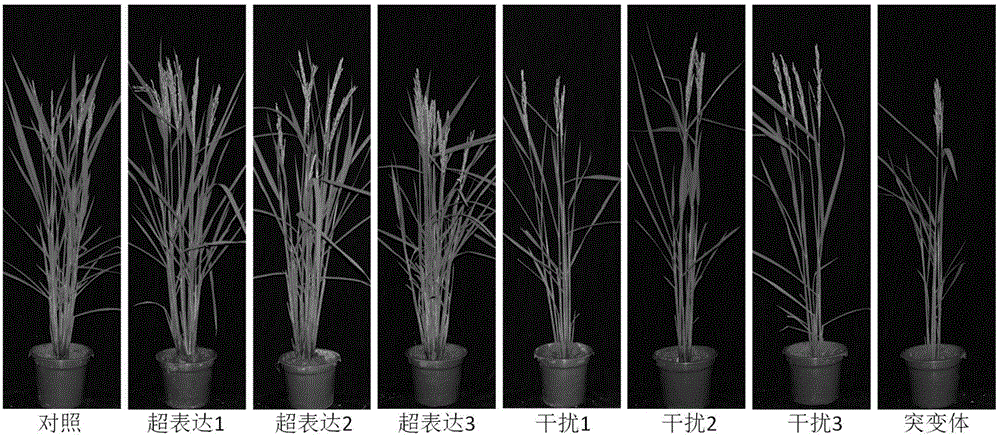
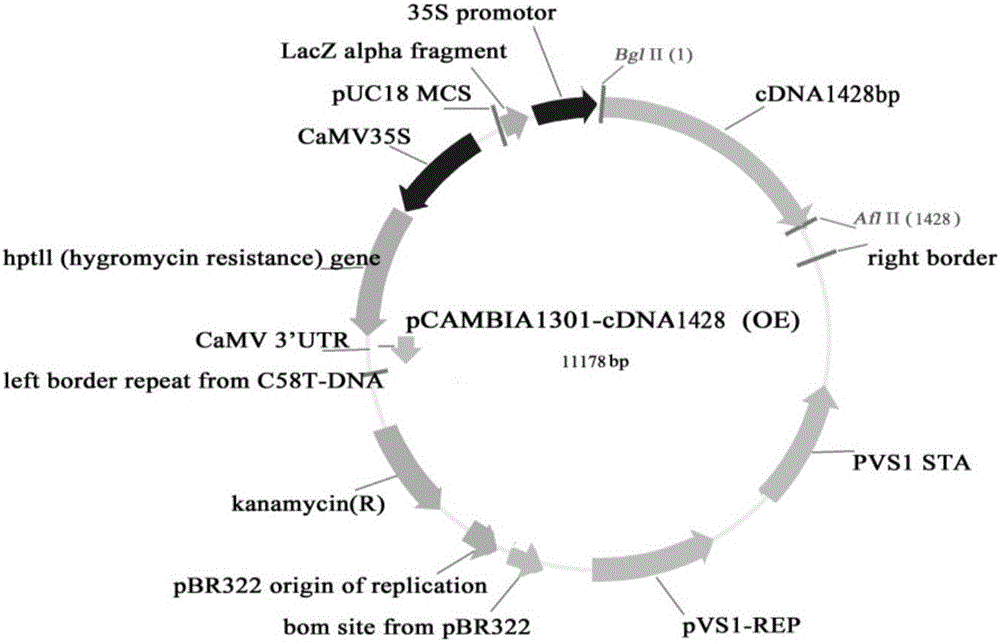
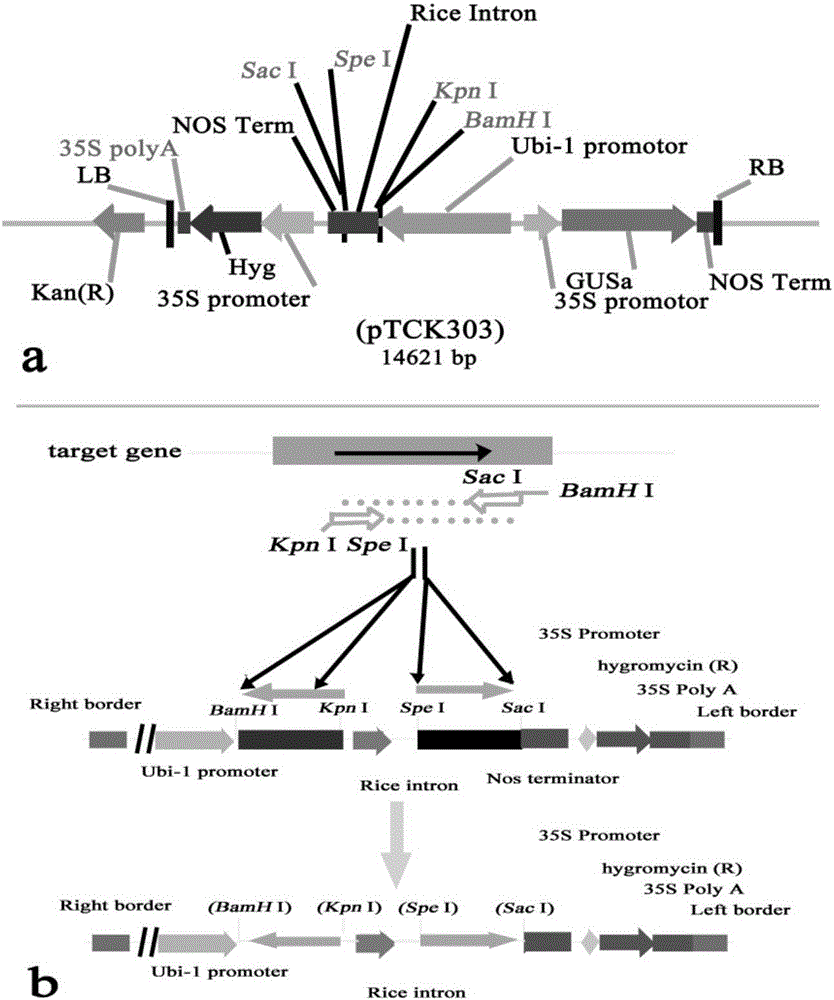
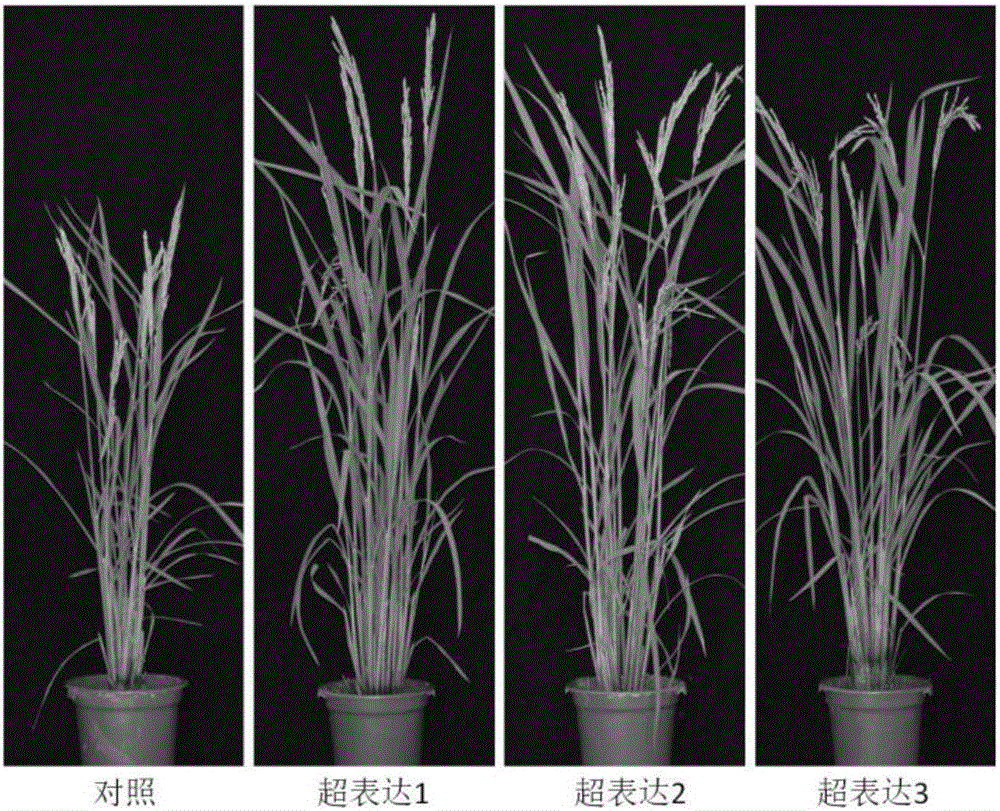
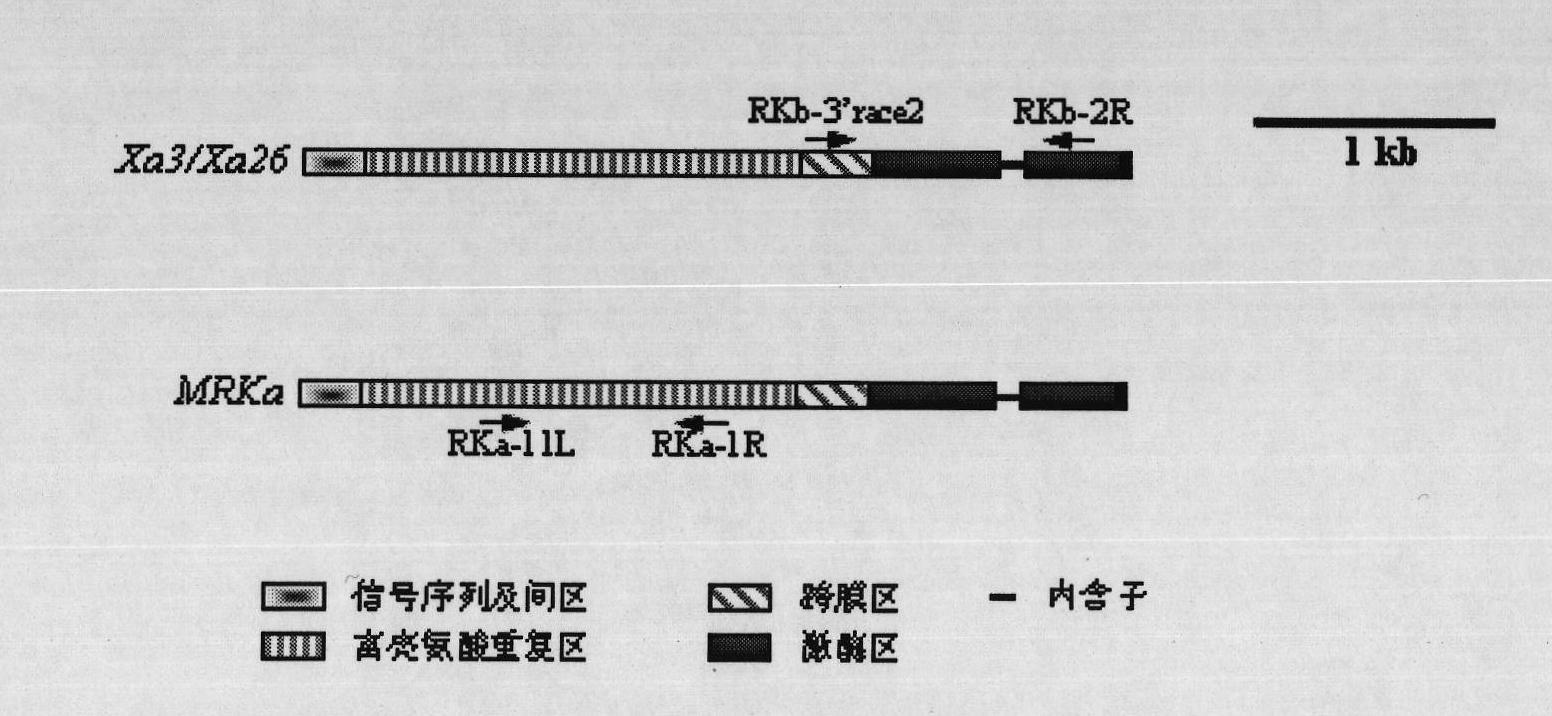
Patents
Literature
1657 results about "Plant genetic engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plant genetic engineering, also known as plant genetic modification or manipulation, is the key that opens up the doors for introducing crops with valuable traits to produce plants that require fewer pesticides, fungicides, or fertilizers, and can be more resistant to stress conditions.
Method for deleting selection marker gene of transgenic rice
ActiveCN104846010AHigh distribution frequencyEasy to operateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetically modified ricePlant genetic engineering
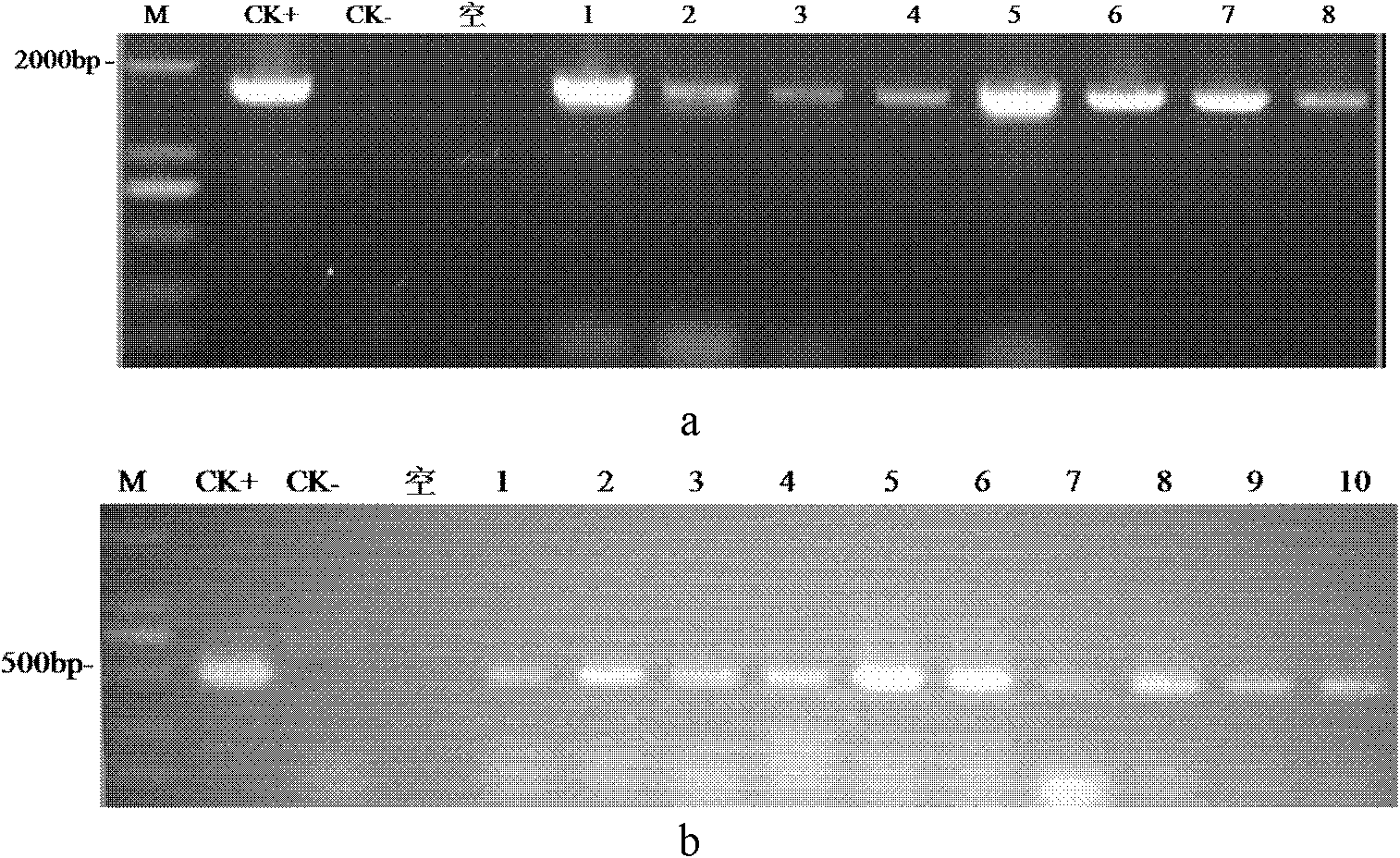
The invention provides a method for deleting a selection marker gene of transgenic rice and belongs to the field of plant gene engineering. The method for efficiently deleting the marker gene of the transgenic rice in a plant level is established by utilizing a genome fixed-point editing technology mediated by a CRISPR / Cas9 system. The whole segment of the marker gene can be effectively deleted by utilizing the method, and only an expression frame of the marker gene is deleted pointedly without change of the expression of other components in the transgenic rice. Thus, the transgenic rice without the selection marker gene can be efficiently bred by utilizing the method, so that the safety doubt of people about the selection marker gene can be completely removed.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for directionally knocking out miRNA (micro Ribonucleic Acid) of paddy rice
ActiveCN106367435AEasy to operateHigh knockout rateNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionLarge fragmentMutant
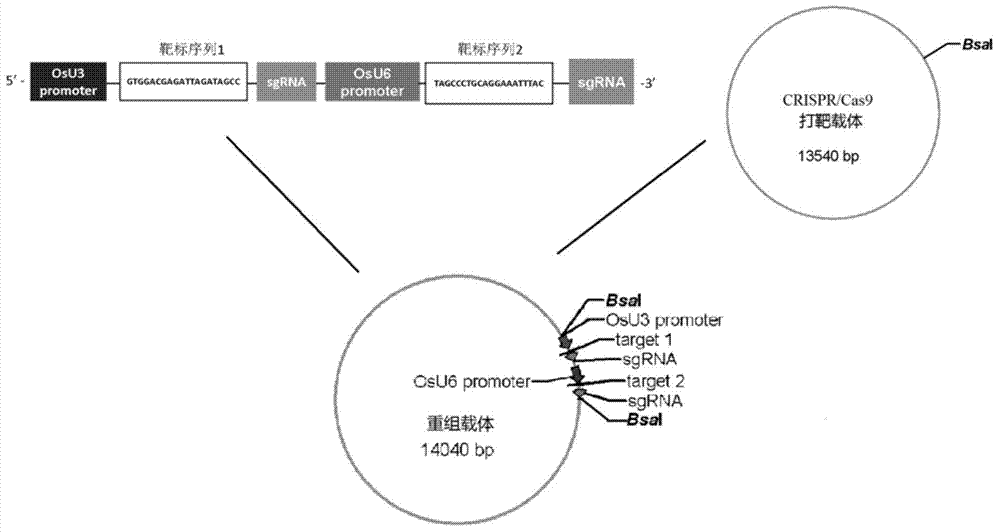
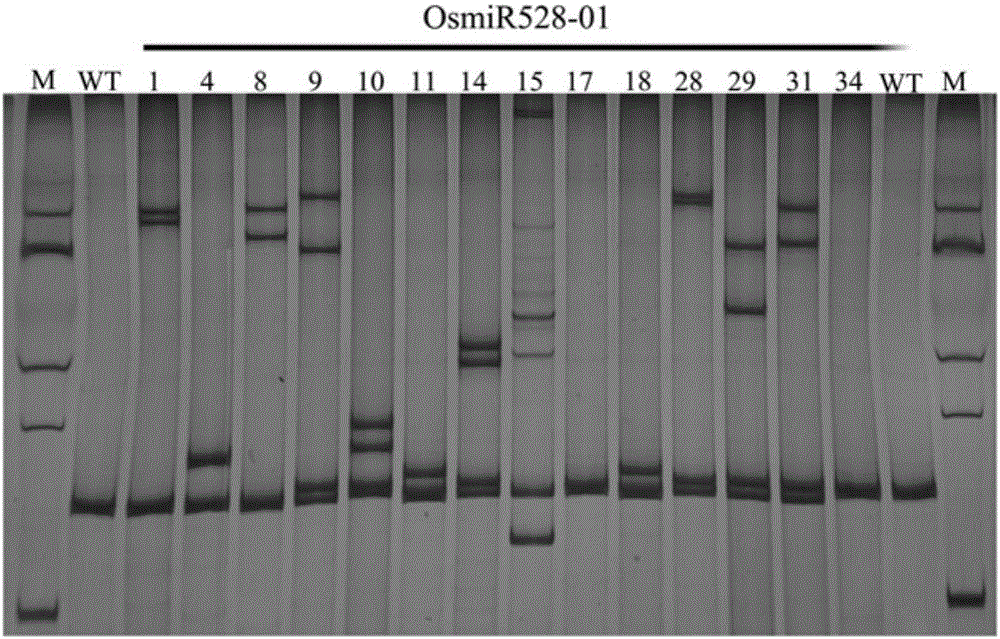
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and specifically relates to a method for directionally knocking out miRNA (micro Ribonucleic Acid) of paddy rice. Aiming at solving the technical problems, a method and a detection means are provided for directionally modifying miRNA sites of plants. The invention discloses a method for obtaining miRNA mutants of the paddy rice; specific operation of the method comprises: knocking out single miRNA, knocking out a plurality of miRNAs or knocking out large fragments of the miRNA by adopting a CRISPR-Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats- associated 9) method. The method provided by the invention is suitable for creation and screening of directionally knocking out the miRNA of the paddy rice.
Owner:成都极谷基因科技有限公司
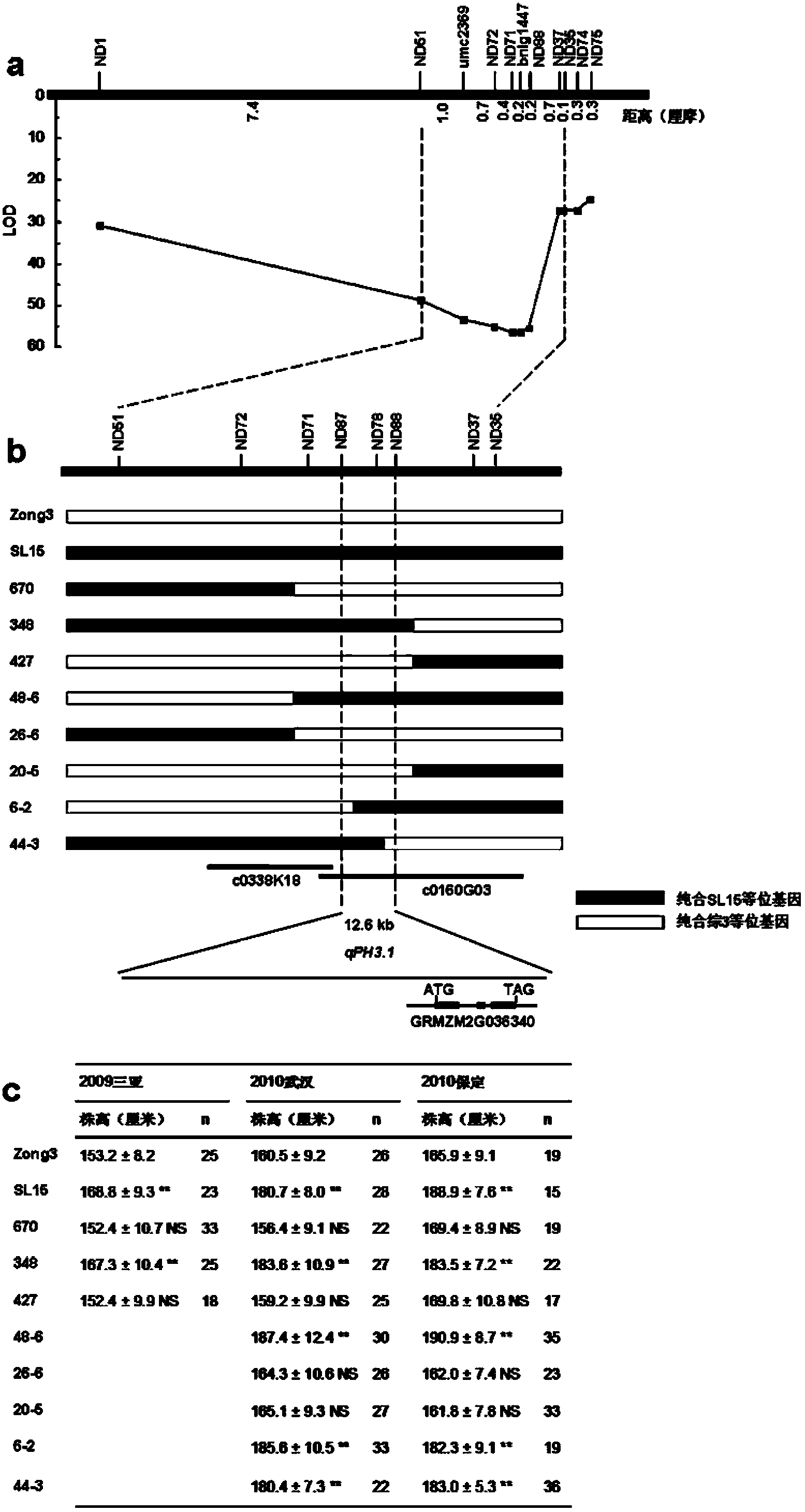
Molecular marker for controlling corn plant height and applications thereof
InactiveCN103451200AConfirm the synthetic relationshipYield is not affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Gene OsPTR9 capable of improving nitrogen absorption efficiency and yield of rice and application thereof
InactiveCN102604962AEnhanced tillering abilityIncrease productionBacteriaClimate change adaptationGrowth plantMutant
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering, and in particular relates to separation, cloning and application of a gene OsPTR9 which can improve nitrogen utilization efficiency and yield of rice. The OsPTR9 is one gene in a rice PTR (peptide transporter family) family, and an encoded protein is a nitrogenous organic matter transporter. In the invention, the OsPTR9 gene is excessively expressed, so that nitrogen fertilizer absorbing efficiency of normal rice is improved, tillering capacity is improved, ear length and thousand seed weight are increased, and functions of the OsPTR9 gene is verified in an OsPTR9 target gene mutant by adopting an RNAi (ribonucleic acid interference) technology. According to the invention, the expression quantity of the OsPTR9 gene is increased or reduced by adopting a genetic engineering technology, which sufficiently shows that the OsPTR9 gene can control the nitrogen absorption, plant tillering, ear length and thousand seed weight andthe like of the rice. The gene has important application values in the aspects of explaining influence of nitrogen on a plant growth and development process, efficiently utilizing nitrogen fertilizerfor the rice and improving the yield.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
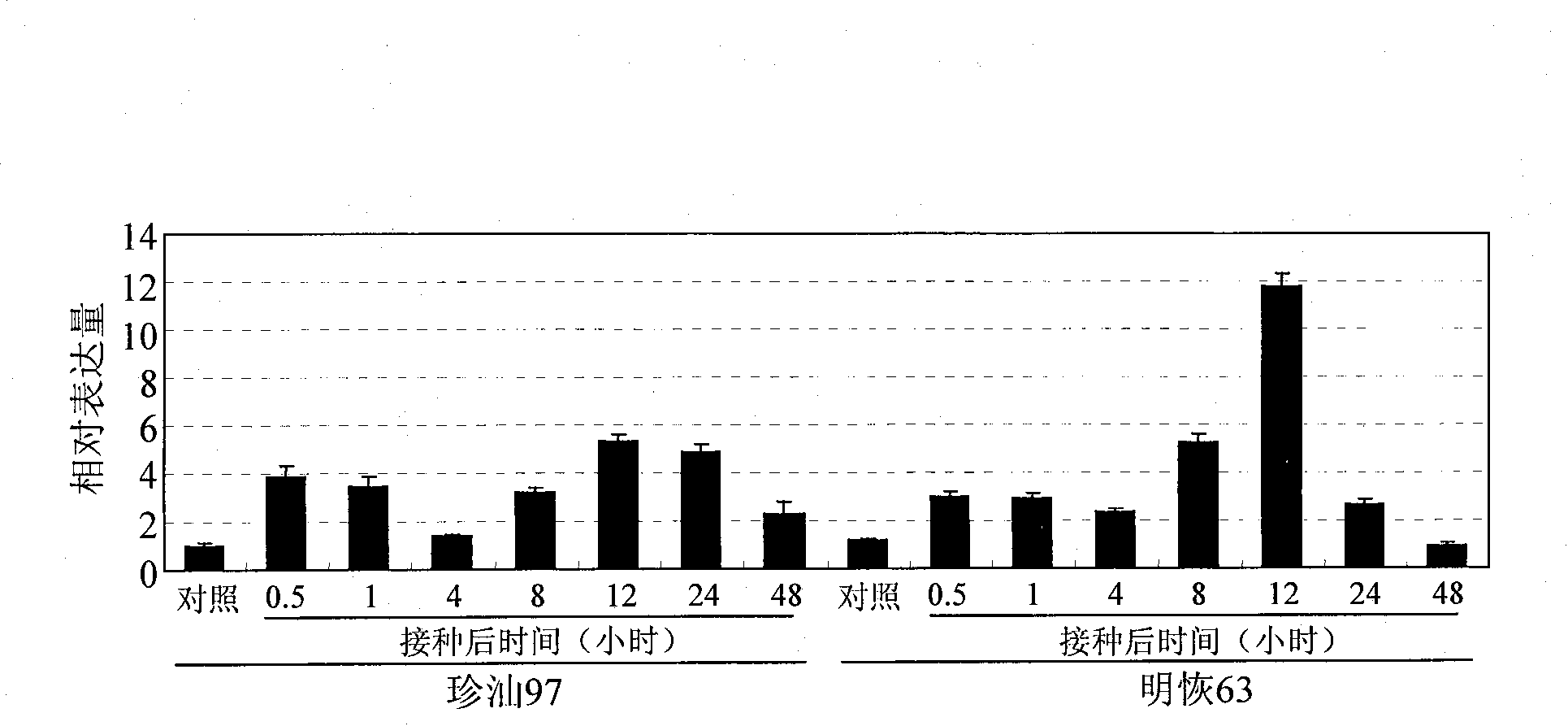
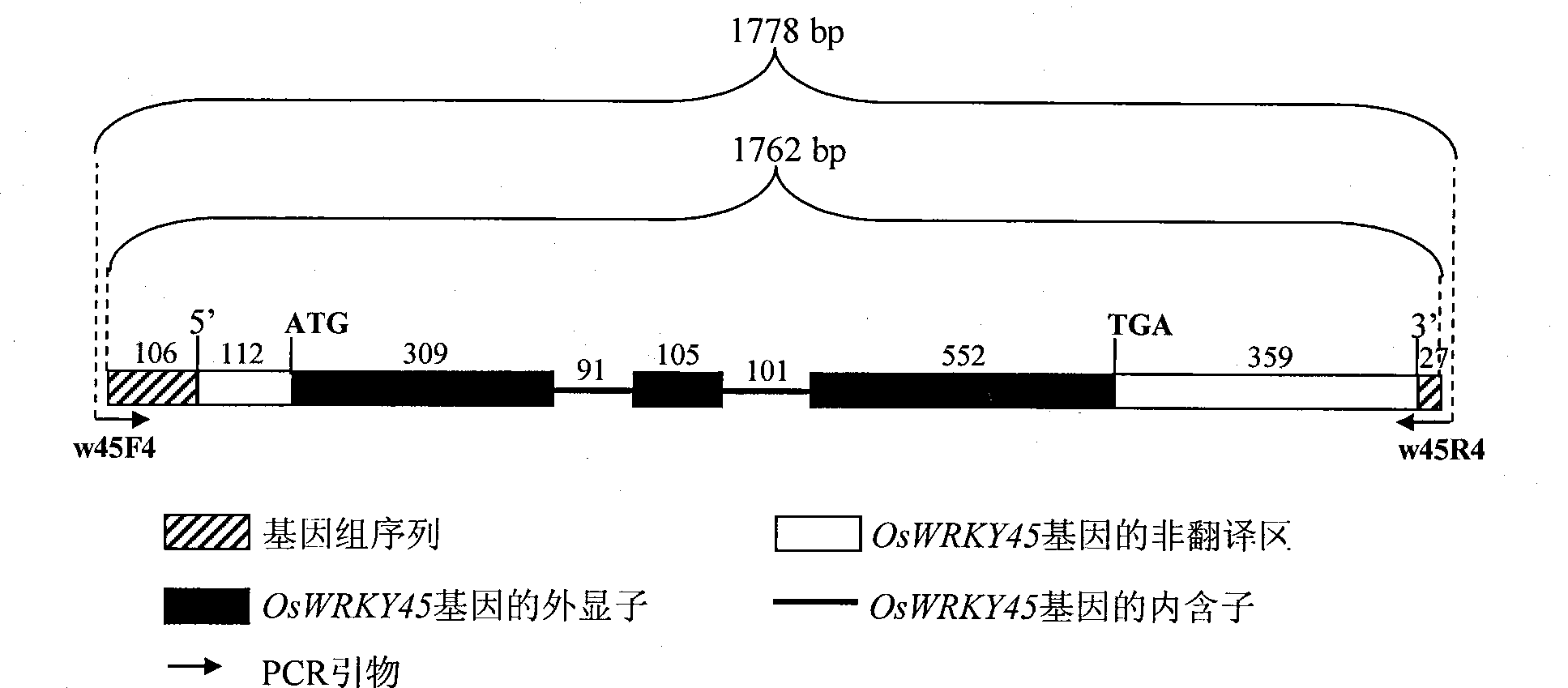
Rice disease resistance relevant gene OsWRKY45-2 and application thereof in improving rice disease resistance
InactiveCN101386856AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified ricePlant genetic engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, in particular relates to isolating clone and functional verification of a DAN fragment containing a gene OsWRKY45-2 related to rice disease resistance. The gene OsWRKY45-2 codes WRKY proteinoids and can endow rice with resistance to the diseases caused by bacterial pathogenic bacteria, namely the leaf blight bacteria (Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae) and fungal pathogenic bacteria, namely the rice blast bacteria (Magnaporthe grisea). The fragment and the exogenous regulatory sequence thereof are directly transferred into rice, thus the resistance capability of transgenic rice with over-expression OsWRKY45-2 against bacterial blight in and rice blast is improved remarkably.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
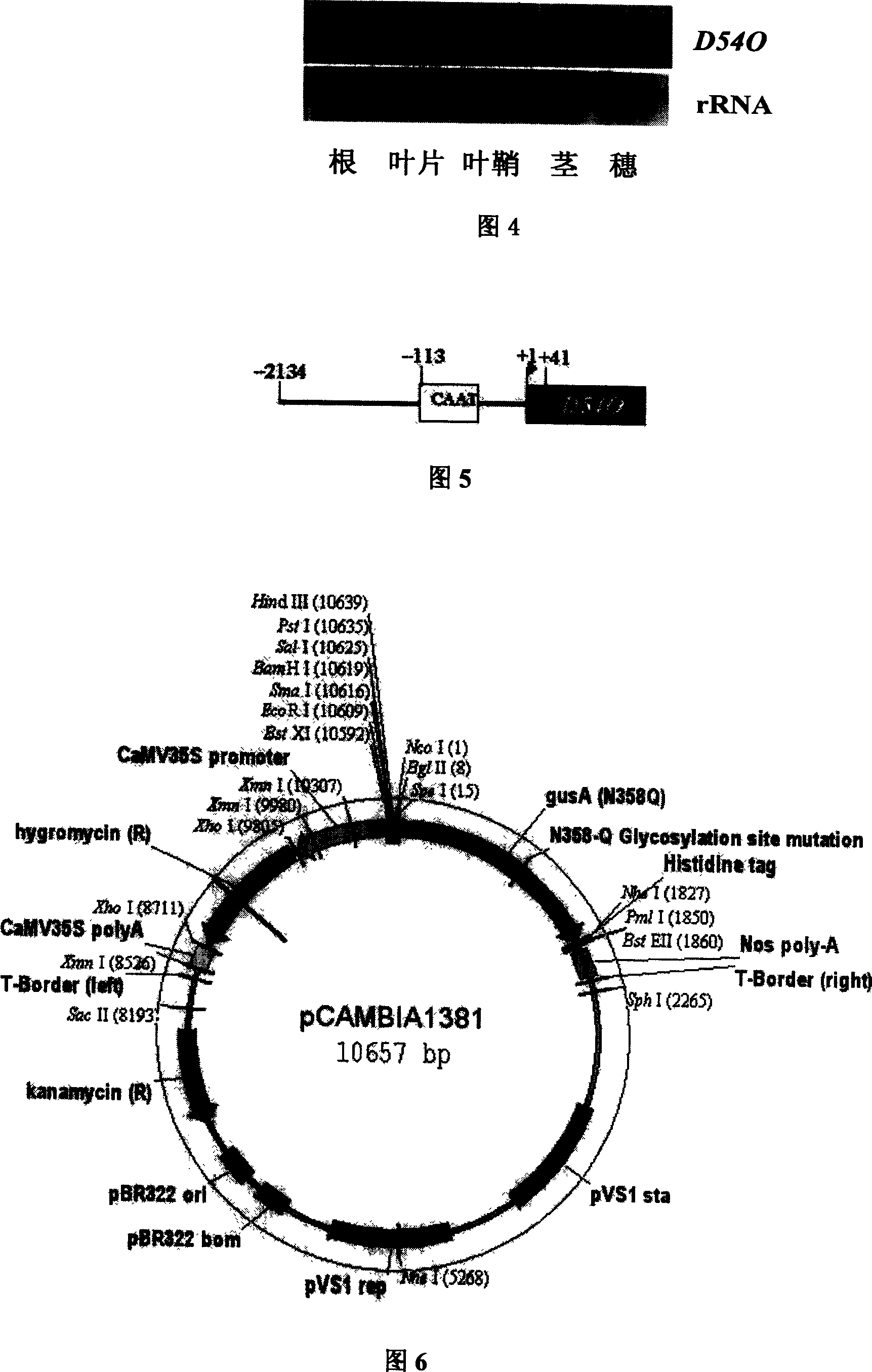
Tissue specificity expression promoter PD540 and application of the same in rice modification
InactiveCN101016546AImprove securityAddress food safety issuesFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPlant genetic engineering
The invention discloses a DNA fragment separating colony and functional checking of rice tissue special expressing promoter PD54O in plant gene engineering technical domain, which is characterized by the following: the PD54O promoter expresses in rice leaf and leaf sheath and does not express in germ and endosperm; transferring genetic rice plant can resist the invasion of borer with the expression of PD54O regulate and control insect-resisting gene; it does not express Bt protein in seeds of food.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Cloning and application of major gene GS5 capable of controlling width and weight of rice grain
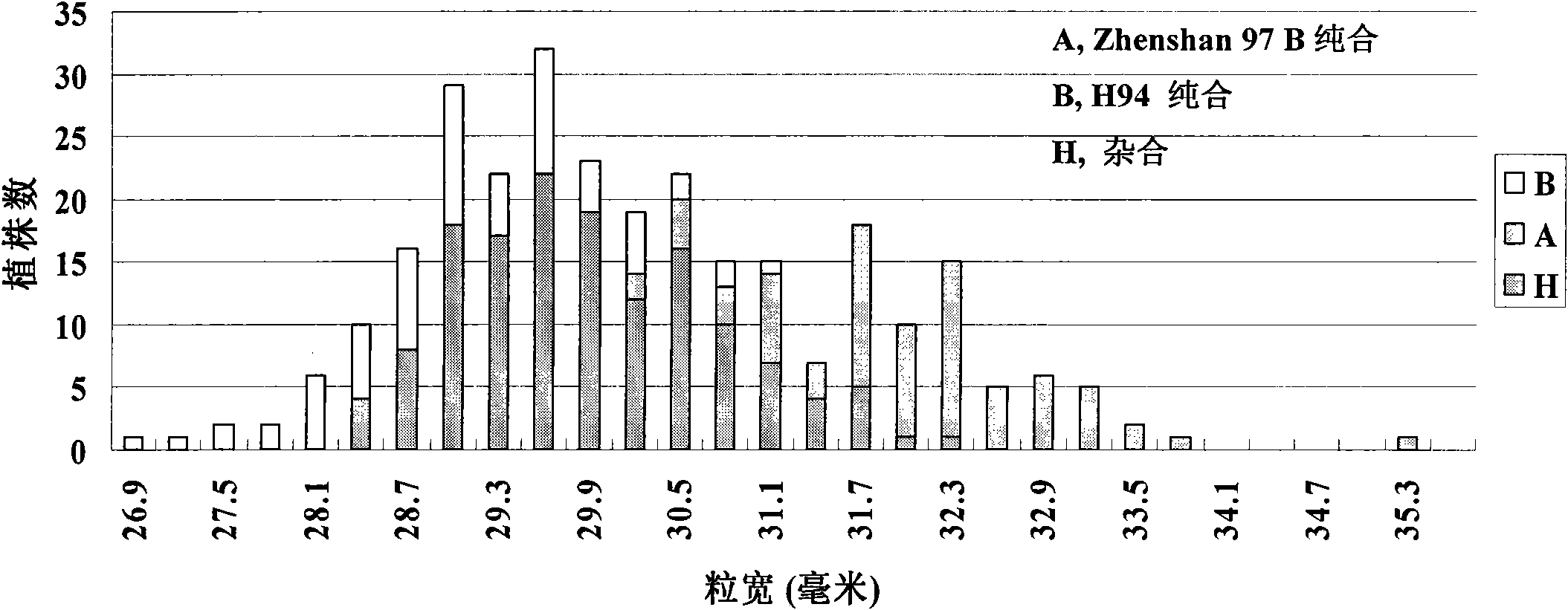
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, disclosing a separated and cloned major gene GS5 capable of controlling the width and the weight of a rice grain and the DNA sequence of the allelic gene of the major gene GS5. The DNA sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 (Zhenshan 97B) and SEQ ID NO.3 (H94) and contains 10 exons. The amino acid sequence of the major gene and the amino acid sequence of the allelic gene are shown as SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.4. By using two large-grain rice varieties and two small-grain rice varieties for comparative sequencing, in an approximately 6.1kb range, 22 common base differences exist between the large-grain variety and the small-grain variety, wherein 18 mutations are in a promoter area, 4 mutations are in a code area and 5 amino acids are caused to be changed. By using a transgenic technology, GS5 transgenic rice plants are obtained and express that the width and the weight of the rice grain are obviously improved when being compared with the control width and the control weight of the rice grain. The character changes are quite coincident with the two genotype expressions of a Zhenshan 97 near-isogenic line and a GS5 near-isogenic line. The invention additionally discloses a method of near-isogenic line breeding, gene cloning and gene transfer and application thereof.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
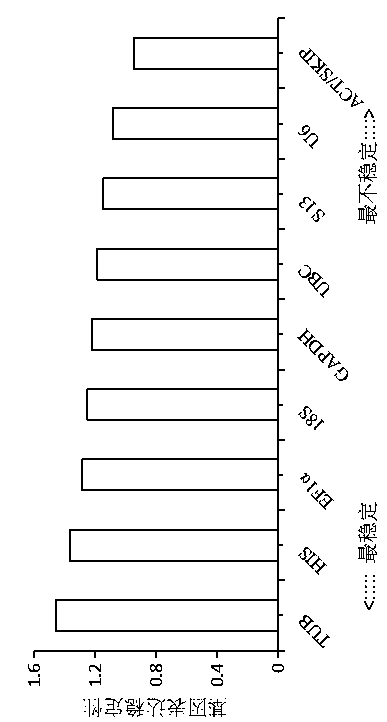
Screening method for real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR reference genes of Hibiscus hamabo Sieb.et Zucc
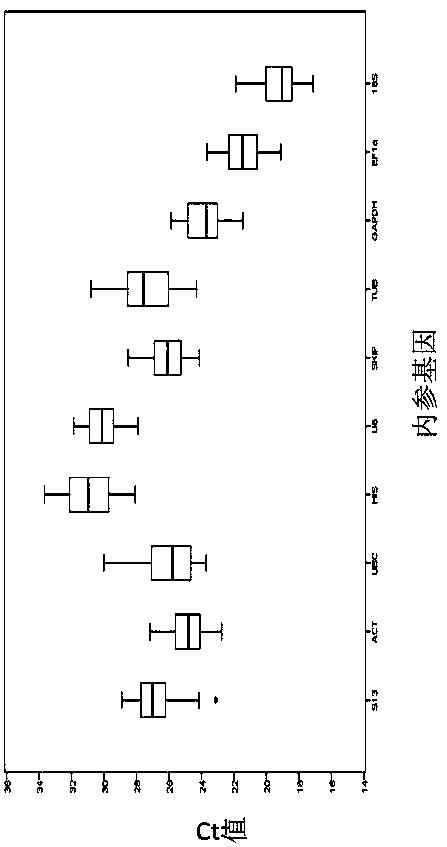
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, and discloses a screening method for real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR reference genes of Hibiscus hamabo Sieb.et Zucc. Thescreening method utilizes a transcriptome database of Hibiscus hamabo Sieb.et Zucc, selects 10 candidate reference genes, and takes 10 candidate reference gene sequences as templates to design real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR specific primers, selects different tissues of Hibiscus hamabo Sieb.et Zucc and Hibiscus hamabo Sieb.et Zucc leaves under various abiotic stresses and hormone treatments as experimental materials for performing a fluorescent quantitative PCR experiment, and finally, performs data analysis by applying geNorm, NormFinder and BestKeeper software. The most stable reference genes in the screening method are ACT and SKIP. The screening method for real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR reference genes of Hibiscus hamabo Sieb.et Zucc establishes a screening system forstable reference genes of hibiscus hamabo, and provides stable reference genes for developing gene function research of Hibiscus hamabo Sieb.et Zucc.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
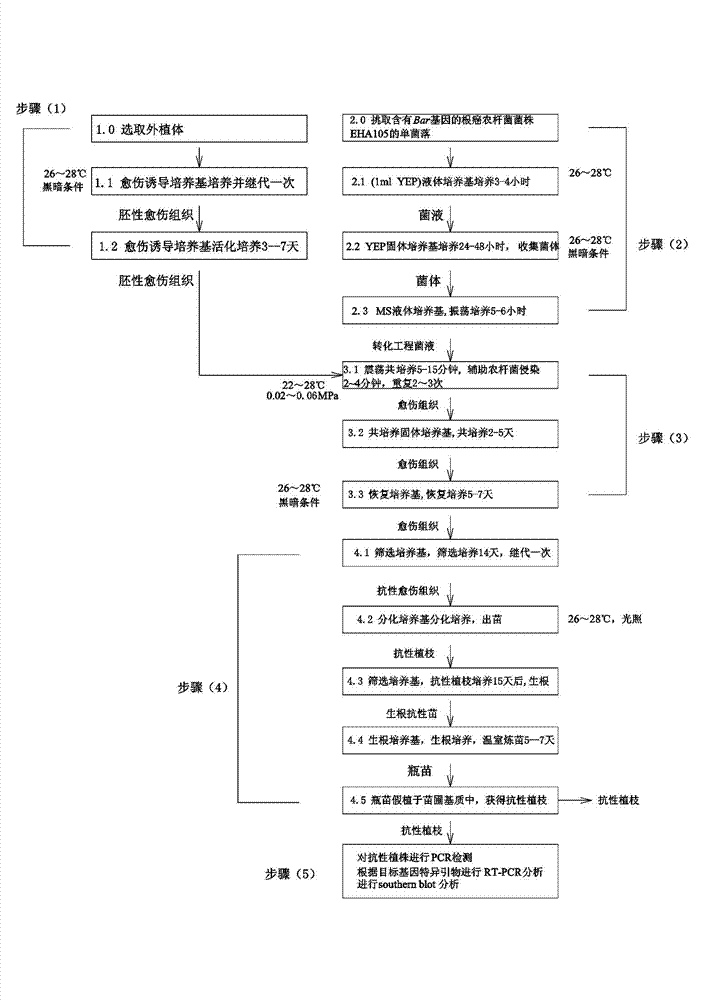
Agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method with vacuum infiltration assistance
InactiveCN103205459APerfect genetic transformation systemIncreased genetic transformation rateGenetic engineeringFermentationTi plasmidBiological activation
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and discloses an agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method with vacuum infiltration assistance. The agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method includes: (1) induction and multiplication of embryonic callus of sugarcane core leaves, (2) activation and cultivation on agrobacterium tumefaciens with target genes, (3) agrobacterium infestation with vacuum infiltration assistance on embryonic callus of sugarcane core leaves, (4) resistant material screening and germination, and (5) resistant material verification. With the agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation method, the agrobacterium can pass through the gaps among callus cells and enter deep cells on vacuum, and tiny wounds can be generated on the surfaces of the cells, so that phenolic substances are secreted by plants to activate shear and transfer of T-DNA (transferred deoxyribonucleic acid) in Ti plasmids. The agrobacterium-mediated sugarcane genetic transformation system is perfected. Genetic transformation rate of sugarcane is remarkably improved as compared with that of the prior art.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SUGARCANE IND RES INST
Pyrophosphatase of ammopiptanthus mongolicus, and coding gene and application thereof
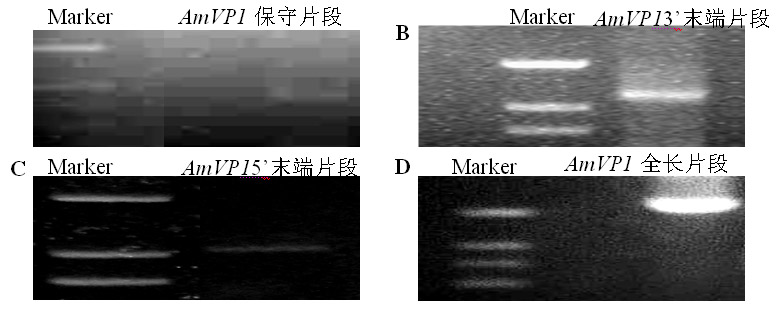
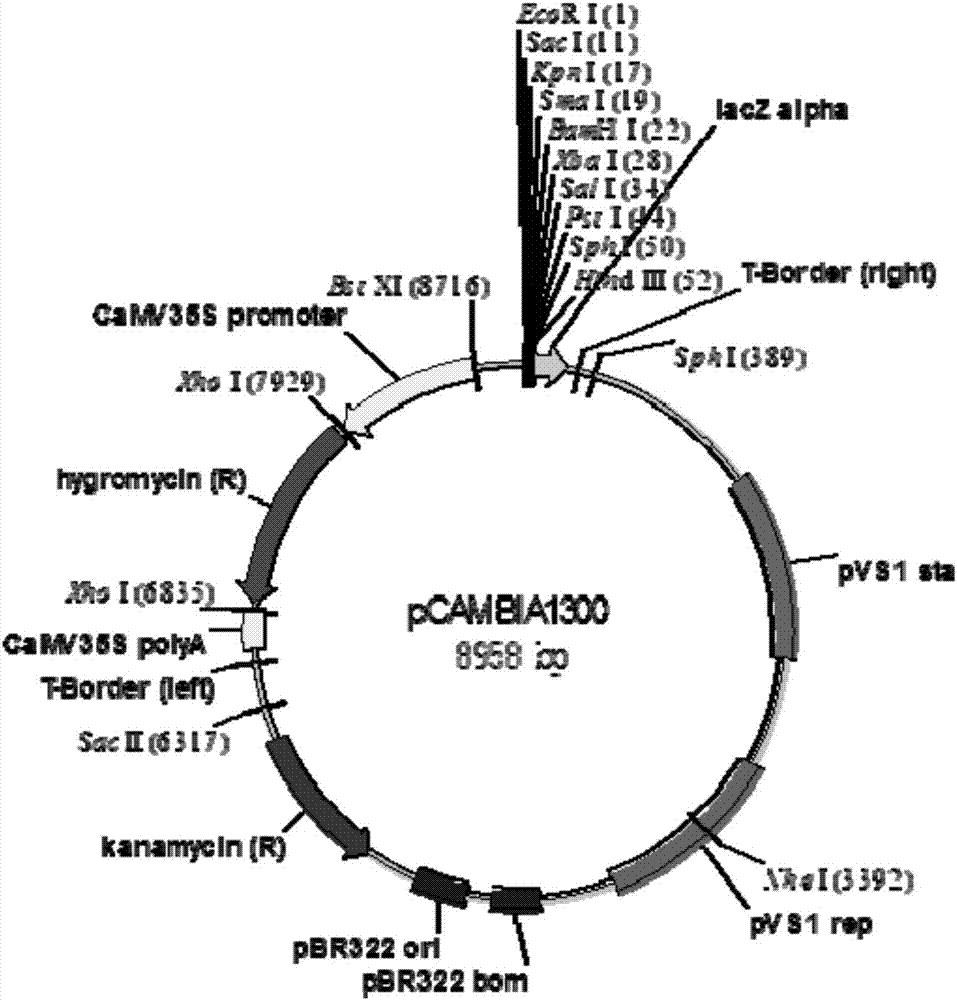
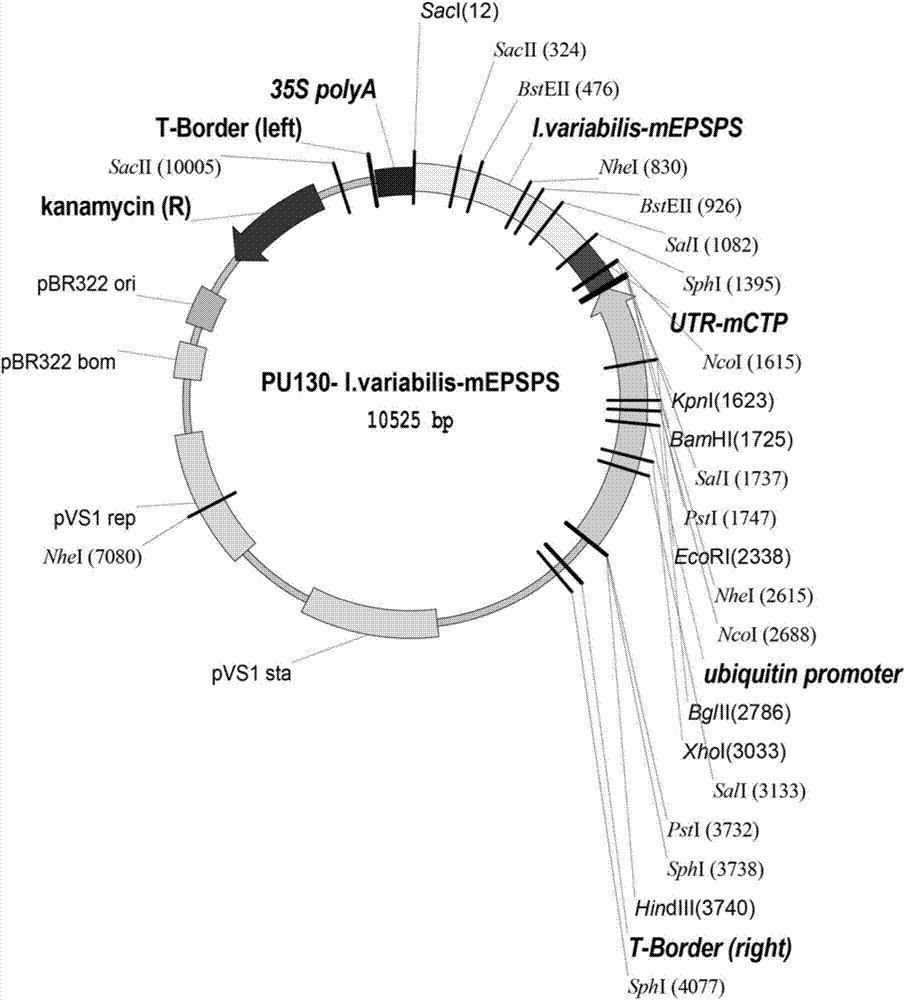
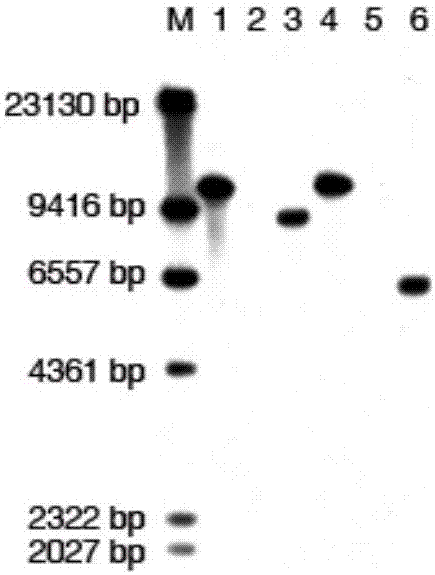
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and in particular relates to pyrophosphatase of ammopiptanthus mongolicus, and a coding gene and application thereof. The pyrophosphatase provided by the invention comes from the ammopiptanthus mongolicus, named AmVP1, wherein the amino acid sequence of the pyrophosphatase is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The coding gene of the pyrophosphatase of the ammopiptanthus mongolicus is one of the following nucleotide sequences: SEQ ID NO.1 and polynucleotide with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The gene of the invention can be applied to the research of the salt-resisting and drought-enduring molecular mechanism of the ammopiptanthus mongolicus, and is used for improving the salt-resisting and drought-enduring property of plants.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Modified glyphosate-resistant gene and glyphosate-resistant rice cultivation method
InactiveCN107129993AIncrease resistanceAgronomic traits do not changeMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, in particular to a modified glyphosate-resistant gene and a glyphosate-resistant rice cultivation method and comprises modification of glyphosate genes, building of plant expression vectors of the glyphosate-resistant gene and a glyphosate-resistant transgenosis rice cultivation method. Artificially-synthesized modified glyphosate-resistant gene serves as a target gene, the sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the target gene is led into rice receptors by an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation method to obtain high glyphosate-resistant transgenosis rice GT28. the glyphosate-resistant gene of GT28 is recombined by the aid of sexual hybridization and somatic hybridization technique to obtain new rice germplasm, and new glyphosate-resistant varieties (strains) of rice are cultivated.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Gene OsPTR10 for improving nitrogen utilization efficiency and yield of rice and applications of gene OsPTR10
ActiveCN106119262AImprove utilization efficiencyIncrease the number of tillersMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesPlant genetic engineeringMutant
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering, and provides a rice nitrogen transporter gene OsPTR10, wherein the protein sequence of the rice nitrogen transporter gene OsPTR10 is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the cDNA sequence of the rice nitrogen transporter gene OsPTR10 is shown as SEQ ID No.2. According to the rice nitrogen transporter gene OsPTR10, through the excessive expression of the OsPTR10 gene, the normal efficiency in absorbing nitrogenous fertilizer of the rice is improved, the content of soluble protein of plants is increased, further, the tiller number is increased, the ear length and filling grain number are increased, and finally, the yield is improved; through the RNAi technology, the expression quantity of the OsPTR 10 gene is reduced, and the functions of the gene are verified in the OsPTR10 target gene mutant. The gene has the significant application values on the aspects of the statement on the influences of the nitrogen element on the growth and development of the plants and on the aspects of the efficient utilization for the nitrogen fertilizer of the rice and the improvement on the yield of the rice.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF BIOENG
Oryza officinalis anti-Xanthomonas oryzae major gene Xa3/Xa26-2 and application for improving disease resistance of rice thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of the plant genetic engineering, in particular to the isolation and cloning and functional verification of the DNA fragment of oryza officinalis anti-Xanthomonas oryzae major gene Xa3 / Xa26-2. The Xa3 / Xa26-2 gene is used to code the leucine-rich protein kinase protein. The Xa3 / Xa26-2 gene ensures that rice can resist diseases caused by bacterial pathogen-Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. The DNA fragment and the regulatory sequence thereof are directly transferred in rice, and the resistance capability to Xanthomonas oryzae of the transgenic rice carrying Xa3 / Xa26-2 is significantly enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Nucleotide sequence of gene for resistance to Cereal cyst nematode, Heterodera avenae and application thereof
InactiveCN102234651AImprove resistance (tolerance)Plant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyAegilops variabilis
The invention, relating to the field of plant genetic engineering, particularly relates to a nucleotide sequence of a gene from an allied specie Aegilops variabilis of wheat for resistance to Cereal cyst nematode, and an application on improving plant resistance to insects based on the gene through the method of biotechnology. The nucleotide sequence of the gene for resistance to Cereal cyst nematode disclosed in the invention is a complete encoding sequence of the gene for resistance to Cereal cyst nematode with the width of 3586bp, comprising 3 exons and 2 introns, and can code 934 amino acids, and is used in improving plant resistance.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
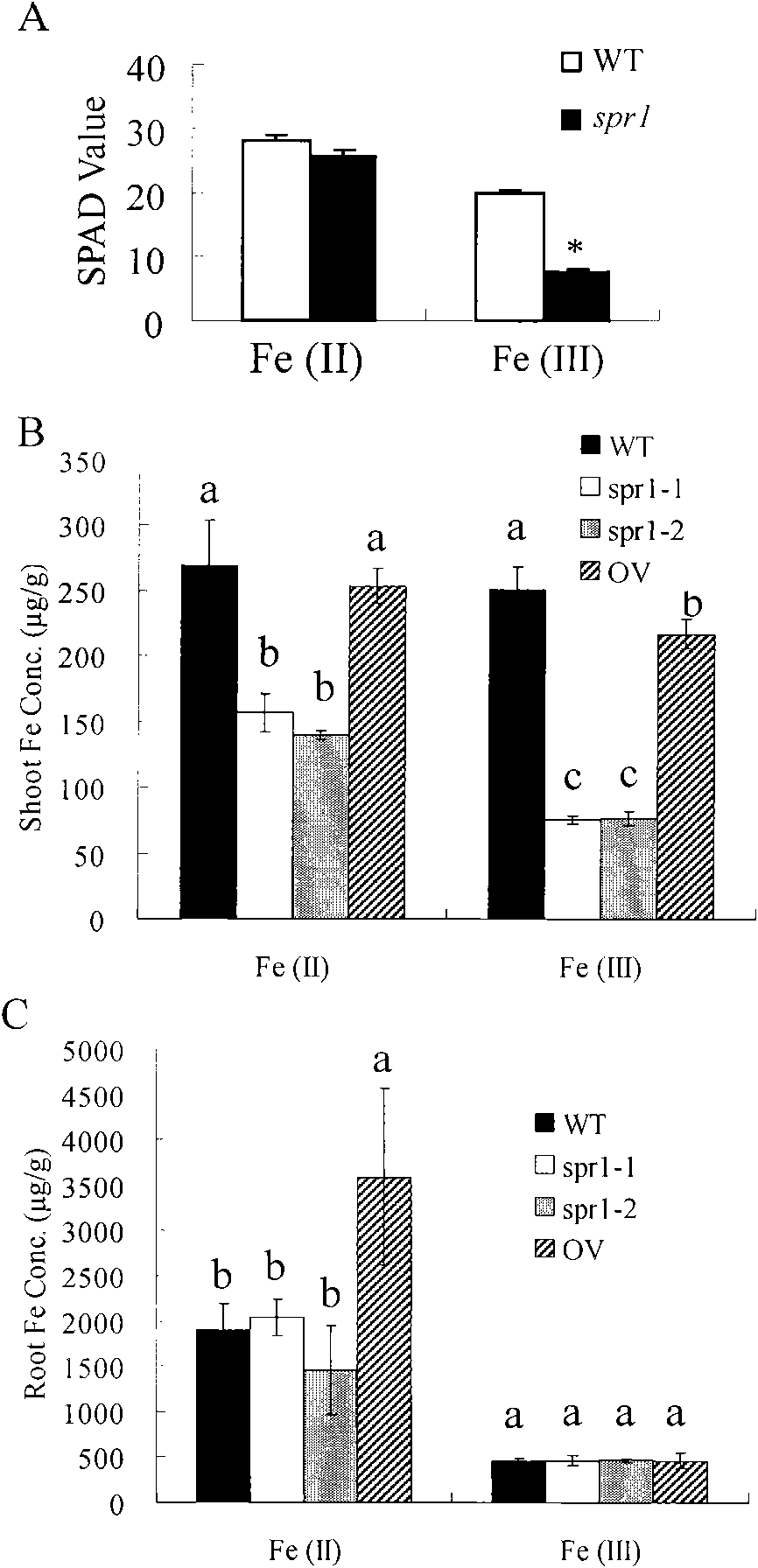
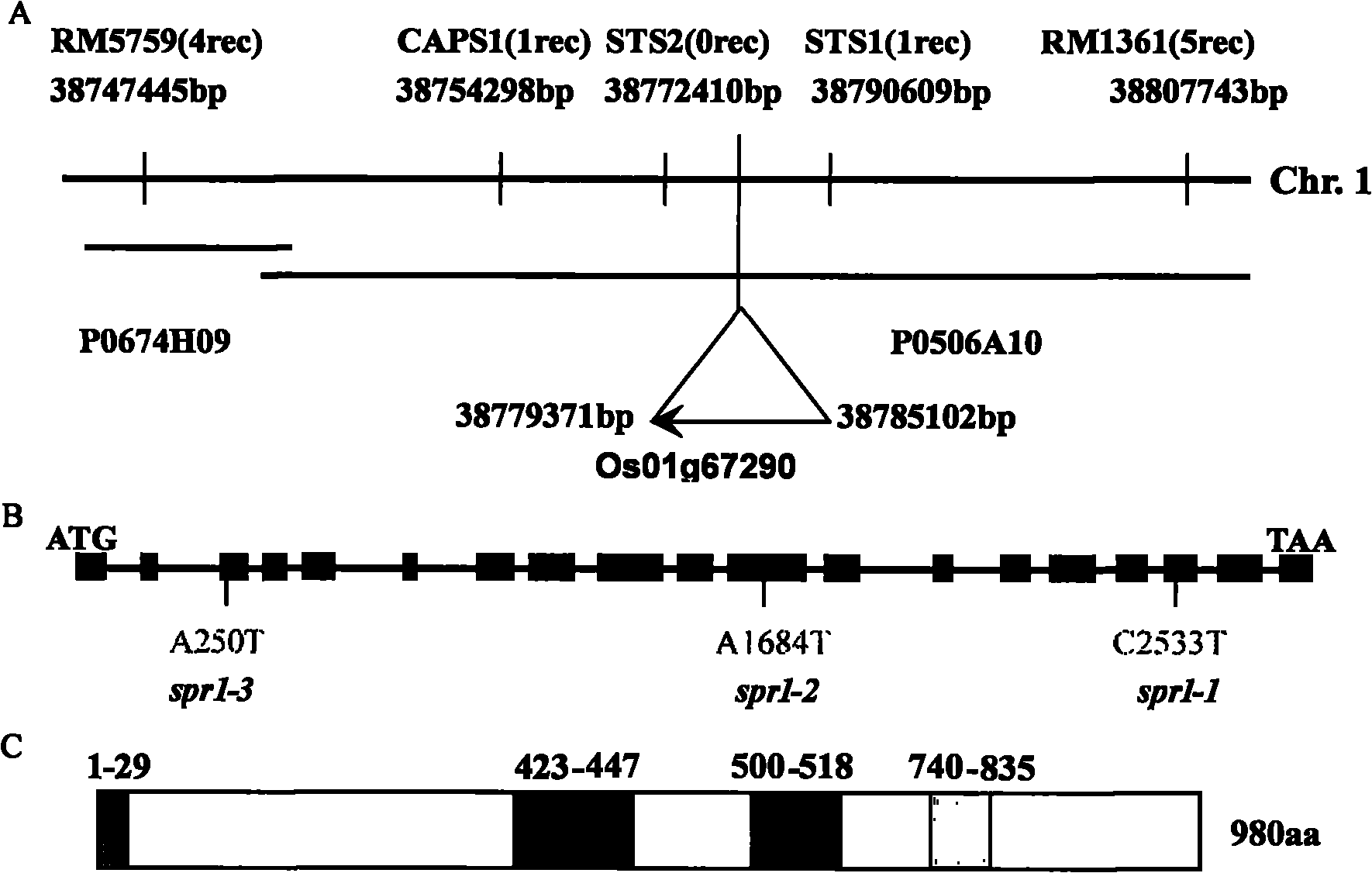
Gene and protein encoded by rice root growth and development control gene OsSPR1
The invention relates to the plant gene engineering field, aiming at providing protein encoded by a rice root growth and development control gene OsSPR1 and a gene for encoding the protein. The protein has an amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:2 and a nucleotide sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1. In the invention, a rice mutant with a short adventitious root and a short branch root is taken as a research material to determine that the gene is involved in regulating and controlling growth and development of the rice root; the functional deletion mutant of the gene shows reduced ferric content of blades, and the ferric content in the root is in accordance with that of wild rice; and recovery of expression of the gene can recover the ferric content in the blades, thus showing that the gene can regulate and control the ferric content in the blades. The invention provides a molecular regulation and control mechanism for rice root growth and development and ferric ion in-vivo transport, and provides a foundation for regulating and controlling a rice root structure and the ferric content by a genetic engineering method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Application of nitrate radical transporter gene OsNRT1.8 in rice breeding
ActiveCN106337055AEnhanced tillering abilityIncrease productionPlant peptidesFermentationGrowth plantNitrogen
The invention discloses application of a nitrate radical transporter gene OsNRT1.8 in rice breeding and belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering. The protein encoding amino acid sequence of the gene OsNRT1.8 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and a cDNA sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. By establishing rice gene OsNRT1.8 overexpression plant and a gene OsNRT1.8 interference plant, it is found that normal rice tiller number and spike number of each plant can be increased by improving gene OsNRT1.8 expression. Therefore, the gene OsNRT1.8 can be used for increasing rice yield in rice breeding. The gene OsNRT1.8 has an important application value on the aspects of elaboration about nitrogen influence on plant growth and development and improvement of rice plant type.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF BIOENG
Application of Chilo suppressalis endogenesis small RNA in rice inset resistance improvement
InactiveCN104673827AIncreased metabolic burdenSmall gene fragmentFermentationPlant genotype modificationGenetically modified riceA-DNA
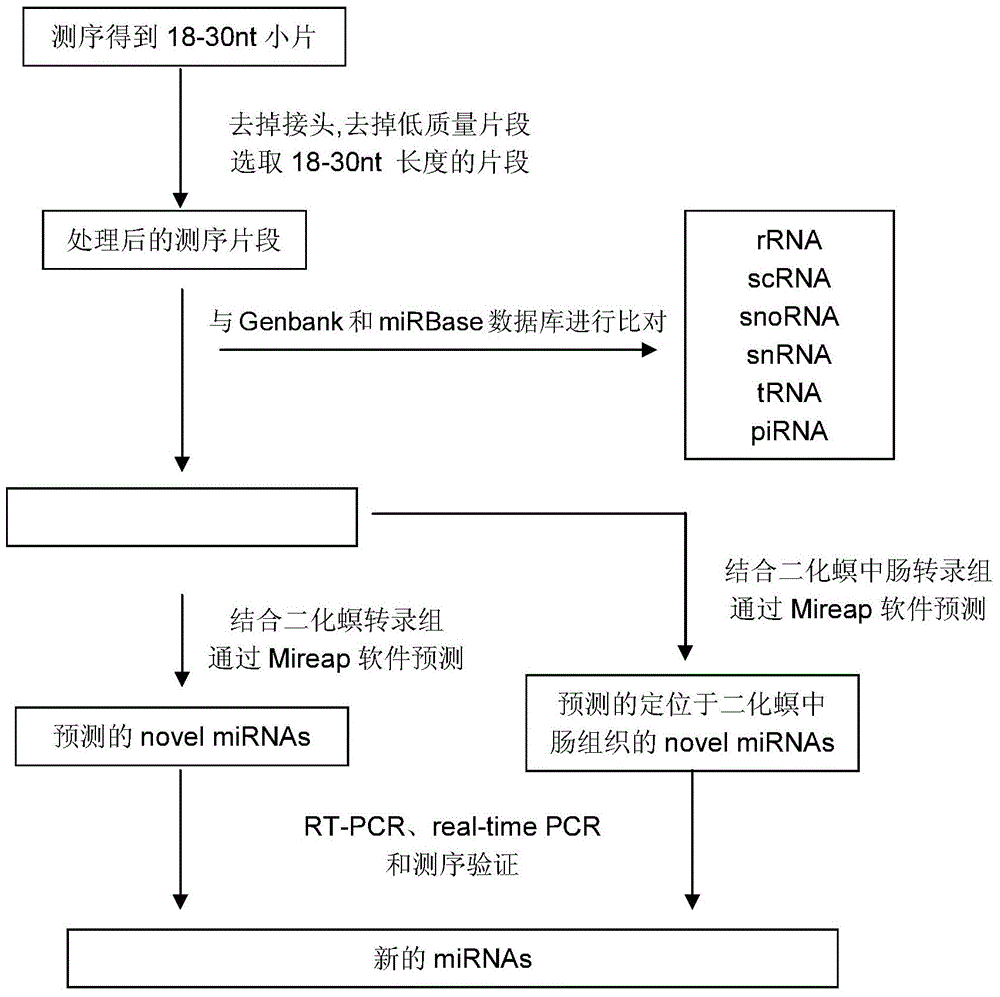
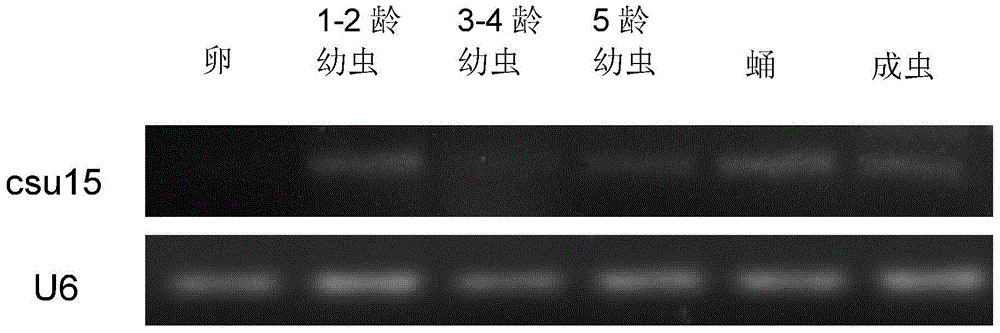
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, in particular relates to application of Chilo suppressalis (Walker) endogenesis small RNA in rice inset resistance improvement, and aims to verify the function and study the application of an obtained Chilo suppressalis endogenesis small RNA sequence. By means of high-flux small RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, a DNA sequence of Chilo suppressalis endogenesis small RNA csu-15, and the nucleotide sequence of the DNA sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The sequence of csu-15 is adopted to establish an artificial microRNA (amiRNA) expression carrier and convert rice. The in-vitro stalk insect inoculation experiment shows that Chilo suppressalis growth can be remarkably inhibited in transgenic rice.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for building high-efficiency regeneration system of superior corn self-bred line agriculture line 531
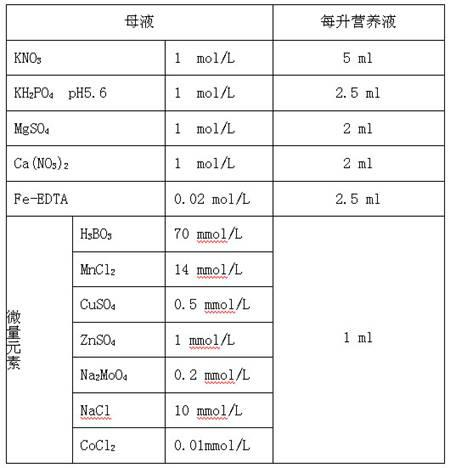
InactiveCN101779598AHigh induction ratePromote rapid proliferationCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureField cropNutrient solution
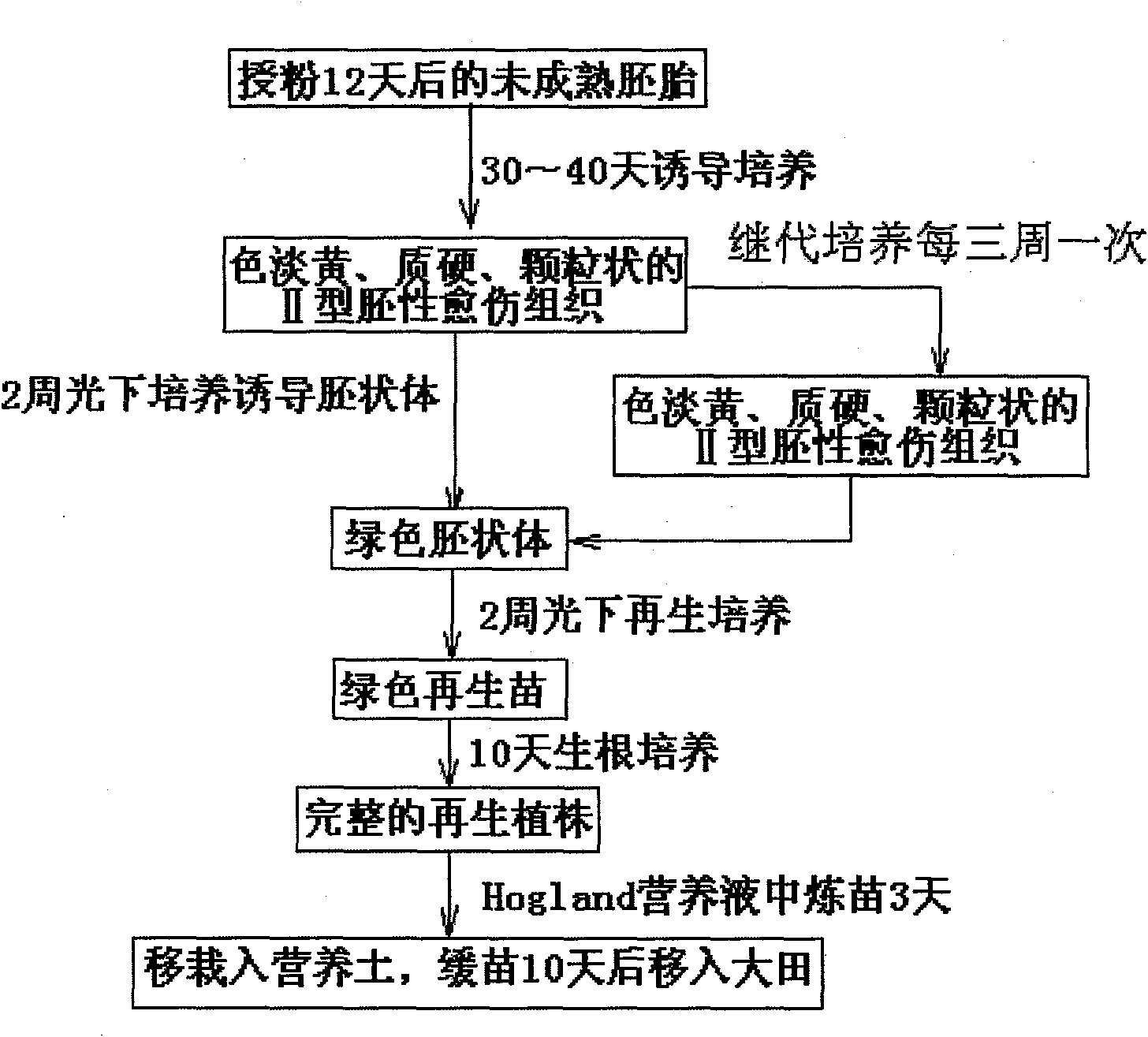
The invention discloses a method for building a high-efficiency regeneration system of superior corn self-bred line agriculture line 531, belonging to the field of plant genetic engineering and transgenosis breeding. The invention takes an agriculture line 531 rataria as an explant, induces in a callus induction medium and produces an II-type embryonic callus; the II-type embryonic callus is subjected to embryoid induction under light in an embryoid induction medium to produce a green embryoid; then, the green embryoid is transported to a regeneration medium and is cultured into a regeneration plant under light; root induction is carried out in a rooting medium, and acclimatization is carried out in Hogland nutrient solution to ensure that a new thick root grows on the root of the regeneration plant; the root is transplanted to nutritional soil for rejuvenation culture; and finally, the root is transplanted to a land for growing field crops to normally grow and seed. The regeneration technology is suitable for the superior corn self-bred line agriculture line 531 with high application value, can ensure that the superior quality of agriculture line 531 corn can be inherited in the corn transgenosis breeding process, and has an important meaning for functional genome group research.
Owner:GRAIN RES INST HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
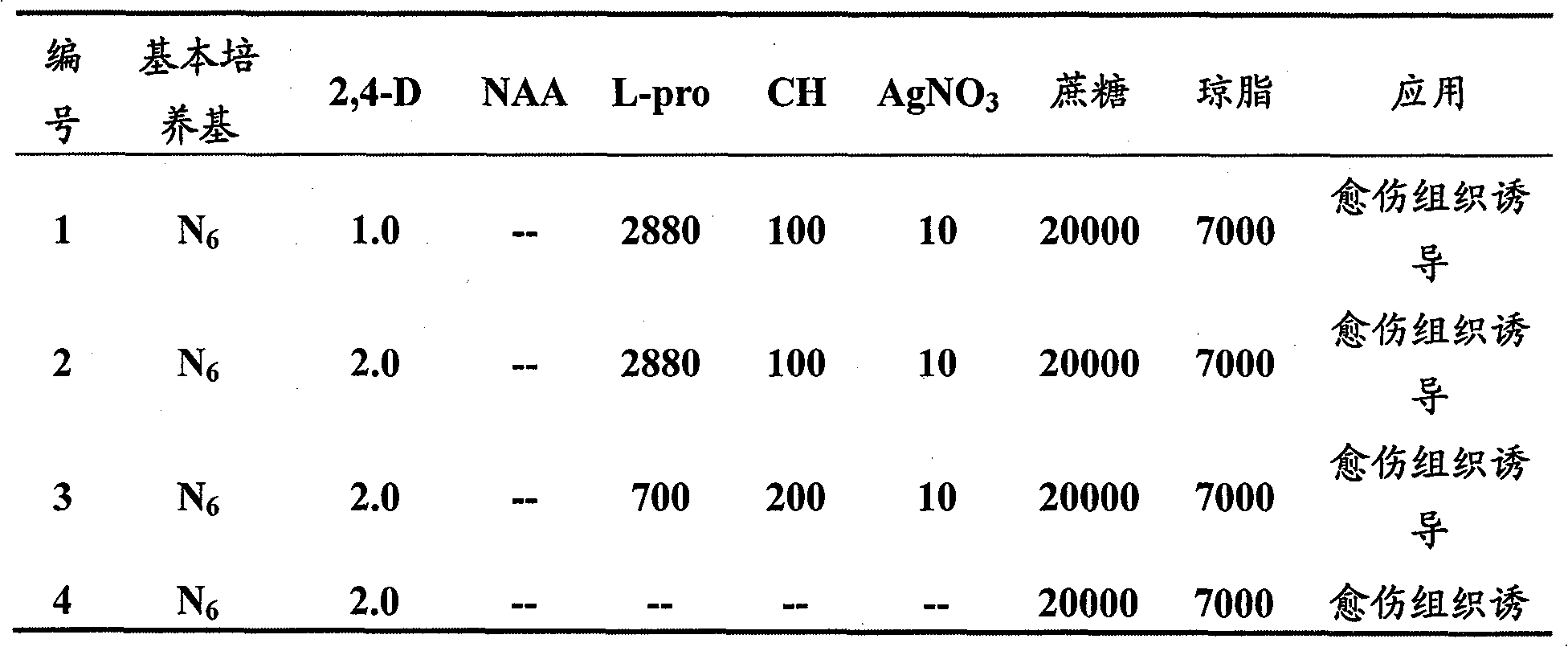
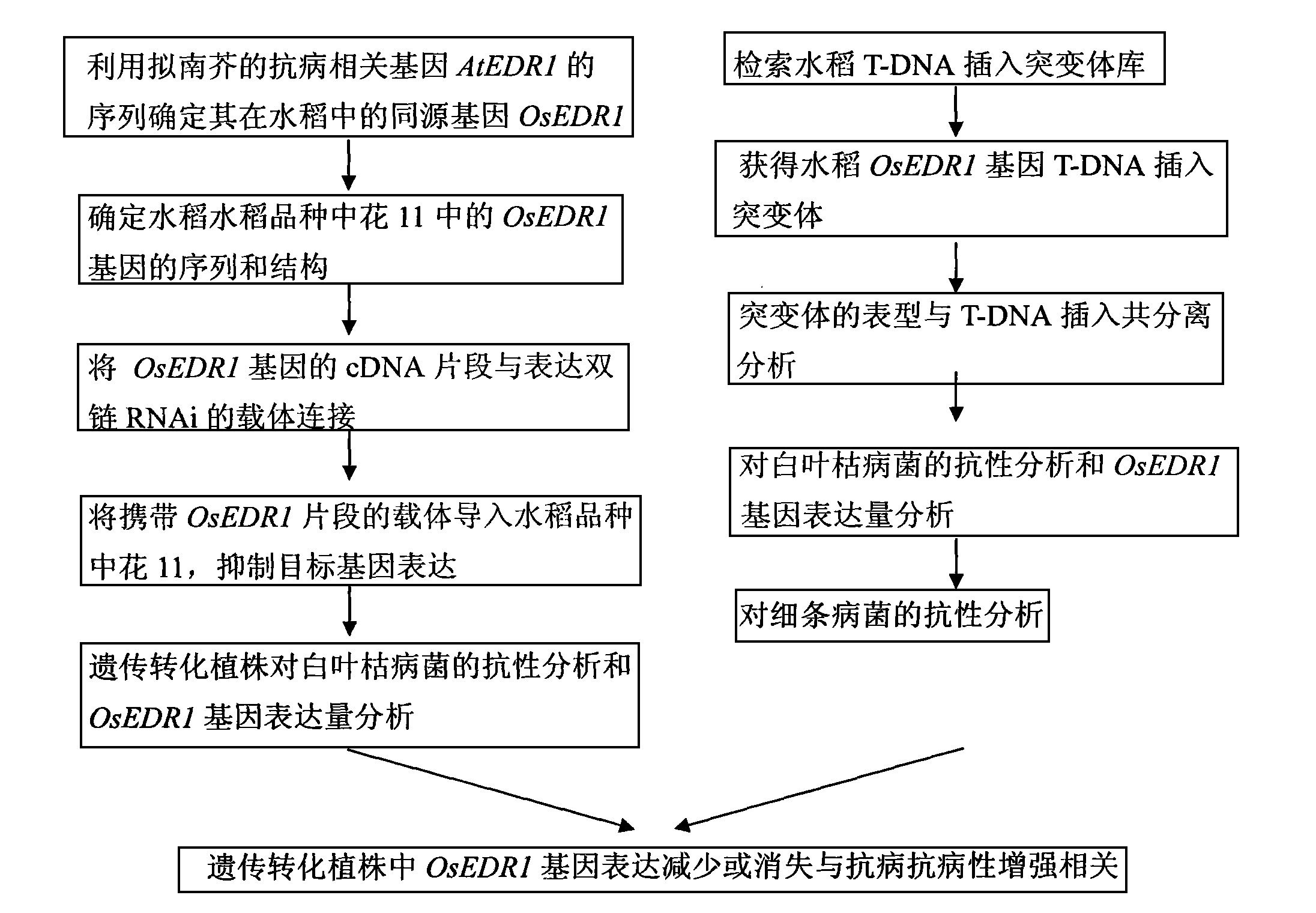
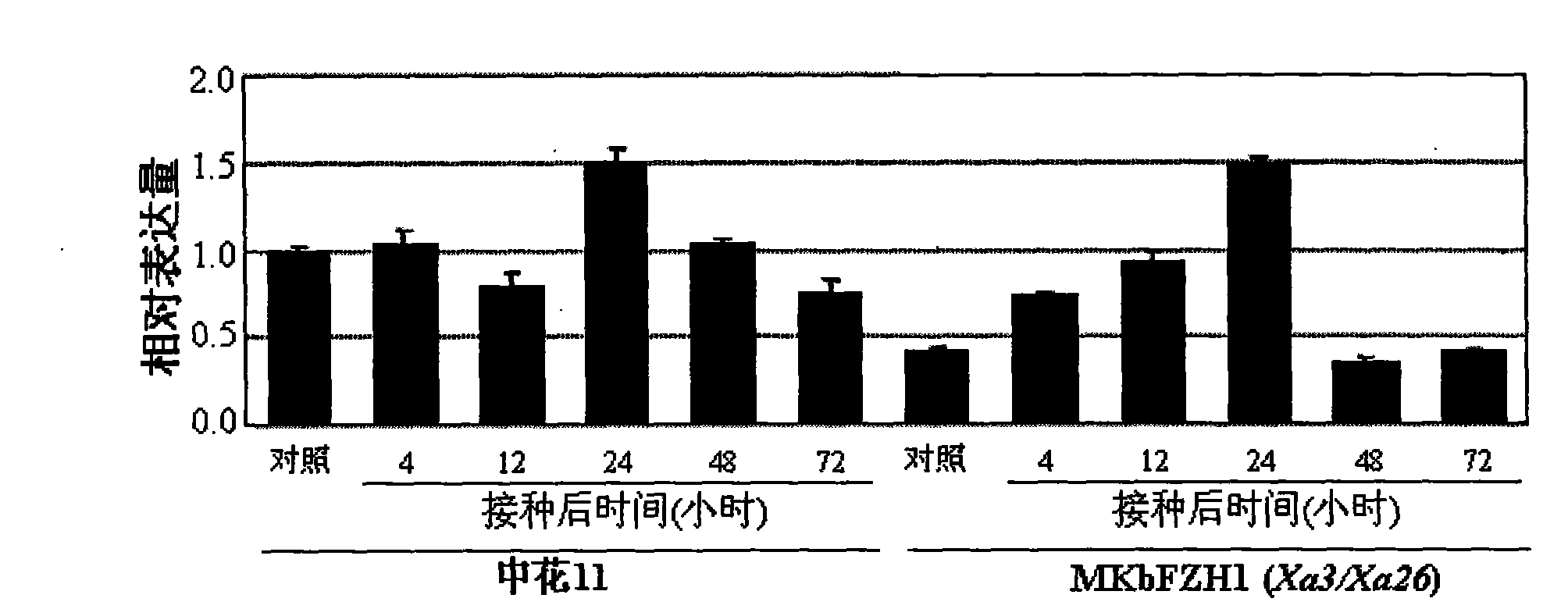
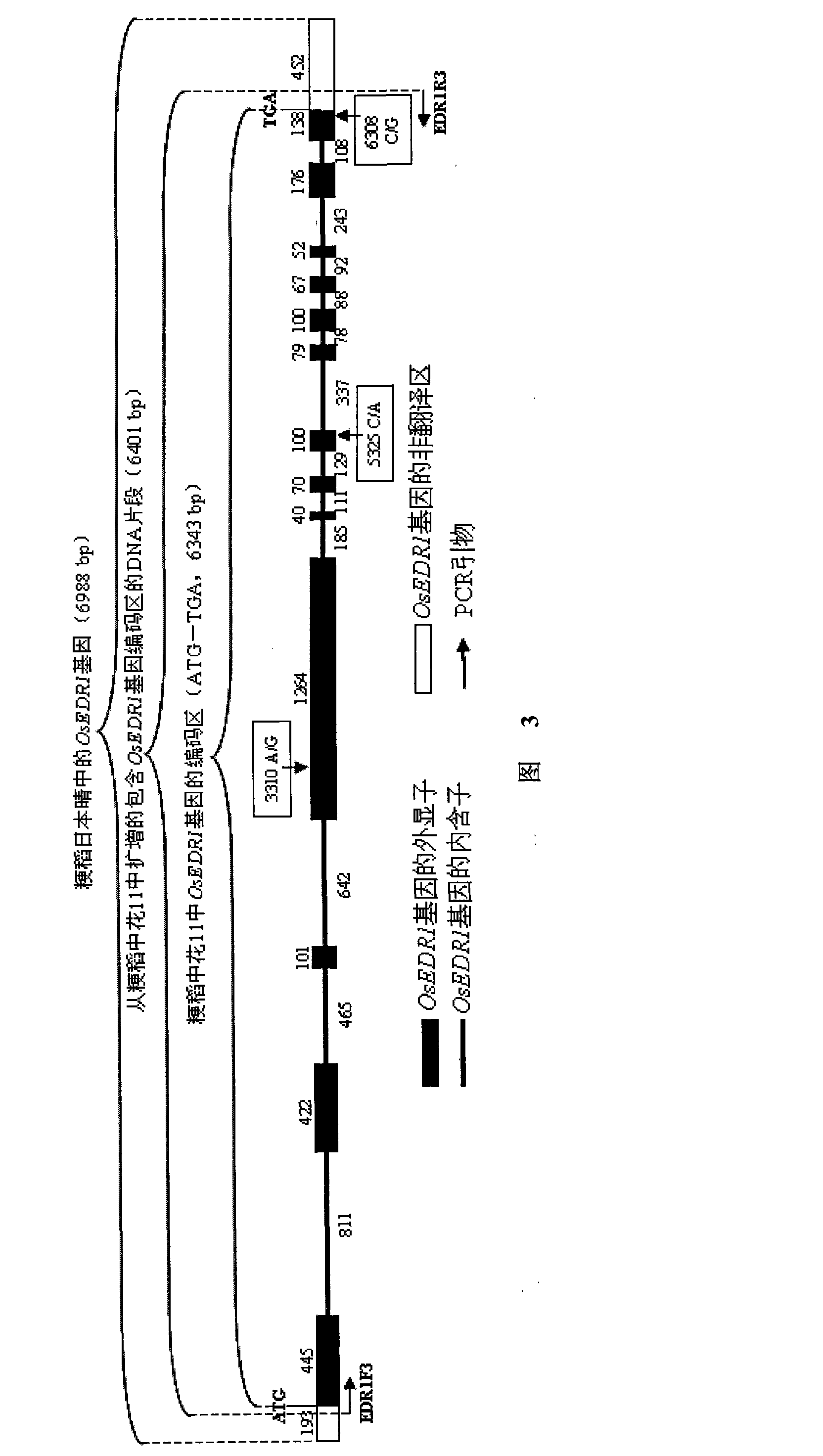
Paddy disease-resistant related gene OsEDR1 and application thereof in improved paddy disease resistance
InactiveCN101514343AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDiseasePlant genetic engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and more particularly relates to separated clone and functional verification of DNA segments of paddy disease-resistant related gene OsEDR1. By utilizing transgenic technology based on RNA interference (RNAi) principle, part of the DNA segments of the OsEDR1 gene are connected with a vector expressing double-strand RNA to be converted into rice varieties, and the expression of the OsEDR1 gene in the rice varieties can be inhibited. Genetic transformation rice with obviously reduced OsEDR1 gene expression quantity has the remarkably improved resistibility for bacterial blight and bacterial streak disease, so as to prove that the OsEDR1 gene is negative regulatory factor in the reaction of resisting bacterial blight and bacterial streak disease of rice, thus the disease resistance of the rice can be improved by inhibiting the expression of the OsEDR1 gene.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
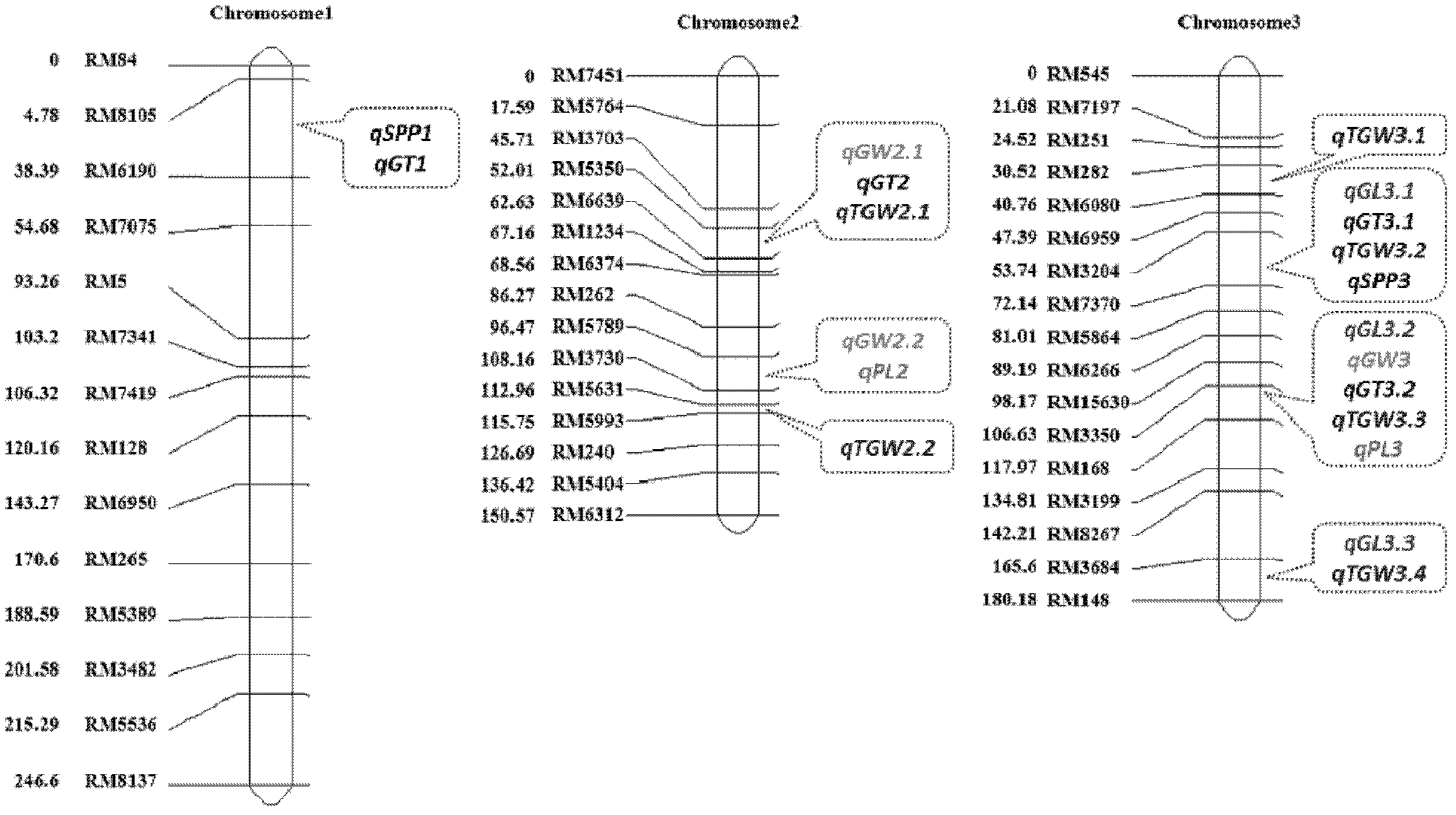
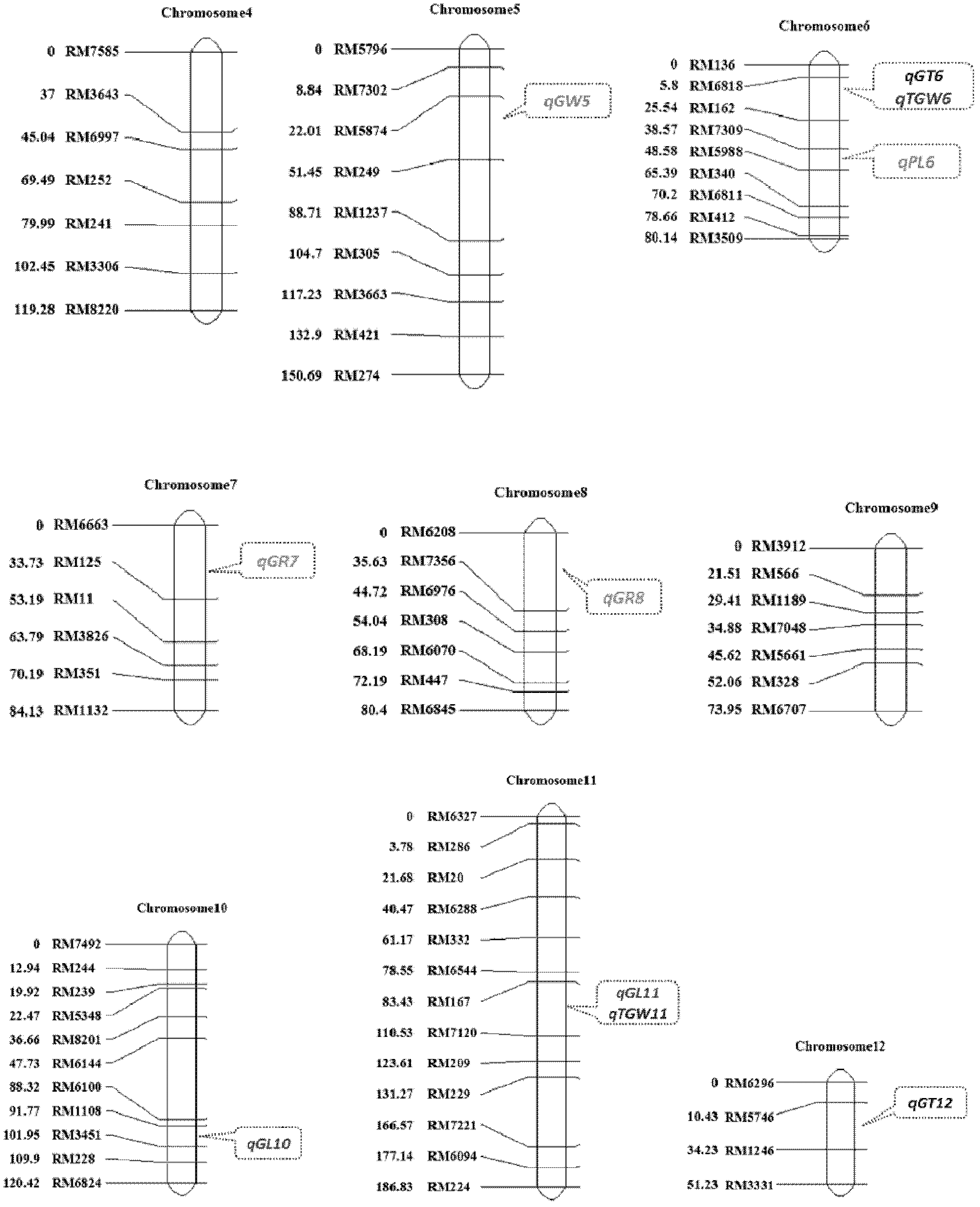
Clone and application of semi-dominant gene qGL3 capable of controlling grain length and grain weight of rice kernel
ActiveCN102352367AIncrease the lengthIncrease grain weightHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGrain weight
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and discloses clone and application of semi-dominant gene qGL3 capable of controlling grain length and grain weight of rice kernel. In the invention, a main-effective QTL (quantitative trait loci) SEQ ID NO:1 which is capable of simultaneously controlling the grain length and grain weight of rice kernel and a semi-dominant allelic gene SEQ ID NO:3 having advantageous function are separated and cloned; the two genes have the capacities of modifying the yield and appearance quality of rice; and at the same time, the two homologous genes of the two genes in rice are cloned and a fact that the two homologous genes have regulation effect on the length of rice kernel as well is proved. Thus, the gene qGL3 and the advantageous allelic gene qGL3-D thereof as well as the two homologous genes of the gene qGL3 all can be applied to crop genetic modification.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
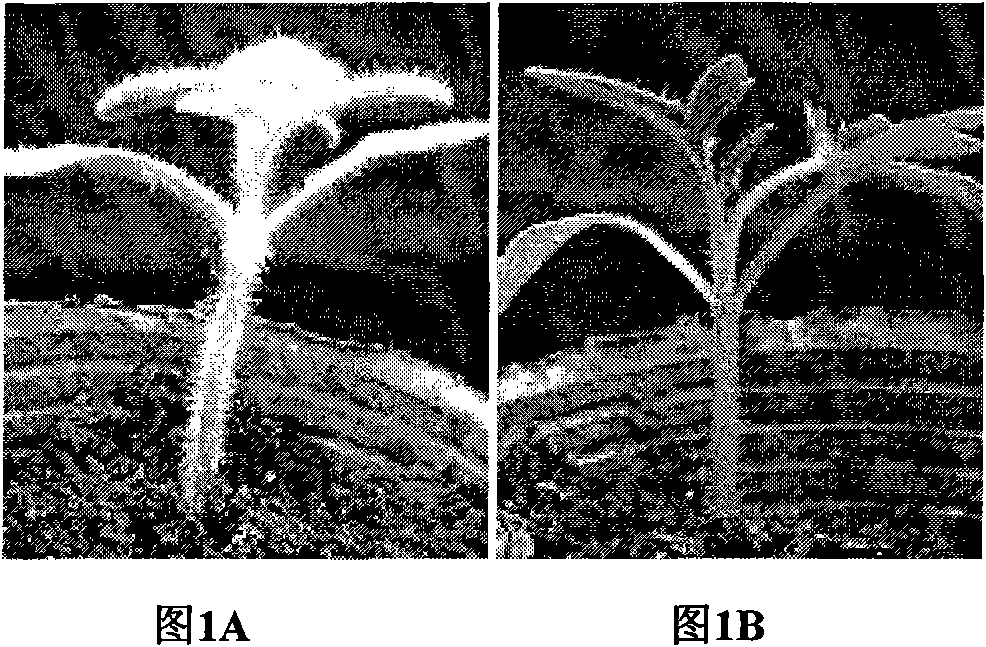
Cloning and application of key gene Wo for controlling tomato hair generation
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and specifically relates to cloning and an application of a Wo gene which is related to tomato hair generation. The cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of the cloned Wo gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1(sequence identity number 1) in a sequence table, the corresponding amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the Wo gene encodes 731 amino acids. The invention further relates to a promoter of the Wo gene and cloning of two allelic genes of the Wo gene. The Wo gene is over-expressed in tomatoes and can improve the amount of epidermal hair of the tomatoes, significantly enhance the insect resistance of the tomatoes and enhance the anti-virus capability.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Arabidopsis thaliana floral organ specificity promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN103589726AImplement directional operationsVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyOrgan Specificity
The invention relates to a newly discovered DNA sequence which can be used as a promoter for regulating and controlling a target gene to be specifically expressed in a floral organ of arabidopsis thaliana. An AtcpSecY1 gene promoter sequence is cloned from a model plant arabidopsis thaliana; subsequently in a transgenic arabidopsis thaliana, the promoter is confirmed to be capable of driving a GUS reporter gene to be specifically expressed in the floral organ of arabidopsis thaliana. With the application of the promoter, a 'floral organ specificity promoter-target gene to be expressed' fusion gene is obtained by construction, arabidopsis thaliana is transformed, and the transgenic plant having the target gene specifically expressed in the floral organ can be obtained. The promoter not only provides important molecular elements for in-depth research of plant floral organ differentiation, formation, growth and development molecular mechanisms and other theory researches, but also provides important molecular regulating and controlling elements for plant genetic engineering seed breeding, especially the gene engineering seed breeding for regulating and controlling flower shapes, flower colors, flower aromas, ornamental life and the like of famous and valuable flowers, and has wide application value.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
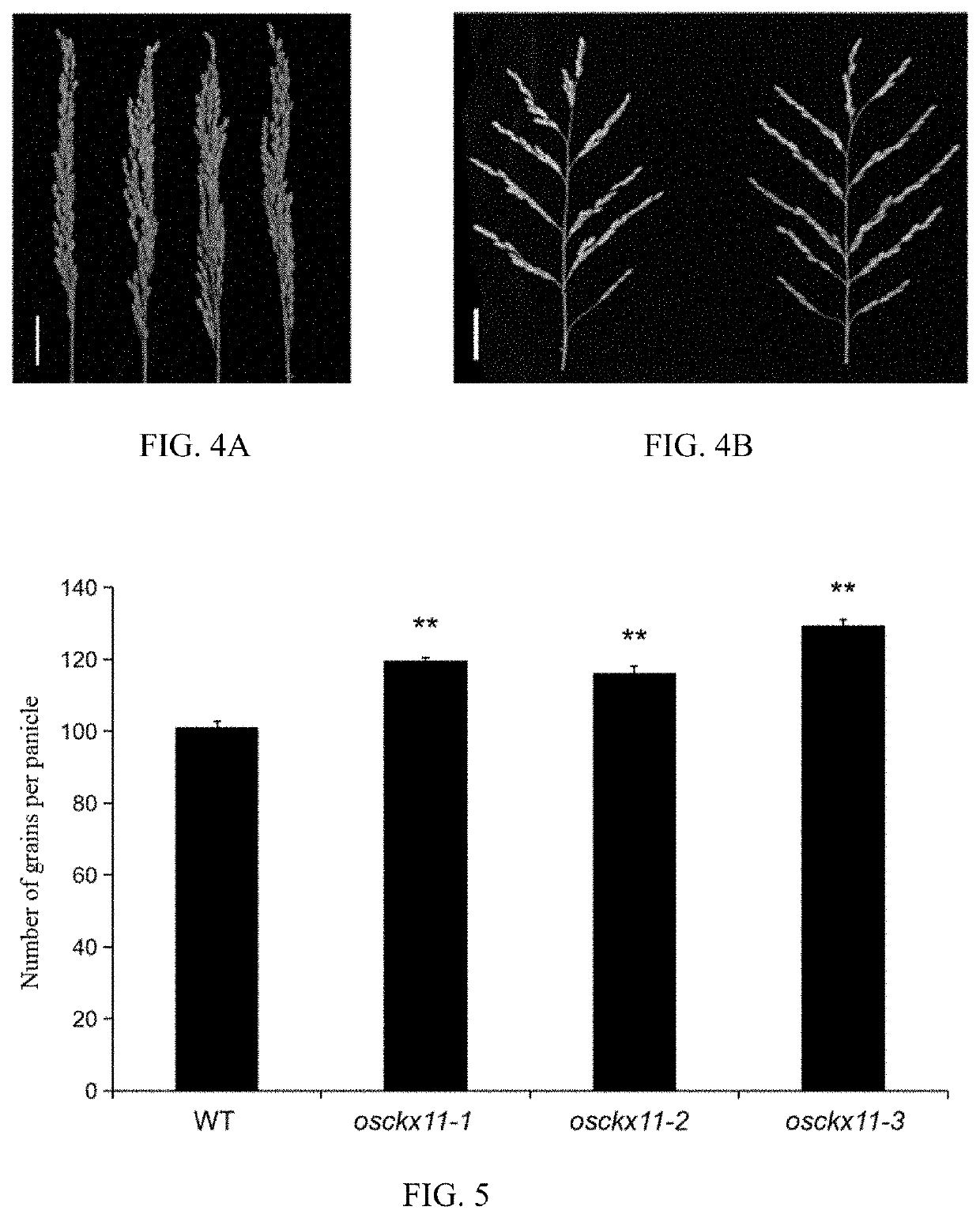
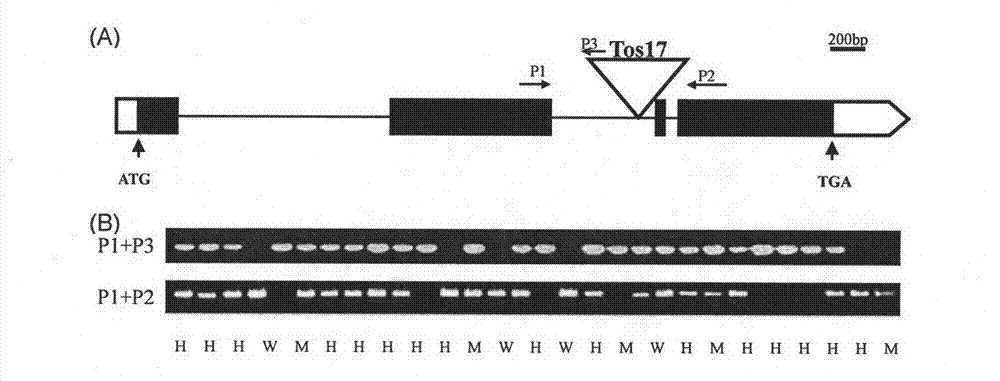
A gene osckx11 for controlling rice grain number and use thereof
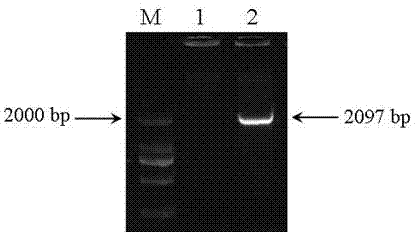
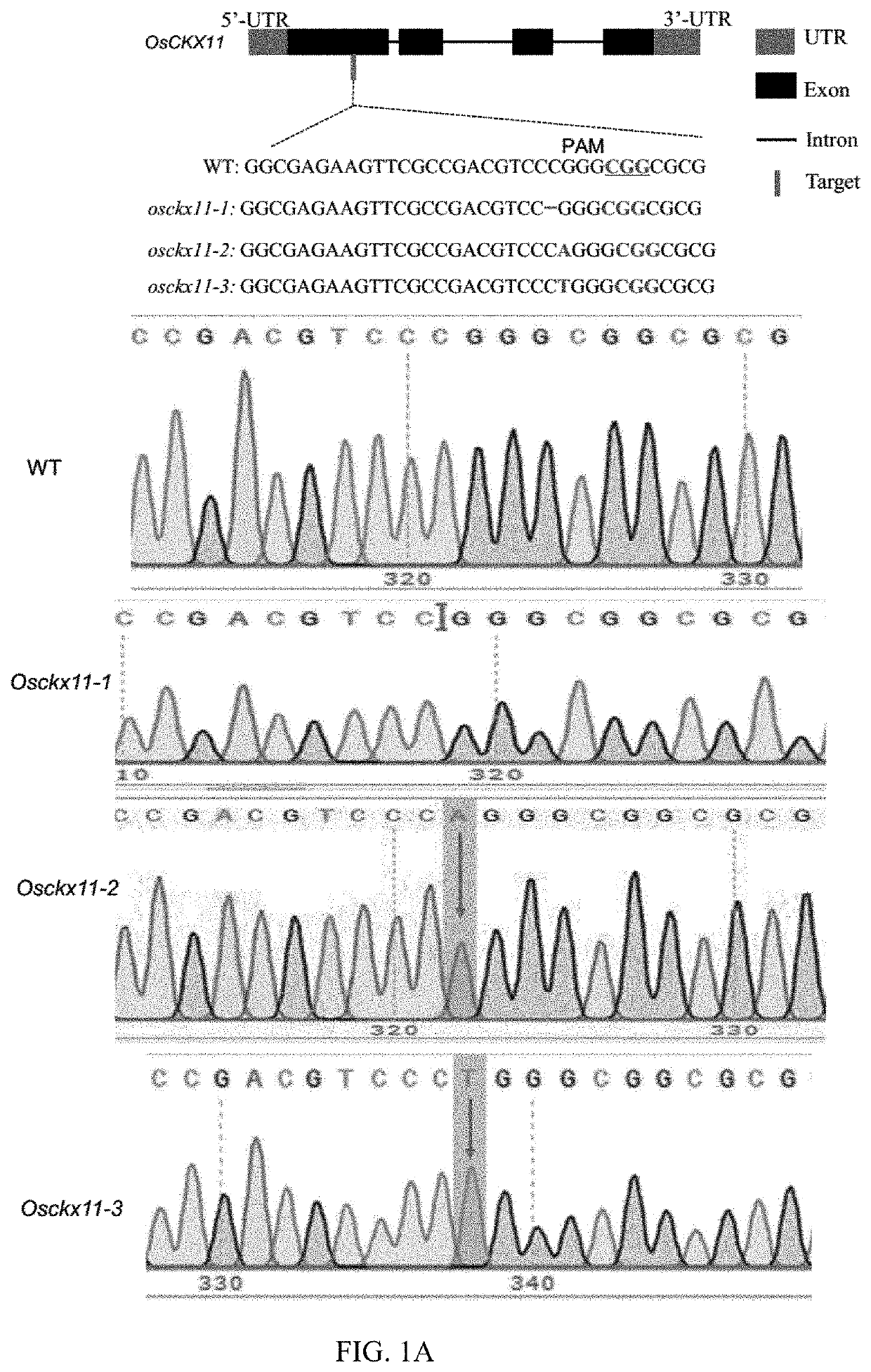
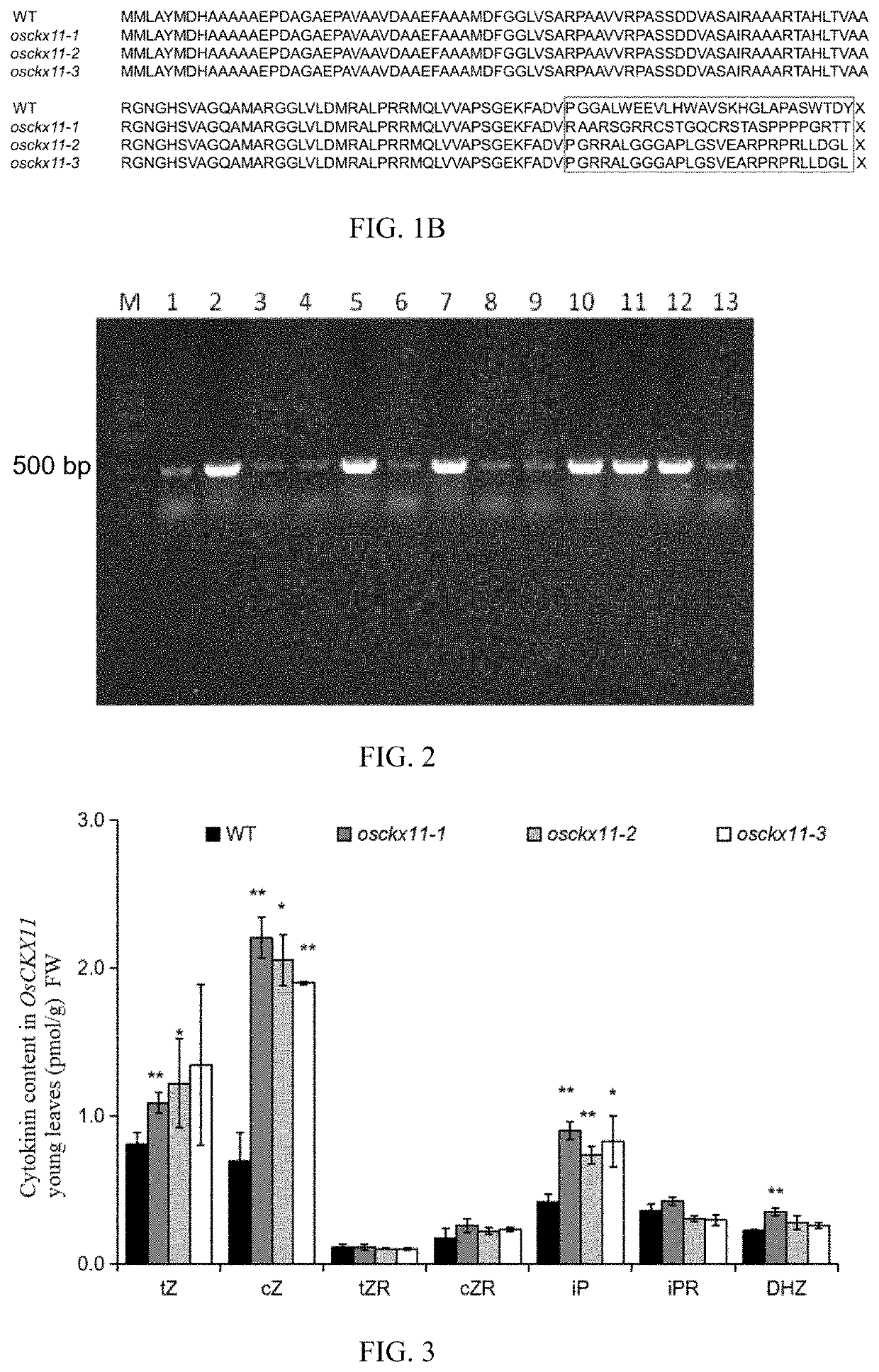
PendingUS20210324397A1Reduce expressionSignificant positive effectOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotidePlant genetic engineering
The present disclosure belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and discloses a gene for controlling the rice grain number per panicle and its use. Nucleotide sequence of OsCKX11 is SEQ ID NO. 1, nucleotide sequence for coding protein region is SEQ ID NO. 2, amino acid sequence of the encoded protein is SEQ ID NO. 3. The disclosure constructs an OsCKX11-knocked-out vector using CRISPR / Cas9, and identifies multiple independent homozygous lines through PCR amplification and sequencing methods, and provides a mutant in which specific knockout of gene OsCKX11 of the rice leads to an increase in cytokinin levels and an increase in grain number per panicle. Based on the biological function of OsCKX11 to increase the rice grain number per panicle, methods such as gene editing, natural allele replacement, RNA interference, or molecular assisted breeding can be used to improve existing rice varieties.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Gene for regulating and controlling corn drought stress resistance and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, in particular to a gene for regulating and controlling the corn drought stress resistance. The gene is a ZmPP2CA10 deletion mutation gene; the deletion segment is a continuous base sequence with a distance being 301bp away from the upstream of the ZmPP2CA10 initial codon ATG; the continuous basic group sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1; the nucleotide sequence of the mutated ZmPP2CA10 promoter is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The deletion mutation gene can be used for corn drought resistance relevant molecular marker auxiliary breeding and corn drought resistance auxiliary identification; the operation is convenient; the accuracy rate is high.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
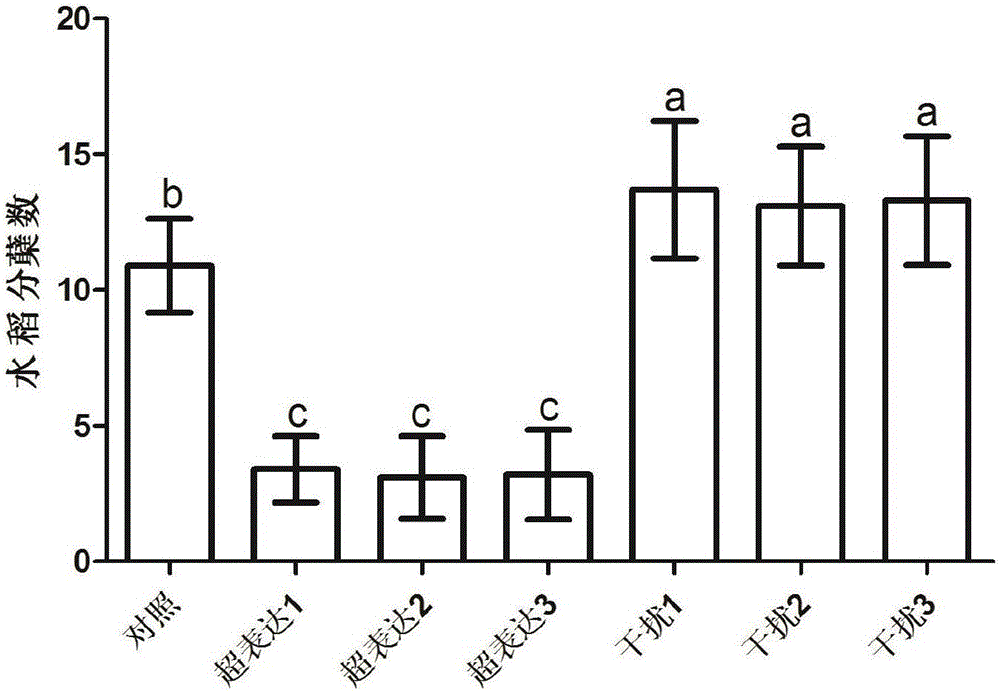
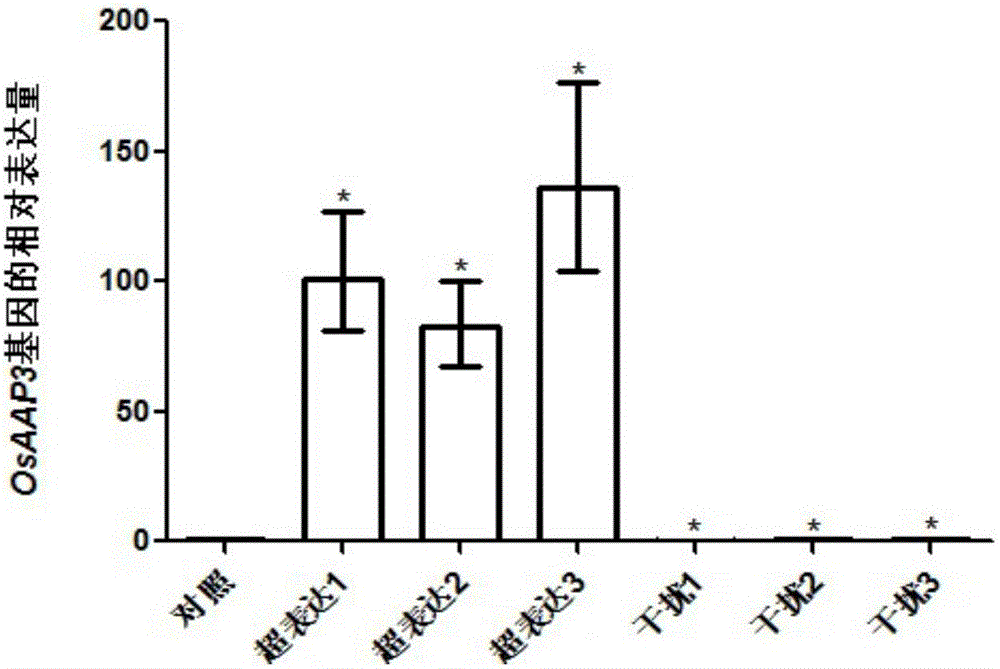
Application of amino acid transporter gene OsAAP3 in rice seed selection
ActiveCN106518993AEnhanced tillering abilityIncrease the number of tillersHydrolasesPlant peptidesPlant genetic engineeringGenetic engineering
The invention discloses application of an amino acid transporter gene OsAAP3 in rice seed selection, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. An amino acid sequence of encoded protein of the gene OsAAP3 is specified in SEQ ID NO.1, and a Cdna sequence is specified in SEQ ID NO.2. According to the application of the amino acid transporter gene OsAAP3 in rice seed selection, by constructing a rice plant which is interfered by the gene OsAAP3, and constructing a rice plant which is over-expressed by the gene OsAAP3, it is discovered that reduction of genetic expression of the gene OsAAP3 can increase tiller number of the rice and spike number in each rice plant, and therefore the gene OsAAP3 can be used in rice seed selection for increasing the rice yield. The gene OsAAP3 has important application value in expounding influence of amino acid transportation on growth and development process of the plant.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF BIOENG
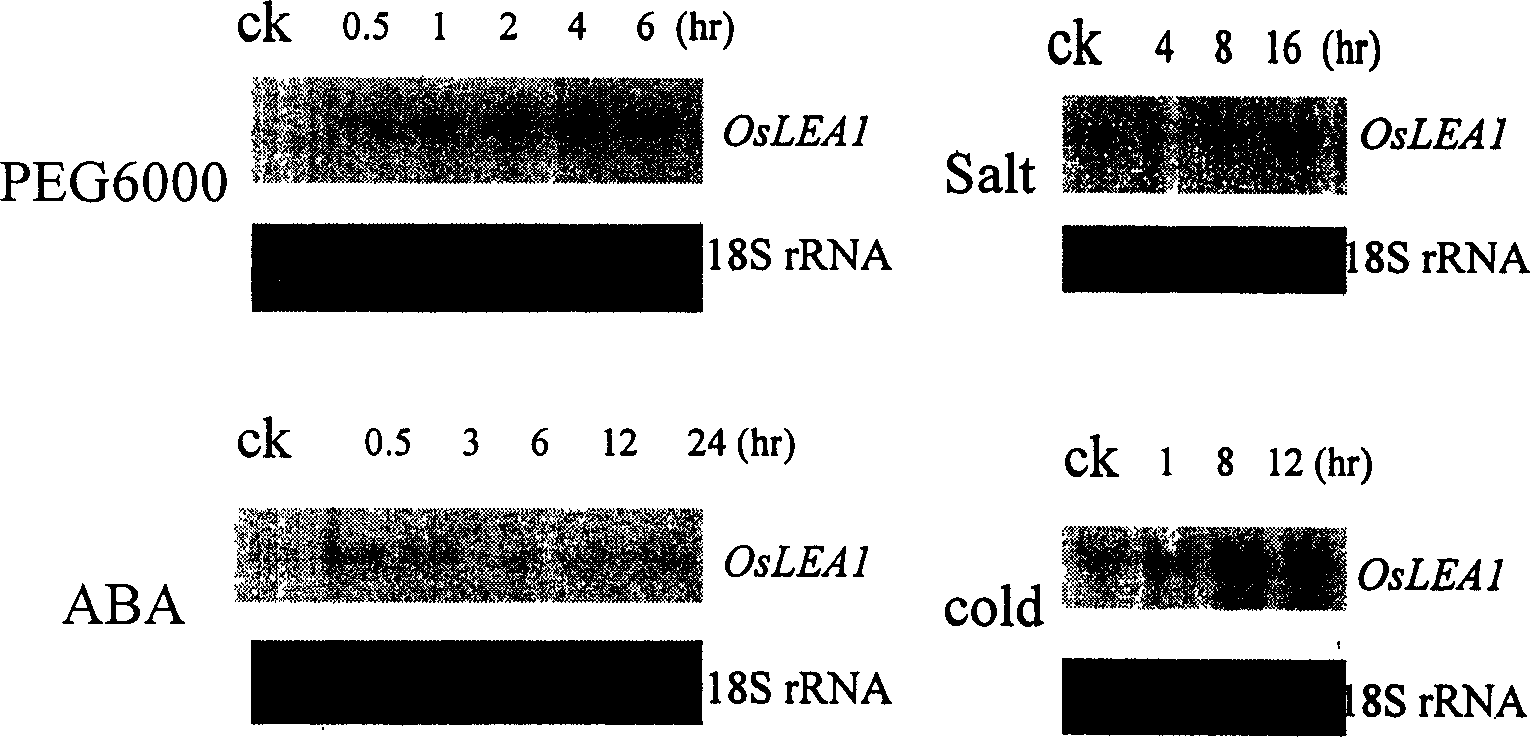
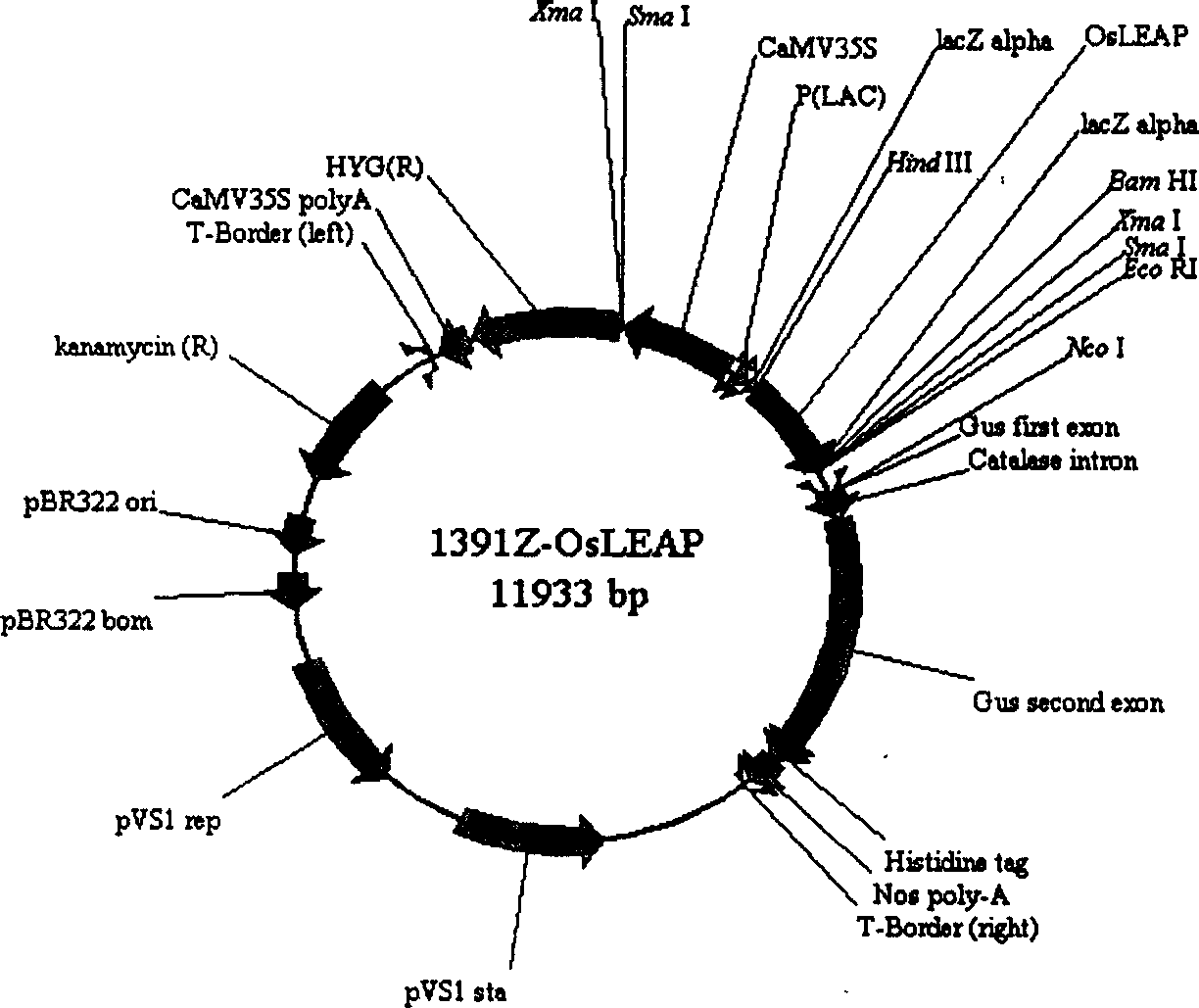
Improving drought-resistant property of plant by rice drought inducing gene promoter LEAP
InactiveCN1624133AImprove drought toleranceImprove drought resistanceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideCis acting
A method for using the promotor LEAP of rice's drought inducting gene to improve the resistance of plant to drought features that the promotor LEAP of rice OsLEAl gene is cloned. Its nucleotide sequence is shown by SEQ ID No.1 and is used to code a drought induced expression protein. Two cis-acting elements ABRE contained in its promotor region can be specifically response to drought and ABA. Its inductive expression carrier can stongly induce the expression of target gene when the drought stress is applied to a plant. The method for culturing the drought-resistant plant is also disclosed.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
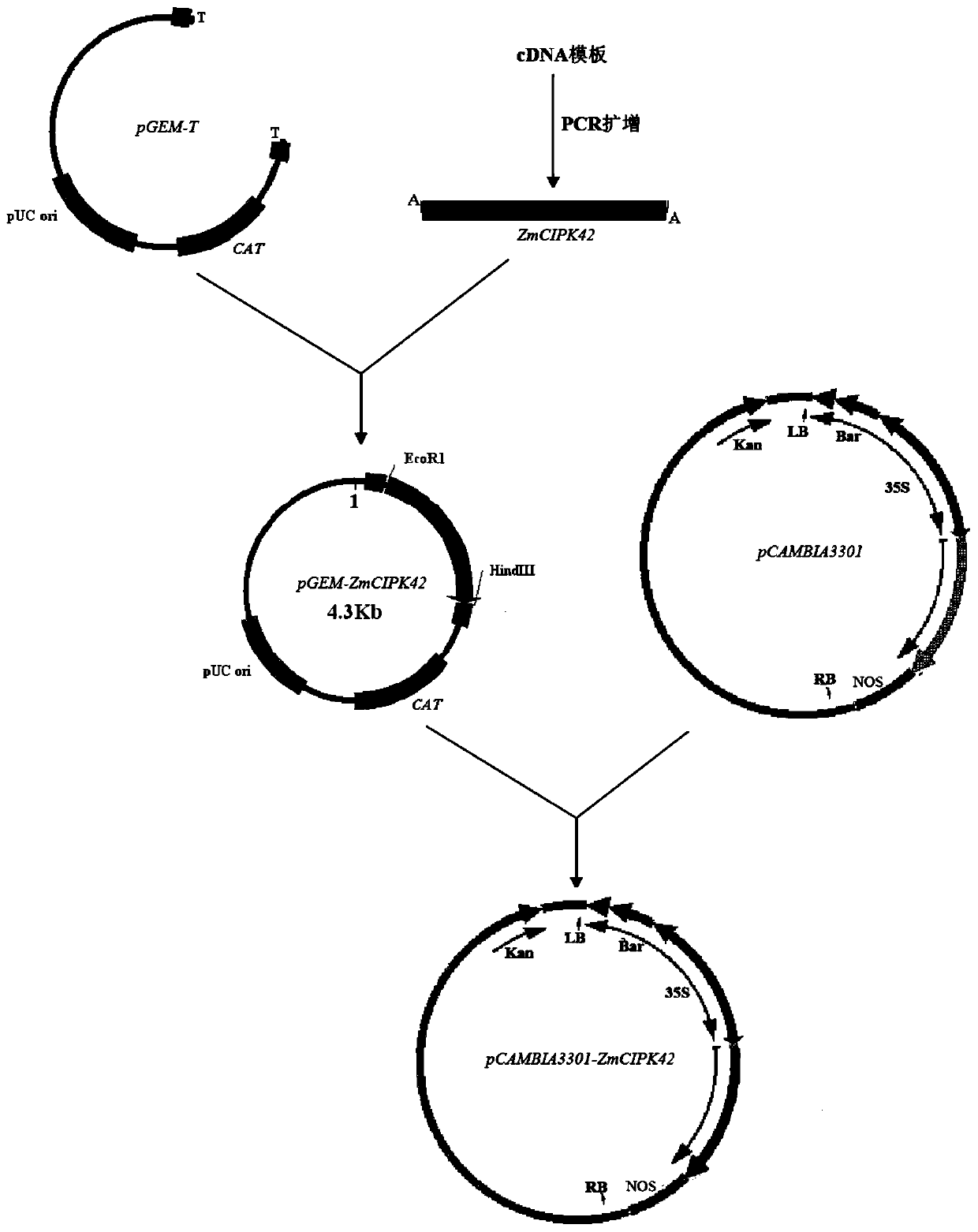
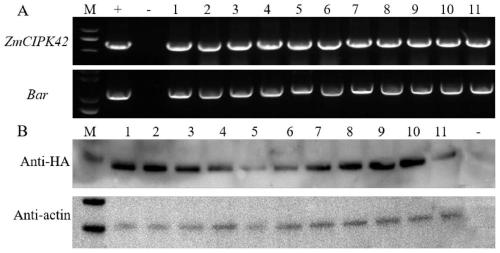
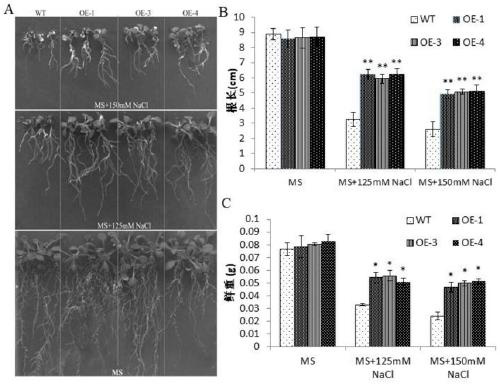
Application of corn CIPK42 protein and coding gene of corn CIPK42 protein in regulation and control of salt stress tolerance of plants
ActiveCN111172131AImprove salt toleranceImprove growth performanceTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologySalt Tolerant Plants
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly discloses an application of a corn CIPK42 protein and a coding gene of the corn CIPK42 protein in regulationand control of salt stress tolerance of plants. The corn ZmCIPK42 gene is found to be able to positively regulate and control the salt tolerance of the plants; and the salt tolerance of the plants can be effectively improved by increasing of the expression quantity of the ZmCIPK42 gene. According to the invention, transgenic corn and arabidopsis thaliana plants with ZmCIPK42 overexpression are constructed; and compared with a non-transgenic wild type, the transgenic corn and arabidopsis thaliana plants are significantly improved in salt tolerance and growth. Discovery of the salt-tolerant function of the ZmCIPK42 gene provides a novel gene target and resource for cultivation of salt-tolerant plant varieties, is of great significance to research of a salt-tolerant molecular mechanism of the plants, and lays a certain theoretical foundation for research of a salt stress response mechanism of the plants and a molecular mechanism of resisting adverse environments.
Owner:新疆农业科学院核技术生物技术研究所(新疆维吾尔自治区生物技术研究中心)
Method for building high-efficiency regenerating and transforming system of Oryza sativaL. subsp. japonica 11
InactiveCN102220277AHigh induction rateEnough to transform the materialFermentationGenetic engineeringGenetically modified riceRice plants
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering of plants and discloses a method for building a high-efficiency regenerating and transforming system of Oryza sativaL. subsp. japonica 11 through cultivation of induction of embryogenic callus, subculture multiplication of embryogenic callus, transformation mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens, cocultivation of embryogenic callus and agrobacterium tumefaciens, screening and cultivation of resistant callus and seedlings differentiation of resistant callus. The method has the advantages of simple technological processes, low production cost, and capabilities of obviously increasing the inductivity of the embryogenic callus, the subculture multiplication rate and the differentiation and regeneration rate of the embryogenic callus of the Oryza sativaL. subsp. japonica 11 and simultaneously shortening the period of obtaining regenerative rice plants; and on the basis, an improved agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated method can be used for remarkably increasing the efficiency of obtaining the transgenosis rice plants and shortening the period of obtaining regenerative rice plants.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Inducible promoter for pathogenic bacteria of rice
InactiveCN103074342AAngiosperms/flowering plantsDNA/RNA fragmentationSalicylic acidPlant genetic engineering
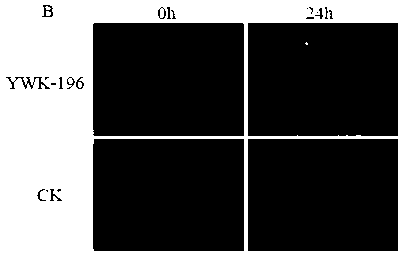
The invention relates to the technical field of plant gene engineering and provides an inducible promoter for pathogenic bacteria of rice. The promoter can be activated by rice bacterial leaf blight bacterium xanthomonas PXO99 and PXO61, a rice baeterial leaf streak bacterium RS105 and a corn banded sclerotial blight bacterium YWK-196, and can also be activated by abscisic acid, gibberellic acid, salicylic acid and sodium chloride. Truncation of the promoter verifies that two sections from -513bp to -411bp and from -411bp to -309bp are critical areas induced by the pathogenic bacteria. Various plant expression vectors can be constructed with the adoption of the promoter, and the promoter can be used for improving plant quality and other beneficial production traits through a plant gene engineering technology.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of OsELF 3 gene in controlling heading stage of paddy rice
InactiveCN102776201ABig pushDoes not affect other agronomic traitsPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyPlant genetic engineering
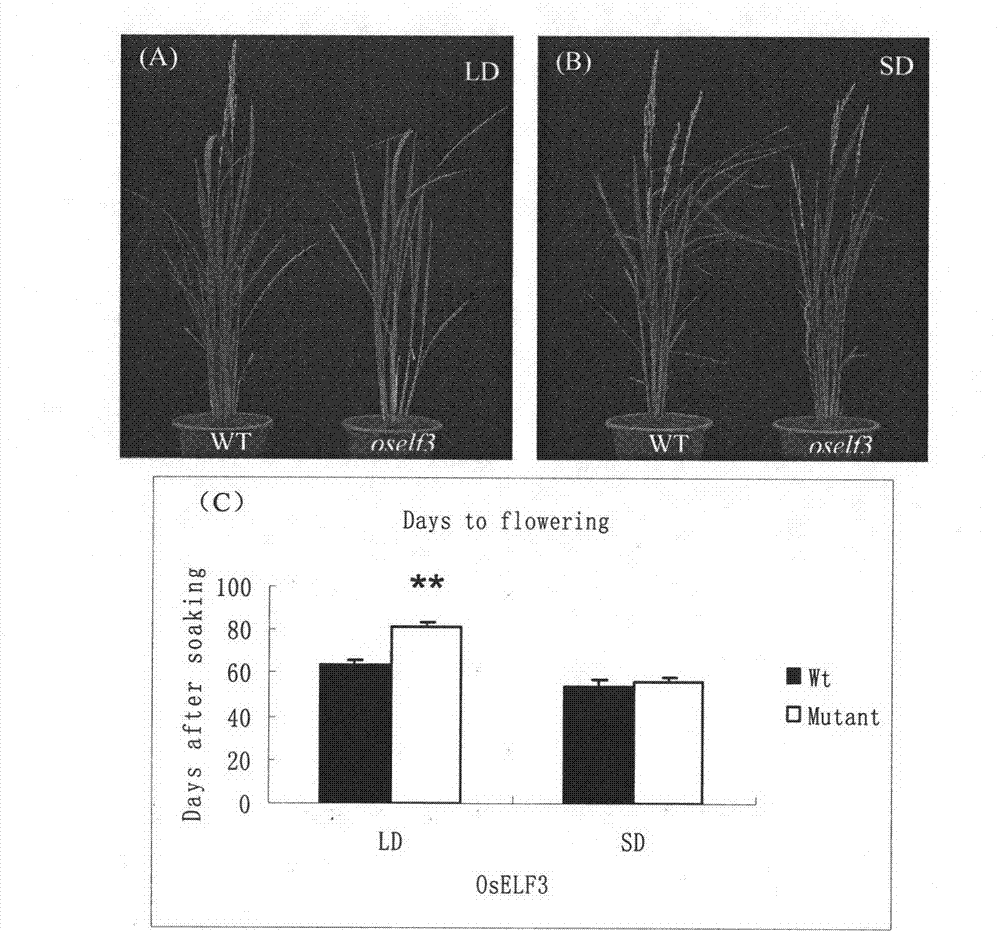
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering and specifically relates to isolation and cloning and application of OsELF 3 gene capable of controlling the heading stage of paddy rice. According to results of functional complementation experiments of the gene, the OsELF 3 gene has the function of controlling the heading stage of paddy rice, the heading stage of plants can be regulated through improving or weakening the expression level of the OsELF 3 gene by using genetic engineering technology, and therefore, the heading stage of a variety is improved to be adapted to the variety to different areas and seasons. The gene cloned in the invention and coded protein thereof can be extensively used for regulating flowering characteristics of plants and improving growth stages of plant varieties and have critical application values.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com