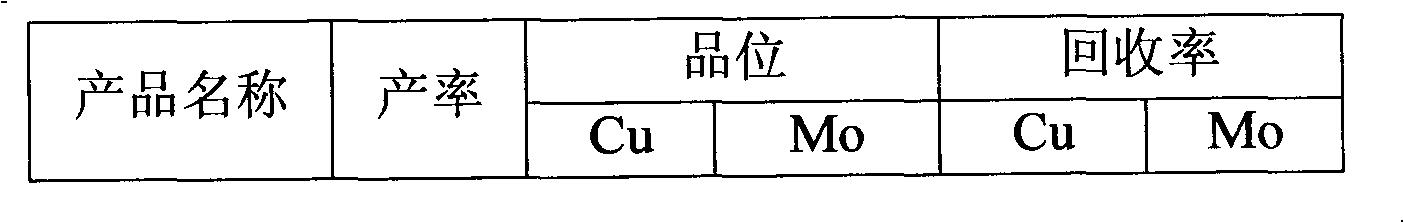
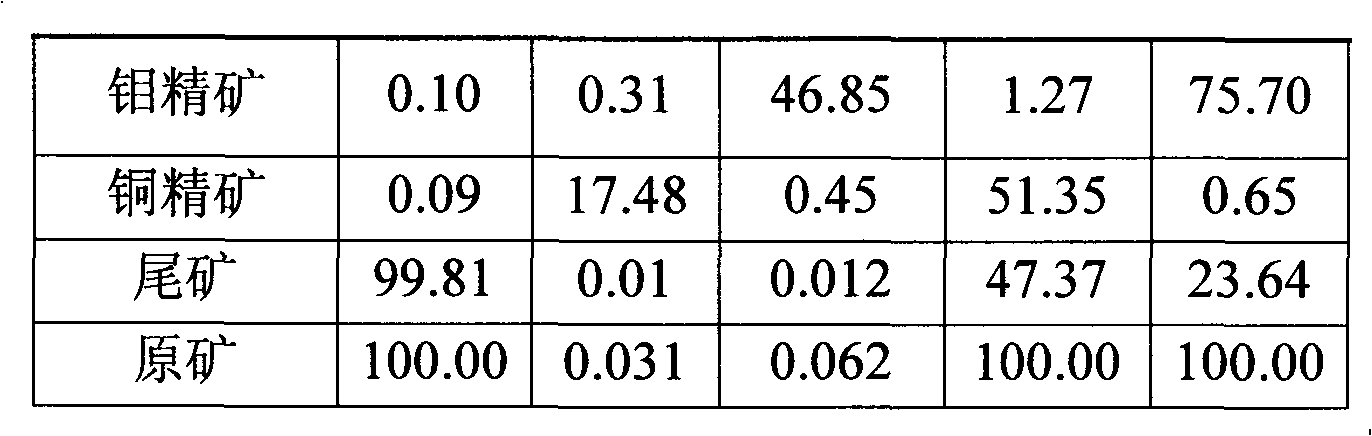
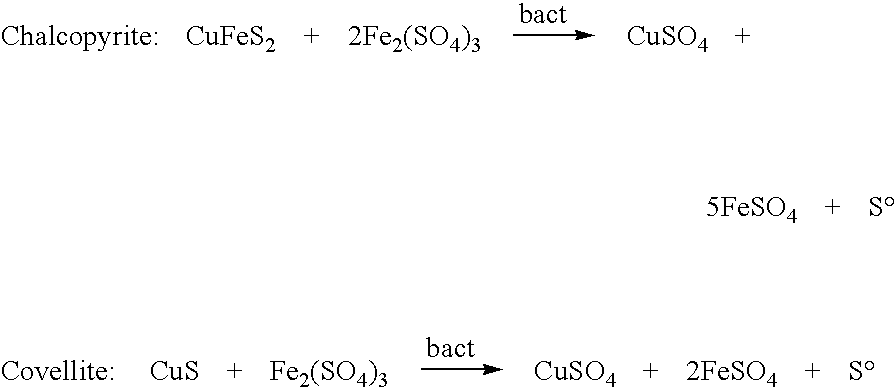Patents
Literature
316 results about "Chalcopyrite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
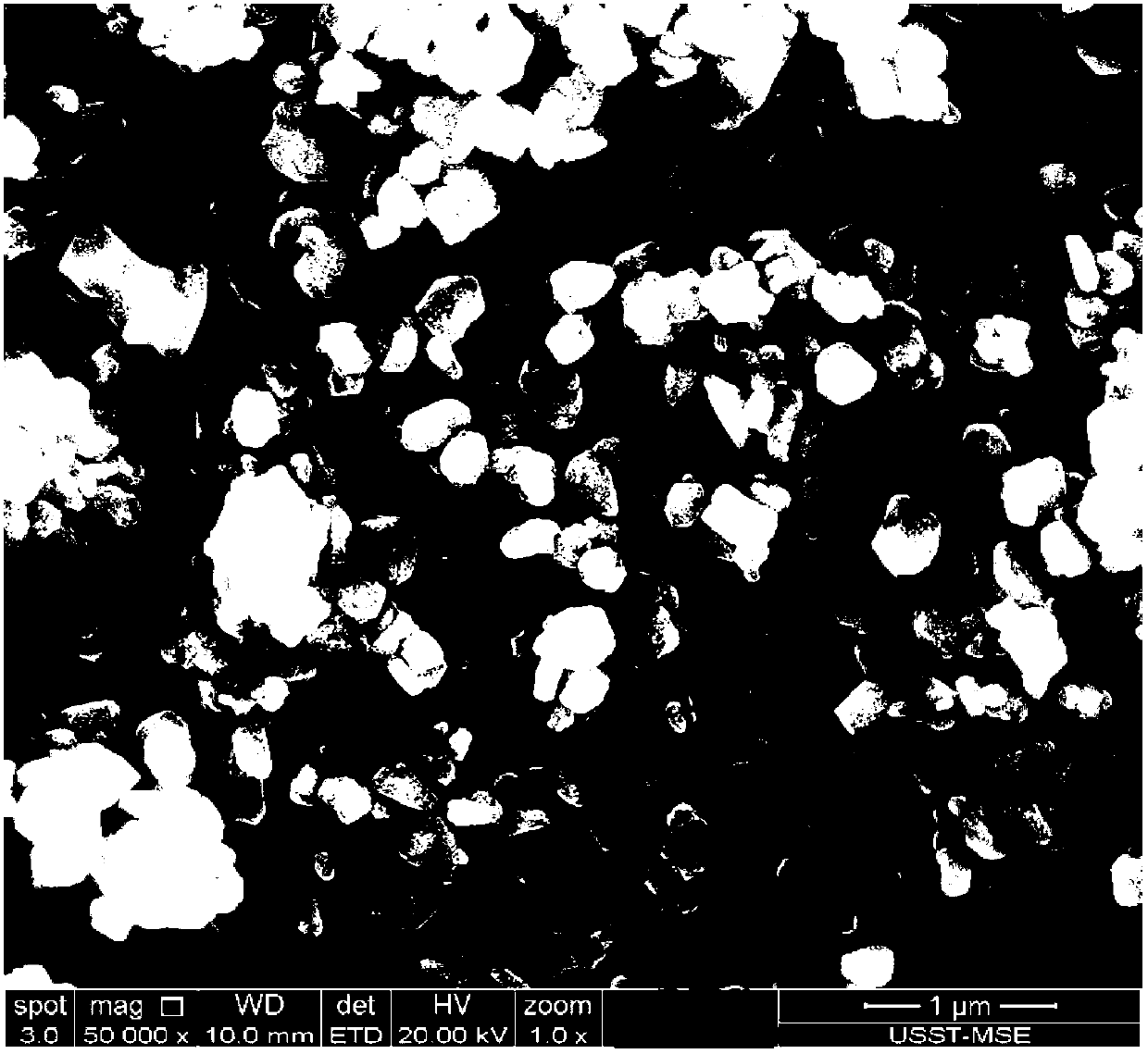
Chalcopyrite ( /ˌkælkəˈpaɪraɪt, -koʊ-/ KAL-ko-PY-ryt) is a copper iron sulfide mineral that crystallizes in the tetragonal system. It has the chemical formula CuFeS₂. It has a brassy to golden yellow color and a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale. Its streak is diagnostic as green tinged black.
Single-source precursors for ternary chalcopyrite materials, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS6992202B1Effective yieldFurnaces without endless coreMaterial nanotechnologyChalcopyriteQuantum dot
A single source precursor for depositing ternary I-III-VI2 chalcopyrite materials useful as semiconductors. The single source precursor has the I-III-VI2 stoichiometry “built into” a single precursor molecular structure which degrades on heating or pyrolysis to yield the desired I-III-VI2 ternary chalcopyrite. The single source precursors effectively degrade to yield the ternary chalcopyrite at low temperature, e.g. below 500° C., and are useful to deposit thin film ternary chalcopyrite layers via a spray CVD technique. The ternary single source precursors according to the invention can be used to provide nanocrystallite structures useful as quantum dots. A method of making the ternary single source precursors is also provided.
Owner:OHIO AEROSPACE INST +1
Process for the rapid leaching of chalcopyrite in the absence of catalysts
InactiveUS6277341B1Increase surface areaImprove misalignmentSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
Owner:MINTEK
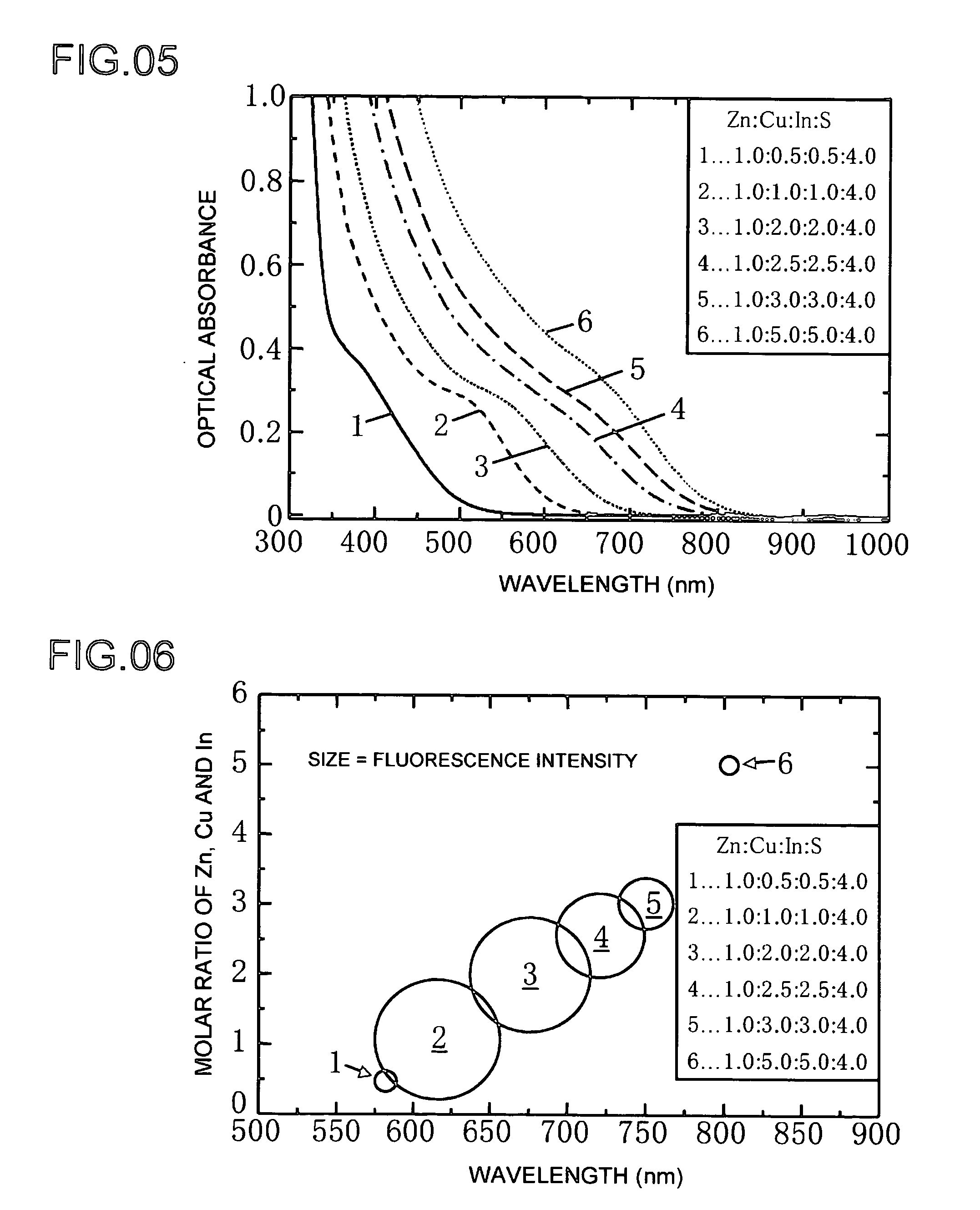
Phosphor And Production Process Of Same
InactiveUS20080277625A1Low toxicLow toxicityLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devicesIndiumChalcopyrite
The present invention provides a lowly toxic phosphor and a production process thereof, and more particularly, the synthesis of nanoparticles having a chalcopyrite structure, a phosphor by compounding with a metal chalcogenite, and a production process thereof. The phosphor is a first compound composed of elements of groups I, III and VI having a chalcopyrite structure, or composite particles or composite compound containing the first compound, and the particle diameter of the first compound, or the composite particles or composite compound, is 0.5 to 20.0 nm. The phosphor is produced by mixing a first solution (Solution A), in which one or more of copper (I), copper (II), silver (I), indium (III), gallium (III) and aluminum (III) are respectively dissolved and mixed in a solution to which has been added a complexing agent, and a second solution (Solution C), in which a chalcogenite compound has been dissolved, followed by heat-treating under pre-determined synthesis conditions.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
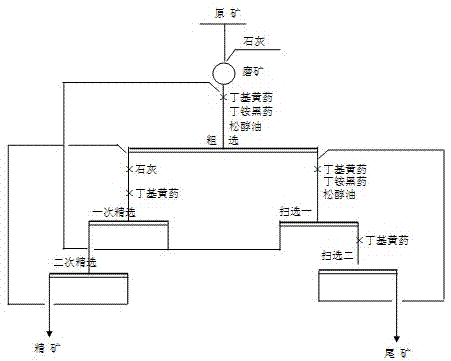
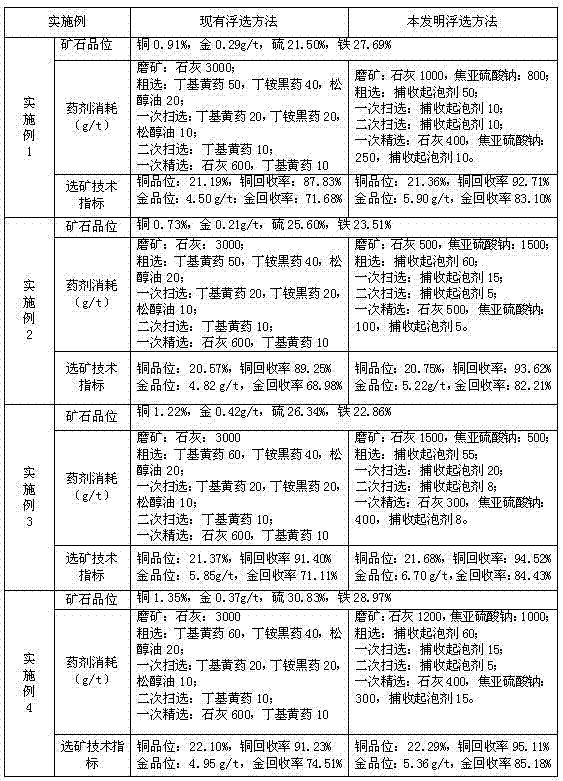
Method for floating high-sulfur gold-bearing copper ore
ActiveCN103691569AEnhanced inhibitory effectImprove beneficiation indexFlotationPropionitrileEthyl group
The invention discloses a method for floating high-sulfur gold-bearing copper ore, which aims at solving the problems that the existing beneficiation method is lower in copper and gold recovery rate under high-alkali condition, and problems that xanthate and black powder are adopted as high-sulfur gold-bearing copper ore collecting agents, the collecting power is stronger, the selectivity is poor, the separation difficulty of copper and sulfur can be aggravated and the consumption of inhibitors is increased. The method comprises the steps of by adopting lime and sodium metabisulfite as an ore pulp pH regulator and a pyrite inhibitor, and the mixture of isopropyl xanthogen propionitrile ester, black powder acid and ethyl dithiocarboxyl propionitrile ester according to certain proportion as a collecting foaming agent, carrying out ore grinding, rough concentration, primary scavenging, secondary scavenging, primary concentration, and secondary concentration on a crude ore, thus realizing the high-efficiency recovery on copper and gold in the high-sulfur gold-bearing copper ore. According to the method, through reasonable combination and addition of medicaments, the selective adsorption of the collecting agent on target mineral-copper pyrite and other copper sulfide minerals and gold minerals can be reinforced, and the copper recovery rate and the gold recovery rate can be improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
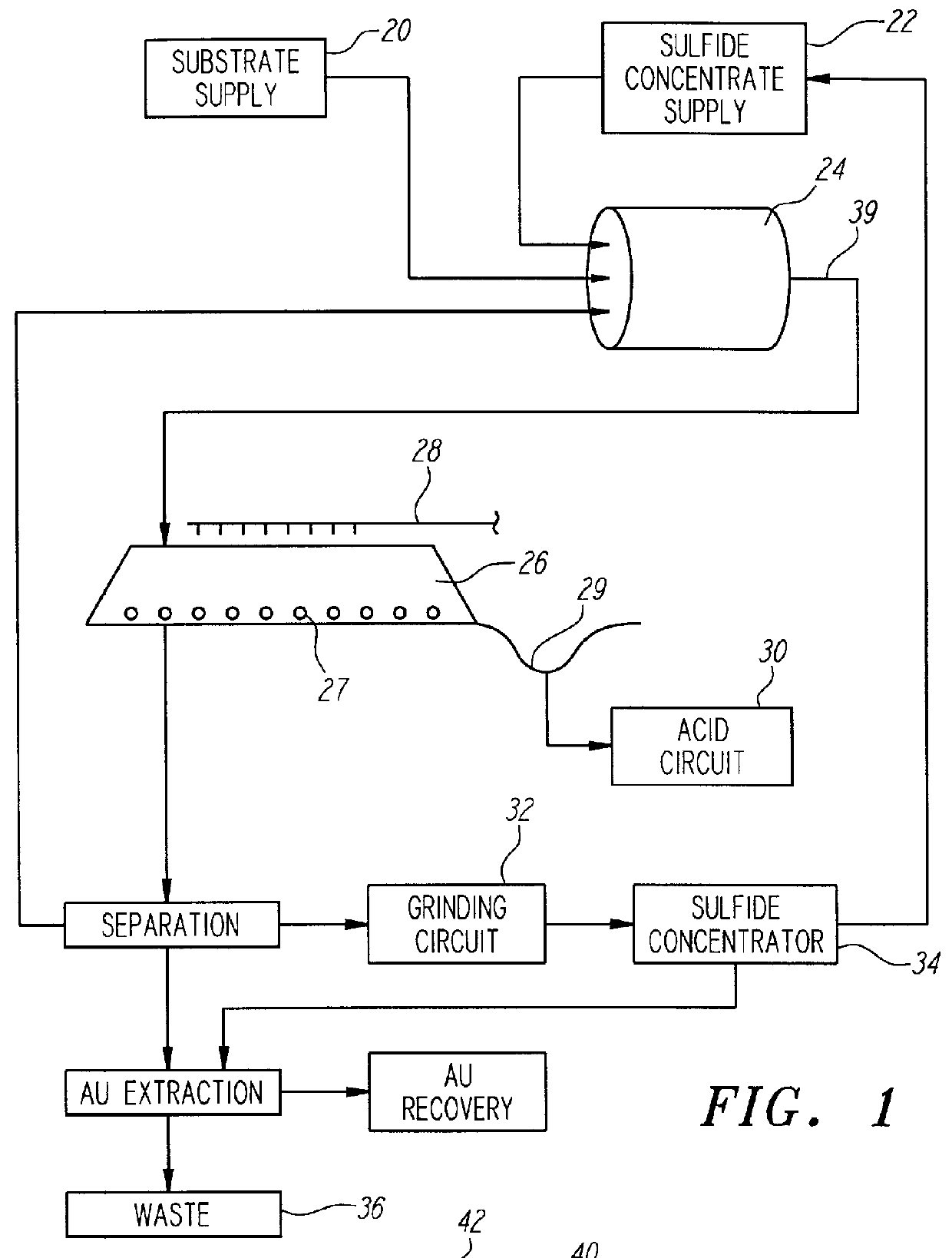
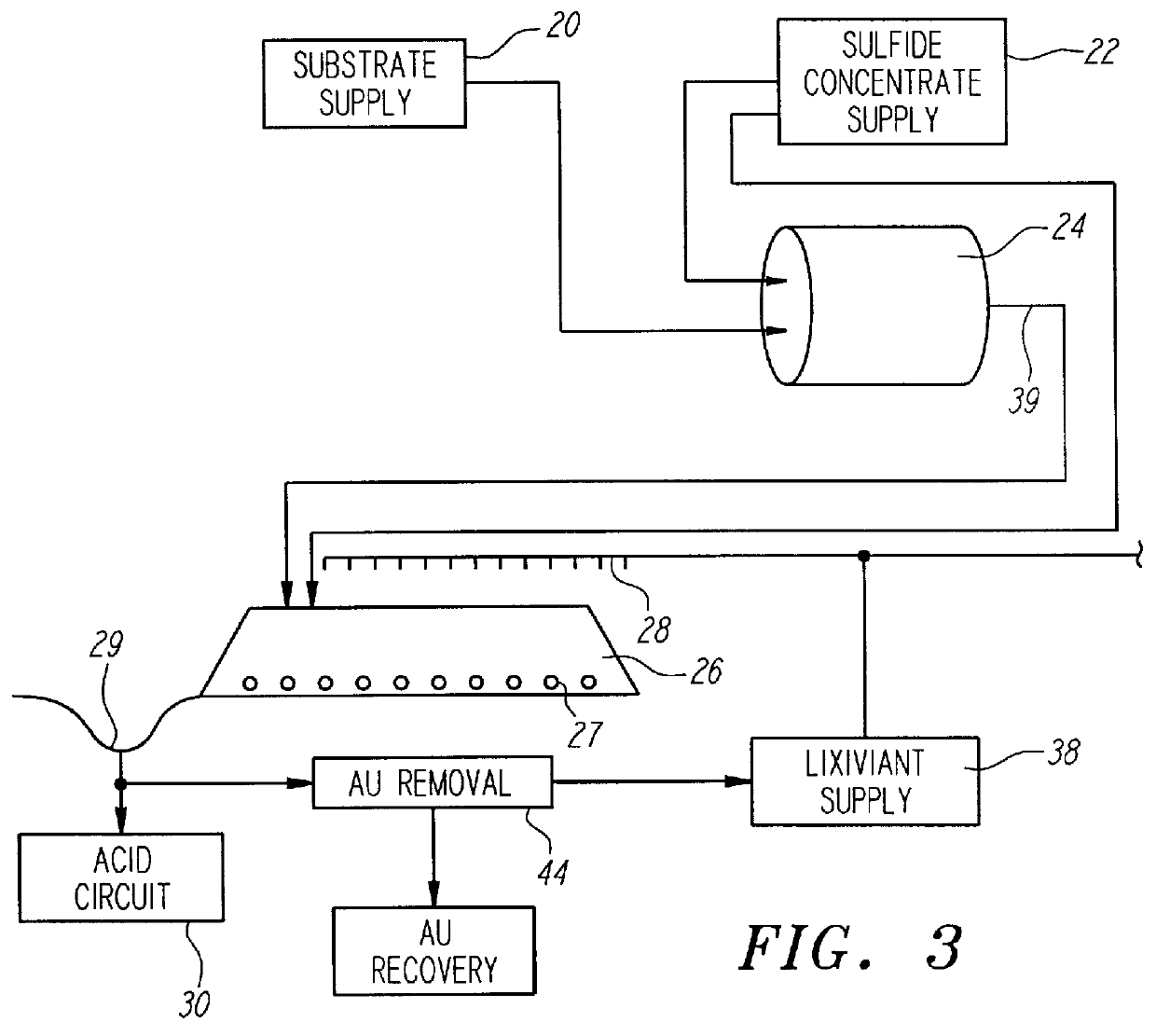
Nonstirred bioreactor for processing refractory sulfide concentrates and method for operating same
InactiveUS6083730AReduced pHIncrease equipment costSolvent extractionContaminated soil reclamationSulfide mineralsMetallic sulfide
A method of biooxidizing sulfide minerals in a nonstirred bioreactor is provided. According to the disclosed method, a concentrate of sulfide minerals is coated onto a substrate, such as coarse ore particles, lava rock, gravel or rock containing mineral carbonate as a source of CO2 for the biooxidizing bacteria. After the sulfide minerals are coated onto the substrate, a heap is formed with the coated substrates or the coated substrates are placed within a tank. The sulfide minerals are then biooxidized to liberate the metal value of interest. Depending on the particular ore deposit being mined, the sulfide mineral concentrates used in the process may comprise sulfide concentrates from precious metal bearing refractory sulfide ores or they may comprise sulfide concentrates from metal sulfide type ores, such as chalcopyrite, millerite or sphalorite. The distinction being that in the former, the metal of interest is a precious metal occluded within the sulfide minerals, whereas in the latter, the metal to be recovered is copper, nickel or zinc and is present as a metal sulfide in the sulfide concentrate.
Owner:GEOSYNFUELS LLC (US)
Moderate thermophilic enriched substance used for mineral leaching of copper pyrites
InactiveCN101560485APromote leachingReduce inhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationFerroplasma thermophilum
The invention discloses a moderate thermophilic enriched substance used for mineral leaching of copper pyrites, comprising five mineral leaching microorganisms: acidithiobacillus caldus S2, leptospirillum ferriphilum YSK, sulfobacillus acidophilus ZW-1, sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans YN22 and ferroplasma thermophilum L1; the pH value and the temperature which are most suitable for the growth of the enriched substance are respectively 1.4-2.0 and 45-48 DEG C. Compared with the existing microorganisms used for brass bio-heap leaching, the enriched substance not only improves the leaching reaction kinetics and shortens the leaching period, but also reduces the passivation inhibition phenomenon and increases the bioleaching speed and the leaching rate of the copper pyrites; furthermore, the enriched substance can endure high concentration metallic ion at the late stage of bioleaching.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of leaching copper sulfide ore with the use of iodine
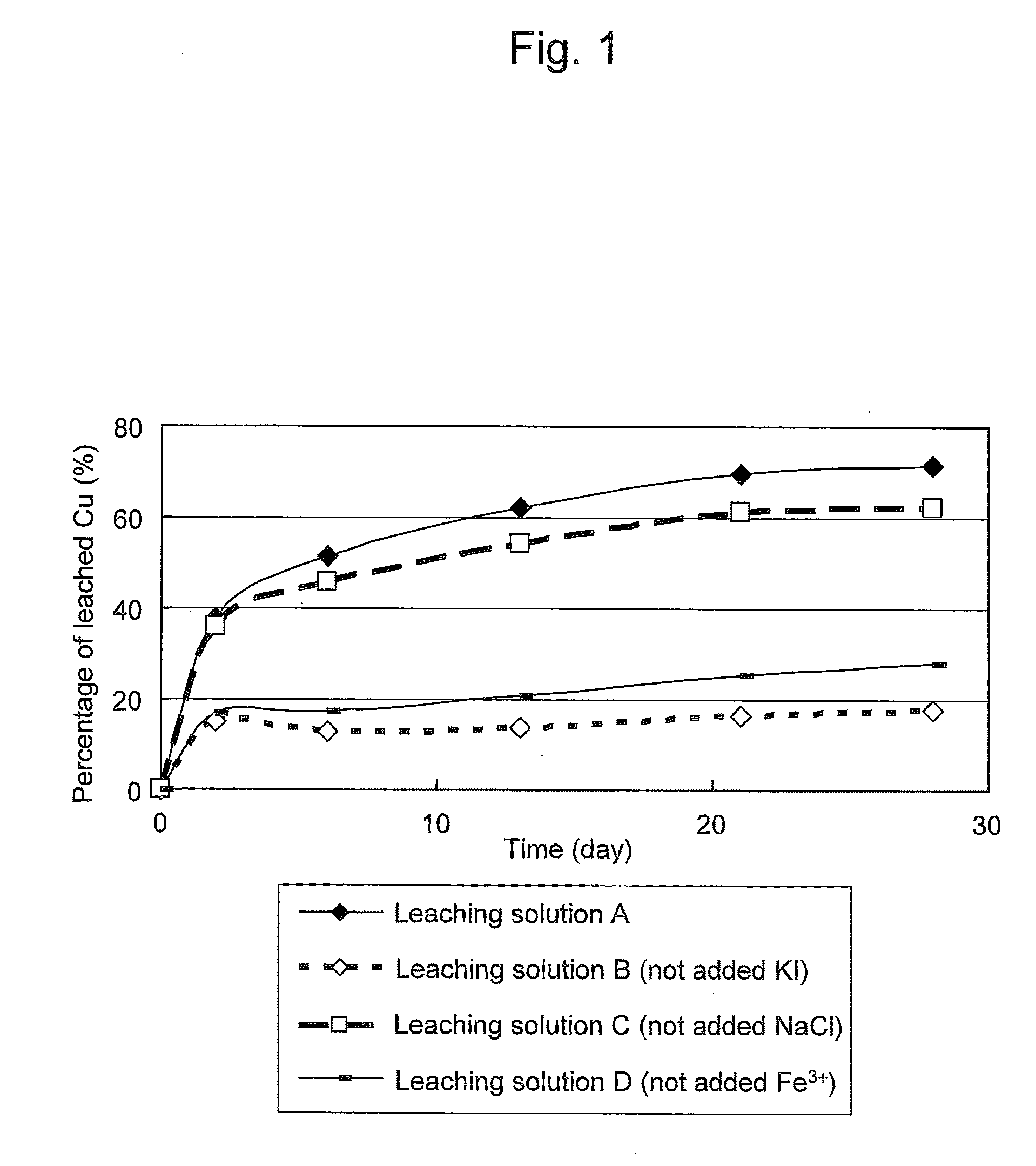
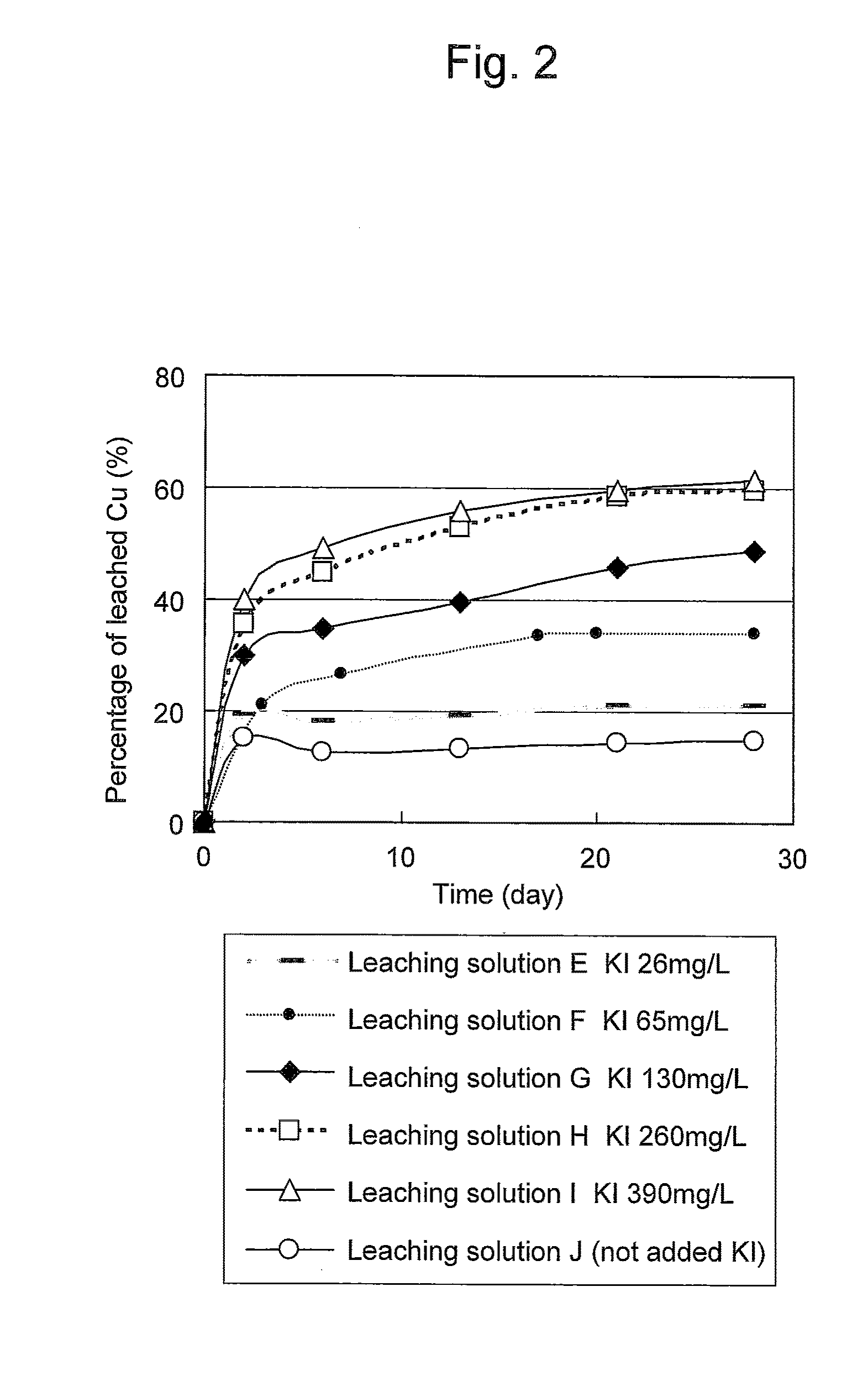
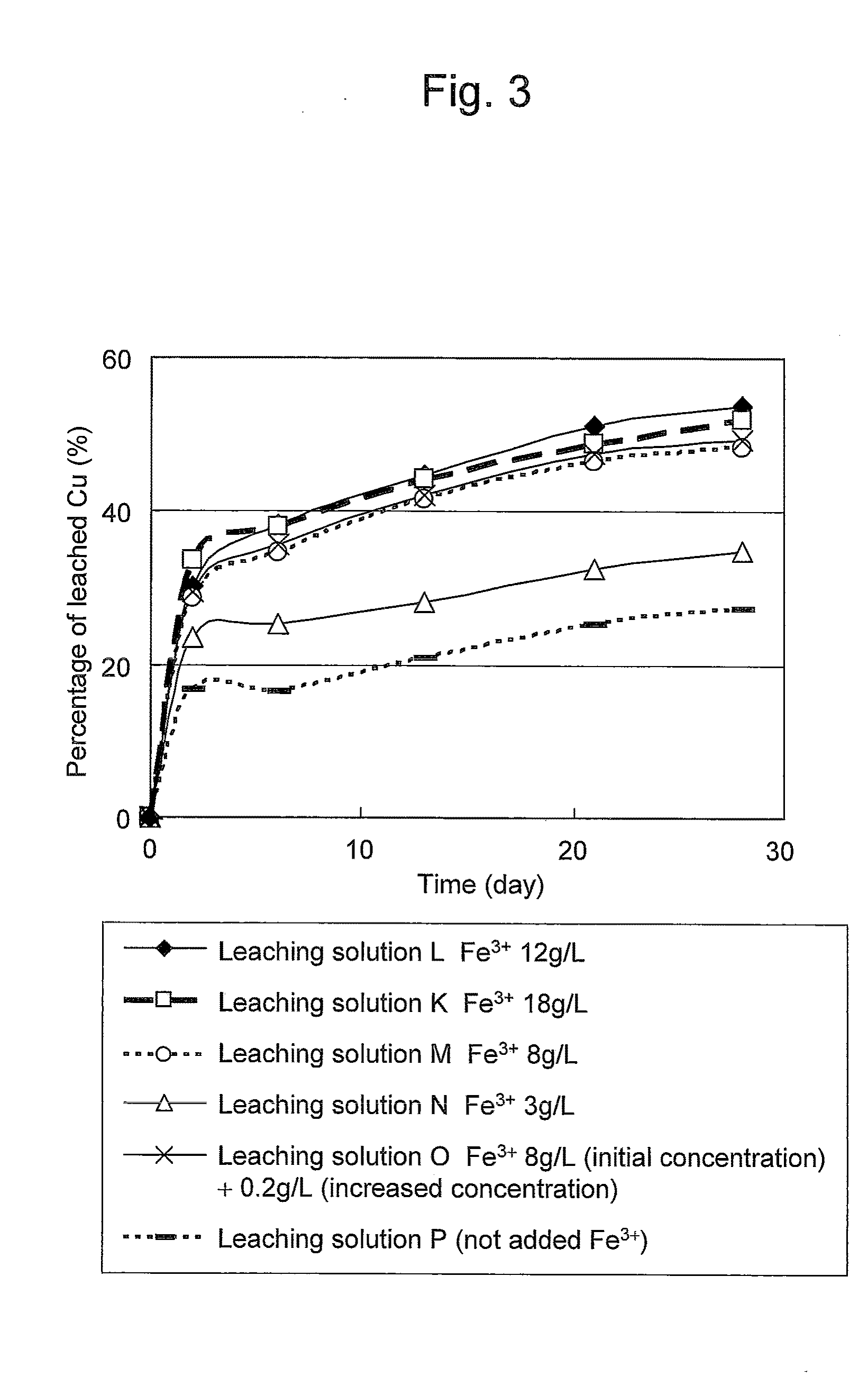
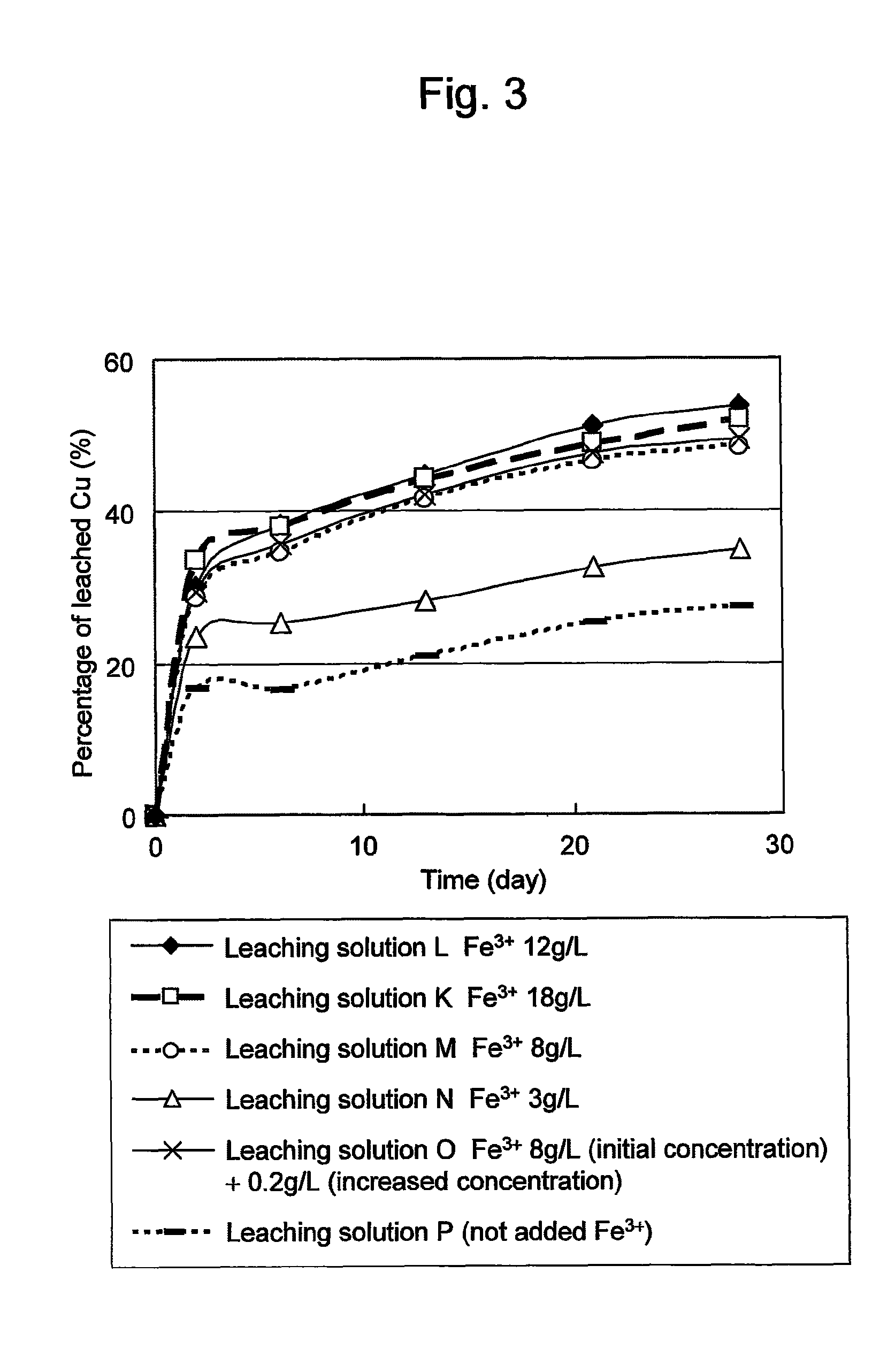
ActiveUS20100018349A1Efficient leachingEfficient executionSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
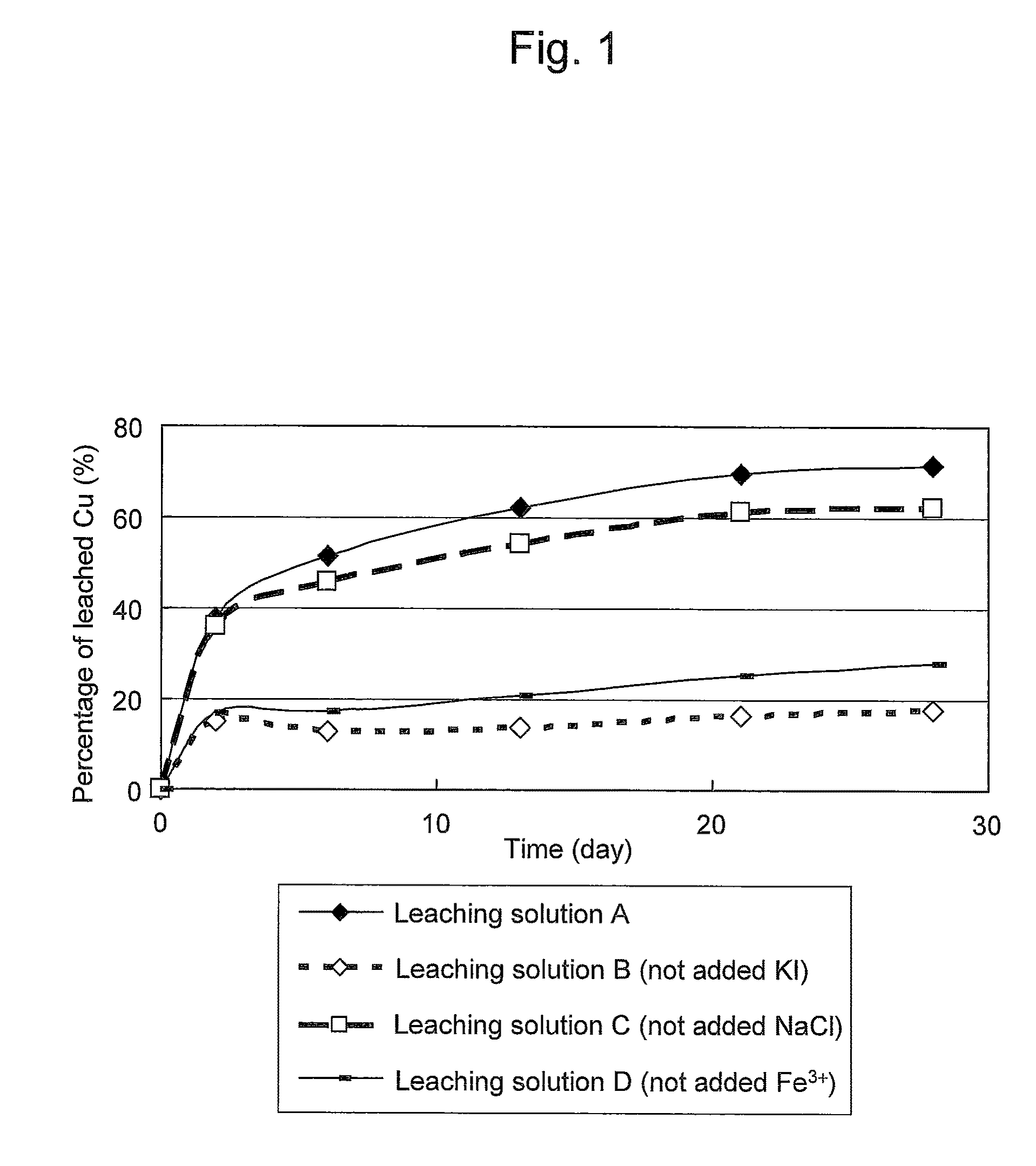
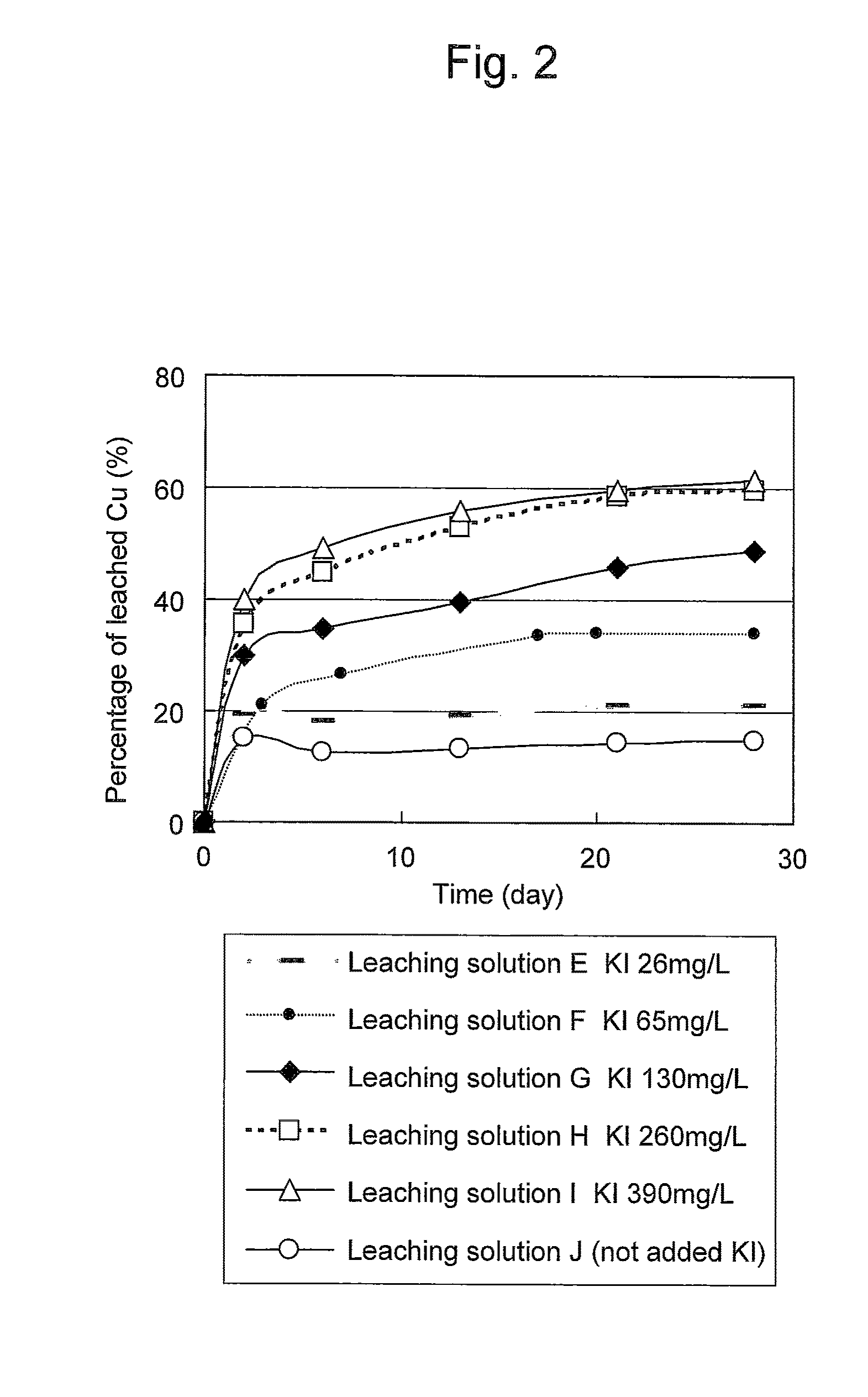
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of efficiently leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore containing chalcopyrite or enargite as a main constituent under versatile conditions for actual operation.A method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising using, as a leaching solution, a sulfuric acid solution containing iodide ions and ferric (III) ions in an excessive amount relative to the iodide ions and leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore; or a method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore with the use of a leaching solution further containing water-soluble ligands such as chloride ions that can stabilize ferric (III) ions in addition to the above components, is provided.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
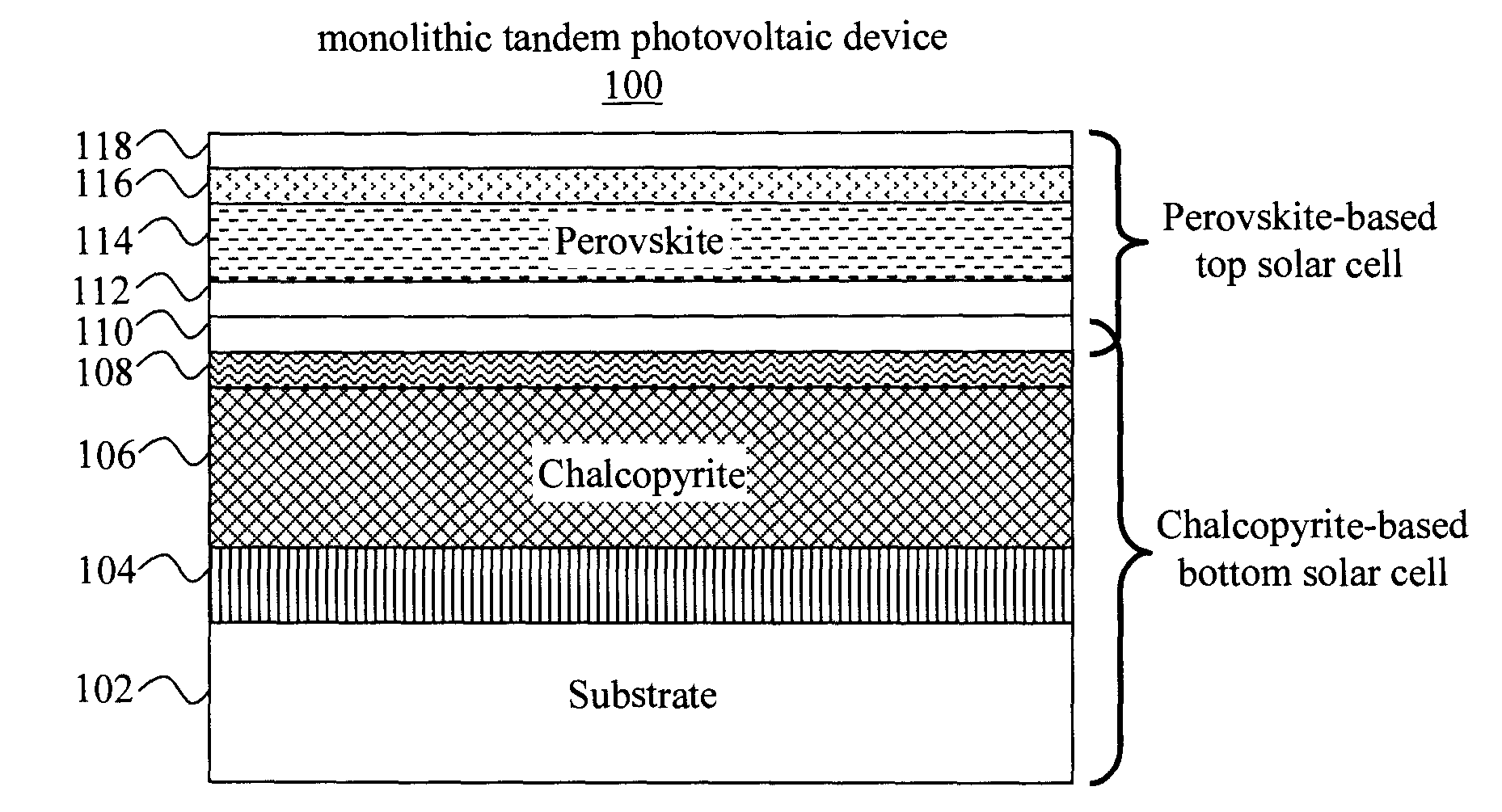
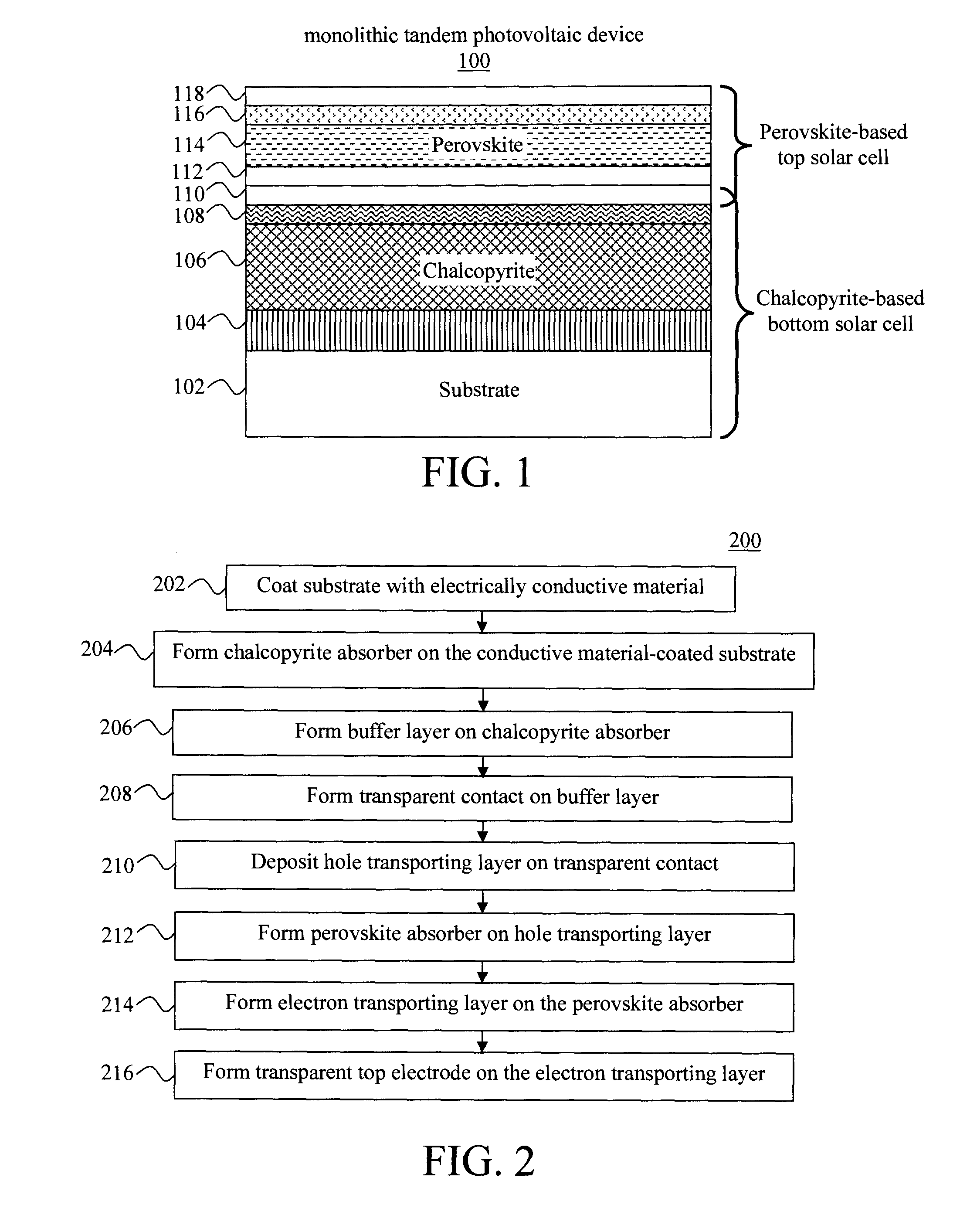
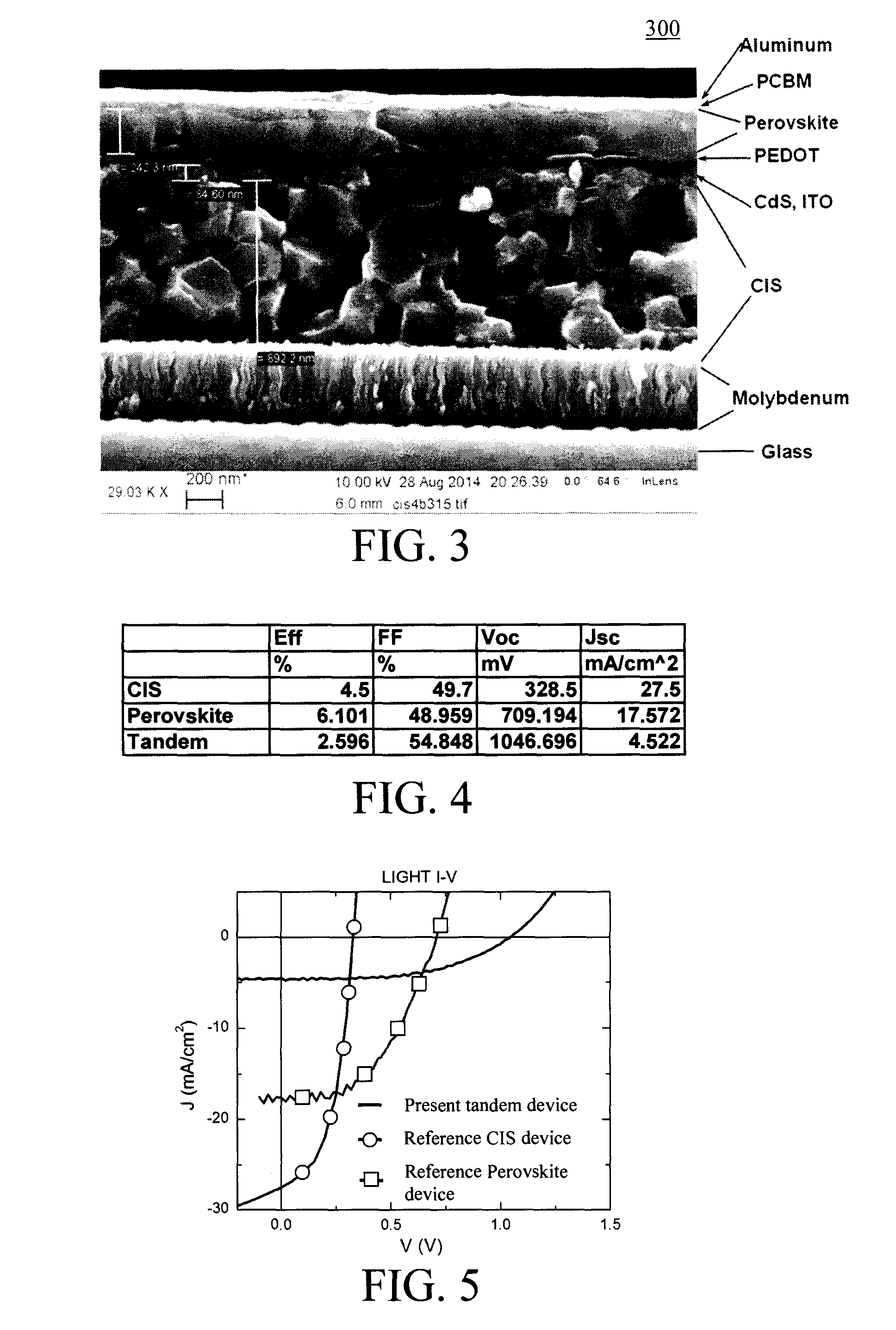
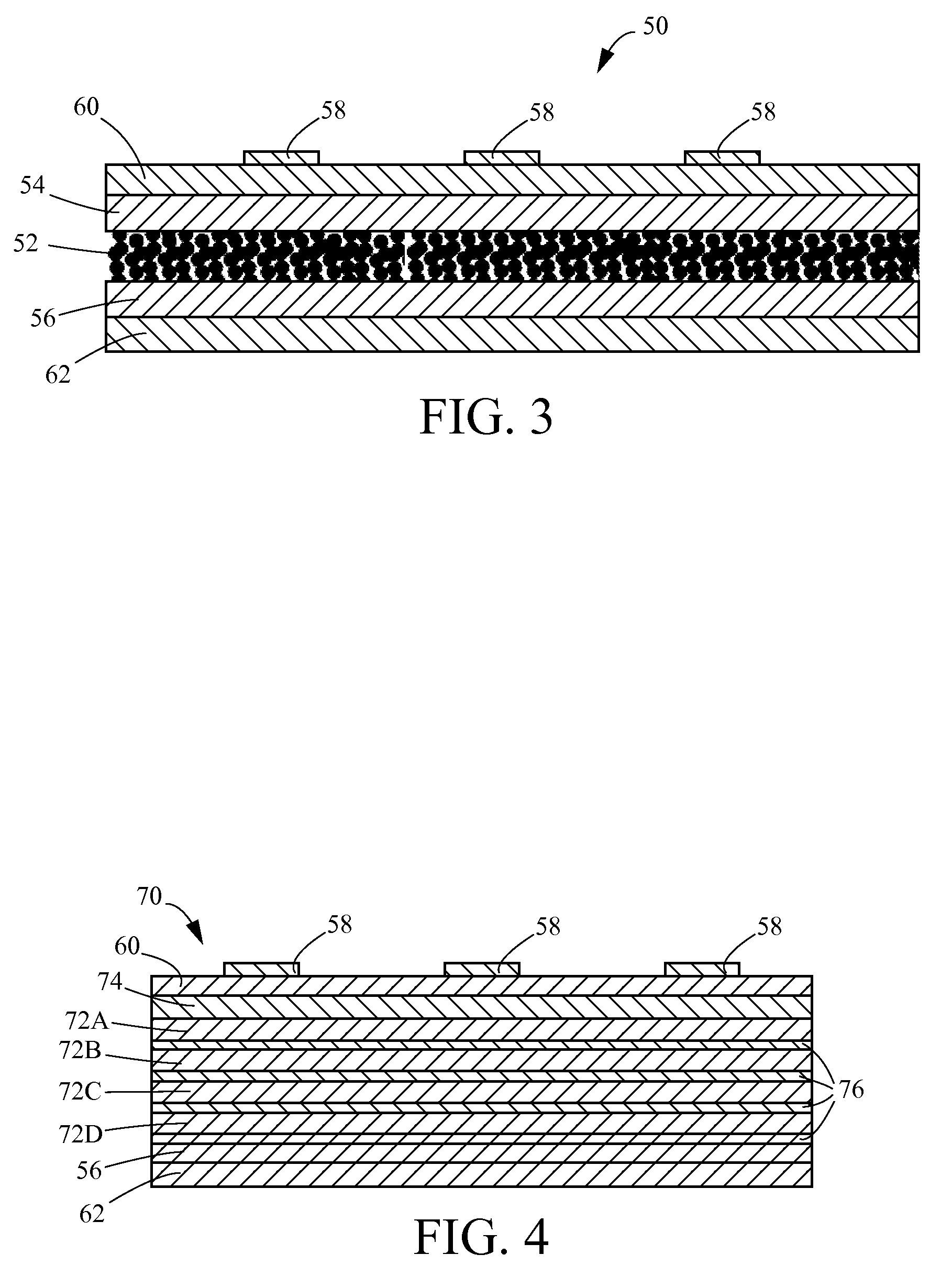
Monolithic Tandem Chalcopyrite-Perovskite Photovoltaic Device
Monolithic tandem chalcopyrite-perovskite photovoltaic devices and techniques for formation thereof are provided. In one aspect, a tandem photovoltaic device is provided. The tandem photovoltaic device includes a substrate; a bottom solar cell on the substrate, the bottom solar cell having a first absorber layer that includes a chalcopyrite material; and a top solar cell monolithically integrated with the bottom solar cell, the top solar cell having a second absorber layer that includes a perovskite material. A monolithic tandem photovoltaic device and method of formation thereof are also provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
Chalcogenide-based materials and improved methods of making such materials
InactiveUS20110226336A1Reduce void areaSmall sizeDiffusing elementsFinal product manufactureChalcopyriteSulfur
The present invention provides strategies for making high quality CIGS photoabsorbing materials from precursor films that incorporate a sub-stoichiometric amount of chalcogen(s). Chalcogen(s) are incorporated into the CIGS precursor film via co-sputtering with one or more other constituents of the precursor. Optional annealing also may be practiced to convert precursor into more desirable chalcopyrite crystalline form in event all or a portion of the precursor has another constitution. The resultant precursors generally are sub-stoichiometric with respect to chalcogen and have very poor electronic characteristics. The conversion of these precursors into CMS photoabsorbing material via chalcogenizing treatment occurs with dramatically reduced interfacial void content. The resultant CIGS material displays excellent adhesion to other layers in the resultant photovoltaic devices. Ga migration also is dramatically reduced, and the resultant films have optimized Ga profiles in the top or bottom portion of the film that improve the quality of photovoltaic devices made using the films.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
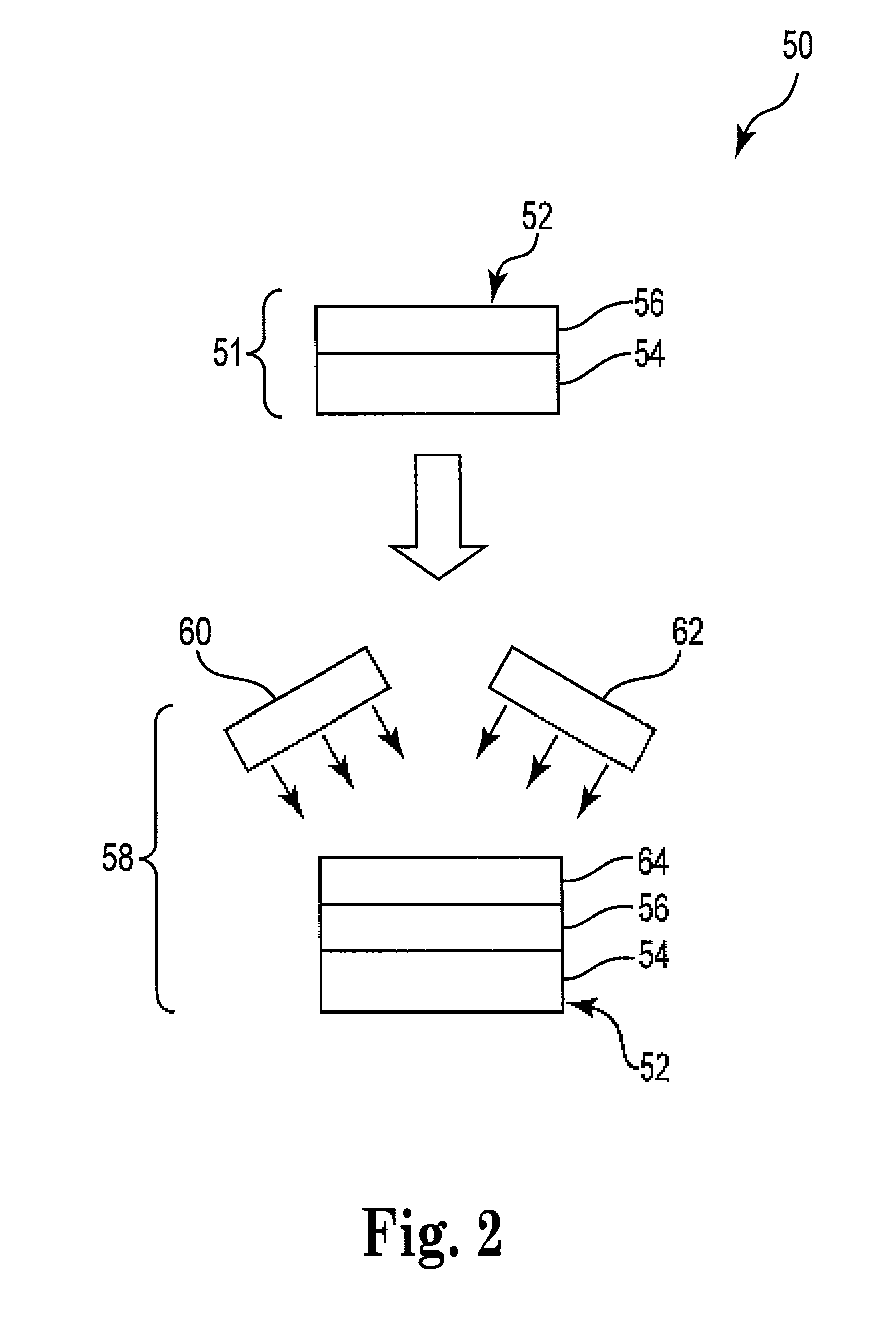
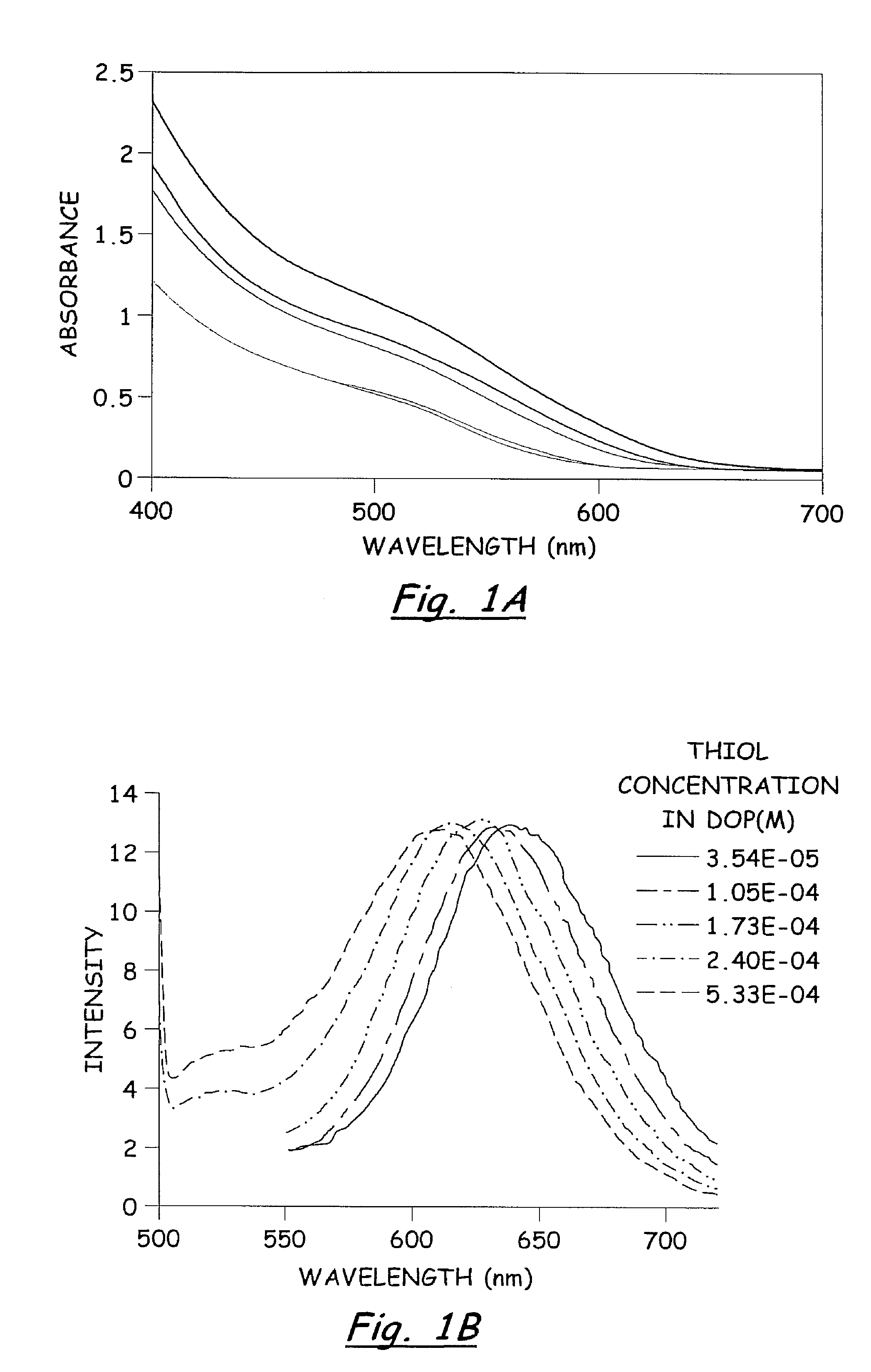
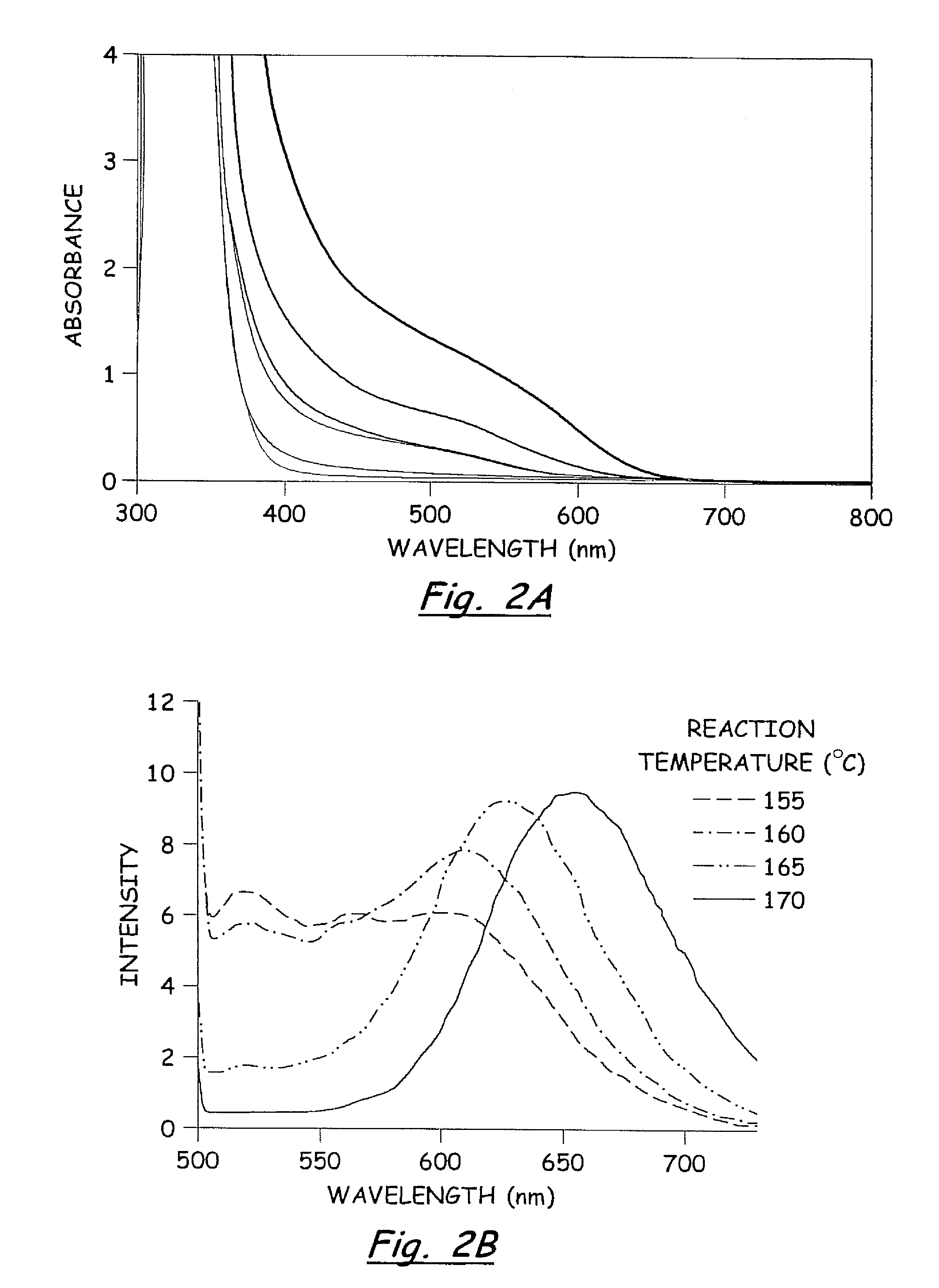
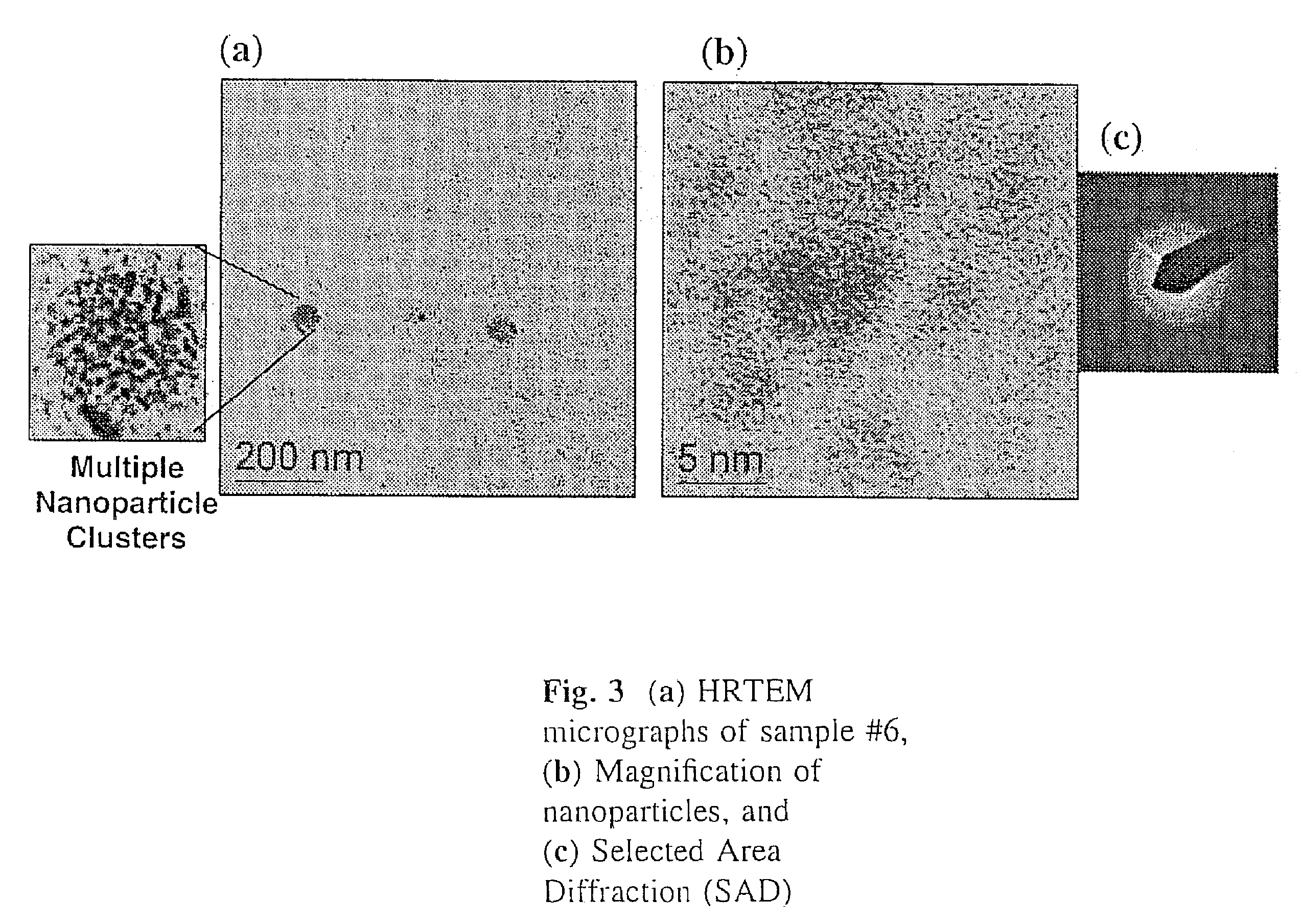
Rapid synthesis and size control of chalcopyrite-based semi-conductor nanoparticles using microwave irradiation
ActiveUS7892519B2Increases microscopic temperature of reactionImprove homogeneityNanotechPolycrystalline material growthChalcopyritePhotoluminescence
CuInS2 nanoparticles have been prepared from single source precursors via microwave irradiation. Also, CuInGaS2 alloy nanoparticles have been prepared. Microwave irradiation methods have allowed an increase in the efficiency of preparation of these materials by providing increased uniformity of heating and shorter reaction times. Nanoparticle growth has been controlled in the about 1 to 5 nm size range by variation of thiolated capping ligand concentrations as well as reaction temperatures and times. Investigation of the photophysical properties of the colloidal nanoparticles has been performed using electronic absorption and luminescence emission spectroscopy. Qualitative nanoparticles sizes have been determined from the photoluminescence (PL) data and compared to TEM images.
Owner:IDAHO STATE UNIVERSITY
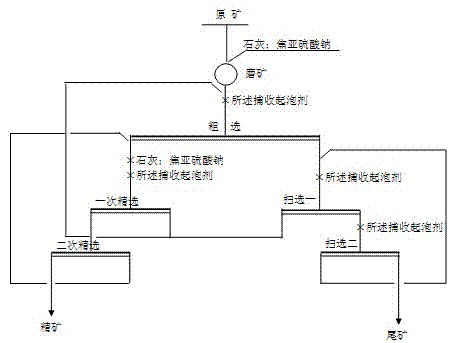
Beneficiation method for separating chalcopyrite, galena, zinc blende and ironpyrite
The invention discloses a flotation separation method for chalcopyrite, galena, zinc blende and ironpyrite by a composite inhibitor which comprises sodium pyrosulfite, sodium sulfite and ferrous sulfate, has an inhibition effect on the galena, the zinc blende and the ironpyrite under the condition of a natural pH value, and is easy to degrade and activate after inhibition during a separation process of the chalcopyrite, the galena, the zinc blende and the ironpyrite. According to the flotation separation method, the flotation is performed under the condition of a neutral medium, the adopted composite inhibitor has the inhibition effect on three metal sulphide ores of the galena, the zinc blende and the ironpyrite; environment pollution caused by adoption of heavy metal salt inhibitors is prevented; pipeline scaling caused by adoption of lime is prevented; and the inhibiting capacity of the composite medicament is relatively weaker and added segmentally, an activation difficulty of follow-up operation due to overinhibition in a flotation process is prevented, and the improvement of the metal recovery rate is further facilitated.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
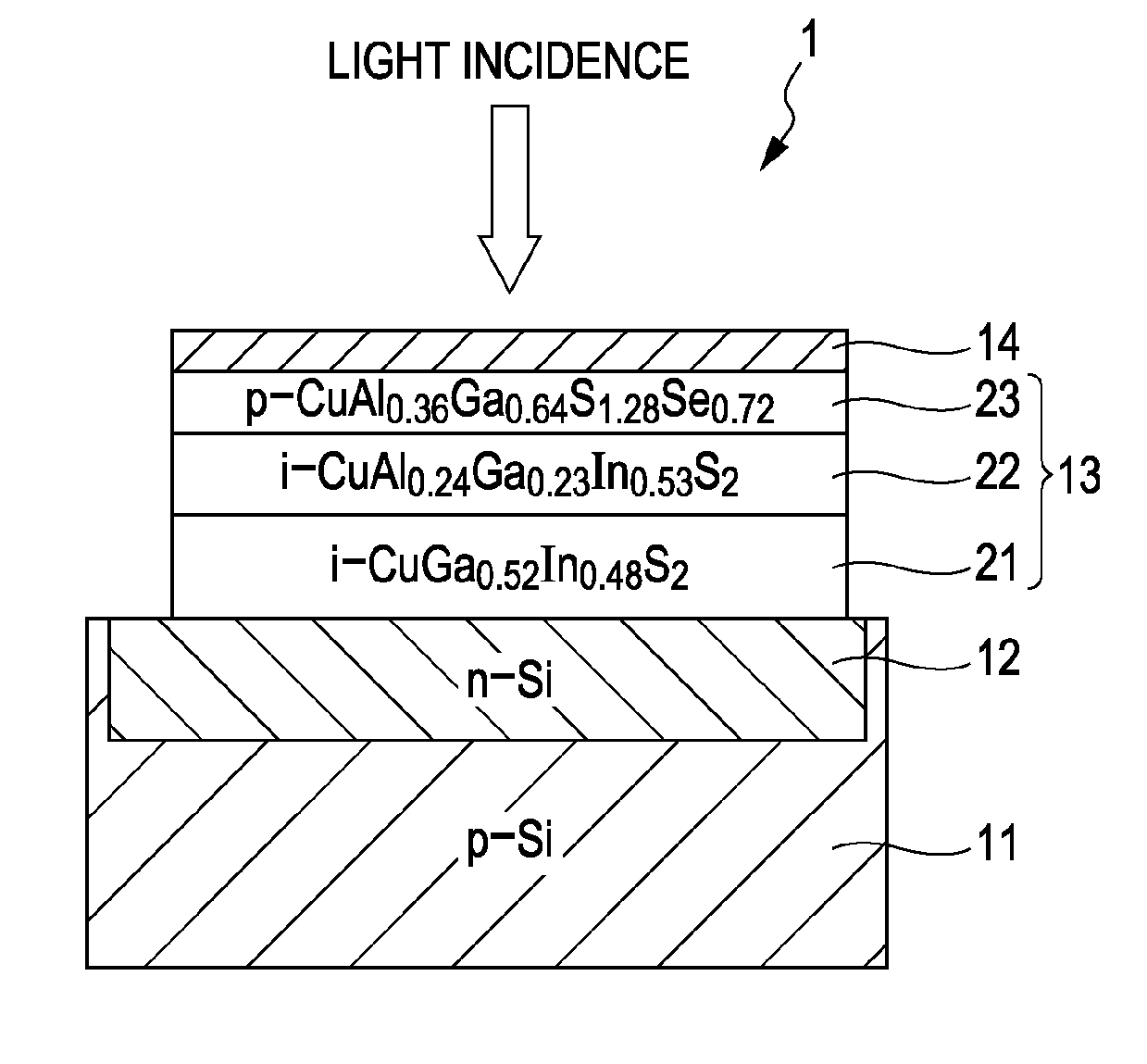
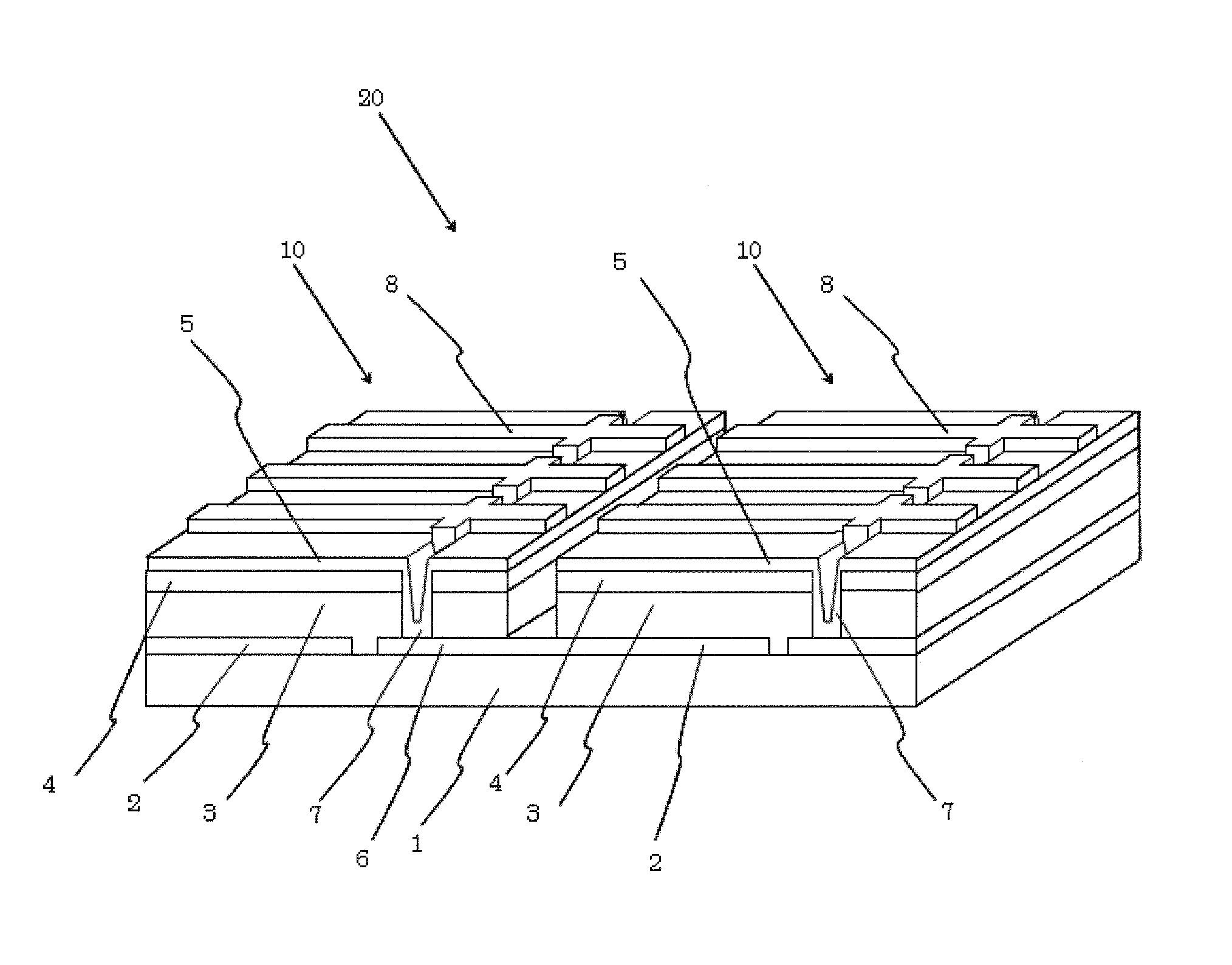
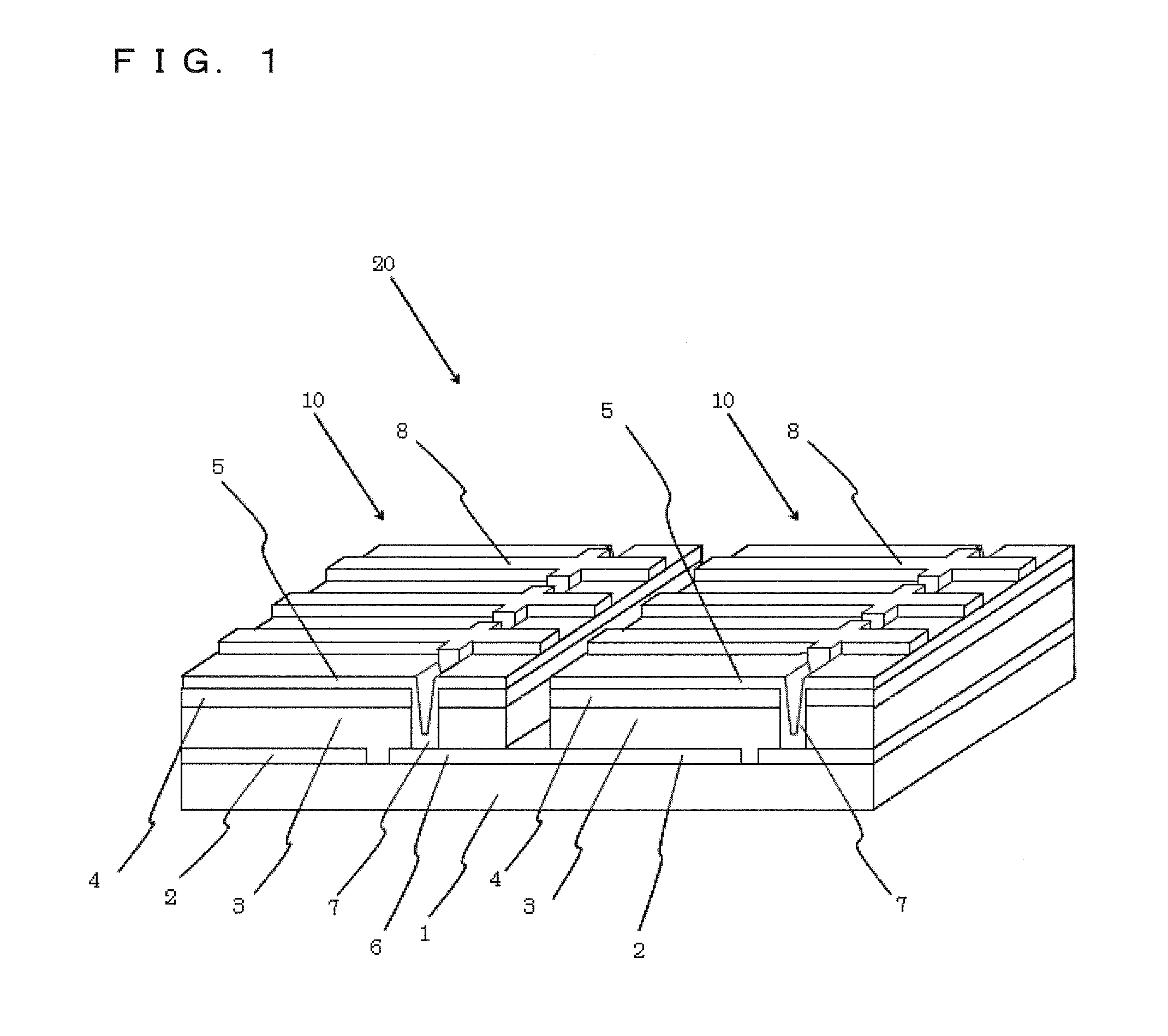
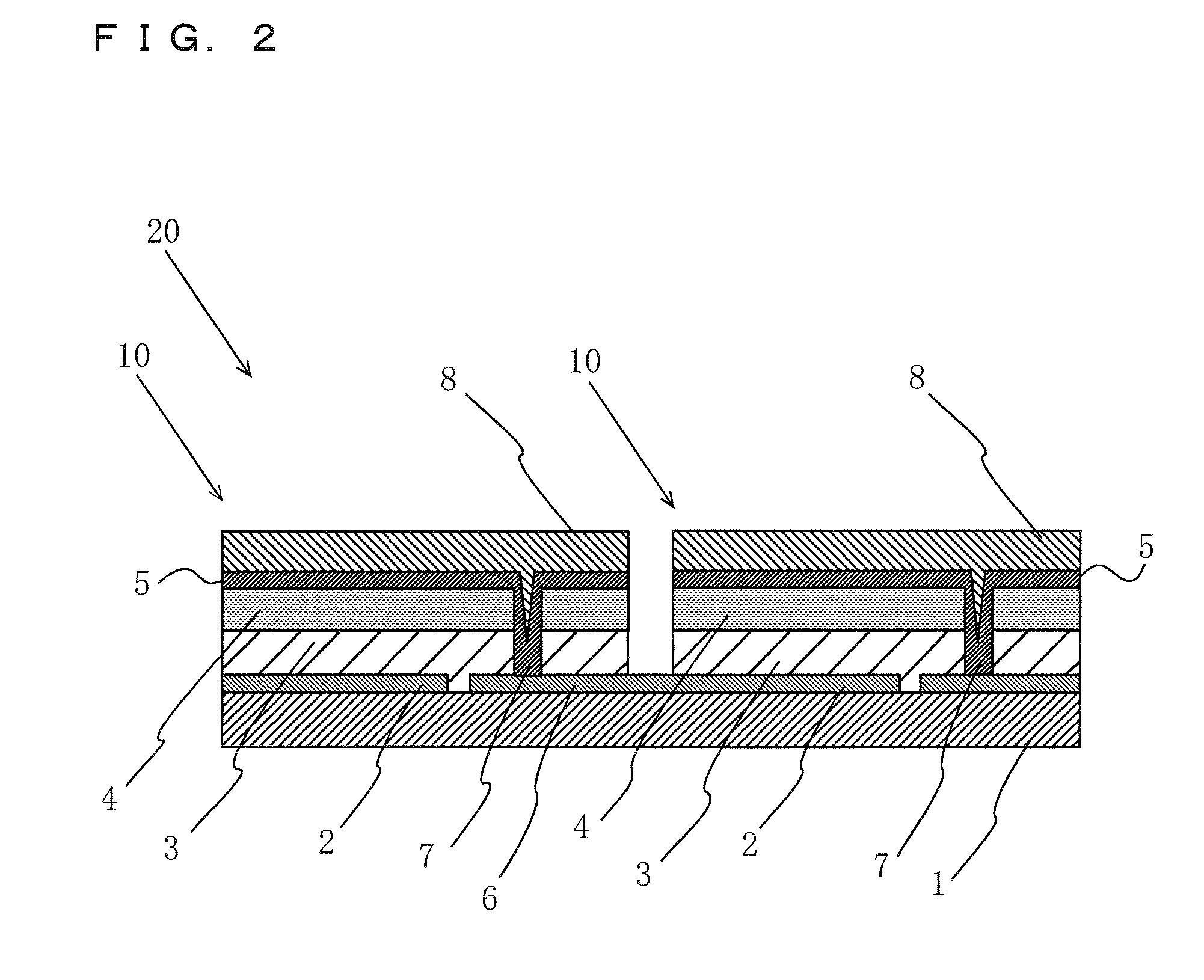
Solid-state image device, method for producing the same, and image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20100182471A1Avoid desensitizationSmall sizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsIndiumChalcopyrite
A solid-state image device includes a silicon substrate, and a photoelectric conversion layer arranged on the silicon substrate and lattice-matched to the silicon substrate, the photoelectric conversion layer being composed of a chalcopyrite-based compound semiconductor of a copper-aluminum-gallium-indium-sulfur-selenium-based mixed crystal or a copper-aluminum-gallium-indium-zinc-sulfur-selenium-based mixed crystal.
Owner:SONY CORP
Applications of specific restraining agent in complicated sulfuration mine
The invention discloses a specific inhibitor application in complex sulfide ore. The inventive organic compound contains mineral-philic group -SH, hydrophilic group -COOH, -OH, -SO3, etc. in molecular structure, which fully shows the inhibiting property against pyrrhotite, pyrite and chalcopyrite in complex sulfide ore flotation separation, and is a high selectivity desulphurizing inhibitor. Compared with the prior inorganic inhibitors such as cyanide, lime, zinc sulfate, trisodium phosphate, dichromate, potassium permanganate, sodium sulfide, sulfite, etc., the inventive inhibitor has the advantages of low usage amount, good index and no pollution.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
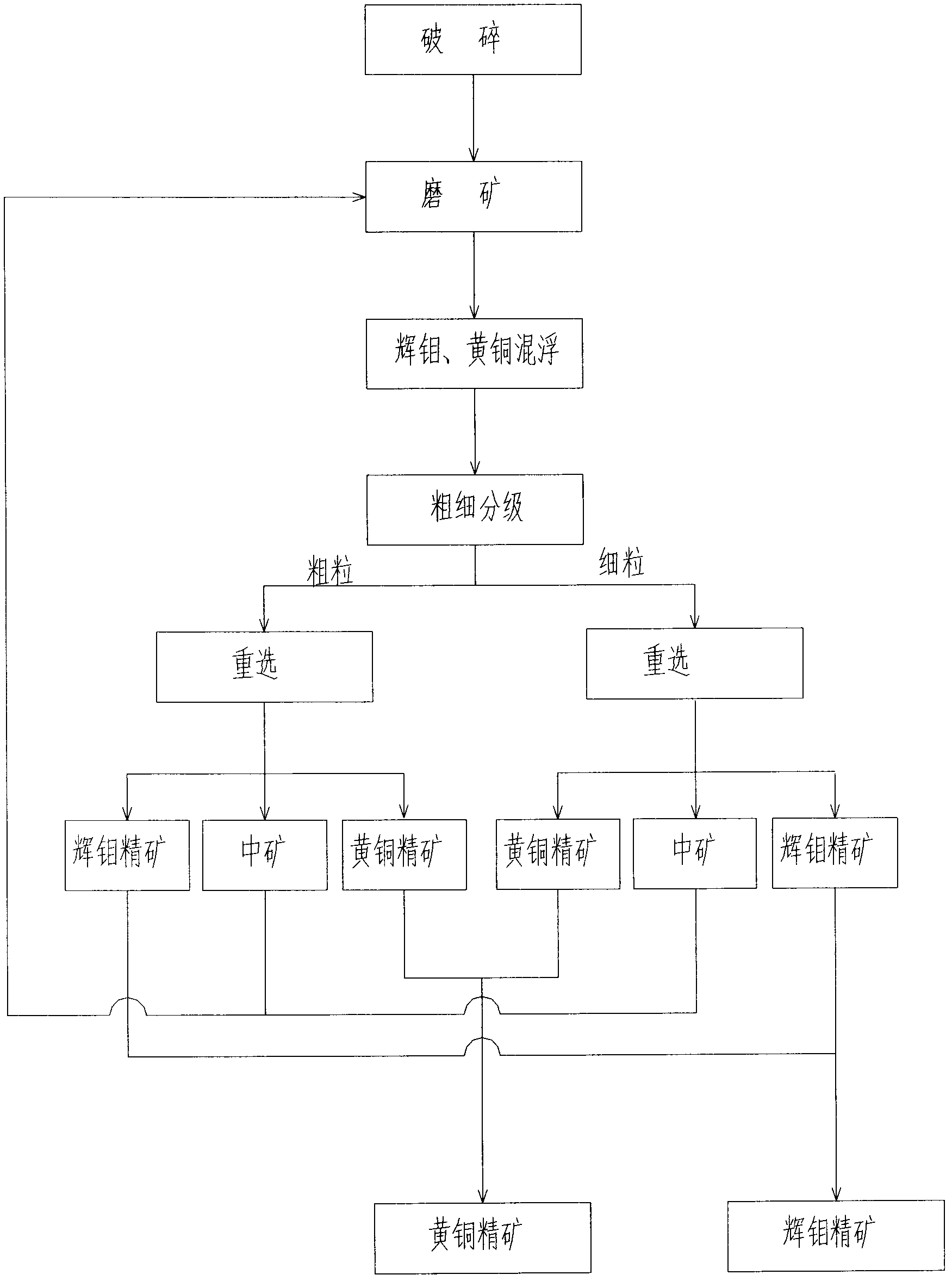
Method for separating bright molybdenum and brass in refractory molybdenum copper sulphide ore
InactiveCN102824954ALow recovery rateHigh recovery rateFlotationWet separationChalcopyriteRefractory
The invention discloses a method for separating bright molybdenum and brass in refractory molybdenum copper sulphide ore. According to the method, primordial bright molybdenum and brass ore are used as raw materials and are subject to general floatation after being crushed and ground, thereby enriching bright molybdenum and brass; the bright molybdenum and brass are subject to thickness grading in order to separate out coarse and fine products, the coarse particle portion and the fine particle portion are respectively subject to table re-separation in order to separate bright molybdenum and brass, thereby obtaining the qualified bright molybdenum and brass ore concentrate, mixed intermediate ore of bright molybdenum ore and brass ore, and qualified brass ore; the mixed intermediate ore is returned back to the re-grinding technique and introduced into the circulating system, thereby realizing the separation of the refractory bright molybdenum and brass. The technique has the following advantages that the disadvantages of greatly increased cost caused by the addition of a large amount of inhibitors in the common separation of bright molybdenum and brass for inhibiting the brass ore and the removing of the regents when brass is recovered from the tailings, in particular the disadvantages of the reduction of recovering ratio of the bright molybdenum particularly the brass when a large amount of brass ore inhibitors are existent in the water system, and the environmental impact due to the need of reagents in the common floating separation, are avoided.
Owner:北京华夏建龙矿业科技有限公司
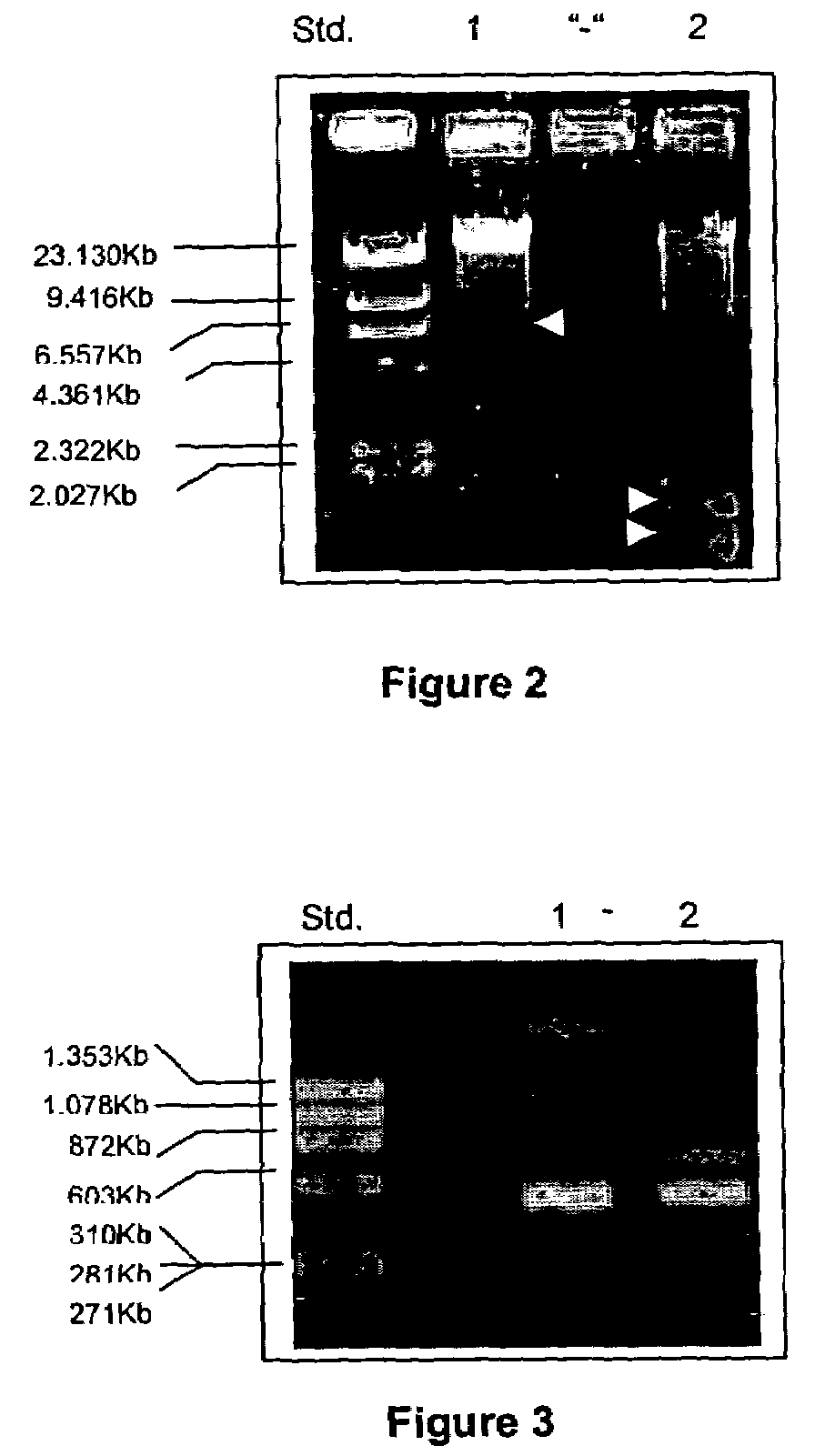
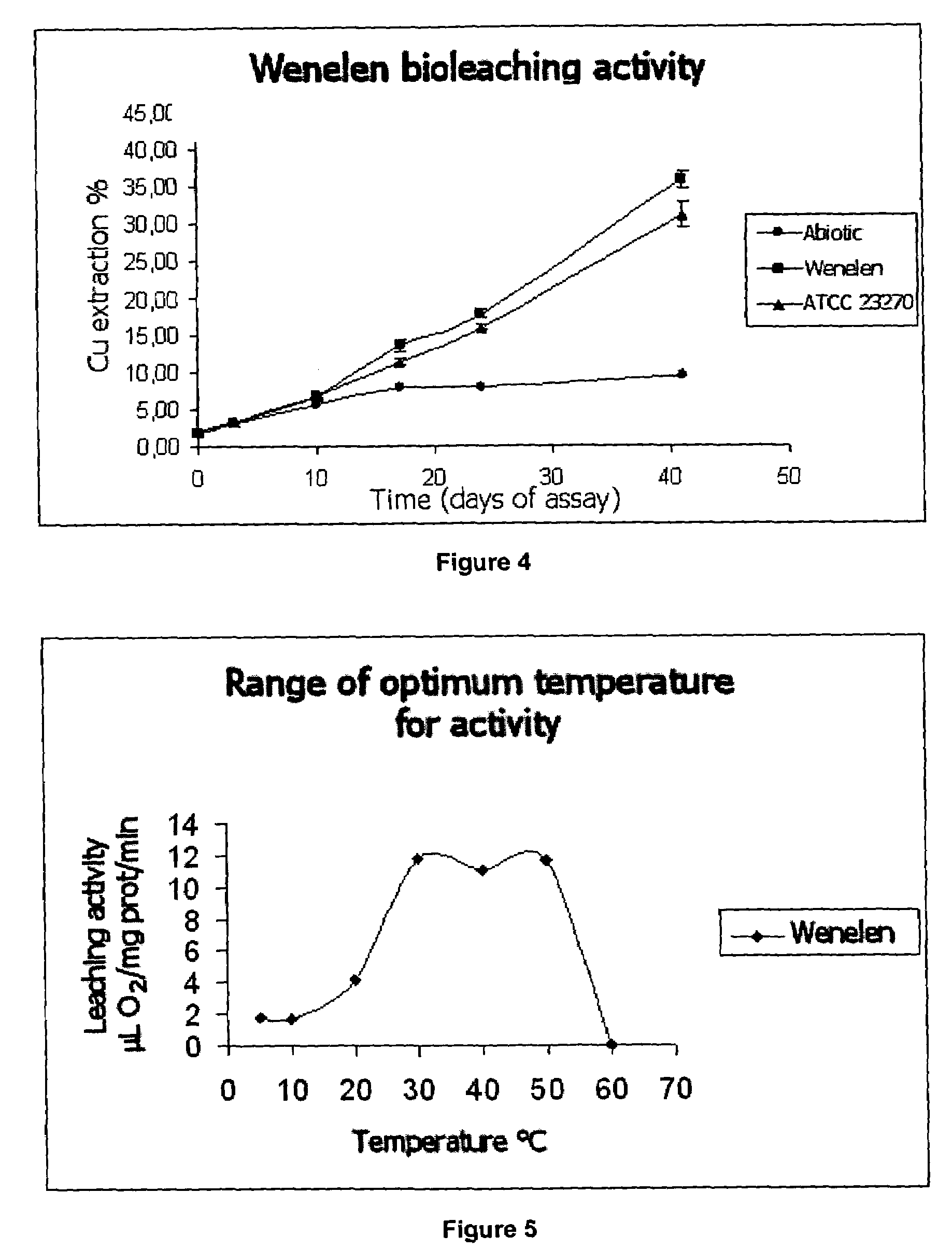
Bacteria strain wenelen DSM 16786, use of said bacteria for leaching of ores or concentrates containing metallic sulfide mineral species and leaching processes based on the use of said bacteria or mixtures that contain said bacteria
The present invention is related to an isolated chemolithotrophic bacterial strain belonging to the specie Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, named “Wenelen” and deposited at the Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH—DSMZ under classification number DSM 16786, the use of said bacteria for leaching ores or concentrates containing of metallic sulfide species and leaching processes based on the use of said bacteria or mixtures that contain said bacteria. This Wenelen DSM 16786 strain has an increased oxidizing activity, especially regarding chalcopyrite, when compared to known bacteria. Due to the former feature, this bacteria strain show great interest for biomining applications and it is presently being subjected to annotation processes after sequencing.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
A Composite Depressant for Inhibiting the Flotation of Copper Sulfide Minerals
The present invention relates to a composite depressant for inhibiting the flotation of copper sulfide minerals. Sodium acetate 20% ~ 80%; The preparation method is: According to the above ratio, under normal temperature and pressure, stir and mix evenly at a speed of 300 ~ 1000rad / min to obtain a compound inhibitor. The present invention overcomes (1) the environmental pollution caused by the application of cyanide; (2) the large amount of sodium sulfide used, the high expense of the medicament, and the poor economic benefit; Activation of sulfide ions on chalcopyrite, pyrite, etc. The compound depressant has improved inhibition effect and inhibition effect, and has the characteristics of wide source of raw materials, easy preparation, low processing cost, stable flotation performance, relatively low price and easy popularization.
Owner:SHENYANG RES INST OF NONFERROUS METALS
Floatation separation method for copper pyrites and iron pyrites
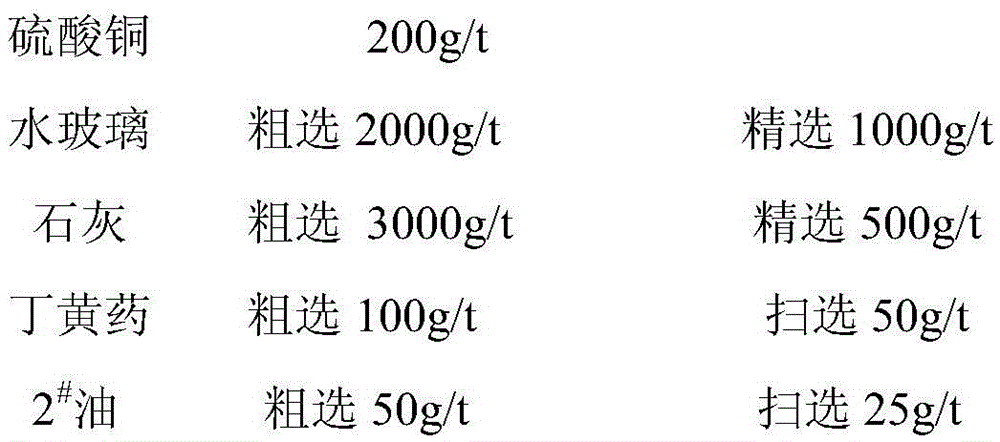
The invention discloses a floatation separation method for copper pyrites and iron pyrites. According to the method, copper sulfate serves as an activating agent of the copper pyrites, sodium silicate, sodium hexametaphosphate and the like serve as an inhibitor of a gangue mineral and a pulp dispersing agent, sesbania gum serves as an inhibitor of the iron pyrites, Z200 and the like serve as a collecting agent of the copper pyrites, 2# oil serves as a foaming agent, the floatation separation is carried out, and flotation of the iron pyrites can be effectively restrained. Under the neutrality condition, floatation separation of the copper pyrites and the iron pyrites can be effectively achieved, and under the condition that the copper content of fed ore is 0.5%-0.9% and the sulfur content is 3%-11%, the copper concentrate with the copper content of 18%-21% can be obtained after flotation separation, and the recycling rate can reach 77%-85%.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of leaching copper sulfide ore with the use of iodine
ActiveUS8163063B2Efficient leachingEfficient executionSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of efficiently leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore containing chalcopyrite or enargite as a main constituent under versatile conditions for actual operation.A method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising using, as a leaching solution, a sulfuric acid solution containing iodide ions and ferric (III) ions in an excessive amount relative to the iodide ions and leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore; or a method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore with the use of a leaching solution further containing water-soluble ligands such as chloride ions that can stabilize ferric (III) ions in addition to the above components, is provided.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
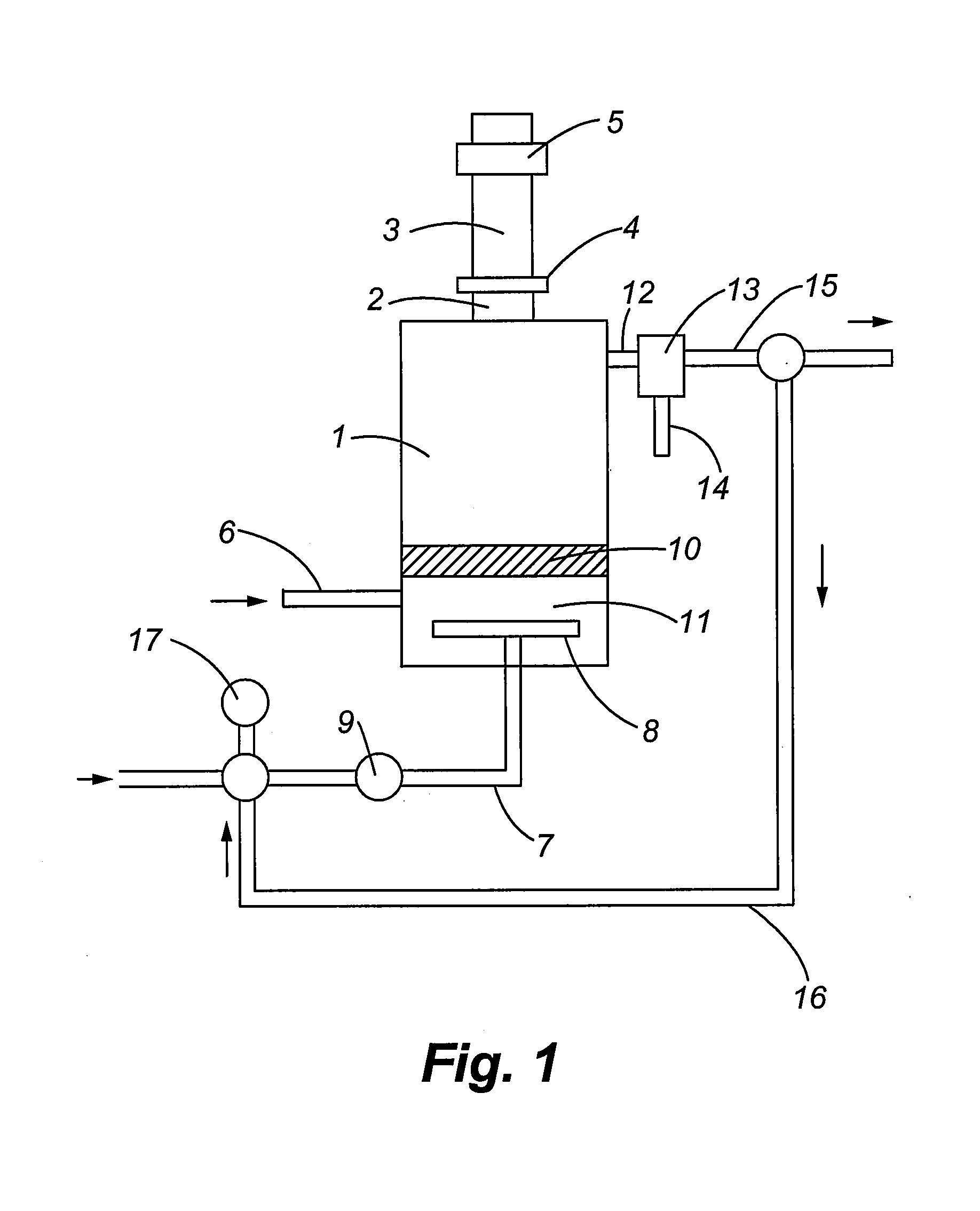
Method for Producing a Thin-Film Chalcopyrite Compound
InactiveUS20080044570A1Polycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsChalcopyriteSolid film
The invention concerns a method which consists in depositing on a substrate a solution containing metal mineral salts constituting chalcopyrite and an organic binder; then drying to obtain a solid film on the substrate; and finally contacting the film with an atmosphere containing one or more elements of group 16 of the periodic table and forming chalcopyrite by thermal reaction.
Owner:SOLARONIX
Method for recycling copper from copper smelting slag
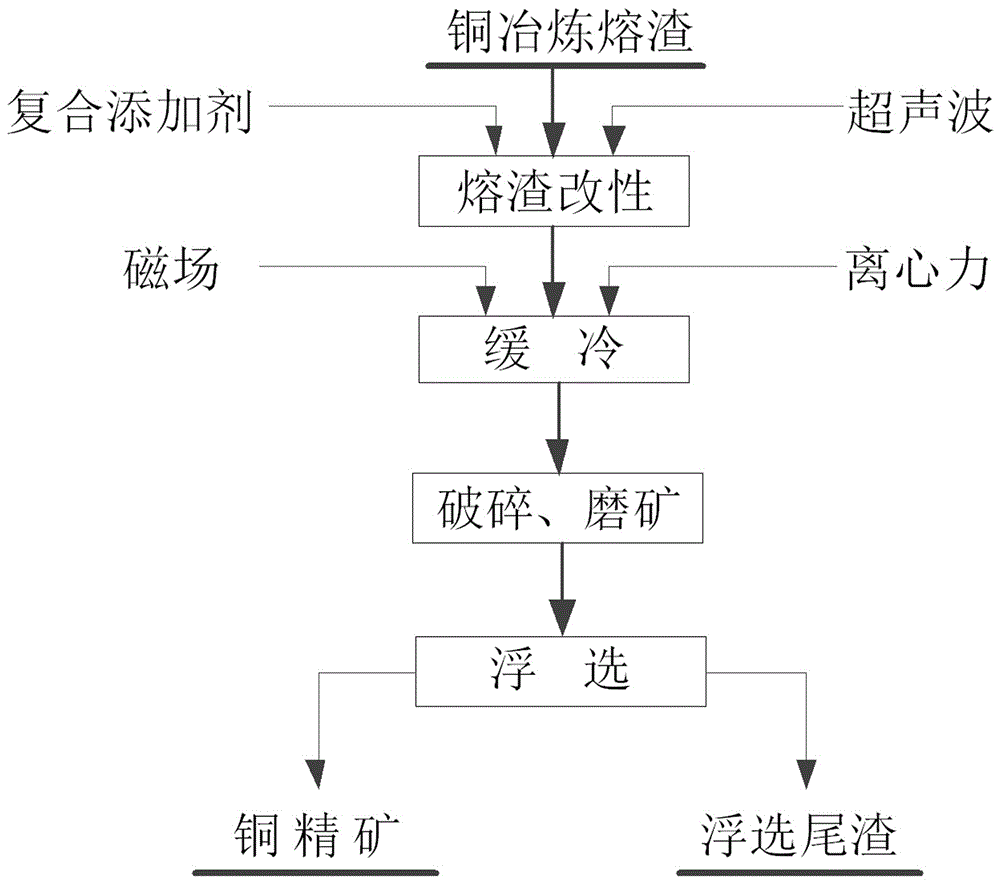
ActiveCN106824543AAchieve recyclingLow viscosityFlotationProcess efficiency improvementMolten stateUltrasound - action
The invention relates to a method for recycling copper from copper smelting slag. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, modifying copper smelting molten slag: adding 3 percent to 5 percent of a compound additive into the copper smelting molten slag with a molten state according to the mass ratio of the molten slag; carrying out ultrasonic treatment and sufficiently and uniformly blending and smelting, wherein the compound additive is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 40 percent to 50 percent of pyrite, 5 percent to 10 percent of chalcopyrite, 40 percent to 50 percent of coke powder, 5 percent to 15 percent of sodium humate, and the sum is 100 percent; step 2, slowly cooling the smelting slag: slowly cooling the modified smelting slag under the action of a centrifugal force and a magnetic field; step 3, carrying out flotation: carrying out crushing and ore milling on the slowly cooled modified slag and carrying out flotation treatment to obtain floated copper concentrate and tailings. According to the method provided by the invention, a mineral phase of the copper smelting molten slag is reconstructed and comprehensive recycling of copper and iron is realized; an experiment proves that the copper concentrate with the copper content more than 20 percent is obtained through flotation and the recycling rate of the copper is 71 percent to 80 percent.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Sulfide ore treatment technology by thermoacidophile
InactiveCN1827805AReduced Cooling NeedsFast oxidationProcess efficiency improvementMetaboliteSulfide
The invention relates the technology of using thermophilic and acidophilic bacteria to treat sulphide field, comprising the following steps: screening and domesticating the thermophilic and acidophilic bacteria to get the high effective biooxidation strain; training it to get inoculation liquid whose thalline density is above 1X108 per liter; mixing the inoculation liquid, sulphide powder and culture medium of thermophilic and acidophilic bacteria, carrying out biological oxidation reaction, and when the copper ion of chalcopyrite in sulphide powder dissolving out above 70%, or 70% lattice structure of chalcopyrite destroyed, terminating the reaction. The technology uses the microbe direct oxidation action and metabolite indirect oxidation action to oxygenize the sulphide in ore to sulphate, destroying the sulphide lattice and discharging the precious metal ion.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Methods for forming particles from single source precursors, methods of forming semiconductor devices, and devices formed using such methods
ActiveUS20090233398A1Simplify the viewing processNanotechPhosphorus sulfur/selenium/tellurium compoundsSemiconductor materialsChalcopyrite
Single source precursors are subjected to carbon dioxide to form particles of material. The carbon dioxide may be in a supercritical state. Single source precursors also may be subjected to supercritical fluids other than supercritical carbon dioxide to form particles of material. The methods may be used to form nanoparticles. In some embodiments, the methods are used to form chalcopyrite materials. Devices such as, for example, semiconductor devices may be fabricated that include such particles. Methods of forming semiconductor devices include subjecting single source precursors to carbon dioxide to form particles of semiconductor material, and establishing electrical contact between the particles and an electrode.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Bacteria strain wenelen DSM 16786, use of said bacteria for leaching of ores or concentrates containing metallic sulfide mineral species and leaching processes based on the use of said bacteria or mixtures that contain said bacteria
The present invention is related to an isolated chemolithotrophic bacterial strain belonging to the specie Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, named “Wenelen” and deposited at the Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH—DSMZ under classification number DSM 16786, the use of said bacteria for leaching ores or concentrates containing of metallic sulfide species and leaching processes based on the use of said bacteria or mixtures that contain said bacteria. This Wenelen DSM 16786 strain has an increased oxidizing activity, especially regarding chalcopyrite, when compared to known bacteria. Due to the former feature, this bacteria strain show great interest for biomining applications and it is presently being subjected to annotation processes after sequencing.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
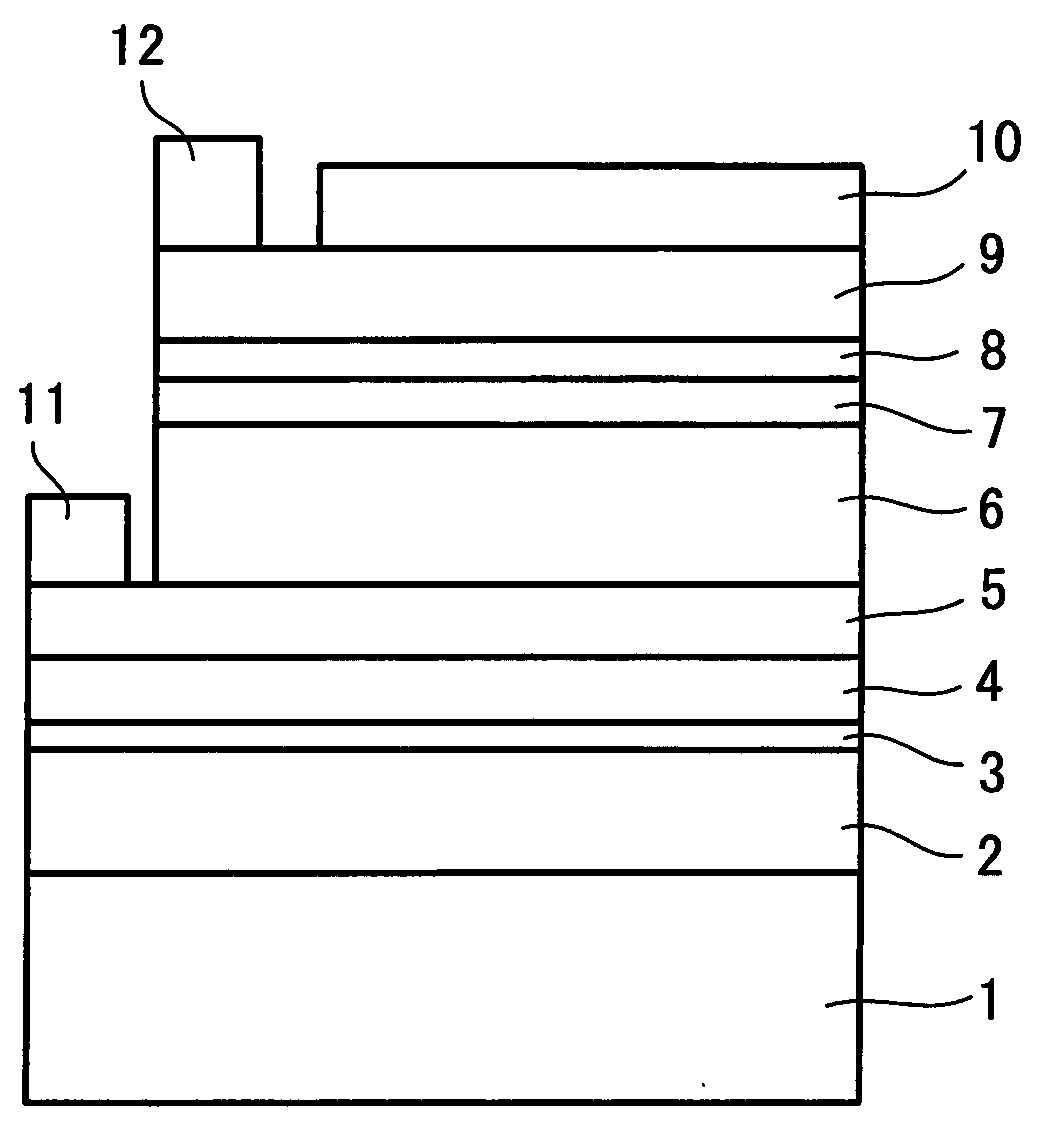
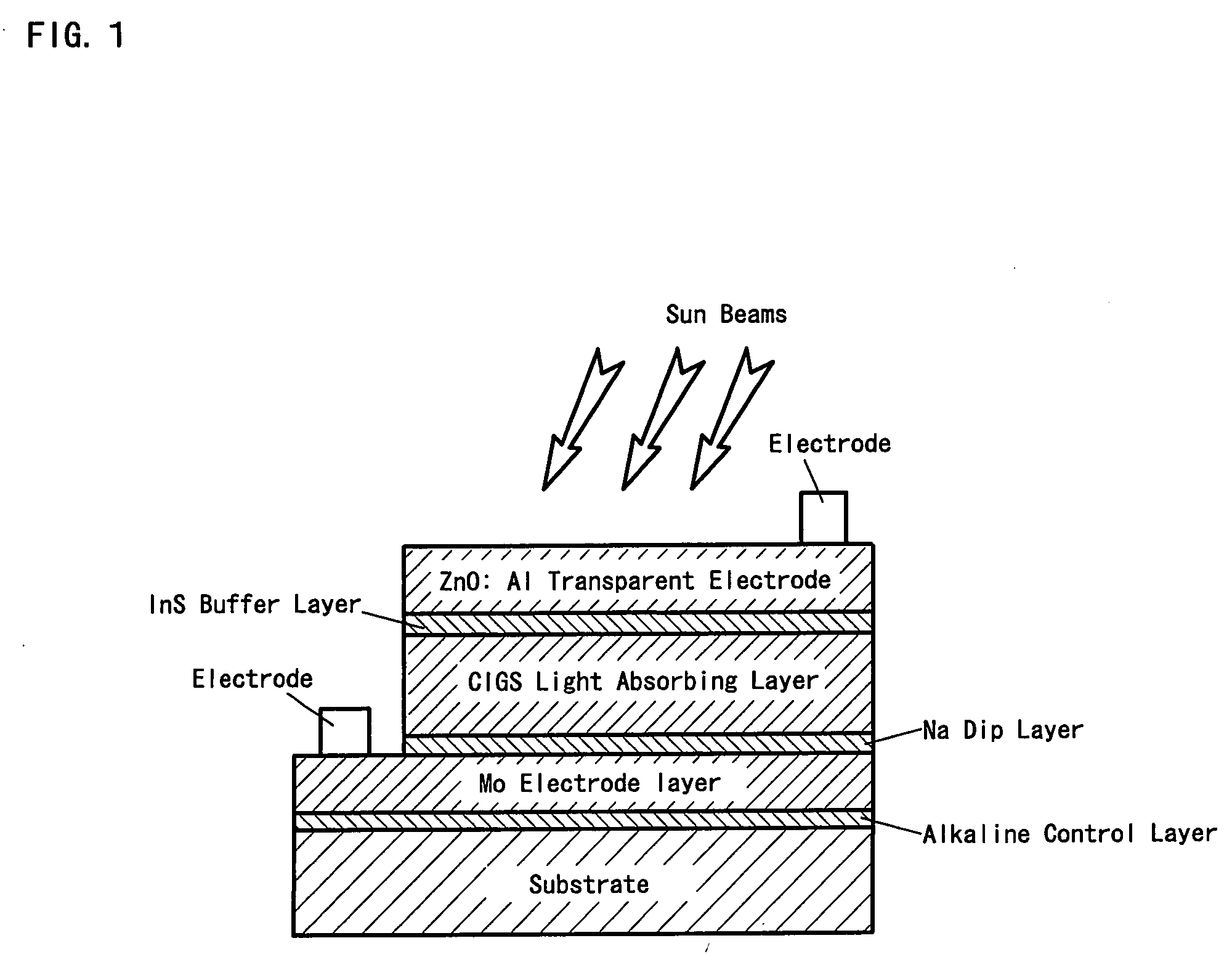
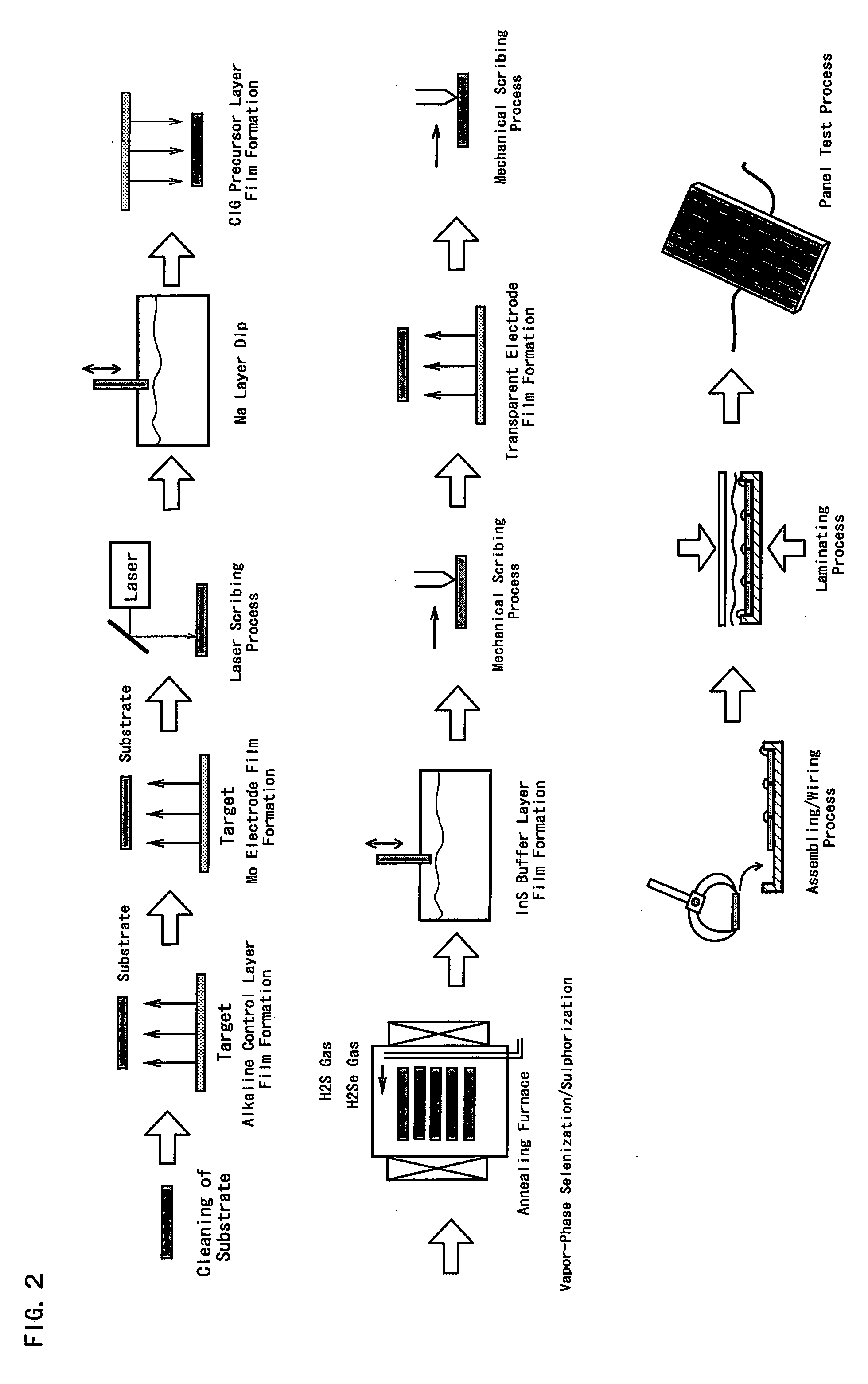
Chalcopyrite Solar Cell and Manufacturing Method Thereof
InactiveUS20090205715A1Light weightIncrease flexibilityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phasePliability
A solar cell having high conversion efficiency and excellent flexibility is realized. A mica substrate or laminated mica substrate is used as substrate 1. The mica and laminated mica have high insulating property and heat resistance temperature, which can be selenized at an appropriate treatment temperature through vapor-phase selenization process, high conversion efficiency and excellent flexibility resultantly suitable for mass-production can be obtained. On the other hand, because the surfaces of the mica and laminated mica have large surface roughnesses, it is impossible to induce leakage to obtain high conversion efficiency in the case where a chalcopyrite based light absorbing layer 6 is simply formed. In the present invention, an intermediate layer 2 of ceramic based material and binder layer 4 are interposed between the mica substrate 1 and a molybdenum electrode 5. By providing the intermediate layer 2 and binder layer 4, surface coating property is enhanced and a solar cell having high conversion efficiency can be realized.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
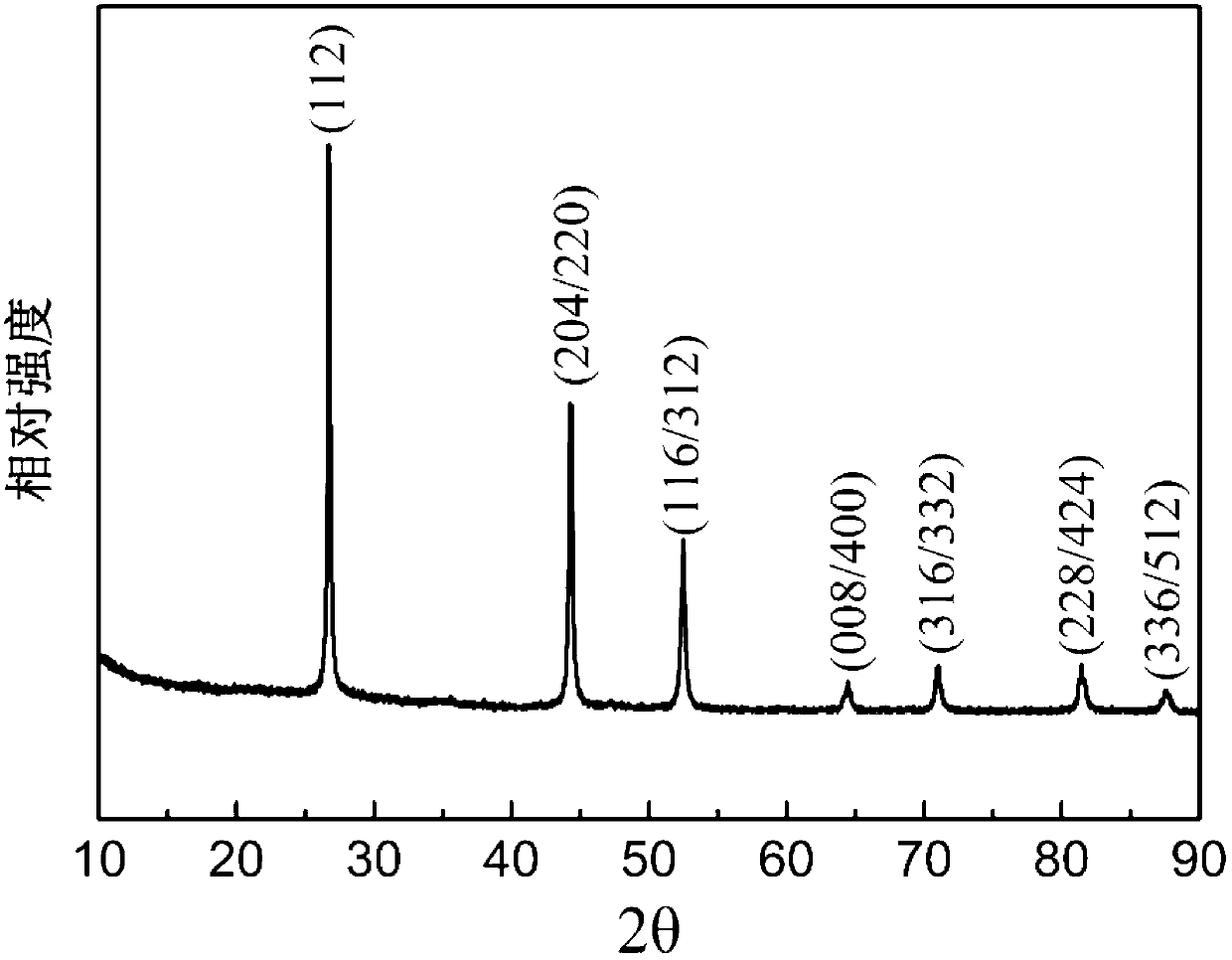
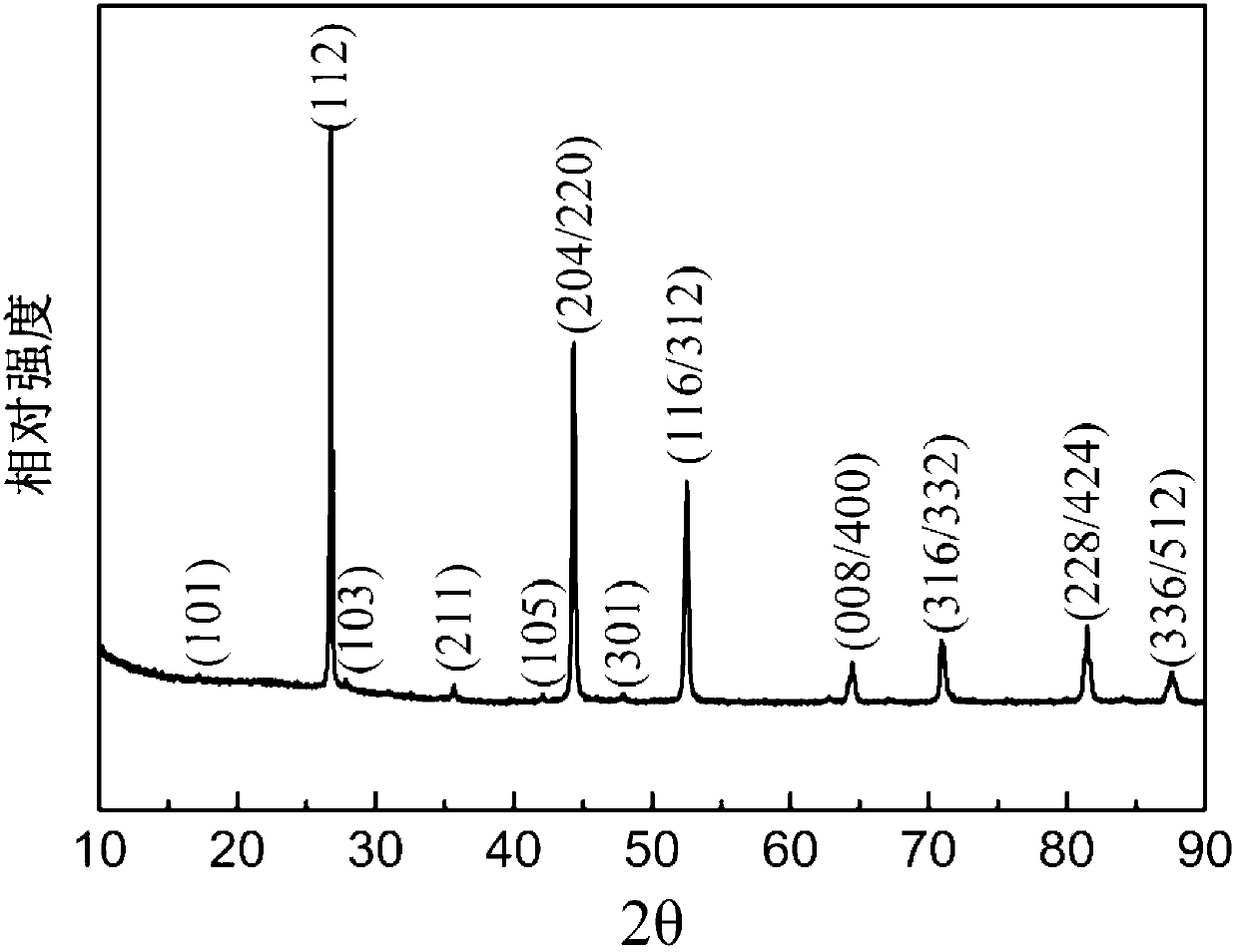
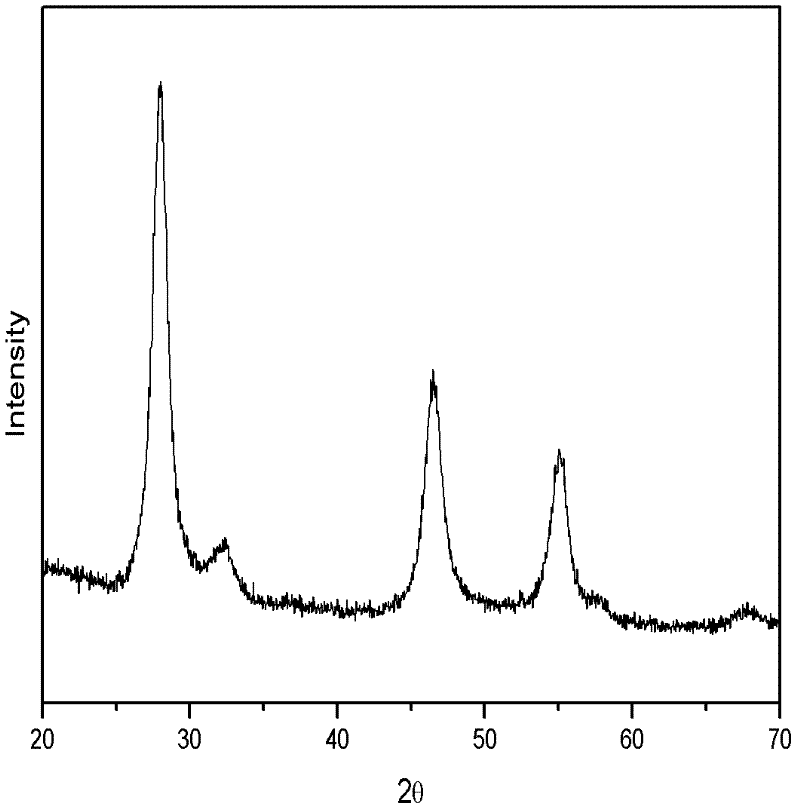
Preparation method of CuInSe2 with a chalcopyrite structure and CuIn1-xGazSe2 nano particles
InactiveCN103213956AGood dispersionHigh phase purityMaterial nanotechnologySelenium/tellurium compundsChalcopyriteCentrifugation
The invention relates to a preparation method of CuInSe2 with a chalcopyrite structure and CuIn1-xGazSe2 nano particles. Firstly, a metal precursor solution containing Cu+ or Cu2+, In3 or Ga3+ cation and a Se powder precursor solution are respectively prepared, and then the metal precursor solution and the Se powder precursor solution are mixed and uniformly stirred, and the solution is heated to 200-285 DEG C. with high purity nitrogen protection and reacted for 0.5-2 hours, and then the CuInSe2 or CuIn1-xGazSe2 nano particle solution is obtained, after high speed centrifugation, cleaning and drying steps, the CuInSe2 or CuIn1-xGazSe2 nano particles are obtained. The CuInSe2 or CuIn1-xGazSe2 nano particle has the advantages of chalcopyrite crystal structure, good dispersibility and high phase purity, and the element ingredient approaches to the stoichiometric ratio, thereby laying a foundation for preparing a high conversion efficiency film solar energy battery. The invention employs cheap metal salt and selenium powder as precursors, and employs a simple one-pot synthetic method, and has the advantages of simple operation, short synthesis period, strong repeatability without injection, and is suitable for mass production.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Floatation separation process for galenite and chalcopyrite
InactiveCN101745469ANo pollution in the processReduce manufacturing costFlotationChalcopyriteFoaming agent
The invention relates to a floatation separation process for galenite and chalcopyrite. The process adopts the match of sodium humate and calcium chloride to inhibit the galenite; and sodium xanthogenate or O-isopropyl-N-ethylthionocarbamate is used as a collecting agent and butyl ether alcohol, ethyl ether alcohol or terpineol is used as a foaming agent. The combined inhibitor adopted can inhibit the floatation of the galenite; and the chalcopyrite can float upwards; therefore, the floatation separation of the galenite and the chalcopyrite can be achieved; and the process has no pollution and low production cost.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS8653616B2Reduce generationImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorChalcopyrite
It is aimed to provide a photoelectric conversion device having high adhesion between a first semiconductor layer and an electrode layer as well as high photoelectric conversion efficiency. A photoelectric conversion device comprises an electrode layer, a first semiconductor layer located on the electrode layer and comprising a chalcopyrite-based compound semiconductor of group I-III-VI and oxygen, and a second semiconductor layer located on the first semiconductor layer and forming a pn junction with the first semiconductor layer. In the photoelectric conversion device, the first semiconductor layer has a higher molar concentration of oxygen in a part located on the electrode layer side with respect to a center portion in a lamination direction of the first semiconductor layer than a molar concentration of oxygen in the whole of the first semiconductor layer.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
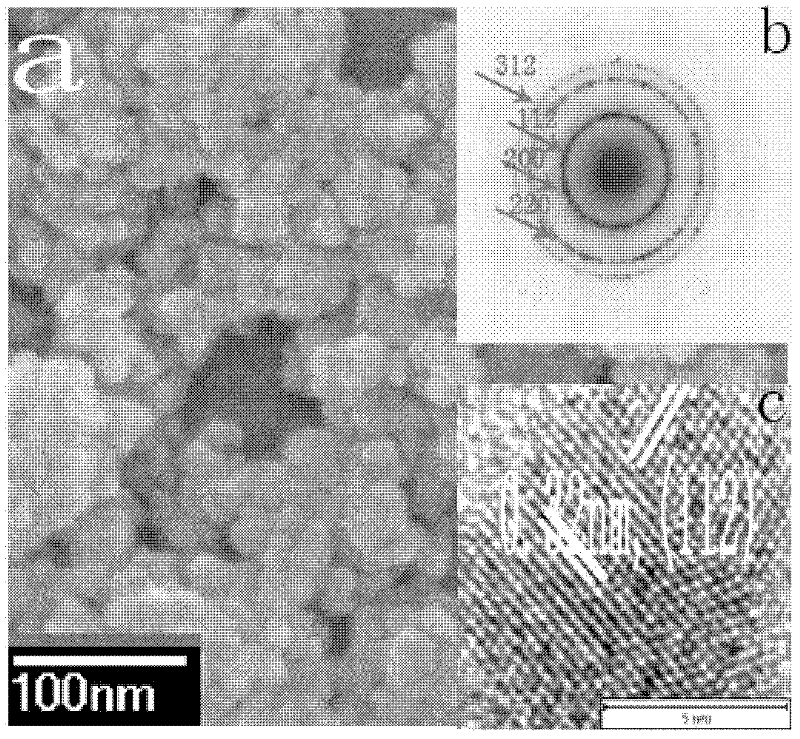
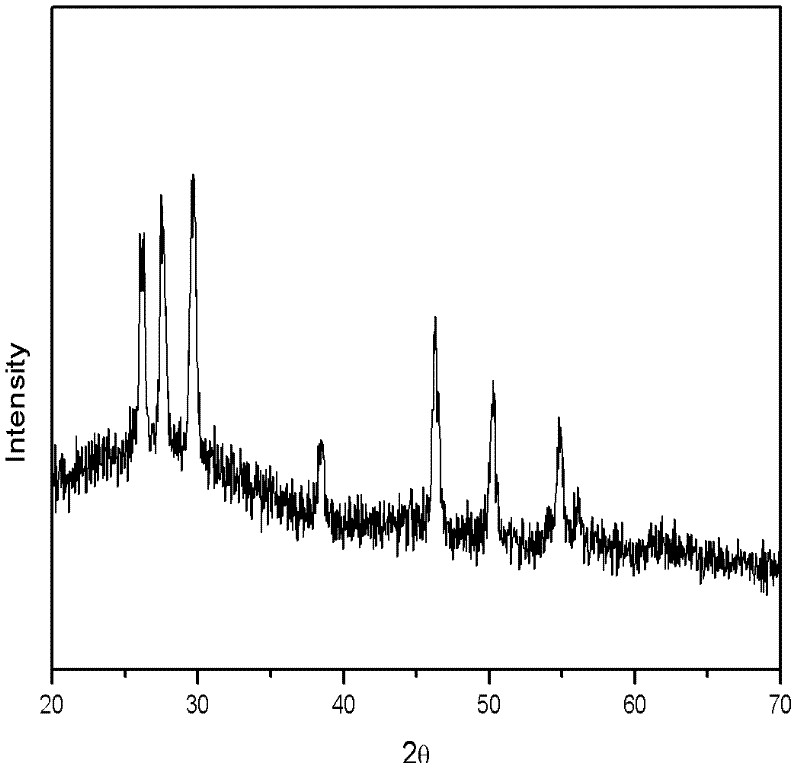
Simple and controllable preparation method of copper-indium-sulfur ternary semiconductor nano granules
ActiveCN102502788AThe size is easy to controlEasy to makeGallium/indium/thallium compoundsNanotechnologyIndiumCopper salt
The invention relates to a simple and controllable preparation method of copper-indium-sulfur ternary semiconductor nano granules, namely a preparation method of copper-indium-sulfur ternary semiconductor nano particles. The preparation method comprises the steps of: dissolving a copper salt and an indium salt in a certain amount of water, adding a proper amount of mercaptan acid, adjusting pH to a certain range, then adding a sulfur source, uniformly stirring, transferring the obtained solution into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, and carrying out hydrothermal reaction at a certain temperature; and cooling obtained colloidal solution to room temperature, and carrying out centrifugal settling to copper the copper-indium-sulfur semiconductor nano particles. The obtained copper-indium-sulfur semiconductor nano particles are divided into a chalcopyrite phase and a wurtzite phase, wherein the chalcopyrite granules are near-spherical and have granular size of 10-30 nm; and the wurtzite phase is of an irregular shape and a hexagonal laminated structure, and the size of the hexagonal laminated structure is 100-200 nm.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
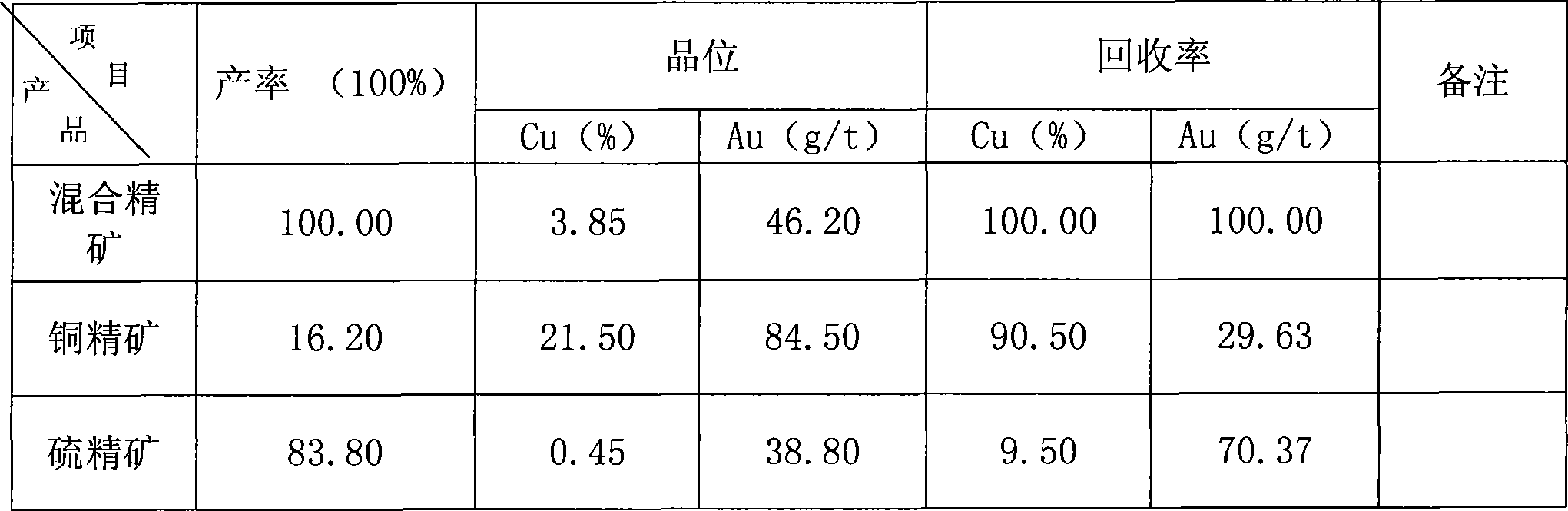
Copper-sulfur separation floatation method
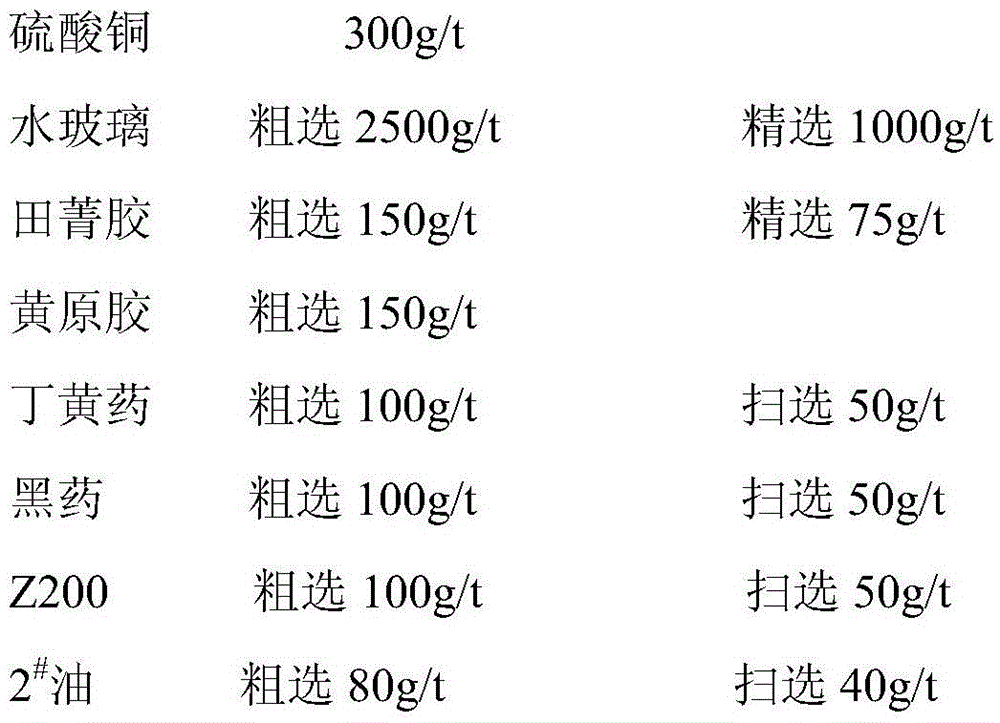
The invention discloses a copper-sulfur separating flotation method, wherein a regulator is used according to the difference of the charge, the point of zero charge (PZC) and the pH value of the point of zero charge (PHPZC) on the surface of chalcopyrite and pyrite in collective alloy concentrate; the pH value of ore slurry of the collective alloy concentrate is adjusted and controlled to be between 12.5 and 13; a combined inhibitor is adopted to inhibit the flotability of the pyrite; a collector is adopted to change the flotability of the chalcopyrite; No. 2 flotation oil is adopted as a foaming agent; and the ore slurry of the collective alloy concentrate is subjected to the flotation flow of primary roughing, secondary scavenging and tertiary refining. After the collective alloy concentrate (the chalcopyrite and the pyrite) are floated by the method, foam products are concentrate containing gold copper, and underflow is concentrate containing gold sulfur; the total amount of gold metals and copper metals is balanced before and after separation, and only the existence form is different; the value of gold is unchanged; and the grade of copper is improved from 3.85 percent to 21.50 percent, and the sale price of the copper is improved from 4,000 RMB per metal ton to 13,000 RMB per metal ton, so that significant economic benefit is generated.
Owner:LINGBAO CITY JINYUAN MINING
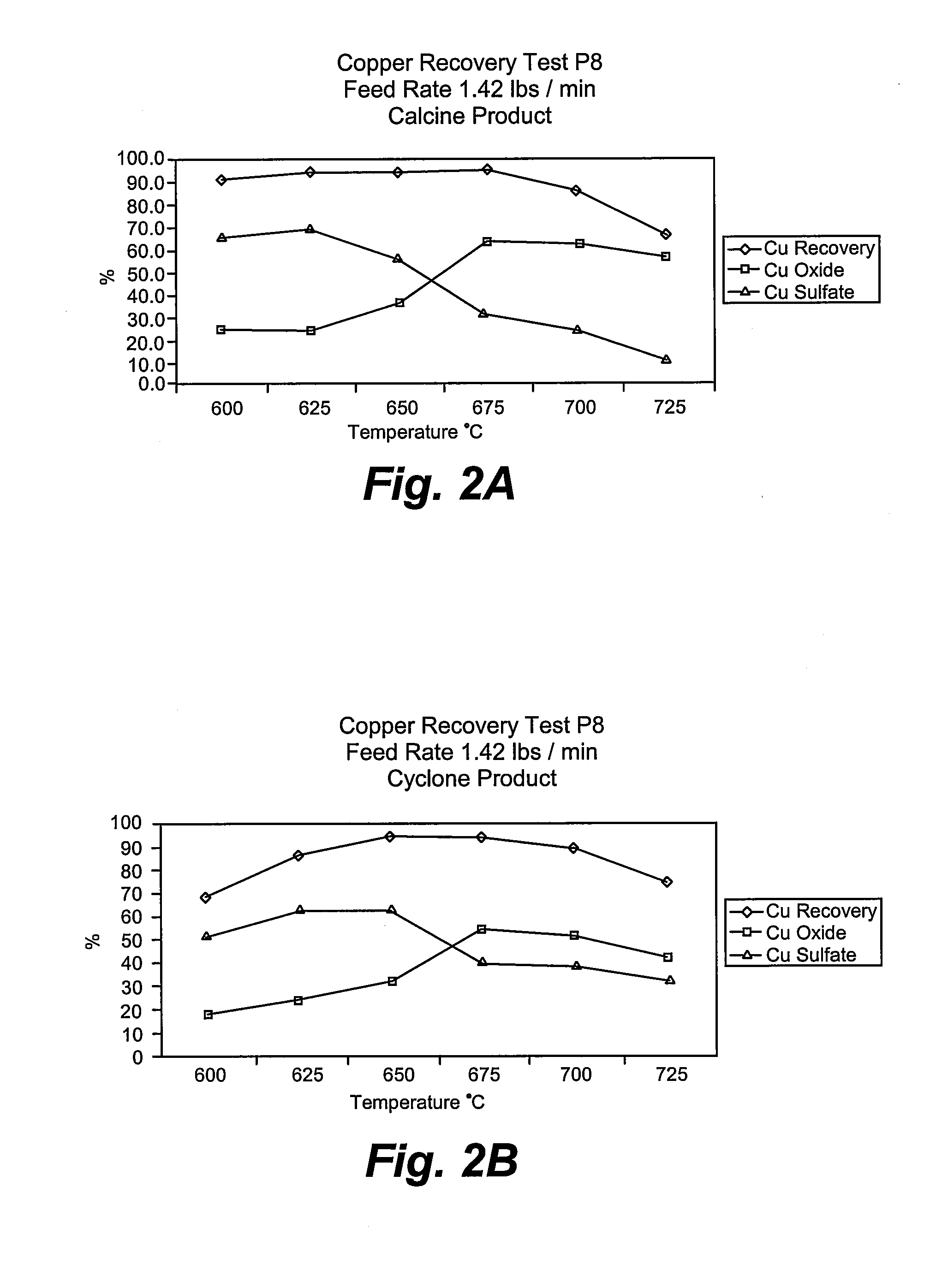
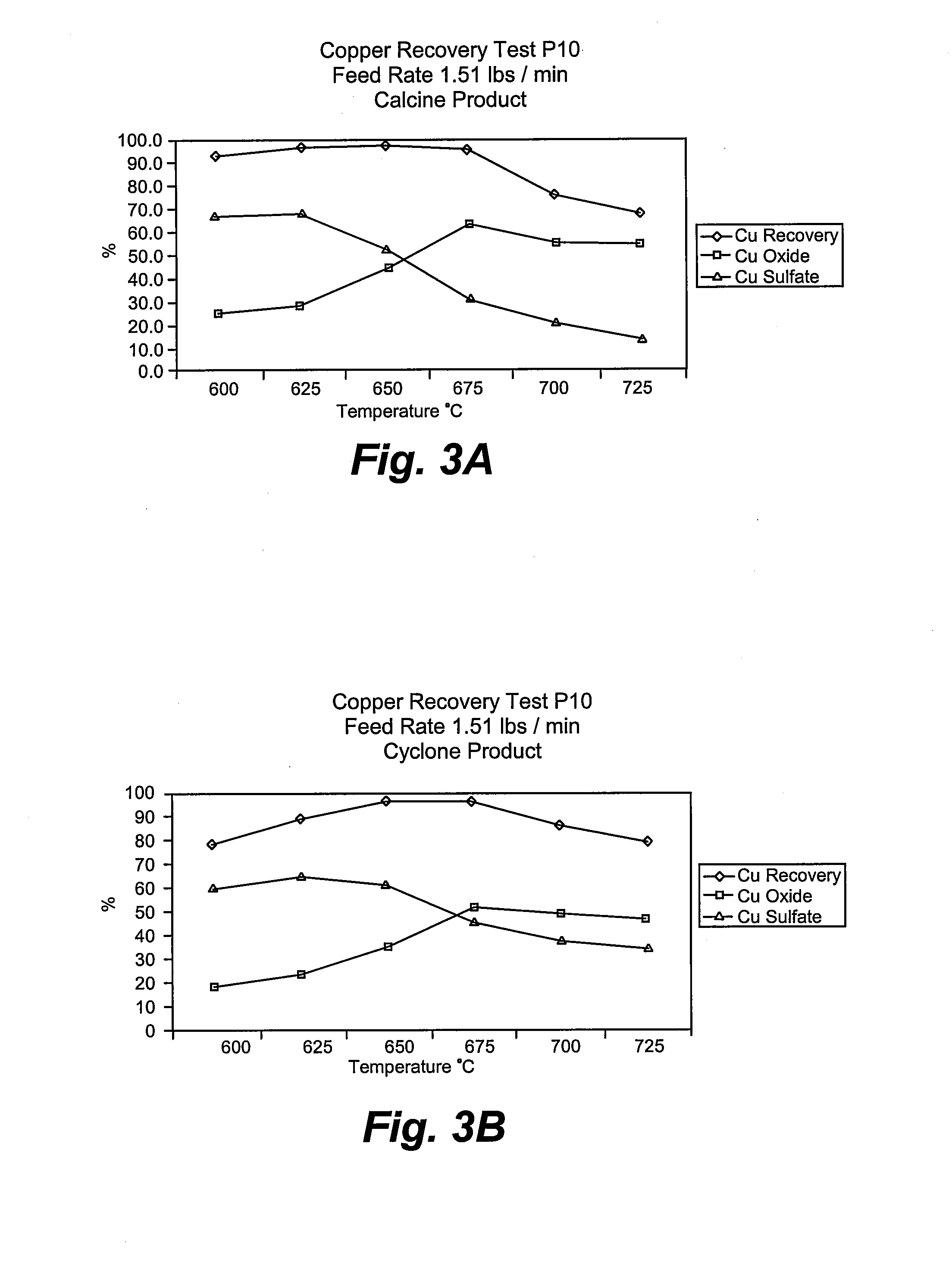
Method and means for using microwave energy to oxidize sulfidic copper ore into a prescribed oxide-sulfate product
InactiveUS20080118421A1Highly solubleLow costOxide/hydroxide preparationCobalt sulfatesMicrowaveChalcopyrite
The present invention is directed to the microwave treatment of a class of selected metal ores and concentrates, particularly those known as chalcopyrite, in a fluidized bed reactor. The end product is commonly a mixture of copper oxide and copper sulfate, both of which are liquid soluble and directly recoverable by known techniques. The ratio of the oxide-sulfate mixture end product may be controlled by suitable control of microwave parameters.
Owner:HW PROCESS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com