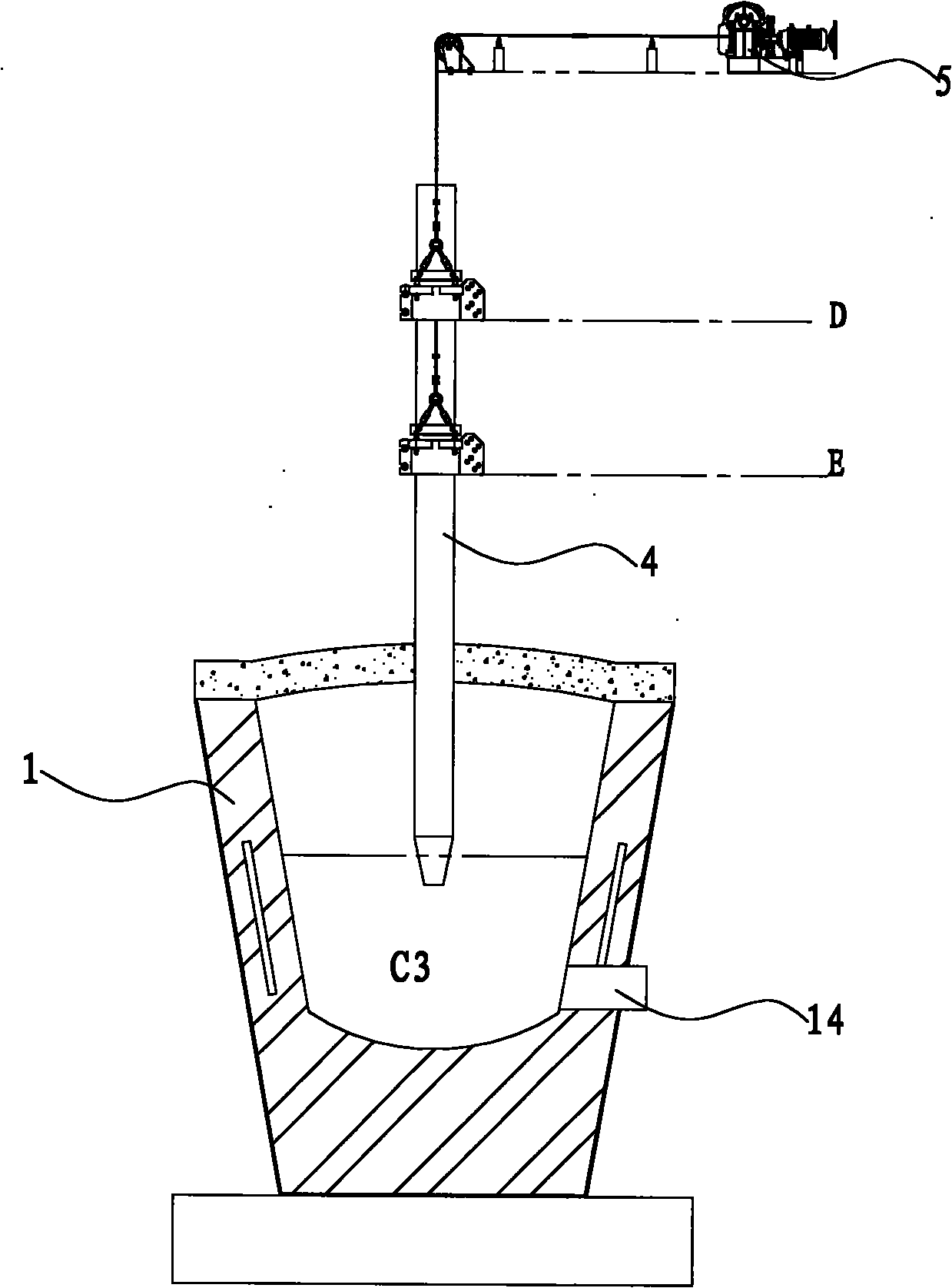
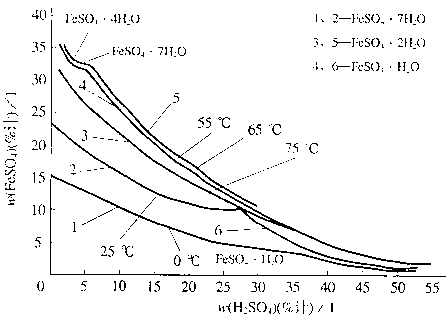
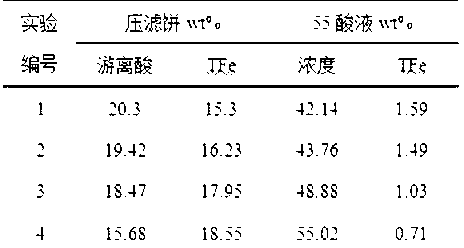
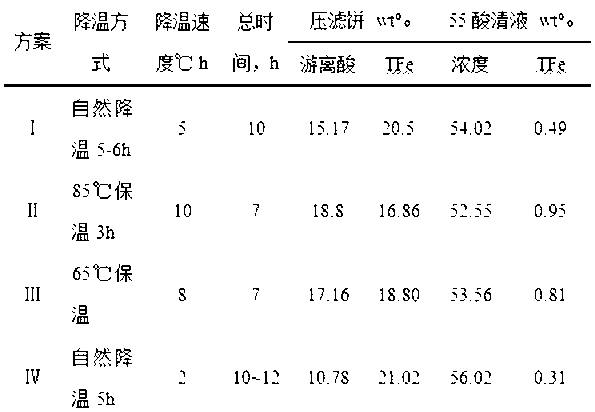
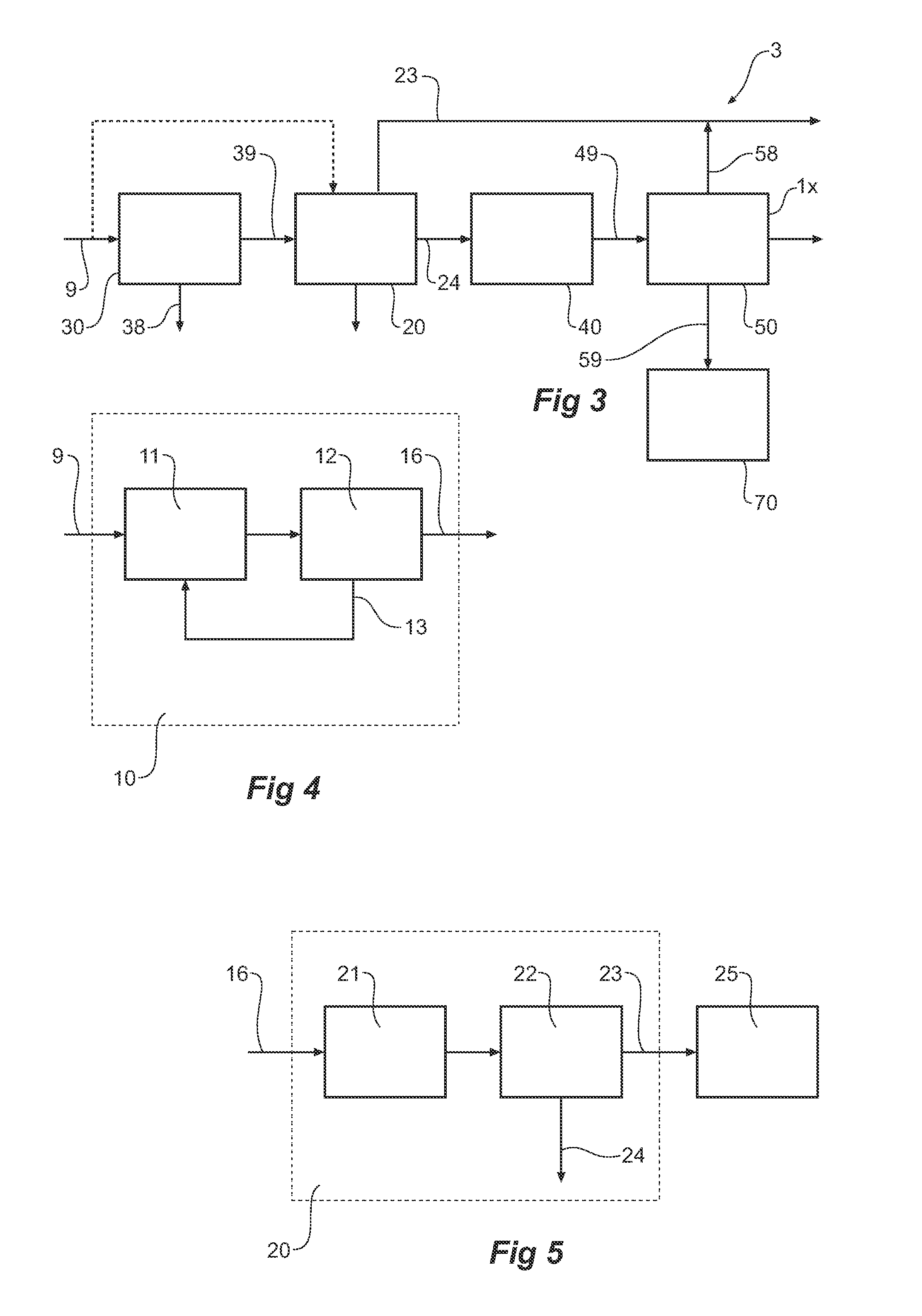
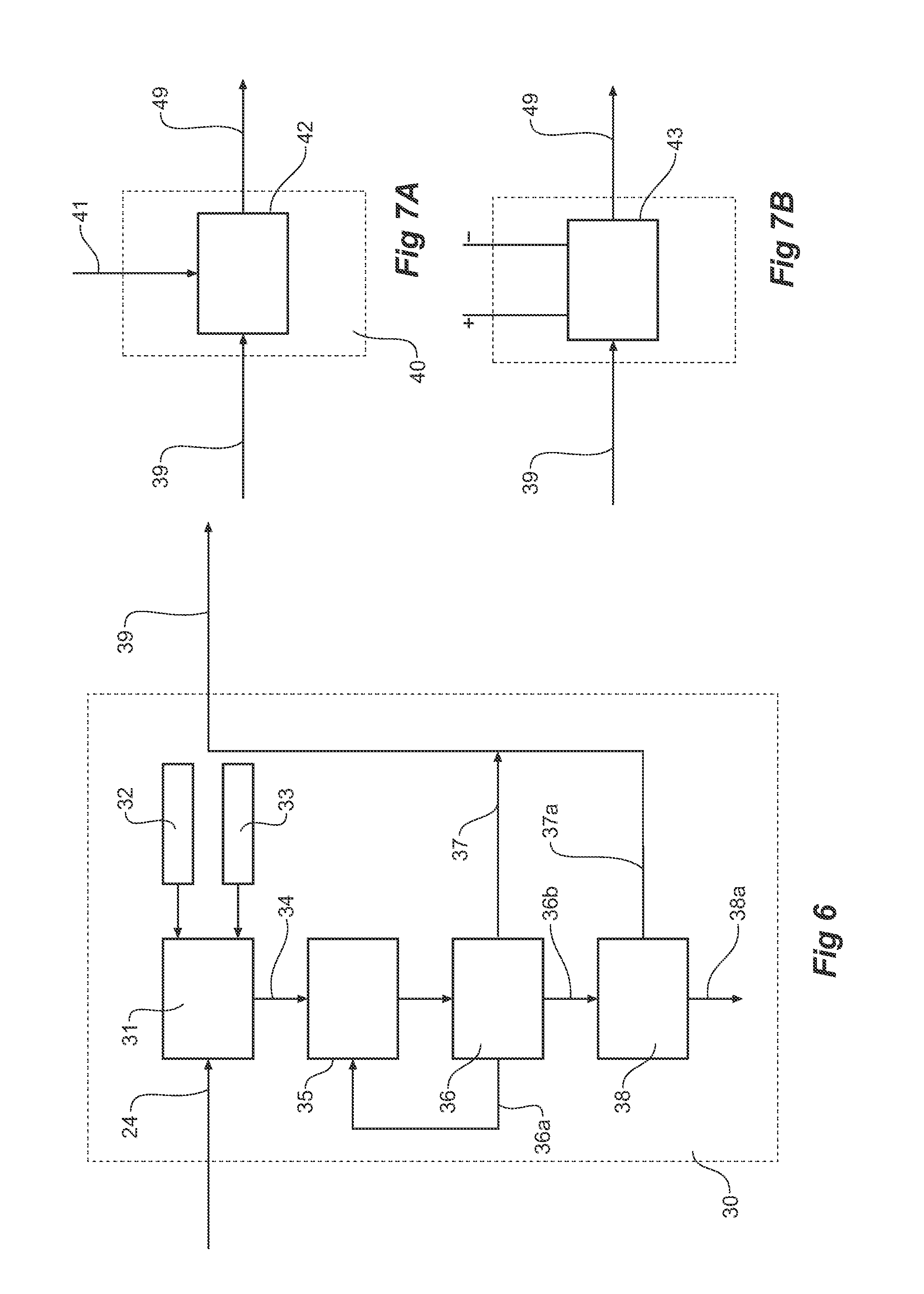
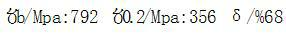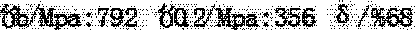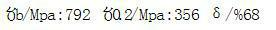Patents
Literature
410results about How to "Lower iron levels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
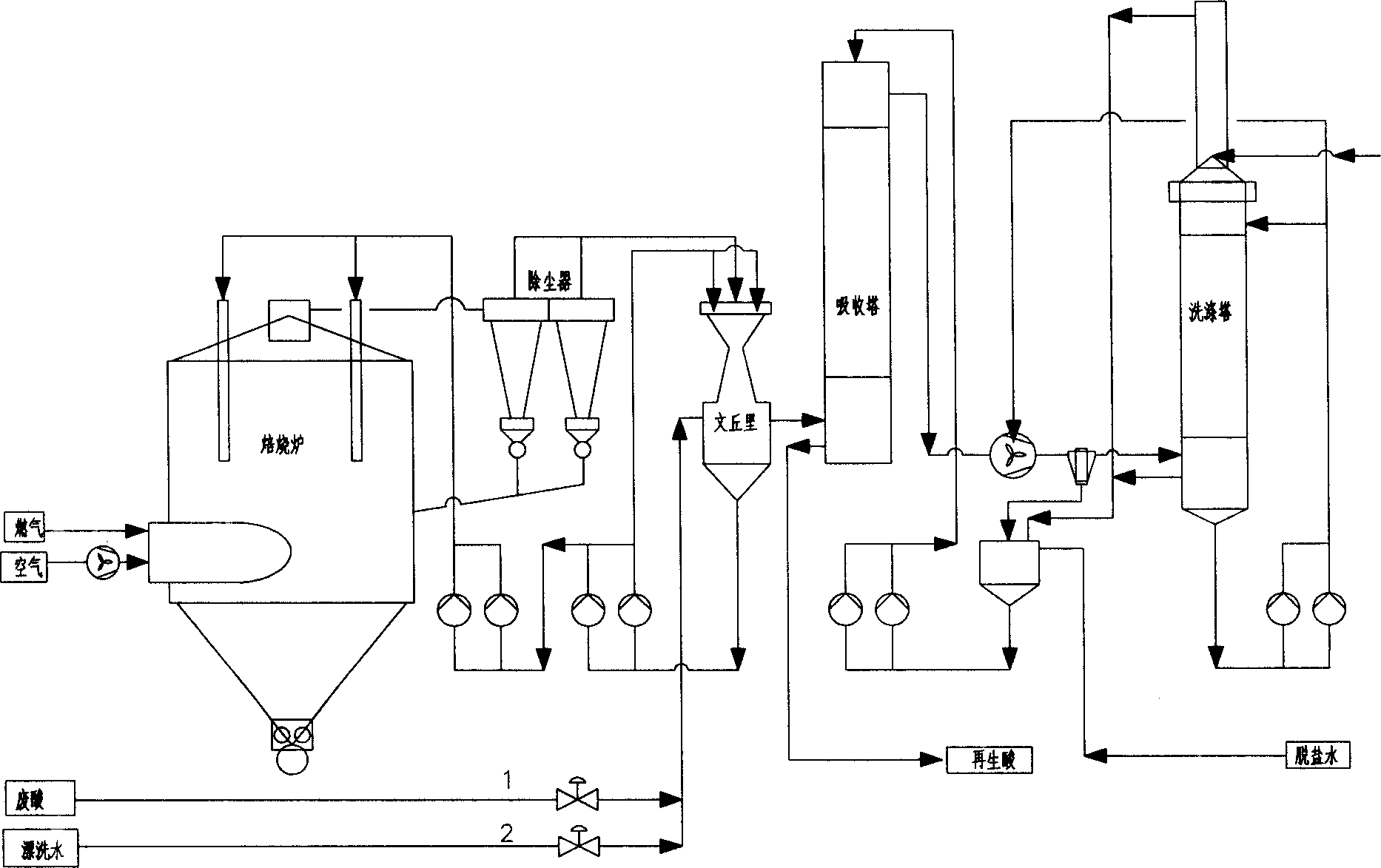
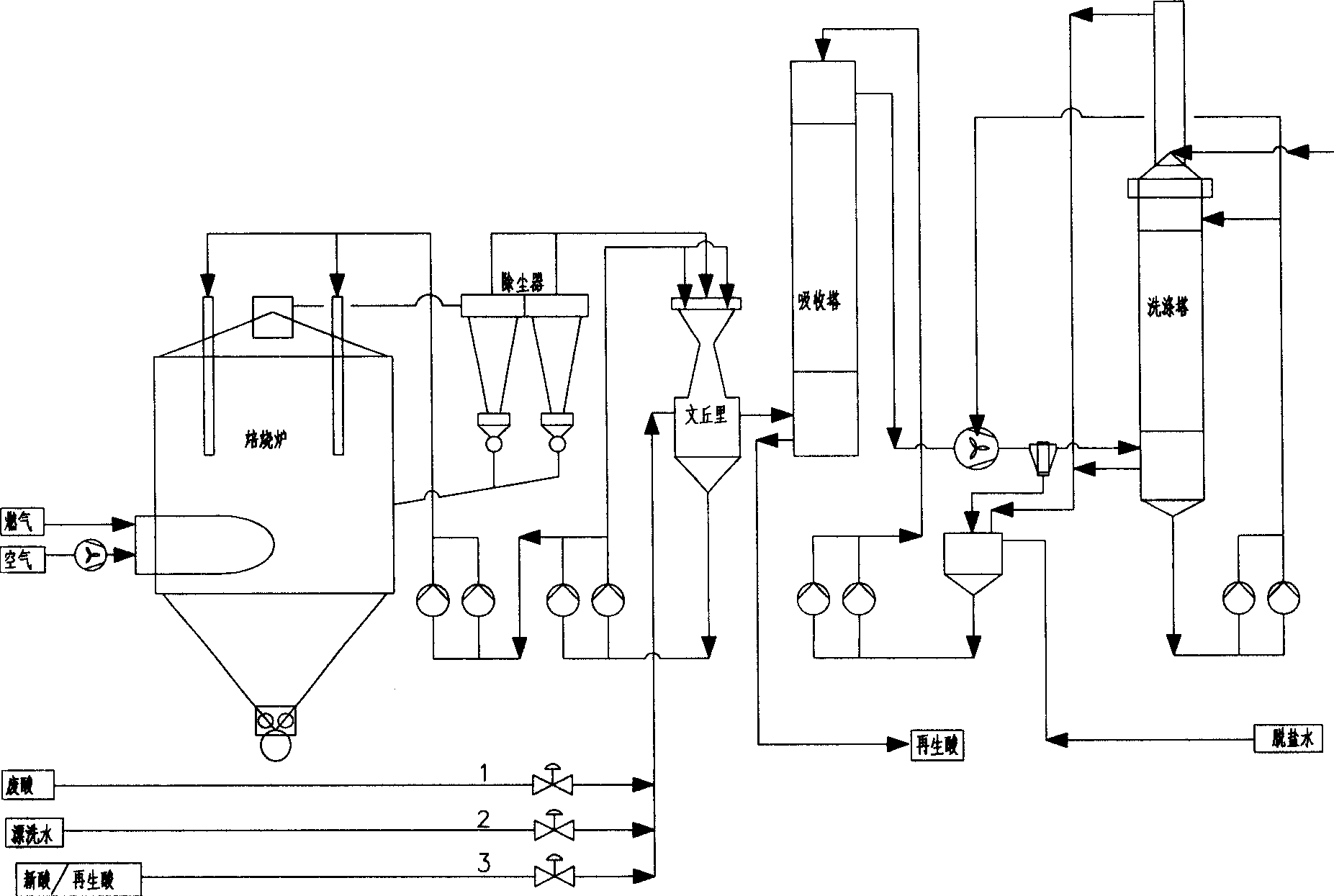
Hydrochloride waste regenerating process for spray roasting
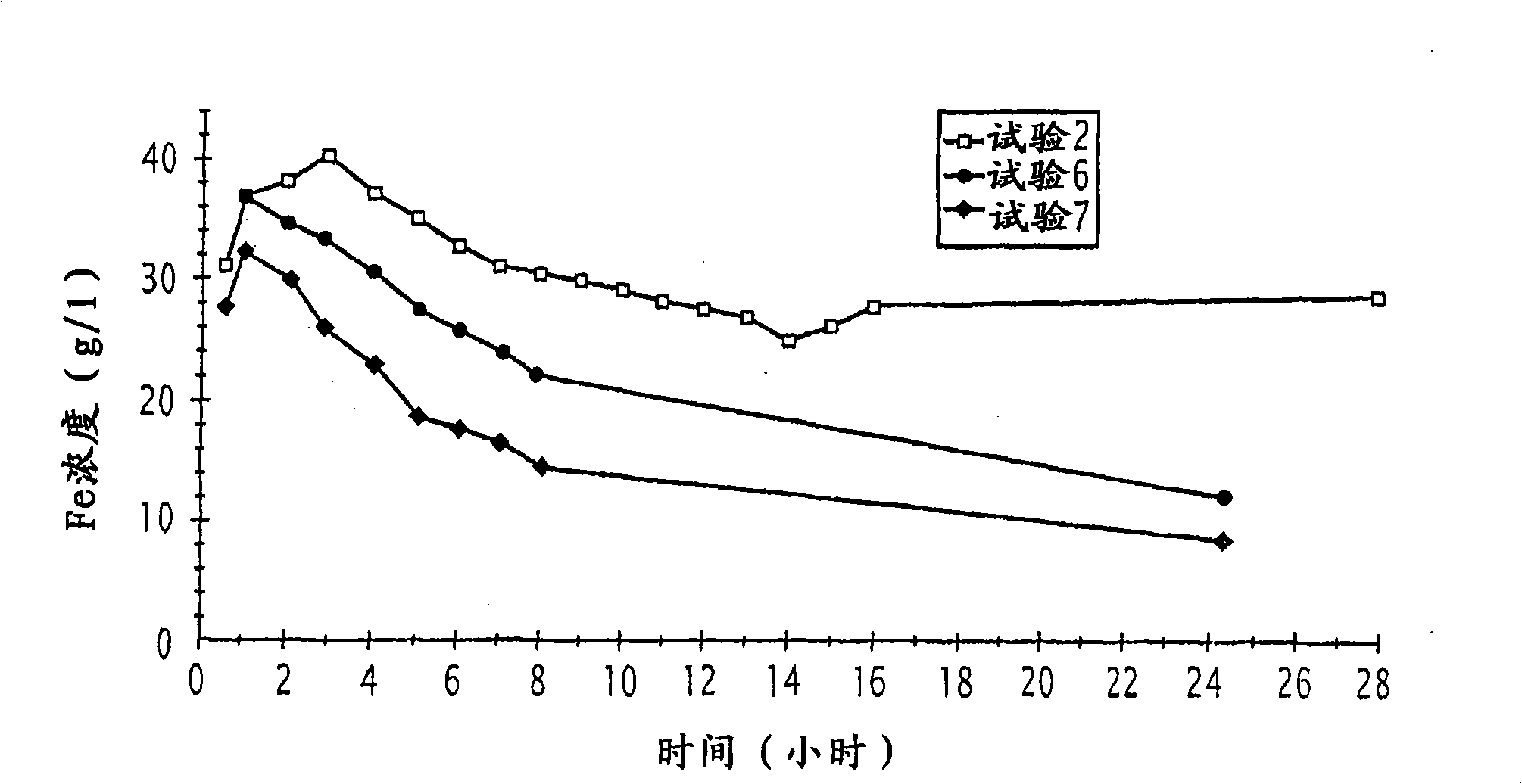
ActiveCN1851320AReduce the concentration of iron oxide powderLower iron levelsIncinerator apparatusVolumetric Mass DensityHydrogen chloride
The invention relates to hydrochloric acid exhausted liquid reclaiming process. It includes the following steps: water operation after 390 centigrade degree; adding 18-20 percent hydrochloric acid before acid operation 5-10 minutes; acid operation; and blowing out. It can reduce brown iron oxide density of discharging gas, and the iron content in reclaimed acid.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
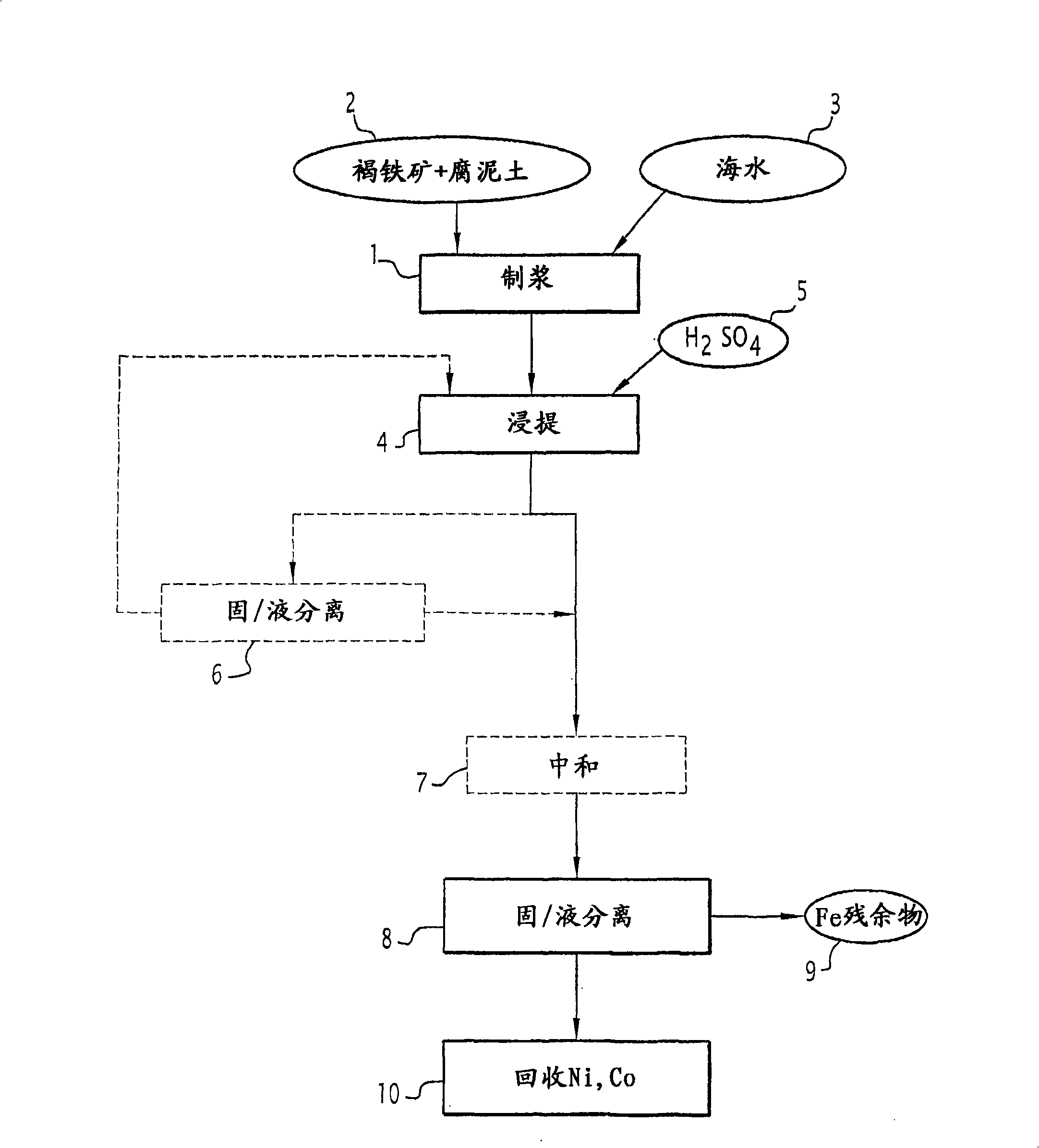
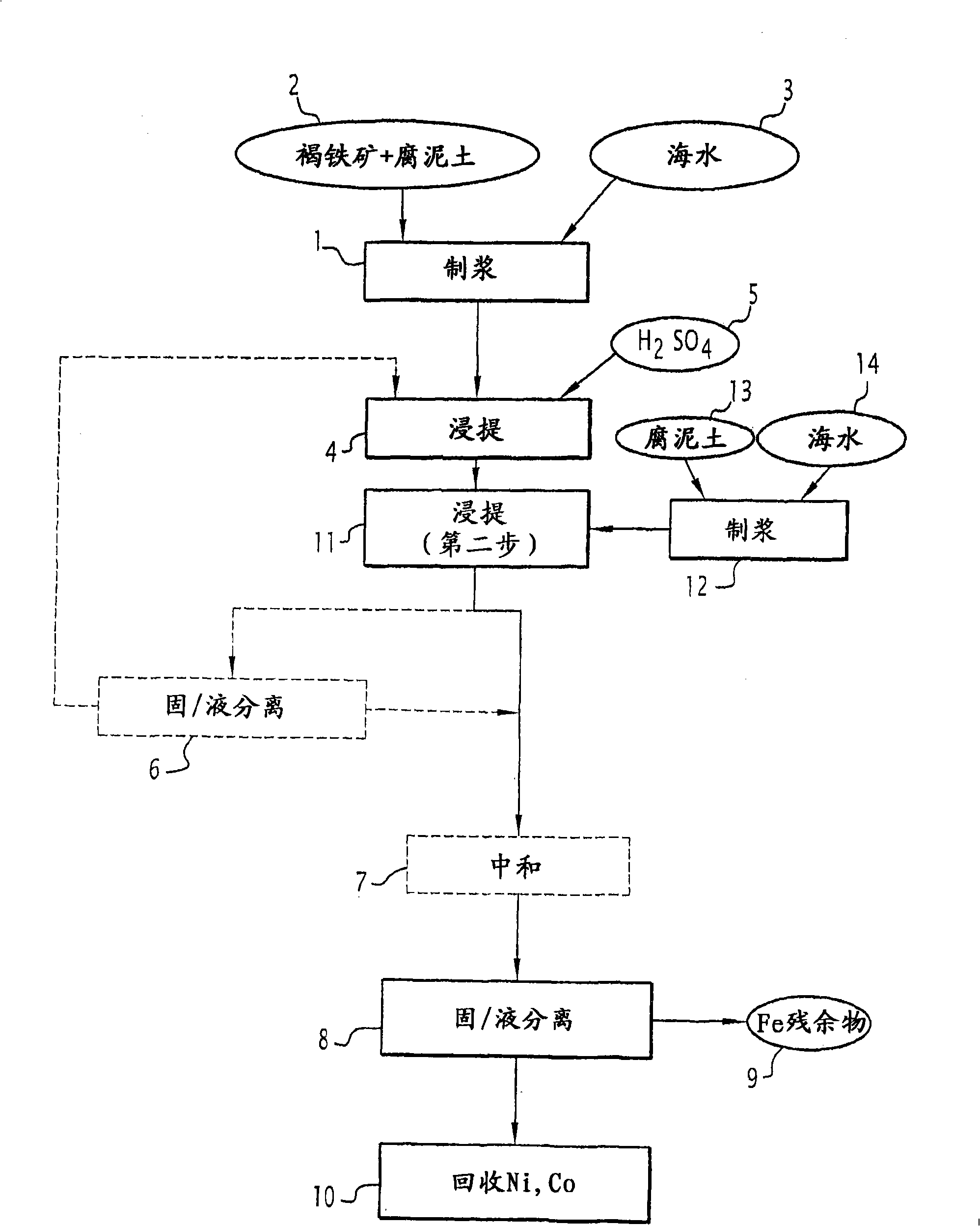
Process for the hydrometallurgical treatment of a lateritic nickel/cobalt ore and process for producing nickel and/or cobalt intermediate concentrates or commercial products using it
ActiveCN101541985ASimple structureShorten the durationProcess efficiency improvementBoiling pointHydrometallurgy
Process for the treatment of a lateritic nickel / cobalt ore consisting of a mixture (2) of limonite and saprolite, characterized in that: the mixture (2) in the presence of an iron-precipitating agent is made into a pulp (1), having a solids content of between 10 and 40% by weight; the pulp undergoes a leaching operation (4) with sulphuric acid (5), at a temperature between 70 DEG C and the boiling point and at atmospheric pressure; and a solid-liquid separation (8) is carried out so as to obtain an iron-containing solid residue (9) and a solution containing nickel and cobalt ions. Process for producing nickel and / or cobalt intermediate concentrates or commercial products using the above process.
Owner:ERAMET
Iron-Containing Human Milk Fortifier With Improved Antimicrobial Properties
InactiveUS20080274230A1Reducing and eliminating inherent activityHigh iron concentrationNervous disorderAntipyreticHuman milk fortifierMicroorganism
Disclosed are human milk fortifier compositions, in either powder or liquid forms, comprising nutrients and selected iron-containing materials, wherein the fortifiers when added to human milk do not significantly inhibit or otherwise eliminate the inherent, in-vitro antimicrobial properties of the milk. This is accomplished by formulating the compositions with iron-containing insoluble iron, soluble bound iron, or combinations thereof, with little or no soluble unbound iron. Also disclosed are methods of providing nutrition to infants, especially preterm infants, by adding the human milk fortifier described herein with human milk to form a fortified human milk, and then administering the fortified human milk to the infant. The fortifier can also be used to fortify other infant formulas.
Owner:JOHNS PAUL W +2
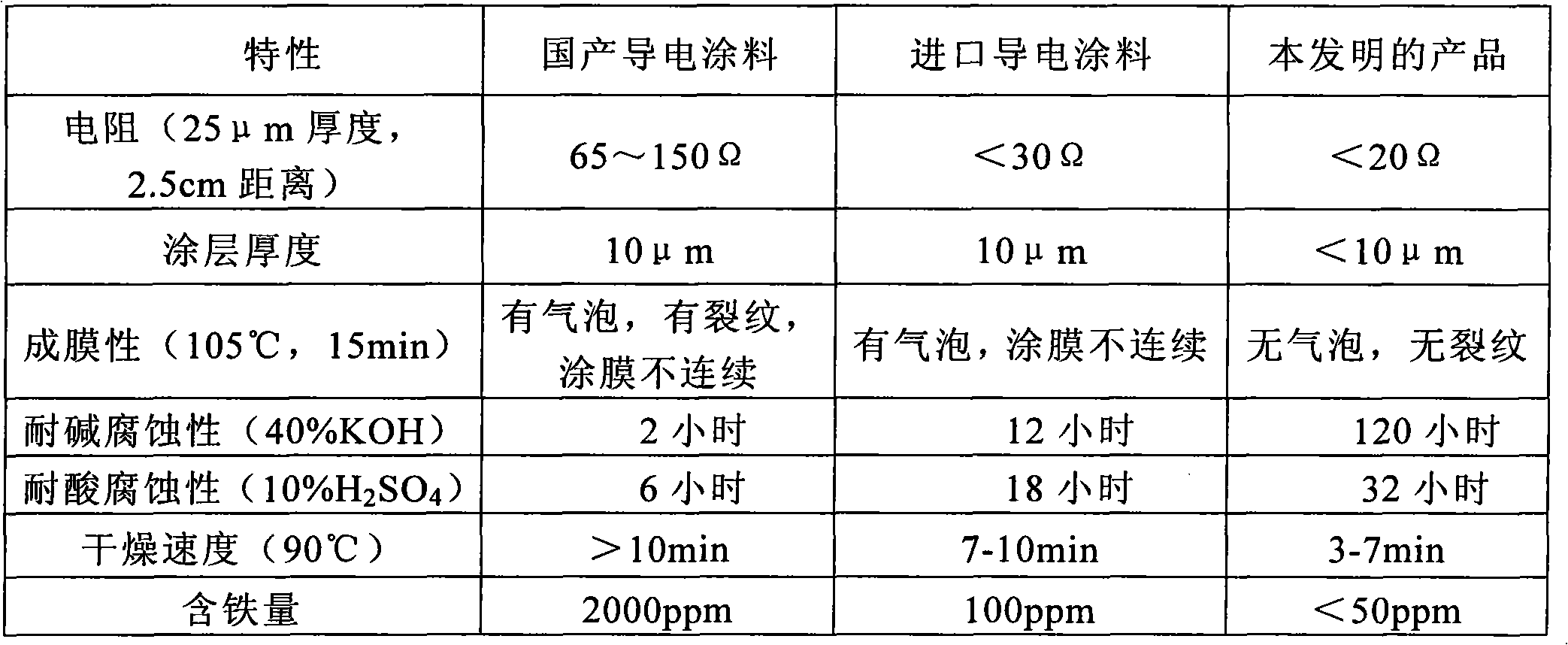
Supercapacitor electrode corrosion-resistant conductive coating
ActiveCN101899233AImprove conductivityReduce volumeAlkali metal silicate coatingsElectrolytic capacitorsConductive coatingSupercapacitor
The invention discloses a supercapacitor electrode corrosion-resistant conductive coating, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 10 to 35 percent of conductive agent, 0.1 to 3.5 percent of dispersing agent, 2.0 to 15 percent of binder, 0.1 to 8.0 percent of pH regulator, and 50 to 70 percent of pure water. The supercapacitor electrode corrosion-resistant conductive coating is prepared by the following steps of: fully mixing and uniformly stirring the components, adding the components into a ball mill for peptizing and dispersing, and discharging to obtain the supercapacitor electrode corrosion-resistant conductive coating. Compared with the conventional like products at home and abroad, the supercapacitor electrode corrosion-resistant conductive coating has the advantages of greatly improving the acid and alkali corrosion resistance, having no bubbles, falling off, corrosion and other phenomena after being soaked in alkaline solution for 120 hours and in acid solution for 32 hours, and improving the conductivity, adhesiveness and drying speed. The product can be diluted and adjusted according to need during use.
Owner:SHANGHAI HANBO ENTERPRISE +1
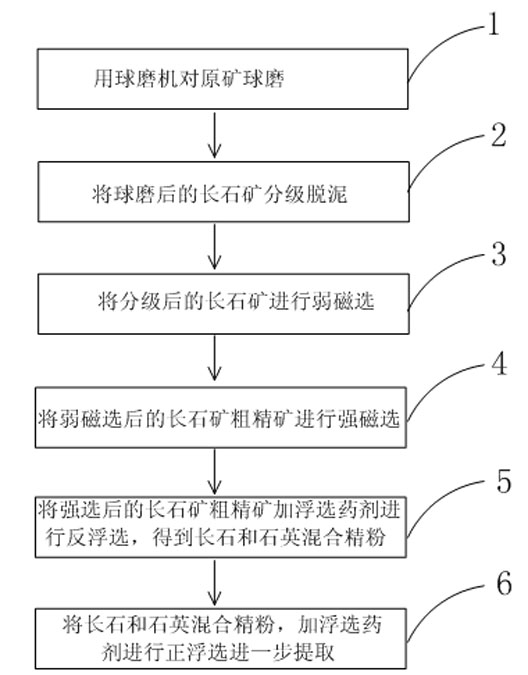
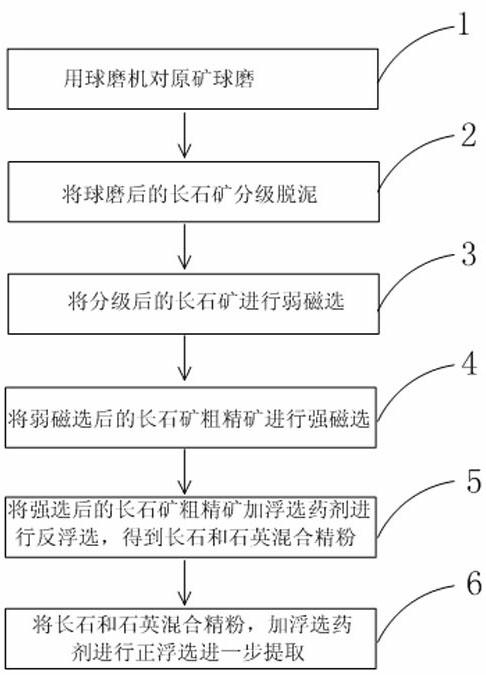
Method for separating and extracting feldspar ore with complex impurity components
InactiveCN102069033AEfficient removalImprove burnt board whitenessWet separationHigh intensityReverse flotation
The invention relates to a method for separating and extracting feldspar ore with complex impurity components, which comprises the following steps of: 1) performing ball milling on the feldspar ore with complex impurity components through a ball mill; 2) performing classification and de-sliming on the milled feldspar ore by using an improved hydraulic classifier; 3) performing low-intensity magnetic separation on the classified feldspar ore through a low-intensity magnetic separator to obtain high-intensity magnetic substances and rough feldspar concentrate for high-intensity magnetic separation; 4) performing high-intensity magnetic separation on the rough feldspar concentrate obtained by the low-intensity magnetic separation through a high-intensity magnetic separator to obtain low-intensity magnetic substances and rough feldspar concentrate for flotation; and 5) performing size mixing and segmentation on the rough feldspar concentrate obtained by the high-intensity magnetic separation, adding a flotation agent, and performing reverse flotation, impurity removal and dehydration through a flotation machine to remove impurities and obtain fine feldspar and quartz mixed powder and flotation water.
Owner:烟台宜陶矿业有限公司
Method for preparing iron-free aluminium sulfate and superfine active carbon white utilizing aluminium first-class ore
InactiveCN1850607AConcentration easyDo not reduce the concentrationSilicaAluminium sulfatesSurface-active agentsActive particles
The invention discloses a method for preparing iron-free aluminum sulfate and superfine active white carbon black with bauxite, crushing the bauxite and removing dissociative iron source by magnetic separation, and then reacting with vitriol; adding in dithiocarbamate with medium and high molecular weights and multiple functionalities to remove iron ions by solid phase reaction, and filtering, where the filtrate is iron-free aluminum sulfate; washing filter residue with alkaline water solution, surface active agent water solution, and tap water, respectively, to neutralize it, then after reacting with alkali, filtering, making filtrate, inorganic acid and active particles react mutually, filtering, water-washing, and drying to obtain the superfine active white carbon black. And the method has simple process, and low cost, applied to industrialized production, where the iron content of the prepared aluminum sulfate is less than 15 ppm, and the grain size, specific surface area, tensile strength, added value of the superfine white carbon black are 0.5-5 mum, greater than 200 m2 / g, higher than 17.0 MPa, and high, respectively.
Owner:杭州百事特实业股份有限公司
Electromagnetic filter method for removing iron element from aluminium-silicon alloy
The electromagnetic filtering method for removing iron element from aluminium silicon alloy includes the following steps: firstly, adding managanese in eutectic aluminium-silicon alloy melt and making the iron element separate out in the form of nascent iron-rich phase in the melt; then according to the difference of electric conductivity between the nascent iron-rich phase and melt self-body to make the nascent phase be separated out from the melt, under the action of eledctromagnetic force adopting the method for electromagnetically filtering nascent iron-rich phase to reduce iron content in the aluminium-silicon alloy melt. The electromaglnetic force application mode can adopt D.C. current applied stable and constant magnetic field or high-frequency magnetic field. Said ivnention features simple process, high efficiency and continuous treatment, and can raise purity of metal melt.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Bayer process red mud processing method
The invention discloses a treatment method of Bayer method red mud, comprising the following steps: (a) the red mud is sorted by a beneficiation method and divided into three parts, namely, rough sand, fine sand and soil mortar; (b) milling grinding and settling separation are carried out to the rough sand in the step (a) to obtain rough sand one and tailing ore slurry one; (c) after the rough sand one in the step (b) and the fine sand in the step (a) are mixed, magnetic separation is carried out to obtain iron powder and quartz powder; (d) the iron powder obtained in the step (c) is refined and sorted by a magnetic separator to obtain fine iron powder F and fine iron powder P; and (e) the soil mortar in step (a) is pulse magnetic separated to obtain tailing ore slurry and fine iron powder PI. The method can reduce 35-40 percent of red mud discharge, the iron element effective utilization rate can reach more than 70 percent, and the monomer quartz extraction yield can reach 80 percent. The method optimizes the production flow of alumina by using a combination method, reduces the red mud discharge, protects the environment, reduces the production cost of alumina and improves the alumina production capacity.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
Magnesium alloy boride iron illiminating flux and its production method
A deironing boride flux for Mg-alloy contains magnesium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium chloride, calcium chloride, calcium fluoride, barium chloride, and boron oxide and / or sodium borate as deironing agent. Its advantages are high power removing impurities and Fe from molten Mg-alloy, easy separation, and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAOHUA MOLD
Method for enriching niobium by high-temperature roasting and low-intensity magnetic separation
InactiveCN104498737AAchieve separationIncrease productivityMagnetic separationIron reductionRoasting
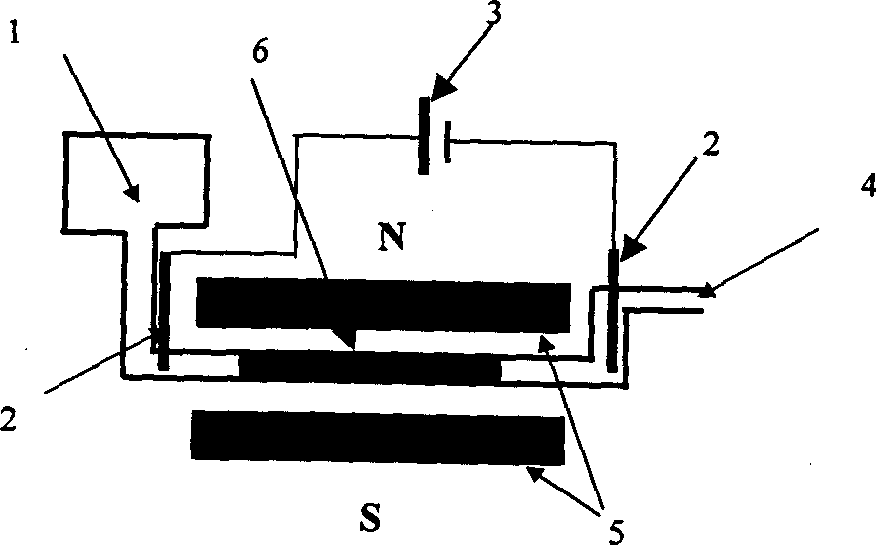
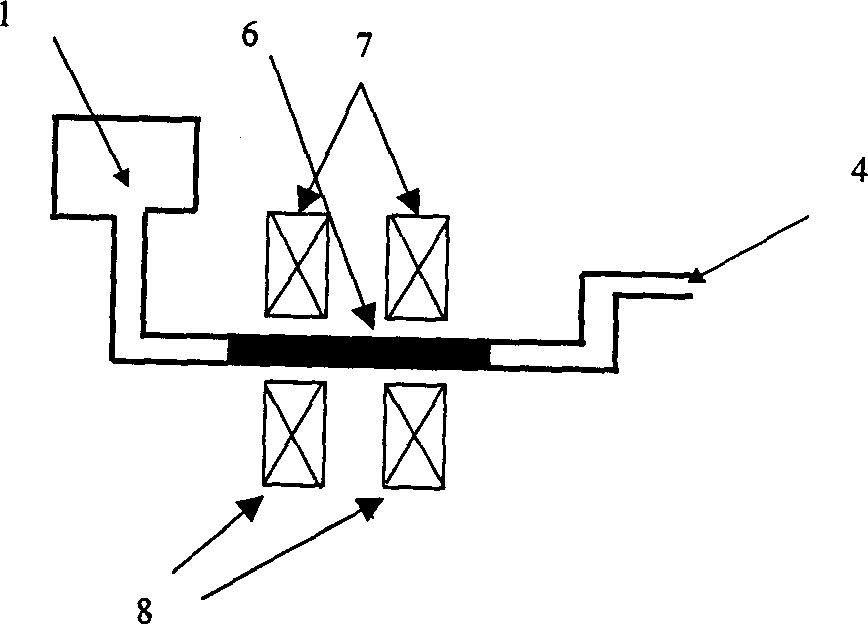
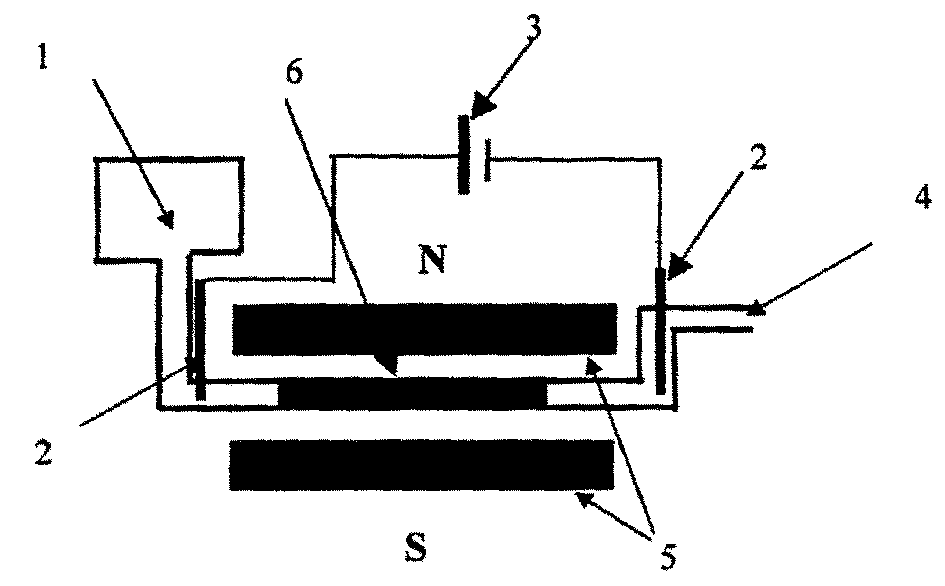
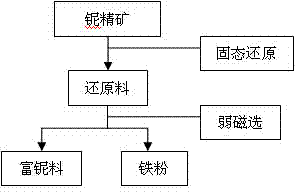
The invention relates to a method for enriching niobium by high-temperature roasting and low-intensity magnetic separation and belongs to the technical field of mineral extraction metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: performing solid-state reduction of a niobium ore concentrate to obtain a reduced ore containing the niobium and metal iron; ball-milling the reduced ore containing the niobium and the metal iron and then performing low-intensity magnetic separation to obtain a niobium-rich material. According to the method disclosed by the invention, iron oxide in the niobium ore concentration is selectively reduced in a solid state, so that the metal transformation rate is above 90%; by reduction of the iron oxide, a mineral structure of niobium-iron rutile in the original ore is damaged; subsequently niobium oxide can be separated from the metal iron by low-intensity magnetic separation; finally the content of iron in the obtained niobium-rich material is lower than 8%; compared with the original 'solid-state iron reduction-high-temperature melt separation-smelting' method, the method disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing the niobium-rich material of which the iron content is basically the same and also has the advantages of saving power consumption, reducing emission and improving the efficiency.
Owner:包钢集团矿山研究院(有限责任公司)
Smelting furnace for nickel-bearing laterite ore
The invention discloses a smelting furnace for nickel-bearing laterite ore, comprising a furnace body, a gunjet for top combustion, a side-blown jugjet and an electrode. A hearth is limited in the furnace body; a smelting bath is arranged at the lower part of the hearth, and the furnace body is provided with a charging hole for adding materials to the hearth, a smoke outlet, a nickel outlet and a dreg outlet; the lower end of the gunjet for top combustion extends from the top of the furnace body to the hearth and is located at the upper side of the smelting bath and sprays pulverized coal and oxygen to the upper part of the hearth towards the smelting bath; the side-blown gunjet extends from the lateral side of the furnace body to the smelting bath to spray the pulverized coal and oxygen; and the lower end of the electrode extends to the smelting bath to heat the melt in the smelting bath and clarify and separate dregs from nickel and ferrum. The smelting furnace for the nickel-bearing laterite ore has the advantages of low cost and energy consumption, good operating environment, low pollution and simple process.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Method for concentrating and purifying titanium dioxide waste acid by using complex acid
InactiveCN103011272AHigh yieldReduce enrichment costsSulfur compoundsEnergy inputPhysical chemistryAcid concentration
The invention discloses a method for concentrating and purifying titanium dioxide waste acid by using complex acid. The method comprises the following specific steps of: titanium recovery: primarily concentrating waste acid produced in a titanium dioxide production process by using waste heat of calcining tail gas of a ring kiln to achieve the mass concentration being 25-32%, and then recovering titanium; acid mixing: uniformly mixing the waste acid subjected to titanium recovery and concentrated sulfuric acid in an acid mixing tank according to a mass proportion of (1.2-4):1 to obtain mixed acid; and crystallization: carrying out gradient cooling, crystallizing, curing and filtering on the mixed acid gradually in the acid mixing tank, and when the temperature of the mixed acid is reduced to 60-65 DEG C, pumping the mixed acid into a filter press for solid-liquid separation to obtain concentrated sulfuric acid and ferrous dregs. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantage of changing the traditional method for concentrating the titanium dioxide waste acid by depending on natural gas, steam, fire coal hot gas and other heat sources, is free from consuming a large amount of energy sources and capable of reducing the cost in waste acid concentration, and is high in recovery rate of the waste acid.
Owner:SICHUAN LOMON TITANIUM IND CO LTD
Method for preparing titanium dioxide for delustering chemical fibers
The invention belongs to the field of fine chemical engineering, and particularly relates to a method for preparing titanium dioxide for delustering chemical fibers. The method comprises the following technological flows: slurry making, iron-removal filtering, wet grinding, diluting, iron-removal filtering, grading, surface treatment, washing settling, atomized drying, grinding and packaging. The method provided by the invention has the advantageous effects as follows: 1, the prepared products have controllable particle sizes and stable dispersity; 2, the impurity removal effect is good; 3, the removal effect of soluble slats is good; and 4, the product quality is guaranteed.
Owner:JIAXING GAOSHENG NEW MATERIAL TECH
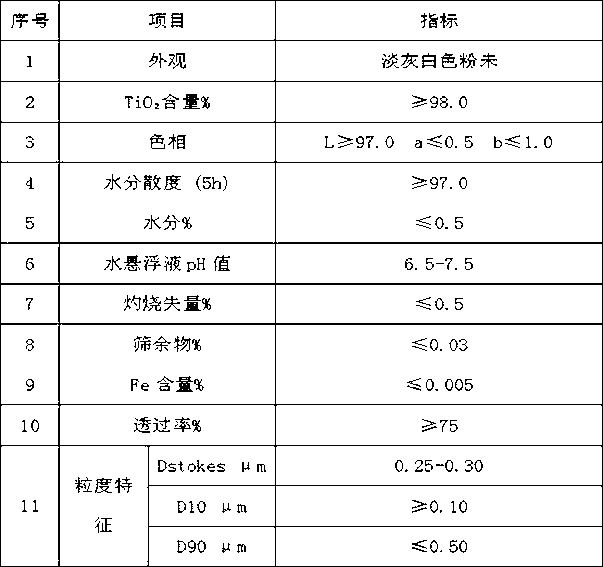
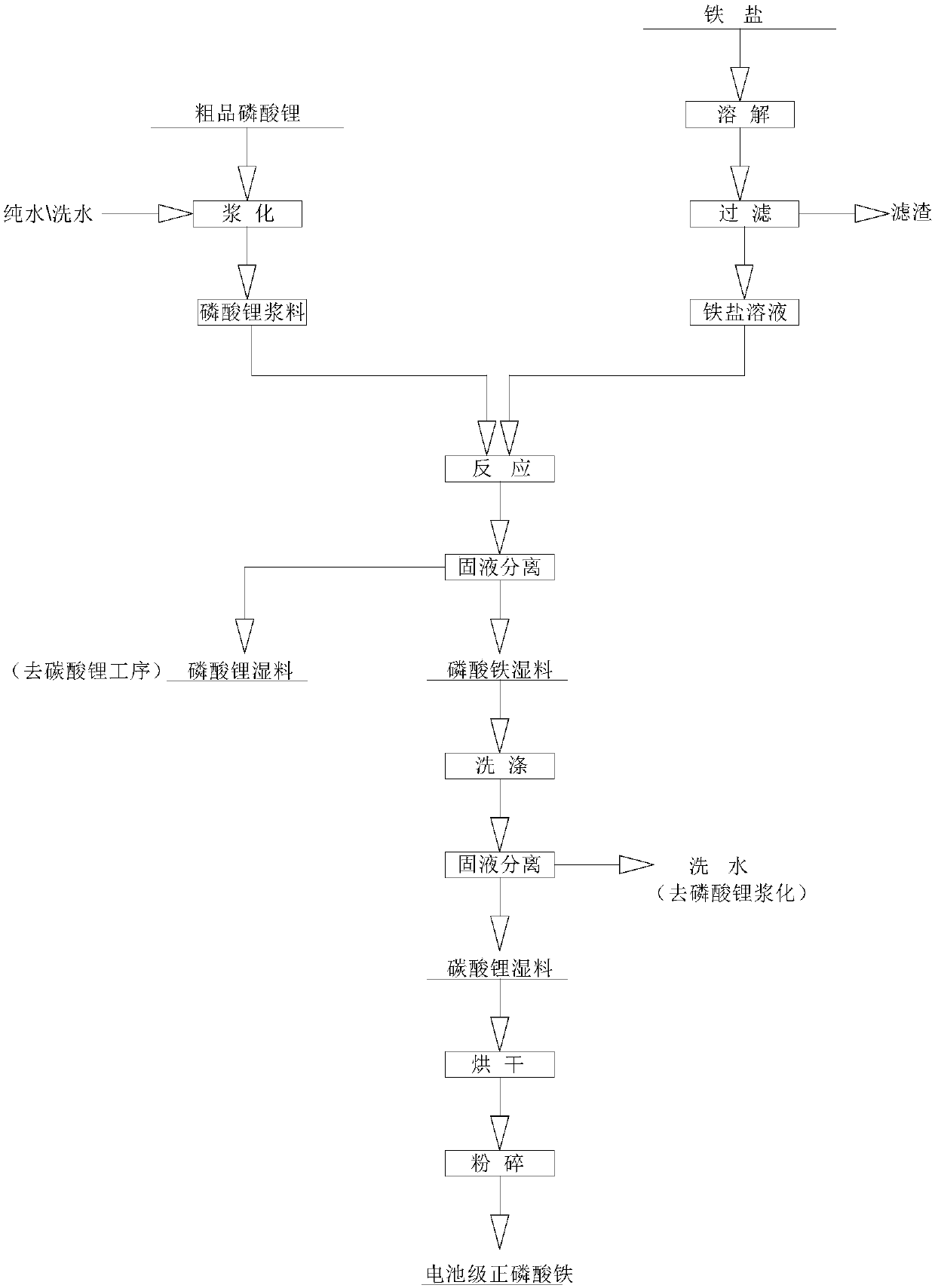
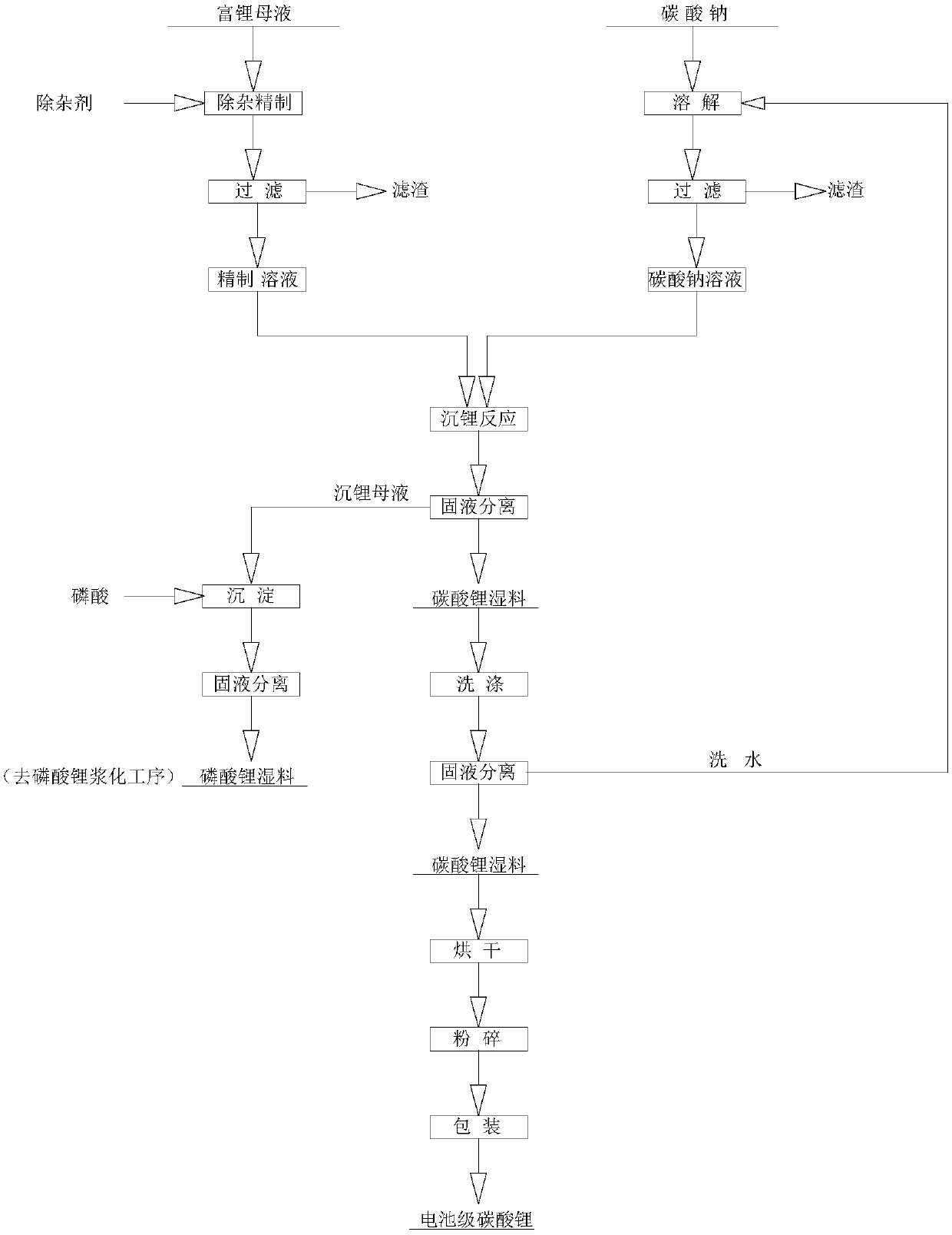
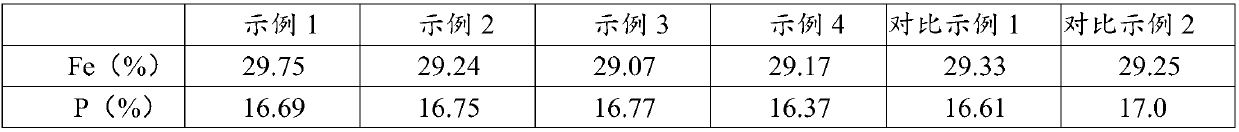
Process for recovering lithium phosphorous from lithium phosphate crude product to prepare battery-level lithium carbonate and iron phosphate
ActiveCN107720716AAchieve recyclingIncrease surface areaPhosphorus compoundsLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesWater basedPhosphoric acid
The invention provides a process for recovering lithium phosphorous from a lithium phosphate crude product to prepare battery-level lithium carbonate and iron phosphate, and belongs to the technical field of resource recycling. The process comprises: lithium phosphate slurrying: adding pure water or washing water to the lithium phosphate crude product to prepare slurry, and performing high-speed dispersion and grinding dispersion to obtain uniform lithium phosphate slurry; iron solution preparation: filtering an iron solution to obtain a refined iron solution; iron orthophosphate preparation:adding inorganic acid into a pure water base solution to regulate pH to 2-3, adding the lithium phosphate slurry and the refined iron solution after temperature rise, performing solid-liquid separation after reaction is completed, initially washing a solid by the pure water, re-washing the solid by slurry mixing, and drying and crushing the solid, so as to obtain iron orthophosphate; battery-levellithium carbonate preparation: purifying a lithium-containing mother solution obtained by preparing the iron orthophosphate, and inputting into a mixed solution of sodium carbonate and EDTA to perform lithium deposition reaction, and performing separation, washing, drying and crushing to obtain lithium carbonate. The lithium phosphate crude product is treated by means of the process of the invention, so that iron orthophosphate and lithium carbonate products meeting quality requirements of a lithium battery can be obtained.
Owner:CHENGDU CHEMPHYS CHEM IND
Method for processing motorcycle hub
The invention provides a processing method for a motorcycle hub. When the hub is processed by the method of the invention, the processing cost is low and the performance is stable. The processing method is characterized in that the processing method comprises the steps as follows: aluminium solution melting, casting blank, riser cutting, bottom pore drilling, air nozzle drilling, grinding, T6 heat disposal, shot blasting, single-board computer, cleaning, coating, numerical control processing, finished product detecting, cleaning, packaging, and warehousing. The processing method is characterized in that the contents of all components in the aluminium solution are 6.5 to7.5 percent of Si, less than 0.25 percent of Fe, less than 0.25 percent of Mg, and 0.2 percent of Zn, 92.5 percent of Al; the melting temperature of the aluminium solution is ranging from 705 DEG C to 735 DEG C; and the casting blank is cast by gravity.
Owner:WUXI WANXUAN METAL PROD
Method for continuous production of aligned nanostructures on a running substrate and related device
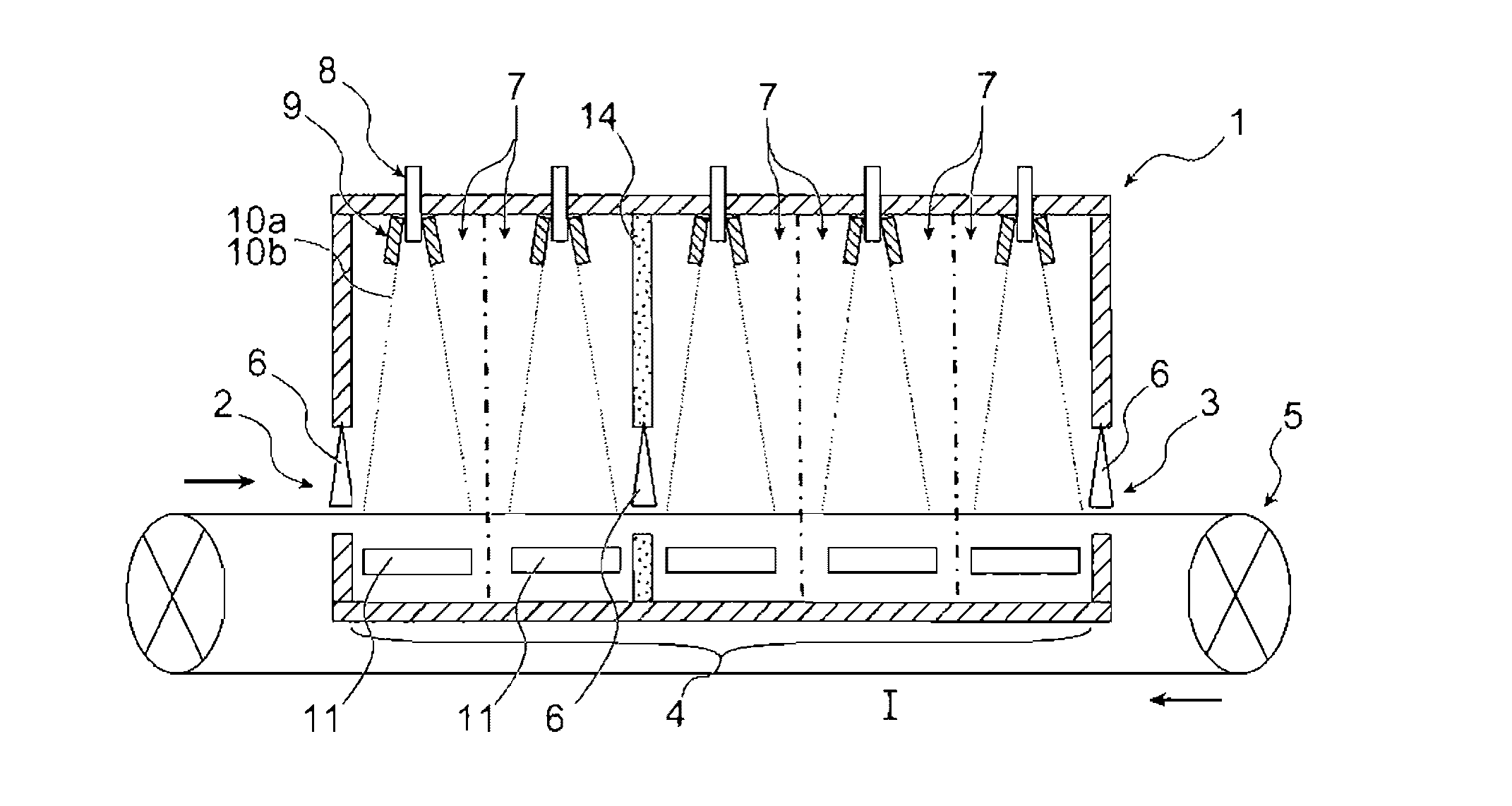
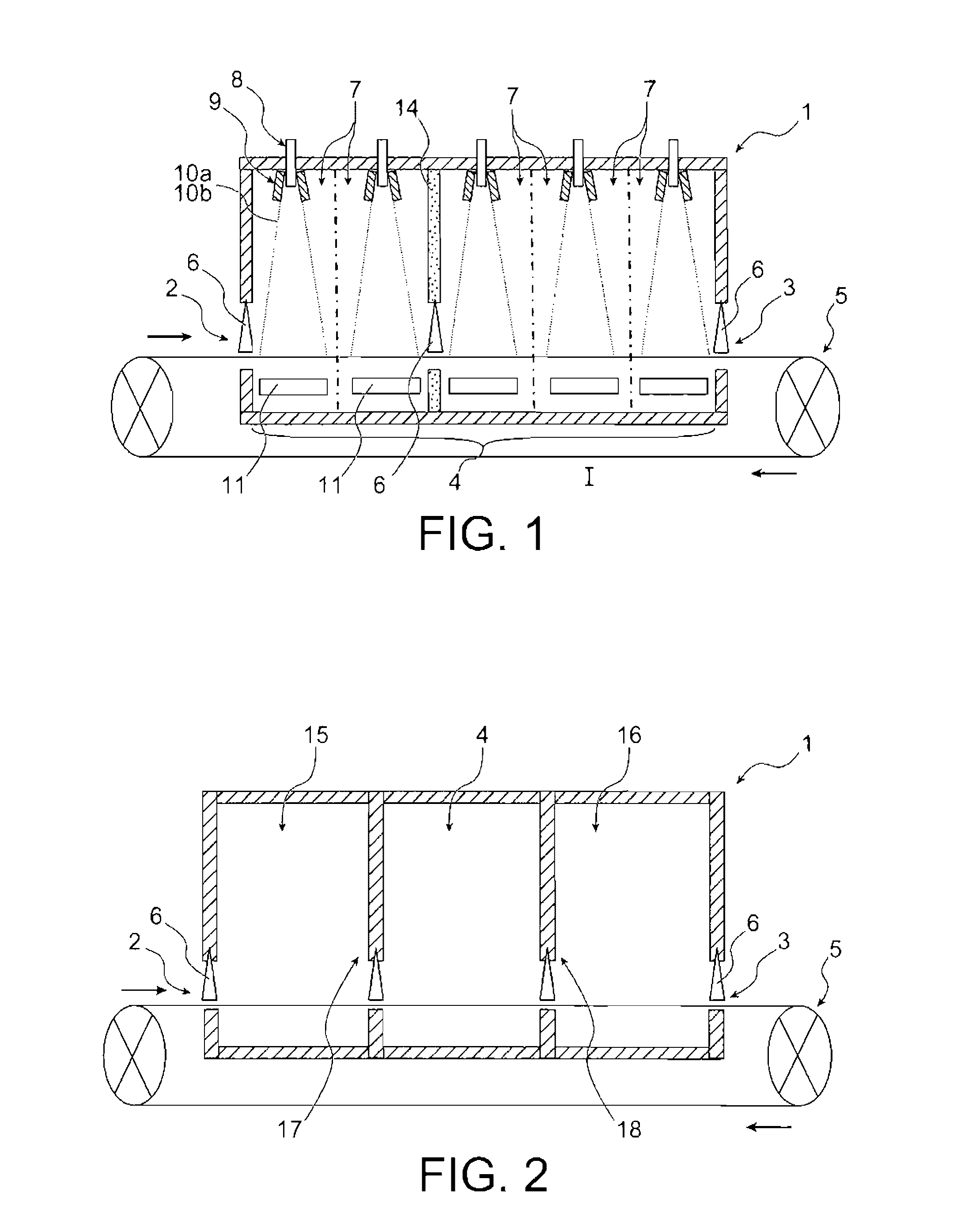
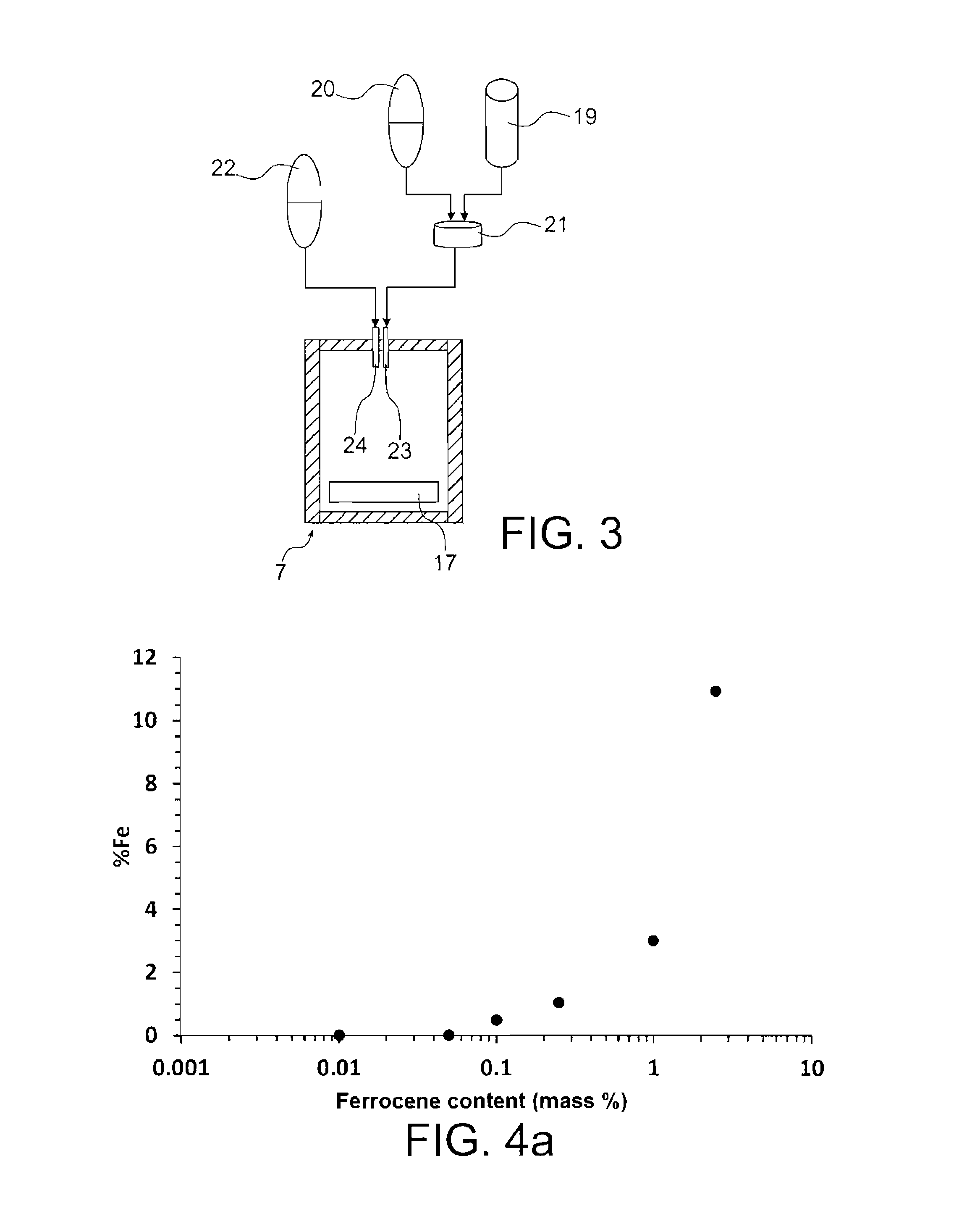
InactiveUS20160289826A1High purityLower iron levelsMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChemical compositionGas phase
The invention relates to a method for continuously manufacturing aligned nanostructures on a running support, which comprises conveying the support through a heated space and synthesising, in this space, aligned nanostructures on the support by catalytic chemical vapour deposition. The heated space is divided into n consecutive zones in the conveying direction of the support (n being an integer ≧2), and the synthesis of the nanostructures results from heating and injection operations, in each of these n zones, of a flux of an aerosol containing a catalytic precursor and a source precursor of the material of the nanostructures to be formed, carried by a carrier gas. The injection operations are made by modifying, in at least two of the n zones, at least one parameter chosen among the flow rate of the carrier gas flux, the chemical composition of the carrier gas, the mass concentration of the catalytic precursor in the catalytic precursor and source precursor mixture. The invention also relates to a device for implementing this method.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Extraction of uranium from wet-process phosphoric acid
ActiveUS20100028226A1Lower iron levelsReduced valencyCobalt ammonia complexesPhotography auxillary processesFiltrationIon exchange
A process for the extraction of uranium compounds from wet-process phosphoric acid includes lowering the iron concentration of the wet-process phosphoric acid and reducing the valency of any remaining ferric iron in the wet-process phosphoric acid to ferrous iron, and then extracting uranium compounds from the wet-process phosphoric acid. The process can include separating a side stream from a feed stream of wet-process phosphoric acid, wherein the side stream has a greater concentration of the uranium compounds than the feed stream by filtration. Extracting uranium compounds from the wet-process phosphoric acid can be by ion exchange process or by solvent extraction.
Owner:URTEK
High purity metallurgical silicon and method for preparing same
InactiveUS20050053539A1Lower iron levelsEasy to operateSiliconFinal product manufactureForming gasNeutral atmosphere
The invention concerns a silicon designed in particular for making solar cells containing a total of impurities ranging between 100 and 400 ppm, a boron content ranging between 0.5 and 3 ppm, a phosphorus / boron content ratio ranging between 1 and 3, and a content of metal elements ranging between 30 and 300 ppm. The invention also concerns a method for making such a silicon from an oxygen- or chorine-refined metallurgical silicon containing at least 500 ppm of metal elements, and comprising: refusion under neutral atmosphere of the refined silicon, in an electric furnace equipped with a hot crucible; transferring the molten silicon, to provide a plasma refining, in an electric furnace equipped with a hot crucible; plasma refining with as plasma-forming gas a mixture of argon and of at least a gas belonging the group consisting of chlorine, fluorine, HCI and HF; casting under controlled atmosphere in an ingot mould wherein is produced segregated solidification.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
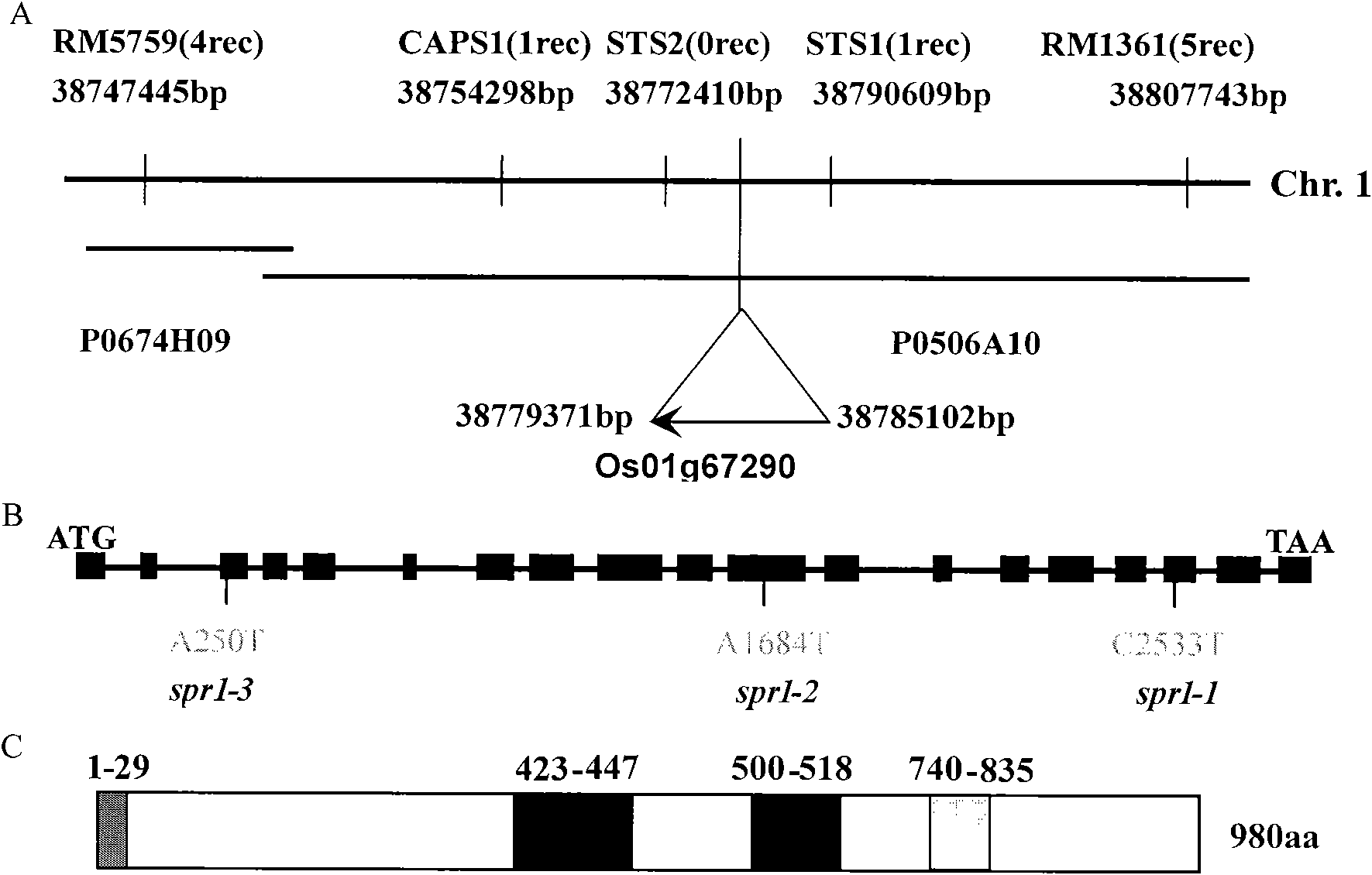
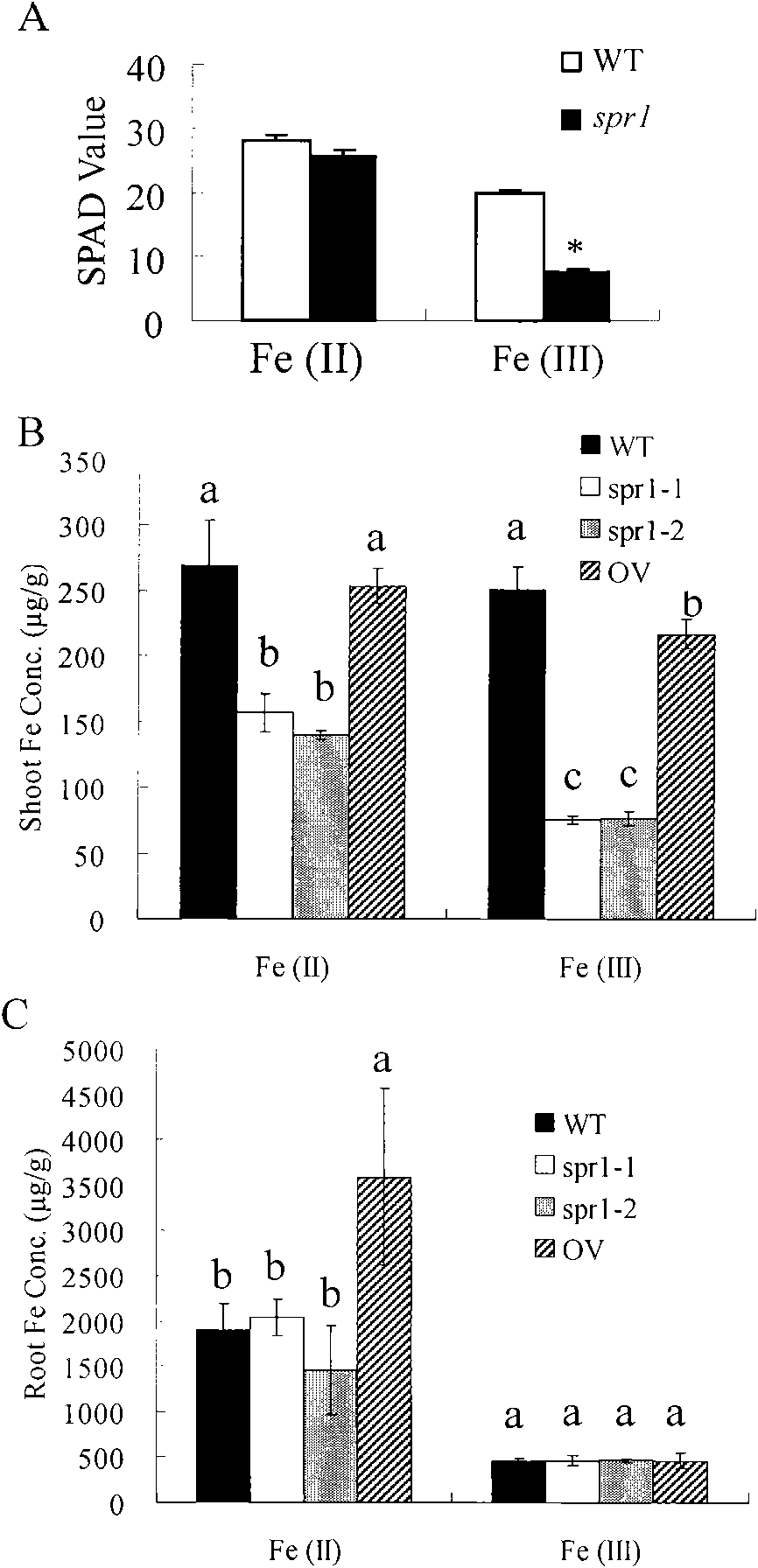
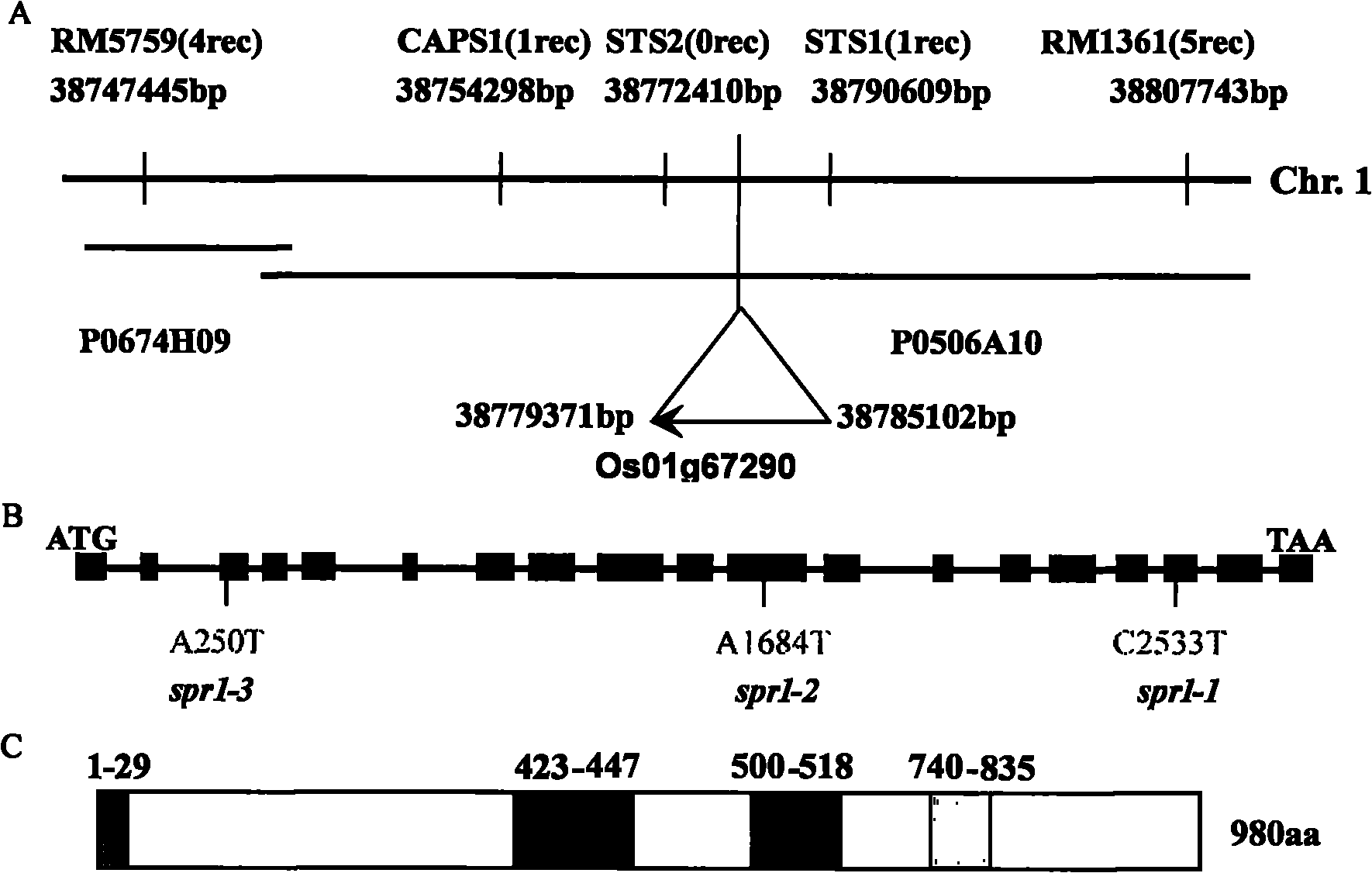
Gene and protein encoded by rice root growth and development control gene OsSPR1
The invention relates to the plant gene engineering field, aiming at providing protein encoded by a rice root growth and development control gene OsSPR1 and a gene for encoding the protein. The protein has an amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:2 and a nucleotide sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1. In the invention, a rice mutant with a short adventitious root and a short branch root is taken as a research material to determine that the gene is involved in regulating and controlling growth and development of the rice root; the functional deletion mutant of the gene shows reduced ferric content of blades, and the ferric content in the root is in accordance with that of wild rice; and recovery of expression of the gene can recover the ferric content in the blades, thus showing that the gene can regulate and control the ferric content in the blades. The invention provides a molecular regulation and control mechanism for rice root growth and development and ferric ion in-vivo transport, and provides a foundation for regulating and controlling a rice root structure and the ferric content by a genetic engineering method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Glass plate and process for its production
ActiveUS20130203584A1Lower iron levelsHigh TeGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusGlass sheetMaterials science
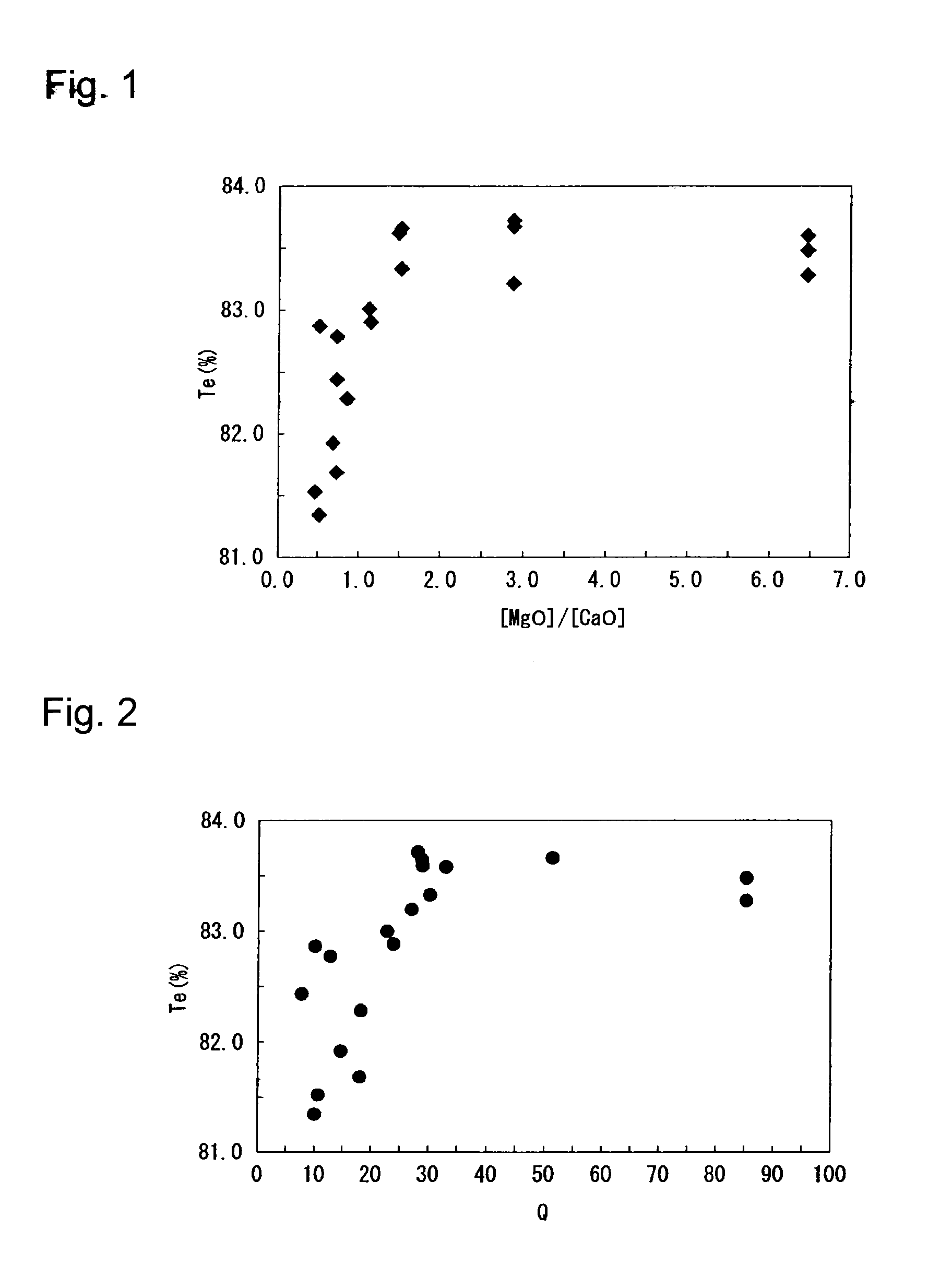
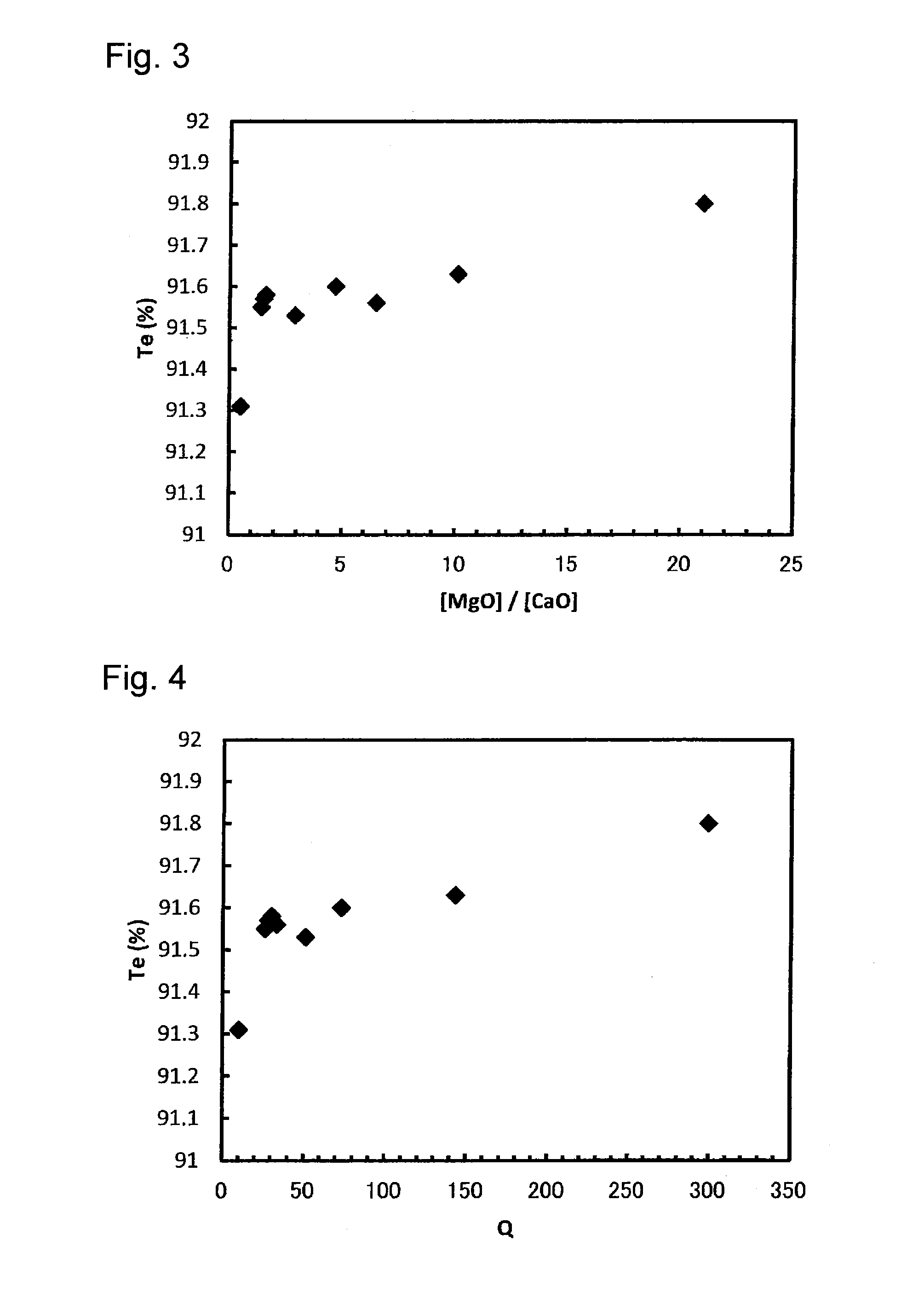
A glass plate made of soda lime silica glass containing at least MgO, CaO, Na2O and Al2O3 produced by a float process or a downdraw method, wherein [MgO] is at least 4.5%, [MgO] / [CaO] is larger than 1, and Q=([MgO] / [CaO])×([CaO]+[Na2O]−[Al2O3]) is at least 20, wherein [MgO] is the content of MgO, [CaO] is the content of CaO, [Na2O] is the content of Na2O, and [Al2O3] is the content of Al2O3 (each being as represented by mass percentage based on oxide) and a process for the glass plate.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Ultralow-temperature welded alloy steel and production method thereof
Owner:JIANGSU TIANYE ALLOY MATERIAL
Method for collecting nickel and cobalt from laterite-nickel ore lixivium by using sulfide precipitation
InactiveCN101302584AUniform natureUniform precipitationProcess efficiency improvementHydrogenSulfide
The invention provides a method for enriching nickel and cobalt from lateritic nickel ore lixivium. The method comprises the steps of concentration and pH value adjustment of pickle liquor, precipitation through adopting composite vulcanizing agent, solid-liquid separation, washing and filtrate processing. The composite vulcanizing agent consists of vulcanizing agent A containing hydrogen ions and vulcanizing agent B without the hydrogen ions. The method uses 1 to 95 percent of the vulcanizing agent A and 5 to 99 percent of the vulcanizing agent B in the composite vulcanizing agent. The pH value of the pickle liquor can be maintained or changed slowly through adjusting the pH value of the pickle liquor of the lateritic nickel ore to be a set value and slowly adding the composite vulcanizing agent, thereby acquiring a sulphide product enriched with nickel-cobalt. The mass ratio of nickel and the vulcanizing agent is between 1 to 1.6 and 5. A buffer system formed by the vulcanizing agent A and the vulcanizing agent B in the invention adjusts and controls changes of the pH value during the process of sulphuration precipitation, prevents iron chloride and magnesium chloride from being hydrolyzed into hydroxide and entering a sulphide, and improves the separation rate of nickel and cobalt and the separation rate of iron and magnesium; the acquired precipitation of the sulphide can be easily filtered; and the dosage of the vulcanizing agent is small.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
High-performance stainless steel surfacing nickel-based special welding wire and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108406164AHigh tensile strengthImprove intergranular corrosion resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaRare-earth elementCrack resistance
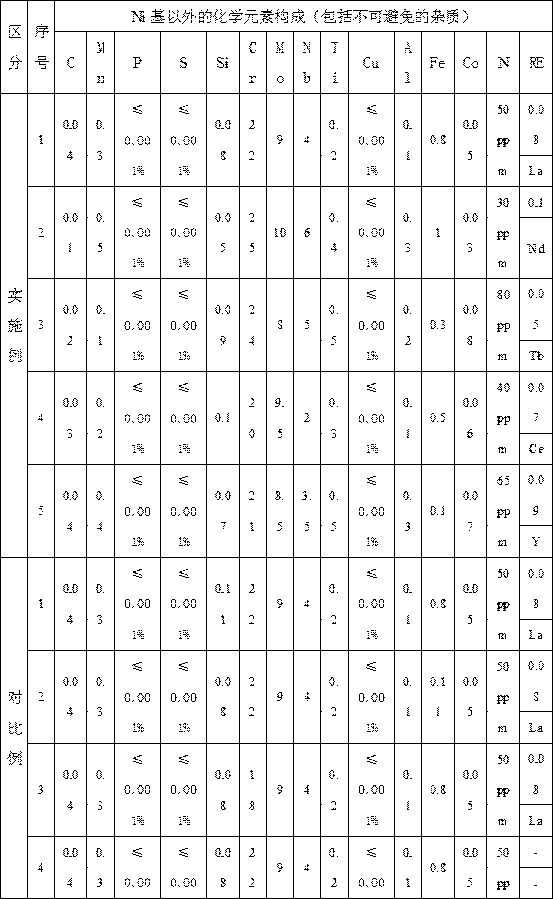
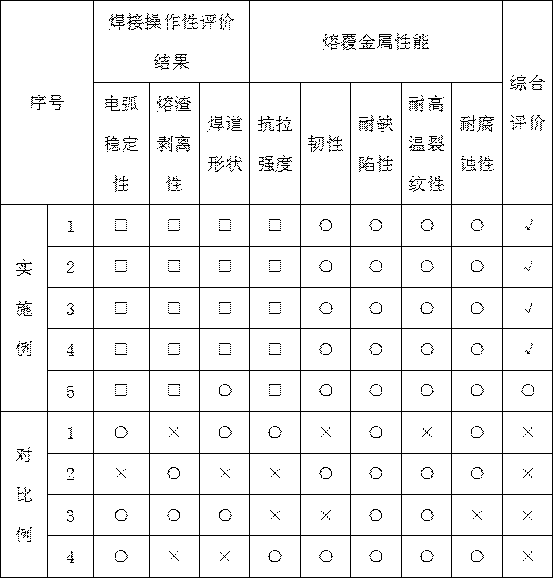
The invention belongs to the field of welding materials and particularly relates to a high-performance stainless steel surfacing nickel-based special welding wire and a preparation method thereof. Thewelding wire comprises chemical elements including, by mass, not greater than 0.04% of C, 0.1-0.5% of Mn, not greater than 0.001% of P, not greater than 0.001% of S, 0.05-0.1% of Si, 20-25% of Cr, 8-12% of Mo, 2-6% of Nb, 0.2-0.5% of Ti, not greater than 0.001% of Cu, 0.1-0.3% of Al, not greater than 1% of Fe, 0.03-0.08% of Co, 0.05-0.1% of the rare earth element RE, 30-80 ppm of N and the balance Ni and inevitable impurity elements. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) vacuum electric-furnace smelting; (2) VOD external refining; (3) horizontal continuous casting; (4) tandem rolling; and (5) tandem drawing. The welding wire provided by the invention has the good properties of active gas resistance and reducing acid medium corrosion resistance, the electric arc stability and slag stripping performance are excellent during welding, and welding metal with high strength, good tenacity, flaw resistance, high temperature cracking resistance and corrosion resistance is obtained;and the preparation technology is simple, the raw material and manufacturing cost is low, environmental friendliness is achieved, no pollution is generated, and the welding wire and the preparation method are suitable for industrial volume production and remarkable in economic benefit.
Owner:DANYANG HUALONG SUPERIOR STEEL
Thermomechanical processing of aluminum alloys
ActiveUS8163113B2Good molding effectNot adversely affect formabilitySolid solutionUltimate tensile strength
A cast aluminum alloy containing up to about 0.35% by weight chromium is heated to a first elevated temperature to homogenize the casting and dissolve the chromium content in an aluminum-based matrix phase. The alloy is then heated at a lower elevated temperature to cause the precipitation of a portion of the chromium as an aluminum-containing and chromium-containing intermetallic compound. A suitable amount of chromium is retained in solid solution in aluminum. Thus, the concentration of dissolved chromium in an aluminum alloy may be controlled to fall within specified ranges which result in improvements in both the strength and ductility of the alloy. Impurity amounts of iron may also be precipitated as intermetallic particles from the aluminum matrix to enhance the ductility of the aluminum-based alloy.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
Method for preparing high-purity low-chlorine electroplating-grade cupric oxide
InactiveCN103101957AAvoid bringing inGuaranteed purityEnergy inputCopper oxides/halidesDecompositionCarbonization
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity low-chlorine electroplating-grade cupric oxide. According to the method, copper, liquid ammonia and high-purity carbon dioxide are taken as raw materials, stronger ammonia water is prepared firstly, carbonated ammonia water is obtained through introducing the high-purity carbon dioxide into the stronger ammonia water and controlling carbonization degree, the carbonated ammonia water reacts with the copper under certain air pressure so as to prepare copper-ammonia complexation liquid, the copper-ammonia complexation liquid is then subjected to heating, ammonia distilling, separating, washing, drying and sieving so as to prepare high-purity heavy basic copper carbonate, and the heavy basic copper carbonate is then subjected to heating calcination and decomposition, thereby preparing the high-purity low-chlorine electroplating-grade cupric oxide. According to the method, the carbon dioxide is directly used as a raw material, so that the problems of the traditional method that impurities, such as heavy metal ions and chloride ions, are introduced by raw materials used in the production of basic copper carbonate are solved, the rate of reaction is increased, the production cycle is shortened, the production efficiency is greatly increased, and products are low in impurity content, high in purity, high in activity and wider in application; and meanwhile, the method is high in yield, low in energy consumption, and low in cost and hardly causes pollution.
Owner:TAIXING SMELTING PLANT
Laminated glass and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN109572109ALess impuritiesLower iron levelsSynthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsTransmittanceHigh pressure
The invention discloses laminated glass, comprising an upper super-white coated glass layer, SGP (SentryGlas Plus) film and a lower super-white coated glass layer. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the laminated glass, comprising the steps of providing a raw sheet, cutting, polishing edge, washing, tempering, coating, washing, laminating, pressing primarily, vacuumizing, heatingand pressurizing in a high-pressure kettle, holding the temperature and pressure in the high-pressure kettle, lowering the temperature and pressure in the high-pressure kettle, removing from the kettle, trimming and dressing, finishing, packaging, and allowing the finished glass to leave a factory. The heating mode is modified to a mode with a heating tube and a convection fan, so that heating uniformity of glass is improved, glass heating efficiency is improved, SGP laminated glass has better visible light transmittance and strength, production time of the SGP laminated glass is shortened, and energy consumption is lowered.
Owner:JIANGYIN MUXIANG ENERGY SAVING DECORATION MATER
Online repair method for local damage of aluminum electrolytic cell cathode
The invention provides an online repair method for local damage of an aluminum electrolytic cell cathode. When it is monitored that the content of iron in electrolytic cell primary molten aluminum rises abnormally, after the damaged portion of the electrolytic cell cathode is confirmed through the monitoring of the cell shell temperature, monitoring of the cathode square steel temperature and electrode extraction and furnace bottom groping of an electrolytic cell, the damaged portion of the cathode of the electrolytic cell is repaired on line. Compared with the prior art, the online repair method has the following beneficial effects that normal operation of the electrolytic cell is not affected; mixed materials used in the method are common or spare materials in electrolysis production, and the materials are obtained conveniently and fast without being specially purchased; the content of the iron in the repaired electrolytic cell primary molten aluminum can be decreased rapidly to be within the required range of aluminum ingot remelting; and further damage of the repaired portion can be inhibited through process adjustment and control over electrode change work.
Owner:云南云铝泽鑫铝业有限公司
Novel boron compound-containing aluminium alloy deironing flux
The invention provides aluminium alloy deironing flux, which is characterized by comprising the following components by weight: 10-20% of sodium chloride (NaCl), 10-20% of potassium chloride (KCl), 10-20% of cryolite (Na3AlF6), 10-20% of sodium fluoride (NaF), 30-40% of boric acid (H3BO3) and / or boron carbide (B4C). The purifying flux provided by the invention has the advantages of continuous deironing, convenient operation and the like, and can effectively remove iron element in aluminium melt. When in use, the boron compounds in the flux react with the impurity of iron element to form high-melting point boron iron compounds which are captured by slag and mixed with the slag, so as to effectively reduce the iron content in aluminium alloy. The flux is suitable for melting requirements of aluminium alloy, has excellent viscosity and surface tension, and is good in separability from aluminium. The flux is good in chemical stability and less in harmful gas amount, and meets industrial hygienic standards and exhaust gas discharge standards. In addition, the flux is convenient to add, simple in operation process, and low in cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGCAI ENG DETECTION CO LTD
Feldspar quarry beneficiation process
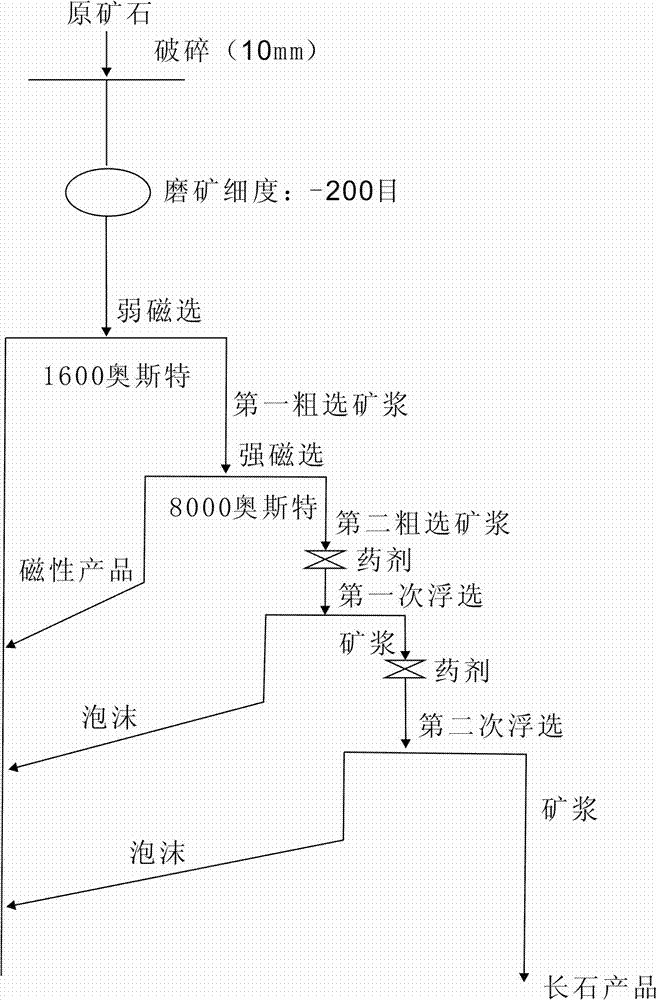
The invention discloses a feldspar quarry beneficiation process which includes conducting breaking and grinding on feldspar quarry raw ore, adopting SLon magnetic separators to conduct strong magnetic separation and weak magnetic separation, then conducting secondary floatation to obtain feldspar concentrate with the content of Fe2O3 smaller than 0.1%. The beneficiation process is characterized in that under the condition that the raw ore is ground to certain fineness, a weak SLon magnetic separator and a strong SLon magnetic separator are sequentially adopted to conduct magnetic separation, then floatation is conducted under the specific process condition to enable the content of iron in the feldspar quarry raw ore to be reduced to below 0.1% to obtain good feldspar quarry and reach the use standard in the glass industry. The process turns waste into wealth, adopts the mode that magnetic separation is conducted first and then floatation is conducted, the content of medicament added later is greatly reduced, the pollution is small, and the cost is lower.
Owner:四川南江新兴矿业有限公司
Method for preparing double-acid ferro-aluminum flocculating agent
InactiveCN101691252ALow priceEase of industrial productionWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationLiquid productSocial benefits
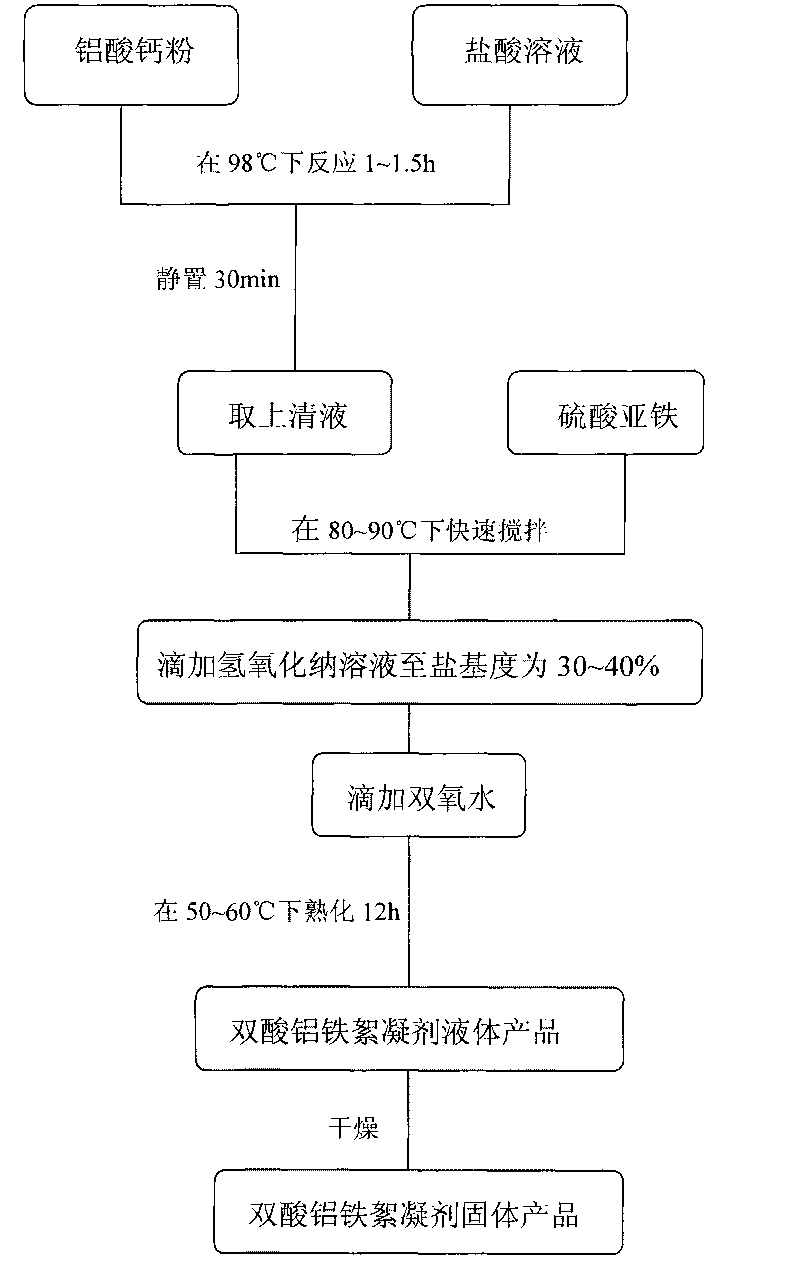
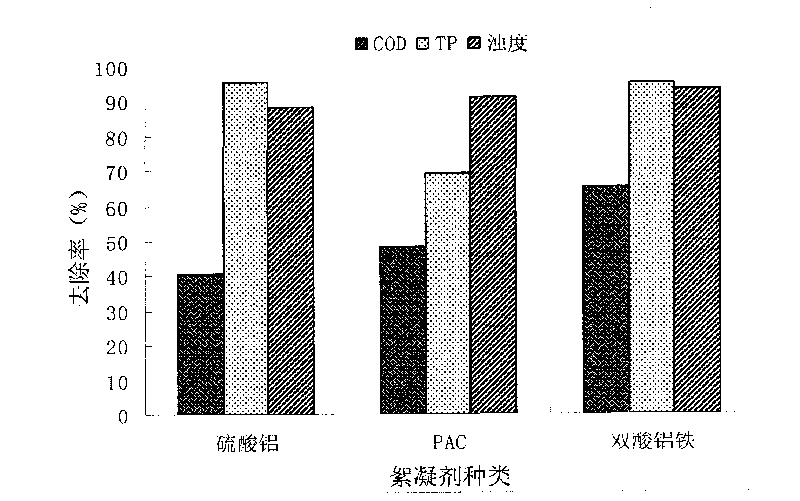
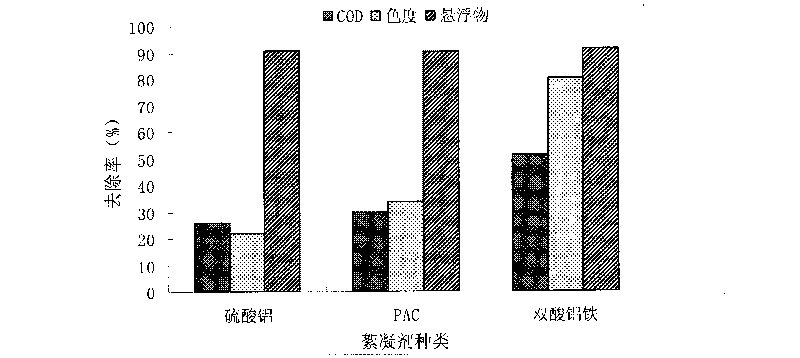
The invention discloses a method for preparing a double-acid ferro-aluminum flocculating agent, which relates to a process for preparing the double-acid ferro-aluminum flocculating agent by using calcium aluminate powder. The method comprises the following steps of: taking the calcium aluminate powder of which the particle size is smaller than 60 meshes, putting the calcium aluminate powder into a hydrochloric acid solution in a part mass ratio of the hydrochloric acid solution to the calcium aluminate powder of 3-5:1, reacting the two materials at a temperature of 98 DEG C for 1 to 1.5 hours, standing the mixture for 30 minutes, and then taking a supernatant to obtain AlCl3 liquid; adding ferrous sulfate to the mixture in a part mass ratio of the calcium aluminate powder to the ferrous sulfate of 9-11:1 at a temperature of between 80 and 90 DEG C, dropwise adding a sodium hydroxide solution of which the concentration is 0.5 mol / L into the mixture after 15 minutes, dropping oxyful into the mixture in a part mass ratio of the ferrous sulfate to the oxyful of 1:1-1.5 when the basicity is 30 to 40 percent, stirring the mixture continuously for 15 to 20 minutes, and then curing the mixture at a temperature of between 50 and 60 DEG C for 12 hours to obtain a liquid product of the double-acid ferro-aluminum flocculating agent; and drying the liquid product of the double-acid ferro-aluminum flocculating agent to obtain a double-acid ferro-aluminum solid product. Tests show that in the solid product, Al2O3 is over 30 percent, the total iron is over 1 percent, the insoluble substances is less than 1 percent, and other indexes accord with the national standards. The method has a simple process and a low cost, and the prepared product has a good coagulation effect and high economic and social benefits.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com