Patents
Literature
973 results about "Ferric ion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This means that ferric iron needs to share three electrons with an oxygen molecule to make the ion neutral, while ferrous iron only needs two more electrons. With the addition of oxygen, the ferrous ion can easily become a ferric ion.
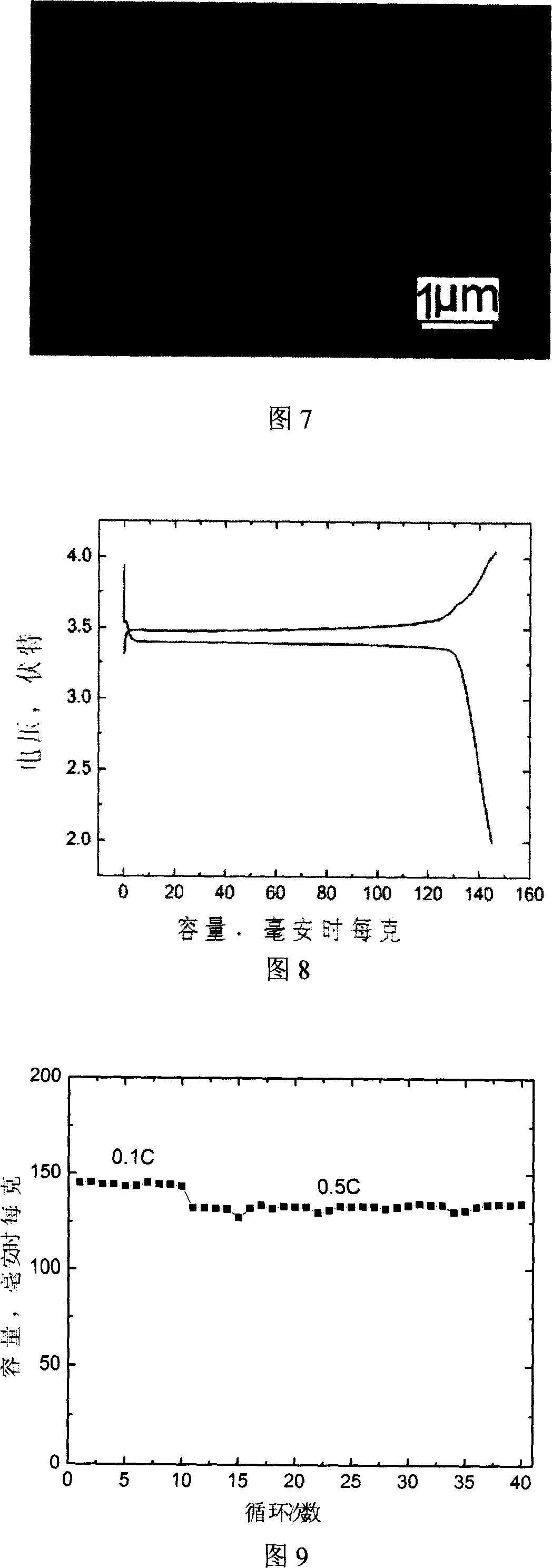
Particle appearance regulatory lithium iron phosphate preparation method
ActiveCN101007630AGood for solid phase diffusionUniform size distributionCell electrodesPhosphorus compoundsLithium iron phosphatePhosphate ion
The invention discloses a modulating method of LiFePO4 particle shape, which comprises the following steps: blending one or more composition with lithium ion, ferric ion and phosphate radical ion; adding solvent and certain quantity of crystal growing inhibitor; proceeding solvent heat reaction under certain temperature; washing; filtering; drying; sintering to improve crystallizing property; obtaining the product with regular shape and size.
Owner:QINGHAI TAIFENG XIANXING LITHIUM ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Process for producing carbon coated iron lithium phosphate
InactiveCN101172599AElectrode manufacturing processesPhosphorus compoundsShortest distancePhosphate ion
The invention relates to a preparation method of lithium iron phosphate for the carbon cladding of a lithium ion battery. The prior lithium iron phosphate preparation technical art is complex, and has high cost. The invention has the synthetic process that: ferric oxide, phosphoric acid, simple organics and doped element compound are mixed and dried, the mol ratio of phosphate radical ion, ferric ion and doped element ion is 1:y:z, wherein, y is larger than or equal to 0.95 and smaller than or equal to 1, and y plus z is equal to 1; the mixture is added with lithium source compound, added with water to be mixed and dried, the mol ratio of lithium ion and phosphate radical ion is x:1, and x is larger than or equal to 0.95 and smaller than or equal to 1.05; the mixture which reacts for 2 to 20 hours under 500 to 800 DEG C is cooled in a furnace. The invention finally produces the precursor uniformly mixed with superfine crystal grain, and during the subsequent high temperature solid phase reaction, the end product lithium iron phosphate can be produced through shorter distance diffuseness of atoms. The end product has high purity, the crystallisation is good, the capacity is high, and the cycle stability is good.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
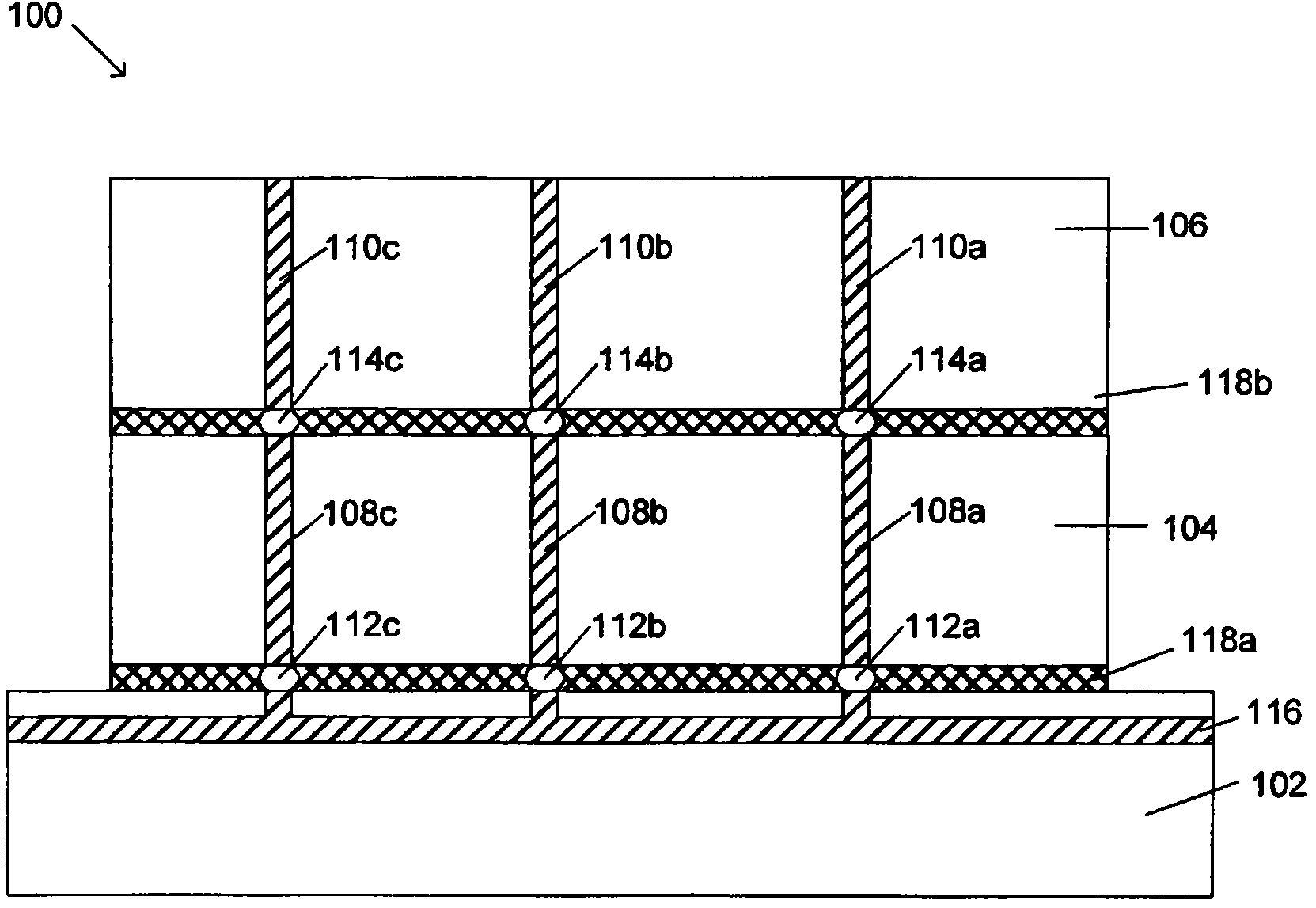
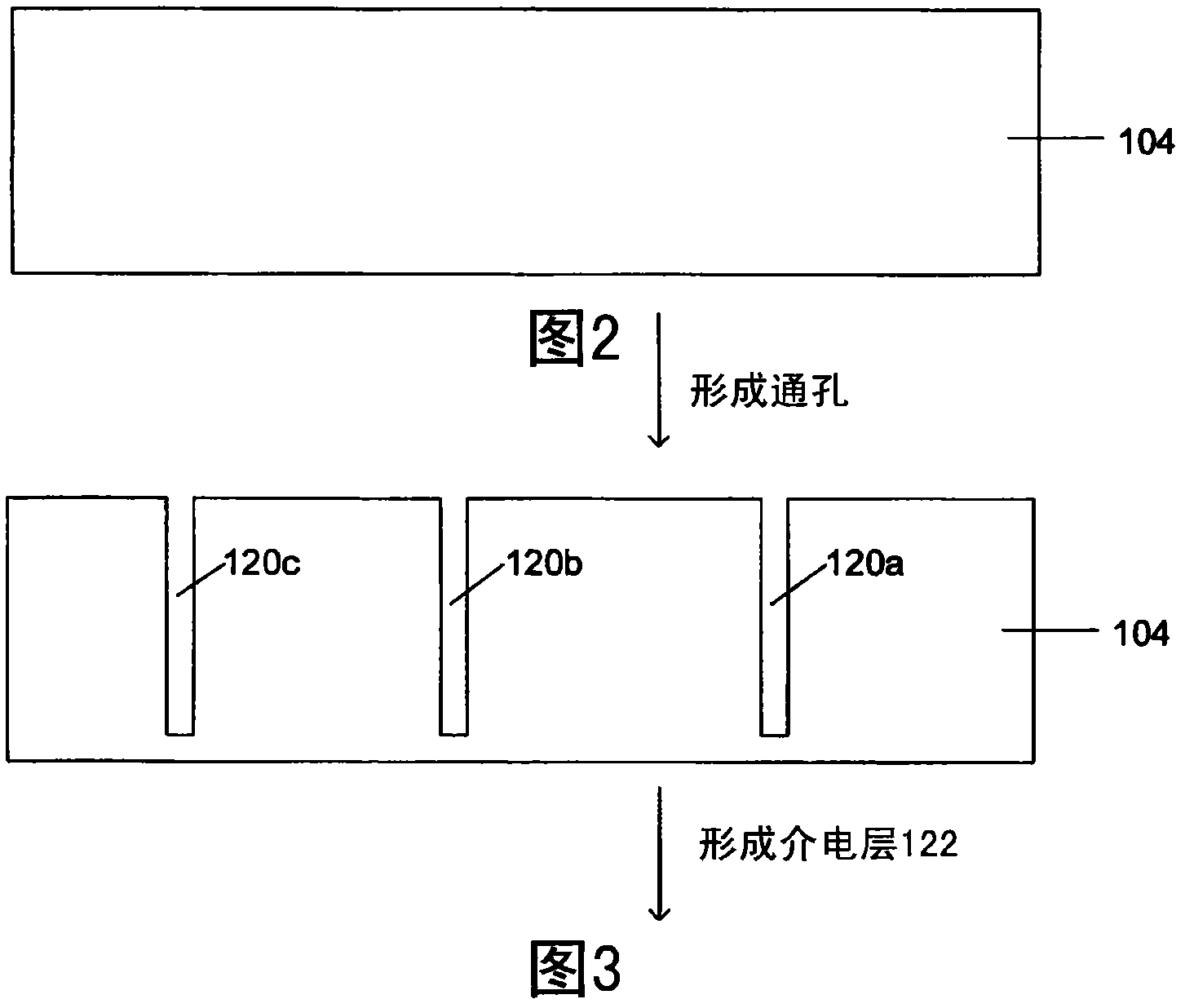
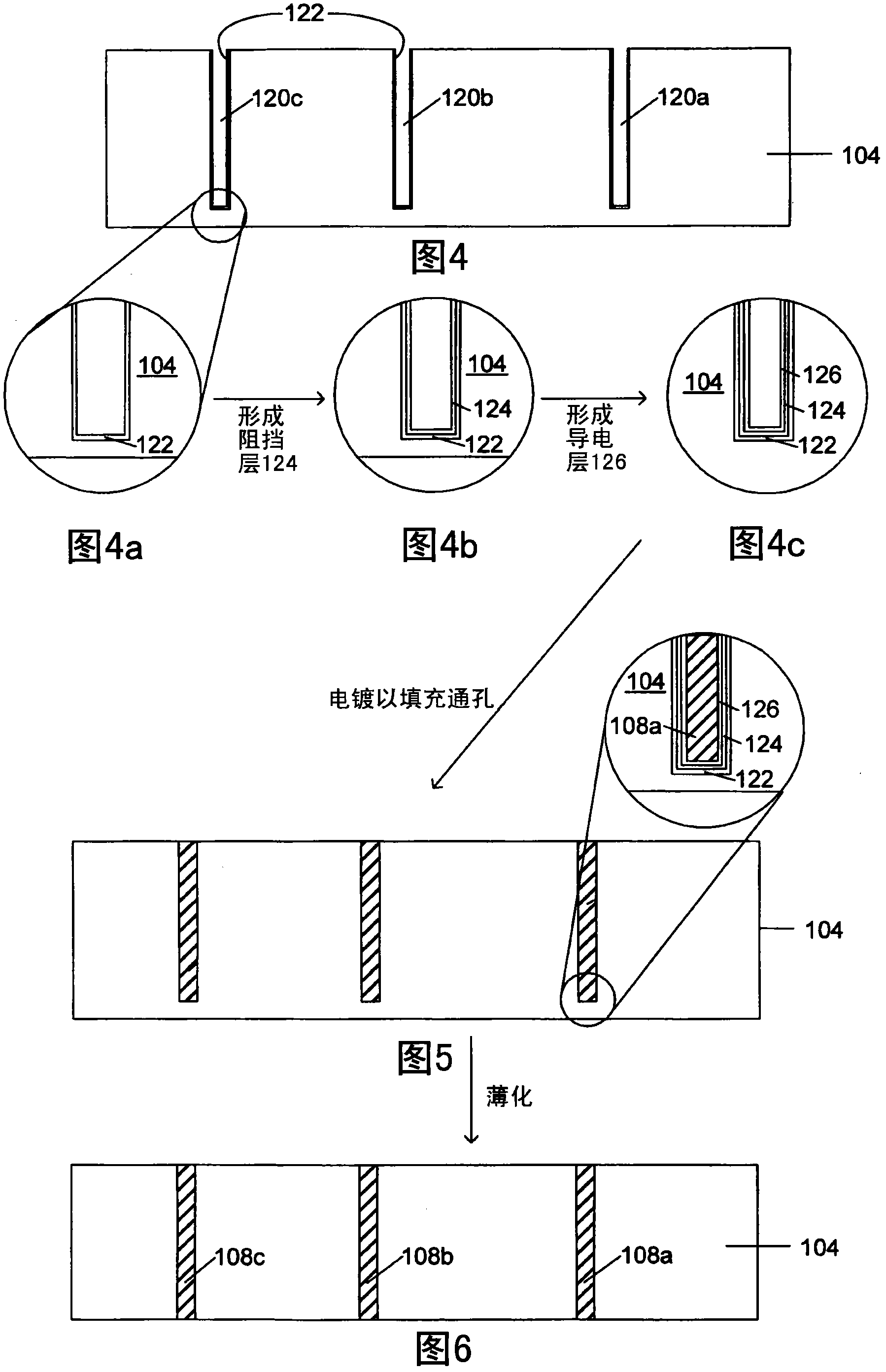
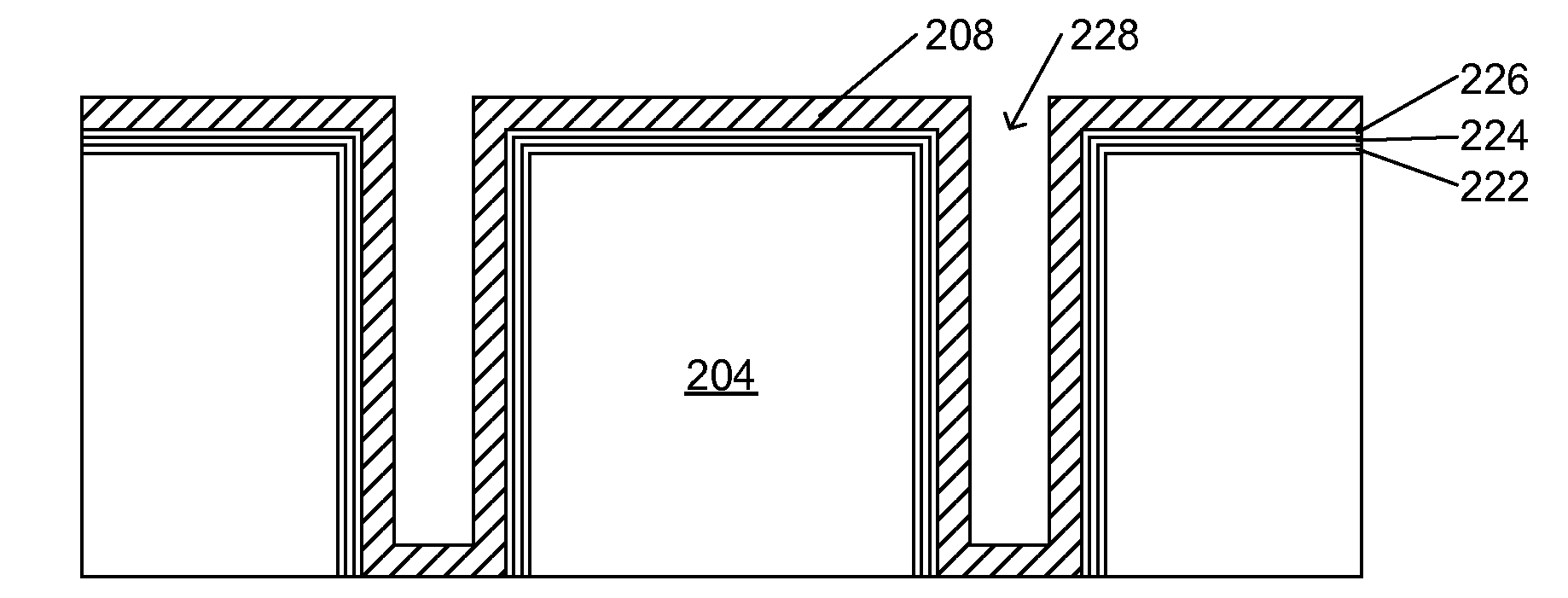
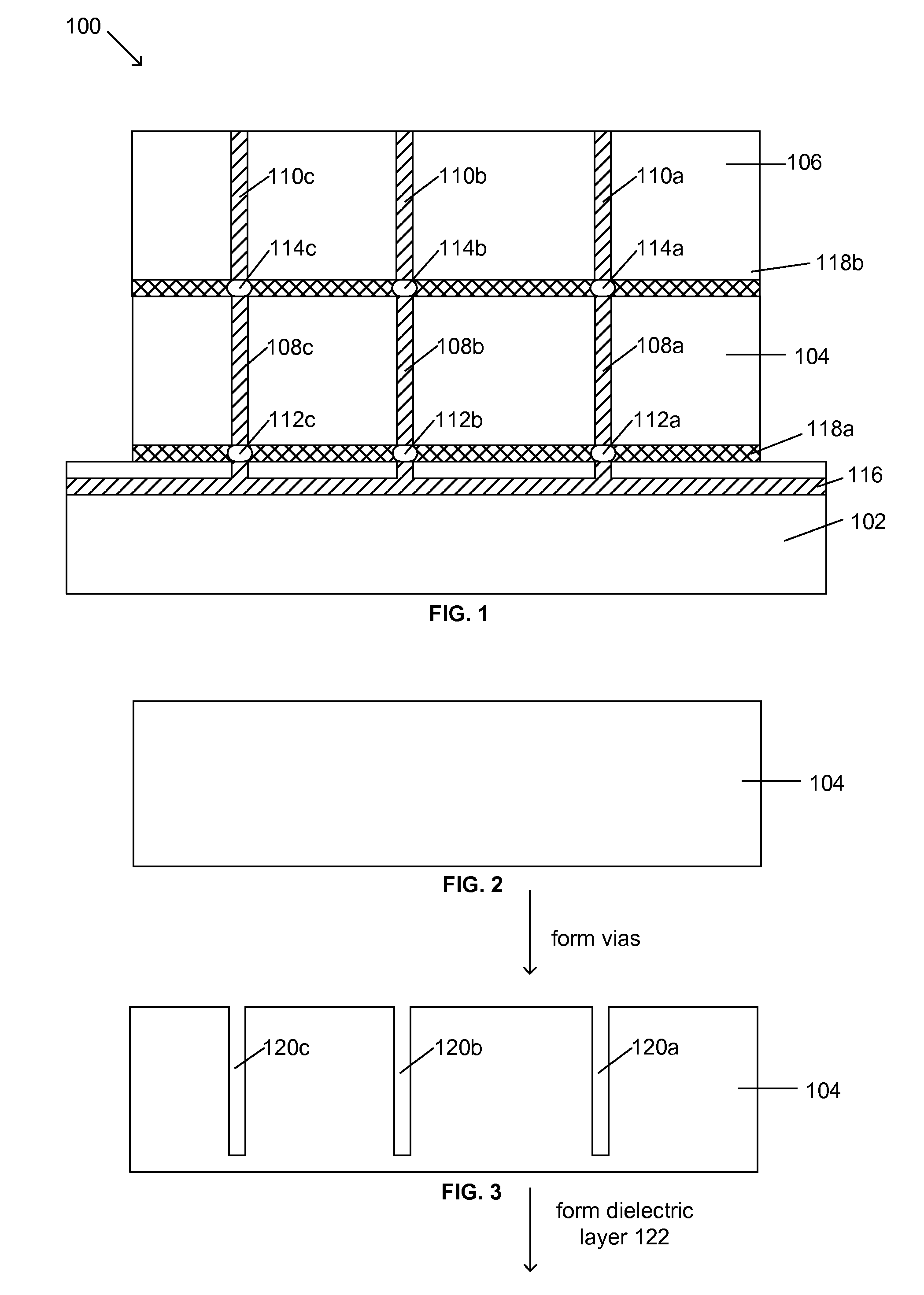
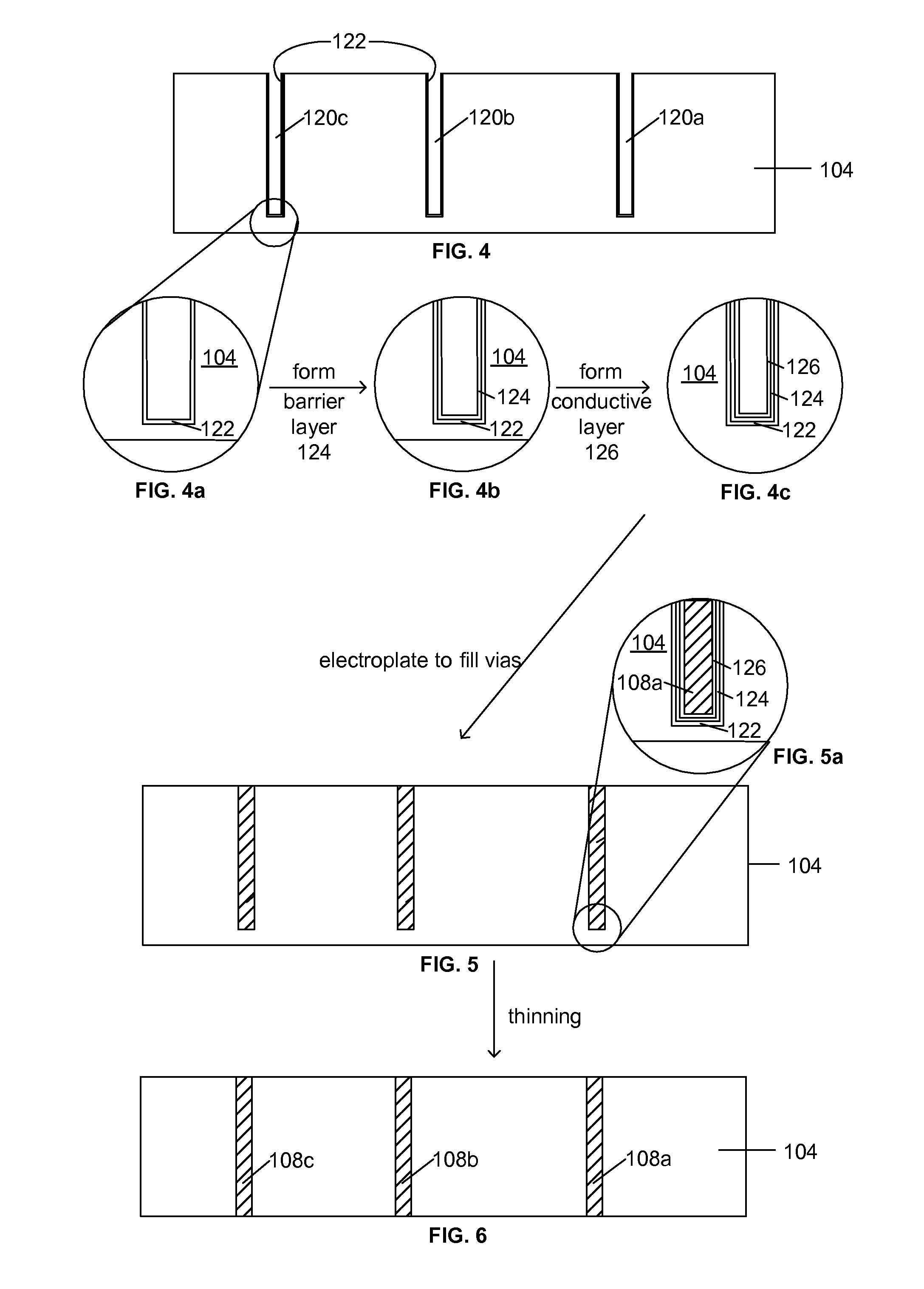
Process for electrodeposition of copper chip to chip, chip to wafer and wafer to wafer interconnects in through-silicon vias (TSV)
InactiveCN102318041AAvoids disadvantages of known processesAvoid disadvantagesCellsSolid-state devicesElectrolysisCopper plating
A process of electrodepositing high purity copper in a via in a silicon substrate to form a through-silicon-via (TSV), including immersing the silicon substrate into an electrolytic bath in an electrolytic copper plating system in which the electrolytic bath includes an acid, a source of copper ions, a source of ferrous and / or ferric ions, and at least one additive for controlling physical-mechanical properties of deposited copper; and applying an electrical voltage for a time sufficient to electrodeposit high purity copper to form a TSV, in which a Fe+2 / Fe+3 redox system is established in the bath to provide additional copper ions to be electrodeposited by dissolving copper ions from a source of copper metal.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Process for electrodeposition of copper chip to chip, chip to wafer and wafer to wafer interconnects in through-silicon vias (TSV)
InactiveUS20100206737A1Maximizes electrodeposited fillingStress minimizationCellsSolid-state devicesElectrolysisCopper plating
A process of electrodepositing high purity copper in a via in a silicon substrate to form a through-silicon-via (TSV), including immersing the silicon substrate into an electrolytic bath in an electrolytic copper plating system in which the electrolytic bath includes an acid, a source of copper ions, a source of ferrous and / or ferric ions, and at least one additive for controlling physical-mechanical properties of deposited copper; and applying an electrical voltage for a time sufficient to electrodeposit high purity copper to form a TSV, in which a Fe+2 / Fe+3 redox system is established in the bath to provide additional copper ions to be electrodeposited by dissolving copper ions from a source of copper metal.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Acid fracturing process of oil gas well mining temperature control various mucic acid
ActiveCN101353958AReduce fluid lossEasy to form non-uniform etchingFluid removalDrilling compositionAcid etchingMucic acid
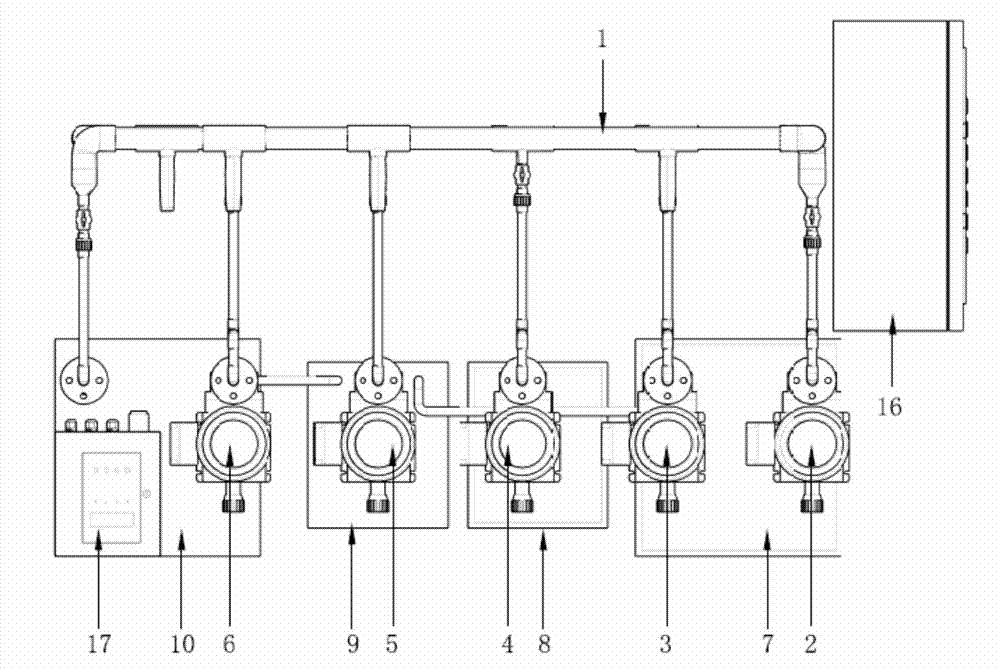
The invention relates to an acid fracturing method of a temperature-control and variable-viscosity acid in the exploitation of an oil-gas well, which comprises the steps that: a common chlorohydric acid pickling process is firstly used for removing the pollution of an embrasure; then, the temperature-control and variable-viscosity acid fracturing process, or an ahead-fluid temperature-control and variable-viscosity acid fracturing process, or a temperature-control and variable-viscosity acid fracturing enclosed acidizing process, or an ahead-fluid temperature-control and variable-viscosity acid fracturing enclosed acidizing process is adopted; the weight ratio of the components of the temperature-control and variable-viscosity acid are as follows: 100 portions of basic acid solution, 0.5 portion to 1.5 portions of the main agent of the temperature-control and variable-viscosity acid, 1 portion to 3 portions of a corrosion inhibitor of the temperature-control and variable-viscosity acid, 0.5 portion to 1 portion of an emulsion breaker, 0.5 portion to 1 portion of a ferric ion stabilizer and 0.5 portion to 1 portion of a high efficient discharge aiding agent; 2-percent KCL clear water is used for displacing the temperature-control and variable-viscosity acid into the stratum. The temperature-control and variable-viscosity acid is easily prepared on site, with low friction drag and strong pumpability, thereby being capable of being applied to high-discharge construction; under the high temperature condition of a storing layer, both the fresh acid and the residue acid have high viscosity, thus increasing the length of acid-etching cracks. After the construction is finished, the viscosity of the residue acid is reduced, which is beneficial to the back discharge of the residue acid.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
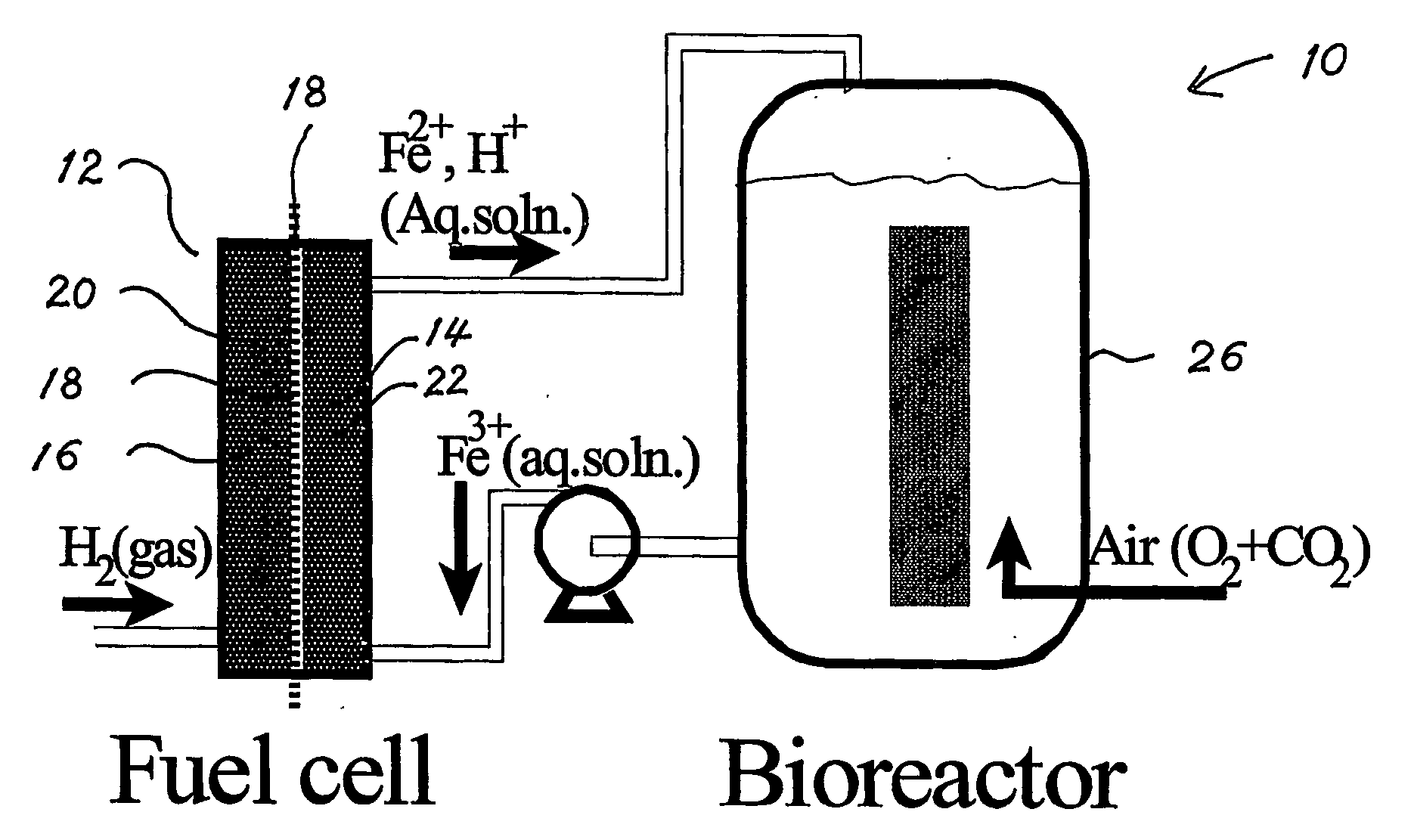
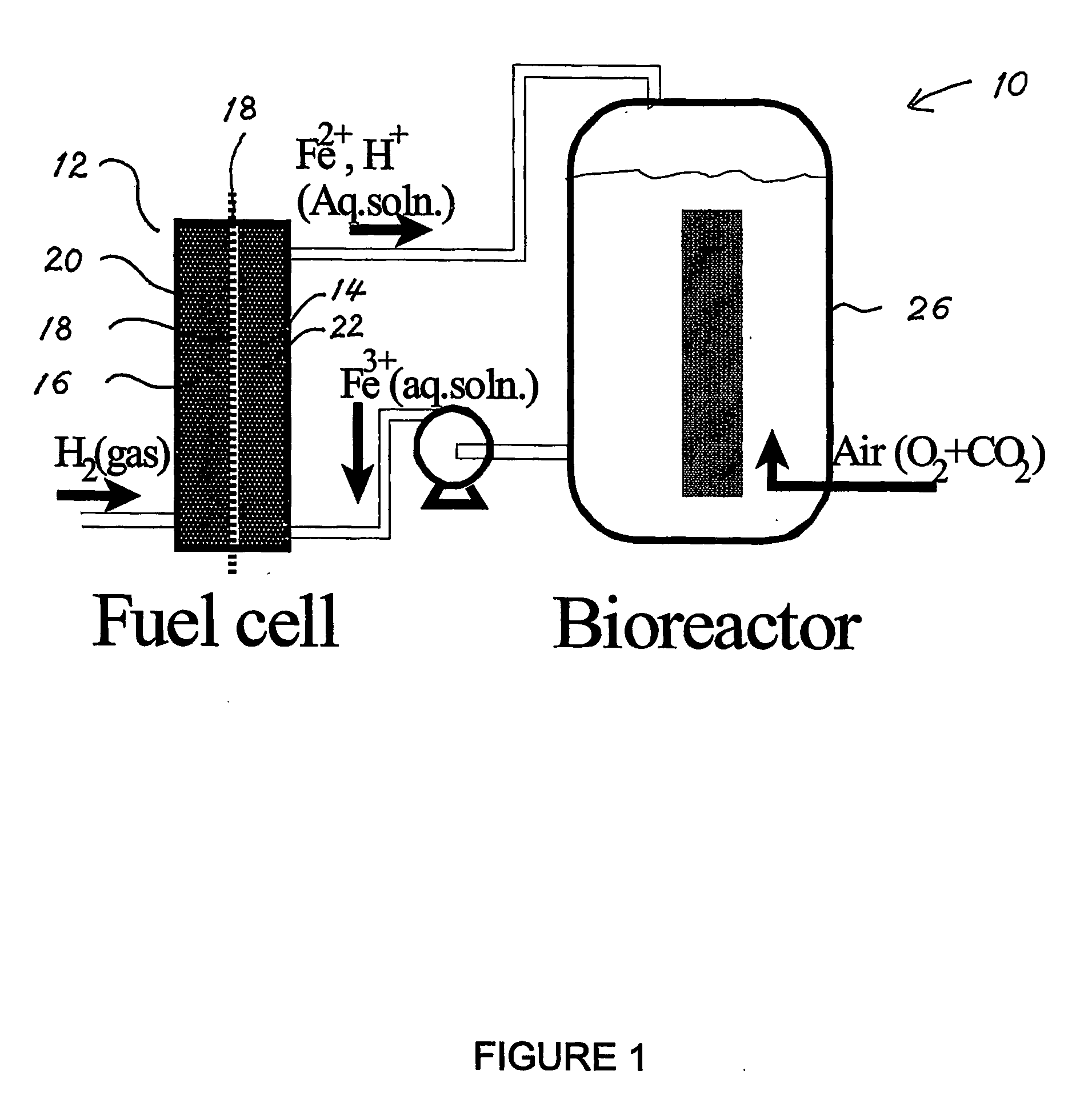
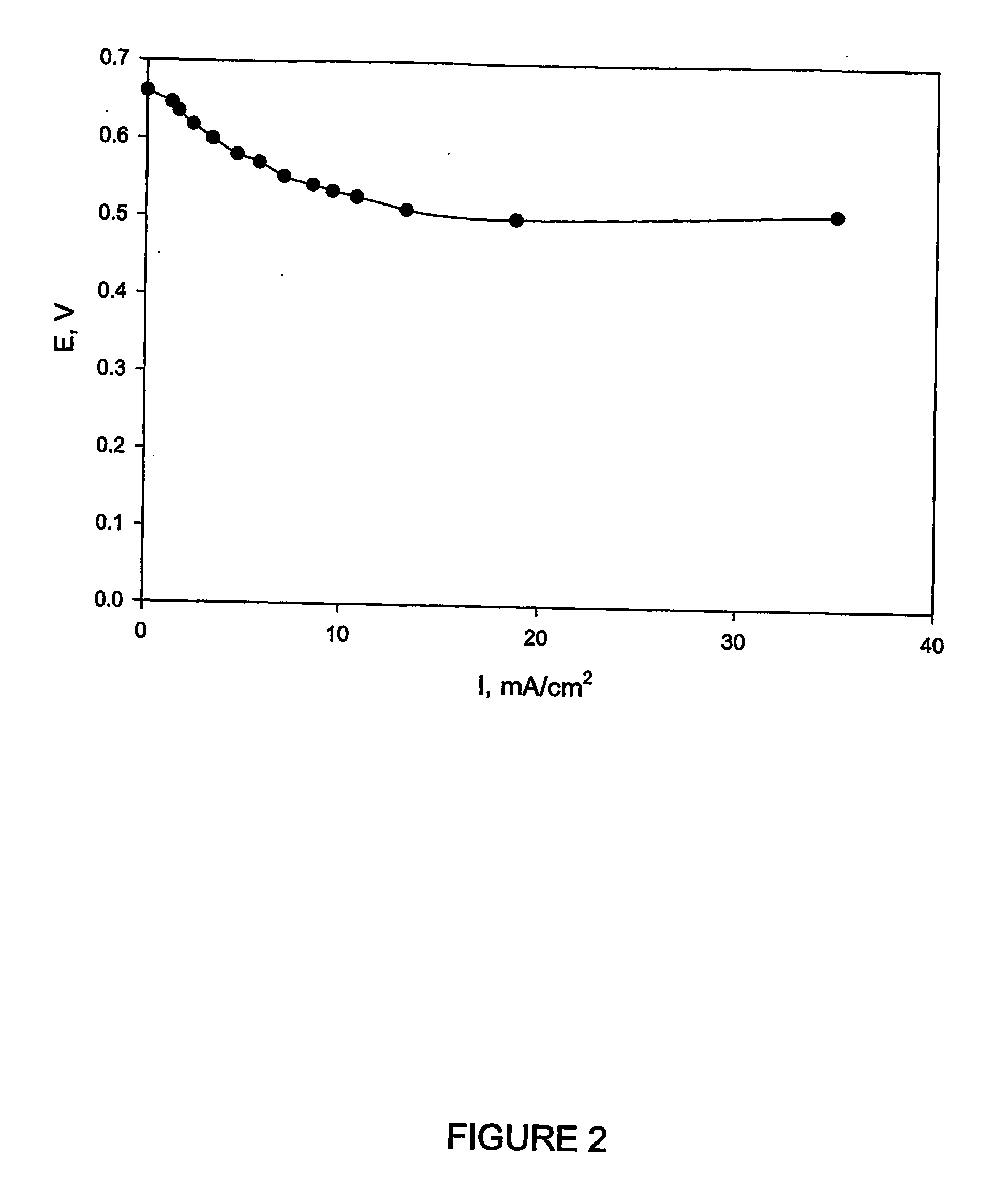
Biofuel cell
InactiveUS20060251959A1Promote growthElectrolyte holding meansRegenerative fuel cellsMicroorganismHydrogen
The present invention discloses a new type of biofuel cell, based on the microbial regeneration of the oxidant, ferric ions. The bio-fuel cell is based on the cathodic reduction of ferric to ferrous ions, coupled with the microbial regeneration of ferric ions by the oxidation of ferrous ions, with fuel (such as hydrogen) oxidation on the anode. The microbial regeneration of ferric ions is achieved by chemolithotrophic microorganisms such as Acidithiobacillus ferroxidans. Electrical generation is coupled with the consumption of carbon dioxide from atmosphere and its transformation into microbial cells, which can be used as a single-cell protein.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Formula and production method for preparing deep yellow wheat straw dye
InactiveCN103554972AWide variety of sourcesAvoid harmReed/straw treatmentNatural dyesSennaOrganic chemistry
The invention discloses a formula and a production method for preparing a deep yellow wheat straw dye. Gamboge tree resin, grass bouquet box, amur corktree, madder, senna leaf, alumen, a ferric ion compound solution and spring water are taken as main raw materials. The production method comprises the following main technological processes: sorting, cropping, drying, soaking, hot boiling, mixing, participating, dyeing, and forming a product. According to the formula and the production method for preparing the deep yellow wheat straw dye, the deep yellow wheat straw dye prepared from pure natural plants is pure natural, free of pollution, green and environment-friendly, and free of toxic and side effects on a human body.
Owner:HARBIN ARTS & CRAFTS
Method for treating complexed chemical nickel electroplating wastewater
InactiveCN103833123AImprove processing efficiencyGood effectWaste water treatment from metallurgical processWater/sewage treatment by oxidationPotassium ferrateAdsorption effect
The invention provides a method for treating complexed chemical nickel electroplating wastewater and aims at the problem in the existing complexed chemical nickel electroplating wastewater treatment processes that the nickel ion removal efficiency is inadequate. The method comprises the main processes of firstly adding calcium hydroxide into the wastewater, adjusting the pH to 8-9 so as to form calcium phosphate precipitates, adding sulfuric acid into a supernatant liquid so as to adjust the pH of the liquid to 4-5, then, adding a potassium ferrate liquid with strong oxidizing power so as to decomplex in a strong oxidizing manner and change complexed nickel ions into free-state nickel ions, then, adding calcium hydroxide, adjusting the pH to 10-11 so as to enable the free-state nickel ions to form precipitates to be removed from the wastewater, enabling trivalent ferric ions with excellent flocculation function generated after oxidation of ferric acid radical ions to have flocculation with hydroxide precipitates with an adsorption effect, and finally, adding polyacrylamide (PAM) to coagulate and precipitate, thereby removing nickel ions from the electroplating wastewater. The method has the advantages that the condition that the nickel ions obtained after the complexed chemical nickel electroplating wastewater is treated reach the national standards can be effectively guaranteed, the treatment efficiency is high, and the requirements on emission are met.
Owner:陈瀚翔
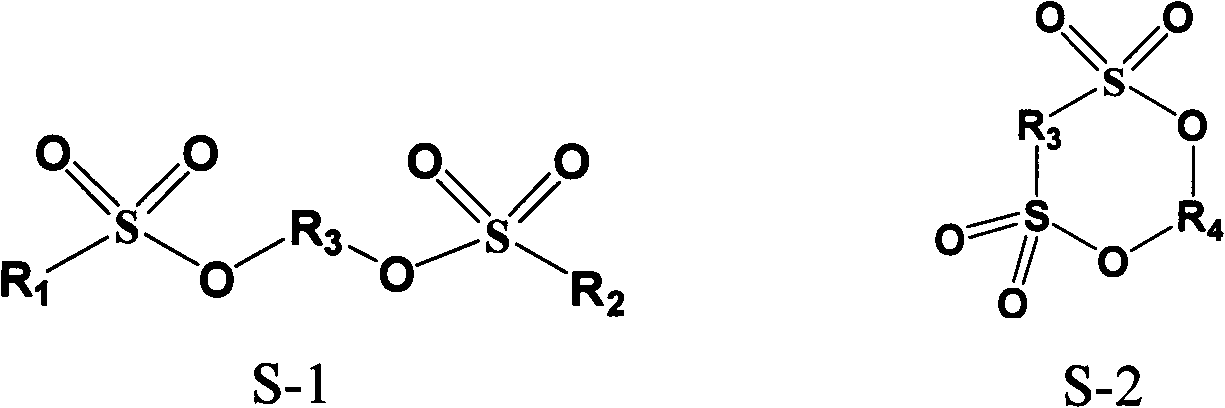
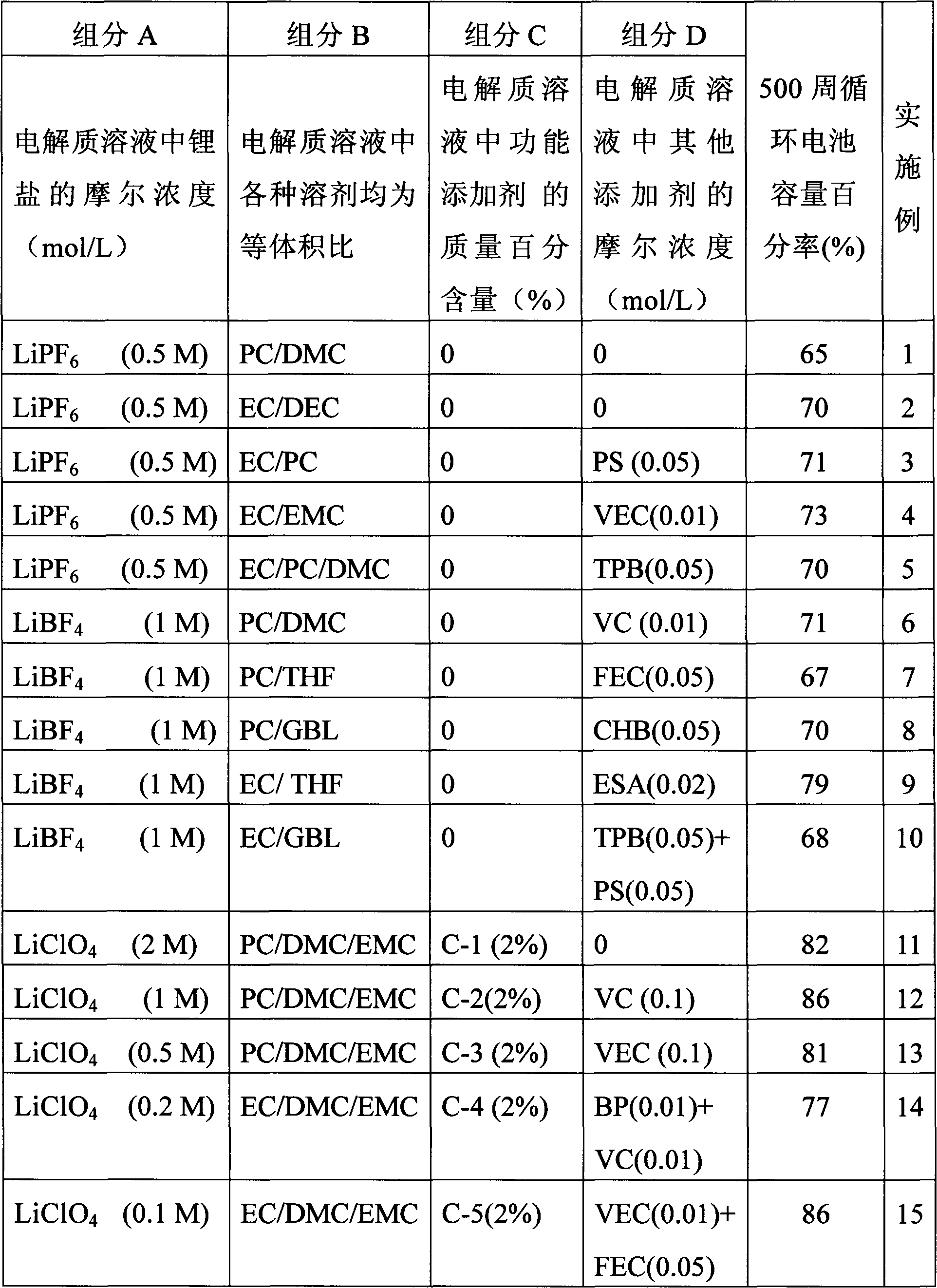
Nonaqueous electrolyte solution for lithium iron phosphate lithium-ion battery
ActiveCN102983358AImprove cycle lifeExtended service lifeSecondary cellsPower batteryLithium iron phosphate
The invention discloses a nonaqueous electrolyte solution for a lithium iron phosphate lithium-ion battery. The nonaqueous electrolyte solution comprises 0.001 to 2mol / L of a lithium salt, 0.01 to 20% by mass of functional additives, a carbonic ester and / or ether organic solvent, and 0 to 0.5mol / L of other additives. Through interaction with iron ions dissolved out, the nonaqueous electrolyte solution reduces reduced iron ions on the surface of a cathode, improves a battery cycle life and a battery service life, improves a battery capacity retention rate and a battery cycle life in a high-temperature environment, and can be used for manufacture of a lithium iron phosphate power battery and an energy-storage battery.
Owner:轻工业化学电源研究所 +1
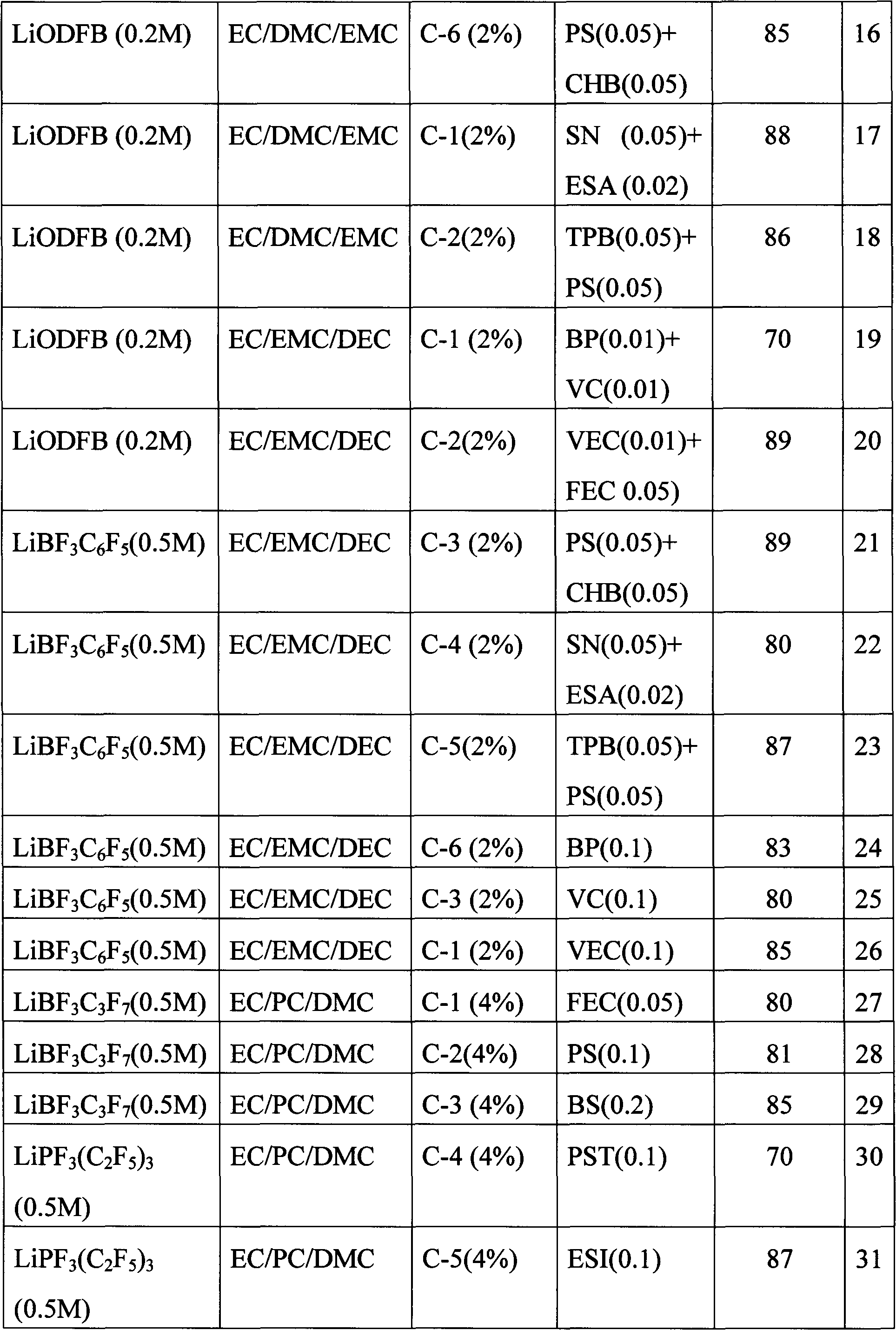
Method for treating organic waste water by using electrochemistry under assistance of persulfate
InactiveCN102249378AReduce dosageLess side effectsWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationElectrochemical responseSulfate radicals
The invention relates to a method for treating organic waste water by using electrochemistry under the assistance of persulfate. The method comprises the following steps of: putting sulfate, a divalent or tervalent ferric salt and organic waste water into an electrochemical reactor consisting of a DSA (Dimensional Stable Anode) and an anti-corrosive cathode; adjusting the pH value of a reaction liquid to 3-9; stirring; and switching on a power supply for reacting. The method is characterized in that: special requirement on the ferric salt is not made, the ferric salt can be divalent or tervalent, generated free sulfate radicals can be used for effectively treating organic pollutants in water; meanwhile, in the electrochemical reactor, reutilization of divalent ferric ions can be realized under the reducing action of the cathode, so that the adding amount of the ferric salt is reduced, side reactions between an excessive amount of ferric salt and free sulfate radicals are reduced, ineffective consumption of free sulfate radicals is avoided, and the generation of iron sludge is reduced simultaneously.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Prussian-blue type sodium ion battery positive electrode material and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN106920964AImprove performanceImprove structural stabilityCell electrodesSecondary cellsOctahedronConcentration gradient
The invention discloses a prussian-blue type sodium ion battery positive electrode material and a preparation method therefor. According to the material, iron ions in iron-nitrogen octahedron in prussian-blue crystal lattices are substituted by transitional metal elements from the interiors to the surfaces of crystal particles based on concentration gradient; the molecular formula of the positive electrode material is Na<x>M<y>Fe<1-y>[Fe(CN)<6>]<z>.nH<2>O, wherein M is a substituting element. The preparation method comprises the following steps of dissolving sodium ferrocyanide, ferrous chloride, and a mixture of substituting element chloride and ferrous chloride into deionized water separately to obtain each precursor solution; then performing a co-precipitation reaction to obtain a prussian-blue turbid liquid, wherein the substituting element is distributed from the interiors to the surfaces of the crystal particles based on concentration gradient; and performing centrifuging, washing and vacuum drying to prepare the positive electrode material. The positive electrode material has the characteristics of high capacity, high cycling stability, simple preparation and the like.
Owner:湖州超钠新能源科技有限公司
Method for recycling acidic copper-etching waste solution
InactiveCN102912352AAchieving "zero" emissionsShort production processLiquid wastePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for recycling acidic copper-etching waste solution. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1, recovering copper form the acidic copper-etching waste solution, filling the acidic copper-etching waste solution in a reaction kettle, adding reduced iron while stirring so as to replace copper ions in the etching solution and separate out spongy copper, and performing solid-liquid separation treatment so as to obtain a spongy copper product having a water content of 50% and the solution containing lots of ferrous ions after the replacement; and step 2, preparing ferric trichloride from the solution after copper extraction: adjusting the solution according to the ferrous ion content and the pH value of the ferrum-containing solution after the replacement in the step 1, and then charging chlorine and reacting the ferrous ions with the chlorine to generate ferric ions, so as to prepare an effluent treatment agent, namely, ferric trichloride. The method disclosed by the invention is short in production flow, simple in process, low in energy consumption, wide in adaptability, capable of reutilizing all the remainder effective cost of the waste solution after the copper extraction while effectively extracting copper powder in the etching waste solution, and capable of realizing zero-discharge of the acidic etching waste solution of a printer circuit board and effectively protecting environment.
Owner:SHANGHAI LVCHENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
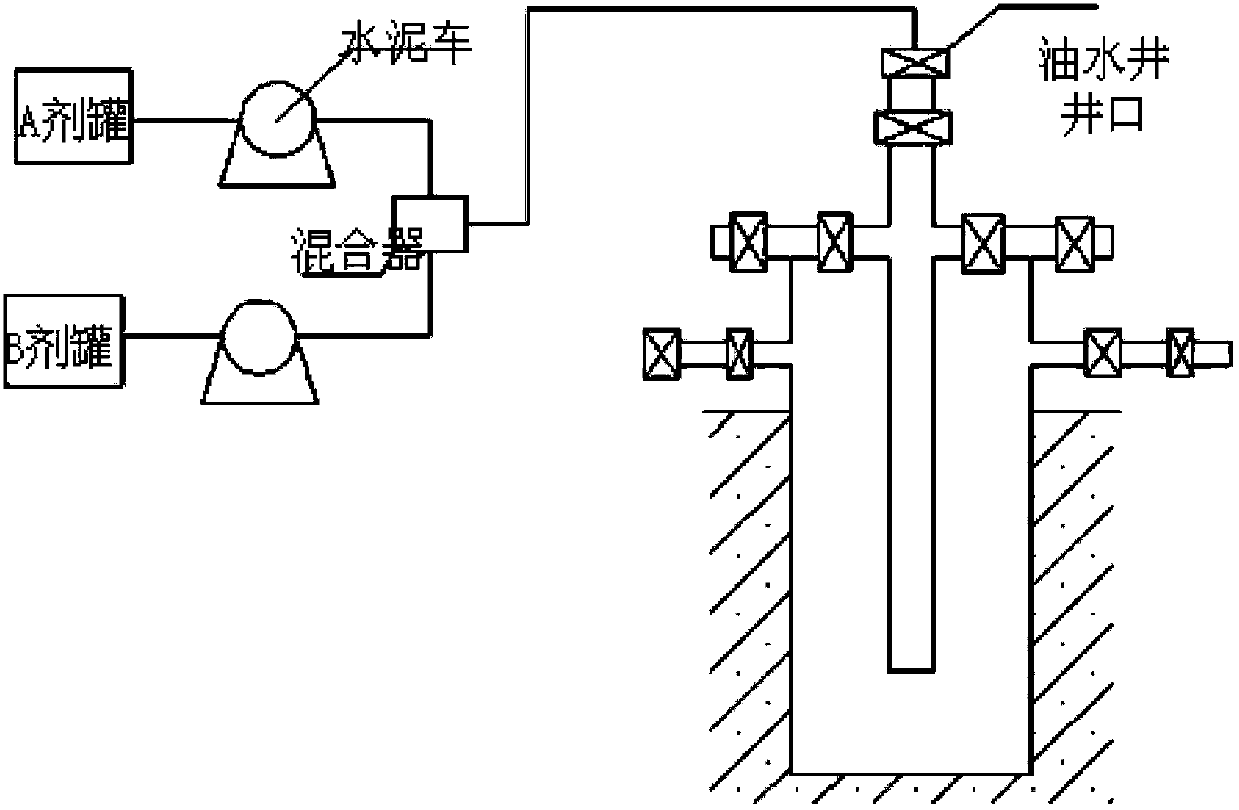
Self-generating foam blocking removal agent for oil-water well and blocking removal process
The invention relates to a self-generating foam blocking removal agent for an oil-water well and a blocking removal process. The foam blocking removal agent is composed of an agent formula A and an agent formula B, wherein the agent formula A is composed of inorganic acid, organic acid, quinoline quaternary ammonium salt, alkynol, iodine salt, imidazoline acetate, polyethenoxy ether sulfonic acid, dodecyl trimethyl quaternary ammonium salt and clear water; and the agent formula B is composed of carbonate, peroxide, fluorosurfactant, salt-free imidazoline, ferric ion stabilizer, foam stabilizer and clear water. The blocking removal process comprises the following steps: injecting a certain amount of prepad fluid through a cementing truck; then, injecting the agent A through one cementing truck and the agent B through another cementing truck; after the injection of the agent A and the agent B is finished, injecting displacement fluid; then injecting clear water; and shutting in the well, and then performing flowback or directly transferring into production. According to the invention, based on the synergic effect between the surfactants, the injected blocking removal agent has blocking removal effect and simultaneously has profile control and displacement effect for an injection well; and the injected blocking removal agent has blocking removal effect and simultaneously has foam huff and puff effect on an oil well.
Owner:陕西一诺油气工程技术服务有限公司
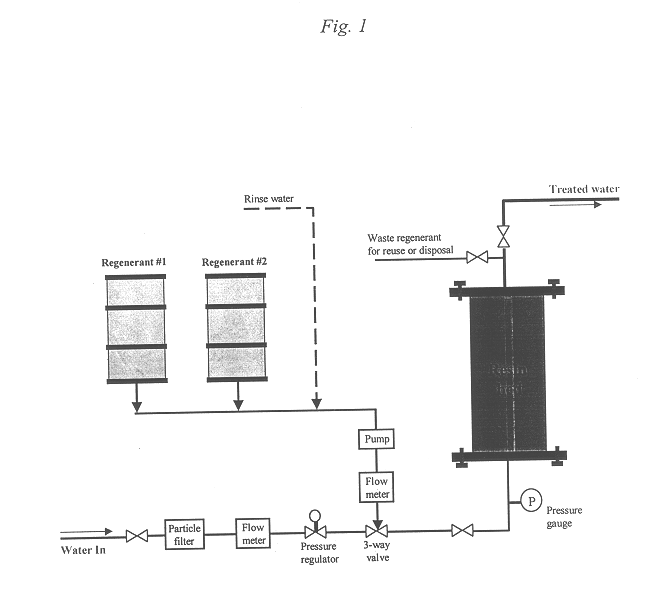
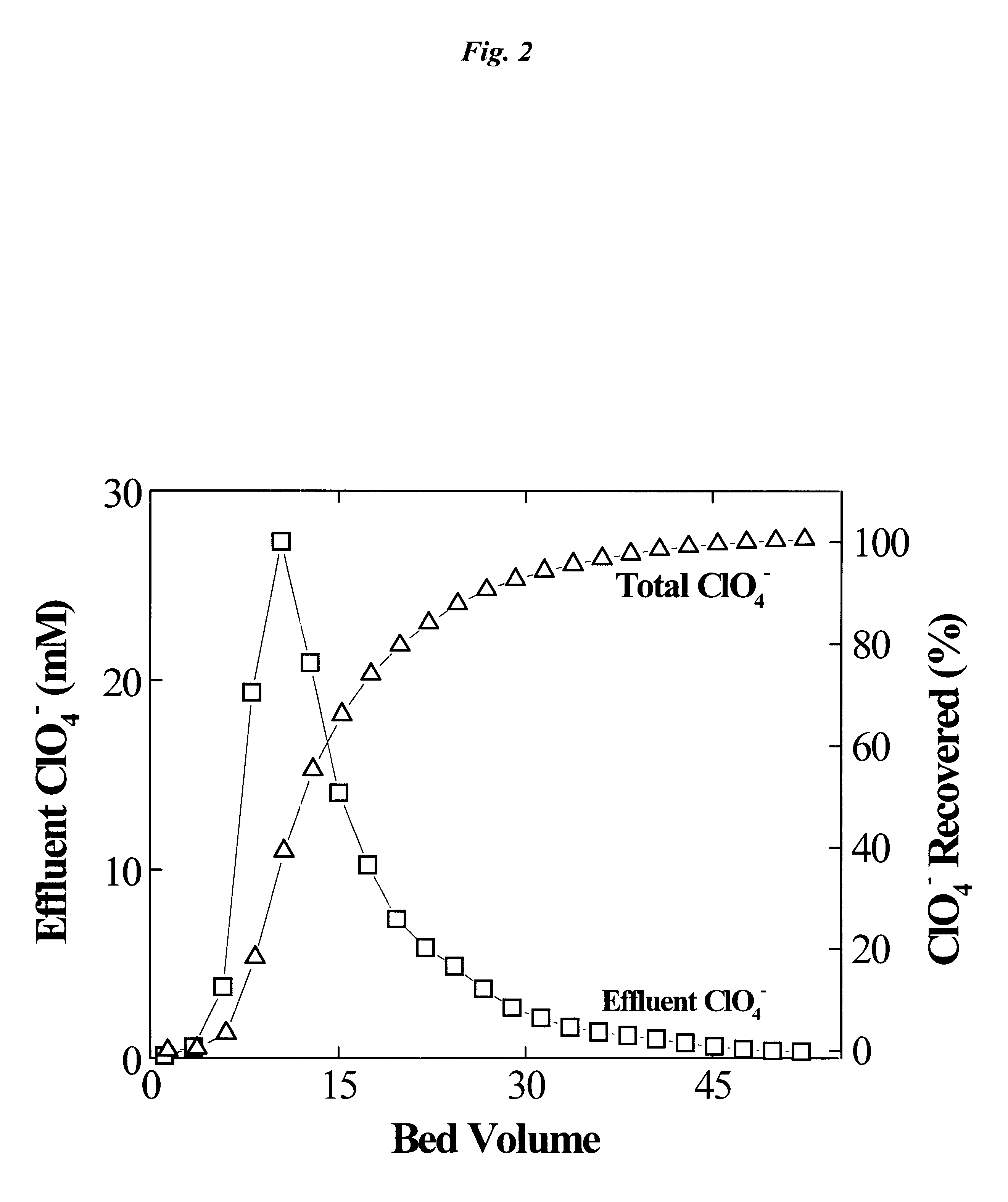
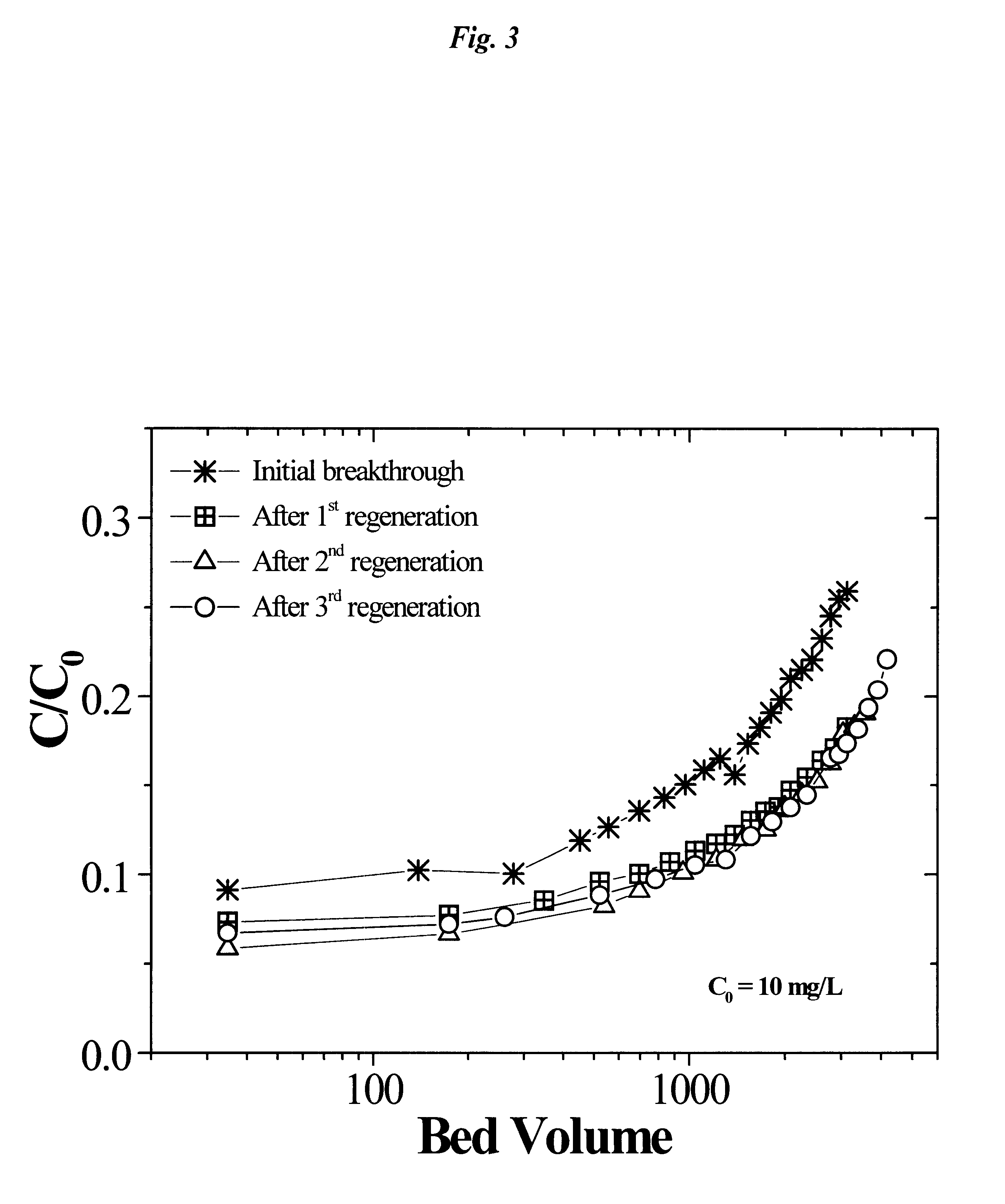
Regeneration of strong-base anion-exchange resins by sequential chemical displacement
A method for regenerating strong-base anion exchange resins utilizing a sequential chemical displacement technique with new regenerant formulation. The new first regenerant solution is composed of a mixture of ferric chloride, a water-miscible organic solvent, hydrochloric acid, and water in which tetrachloroferrate anion is formed and used to displace the target anions on the resin. The second regenerant is composed of a dilute hydrochloric acid and is used to decompose tetrachloroferrate and elute ferric ions, thereby regenerating the resin. Alternative chemical displacement methods include: (1) displacement of target anions with fluoroborate followed by nitrate or salicylate and (2) displacement of target anions with salicylate followed by dilute hydrochloric acid. The methodology offers an improved regeneration efficiency, recovery, and waste minimization over the conventional displacement technique using sodium chloride (or a brine) or alkali metal hydroxide.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
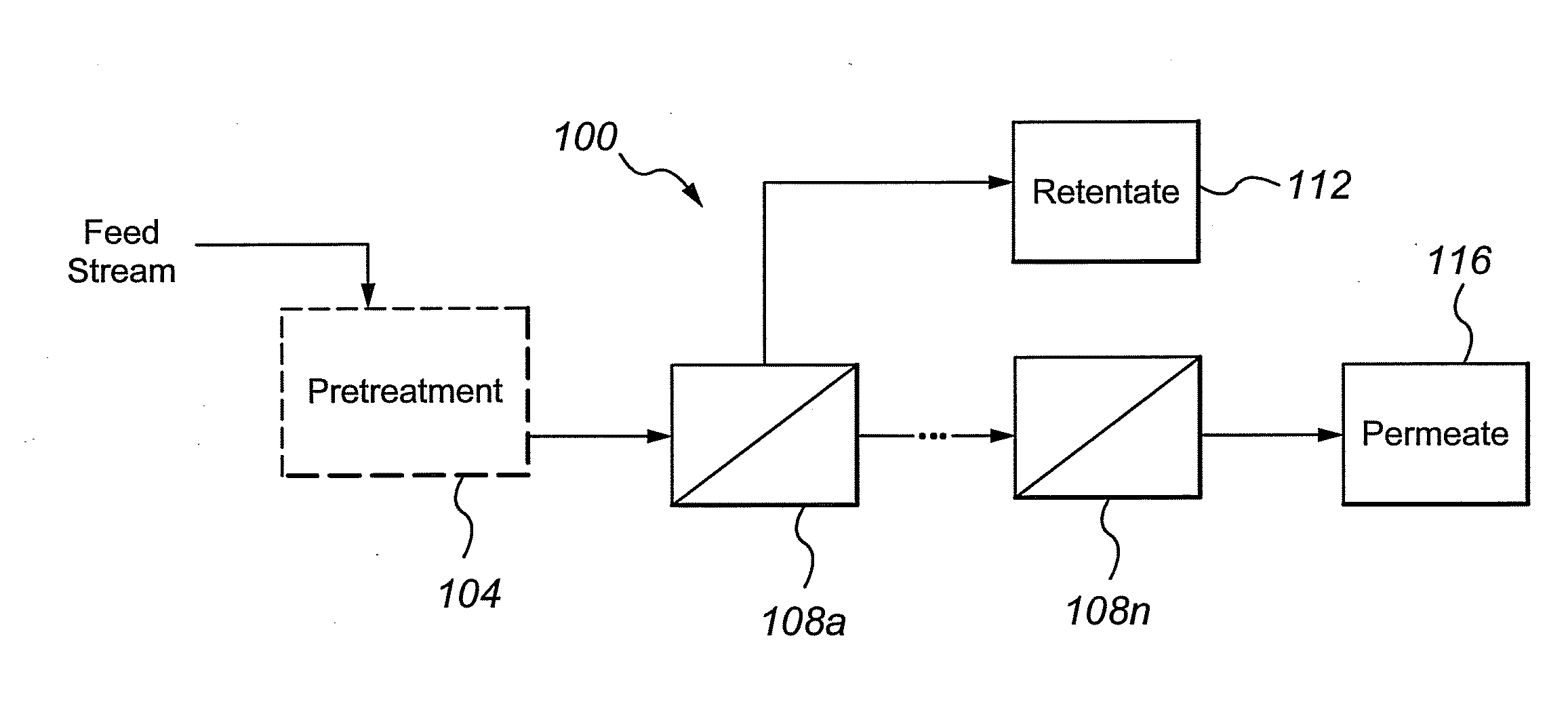
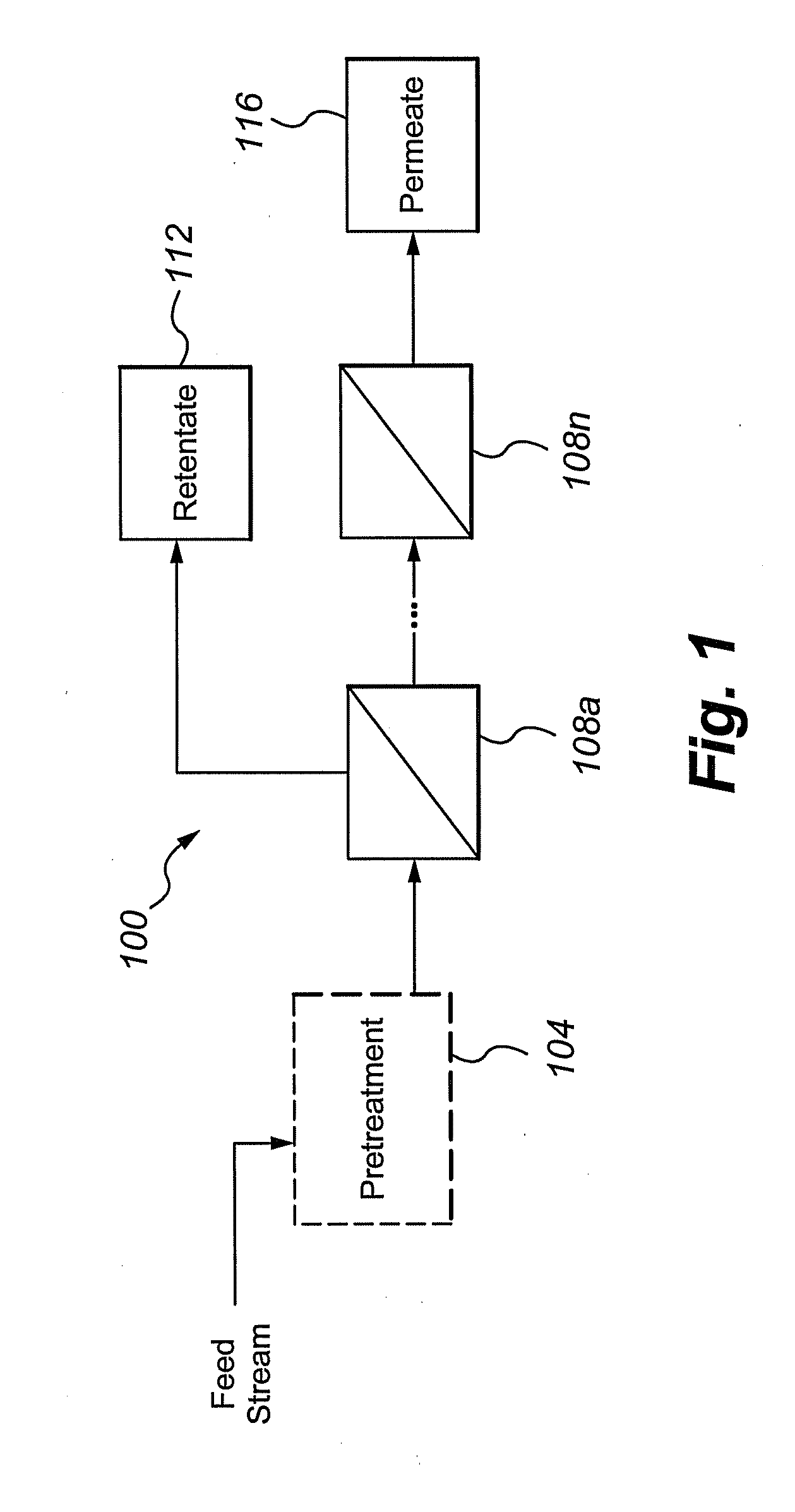
Multivalent iron ion separation in metal recovery circuits
InactiveUS20080069748A1High sulfide sulfur oxidation rateReduce electricity costsSolvent extractionFerrous oxidesPhysical chemistryFerric ion
Owner:HW PROCESS TECH
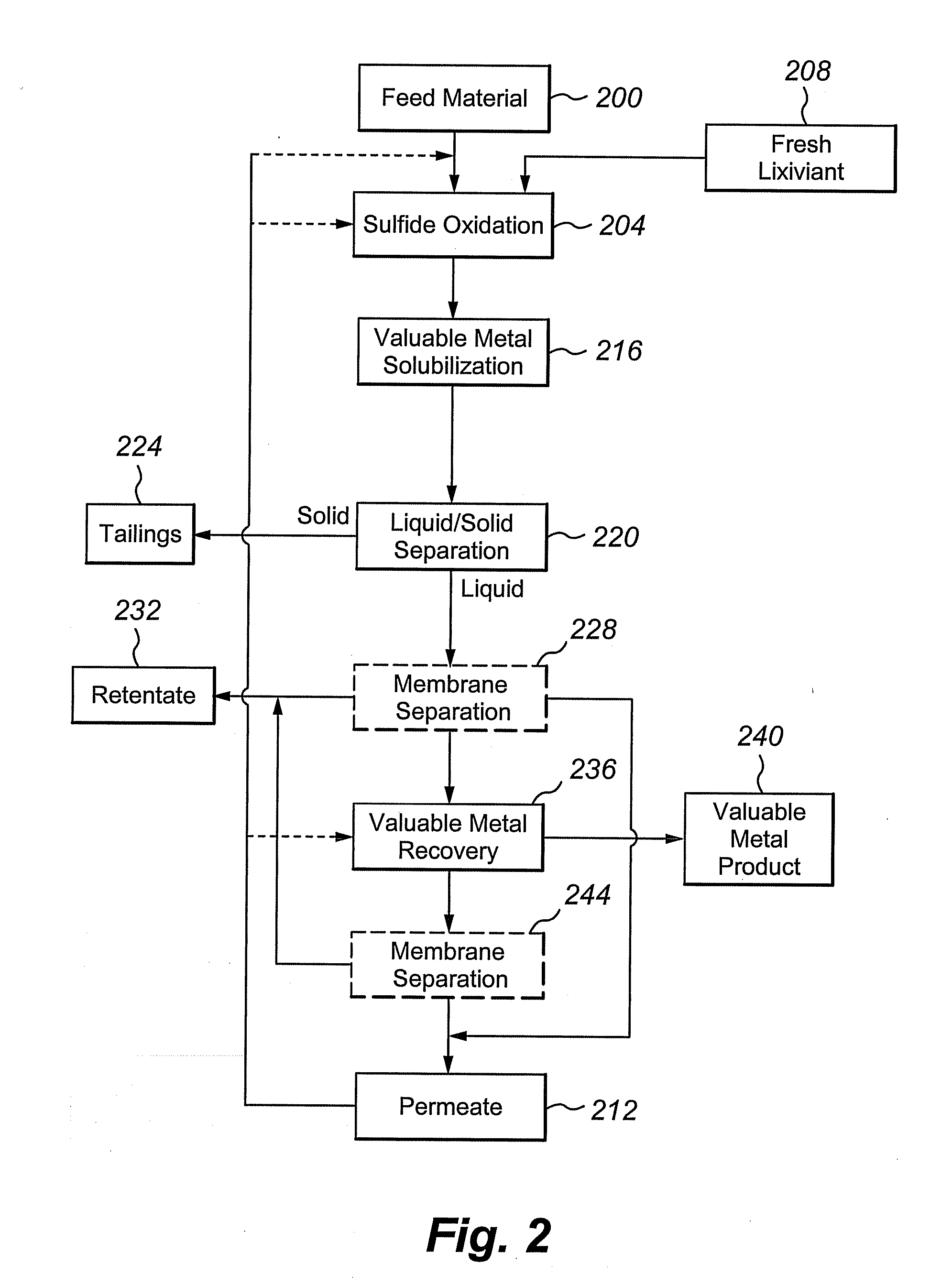
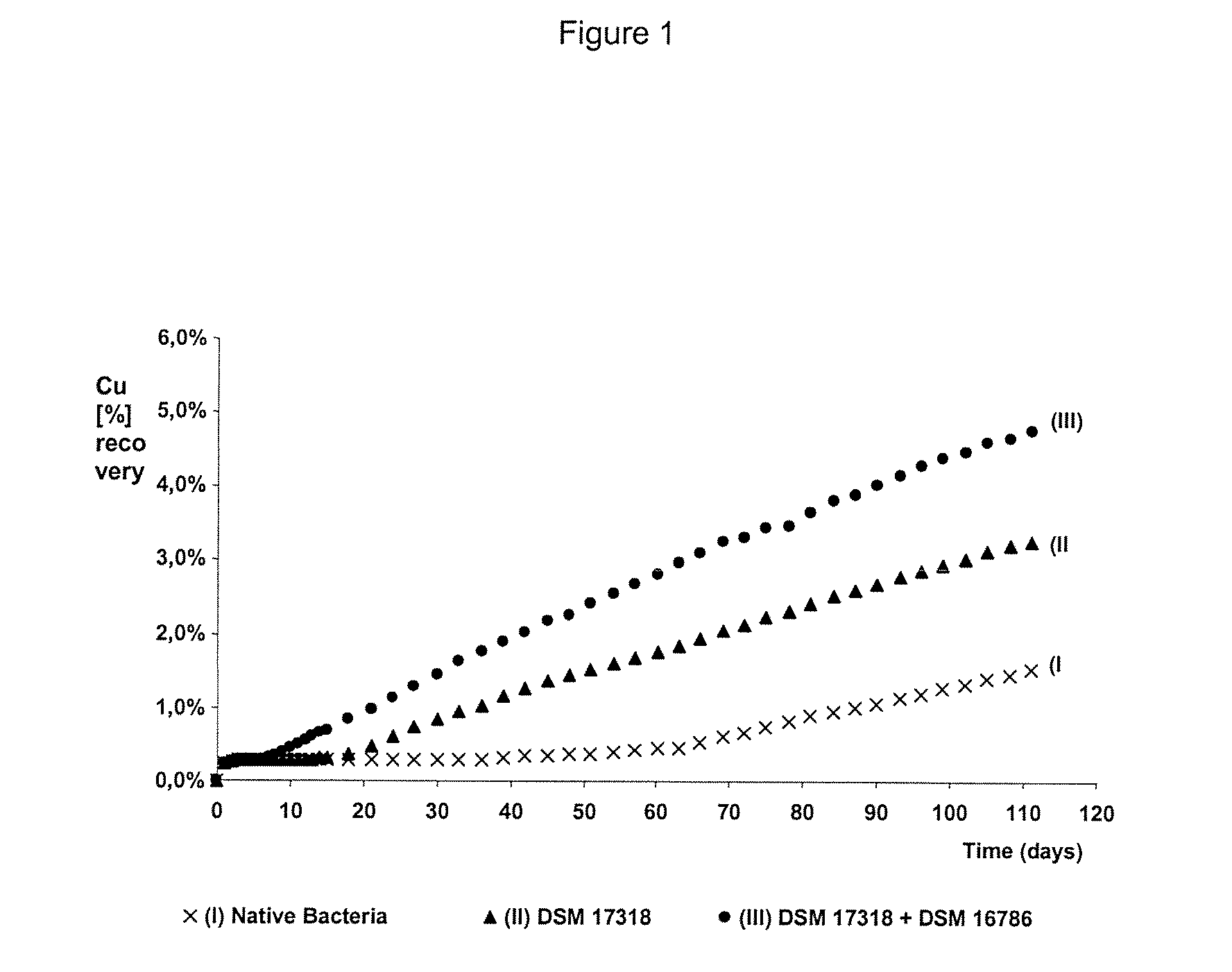
Process to increase the bioleaching speed of ores or concentrates of sulfide metal species, by means of continuous inoculation with leaching solution that contains isolated microorganisms, with or without presence of native microorganisms
ActiveUS20080127779A1Decrease ore bioleaching timeImprove bioleaching conditionSolvent extractionGold compoundsTailings damPotassium
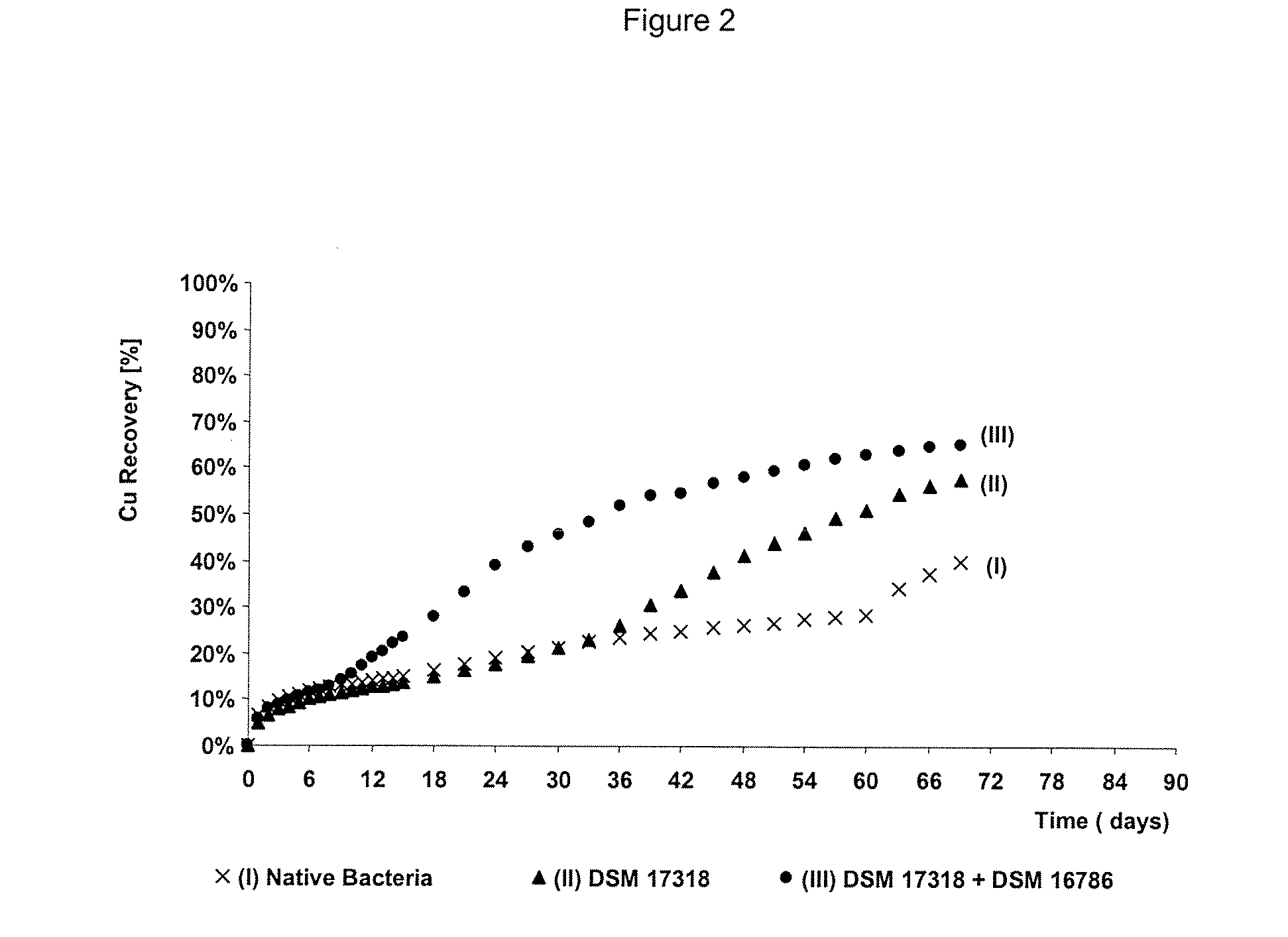
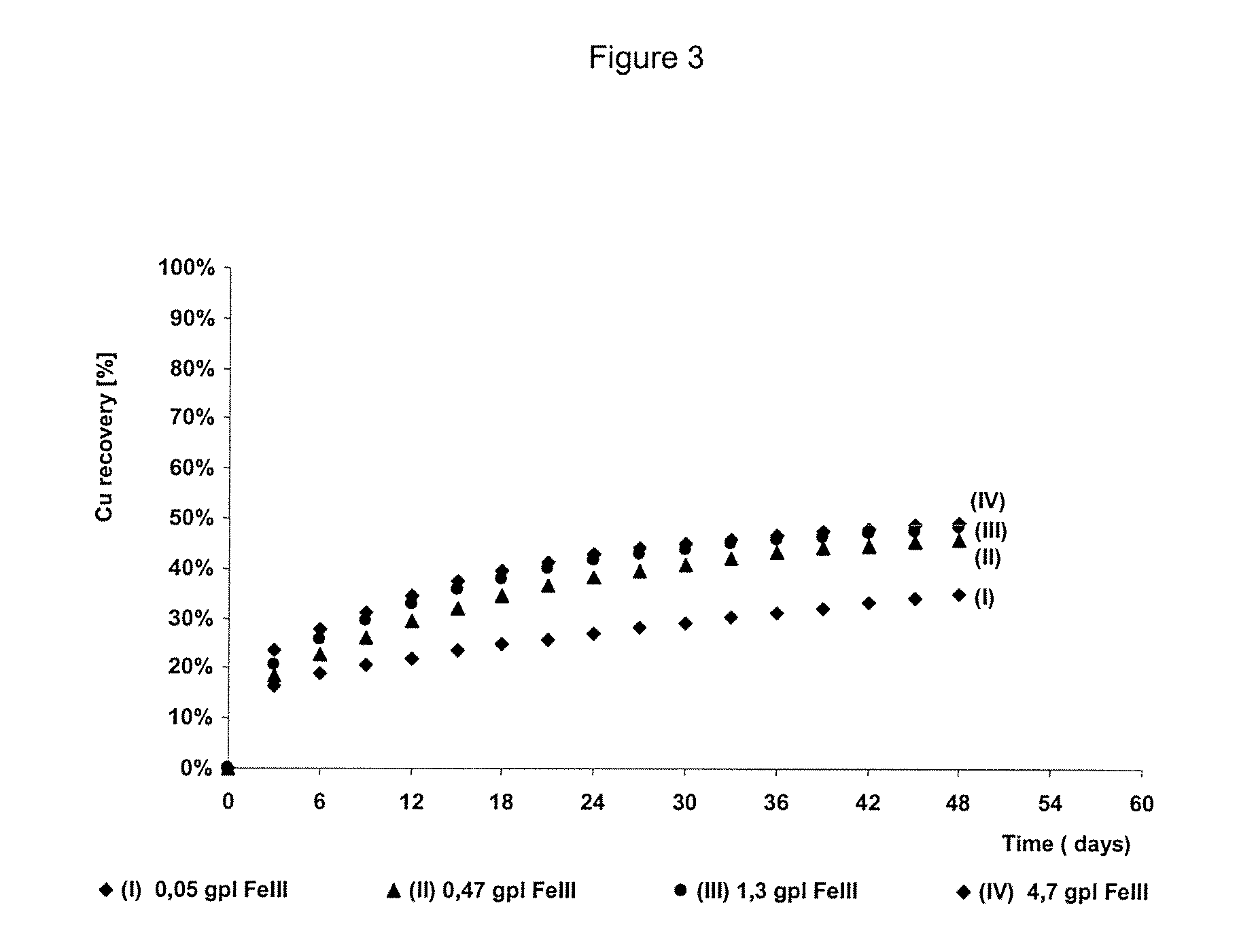
The invention publishes a process to increase the bioleaching speed of ores or concentrates of sulfide metal species in heaps, tailing dams, dumps, or other on-site operations. The process is characterized by the continuous inoculation of the ores or concentrates with isolated microorganisms of the Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans type, together with isolated microorganisms of the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans type, with or without native microorganisms, in such a way that the total concentration of microorganisms in the continuous inoculation flow is of around 1×107 cells / ml to 5,6×107 cells / ml. In particular, the invention publishes the continuous inoculation of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans Licanantay DSM 17318 together with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Wenelen DSM 16786 microorganisms, or with other native microorganisms at a concentration higher than 5×107 cells / ml. In addition to the inoculation of isolated bacteria, the invention includes the addition of oxidizing agents such as the ferric ion produced externally, together with nutrients in the shape of salts of ammonium, magnesium, iron, potassium, as well as air enriched continuously with carbon dioxide to promote bacterial action in the bioleaching process of ores or concentrates.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Method of leaching copper sulfide ore with the use of iodine
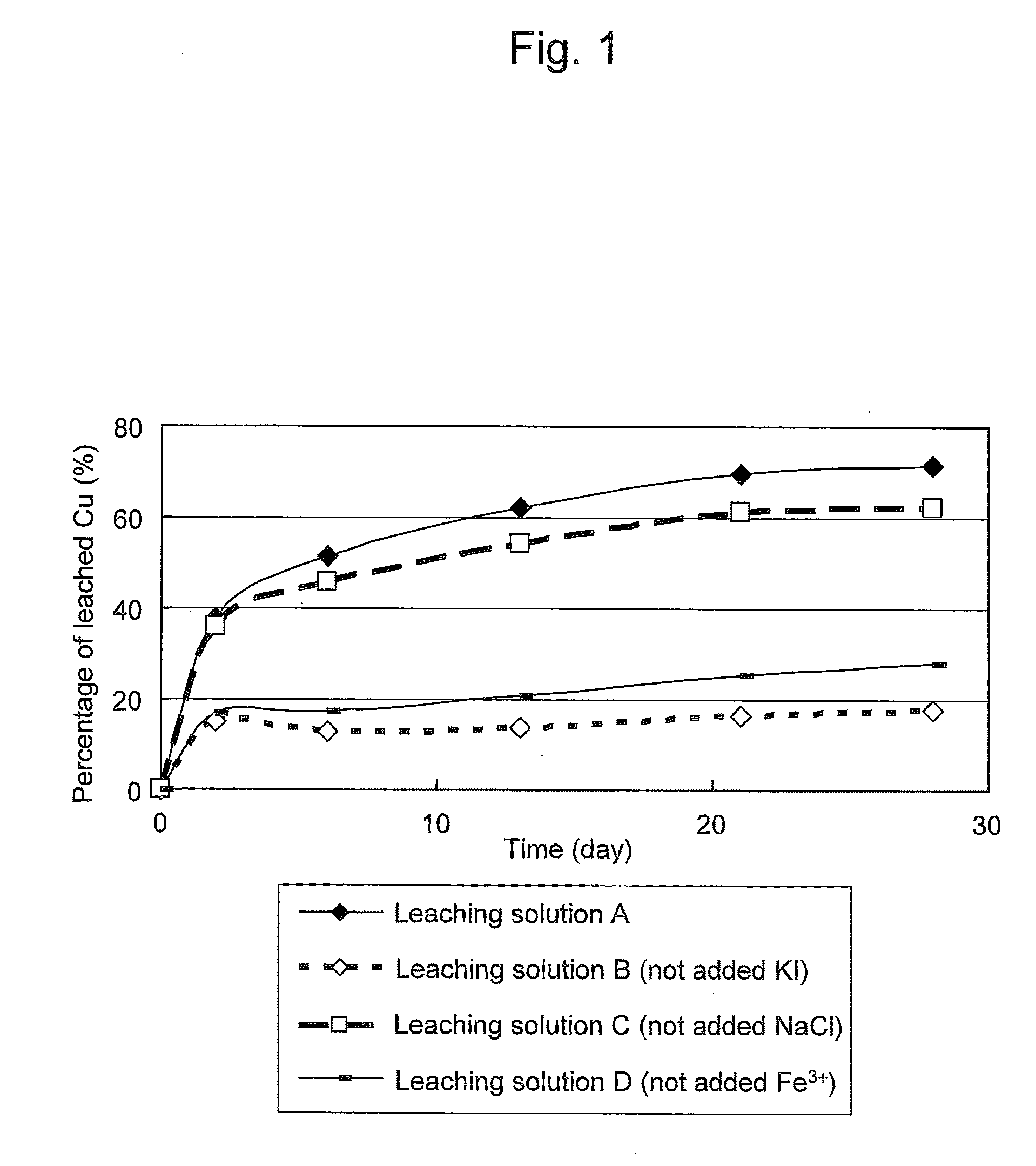
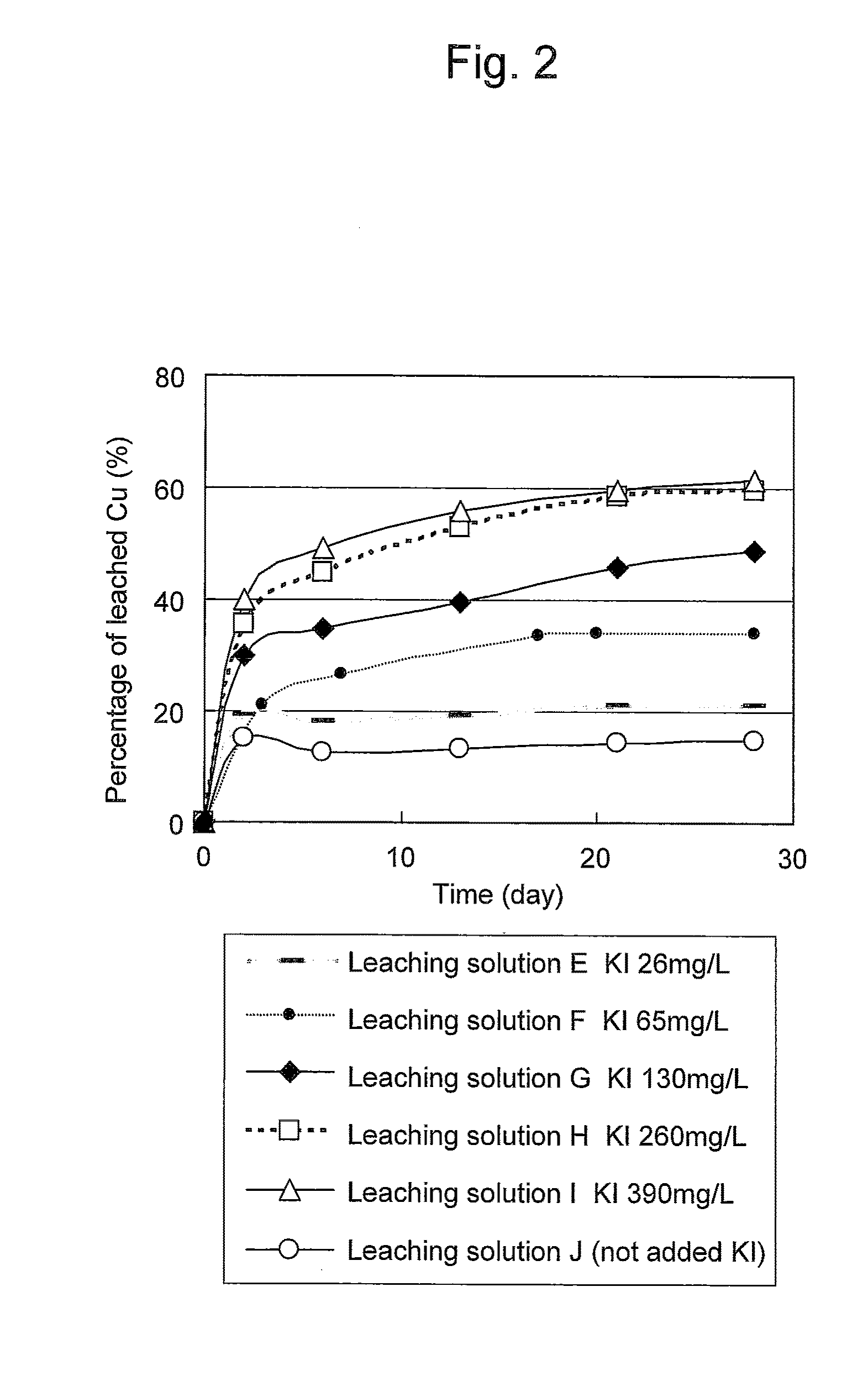
ActiveUS20100018349A1Efficient leachingEfficient executionSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
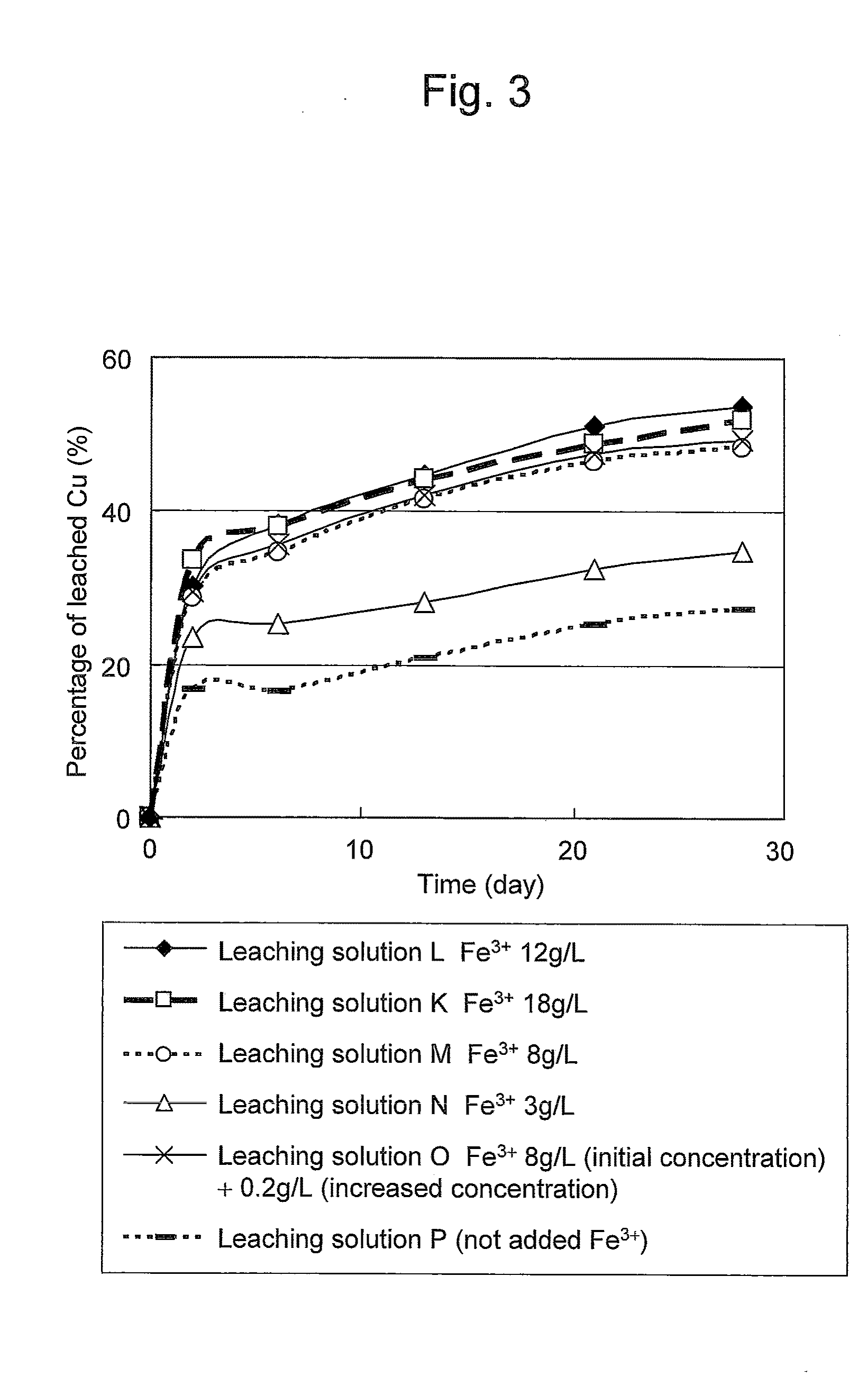
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of efficiently leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore containing chalcopyrite or enargite as a main constituent under versatile conditions for actual operation.A method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising using, as a leaching solution, a sulfuric acid solution containing iodide ions and ferric (III) ions in an excessive amount relative to the iodide ions and leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore; or a method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore with the use of a leaching solution further containing water-soluble ligands such as chloride ions that can stabilize ferric (III) ions in addition to the above components, is provided.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Nano-crystalline Fe*O* particles with high absorption capacity and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101445277AImprove adsorption capacityImprove propertiesOther chemical processesFerroso-ferric oxidesChemical reactionHigh absorption
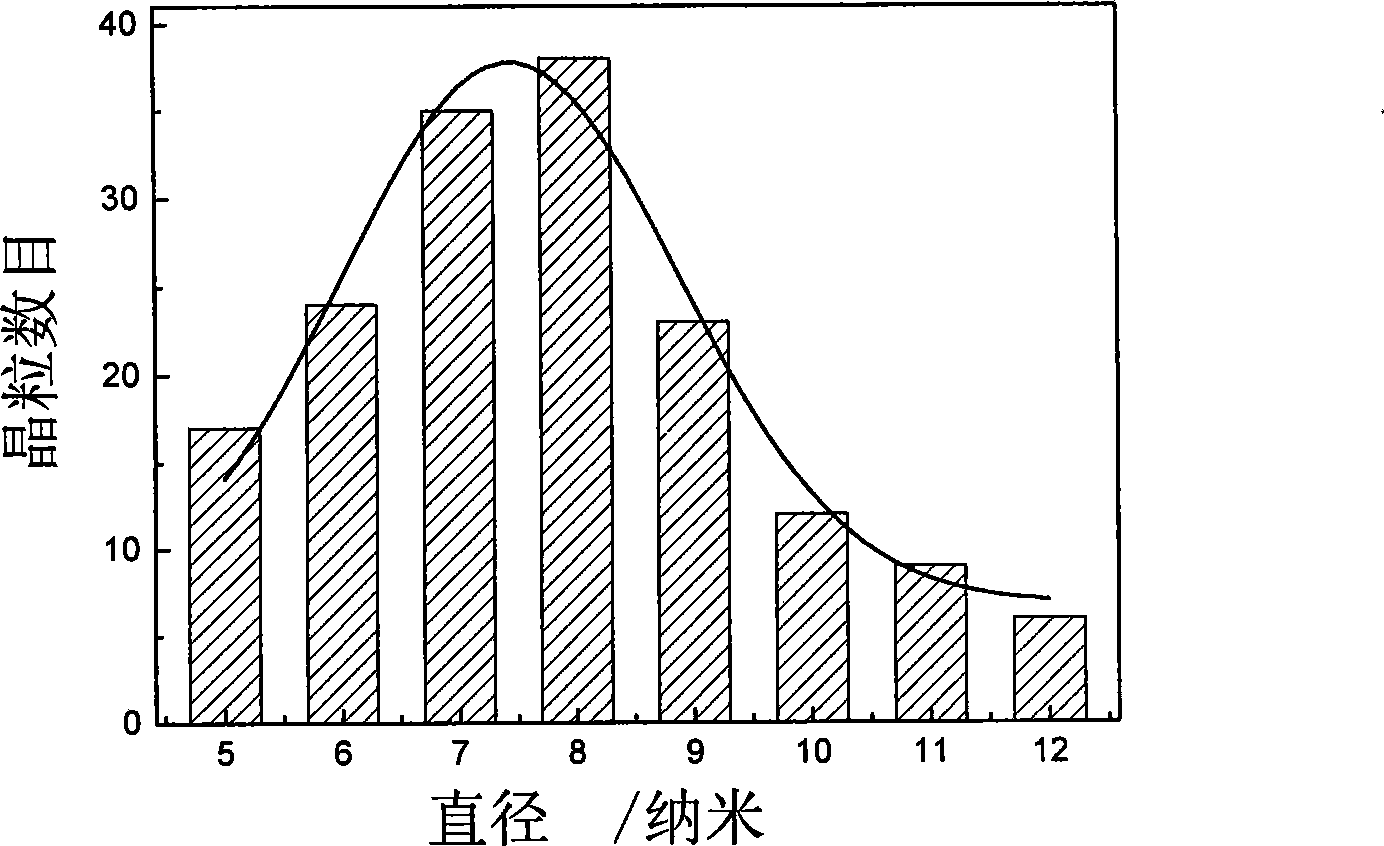
The invention relates to nano-crystalline Fe3O4 particles with high absorption capacity and a preparation method thereof which belong to the field of material science. The microstructure of the particles comprises equiaxed nano-grains, and the particle size of the nano-grains is 5-100nm; the average particle size is 8-25nm, and the saturated magnetization MS is 6.7-7.2 multiplied by 10<minus 3>A / m. The preparation method is as follows: solution containing ferric ions and ferrous ions is prepared, ammonia solution is added under nitrogen atmosphere, ultrasonic waves are transmitted to carry out the ultrasonic dispersion, and heating, stirring and reaction are carried out; solids are washed till neutral by water under the condition of a magnetic field; water is removed by drying after the centrifugal separation. The invention utilizes the simple chemical reaction co-precipitation technology and combines the ultrasonic stirring, the centrifugal separation, the vacuum drying and other technologies to obtain the Fe3O4 powder materials with the average particle size of 8-25nm and the higher saturated magnetization.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Coumarin-oxacalix[3]arene fluorescent reagents as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103435603AConformation variableEasy to retouchOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceOrganic synthesisEthyl group
The invention discloses coumarin-oxacalix[3]arene fluorescent reagents as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the fields of organic synthesis and analytical chemistry. The invention respectively synthesizes two coumarin-oxacalix[3]arene fluorescent reagents: chemical name a: 7,15,23-tertiary butyl-25,26,27-tri{1-[N-(7-coumarin oxyethyl)-1,2,3-triazole]-4-methoxy}-3,11,19-trioxacalix[3]arene; b: 7,15,23-triethoxycarbonyl -25,26,27-tri{1-[N-(7-coumarin oxyethyl)-1,2,3-triazole]-4-methoxy}-3,11,19-trioxacalix[3]arene. Meanwhile, the invention discloses a synthesis method and process conditions. According to the invention, the two coumarin-oxacalix[3]arene fluorescent reagents, in detecting ferric ions, have characteristics of high selectivity and high sensitivity; the fluorescent reagents are applicable to qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
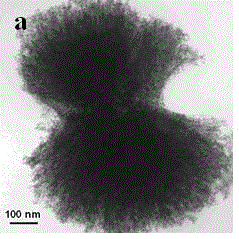
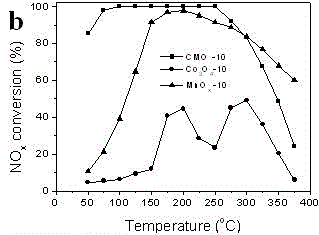
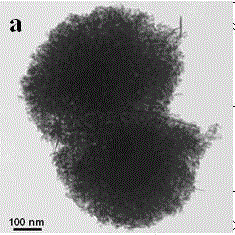
Synthesis method for low-temperature manganese-based compound metal oxide denitration catalysts
InactiveCN104001520AInhibition of agglomerationGood resistance to low temperature freezingDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNickel saltPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the technical field of material preparation, and particularly relates to a synthesis method for low-temperature manganese-based compound metal oxide denitration catalysts. According to the method, a manganese salt and a salt from a cobalt salt, a ferric salt or a nickel salt are dissolved in ethylene glycol in a mixed manner; a sodium carbonate water solution is dripped at a low temperature, and coprecipitation is carried out; and coprecipitation products are washed by water, are dried, and are calcined in the air, and products can be obtained. The synthesis method provided by the invention adopts a low-temperature artificially induced crystal splitting technology, one kind of ions from cobalt ions, ferric ions and nickel ions are added, and manganese ion precipitate crystals are induced to split in the manganese ion precipitate crystal growth process. The split crystals do not agglomerate during the growing in low-temperature environment. After the crystals after splitting growth are calcined, manganese-based compound metal oxides with high specific surface area can be obtained, and the manganese-based compound metal oxides can show excellent low-temperature catalytic activity when being used for catalyzing a denitration reaction. The synthesis method has the advantages that the operation is simple, the control is easy, and raw materials can be easily obtained, so the synthesis method is suitable for large-scale production, and in addition, the environment pollution is little.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
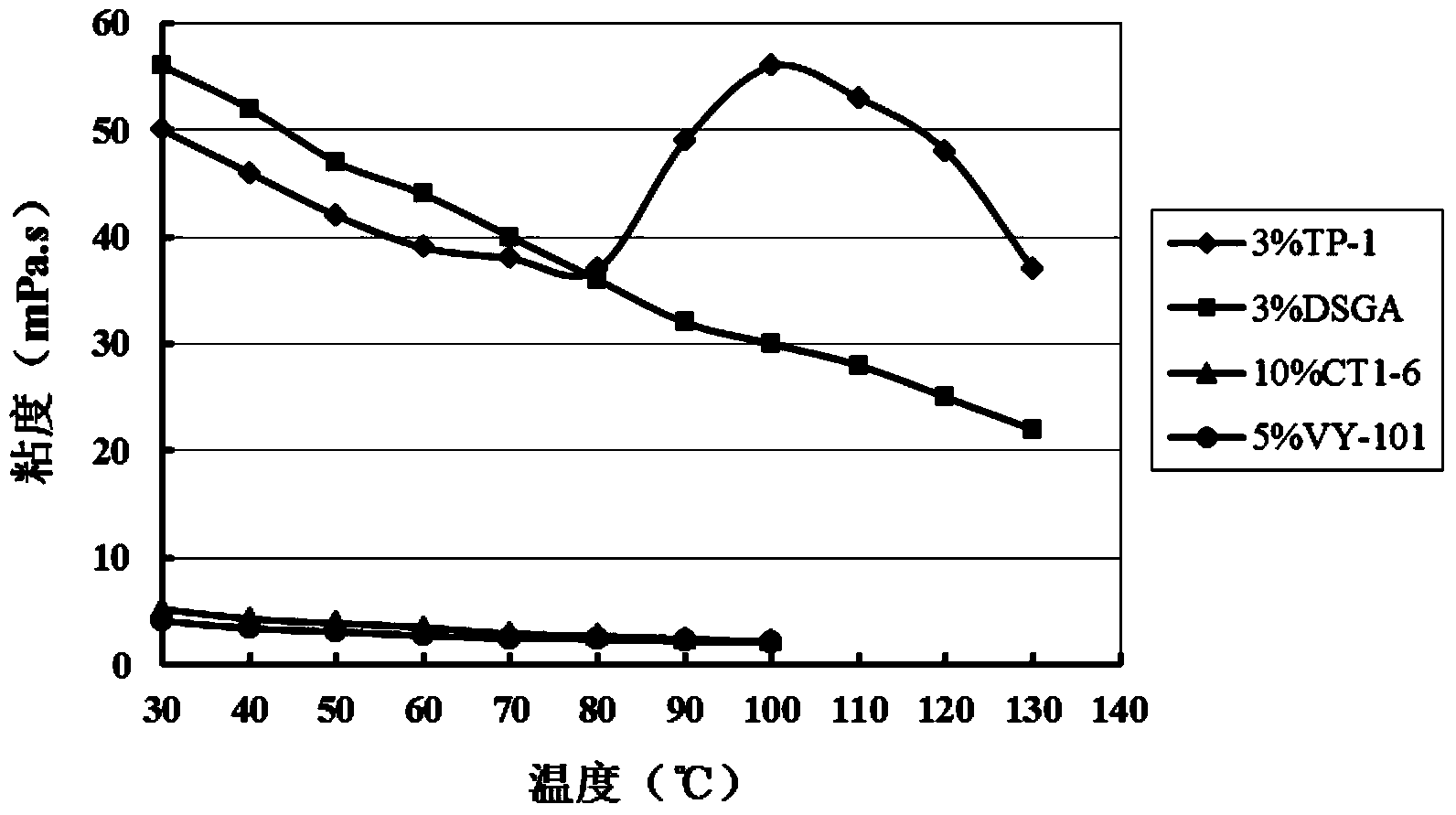
Gelled acid used for acid fracturing of high-temperature fractured-vuggy type carbonate reservoir
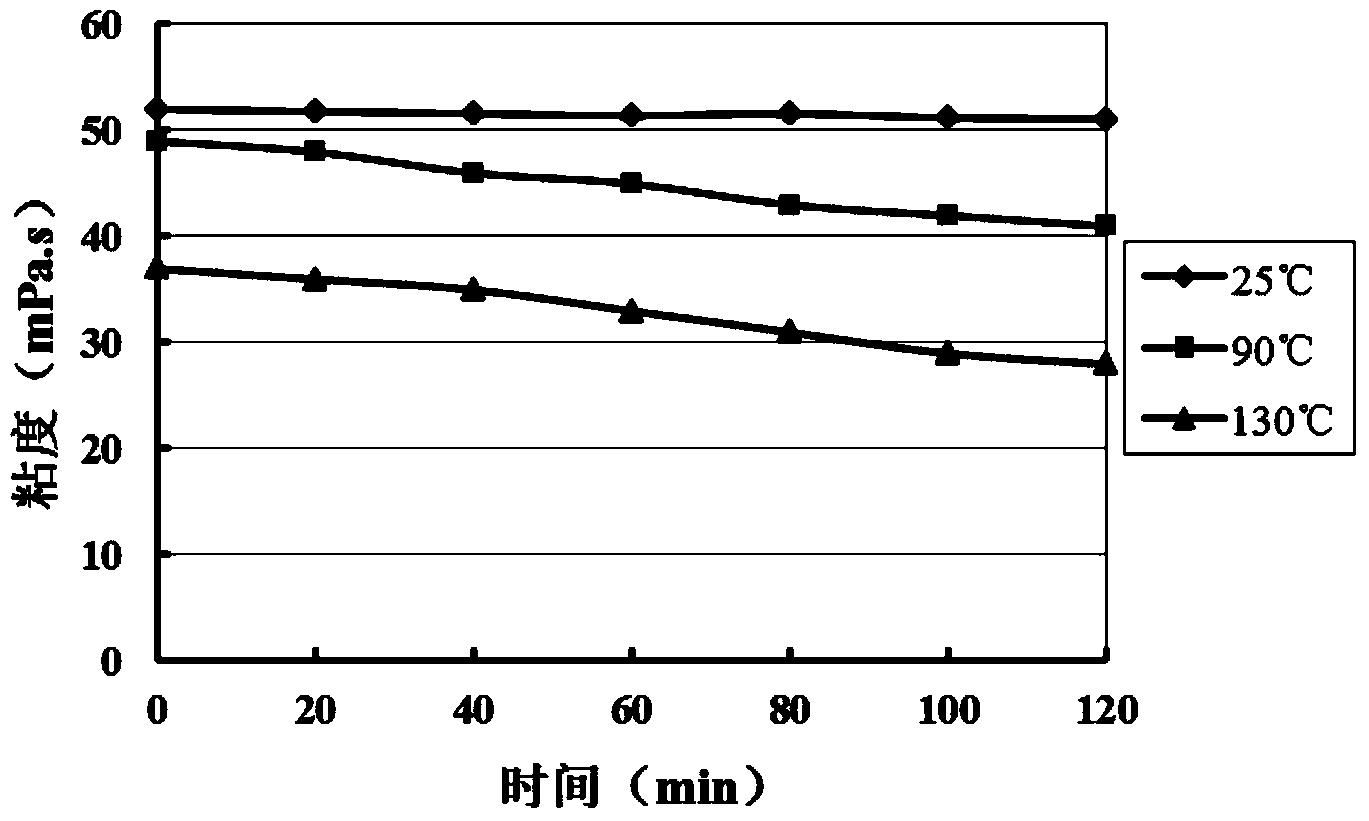
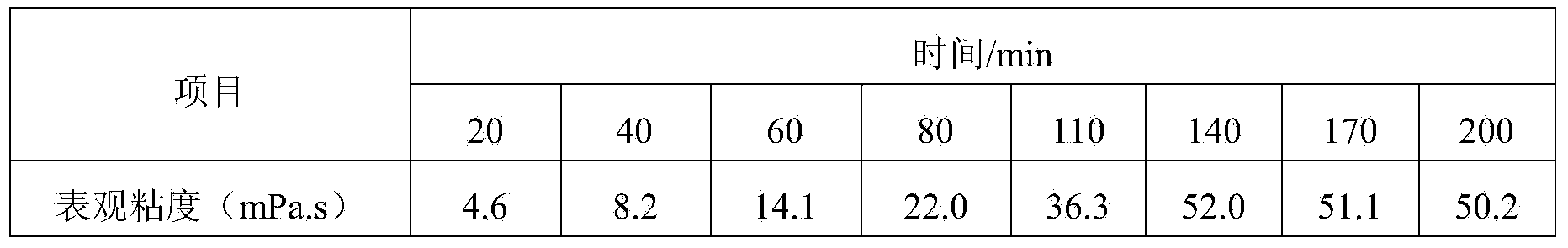
InactiveCN103820100AGood compatibilityGood filter loss reduction effectDrilling compositionAcid fracturingFiltration
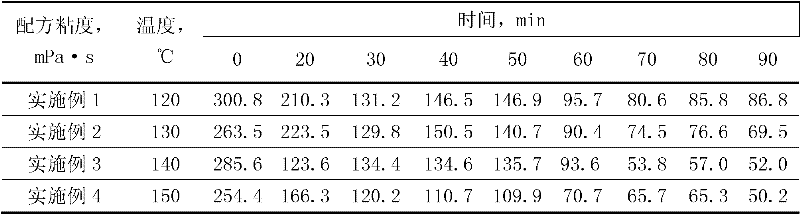
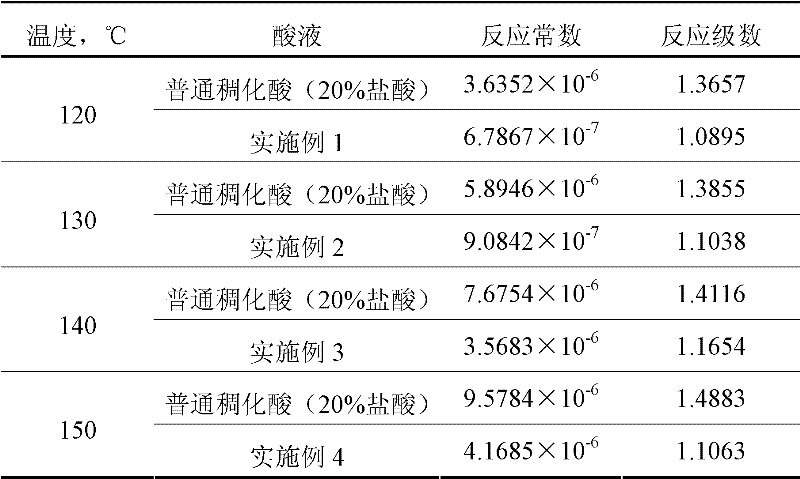
The invention relates to gelled acid used for acid fracturing of a high-temperature fractured-vuggy type carbonate reservoir. The gelled acid comprises components in percentage by weight as follows: 20% of hydrochloric acid (HCl), 3% of a gelling agent (TP-1), 2% of a corrosion inhibitor (MC50), 1.5% of a ferric ion stabilizer (FL4-7), 0.05% of a demulsifying agent (PRJ), 1.5% of a discharge aiding agent (AD12) and the balance of water. The gelled acid can resist a temperature of 130 DEG C, and has an excellent rheological property and shearing resistance, good compatibility and filtration reduction performance and low frictional resistance; compared with common acid (20% of HCl), the acid-rock reaction speed can be reduced by 52%; under the condition of high temperature, the processing depth of the gelled acid to the stratum is enlarged, acidulating efficiency and success rate are increased, and pipe column corrosion and formation damage can be effectively reduced simultaneously, the gelled acid is prone to flowback and has a capacity of carrying solid-phase particles, the acid dissolution time of the gelling agent is short, so that field preparation is facilitated, and the gelled acid is very suitable for acid fracturing improvement of the high-temperature fractured-vuggy type carbonate reservoir.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Bioreactor for continuous production of bioleaching solutions for inoculation and irrigation of sulfide-ore bioleaching heaps and dumps
InactiveUS20110045581A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWaste Dump SitesCulture mediums
The invention discloses an air-lift bioreactor, with internal recirculation, for producing sulfide-ore and minerals bioleaching solutions, with a phase-separating and solids-recirculation system without needing to impel the suspension containing the solids to the bioreactor by means of pumps, using diatomaceous earth and / or ferric precipitates as solid support to immobilize iron and sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms. Specifically speaking, the invention describes a bioreactor that continuously produces bioleaching solutions containing microorganisms for inoculation and irrigation of sulfide-ore heaps and dumps processed by bioleaching. The bioreactor is stirred pneumatically, and is generally made up of an air diffuser, a reaction zone, a de-gasification zone, a solids separation zone, a culture media inlet, and a bioleaching solution outlet. Depending on the source of energy supplied for the growth of microorganisms, the bioreactor can produce a solution concentrated in ferric ions, iron-oxidizing bacteria and reduced-sulfur-compound-oxidizing bacteria.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Iron Precipitation
InactiveUS20110120267A1Reduce lossesIncreased formationSolvent extractionIron compoundsFerric hydroxide oxideResidence time
A process for the treatment of a solution containing at least ferric ions, and one or more metal values, said process including the step of maintaining a controlled concentration of ferric ions in solution for a sufficient residence time to control iron hydroxide or oxide crystal growth, and precipitating the iron as a relatively crystalline iron hydroxide or oxide while minimising the loss of the ore or more metal values with the iron hydroxide or oxide.
Owner:BHP BILLITON SSM TECH PTY LTD
Method for electrically restoring soil and underground water
InactiveCN101698521AInhibitionAvoid alkalizationWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationGroundwater remediationOxygen
The invention provides a method for electrically restoring soil and underground water, which is realized in a way that: soil or underground water which needs to be restored is used as the conducting medium, metallic iron is used as the anode, a ferric salt solution is used as the working solution, the anode iron is oxidized into ions after losing electrons, the ions enter the anode working solution and move towards the cathode into the soil or underground water as the current carrier with positive charges under the action of an electric field; and copper or copper-coated iron or iron is used as the cathode, a cupric salt or ferric salt solution is used as the working solution, cupric ions or trivalent ferric ions are reduced into elementary substance copper or bivalent ferric ions, meanwhile, small amounts of heavy metal cations transferring from the soil to the cathode working liquid are also reduced, and acid radicals of cupric salts or ferric salts move towards the anode under the action of the electric field and enter the soil and the underground water. The method can restore soil and underground water which are polluted by heavy metals, acids or alkalis, does not change the pH value of the soil and the underground water, does not produce hydrogen, oxygen or chlorine with hidden danger and has the advantages of high current efficiency, low price and easy obtainment of the anode material.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
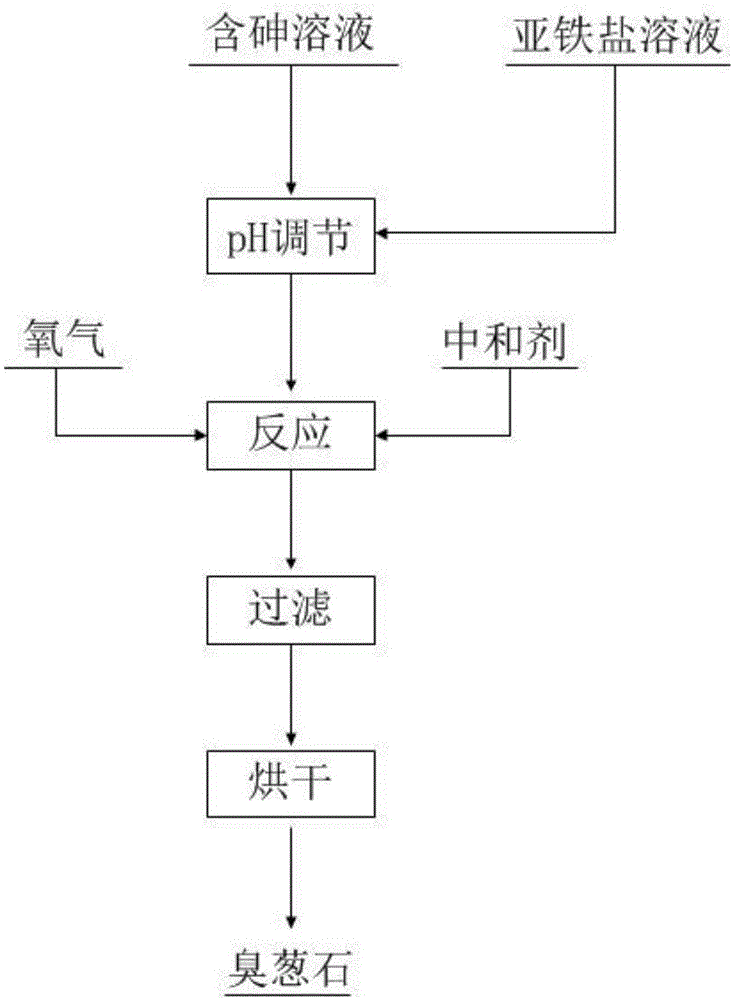
Treatment method of arsenic wastewater
ActiveCN103112974AShort process routeShort construction periodMultistage water/sewage treatmentFlocculationResource recovery
The invention discloses a treatment method of arsenic wastewater. The treatment method comprises the following steps: optionally adding acid liquor into the arsenic wastewater to adjust the pH value to 0-5; introducing the arsenic wastewater into a reaction unit, continuously removing arsenic by adding sulfide in multistage manner; carrying out solid-liquid separation on the effluent after reaction, recycling the separated arsenic slag; adding alkali into the separated effluent to perform electrochemical advanced treatment, wherein the electrochemical advanced treatment includes an electrolytic coagulation step, an electrolytic flotation step and an electrolytic oxidation reduction step, in the electrolytic coagulation, cations are generated by the electrolyzation of a soluble anodic iron plate for flocculation; carrying out aerated oxidation on the effluent after flocculation to generate floc and micelle sediment including ferric ions, and then carrying out solid-liquid separation, wherein the liquid supernatant after separation can be recycled or reach the standard and drain outwards. The treatment method of arsenic wastewater has the advantages of simple technology, low investment, low cost and high resource recovery and recycling rate, and being green and environment-friendly, and being capable of treating continuously and the like.
Owner:CHANGSHA HASKY ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH DEV CO LTD
Preparation method of multi-component organic cross-linked acid liquid
The invention relates to a preparation method of multi-component organic cross-linked acid liquid, which comprises base liquid and a cross-linking agent, wherein the weight ratio of the base liquid and the cross-linking agent is 100:0.6-0.8; the base liquid comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 3.6-9 percent of formic acid, 4.8-12 percent of acetic acid, 5.5-13.75 percent ofhydrochloric acid, 0.6-0.8 percent of thickening agent, 4.0-5.0 percent of high-temperature corrosion inhibitors, 0.5-1.0 percent of long-term clay stabilizer, 1.0-1.5 percent of ferric ion stabilizers, 0.5-1.0 percent of broken emulsion discharge aiding agent and the balance is water; and the sum of the mass percentages of all the components is 100%. The method has the beneficial effects that the acid liquid system can be cross-linked under the conditions of high temperature and strong acid and is good in temperature resistance and shear resistance, less in filtration and complete in gelout;after the acid liquid is cross-linked, an acid rock is remarkably lower than ordinary gelled acid in reaction speed and is good in speed retarding performance; and the multi-component organic cross-linked acid liquid can be used for realizing the modification of depth acid pressure in a high-temperature deep well of a carbonate rock.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
Clean manufacturing technique of extracting vanadium pentoxide from vanadium-contained stone coal
InactiveCN101597697AEffective destructionImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementSlurrySolvent
The invention discloses a clean manufacturing technique of extracting vanadium pentoxide from vanadium-contained stone coal, comprising the following steps: grinding the vanadium-contained stone coal until the granularity is less than 2mm, baking in the industrial microwave device at temperature of 700 to 800 DEG C for 1h to 2h, fine grinding the clinker after baking until the granularity is less than 0.15mm, adding water to prepare ore slurry, in which the volume mass ratio of water to vanadium-contained stone coal is 1-1.5 to 1, adding sulphuric acid to leach at temperature of 80 to 95 DEG C for 2h to 20h, in which the amount of sulphuric acid is 10% to 25% of vanadium-contained stone coal, adding ferrous powder in the extract to reduce ferric ion, adjusting the pH value with lime and ammonia water to be 2.8 to 3.0, and obtaining ammonium polyvanadate precipitate after solvent extraction, oxidization and adding ammonia water. The ammonium polyvanadate is calcined to prepare powdery vanadium pentoxide product. The invention has beneficial effects of 1. effectively breaking structures of minerals such as vanadium-contained mica and kaolin by using microwave device to roast the vanadium-contained stone coal; 2. compared with stone coal direct acid leaching technique, reducing sulphuric acid amount by 10% to 15%, as the sulphuric acid amount when acid leaching is 10% to 25% of mineral mass; and 3. without any additive in the baking process or air pollution, belonging to clean manufacturing technique.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Method for synthesizing ferrum-aluminium spinelle
The invention relates to a synthesis method of hercynite and has the technical proposal that aluminium compound and iron compound are mixed according to the mol ratio of Al ion to Fe ion of two to one, added with TiO2 fine powder of 1-20wt percent of the mixture obtained from the mixing of the aluminium compound and the iron compound and 1-6wt percent of binding agent to be mixed for 5 to 180 minutes for formation and then dried for 20 to 30 hours under the temperature of 90 to 120 DEG C and warmed up to 1100 to 1700DEG C with a temperature rising speed of 0.5 to 10 DEG C / min in the atmosphere of nitrogen to be kept warm for 5 to 600 minutes and next naturally cooled so as to obtain the hercynite. The invention is characterized by simple technology, low reaction temperature, low cost of raw materials and no environmental pollution; due to the low oxygen content in the atmosphere of the nitrogen, Fe elements exist in the form of Fe<2+> and all aluminium and iron are transformed to FeAl2O4 under the firing temperature; in addition, as the TiO2 is introduced, Ti<4+> can easily enter into crystal lattice of the FeAl2O4 to produce oxygen-iron vacancy concentration and ferric-ion vacancy concentration so as to promote the sintering with apparent porosity less than or equal to 2 percent after sintering.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of lithium iron phosphate
ActiveCN101826617AImprove conductivityHigh specific capacityCell electrodesLithium iron phosphatePhosphate
The invention provides a preparation method of lithium iron phosphate, which comprises the following steps: 1, dissolving an iron source in water to obtain ferric ion / ferrous ion; adding ascorbic acid, phosphorus source solution and aqueous alkali and adjusting the pH value; and filtering to obtain ferrous phosphate sediment and drying the ferrous phosphate sediment; 2, dispersing the ferrous phosphate into the deionized water, adding phosphoric acid solution, heating and mixing the solution and stirring; and adding a lithium source solution into the mixed solution for reaction to obtain suspension; 3 dissolving a sugar source into the water and adding into the suspension obtained in step 2, stirring and drying to obtain the precursor of lithium iron phosphate; and 4, under the protection of inert gas, increasing, keeping and then reducing the temperature of the lithium iron phosphate obtained in step 3, to obtain lithium iron phosphate; and crushing lithium iron phosphate until the particle size is less than 15 mu m, to obtain the finished product. The lithium iron phosphate product prepared by the method of the invention has perfect electrical conductivity, large specific capacity and uniform particle size.
Owner:黄博
Method for obtaining high-leaching stability scorodite by precipitating arsenic-containing solution
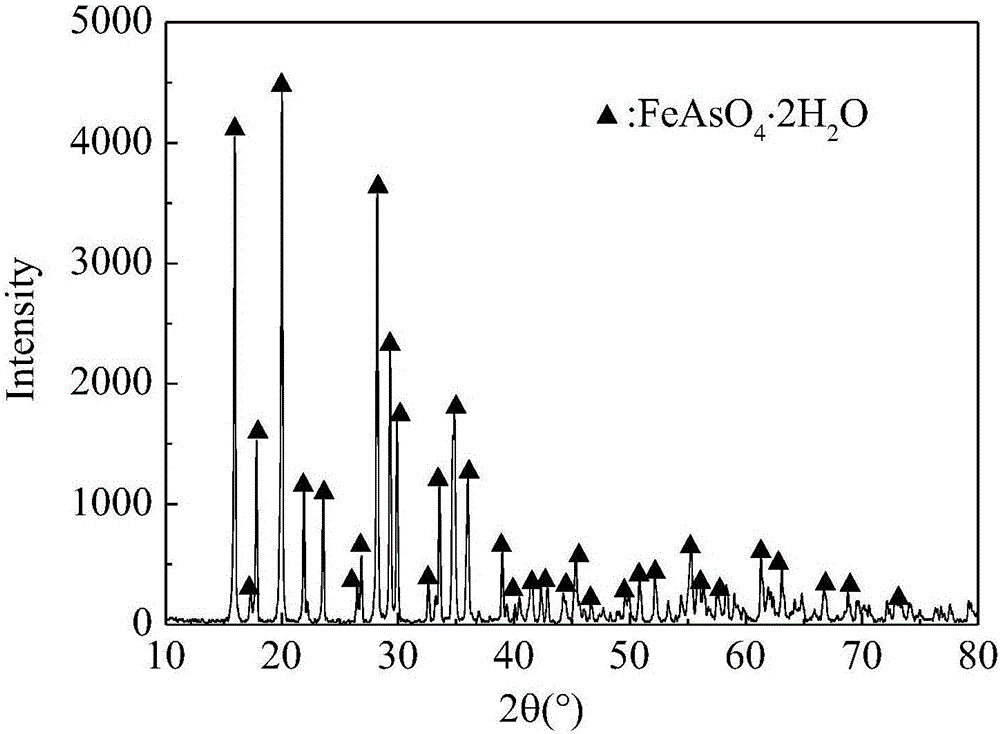
The invention relates to a method for obtaining high-leaching stability scorodite by precipitating an arsenic-containing solution. The method comprises the following steps: adding a ferrite solution as an arsenic precipitating agent in a continuous feeding mode, and simultaneously adding a neutralizing agent in a certain concentration; continuously introducing oxygen for oxidizing ferrous ions into ferric ions, and then reacting with arsenic in the solution, thus generating the high-leaching stability scorodite. The obtained scorodite can be stably stacked and stored within a pH (Potential of Hydrogen) value range of 2 to 11 and under a strong reducing condition.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

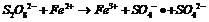
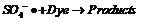
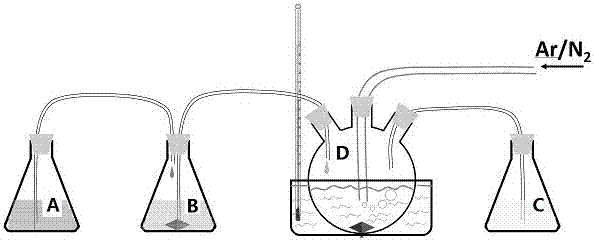


![Coumarin-oxacalix[3]arene fluorescent reagents as well as preparation method and application thereof Coumarin-oxacalix[3]arene fluorescent reagents as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e78a47b1-2e36-4e56-a201-f23b2c02df82/797226DEST_PATH_IMAGE012.png)
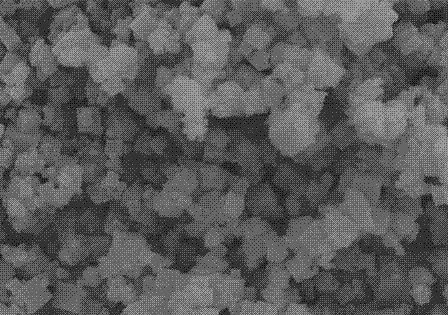
![Coumarin-oxacalix[3]arene fluorescent reagents as well as preparation method and application thereof Coumarin-oxacalix[3]arene fluorescent reagents as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e78a47b1-2e36-4e56-a201-f23b2c02df82/995070DEST_PATH_IMAGE007.png)
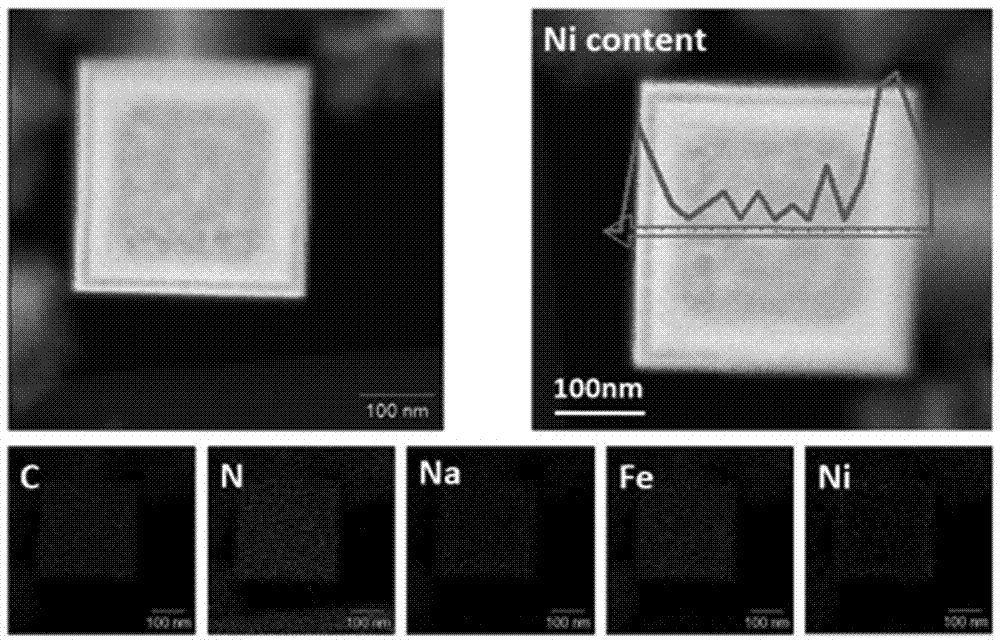
![Coumarin-oxacalix[3]arene fluorescent reagents as well as preparation method and application thereof Coumarin-oxacalix[3]arene fluorescent reagents as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e78a47b1-2e36-4e56-a201-f23b2c02df82/130822154350.png)